Examination of subjects using photon migration with high directionality techniques
a high-directionality, photon migration technology, applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, instruments, applications, etc., can solve the problems of inapplicability of certain aspects of cross-sectional imaging techniques, and none of those techniques have fully satisfied all situations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
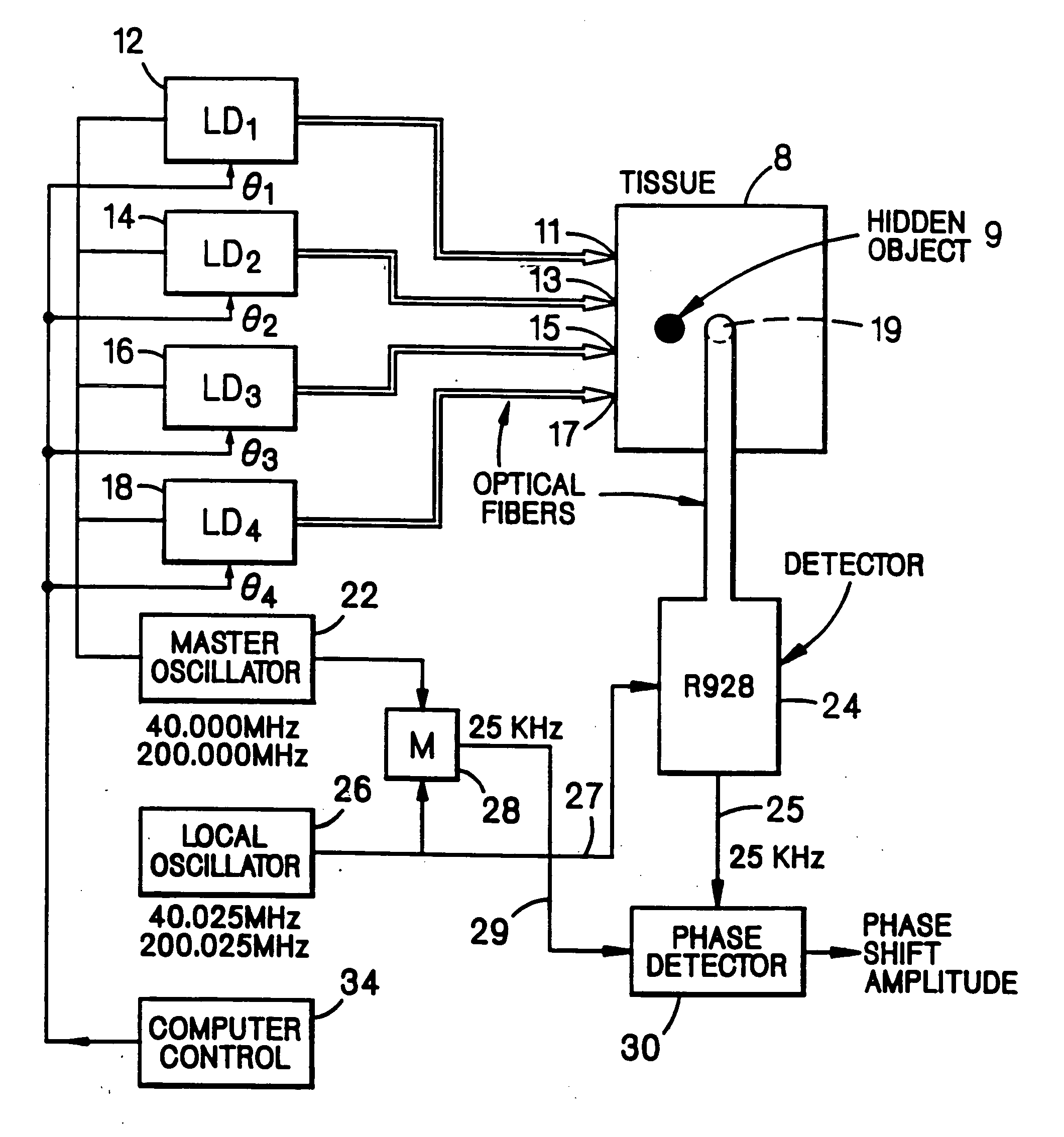
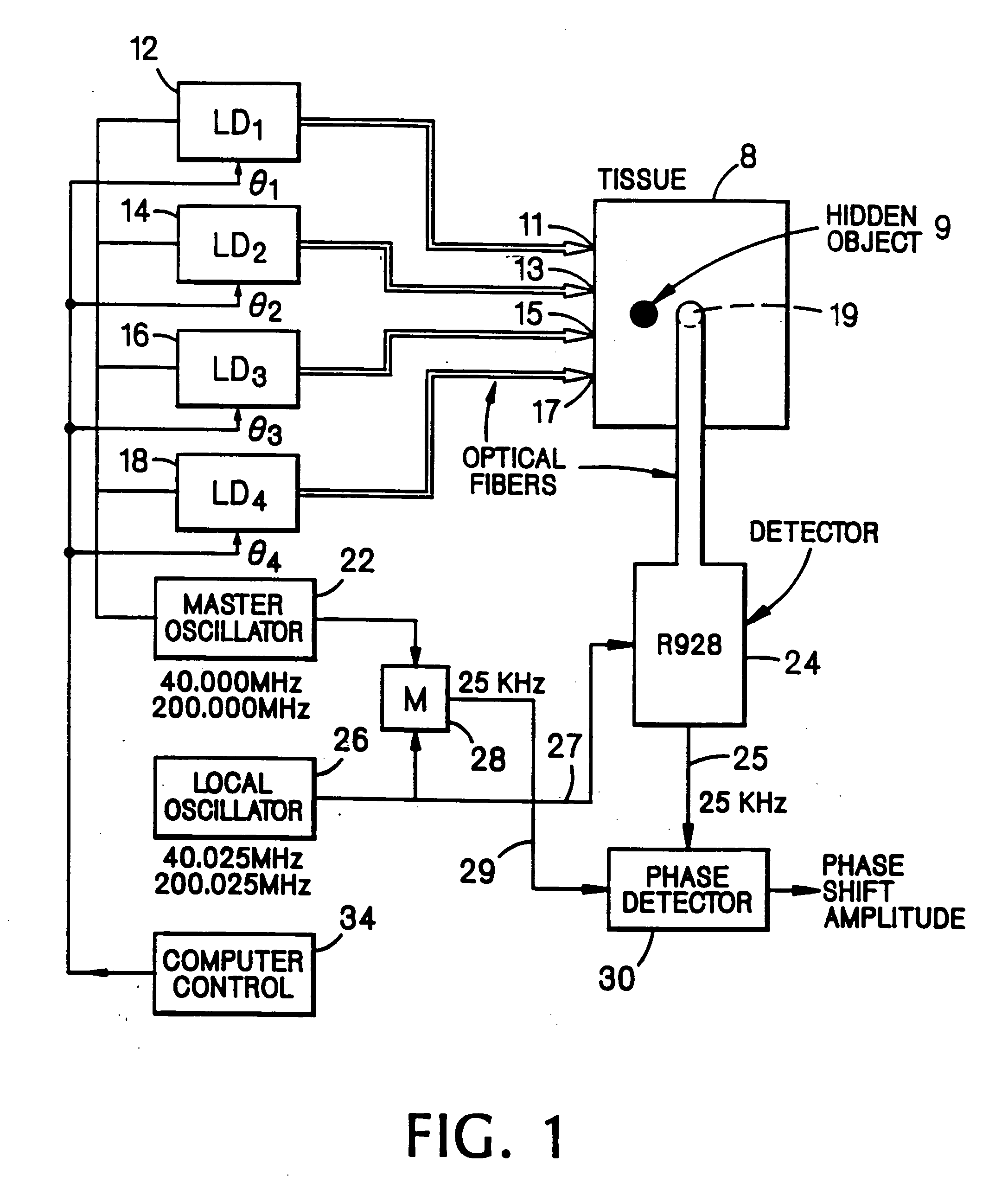
