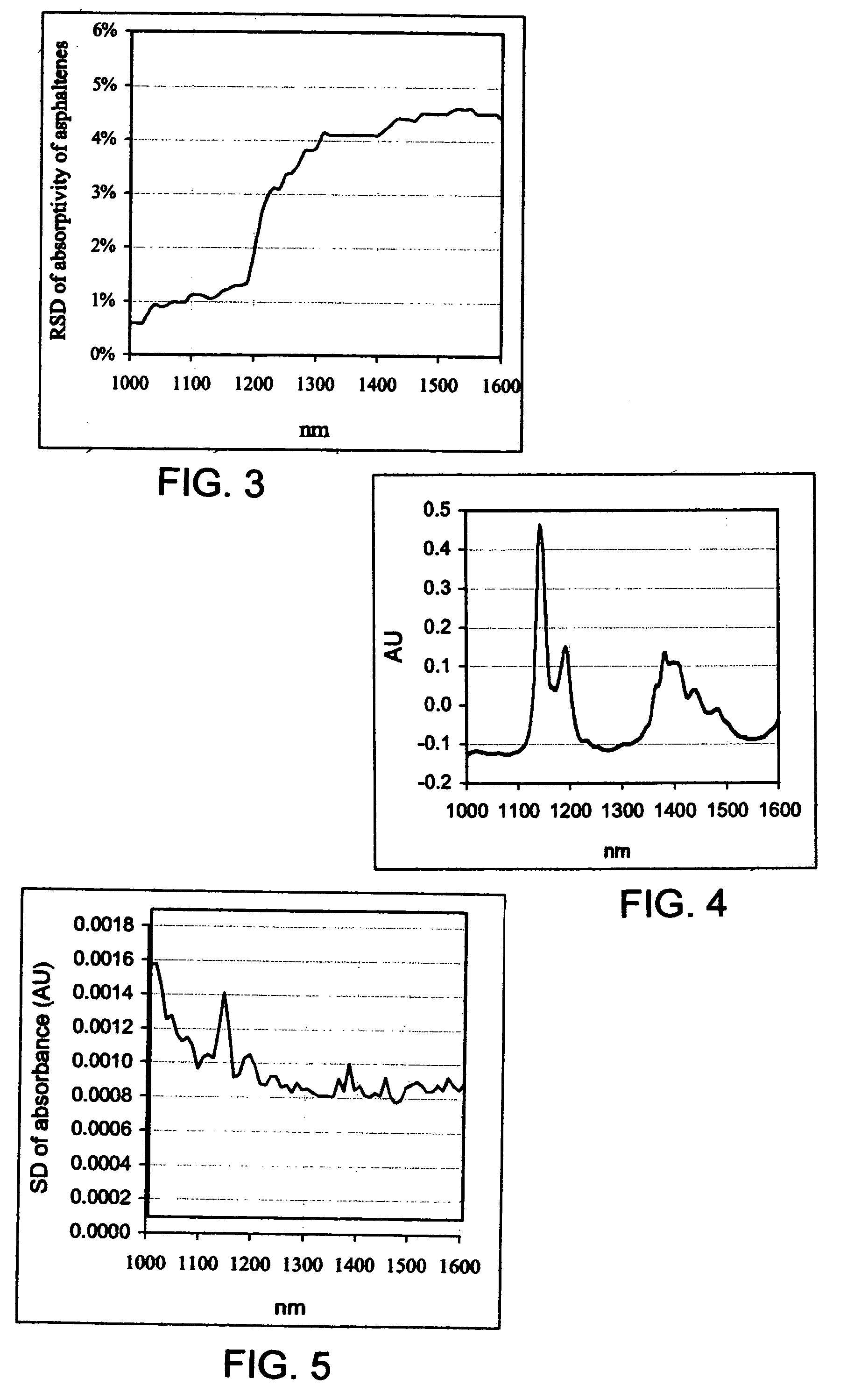
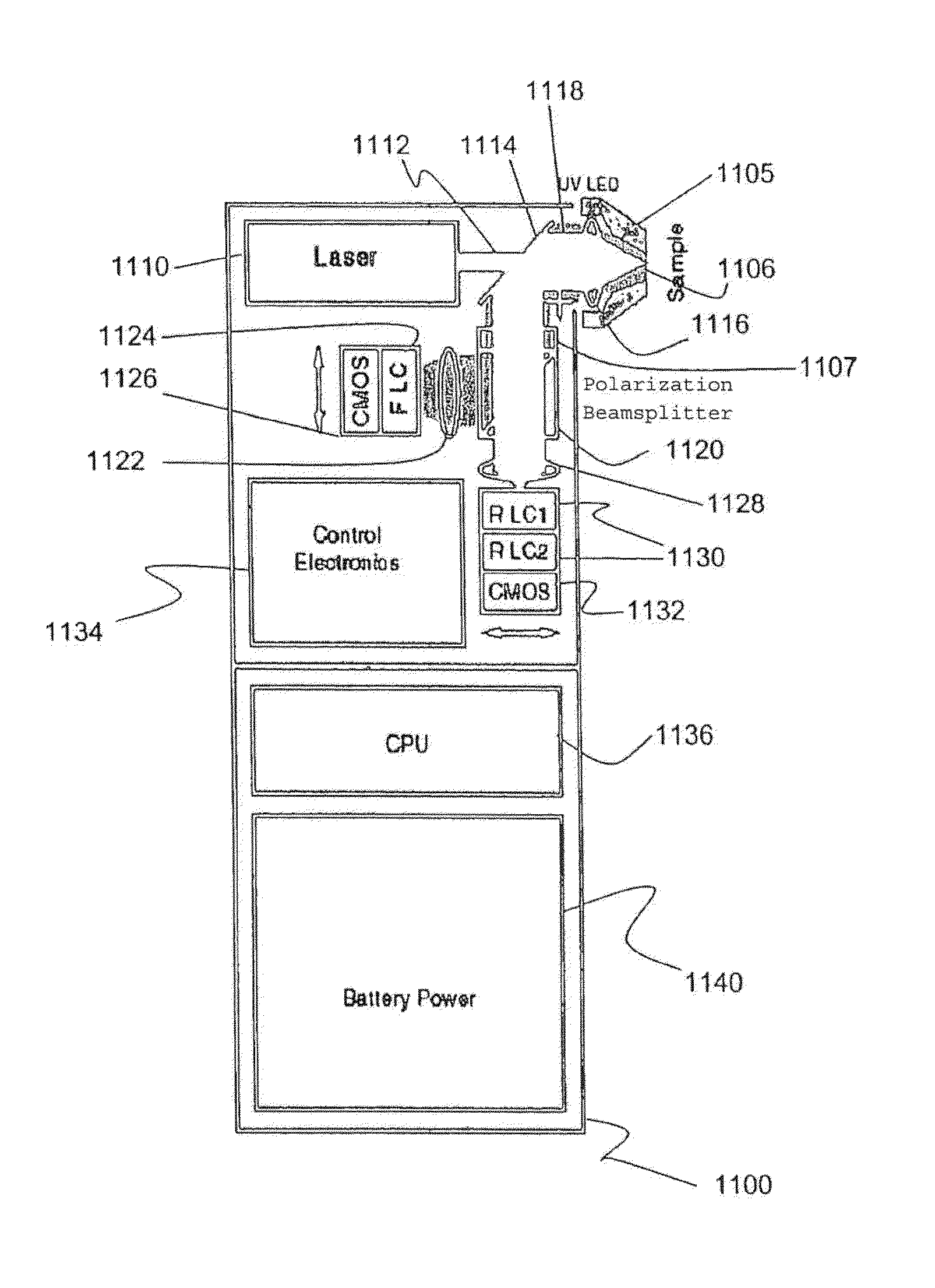
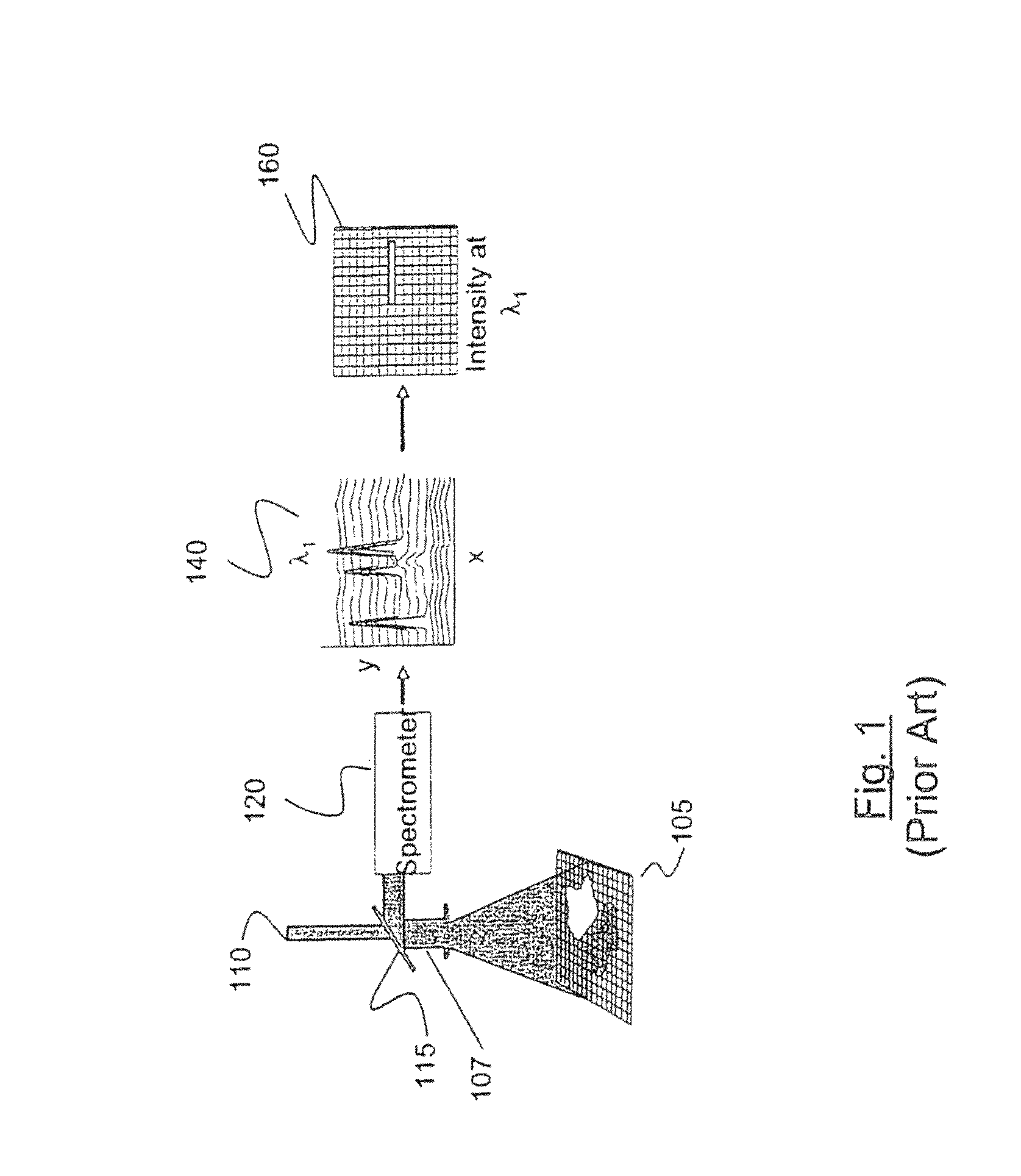
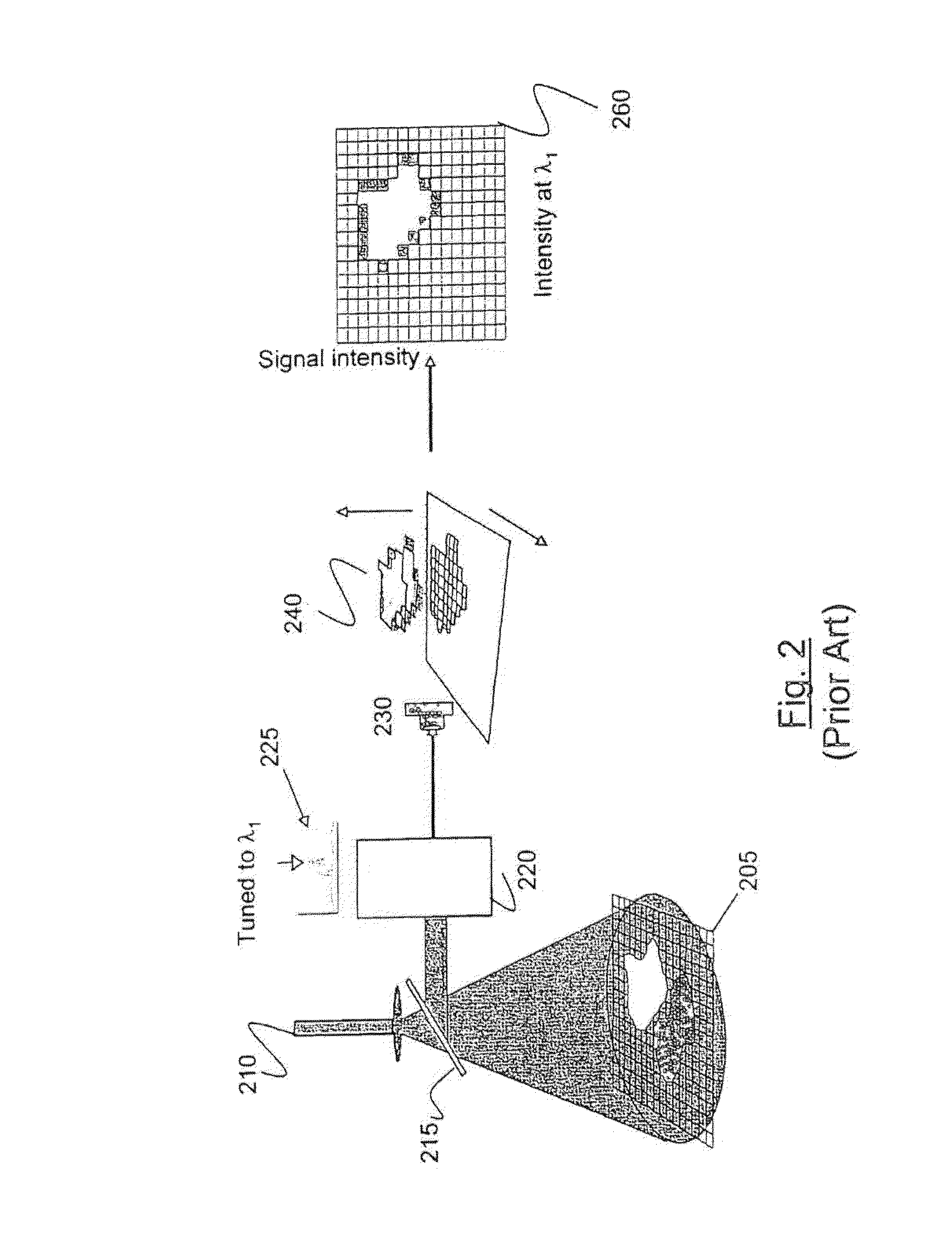
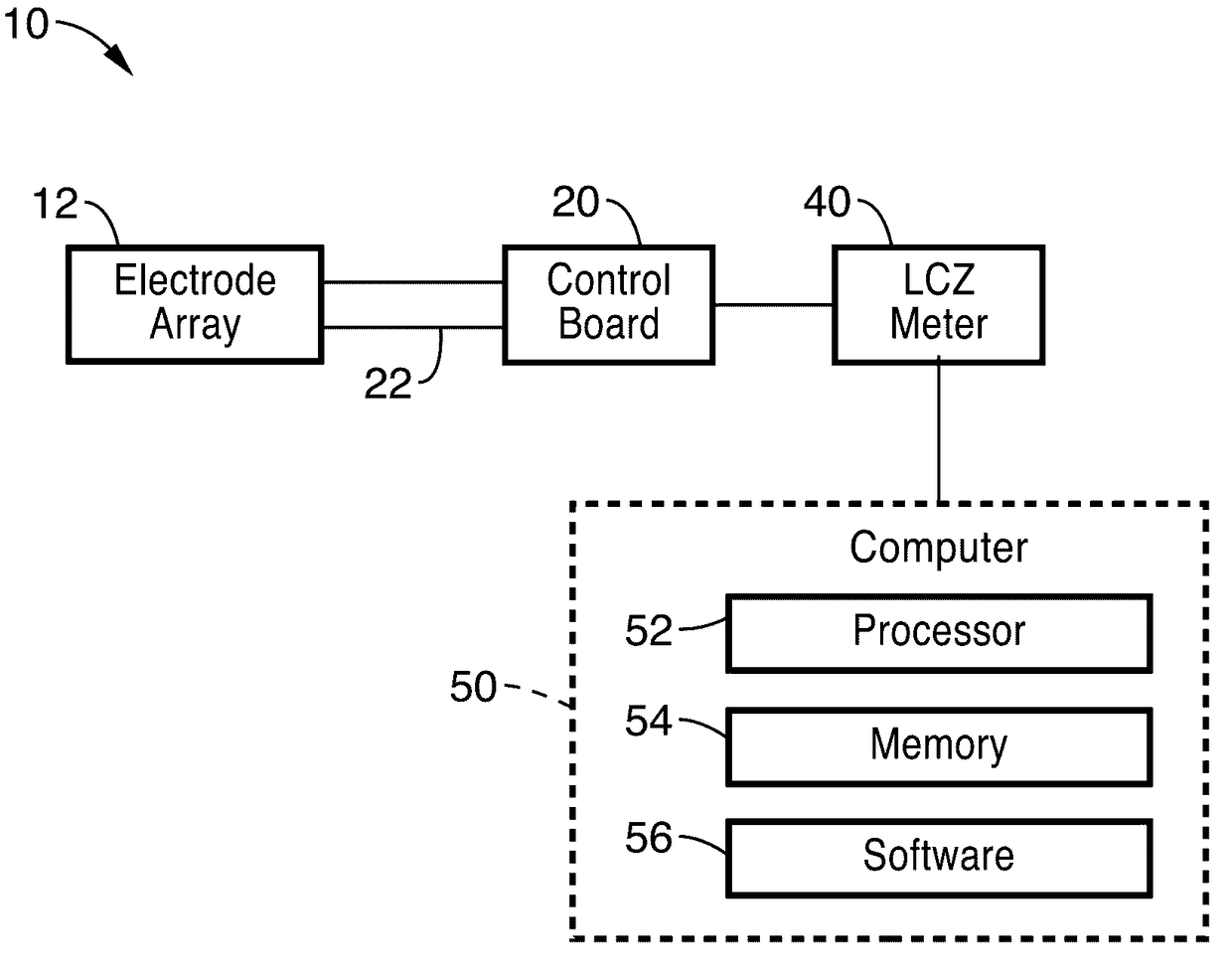
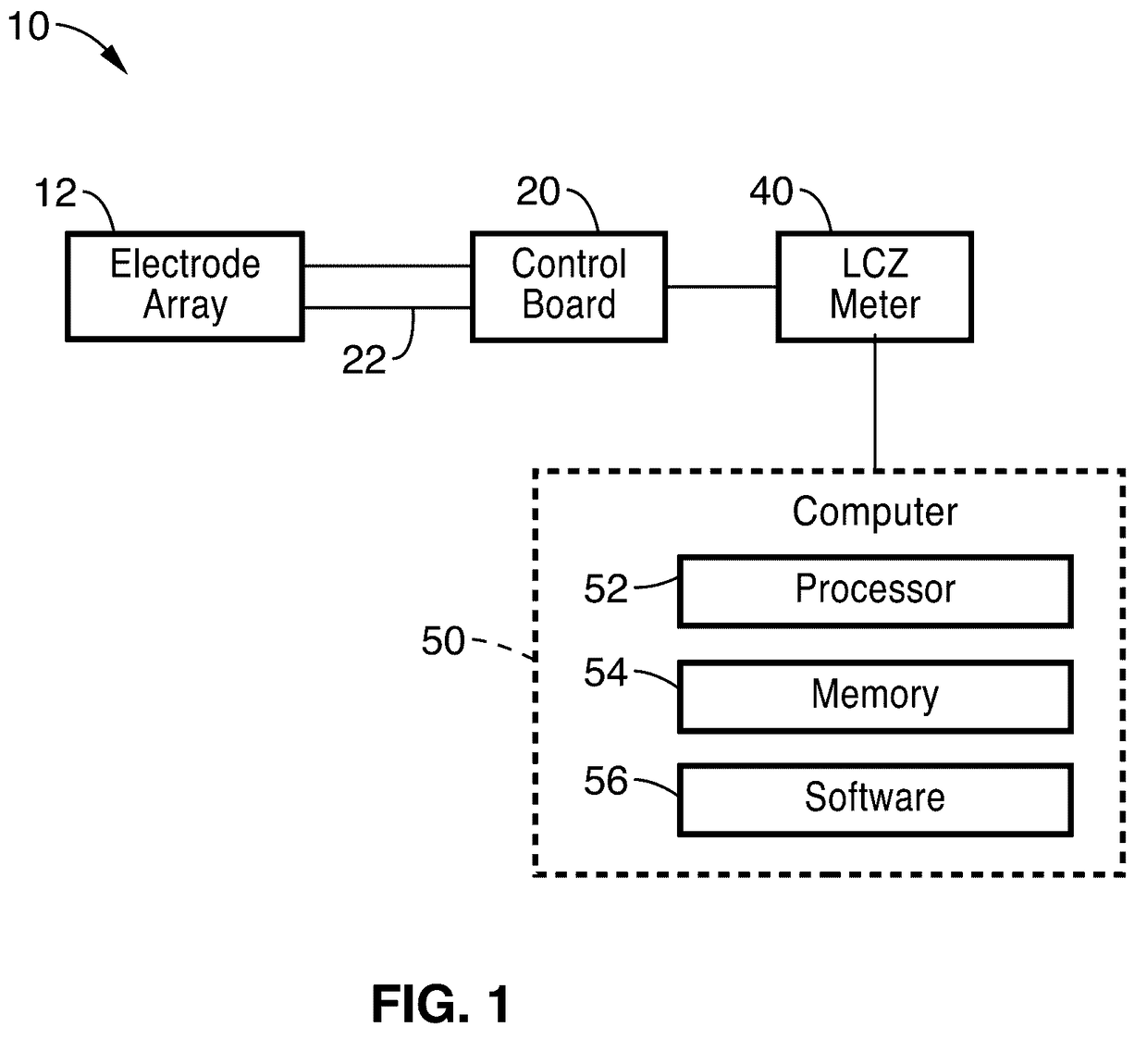
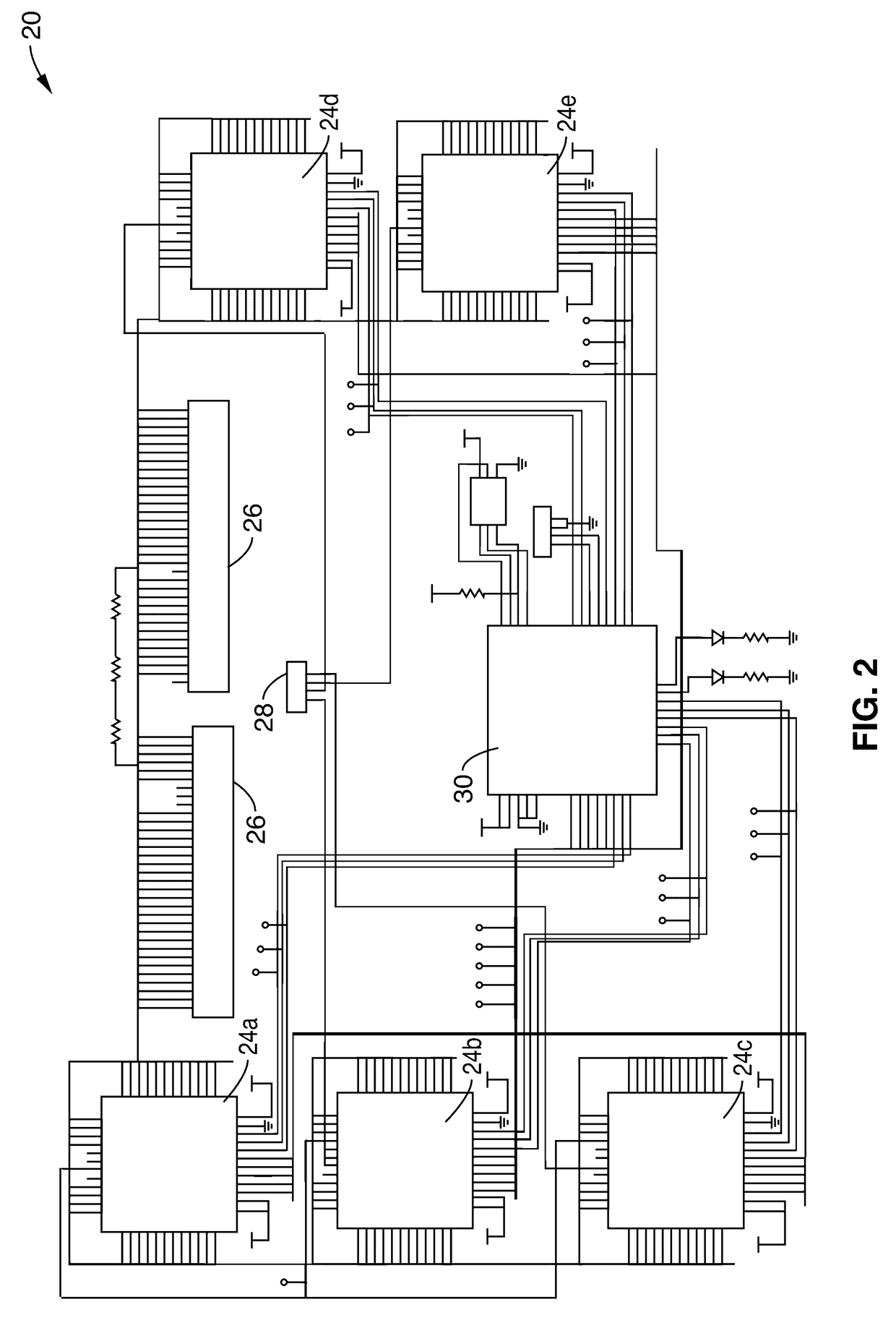
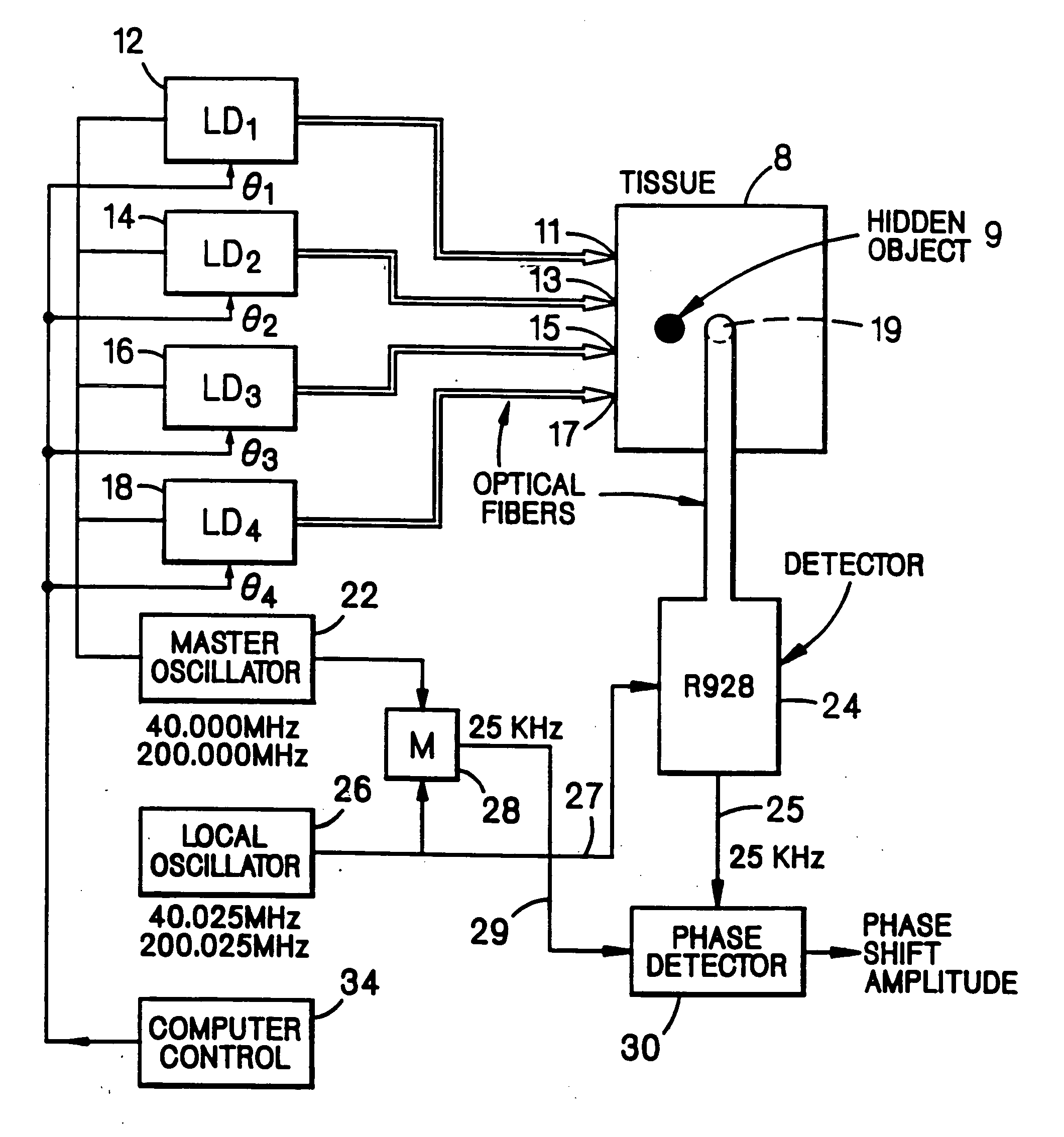
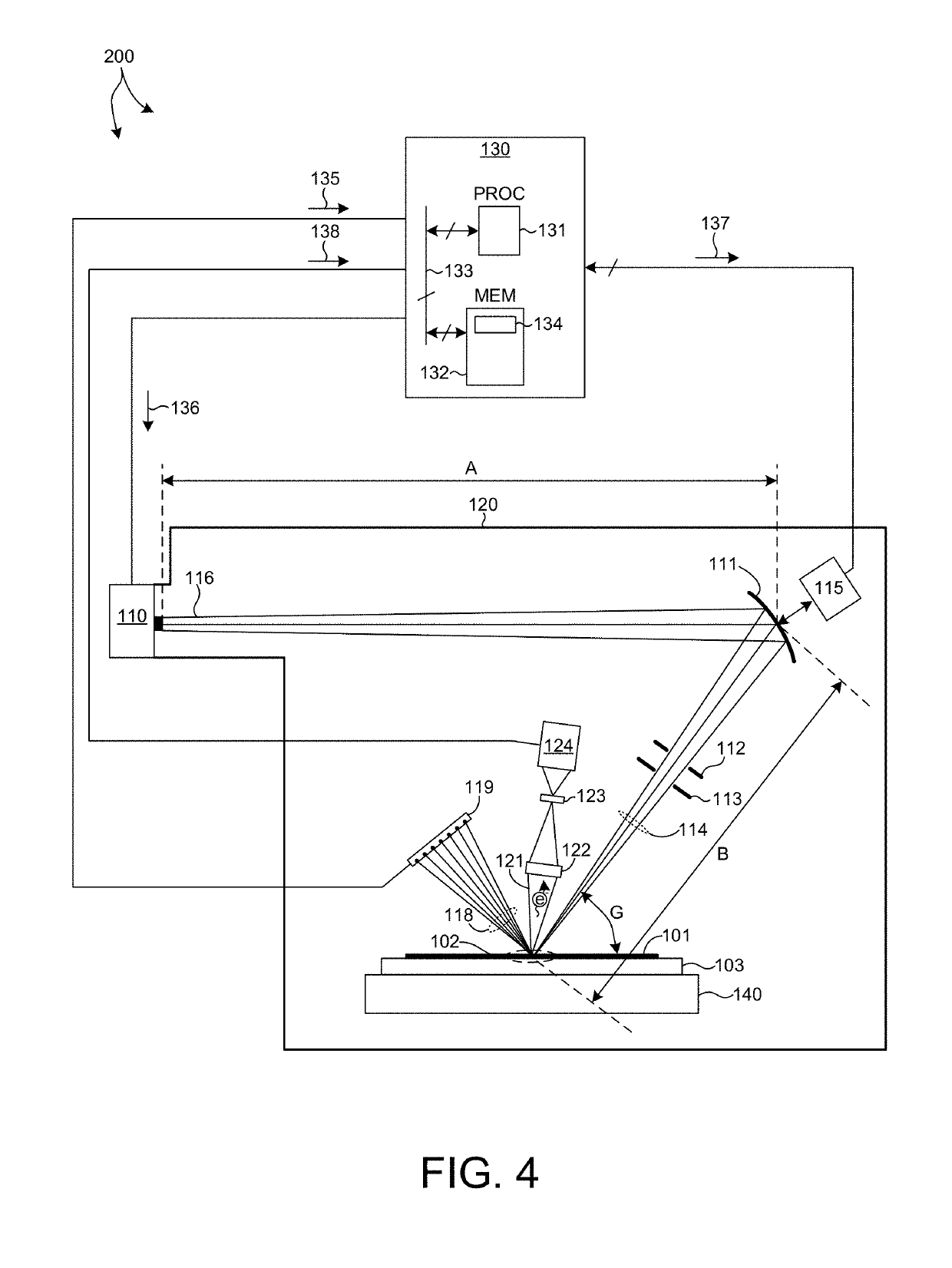
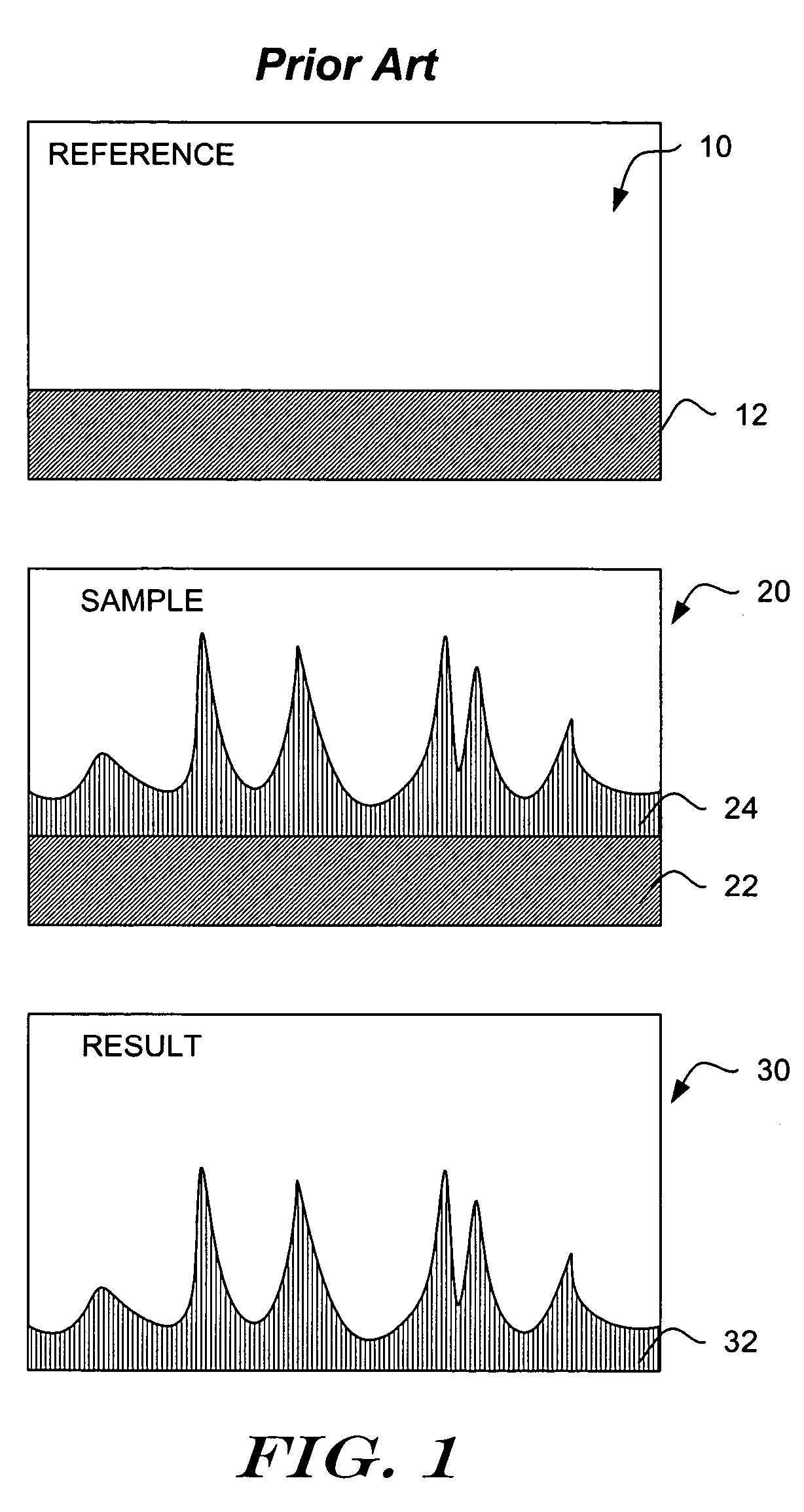
Patents
Literature
254 results about "Spectroscopy methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
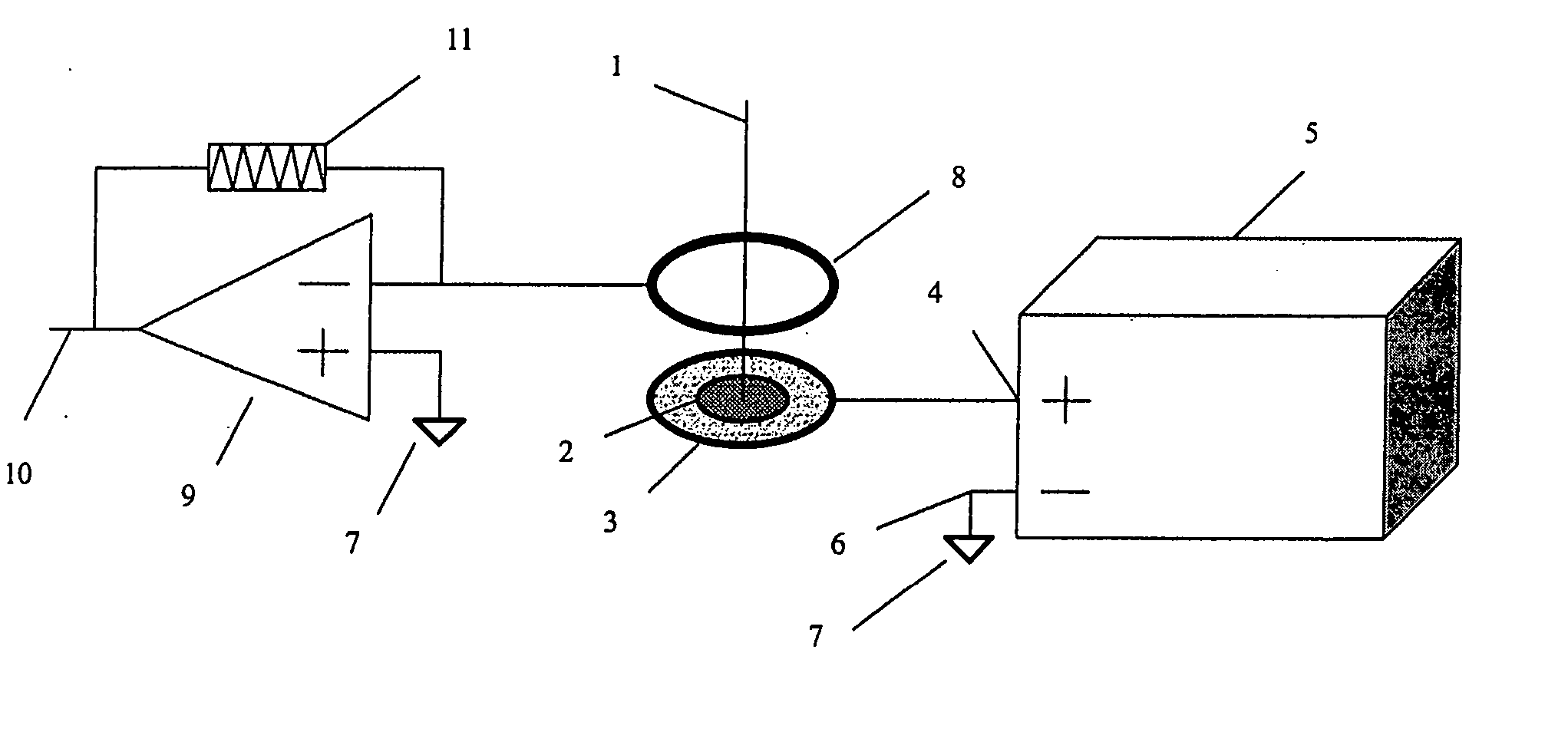
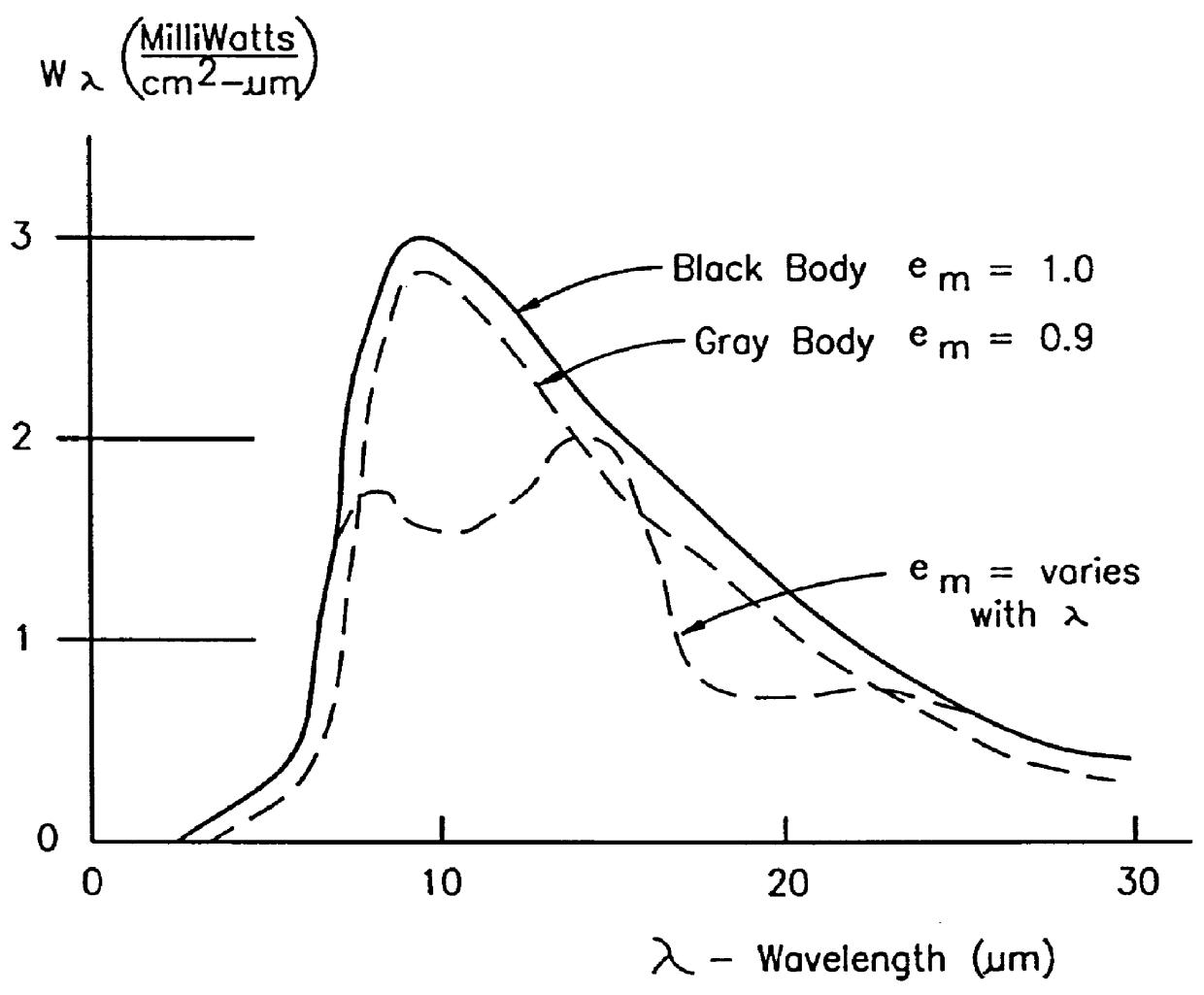
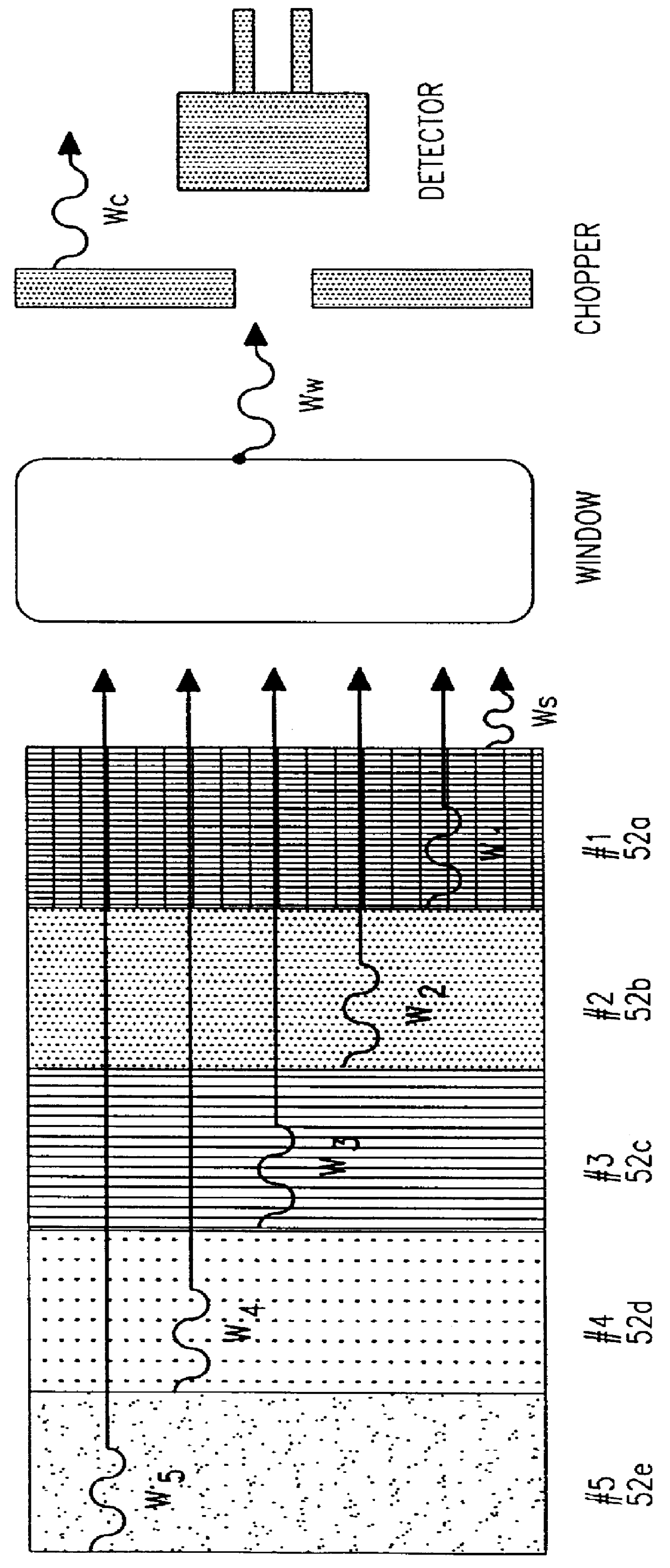
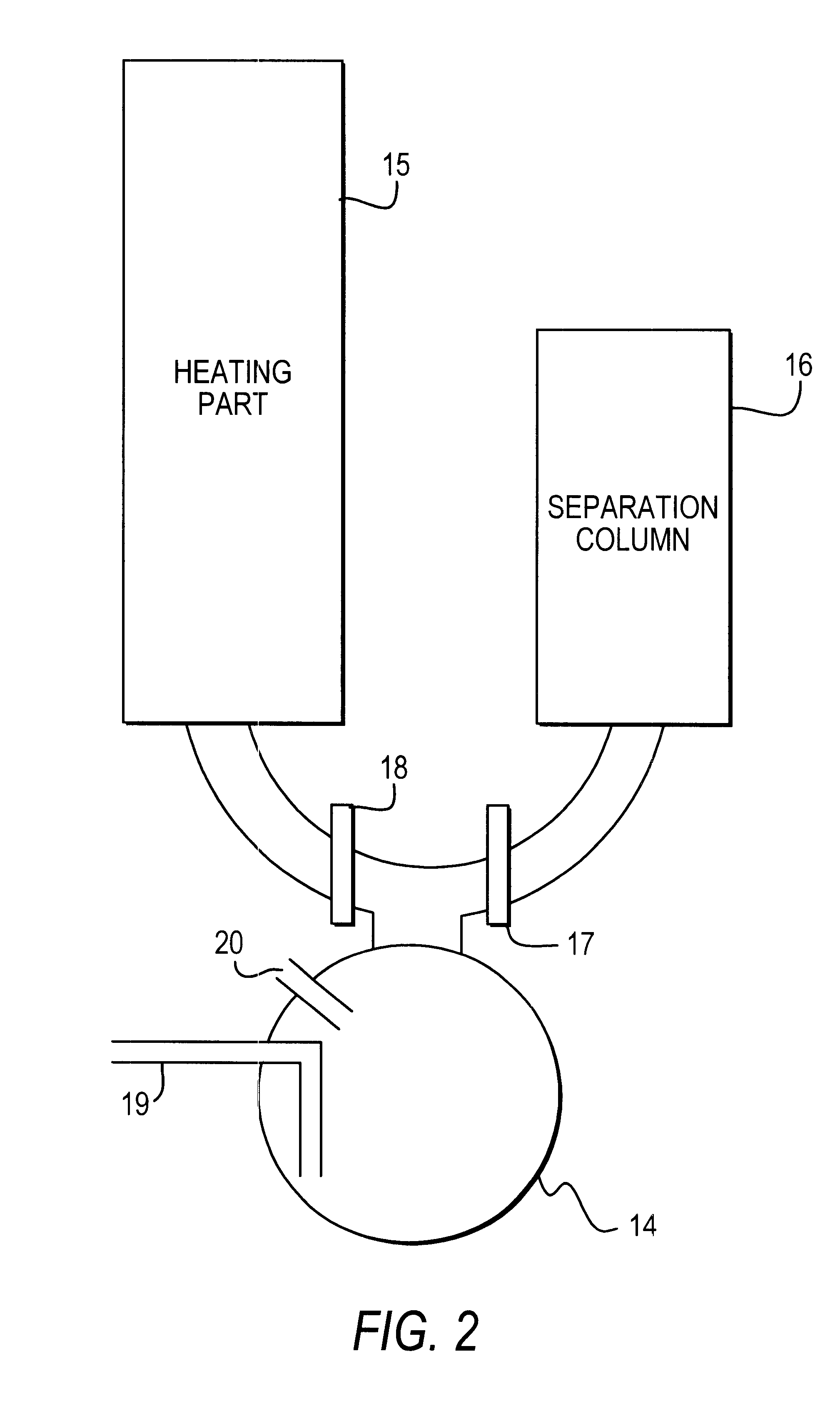
Spectroscopic methods. A common spectroscopic method for analysis is Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, where chemical bonds can be detected through their characteristic infrared absorption frequencies or wavelengths.
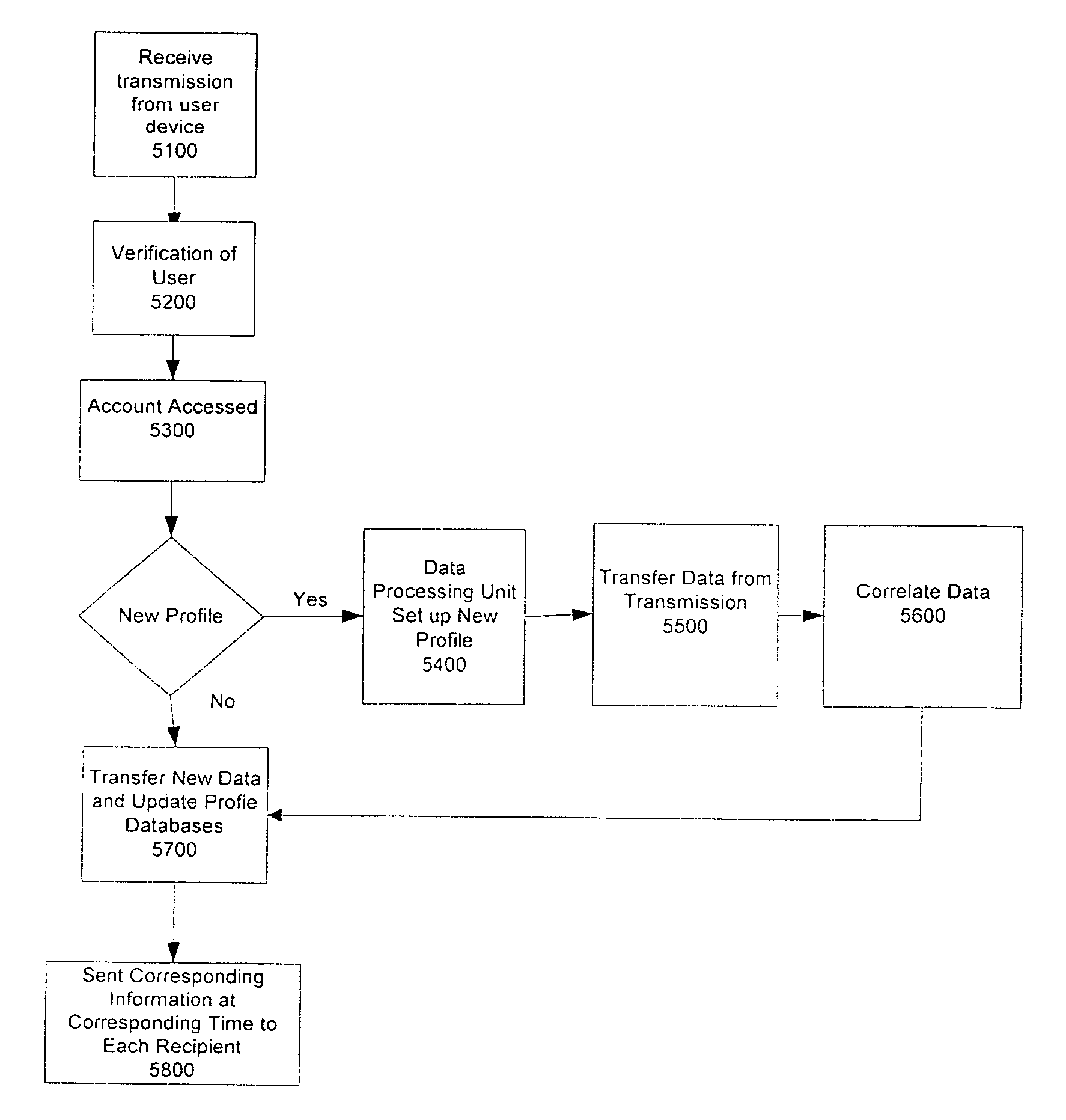
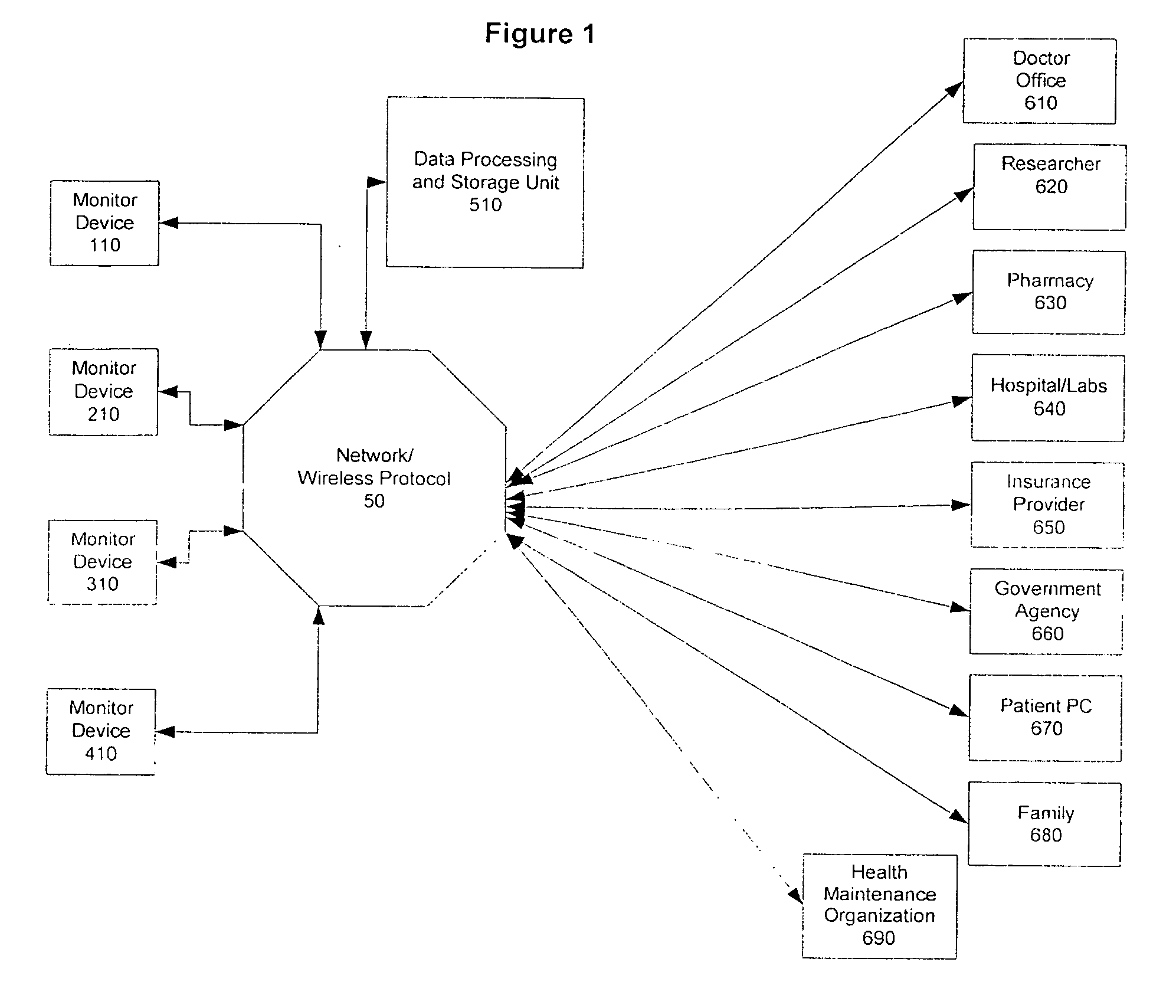
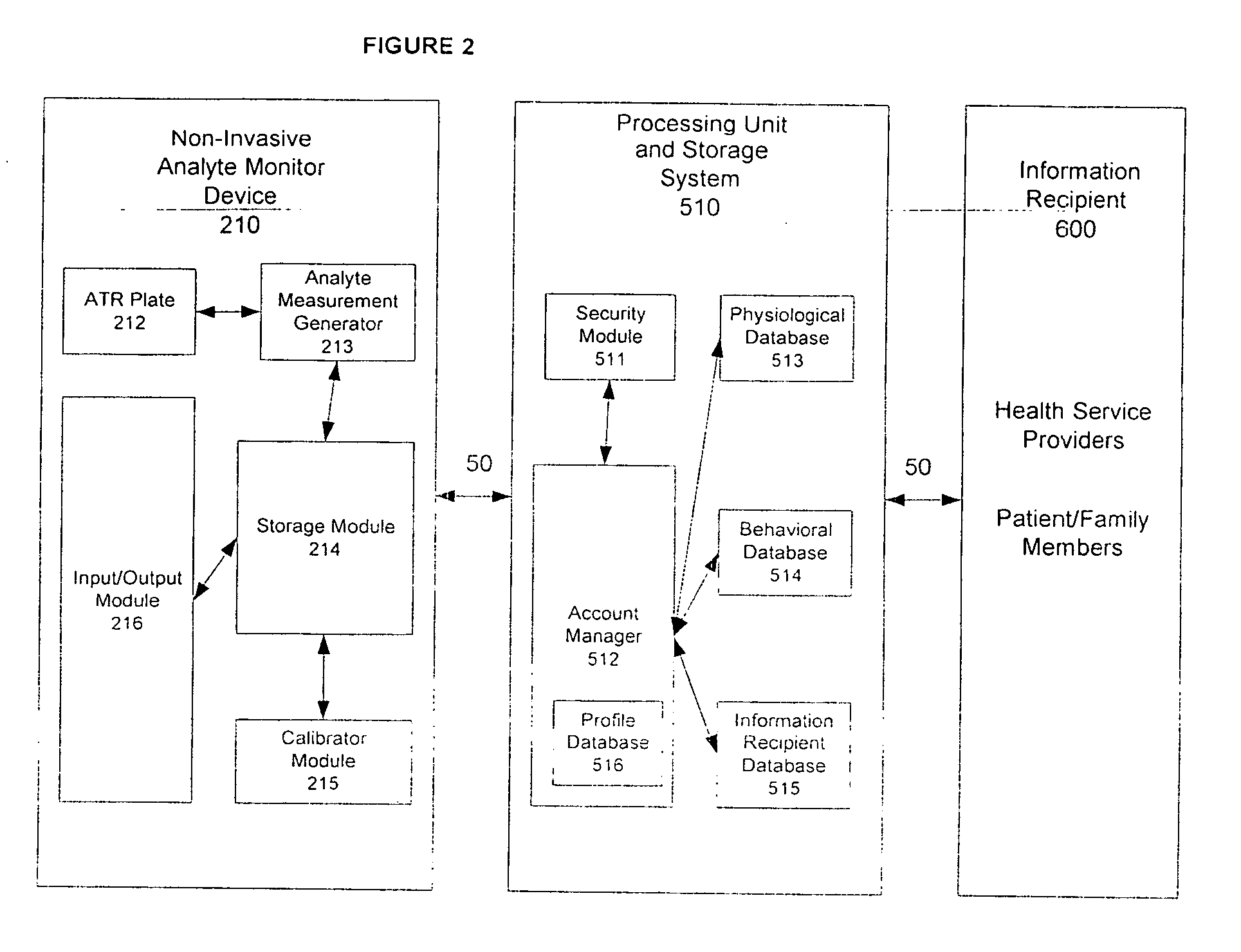
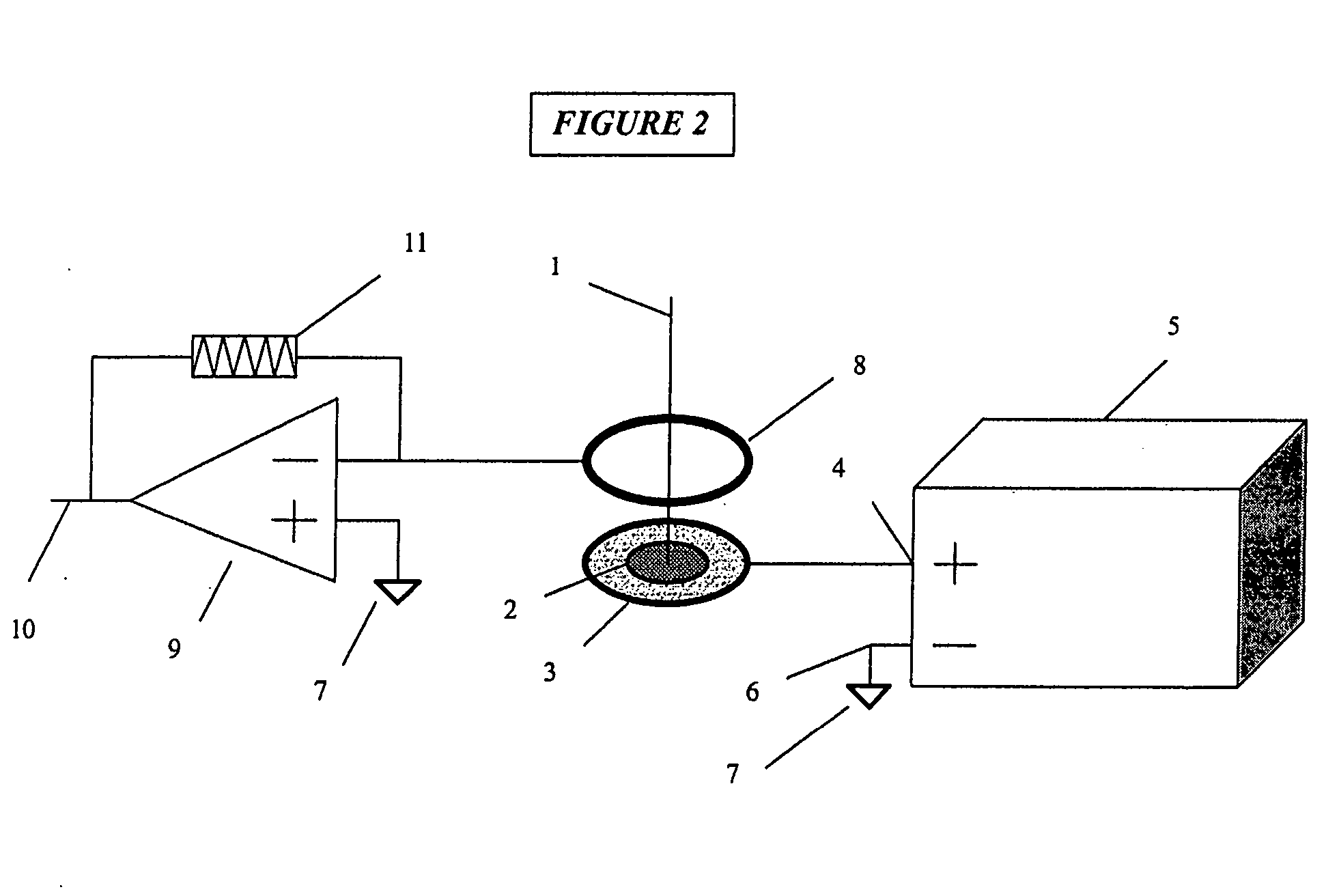
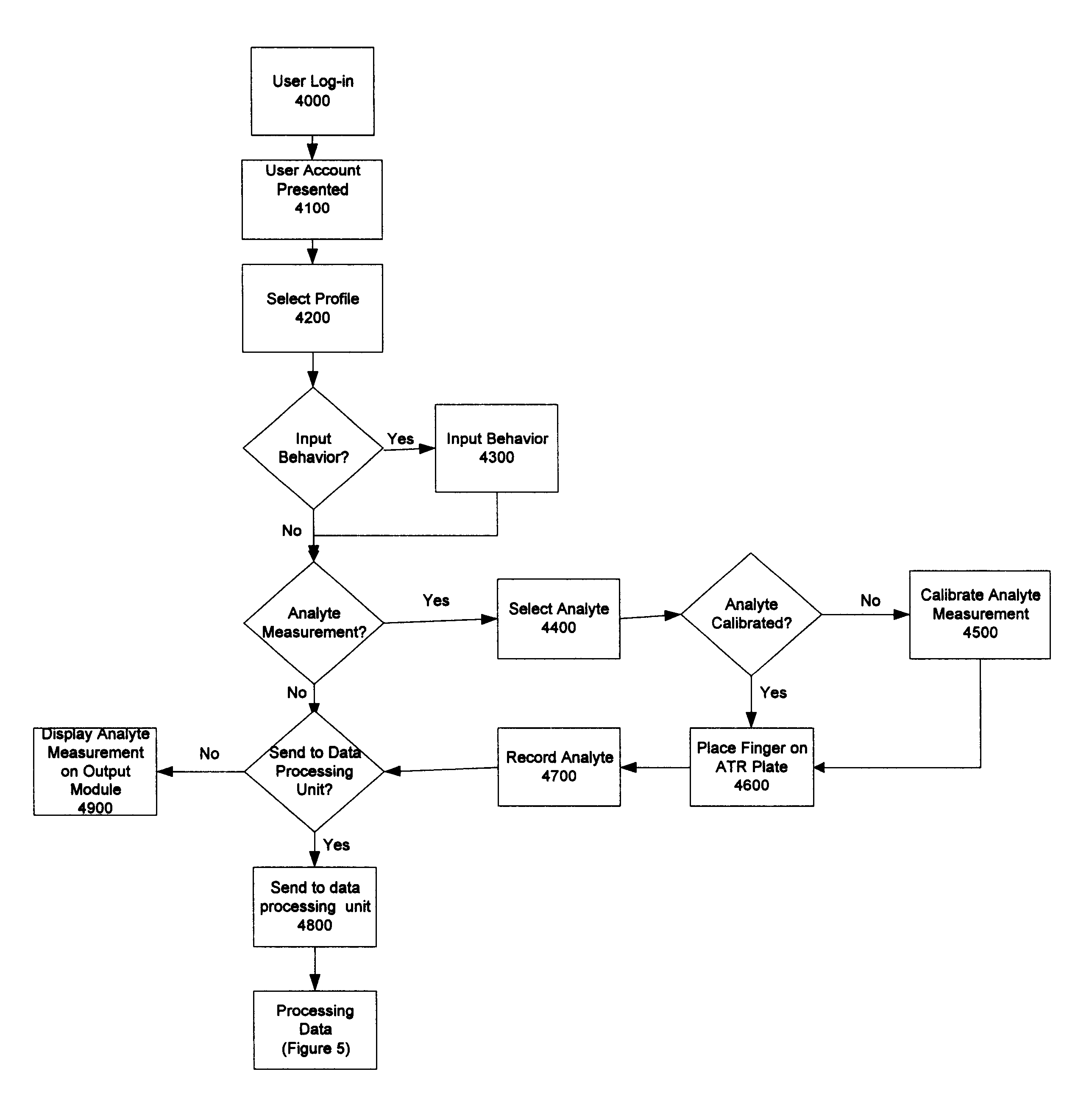
