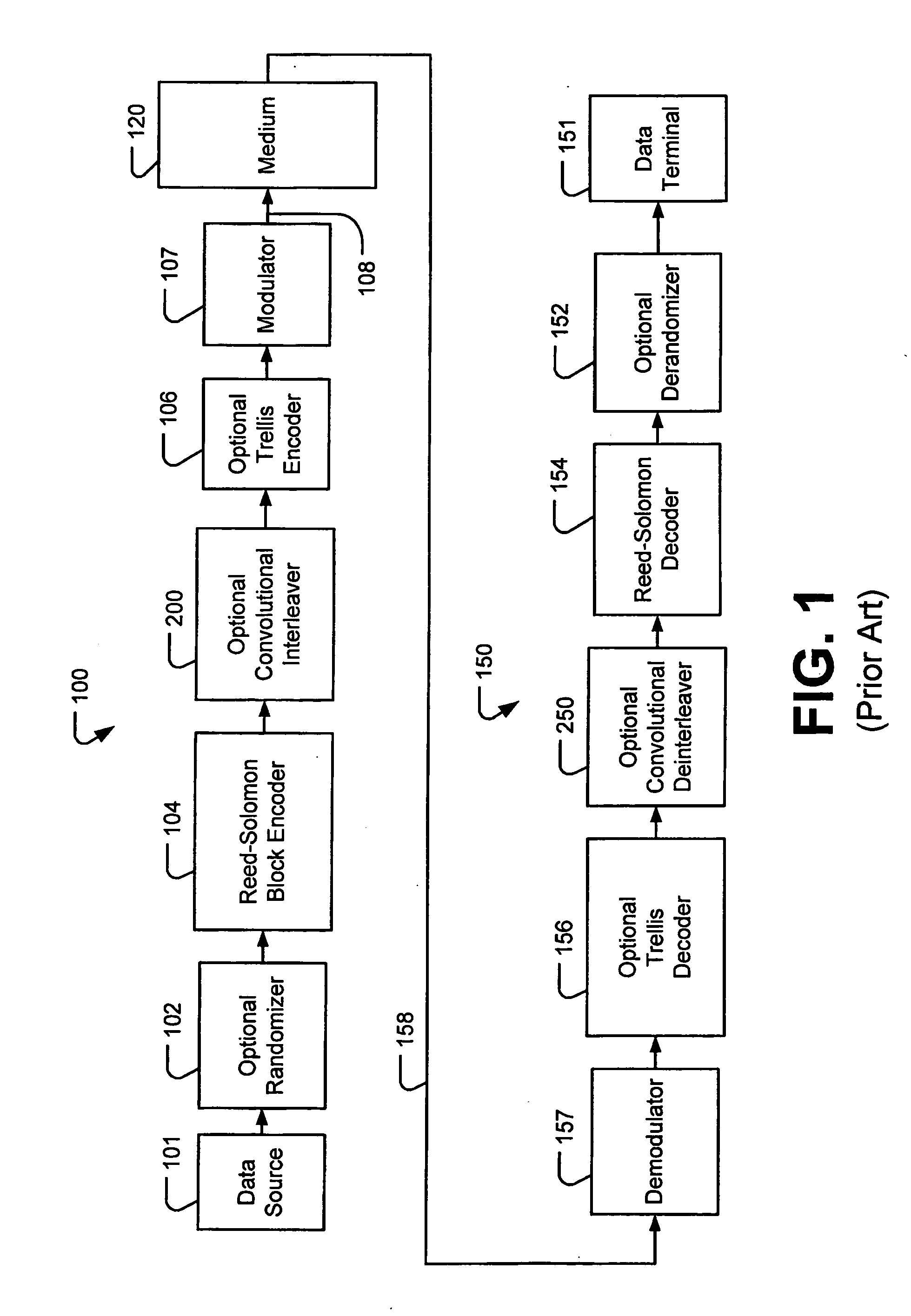
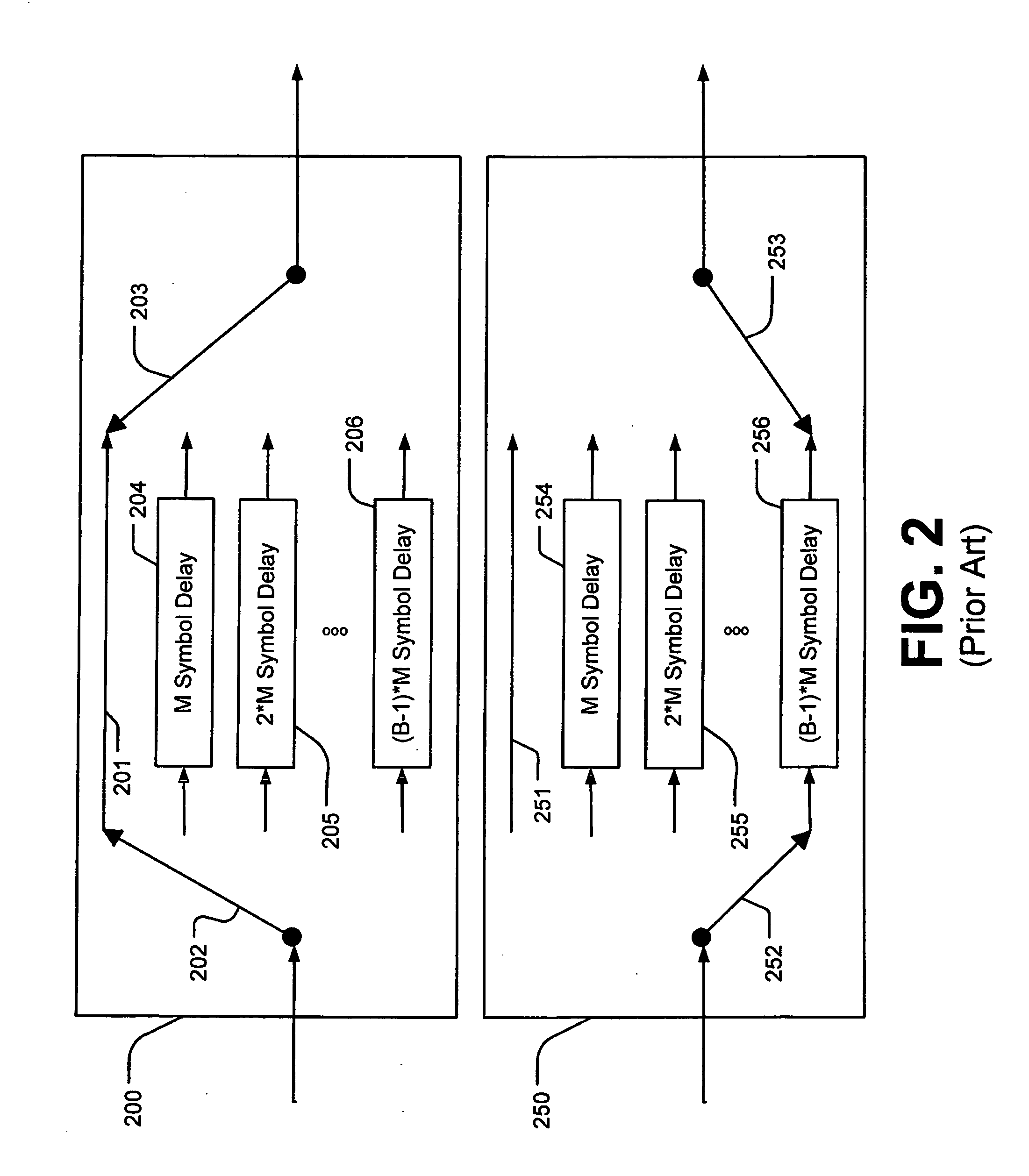
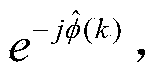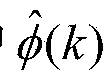Patents
Literature
264 results about "Burst error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
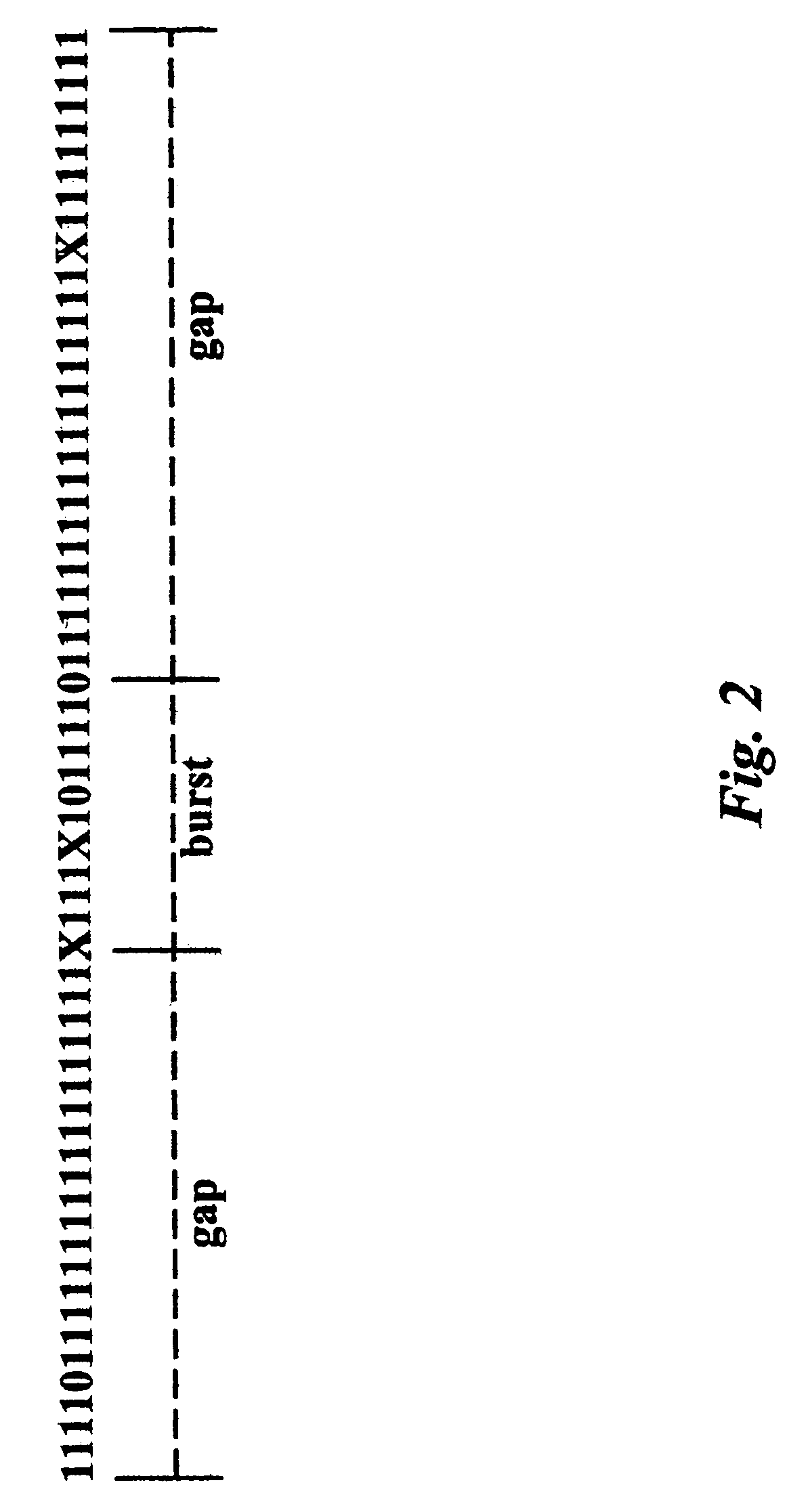
In telecommunication, a burst error or error burst is a contiguous sequence of symbols, received over a communication channel, such that the first and last symbols are in error and there exists no contiguous subsequence of m correctly received symbols within the error burst.
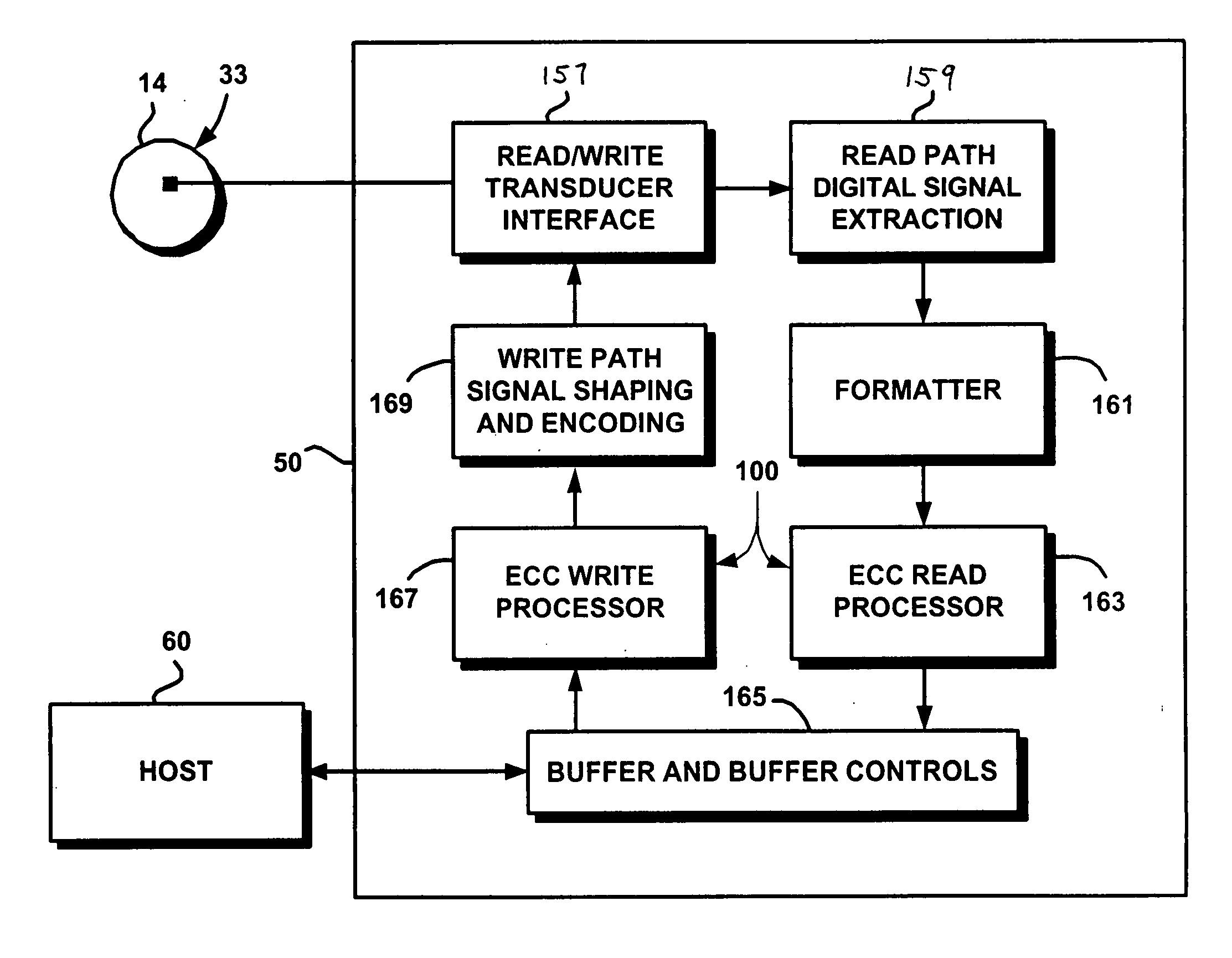
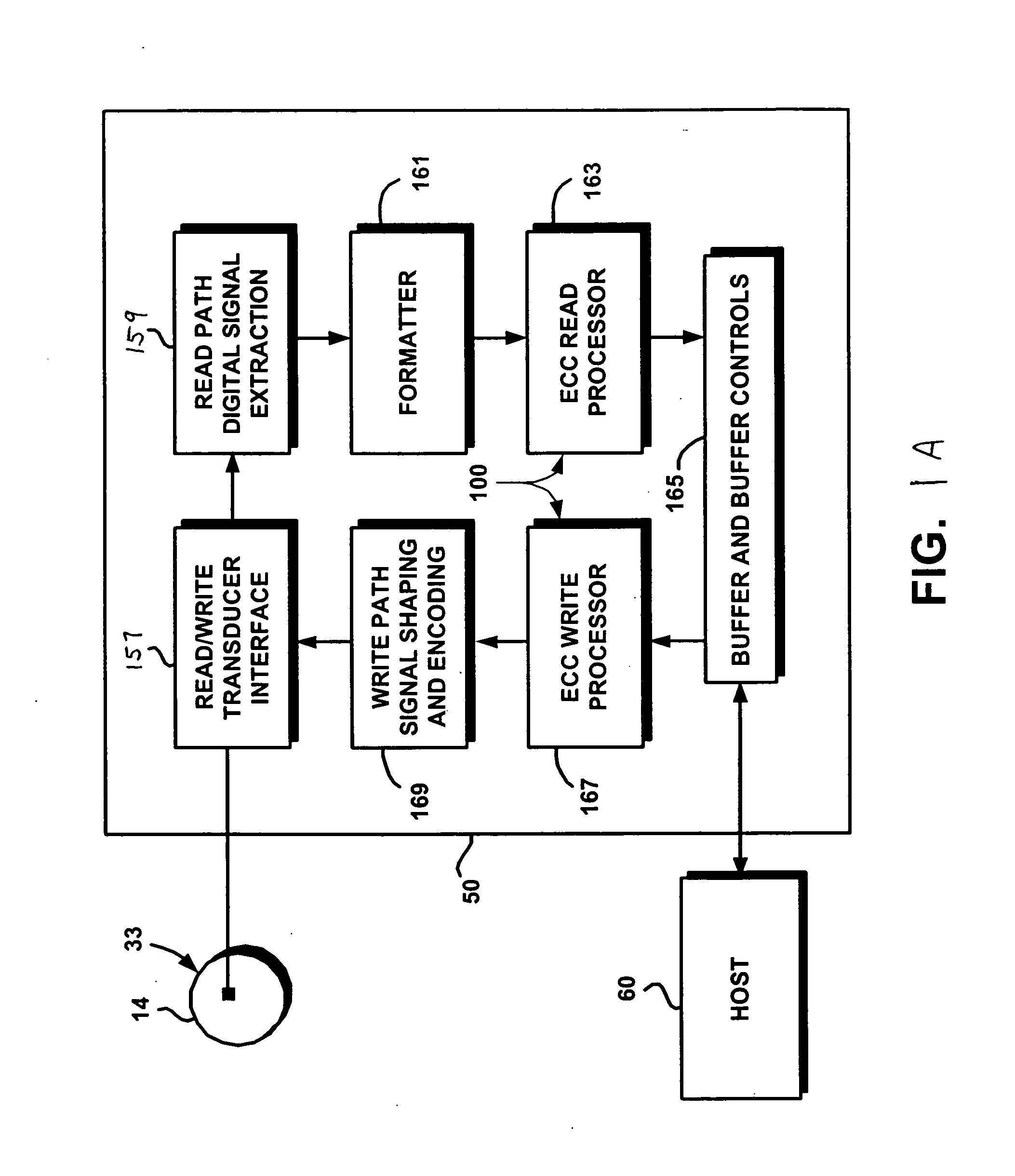
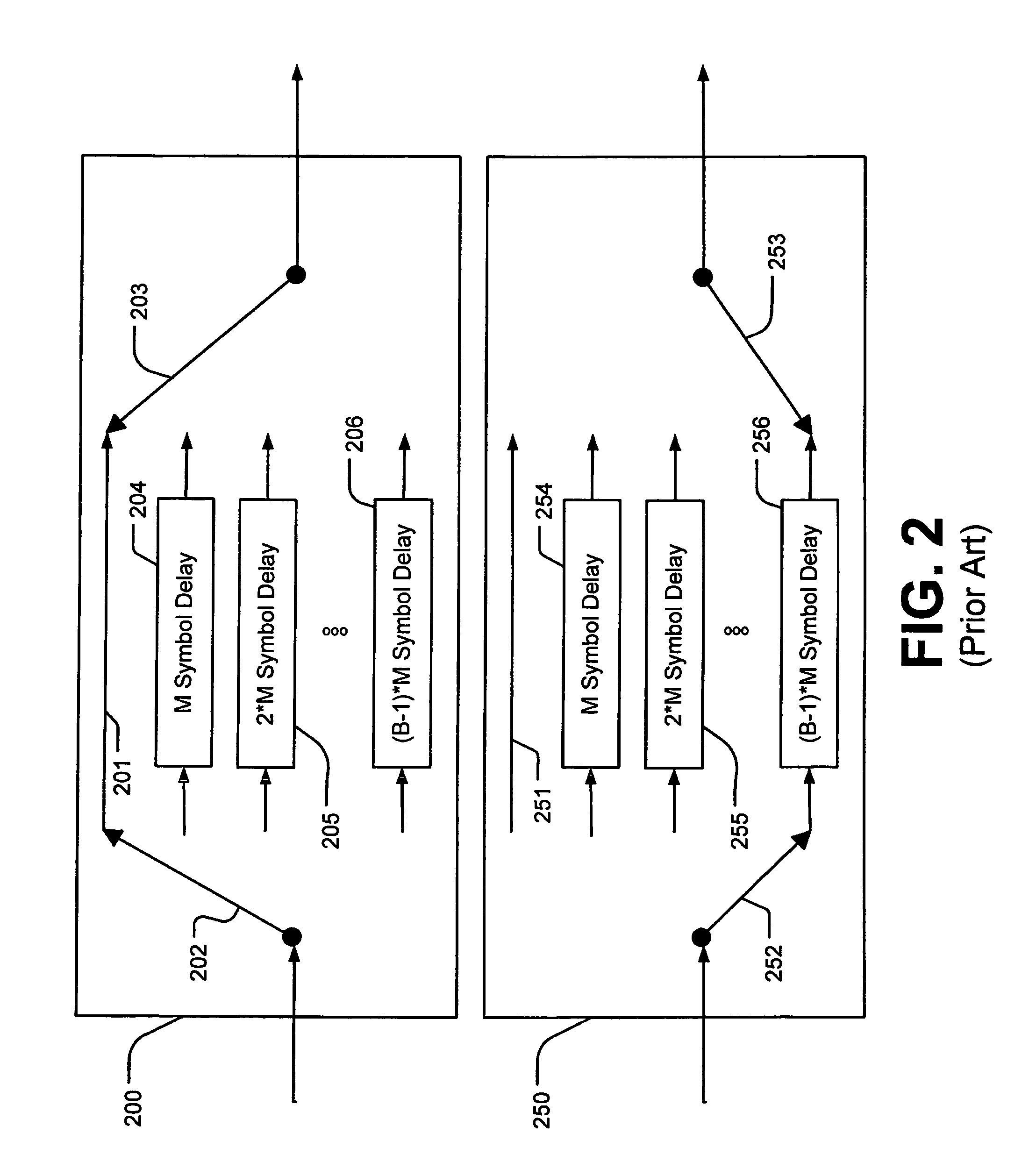
Techniques for detecting and correcting errors using multiple interleave erasure pointers
InactiveUS20050229069A1Correction capabilityTransmission systemsCode conversionBlock codeError location
Techniques for detecting and correcting burst errors in data bytes formed in a two-level block code structure. A second level decoder uses block level check bytes to detect columns in a two-level block code structure that contain error bytes. The second level decoder generates erasure pointers that identify columns in the two-level block structure effected by burst errors. A first level decoder then uses codeword check bytes to correct all of the bytes in the columns identified by the erasure pointers. The first level decoder is freed to use all of the codeword check bytes only for error byte value calculations. The first level decoder does not need to use any of the codeword check bytes for error location calculations, because the erasure pointers generated by the second level decoder provide all of the necessary error locations. This techniques doubles the error correction capability of the first level decoder.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV +1
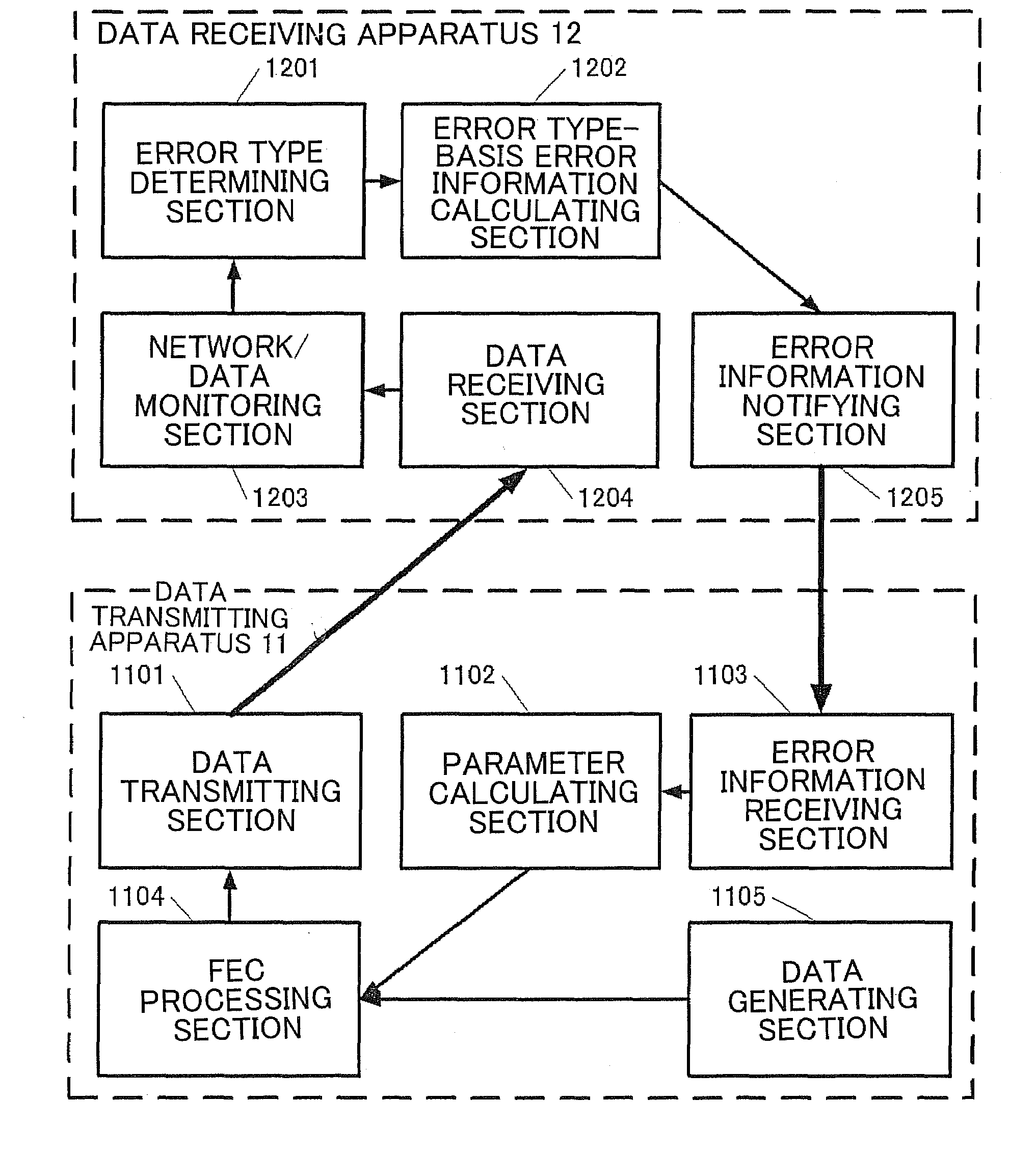
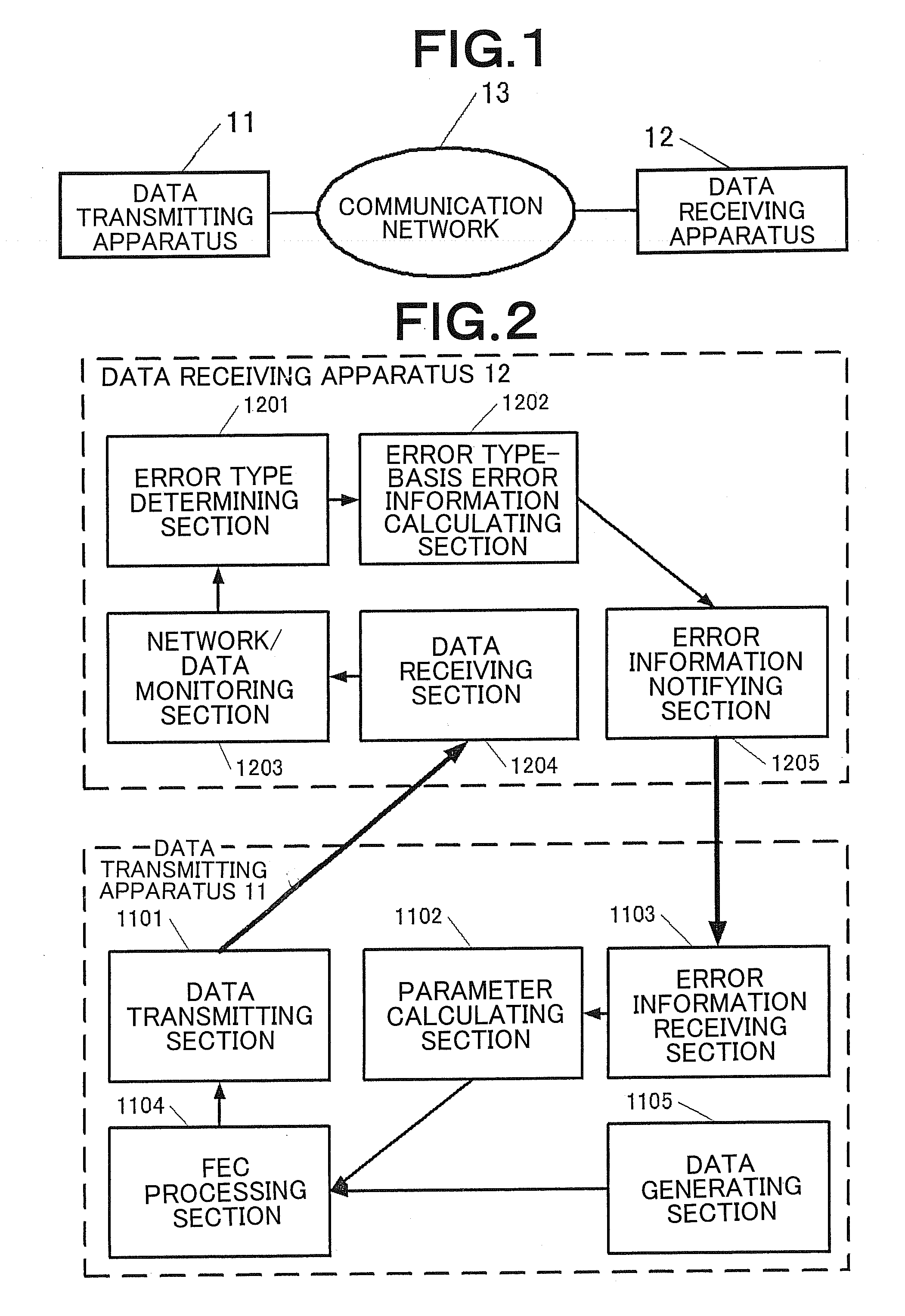
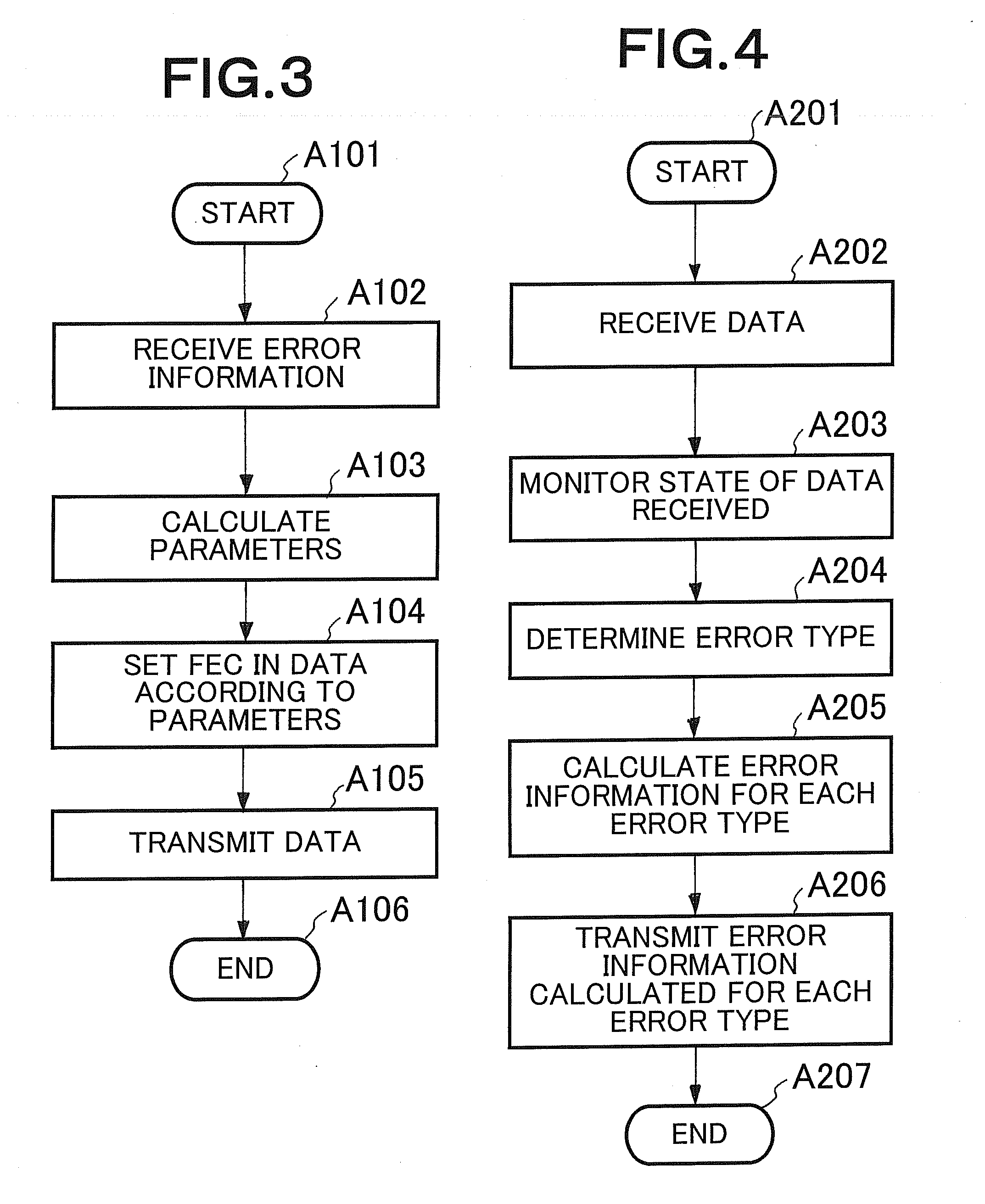
Data communication apparatus, method, and program
InactiveUS20080184081A1Optimal FEC redundancy degreeDegree of avoidanceError detection/correctionChannel coding adaptationError ratioBurst error
A data communication apparatus determines whether the error type is a burst error or not based on an error occurrence state of the data received from a data transmitting apparatus and transmits error type-basis error information. The data communication apparatus receives the error type-basis error information and sets the redundancy degree of an FEC processing section based on the error rate of the errors other than a burst error.
