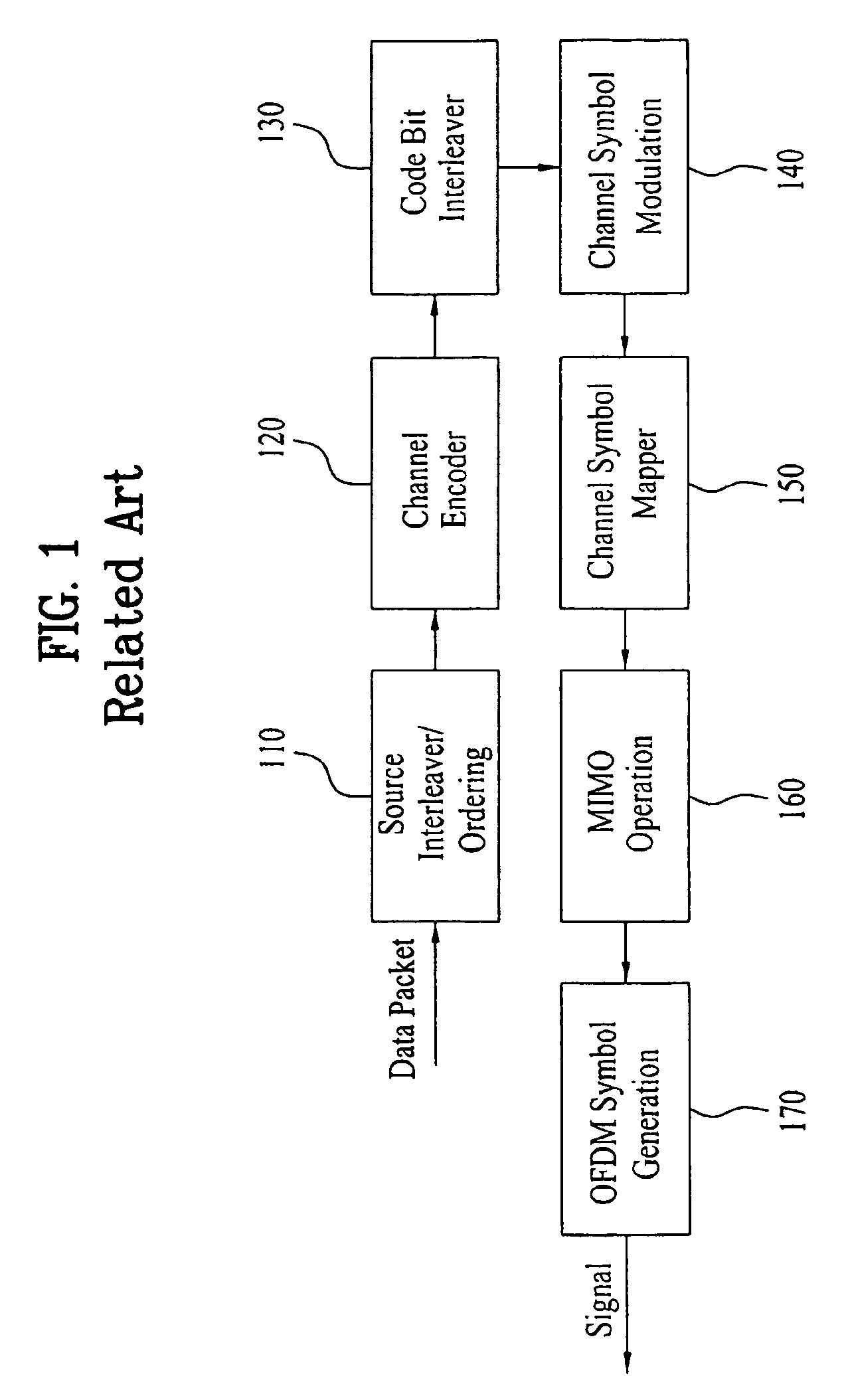
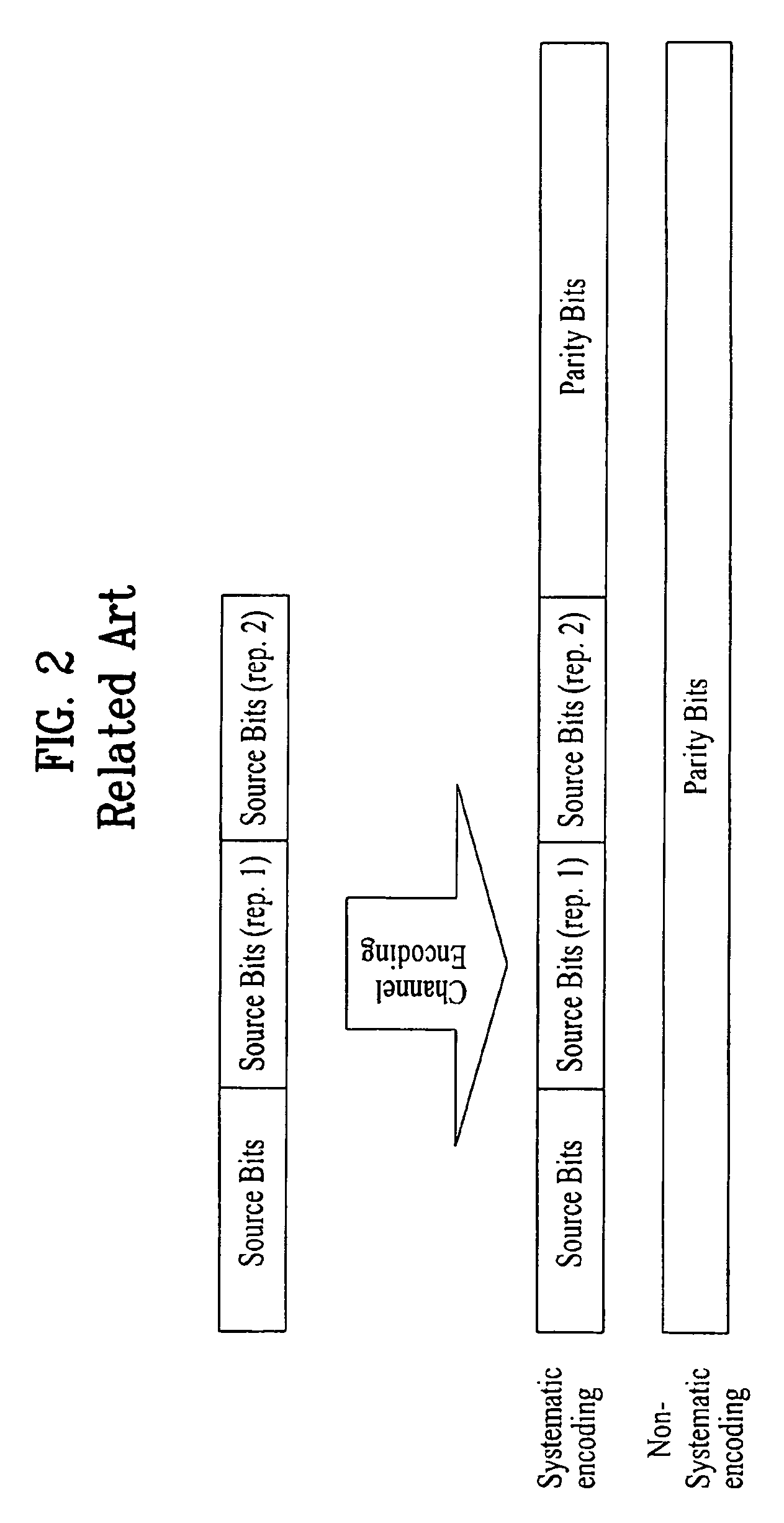
Patents
Literature
113 results about "Repetition code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
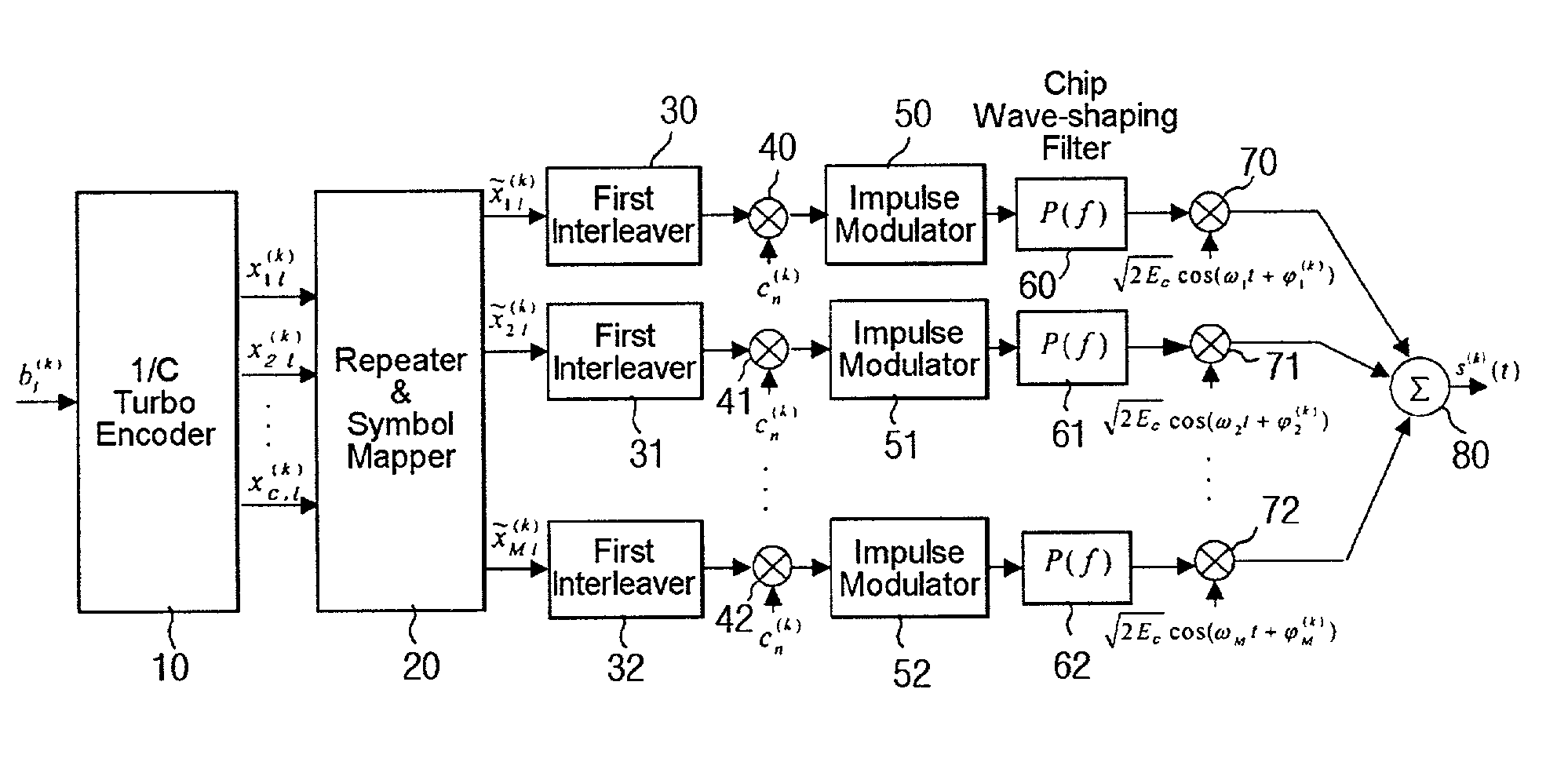
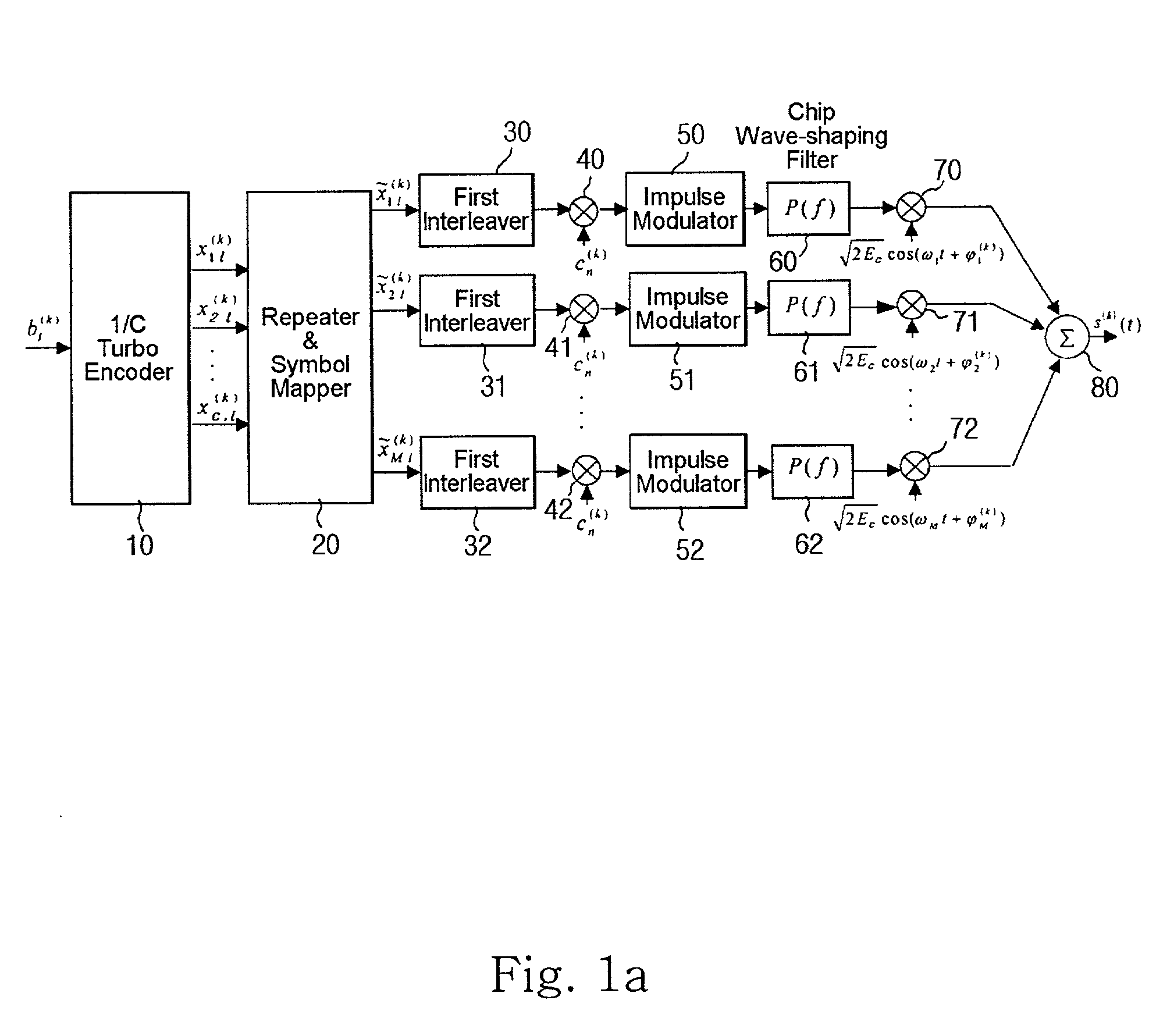
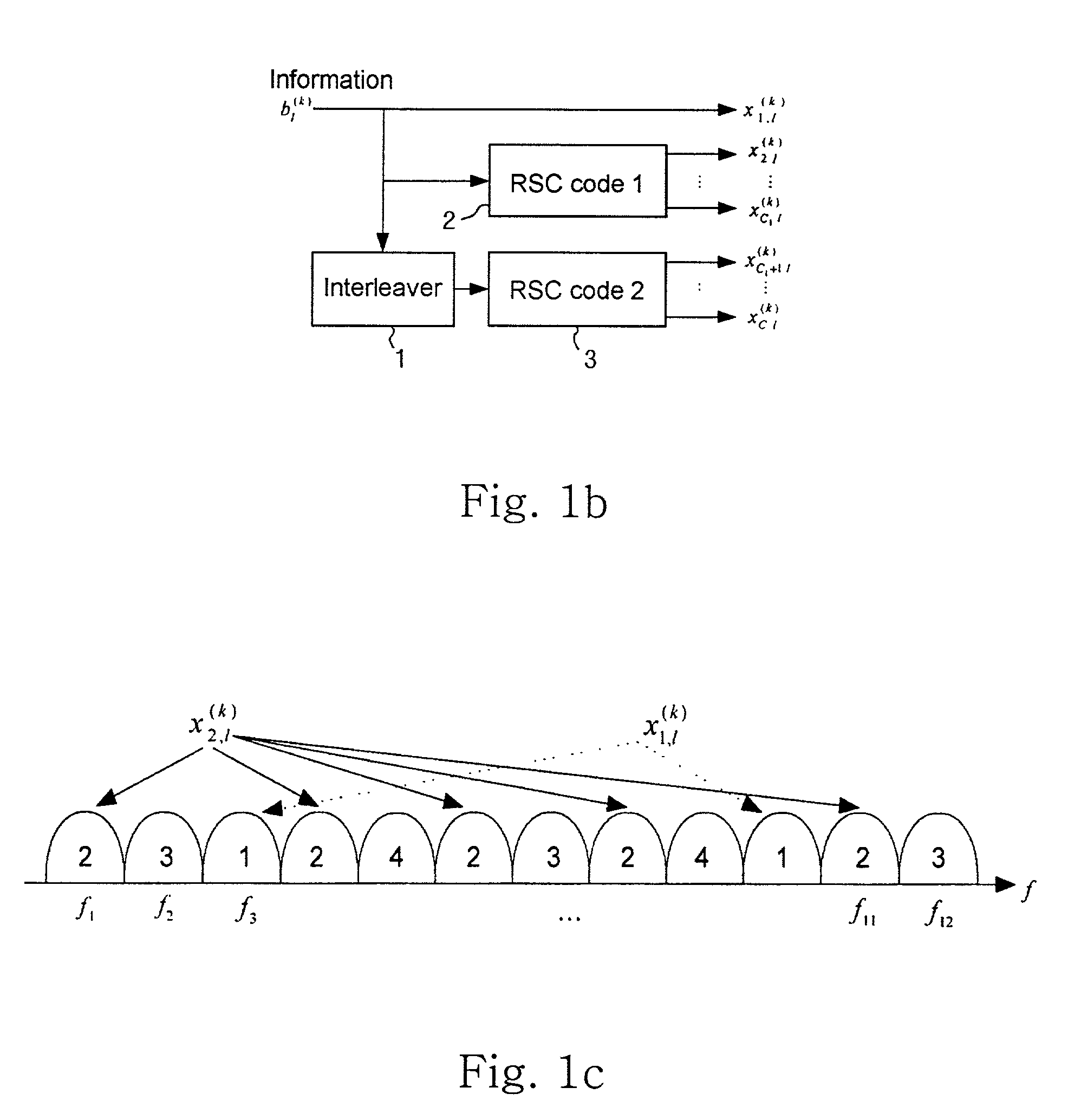
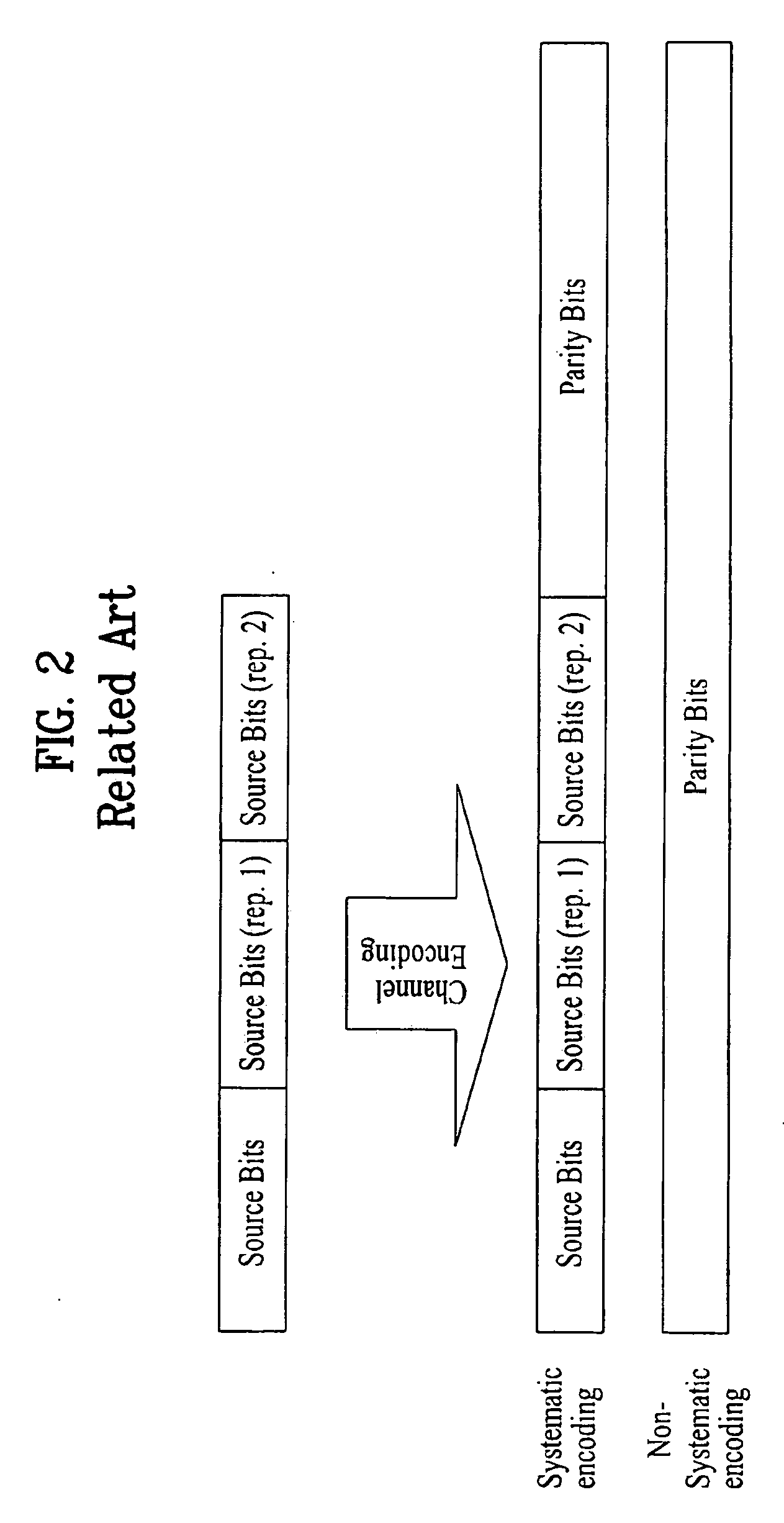
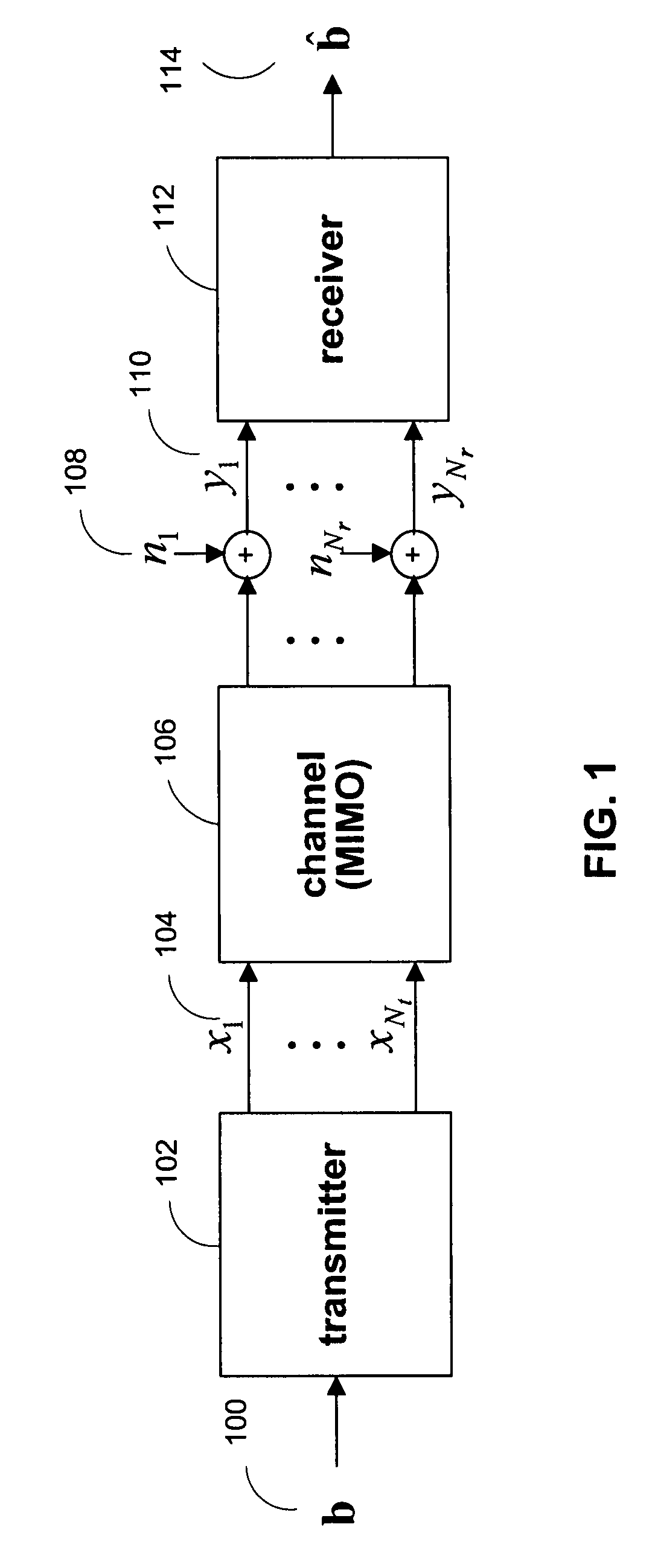
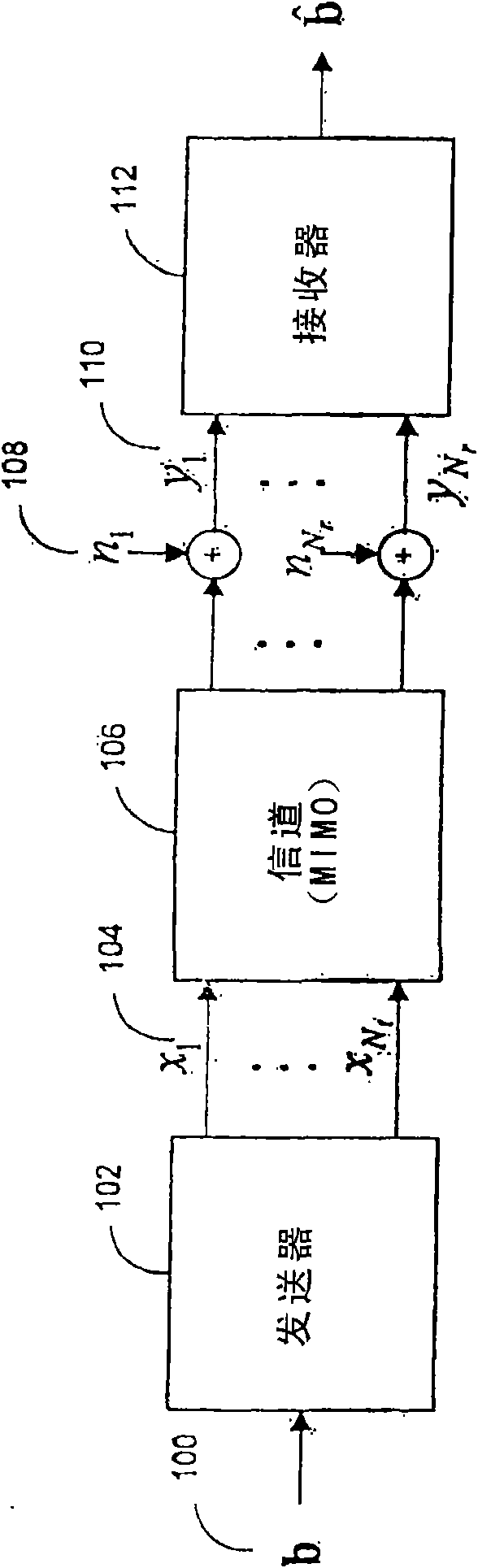
In coding theory, the repetition code is one of the most basic error-correcting codes. In order to transmit a message over a noisy channel that may corrupt the transmission in a few places, the idea of the repetition code is to just repeat the message several times. The hope is that the channel corrupts only a minority of these repetitions. This way the receiver will notice that a transmission error occurred since the received data stream is not the repetition of a single message, and moreover, the receiver can recover the original message by looking at the received message in the data stream that occurs most often.
