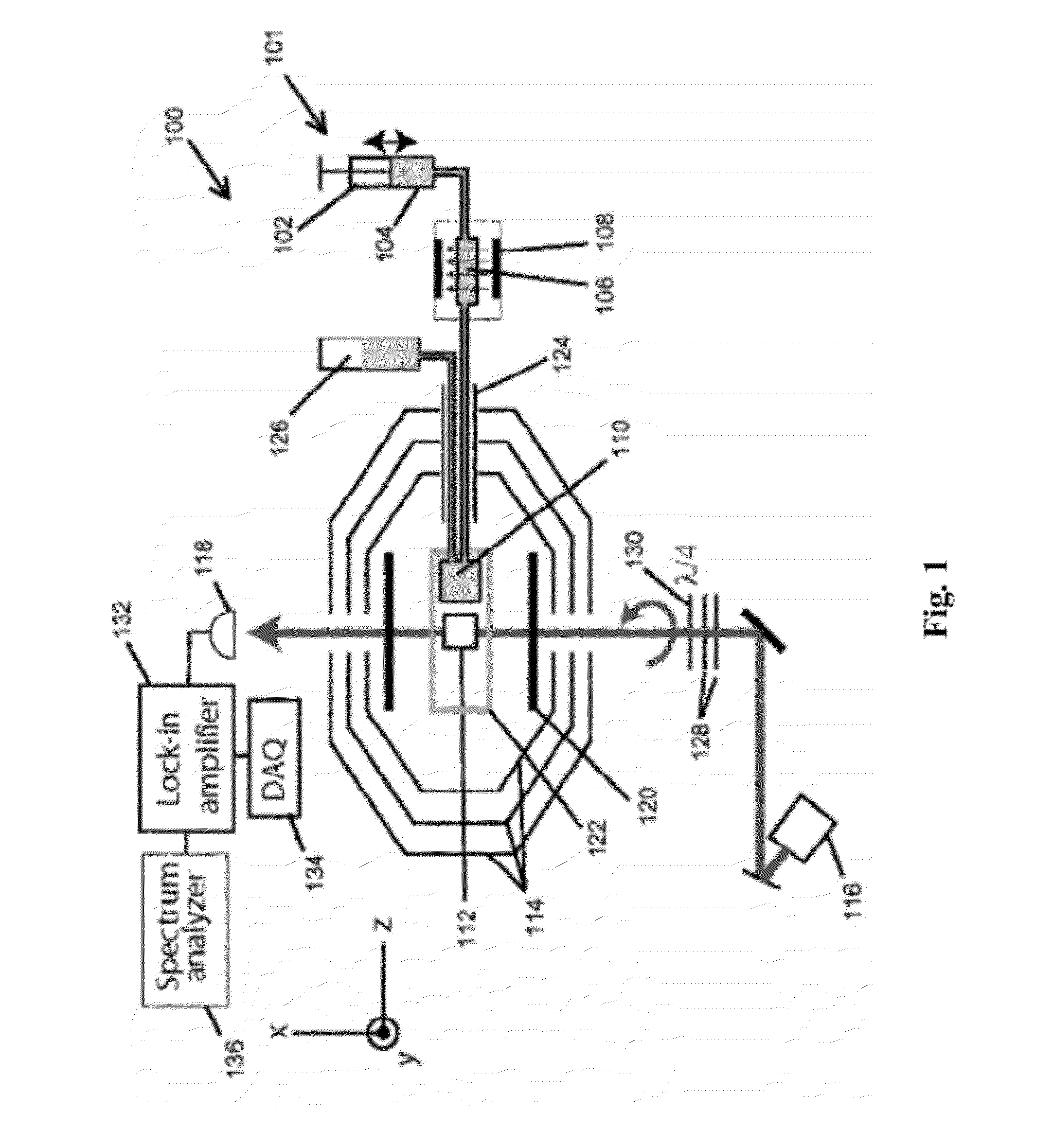
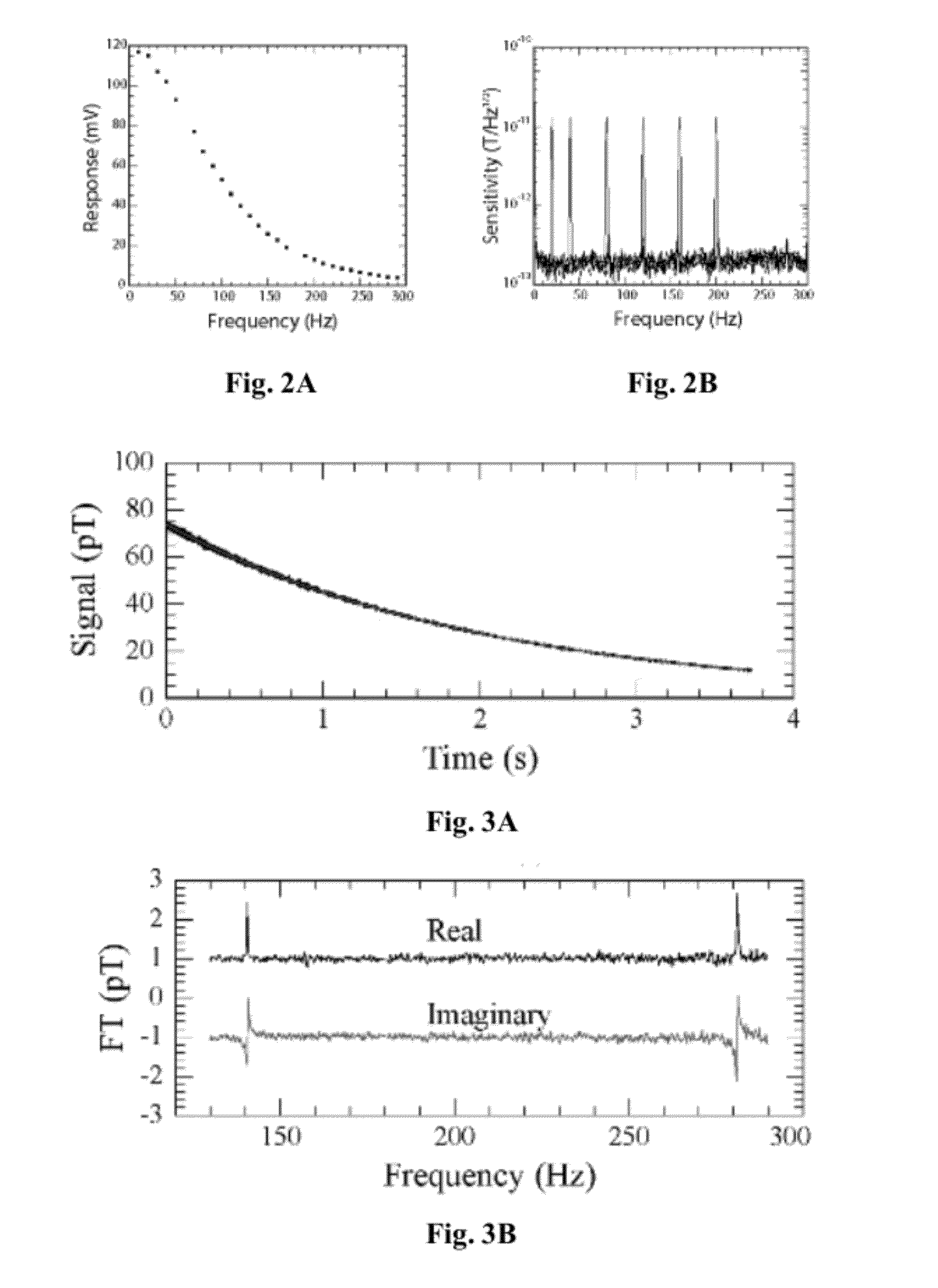
Patents
Literature
224 results about "Atomic magnetometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
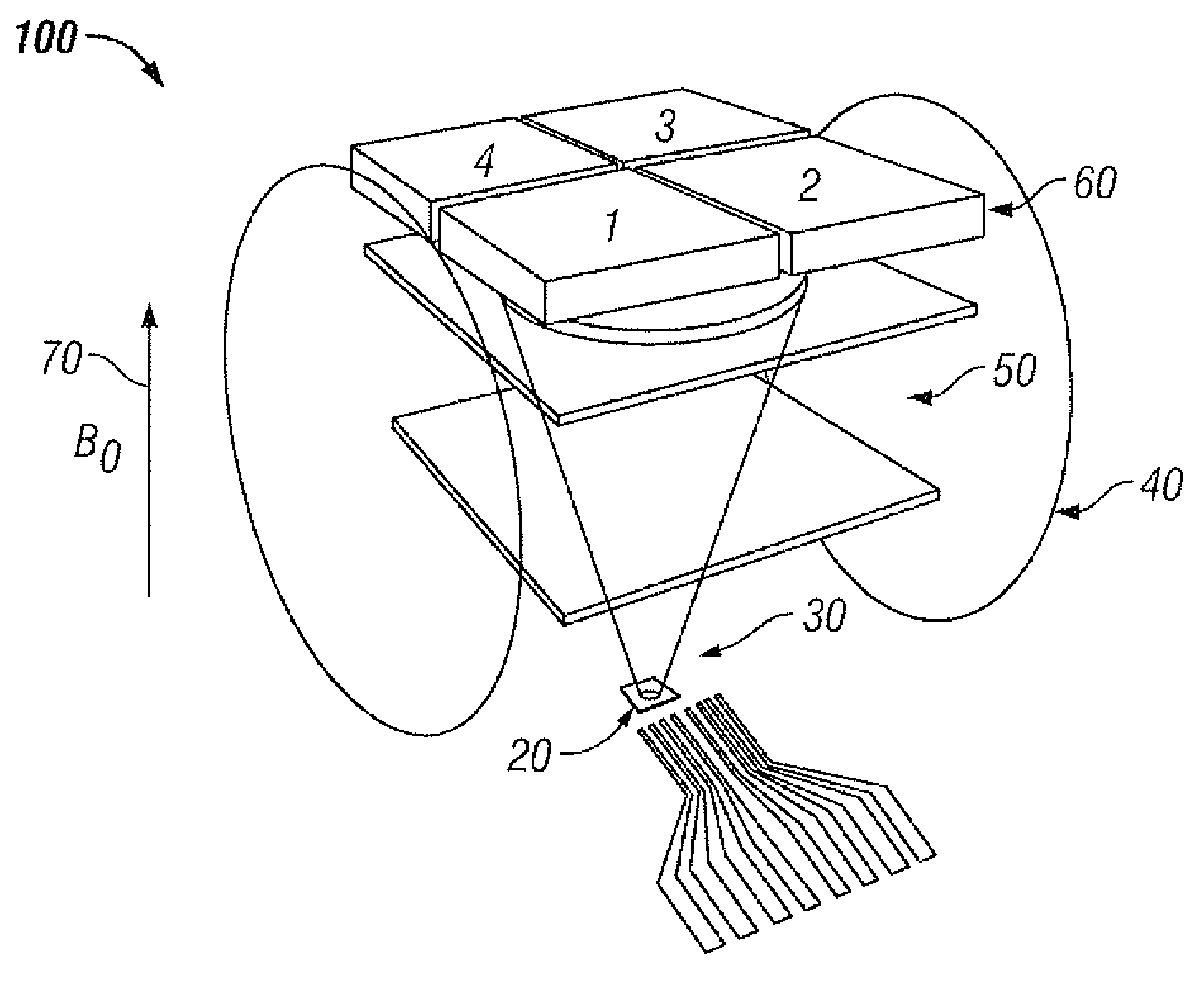
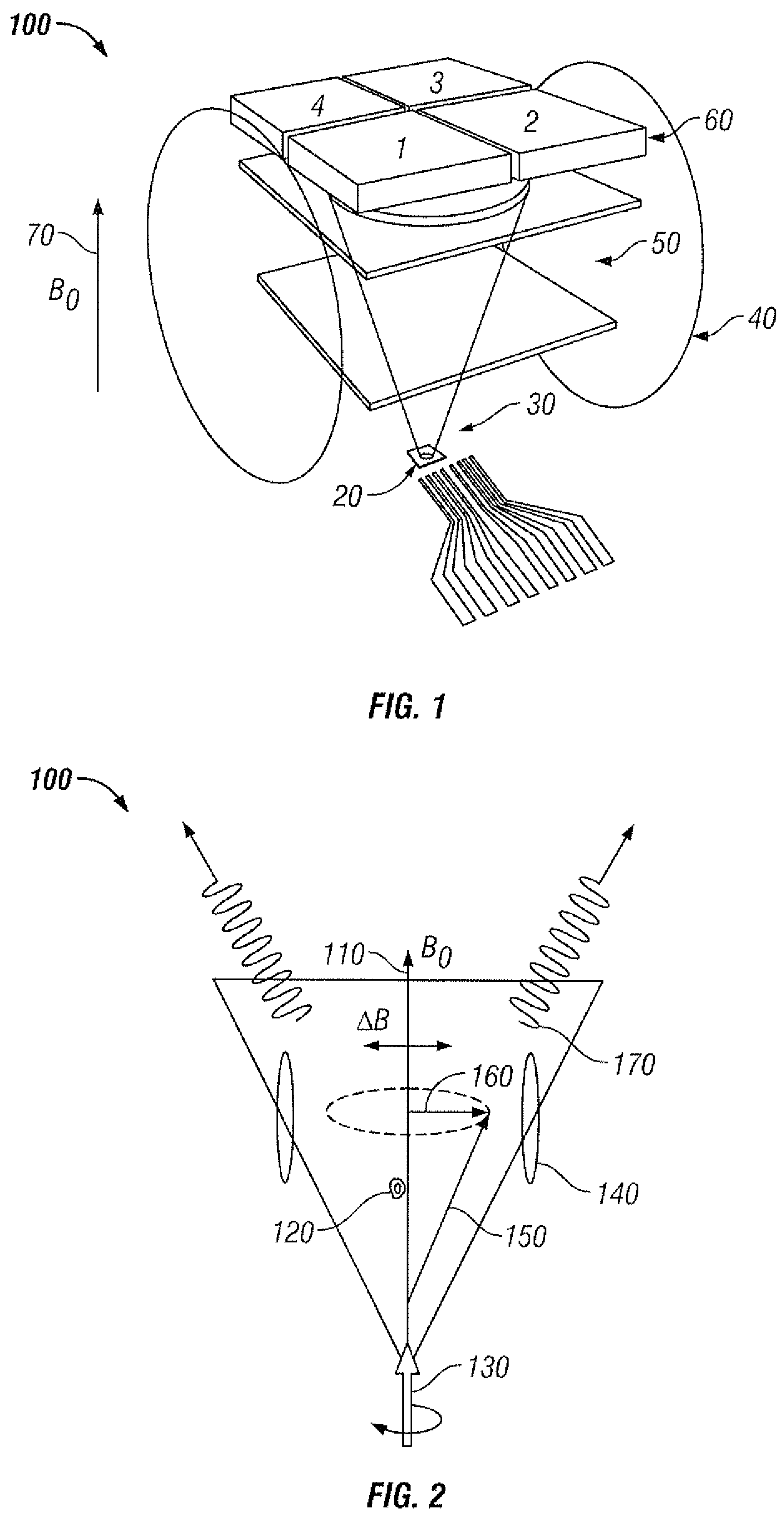
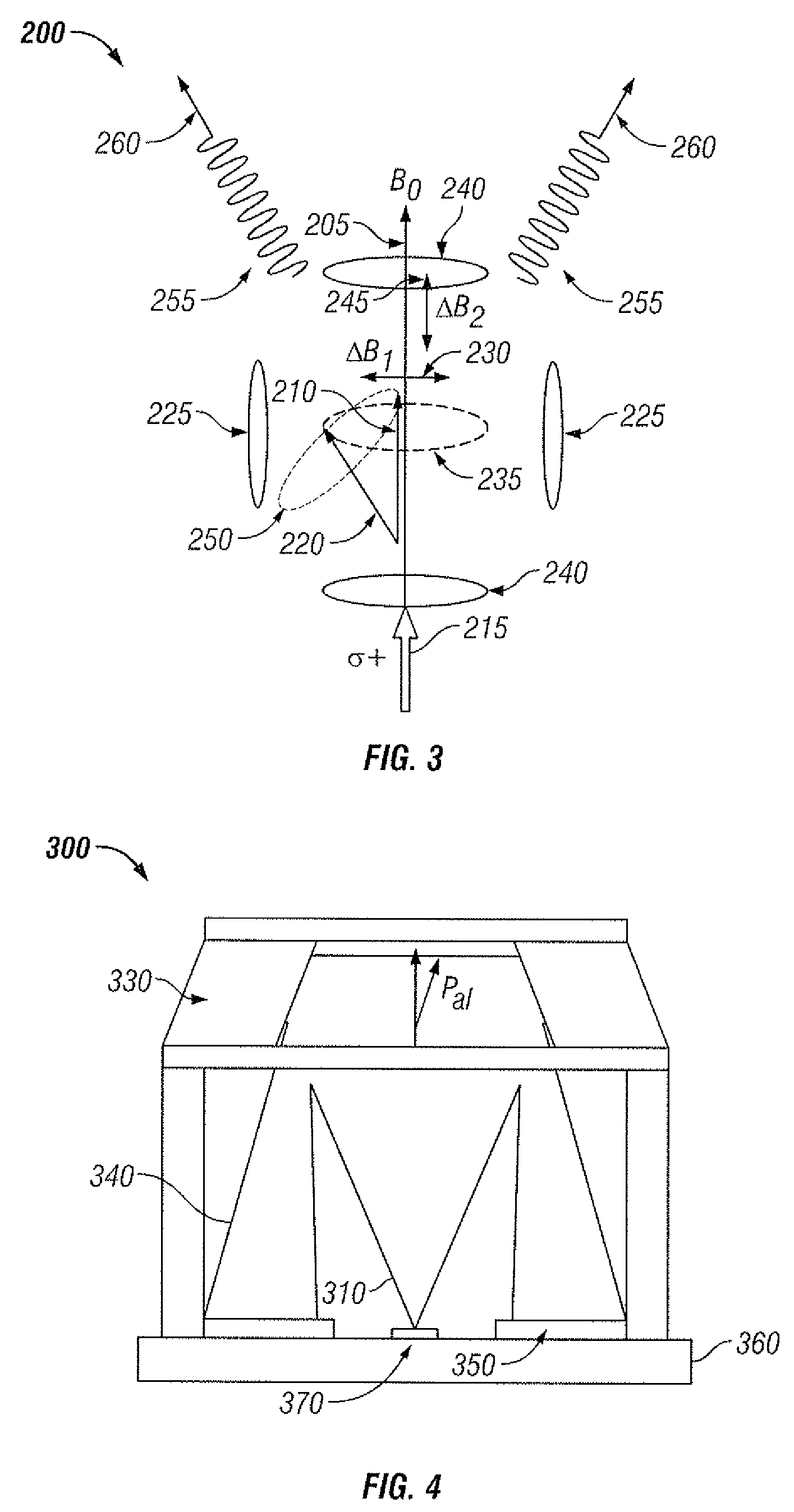
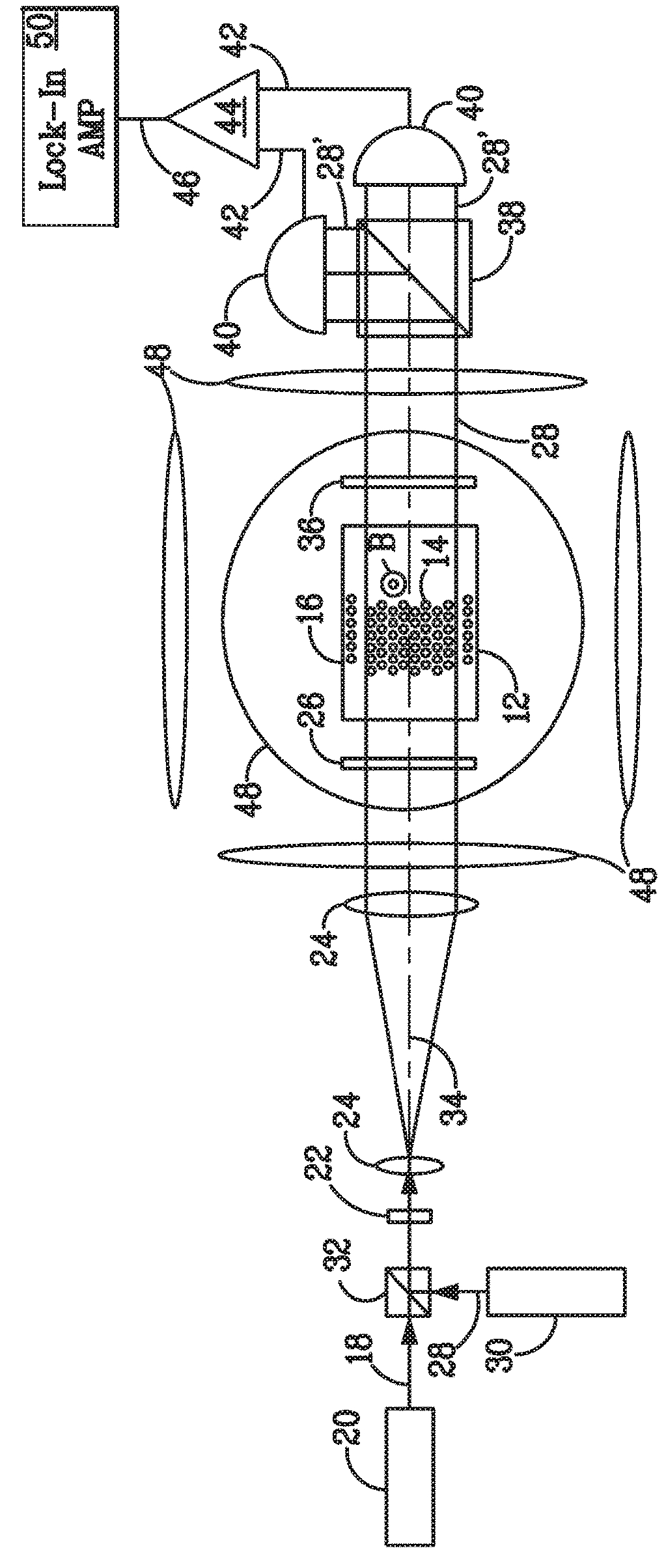
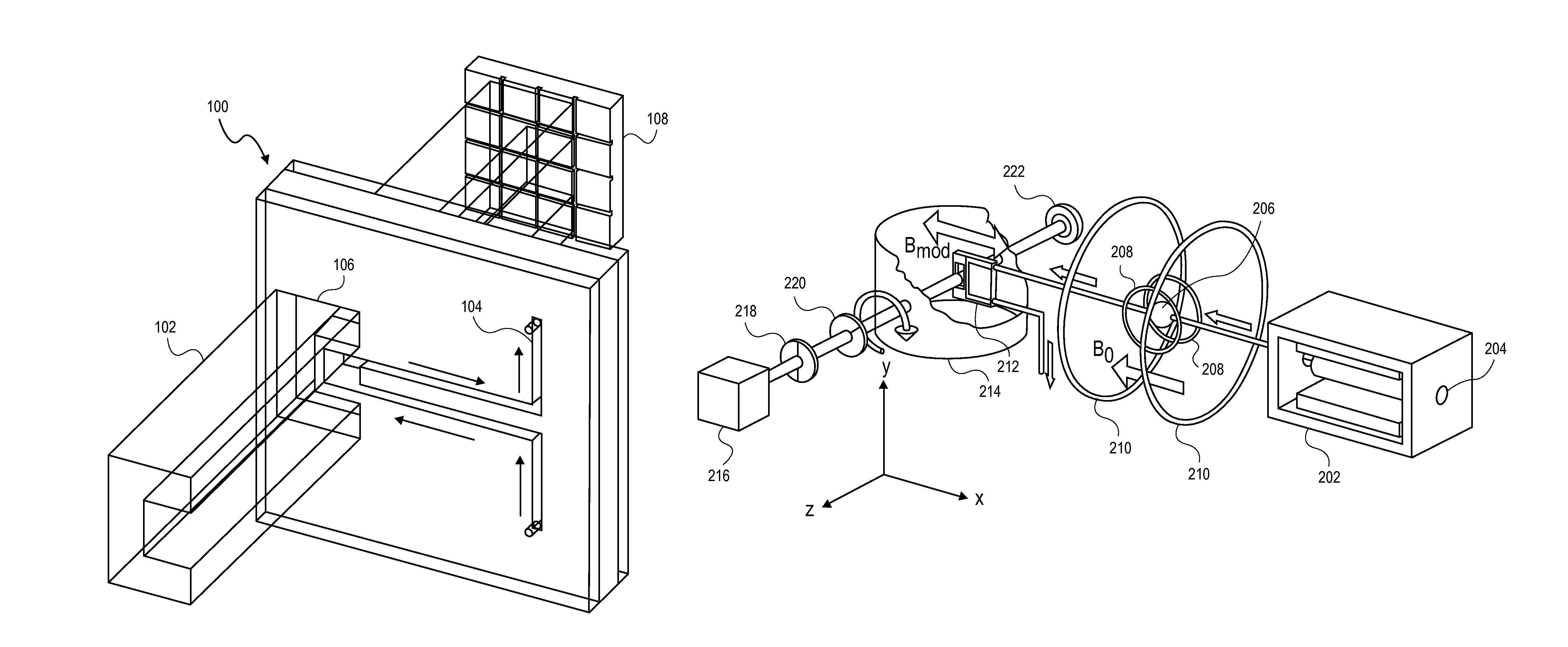
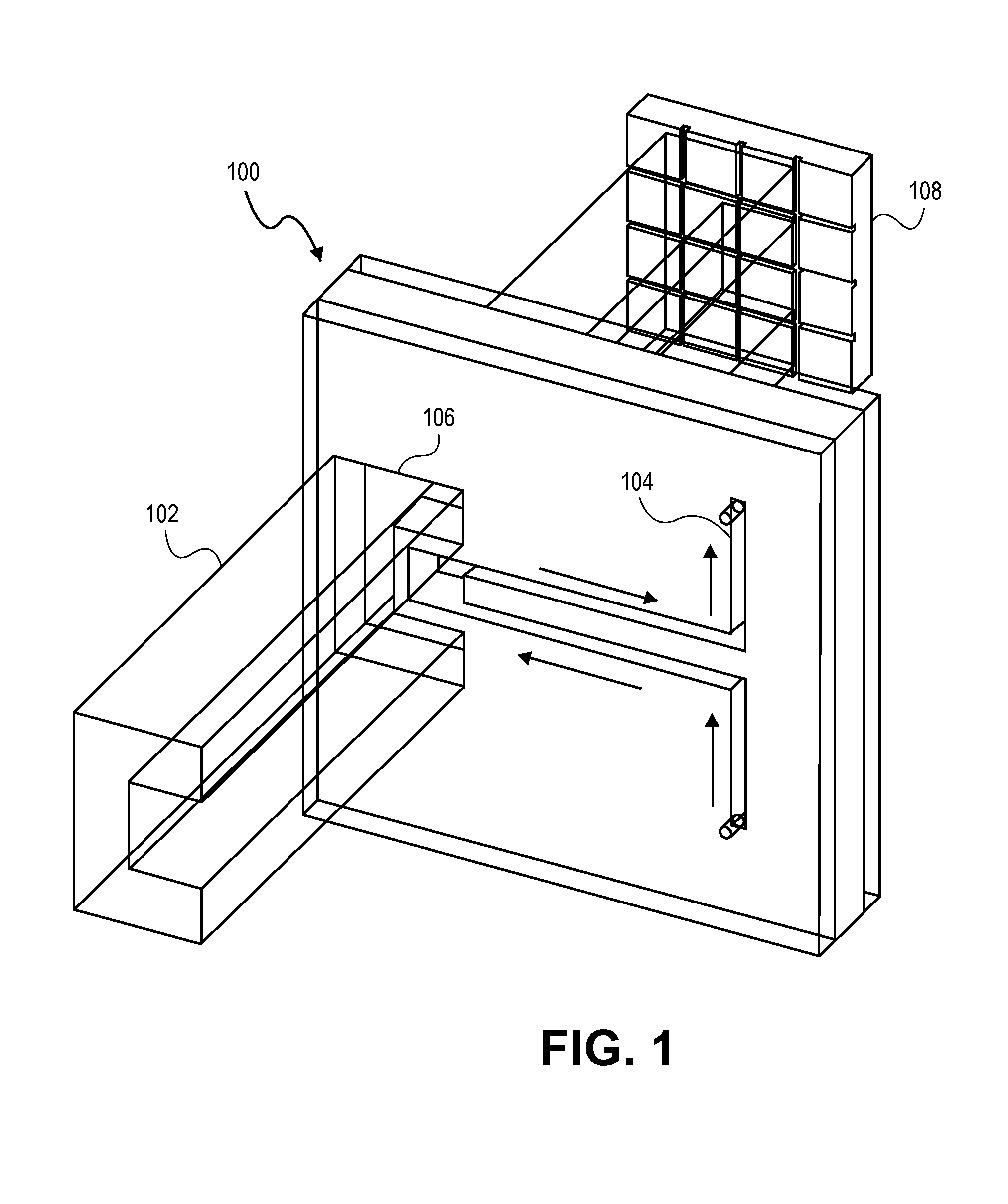
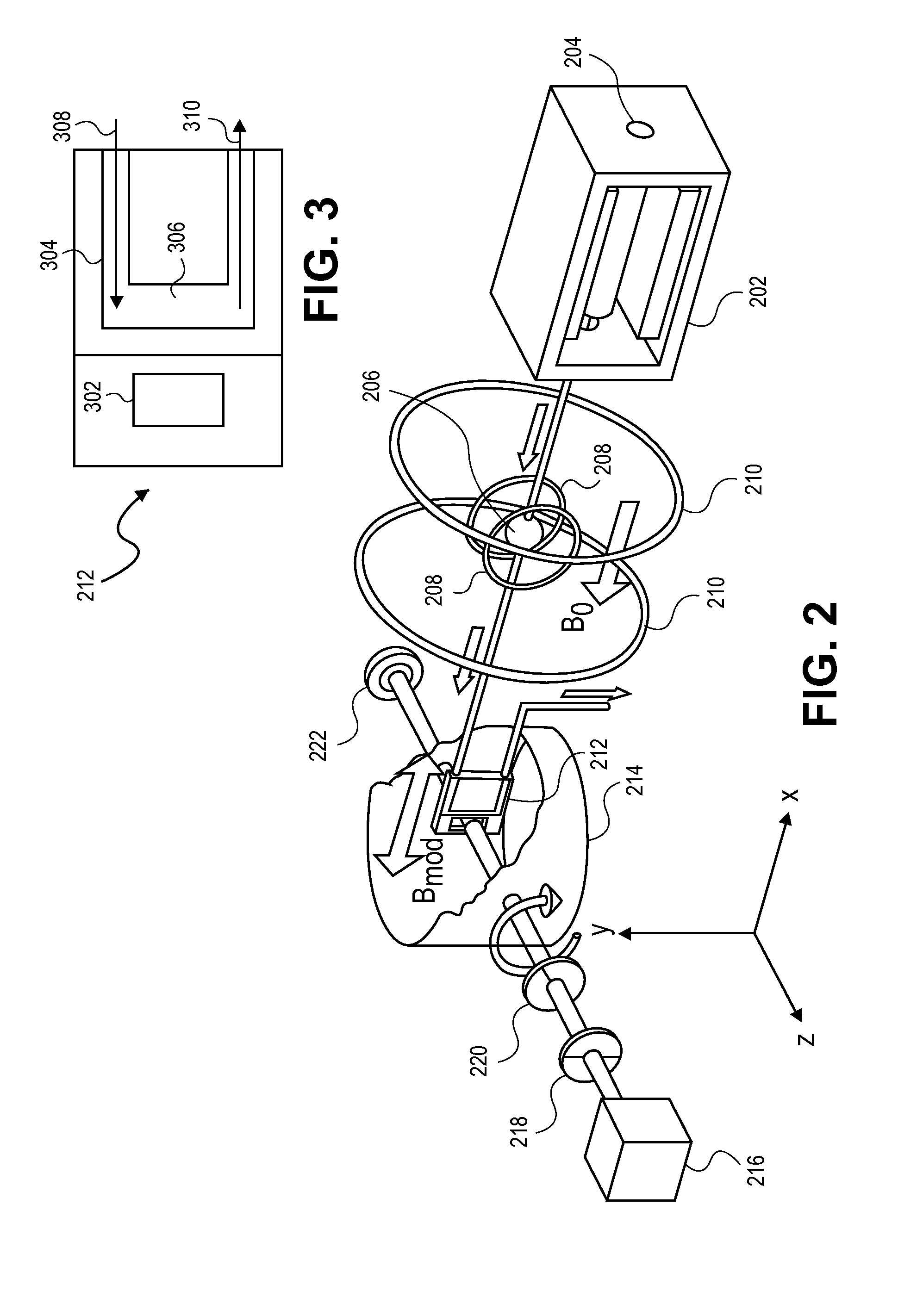
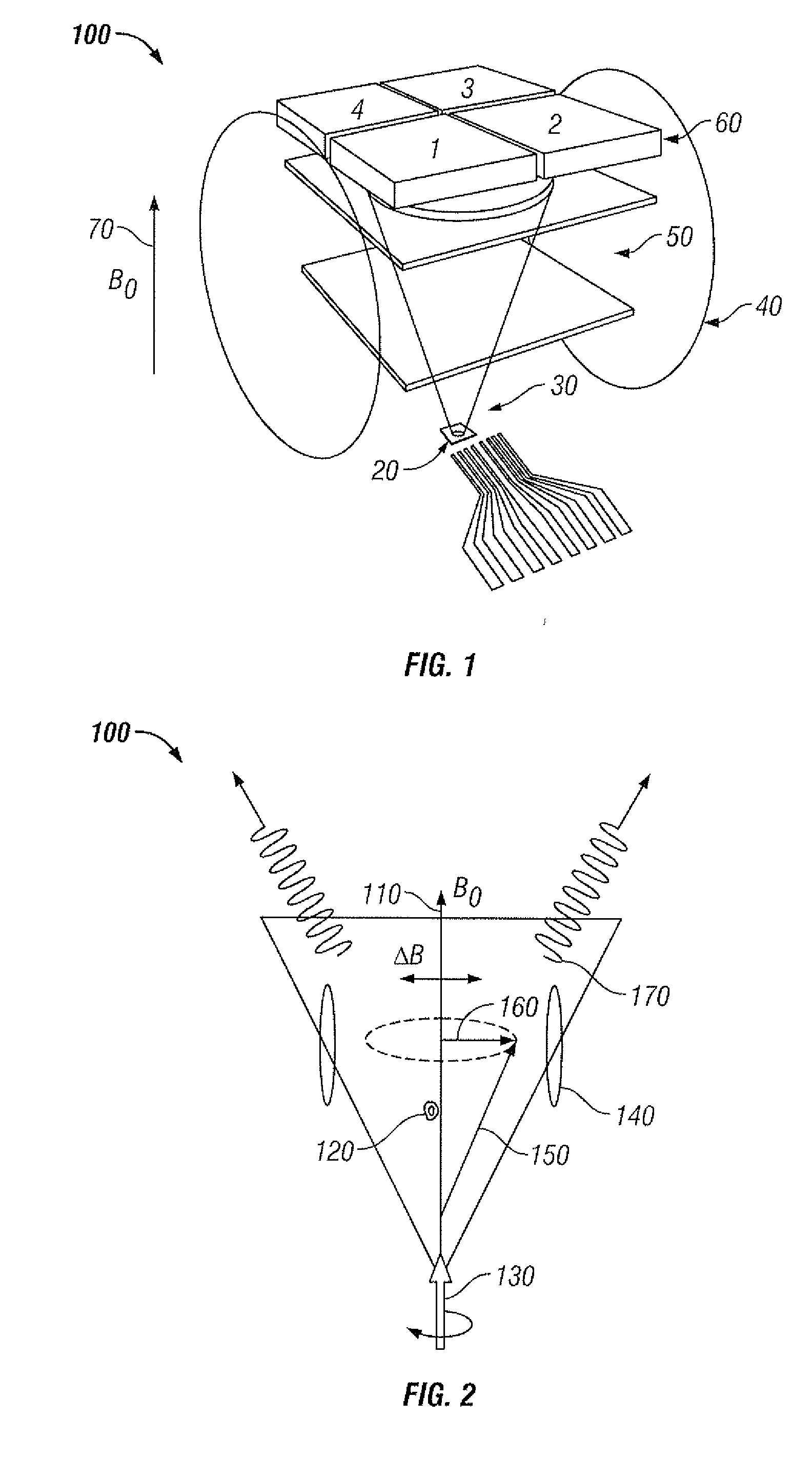
Atomic magnetometer
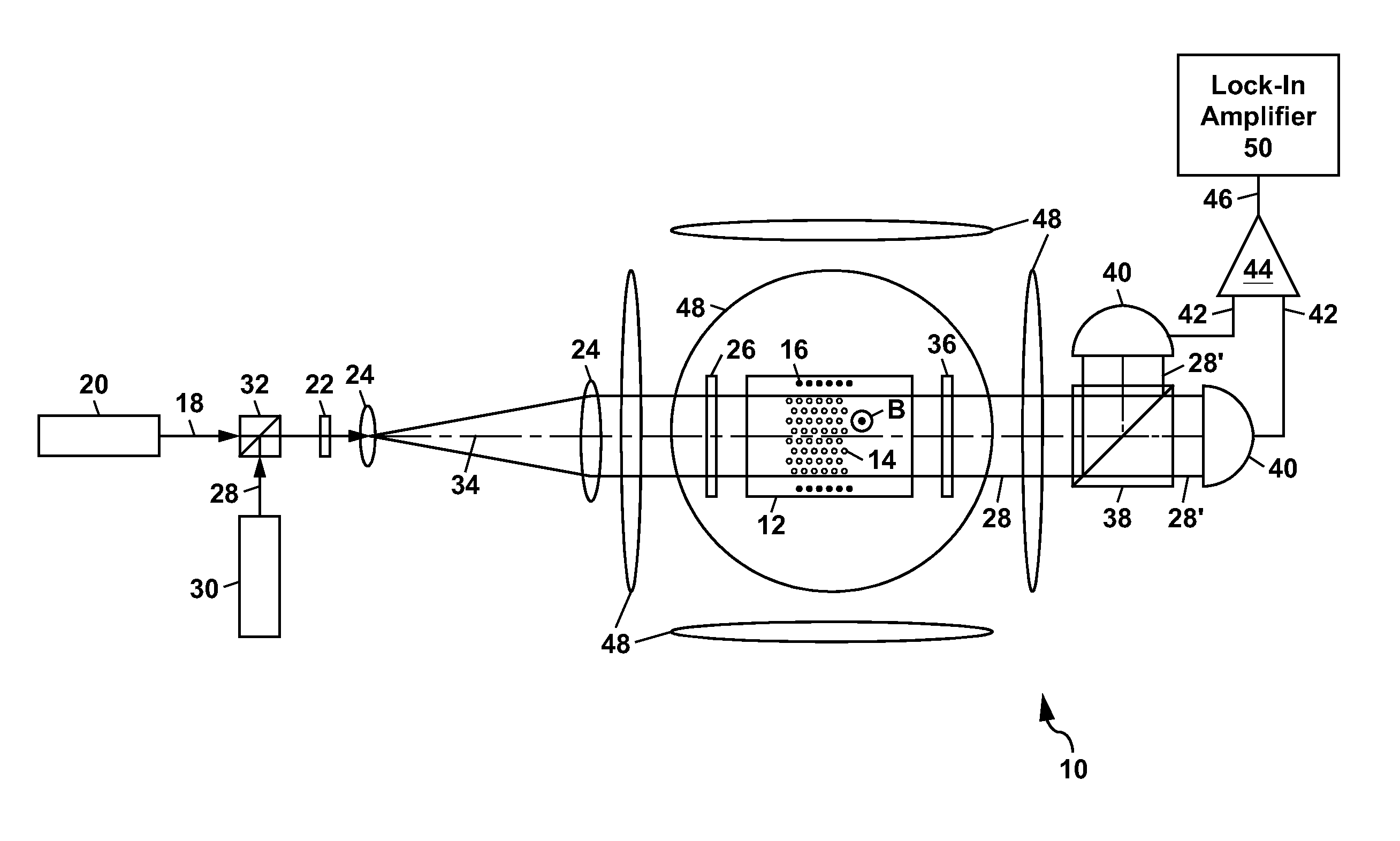
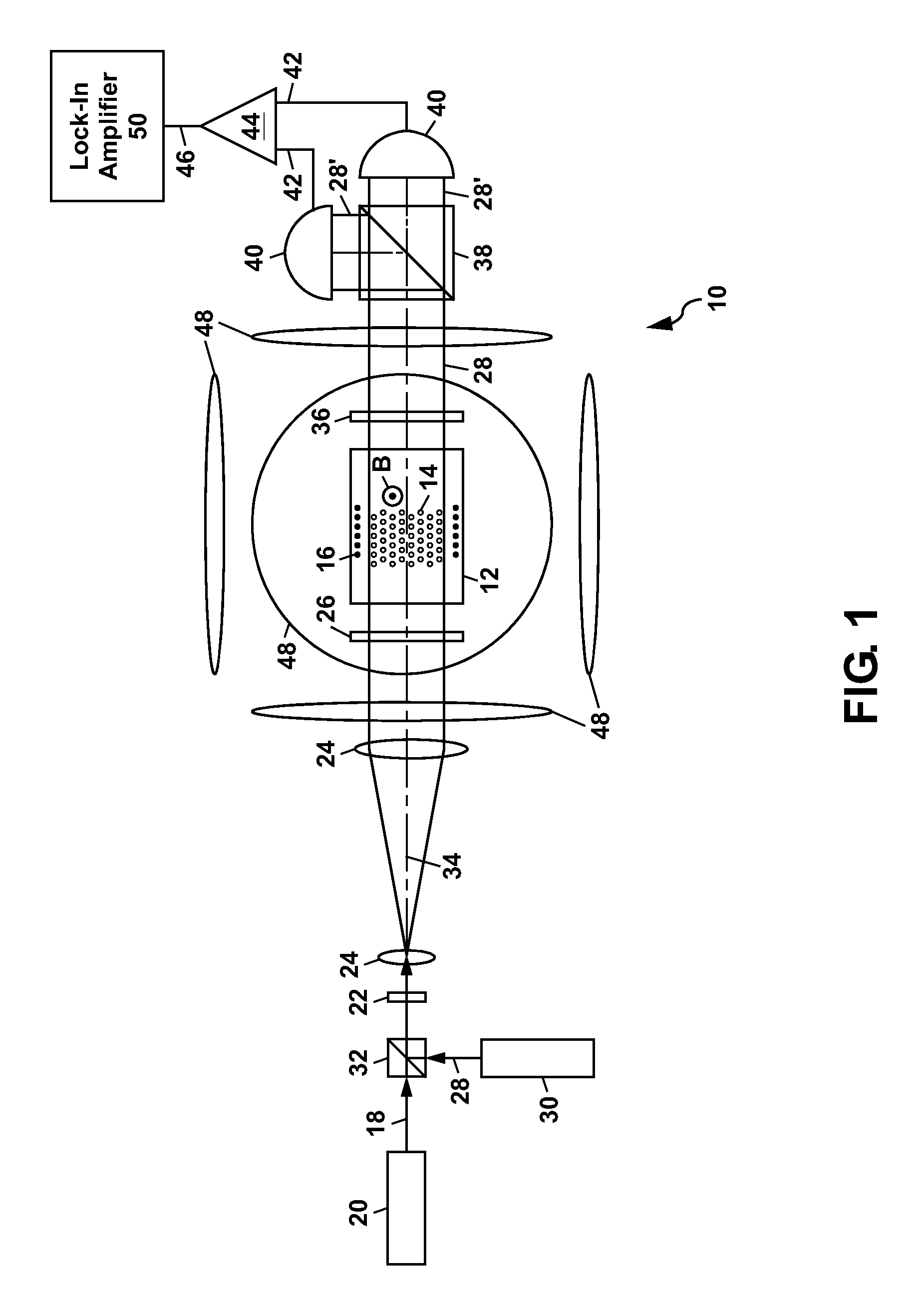
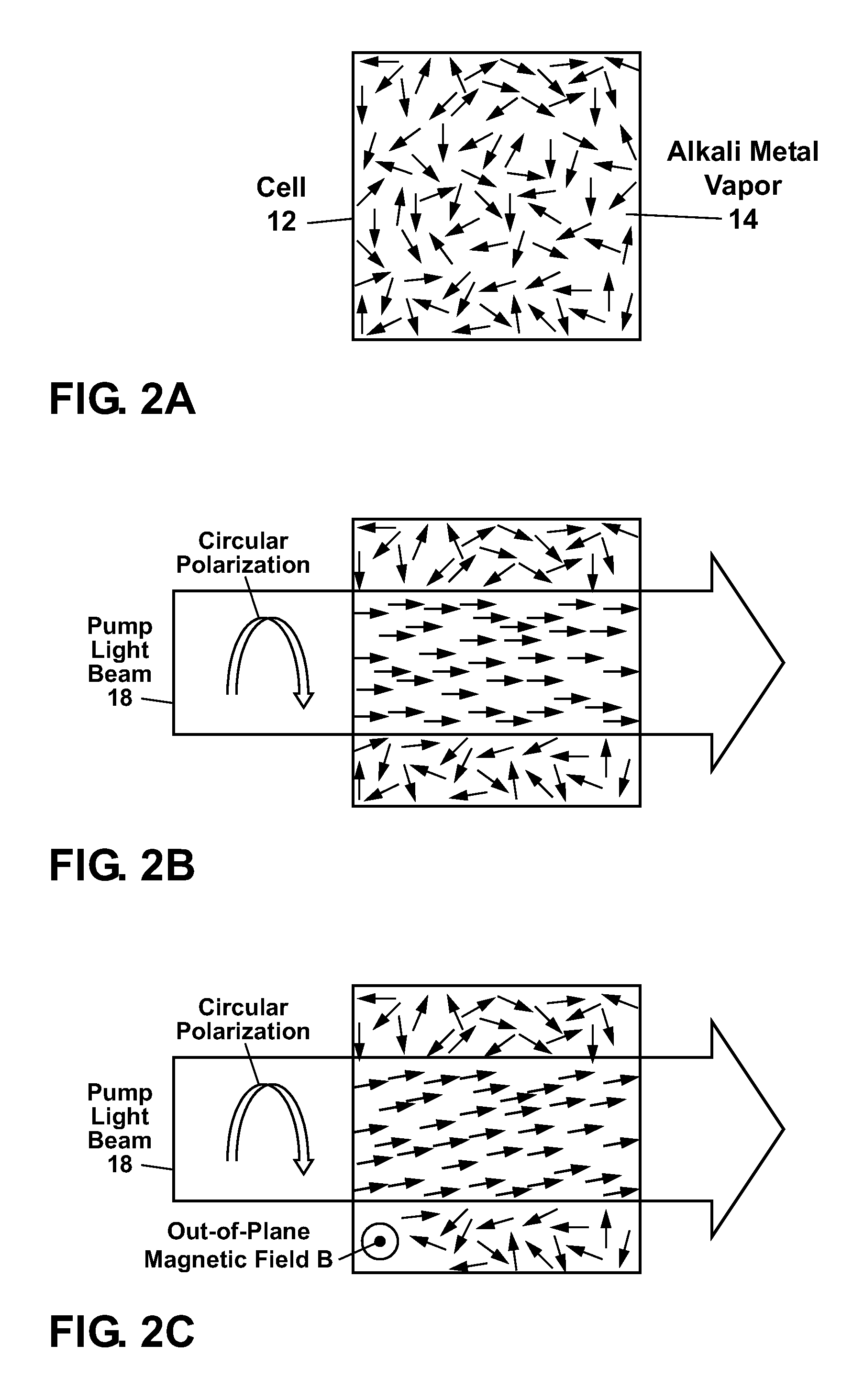
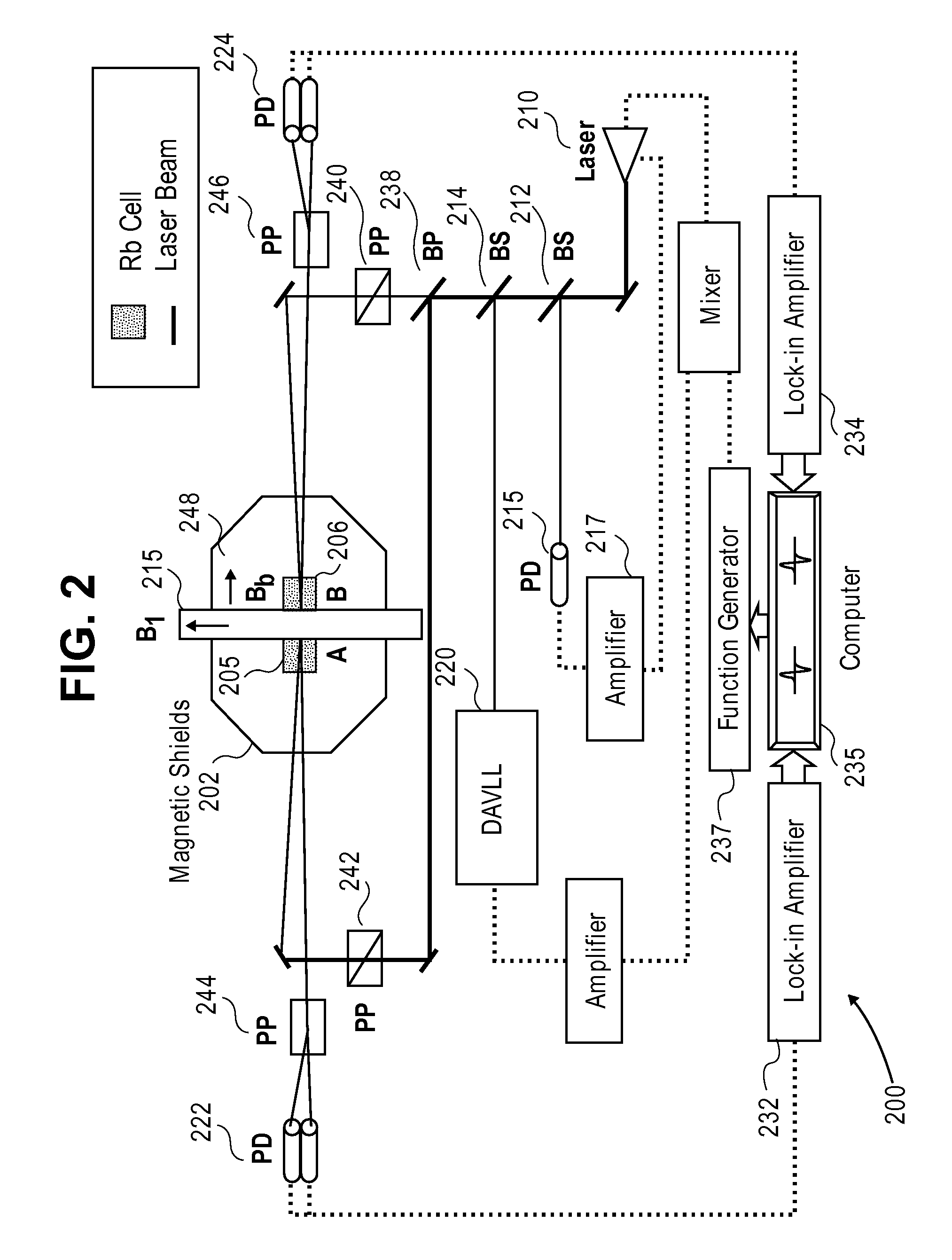
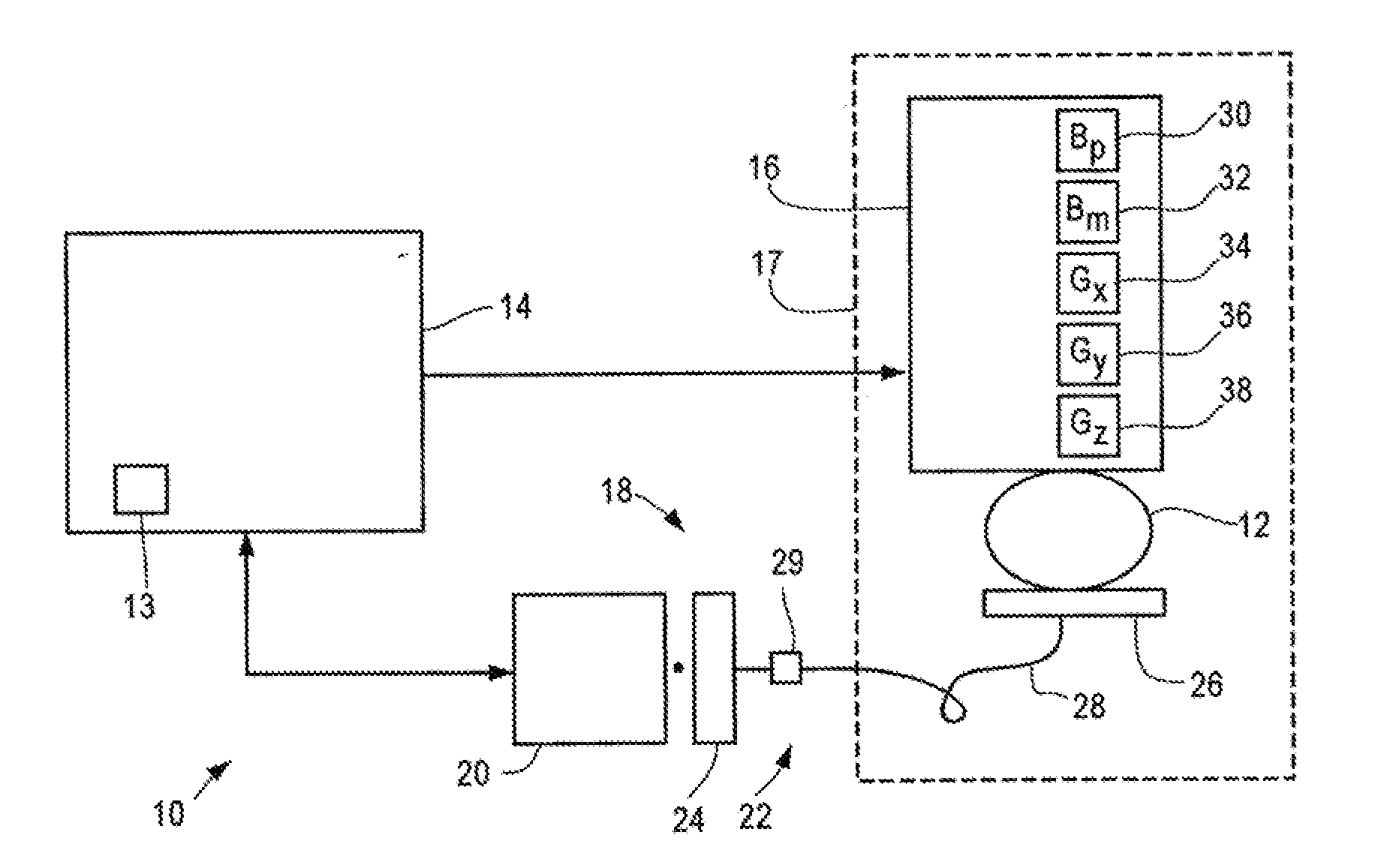
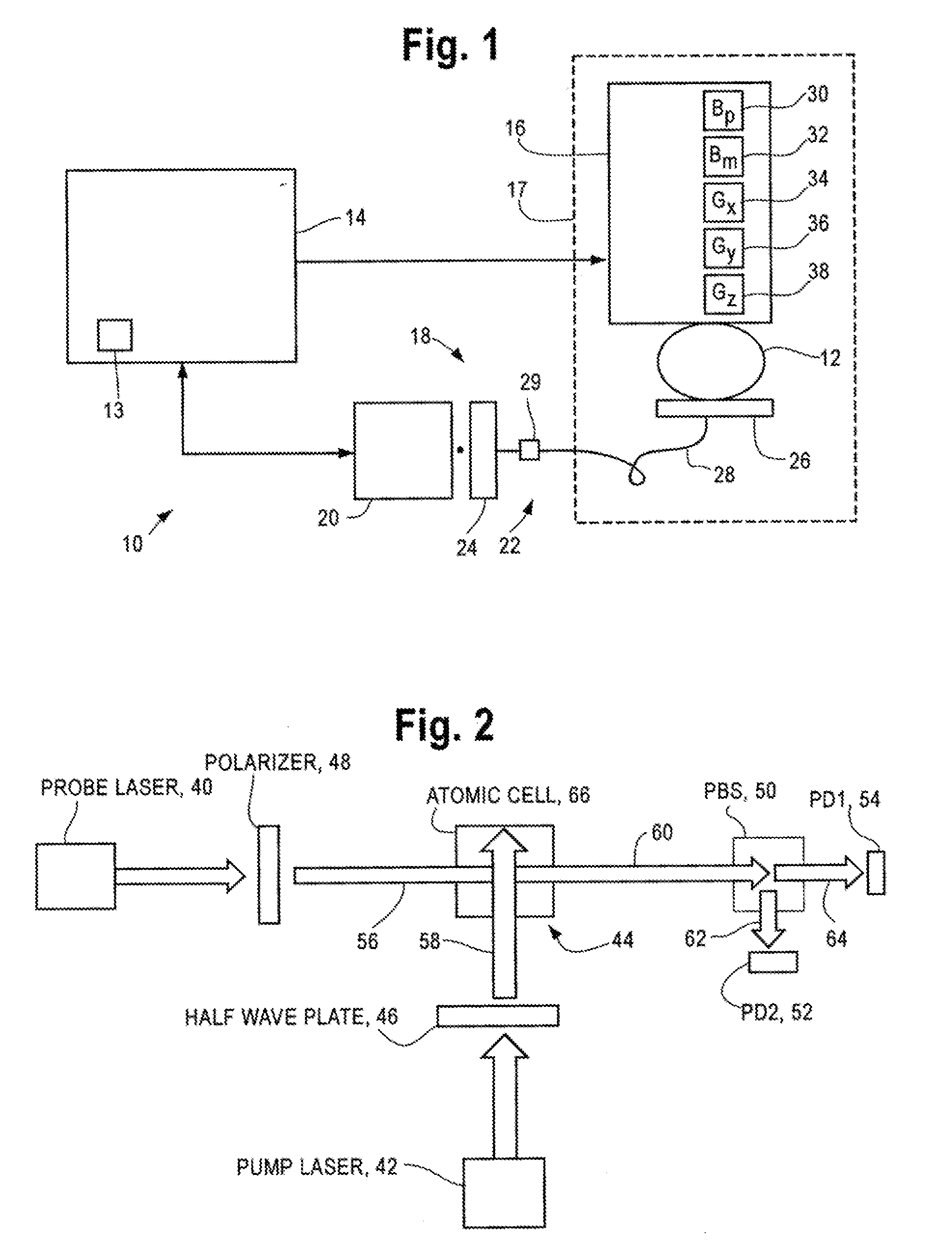
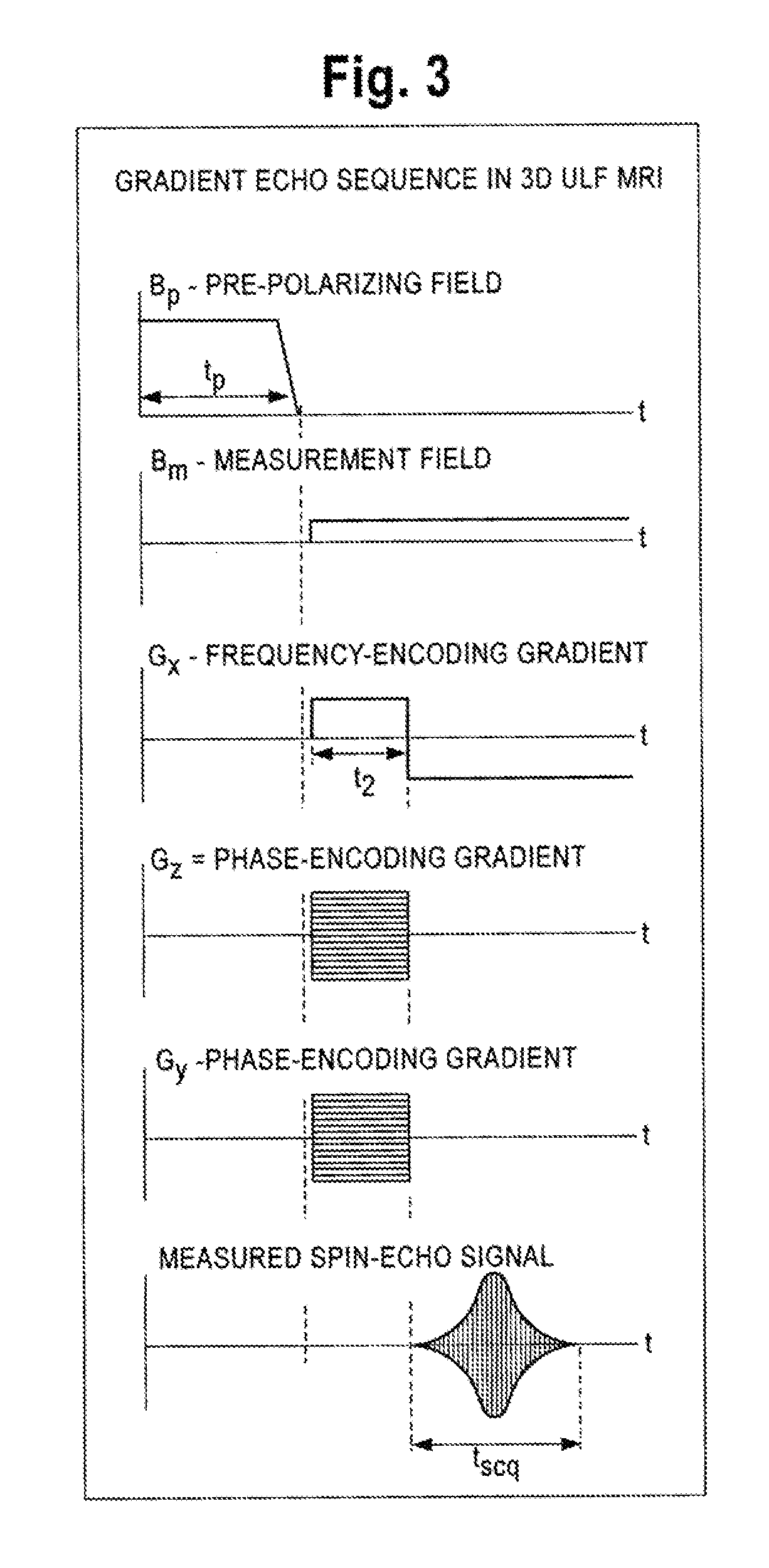
ActiveUS8212556B1Improve signal-to-noise ratioElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonancePhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
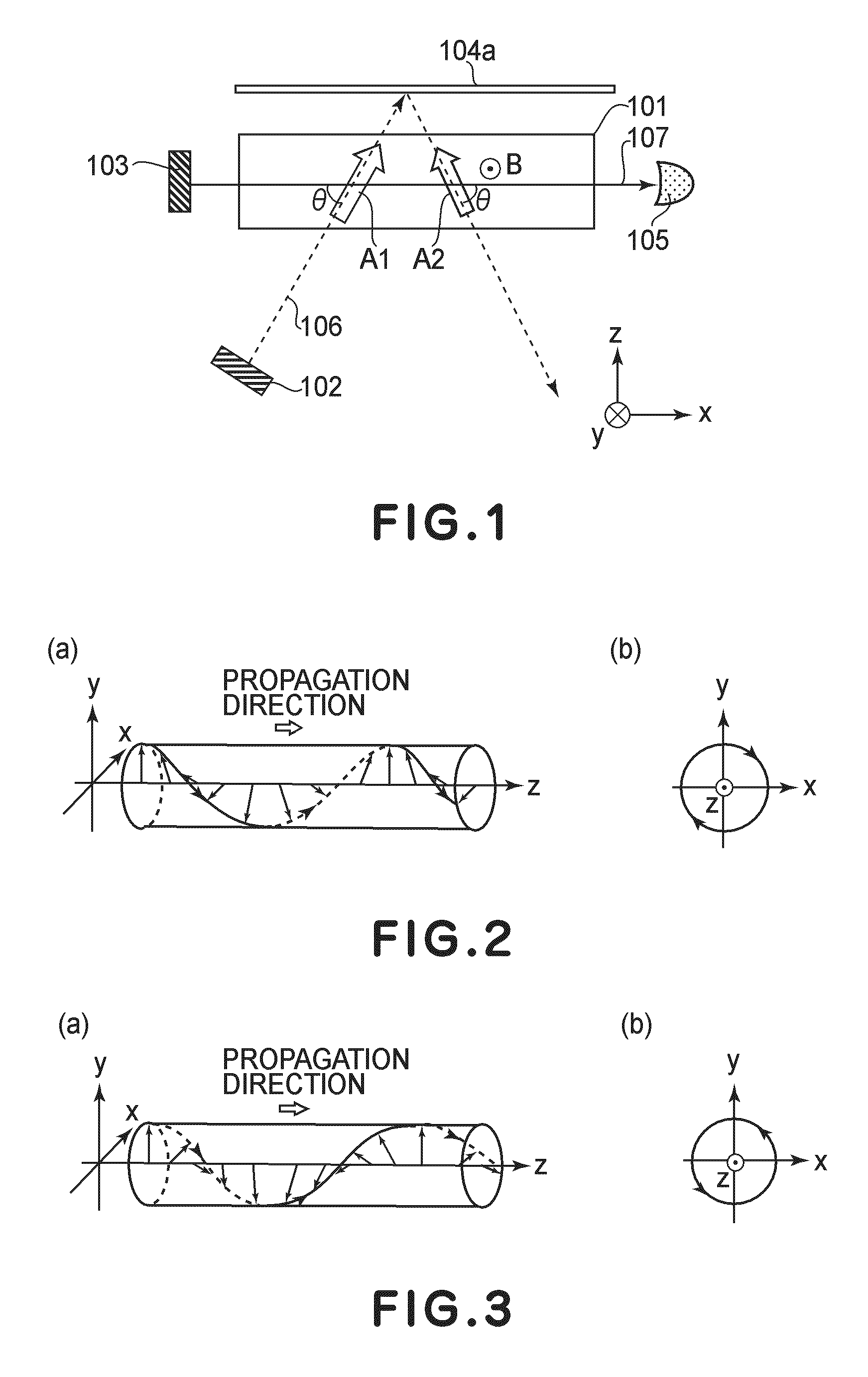
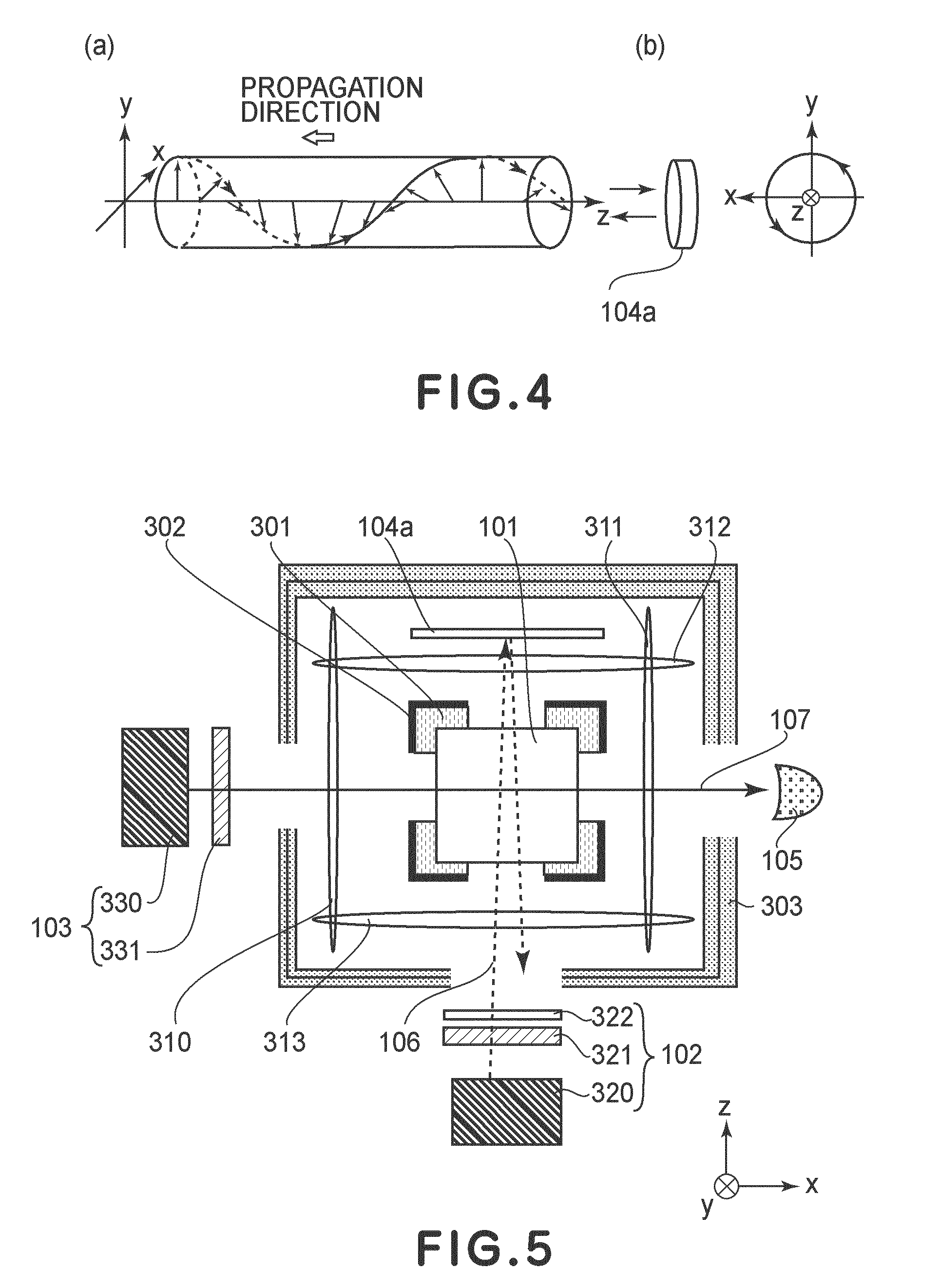
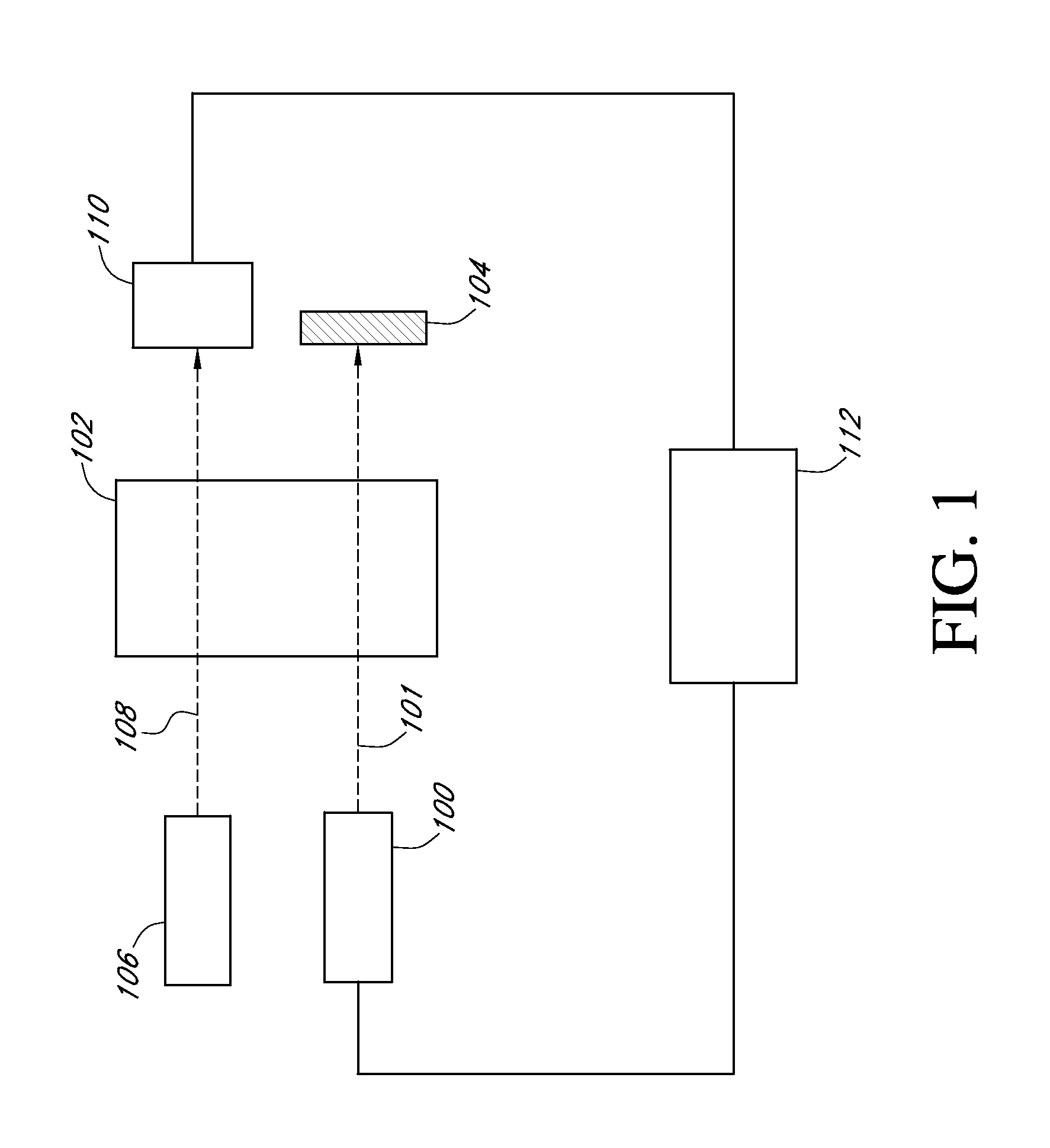
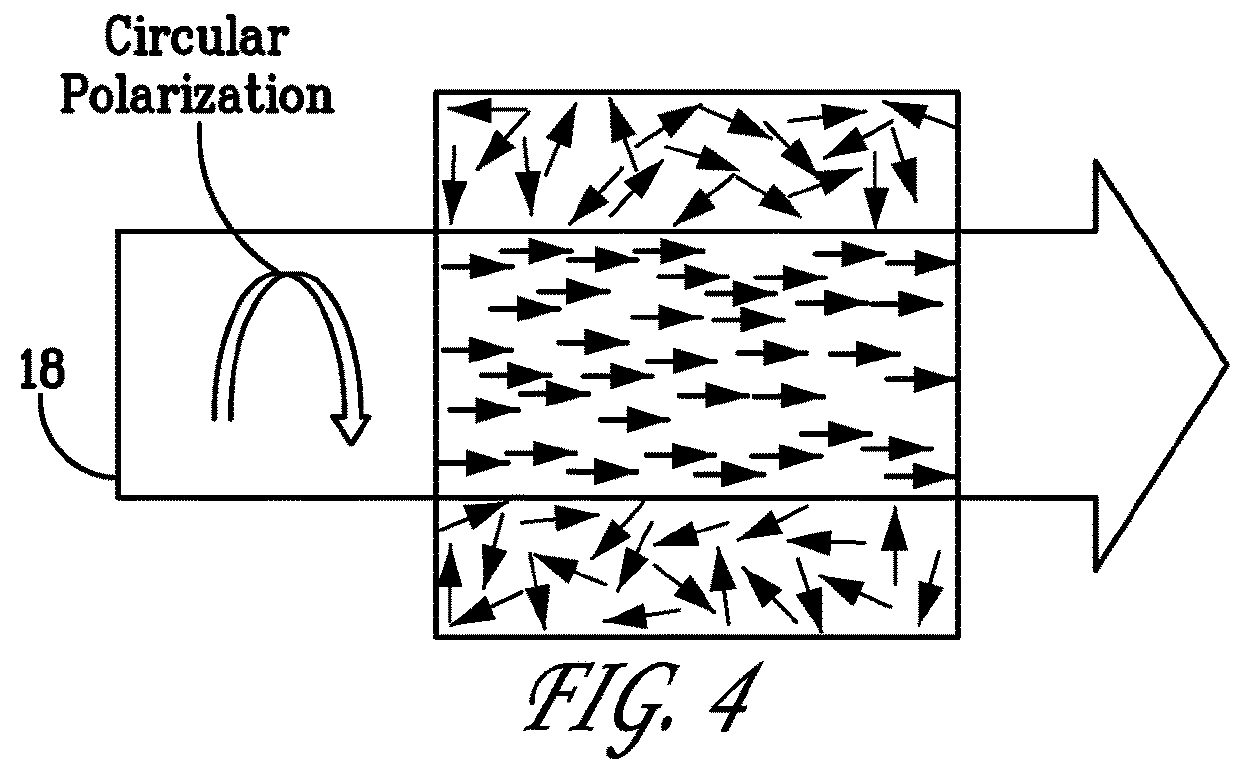
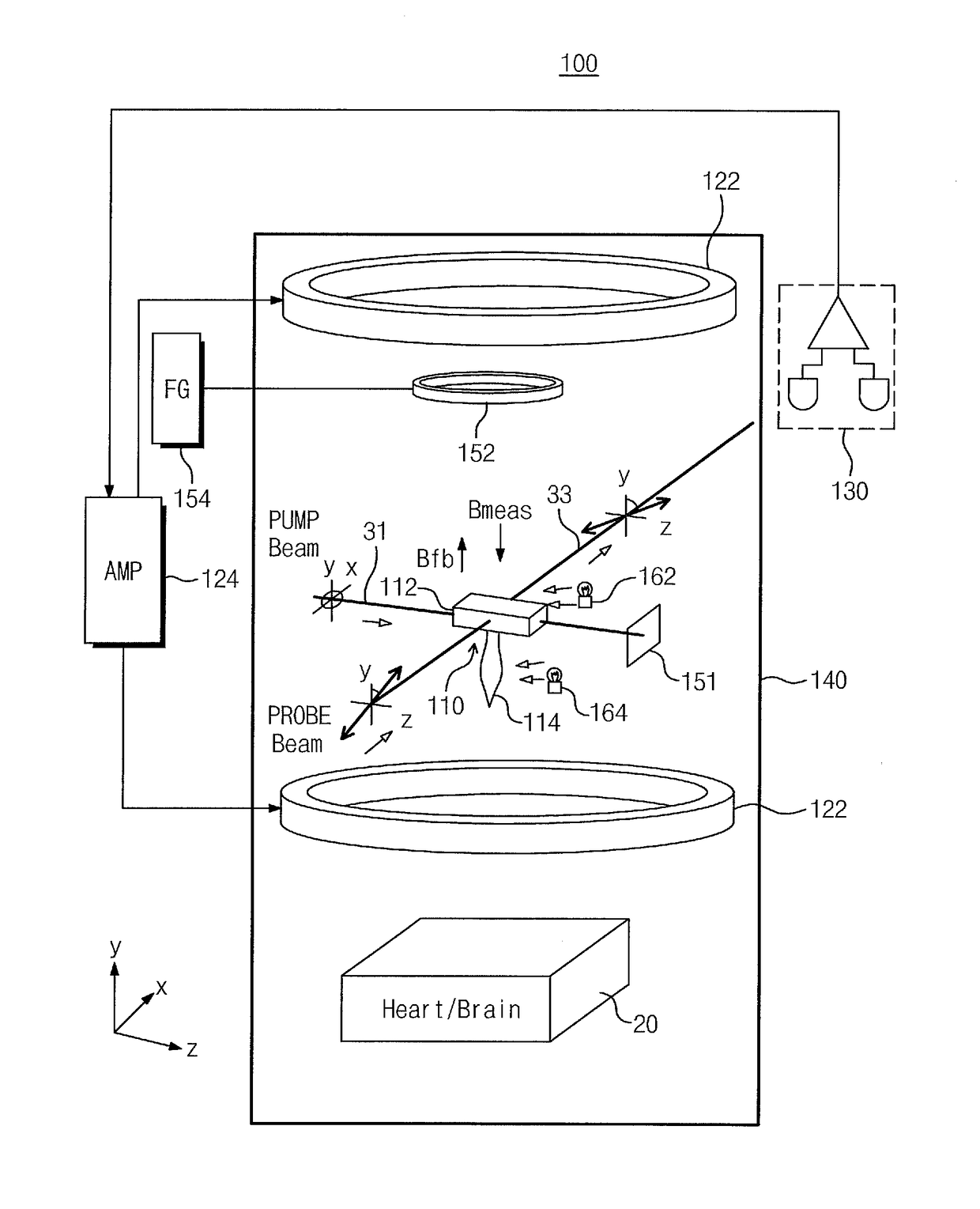
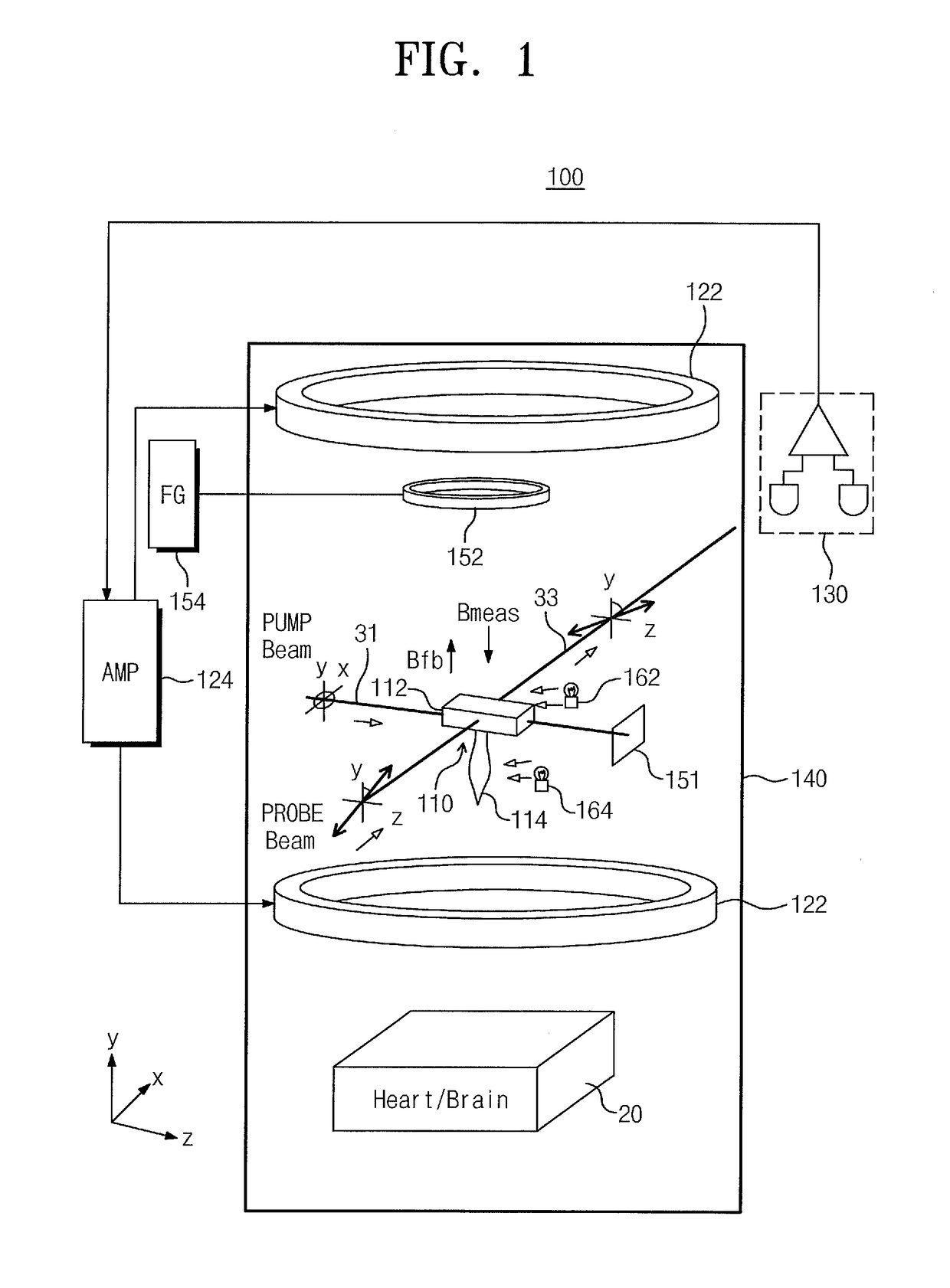
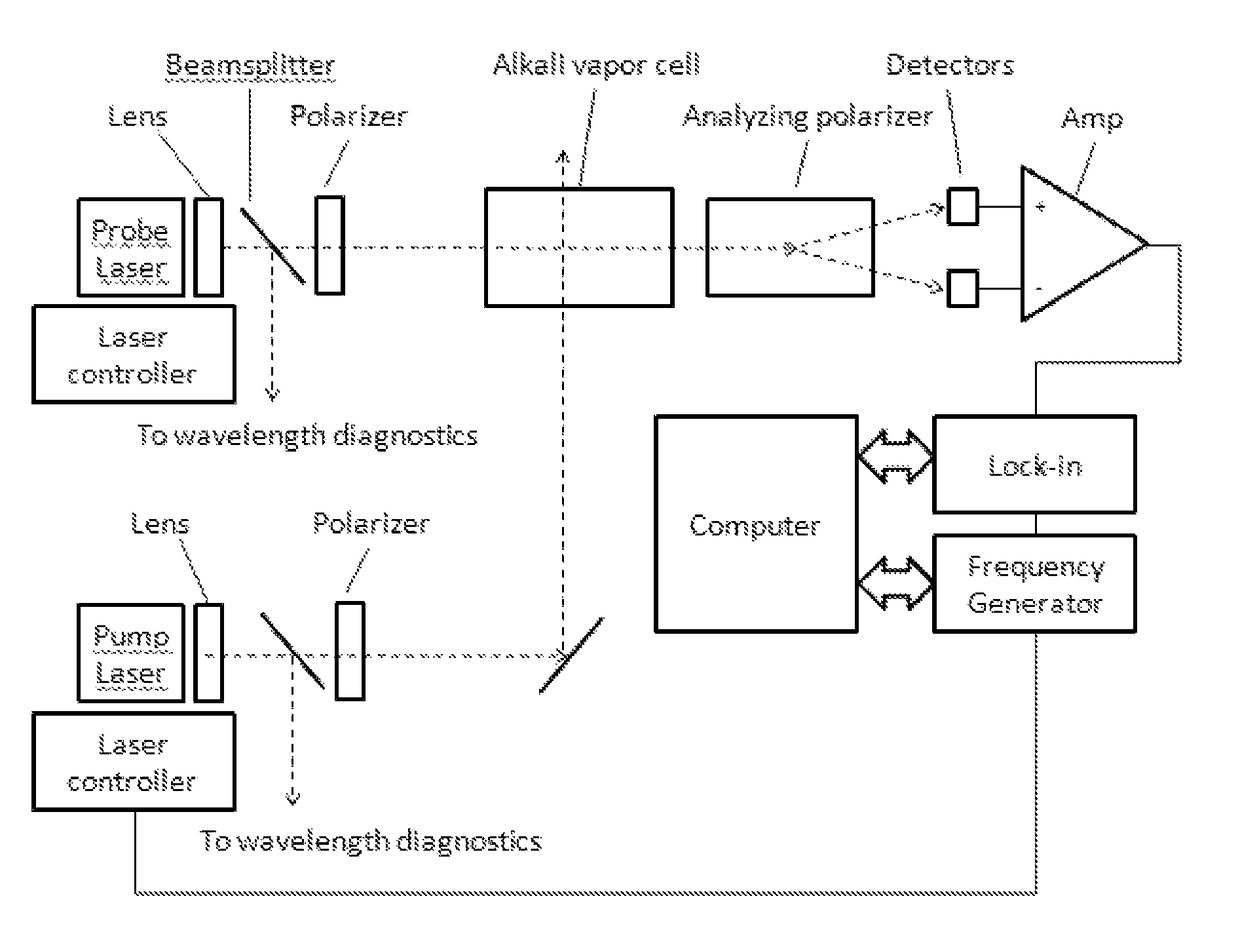
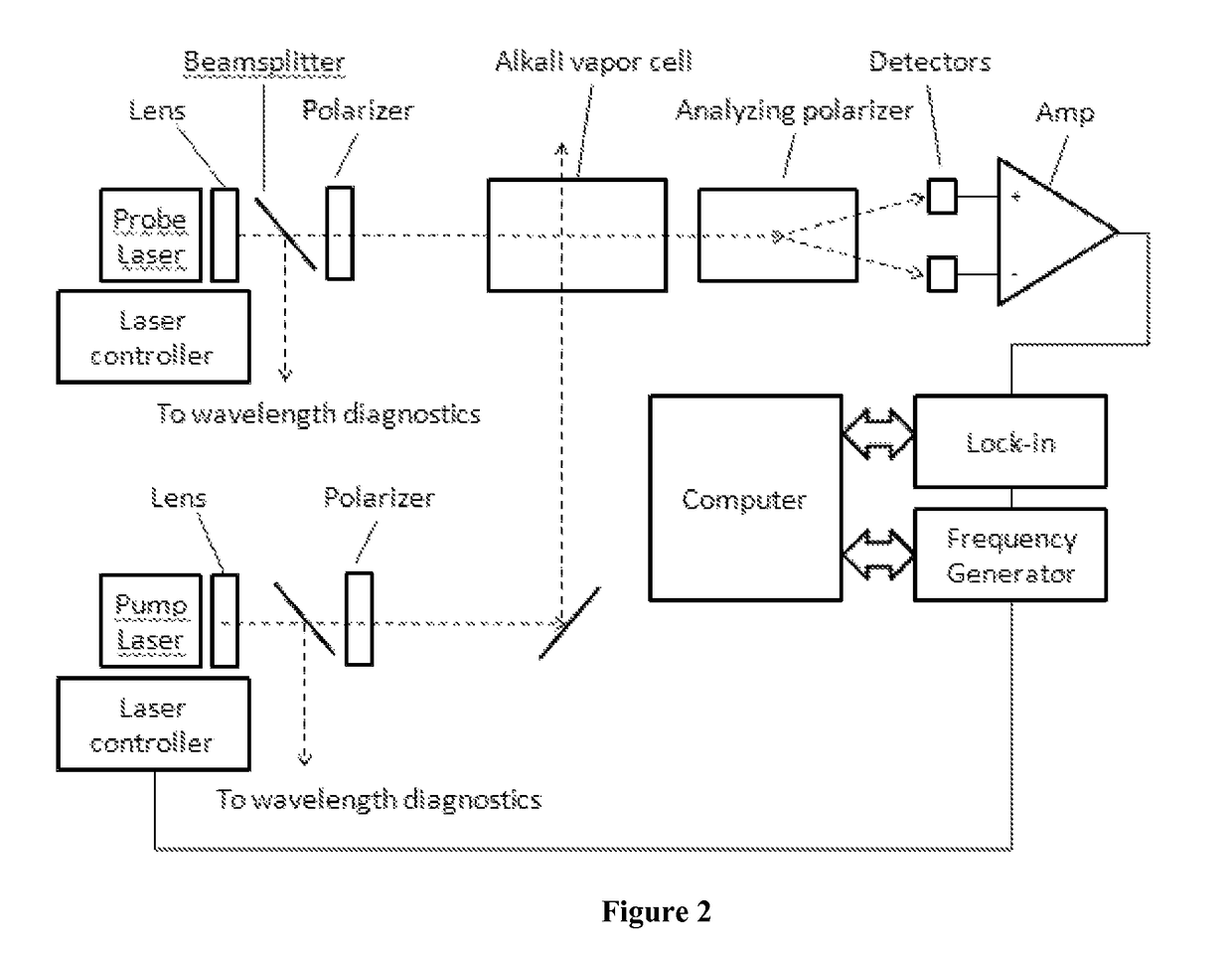
An atomic magnetometer is disclosed which uses a pump light beam at a D1 or D2 transition of an alkali metal vapor to magnetically polarize the vapor in a heated cell, and a probe light beam at a different D2 or D1 transition to sense the magnetic field via a polarization rotation of the probe light beam. The pump and probe light beams are both directed along substantially the same optical path through an optical waveplate and through the heated cell to an optical filter which blocks the pump light beam while transmitting the probe light beam to one or more photodetectors which generate electrical signals to sense the magnetic field. The optical waveplate functions as a quarter waveplate to circularly polarize the pump light beam, and as a half waveplate to maintain the probe light beam linearly polarized.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
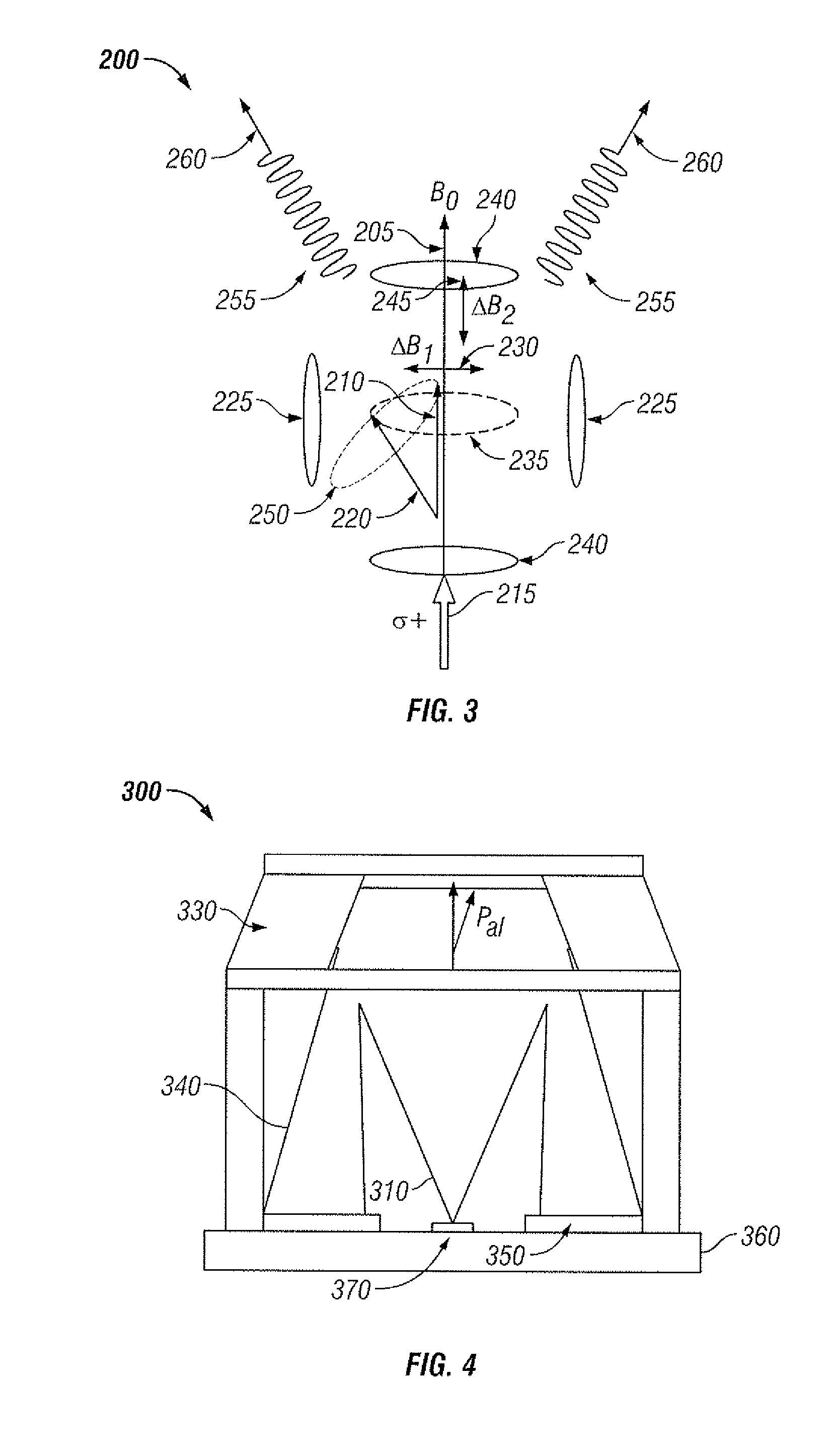
Atomic magnetometer and operating method of the same
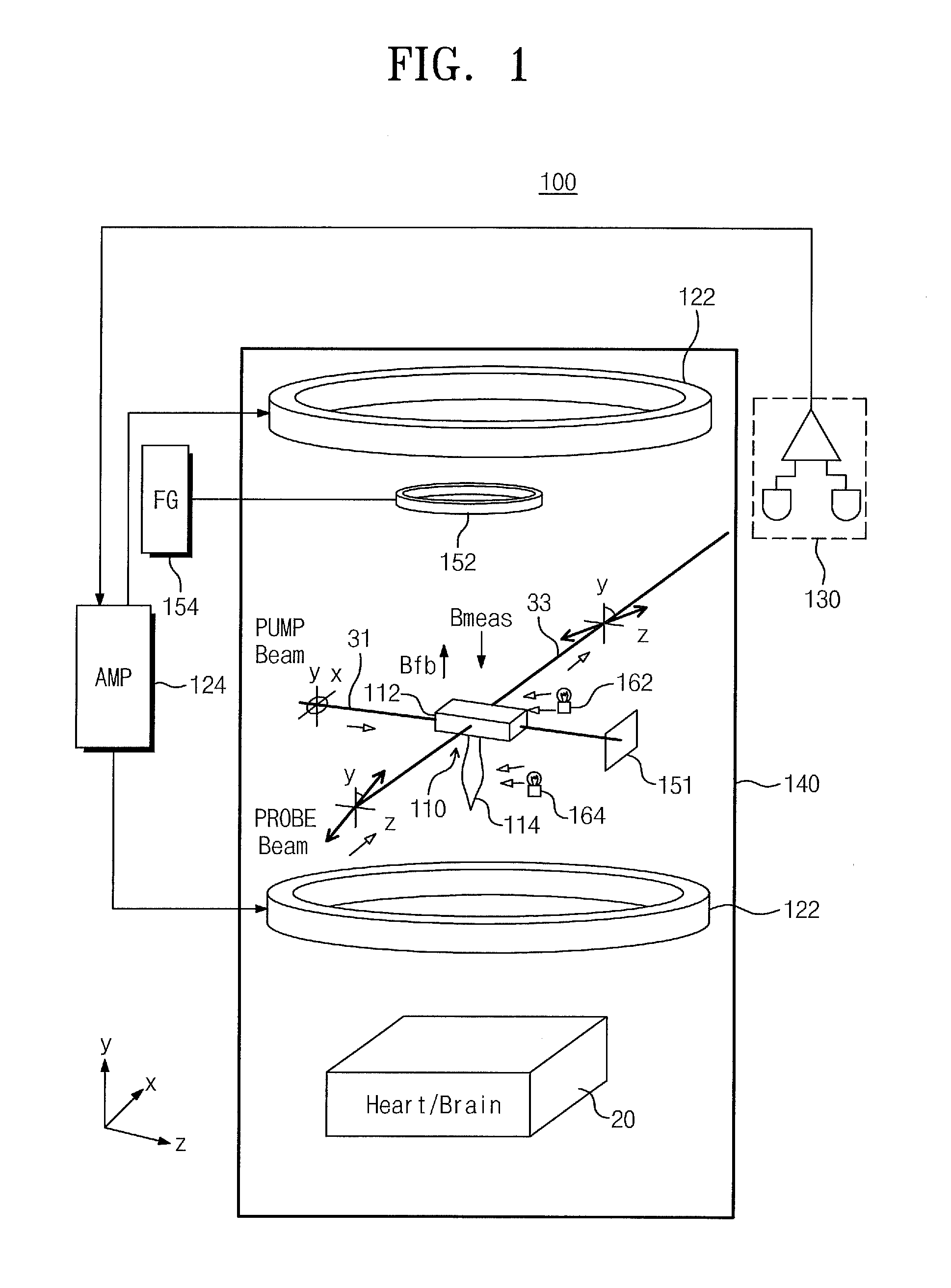
