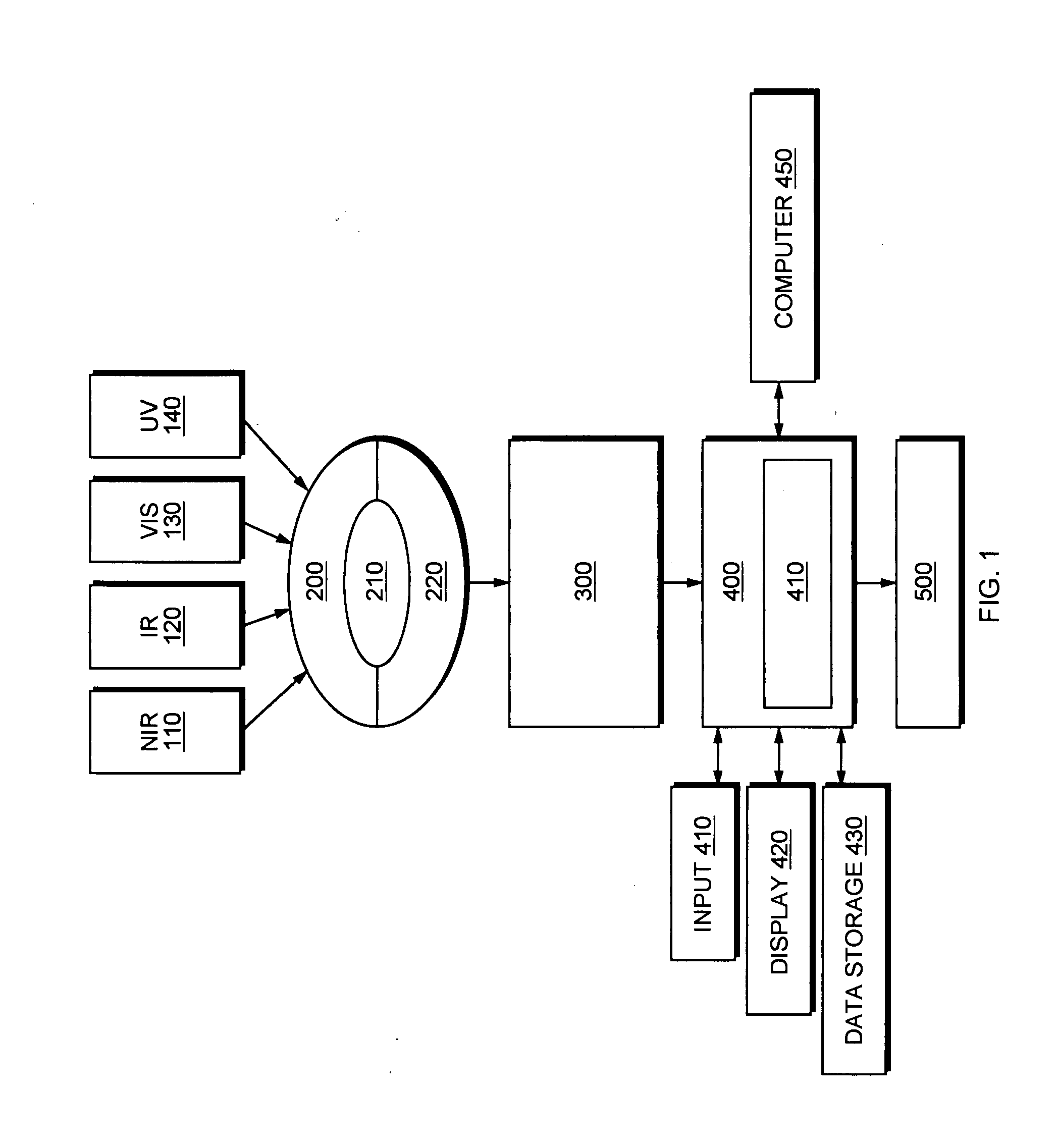
Patents
Literature
2278 results about "Raman spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Raman spectroscopy (/ˈrɑːmən/); named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified.
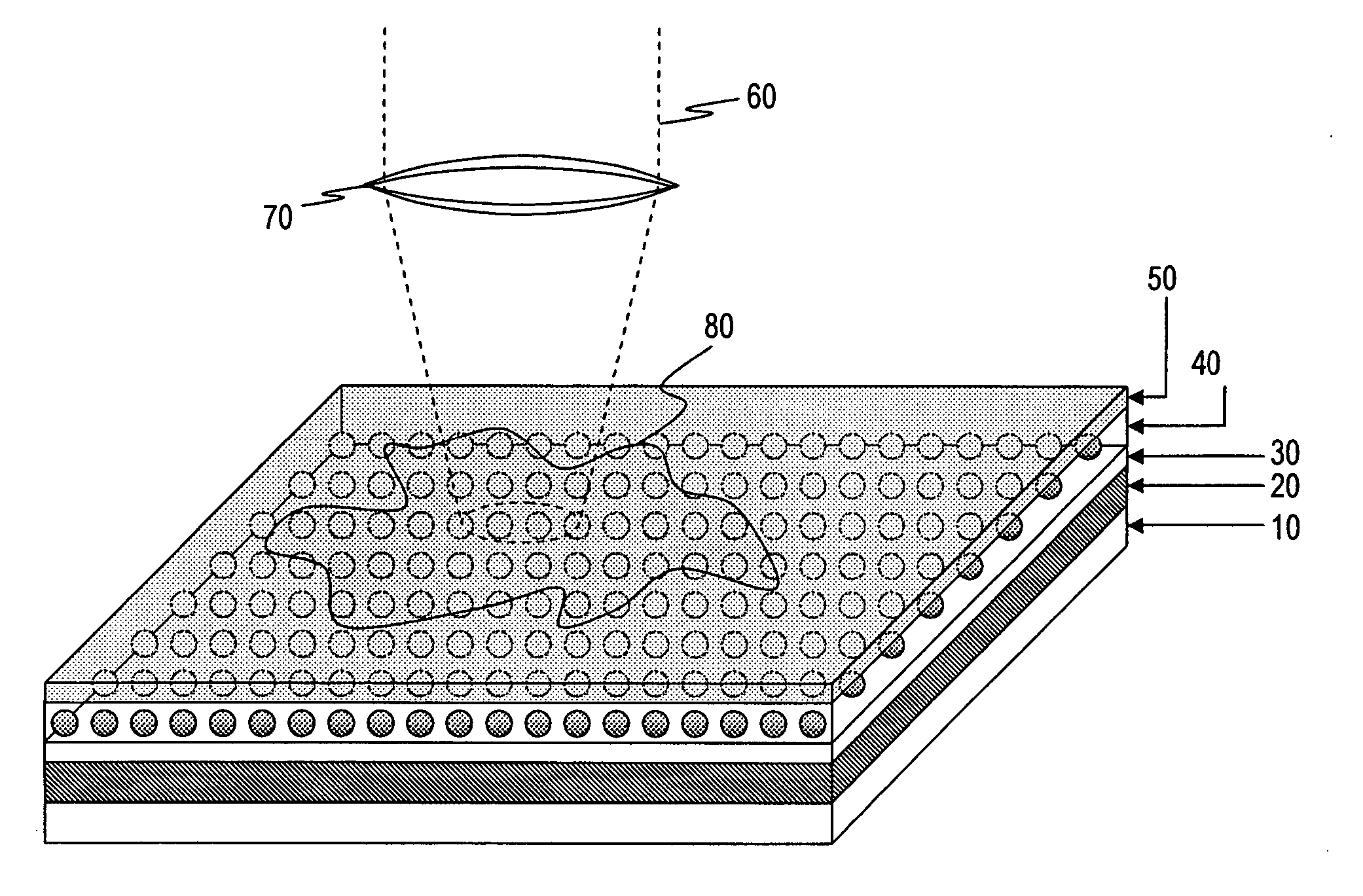
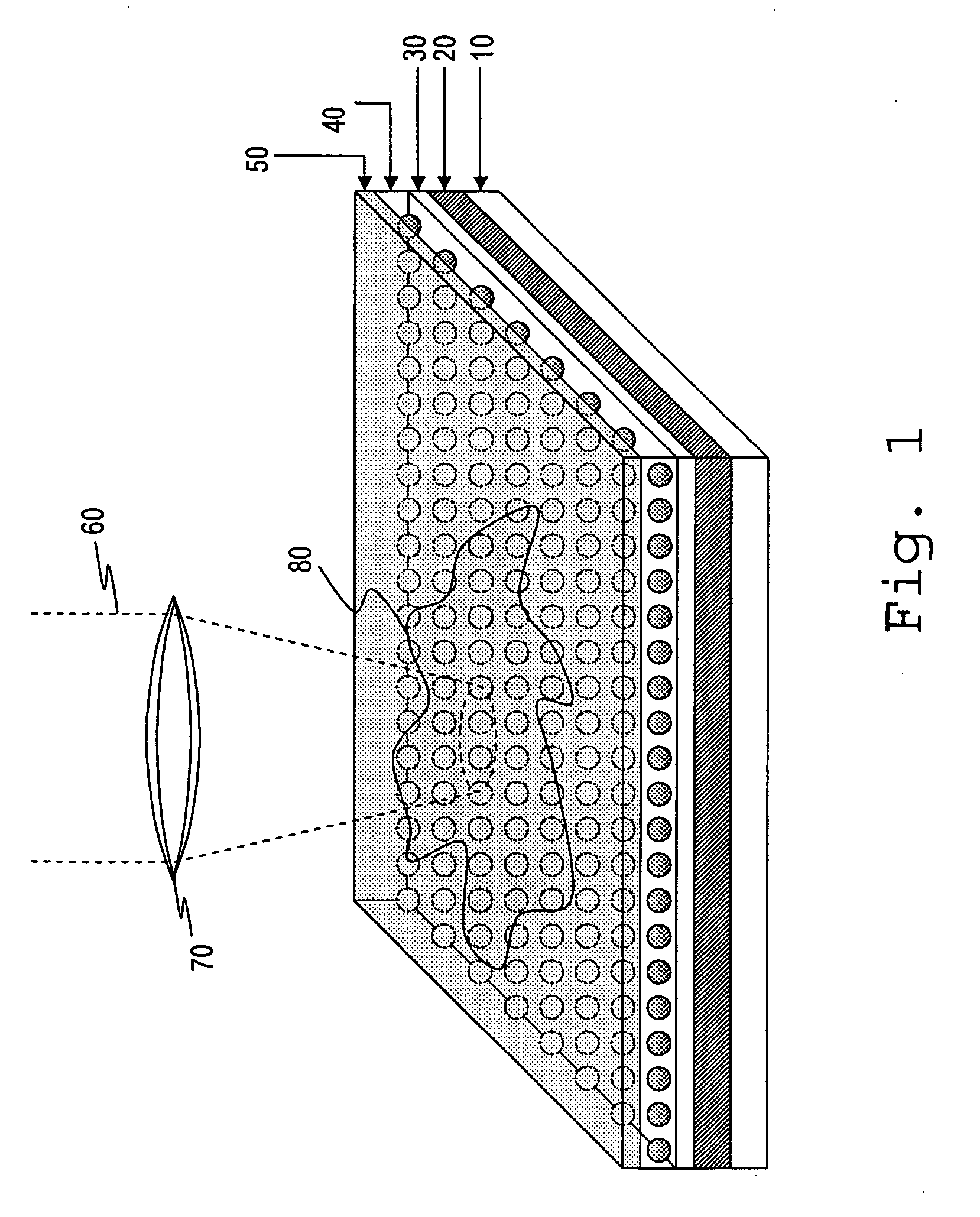
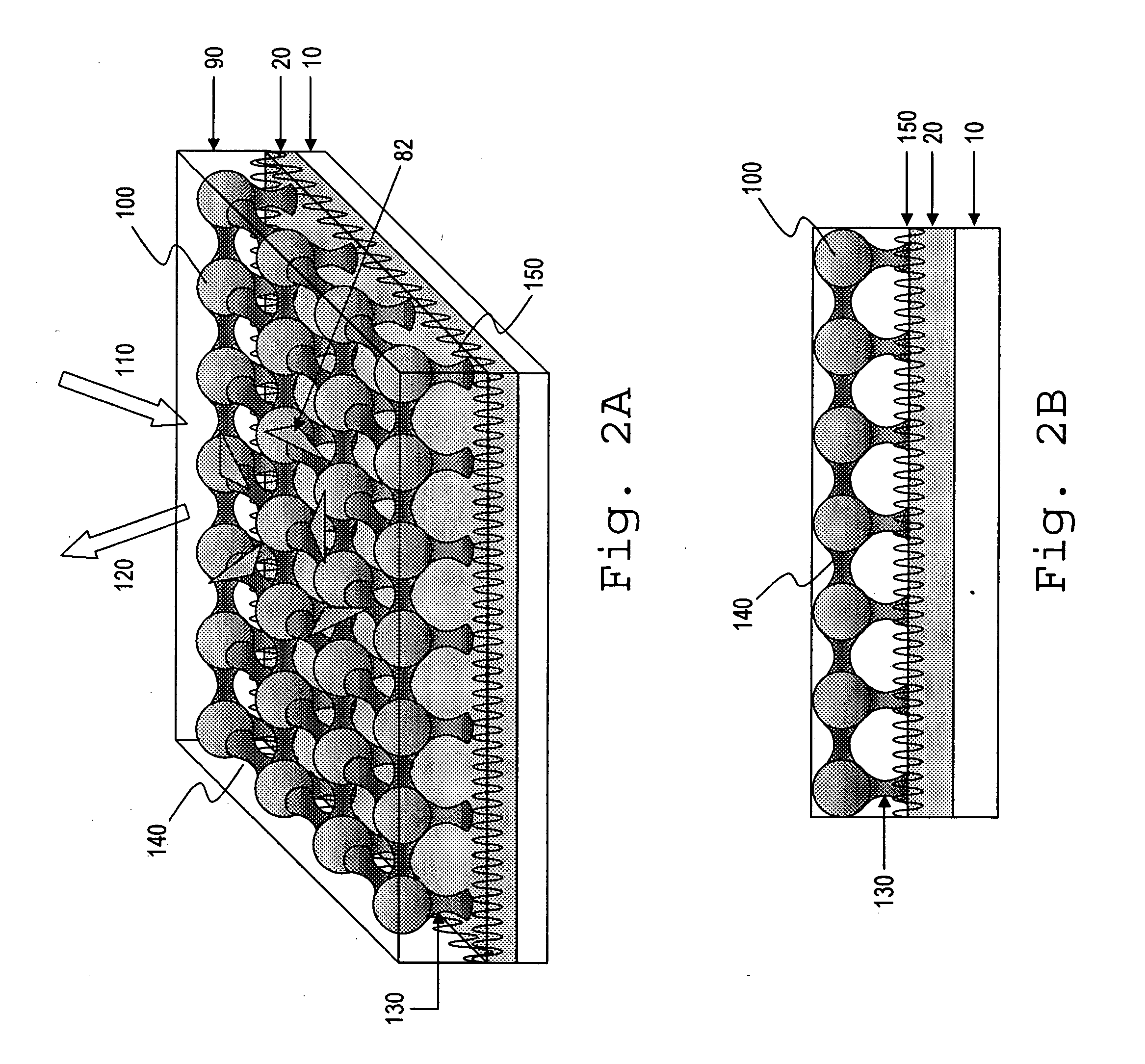
