Patents
Literature
648 results about "Cw laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
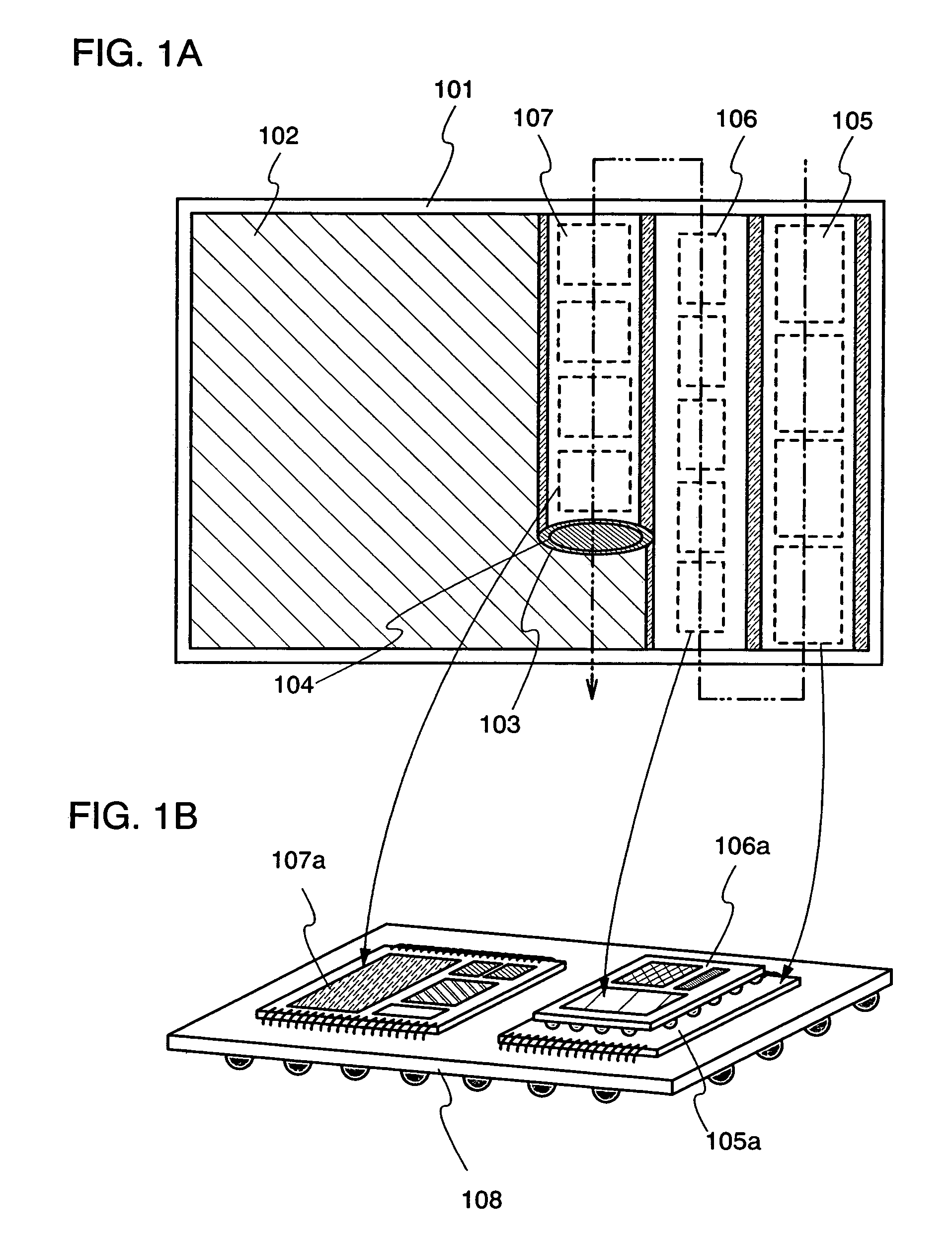
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070087488A1Improve driving abilitySmall characteristic variationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialPlane orientation
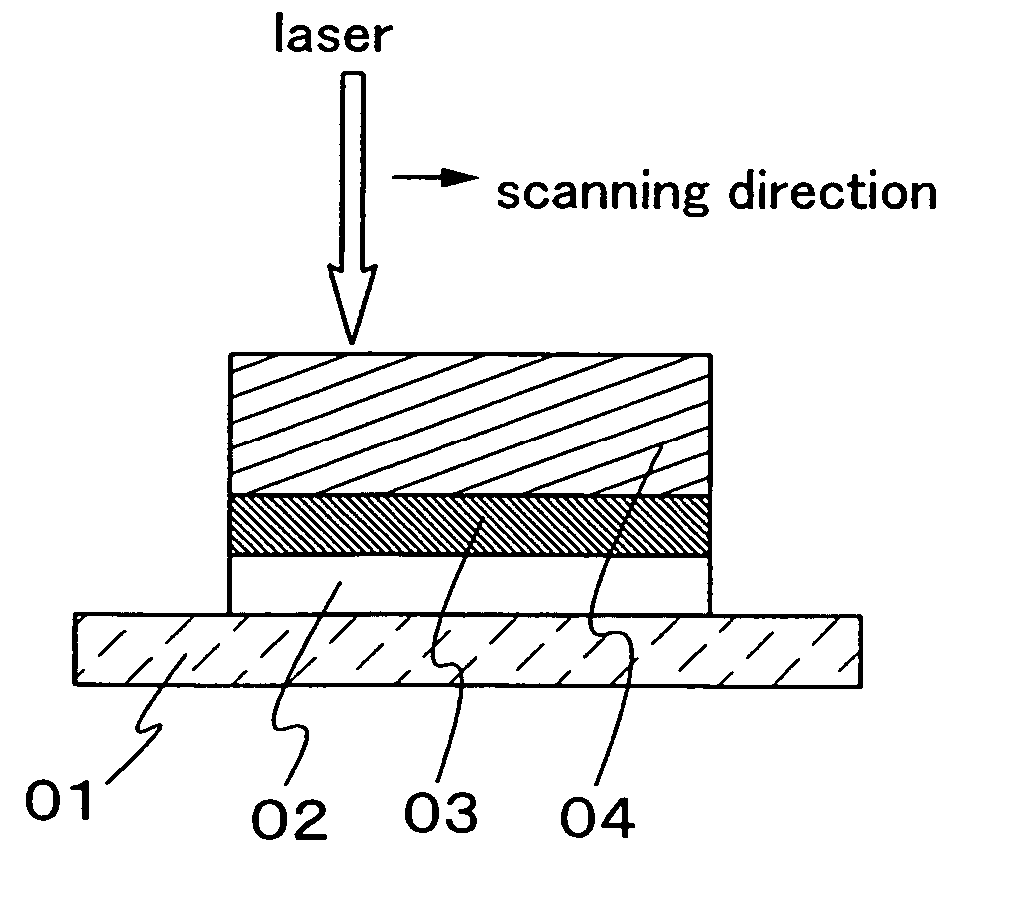
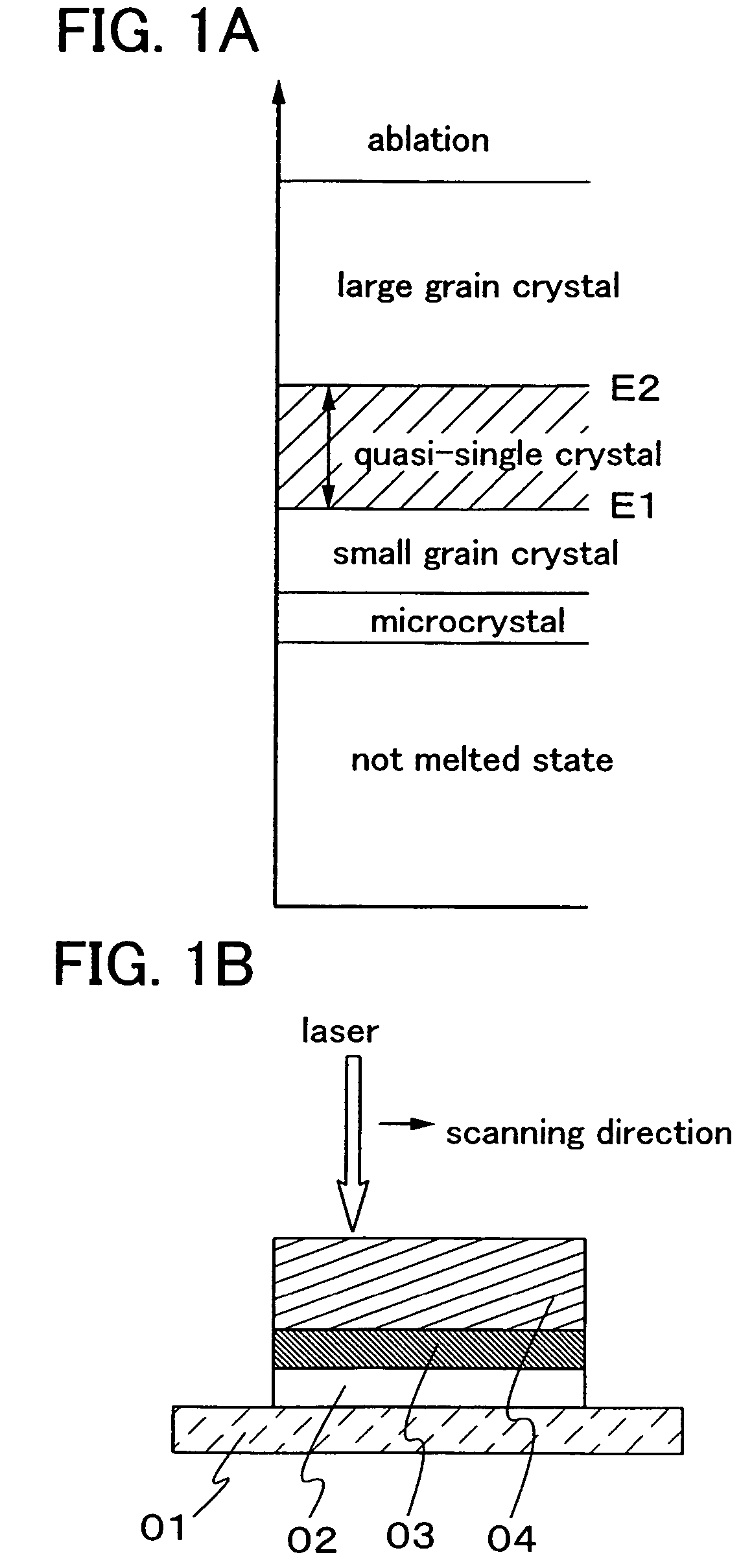
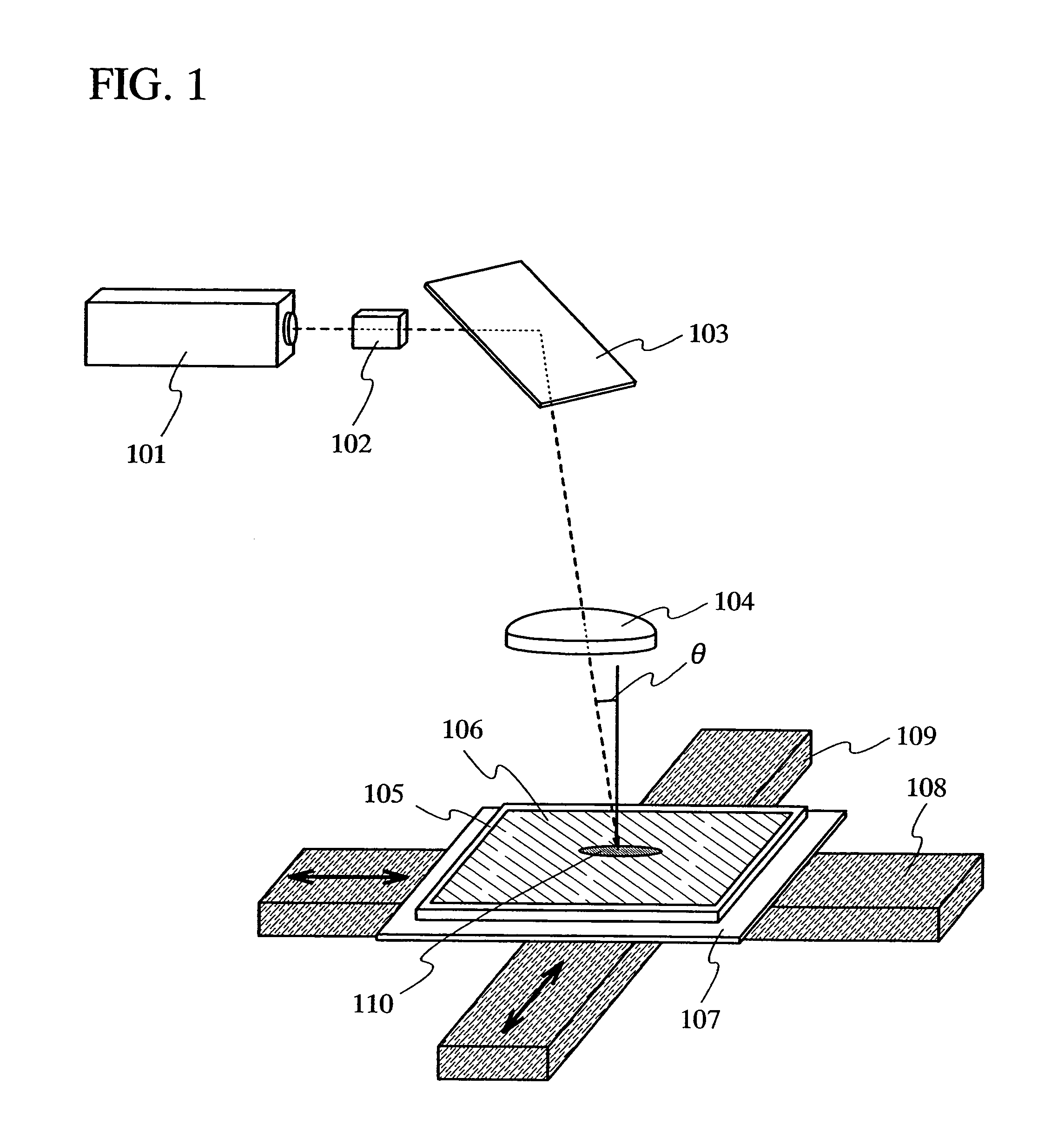
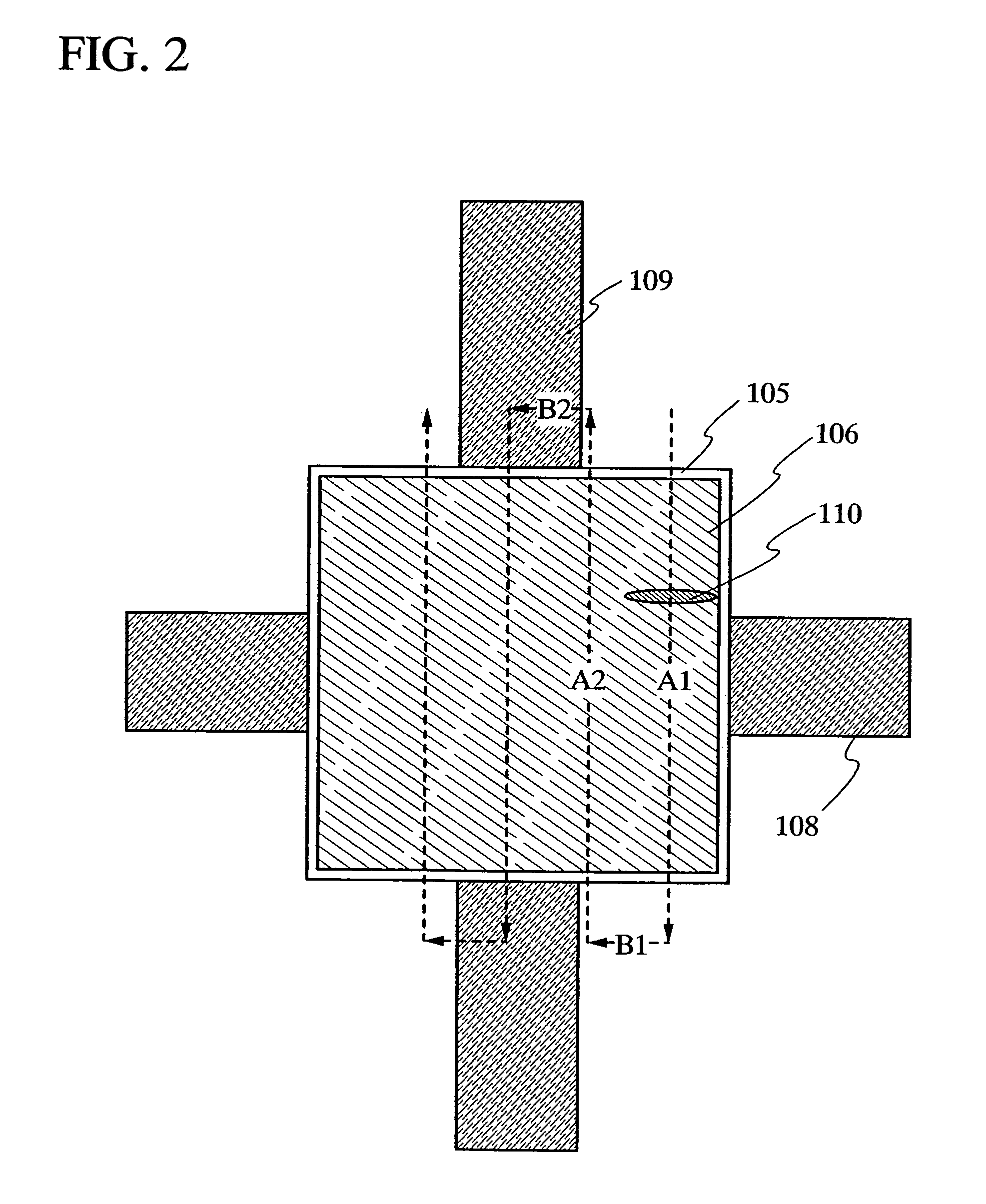
It is an object of the present invention to control the plane orientation of crystal grains obtained by using a laser beam, into a direction that can be substantially regarded as one direction in an irradiation region of the laser beam. After forming a cap film over a semiconductor film, the semiconductor film is crystallized by using a CW laser or a pulse laser having a repetition rate of greater than or equal to 10 MHz. The obtained semiconductor film has a plurality of crystal grains having a width of greater than or equal to 0.01 μm and a length of greater than or equal to 1 μm. In a surface of the obtained semiconductor film, a ratio of an orientation {211} is greater than or equal to 0.4 within the range of an angle fluctuation of ±10°.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
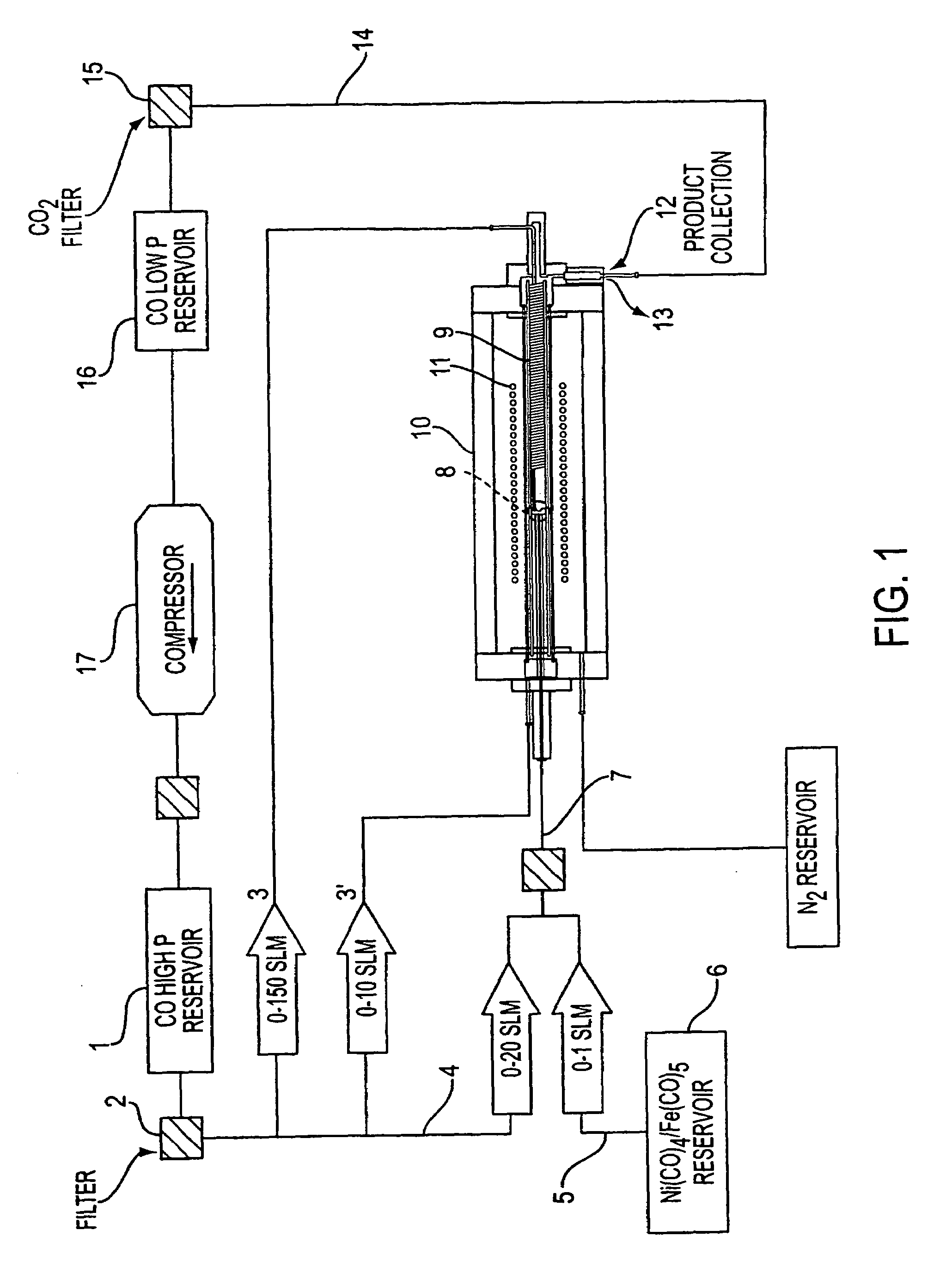
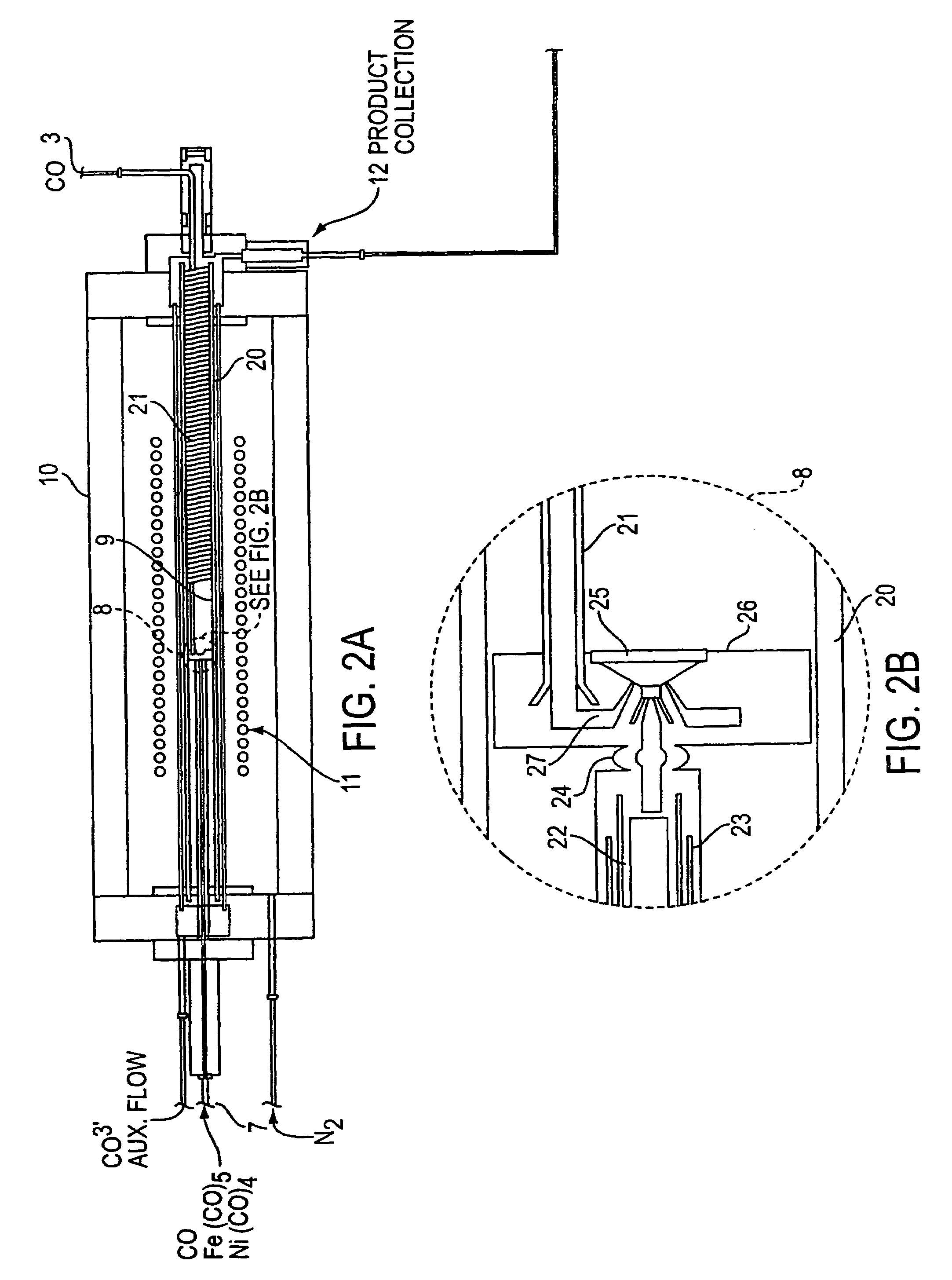
Single-wall carbon nanotubes from high pressure CO
InactiveUS7204970B2Promote rapid formationIncrease pressureMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureDecompositionCarbon nanotube
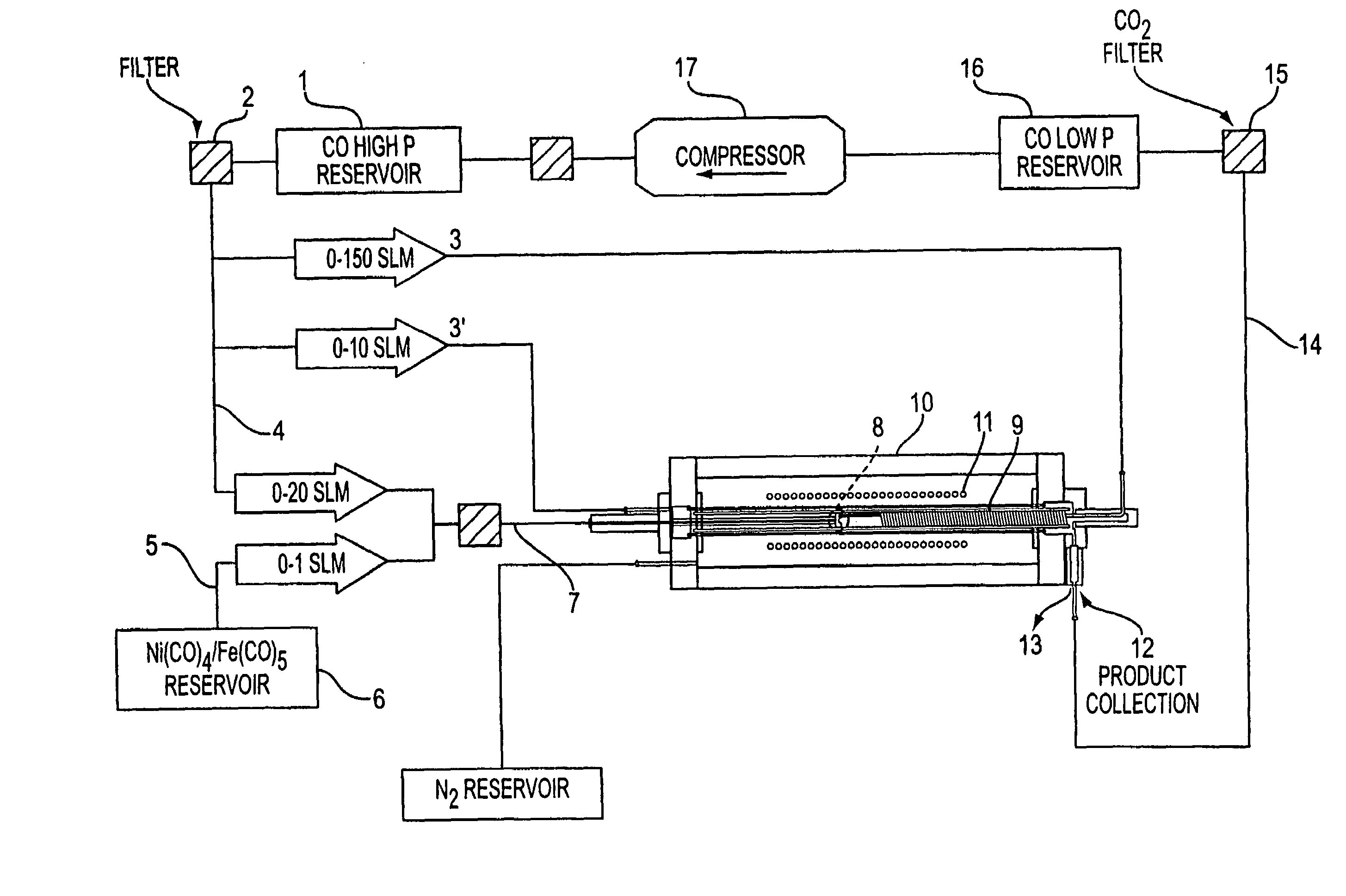
The present invention discloses the process of supplying high pressure (e.g., 30 atmospheres) CO that has been preheated (e.g., to about 1000° C.) and a catalyst precursor gas (e.g., Fe(CO)5) in CO that is kept below the catalyst precursor decomposition temperature to a mixing zone. In this mixing zone, the catalyst precursor is rapidly heated to a temperature that results in (1) precursor decomposition, (2) formation of active catalyst metal atom clusters of the appropriate size, and (3) favorable growth of SWNTs on the catalyst clusters. Preferably a catalyst cluster nucleation agency is employed to enable rapid reaction of the catalyst precursor gas to form many small, active catalyst particles instead of a few large, inactive ones. Such nucleation agencies can include auxiliary metal precursors that cluster more rapidly than the primary catalyst, or through provision of additional energy inputs (e.g., from a pulsed or CW laser) directed precisely at the region where cluster formation is desired. Under these conditions SWNTs nucleate and grow according to the Boudouard reaction. The SWNTs thus formed may be recovered directly or passed through a growth and annealing zone maintained at an elevated temperature (e.g., 1000° C.) in which tubes may continue to grow and coalesce into ropes.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Mode-locked multi-mode fiber laser pulse source
InactiveUS20050008044A1High energy storageIncrease the sectionCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersPeak value
A laser utilizes a cavity design which allows the stable generation of high peak power pulses from mode-locked multi-mode fiber lasers, greatly extending the peak power limits of conventional mode-locked single-mode fiber lasers. Mode-locking may be induced by insertion of a saturable absorber into the cavity and by inserting one or more mode-filters to ensure the oscillation of the fundamental mode in the multi-mode fiber. The probability of damage of the absorber may be minimized by the insertion of an additional semiconductor optical power limiter into the cavity. To amplify and compress optical pulses in a multi-mode (MM) optical fiber, a single-mode is launched into the MM fiber by matching the modal profile of the fundamental mode of the MM fiber with a diffraction-limited optical mode at the launch end, The fundamental mode is preserved in the MM fiber by minimizing mode-coupling by using relatively short lengths of step-index MM fibers with a few hundred modes and by minimizing fiber perturbations. Doping is confined to the center of the fiber core to preferentially amplify the fundamental mode, to reduce amplified spontaneous emission and to allow gain-guiding of the fundamental mode. Gain-guiding allows for the design of systems with length-dependent and power-dependent diameters of the fundamental mode. To allow pumping with high-power laser diodes, a double-clad amplifier structure is employed. For applications in nonlinear pulse-compression, self phase modulation and dispersion in the optical fibers can be exploited. High-power optical pulses may be linearly compressed using bulk optics dispersive delay lines or by chirped fiber Bragg gratings written directly into the SM or MM optical fiber. High-power cw lasers operating in a single near-diffraction-limited mode may be constructed from MM fibers by incorporating effective mode-filters into the laser cavity. Regenerative fiber amplifiers may be constructed from MM fibers by careful control of the recirculating mode. Higher-power Q-switched fiber lasers may be constructed by exploiting the large energy stored in MM fiber amplifiers.