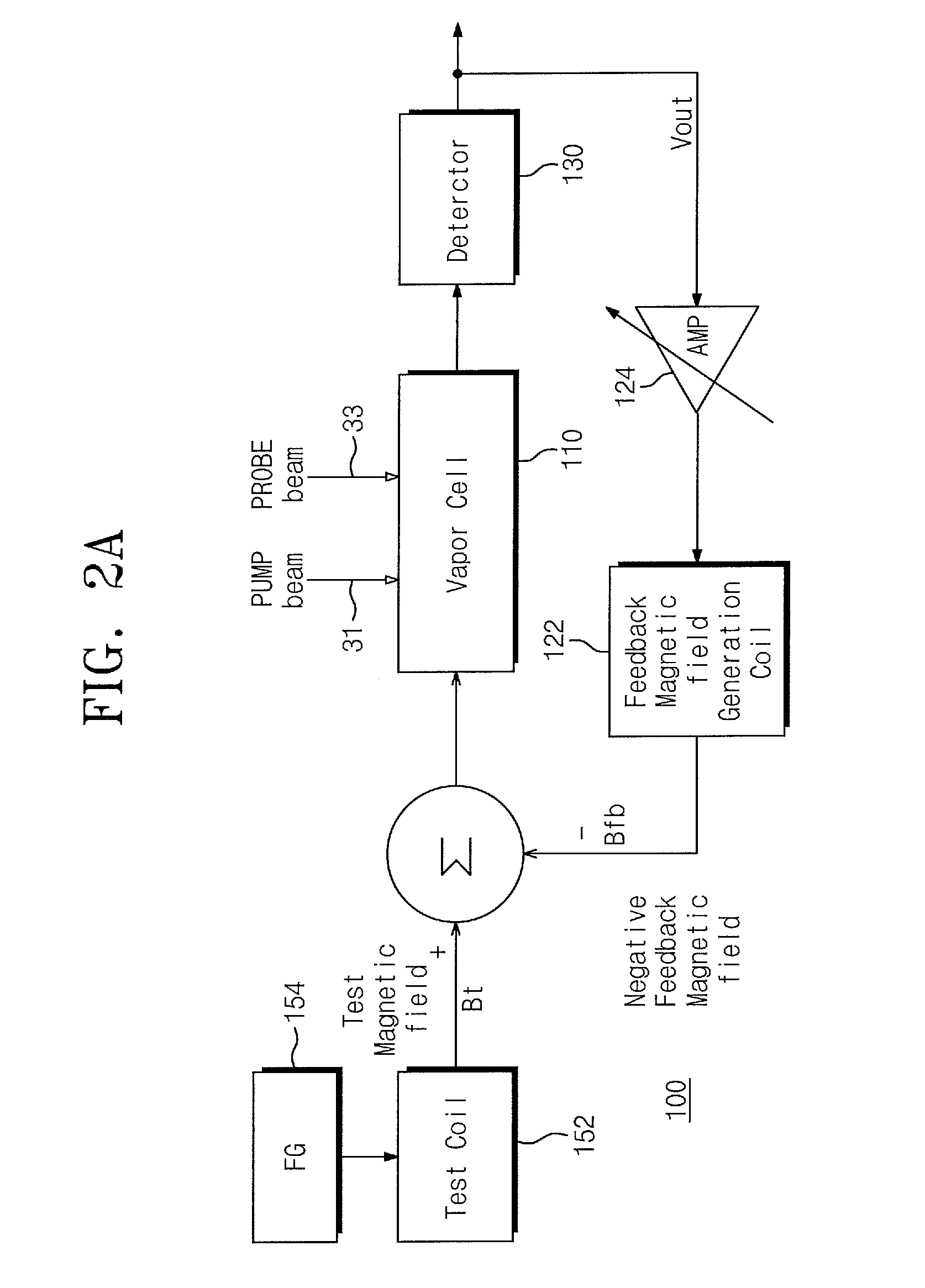
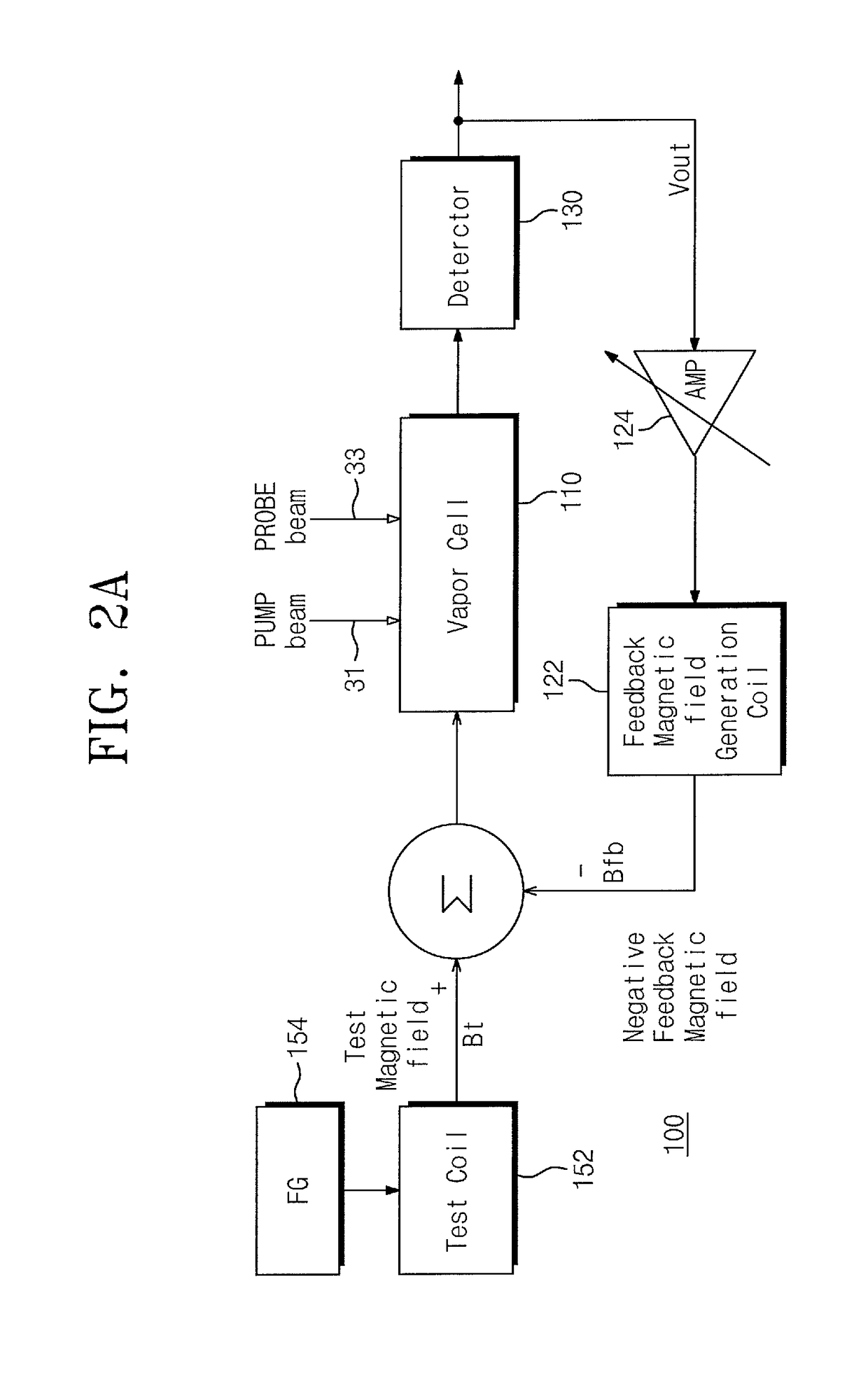
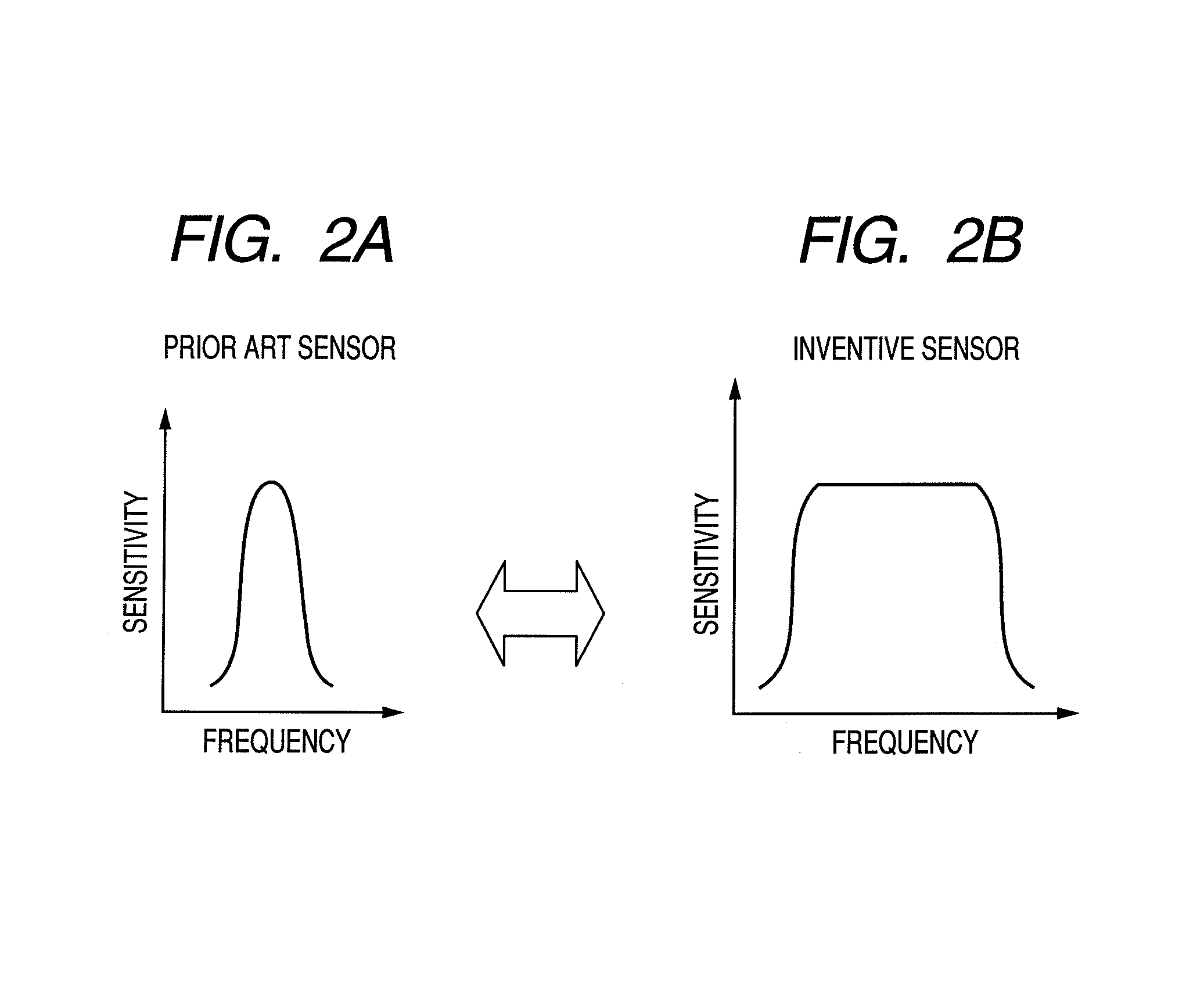
ActiveUS20160116553A1Extend detection bandwidthHigh bandwidthMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesElectric/magnetic detectionNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
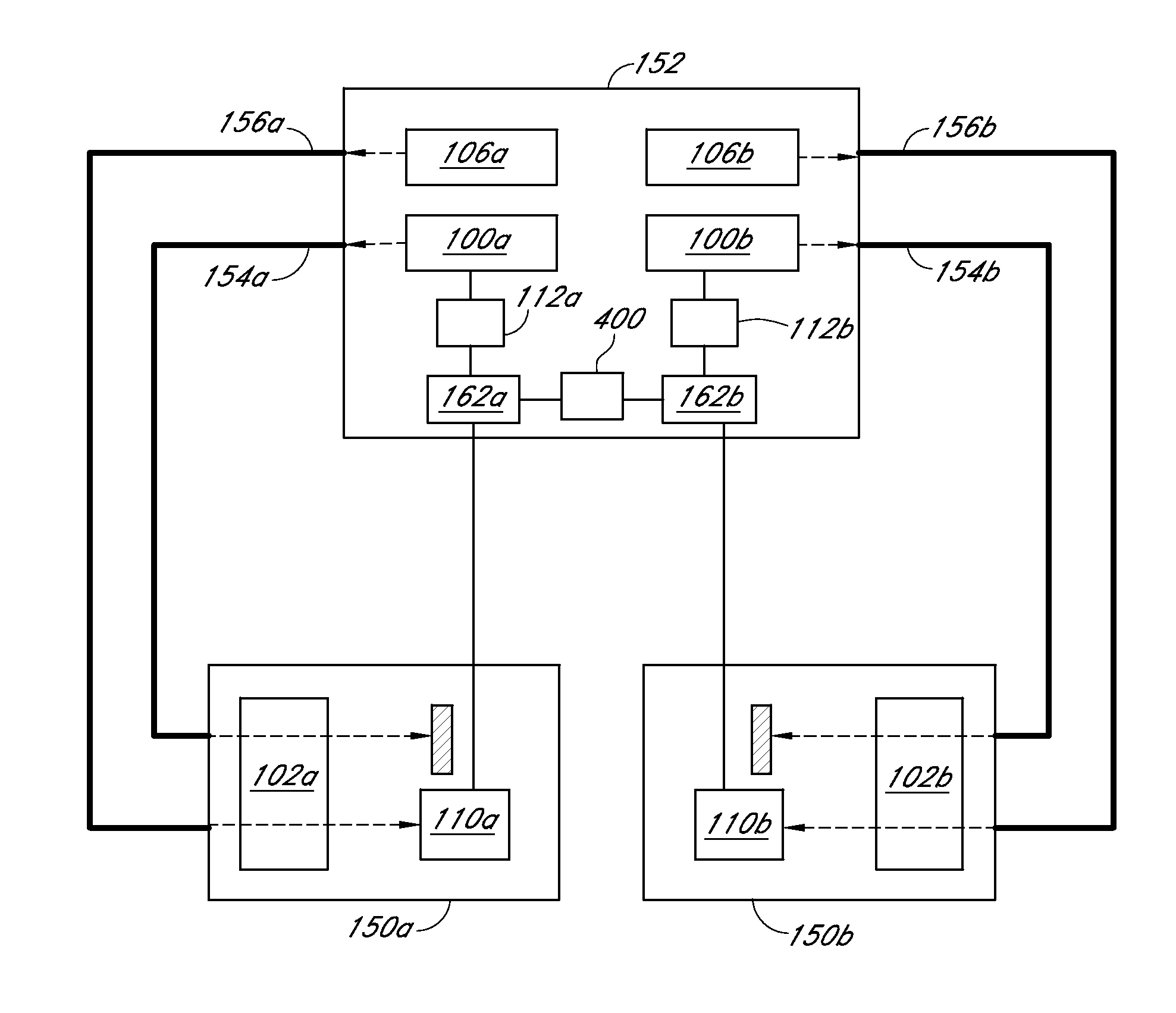
Provided are an atomic magnetometer and an operating method of the same. The atomic magnetometer includes a vapor cell receiving a circularly polarized pump beam and a linearly polarized probe beam and containing an alkali metal vapor, a detector adapted to receive the probe beam passing through the vapor cell to measure magneto-optical rotation of the probe beam, a feedback coil to establish a negative feedback magnetic field signal orthogonal to a first plane defined by traveling directions of the probe beam and the pump beam and provide the negative feedback magnetic field signal to the vapor cell, and a feedback amplifier adapted to provide feedback current to the feedback coil such that the negative feedback magnetic field proportional to a measurement magnetic field is established. The measurement magnetic field of a measurement target provides magneto-optical rotation of the probe beam in the vapor cell.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Atomic magnetic gradiometer for room temperature high sensitivity magnetic field detection
InactiveUS20070205767A1Reduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSingle polarizationGradiometer
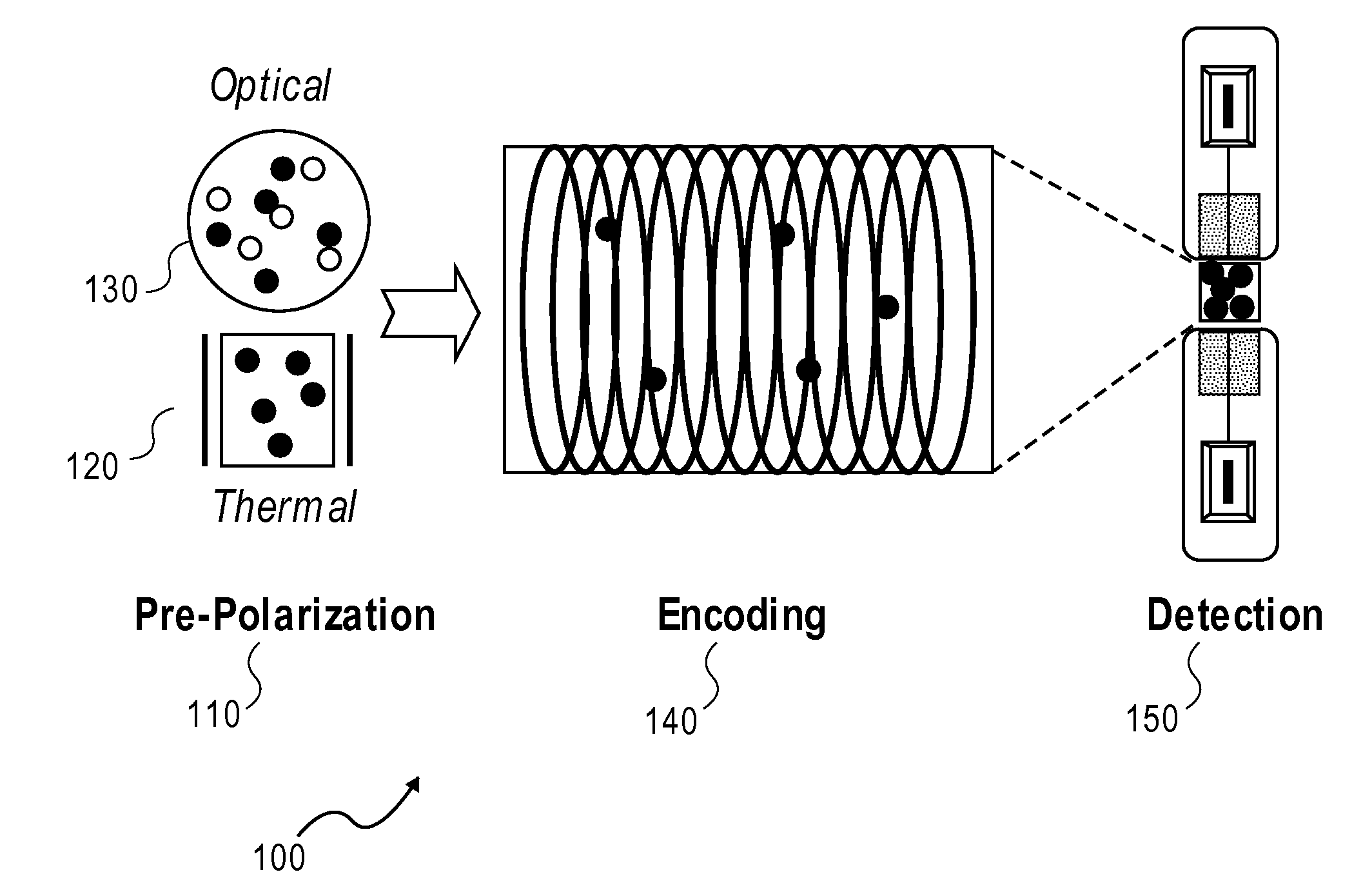
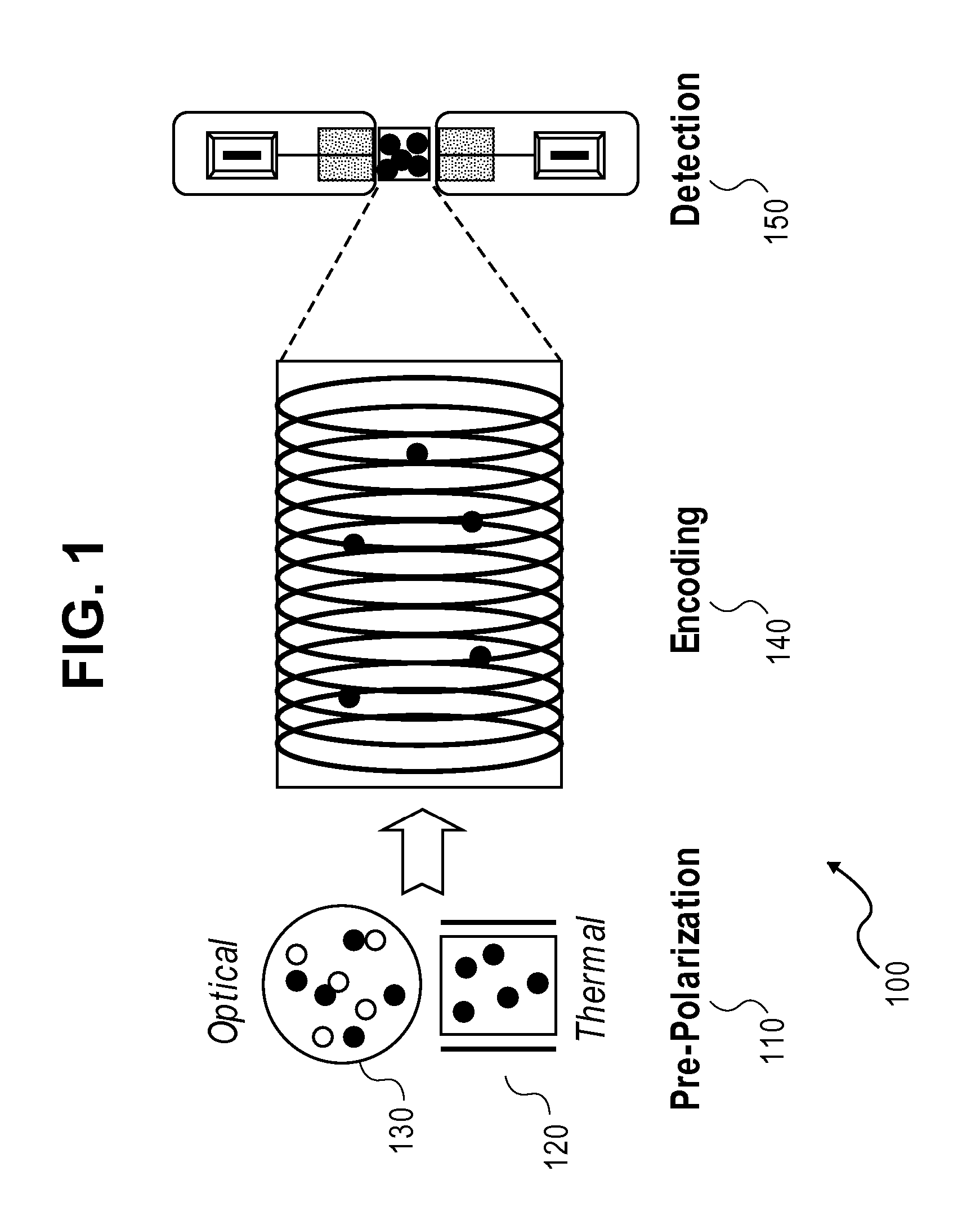
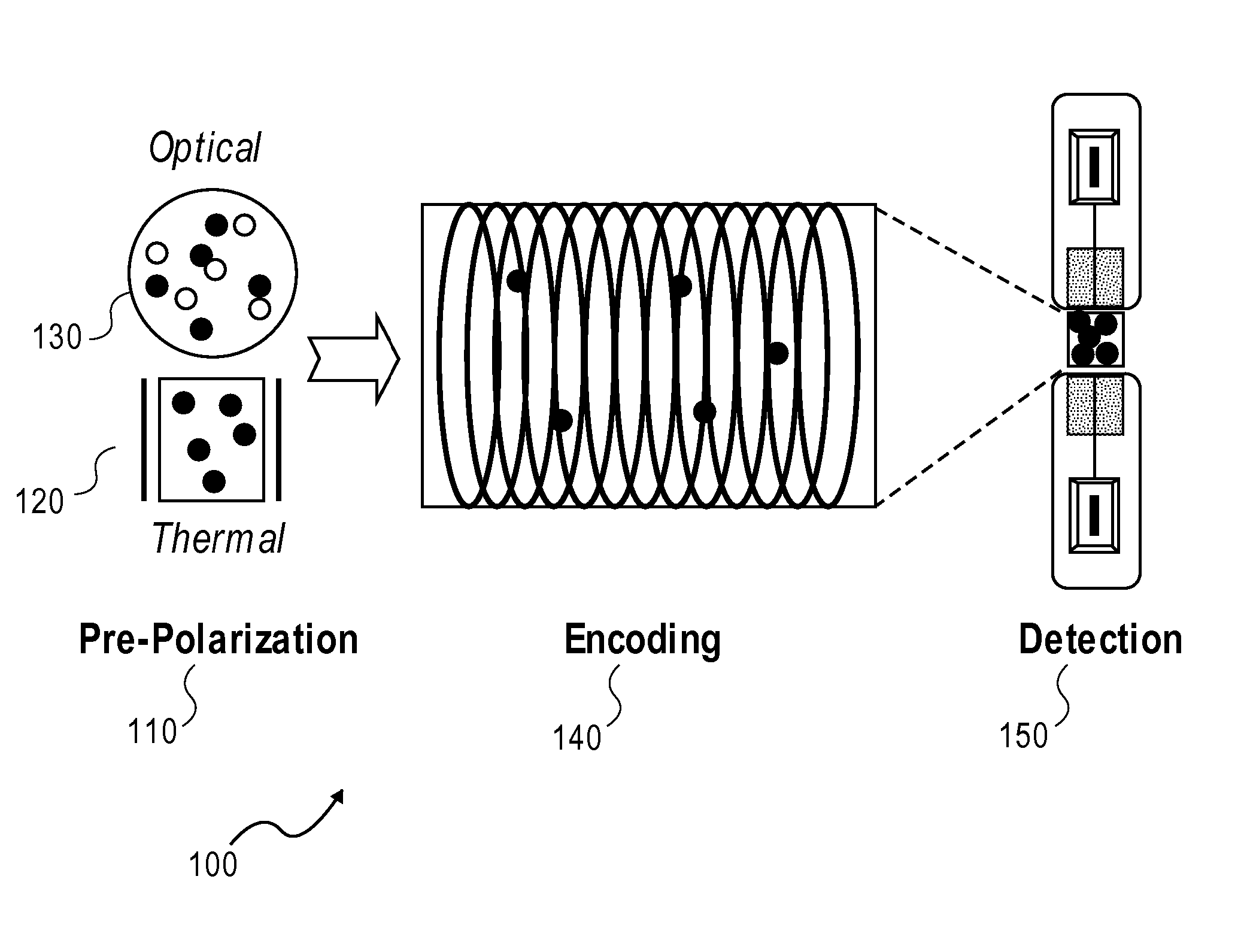
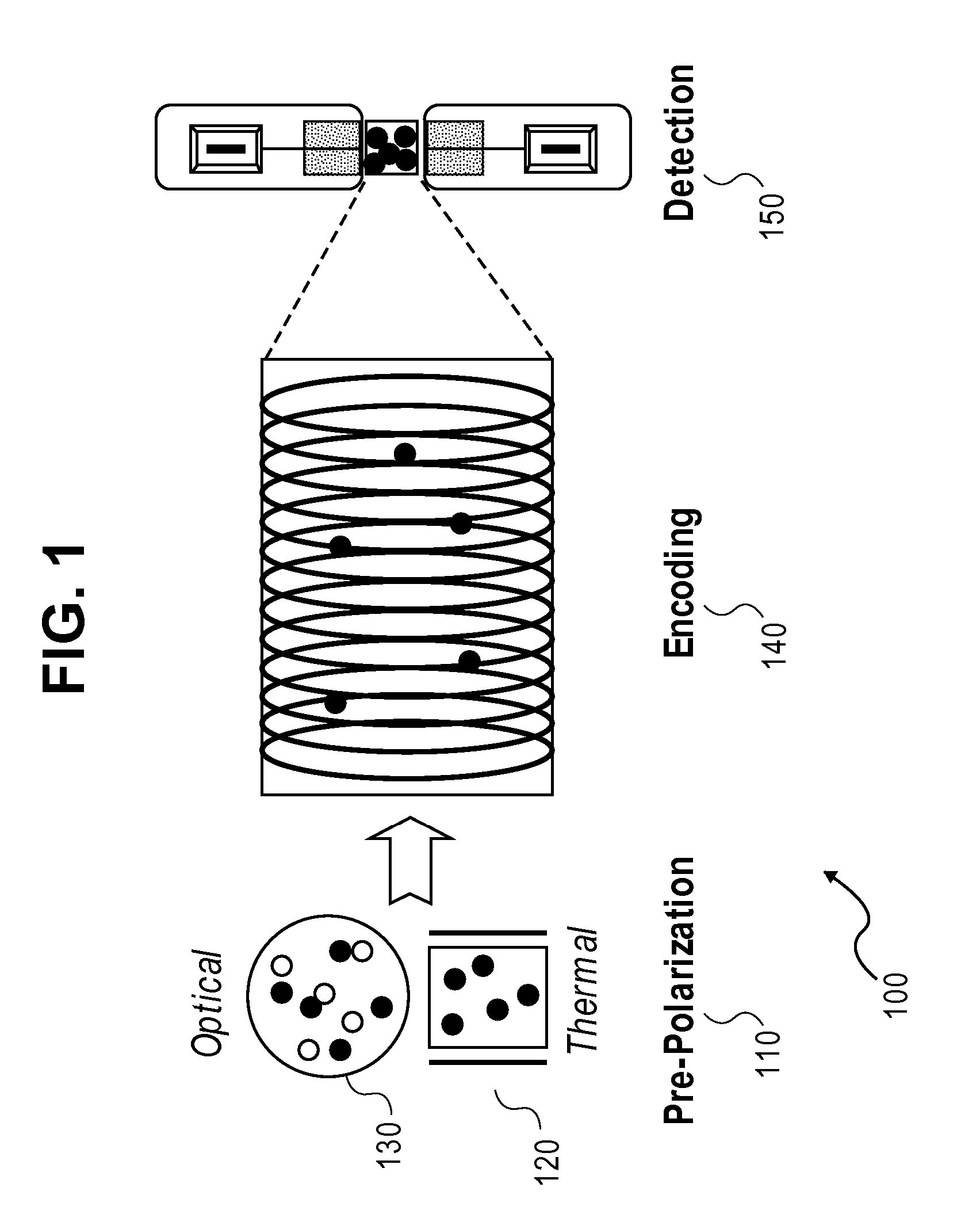
A laser-based atomic magnetometer (LBAM) apparatus measures magnetic fields, comprising: a plurality of polarization detector cells to detect magnetic fields; a laser source optically coupled to the polarization detector cells; and a signal detector that measures the laser source after being coupled to the polarization detector cells, which may be alkali cells. A single polarization cell may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) by prepolarizing the nuclear spins of an analyte, encoding spectroscopic and / or spatial information, and detecting NMR signals from the analyte with a laser-based atomic magnetometer to form NMR spectra and / or magnetic resonance images (MRI). There is no need of a magnetic field or cryogenics in the detection step, as it is detected through the LBAM.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tuned optical cavity magnetometer
