Patents
Literature
540 results about "Laser probe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
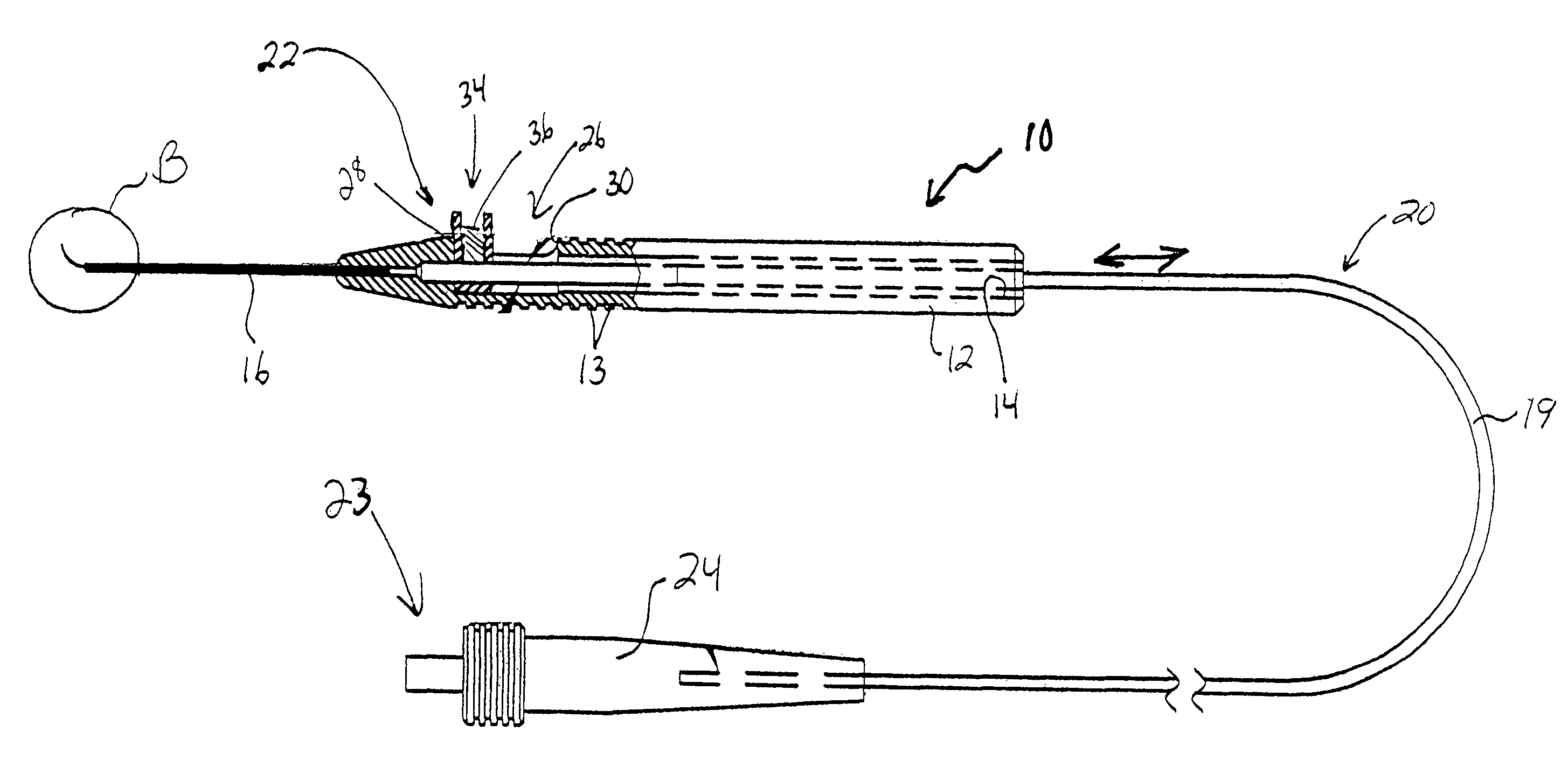
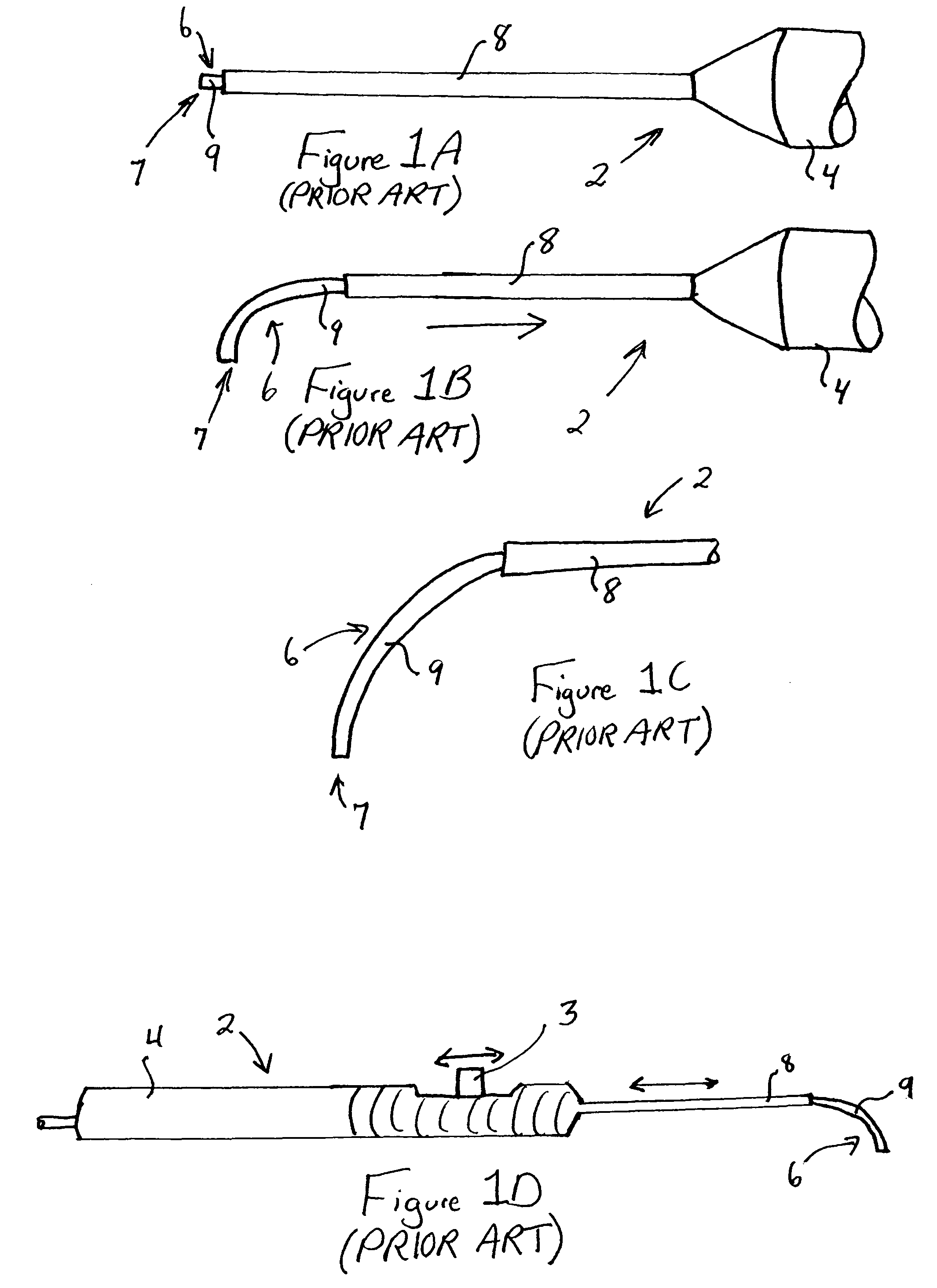
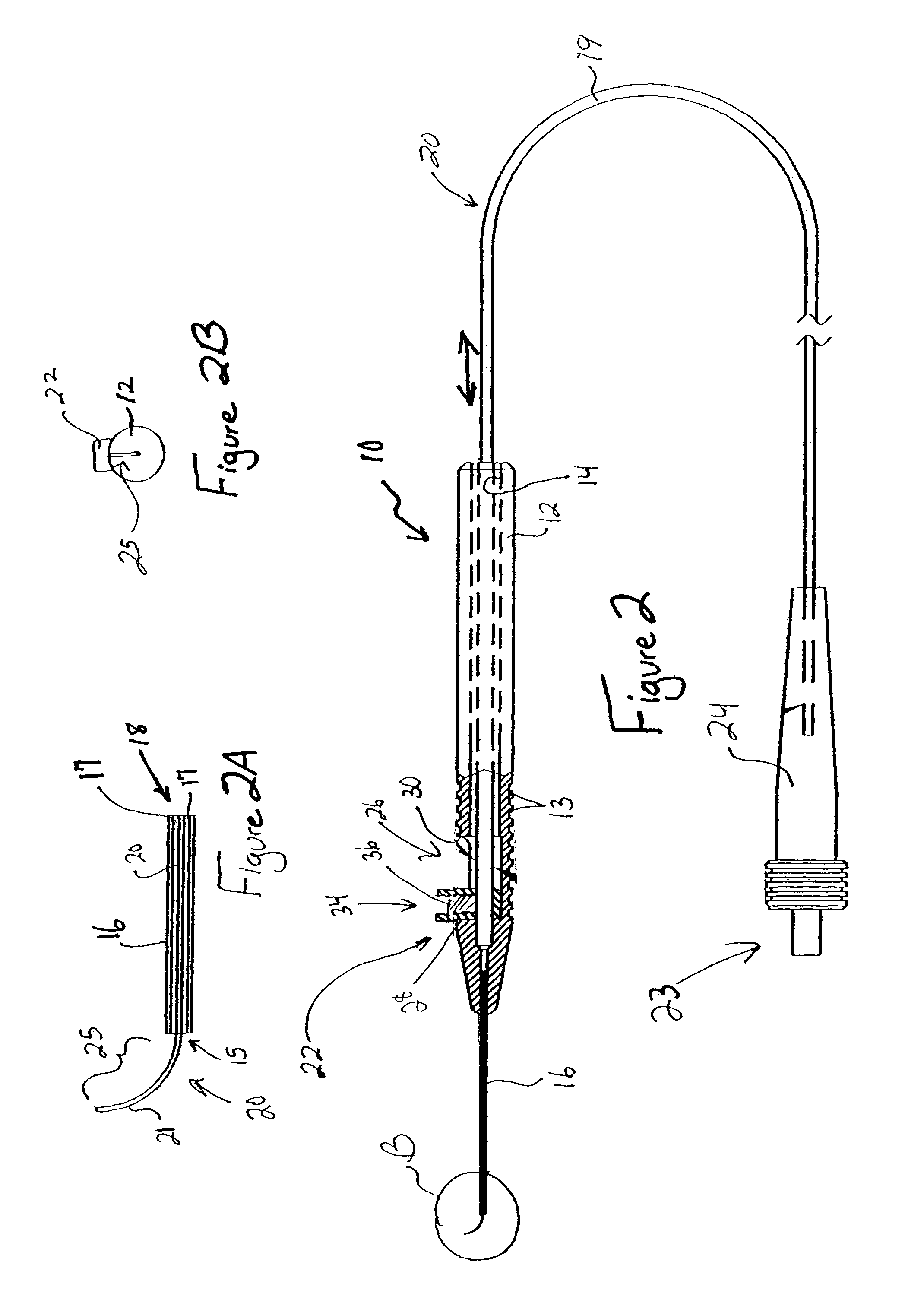
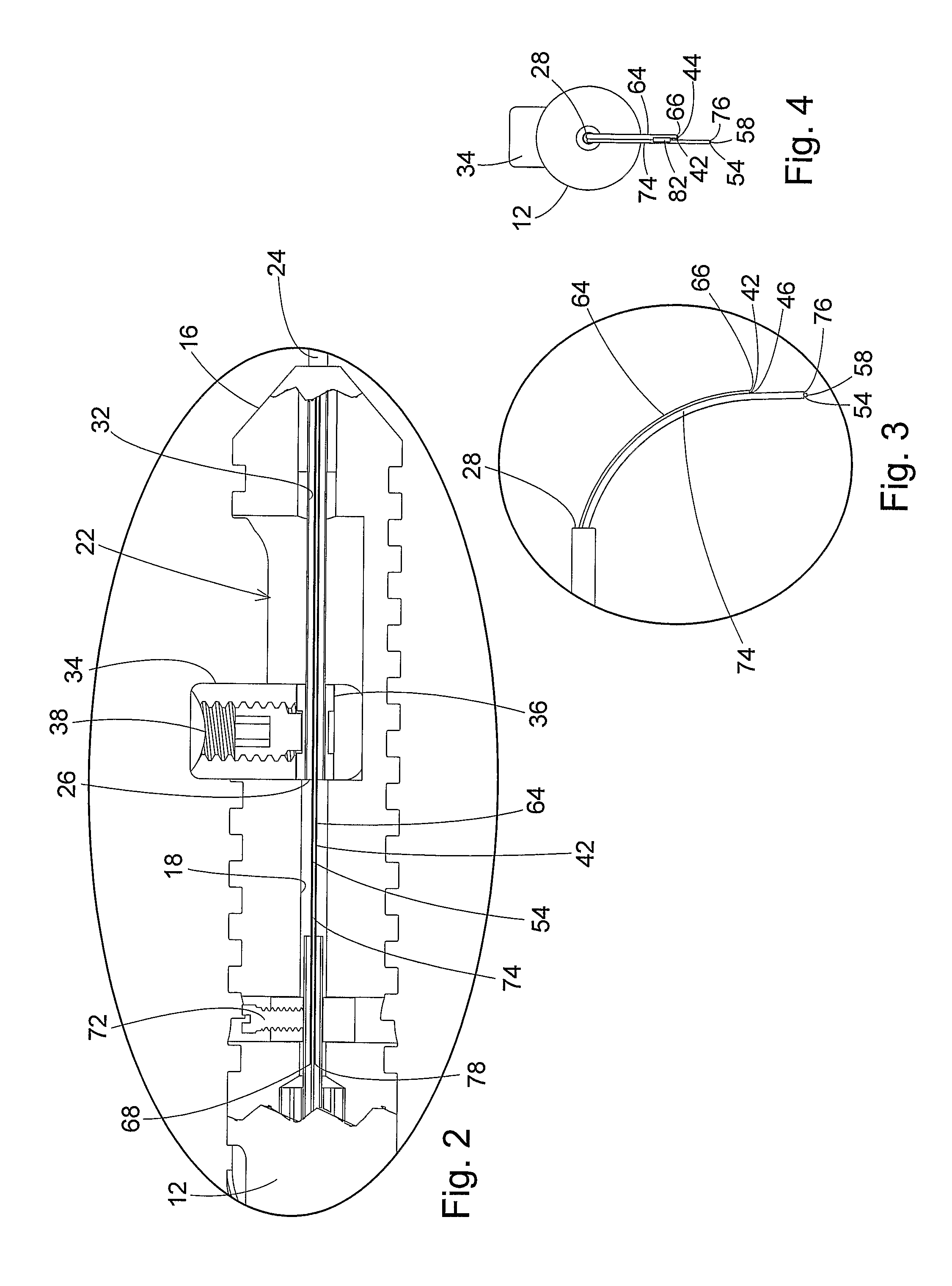
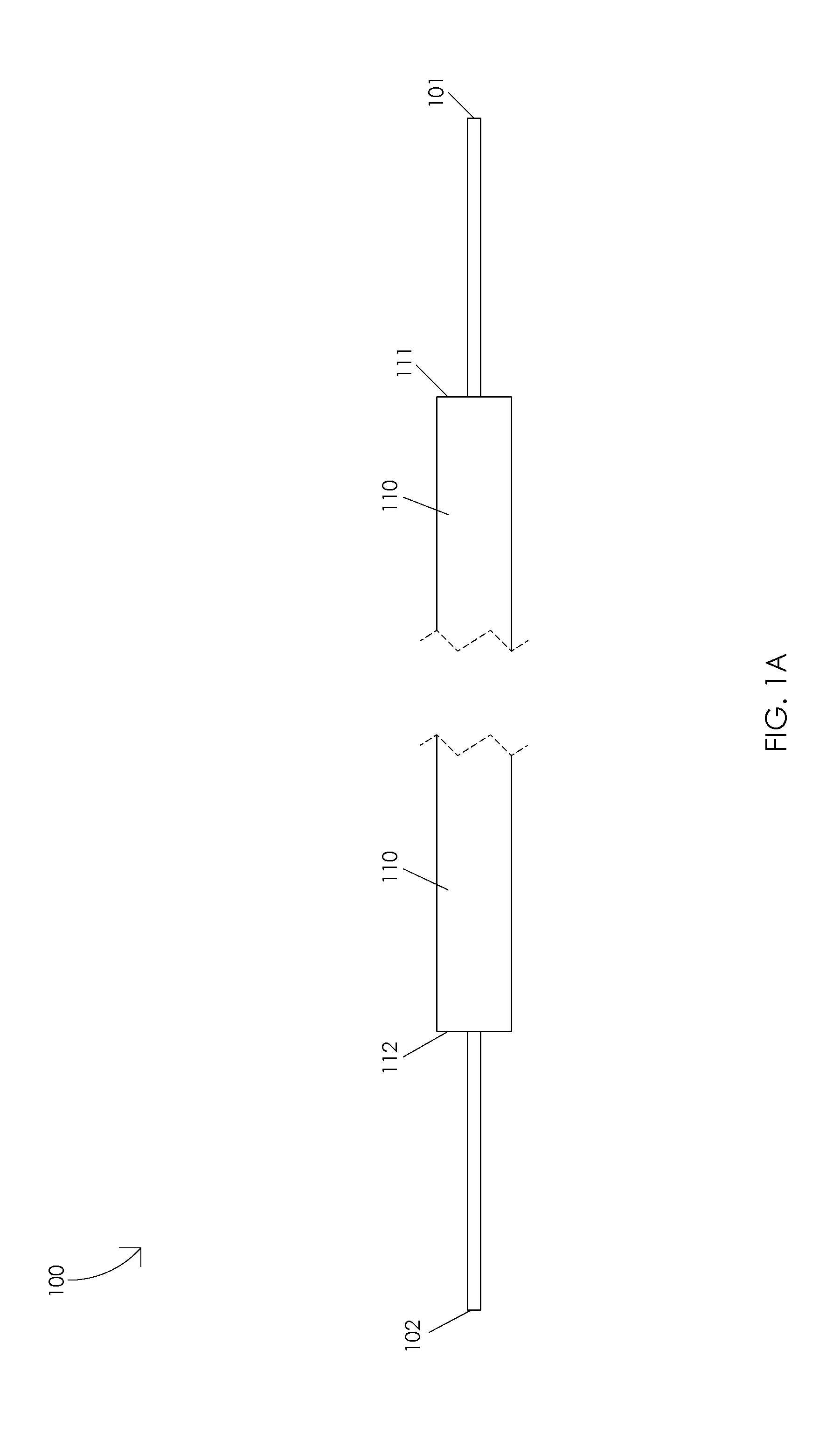
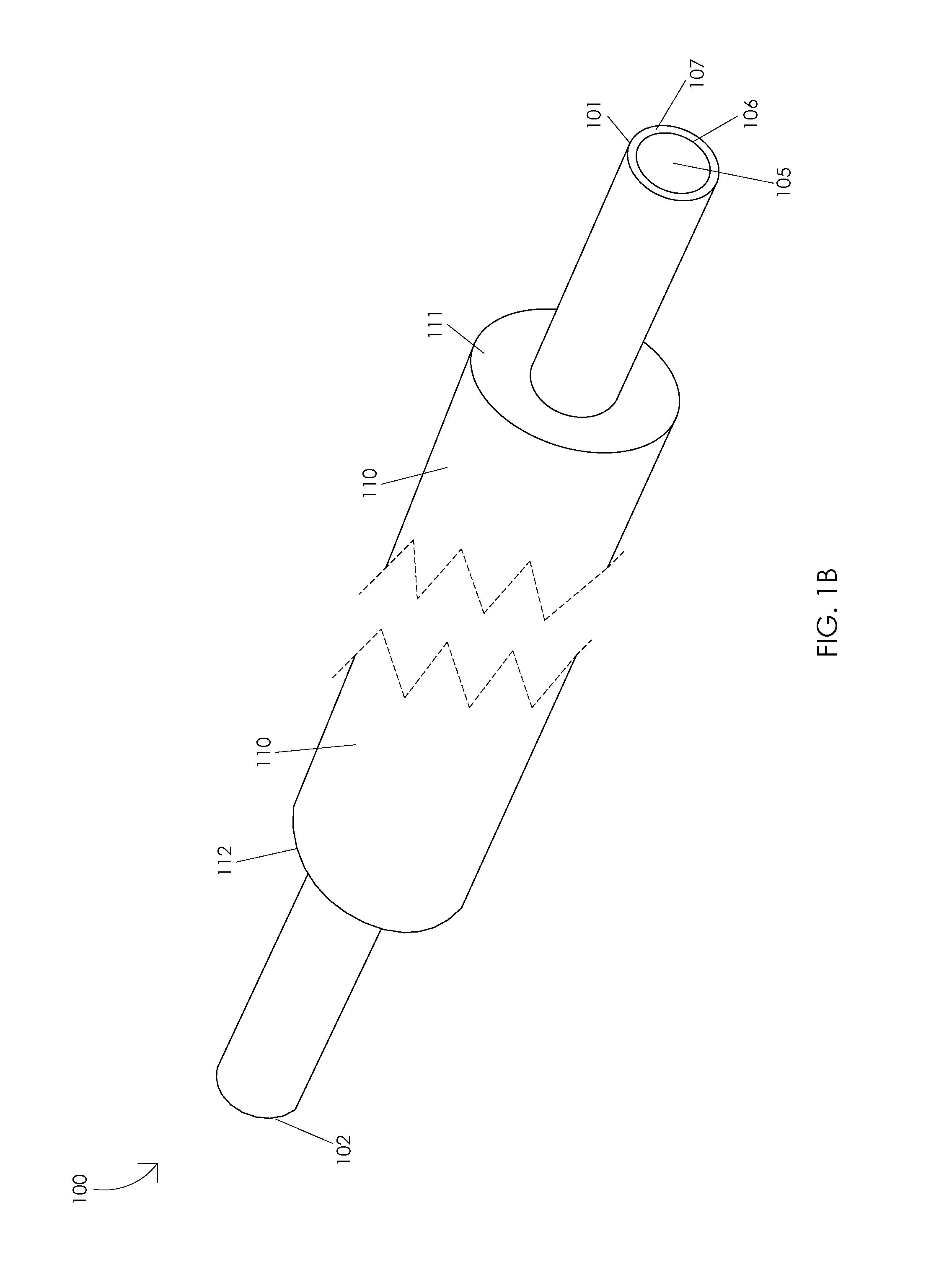
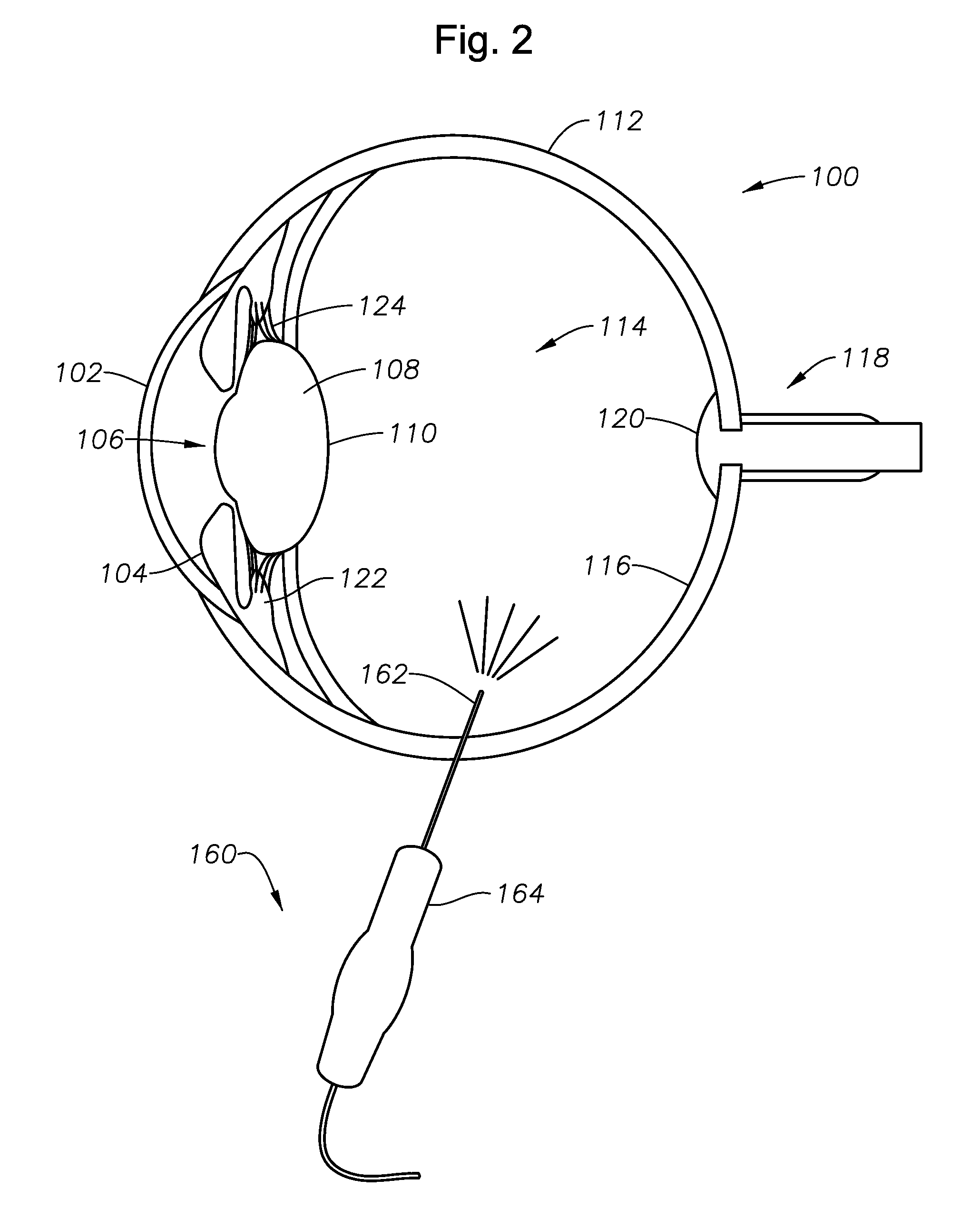
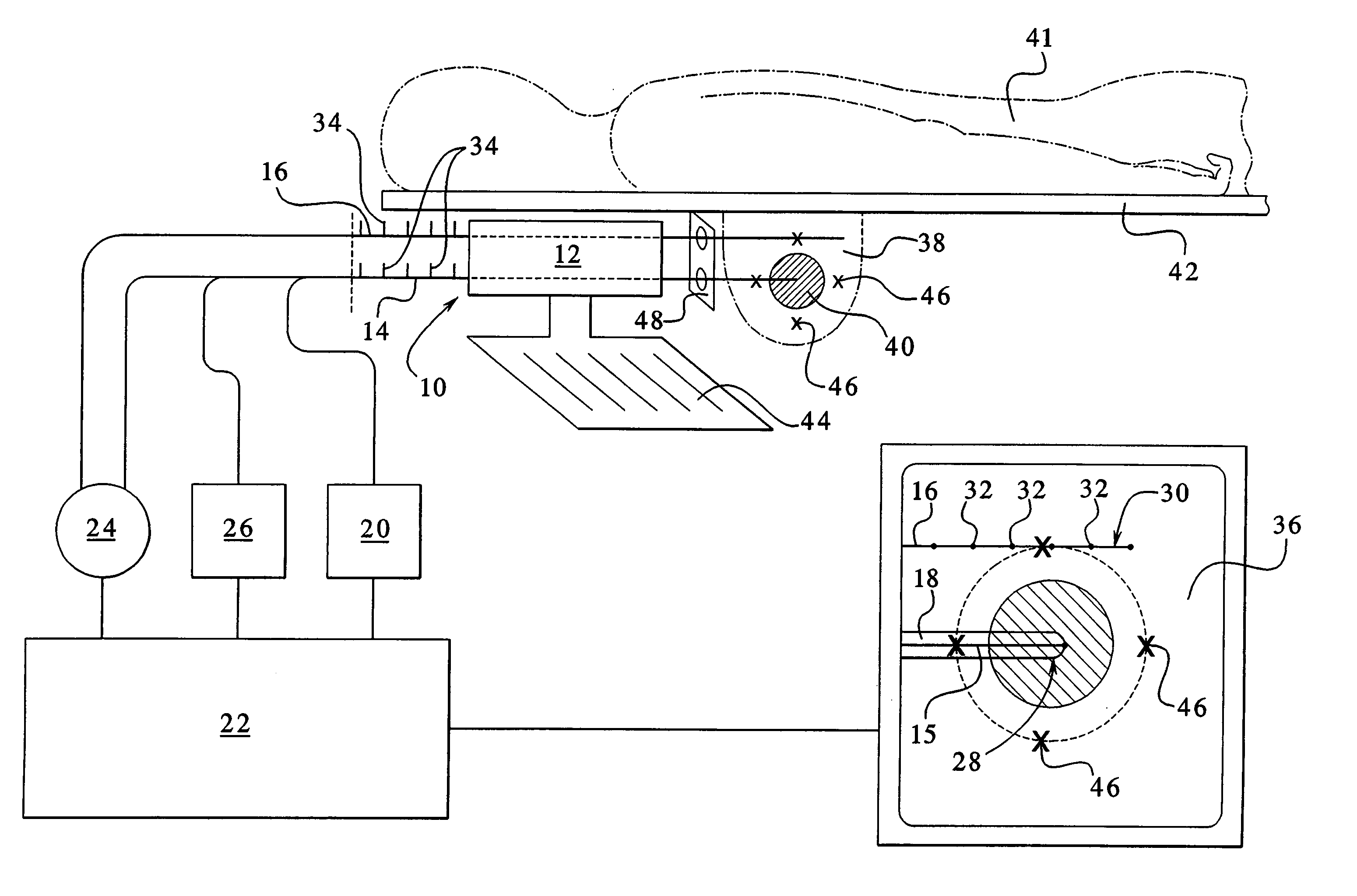
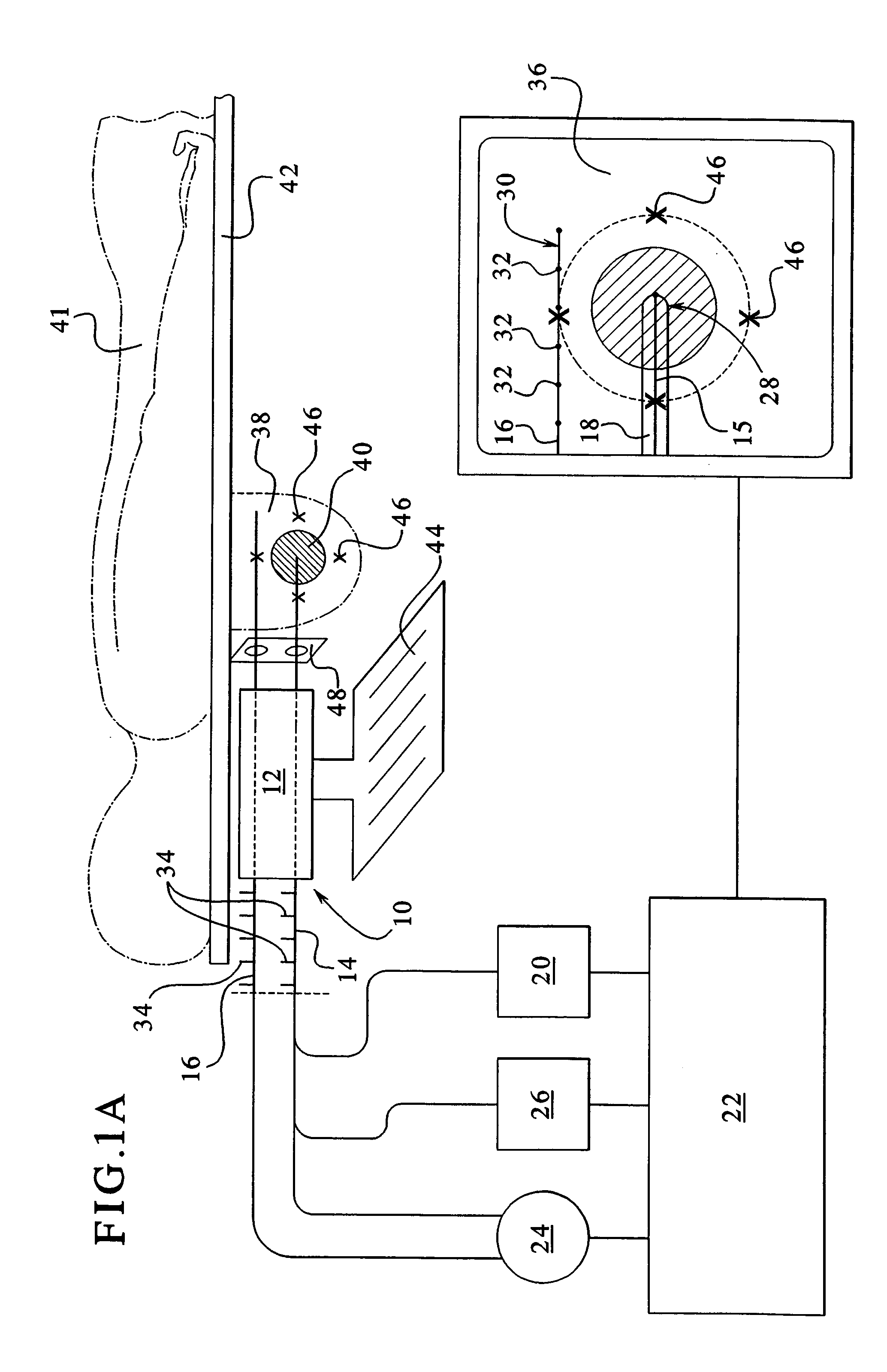
Adjustable laser probe for use in vitreoretinal surgery
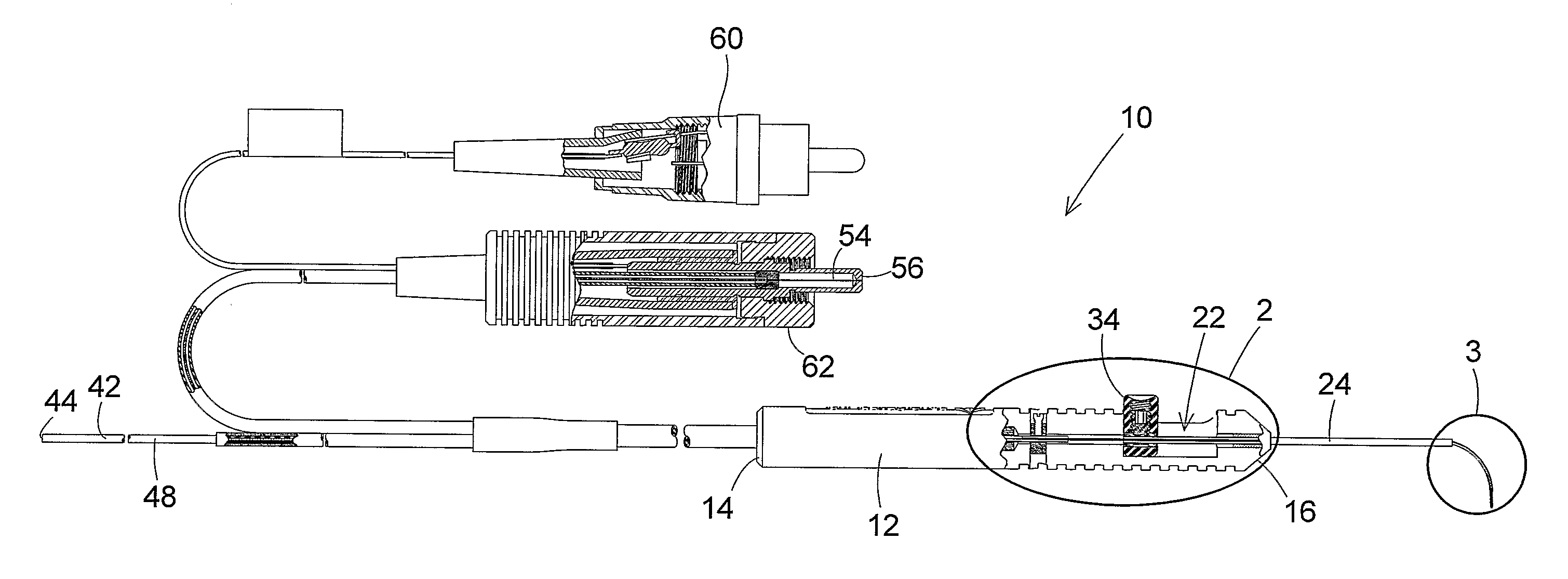
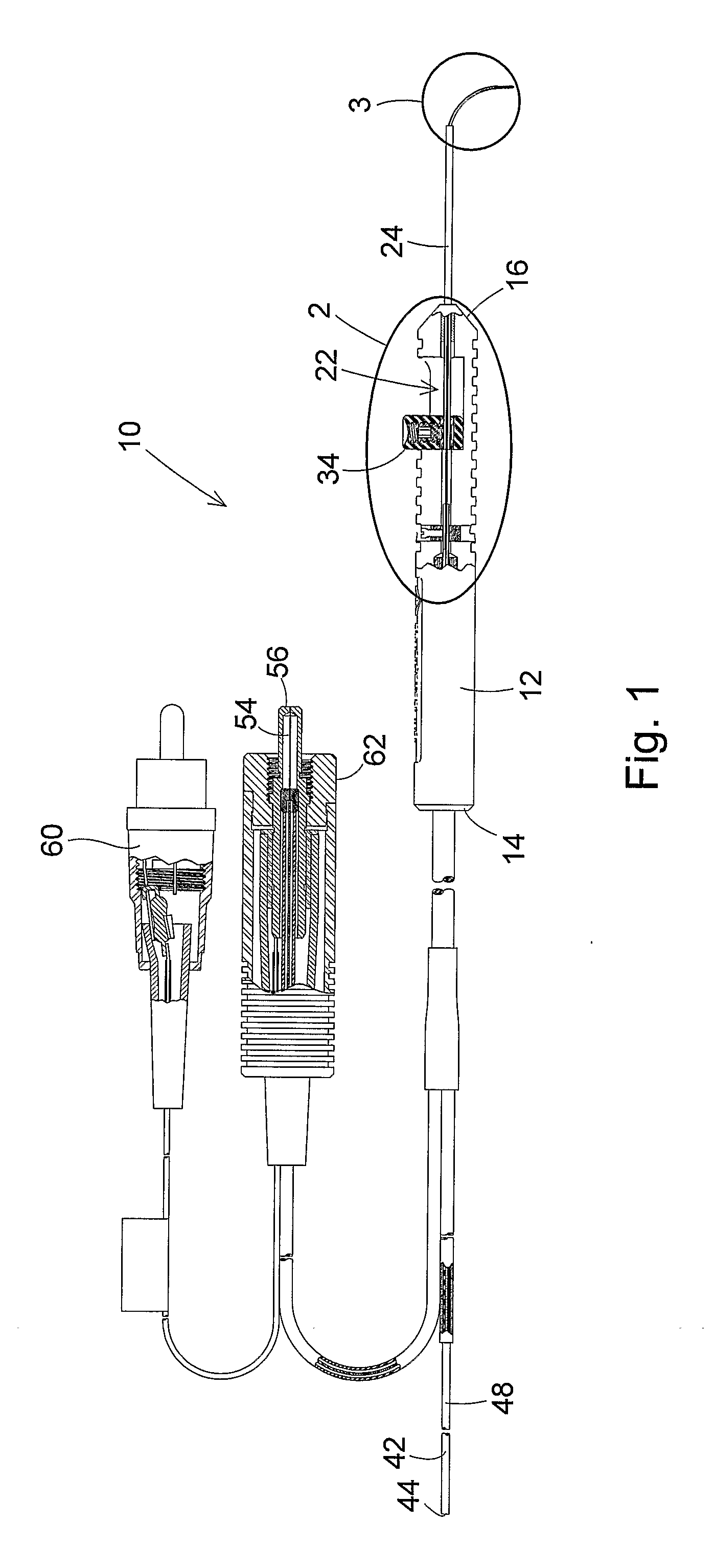
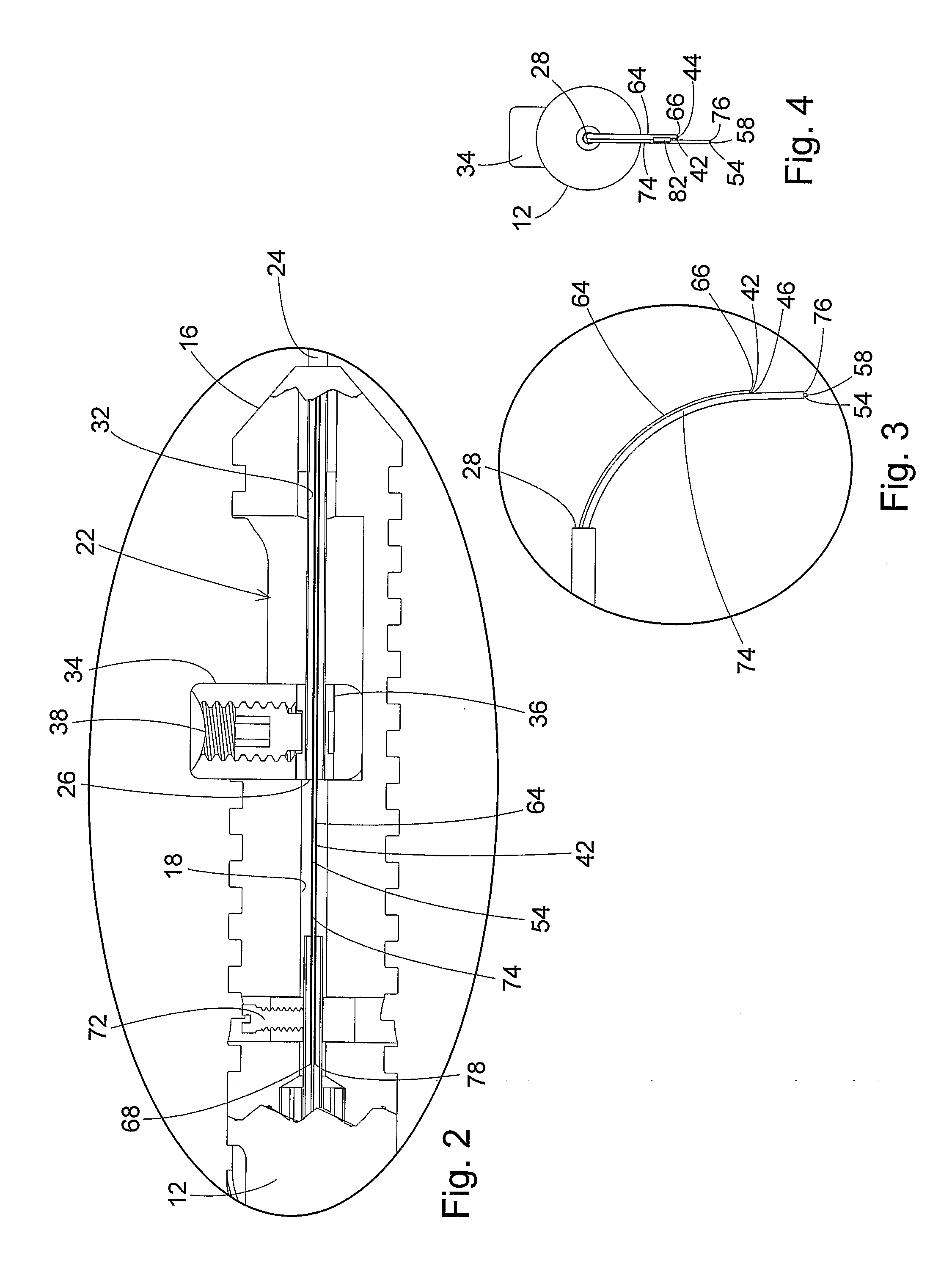
ActiveUS7766904B2Avoid damagePrevent movementLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFiberLaser probe
A laser probe including a handpiece and a rigid cannula fixed to the handpiece to prevent relative translational movement-therebetween. An optical fiber for delivering laser energy is supported for translational movement relative to the handpiece. A slidable button is fixed to the optical fiber via a rigid sleeve such that the button and optical fiber move together in the same direction during operation. The fiber may be selectively positioned relative to the button to cause the button to act as a visual indicator of the direction in which the fiber will extend from the cannula. The button may be specially configured with an enlarged head portion to enhance grippability and smooth operation of the button.