Owner:FERMANN MARTIN E +1
Laser irradiation method, laser irradiation apparatus and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070178672A1High output powerImprove mobilityPolycrystalline material growthBy zone-melting liquidsNonlinear opticsDevice material
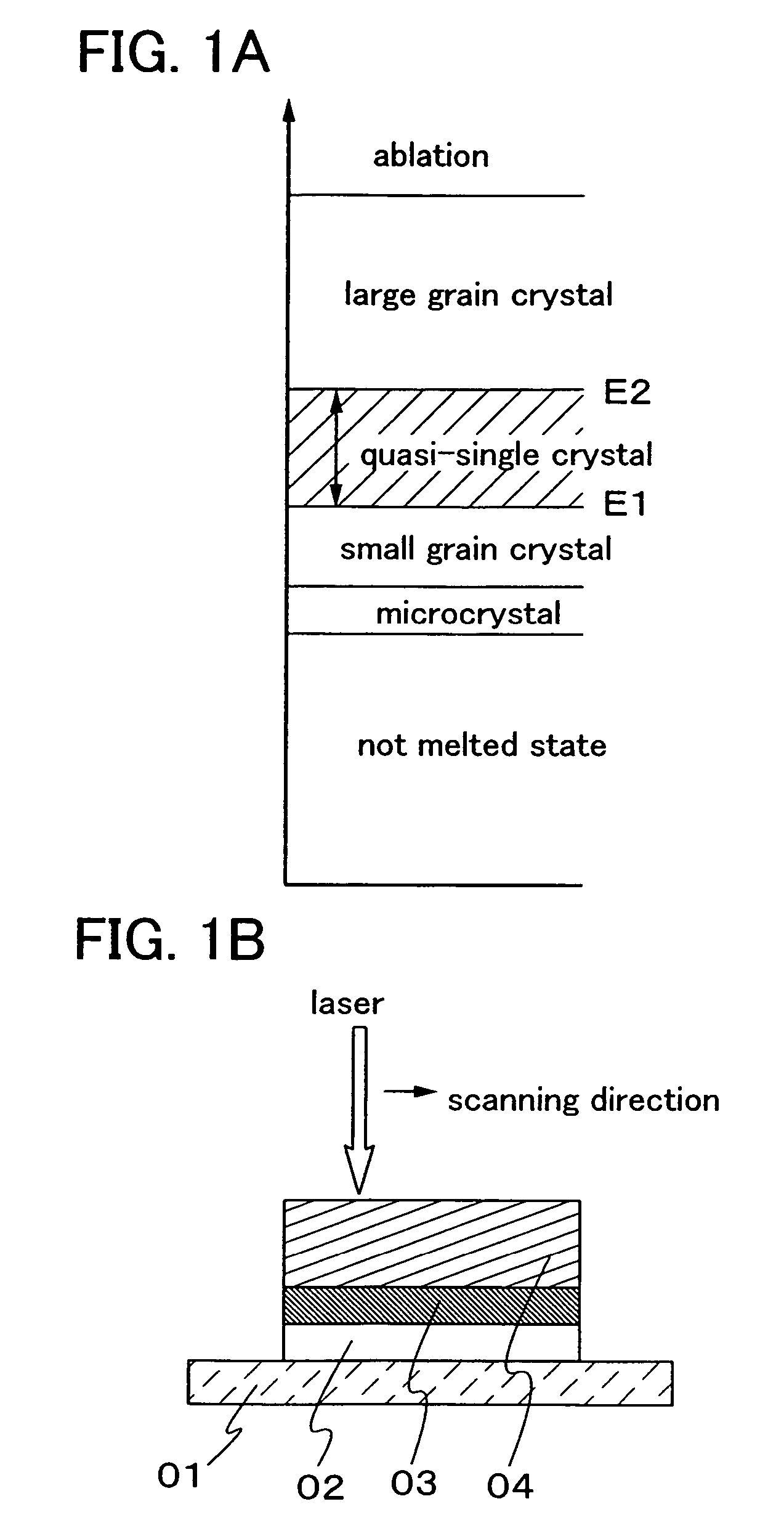
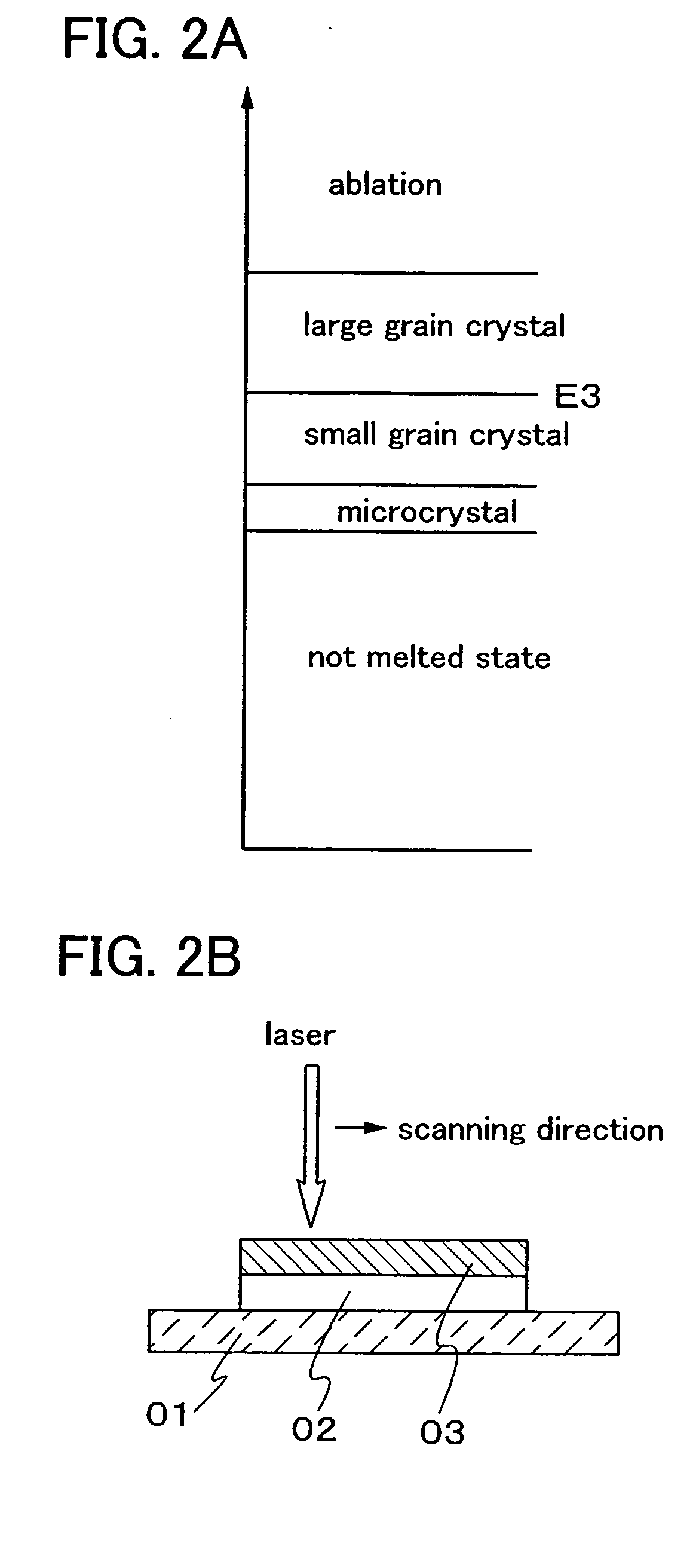
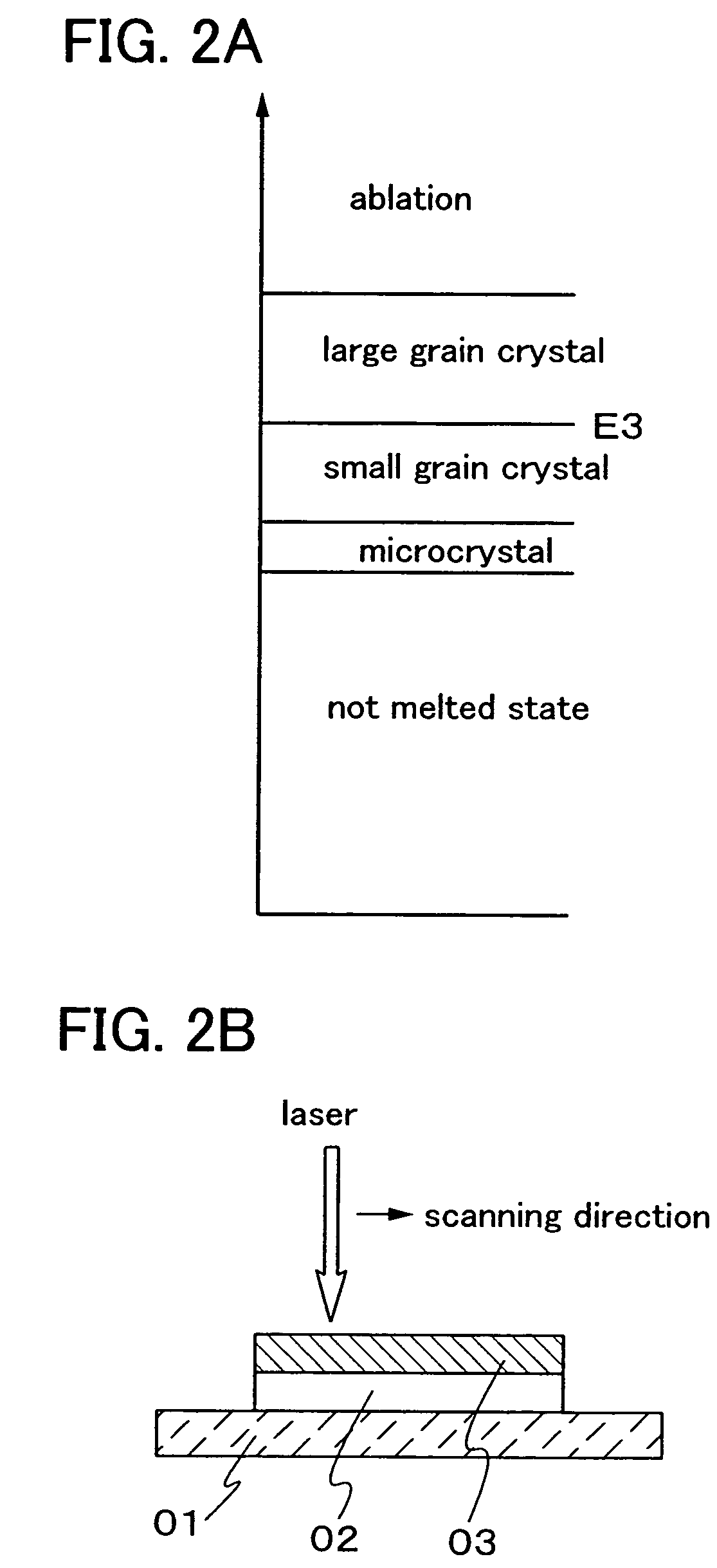
In conducting laser annealing using a CW laser or a quasi-CW laser, productivity is not high as compared with an excimer laser and thus, it is necessary to further enhance productivity. According to the present invention, a fundamental wave is used without putting laser light into a non linear optical element, and laser annealing is conducted by irradiating a semiconductor thin film with pulsed laser light having a high repetition rate. A laser oscillator having a high output power can be used for laser annealing, since a non linear optical element is not used and thus light is not converted to a harmonic. Therefore, the width of a region having large grain crystals that is formed by scanning once can be increased, and thus the productivity can be enhanced dramatically.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
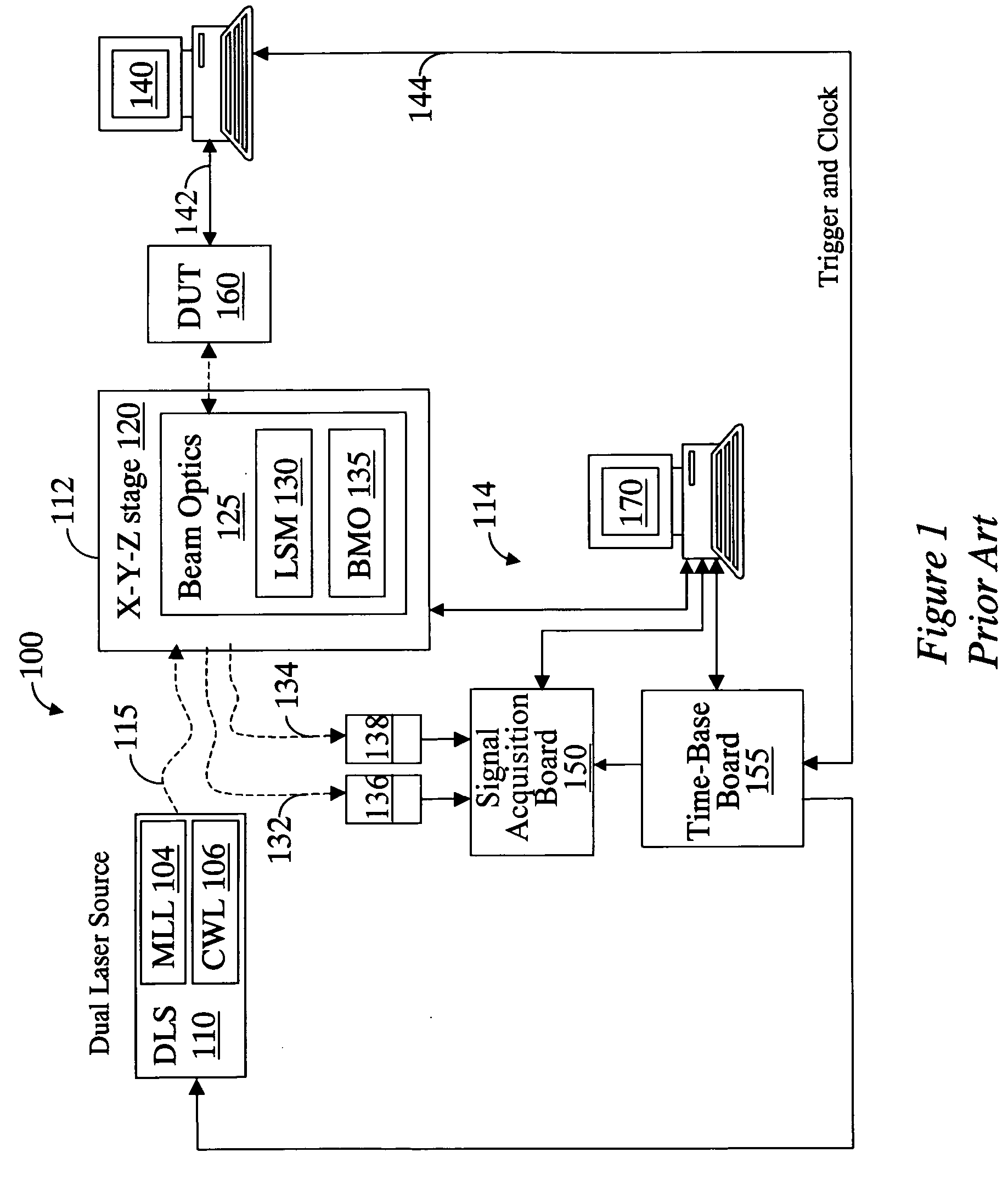
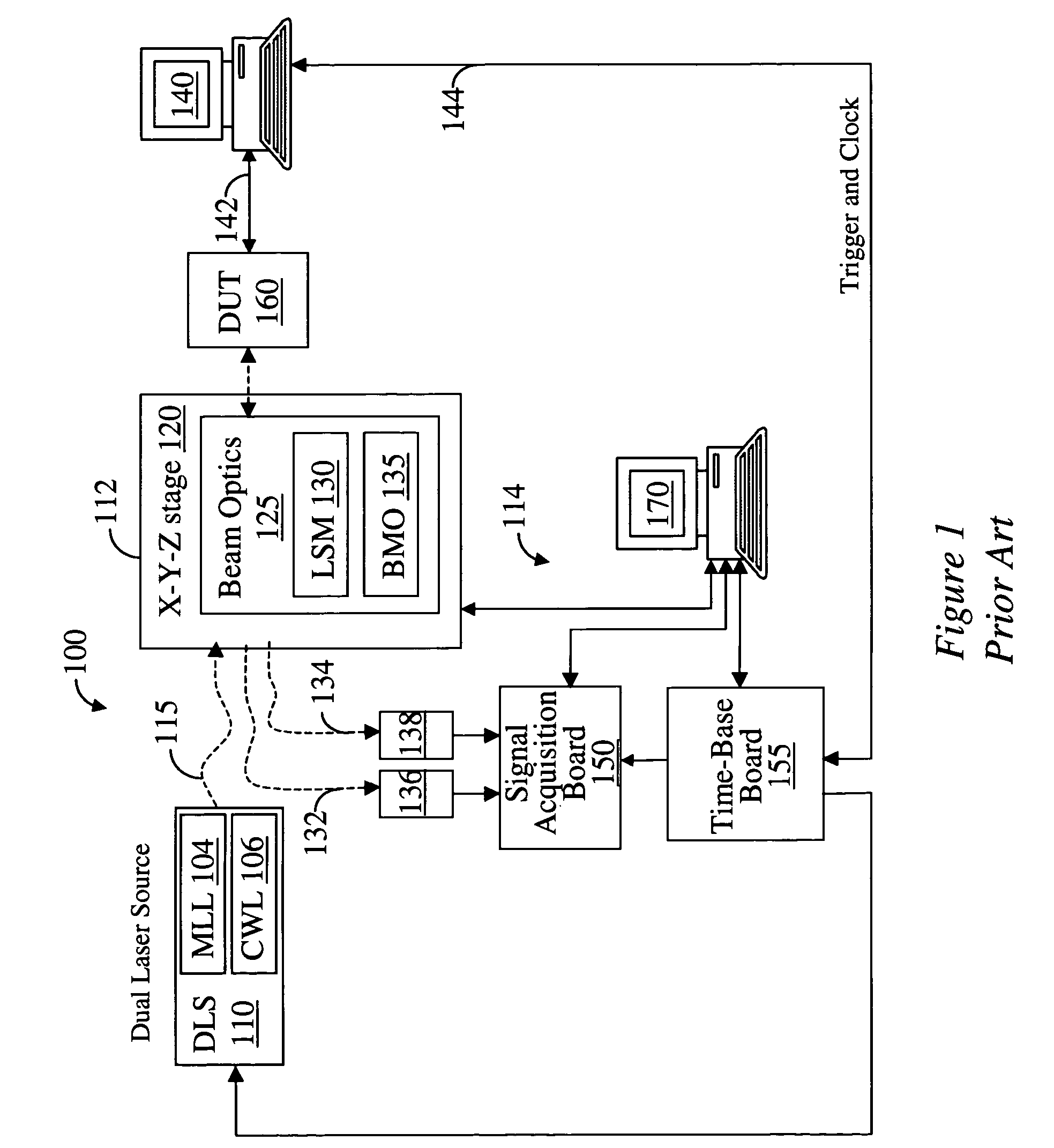
Apparatus and method for dynamic diagnostic testing of integrated circuits
InactiveUS6859031B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMagnetic property measurementsPhoton counting detectorElectricity
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Method for manufacturing semiconductor apparatus, and semiconductor apparatus and electric appliance
ActiveUS7056810B2Low costImprove throughputPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringCw laser
According to the package and the method for manufacturing the package of the present invention, a chip can be formed extremely to be thin, and manufactured at lower cost and higher throughput, and the variations of a chip thickness can be reduced without back grind that causes cracks or polishing marks. In the present invention, a semiconductor film with a thickness of at most 500 μm deposited over a substrate serving as a support medium is crystallized with a CW laser light, and a chip having a semiconductor device is formed to have a total thickness of 5 μm, preferably at most 2 μm by using the crystallized semiconductor film. Consequently, the chip is mounted on an interposer after separating a substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Fiber lasers
ActiveUS7778290B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove abilitiesLaser using scattering effectsDouble-clad fiberPolarizer
Fiber lasers for producing Band I wavelengths include a laser cavity having an optical fiber with specific parameters in length and thickness and doping concentration, and having high reflectivities. Examples show the feasibility of producing such fiber lasers. Fiber lasers for producing Band IV wavelengths include a depolarized laser oscillator, at least one amplifier and a polarizer. Depolarized laser oscillator is an inherently depolarized CW laser, or a depolarized laser diode, which is depolarized by a depolarizer. Additional fiber lasers in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include a double clad active optical fiber having a pump power entry point for sending pump energy through the active optical fiber in a first direction, and a loop portion at a second end of the fiber for sending pump energy through the active optical fiber in a second direction which is opposite to the first direction. A system for coupling light into a fiber in accordance with embodiments of the present invention include a first fiber, a second double clad fiber, and a bulk optic component positioned between the first and second fibers. A mode stripper included within the second fiber allows for removal of high power light which is propagated through the outer clad rather than launched into the core of the second fiber.
