Patents
Literature
45 results about "Energy dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
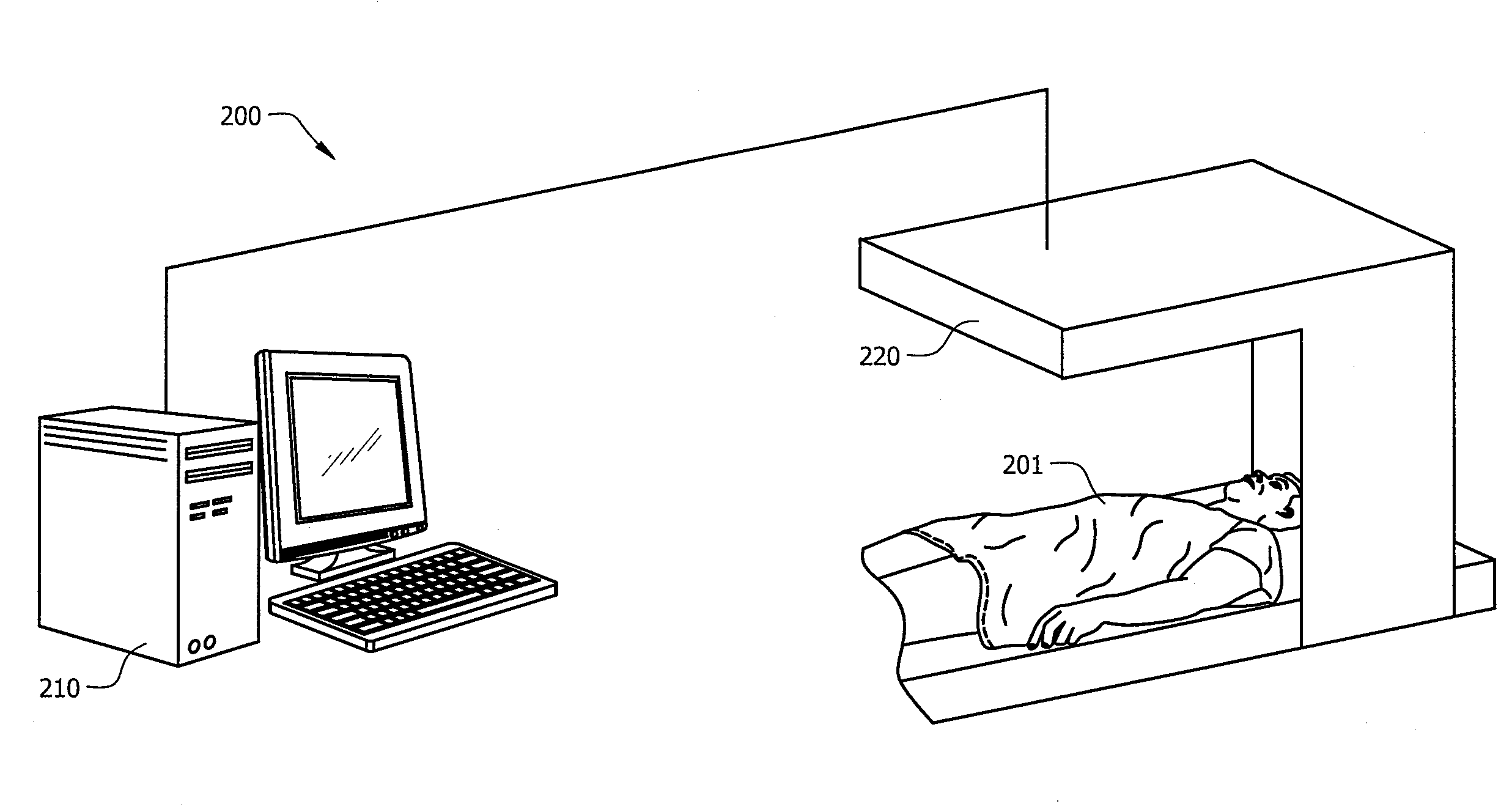
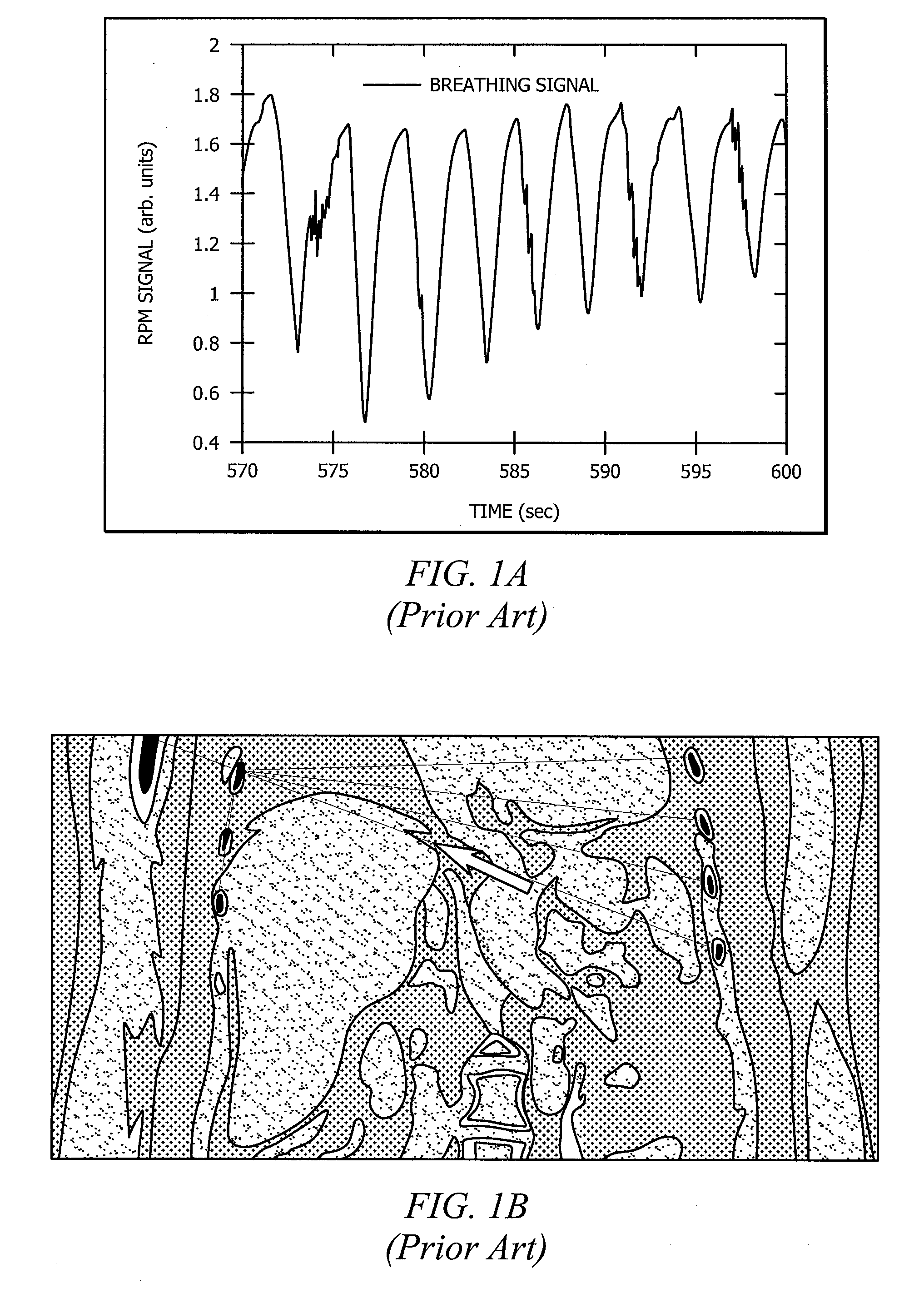
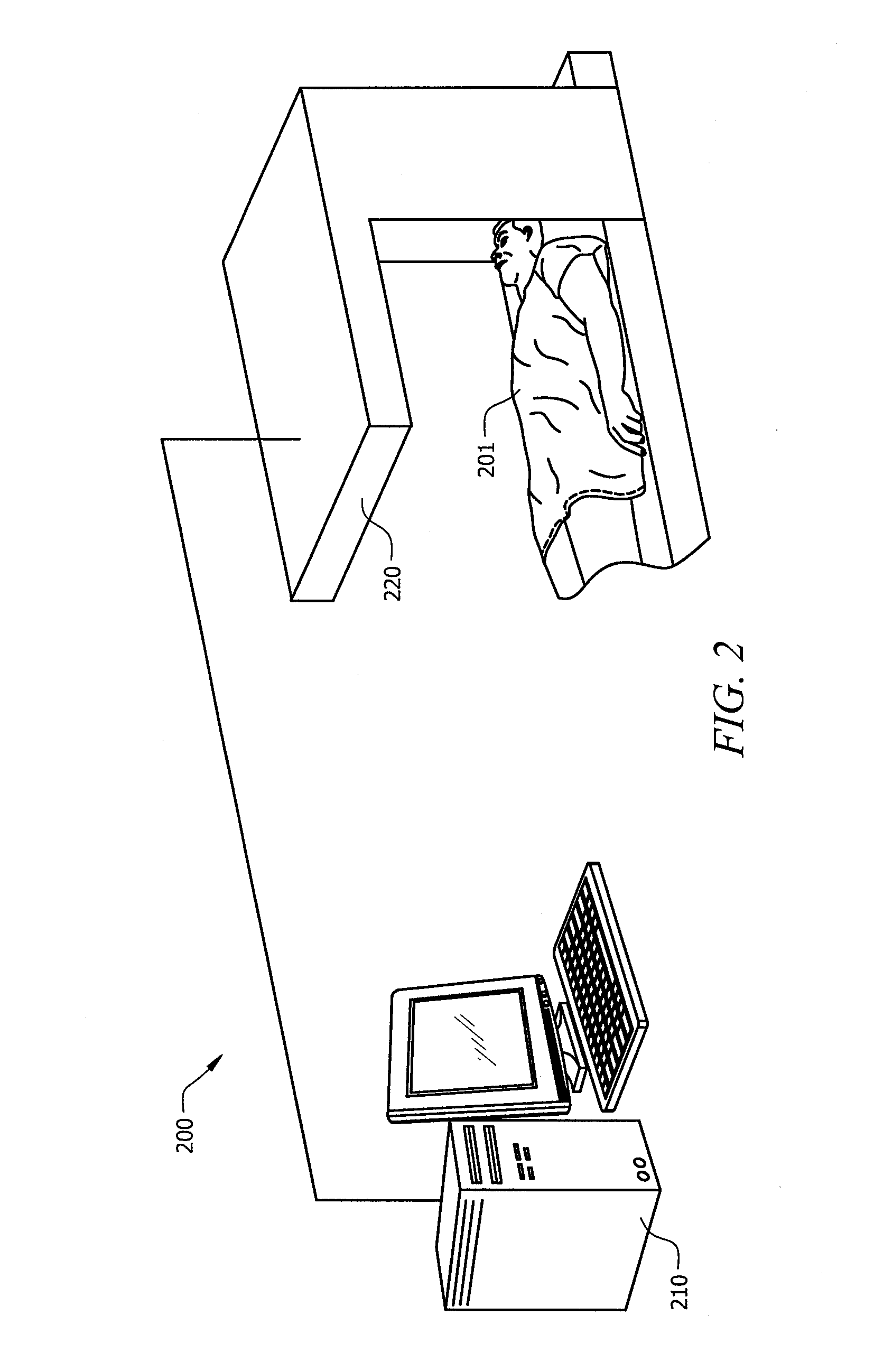
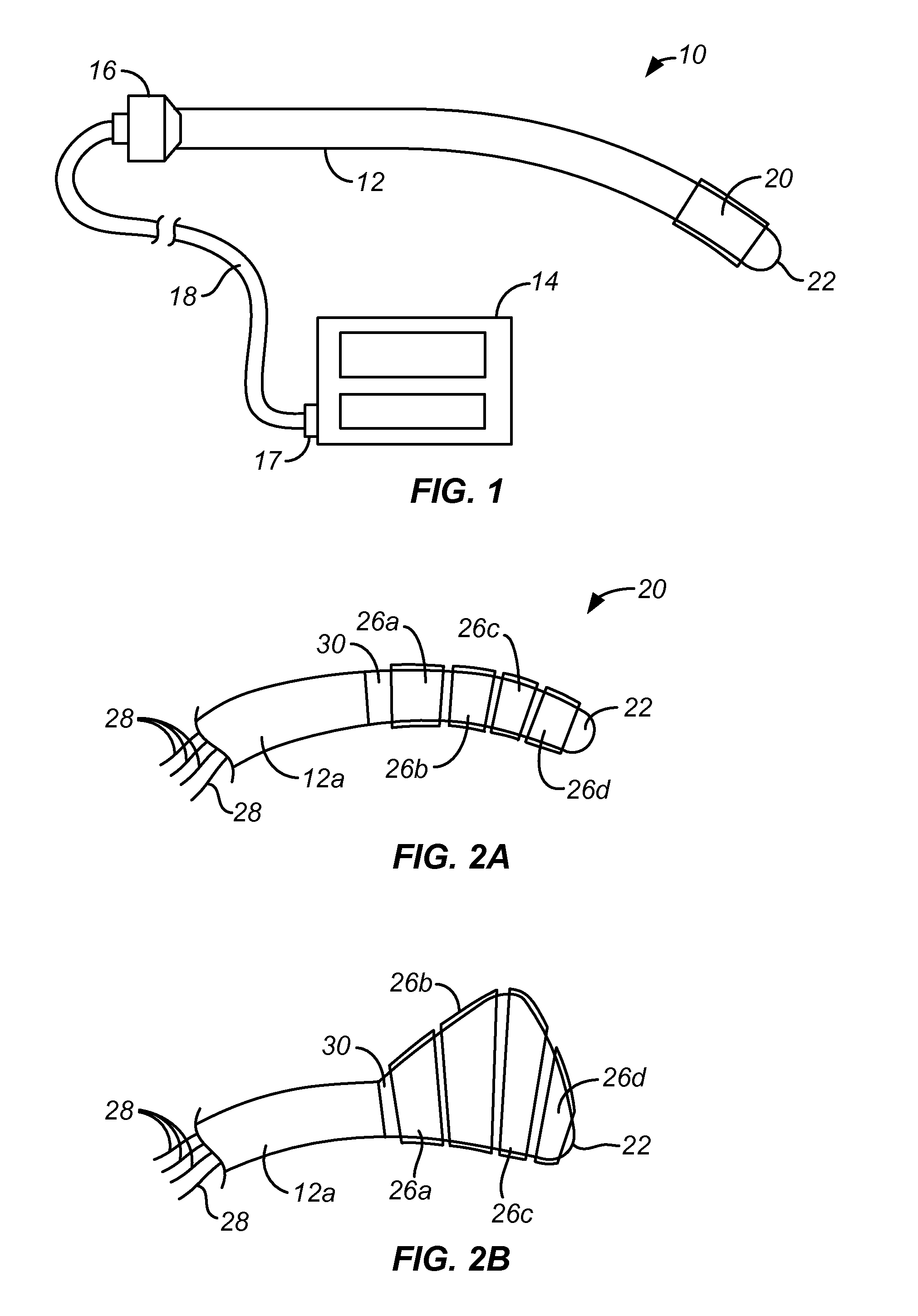
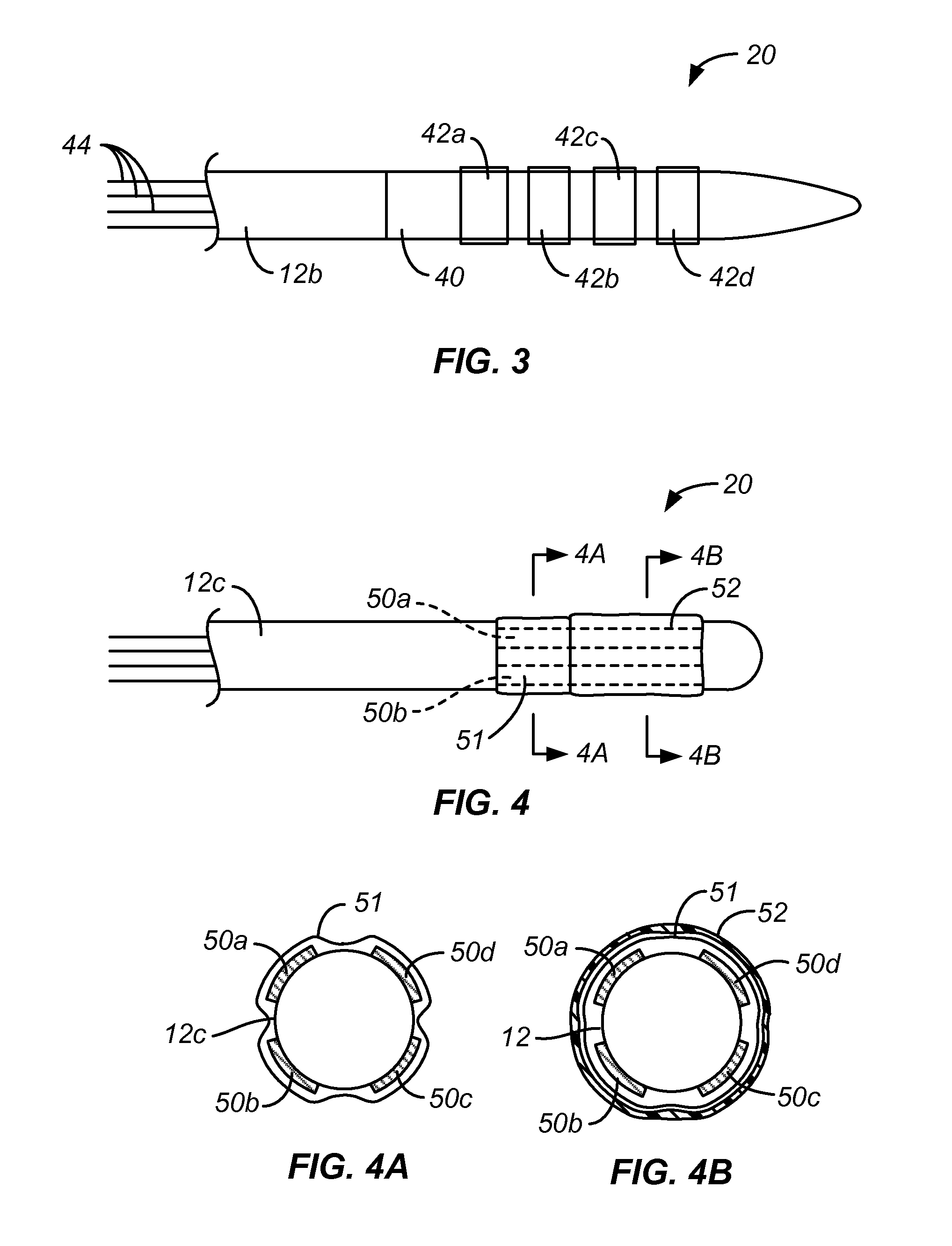
Image reconstruction incorporating organ motion
InactiveUS20120201428A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioPromote lowerUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
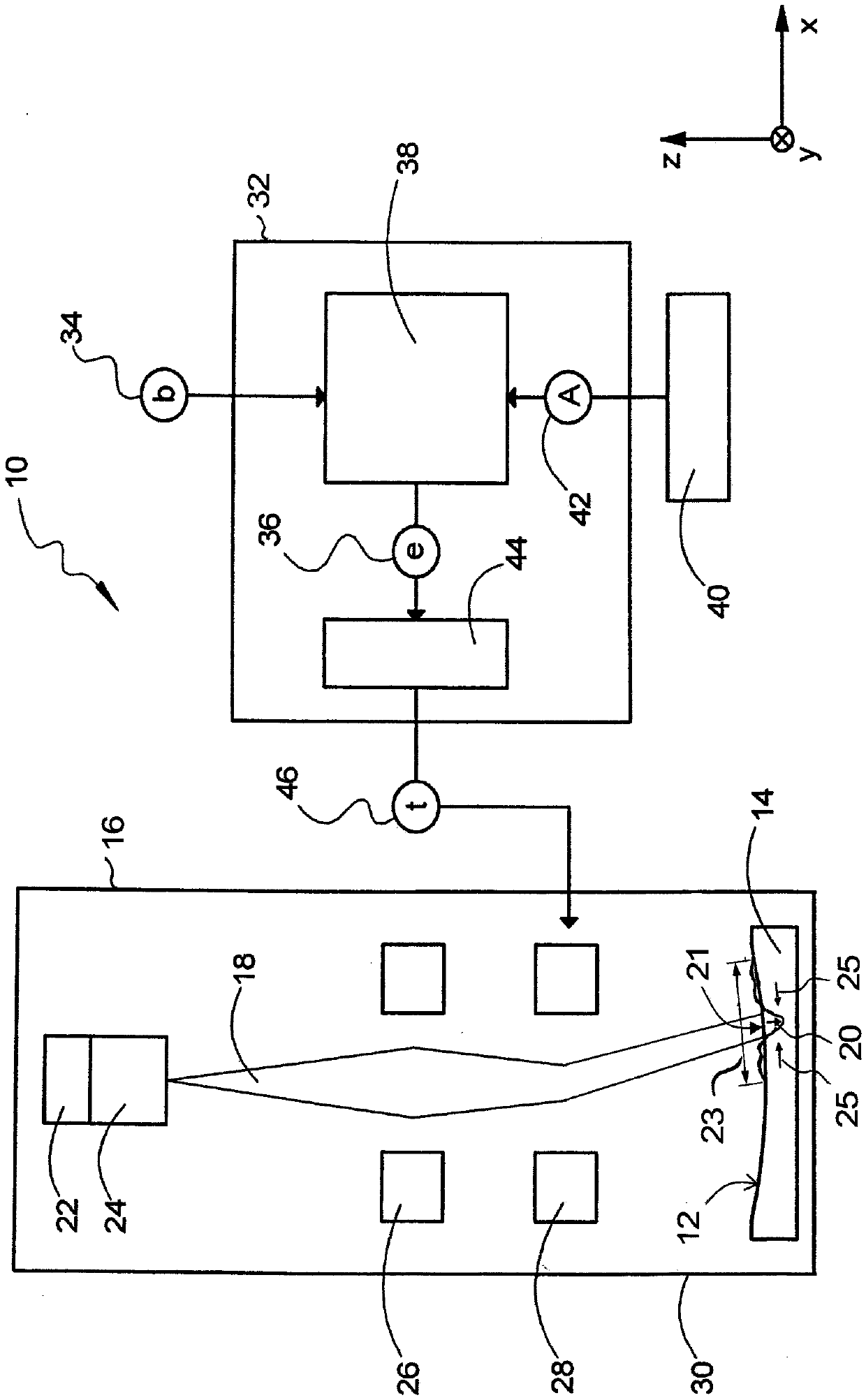
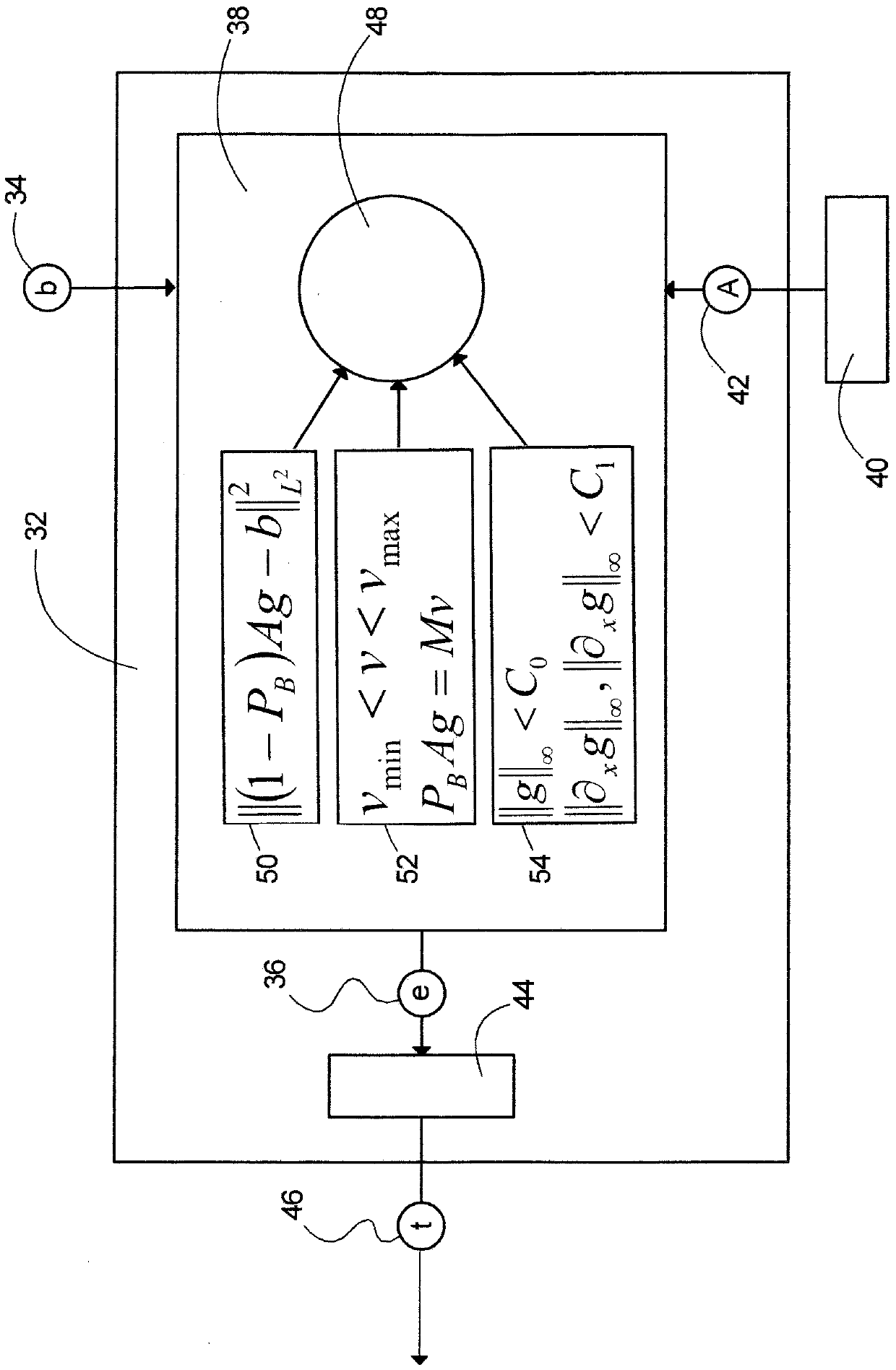
Systems and methods which implement an image reconstruction framework to incorporate complex motion of structure, such as complex deformation of an object or objects being imaged, in image reconstruction techniques are shown. For example, techniques are provided for tracking organ motion which uses raw time-stamped data provided by any of a number of imaging modalities and simultaneously reconstructs images and estimates deformations in anatomy. Operation according to embodiments reduces artifacts, increase the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and facilitates