Patents
Literature
119 results about "Burst noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
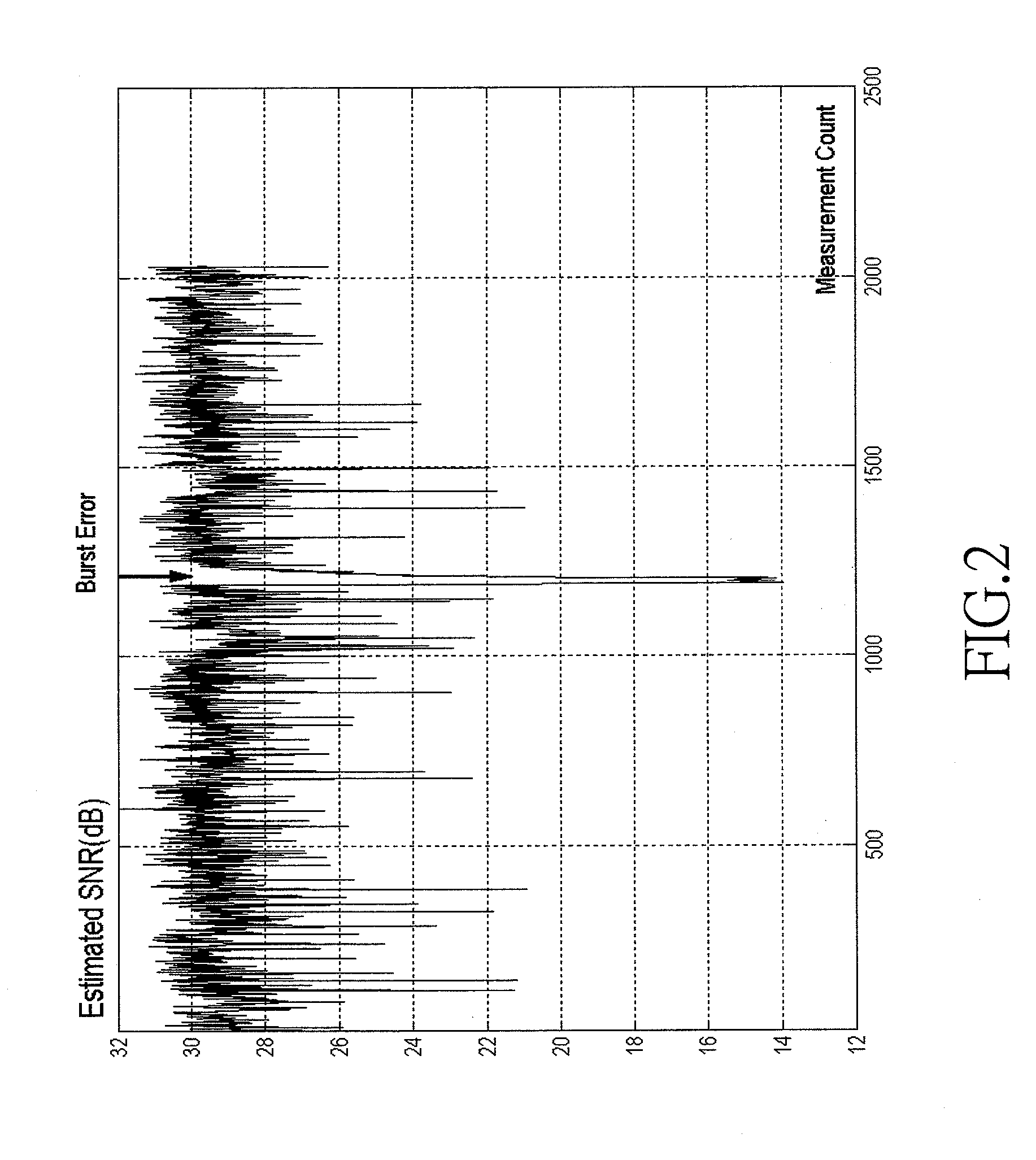
Burst noise is a type of electronic noise that occurs in semiconductors and ultra-thin gate oxide films. It is also called random telegraph noise (RTN), popcorn noise, impulse noise, bi-stable noise, or random telegraph signal (RTS) noise.
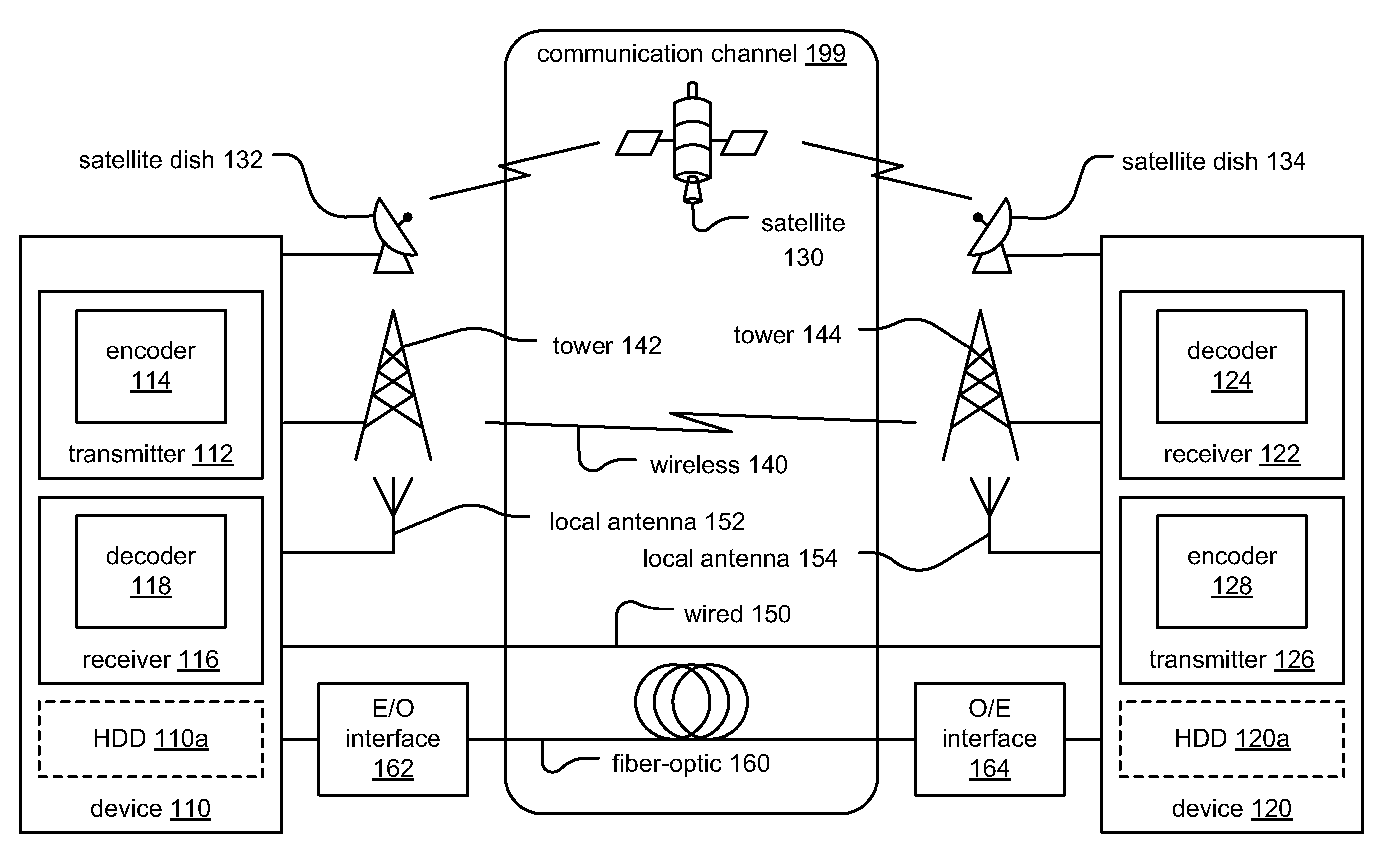
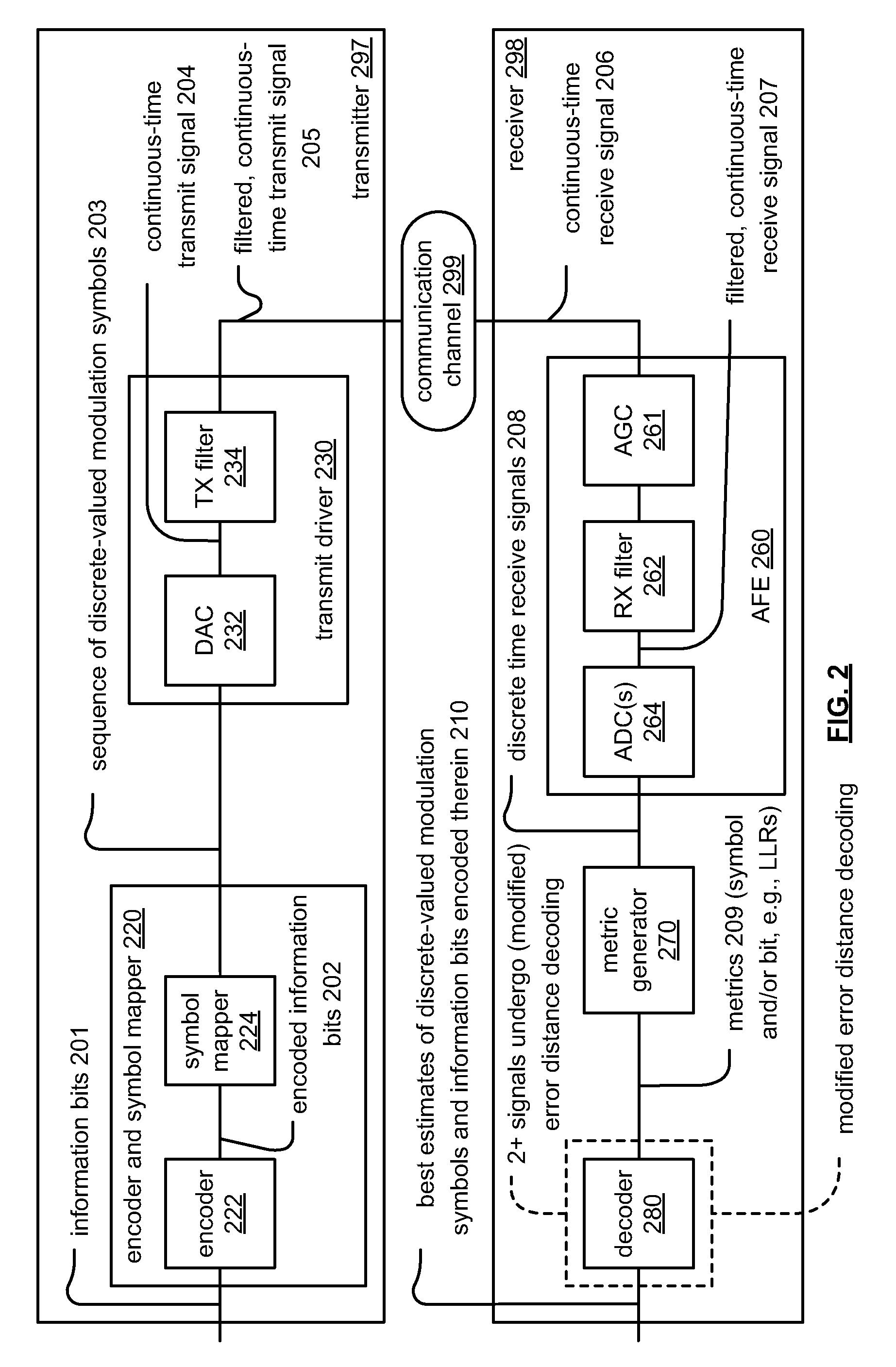
Modified error distance decoding
InactiveUS20110072330A1Code conversionDiversity/multi-antenna systemsCommunications systemMinimum distance estimation
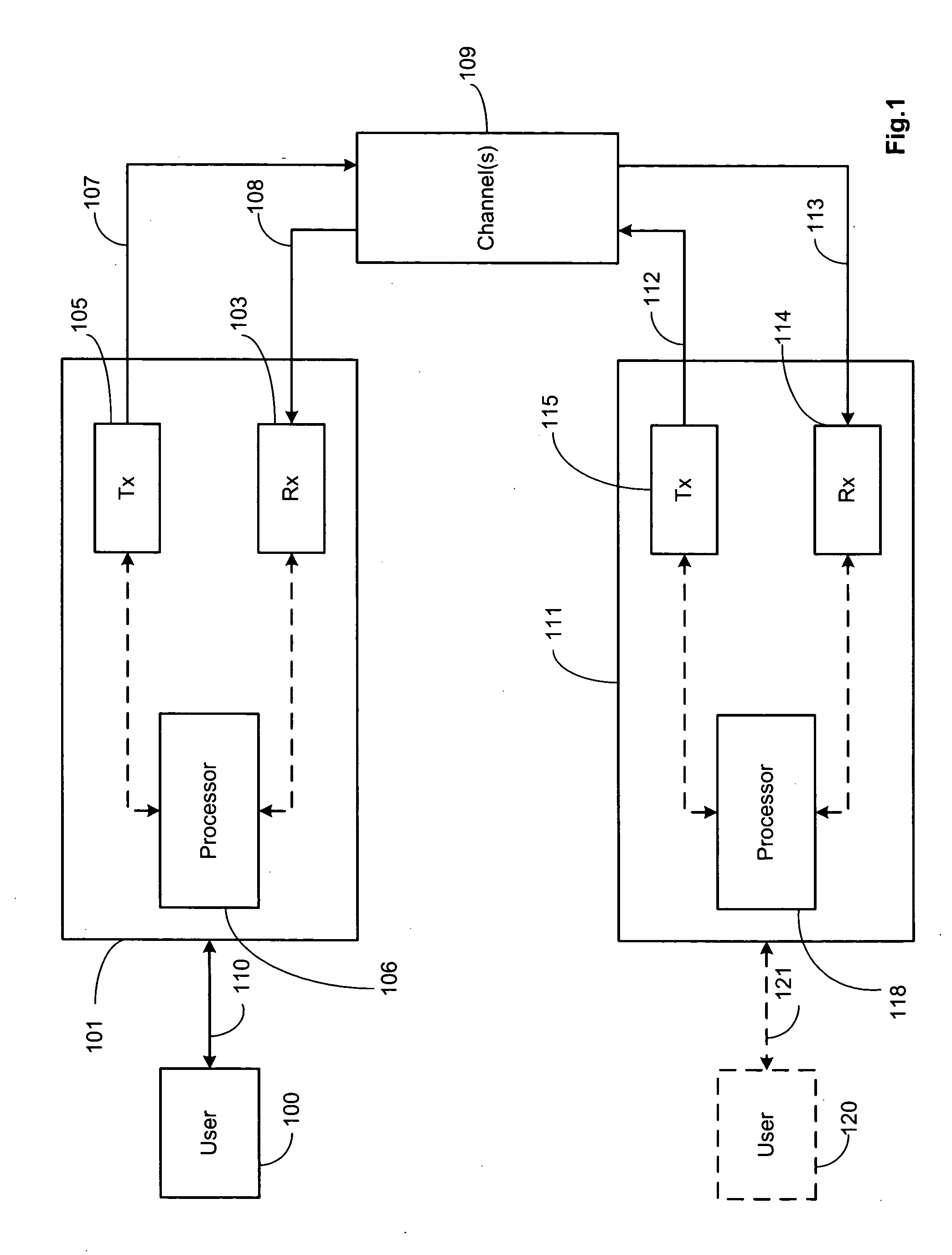
Modified error distance decoding. In certain communication systems, multiple signals (e.g., which may be viewed as being codewords, groups / sets of bits or symbols, etc.) can be commonly affected by such deleterious phenomenon as burst noise when traversing a communication channel (e.g., from a transmitter communication device to a receiver communication device). In such instances, a test error pattern may be identified which covers those affected bits (or symbols) among at least two respective signals (e.g., all of the respective signals or any subset thereof). Various respective test error patterns may be employed, each having a different respective weight, to the desired group of signals (e.g., codewords, groups / sets of bits or symbols, etc.). As such, more than one possible estimate of each respective signal may be generated. A variety of selection operations may be employed when more than one possible estimate exists (e.g., random selection, that estimate with minimum distance, etc.).
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
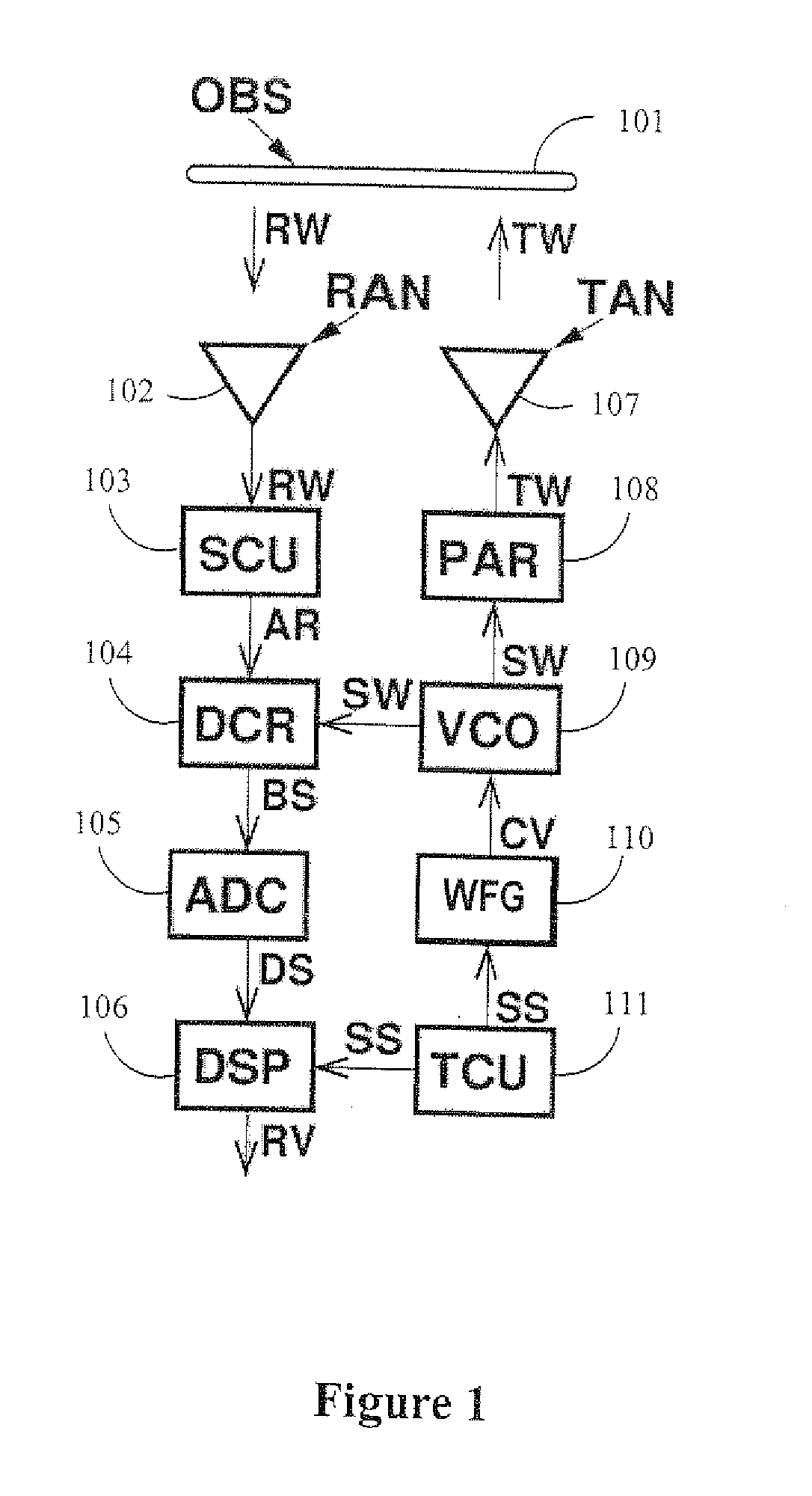
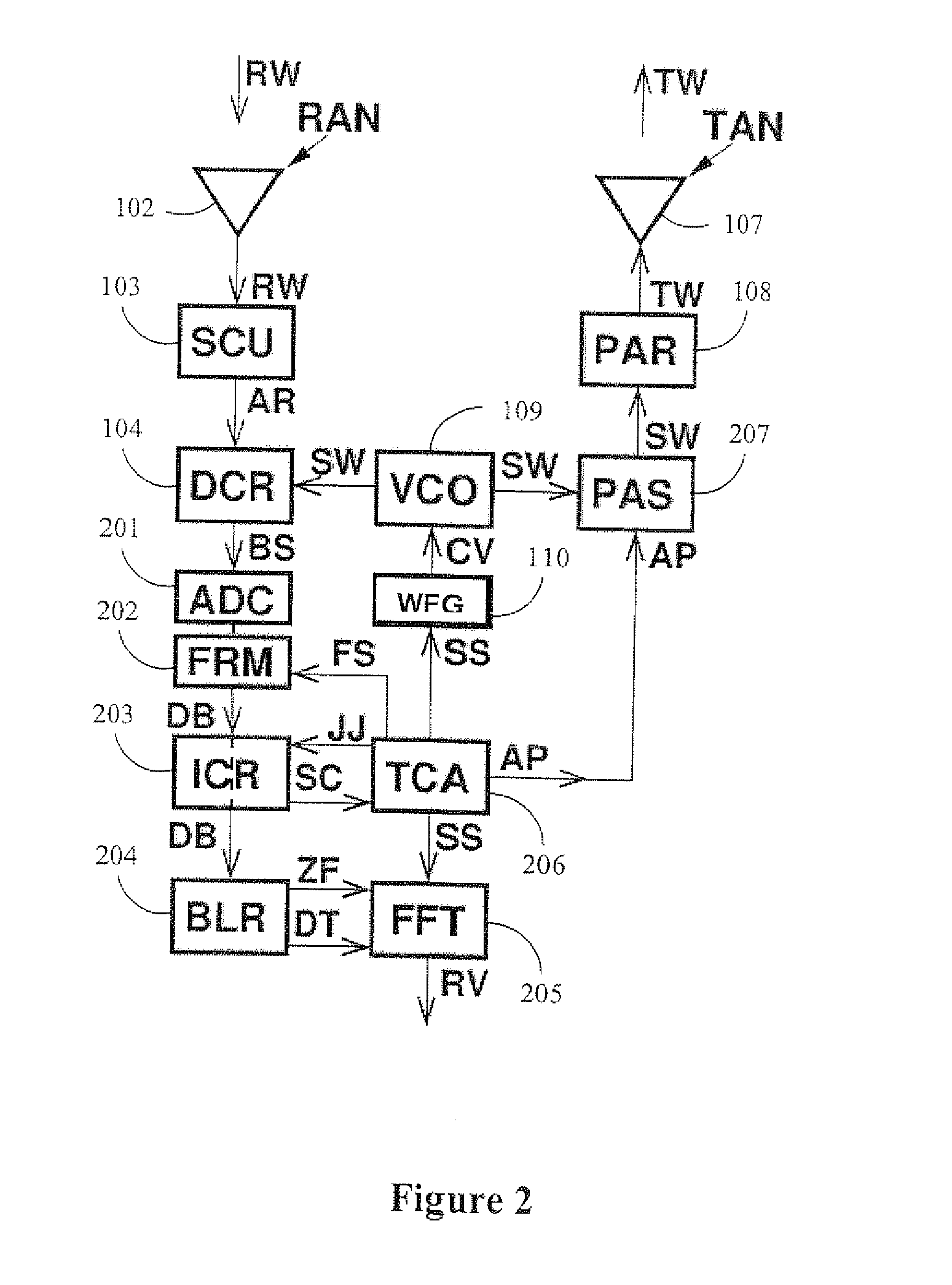
Automotive radar with radio-frequency interference avoidance
ActiveUS20110291875A1Good estimateVelocity increasesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsRadar waveforms
An automotive radar system is disclosed that comprises an interference classifier 203 for determining a type of interference in a signal received from a multiuser environment. A sweep pattern comprising frequency sweep signals for a transmitted radar waveform is then advantageously determined in dependence upon the level of interference experienced by frequency sweep signals for the determined type of interference. The automated radar system comprises: a receiver 102 operable to receive a noise signal comprising burst noise, frequency chirp signals generated by one or more other users, or a combination thereof; a signal generator 109, 110 operable to generate a plurality of different frequency sweep signals; a signal combiner 104 operable to combine each frequency sweep signal with a received noise signal to generate a combined signal for each frequency sweep signal; an interference classifier 203 operable to identify combined signals corresponding to received noise signals comprising frequency chirp signals and to determine the noise levels of said combined signals corresponding to received noise signals comprising frequency chirp signals; and a selector 206 operable to select a plurality of frequency sweep signals in dependence upon the noise level determinations by the interference classifier 203 on the combined signals corresponding to received noise signals comprising frequency chirp signals; and a control unit 206 operable to determine a sweep pattern comprising the selected plurality of frequency sweep signals to be transmitted as an output radar waveform.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
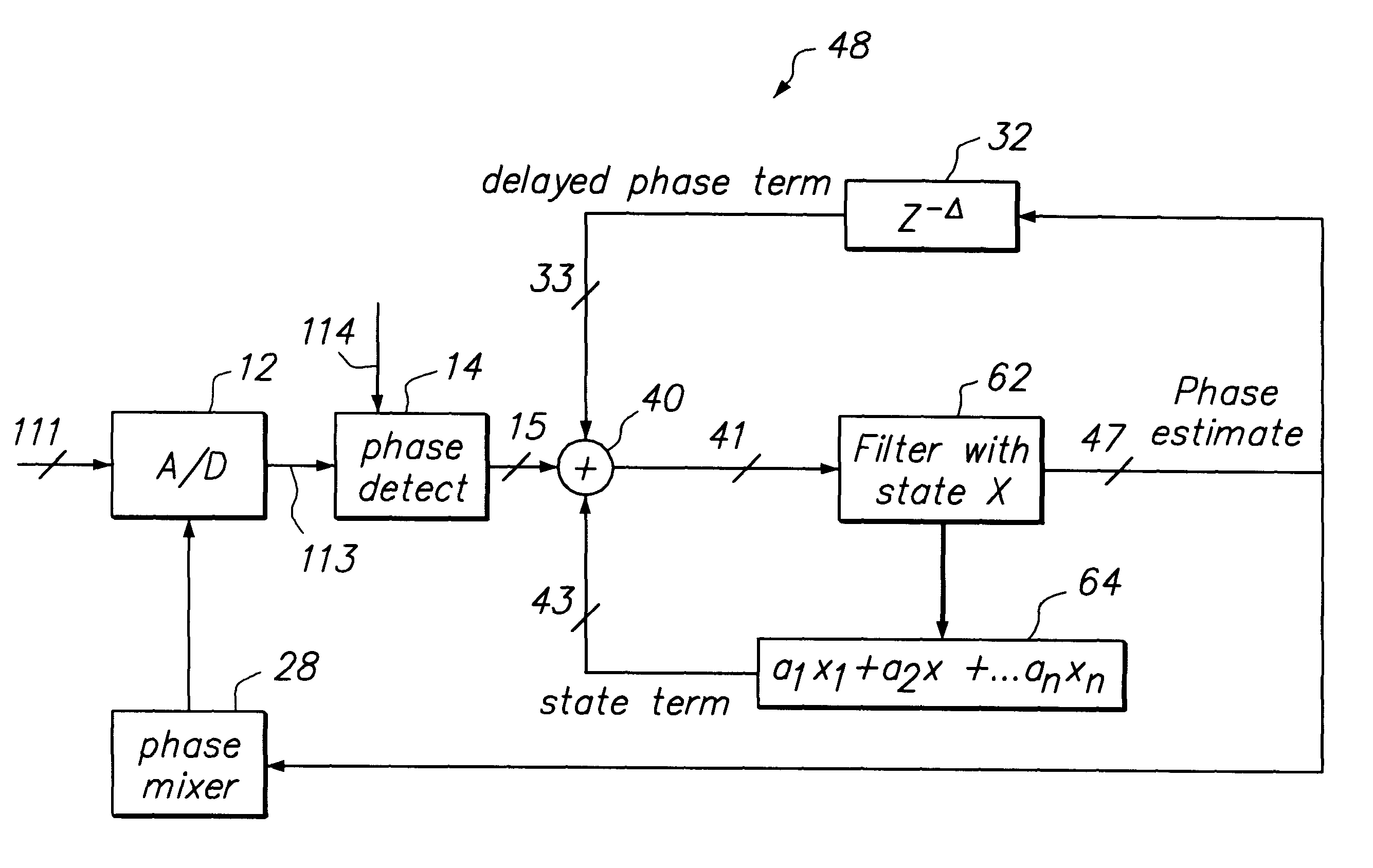
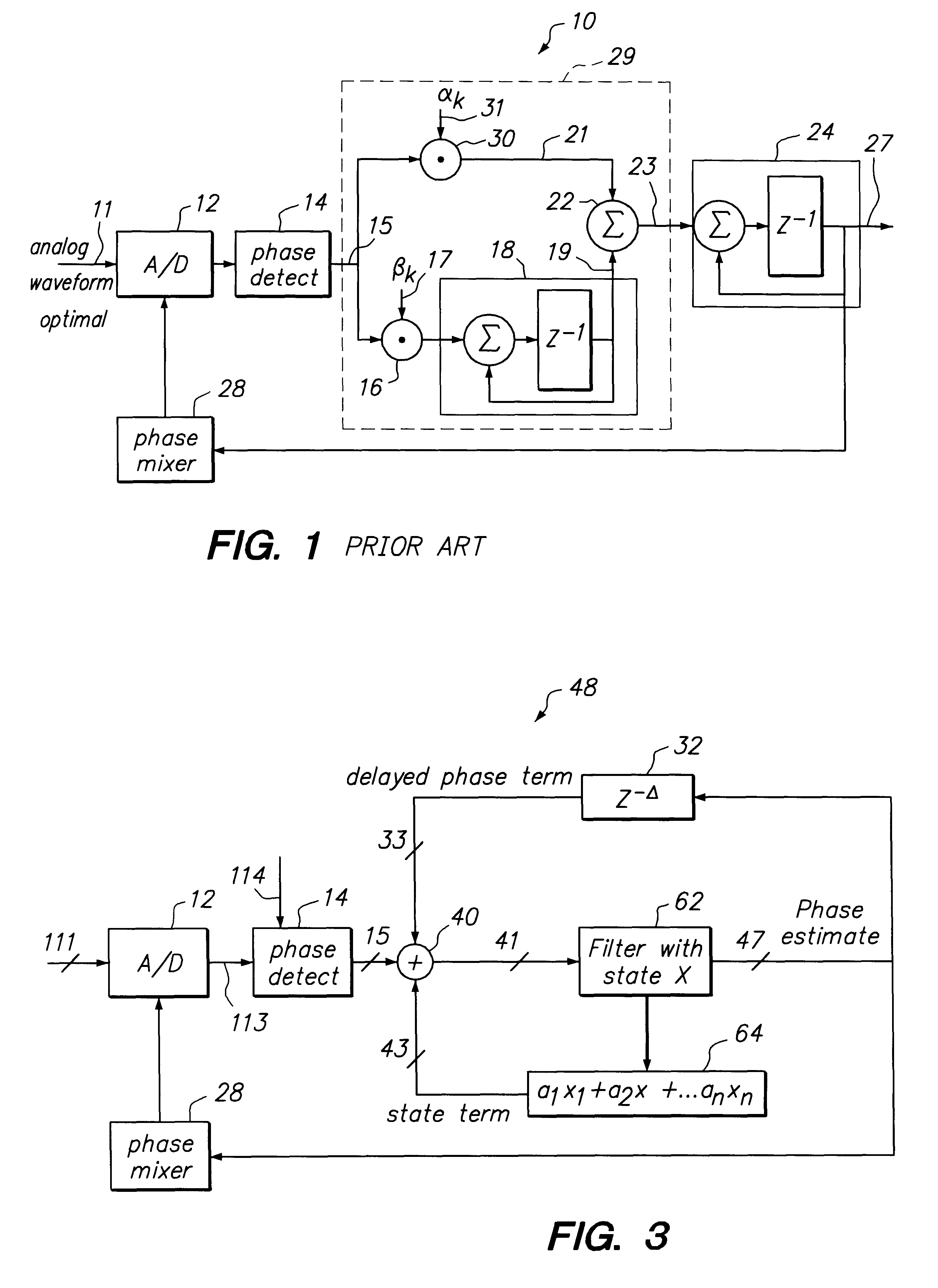
Loop latency compensated PLL filter
InactiveUS6236343B1Minimize jitterReduce sensitivityAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsPhase detectorSquare waveform
The loop latency compensated PLL filter comprising two additional feedback terms, a delayed phase compensation signal and a state compensation signal, that are provided as input of a PLL filter. Accordingly, the PLL filter input comprises two additional compensation input signals: the delayed phase compensation signal and the state compensation signal in addition to a phase estimated error output from a phase detector that is also coupled to the input of the PLL filter. Consequently, PLL filter thus is able to provide a latency compensated phase error control output that is fedback to control a phase mixer to generate a square waveform used to drive an A / D of the PLL in accordance with the principles of this invention. The loop latency compensated PLL of this invention thus minimizes the jitter of the PLL circuit, provides higher format efficiency, and also has reduced sensitivity to large bursty noises.