Owner:IRIDEX CORP
Laser probes for drug permeation
InactiveUS6389313B1Improve diffusivityImprove permeabilityElectrotherapyEar treatmentHigh concentrationLaser probe
Owner:SPECTRAL BIOSYST
Illuminated directional laser probe
Owner:SYNERGETICS
Apparatus and method for dynamic diagnostic testing of integrated circuits
InactiveUS6859031B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMagnetic property measurementsPhoton counting detectorElectricity
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Systems and methods for monitoring temperature during electrosurgery or laser therapy
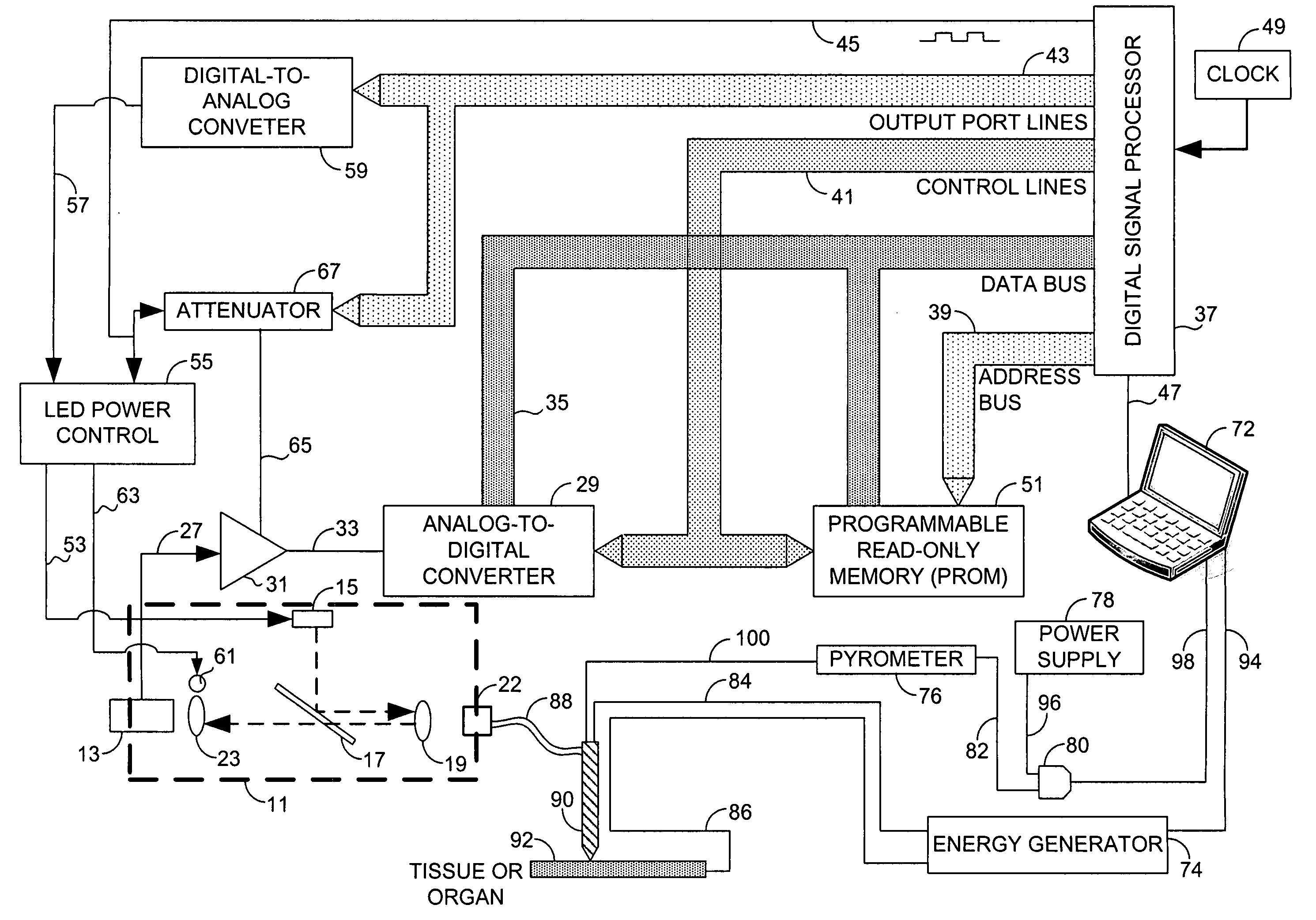
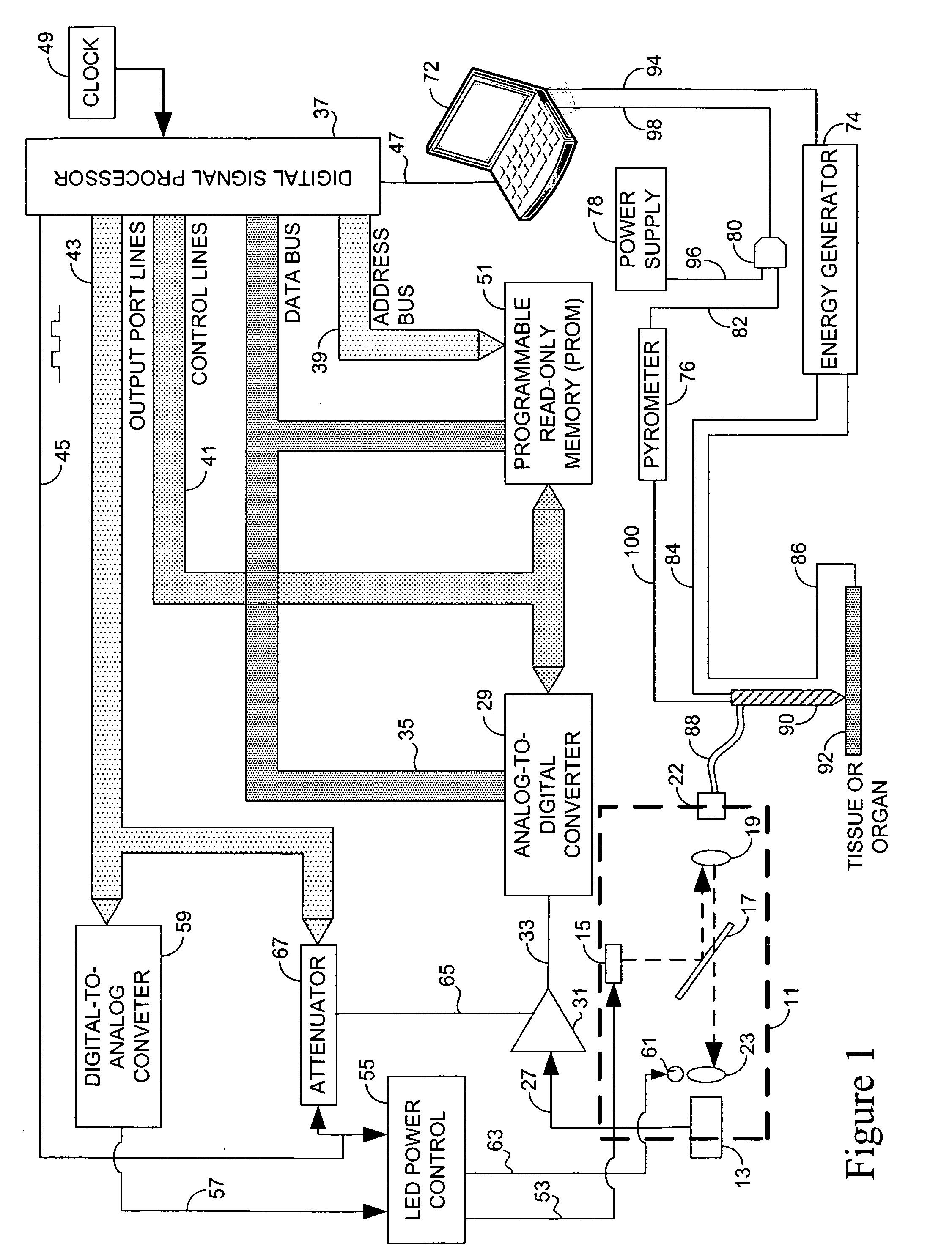
InactiveUS20080033300A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingLaser probeHigh heat
Systems that measure temperatures of tissue during electrosurgery or laser therapy of the tissue or organs is provided. One system provides a pyrometer that measures infrared electromagnetic energy emitted by a surface of a tissue or organ thereby determining a sub-surface temperature of the tissue or organ. The system further has an energy generator and an ablation electrode or laser probe that delivers energy from the energy generator to a tissue or organ, responsive to a sub-surface temperature determined by the pyrometer. The pyrometer can be calibrated using a luminescent material having known optical properties as a function of temperature. The luminescent material can be positioned on the surface of the tissue or organ or inserted directly into the tissue or organ using a catheter. Methods in which the surface or sub-surface temperature of the tissue is measured during therapy are also provided.
Owner:LUMASENSE TECH HLDG
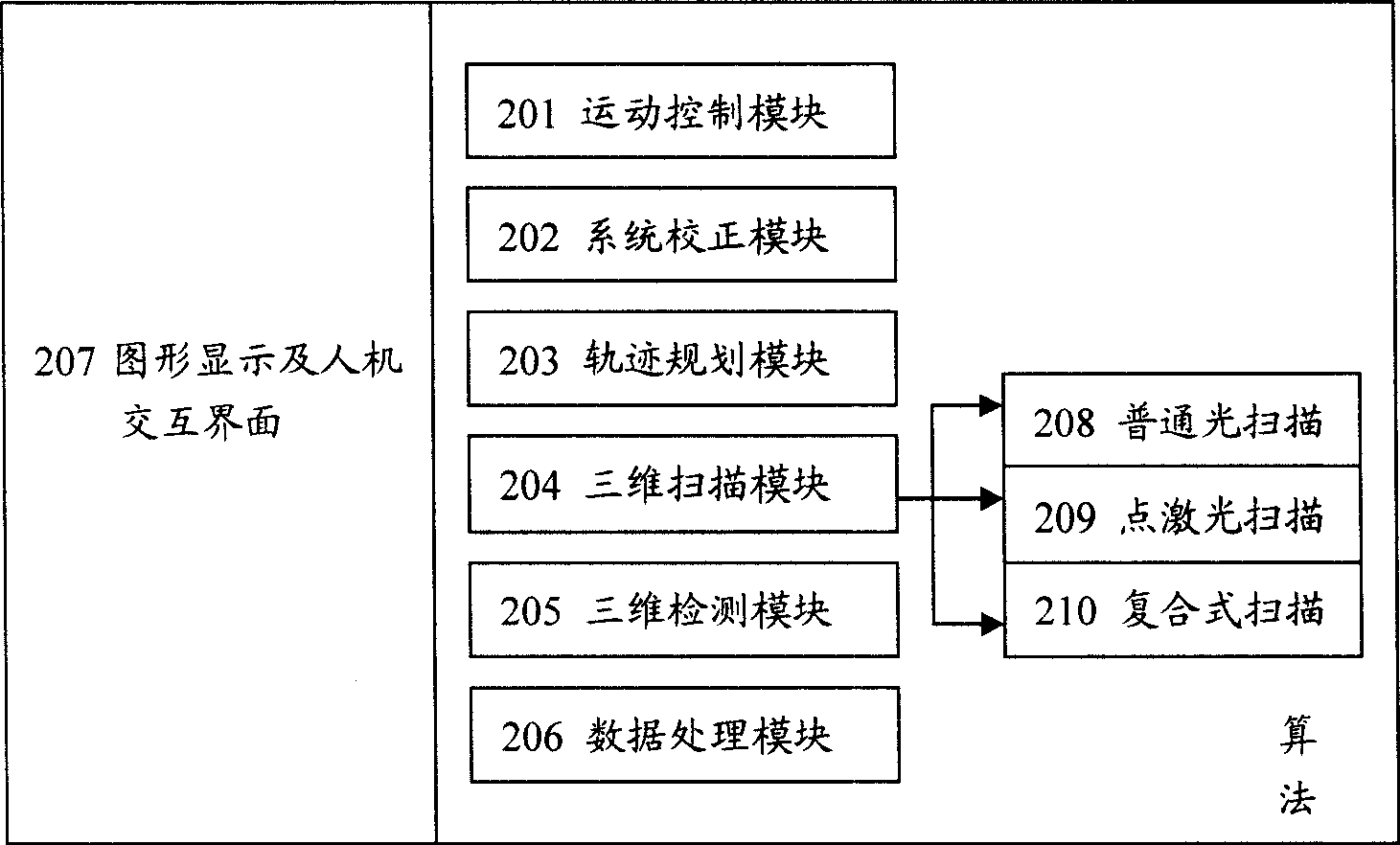
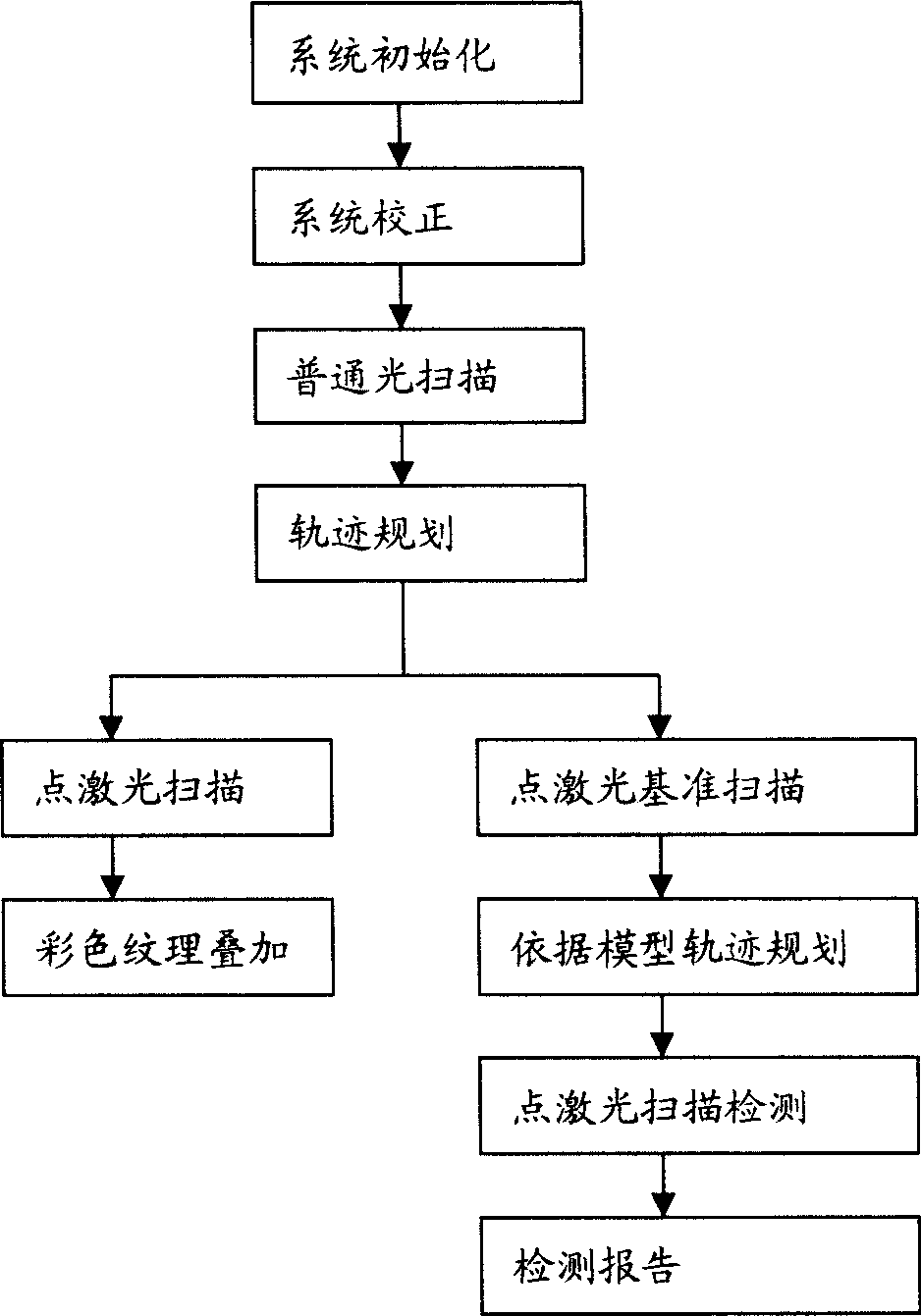
Composite three-dimensional laser measurement system and measurement method
InactiveCN101520319ARealize automated high-speed measurementAdjust light outputPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryUsing optical meansPoint cloudLaser probe
The invention provides a composite three-dimensional point laser measurement system and a measurement method, comprising three-dimensional scanning and three-dimensional detection. Normal optical scanning is adopted so as to obtain the profile information of the article quickly and establish a three-dimensional model; motion trajectory planning is carried out by the profile data; and a point laser probe is guided to carry out more precise measurement so as to obtain the three-dimensional point cloud data of higher precision and higher quality. The three-dimensional non-contact detection to the characteristic position, appointed section line and integer of the workpiece is obtained further on the basis of comparing the point cloud and model data. The system and the method have the advantages that the non-contact measurement can obtain the point cloud of good quality and high precision, the article can be positioned freely, precise clamping devices are not needed, the measurement speed is quick, the process is automatic and the measured article has wide applicable range.
Owner:深圳市精易迅科技有限公司
Venous heated ablation catheter
InactiveUS20130030410A1Improve efficiencyFluid handlingBalloon catheterMedical devicesVeinLaser probe
A catheter for delivery of sclerosant to a tubular member or vein of the body to cause ablation. The catheter has one or more balloons located near the distal end to enhance effectiveness of the sclerosant and prevent its delivery to the deep venous system. The catheter has an orifice located near the distal end of the catheter to direct the sclerosant into the vessel and one or more effluent openings to provide for removal of the sclerosant fluid. A heating member such as an electrical resistance element, a Laser probe, or an RF electrode located within the catheter lumen or on the outside of the catheter shaft heats the sclerosant fluid to improve its ablation effectiveness.
Owner:DRASLER WILLIAM JOSEPH +2
Three-dimensional photographing process based on laser probe array and device utilizing same
InactiveCN102494609AAvoid damageAvoid submersionUsing optical meansStereoscopic photographyMatch treatmentStereo matching
The invention discloses a three-dimensional photographing process based on a laser probe array and a device utilizing the same, and belongs to the field of three-dimensional photographing and measuring. Thousands of laser probes are projected to preset space positions according to the digital optical phase conjugation principle, reflection of the laser probes on surfaces of articles is monitored by a general two-dimensional camera, and then three-dimensional coordinate measurement is realized. Meanwhile, since the laser probe array is combined with a pair of three-dimensional cameras, more three-dimensional coordinates can be acquired by means of three-dimensional reconstruction, and accurate and compact three-dimensional coordinate measurement for large sites can be realized. Accordingly, three-dimensional matching treatment accuracy of three-dimensional images in the three-dimensional reconstruction process can be improved, matching treatment time is shortened, images picked up by the three-dimensional cameras can be compensated at the post stage, error in focal length and installation of the two cameras is eliminated, and requirements for the previous stage installation and synchronization of the focal length in the actual photographing process of the three-dimensional cameras are lowered. The three-dimensional photographing process based on the laser probe array and the device utilizing the same are applicable to fields of three-dimensional films, robots, intelligent driving, quick detection for obstacles, automatic measurement for industrial parts, and the like.
Owner:李志扬
Illuminated Directional Laser Probe
An ophthalmic surgery illuminated directional laser probe has a handle and a rigid tubular tip projecting from the handle, and has an illumination optic fiber and a laser optic fiber that extend through the handle and the tip. A mechanism on the handle is operable to extend distal ends of the illumination optic fiber and the laser optic fiber from the distal end of the instrument tip, and to retract the distal ends of the illumination optic fiber and the laser optic fiber back into the interior of the tip. At least one of the distal ends of the illumination optic fiber and the laser optic fiber is held in a curved configuration. The distal ends of the illumination optic fiber and the laser optic fiber are secured to each other, whereby both the illumination optic fiber and the laser optic fiber curve into a bent configuration as the distal ends of the illumination optic fiber and the laser optic fiber are extended from the distal end of the instrument tip.
Owner:SYNERGETICS
Laser probe with a replaceable optic fiber
A laser probe with a replaceable optic fiber may include a reusable handle, a reusable housing tube, a reusable handle adapter, a reusable machine adapter, and a replaceable optic fiber. The handle adapter may interface with a proximal end of the handle. The machine adapter may interface with a surgical machine. The replaceable optic fiber may include an optic fiber having a first optic fiber end and a second optic fiber end, a first connector, and a second connector. The optic fiber may be disposed within the first connector and the second connector. The first connector may be temporarily fixed within the handle adapter and the second connector may be temporarily fixed within the machine adapter.
Owner:KATALYST SURGICAL
Single-fiber multi-spot laser probe for ophthalmic endoillumination
ActiveUS20110122366A1Eliminates and reduces disadvantageEliminates and reduces and problemLaser surgeryLaproscopesDiffraction orderGrating
An ophthalmic endoilluminator is provided. The ophthalmic endoilluminator includes a light source, a first optical assembly, an optical coupling element, and an optical fiber having an optical grating located distally on the optical fiber, the optical fiber optically coupled to the optical coupling element. The first optical assembly receives and substantially collimates the white light. The optical coupling element receives the substantially collimated white light from the first optical assembly and directs the light to an optical fiber. The optical grating couples to the distal end of the optical fiber, the optical grating having a surface relief grating, and an overlayer optically coupled to the surface relief grating. The optical grating is operable to substantially diffract incident light into N diffraction orders, the N diffraction orders having a substantially uniform intensity.