reduced image modality energy dosing to patients. The technology also facilitates the incorporation of physical properties of organ motion, such as the conservation of local tissue volume. This approach is accurate and robust against noise and irregular breathing for tracking organ motion.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
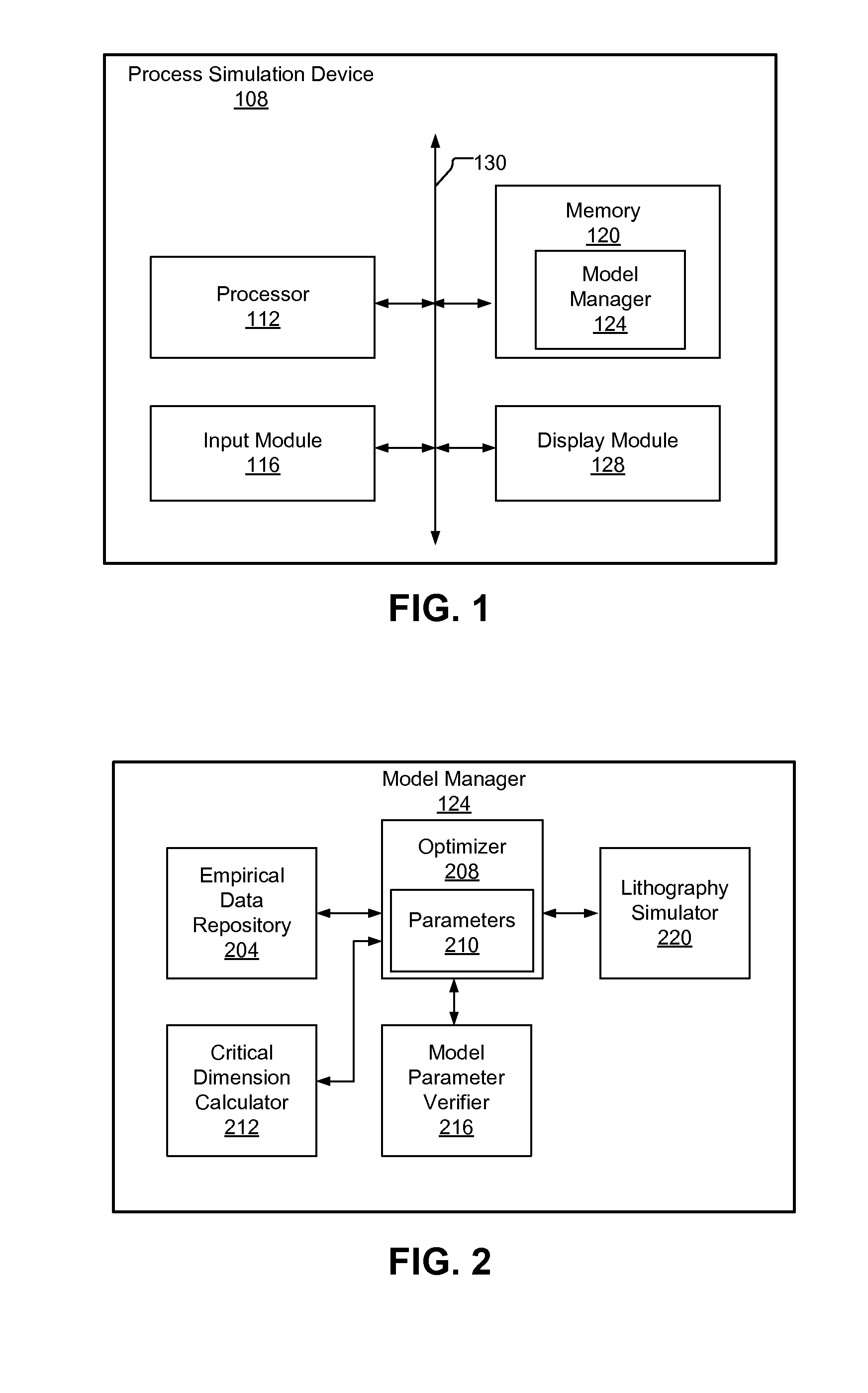
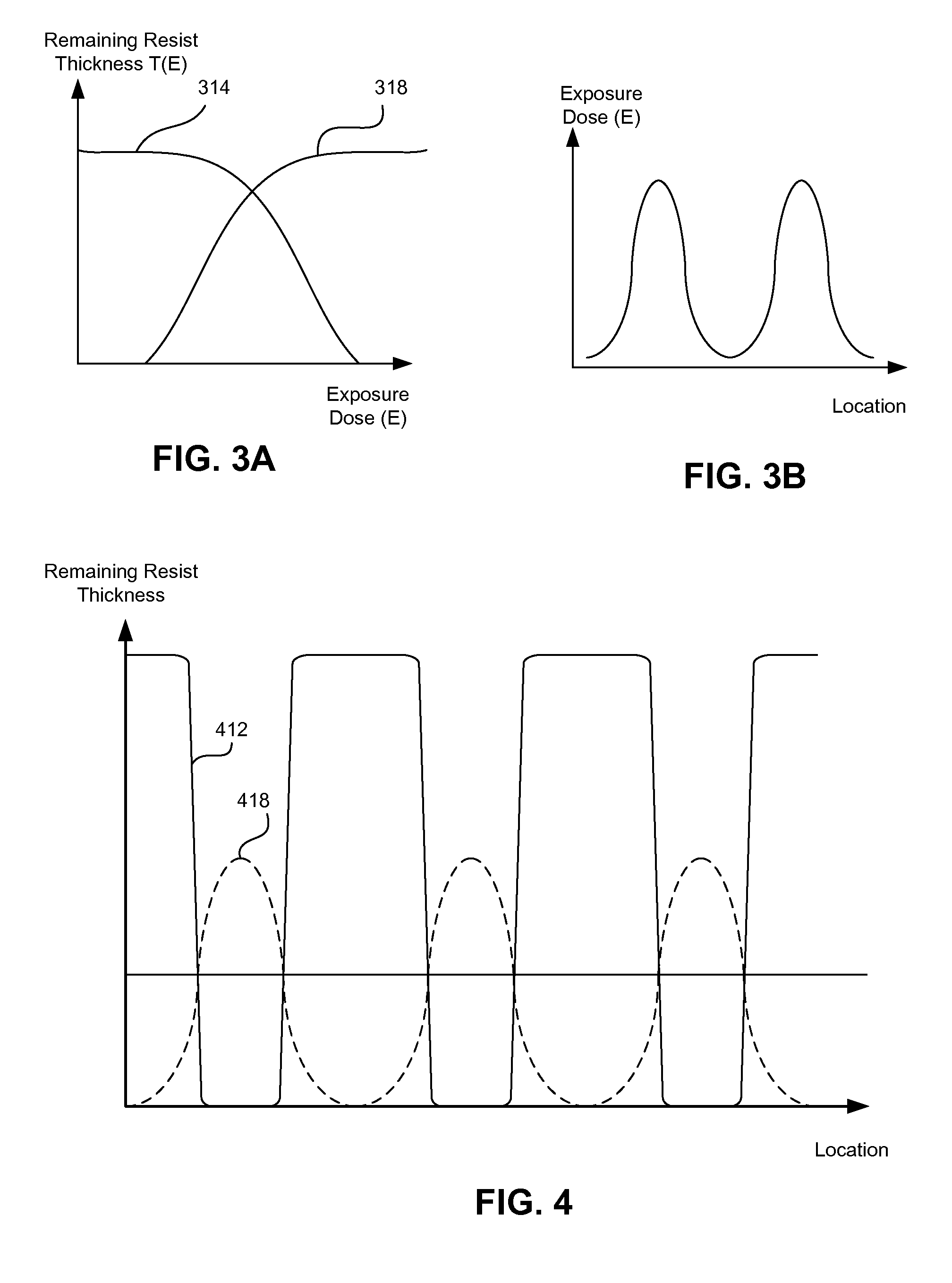
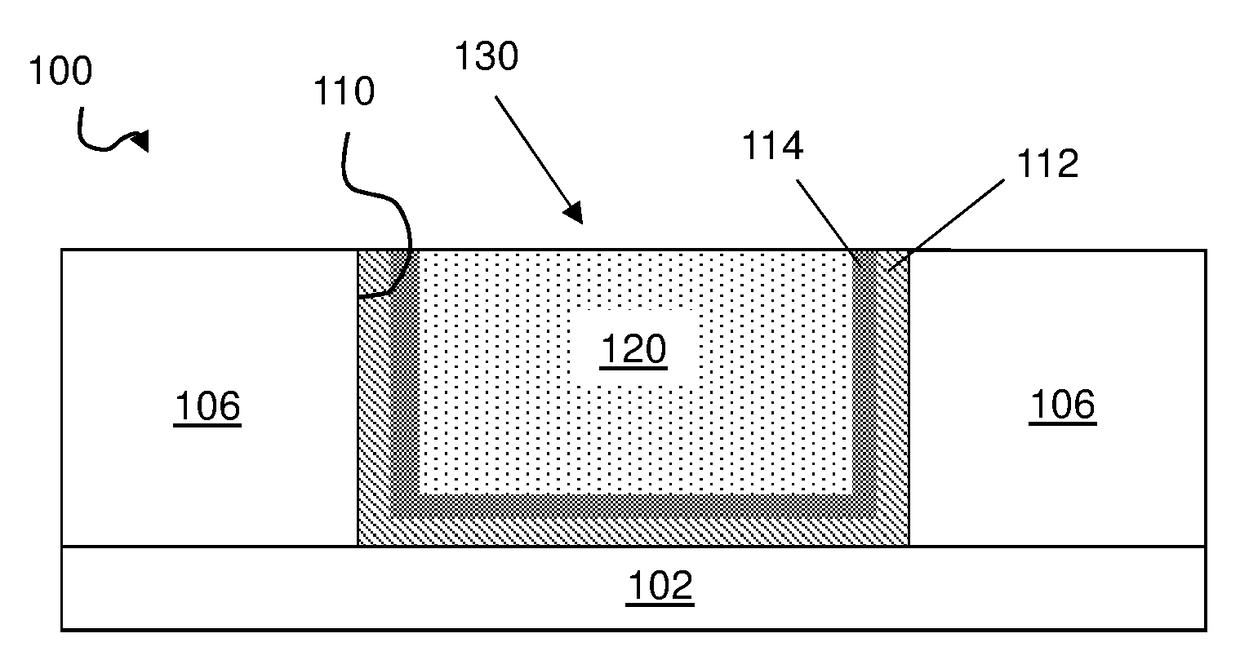
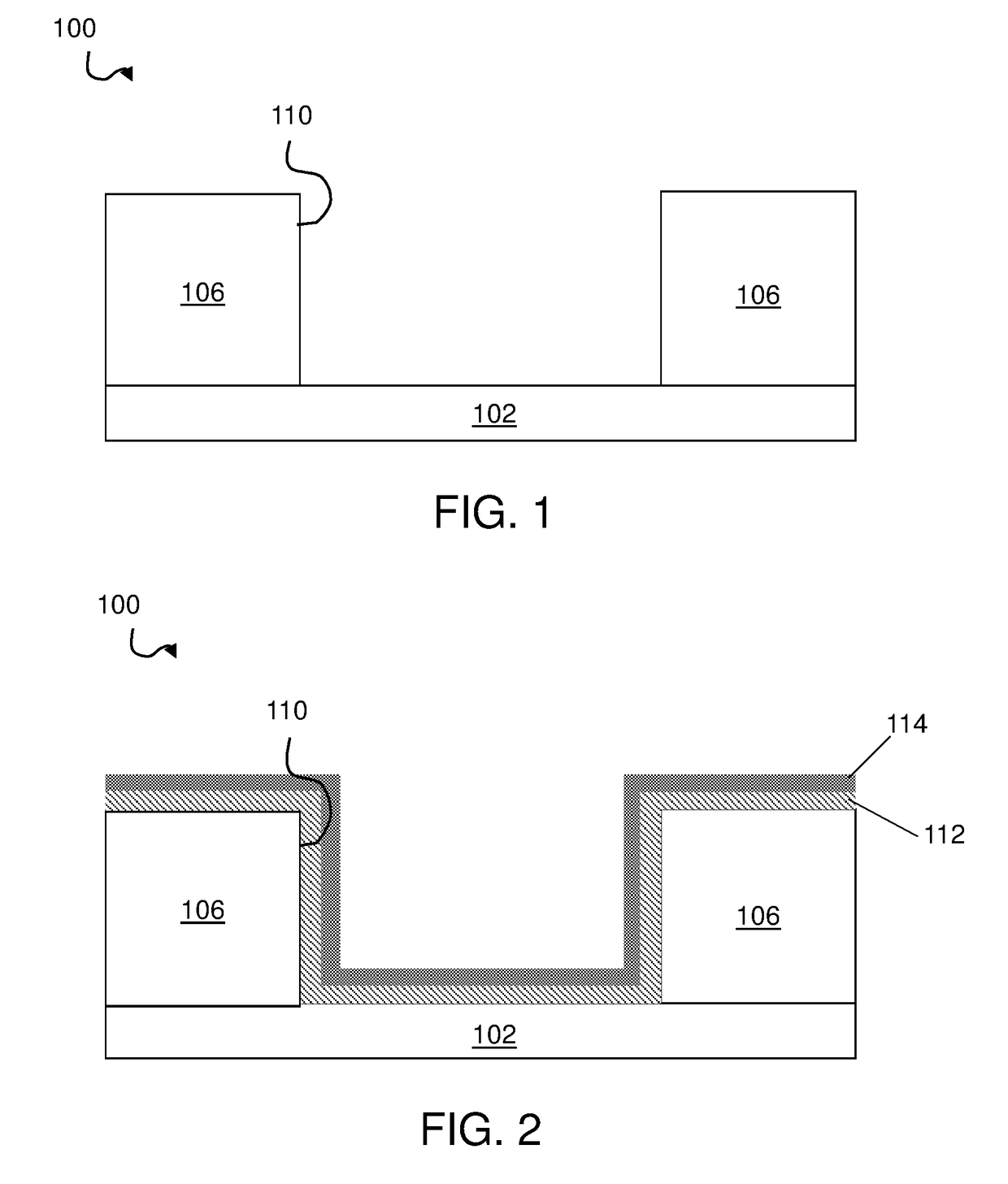
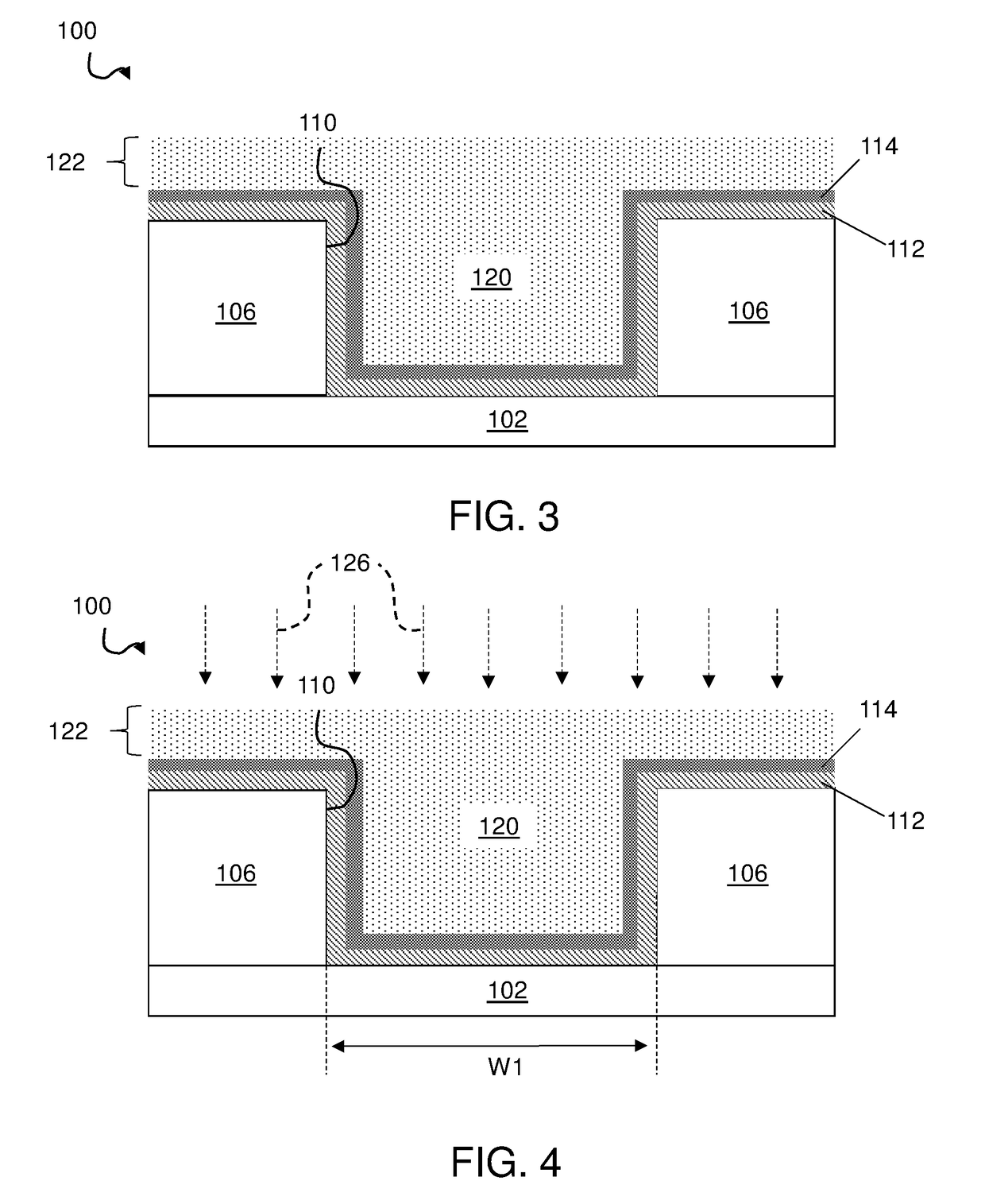
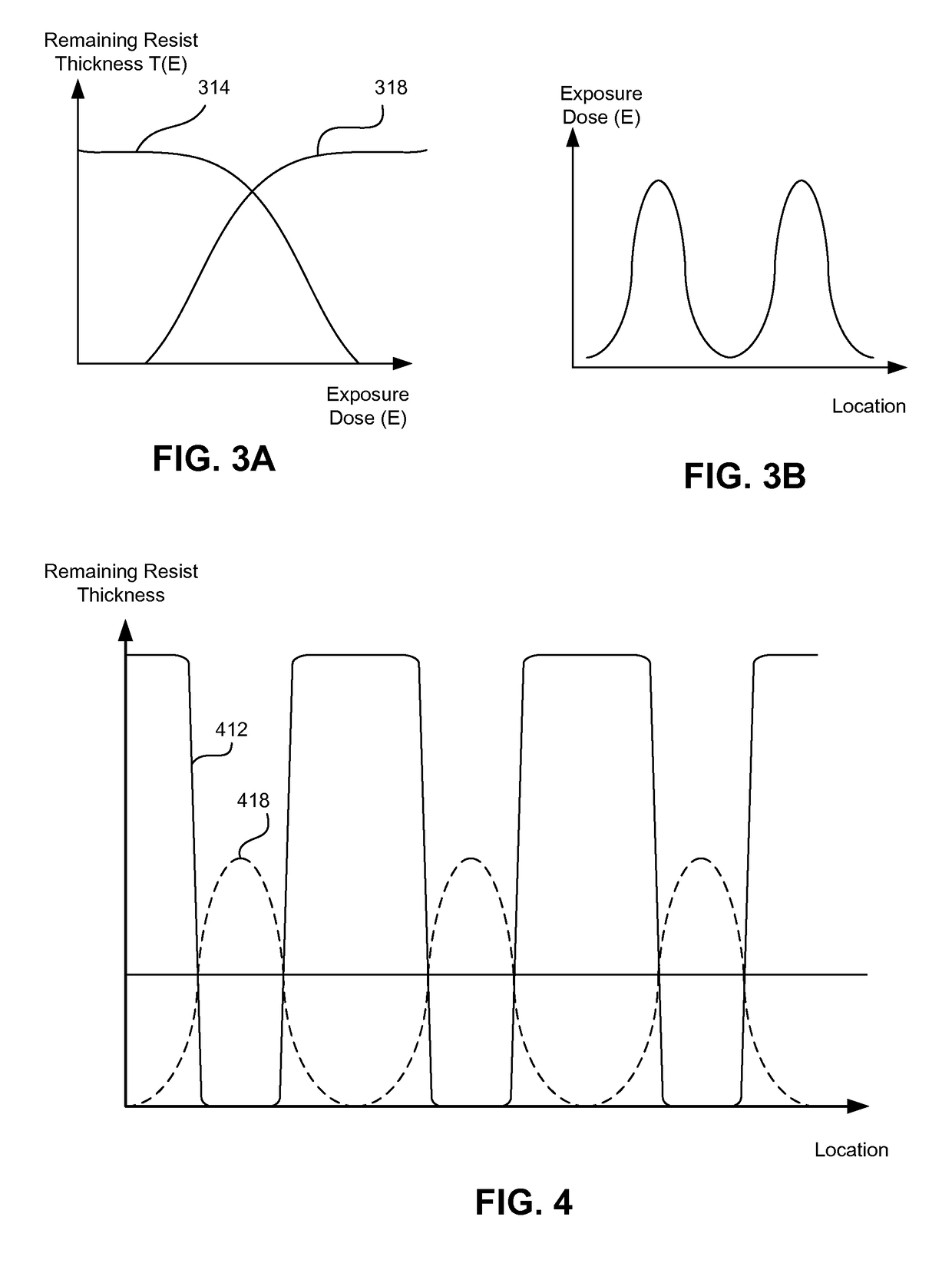
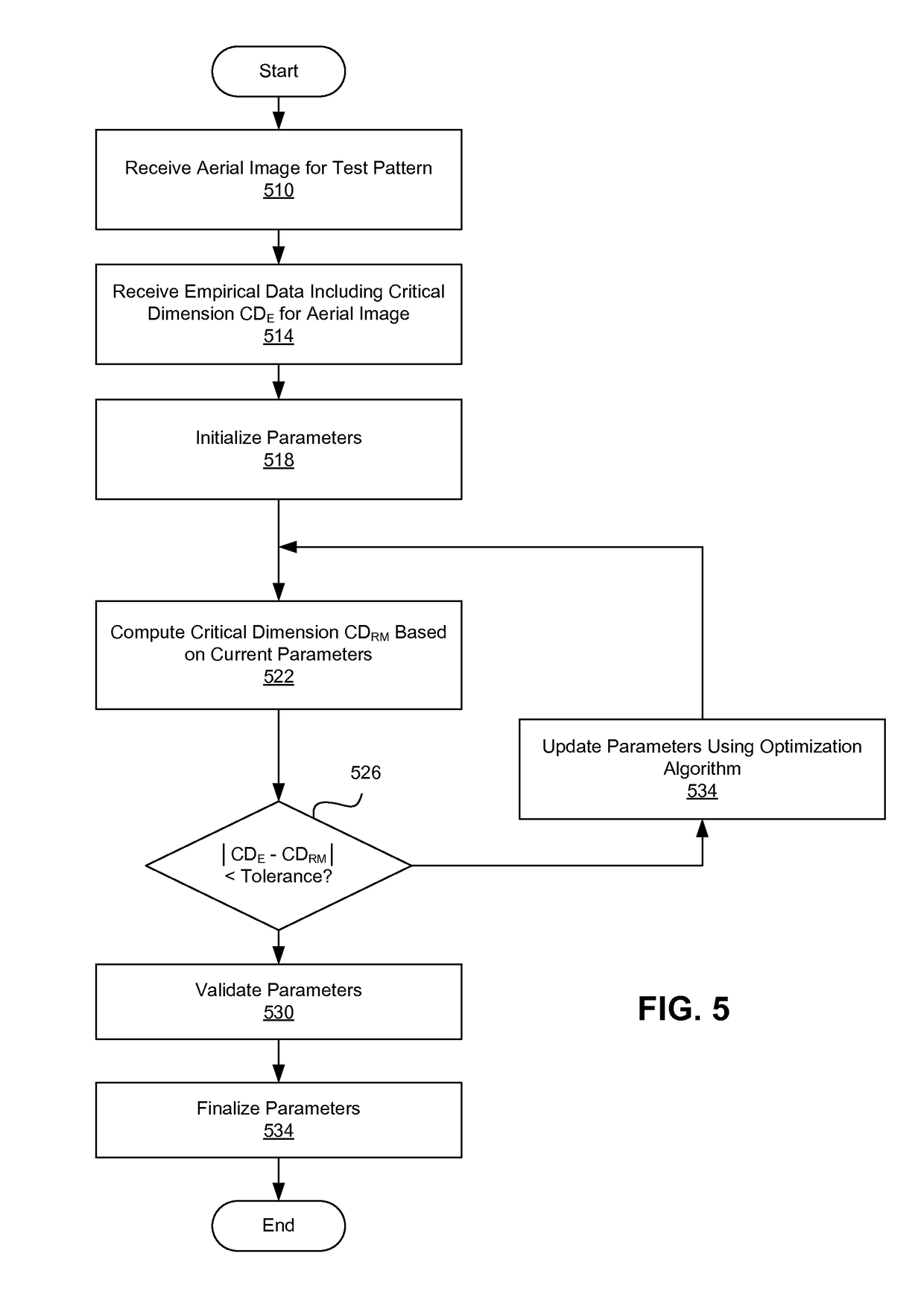
Fast Photolithography Process Simulation to Predict Remaining Resist Thickness
ActiveUS20110224963A1Account for effectAvoid excessive computationAnalogue computers for electric apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusResistSoftware development process
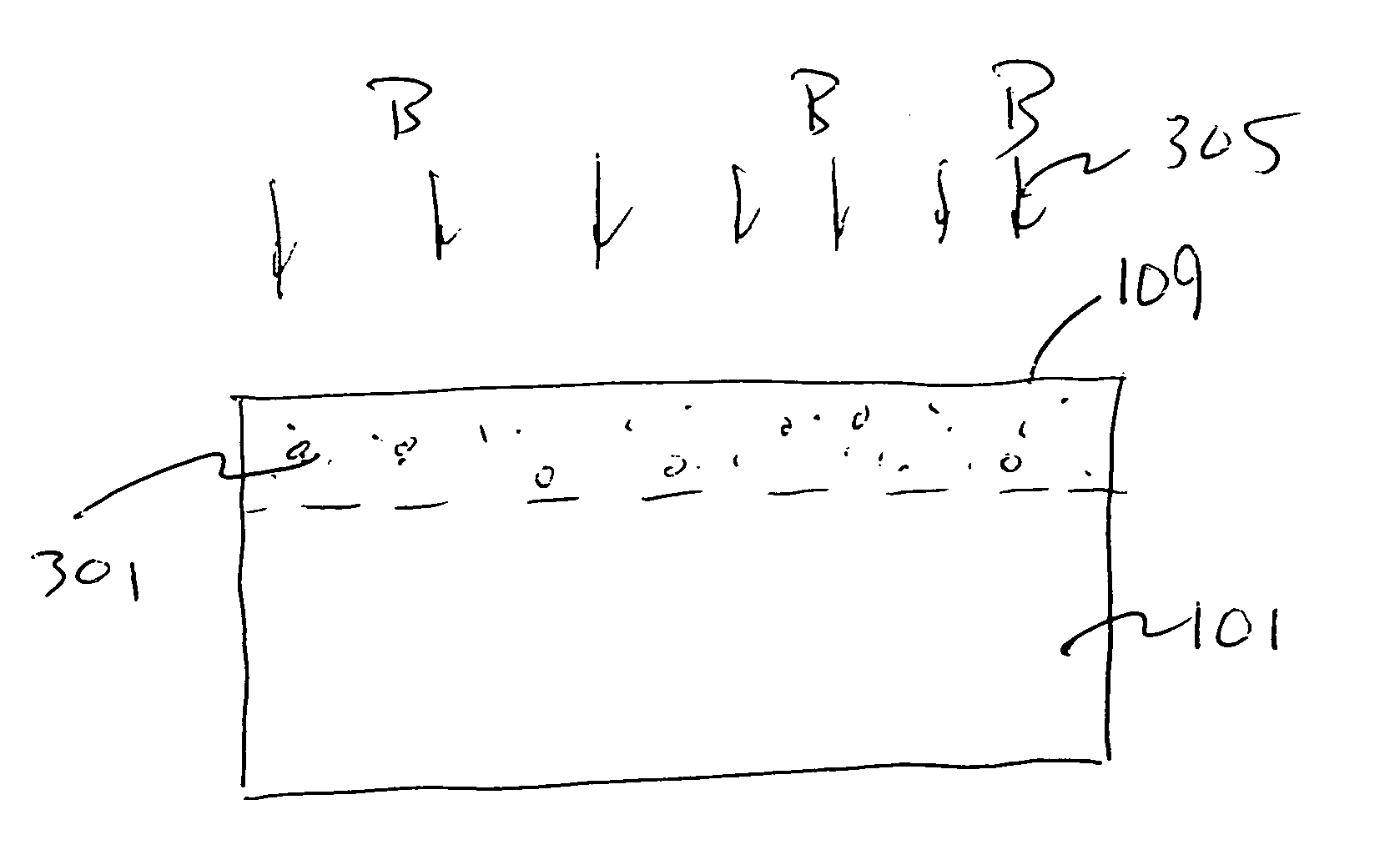
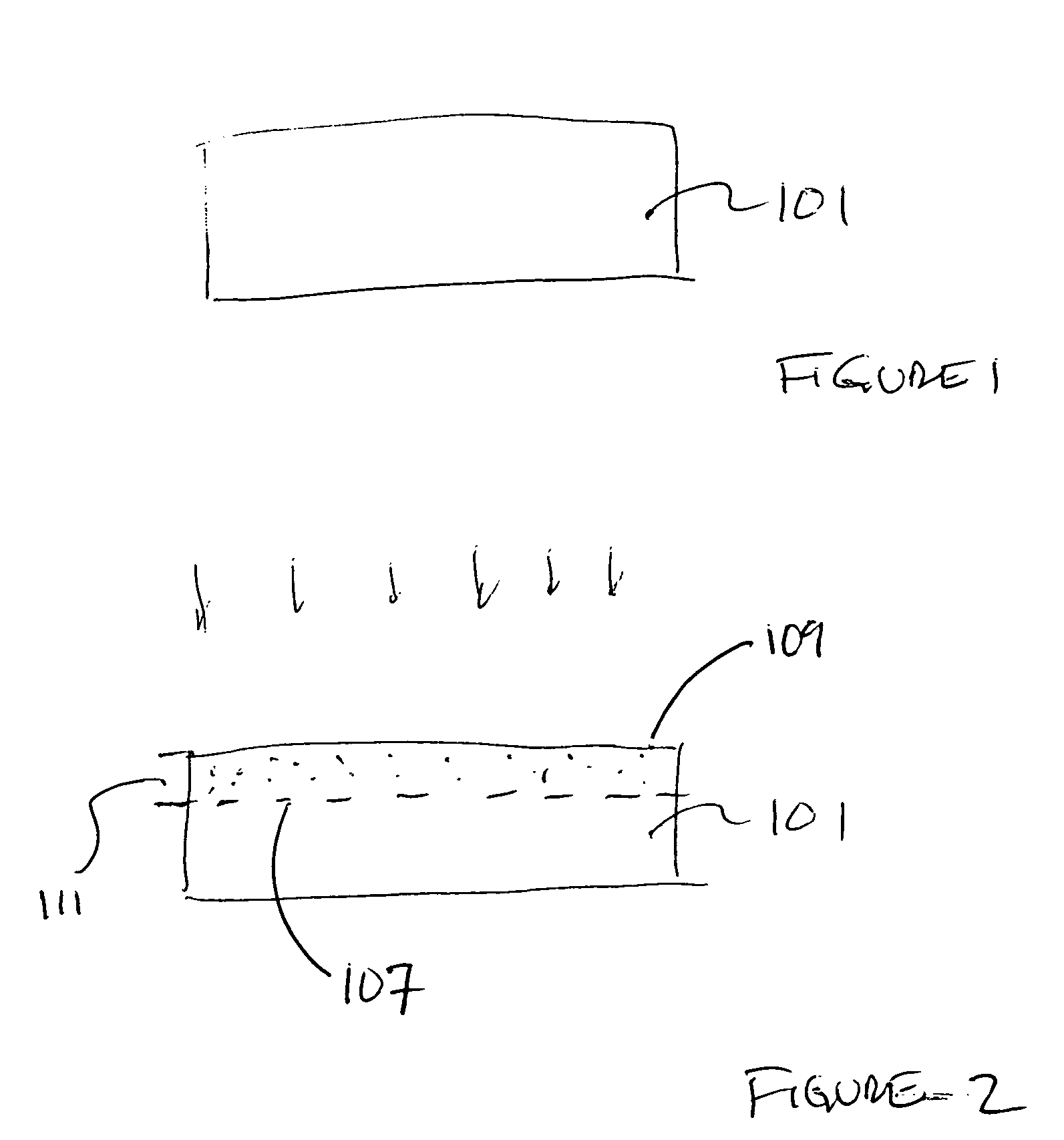
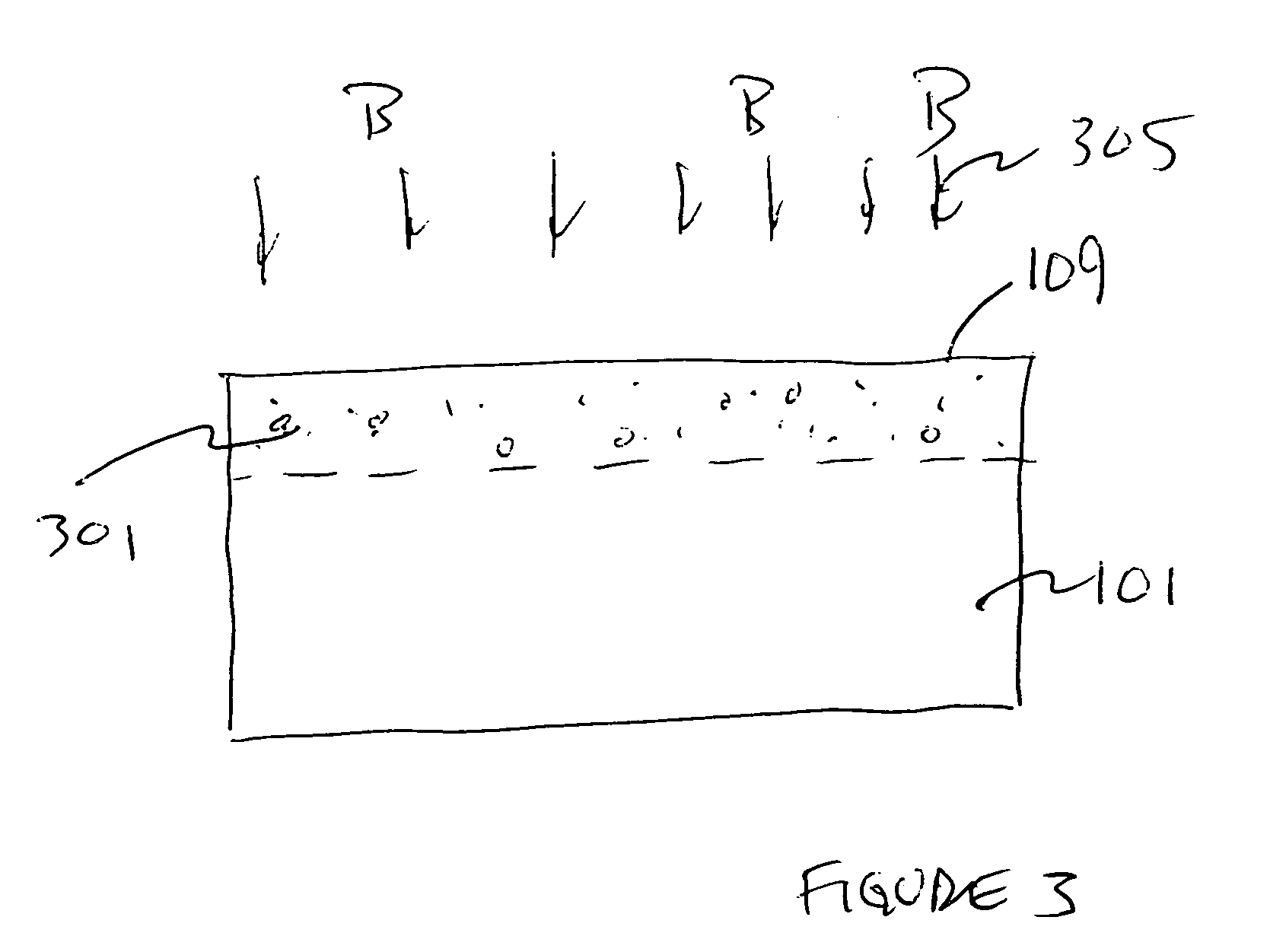
A lithography model uses a transfer function to map exposure energy dose to the thickness of remaining photoresist after development; while allowing the flexibility to account for other physical processes. In one approach, the model is generated by fitting empirical data. The model may be used in conjunction with an aerial image to obtain a three-dimensional profile of the remaining photoresist thickness after the development process. The lithography model is generally compact, yet capable of taking into account various physical processes associated with the photoresist exposure and / or development process for more accurate simulation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Multiple Aperture Hand-Held Laser Therapy Apparatus
ActiveUS20130317571A1Easy to changeIncrease the areaLaser detailsControlling energy of instrumentHigh energyHand held
A hand-held therapeutic laser apparatus with a special opto-mechanical construction, which enables changeability of a front collimating lens to create different effective laser apertures. A smaller effective aperture has a comparatively higher radiant flux density for treatment of a small area that requires a higher energy dose, while a larger effective aperture facilitates treatment of a large area at a relatively reduced radiant intensity.