Owner:NEC CORP
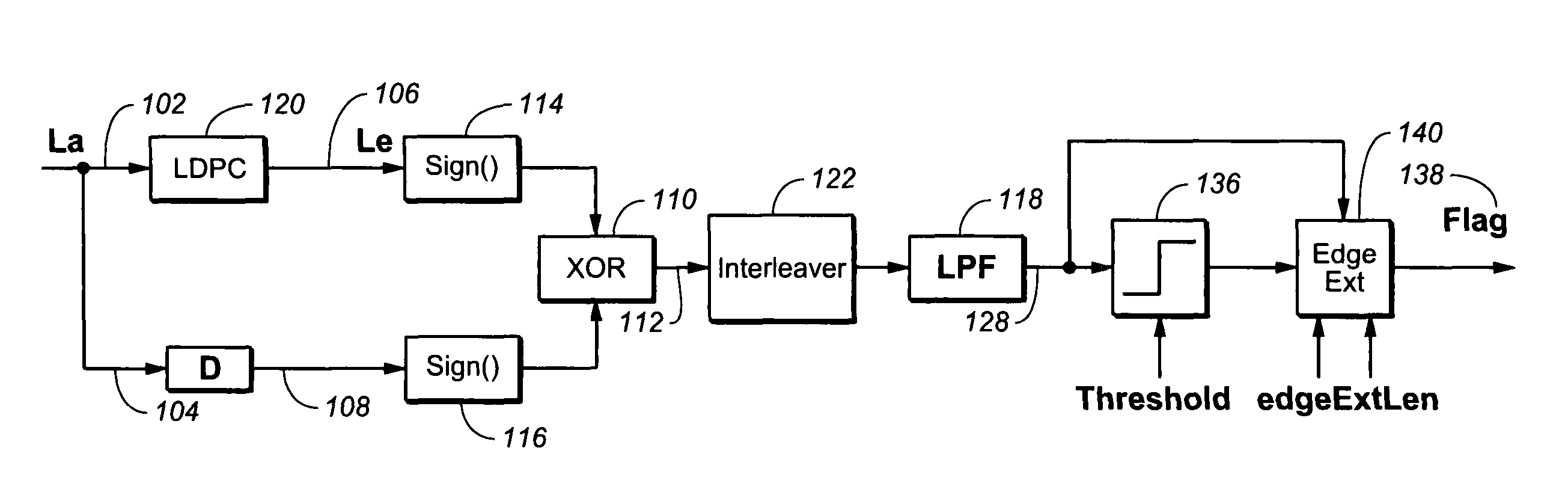
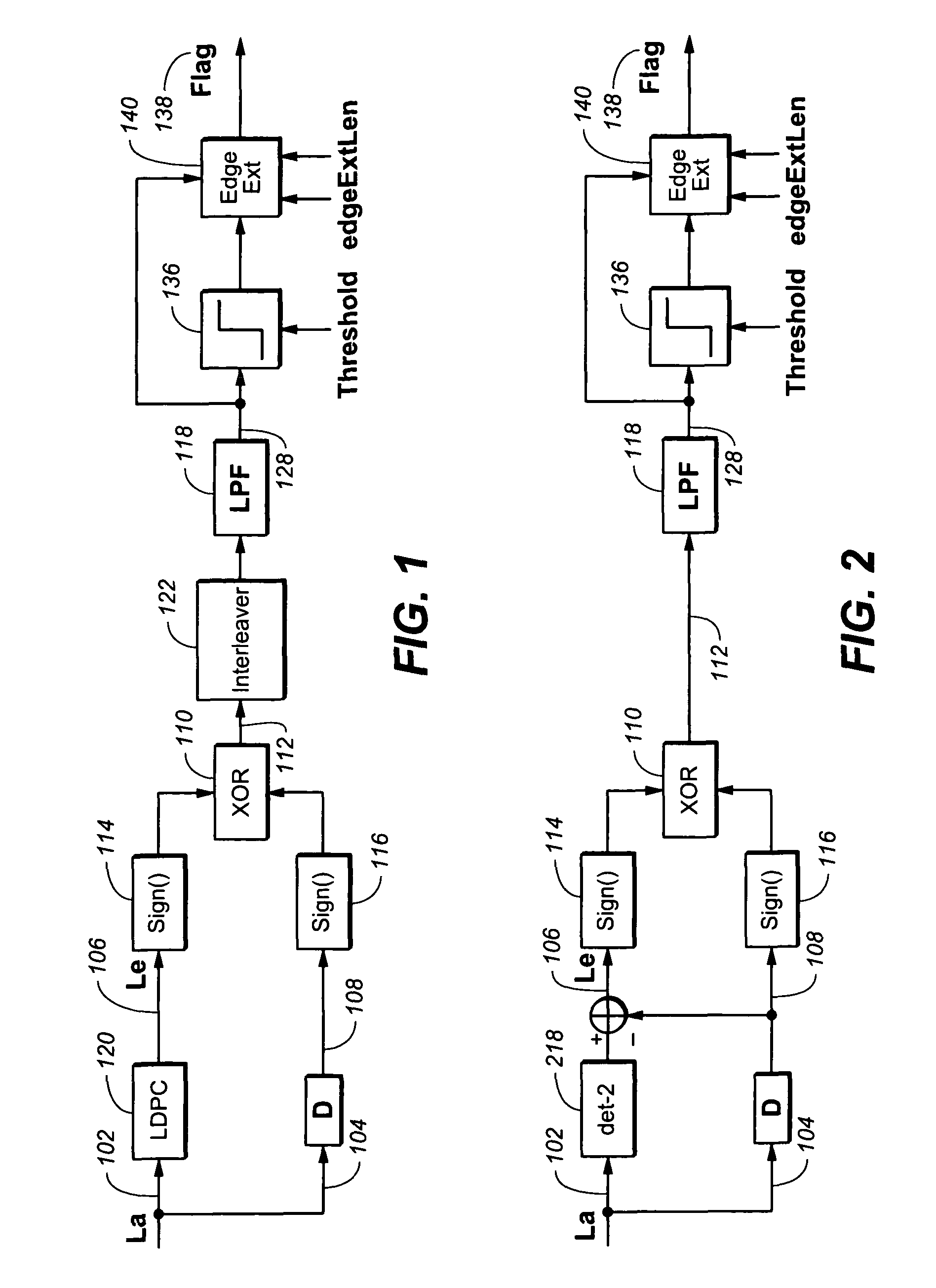
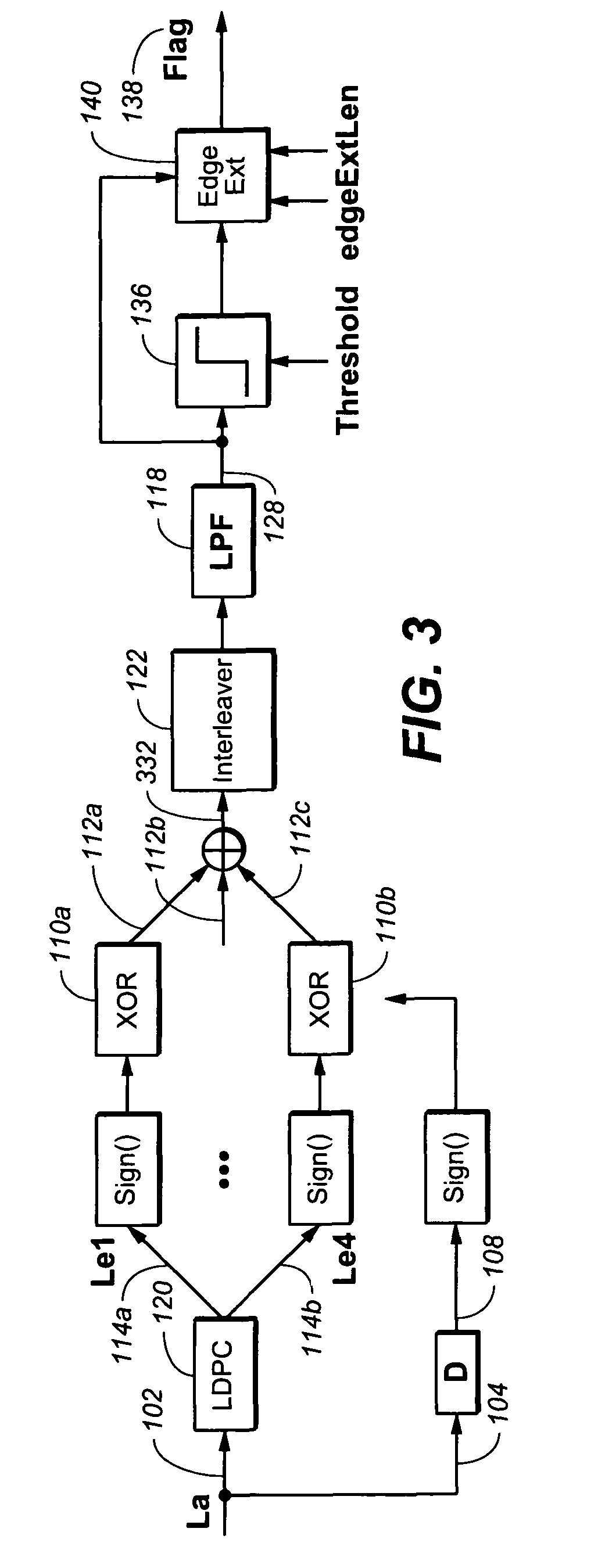
Method for detecting short burst errors in LDPC system
The present invention is a device for detecting short burst errors. The device includes a first signal input, wherein the first signal input is configured to receive a first signal. The device includes a second signal input, wherein the second signal input is configured to receive a second signal. The device includes a logic gate, wherein the logic gate is operable for receiving the first signal vial the first signal input, receiving the second signal via the second signal input, and generating a logic output gate signal based on the received first signal and the second signal. Furthermore, the device includes a filter, wherein the filter is configured for receiving the logic output gate signal from the logic gate and generates a filter output signal based upon the received logic output gate signal, wherein the filter output signal is operable for flagging errors.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Robust DTV signals that can overcome burst errors up to 1040 bytes or more in length
InactiveUS20070217499A1Easy to optimizeImprove abilitiesColor television with pulse code modulationModulated-carrier systemsForward error correctionByte
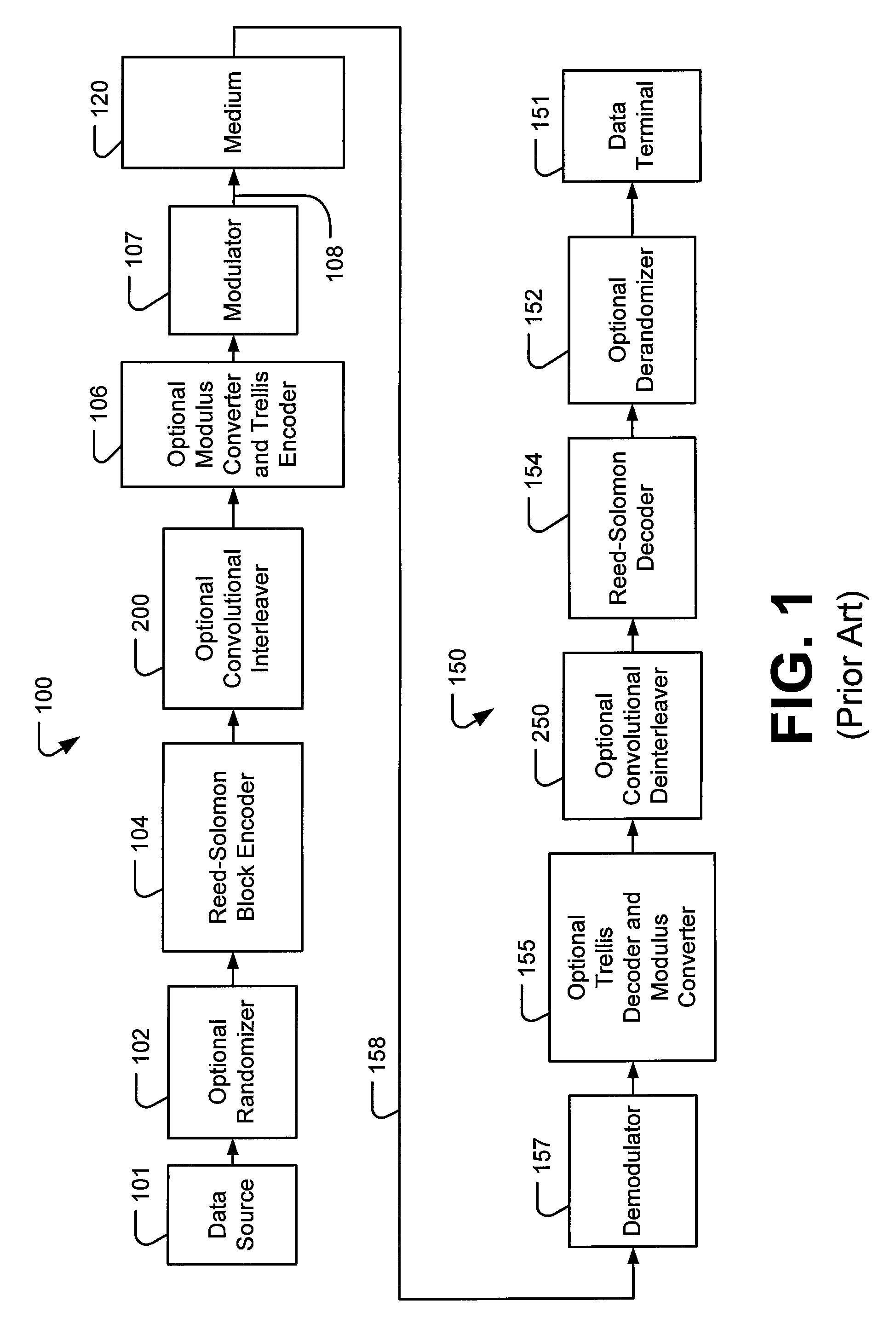
Electromagnetic signals for transmitting television and other information more robustly have amplitudes modulated in accordance with a digital signal generated by convolutional interleaving and trellis coding of segments of successive data fields, each of which segments contains a prescribed number of bytes. In improvements of these signals, respective fractional portions of a Reed-Solomon forward-error-correction codeword are transmitted in respective ones of a plurality of the segments of the successive data fields. The respective ones of the plurality of segments are separated from each other within the successive data fields, such that their individual bytes do not interleave with each other after the convolutional interleaving and trellis coding are completed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
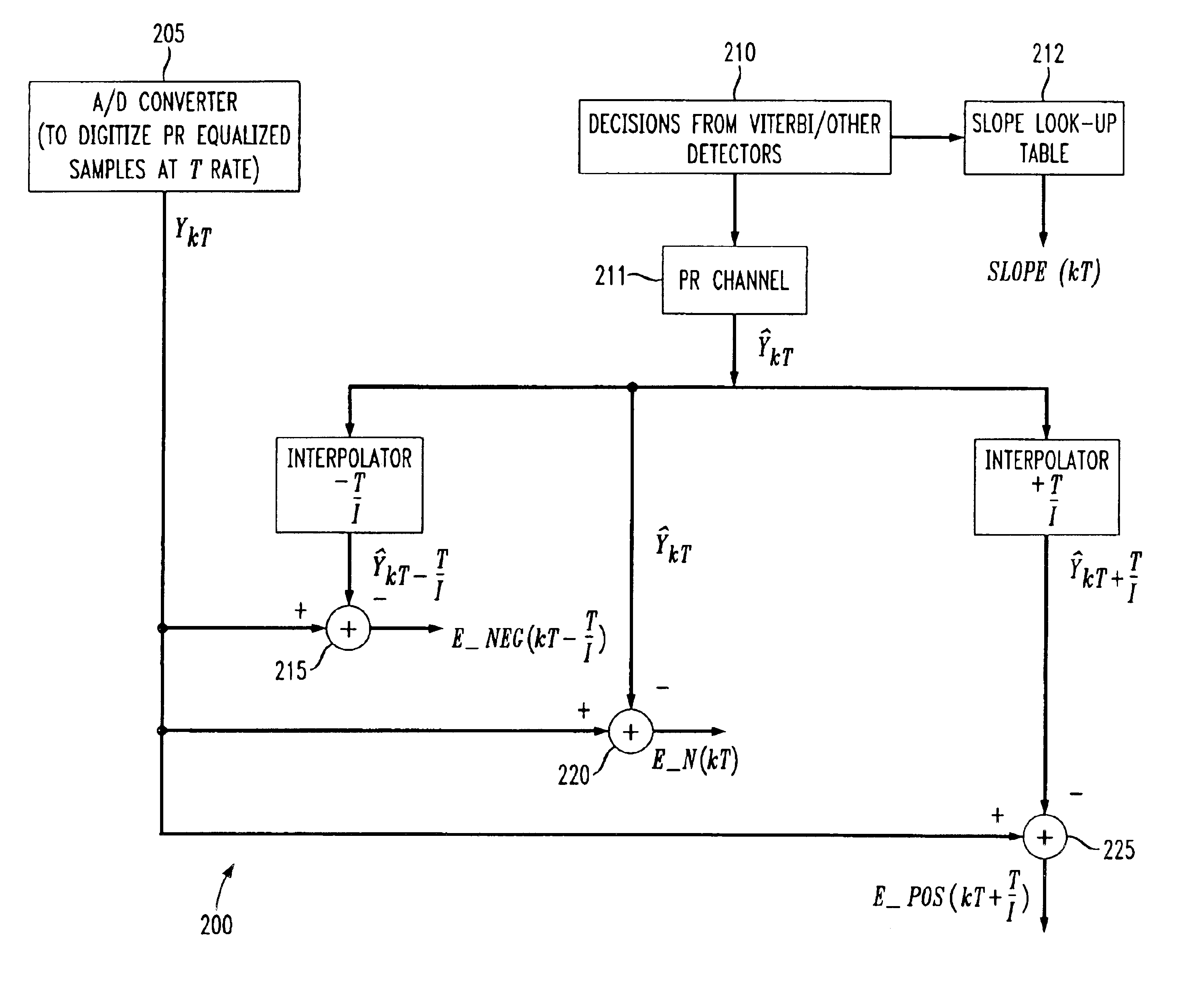
Scheme to improve performance of timing recovery systems for read channels in a disk drive
InactiveUS6856183B2Pulse automatic controlVoltage-current phase anglePhase locked loop circuitEngineering
A digital phase lock loop circuit including an error generation circuit for generating at least three error signals and a phase error adjustment circuit for generating at least one phase error adjustment signal from the at least three error signals. By using at least three error signals, as opposed to just one, the drift in the sampling phase of the recovered clock is easily detected and corrected to reduce burst errors and to improve loss of lock (LOL) performance.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
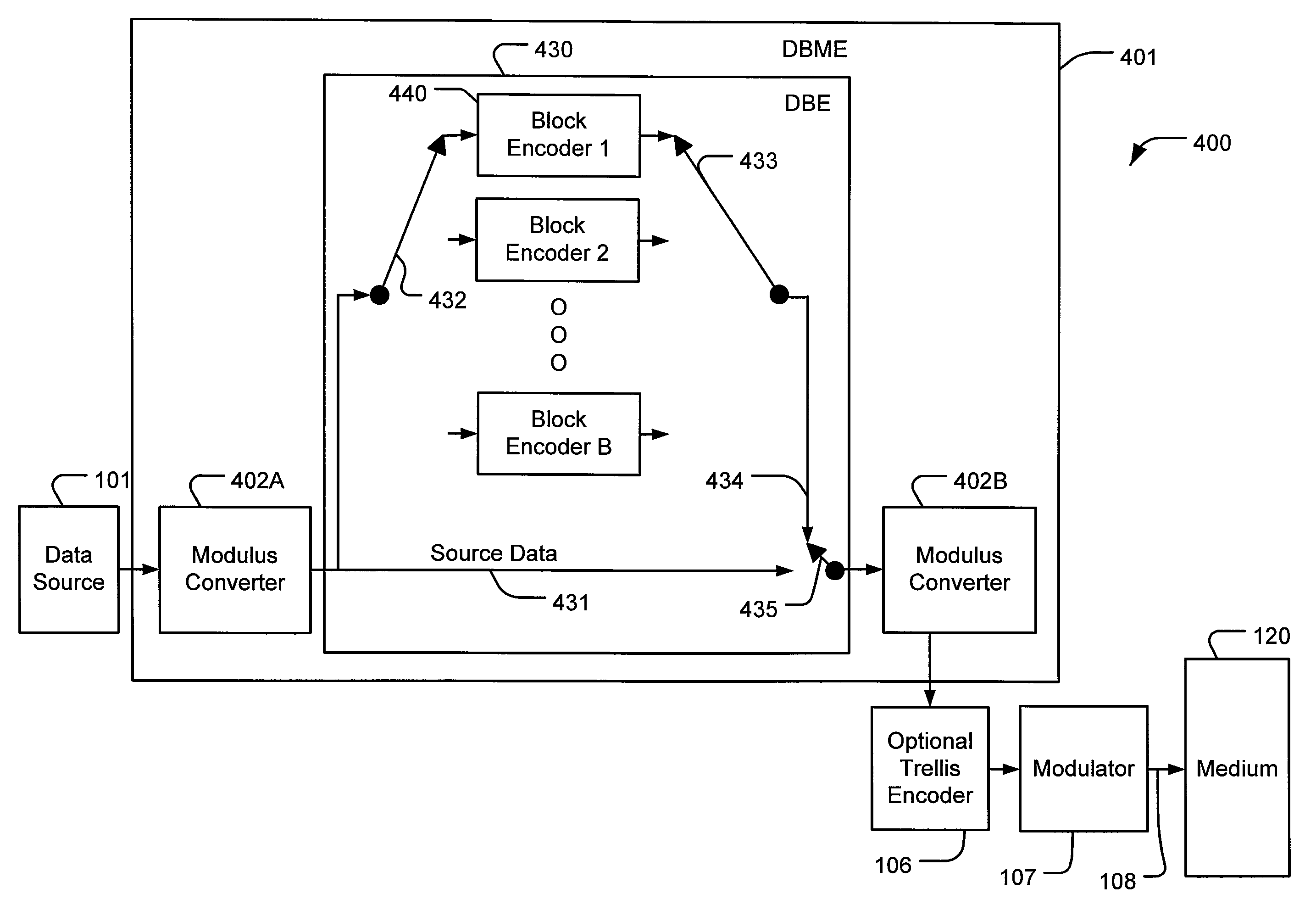
Block Modulus Coding (BMC) Systems and Methods for Block Coding with Non-Binary Modulus
InactiveUS20090204877A1Reduce memory requirementsFacilitate interleavingData representation error detection/correctionOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemBlock code
Block modulus coding (BMC) systems implement block coding on non-binary modulus m symbols, where m is greater than 2. BMC systems can be used for, among other things, forward error correction (FEC) of source data in communication systems or parity backup for error correction of source data in storage systems where the source data is represented by non-binary symbols that may be corrupted by burst errors. The block coding is preferably performed using a distributed arrangement of block encoders or decoders. A distributed block modulus encoder (DBME) encodes sequential source data symbols of modulus m with a plurality of sequential block encoders to produce interleaved parity codewords. The codewords utilize modulus m symbols where the medium can reliably resolve m symbol states. The interleaved parity codewords enable decoding of error-corrected source data symbols of modulus m with a distributed block modulus decoder (DBMD) that utilizes a plurality of sequential block decoders to produce the error-corrected source data symbols.
