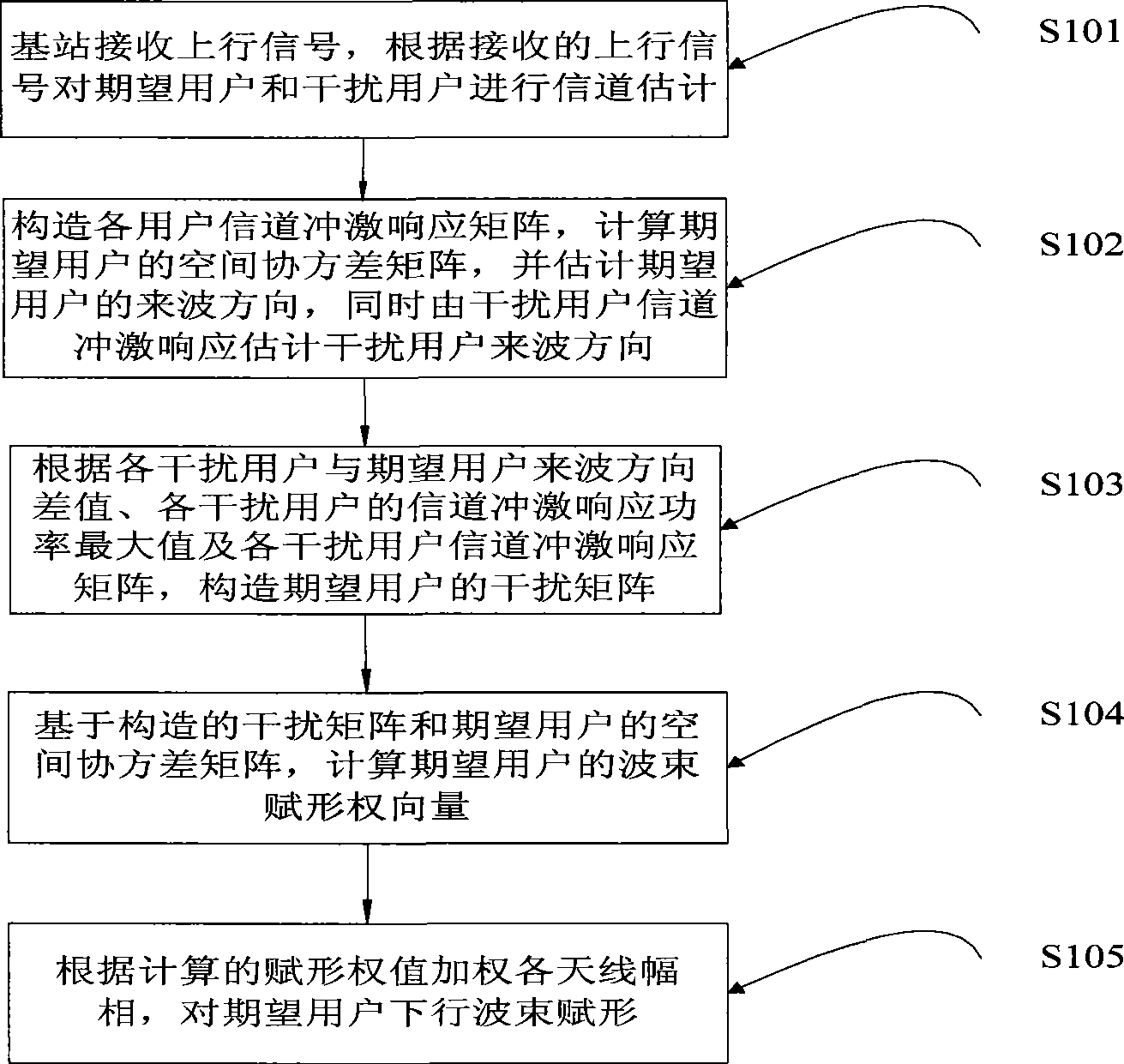
Patents
Literature
229 results about "Beam size" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
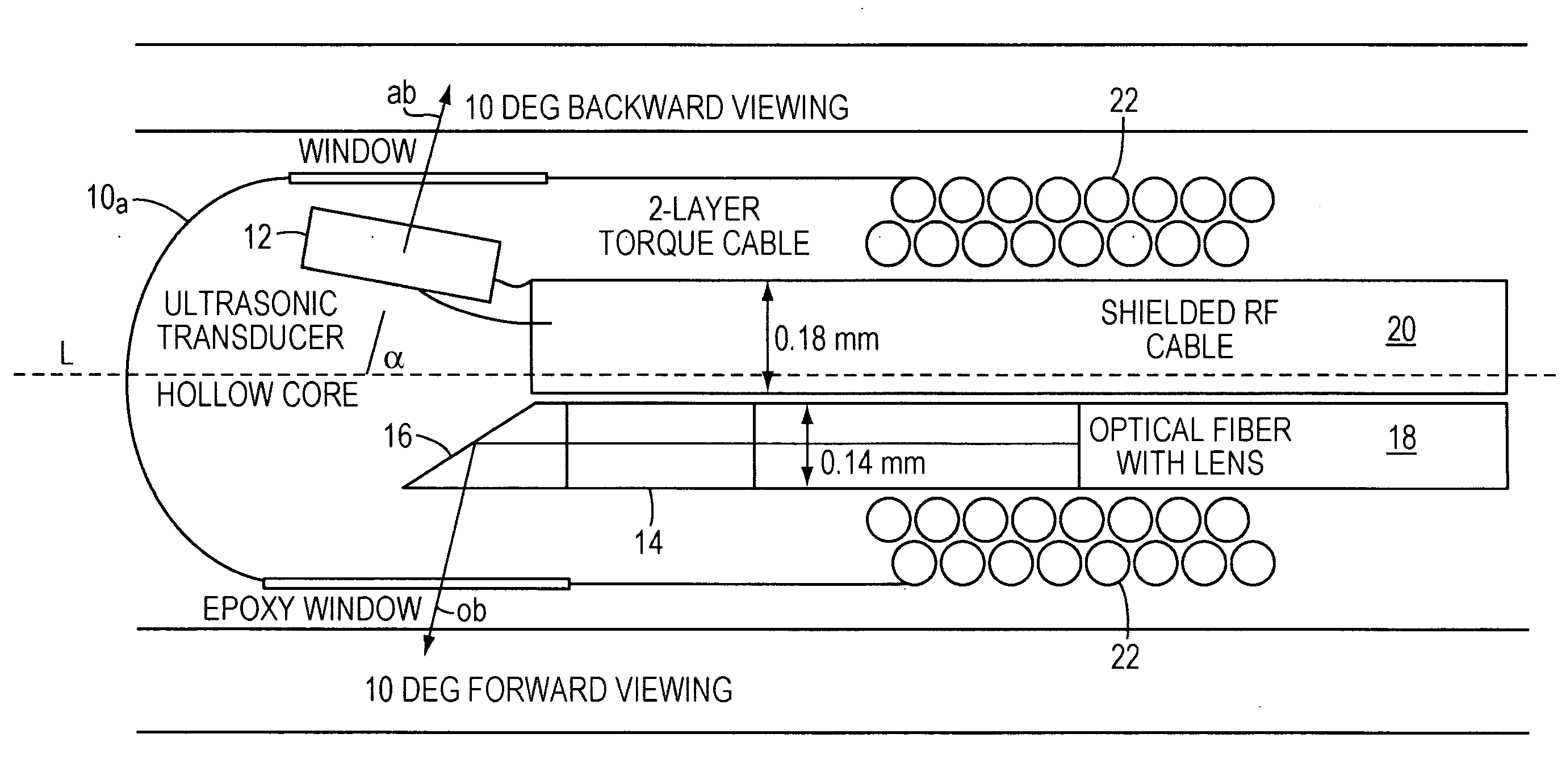
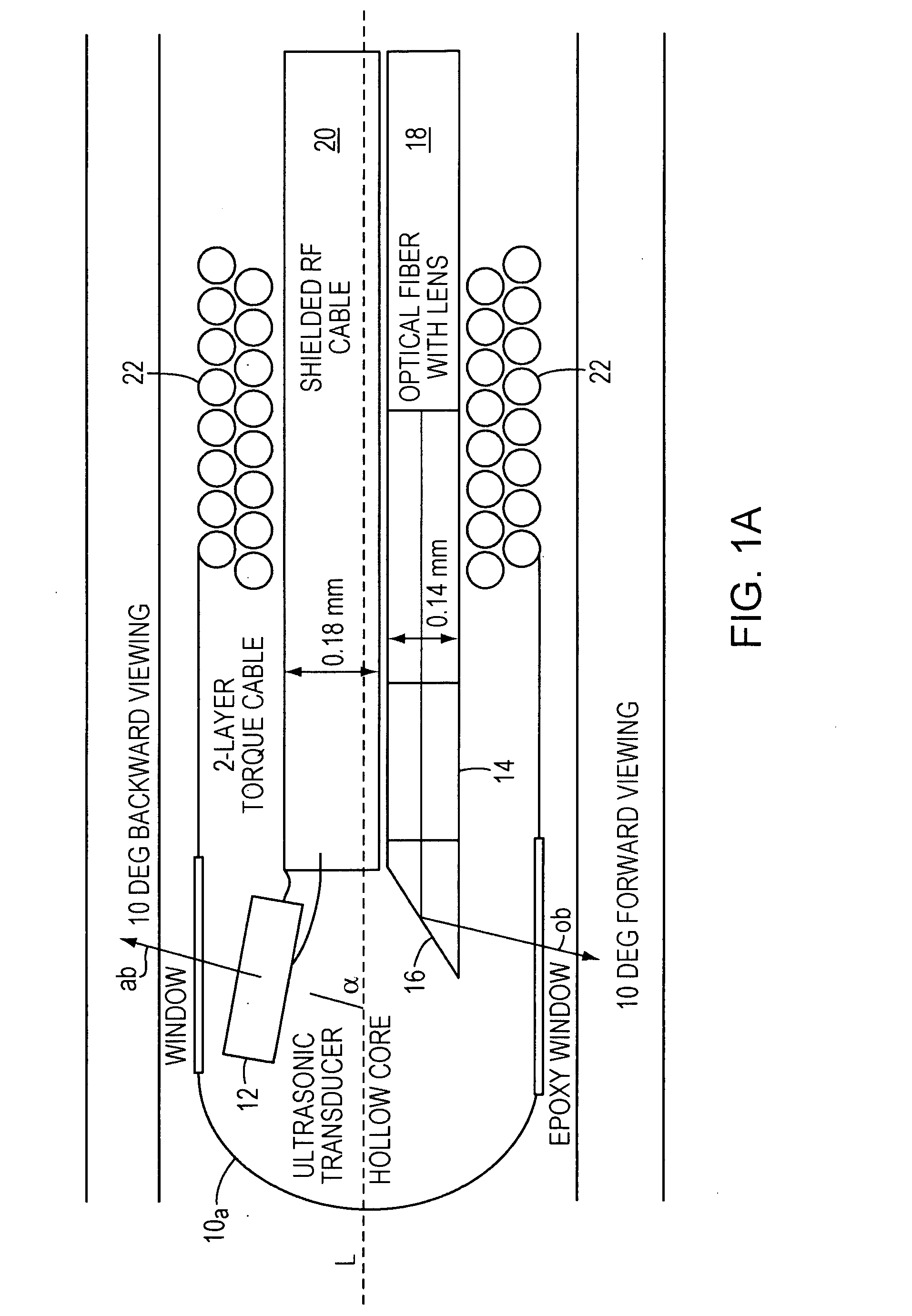
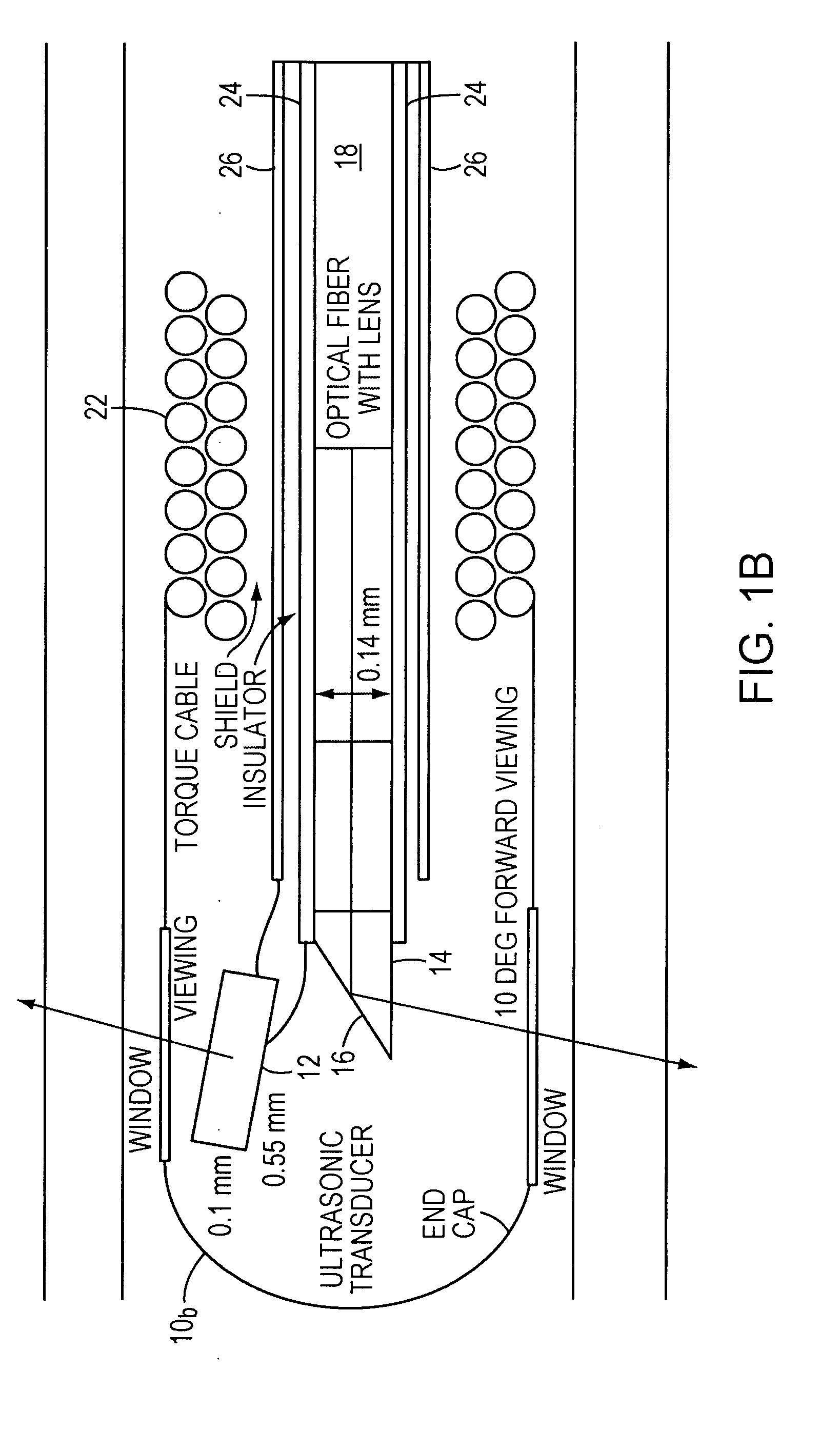
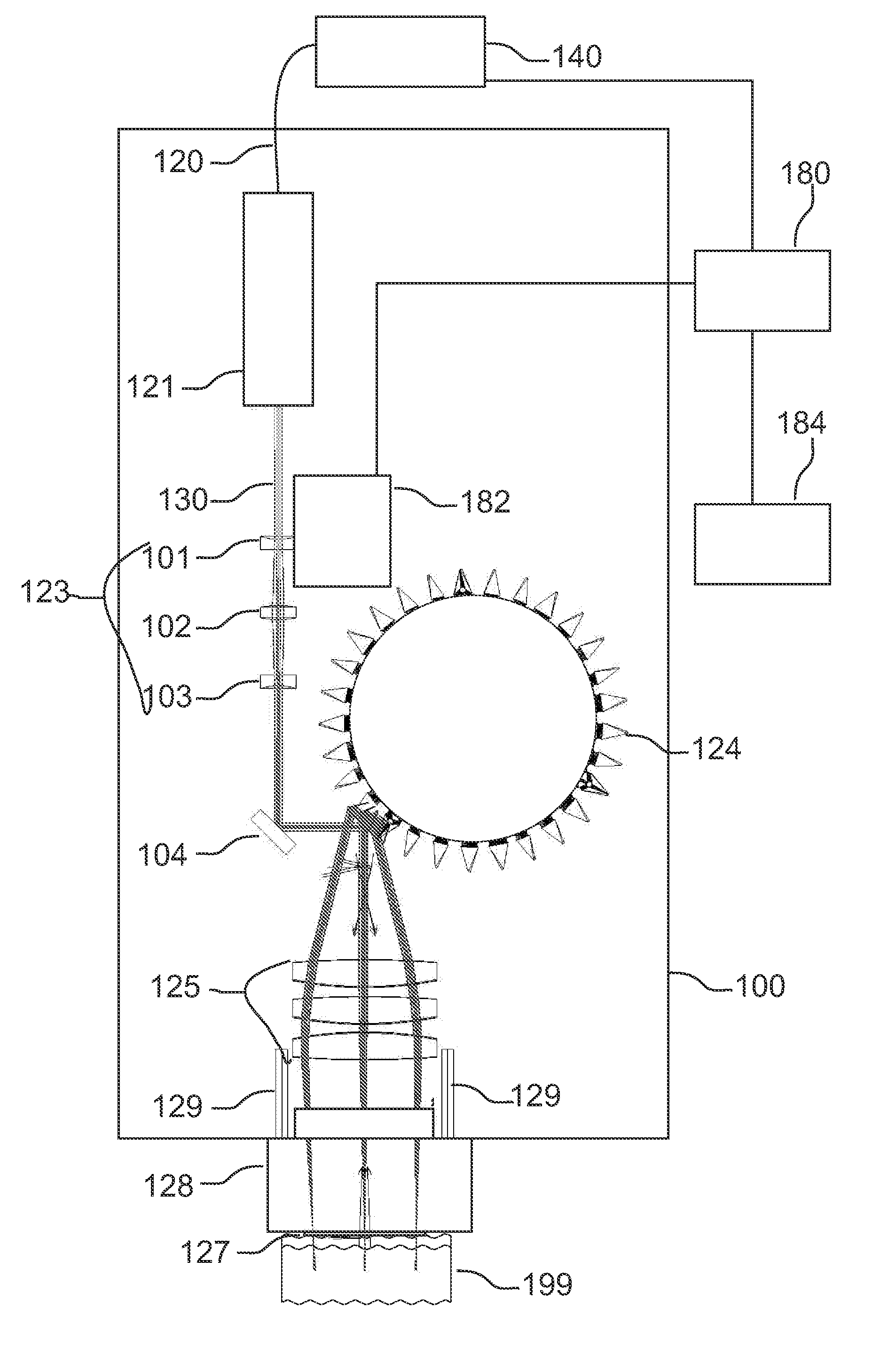
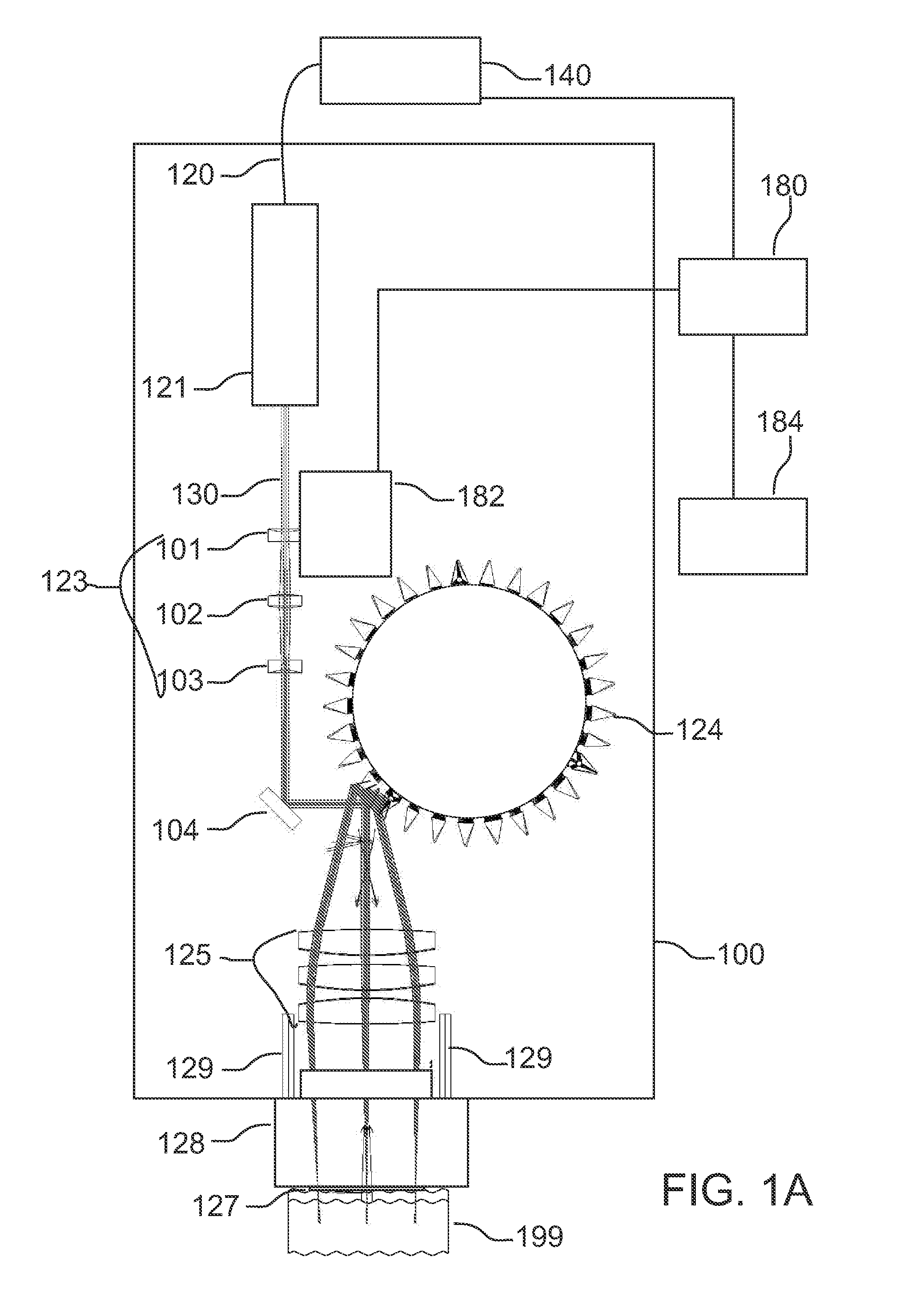
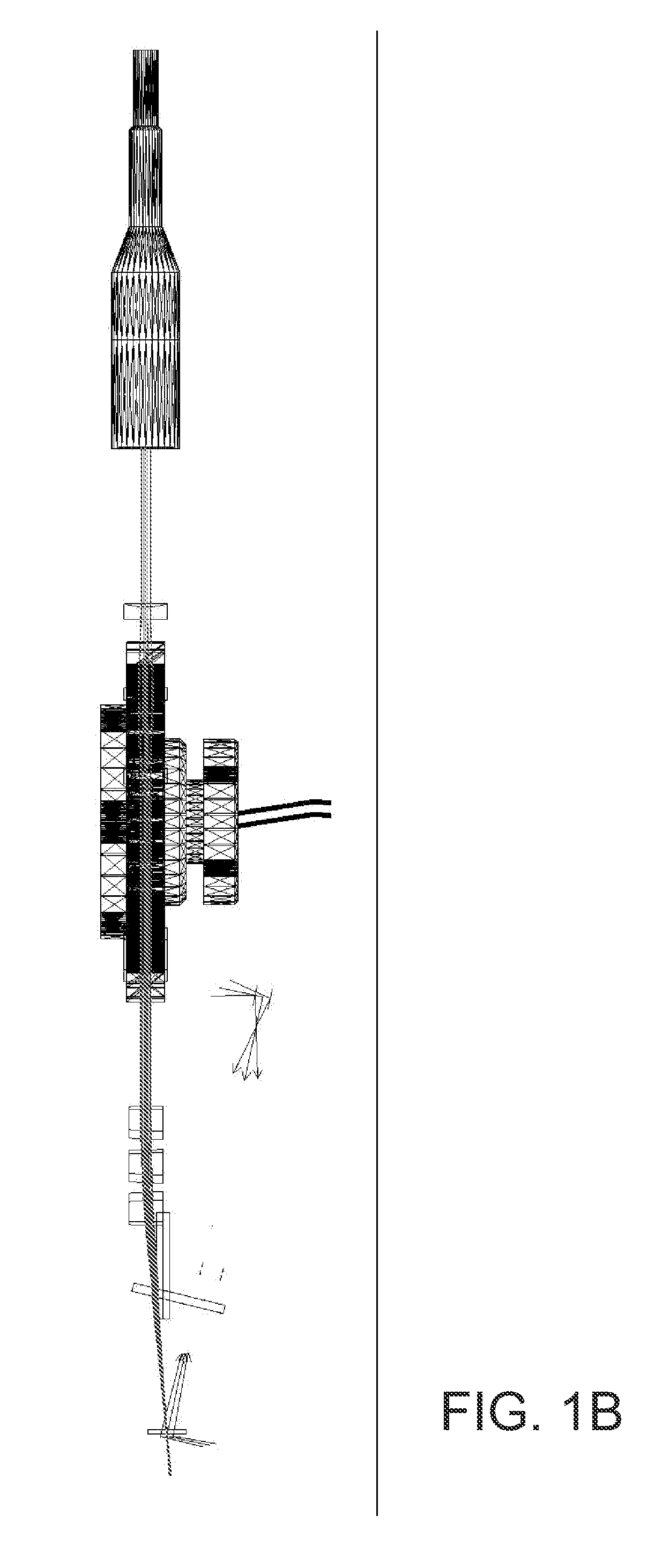
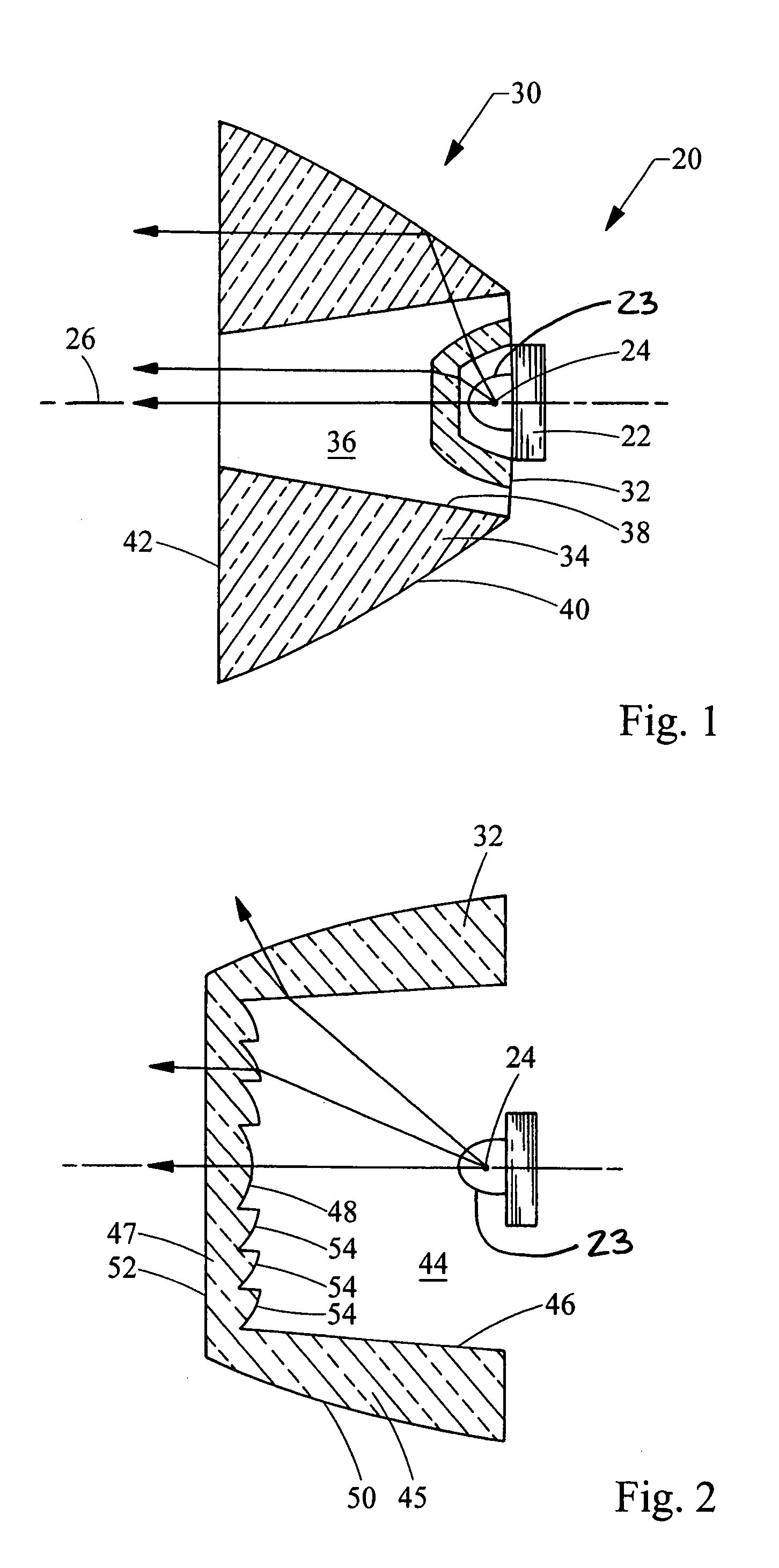
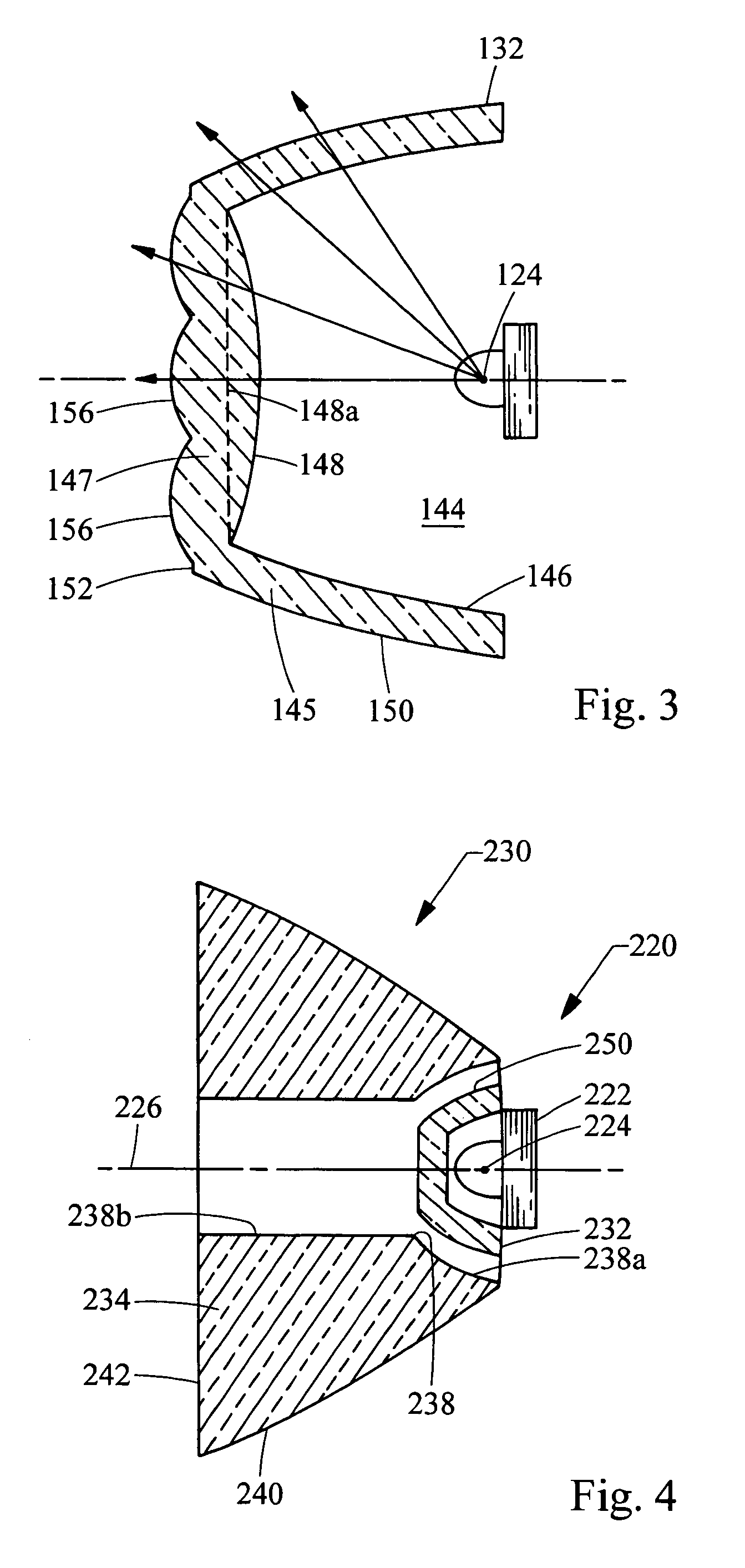
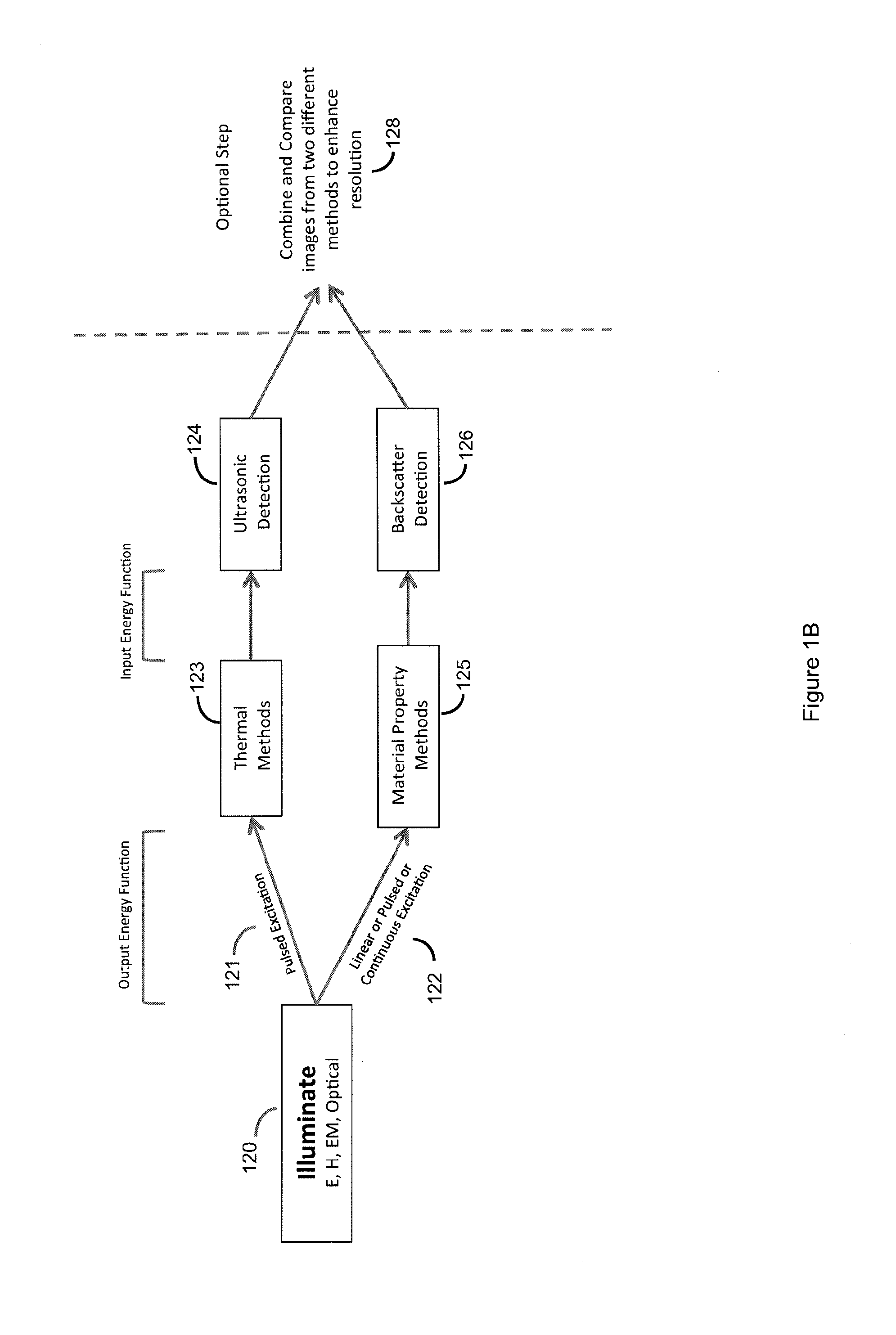
Opto-acoustic imaging devices and methods
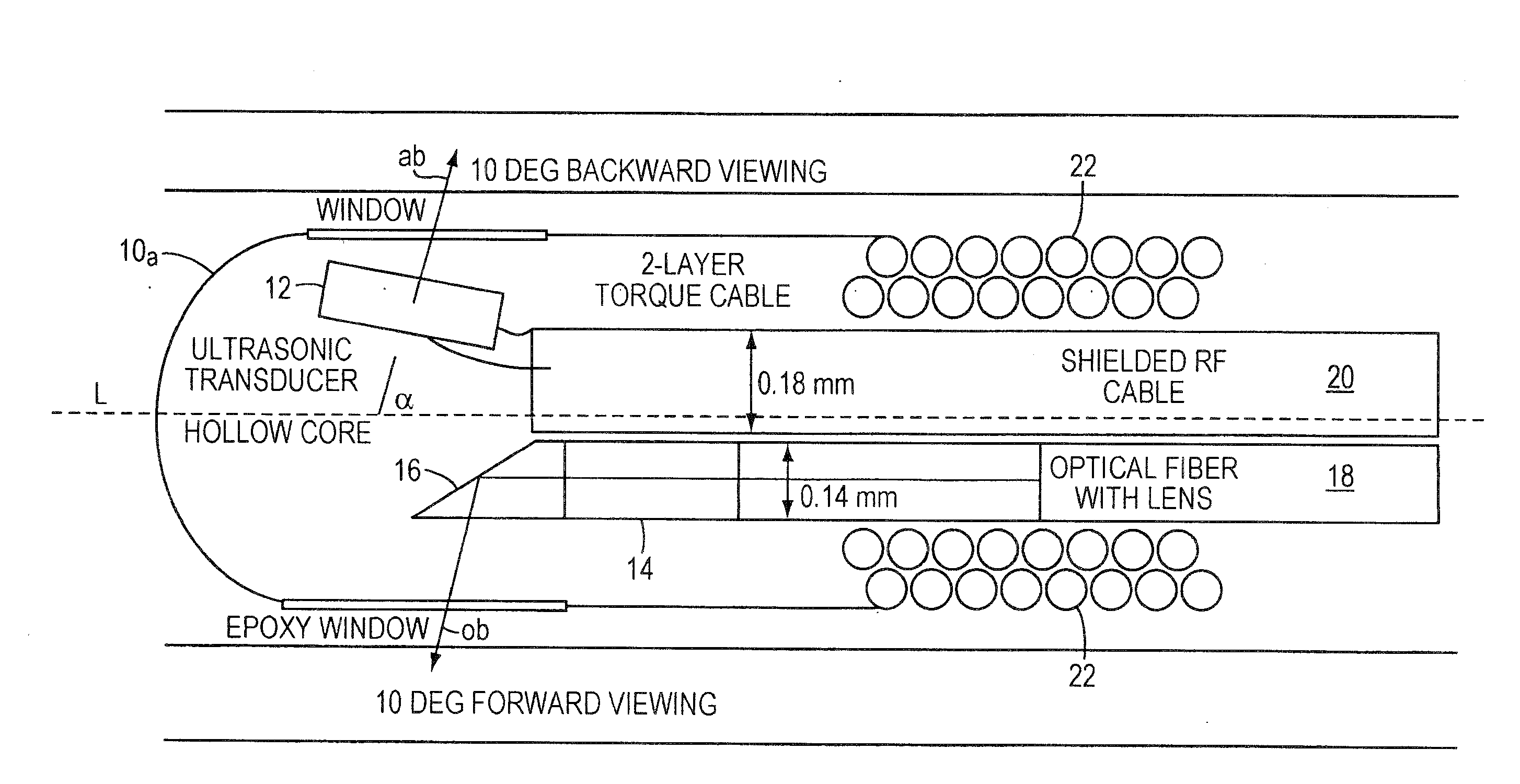
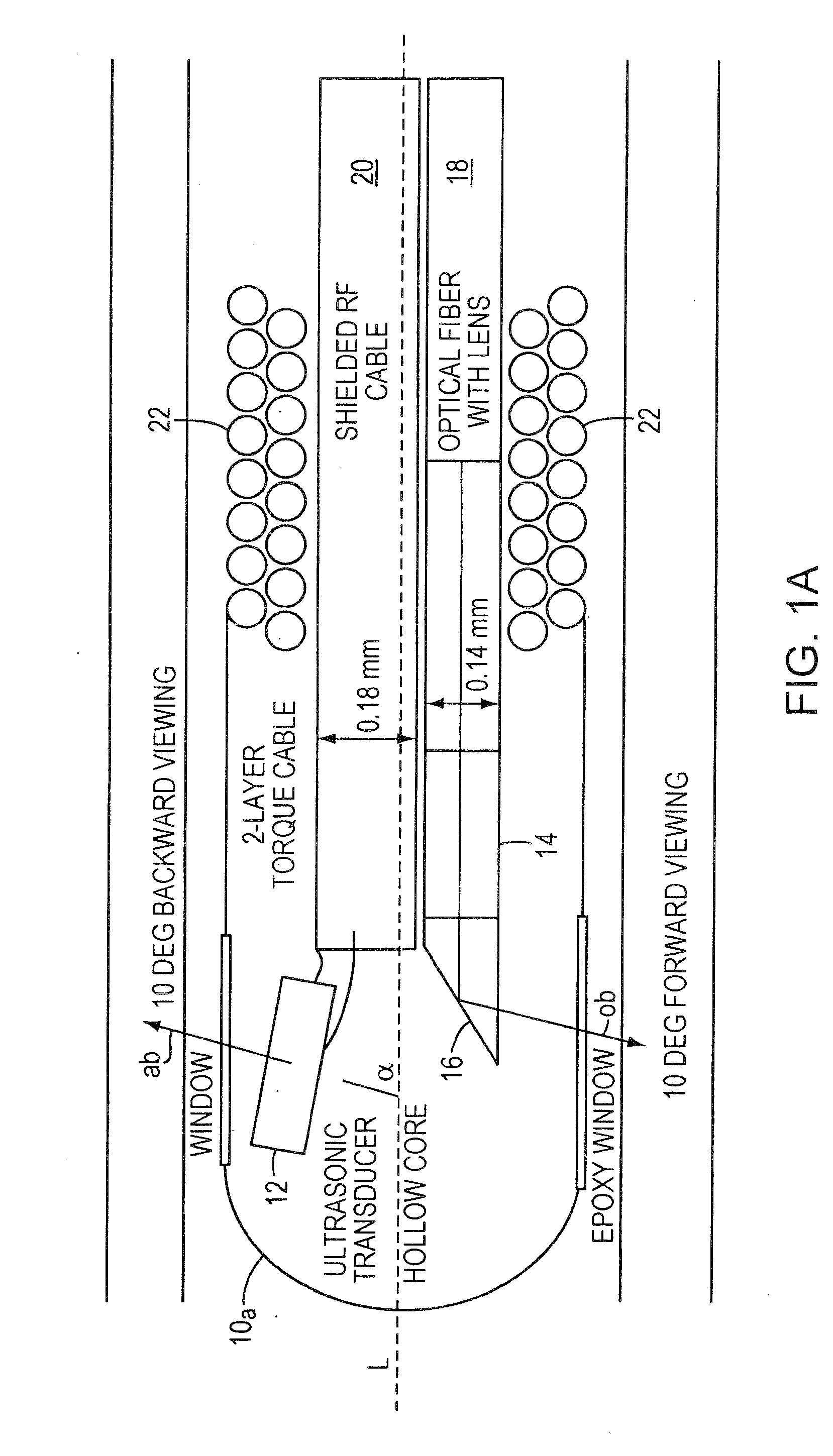
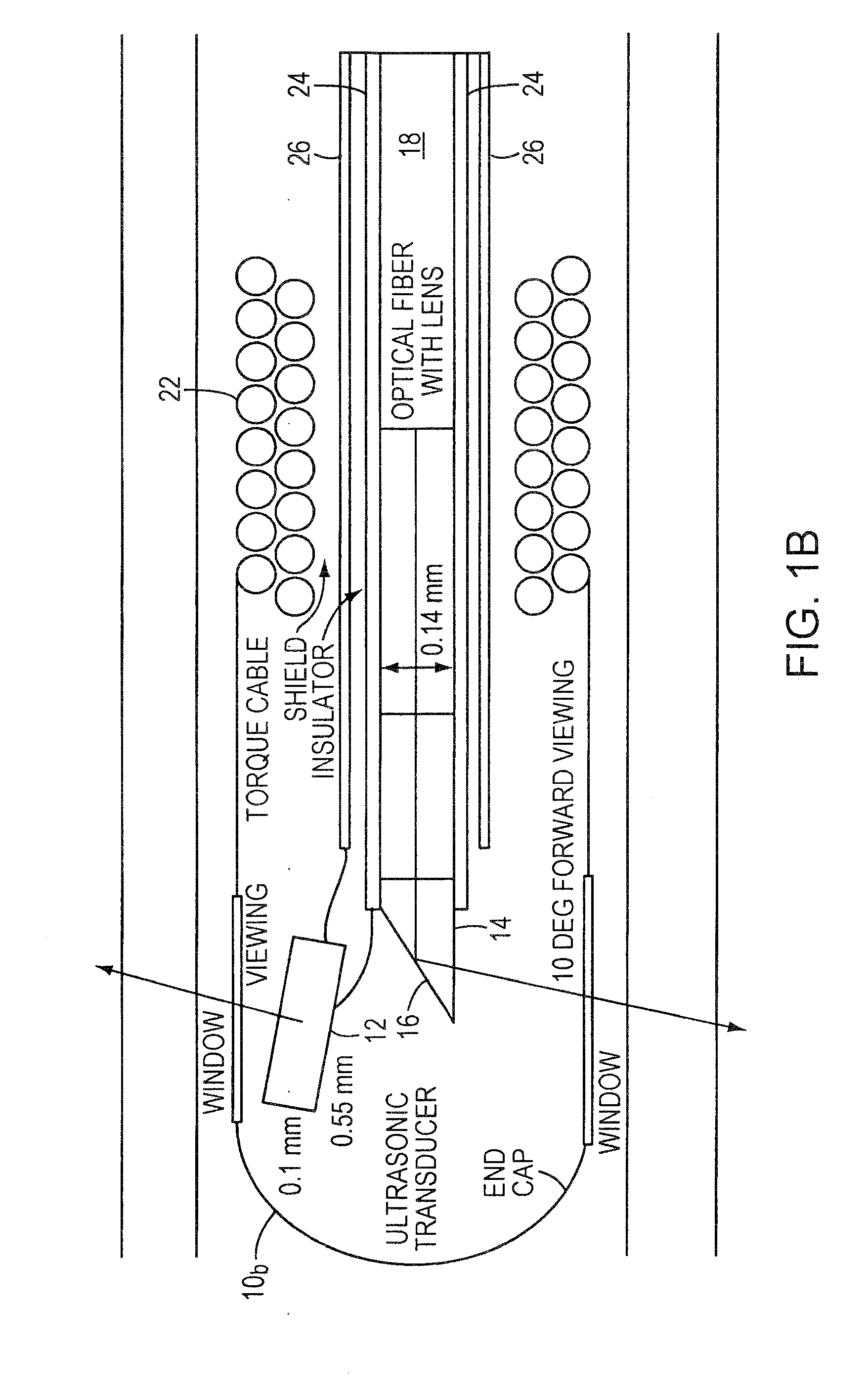
ActiveUS20080161696A1Improve accuracyFacilitate proper co-registrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterLight beamPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