Owner:ALCON INC
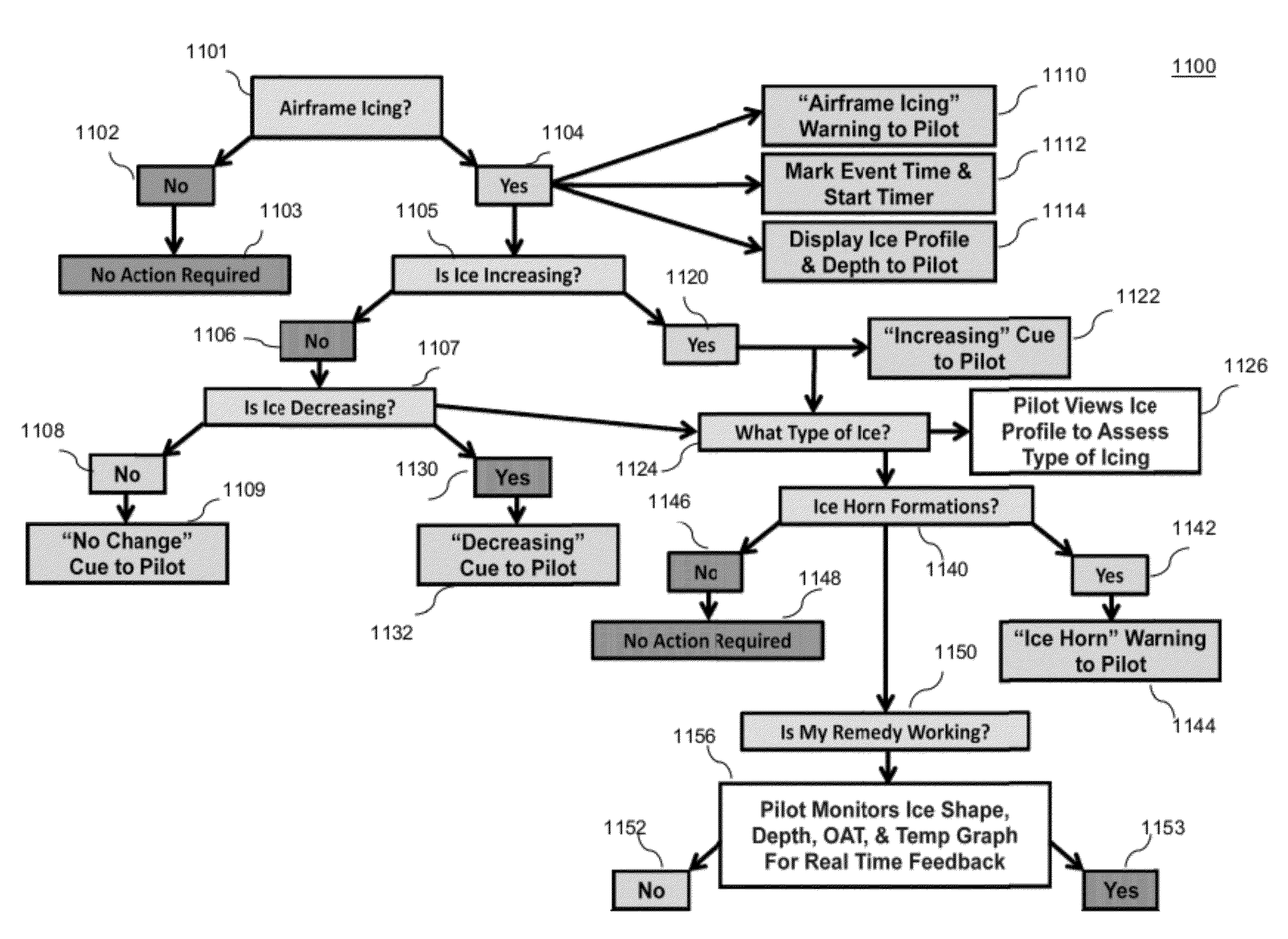
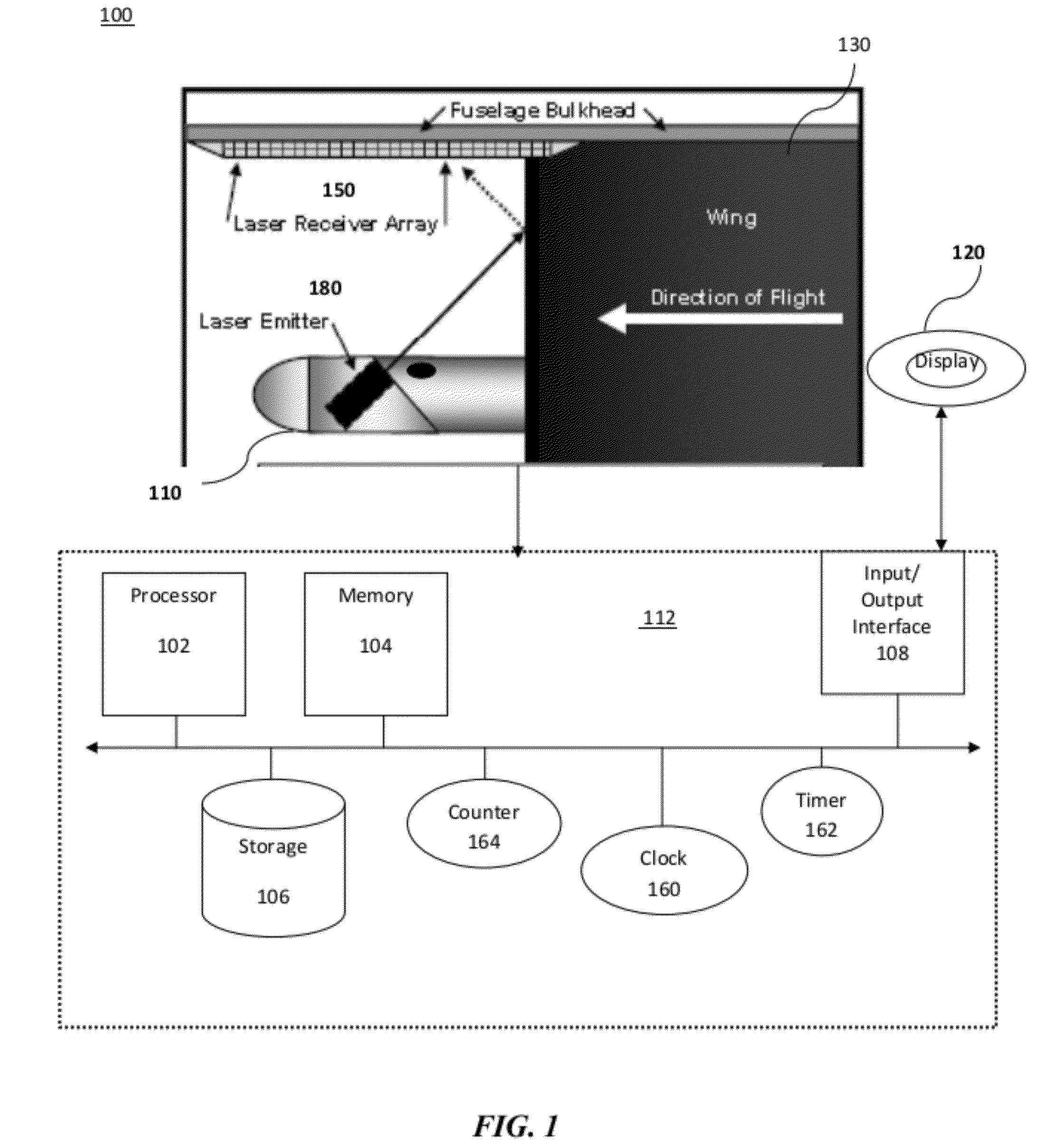
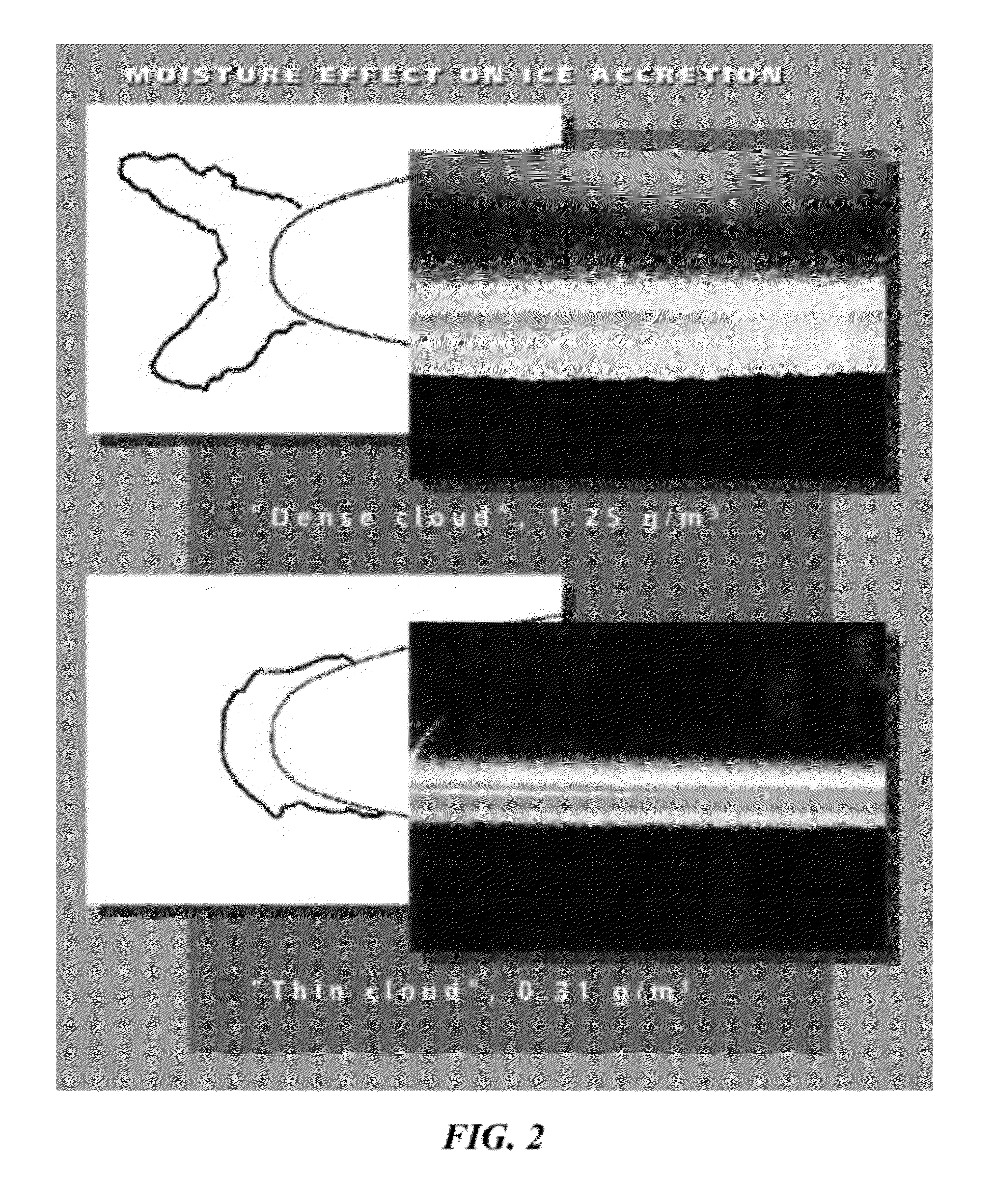
Aircraft icing detector
A method for aircraft surface contamination detection and measurement includes: mounting a laser probe on an airfoil; positioning the laser probe to emit laser energy at multiple pre-determined surface points along the leading edge of the airfoil; and using a processor device for activating the laser probe and obtaining measurement data for generating a surface contour of the shape and accurate measurement of the depth of airfoil icing in the surface target area. The icing data is presented to the pilot in a display that alerts him to the icing and accurately shows the depth and shape of the airfoil icing.
Owner:LUMEN INT
Skin laser treatment auxiliary robot and auxiliary method thereof
ActiveCN105288865AImprove accuracyEfficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorSurgical instrument detailsLaser probeEngineering
The invention provides a skin laser treatment auxiliary robot and an auxiliary method thereof. The skin laser treatment auxiliary robot comprises an accurate positioning mobile robot, a therapeutic instrument laser probe, a visual identification and control system, a range finding device and a safety device. The therapeutic instrument laser probe is installed at the front end of the tail position of the mechanical arm of the accurate positioning mobile robot. The range finding device is installed at the side surface of the therapeutic instrument laser probe. The CMOS probe of the visual identification and control system is installed at the other side surface of the therapeutic instrument laser probe. The safety device is installed at the front end of the therapeutic instrument laser probe. The measured value outputted by the range finding device and the sensing signal outputted by the safety device are connected with the input end of the visual identification and control system. Output of the visual identification and control system is connected with and controls the accurate positioning mobile robot. Manual operation on a skin laser therapeutic instrument is replaced by the accurate positioning mobile robot so that the skin laser treatment auxiliary robot and the auxiliary method thereof have advantages of high degree of automation and accurate positioning and movement, and high-curative-effect, high-efficiency, safe and reliable skin laser treatment can be guaranteed.
Owner:康健
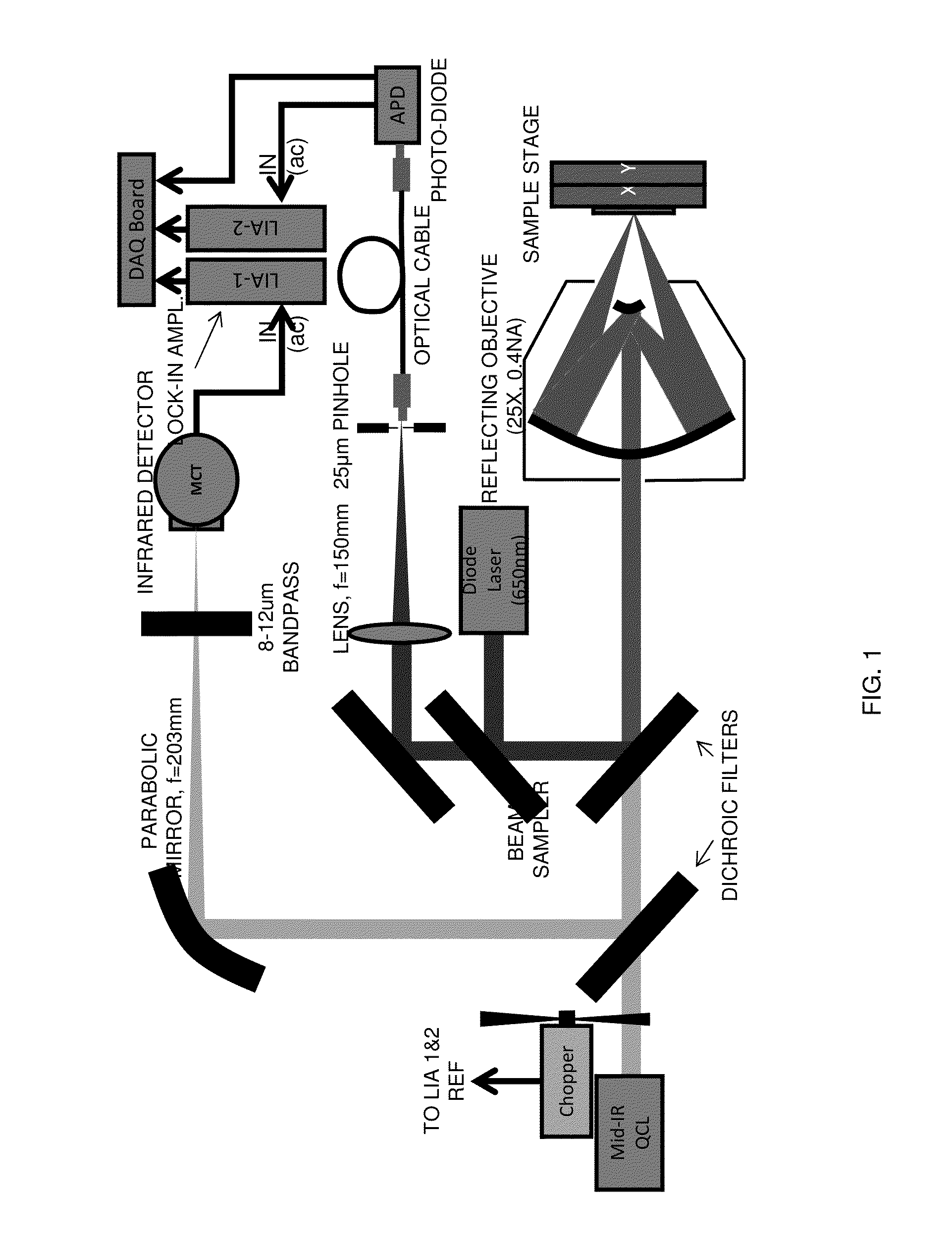
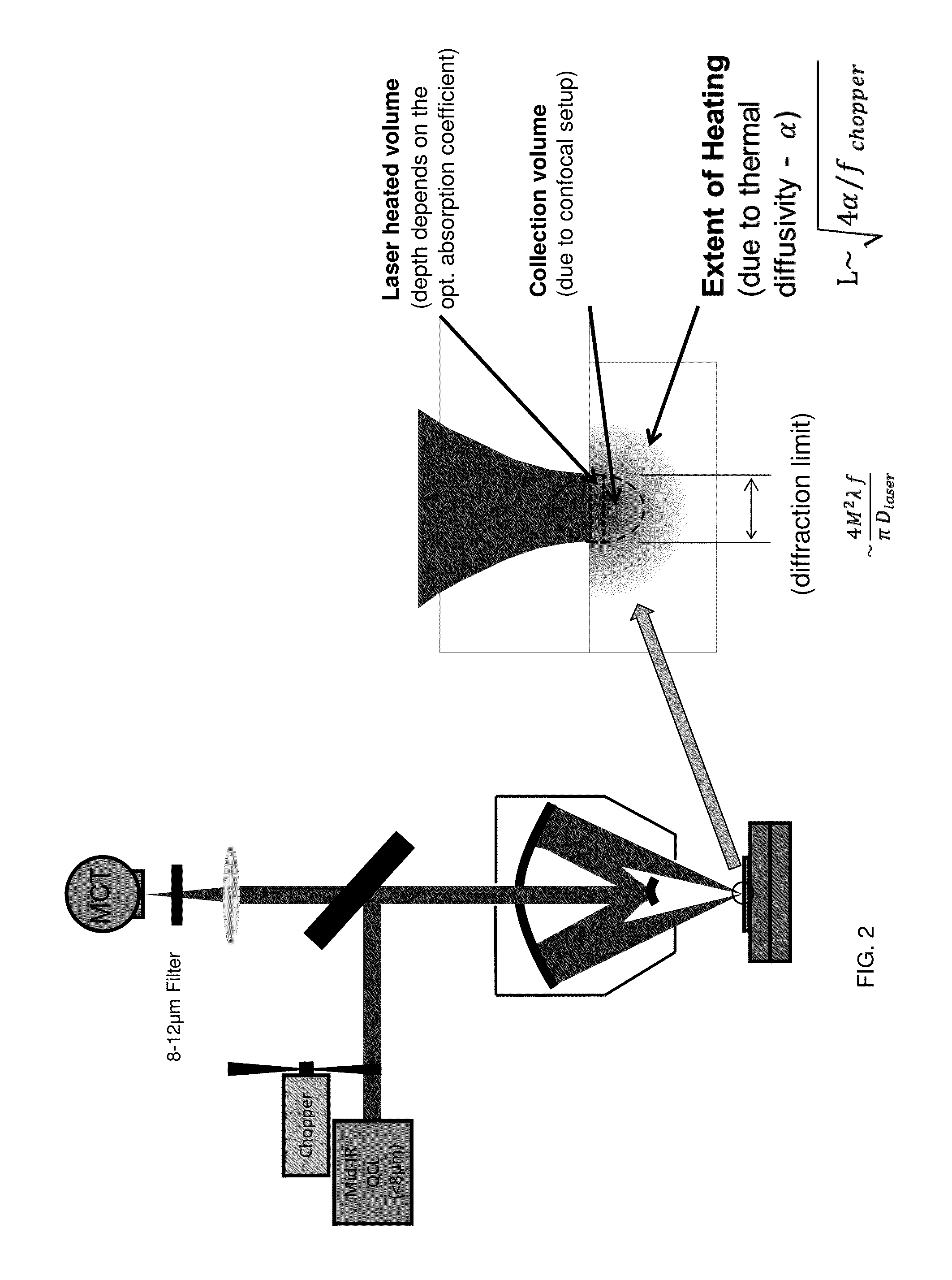
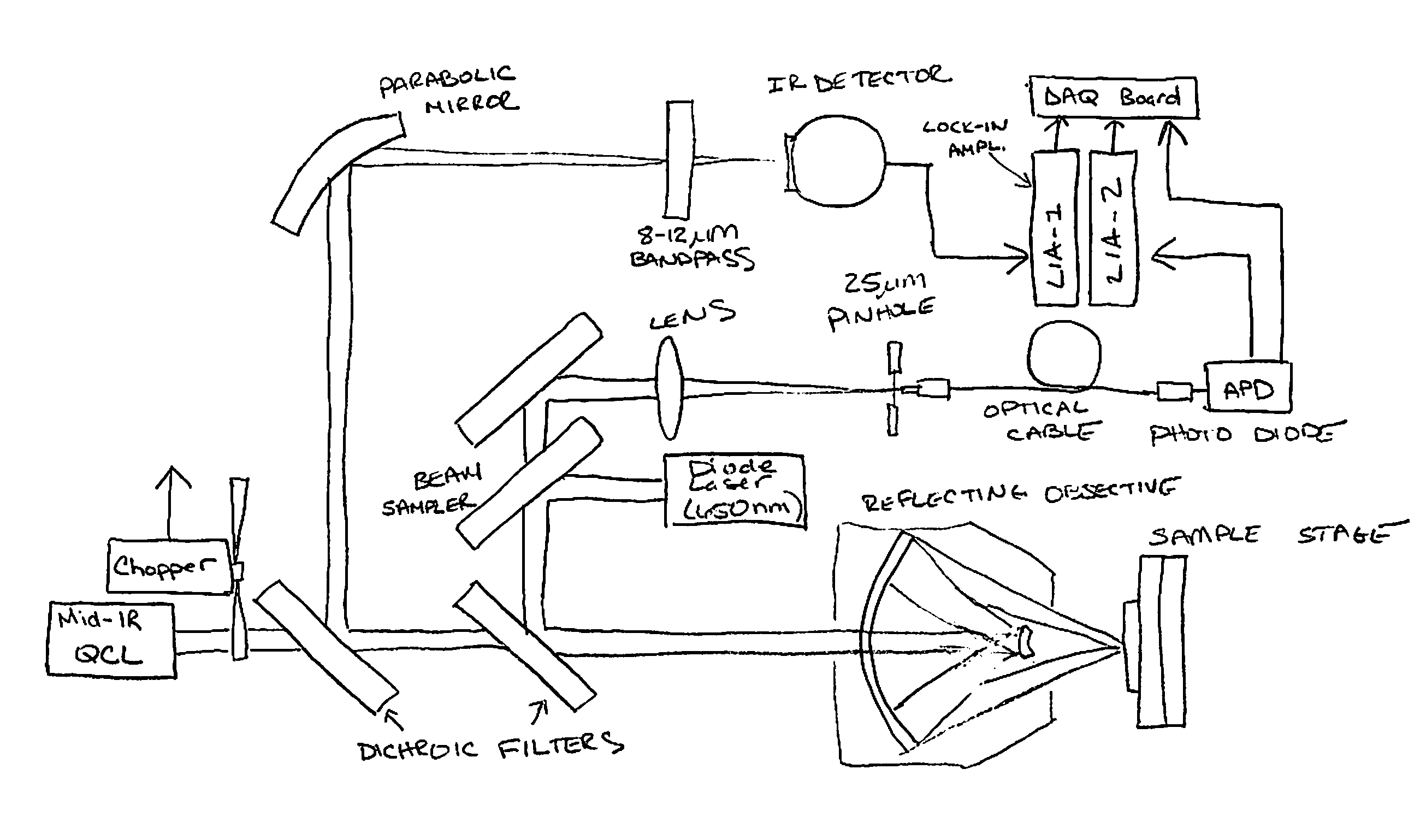
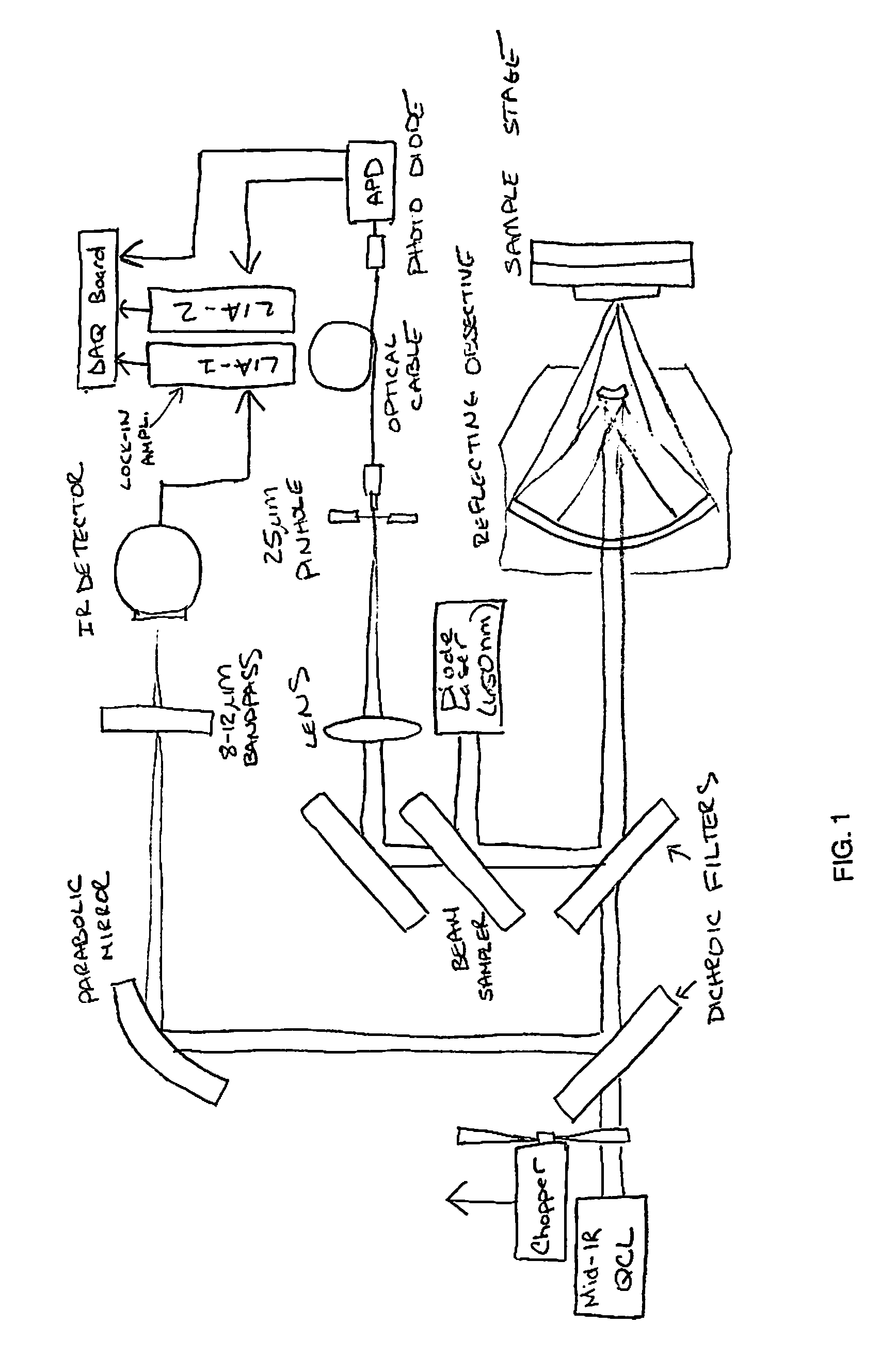
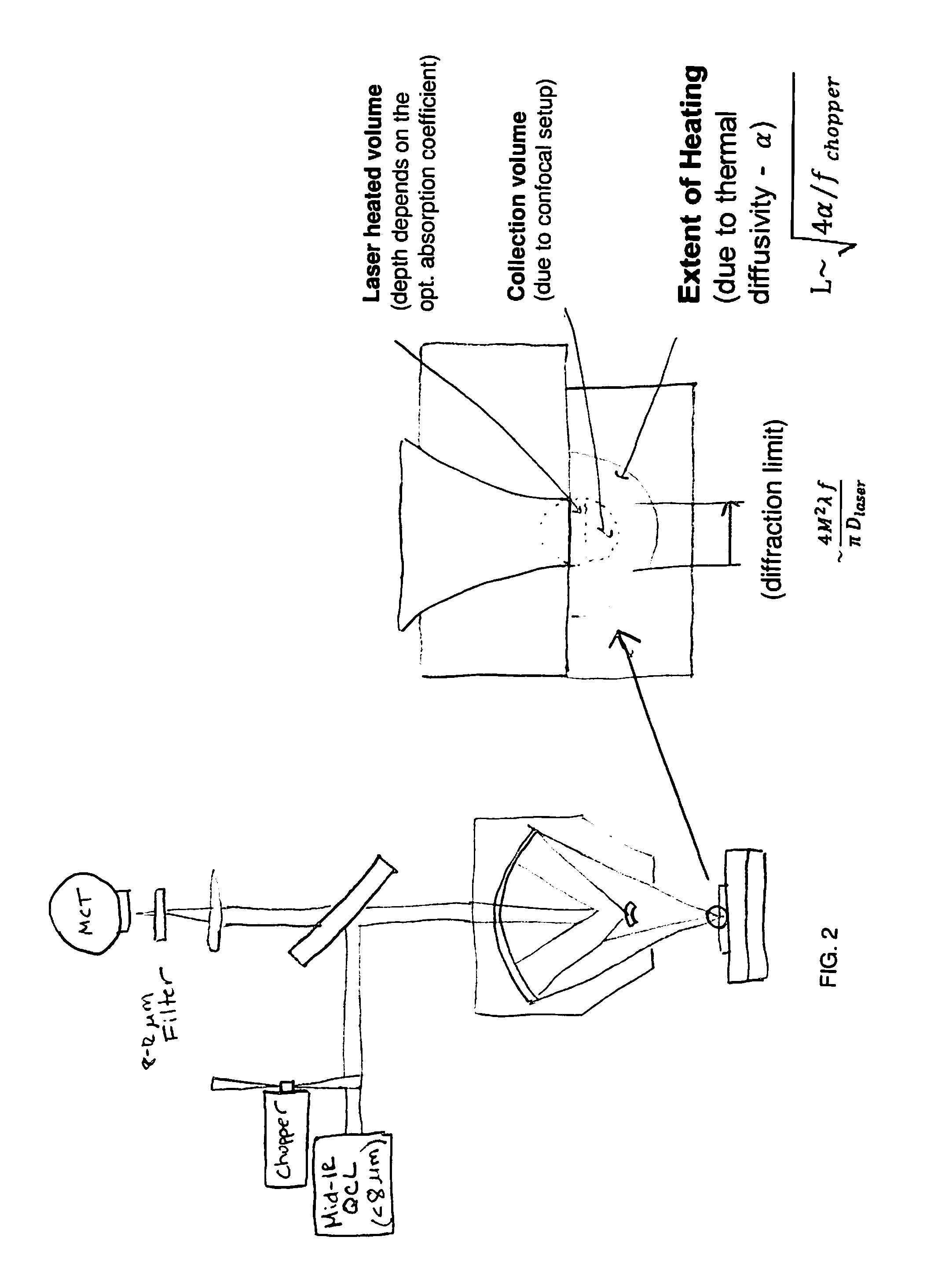
Chemical mapping using thermal microscopy at the micro and NANO scales
ActiveUS20130134310A1Small sizeReduce impactEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryThermionic emissionLaser probe
A non-destructive method for chemical imaging with ˜1 nm to 10 μm spatial resolution (depending on the type of heat source) without sample preparation and in a non-contact manner. In one embodiment, a sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using an IR laser and the resulting increase in thermal emissions is measured with either an IR detector or a laser probe having a visible laser reflected from the sample. In another embodiment, the infrared laser is replaced with a focused electron or ion source while the thermal emission is collected in the same manner as with the infrared heating. The achievable spatial resolution of this embodiment is in the 1-50 nm range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
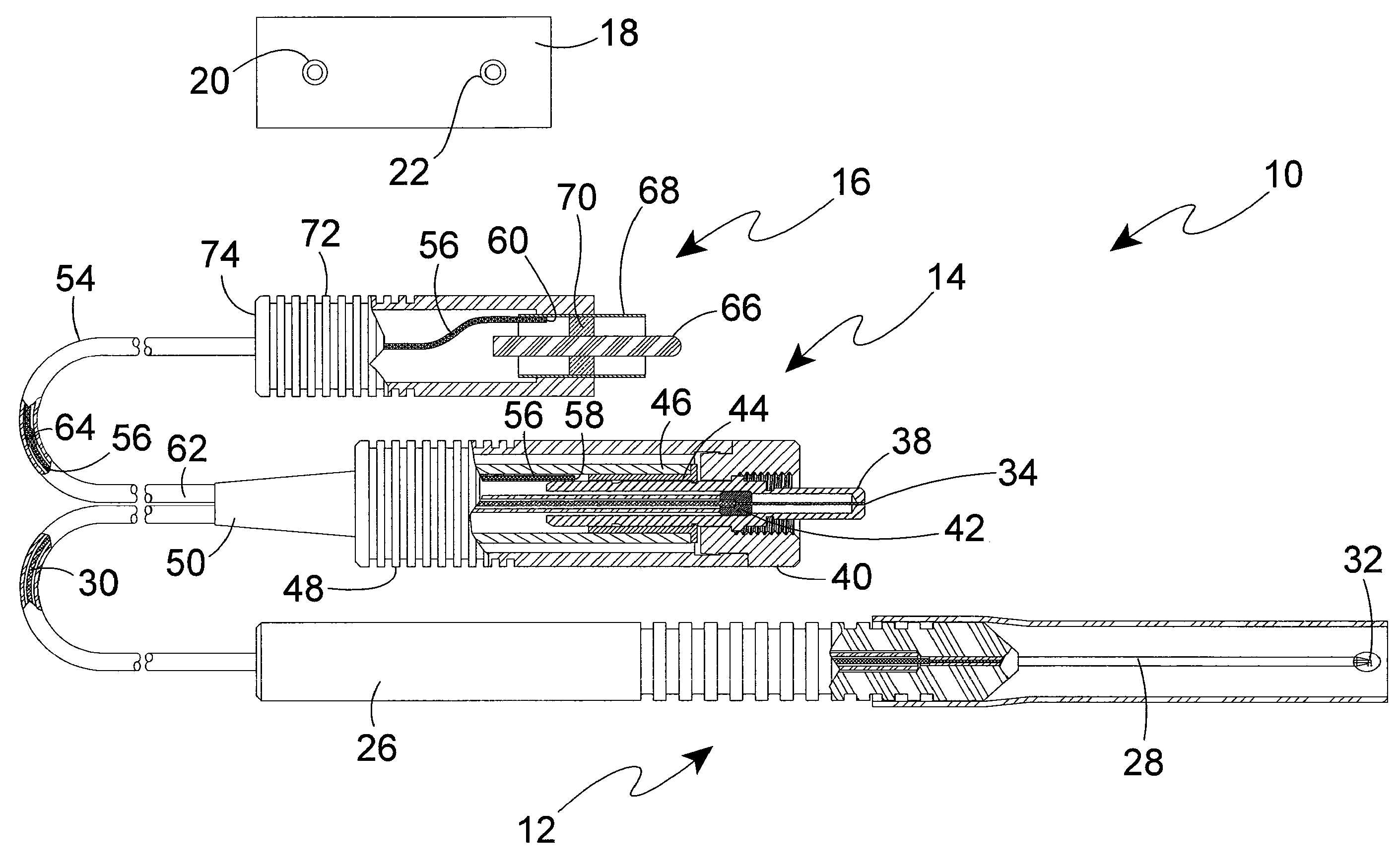
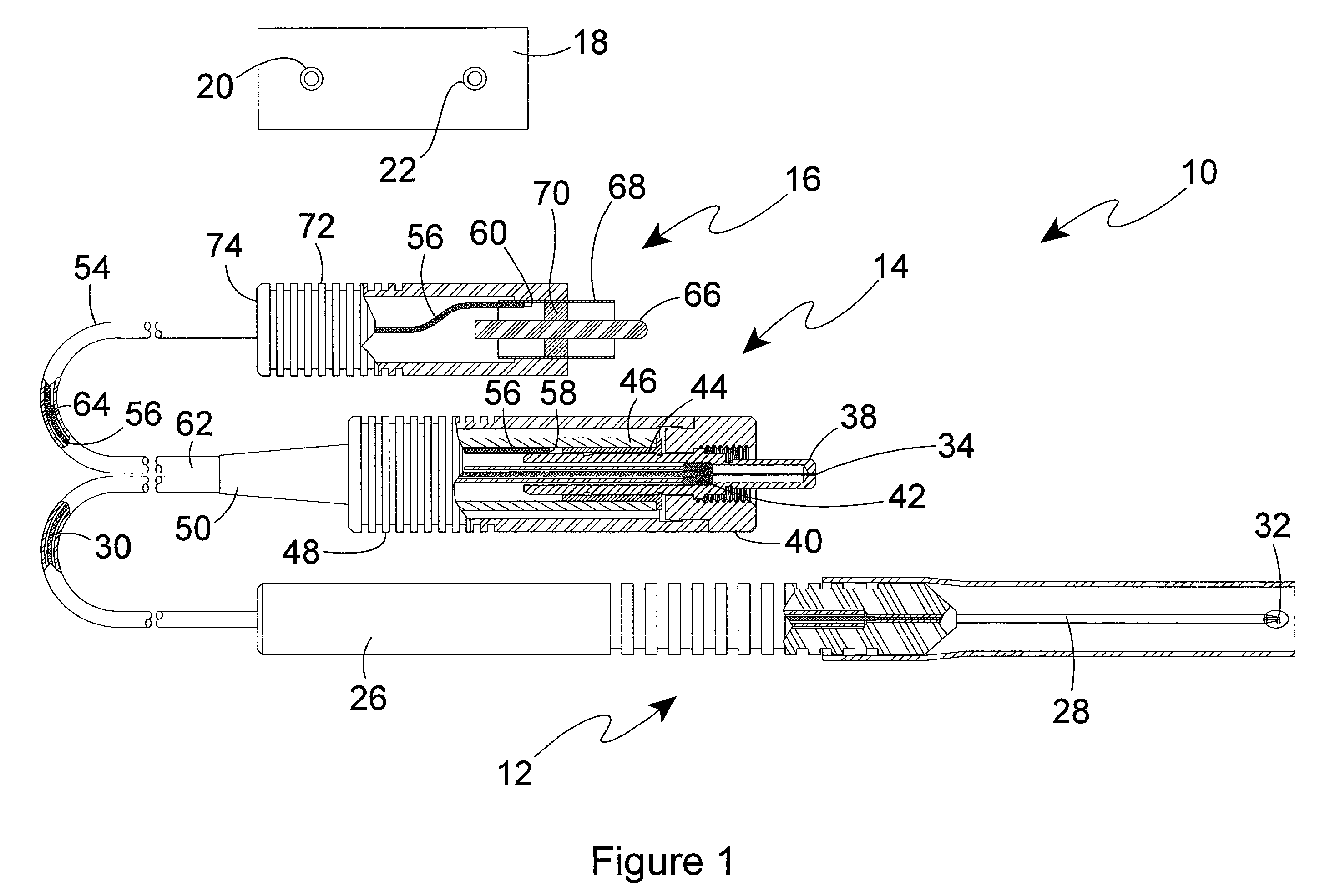
Laser Probe Assembly with Laser Light Source Connector and Electronic Identification Connector
An optic fiber surgical instrument is removably connectable to a surgical light source. The instrument is provided with an optic fiber connector and a separate auxiliary or electric identification connector. The optic fiber connector is removably connectable to a laser light output of a laser light source to convey the laser light through the optic fiber of the instrument, whereby manipulation of the instrument by a user can direct the laser light to a surgical site. The auxiliary connector is connectable to a ground connection of the surgical light source to establish an electric circuit through the instrument and the surgical light source, whereby an electrical identification device on the instrument identifies the instrument for the surgical light source.