Owner:SUNRISE IP
Method and system for correcting burst errors in communications networks, related network and computer-program product
ActiveUS20060253763A1Satisfactory treatmentFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsDigital dataData pack
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
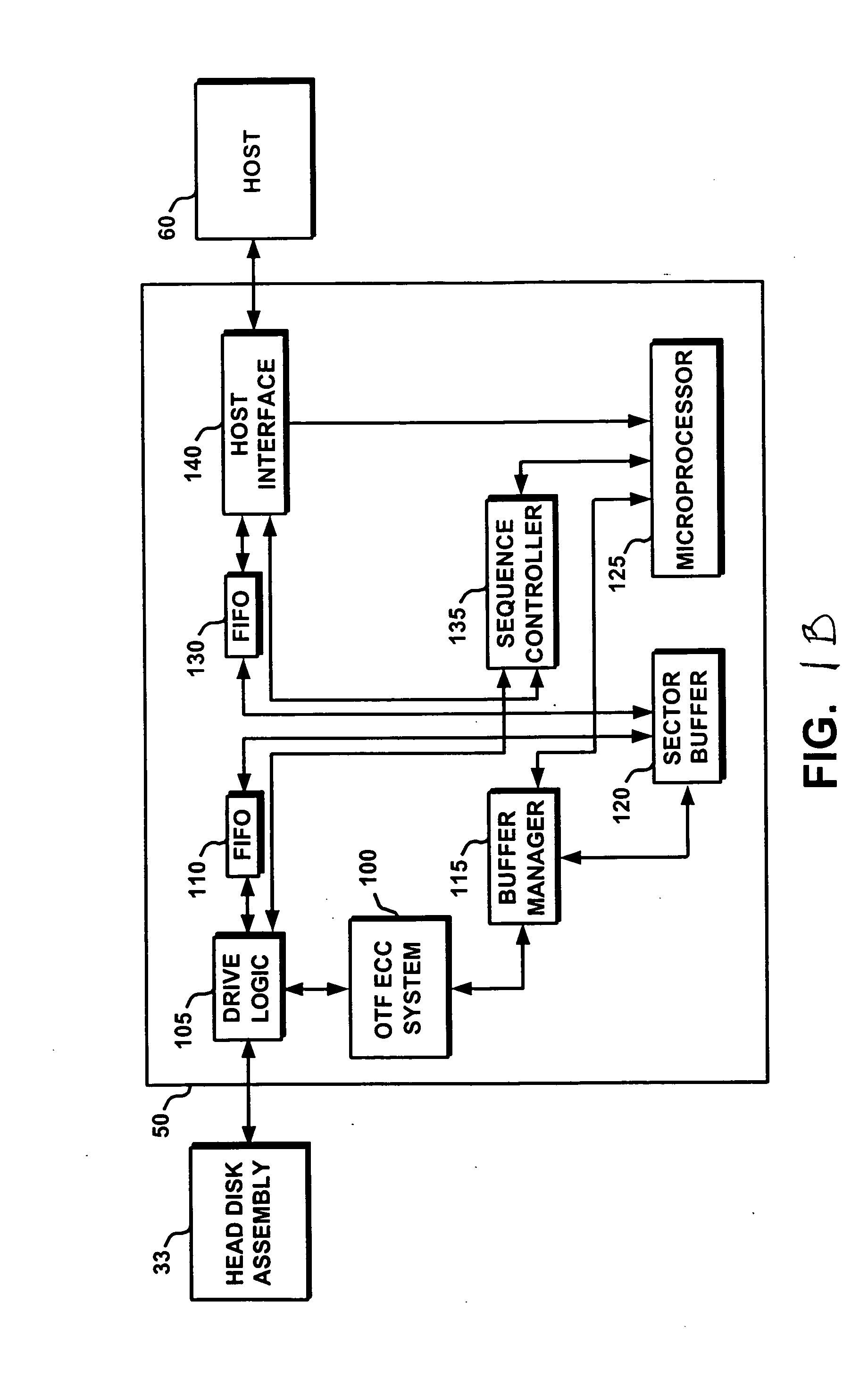
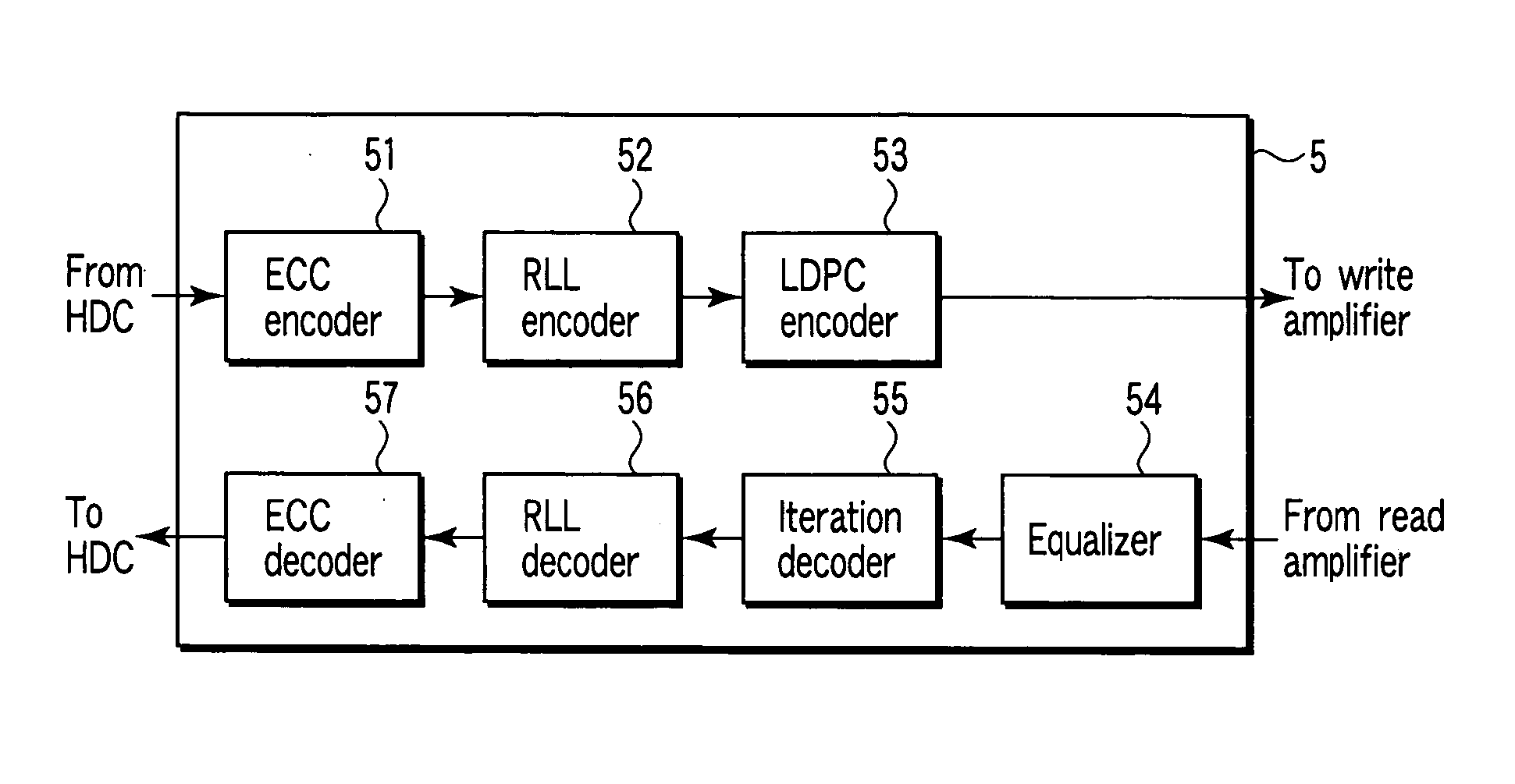
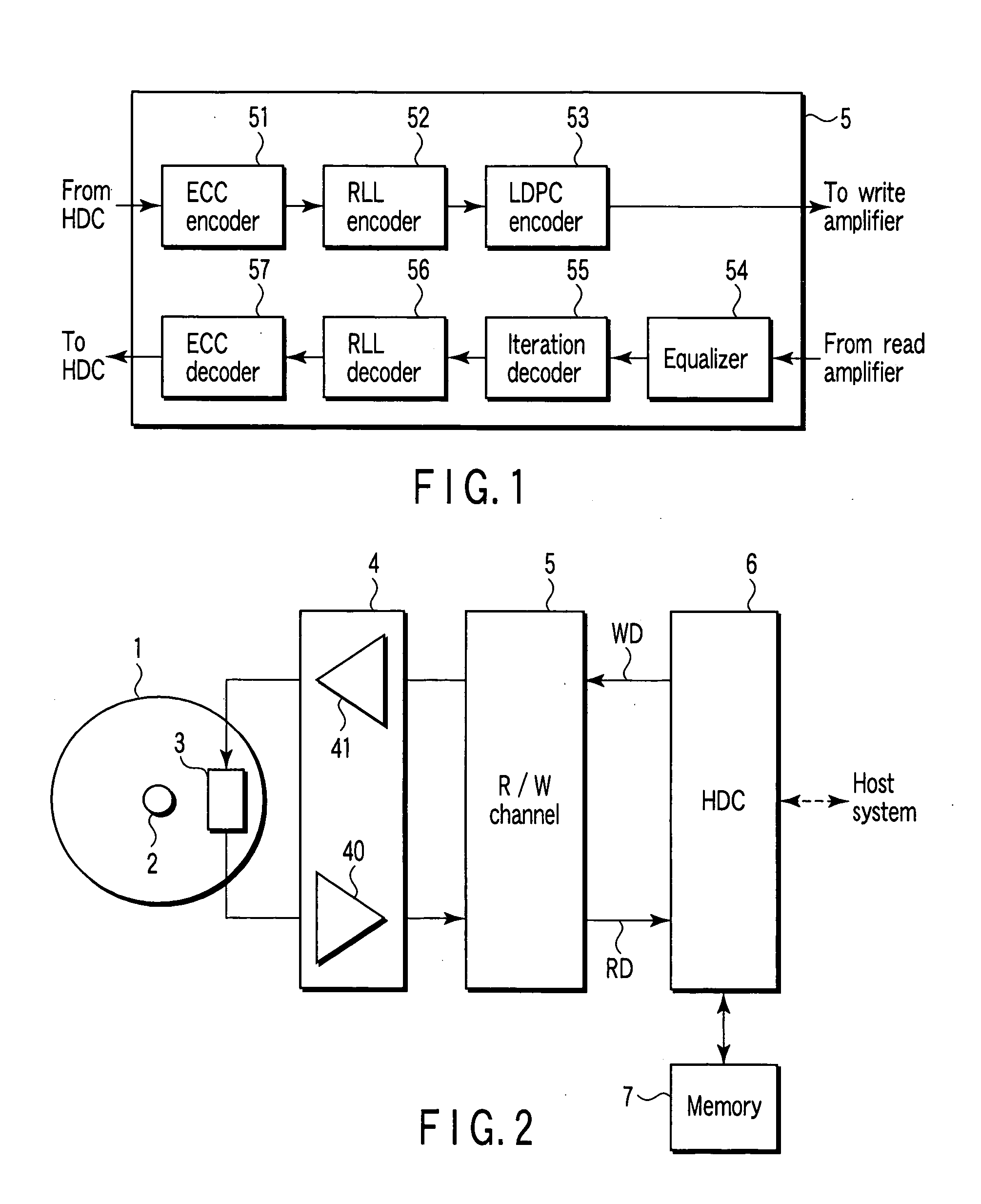
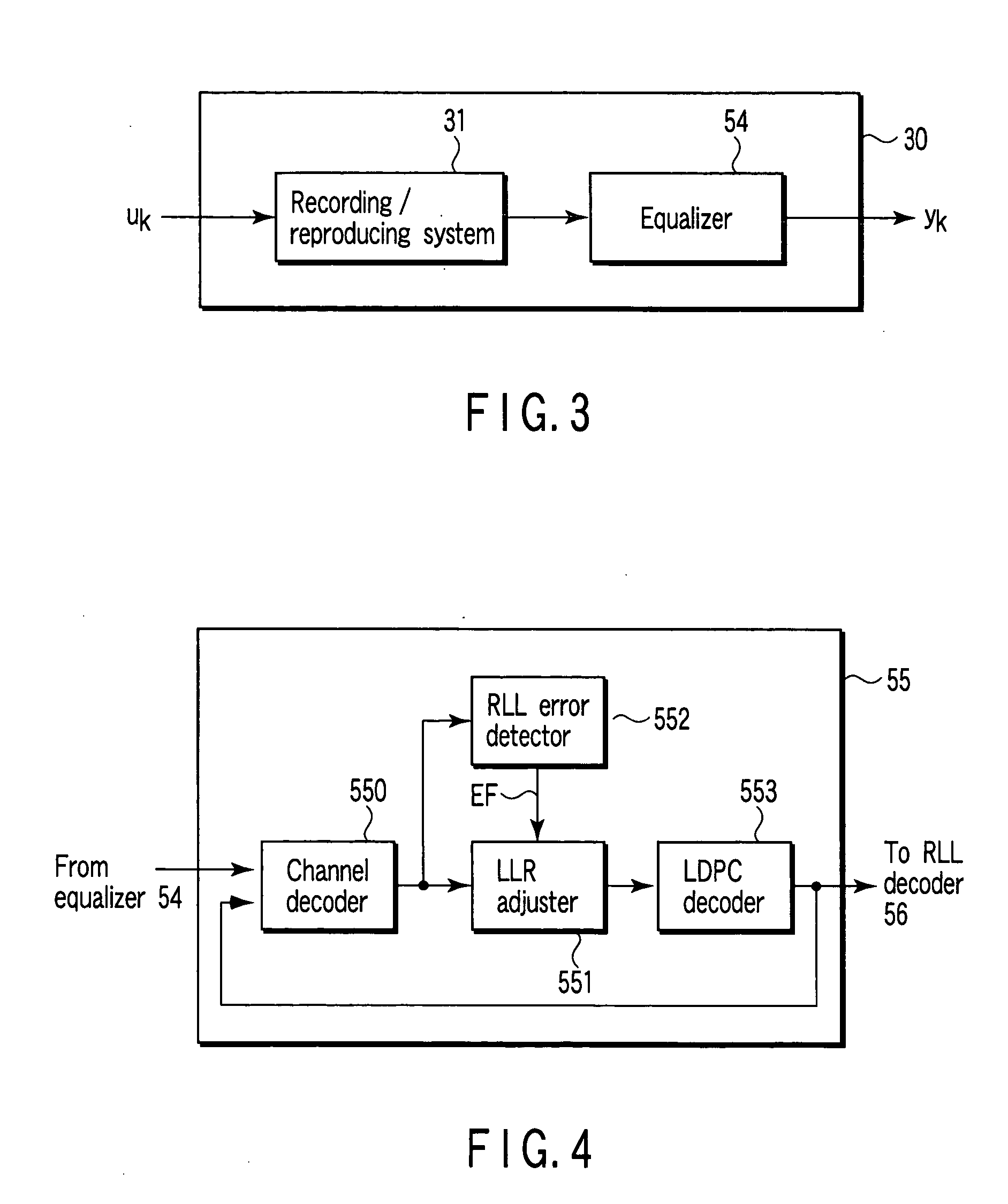
Method and apparatus for data reproducing using iterative decoding in a disk drive
InactiveUS20050120286A1Precise functionJoint error correctionOther decoding techniquesChannel decoderBurst error
A disk drive using a read / write channel including an iteration decoder for performing iterative decoding processing is disclosed. The iteration decoder has an RLL error detector for detecting a burst error portion from an LLR group output from the channel decoder, and an LLR adjuster. The LLR adjuster makes adjustment by reducing the value of the LLR group corresponding to the detected burst error portion.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
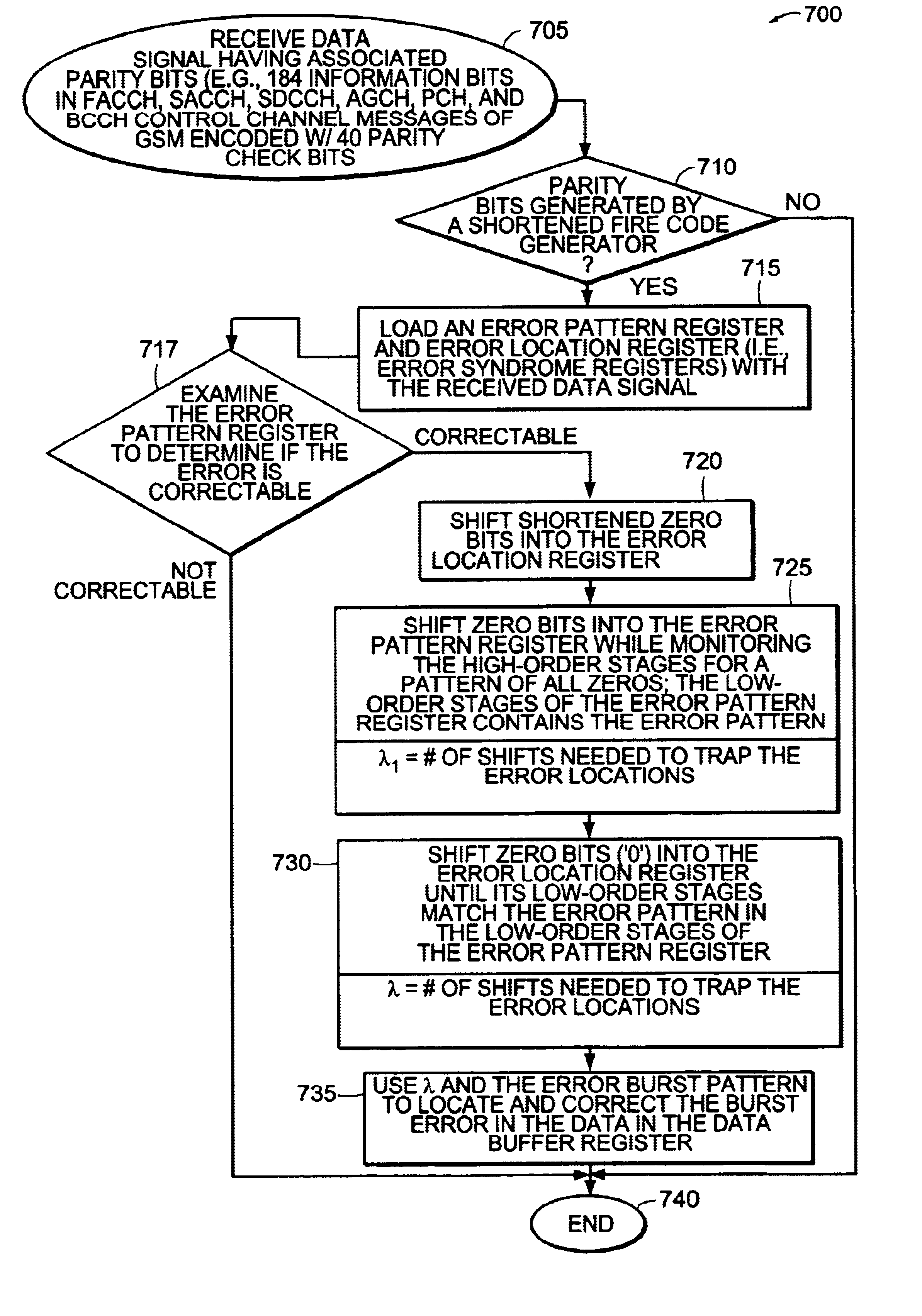
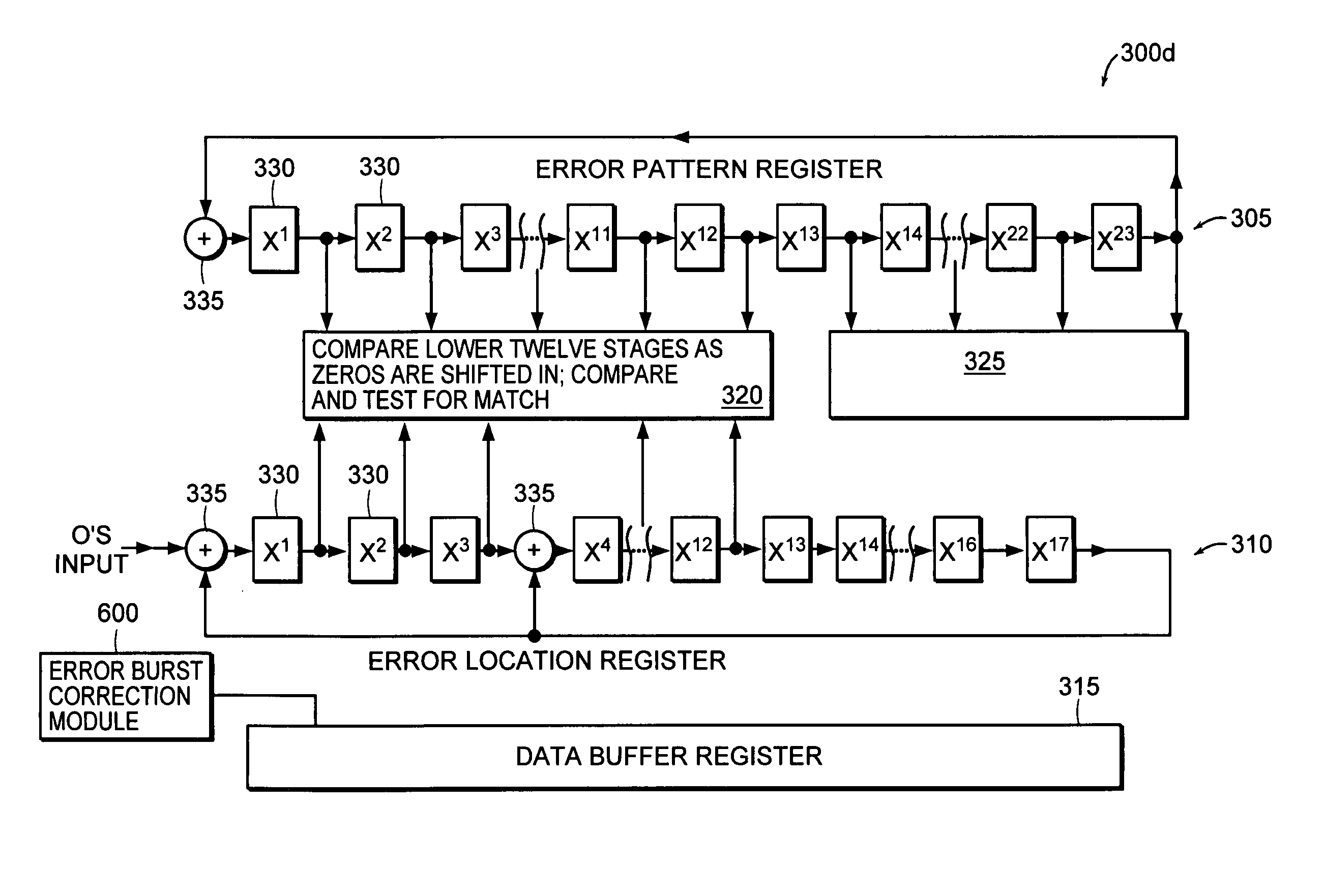
Method and apparatus for using fire decoder to correct burst errors in a real-time communications system
InactiveUS6754871B1Error preventionBurst error correctionProcessor registerReal time communication systems
Error bursts are detected and corrected in a communication system using shortened cyclic codes, such as shortened Fire codes. Data is loaded into a first error syndrome register and a second error syndrome register. The data in the registers may be evaluated to determine if the data bits contain a correctable error. Shortened zero bits are shifted into the second error syndrome register. A number of zero bits are shifted into the first error syndrome register to trap an error burst pattern in the data. A determination is made as to the number of zero bits shifted into the second error syndrome register to trap the location of the error burst in the data. Using the number of zero bits shifted into the second error syndrome register and the error burst pattern, the error in the data is located and corrected.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for generating bit errors in a forward error correction (FEC) system to estimate power dissipation characteristics of the system
ActiveUS7073117B1Precision productionPower dissipationData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionFir systemForward error correction
A method and apparatus for generating and inserting bit errors in data words that have been encoded in a forward error correction (FEC) system in order to estimate power dissipation. In accordance with the present invention, it has been determined that a burst error generator that is capable of erroring the maximum number of correctable data bits in every FEC encoded frame, which allows the designer to accurately produce test vectors that are suitable for use in commercially available power estimation tools. In addition, after the IC is produced, the burst error generator of the present invention can be enabled to provide real-time FEC power dissipation data for use in system thermal modeling, thus obviating the need to use costly external devices that emulate a given error rate. Furthermore, the power dissipation data obtained in real-time may be used to refine the initial design power estimate, which will then allow the designer to develop a more accurate prediction of power consumption for future IC designs. Thus, the burst error generator of the present invention is capable of reducing iterations of IC designs by accurately estimating the worst-case power dissipation of FEC decoders.
Owner:CIENA
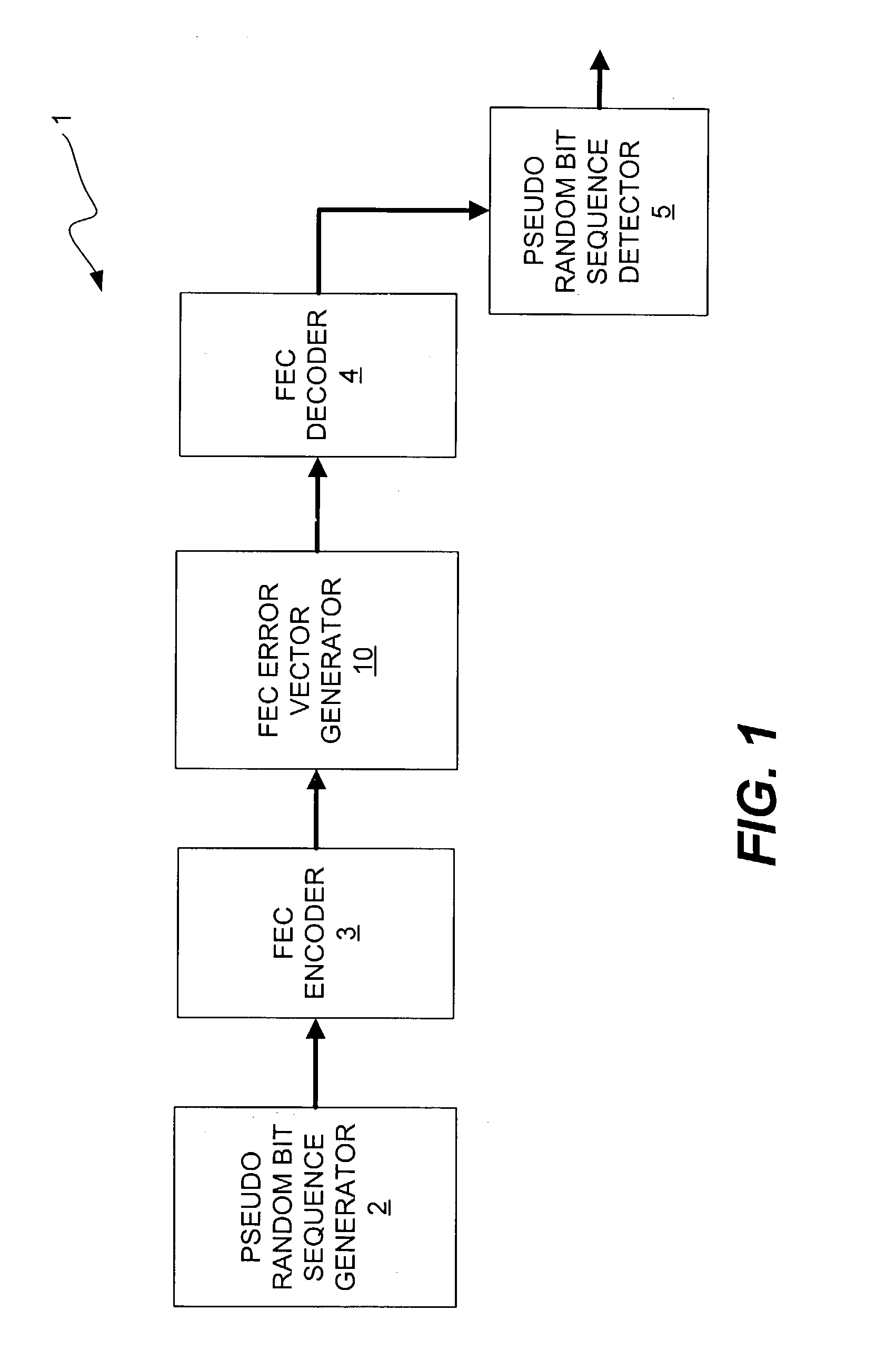
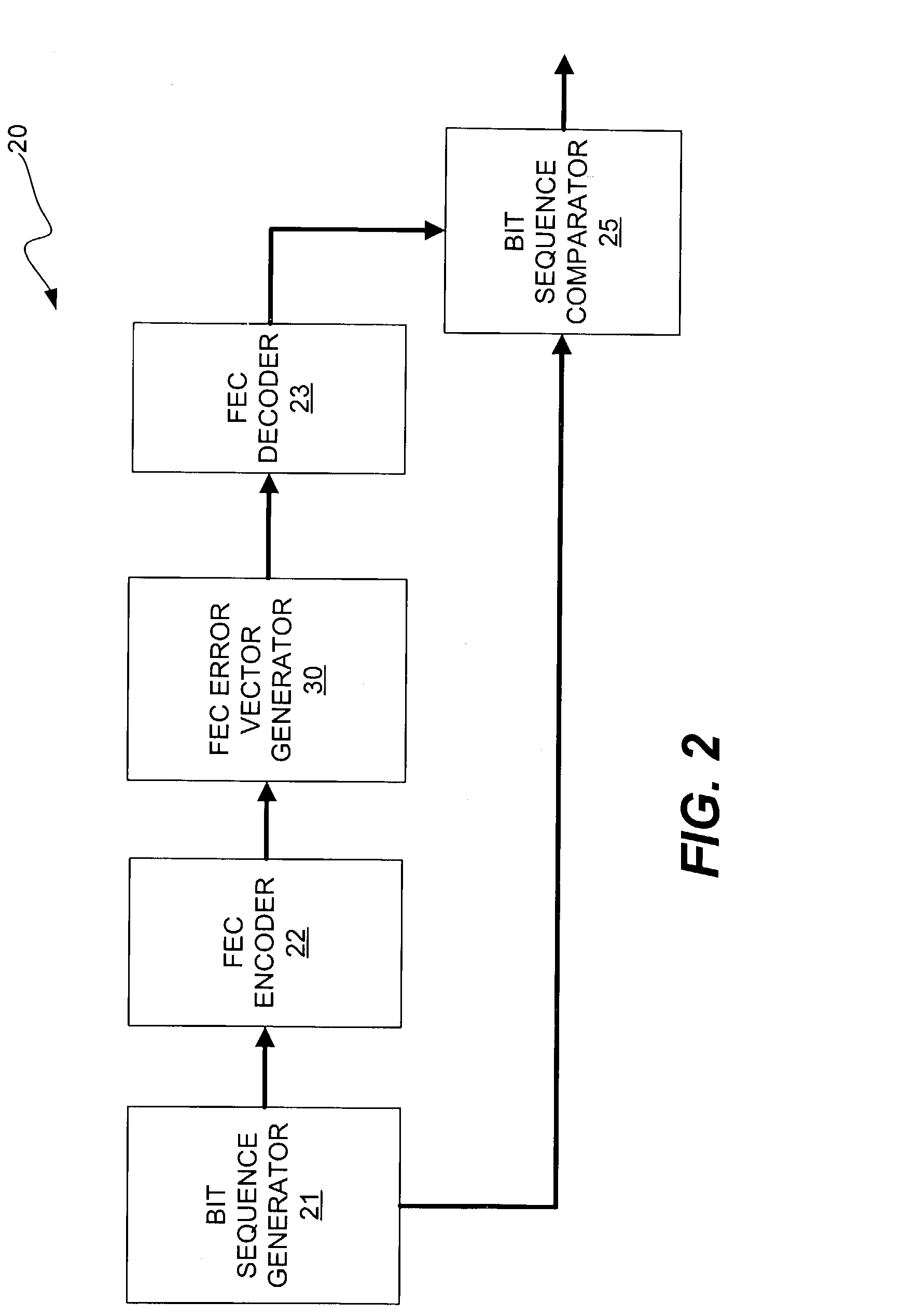
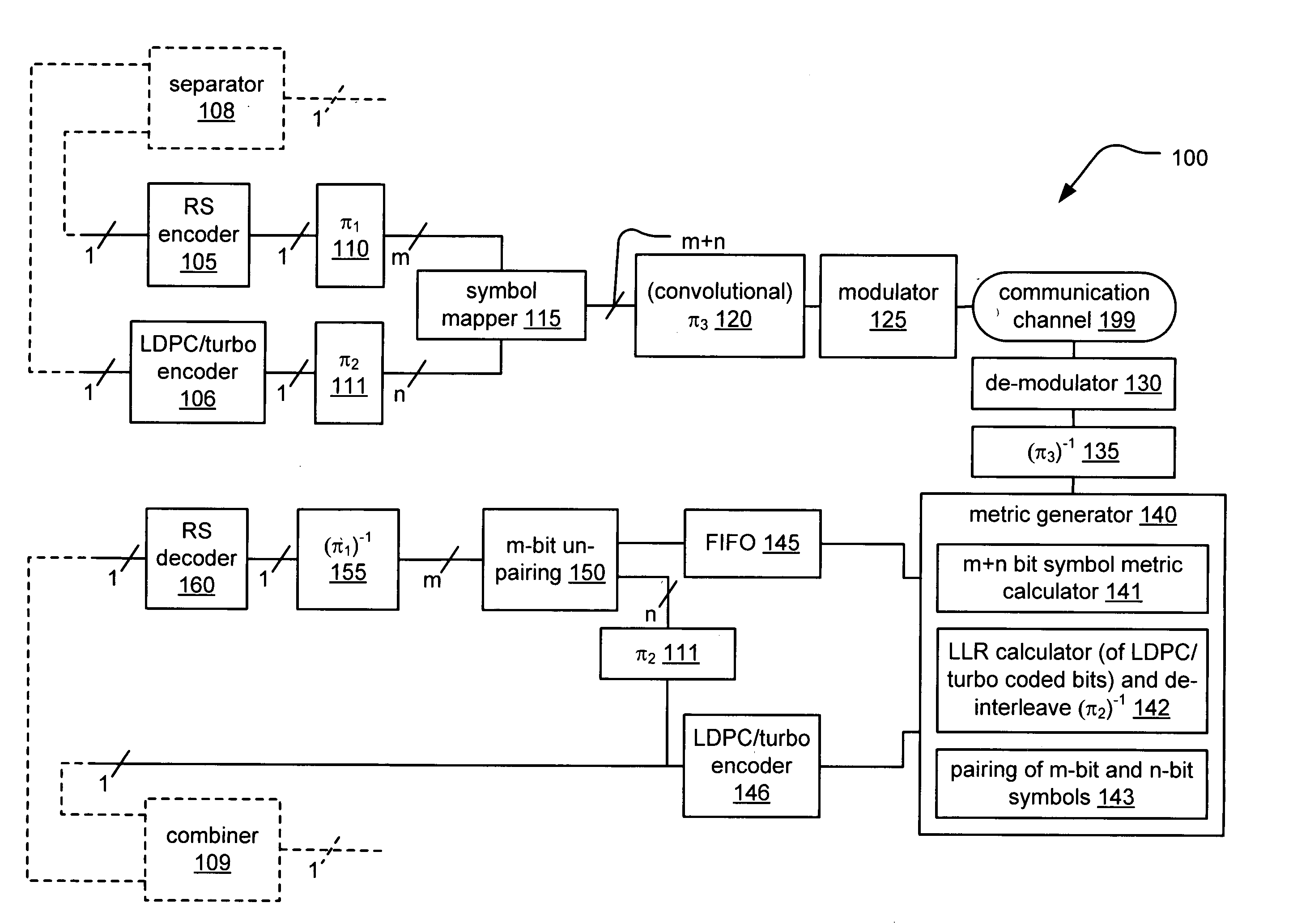
