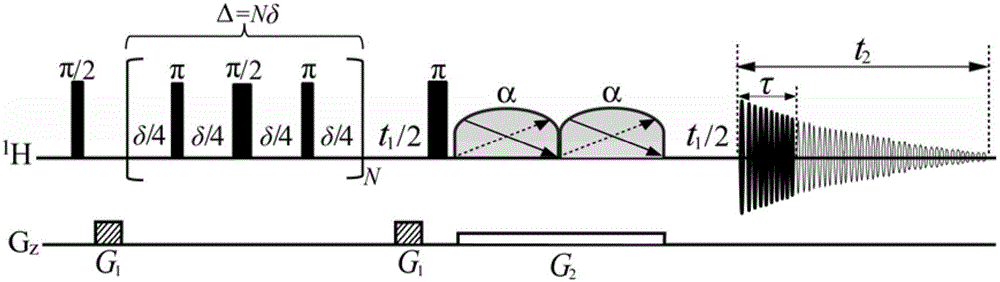
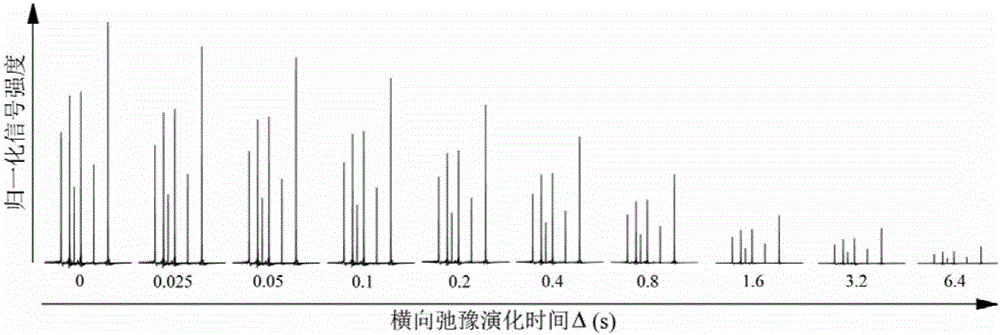
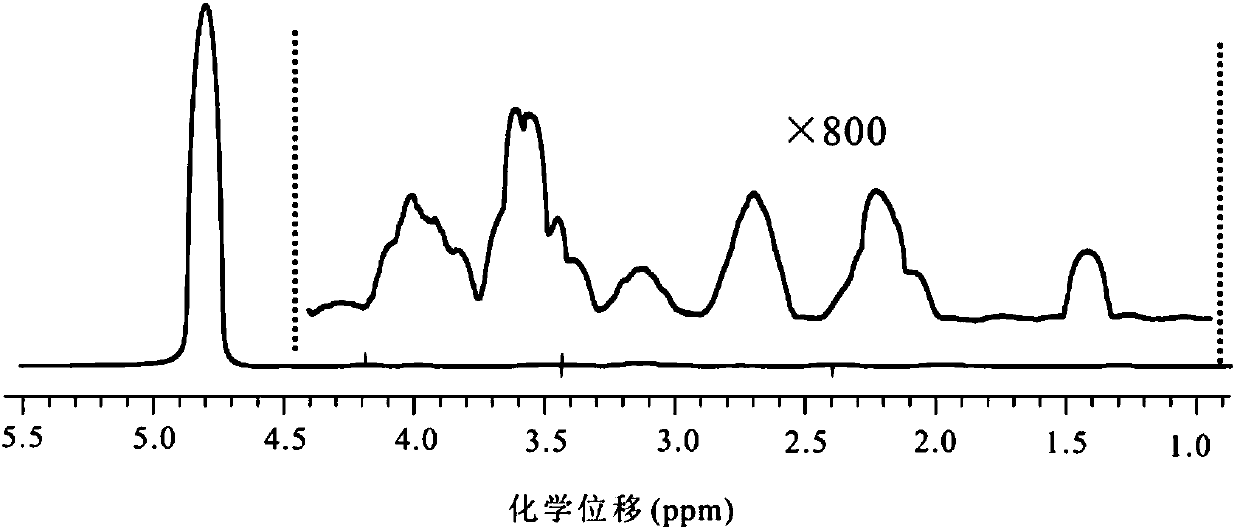
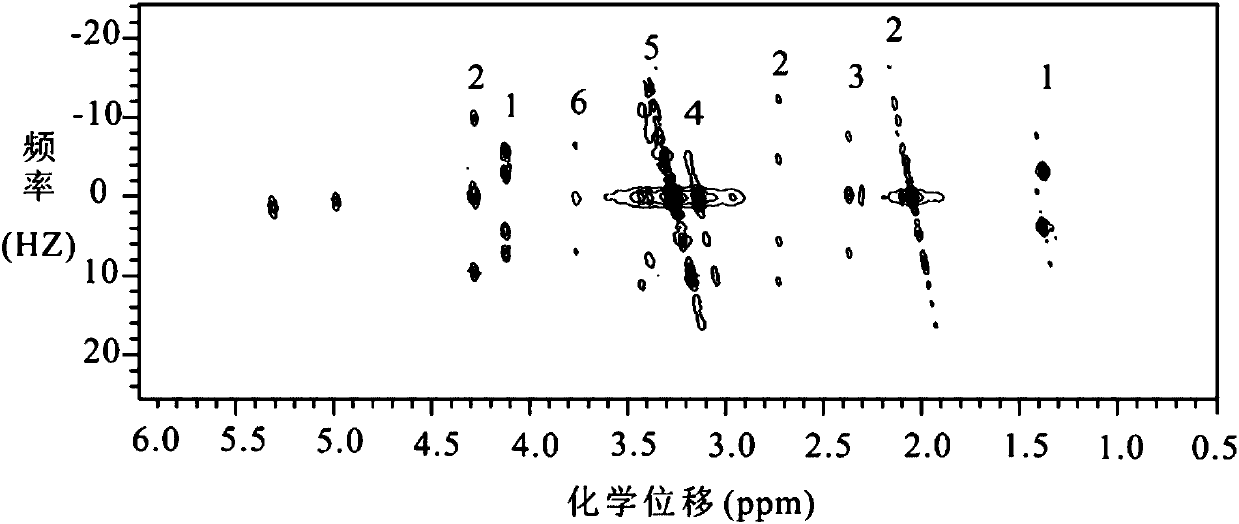
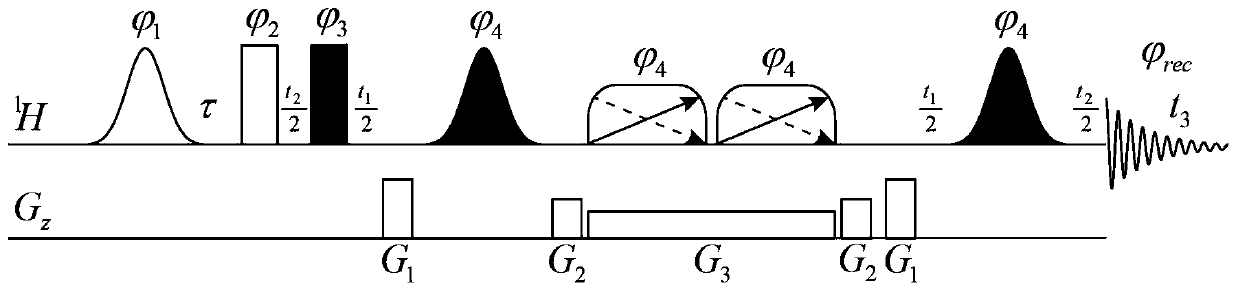
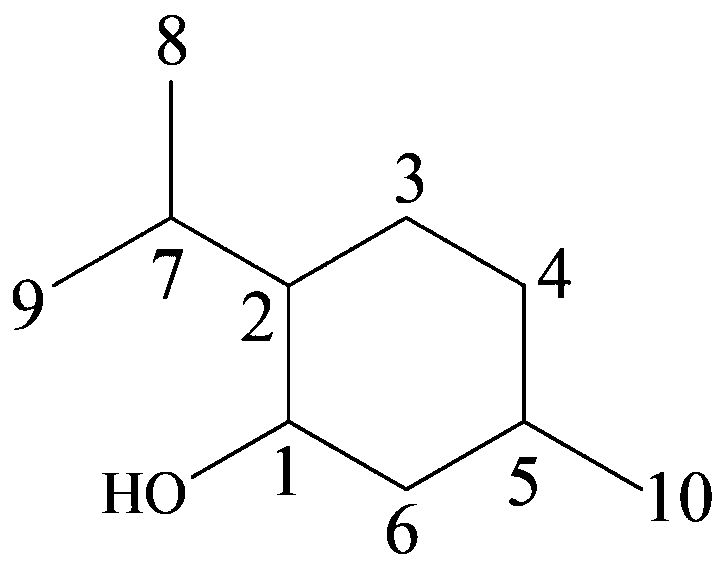
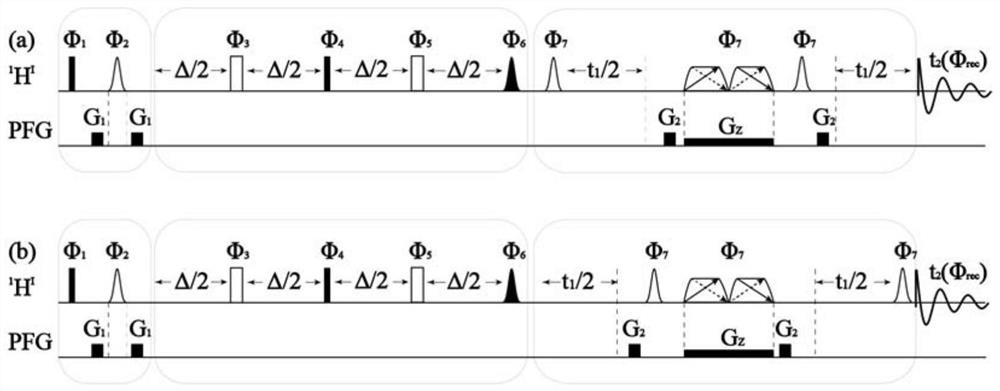
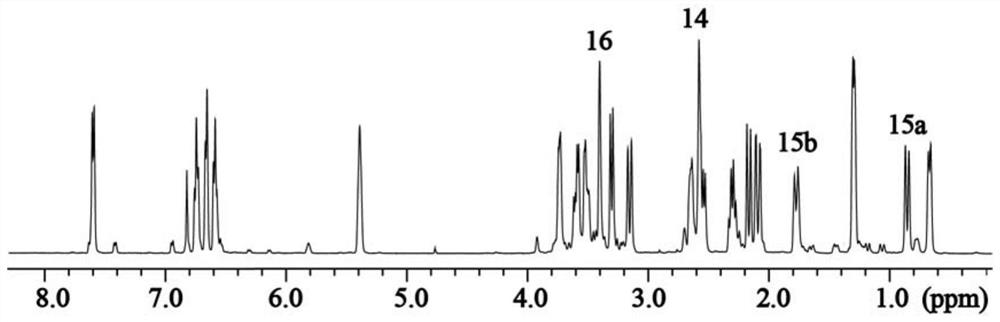
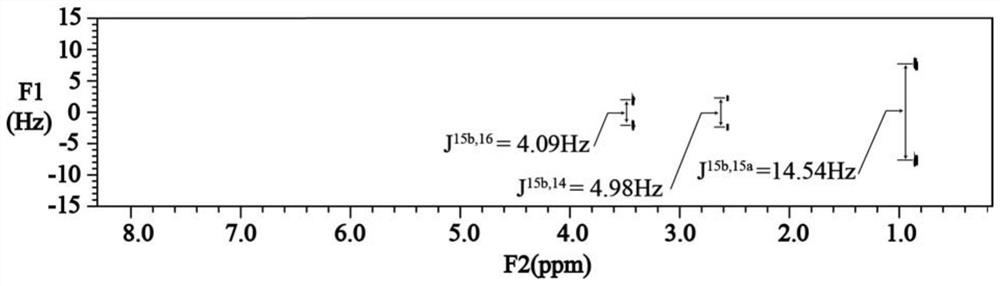
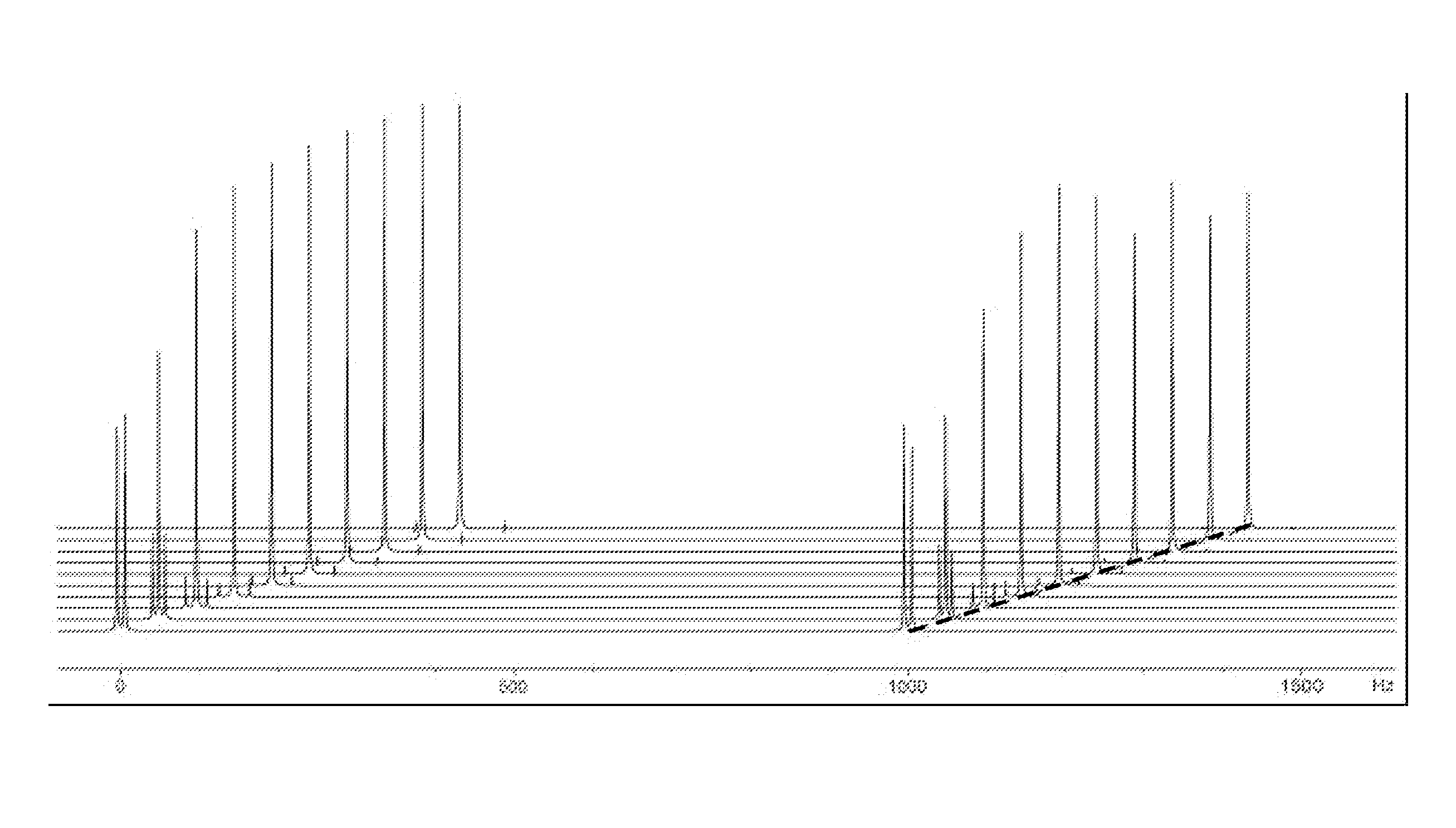
Patents
Literature
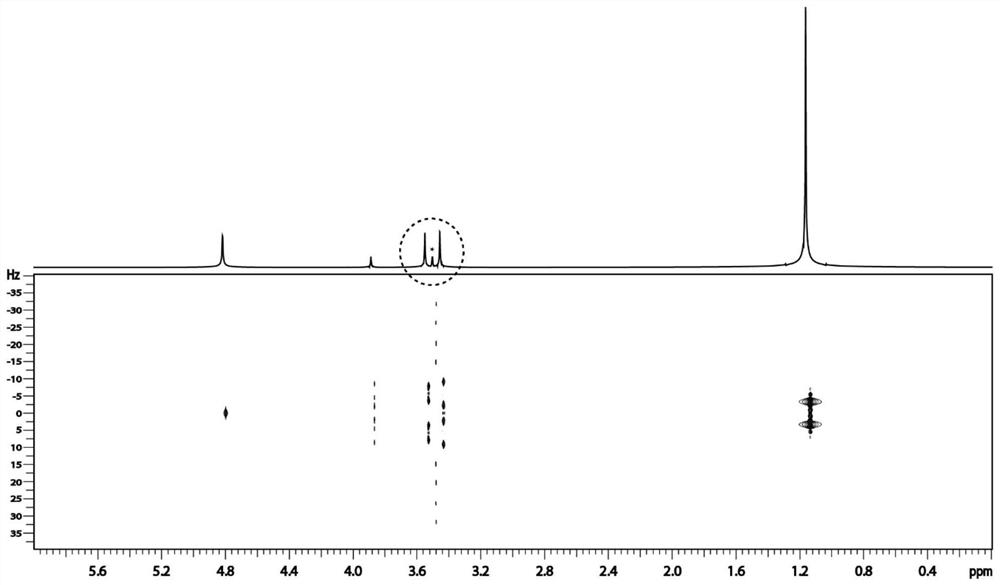
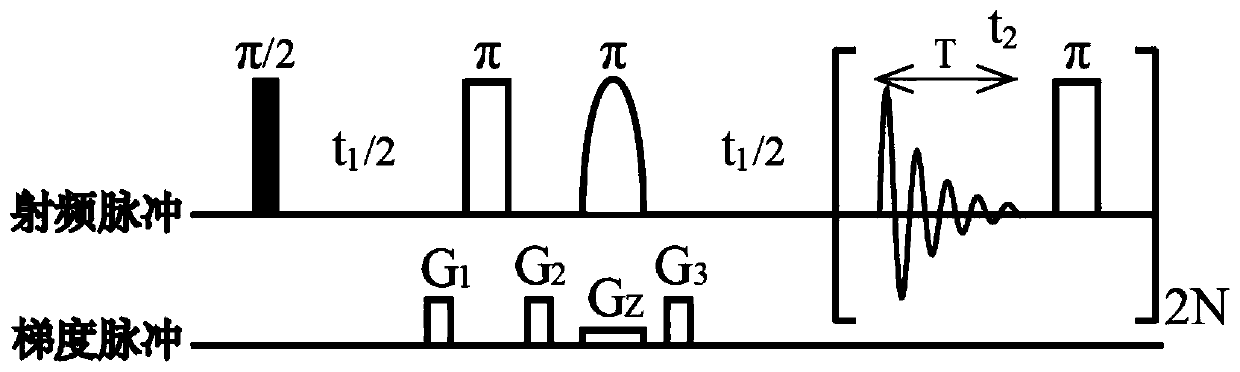
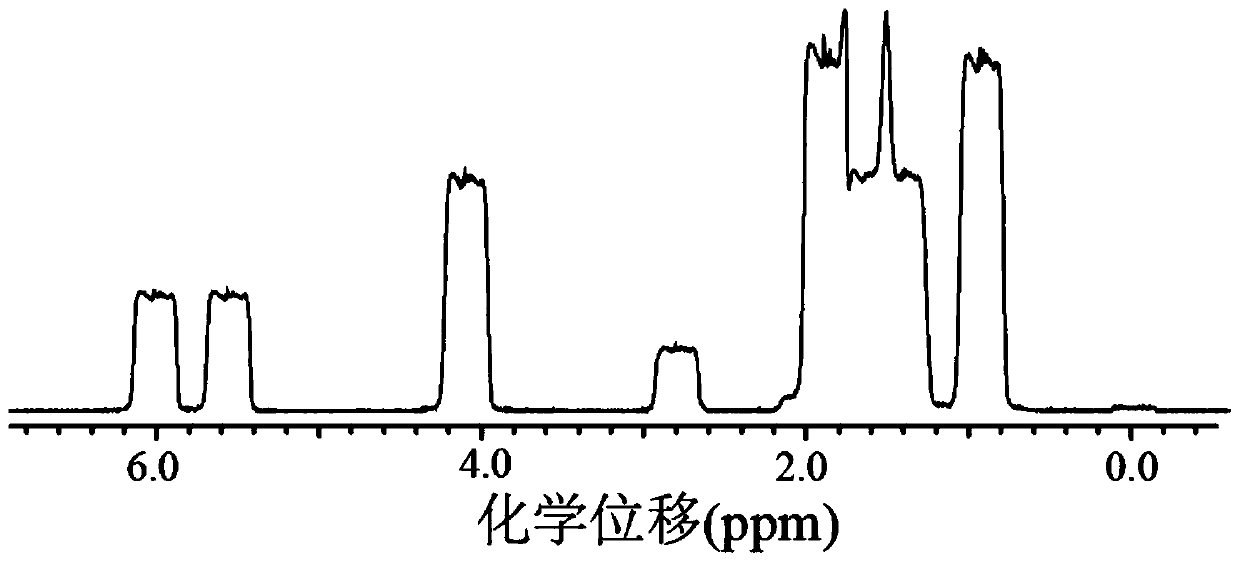
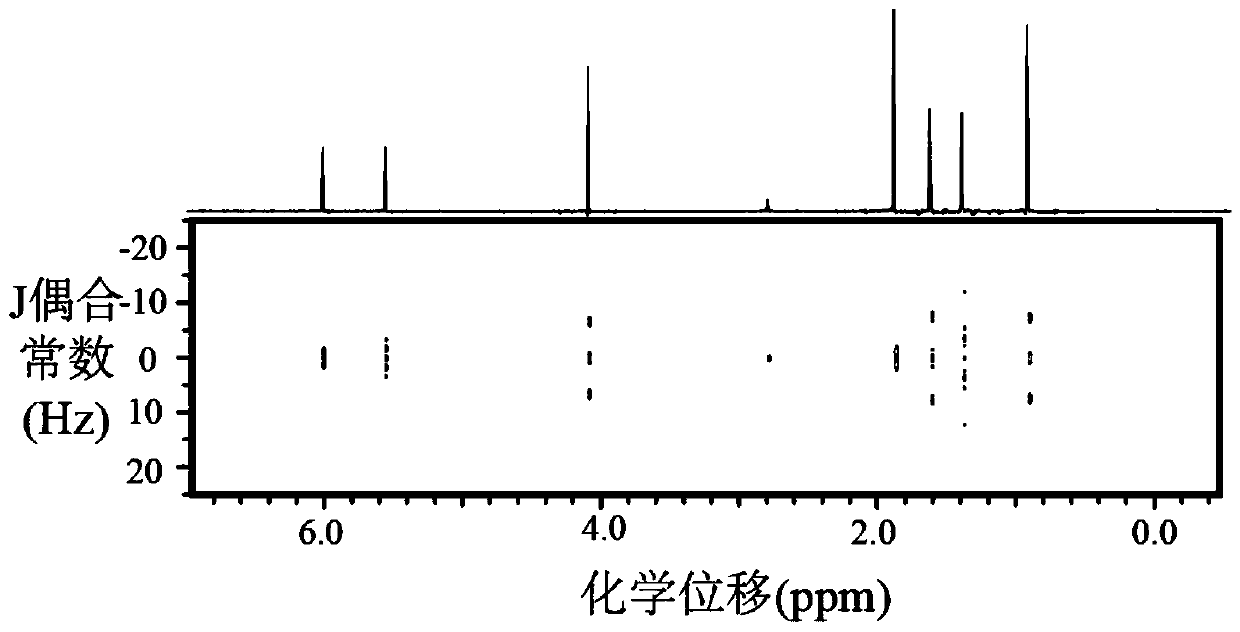
42 results about "J-coupling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
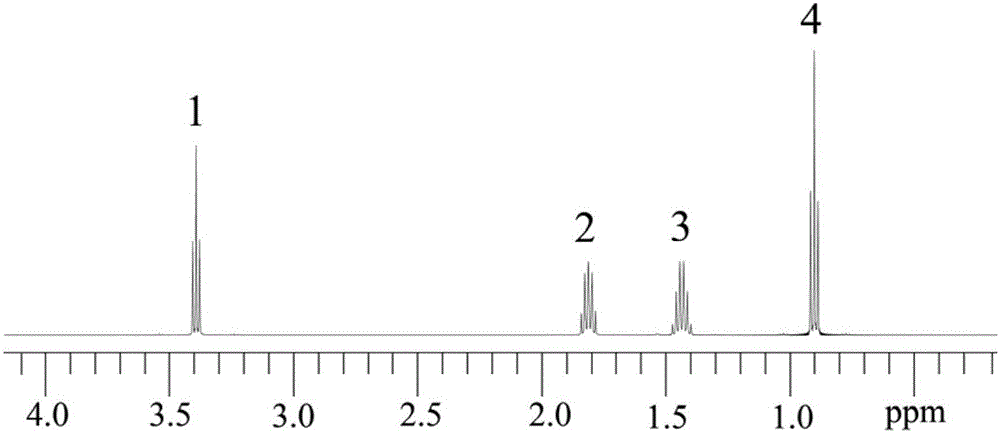
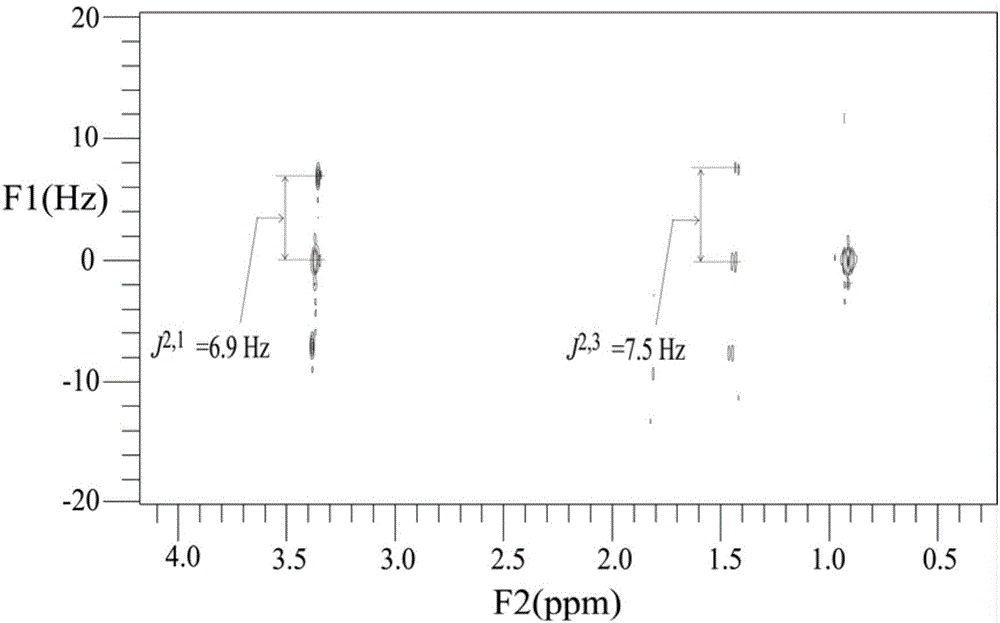
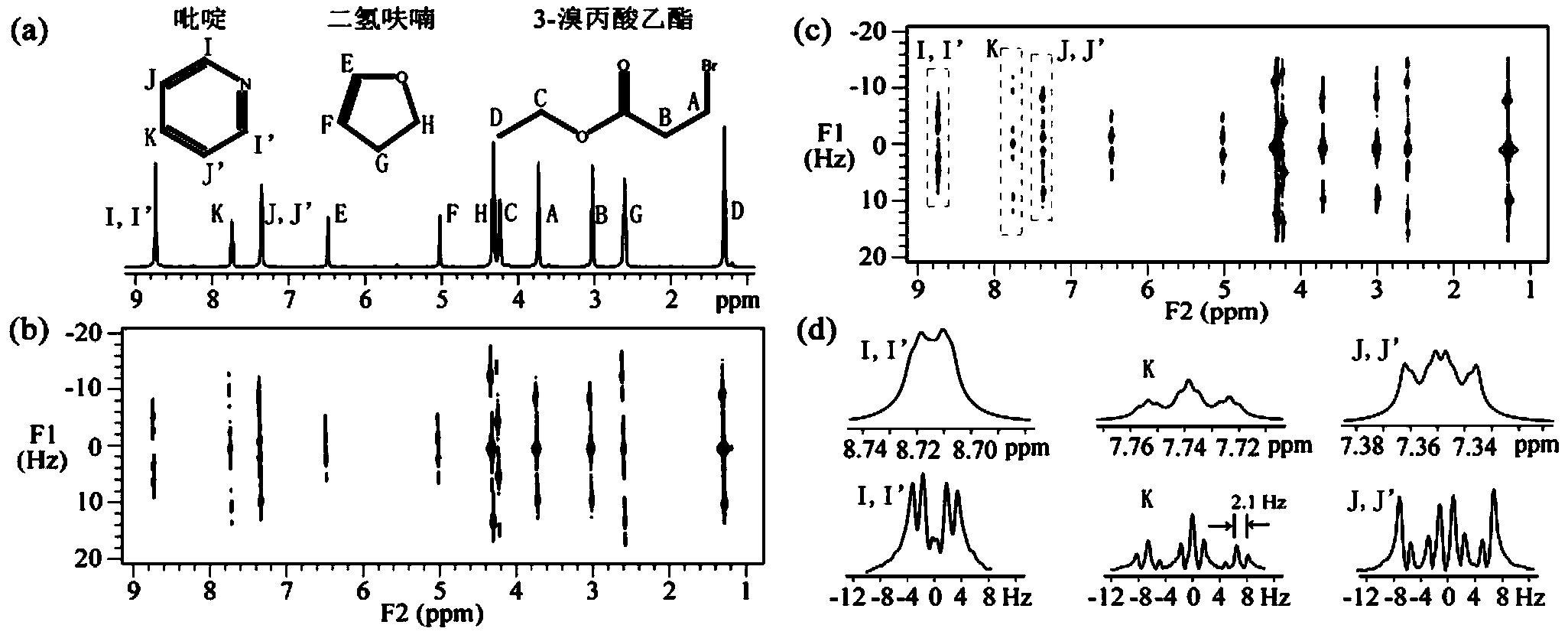
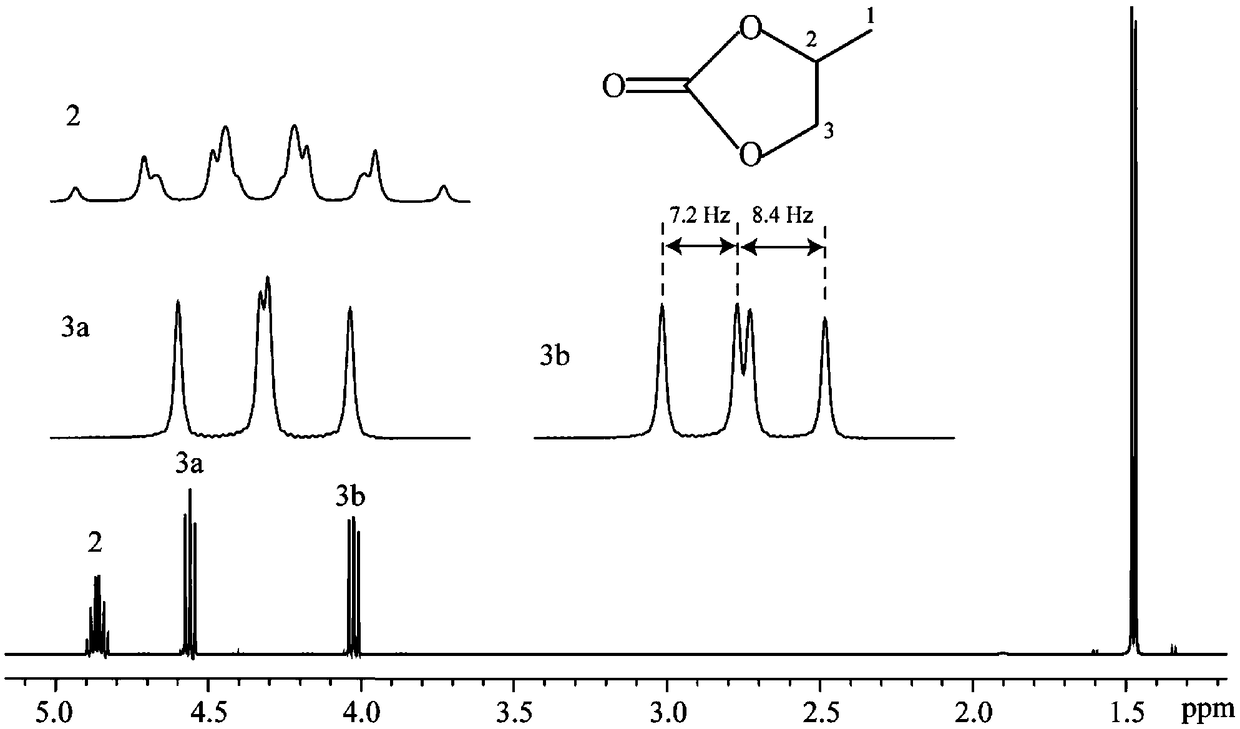
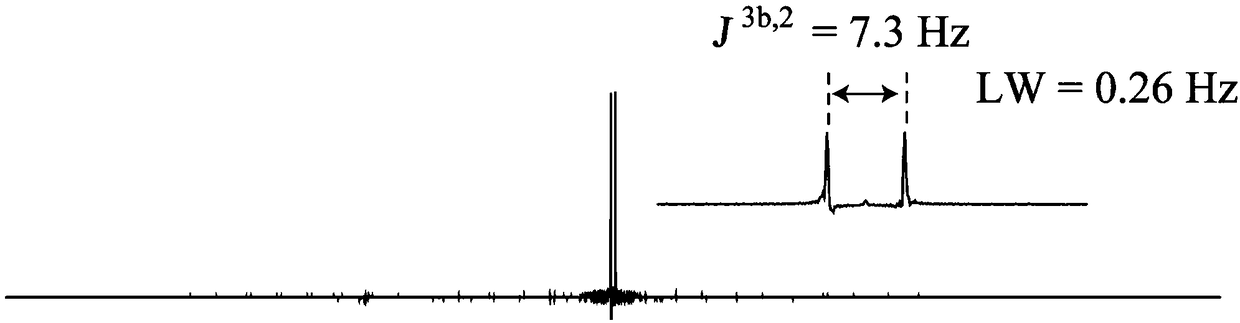
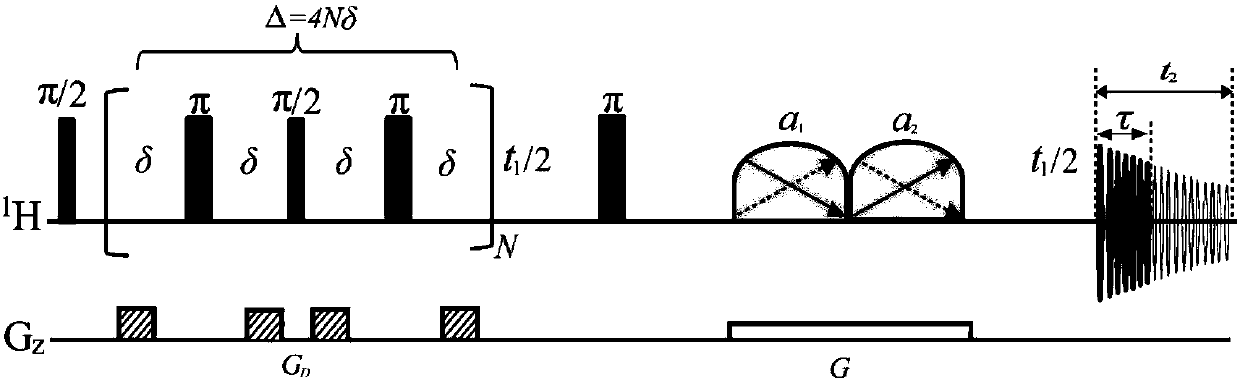
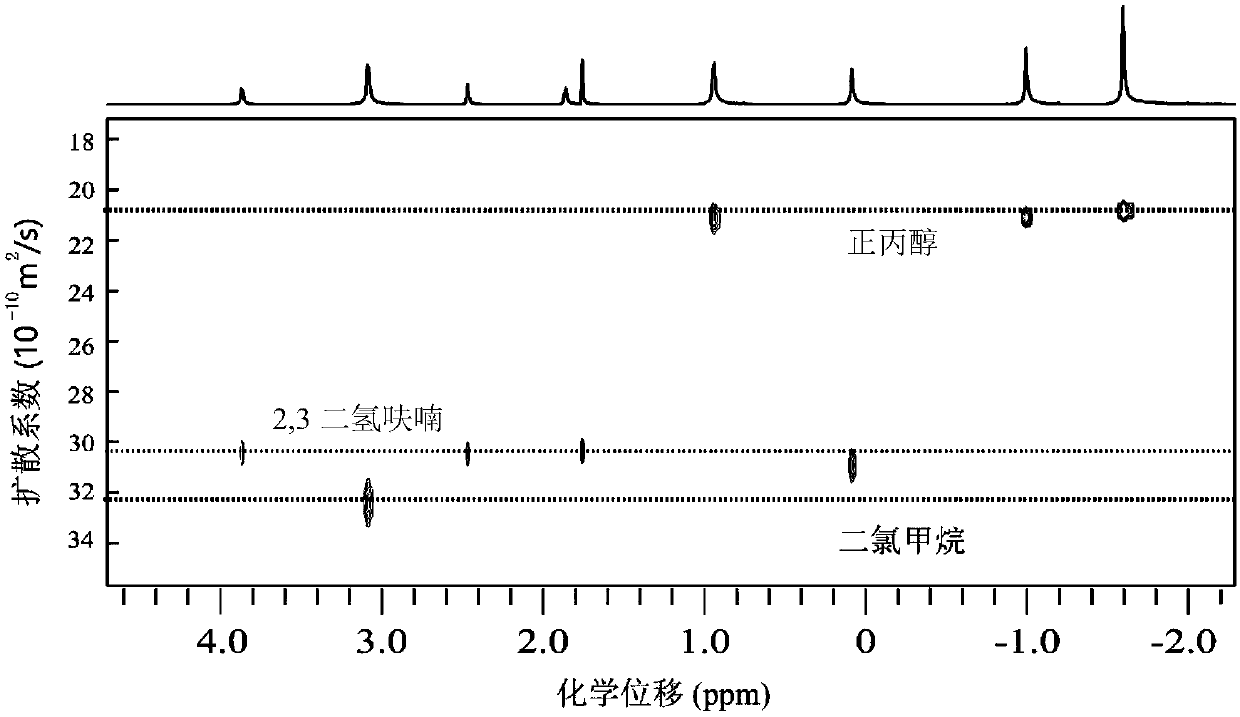