Owner:MAXTOR
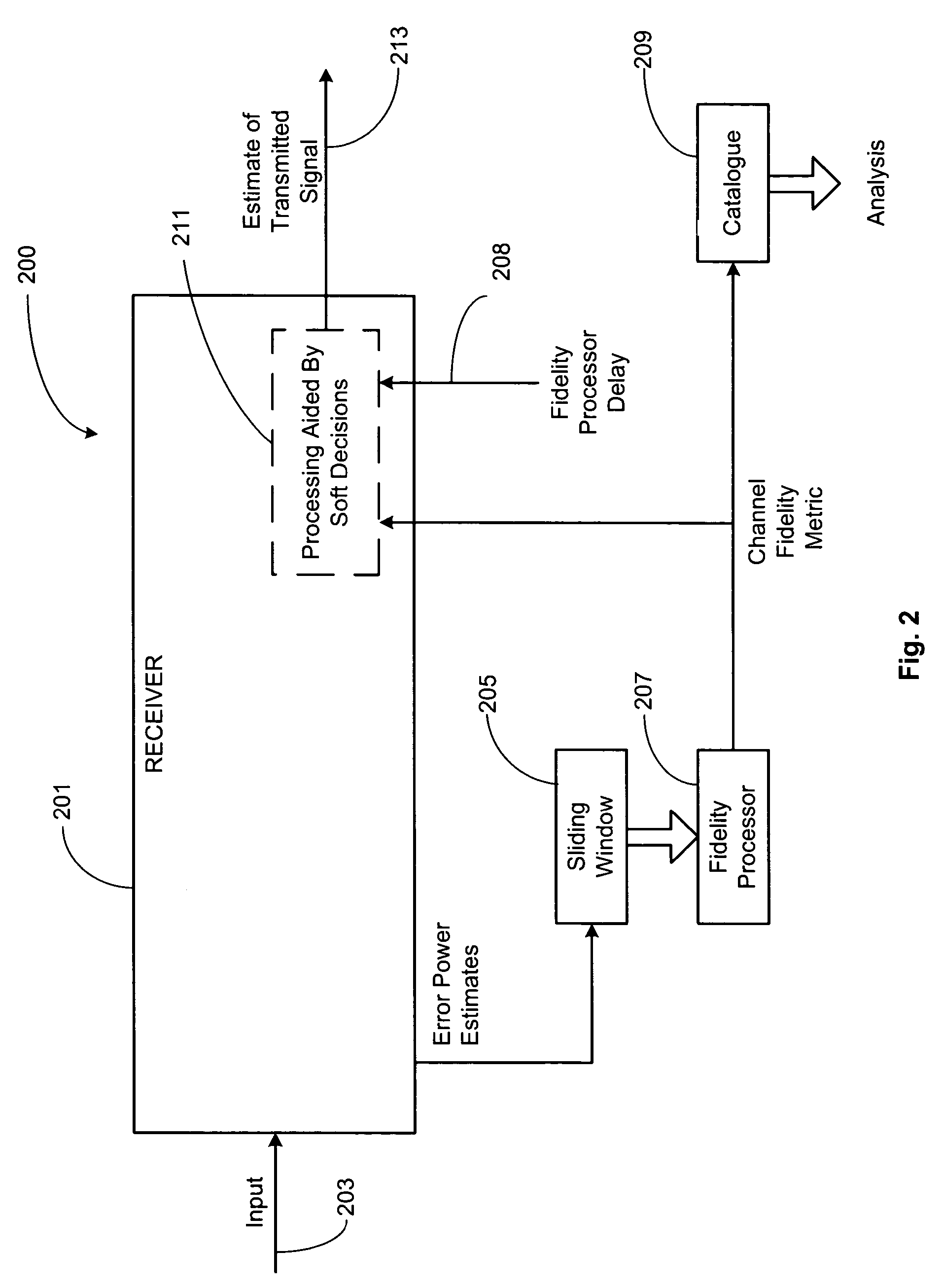
Receiver
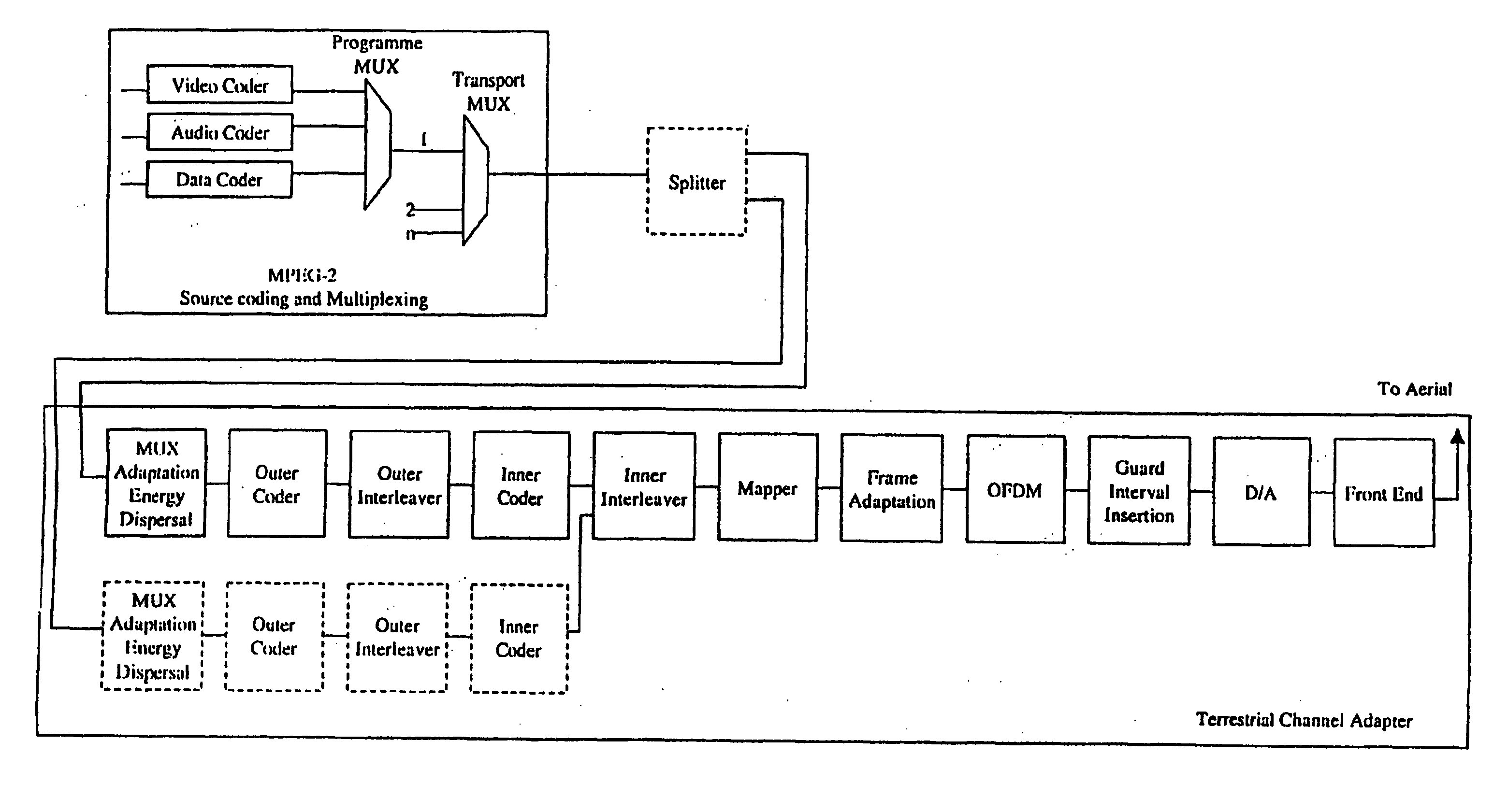
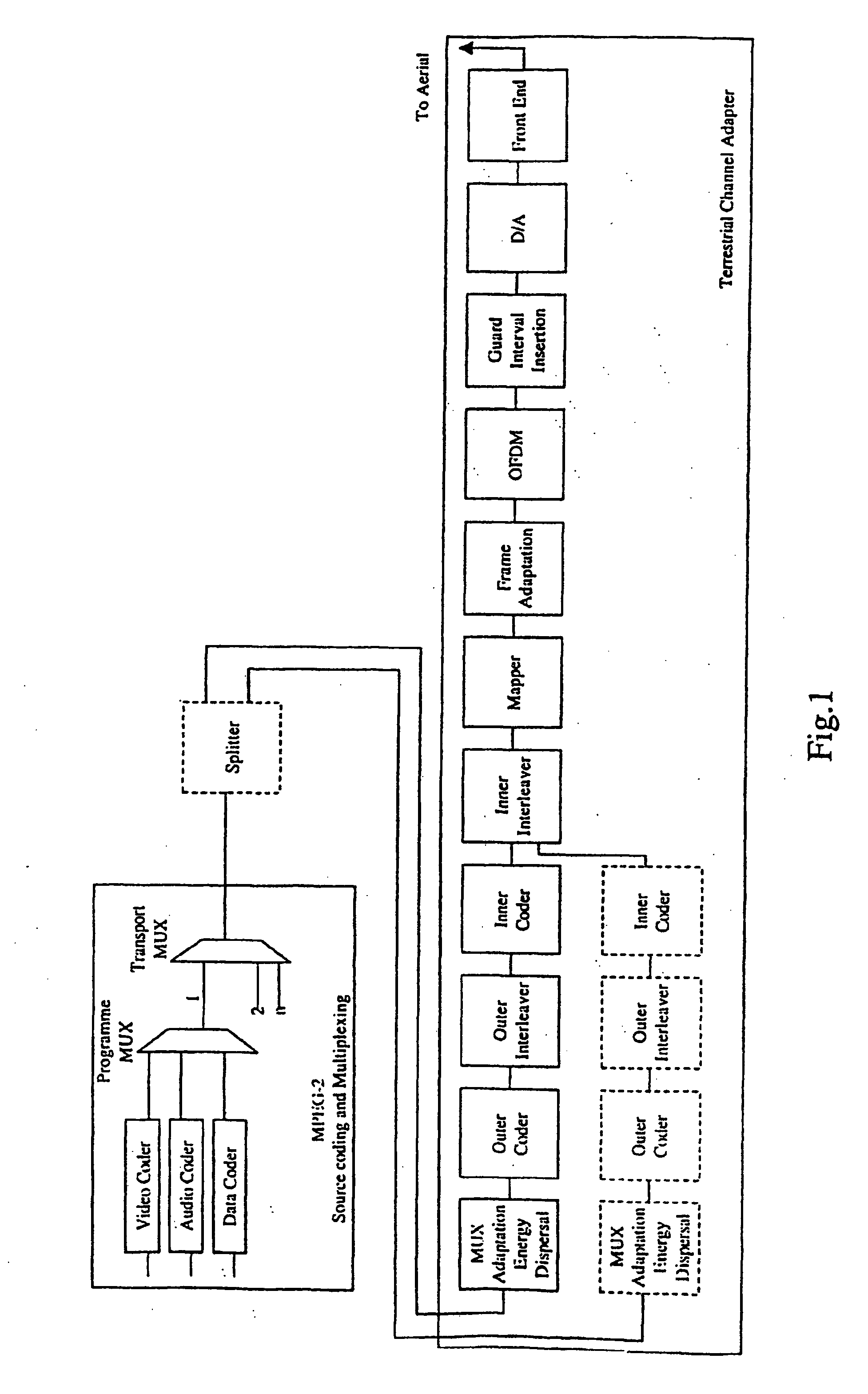
ActiveUS20030210749A1Improve integrityFacilitate communicationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCarrier signalFourier transform on finite groups
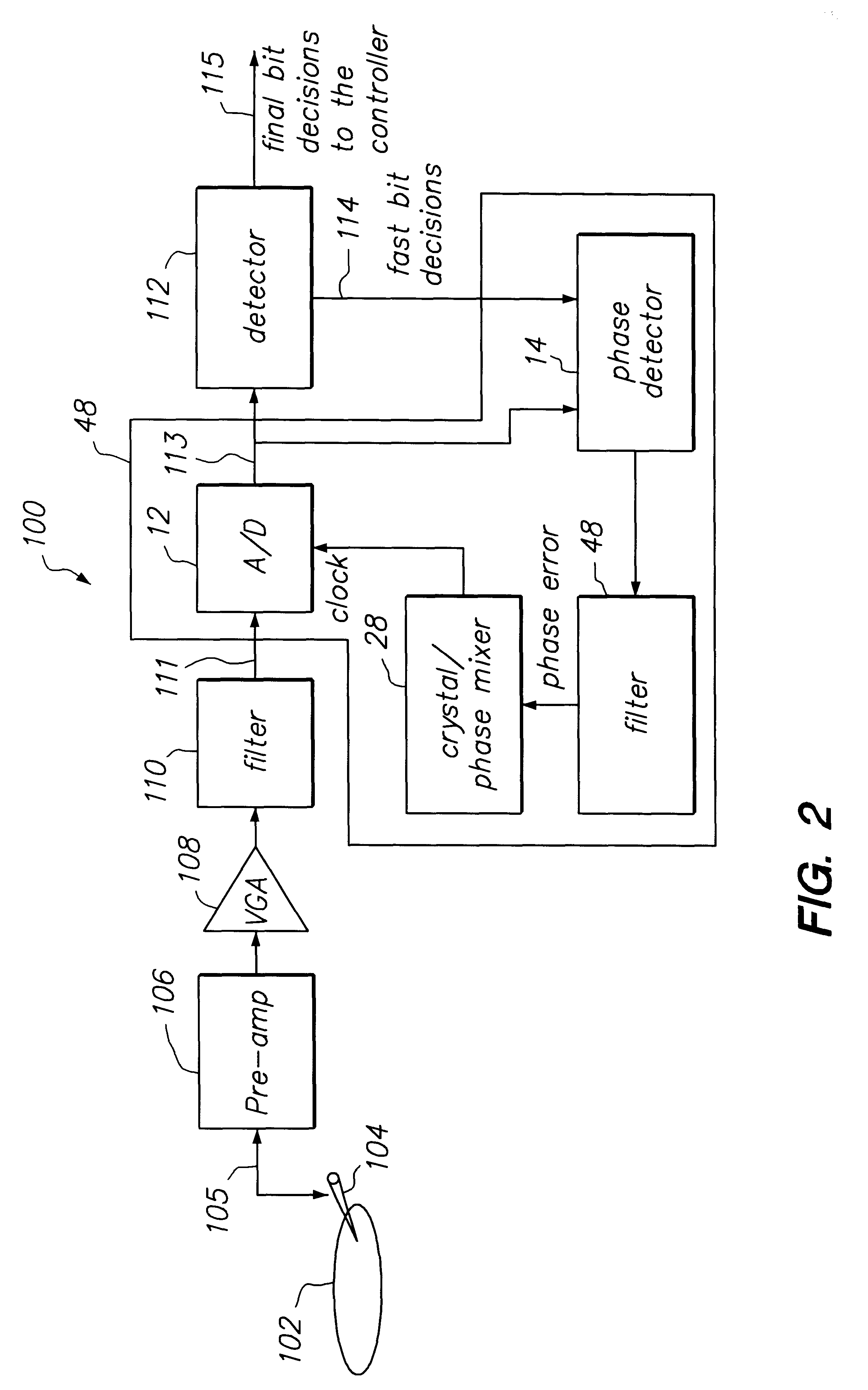
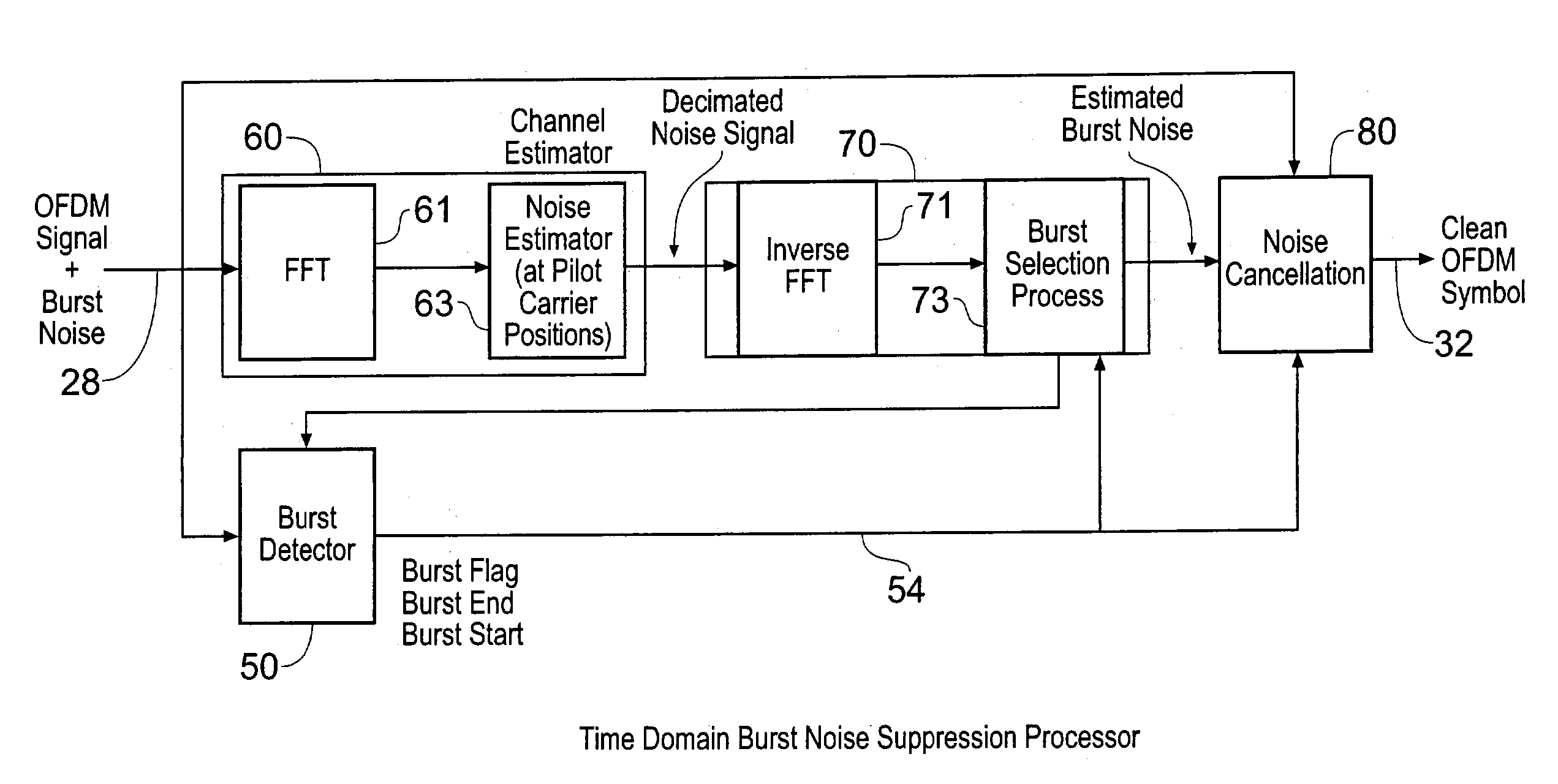
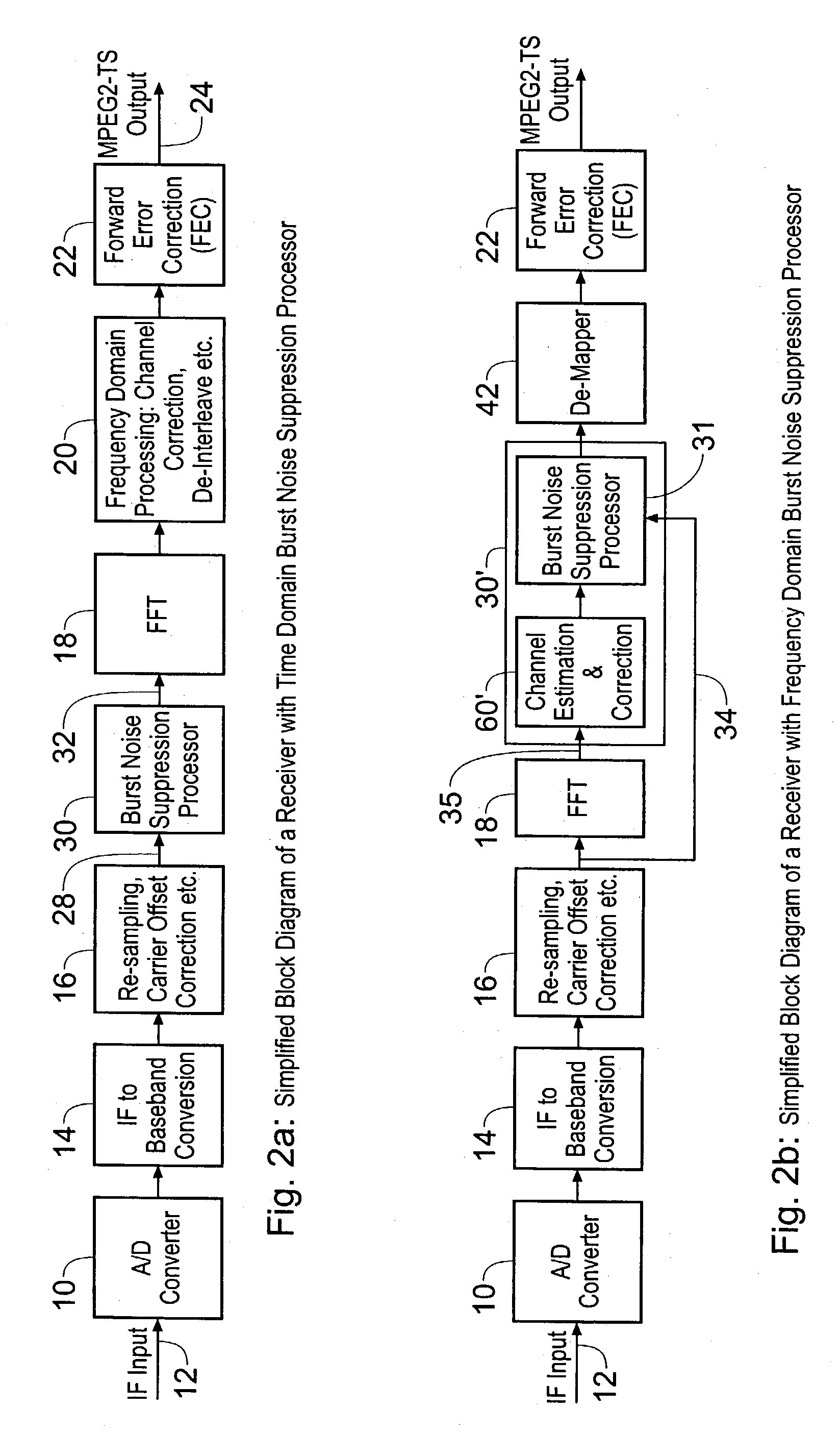
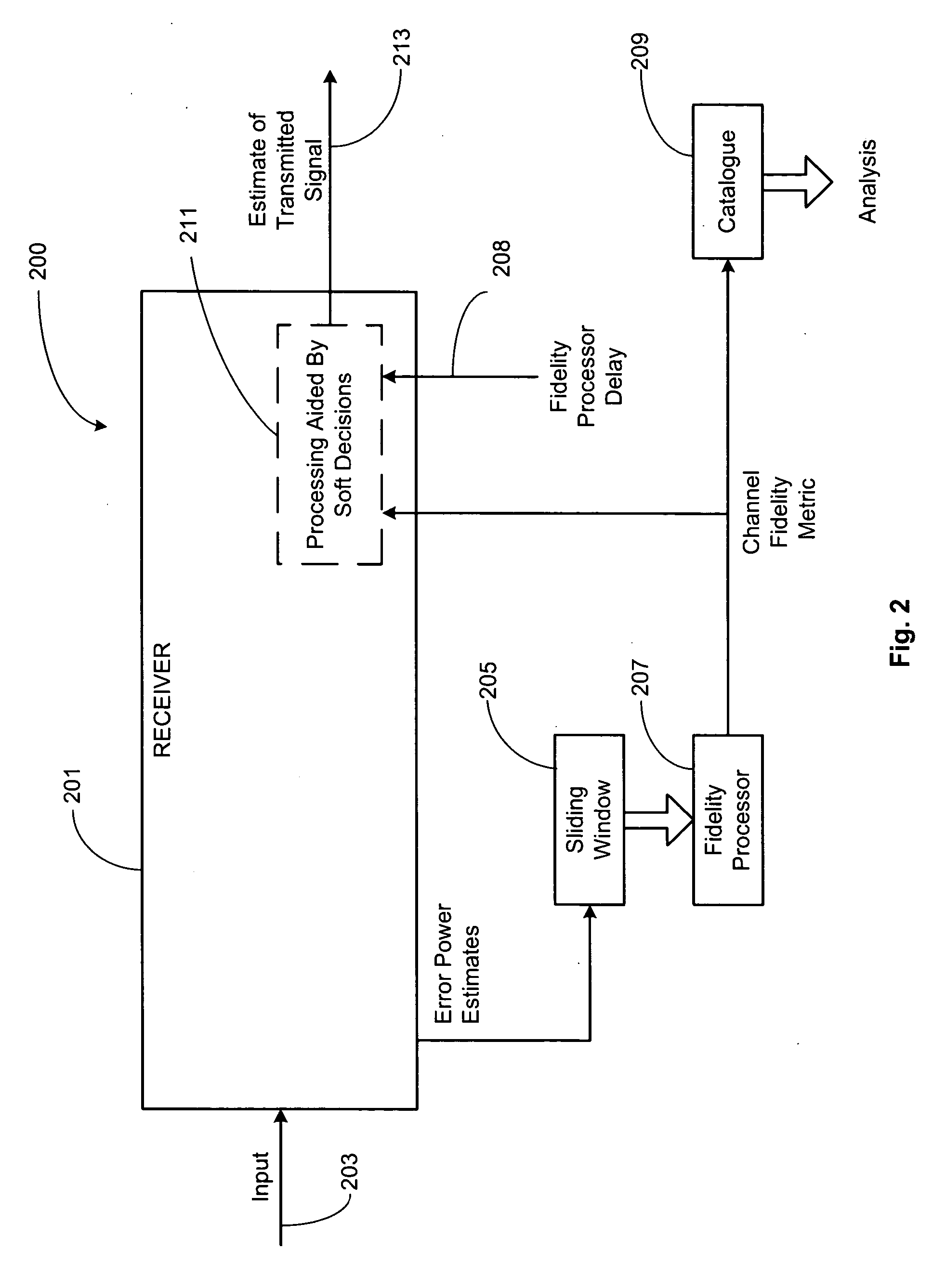
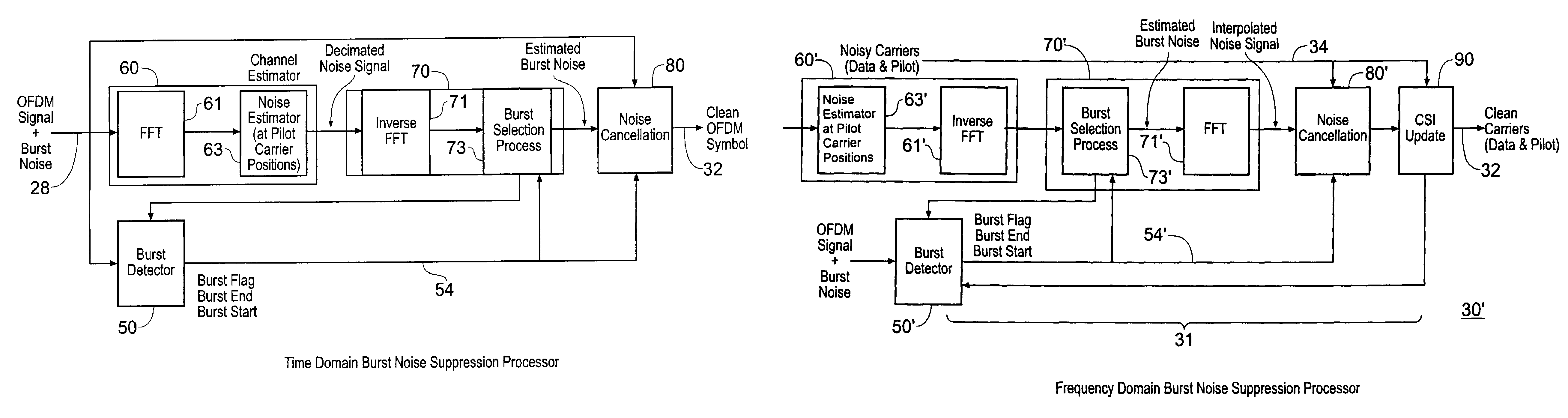
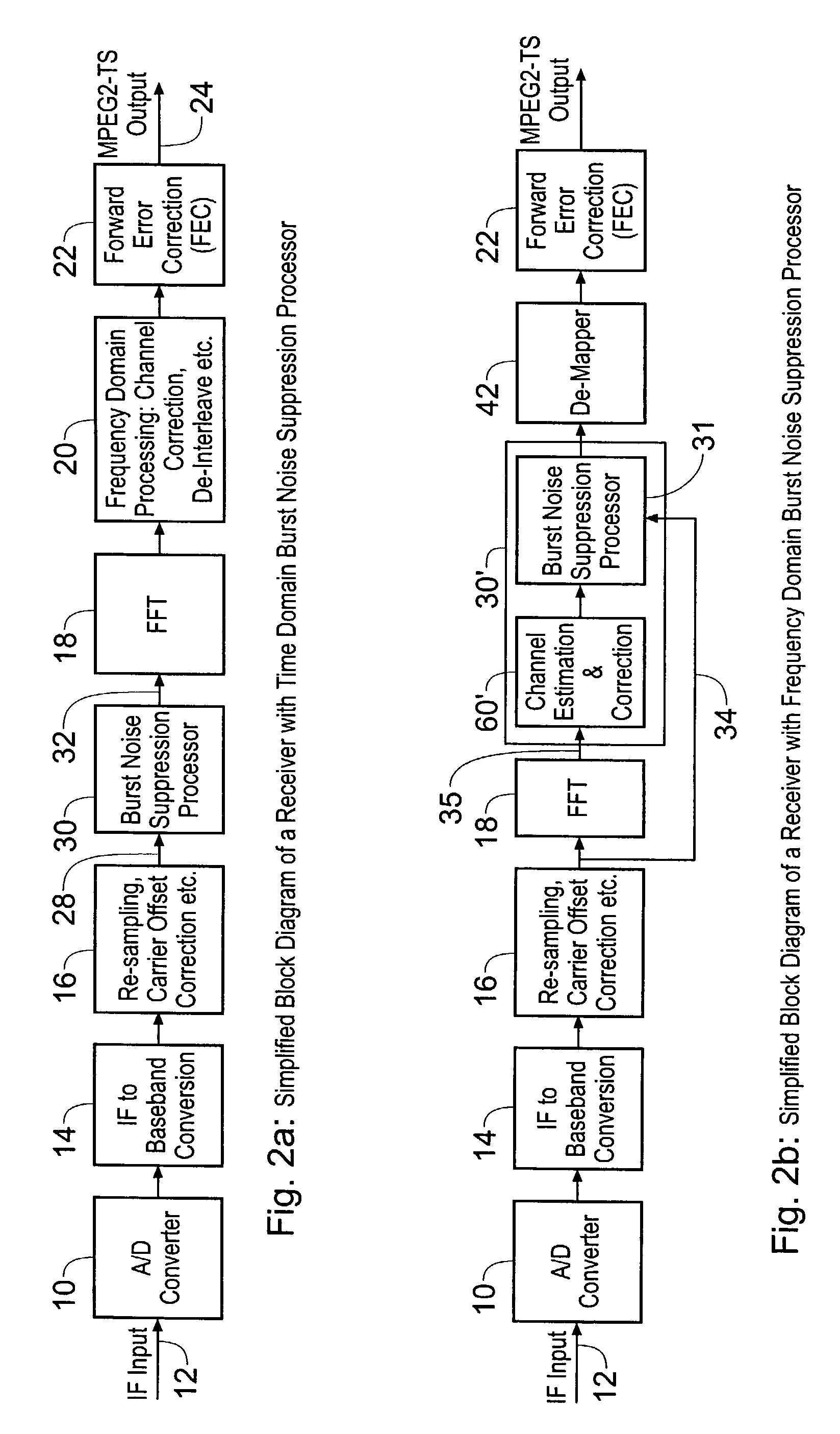
A receiver for receiving a multi-carrier modulated symbol is arranged to suppress a burst noise signal which may have been induced in the symbol. The symbol includes a plurality of pilot carriers as well as a plurality of data bearing carriers. The receiver comprises a burst noise detection processor operable to detect the temporal position of the burst noise signal which may have corrupted the symbol within a period occupied by the symbol, and a channel estimation processor operable to generate a decimated noise signal corresponding to the burst noise, from the recovered pilot carriers. An inverse Fourier transform of the decimated noise signal provides a plurality of estimated versions of the burst noise signal. A noise signal processor is operable to generate an estimate of the burst noise signal by identifying one of the plurality of estimated burst noise versions at the detected temporal location of the burst noise signal. The noise signal processor may be operable to set the signal samples other than the identified estimate of the burst noise signal to zero and to perform a Fourier transform, to provide a frequency domain version of the burst noise signal, thereby interpolating the decimated noise signal. The frequency domain noise signal estimate may be cancelled from the symbol by a noise cancellation processor in the frequency domain, before data is recovered from the symbol. The receiver finds application for Digital Video Broadcasting in which COFDM is employed.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC +1
Method and system for receiving a multi-carrier signal
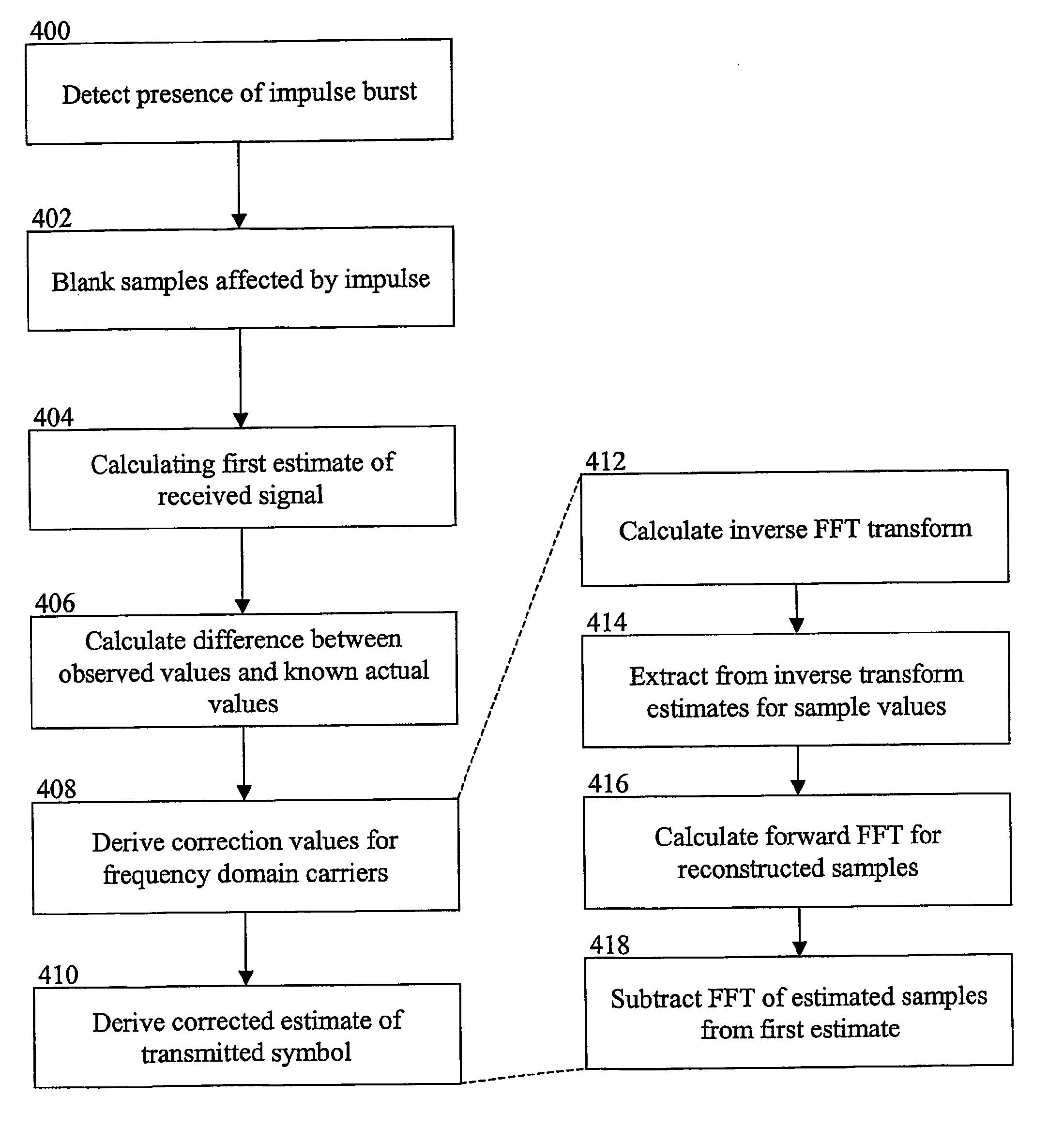
Method and system for reducing impulsive burst noise in less delayed reception in pilot based OFDM systems, especially using DVB-T standard such as Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is provided. The method contains following steps: 1) recognition of the impulse position and possibly length in the time domain symbol, 2) blanking of those samples of the symbol where significant amount of impulse noise is present, 3) calculating the first estimate of the received signal from the blanked symbol, 4) deriving correction values for the carrier estimates by applying prior information (pilot carriers), and 5) the corrected estimate of the received symbol is derived by subtracting the correction values of step 4 from the first estimate of carriers derived in step 3. The method and arrangement allow correction of fairly long bursts of impulse noise with minor degradation only. The complexity of the scheme and the additional energy consumption are fairly low. The method provides considerably more effective more simple and less delay in broadcast data reception than previously known solutions in interfered multi-carrier signal reception.