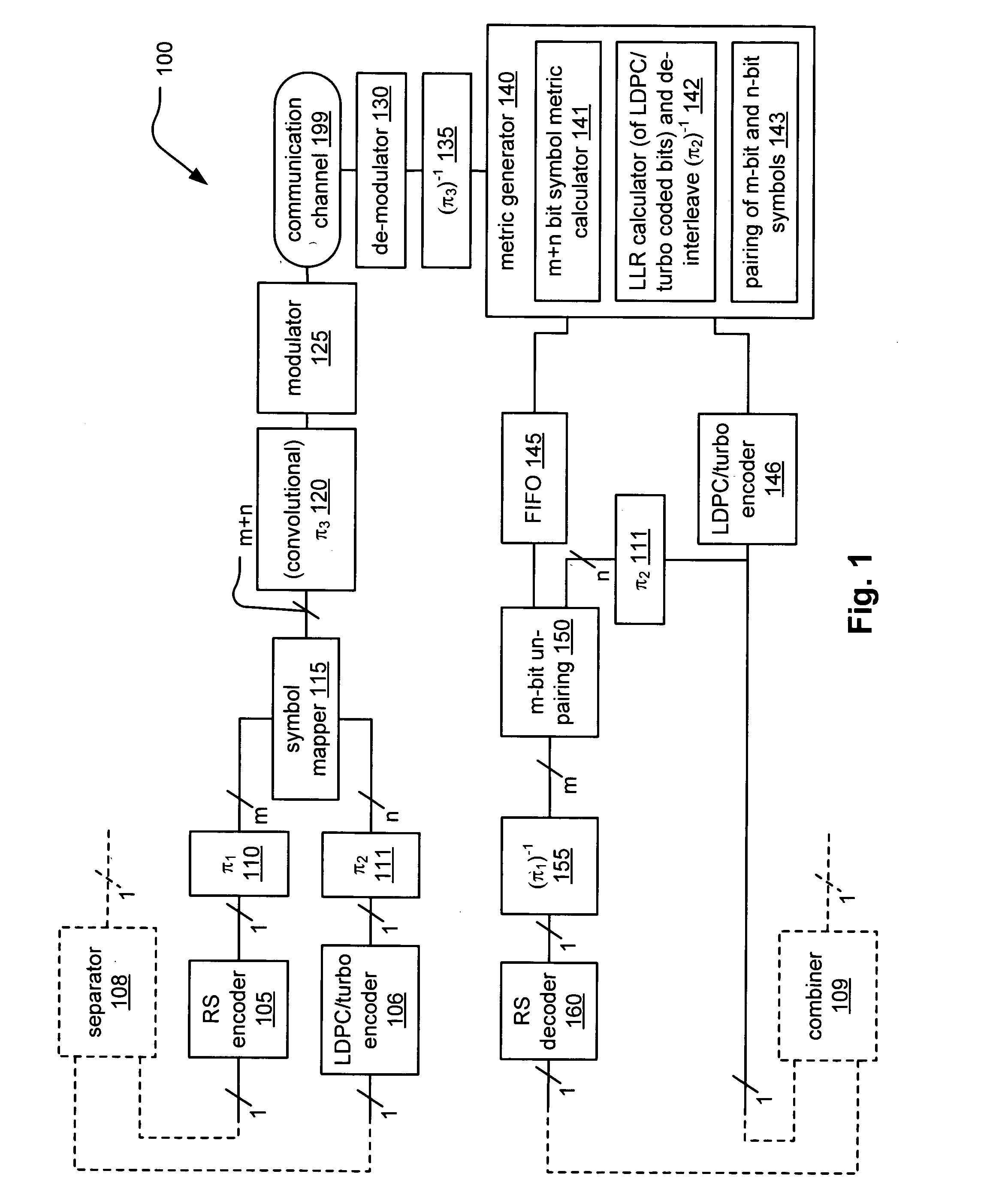
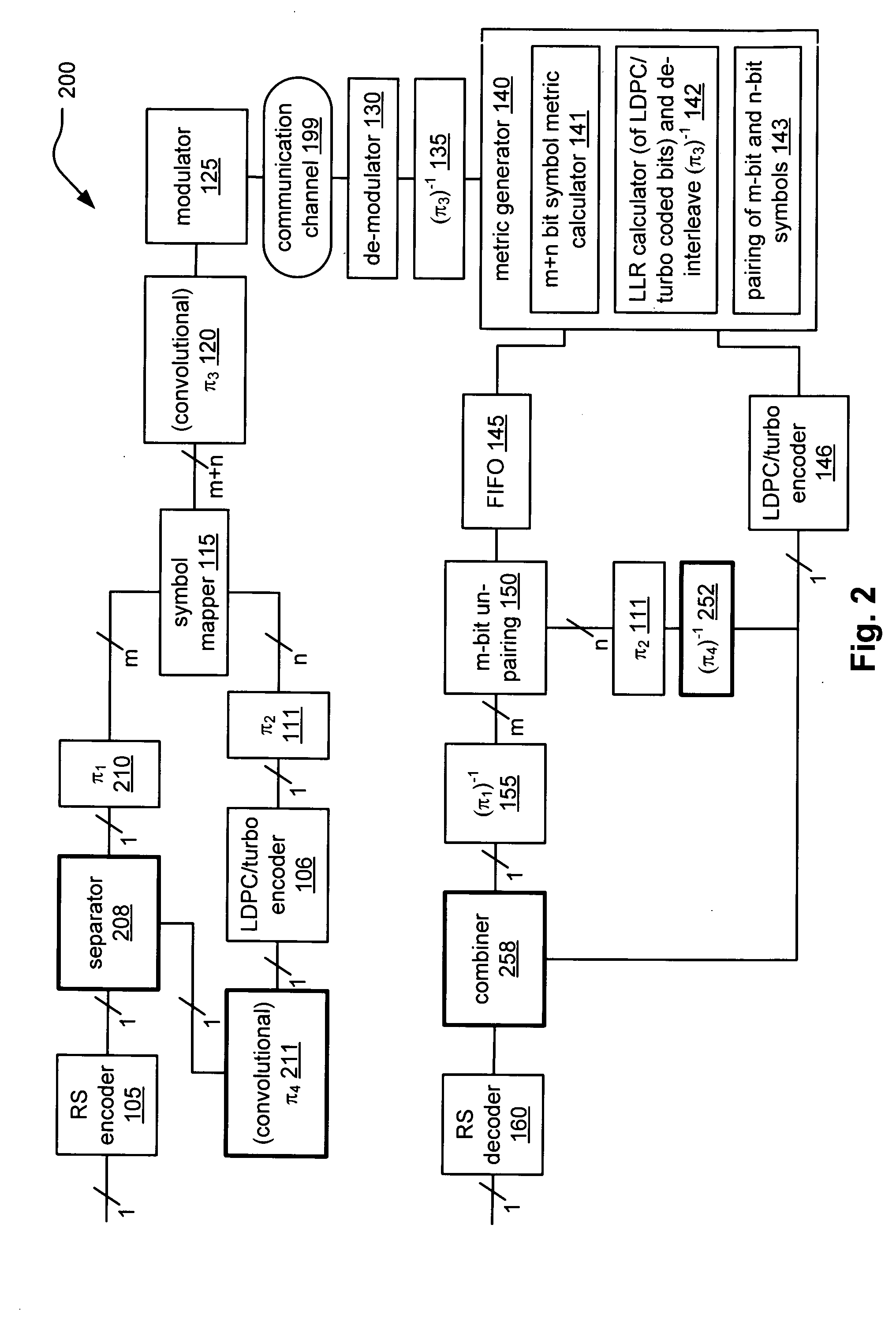
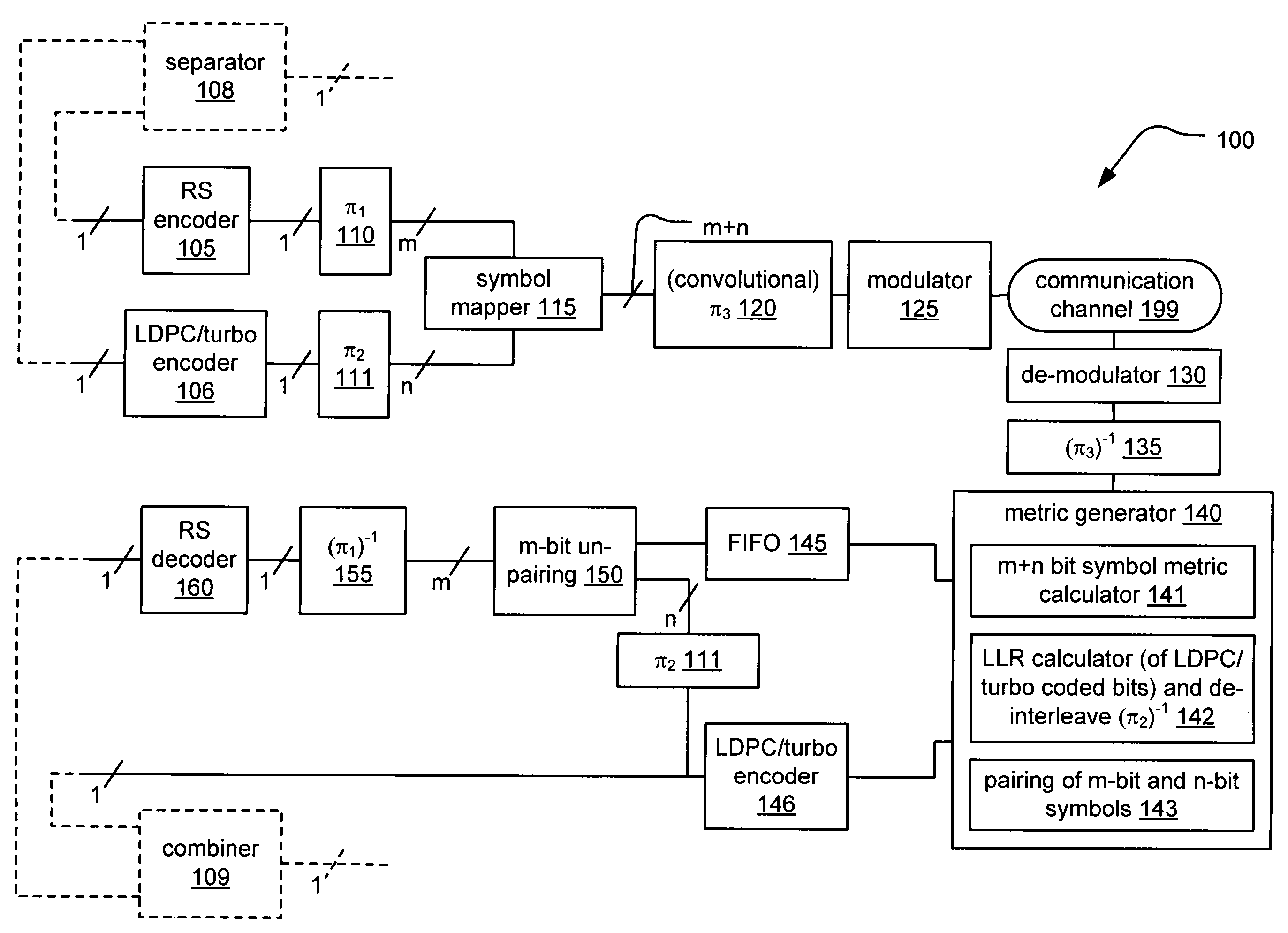
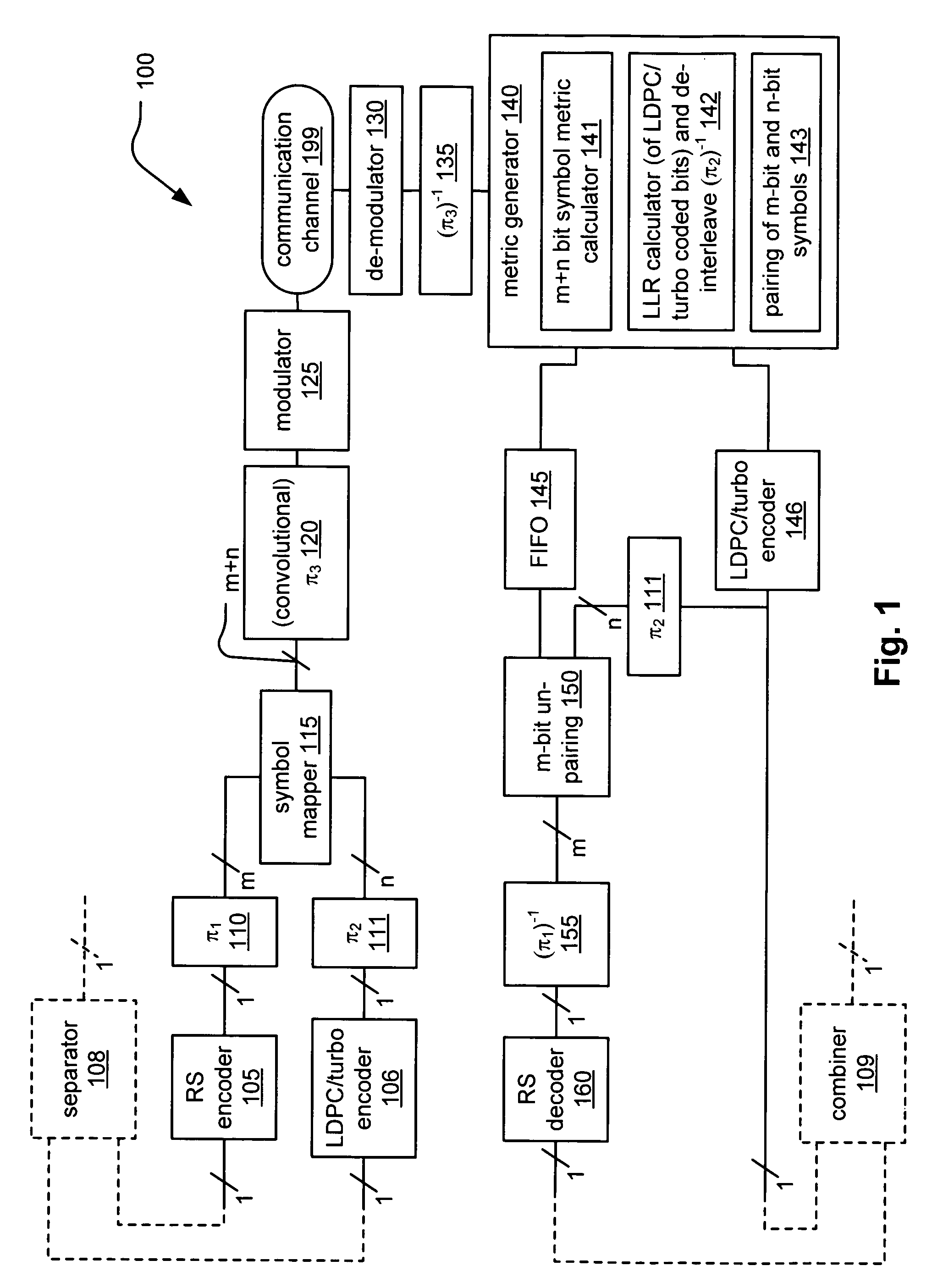
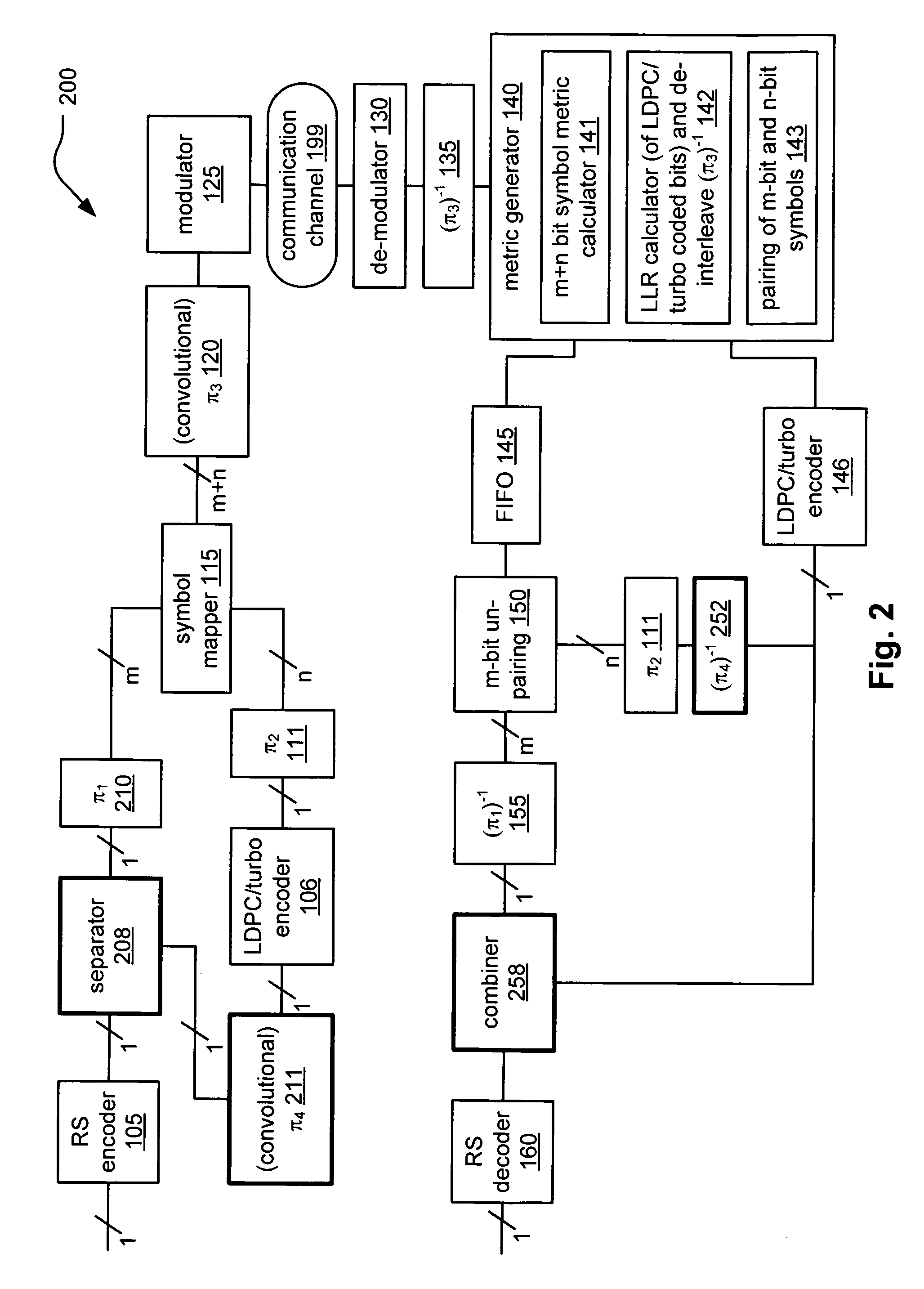
System correcting random and/or burst errors using RS (Reed-Solomon) code, turbo/LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and convolutional interleave
InactiveUS20060224935A1Error correction/detection using concatenated codesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareBurst error
System correcting random and / or burst errors using RS (Reed-Solomon) code, turbo / LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and convolutional interleave. A novel approach is presented that combines different coding types within a communication system to perform various types of error correction. This combination of accommodating different coding types may be employed at either end of a communication channel (e.g., at a transmitter end when performing encoding and / or at a receiver end when performing decoding). By combining different coding types within a communication system, the error correcting capabilities of the overall system is significantly improved. The appropriate combination of turbo code and / or LDPC code along with RS code allows for error correction or various error types including random error and burst error (or impulse noise).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
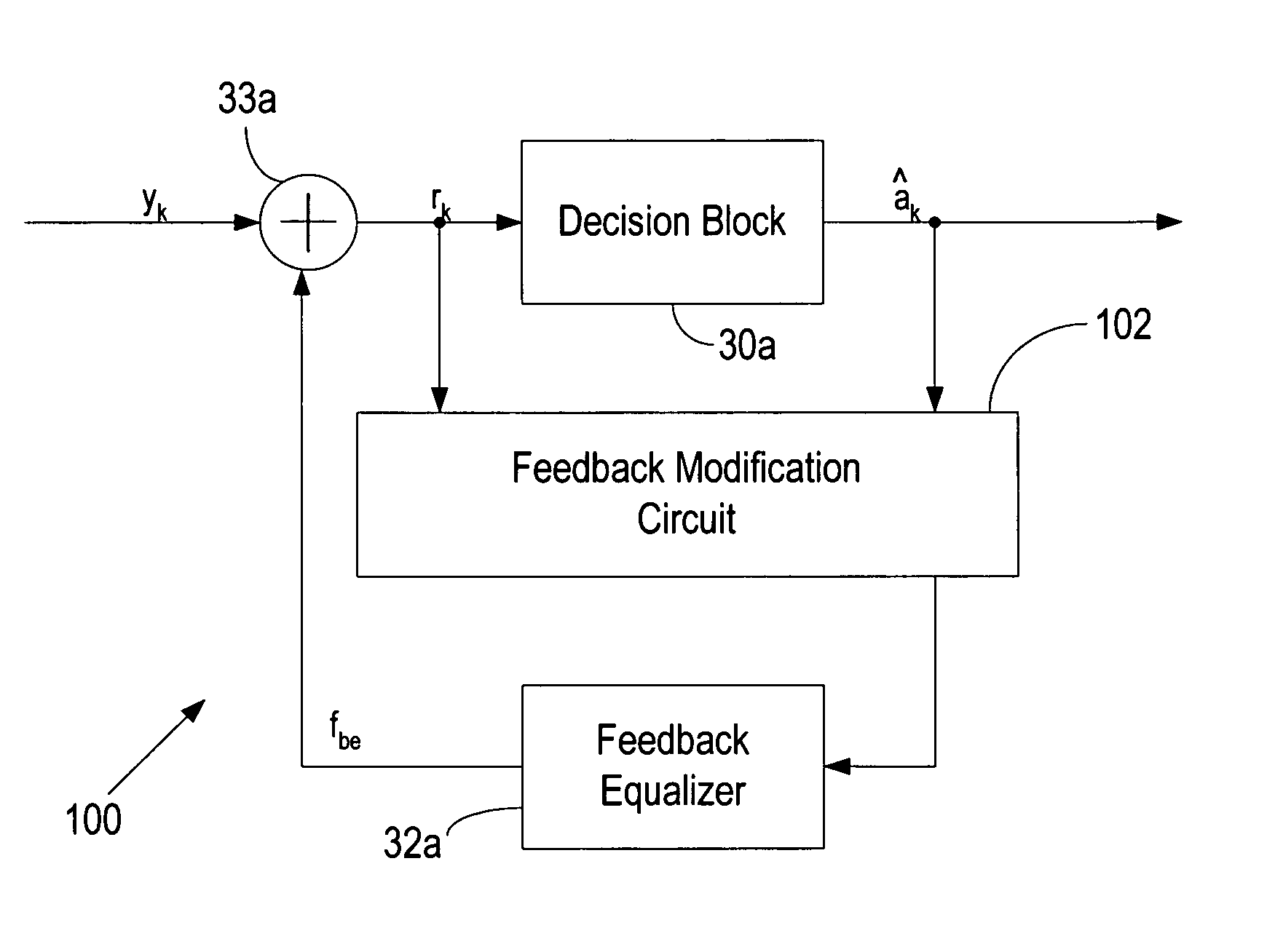
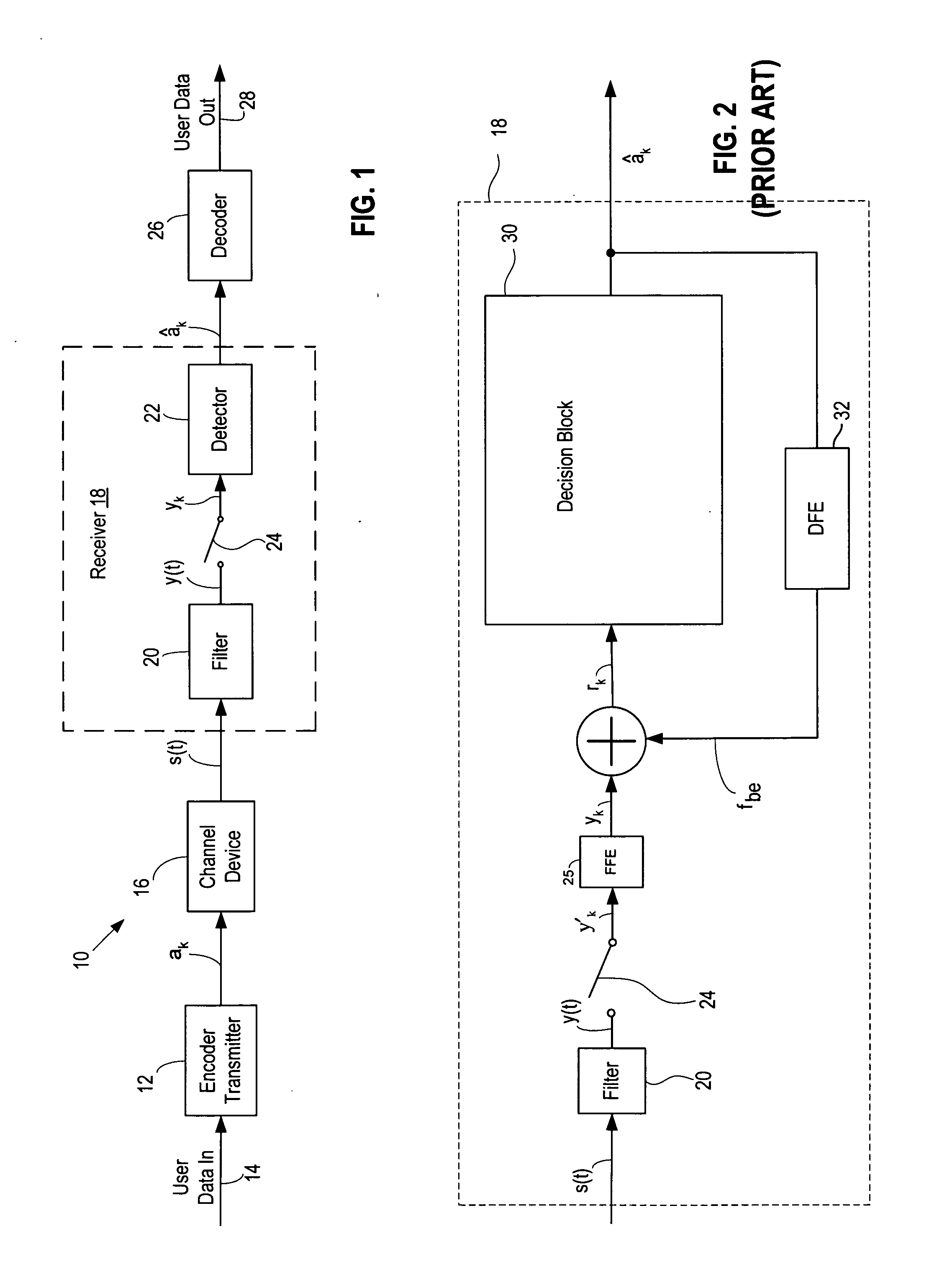
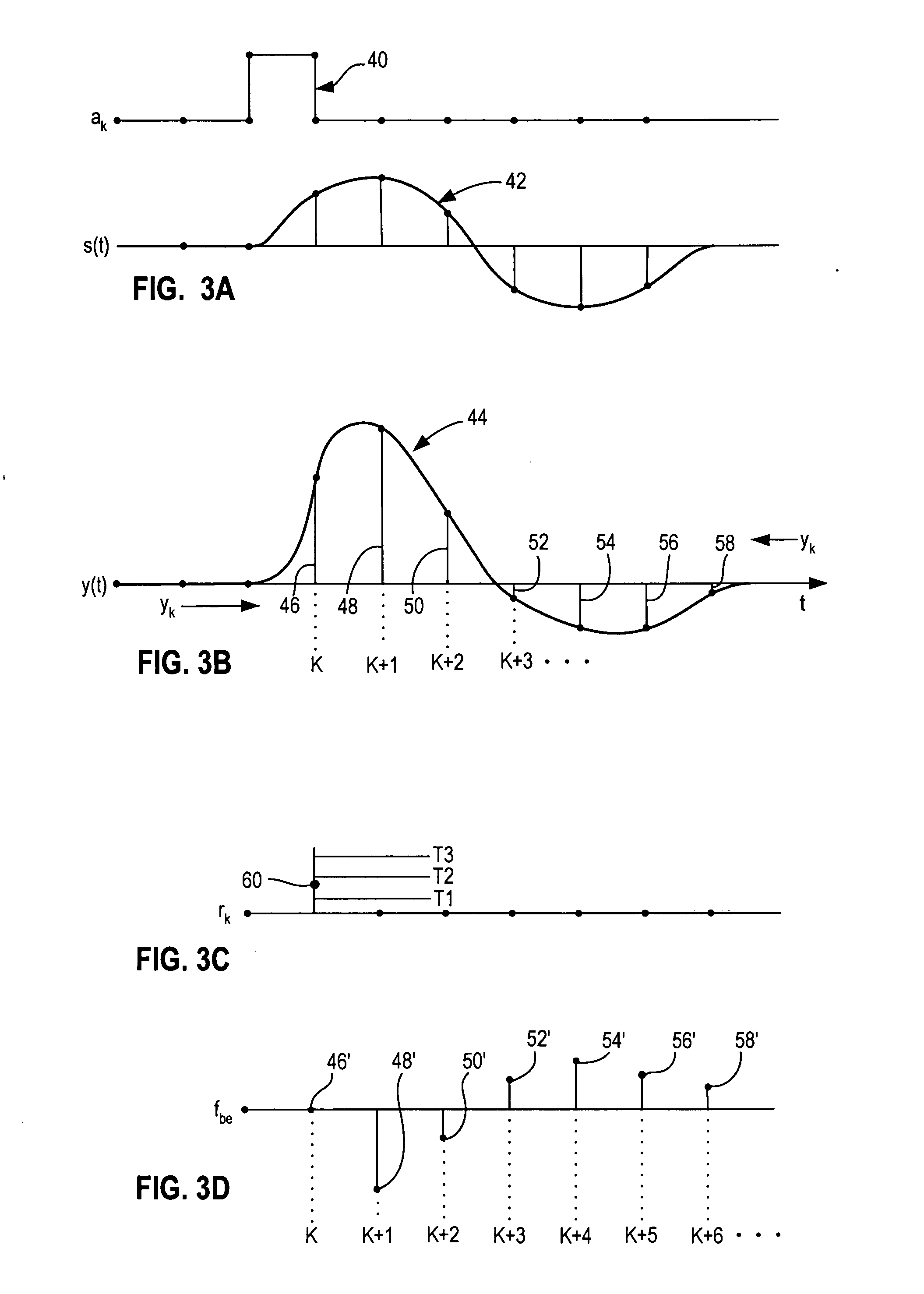
Burst error limiting feedback equalizer system and method for multidimensional modulation systems
A burst error limiting symbol detector system includes a symbol detector circuit responsive to a corrected sample signal for detecting multilevel or multidimensional symbols encoded in the corrected sample signal with reference to a plurality of associated thresholds. A feedback equalizer circuit provides a feedback equalizer signal for cancelling undesired distortion in an input signal. A summing circuit is responsive to the input signal and the feedback equalizer signal to provide the corrected sample signal to the symbol detector circuit. A feedback modification circuit is responsive to the corrected sample being within one of a plurality of valid symbol windows to feed back the detected symbol to the feedback equalizer and is responsive to the corrected sample being within one of plurality of marginal threshold windows to feed back a corresponding intermediate value to the feedback equalizer.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Method and system for transport of frame relay traffic over satellite/wireless networks
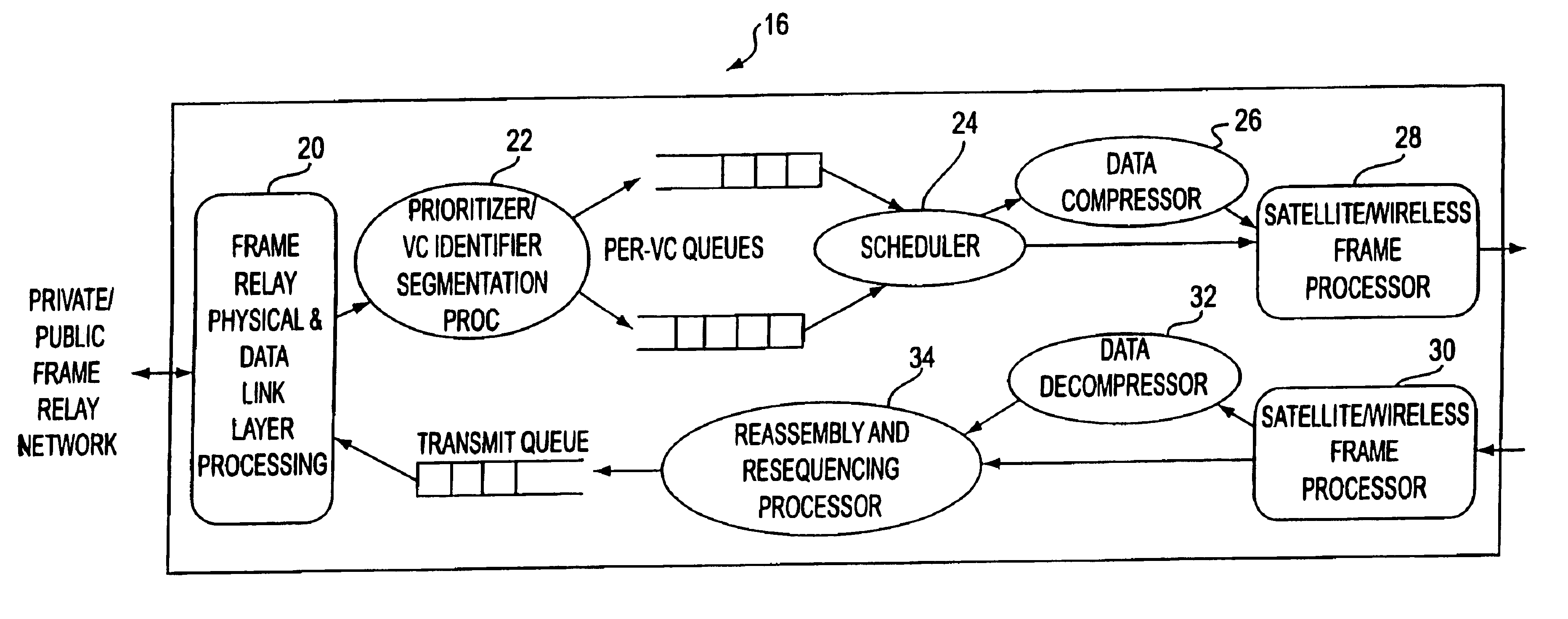
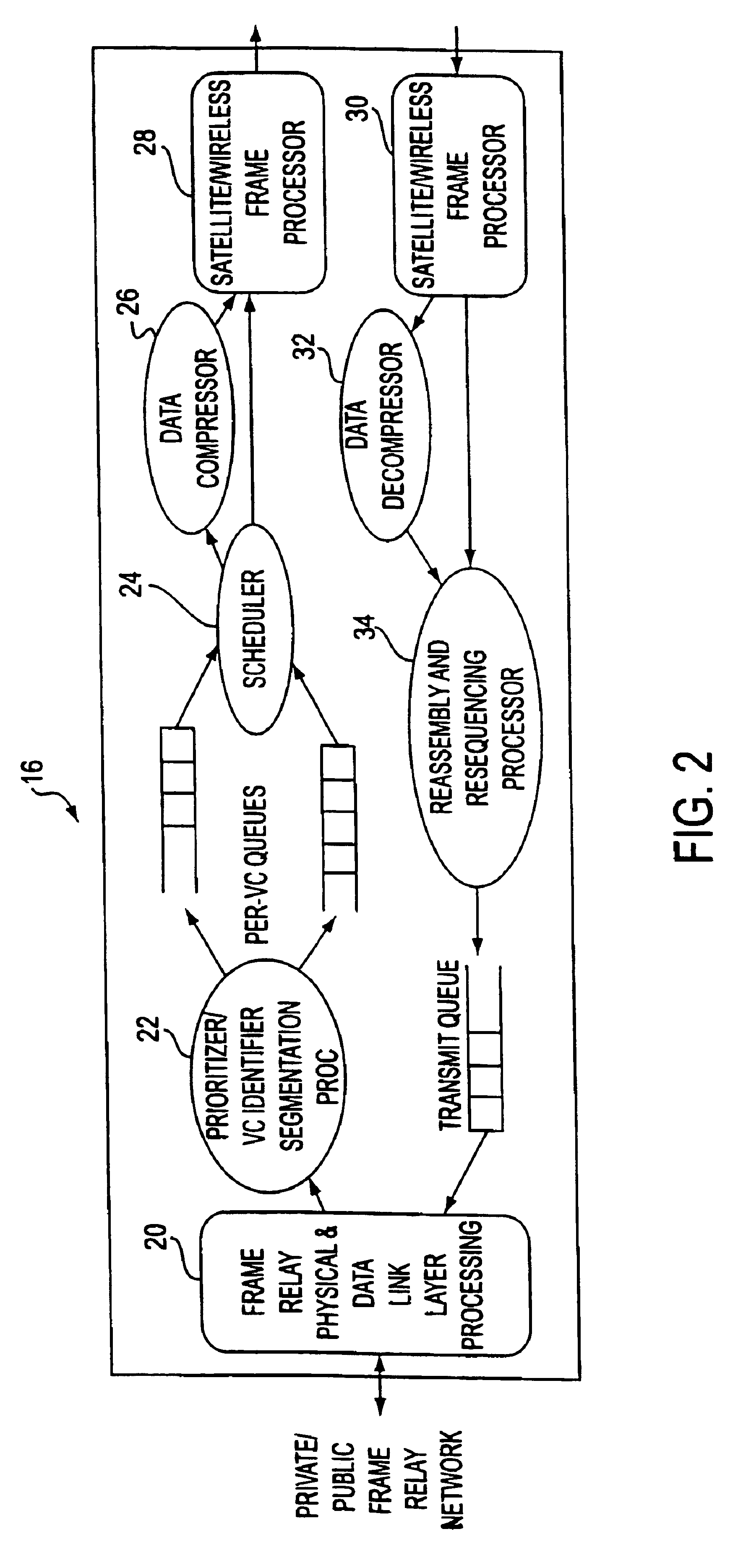
InactiveUS6859442B1Guaranteed normal transmissionQuality improvementTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationWireless mesh networkFrame Relay
To efficiently transmit frame relay packets between terrestrial frame relay networks (10, 12) over a satellite / wireless network (14), the packets are processed by frame relay processors (16, 18) at both ends of the satellite / wireless network (14). Variable length frame relay packets are segmented into smaller packets called spackets. The system utilizes priority queueing and a scheduler (24) transmits the spackets over the satellite / wireless link. To enhance the quality of the satellite / wireless link, each frame contains a variable number of Reed-Solomon (RS) check bytes used for error correction. Further, several frames are interleaved before transmission over the satellite / wireless link to spread the effect of burst errors over several frames. Additionally, a header compression technique saves bandwidth by compressing a Virtual Circuit (VC) identifier of the frame relay packet into a smaller value and maps the VCs to a value as specified by the size of the compressed VC field.