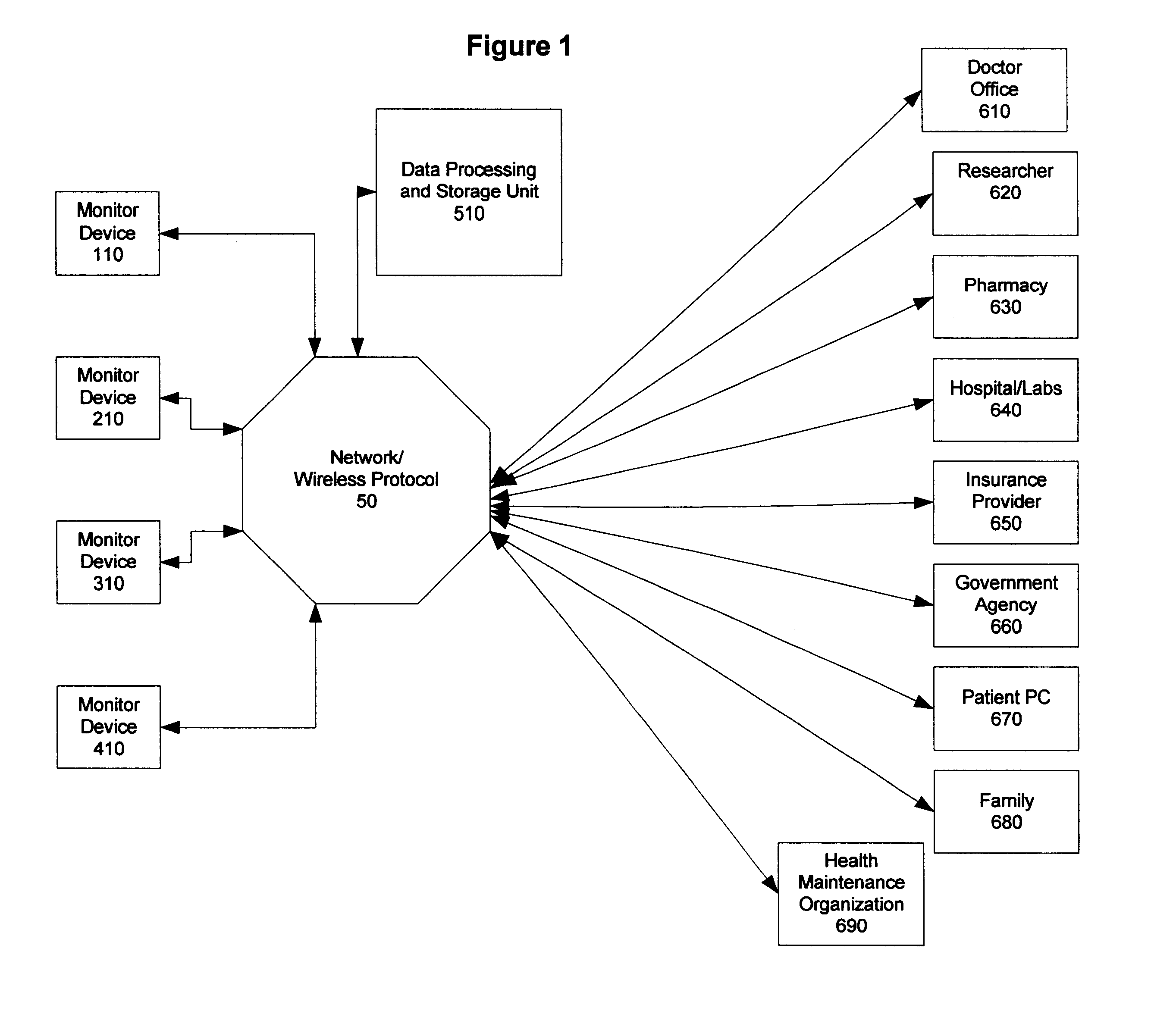
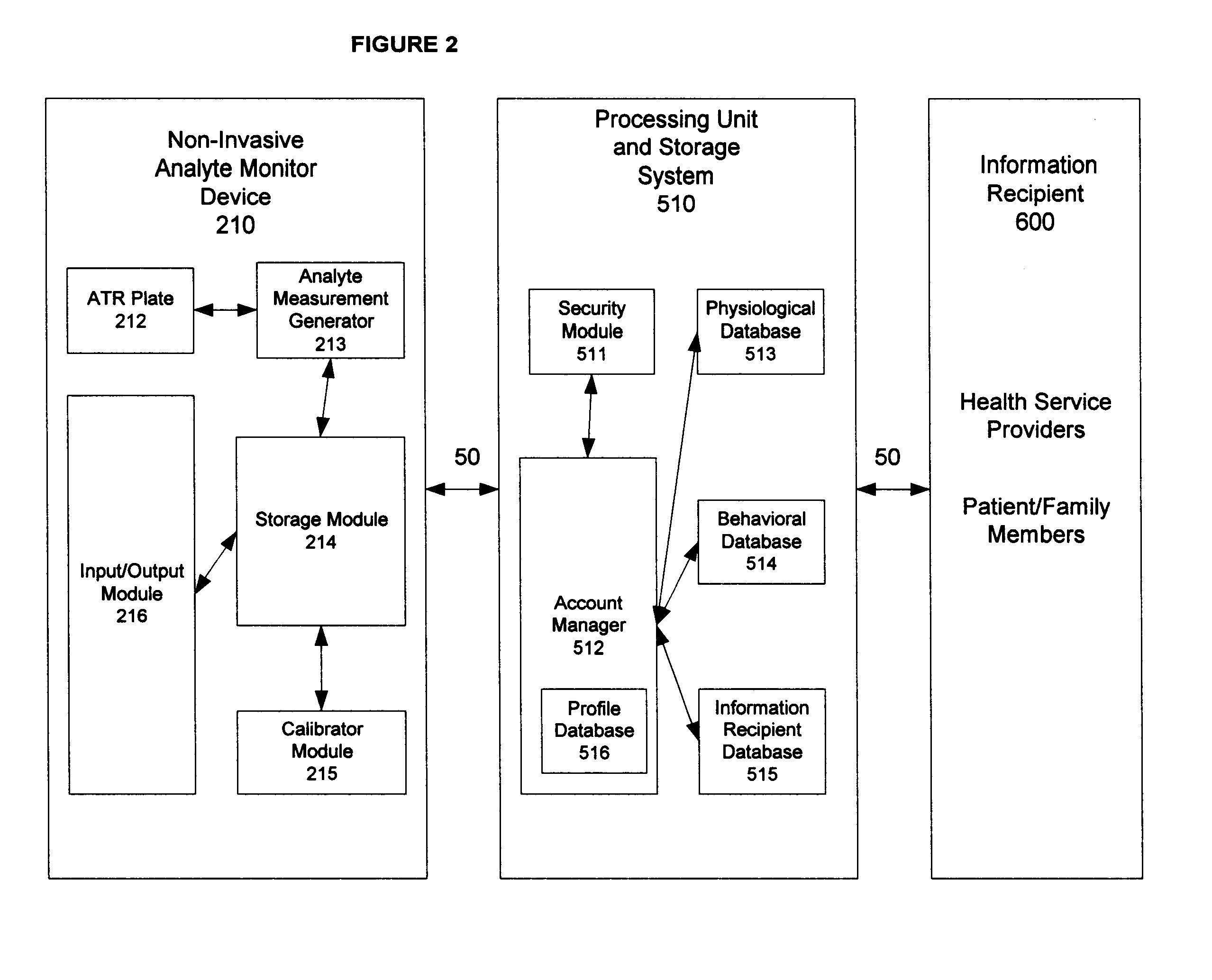
Method and system of monitoring a patient
A patient monitor system implemented by a service provider for users via recording a patients analytes measurements by an attenuated total reflection (ATR) infrared total spectroscopy method. The system comprises an input module that provides a non-invasive method in measuring analytes in a patient, such as a measurement of the glucose level and other blood analytes. The measurement is shared among a plurality of output devices such as computers, personal digital assistants (PDAs), cellular phones, and pagers that are stationed or held by various users such as doctors, patients, researchers, pharmacies, labs, and health insurers. In addition behavioral attributes are recorded and correlated with the analytes measurements to generate a profile. The profile is selectively sent to output devices based on the user profile corresponding to the output device. Also, access to the profile is monitored by a security module that encrypts the profile to prevent access by un-authorized users.