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Chip blanking and processing in SCDMA to mitigate impulse and burst noise and/or distortion
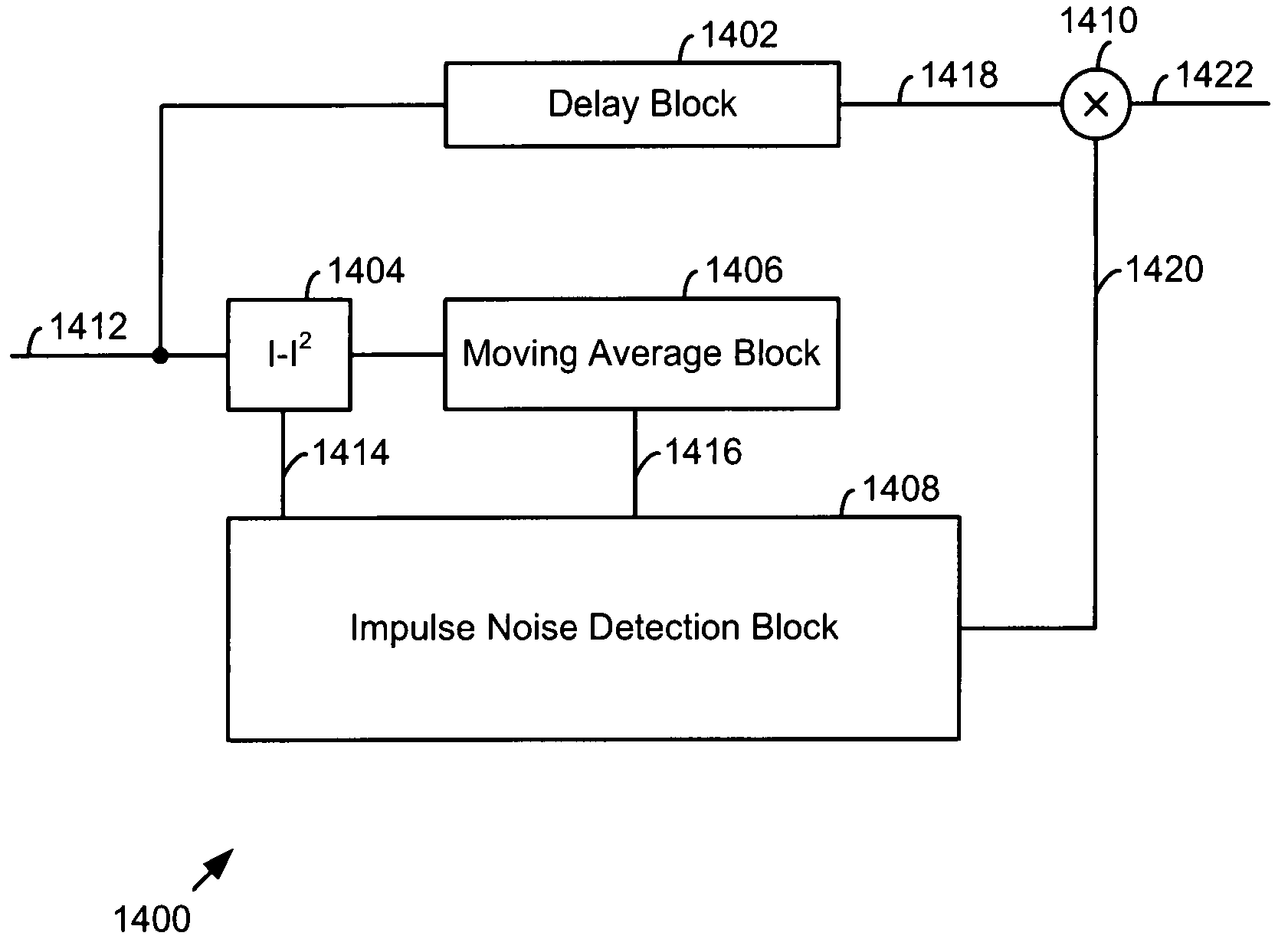
InactiveUS20050047489A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMoving averageCommunications system
A system for mitigating impairment in a communication system includes a delay block, a signal level block, a moving average window block, an impulse noise detection block, and a combiner. The delay block receives and delays each chip of a plurality of chips in a spreading interval. The signal level block determines a signal level of each chip of the plurality of chips in the spreading interval. The moving average window block determines a composite signal level for a chip window corresponding to the chip. The impulse noise detection block receives the signal level, receives the composite signal level, and produces an erasure indication for each chip of the plurality of chips of the corresponding chip window. The combiner erases chips of the plurality of chips of the spreading interval based upon the erasure indication.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Decoding distorted symbols
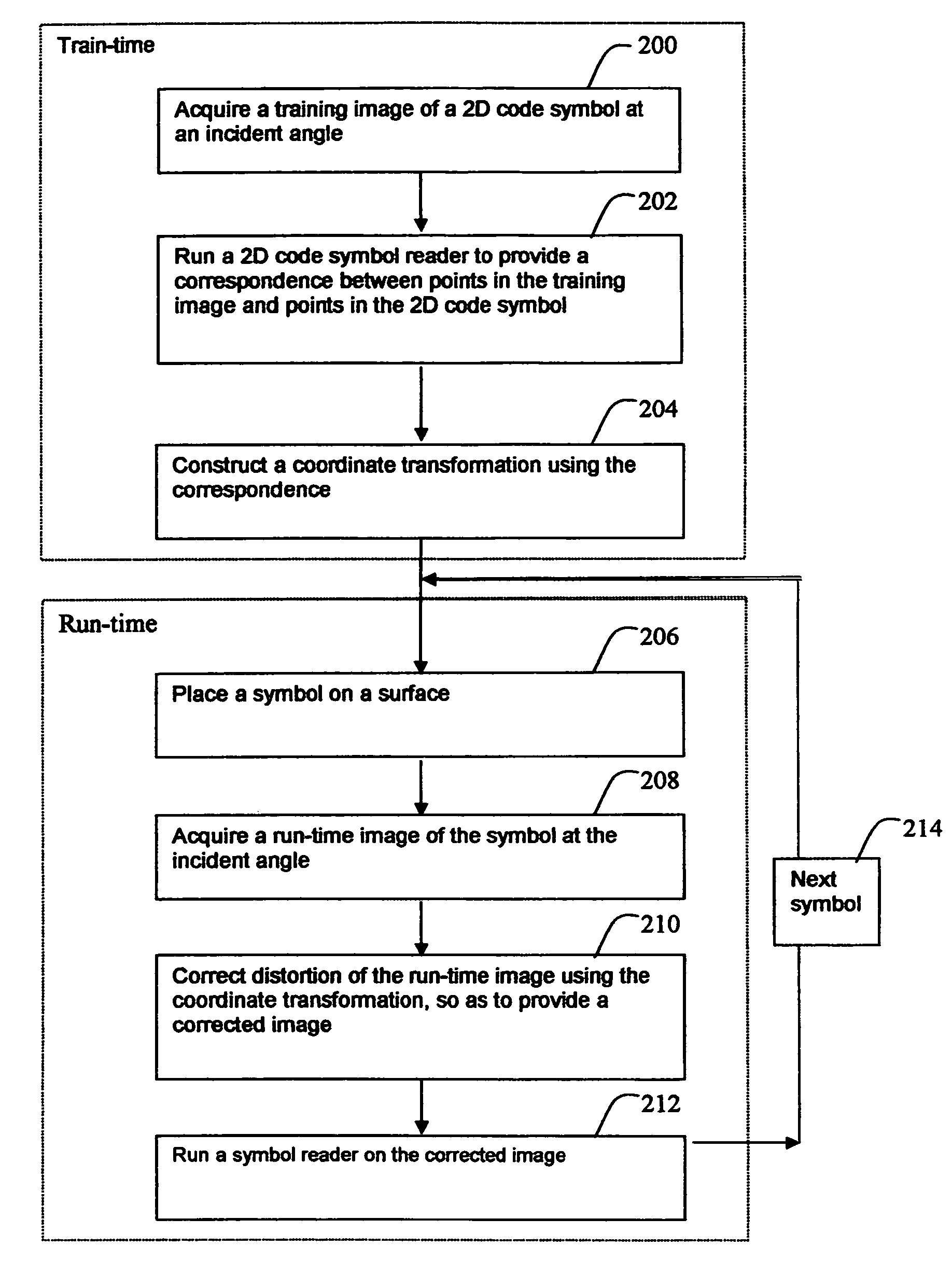
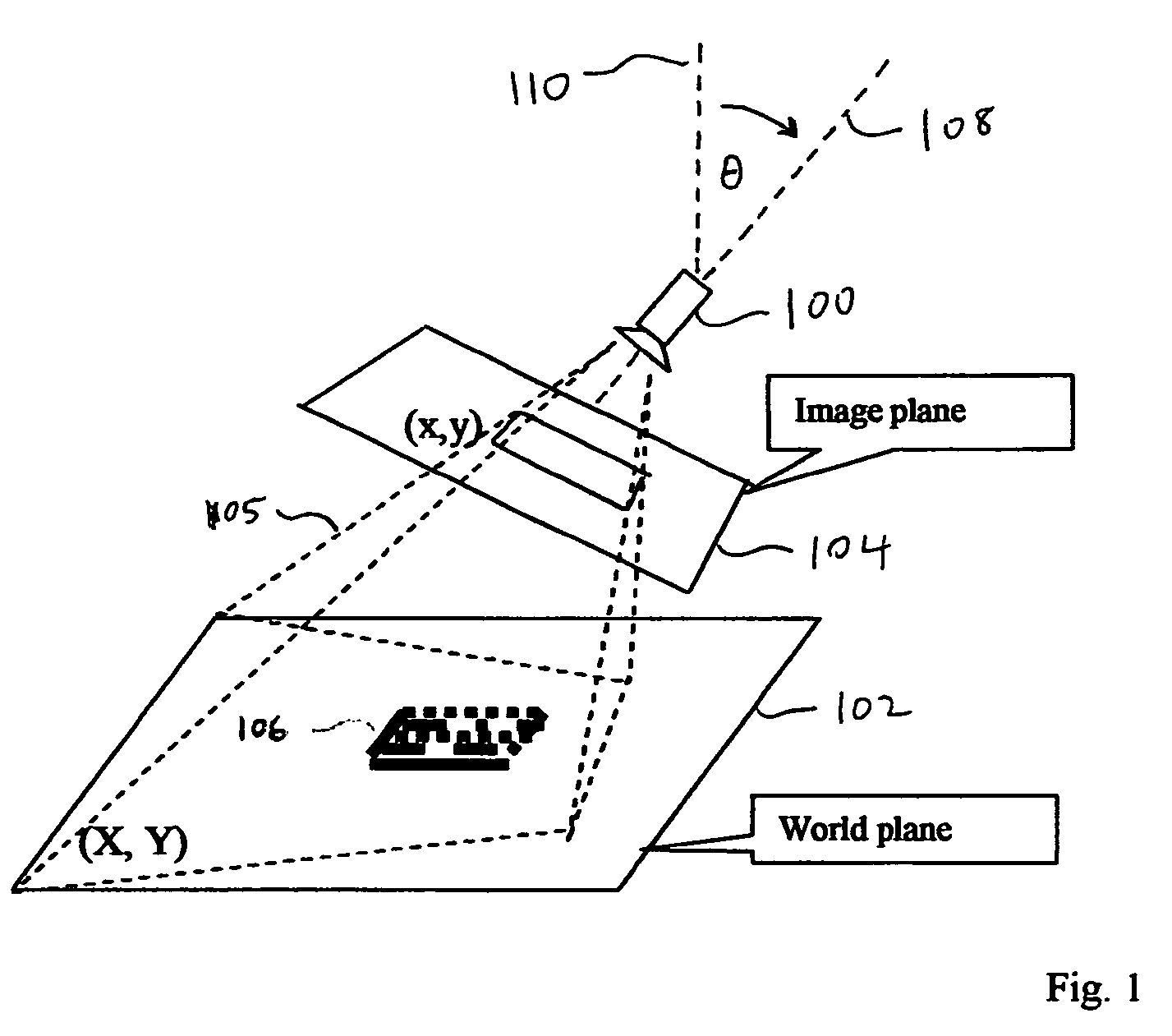
InactiveUS20090090781A1Without excessive computational complexityWithout compromised burst noise handlingGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionDecoding methodsDistortion free
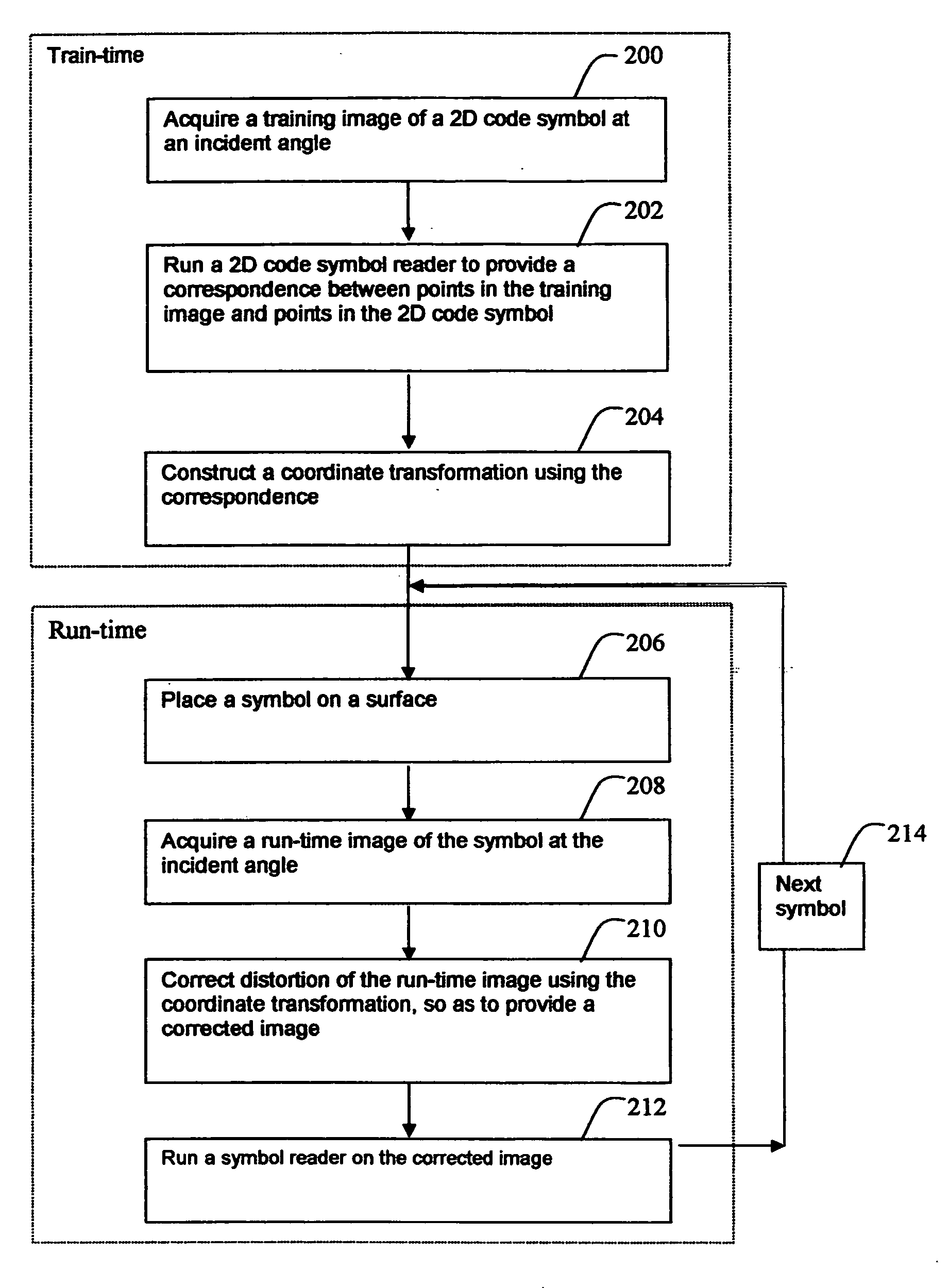
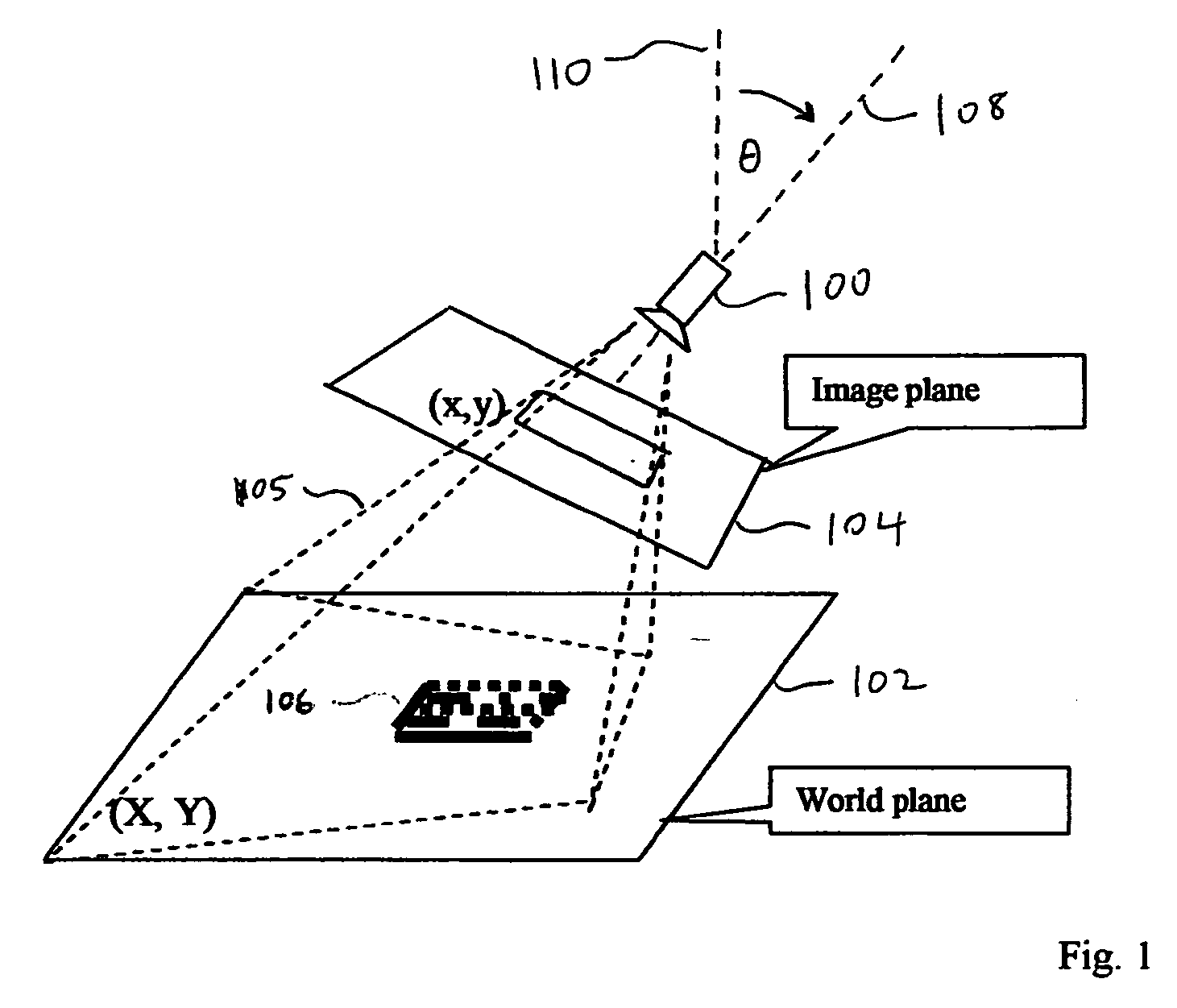
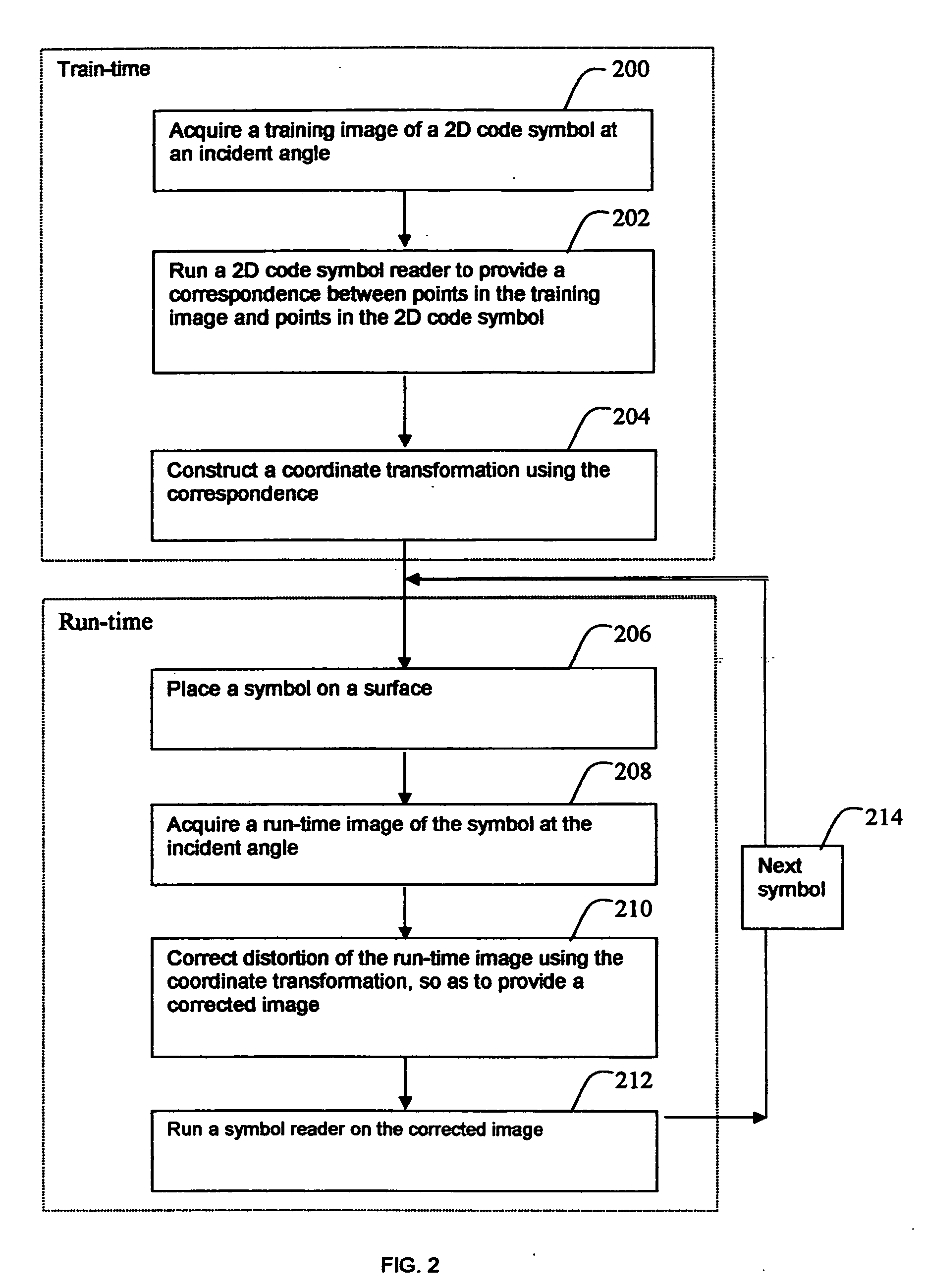
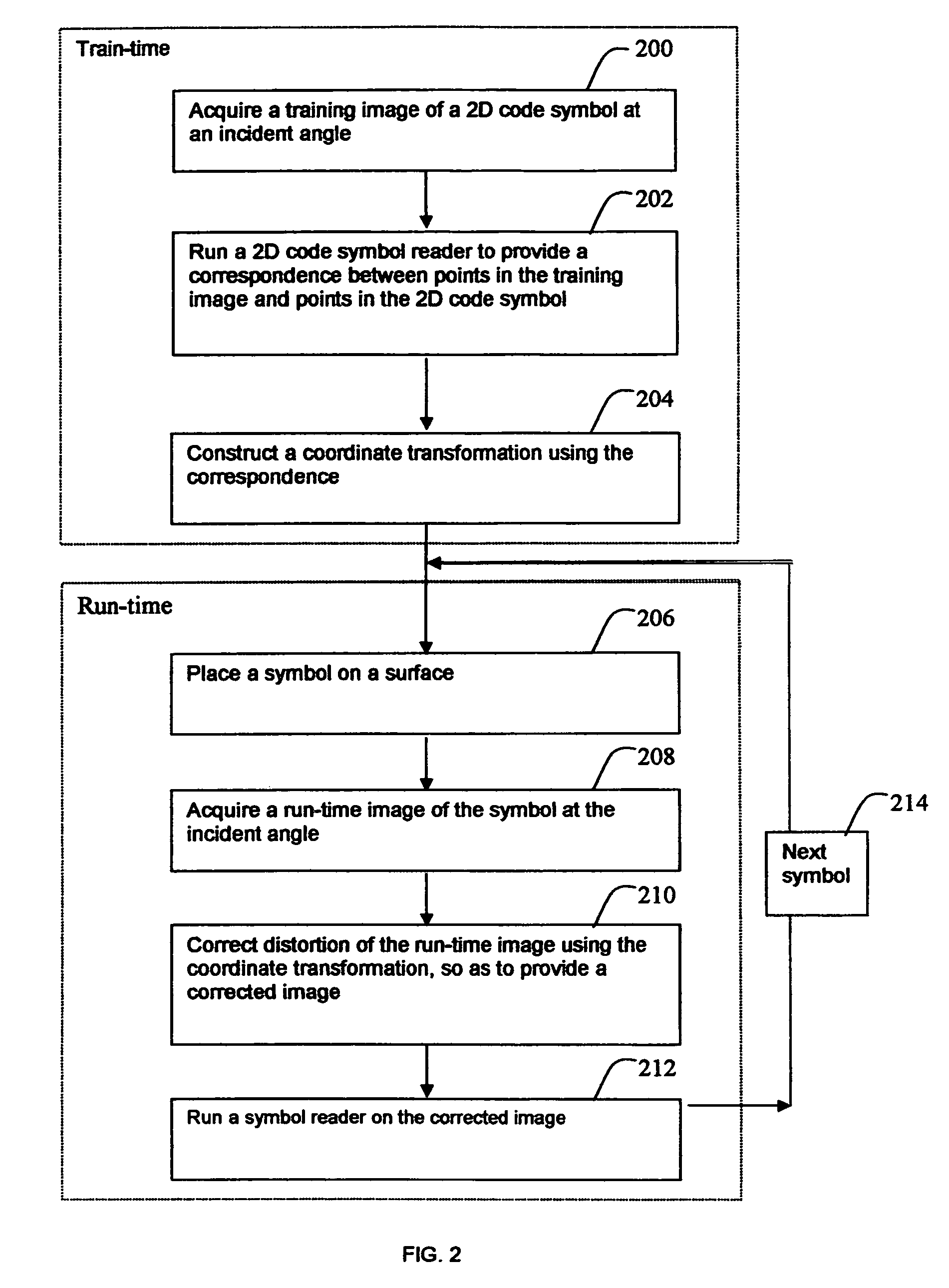
A method is provided for reading distorted optical symbols using known locating and decoding methods, without requiring a separate and elaborate camera calibration procedure, without excessive computational complexity, and without compromised burst noise handling. The invention exploits a distortion-tolerant method for locating and decoding 2D code symbols to provide a correspondence between a set of points in an acquired image and a set of points in the symbol. A coordinate transformation is then constructed using the correspondence, and run-time images are corrected using the coordinate transformation. Each corrected run-time image provides a distortion-free representation of a symbol that can be read by traditional code readers that normally cannot read distorted symbols. The method can handle both optical distortion and printing distortion. The method is applicable to “portable” readers when an incident angle with the surface is maintained, the reader being disposed at any distance from the surface.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