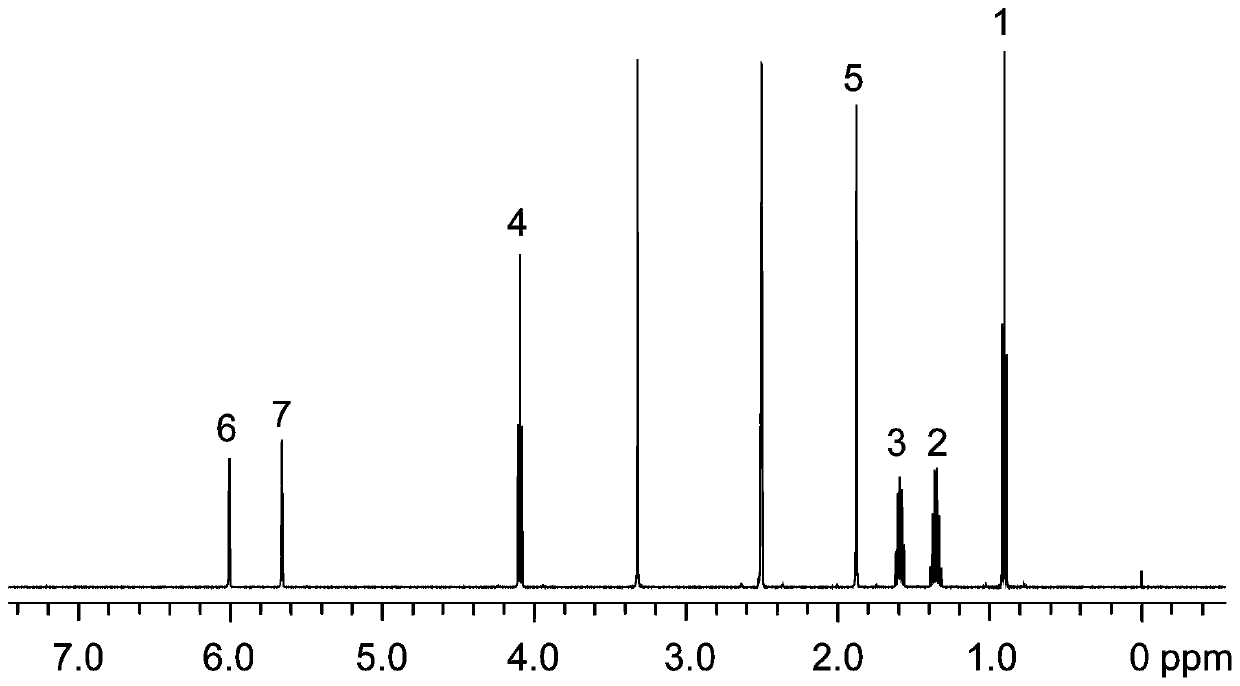
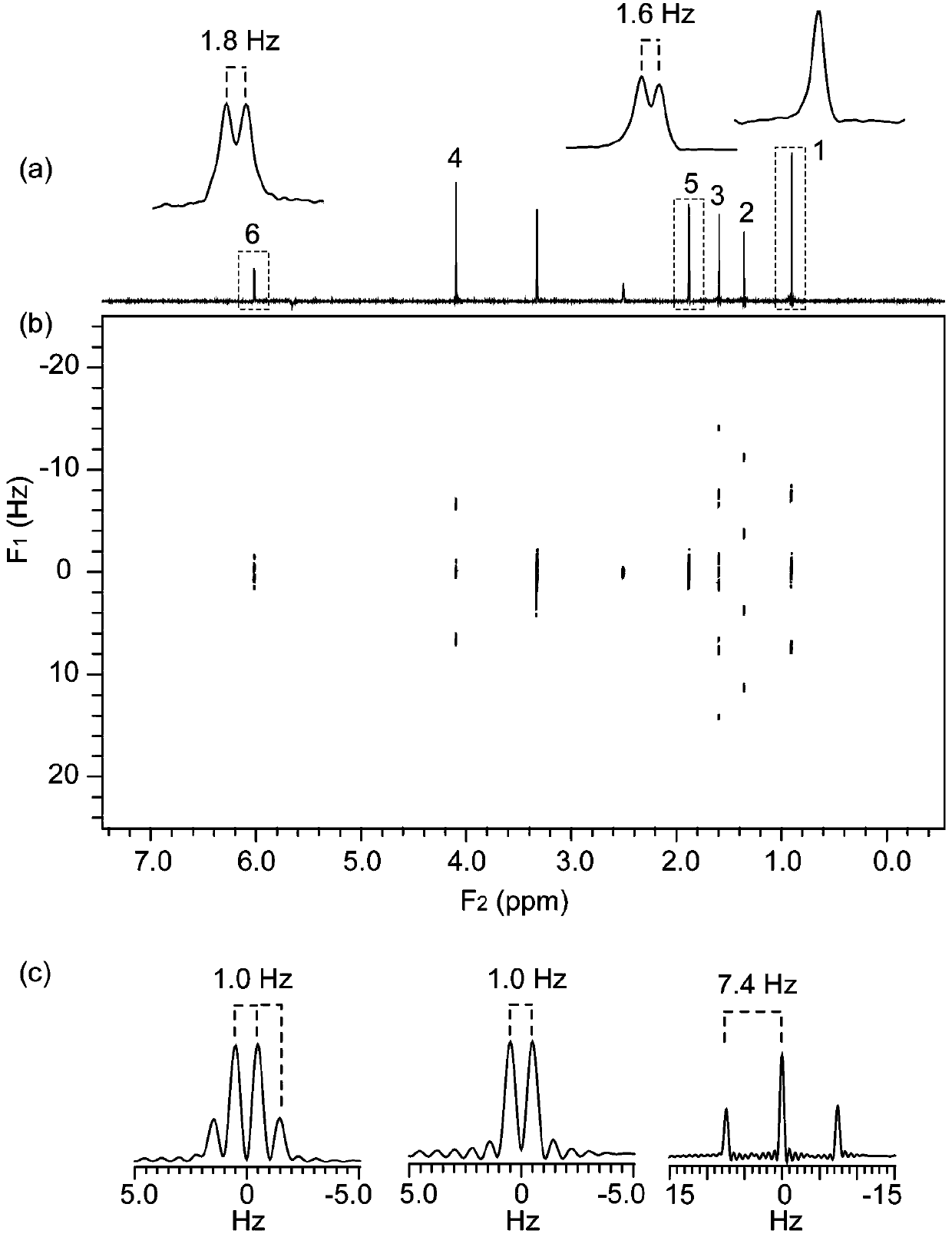
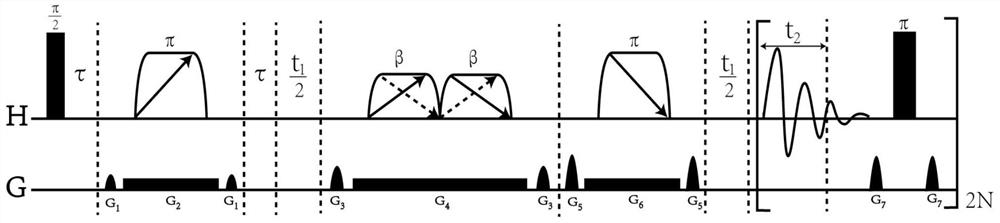
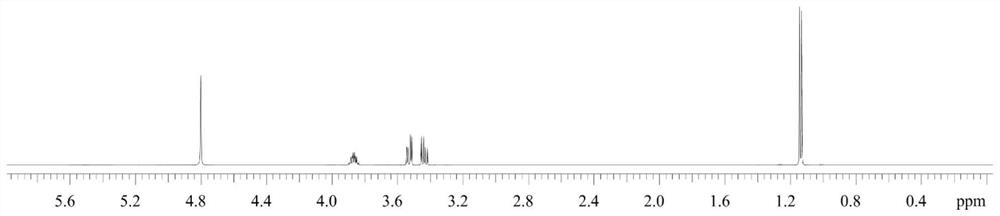
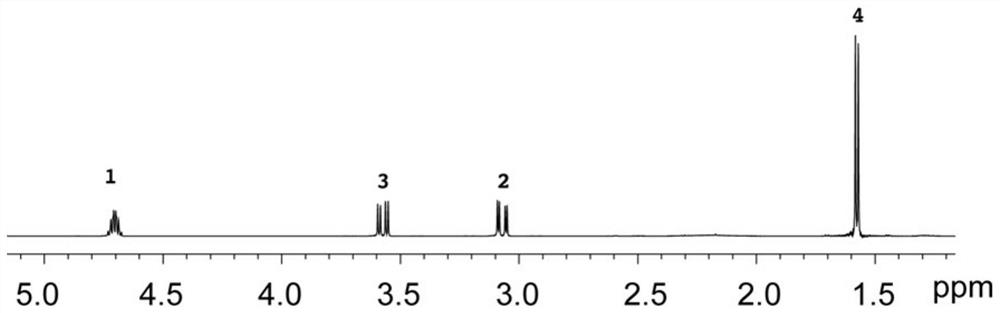
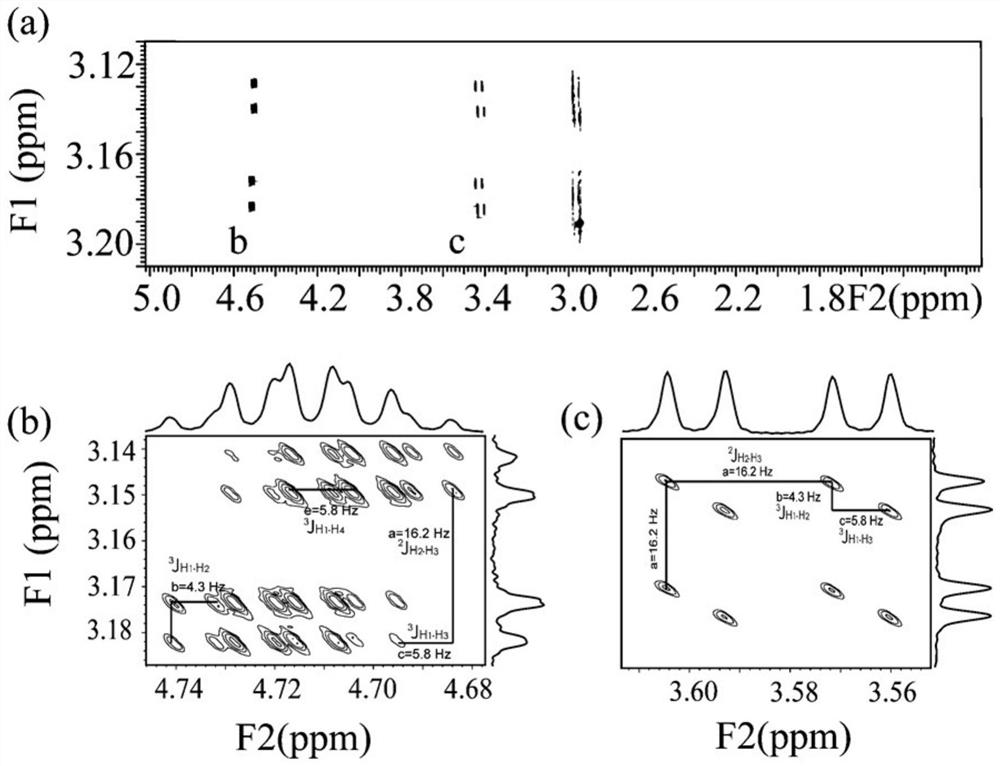
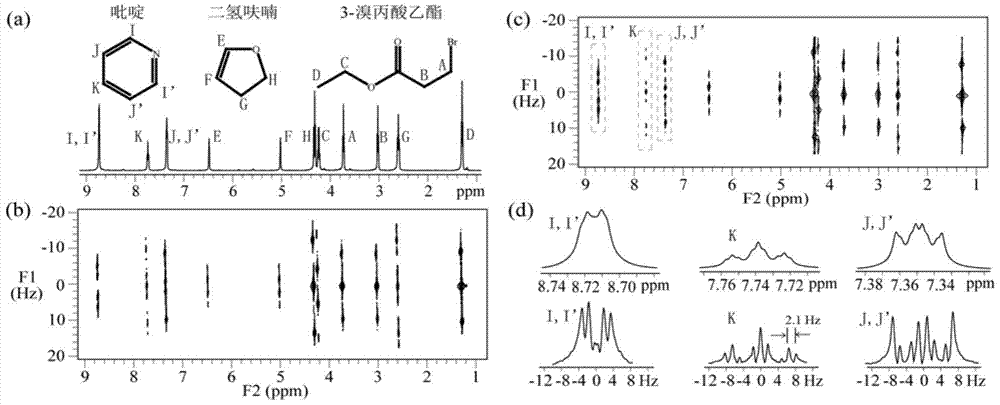
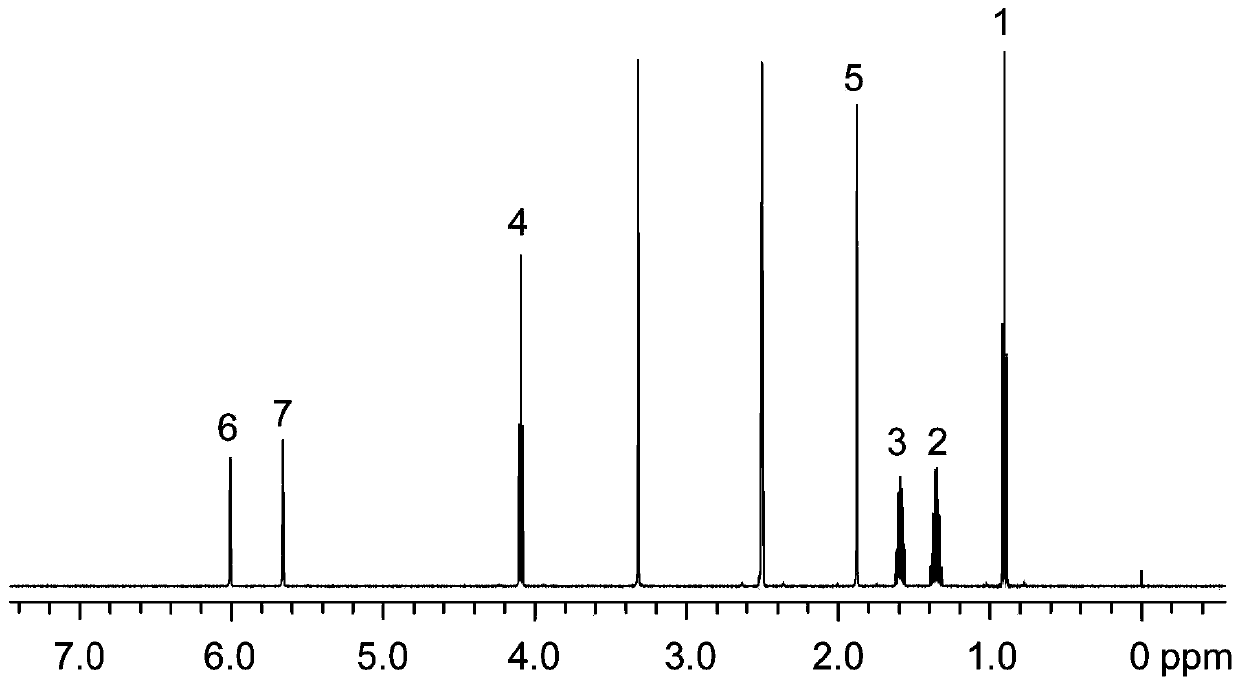
In nuclear chemistry and nuclear physics, Scalar or J-couplings (also called indirect dipole–dipole coupling) are mediated through chemical bonds connecting two spins. It is an indirect interaction between two nuclear spins which arises from hyperfine interactions between the nuclei and local electrons. In NMR spectroscopy J-coupling contains information about relative bond distances and angles. Most importantly, J-coupling provides information on the connectivity of chemical bonds. It is responsible for the often complex splitting of resonance lines in the NMR spectra of fairly simple molecules.