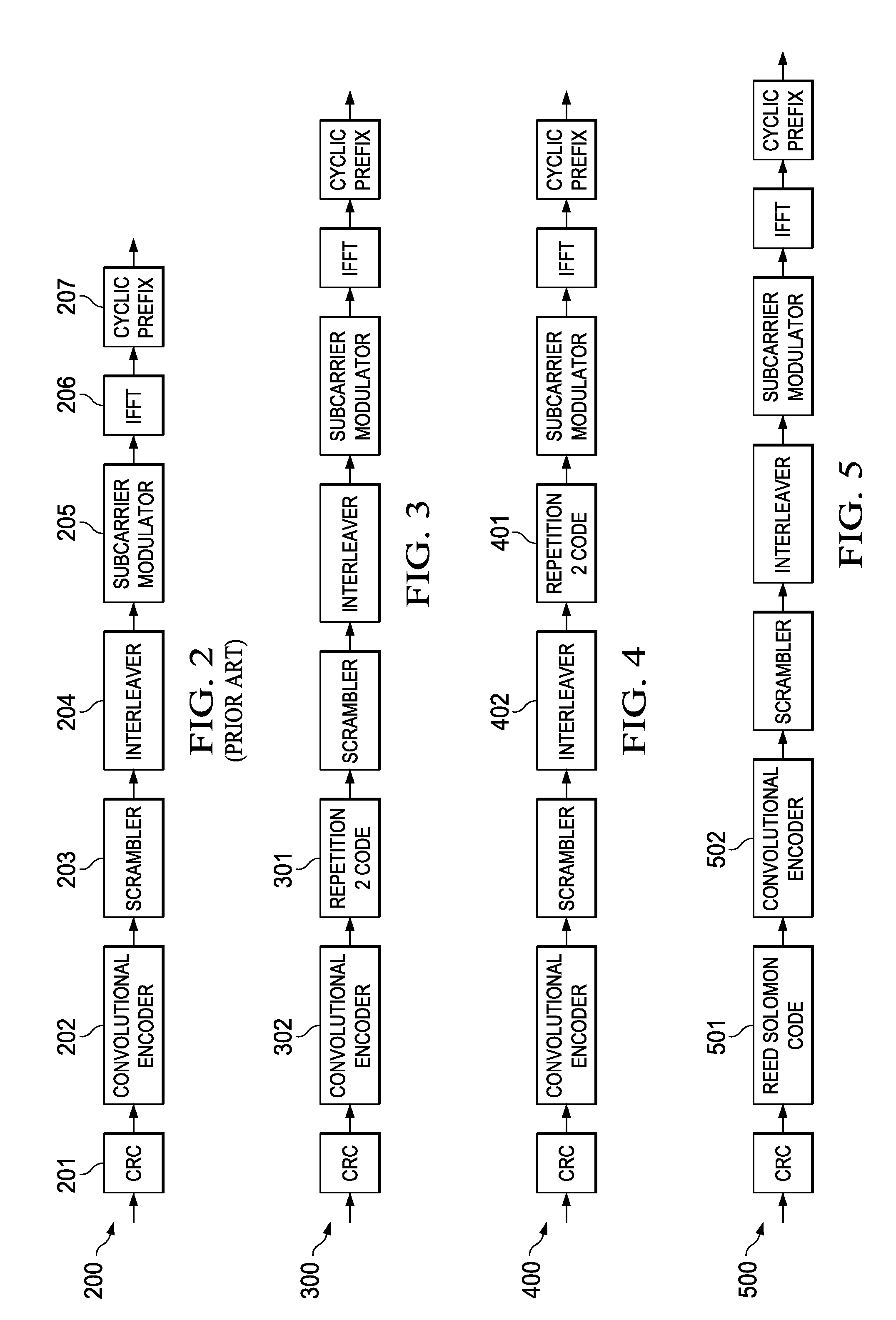
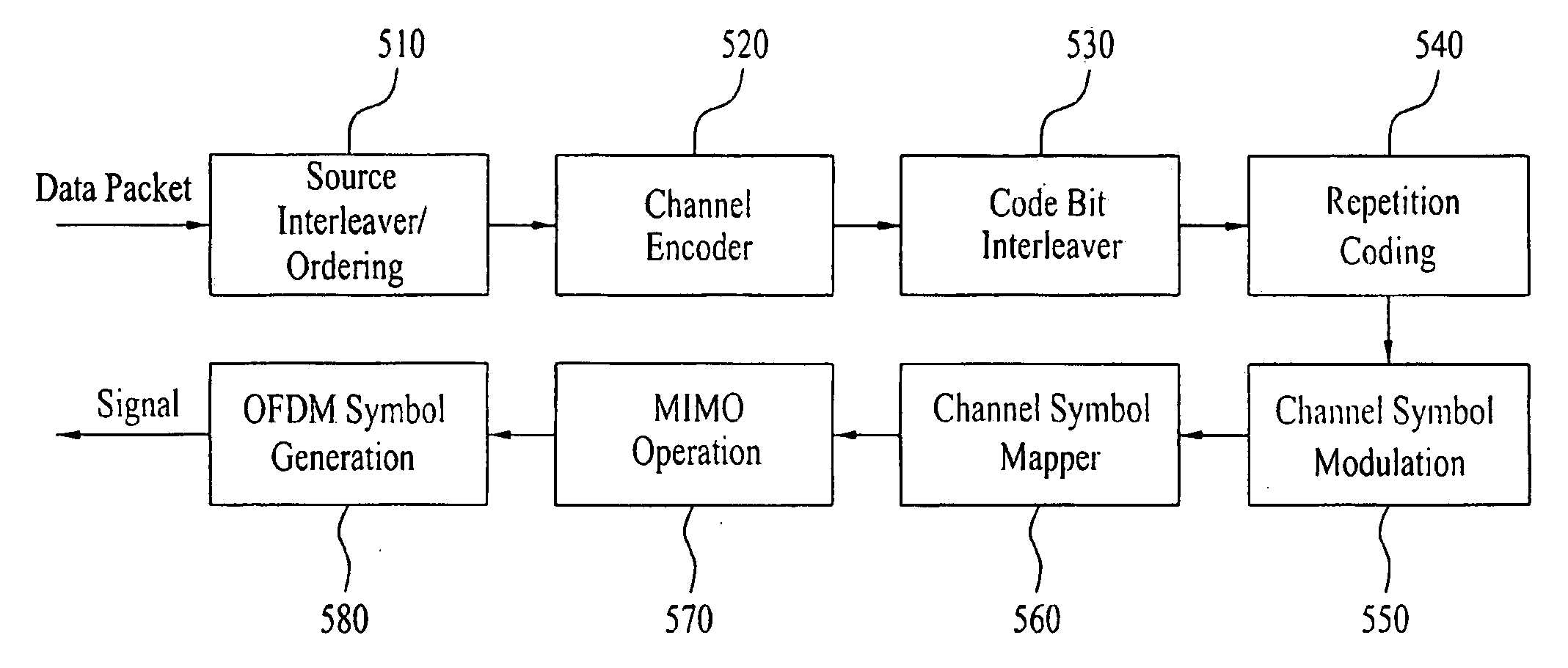
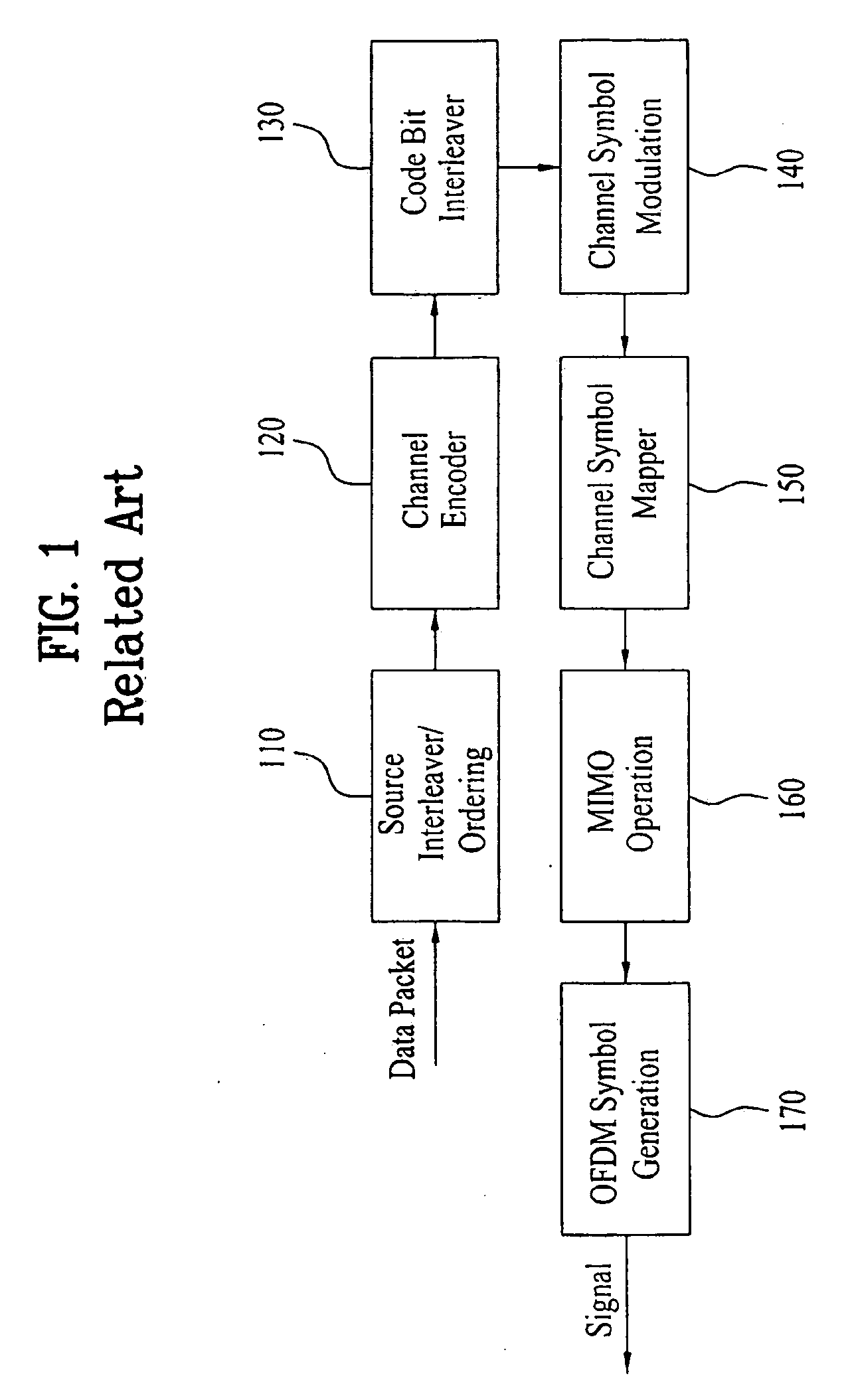
Concatenated Repetition Code with Convolutional Code
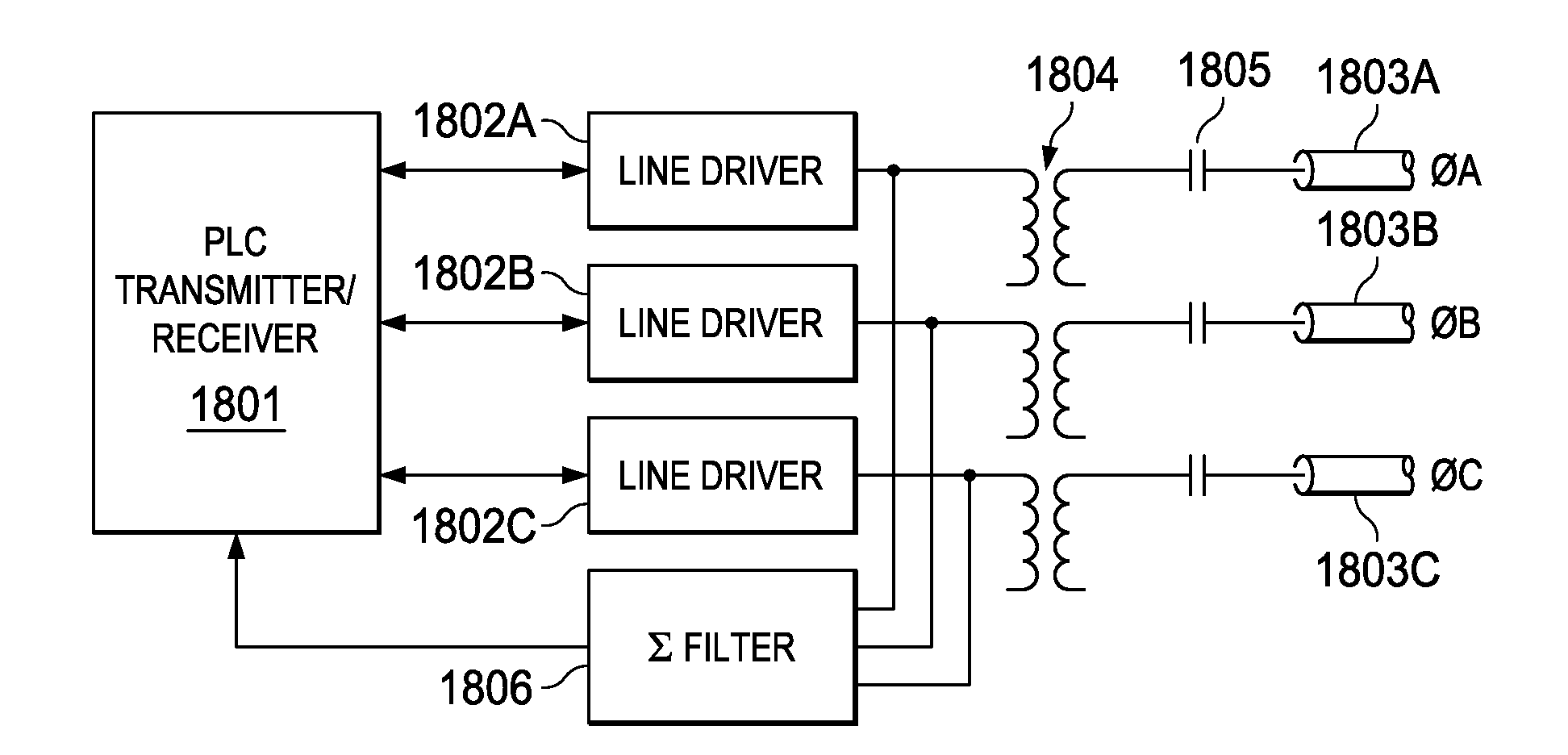
InactiveUS20110043340A1Reliable communicationEasy to implementTransmission/receiving by adding signal to waveElectric controllersComputer hardwarePower line network
A system and method for modulating and coding a signal is disclosed. Data from a Media Access Control (MAC) layer is convolutionally encoded. Robust coding of the data from the MAC layer is performed either before or after the convolutional encoding. The coded data is differentially modulating and then Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed to create an OFDM output signal adapted to be transmitted on a power line network. The robust coding may be a repetition 2 coding or a repetition N coding. The robust coding may add an outer code prior to the convolutional encoding. The robust coding may be Reed Solomon coding performed prior to the convolutional encoding. An optional header for identifying the robust coding is also disclosed along with a method for decoding the header.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
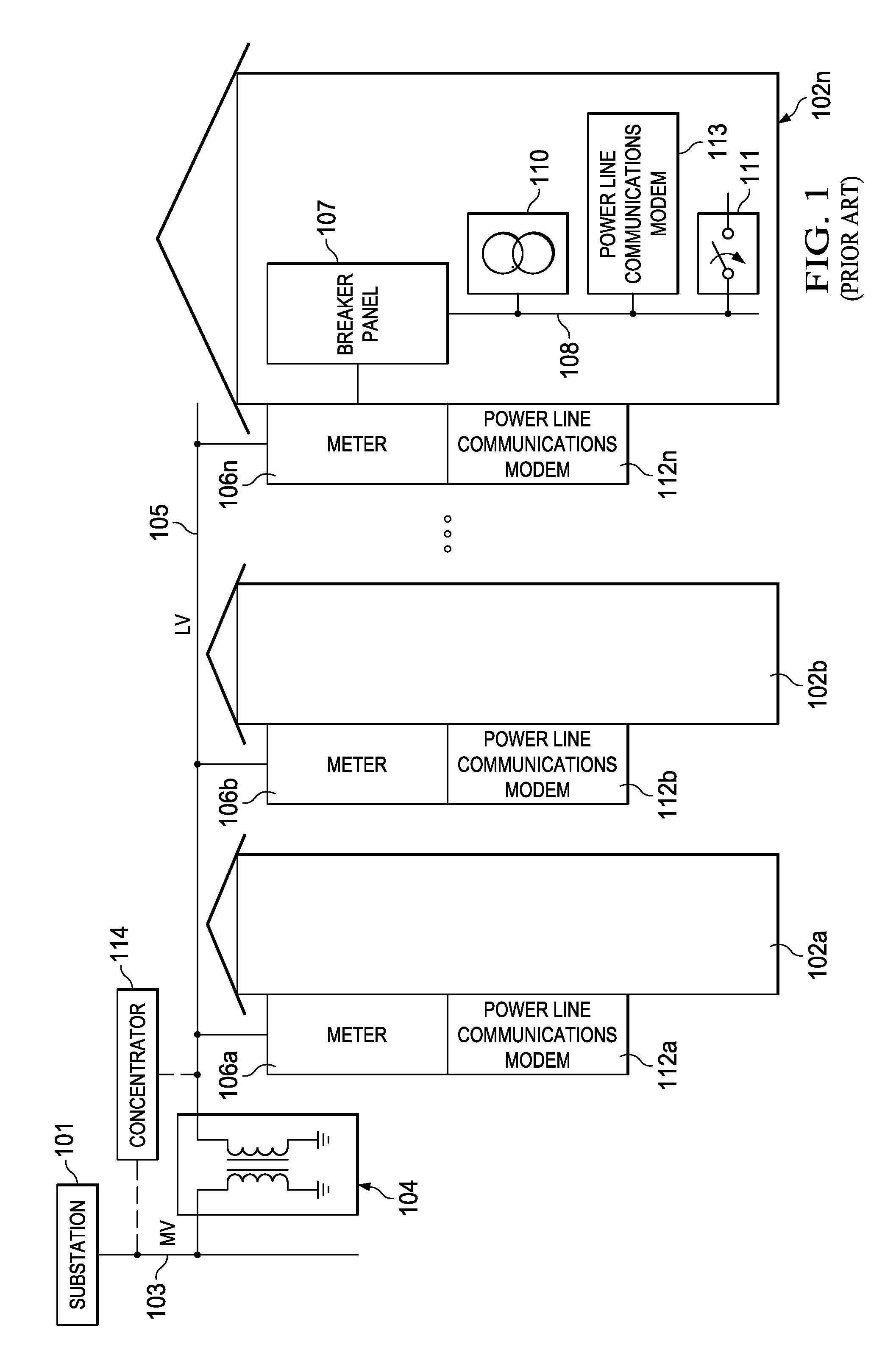
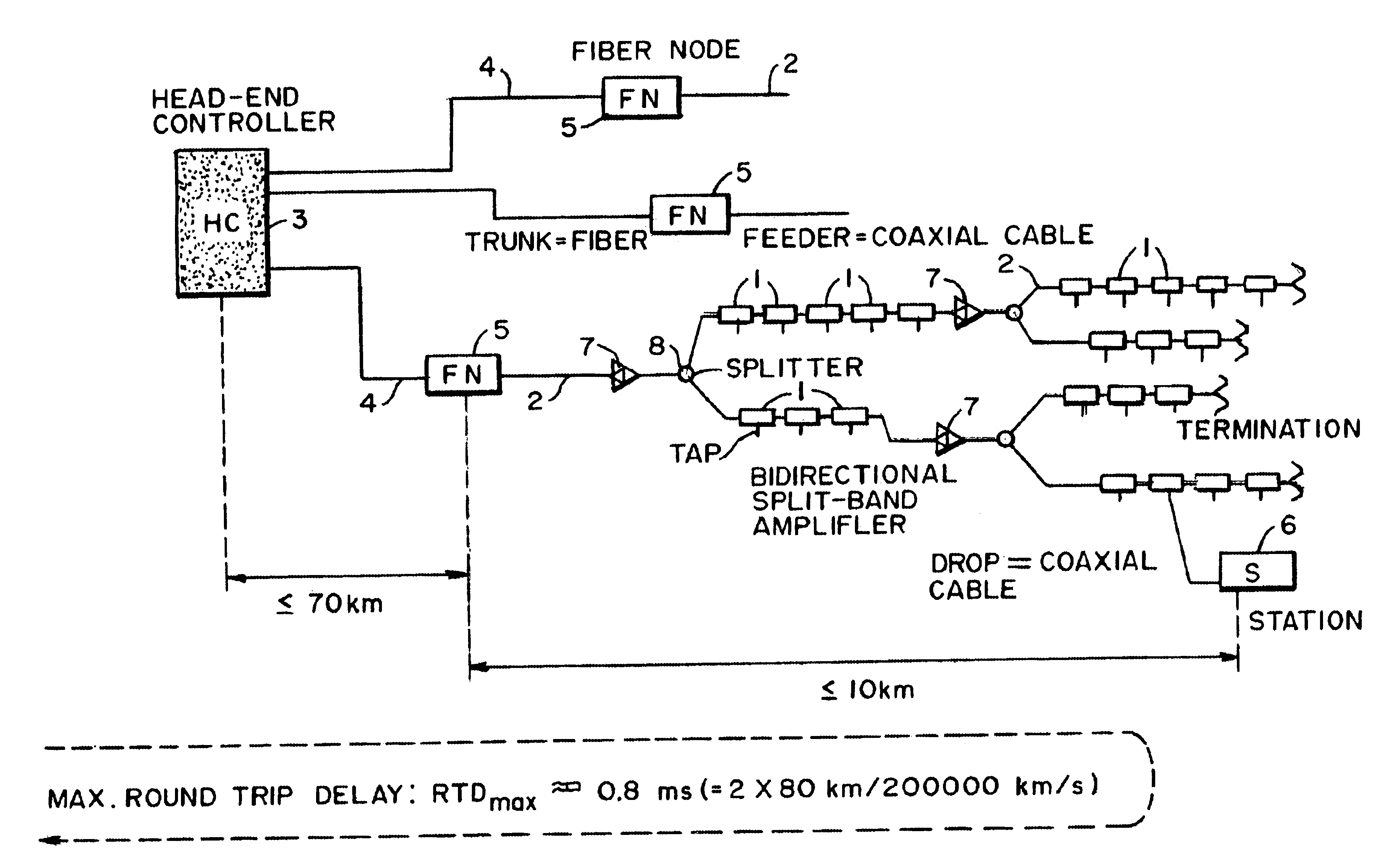
Communication network system
InactiveUS6735221B1Increase flexibilityFrequency-division multiplexLine-faulsts/interference reductionFrequency spectrumData stream
A digital communications network system for multiple access has a head-end node and at least one station node at at least one other end node; the system comprises a head-end controller (3) capable of transmitting data and medium-access control information to at least one station (6), preferably a plurality of station means, over a set of downstream channels within a first frequency range, and receiving information from the station or stations over an upstream channel within a second frequency range; the upstream channel comprises at least one upstream subchannel, preferably a plurality of upstream subchannels; the system further comprises at least one connection, preferably a plurality of connections, for connecting the head-end controller with the station or stations; each station includes means for receiving data and medium-access control information from the head-end controller; further means are provided for sending a data stream at a first signal level over at least one upstream subchannel, preferably a plurality of upstream subchannels; the station further includes means for sending at least one ranging request message to the head-end controller over at least one upstream subchannel; the ranging request message of messages has / have a signal level that is lower than the first signal level of the data stream; the ranging request message or messages is / are being transmitted using repetition coding enabling the head-end controller to detect the ranging request message or messages having a signal level lower than the first signal level of the data stream; the repetition coding is selected for enhancing the level of spectral containment of the ranging request message(s) and for reducing interference with transmission over adjacent upstream subchannels.