Method and system for receiving a multi-carrier signal
InactiveUS20050220001A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsTime domainPrior information
Method and system for tolerating impulsive burst noise in pilot based OFDM systems, especially using DVB-T standard. The method contains following steps: 1) recognition of the impulse position and possibly length in the time domain symbol, 2) blanking of those samples of the symbol where significant amount of impulse noise is present, 3) calculating the first estimate of the received signal from the blanked symbol, 4) using a prior information (guard band carriers, pilot carriers) an estimate of the blanked symbol is calculated using inverse FFT on the differences of the observed carrier values from the known values in the frequency domain, 5) correction values for the frequency domain carriers are derived taking the FFT of the restored time domain samples, 6) finally the corrected estimate of the received symbol is derived by summing the correction values of step 5 to the first estimate of carriers derived in step 3. The method allows correction of relatively long bursts of impulse noise with minor degradation. The method provides considerably reliable data reception in broadcast systems.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
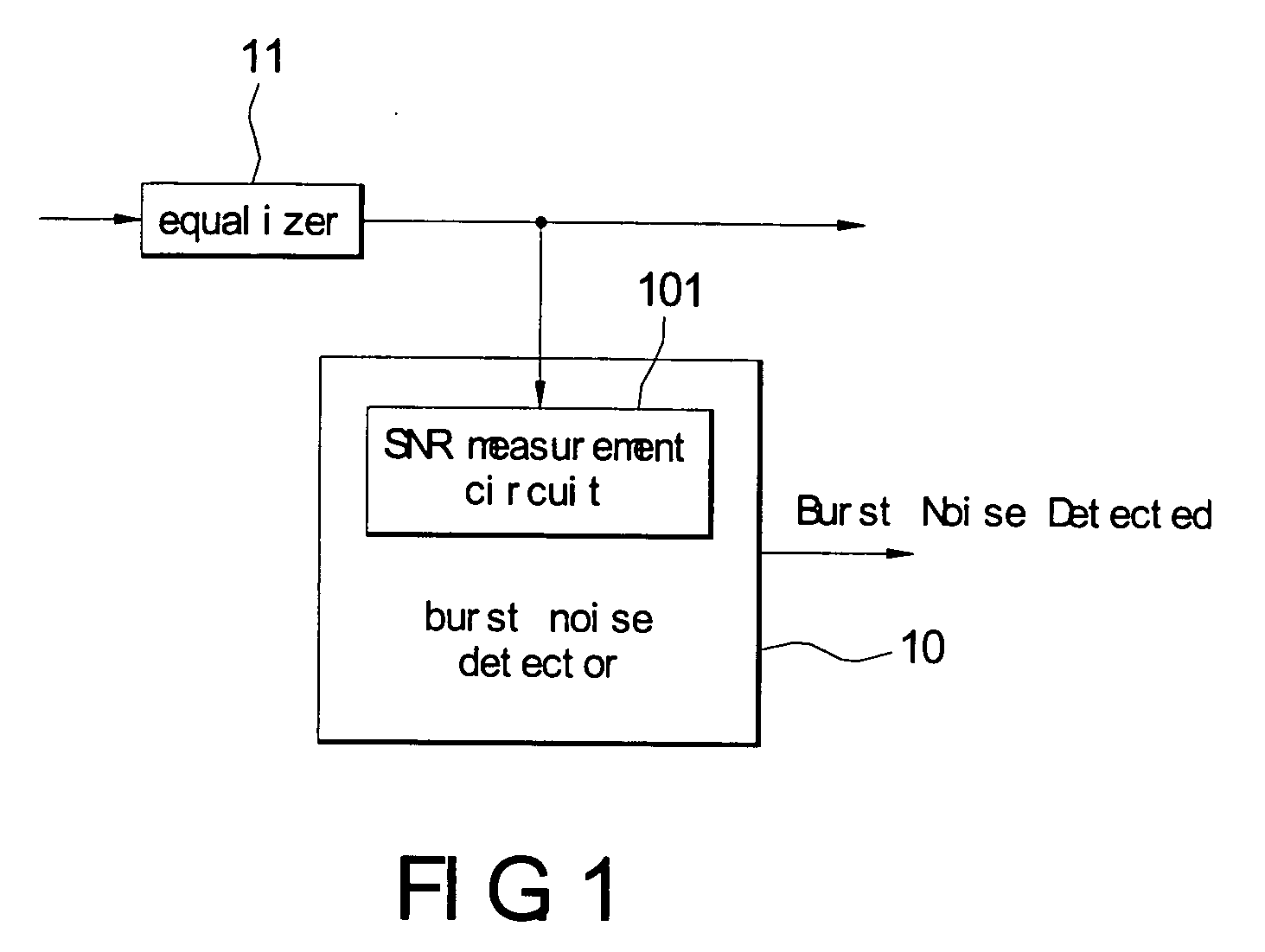
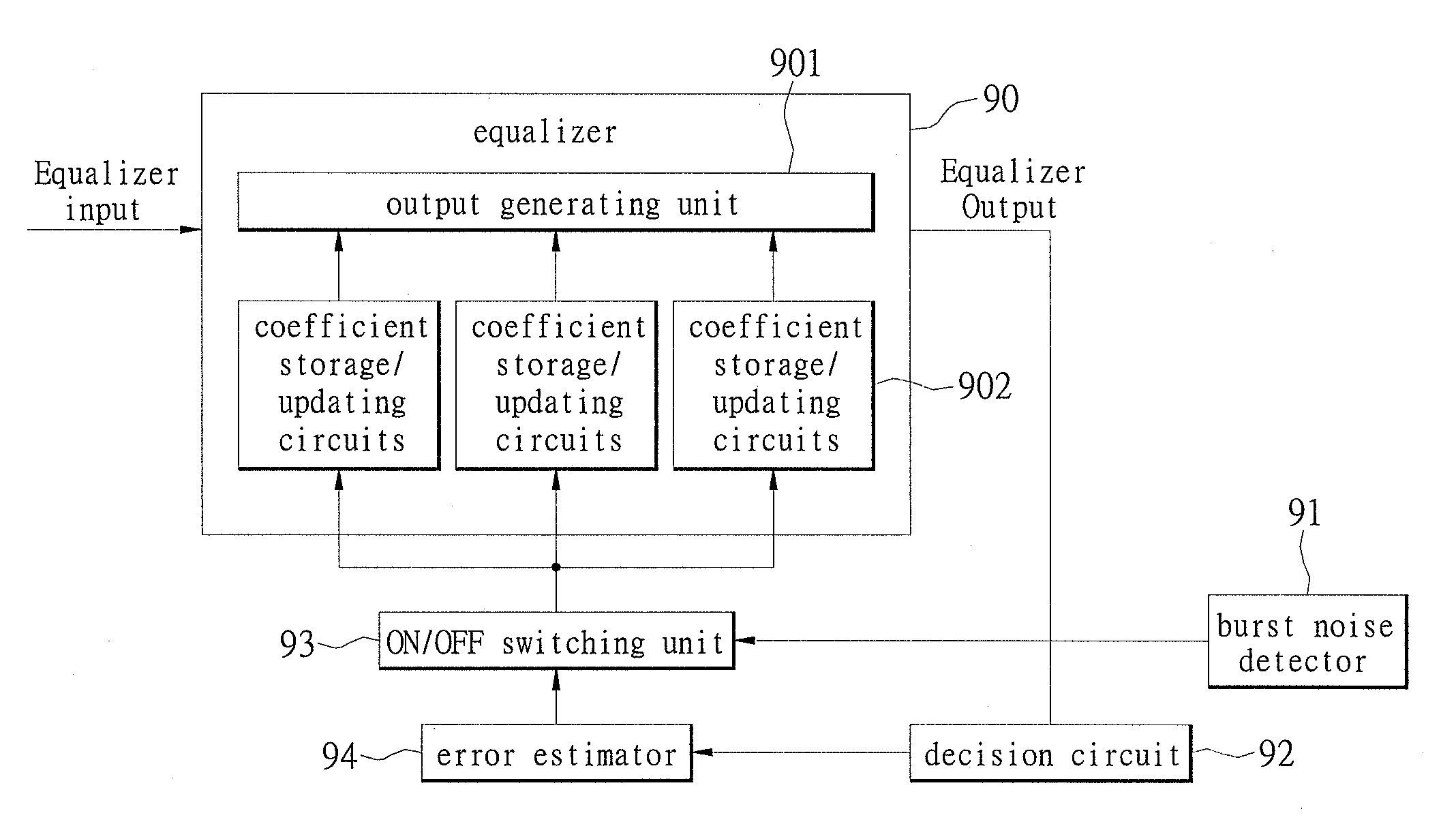
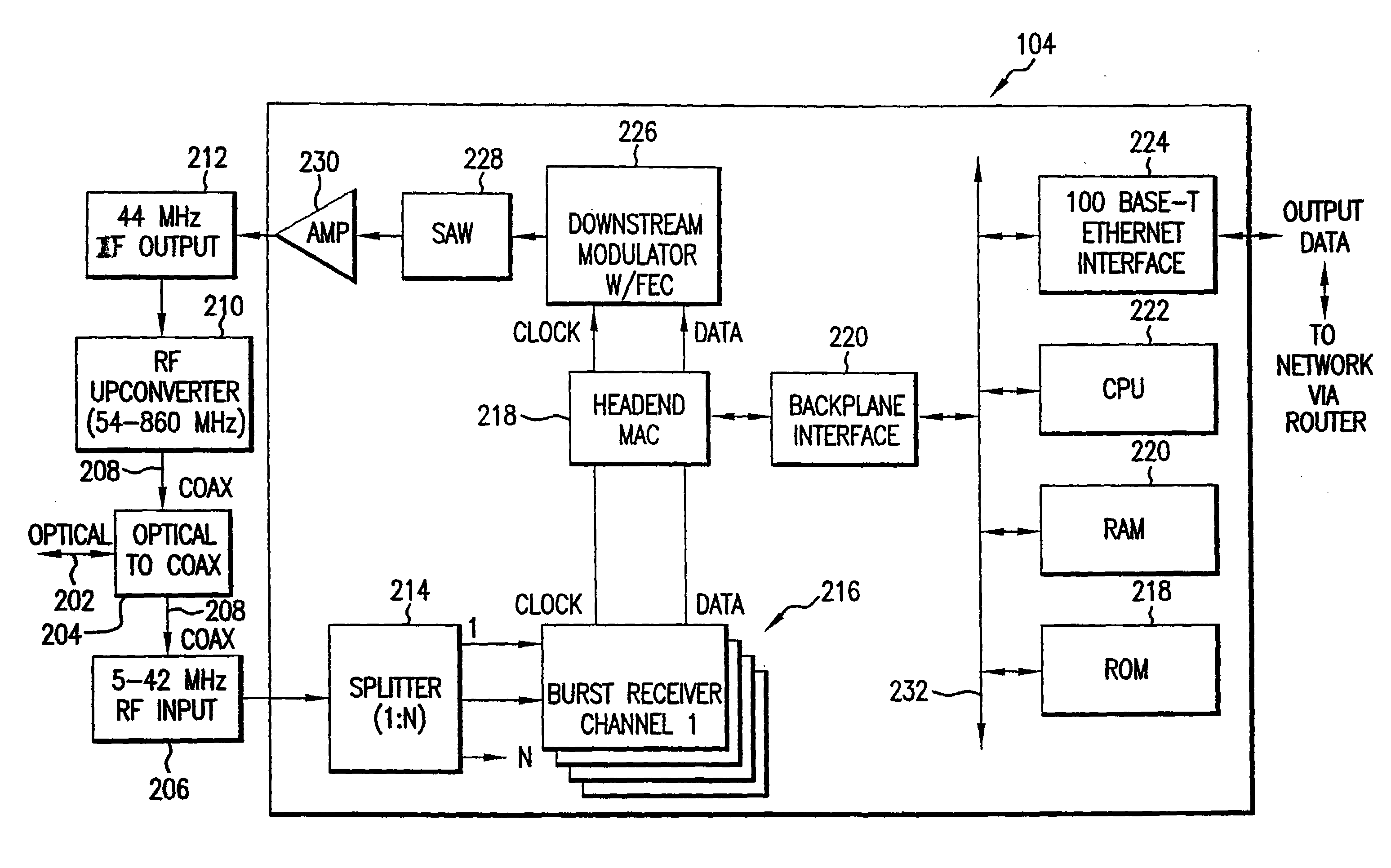
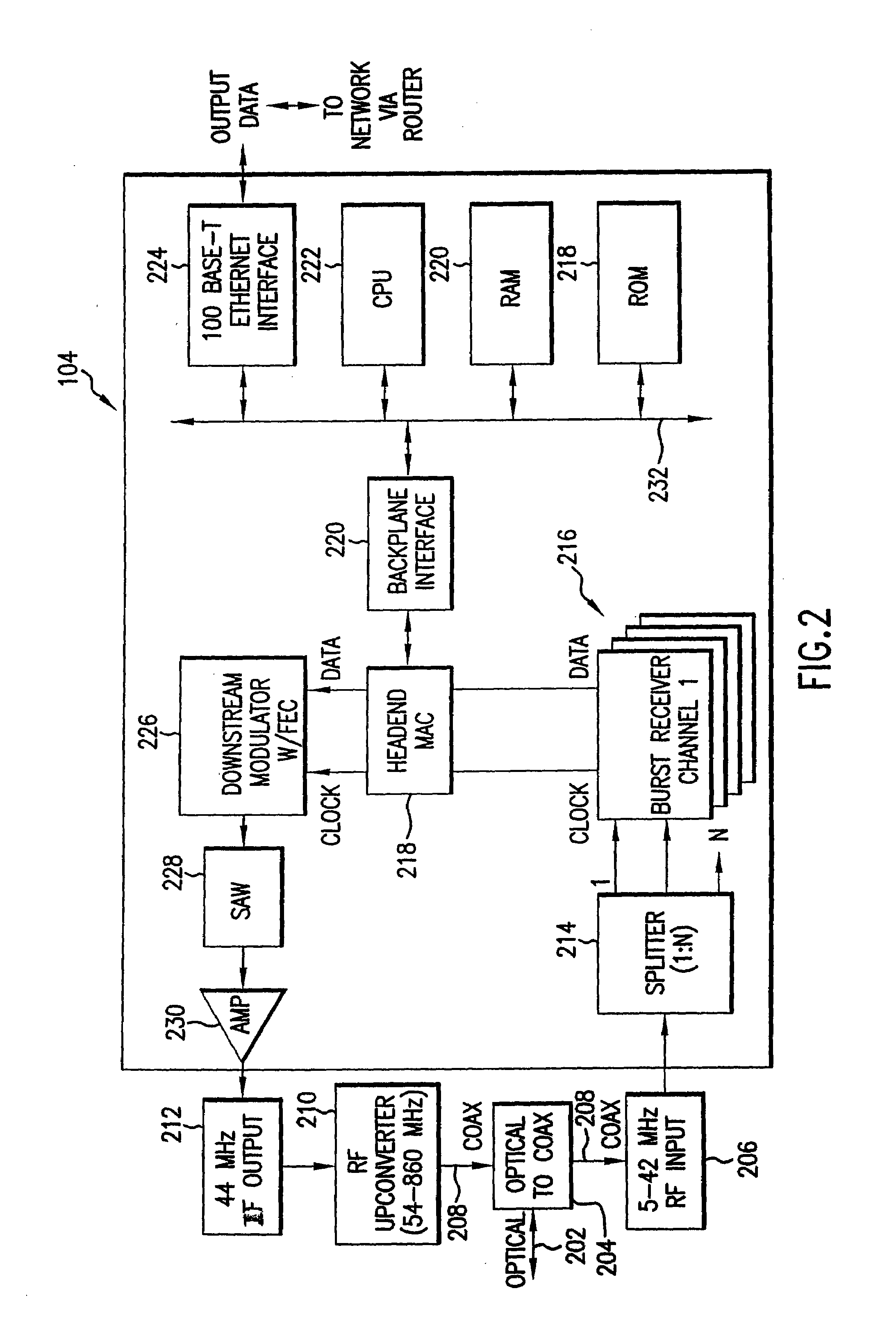
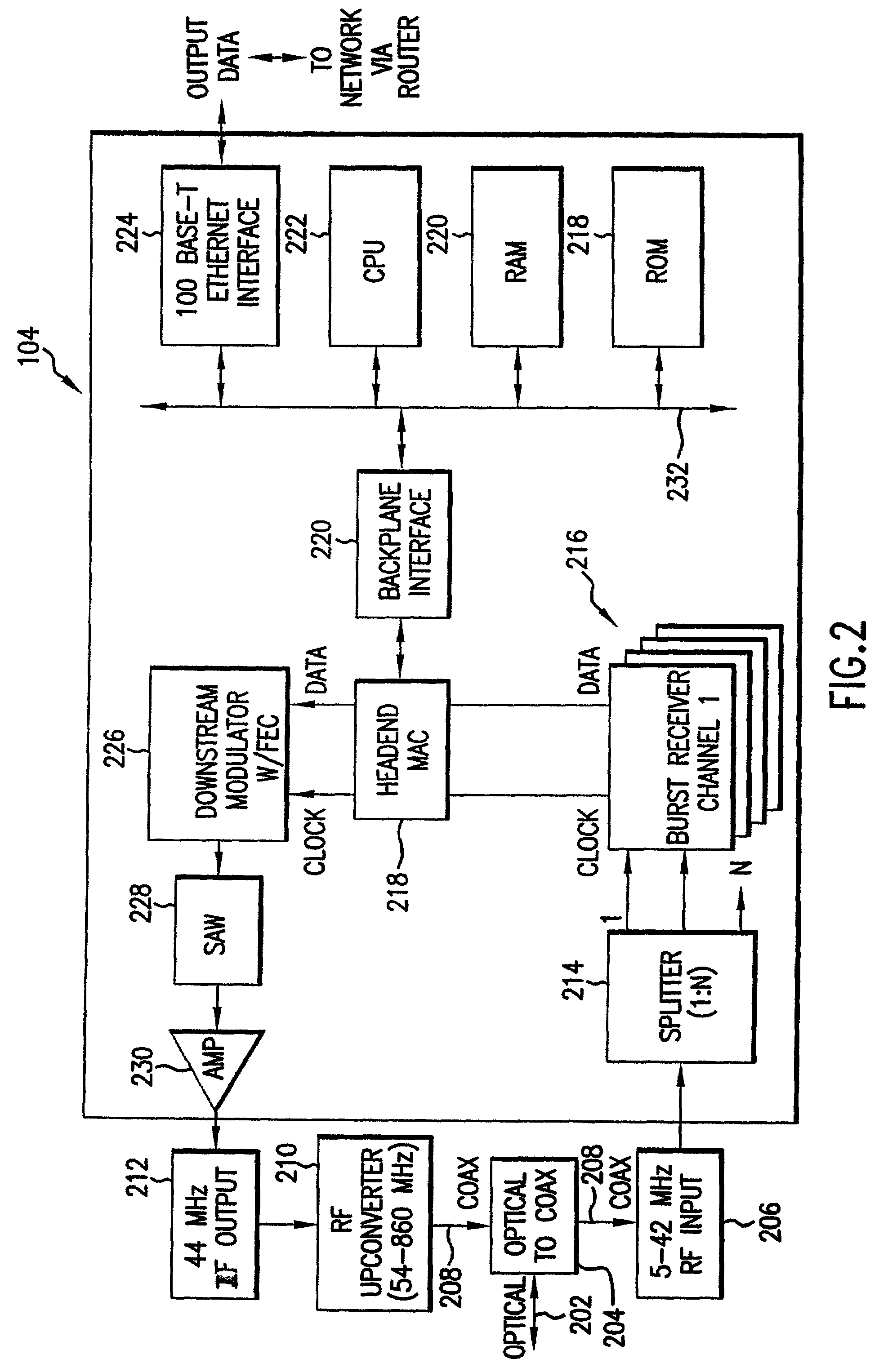
Apparatus for suppressing burst noise and method thereof
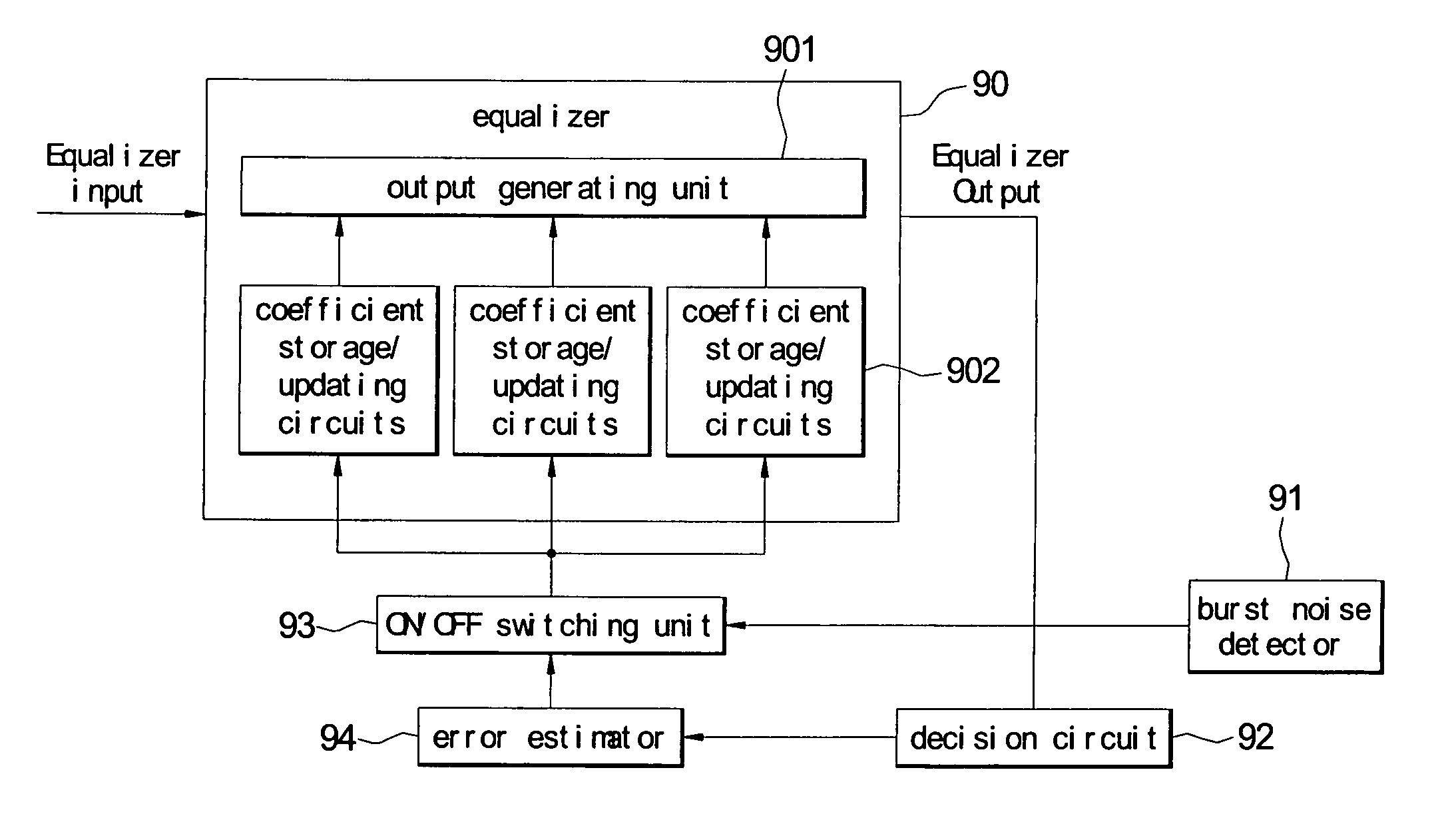
ActiveUS20060274866A1Suppressing burst noiseReduce distractionsMultiple-port networksError preventionEngineeringBurst noise
An apparatus performs burst noise detection and then reduce the interference of the burst noise by controlling an operation of an adaptive apparatus, such as an equalizer. It includes: an adaptive apparatus having multiple coefficients, processing incoming signals according to these coefficients, and employing an error estimator to update the coefficients; a burst noise detector used to detect a burst noise; and an ON / OFF switching unit used to stop the error estimator from updating the coefficients when the burst noise is detected.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
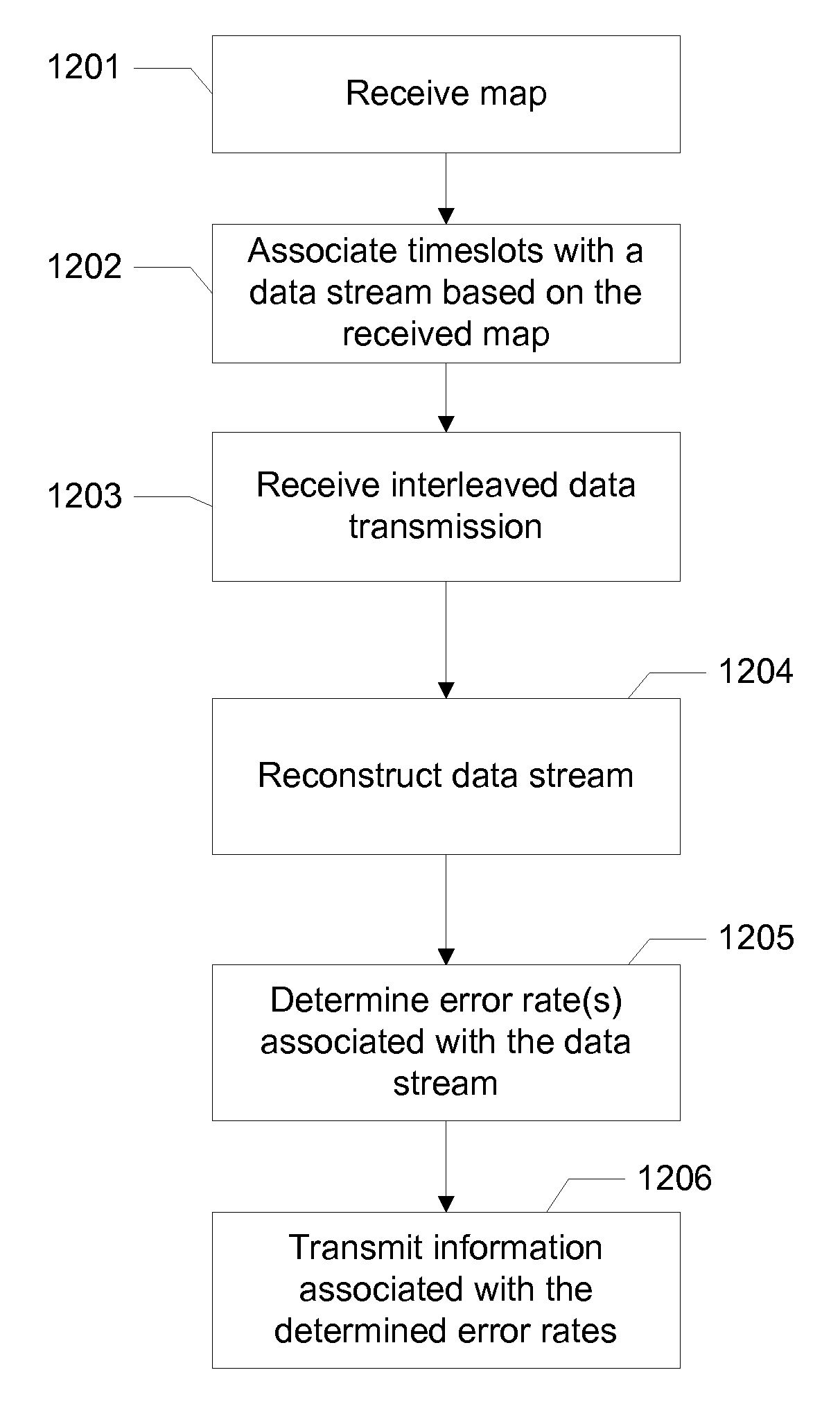
Variable Interleave Data Transmission
ActiveUS20100332941A1Depth adjustableLower latencyCode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesData streamModem device
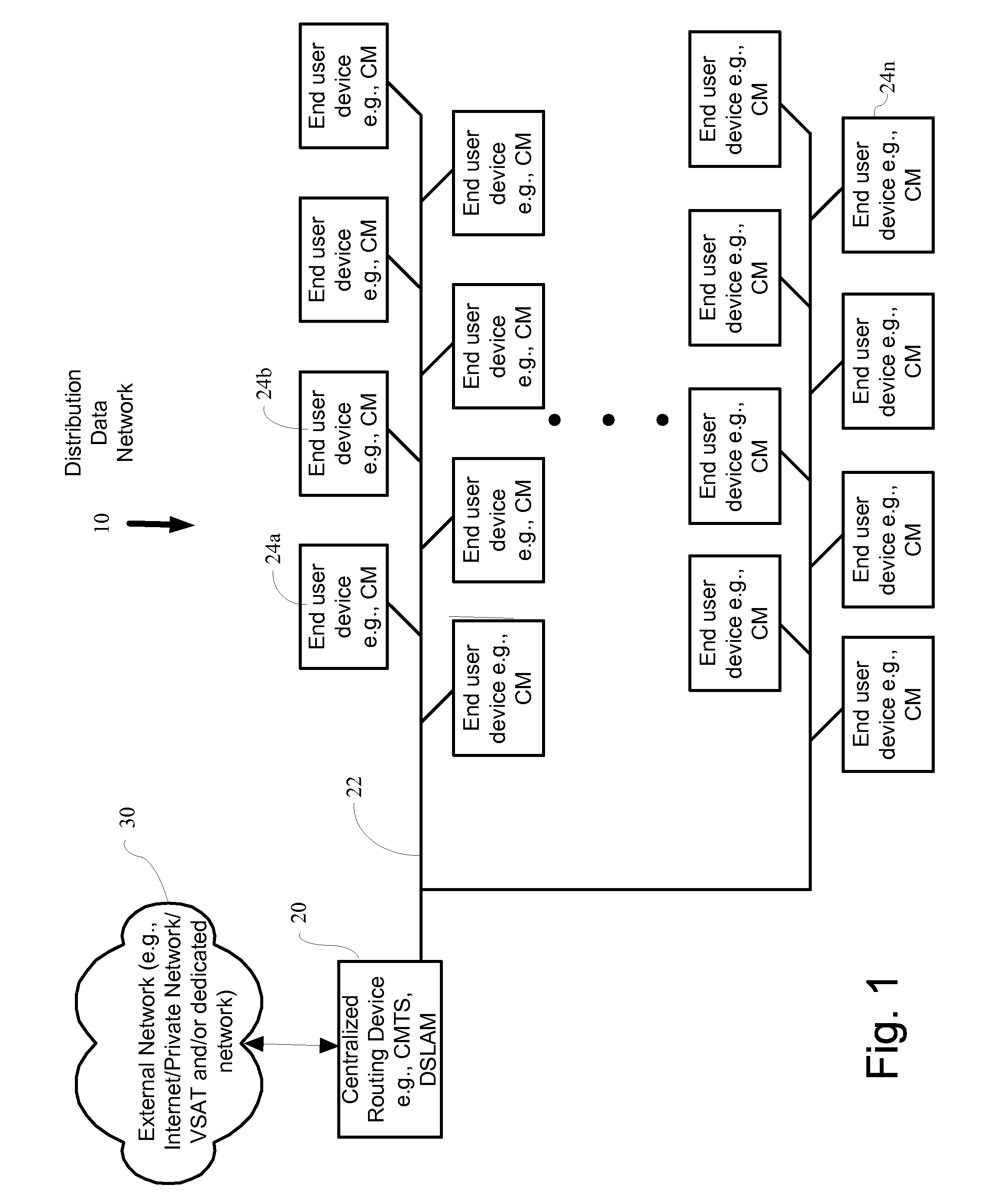
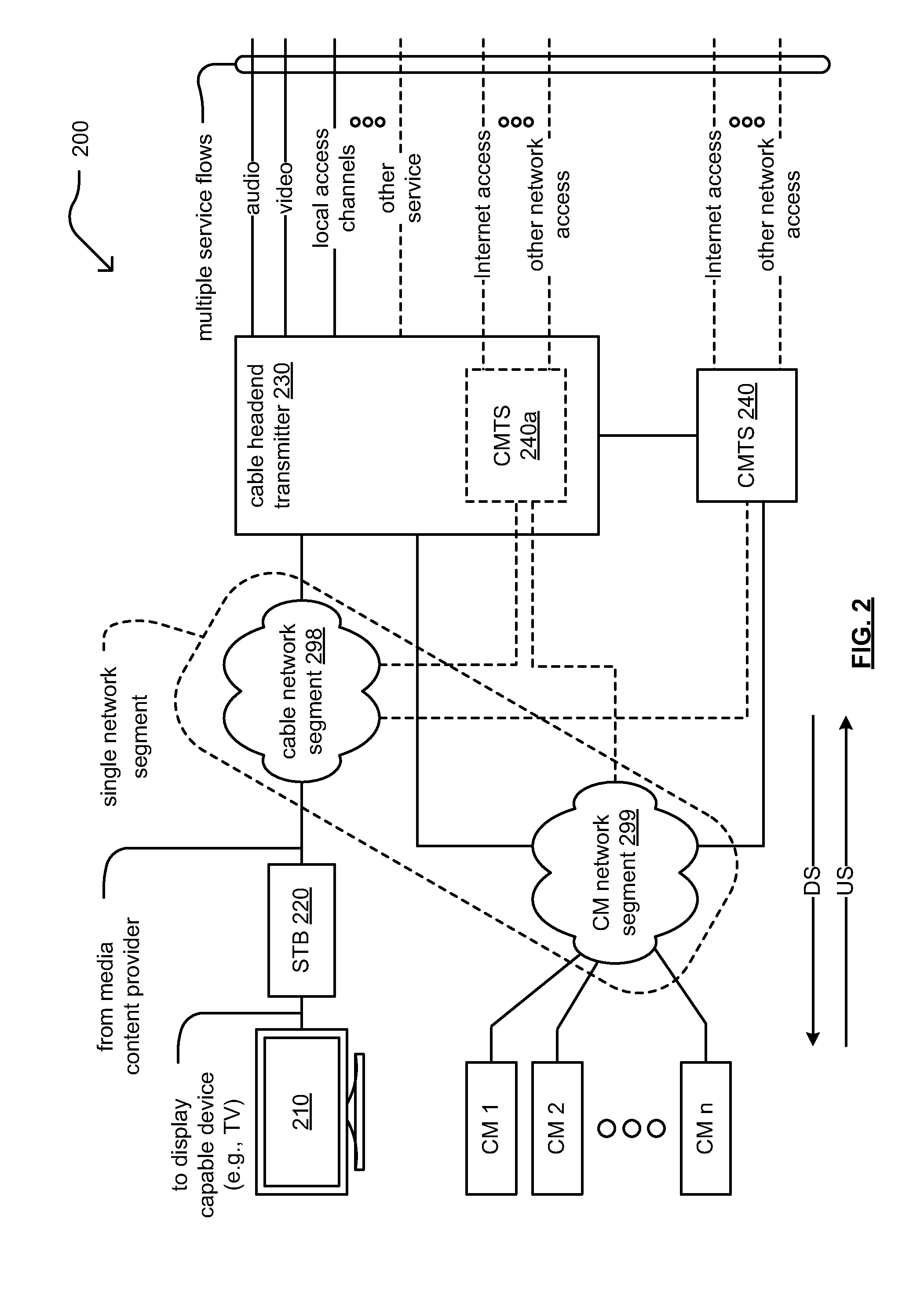
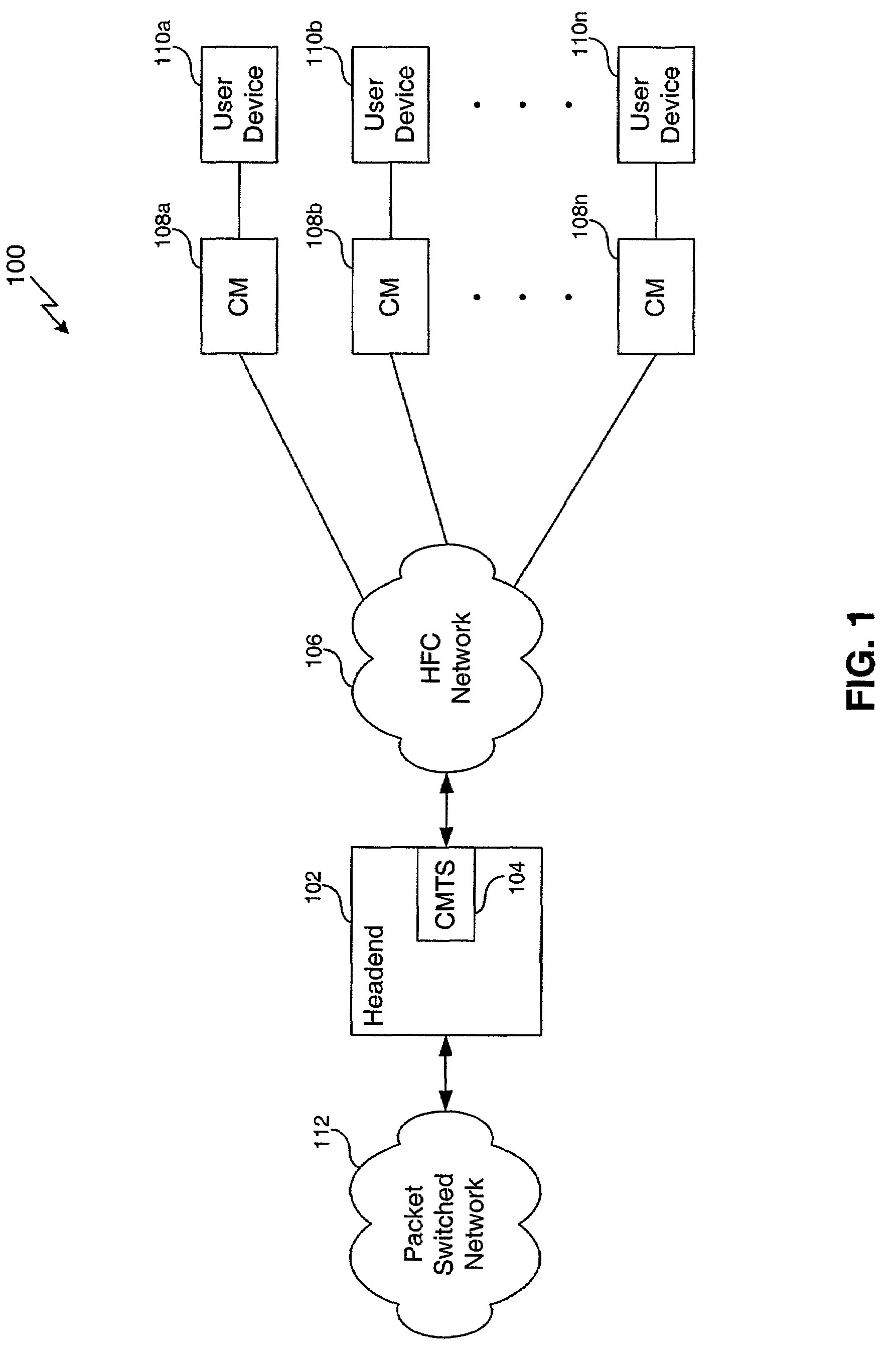