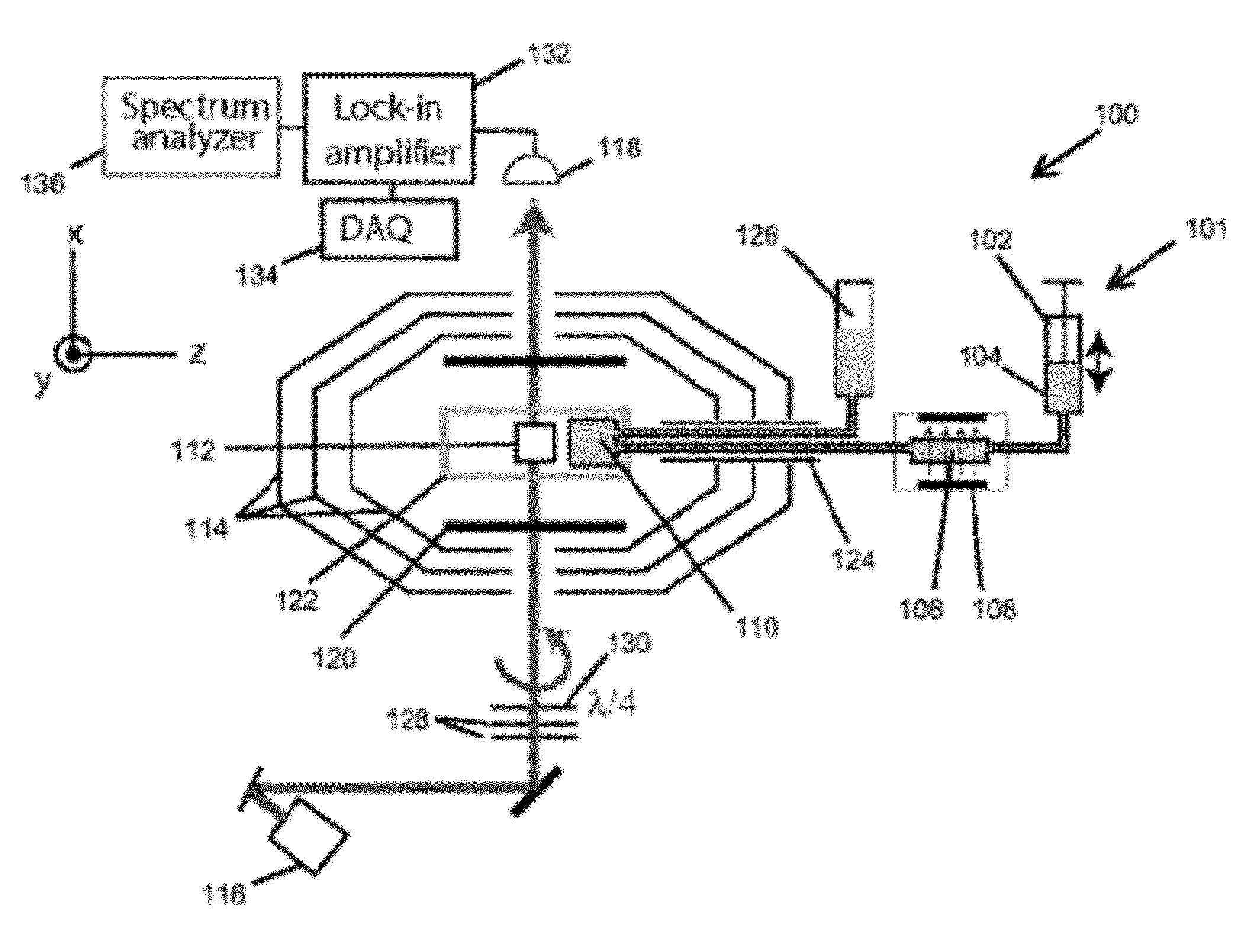
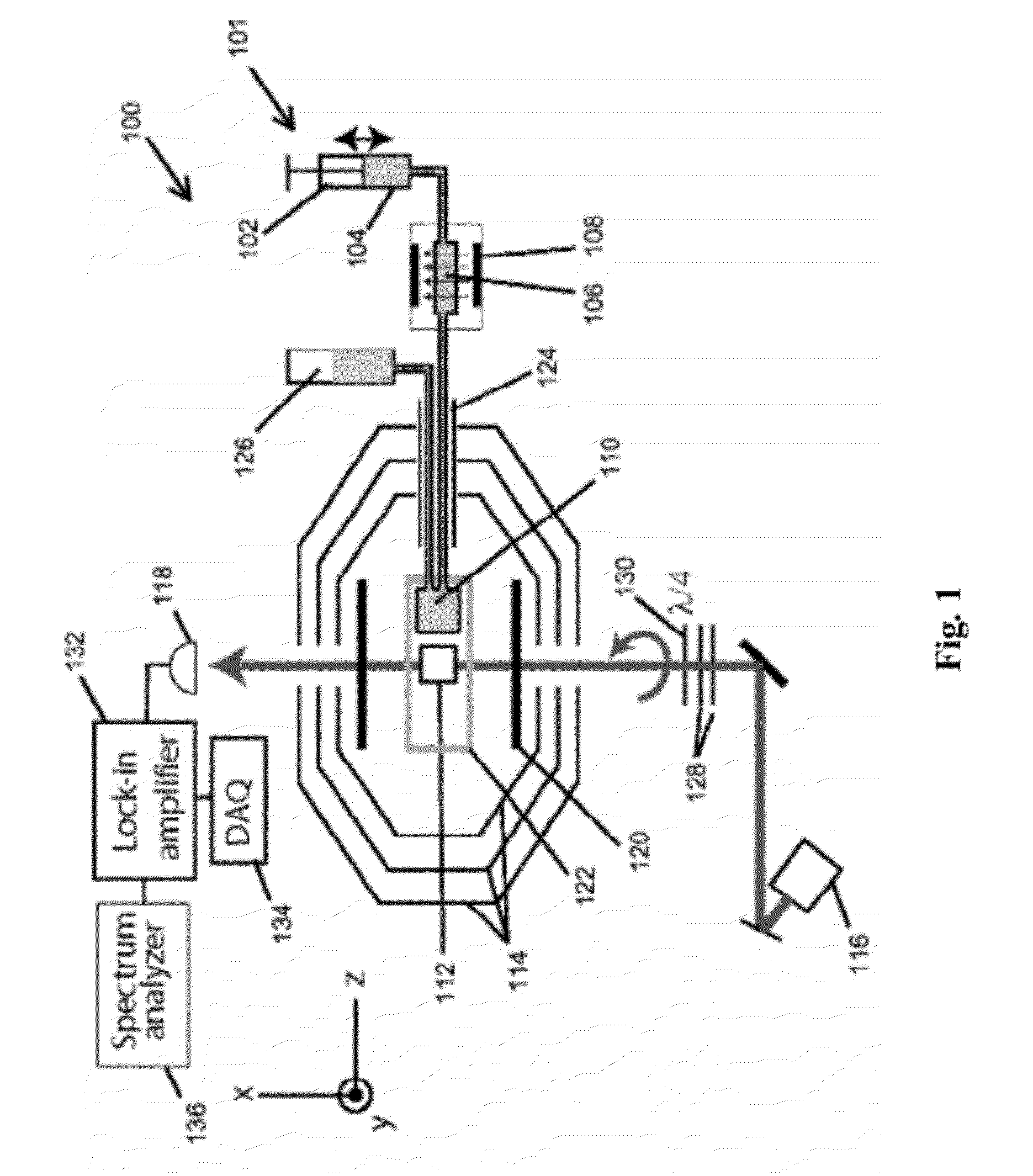
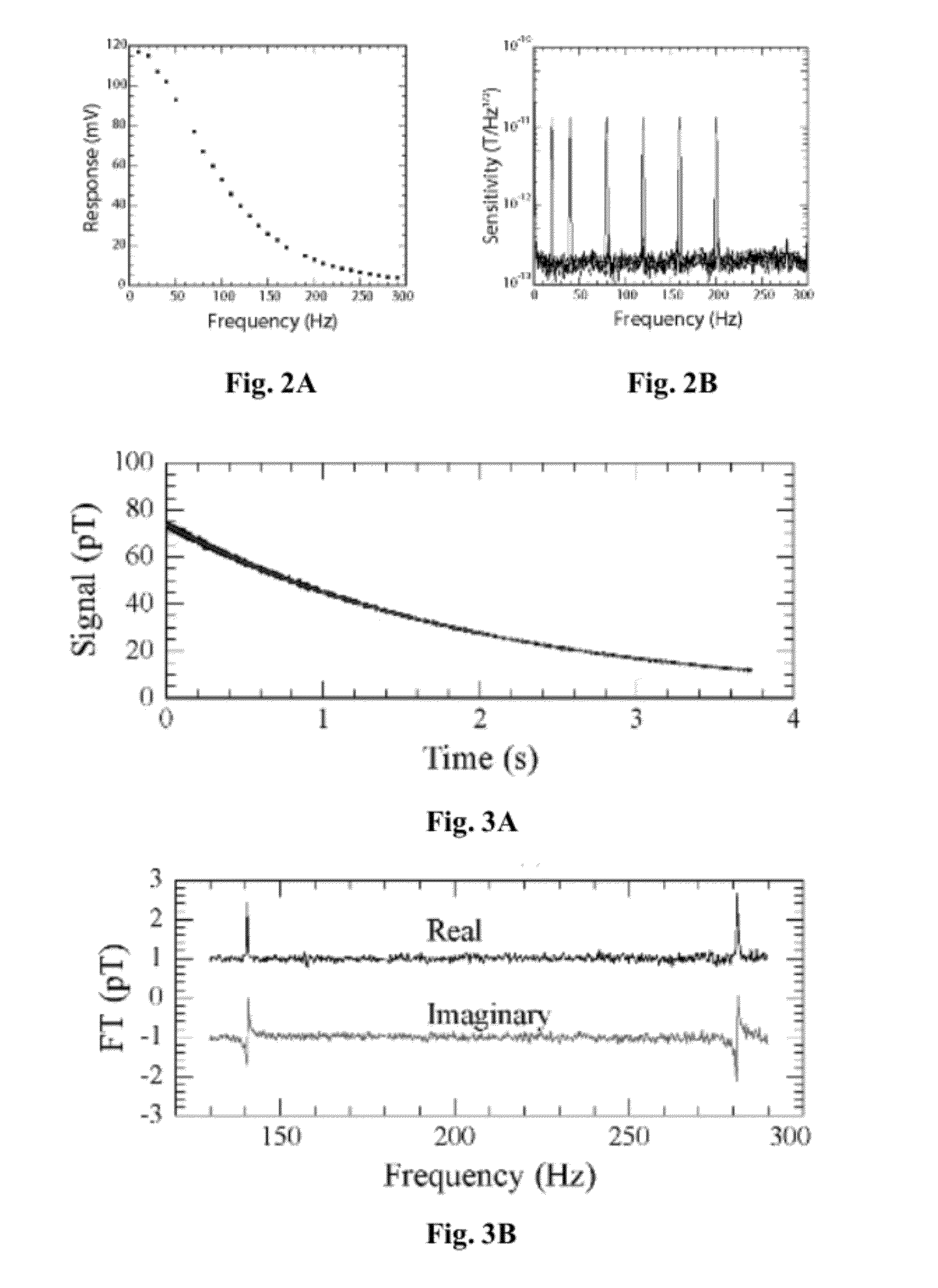
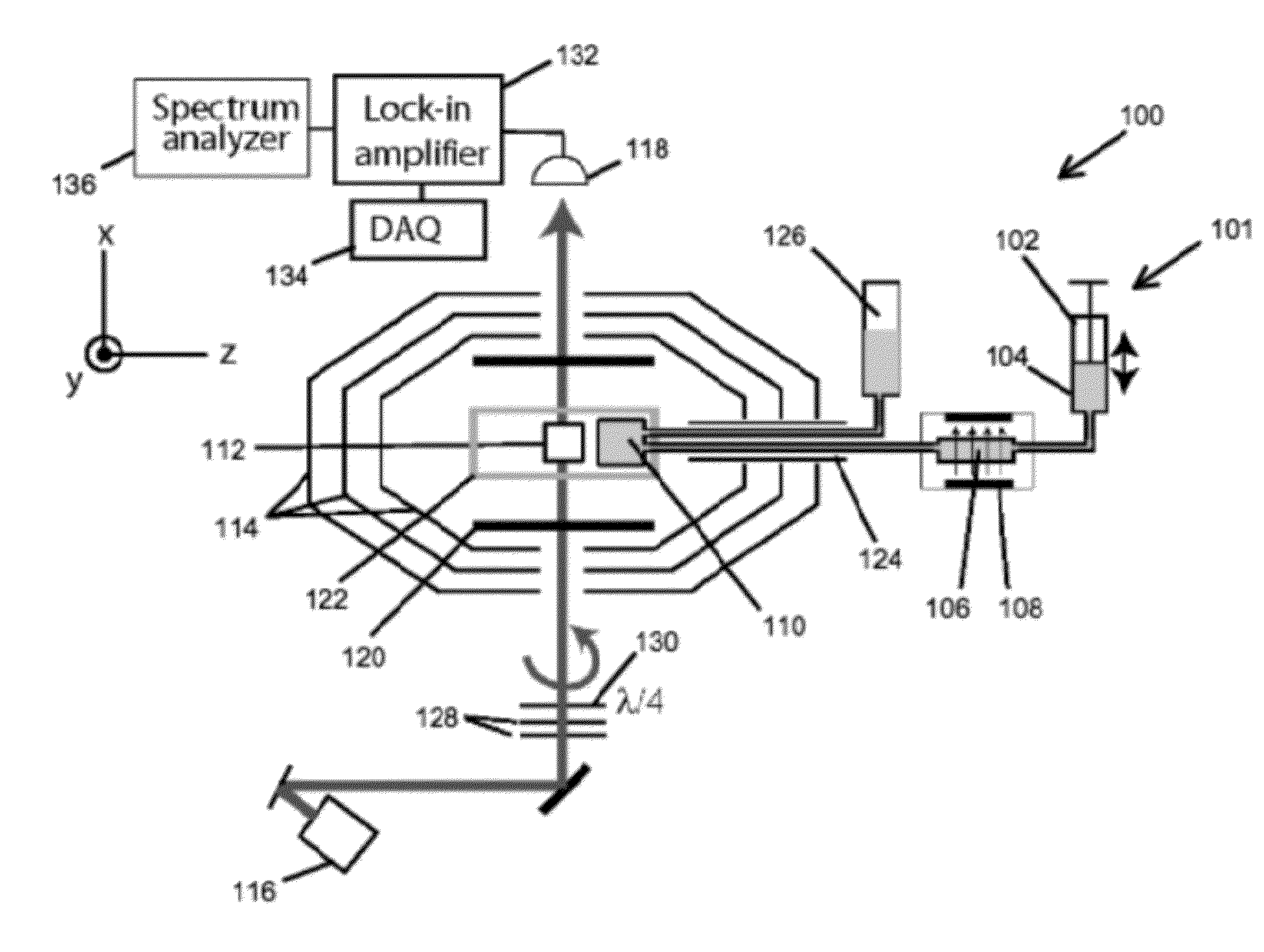
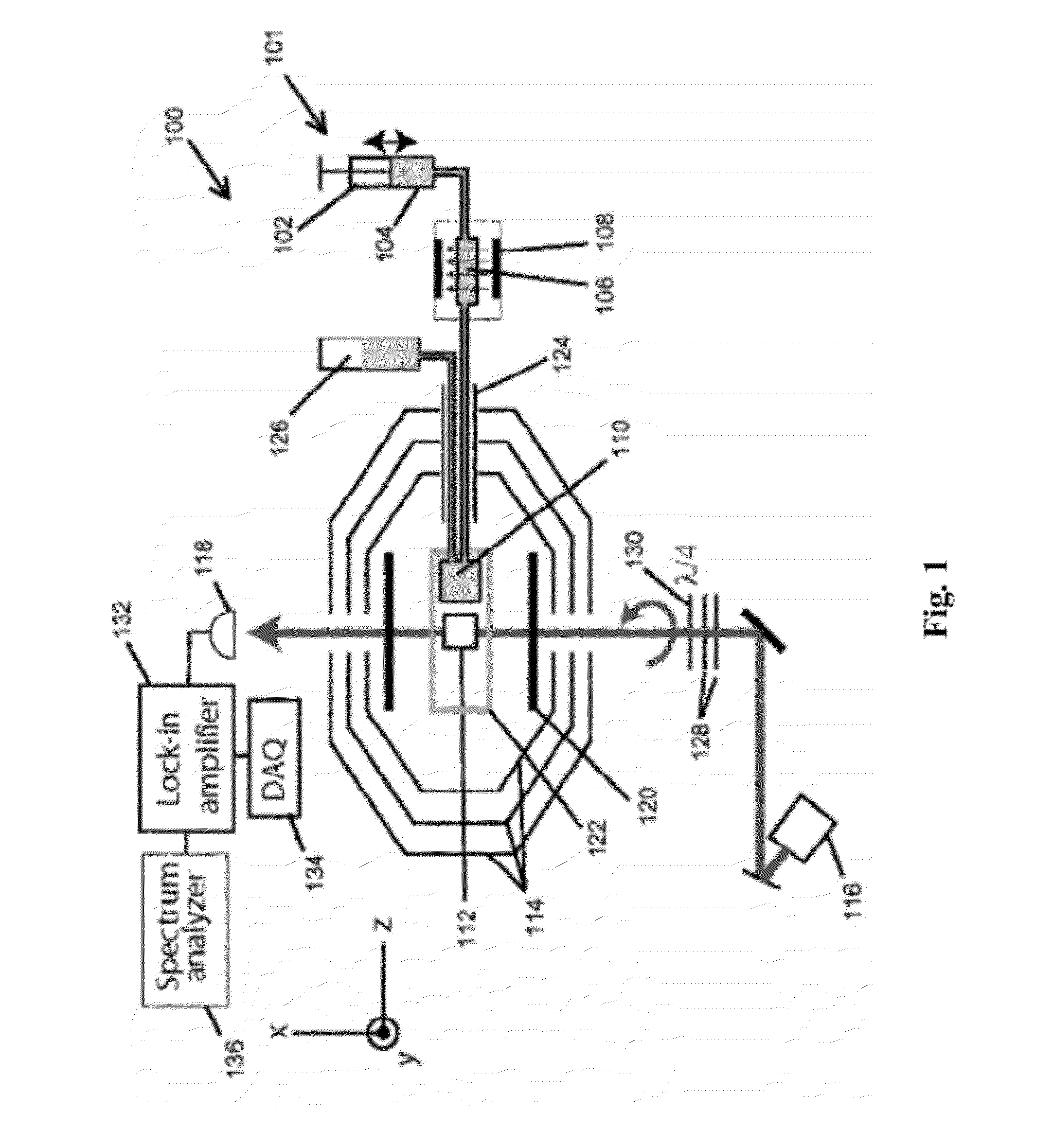
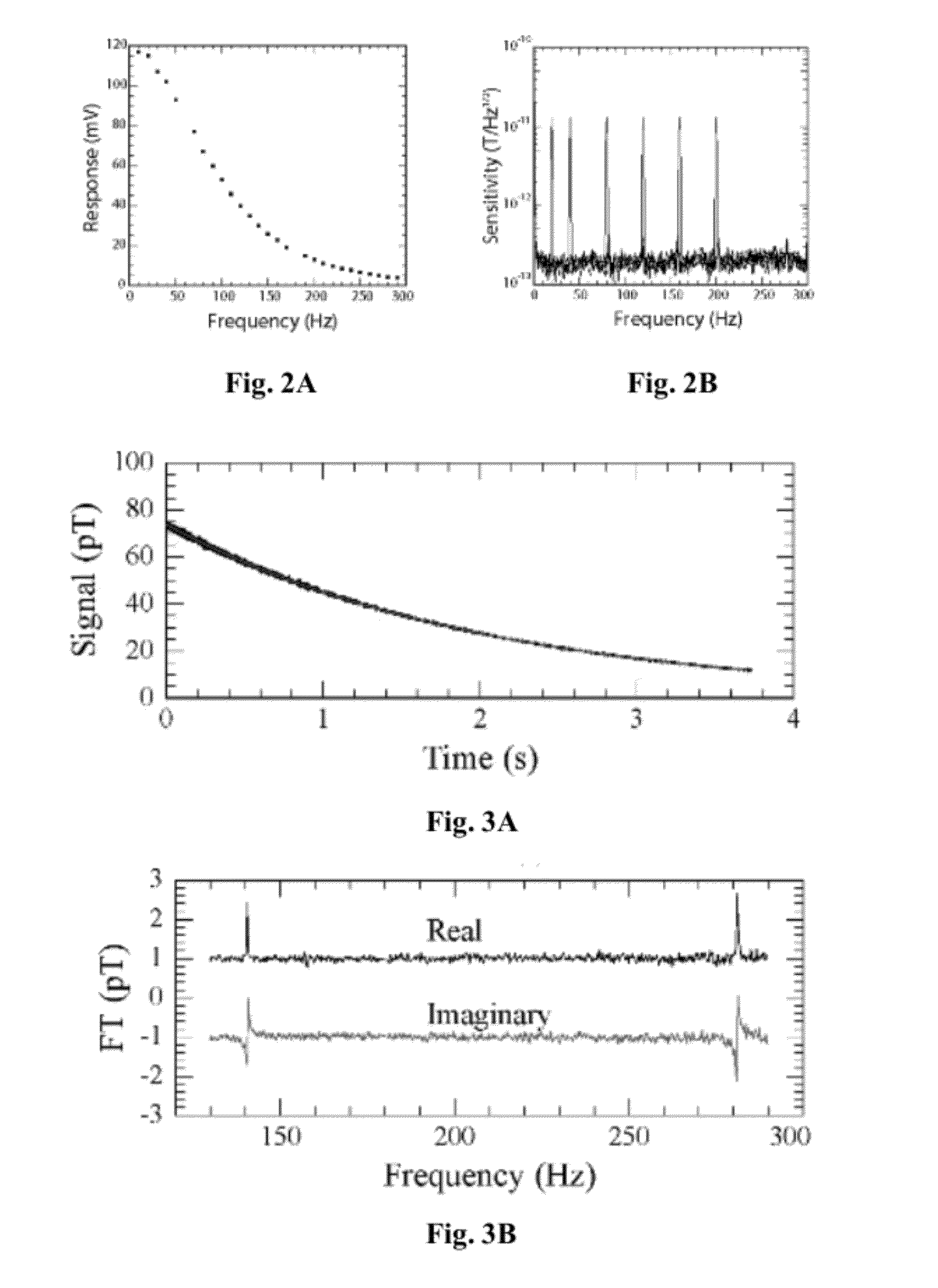
Detection of J-coupling using atomic magnetometer
ActiveUS9140657B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceJ-couplingAnalyte
An embodiment of a method of detecting a J-coupling includes providing a polarized analyte adjacent to a vapor cell of an atomic magnetometer; and measuring one or more J-coupling parameters using the atomic magnetometer. According to an embodiment, measuring the one or more J-coupling parameters includes detecting a magnetic field created by the polarized analyte as the magnetic field evolves under a J-coupling interaction.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY +1
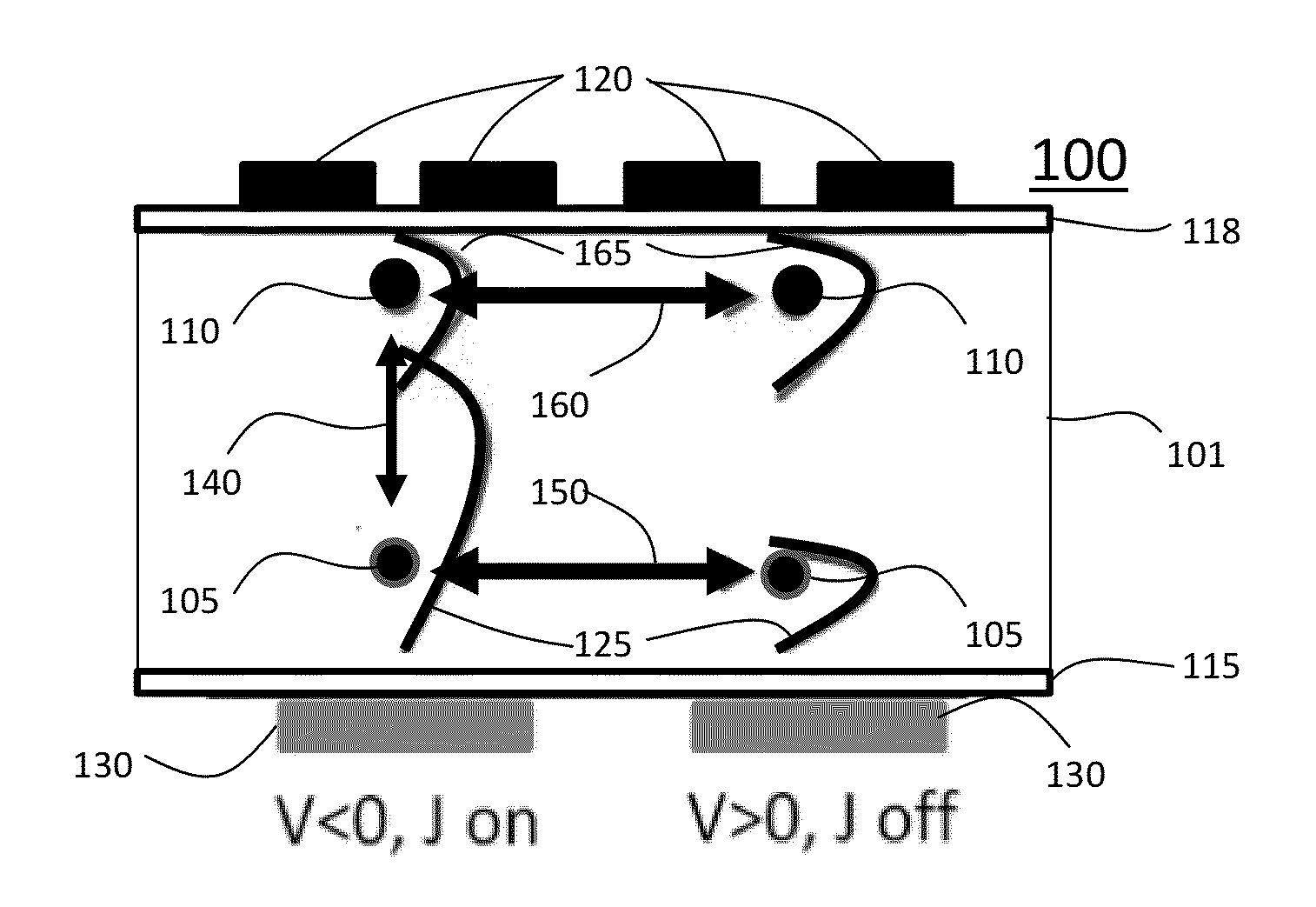
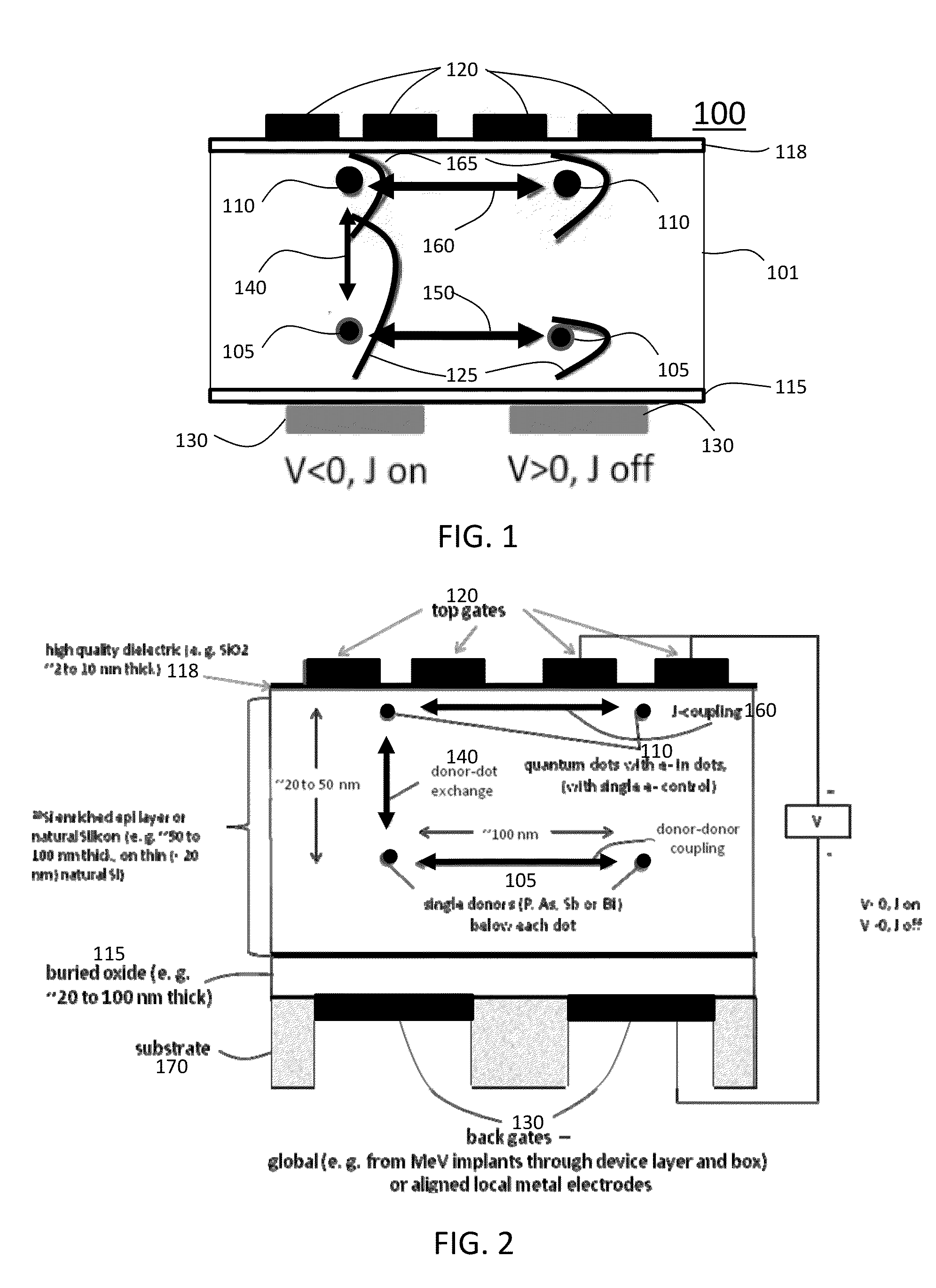
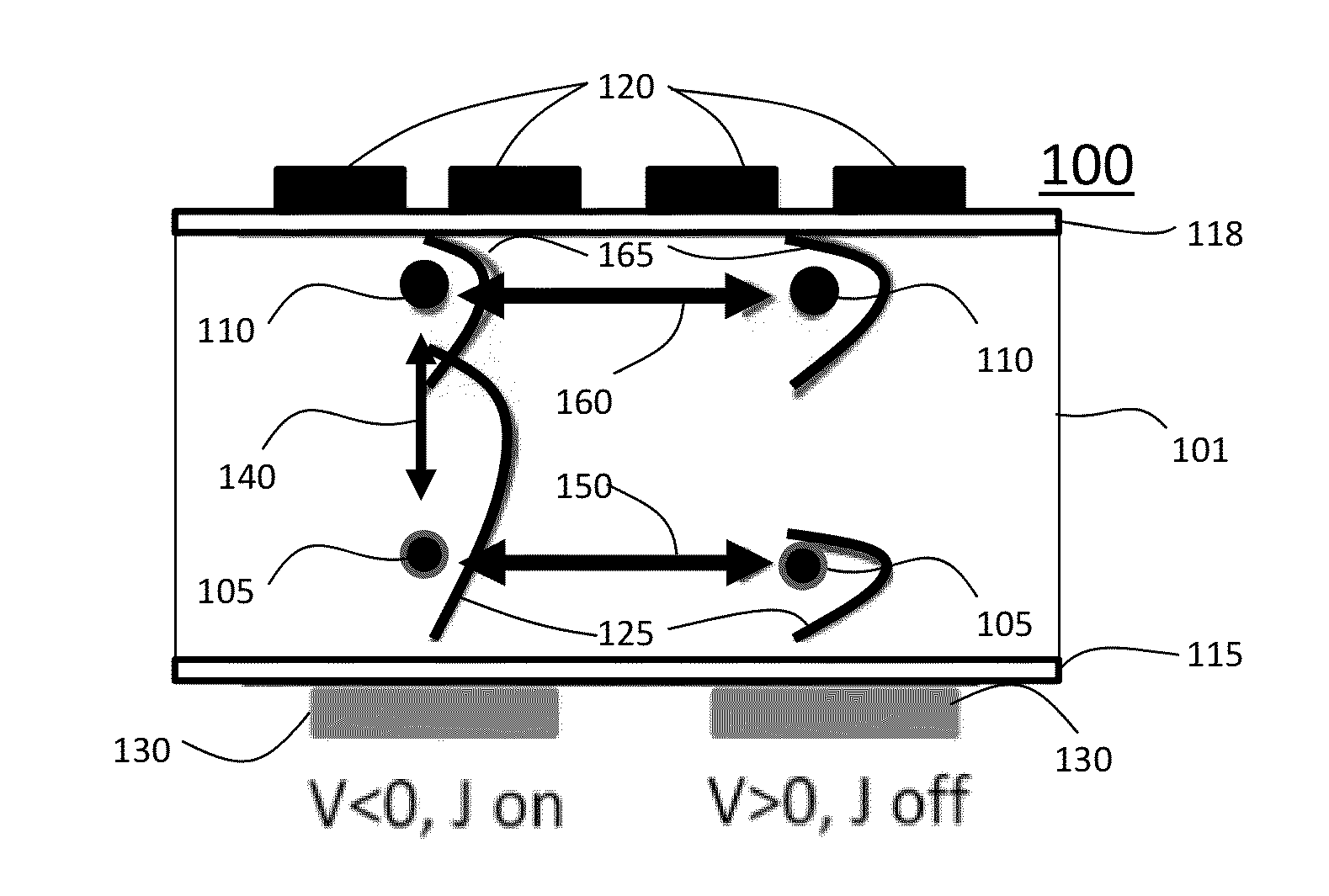
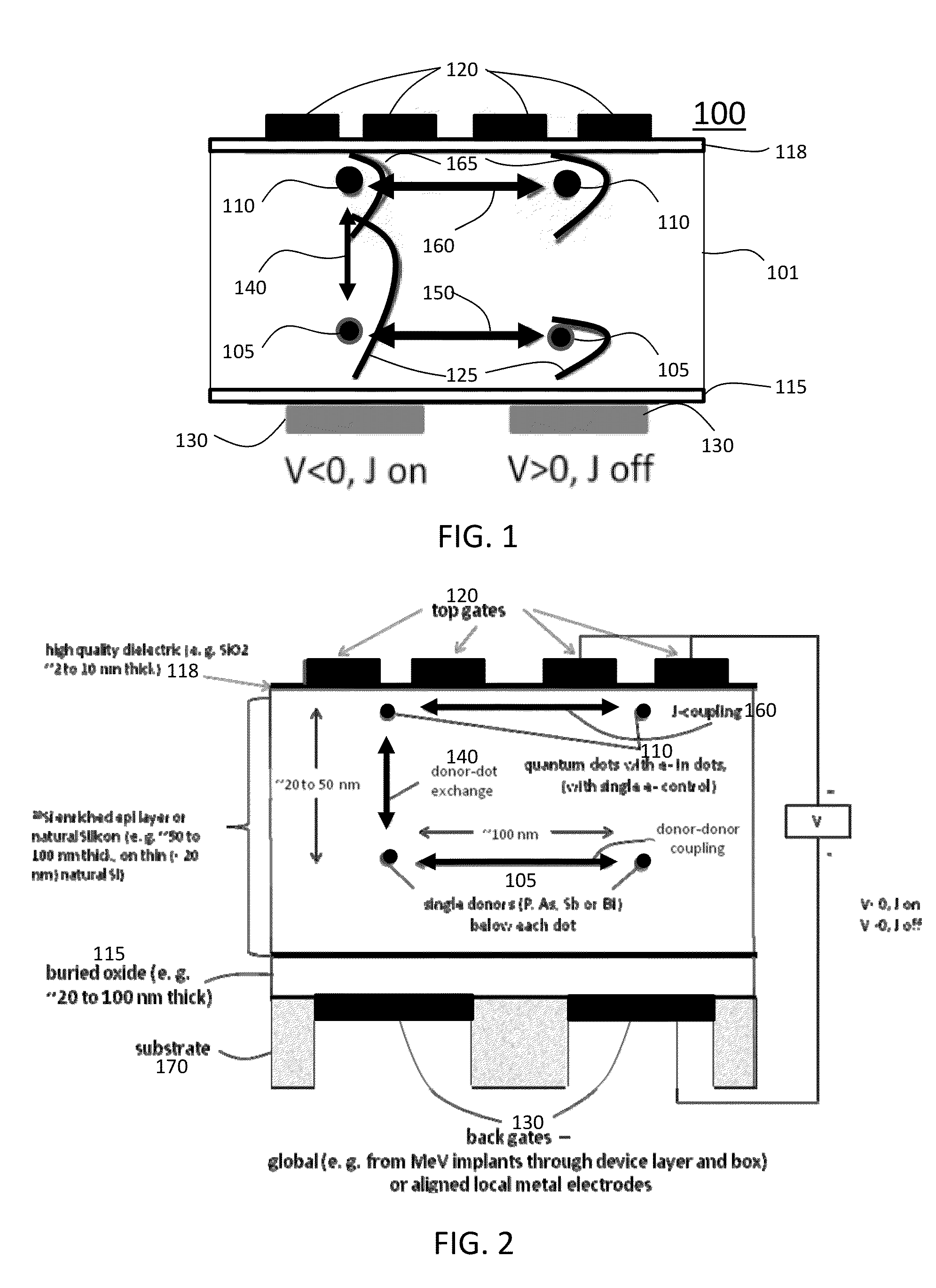
Scalable quantum computer architecture with coupled donor-quantum dot qubits
A quantum bit computing architecture includes a plurality of single spin memory donor atoms embedded in a semiconductor layer, a plurality of quantum dots arranged with the semiconductor layer and aligned with the donor atoms, wherein a first voltage applied across at least one pair of the aligned quantum dot and donor atom controls a donor-quantum dot coupling. A method of performing quantum computing in a scalable architecture quantum computing apparatus includes arranging a pattern of single spin memory donor atoms in a semiconductor layer, forming a plurality of quantum dots arranged with the semiconductor layer and aligned with the donor atoms, applying a first voltage across at least one aligned pair of a quantum dot and donor atom to control a donor-quantum dot coupling, and applying a second voltage between one or more quantum dots to control a Heisenberg exchange J coupling between quantum dots and to cause transport of a single spin polarized electron between quantum dots.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Detection of J-Coupling Using Atomic Magnetometer
ActiveUS20120176130A1Magnetic property measurementsMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyJ-couplingAnalyte
An embodiment of a method of detecting a J-coupling includes providing a polarized analyte adjacent to a vapor cell of an atomic magnetometer; and measuring one or more J-coupling parameters using the atomic magnetometer. According to an embodiment, measuring the one or more J-coupling parameters includes detecting a magnetic field created by the polarized analyte as the magnetic field evolves under a J-coupling interaction.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TEHCNOLOGY +1
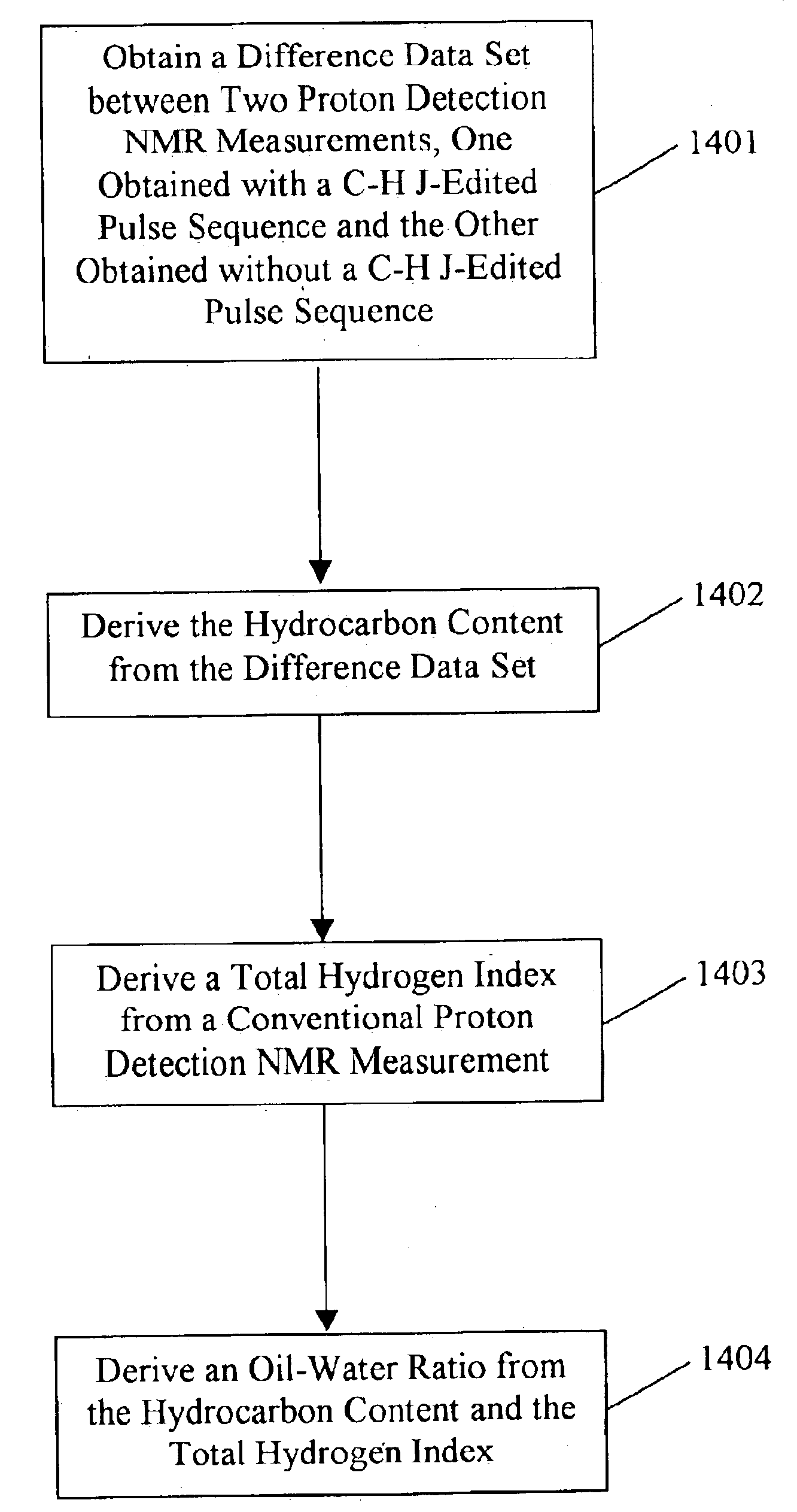
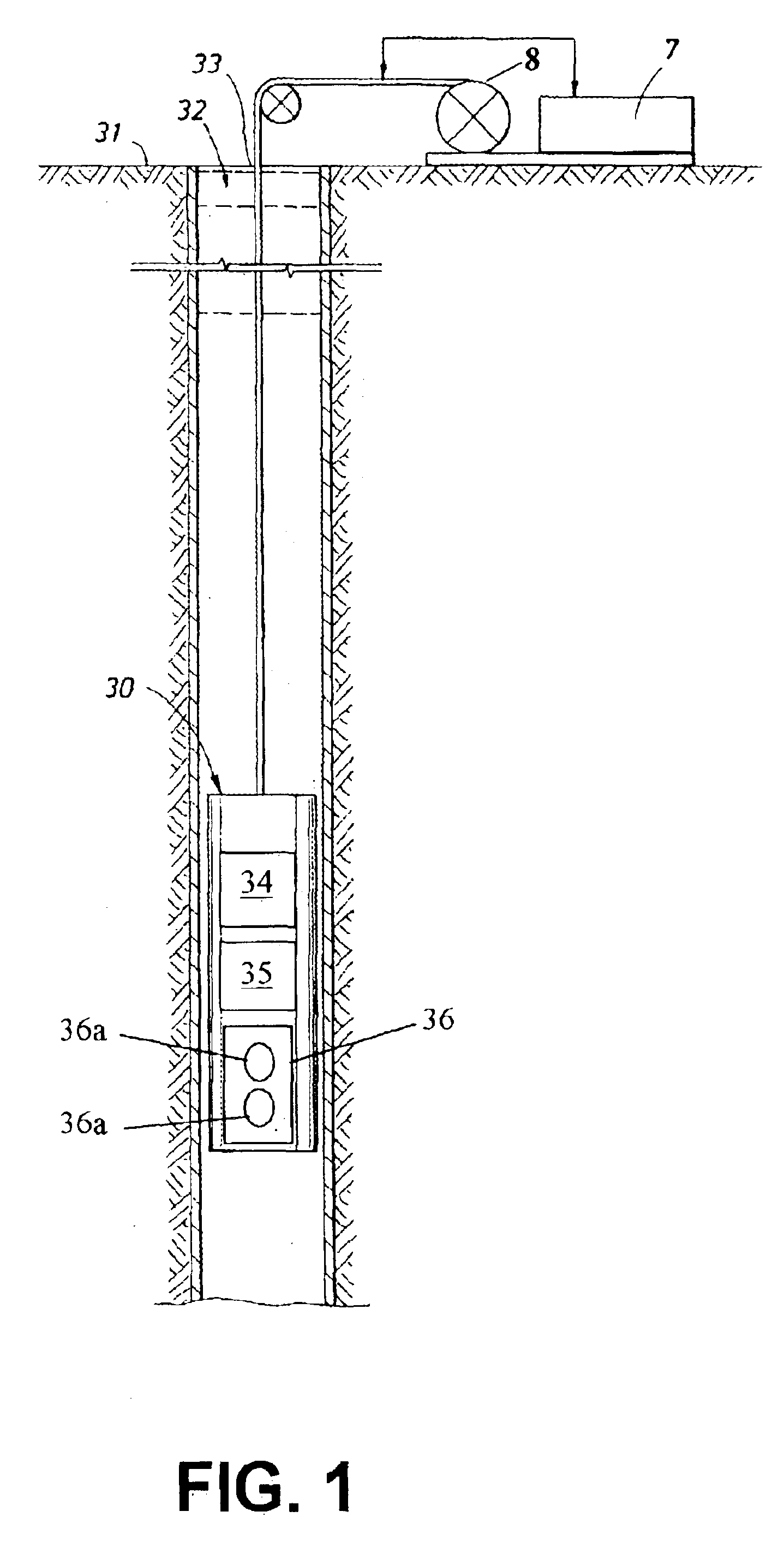
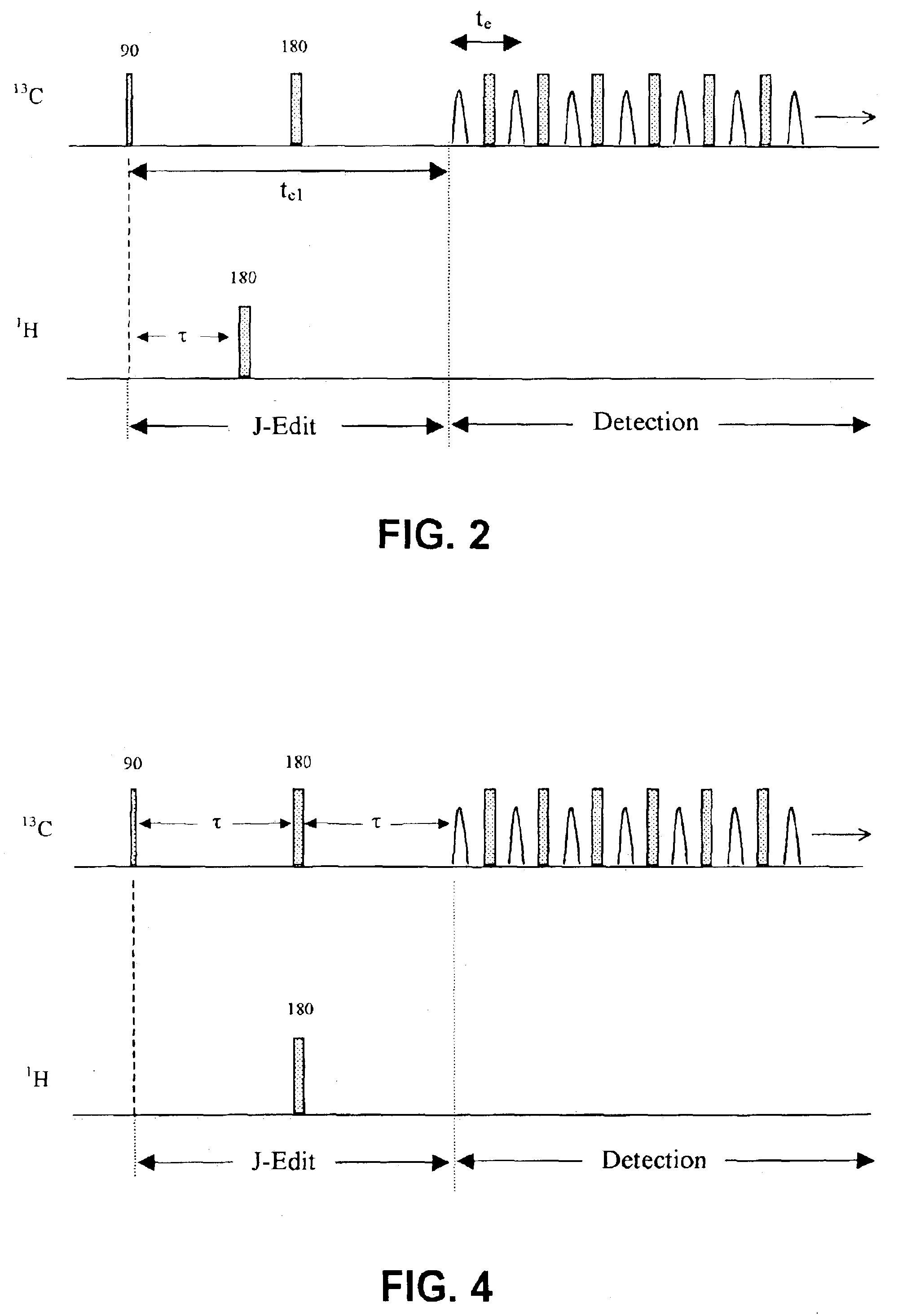
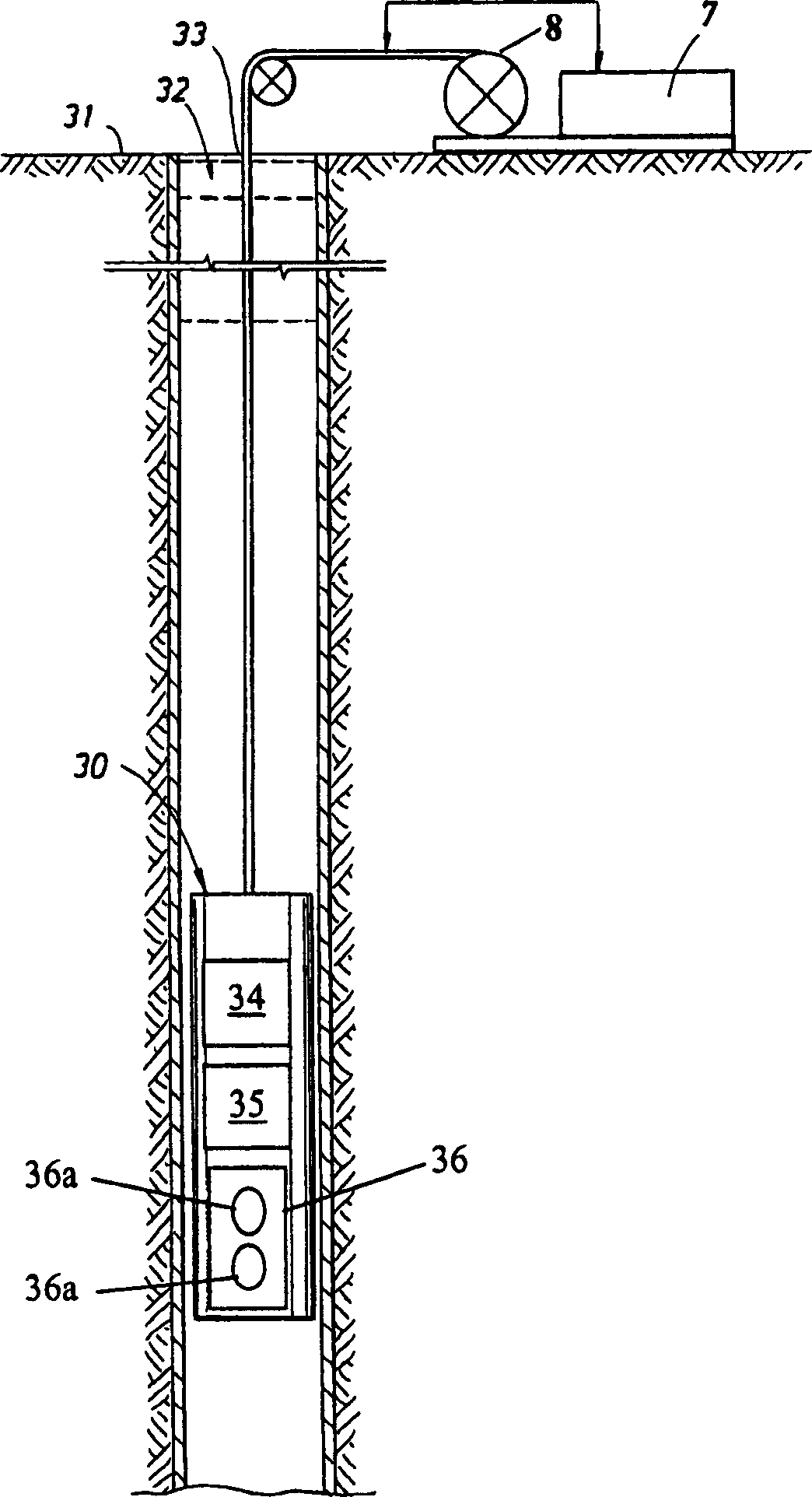
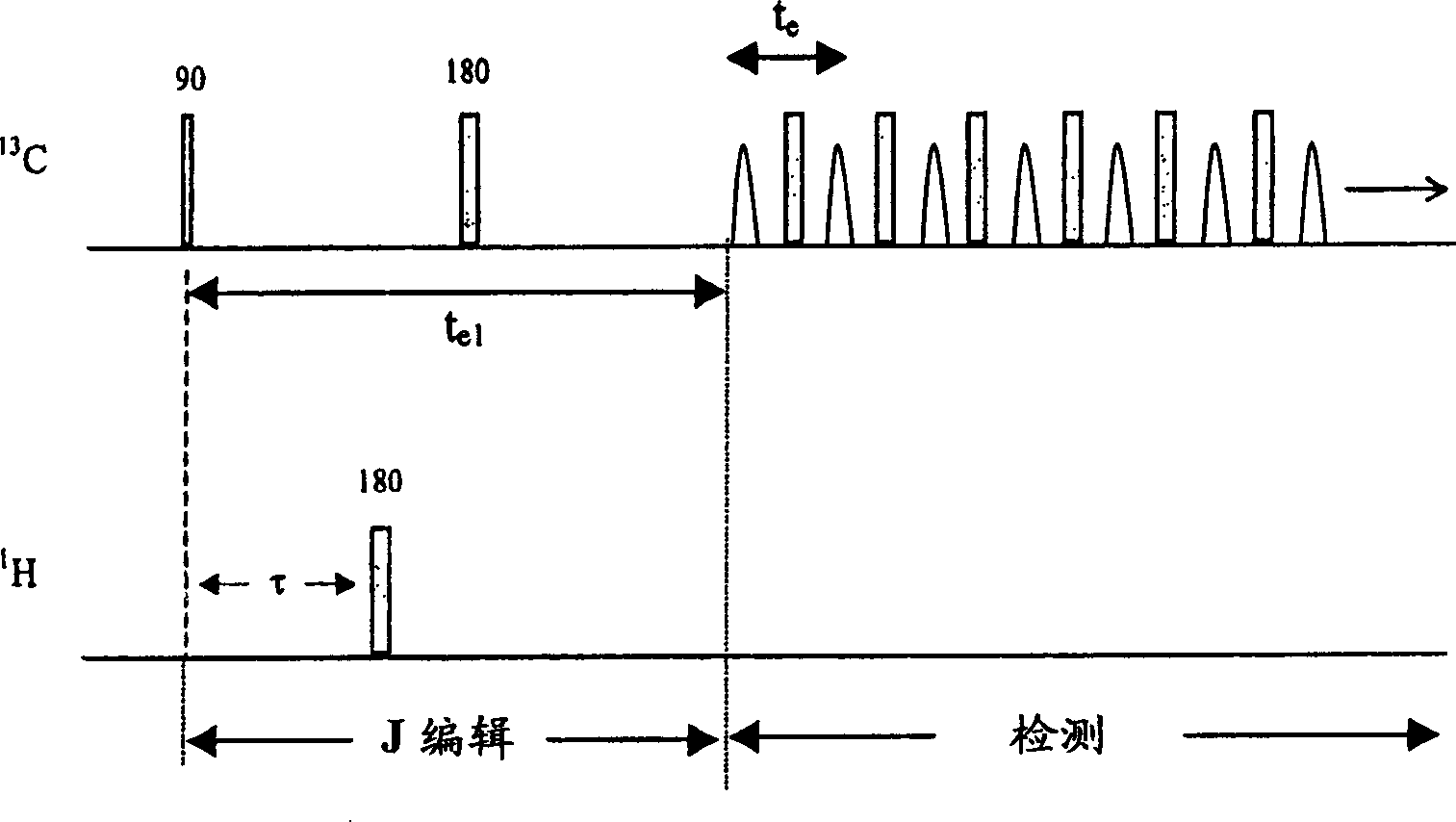
Apparatus and methods for J-edit nuclear magnetic resonance measurement
ActiveUS6958604B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
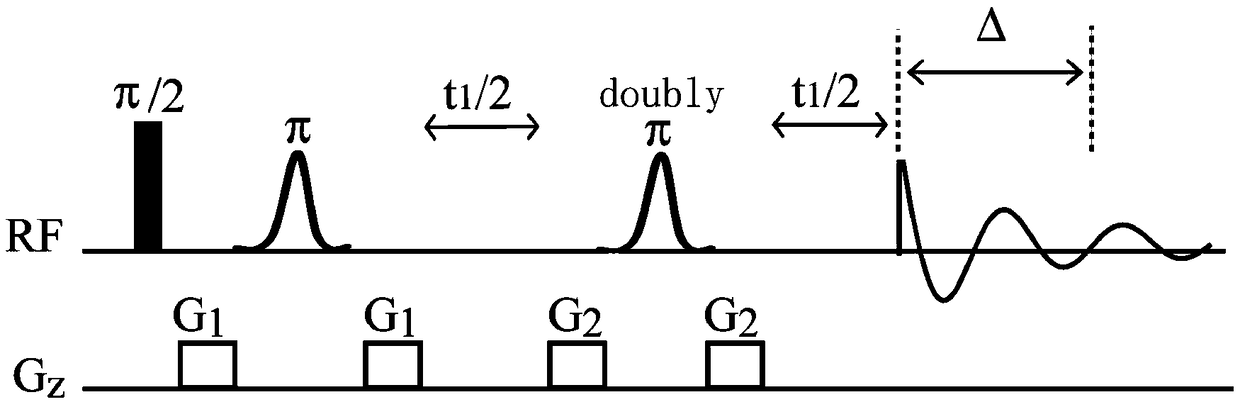
A method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance measurements includes inducing a static magnetic field in a formation fluid sample; applying an oscillating magnetic field to the fluid sample according to a preparation pulse sequence that comprises a J-edit pulse sequence for developing J modulation; and acquiring the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements using a detection sequence, wherein the detection sequence comprises at least one 180-degree pulse. The method may further include acquiring the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements a plurality of times each with a different value in a variable delay in the J-edit pulse sequence; and analyzing amplitudes of the plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements as a function of the variable delay to provide J coupling information.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Nuclear magnetic resonance multi-spectral method for measuring hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of plurality of coupling networks
InactiveCN106706694ASimple and convenient NMR methodMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientJ-coupling
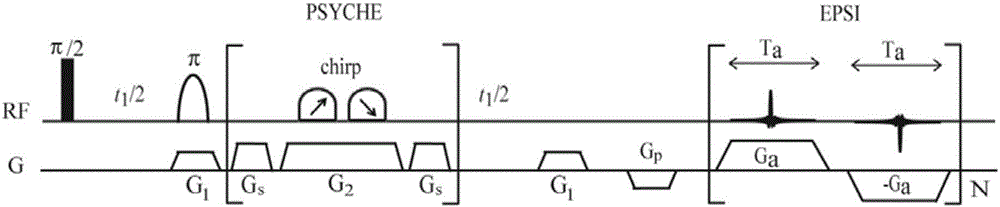
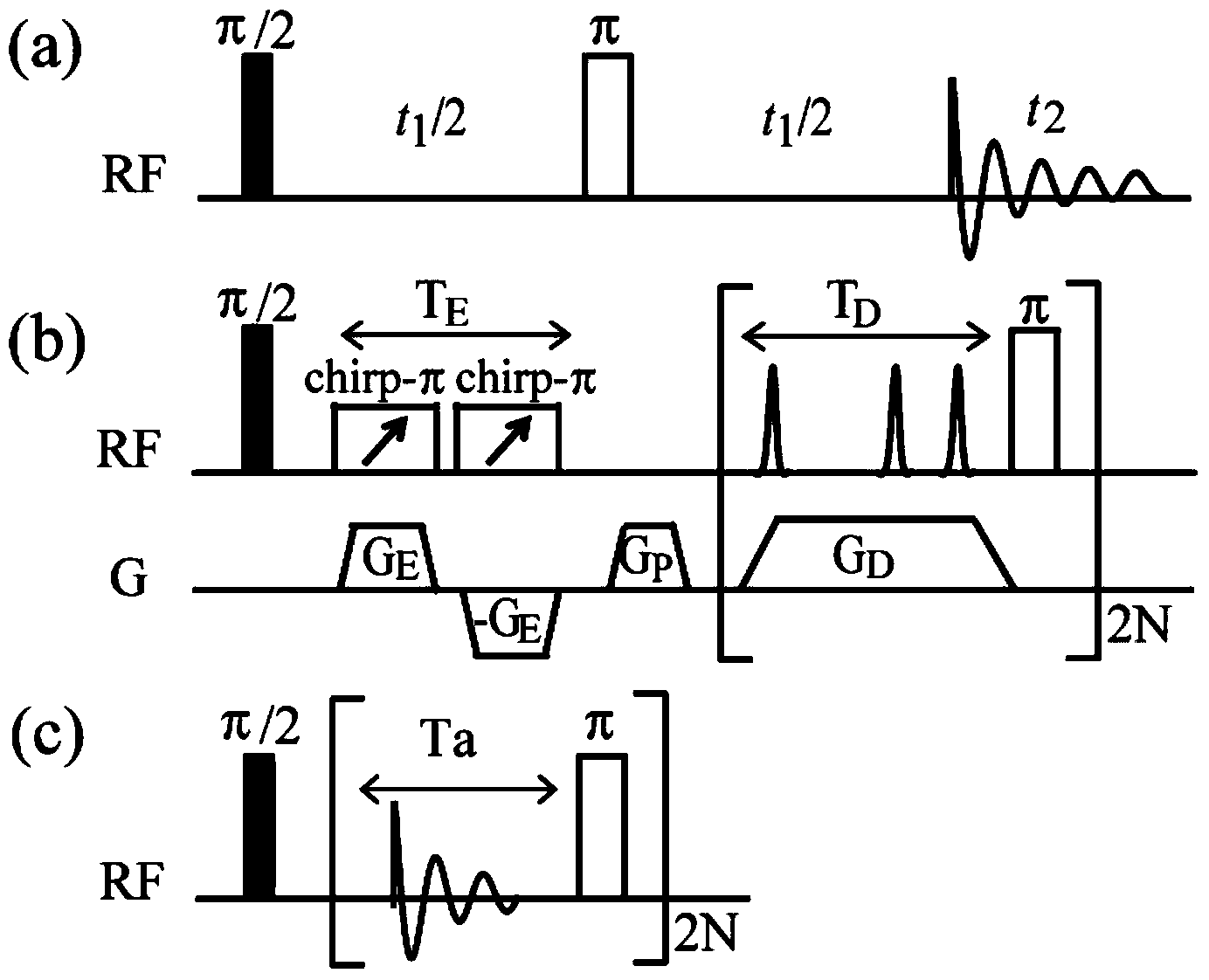
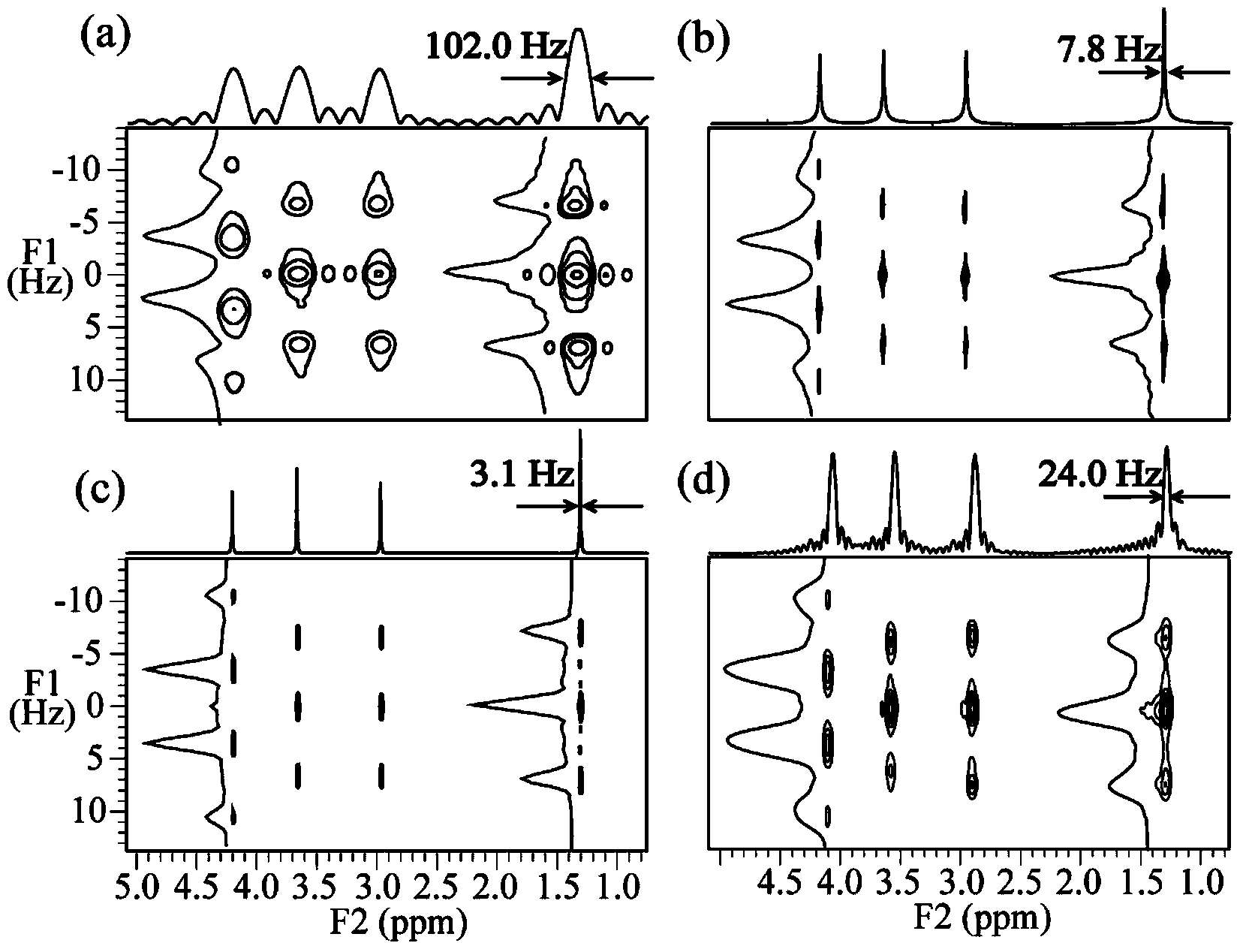
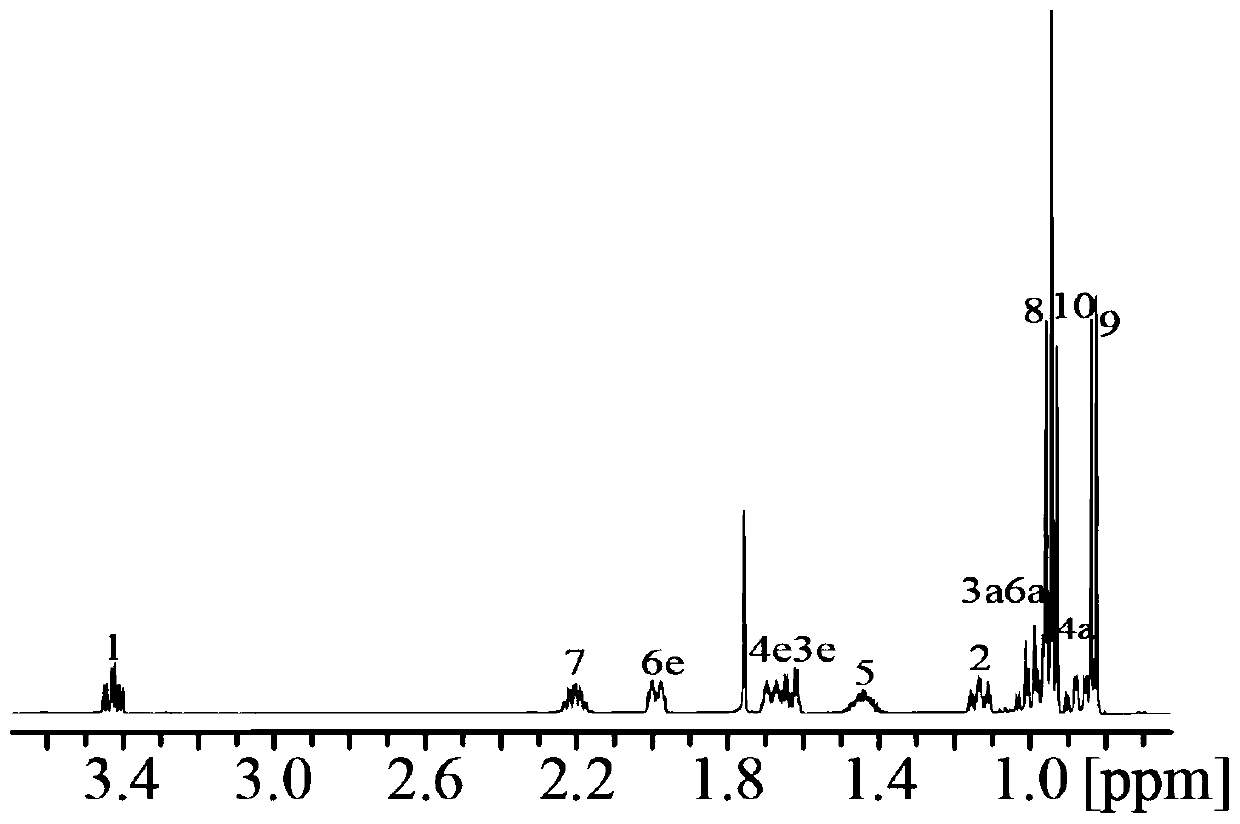
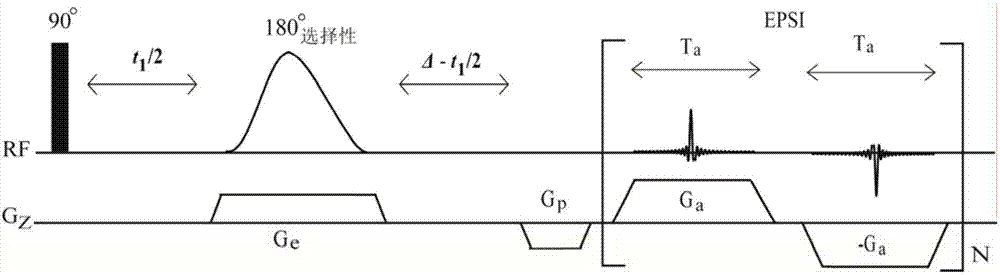
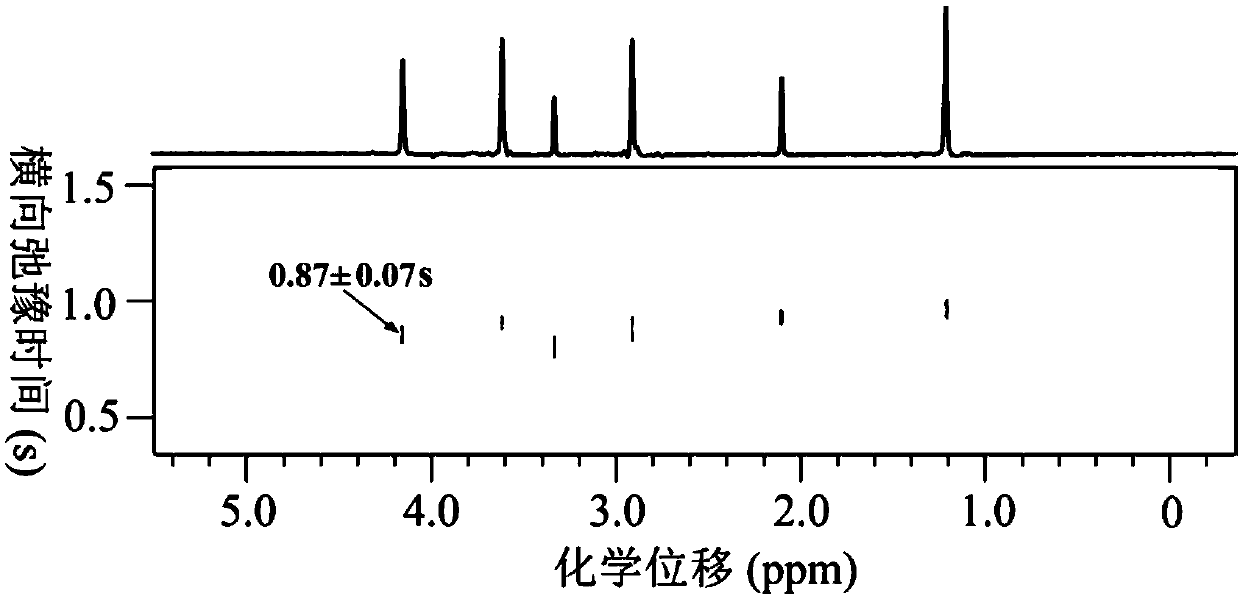
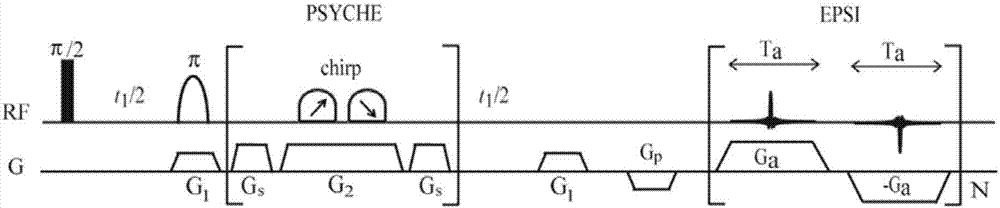
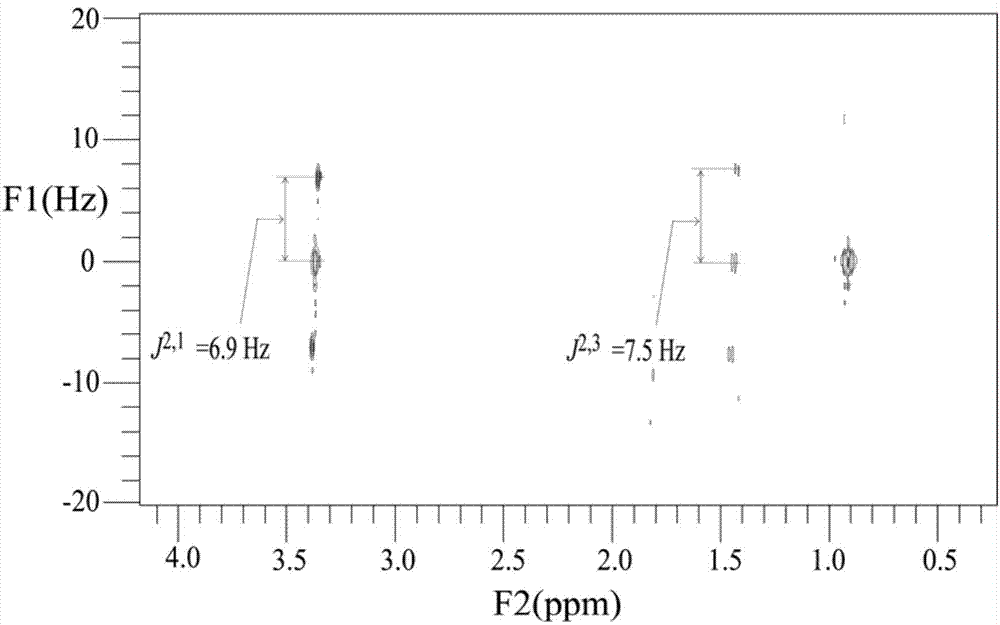
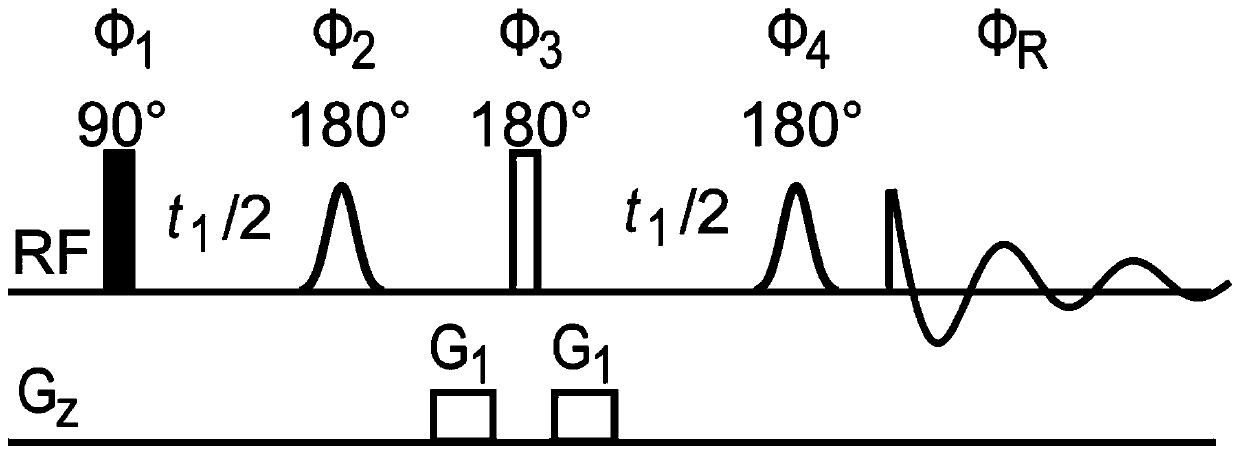
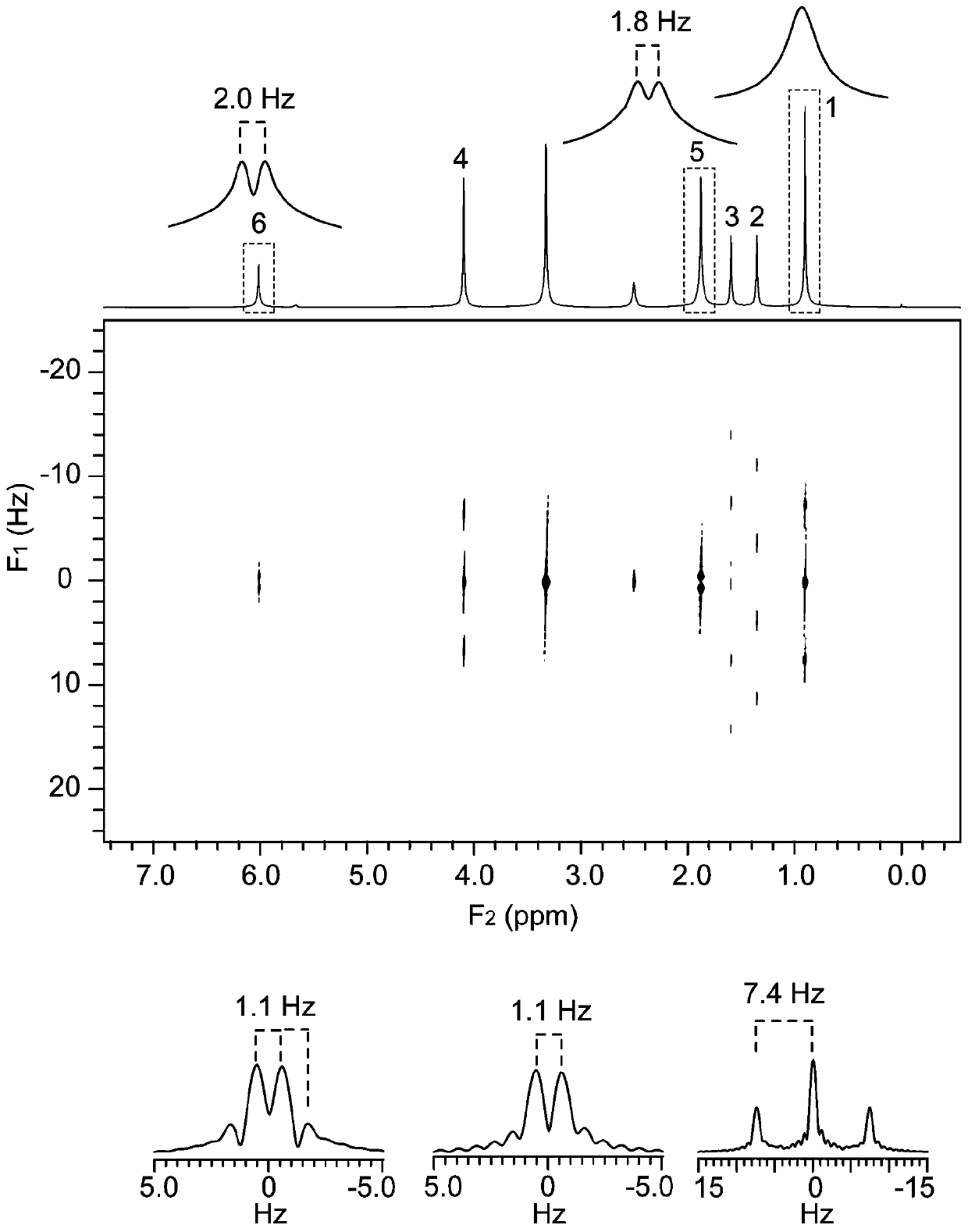
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance multi-spectral method for measuring the hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of a plurality of coupling networks. The method comprises the following steps: applying a 90 DEG hard pulse to make a magnetization vector rotate to the XY plane from the Z direction; applying a selective 180 DEG soft pulse and a magnetic field gradient in the Z direction t1 / 2 time later in order to excite different nuclei in different space positions; applying a PSYCHE module; applying gradients with the same intensity and the same direction to two sides of the PSYCHE module to disperse unwanted signals; adopting an EPSI sampling module t1 / 2 time later to obtain chemical displacement information and space position information; coupling other nuclei obtained at different layers and the nuclei excited by he 180 DEG soft pulse in the same layer to make the couplings have split peaks in indirect dimension; and measuring a corresponding J coupling constant from the split peaks.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for acquiring two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy of magnetic resonance by single sweeping
InactiveCN104237820AShorten the timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyChemical reactionMetabolite
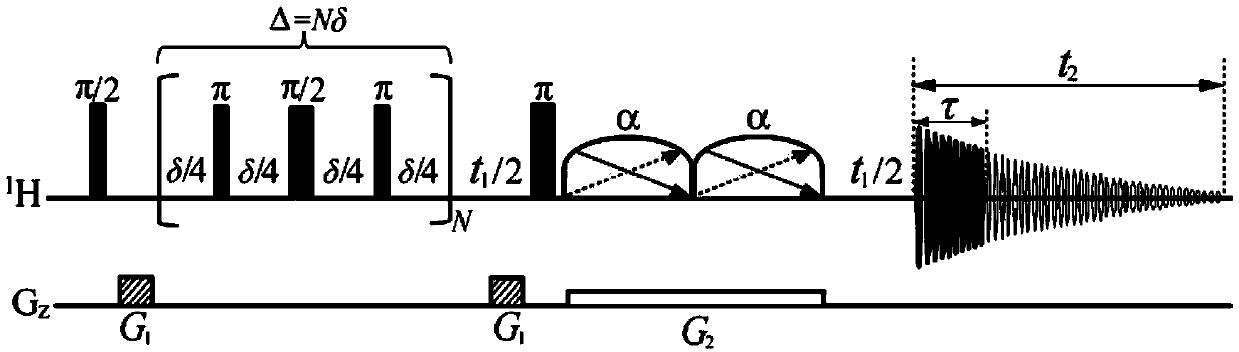