Owner:IBM CORP
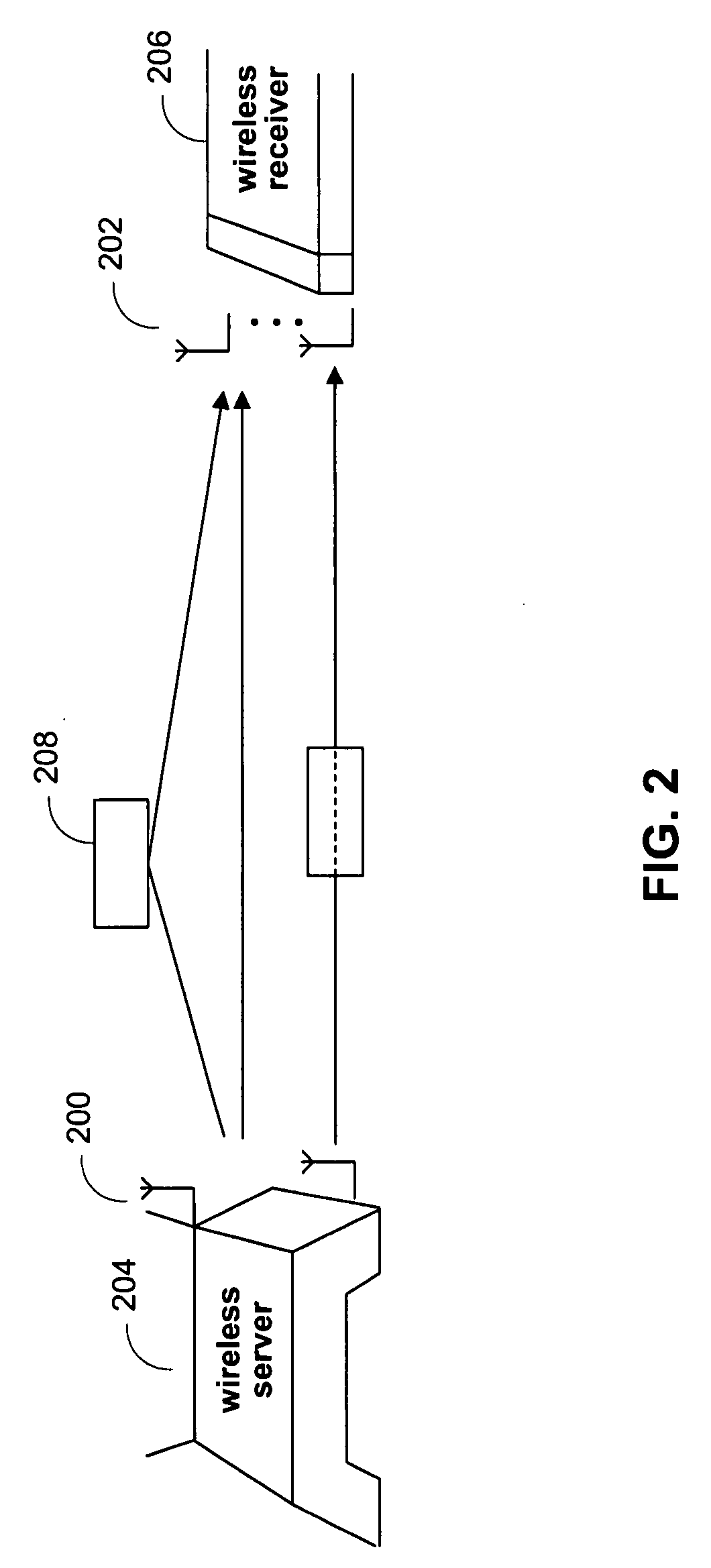
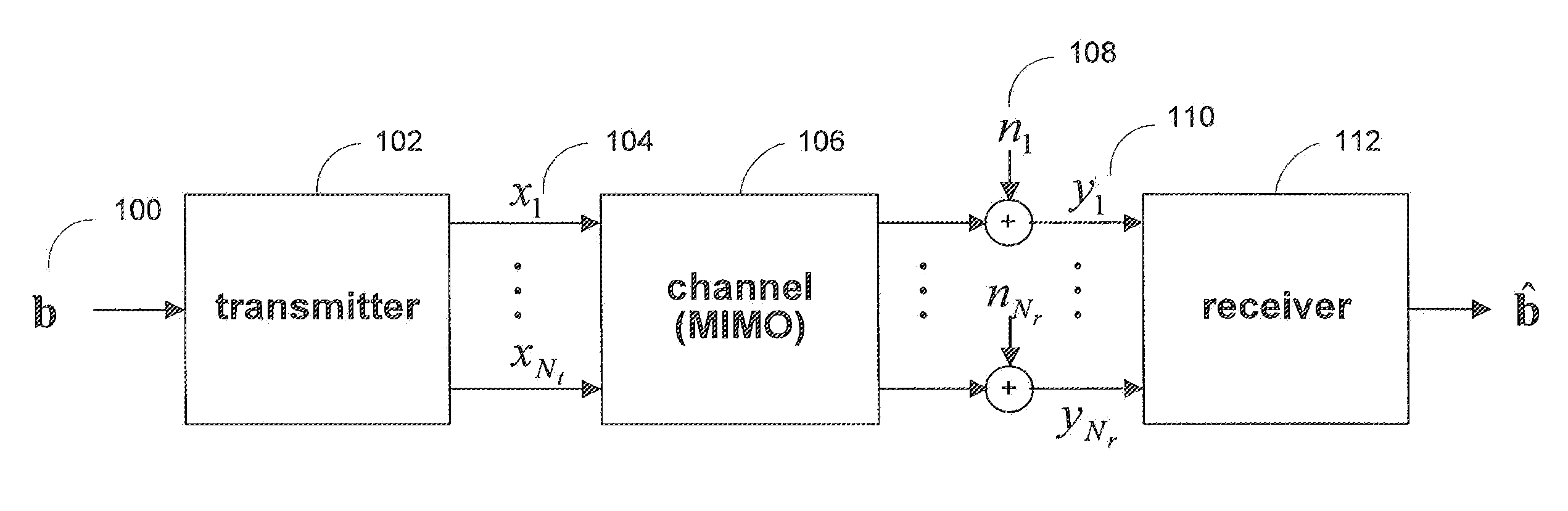
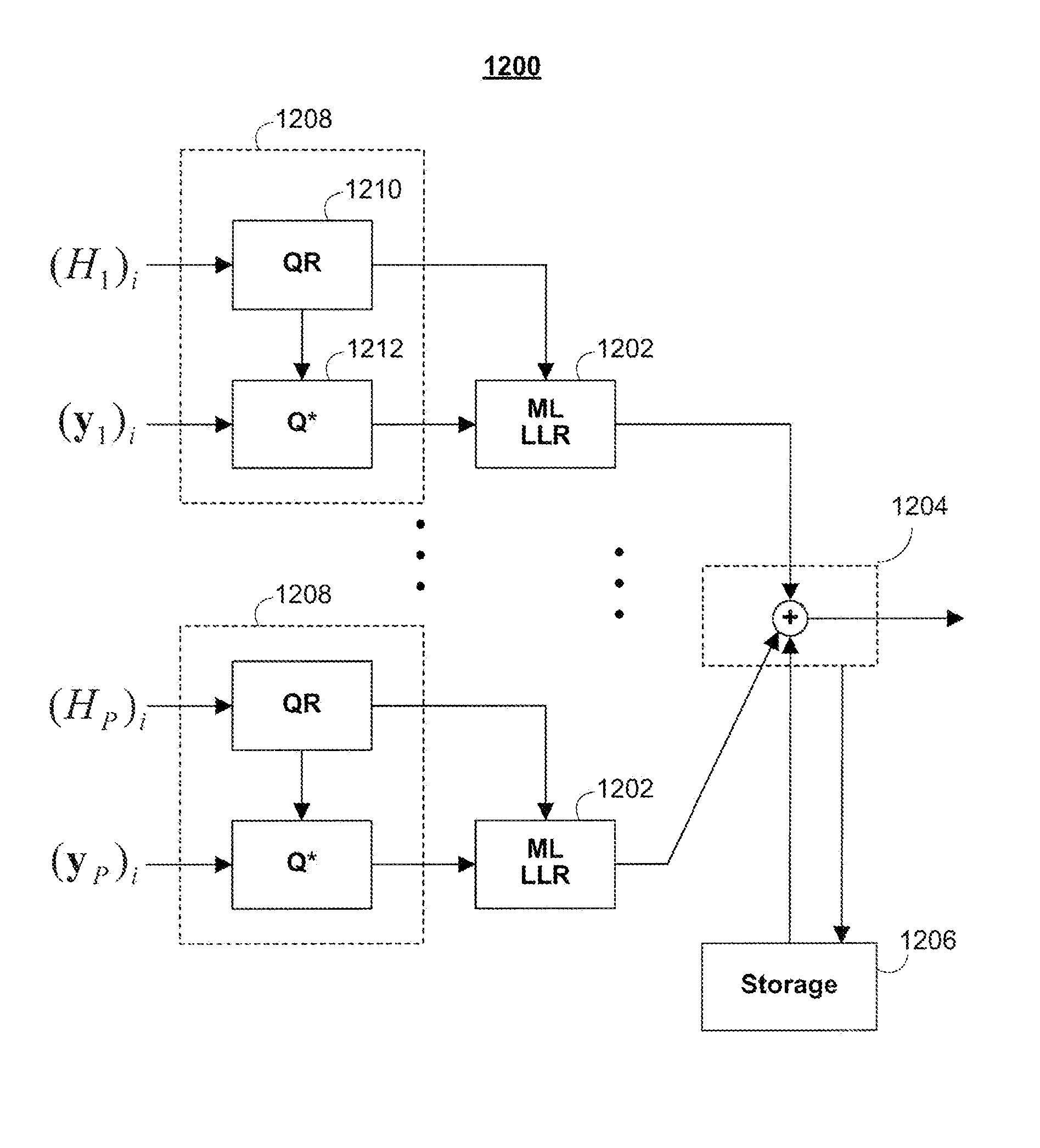
Concatenation-assisted symbol-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS20080025429A1Reduce receiver complexityReduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityMimo systemsComputer science
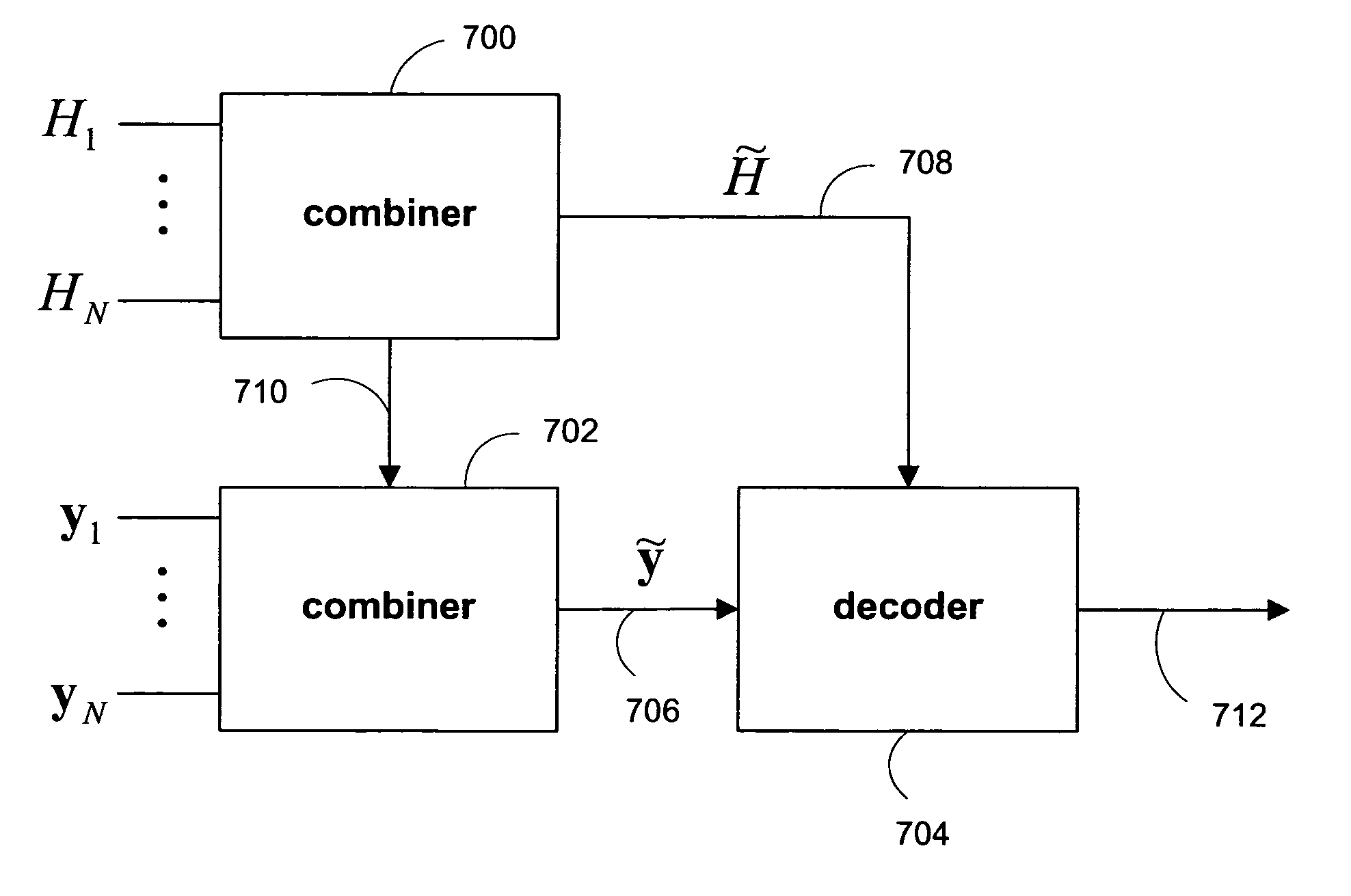
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from the same transmitted vector. The receiver combines the received vectors by vector concatenation The concatenated vector may then be decoded using, for example, maximum-likelihood decoding. In some embodiments, the combined signal vector is equalized before decoding.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Symbol-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS20080025427A1Reduce decoding complexityWhitens noiseSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCritical path methodMimo systems
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from the same transmitted vector. The symbols of the received signal vectors are combined, forming a combined received signal vector that may be treated as a single received signal vector. The combined signal vector is then decoded using a maximum-likelihood decoder. In some embodiments, the combined received signal vector may be processed prior to decoding. Systems and methods are also provided for computing soft information from a combined signal vector based on a decoding metric. Computationally intensive calculations can be extracted from the critical path and implemented in preprocessors and / or postprocessors.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Multicarrier DS/CDMA system using a turbo code with nonuniform repetition coding
ActiveUS20040202138A1Increase the number ofReduce fadingError correction/detection using convolutional codesCode conversionProgramming languageConvolutional code
The present invention relates to a multicarrier direct sequence code division multiple access (DS / CDMA) system using a turbo code with nonuniform repetition coding. In particular, it relates to a multicarrier DS / CDMA system using a turbo code with unequal diversity order in its code symbols instead of using a convolutional code.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
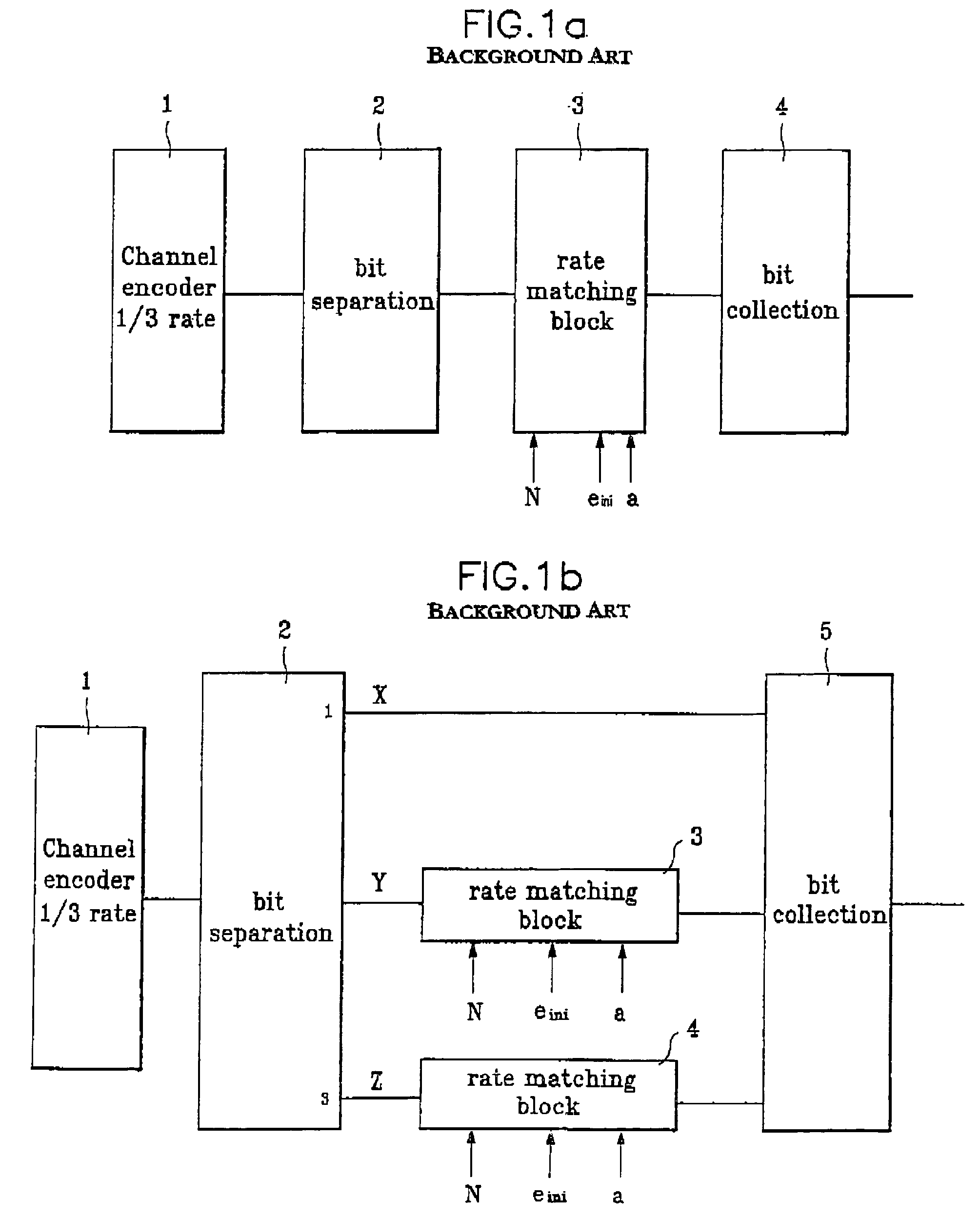
Method for matching rate in mobile communication system
InactiveUS7076726B1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionCode division multiple accessMobile communication systems
A method for matching a rate in a mobile communication system causes puncturing or repetition in a fixed pattern, in which puncturing or repetition is applied to each bitstream on transport channels supporting different services in a next generation mobile communication system of the W-CDMA (Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) system. The method comprises the steps of (1) subjecting a bitstream on a transport channel for use in supporting a particular service to channel coding, (2) determining an initial error offset value for use in avoiding all the puncturing only in a particular bitstream among one or more than one bitstreams produced by the channel coding, (3) periodically subtracting a decrement from the determined initial error offset value, for puncturing a bit at a relevant position when a result of the subtraction satisfies a puncturing condition, (4) adding an update error parameter determined as the maximum bit size among TF (Transport Format) transportable during one TTI (Transport Time Interval) of the transport channel after the puncturing to a result of the subtraction, for updating an initial error offset value, and (5) periodically subtracting a decrement from the updated initial error offset value, for determining a position of a relevant bit to be punctured at the next time.