In cable modem termination systems (CMTS) and other information transmission systems, a method for changing the interleave depth associated with each data stream is provided. This may be done dynamically, and for any subset of downstream devices such as modems. The interleave depth may be set on an individual device level. Embodiments may decrease data receiving latency on devices that do not suffer from error rates, such as caused by burst noise, while maintaining throughput on devices with high error rates.
Owner:TIVO CORP
Chip blanking and processing in SCDMA to mitigate impulse and burst noise and/or distortion
InactiveUS7366258B2Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsMoving averageCommunications system
A system for mitigating impairment in a communication system includes a delay block, a signal level block, a moving average window block, an impulse noise detection block, and a combiner. The delay block receives and delays each chip of a plurality of chips in a spreading interval. The signal level block determines a signal level of each chip of the plurality of chips in the spreading interval. The moving average window block determines a composite signal level for a chip window corresponding to the chip. The impulse noise detection block receives the signal level, receives the composite signal level, and produces an erasure indication for each chip of the plurality of chips of the corresponding chip window. The combiner erases chips of the plurality of chips of the spreading interval based upon the erasure indication.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
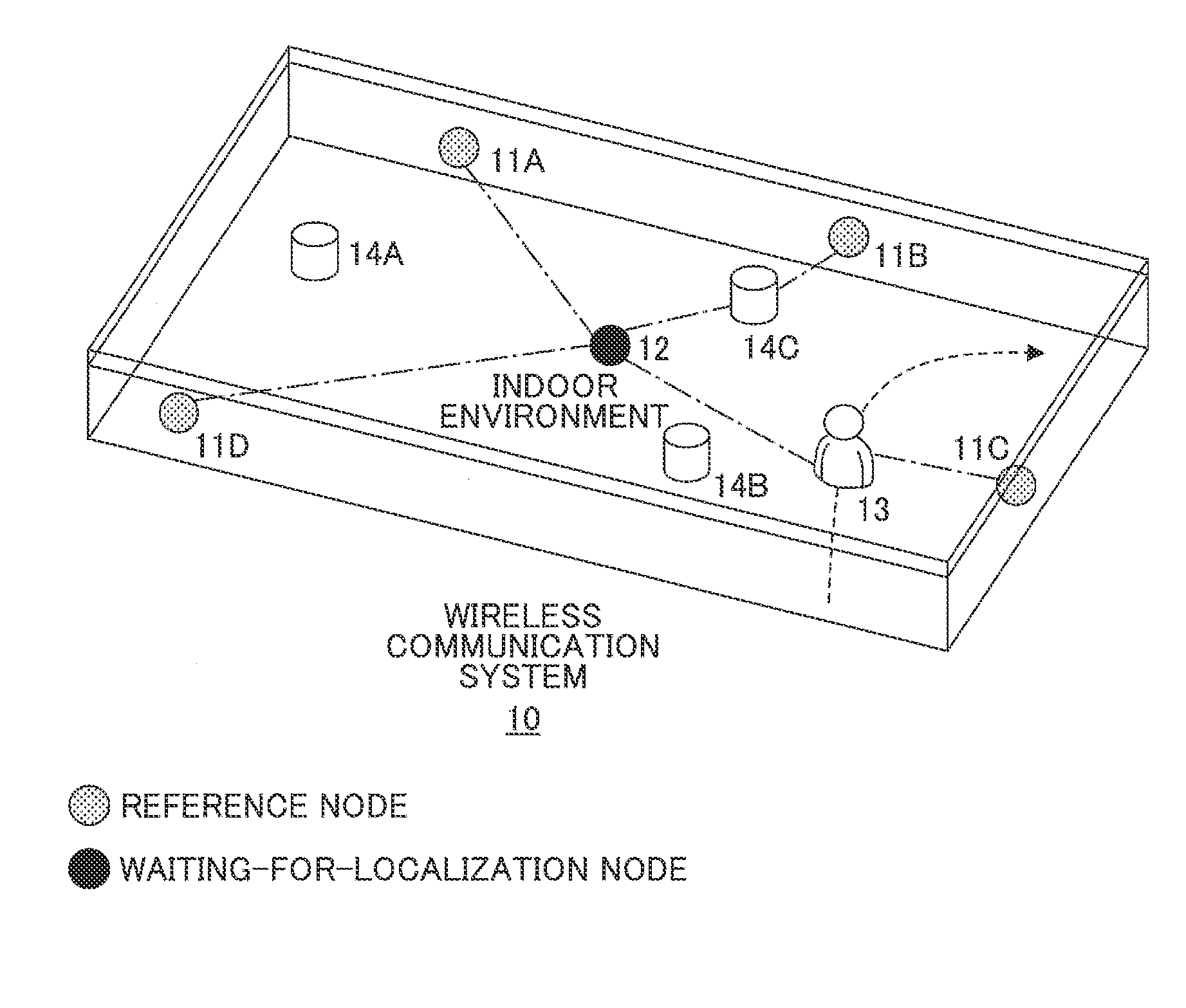
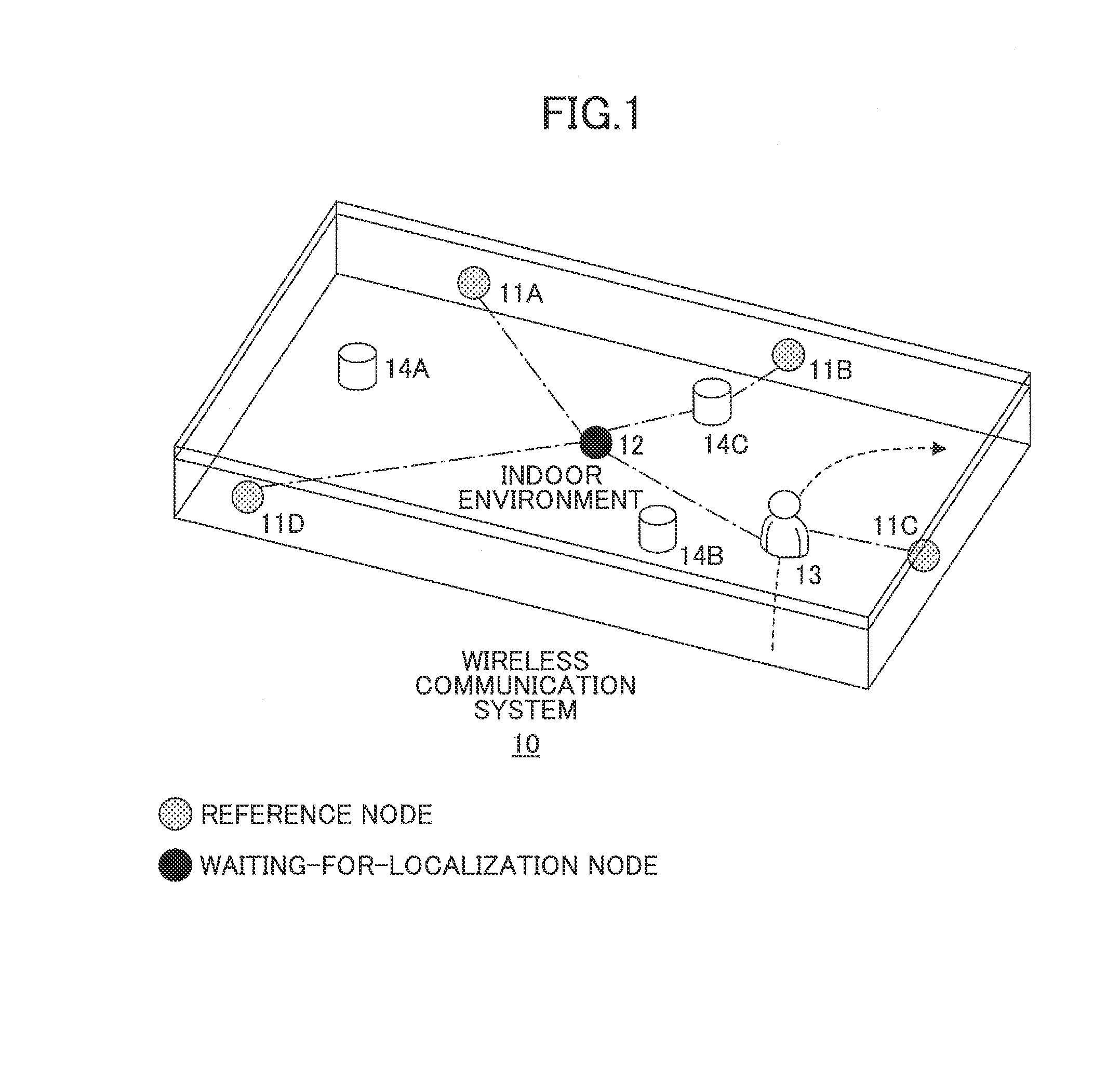
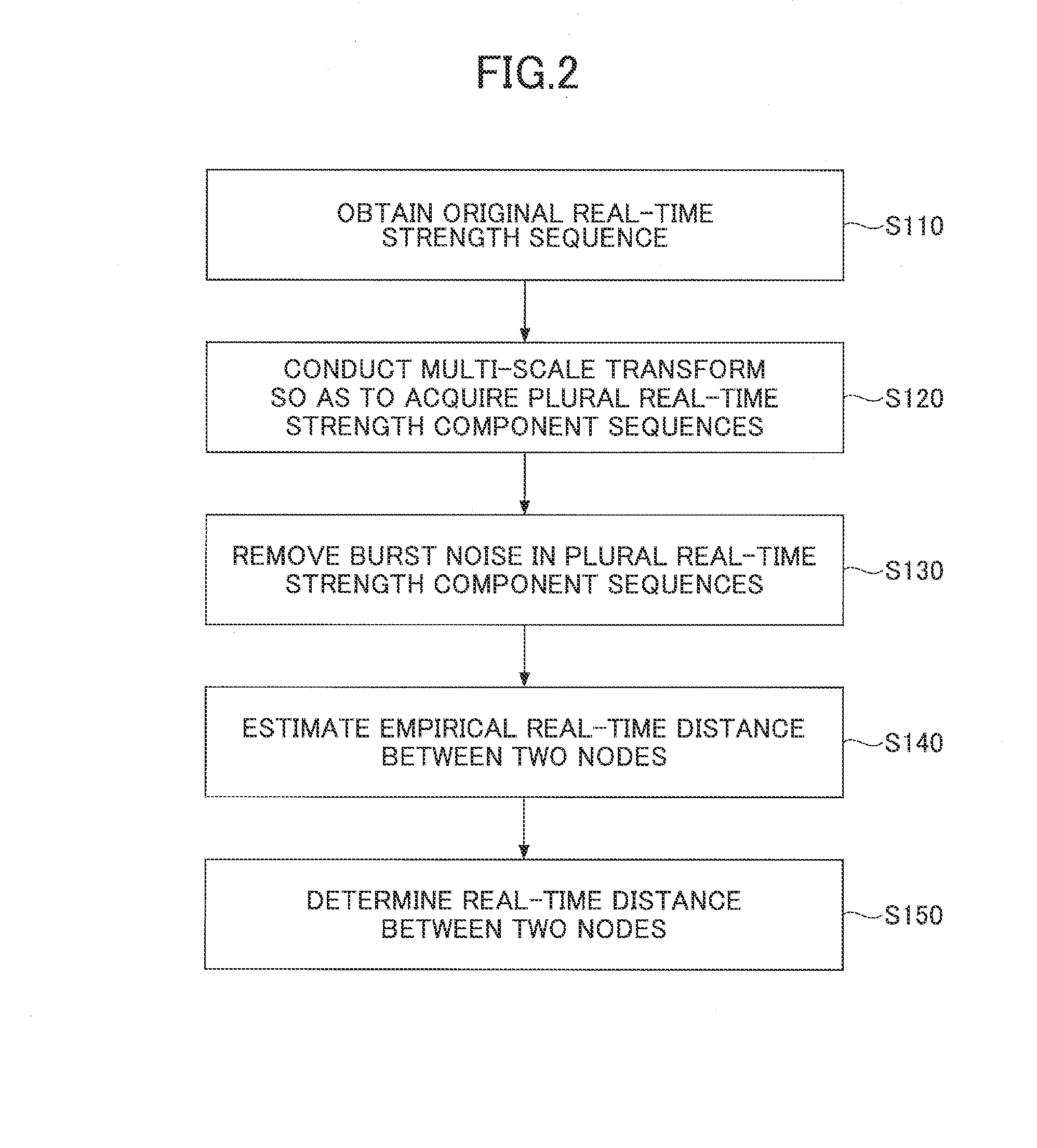
Distance estimation method and device as well as node localization method and apparatus
ActiveUS20160131750A1Accurately localizeAccurate removalDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationAlgorithmTime segment
Disclosed is a method of estimating the distance between two nodes. The method includes obtaining an original real-time strength sequence, its elements being strengths of signals between the two nodes at respective time slots of a first time period; conducting multi-scale transform with respect to the original real-time strength sequence so as to acquire plural real-time strength component sequences which are results of the original real-time strength sequence projected onto plural scales; removing at least one burst noise element in each real-time strength component sequence so as to get plural updated real-time strength component sequences; estimating, based on the plural updated real-time strength component sequences and a multi-scale empirical mapping relationship, an empirical real-time distance, the multi-scale empirical mapping relationship being used for expressing correspondence relations between strength components and distance components; and determining, based on at least the empirical real-time distance, a real-time distance between the two nodes.