Owner:MEDICAL COHERENCE
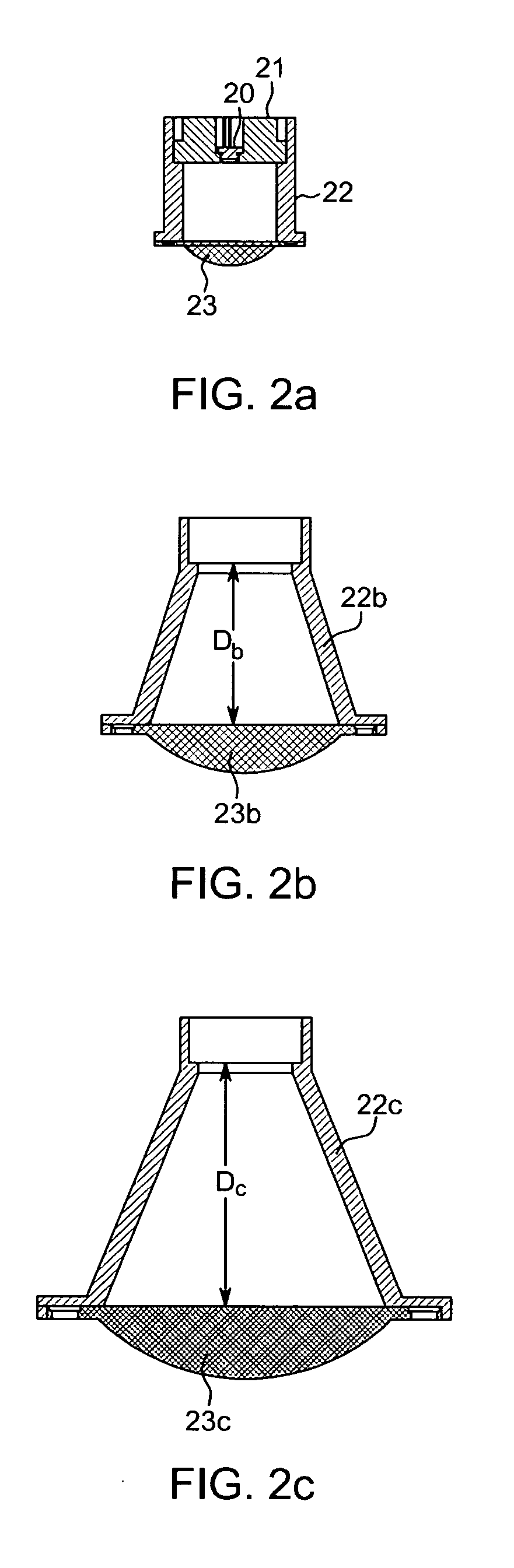
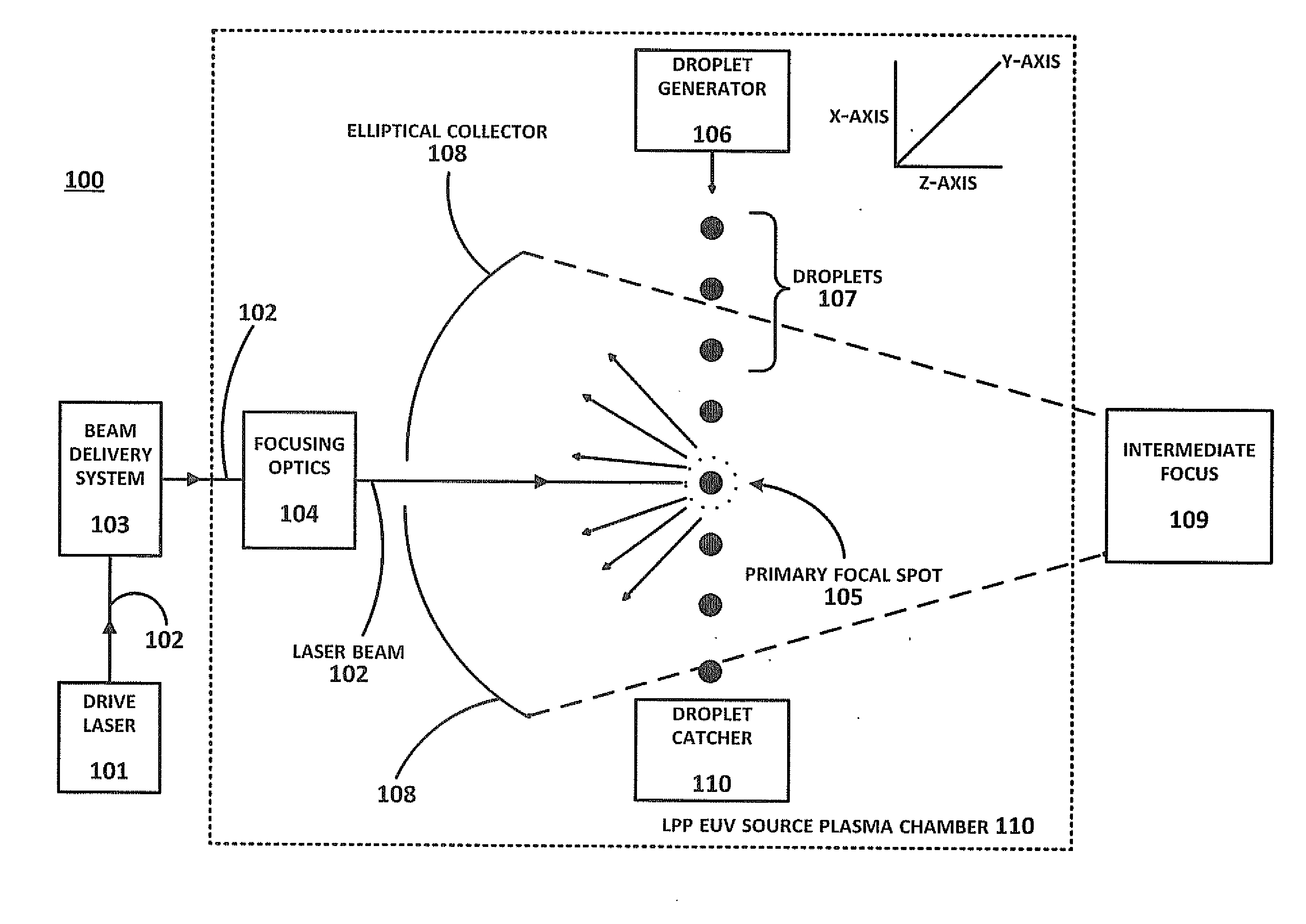
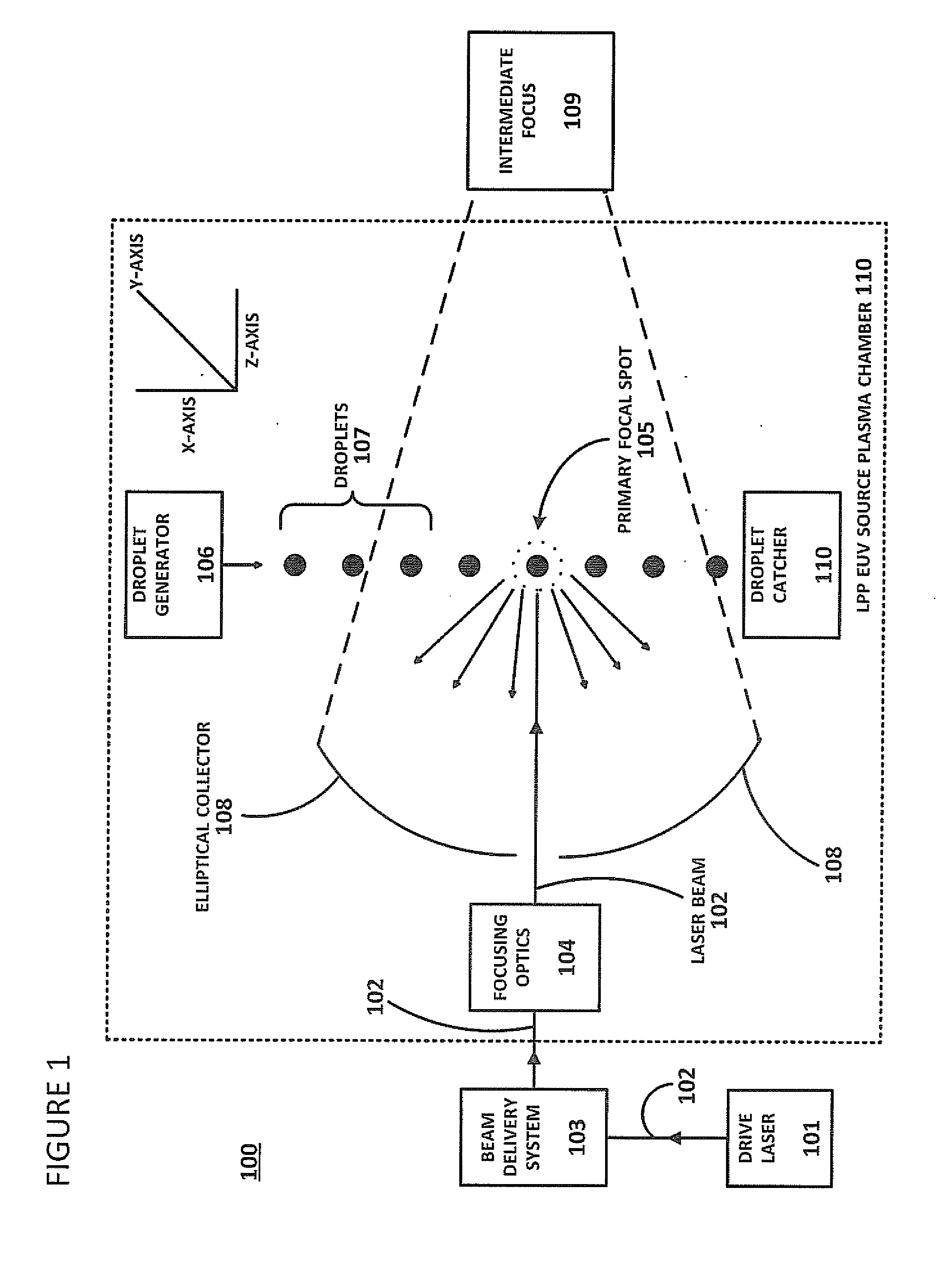
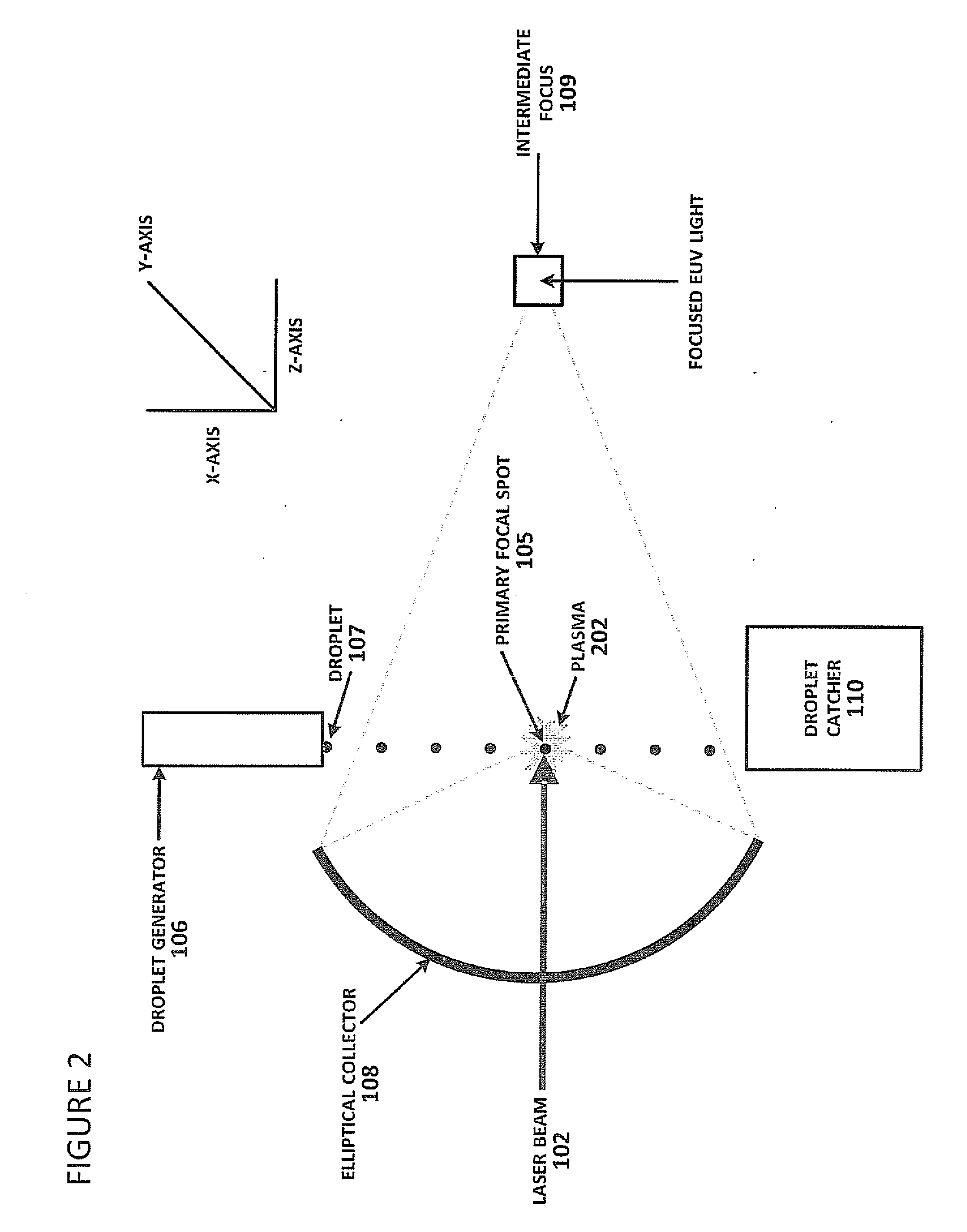
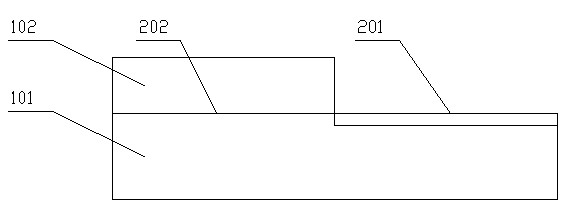
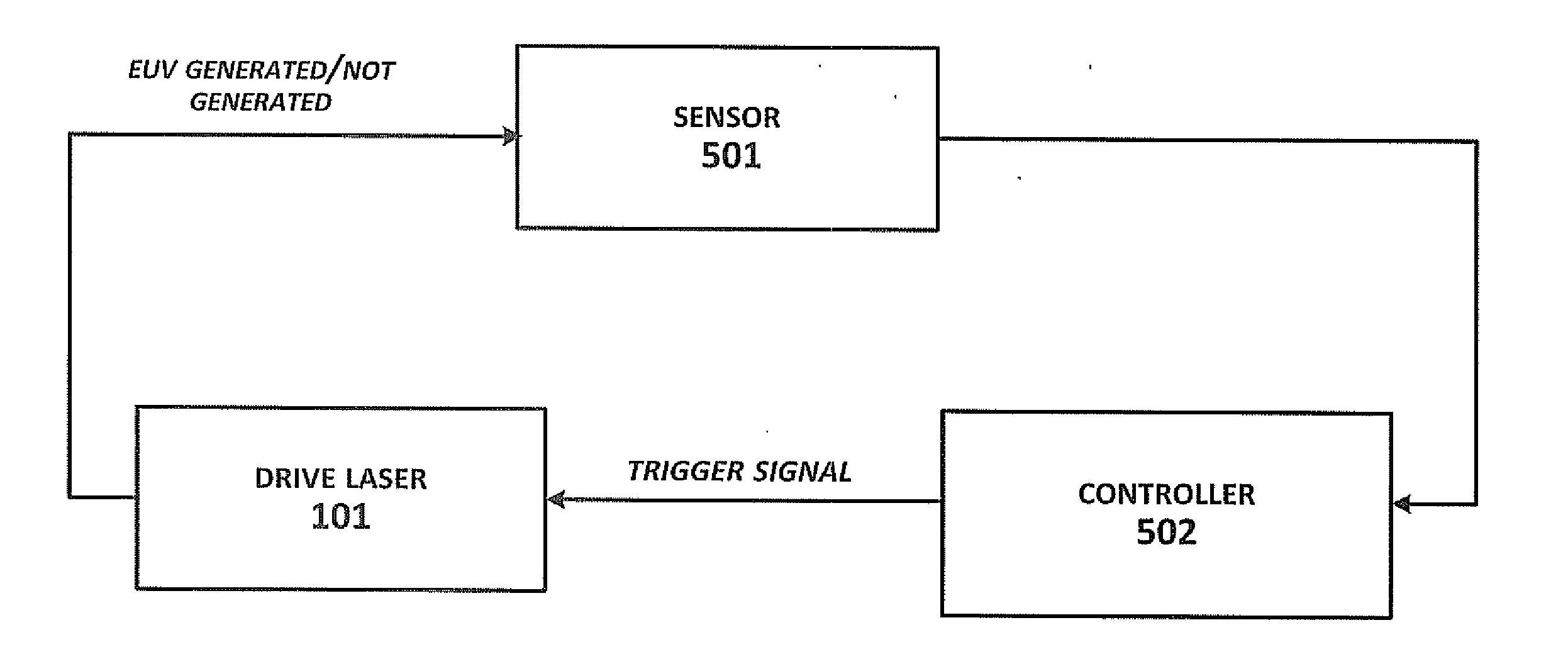
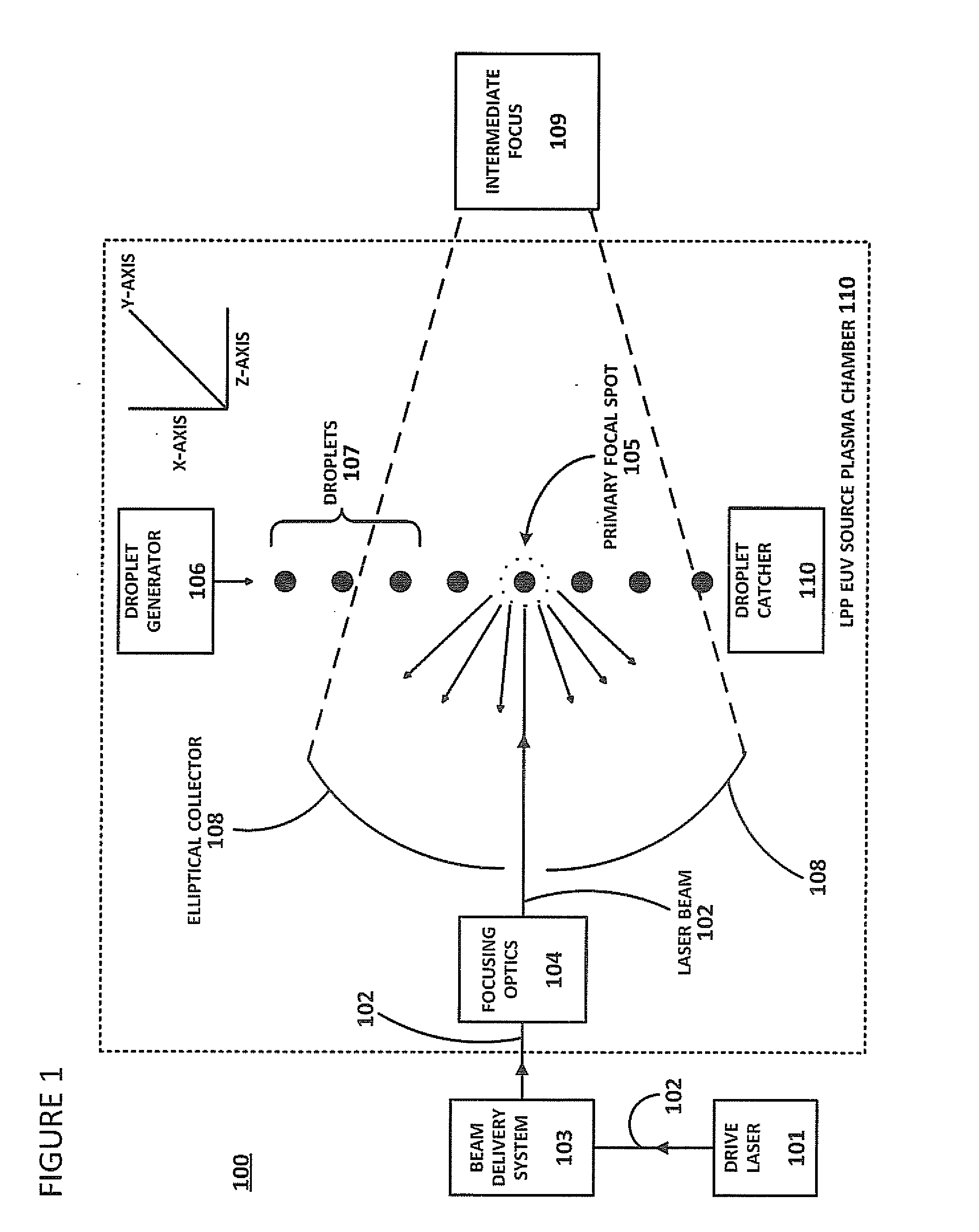
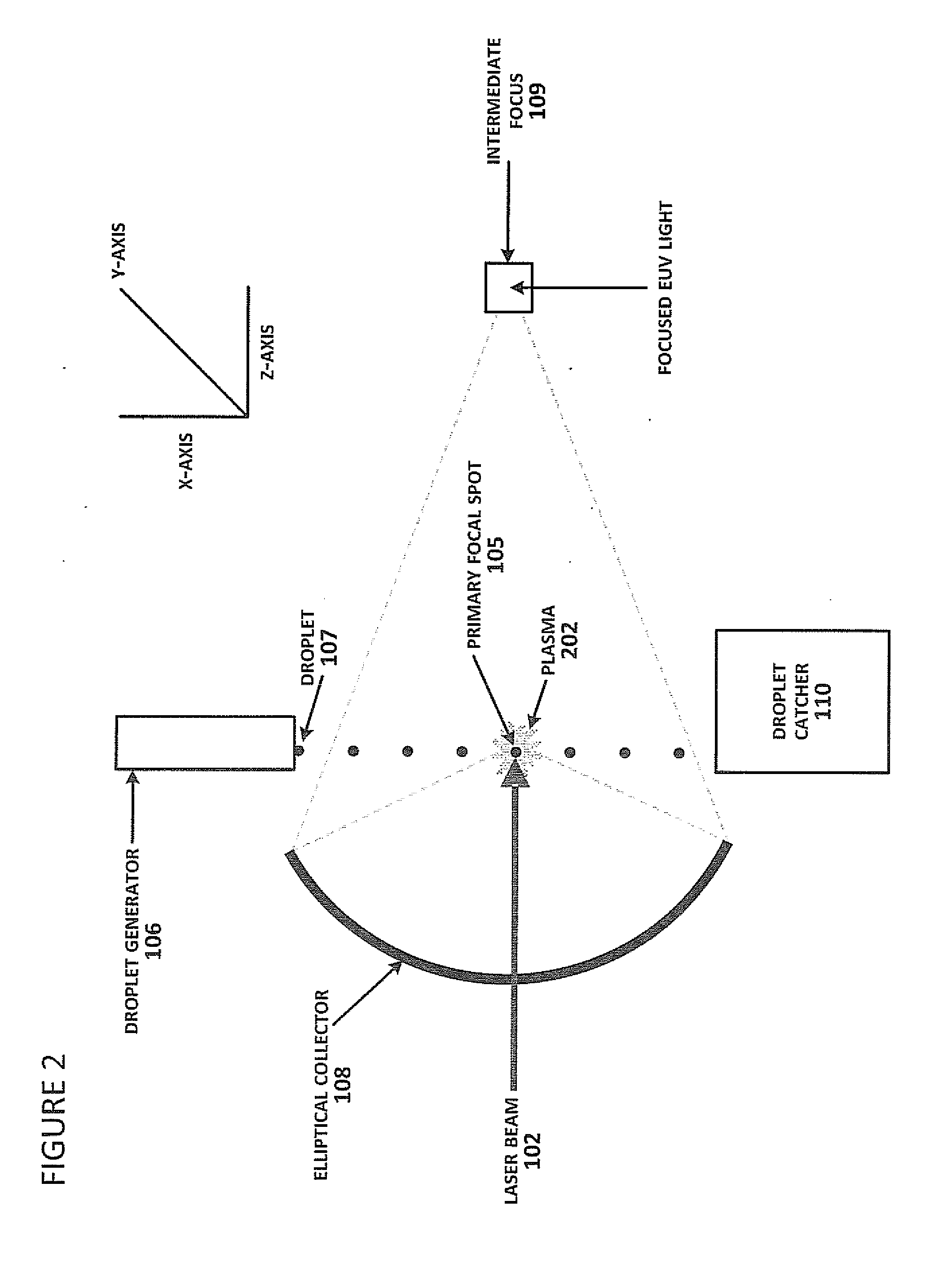
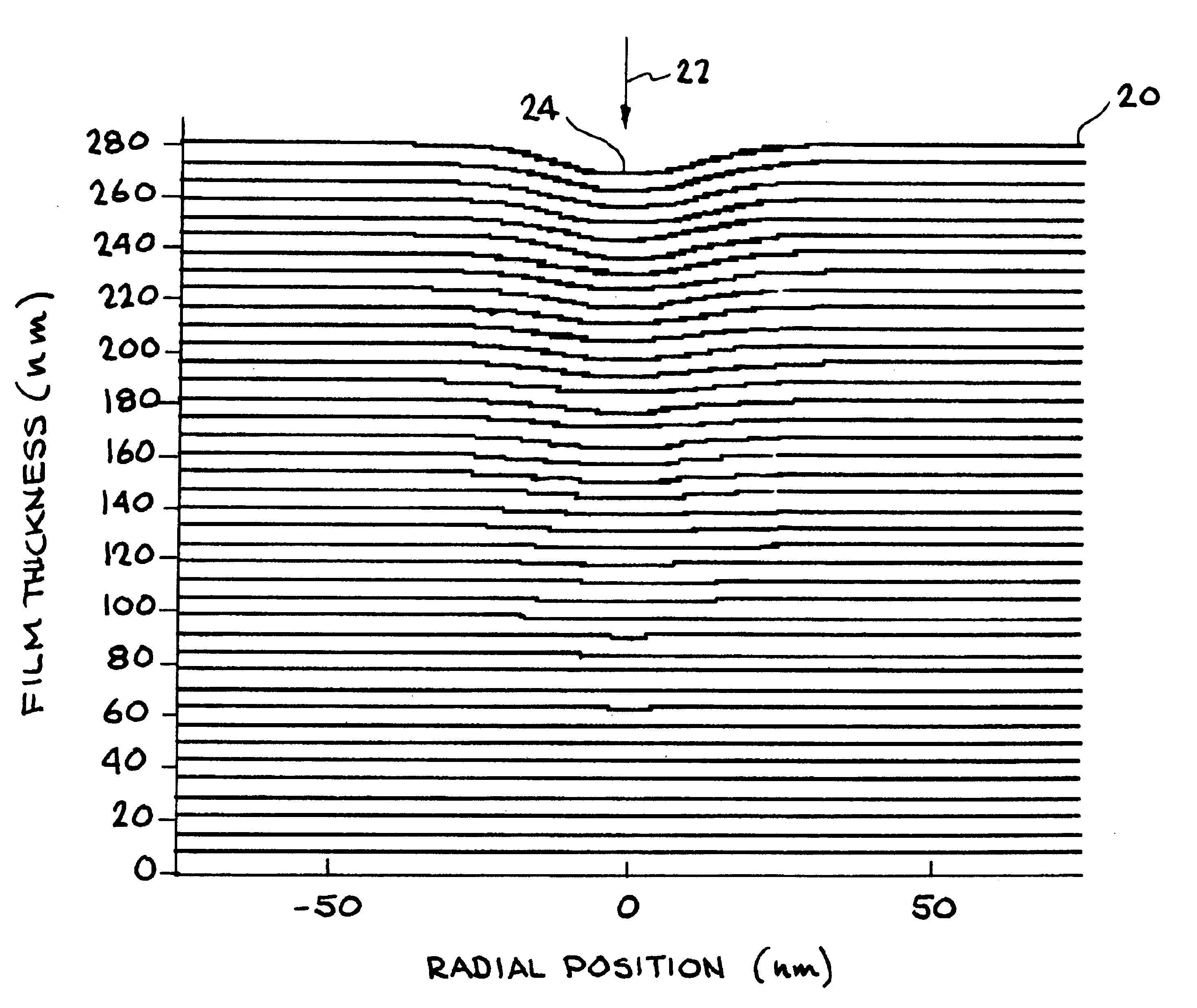
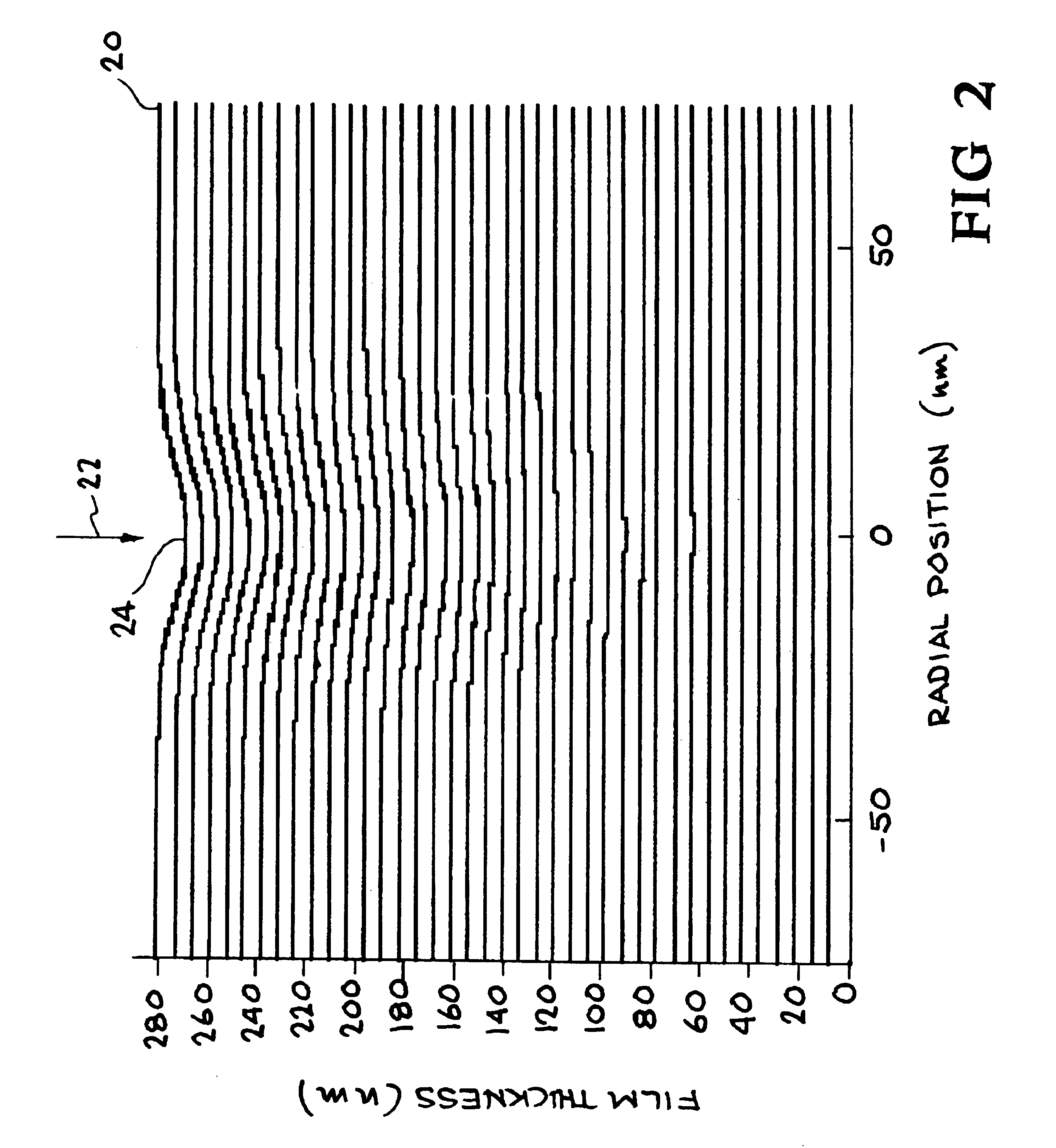
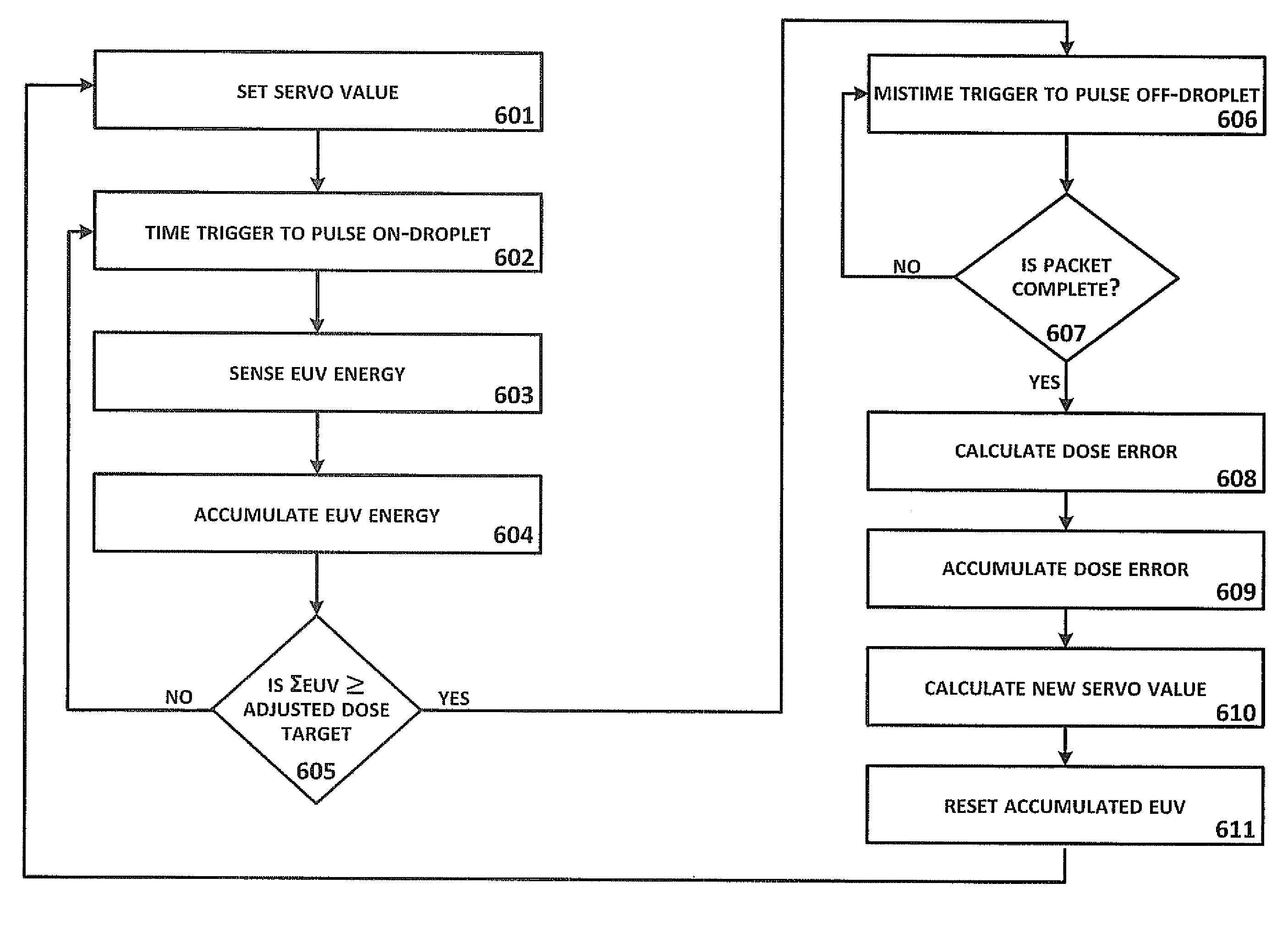
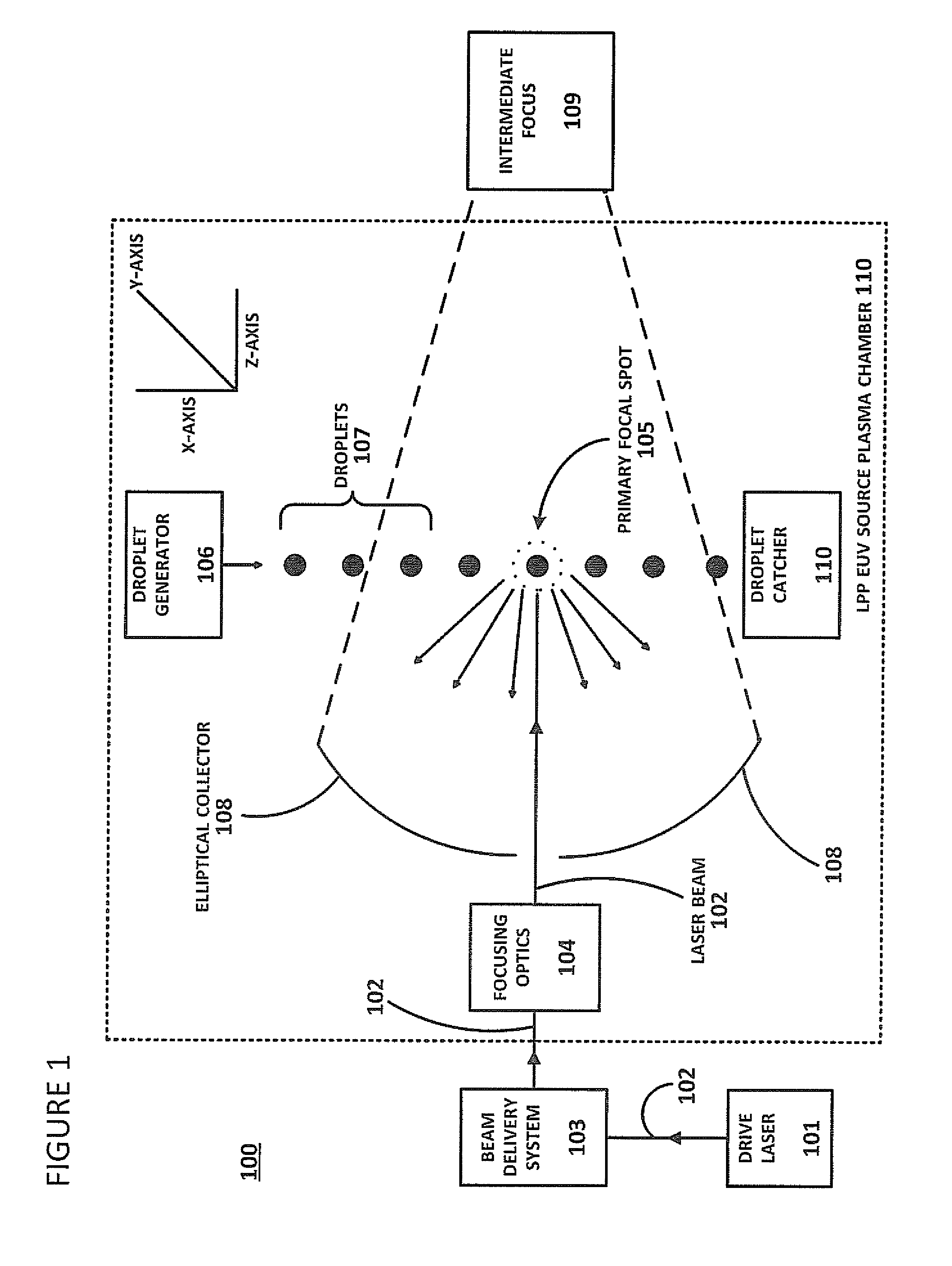
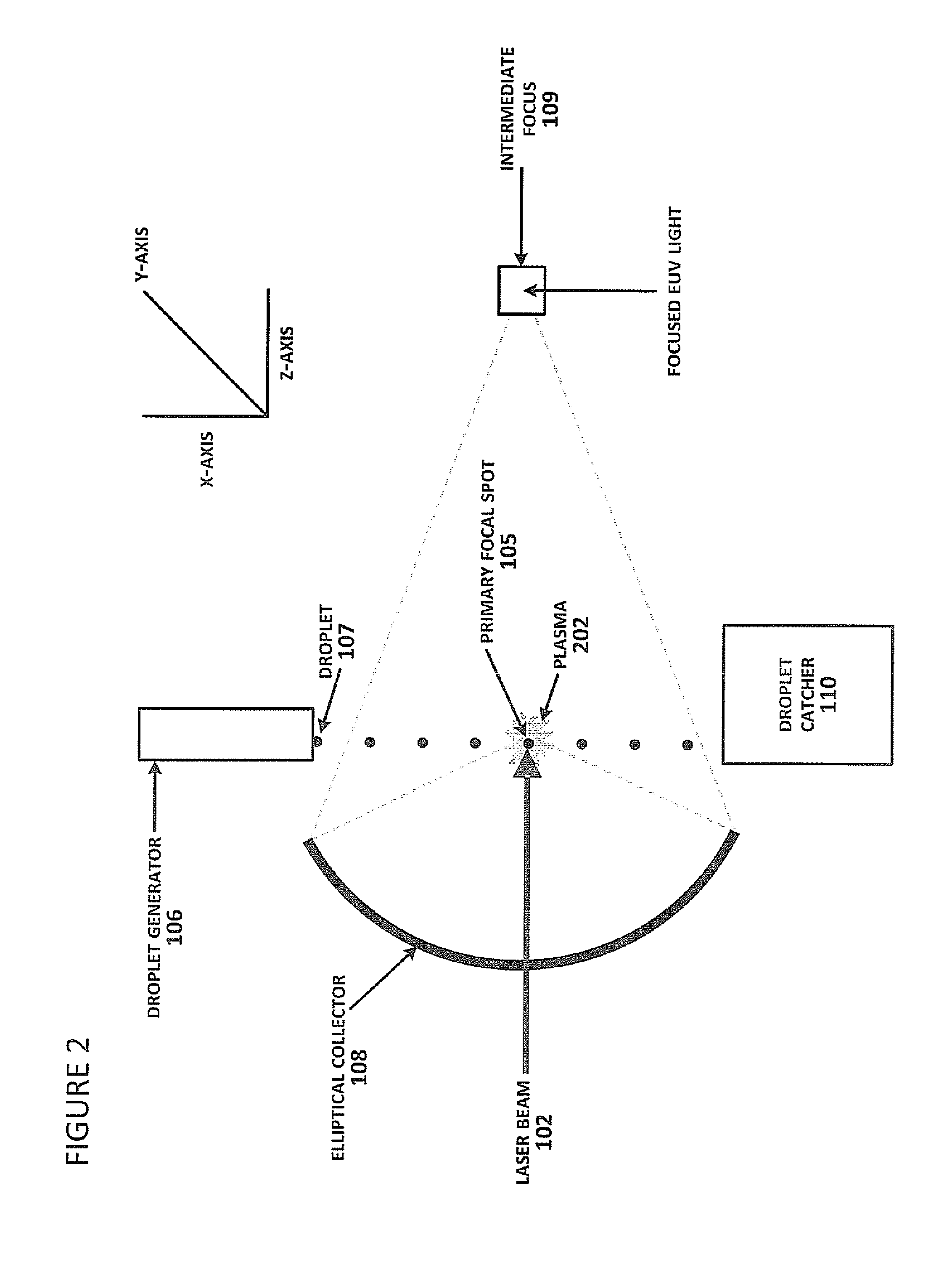
Method of Timing Laser Beam Pulses to Regulate Extreme Ultraviolet Light Dosing
ActiveUS20140191132A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsOptoelectronicsLighting system
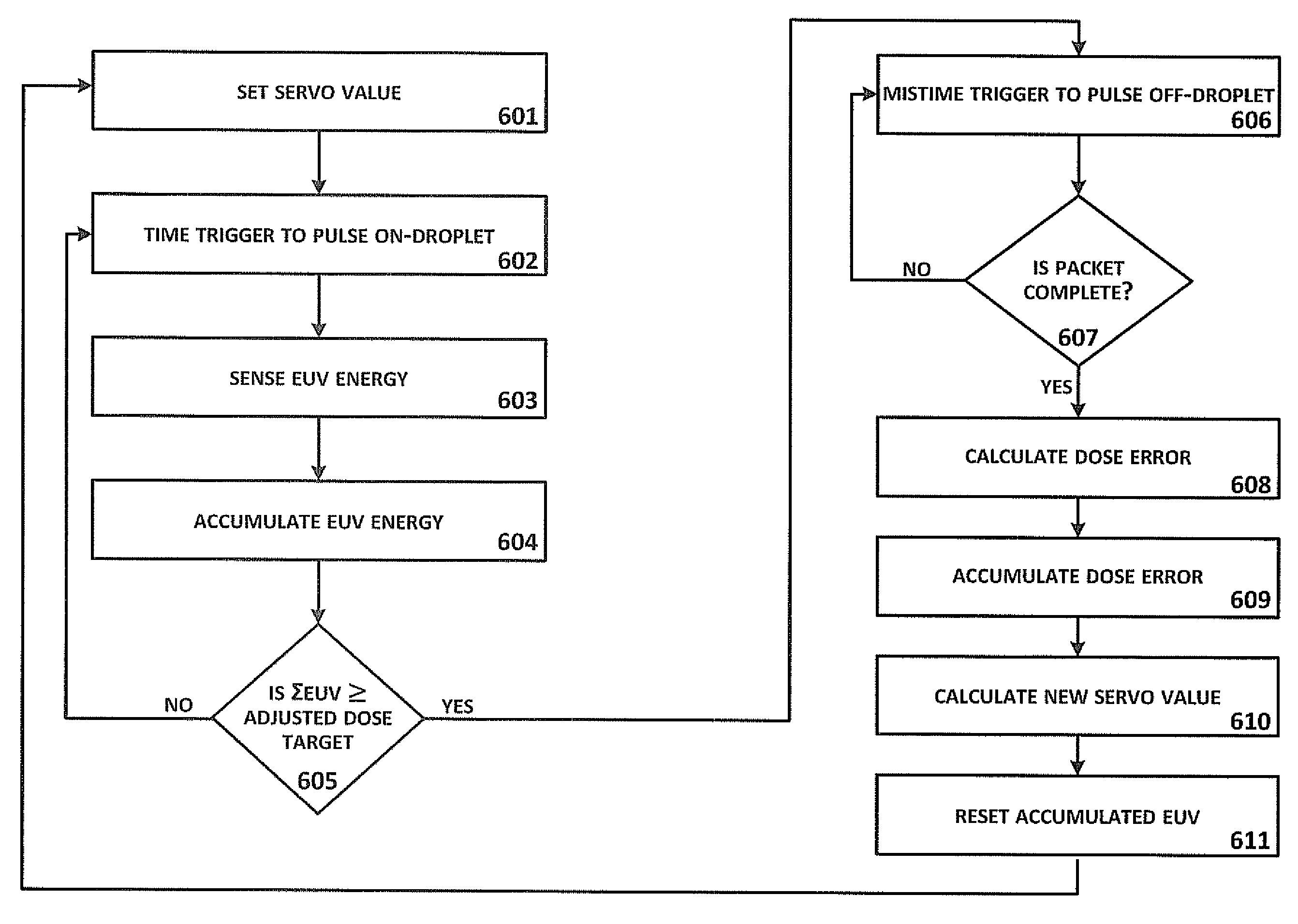
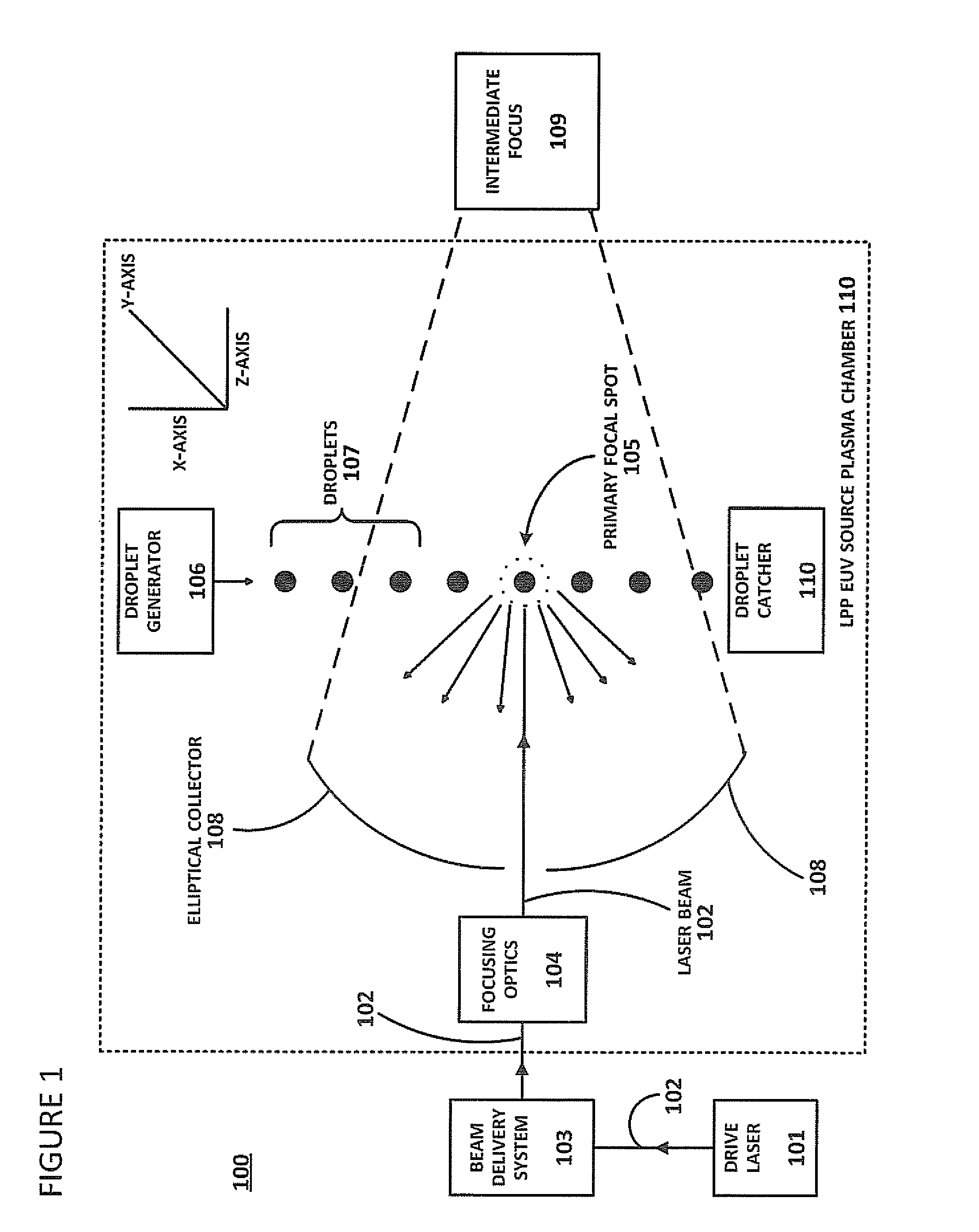
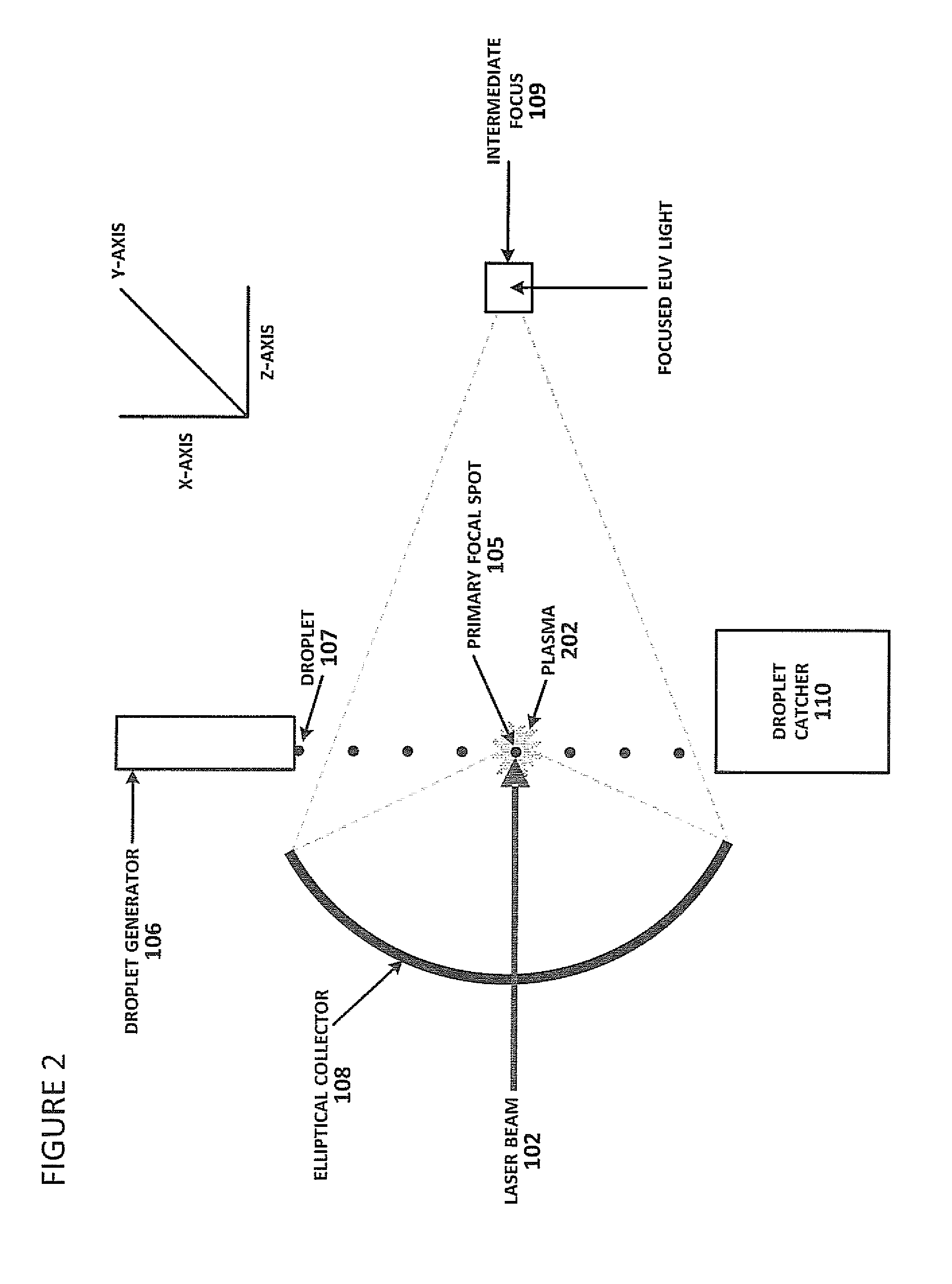
Described herein are embodiments of a method to control energy dose output from a laser-produced plasma extreme ultraviolet light system by adjusting timing of fired laser beam pulses. During stroboscopic firing, pulses are timed to lase droplets until a dose target of EUV has been achieved. Once accumulated EUV reaches the dose target, pulses are timed so as to not lase droplets during the remainder of the packet, and thereby prevent additional EUV light generation during those portions of the packet. In a continuous burst mode, pulses are timed to irradiate droplets until accumulated burst error meets or exceeds a threshold burst error. If accumulated burst error meets or exceeds the threshold burst error, a next pulse is timed to not irradiate a next droplet. Thus, the embodiments described herein manipulate pulse timing to obtain a constant desired dose target that can more precisely match downstream dosing requirements.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
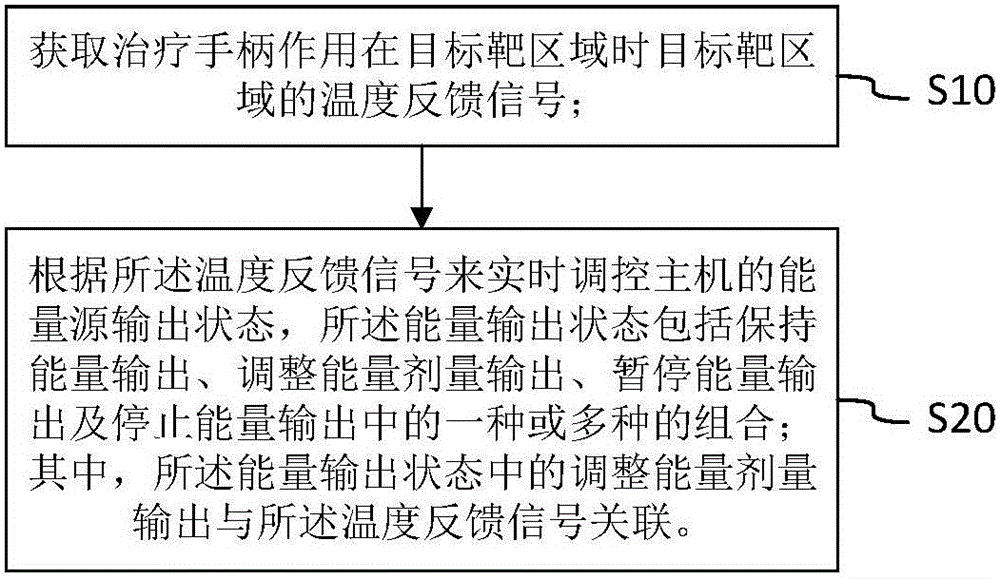
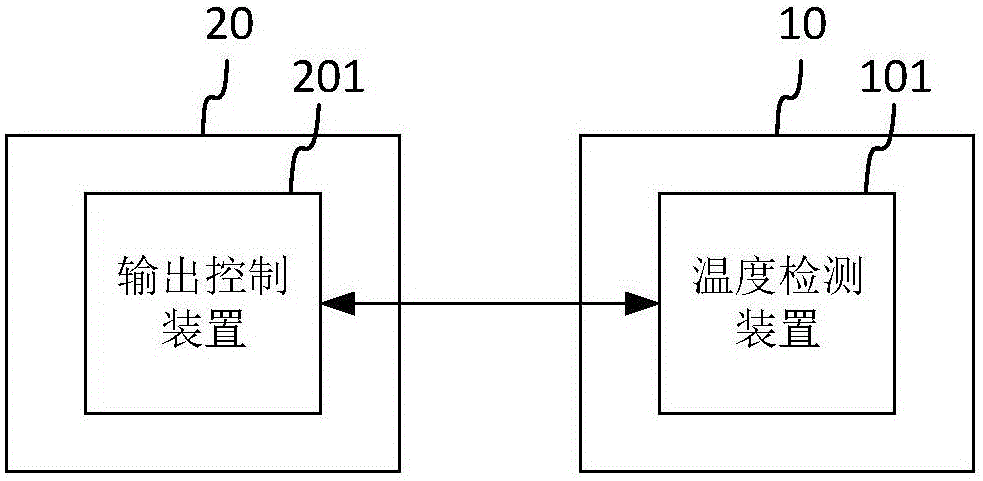
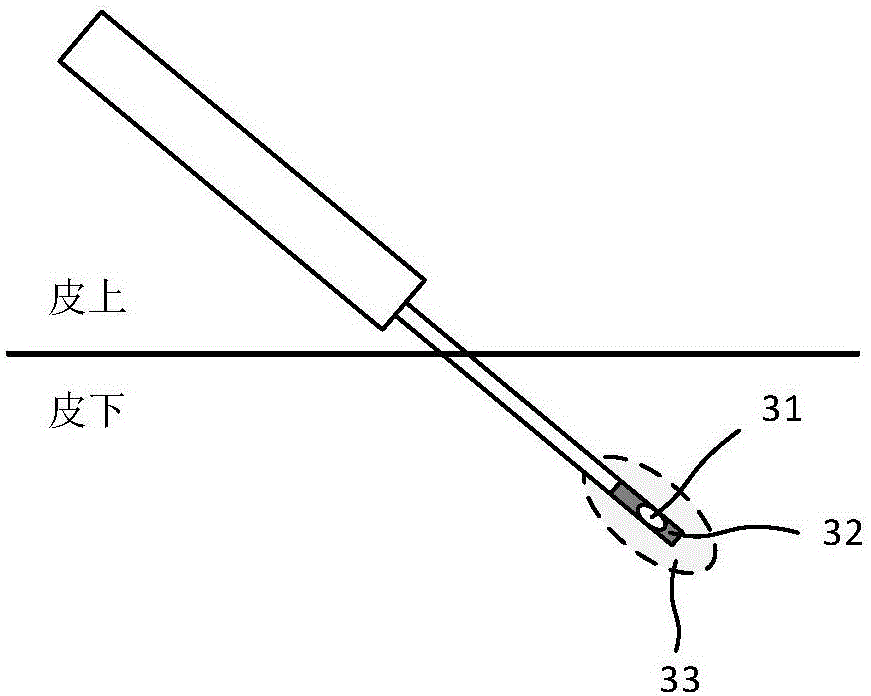
Host, therapeutic handle, control method and system for radio frequency energy output
InactiveCN105079956AReduce the difficulty of operationImprove securityElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyControl systemEngineering
The invention provides a host, a therapeutic handle, a control method and a control system for radio frequency energy output. The energy output state of the host is adjusted by acquiring a temperature feedback signal of a target area in real time at the therapeutic handle, wherein the energy output state includes one or more of keeping energy output, adjusting energy dose output, suspending energy output and stopping energy output; and the energy dose output adjustment in the energy output state is associated with the temperature feedback signal. By adopting the temperature as the dose adjusting standard, the operation difficulty of doctors is greatly reduced, and the safety and the effectiveness are improved.
Owner:CHONGQING DEMA PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Method for controlling thickness of oxidation film through ion injection process
InactiveCN102420130ASTI edge dimples do not appearSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingState of artGate oxide
The invention discloses a method for controlling the thickness of an oxidation film through an ion injection process. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the problem that the performance of a device is influenced by an STI (Shallow Trench Isolation) edge divot due to a process method of growing thick oxide, removing a region of a second kind of thickness gate oxide by adopting a wet method and growing a second kind of gate oxide is solved. The invention provides a special process method for controlling the thickness of a thermal oxidation film; the decrystallized thickness of a thick gate oxide zone on the surface of a silicon chip is controlled by injecting different energy doses; and furnace tube oxidation is subsequently carried out to grow oxidation films with various thicknesses. Since no wet-method process is used in the implementation process of the process, the STI edge divot is avoided; in addition, the oxidation films with various thicknesses can be simultaneously integrated.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Method of Timing Laser Beam Pulses to Regulate Extreme Ultraviolet Light Dosing