Owner:SYNERGETICS
Grin fiber multi-spot laser probe
A surgical probe includes a cannula assembly, having a graded index (GRIN) fiber that is configured to receive a multi-spot light beam at a proximal end and to emit the multi-spot light beam at a distal end ; an adapter, having a distal end, configured to receive the cannula assembly, with the proximal end of the GRIN fiber, a proximal end, configured to couple to a light guide via a connector and to receive a light delivered by the light guide from a laser source to the adapter, and an interface, configured to couple the light delivered by the light guide to the proximal end of the GRIN fiber; wherein a length of the GRIN fiber is sufficiently long that the interface is outside a patient's eye during a photocoagulation procedure.
Owner:ALCON INC
Laser probe micro-area component analyzer based on double laser light source
ActiveCN101782517AAchieve accuracyTo achieve the purpose of precise quantitative analysisAnalysis by material excitationMountingsFiberLaser probe
The invention belongs to the technical field of laser probing, in particular to a laser probe micro-area component analyzer based on a double laser light source. The laser probe micro-area component analyzer comprises a fixed wavelength laser device, an attenuator, a beam expanding mirror and an aperture diaphragm; first semi-permeable half-mirrors are arranged on the same horizontal light path according to the structure; after a wavelength tunable laser device is reflected onto the first semi-permeable half-mirrors by a second totally reflecting mirror, the wavelength tunable laser device has the same light path with the laser beam of the fixed wavelength laser device; the fixed wavelength laser device and the wavelength tunable laser device can be arranged up and down or in parallel, and the starting sequence and the time delay thereof can be controlled by a digital delay generator; a fibre-optical probe receives laser, then the laser is transmitted to a grating spectrometer by the optical fibre, and the acquisition time of a plasma spectra reaching enhancement mode CCD is controlled by the digital delay generator. The laser probe machine stimulated by the double laser light sources has low detection limit, high element analysis precision and favourable element selectivity, is reliable and safe, and can be used for accurately determining the nature of microelements and trace elements of the micro-areas of various substances as well as carrying out accurate quantitative analysis.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
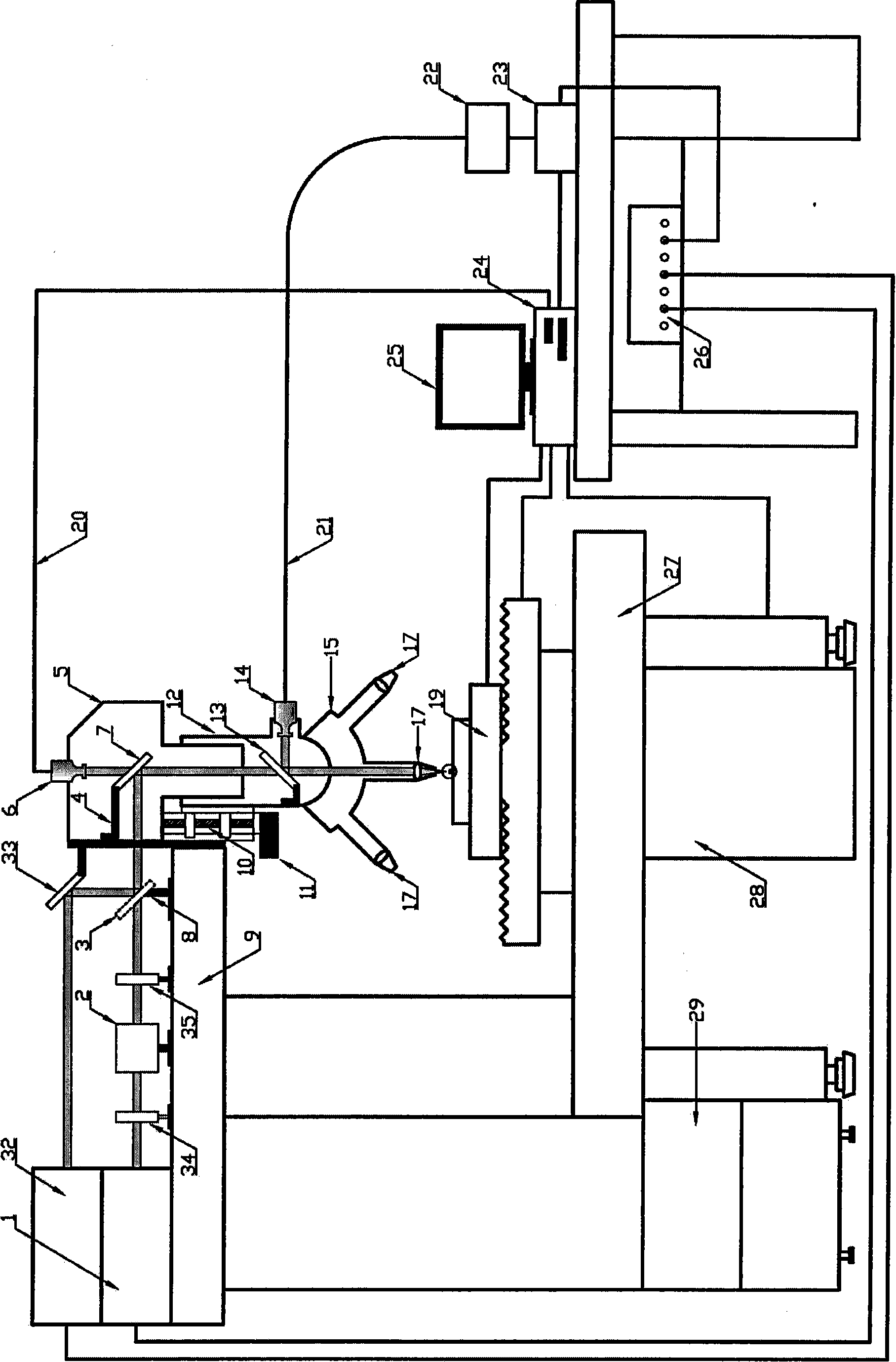
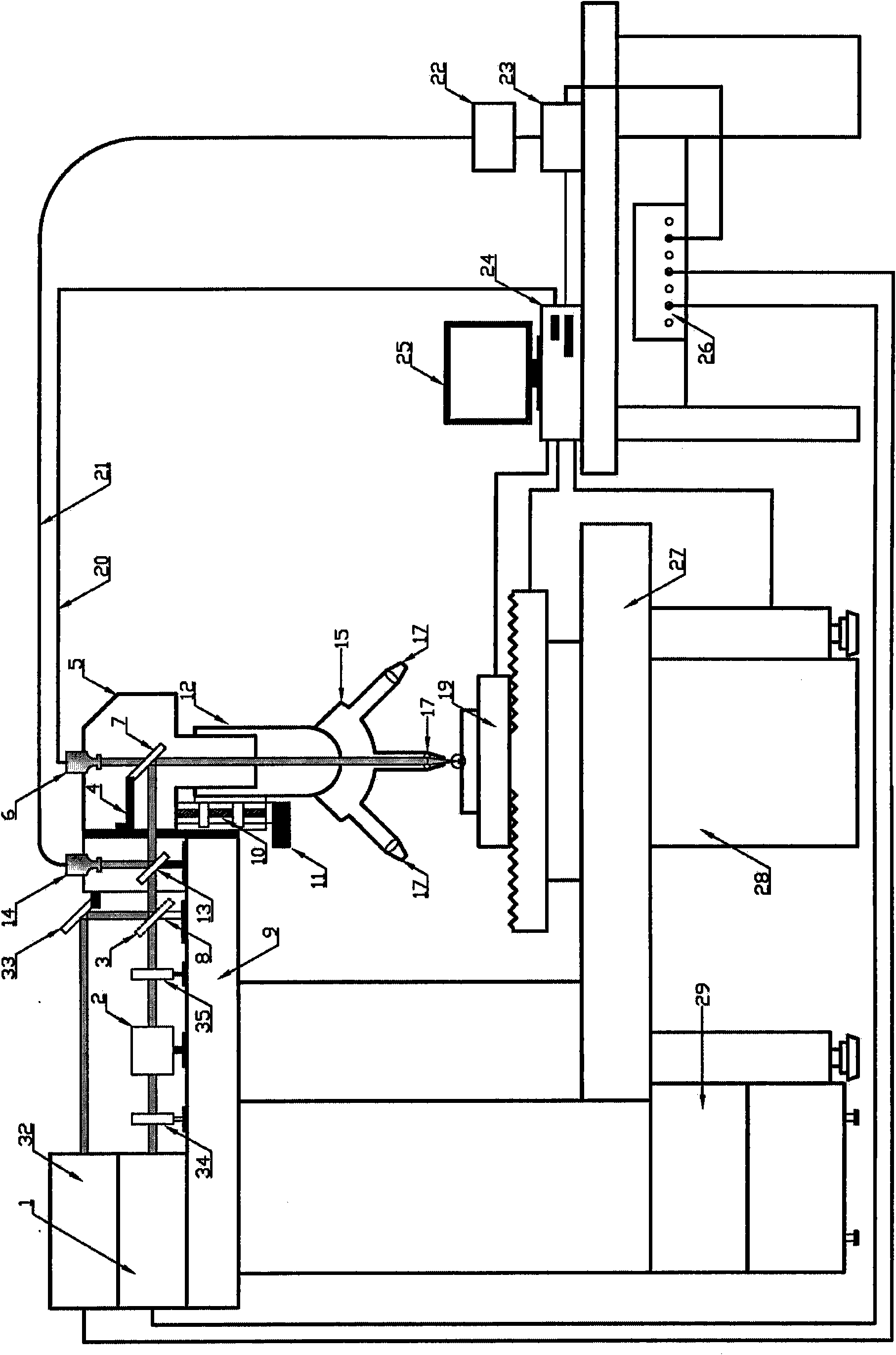
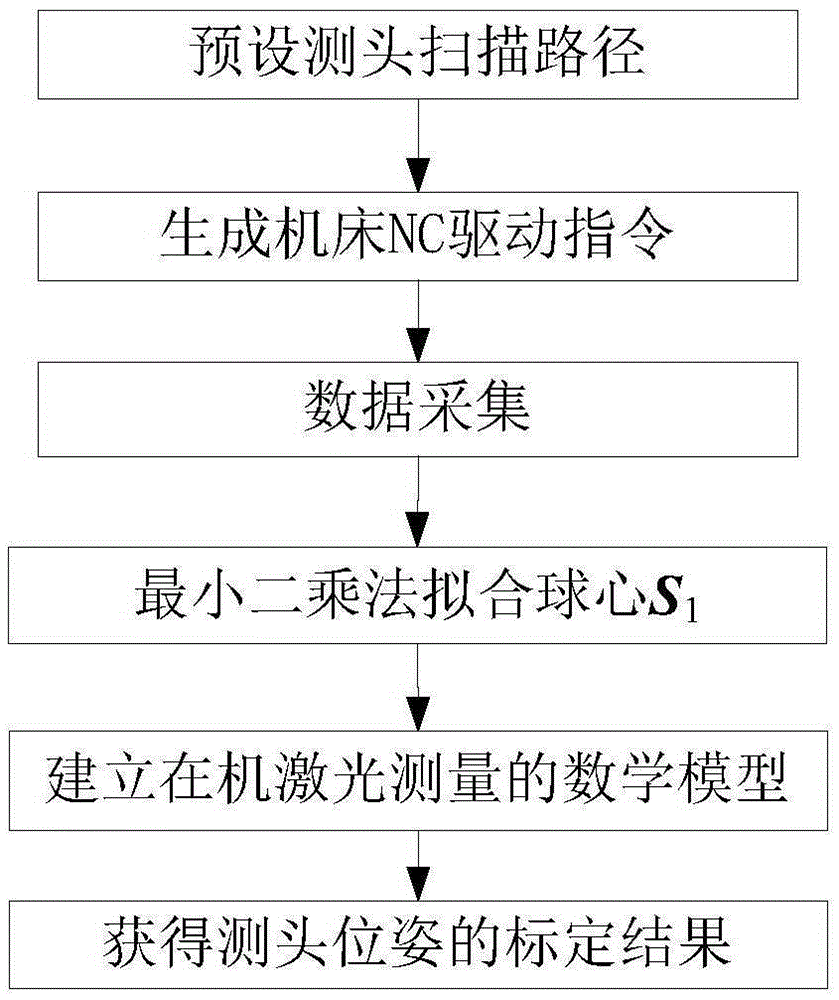
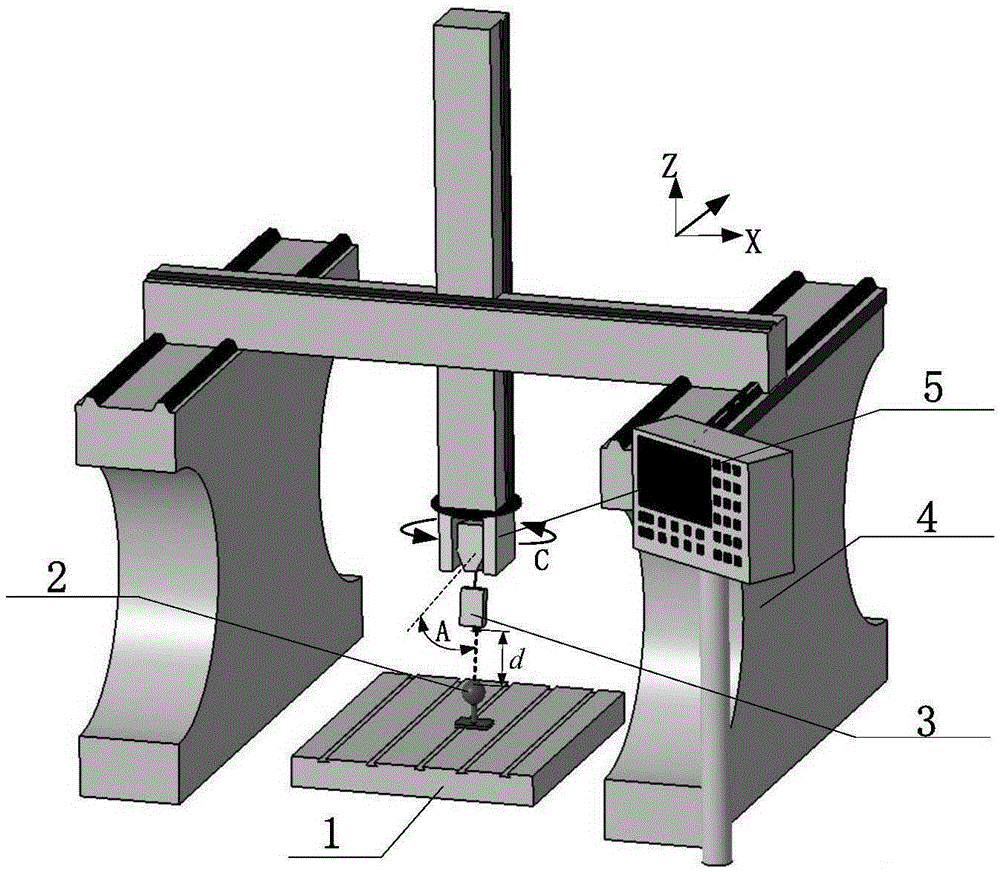
Probe position linearization calibration method for on-machine laser measurement
ActiveCN105404238AAvoid calculationAvoid stabilityProgramme controlComputer controlLaser probeInstability
The invention discloses a probe position linearization calibration method for on-machine laser measurement. The method comprises steps that, a measurement model of a laser probe moving along with a machine tool is established, a machine tool motion program is generated in an offline mode, the laser probe is driven by the machine tool to carry out multi-angle scanning of a standard ball for ball center fitting, a linear equation group of a standard ball center under multiple machine tool rotation angles and a probe mounting position relationship is acquired, probe mounting position parameters can be acquired through solving the equation group, that a calibration problem is expressed as a nonlinear optimization problem with constraint is not required, and problems of massive calculation and instability existing in nonlinear optimization solution can be avoided.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Apparatus and method for delivering ablative laser energy and determining the volume of tumor mass destroyed
InactiveUS7171253B2Complete efficientlyEffective destructionBlood flow measurement devicesSurgical needlesTumour volumeVisual monitoring
