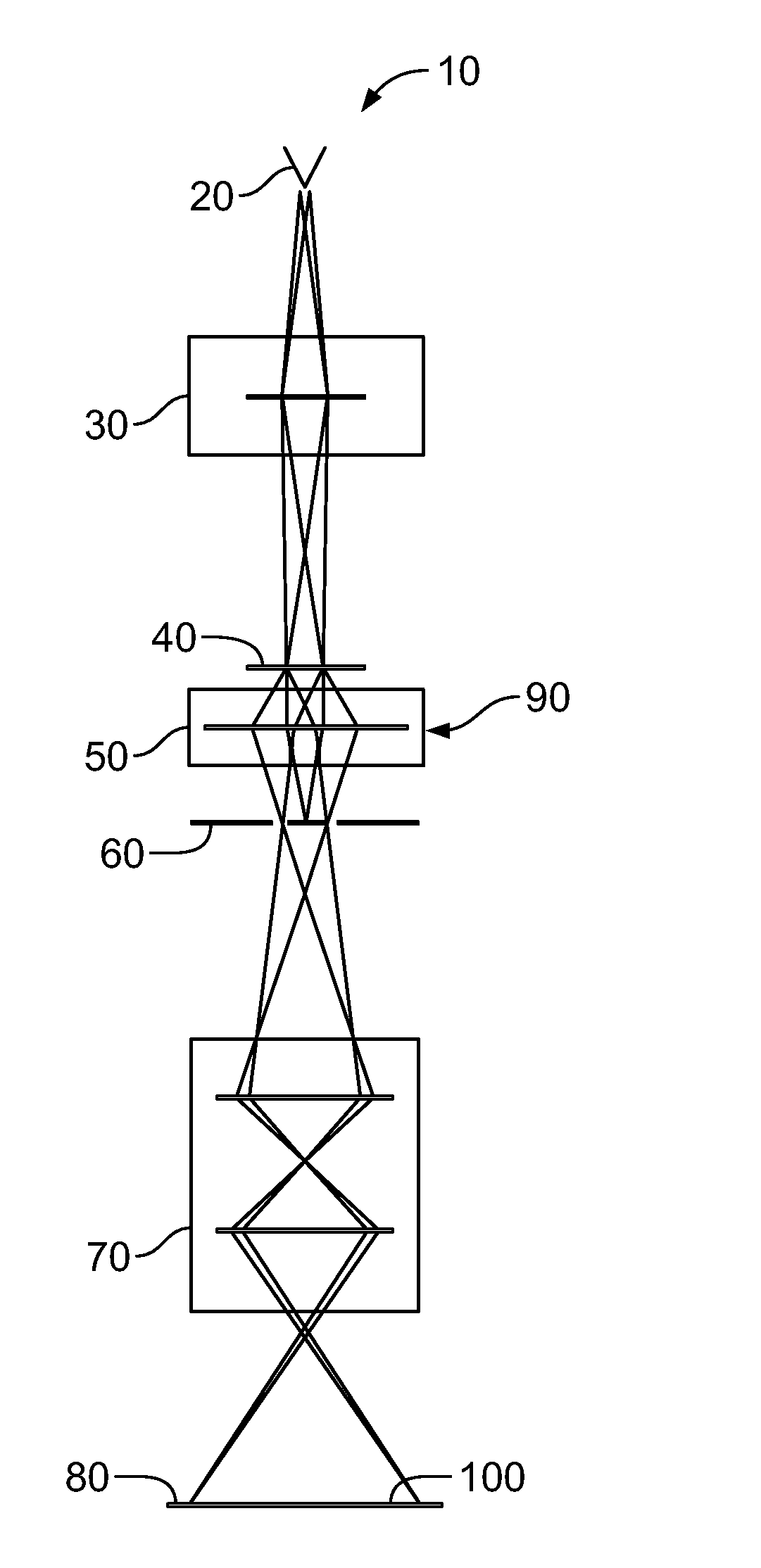
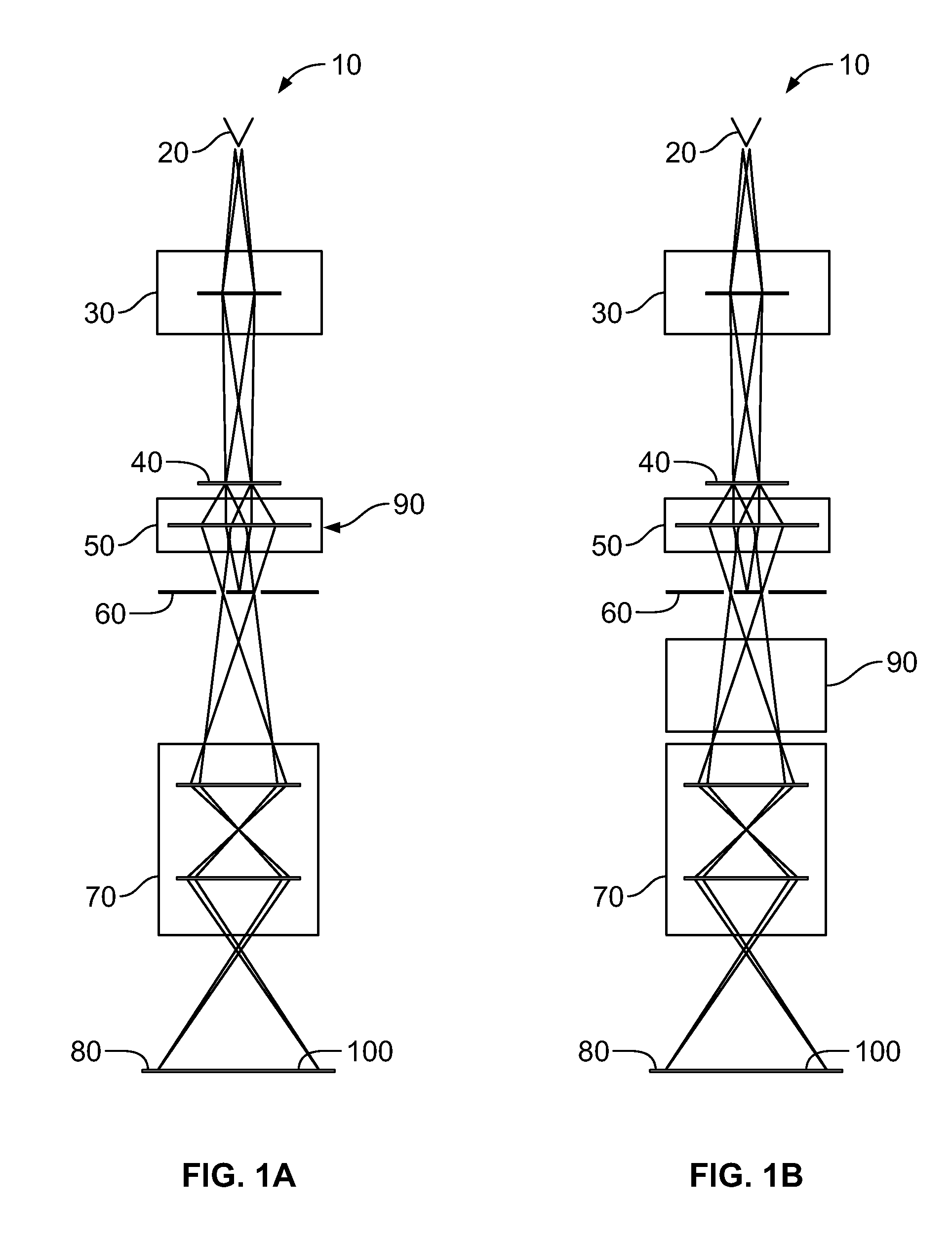
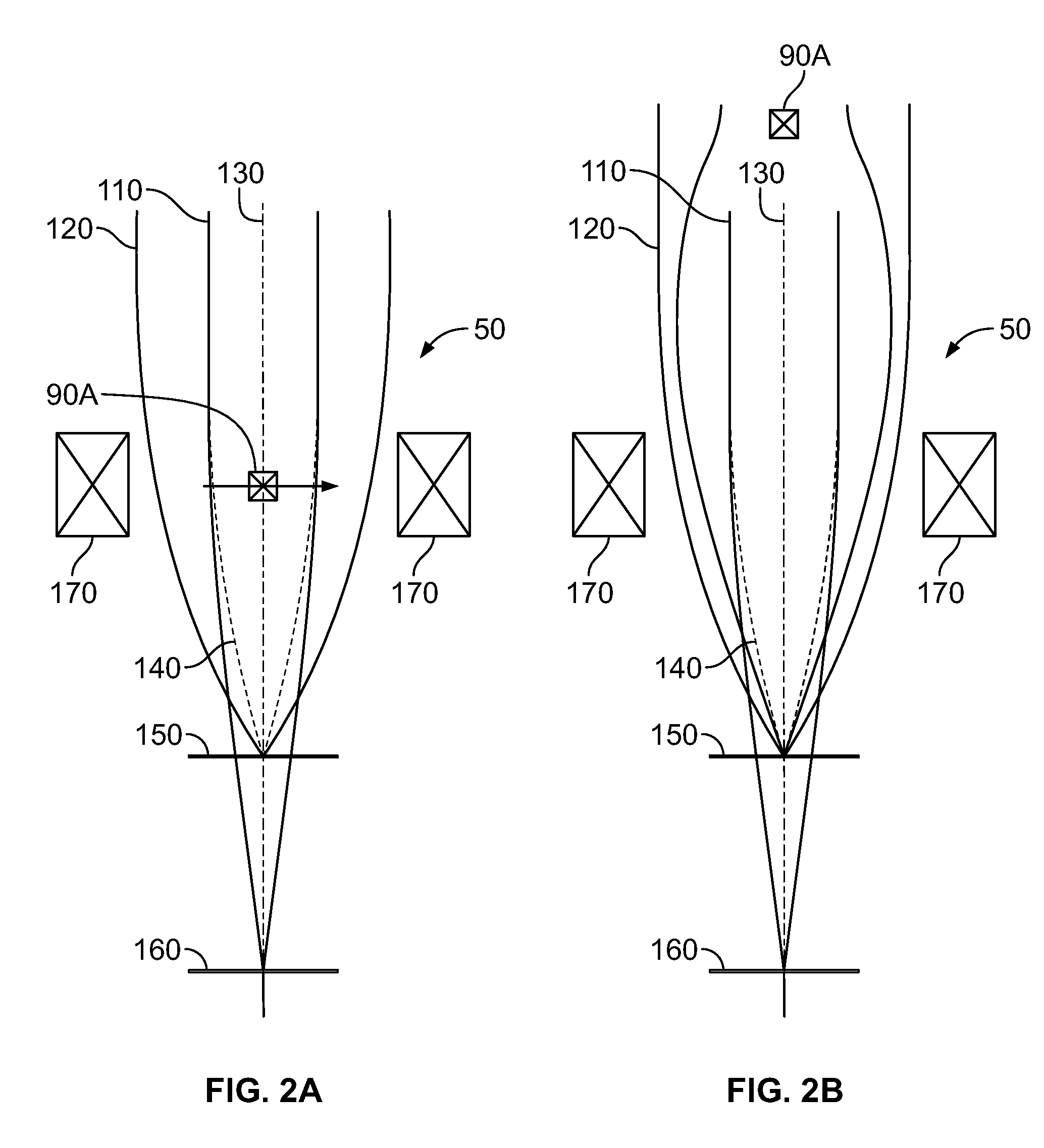
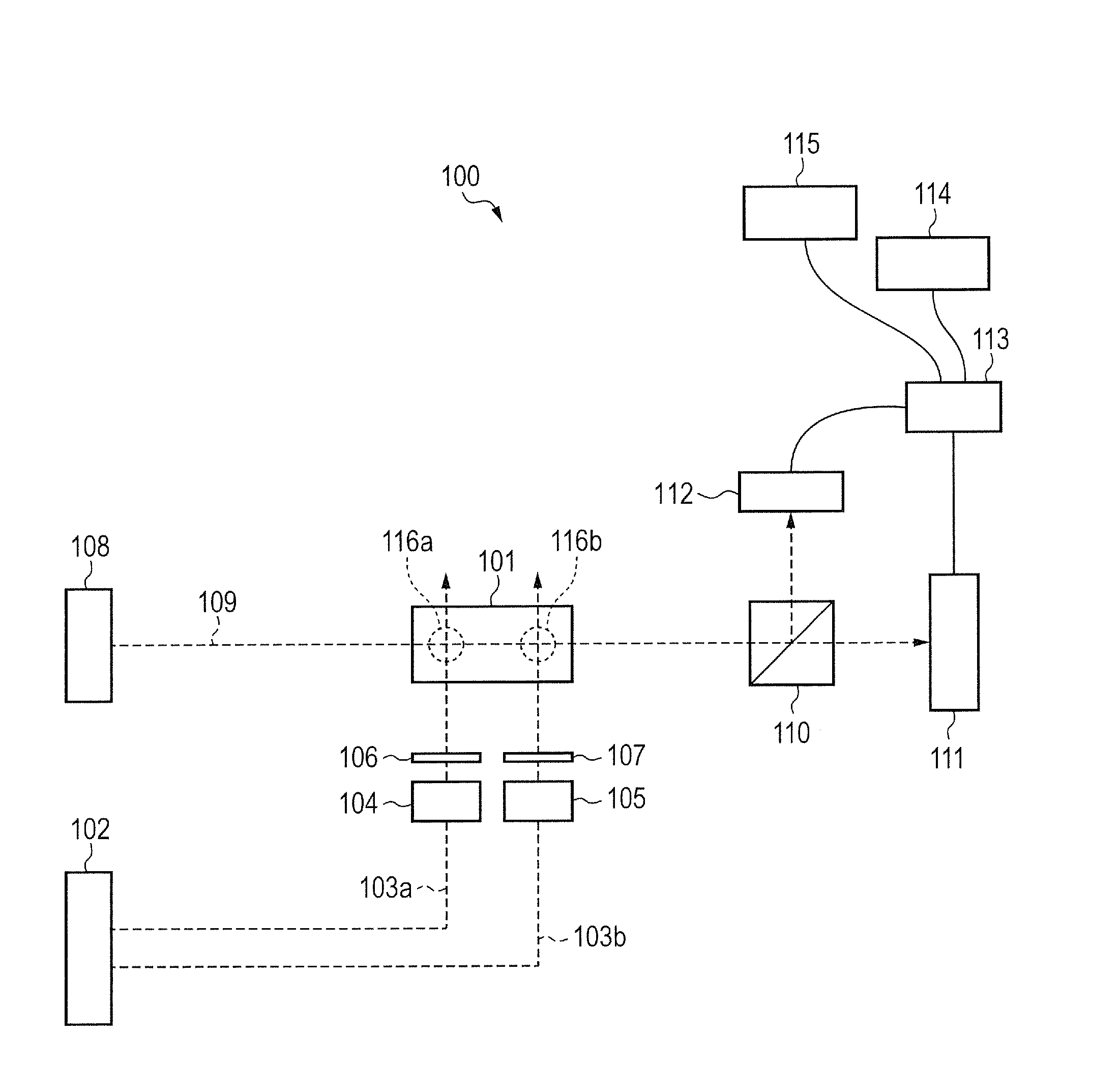
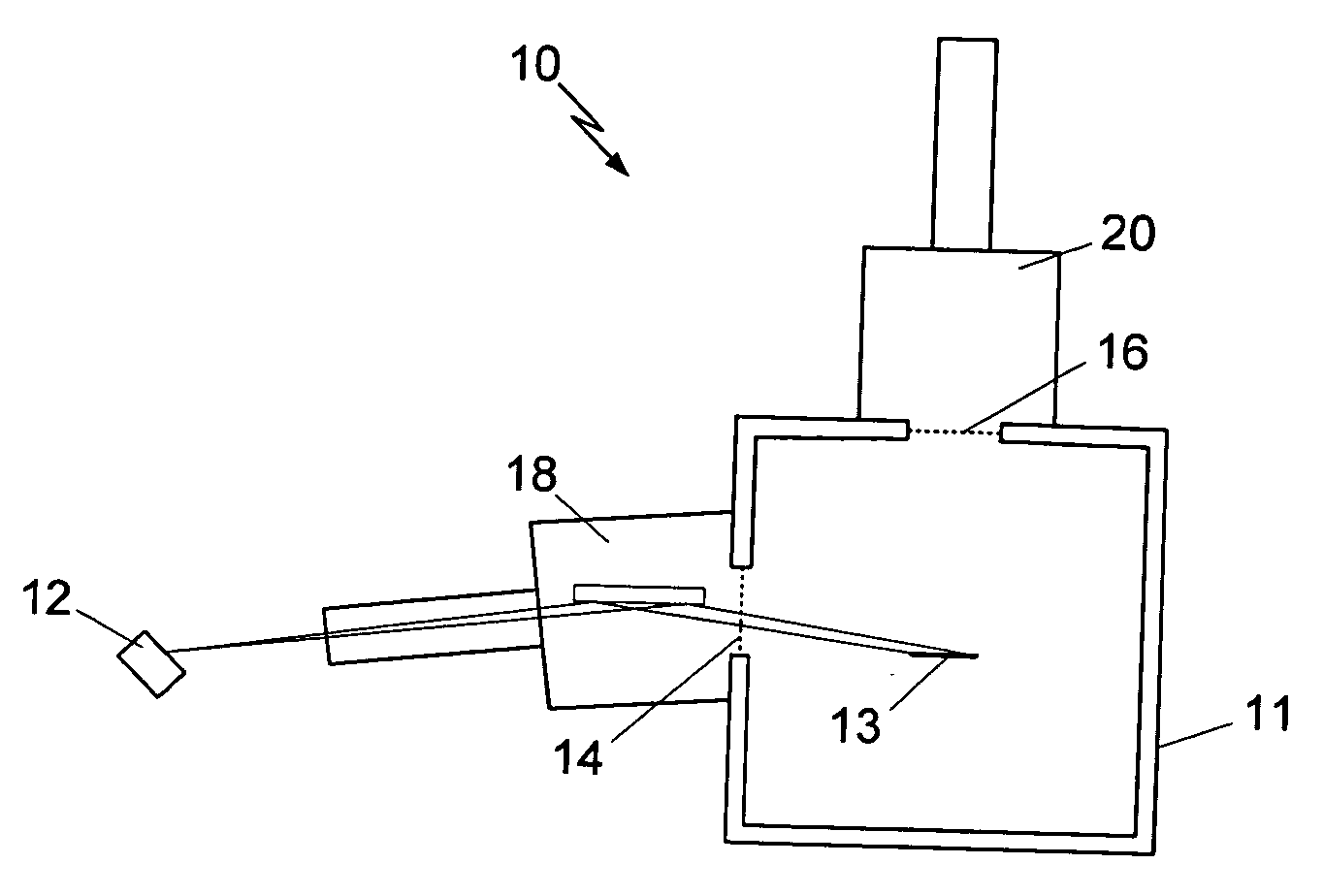
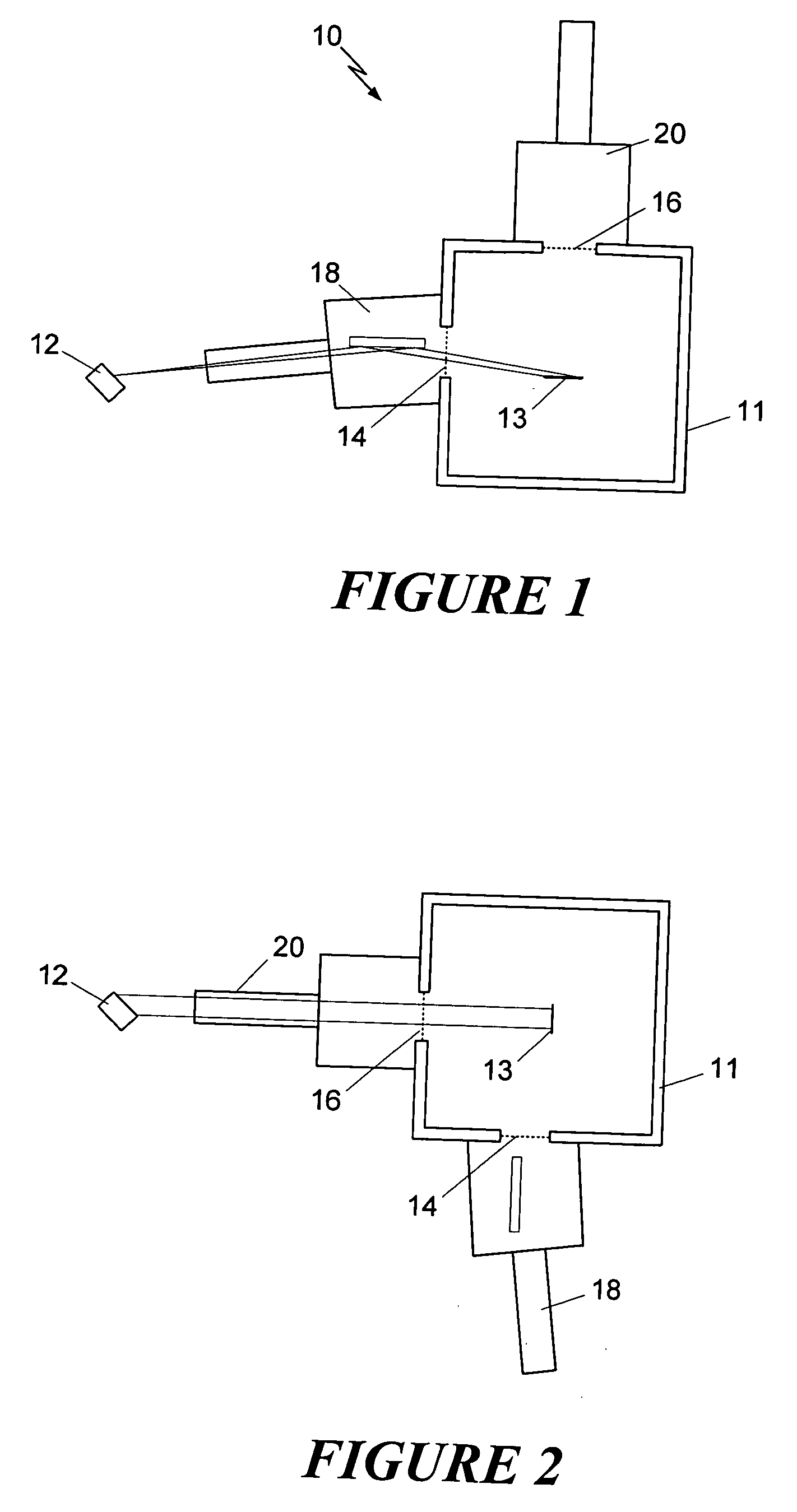
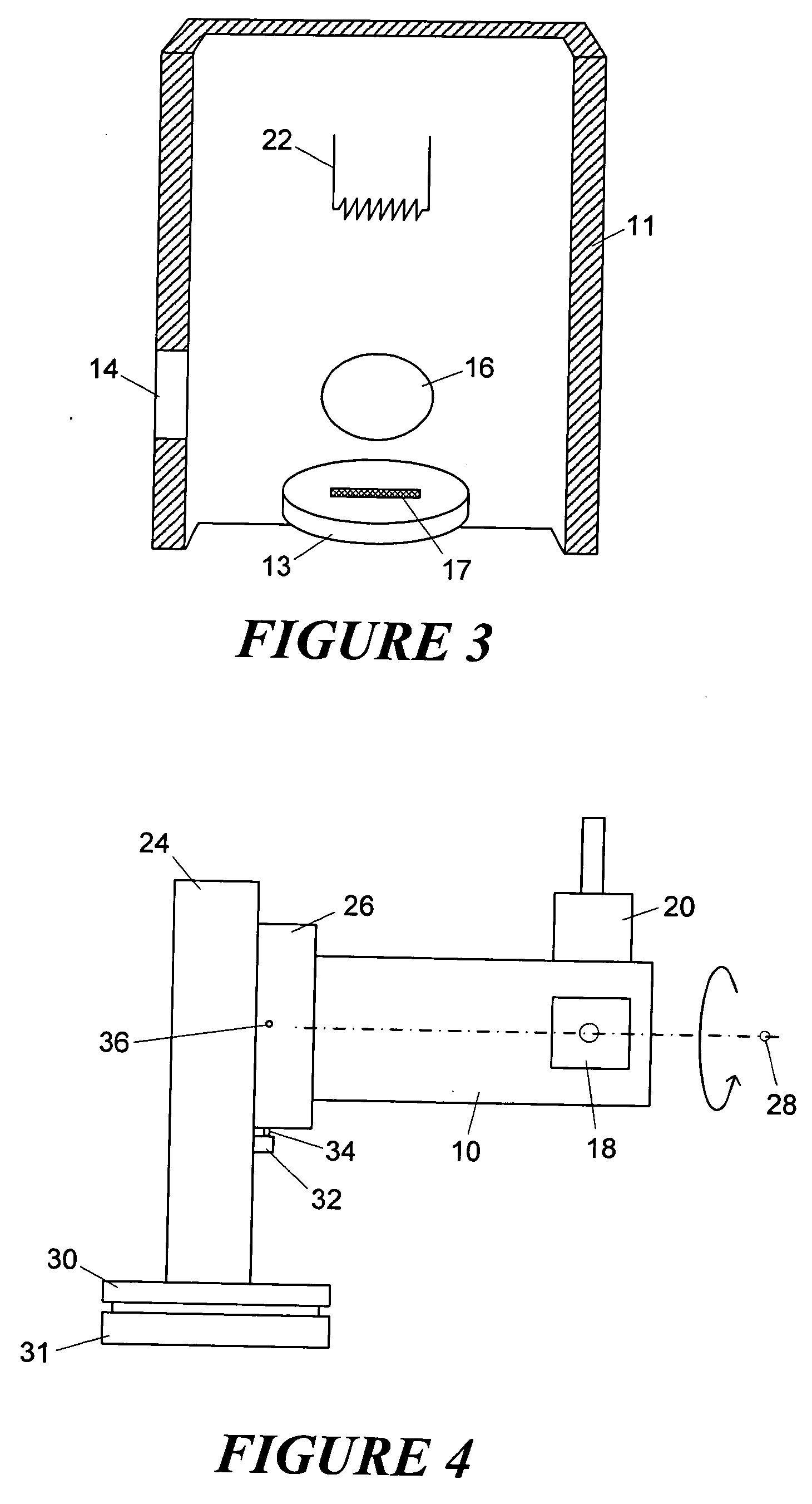
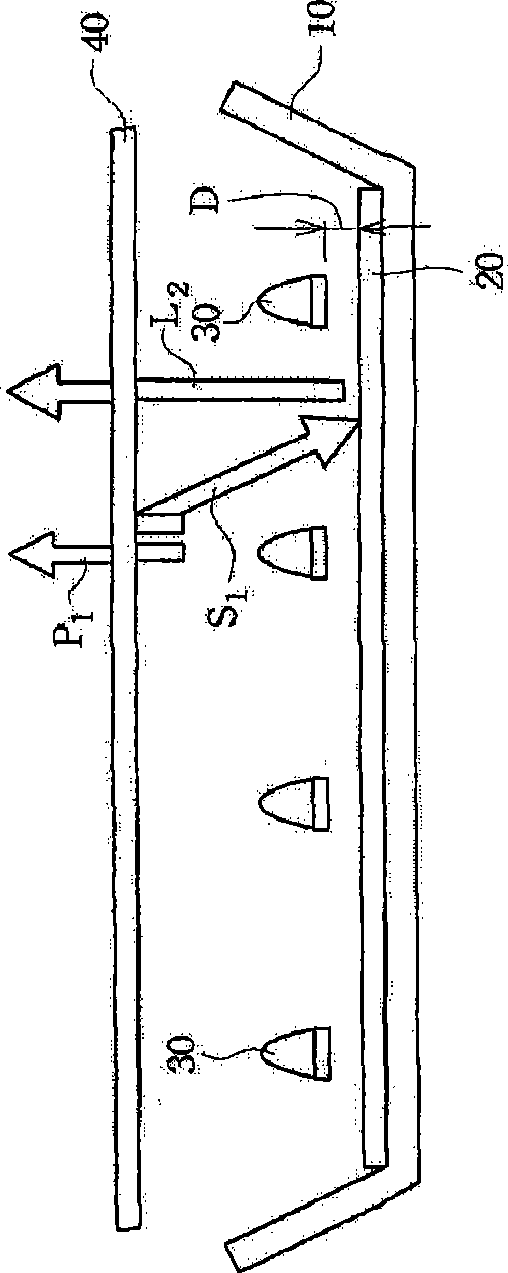
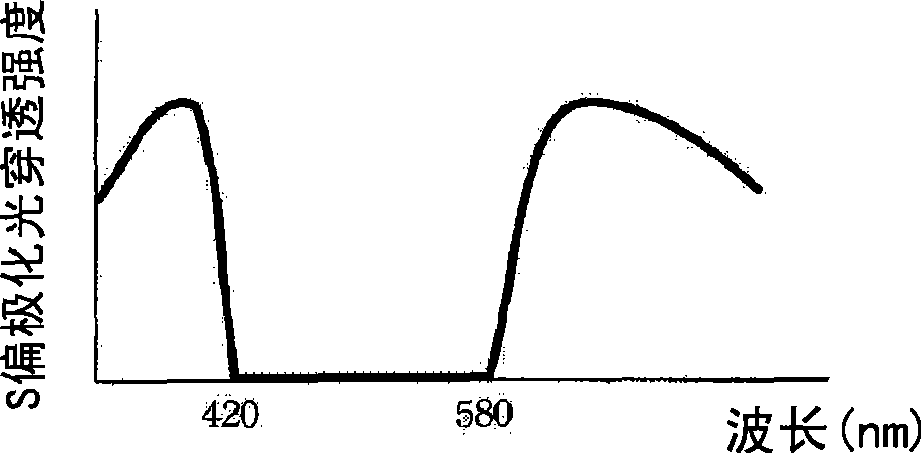
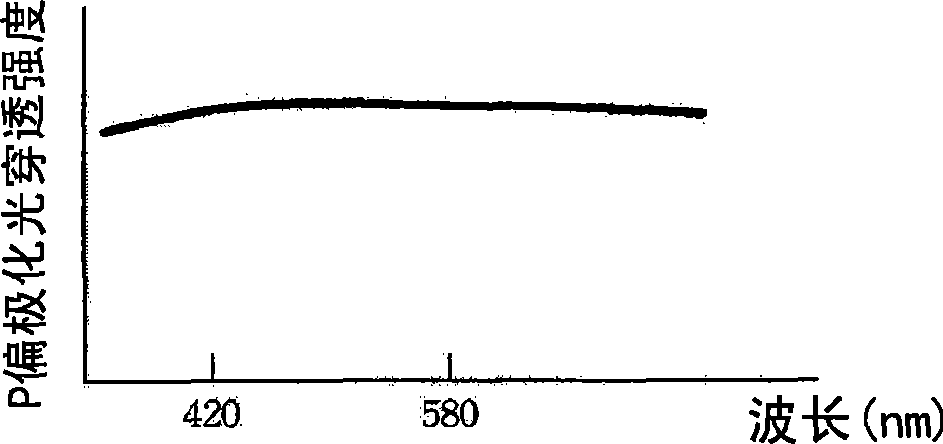
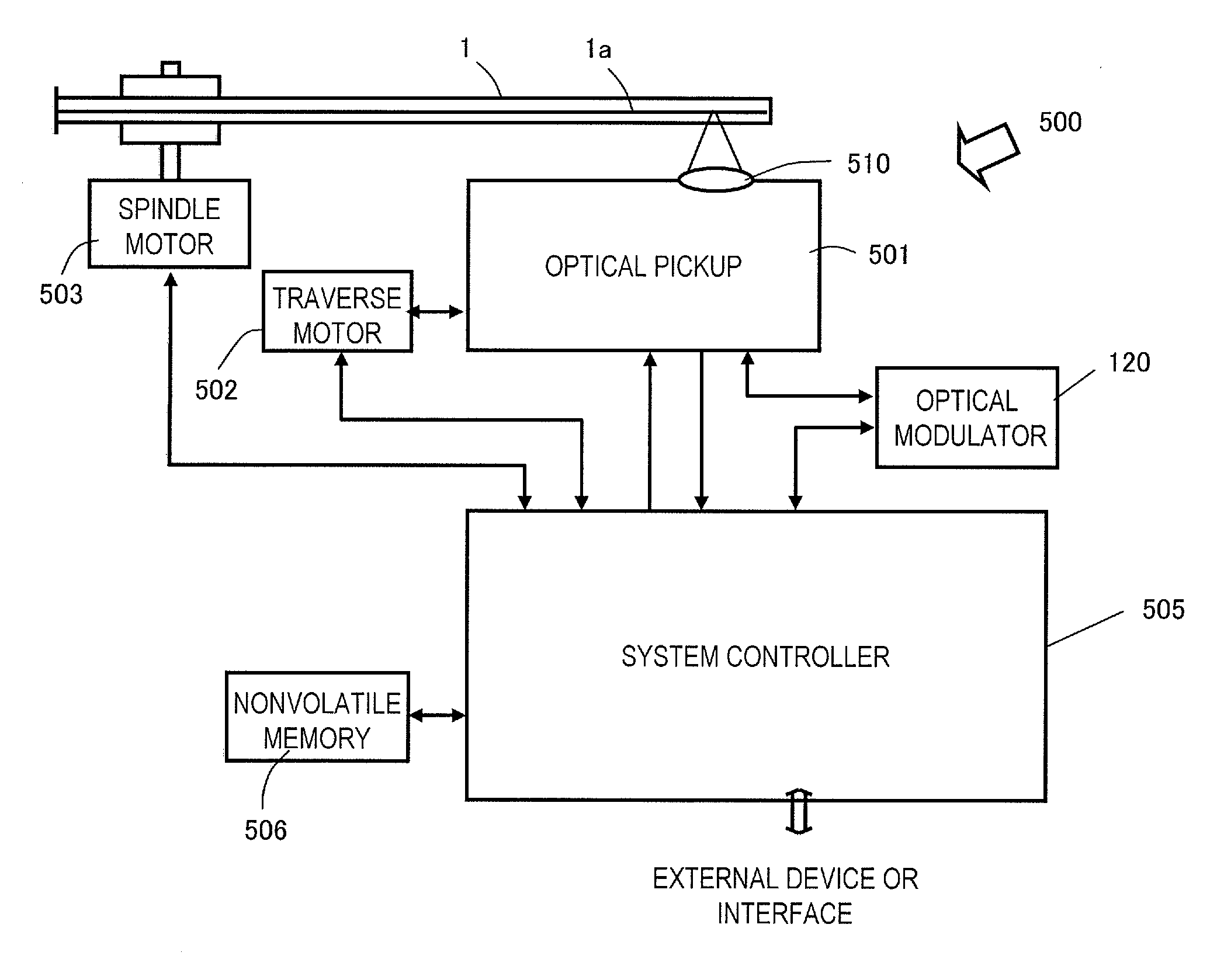
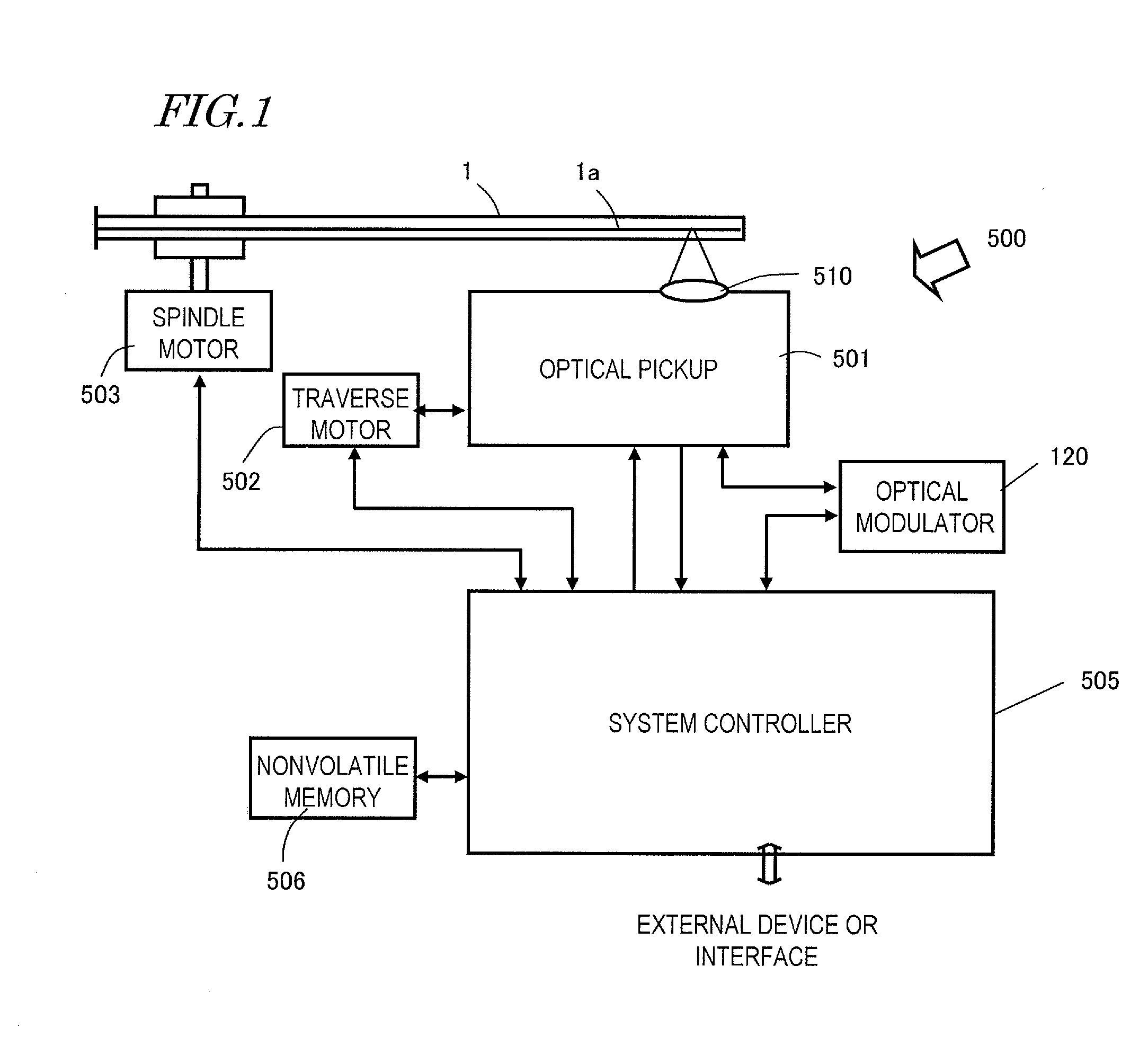
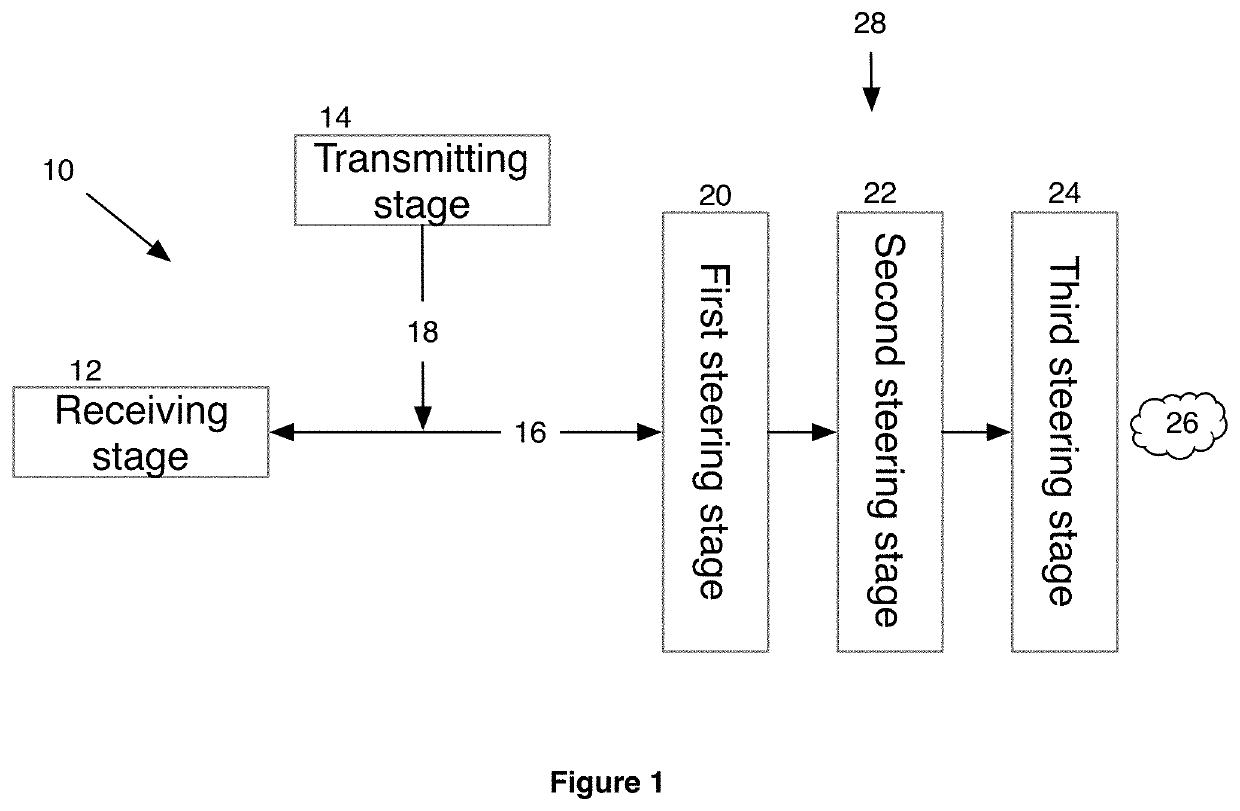
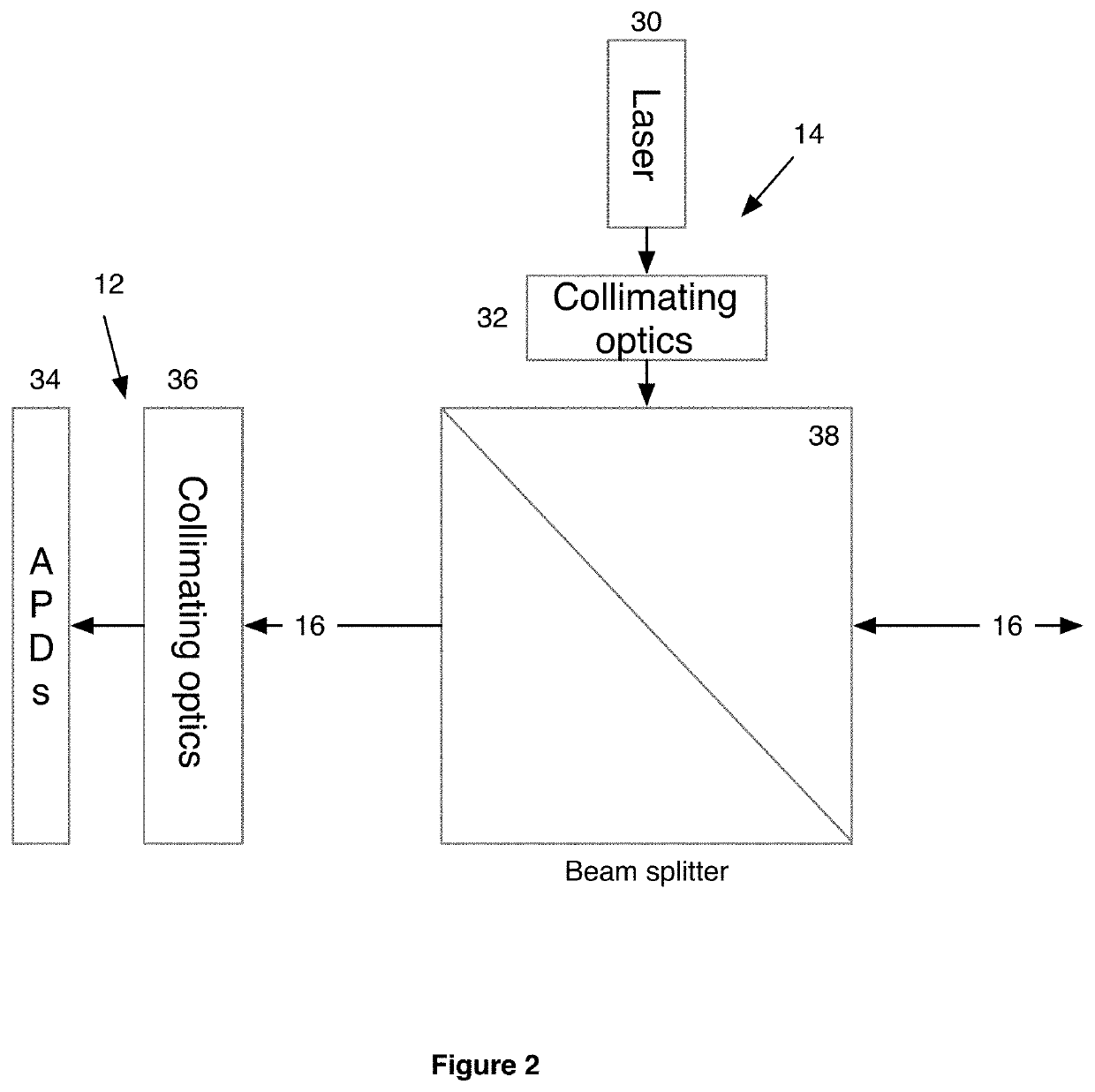
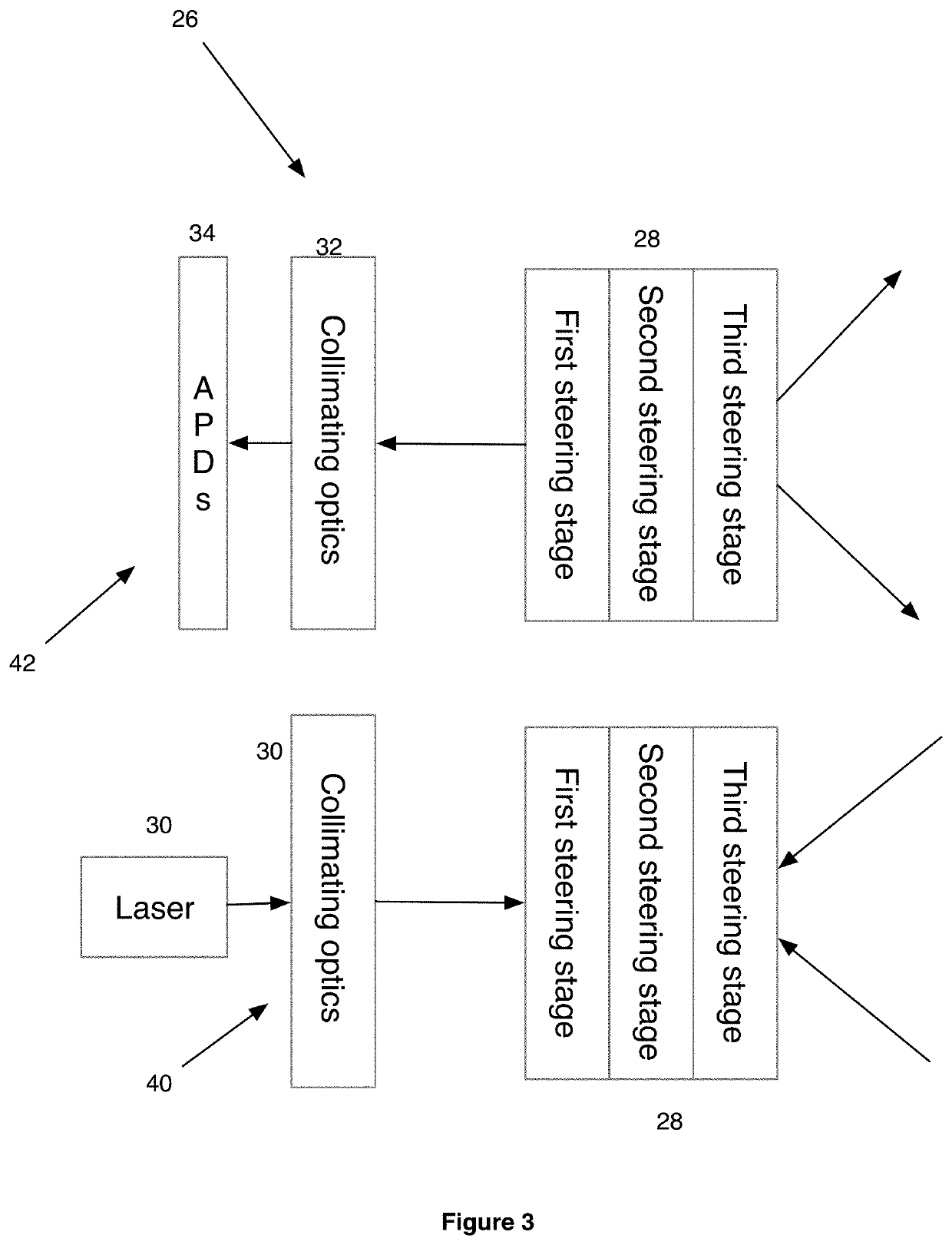
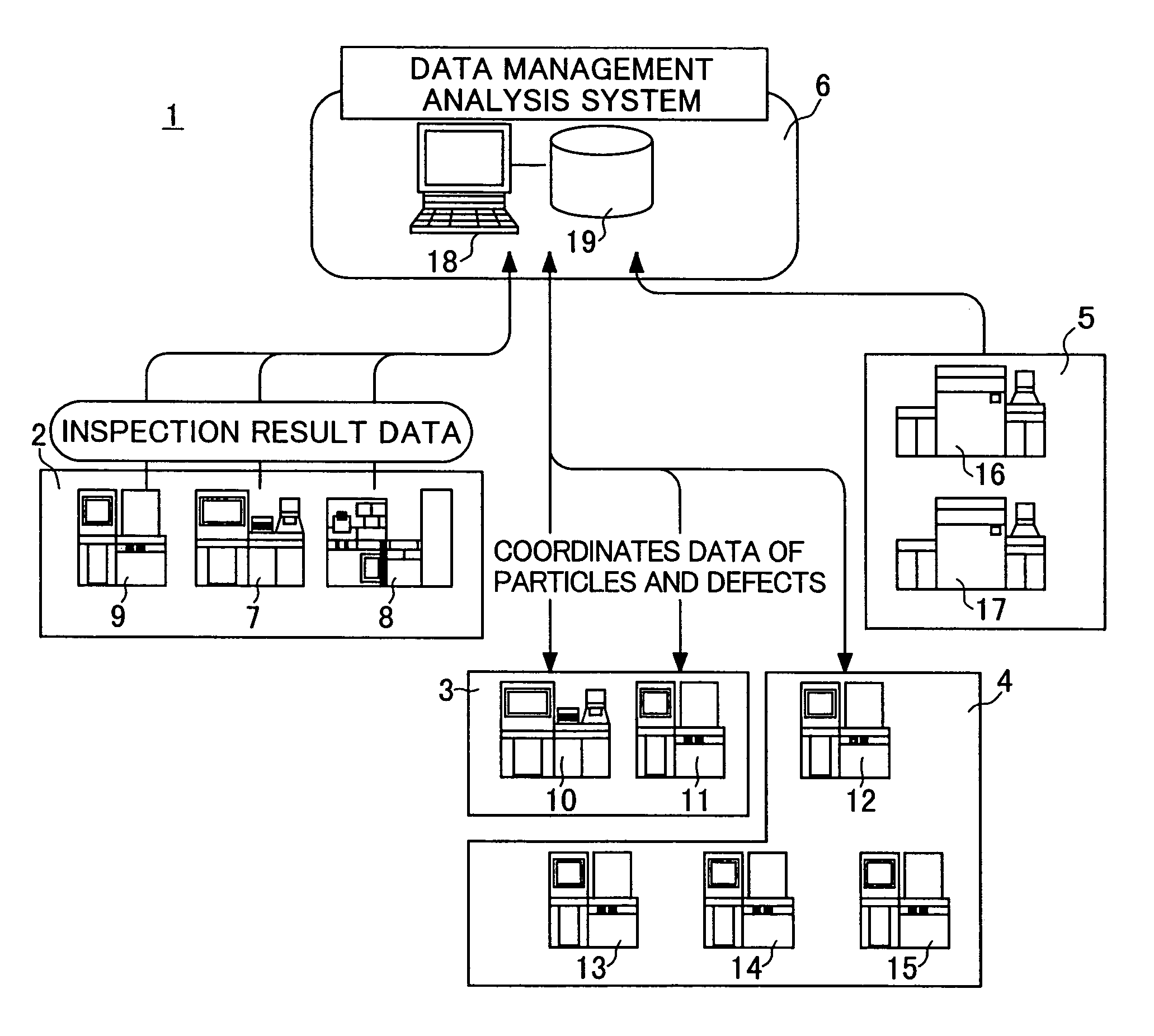
Patents
Literature
152 results about "Beam optics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aberration-correcting dark-field electron microscopy
ActiveUS20110192976A1Thermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationBeam sourceLight beam
A transmission electron microscope includes an electron beam source to generate an electron beam. Beam optics are provided to converge the electron beam. An aberration corrector corrects the electron beam for at least a spherical aberration. A specimen holder is provided to hold a specimen in the path of the electron beam. A detector is used to detect the electron beam transmitted through the specimen. The transmission electron microscope operates in a dark-field mode in which a zero beam of the electron beam is not detected. The microscope may also be capable of operating in an incoherent illumination mode.