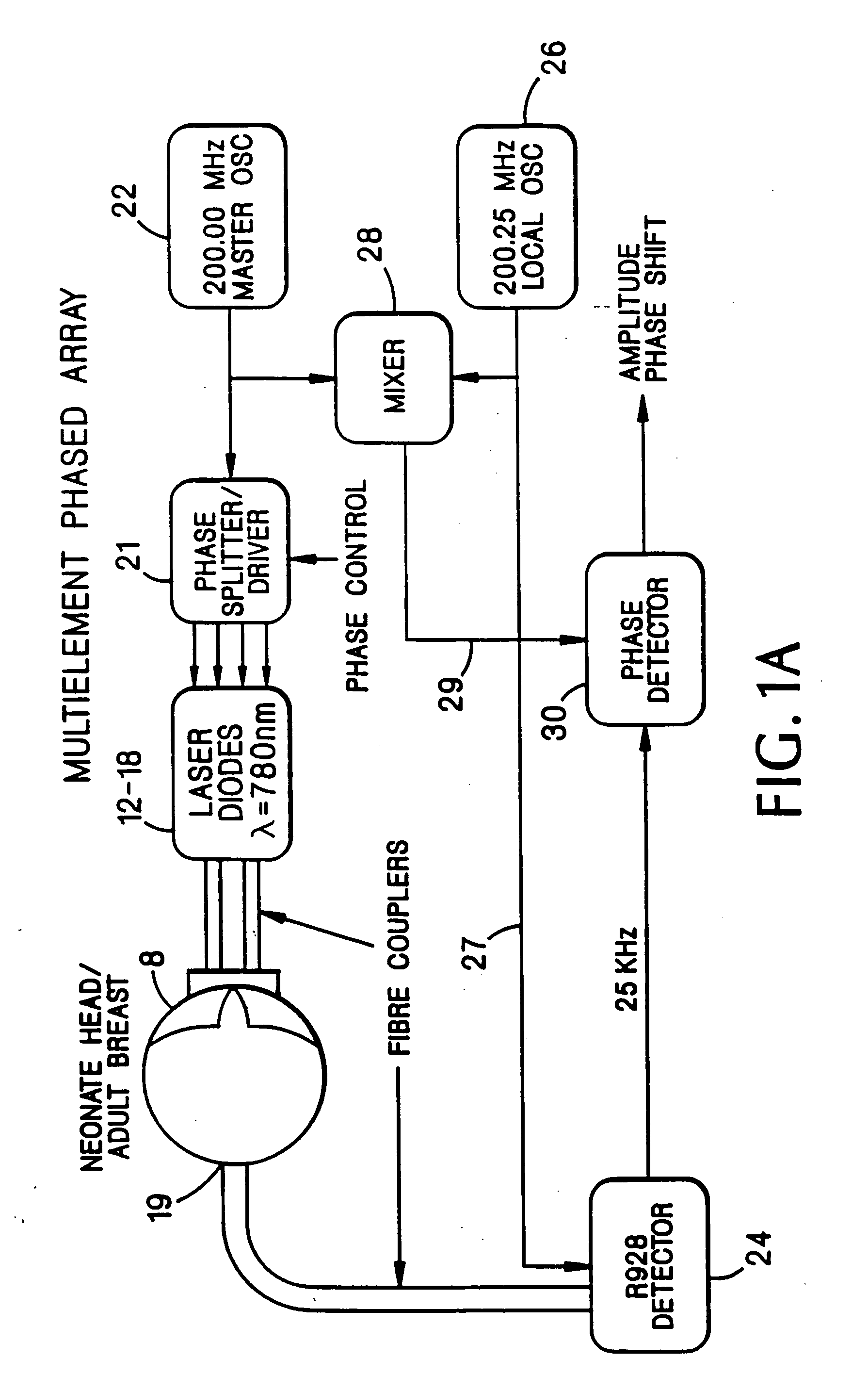
[0057]Imaging system embodiments of the present invention based upon interference effects of radiation migrating in a subject having scattering and absorptive properties are shown in FIGS. 1, 2, and 3. The systems effectively utilize, in this scattering medium, a directional beam of visible or IR radiation generated and / or detected by an array of sources and / or detectors, respectively. For instance, in the case of an array of sources, each source is placed at a selected location in the array and emits intensity modulated radiation, preferably coherent radiation from a laser diode, of a selected intensity and phase. The criteria for selecting the source locations, the intensities, and the phases of the respective sources is the shape of the desired beam that at any time point possesses a substantial photon density gradient produced by interference effects of radiation from the various sources. This gradient of photon density is localized and has directional properties. Overall, the r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com