The invention provides a method for acquiring two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy of magnetic resonance by single sweeping. Through a module executing 'sampling and 180-degree pulsing' repeatedly after exciting a magnetization vector to an XY plane, data needed for two-dimensional J- resolved spectroscopy can be acquired by only one-time excitation. In order to acquire better resolution on a direct dimension F2 of a spectrogram, raw data are predicted along the direct dimension F2, and signals are attenuated completely. Compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantage that time of experiment is shortened greatly; compared with a previous spatial encoding method, the method is equivalent to the previous method in experimental time, can provide higher signal to noise ratio and resolution, and is simple in sequence and convenient to operate; compared with a one-dimensional spectroscopy method, the method is equivalent to the method in experimental time, but can provide finer J-coupling split peak information. The simple and efficient method plays an important role in metabolite batch testing, organic chemistry reaction and bioassay.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Scalable quantum computer architecture with coupled donor-quantum dot qubits
A quantum bit computing architecture includes a plurality of single spin memory donor atoms embedded in a semiconductor layer, a plurality of quantum dots arranged with the semiconductor layer and aligned with the donor atoms, wherein a first voltage applied across at least one pair of the aligned quantum dot and donor atom controls a donor-quantum dot coupling. A method of performing quantum computing in a scalable architecture quantum computing apparatus includes arranging a pattern of single spin memory donor atoms in a semiconductor layer, forming a plurality of quantum dots arranged with the semiconductor layer and aligned with the donor atoms, applying a first voltage across at least one aligned pair of a quantum dot and donor atom to control a donor-quantum dot coupling, and applying a second voltage between one or more quantum dots to control a Heisenberg exchange J coupling between quantum dots and to cause transport of a single spin polarized electron between quantum dots.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum
ActiveCN106841270AHigh spectral resolutionImprove spectral qualityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceFrequency spectrumData acquisition
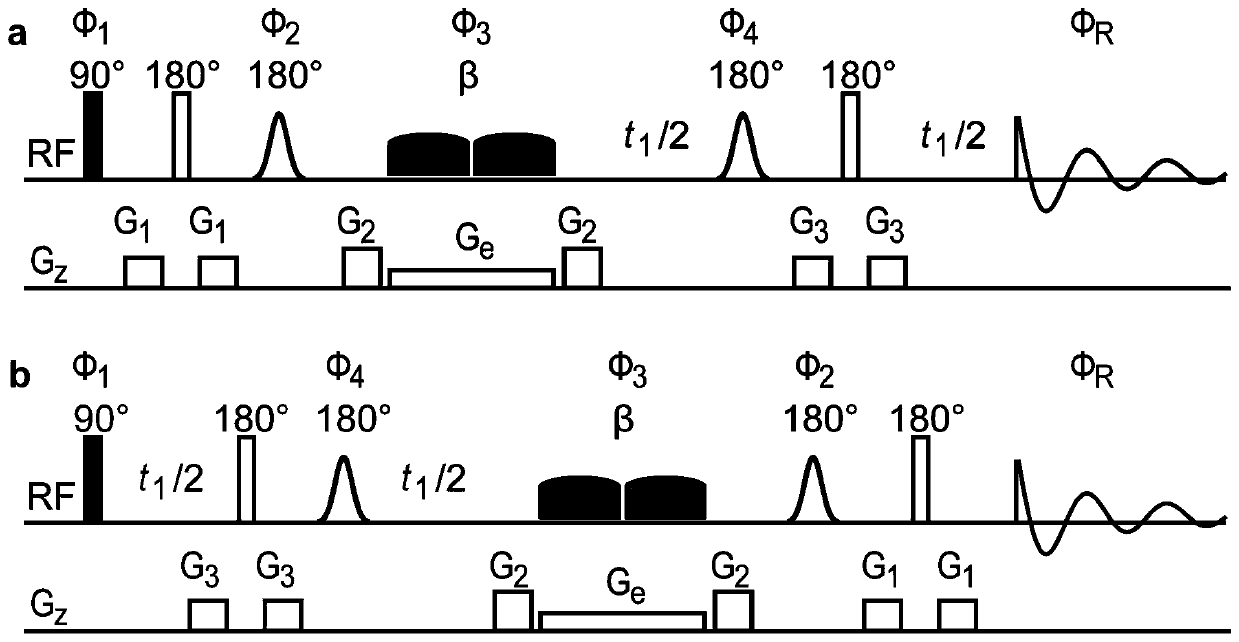
The invention relates to a method for obtaining a nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum. The method comprises the following steps: putting a to-be-tested sample into a nuclear magnetic tube and conveying the nuclear magnetic tube loaded with the to-be-tested sample into a detection chamber of a magnetic resonance spectrometer; invoking a conventional one-dimensional hydrogen spectrum pulse sequence to acquire a one-dimensional hydrogen spectrum, obtaining signal peak distribution and spectrum width information, and measuring the non-selective 90-degree radio frequency pulse width; inputting a compiled two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum pulse sequence into the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, opening a chiro pulse weak selection layer gradient combination module and a two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum pulse sequence sampling module of the two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum pulse sequence; setting two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum pulse sequence experiment parameters, inspecting that the experiment parameters are set correctly, and then executing data sampling; after the completion of data sampling, performing corresponding data splicing and two-dimensional Fourier transform to obtain a two-dimensional frequency spectrum containing J coupling information and chemical displacement information; performing two-dimensional phase-sensitive treatment on the obtained two-dimensional frequency spectrum to obtain the two-dimensional phase-sensitive J spectrum.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation measurement method without J-coupling-effect interference
ActiveCN106814337AAccurate measurementEliminate signal modulation effectsMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
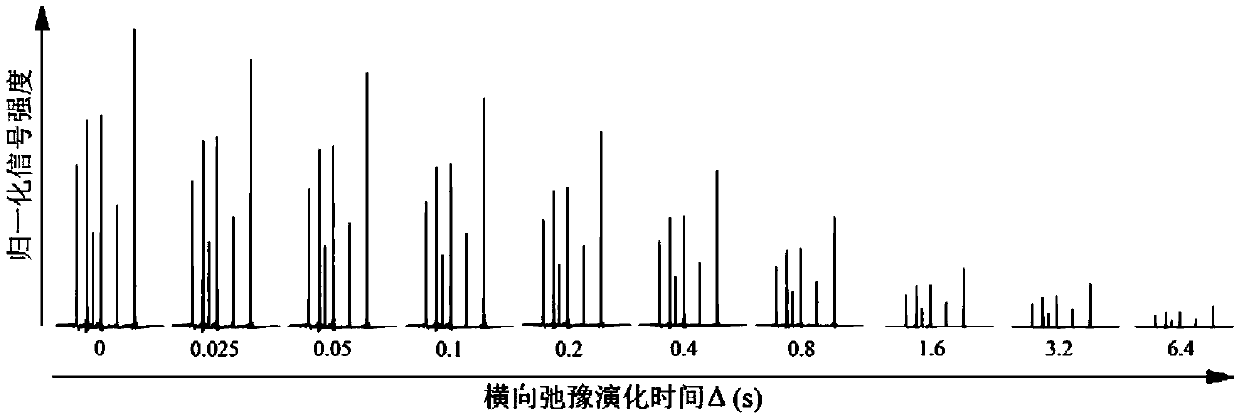
A nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation measurement method without J-coupling-effect interference is suitable for a routine liquid magnetic resonance spectrometer. The nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation measurement method without J-coupling-effect interference can eliminate the J-coupling-effect interference. The method comprises the steps of (1), measuring a pi / 2 nonselective RF pulse width required for exciting a sample; (2), introducing a nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence into the magnetic resonance spectrometer; (3), starting a transverse relaxation evolution module and a pure chemical shift decoupling module based on a perfect echo for the nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence, and setting experiment parameters of the transverse relaxation evolution module and the pure chemical shift decoupling module; (4), performing three-dimensional data sampling; and (5), after data sampling, performing related data after-processing operation, and obtaining a two-dimensional spectrum of which the direct dimension is the pure chemical shift information and the indirect dimension is the transverse relaxation time and error, namely a pure chemical shift-transverse relaxation time two-dimensional correlation spectrum.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance multi-dimensional spectrum method for measuring hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of specific hydrogen nucleus
InactiveCN109187613AStrong spectrogram signalAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientJ-coupling
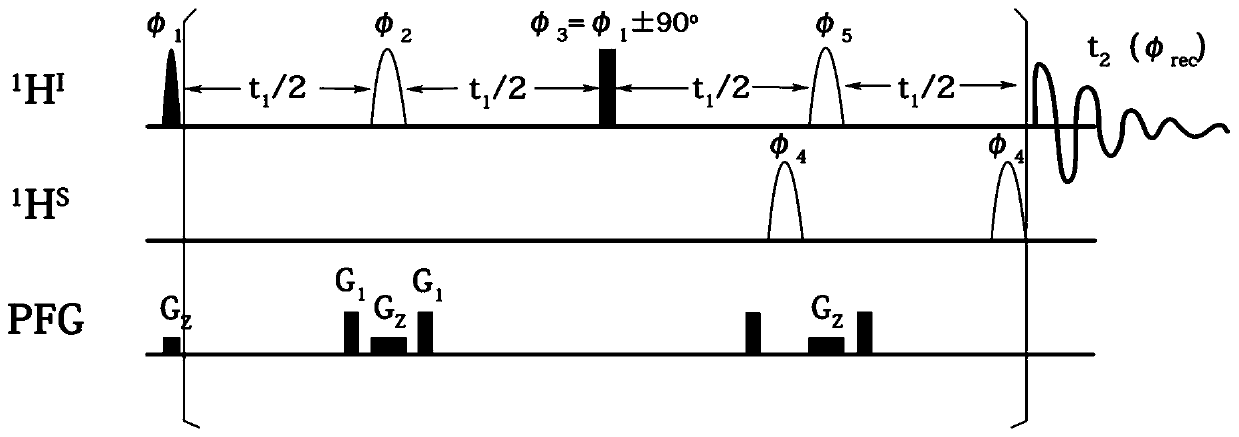
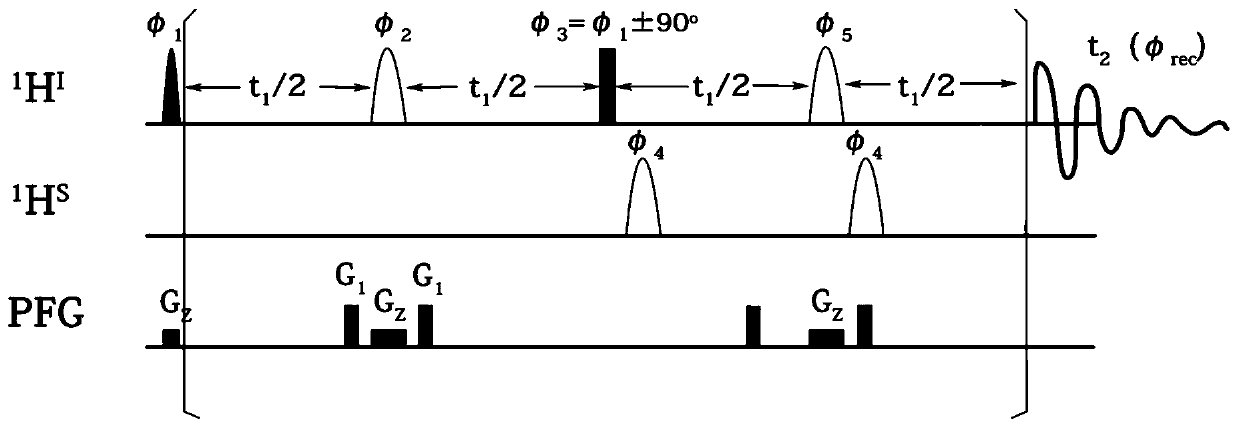