An atomic magnetometer is disclosed which utilizes an optical cavity formed from a grating and a mirror, with a vapor cell containing an alkali metal vapor located inside the optical cavity. Lasers are used to magnetically polarize the alkali metal vapor and to probe the vapor and generate a diffracted laser beam which can be used to sense a magnetic field. Electrostatic actuators can be used in the magnetometer for positioning of the mirror, or for modulation thereof. Another optical cavity can also be formed from the mirror and a second grating for sensing, adjusting, or stabilizing the position of the mirror.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Optically pumped atomic magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS20160061913A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceLight beamOptic system
Provided is an optically pumped atomic magnetometer that can separate and acquire magnetic information of spatially different places at the same time by one probe beam. The optically pumped atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing alkali metal atoms, a pump beam optical system introducing pump beams including circularly polarized light component to different locations of the cell, a probe beam optical system introducing a probe beam including linearly polarized light component to the cell, a detection unit detecting a signal reflecting a rotation angle of a plane of polarization of the probe beam after intersecting with the pump beams, and an information acquisition unit acquiring information related to a magnetic field intensity of each of the different locations from the detected signal. The pump beam optical system includes a modulation unit modulating the pump beams so that one of frequencies and phases of the pump beams is different.
Owner:CANON KK
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic force measuring method
ActiveUS8054074B2High sensitivityNanomagnetismElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic tension forceAtomic group