Owner:ELBIT SYST ELECTRO OPTICS ELOP
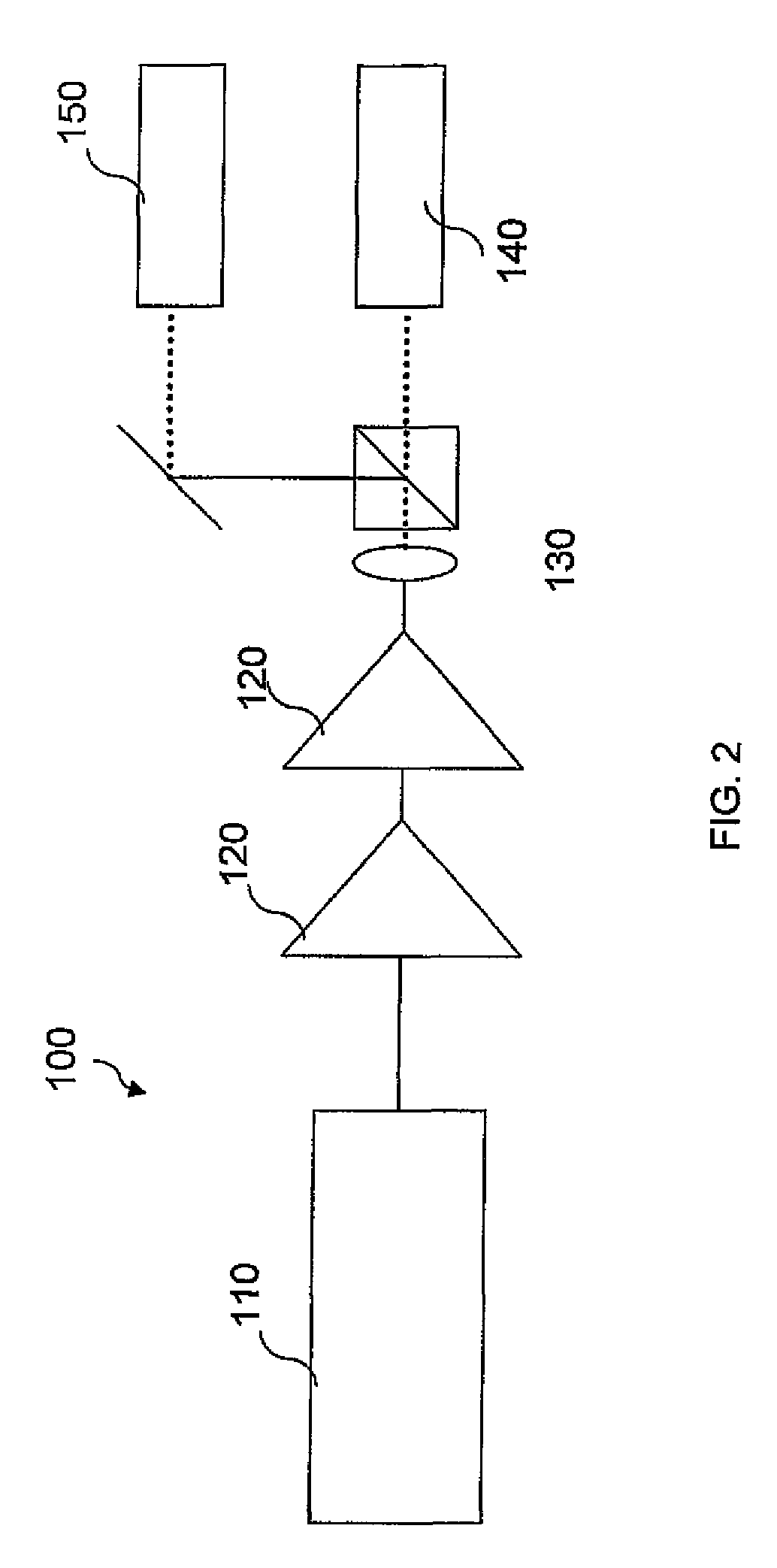
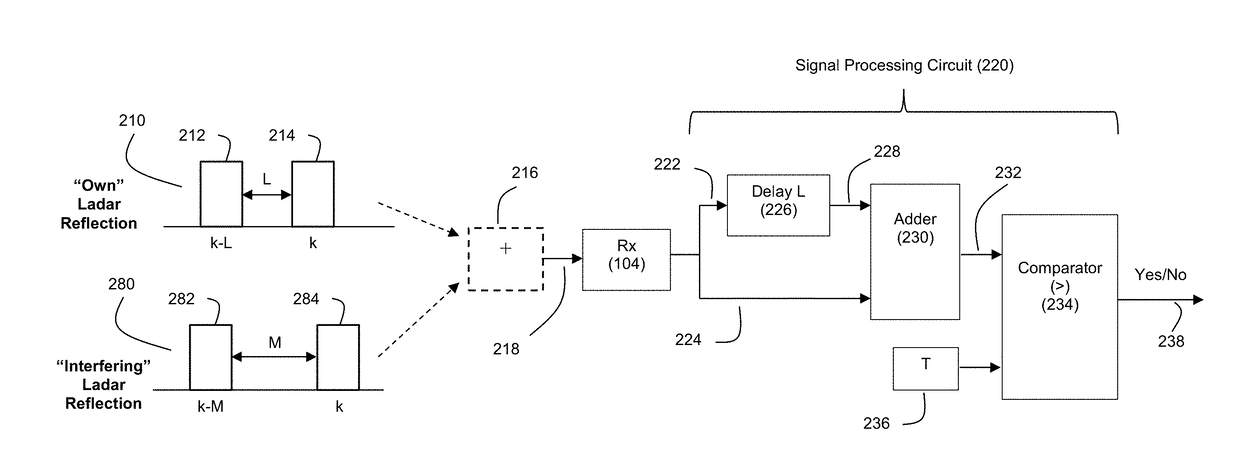
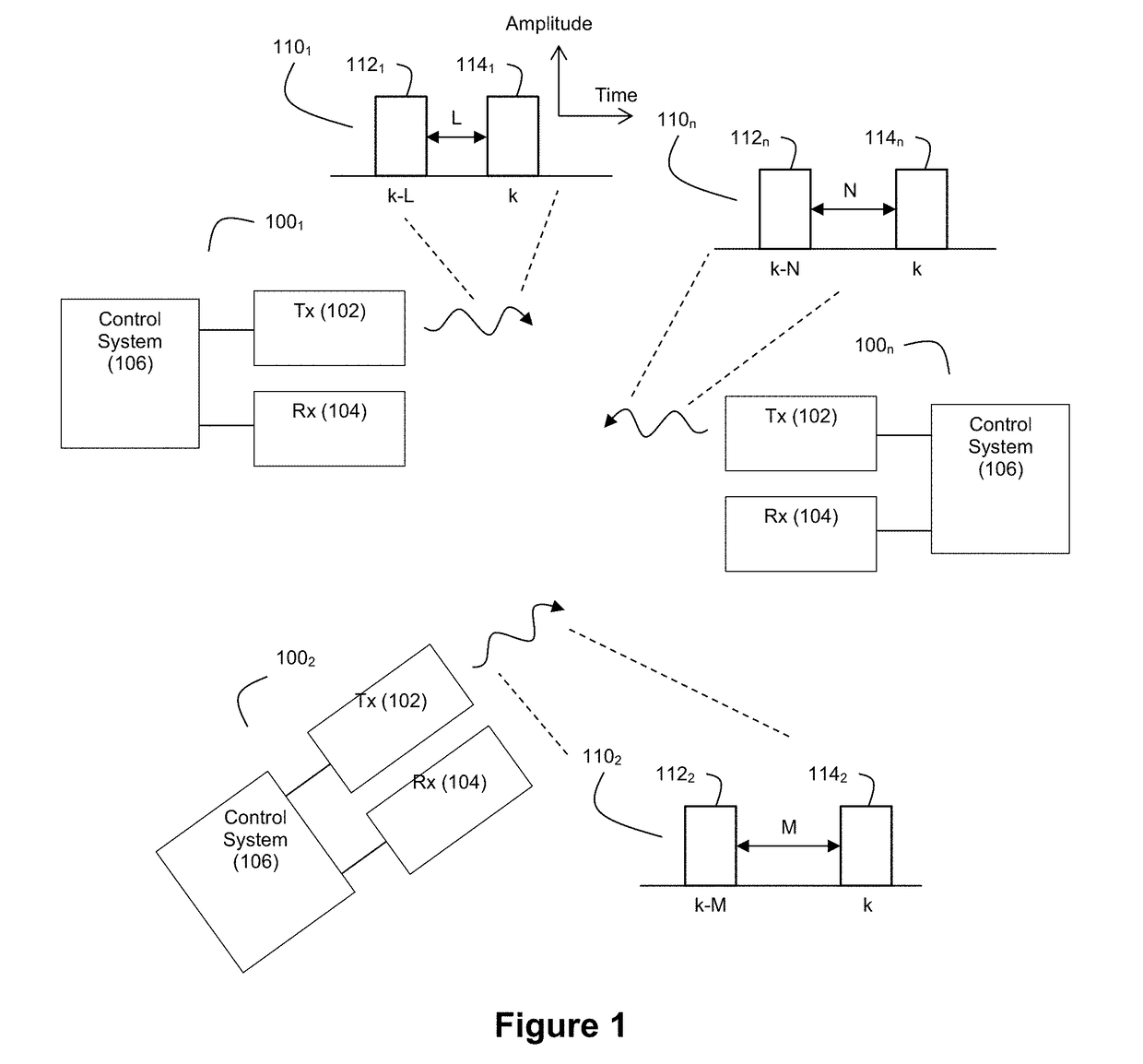
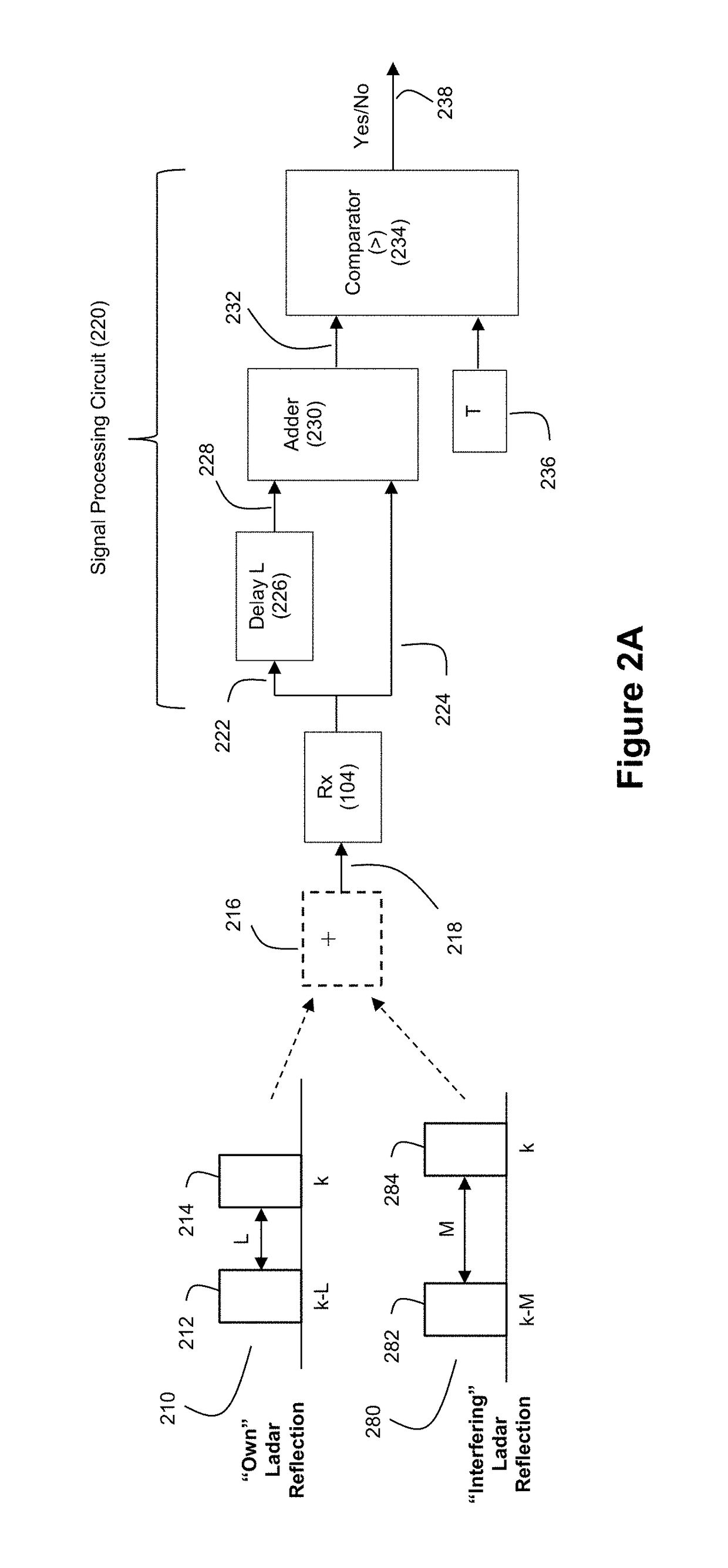
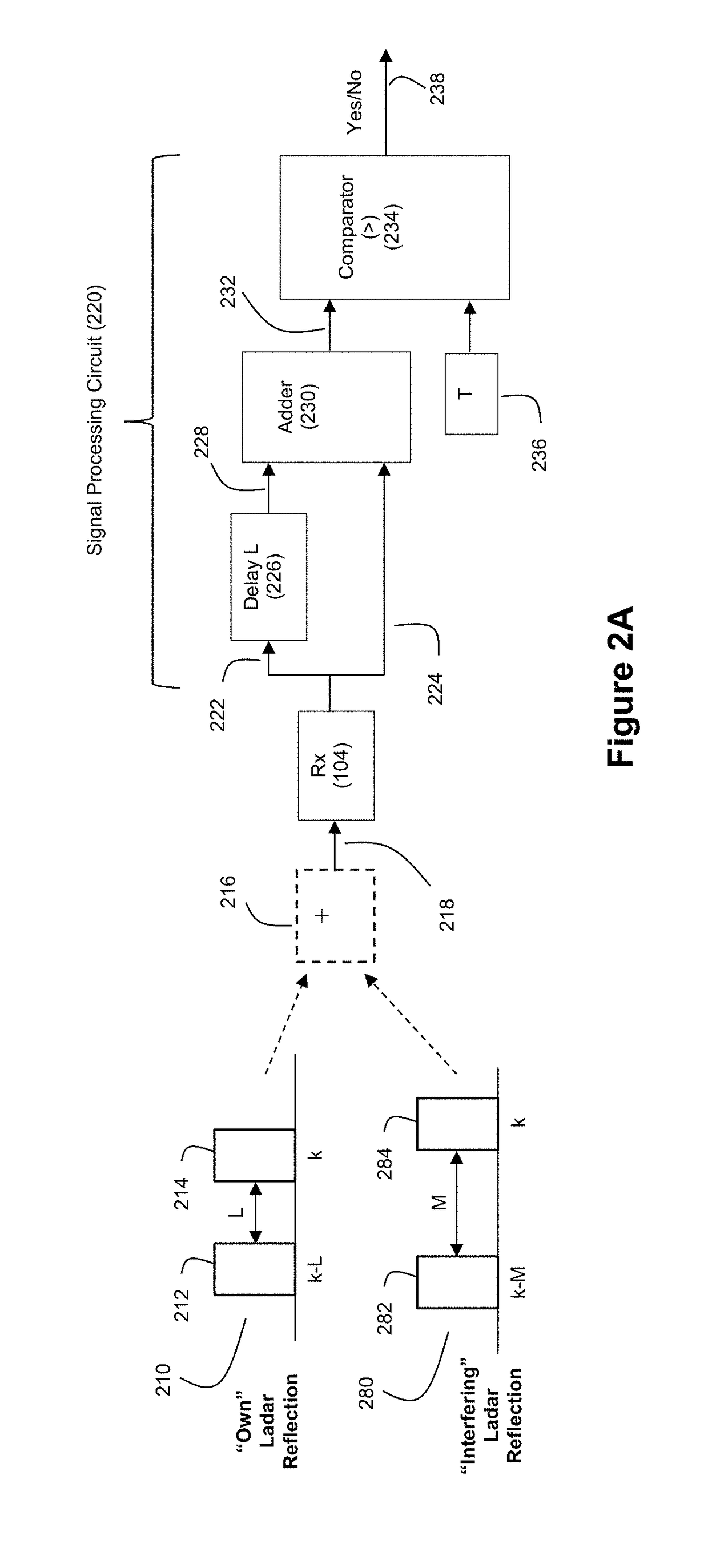
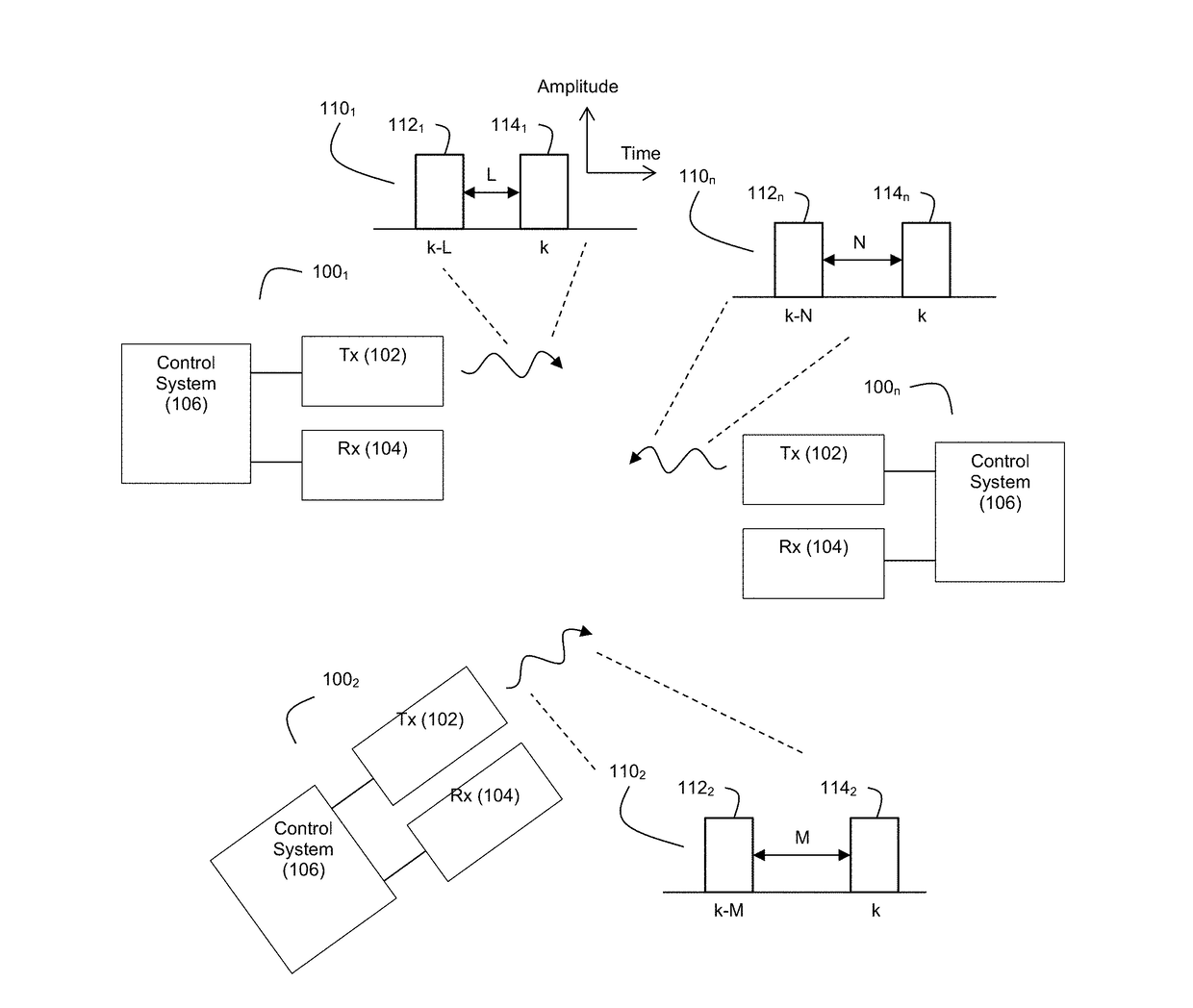
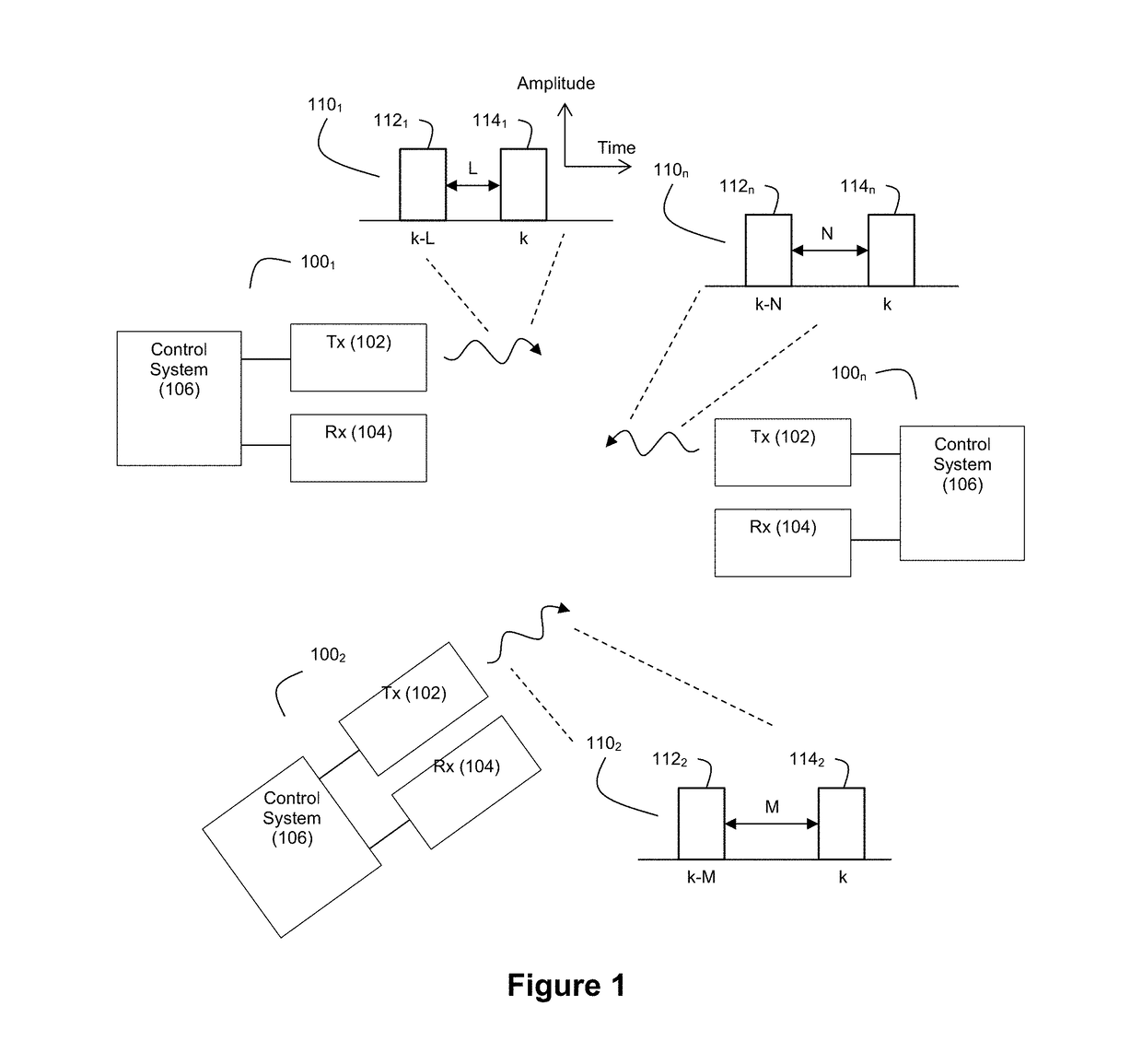
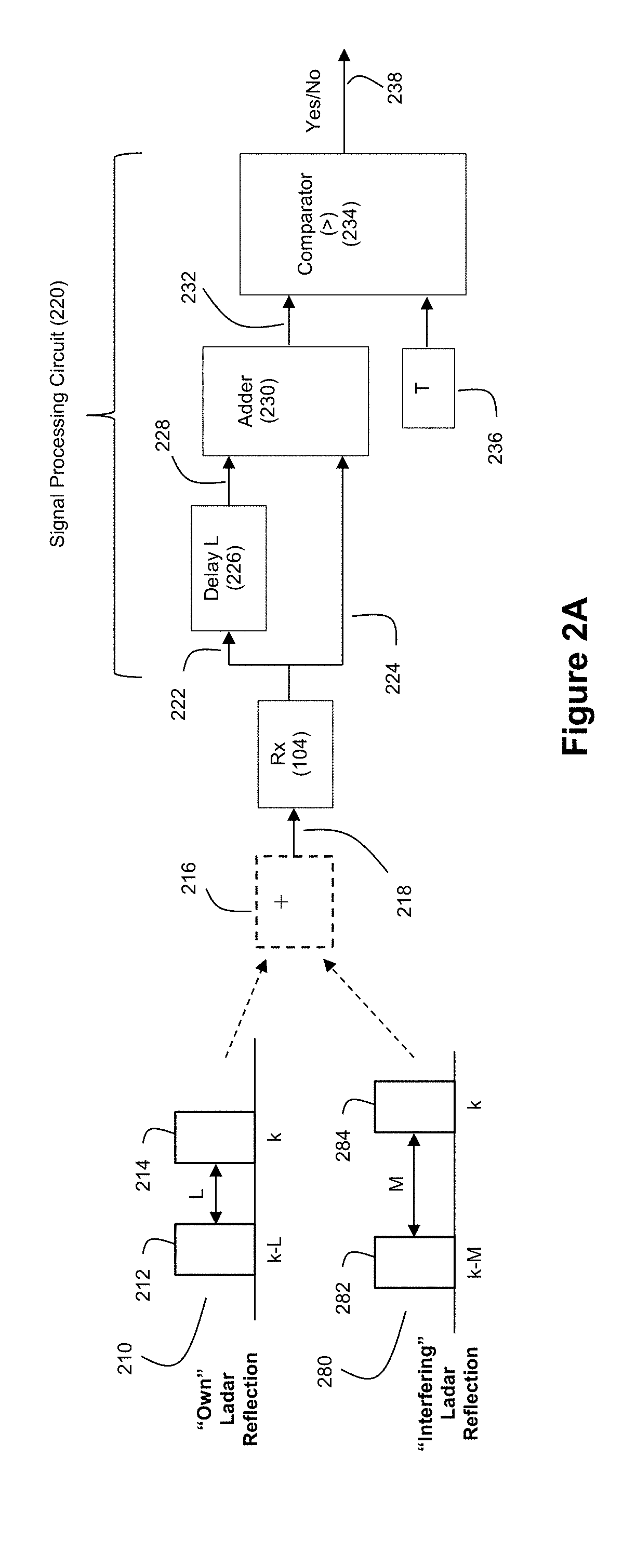
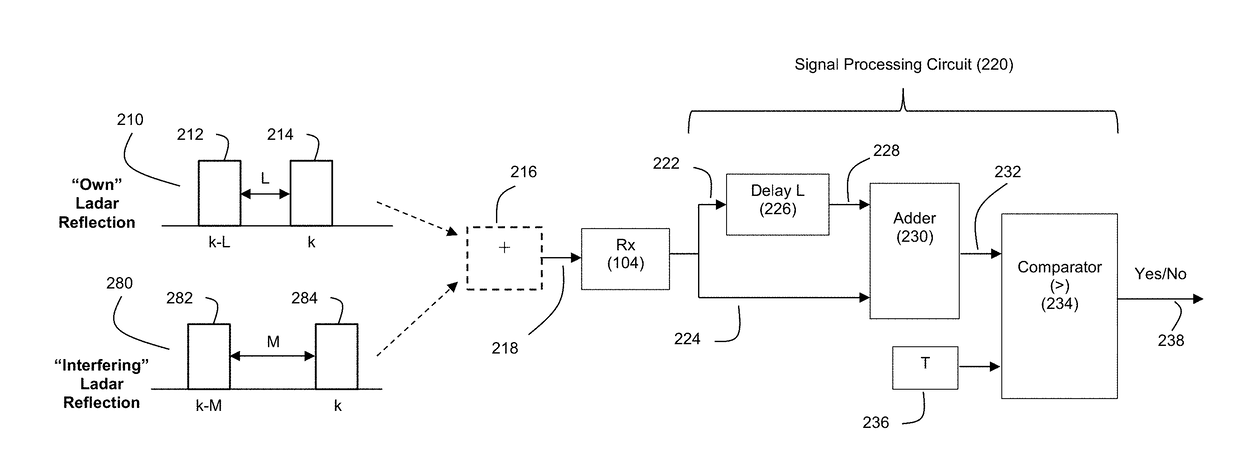
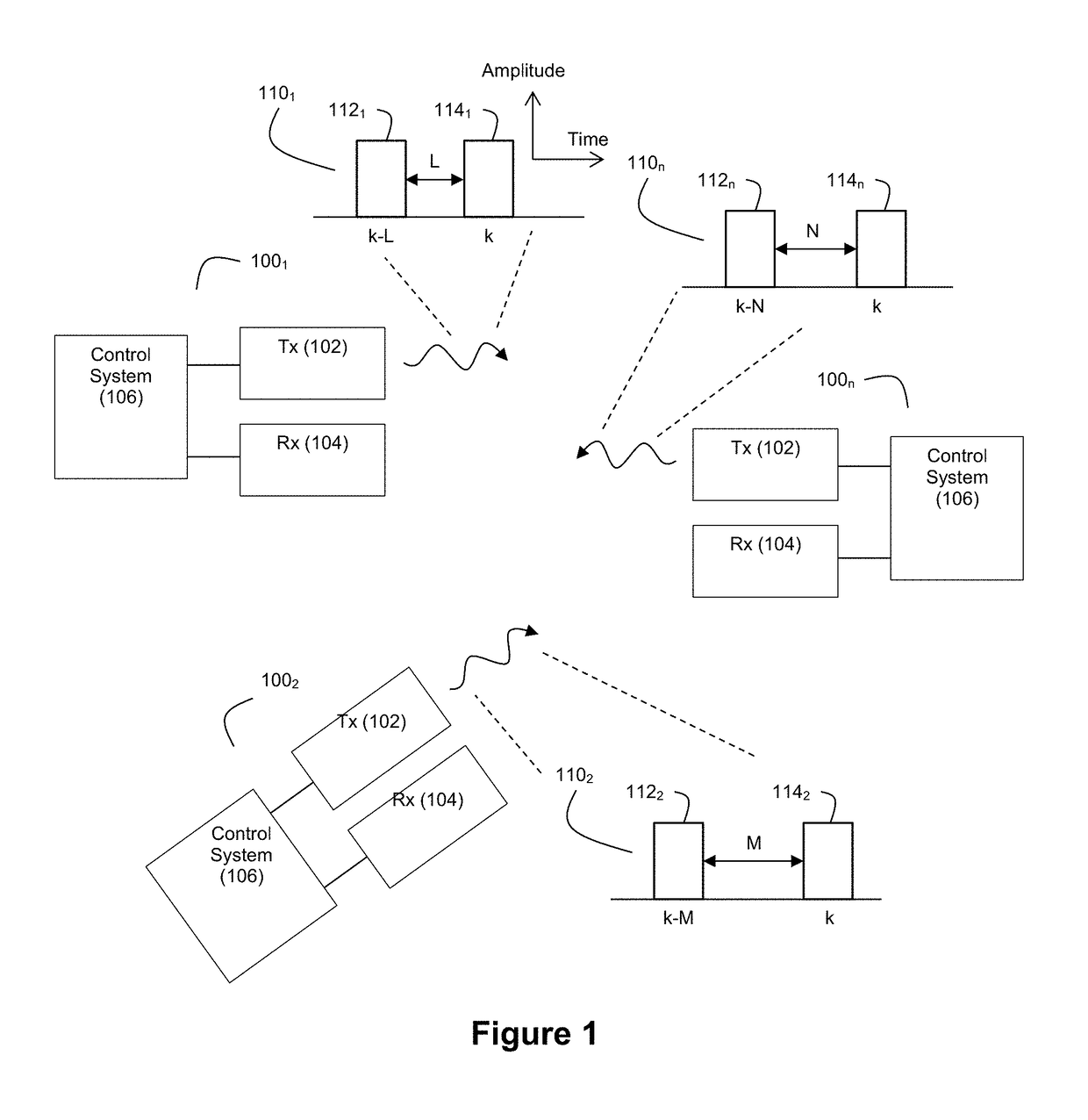
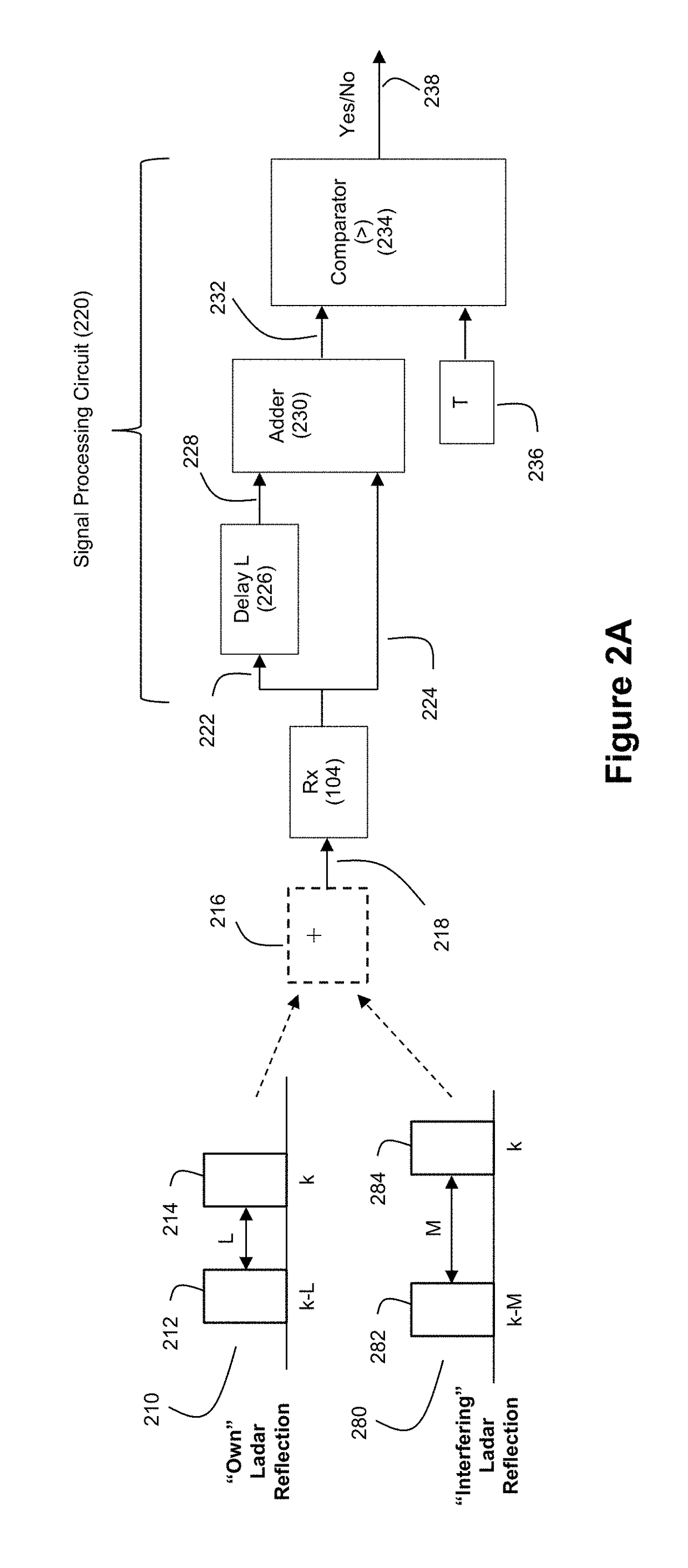
Ladar Pulse Deconfliction Apparatus
ActiveUS20180238998A1Short time intervalReduce the numberElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCommunications systemRadar systems
Disclosed herein are a number of example embodiments that employ controllable delays between successive ladar pulses in order to discriminate between “own” ladar pulse reflections and “interfering” ladar pulses reflections by a receiver. Example embodiments include designs where a sparse delay sum circuit is used at the receiver and where a funnel filter is used at the receiver. Also, disclosed are techniques for selecting codes to use for the controllable delays as well as techniques for identifying and tracking interfering ladar pulses and their corresponding delay codes. The use of a ladar system with pulse deconfliction is also disclosed as part of an optical data communication system.
Owner:AEYE INC
Semiconductor light-emitting device, surface-emission laser diode, and production apparatus thereof, production method, optical module and optical telecommunication system
A semiconductor light-emitting device has a semiconductor layer containing Al between a substrate and an active layer containing nitrogen, wherein Al and oxygen are removed from a growth chamber before growing said active layer and a concentration of oxygen incorporated into said active layer together with Al is set to a level such that said semiconductor light-emitting device can perform a continuous laser oscillation at room temperature.
Owner:RICOH KK
Pulsed laser light source
A pulsed laser light source is provided. A continuous light beam is first generated by a CW laser source such as a laser diode, a superfluorescent source or a CW solid state laser. The continuous light beam is then modulated by a first modulator, and further shaped by a second modulator at least in partial synchronization with the first. The first and second modulators are preferably each followed by a gain medium for signal amplification.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Method and System for Ladar Pulse Deconfliction Using Delay Code Selection
ActiveUS20180239000A1Short time intervalReduce the numberElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsCommunications system
Disclosed herein are a number of example embodiments that employ controllable delays between successive ladar pulses in order to discriminate between “own” ladar pulse reflections and “interfering” ladar pulses reflections by a receiver. Example embodiments include designs where a sparse delay sum circuit is used at the receiver and where a funnel filter is used at the receiver. Also, disclosed are techniques for selecting codes to use for the controllable delays as well as techniques for identifying and tracking interfering ladar pulses and their corresponding delay codes. The use of a ladar system with pulse deconfliction is also disclosed as part of an optical data communication system.