In one aspect, the invention relates to a probe. The probe includes a sheath, a flexible, bi-directionally rotatable, optical subsystem positioned within the sheath, the optical subsystem comprising a transmission fiber, the optical subsystem capable of transmitting and collecting light of a predetermined range of wavelengths along a first beam having a predetermined beam size. The probe also includes an ultrasound subsystem, the ultrasound subsystem positioned within the sheath and adapted to propagate energy of a predetermined range of frequencies along a second beam having a second predetermined beam size, wherein a portion of the first and second beams overlap a region during a scan.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
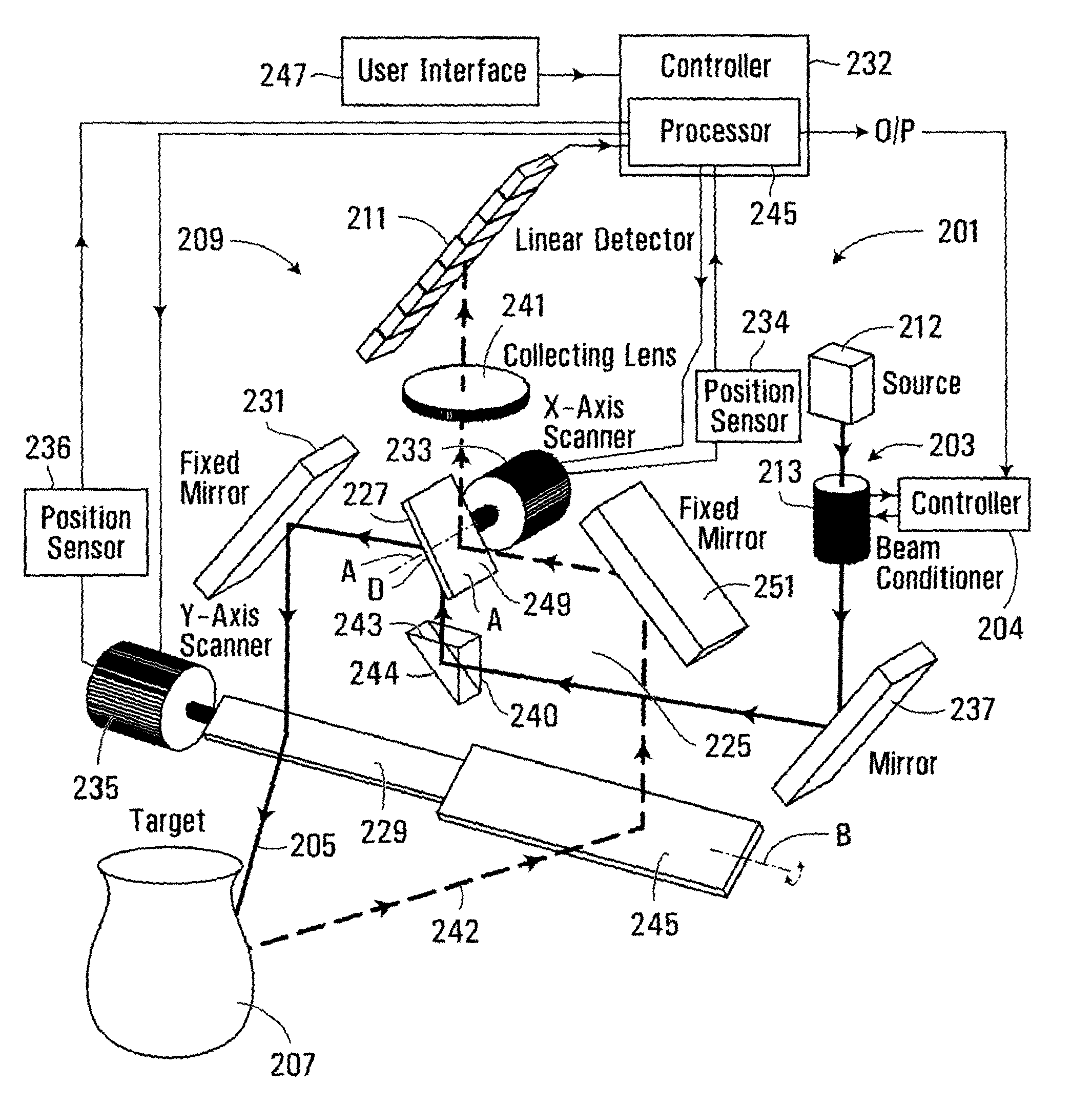
Imaging system and method
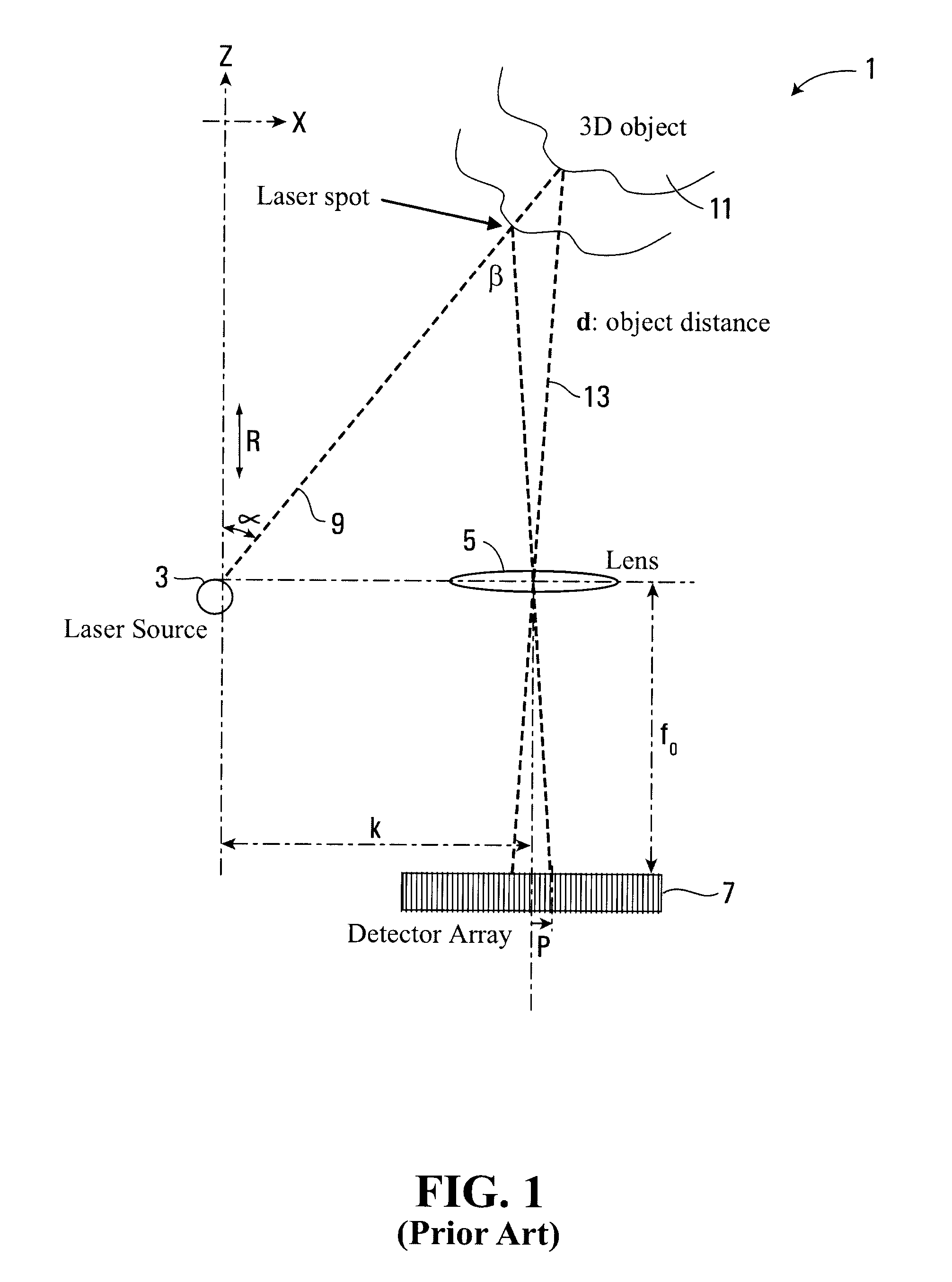
InactiveUS20090195790A1Reduce edge effectsReduce errorsUsing optical meansBeam expanderTarget surface
An apparatus for measuring the coordinates of a point on the surface of an object comprises a projection system for projecting a beam of energy onto the surface of the object, a receiving system for receiving reflected beam energy from the target surface, and a detector for detecting the received energy. The projection system comprises a beam expander for expanding the width of the beam, and a focussing device for focussing the projected beam. The position of the reflected beam energy at the detector provides a measure of the range of the point on the target surface using triangulation and the direction of the projected beam provides the x and y coordinates. The focussing device can be controlled to vary the focal length of the projected beam and to control the beam size at the target object to vary the area of the target surface illuminated by the beam and thereby to control the resolution of the measurements.