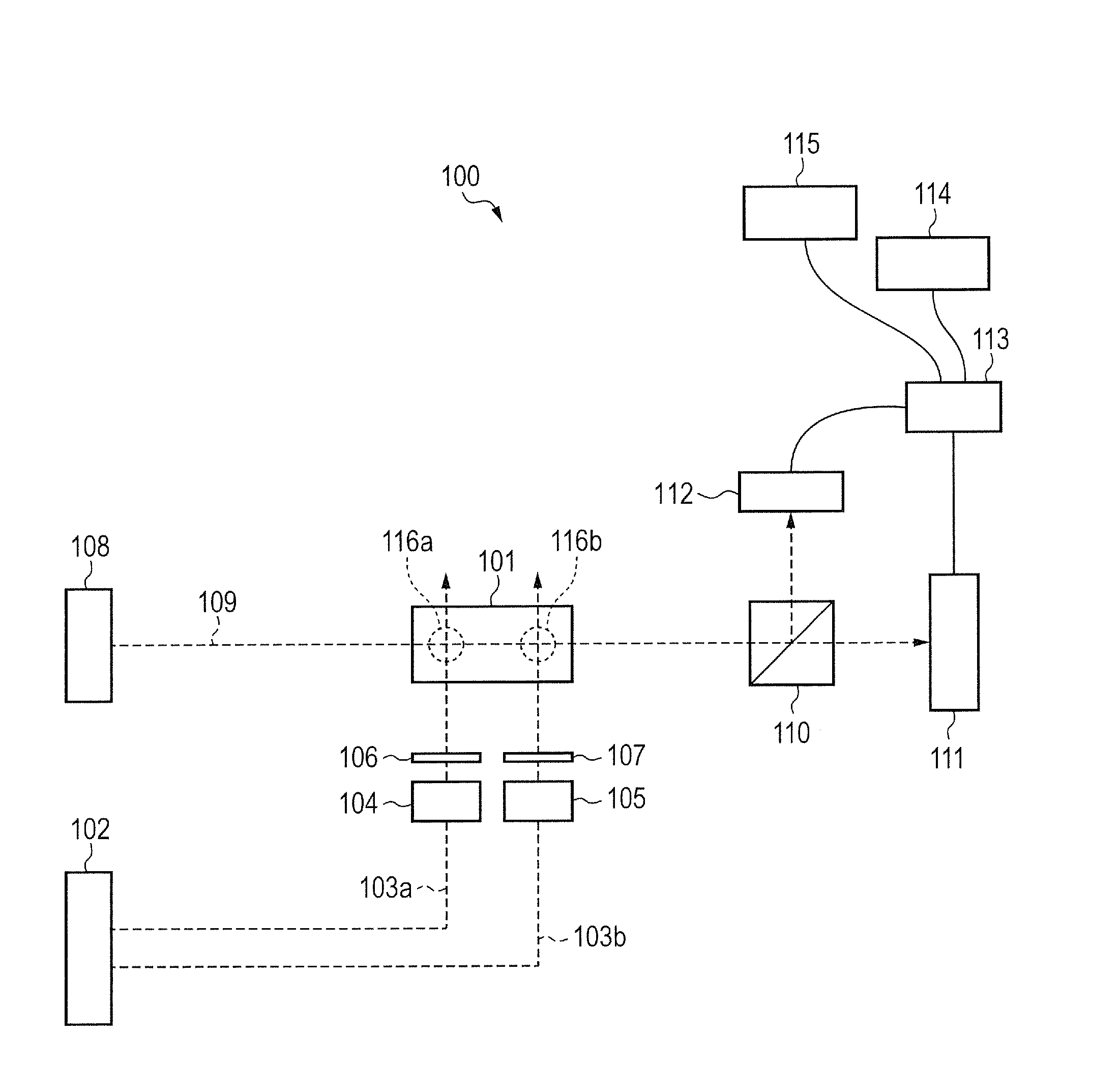
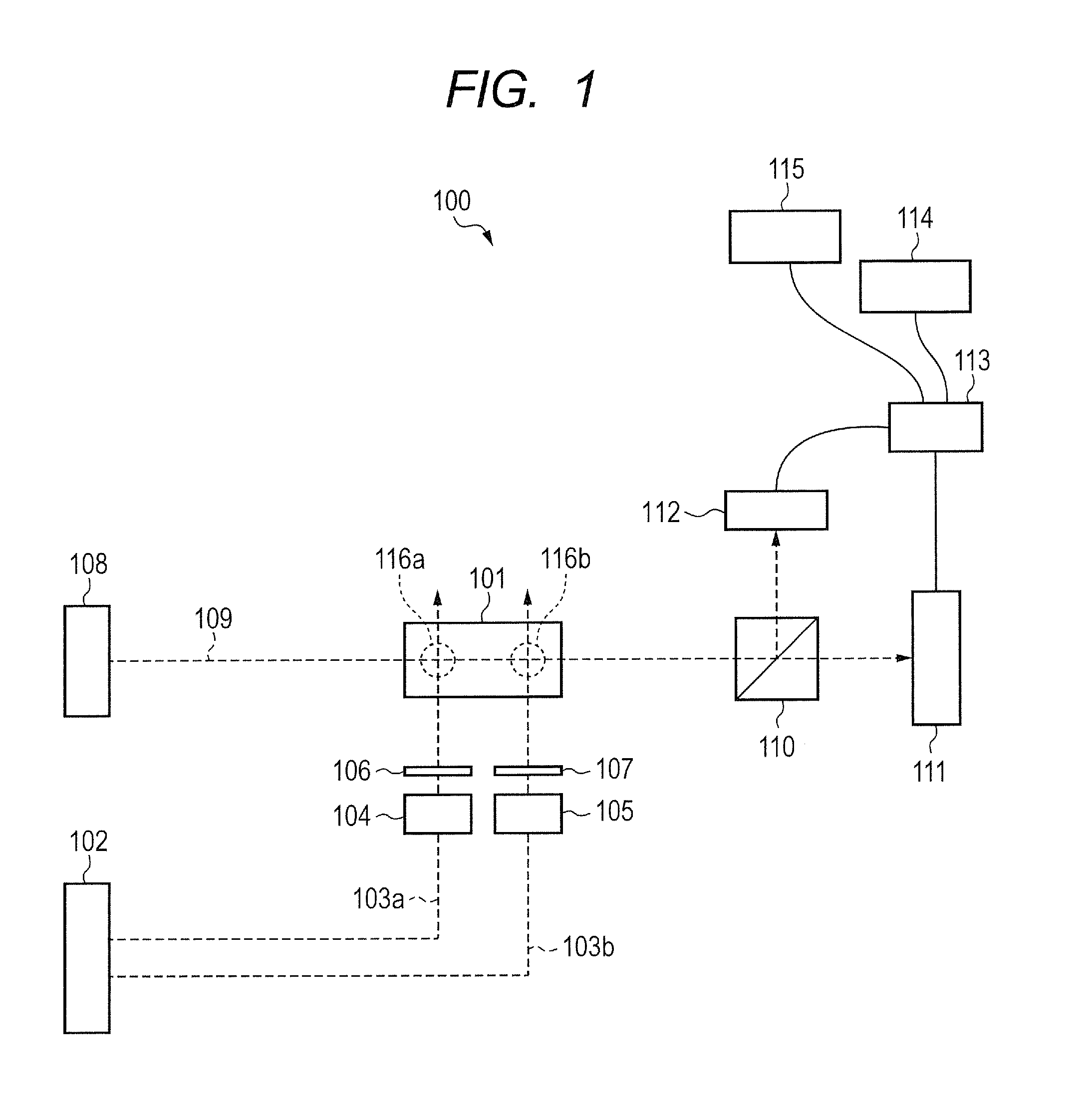
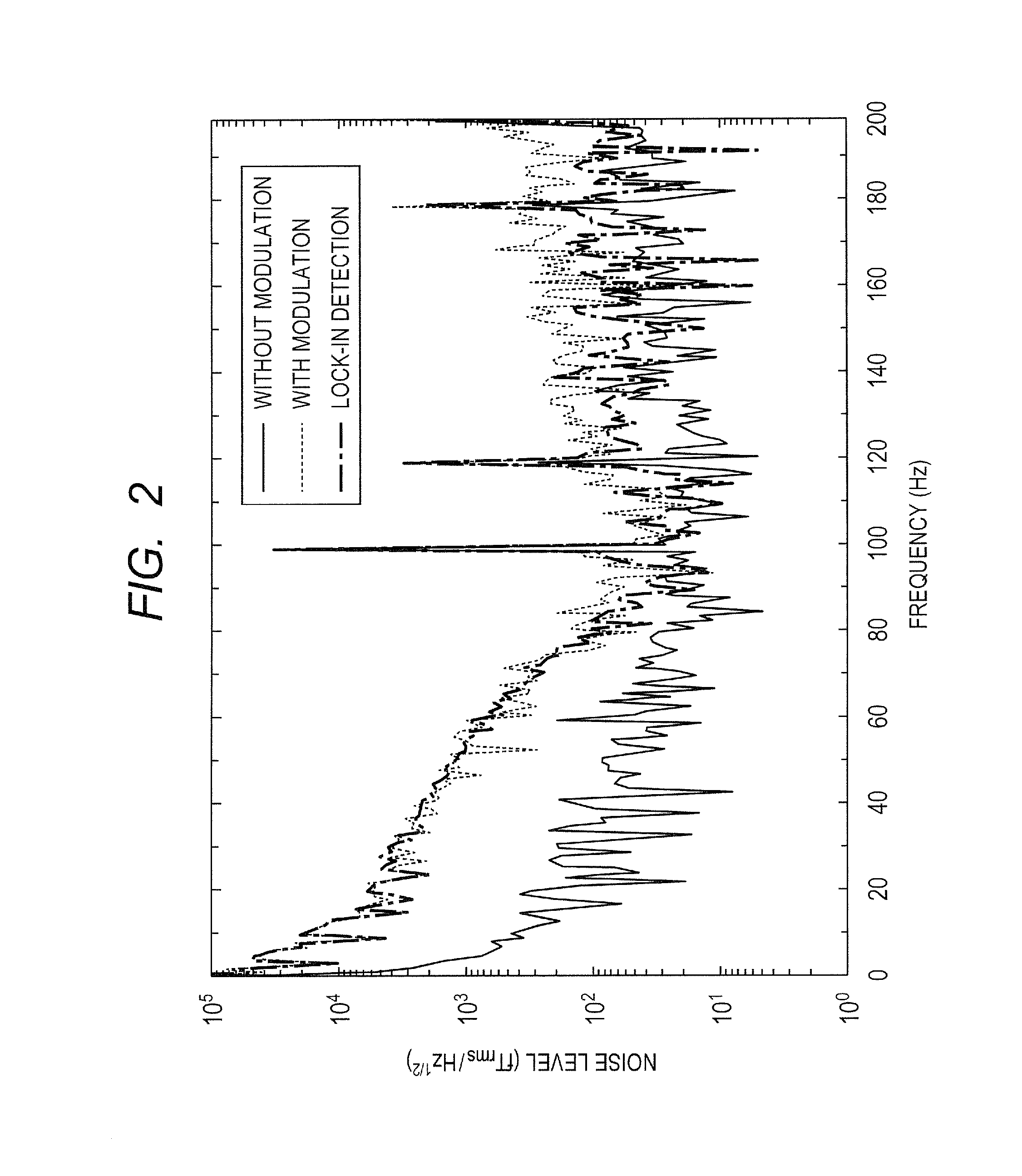
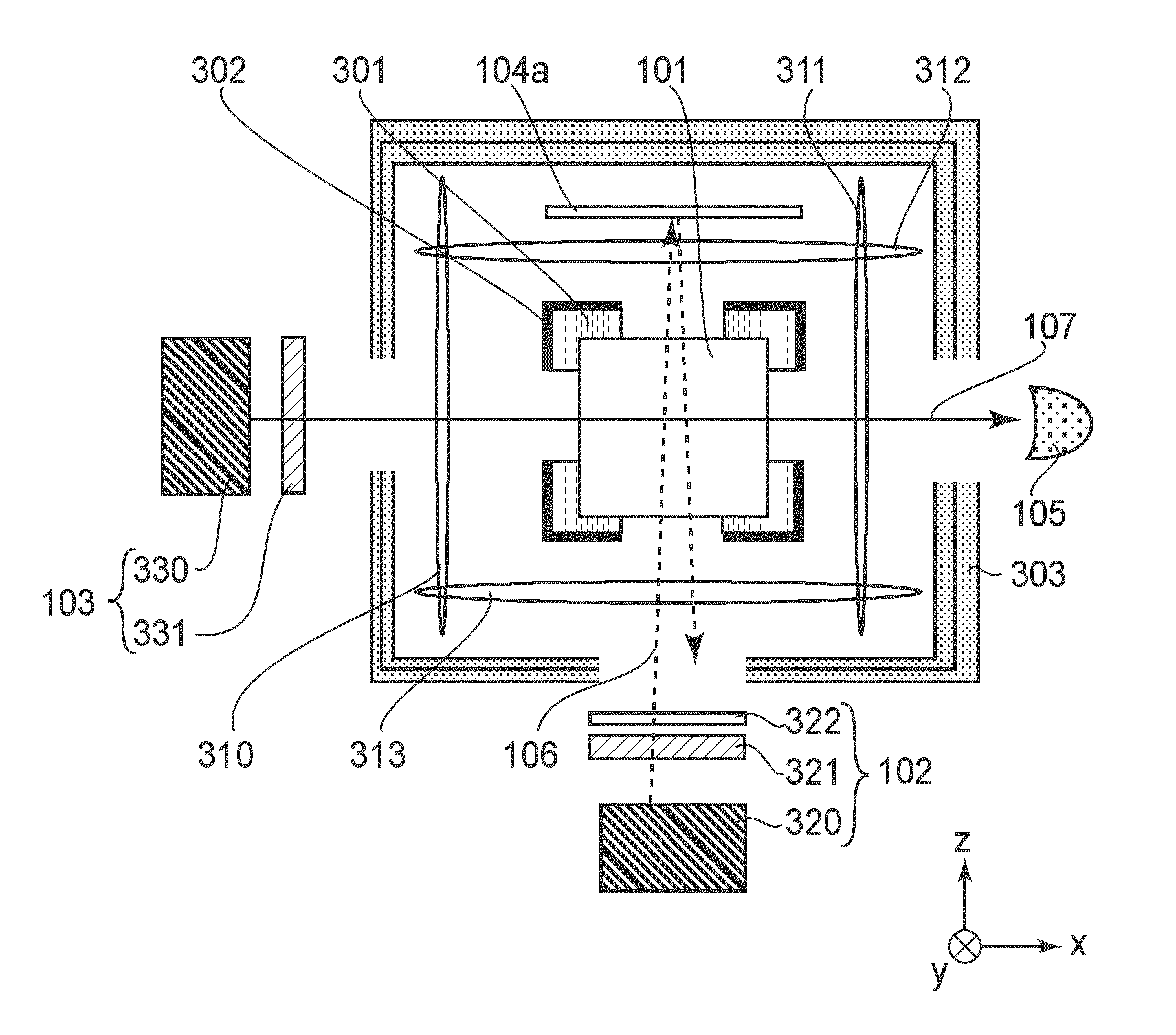
An atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing an atomic group, a pump light source, a probe light source, a mirror, and a detector. The cell is disposed between the pump light source and the mirror and between the probe light source and the detector. A pump beam emitted from the pump light source is circularly polarized light. The pump beam passes through the cell and is reflected by the mirror and then passes through the cell again. The probe beam emitted from the probe light source is linearly polarized light. An optical path of the probe beam is parallel to the plane of incidence of the pump beam and is also parallel to the surface of the mirror. The optical path of the probe beam crosses the optical path of the pump beam in the cell. The probe beam which has passed through the cell enters the detector.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS8587304B2Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSelf-oscillationLight beam
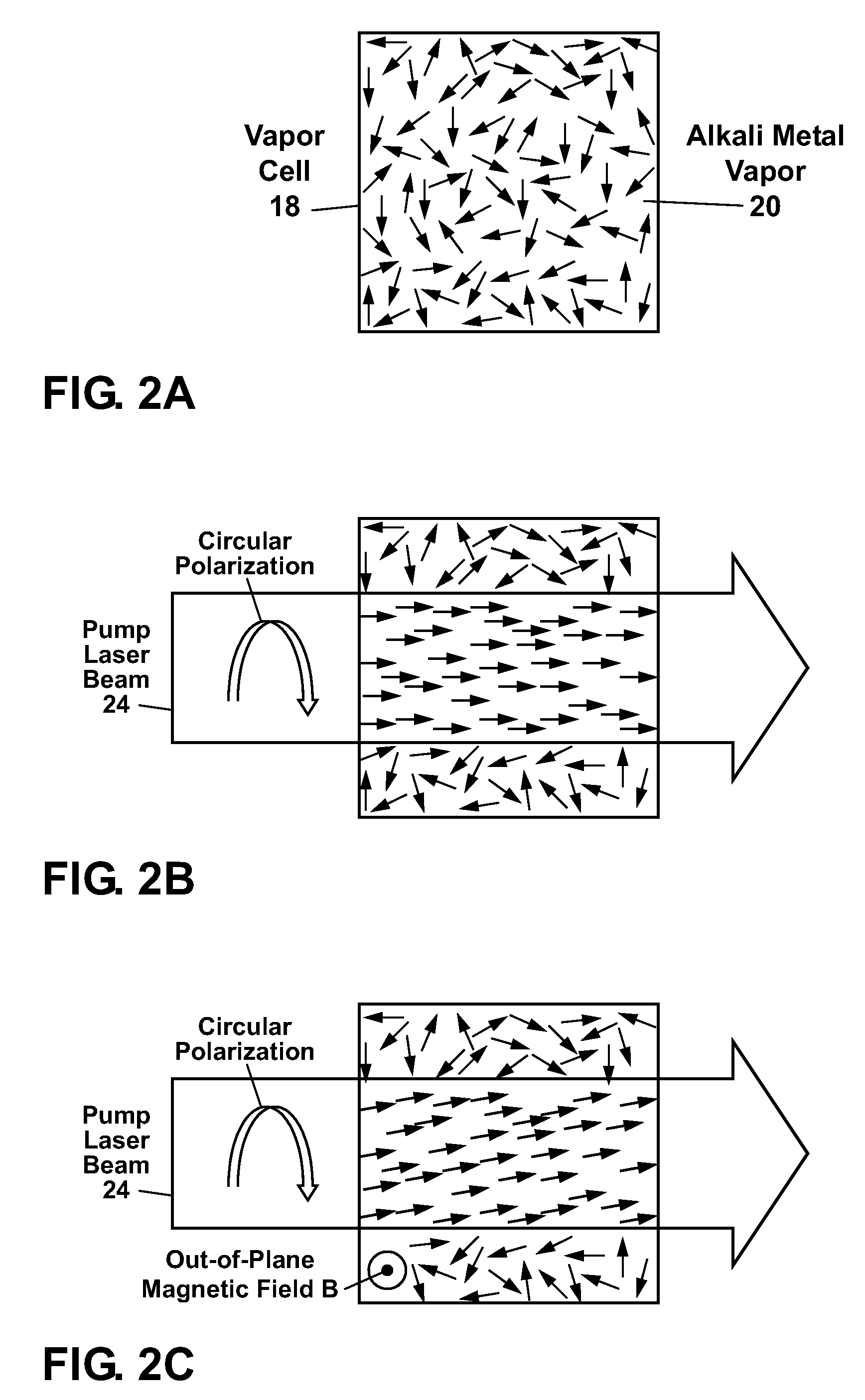
An optical atomic magnetometers is provided operating on the principles of nonlinear magneto-optical rotation. An atomic vapor is optically pumped using linearly polarized modulated light. The vapor is then probed using a non-modulated linearly polarized light beam. The resulting modulation in polarization angle of the probe light is detected and used in a feedback loop to induce self-oscillation at the resonant frequency.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Radio frequency atomic magnetometer
InactiveUS20100289491A1Enhance nuclear magnetizationEnhanced magnetizationElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRRadio frequency signalLight beam
An atomic magnetometer is used to detect radio frequency magnetic fields, such as those generated in nuclear resonance experiments. The magnetometer is based on nonlinear magneto-optical rotation and pumps an atomic vapor into a quadrupole aligned state. Detection of the modulation of the polarization of a linearly polarized beam provides the radio frequency signal, which can then be processed to extract the component frequencies.