An apparatus and method for determining a volume of tumor mass destroyed. The present invention includes a temperature probe and a laser probe having a temperature sensor. The laser probe and temperature probe are inserted to measure a temperature of the tumor mass and a temperature of tissue mass surrounding the tumor mass. By determining the volume of tumor mass destroyed, a graphical representation of the volume of tumor mass destroyed is provided whereby real-time visual monitoring of the destruction of the tumor mass is achieved.
Owner:NOVIAN HEALTH INC
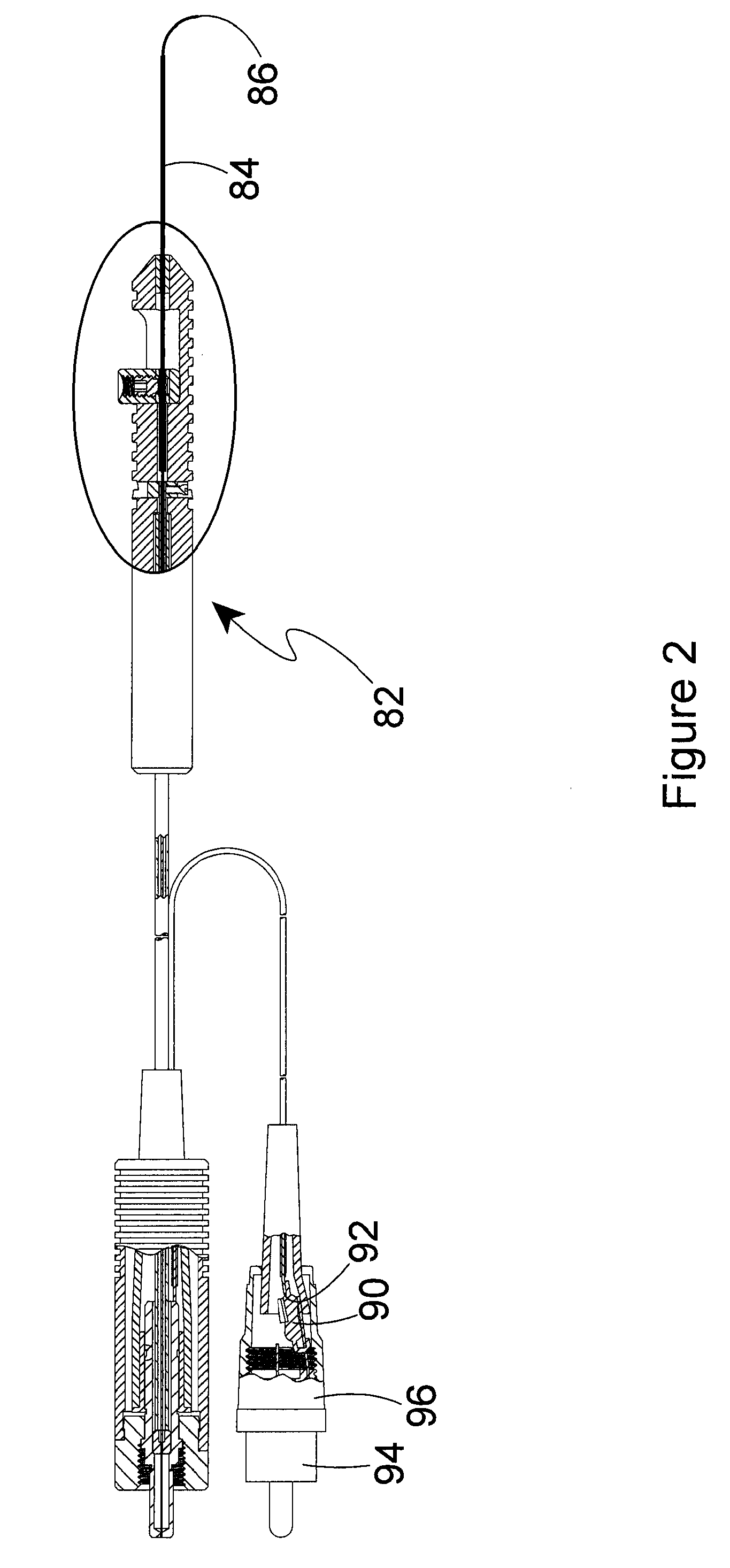
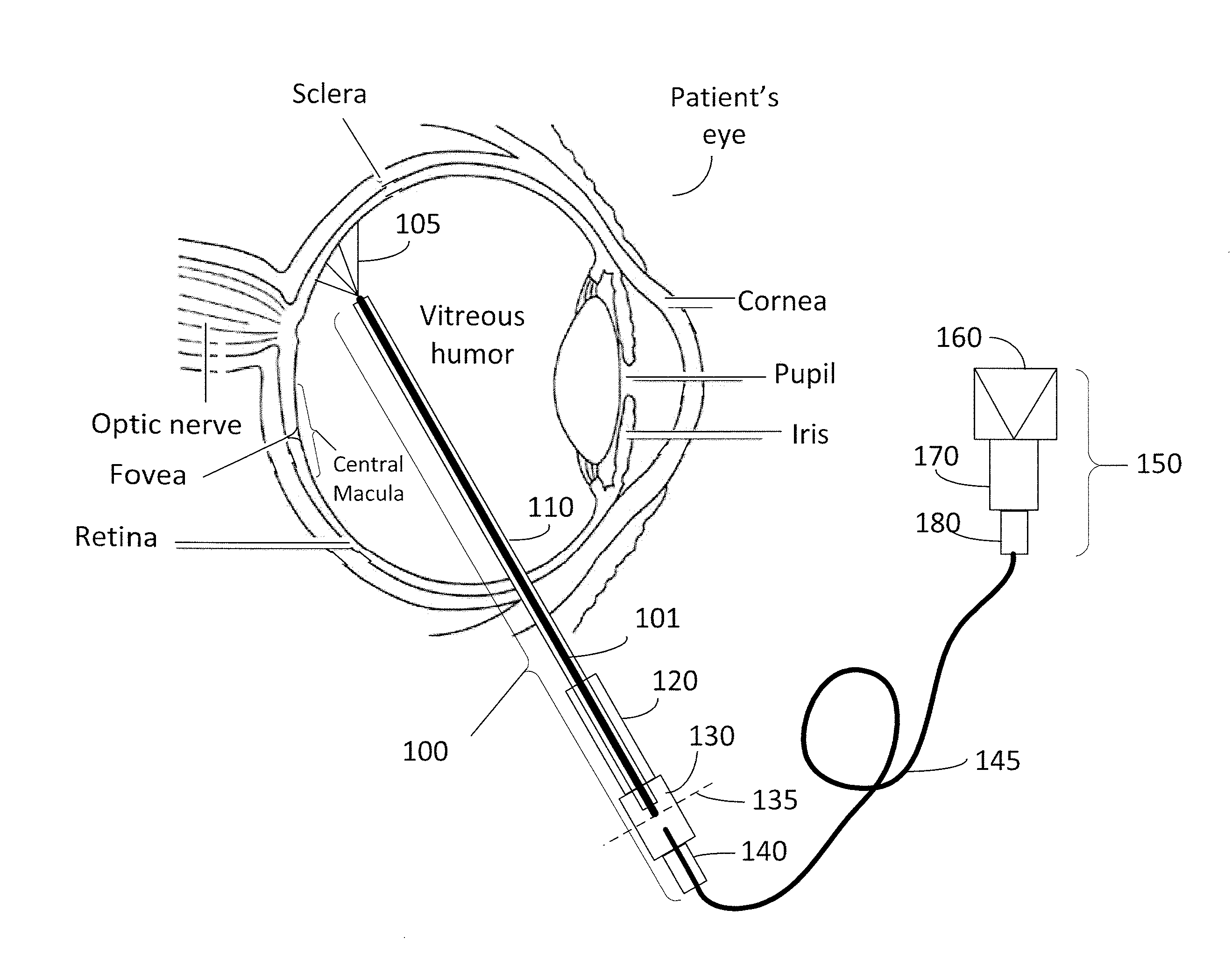
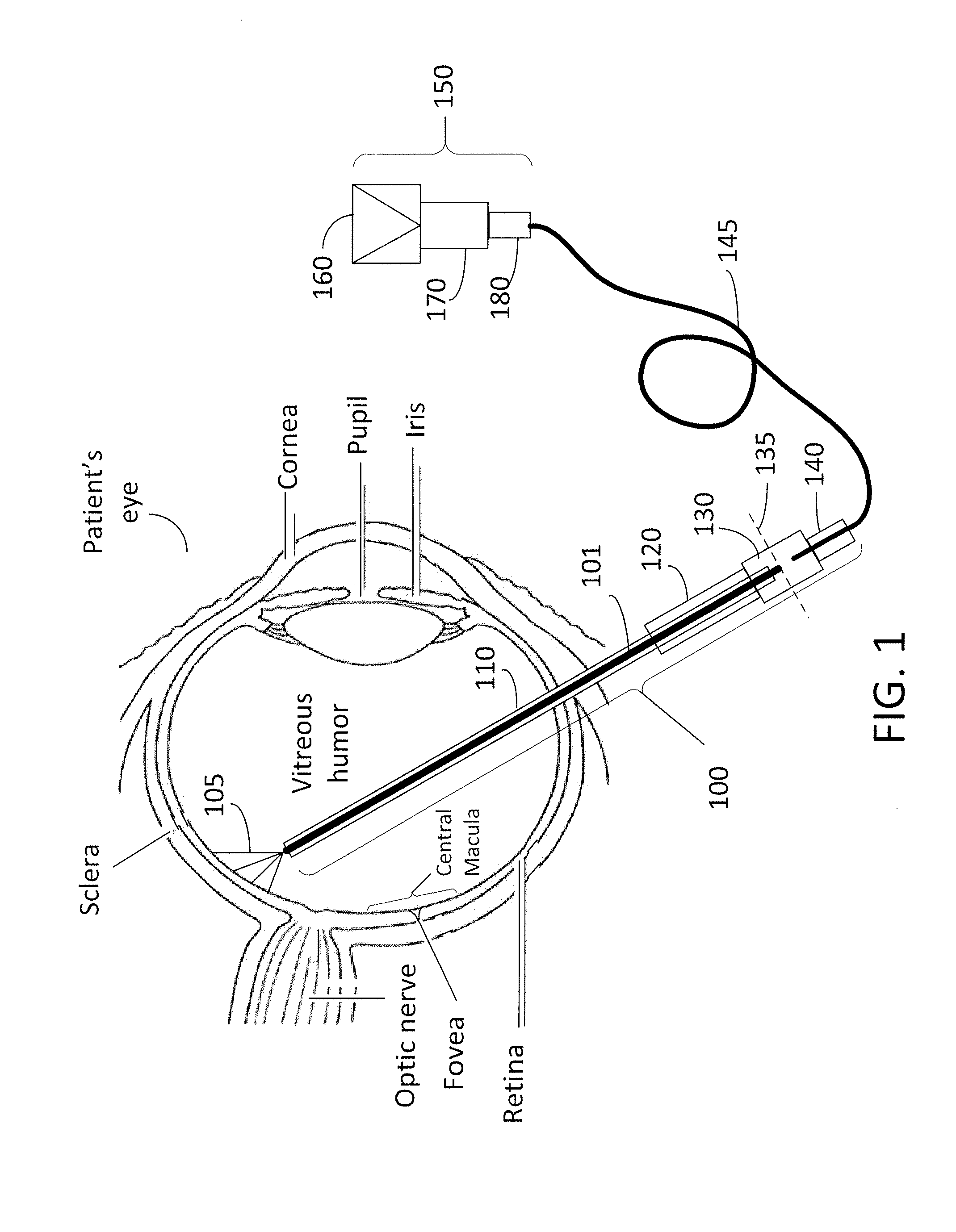
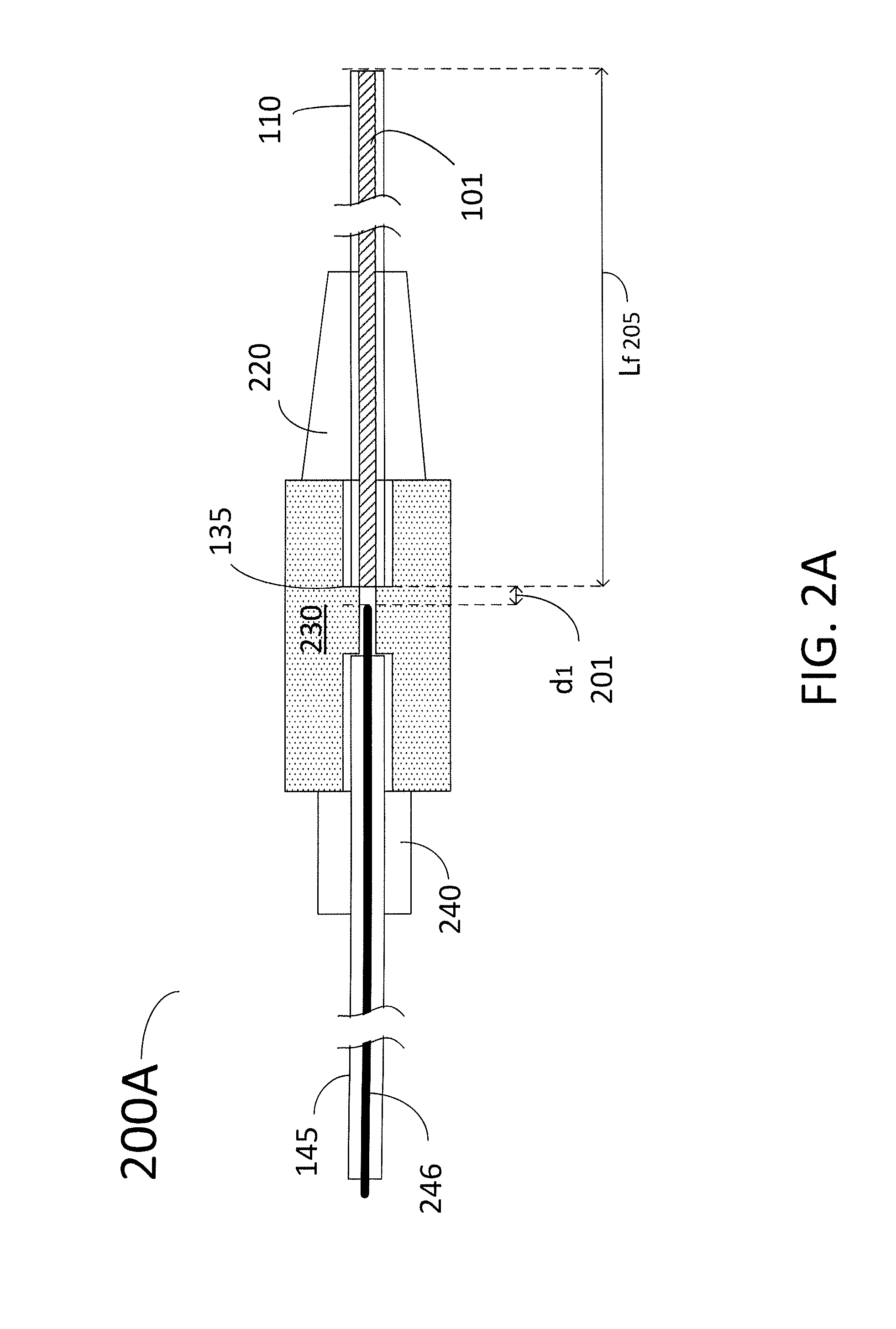
Directional laser probe
InactiveUS20060004348A1Increase deflectionPrecise positioningLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFiberLaser probe
Owner:SYNERGETICS
Component analyzer for laser probe micro-area
ActiveCN101587074AHigh absolute analytical precisionBig room for expansionFluorescence/phosphorescenceMountingsLaser probeTrace element
The invention belongs to the technical field of laser detection, specifically relates to a component analyzer for laser probe micro-area. The structure thereof comprises that: a laser, a beam expanding lens and a first total reflector are sequentially positioned on the same horizontal optical path; an included angle between the reflection plane of the first total reflector and the horizontal optical path is 45 degrees; an industrial CCD is positioned above the first total reflector, the industrial CCD and a first focusing object lens are sequentially arranged from top to bottom and optical axes thereof are superposed; the surface of a three-dimensional workbench is positioned below the first focusing object lens; the total reflector is movably mounted on the reflection optical path of a sample, an optical cable probe is positioned the reflection optical path of the total reflector; the industrial CCD is connected via the optical cable with a computer having a display, the optical cable probe is connected with a grating spectrograph, an enhanced CCD and the computer. The laser probe instrument can probe micro-area elements of substances losslessly, can satisfy rapid qualitative analysis for element components of devices having various materials and sizes, and can also implement high-accuracy quantitative analysis on micro elements and trace elements in the micro area of the sample.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
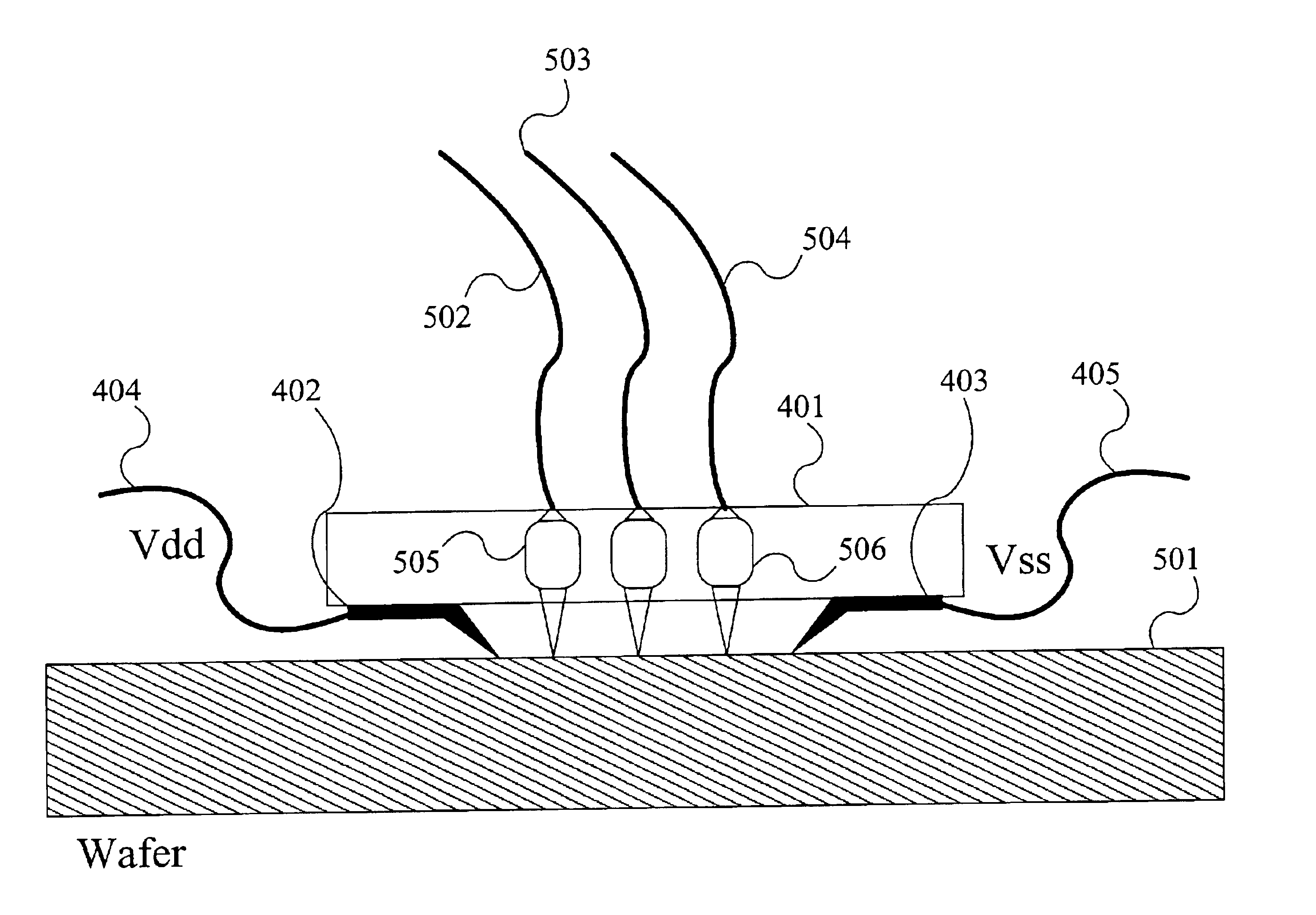
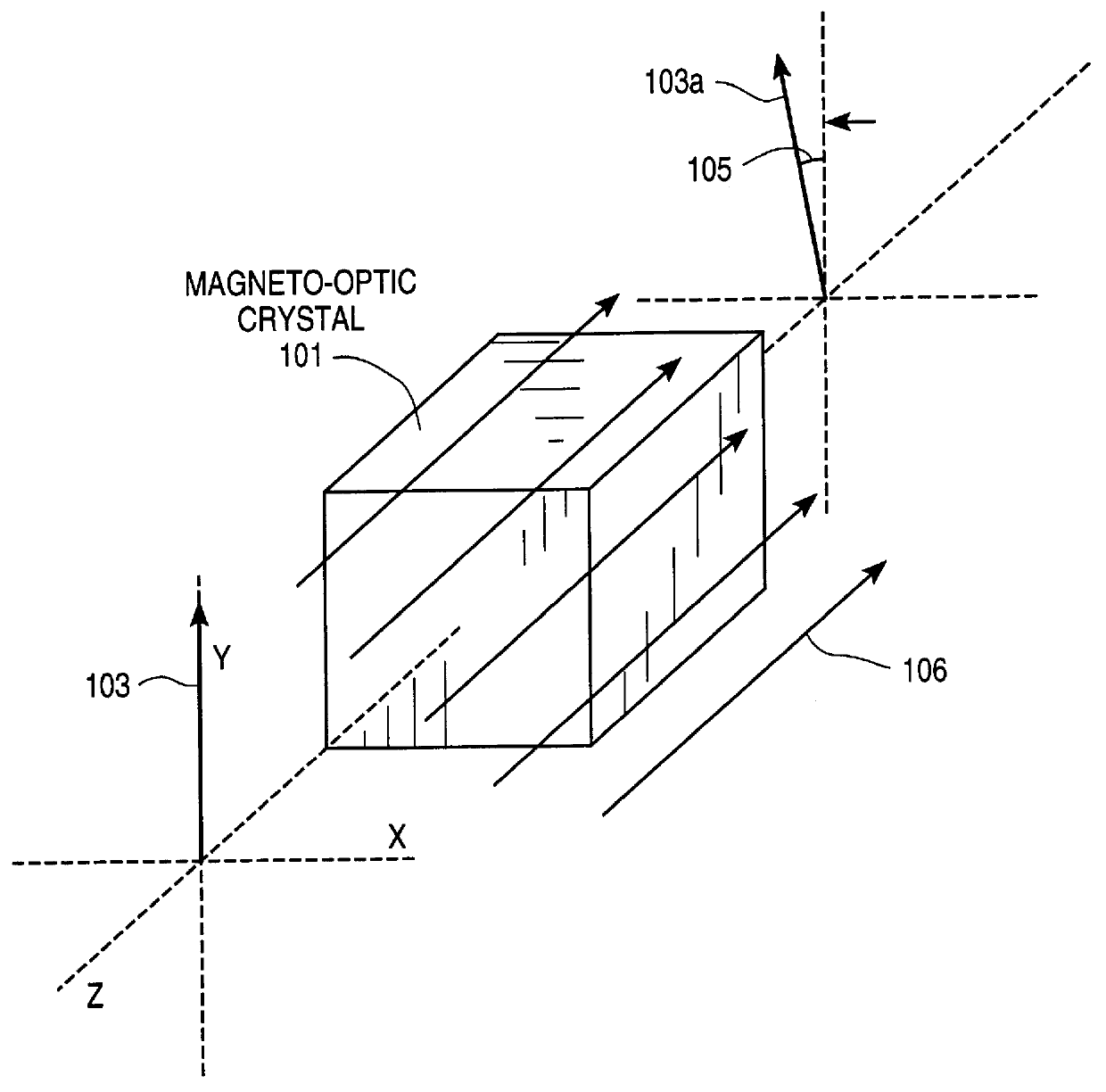
Method for performing quantitative measurement of DC and AC current flow in integrated circuit interconnects by the measurement of magnetic fields with a magneto optic laser probe
InactiveUS6084396AVoltage/current isolationMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsElectrical conductorIntegrated circuit interconnect
A laser probe for measuring a magnetic field is disclosed. A polarized laser beam is passed through a magneto-optic crystal in the presence of an unknown magnetic field. The rotation of the polarization which occurs through the magneto-optic crystal is measured in order to determine the magnitude of the magnetic field. The measured magnetic field is used to determine, for example, the current through a conductor such as an interconnect line on a semiconductor chip. A method of calibrating the magnetic field using a known magnetic from a solenoid is also disclosed. Further disclosed is a method of providing a zero-reference current by momentarily stopping the chip clock.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multi-spot laser probe with micro-structured distal surface
An optical surgical probe, configured to optically couple to a light source; comprising a cannula; a light guide within the cannula, configured to receive a light beam from the light source, to guide the light beam to a distal end of the light guide, and to emit the light beam at the distal end of the light guide; and a multi-spot generator at a distal end of the cannula, the multi-spot generator having a faceted proximal surface with oblique facets, configured to receive the light beam emitted at the distal end of the light guide and to split the received light beam into multiple beam-components, and a distal surface through which the multiple beam-components exit the multi-spot generator, wherein the distal surface is micro-structured with a modulation length smaller than a wavelength of the light beam in order to reduce the reflectance of light back into the probe.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Dual Core Optic Fiber Illuminated Laser Probe