Owner:NEPTEC
Irradiation system ion beam and method to enhance accuracy of irradiation
ActiveUS20060113493A1Improve beam irradiation accuracyImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon beam tubesTransformerLight beam
The present invention is a method to enhance accuracy of irradiation with beam for an irradiation system with a beam. The irradiation system comprises a beam generation source, a mass analysis device, a beam transformer, a scanner which swings the beam reciprocally with high speed, a beam parallelizing device, an acceleration / deceleration device, an energy filtering device, and beam monitors. The beam transformer comprises a vertically focusing synchronized quadrupole electromagnet syQD and a horizontally focusing synchronized quadrupole electromagnet syQF. Consequently, it is possible to correct at least one of a deviation in beam divergence angle and a deviation in beam size within a range between a center trajectory and an outer trajectory after swinging of the beam by the scanner.
Owner:SENCORP
Beam reconfiguration method and apparatus for satellite antennas
InactiveUS20040189538A1Increased complexityIncrease costCollapsable antennas meansAntenna supports/mountingsSatellite antennasLight beam
A method, apparatus, article of manufacture, and a memory structure for generating reconfigurable beams is disclosed herein. The apparatus comprises a stationary feed array having a plurality of selectably activatable feed array elements, the feed array having a feed array sensitive axis; a reflector, illuminated by the selectably activatable feed array elements; a first mechanism, coupled to the reflector, for varying a position of the reflector along the feed array axis; wherein a desired beam size of the antenna system is selected by varying the reflector position along the feed array sensitive axis and by selectably activating the feed array elements.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Optical measuring device
ActiveUS7003075B2Accurate measurementRadiation pyrometryX-ray spectral distribution measurementMeasurement deviceOptical property
The present invention provides a measuring device by which, even if a radiation intensity from a light source, a beam size or a beam intensity distribution of the light source changes, an optical characteristic of an optical element to be measured can be measured very precisely. In a measuring device according to the present invention, to this end, light from a light source is diffracted by a diffracting grating to thereby resolve the same into plural light beams, and by using different light beams, the object to be measured is measured and the intensity of incident light from the light source is measured. With this structure, even if the light from the light source changes, the intensity of the light from the light source is specified concurrently, and therefore, the optical characteristic of the object to be measured can be measured very accurately.
Owner:CANON KK
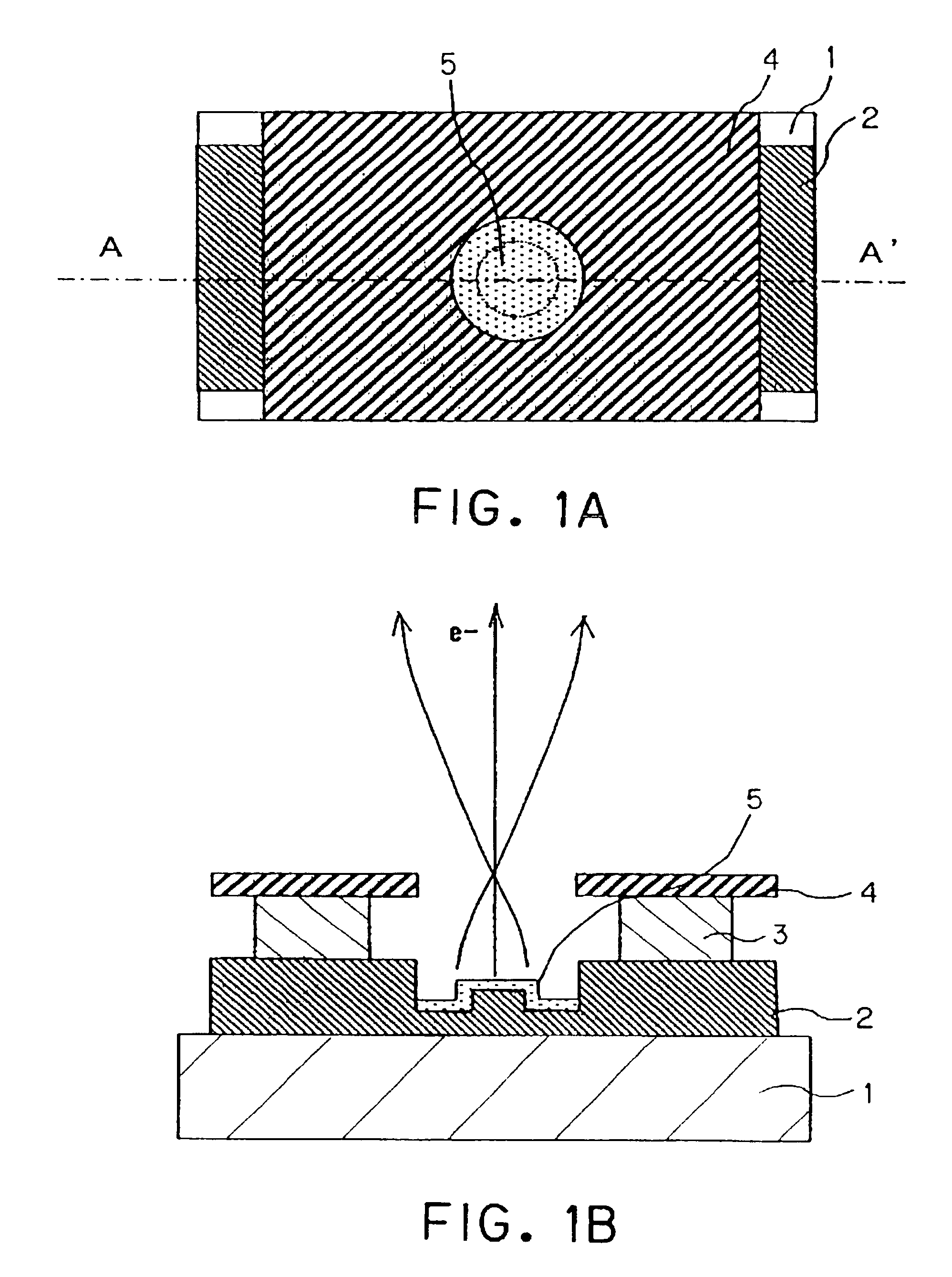
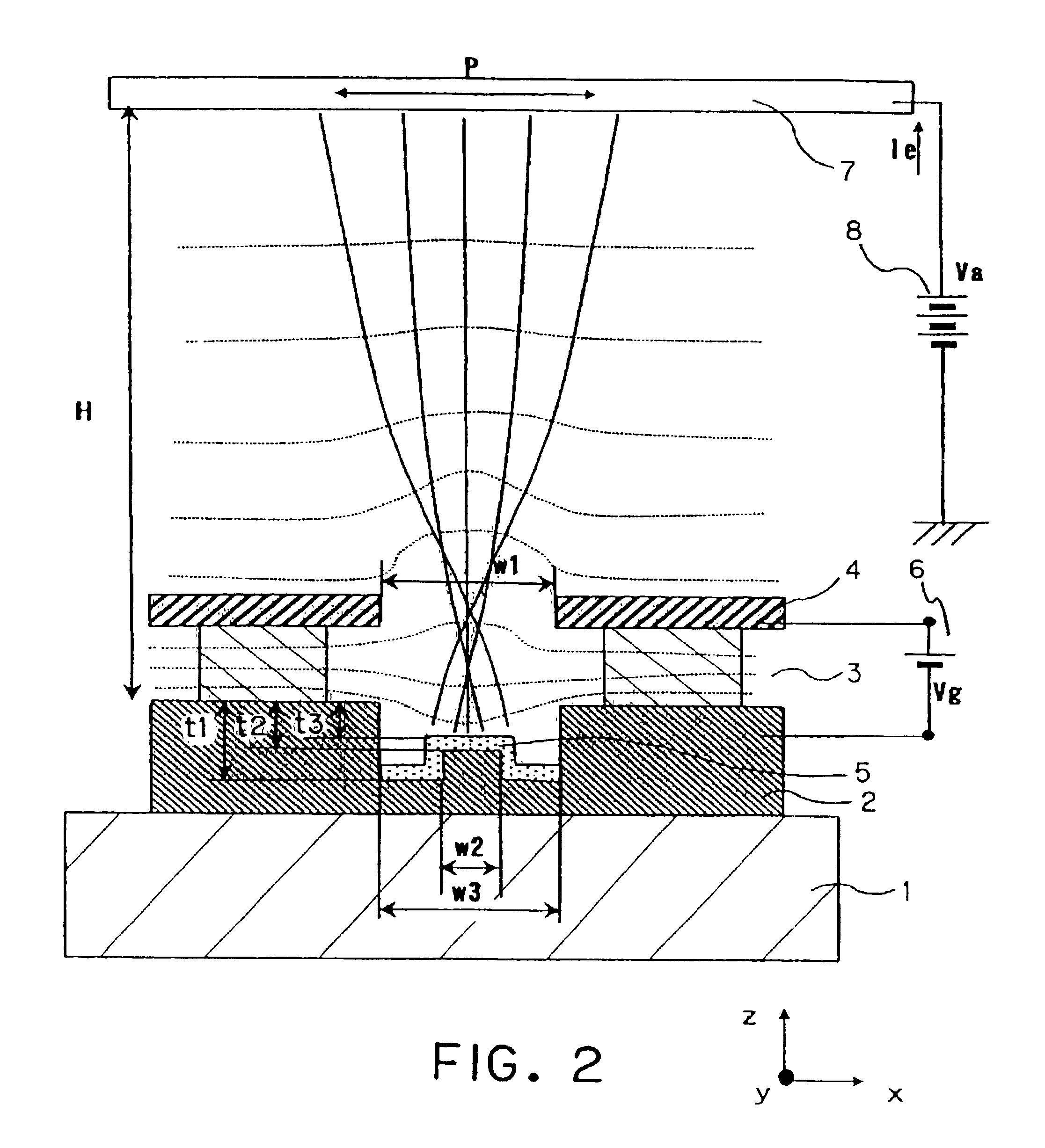
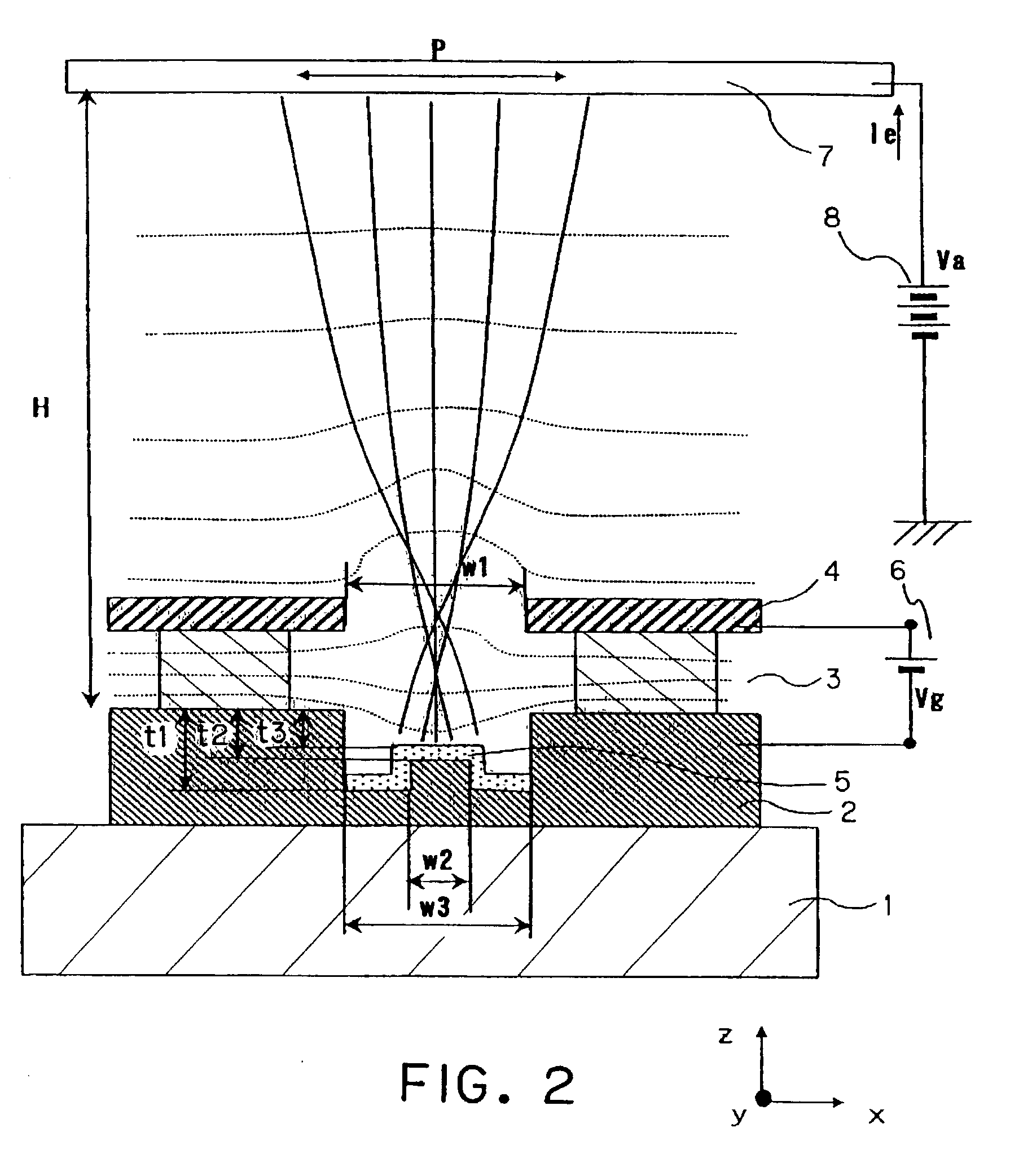
Electron-emitting device and image-forming apparatus
An electron-emitting device having a small electron beam size is proposed. In order to provide a high definition image display device having high image quality by utilizing this type of electron-emitting device and an electron source, a cathode electrode (2) has an opening which is trenched in a portion thereof, and further, the depth at which the opening is trenched is deep at a peripheral portion of the opening bottom face, and shallow at a central portion of the opening bottom face. A surface of an electron-emitting material is formed in a portion deeper than a boundary surface between the cathode electrode and an insulating layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Lens assembly for an automobile light assembly having LED light source
InactiveUS20060209558A1Reduce thicknessNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLight beamOptoelectronics
A light assembly is provided having a lens assembly that splits the function of a near field lens into two components, thereby permitting a manufacturable lens that achieves the desired beam size and intensity. At the same time, increased flexibility and control over the beam spread characteristics is achieved. The first component is an inner lens, while the second component may be a reflector or a second lens.
Owner:VARROC LIGHTING SYST SRO
Multi-beam and multi-band antenna system for communication satellites
An antenna system includes a reflector having a modified-paraboloid shape; and a multi-beam, multi-band feed array located at a focal point of the reflector so that the antenna system forms a multiple congruent beams that are contiguous. The system has a single reflector with non-frequency selective surface. The reflector is sized to produce a required beam size at K-band frequencies and is oversized at EHF-band frequencies. The synthesized reflector surface is moderately shaped and disproportionately broadens EHF-band and Ka-band beams compared to K-band beams. The synthesized reflector surface forms multiple beams each having a 0.5-degree diameter at K-band, Ka-band, and EHF band. The multi-beam, multi-band feed array includes a number of high-efficiency, multi-mode circular horns that operate in focused mode at K-band and defocused mode at Ka-band and EHF-band by employing “frequency-dependent” design for the horns.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Opto-Acoustic Imaging Devices and Methods
ActiveUS20110172511A1Improve accuracyEfficient methodUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterLight beamPhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
In one aspect, the invention relates to a probe. The probe includes a sheath, a flexible, bi-directionally rotatable, optical subsystem positioned within the sheath, the optical subsystem comprising a transmission fiber, the optical subsystem capable of transmitting and collecting light of a predetermined range of wavelengths along a first beam having a predetermined beam size. The probe also includes an ultrasound subsystem, the ultrasound subsystem positioned within the sheath and adapted to propagate energy of a predetermined range of frequencies along a second beam having a second predetermined beam size, wherein a portion of the first and second beams overlap a region during a scan.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Method of detecting and classifying scratches, particles and pits on thin film disks or wafers
InactiveUS20050057747A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationDual beamLight beam
Scratches, pits and particles which are smaller or larger than the beam size may be measured and identified by a dual beam technique. This invention uses a pair of orthogonally oriented laser beams, one in the radial and one in the circumferential direction. The scattered light from radial and circumferential beams allows the detection and classification of particles, pits and scratches.
Owner:MEEKS STEVEN W
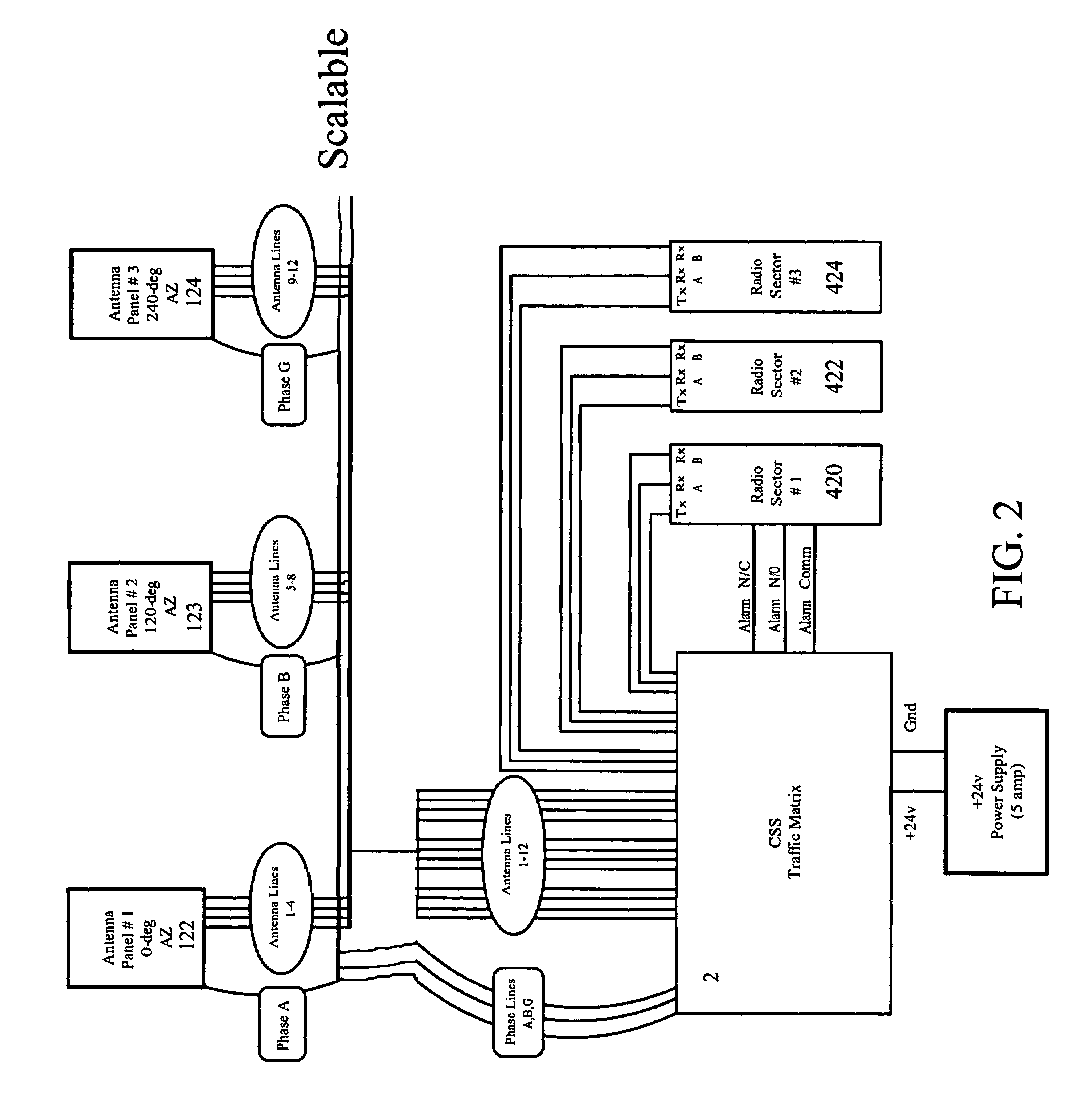
Wireless antenna traffic matrix
InactiveUS7245938B2Simple procedureNo equipment failure or downtimePolarisation/directional diversityAntenna supports/mountingsTraffic capacityPatch panel
A beam shaping antenna matrix for use in wireless cell towers that is manually-configured at a patch panel by a wireless operator based on selection of a desired beam size and point of direction. The traffic matrix allows a wireless operator to sculpt and resculpt the beams to accommodate demographic or other changes preferably without a large amount of hardware or intensive processing capability.