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance multi-dimensional spectrum method for measuring the hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of a specific hydrogen nucleus. The nuclear magnetic resonance multi-dimensional spectrum method comprises: applying a selective 90 DEG soft pulse while applying a Z-direction magnetic field gradient; applying a perfect echo module, and applying Z-direction magnetic field gradients with the same strength and the same direction on both sides of the selective 180 DEG soft pulse of the perfect echo; adding the 180 DEG soft pulse of an S nucleus after the first t1 / 2 evolution time in the second echo of the perfect echo so as to retain the J-coupling information of the S nucleus; adding the 180 DEG soft pulse of the S nucleus after the second t1 / 2 to compensate phase distortion; respectively applying the 180 DEG soft pulse of the selective S nucleus before the two t1 / 2 evolution times in the second echo so as to obtain a R type sequence corresponding toa N type sequence; and finally carrying out addition on a N type spectrum and a R type spectrum inverted along indirect dimension to obtain a phase-sensitive two-dimensional spectrum, and obtaining the corresponding J-coupling constant by measuring from the splitting of the peak in the indirect dimension.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
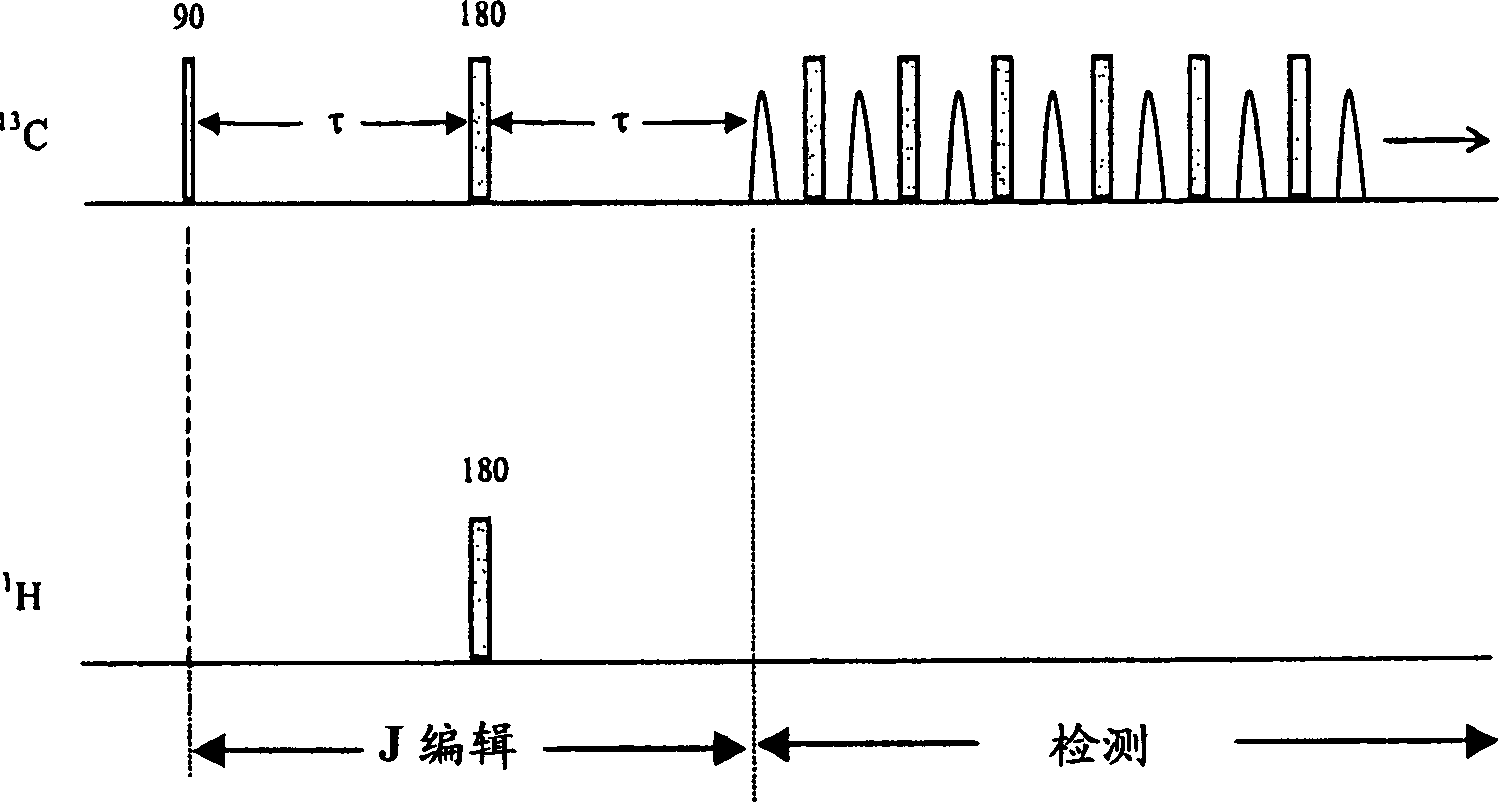
Apparatus and methods for J-edit nuclear magnetic resonance measurement
InactiveCN1611965AElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance measurements includes inducing a static magnetic field in a formation fluid sample; applying an oscillating magnetic field to the fluid sample according to a preparation pulse sequence that comprises a J-edit pulse sequence for developing J modulation; and acquiring the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements using a detection sequence, wherein the detection sequence comprises at least one 180-degree pulse. The method may further include acquiring the nuclear magnetic resonance measurements a plurality of times each with a different value in a variable delay in the J-edit pulse sequence; and analyzing amplitudes of the plurality of nuclear magnetic resonance measurements as a function of the variable delay to provide J coupling information.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER OVERSEAS SA
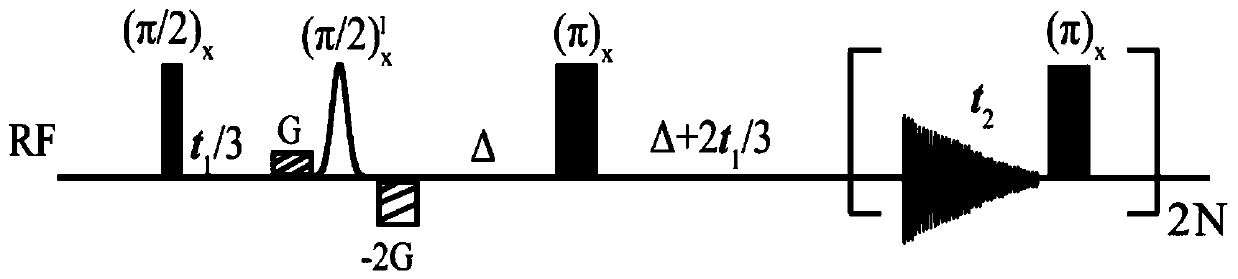
Fast two-dimensional J spectrum method applied to non-uniform magnetic field
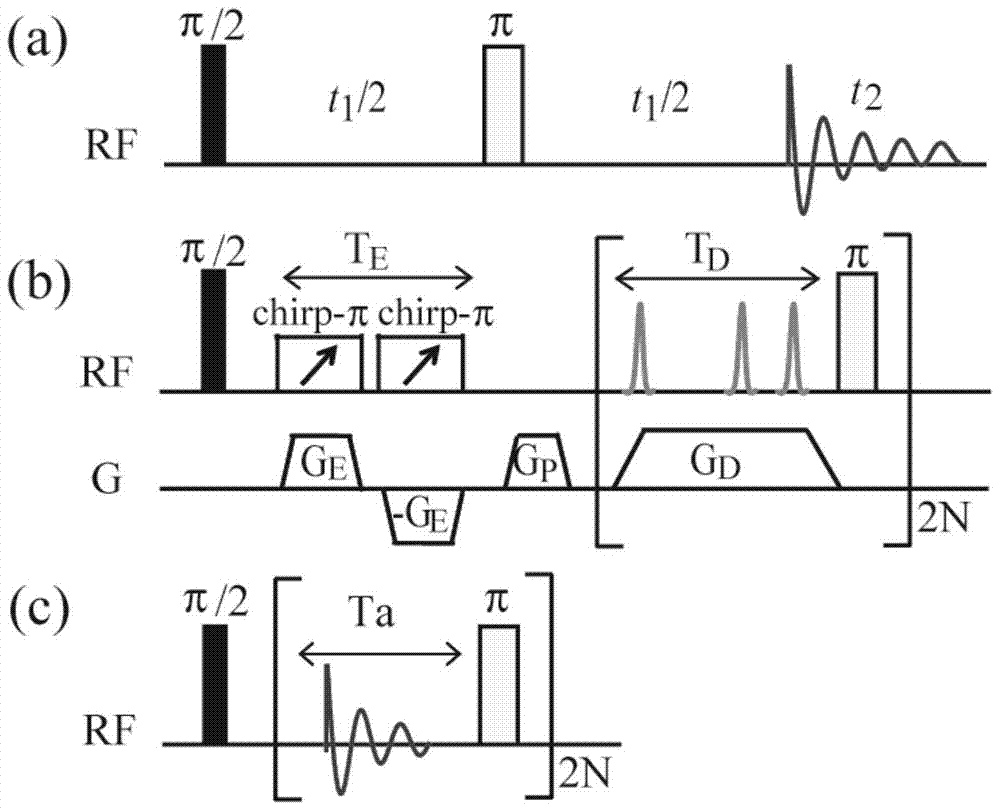
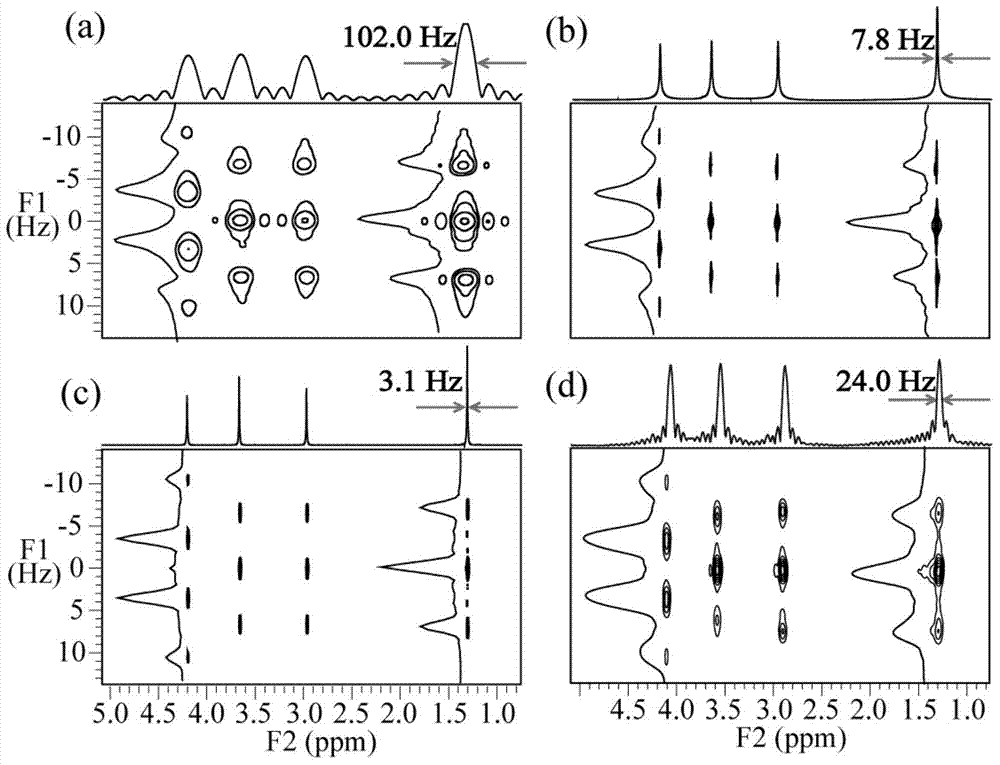
Provided is a fast two-dimensional J spectrum method applied to a non-uniform magnetic field. By using the characteristic that intermolecular double-quantum coherence signals are immune for non-uniformity of the field, the two-dimensional J spectrum method combining an intermolecular double-quantum indirect dimensional delayed evolution module and a J resolution sampling module is designed, wherein a high-resolution two-dimensional J spectrum can be obtained in the non-uniform filed through fast sampling. According to the intermolecular double-quantum indirect dimensional delayed evolution module, a pair of regression linear selection gradients with the strength radio of 1:(-2) are used for selecting the needed intermolecular double-quantum coherence signals, an complete indirect dimensional evolution period t1 is divided into t1 / 3 and 2t1 / 3, and finally, chemical shift evolution information immune for non-uniform filed interference of the field is obtained. The J resolution sampling module is composed of a sampling period t2 and a nonselective pi pulse, and repeated for 2N times, and J coupling evolution information immune for the non-uniform interference of the field can be fastobtained through once scanning. Finally, through specific data fitting treatment, the high-resolution two-dimensional J spectrum is obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Spin coupling network phase sensitive spectrum implementation method based on pure chemical shift
ActiveCN110988006AOvercoming Phase Distortion ProblemsAccurate measurementAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceJ-couplingPhase sensitive
The invention provides a spin coupling network phase sensitive spectrum implementation method based on pure chemical shift. The method mainly relates to spin excitation, selective repolymerization, pure chemical shift and phase-sensitive implementation. The method comprises: sending the uniformly stirred sample to be detected into a detection cavity of a nuclear magnetic spectrometer; performing tuning, shimming and field locking; measuring the non-selective pi / 2 pulse width; acquiring a hydrogen spectrum by utilizing the standard sequence to obtain spectrum peak information; importing a preset sequence and setting experimental parameters, and executing data sampling; carrying out pure chemical shift data processing to obtain a two-dimensional spectrum containing J coupling information andpure chemical shift; and carrying out two-dimensional phase-sensitive processing on the obtained spectrogram. The method has the beneficial effects that (1) a single spin coupling network two-dimensional spectrum with a pure absorption peak line type can be obtained by only one experiment; (2) the J coupling constant can be accurately measured.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance method for measuring all hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constants in molecule
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance method for measuring all hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constants in a molecule. The nuclear magnetic resonance method comprises the following steps: firstly applying one 90-degree hard pulse to rotate a magnetization vector to an XY plane from a Z direction, setting a sampling point at one fixed moment delta after the 90-degree hard pulse; enabling a selective 180-degree soft pulse applied at the same time with Z direction magnetic field gradient to move between the 90-degree hard pulse and the sampling point along with variation of indirect dimension evolution time t1; under the action of the magnetic field gradient, overturning different nucleuses at different spatial positions by the selective 180-degree soft pulse; acquiring chemical displacement information and spatial position information at the same time by adopting an EPSI sampling module, so that couplings of other nucleuses and the nucleus overturned by the 180-degree soft pulse at the same layer can be obtained at different layers, the couplings can show up split peaks at an indirect dimension, and corresponding J coupling constants can be measured from the split peaks.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Fourier Tickling For Homonuclear Decoupling in NMR