Owner:MOCHII VOXA
Optically pumped atomic magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS20160061913A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceLight beamOptic system
Provided is an optically pumped atomic magnetometer that can separate and acquire magnetic information of spatially different places at the same time by one probe beam. The optically pumped atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing alkali metal atoms, a pump beam optical system introducing pump beams including circularly polarized light component to different locations of the cell, a probe beam optical system introducing a probe beam including linearly polarized light component to the cell, a detection unit detecting a signal reflecting a rotation angle of a plane of polarization of the probe beam after intersecting with the pump beams, and an information acquisition unit acquiring information related to a magnetic field intensity of each of the different locations from the detected signal. The pump beam optical system includes a modulation unit modulating the pump beams so that one of frequencies and phases of the pump beams is different.
Owner:CANON KK
Scanning beam optical imaging system for macroscopic imaging of an object
A new high resolution confocal and non-confocal scanning laser macroscope is disclosed which images macroscopic specimens in reflected light, transmitted light, fluorescence, photoluminescence and multi-photon fluorescence. The optical arrangement of a scanning laser macroscope has been altered to include a liquid-immersion laser scan lens, providing higher numerical aperture and higher resolution; and higher intensity at the focal spot, which makes the macroscope particularly well suited for multiphoton imaging. Several applications of the imaging system are described. A liquid-immersion laser scan lens with spring-loaded bottom element and method for containing the immersion liquid are also disclosed.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL PHOOMETRICS
Method and apparatus for measuring high-bandwidth electrical signals using modulation in an optical probing system
ActiveUS20070002328A1Improve time resolutionUsing optical meansLight polarisation measurementLaser sourceOperating frequency
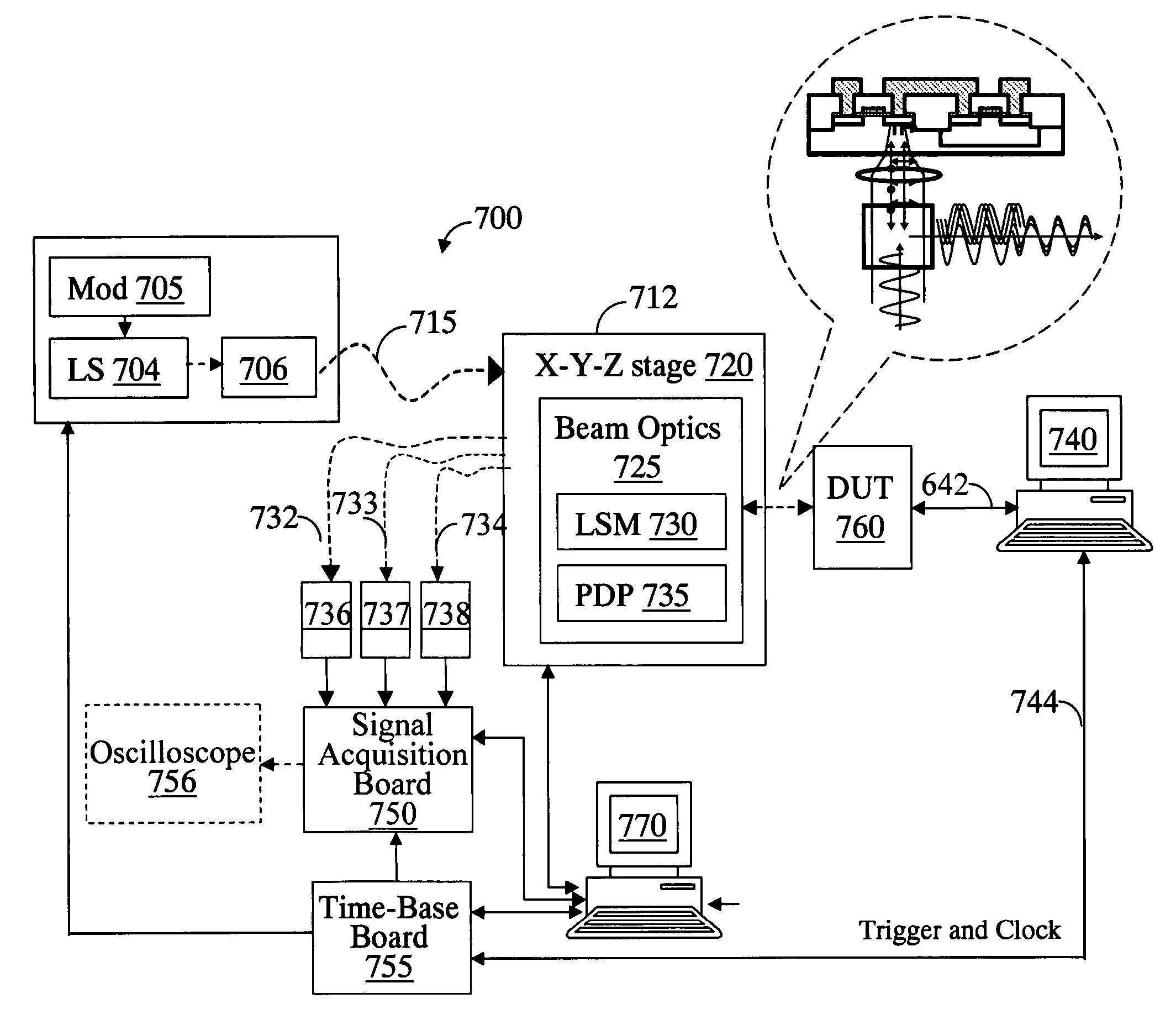
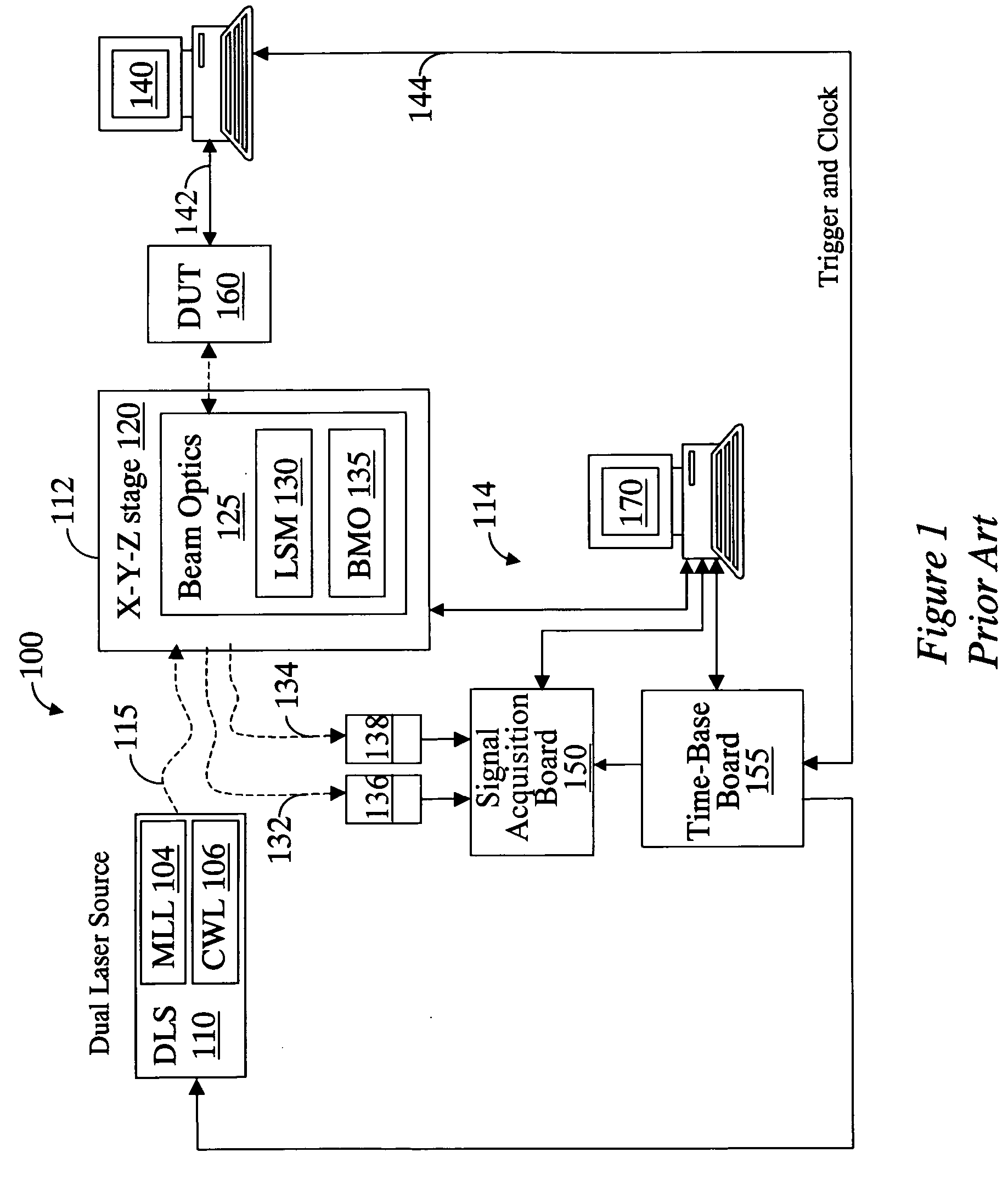
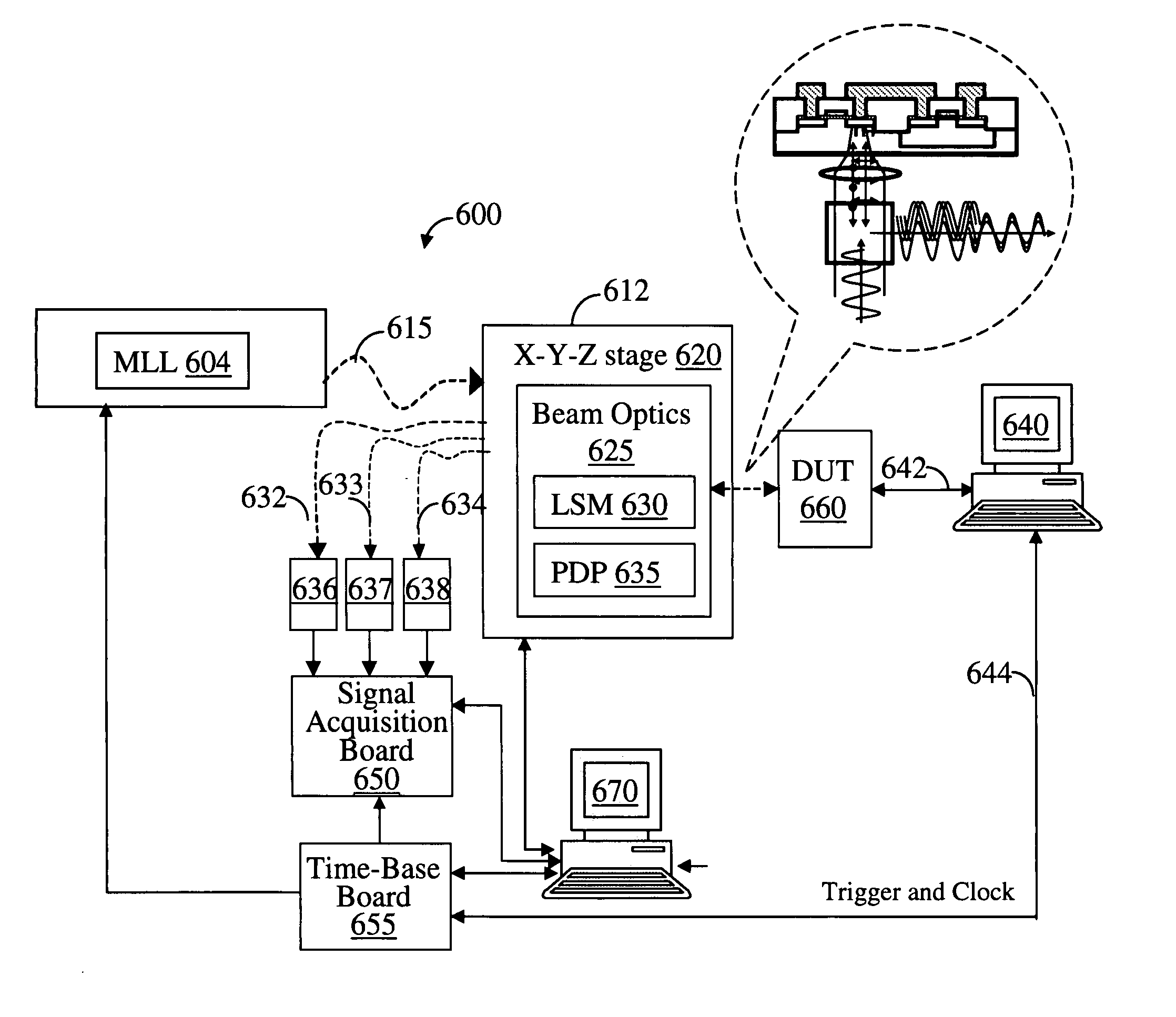
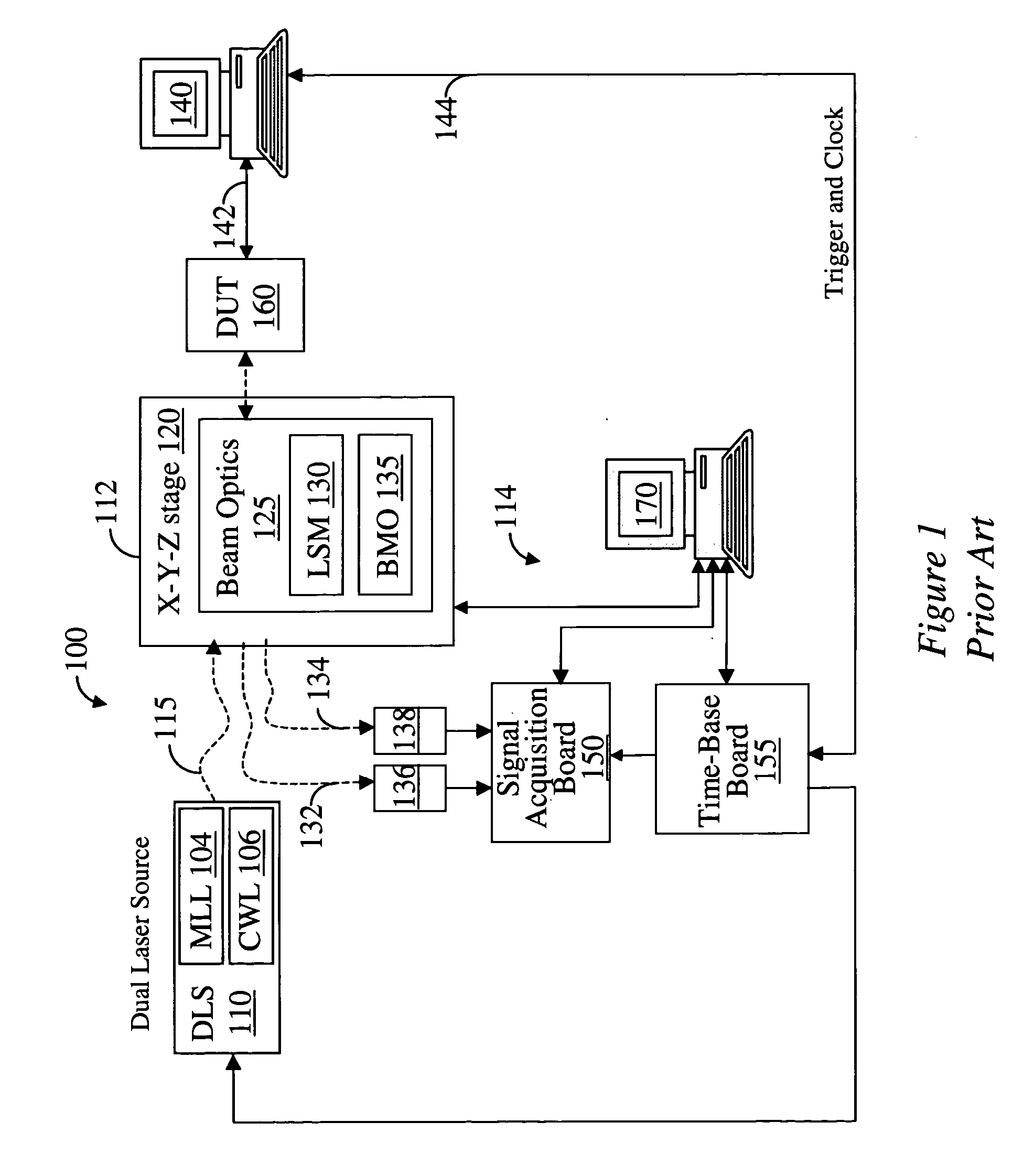
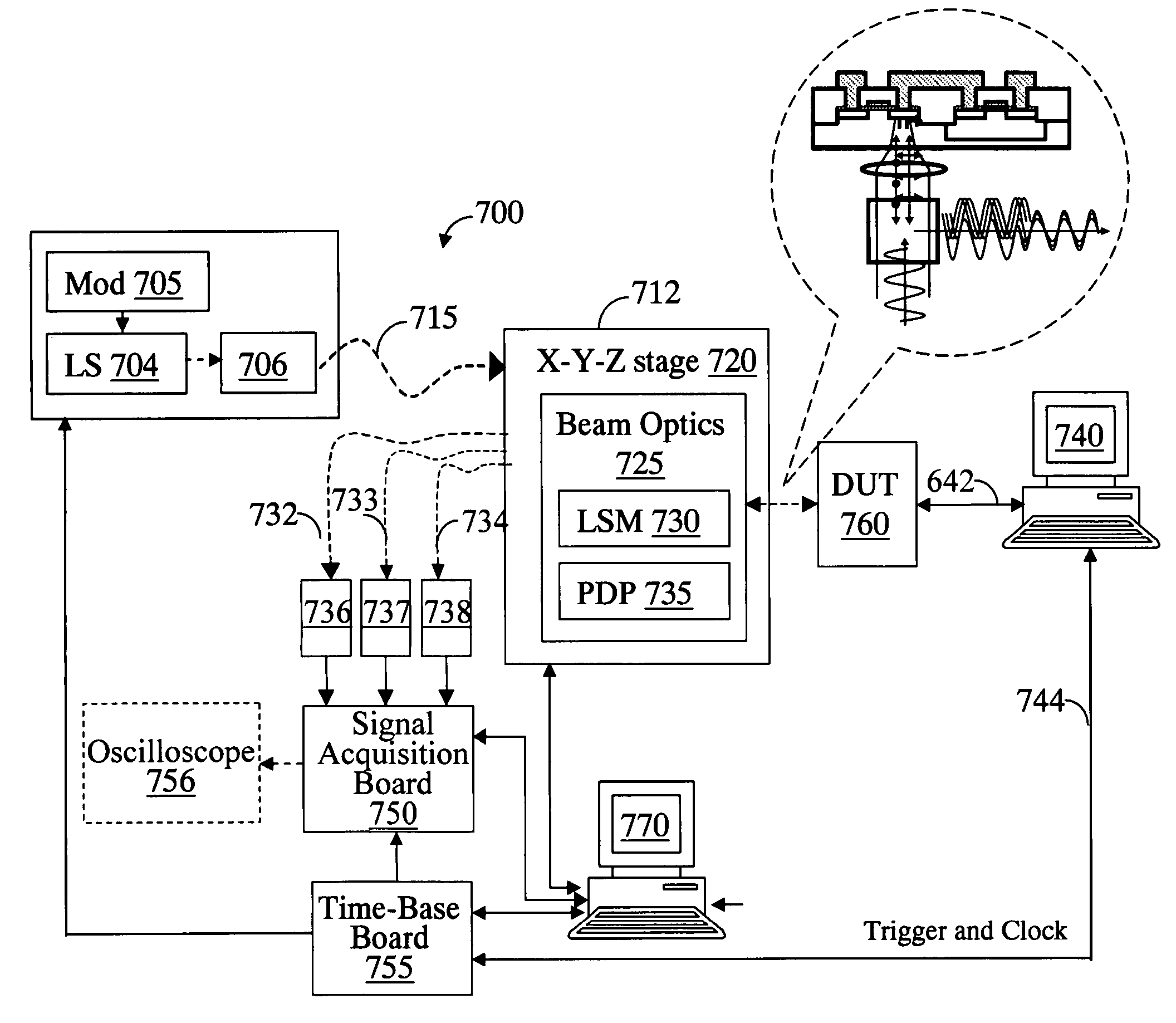
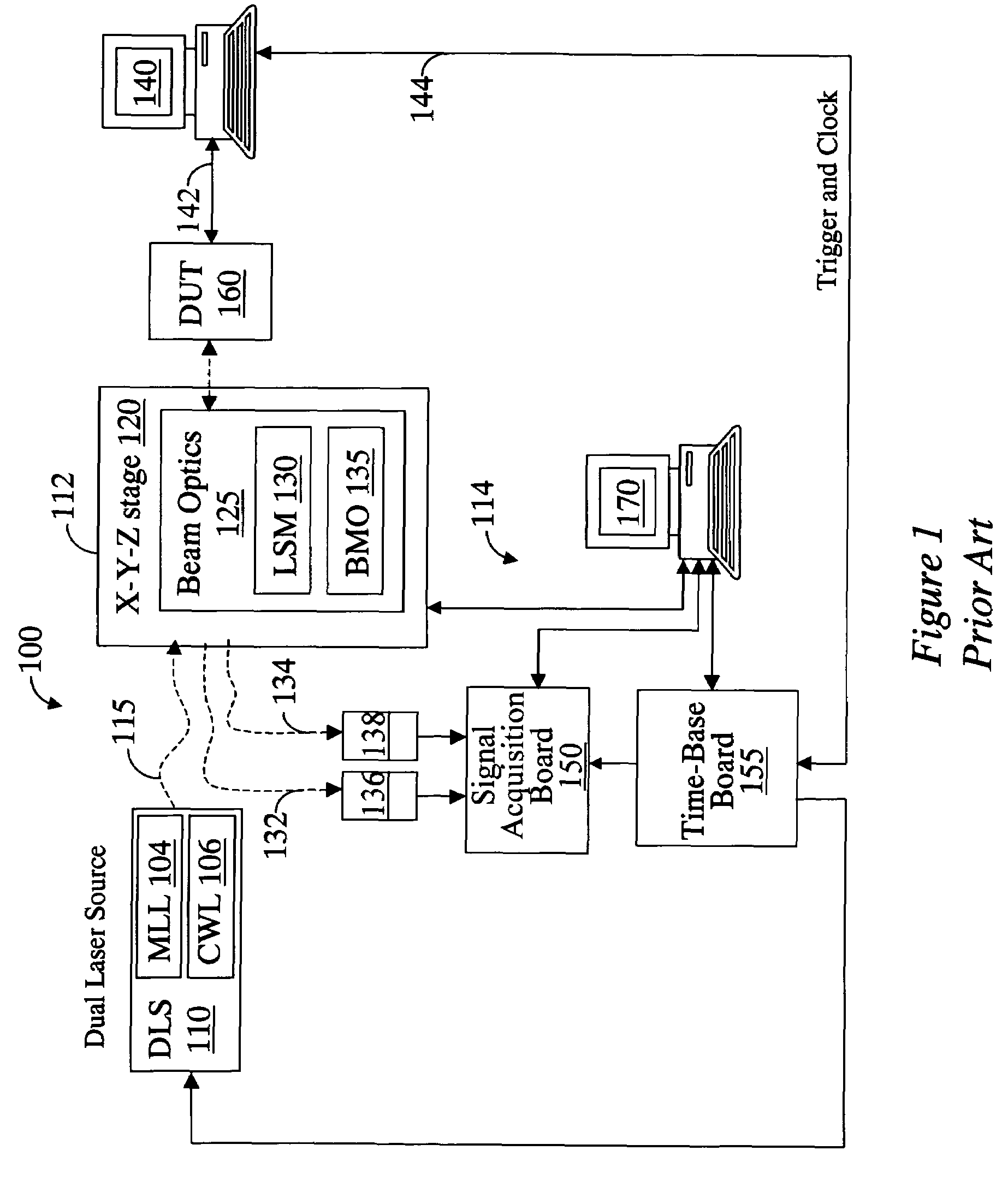
A system for probing a DUT is provided, the system comprising a tunable or CW laser source, a modulator for modulating the output of the laser source, a beam optics designed to point a probing beam at a designated location on the DUT, optical detector for detecting the reflected beam, and collection and signal processing electronics. The system deciphers perturbations in the reflected beam by detecting beat frequency between operation frequency of the DUT and frequency of the modulation. In an alternative embodiment, the laser is CW and the modulation is applied to the optical detector.