Owner:CSS ANTENNA
Laser optical system
InactiveUS20080151951A1Simple designSmall sizeLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSystems designLuminous flux
A compact optical system is provided for delivering laser radiation with high optical efficiency and uniformity. The optical system includes, in order of the propagation of light, a refractive beam expander to adjust beam size and energy density, a beam flattening module to increase throughput and beam uniformity, an anamorphic corrector to equalize ray distribution in both axes, an attenuator assembly to adjust beam intensity, galvanometer mirrors to scan the beam across a substrate surface, and a focusing lens containing a plurality of refractive elements to deliver the beam at the substrate plane. The laser optical system shapes the laser source beam to increase its effective width for greater productivity in manufacturing, and reduces peak intensity to minimize substrate damage. The laser optical system design is optimized for maximum transmission and optical efficiency for low cost operation with a small laser.
Owner:UVTECH SYST
Method and apparatus for rapid grain size analysis of polycrystalline materials
InactiveUS6882739B2Remove background noiseEliminate DiffractionMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionHighly skilledX-ray
An apparatus and method for performing rapid grain size analysis on a textured polycrystalline material, by generating average grain size and grain size distribution data from x-ray diffraction data of such material. Raw diffraction data is obtained by capturing a plurality of diffraction arcs within a single data capture frame. The raw diffraction data is digitally registered; (3) and the registered diffraction data is filtered to remove background noise, exclude diffraction overlaps or truncations, and compensate for biased data obtained from regions of highly preferred orientations. Average grain size and grain size distribution data are then correlated with the filtered diffraction data. The apparatus for acquiring raw diffraction data includes a collimated x-ray source having means for adjusting beam size and divergence of the x-ray generated, a 2-dimensional area detector for registering diffracted x-ray, and a sample motion assembly for moving the sample in the sample plane. The resulting system is fast, accurate, amenable to automation, and does not require highly skilled personnel to operate.
Owner:NOVA MEASURING INSTR LTD
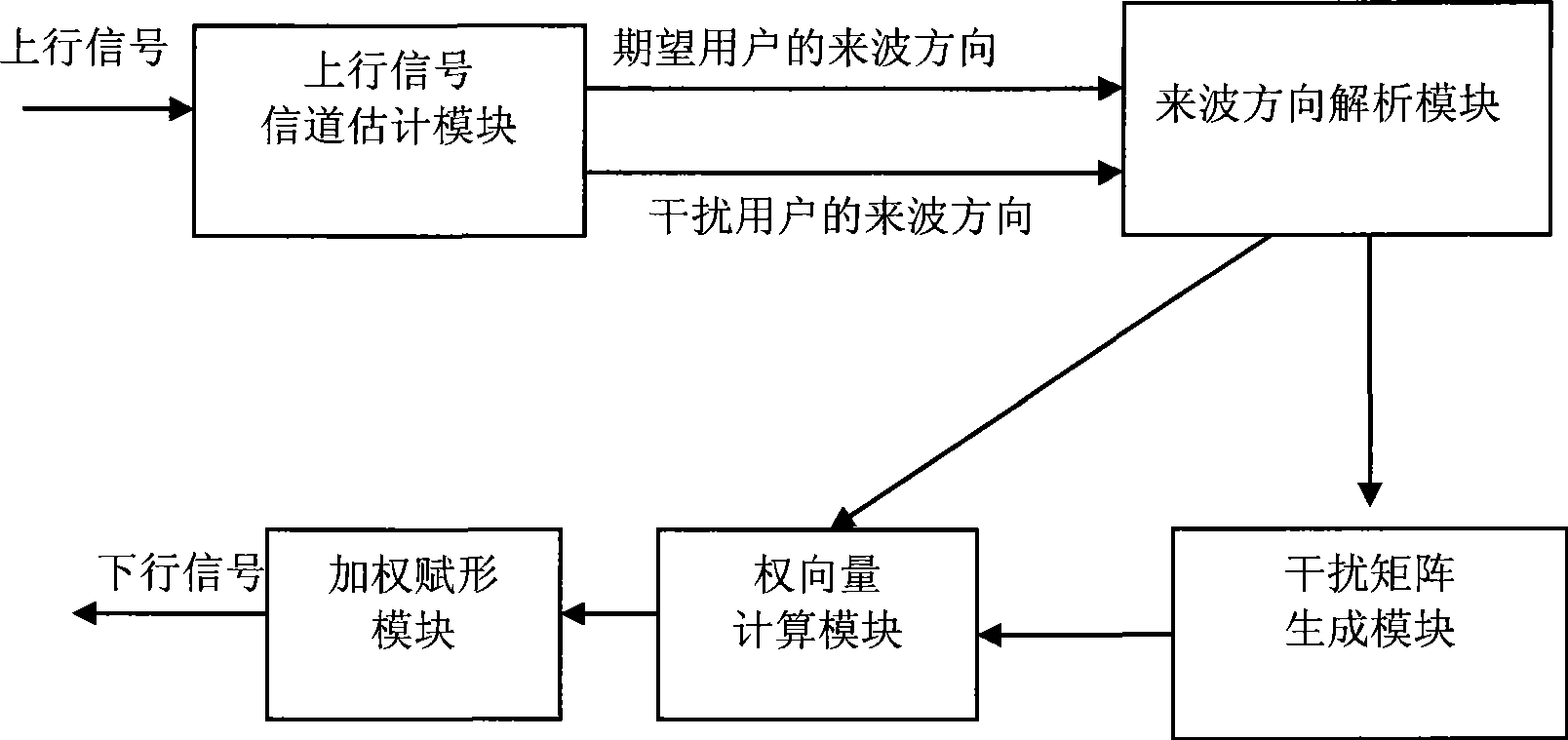
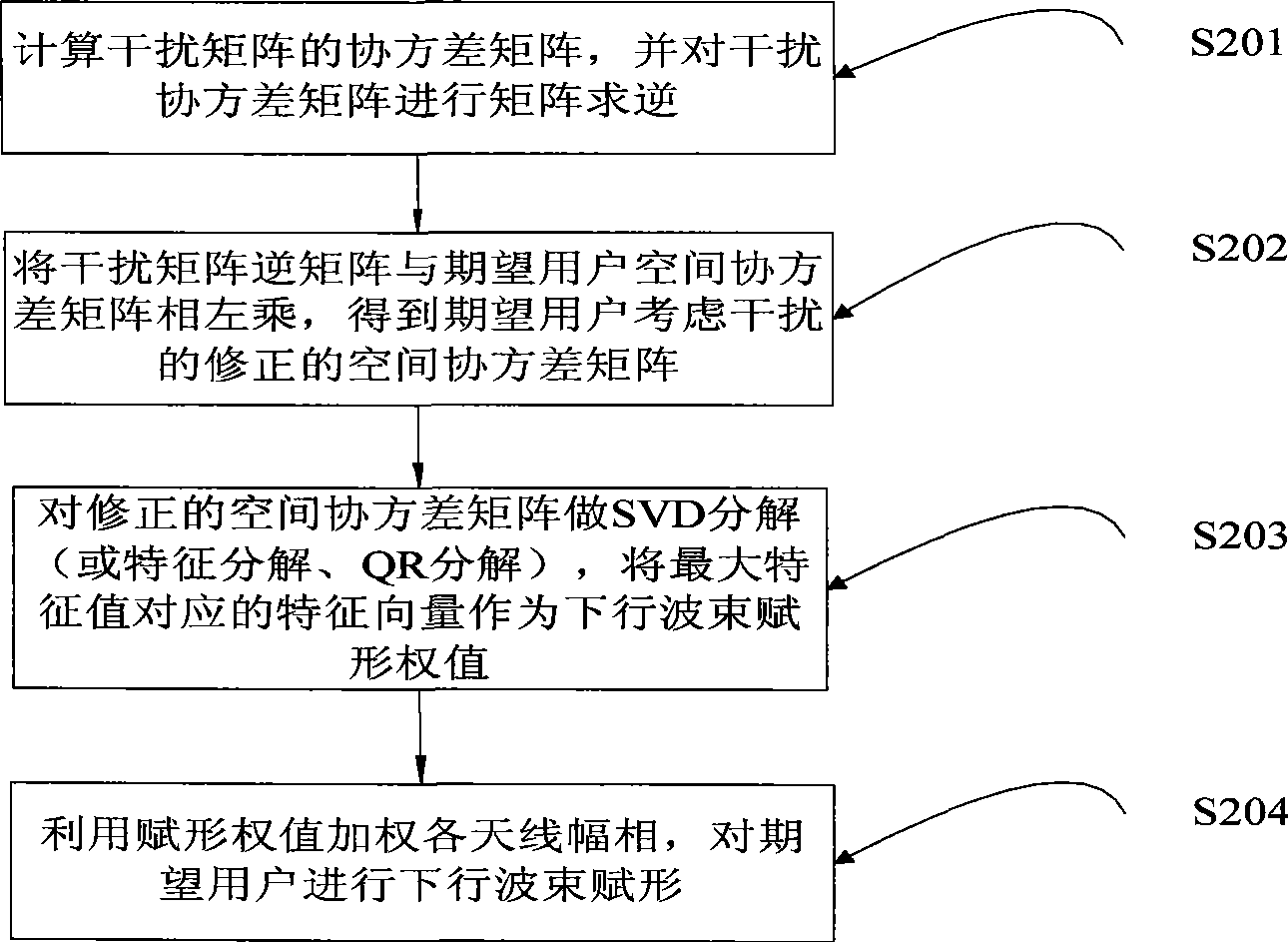
Beam size enlargement apparatus and method for restraining interference of intelligent antenna
InactiveCN101436893ACorrectly determine the spatial characteristicsSuppress interferenceSpatial transmit diversitySmart antennaEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of communication, and in particular discloses a beam forming method and a device for inhibiting interference in an intelligent antenna. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, according to received uplink signals, carrying out channel estimation on an expected user and an interferential user, and estimating an incoming wave direction of the expected user and an incoming wave direction of the interferential user; secondly, constructing an interference matrix of the expected user; thirdly, calculating a beam forming weight vector of the expected user based on the interference matrix of the expected user and a spatial covariance matrix covariance matrix; and finally, using the beam forming weight vector of the expected user as a formingweight value to weigh each antenna magnitude phase, and forming downlink beams for the expected user. A beam forming device is used for carrying out beam forming treatment according to the beam forming method. The method can inhibit interference, can still accurately determine spatial characteristics of the expected user, and achieve better downlink beam forming.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Multifunction laser power meter
ActiveUS20120134386A1Small effective diameterThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsPhotometryOptical power meterThermopile
A laser power meter incorporating an absorber disc with a peripheral thermopile ring, either continuous or segmented, and an additional temperature detection element in the central portion, that enables measurement of beam size. This detection element can be a thermopile element, generally a ring of smaller diameter than the peripheral thermopile used, and located closer to the center of the absorber disc. With this arrangement the beam size can be measured, in addition to measurements of the power and the position of the beam. Alternatively, this centralized detection element can be a single thermocouple junction located at the center of the disc, which acts as the hot junction of a thermocouple pair. The second or cold junction is effectively located on the disc close to the peripheral thermopile. Alternatively, two temperature measuring elements can be used, one at the disc center and one at the periphery.
Owner:OPHIR OPTRONICS SOLUTIONS
Apparatus and Method for Adjustable Fractional Optical Dermatological Treatment
ActiveUS20080015556A1System can be further enhancedControlling energy of instrumentLight therapyLight beamLasing wavelength
A fractional treatment system can be configured with a laser wavelength that is selected such that absorption of the laser wavelength within the tissue increases as the tissue is heated by the laser (e.g., 1390-1425 nm). Desirably, the laser wavelength is primarily absorbed within a treated region of skin by water and has a thermally adjusted absorption coefficient within the range of about 8 cm−1 to about 30 cm−1. An adjustable mechanism can be used to adjust the beam shape, beam numerical aperture, beam focus depth, and / or beam size to affect the treatment depth and or the character of the resulting lesions. The system may be designed to be switchable between a treatment mode that is semi-ablative and a treatment mode that is not semi-ablative. Adjustment of these parameters can improve the efficiency and efficacy of treatment. Illustrative examples of adjustable mechanisms include a set of spacers of different lengths, a rotatable turret with lens elements of different focal distances, an optical zoom lens, and a mechanical adjustment apparatus for adjusting the spacing between two optical lens elements.
Owner:SOLTA MEDICAL
Apparatus and Method for Adjustable Fractional Optical Dermatological Treatment
ActiveUS20080015557A1Control over selected characteristicOvercome limitationsControlling energy of instrumentLight therapyLight beamLasing wavelength
In a fractional treatment system, an adjustable mechanism can be used to adjust the beam shape, beam numerical aperture, beam focus depth, and / or beam size to affect the treatment depth and or the character of the resulting lesions. Adjustment of these parameters can improve the efficiency and efficacy of treatment. Illustrative examples of adjustable mechanisms include a set of spacers of different lengths, a rotatable turret with lens elements of different focal distances, an optical zoom lens, and a mechanical adjustment apparatus for adjusting the spacing between two optical lens elements. In one aspect, the fractional treatment is configured with a laser wavelength that is selected such that absorption of the laser wavelength within the tissue decreases as the tissue is heated by the laser (e.g., 1480-1640 nm). Desirably, the laser wavelength is primarily absorbed within a treated region of skin by water and has a thermally adjusted absorption coefficient within the range of about 7 cm−1 to about 26 cm−1.
Owner:SOLTA MEDICAL
Lens assembly for an automobile light assembly having LED light source
Owner:VARROC LIGHTING SYST SRO
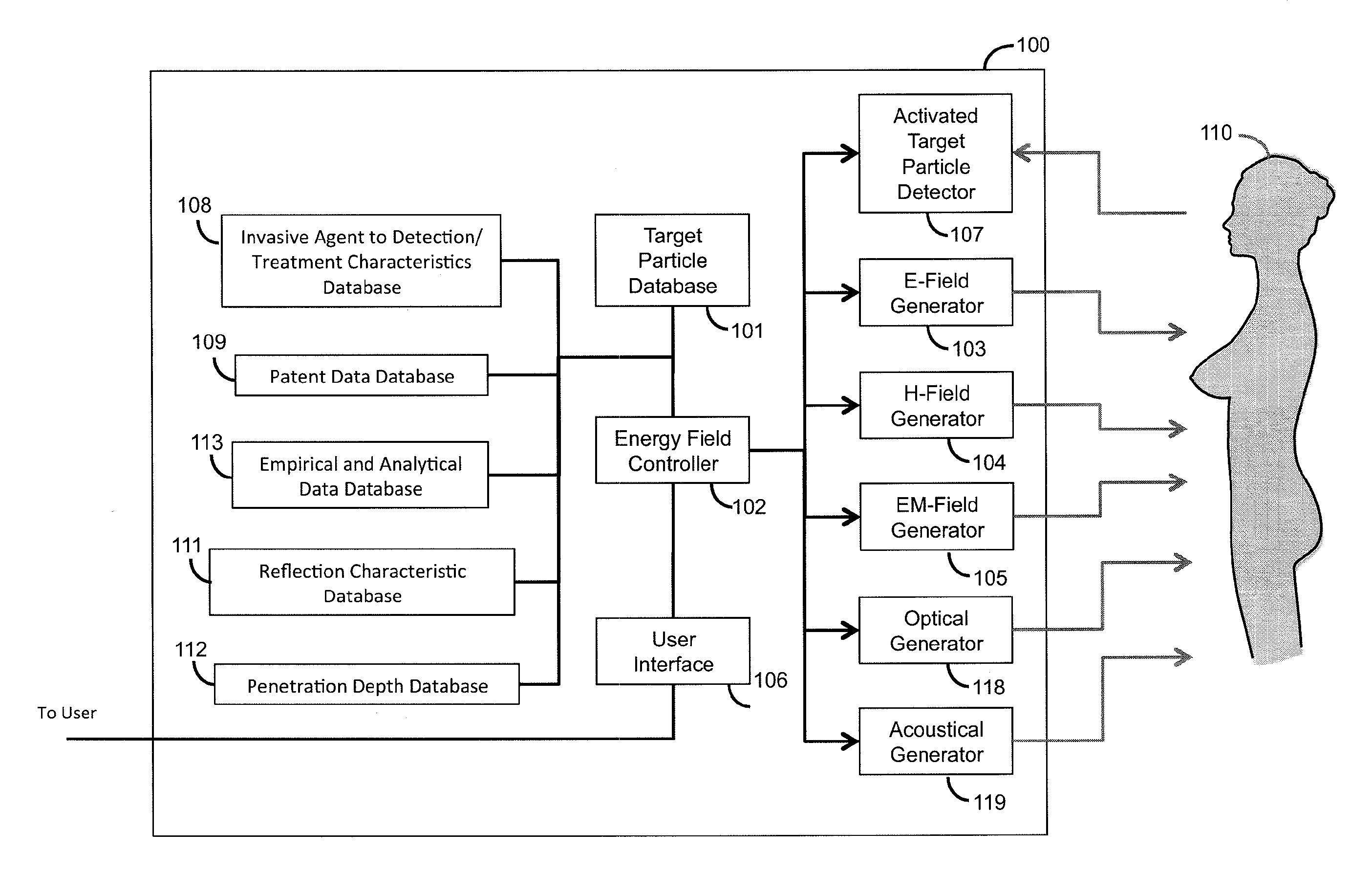
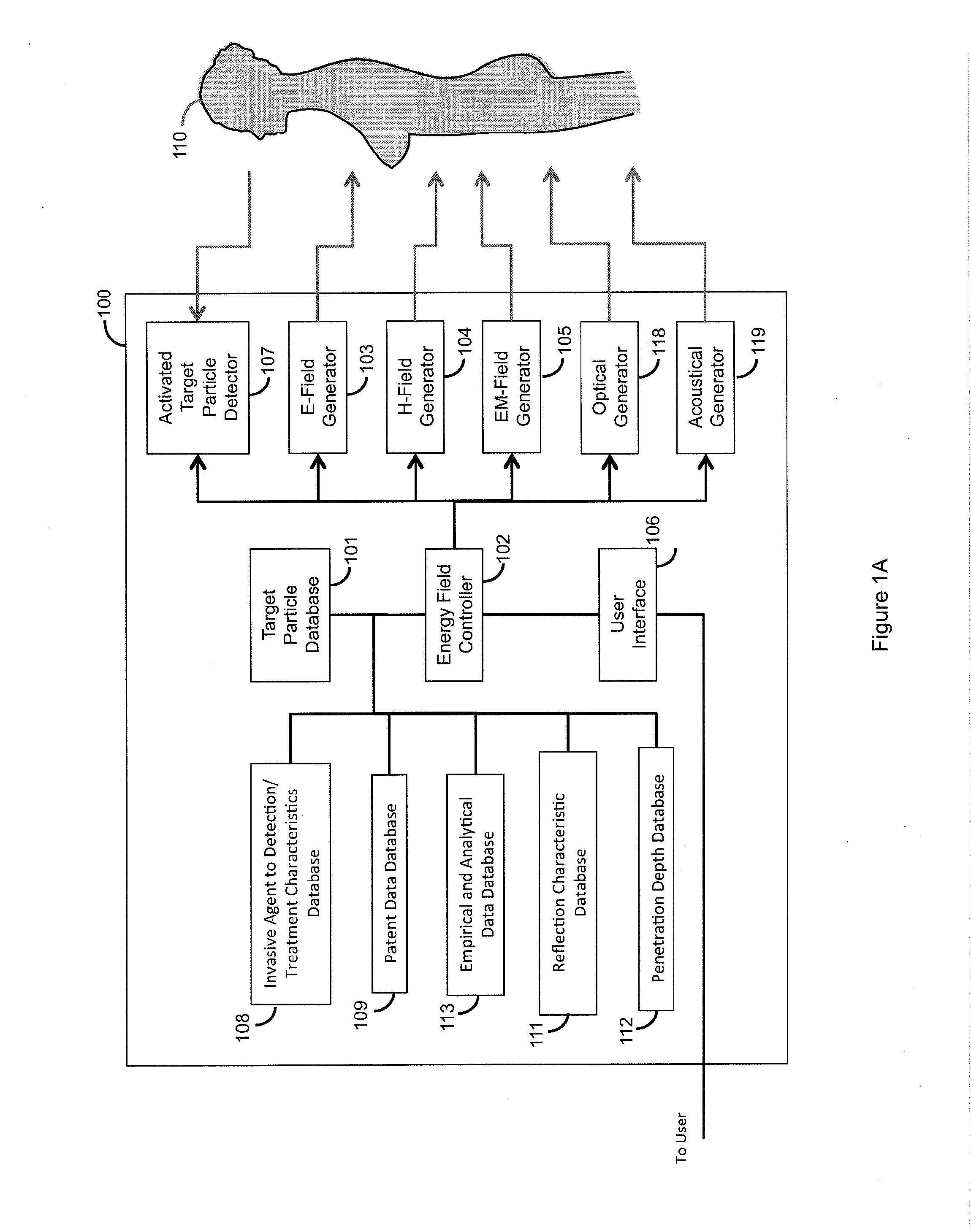
System for correlating energy field characteristics with target particle characteristics in the application of an energy field to a living organism for imaging and treatment of invasive agents
ActiveUS20120190912A1Extreme level of contrastEasy to separateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyBiological bodyParticle physics
The Energy Field and Target Correlation System automatically correlates the characteristics of target particles and a living organism to compute the characteristics of an energy field that is applied to a living organism to activate the target particles which are bound to or consumed or taken up by invasive agents in the living organism to produce detectable effects which can be used to image and treat the invasive agents. The energy field must be crafted to properly control the response and localize the extent of the illumination. The System automatically selects a set of energy field characteristics, including: field type, frequency, field strength, duration, field modulation, repetition frequency, beam size, and focal point. The determined energy field characteristics then are used to activate field generators to generate the desired energy field.