Owner:VIASAT INC
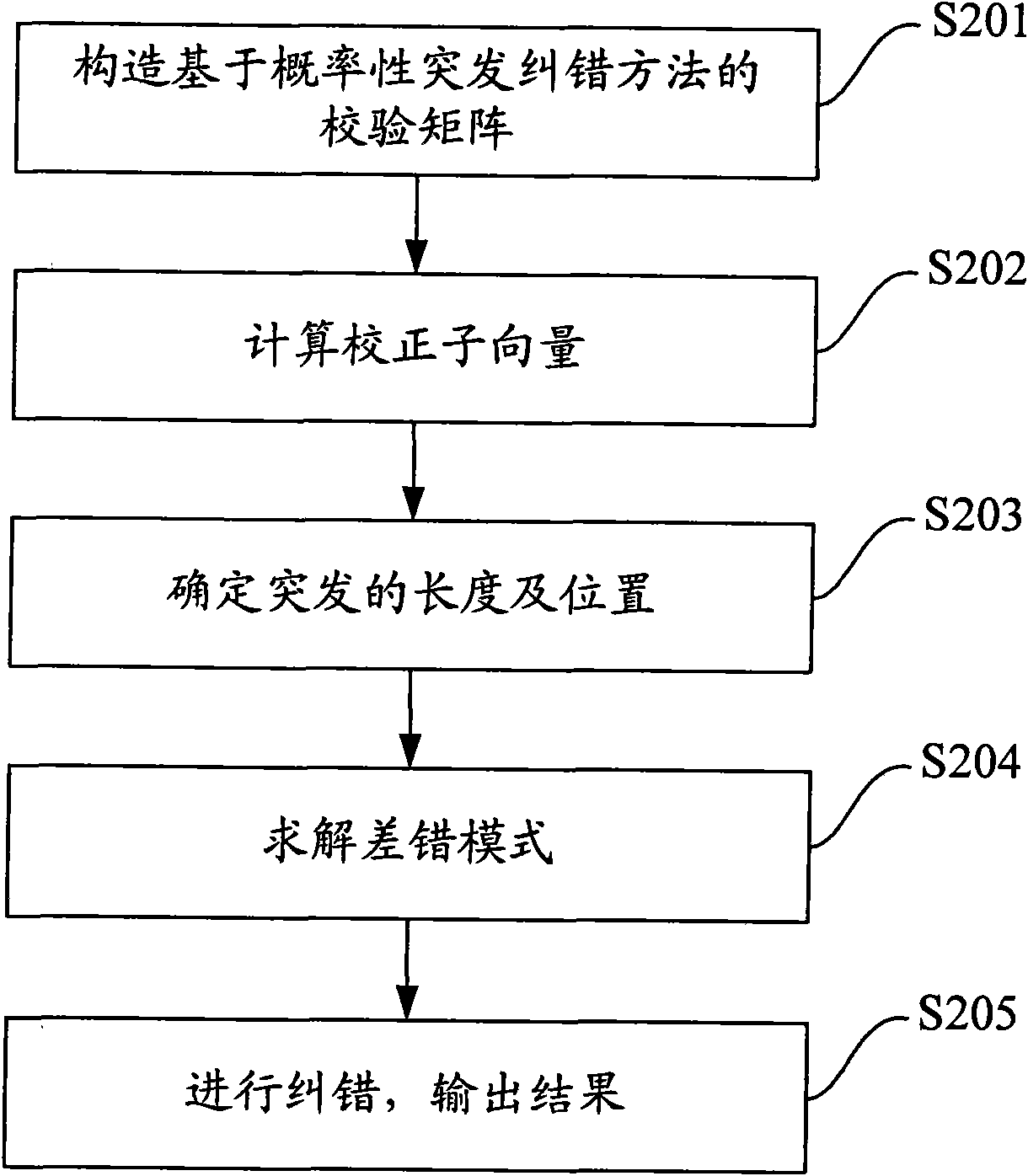
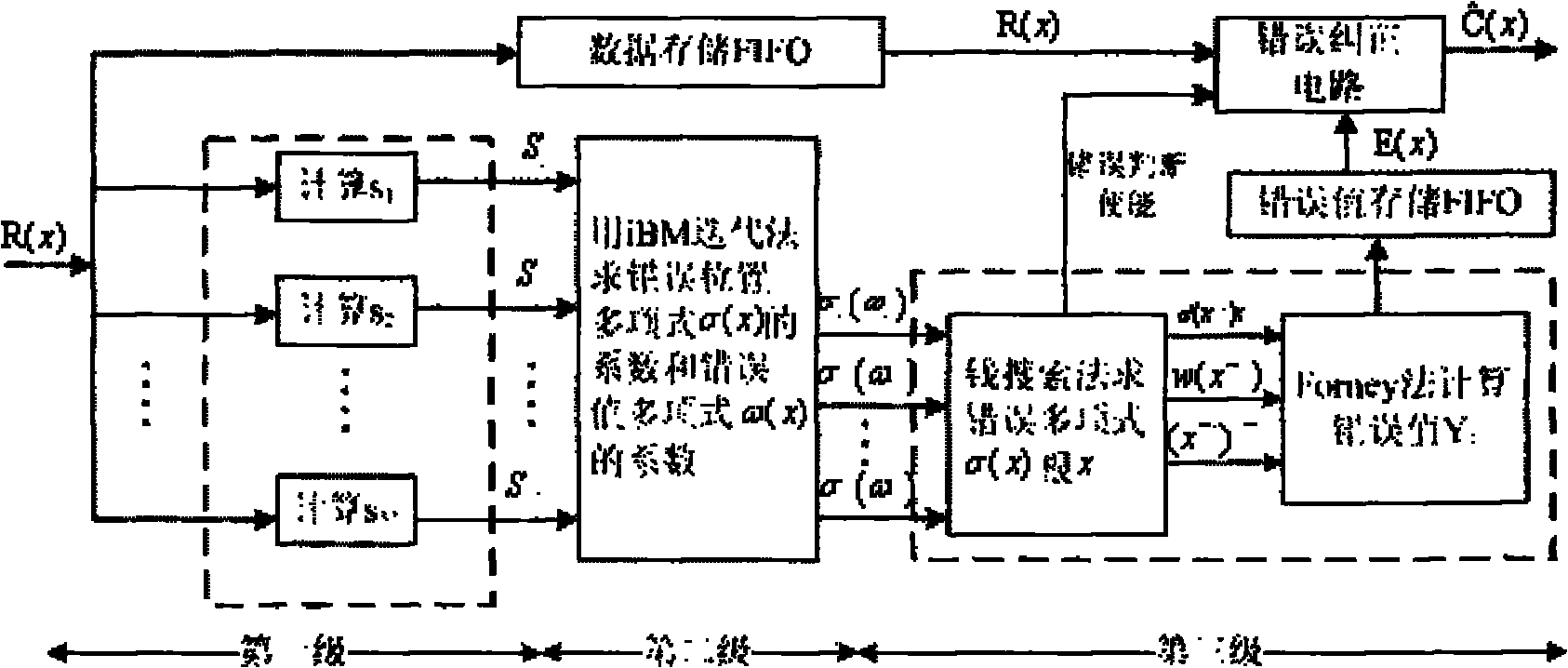
Burst correcting method, equipment and device
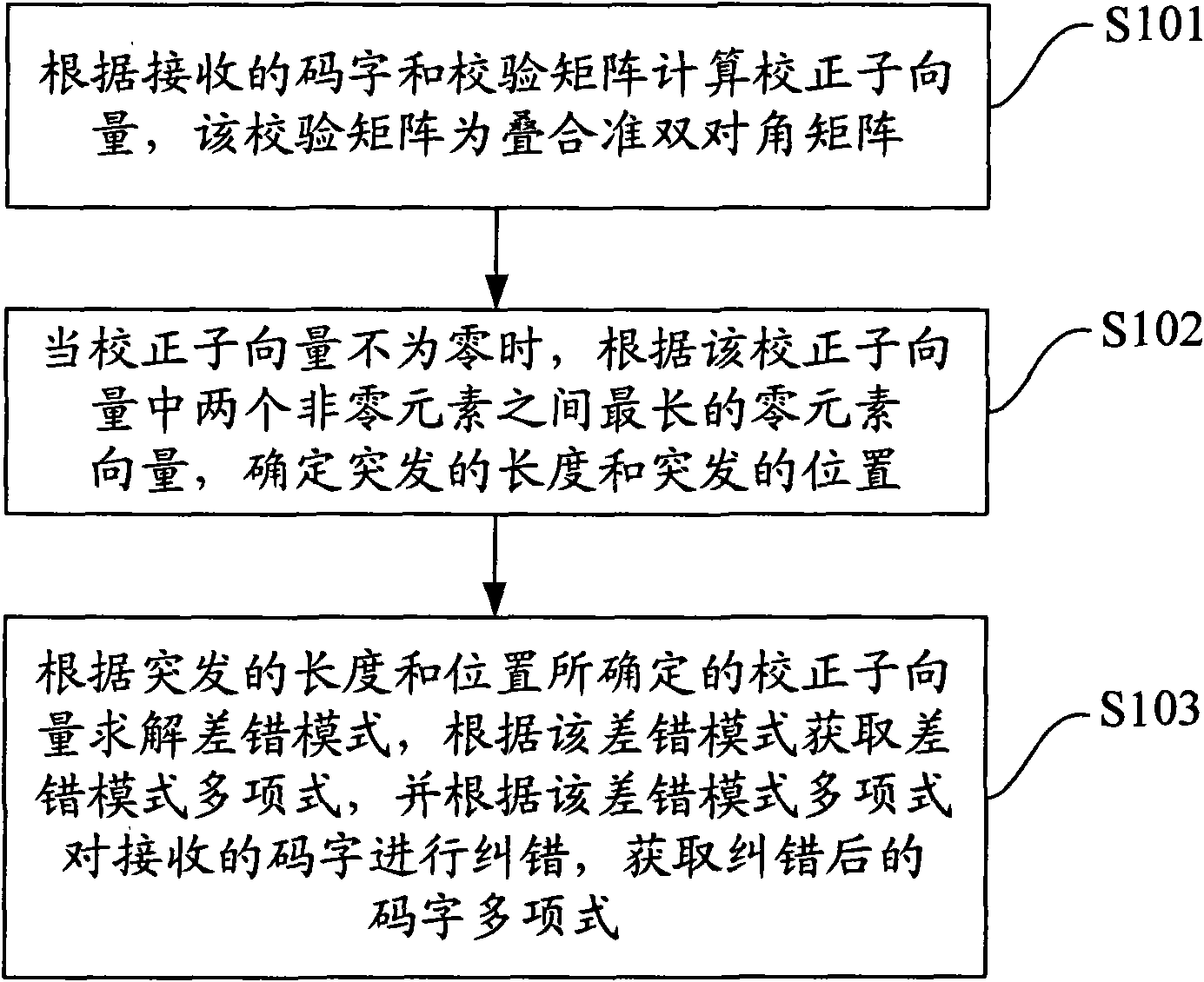
ActiveCN101621299AError correction burst errorError preventionBurst error correctionEuclidean vectorBurst error
The embodiment of the invention discloses a burst correcting method, equipment and a device. The burst correcting method comprises calculating a corrector subvector according to received codes and a rectifying matrix, wherein, the rectifying matrix is an overlapped quasi-bidiagonal matrix; determining the burst length and the burst position according to the longest zero element vector between thetwo non-zero element vectors in the corrector subvector when the corrector subvector is non-zero element vector; solving an error mode according to the determined corrector subvector based on the burst length and the burst position, obtaining a multinomial error mode according to the error mode, and correcting the received codes according to the multinomial error mode to obtain a corrected multinomial code. The embodiment of the invention provides a concrete implementation method which regards circulating codes, is based on probabilistic burst correction, and can correct more burst errors in comparison with regular circulating code deciphering method.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
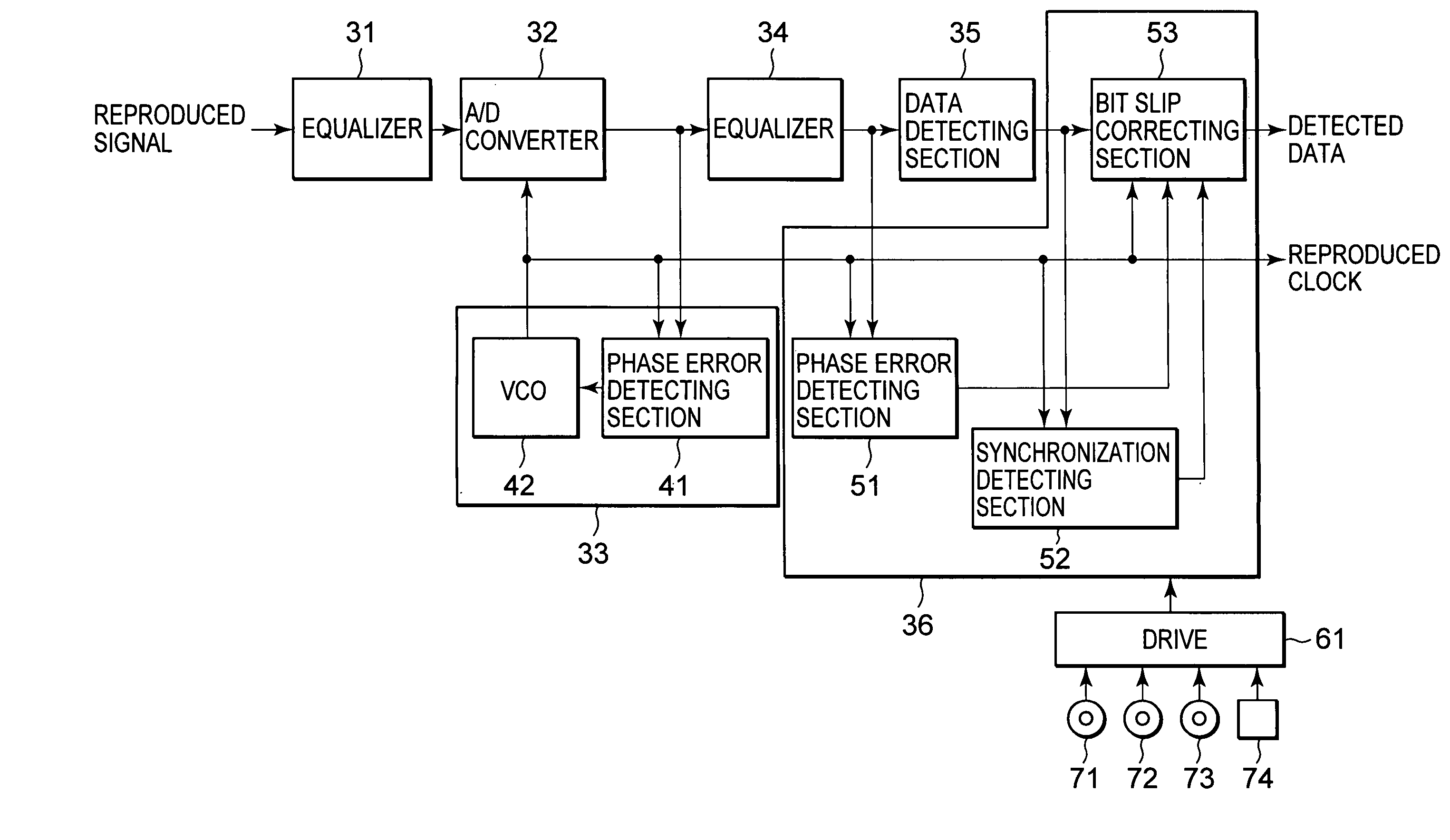
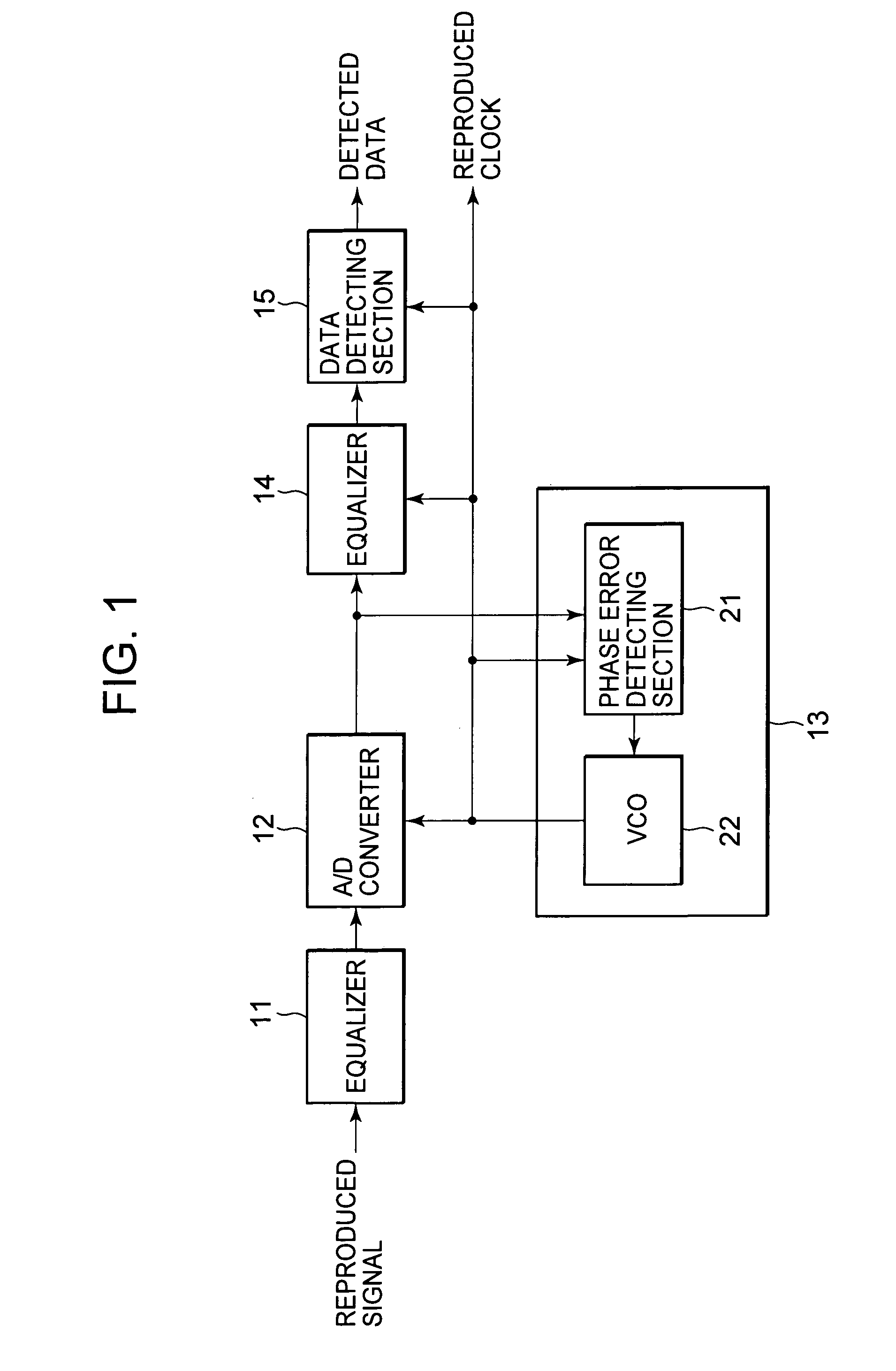
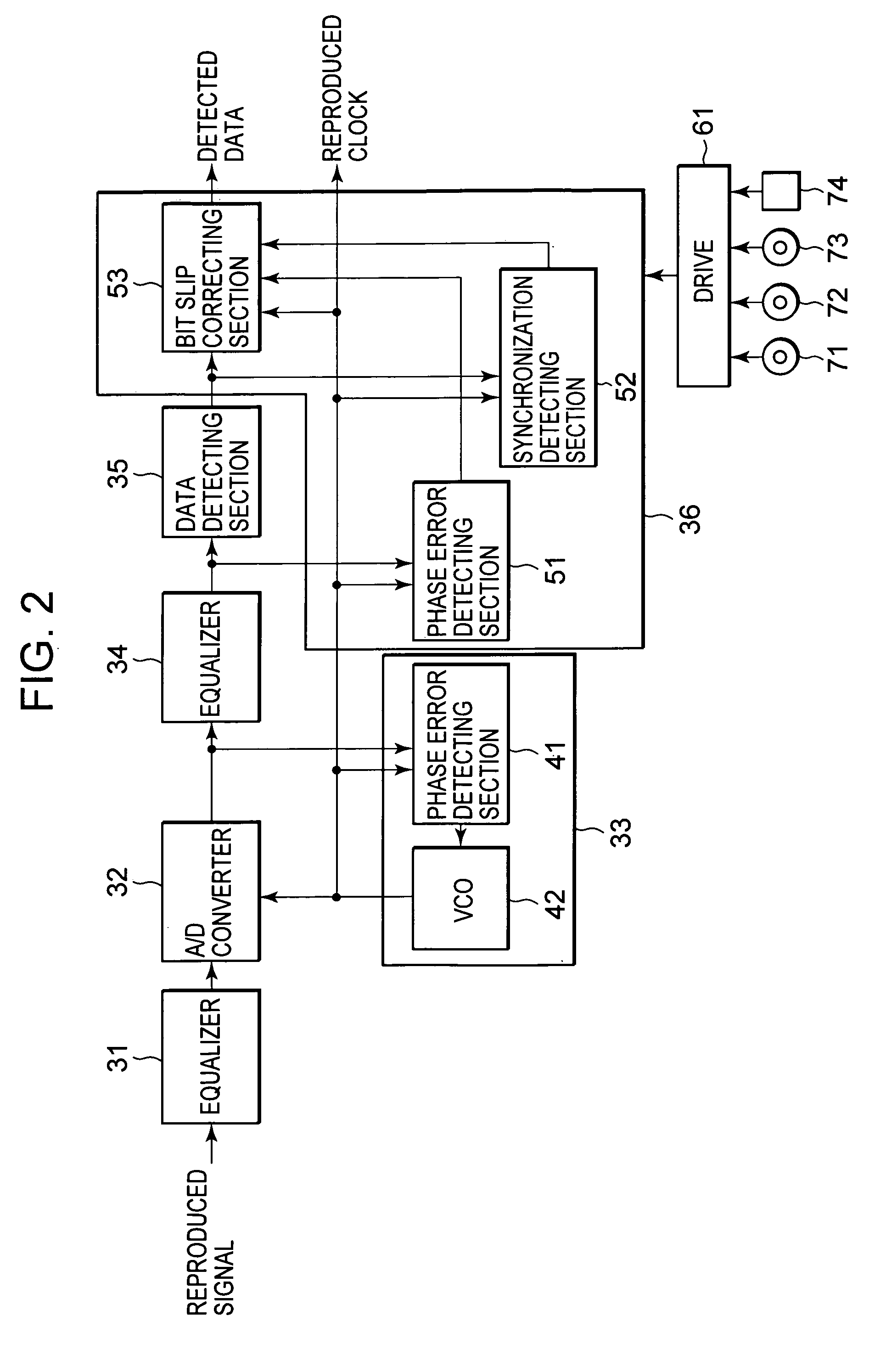
Reproduction device and method, recording medium, and program
InactiveUS20070103805A1Television system detailsModification of read/write signalsComputer hardwareError reduction
The present invention relates to a reproducing apparatus which, in a case where a burst error has occurred, corrects an error preceding a synchronization pattern detected thereafter to have less errors. A bit slip judging section81 in a bit slip correcting section 53 calculates a bit slip correction amount and a bit slip correction position on the basis of phase error signals detected by a phase error detecting section 51, synchronization pattern signals detected by a synchronization detecting section 52, reproduced clocks and detected data. A FIFO control section 82 controls a FIFO buffer 83 on the basis of the bit slip correction amount and the bit slip correction position, to perform bit slip correction. As a result, in the case where a burst error has occurred, an error preceding a synchronization pattern detected thereafter is corrected, whereby an error reduction can be implemented. The present invention is applicable to a reproducing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
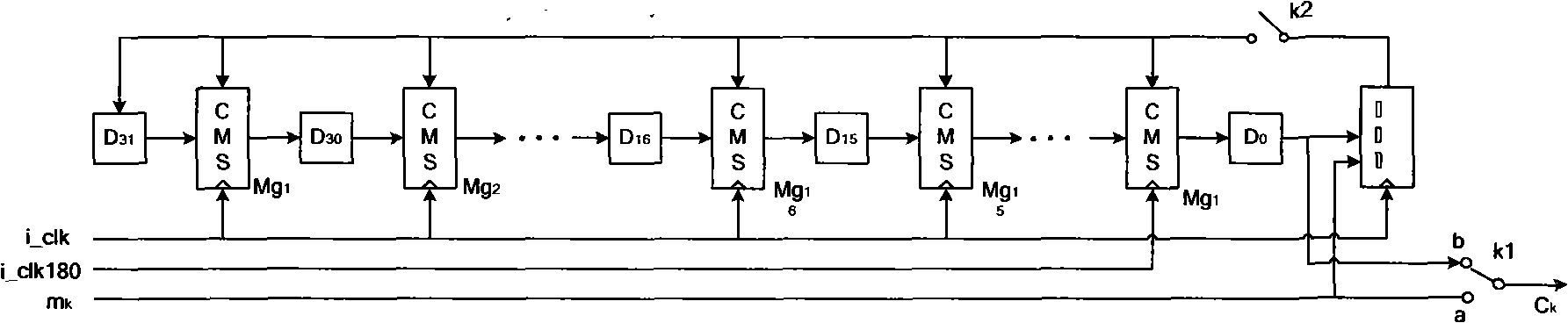
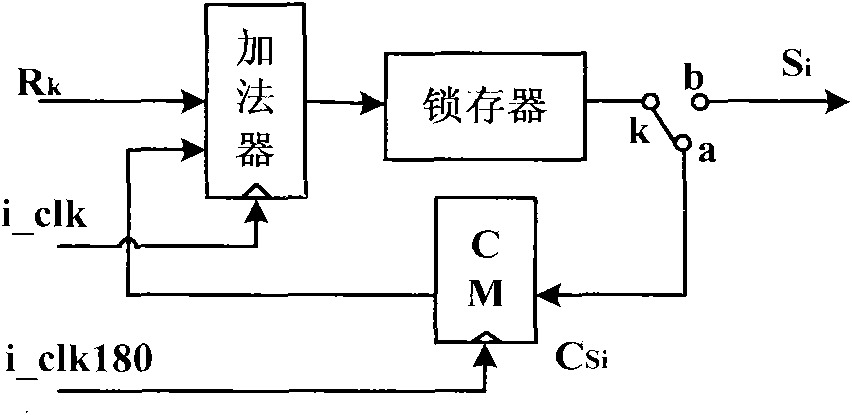
Implementation method of high-speed reed-solomon (RS) codec based on field programmable gate array (FPGA)
InactiveCN102122964AHigh data pass rateImprove efficiencyError preventionCyclic codesThree levelComputer architecture
The invention discloses an implementation method of a high-speed reed-solomon (RS) codec based on a field programmable gate array (FPGA), comprising FPGA implementation of a high-speed RS (244, 212) coder and FPGA implementation of a high-speed RS (244, 212) decoder. In the invention, the high-speed RS coder is a circuit based on polynomial division, and the high-speed RS decoder is based on three-level pipeline architecture, and dual-clock driving based on clock i_clk and reverse clock i_clk180 is adopted; In addition, based on a common Galois field (GF) multiplying unit, three basic computing units, including a constant coefficient GF multiply-add fused unit, a constant coefficient GF multiplying unit and a dual-clock period controlled GF multiplying unit are provided, thereby greatly improving the computing speed and reducing hardware complexity. The implementation method has the advantages of high supporting throughput rate and strong capacity of correcting burst errors and can be applied to many aspects.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
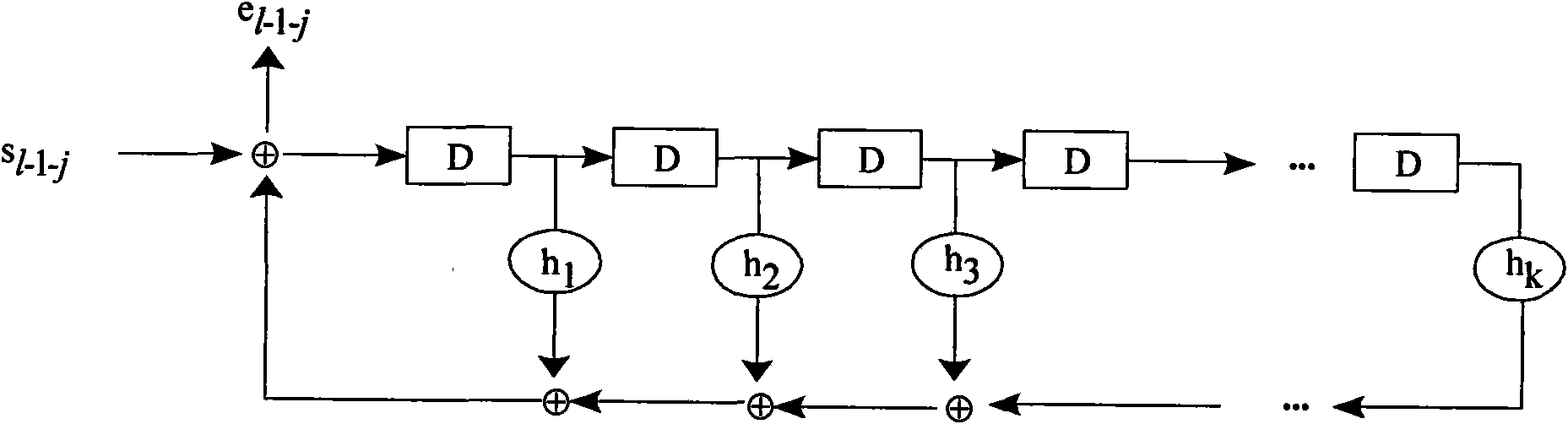
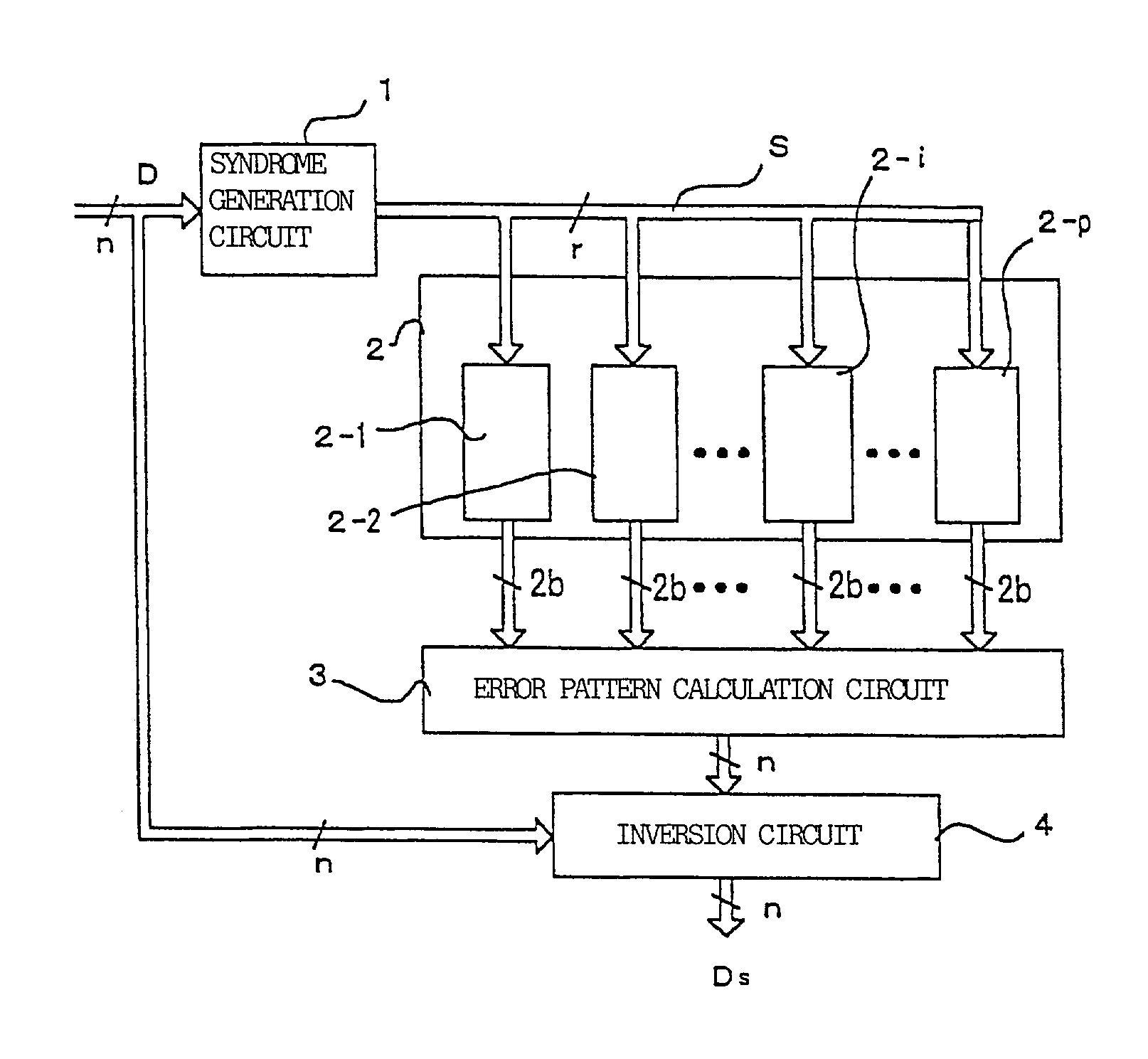
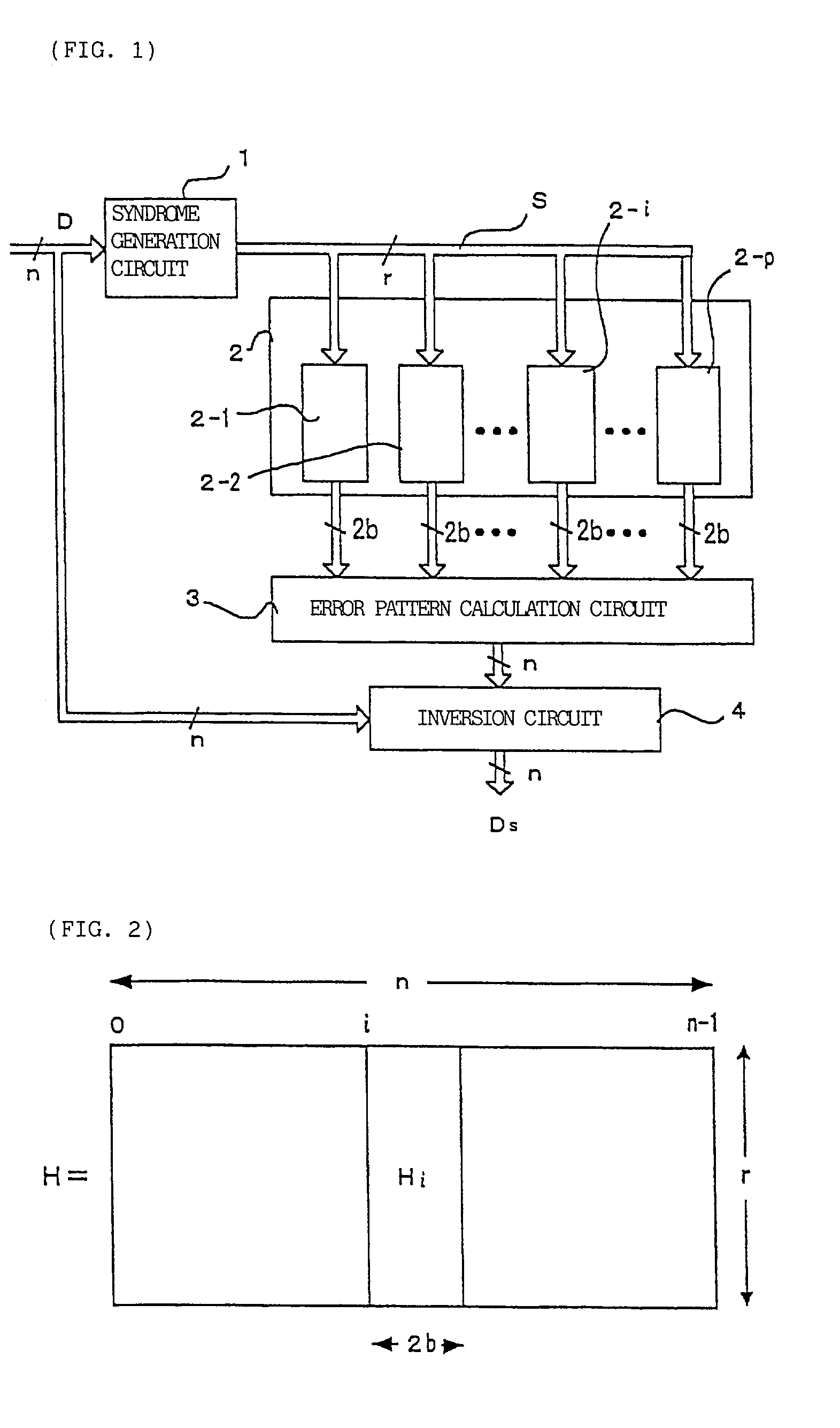
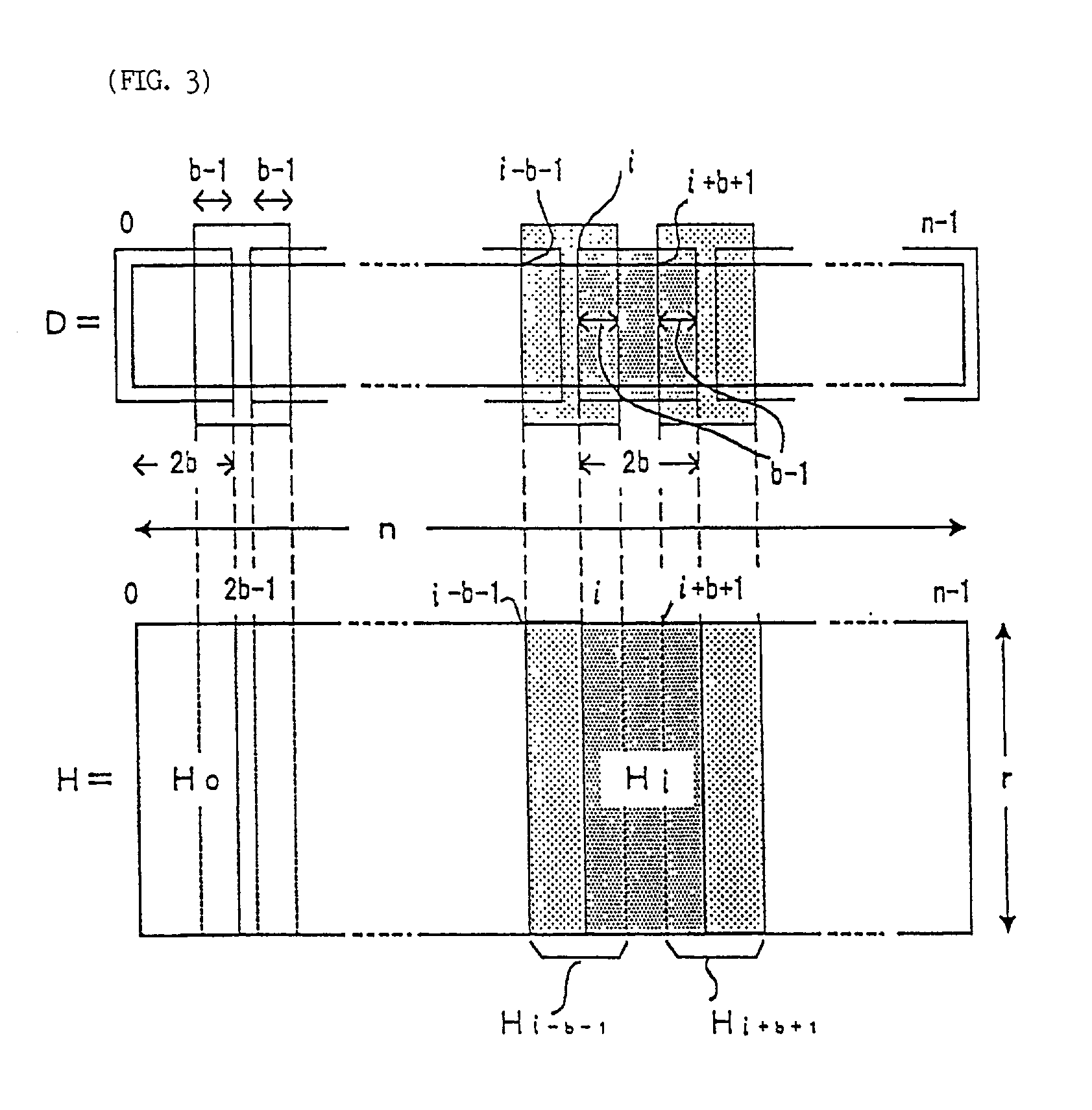
Burst error pattern generation method, and burst and byte error detection correction apparatus
A syndrome S is found from a received information D and a parity check matrix for correcting burst errors up to b bits. The syndrome S is inputted to p sets of burst error pattern generation circuits that correspond to information frames overlapping each other by (b−1) bits and each having a length of 2b bits. If a burst error is included entirely in any one of the p sets of burst error pattern generation circuits, then the burst error pattern is outputted. An error pattern calculation circuit executes OR respectively on overlapping bits output from the error pattern generation circuits. By executing exclusive OR on an output of the error pattern calculation circuit and received information D, corrected information Ds is obtained. As a result, a burst error in the received information can be detected and corrected.