Owner:3G LICENSING SA
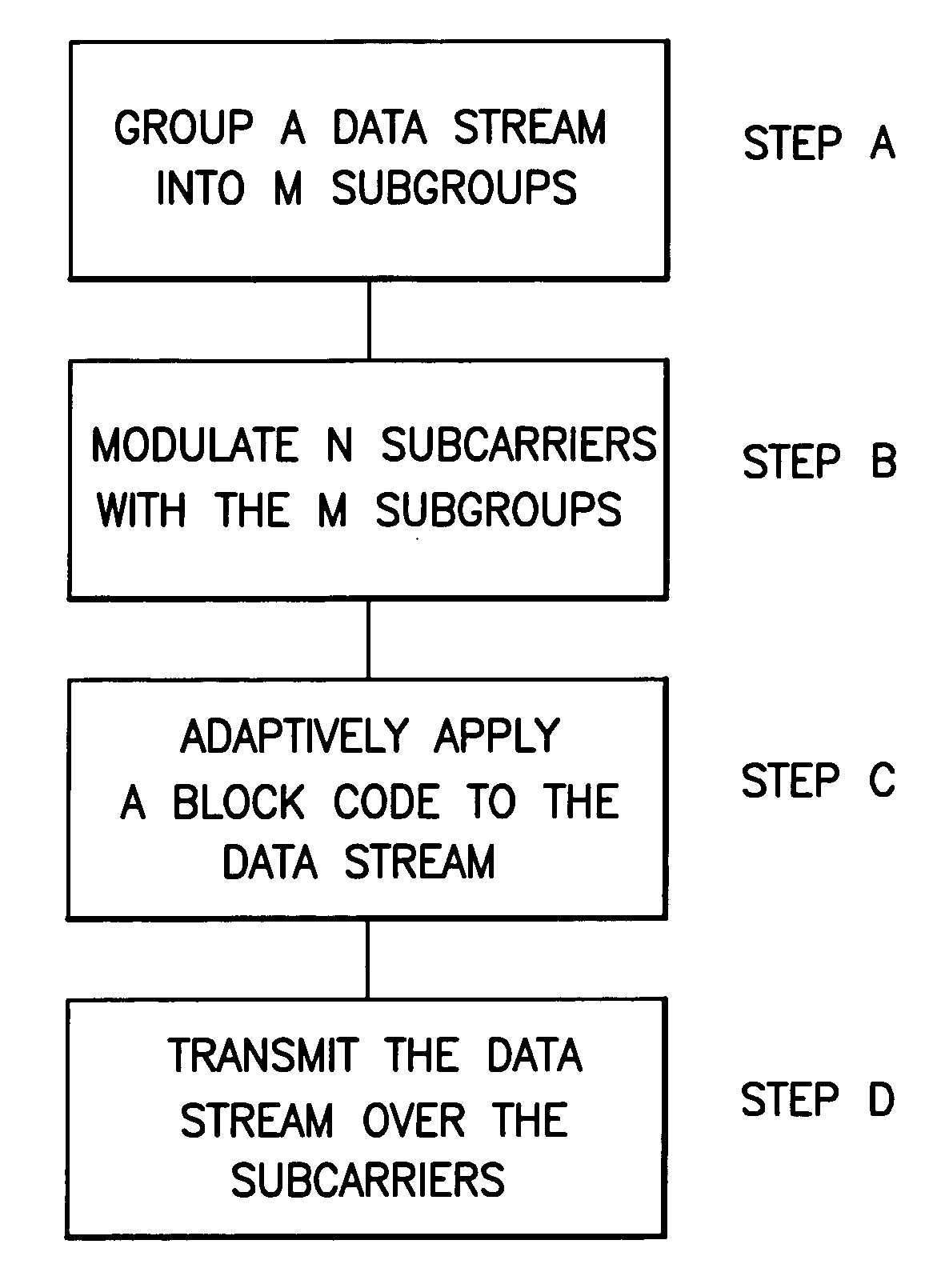
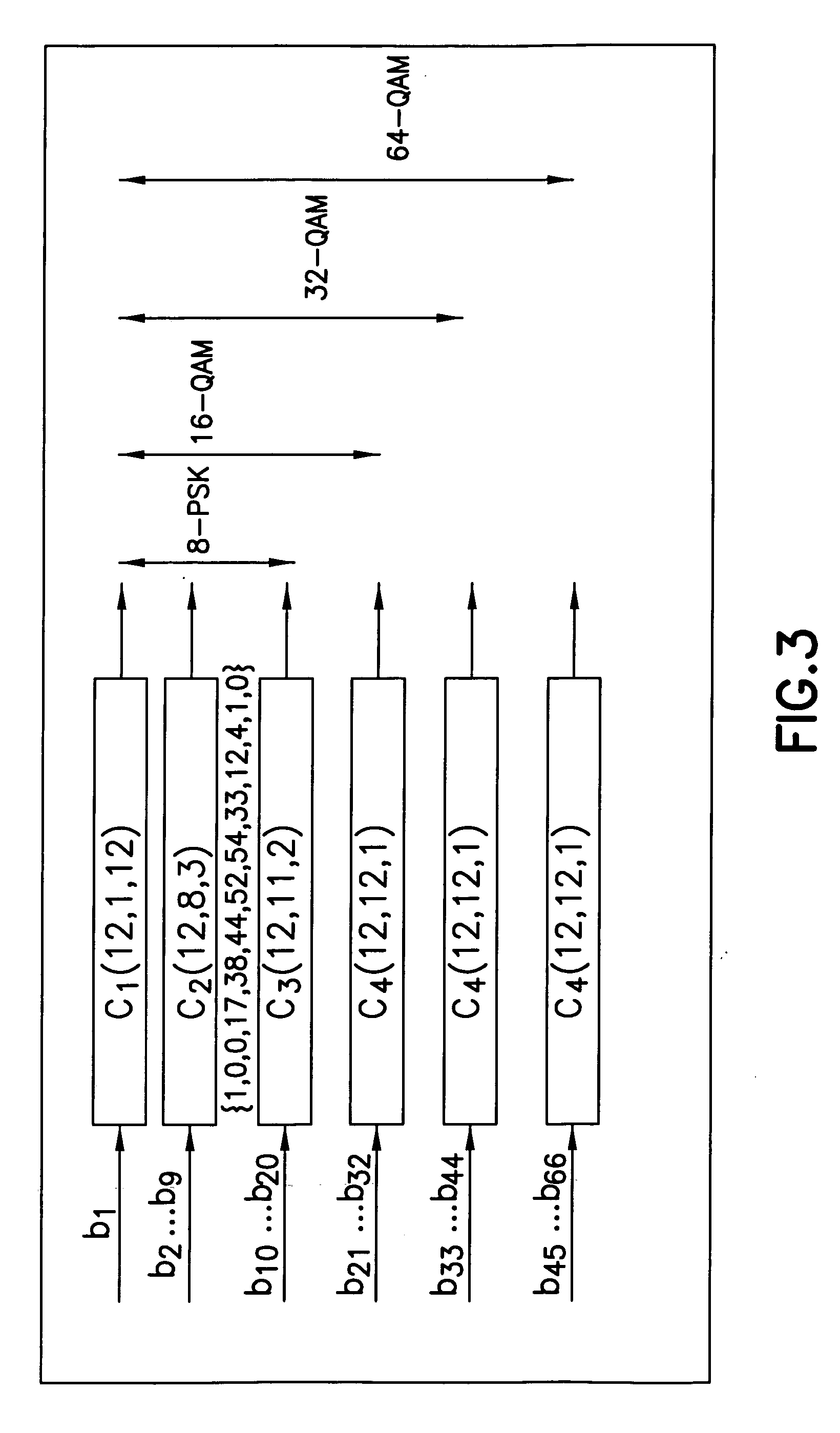
Adaptive multilevel block coded modulation for OFDM systems
InactiveUS20070019753A1Multiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsError correction/detection using block single space codingHamming codeData stream
A method includes grouping a data stream into a first plurality of subgroups, modulating a plurality of subcarriers with the first plurality of subgroups, adaptively applying a block code to said data stream comprising a repetition code, a Hamming code, and a plurality of uncoded bits based upon a channel characteristic of each of said plurality of subcarriers, and transmitting the data stream on the plurality of subcarriers.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
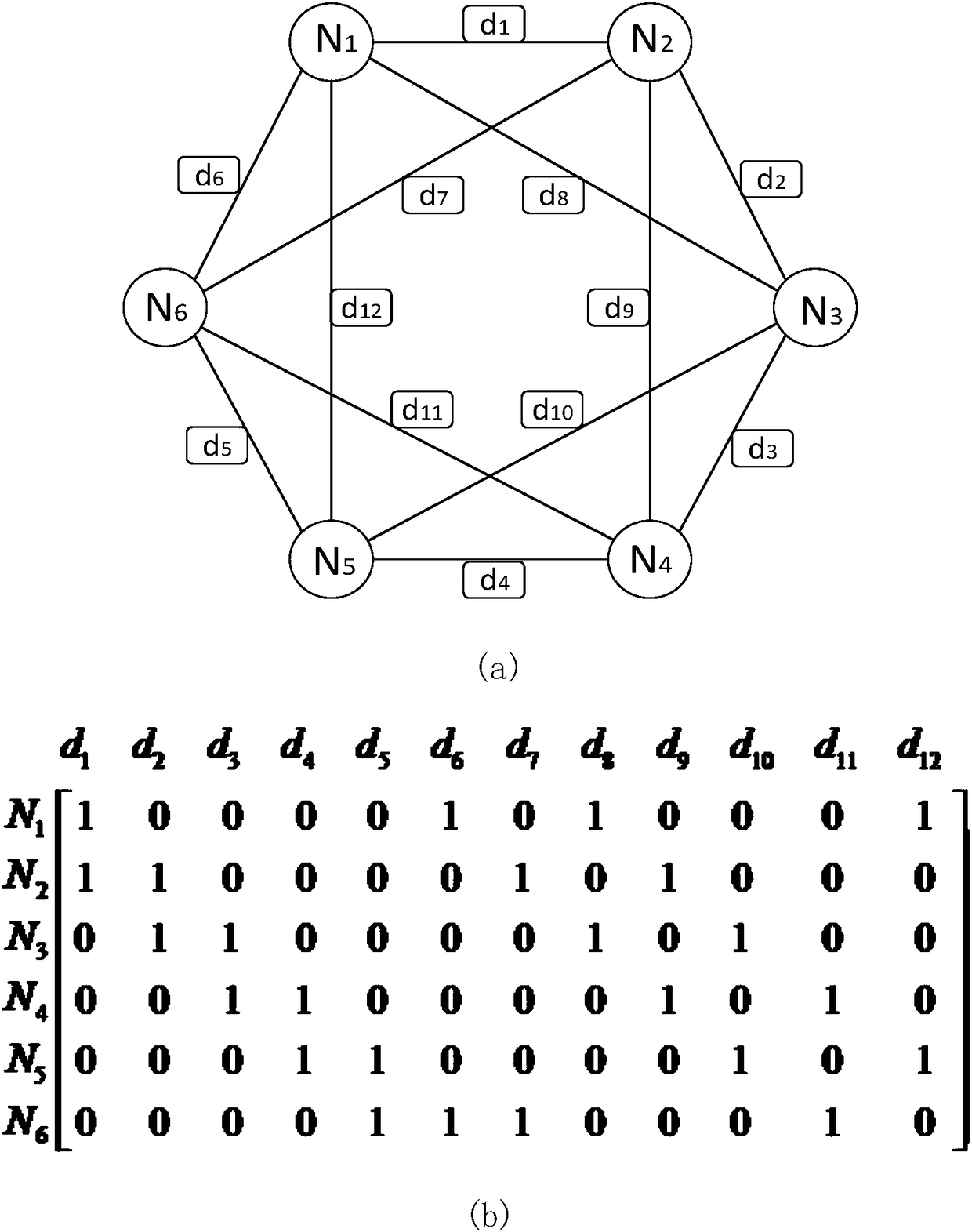
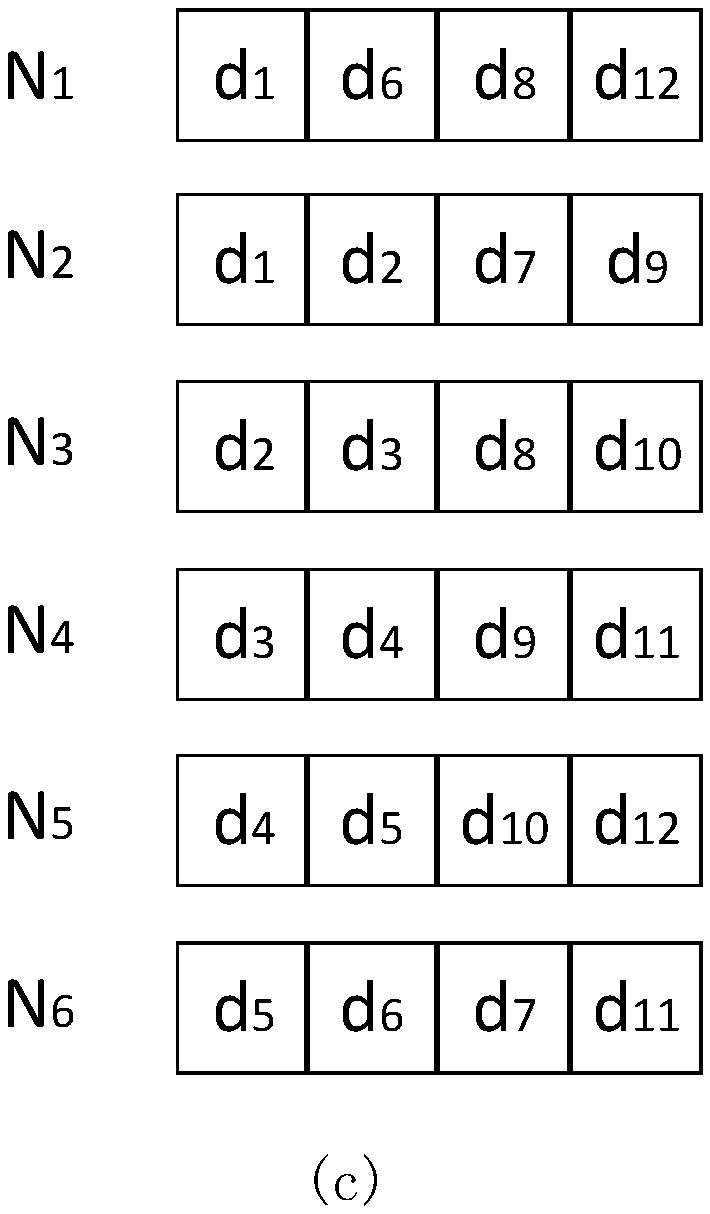
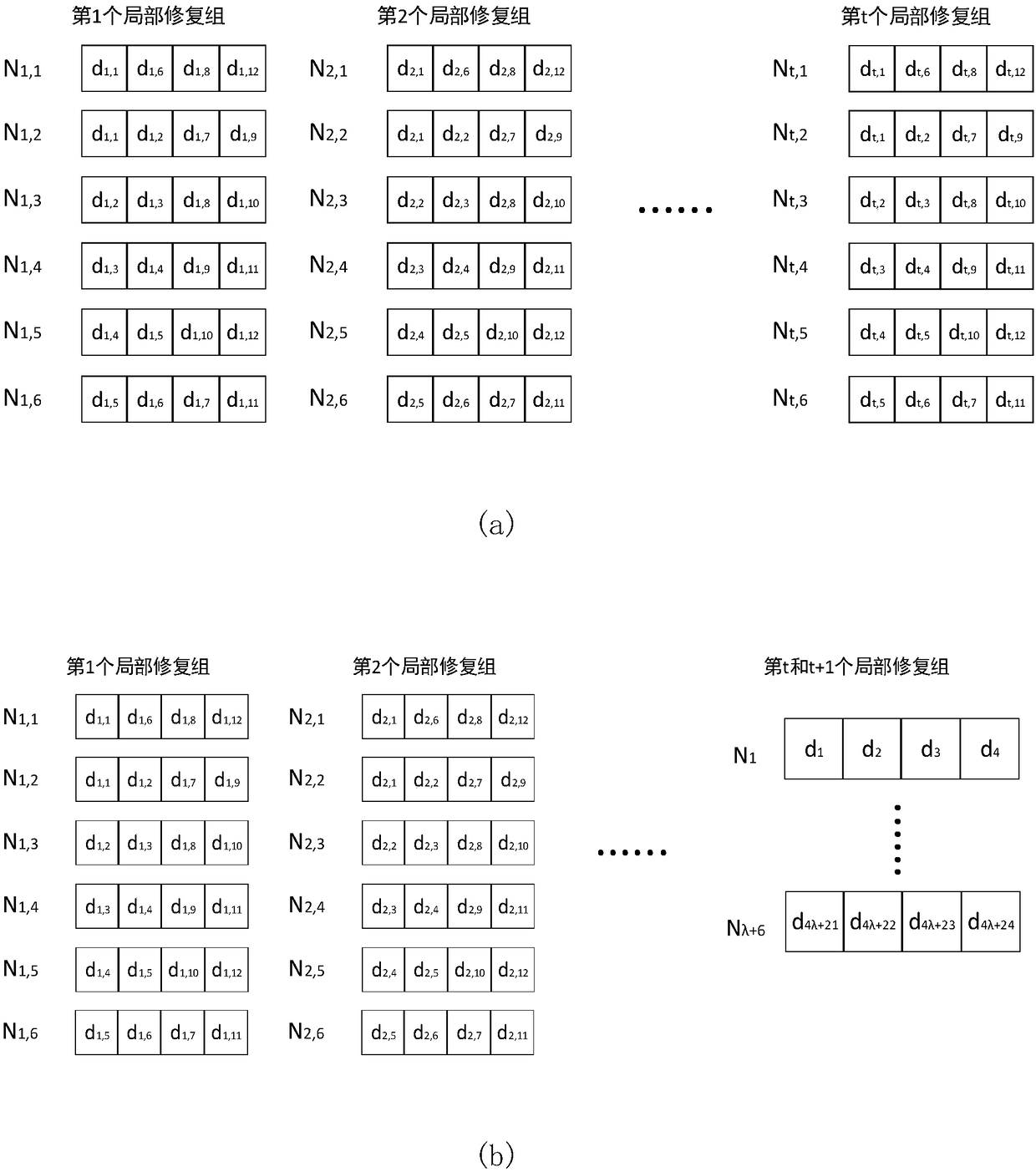
Local repairing coding method based on fractional repetition codes and node failure repairing method
ActiveCN108540520AGuaranteed Storage OverheadControl the amount of stored dataForward error control useData switching networksAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a local repairing coding method based on fractional repetition codes and a node failure repairing method, the local repairing coding method based on the fractional repetition codes is used for realizing storage of data, the number of nodes in a local repairing group and the quantity of stored data in the local repairing group can be controlled, and thus, storage overhead ofthe nodes can be guaranteed; and when single node failure and two-node failure exist in the local repairing group, data reconstruction of the failed nodes in the local repairing group can be realizedquickly just by finite live nodes in the local repairing group, and data of the failed nodes can be recovered quickly.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
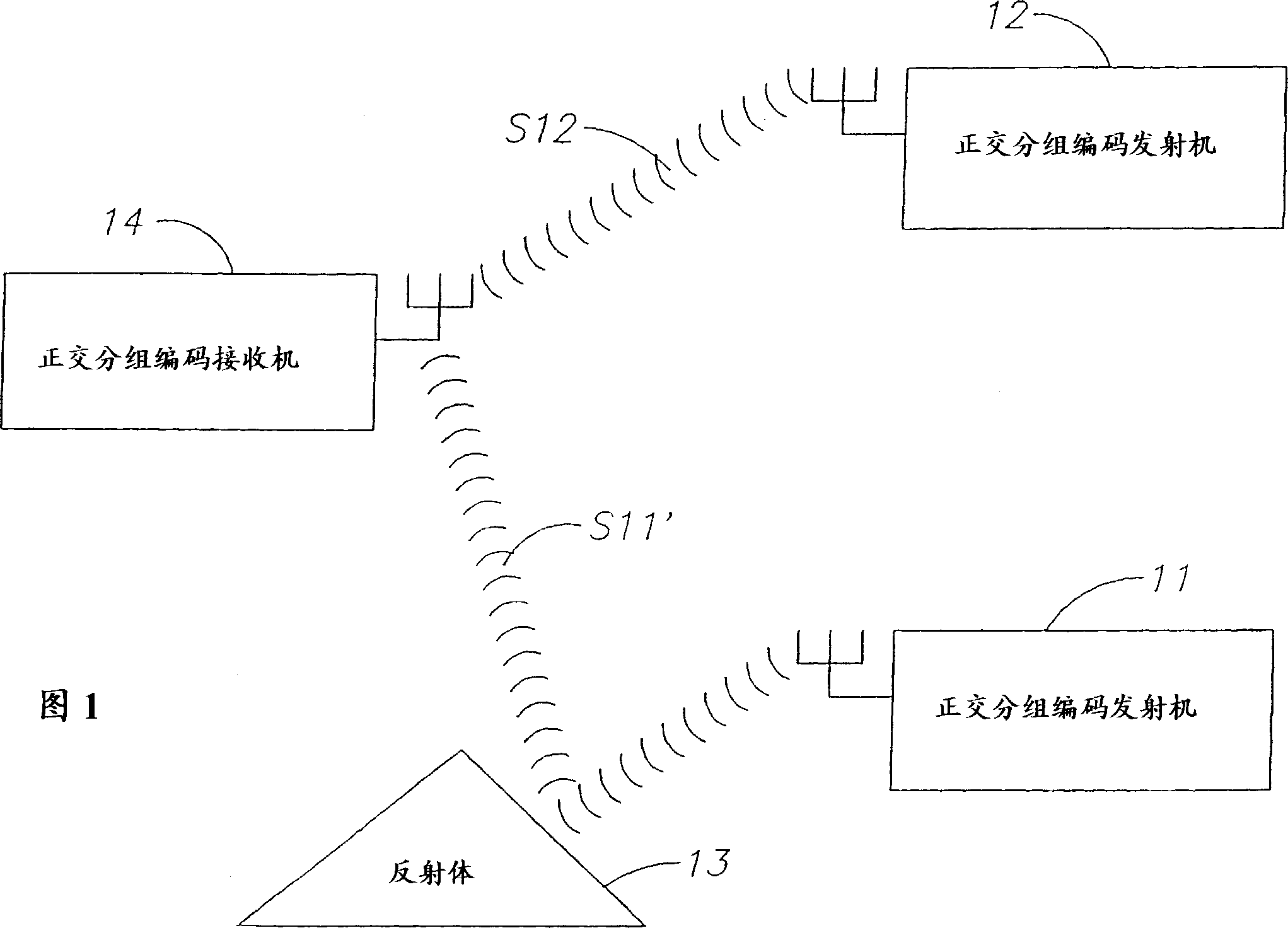
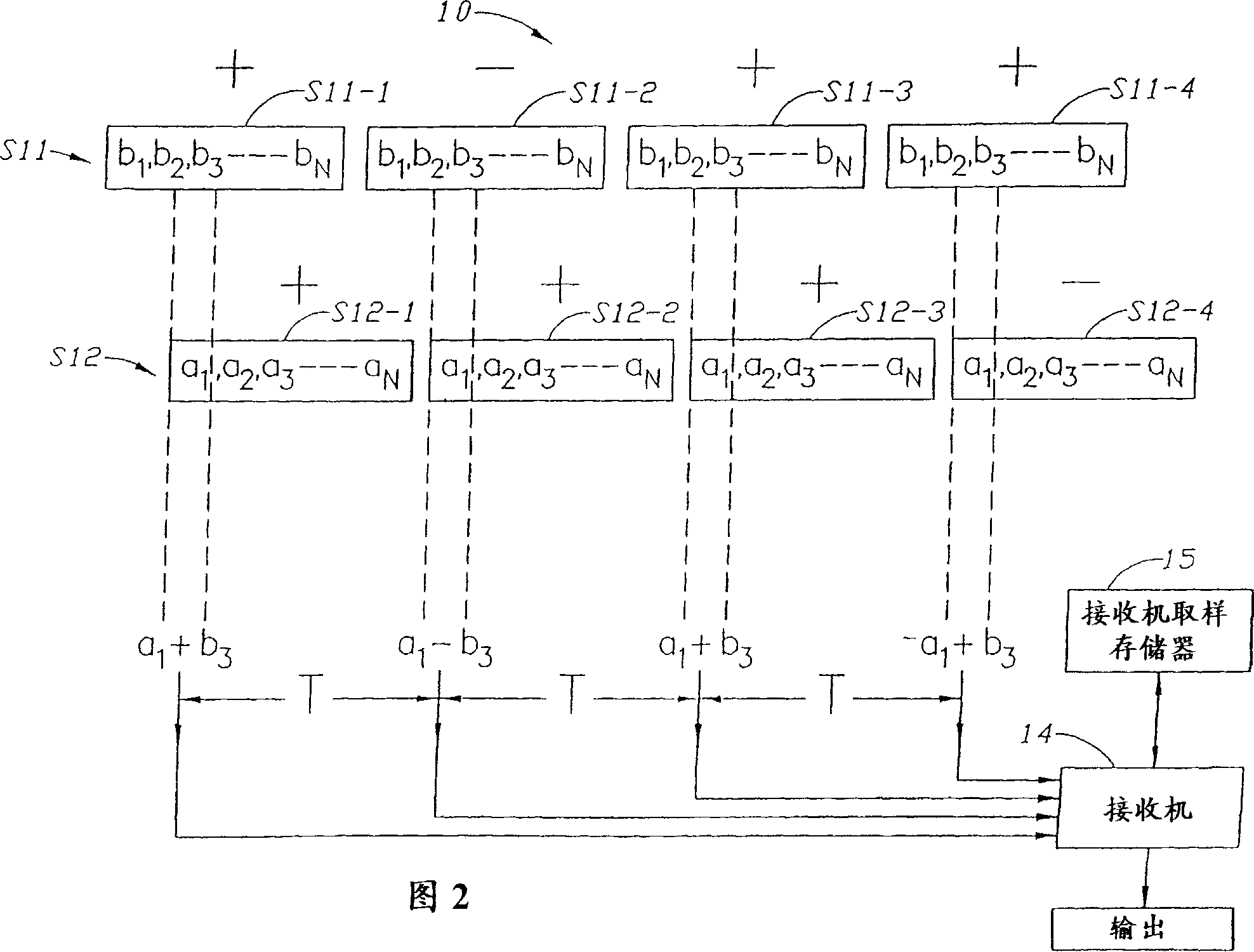
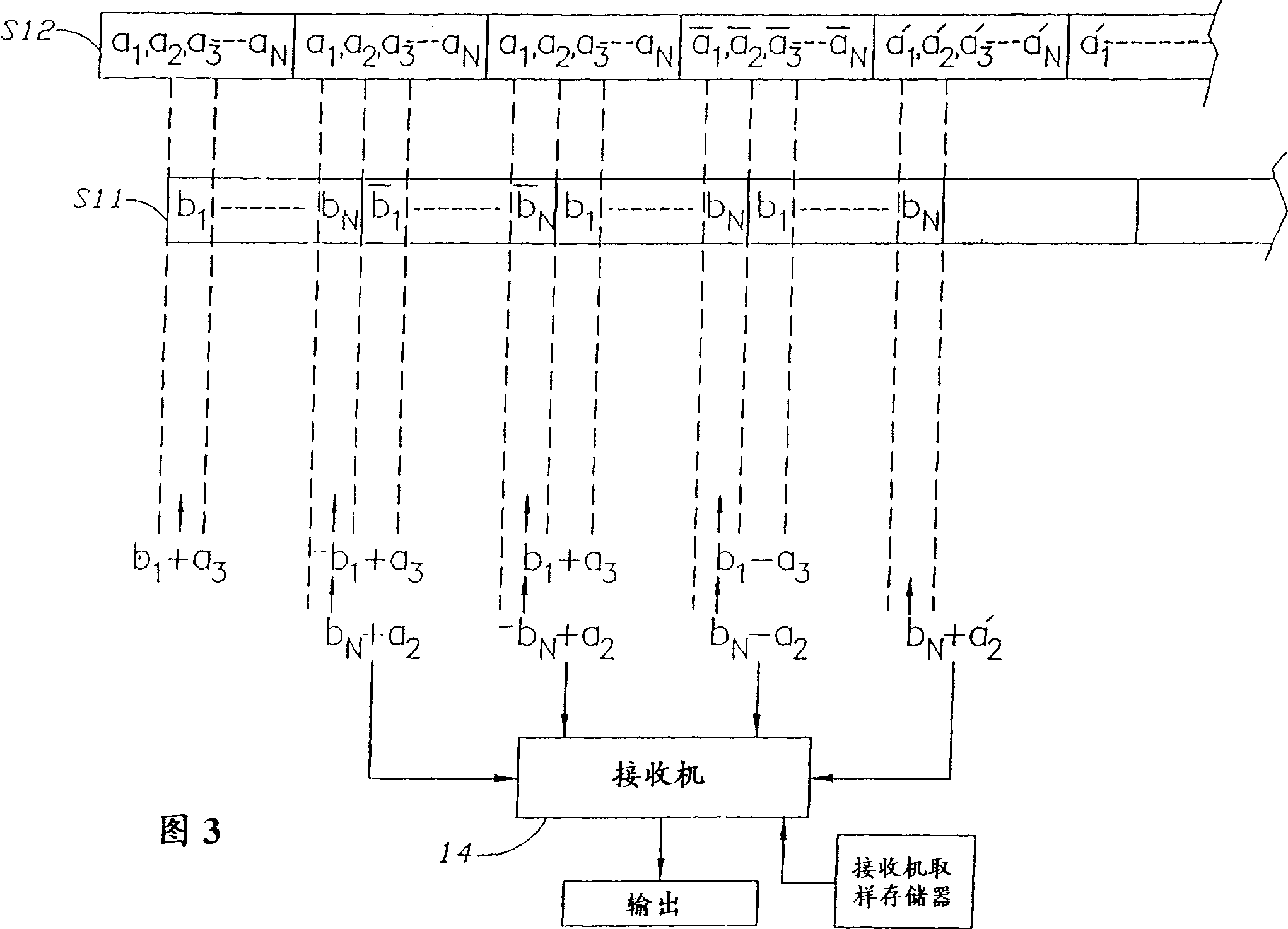
Communication system and method with orthogonal block encoding
A communication system and method with orthogonal, block encoding is provided. Encoded signals are transmitted by repeating transmissions of symbol blocks with a phase or sign change selected for each block from a sequence of phase or sign changes. Different symbols are transmitted using orthogonal sequences. The decoding uses different orthogonal sequences for separating the received encoded signals into corresponding separate channels. The orthogonal encoding is removed from the encoded transmitted signals and corresponding ones of the repeated symbols are added in successively received repeated blocks after the orthogonal encoding is removed. A transmitter uses a digital source encoder to encode information into symbols, and each symbol is repeated a preselected number of times to successively produce groups of repeated bits. Each repeat bit is changed in phase or sing by application of a sign or phase change determined by a selected assigned orthogonal code associated with the transmitter. The sign changed bits are interleaved from a number of such groups to successively generate a number of blocks, each composed of the different sign or phase changed bits of the preselected number of repeated groups and having a collective sign or phase change corresponding to a common sign change or phase shared by all bits of the block. The interleaved blocks then modulate a radio signal for transmission.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Infrared remote control, infrared code learning method and infrared code emission method
InactiveCN103426292AWith continuous control functionNon-electrical signal transmission systemsInfraredRemote control
The invention discloses an infrared remote control, an infrared code learning method and an infrared code emission method to achieve the learning and the restoration of infrared code information of the infrared remote control. According to the infrared remote control, the infrared code learning method and the infrared code emission method, the infrared code information can be divided into non-repetition code information and repetition code information, repeatedly-transmitted code information in the infrared code information can be recognized through the learning method without analyzing the specific protocol of the infrared code information, and when the infrared code information is transmitted, the effect that a function key has the continuous control function when unceasingly pressed actually reoccurs. The infrared remote control can be provided with a plurality of function keys, infrared remote controls of different devices can conduct learning through the different function keys of one of the infrared remote controls, and the one of the infrared remote controls can control the plurality of devices.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