A microsurgical laser probe primarily used in ophthalmic surgery provides both laser light and illumination light to a surgical site from a single light source. The laser probe has a dual core optic fiber that transmits both laser light and illumination light to the surgical site. A center core of the optic fiber transmits the laser light through the optic fiber and emits the laser light at the surgical site. The center core of the fiber is surrounded by an outer fiber core. The outer fiber core has an interior bore that contains the center core optic fiber. The outer fiber core transmits illumination light through the optic fiber and emits the illumination light at the surgical site.
Owner:SYNERGETICS
Chemical mapping using thermal microscopy at the micro and nano scales
ActiveUS9091594B2Small sizeReduce impactEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryThermionic emissionLaser probe
A non-destructive method for chemical imaging with ˜1 nm to 10 μm spatial resolution (depending on the type of heat source) without sample preparation and in a non-contact manner. In one embodiment, a sample undergoes photo-thermal heating using an IR laser and the resulting increase in thermal emissions is measured with either an IR detector or a laser probe having a visible laser reflected from the sample. In another embodiment, the infrared laser is replaced with a focused electron or ion source while the thermal emission is collected in the same manner as with the infrared heating. The achievable spatial resolution of this embodiment is in the 1-50 nm range.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
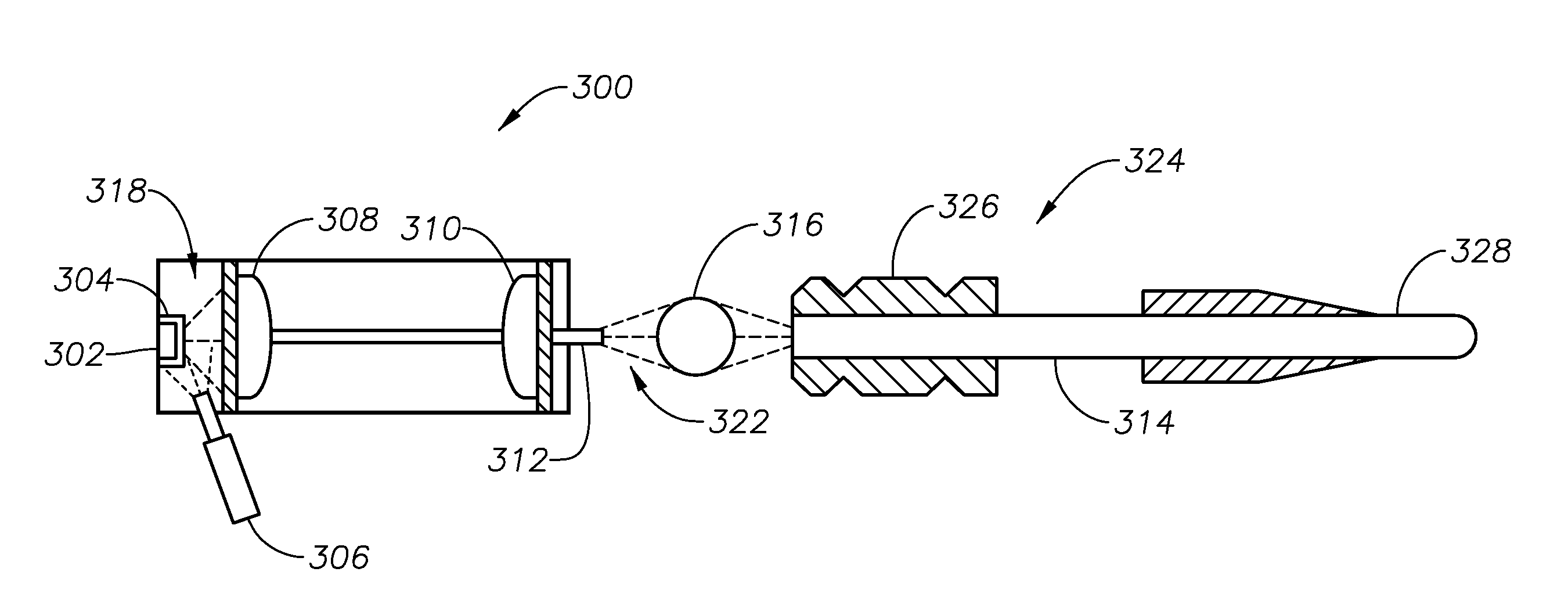
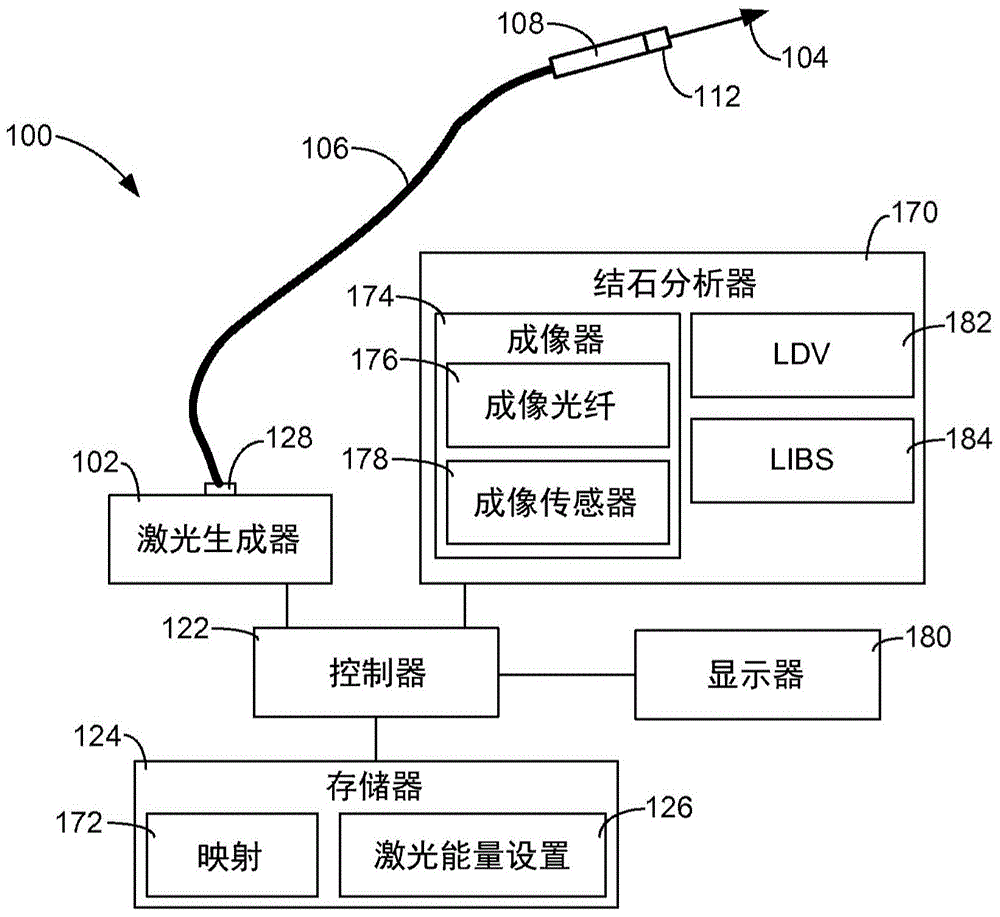
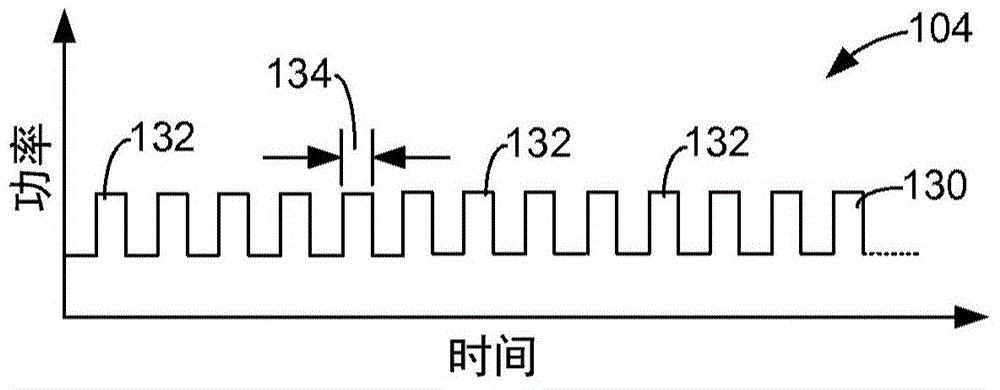
Surgical laser systems and laser lithotripsy techniques
ActiveCN104619281ADiagnostics using vibrationsDiagnostics using spectroscopyLaser probeLaser lithotripsy
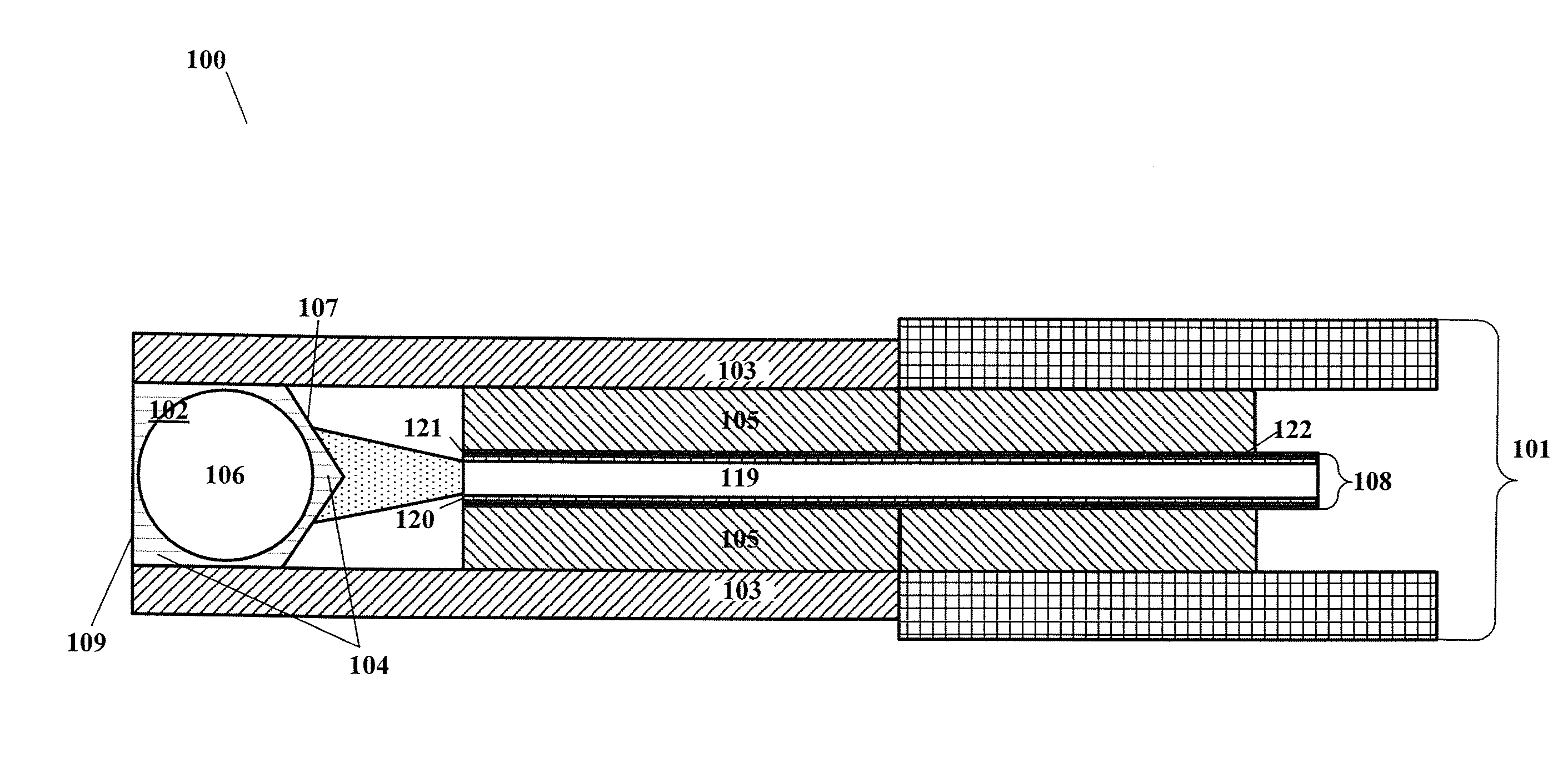
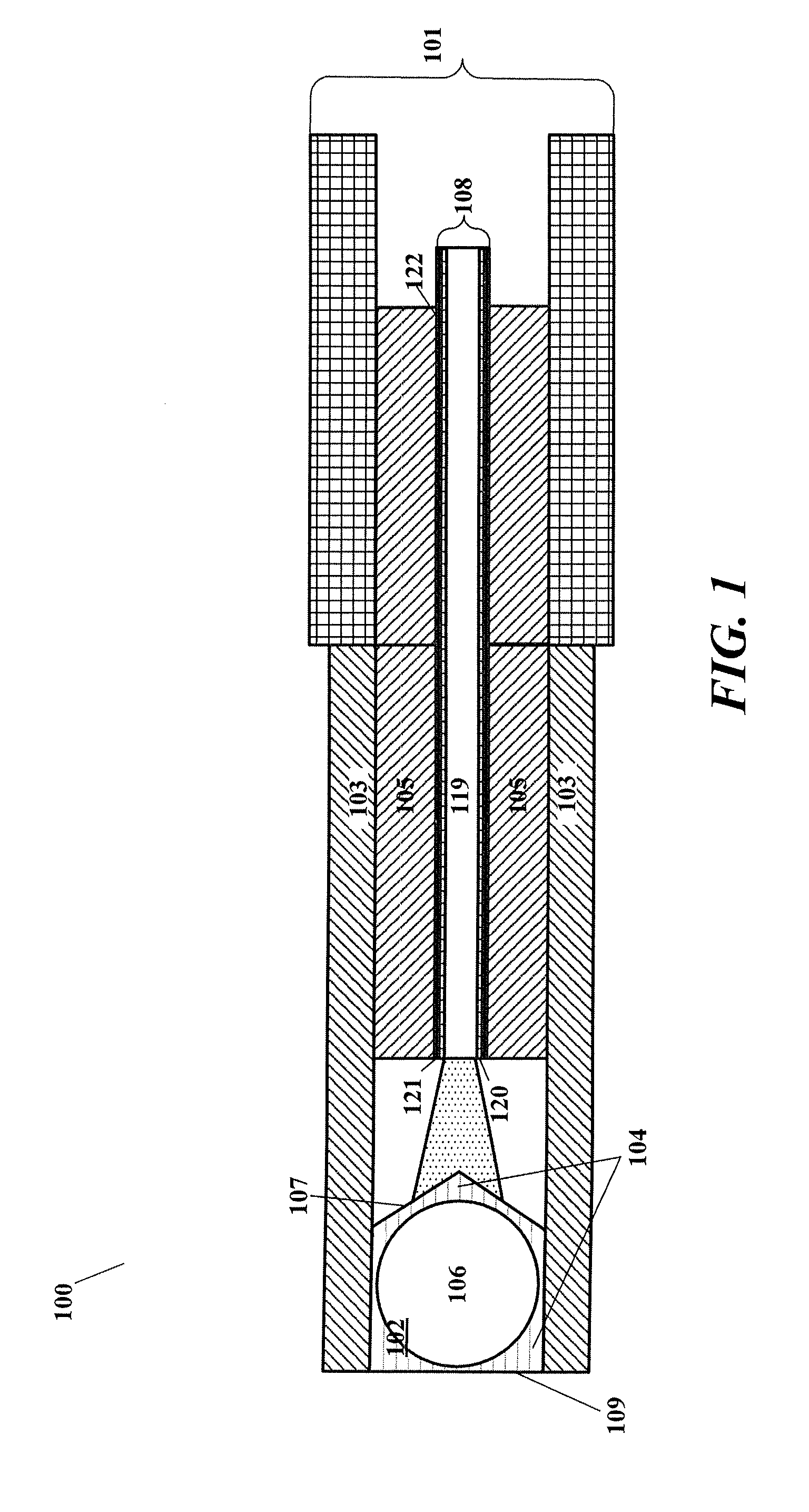
A surgical laser system (100) includes a first laser source (140A), a second laser source (140B), a beam combiner (142) and a laser probe (108). The first laser source is configured to output a first laser pulse train (144, 104A) comprising first laser pulses (146). The second laser source is configured to output a second laser pulse train (148, 104B) comprising second laser pulses (150). The beam combiner is configured to combine the first and second laser pulse trains and output a combined laser pulse train (152, 104) comprising the first and second laser pulses. The laser probe is optically coupled to an output of the beam combiner and is configured to discharge the combined laser pulse train.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
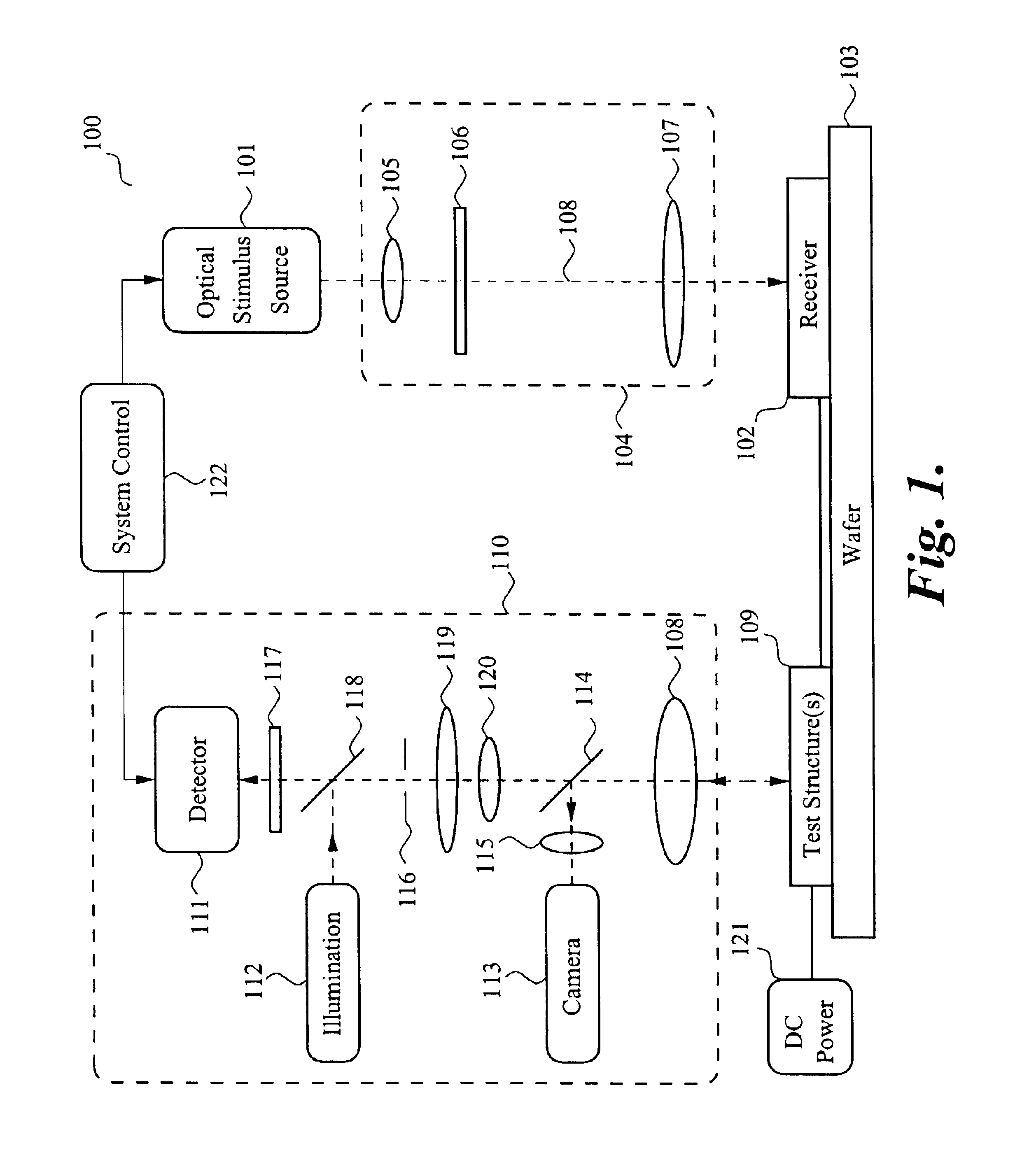
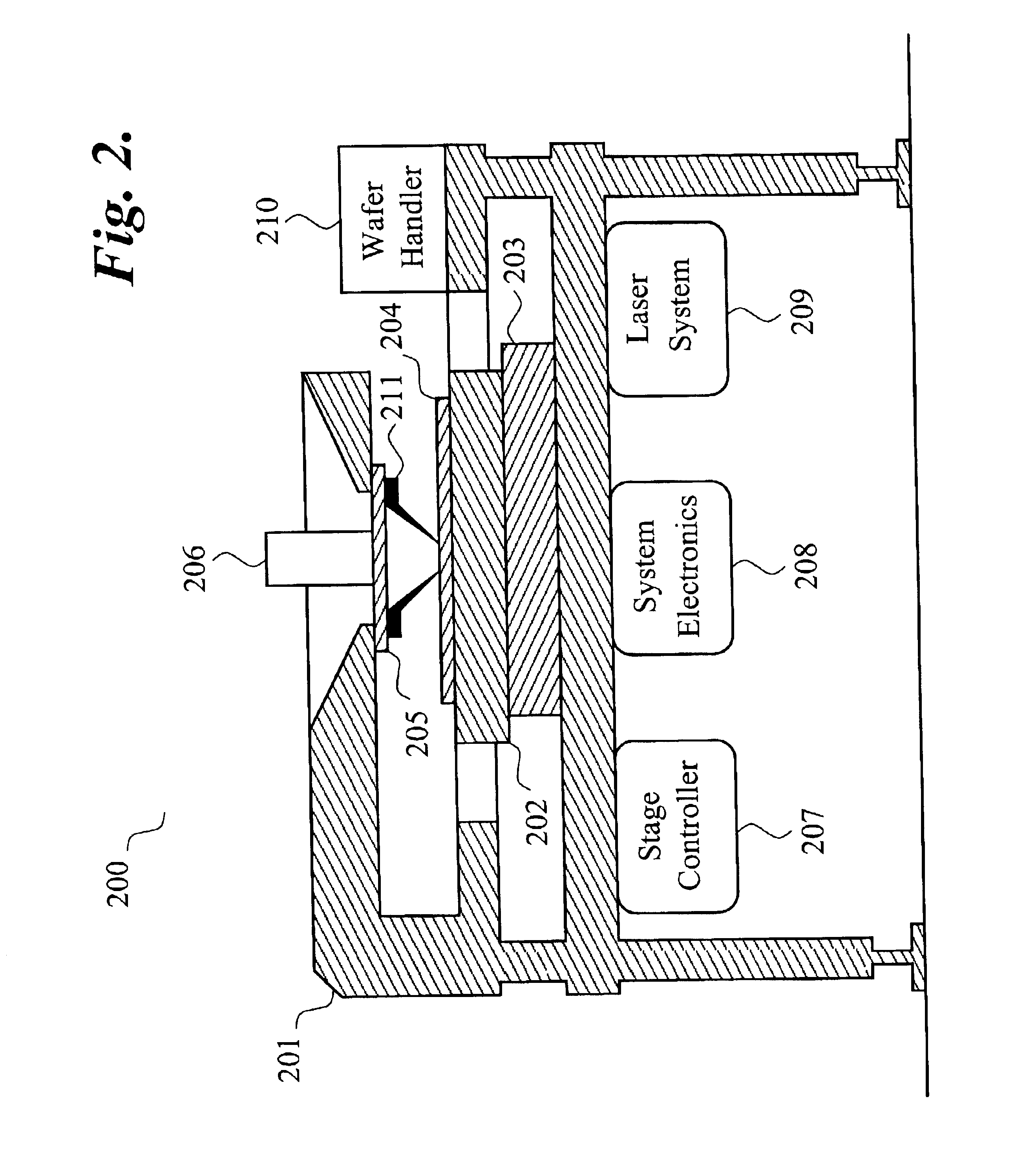
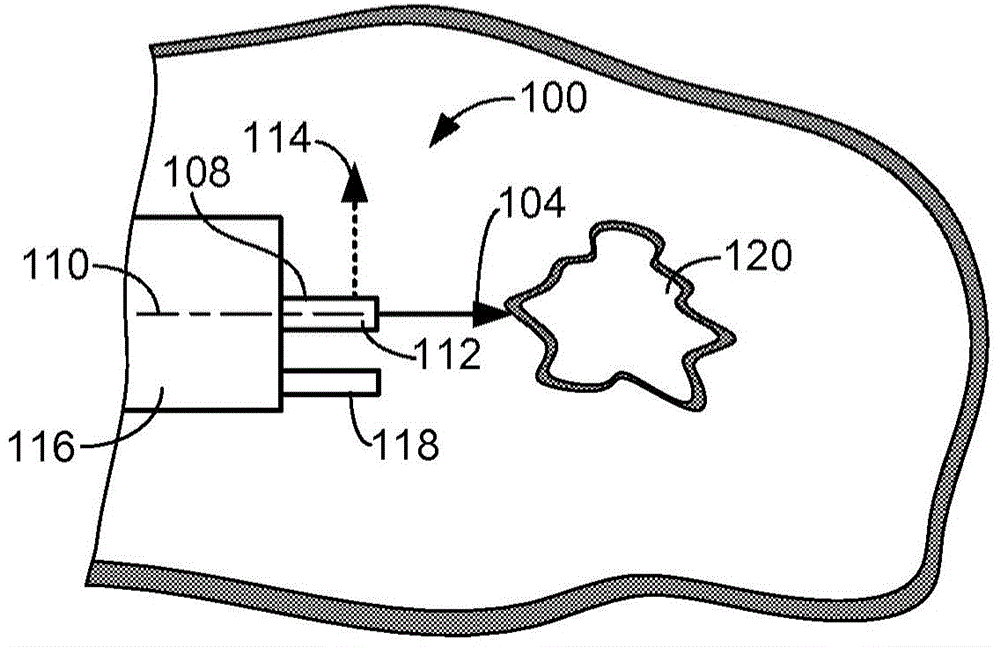
Laser probing system for integrated circuits
InactiveUS20070046947A1Improve time resolutionUsing optical meansLight polarisation measurementLaser probeLaser source
A system for probing a DUT is disclosed, the system having a pulsed laser source, a CW laser source, beam optics designed to point a reference beam and a probing beam at the same location on the DUT, optical detectors for detecting the reflected reference and probing beams, and a collection electronics. The beam optics is a common-path polarization differential probing (PDP) optics. The common-path PDP optics divides the incident laser beam into two beams of orthogonal polarization - one beam simulating a reference beam while the other simulating a probing beam. Both reference and probing beams are pointed to the same location on the DUT. Due to the intrinsic asymmetry of a CMOS transistor, the interaction of the reference and probing beams with the DUT result in different phase modulation in each beam. This difference can be investigated to study the response of the DUT to the stimulus signal.
Owner:DCG SYST
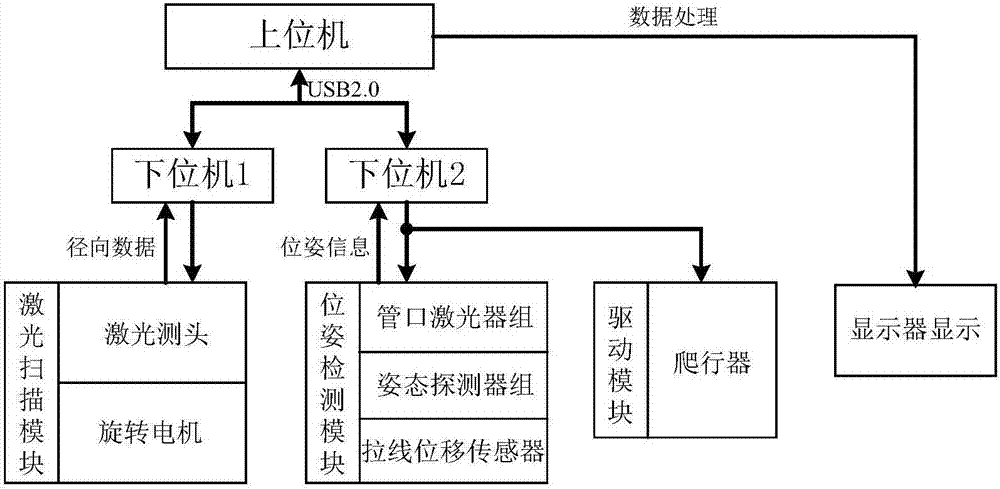
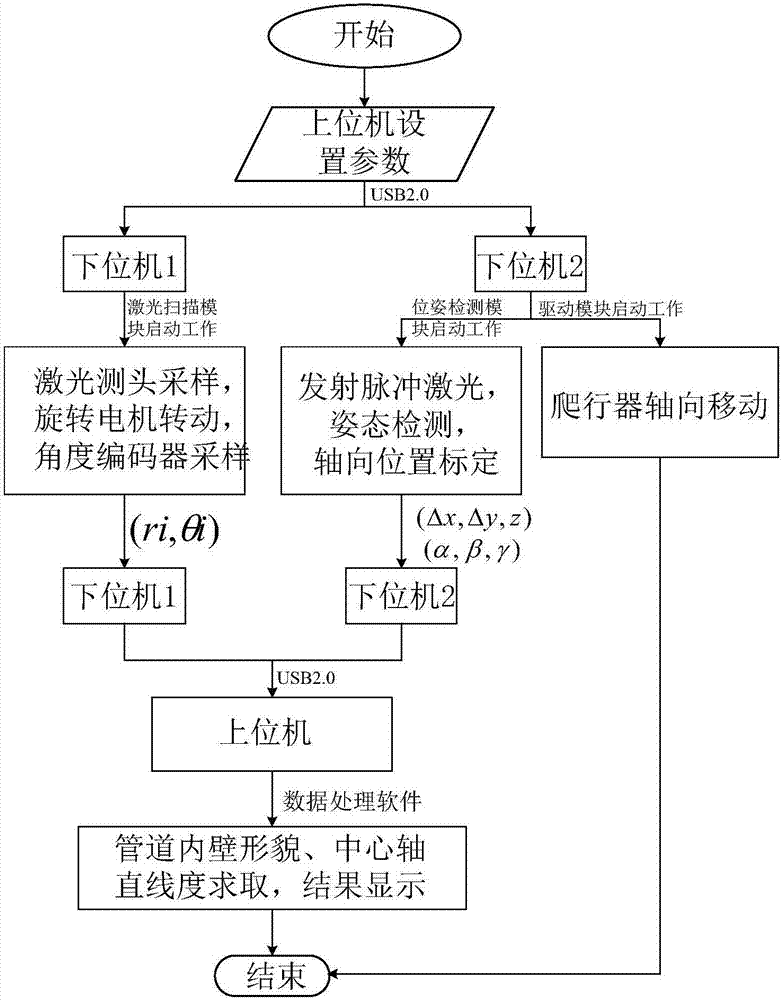
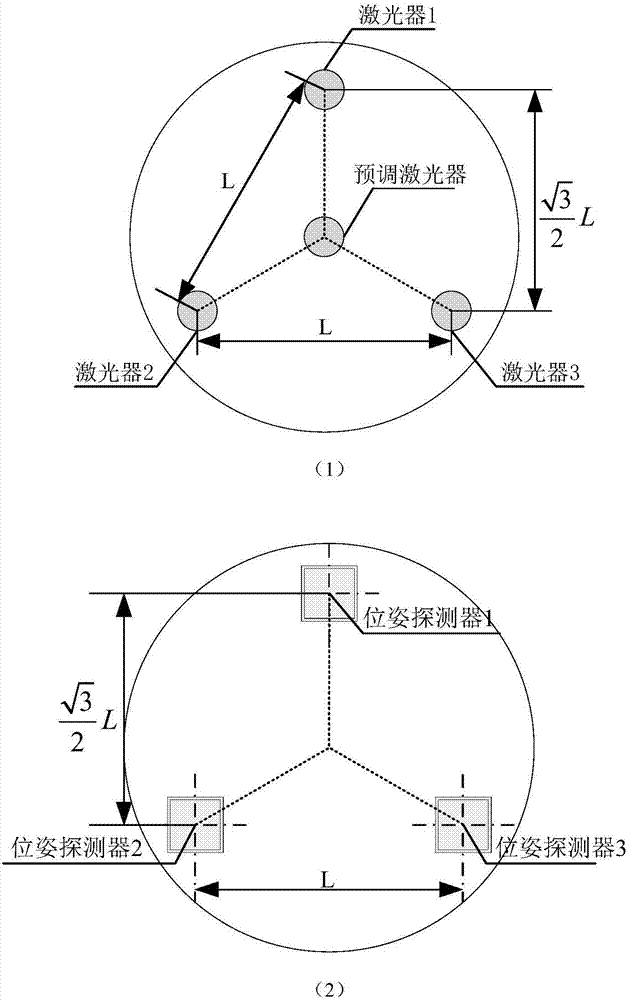
Pipeline inner wall morphology and center axis straightness measuring device and method
ActiveCN107063119AEliminate errorsHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansLaser probePre conditioning