Owner:FANUC LTD +1
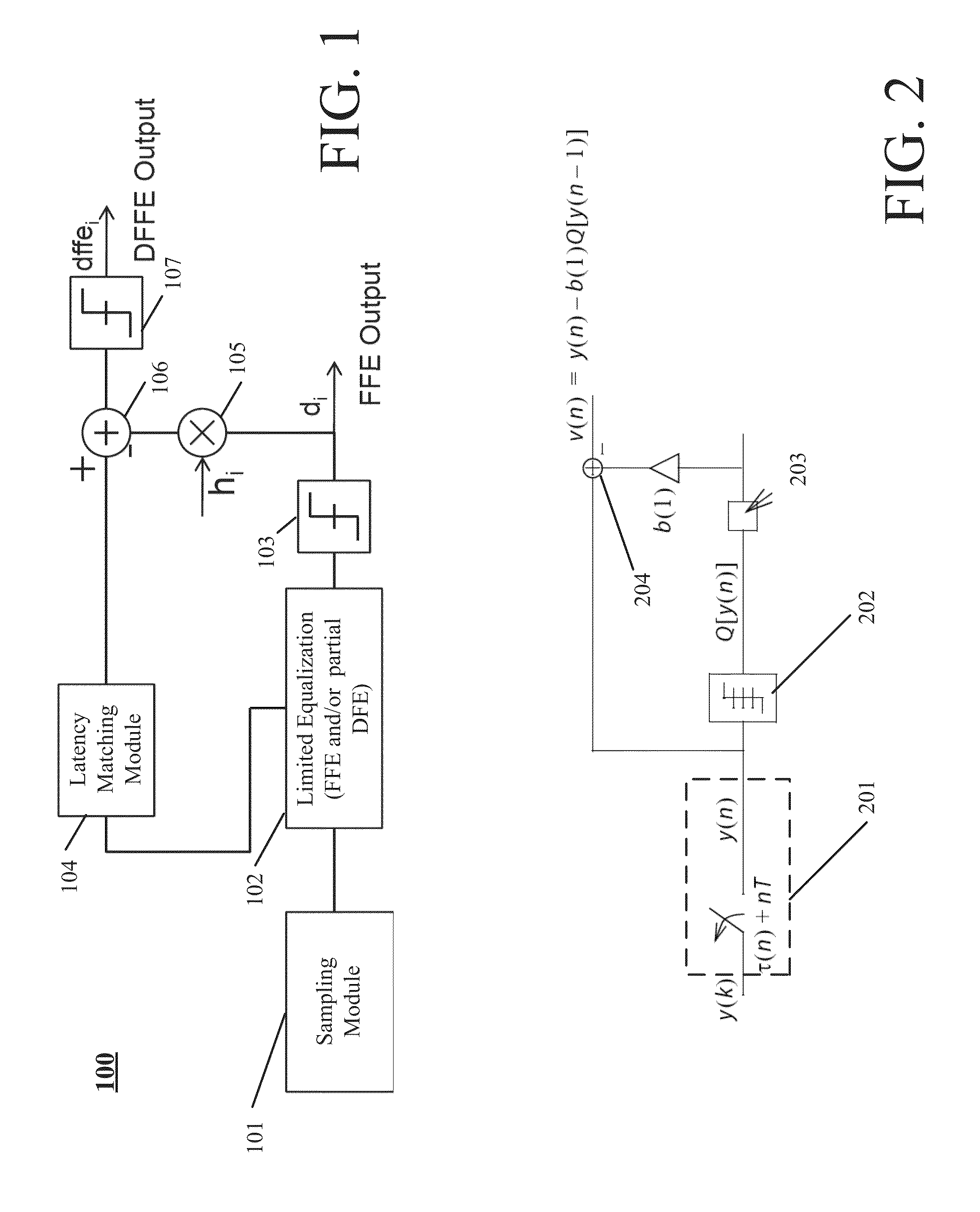
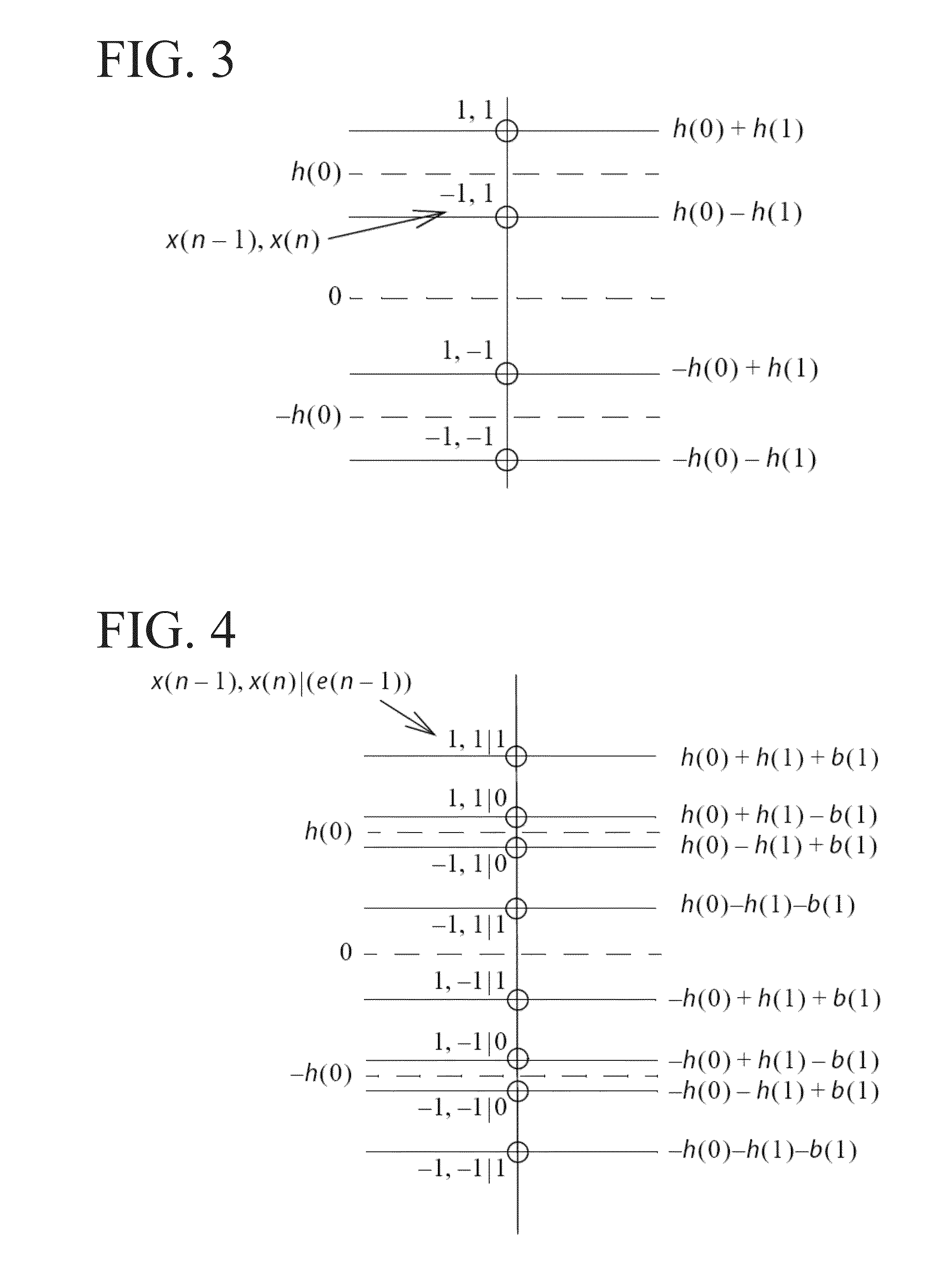
Decision feedforward equalization
InactiveUS20130243066A1Well formedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsPathPingSoftware engineering
In described embodiments, a Decision Feed Forward Equalizer (DFFE) comprises a hybrid architecture combining features of a Feed Forward Equalizer (FFE) and a Decision Feedback Equalizer (DFE). An exemplary DFFE offers relatively improved noise and crosstalk immunity than an FFE implementation alone, and relatively lower burst error propagation than a DFE implementation alone. The exemplary DFFE is a relatively simple implementation due few or no critical feedback paths, as compared to a DFE implementation alone. The exemplary DFFE allows for a parallel implementation of its DFE elements without an exponential increase in the hardware for higher numbers of taps. The exemplary DFFE allows for cascading, allowing for progressive improvement in BER, at relatively low implementation cost as a solution to achieve multi-tap DFE performance.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Hybrid spread spectrum communication system based on low density parity code (LDPC) encoding and method thereof
ActiveCN103701490ASolve the delay problemEasy to implementError preventionBurst errorFrequency offset
The invention discloses a hybrid spread spectrum communication system based on low density parity code (LDPC) encoding and a method thereof. The problems of leakage capture, high leakage capture probability, slow convergence of a phase-locked loop and low decoding performance of the existing synchronous capture method are mainly solved. The system comprises a transmitting part and a receiving part, wherein the transmitting part is used for carrying out pretreatment on original information; the pretreatment data are subjected to frequency hopping treatment and transmitted after being modulated and filtered by a base band; the receiving part is used for obtaining a synchronization point position and a frequency offset value in the received signal through synchronous capture, and intercepting useful data to carry out de-hopping according to the synchronization point position; the base band demodulates and filters; the filtering data are subjected to frequency offset compensation according to the frequency offset value; the data after frequency offset compensation are subjected to dispreading and frequency offset rectification; the frequency offset rectification data are decoded and the decoding result is output. The hybrid spread spectrum communication system has the advantages of being strong in burst error resisting ability, high in real-time synchronization capture speed, high in capture accuracy, high in convergence speed of the phase-locked loop, and good in decoding performance, and can be applied to reliable communication under the condition of very low powder spectral density.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Client for video stream play and method thereof
InactiveUS20050232290A1Efficient executionReduce gapTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionBurst errorSelf adaptive
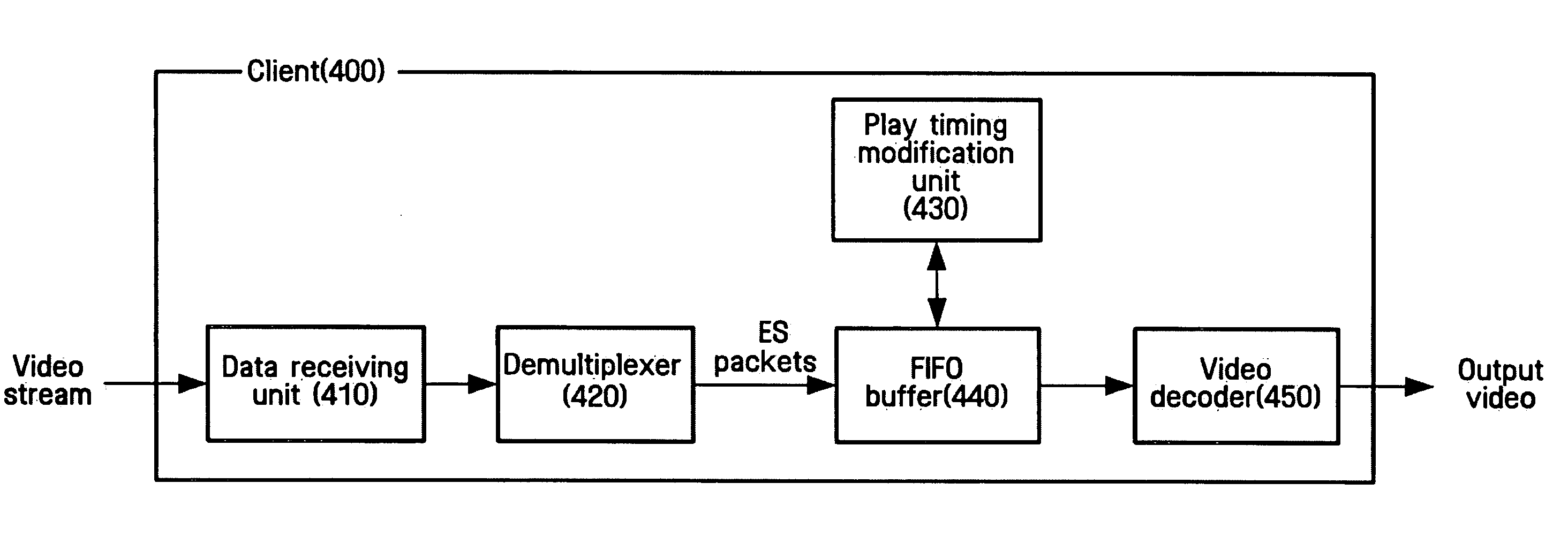
A client for playing a video stream and a method thereof adaptively control the video play in accordance with variable communication environments and the size of the video stream to be transmitted. The client includes a demultiplexer for generating elementary stream (ES) packets by demultiplexing a video stream; a FIFO buffer for temporarily storing the ES packets; a play timing modification unit for reducing a gap of a play time caused by a burst error by modifying time stamps of the ES packets that exist in the FIFO buffer if it is judged that the burst error occurs; and a video decoder for generating an output video by decoding the ES packets of which the time stamps are modified. The client can relatively improve the quality of the video streaming in multimedia communications through a wireless or wire network.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
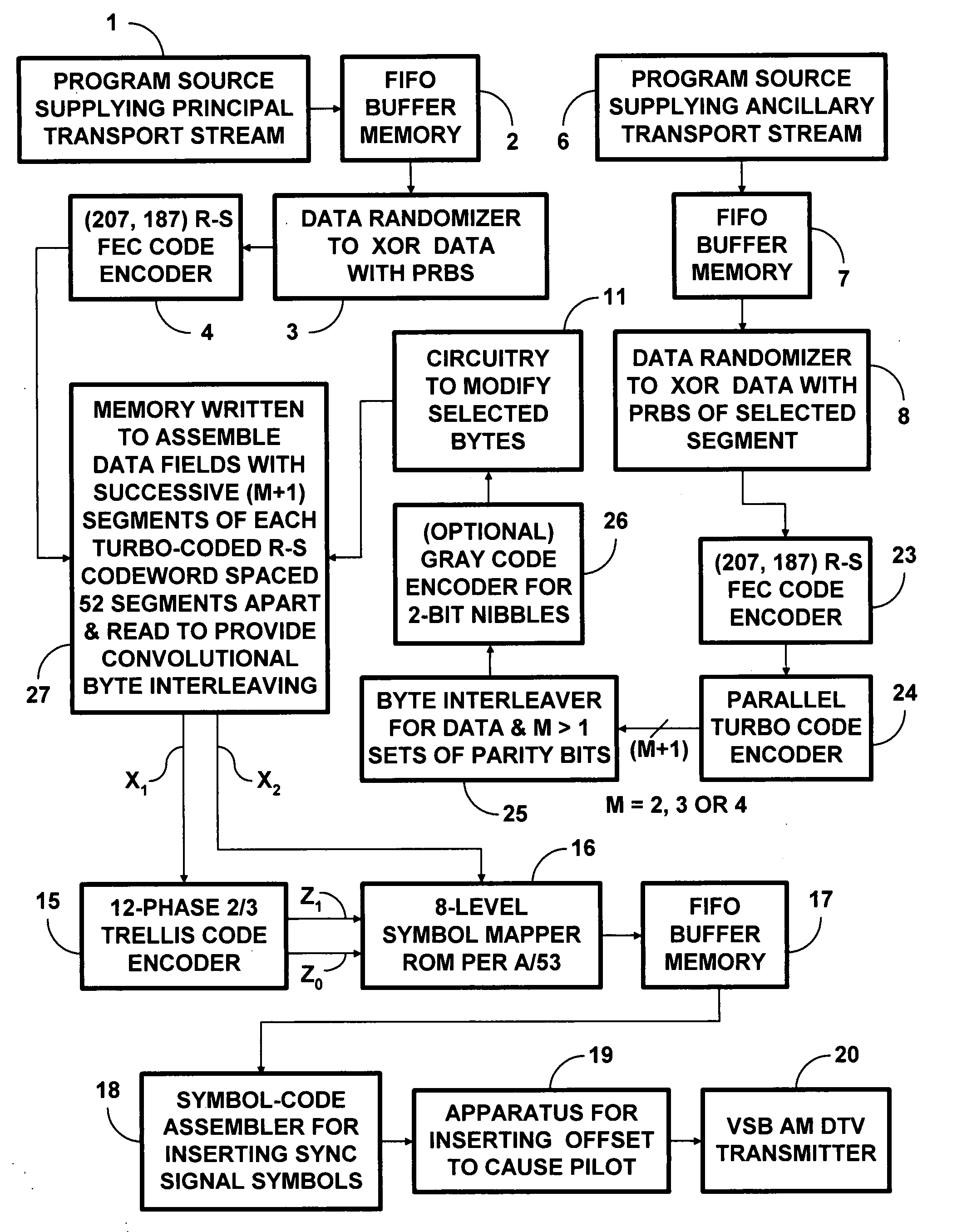
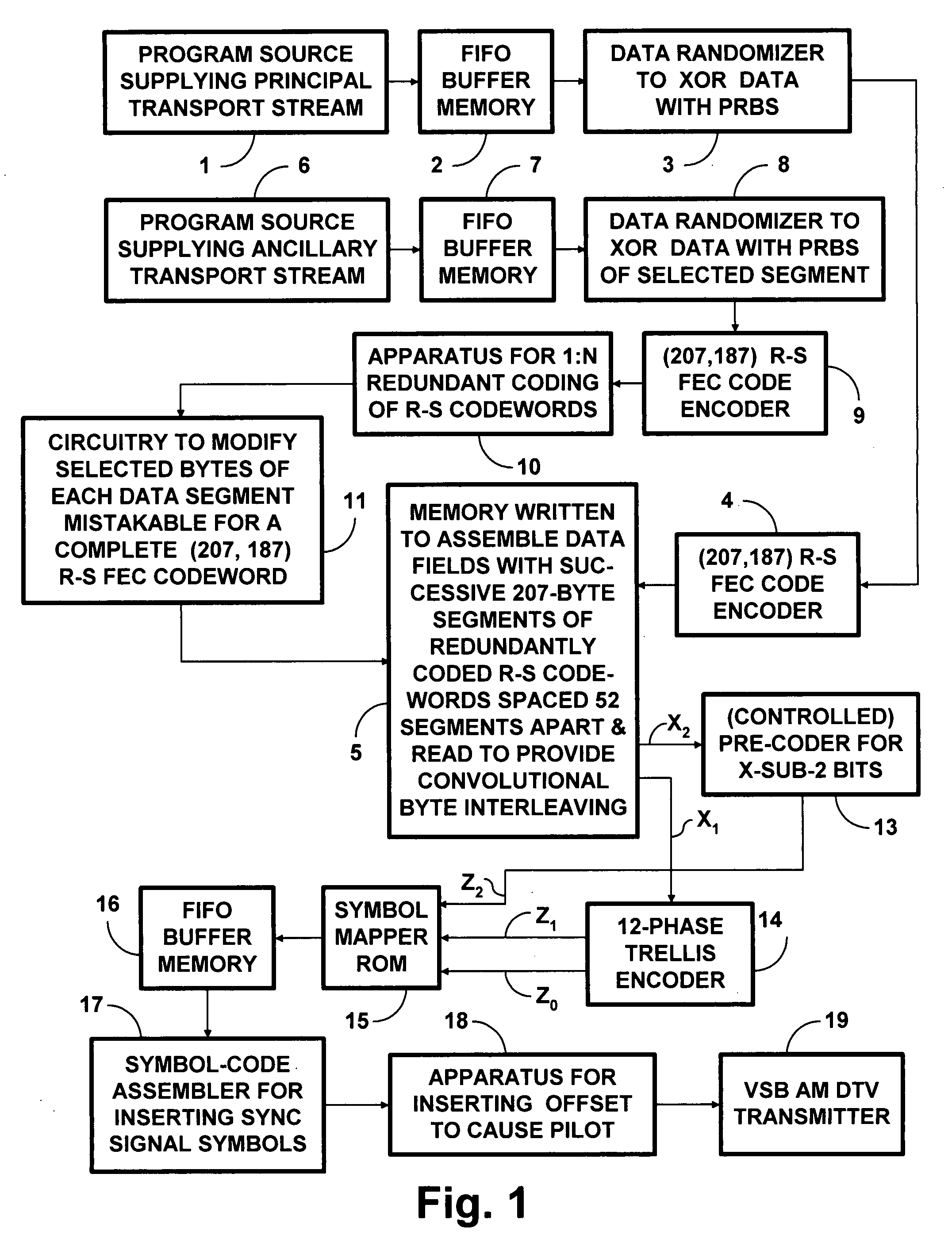
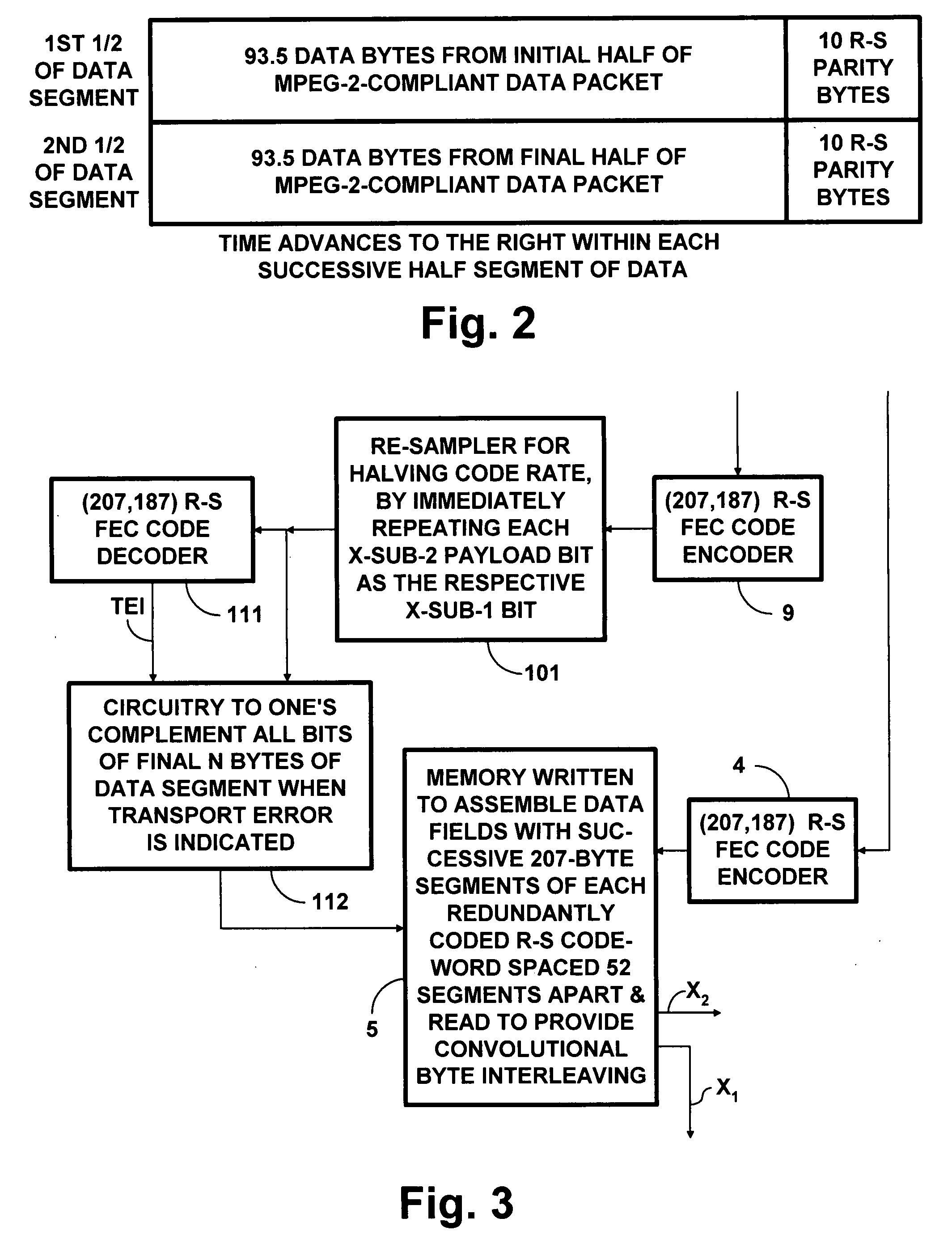
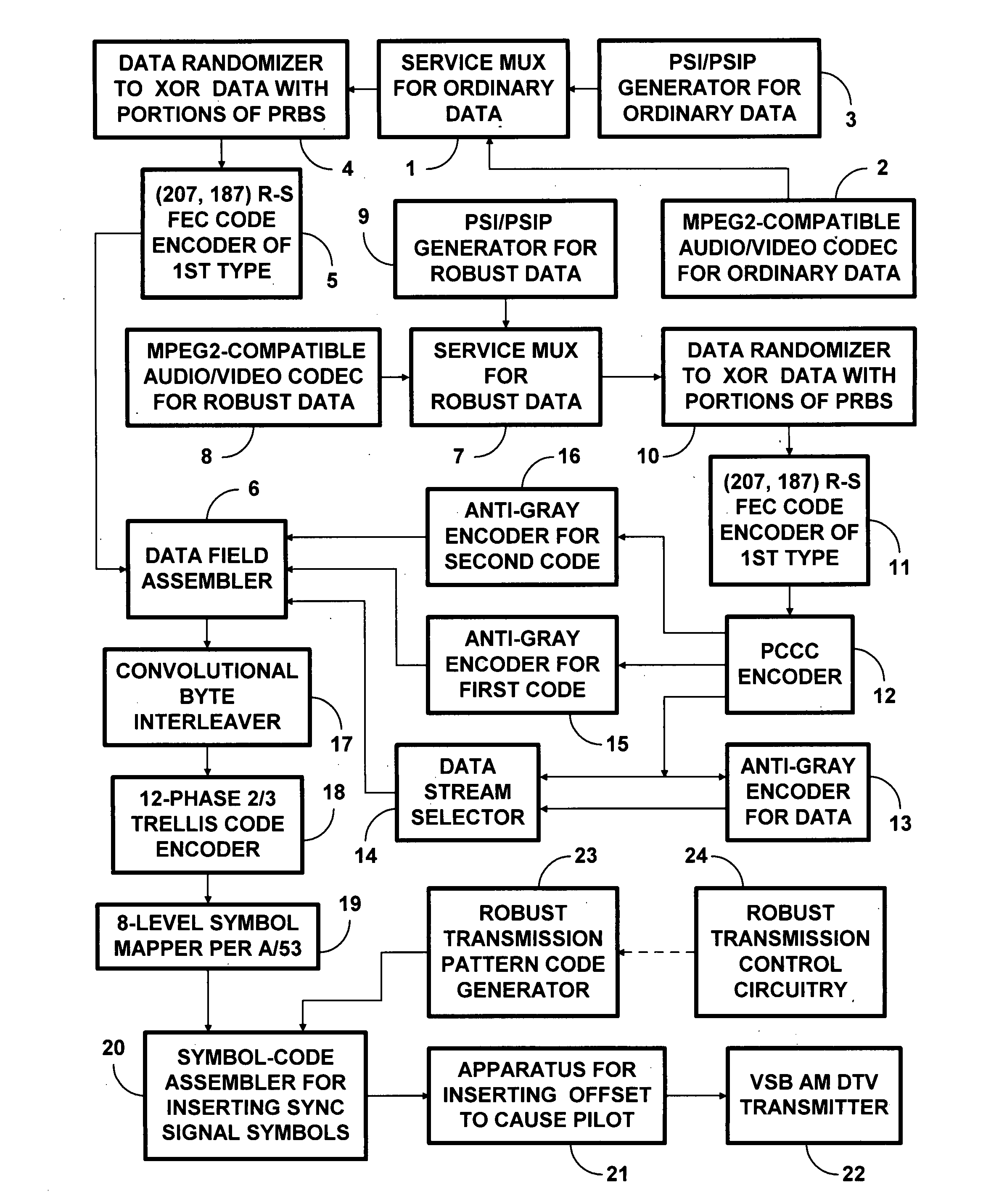
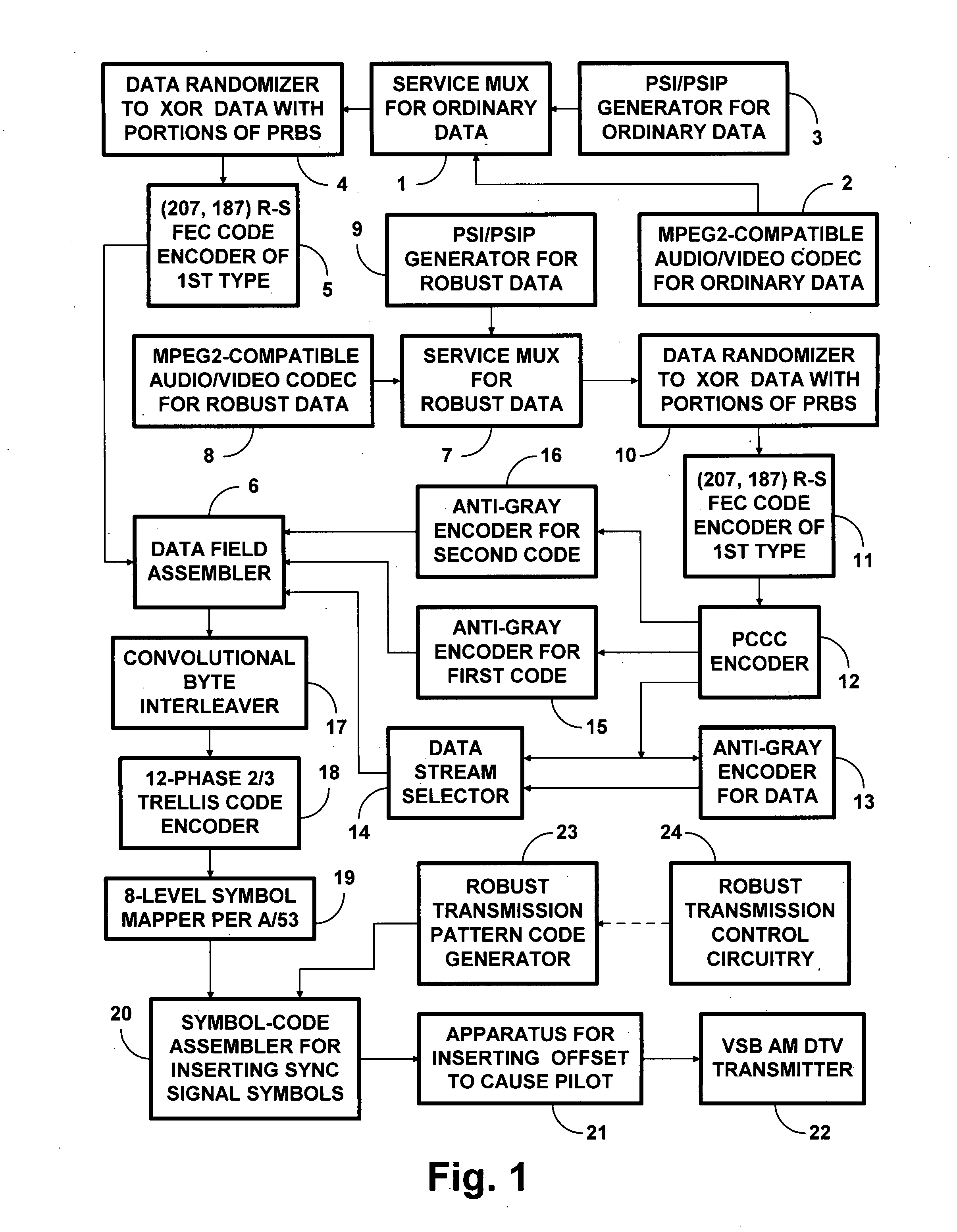
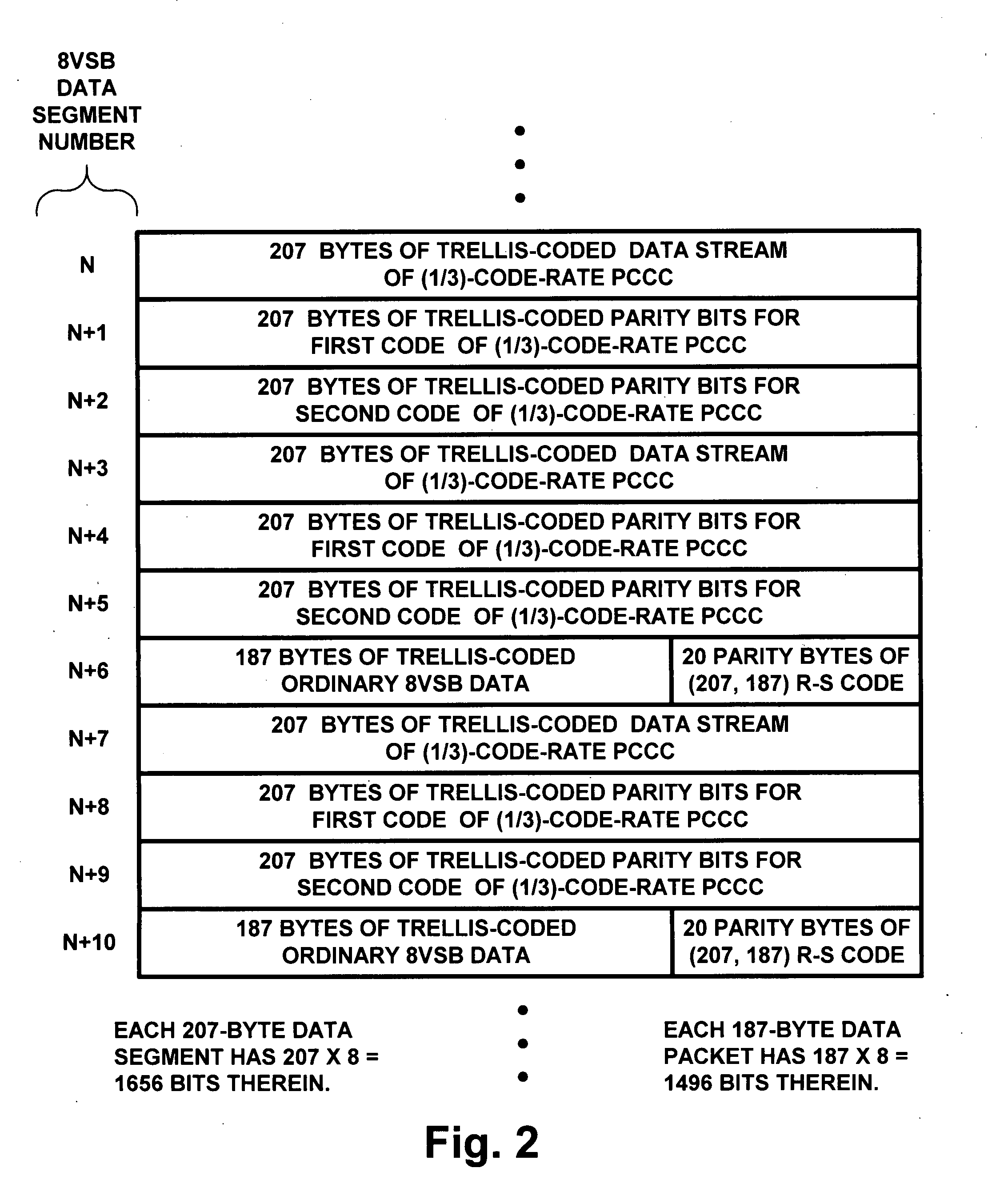
8VSB DTV signals with PCCC and subsequent trellis coding
InactiveUS20090003459A1Improve abilitiesReduce code rateData representation error detection/correctionPulse modulation television signal transmissionNetwork packetSymbol mapping
Data to be more robustly transmitted within 8VSB broadcast DTV signals are turbo coded using parallelly concatenated convolutional coding (PCCC) and incorporated within the segments of data fields, the bytes of which are convolutionally interleaved before trellis coding and 8VSB symbol mapping. Packing the PCCC into payload fields of MPEG-2-compatible null data packets and Reed-Solomon coding the packets to generate the segments of data fields, the bytes of which are convolutionally interleaved, conditions legacy DTV receivers to disregard PCCC components not useful to them. Transversal packing turbo-coded Reed-Solomon codewords into the payload fields of MPEG-2-compatible null data packets increases the capability of those turbo-coded Reed-Solomon codewords to overcome burst errors. Repeated transmissions of the transversally packed turbo-coded Reed-Solomon codewords in whole or in part allows them to overcome protracted deep fades encountered during mobile reception of 8VSB DTV signals.