Owner:BUDKER DIMITRY +2
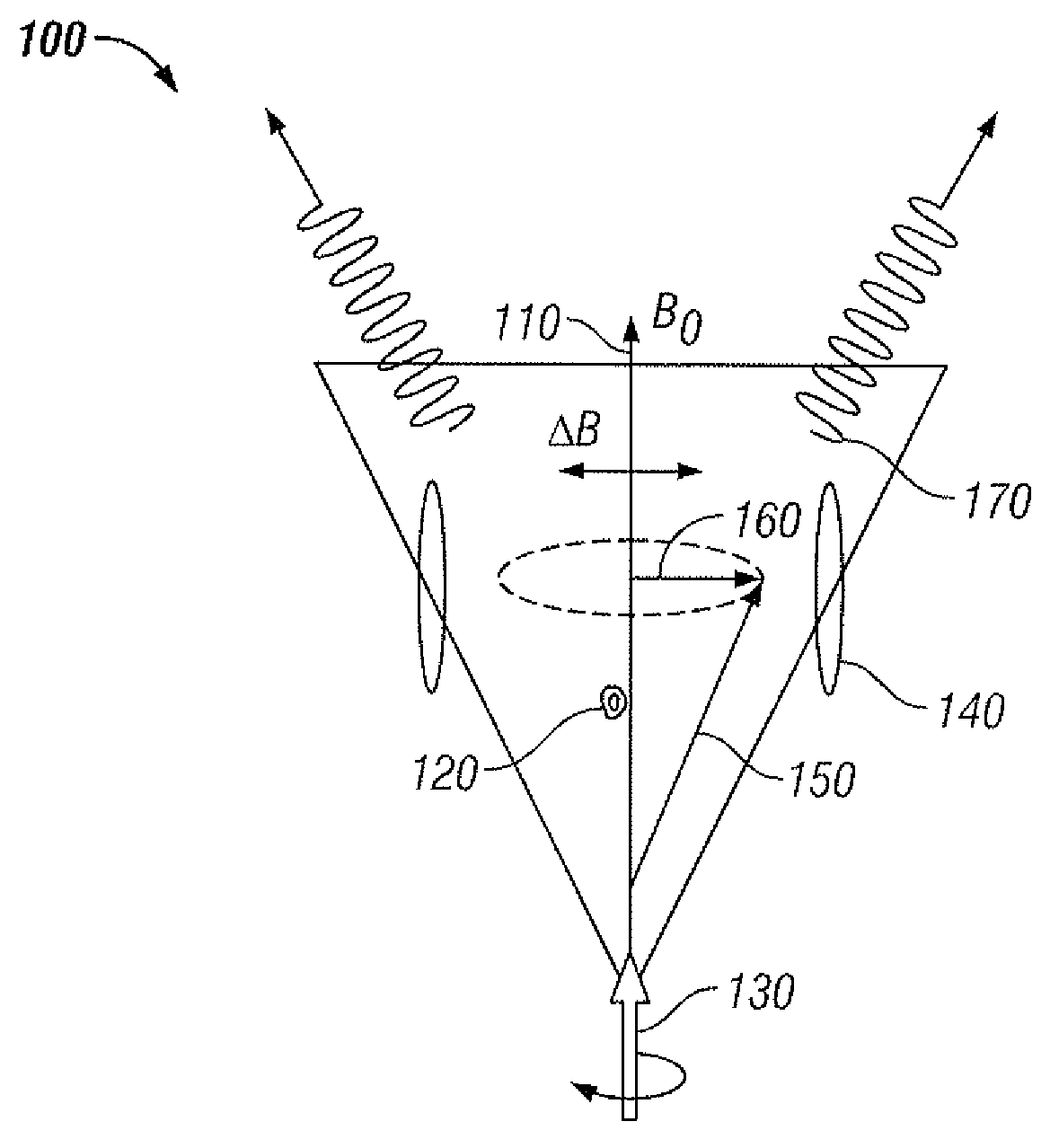
Compact atomic magnetometer and gyroscope based on a diverging laser beam
InactiveUS7872473B2Improve compactnessLow costTurn-sensitive devicesElectric/magnetic detectionAtomic systemGyroscope
An atomic magnetometer that simultaneously achieves high sensitivity, simple fabrication and small size. This design is based on a diverging (or converging) beam of light that passes through an alkali atom vapor cell and that contains a distribution of beam propagation vectors. The existence of more than one propagation direction permits longitudinal optical pumping of atomic system and simultaneous detection of the transverse atomic polarization. The design could be implemented with a micro machined alkali vapor cell and light from a single semiconductor laser. A small modification to the cell contents and excitation geometry allows for use as a gyroscope.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Atomic magnetometer with multiple spatial channels
An atomic magnetometer includes an atomic vapor cell, an optical system conformed to transmit pump radiation and probe radiation through the vapor cell, and an optical detection system arranged to receive and detect probe radiation after it exits the vapor cell. Improvements in the separation of spatial channels are achieved by using a a diffractive optical element arranged to divide at least the pump radiation into a plurality of separate diffracted beams that traverse the vapor cell.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Method and system for operating a laser self-modulated at alkali-metal atom hyperfine frequency
InactiveUS7323941B1Boost up CPT signalImprove performancePulse automatic controlGaseous masersPhotodetectorPush pull
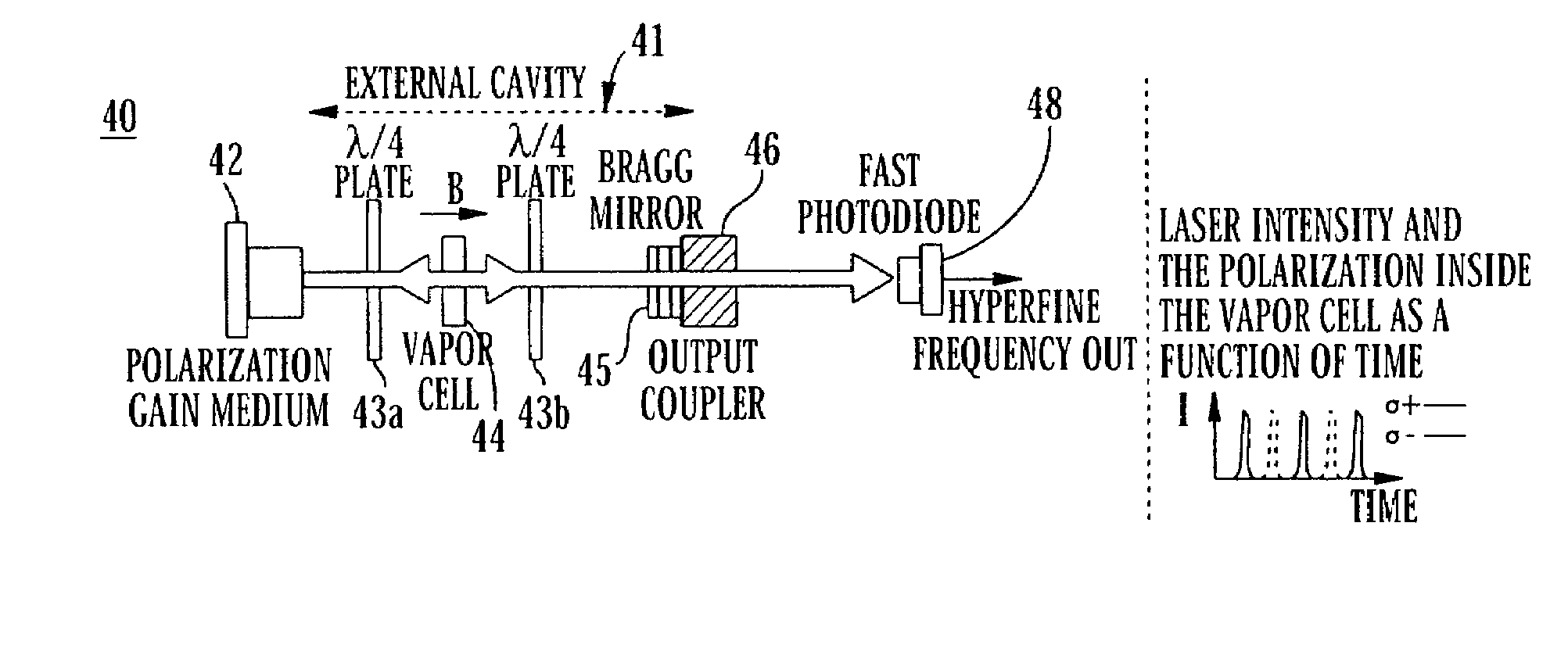
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for making atomic clocks or atomic magnetometers as self-modulated laser systems based on the physics of push-pull optical pumping. An atomic vapor cell is required to be in the laser cavity. With proper conditions, spontaneous push-pull optical pumping can occur inside the laser cavity. This causes the laser beam to be modulated at hyperfine-resonance frequency. With a fast photodetector, the modulated laser signal can be converted into the electrical signal, which serves as the atomic clock ticking signal or magnetometer signal. The self-modulated laser system does not use any local oscillator and the microwave circuit to lock the oscillator frequency to the hyperfine-resonance frequency, and therefore can consume less power and become more compact than conventional systems. This invention will benefit applications of time measurements and magnetic-field measurements.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
Micro-fabricated atomic magnetometer and method of forming the magnetometer
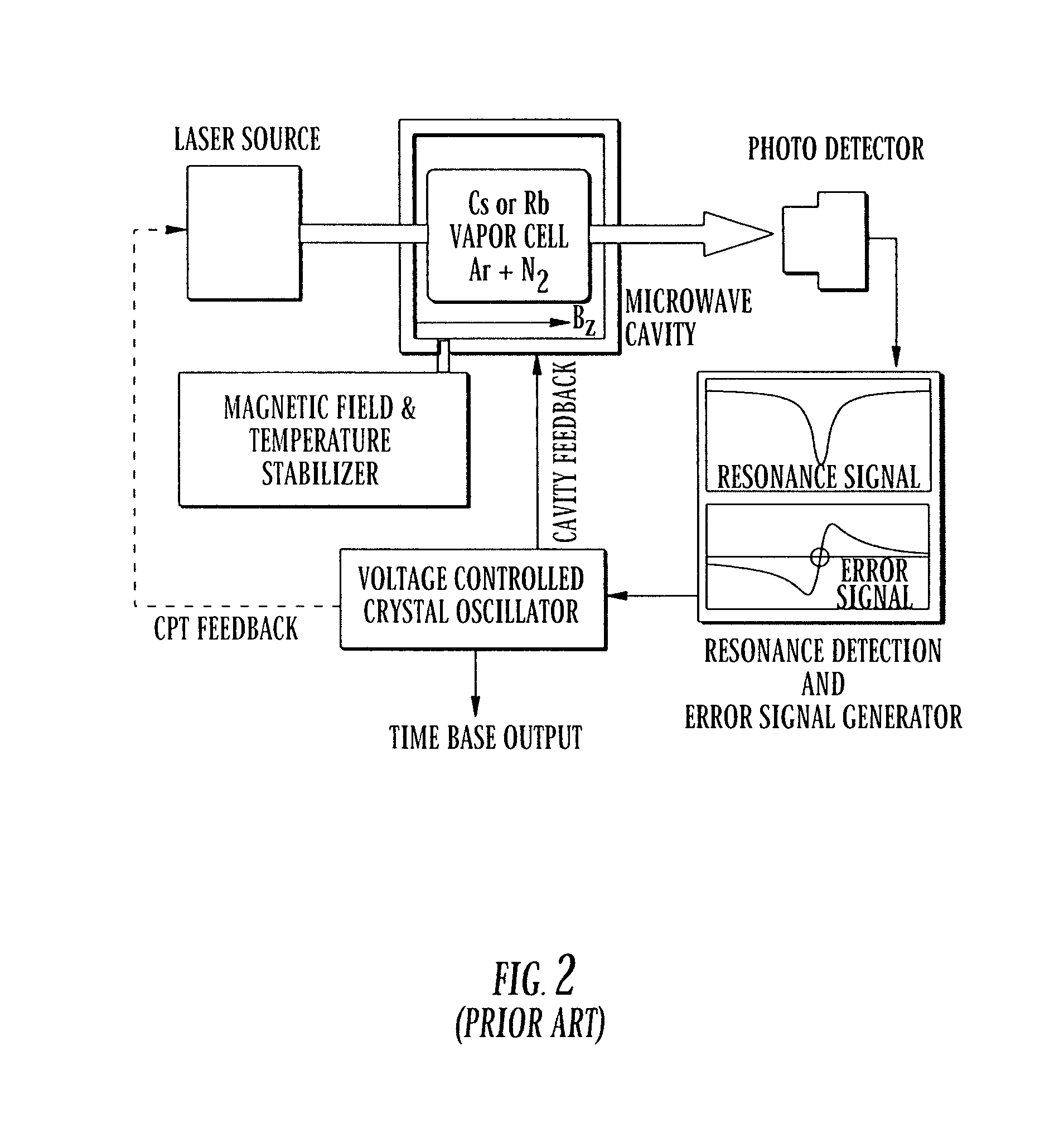
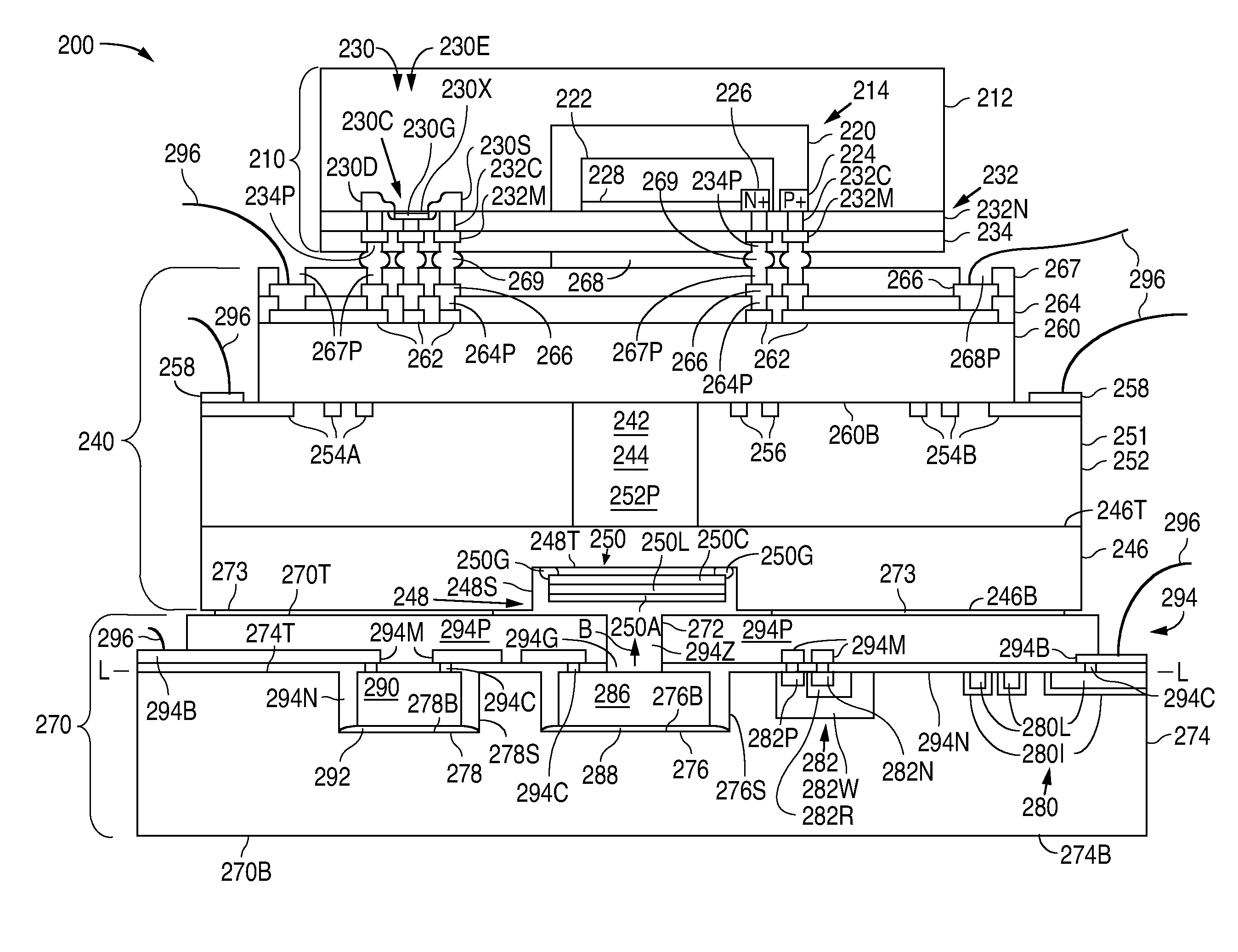
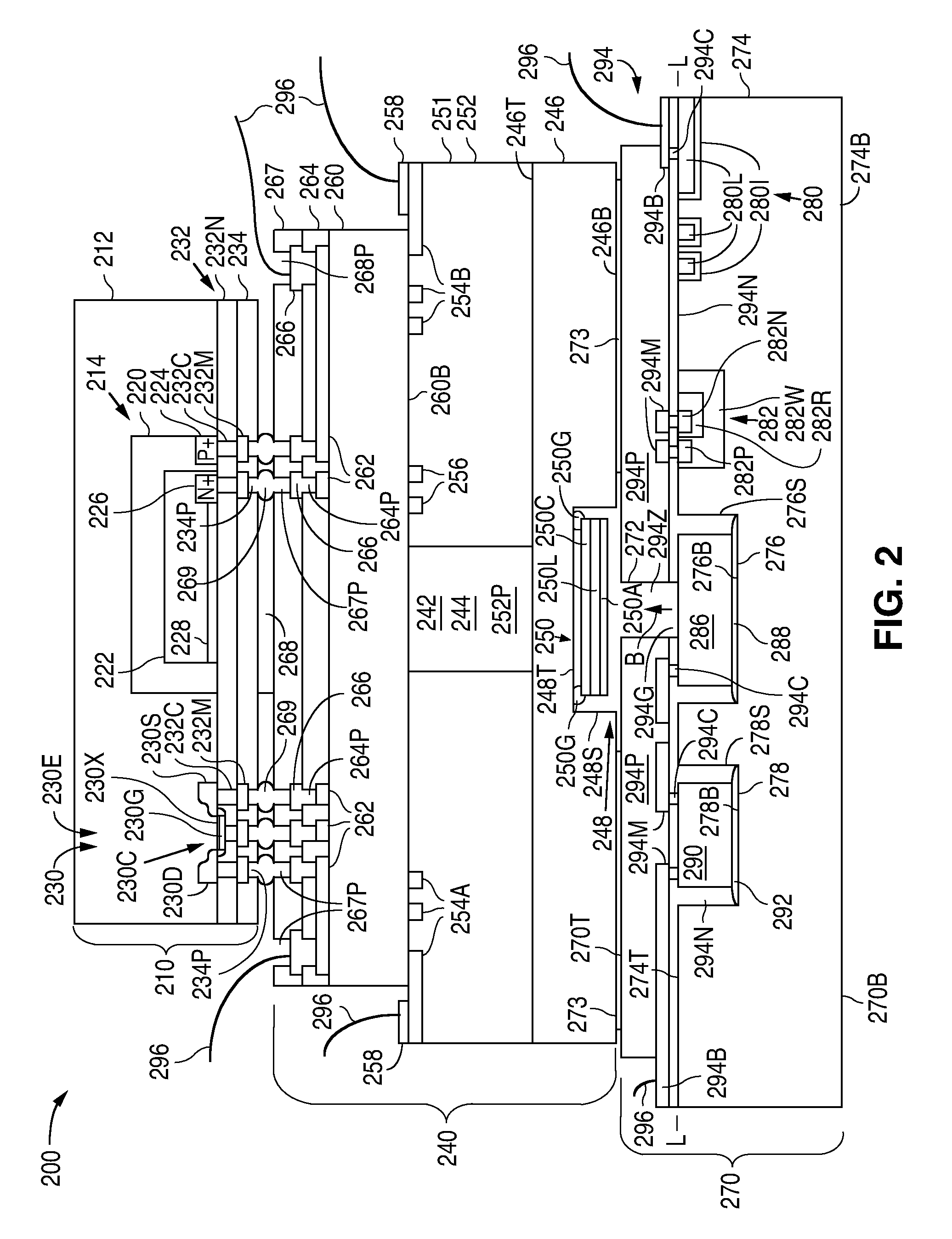
ActiveUS8836327B2Low costSmall sizeSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesLaser lightPhotodiode
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic force measuring method
ActiveUS20090243610A1High sensitivityNanomagnetismElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic tension forceAtomic group
An atomic magnetometer includes a cell containing an atomic group, a pump light source, a probe light source, a mirror, and a detector. The cell is disposed between the pump light source and the mirror and between the probe light source and the detector. A pump beam emitted from the pump light source is circularly polarized light. The pump beam passes through the cell and is reflected by the mirror and then passes through the cell again. The probe beam emitted from the probe light source is linearly polarized light. An optical path of the probe beam is parallel to a plane of incidence of the pump beam and is also parallel to a surface of the mirror. The optical path of the probe beam crosses an optical path of the pump beam in the cell. The probe beam which has passed through the cell enters the detector.