Owner:ENDOMAGNETICS LTD
Stereo projection apparatus and stereo projection system with low throw ratio and high light efficiency
ActiveUS20150109539A1Low throw ratioHigh light efficiencyProjectorsStereoscopic photographyFrame sequenceBeam splitter
A stereo projection apparatus includes a polarized beam splitter assembly for splitting a projecting light beam into a transmitted light beam, a first reflective light beam and a second reflective light beam; a polarization state transforming assembly for adjusting the polarization state of the transmitted light beam or the polarization state of the first reflective light beam and second reflective beam; a light path direction adjustment assembly for adjusting a travel direction of the transmitted light beam or a travel direction of the first reflective light beam and the second reflective light beam; a light beam size adjustment assembly for adjusting a coverage range of the transmitted light beam or a coverage range of the first reflective light beam and the second reflective light beam; and a light modulator for modulating the adjusted transmitted light beam, first reflective light beam and second reflective light beam to left-circularly polarized light and right-circularly polarized light in accordance with a frame sequence. The stereo projection apparatus can effectively reduce the optical path difference between the reflective light and transmitted light, thereby significantly reducing the size of the entire device and making overlapping of the various light beams easier.
Owner:SHENZHEN TIME WAYING TECH
Adjustable ring vector light beam producing system
InactiveCN101363964AChange horizontal sizeLow incident beam requirementsMirrorsPolarising elementsBeam polarizationCircular cone
The invention relates to an adjustable ring-shaped vector beam generating system. The prior art has high incident beam requirements, and cannot realize the ring-shaped vector beam and the beam size adjustment. In the invention, the incident beam sequentially passes through a beam expanding shaper, an external reflection circular conical surface reflector, a cylindrical curved polarizer, an internal reflection circular conical surface reflector, and two halfwave plates positioned in parallel; after a light source emergent beam passes through the beam expanding shaper and the external reflection circular conical surface reflector, a radial propagating beam is formed; a ring-shaped rotation vector polarized beam is formed by the reflection of the internal reflection circular conical surface reflector after the radial propagating beam passes through the cylindrical curved polarizer; the polarization state is changed by adjusting the optical axis angle of the two halfwave plates through a rotary motion part; and the transverse size of the beam is changed by adjusting the space between the external reflection circular conical surface reflector and the internal reflection circular conical surface reflector through an axial motion part. The invention has the advantages of low incident beam requirements, ring-shaped vector beam output, convenient beam polarization state and transverse size adjustment, etc.
Owner:高秀敏
Electron-emitting device and image-forming apparatus
InactiveUS20030067259A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsElectron sourceImaging quality
An electron-emitting device having a small electron beam size is proposed. In order to provide a high definition image display device having high image quality by utilizing this type of electron-emitting device and an electron source, a cathode electrode (2) has an opening which is trenched in a portion thereof, and further, the depth at which the opening is trenched is deep at a peripheral portion of the opening bottom face, and shallow at a central portion of the opening bottom face. A surface of an electron-emitting material is formed in a portion deeper than a boundary surface between the cathode electrode and an insulating layer.
Owner:CANON KK
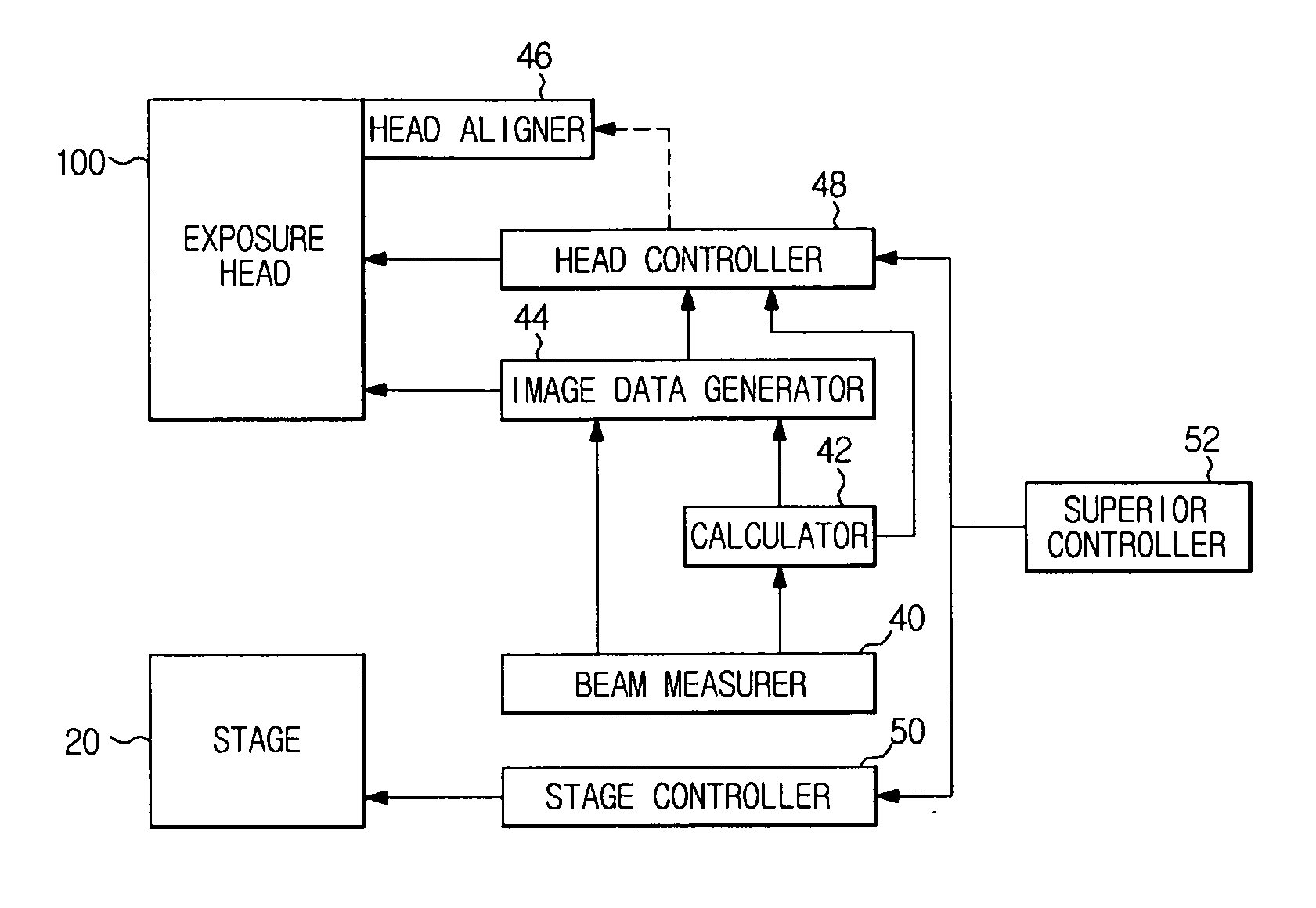
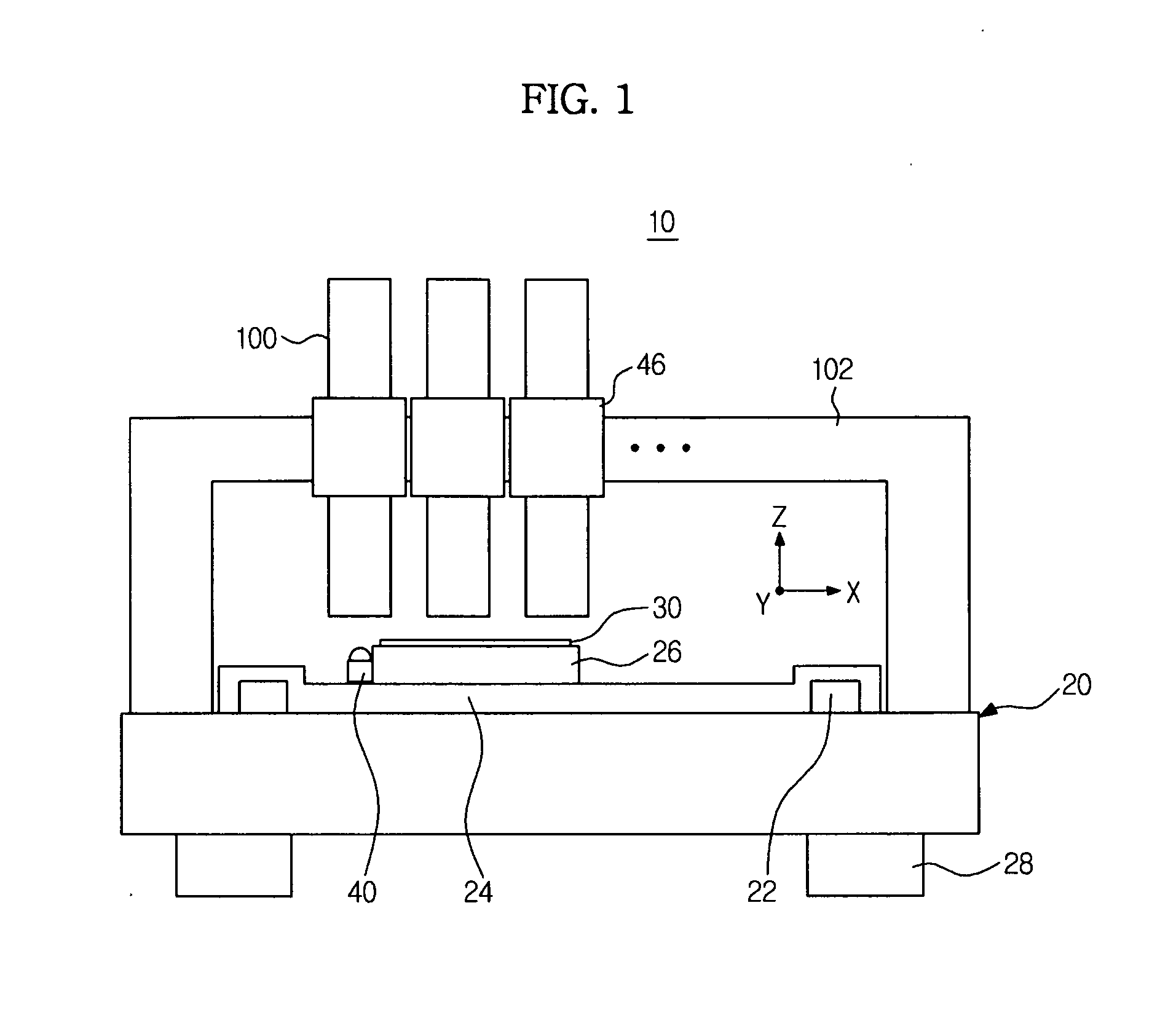
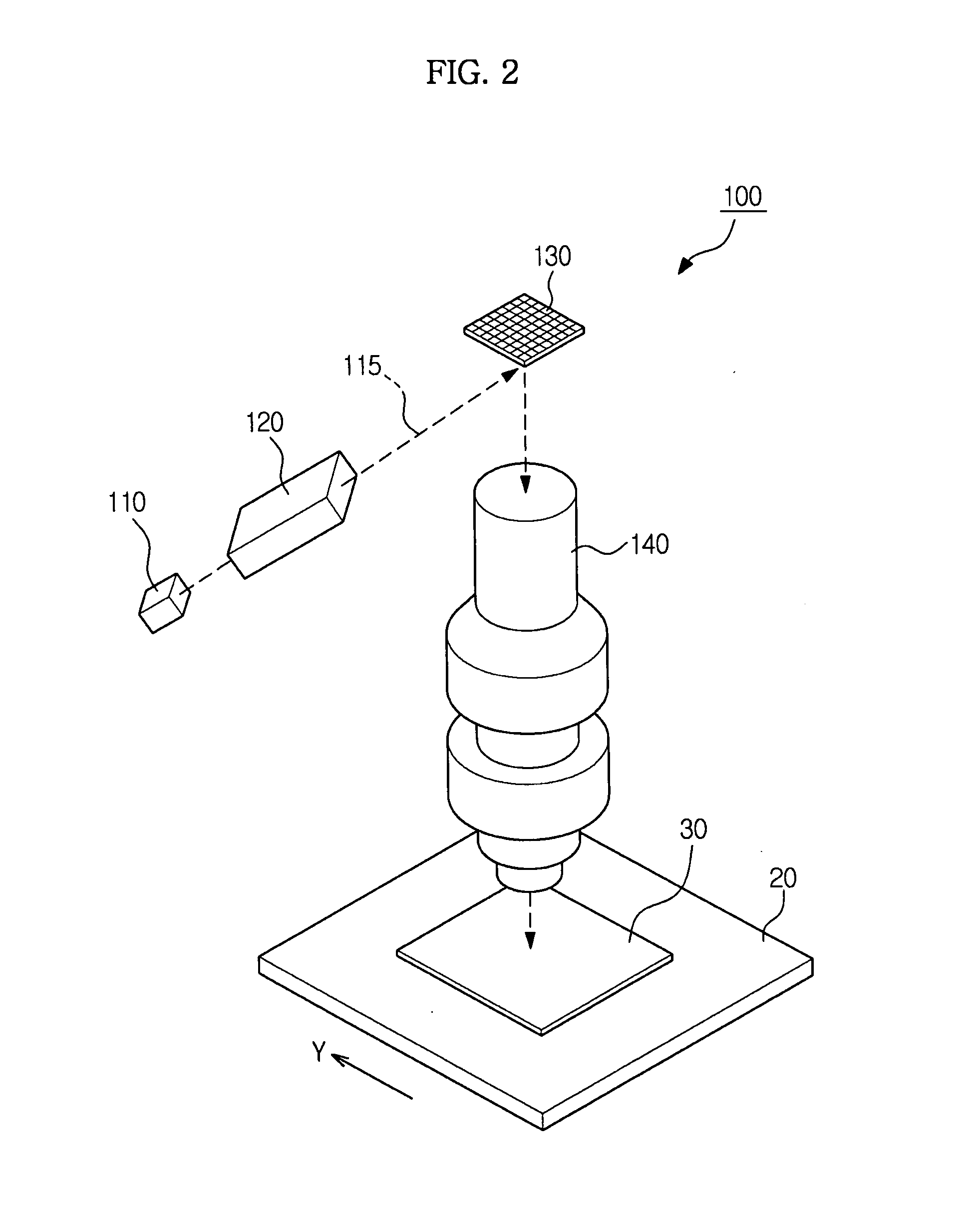
Maskless exposure apparatus and stitching exposure method using the same
ActiveUS20110267594A1Photomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDose uniformityImaging data