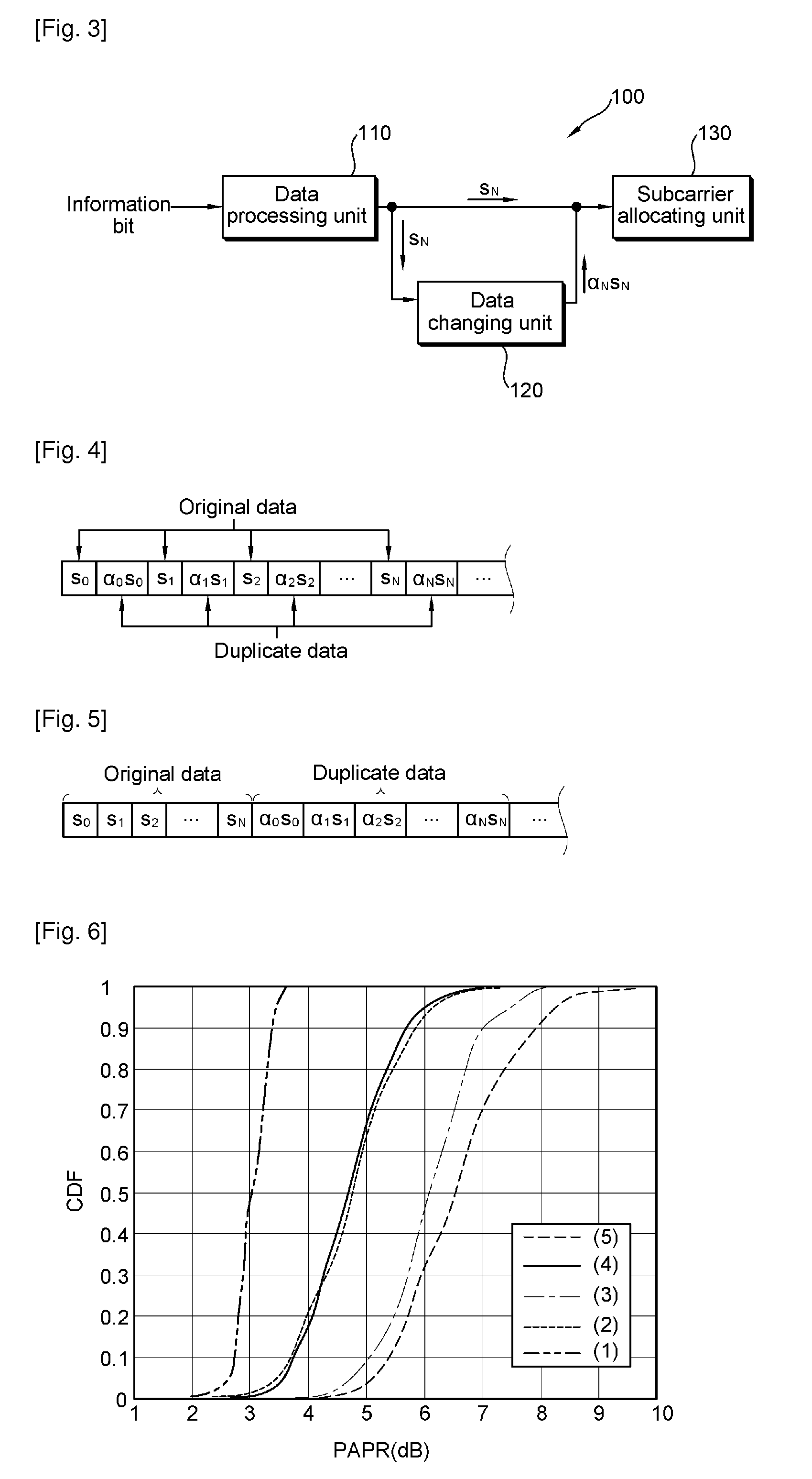
Method of Transmitting Data Using Repetition Coding
ActiveUS20100239046A1Reduce PAPRSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsPhase shiftedCommunications system
A method of transmitting data in a wireless communication system is provided. The method includes generating duplicate data by using repetition coding, the duplicate data being the same as original data, shifting the phase of the duplicate data, and transmitting the original data and the phase-shifted duplicate data. The duplicate data is mapped to a modulation symbol having a different size or phase as that of the original data, thus to reduce the PAPR unlike the general repetition coding.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
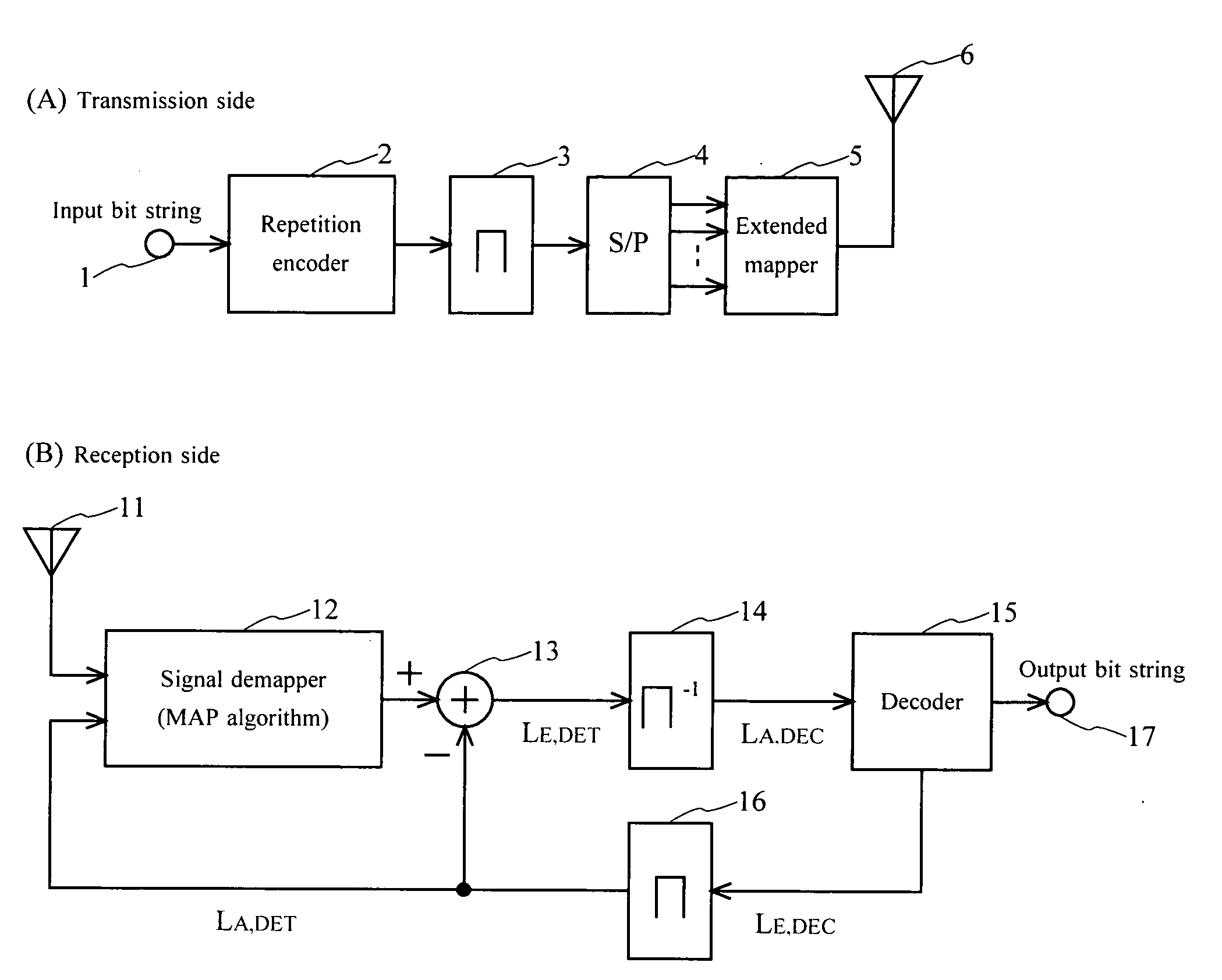
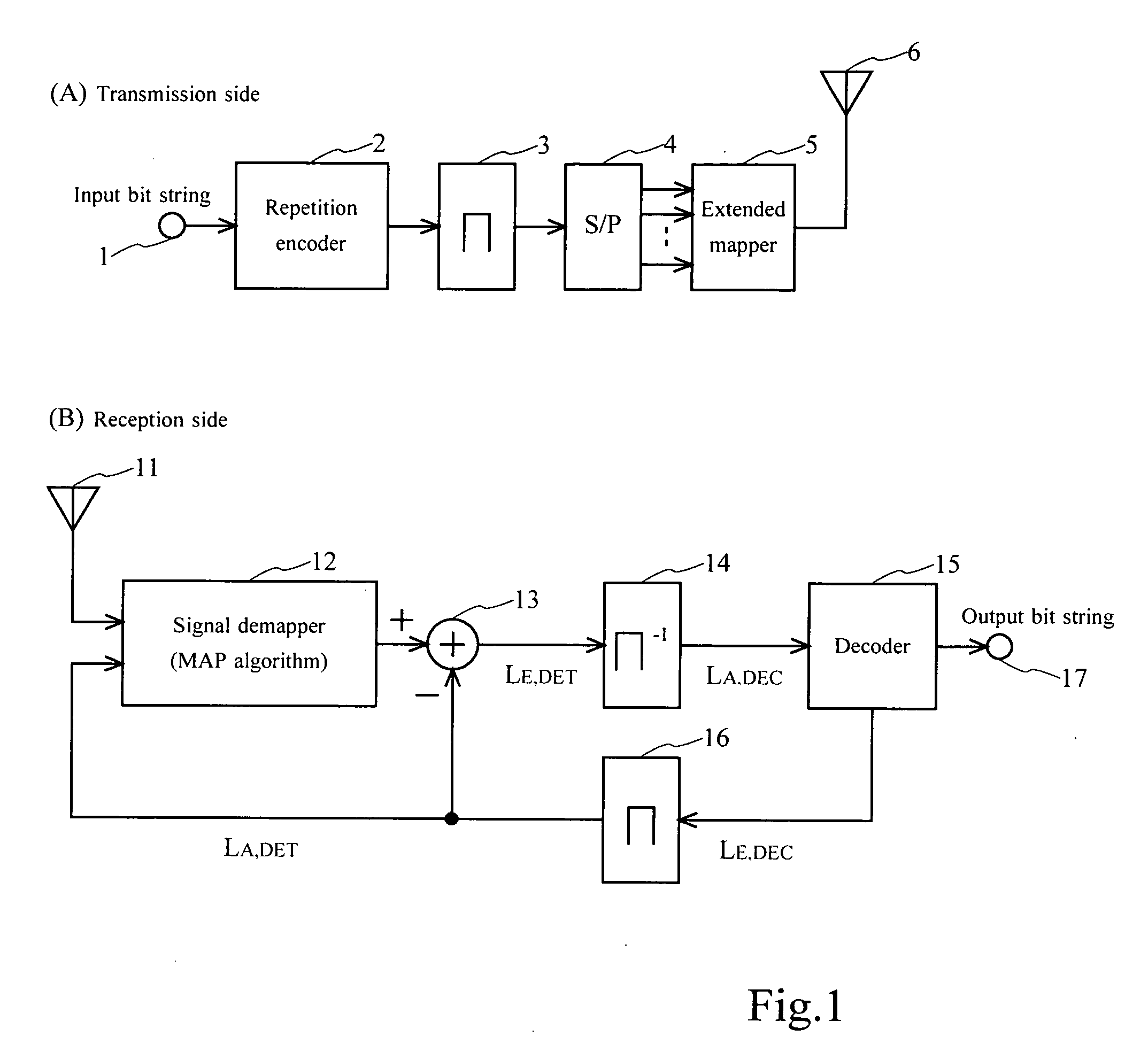
Communication system
InactiveUS20090245432A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationCommunications systemMutual information
A communication system receives a signal that is coded using a repetition encoder (2) in a transmitter side, thereafter extended-mapped by an extended mapper (5), and transmitted by a transmitter (6). A demapper (12) demaps the received signal, corresponding to the extended mapping. The decoding unit (15) decodes a result of the demapping, corresponding to the coding using the repetition code. Mutual information between the transmitter coded bits and the log likelihood ratios of the demapping and decoding results is increased by exchanging the likelihood ratio between the demapper (12) and the decoder (15).
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
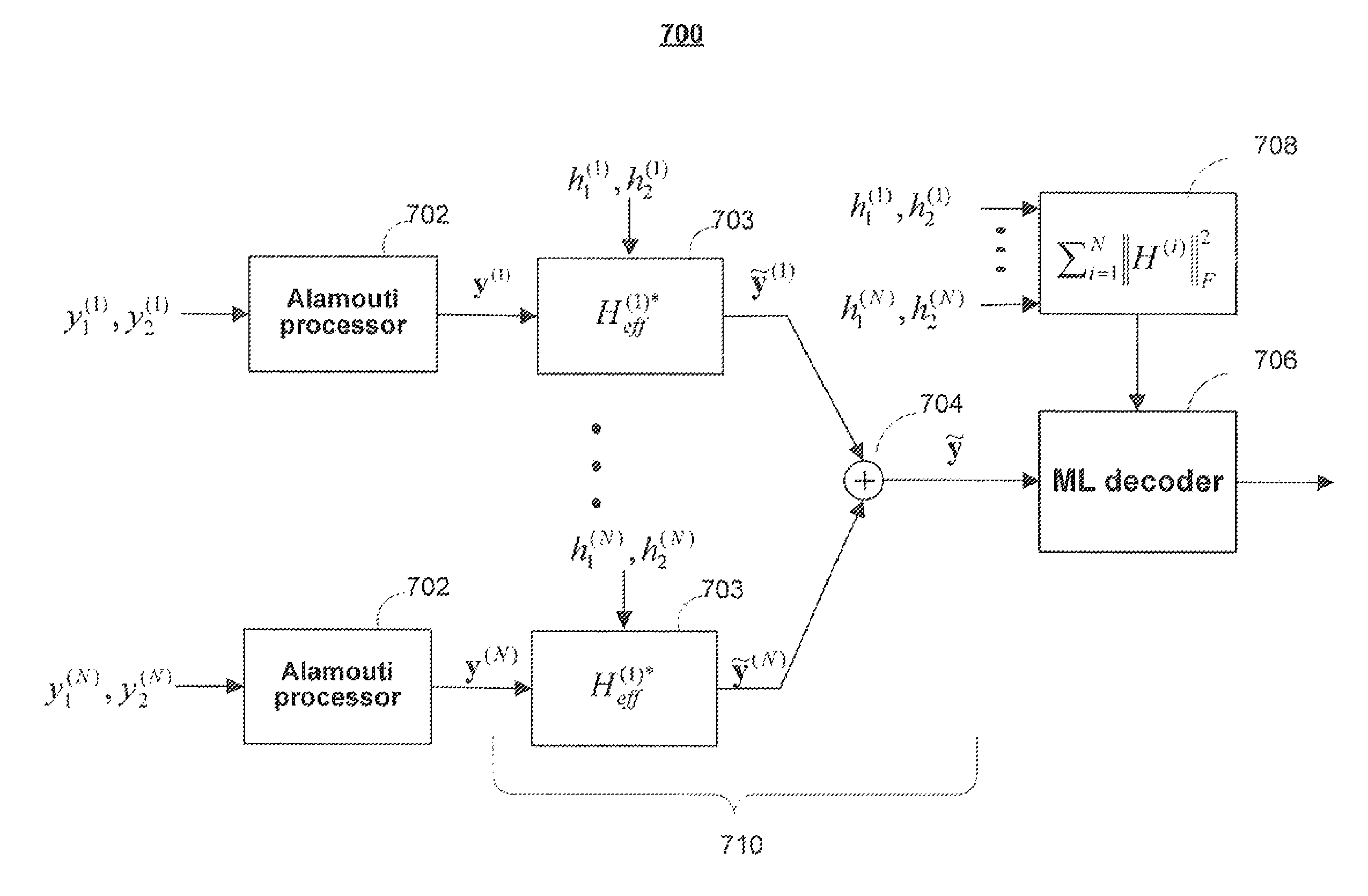
Decoding method for Alamouti scheme with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS8014470B2High data rateIncrease data ratePolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsDecoding methodsDiversity scheme
Systems and methods are provided for decoding a signal vector in a transmission scheme that uses transmit diversity as well as HARQ, repetition coding, or any other protocol that allows a receiver to obtain multiple reception of common transmit information. Information obtained in more than one symbol period are treated as a single received vector, and each of the received signal vectors may be processed to reduce or remove phase rotations caused by the channel. The received signal vectors may be combined by addition and decoded using a maximum-likelihood decoder. In some embodiments, the transmitter and receiver are configured to communicate using the transmit diversity scheme and a spatial multiplexing scheme. The scheme may be chosen based on the quality of the channel through which communication takes place.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Multiple streams using STBC with higher data rates and diversity gain within a wireless local area network
InactiveUS20050281349A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsMulti-frequency code systemsData streamData rate
A method of communicating data to M receiving antennas from N transmitting antennas, where M and N are integers, the method includes the steps of producing N data streams from outbound data, applying the N data streams to a space / time encoder to produce N encoded signals and transmitting the N encoded signals from N transmitting antennas. At least P transmitting antennas transmit space-time block-coded signals and (N-P) transmitting antennas transmit repetition code signals, where P is an integer. The transmission of the N encoded signals is performed such that the M receiving antennas receive at least three Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbols per tone.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Optimal linear equalizer for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS8411778B1Reduce complexityPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEqualizationMimo systems
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors based on the same transmitted vector. The symbols of the received signal vectors are combined, forming a combined received signal vector that may be treated as a single received signal vector. The combined received signal vector may be equalized by, for example, a zero-forcing or minimum-mean-squared error equalizer or another suitable linear equalizer. Following equalization, the equalized signal vector may be decoded using a simple, linear decoder.