Owner:VIVOMEDICAL INC
Laser ablation feedback spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050061779A1Precise depth controlReduce the amount requiredWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusMass spectrometryAblation plasma
Methods, for use with a laser ablation or drilling process, which achieve depth-controlled removal of composite-layered work-piece material by real-time feedback of ablation plasma spectral features. The methods employ the use of electric, magnetic or combined fields in the region of the laser ablation plume to direct the ablated material. Specifically, the electric, magnetic or combined fields cause the ablated material to be widely dispersed, concentrated in a target region, or accelerated along a selected axis for optical or physical sampling, analysis and laser feedback control. The methods may be used with any laser drilling, welding or marking process and are particularly applicable to laser micro-machining. The described methods may be effectively used with ferrous and non-ferrous metals and non-metallic work-pieces. The two primary benefits of these methods are the ability to drill or ablate to a controlled depth, and to provide controlled removal of ablation debris from the ablation site. An ancillary benefit of the described methods is that they facilitate ablated materials analysis and characterization by optical and / or mass spectroscopy.
Owner:BLUMENFELD WALTER +2
Method and apparatus for performing rapid isotopic analysis via laser spectroscopy
InactiveUS6888127B2Accurate and preciseAccurate and Precise MeasurementsRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsIsotopeLaser beams
Method and apparatus for providing real-time data indicative of the isotopic composition of formation fluids during drilling. The method includes the steps of: (a) providing a reference fluid having a known isotopic composition in a reference cell; (b) capturing a sample of formation; (c) providing at least one laser beam; (e) passing a beam through the reference fluid, measuring the reference-measurement beam before and after it passes through the reference fluid; (f) and passing a beam through the sample, measuring the beam before and after it passes through the sample, and calculating a first isotope concentration from those measurements. The measurements can provide information relating to the carbon isotopic composition of individual compounds in hydrocarbon gas mixtures, with the individual compounds including methane, ethane, propane, iso- or normal butane, or iso- or normal pentane.
Owner:CALEB BRETT USA
Method and system of monitoring a patient
Owner:VIVOMEDICAL INC
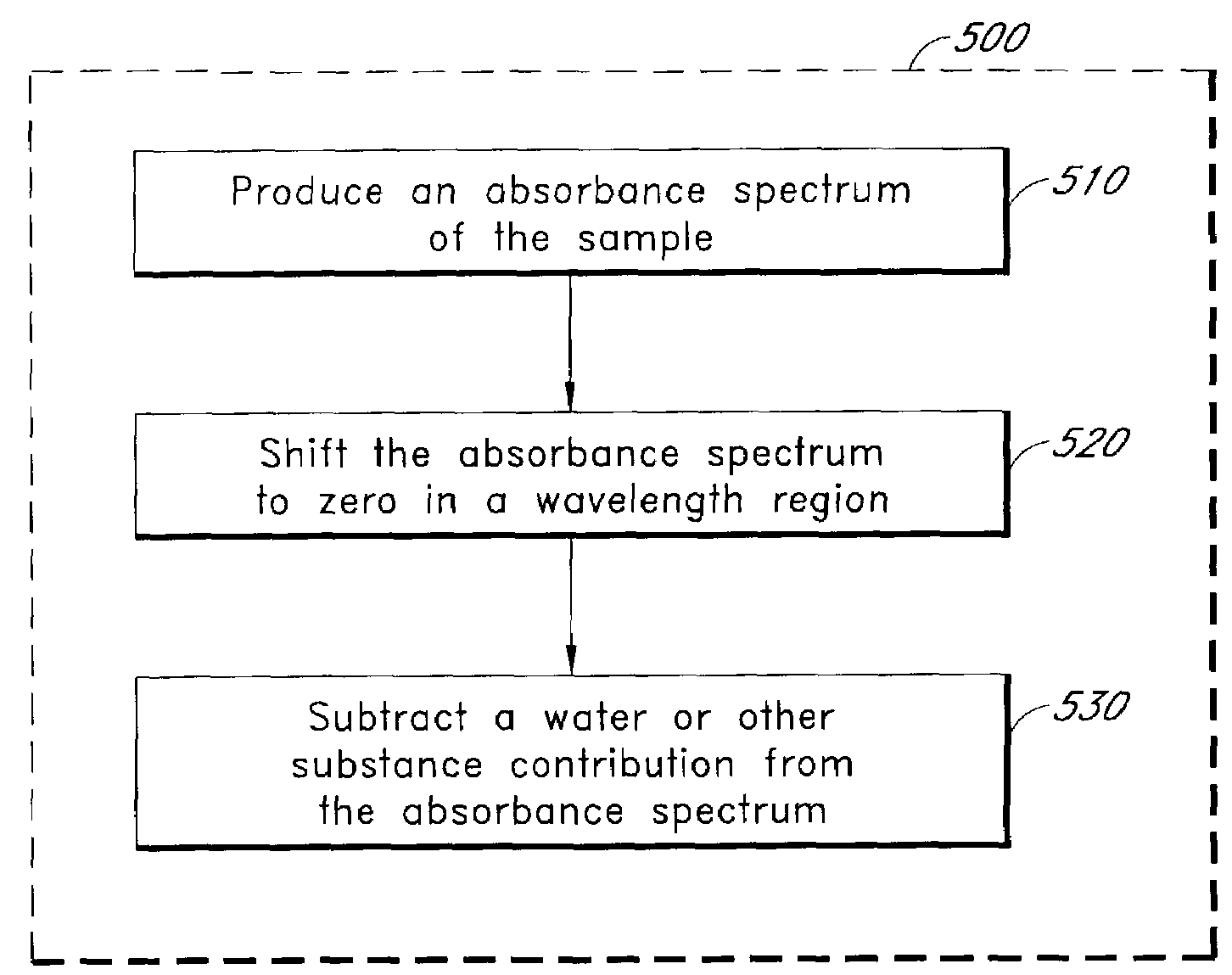
Pathlength-independent methods for optically determining material composition
ActiveUS7009180B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChemical compositionAnalyte
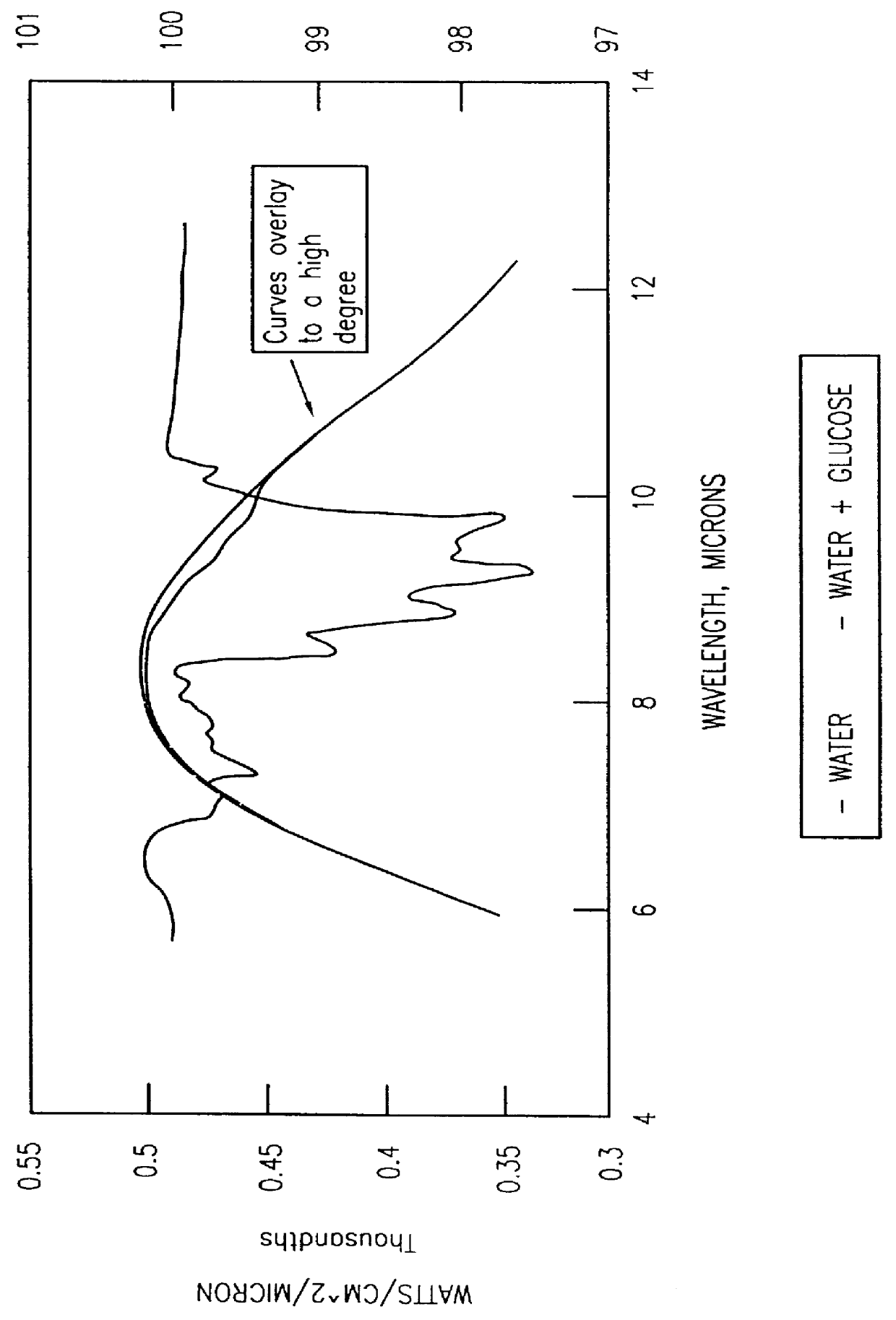
A method uses spectroscopy to determine an analyte concentration in a sample. The method includes producing an absorbance spectrum of the sample. The method further includes shifting the absorbance spectrum to zero in a wavelength region. The method further includes subtracting a water or other substance contribution from the absorbance spectrum.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Spectrometer and method of spectroscopy
InactiveUS6104029AStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersOptical spectrometerEnergy analyser
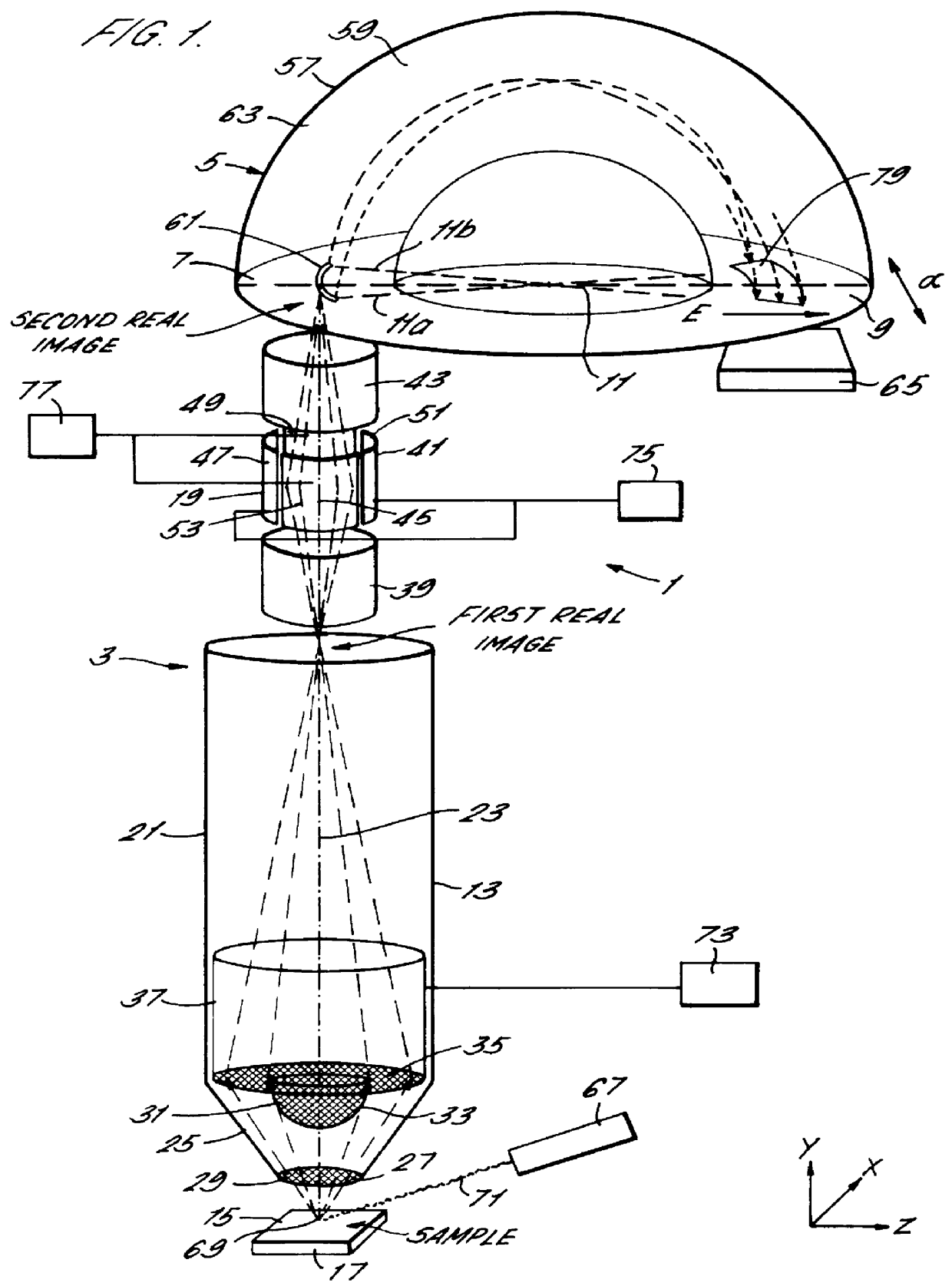
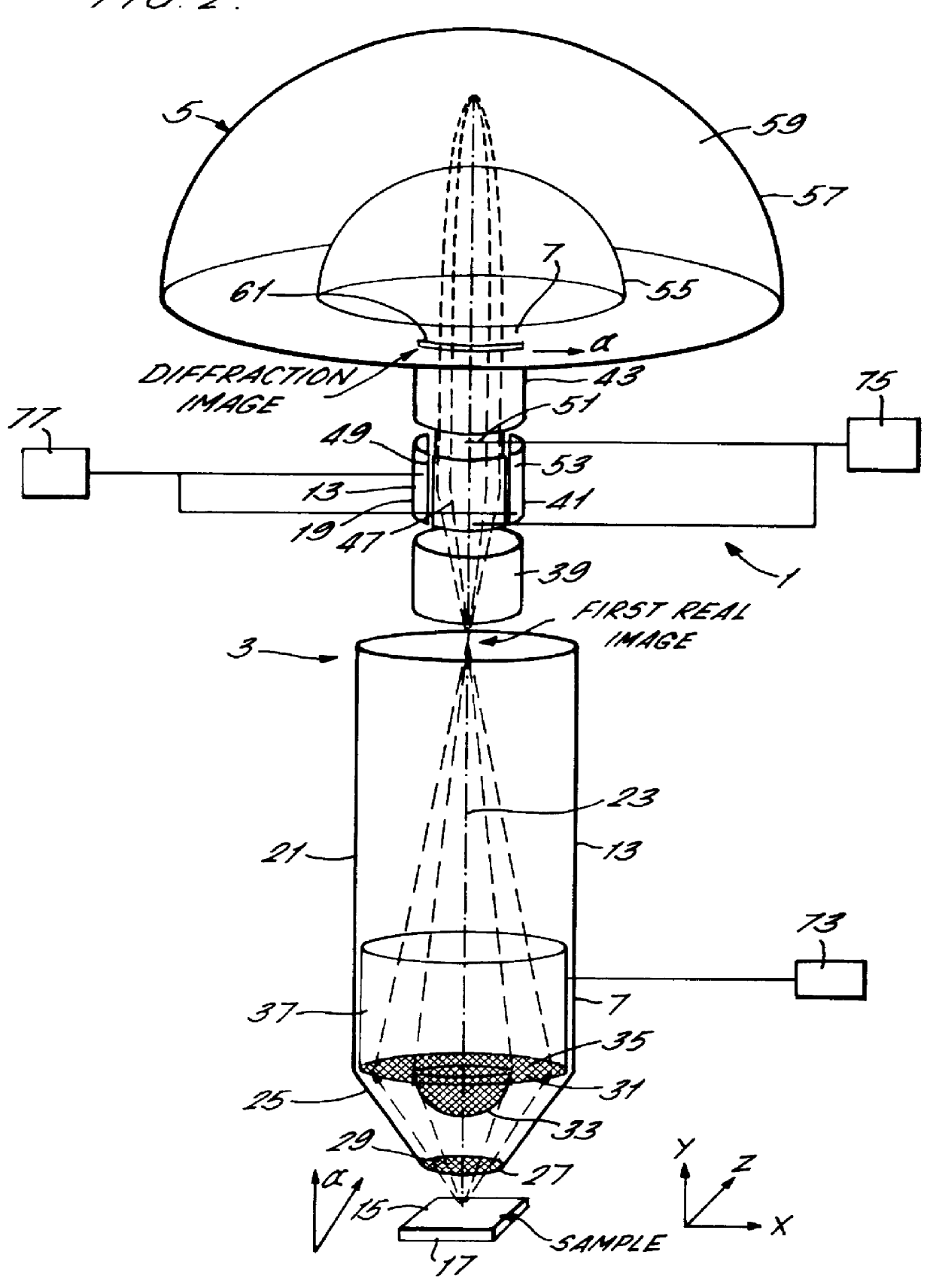
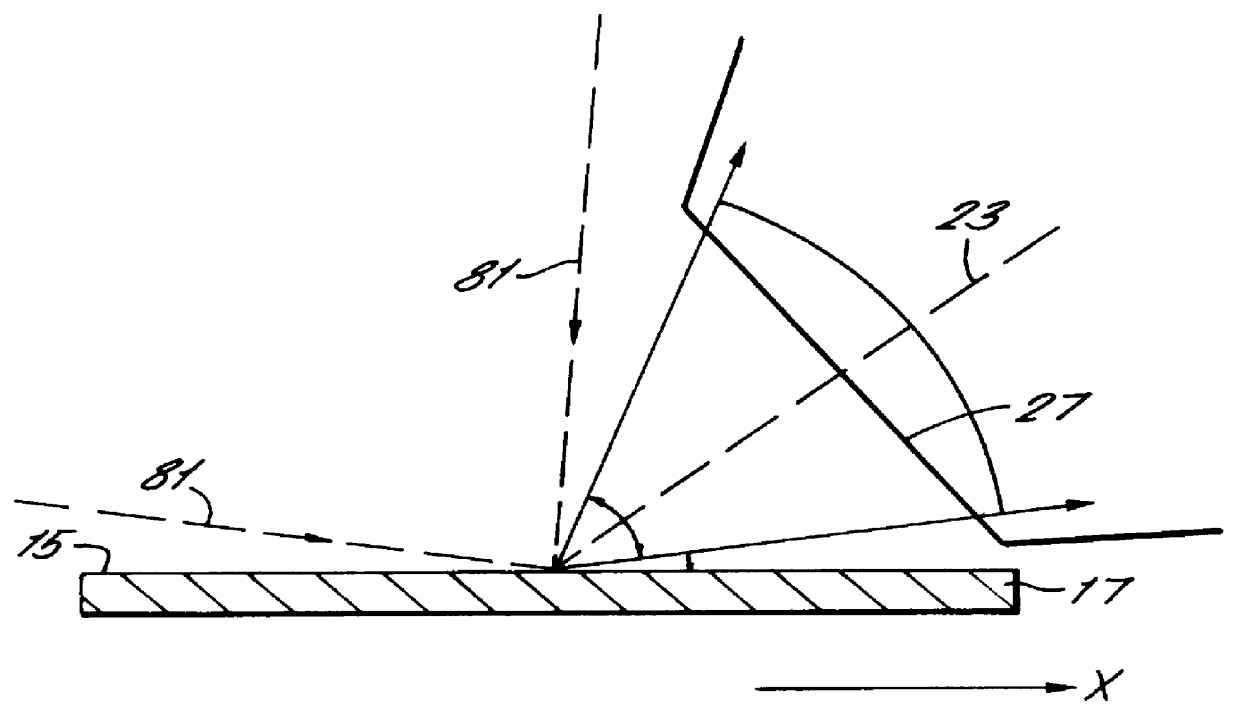
A spectrometer and method of spectroscopy are provided for surface analysis. The spectrometer comprises an energy analyser for analysing the energies of charged particles liberated from a sample, a lens arranged to project a diffraction image of the analysis area at the image plane of the lens and a detector for detecting the charged particles. The analyser and lens are arranged to generate an image at the detector in which the charged particles are distributed along a first direction according to their emission angles and are distributed along another direction according to their energies. The detector is arranged to detect the distribution of charged particles in the image along the first direction to provide angle resolved energy spectra.
Owner:VG SYST
Method and apparatus for performing rapid isotopic analysis via laser spectroscopy
Method and apparatus for providing real-time data indicative of the isotopic composition of formation fluids during drilling. The method includes the steps of: (a) providing a reference fluid having a known isotopic composition in a reference cell; (b) capturing a sample of formation; (c) providing at least one laser beam; (e) passing a beam through the reference fluid, measuring the reference-measurement beam before and after it passes through the reference fluid; (f) and passing a beam through the sample, measuring the beam before and after it passes through the sample, and calculating a first isotope concentration from those measurements. The measurements can provide information relating to the carbon isotopic composition of individual compounds in hydrocarbon gas mixtures, with the individual compounds including methane, ethane, propane, iso- or normal butane, or iso- or normal pentane.