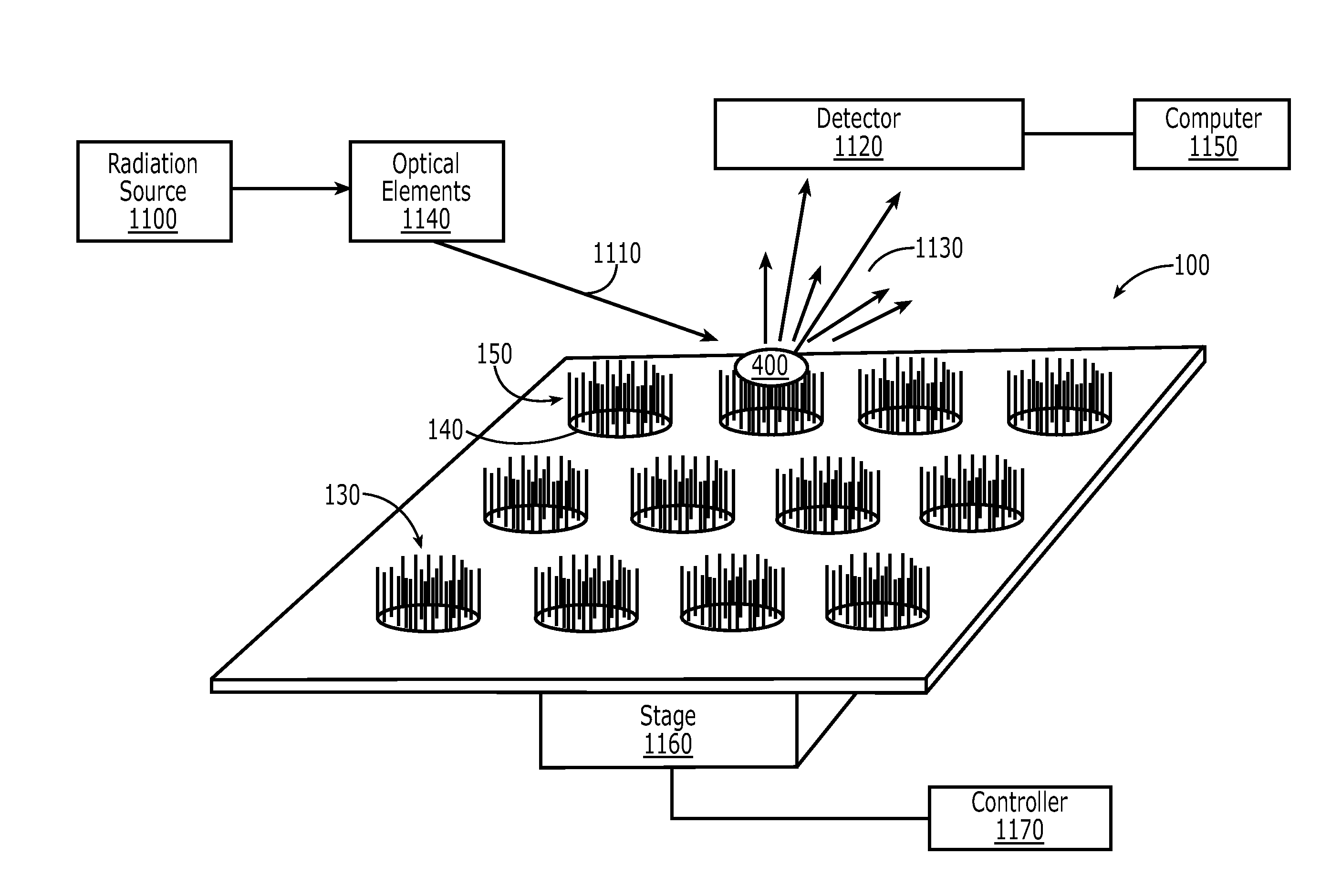
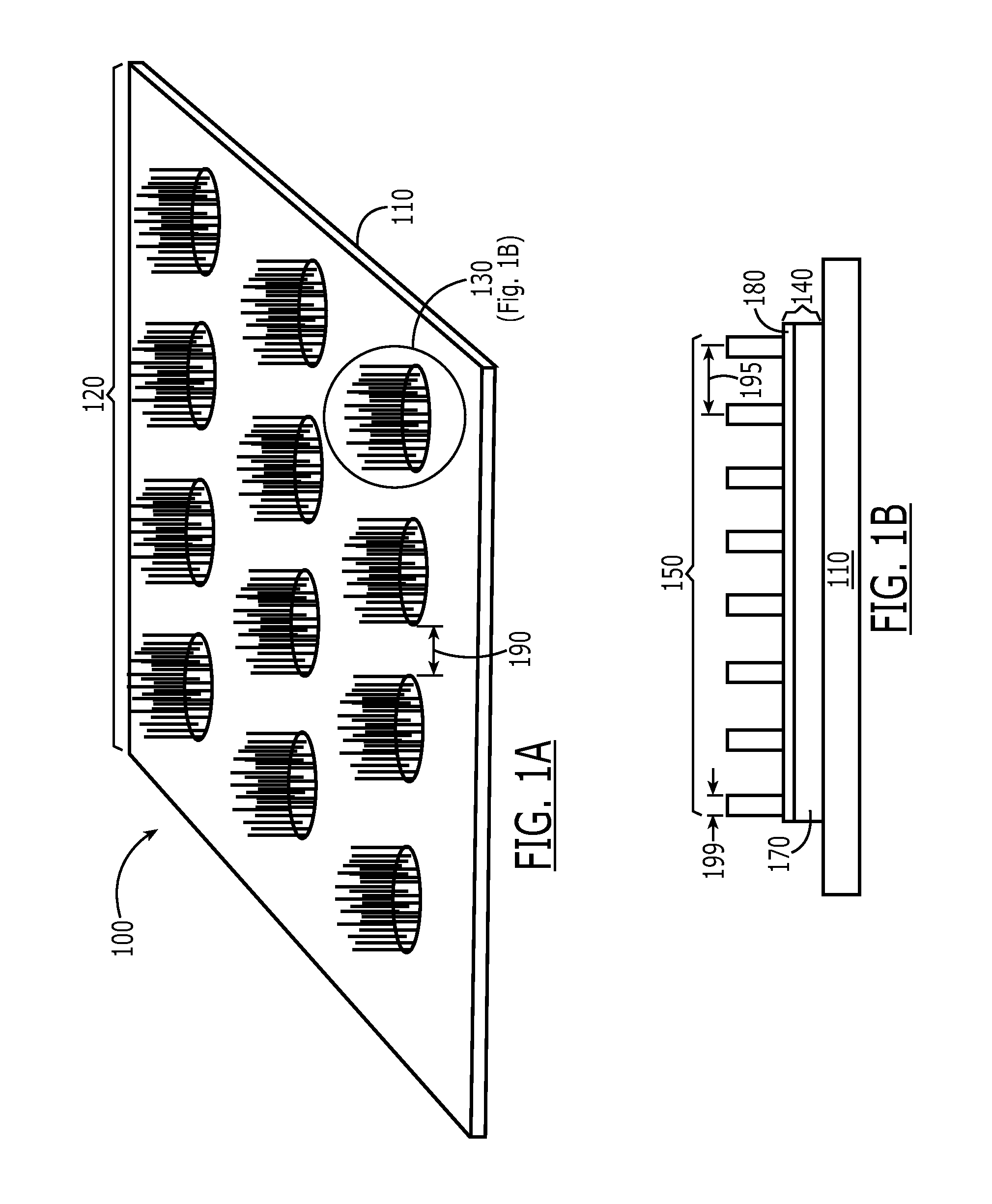
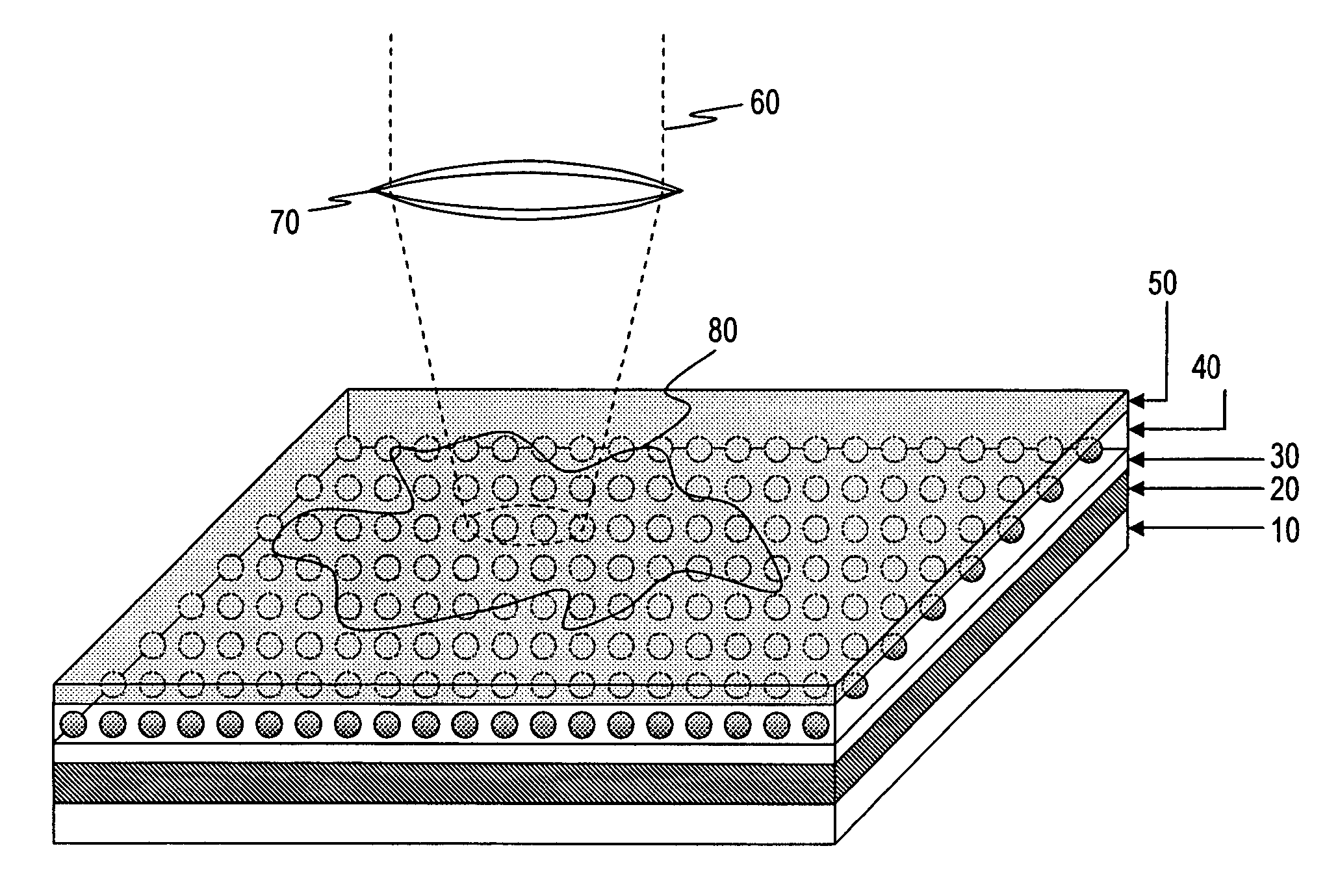
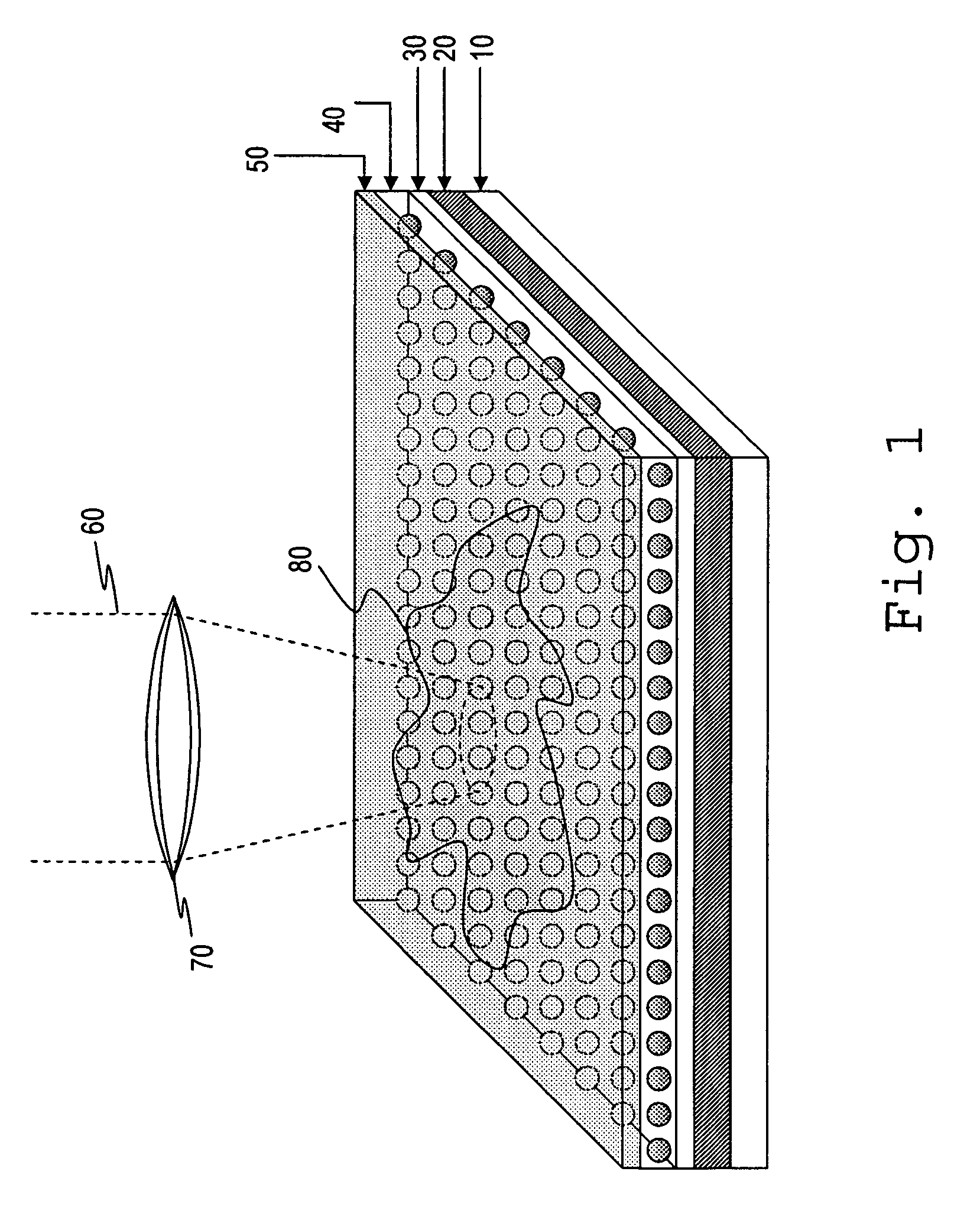
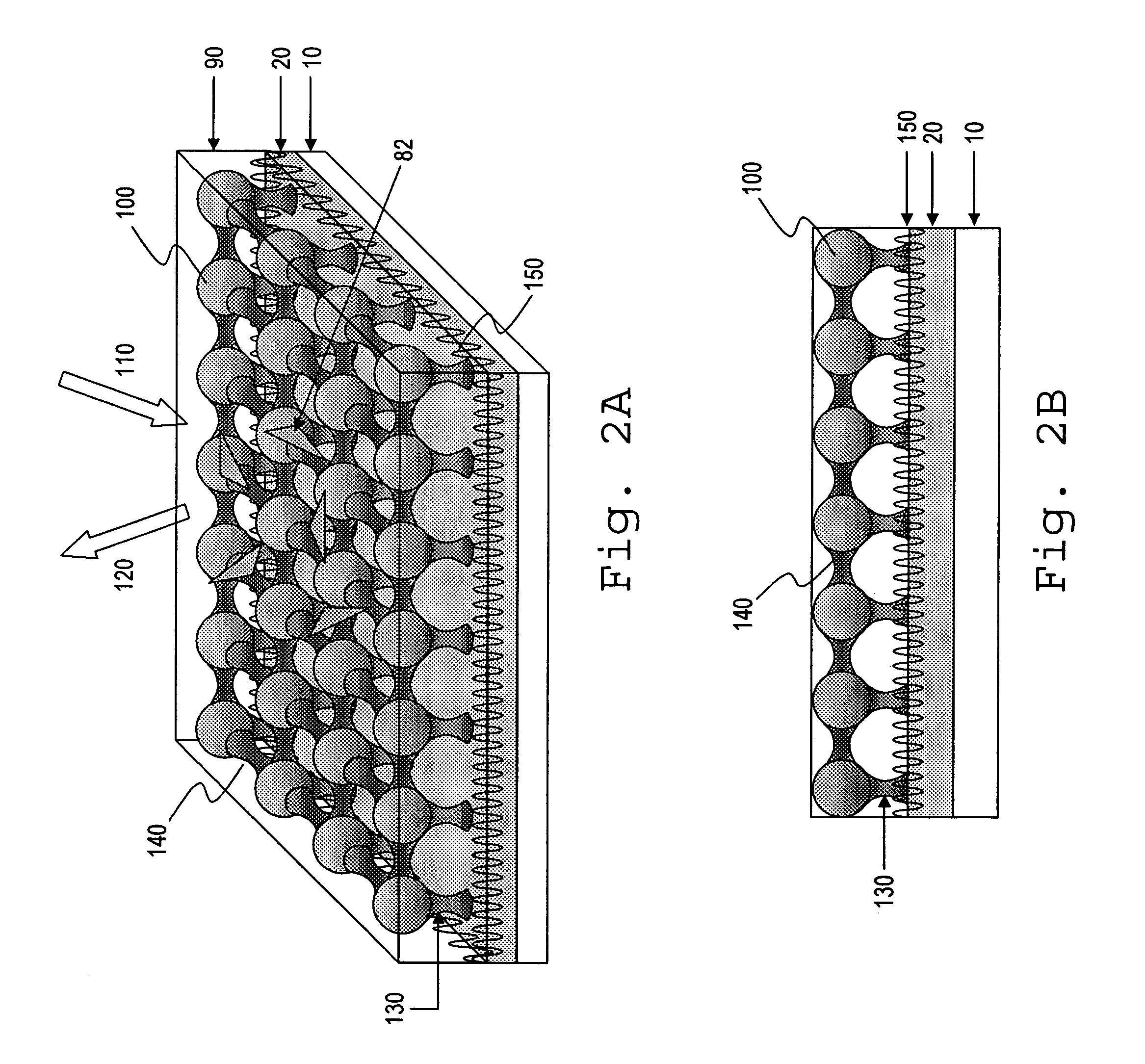
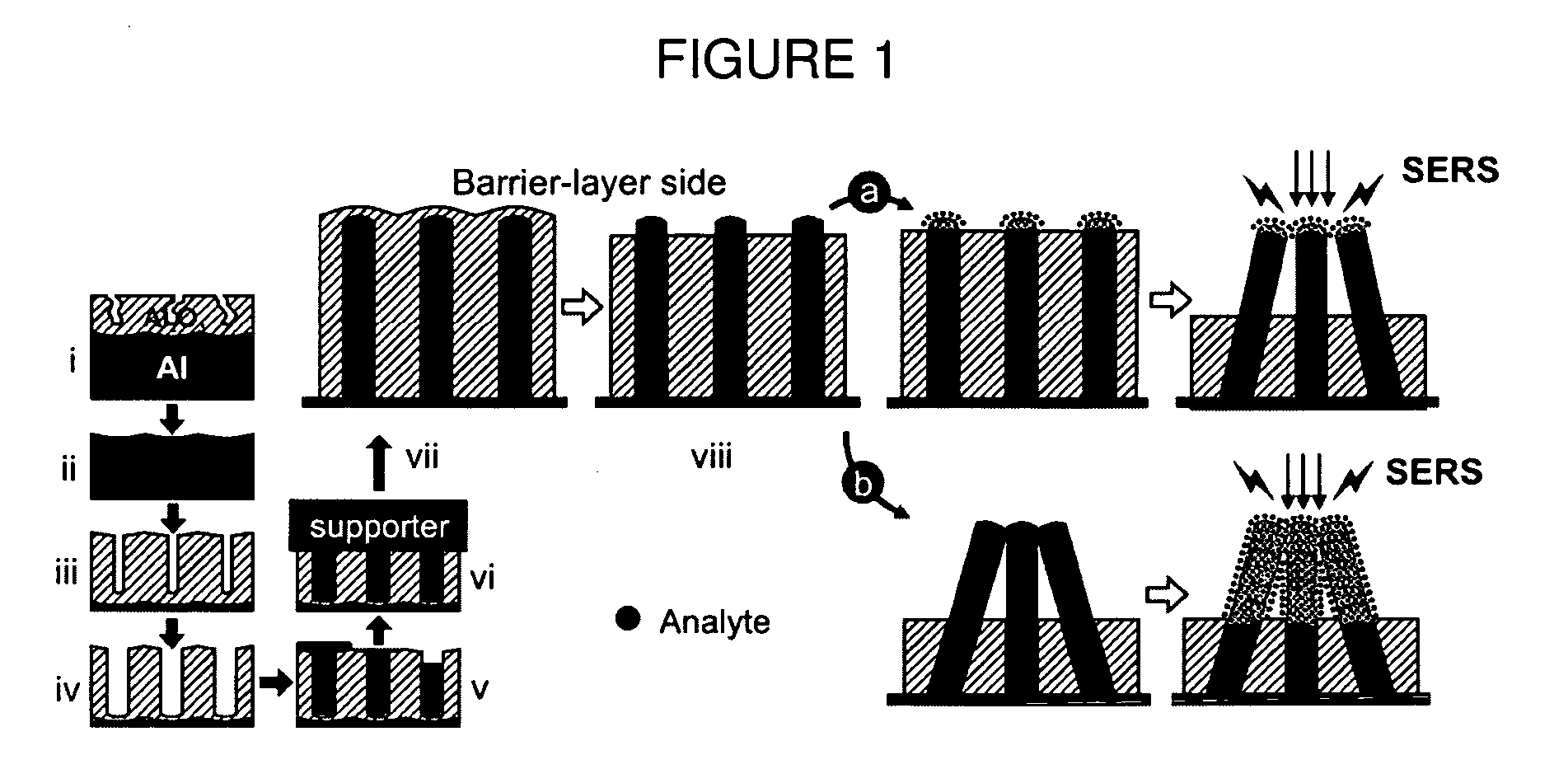
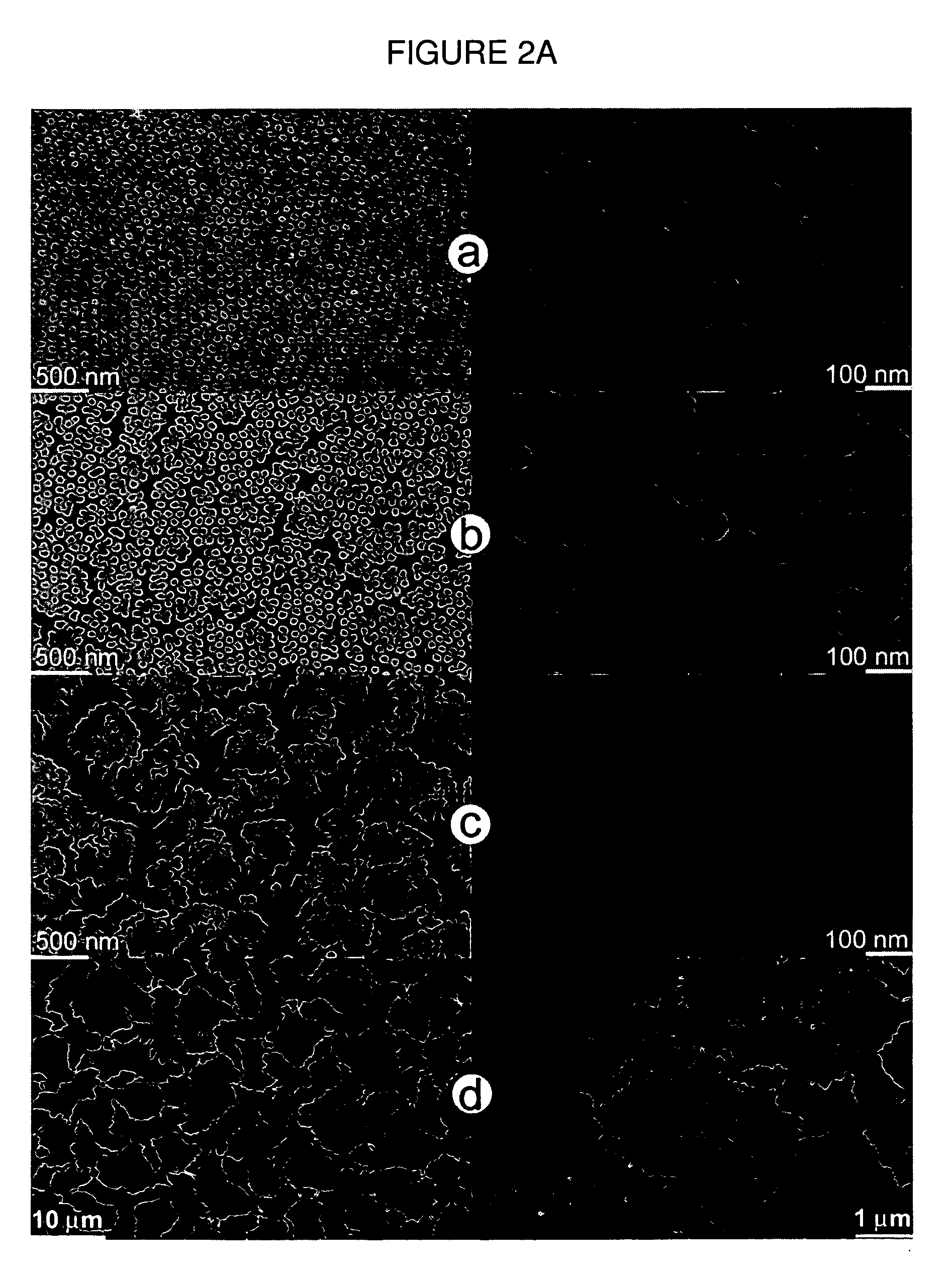
Optical sensor with layered plasmon structure for enhanced detection of chemical groups by SERS