ActiveUS20140191133A1Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsOptoelectronicsLighting system
Described herein are embodiments of a method to control energy dose output from a laser-produced plasma extreme ultraviolet light system by adjusting timing of fired laser beam pulses. During stroboscopic firing, pulses are timed to lase droplets until a dose target of EUV has been achieved. Once accumulated EUV reaches the dose target, pulses are timed so as to not lase droplets during the remainder of the packet, and thereby prevent additional EUV light generation during those portions of the packet. In a continuous burst mode, pulses are timed to irradiate droplets until accumulated burst error meets or exceeds a threshold burst error. If accumulated burst error meets or exceeds the threshold burst error, a next pulse is timed to not irradiate a next droplet. Thus, the embodiments described herein manipulate pulse timing to obtain a constant desired dose target that can more precisely match downstream dosing requirements.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Method for analyzing masks for photolithography
ActiveCN102007454ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusData simulationSpatial image
The invention relates to a method for analyzing masks for photolithography. In this method, an aerial image of the mask for a first focus setting is generated and stored in an aerial image data record. The aerial image data record is transferred to an algorithm that simulates a photolithographic wafer exposure on the basis of this data record. In this case, the simulation is carried out for a plurality of mutually different energy doses. Then, at a predetermined height from the wafer surface, contours which separate regions with photoresist from those regions without photoresist are in each case determined. The result, that is to say the contours, are stored for each of the energy doses in each case in a contour data record with the energy dose as a parameter. Finally, the contour data records are combined to form a three-dimensional multicontour data record with the reciprocal of the energy dose as a third dimension, and, on the basis of the transitions from zero to values different than zero in the contours, a three-dimensional profile of the reciprocal of the energy dose depending on the position on the mask is generated. This profile, the so-called effective aerial image, is output or stored or automatically evaluated. The same can also occur with sections through said profile.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Power generating and control apparatus for the treatment of tissue
ActiveUS9277955B2Calculate system impedanceExact impedanceUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyElectrode ContactBalloon catheter
Apparatus, systems, and methods are provided for the generation and control of energy delivery in a dosage to elicit a therapeutic response in diseased tissue. A balloon catheter can have electrodes attached to a power generator and controller such that the balloon and electrodes contact tissue during energy treatment. Energy selectively may be applied to tissue based on measured impedance to achieve gentle heating. Calibration of the apparatus and identification of attached accessories by computing the circuit impedance prior to energy dosage facilitate regulation of power delivery about a set point. Energy delivery can be controlled to achieve substantially uniform bulk tissue temperature distribution. Energy delivery may beneficially affect nerve activity.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for treating breast lesions using microwaves