Owner:DCG SYST
Apparatus and method for probing integrated circuits using polarization difference probing
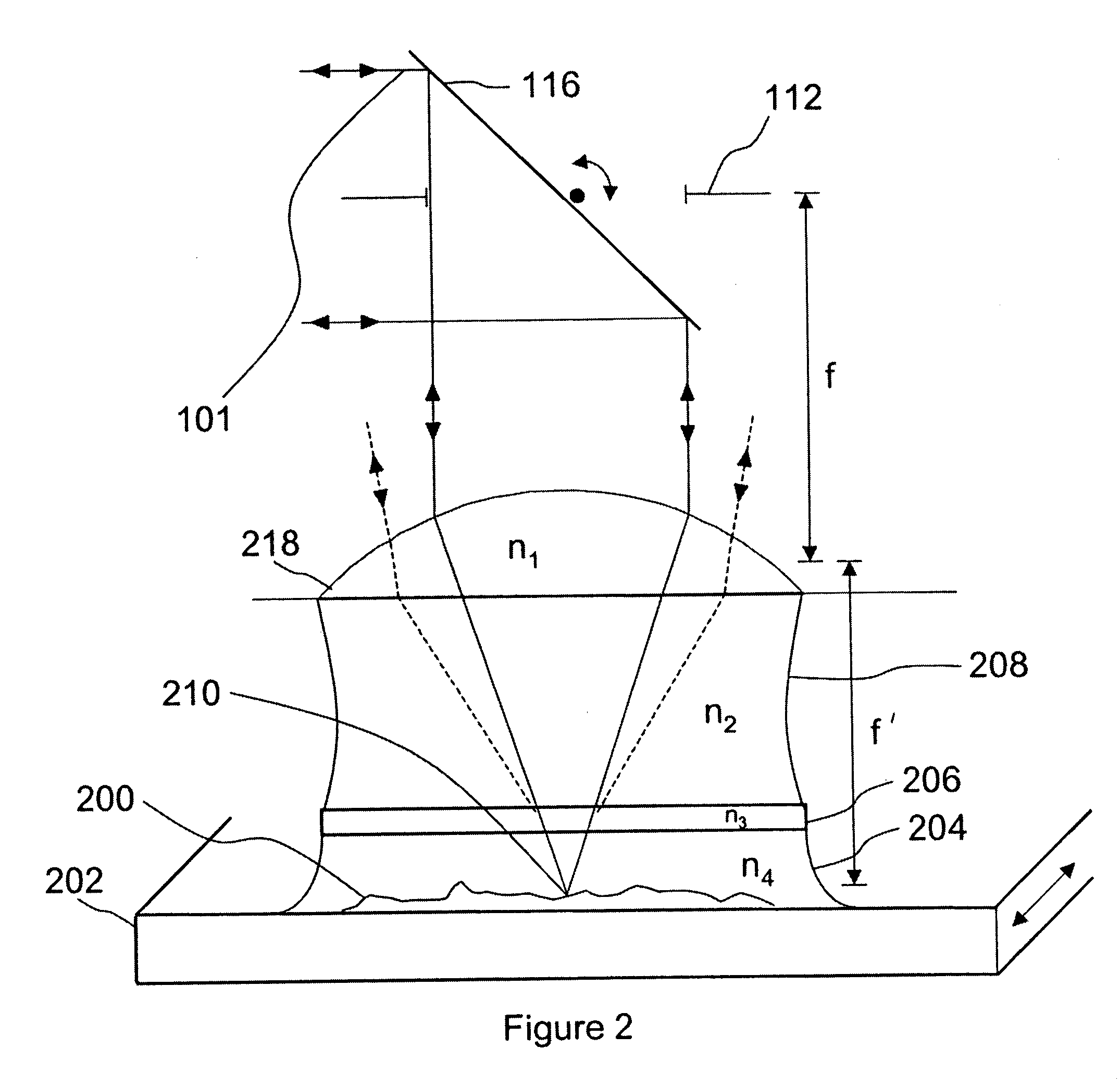
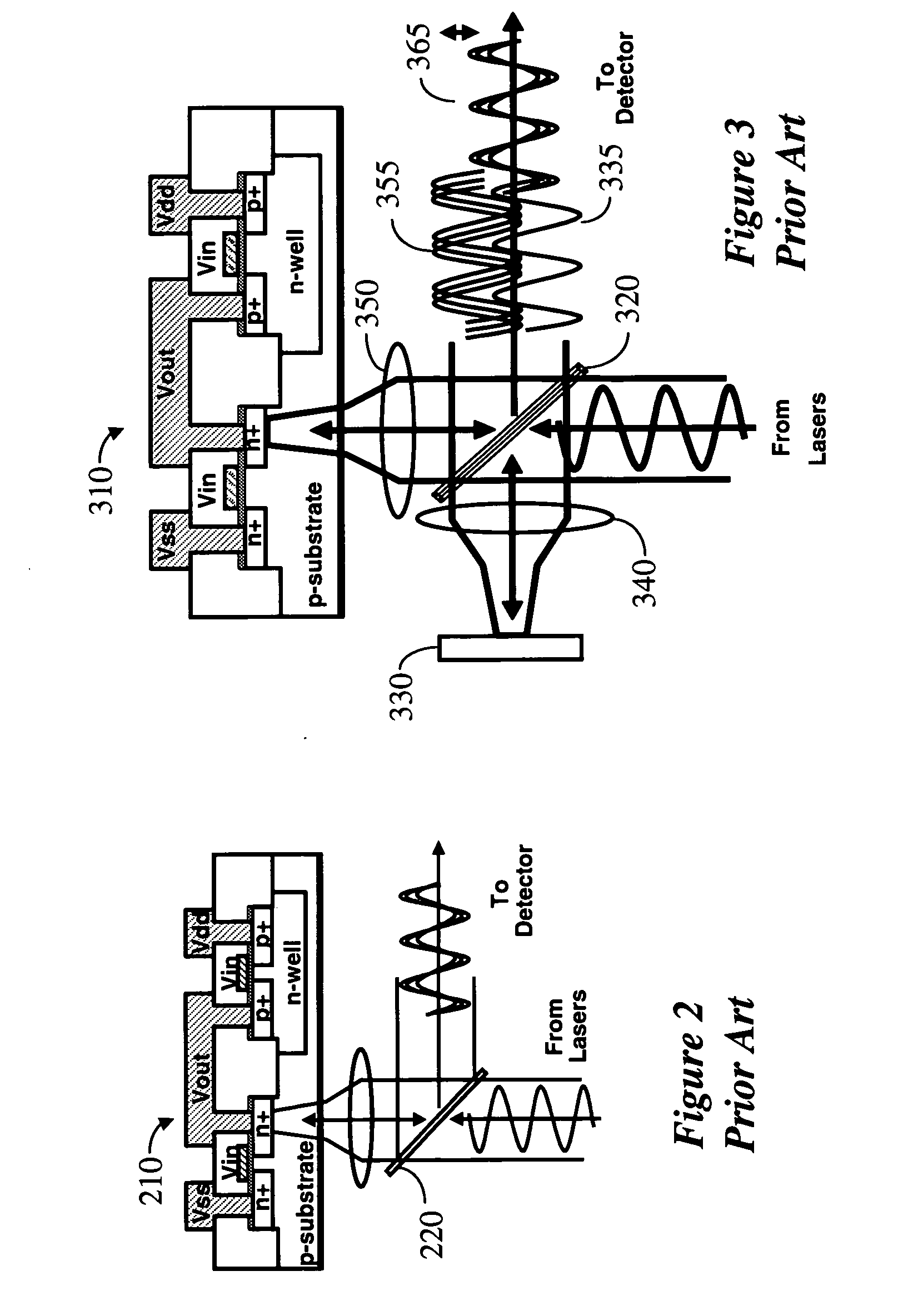
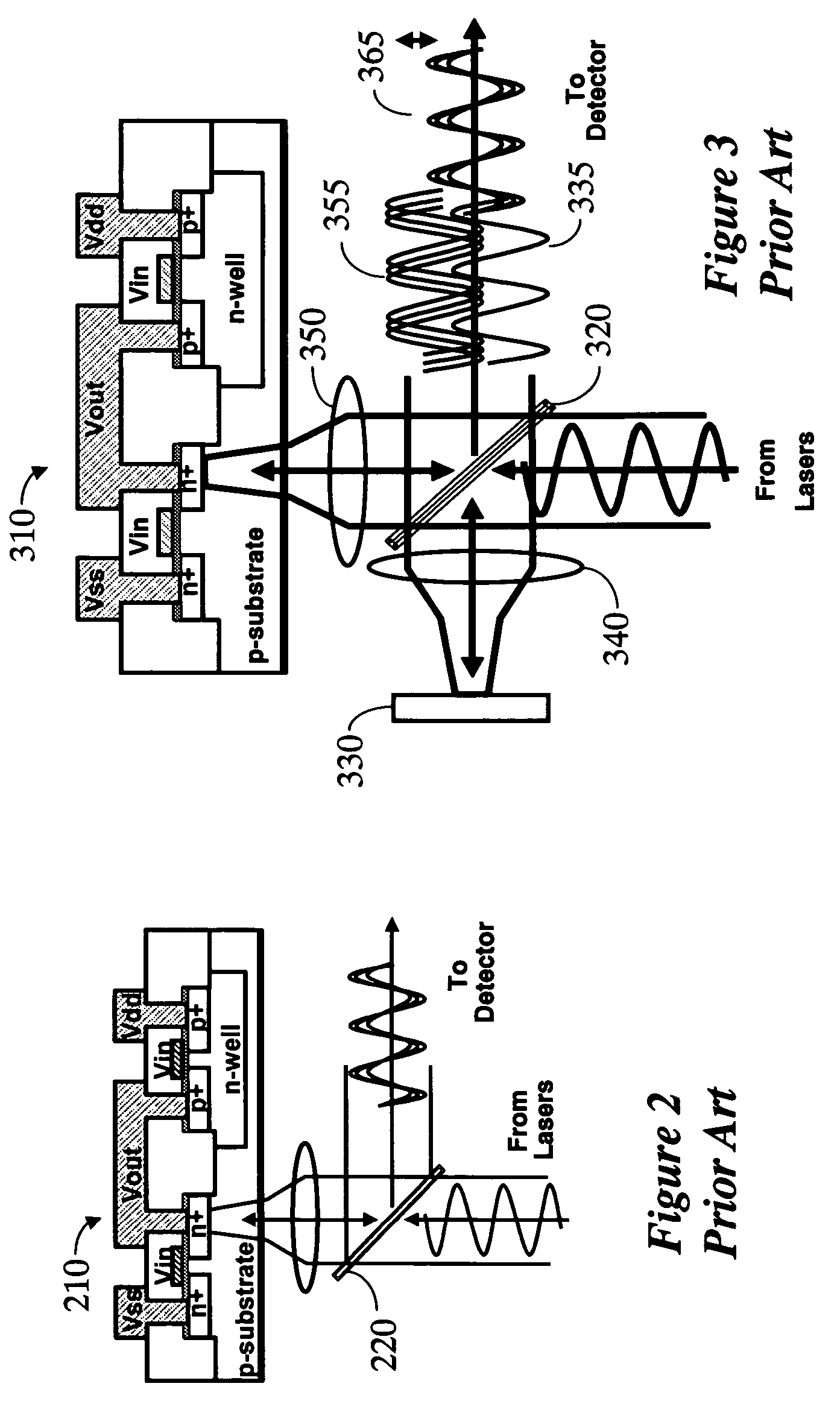
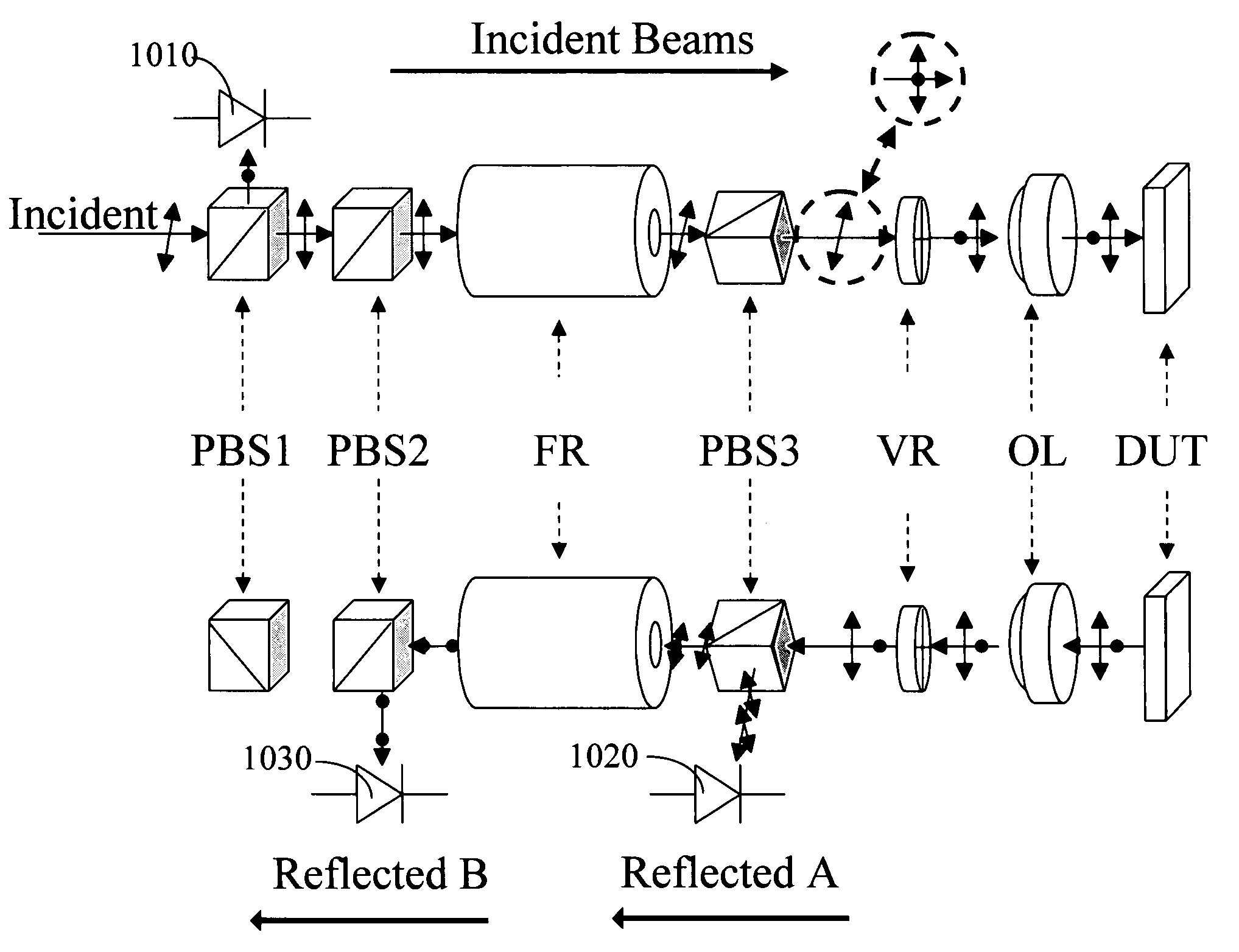
A system for probing a DUT is disclosed, the system having a pulsed laser source, a CW laser source, beam optics designed to point a reference beam and a probing beam at the same location on the DUT, optical detectors for detecting the reflected reference and probing beams, and a collection electronics. The beam optics is a common-path polarization differential probing (PDP) optics. The common-path PDP optics divides the incident laser beam into two beams of orthogonal polarization—one beam simulating a reference beam while the other simulating a probing beam. Both reference and probing beams are pointed to the same location on the DUT. Due to the intrinsic asymmetry of a CMOS transistor, the interaction of the reference and probing beams with the DUT result in different phase modulation in each beam. This difference can be investigated to study the response of the DUT to the stimulus signal.