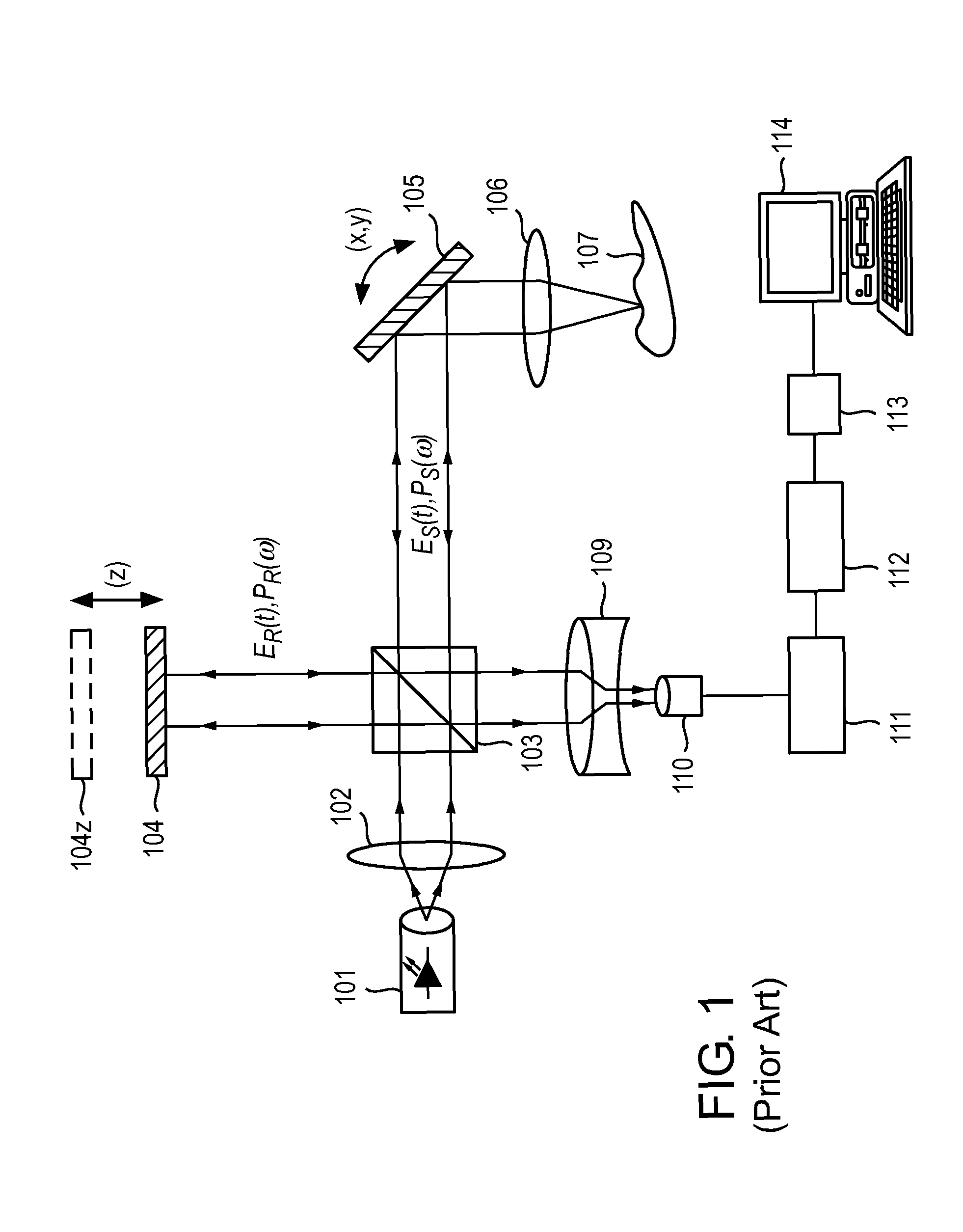
InactiveUS20060034729A1Produced in advanceRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementExcitation beamLight excitation
An optical sensor and method for use with a visible-light laser excitation beam and a Raman spectroscopy detector, for detecting the presence chemical groups in an analyte applied to the sensor are disclosed. The sensor includes a substrate, a plasmon resonance mirror formed on a sensor surface of the substrate, a plasmon resonance particle layer disposed over the mirror, and an optically transparent dielectric layer about 2-40 nm thick separating the mirror and particle layer. The particle layer is composed of a periodic array of plasmon resonance particles having (i) a coating effective to binding analyte molecules, (ii) substantially uniform particle sizes and shapes in a selected size range between 50-200 nm (ii) a regular periodic particle-to-particle spacing less than the wavelength of the laser excitation beam. The device is capable of detecting analyte with an amplification factor of up to 1012-1014, allowing detection of single analyte molecules.