InactiveCN1380833AAvoid damageAvoid the risk of proliferationSurgical instrument detailsMicrowave therapyMedicineMicrowave power
A method for selectively heating cancerous conditions of the breast including invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive glandular lobular carcinoma, and pre-cancerous conditions of the breast including ductal carcinoma in-situ, lobular carcinoma in-situ, and intraductal hyperplasia, as well as benign lesions (any localized pathological change in the breast tissue) such as fibroadenomas and cysts by irradiation of the breast tissue with adaptive phased array focused microwave energy is introduced. Microwave energy provides preferential heating of high-water content breast tissues such as carcinomas, fibroadenomas, and cysts compared to the surrounding lower-water content normal breast tissues. To focus the microwave energy in the breast, the patient's breast can be compressed and a single electric-field probe, inserted in the central portion of the breast, or two noninvasive electric-field probes on opposite sides of the breast skin, can be used to measure a feedback signal to adjust the microwave phase delivered to waveguide applicators on opposite sides of the compressed breast tissue. The initial microwave power delivered to the microwave applicators is set to a desired value that is known to produce a desired increase in temperature in breast tumors. Temperature feedback sensors are used to measure skin temperatures during treatment to adjust the microwave power delivered to the waveguide applicators to avoid overheating the skin. The microwave energy delivered to the waveguide applicators is monitored in real time during treatment, and the treatment is completed when a desired total microwave energy dose has been administered. By heating and destroying the breast lesion sufficiently, lesions can be reduced in size and surrounding normal breast tissues are spared so that surgical mastectomy can be replaced with surgical lumpectomy or the lesions can be completely destroyed so that surgical mastectomy or lumpectomy is avoided.
Owner:CELSION CANADA
Integrated circuit having improved electromigration performance and method of forming same
InactiveUS9679810B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMicrowaveDielectric layer
An aspect of the disclosure is directed to a method of forming an interconnect for use in an integrated circuit. The method comprises: forming an opening in a dielectric layer on a substrate; filling the opening with a metal such that an overburden outside of the opening is created; subjecting the metal to a microwave energy dose such that atoms from the overburden migrate to within the opening; and planarizing the metal to a top surface of the opening to remove the overburden, thereby forming the interconnect.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
EUV lithography reticles fabricated without the use of a patterned absorber
InactiveUS7049033B2Significant commercial potentialLow costElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsElectronEnergy dose
Absorber material used in conventional EUVL reticles is eliminated by introducing a direct modulation in the complex-valued reflectance of the multilayer. A spatially localized energy source such as a focused electron or ion beam directly writes a reticle pattern onto the reflective multilayer coating. Interdiffusion is activated within the film by an energy source that causes the multilayer period to contract in the exposed regions. The contraction is accurately determined by the energy dose. A controllable variation in the phase and amplitude of the reflected field in the reticle plane is produced by the spatial modulation of the multilayer period. This method for patterning an EUVL reticle has the advantages (1) avoiding the process steps associated with depositing and patterning an absorber layer and (2) providing control of the phase and amplitude of the reflected field with high spatial resolution.