Owner:DCG SYST
Light-emitting unit array, method for fabricating the same and projection apparatus
A projection apparatus (1200) is provided. The projection apparatus (1200) includes a light-emitting unit array (1210), an optical sensor (1230), and a control unit (1220). The light-emitting unit array (1210) is for emitting an image beam projected onto a screen (60). The optical sensor (1230) is for detecting electromagnetic waves from at least one of the screen (60) and an environment (70) so as to generate a signal. The control unit (1220) is electrically coupled to the light-emitting unit array (1210) and the optical sensor (1230) for controlling emission of the light-emitting unit array (1210) according to the signal from the optical sensor (1230). A light-emitting unit array (1210) and a method for fabricating a light-emitting unit array (1210) are also provided.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Planar light source module and optical film
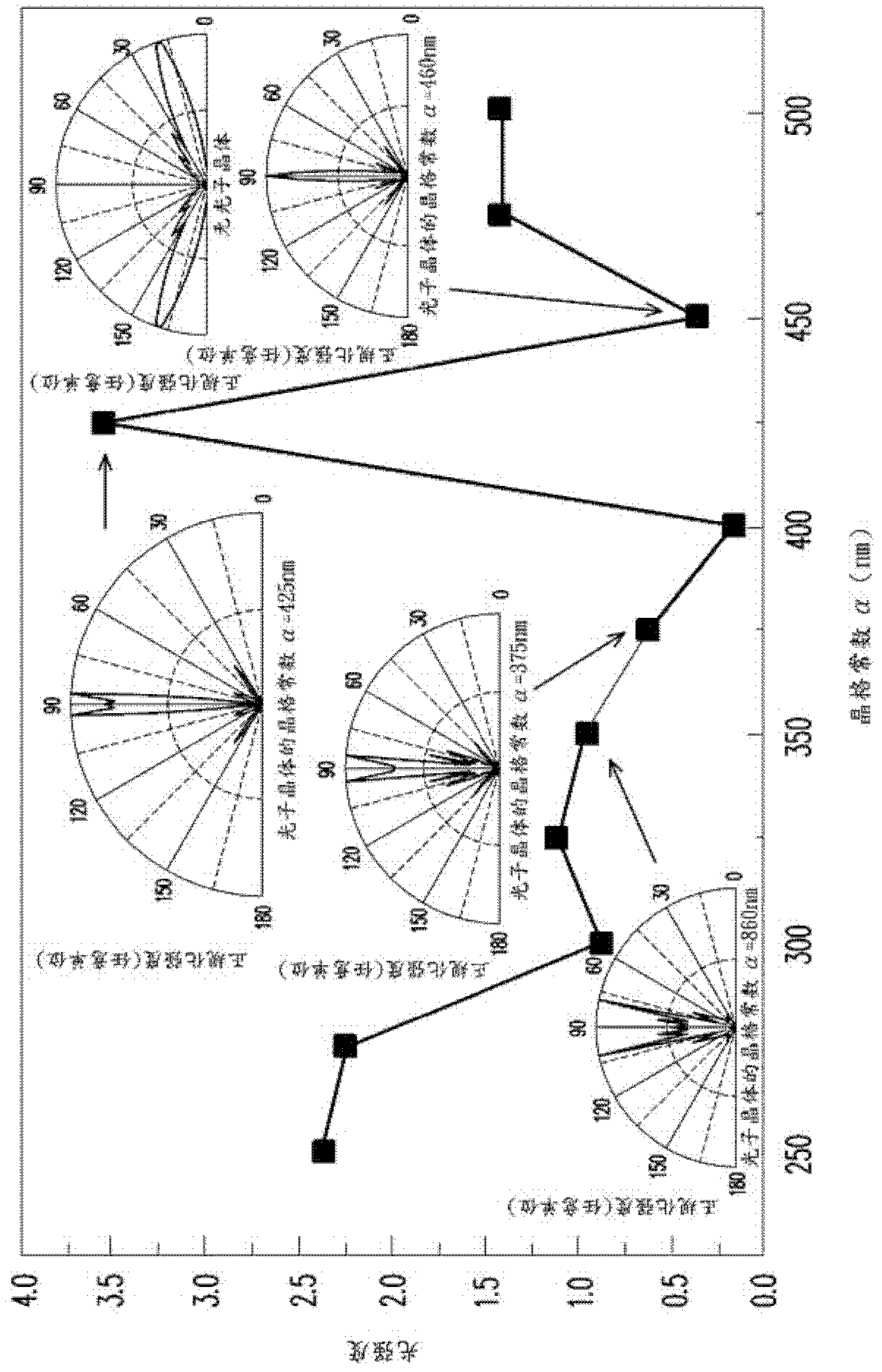
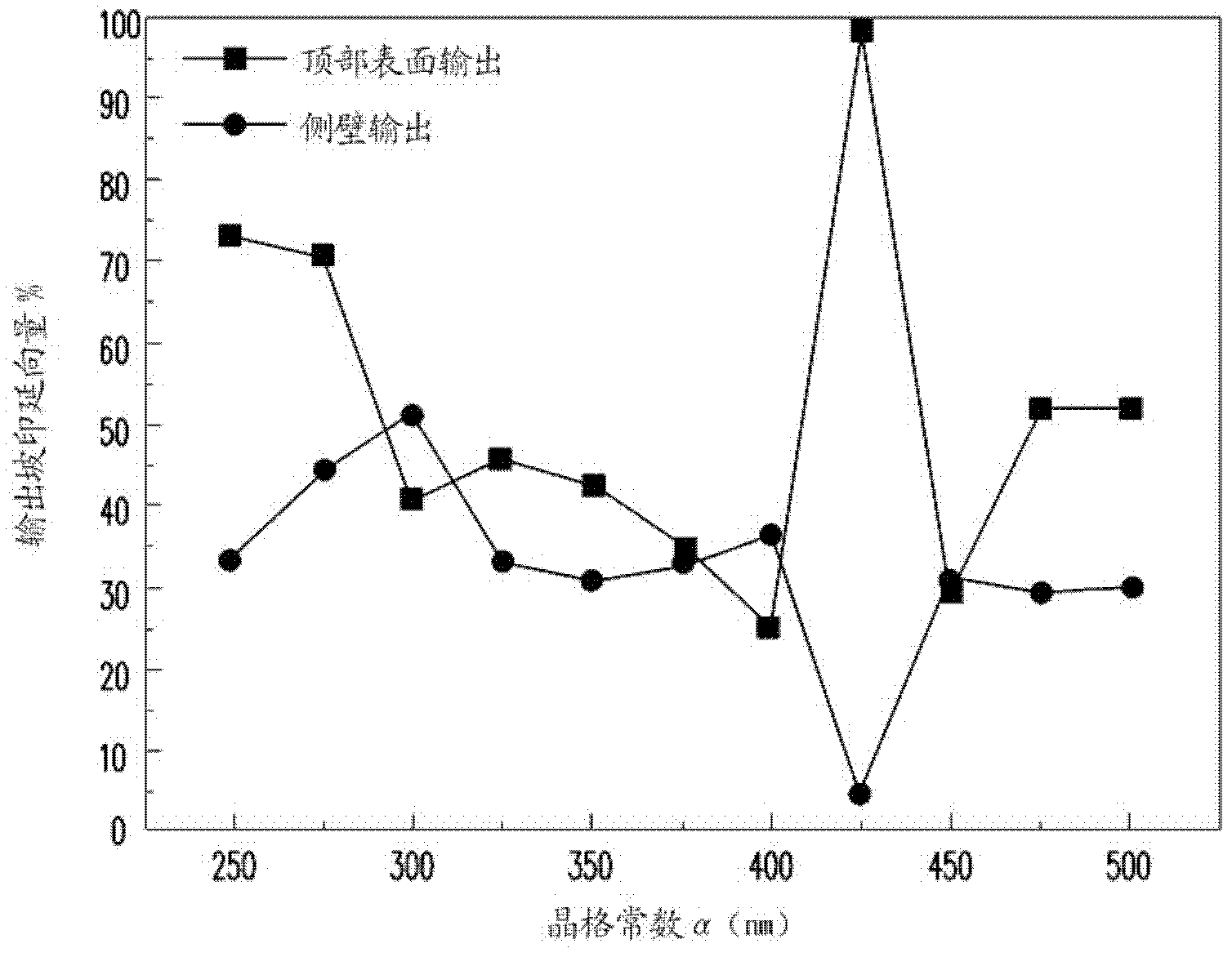
InactiveUS20110141765A1Good collimationHighly collimated characteristicPolarising elementsReflectorsLight guideLight beam
A planar light source module including a light guide plate (LGP), a light source, an optical film, and a reflector is provided. The light source for emitting a light beam is disposed adjacent to the side light-incident surface, wherein the light beam enters the LGP from a side light-incident surface and leaves the LGP from a light-emergence surface in an emergence angle θ1, θ1≧70 degrees. The optical film is disposed above the LGP to collimate the light beam from the LGP. The optical film includes a prism layer module and a bonding layer module stacked alternately. The prism layer module comprises prism layers and each prism layer includes micro-prisms. The bonding layer module comprises at least one bonding layer bonded with two prism layers adjacent thereto. The refraction index of the prism layers is greater than that of the bonding layer. The reflector is disposed under the bottom surface.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
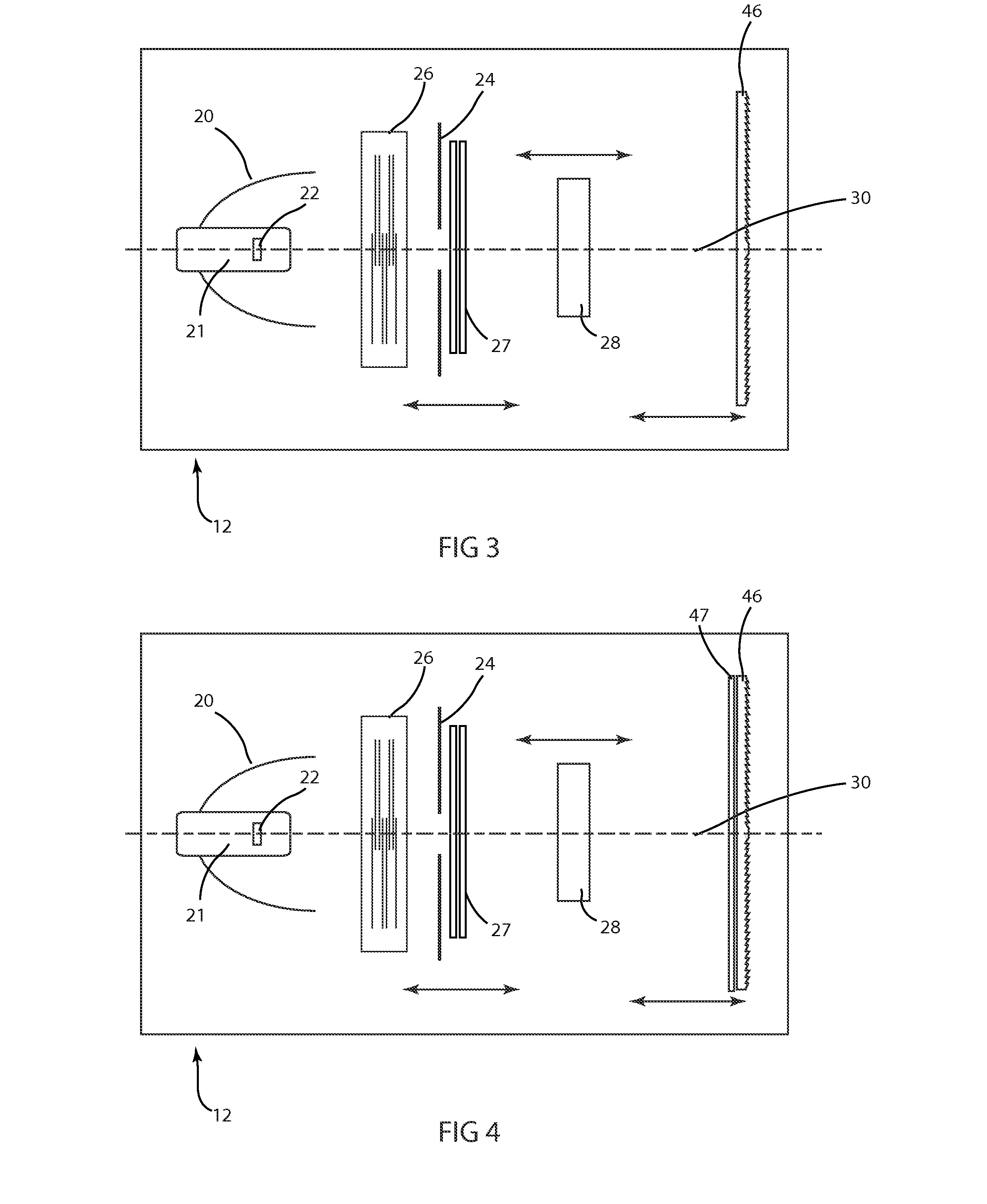
Beam Optical Component Having a Charged Particle Lens
InactiveUS20080230694A1Reduce optical aberrationImprove spatial resolutionThermometer detailsElectrode and associated part arrangementsLight beamAtomic physics
The present invention relates to a beam optical component including a charged particle lens for focusing a charged particle beam, the charged particle lens comprising a first element having a first opening for focusing the charged particle beam; a second element having a second opening for focusing the charged particle beam and first driving means connected with at least one of the first element and the second element for aligning the first opening with respect to the second opening. With the first driving means, the first opening and the second opening can be aligned with respect to each other during beam operation to provide a superior alignment of the beam optical component for a better beam focusing. The present invention also relates to a charged particle beam device that uses said beam optical component for focusing the charged particle beam, and a method to align first opening and second opening with respect to each other.
Owner:ICT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TESTING GESELLSCHAFT FUER HALBLEITERPRUEFTECHNIK GMBH
Laser probing system for integrated circuits
InactiveUS20070046947A1Improve time resolutionUsing optical meansLight polarisation measurementLaser probeLaser source
A system for probing a DUT is disclosed, the system having a pulsed laser source, a CW laser source, beam optics designed to point a reference beam and a probing beam at the same location on the DUT, optical detectors for detecting the reflected reference and probing beams, and a collection electronics. The beam optics is a common-path polarization differential probing (PDP) optics. The common-path PDP optics divides the incident laser beam into two beams of orthogonal polarization - one beam simulating a reference beam while the other simulating a probing beam. Both reference and probing beams are pointed to the same location on the DUT. Due to the intrinsic asymmetry of a CMOS transistor, the interaction of the reference and probing beams with the DUT result in different phase modulation in each beam. This difference can be investigated to study the response of the DUT to the stimulus signal.
Owner:DCG SYST
Method and apparatus for measuring high-bandwidth electrical signals using modulation in an optical probing system
A system for probing a DUT is provided, the system comprising a tunable or CW laser source, a modulator for modulating the output of the laser source, a beam optics designed to point a probing beam at a designated location on the DUT, optical detector for detecting the reflected beam, and collection and signal processing electronics. The system deciphers perturbations in the reflected beam by detecting beat frequency between operation frequency of the DUT and frequency of the modulation. In an alternative embodiment, the laser is CW and the modulation is applied to the optical detector.
Owner:DCG SYST
Versatile beam and wash optical system for an automated luminaire
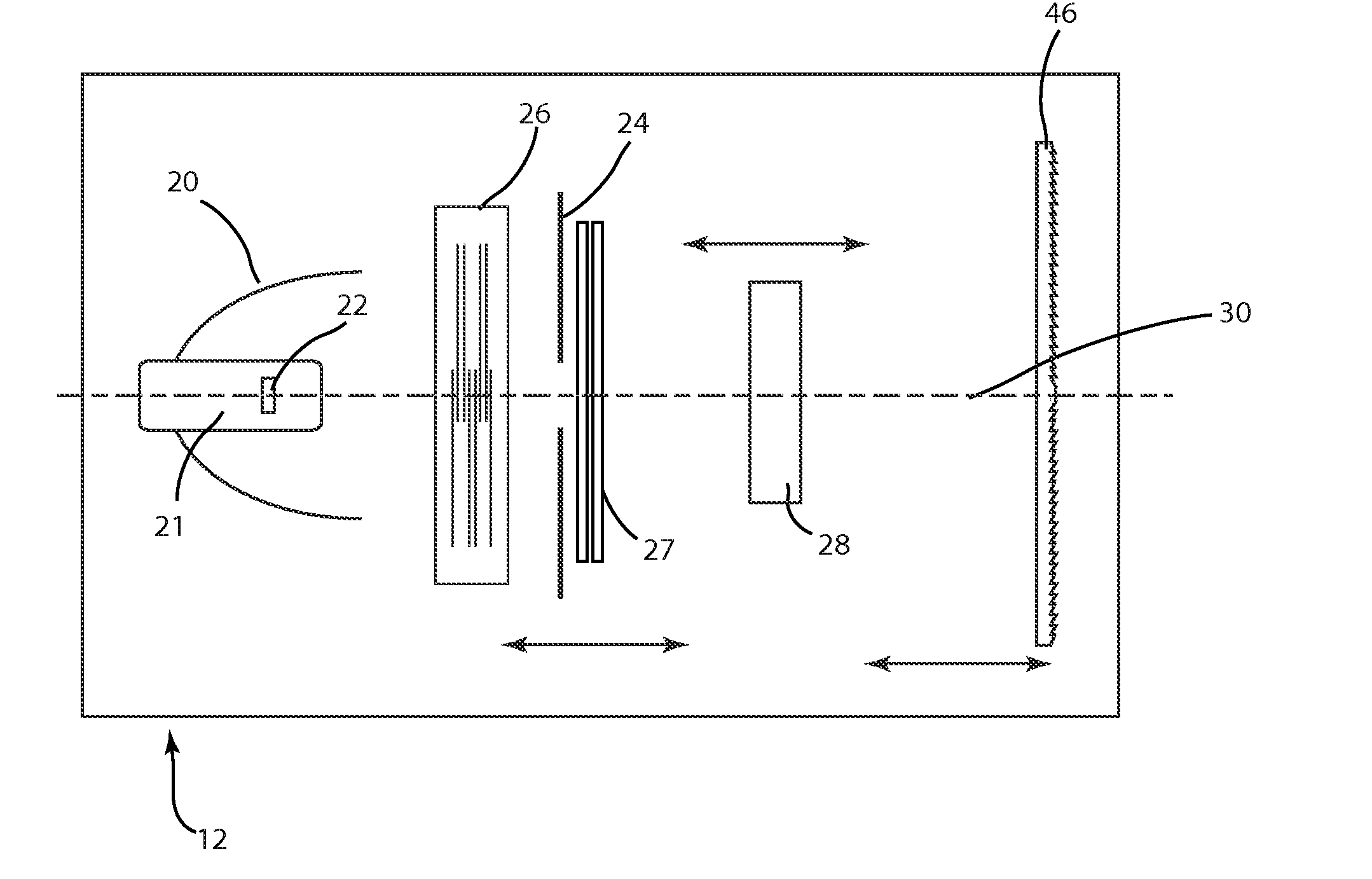
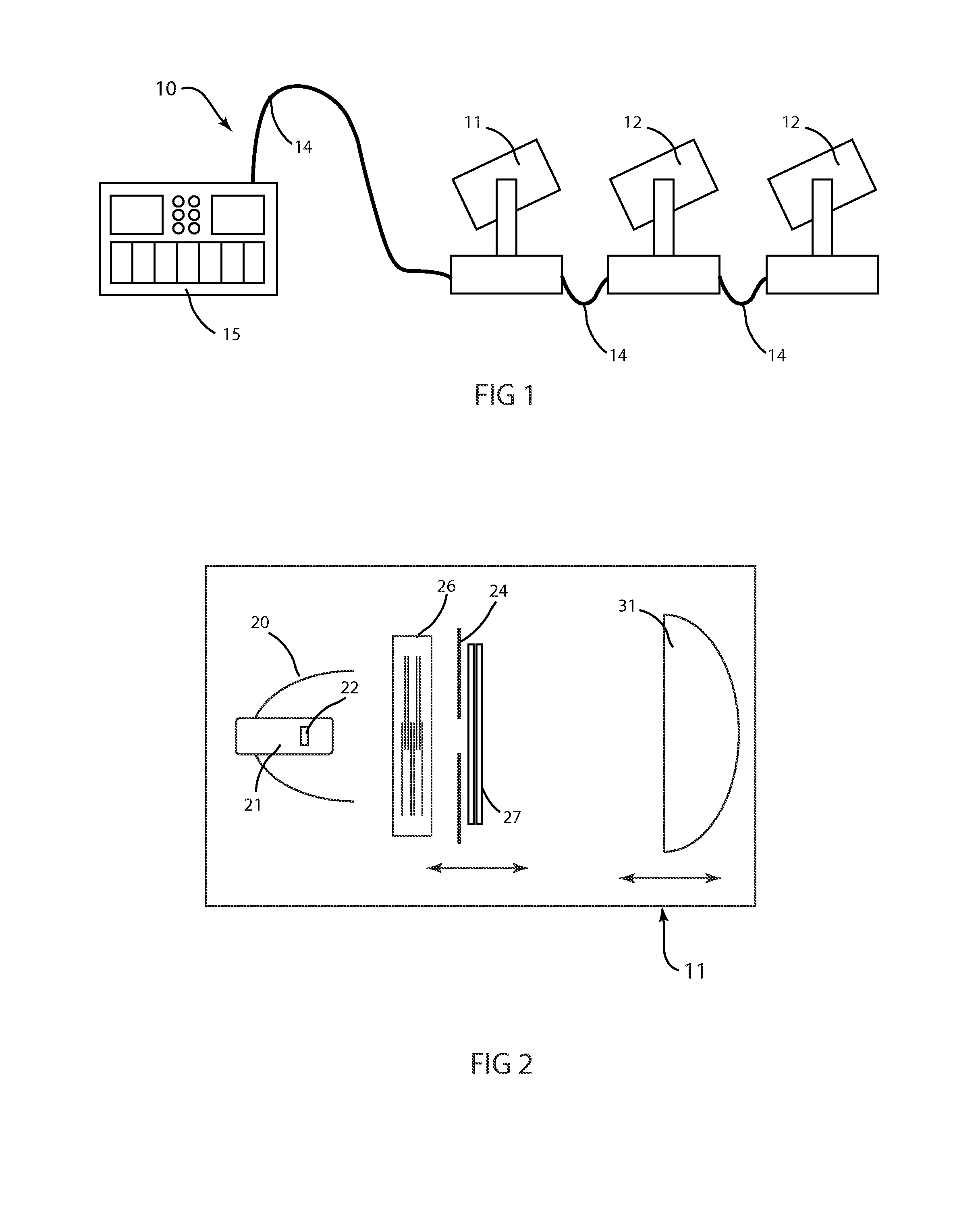
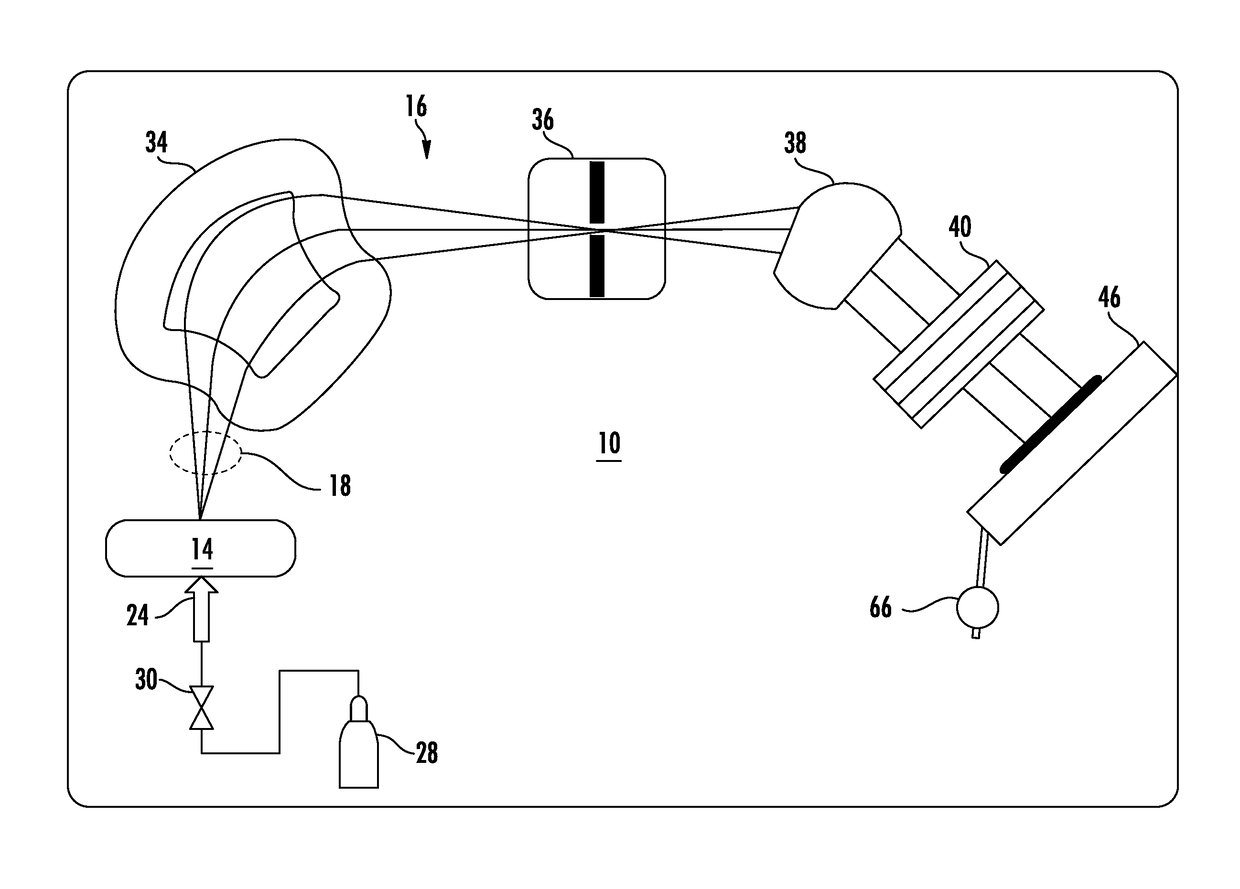
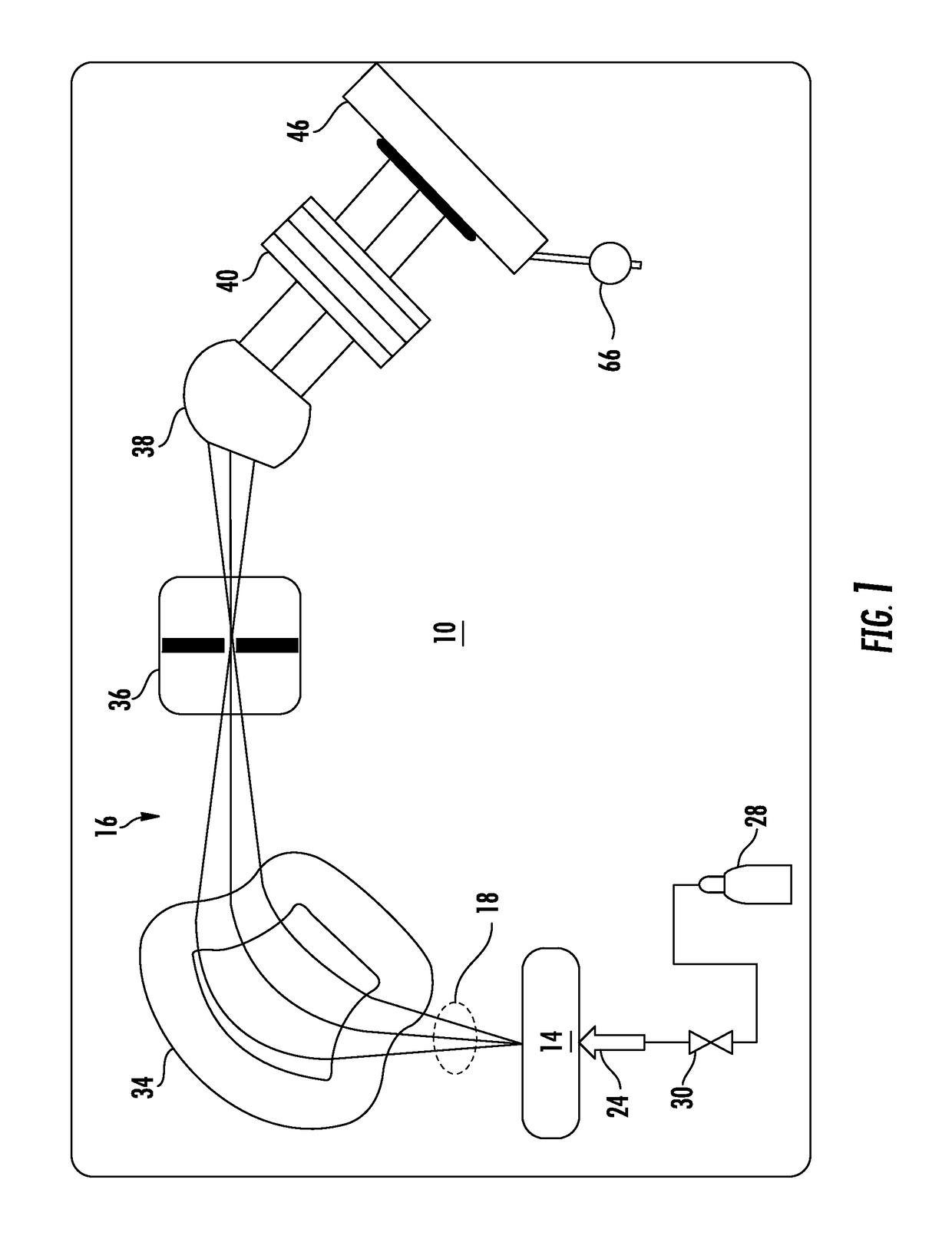
Described are an improved automated luminaire 12 and luminaire systems 10 employing an improved output Fresnel lens 46 with an optically planar surface 34 combined with an articulable stippling plate 47. The stippling plate 47 may be inserted and removed immediately behind and adjacent to the planar rear surface of the lens 46 in order to transform the optical system from beam optics to wash optics or immediately adjacent to another articulable lens system 29 directly the light beam toward the previously described Fresnel lens. Further embodiment may include an articulable beam spreader.
Owner:ROBE LIGHTING
Navigation and sample processing using an ion source containing both low-mass and high-mass species
ActiveUS8455822B2Simple methodMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesLight beamImproved method
Owner:FEI CO
Apparatus and method for probing integrated circuits using laser illumination
InactiveUS7616312B2Using optical meansLight polarisation measurementGlobal illuminationHigh temporal resolution
An apparatus and method for laser probing of a DUT at very high temporal resolution is disclosed. The system includes a CW laser source, a beam optics designed to point two orthogonally polarized beams at the same location on the DUT, optical detectors for detecting the reflected beams, collection electronics, and an oscilloscope. The beam optics defines a common-path polarization differential probing (PDP) optics. The common-path PDP optics divides the laser beam into two beams of orthogonal polarization. Due to the intrinsic asymmetry of a CMOS transistor, the interaction of the beams with the DUT result in different phase modulation in each beam. This difference can be investigated to study the response of the DUT to the stimulus signal.