Owner:AEYE INC
Method and System for Optical Data Communication via Scanning Ladar
ActiveUS20180239005A1Short time intervalReduce the numberElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCommunications systemRadar systems
Disclosed herein are a number of example embodiments that employ controllable delays between successive ladar pulses in order to discriminate between “own” ladar pulse reflections and “interfering” ladar pulses reflections by a receiver. Example embodiments include designs where a sparse delay sum circuit is used at the receiver and where a funnel filter is used at the receiver. Also, disclosed are techniques for selecting codes to use for the controllable delays as well as techniques for identifying and tracking interfering ladar pulses and their corresponding delay codes. The use of a ladar system with pulse deconfliction is also disclosed as part of an optical data communication system.
Owner:AEYE INC
Method and System for Ladar Pulse Deconfliction to Detect and Track Other Ladar Systems
ActiveUS20180239001A1Short time intervalReduce the numberElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsCommunications system
Disclosed herein are a number of example embodiments that employ controllable delays between successive ladar pulses in order to discriminate between “own” ladar pulse reflections and “interfering” ladar pulses reflections by a receiver. Example embodiments include designs where a sparse delay sum circuit is used at the receiver and where a funnel filter is used at the receiver. Also, disclosed are techniques for selecting codes to use for the controllable delays as well as techniques for identifying and tracking interfering ladar pulses and their corresponding delay codes. The use of a ladar system with pulse deconfliction is also disclosed as part of an optical data communication system.
Owner:AEYE INC
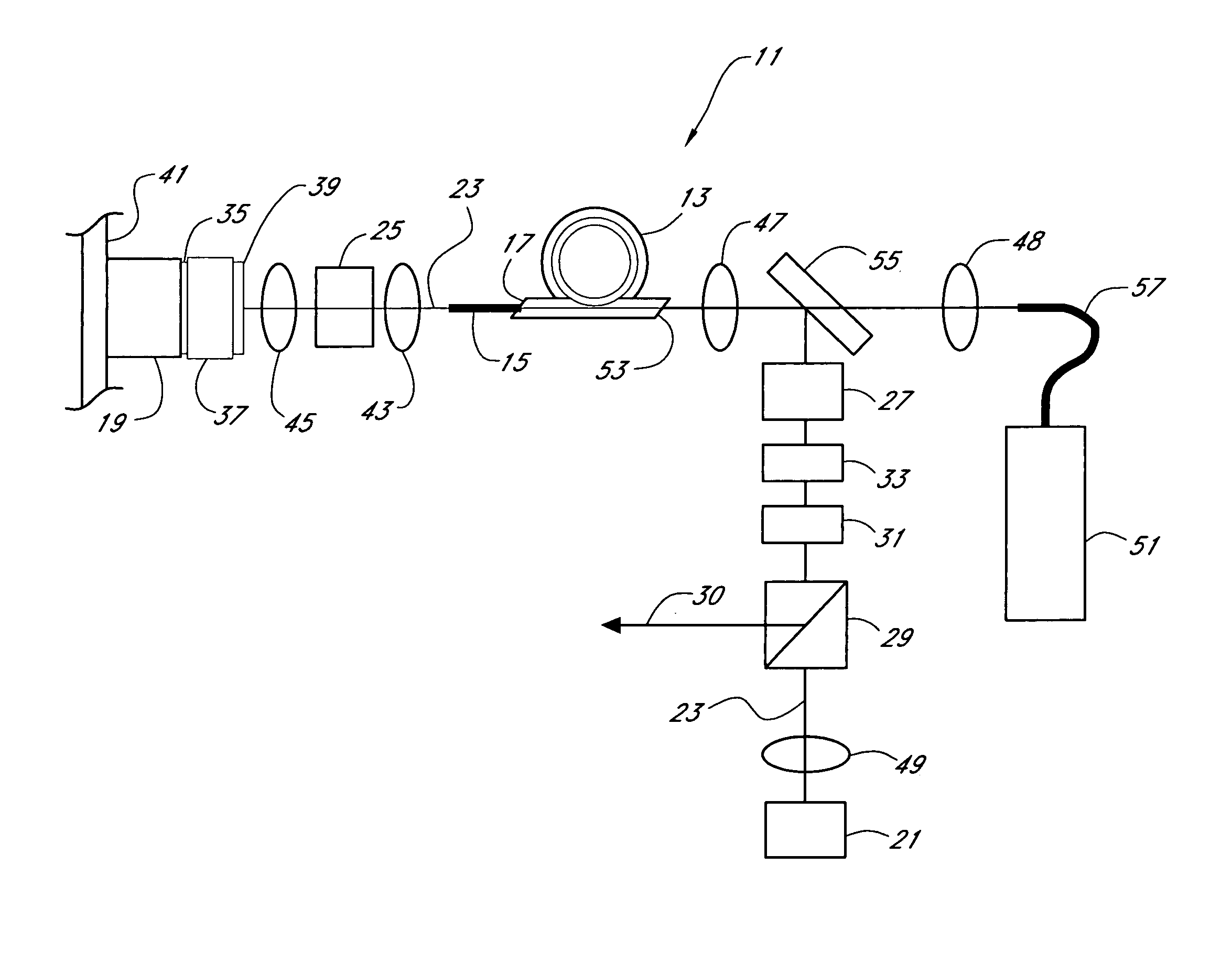
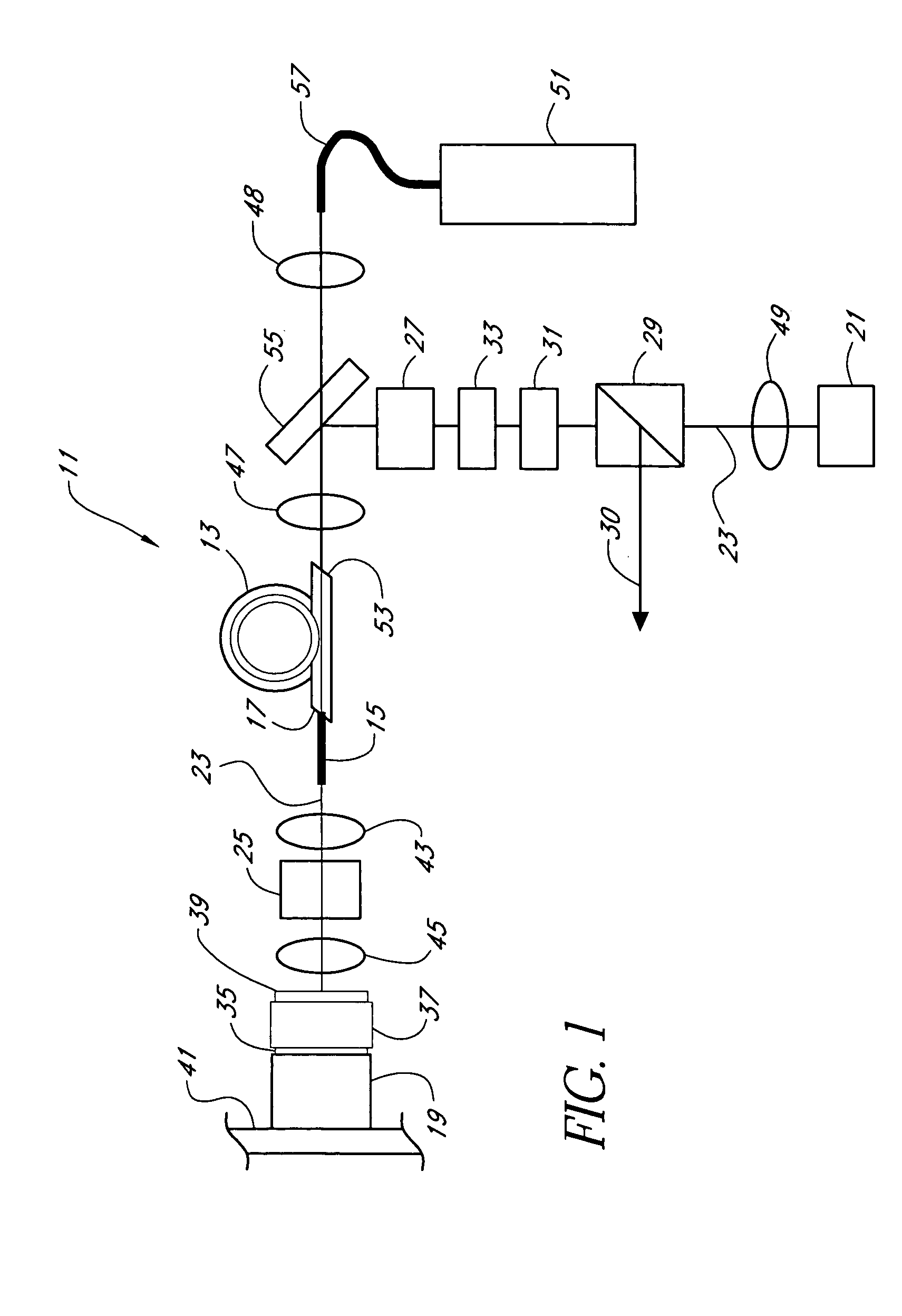
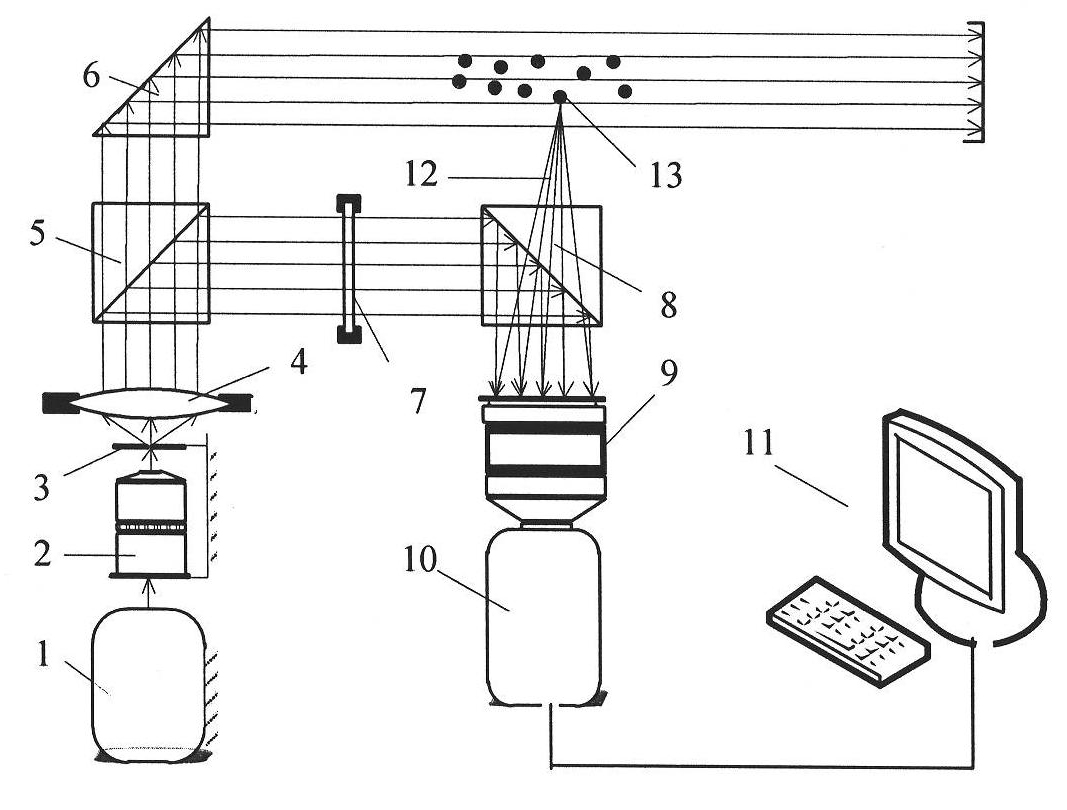
Method and device for simultaneously measuring droplet position, particle sizes and complex refractive index
InactiveCN102003936AReconstruction Spatial PositionEasy to implementPhase-affecting property measurementsParticle size analysisMeasurement deviceRainbow
The invention relates to technology for simultaneously measuring multi-phase flow particles online through multi-parameter, and aims to provide a method and a device for simultaneously measuring droplet positions, particle sizes and a complex refractive index. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) dividing a highly coherent continuous laser beam into two beams after spatial filtering and collimating beam expansion, wherein one beam radiates particles in a detected flow field region, and the other beam is used as a reference beam; (2) mixing scattered light of a lateral 30-degree to 90-degree region of particles in the detected flow field region and the attenuated reference beam to perform interference so as to form a hologram, storing the hologram in a computer after being recorded by a digital camera through an imaging device; (3) acquiring a series of reconstructed images of the detected particles along the depth direction by utilizing digital reconstruction technology; and (4) identifying the reflective spot and the refractive spot of the particles from the reconstructed images by utilizing digital image processing technology so as to acquire space coordinates and scattered light intensity ratios. Compared with rainbow measurement technology, the measurement method has the advantages that: a light path system of the measurement device is relatively simple and is easy to implement.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Lidar
ActiveUS20140233013A1Easy to measureSimple configuration without complicating the configurationOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationMultiplexingRadar
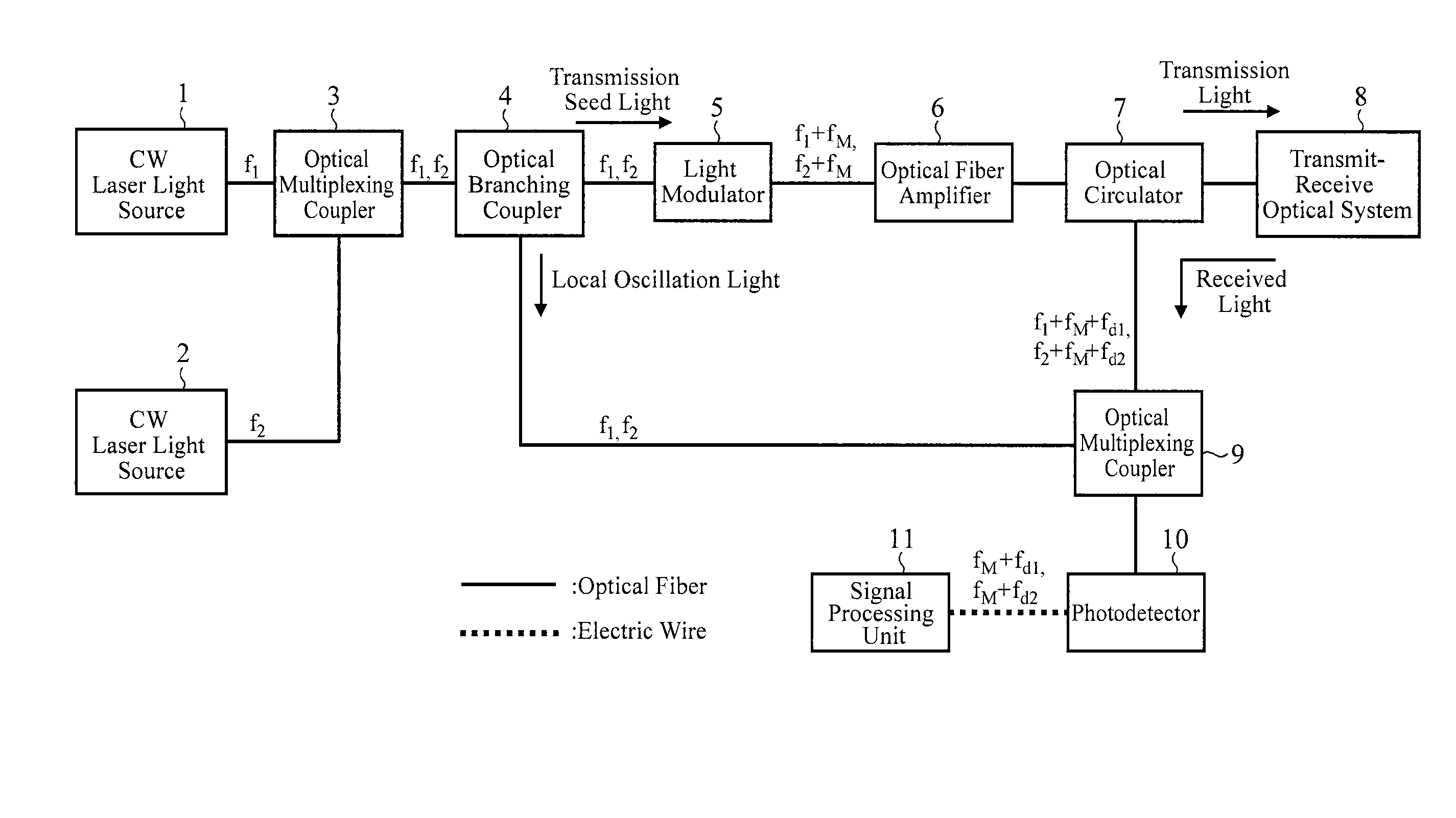
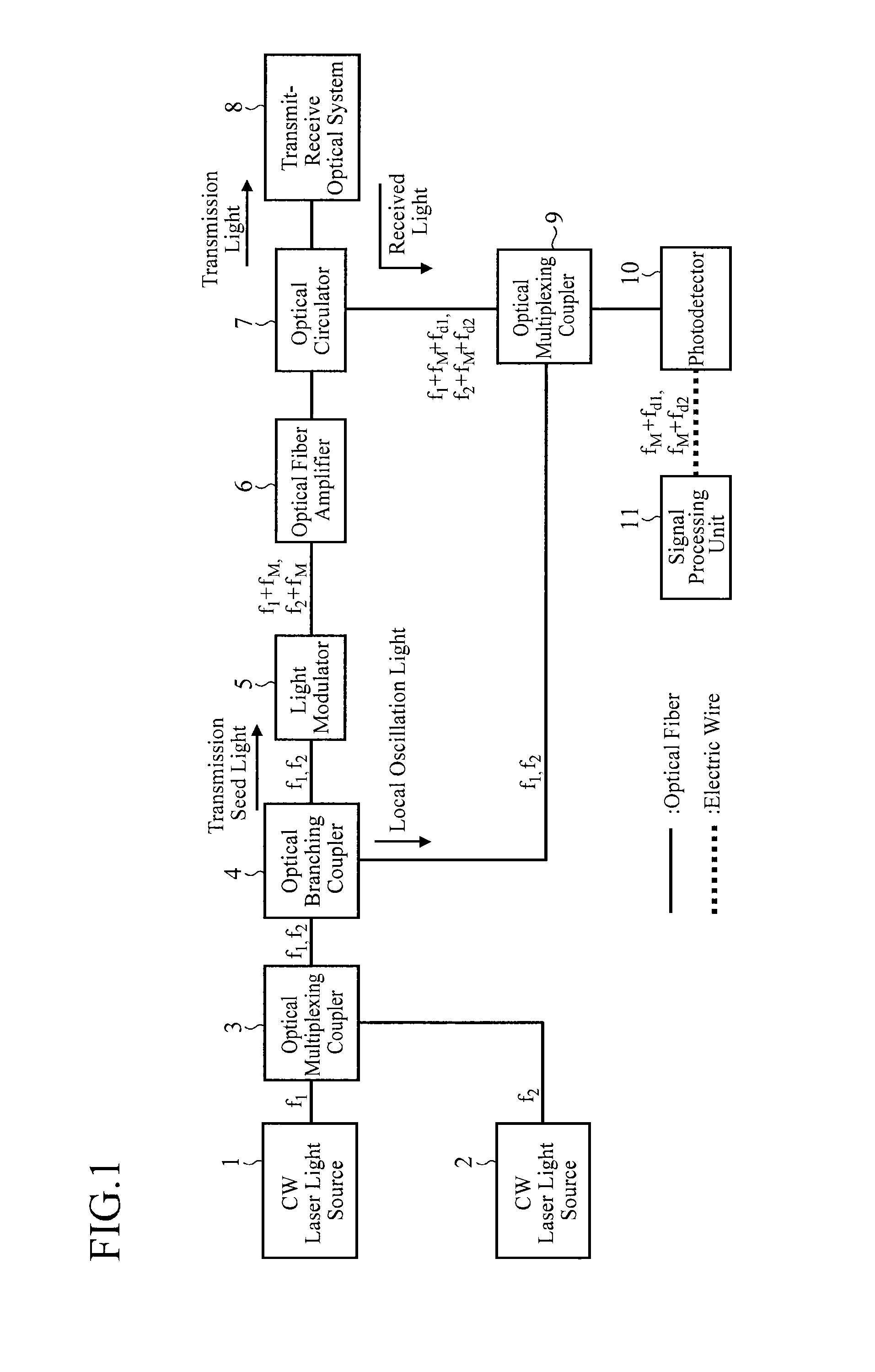
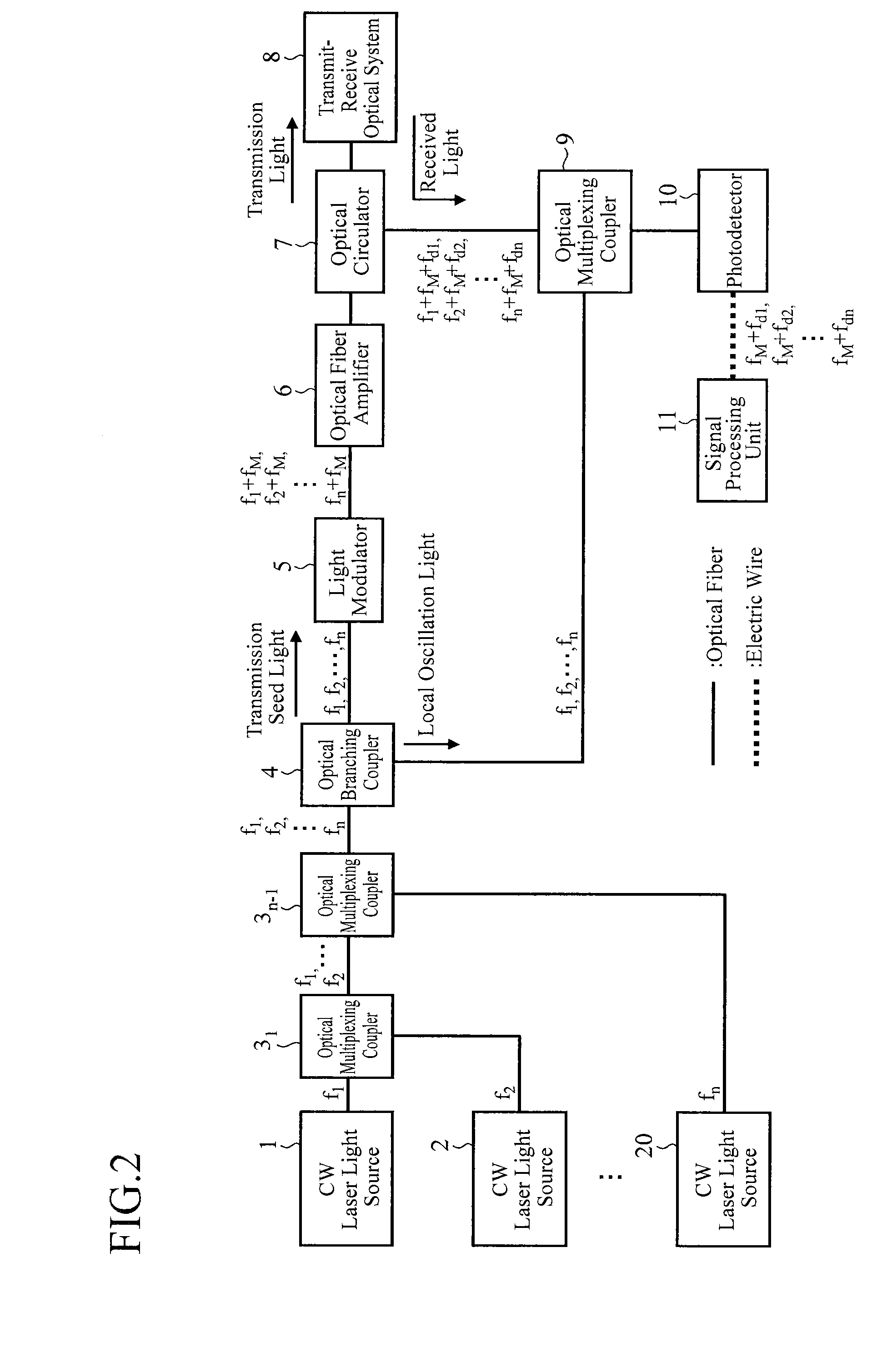