Disclosed herein are a maskless exposure apparatus configured to perform exposure by tilting a beam spot array with respect to a scan direction (Y-axis direction) thus preventing stitching stripes and a stitching method using the same. A step distance, in which exposure dose uniformity in a stitching area is within a tolerance range, is calculated using actual position data of beam spots constituting the beam spot array on an exposure plane, and if necessary, using beam power data and / or beam size data. As exposure is performed based on image data conforming to the step distance, the stitching area has a uniform exposure dose, enabling exposure without stitching stripes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ophthalmic system and method
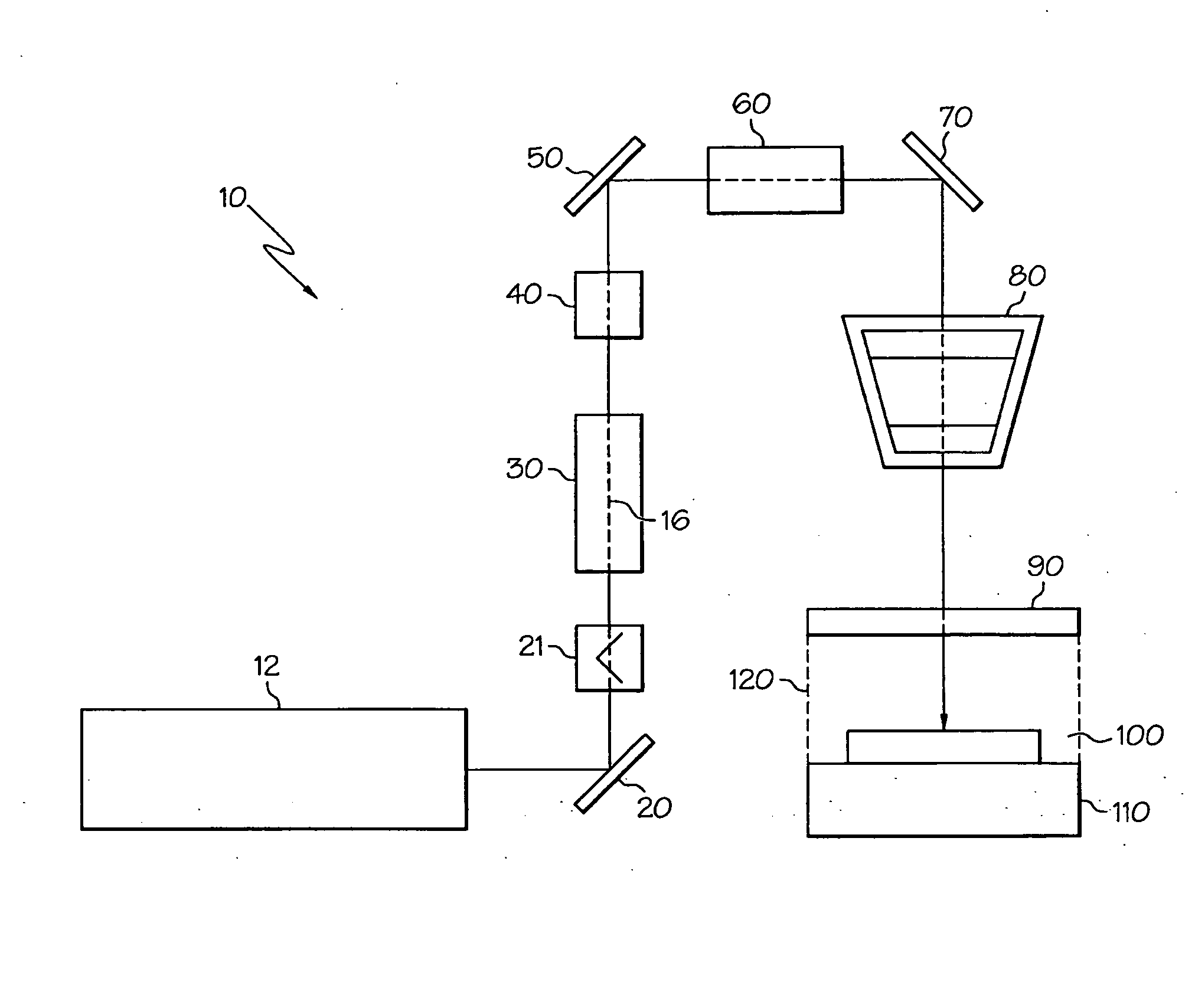
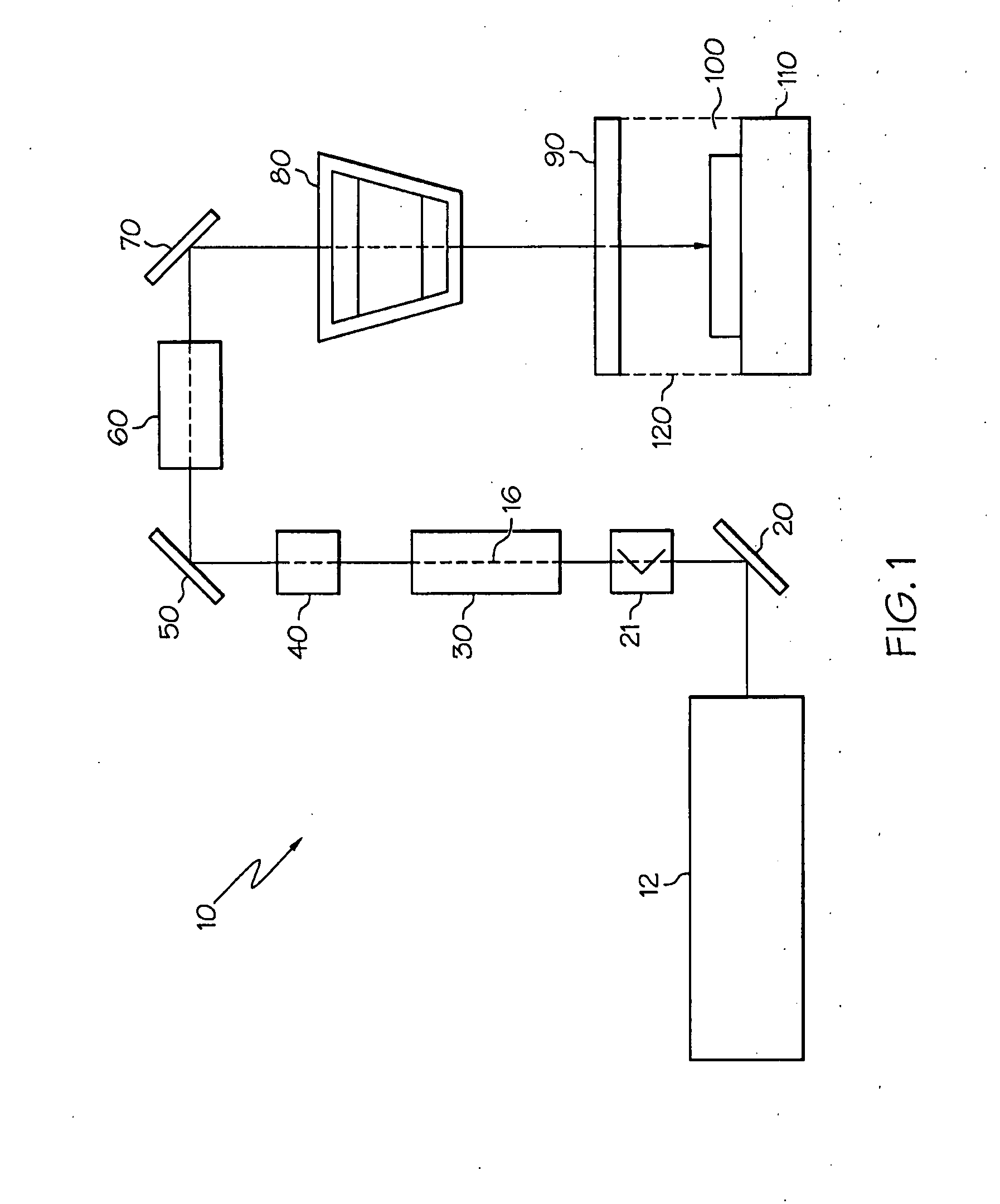
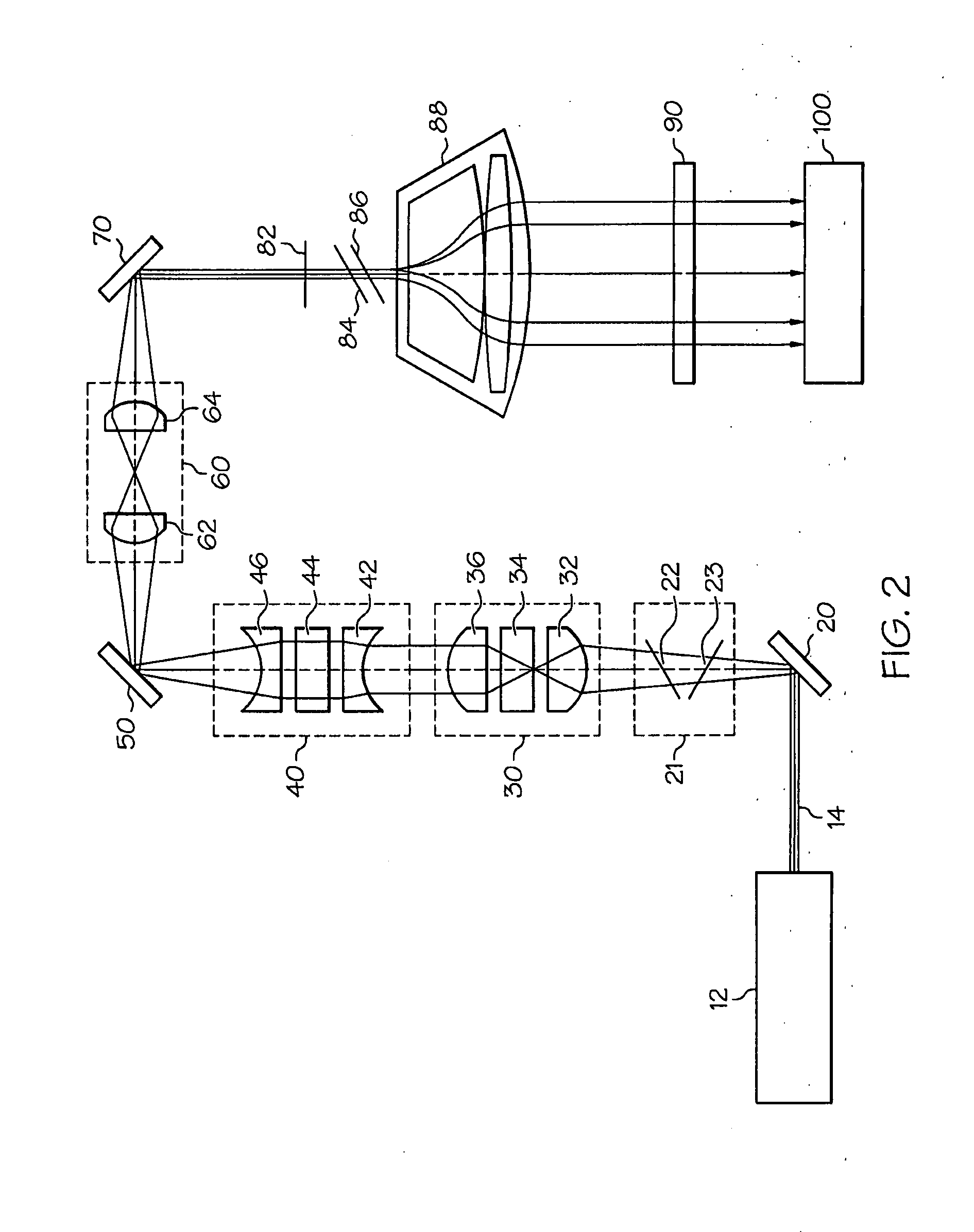
InactiveUS20080084541A1Eliminates focusedMinimizing speckleEye diagnosticsVergence movementLaser probe
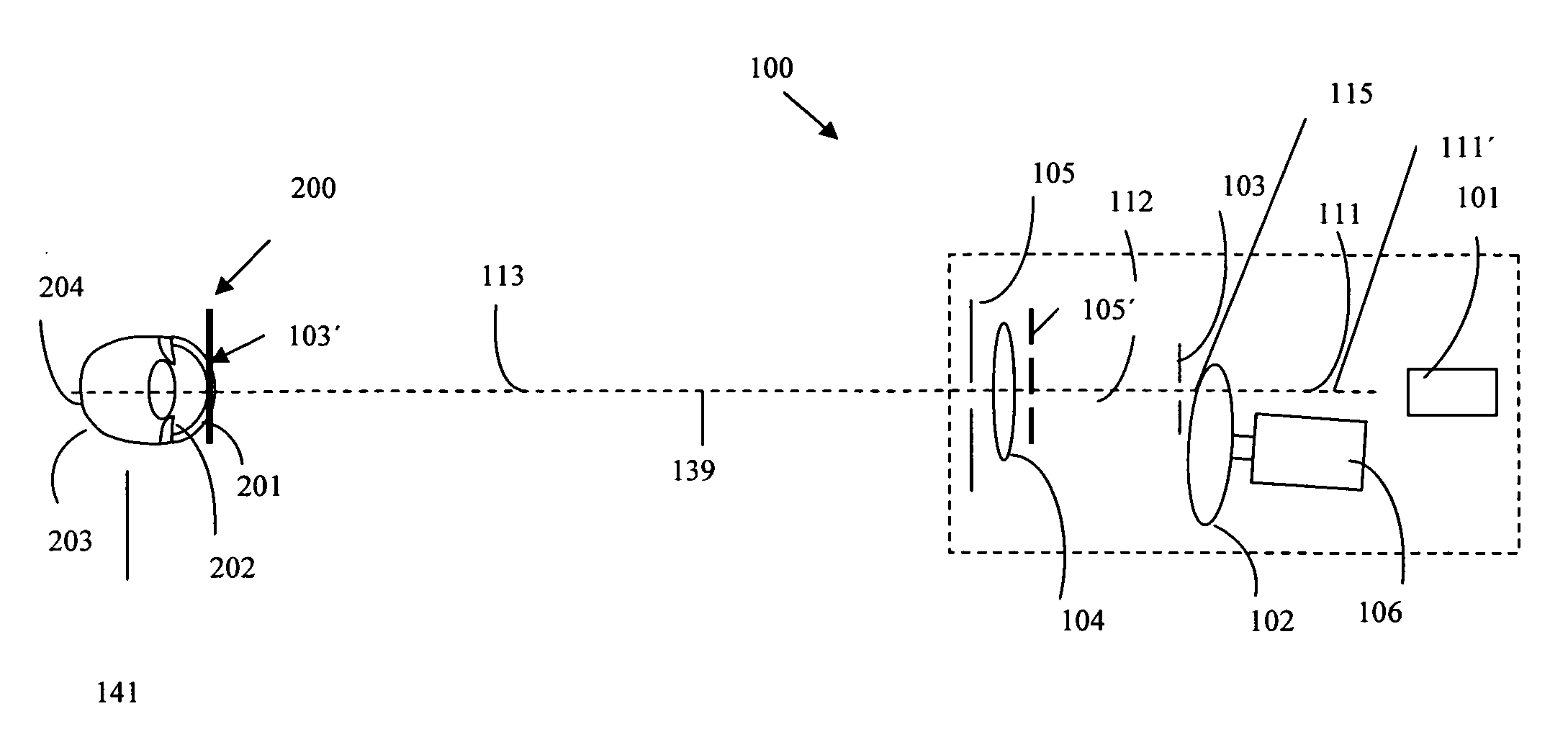
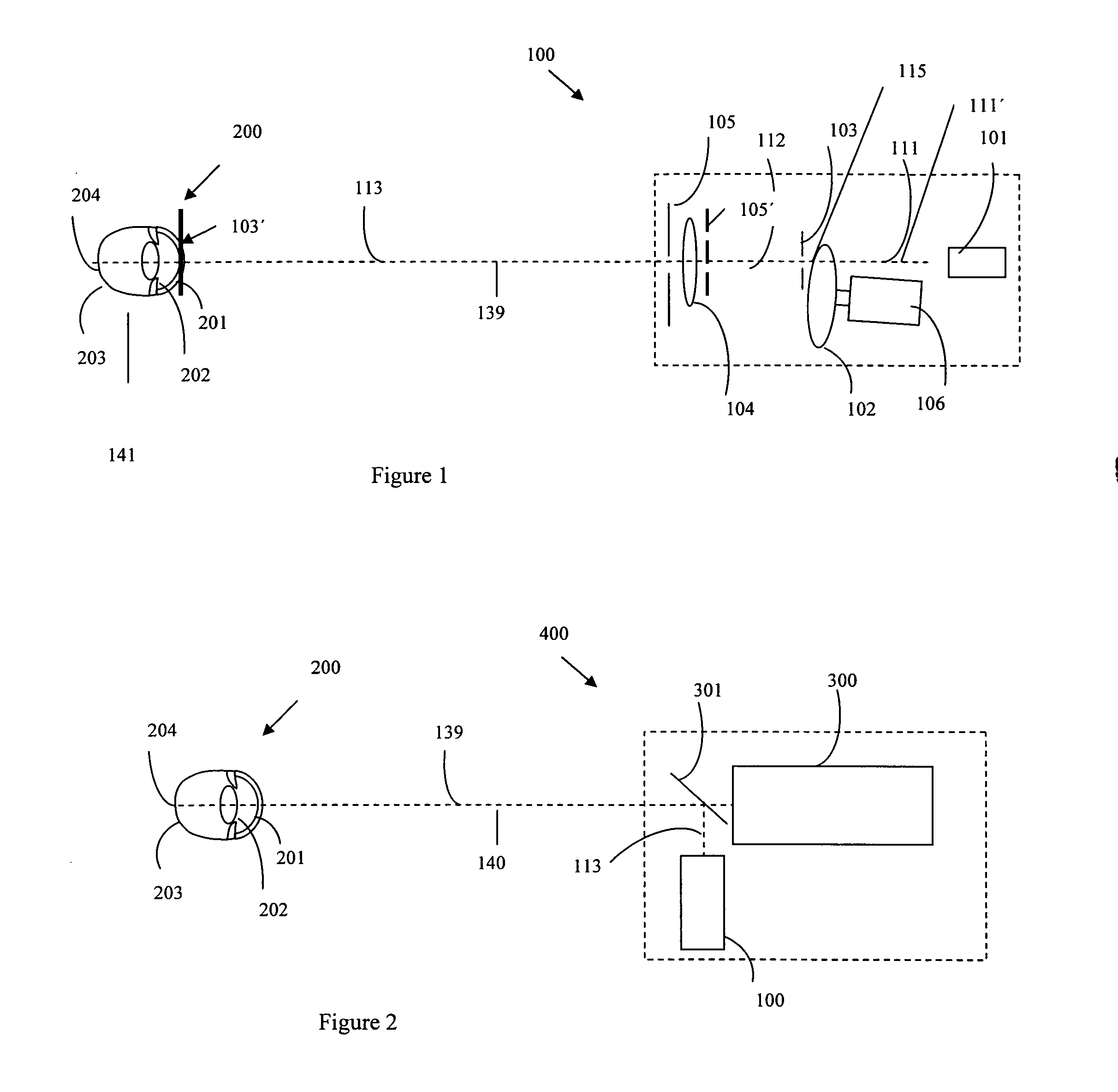
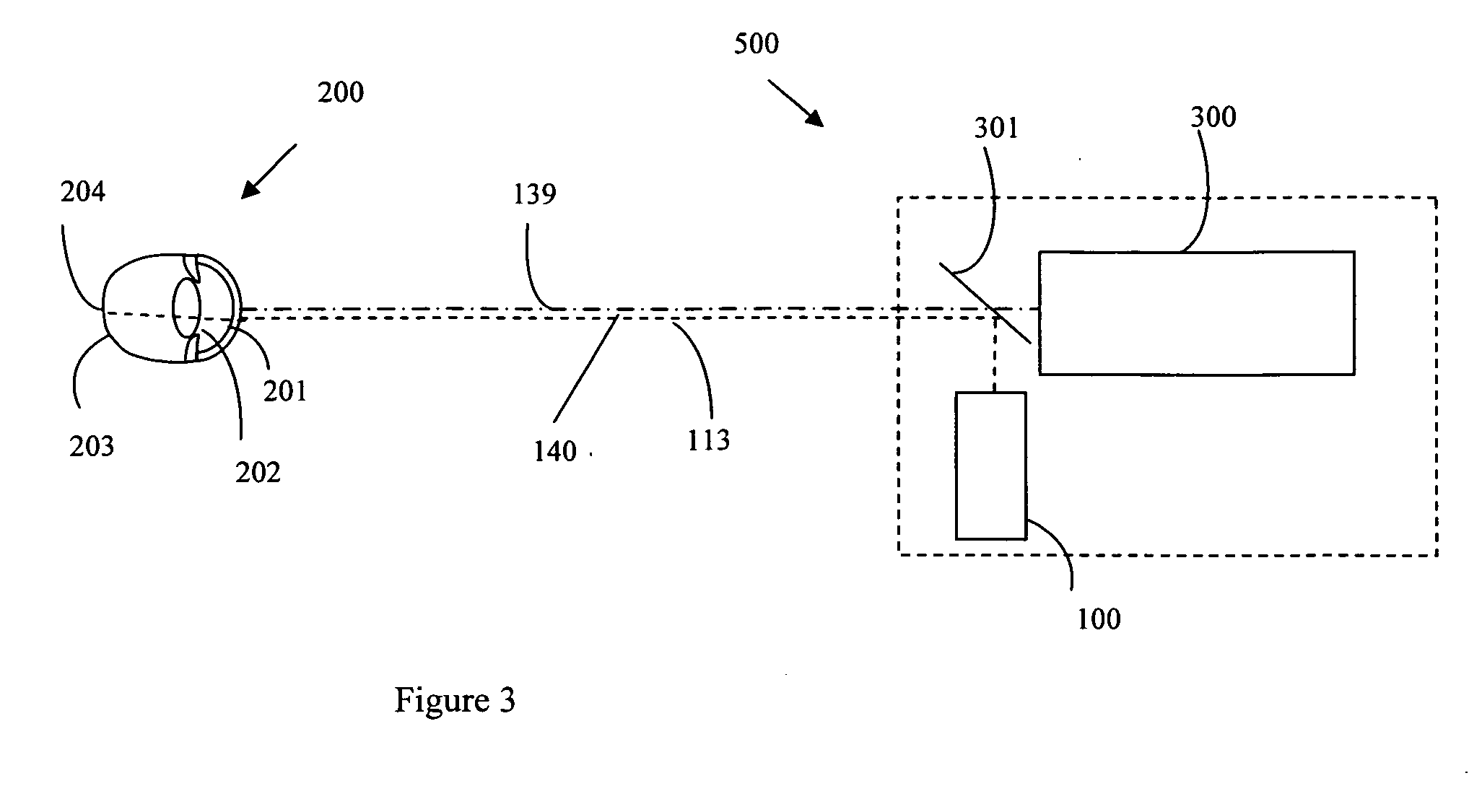
Ophthalmic system and method particularly suited to providing a laser probe beam for a Hartmann-Shack ophthalmic aberrometer. The laser probe beam produced by the system and method has a confined image spot at both the cornea and the retina. The probe beam can be generated with a laser beam passing through a moving holographic diffuser and two pinhole apertures. The holographic diffuser randomizes the spatial phase across the laser probe beam to substantially eliminate laser speckle from the Hartmann-Shack images. An imaging lens forms the probe beam and a first pinhole aperture image on the cornea, which eliminates beam size variation due to laser parameters and misalignment. A second-pinhole aperture is used to control the vergence of the probe beam and the probe beam spot size on the retina. The spot size on the retina is thus insensitive to the defocus power range of various subjects' eyes. The confined image spot on the retina substantially eliminates the possibility of an over-tight laser focal spot and allows the injection of higher laser power into the eye.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
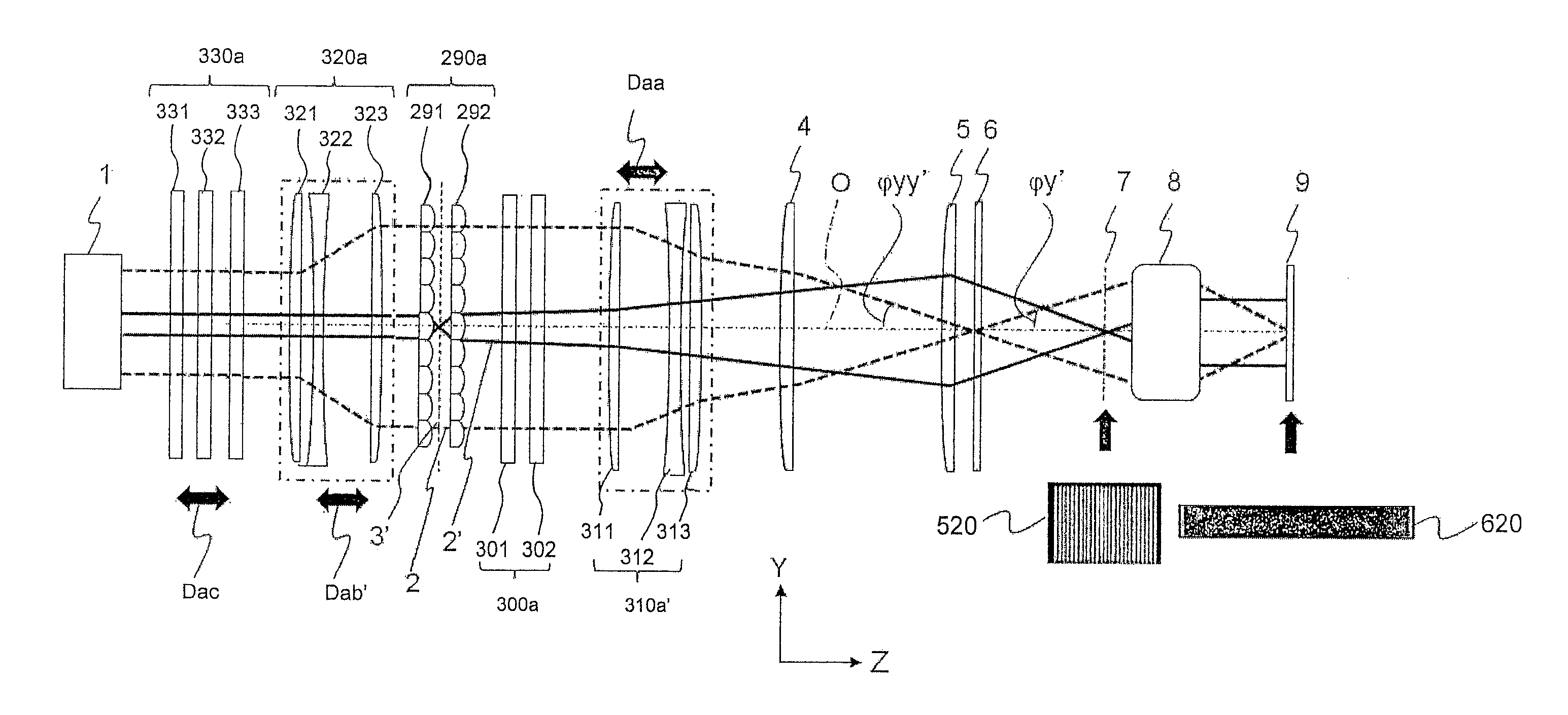
Adjustable Beam Size Illumination Optical Apparatus and Beam Size Adjusting Method
InactiveUS20110228537A1Small sizeUniform strengthCondensersLaser beam welding apparatusLight beamOptoelectronics
An adjustable beam size illumination optical apparatus includes a beam size adjusting optical system which includes groups of cylindrical array lenses disposed correspondingly to the long and short axis directions respectively and having variable intervals among the lenses, and a group of cylindrical telescope lenses disposed correspondingly to one of the long and short axis directions and having variable intervals among the lenses, and adjusts parallel light from a light source in size in accordance with the two axis directions orthogonal to each other. The lens interval of one of the cylindrical array lens groups and the cylindrical telescope lens group is changed to adjust a beam size on a projection surface in accordance with the long axis direction or the short axis direction. Thus, it is possible to adjust the beam size in accordance with the long axis direction and the short axis direction individually, and it is possible to make irradiation with the beam with uniform intensity.
Owner:HITACHI SEIKO LTD
Multi-beam and multi-band antenna system for communication satellites
An antenna system includes a reflector having a modified-paraboloid shape; and a multi-beam, multi-band feed array located at a focal point of the reflector so that the antenna system forms a multiple congruent beams that are contiguous. The system has a single reflector with non-frequency selective surface. The reflector is sized to produce a required beam size at K-band frequencies and is oversized at EHF-band frequencies. The synthesized reflector surface is moderately shaped and disproportionately broadens EHF-band and Ka-band beams compared to K-band beams. The synthesized reflector surface forms multiple beams each having a 0.5-degree diameter at K-band, Ka-band, and EHF band. The multi-beam, multi-band feed array includes a number of high-efficiency, multi-mode circular horns that operate in focused mode at K-band and defocused mode at Ka-band and EHF-band by employing “frequency-dependent” design for the horns.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Power scalable multi-pass faraday rotator