Owner:DCG SYST
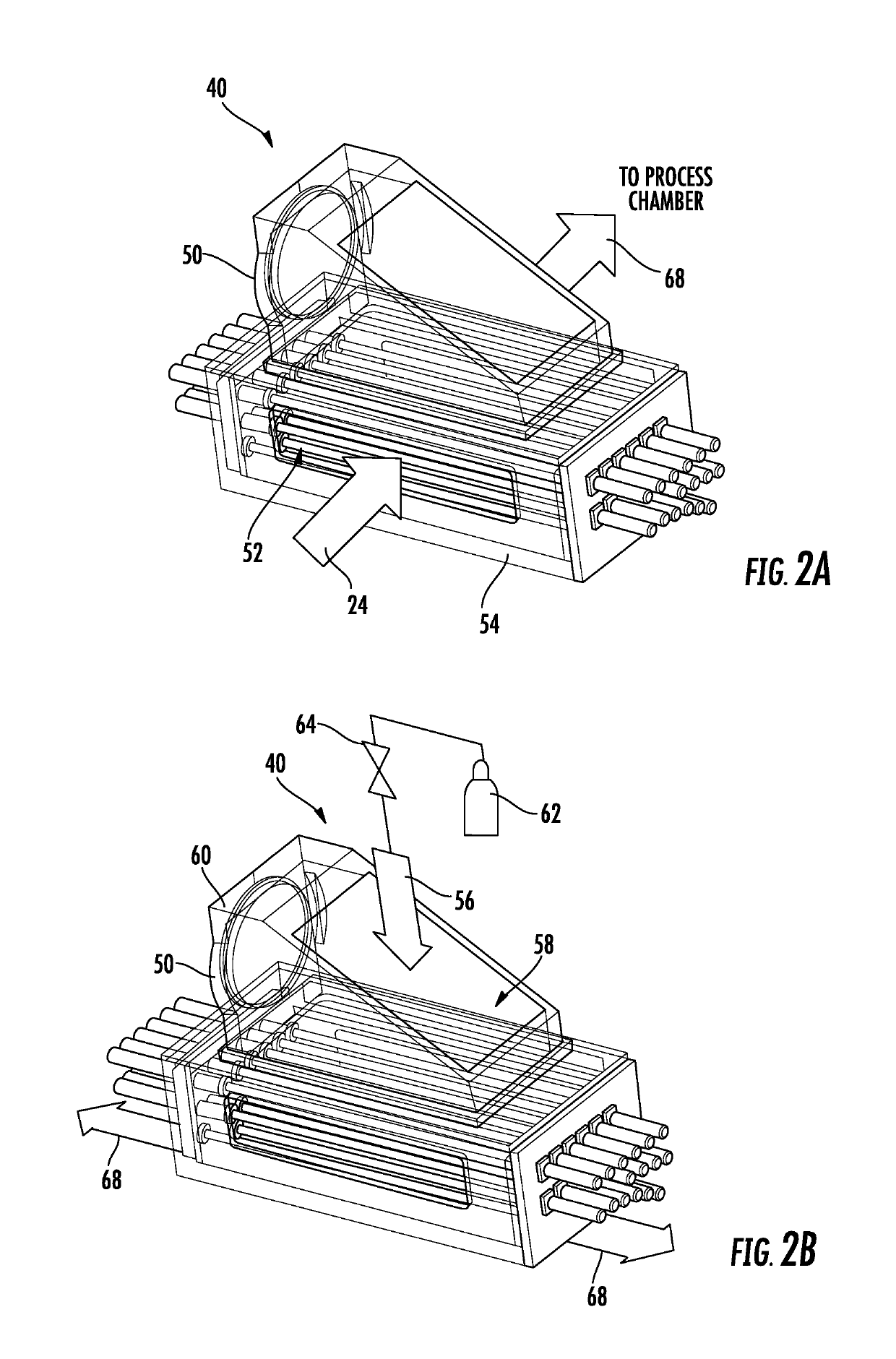
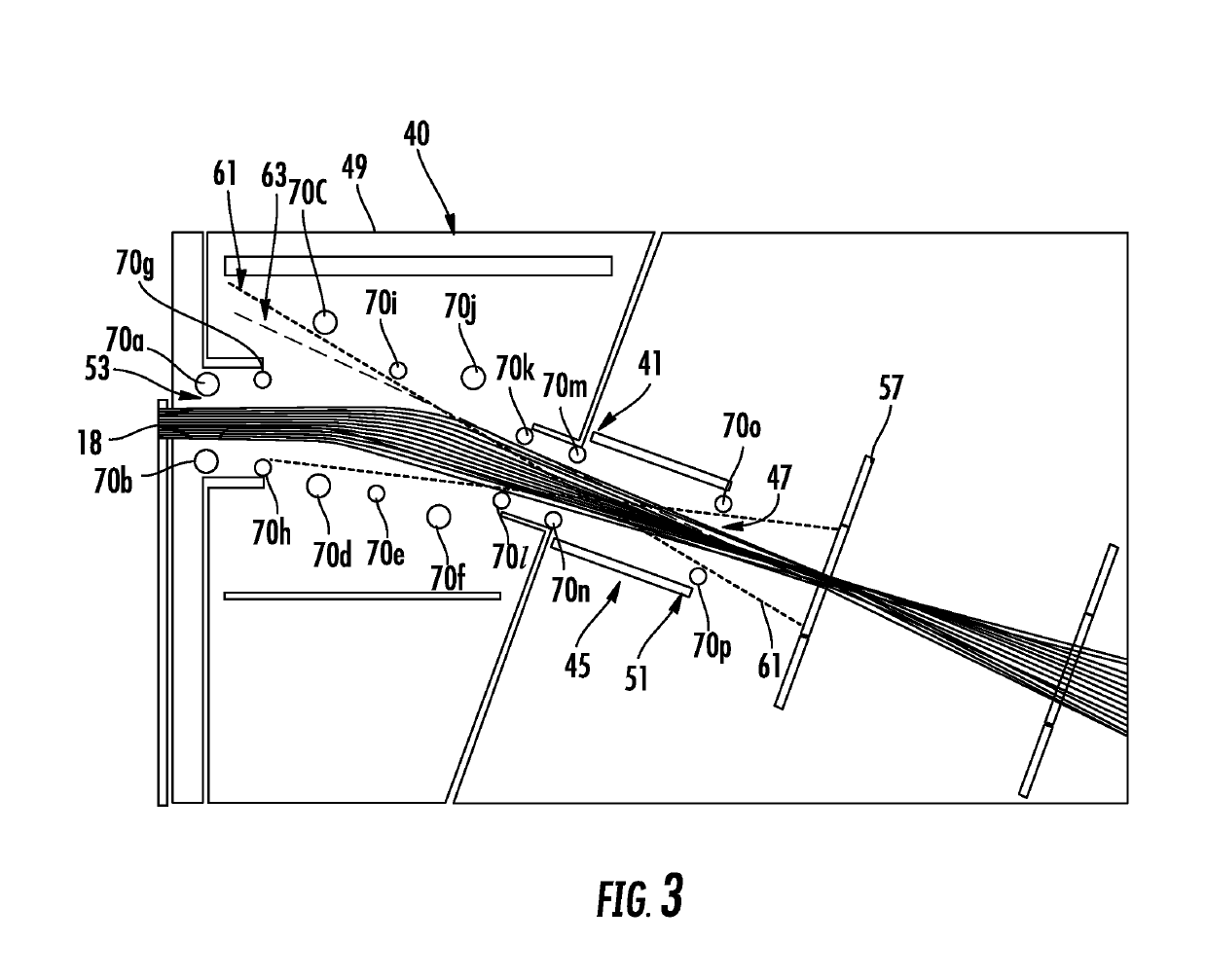
Gas purge system and methods
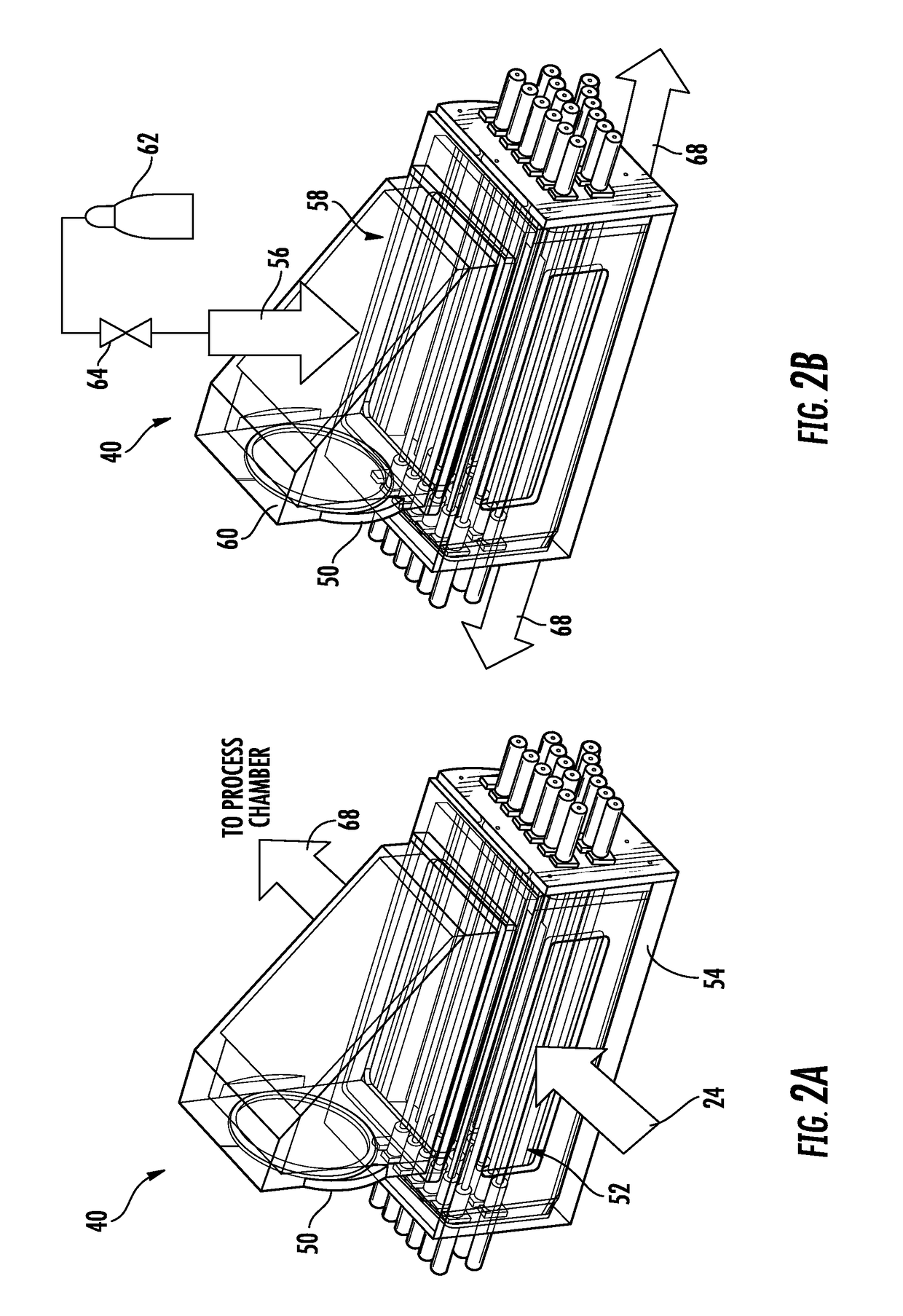
ActiveUS7420681B1Faster purge timeIncrease in sizePolarisation spectroscopyMaterial analysis by optical meansProcess engineeringNose cone
Gas purge systems and methods and a spectroscopic ellipsometer are disclosed. A purge gas system may include an input beam optics housing, a collection optics housing and a gas purge manifold. The input beam optics housing may include a first gas flow path between a first gas inlet and an aperture in a first nose cone proximate a measurement position. The collection optics housing may include a second gas flow path between a second gas inlet and an aperture in a second nose cone proximate the measurement position. The gas purge manifold may be disposed between the input beam optics housing and the collection optics housing. The gas purge manifold has a third gas flow path between a third gas inlet and an aperture in the gas manifold proximate the measurement position. The ellipsometer may include input beam optics in the input beam optics housing and collection optics in the collection optics housing. First, second, and third flows of purge gas may be supplied through the input beam optics housing, collection optics housing and gas purge manifold respectively. The purge gas is delivered directly to a measurement position of a surface of a substrate through the gas purge manifold, the first nosecone and the second nose cone.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
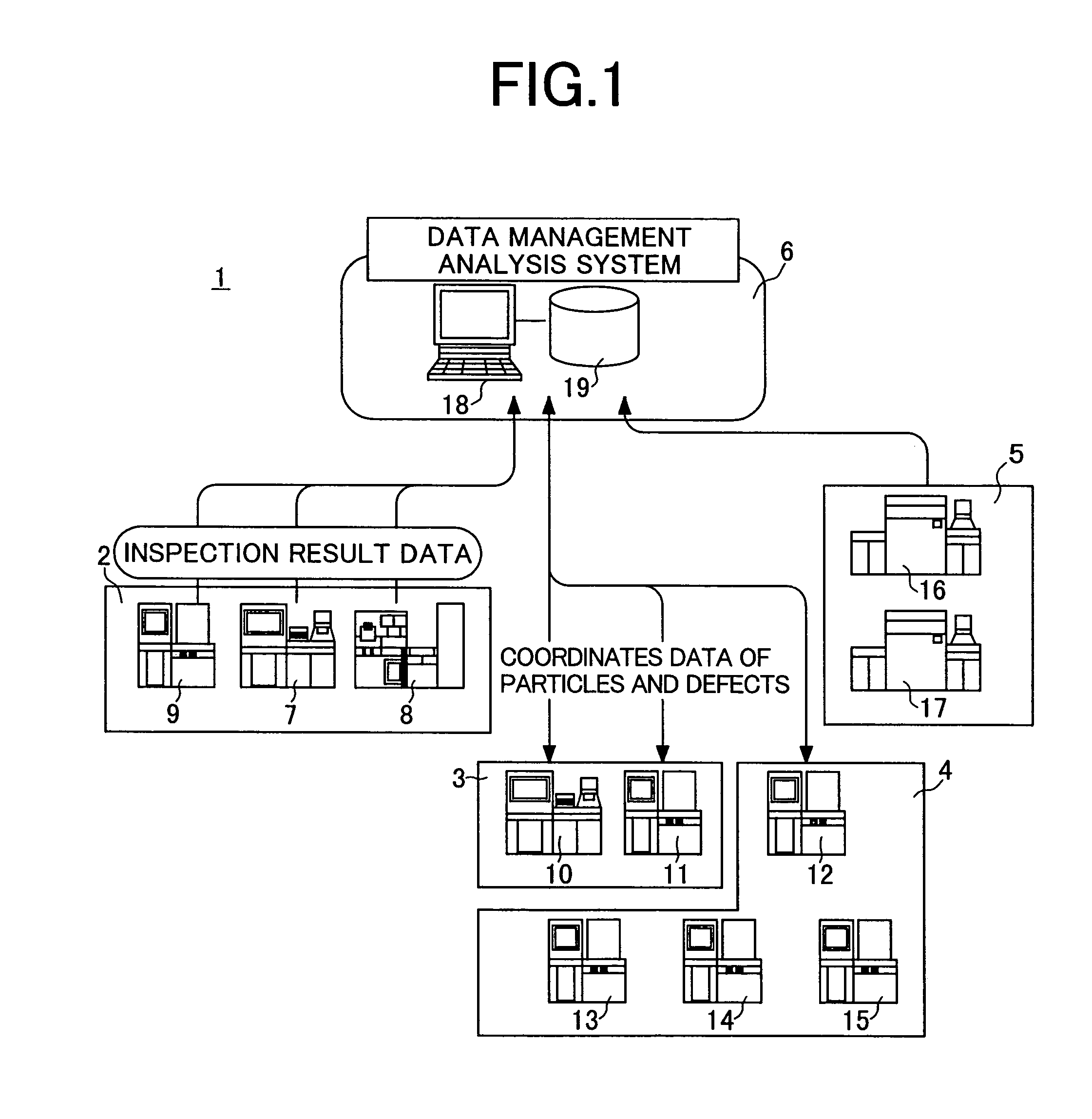
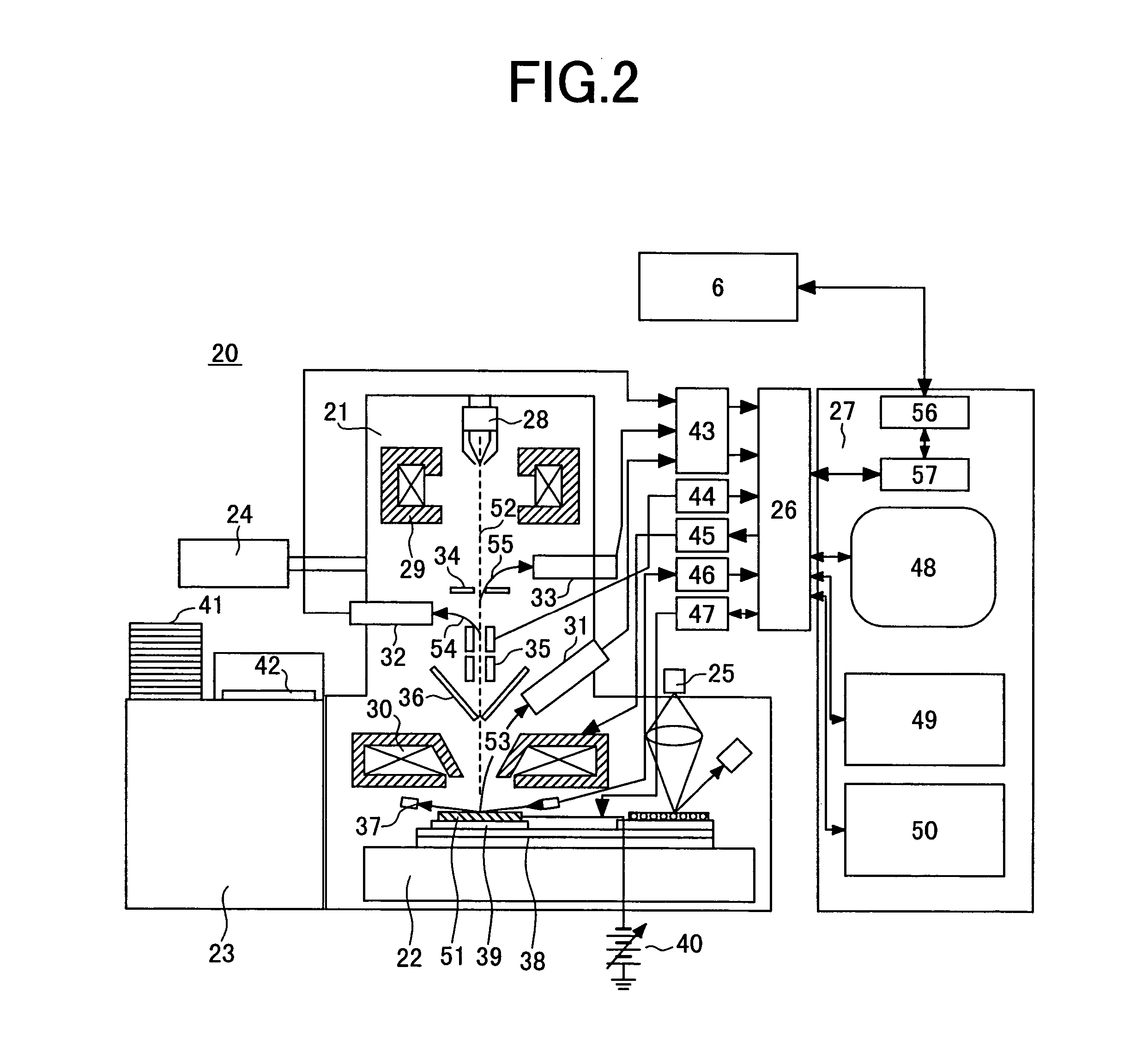
Method of inspecting pattern and inspecting instrument
InactiveUS20050006583A1Highly accurate sight detection of defectEasy to set upImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingElectron
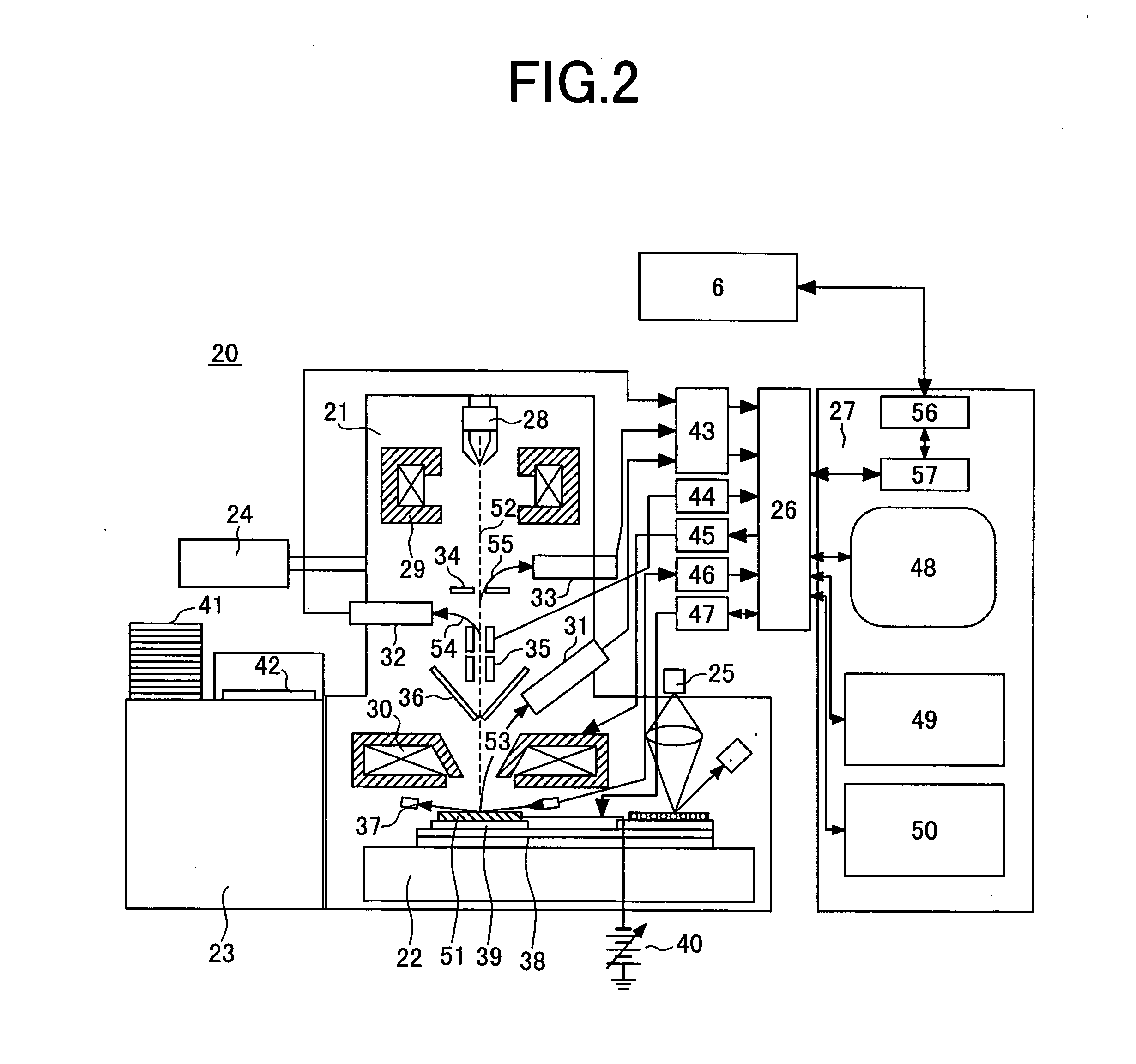
A sample inspection system having a sample stage holding a sample to be inspected corresponding to a selected file, electron beam optics so as to radiate an electron beam to the sample, a detector unit that detects a secondly generated signal attributable to the electron beam, a storage for storing a plurality of images obtained from the secondly generated signal and information for classifying the plurality of images by a type of defect in the sample, and an image processing unit. The image processing unit retrieves any of the plurality of images and classifies the retrieved image depending on the type of defect including an electrical defect and a defect in the figure.