Owner:EUV
Method of timing laser beam pulses to regulate extreme ultraviolet light dosing
ActiveUS8872122B2Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsLight doseLighting system
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Self-aligned alternating phase shift mask patterning process
InactiveUS20030228526A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAnti-reflective coatingPhase shifted
A method and apparatus for making phase shift masks are provided wherein an anti-reflective coating used on an opaque pattern layer of the mask fully covers the opaque pattern layer and has not been etched in the etching process to form the phase shift mask. A two-exposure method to form the phase shift mask is used wherein a photoresist having a defined dose-to-clear level is coated on the surface of the mask and the lower surface of the mask is exposed to a blanket exposure in an energy amount less than the dose-to-clear level. The open areas of the upper surface of the mask to be etched are exposed to an energy dose in an amount less than the dose-to-clear level, with the sum of the amounts of the lower surface energy and upper surface energy being at least the dose-to-clear level. The method and apparatus minimizes and / or avoids etching of the anti-reflective coating.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
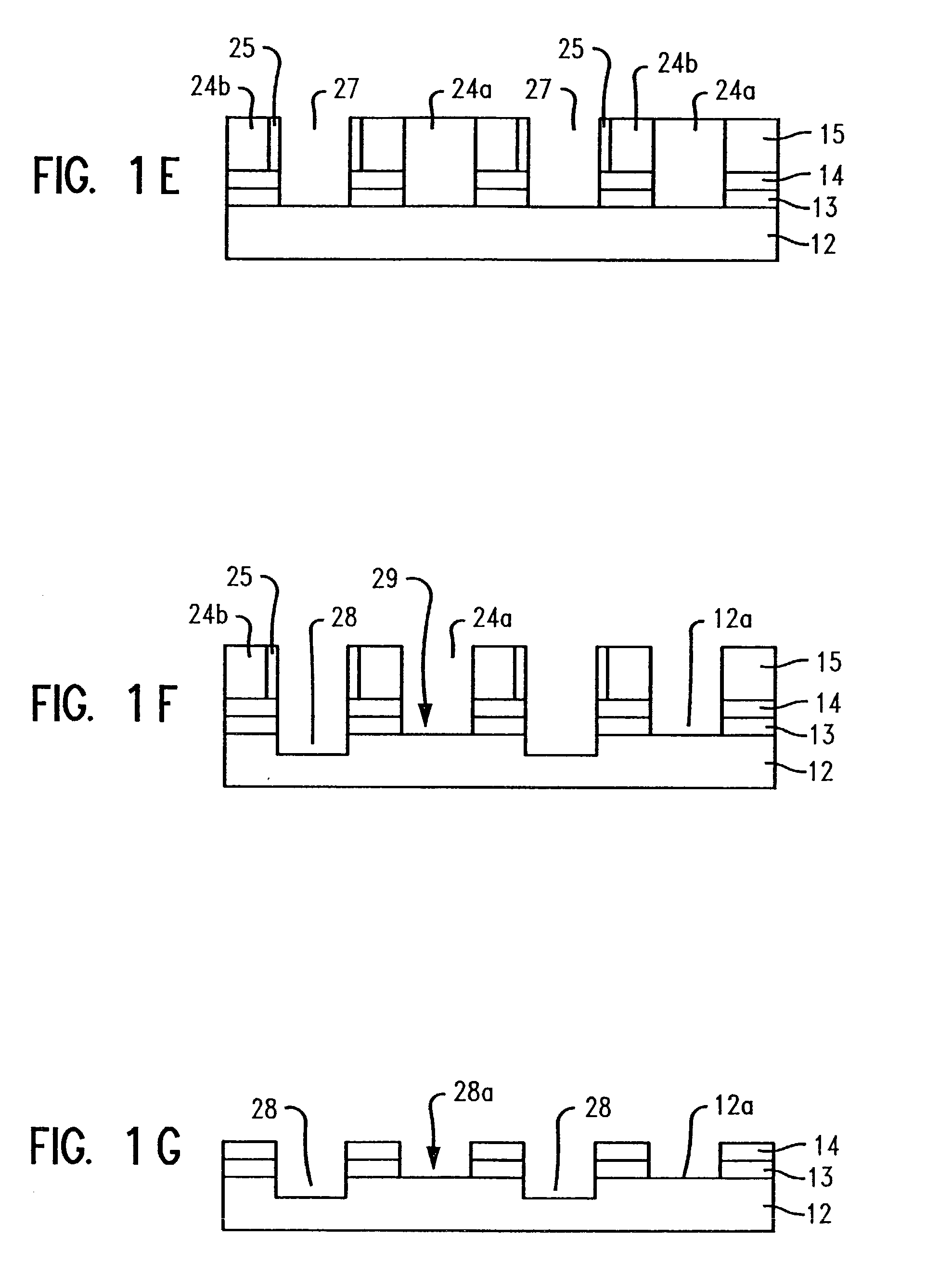
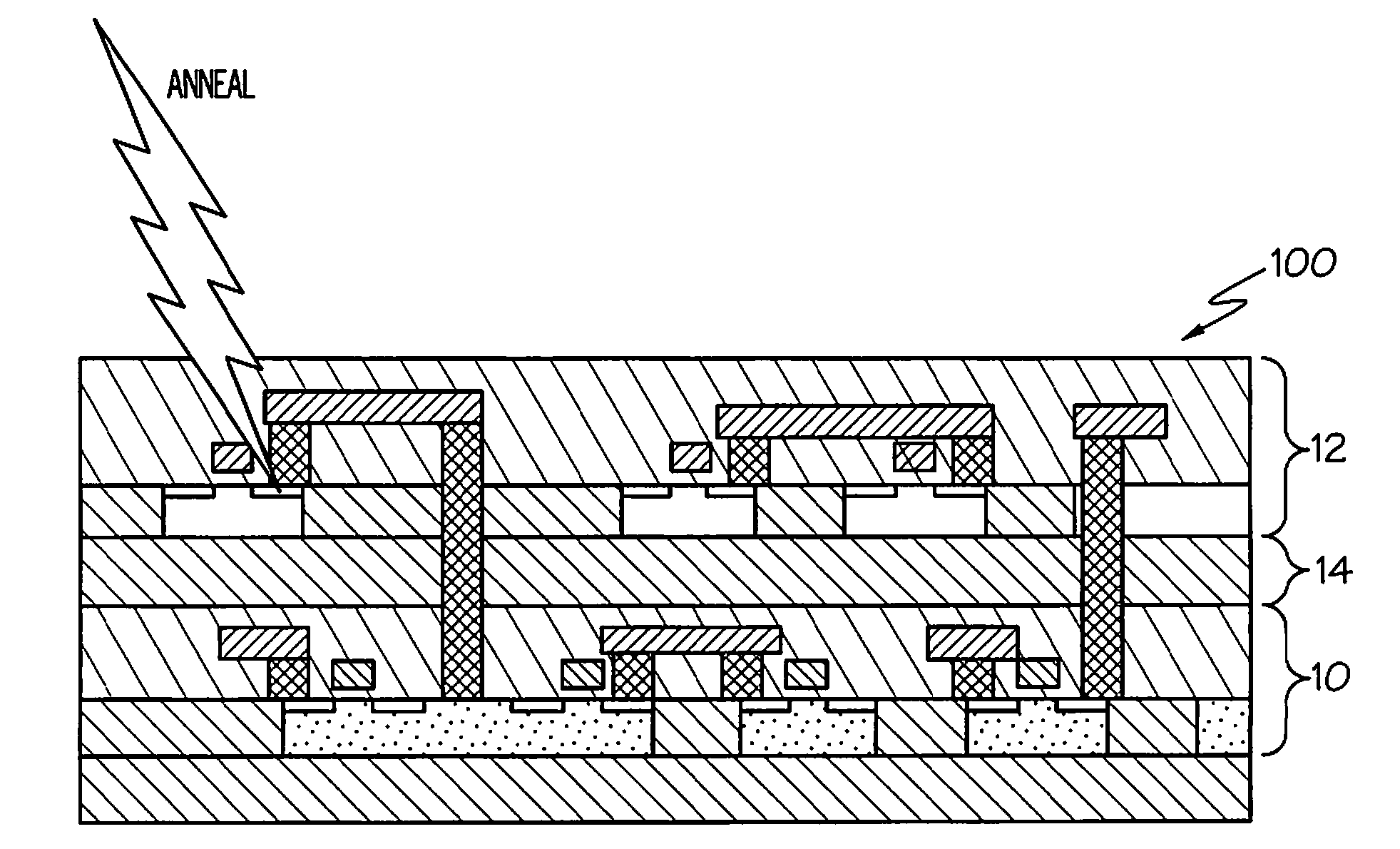
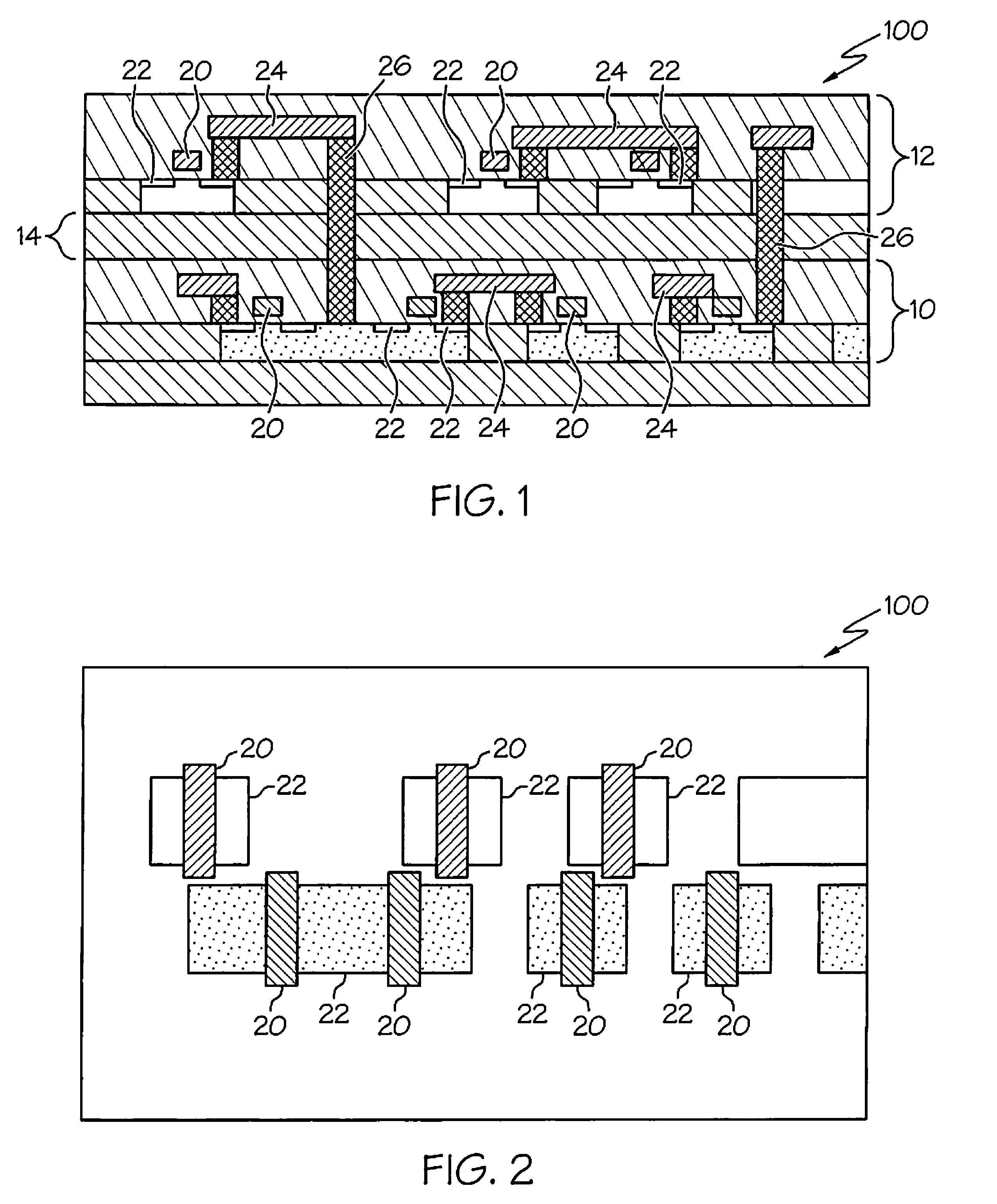
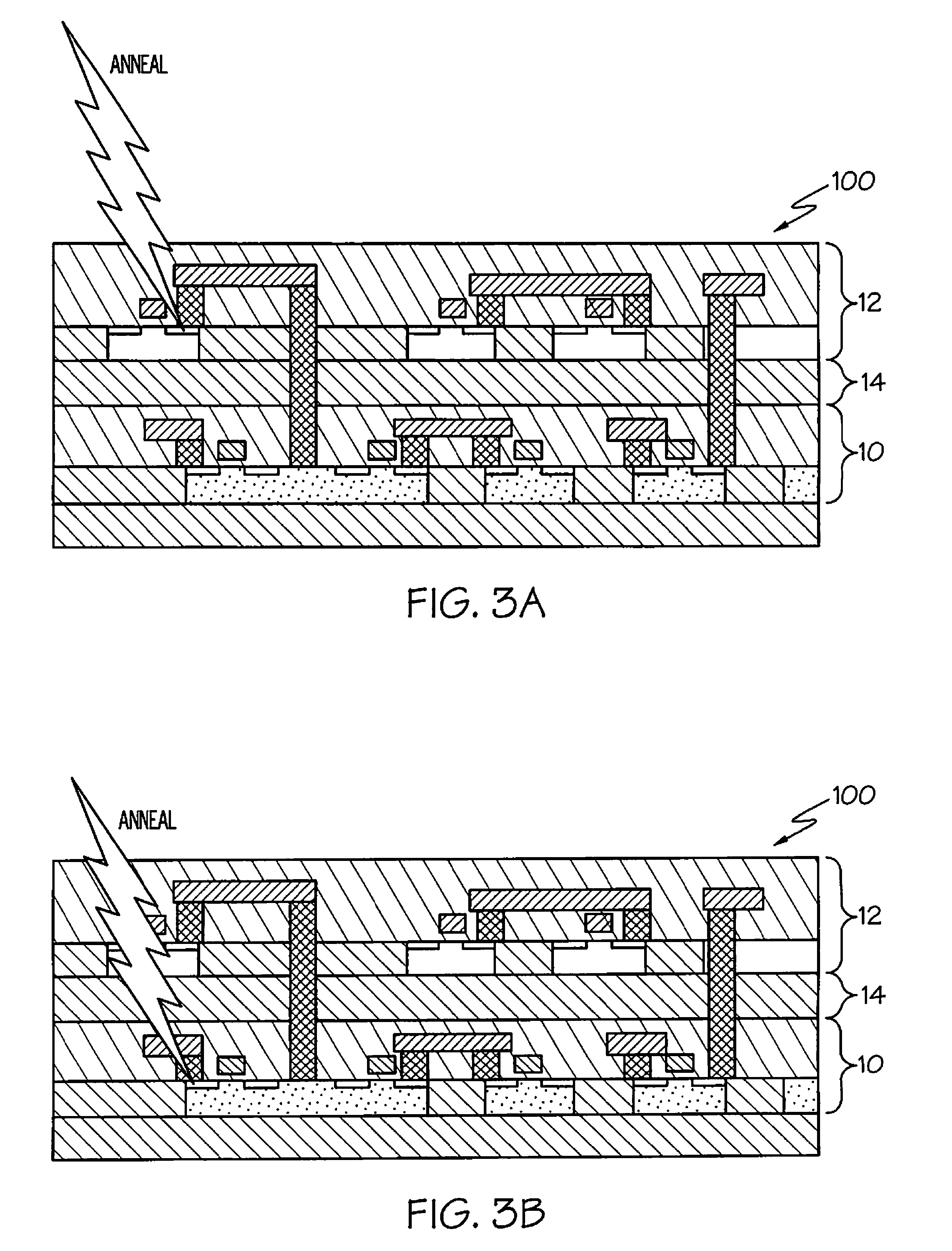
Laser annealing for 3-D chip integration
A laser annealing method for annealing a stacked semiconductor structure having at least two stacked layers is disclosed. A laser beam is focused on a lower layer of the stacked layers. The laser beam is then scanned to anneal features in the lower layer. The laser beam is then focused on an upper layer of the stacked layers, and the laser beam is scanned to anneal features in the upper layer. The laser has a wavelength of less than one micrometer. The beam size, depth of focus, energy dosage, and scan speed of the laser beam are programmable. Features in the lower layer are offset from features in the upper layer such that these features do not overlap along a plane parallel to a path of the laser beam. Each of the stacked layers includes active devices, such as transistors. Also, the first and second layers may be annealed simultaneously.
Owner:ULTRATECH INT INC
Low energy dose monitoring of implanter using implanted wafers
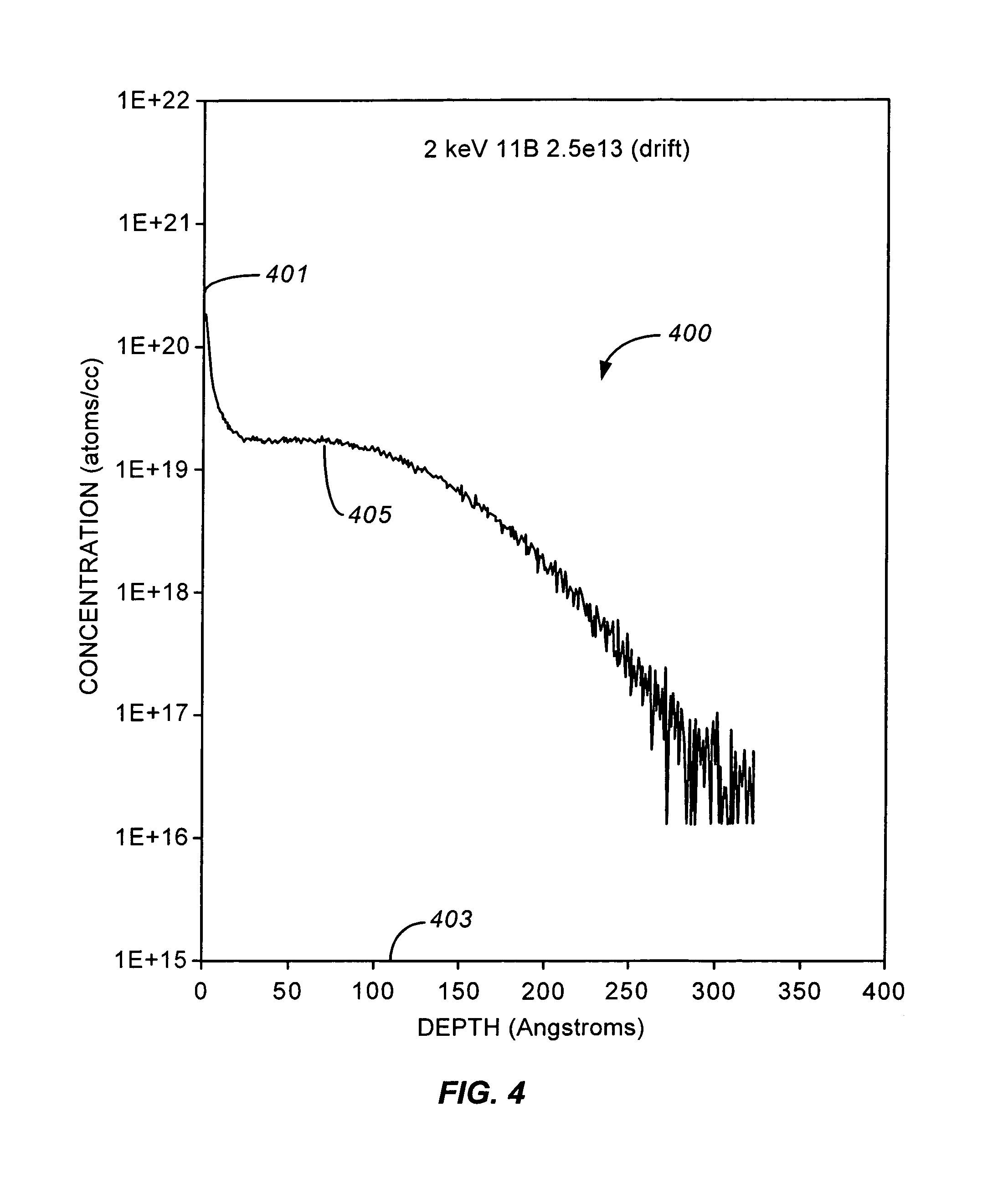
ActiveUS20050142671A1Easy to useHigh device yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesDopantCrystalline materials
A method for processing semiconductor wafers, e.g., silicon. The method includes providing a monitor wafer, which is made of a crystalline material. The method includes introducing a plurality of particles within a depth of the material, whereupon the plurality of particles cause the crystalline material to be in an amorphous state. The method also includes introducing a plurality of dopant particles into a selected depth of the crystalline material in the amorphous state using an implantation tool. The amorphous state traps the dopant particles. The method includes subjecting the monitor wafer including the plurality of particles and dopant particles into thermal anneal process to activate the dopant. The sheet resistivity is measured. The method operates the implantation tool using one or more production wafers if the dose of the dopant particles in the monitor water is within a tolerance of a specification limit.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Method for integrated circuit patterning
ActiveCN104916530AHas a first etch rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusResistRadiation sensitivity
Provided is a method of forming a pattern for an integrated circuit. The method includes forming a first layer over a substrate, wherein the first layer's etch rate is sensitive to a radiation, such as an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) radiation or an electron beam (e-beam). The method further includes forming a resist layer over the first layer and exposing the resist layer to the radiation for patterning. During the exposure, various portions of the first layer change their etch rate in response to an energy dose of the radiation received therein. The method further includes developing the resist layer, etching the first layer, and etching the substrate to form a pattern. The radiation-sensitivity of the first layer serves to reduce critical dimension variance of the pattern.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for uniformly metallization on substrate
ActiveCN105190859AElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltimate tensile strengthPower intensity
The present invention relates to applying at least one ultra / mega sonic device and its reflection plate for forming standing wave in a metallization apparatus to achieve highly uniform metallic film deposition at a rate far greater than conventional film growth rate in electrolyte. In the present invention, the substrate is dynamically controlled so that the position of the substrate passing through the entire acoustic field with different power intensity in each motion cycle. This method guarantees each location of the substrate to receive the same amount of total sonic energy dose over the interval of the process time, and to accumulatively grow a uniform deposition thickness at a rapid rate.