Owner:BROADQAST SOLUTIONS
System correcting random and/or burst errors using RS (Reed-Solomon) code, turbo/LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and convolutional interleave
ActiveUS7447984B2Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionComputer hardwareCommunications system
System correcting random and / or burst errors using RS (Reed-Solomon) code, turbo / LDPC (Low Density Parity Check) code and convolutional interleave. A novel approach is presented that combines different coding types within a communication system to perform various types of error correction. This combination of accommodating different coding types may be employed at either end of a communication channel (e.g., at a transmitter end when performing encoding and / or at a receiver end when performing decoding). By combining different coding types within a communication system, the error correcting capabilities of the overall system is significantly improved. The appropriate combination of turbo code and / or LDPC code along with RS code allows for error correction or various error types including random error and burst error (or impulse noise).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for using fire decoder to correct burst errors in a real-time communications system
InactiveUS7231579B1Delay minimizationError preventionBurst error correctionCommunications systemAlgorithm
Error bursts are detected and corrected in a communication system using shortened cyclic codes, such as shortened Fire codes. Data is loaded into a first error syndrome register and a second error syndrome register. The data in the registers may be evaluated to determine if the data bits contain a correctable error. Shortened zero bits are shifted into the second error syndrome register. A number of zero bits are shifted into the first error syndrome register to trap an error burst pattern in the data. A determination is made as to the number of zero bits shifted into the second error syndrome register to trap the location of the error burst in the data. Using the number of zero bits shifted into the second error syndrome register and the error burst pattern, the error in the data is located and corrected.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Techniques for detecting and correcting errors using multiple interleave erasure pointers
InactiveUS7231578B2Correction capabilityTransmission systemsBurst error correctionBlock codeError location
Techniques for detecting and correcting burst errors in data bytes formed in a two-level block code structure. A second level decoder uses block level check bytes to detect columns in a two-level block code structure that contain error bytes. The second level decoder generates erasure pointers that identify columns in the two-level block structure effected by burst errors. A first level decoder then uses codeword check bytes to correct all of the bytes in the columns identified by the erasure pointers. The first level decoder is freed to use all of the codeword check bytes only for error byte value calculations. The first level decoder does not need to use any of the codeword check bytes for error location calculations, because the erasure pointers generated by the second level decoder provide all of the necessary error locations. This techniques doubles the error correction capability of the first level decoder.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV +1
Reducing scintillation effects for optical free-space transmission
InactiveUS6868519B2Affordable costLow costMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCode conversionBurst errorOptical communication
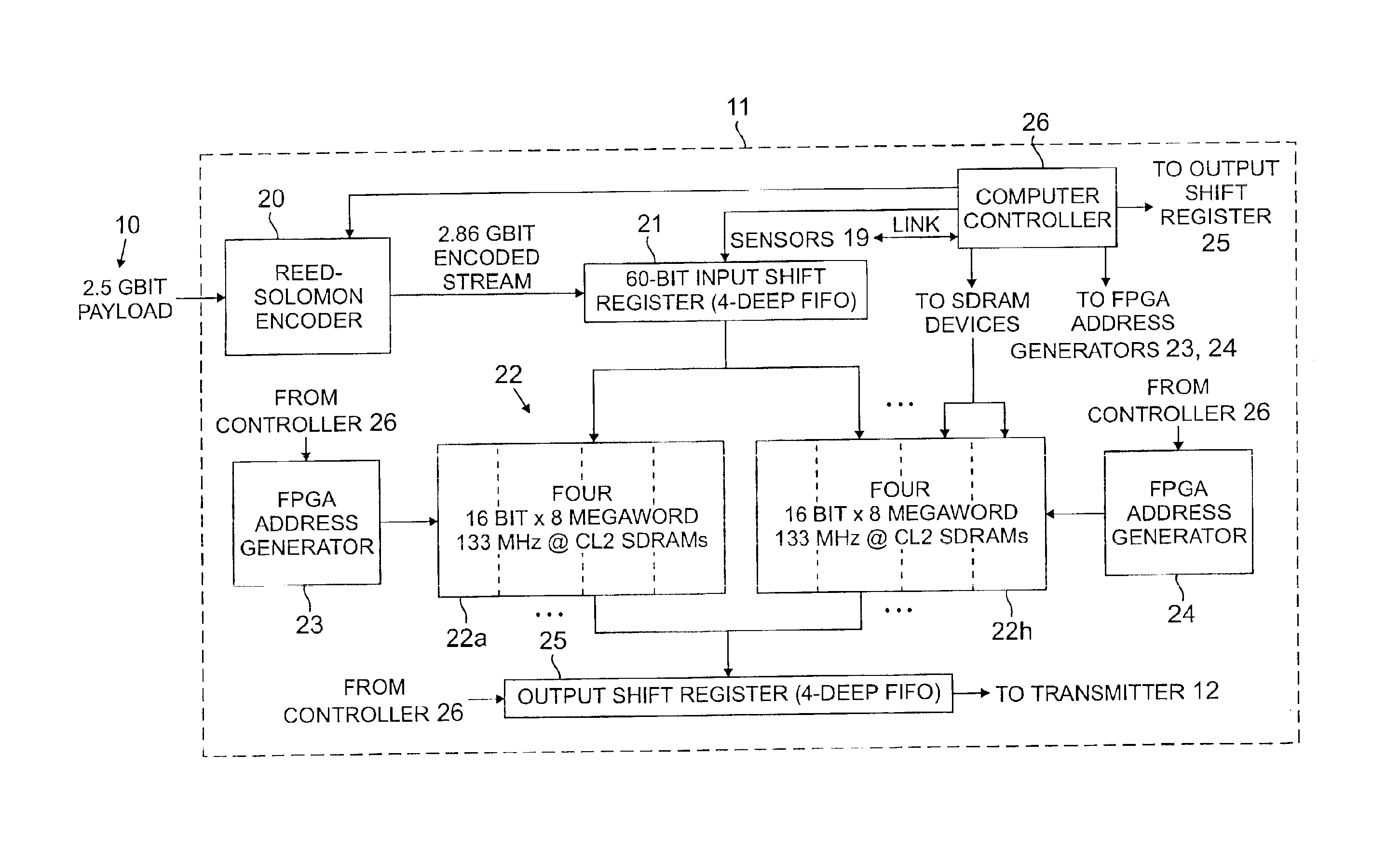
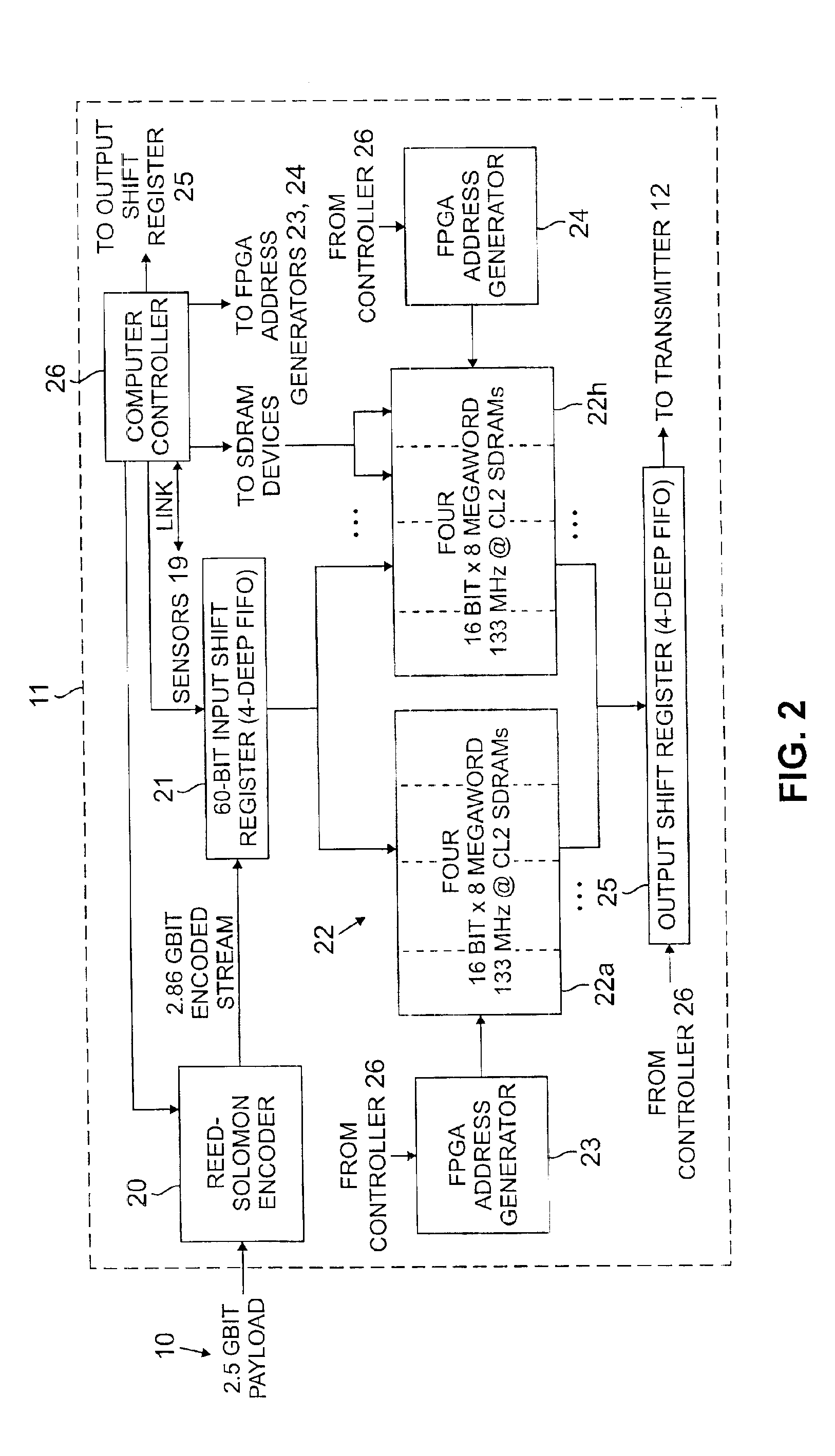
A process and apparatus is described for recovering from optical transmission degradation due to scintillation effects in optical free space. A payload bit stream is encoded into Reed-Solomon codewords. These are fragmented and distributed as interleaved segments over a cell matrix of a SDRAM buffer store which is made large enough to correct a burst error occurring over 20 million consecutive bits. The rate imbalance between conventional read vs. write operations for SDRAM devices, which would otherwise obviate their use in this application by preventing real time operation, is overcome by an address remapping that avoids having to changing page addresses each time SDRAM memory is referenced. The remapping facilitates a more nearly equal allocation of READ overhead and WRITE overhead. An optical communications system employs at both the transmit and receive ends, substantially equivalent SDRAM buffer with address remapping capability.