Owner:CALEB BRETT USA
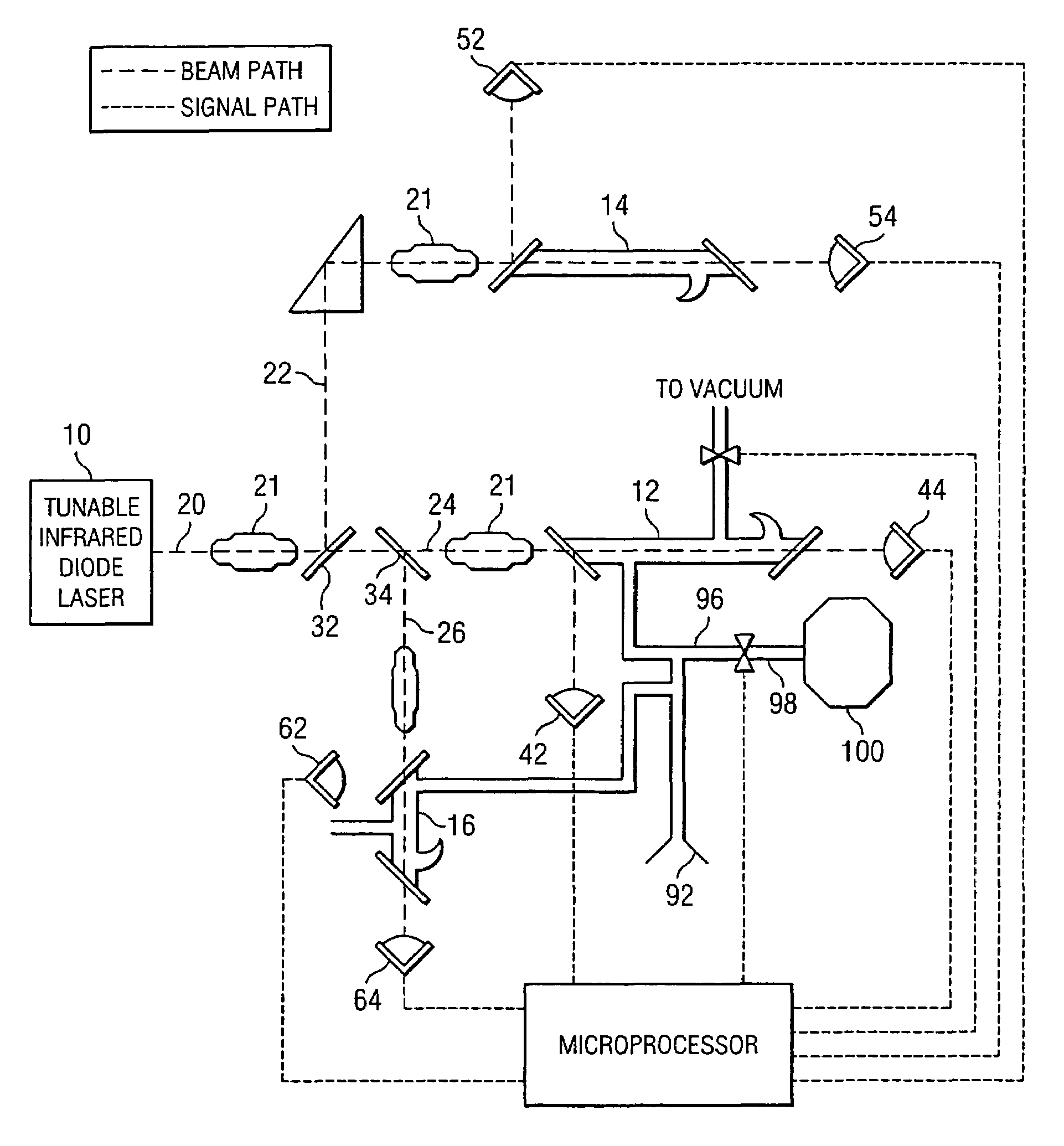
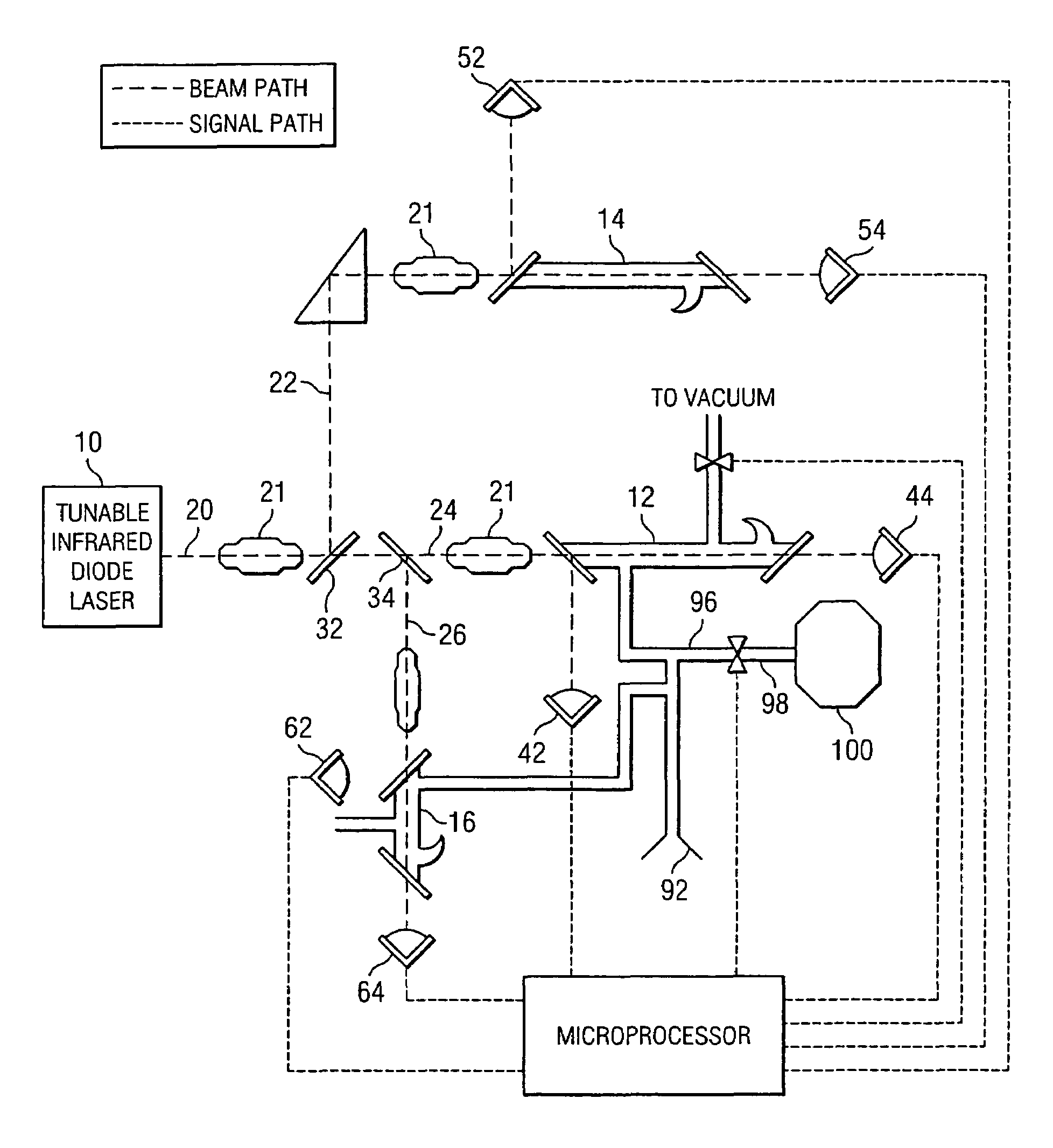
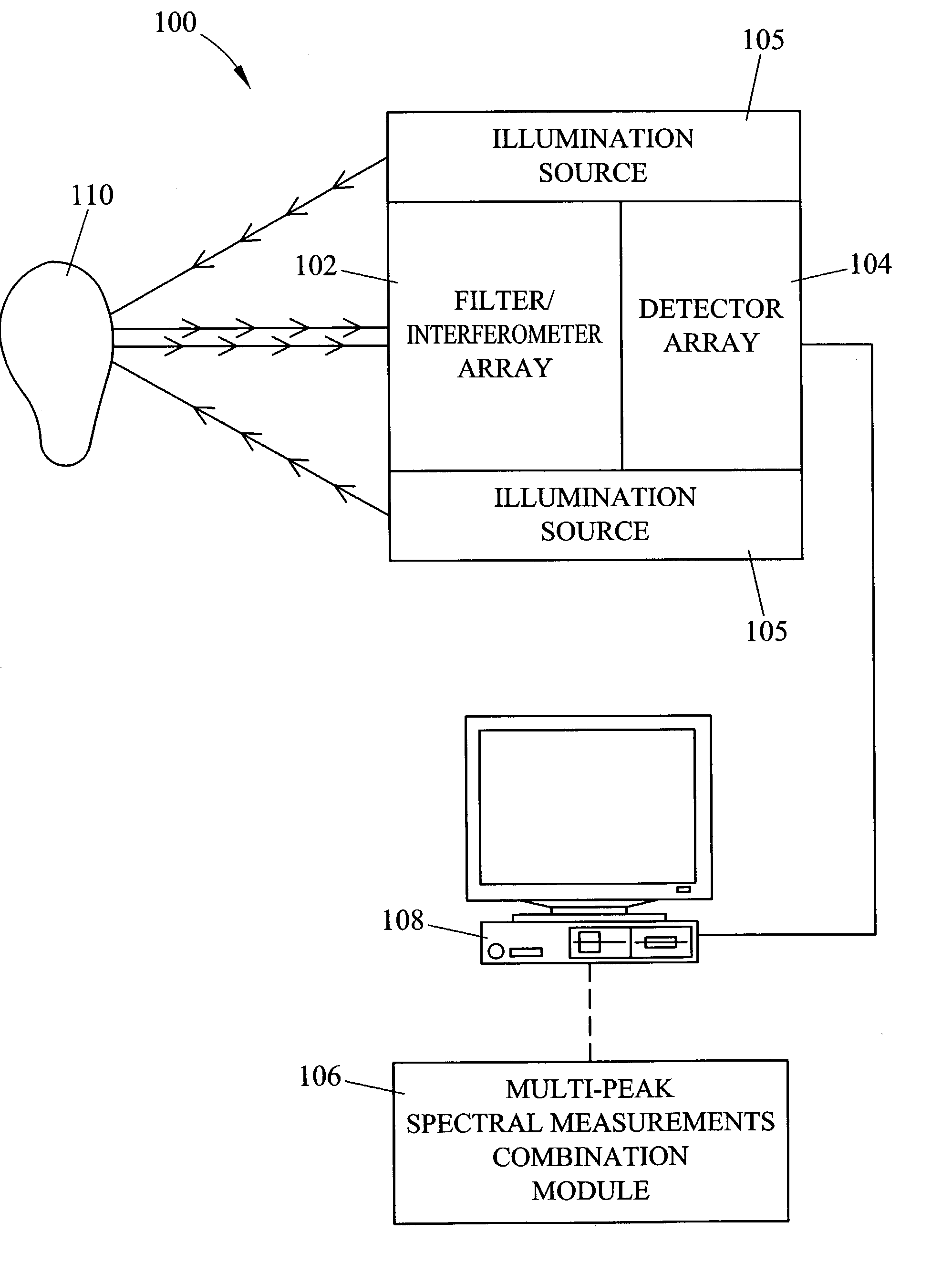
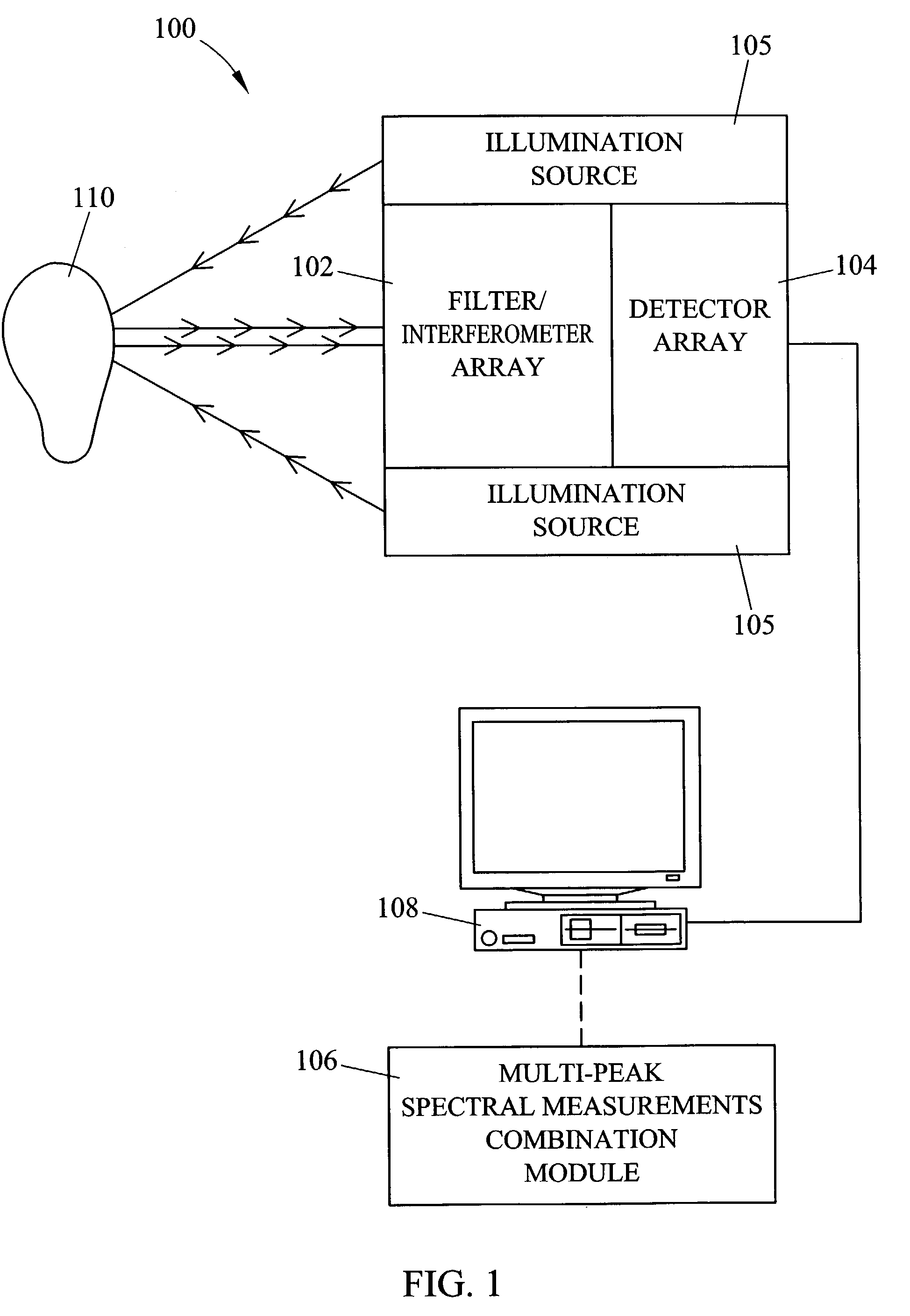
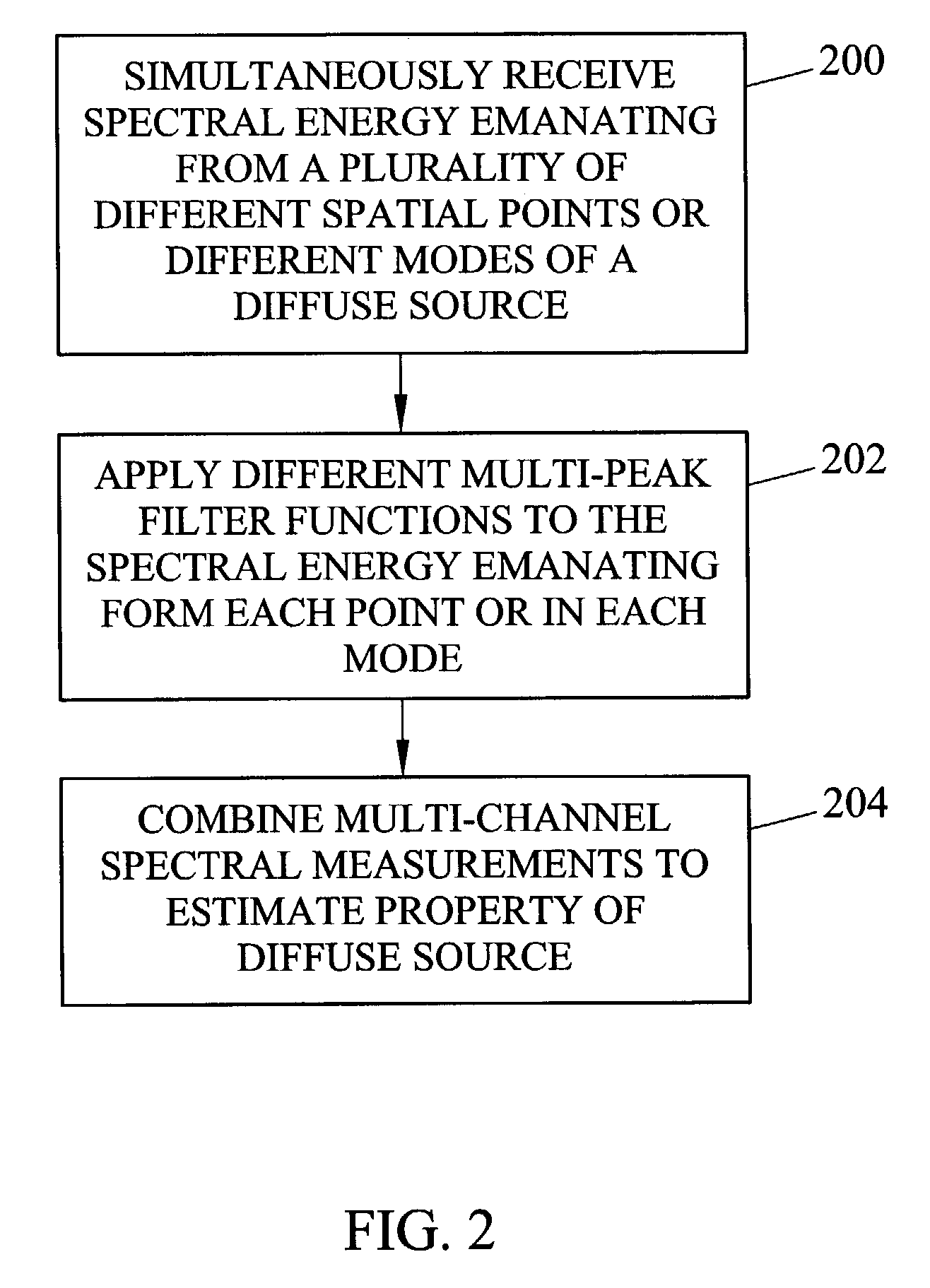
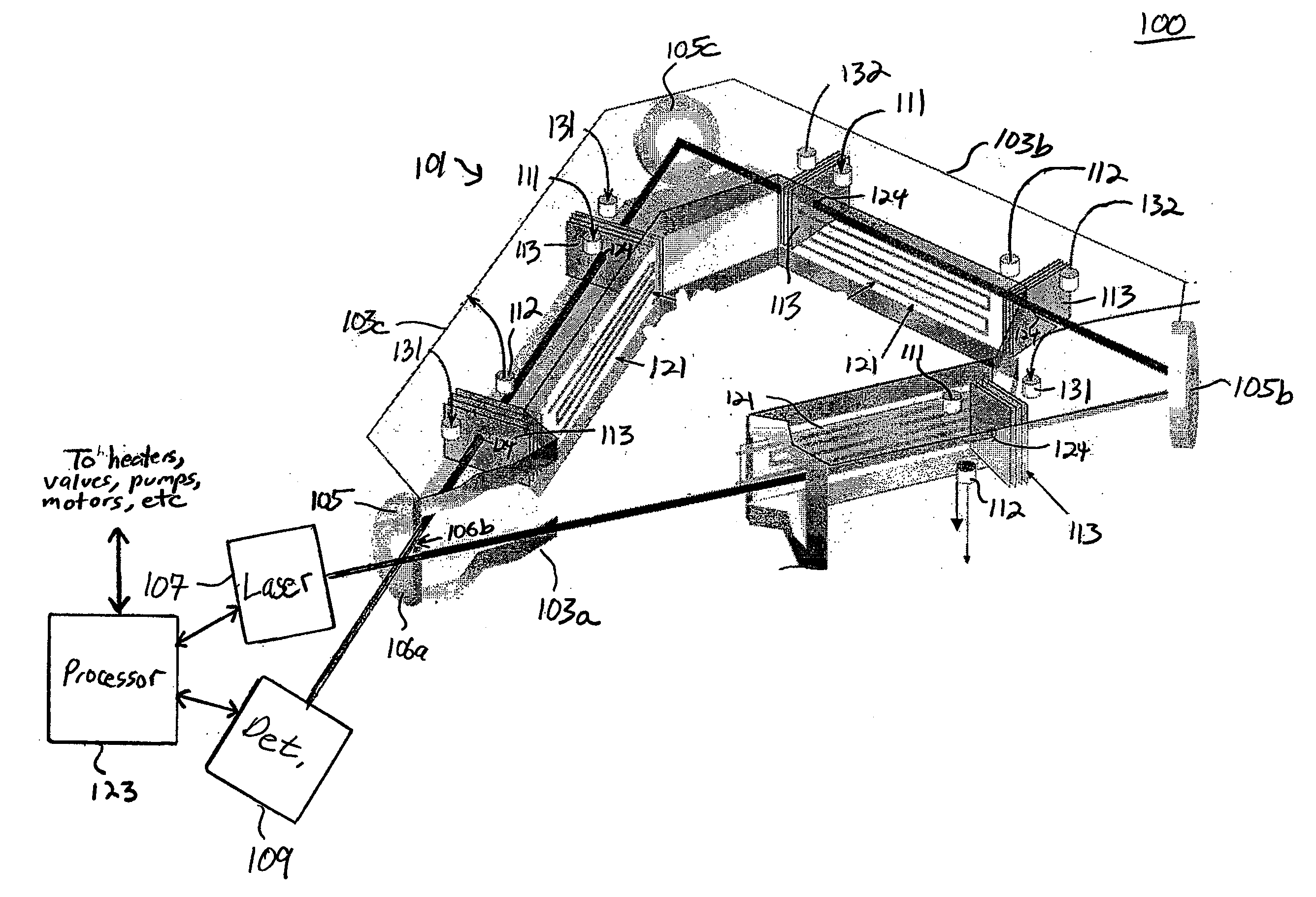
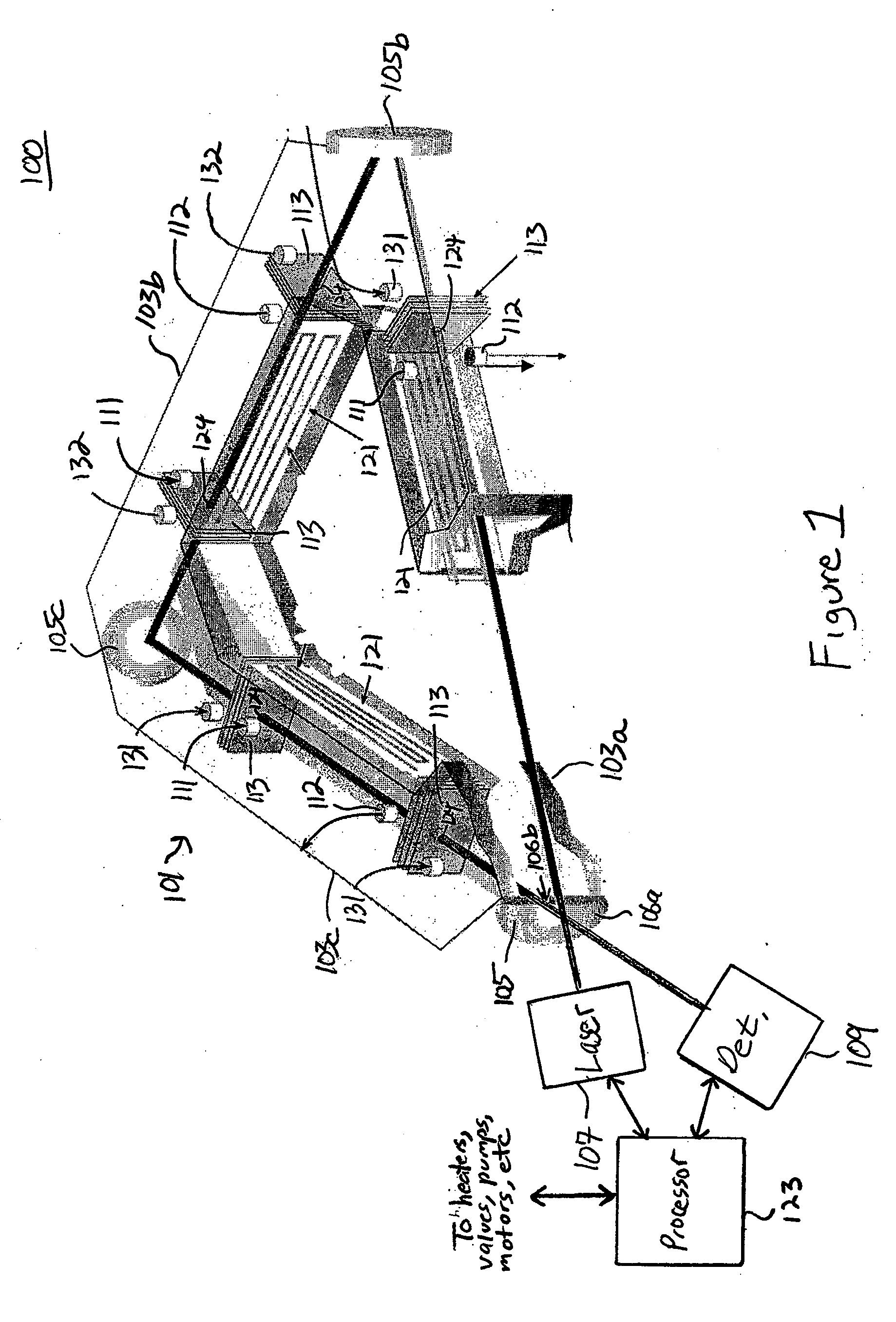
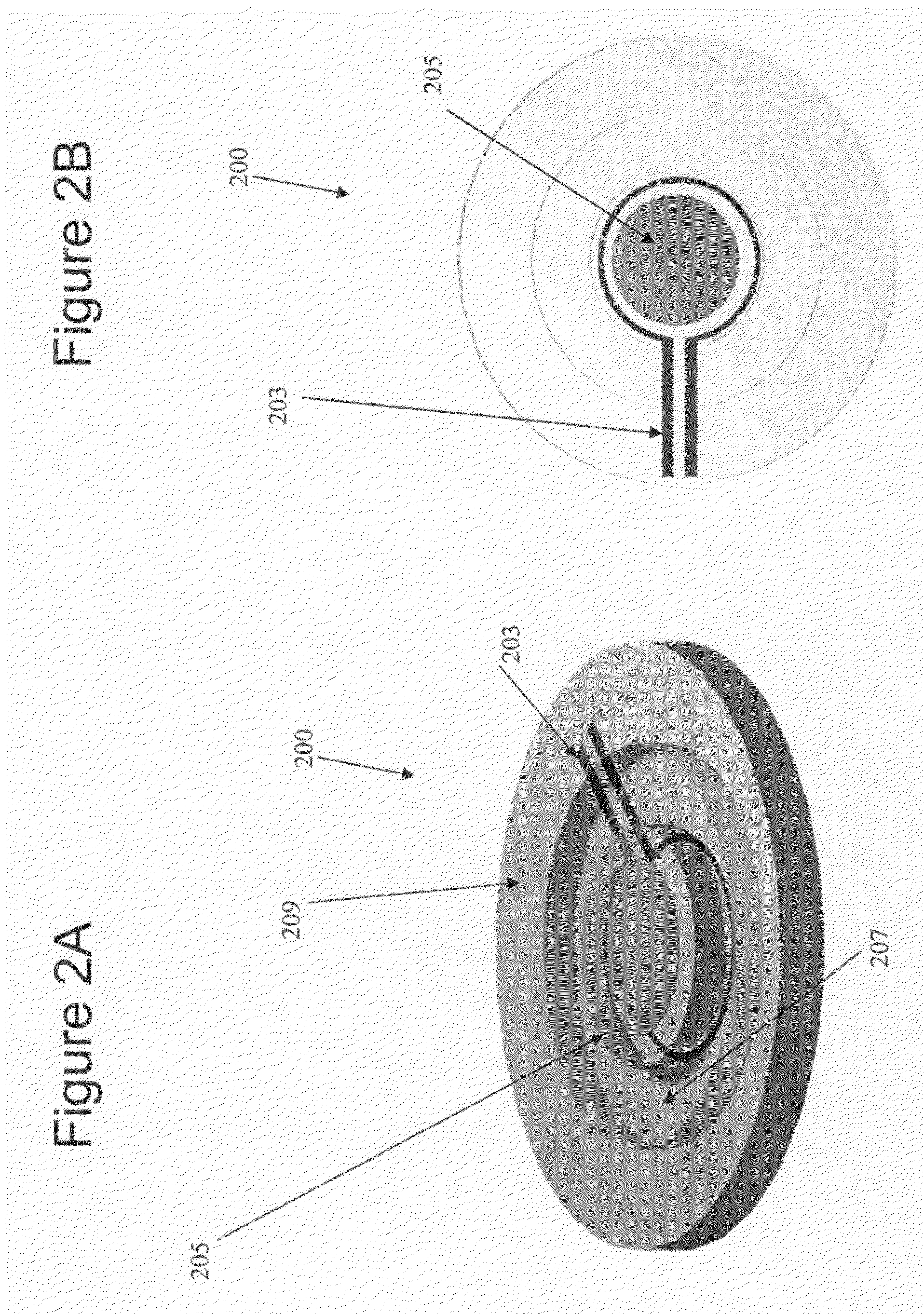
Methods and systems for static multimode multiplex spectroscopy
ActiveUS7092101B2Accurately and efficiently measuring spectral propertyIncrease speedRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectroscopy methodsStatics
Methods and systems for static multimode multiplex spectroscopy are disclosed. According to a method for static multimode multiplex spectroscopy, spectral energy emanating from different points of a diffuse source is simultaneously received. Different multi-peak filter functions are applied to the spectral energy emanating from the different points to produce a multi-channel spectral measurement for each point. The multi-channel spectral measurements are combined to estimate a property of the diffuse source.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
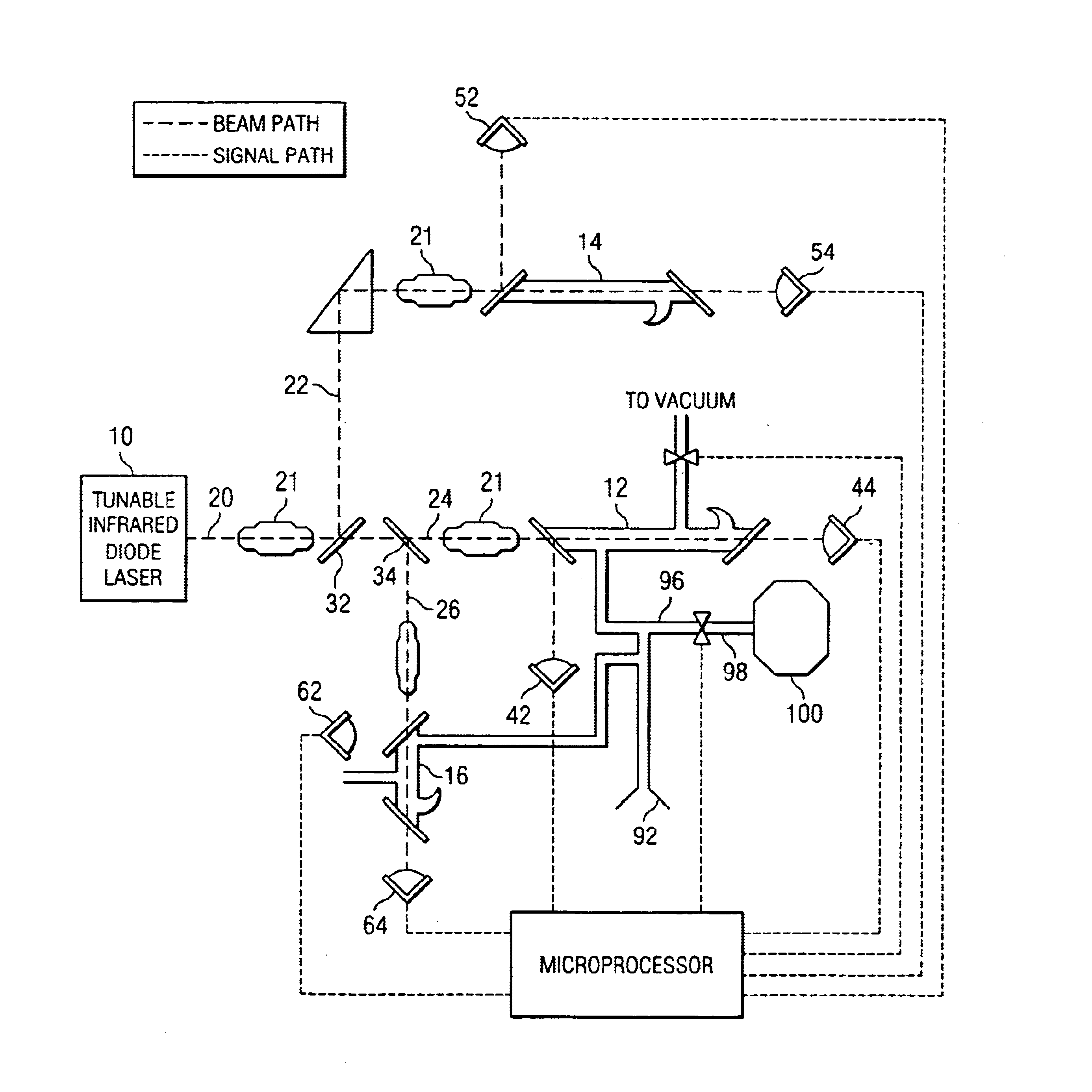
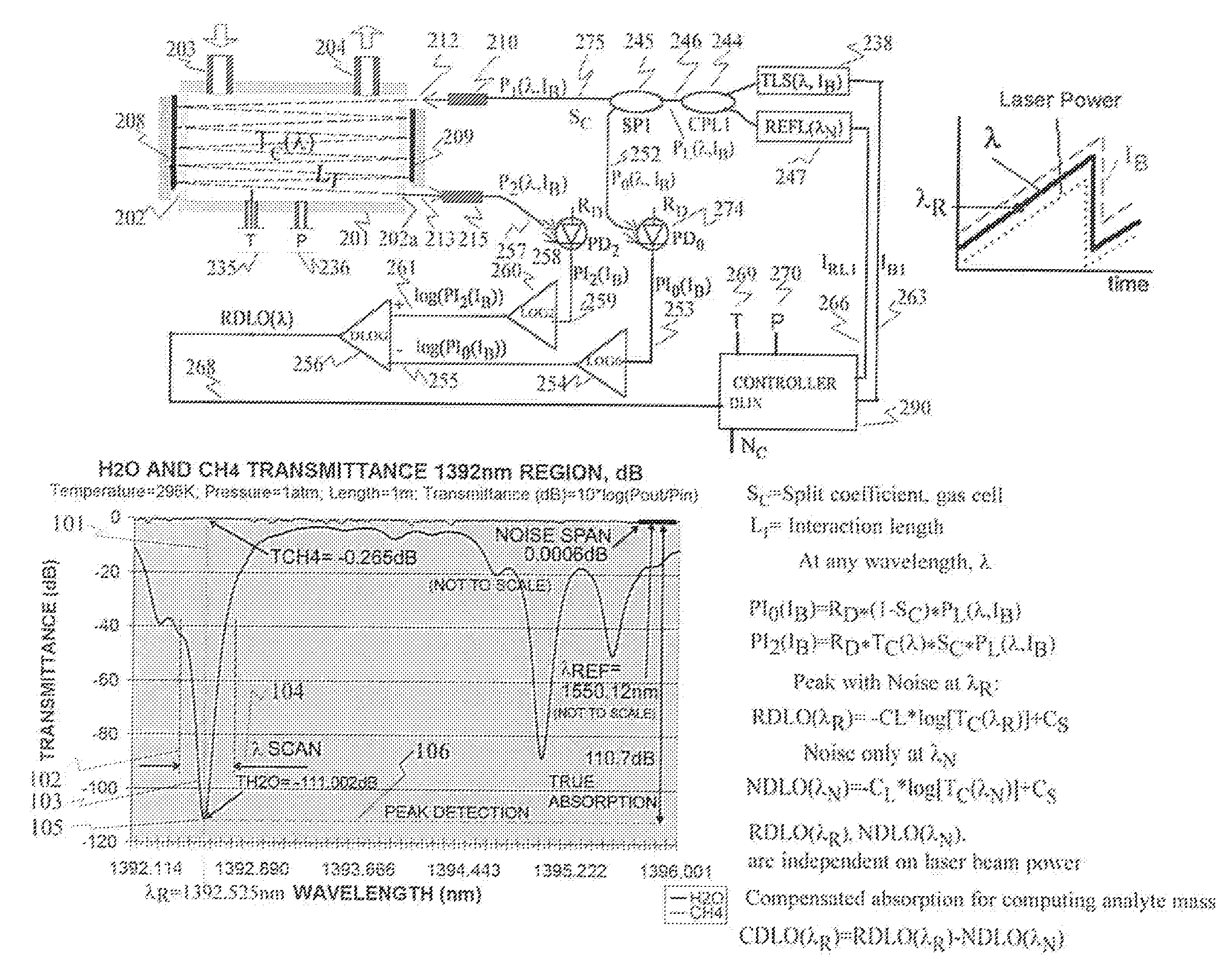
Spectroscopy Method and Apparatus for Detecting Low Concentration Gases
InactiveUS20080151248A1Reduce concentrationAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsRing downOptical cavity
The invention is a method and apparatus capable of detecting constituents of a gas at extremely low concentrations comprising providing a medium that is absorbent of at least a first particular gas under a first environmental condition and desorbent of the particular gas under a second environmental condition, exposing the medium to a sample gas for a first period of time under the first environmental condition, during a second period of time after the first period of time, exposing the medium to the second environmental condition to cause the medium to desorb gas into an optical cavity of a cavity ring down spectrometer and introducing electromagnetic radiation into the cavity, during a third period of time after the second period of time, ceasing introduction of the electromagnetic radiation into the cavity and detecting the decay of the electromagnetic radiation in the cavity, and analyzing the decay of the light in the cavity to obtain a spectral analysis of the sample gas.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
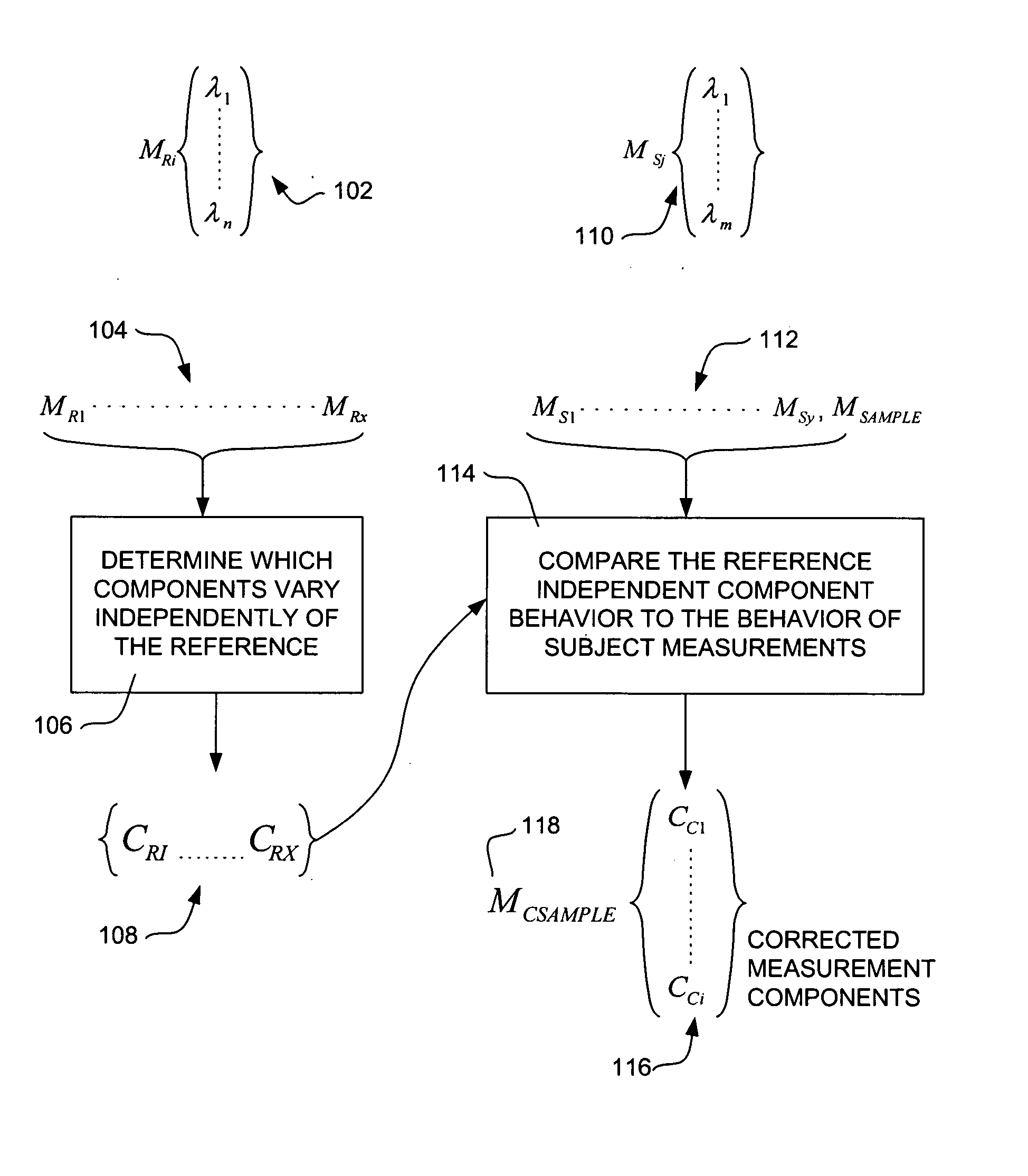
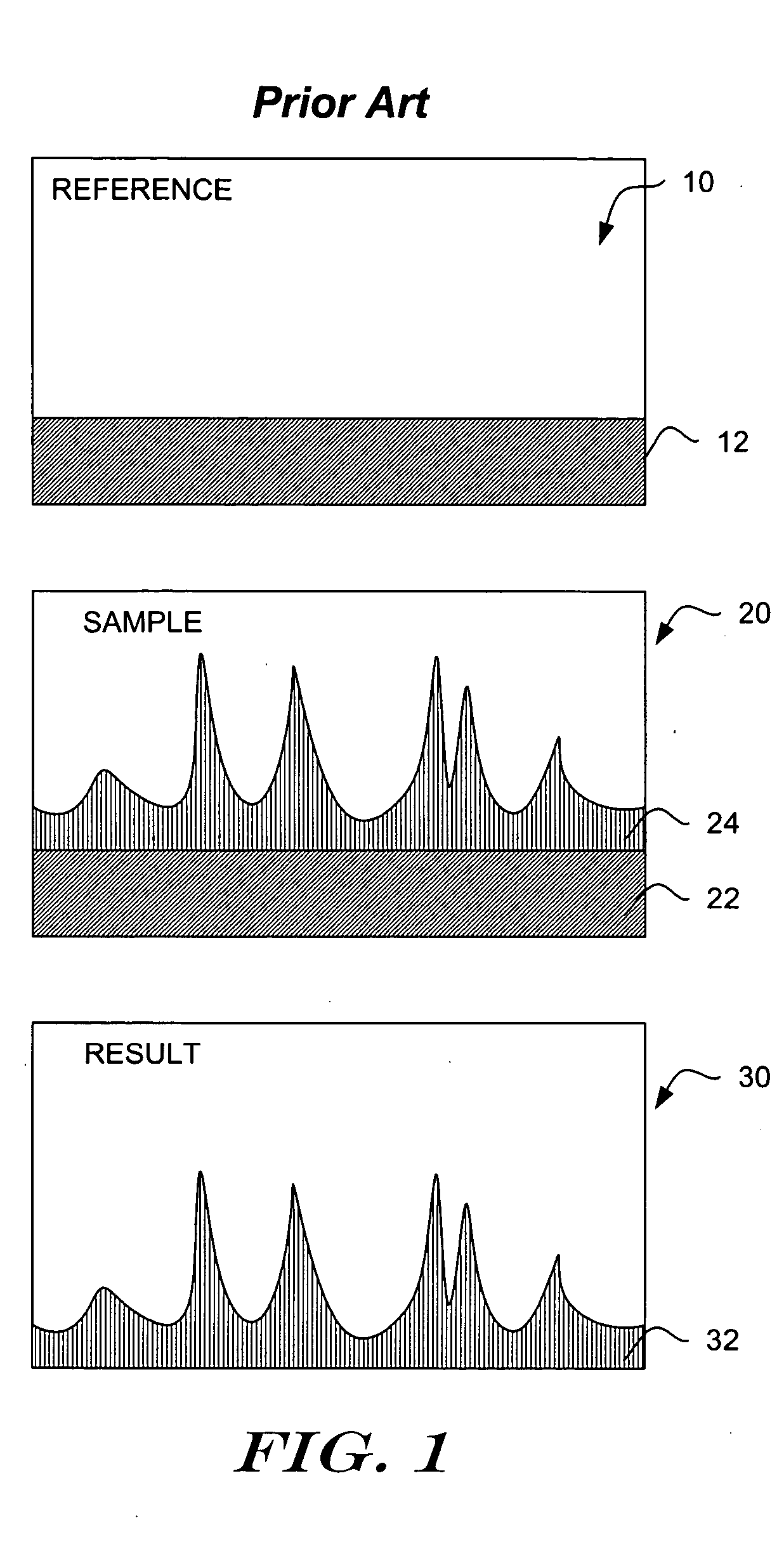
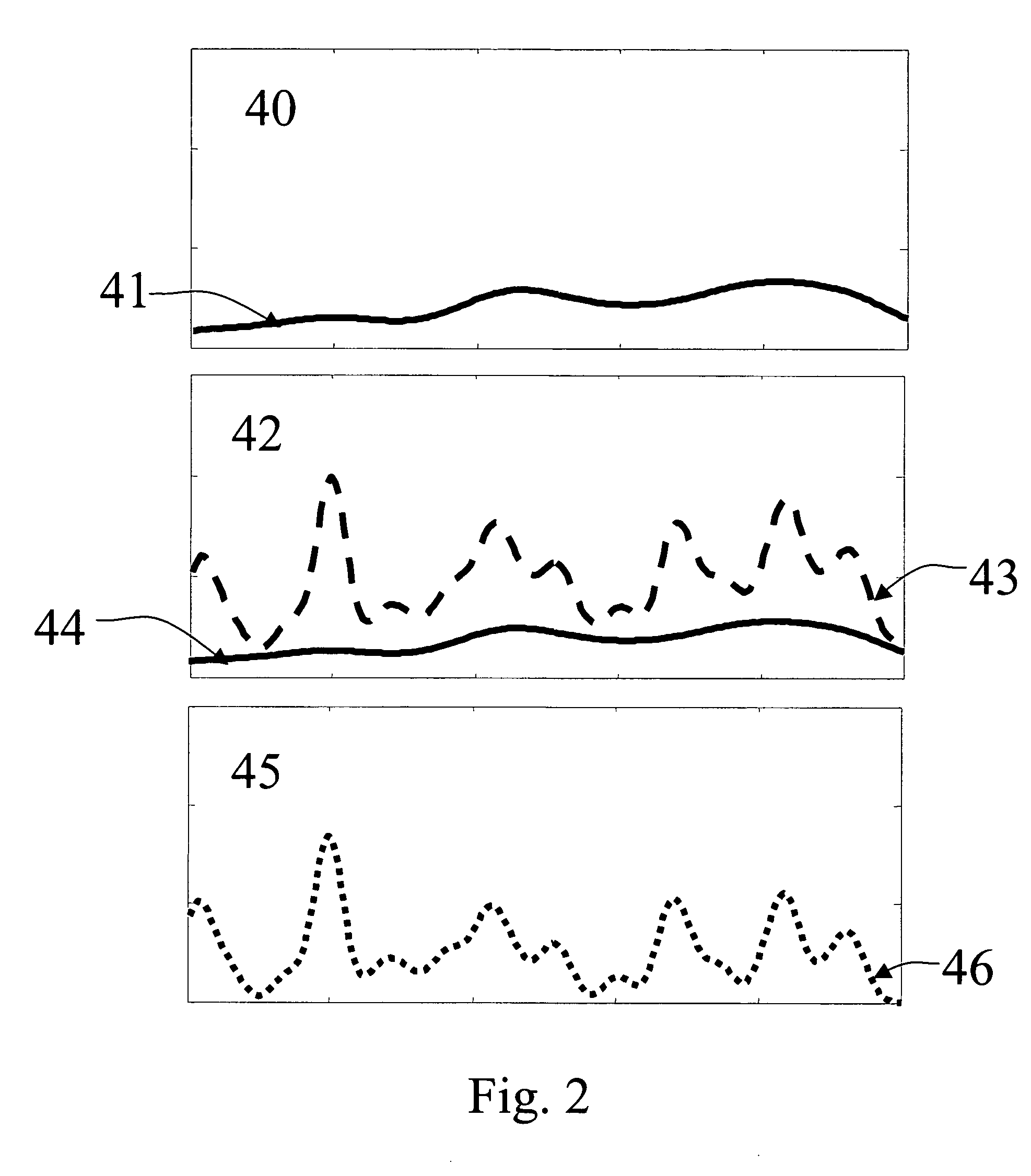
Adaptive compensation for measurement distortions in spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050143943A1Compensation DistortionSpectrum investigationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMeasurement deviceSpectroscopy methods