A lidar includes CW laser light sources that oscillate CW laser light rays with wavelengths different from each other; an optical multiplexing coupler that mixes the CW laser light rays oscillated by the CW laser light sources; an optical branching coupler that splits the CW laser light passing through the mixing by the optical multiplexing coupler; a light modulator that modulates first CW laser light split by the optical branching coupler; and an optical fiber amplifier that amplifies the laser light modulated by the light modulator, in which a transmit-receive optical system irradiates a target with the laser light amplified by the optical fiber amplifier, and receives scattered light of the laser light by the target.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for manufacturing semiconductor apparatus, and semiconductor apparatus and electric appliance
ActiveUS20060220211A1Thickness drasticallyLow costPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCrazingDevice material
According to the package and the method for manufacturing the package of the present invention, a chip can be formed extremely to be thin, and manufactured at lower cost and higher throughput, and the variations of a chip thickness can be reduced without back grind that causes cracks or polishing marks. In the present invention, a semiconductor film with a thickness of at most 500 μm deposited over a substrate serving as a support medium is crystallized with a CW laser light, and a chip having a semiconductor device is formed to have a total thickness of 5 μm, preferably at most 2 μm by using the crystallized semiconductor film. Consequently, the chip is mounted on an interposer after separating a substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
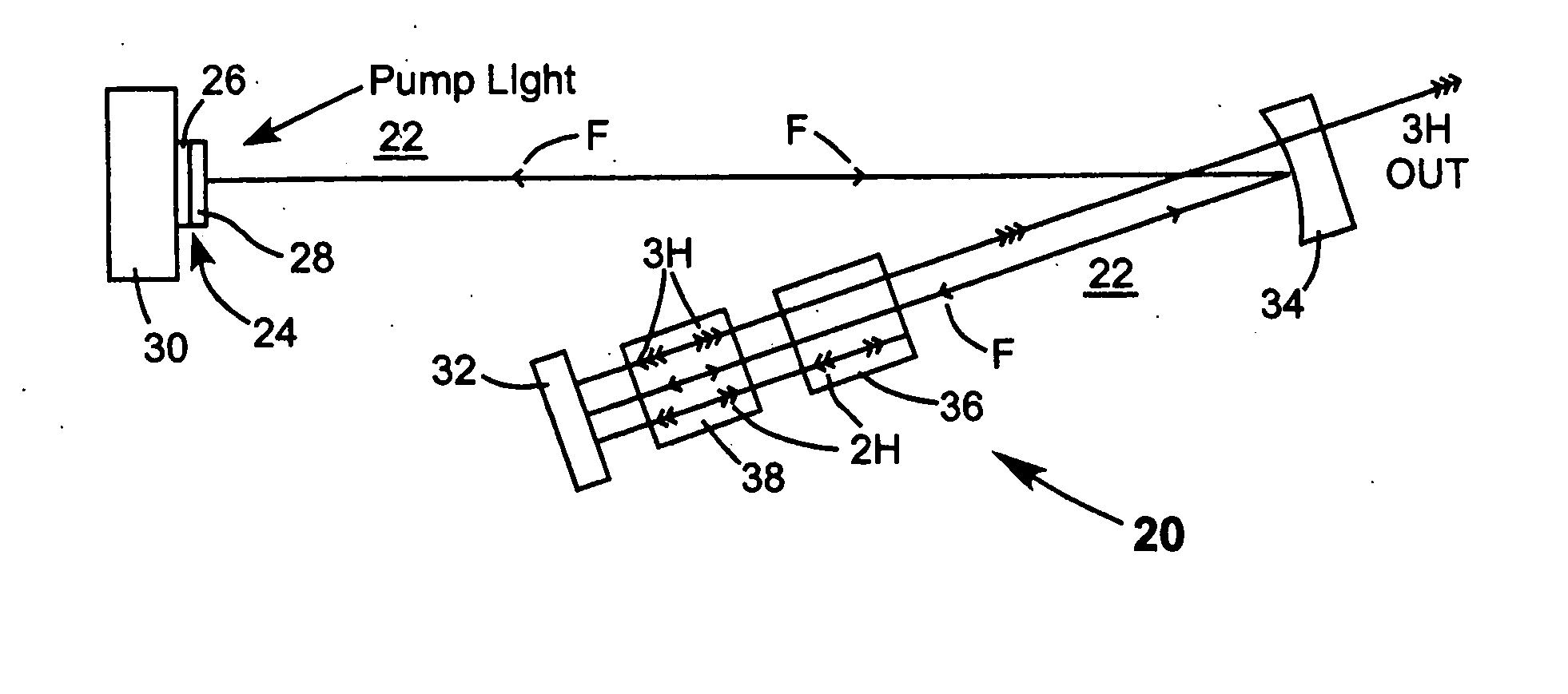
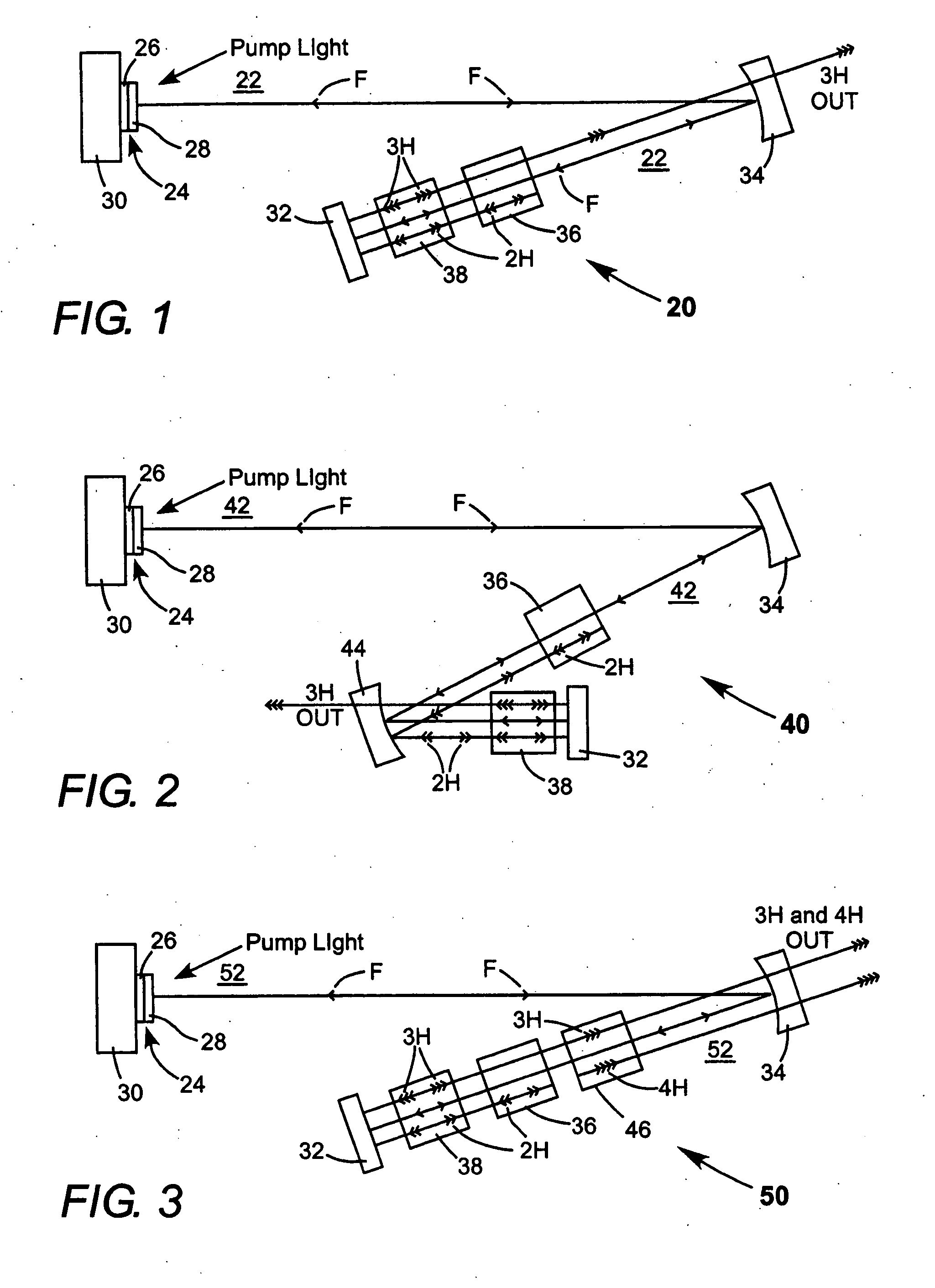
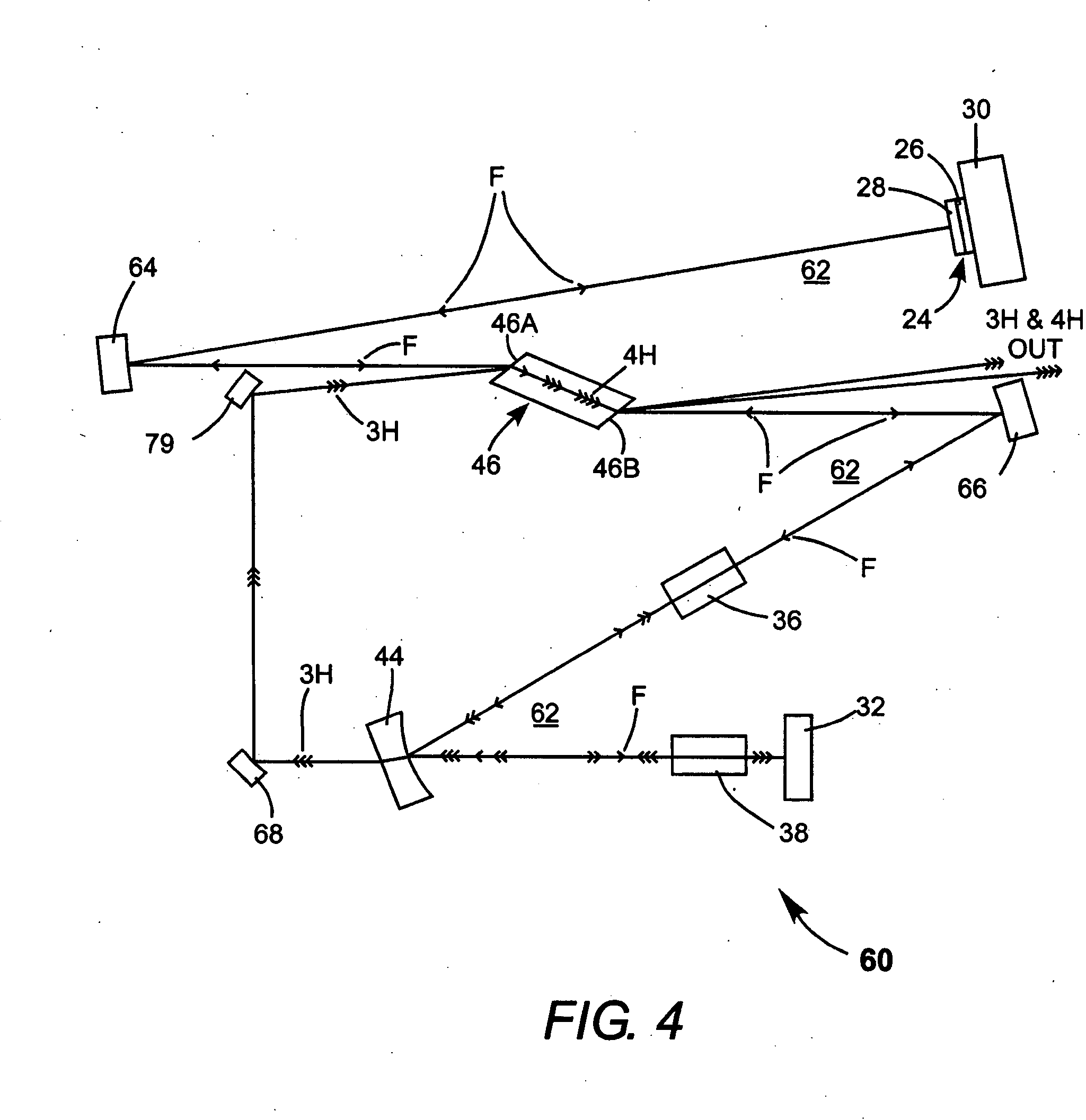
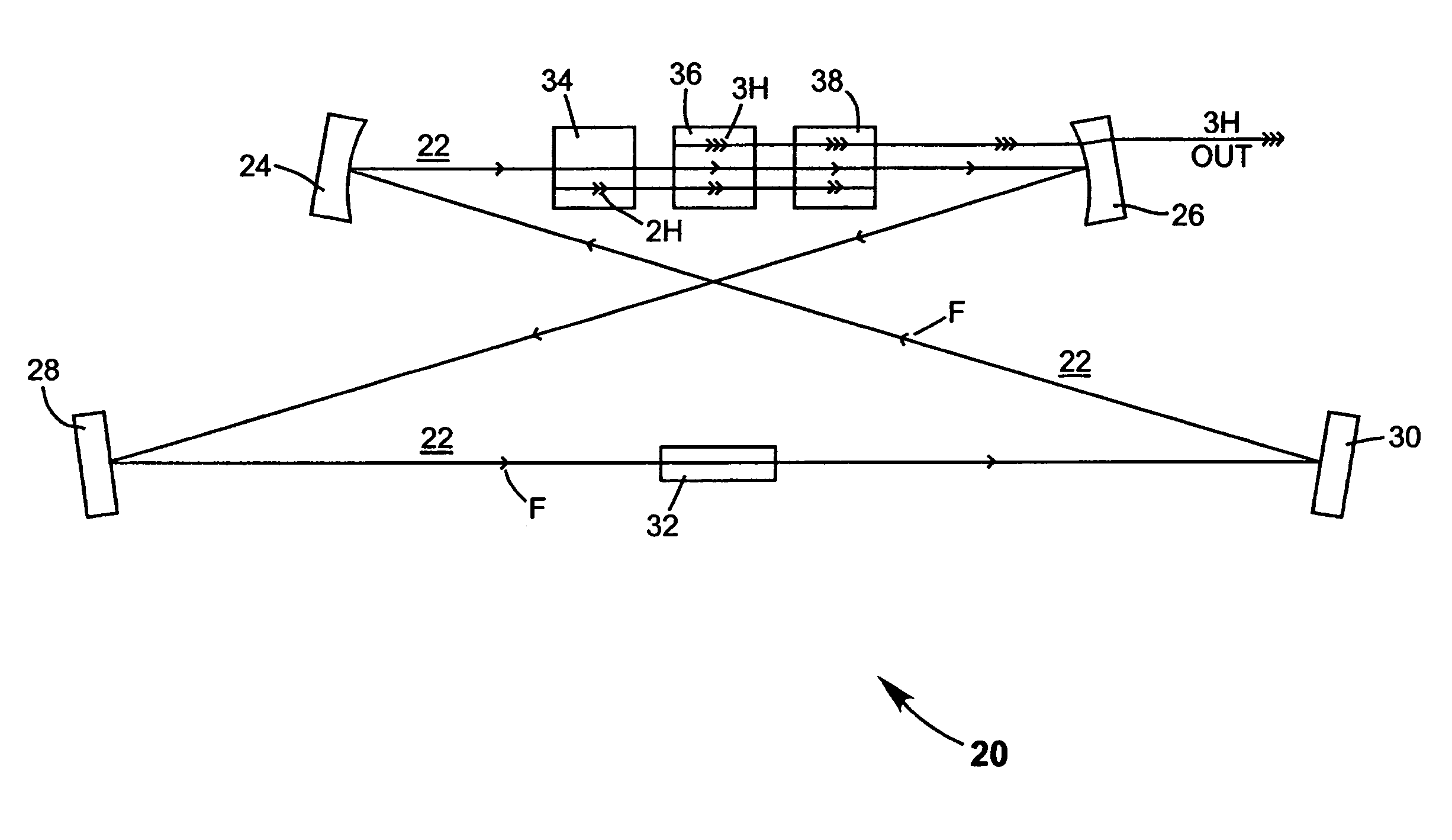
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser
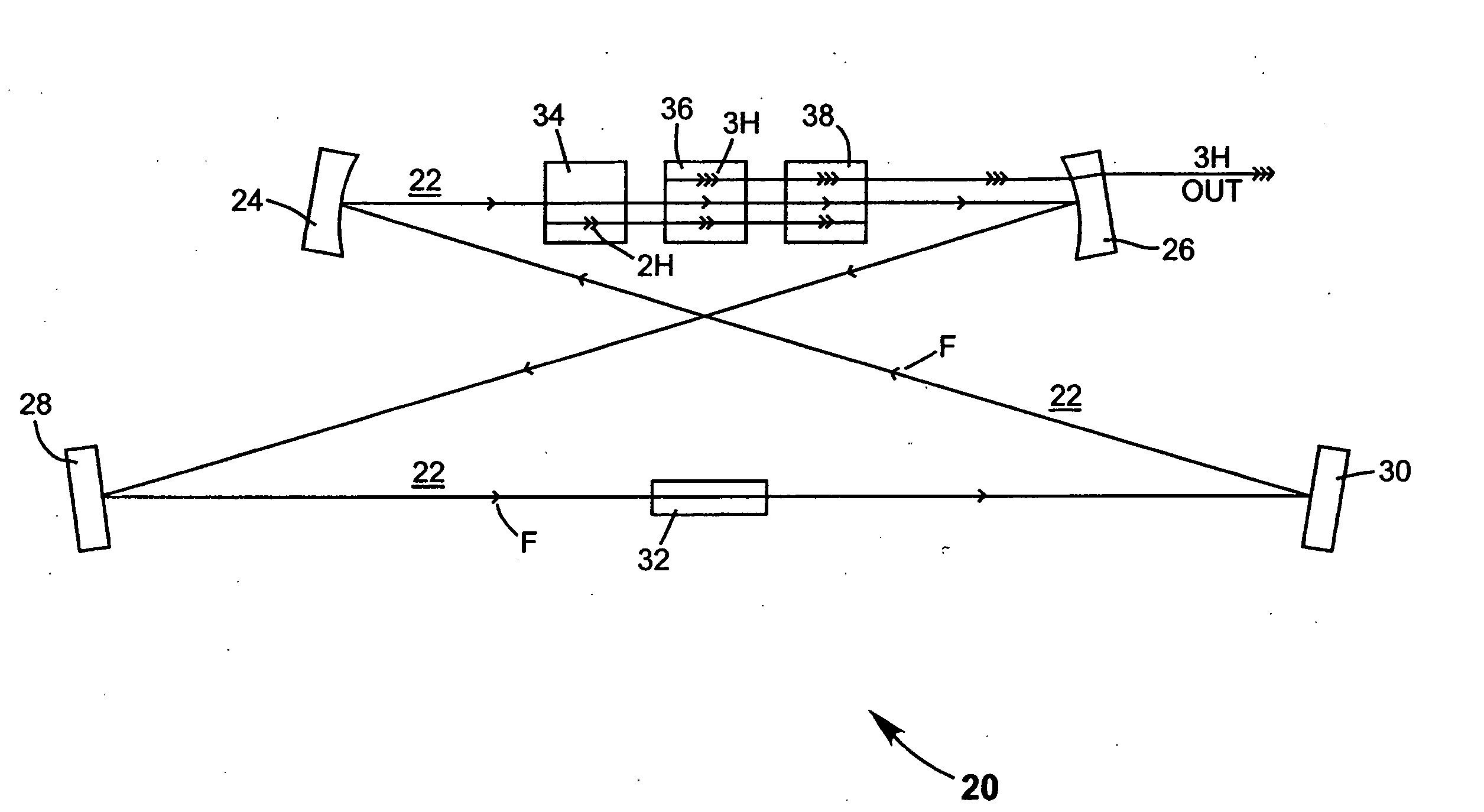
InactiveUS20050078718A1High frequencyImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusNonlinear crystalsPhysics
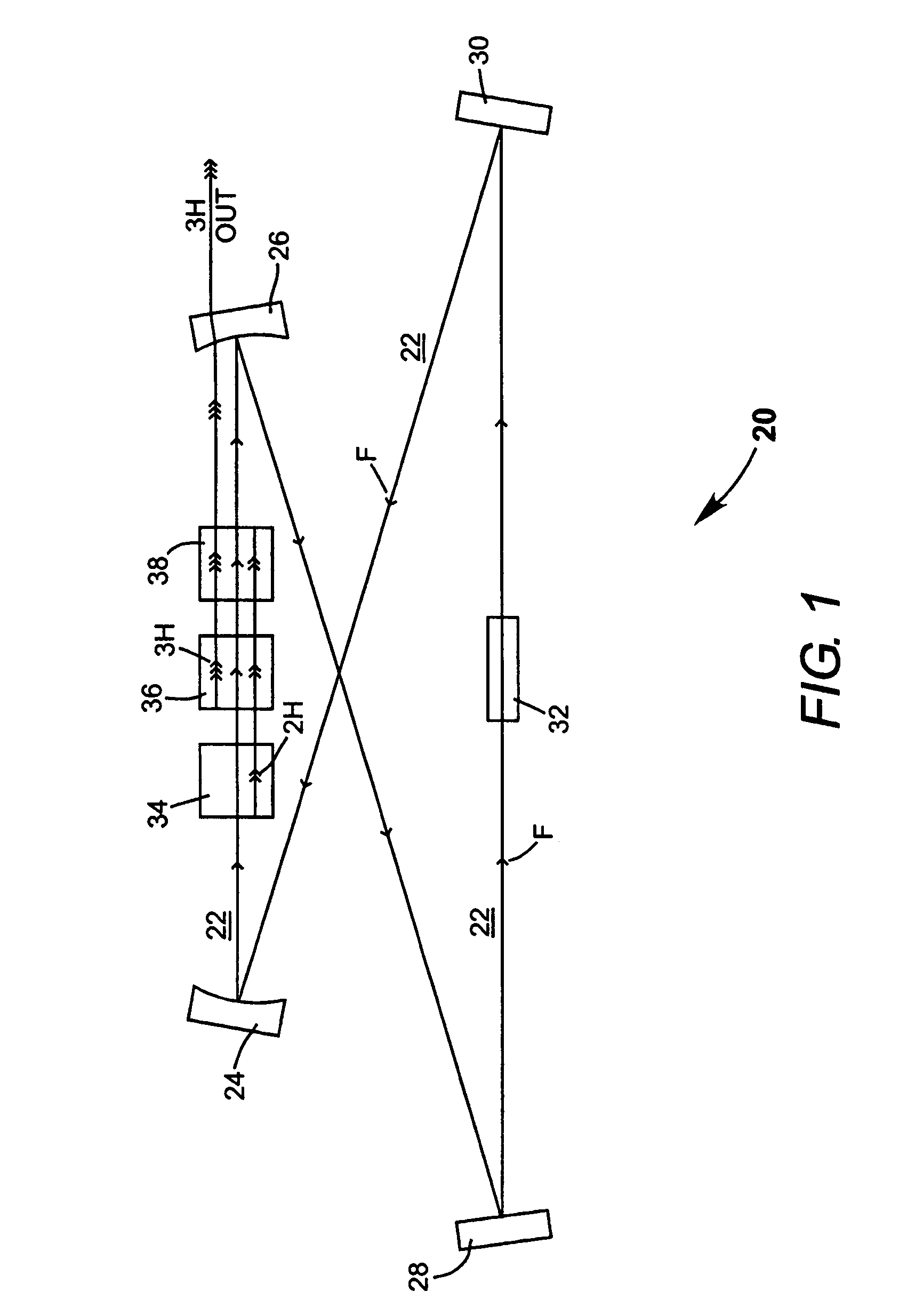
A method of intracavity frequency conversion in a CW laser includes causing fundamental radiation to circulate in a laser resonator. The fundamental radiation makes a first pass through an optically nonlinear crystal where a fraction of the fundamental radiation generates second-harmonic radiation in a forward pass through the crystal. The residual fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation are then sum-frequency mixed in forward and reverse passes through an optically nonlinear crystal such that a fraction of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. The residual second-harmonic radiation and fundamental radiation from the sum-frequency mixing then make a reverse pass through the second-harmonic generating crystal where the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation, or can be used to pump another optically nonlinear crystal in an optical parametric oscillator. Second-harmonic radiation can also be used to pump an optical parametric oscillator.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7709309B2Efficient use ofReduce energy densitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlane orientationCw laser
It is an object of the present invention to control the plane orientation of crystal grains obtained by using a laser beam, into a direction that can be substantially regarded as one direction in an irradiation region of the laser beam. After forming a cap film over a semiconductor film, the semiconductor film is crystallized by using a CW laser or a pulse laser having a repetition rate of greater than or equal to 10 MHz. The obtained semiconductor film has a plurality of crystal grains having a width of greater than or equal to 0.01 μm and a length of greater than or equal to 1 μm. In a surface of the obtained semiconductor film, a ratio of an orientation {211} is greater than or equal to 0.4 within the range of an angle fluctuation of ±10°.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Optical synchronization system for femtosecond x-ray sources
ActiveUS20080043784A1Compensation differenceLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionMode locked fiber laserX-ray