Owner:HITACHI TOKYO ELECTRONICS
Optical module for a motor vehicle capable of selectively lighting a zone
InactiveUS20100091514A1Convenient lightingSimple structureVehicle headlampsPoint-like light sourceMobile vehicleOptical Module
A headlamp for a motor vehicle, this headlamp comprising at least one optical module capable of emitting a plurality of light beams, including a low beam and at least one additional light beam. The optical module is equipped with a cover plate which can be moved between at least two positions, this movable cover plate being configured along a shaft mounted so as to rotate in the optical module and driven in rotation at least by a motor. The shaft comprises at least one first cut-off member configured as a double-edged cover plate providing an oblique cut-off for emission of the low beam, and at least one second cut-off member configured as a wall of substantially constant height, angularly offset relative to the first cut-off member and providing at least one substantially vertical cut-off line for emission of a high beam.
Owner:VALEO VISION SA
Lidar
ActiveUS7428041B2Reduce dispersionEfficient preparationOptical rangefindersMaterial analysis by optical meansRadarLight beam
A lidar, which includes a transmitter and a receiver, as well as an optical system, which is arranged to direct at least part of the light sent by the transmitter as a transmitter beam progressing towards an object and to define the receiver beam to the receiver, at least part of the light arriving from the zone of which is focussed on the receiver. The optical system of the lidar is implemented in such a way that the beams immediately in front of the lidar are located essentially outside of each and one of the beams at least partially surrounds the other beam. The optical system includes an integrated optical, which has a first area for forming the transmitter beam, and a second area for forming the receiver beam.
Owner:VAISALA
Optical shape sensing system and method for sensing a position and/or shape of a medical device using backscatter reflectometry
ActiveUS20180128600A1Avoid dataInterfere with accurateSurgical navigation systemsEndoscopesFiberSpectrometer
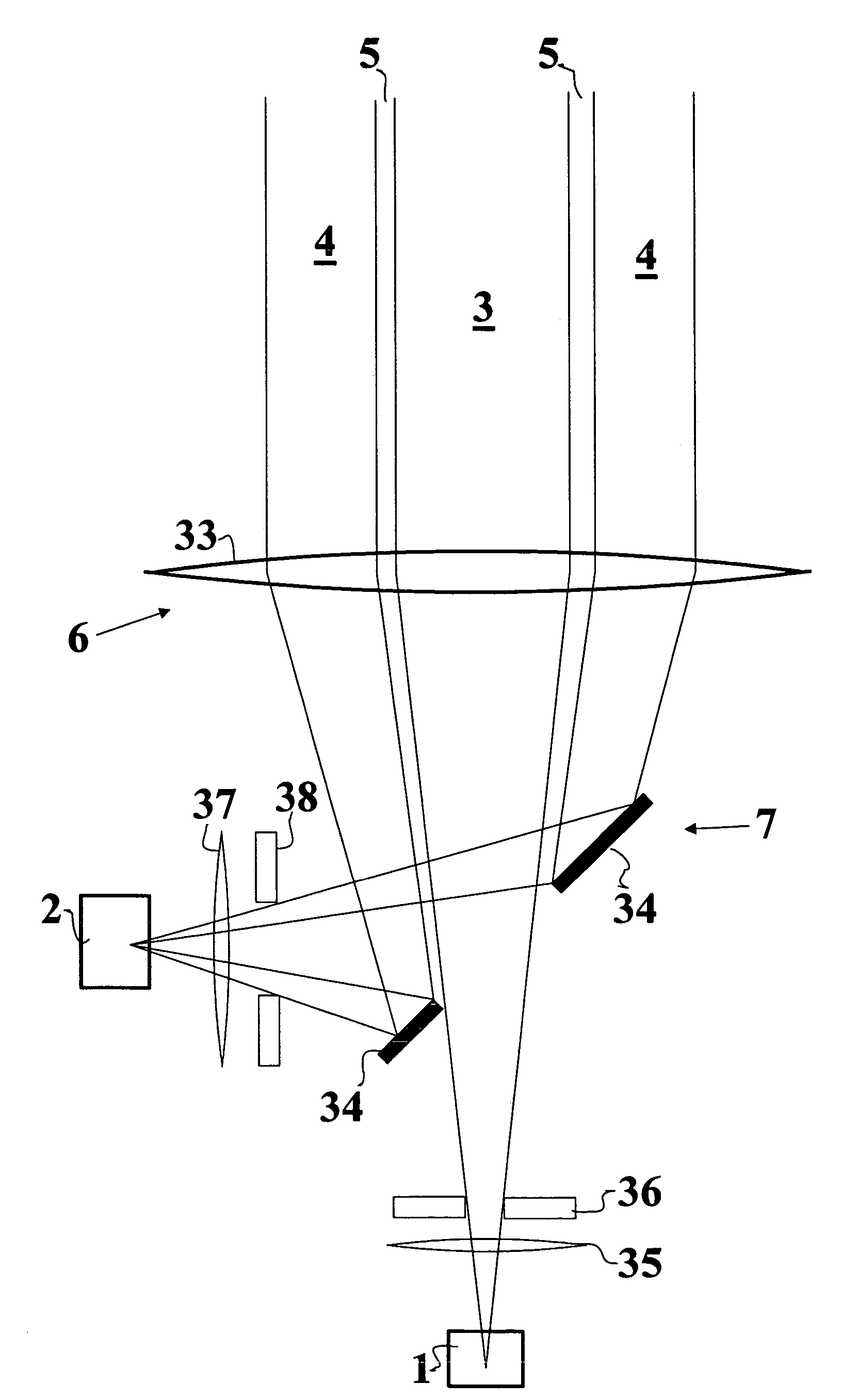
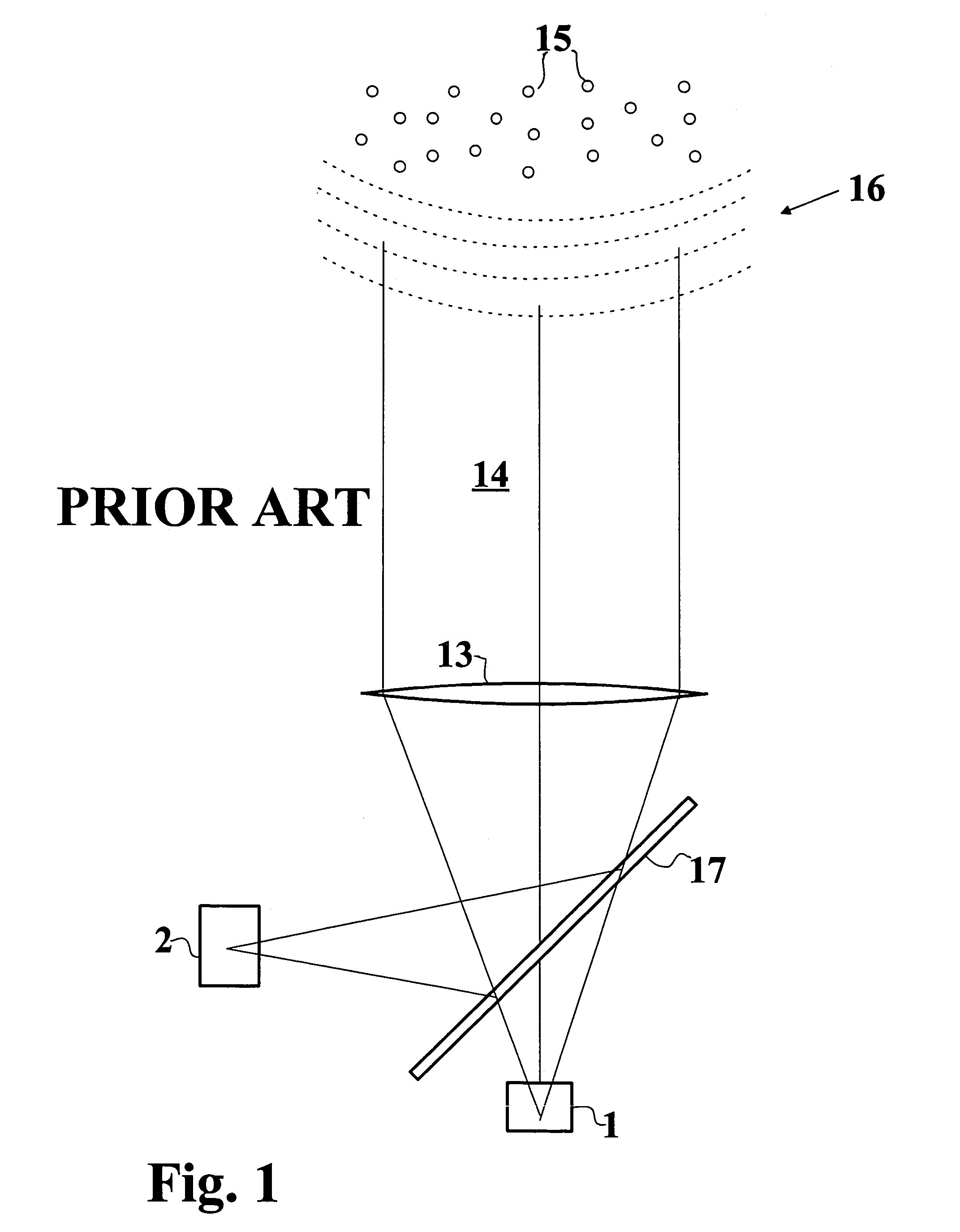
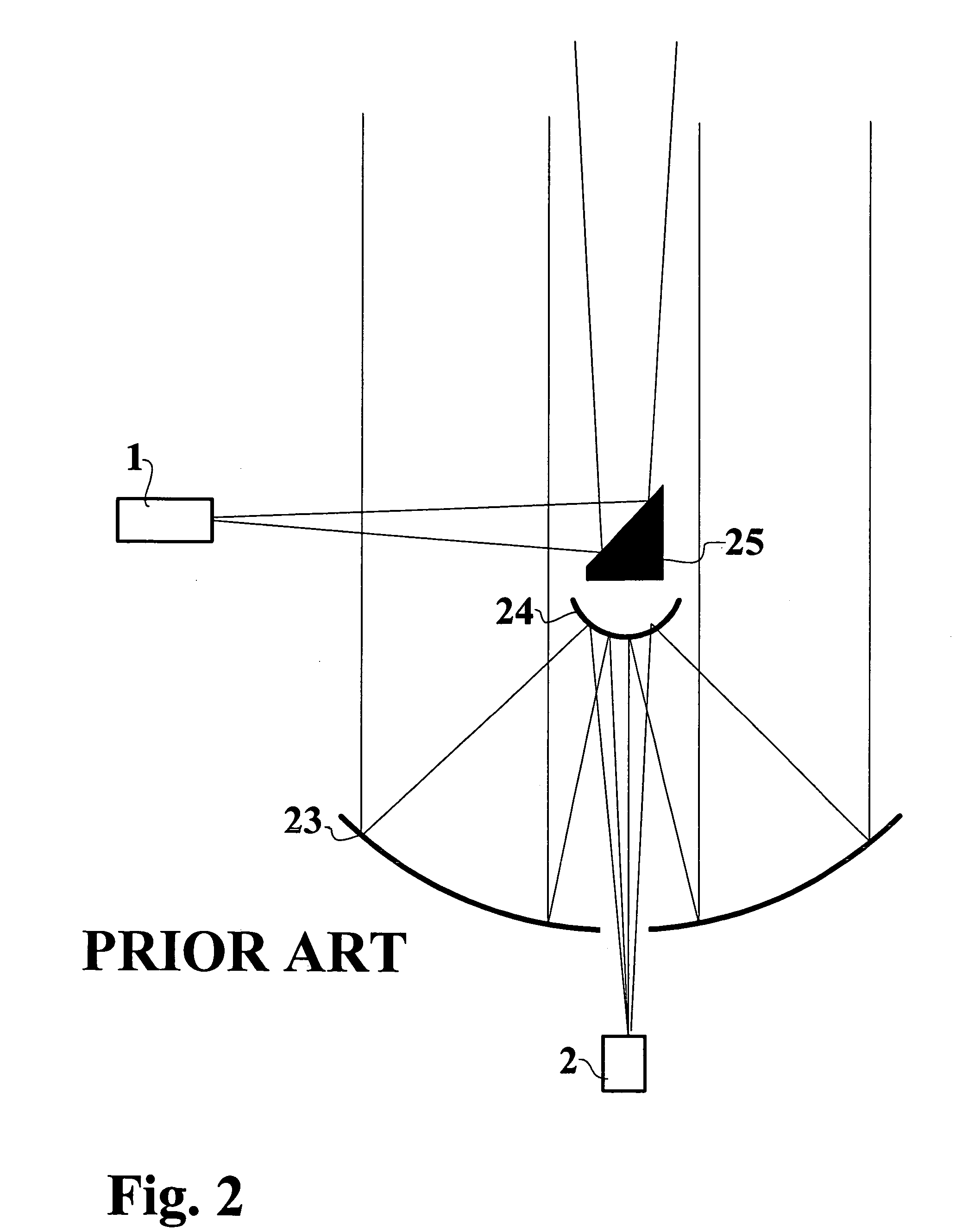
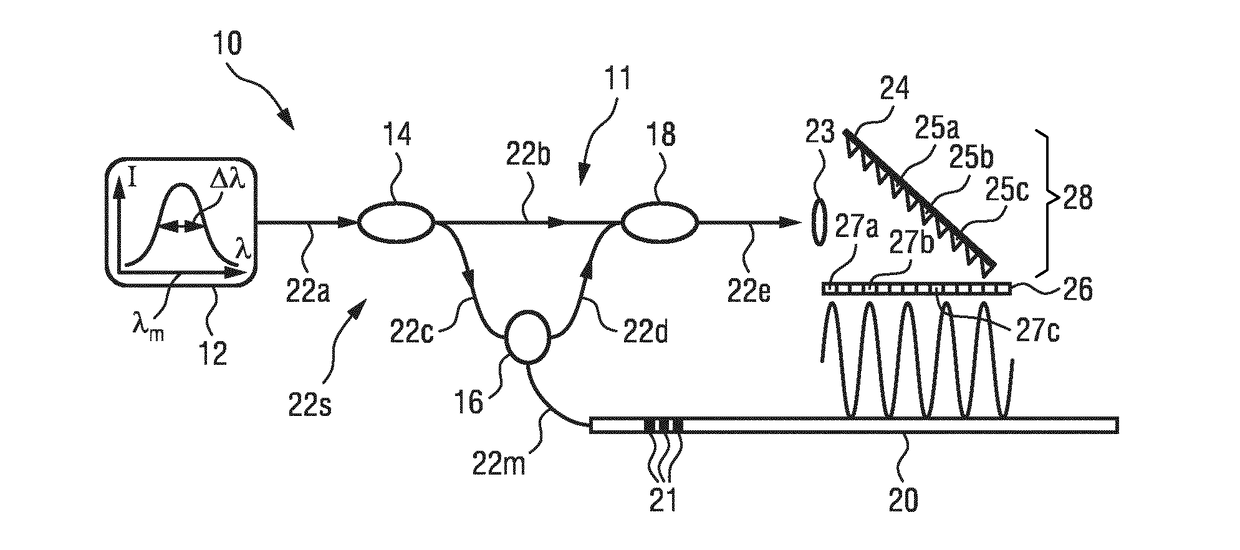
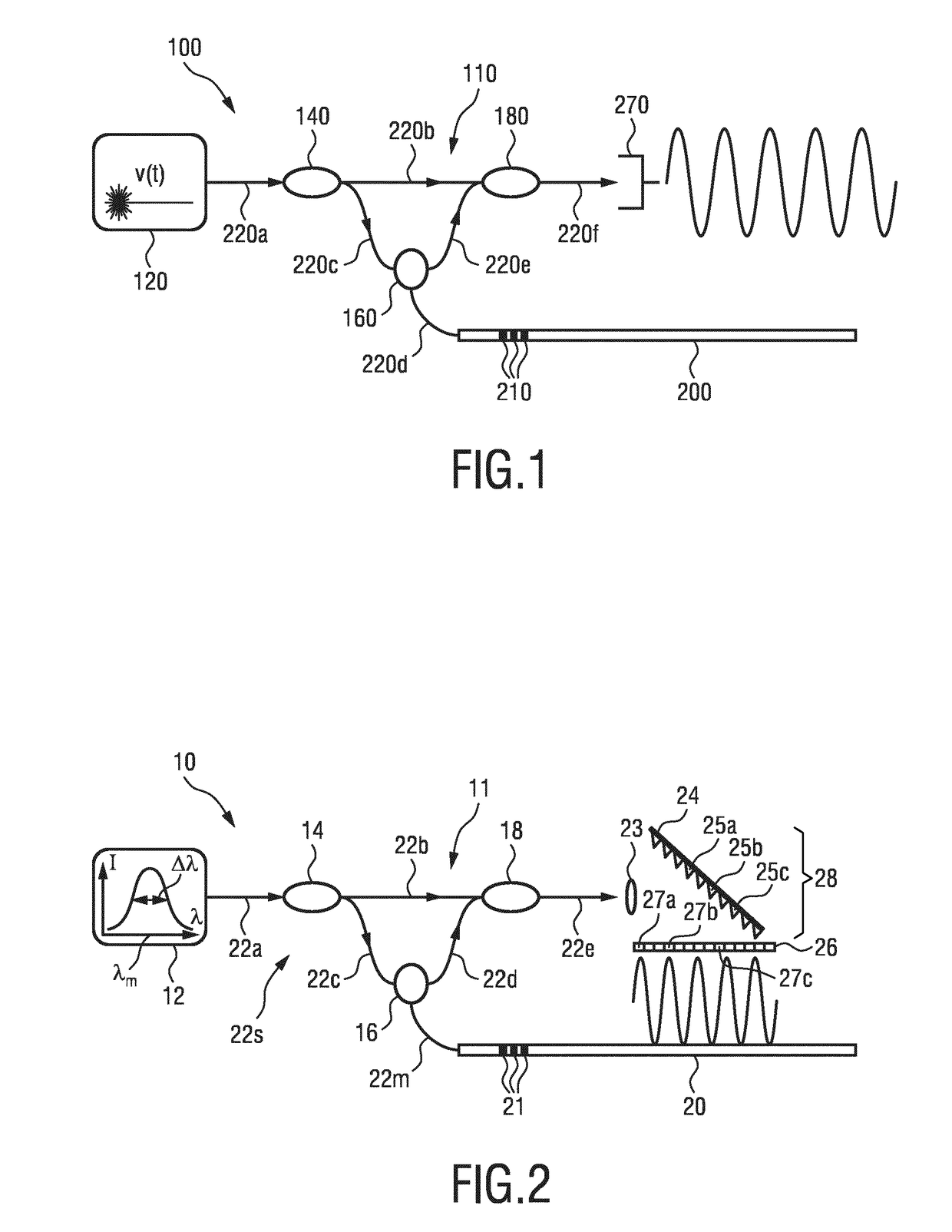
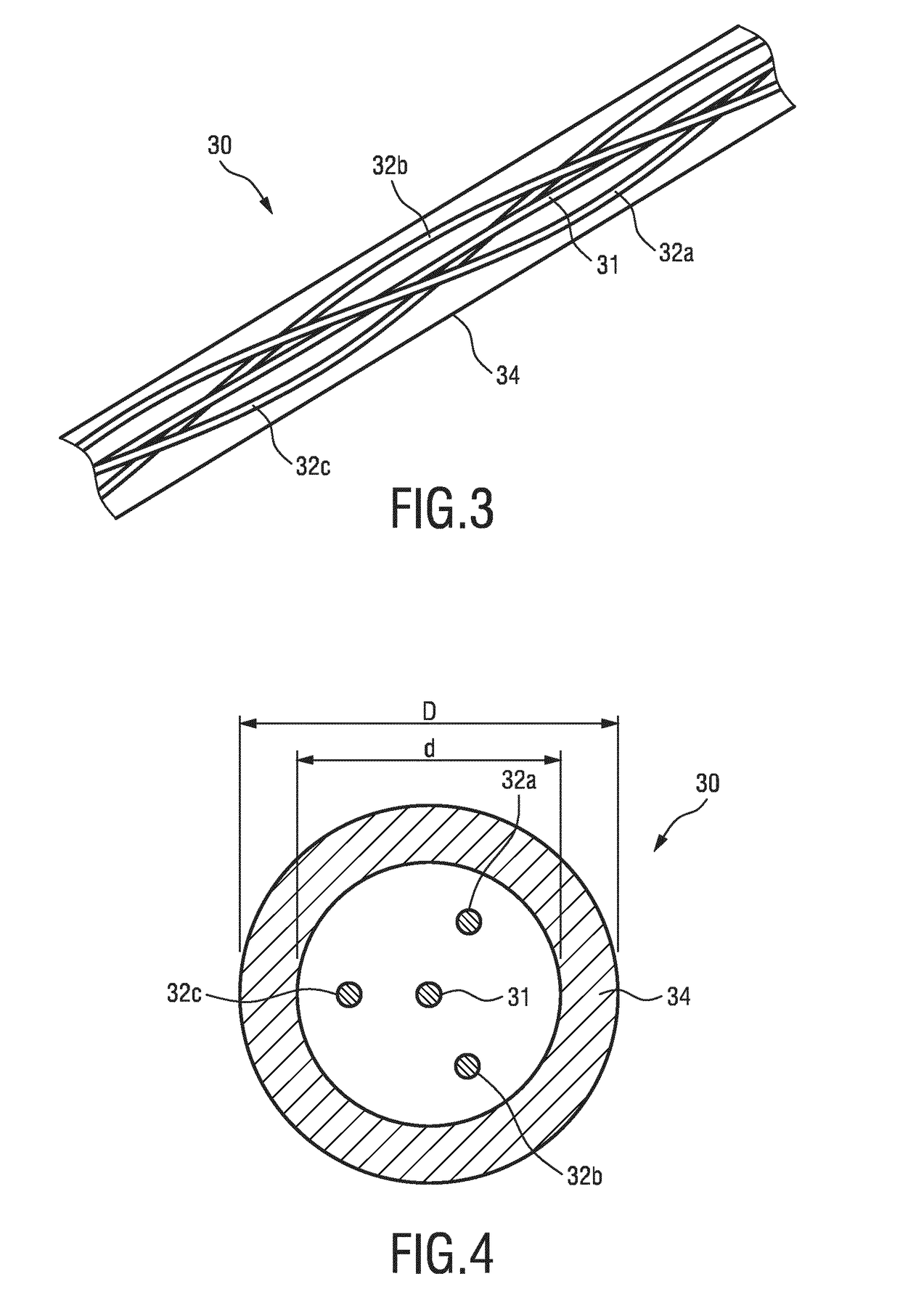
Optical shape sensing system for sensing a position and / or shape of a medical device (20) using backscatter reflectometry, comprising a broadband light source (12) for generating input light of multiple wavelengths of a broadband spectrum, an interferometer arrangement (11) comprising a plurality of interferometers including a multi-core optical fiber (22m, 30), the multi-core optical fiber (22m, 30) comprising at least two fiber cores (31, 32a,b,c), wherein each of the interferometers is configured to perform backscatter reflectometry separately with a corresponding one of a plurality of input light beams divided from the input light and comprises a fiber splitter (14) for dividing the corresponding input light beam into a reference beam and a device beam, an additional optical fiber (22s) for guiding the reference beam, a corresponding fiber core (31, 32a,b,c) of the multi-core optical fiber (22m, 30) for guiding the device beam to be reflected within the medical device (20) and for guiding the reflected device beam, and a fiber coupler (18) for coupling the reflected device beam with the reference beam to form an output light beam, the optical shape sensing system further comprising a spectrometer (28) for receiving and interacting with the output light beam, the spectrometer (28) comprising a detector unit (26) for detecting the output light beam.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
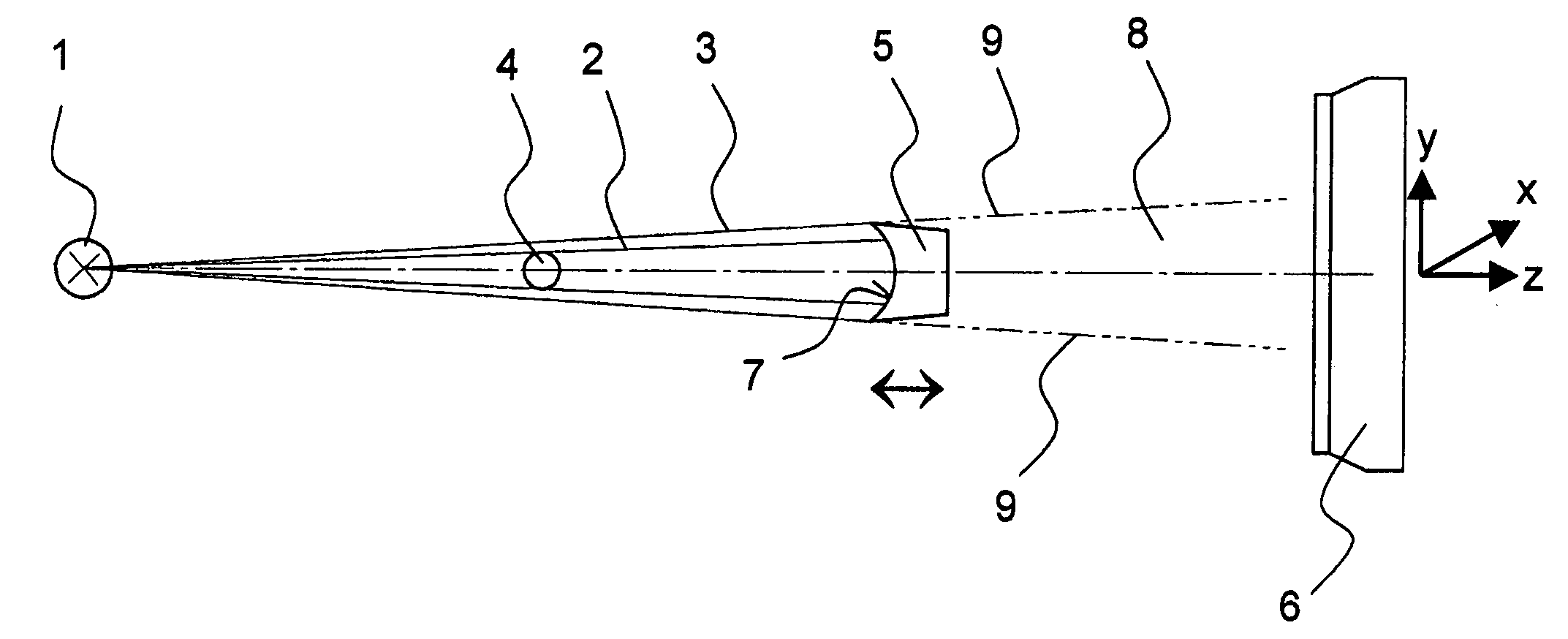
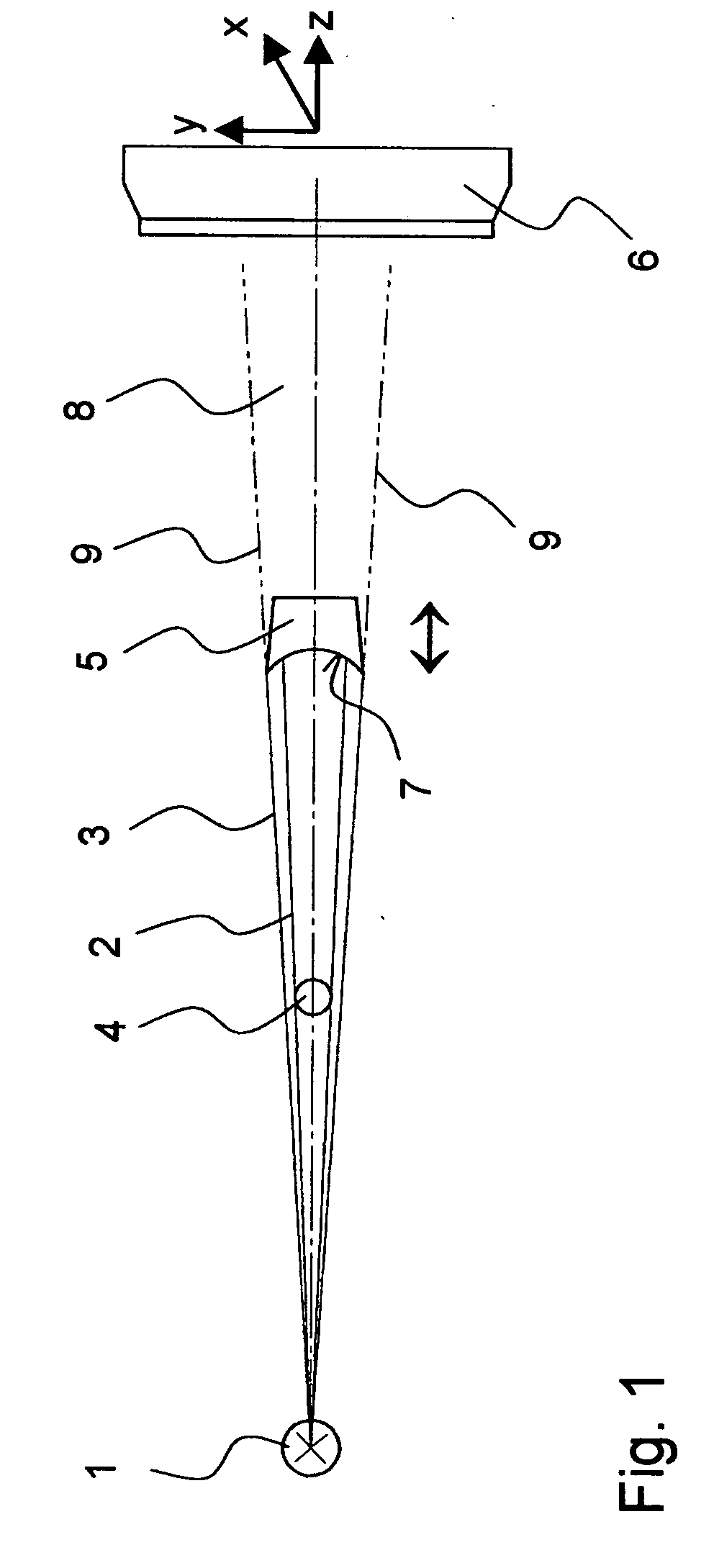
Method for operating a primary beam stop
ActiveUS7295650B2Easy to adjustFast measurement speedMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing wave/particle radiation meansX-rayLight beam
A method for operating an X-ray or neutron-optical system and beam stop comprising an X-ray or neutron source (1) from which corresponding radiation is guided as a primary beam (2) to a sample (4) under investigation, with an X-ray or neutron detector (6) for receiving radiation diffracted or scattered from the sample (4), wherein the source (1), the sample and the detector are disposed substantially on one line (=z-axis) and wherein a beam stop (5; 31; 41) is provided between the sample and the detector whose cross-sectional shape is adjusted to the cross-section of the primary beam is characterized in that the beam stop is disposed to be displaceable along the z-direction for optimum adjustment of the amounts of useful and interfering radiation impinging on the detector. This protects the detector from the influence of the primary beam while allowing a maximum amount of diffracted or scattered radiation to reach the detector, wherein the beam stop can be easily adjusted to temporally changing properties of the beam optics.