Methods of reducing the effects of measurement device artifacts on a measurement of a sample are presented. A number of reference measurements performed with the measurement device are observed to identify reference independent components of the reference measurements. The variations of the reference independent components are used as surrogates for possible artifacts of the measurement device. A number of measurements of subjects similar to the sample are observed, and similarity components of the subject measurements that vary in a manner similar to the reference independent components may be identified. The sample measurement is then adjusted to remove at least part of the similarity components that correspond to the variations in the reference independent components. The adjustment of the sample measurement is thereby improved by reducing the effects of artifacts of the measurement device.
Owner:INLIGHT SOLUTIONS
Differential time domain spectroscopy method for measuring thin film dielectric properties
InactiveUS6556306B2Large dynamic rangeRaise the ratioPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansTime domainDielectric
A non-contact, free-space method for determining the index of refraction of a thin film at a desired angular frequency. The method includes generating an input desired-frequency pulse and an optically detectable probe pulse. The thin film is moved in and out of the path of the input pulse, creating an output pulse that alternates between a transmitted signal, created when the film intercepts the input pulse path, and a reference signal, created when the sample is outside the input pulse path. The output pulse modulates the probe pulse, which is then detected with a photo detector, and the difference between the transmitted signal and the reference signal is calculated. The above steps are repeated over a plurality of delay times between the input pulse and the probe pulse until a complete field waveform of the differential signal is characterized. The index of refraction is calculated as a function of a ratio between the differential signal for the thin film and the reference signal. A complete field waveform of the reference signal may be characterized by repeating the above steps for a reference plate identical to the sample except having a non-transmissive film instead of the thin, transmissive film.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
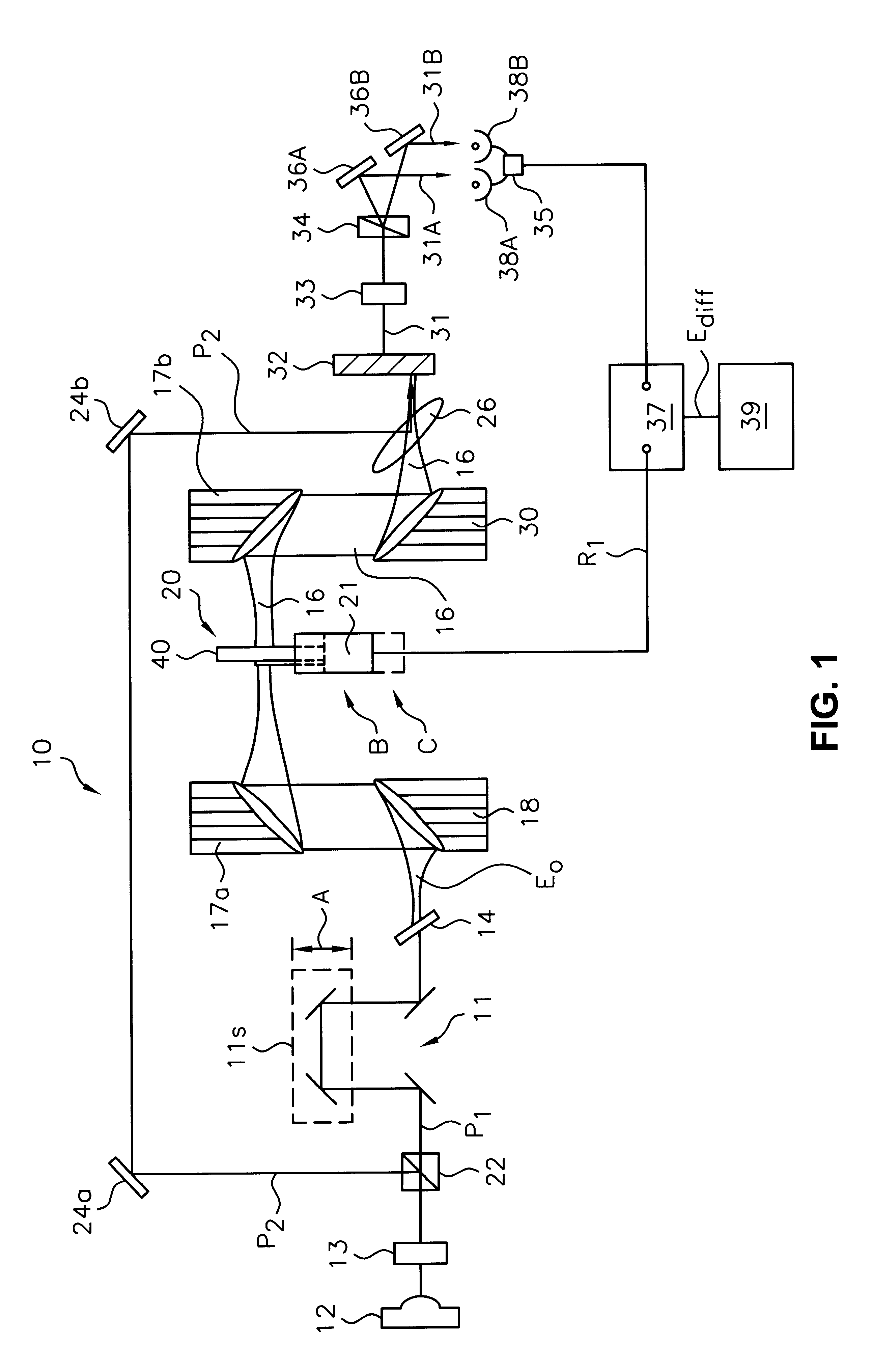
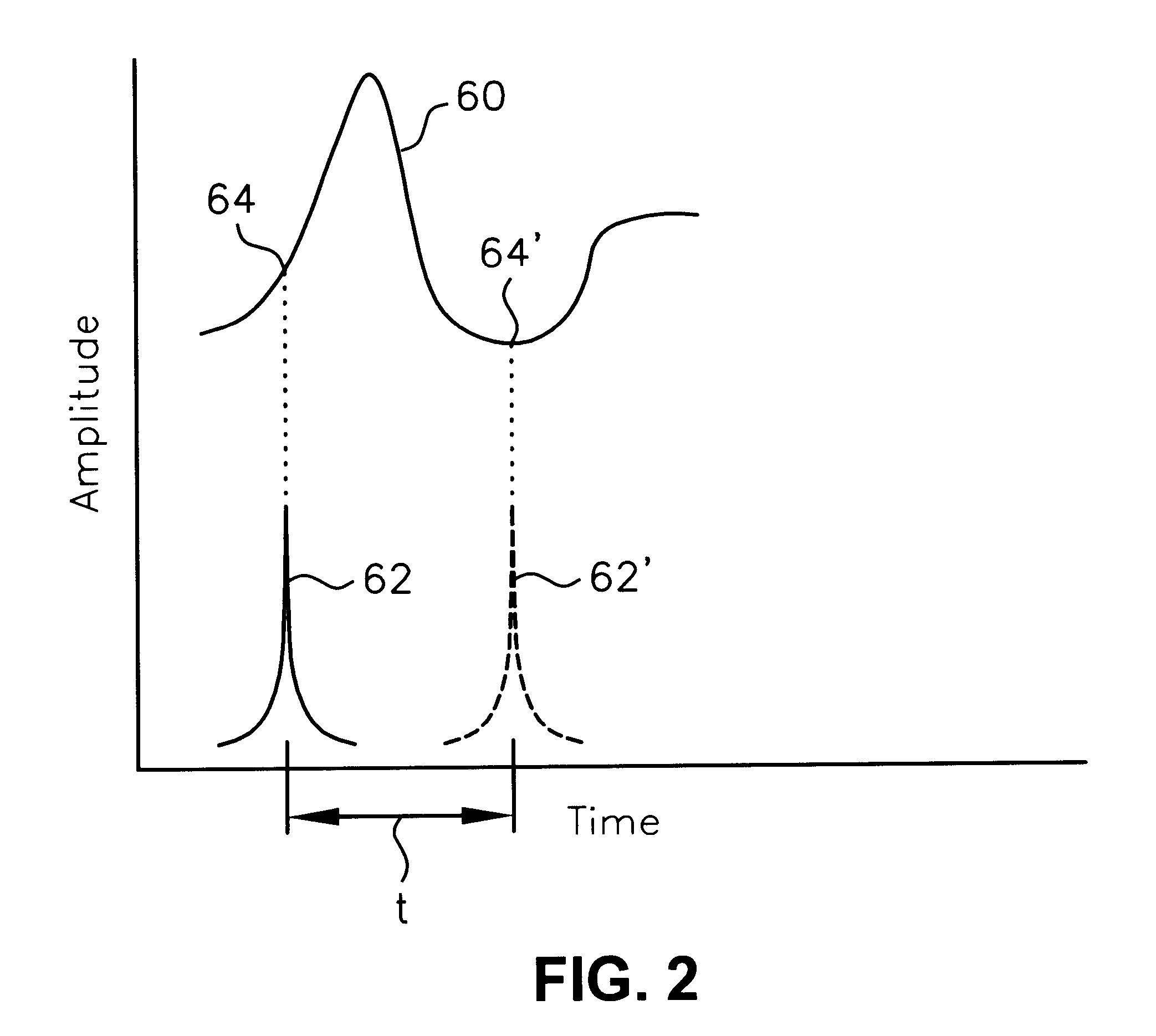
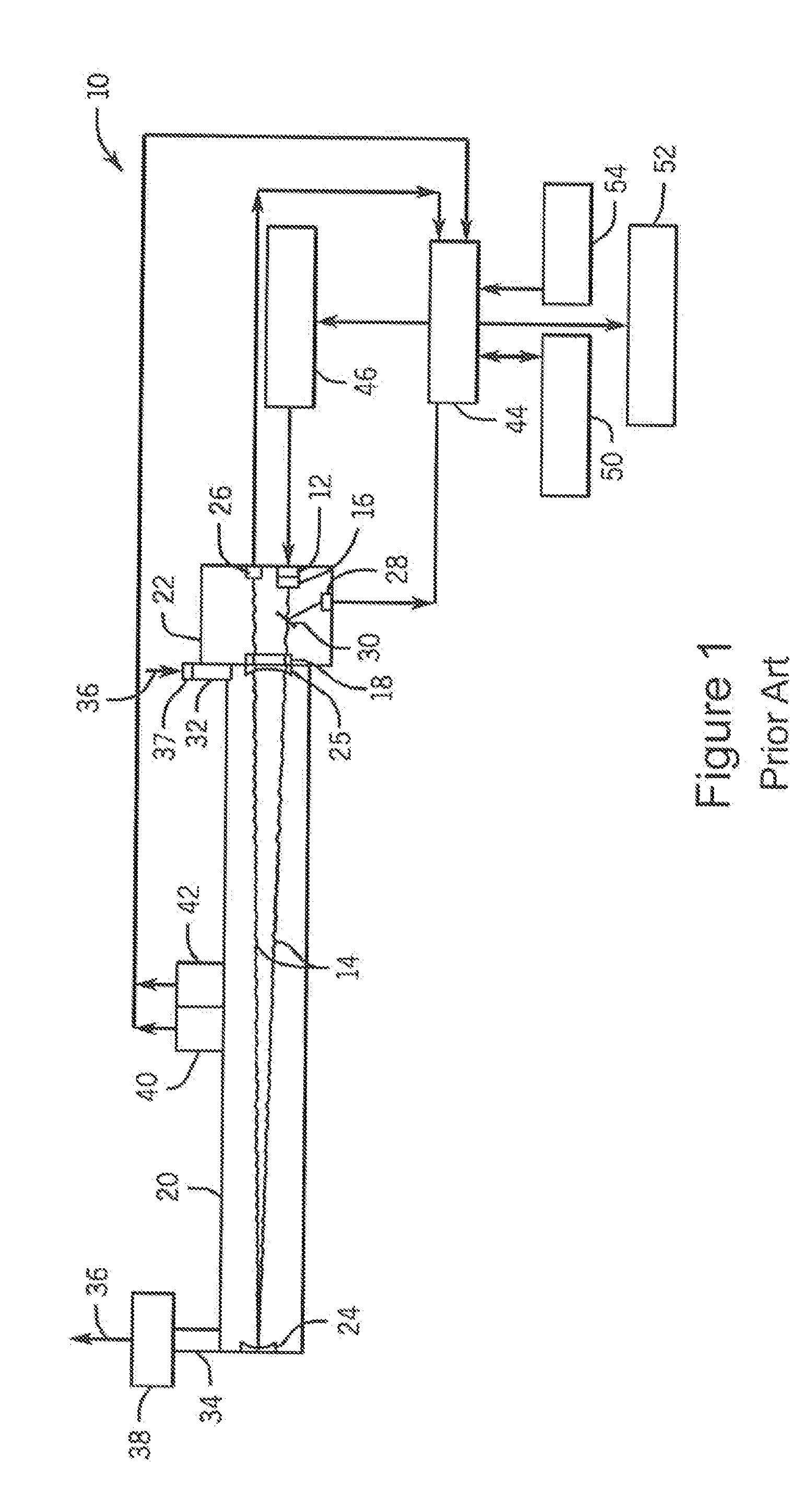
Analytes monitoring by differential swept wavelength absorption spectroscopy methods
ActiveUS20160084757A1High sensitivityAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteGas phase
The present invention relates to a method, apparatus and system for measuring the content of either one or more gas analytes that may be part of a gas. The present invention applies a spectroscopic method that utilizes an extremely narrow linewidth laser beam that is absorbed when its wavelength is swept across the interval containing the absorption line of the analyte. The method, apparatus and system of the present invention is applicable to any analyte in gas phase that is part of a gas mixture, or to any analyte in a plasma phase, as well as analytes in other environments.