Owner:POPONIN VLADIMIR
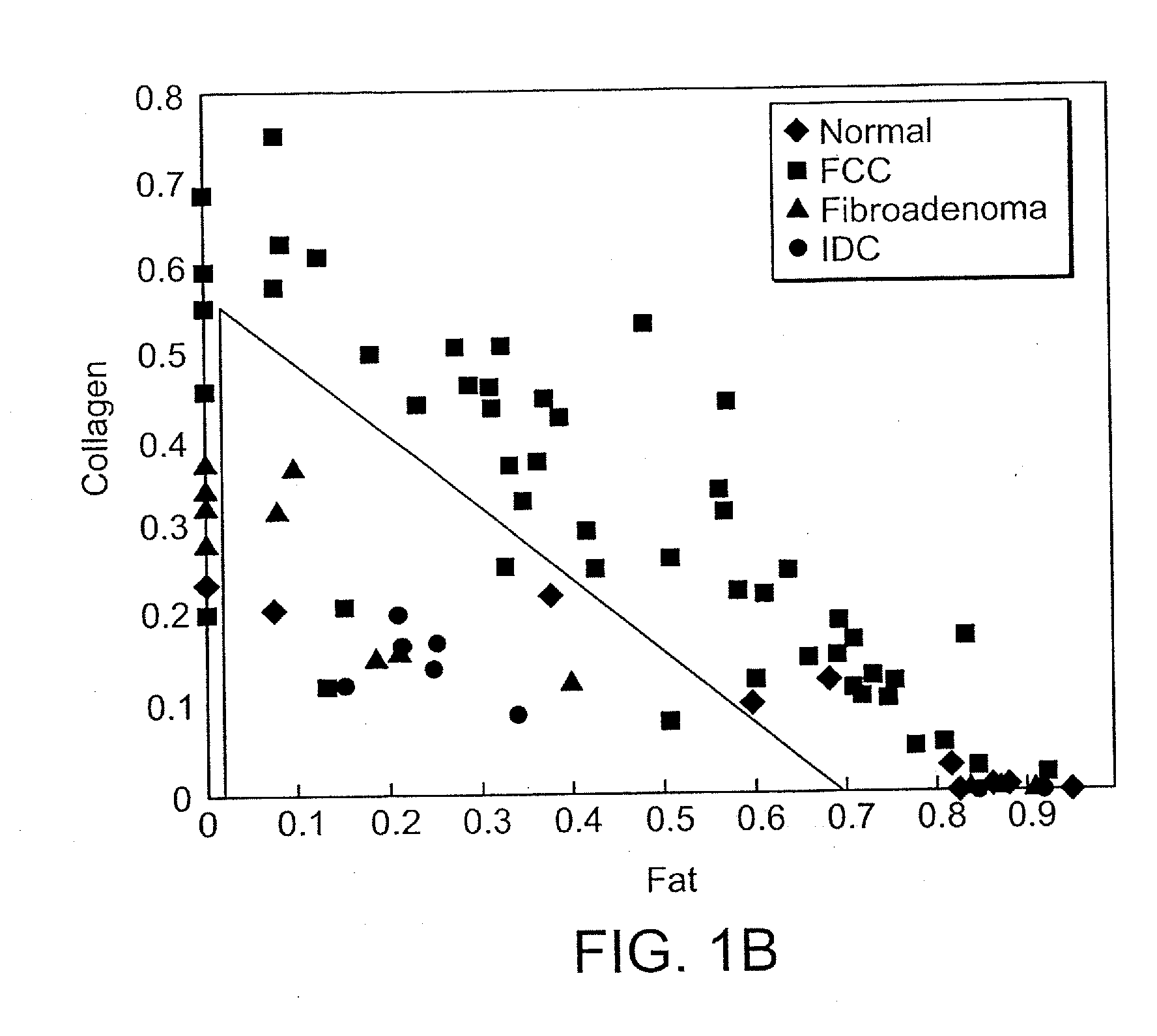
Detection and monitoring of changes in mineralized tissues or calcified deposits by optical coherence tomography and Raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050283058A1Minimal disruptionHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansMedicineCarious lesion
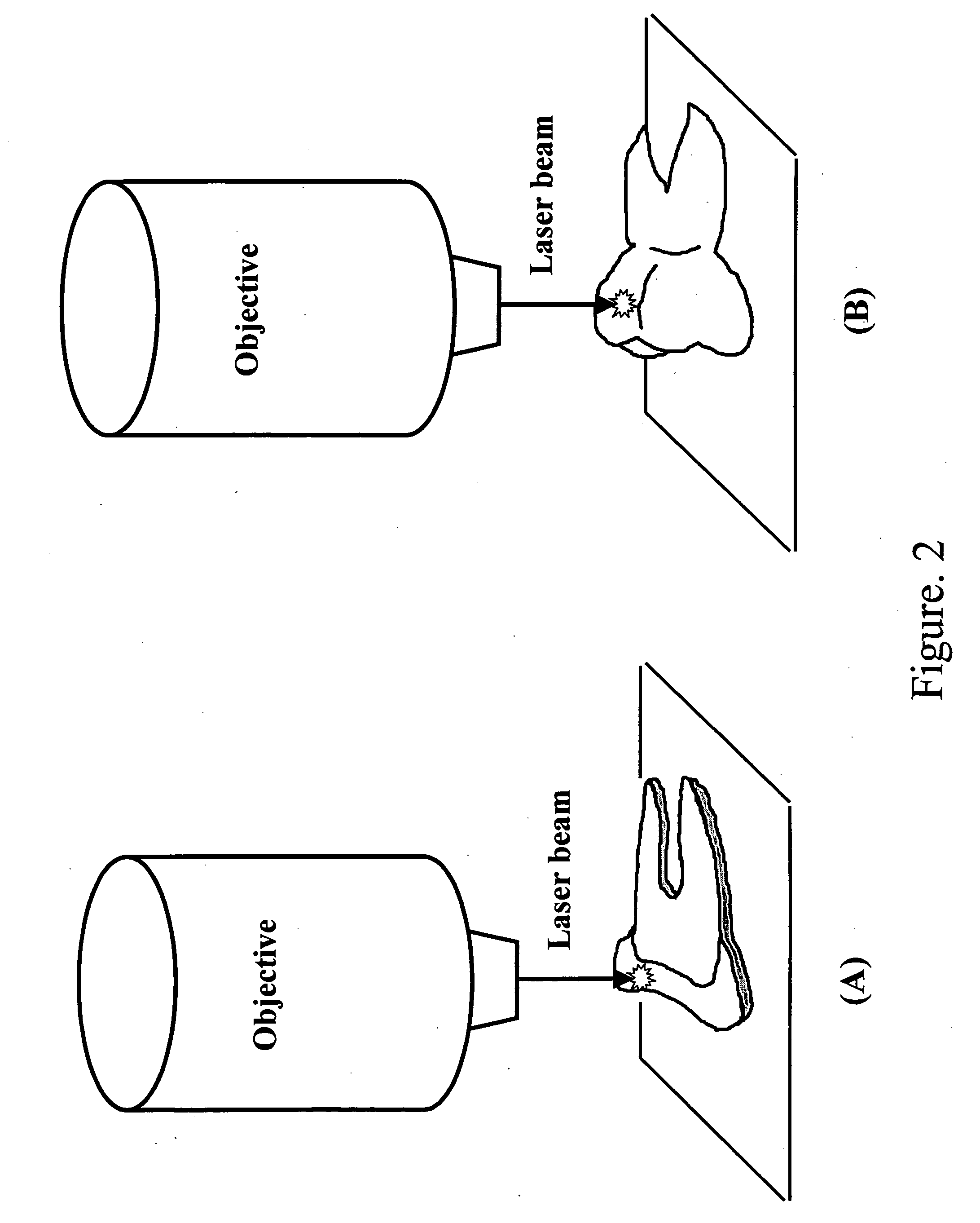
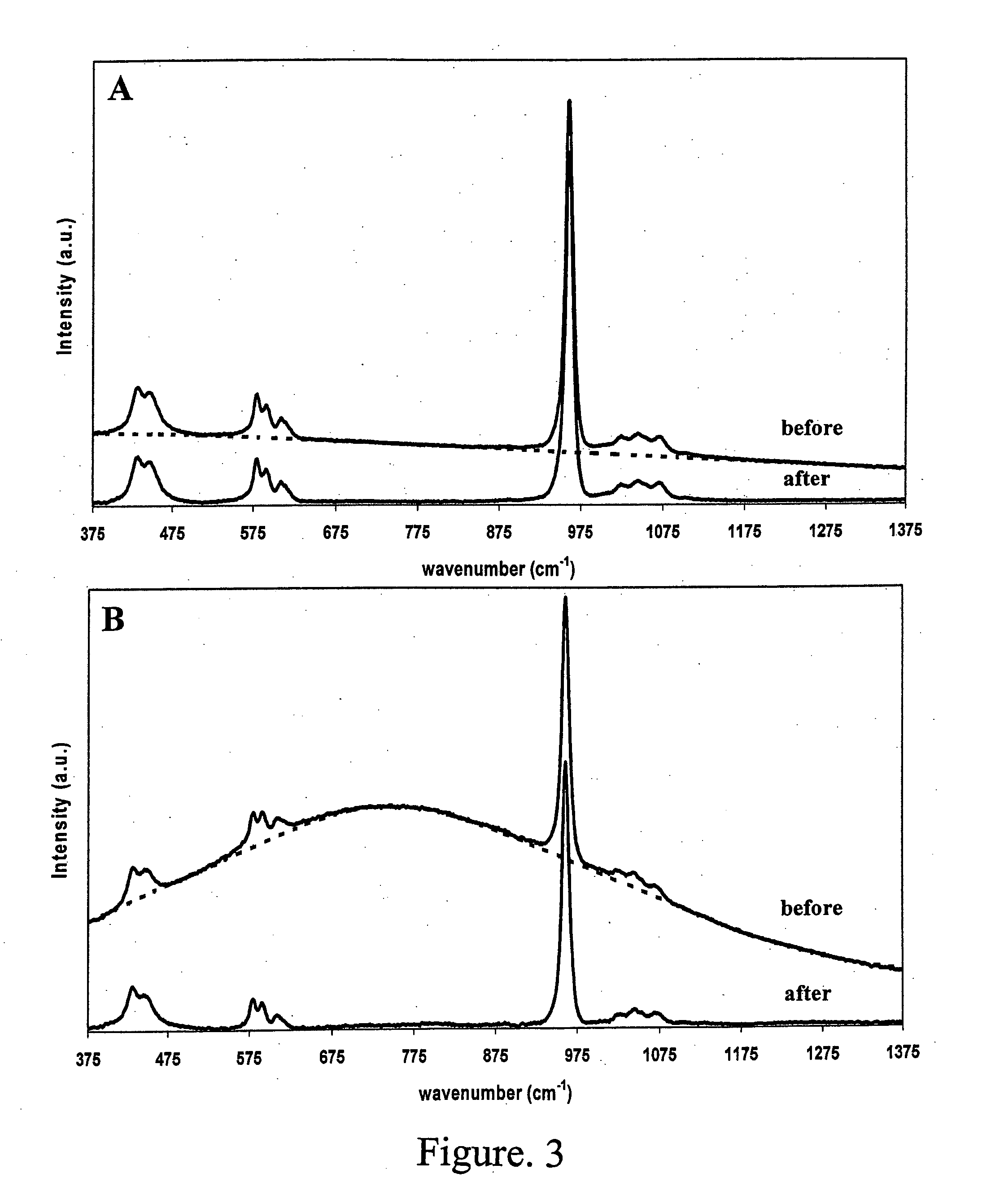
Early dental caries detection is carried out by a method that combines optical coherence tomography (OCT) and Raman spectroscopy to provide morphological information and biochemical specificity for detecting and characterizing incipient carious lesions found in extracted human teeth. OCT imaging of tooth samples demonstrated increased light back-scattering intensity at sites of carious lesions as compared to the sound enamel. Raman microspectroscopy and fibre-optic based Raman spectroscopy are used to characterize the caries further by detecting demineralization-induced alterations of enamel crystallite morphology and / or orientation. OCT imaging is useful for screening carious sites and determining lesion depth, with Raman spectroscopy providing biochemical confirmation of caries. The combination is incorporated into a common probe operable without movement to scan the tooth surface and to provide an output for the dentist.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA +2
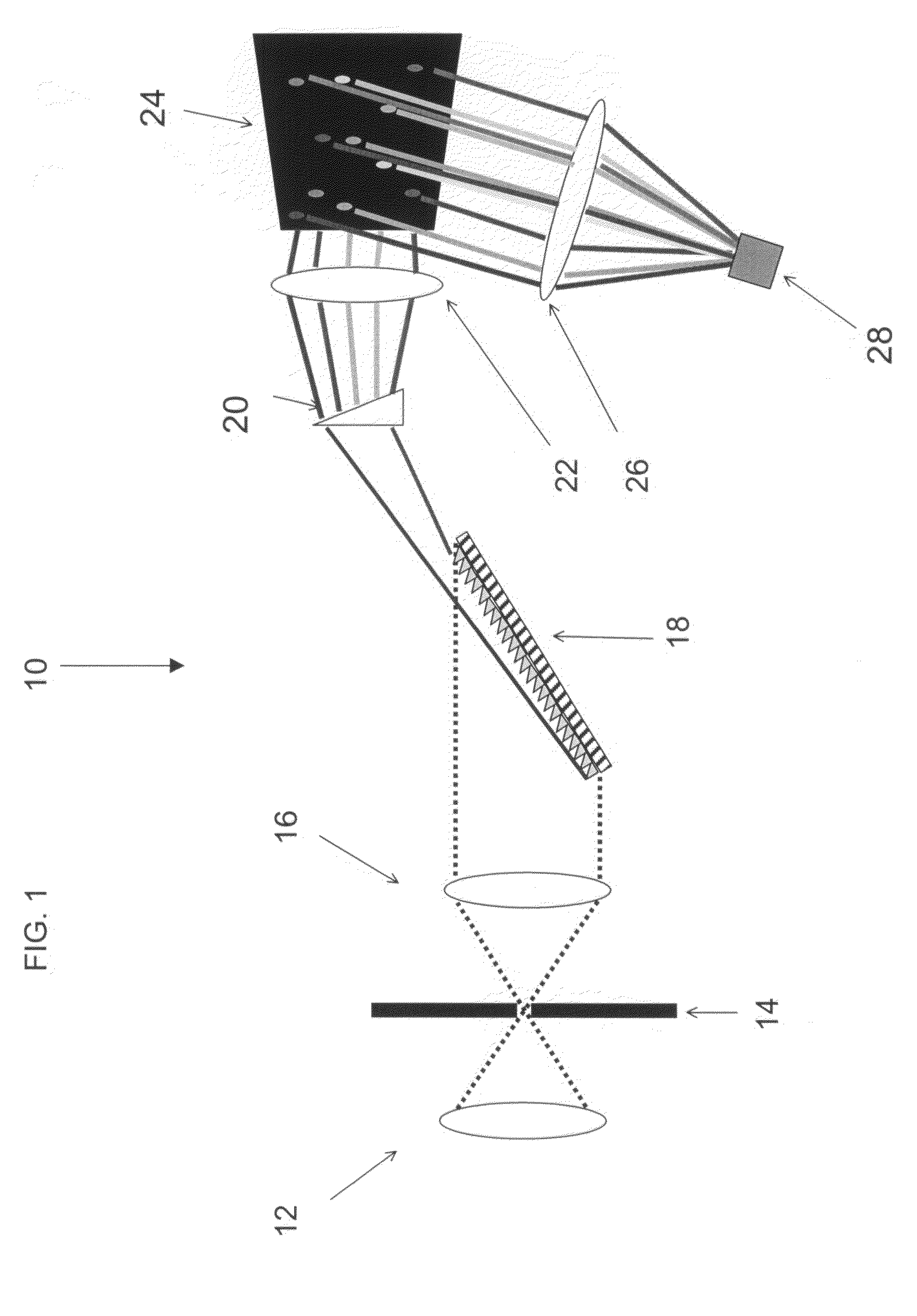
Methods and apparatus for imaging with multimode optical fibers
ActiveUS20150015879A1Radiation pyrometryOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingLight dispersionImage resolution
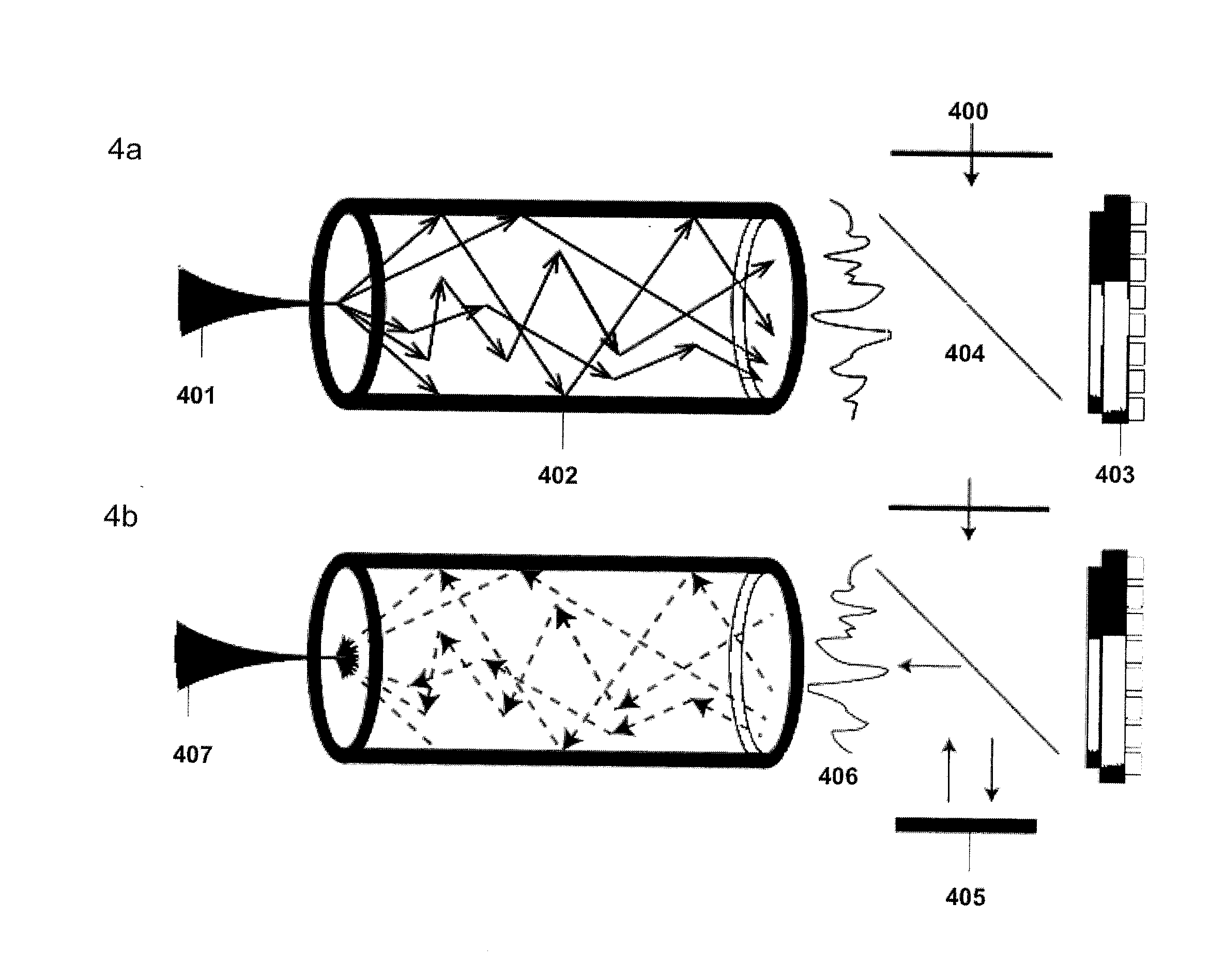