Owner:CANON KK
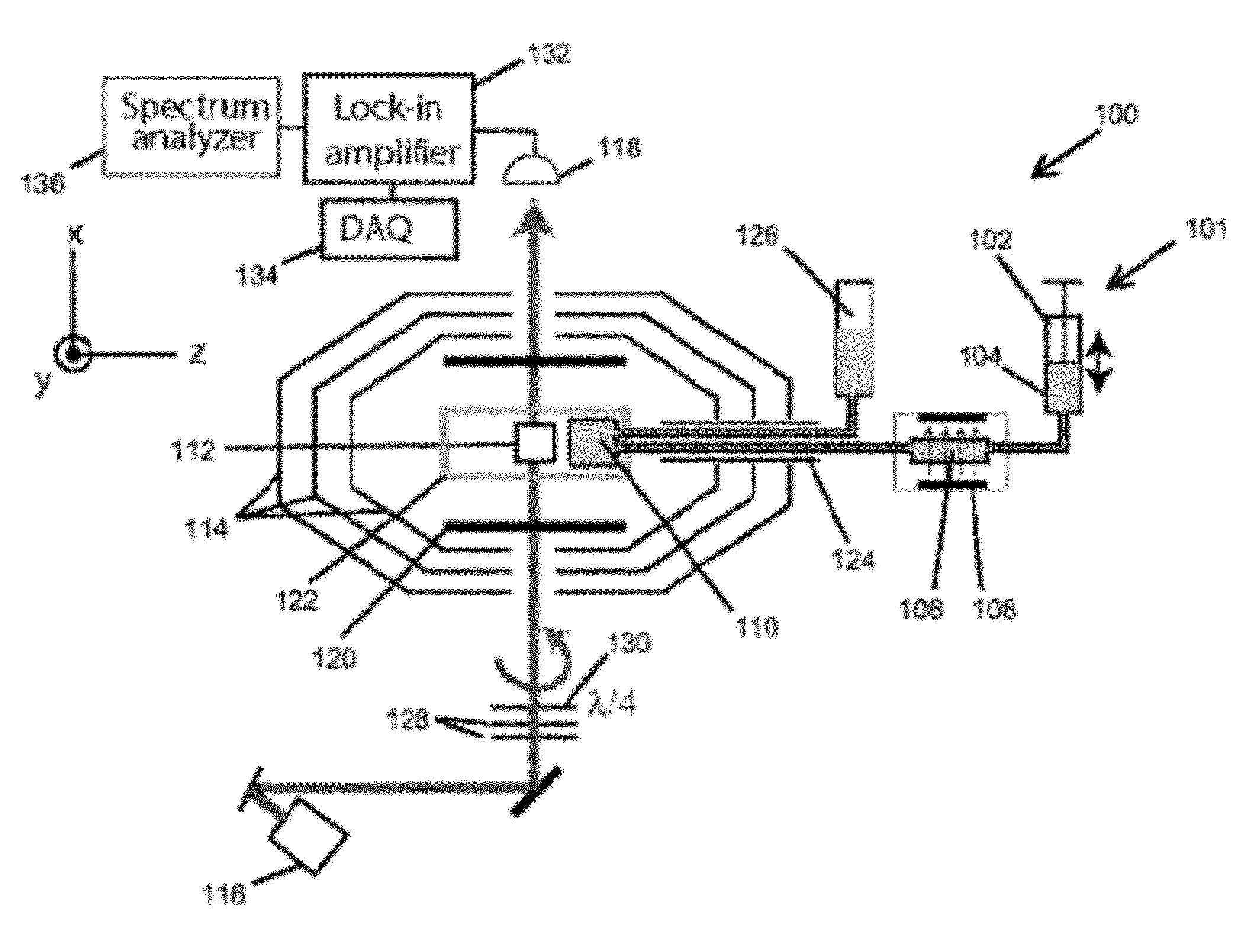
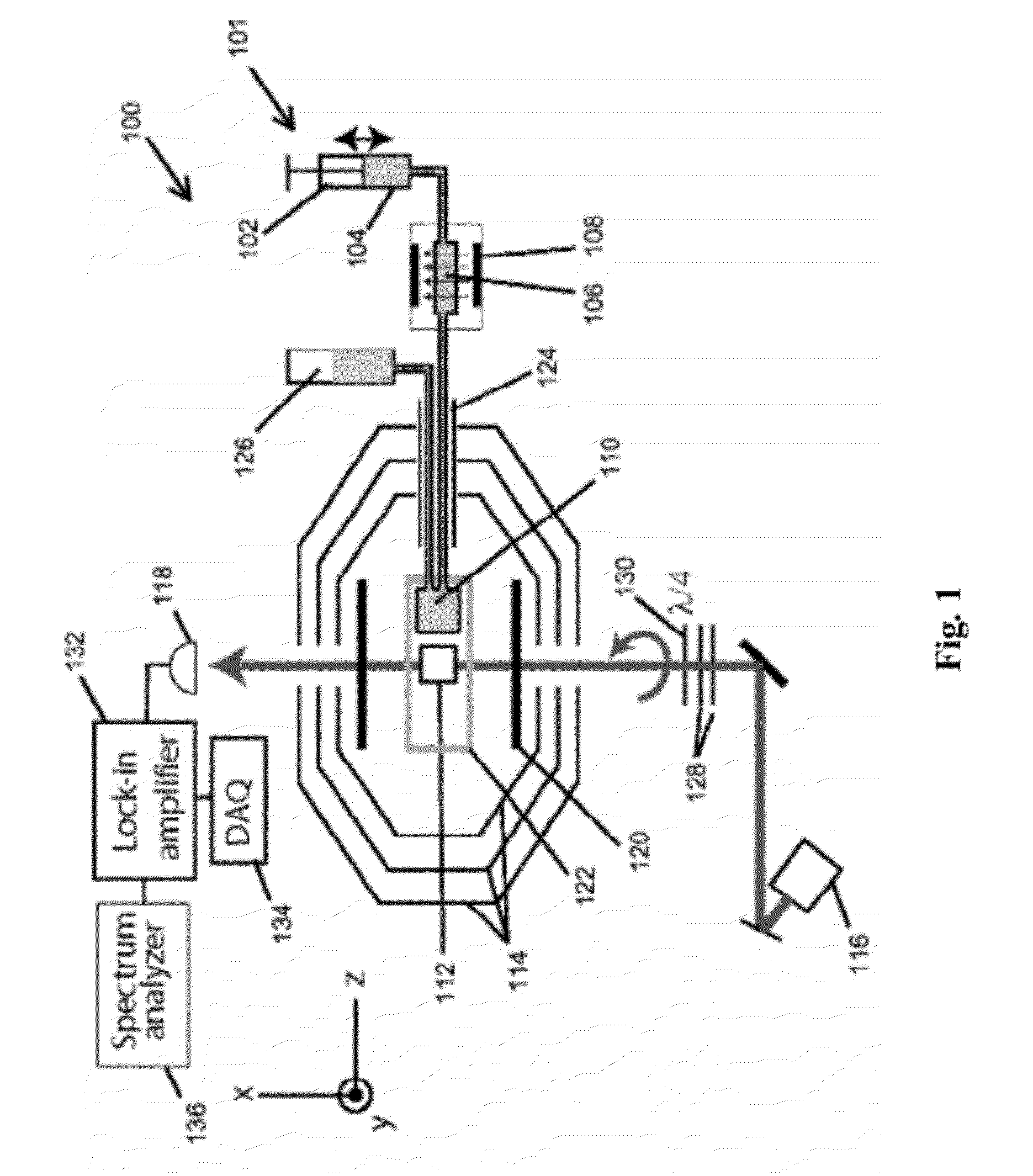
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
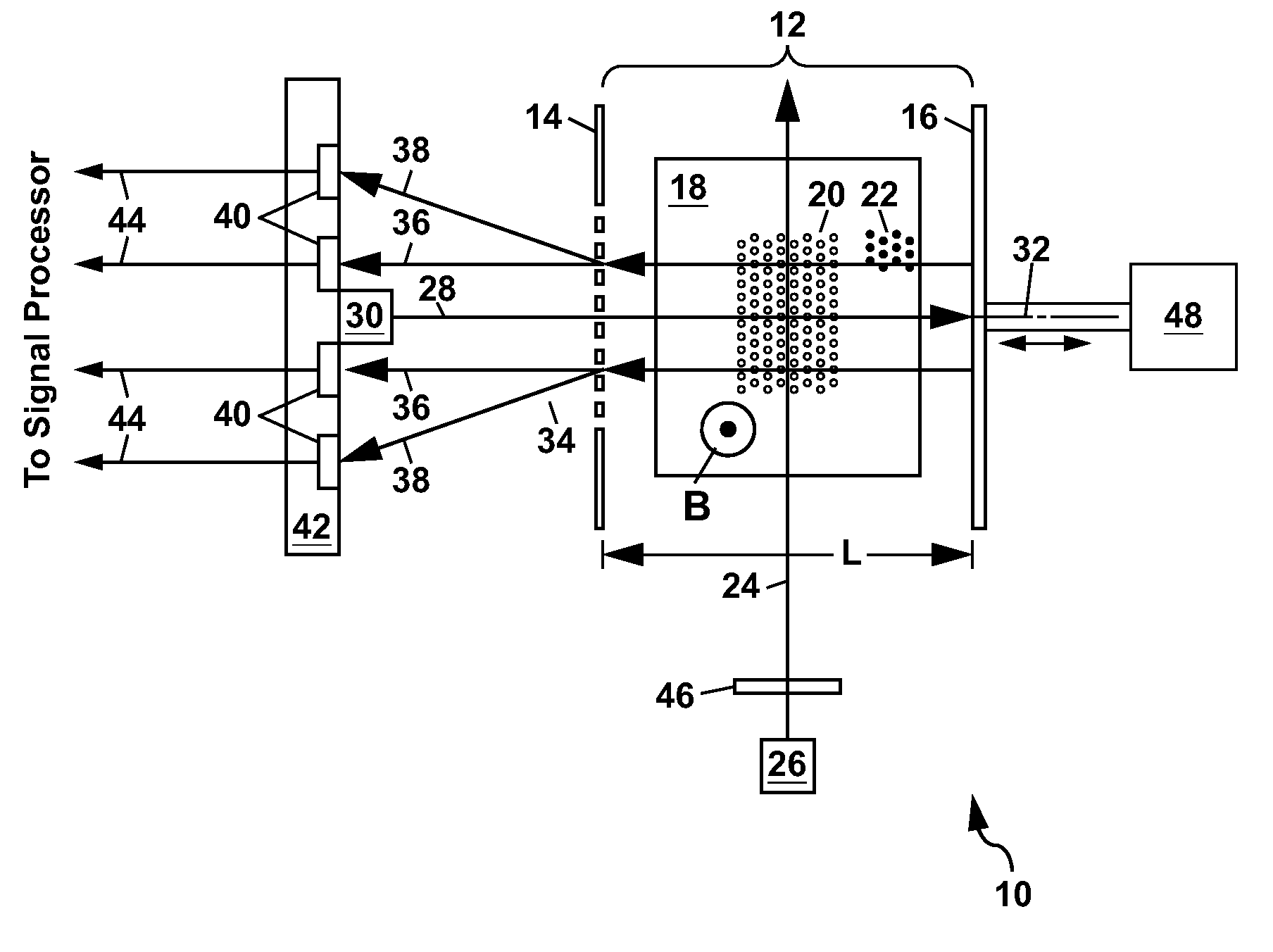
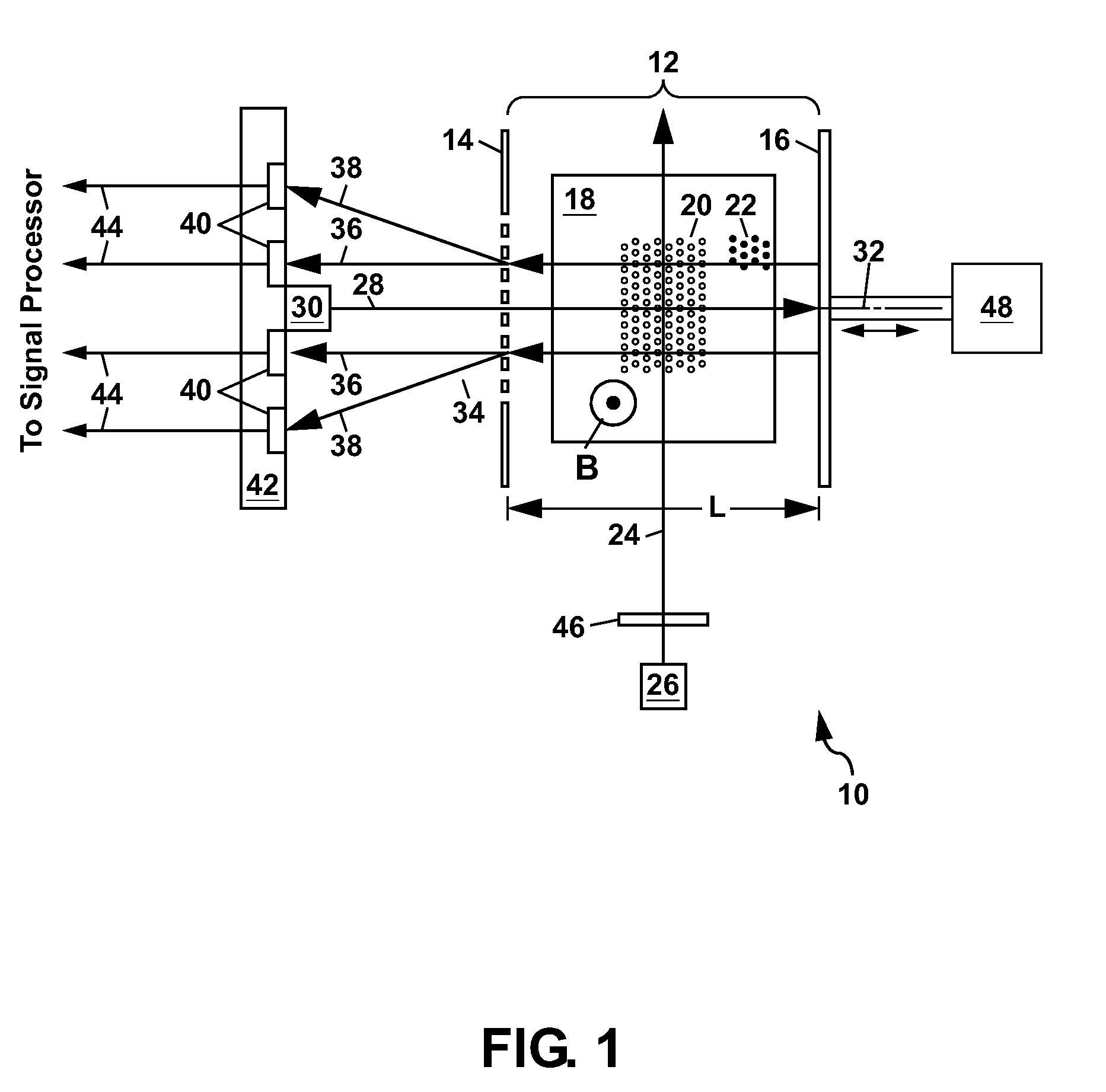
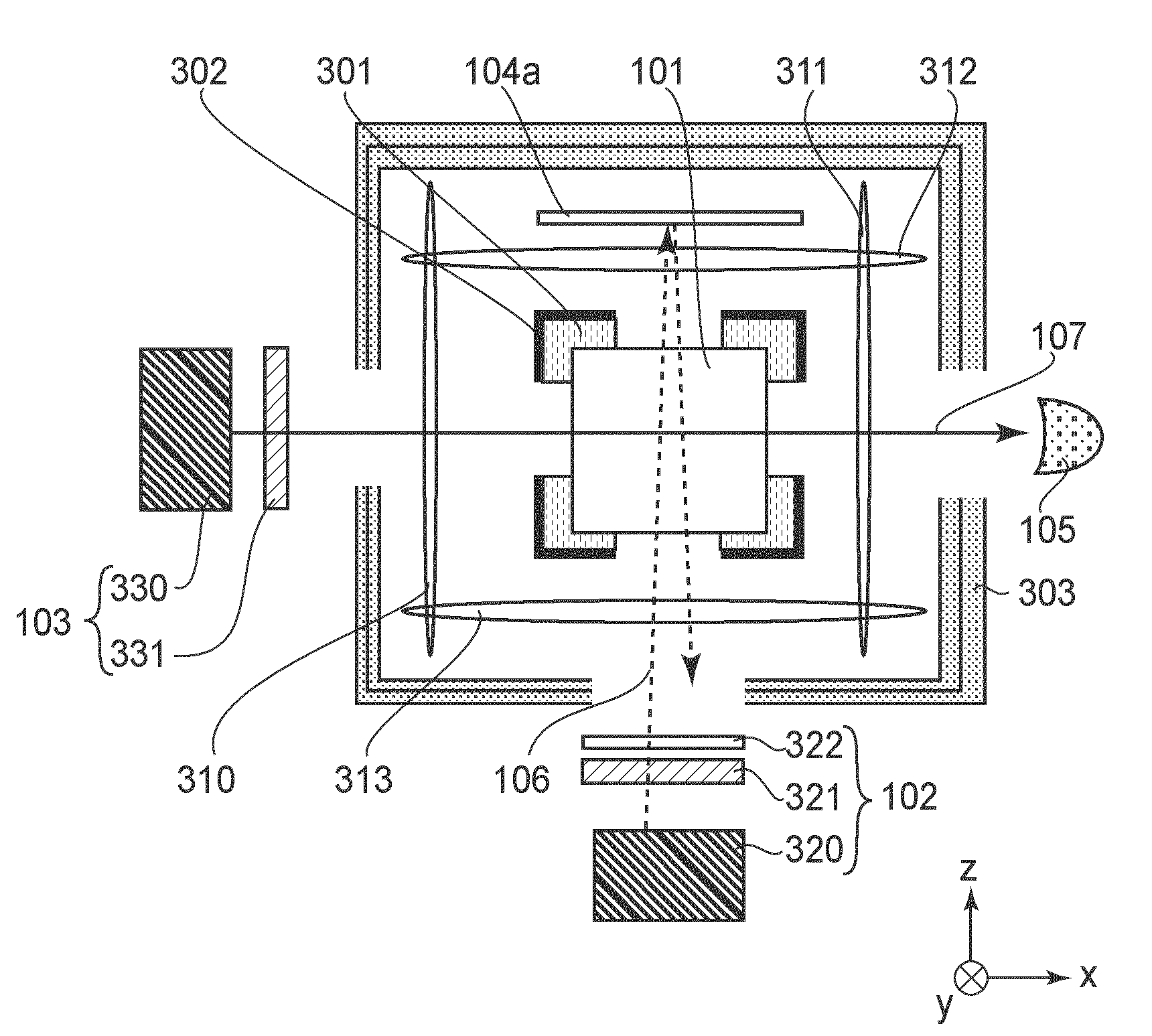
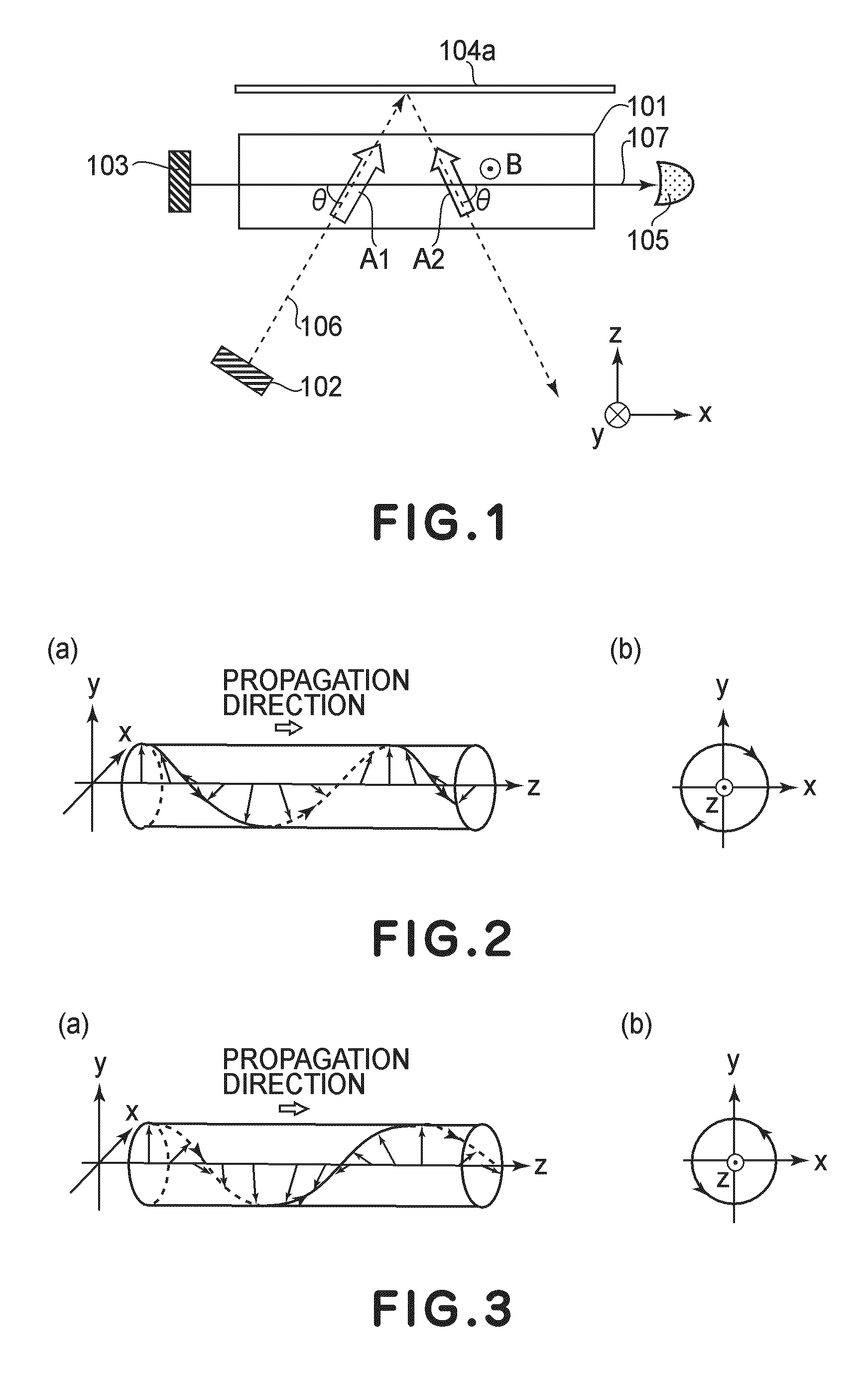
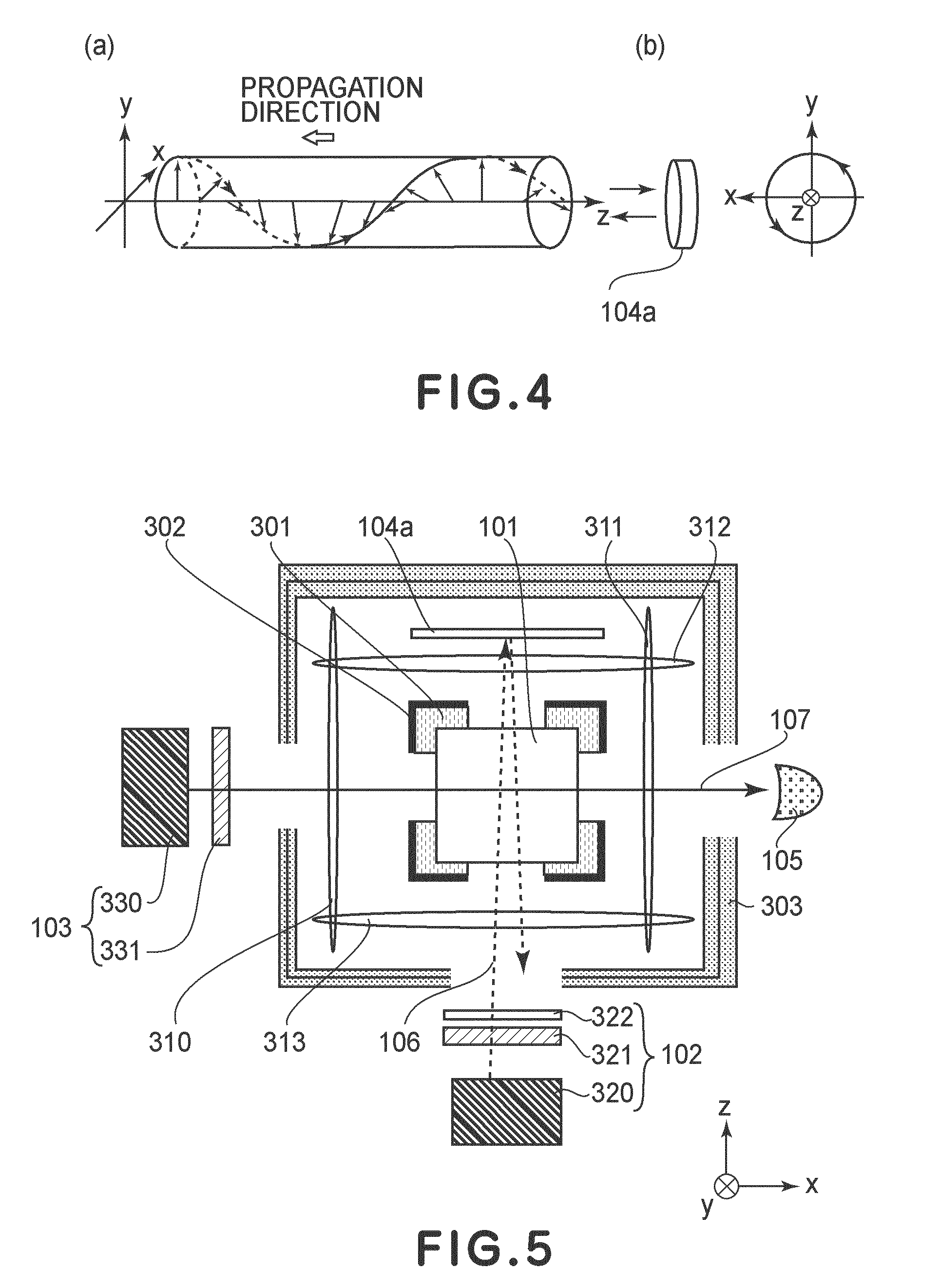
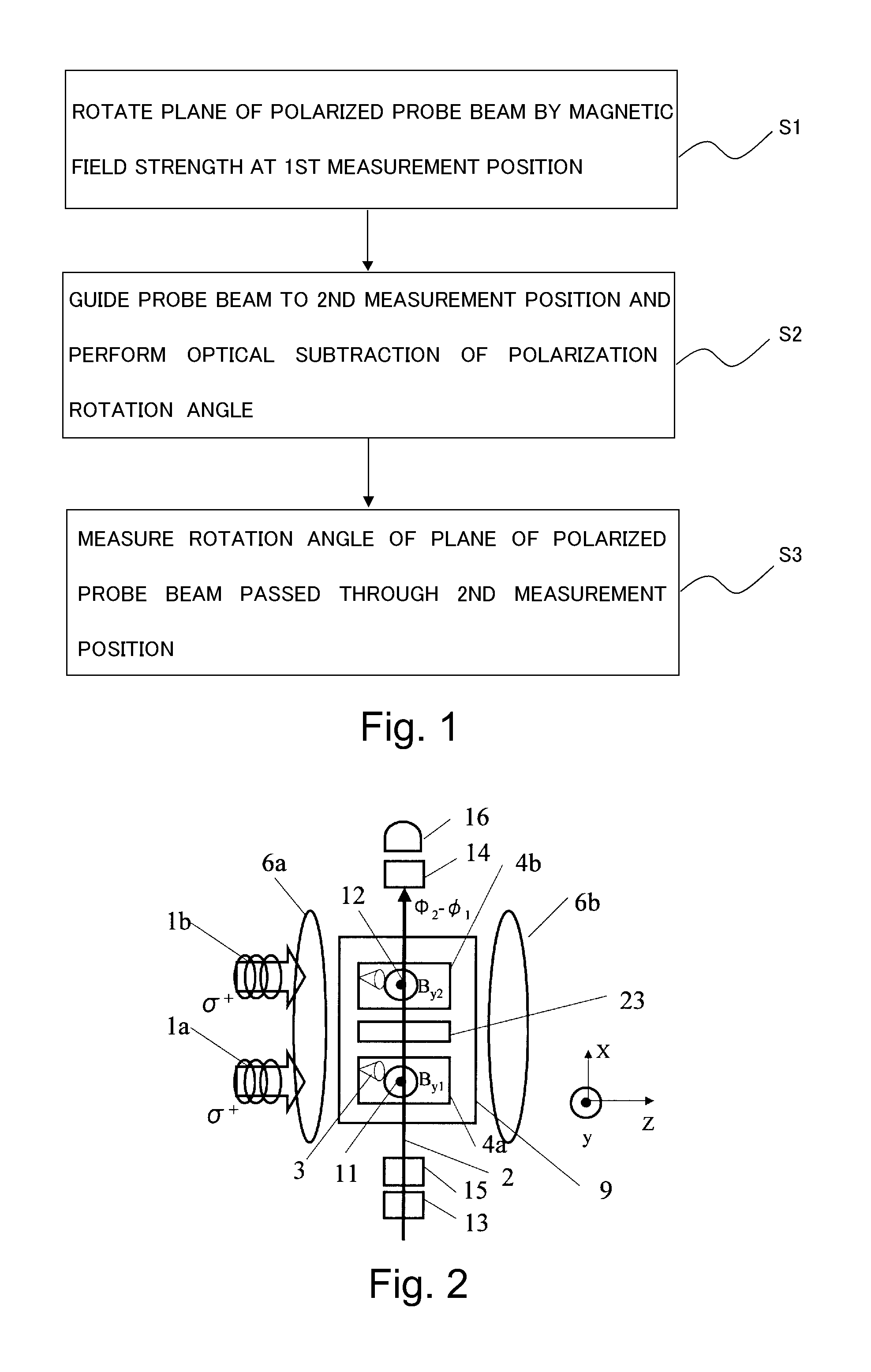
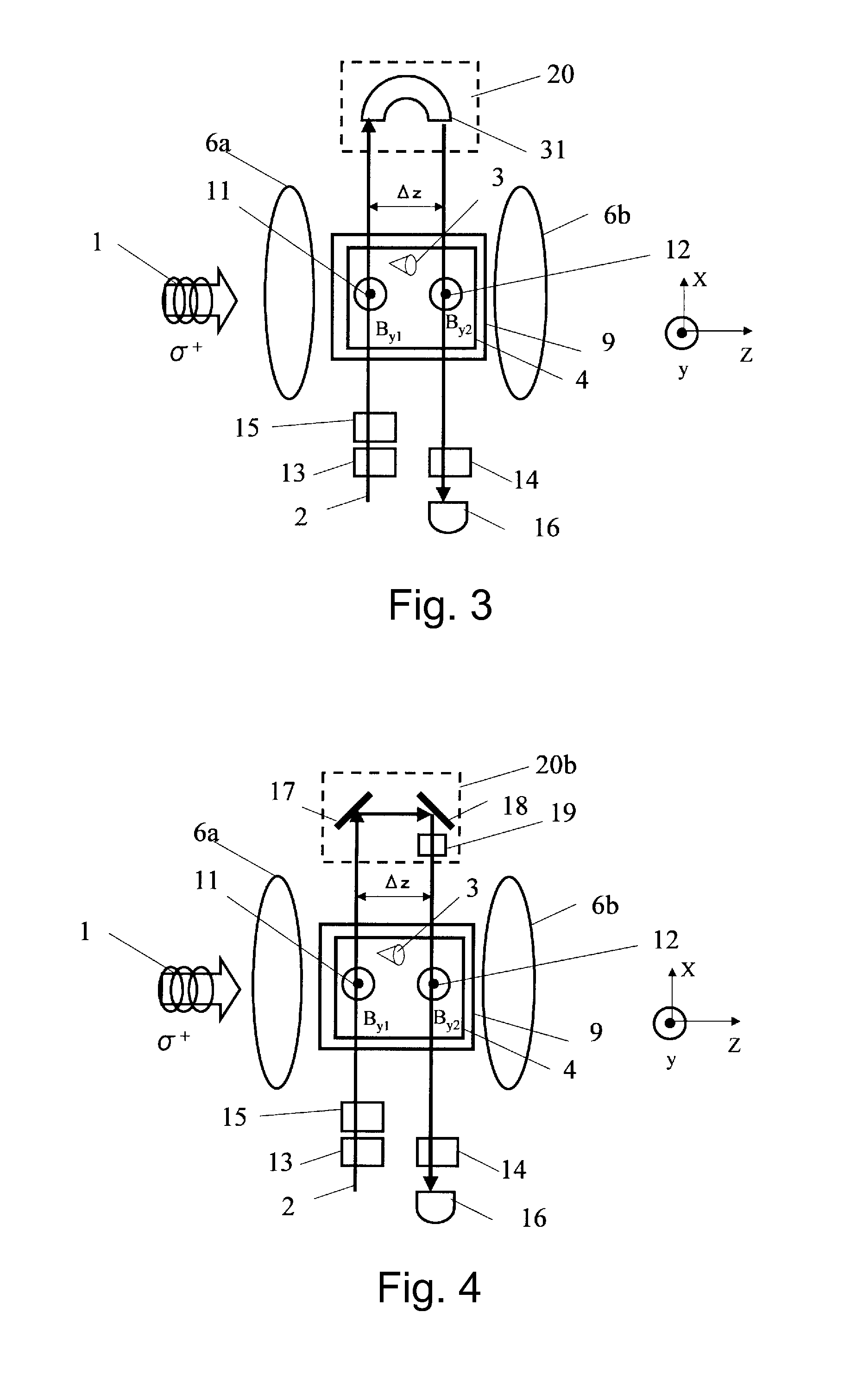
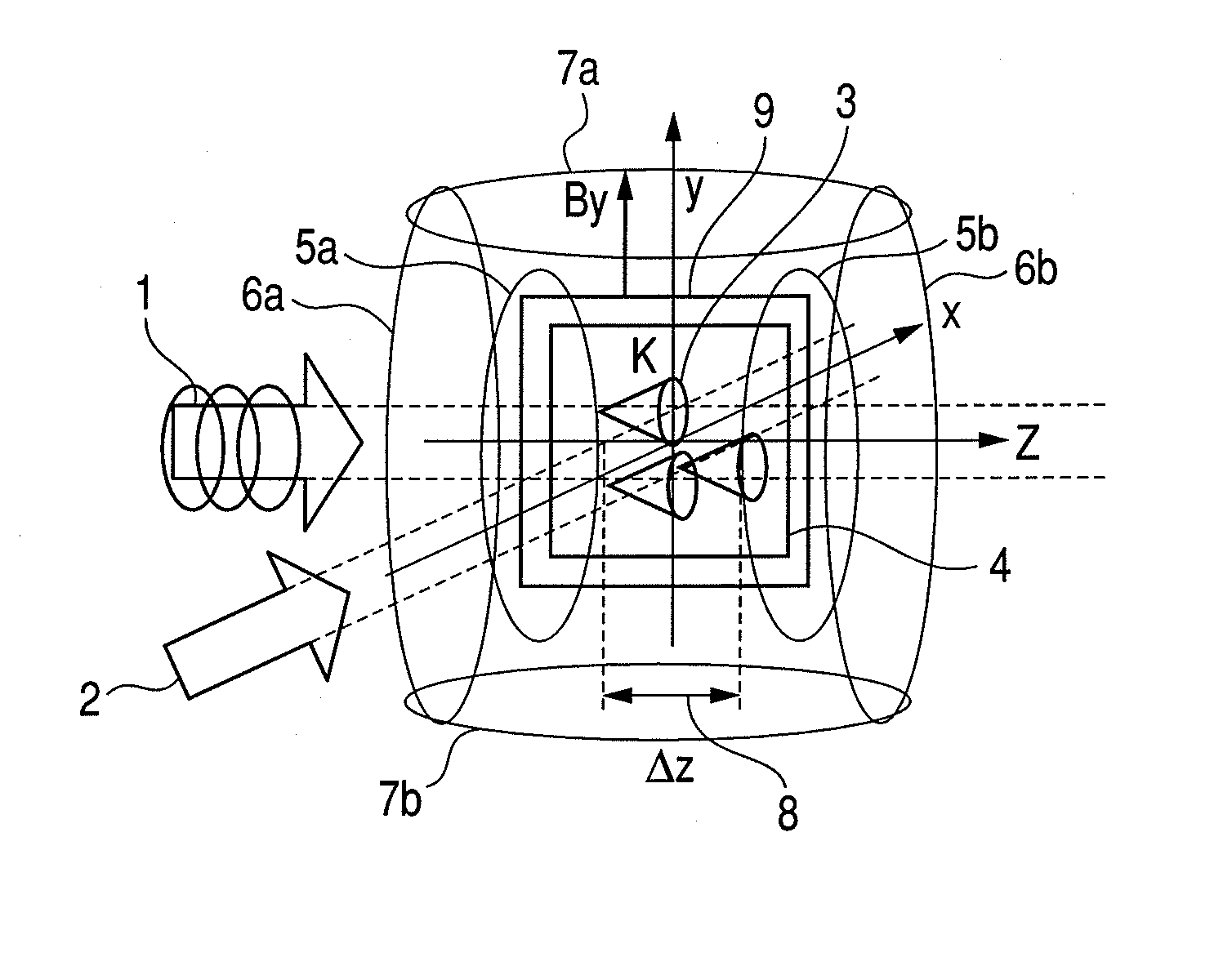
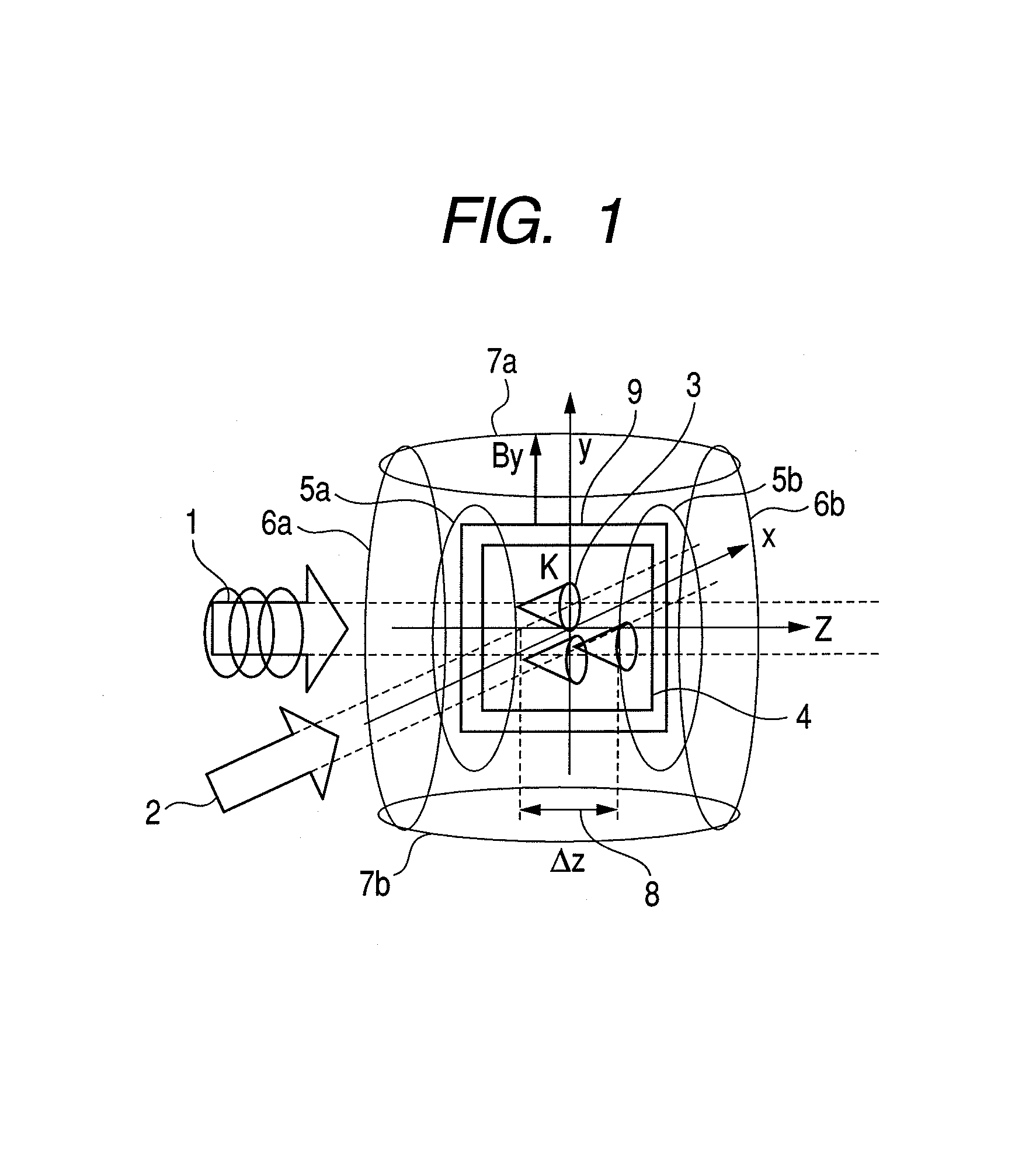
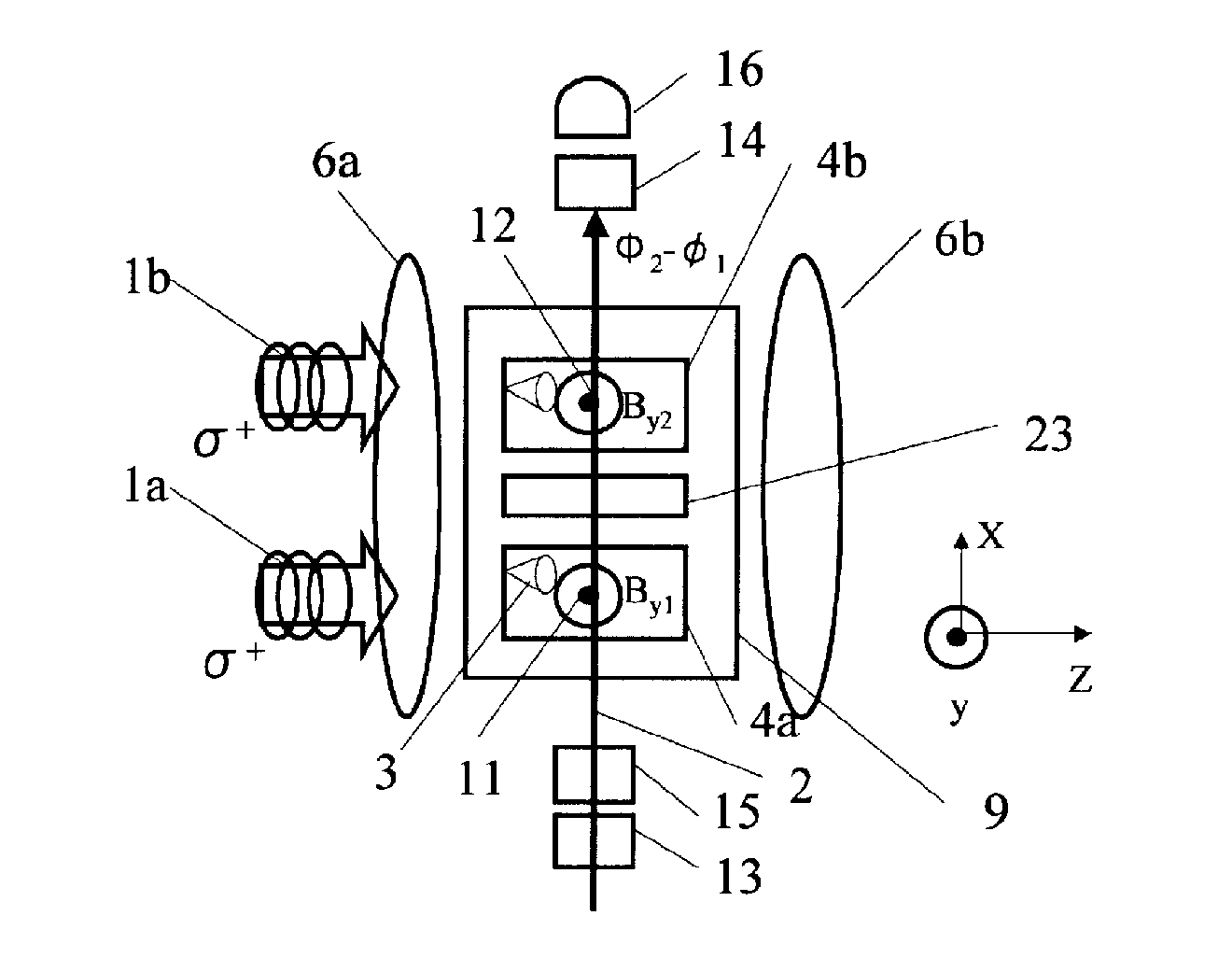
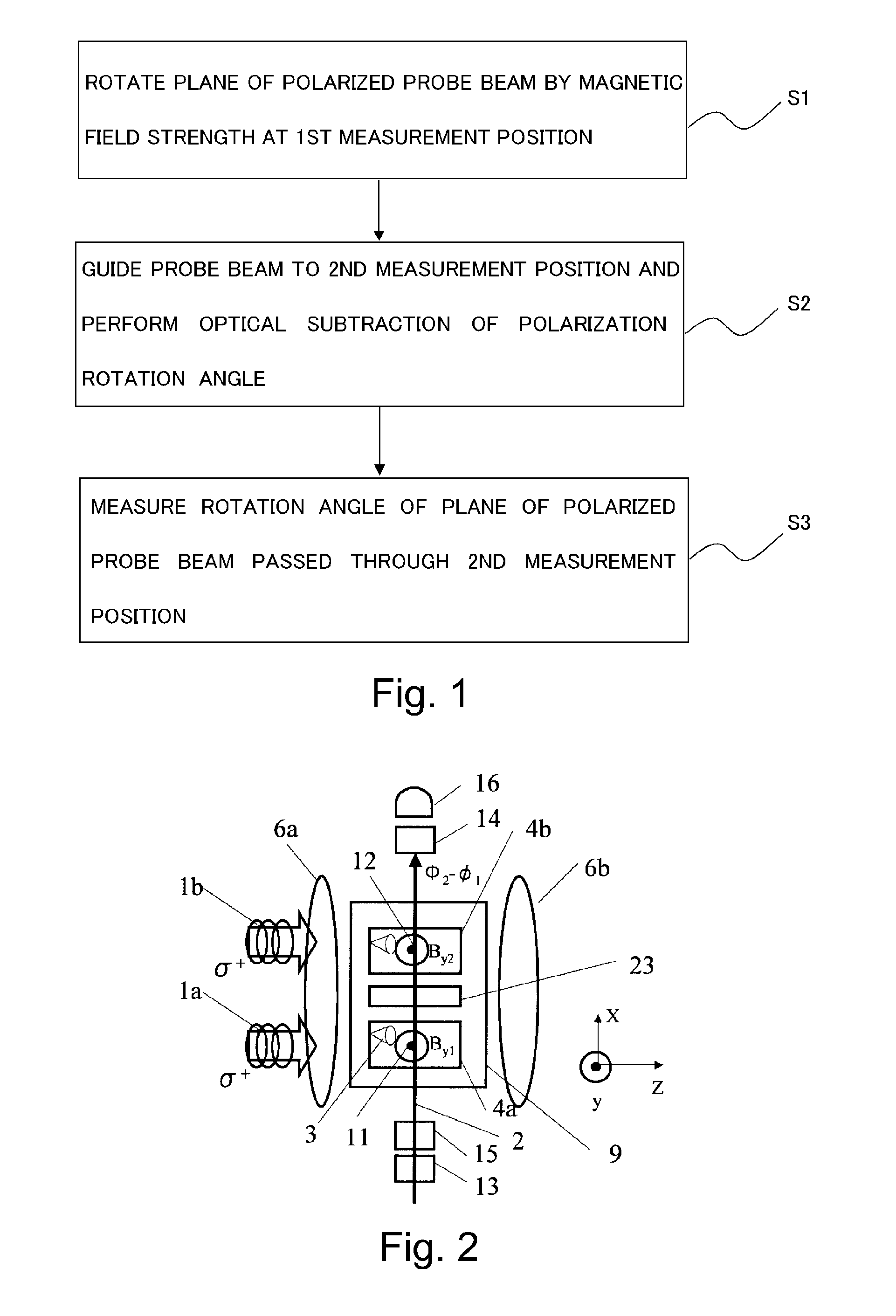
ActiveUS8405389B2High-sensitivity sensorMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic gradient measurementsLight beamAtomic magnetometer
An atomic magnetometer includes a light source for a probe beam and a medium in which the probe beam is to be propagated. The medium is a substance which changes a polarization rotation angle of the probe beam depending on a magnetic field intensity at a first measurement position and a magnetic field intensity at a second measurement position different from the first measurement position. The atomic magnetometer directly measures a difference between the magnetic field intensity at the first measurement position and the magnetic field intensity at the second measurement position as a difference in polarization rotation angle, along a propagation path of the probe beam.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS20110025323A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceSelf-oscillationLight beam
An optical atomic magnetometers is provided operating on the principles of nonlinear magneto-optical rotation. An atomic vapor is optically pumped using linearly polarized modulated light. The vapor is then probed using a non-modulated linearly polarized light beam. The resulting modulation in polarization angle of the probe light is detected and used in a feedback loop to induce self-oscillation at the resonant frequency.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
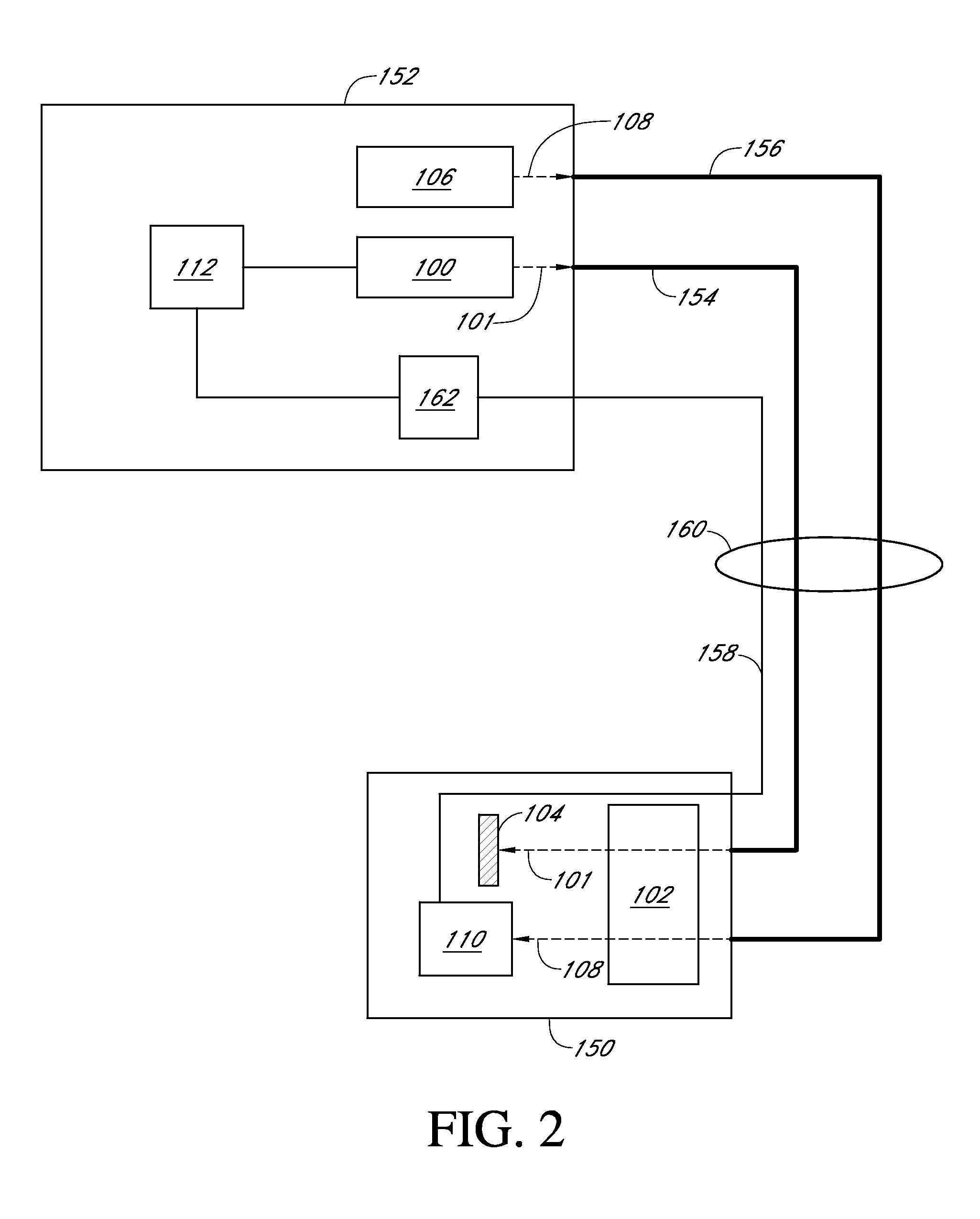
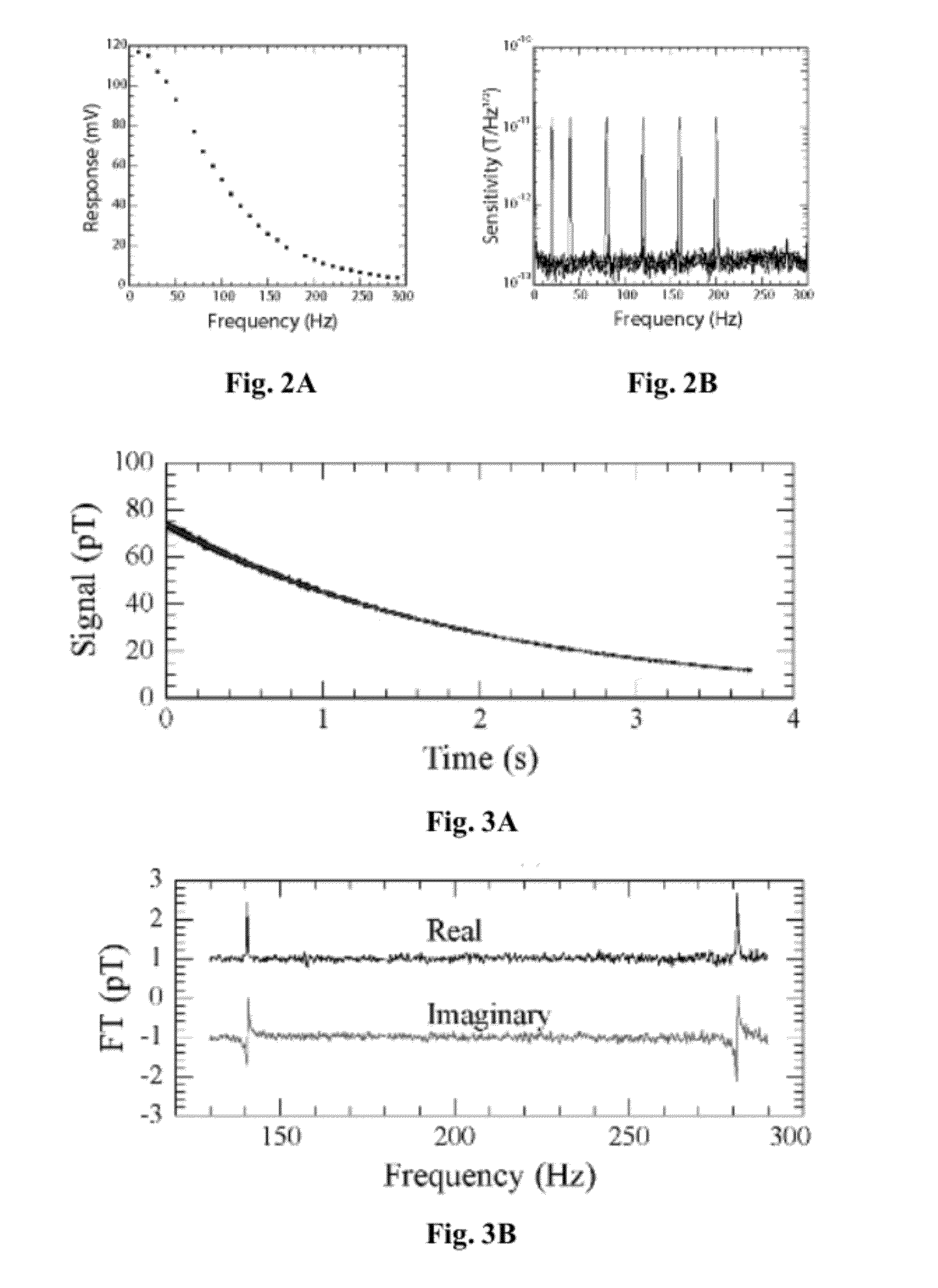
Detection of J-coupling using atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS9140657B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceJ-couplingAnalyte
An embodiment of a method of detecting a J-coupling includes providing a polarized analyte adjacent to a vapor cell of an atomic magnetometer; and measuring one or more J-coupling parameters using the atomic magnetometer. According to an embodiment, measuring the one or more J-coupling parameters includes detecting a magnetic field created by the polarized analyte as the magnetic field evolves under a J-coupling interaction.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY +1
Integrated microchip incorporating atomic magnetometer and microfluidic channel for NMR and MRI
ActiveUS7994783B2Improve scalabilityLow costElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMicrofluidic channel
An integral microfluidic device includes an alkali vapor cell and microfluidic channel, which can be used to detect magnetism for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Small magnetic fields in the vicinity of the vapor cell can be measured by optically polarizing and probing the spin precession in the small magnetic field. This can then be used to detect the magnetic field of in encoded analyte in the adjacent microfluidic channel. The magnetism in the microfluidic channel can be modulated by applying an appropriate series of radio or audio frequency pulses upstream from the microfluidic chip (the remote detection modality) to yield a sensitive means of detecting NMR and MRI.
Owner:GOVERNMNET OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TECH +1
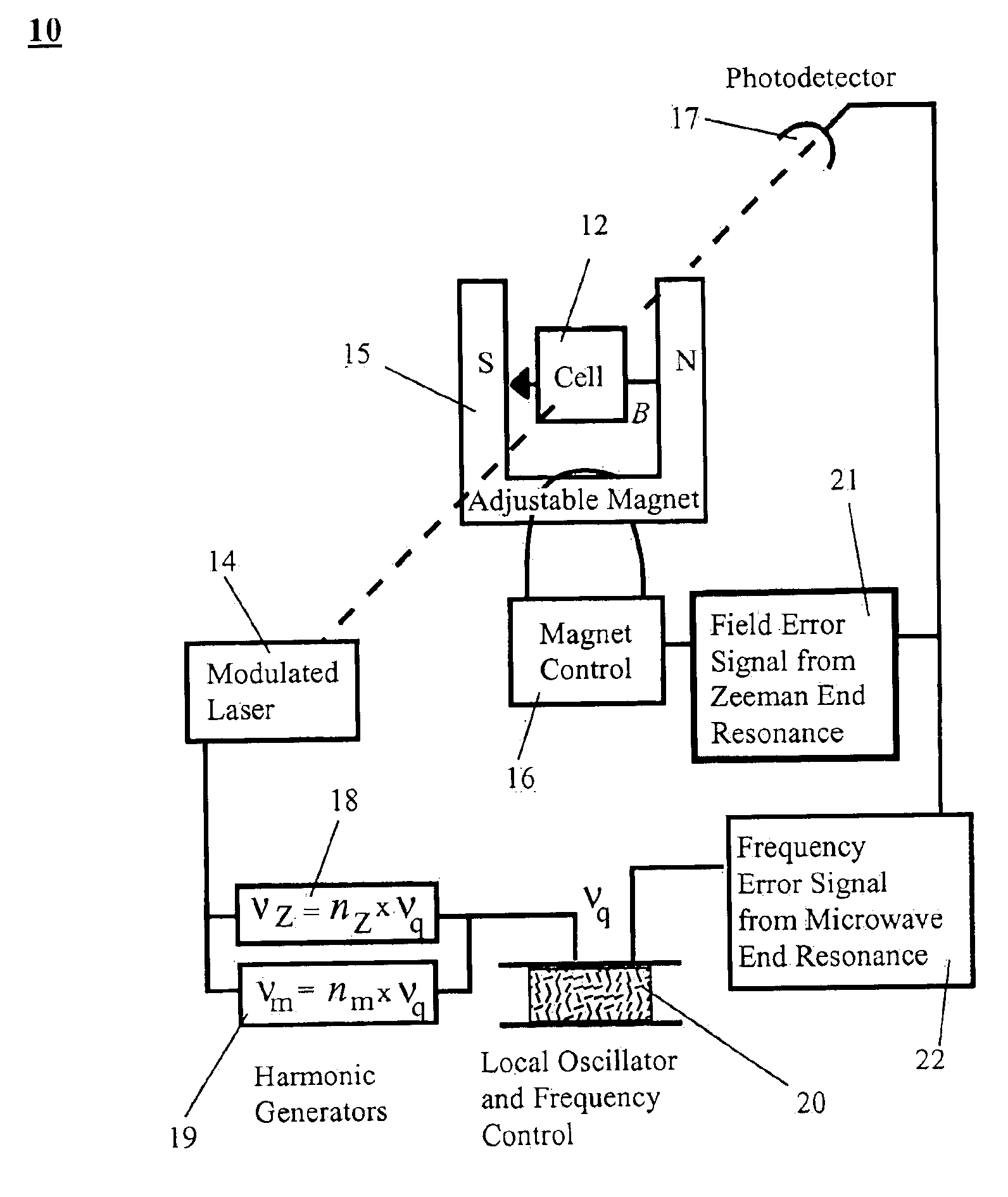