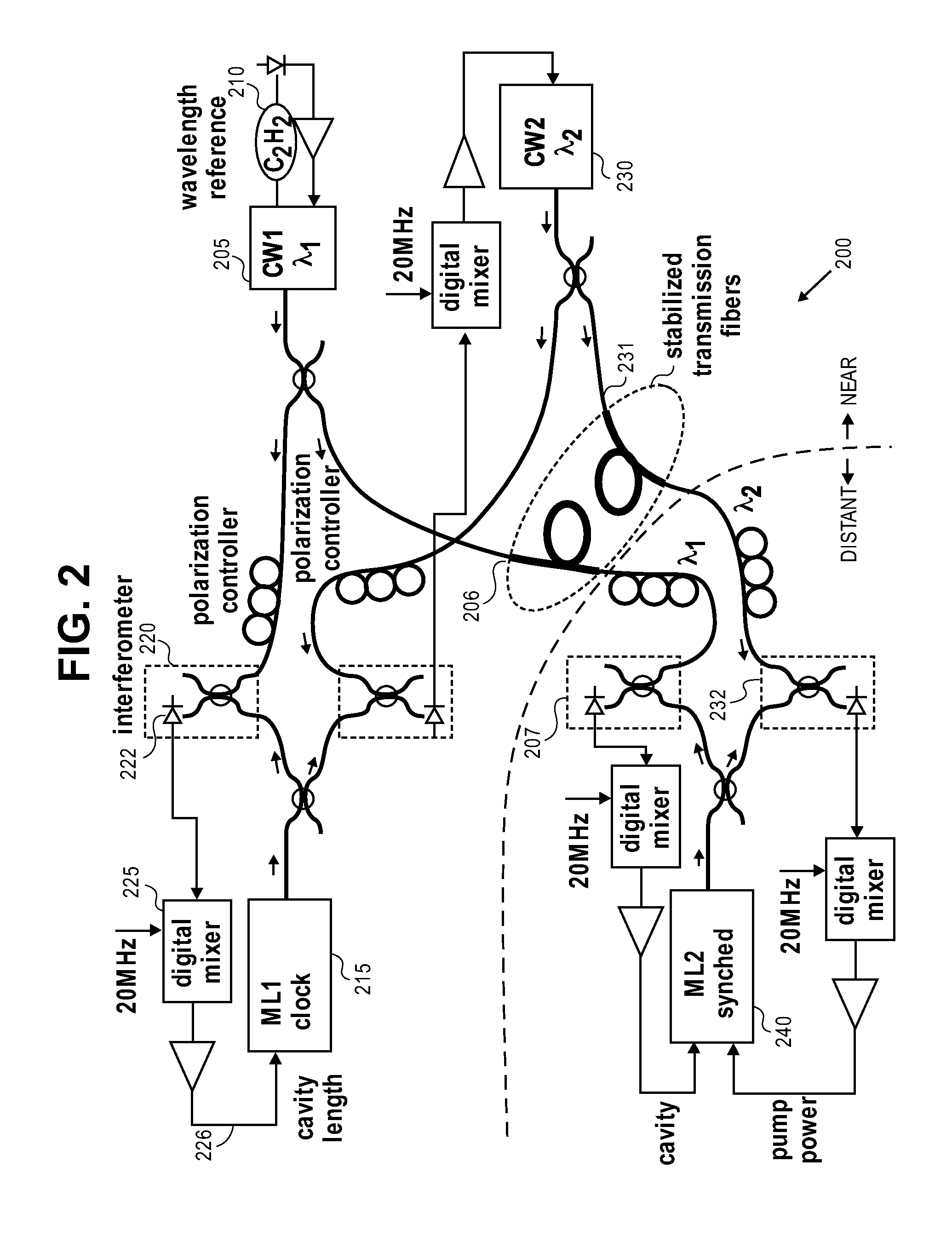
Femtosecond pump / probe experiments using short X-Ray and optical pulses require precise synchronization between 100 meter-10 km separated lasers in a various experiments. For stabilization in the hundred femtosecond range a CW laser is amplitude modulated at 1-10 GHz, the signal retroreflected from the far end, and the relative phase used to correct the transit time with various implementations. For the sub-10 fsec range the laser frequency itself is upshifted 55 MHz with an acousto-optical modulator, retroreflected, upshifted again and phase compared at the sending end to a 110 MHz reference. Initial experiments indicate less than 1 fsec timing jitter. To lock lasers in the sub-10 fs range two single-frequency lasers separated by several teraHertz will be lock to a master modelocked fiber laser, transmit the two frequencies over fiber, and lock two comb lines of a slave laser to these frequencies, thus synchronizing the two modelocked laser envelopes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Measurement method for reflectivity of high-reflection mirror
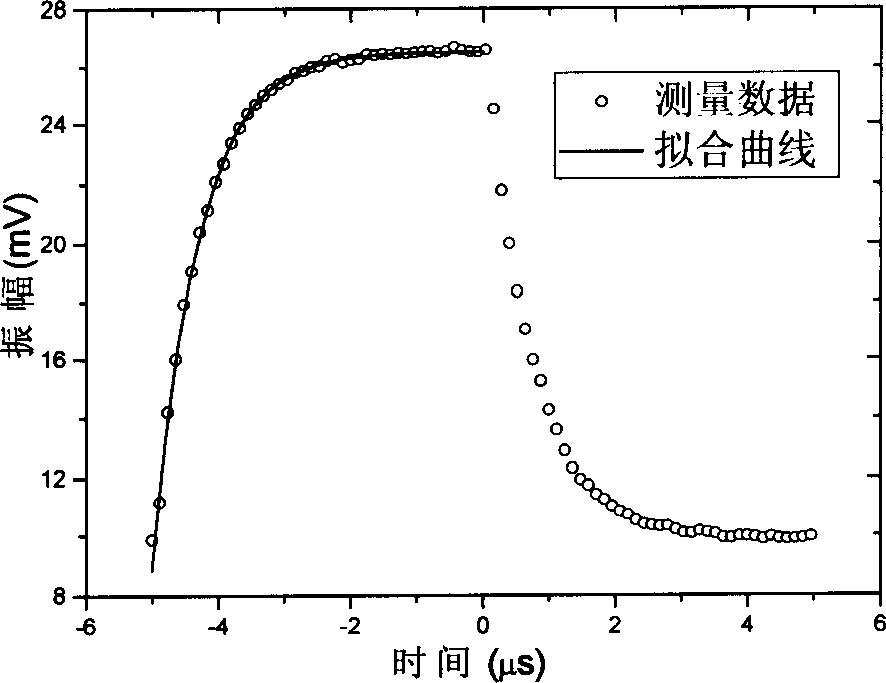
InactiveCN1804572AStable output powerHigh measurement accuracyScattering properties measurementsTesting optical propertiesHarmonicCurve fitting
The invention relates to a method for measuring high reflector reflection index which is characterized in that it adopts square wave or sinusoidal wave modulated wide-spectrum continuous laser as light source which enters into the stable resonator formed by two blocks of high reflectors; it uses square wave to modulate the up stage and down stage of the single period wave to obtain the lasting time and the channel reflecting index or uses fixed phase mode to detect the one-time or odd harmonic of light channel output signal; it uses the amplitude and the phase spiked value to modulate the angle frequency changing curve to obtain the lasting time and the channel reflecting index.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
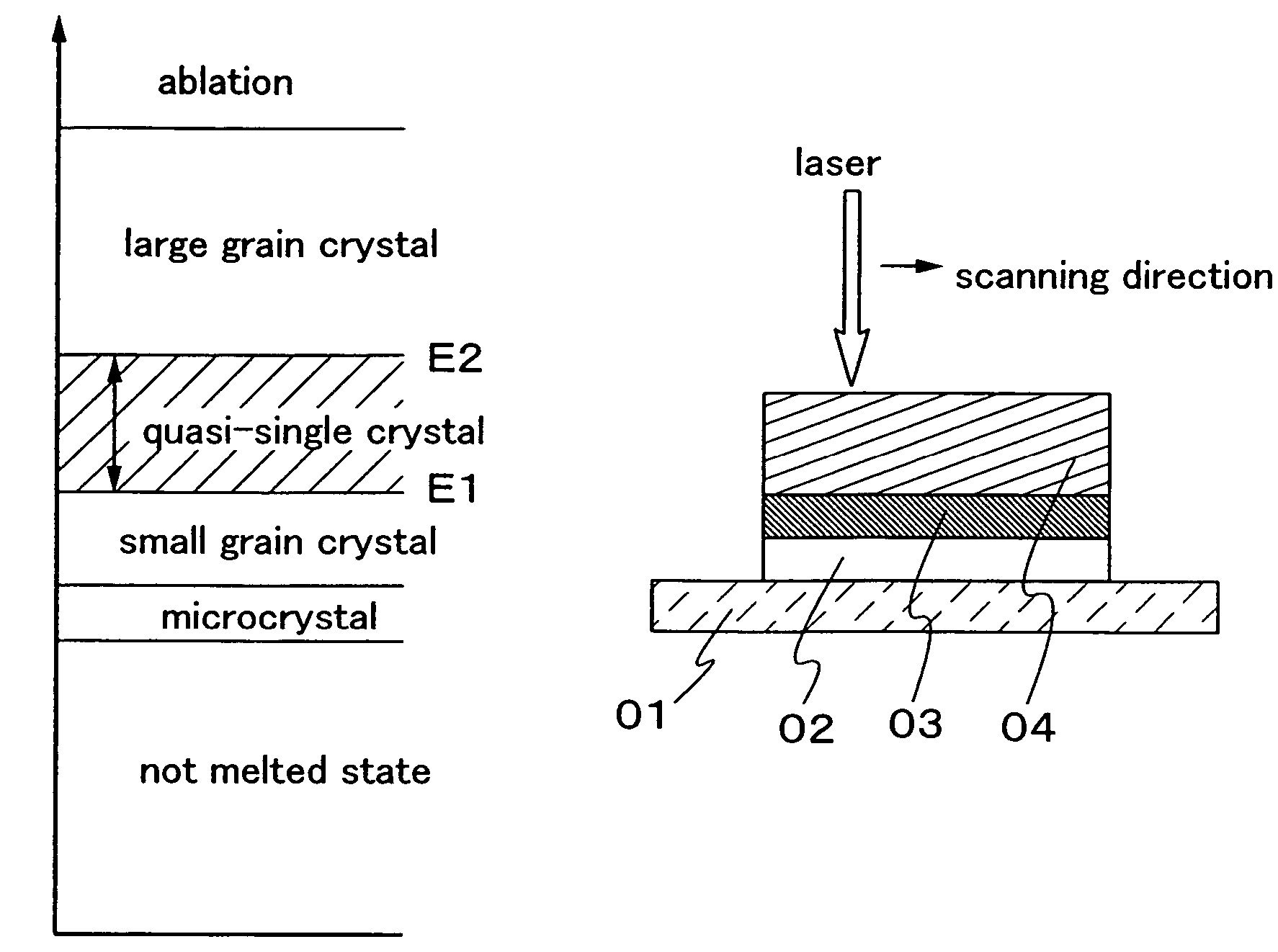
Laser irradiation method, laser irradiation apparatus, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
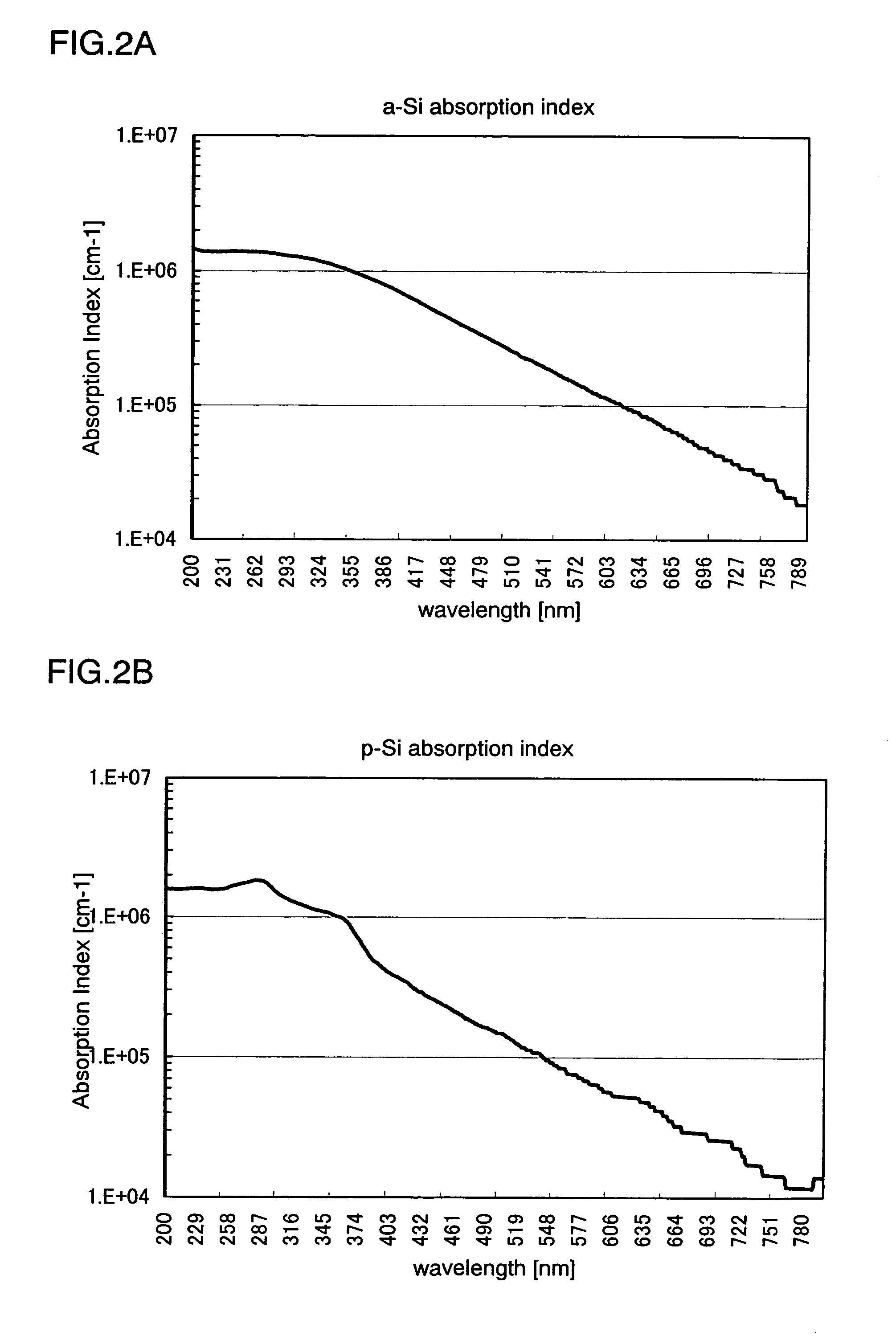
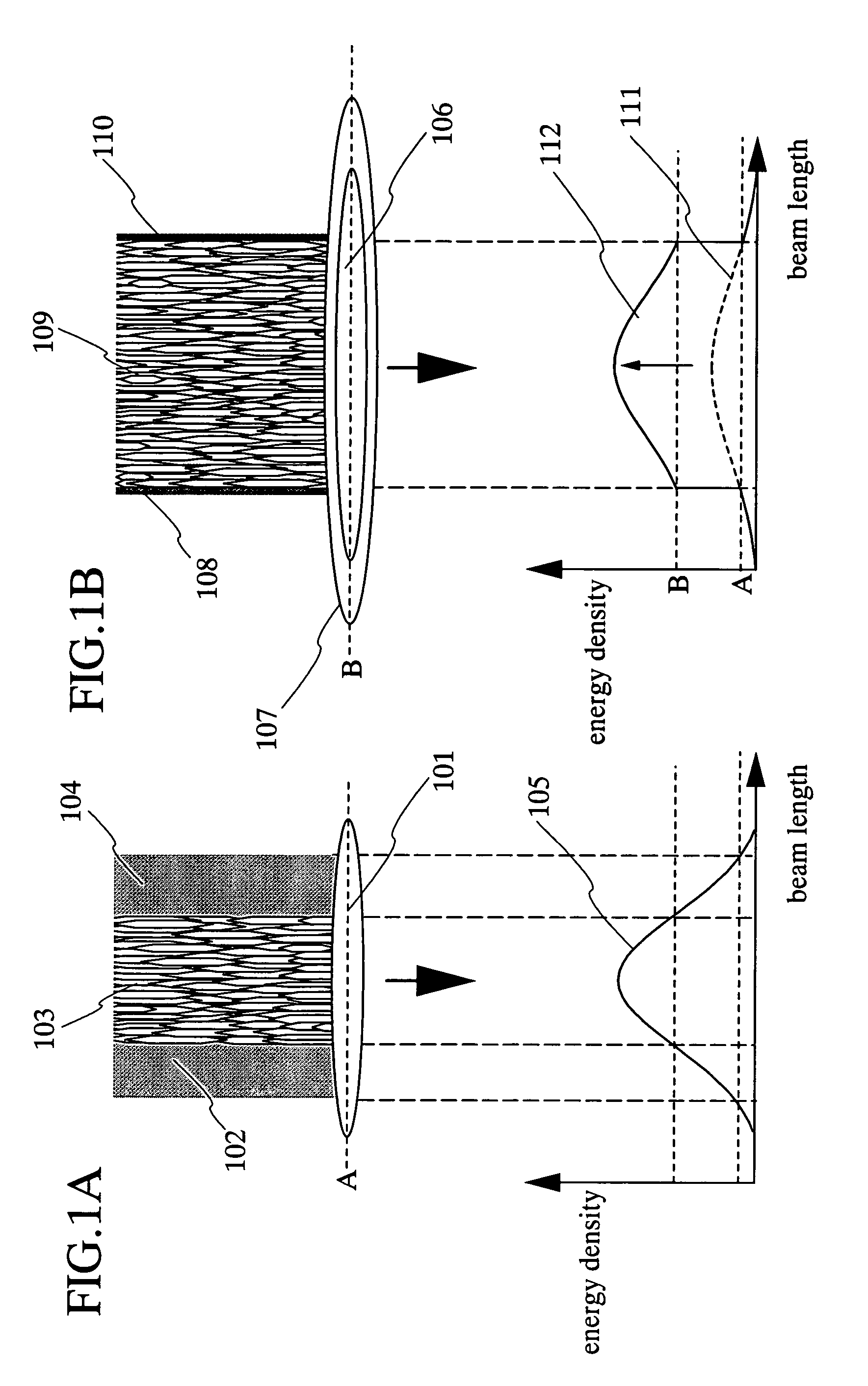
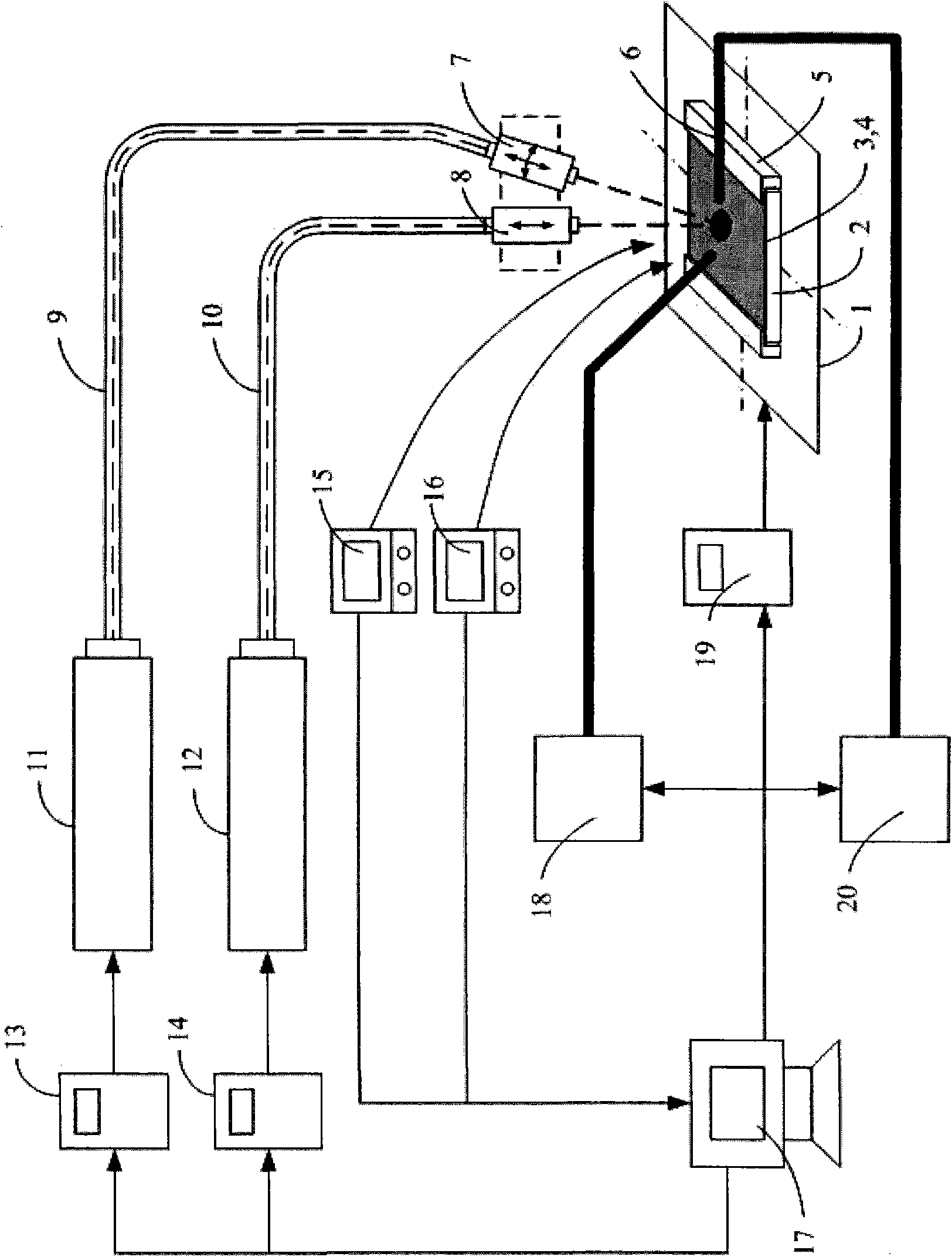
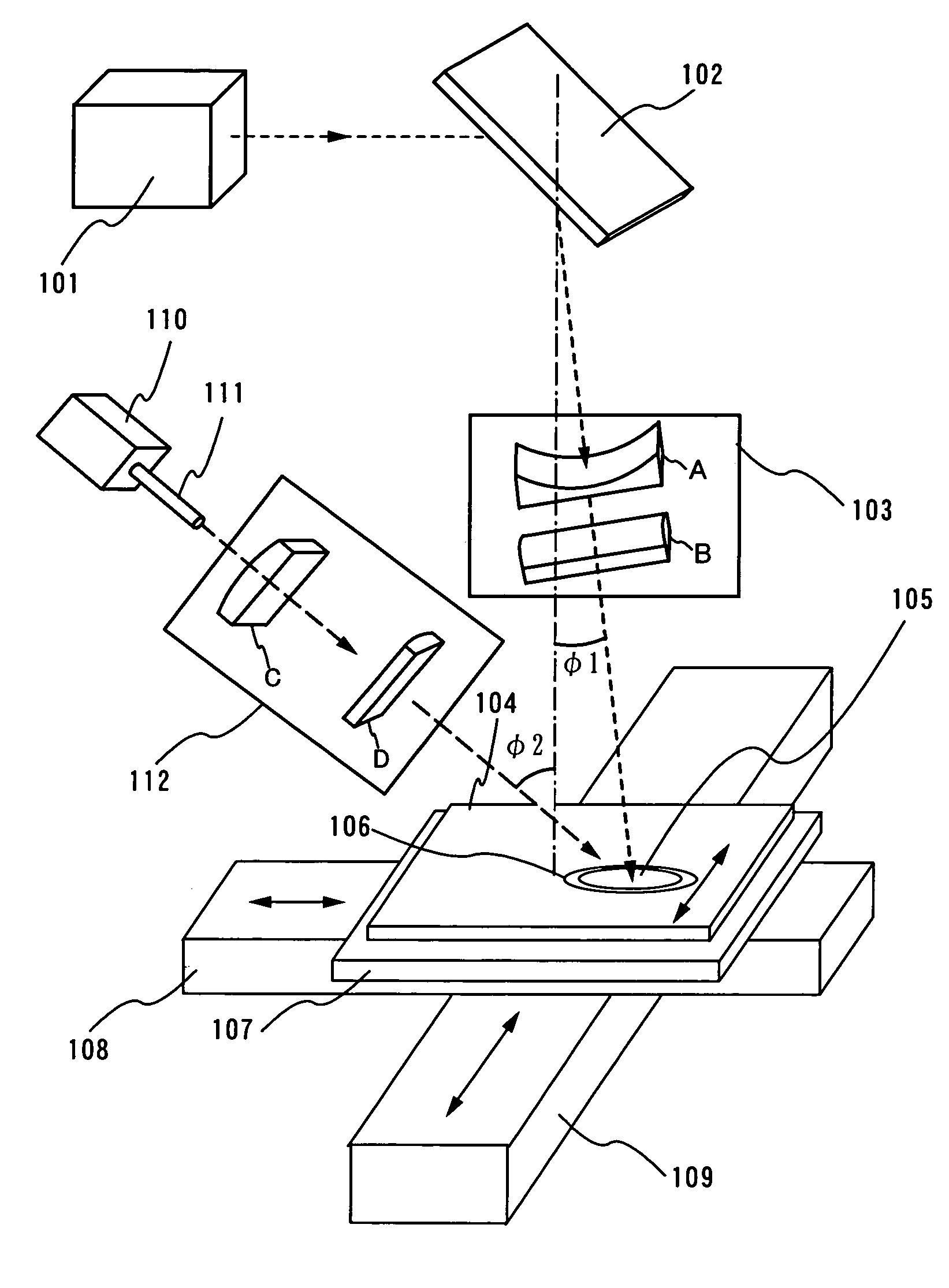
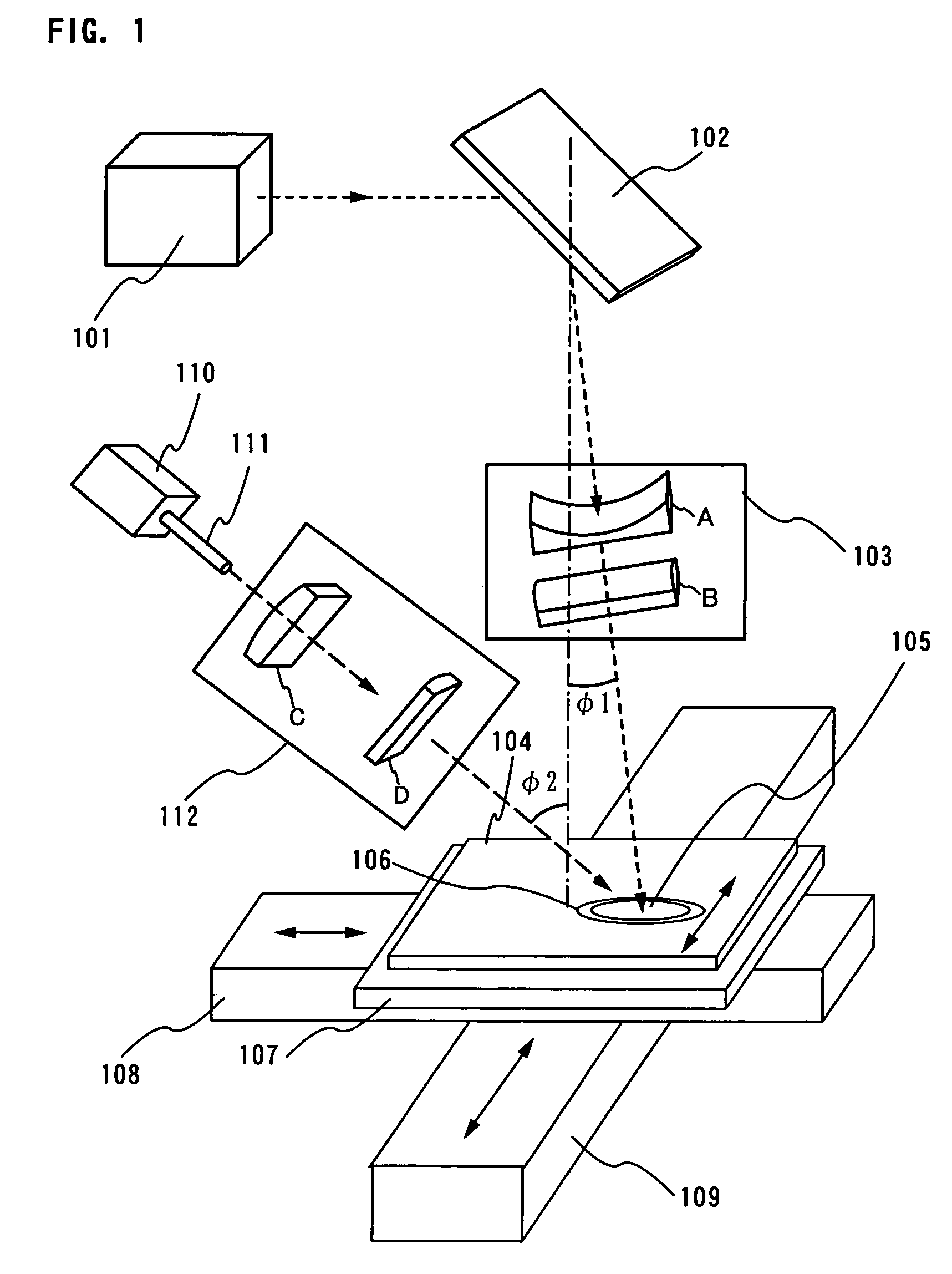
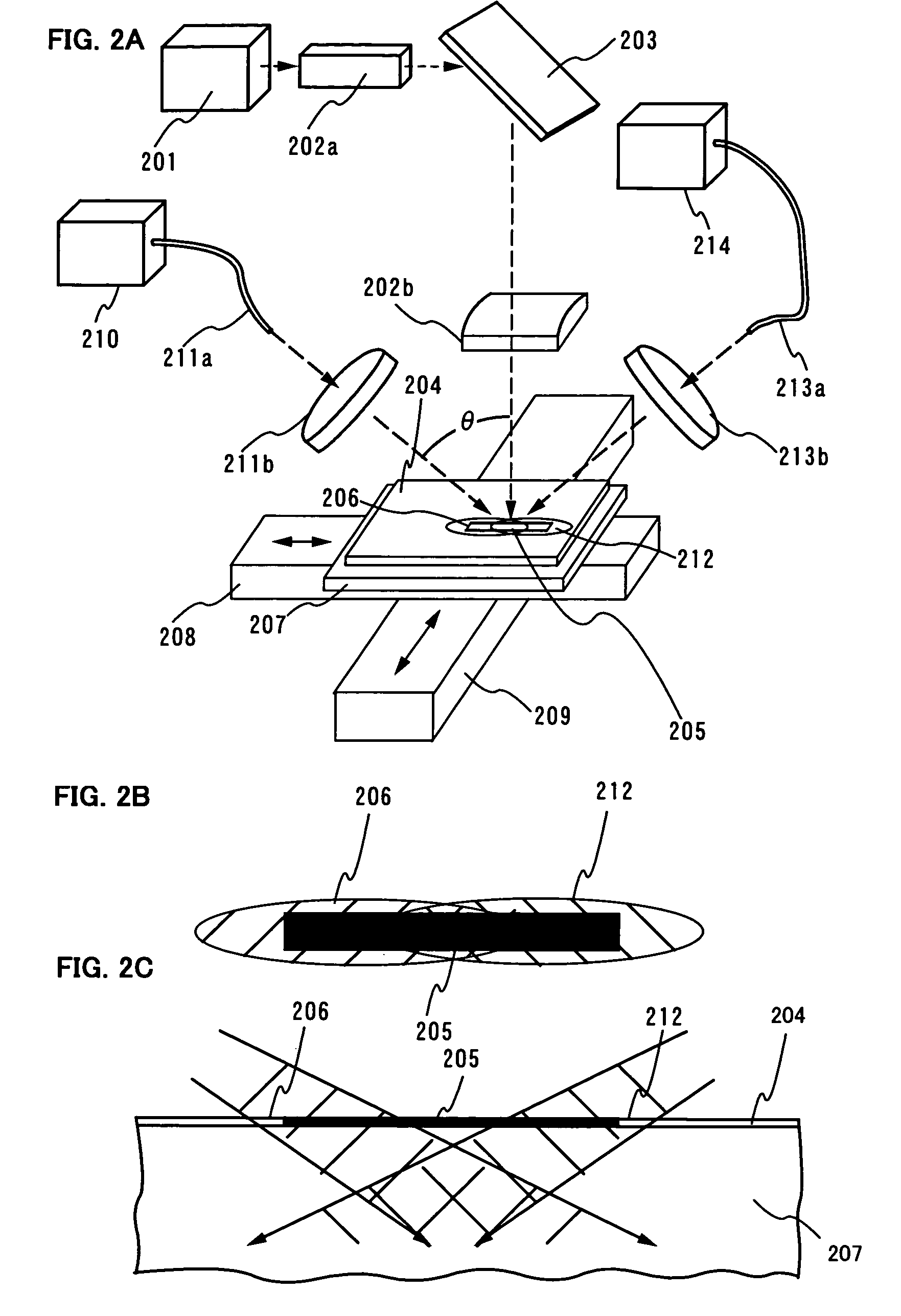
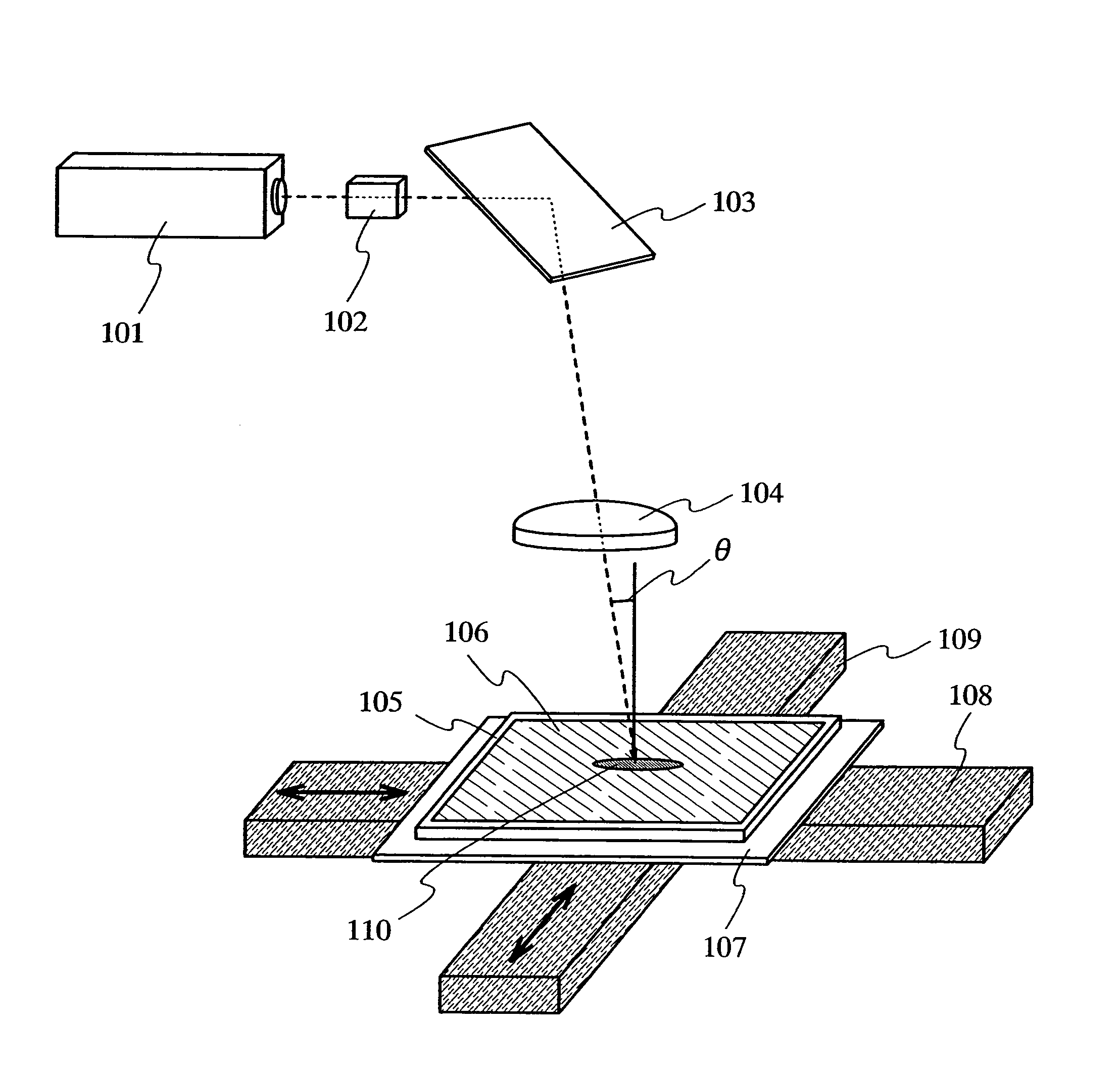
InactiveUS7700462B2Avoid formingReduced areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh energyHarmonic
When the CW laser oscillator is employed in the manufacturing process of the semiconductor device, it is expected to obtain the device of high performance. However, the CW oscillator provides only a small beam spot and forms an inferior crystalline region when it is scanned on the semiconductor film. It is necessary to minimize such an inferior crystalline region because it gives a problem in terms of high integration of the semiconductor element. In view of the problem, the present invention is to form a long crystalline region as suppressing the formation of the inferior crystalline region by irradiating the fundamental wave with the harmonic supplementarily (refer to FIG. 1). The present invention also includes a constitution in which a part having high energy density in the fundamental wave is irradiated to a part having low energy density in the harmonic.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
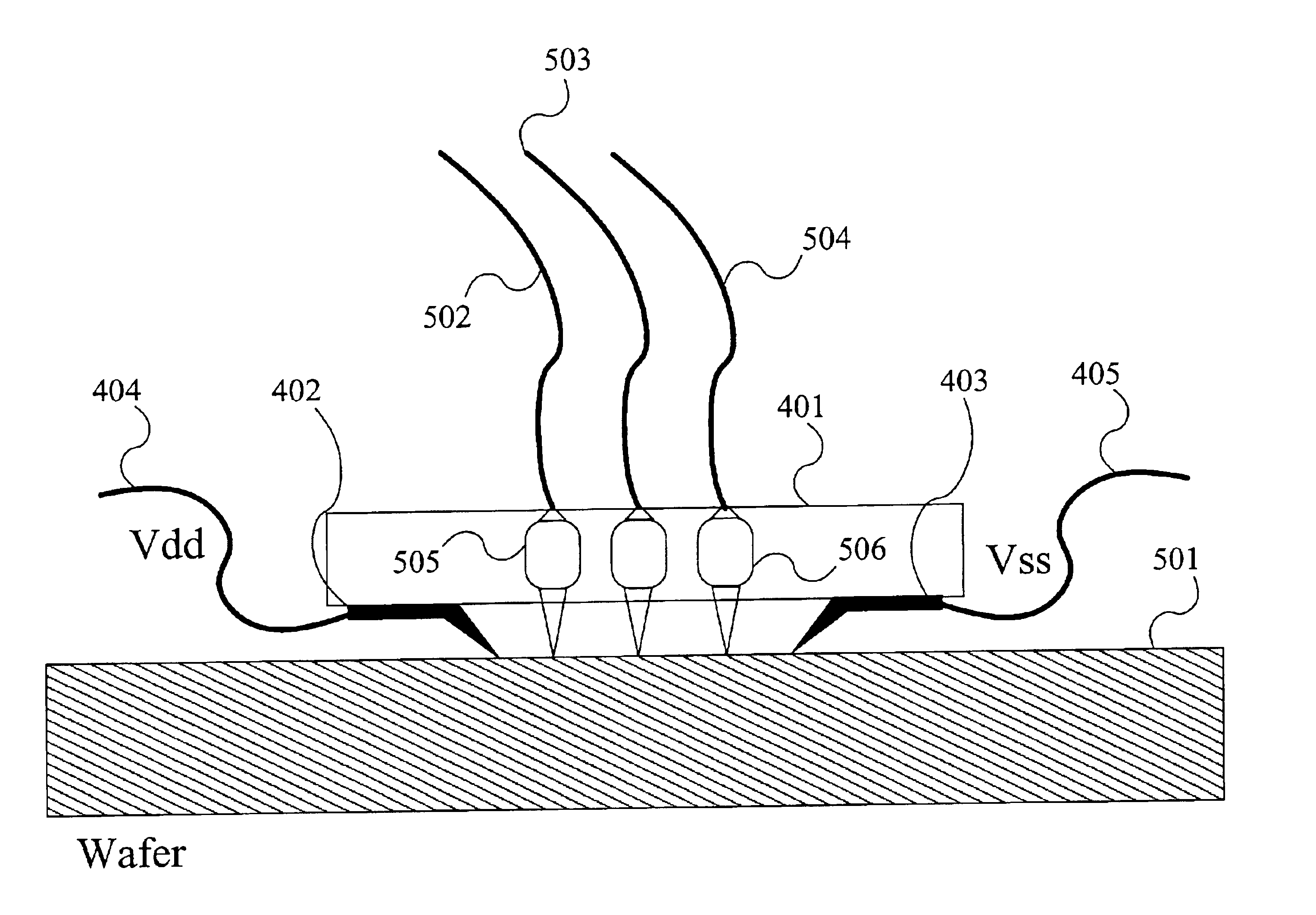
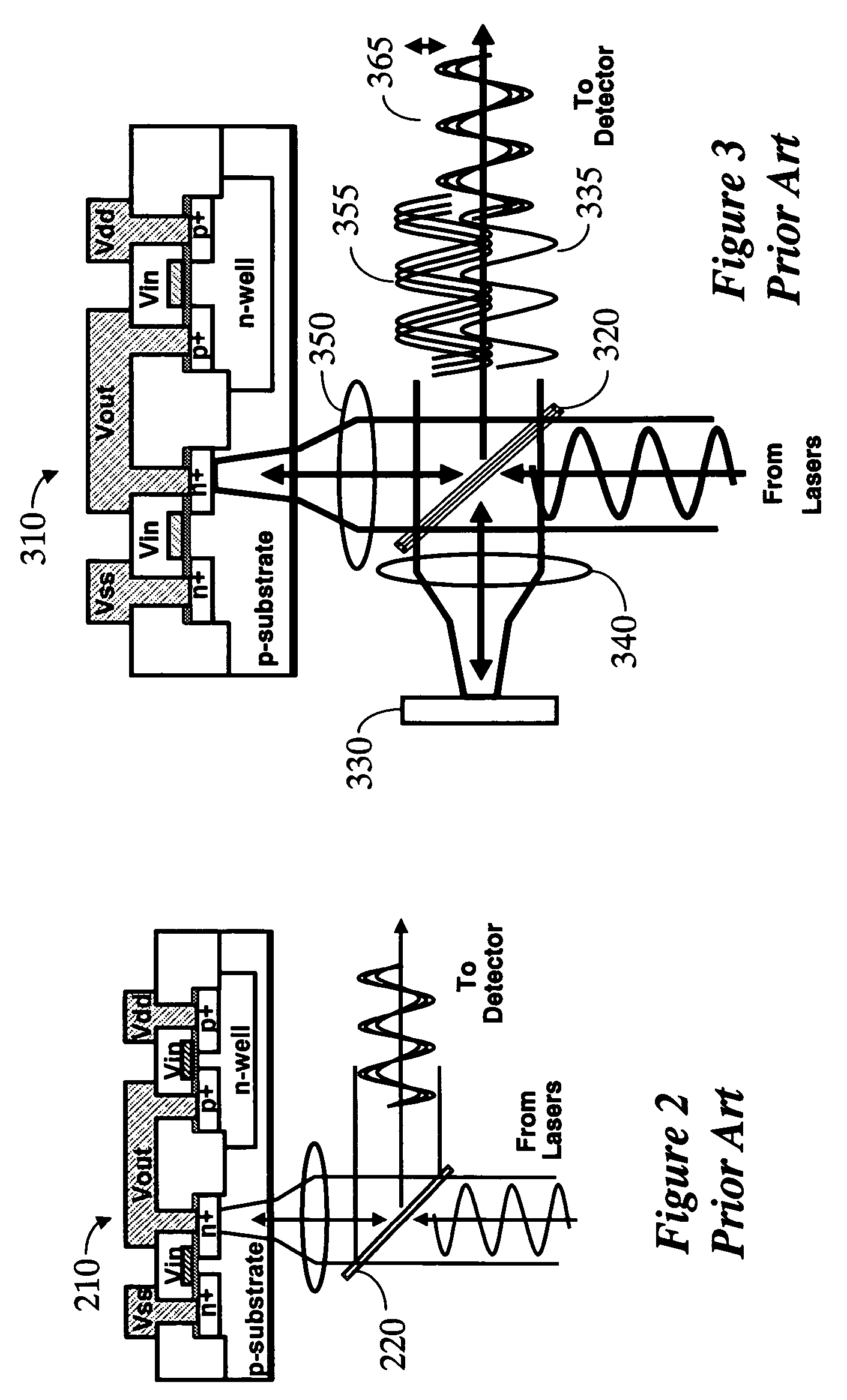
Method and apparatus for measuring high-bandwidth electrical signals using modulation in an optical probing system
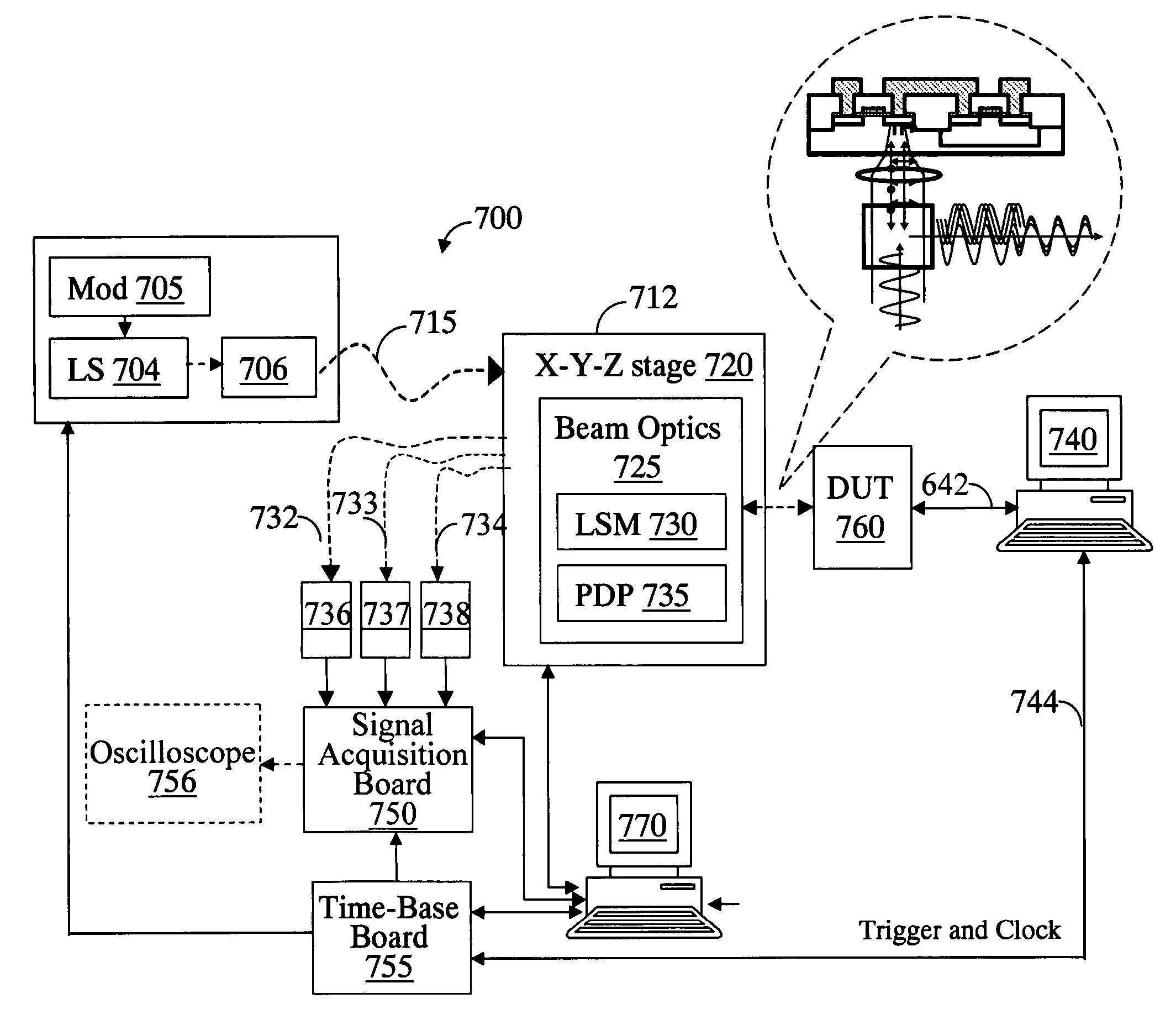
ActiveUS20070002328A1Improve time resolutionUsing optical meansLight polarisation measurementLaser sourceOperating frequency
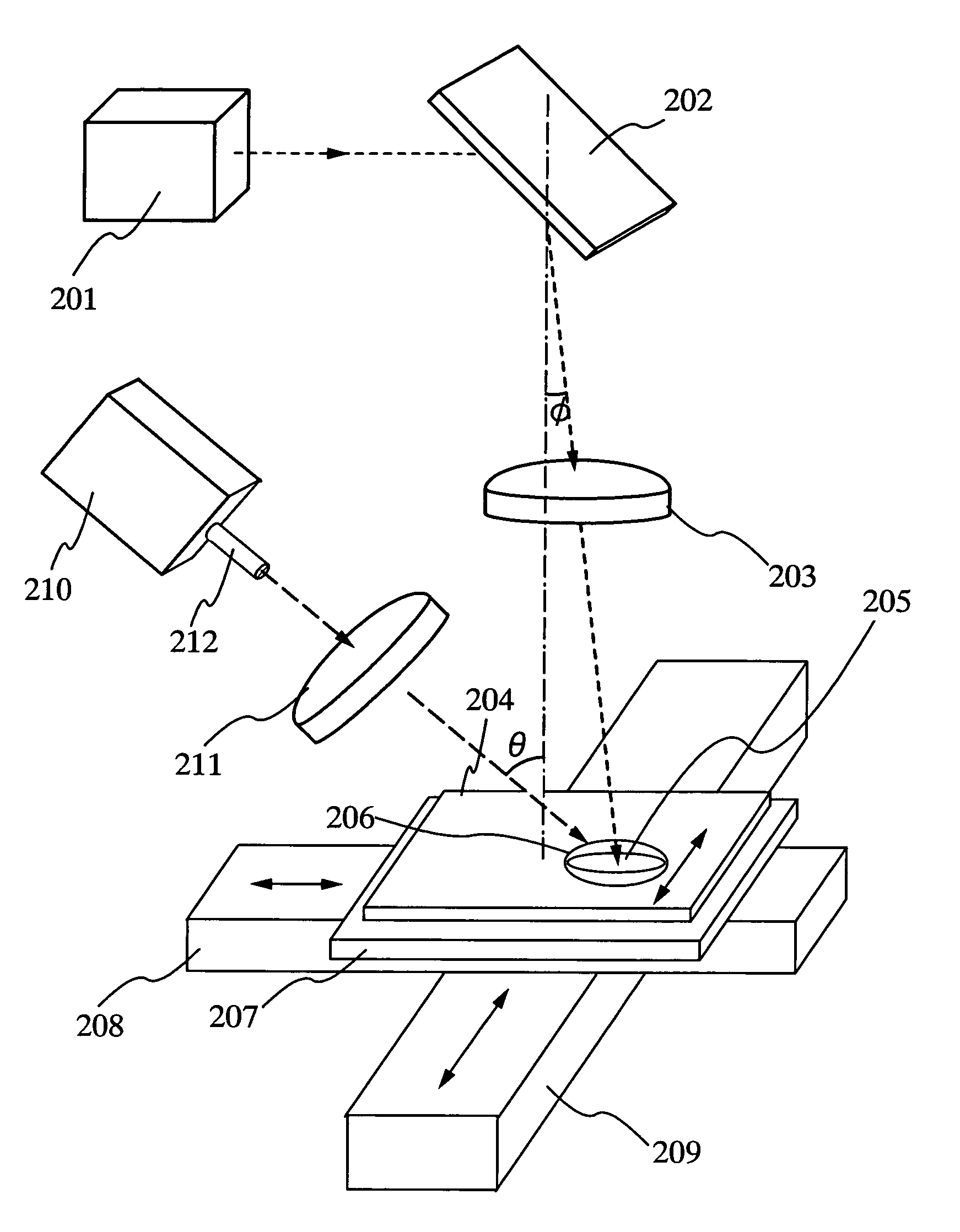
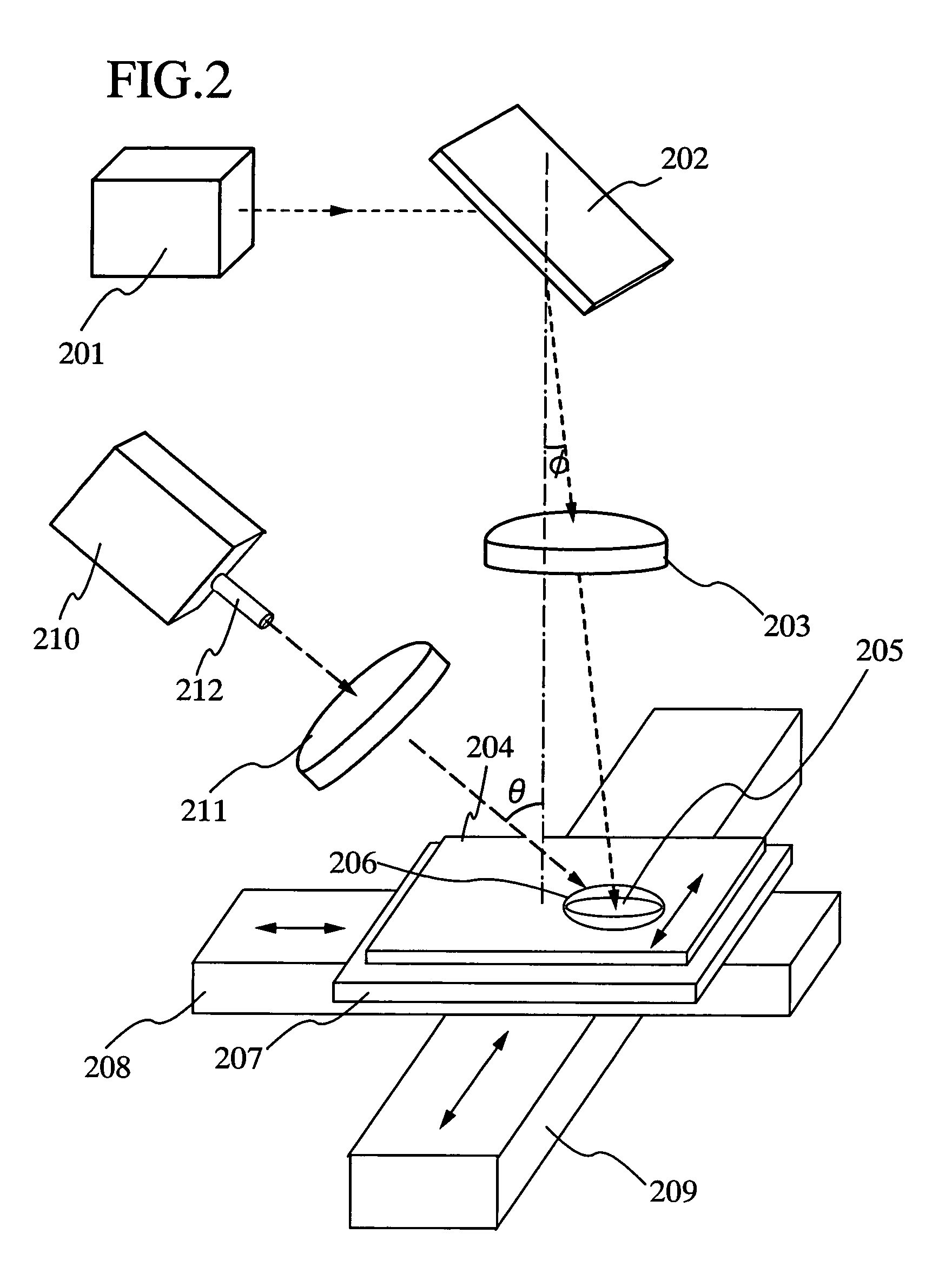