Owner:ACM RES SHANGHAI
Self-aligned alternating phase shift mask patterning process
InactiveUS6824932B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAnti-reflective coatingPhase shifted
A method and apparatus for making phase shift masks are provided wherein an anti-reflective coating used on an opaque pattern layer of the mask fully covers the opaque pattern layer and has not been etched in the etching process to form the phase shift mask. A two-exposure method to form the phase shift mask is used wherein a photoresist having a defined dose-to-clear level is coated on the surface of the mask and the lower surface of the mask is exposed to a blanket exposure in an energy amount less than the dose-to-clear level. The open areas of the upper surface of the mask to be etched are exposed to an energy dose in an amount less than the dose-to-clear level, with the sum of the amounts of the lower surface energy and upper surface energy being at least the dose-to-clear level. The method and apparatus minimizes and / or avoids etching of the anti-reflective coating.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Control of implant critical dimensions using an sti step height based dose offset
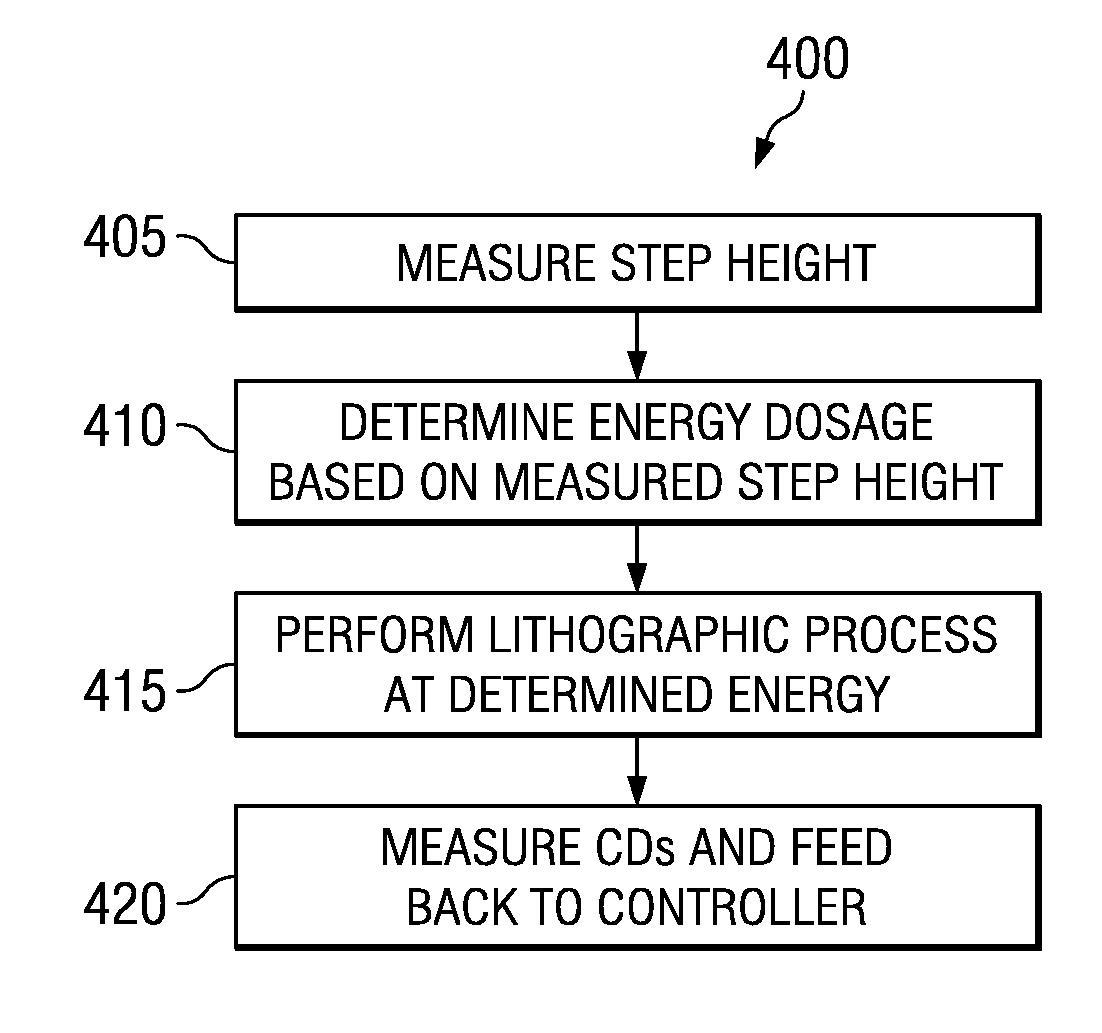
ActiveUS20090170222A1Improved control of overall CDImproving ion implant critical dimensionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringStep height
A method for semiconductor processing is provided, wherein a semiconductor wafer having undergone polishing is provided. The semiconductor wafer has an active region positioned between one or more moat regions, wherein the one or more moat regions have an oxide disposed therein. A top surface of the active region is recessed from a top surface of the moat region, therein defining a step having a step height associated therewith. A step height is measured, and a photoresist is formed over the semiconductor wafer. A modeled step height is further determined, wherein the modeled step height is based on the measured step height and a desired critical dimension of the photoresist. A dosage of energy is determined for patterning the photoresist, wherein the determination of the dosage of energy is based, at least in part, on the modeled step height. The photoresist is then patterned using the determined dosage of energy.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Methods and systems for controlled thermal tissue
InactiveUS20100217250A1High power transmissionFine surfaceSurgical instruments for heatingFixed energyScar tissue
A body passage having an interior wall with a lining is occluded by introducing a thermal delivery catheter to the passage. The thermal delivery catheter has a thermal transfer region which can deliver both a coagulative tissue necrosis energy dosage and a thermally fixing energy dosage. The coagulative necrosis dosage will result in scar tissue formation, while the thermally fixing tissue dosage will prevent regrowth of the tissue lining from neighboring untreated tissue regions which could compromise the integrity of the occlusion which is formed.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Image reconstruction incorporating organ motion
InactiveUS8824756B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioPromote lowerUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsReconstruction from projectionImaging modalitiesSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
Systems and methods which implement an image reconstruction framework to incorporate complex motion of structure, such as complex deformation of an object or objects being imaged, in image reconstruction techniques are shown. For example, techniques are provided for tracking organ motion which uses raw time-stamped data provided by any of a number of imaging modalities and simultaneously reconstructs images and estimates deformations in anatomy. Operation according to embodiments reduces artifacts, increase the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and facilitates reduced image modality energy dosing to patients. The technology also facilitates the incorporation of physical properties of organ motion, such as the conservation of local tissue volume. This approach is accurate and robust against noise and irregular breathing for tracking organ motion.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method of timing laser beam pulses to regulate extreme ultraviolet light dosing
ActiveUS8872123B2Material analysis by optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsLighting systemLight dose
Described herein are embodiments of a method to control energy dose output from a laser-produced plasma extreme ultraviolet light system by adjusting timing of fired laser beam pulses. During stroboscopic firing, pulses are timed to lase droplets until a dose target of EUV has been achieved. Once accumulated EUV reaches the dose target, pulses are timed so as to not lase droplets during the remainder of the packet, and thereby prevent additional EUV light generation during those portions of the packet. In a continuous burst mode, pulses are timed to irradiate droplets until accumulated burst error meets or exceeds a threshold burst error. If accumulated burst error meets or exceeds the threshold burst error, a next pulse is timed to not irradiate a next droplet. Thus, the embodiments described herein manipulate pulse timing to obtain a constant desired dose target that can more precisely match downstream dosing requirements.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Integrated circuit having improved electromigration performance and method of forming same
InactiveUS20170236780A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMicrowaveEngineering physics
An aspect of the disclosure is directed to a method of forming an interconnect for use in an integrated circuit. The method comprises: forming an opening in a dielectric layer on a substrate; filling the opening with a metal such that an overburden outside of the opening is created; subjecting the metal to a microwave energy dose such that atoms from the overburden migrate to within the opening; and planarizing the metal to a top surface of the opening to remove the overburden, thereby forming the interconnect.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
Fast photolithography process simulation to predict remaining resist thickness
ActiveUS8473271B2Avoid excessive computationPhotomechanical apparatusSpecial data processing applicationsResistEngineering
A lithography model uses a transfer function to map exposure energy dose to the thickness of remaining photoresist after development; while allowing the flexibility to account for other physical processes. In one approach, the model is generated by fitting empirical data. The model may be used in conjunction with an aerial image to obtain a three-dimensional profile of the remaining photoresist thickness after the development process. The lithography model is generally compact, yet capable of taking into account various physical processes associated with the photoresist exposure and / or development process for more accurate simulation.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Skin treatment apparatus utilising intense pulsed light (IPL)
ActiveUS20200179048A1Quick cureImprove accuracySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyLight energyEnergy dose
The present invention relates to an apparatus for treating skin by means of intense pulsed light (IPL). Such apparatus may be used for the treatment of, for example, cosmetic purposes such as hair depilation or dermatological treatment of skin conditions such as acne or rosacea. The present invention provides an improved apparatus that can be used by a non-medical practitioner and comprises a light source comprising a light emitting element for transmitting light energy to the skin and a charge storage device for discharging an energy dose to the light emitting element. There is further provided at least one sensor for measuring a parameter of the skin and a control system configured to determine the treatment energy dose to be delivered. This treatment energy dose is de-rived using the sensor measurement and means of reduction in unwanted time delay associated with charging or discharging of the charge storage device in sole dependence on the current or most recently measured skin parameter.
Owner:I-PULSE CO LTD
Proton linear accelerator system for irradiating tissue with two or more RF sources
ActiveUS11406847B2Reduce harmLittle timeLinear acceleratorsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyBragg peakCancer cell
Proton beams are a promising alternative to X-rays for therapeutic purposes because they may also destroy cancer cells, but with a greatly reduced damage to healthy tissue. The energy dose in tissue may be concentrated at the tumor site by configuring the beam to position the Bragg Peak proximate the tumor. The longitudinal range of a proton beam in tissue is generally dependent upon the energy of the beam. However, after switching energies, the proton-beam system requires some time for the beam energy to stabilize before it may be used for therapy. A proton linear accelerator system is provided for irradiating tissue with an improved beam energy control, configured to provide RF energy from a first RF energy source during the on-time of the proton beam operating cycle for changing the energy of the proton beam, and to provide RF energy from a second distinct RF energy source during the off-time of the proton beam operating cycle for increasing or maintaining the temperature of the cavity. Each RF source is operated independently, allowing higher RF pulse rates to reach the cavity, supporting a smaller time between proton beam energy pulses. In addition, the peak power requirements for the second RF energy source may, in general, be less than for the second RF energy source, allowing a less costly type to be used for the second source. The use of a first and second RF source may reduce the cavity settling time from minutes to less than 10 seconds.
Owner:ADAM SA
Device for changing a surface shape of an optical element by means of electron irradiation
ActiveCN109073787AHigh precisionMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusCamera lensSpatially resolved
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Low energy dose monitoring of implanter using implanted wafers
ActiveUS7259027B2Easy to useHigh device yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesDopantCrystalline materials
A method for processing semiconductor wafers, e.g., silicon. The method includes providing a monitor wafer, which is made of a crystalline material. The method includes introducing a plurality of particles within a depth of the material, whereupon the plurality of particles cause the crystalline material to be in an amorphous state. The method also includes introducing a plurality of dopant particles into a selected depth of the crystalline material in the amorphous state using an implantation tool. The amorphous state traps the dopant particles. The method includes subjecting the monitor wafer including the plurality of particles and dopant particles into thermal anneal process to activate the dopant. The sheet resistivity is measured. The method operates the implantation tool using one or more production wafers if the dose of the dopant particles in the monitor water is within a tolerance of a specification limit.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Method used to yield irradiation product with minimal impurity for solid target for gallium (Ga)-68/germanium (Ge)-68 generator
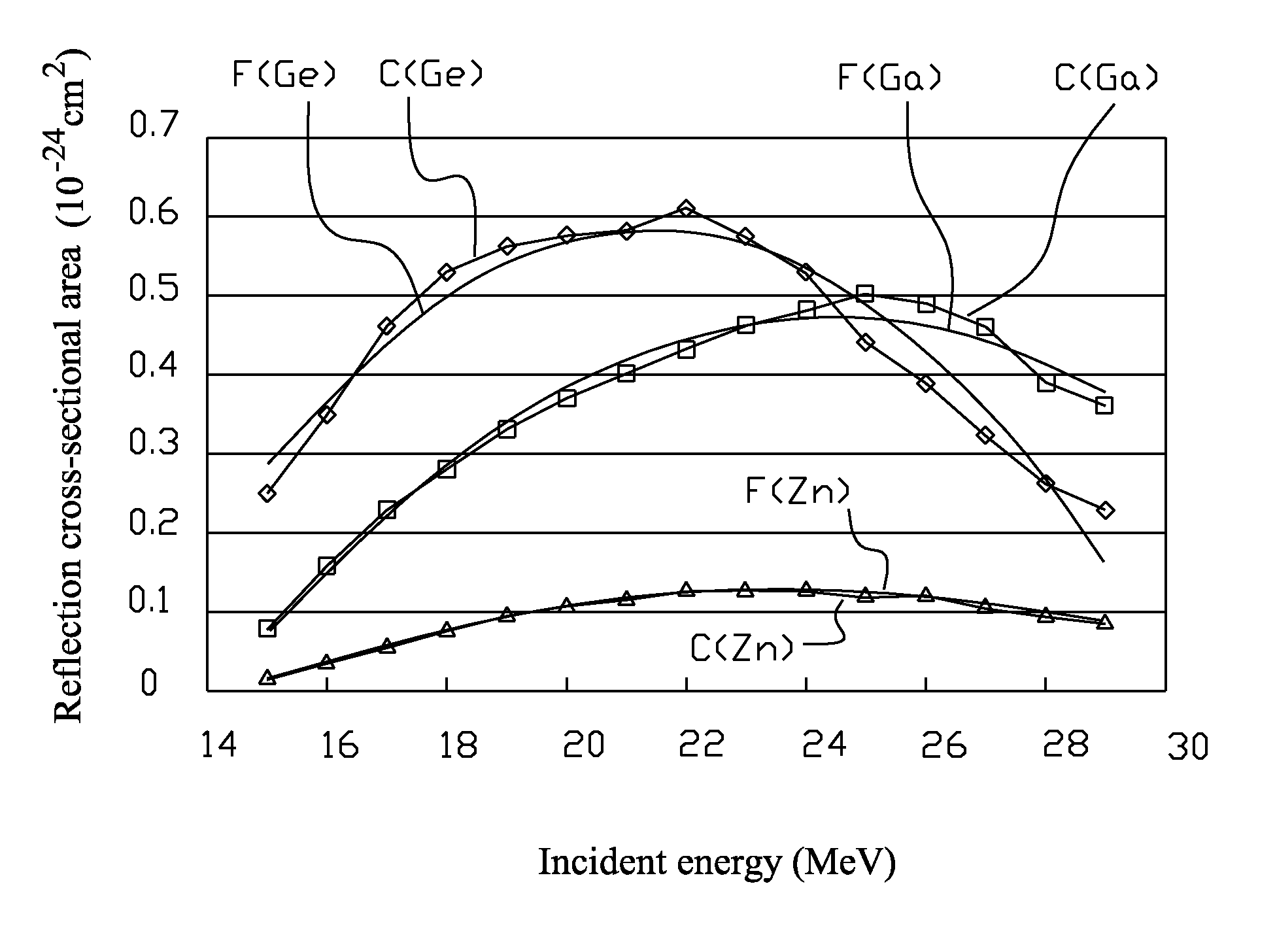
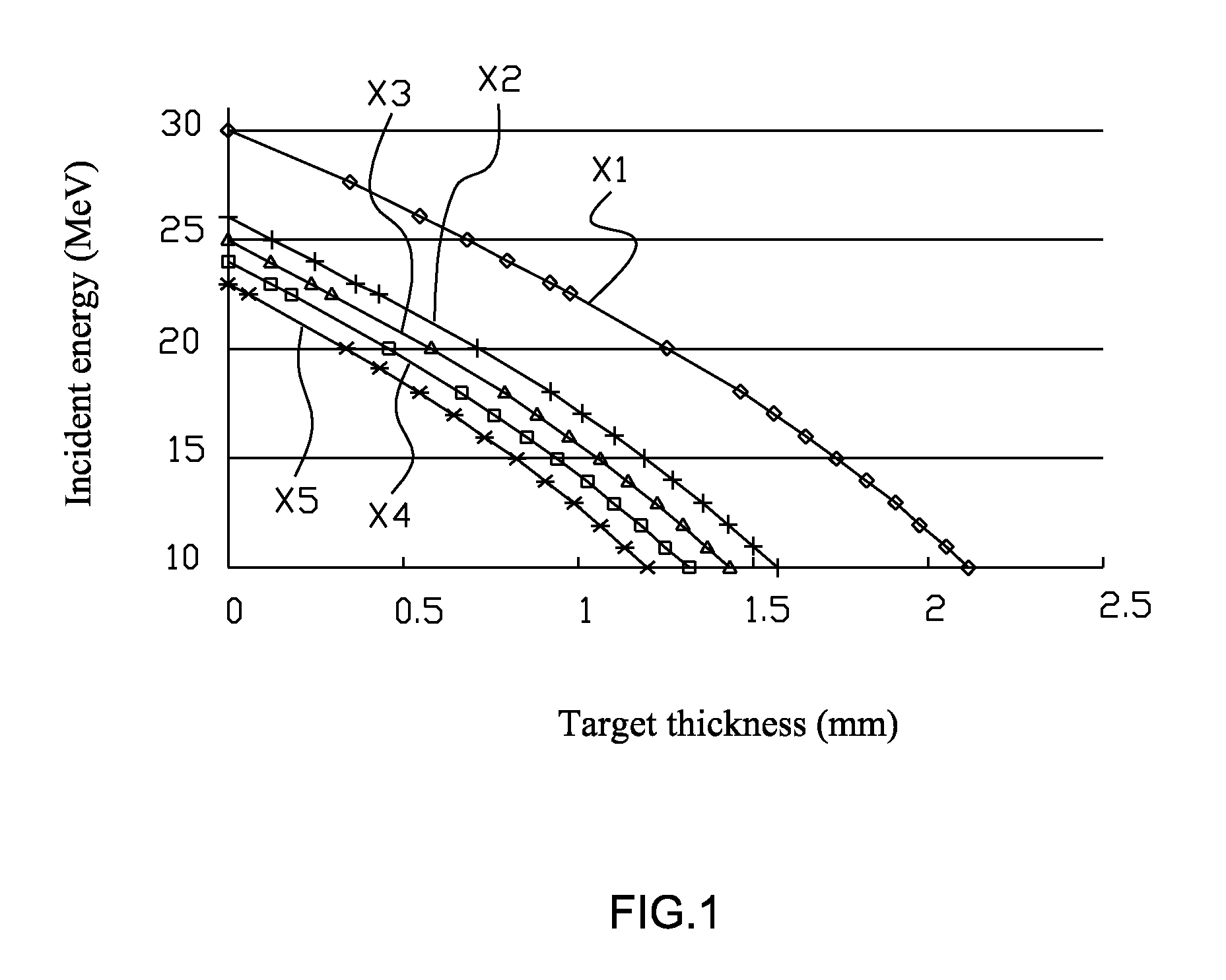
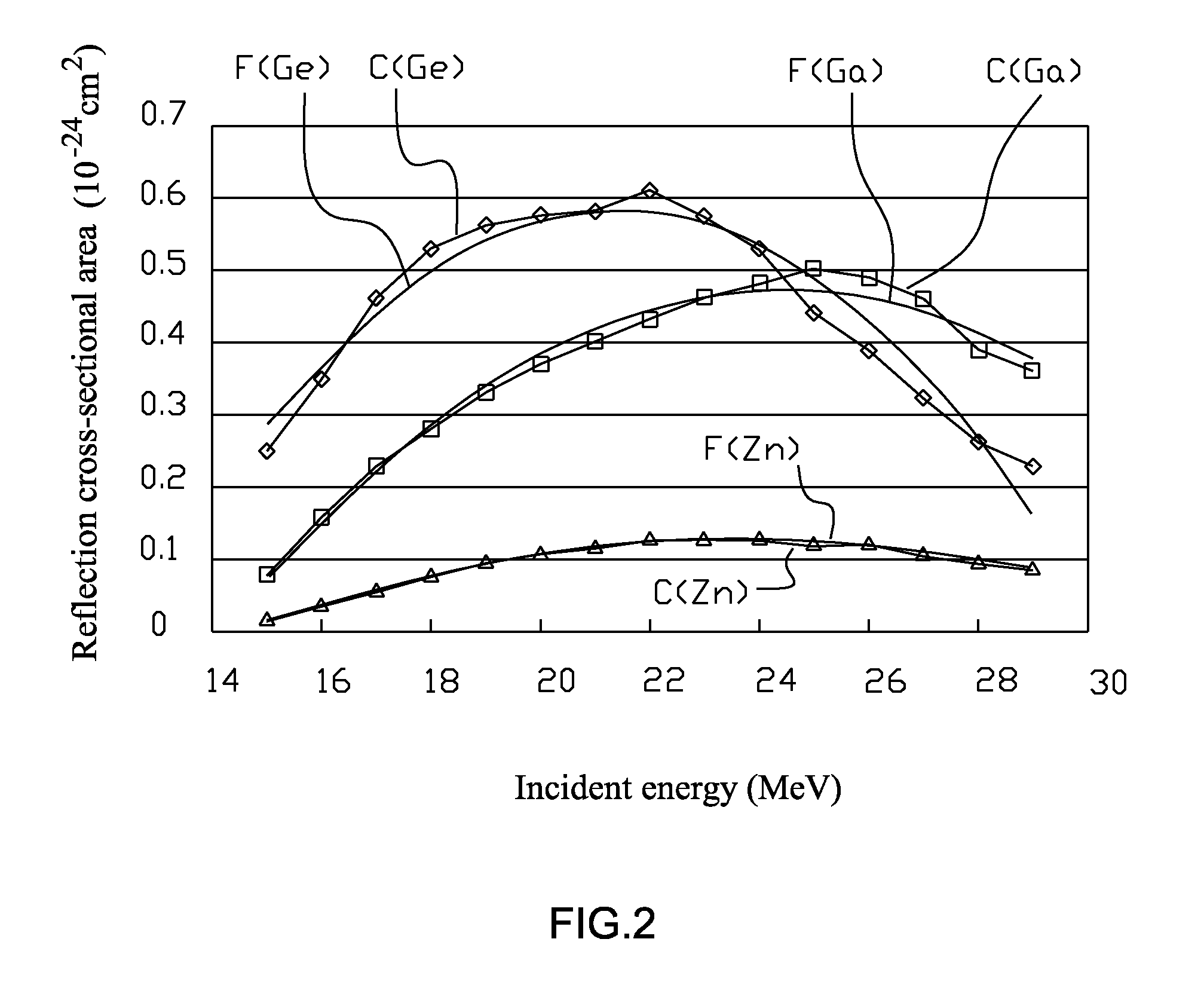
ActiveUS8239159B2Easy to operateQuality of (Ge)-6 is stable and consistentTransuranic element compoundsConversion outside reactor/acceleratorsIncident energyDecay curve
A method used to yield irradiation product with minimal impurity for the solid target for gallium (Ga)-68 / germanium (Ge)-68 generator mainly consists of the procedures: first calculate the thickness d for the electroplated gallium (Ga)-69 on the solid target; and then through a graph of decay curves including 69Ga(p, 2n) 68Ge target thickness and incident energy with 5 different incident energy doses, derive the corresponding irradiation energy dose Yi for each group after decay; and through the graph including 69Ga(p,2n)68Ge incident energy and reaction cross-sectional area, derive the nuclear reaction cross-sectional area for each group for germanium(Ge)-68, gallium (Ga)-68, zinc (Zn)-65 and figure out the mean reaction area (MRA) from the reaction cross-sectional area of each group; and select the maximum germanium(Ge)-68 MRA value and the minimum gallium (Ga)-68 and zinc (Zn)-65 MRA values; and generate the required default irradiation energy for the MRA of each group.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com