Method and system for operating an atomic clock with simultaneous locking of field and frequency
InactiveUS6888780B2Eliminates concern about magnetic-field dependenceHigh light transmittanceMechanical clocksPulse automatic controlTrappingLaser light
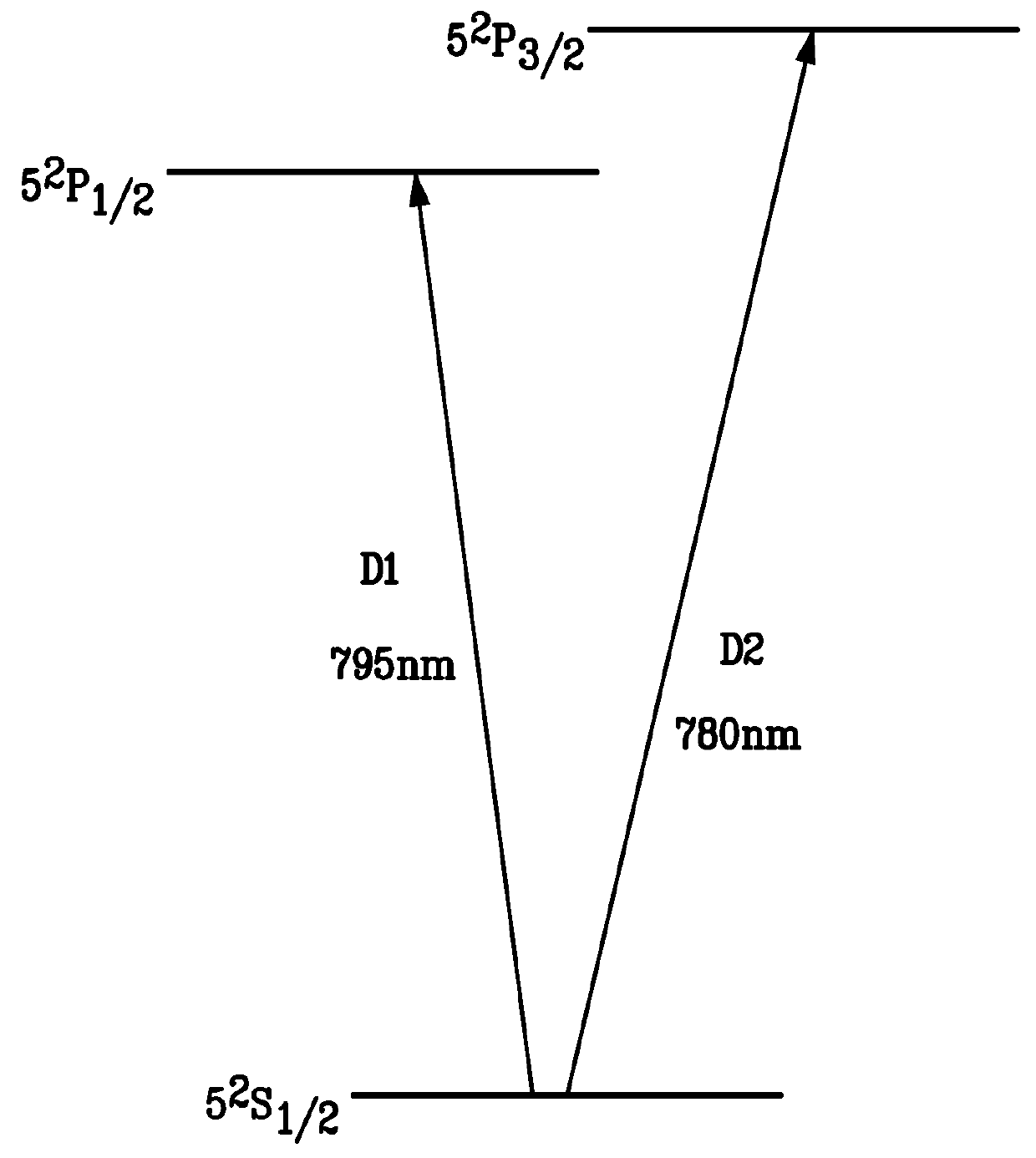
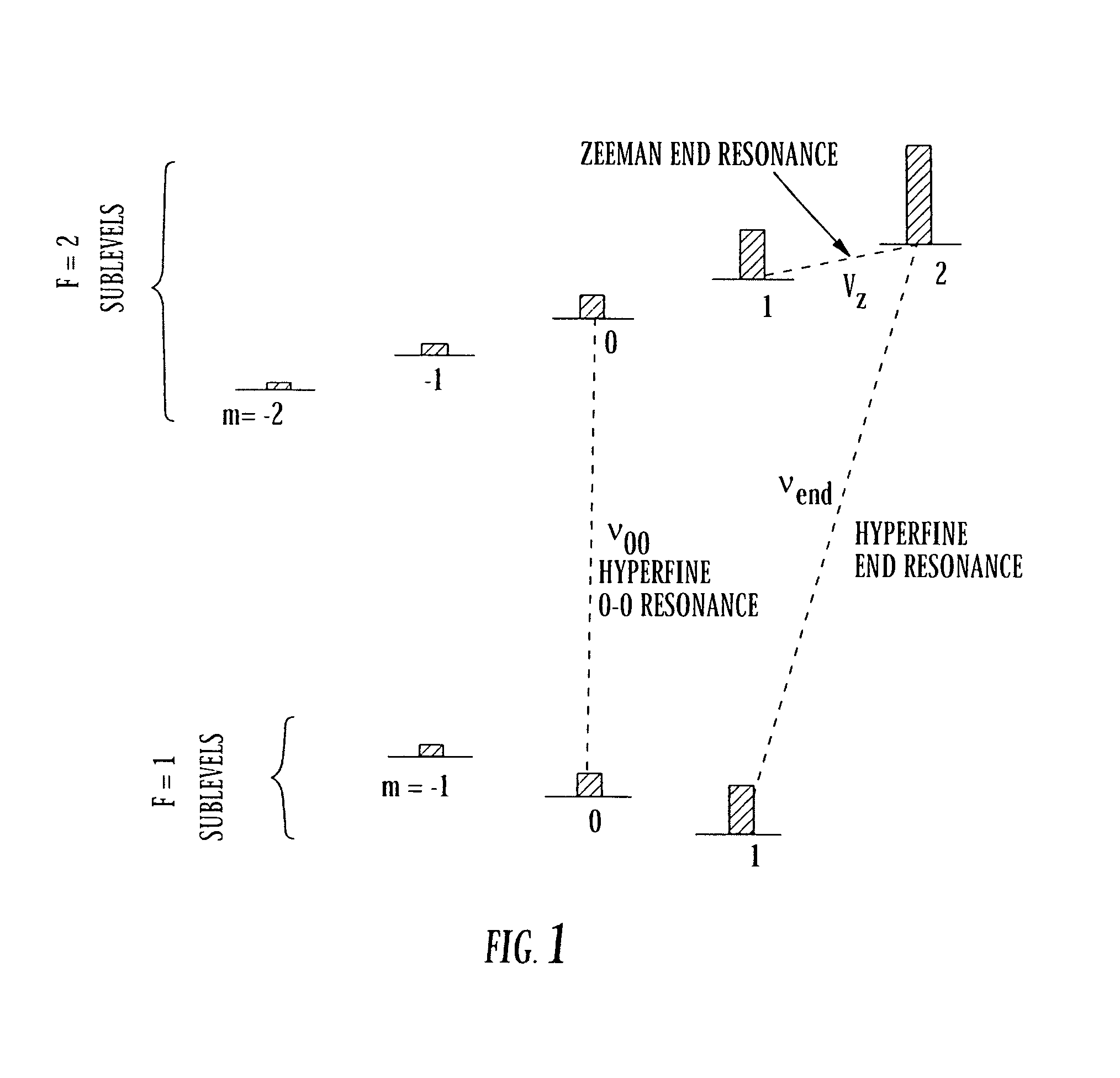
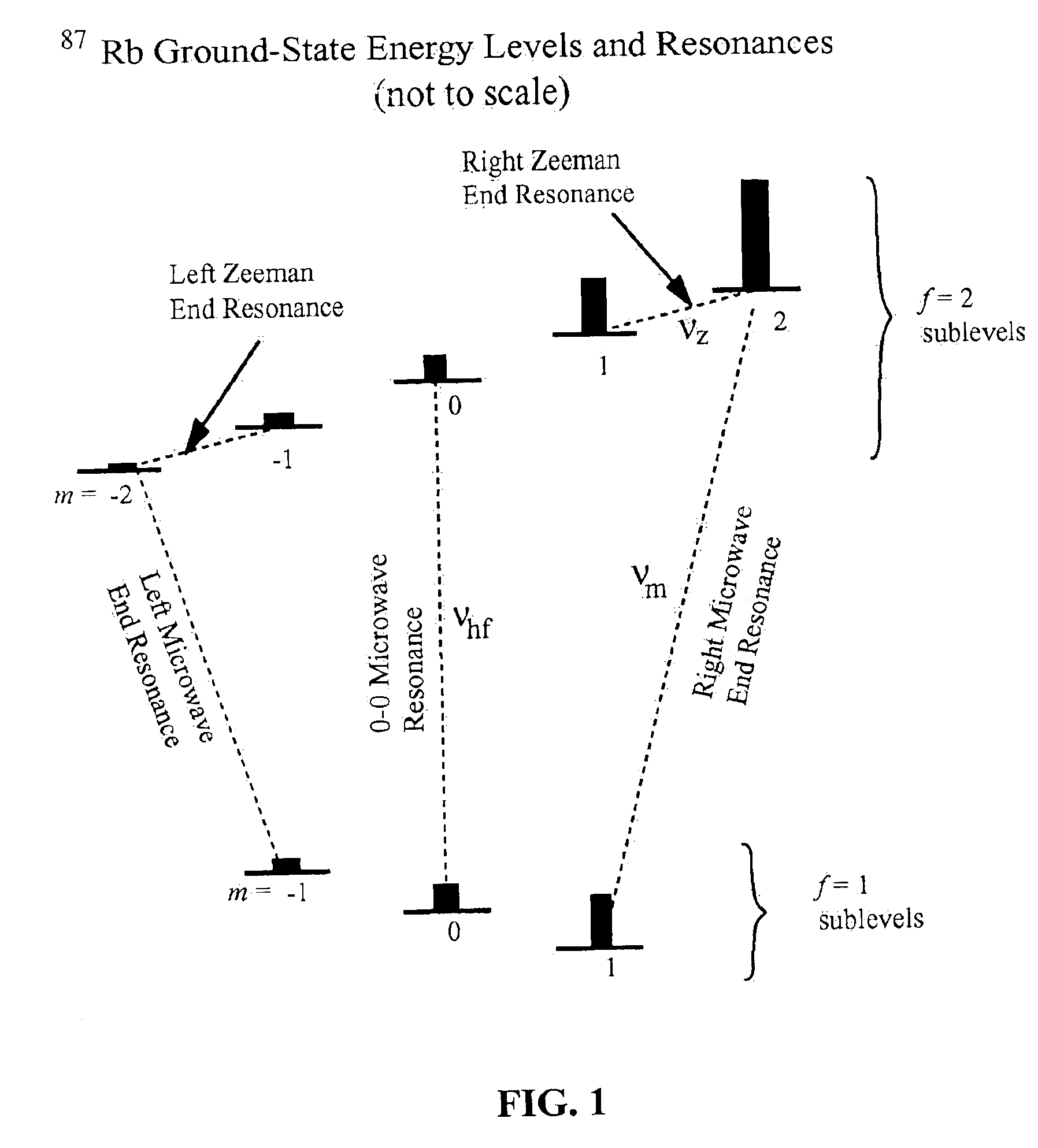
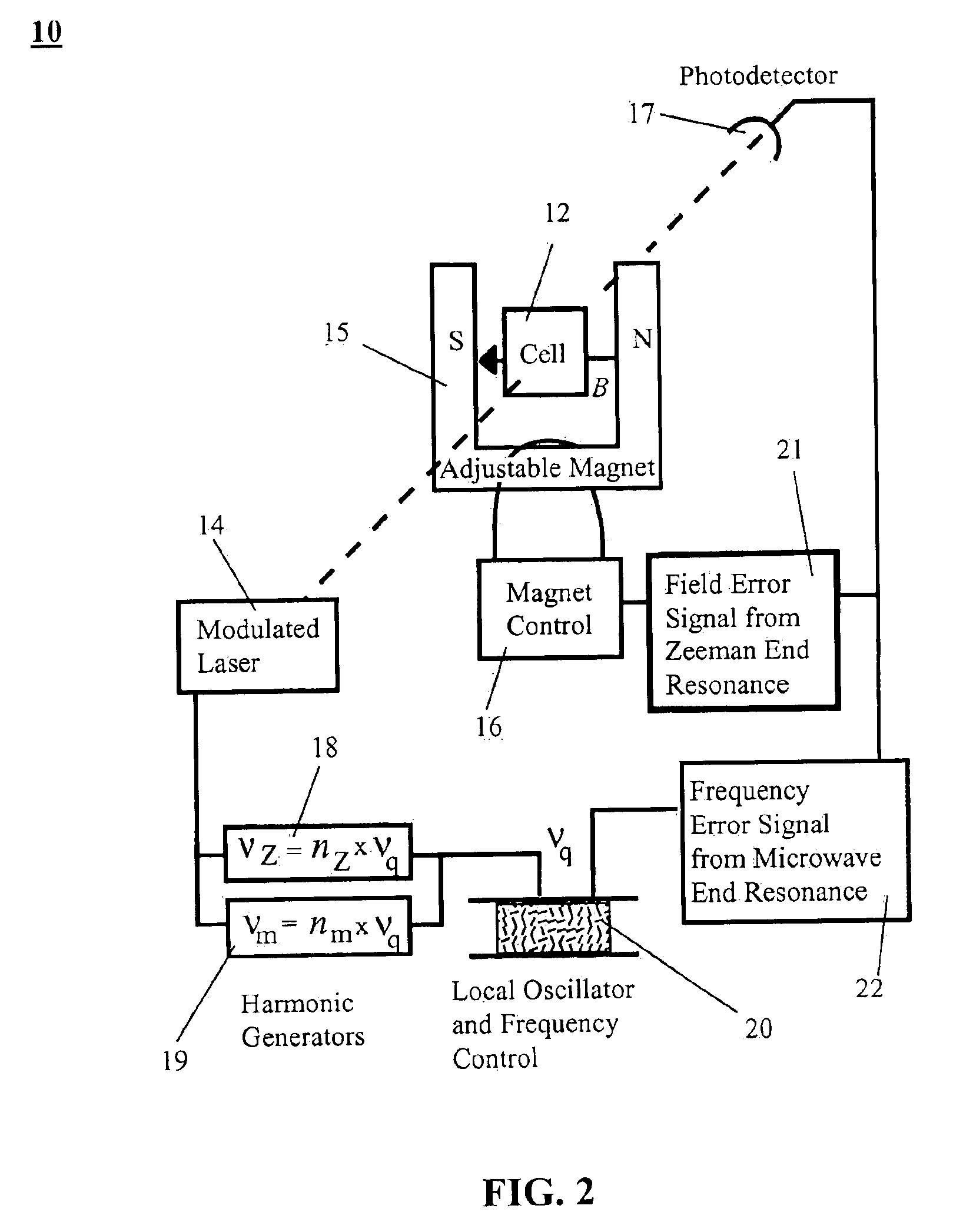
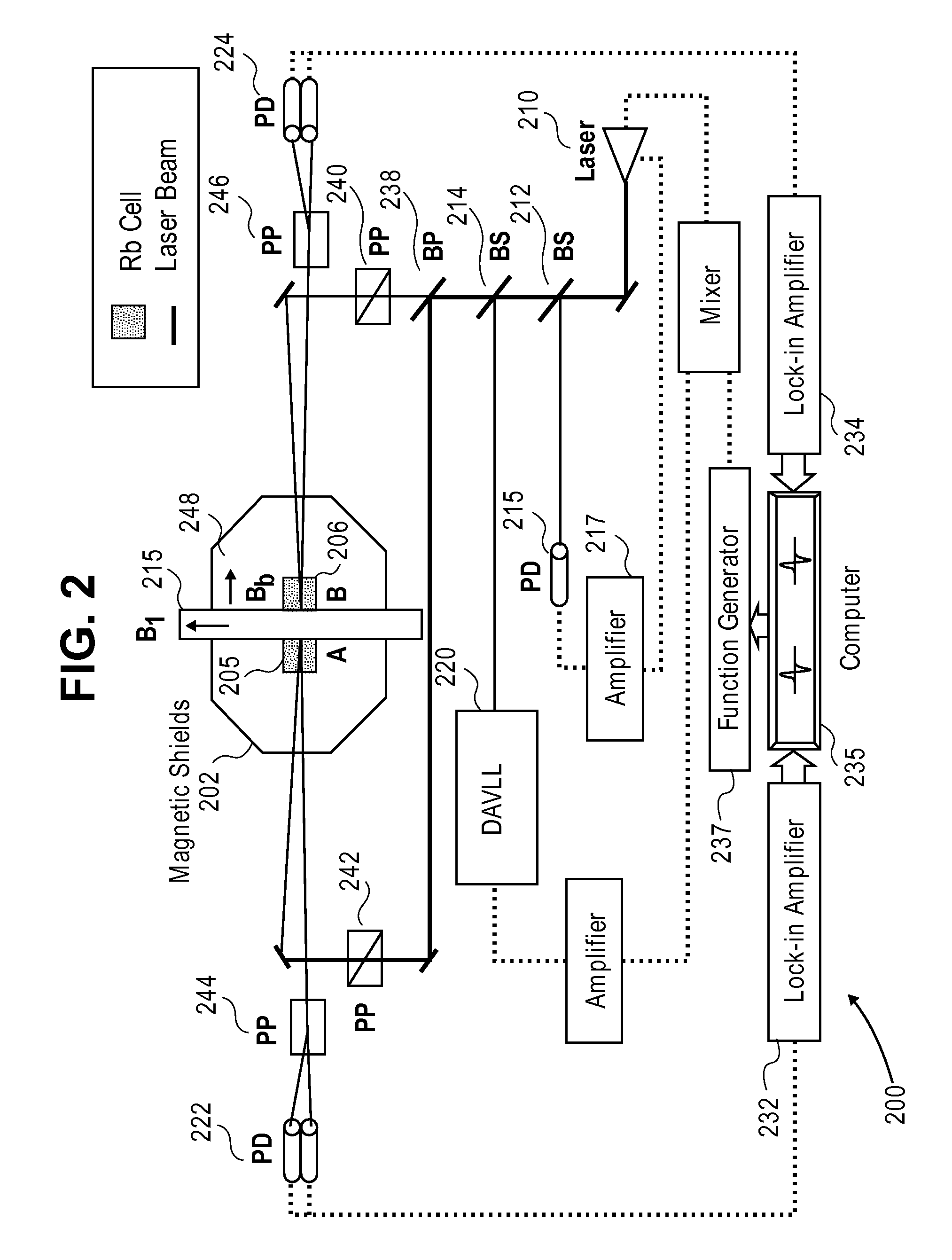
The present invention provides a method and system to simultaneously use the microwave and Zeeman end resonances associated with the same sublevel of maximum (or minimum) azimuthal quantum number m to lock both the atomic clock frequency and the magnetic field to definite values. This eliminates the concern about the field dependence of the end-resonance frequency. In an embodiment of the system of the present invention, alkali metal vapor is pumped with circularly-polarized D1 laser light that is intensity-modulated at appropriate resonance frequencies, thereby providing coherent population trapping (CPT) resonances. In another embodiment, pumping with constant-intensity circularly-polarized D1 laser light enhances magnetic resonances that are excited by alternating magnetic fields oscillating at appropriate resonance frequencies. In both embodiments, the resonances are greatly enhanced by concentrating most of the atoms in the initial state of the resonances, and by diminishing the spin-exchange broadening of the resonances. This leads to greater stability of optically pumped atomic clocks. This invention can also be used to operate an atomic magnetometer, where the feedback signal used to stabilize the magnetic field at the alkali-vapor cell can serve as a sensitive measure of the ambient magnetic field.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
Atomic magnetometer and operating method of the same
ActiveUS9927501B2High bandwidthMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Atomic magnetic gradiometer for room temperature high sensitivity magnetic field detection
InactiveUS7573264B2Reduce noiseElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceProton NMRSingle polarization
A laser-based atomic magnetometer (LBAM) apparatus measures magnetic fields, comprising: a plurality of polarization detector cells to detect magnetic fields; a laser source optically coupled to the polarization detector cells; and a signal detector that measures the laser source after being coupled to the polarization detector cells, which may be alkali cells. A single polarization cell may be used for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) by prepolarizing the nuclear spins of an analyte, encoding spectroscopic and / or spatial information, and detecting NMR signals from the analyte with a laser-based atomic magnetometer to form NMR spectra and / or magnetic resonance images (MRI). There is no need of a magnetic field or cryogenics in the detection step, as it is detected through the LBAM.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
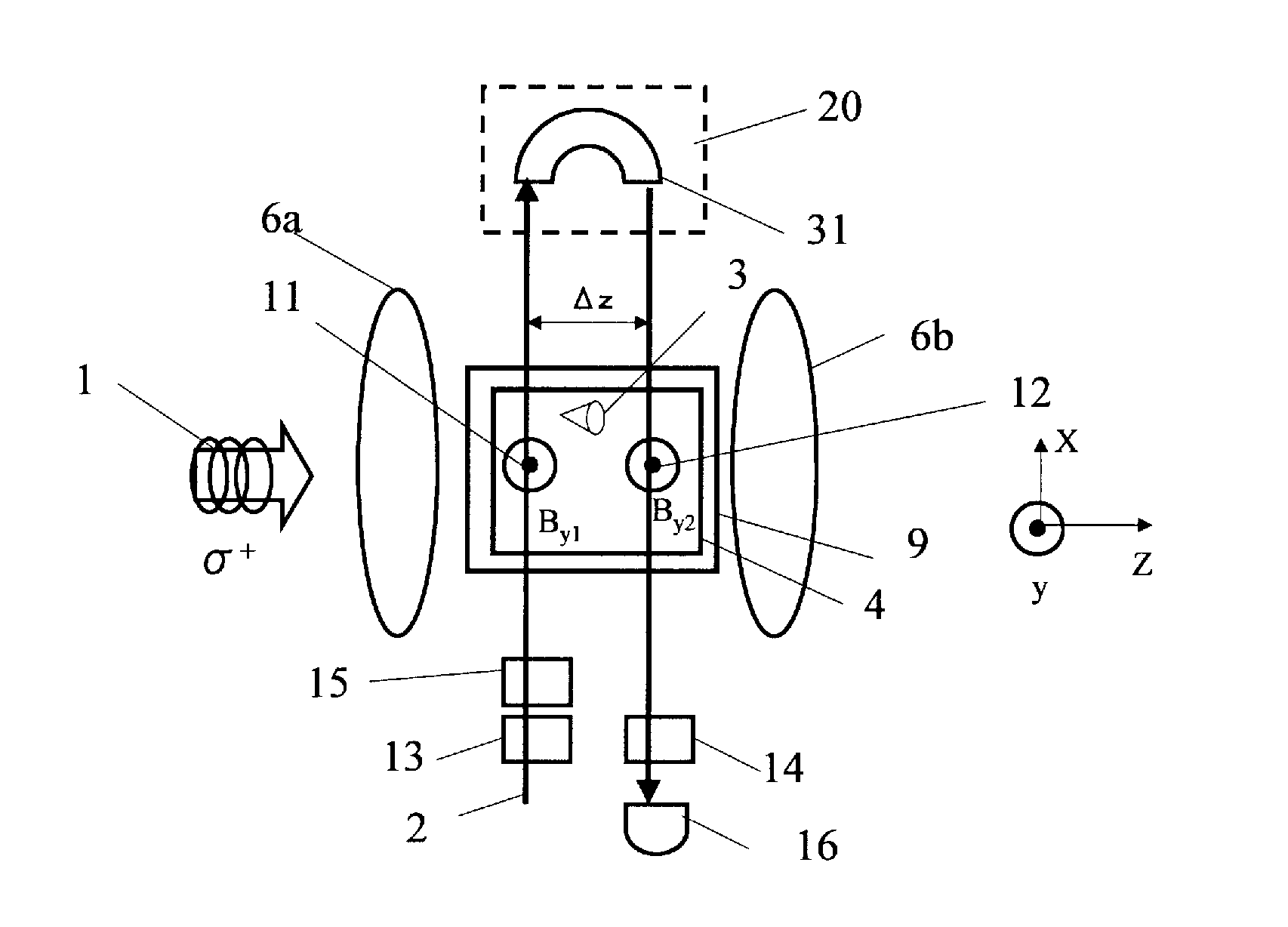
Magnetic sensing method, atomic magnetometer and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveUS8373413B2Increase the frequency bandMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionAtomic magnetometerOptical polarization
A magnetic sensing method comprises irradiating a pump light having a circularly polarized component and a probe light having a linearly polarized component onto a group of atoms contained in a cell so as to make the lights produce an intersection region and detecting a change of rotation angle of a plane of polarization of the probe light before and after passing the cell. The pump light and the probe light are irradiated in a state where a magnetic field of the direction in which the pump light strikes the intersection region is provided with a gradient.