Owner:LGS INNOVATIONS
Method of Timing Laser Beam Pulses to Regulate Extreme Ultraviolet Light Dosing
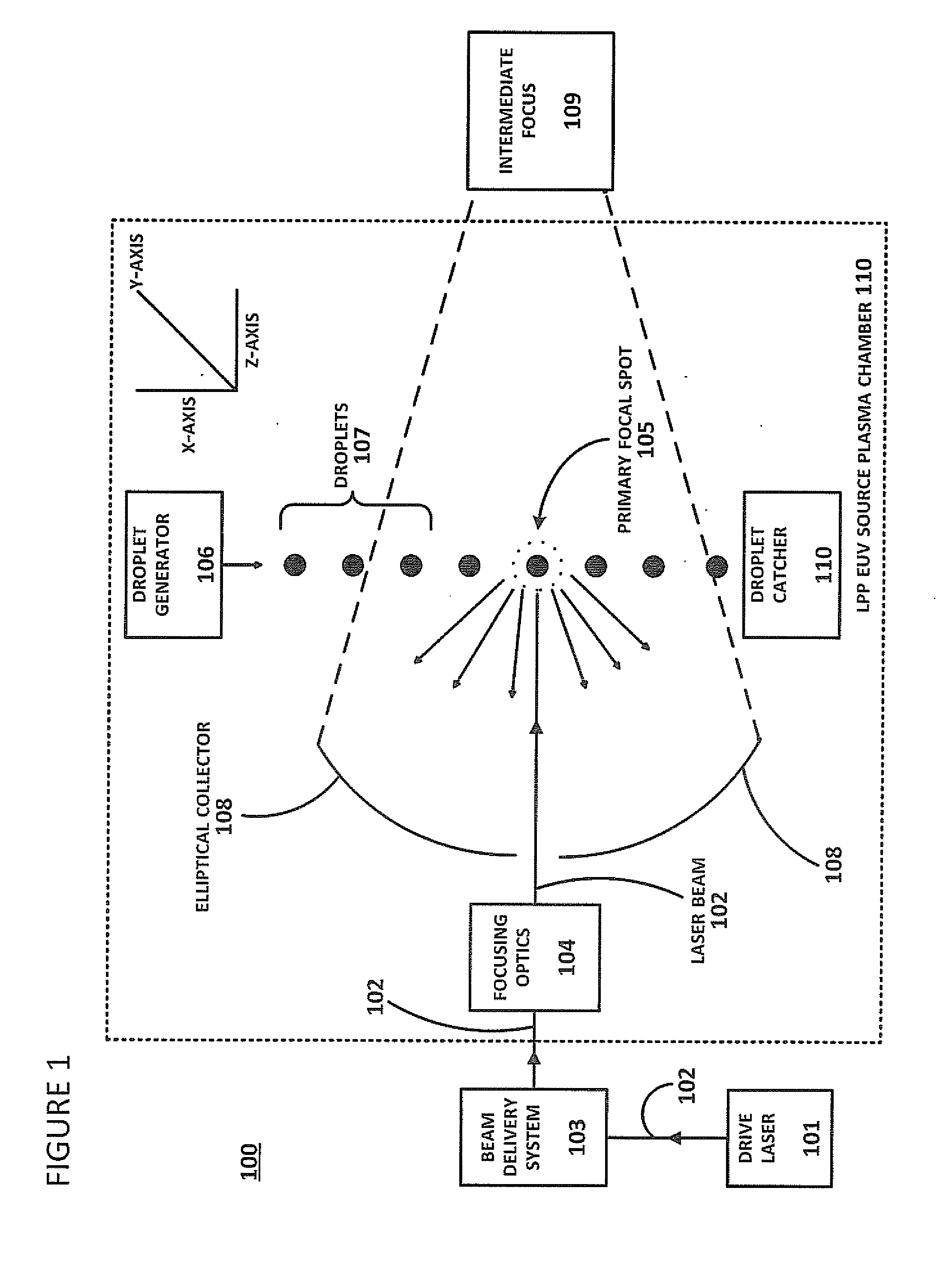
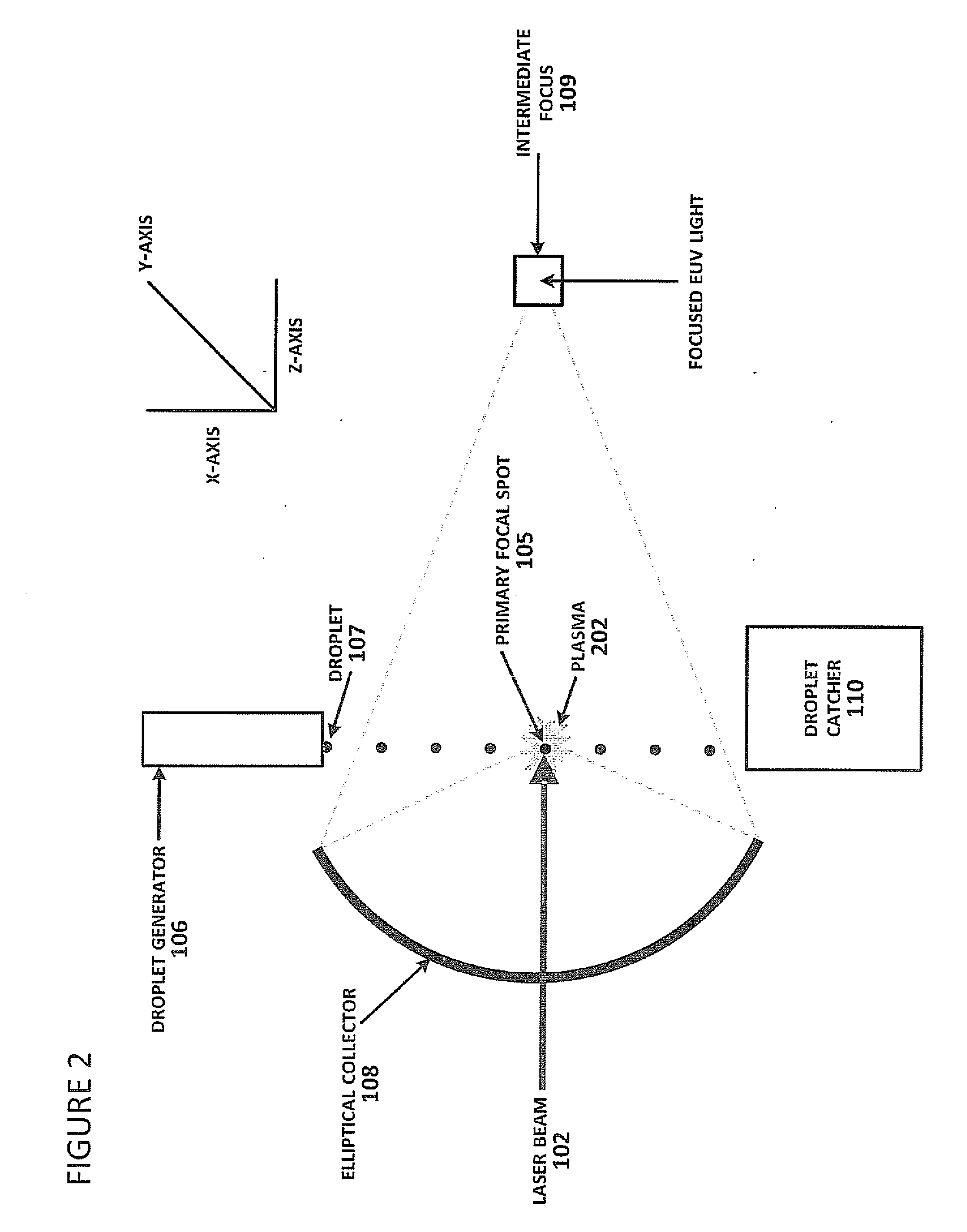
ActiveUS20140191132A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsOptoelectronicsLighting system
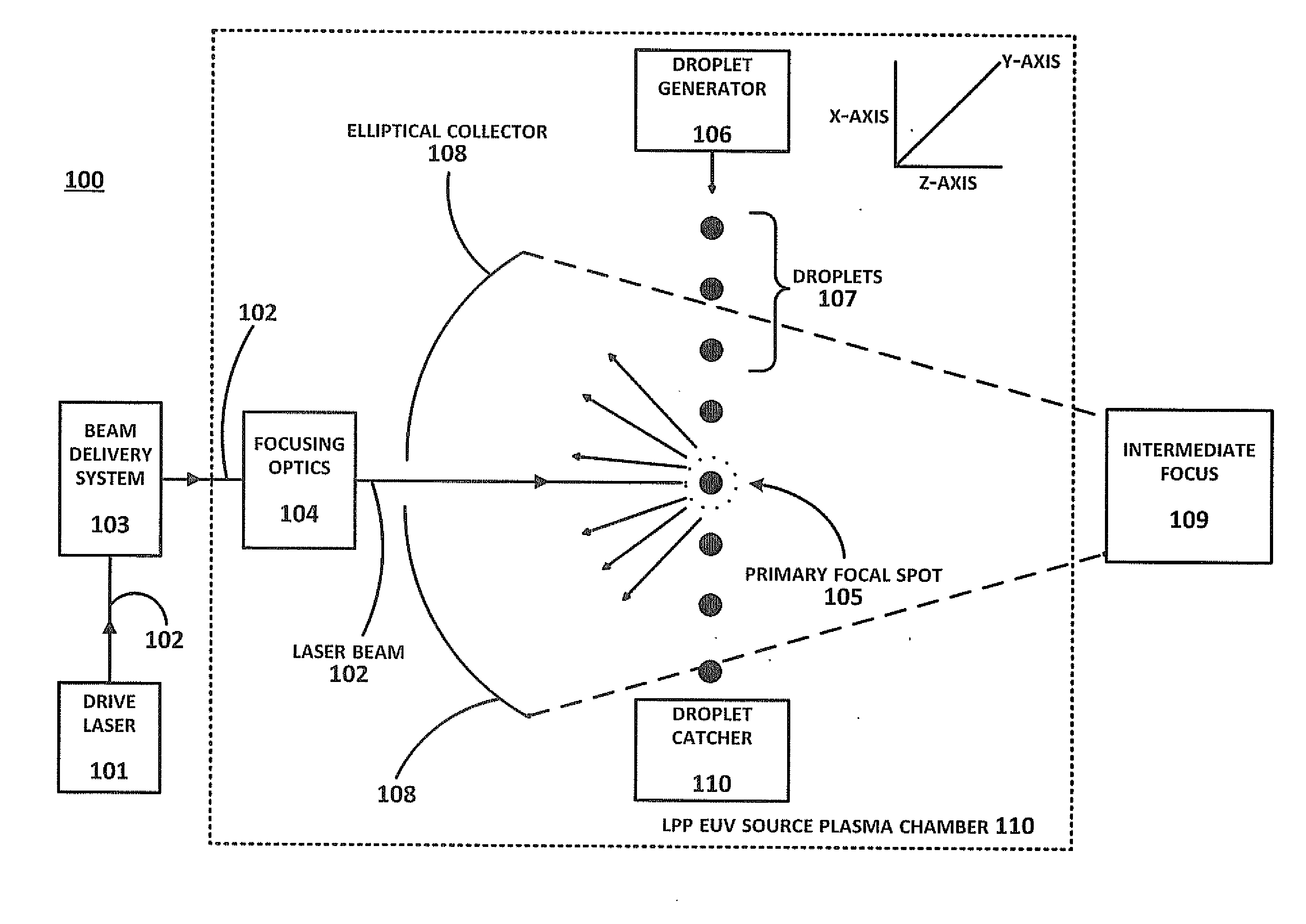
Described herein are embodiments of a method to control energy dose output from a laser-produced plasma extreme ultraviolet light system by adjusting timing of fired laser beam pulses. During stroboscopic firing, pulses are timed to lase droplets until a dose target of EUV has been achieved. Once accumulated EUV reaches the dose target, pulses are timed so as to not lase droplets during the remainder of the packet, and thereby prevent additional EUV light generation during those portions of the packet. In a continuous burst mode, pulses are timed to irradiate droplets until accumulated burst error meets or exceeds a threshold burst error. If accumulated burst error meets or exceeds the threshold burst error, a next pulse is timed to not irradiate a next droplet. Thus, the embodiments described herein manipulate pulse timing to obtain a constant desired dose target that can more precisely match downstream dosing requirements.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
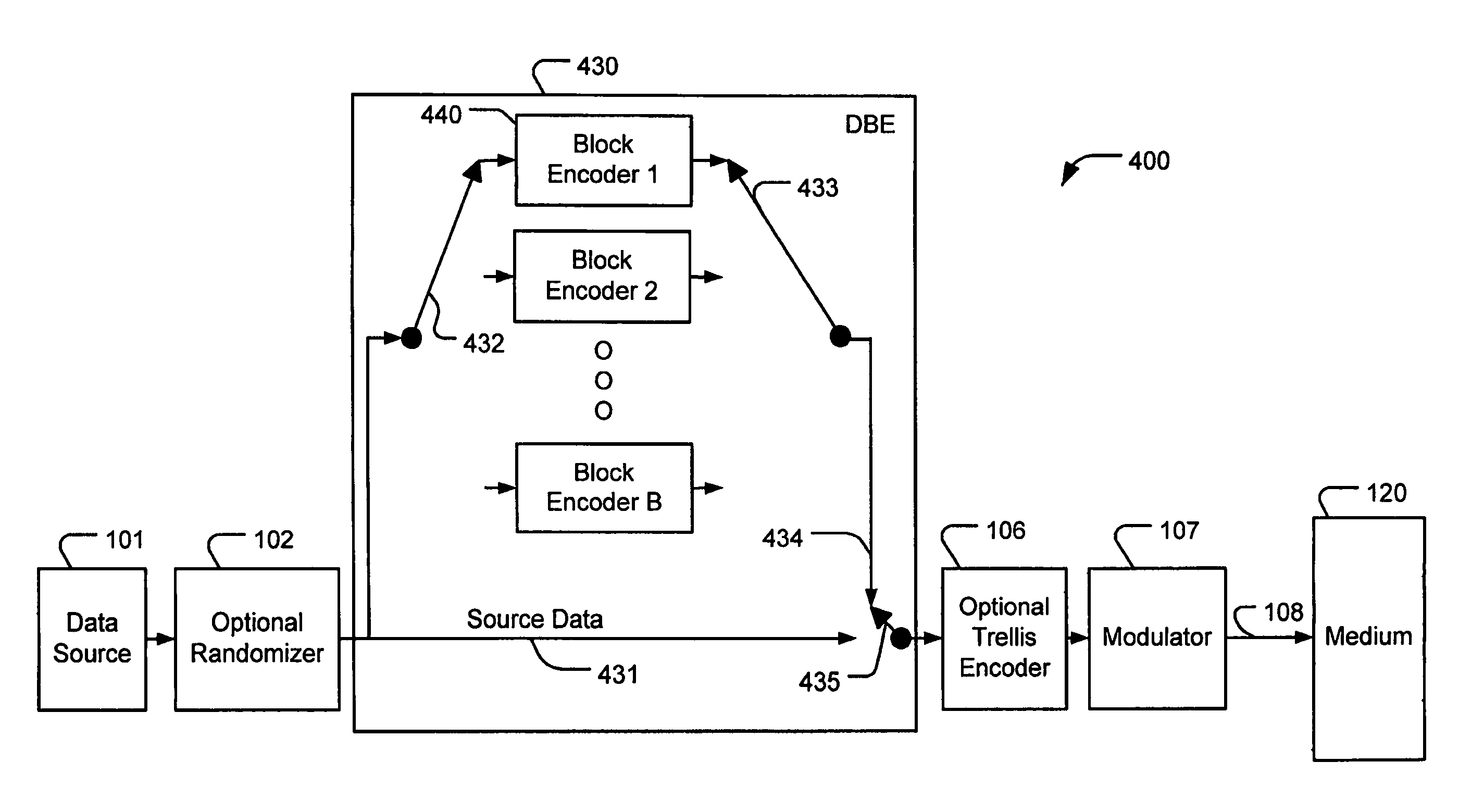
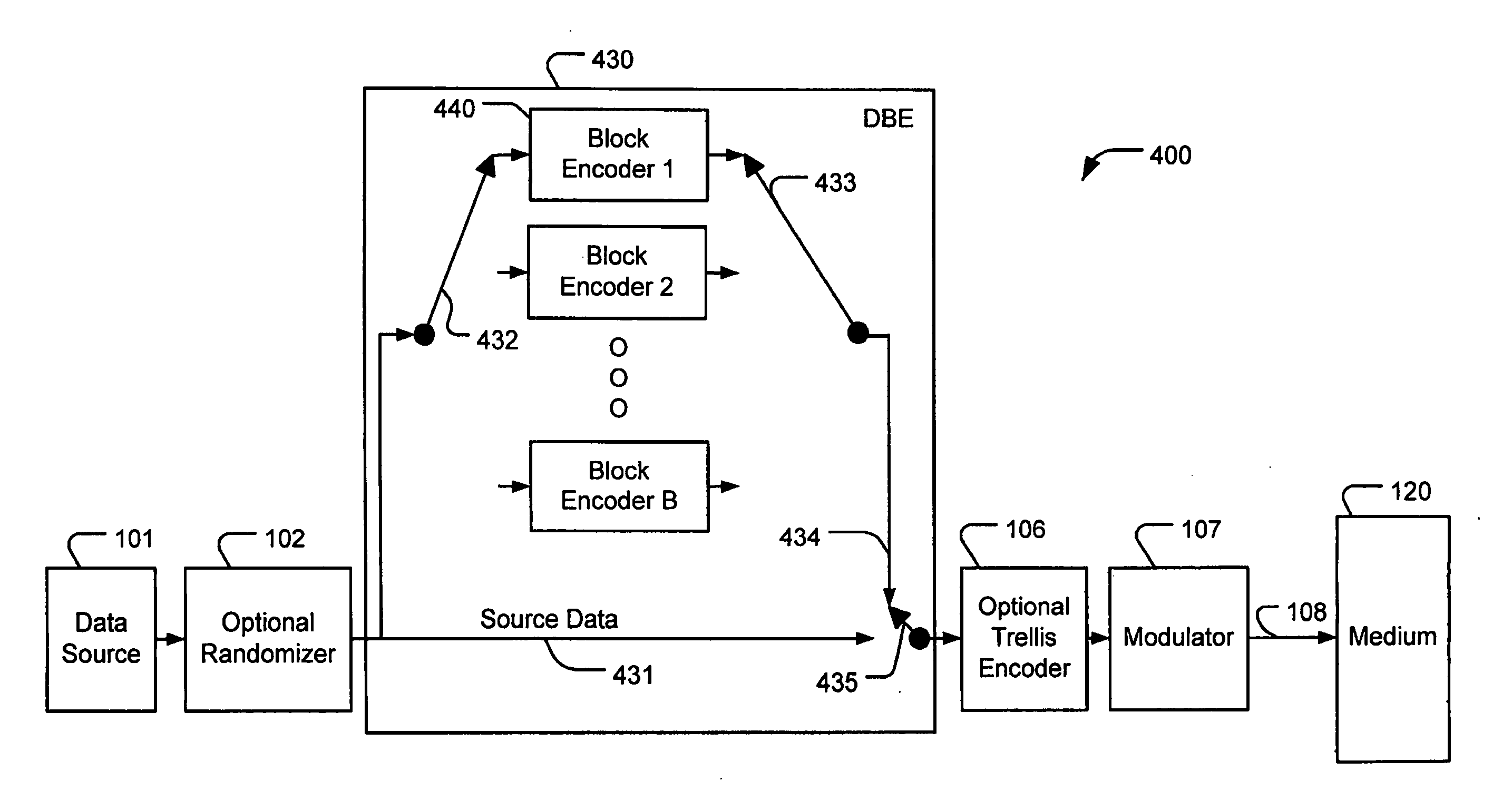
Distributed block coding (DBC)
InactiveUS7958426B2Reduce memory requirementsFacilitate interleavingOther error detection/correction/protectionError detection/correctionDBcCommunications system
Various embodiments implement distributed block coding (DBC). DBC can be used for, among other things, distributed forward error correction (DFEC) of source data in communication systems or parity backup for error correction of source data in storage systems where the source data may be corrupted by burst errors. A distributed block encoder (DBE) encodes sequential source data symbols with a plurality of sequential block encoders to produce interleaved parity codewords. The interleaved parity codewords enable decoding of error-corrected source data symbols with a distributed block decoder (DBD) that utilizes a plurality of sequential block decoders to produce the error-corrected source data symbols. A distributed register block encoder (DRBE) and a distributed register block decoder (DRBD) can each be implemented in a single block encoder and a single block decoder, respectively, by using a distributed register arrangement.
Owner:SUNRISE IP
Algebraic decoder and method for correcting an arbitrary mixture of burst and random errors
InactiveUS7131052B2Combine accuratelyError detection/correctionCode conversionAlgebraic decodingByte
An error correction algebraic decoder and an associated method correct a combination of a B-byte burst of errors and t-byte random errors in a failed sector, by iteratively adding and removing an erasure (N−B) times until the entire failed sector has been scanned, provided the following inequality is satisfied: (B+2t)≦(R−1), where N denotes the number of bytes, B denotes the length of the burst of errors, t denotes the total number of random errors, and R denotes the number of check bytes in the failed sector. This results in a corrected sector at a decoding latency that is a generally linear function of the number of the check bytes R, as follows: Decoding Latency=5R(N−B).
Owner:LINKEDIN
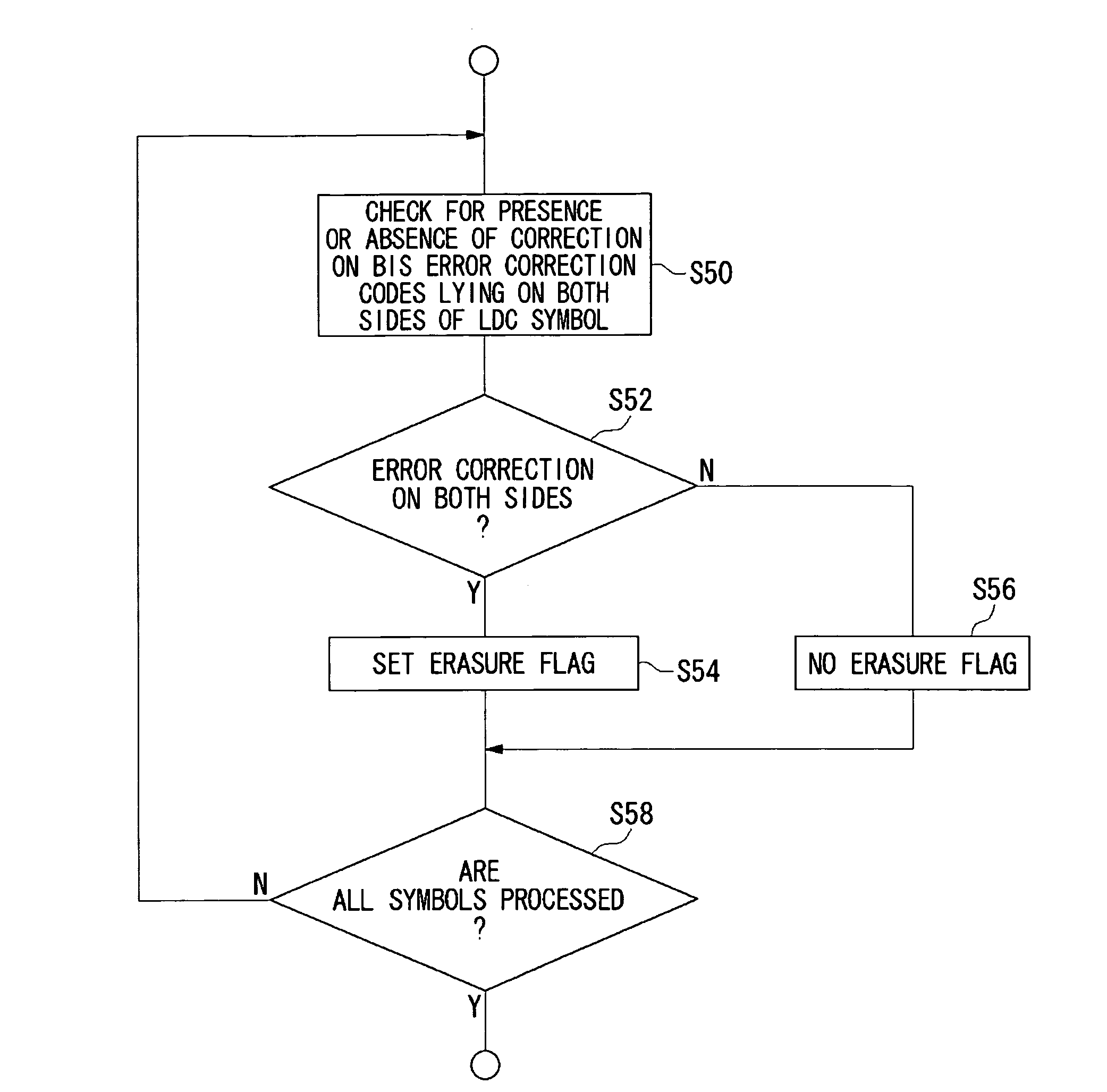
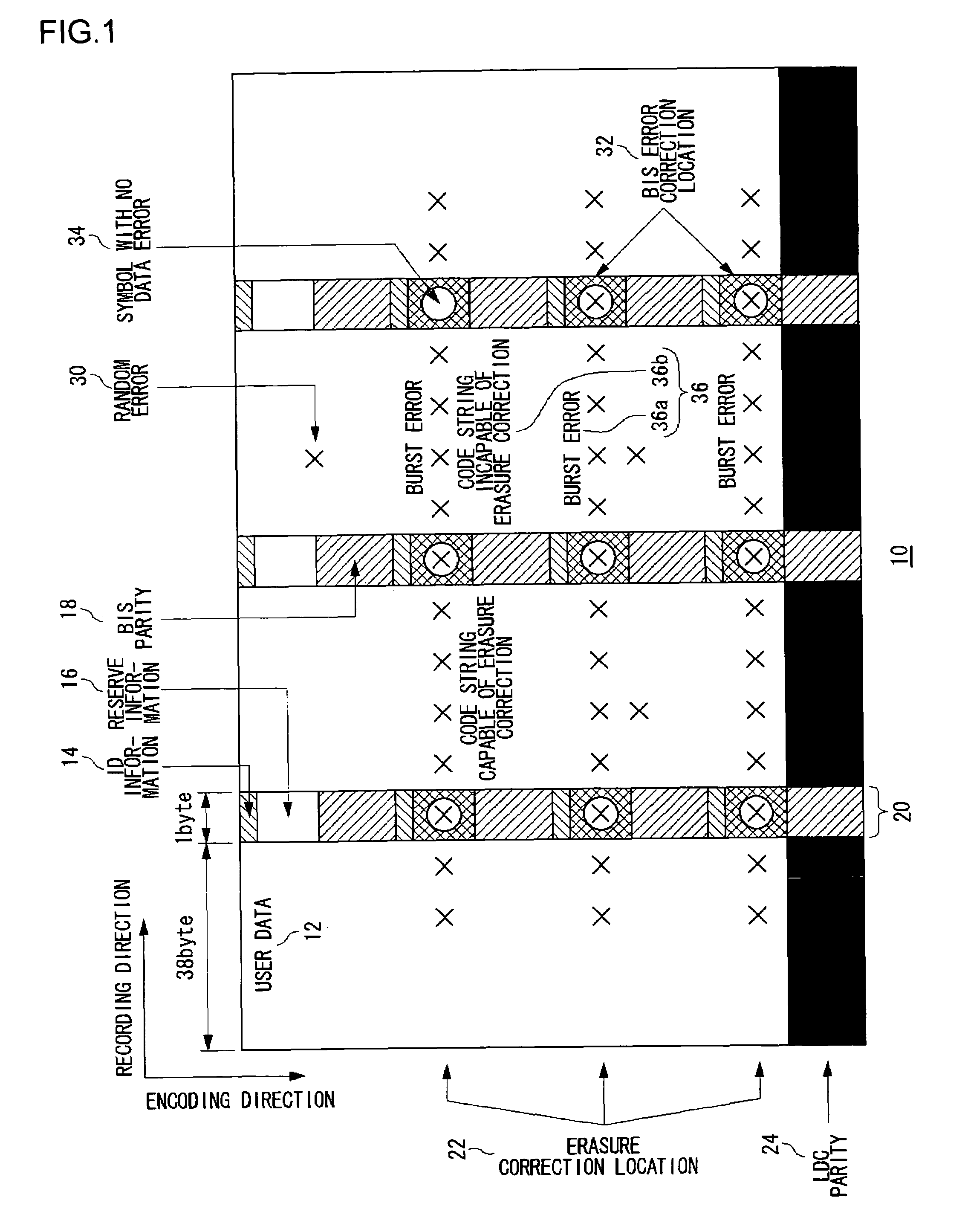
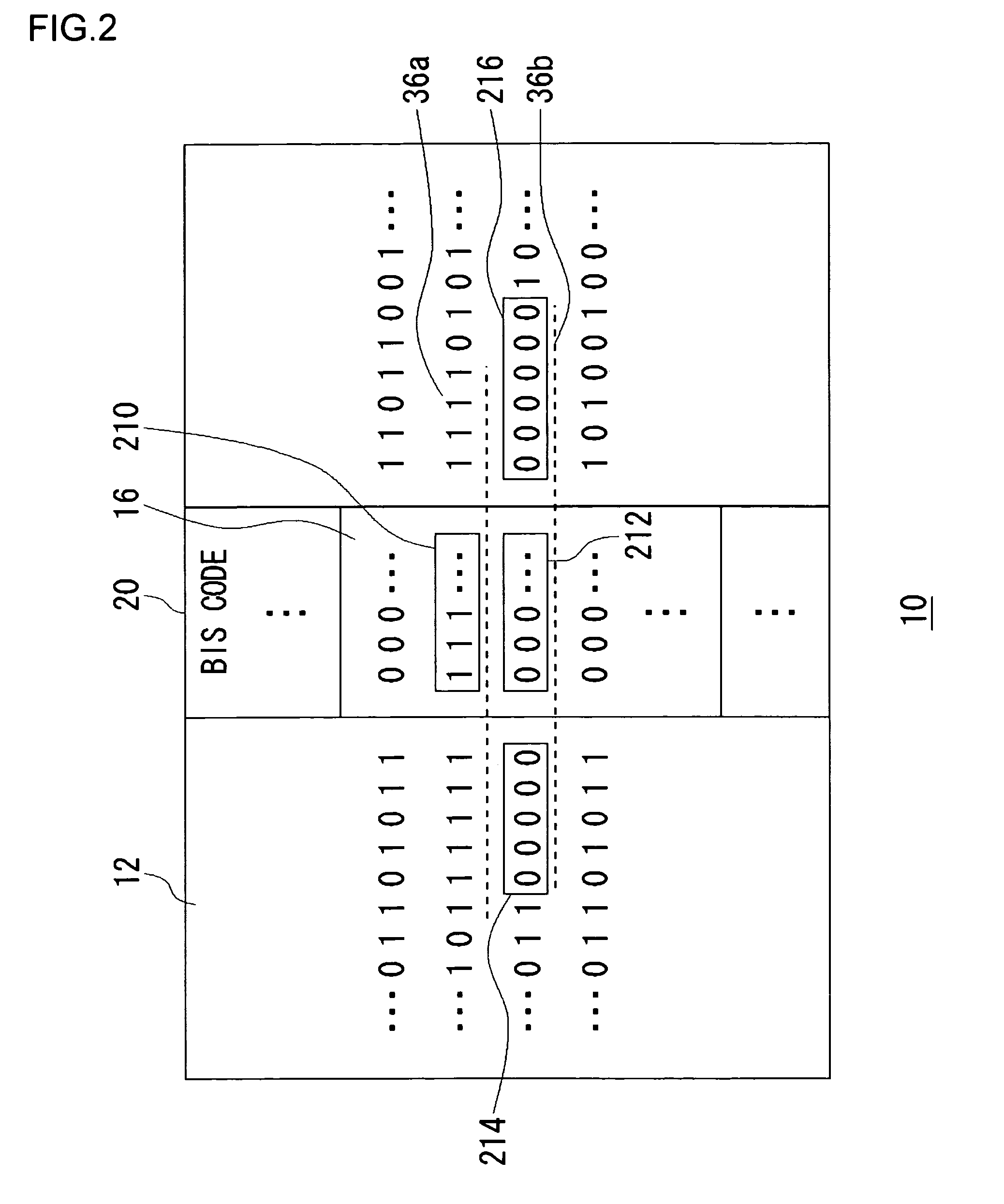
Method of detecting error location, and error detection circuit, error correction circuit, and reproducing apparatus using the method
InactiveUS7478306B2Easy to detectImprove error performanceData representation error detection/correctionTransmission systemsData signalError location
An error correction circuit capable of detecting burst errors included in a data signal with reliability. The error correction circuit comprises a reading unit, a first estimation unit, a second estimation unit, and a correction unit. The reading unit reads the data signal. The first estimation unit estimates error locations based on BIS code included in the data signal, and stores the locations into an error location storing unit. The second estimation unit estimates error locations based on characteristics of bit strings adjoining the BIS code, and stores the locations into the error location storing unit. The correction unit identifies erasure locations based on the error locations stored in the error location storing unit, and performs erasure correction on the erasure locations identified. Since the error locations are estimated based on the BIS code and the characteristics of the bit strings adjoining the BIS code as well, it is possible to detect burst errors without fail.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Distributed block coding (DBC)
InactiveUS20080065971A1Avoid excessive delayReduce complexityOther error detection/correction/protectionError detection/correctionDBcCommunications system
Various embodiments implement distributed block coding (DBC). DBC can be used for, among other things, distributed forward error correction (DFEC) of source data in communication systems or parity backup for error correction of source data in storage systems where the source data may be corrupted by burst errors. A distributed block encoder (DBE) encodes sequential source data symbols with a plurality of sequential block encoders to produce interleaved parity codewords. The interleaved parity codewords enable decoding of error-corrected source data symbols with a distributed block decoder (DBD) that utilizes a plurality of sequential block decoders to produce the error-corrected source data symbols. A distributed register block encoder (DRBE) and a distributed register block decoder (DRBD) can each be implemented in a single block encoder and a single block decoder, respectively, by using a distributed register arrangement.
Owner:SUNRISE IP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com