A system for probing a DUT is provided, the system comprising a tunable or CW laser source, a modulator for modulating the output of the laser source, a beam optics designed to point a probing beam at a designated location on the DUT, optical detector for detecting the reflected beam, and collection and signal processing electronics. The system deciphers perturbations in the reflected beam by detecting beat frequency between operation frequency of the DUT and frequency of the modulation. In an alternative embodiment, the laser is CW and the modulation is applied to the optical detector.
Owner:DCG SYST
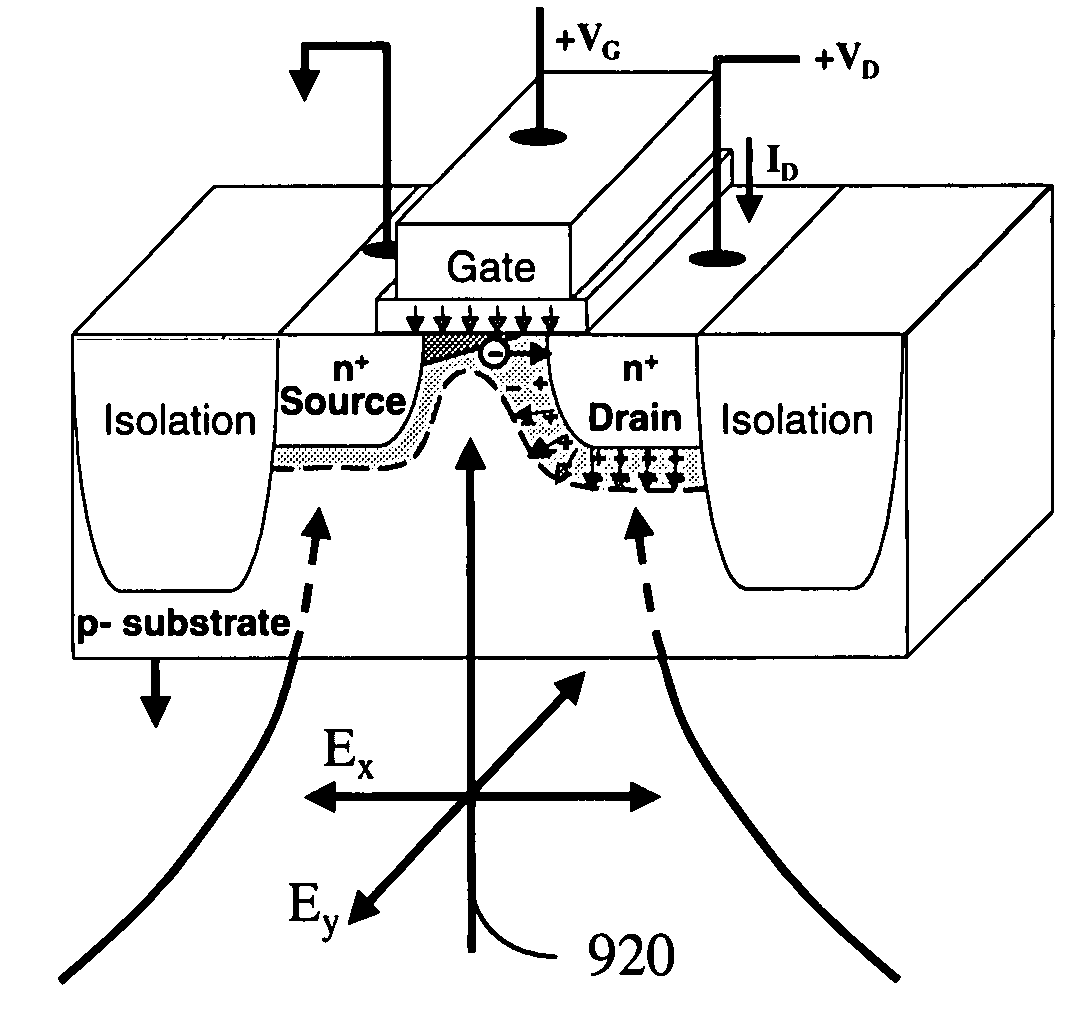
Apparatus and method for probing integrated circuits using polarization difference probing
A system for probing a DUT is disclosed, the system having a pulsed laser source, a CW laser source, beam optics designed to point a reference beam and a probing beam at the same location on the DUT, optical detectors for detecting the reflected reference and probing beams, and a collection electronics. The beam optics is a common-path polarization differential probing (PDP) optics. The common-path PDP optics divides the incident laser beam into two beams of orthogonal polarization—one beam simulating a reference beam while the other simulating a probing beam. Both reference and probing beams are pointed to the same location on the DUT. Due to the intrinsic asymmetry of a CMOS transistor, the interaction of the reference and probing beams with the DUT result in different phase modulation in each beam. This difference can be investigated to study the response of the DUT to the stimulus signal.
Owner:DCG SYST
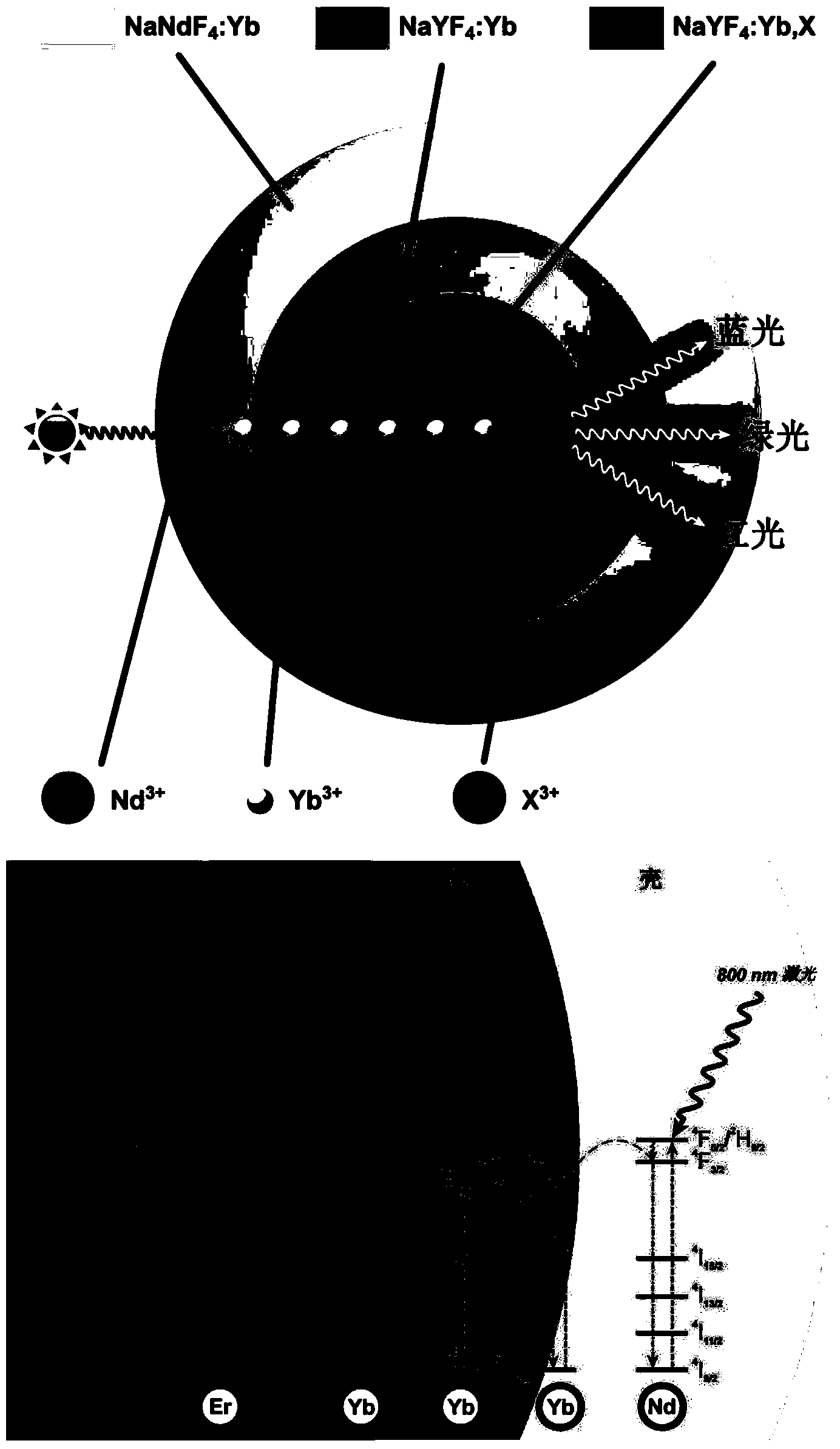
800-nanometer continuous laser excited rare earth upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs), and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103450875AEffective absorptionAvoid quenchingLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceNanoparticle
The invention provides 'core-shell-shell' rare earth upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) using Nd as a sensitizing agent. The rare earth UCNPs are characterized in that the shell layer of the rare earth UCNPs contains Nd<3+> and each layer contains Yb<3+>. The special microscopic nanostructure solves the problem about the quenching effect on upconversion fluorescence in an Nd doping process, so bright upconversion fluorescence can be obtained. Compared with the traditional Yb-sensitized UCNPs, the Nd-sensitized UCNPs have higher infrared absorption intensity so as to greatly improve upconversion efficiency and fluorescence. The Nd-sensitized UCNPs adopt 800-nanometer instead of 980-nanometer laser as an exciting light source, so the Nd-sensitized UCNPs have smaller overheating effect and stronger biological tissue penetrating power. Therefore, the novel rare earth upconversion material is expected to be widely applied in the field of biomedicines.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
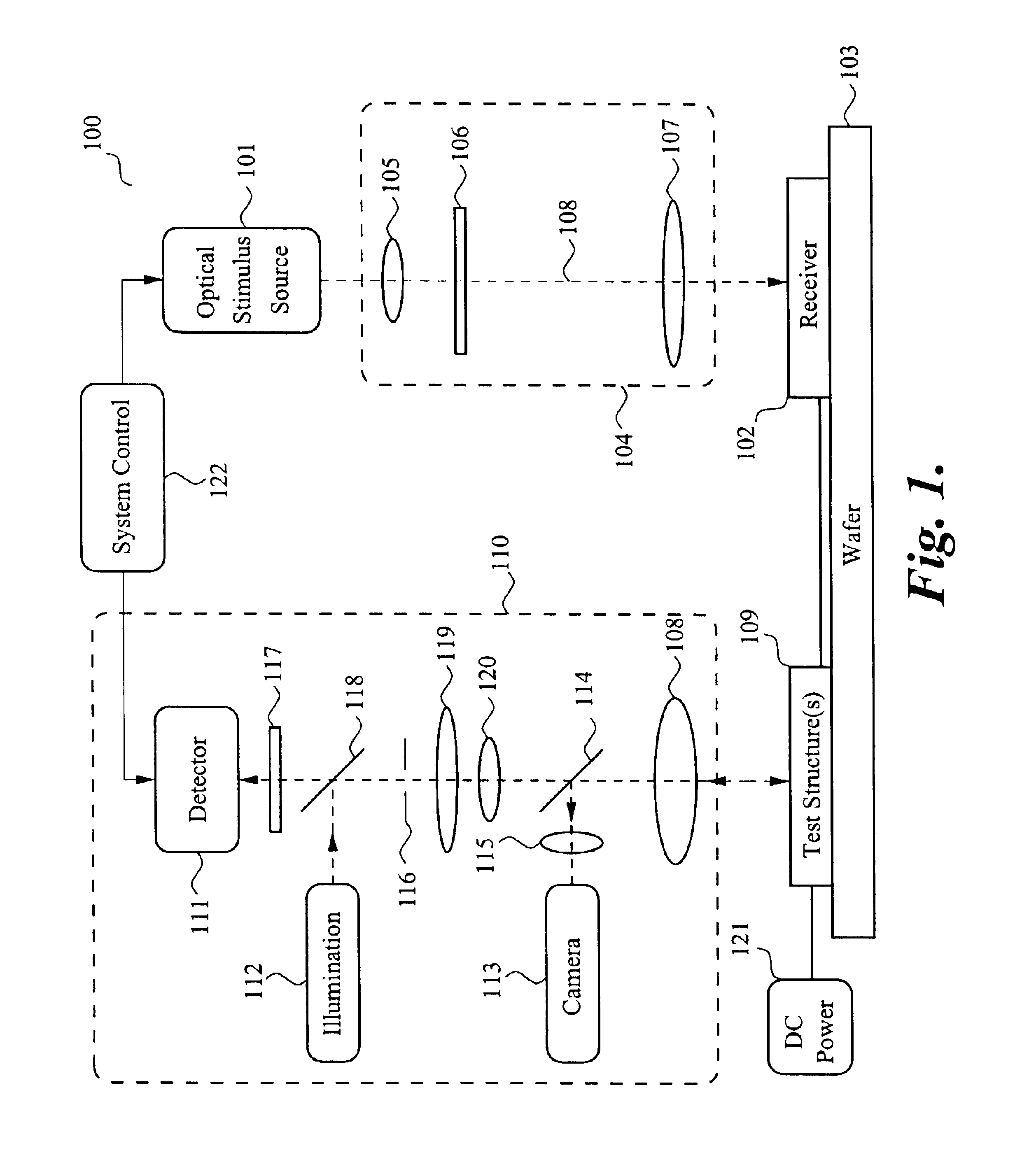
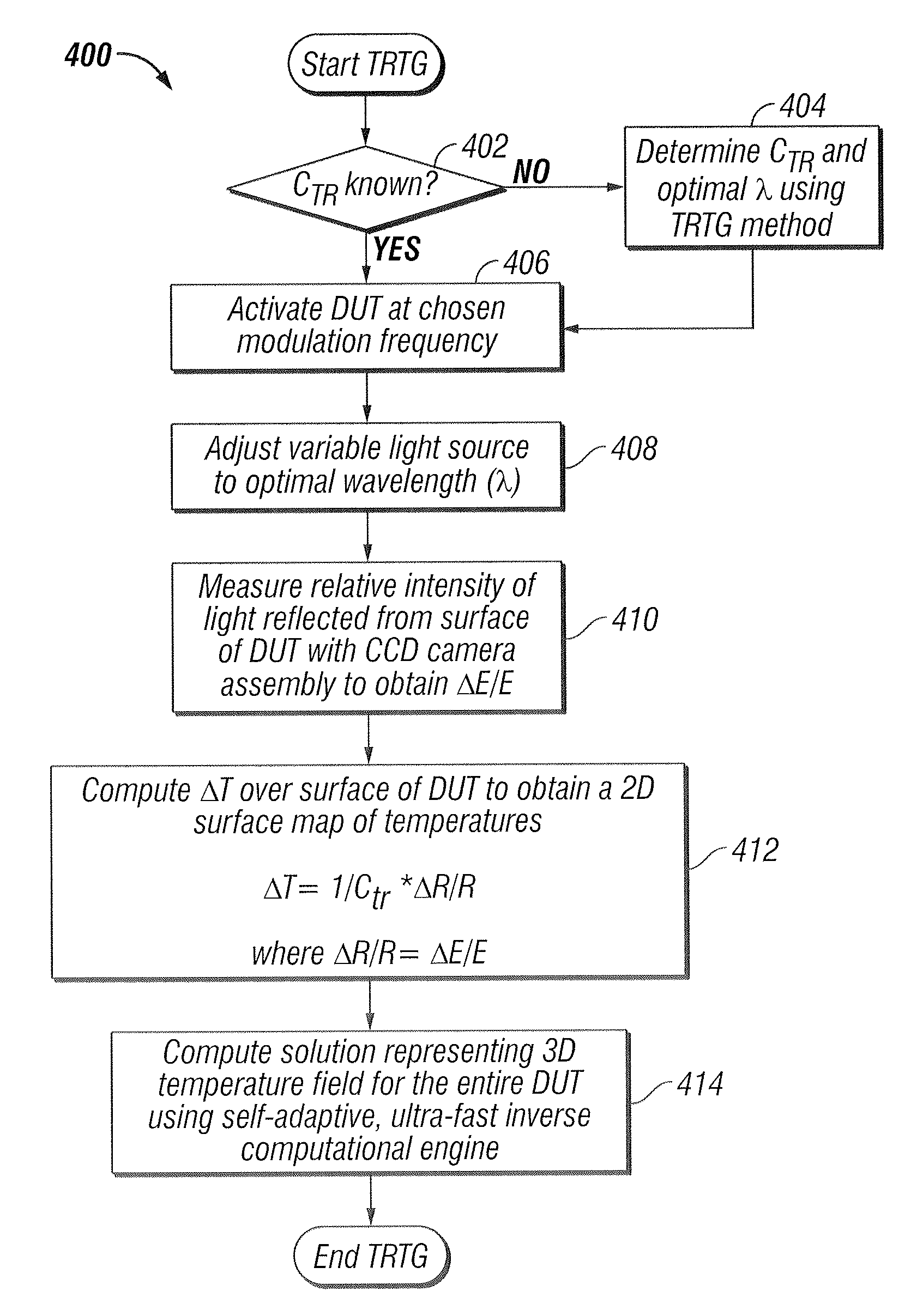
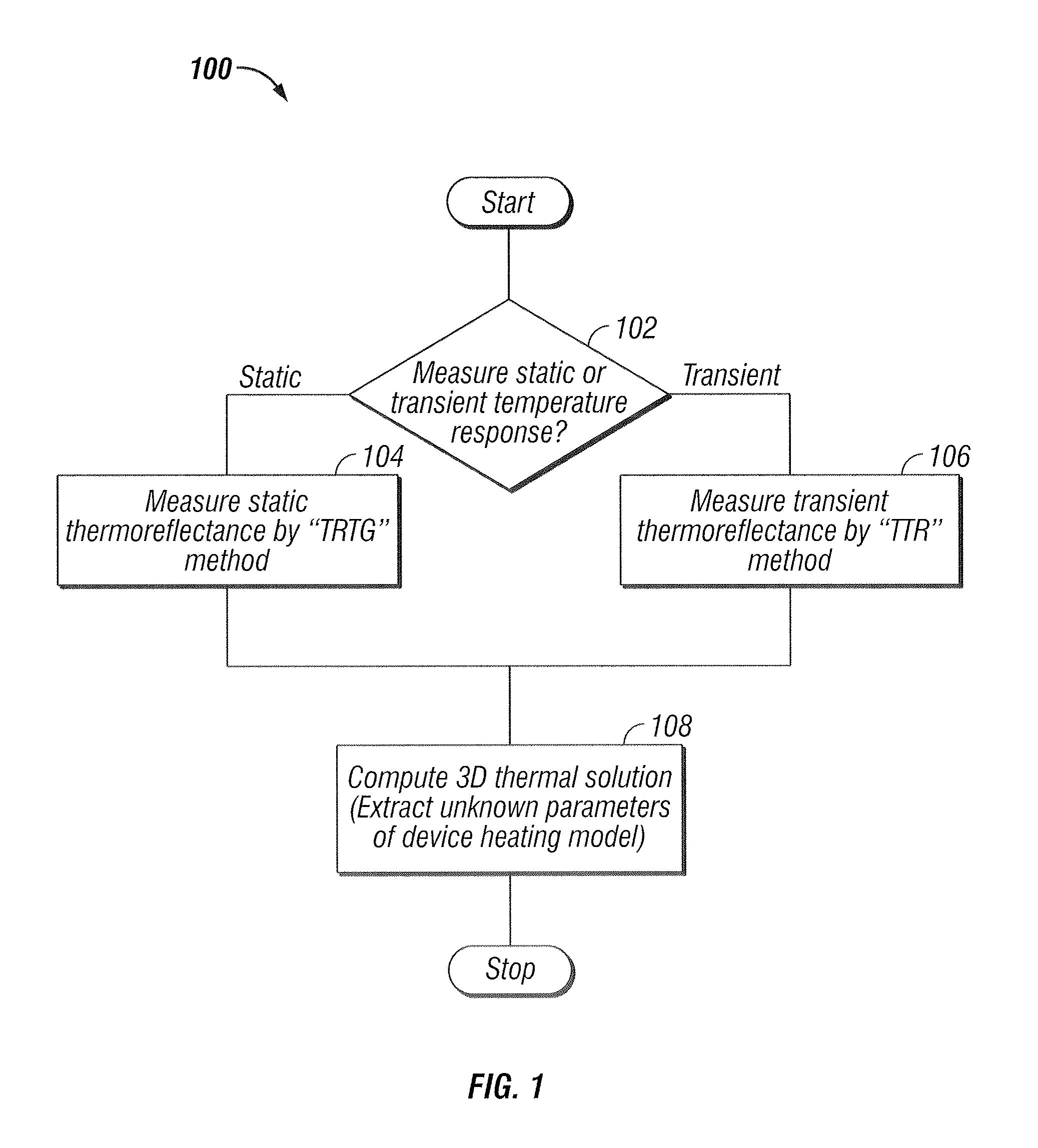
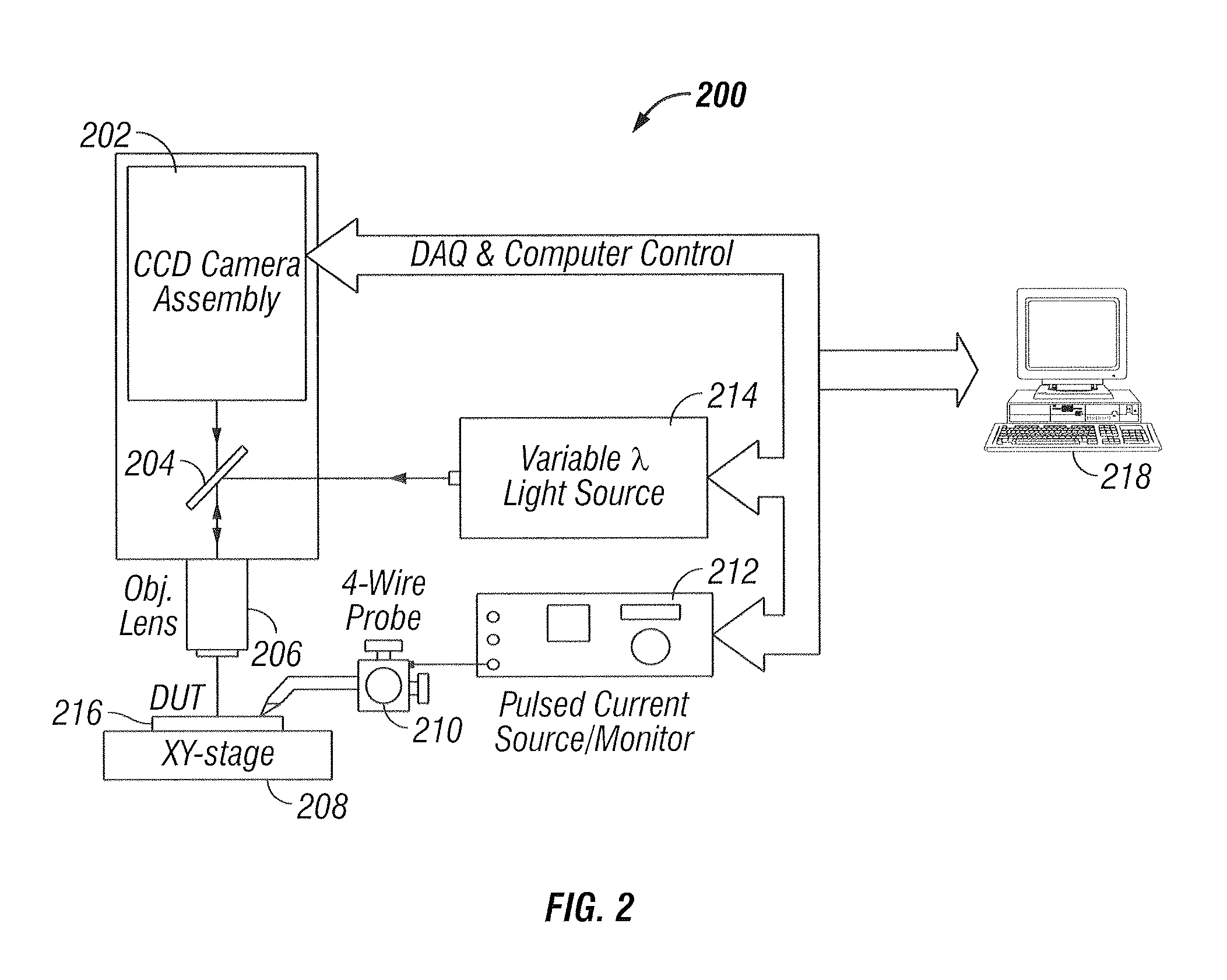
Thermography measurement system for conducting thermal characterization of integrated circuits
ActiveUS20080082288A1High spatialHigh temporal accuracyCounting objects with random distributionSpecial data processing applicationsLight energyPhotodetector
A system and method to fully characterize the thermal behavior of complex 3D submicron electronic devices. The system replaces and / or supplements laser-based surface temperature scanning with a CCD camera-based approach. A CCD camera records multiple points of light energy reflected from an integrated circuit to obtain a static temperature measurement. The system is used to non-invasively measure with submicron resolution the 2D surface temperature field of an activated device. A CW laser illuminates a single point on the surface of an active device and a photodetector records the reflected light energy to obtain a transient temperature measurement. The measured 2D temperature field is used as input for an ultra-fast inverse computational solution to fully characterize the thermal behavior of the complex 3D device. The system extracts geometric features of a known device, assessing the system's ability to combine measured results and computations to fully characterize complex 3D electronic devices.