Owner:NGP
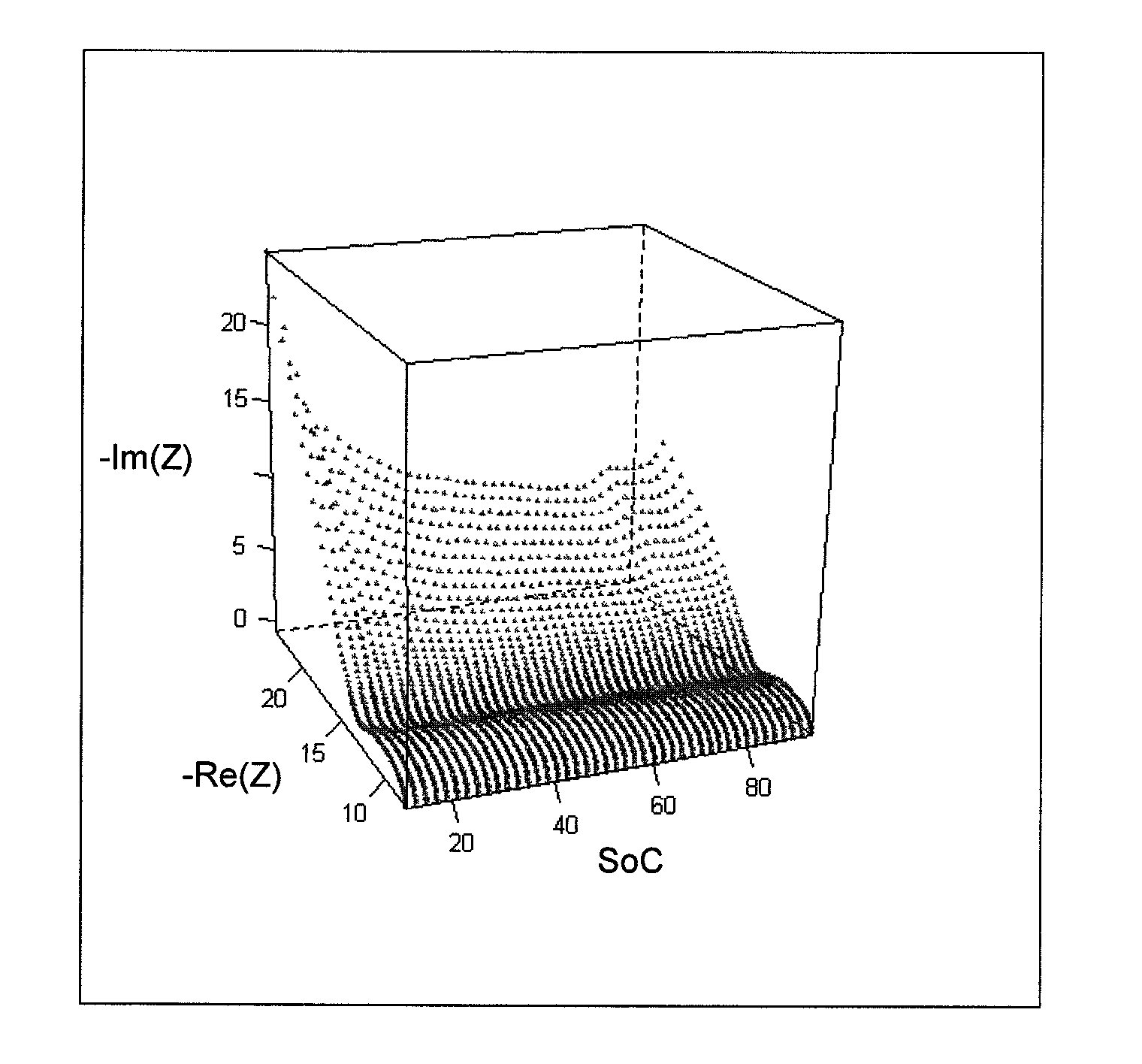
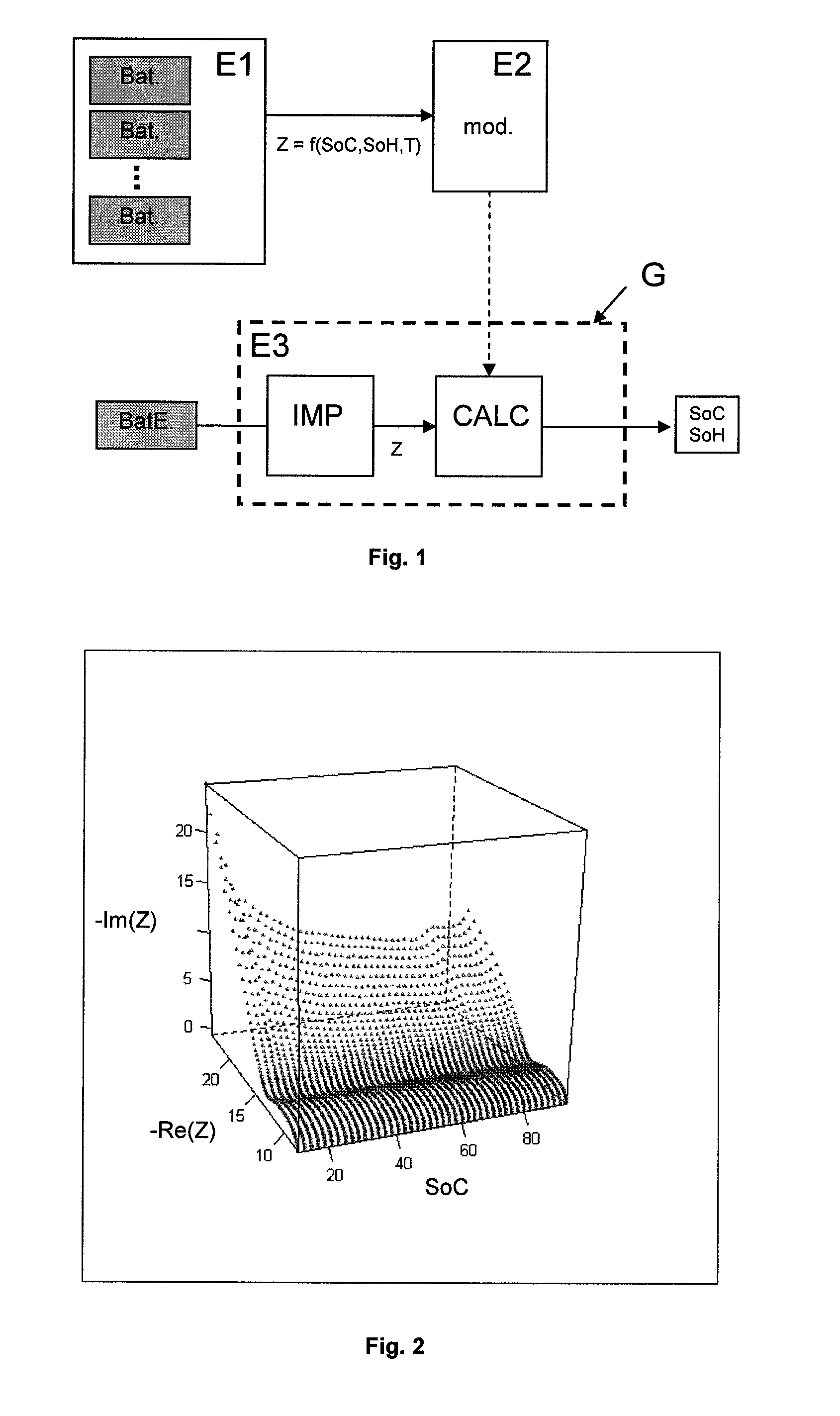
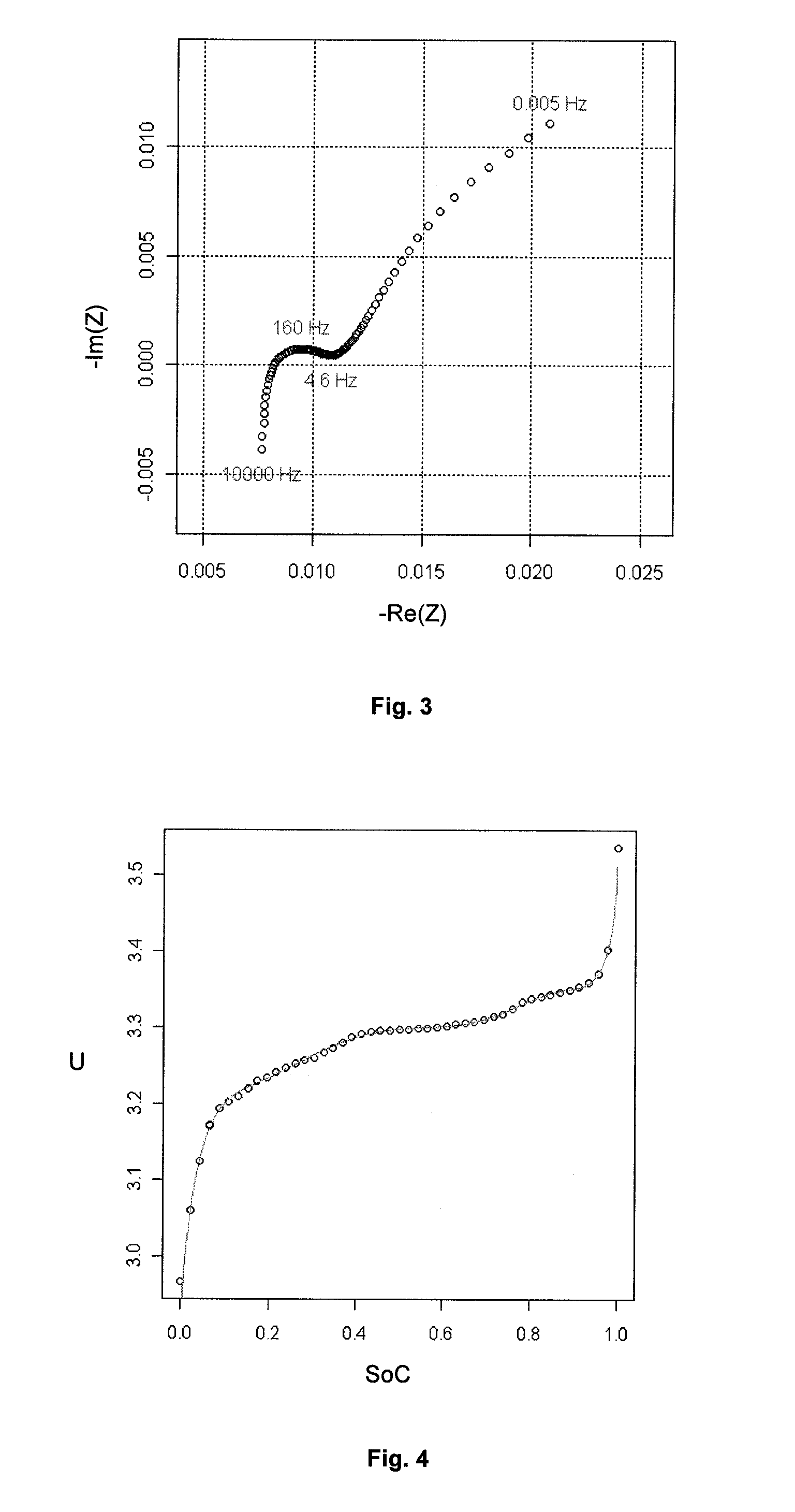
In-situ battery diagnosis method using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20120078552A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrical testingSpectroscopy methodsEngineering
Method of estimating the internal state of an electrochemical system for electric power storage, such as a battery.The SoC and the electrochemical impedance are determined for various internal states of an electrochemical system of the same type as the electrochemical system studied. An electrochemical impedance model is then defined as a function of the SoC and of parameters. These parameters are calibrated through adjustment on the electrochemical impedance measurements obtained for the various internal states. The electrochemical impedance Z of the system studied is determined and its SoC is estimated using the model applied to electrochemical impedance Z.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
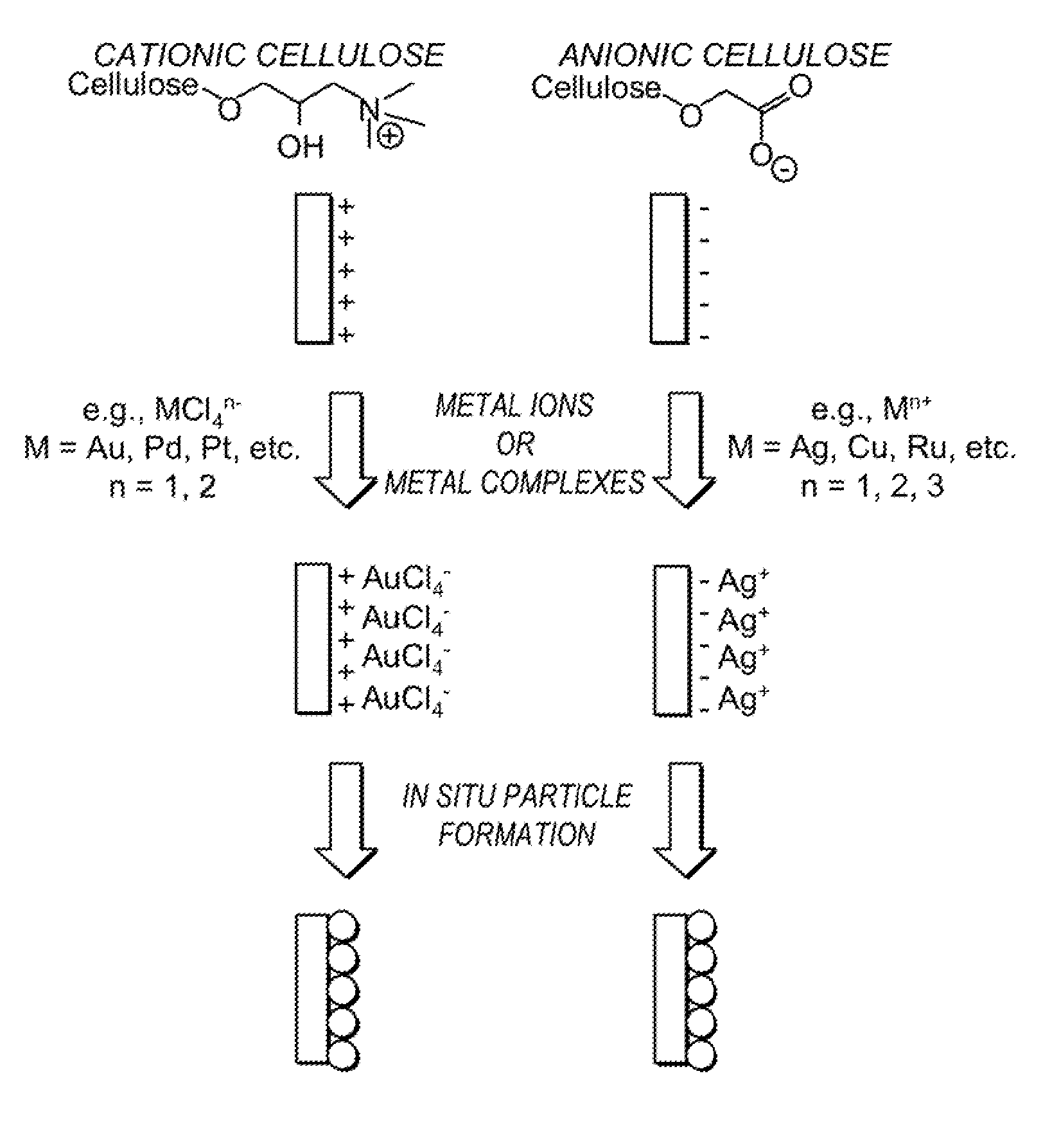
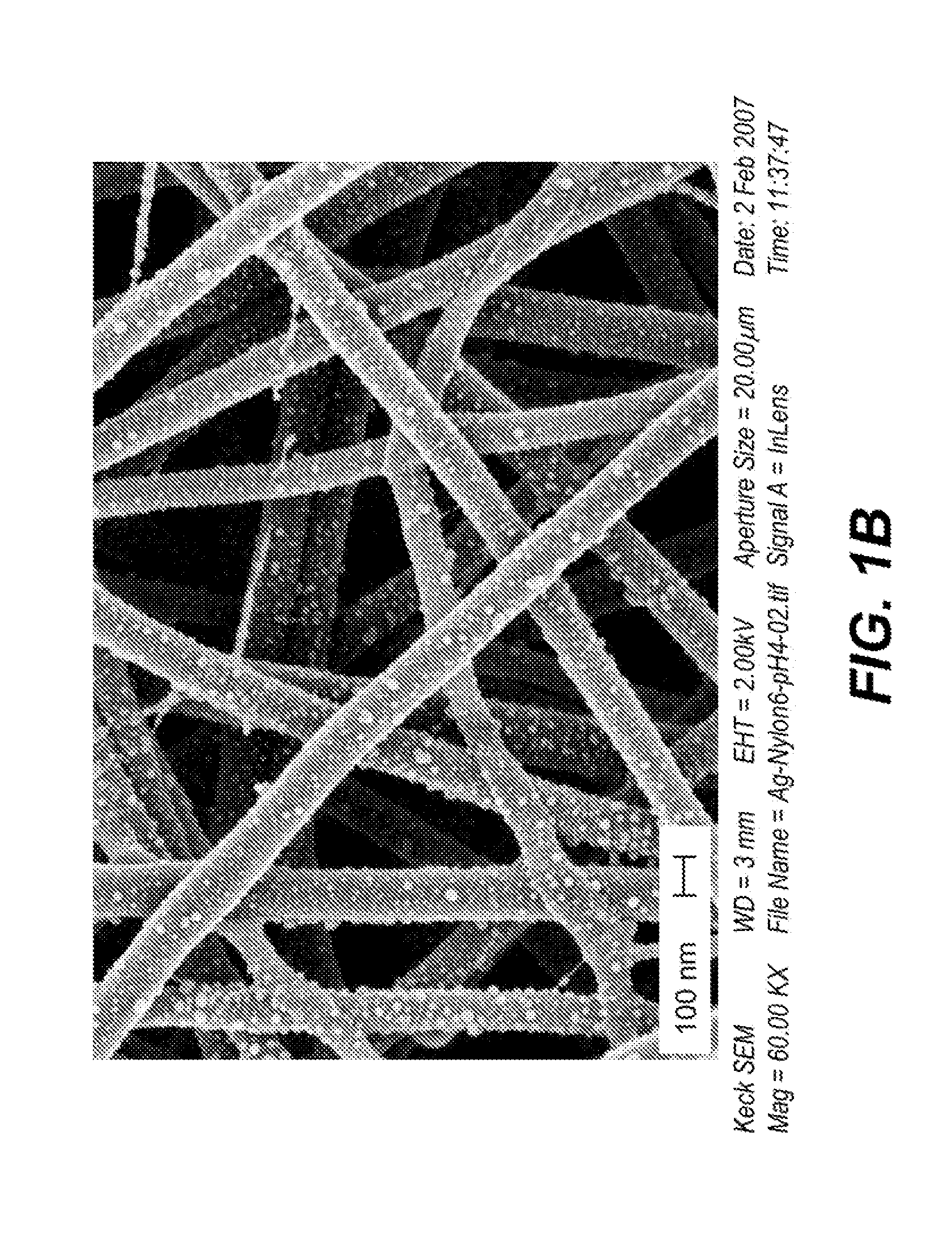
Conformal particle coatings on fiber materials for use in spectroscopic methods for detecting targets of interest and methods based thereon
InactiveUS20120058697A1Good spectral characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsTextile fiberFluorescence
Textile fibers and other fibrous substrates functionalized with particles are provided for use in the detection of targets of interest by spectroscopic methods. In one embodiment, a substrate is provided that comprises a conformal coating on its surface, wherein the coating comprises a plurality of chemically functional particles that are spectroscopically enhancing. Methods for producing such functionalized textile fibers are also provided. These textiles can be used as platforms for spectroscopic detection, including surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA), and surface-enhanced fluorescence (SEF). Functionalized textile fibers for use in the signature detection methods are produced by performing layer-by-layer self-assembly of particles on natural and synthetic textile substrates.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
NIR spectroscopy method for analyzing chemical process components
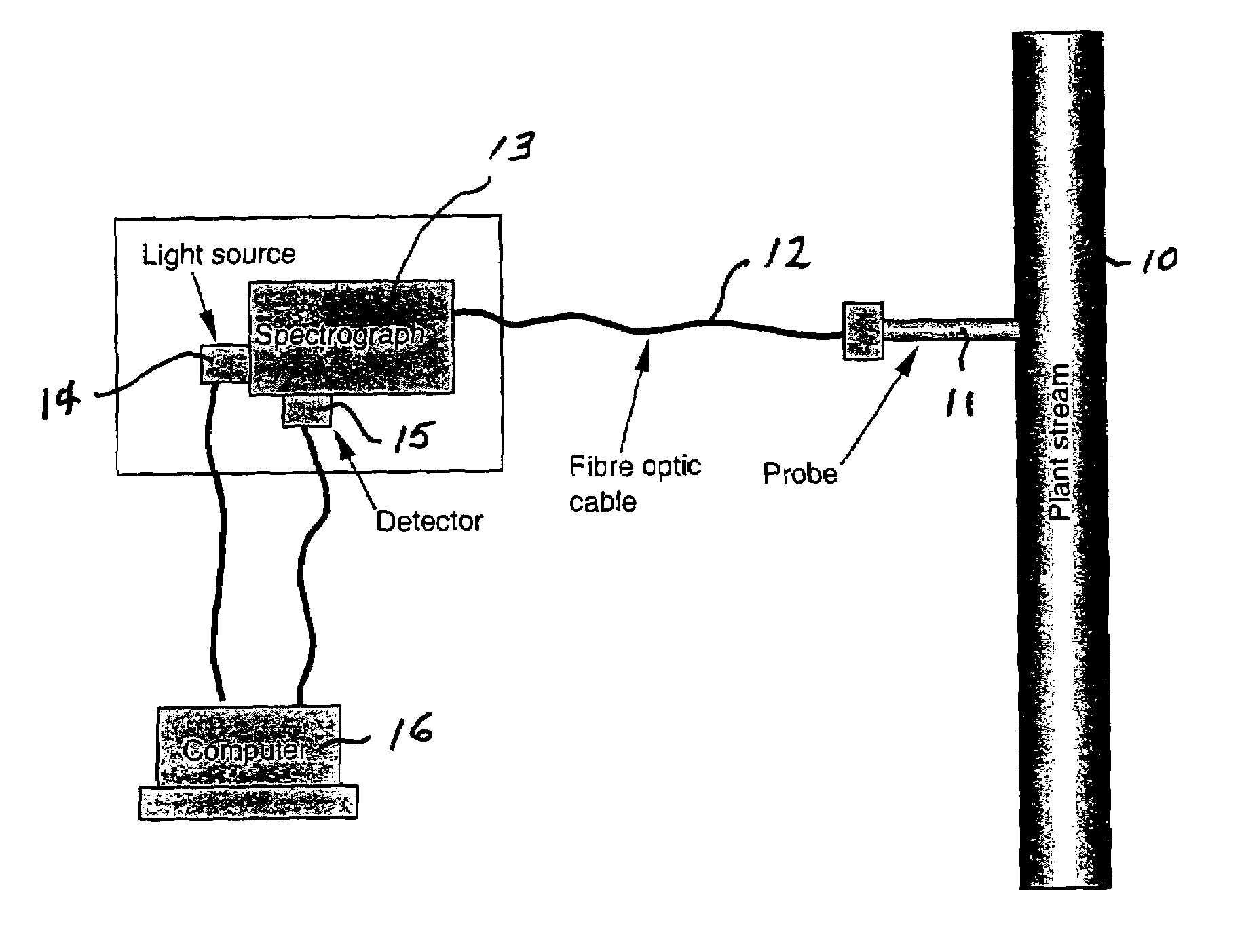
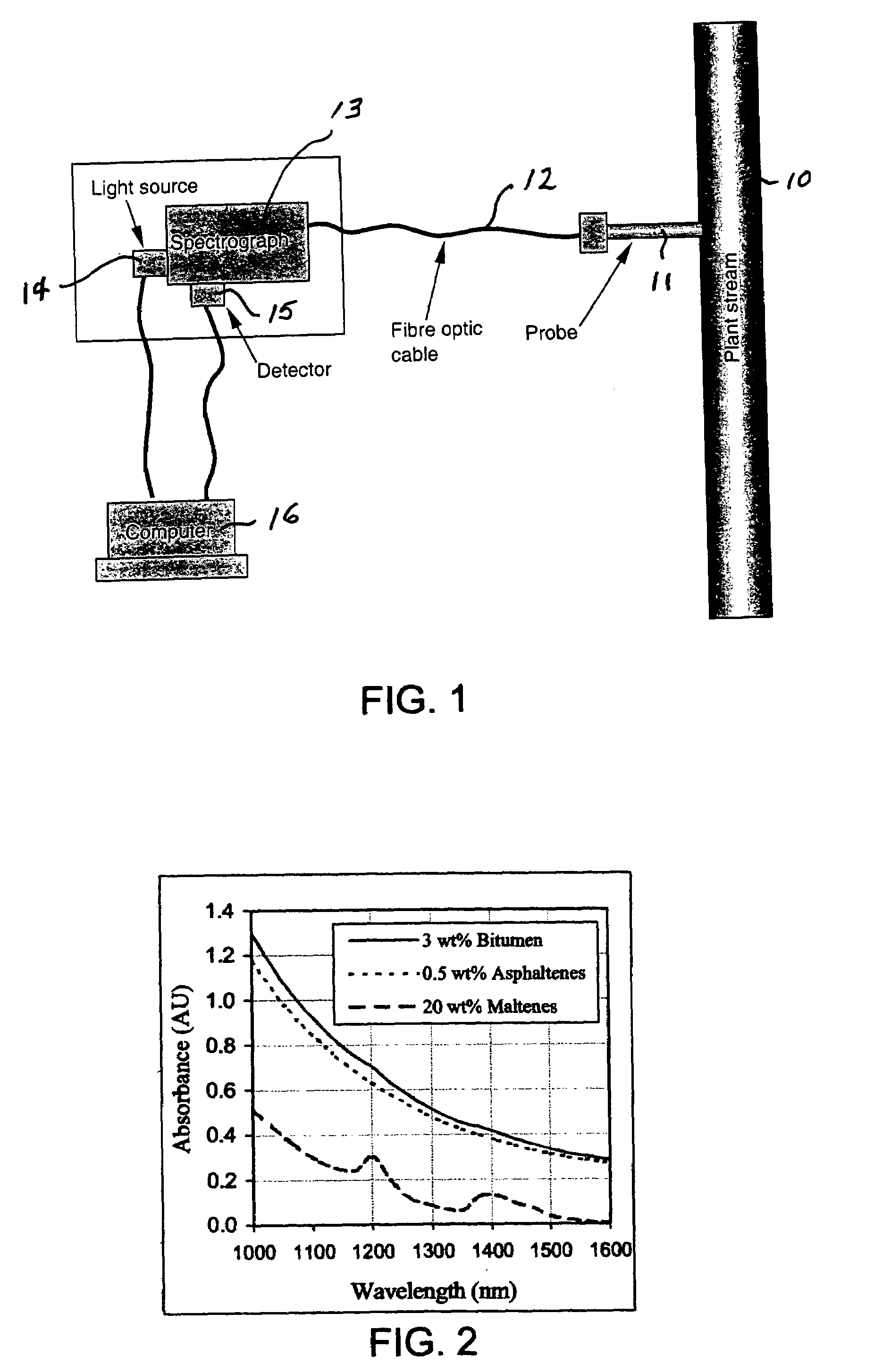
ActiveUS7067811B2Minimize temperature effectRadiation pyrometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsInfraredFiber
A method is described for providing rapid on-line analyses of chemical compositions such as chemical process streams, utilizing near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy in combination with chemometrics. In the method, for each type of analysis to be conducted, a database is provided by analyzing a series of samples using standard laboratory analytical procedures, utilizing the results as reference values to establish quantitative calibration models from NIR spectroscopy using chemometric techniques and storing this information in a computer database. An NIR spectroscopic system is also provided comprising a transflectance or a transmittance probe coupled via fiber-optic cables to a stable white light source and a spectrograph. The probe is inserted into a test sample or chemical process stream to be analyzed, a stable white light of selected wavelength range is beamed to the probe and the spectra obtained on the spectrograph are recorded. Finally the spectra obtained are correlated to the reference data stored in the computer to obtain a rapid measurement of the analysis desired.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF NATURAL RESOURCES
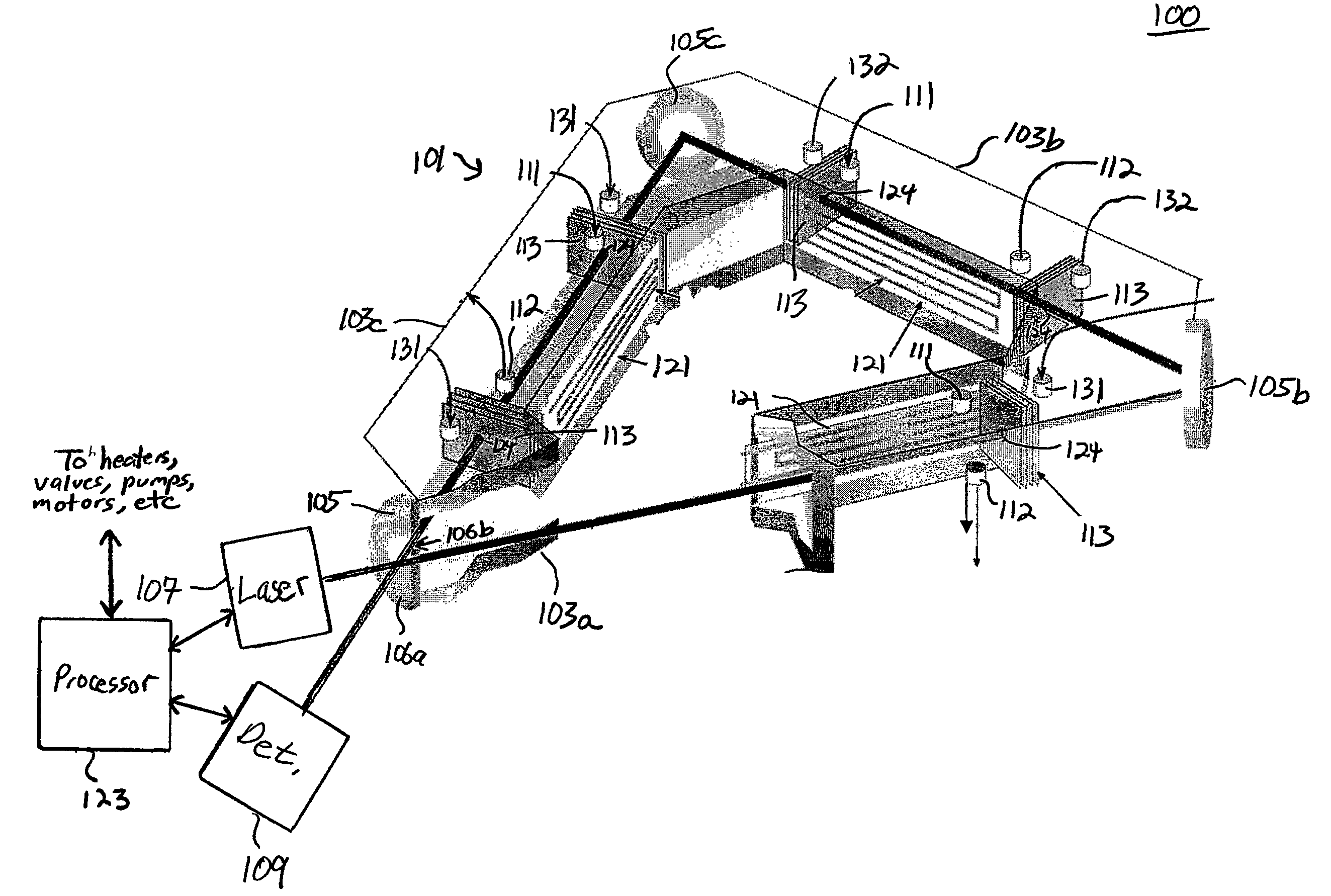
Method and apparatus for compact spectrometer for multipoint sampling of an object
A method and a portable device for assessing the occurrence of an agent in a sample. A sample is illuminated with photons emanating from a portable device to produce photons reflected, emitted, or absorbed from a set of multiple points in the sample having a defined geometric relationship. The portable device is used to simultaneously illuminate the sample and analyze the photons reflected, emitted, or absorbed from the set of multiple points using spectroscopic methods, including infrared, fluorescence, and UV / visible. The agent assessed may include a hazardous agent, a chemical agent, a biological agent, a microorganism, a bacterium, a protozoan, a virus, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Subsurface thermal gradient spectrometry
InactiveUS6049081AFast and efficient calibrationAvoid measuringRadiation pyrometryCalibration apparatusPhysicsOptical path length
Spectrometric methodology for non-invasively obtaining optical spectra from heterogeneous material for the identification and quantification of constituent compounds. There is provided a transient or steady state subsurface thermal gradient spectroscopic methodology for obtaining in vivo optical spectra relating to the concentration of n analytes at depths to around 330 microns in human tissue, and for determining that concentration from the spectra. The methodology is employable on a wide variety of spectrometric devices, and enables: a real time determination of both surface and reference intensities; a fast, efficient calibration of the spectrometric device; and results in the provision of an analytical parameter which avoids the measurement of the optical path length to enable the extremely accurate calculation of a ratio of concentrations of n analytes in the system under analysis.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
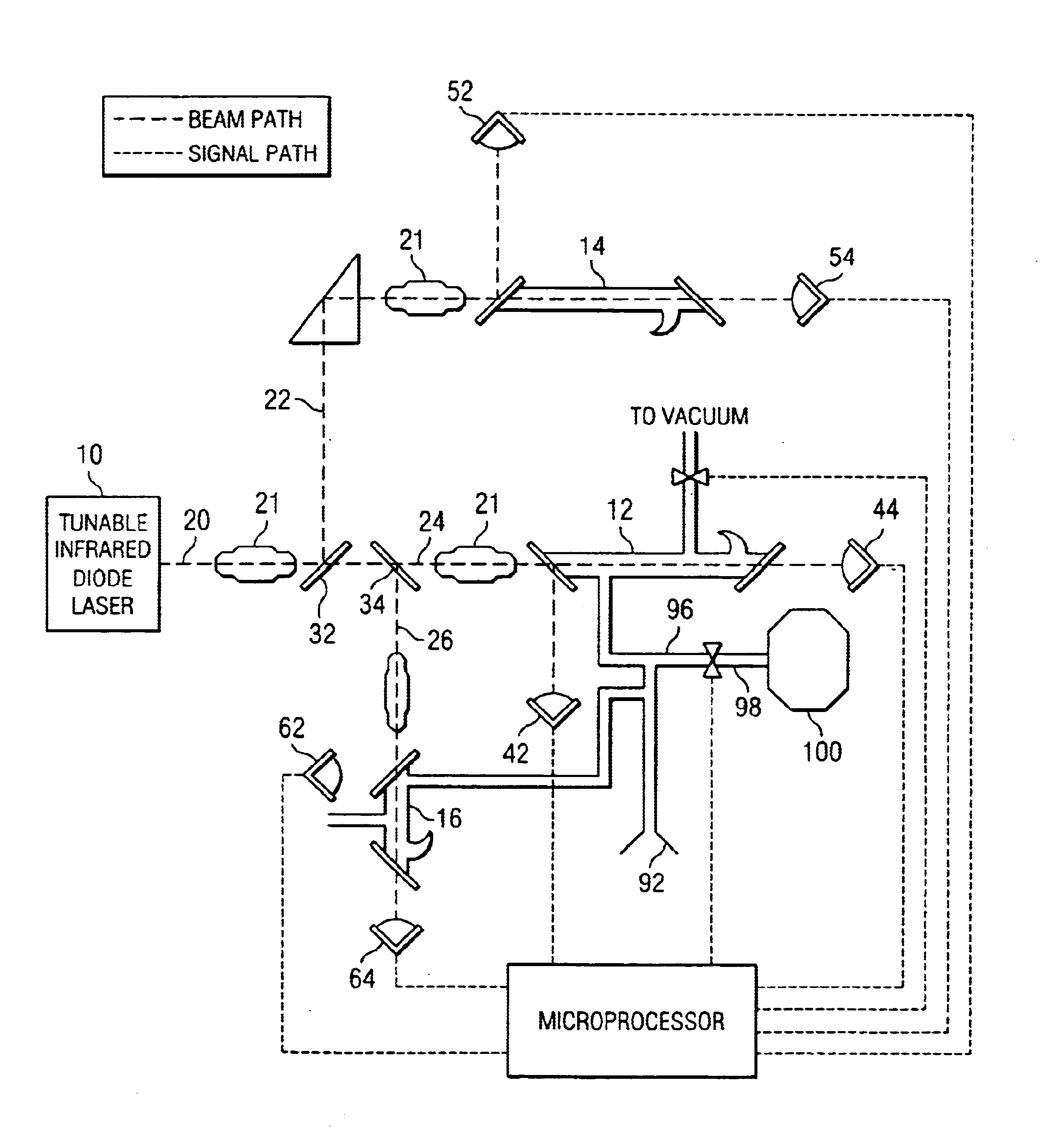
Spectroscopy method and apparatus for detecting low concentration gases
InactiveUS7612885B2Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsRing downOptical cavity
The invention is a method and apparatus capable of detecting constituents of a gas at extremely low concentrations comprising providing a medium that is absorbent of at least a first particular gas under a first environmental condition and desorbent of the particular gas under a second environmental condition, exposing the medium to a sample gas for a first period of time under the first environmental condition, during a second period of time after the first period of time, exposing the medium to the second environmental condition to cause the medium to desorb gas into an optical cavity of a cavity ring down spectrometer and introducing electromagnetic radiation into the cavity, during a third period of time after the second period of time, ceasing introduction of the electromagnetic radiation into the cavity and detecting the decay of the electromagnetic radiation in the cavity, and analyzing the decay of the light in the cavity to obtain a spectral analysis of the sample gas.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