A multimode waveguide illuminator and imager relies on a wave front shaping system that acts to compensate for modal scrambling and light dispersion by the multimode waveguide. A first step consists of calibrating the multimode waveguide and a second step consists in projecting a specific pattern on the waveguide proximal end in order to produce the desire light pattern at its distal end. The illumination pattern can be scanned or changed dynamically only by changing the phase pattern projected at the proximal end of the waveguide. The third and last step consists in collecting the optical information, generated by the sample, through the same waveguide in order to form an image. Known free space microscopy technique can be adapted to endoscopy with multimode waveguide, such as, but not limited to, fluorescence imaging or Raman spectroscopy or imaging, 3D linear scattering imaging or two-photon imaging. Super-resolution, i.e., resolution below the diffraction limit, is achieved for example but not limited to, using the STimulated Emission Depletion microscopy (STED) technique or the Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM) technique or a stochastic illumination based method (PALM, STORM) in combination with the multimode waveguide imaging method.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Portable raman diagnostic system
ActiveUS20120035442A1Small sizeReduce weightRaman scatteringDiagnostic recording/measuringSpectral bandsRaman Optical Activity Spectroscopy
The present invention further relates to the selection of the specific filter combinations, which can provide sufficient information for multivariate calibration to extract accurate analyte concentrations in complex biological systems. The present invention also describes wavelength interval selection methods that give rise to the miniaturized designs. Finally, this