InactiveUS20140218795A1Reduce thermal gradientReduce gradientPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsOptical isolatorLight beam
Transparent heat-conductive layers of significant thickness are bonded or adhered to opposing optical faces of a Faraday optic to form a Faraday optic structure that can be used with beam-folding mirrors and an external magnetic field to form a multi-pass Faraday rotator with minimal thermal gradient across the beam within the Faraday optic. The transparent heat conductive layers conduct heat through the Faraday optic substantially parallel to the beam propagation axis for each pass through the Faraday optic structure and thereby reduce thermal gradients across the beam cross section that would otherwise contribute to thermal lens focal shifts and thermal birefringence in the Faraday optic structure. The multi-pass Faraday rotator of this invention is suitable for use with any device based upon the Faraday effect such as optical isolators, optical circulators and Faraday mirrors that are scalable with beam size to power levels in excess of 2 kW.
Owner:ELECTRO OPTICS TECH
Process for polishing glass substrate
ActiveUS20070259605A1Improve flatnessVacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsBeam sizeDry etching
A process for polishing a glass substrate, which enables to polish a glass substrate having a large waviness formed by mechanical polishing, to have a surface excellent in flatness, is provided. A process for polishing a glass substrate, comprising a step of measuring the surface profile of a mechanically polished glass substrate to identify the width of waviness present in the glass substrate, and a step of applying dry etching using a beam having a beam size in FWHM (full width of half maximum) value of at most the above size of waviness, to polish the surface of the glass substrate.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Laser welder
A laser welder controls a focus and direction of a laser beam received from a laser oscillator through optical fiber and radiating the controlled laser beam. The laser welder may include a housing; a beam transmission unit expanding a beam size and simultaneously switching direction of the laser beam; a first radiation unit switching direction of the laser beam by reflecting part of the laser beam through a slot mirror and simultaneously reducing the beam size within the housing, thus forming a focus in a first welding unit through a first beam port; and a second radiation unit expanding and reducing a remainder of the laser beam received through the slot mirror of the first radiation unit and simultaneously switching a direction of the remainder, thus forming a focus in a second welding unit through a second beam port.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
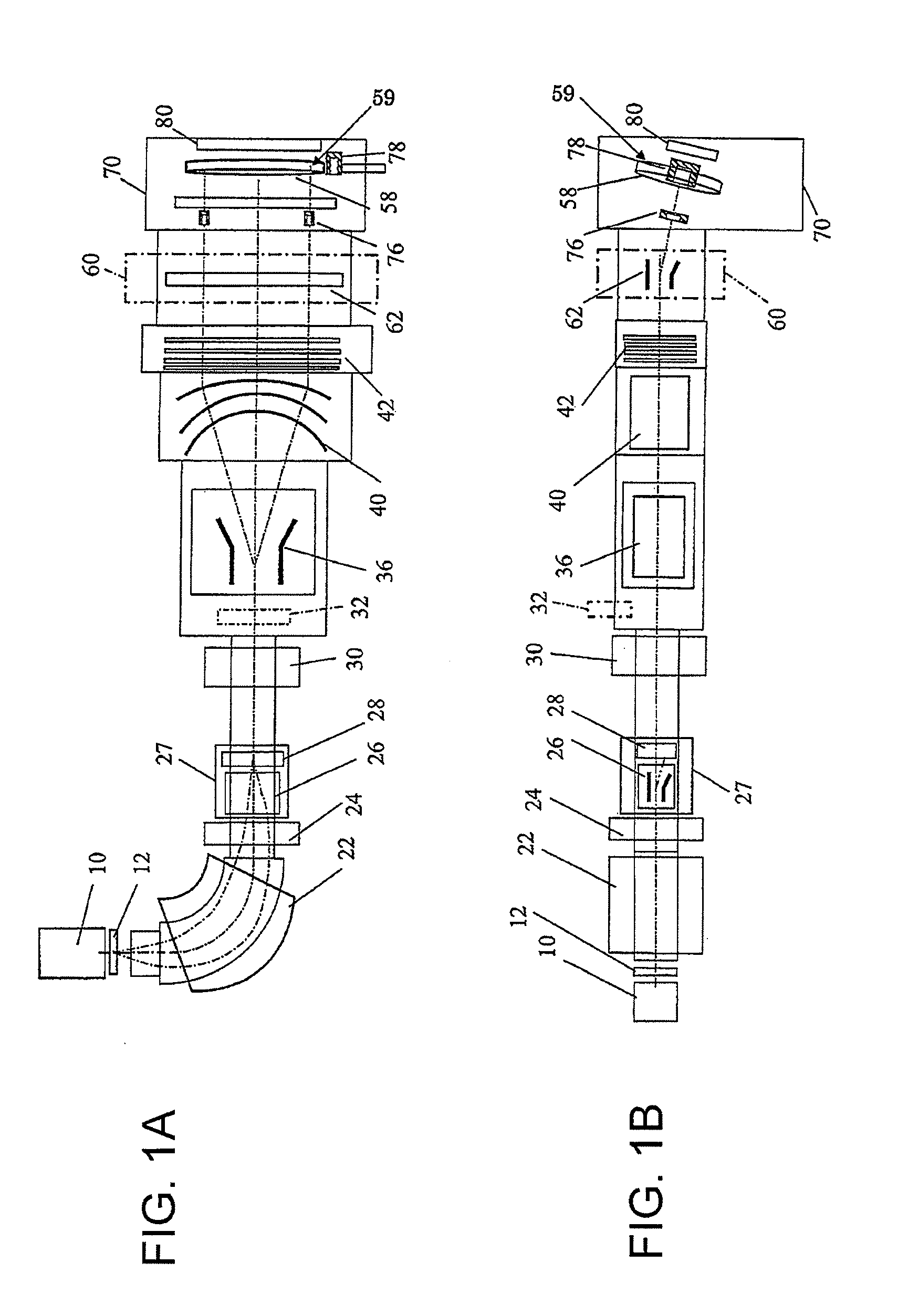
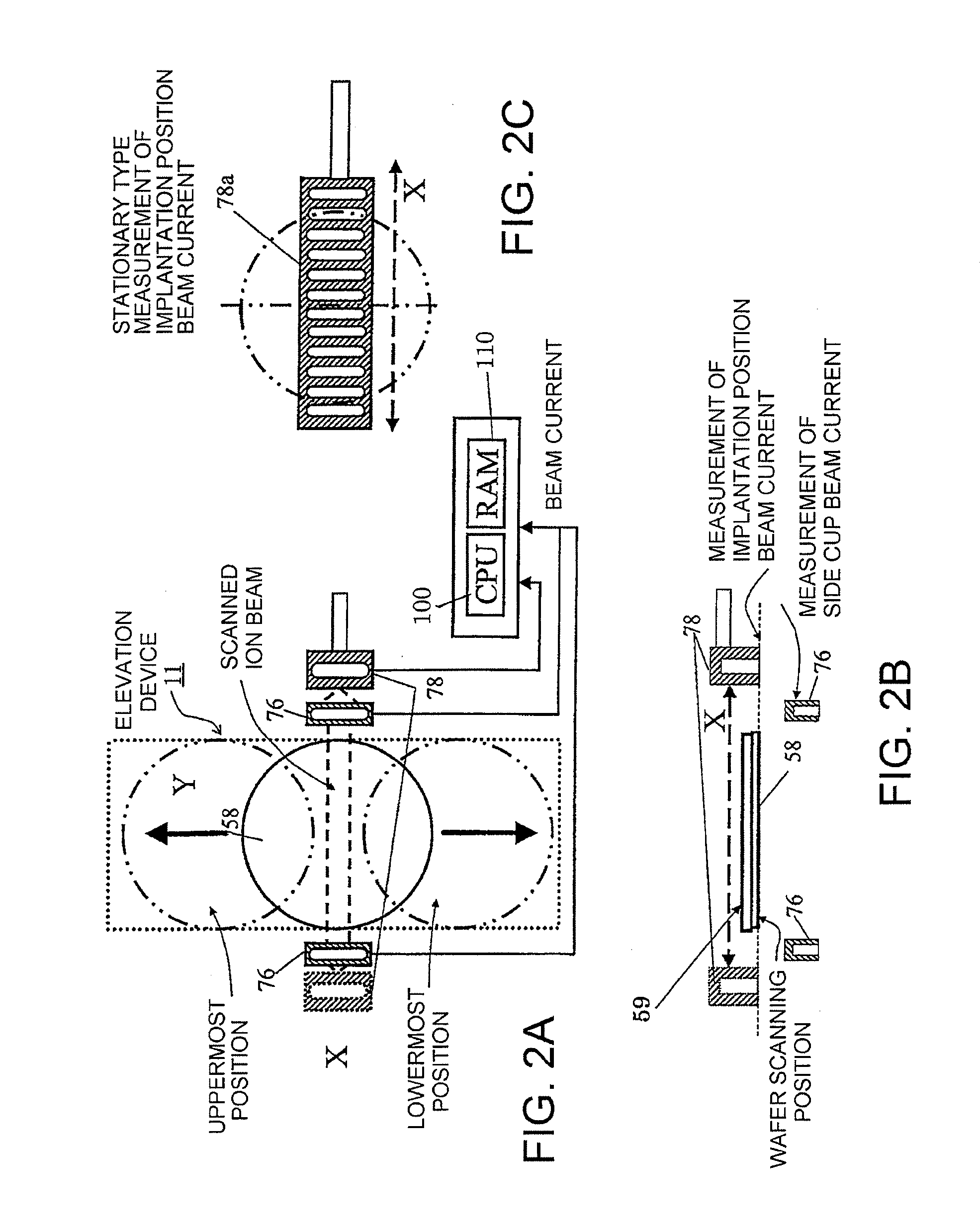
Ion implantation apparatus and control method thereof
ActiveUS20130256566A1Good reproducibilityEasy to adjustElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMeasurement deviceMeasuring instrument
A vertical profile, a horizontal profile, and an integrated current value of an ion beam are measured by a plurality of stationary beam measuring instruments and a movable or stationary beam measuring device. At a beam current adjustment stage before ion implantation, a control device simultaneously performs at least one of adjustment of a beam current to a preset value of the beam current, adjustment of a horizontal beam size that is necessary to secure uniformity of the horizontal ion beam density, and adjustment of a vertical beam size that is necessary to secure the uniformity of the vertical ion implantation distribution on the basis of a measurement value of the stationary beam measuring instruments and the movable or stationary beam measuring device.
Owner:SENCORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com