Owner:BRUKER AXS
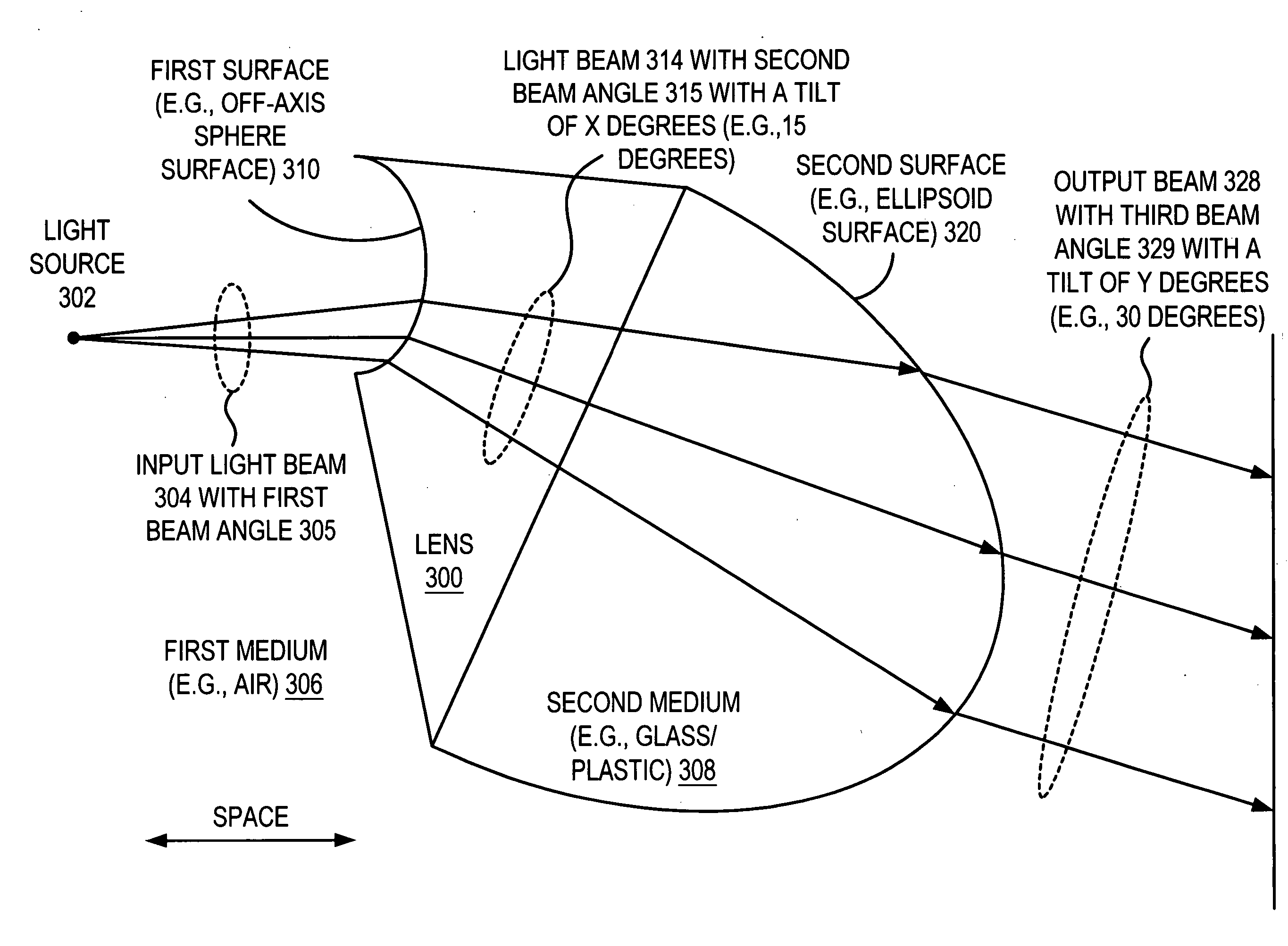
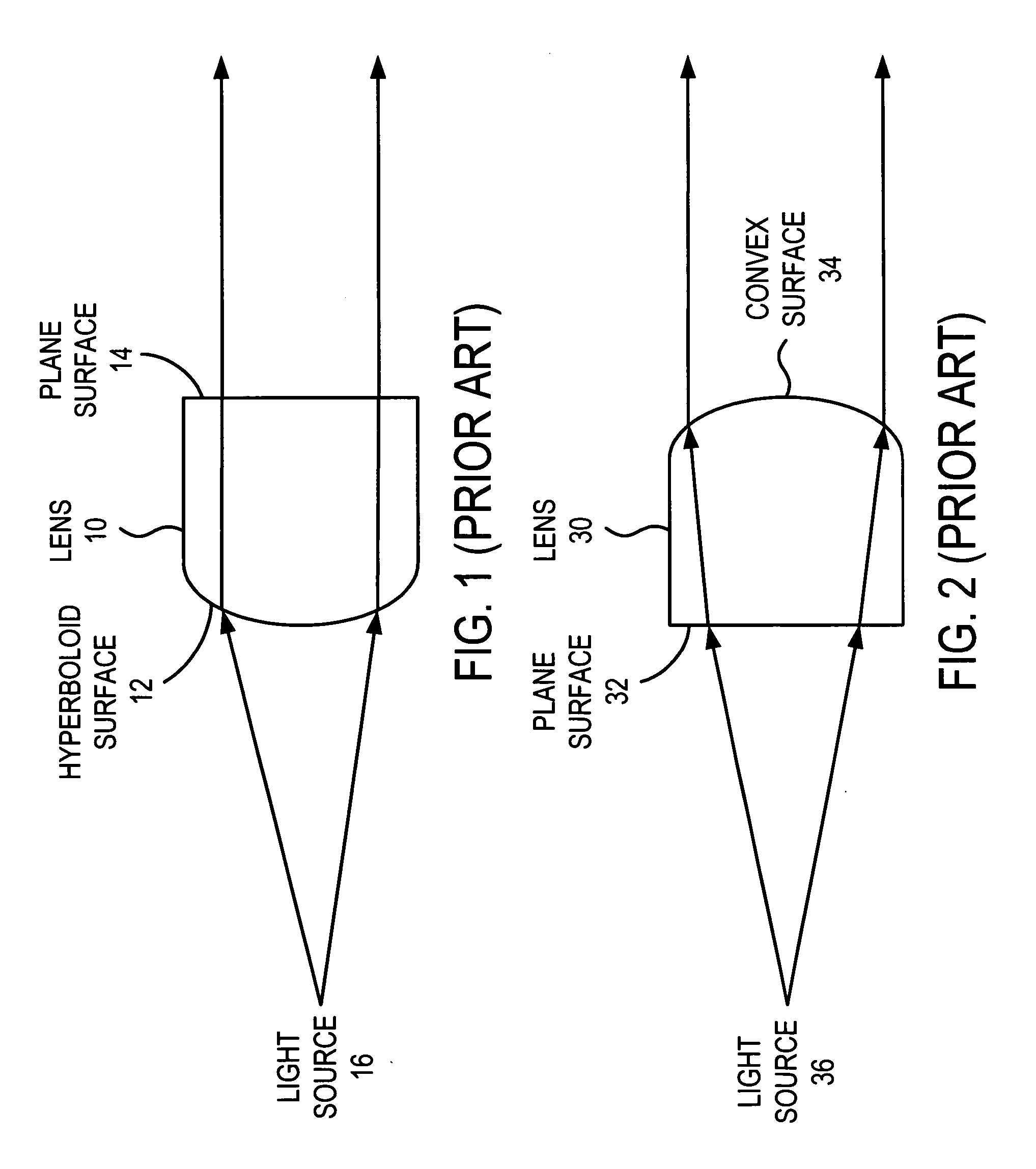
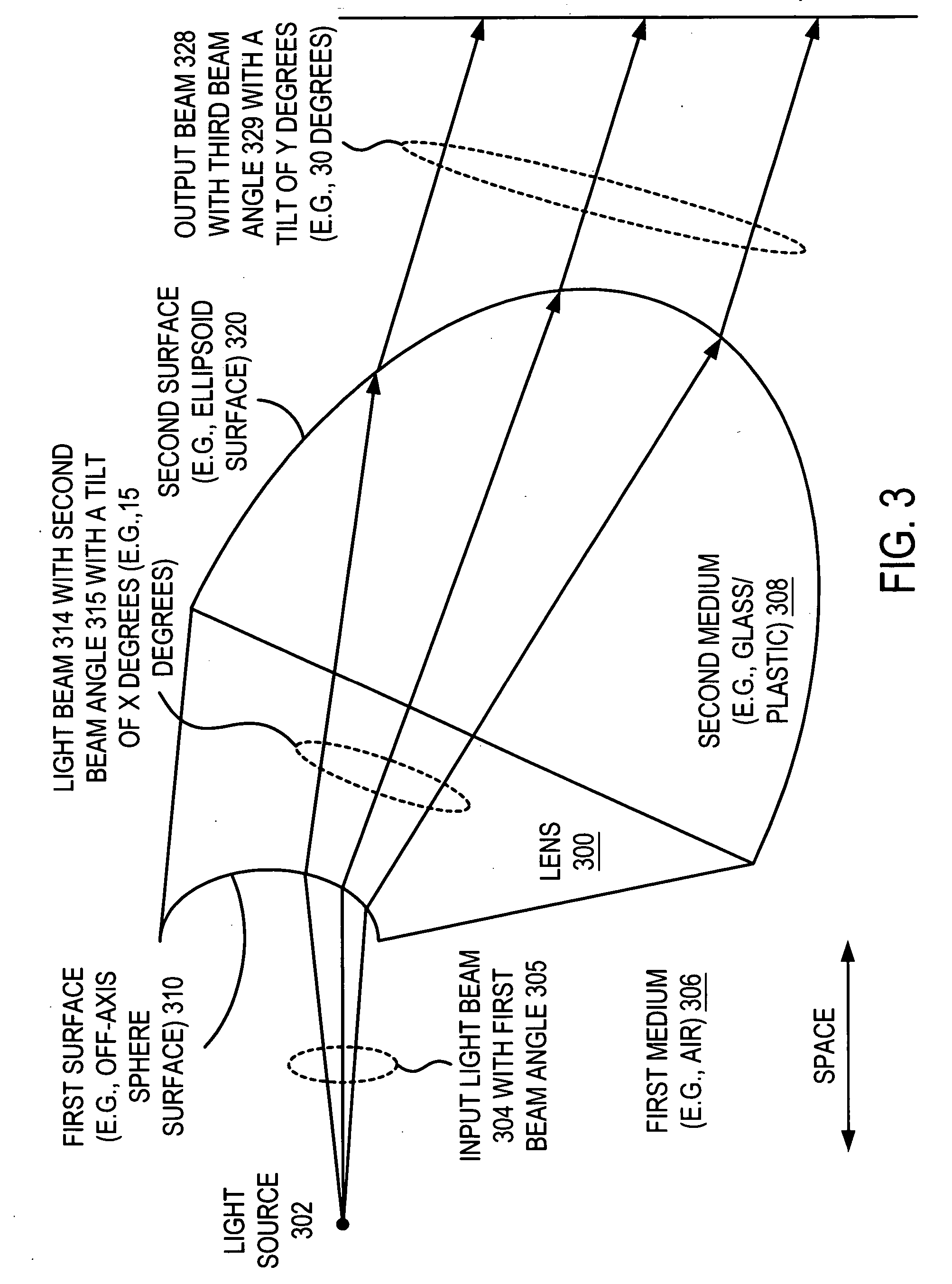
Collimating lens structures
An optic element receives an input light beam with a first beam angle and an axis. The optic element includes a first surface that receives the input light beam and generates an expanded light beam with a second beam angle that is greater than or equal to the first beam angle. The optic element includes a second surface that receives the expanded light beam and generates an output light beam that is either substantially collimated or near collimated. The output light beam is tilted a predetermined degrees with respect to the axis of the input light beam.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multiple-position x-ray tube for diffractometer
ActiveUS20060239408A1Easy to changeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesDiffractometerX-ray
An x-ray source provides both a line focus output and a point focus output, and is mounted on a rotatable support to allow easy changing between the two. A housing has ports at different angular positions relative to an anode, and each port has an associated optic appropriate for an x-ray beam passing through that port. Three or four ports may also be used to allow for different types of beam conditioning. The different beam optics may also do conditioning based on wavelength, and the anode may be of a composite material to provide different wavelength ranges. The rotatable support may be manual or motorized, and a lockout mechanism may be used to ensure that only one port is active at a time. The support may also be located on a movable table that is movable in multiple perpendicular directions.
Owner:BRUKER AXS
Back light module and liquid crystal display
ActiveCN101476684AIncrease brightnessImprove photon utilizationLighting applicationsLight source combinationsLiquid-crystal displayLight beam
The invention relates to a backlight module and a liquid crystal display comprising the same. The backlight module is provided with a reflecting base, and a fluorescent material layer is arranged on the reflecting base; and a plurality of blue light emitting dioxide components are arranged above the reflecting base and the fluorescent material layer and emit first light beams. An optical membrane is arranged above the reflecting base, the fluorescent material layer and the blue light emitting dioxide components, is used for P polarization light of the first light beams to transmit, and reflects S polarization light of the first light beams to the fluorescent layer so as to excite the fluorescent layer to generate second light beams with different wave length from that of the first light beams. The second light beams are reflected to the optical membrane through the reflecting base, then can transmit the optical membrane, and are mixed with the first light beams to generate white light.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Optical read/write apparatus
ActiveUS20130088948A1Limited amountReducing modulated componentRecording verificationRecord information storagePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An optical read / write apparatus as an embodiment of the present invention includes: a light-splitting element configured to split a light beam emitted from a light source into multiple light beams including a write beam and a read beam; an optical system configured to converge the write and read beams onto the same track on an optical storage medium; a photodetector including a light receiving element configured to detect the read beam reflected from the optical storage medium and output an electrical signal; and a divider configured to generate a read signal by dividing the signal detected by the light receiving element by a signal that represents a write modulated component and that is obtained by detecting a part of the light beam emitted from the light source.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
In-situ plasma cleaning of process chamber electrostatic elements having varied geometries
InactiveUS20170092473A1Short timeFacilitate targeted etchingElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlasma densityLight beam
Provided herein are approaches for in-situ plasma cleaning of one or more components of an ion implantation system. In one approach, the component may include a beam-line component having a conductive beam optic, the beam optic having a varied geometry configured to generate a concentrated electric field proximate the beam optic. The system further includes a power supply for supplying a first voltage and first current to the component during a processing mode and a second voltage and second current to the component during a cleaning mode. The second voltage and current may be applied to the one or more beam optics, in parallel, to selectively (e.g., individually) generate plasma in an area corresponding to the concentrated electric field. By providing custom-shaped ion beam optics, plasma density is strategically enhanced in areas where surface contamination is most prevalent, thus improving cleaning efficiency and minimizing tool down time.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Beam-steering device particularly for lidar systems
A beam-steering engine, comprising an optical element switchable between a first operational mode and a second operational mode, in the first operational mode of the optical element the beam-steering engine is configured to output an input light beam incident on the beam-steering engine along a first propagation direction and in the second operational mode of the optical element the beam-steering engine is configured to output the input light beam incident on the beam-steering engine along a second propagation direction. A transition of the optical element between the first and second operational modes is characterized by a transition time period that varies with a temperature of the optical element. The beam-steering engine further includes a device to control a temperature of the solid-state optical element to maintain the transition time period below a certain limit.
Owner:LEDDARTECH INC
Method of inspecting pattern and inspecting instrument
InactiveUS7112791B2High-speed and highly accurate review and classificationImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingElectron
A sample inspection system having a sample stage holding a sample to be inspected, electron beam optics so as to radiate an electron beam to the sample, a detector unit that detects a secondly generated signal generated in response to radiation of the sample by the electron beam, a storage for storing a plurality of images obtained from the generated signal and information for classifying the plurality of images by a type of defect in the sample, and an image processing unit. The image processing unit retrieves any of the plurality of images and classifies the retrieved image depending on the type of defect including an electrical defect and a defect in the figure.
Owner:HITACHI TOKYO ELECTRONICS
Method for operating a primary beam stop
ActiveUS20070007464A1Easy to adjustFast measurement speedMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing wave/particle radiation meansX-rayLight beam
A method for operating an X-ray or neutron-optical system and beam stop comprising an X-ray or neutron source ( 1 ) from which corresponding radiation is guided as a primary beam ( 2 ) to a sample ( 4 ) under investigation, with an X-ray or neutron detector ( 6 ) for receiving radiation diffracted or scattered from the sample ( 4 ), wherein the source ( 1 ), the sample and the detector are disposed substantially on one line (=z-axis) and wherein a beam stop ( 5; 31; 41 ) is provided between the sample and the detector whose cross-sectional shape is adjusted to the cross-section of the primary beam is characterized in that the beam stop is disposed to be displaceable along the z-direction for optimum adjustment of the amounts of useful and interfering radiation impinging on the detector. This protects the detector from the influence of the primary beam while allowing a maximum amount of diffracted or scattered radiation to reach the detector, wherein the beam stop can be easily adjusted to temporally changing properties of the beam optics.
Owner:BRUKER AXS
Optical switch and a control method thereof
InactiveUS20050117838A1Solve the real problemFavorable attitudeCoupling light guidesTransmission monitoringLight beamEngineering
An optical switch for switching communication light beams propagating through a plurality of optical fibers. The switch includes a plurality of input-side lenses, a plurality of moving mirrors, a plurality of output-side lenses, light emitting units, and light receiving units arranged for optical communication. The plurality of input-side lenses include first input-side lenses to which communication light beams coming from first external units and propagating through input-side optical fibers connect optically and second input-side lenses to which the light beams from the light emitting units connect optically. The plurality of output-side lenses include first output-side lenses for causing light beams passing therethrough to optically connect to second output-side optical fibers adapted to propagate the communication light beams to second external units and second output-side lenses for causing the light beams coming from the light emitting units and passing therethrough to optically connect to the light receiving units.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optical connector
ActiveCN104781709AReduce light lossLow cost injection moldingCoupling light guidesLow insertion forceEngineering
Optical connectors are provided for connecting sets of optical waveguides, such as optical fiber ribbons to each other, to printed circuit boards, or to backplanes. The provided connectors utilize expanded beam optics with non-contact optical mating resulting in relaxed mechanical precision requirements. The provided connectors can have low optical loss, are easily scalable to high channel count (optical fibers per connector) and can be compatible with low insertion force blind mating.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Conductive beam optic containing internal heating element
Provided herein are approaches for reducing particles in an ion implanter. An electrostatic filter may include a housing and a plurality of conductive beam optics within the housing. The conductive beam optics are arranged around an ion beam-line directed towards a wafer, and may include entrance aperture electrodes proximate an entrance aperture of the housing. The conductive beam optics may further include energetic electrodes downstream along the ion beam-line from the entrance aperture electrodes, and ground electrodes downstream from the energetic electrodes. The energetic electrodes are positioned farther away from the ion beam-line than the entrance electrodes and the ground electrodes, thus causing the energetic electrodes to be physically blocked from impact by an envelope of back-sputter material returning from the wafer. The electrostatic filter may further include an electrical system for independently delivering a voltage and a current to each of the conductive beam optics.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com