Owner:CANON KK
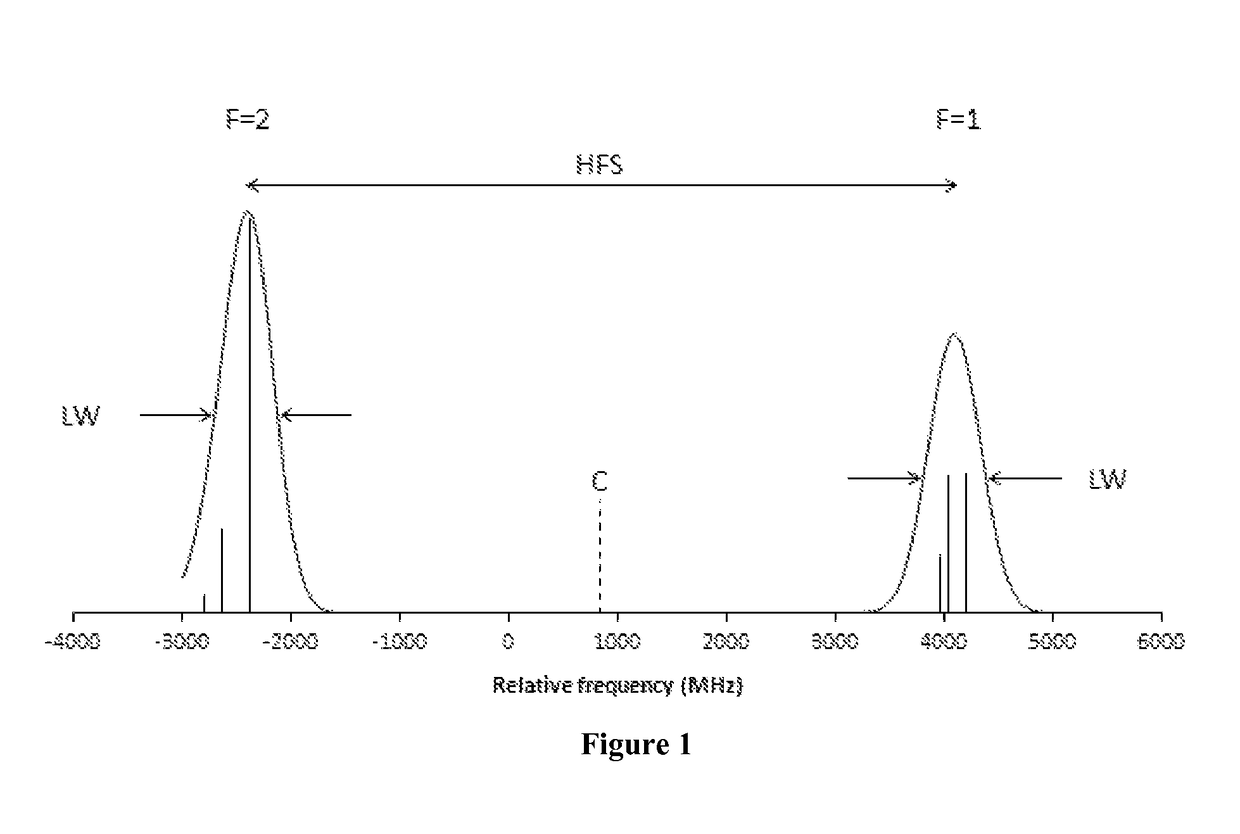
Wavelength-modulated coherence pumping and hyperfine repumping for an atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS9869731B1Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceLight beamWavelength modulation
An FM-NMOR magnetometer and concomitant magnetometry method comprising providing a linearly-polarized pump beam generator, employing a center wavelength approximately equal to a center wavelength of hyperfine peaks, and employing a modulation amplitude in the range HFS-3×LW to HFS.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Atomic magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS20110193555A1High-sensitivity sensorMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetic gradient measurementsLight beamOptical polarization
An atomic magnetometer includes a light source for a probe beam and a medium in which the probe beam is to be propagated. The medium is a substance which changes a polarization rotation angle of the probe beam depending on a magnetic field intensity at a first measurement position and a magnetic field intensity at a second measurement position different from the first measurement position. The atomic magnetometer directly measures a difference between the magnetic field intensity at the first measurement position and the magnetic field intensity at the second measurement position as a difference in polarization rotation angle, along a propagation path of the probe beam.
Owner:CANON KK
Micro-Fabricated Atomic Magnetometer and Method of Forming the Magnetometer
ActiveUS20130147472A1Low costSmall sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser lightPhotodiode
The cost and size of an atomic magnetometer are reduced by attaching a vapor cell structure that has a vapor cell cavity to a base die that has a laser light source that outputs light to the vapor cell cavity, and attaching a photo detection die that has a photodiode to the vapor cell structure to detect light from the laser light source that passes through the vapor cell cavity.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method of performing MRI with an atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS20100090697A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceAtomic magnetometer
A method and apparatus are provided for performing an in-situ magnetic resonance imaging of an object. The method includes the steps of providing an atomic magnetometer, coupling a magnetic field generated by magnetically resonating samples of the object through a flux transformer to the atomic magnetometer and measuring a magnetic resonance of the atomic magnetometer.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Compact atomic magnetometer and gyroscope based on a diverging laser beam
InactiveUS20090039881A1Low costReduce low frequency noiseTurn-sensitive devicesElectric/magnetic detectionAtomic systemGyroscope
An atomic magnetometer that simultaneously achieves high sensitivity, simple fabrication and small size. This design is based on a diverging (or converging) beam of light that passes through an alkali atom vapor cell and that contains a distribution of beam propagation vectors. The existence of more than one propagation direction permits longitudinal optical pumping of atomic system and simultaneous detection of the transverse atomic polarization. The design could be implemented with a micro machined alkali vapor cell and light from a single semiconductor laser. A small modification to the cell contents and excitation geometry allows for use as a gyroscope.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
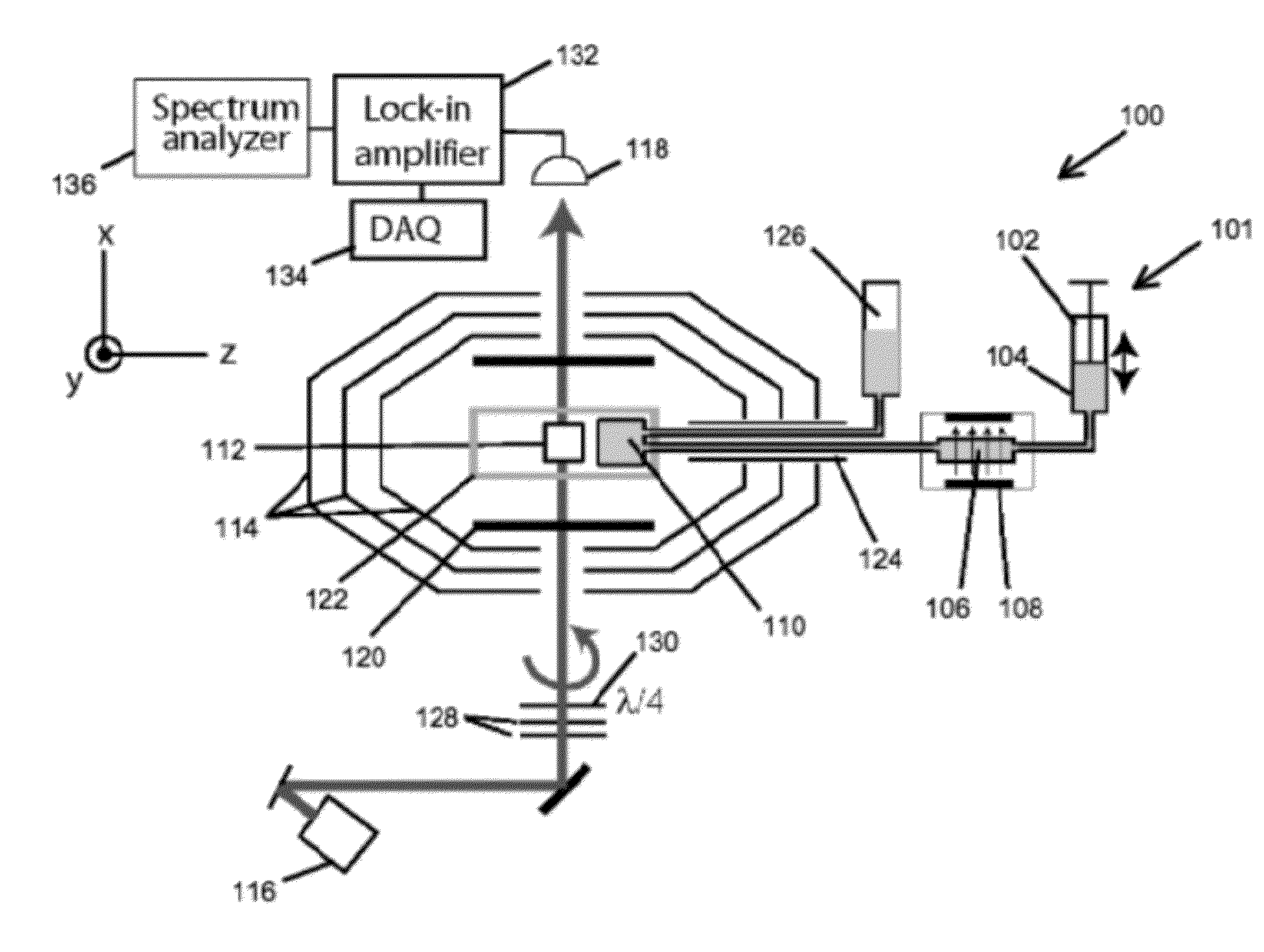
High-sensitivity atomic magnetometer
InactiveCN101441253AHigh sensitivitySimple interfaceMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsSignal detectorUltimate tensile strength
A high-sensitivity atom magnetometer for measuring extremely weak magnetic field consists of laser source, a weak magnetic field probe and a signal detector; the three parts are connected by laser paths to form the integral of the high-sensitivity atom magnetometer. The high-sensitivity atom magnetometer, which can survey the weak magnetic field through measuring the variation of the intensity of the transmission laser which is caused by the combined function of laser, atomic air and weak field, has the advantages of high sensitivity, simple structure, friendly interface, low power consumption, etc.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
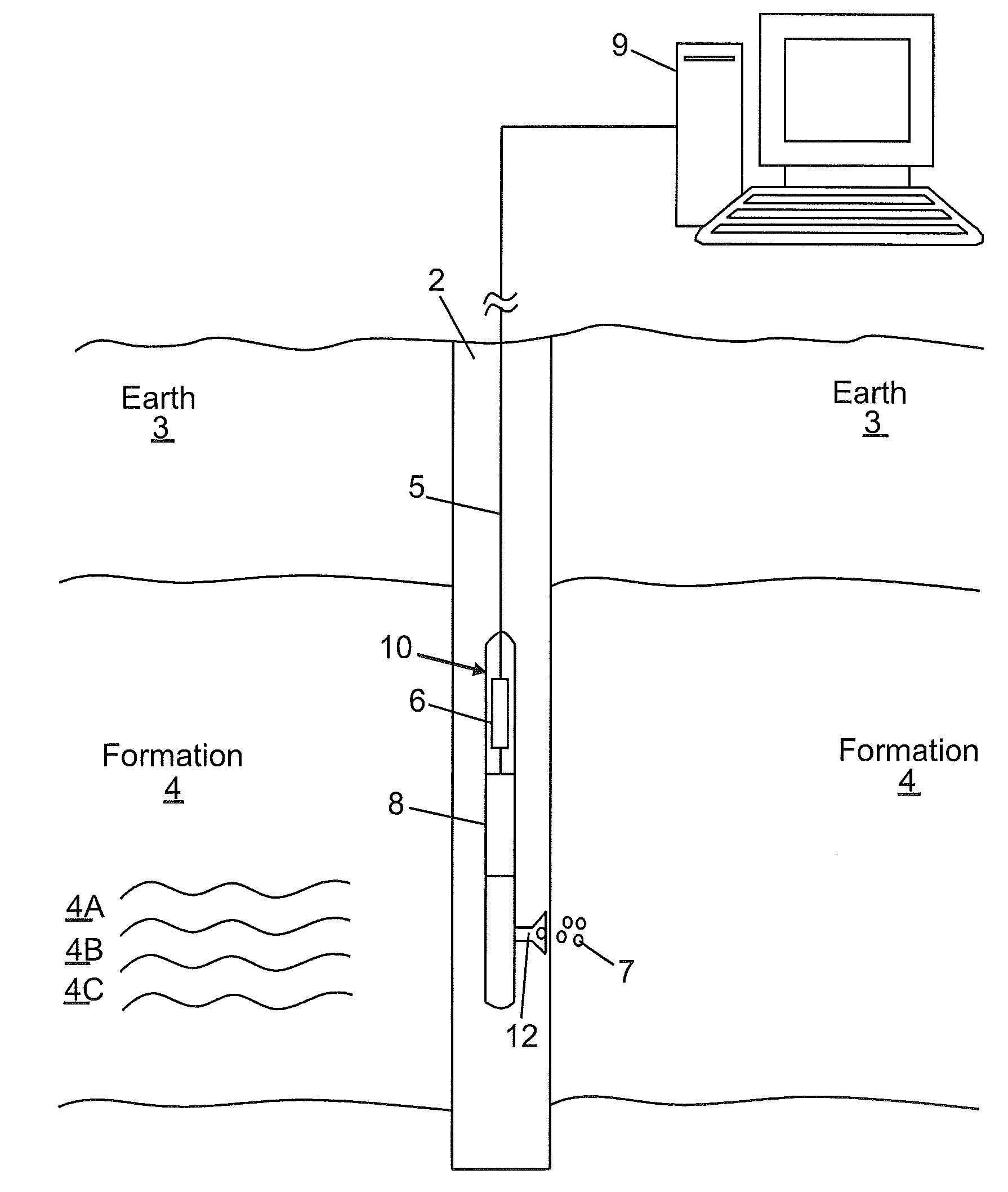
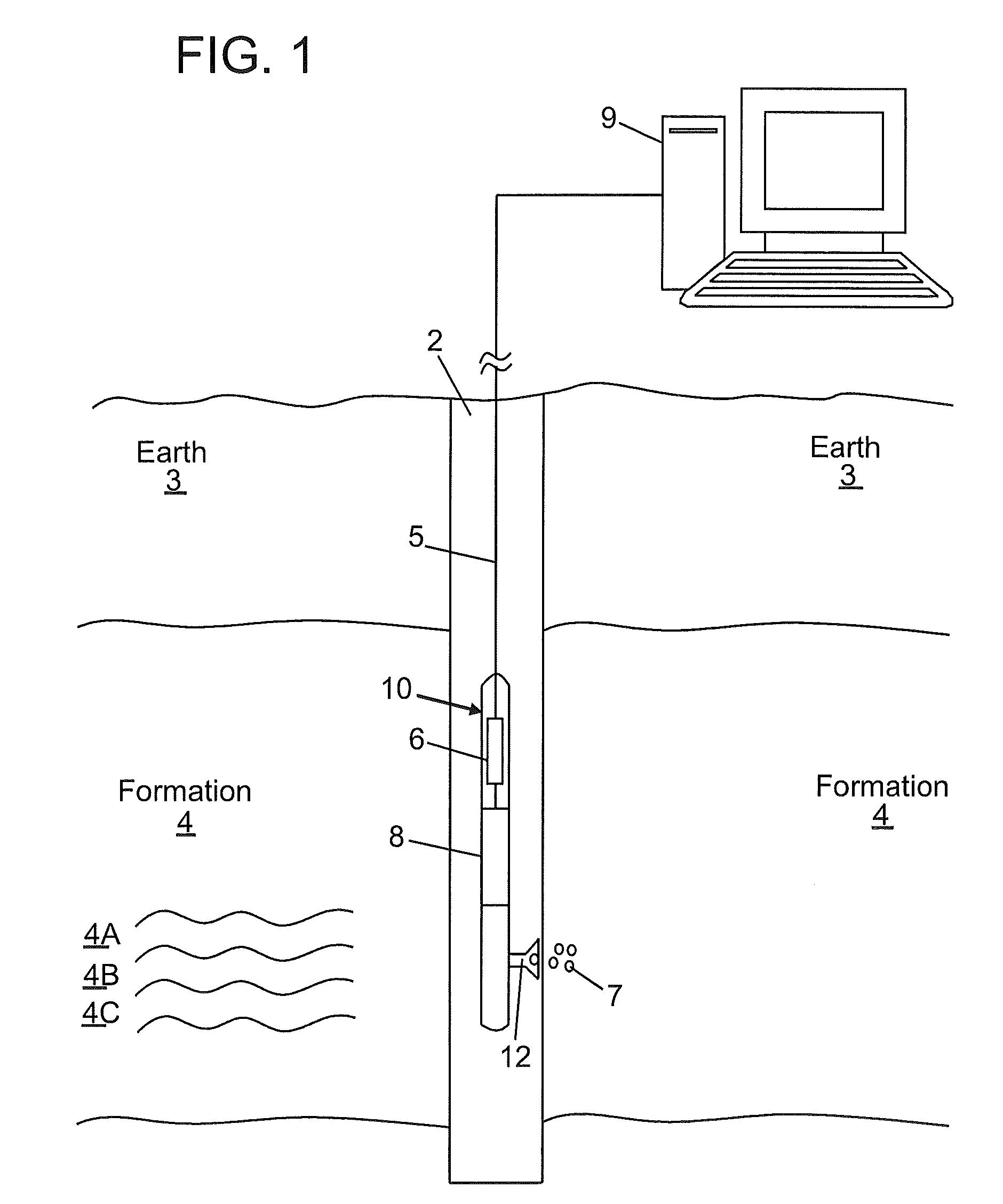
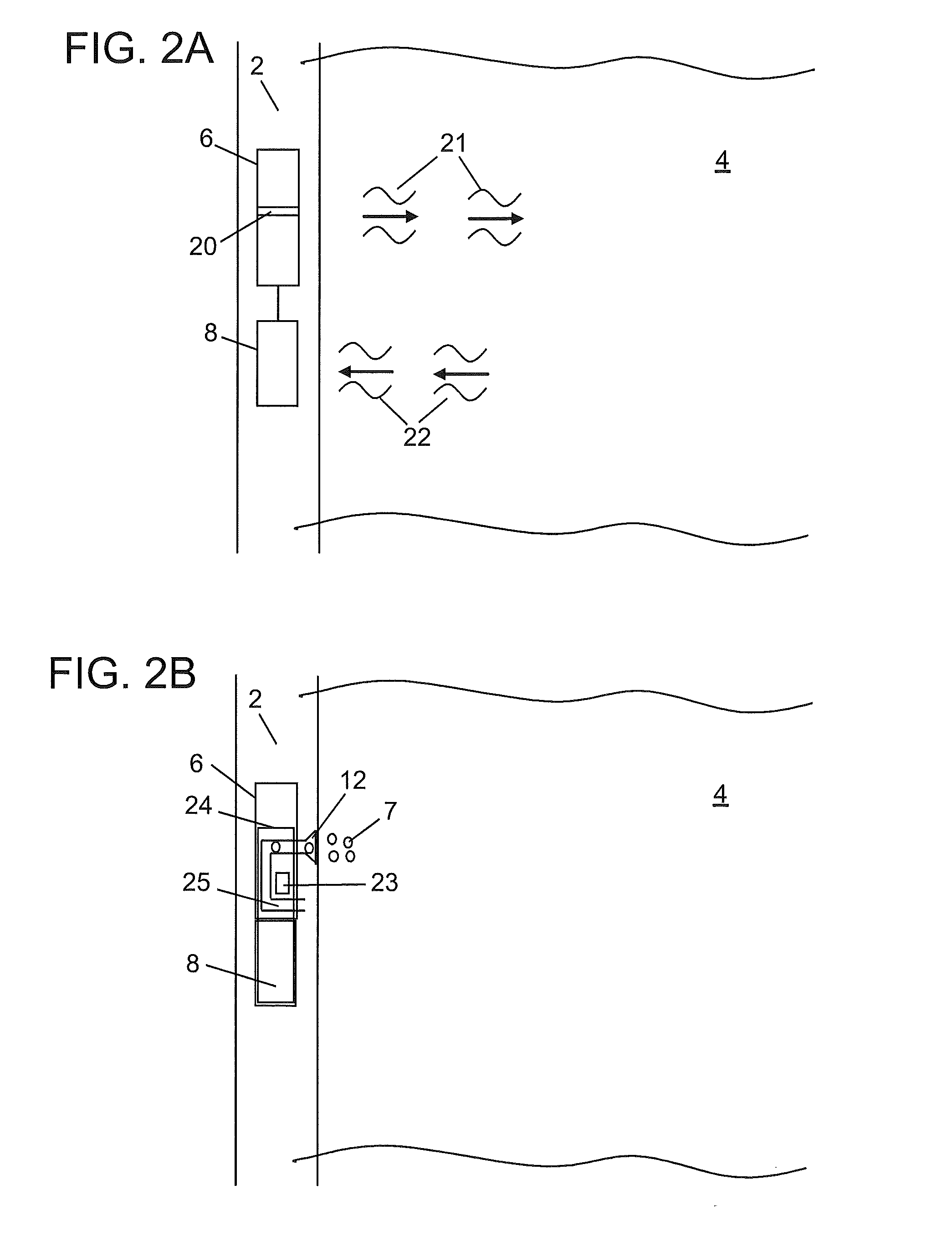
Atomic magnetometers for use in the oil service industry
InactiveUS20100225313A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePetroleumAtomic magnetometer
An apparatus for obtaining information from a subterranean environment, the apparatus includes: an atomic magnetometer configured to measure a magnetic field related to the information. An associated method for obtaining the information is also disclosed.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Rubidium atomic magnetometer and magnetic field measuring method thereof
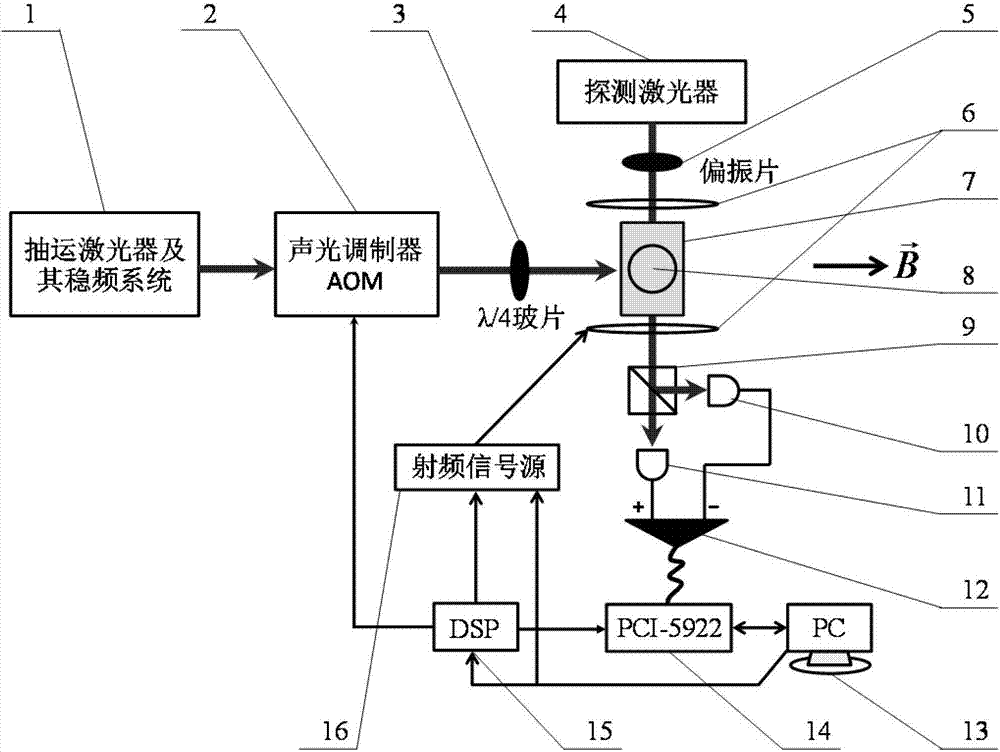
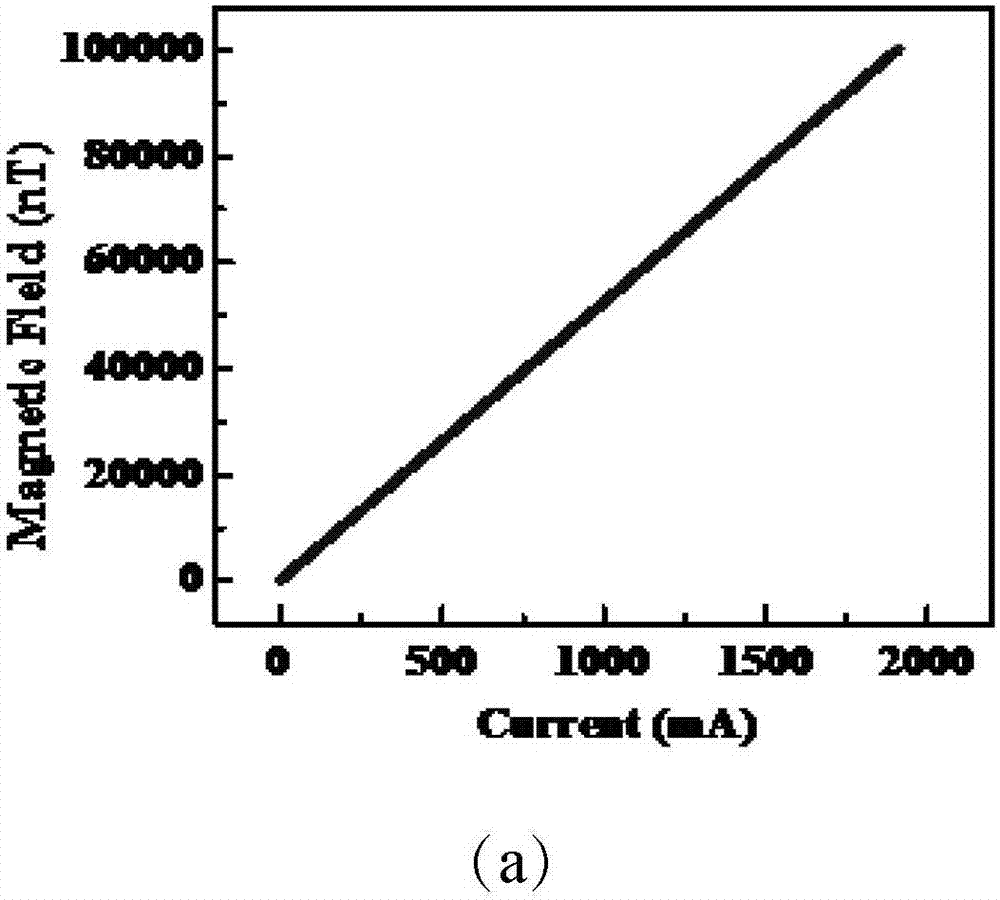
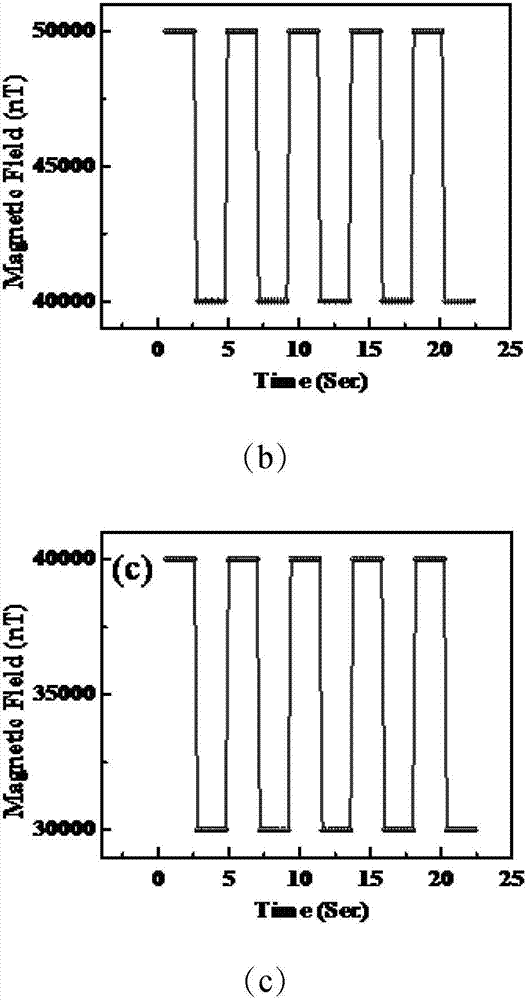
ActiveCN107015172ALarge measuring rangeMagnetic field sampling rate adjustableMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesData acquisitionWork flow
The invention discloses a rubidium atomic magnetometer and a magnetic field measuring method. Based on the principle of nonlinear magneto-optic rotation, and through combination of timing control and tracking type frequency locking control, the atomic magnetometer achieves a large dynamic measurement range, high magnetic field sampling rate and high sensitivity. A DSP timing control module controls on-off of an acousto-optic modulator and a radio-frequency signal source in the physical part of the rubidium atomic magnetometer according to timing combination to adjust the magnetic field sampling rate N. The DSP timing control module further controls acquisition triggering of a data acquisition card. A calculation unit gets the Larmor precession frequency (f) through fast Fourier transform with use of a received rubidium atom Larmor precession free relaxation signal, and further calculates the value of an external magnetic field. The calculation unit selects a high magnetic field sampling rate module or a low magnetic field sampling rate module before measurement according to the pre-judged dynamic range of a to-be-measured magnetic field, and sets whether a tracking type frequency locking work mode is used when the low magnetic field sampling rate module is selected. In the working process, data is acquired and processed, and the value of the magnetic field is output.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Detection of J-Coupling Using Atomic Magnetometer
ActiveUS20120176130A1Magnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyJ-couplingAnalyte
An embodiment of a method of detecting a J-coupling includes providing a polarized analyte adjacent to a vapor cell of an atomic magnetometer; and measuring one or more J-coupling parameters using the atomic magnetometer. According to an embodiment, measuring the one or more J-coupling parameters includes detecting a magnetic field created by the polarized analyte as the magnetic field evolves under a J-coupling interaction.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com