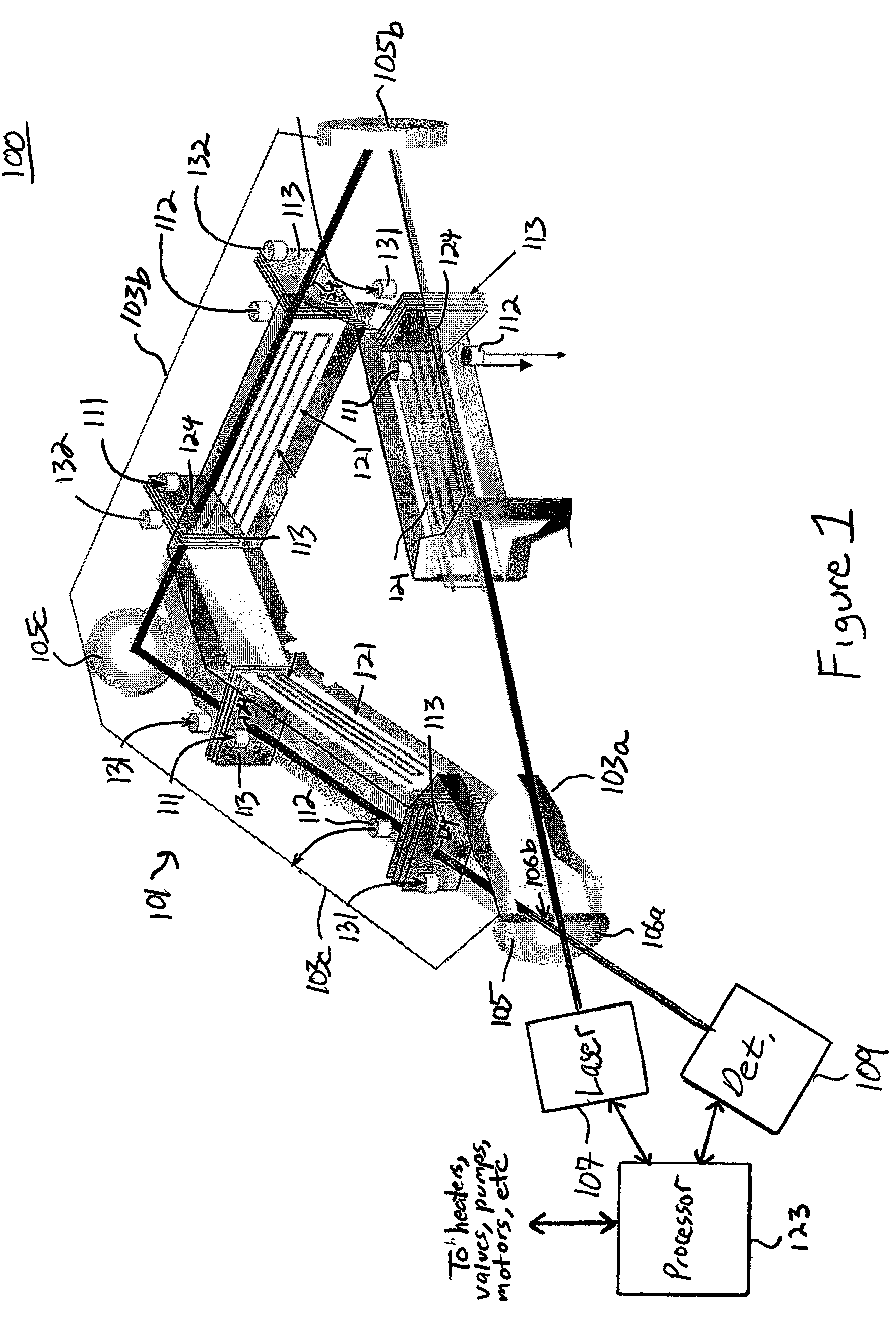
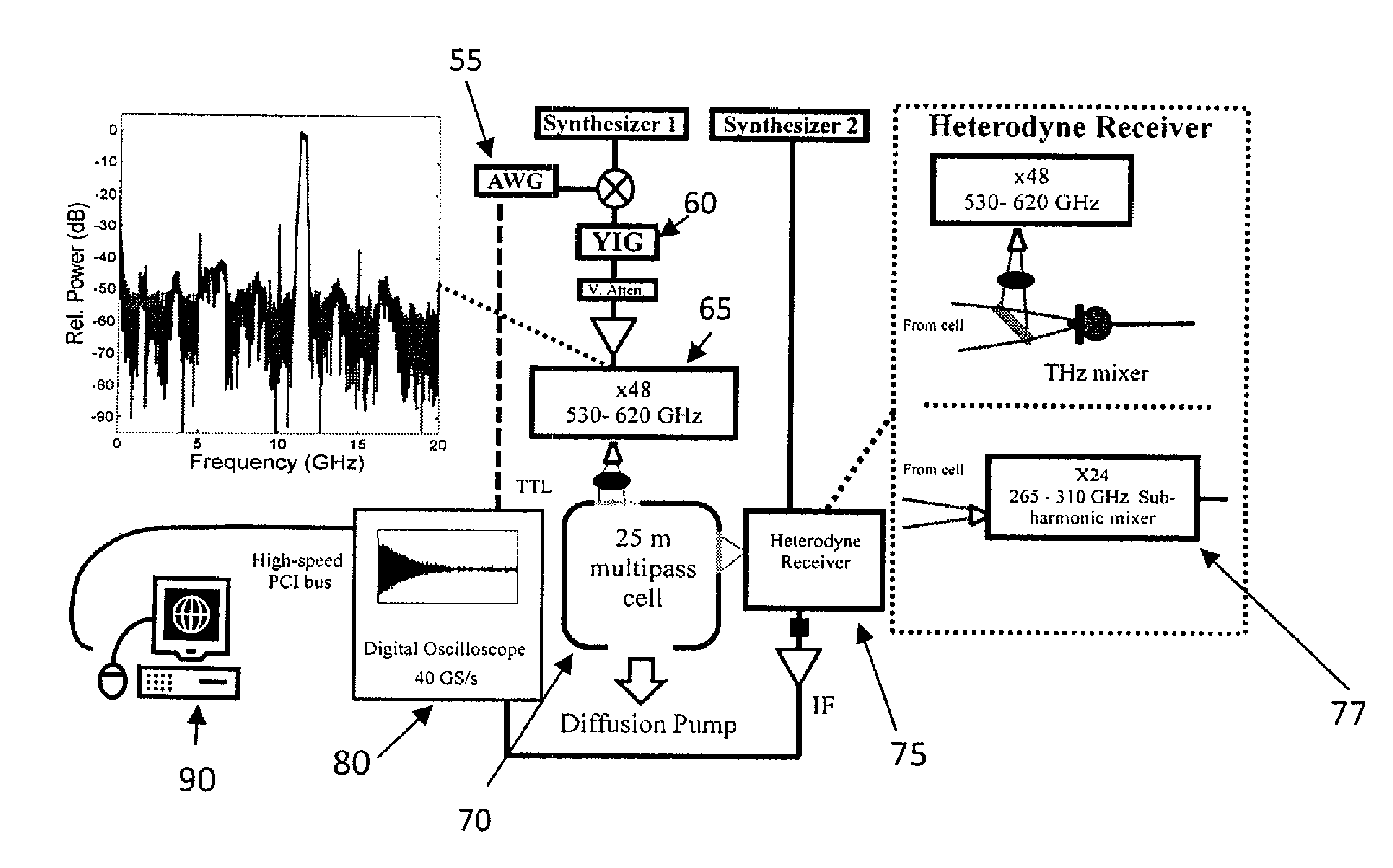
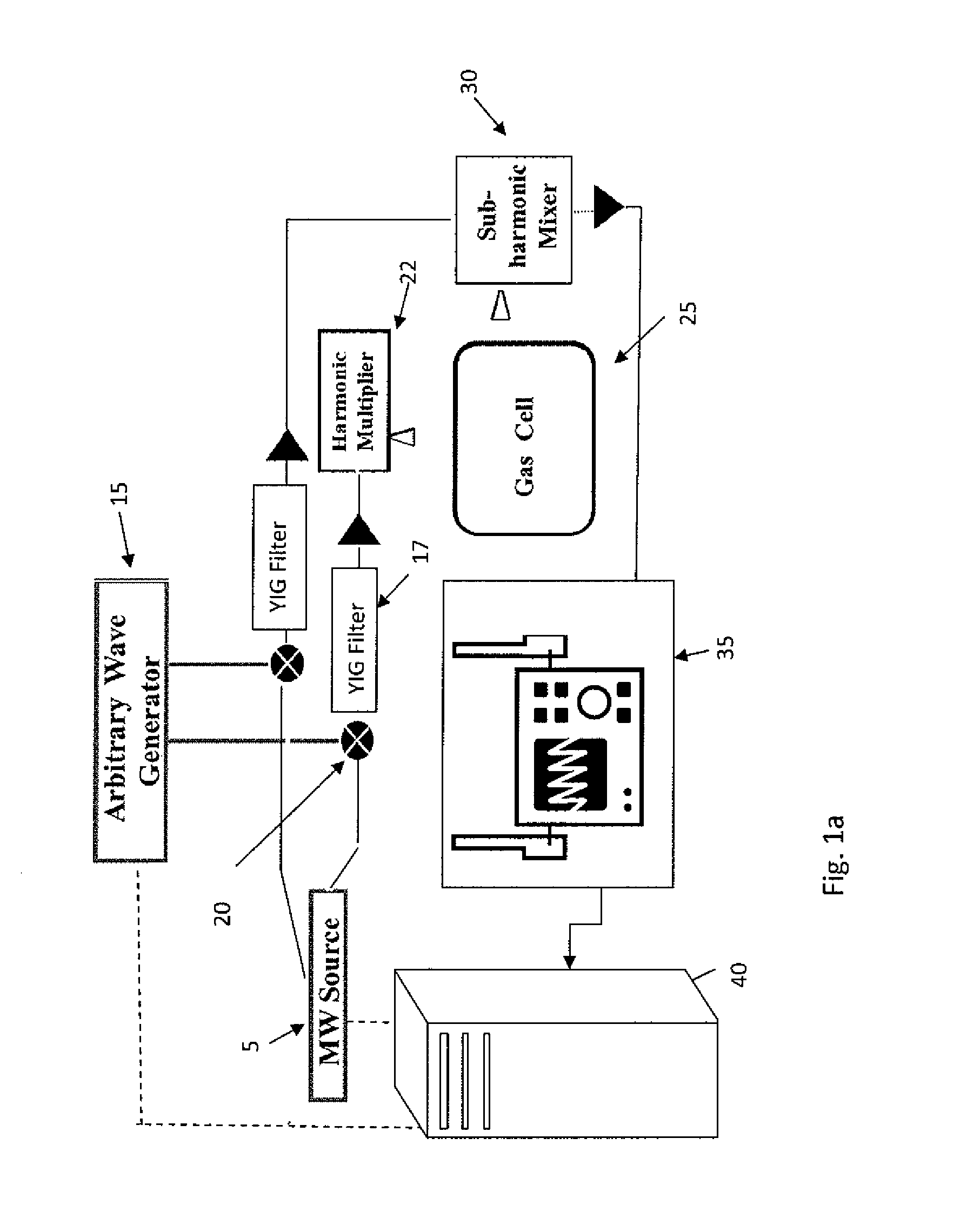
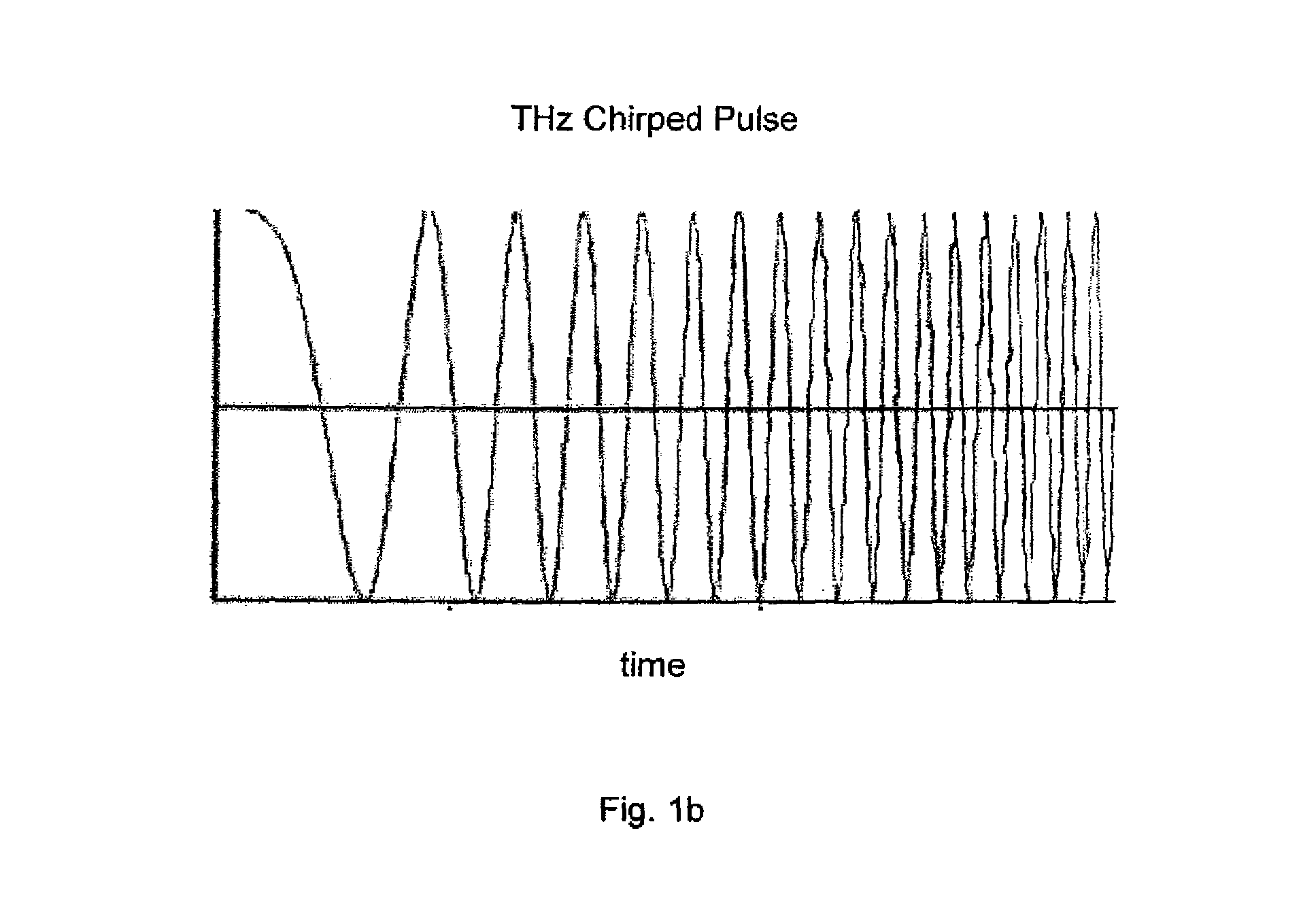
Chirped-pulse terahertz spectroscopy
ActiveUS8748822B1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansSpectroscopy methodsChirp pulse
Terahertz spectroscopy methods that are fast and have excellent spectral resolution and that do not require background correction of the instrument response without sample are disclosed. In one instance, the methods include phase coherent chirp pulse generation and phase coherent detection.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Optical Immersion probe incorporating a spherical lens
InactiveUS20020126289A1High precisionCompact and durable and straightforwardInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsInfraredFluorescence
This invention provides a spherical lens optical immersion probe for use in analysis of solids, liquids, gases, powders, suspensions, slurries, particles and other homogeneous or heterogeneous samples. The use of a spherical lens in an optical immersion probe confers many advantages over traditional immersion probes including ease of use and accuracy of focus. The probe of this invention has applications to many types of optical spectroscopy methods including ultraviolet / visible (UV-Vis), near-infrared (NIR), mid-infrared (FTIR), fluorescence, and Raman spectroscopy. The spherical lens used in this invention is both the optical and sample interface in the analytical system, and may be used to both focus the excitation source and to collecting signal. Importantly, this invention has broad applications to any optical analytical technology that necessitates an optical immersion probe.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Methods and apparatus for monitoring wound healing using impedance spectroscopy
ActiveUS20170156658A1Inhibition formationMonitor progression of wound healingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsWound healingMedicine
Methods and apparatus for real-time, quantifiable monitoring of high-risk areas of biological tissue are described. The methods and apparatus use impedance spectroscopy to detect subtle changes in tissue health.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Examination of subjects using photon migration with high directionality techniques
InactiveUS20080161697A1SurgeryScattering properties measurementsOptical radiationSpectroscopy methods
Owner:CHANCE BRITTON
Systems And Methods For Combined X-Ray Reflectometry And Photoelectron Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20190212281A1High measurement accuracyImprove throughputMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationColor/spectral properties measurementsSemiconductor structureX-ray
Methods and systems for measuring structural and material characteristics of semiconductor structures based on combined x-ray reflectometry (XRR) and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) are presented herein. A combined XRR and XPS system includes an x-ray illumination source and x-ray illumination optics shared by both the XRR and XPS measurement subsystems. This increases throughput and measurement accuracy by simultaneously collecting XRR and XPS measurement data from the same area of the wafer. A combined XRR and XPS system improves measurement accuracy by employing XRR measurement data to improve measurements performed by the XPS subsystem, and vice-versa. In addition, a combined XRR and XPS system enables simultaneous analysis of both XRR and XPS measurement data to more accurately estimate values of one of more parameters of interest. In a further aspect, any of measurement spot size, photon flux, beam shape, beam diameter, and illumination energy are independently controlled.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Adaptive compensation for measurement distortions in spectroscopy
InactiveUS7092832B2Compensation DistortionSpectrum investigationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMeasurement deviceSpectroscopy methods
Owner:INLIGHT SOLUTIONS
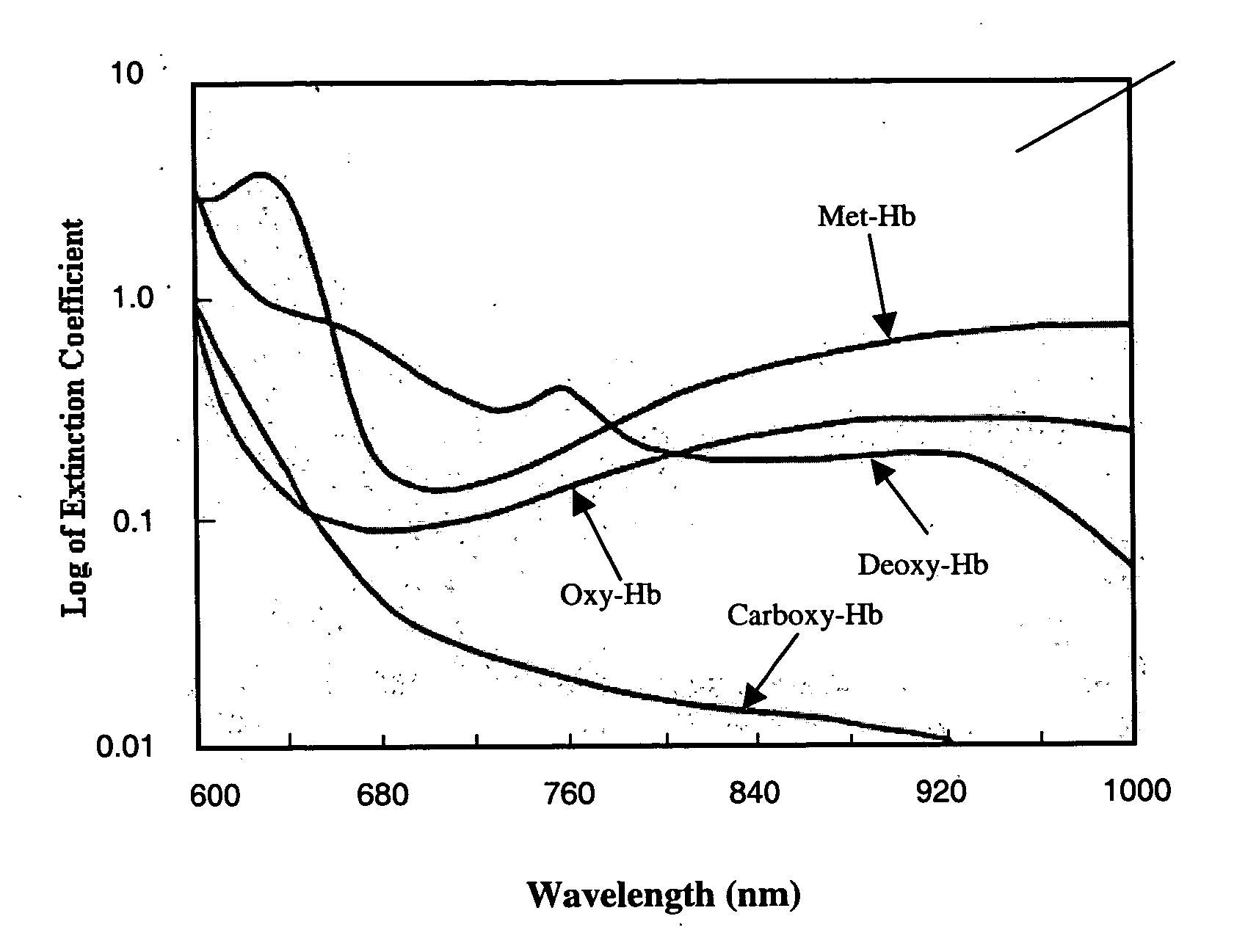
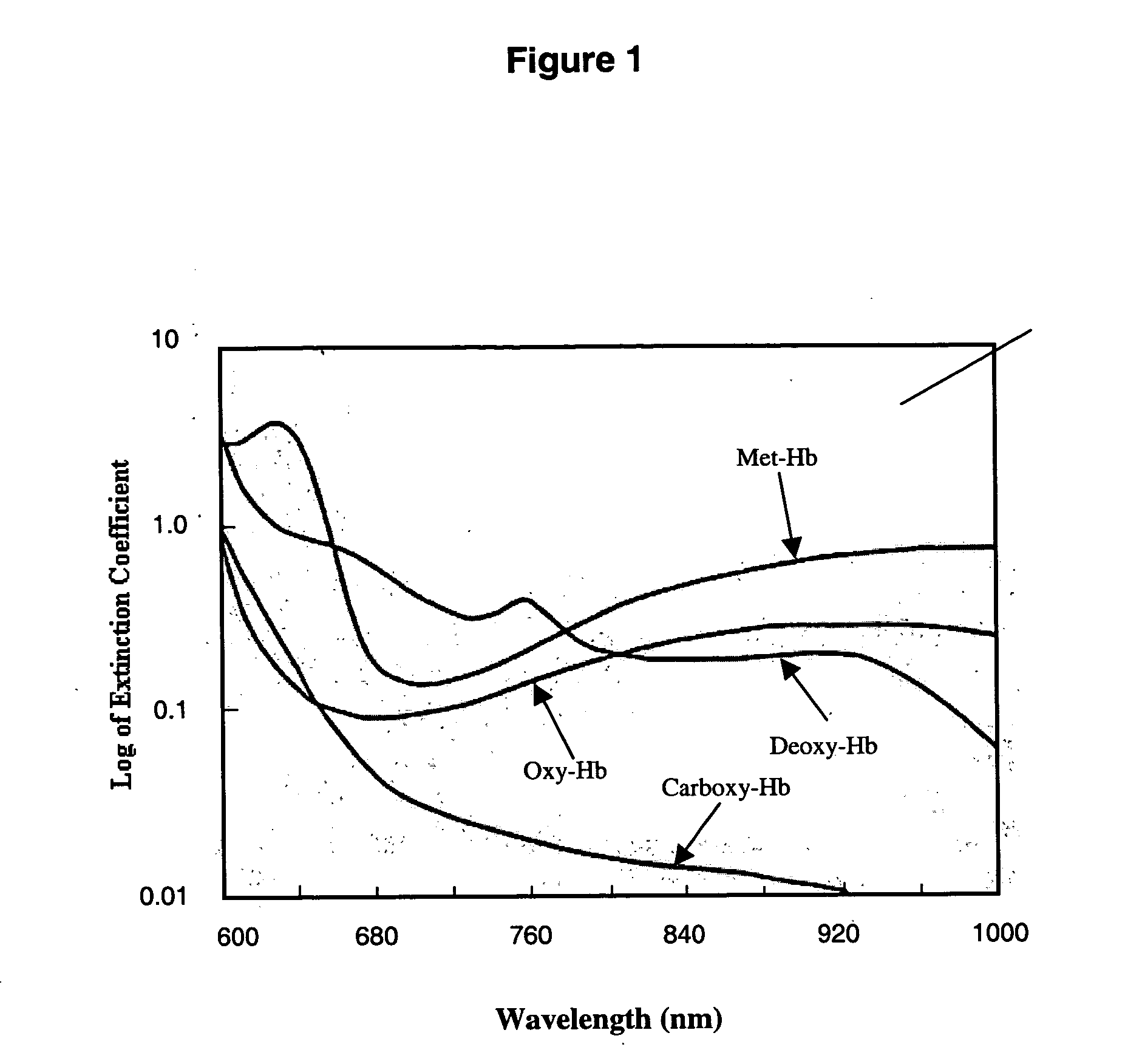
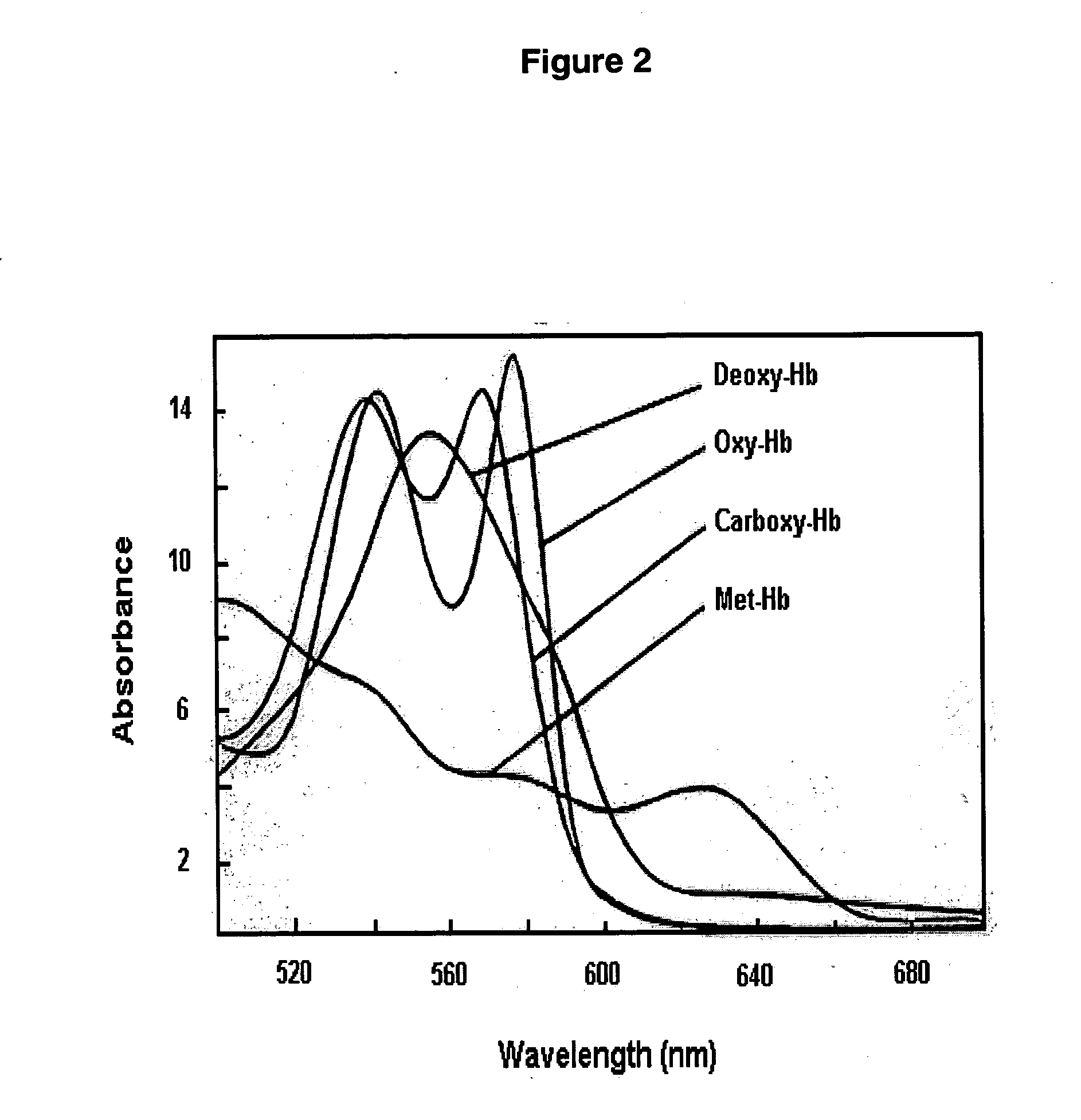
Spectroscopic method and apparatus for total hemoglobin measurement
InactiveUS20050019936A1Scattering properties measurementsLaboratory glasswaresTotal hemoglobinAbsorbance
A method and apparatus for measuring Tot-Hb in a sample are provided. The method comprises collecting absorbance measurements of a sample using a spectroscopic apparatus that comprises a first primary calibration algorithm for one of Oxy-Hb, “Oxy-Hb plus Deoxy-Hb”, or “Total-Hb minus Met-Hb” and a second primary calibration algorithm for one or more than one of Met-Hb, Carboxy-Hb, or Sulf-Hb, or comprising a third primary calibration algorithm obtained by adding terms of the first primary calibration algorithm and the second primary calibration algorithm together. Followed by predicting either a first value for one of Oxy-Hb, “Oxy-Hb plus Deoxy-Hb,” or “Total-Hb minus Met-Hb” and predicting second value for one or more than one of Met-Hb, Carboxy-Hb, or Sulf-Hb in the sample and add the first and second value together, or predicting a value for Total-Hb.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
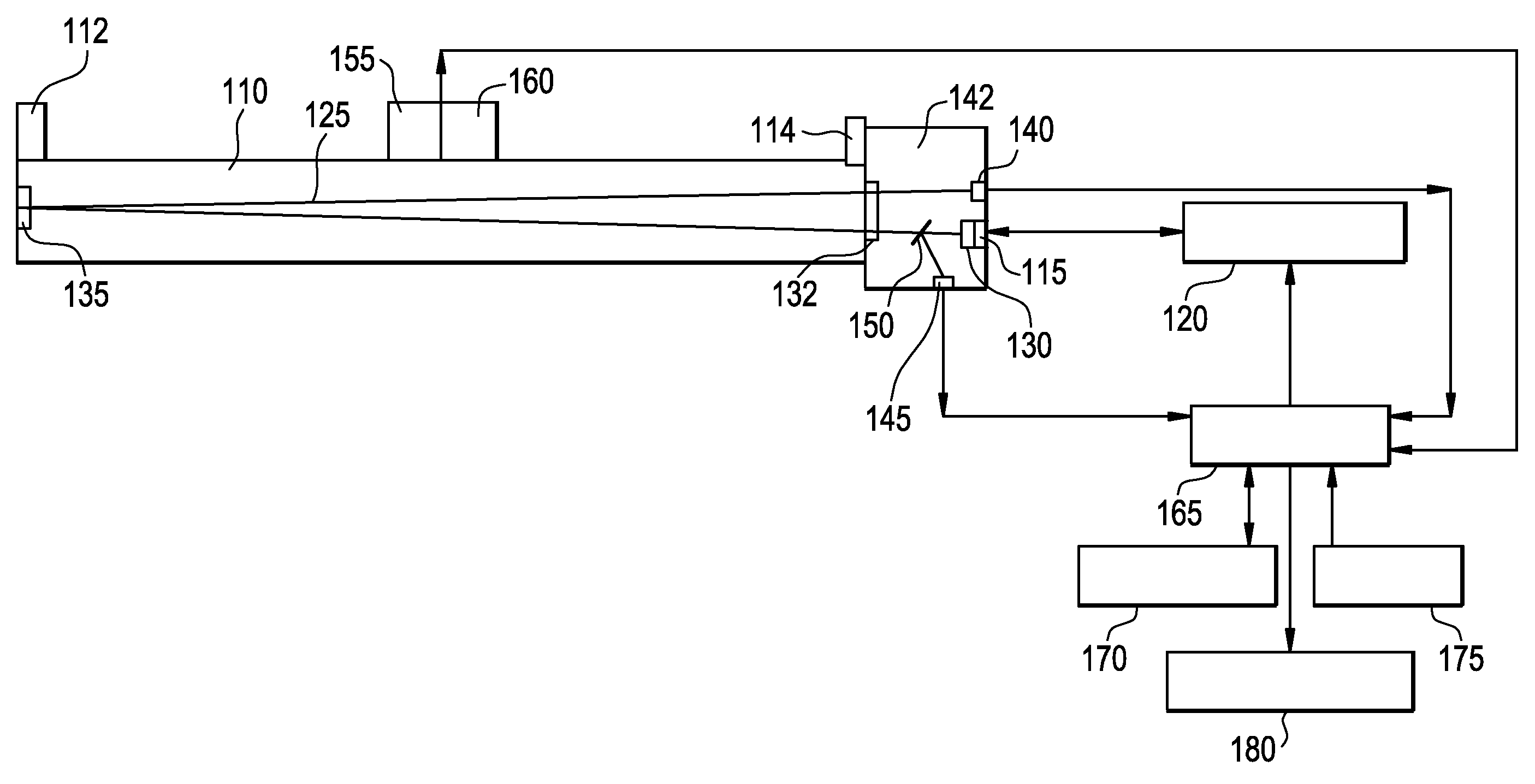
Wavelength-modulation spectroscopy method and apparatus
In one embodiment of the spectroscopy method, the method comprises the steps of modulating the wavelength of a monochromatic radiation at a modulation amplitude and a modulation frequency; determining a first variable representative of an absorbance of an analyte in a sample; and demodulating by phase-sensitive detection the first variable at a harmonic of the modulation frequency to produce a harmonic spectrum of the analyte. In one embodiment of the spectroscopy apparatus, the apparatus comprises a laser diode integrated with a first photodetector configured to detect an intensity of a backward emission from the laser diode and act as a reference detector; a second photodetector configured to detect an intensity of laser radiation exiting a sample; and electronic circuitry coupled to the laser diode and the photodetectors, configured to acquire and process spectra of the sample. In another embodiment, the spectroscopy apparatus comprises a beam splitter configured to split the laser radiation into a first radiation portion and a second radiation portion and a first photodetector configured to detect the intensity of the first radiation portion.