Owner:NXP USA INC
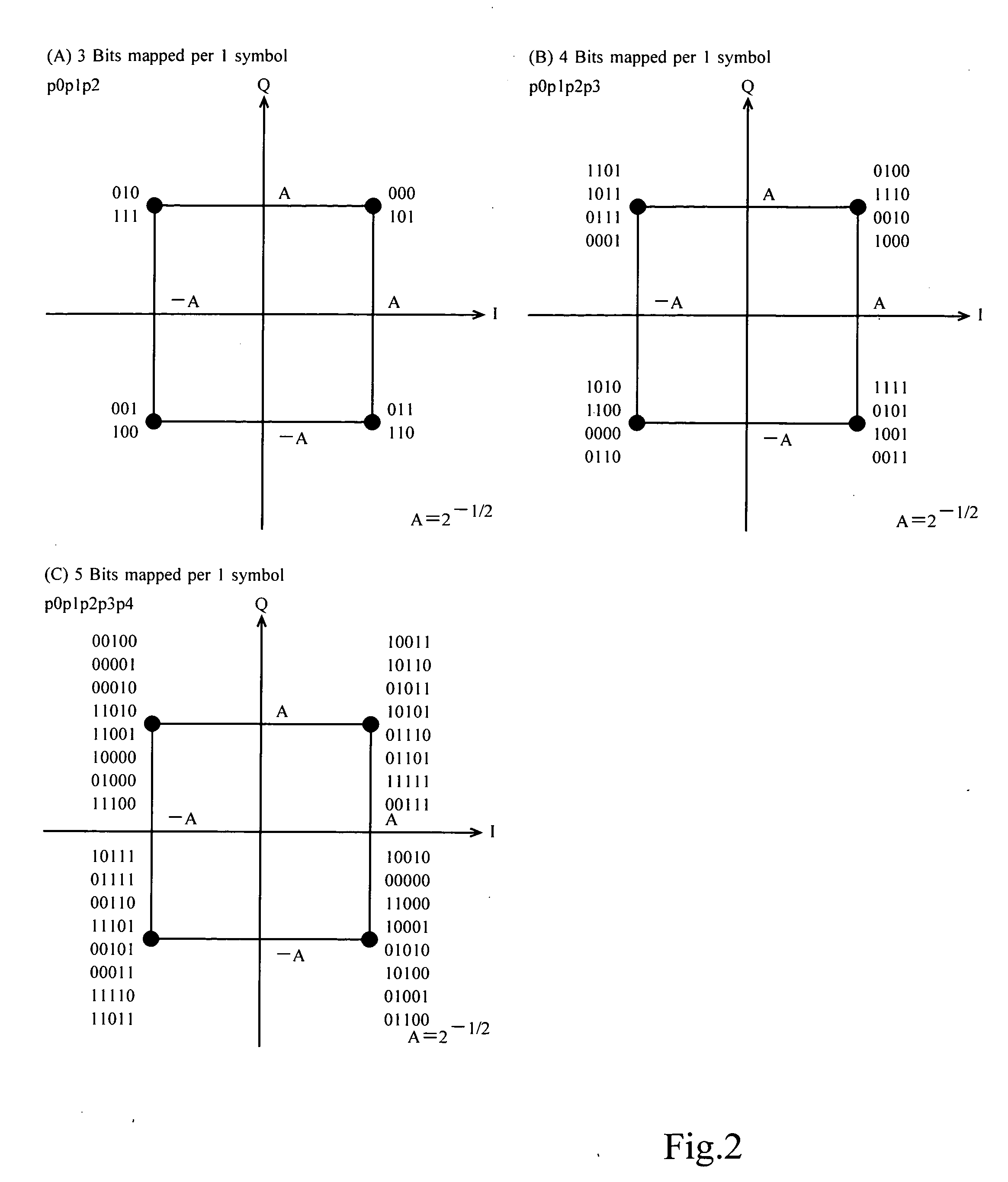
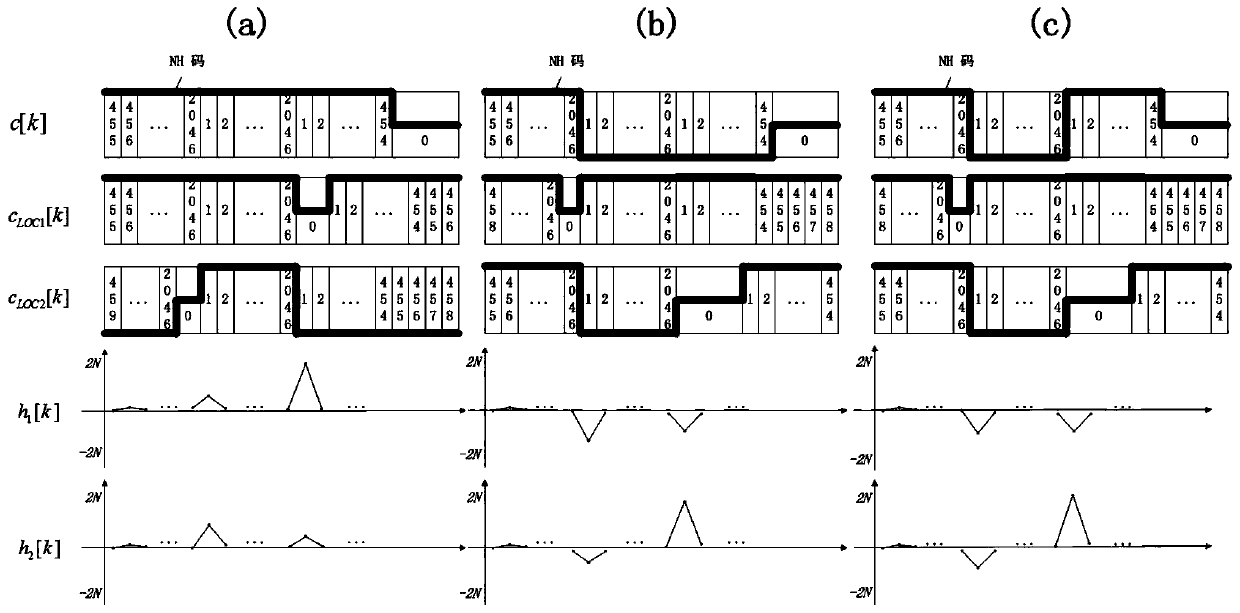
Symbol mapping method for repetition channel coding
ActiveUS20090175373A1DistanceMaximize distanceError prevention/detection by using return channelElectric signal transmission systemsComputer architectureResource block
A symbol mapping method for repetition coding is disclosed. The symbol mapping method comprises performing repetition coding on codeword to output repeated codeword symbols, and mapping the repeated codeword symbols with subcarriers located in different localized resource blocks. According to the embodiments of the present invention, it is possible to obtain maximum reliability in a receiving side by mapping codeword bits with subcarriers to reduce the number of bits having low reliability when a transmitting side uses repetition coding. Also, it is possible to improve decoding throughput and obtain channel diversity.
Owner:OPTIS CELLULAR TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for performing signal correlation
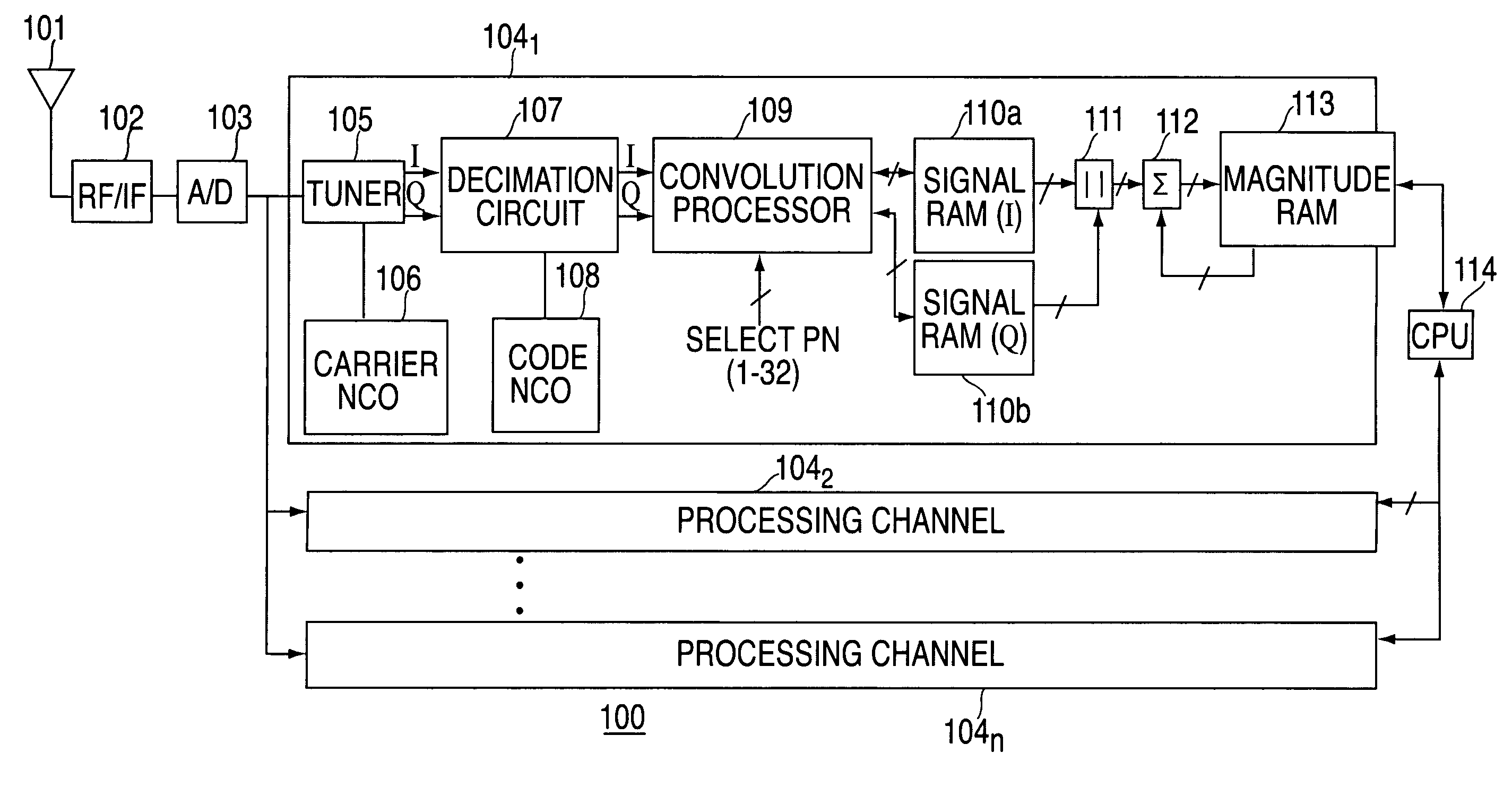
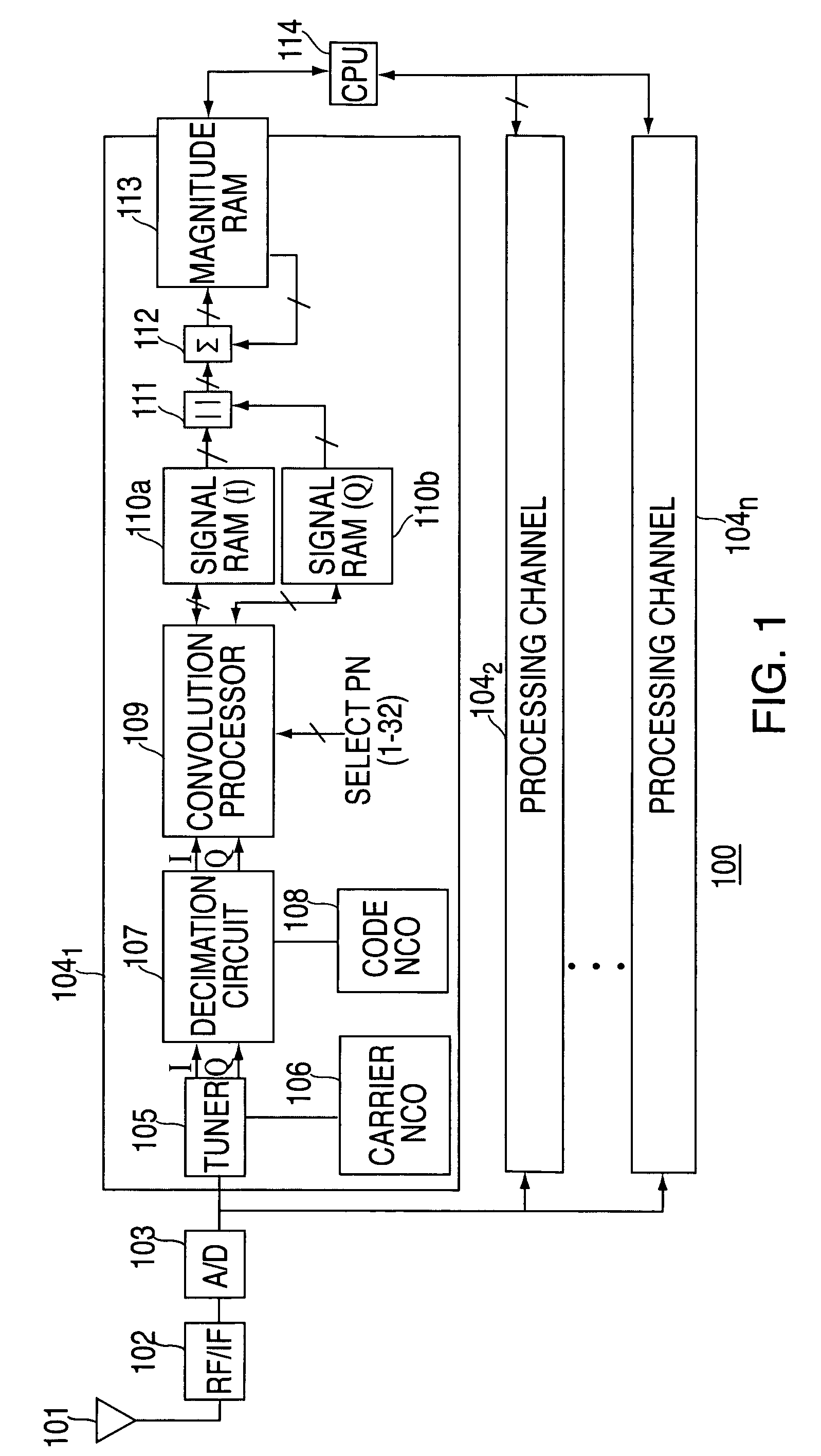
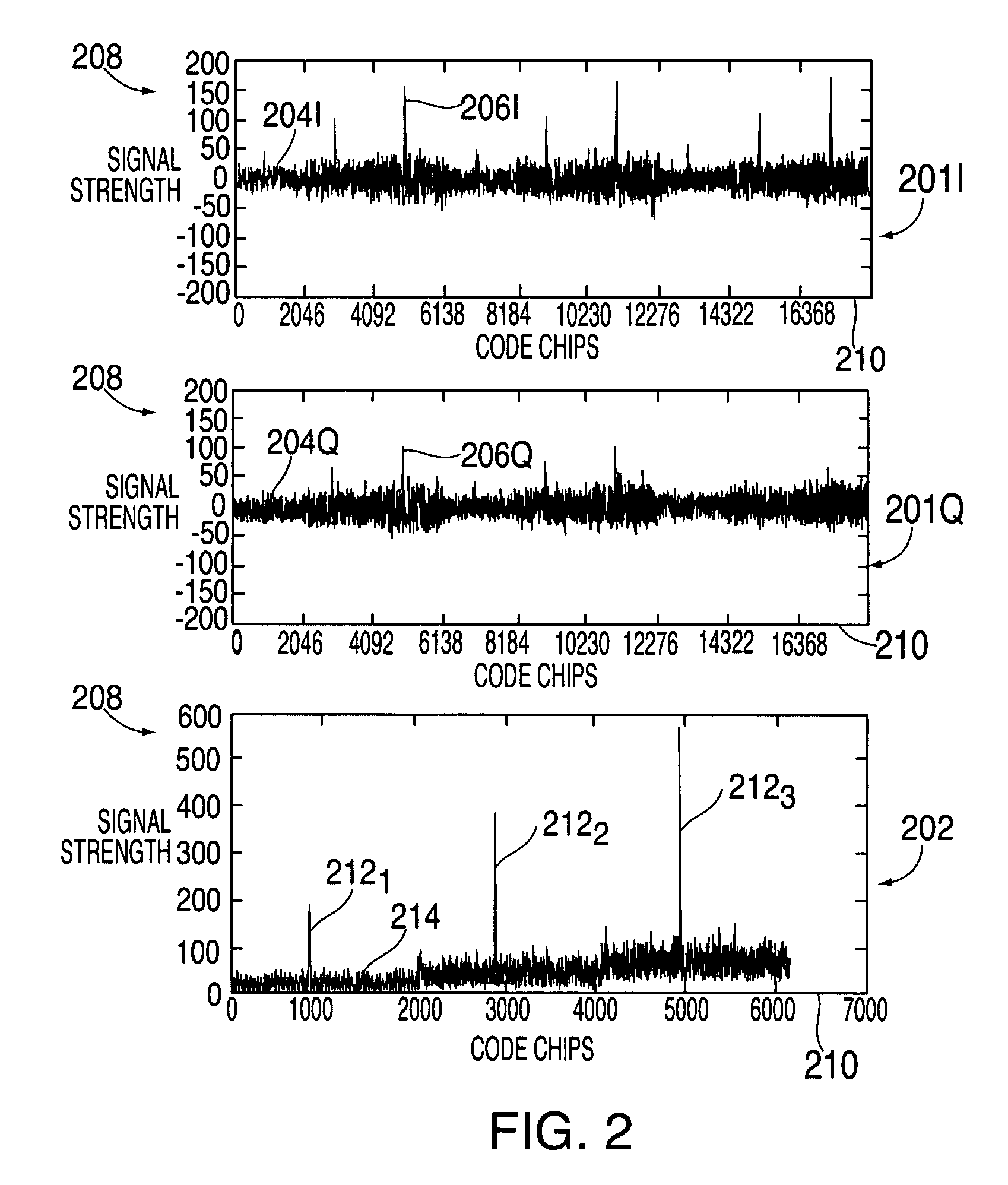
InactiveUS7190712B2Efficient retrievalIncrease clock frequencyBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationEngineeringSignal correlation
A method and apparatus for performing signal correlation is described. In one example, portions of a pseudorandom reference code are multiplied with portions of a repeating code of the digital signal to produce a plurality of inner products. The plurality of inner products are then integrated over a period less than a period of the repeating code to produce a correlation result with a broadened frequency response. In another example, the digital signal is correlated with a pseudorandom reference code to produce a first correlation. The digital signal is then correlated with the pseudorandom code reference code to produce a second correlation. The first and second correlations are then used to determine first and second signal delays. The frequency shift of the digital signal is computed using a difference between the first and second signal delays over time.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Beidou navigation system D1 navigation message capture method
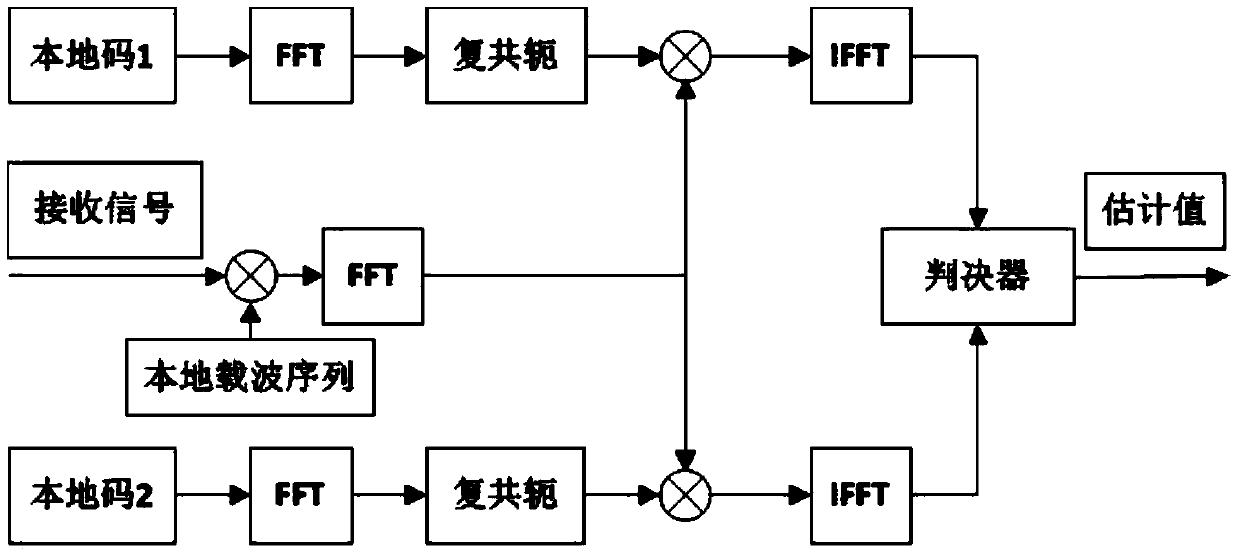
ActiveCN105005057AImprove efficiencyHigh gainSatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalNavigation system
The invention discloses a Beidou navigation system D1 navigation message capture method. The method can adapt to all kinds of bit jump, increases the coherent integral gain, eliminates erroneous carrier frequency estimation caused by correlation peak splitting, and can be used to effectively and reliably capture a Beidou navigation system D1 navigation message. The method comprises the following steps: multiplying the signal sequence of a received D1 navigation message containing interference by a local carrier complex sequence and carrying out frequency mixing to realize carrier Doppler frequency offset stripping; then, expanding a local repetition code in two ways at the same time to obtain a local repetition code A and a local repetition code B; performing correlation operation on each of the two local repetition codes and the frequency mixing result; judging the results of the two correlation operations to obtain a carrier Doppler frequency offset estimated value fd and a ranging code phase delay estimated value Tau; and capturing the D1 navigation message.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
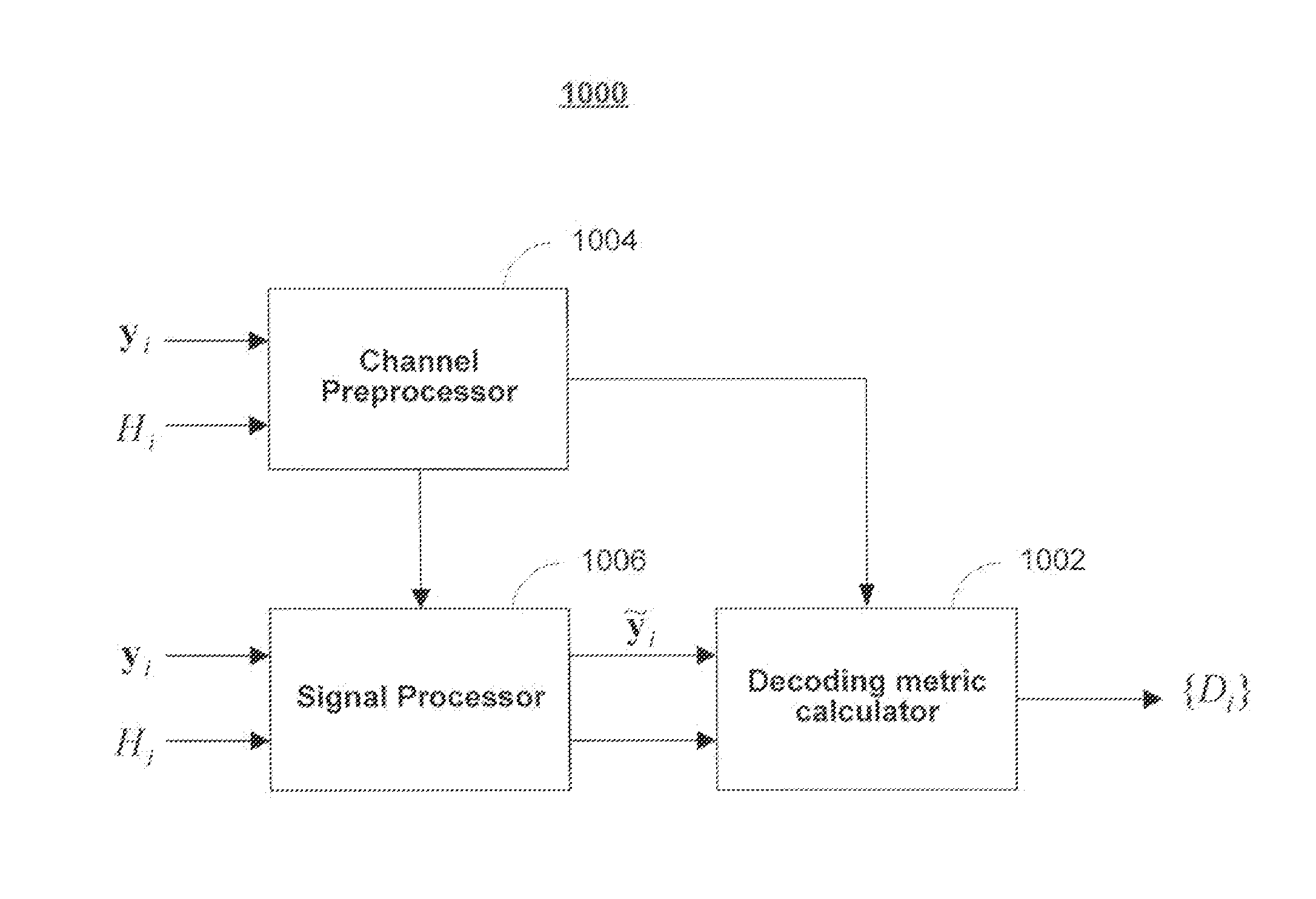
Bit-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS8929472B1Reduce complexityLow hardware requirementsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsRedundant data error correctionHardware complexityLog likelihood
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from a common digital information sequence. Each received signal vector is decoded using, for example, a maximum-likelihood decoder to produce log-likelihood ratios. The results of the decoders are combined by addition to produce a final decoding estimate. In some embodiments, each of the received signals may be processed prior to decoding. The disclosed decoding scheme may utilize all received information without increasing hardware complexity.