Owner:RICOH KK
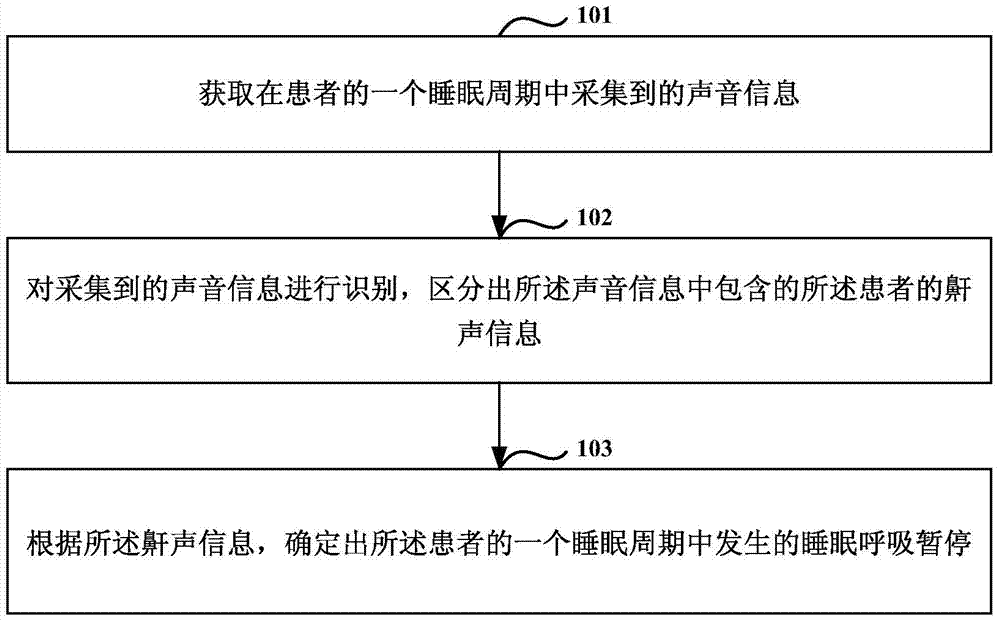
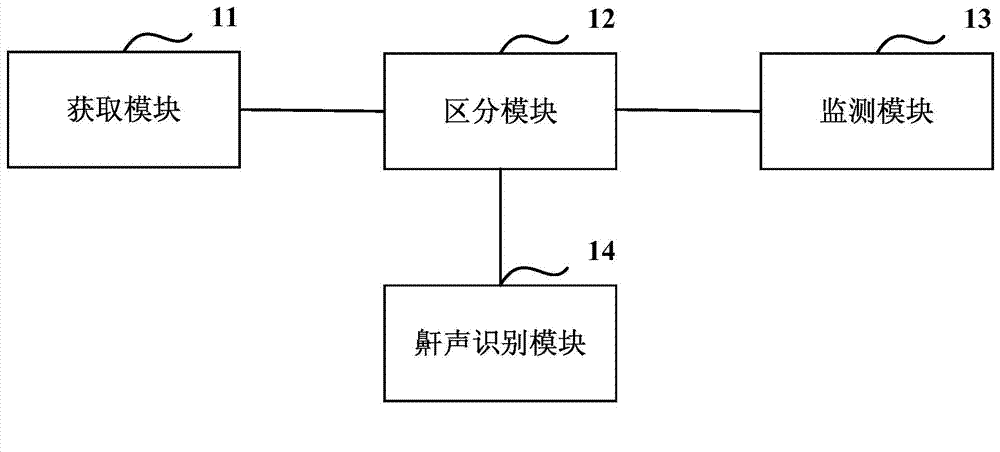
Method and equipment for monitoring sleep apnea
ActiveCN104739412AAvoid the problem of inaccurate monitoringHigh precisionAuscultation instrumentsRespiratory organ evaluationSignal onApnea monitoring
The invention discloses a method and equipment for monitoring sleep apnea. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining sound information collected in a sleeping period of a patient; identifying the collected sound information and distinguishing snore information of the patient in the sound information; determining the sleep apnea in a sleeping period of the patient according to the snore information; and determining the snore information sent in one sleeping period of the patient by analyzing the sound information collected in one sleeping period of the patient, so as to determine the sleep apnea in the sleeping period of the patient according to the snore information. The problem that background noises and burst noises in a sleep scene are greatly overlapped with snore signals on a time-frequency domain when a manner of judging the apnea by analyzing snores is adopted so that the snore signal cannot be accurately monitored is solved, and the apnea monitoring precision is effectively improved.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
Apparatus for suppressing burst noise and method thereof
ActiveUS7760826B2Suppress noiseReduce distractionsMultiple-port networksError preventionEngineeringSelf adaptive
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Impulse and/or burst noise signal to noise ratio (SNR) aware concatenated forward error correction (FEC)
ActiveUS20130227373A1Modulated-carrier systemsOther decoding techniquesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Forward error correction
Impulse and / or burst noise signal to noise ratio (SNR) aware concatenated forward error correction (FEC). Adaptive processing is performed on a signal based on one or more effects which may deleteriously modify a signal. For example, based on a modification of a signal to noise ratio (SNR) associated with one or more impulse or burst noise events, which may be estimated, different respective processing may be performed selectively to differently affected bits associated with the signal. For example, two respective SNRs may be employed: a first SNR for one or more first bits, and a second SNR for one or more second bits. For example, as an impulse or burst noise event may affect different respective bits of a codeword differently, and adaptive processing may be made such that different respective bits of the codeword may be handled differently.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and Method For Mitigating Burst Noise In A Communications System
ActiveUS20090327845A1Avoid packet lossImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemBlock code
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
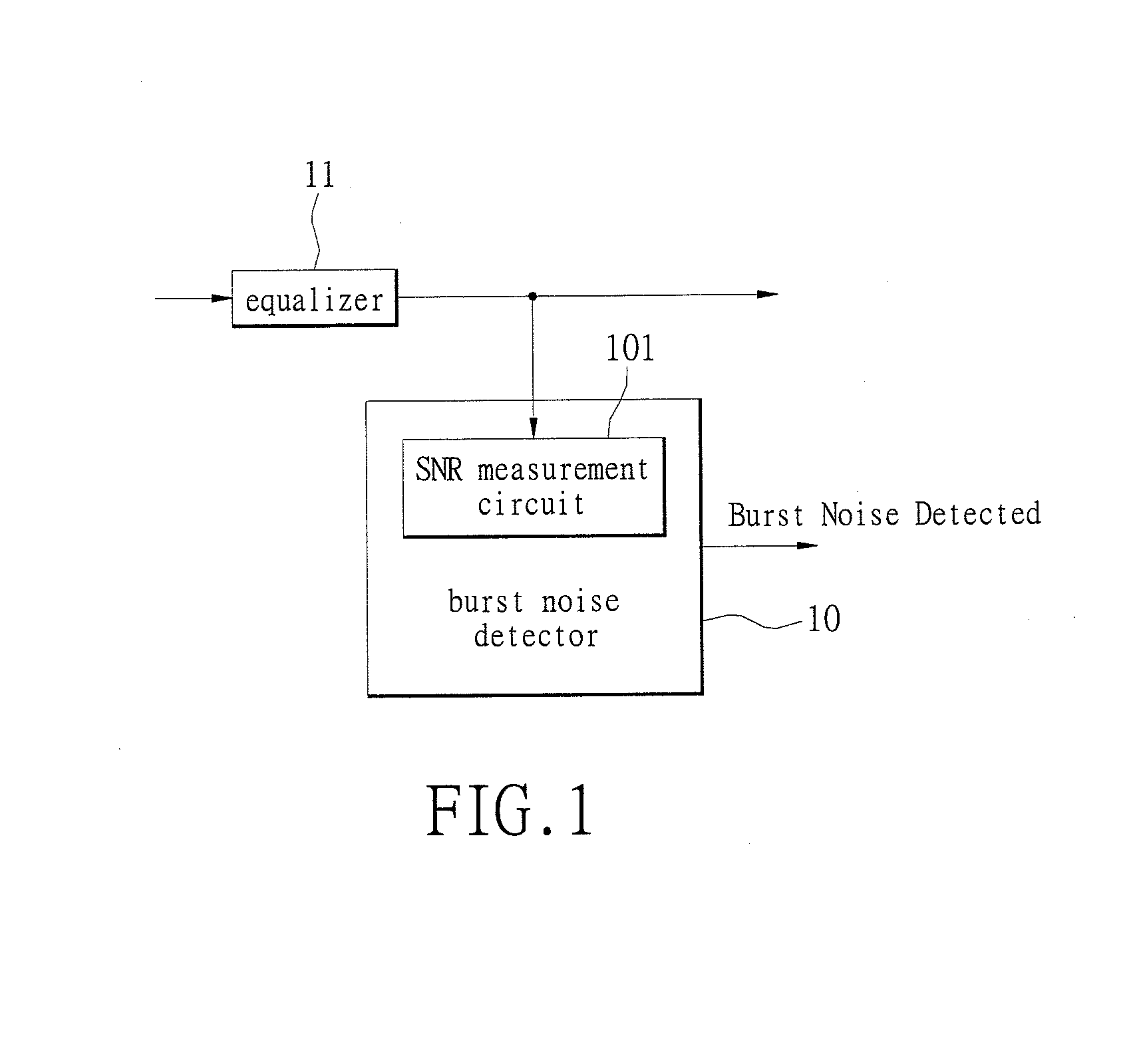
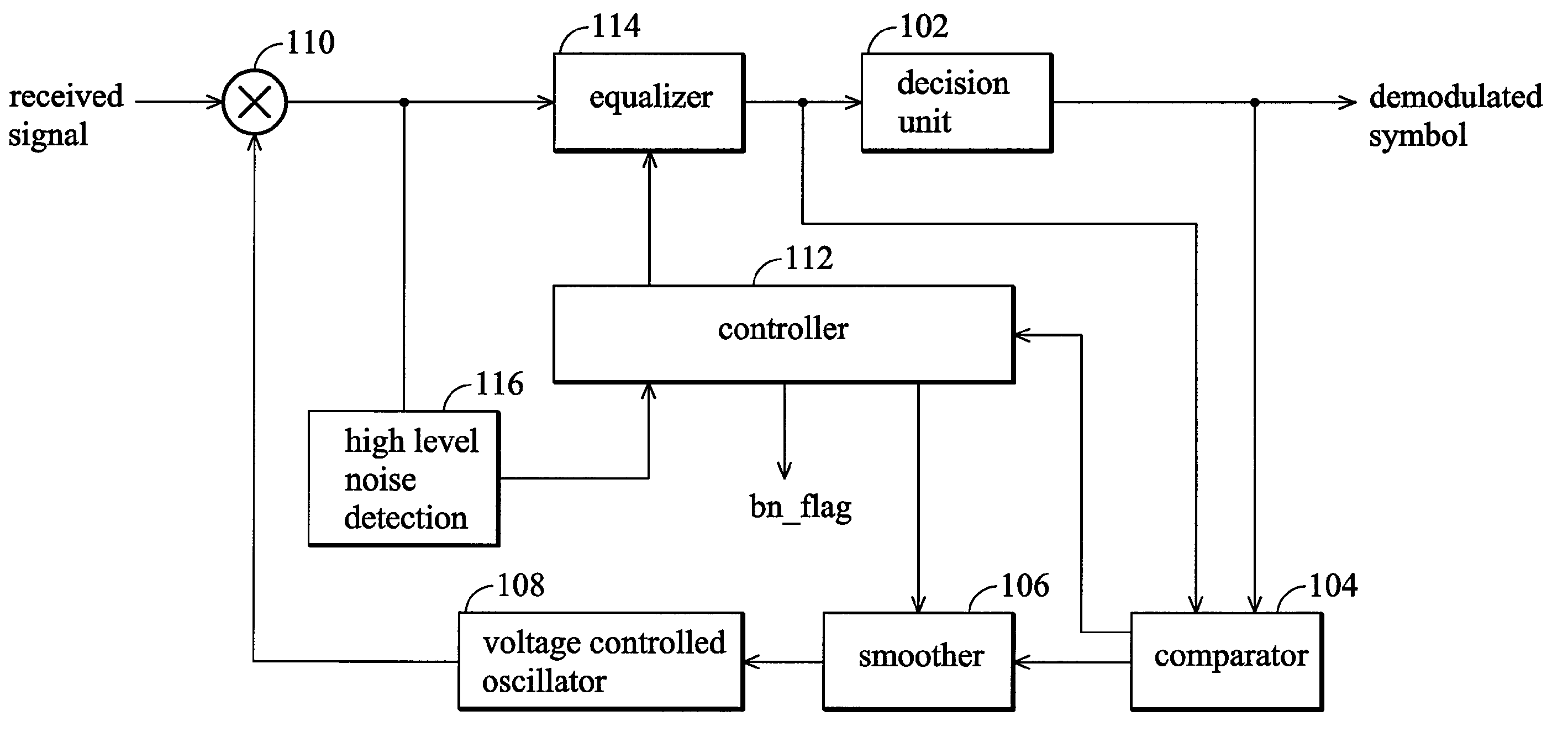
System and method of detecting burst noise and minimizing the effect of burst noise
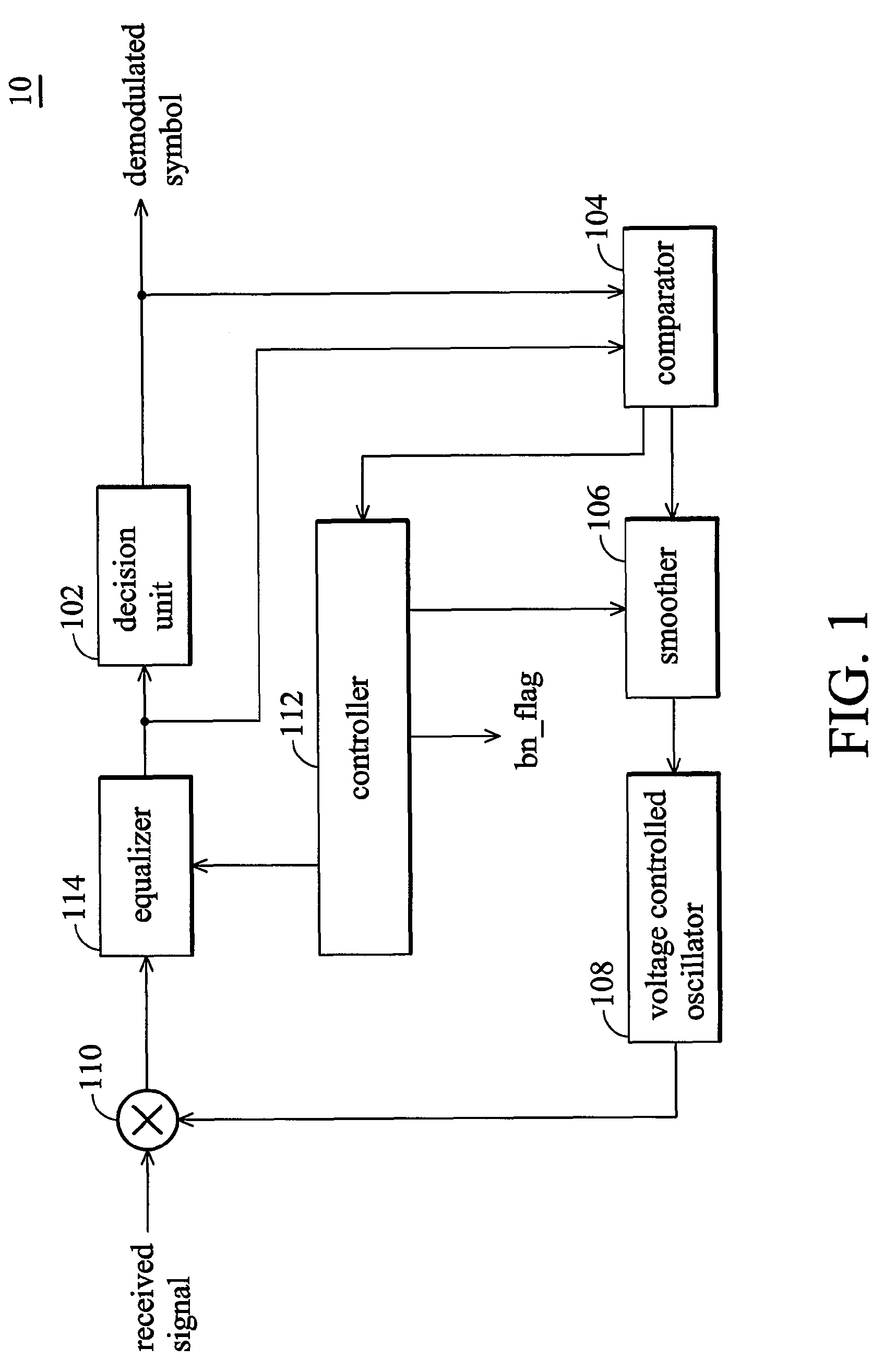
InactiveUS7751514B2Reduce impactHigh noise signalMultiple carrier systemsAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionDecision circuitLoop filter
A communication system and a method which can reduce the effect of burst noise. The communication system comprises a controllable oscillator, a mixer, a decision circuit, a comparator, a loop filter, and a controller. The controllable oscillator generates an oscillating signal. The mixer coupled to the controllable receives input data and mixes the input data with the oscillating signal. The decision circuit receives the mixed input data and generates an estimated symbol. The comparator generates a decision error between the estimated symbol and the mixed input data. The loop filter coupled to the controllable oscillator filters the decision error, and generates a filtered decision error, and the controllable oscillator generates the oscillating signal according to the filtered decision error. The controller reduces a bandwidth of the loop filter according to the decision error.
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
Decoding distorted symbols
InactiveUS7878402B2Without excessive computational complexityWithout compromised burst noise handlingTransmission systemsGeometric image transformationDecoding methodsDistortion free
A method is provided for reading distorted optical symbols using known locating and decoding methods, without requiring a separate and elaborate camera calibration procedure, without excessive computational complexity, and without compromised burst noise handling. The invention exploits a distortion-tolerant method for locating and decoding 2D code symbols to provide a correspondence between a set of points in an acquired image and a set of points in the symbol. A coordinate transformation is then constructed using the correspondence, and run-time images are corrected using the coordinate transformation. Each corrected run-time image provides a distortion-free representation of a symbol that can be read by traditional code readers that normally cannot read distorted symbols. The method can handle both optical distortion and printing distortion. The method is applicable to “portable” readers when an incident angle with the surface is maintained, the reader being disposed at any distance from the surface.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
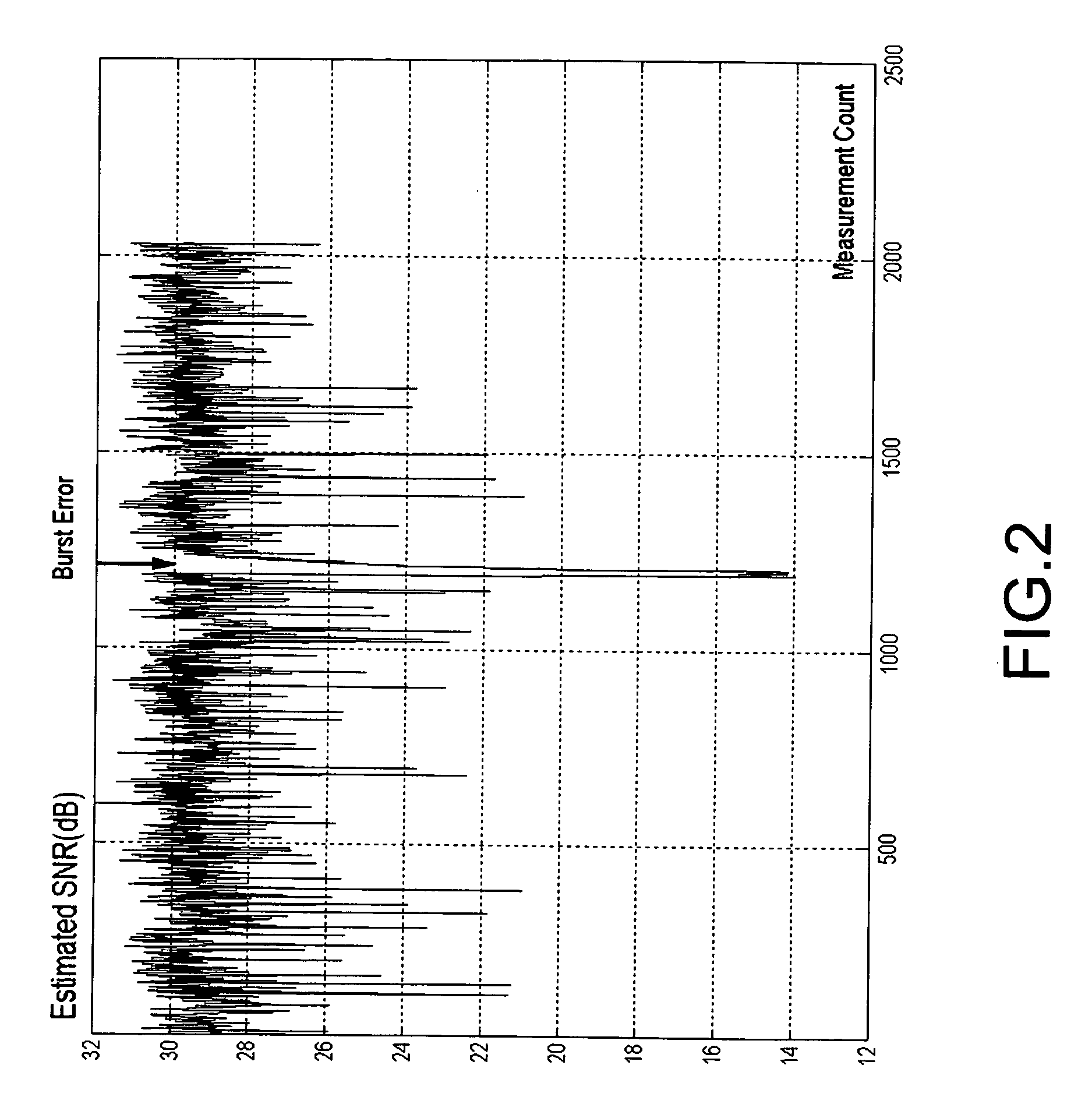
System and Method for Detecting Burst Noise During Quadrature Amplitude Modulation Communications
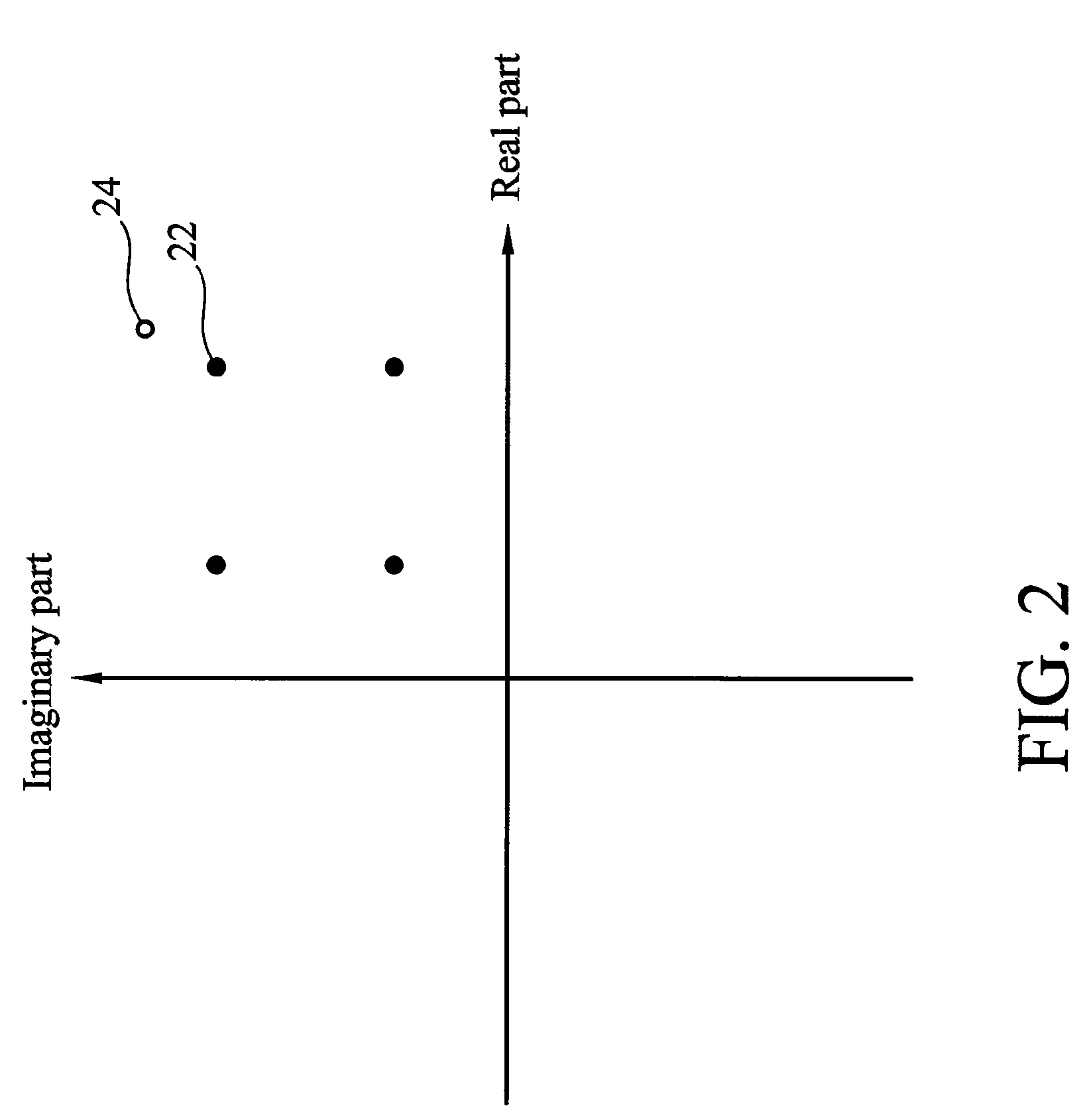
ActiveUS20130182752A1Reducing future burst noiseEqualizer coefficientMultiple carrier systemsDuplex signal operationBurst noiseLoop performance
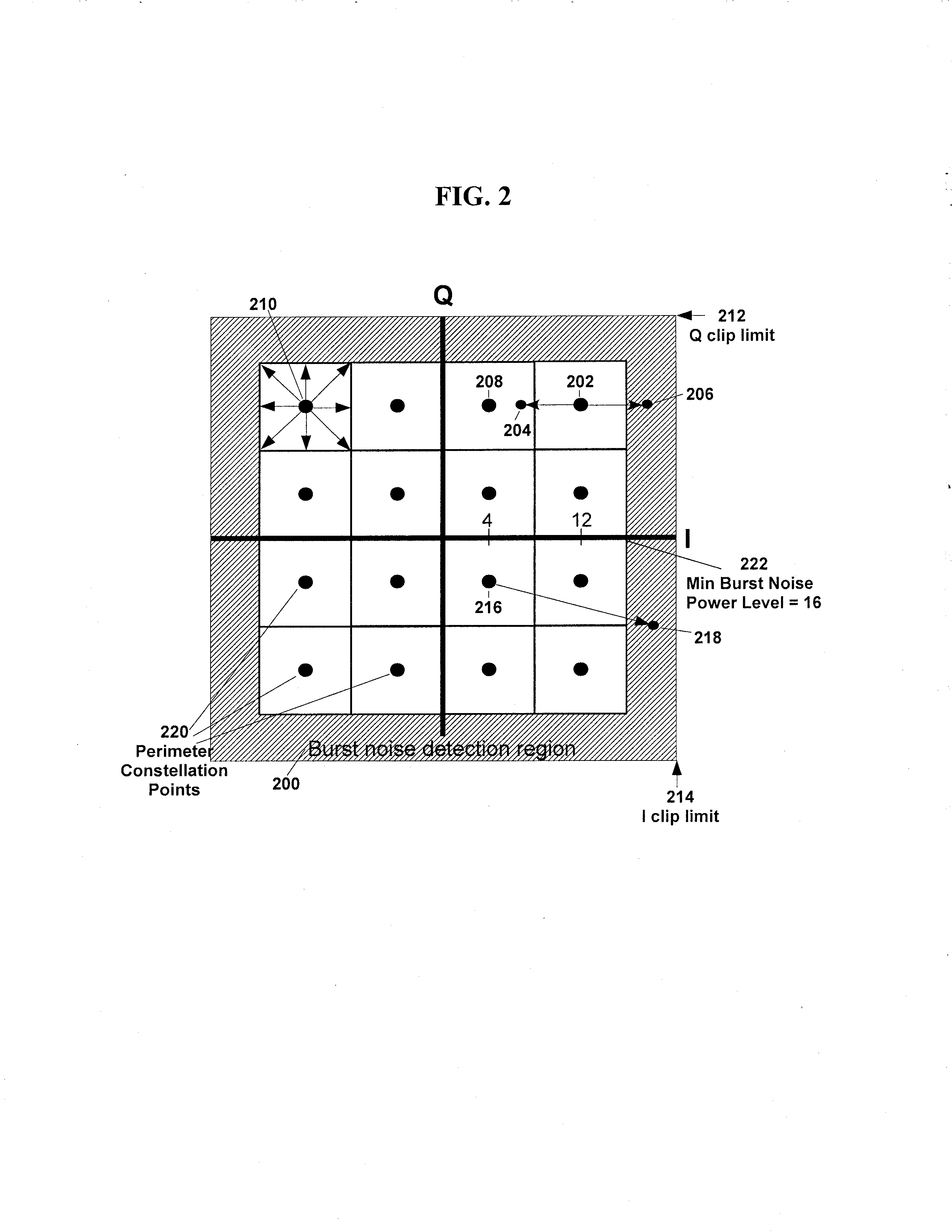
A system and method for detecting burst noise during quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) communications are provided. A QAM signal is acquired at a receiver in communication with a network. The QAM signal is demodulated at the receiver to identify a plurality of symbols. Amplitudes for each of the plurality of symbols are determined, and are compared to a predetermined threshold. For each amplitude that is greater than the predetermined threshold, information is recorded at the receiver relating to a burst noise event. The magnitude of the burst noise can be determined by measuring a difference between a received constellation point and a perimeter constellation point closest to the received constellation point. The information about the burst noise event can be transmitted to an error correction module for reducing future burst noise in the network. Equalizer coefficients and tracking loop performance can be adjusted / enhanced using the burst noise information.
Owner:CASA SYST
Adaptive decoding based on signal to noise ratio (SNR)
ActiveUS20140153673A1Error preventionAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Signal correlation
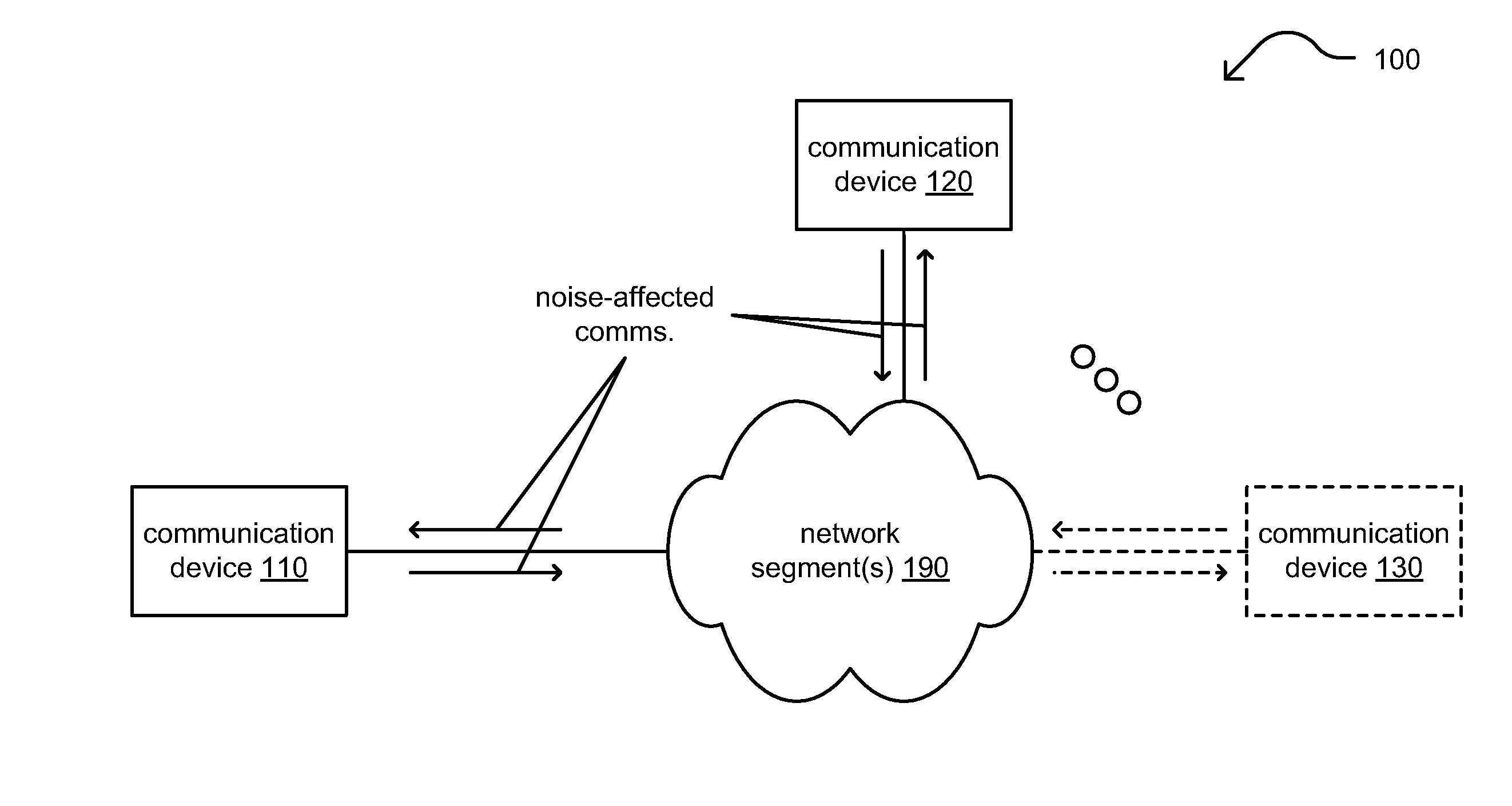
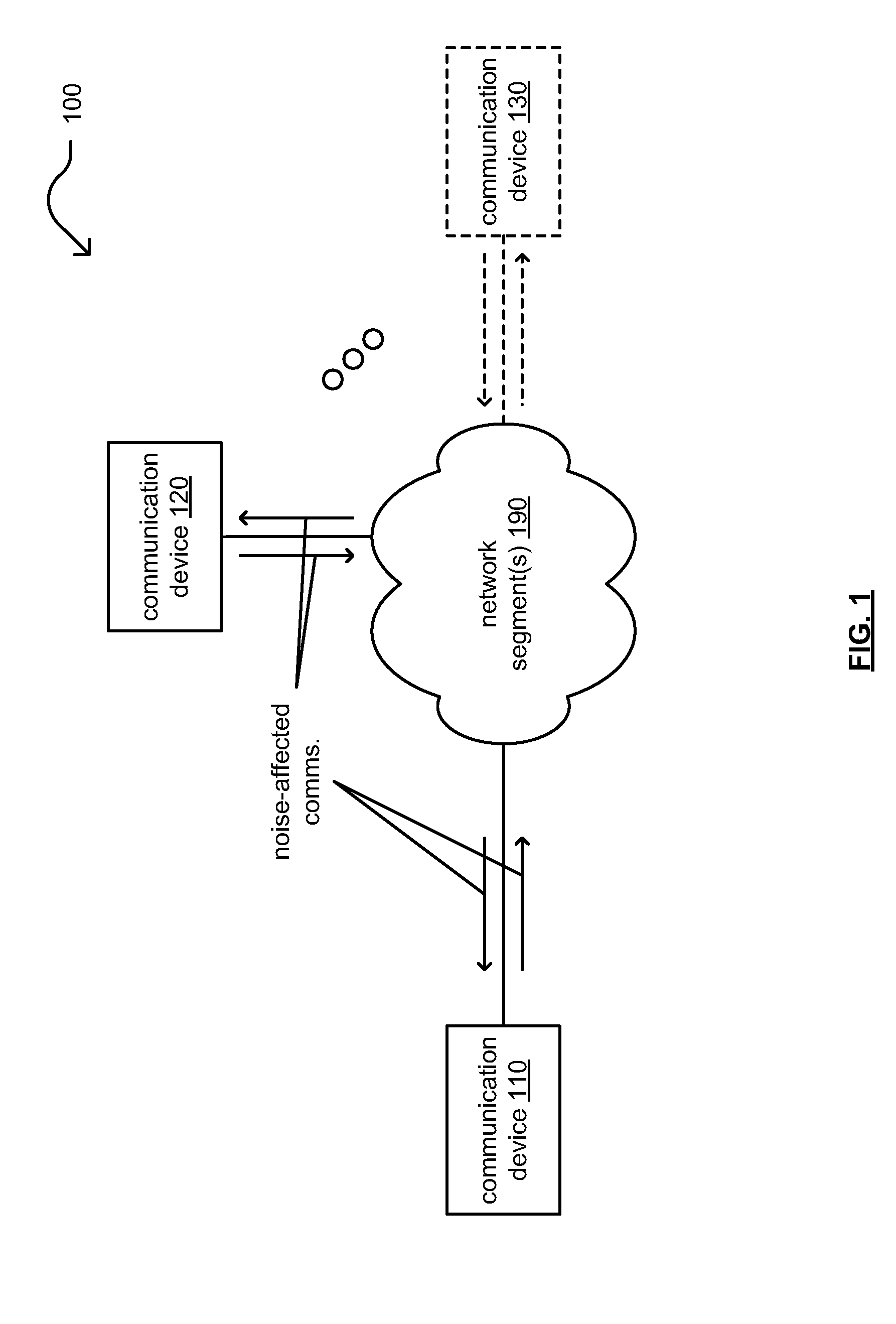
A communication device is configured adaptively to process a receive signal based on noise that may have adversely affected the signal during transition via communication channel. The device may be configured to identify those portions of the signal of the signal that are noise-affected (e.g., noise-affected sub-carriers of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signal), or the device may receive information that identifies those portions of the signal that are noise-affected from one or more other devices. The device may be configured to perform the modulation processing of the received signal to generate log-likelihood ratios (LLRs) for use in decoding the signal. Those LLRs associated with noise-affected portions of the signal are handled differently than LLRs associated with portions of the signal that are not noise-affected. The LLRs may be scaled based on signal to noise ratio(s) (SNR(s)) associated with the signal (e.g., based on background noise, burst noise, etc.).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Audio detection method
ActiveCN104795076APrevent missing alarmsPrevent false alarmsSpeech analysisBurst noiseComputer science
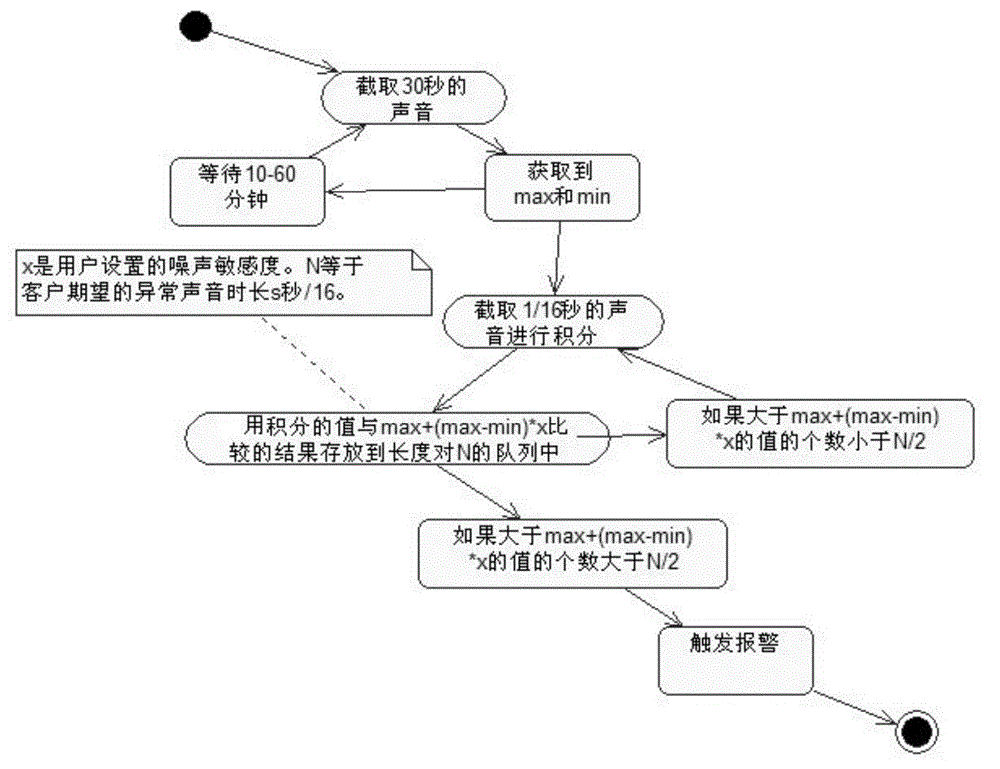
The invention discloses an audio detection method, which comprises the following steps: after audio monitoring is started, environmental background noise is sampled, an energy value corresponding to each sampling point is calculated, and a maximal value and a minimal value are obtained through comparing energy values corresponding to all sampling points during a sampling time of 20 to 40s; sound in a monitoring region is sampled at a sampling time interval deltat of 1 / 64 to 1 / 2s, an energy value corresponding to each sampling point is calculated, an energy value corresponding to each sampling point obtained within a sampling time length S2 is compared with an alarm reference threshold, alarm is triggered when the number of the sampling points whose energy values exceed the alarm reference threshold is larger than a value N / 2, and no alarm is triggered when the number of the sampling points whose energy values exceed the alarm reference threshold is smaller than a value N / 2, wherein the N is a sampling point number S2 / deltat within the sampling time length S2. The method can eliminate surrounding regular noise or surrounding burst noise or interference and can detect abnormal sound.