Owner:GE INFRASTRUCTURE SENSING
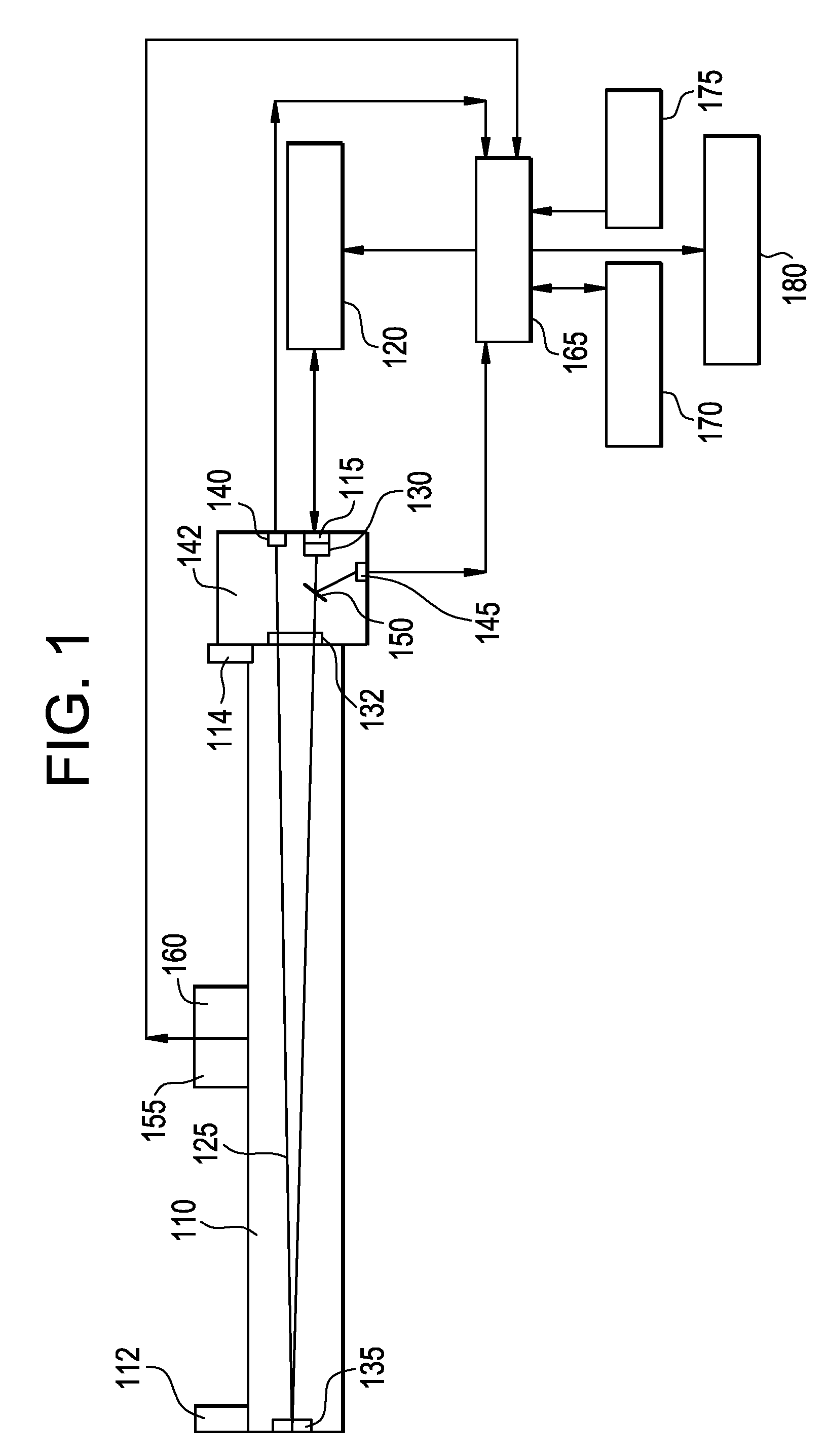
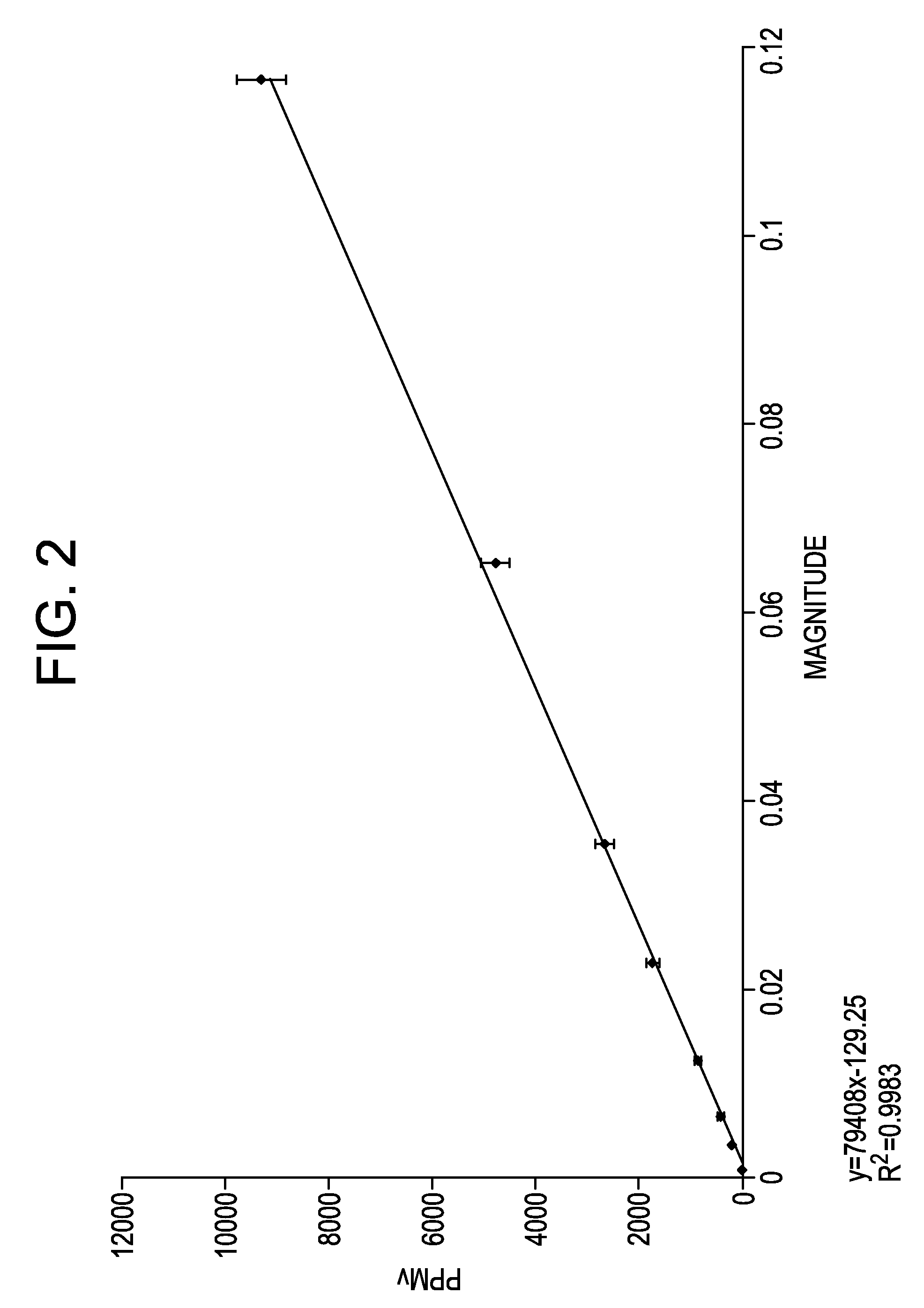
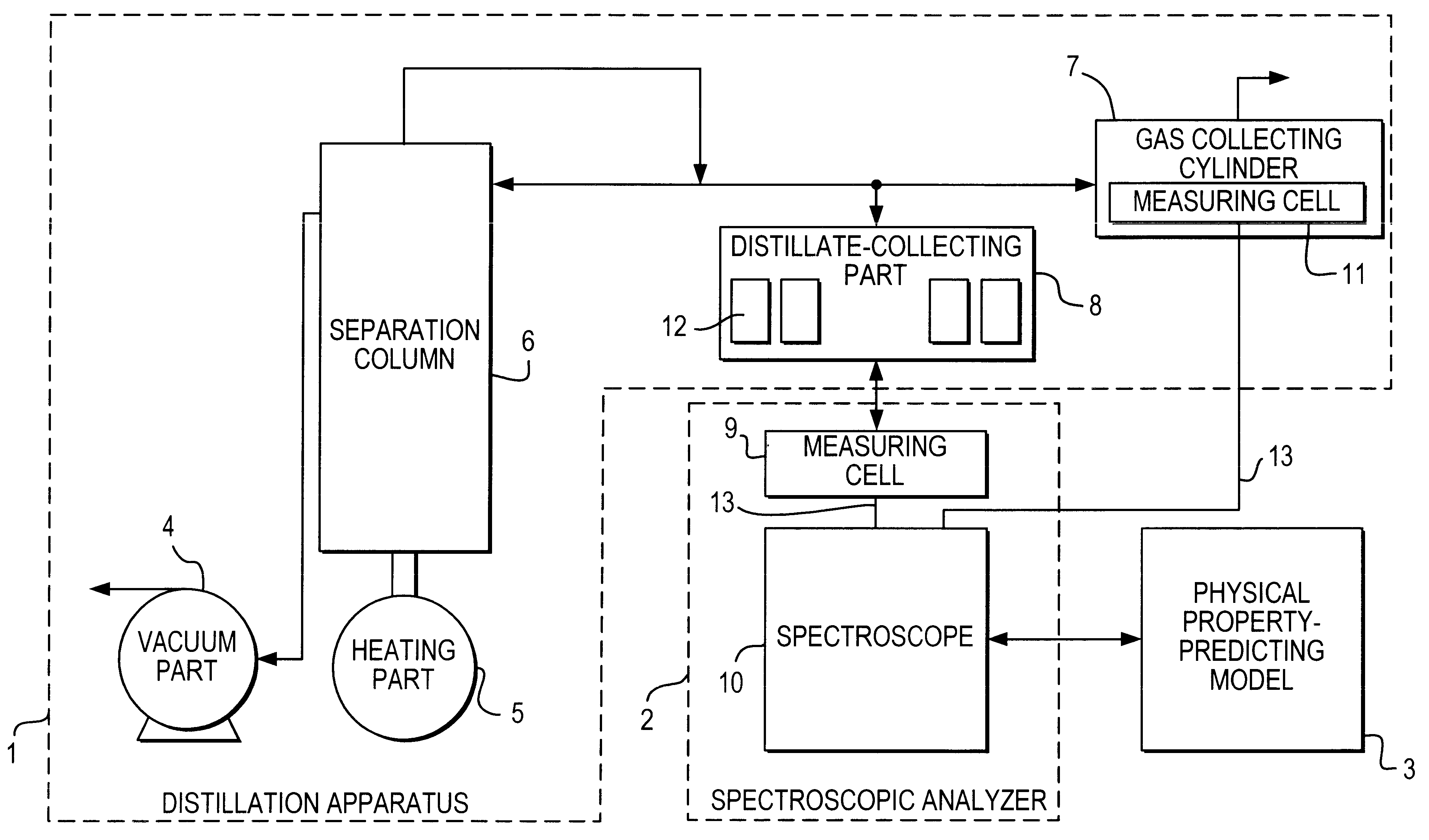
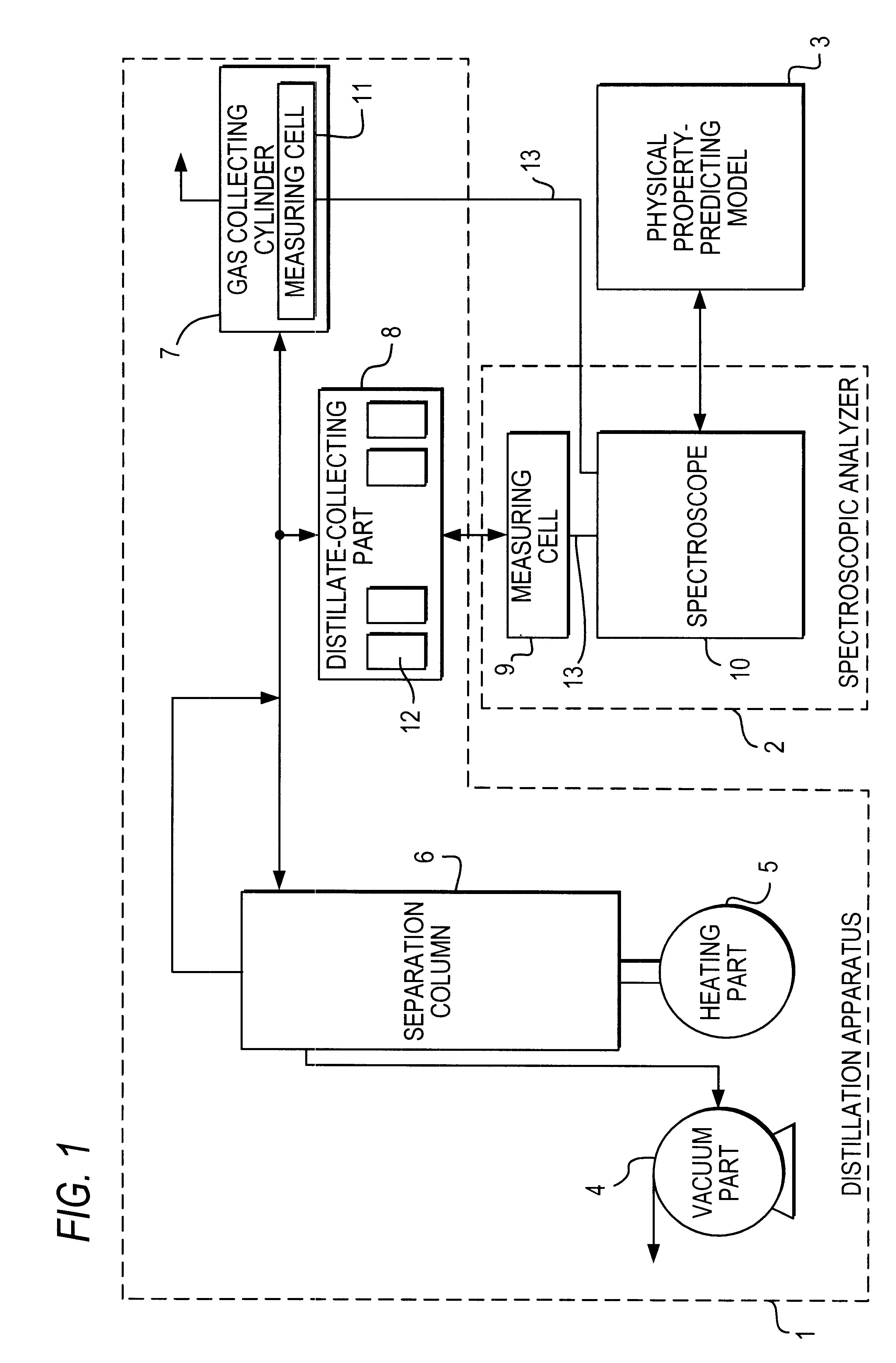
Automatic analysis method of crude petroleum oils using spectroscopy
Disclosed is an automatic analysis method of crude oils, using spectroscopy. A near infrared spectroscopic analysis apparatus is combined with an ordinary distillation apparatus, so as to analyze the physical properties of each oil distillate as soon as it is separated from crude oils, thereby bringing about a significant improvement in analysis accuracy and in an economical aspect. It takes only two days for one person to obtain a full assay data for crude oils by taking advantage of the method. In addition to requiring a significantly reduced equipment cost, the method enables full assay data for crude oils to be obtained quickly, thereby securing more up-to-date information about crude oils and producing an economical benefit.
Owner:SK ENERGY CO LTD (KR)
Optical immersion probe incorporating a spherical lens
InactiveUS6977729B2High precisionCompact and durable and straightforwardInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsInfraredFluorescence
This invention provides a spherical lens optical immersion probe for use in analysis of solids, liquids, gases, powders, suspensions, slurries, particles and other homogeneous or heterogeneous samples. The use of a spherical lens in an optical immersion probe confers many advantages over traditional immersion probes including ease of use and accuracy of focus. The probe of this invention has applications to many types of optical spectroscopy methods including ultraviolet / visible (UV-Vis), near-infrared (NIR), mid-infrared (FTIR), fluorescence, and Raman spectroscopy. The spherical lens used in this invention is both the optical and sample interface in the analytical system, and may be used to both focus the excitation source and to collecting signal. Importantly, this invention has broad applications to any optical analytical technology that necessitates an optical immersion probe.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
High Frequency Deflection Measurement of IR Absorption
ActiveUS20120167261A1Reduce impactEnhanced electric fieldNanotechnologyColor/spectral properties measurementsImage resolutionIr absorption
An AFM based technique has been demonstrated for performing highly localized IR spectroscopy on a sample surface by using the AFM probe to detect wavelength dependent IR radiation interaction, typically absorption with the sample in the region of the tip. The tip may be configured to produce electric field enhancement when illuminated by a radiation source. This enhancement allows for significantly reduced illumination power levels resulting in improved spatial resolution by confining the sample-radiation interaction to the region of field enhancement which is highly localized to the tip.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
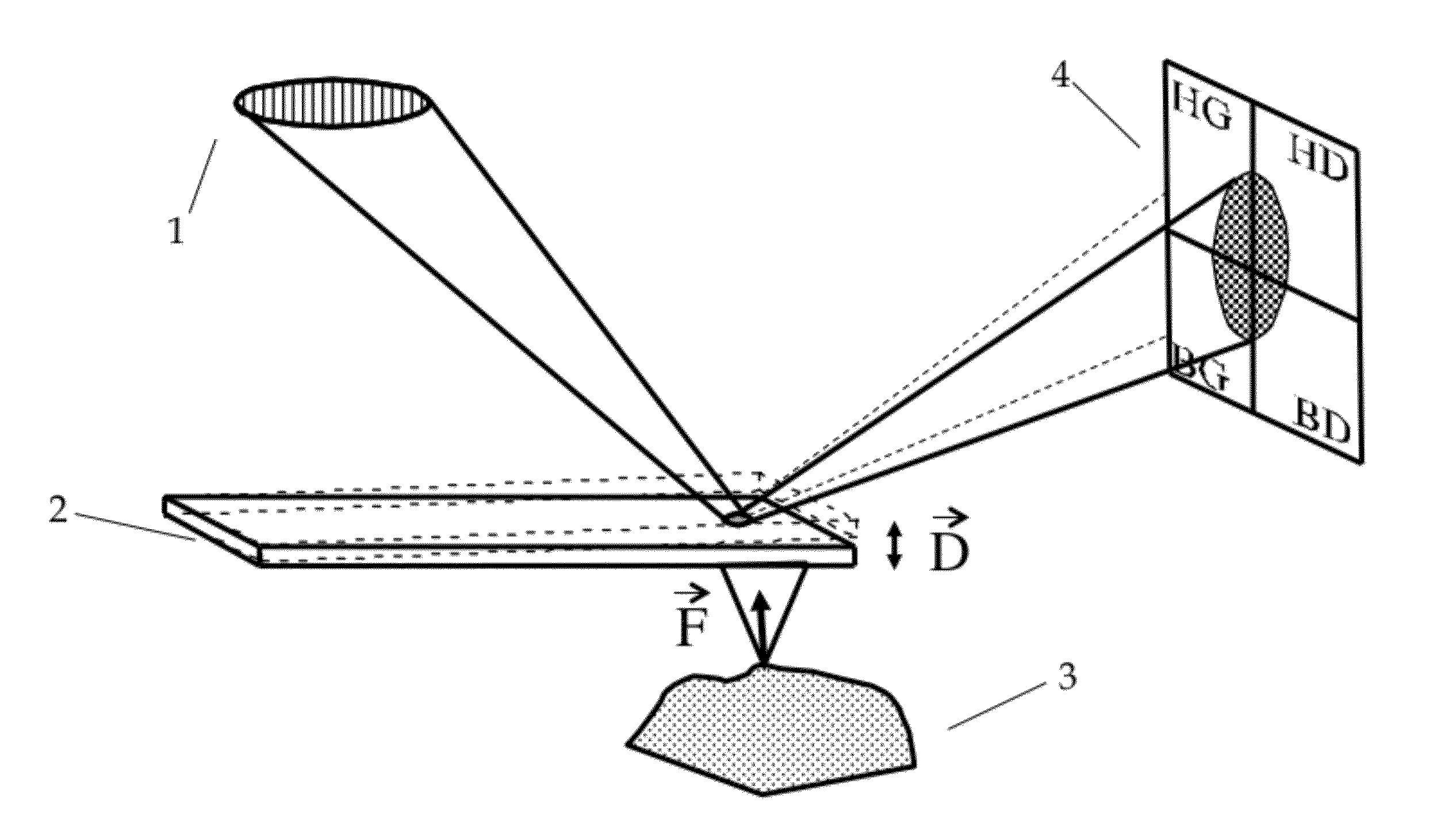
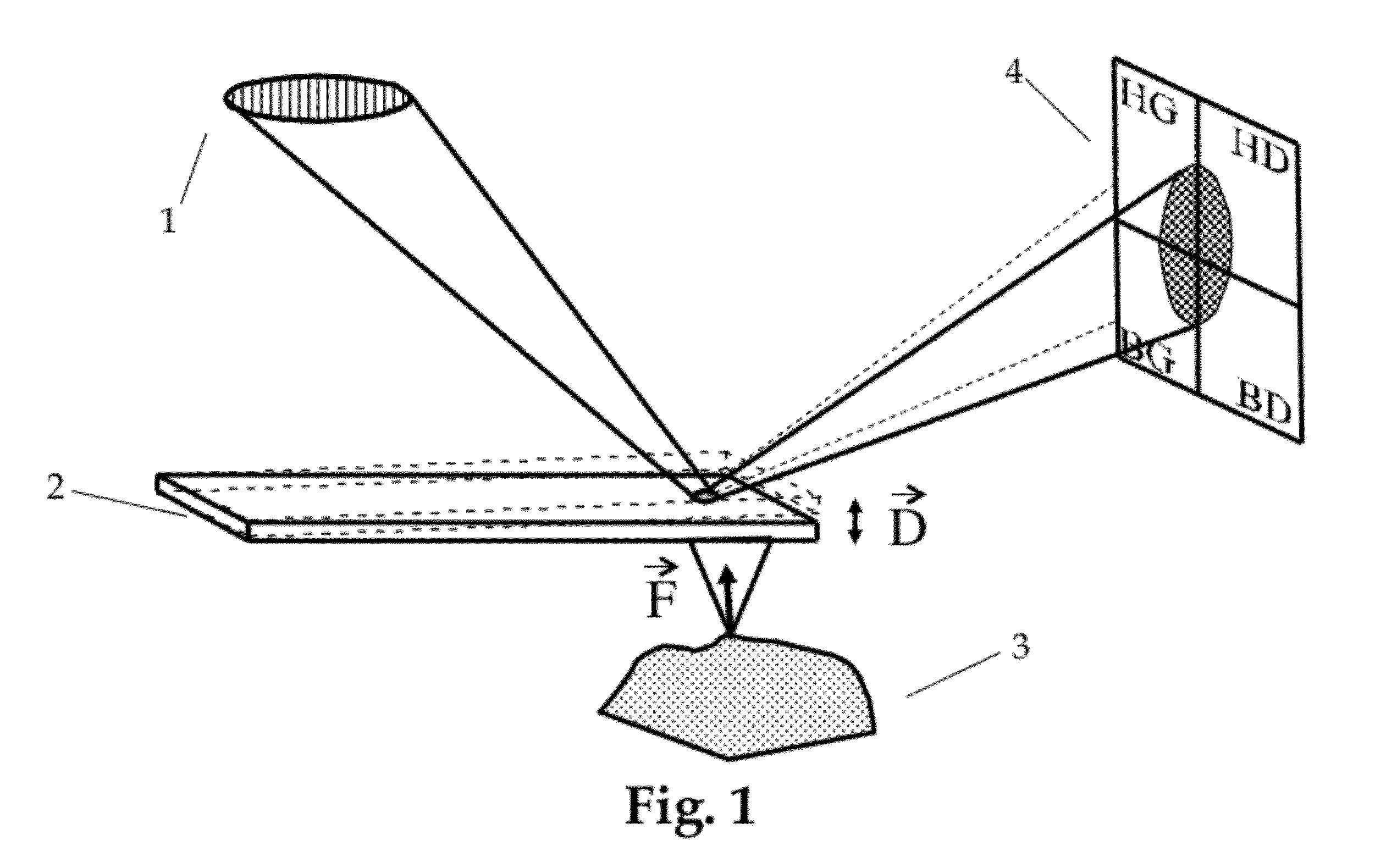
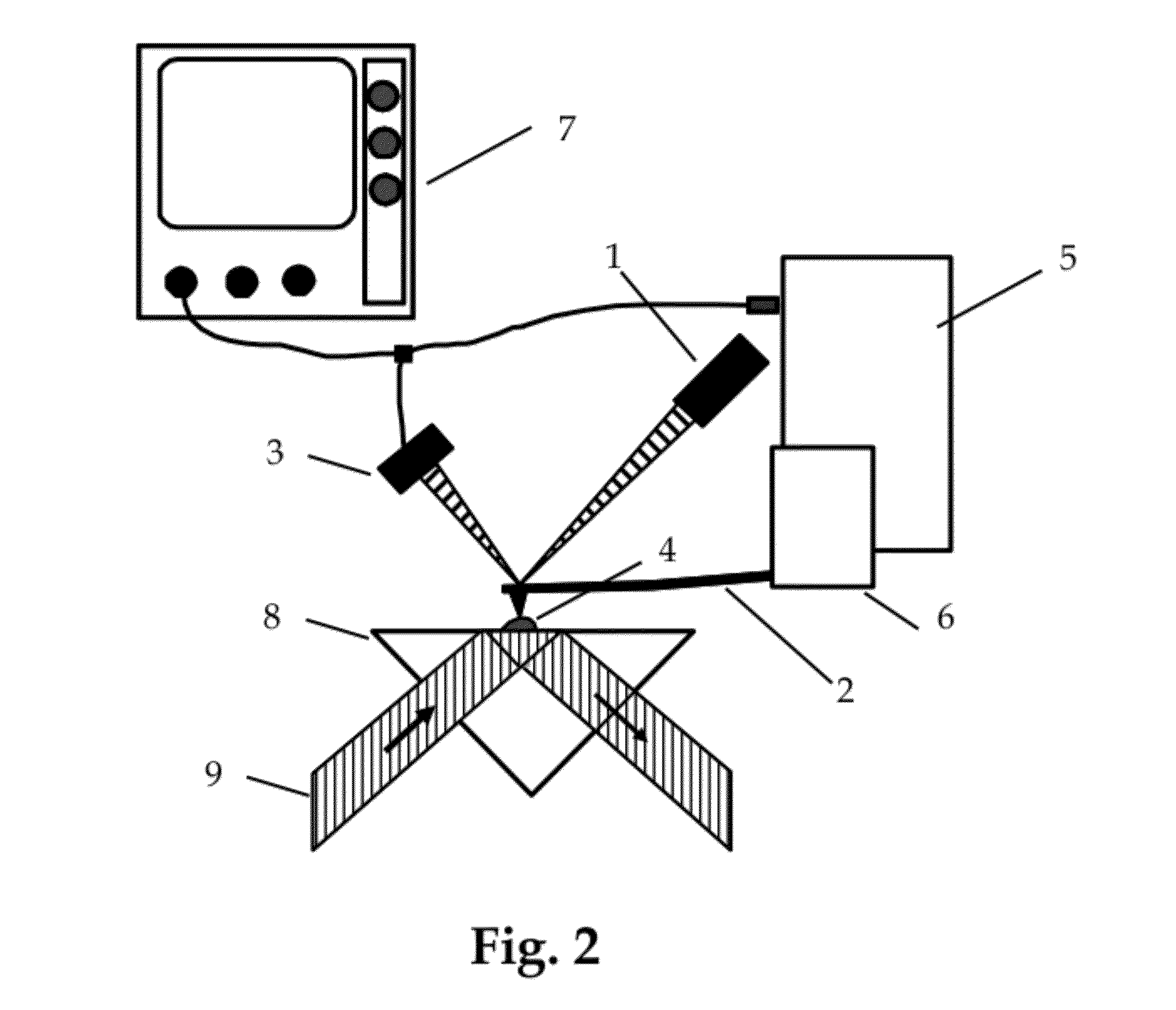
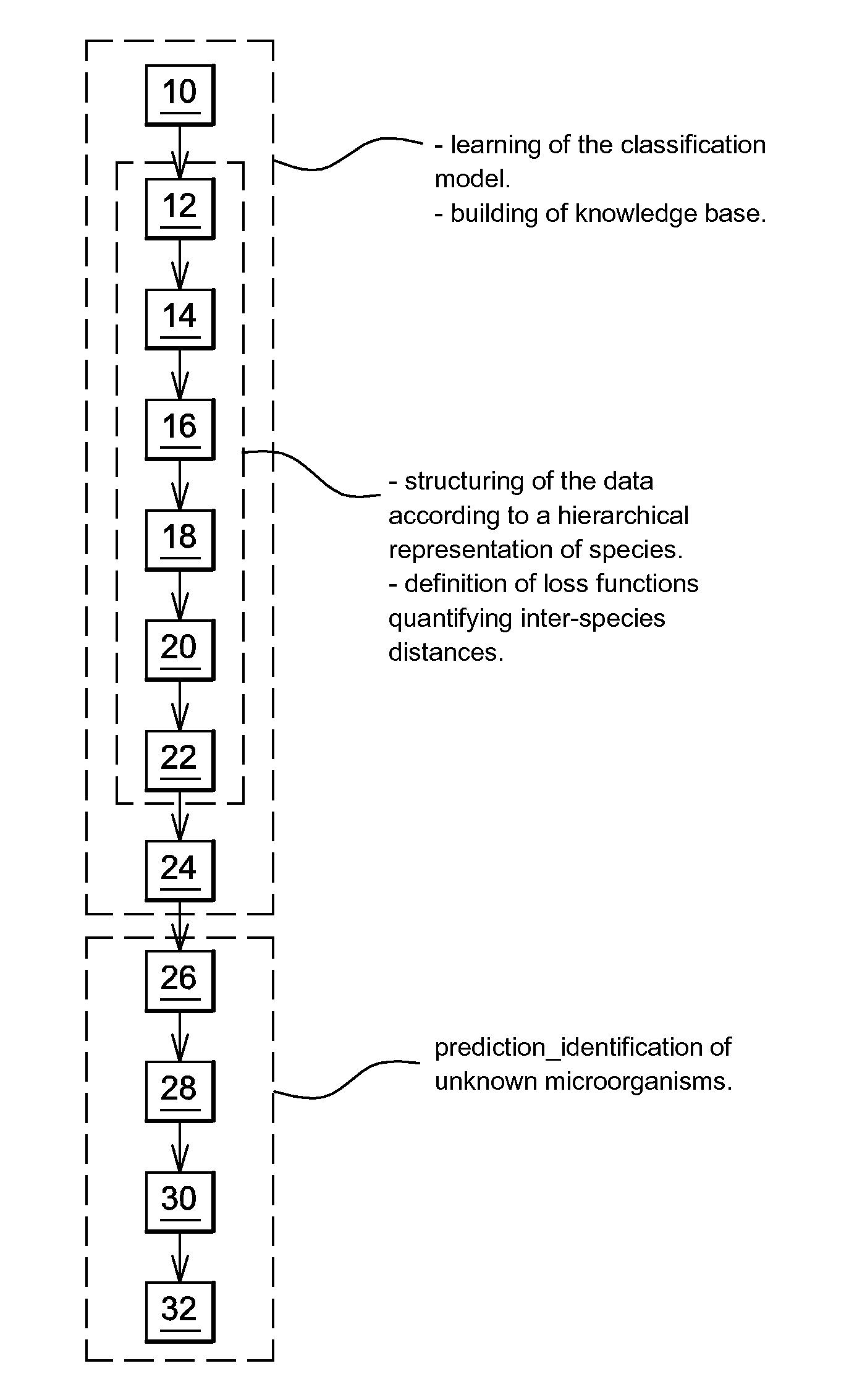
Identification Of Microorganisms By Spectrometry And Structured Classification
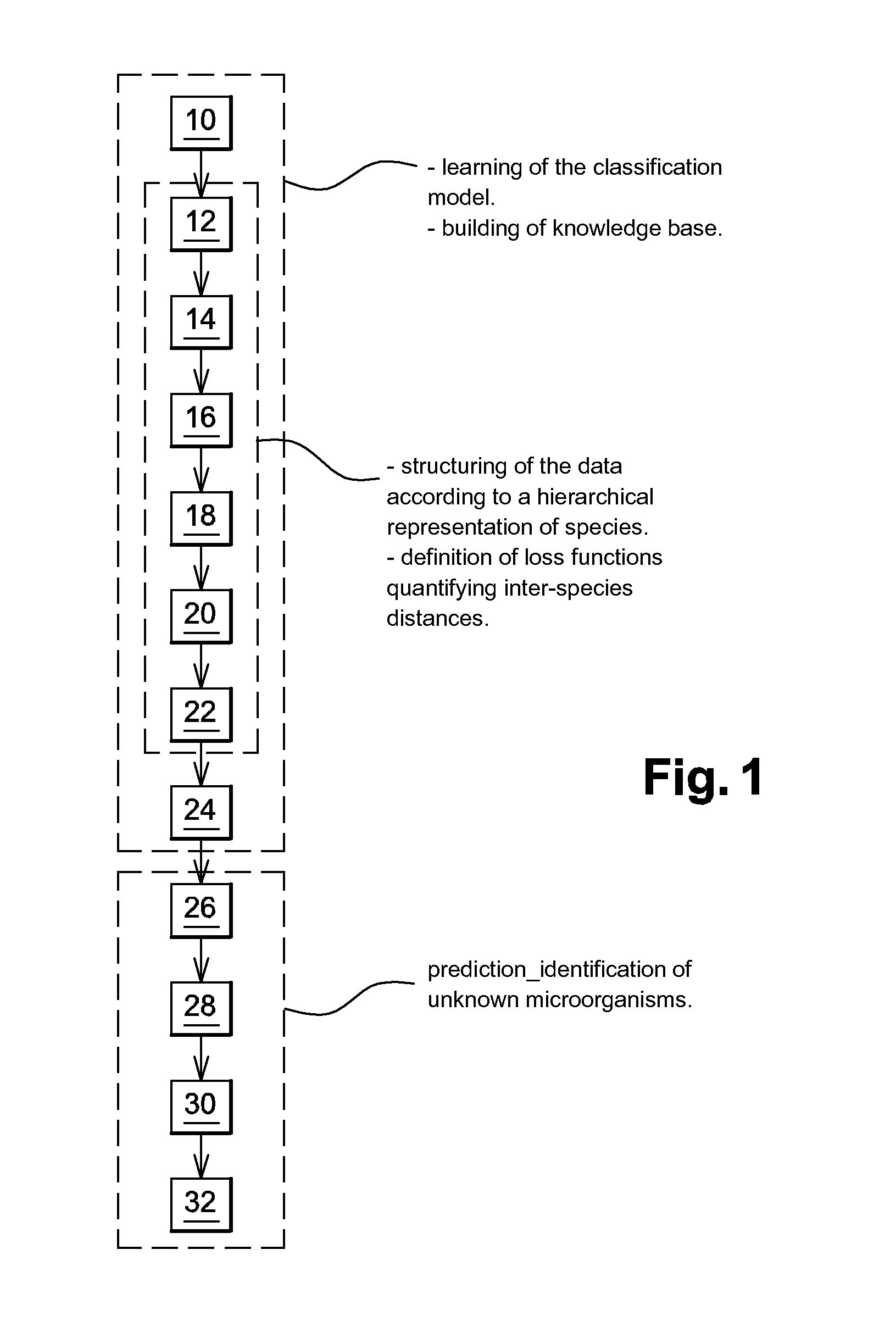
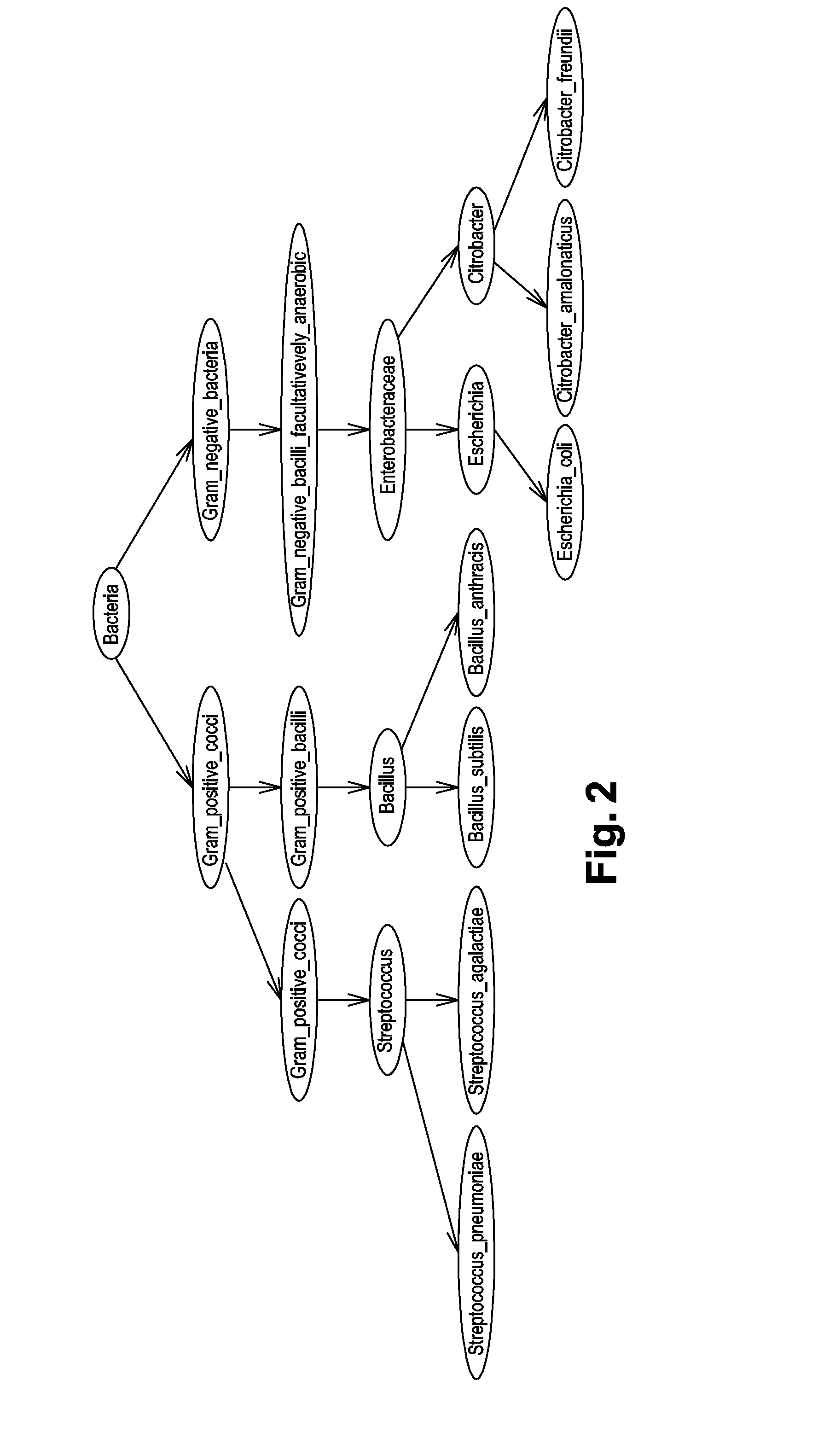
InactiveUS20150051840A1Minimize severityReliable identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsNODALMicroorganism
A method of identifying by spectrometry of unknown microorganisms from among a set of reference species, including a first step of supervised learning of a classification model of the reference species, a second step of predicting an unknown microorganism to be identified, including acquiring a spectrum of the unknown microorganism; and applying a prediction model according to said spectrum and to the classification model to infer at least one type of microorganism to which the unknown microorganism belong. The classification model is calculated by a structured multi-class SVM algorithm applied to the nodes of a tree-like hierarchical representation of the reference species in terms of evolution and / or of clinical phenotype and having margin constraints including so-called “loss” functions quantifying a proximity between the tree nodes.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com