ActiveUS20130021031A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyElectric/magnetic detectionJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
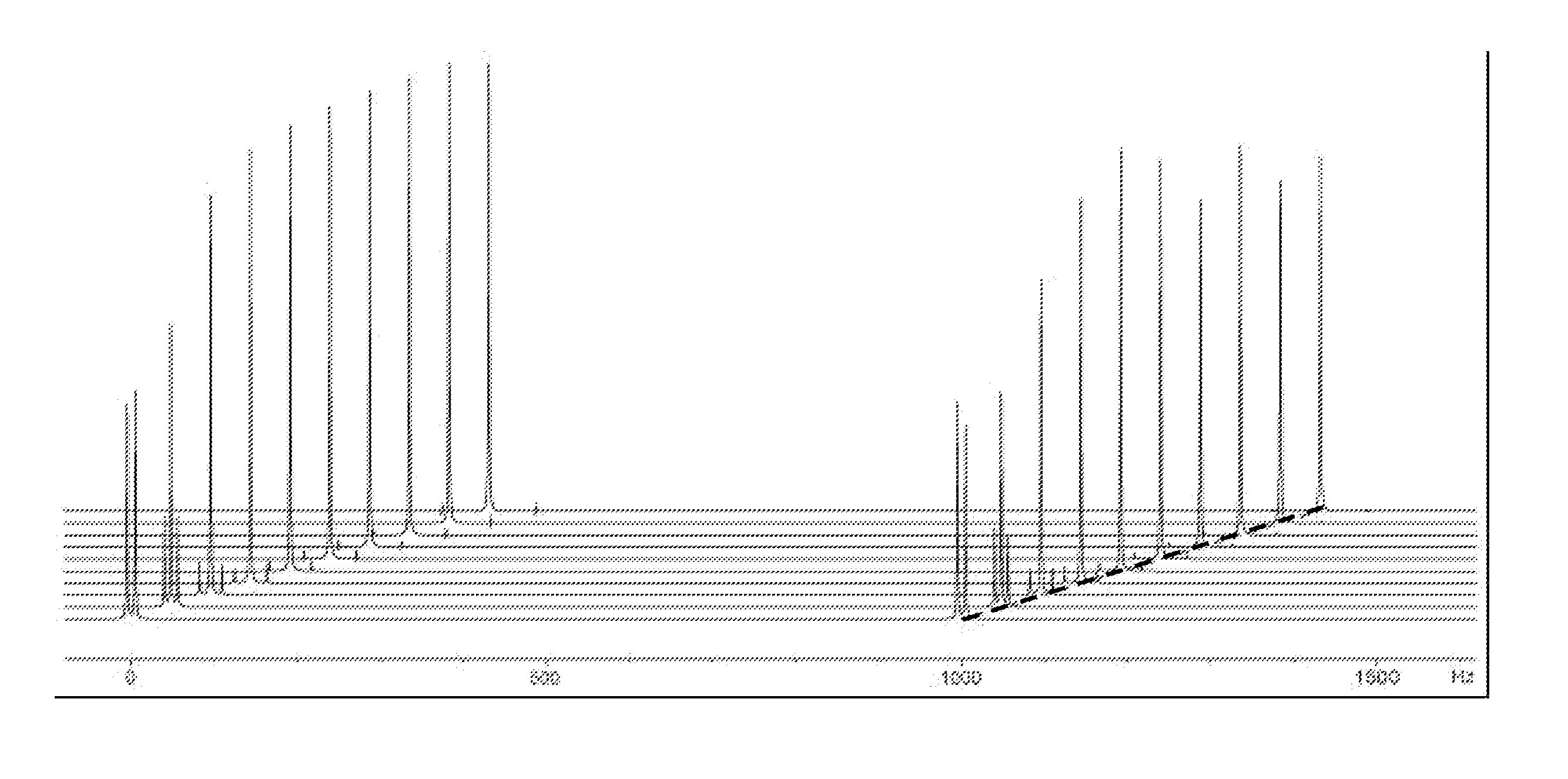
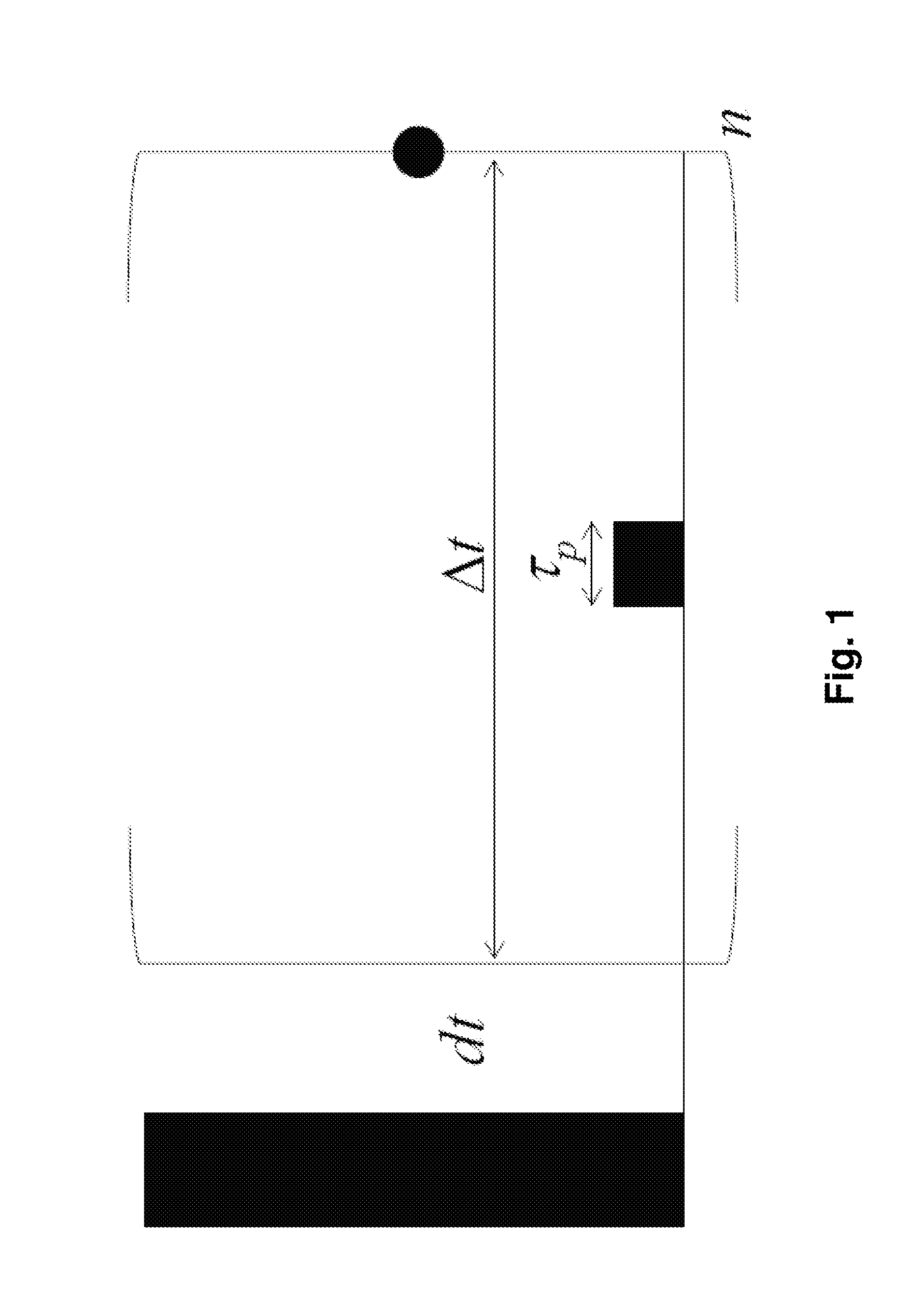
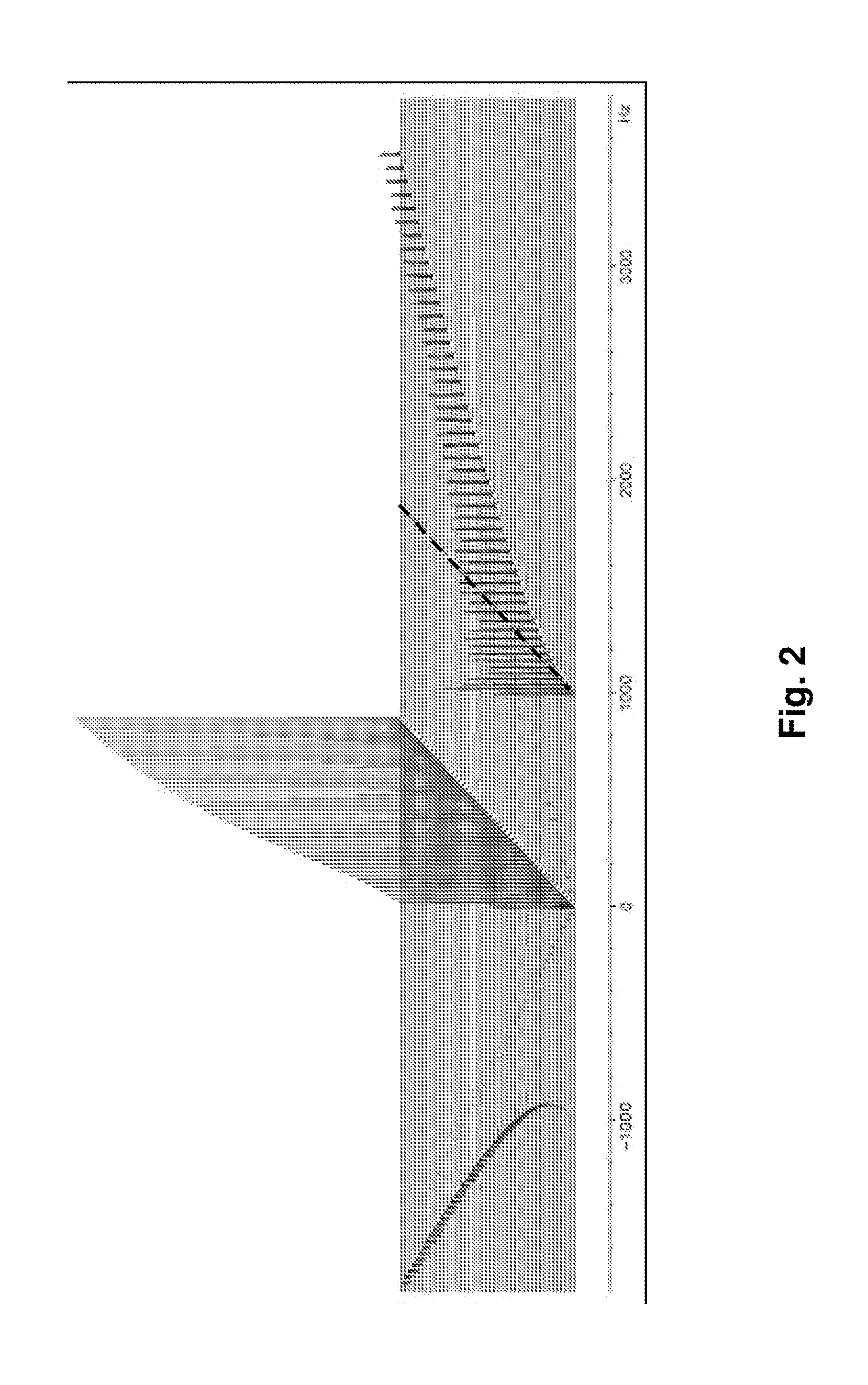
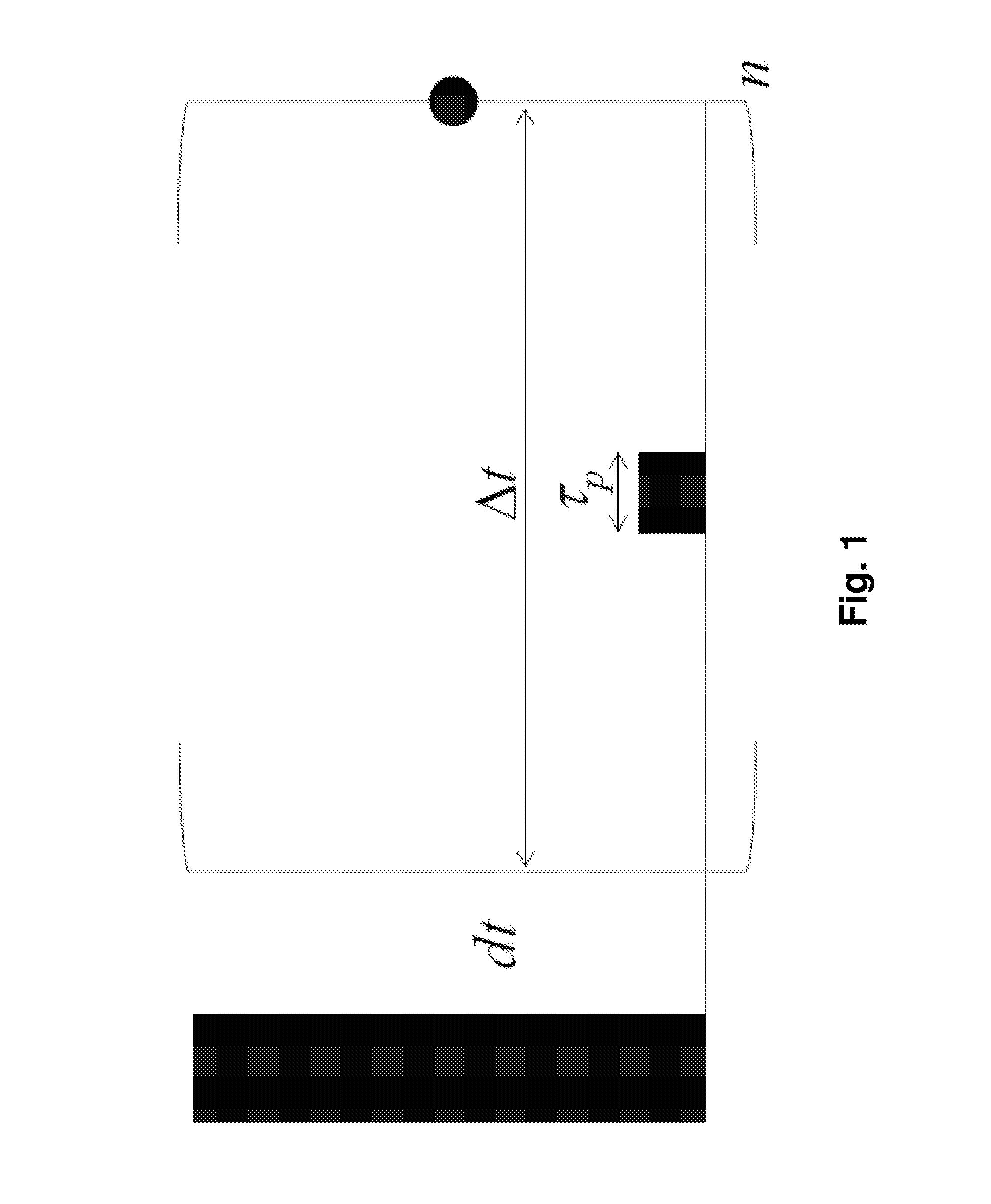
A method for high resolution NMR (=nuclear magnetic resonance) measurements using the application of excitation pulses and the acquisition of data points, whereby a dwell time Δt separates the acquisition of two consecutive data points, which is characterized in that one or more tickling rf (=radio frequency) pulses of duration τp are applied within each dwell time Δt, and that the average rf field amplitude of each of the tickling rf pulses approximately fulfills the condition ω1=ω1τp / Δt=πJ wherein J is the scalar J-coupling constant and ω1=γB1 with γ being the gyromagnetic ratio and B1 being the strength of the magnetic component of each tickling rf pulse. This method is effective in decoupling homonuclear couplings.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL) +1
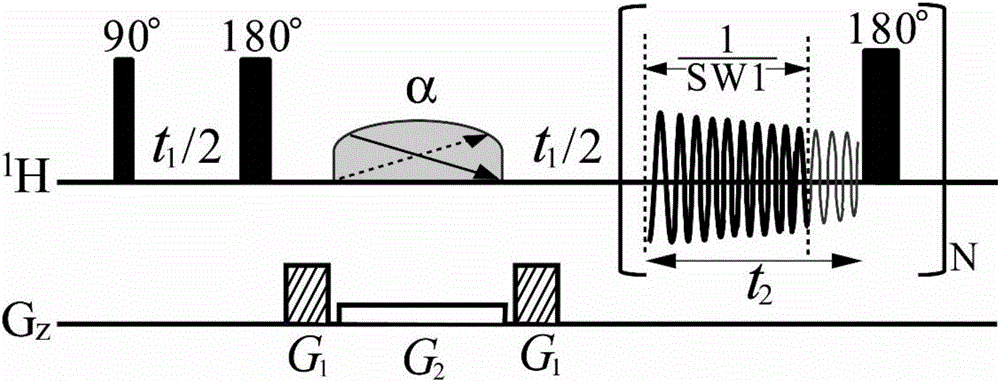
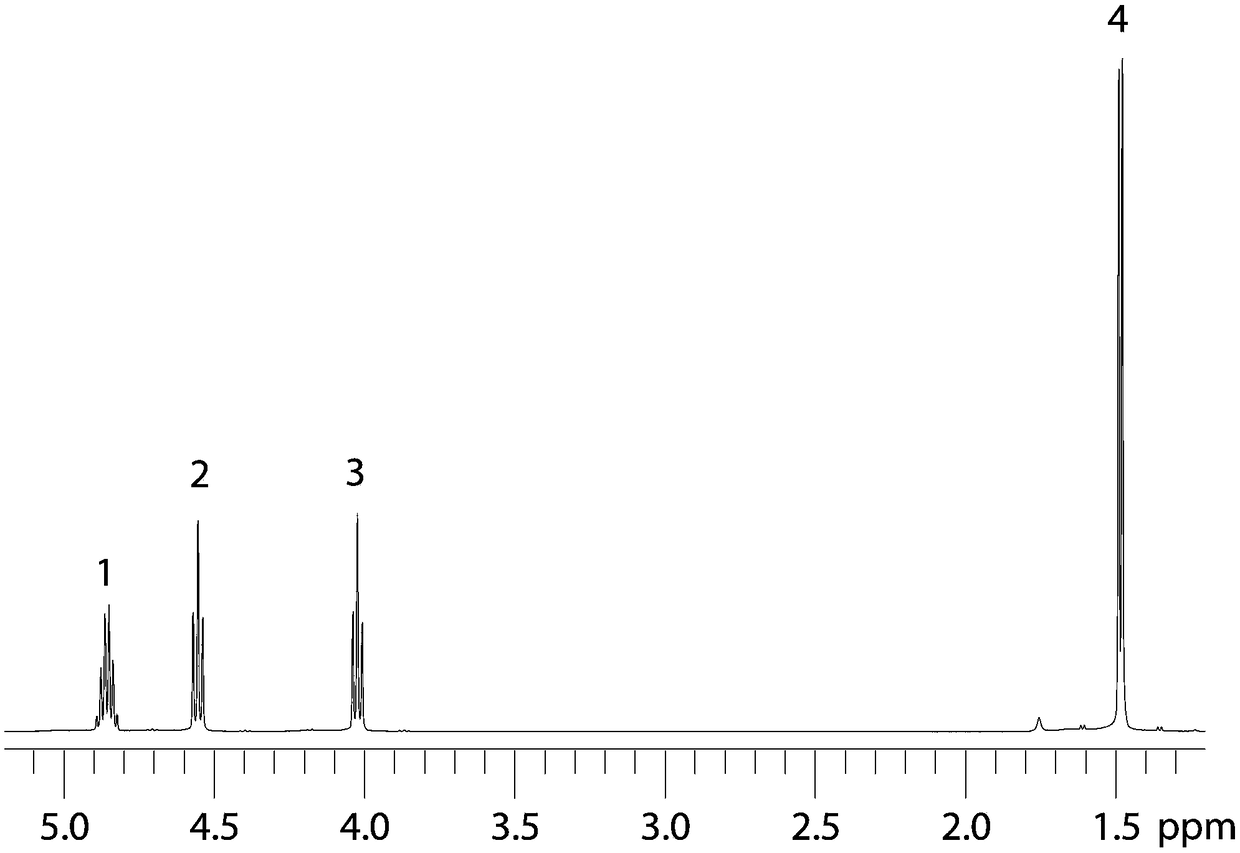
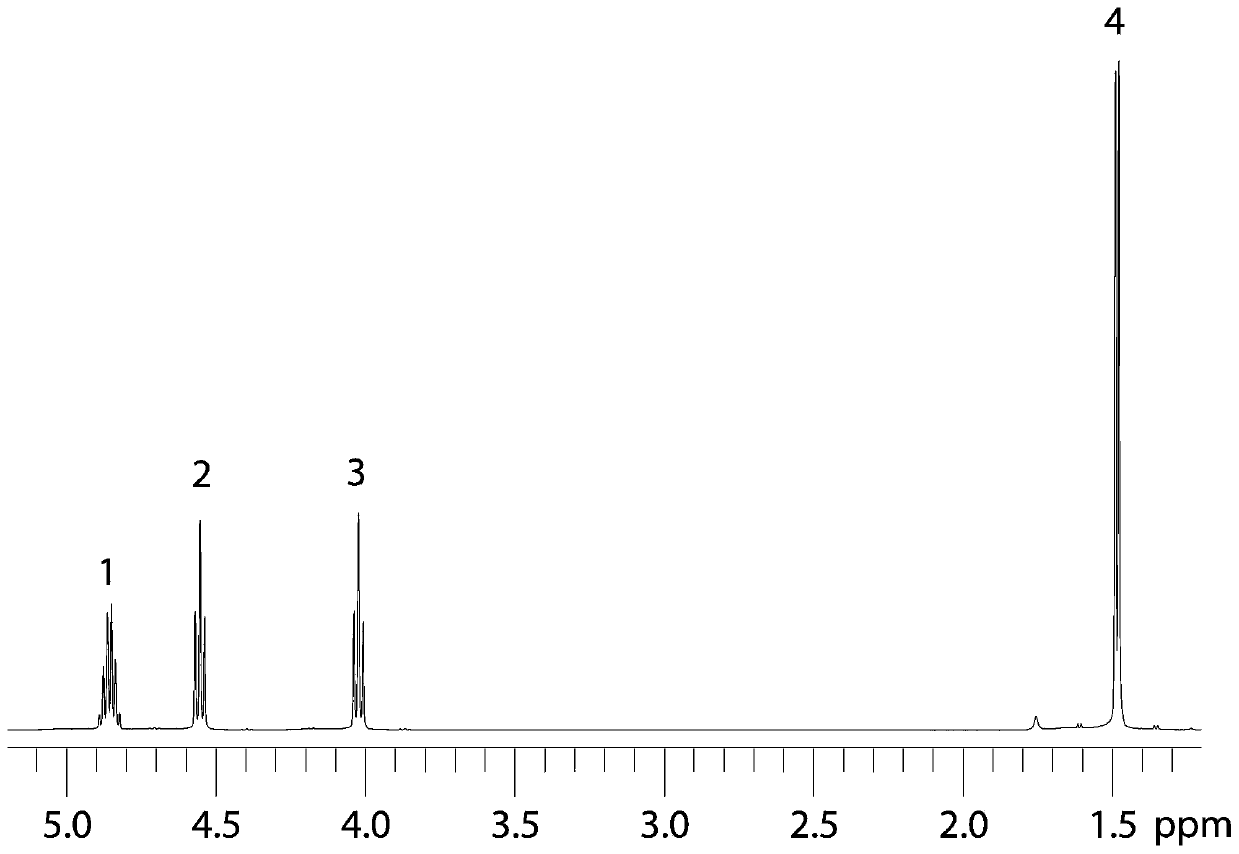
High-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for measuring hydrogen-hydrogen J coupling constant
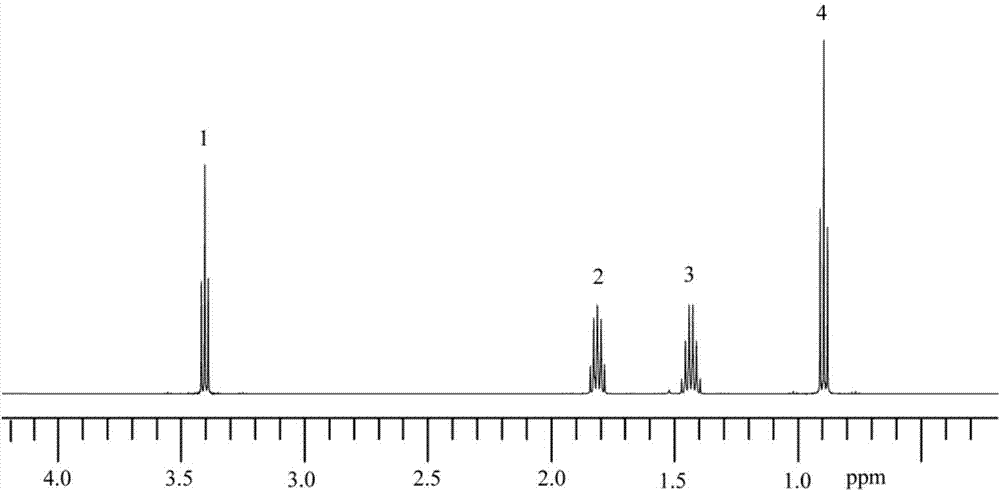
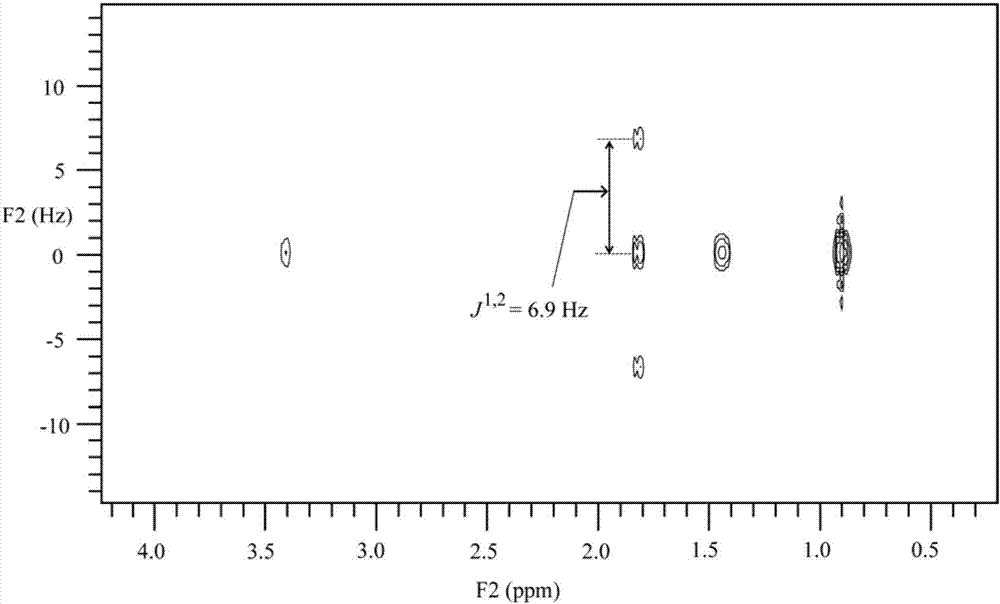
The invention provides a high-resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy for measuring a hydrogen-hydrogen J coupling constant. The method comprises the following steps: after a 90-degree excitation pulse is applied, applying a monochromatic selective 180-degree pulse to a to-be-detected proton, delaying for t1 / 2 time, applying a dichromatic selective 180-degree pulse to the to-be-detectedproton and another proton coupled with the to-be-detected proton, and delaying for t1 / 2 time; carrying out sampling after an evolution period; after the experiment is finished, extracting starting delta time length data from each group of data, and sequentially splicing the data into new one-dimensional data; and carrying out Fourier transform, so as to obtain a new one-dimensional spectrum required by a user, wherein only a signal for detecting the proton selected by the user is maintained, and only J coupling cracking between the proton and another selected proton is maintained. Therefore,the J coupling constant between the two protons can be accurately measured.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Pure chemical shift-based nuclear magnetic resonance diffusion spectroscopy method
ActiveCN107907558AEliminate coupling effect interferenceAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDiffusionJ-coupling
The invention discloses a pure chemical shift-based nuclear magnetic resonance diffusion spectroscopy method, and relates to nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy detection. A response echo diffusion module is used to realize diffusion coefficient evolution; a PSYCHE pure chemical shift decoupling module is used to eliminate J coupling effect induced spectral peak splitting, and one-dimensionalpure chemical shift spectrum information is provided for the measurement of the diffusion coefficient; and specific data fitting processing is carried out to obtain a pure chemical shift-diffusion coefficient related two-dimensional diffusion spectrum, and the two-dimensional diffusion spectrum is used to directly detect the diffusion coefficient of every component in a sample and the error thereof and realize component separation of the sample. The method does not need a special sample processing process, is simple and easy, and is suitable for any routine nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance method for acquiring J coupling constant amplified spectrogram
InactiveCN108279392AQuick measurementHigh-resolutionMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
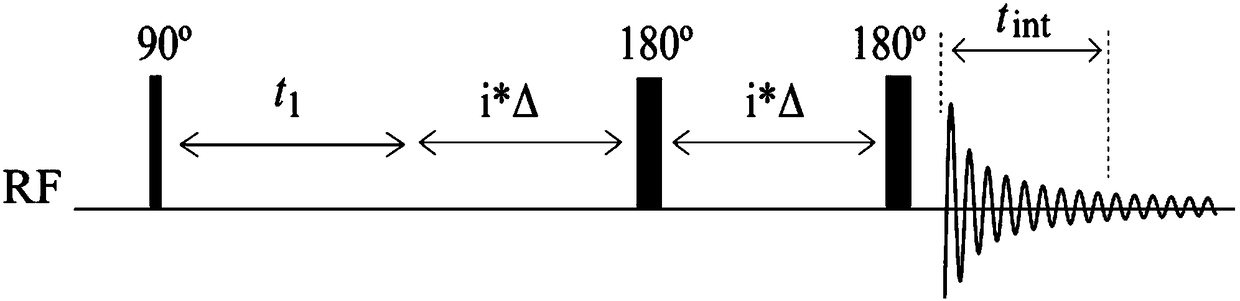
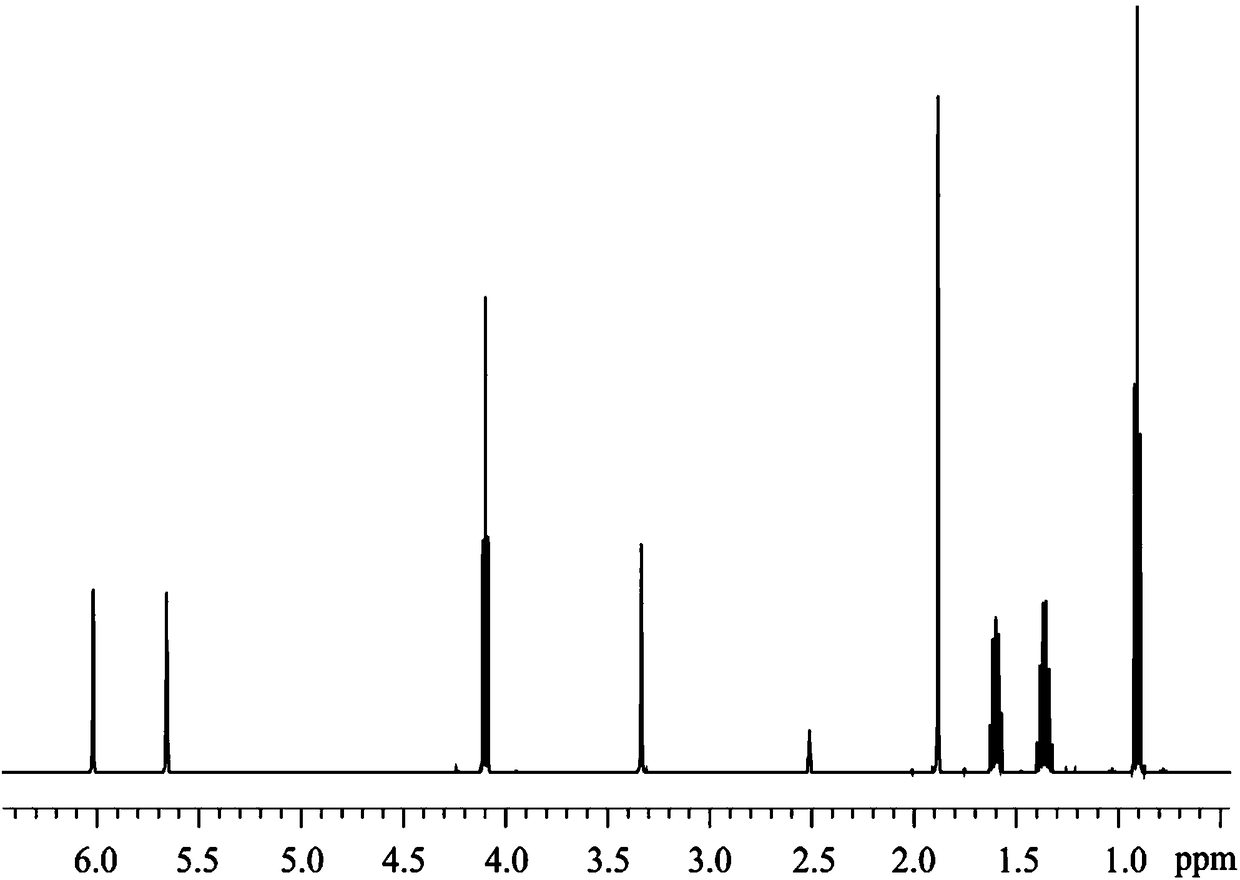
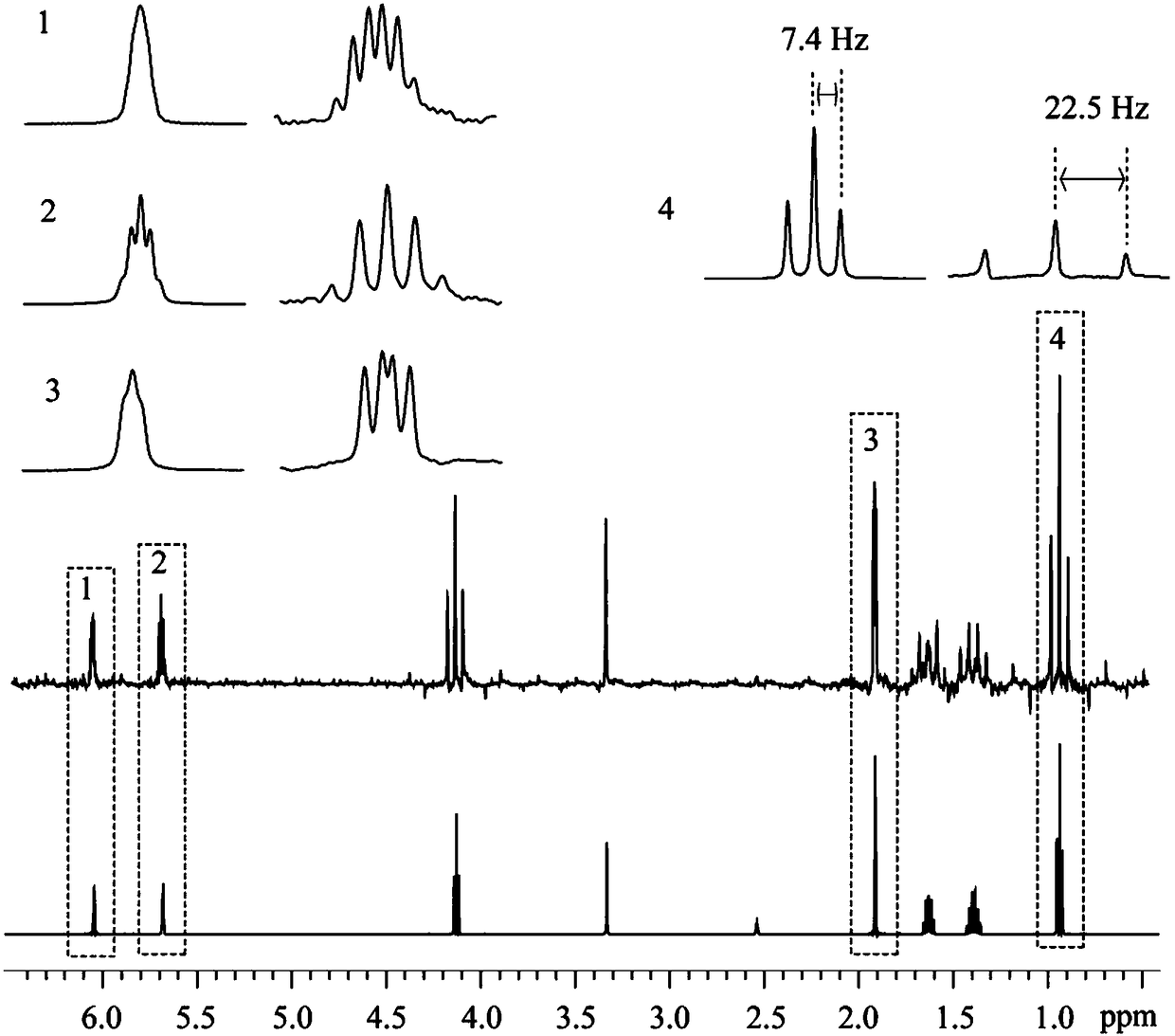
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance method for acquiring a J coupling constant amplified spectrogram. Firstly, a 90-degree hard pulse is applied to turn a magnetization vector from a Zdirection to an XY plane. After time t1, i*delta time is delayed, a 180-degree hard pulse is applied, i*delta time is delayed again, and then sampling is started. The t1 is increased at equal intervals in each time of sampling. The 'i*delta-180-egree pulse-i*delta' is a spin echo module, only J coupling evolution is performed in the meantime, and chemical displacement evolution is reunited. Therefore, in each time of sampling, J coupling evolution time is 2 delta longer than chemical displacement evolution time, so that a J coupling constant can be effectively amplified. After experiments, starting time tint data of data acquired by sampling in each time are extracted and sequentially spliced to obtain new one-dimensional data, and then Fourier transformation is performed to obtain the Jcoupling constant amplified spectrogram.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
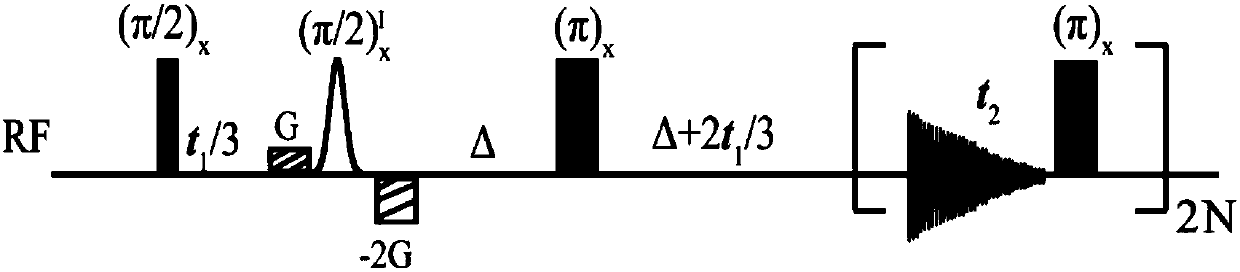
High-resolution magnetic resonant method for measuring two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum of coupling constant
InactiveCN110672650AEasy to measureAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention provides a high-resolution magnetic resonant method for measuring two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum of a coupling constant. The high-resolution magnetic resonant method comprisesthe steps of firstly, applying 90-degree hard pulse to allow a magnetic vector to rotate from a Z direction to an XY plane; secondly, applying an improved spin echo module. Such an effect is in a waythat core-correlated J coupling acting with selected 180-degree pulse is reunited with indirect dimension, so that other J couplings are maintained to be converted in the indirect dimension, and chemical displacement and all J couplings are converted at normal conversion time of direct dimension. By the method, two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum possessing a pure absorption line type can beobtained; after 45-degree rotation on the obtained two-dimensional spectrum, projection spectrum of direct dimension is in a way that pure chemical displacement spectrum of coupling division correlated to the selected core is only maintained, and thus, the J coupling constant can be conveniently measured; and division information of other couplings is maintained by projection of the indirect dimension, and multiplet-mode analysis is helped.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance phase-sensitive two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum method for inhibiting strong coupling pseudo peak