Owner:宁波远志立方能源科技有限公司
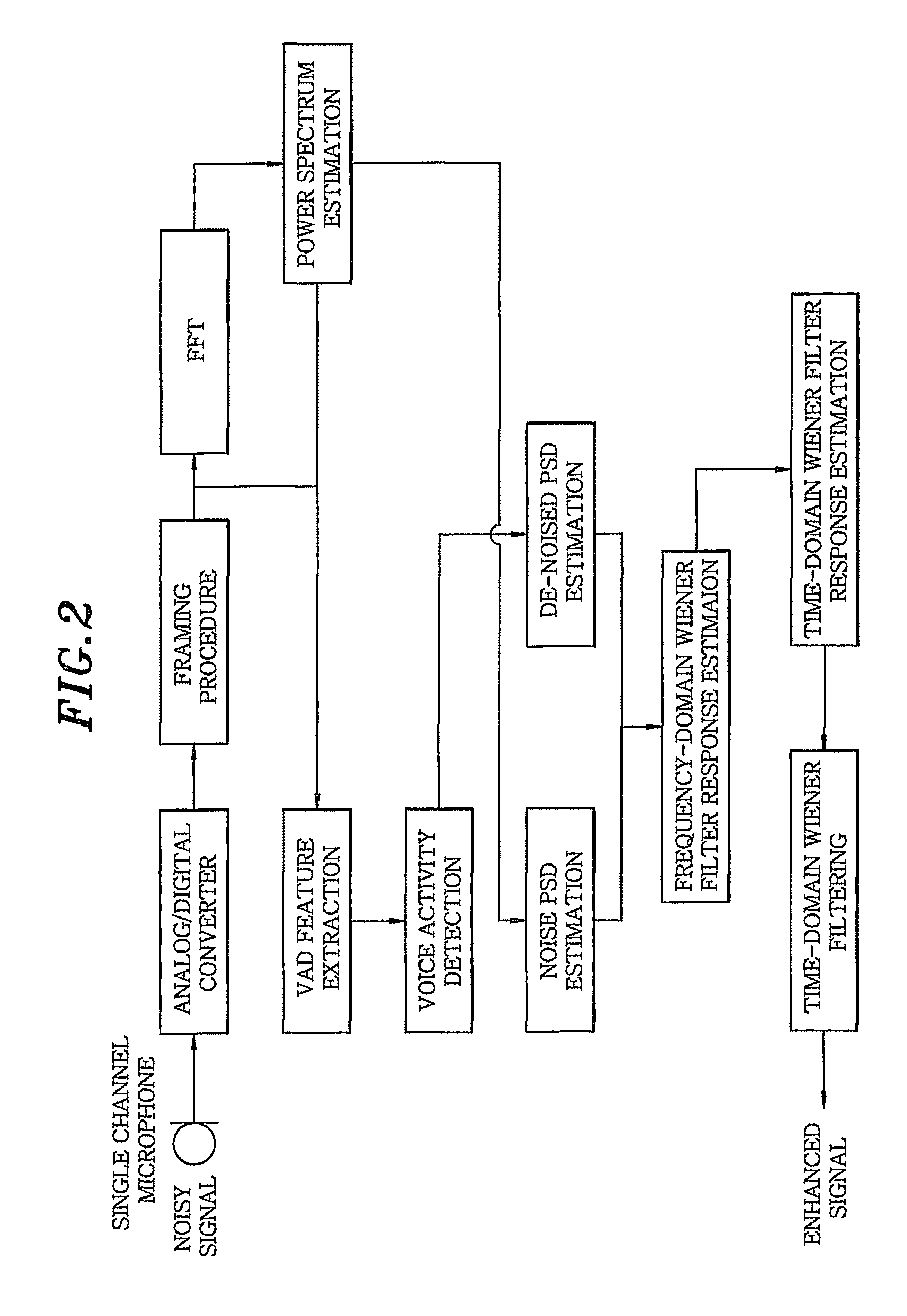
Noise reduction for speech recognition in a moving vehicle
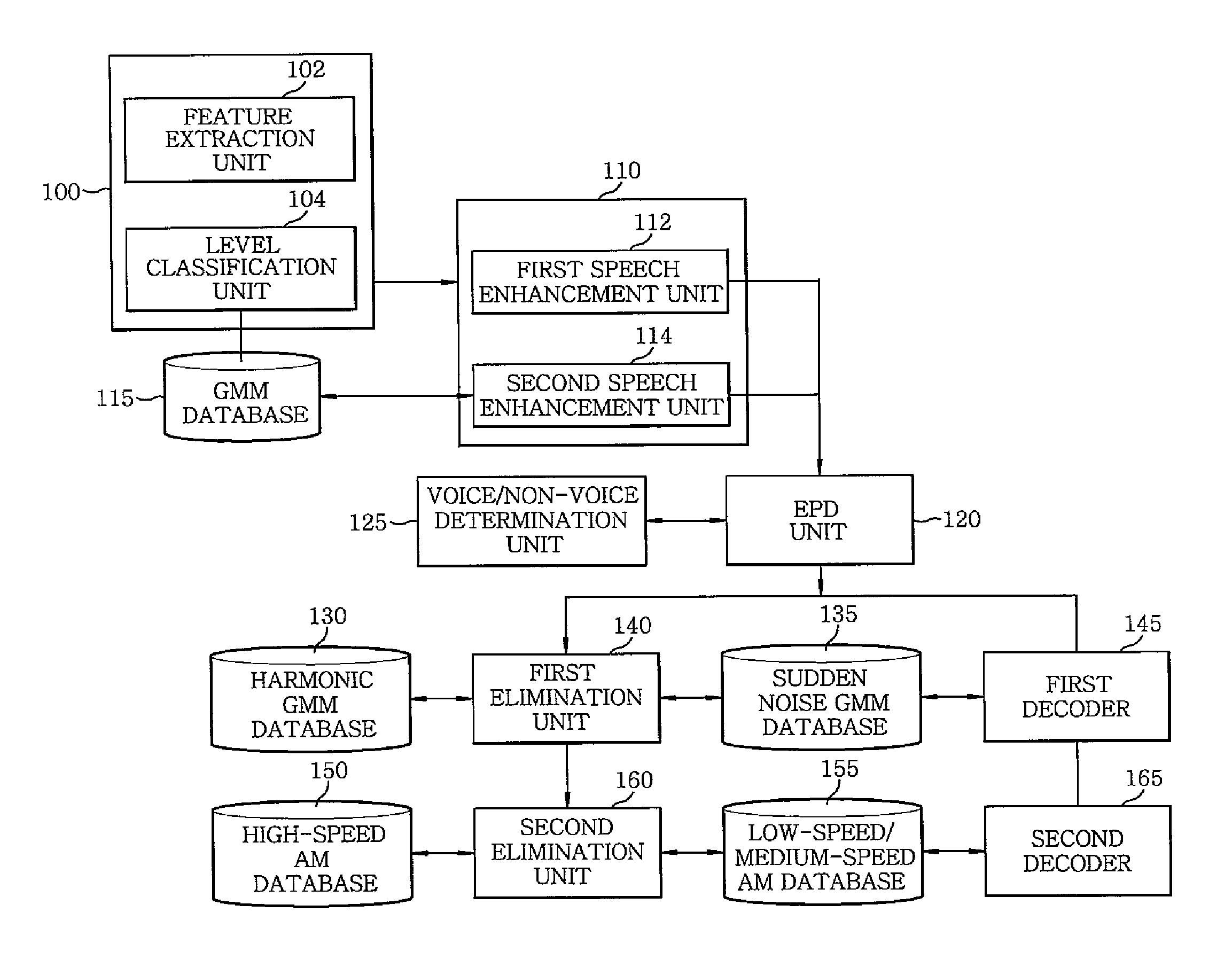
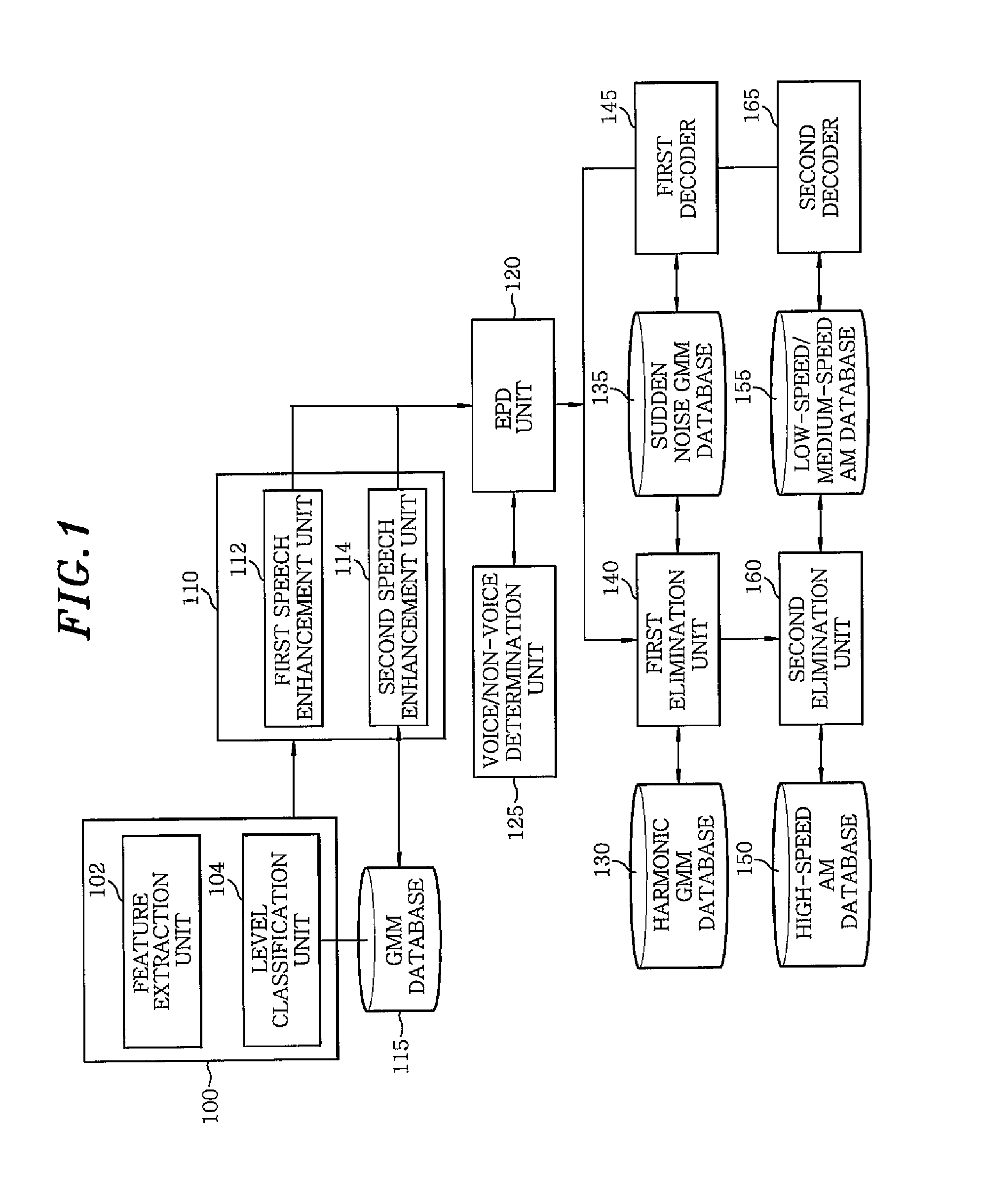
InactiveUS8504362B2Improve sound qualityEfficient detectionSpeech recognitionSound qualitySpeech identification
A speech recognition system includes: a speed level classifier for measuring a moving speed of a moving object by using a noise signal at an initial time of speech recognition to determine a speed level of the moving object; a first speech enhancement unit for enhancing sound quality of an input speech signal of the speech recognition by using a Wiener filter, if the speed level of the moving object is equal to or lower than a specific level; and a second speech enhancement unit enhancing the sound quality of the input speech signal by using a Gaussian mixture model, if the speed level of the moving object is higher than the specific level. The system further includes an end point detection unit for detecting start and end points, an elimination unit for eliminating sudden noise components based on a sudden noise Gaussian mixture model.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
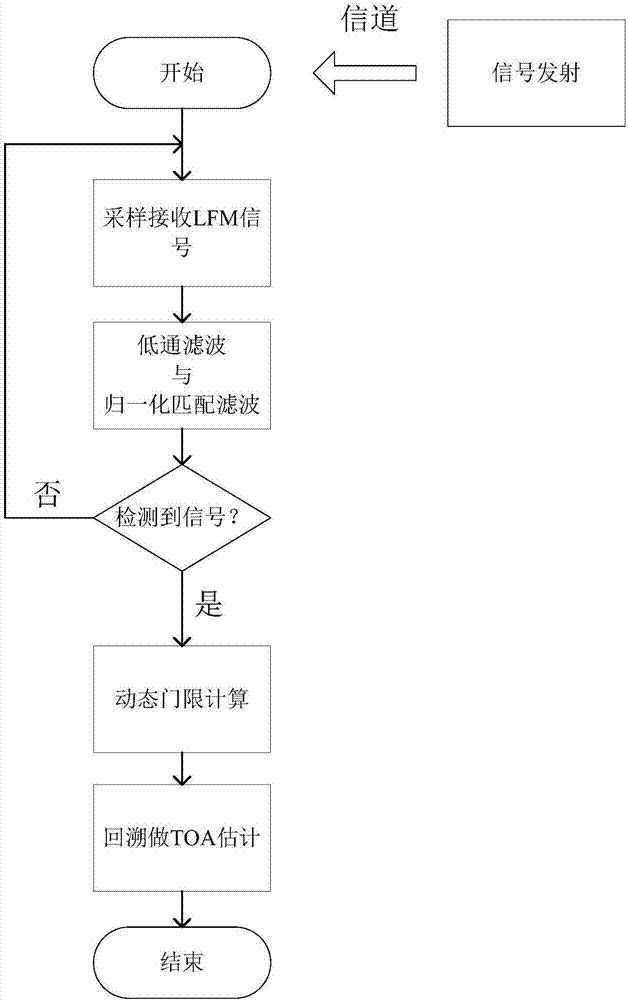
Method for estimating time of arrival of signal in strong multipath environment
ActiveCN106879068AReduce noise interferenceReduce the impactPosition fixationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Peak value
The invention discloses a method for estimating time of arrival of a signal in a strong multipath environment. According to the method, normalized matching and filtering are carried out on a received signal, so that the noise interference is reduced and the influence caused by signal transmission losses is reduced. Meanwhile, the maximum value and the minimum value of the receiving signal filter output are considered in terms of dynamic threshold setting, so that the channel response as well as the signal to noise ratio information is represented. Besides, with a maximum value detection backtracking method, a phenomenon that searching is started at the output starting point of the filter after threshold determination is avoided and the computing load is reduced. Because of a small backtracking range, burst noise peak values fall beyond the backtracking window in most cases, thereby avoiding the possible peak interference to the greatest extent and improving the TOA estimation efficiency and precision. The method has advantages of simple algorithm and accurate TOA estimation and the like. The experiment demonstrates that the method has the high TOA estimation precision on an indoor condition, so that the good foundation can be laid for realizing high-precision positioning.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
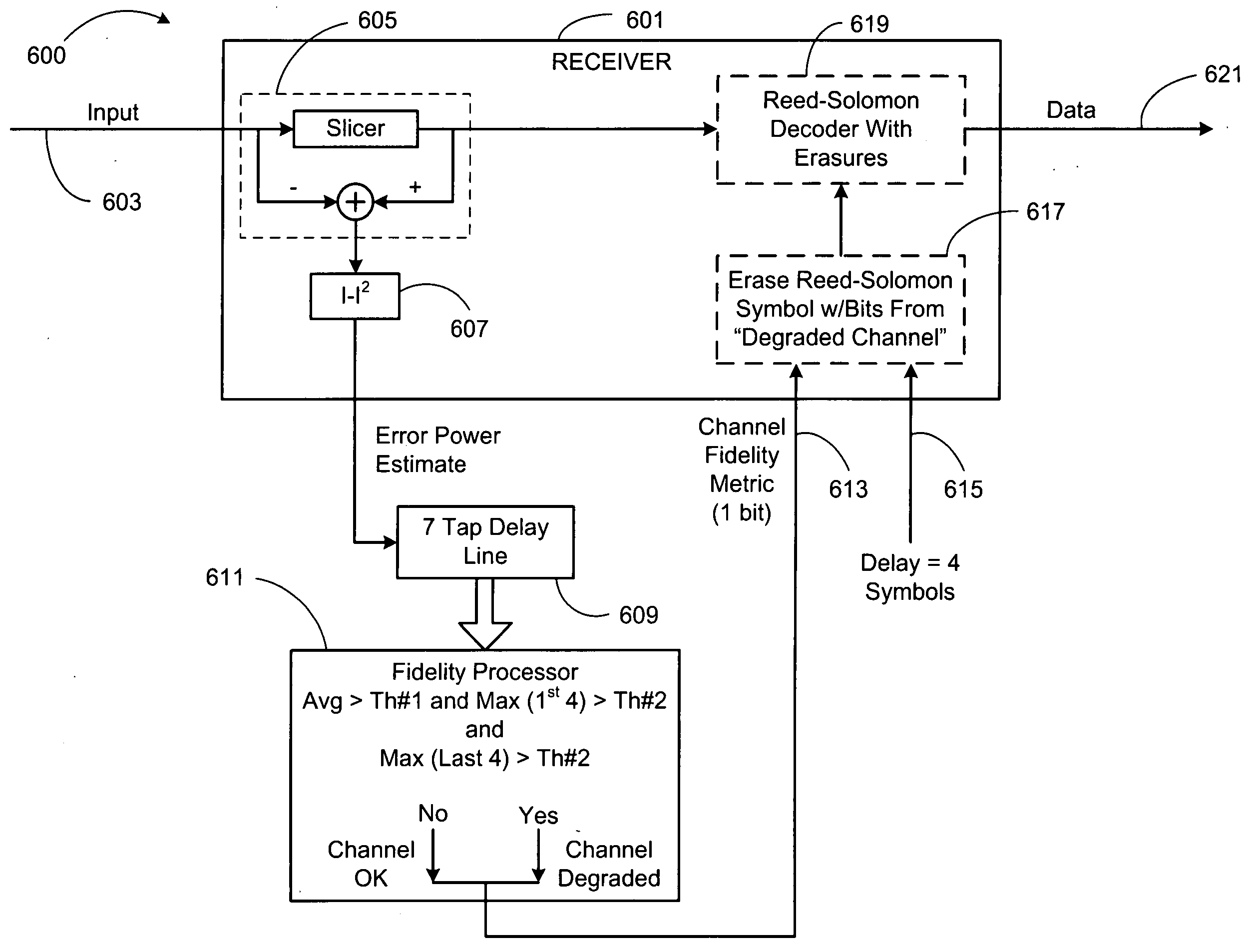
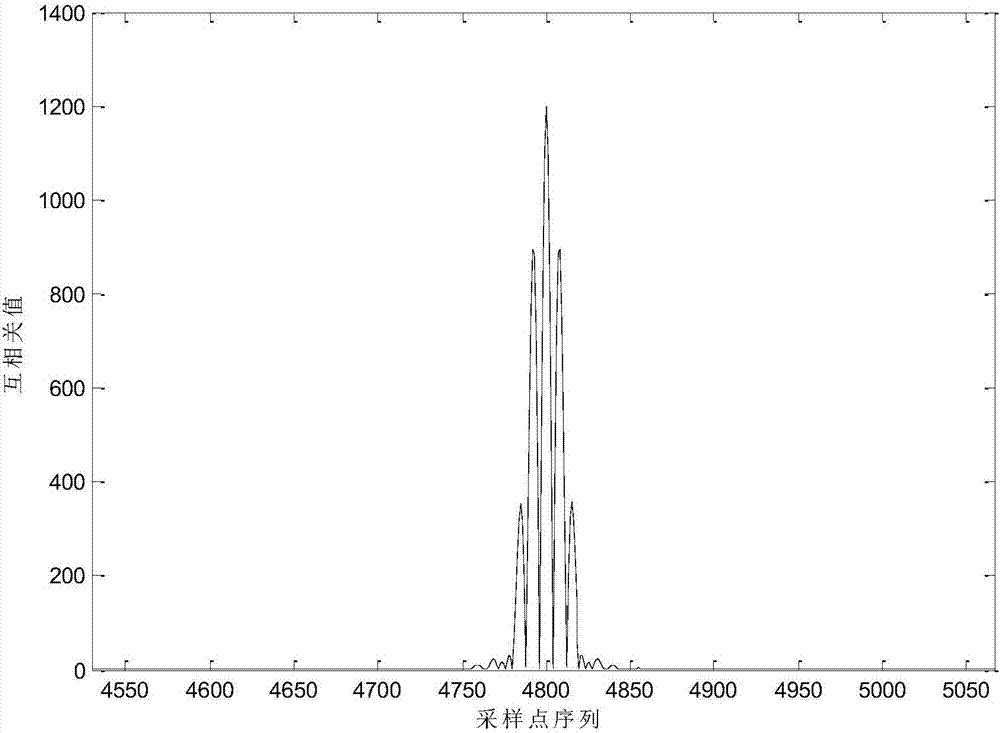
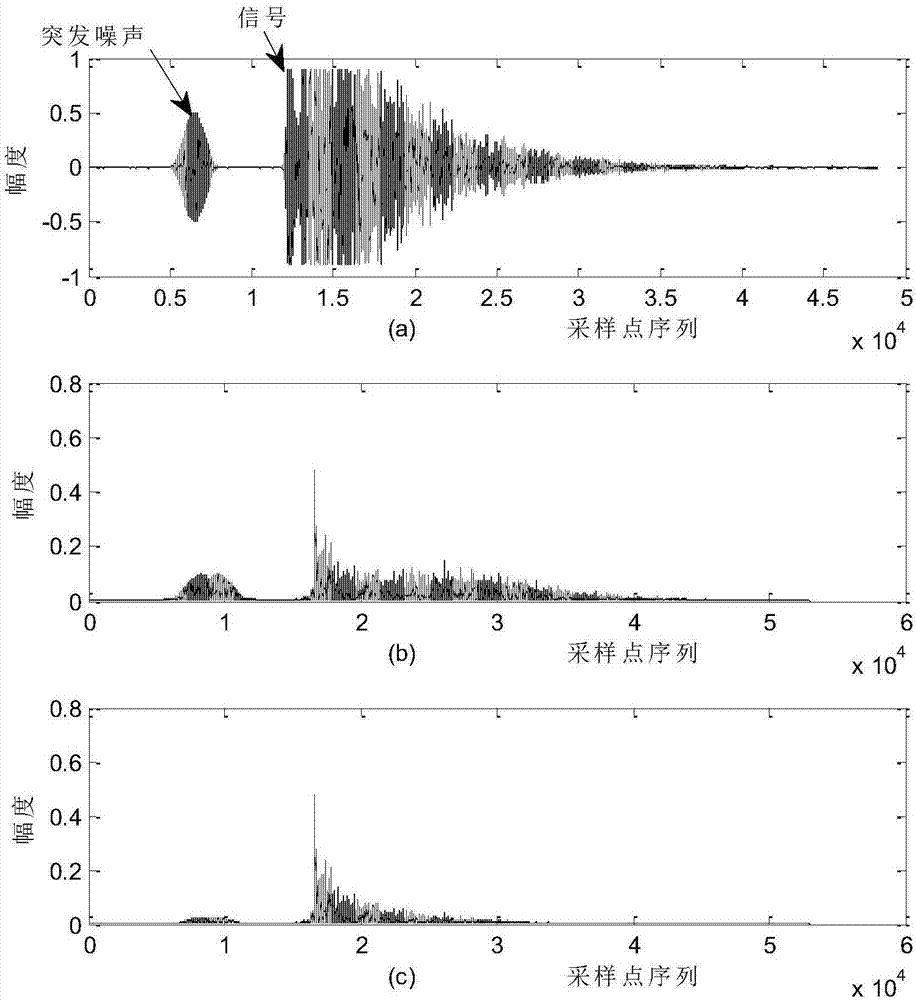
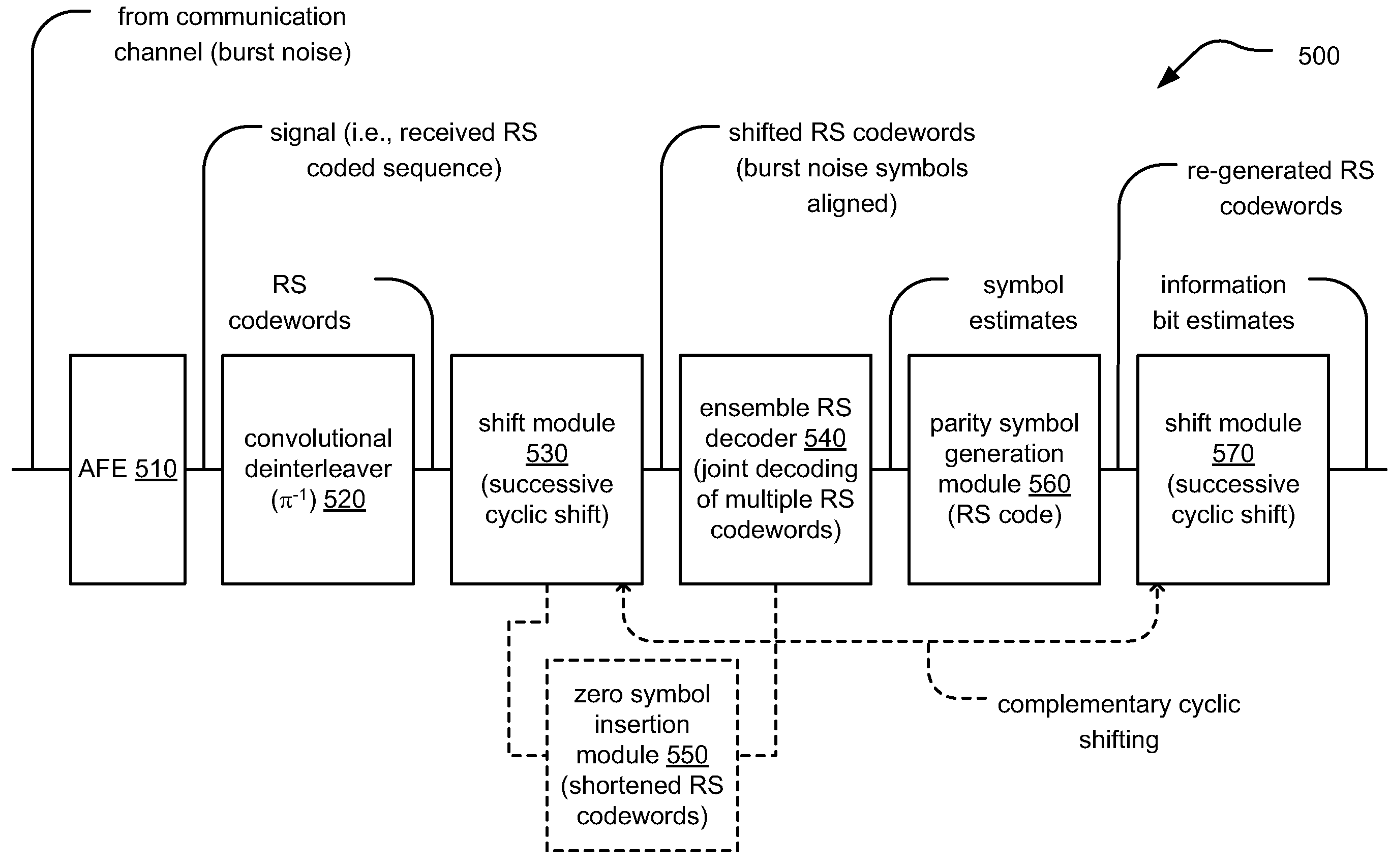
Handling burst error events with interleaved Reed-Solomon (RS) codes
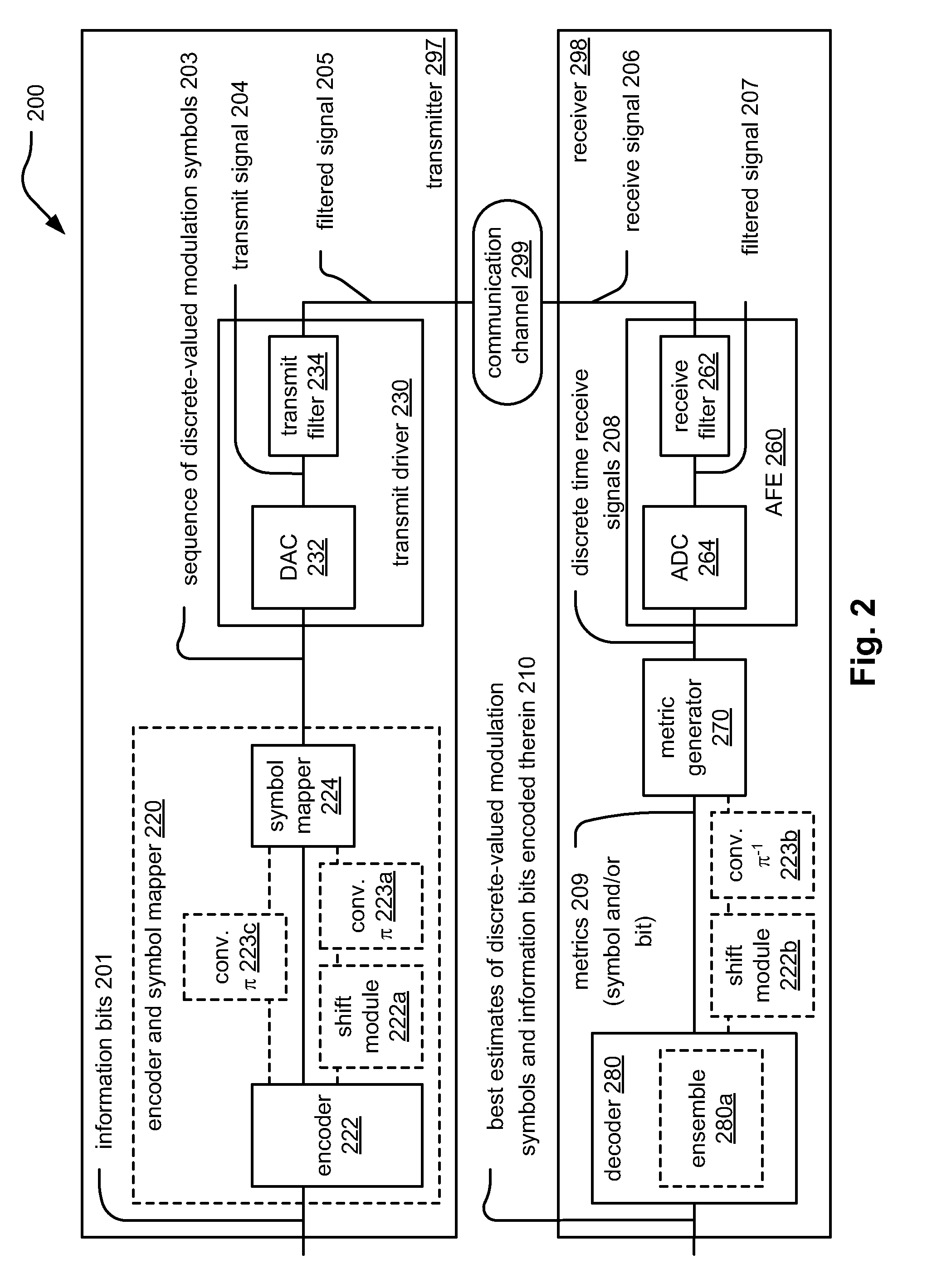
Handling burst error events with interleaved Reed-Solomon (RS) codes. A received signal, that has undergone convolutional interleaving sometime before, is received from a burst noise affected communication channel. The signal undergoes convolutional deinterleaving and the codewords generated there from undergo appropriate successive cyclic shifting to arrange burst noise affected symbols of various codewords into at least some common symbol locations. For example, at least two codewords have burst noise affected symbols in common symbol locations. An ensemble decoder jointly decodes multiple codewords during a same time period (i.e., processes multiple codewords simultaneously). By processing multiple codewords simultaneously, the ensemble decoder has greater error correction capability than a decoder that processes a single codeword at a time.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
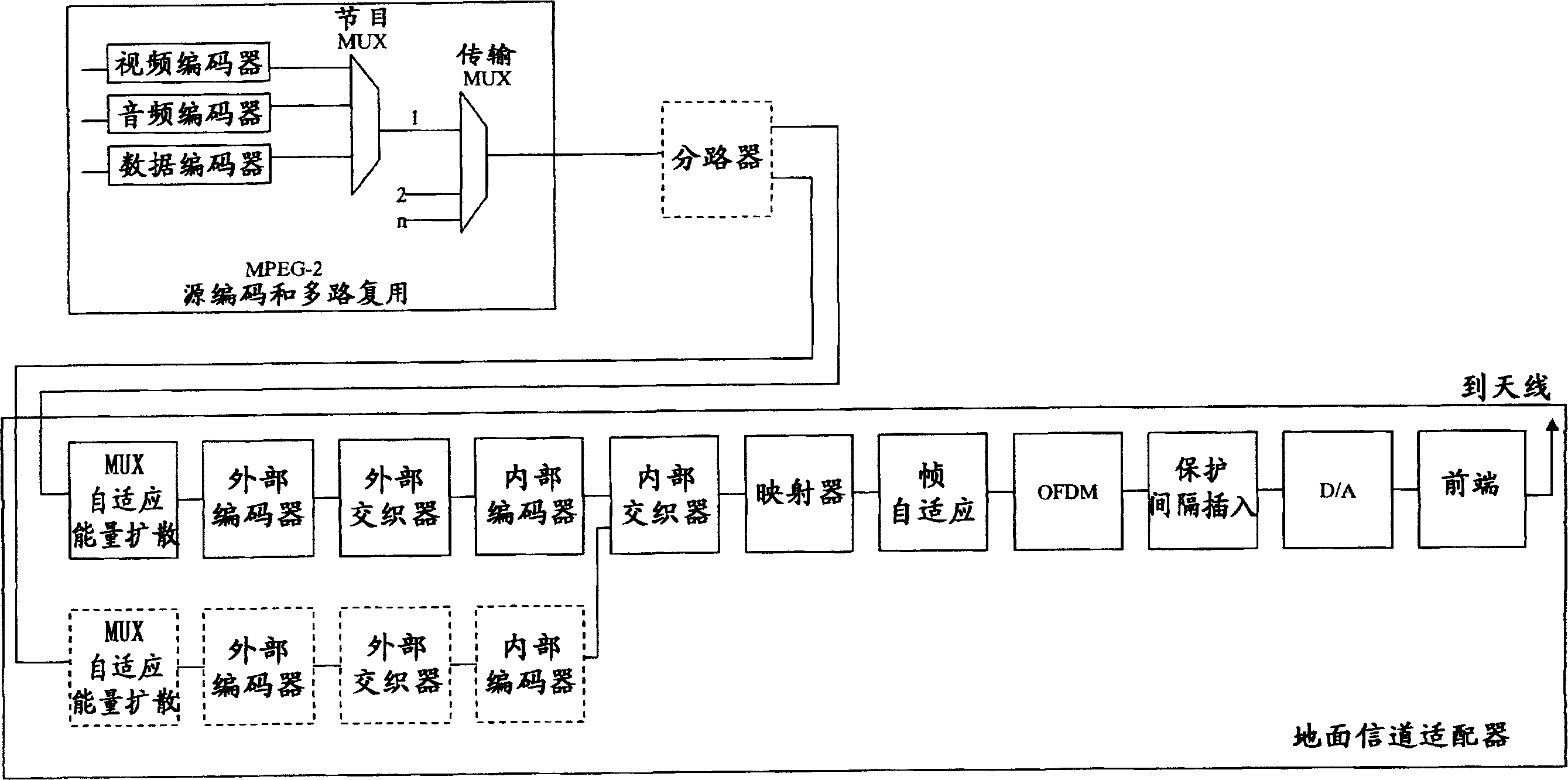
Single carrier transmission system able to reducing signal distortion and its method
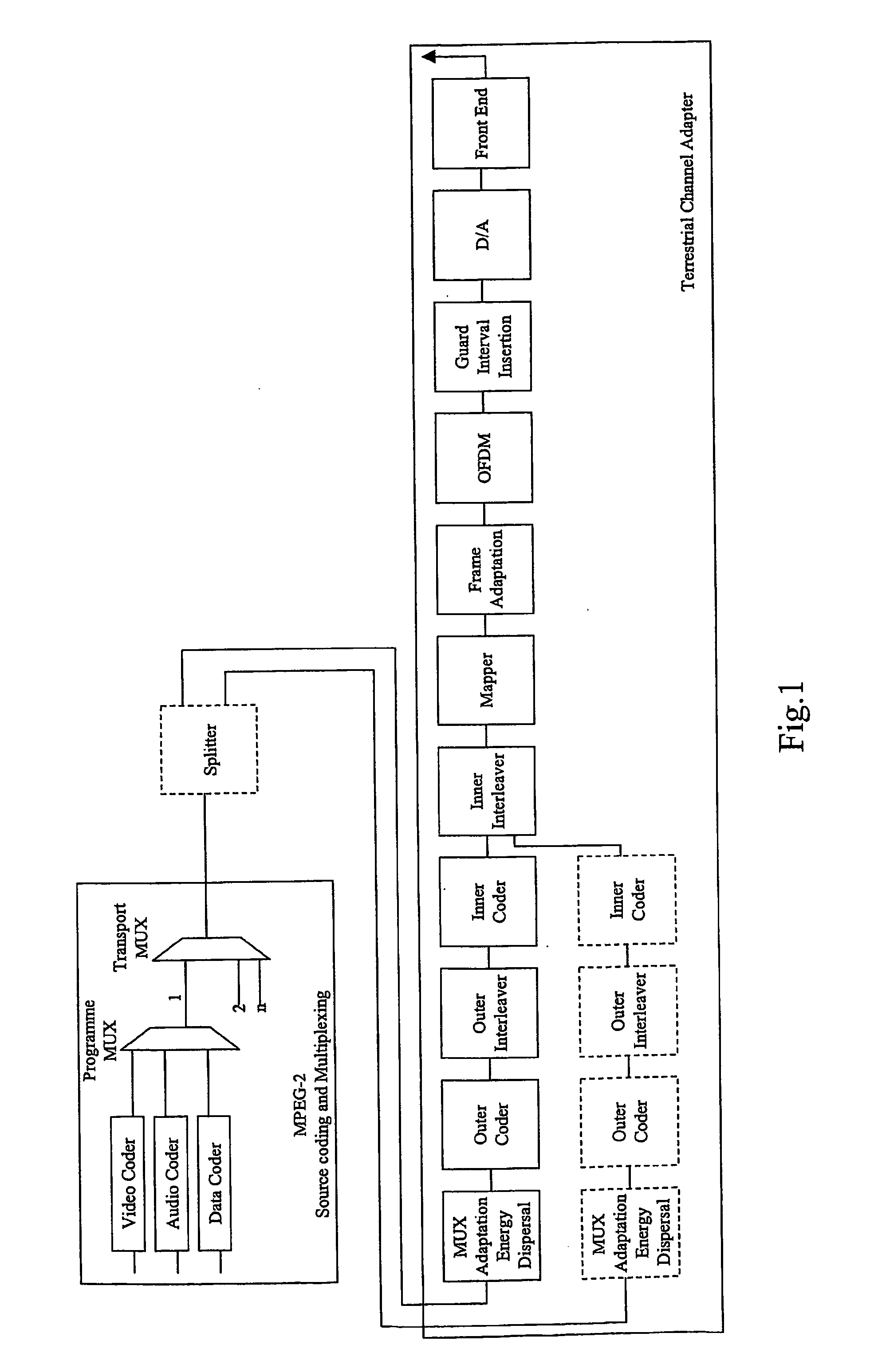
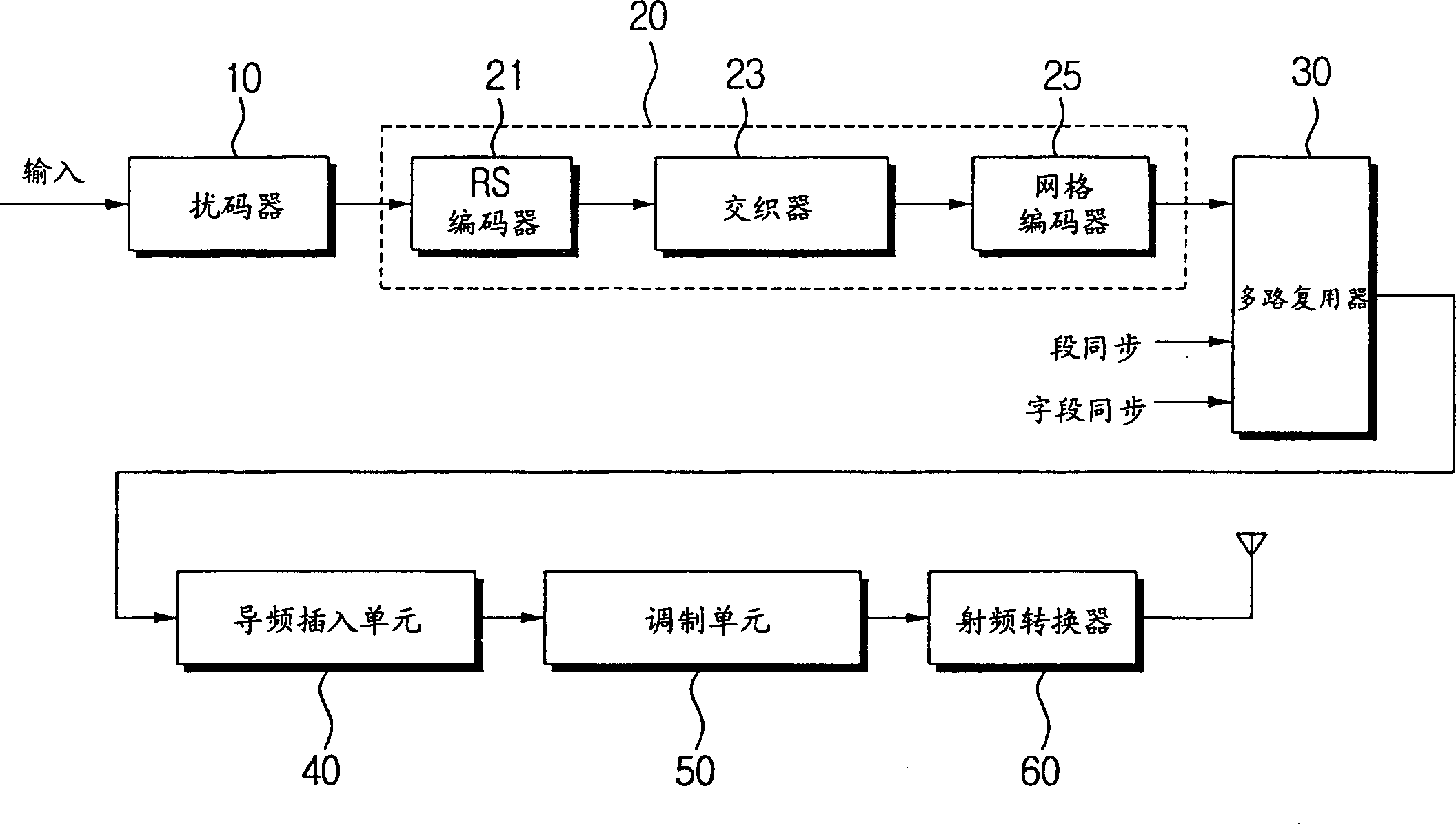
InactiveCN1497916AAppropriately cope with channel environment changesData representation error detection/correctionError preventionMultiplexingData stream
A single carrier transmitting system capable of reducing distortion of transmission signals and a method thereof are provided to reduce distortion of transmission signals in a channel environment where a burst noise exists, and improve the receipt capability of a receiving side. A scrambler(100) randomizes transmitting data signals. An FEC(Forward Error Correction) unit(110) corrects a bit error of an inputted data stream. A section distinguishing unit(141) distinguishes between a frame synchronous section and a data section of a transmission signal. A modulator(143) modulates the distinguished sections in different single carrier methods. A modulation information transmitting unit(145) transmits information related to the modulation methods to a receiving side through the frame synchronous section.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Chip blanking and processing in SCDMA to mitigate impulse and burst noise and/or distortion
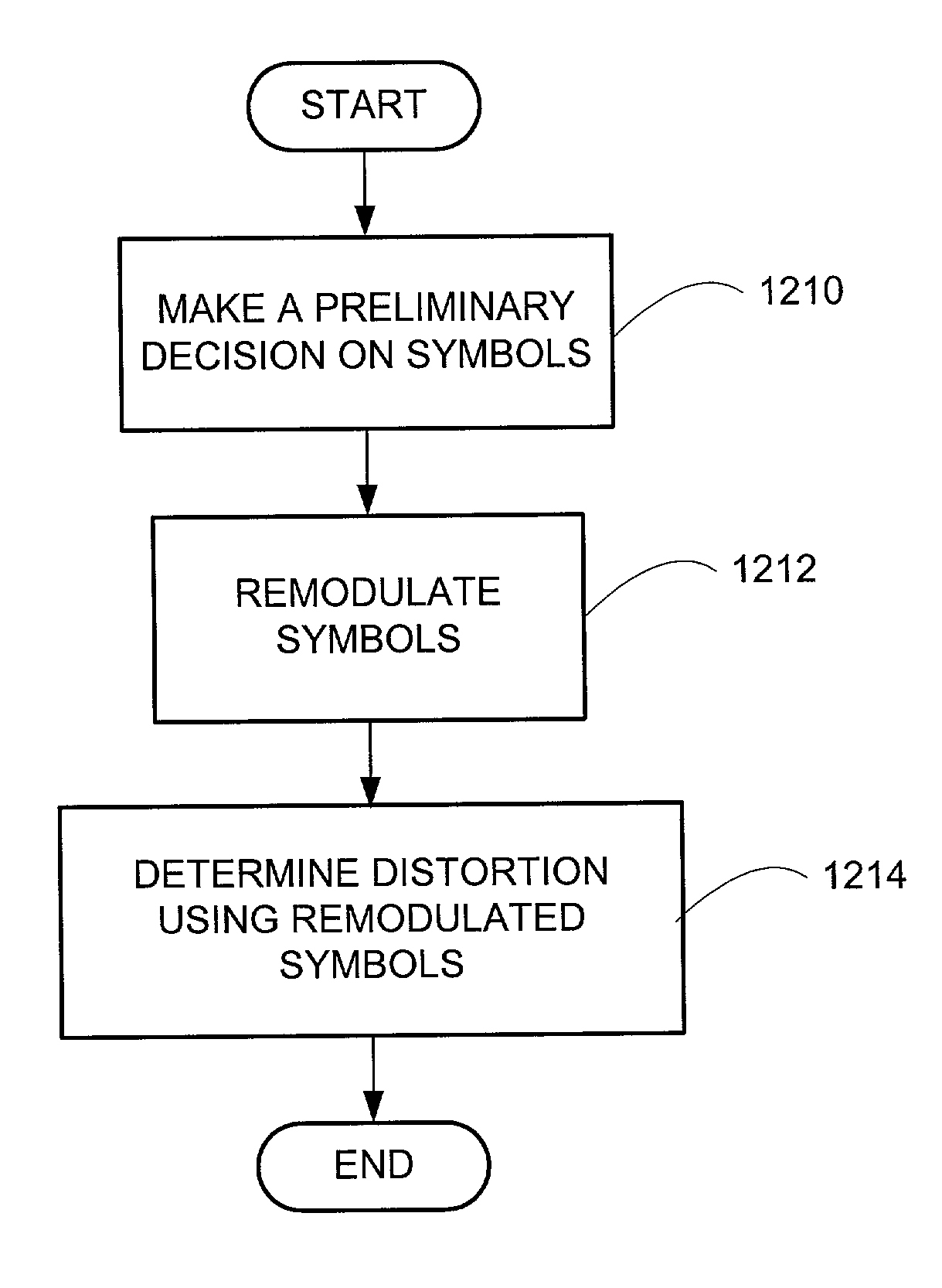