Owner:RAAD PETER E
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser with traveling-wave ring-resonator
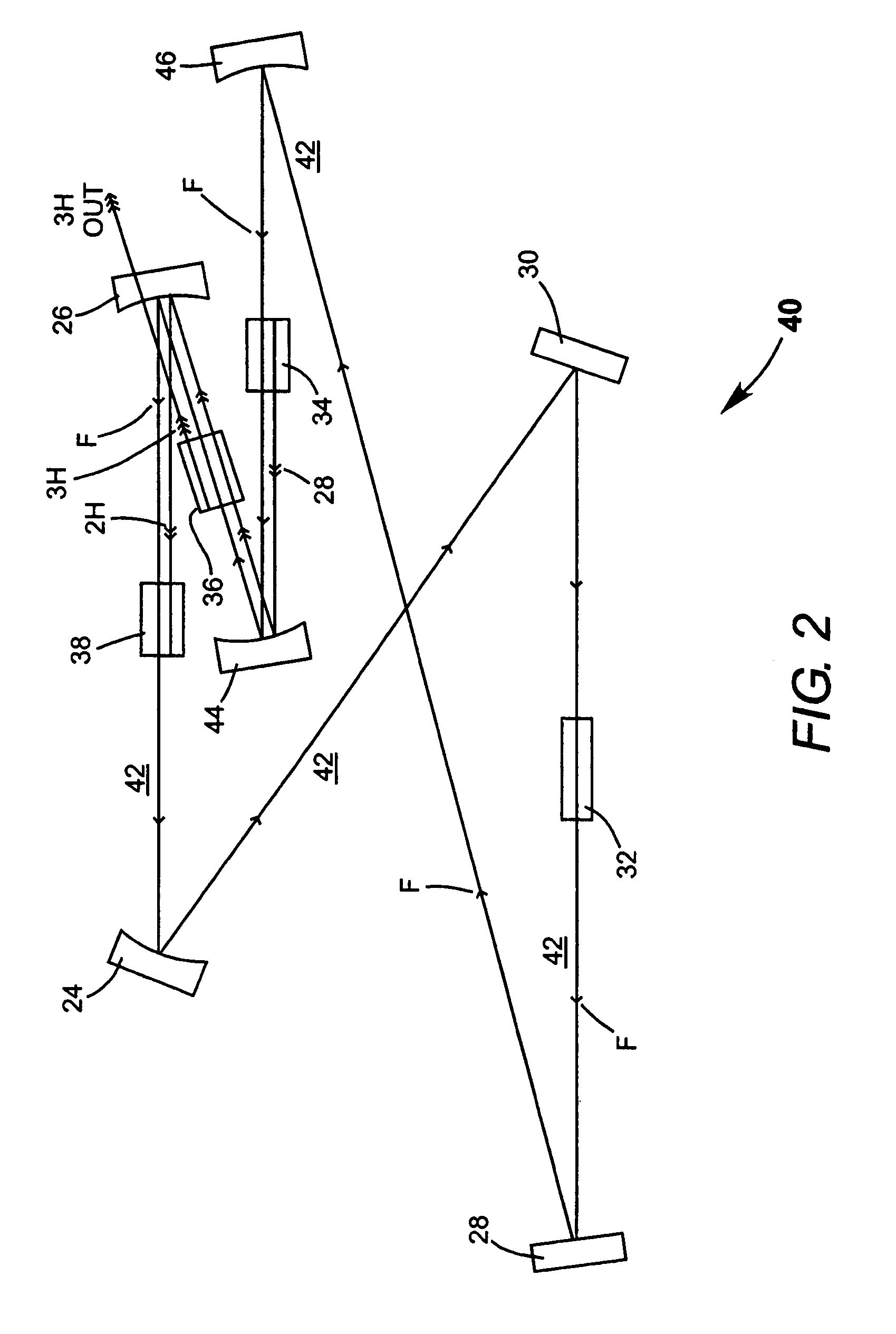
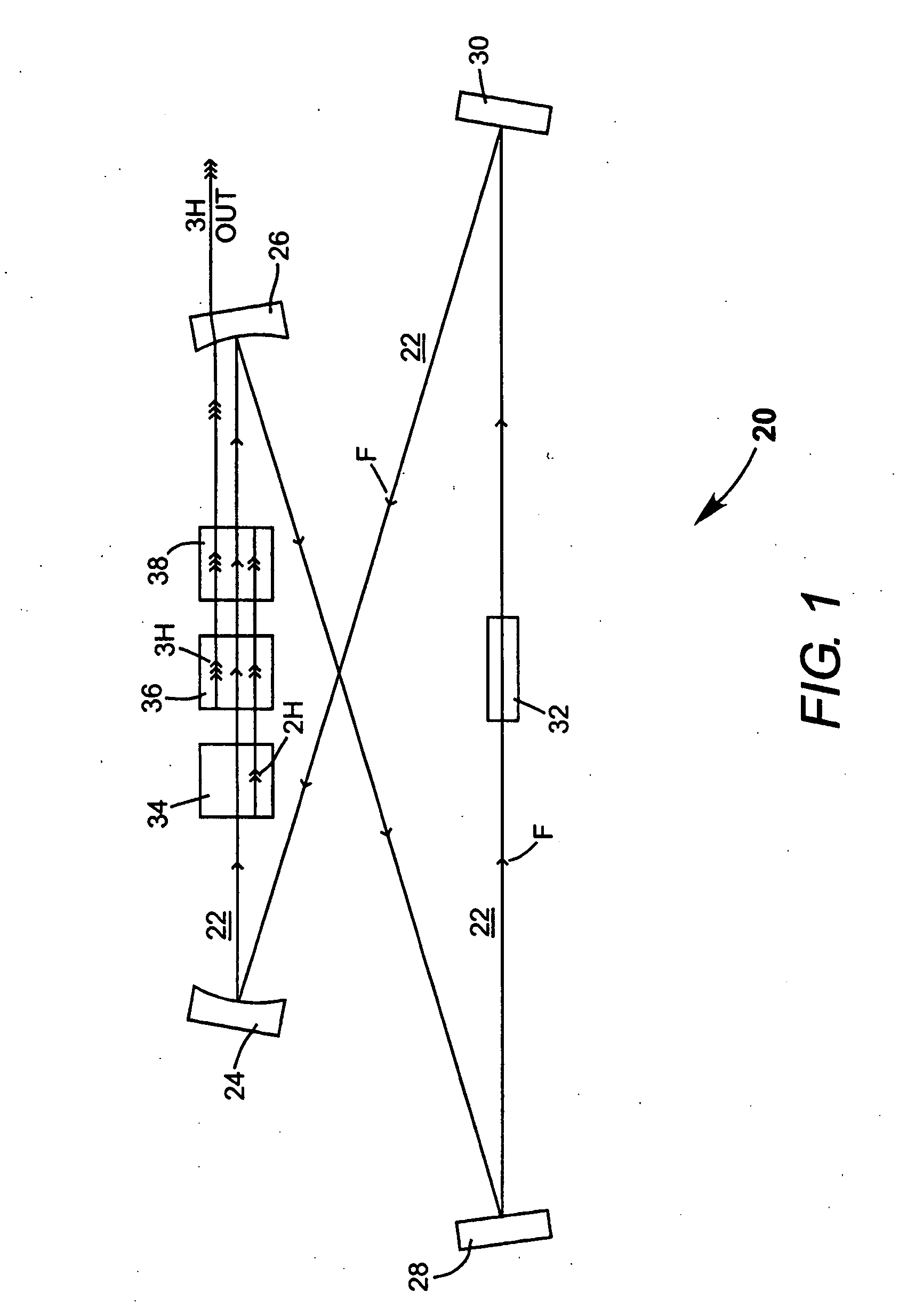
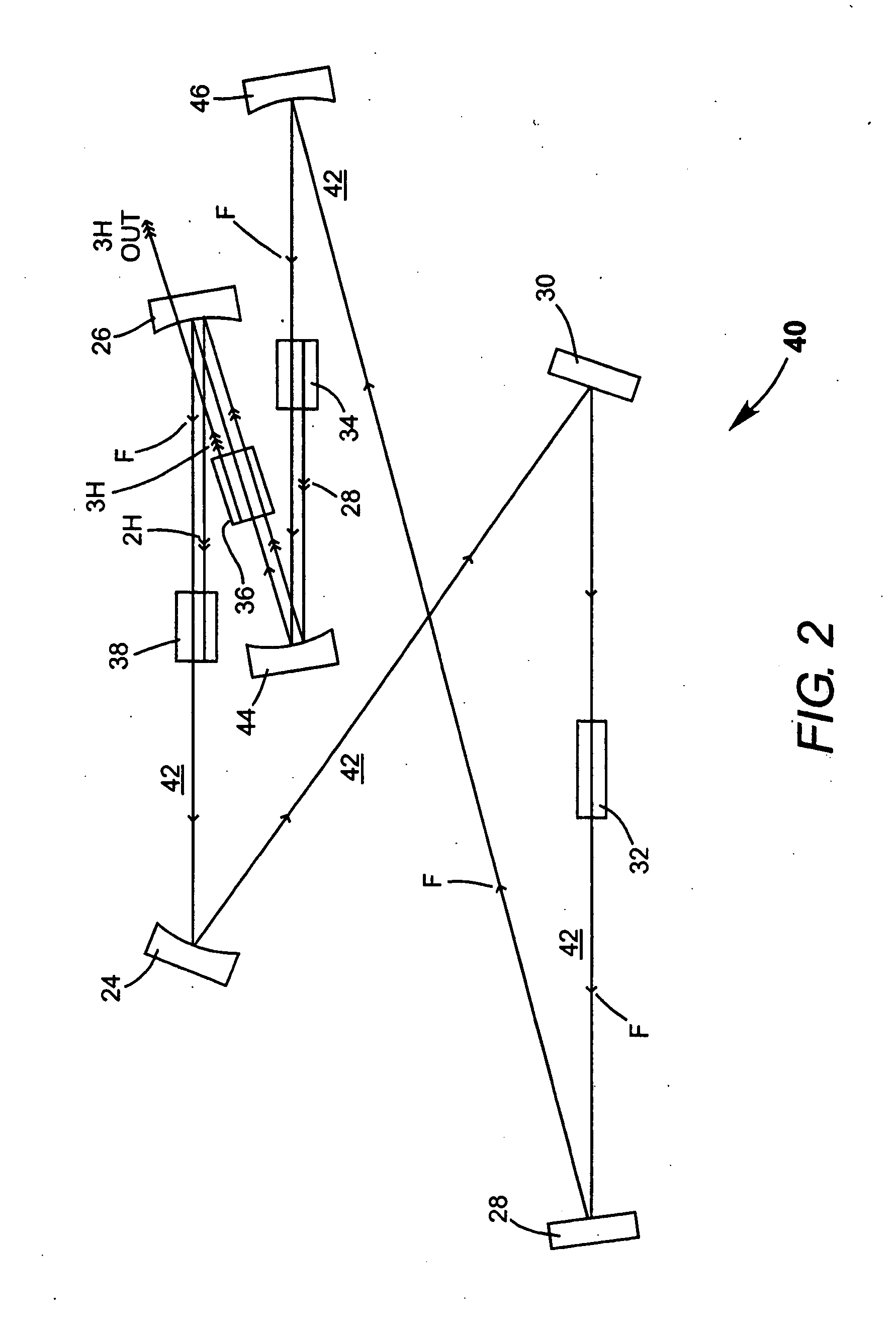
InactiveUS7130321B2Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlFourth harmonicThird harmonic
Owner:COHERENT INC
Device and method for laser shot blasting reinforcement of hard and brittle material
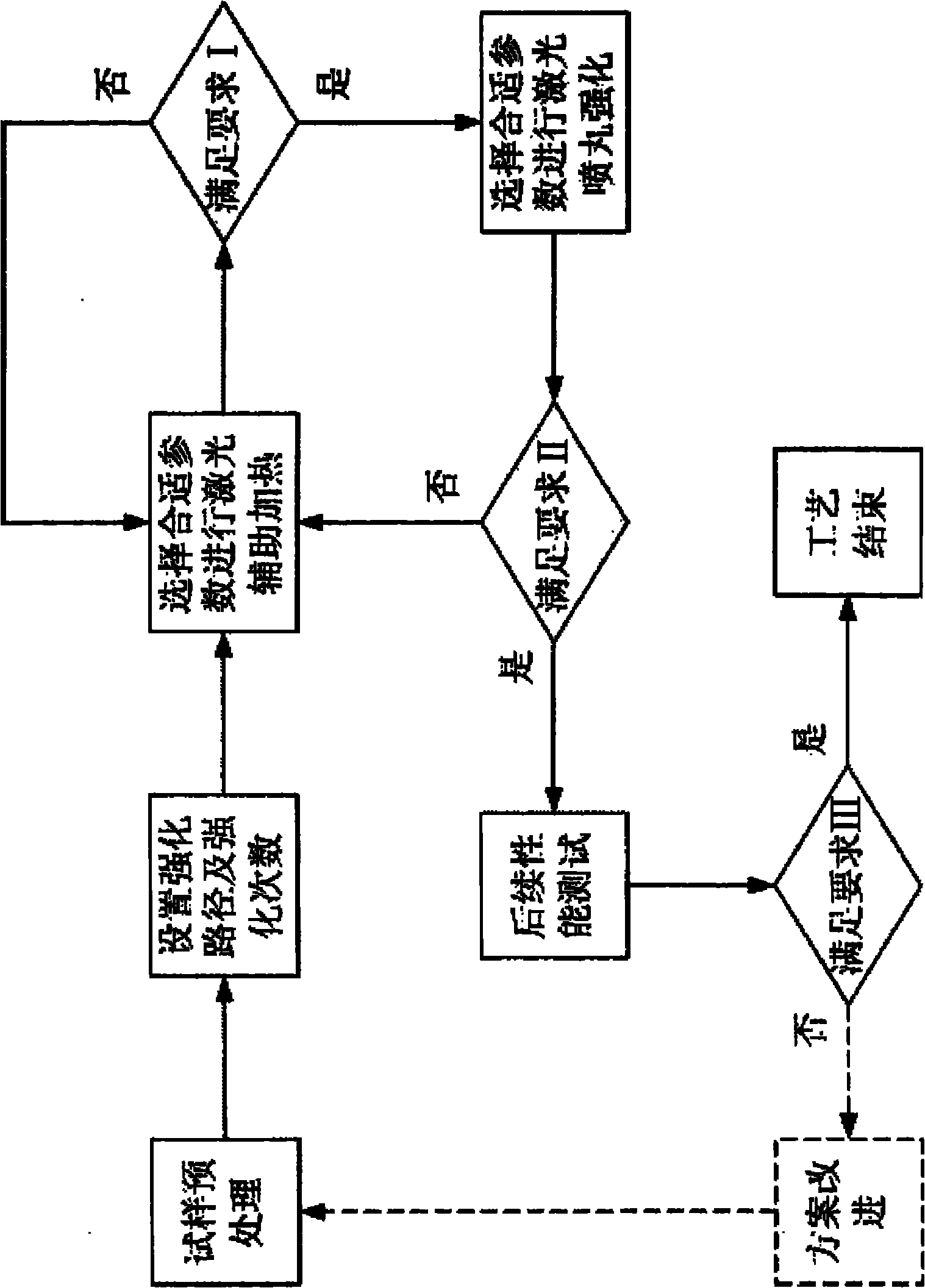
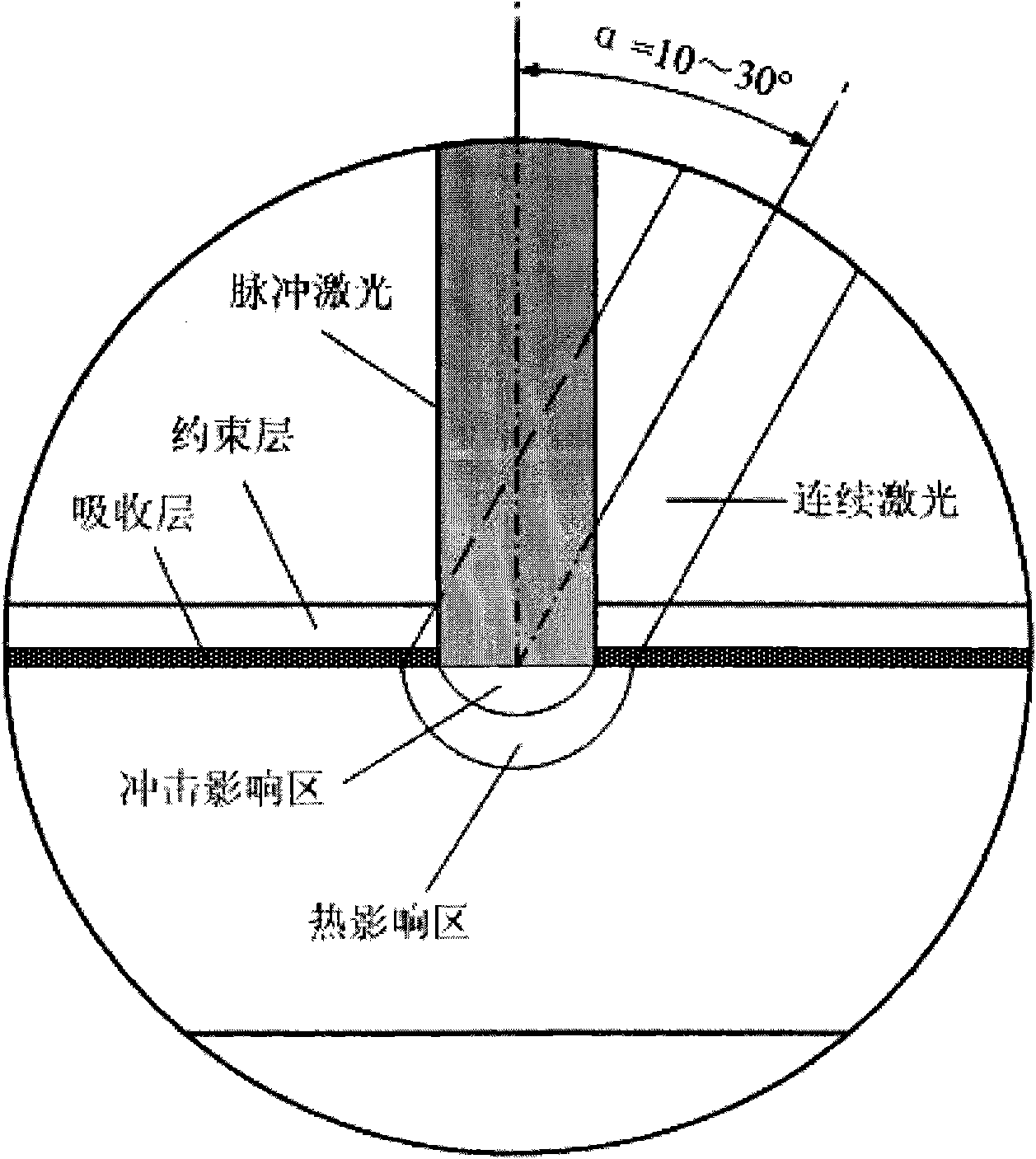
The invention discloses a device and a method for laser shot blasting reinforcement of a hard and brittle material, and relates to the field of mechanical manufacture of hard and brittle material processing and laser application. The device comprises a laser aid heating system, a laser shot blasting reinforcement system, a workpiece clamp system, a computer numerical control system, a measurement feedback system and a protective gas circulating system. The method comprises a laser aid heating stage and a laser shot blasting reinforcement stage, namely performing aid heating treatment on the area to be reinforced by adopting high-power continuous laser, wherein for most metal materials, the plastic performance is improved along with the rise of temperature; and after the temperature of the heating area reaches a predetermined heating temperature, implementing laser shot blasting reinforcement treatment by adopting high-power pulse laser. The device and the method can implement the laser shot blasting reinforcement on the hard and brittle material so as to broaden the application range of the laser shot blasting reinforcement technology, and meanwhile compound the advantages of continuous laser and pulse laser so as to broaden the application field and the application prospect of laser manufacture.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser with traveling-wave ring-resonator
InactiveUS20050163187A1Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlFourth harmonicThird harmonic
A traveling-wave ring laser resonator includes one or more gain-elements for generating fundamental radiation and three optically nonlinear crystals. A portion of the fundamental radiation is converted to second-harmonic radiation in a first of the crystals. Remaining fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation traverse a second of the optically nonlinear crystals where a portion of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. Fundamental and second-harmonic radiation pass through the third of the optically nonlinear crystals where most of the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third-harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation or mixed with the fundamental radiation in a fourth optically nonlinear crystal to generate fourth harmonic radiation. An optical parametric oscillator arrangement is also disclosed.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Laser irradiation apparatus, laser irradiation method, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7125761B2Fully absorbedImprove annealing efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesSingle crystalLaser annealing
An aggregation of crystals extending long in the scanning direction (a long crystal grain region) is formed when a continuous wave laser oscillator (a CW laser oscillator) is employed for annealing the semiconductor film in the manufacturing process of a semiconductor device. The long crystal grain region has a characteristic similar to that of single crystal in the scanning direction, but there is restriction for high integration because of the small output of the CW laser oscillator. pa In order to solve the problem, a pulsed laser beam 1 having a wavelength absorbed sufficiently in the semiconductor film is used in combination with a laser beam 2 having a high output and having a wavelength absorbed sufficiently in the melted semiconductor film. After irradiating the laser beam 1 to melt the semiconductor widely, the laser beam 2 is irradiated to the melted region. And then the laser beam 2 and the semiconductor film are moved relatively while keeping the melting state so as to form the long crystal grain region. The laser beam 2 keeps to be irradiated to the semiconductor film until the laser beam 1 is irradiated, and the output of the laser beam 2 is attenuated when the laser beam 1 is irradiated so as not to give the energy more than is needed so that the very uniform laser annealing becomes possible. Thus the long crystal grain region having a width 10 times as broad as the conventional one can be formed.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com