ActiveCN113281366AEnhanced inhibitory effectSuppression of strong coupling effectsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsJ-couplingMagnetic resonance spectroscopic
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Ultra-high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum method
InactiveCN110361680AHigh-resolutionAlleviate the problem of spectral peak crowdingMagnetic measurementsJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention provides an ultra-high resolution nuclear magnetic resonance phase-sensitive two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum method used for acquiring molecular structure information and accurately measuring a J coupling constant. The method is based on a combined action of a ZS decoupling module and an echo chain sampling module, shortcomings of an existing two-dimensional J-spectrum technology in practical applications are overcome, and a high-resolution two-dimensional phase-sensitive J-decomposition spectrum can be acquired under an uneven magnetic field environment. . By using themethod, a spectral resolution of the two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum is increased. The method is of great significance for structure detection of a complex sample of a crowded spectrum peak,and an application field of the two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum is expanded. And simultaneously, based on a monochromatic pulse excitation method, the invention provides a sensitivity enhancement method based on multi-color pulse excitation sampling realiztion.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
A fast two-dimensional j-spectroscopy method for inhomogeneous magnetic fields
Provided is a fast two-dimensional J spectrum method applied to a non-uniform magnetic field. By using the characteristic that intermolecular double-quantum coherence signals are immune for non-uniformity of the field, the two-dimensional J spectrum method combining an intermolecular double-quantum indirect dimensional delayed evolution module and a J resolution sampling module is designed, wherein a high-resolution two-dimensional J spectrum can be obtained in the non-uniform filed through fast sampling. According to the intermolecular double-quantum indirect dimensional delayed evolution module, a pair of regression linear selection gradients with the strength radio of 1:(-2) are used for selecting the needed intermolecular double-quantum coherence signals, an complete indirect dimensional evolution period t1 is divided into t1 / 3 and 2t1 / 3, and finally, chemical shift evolution information immune for non-uniform filed interference of the field is obtained. The J resolution sampling module is composed of a sampling period t2 and a nonselective pi pulse, and repeated for 2N times, and J coupling evolution information immune for the non-uniform interference of the field can be fastobtained through once scanning. Finally, through specific data fitting treatment, the high-resolution two-dimensional J spectrum is obtained.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
A Clean Isophase Layer-Selected Homonucleus Selective Coherence Spectroscopy Method
ActiveCN112577988BAvoid signal self-cancellationSpectrum is clearAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceJ-couplingSpectroscopy methods
The invention provides a clean and homogeneous layer-selective homonuclear selective coherence spectrum method. The modified perfect echo module is used to realize the coherent transfer between the same phases and combined with selective pulse and dephasing gradient to remove unwanted signals, and finally only the excitation nucleus and the observation nucleus are modulated by the cosine function t 1 , t 2 The temporal J-coupling modulates the signal, and the signal strength is affected by the Δ value. The two-dimensional J-coupling modulation of the excited nucleus and the observed nucleus will present an in-phase square in the spectrum, the coupling information of the observed nucleus and other nuclei is reflected in the lateral offset of the square, and the coupling information of the excited nucleus and other nuclei is reflected in the The vertical offset of the square is on, and since the modulation that causes the horizontal and vertical offset is also a cosine modulation, it will not affect the property that the spectral peaks are in-phase.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
A method for NMR transverse relaxation measurement without j-coupling effect interference
ActiveCN106814337BAccurate measurementMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation measurement method without J-coupling-effect interference is suitable for a routine liquid magnetic resonance spectrometer. The nuclear magnetic resonance transverse relaxation measurement method without J-coupling-effect interference can eliminate the J-coupling-effect interference. The method comprises the steps of (1), measuring a pi / 2 nonselective RF pulse width required for exciting a sample; (2), introducing a nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence into the magnetic resonance spectrometer; (3), starting a transverse relaxation evolution module and a pure chemical shift decoupling module based on a perfect echo for the nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence, and setting experiment parameters of the transverse relaxation evolution module and the pure chemical shift decoupling module; (4), performing three-dimensional data sampling; and (5), after data sampling, performing related data after-processing operation, and obtaining a two-dimensional spectrum of which the direct dimension is the pure chemical shift information and the indirect dimension is the transverse relaxation time and error, namely a pure chemical shift-transverse relaxation time two-dimensional correlation spectrum.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
NMR Multidimensional Spectroscopy Method for Measuring Hydrogen-Hydrogen Coupling Constants of Multiple Coupling Networks