The invention relates to the technical field of photoelectric detection, and relates to a pipeline inner wall morphology and center axis straightness measuring device and method which can measure the pipeline inner wall 3D morphology and the center axis straightness simultaneously, output and display a result and acquire accurate pipeline inner wall morphology data, thereby accurately restoring the pipeline inner wall morphology, and improving the measurement accuracy of the pipeline inner wall morphology and the center axis straightness. The pipeline inner wall morphology and center axis straightness measuring device and method provided by the invention are implemented by the aid of a pre-conditioning device, a laser scanning module, a position and posture detection module and a driving module, wherein the laser scanning module and the position and posture detection module are in rigid connection, the relative positions are determined, a moderate expansion device is arranged, the two modules form a system detection device which is driven by a crawler to crawl continuously in a contact manner along the pipeline inner wall, and the laser scanning module is composed of a laser probe and a rotating motor; the position and posture detection module is composed of a pipe mouth laser group, a posture detector group and a stay wire displacement sensor; and the driving module comprises a crawler. The pipeline inner wall morphology and center axis straightness measuring device and method mainly applied to occasions of pipeline photoelectric detection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Laser probe analyzer based on aerosolization and resonance excitation
ActiveCN103712962AIncrease profitImprove compatibilityAnalysis by thermal excitationCollection systemLaser probe
The invention discloses a laser probe component analyzer. The laser probe component analyzer comprises a Nd. YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet) laser system, a wavelength tunable laser system, an aerosolization system, a spectrum collection system and a computer, wherein the aerosolization system is used for producing an aerosol from a solution to be analyzed; the Nd. YAG laser is used for producing a high-energy laser beam and focusing the laser beam on the aerosol to excite plasma flame; the wavelength tunable laser system is used for producing a pumped laser beam with required resonance excitation wavelength and focusing the laser beam on the plasma flame to produce a resonance excitation effect; and the spectrum collection system is used for collecting characteristic spectral signals produced after resonance excitation, converting the spectral signals to electric signals and then transmitting the electric signals to the computer to analyze substance components in the solution. The system can overcome the shortcomings of the prior art, greatly improve the detection sensitivity of an LIBS (laser induced breakdown spectroscopy) technology in detection of trace elements in the solution, achieve the requirements of actual applications in the fields of environmental monitoring and the like and simultaneously perform online precise qualitative and quantitative analysis of substances in a liquid.
Owner:WUHAN XINRUIDA LASER ENG +1
Auto-focus raman spectrometer system
InactiveUS20160091366A1Simple structureFocusRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyExcitation beamLight beam
An autofocus Raman spectrometer system includes a laser probe assembly, a microprocessor, adjustable stages and a driving means. The laser probe assembly includes an excitation means, a focusing optics provided to focus an excitation beam from the excitation means onto a sample and generate Raman scattering spectrum, a collection optics for collecting the Raman scattering spectrum, and a spectrographic detector for generating a Raman spectrum based on the Raman scattering intensity received from the collection optics. The microprocessor receives the Raman spectra signal therefrom. The laser probe assembly is situated on the adjustable stage. The driving means is coupled to the microprocessor and configured to drive the stage to move with respect to the sample. The microprocessor generates a command to the driving means for moving a position of the adjustable stage to achieve an optimal optical focus based on signal intensity of the spectra peaks measured by the spectrographic detector.
Owner:YANG FR JIANN FU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com