Owner:NXP USA INC
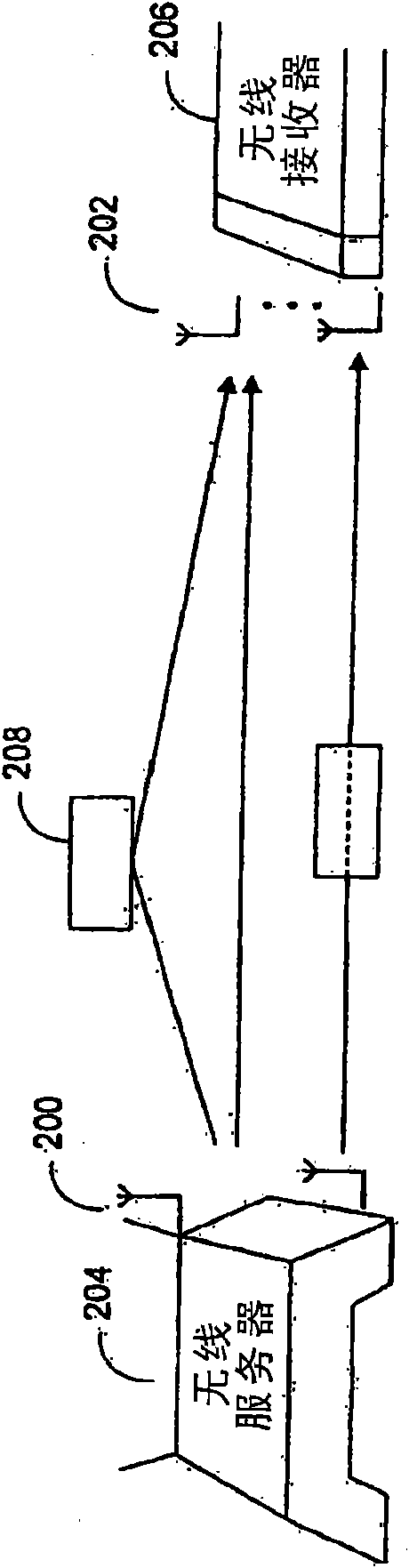
System and Method For Mitigating Burst Noise In A Communications System
ActiveUS20090327845A1Avoid packet lossImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemBlock code
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Concatenation-assisted symbol-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS8121209B2Reduce complexitySpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityMimo systemsMultiple input
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from the same transmitted vector. The receiver combines the received vectors by vector concatenation The concatenated vector may then be decoded using, for example, maximum-likelihood decoding. In some embodiments, the combined signal vector is equalized before decoding.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Symbol-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
InactiveCN101529782AError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityCholesky decompositionCritical path method
The present invention provides systems and methods for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from the same transmitted vector. The symbols of the received signal vectors are combine, forming a combined received signal vector that may be treated as a single received signal vector. The combined signal vector is then decoded using a maximum- likelihood decoder. In some embodiments, the combined received signal vector may be processed prior to decoding. Systems and methods are also provided for computing soft information from a combined signal vector based on a decoding metric. Computationally intensive calculations can be extracted from the critical path and implemented in preprocessors and / or postprocessors. One embodiment considers the MIMO HARQ reception using Cholesky decomposition or factoruzation of the metric.
Owner:MARVELL INT LTD
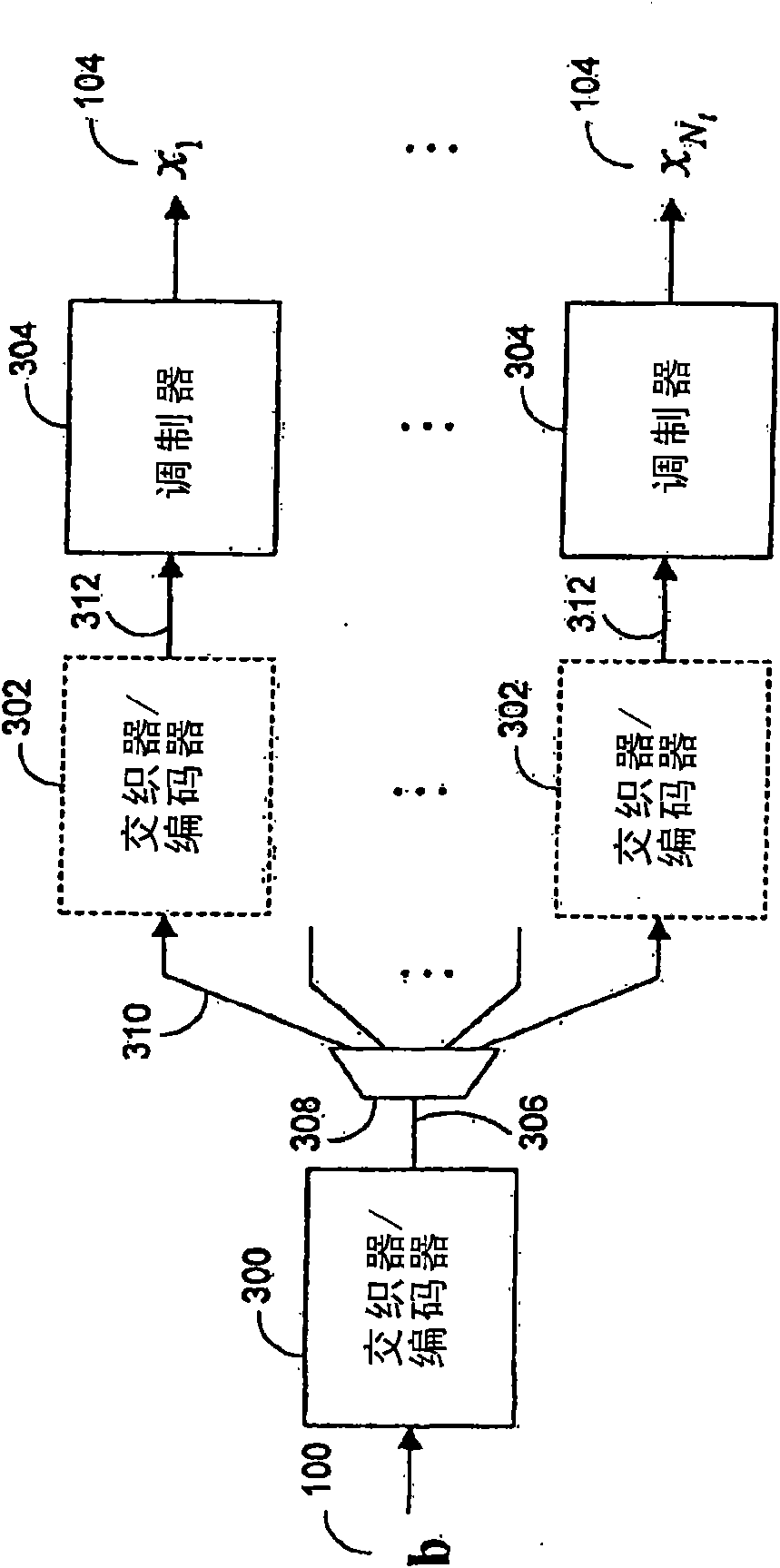
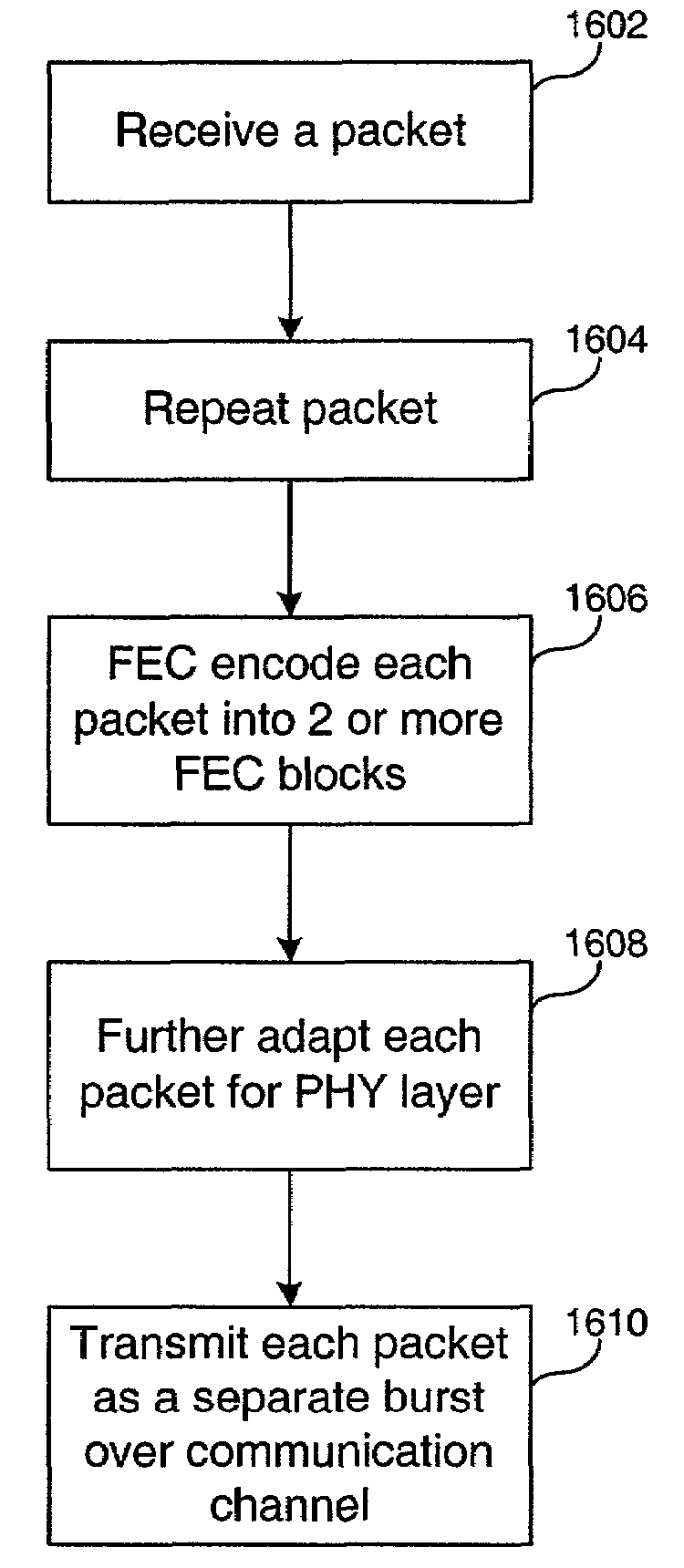
System, method and computer program product for mitigating burst noise in a communications system
ActiveUS7631242B2Reduce the impactIncrease robustness of communicationError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionCommunications systemBlock code
A system, method and computer program product is provided for mitigating the effects of burst noise on packets transmitted in a communications system. A transmitting device applies an outer code, which may include, for example, a block code, an exclusive OR (XOR) code, or a repetition code, to one or more packets prior to adaptation of the packets for transmission over the physical (PHY) layer of the communications system, wherein the PHY layer adaptation may include FEC encoding of individual packets. The outer coded packets are then separately transmitted over a channel of the communications system. A receiving device receives the outer coded packets, performs PHY level demodulation and optional FEC decoding of the packets, and then applies outer code decoding to the outer coded packets in order to restore packets that were erased during transmission due to burst noise or other impairments on the channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multi-rate code encoding method for grouped Markov superposition coding based on time division
ActiveCN104410428AImprove error correction performanceError correction/detection using convolutional codesError detection onlySingle parity checkSuperposition coding
The invention belongs to the fields of digital communication and digital storage and in particular relates to a multi-rate code encoding method for grouped Markov superposition coding based on time division. The method is used for encoding a binary information sequence u- with the length K being equal to (n-2)kBL into code words c- with the length N being equal to (n-2)nB(L+m<k>), wherein n is more than 2, k refers to a range of {1, 2,..., n-1}, namely a code rate set refers to {1 / n, 2 / n,..., (n-1) / n}, L is the number of (n-2)kB sequenced packets of equal length, m<k> is the memory length of subcodes with the code rate of k / n, and the memory length of an encoder is as shown in the specification. The method comprises the following steps: dividing the information sequence u- into L packets of equal length which are as shown in the specification, wherein t is equal to -1, -2,..., -(m<k>-1), -m<k>, and initializing a sequence v-(t) with the length of (n-2)nB; dividing a sequence which is as shown in the specification with the length of (n-2)kB into B packets at the moment t being equal to 0, 1,..., L-1 for performing time division encoding on [n, 1] repetition codes and [n, n-1] single parity check codes, thereby obtaining an encoding sequence which is as shown in the specification with the length of (n-2)nB; and calculating the t-th subsequence of the code words c- by combining the sequence as shown in the specification. The multi-rate codes based on time division provided by the invention are simple in design, wide in code rate range, low in decoding complexity and excellent in performance.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
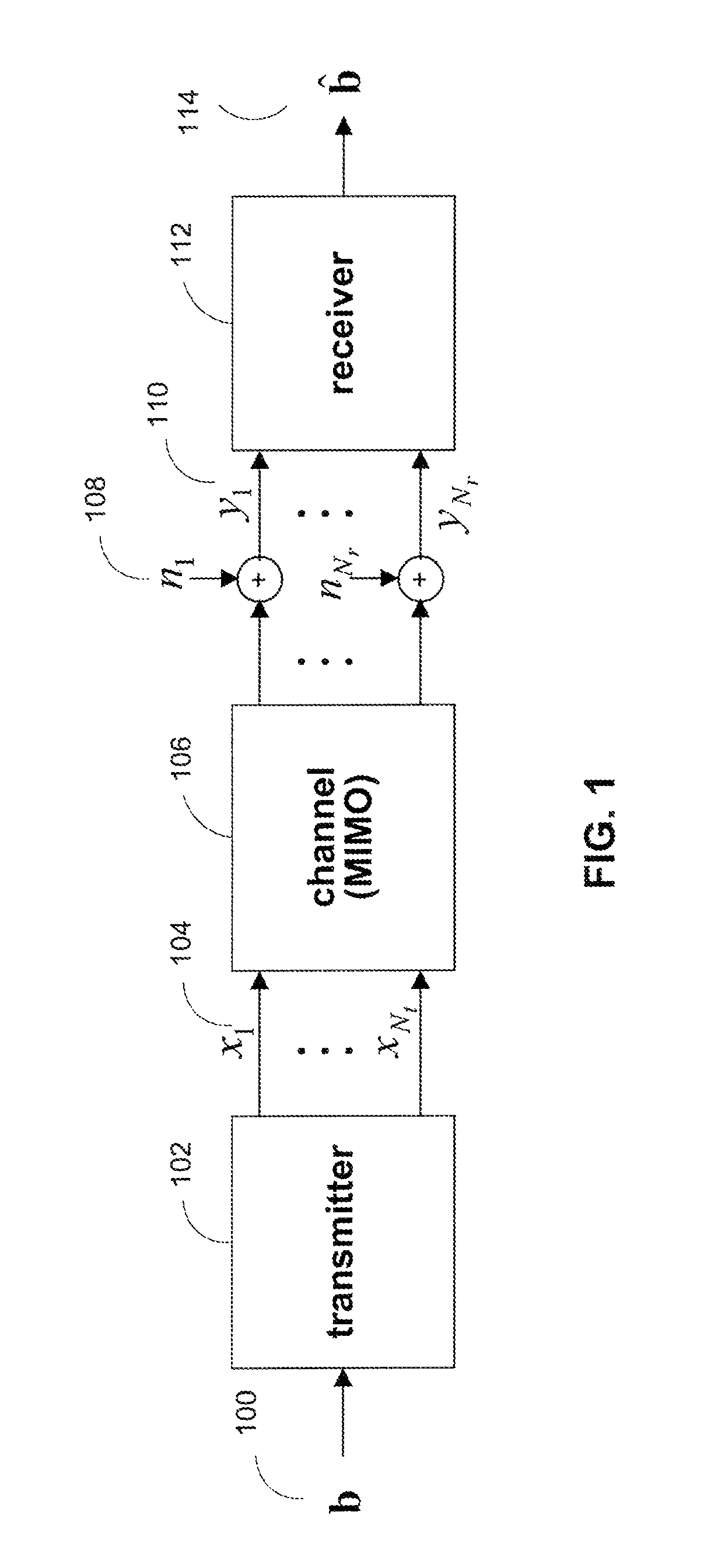
Data transmission method and receiver
ActiveUS20050276313A1Quality improvementSaving in time-delayError preventionModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemData transmission
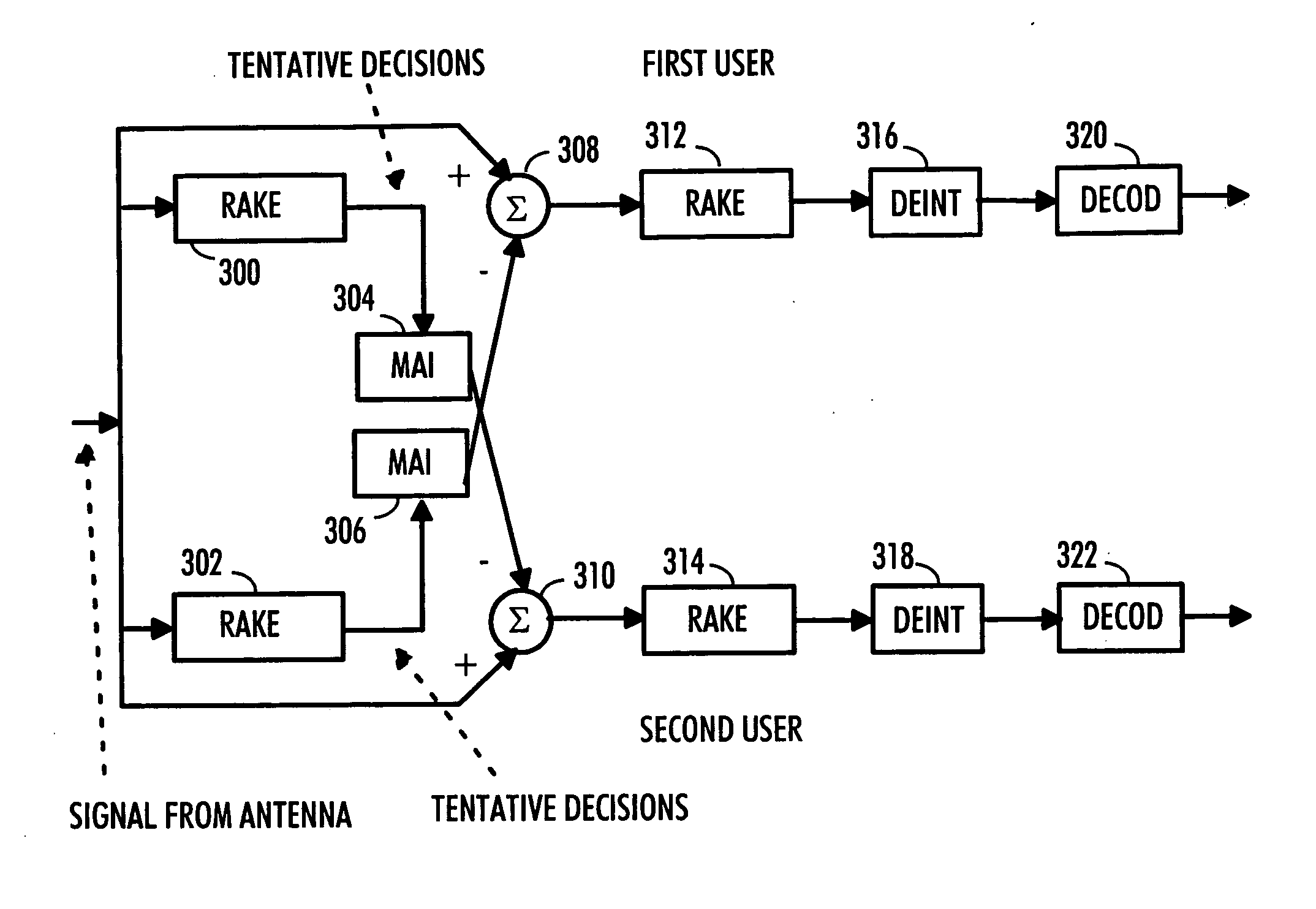
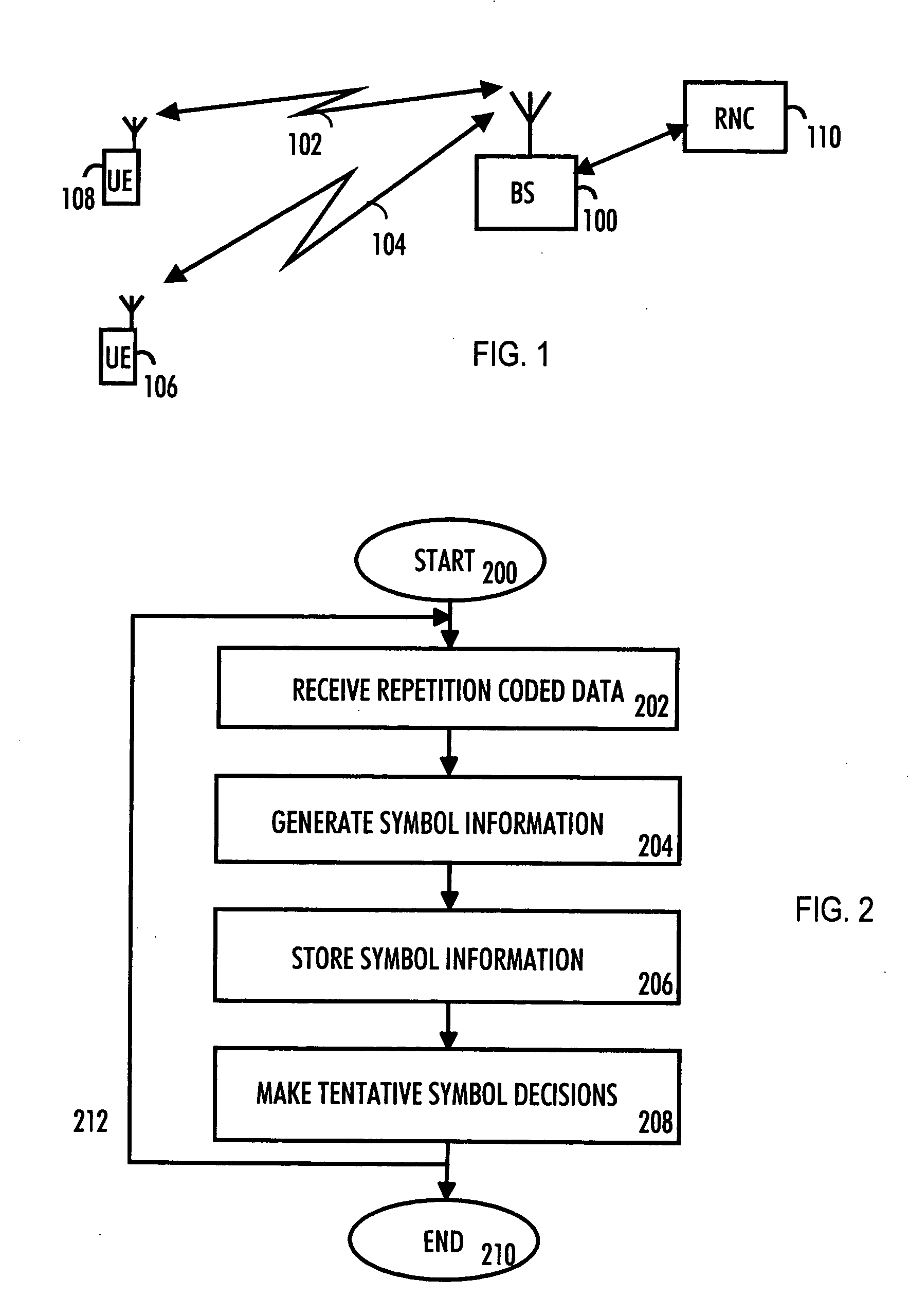
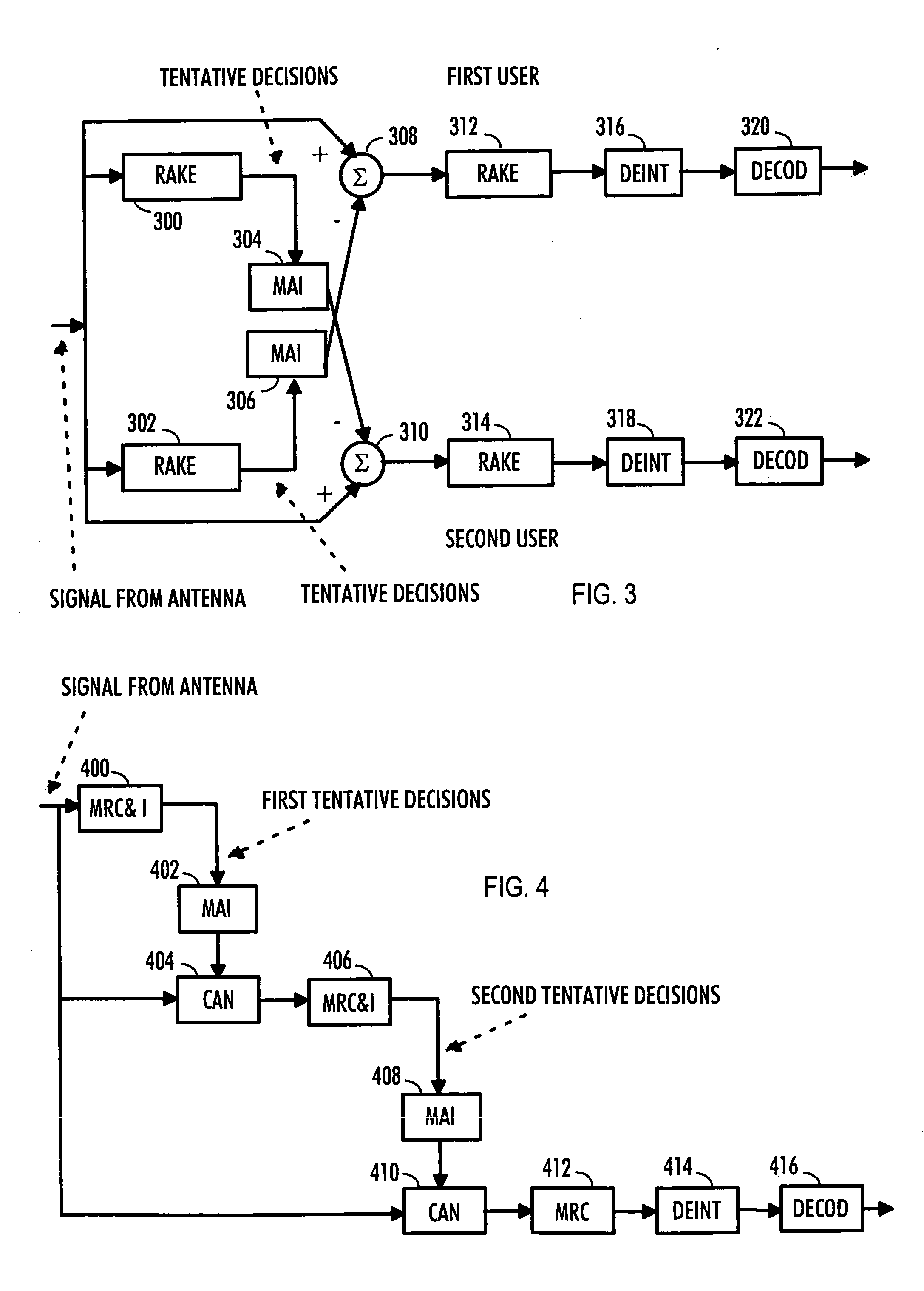
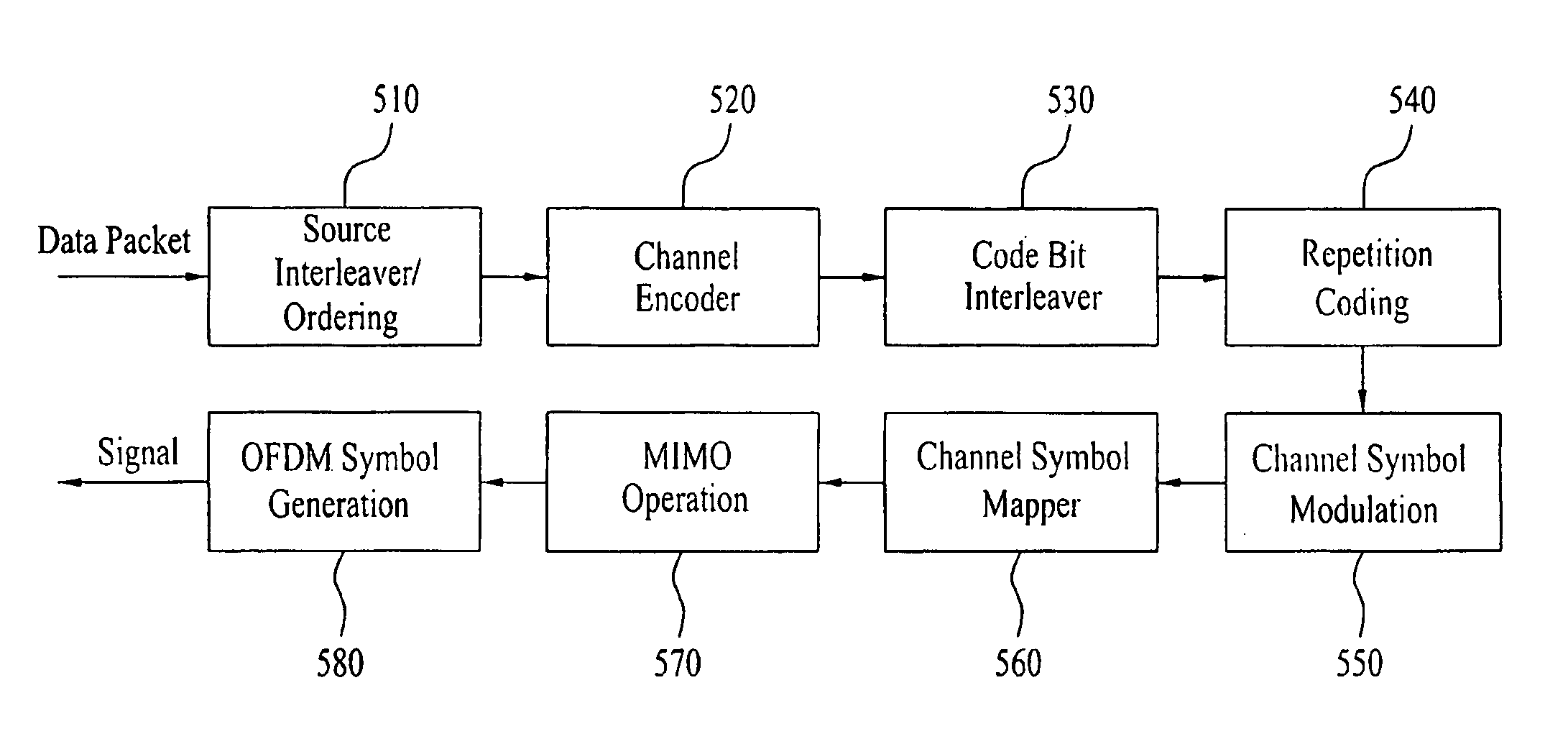
A receiver of a communication system includes means for receiving repetition-coded data. The receiver also includes means for generating symbol information from the received repetition-coded data. The receiver also includes means for storing symbol information over a predetermined period and means for making tentative symbol decisions by combining the stored symbol information.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Symbol mapping method for repetition channel coding
ActiveUS8391405B2Maximum reliabilityReduce in quantityError prevention/detection by using return channelElectric signal transmission systemsComputer architectureSymbol mapping
A symbol mapping method for repetition coding is disclosed. The symbol mapping method comprises performing repetition coding on codeword to output repeated codeword symbols, and mapping the repeated codeword symbols with subcarriers located in different localized resource blocks. According to the embodiments of the present invention, it is possible to obtain maximum reliability in a receiving side by mapping codeword bits with subcarriers to reduce the number of bits having low reliability when a transmitting side uses repetition coding. Also, it is possible to improve decoding throughput and obtain channel diversity.