Systems and methods are disclosed for detecting temporary high level impairments, such as noise or interference, for example, in a communications channel, and subsequently, mitigating the deleterious effects of the dynamic impairments. In one embodiment, a preliminary decision is made on at least one signal transmitted over the communications channel. The at least one signal is remodulated and the impairment is determined using the at least one remodulated signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System, method and computer program product for mitigating burst noise in a communications system
ActiveUS7631242B2Reduce the impactIncrease robustness of communicationError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionCommunications systemBlock code
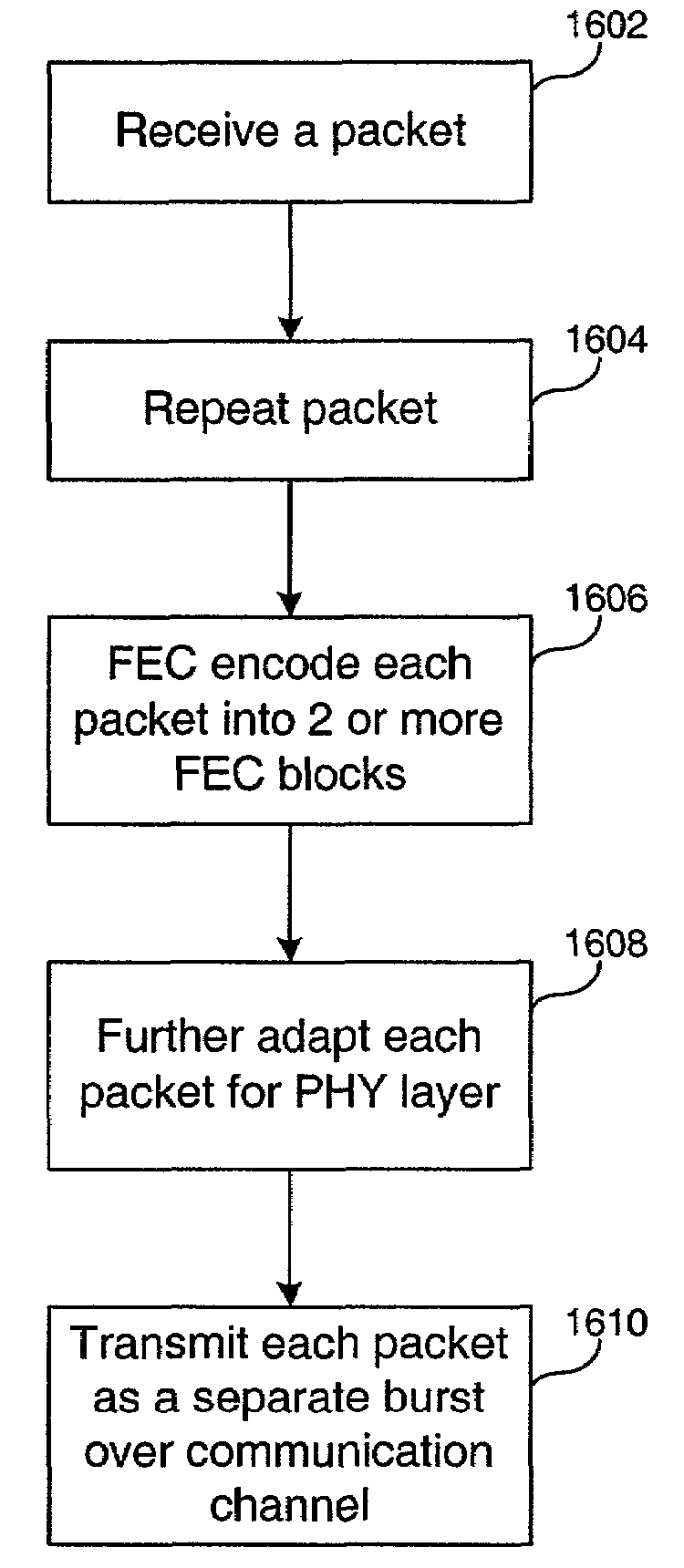
A system, method and computer program product is provided for mitigating the effects of burst noise on packets transmitted in a communications system. A transmitting device applies an outer code, which may include, for example, a block code, an exclusive OR (XOR) code, or a repetition code, to one or more packets prior to adaptation of the packets for transmission over the physical (PHY) layer of the communications system, wherein the PHY layer adaptation may include FEC encoding of individual packets. The outer coded packets are then separately transmitted over a channel of the communications system. A receiving device receives the outer coded packets, performs PHY level demodulation and optional FEC decoding of the packets, and then applies outer code decoding to the outer coded packets in order to restore packets that were erased during transmission due to burst noise or other impairments on the channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
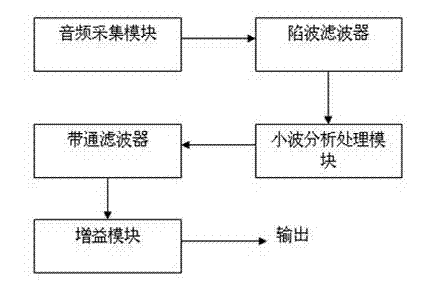
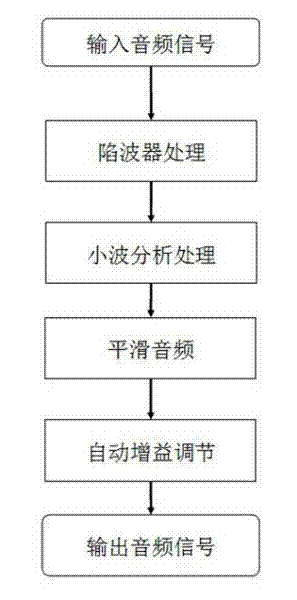
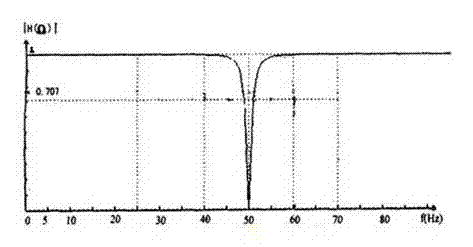
System and method for reducing burst noise through wavelet trapped wave
The invention provides a system and method for reducing burst noise through wavelet trapped wave. The system comprises an audio acquisition module, a trap filter and a wavelet analysis processing module, wherein the audio acquisition module acquires an audio signal, and transmits the audio signal to the trap filter; the trap filter performs trapping processing on the audio signal, filters out power frequency interference, and transmits the audio signal to the wavelet analysis processing module; and the wavelet analysis processing module eliminates high-frequency noise in the audio signal, reconstructs the audio signal, and performs audio output. The system and the method combine the trap filter, can effectively inhibit noise, and restore real audio signals.
Owner:蔡镇滨 +1
Method and sytem for receiving multi-carrier signal
Method and system for reducing impulsive burst noise in less delayed reception in pilot based OFDM systems, especially using DVB-T standard such as Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is provided. The method contains following steps: recognition of the impulse position and possibly length in the time domain symbol, blanking of those samples of the symbol where significant amount of impulse noise is present, calculating the first estimate of the received signal from the blanked symbol, derving correction values for the carrier estimates by applying prior information (pilot carriers), and the corrected estimate of the received symbol is derived by subtracting the correction values of step from the first estimate of carriers derived in step. The method and arrangement allow correction of fairly long bursts of impulse noise with minor degradation only. The complexity of the scheme and the additional energy consumption are fairly low. The method provides considerably more effective more simple and less delay in broadcast data reception than previously known solutions in interfered multi-carrier signal reception.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Receiver for a multi-carrier modulated symbol
ActiveUS7418026B2Improve integrityFacilitate communicationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCarrier signalFourier transform on finite groups
A receiver for receiving a multi-carrier modulated symbol is arranged to suppress a burst noise signal which may have been induced in the symbol. The symbol includes a plurality of pilot carriers as well as a plurality of data bearing carriers. The receiver comprises a burst noise detection processor operable to detect the temporal position of the burst noise signal which may have corrupted the symbol within a period occupied by the symbol, and a channel estimation processor operable to generate a decimated noise signal corresponding to the burst noise, from the recovered pilot carriers. An inverse Fourier transform of the decimated noise signal provides a plurality of estimated versions of the burst noise signal. A noise signal processor is operable to generate an estimate of the burst noise signal by identifying one of the plurality of estimated burst noise versions at the detected temporal location of the burst noise signal. The noise signal processor may be operable to set the signal samples other than the identified estimate of the burst noise signal to zero and to perform a Fourier transform, to provide a frequency domain version of the burst noise signal, thereby interpolating the decimated noise signal. The frequency domain noise signal estimate may be cancelled from the symbol by a noise cancellation processor in the frequency domain, before data is recovered from the symbol. The receiver finds application for Digital Video Broadcasting in which COFDM is employed.
Owner:REDWOOD TECHNOLOGIES LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com