InactiveCN106706694BSimple and convenient NMR methodMagnetic measurementsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientJ-coupling
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
A phase-sensitive selective j-spectroscopy method for suppressing axial peaks
InactiveCN110927643BHigh-resolutionClear resolutionMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a phase-sensitive selective J spectrum method for suppressing an axial peak, and relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance multidimensional spectrum method. The method comprises:applying a 90-degree hard pulse, rotating a magnetization vector to an XY plane from a Z direction, selecting an S core by using a 180-degree selective pulse and a pair of phase dispersion gradients,other transverse magnetization vectors being subjected to phase dispersion, and applying a perfect echo module; setting parameters, an excitation angle and a corresponding gradient of the PSYCHE module; determining the number ni of indirect dimensional sampling points and the spectral width SW1, and ensuring that the J coupling constant measured by the SW1 is large; setting the cycle index Nt ofthe sampling window; performing direct dimensional Fourier transform on the sampled N-type signal and R-type signal, adding real parts of the N-type signal and R-type signal after Fourier transform toserve as a real part of a composite signal, subtracting the real parts to serve as an imaginary part of the composite signal, and performing indirect dimensional Fourier transform on the composite signal to obtain a phase-sensitive selective J spectrum. The method is more accurate, has high spectrogram resolution, and can be widely used in complex compound structure analysis.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
Fourier tickling for homonuclear decoupling in NMR
ActiveUS9086465B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyElectric/magnetic detectionJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A method for high resolution NMR (=nuclear magnetic resonance) measurements using the application of excitation pulses and the acquisition of data points, whereby a dwell time Δt separates the acquisition of two consecutive data points, which is characterized in that one or more tickling rf (=radio frequency) pulses of duration τp are applied within each dwell time Δt, and that the average rf field amplitude of each of the tickling rf pulses approximately fulfills the condition ω1=ω1τp / Δt=πJ wherein J is the scalar J-coupling constant and ω1=γB1 with γ being the gyromagnetic ratio and B1 being the strength of the magnetic component of each tickling rf pulse. This method is effective in decoupling homonuclear couplings.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL) +1
A single-scan method for obtaining two-dimensional j-decomposition spectrum of magnetic resonance
InactiveCN104237820BShorten the timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyChemical reactionMetabolite
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Nuclear magnetic resonance method of two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum
InactiveCN110794350AEasy to measureEasy to analyzeMeasurements using magnetic resonanceJ-couplingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance method of a two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum. The nuclear magnetic resonance method of the two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum is convenient for measuring a coupling constant. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, applying a 90-degree hard pulse to rotate a magnetization vector from a Z direction to an XY plane; secondly, applying an improved spin echo module, namely inserting a selective 180-degree pulse into a conventional 't 1 / 2-180-degree-t 1 / 2' module; and finally, performing two-dimensional Fourier transformto obtain a two-dimensional spectrogram, wherein a signal separation mode arranged along 45 degrees in the conventional two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum is changed into two split signals arranged along 45 degrees, and the distance between the two signals is J coupling related to a kernel acted by the selective 180-degree pulse. The two-dimensional spectrum is rotated by 45 degrees and isprojected to a direct dimension to obtain a pure chemical displacement one-dimensional spectrum, but the J coupling related to the selected kernel is reserved. Therefore, the J coupling constant related to the selected kernel can be conveniently measured from a direct dimension projection spectrum.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
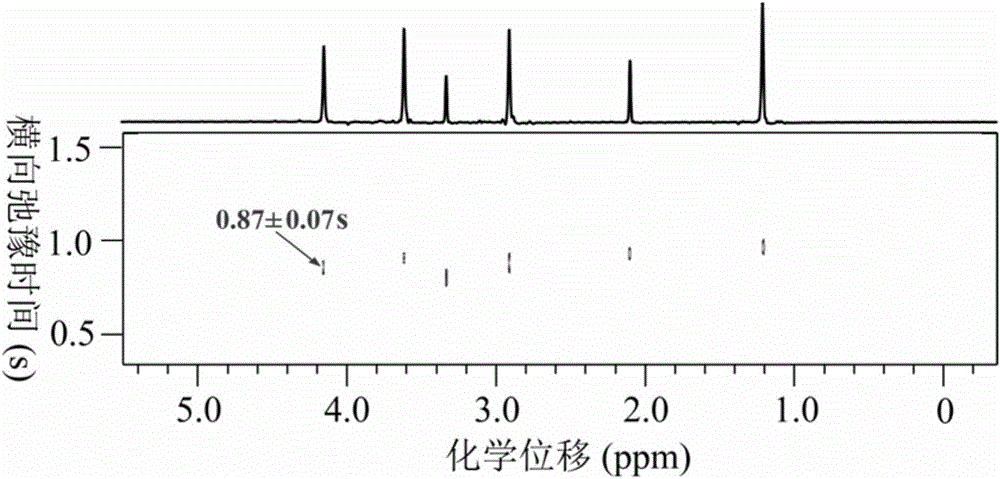
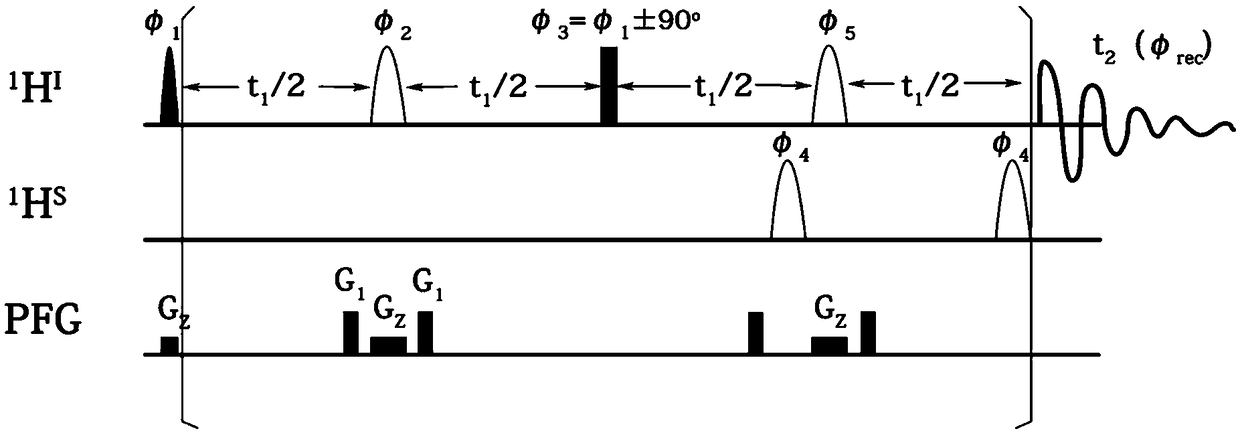
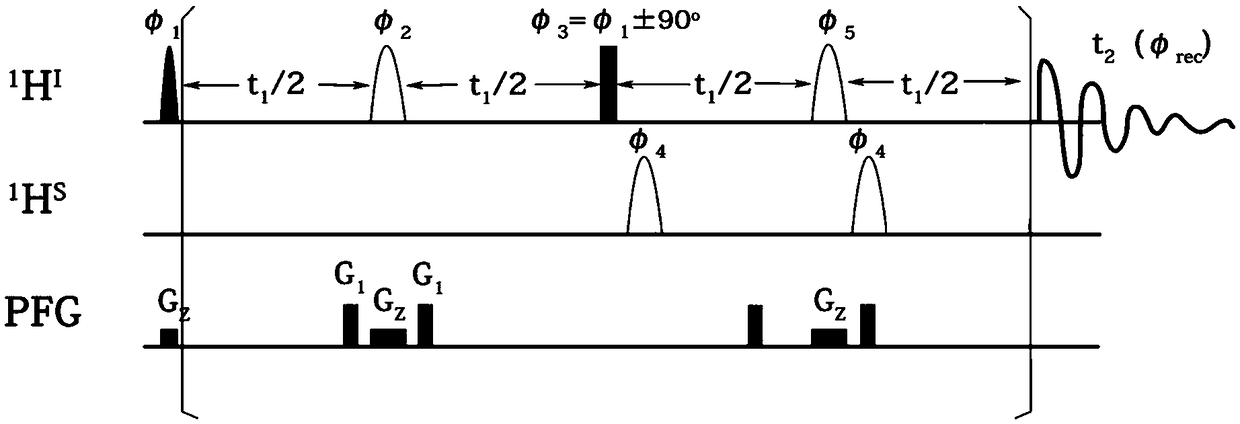
A NMR Multidimensional Spectroscopy Method for Measuring Specific Proton-Nuclear-Hydrogen Coupling Constants
InactiveCN109187613BStrong spectrogram signalAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientJ-coupling
The invention provides a nuclear magnetic resonance multi-dimensional spectrum method for measuring the hydrogen-hydrogen coupling constant of a specific hydrogen nucleus. The nuclear magnetic resonance multi-dimensional spectrum method comprises: applying a selective 90 DEG soft pulse while applying a Z-direction magnetic field gradient; applying a perfect echo module, and applying Z-direction magnetic field gradients with the same strength and the same direction on both sides of the selective 180 DEG soft pulse of the perfect echo; adding the 180 DEG soft pulse of an S nucleus after the first t1 / 2 evolution time in the second echo of the perfect echo so as to retain the J-coupling information of the S nucleus; adding the 180 DEG soft pulse of the S nucleus after the second t1 / 2 to compensate phase distortion; respectively applying the 180 DEG soft pulse of the selective S nucleus before the two t1 / 2 evolution times in the second echo so as to obtain a R type sequence corresponding toa N type sequence; and finally carrying out addition on a N type spectrum and a R type spectrum inverted along indirect dimension to obtain a phase-sensitive two-dimensional spectrum, and obtaining the corresponding J-coupling constant by measuring from the splitting of the peak in the indirect dimension.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com