Owner:OPTIS CELLULAR TECH LLC
Coding method and apparatus in secondary ultrasonic communication
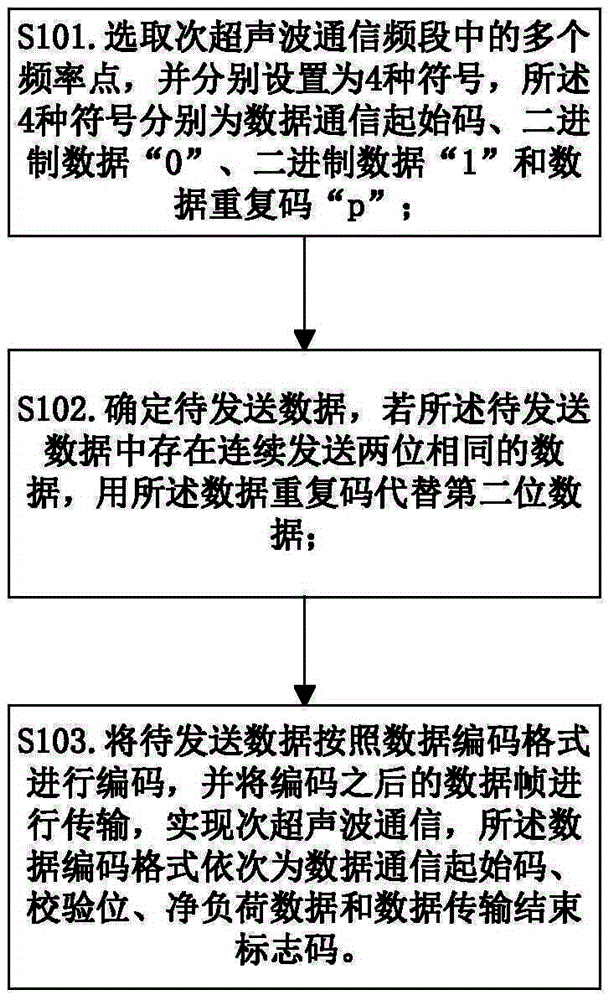
ActiveCN103825675AGuaranteed jumpSolve bit errorsError preventionComputer hardwareData synchronization
The invention provides a coding method and apparatus in secondary ultrasonic communication. A plurality of frequency points in a secondary ultrasonic communication frequency band and four kinds of symbols are respectively set, wherein the four kinds of symbols respectively are a data synchronous code E, binary data "0", binary data "1", and a data repetition code "P"; to-be-sent data are determined and if two bits of identical data for continuous sending exit in the to-be-sent data, the data repetition code is used for replacing the second-bit data; the to-be-sent data are coded according to a data coding format and data frames after coding are transmitted, thereby realizing secondary ultrasonic communication. Besides, the data coding format successively includes a data communication start code, a check code, net load data, and a data transmission end mark code; and the data communication start code is formed by synthesis of the data synchronous code E and the data repetition code P. According to the invention, a problem that an error code occurs due to identical data continuous sending caused by inaccurate communication synchronization in the prior art can be solved; and the transmission accuracy rate can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Transmission method and system of physical hybrid automatic repeat request indicator channel
InactiveCN102340386AAvoid problems that cannot be detected correctlyEliminate distractionsError prevention/detection by using return channelMulti-frequency code systemsPrecodingMultiplexing
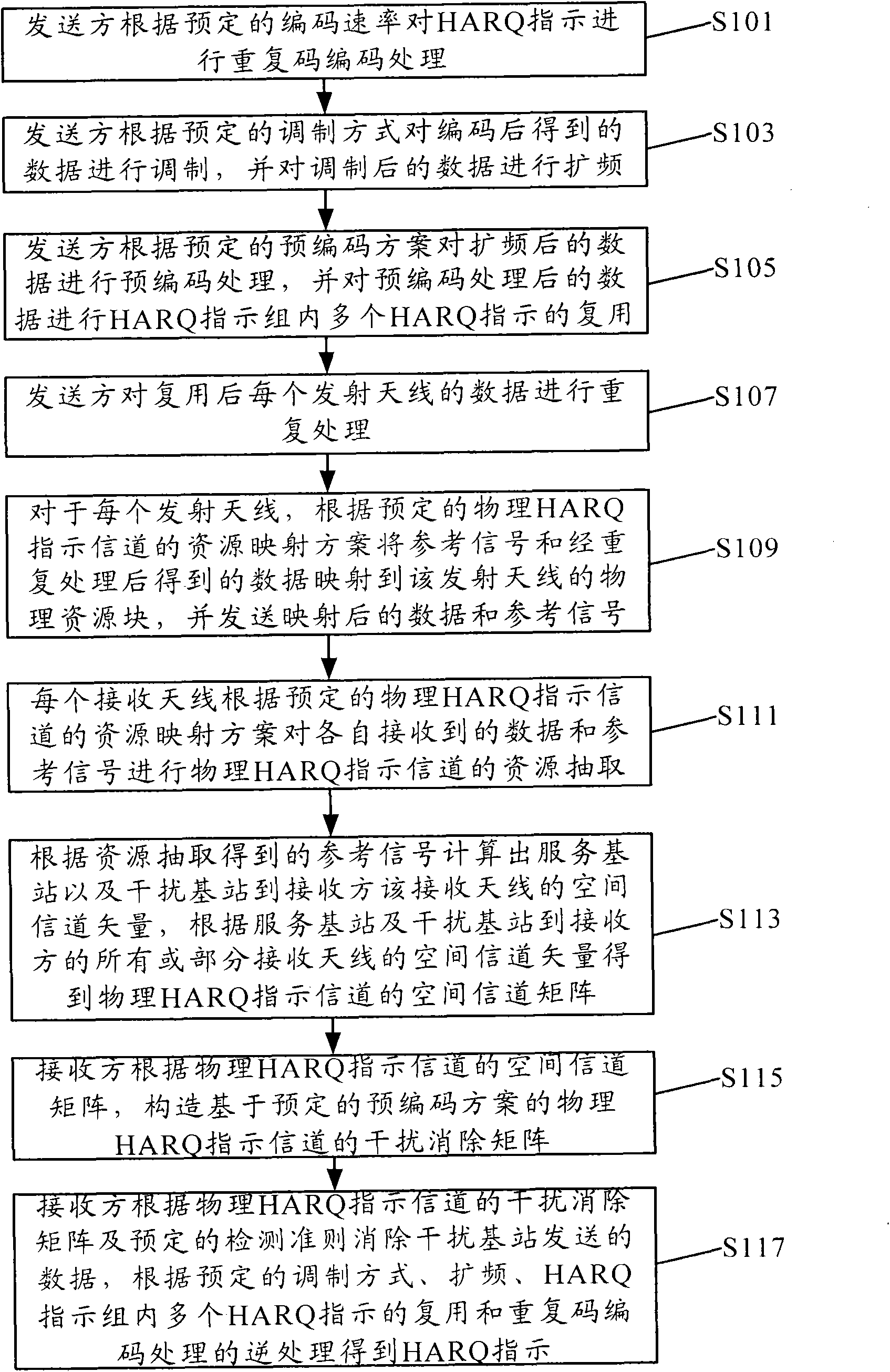
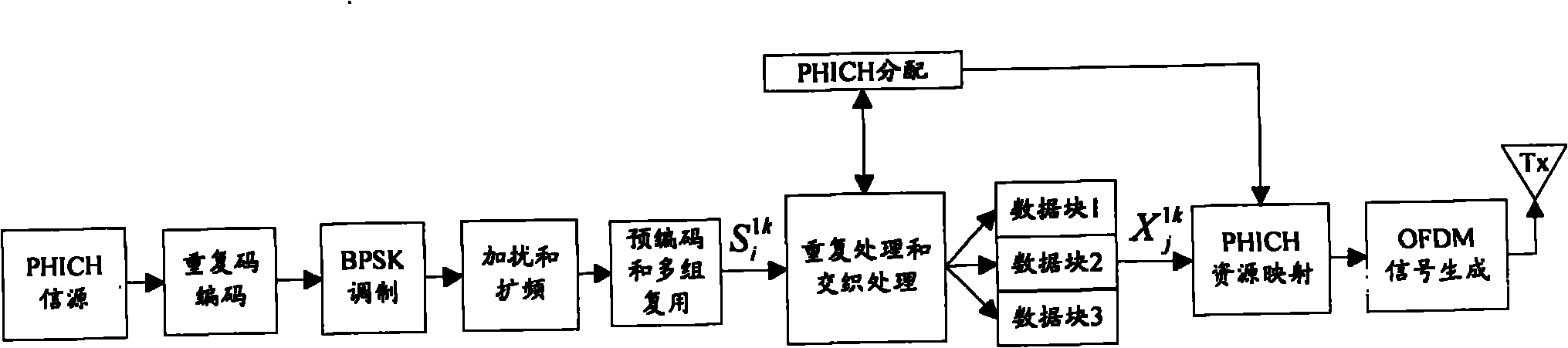
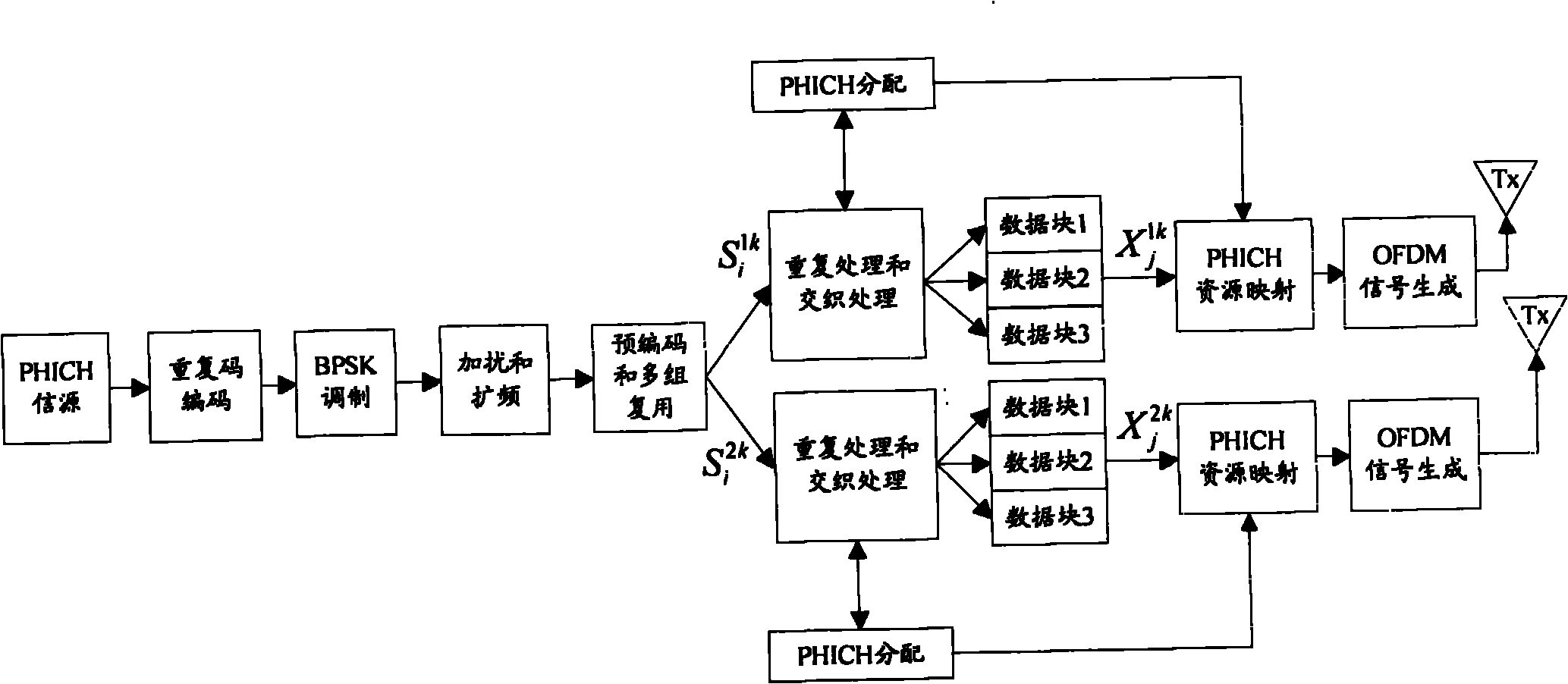
The invention discloses a transmission method and a system of a physical hybrid automatic repeat request indicator channel. The method comprises the steps that repetition code coding processing, modulation, spectrum spreading, pre-coding processing and interclass multiplexing are conducted to a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) indicator; reprocessing is conducted to the data of each transmitting antenna after multiplexing; for each transmitting antenna, reference signals and the data which is obtained after reprocessing are mapped to the physical resource blocks of the transmitting antenna according to the resource mapping scheme of the HARQ indicator channel and then are transmitted; each receiving antenna of a receiving side conducts to resource extraction to the received data and reference signals, space channel vectors from a serving base station and an interference base station to the receiving antenna of the receiving side are calculated according to the obtained reference signals, space channel matrices are obtained accordingly and interference elimination matrices based on a preset pre-coding scheme are constructed; and the receiving side eliminates the data transmitted by the interference base station according to the interference elimination matrices and a preset detection criteria, and the HARQ indicator is obtained through processing inverse to the processing of the transmitting side.
Owner:大连海兰德维通信技术有限公司
Light emitting and receiving device with high flexibility and achieving method thereof
ActiveCN103199937ATake full advantage of coding gainHigh gainWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transceiversPhotovoltaic detectorsOptical signal to noise ratio
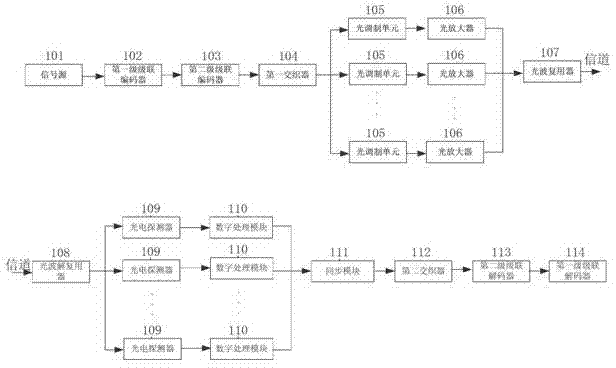
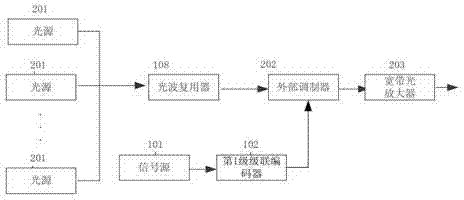
The invention discloses a light emitting and receiving device with high flexibility and an achieving method thereof. The method comprises the following steps that an electric signal generated by a signal source is encoded by a first-stage cascade encoder and is modulated by electro-optical modulation and repetition coding units to be multipath optical signals with repetition code characteristics, the multipath optical signals are finally multiplexed to be optical wave signals to be sent out, the number of the electro-optical modulation and repetition coding units is N, encoding load is (N-1) / N; and the optical wave signals sent by optical channels are multiplexed, multipath partial wave signals are obtained, then the multipath partial wave signals are recovered to a corresponding electric signals by a multipath photoelectricity detector, finally the electric signals are subjected to interweave combination and decoded by the cascade encoder, and corresponding electric signals are obtained. The light emitting and receiving device with high flexibility and the achieving method adopt a multiplying method and enable the independent error rate of each channel to be far smaller than the signal error rate of the whole broadband so as to fully utilize coding gain brought by high coding load. The light emitting and receiving device normally works under the environment with low optical signal to noise ratio.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Distance-level combining for MIMO systems with HARQ and/or repetition coding
ActiveUS20140133610A1Increase system complexityEffectively utilize informationSpatial transmit diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionMimo systemsMultiple input
Systems and methods are provided for decoding signal vectors in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, where the receiver has received one or more signal vectors from the same transmitted vector. For each received signal vector, the receiver evaluates a decoding metric using each possible value of the transmitted signal vector to produce a set of distances. The receiver then combines distances from across the received signal vectors to produce a combined distance associated with each possible value of the transmitted signal vector. Using the combined distances, the receiver may choose among the possible values of the transmit signal vector to determine the actual transmit signal vector.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com