invention presents a plurality of wavelength selection methods and miniaturized spectroscopic apparatus designs and the necessary tools to map from one domain (wavelength selection) to the other (design parameters). Such selection of informative spectral bands has a broad scope in miniaturizing any clinical diagnostic instruments which employ Raman spectroscopy in particular and other spectroscopic techniques in general.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
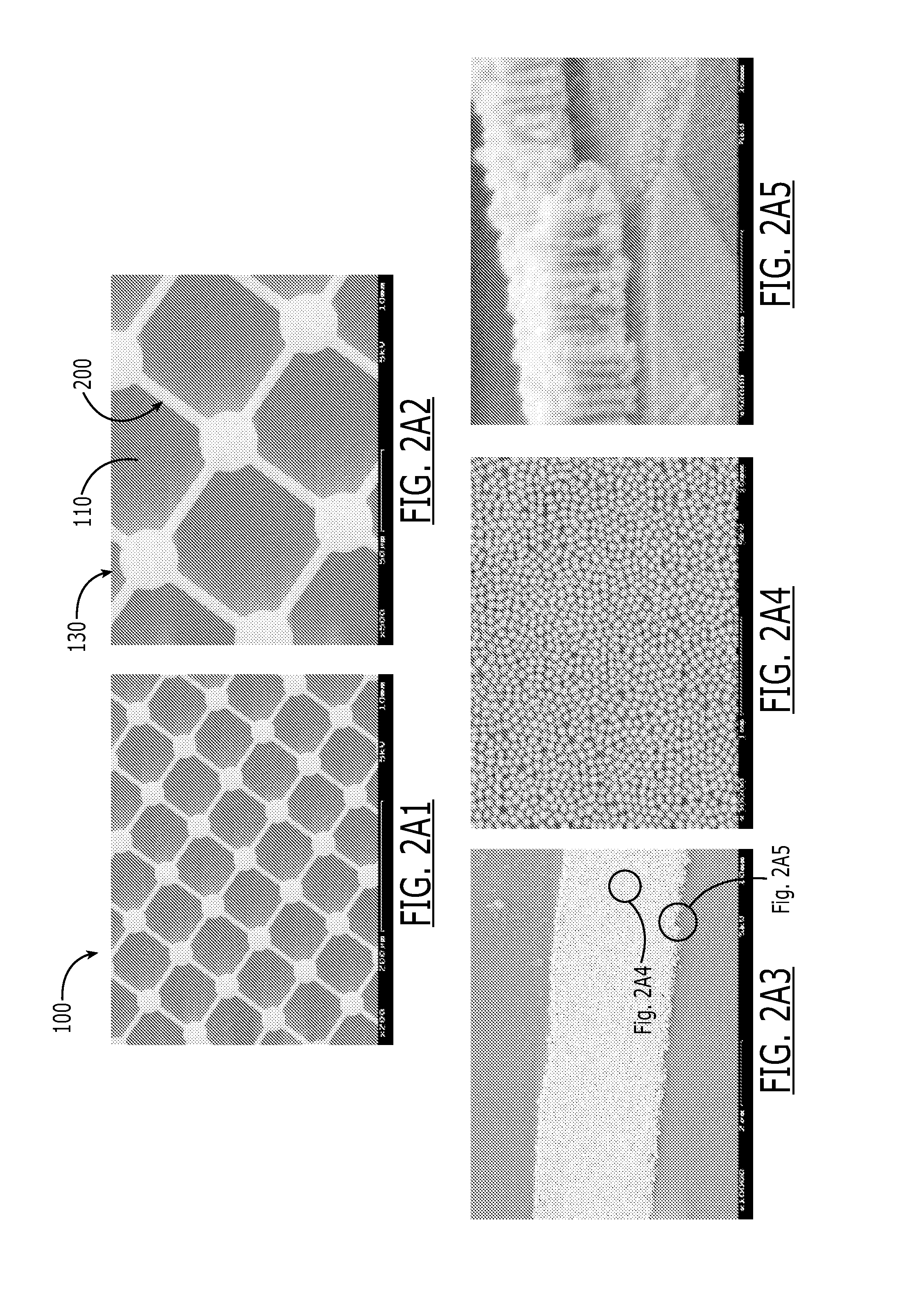
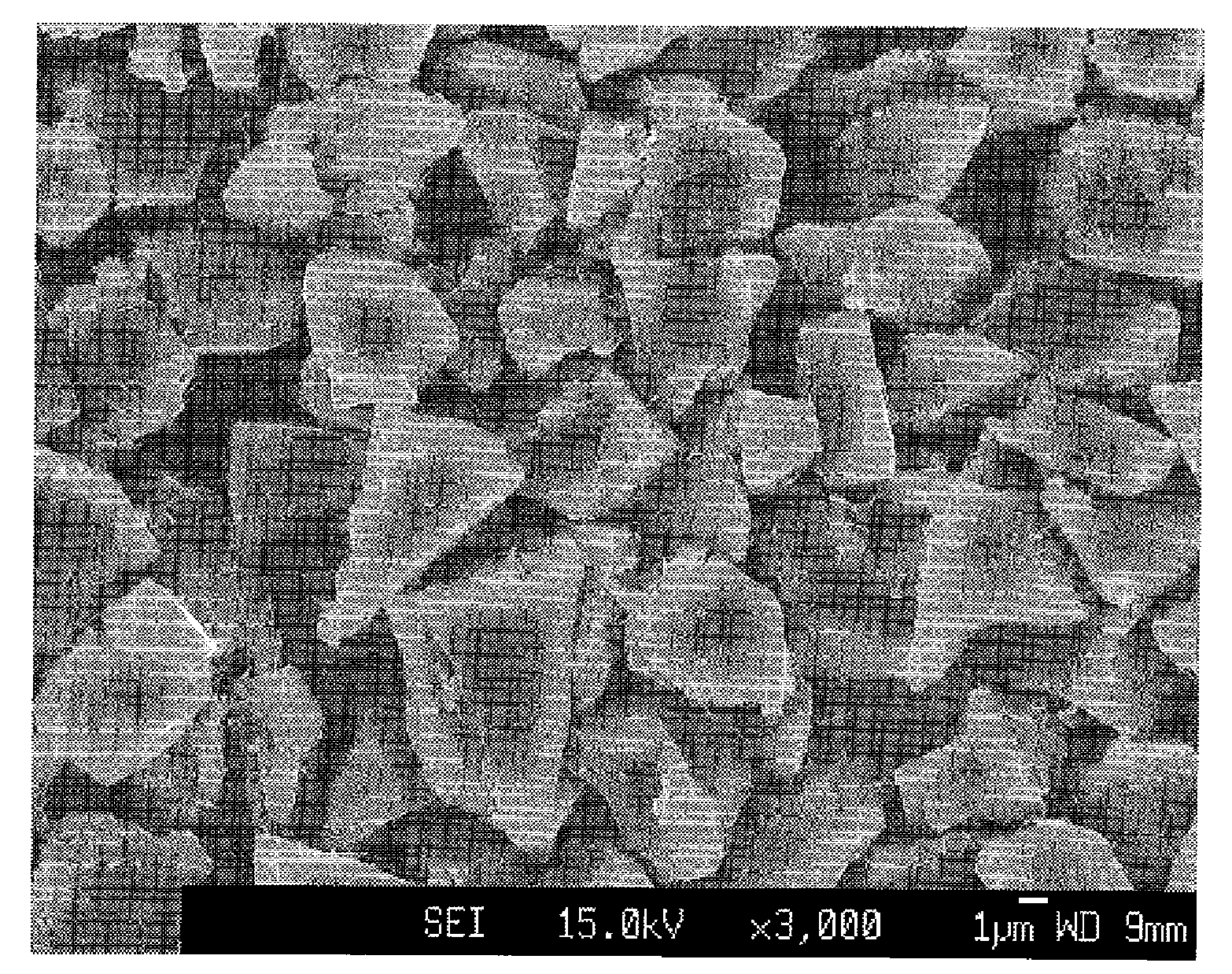
Nanostructured substrates for surface enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS) and detection of biological and chemical analytes by electrical double layer (EDL) capacitance
InactiveUS20110053794A1Enhanced radiationMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsCapacitanceNanopillar
Provided according to embodiments of the invention are nanostructured surfaces that include a substrate; and an array of metallic nanopillar islands on the substrate, wherein each metallic nanopillar island includes a metal base layer on the substrate and a plurality of metallic nanopillars on the metal base layer, and wherein portions of the substrate between adjacent metallic nanopillar islands are free of the metal base layer. Also provided according to some embodiments of the invention are nanostructured surfaces that include a non-conductive substrate; and at least one nanoelectrode defined within the non-conductive substrate, wherein the at least one nanoelectrode is sized and / or shaped to immobilize an analyte or a probe molecule. Also provided are apparatuses and methods for SERS and detection of analytes or biological binding by EDL capacitance.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
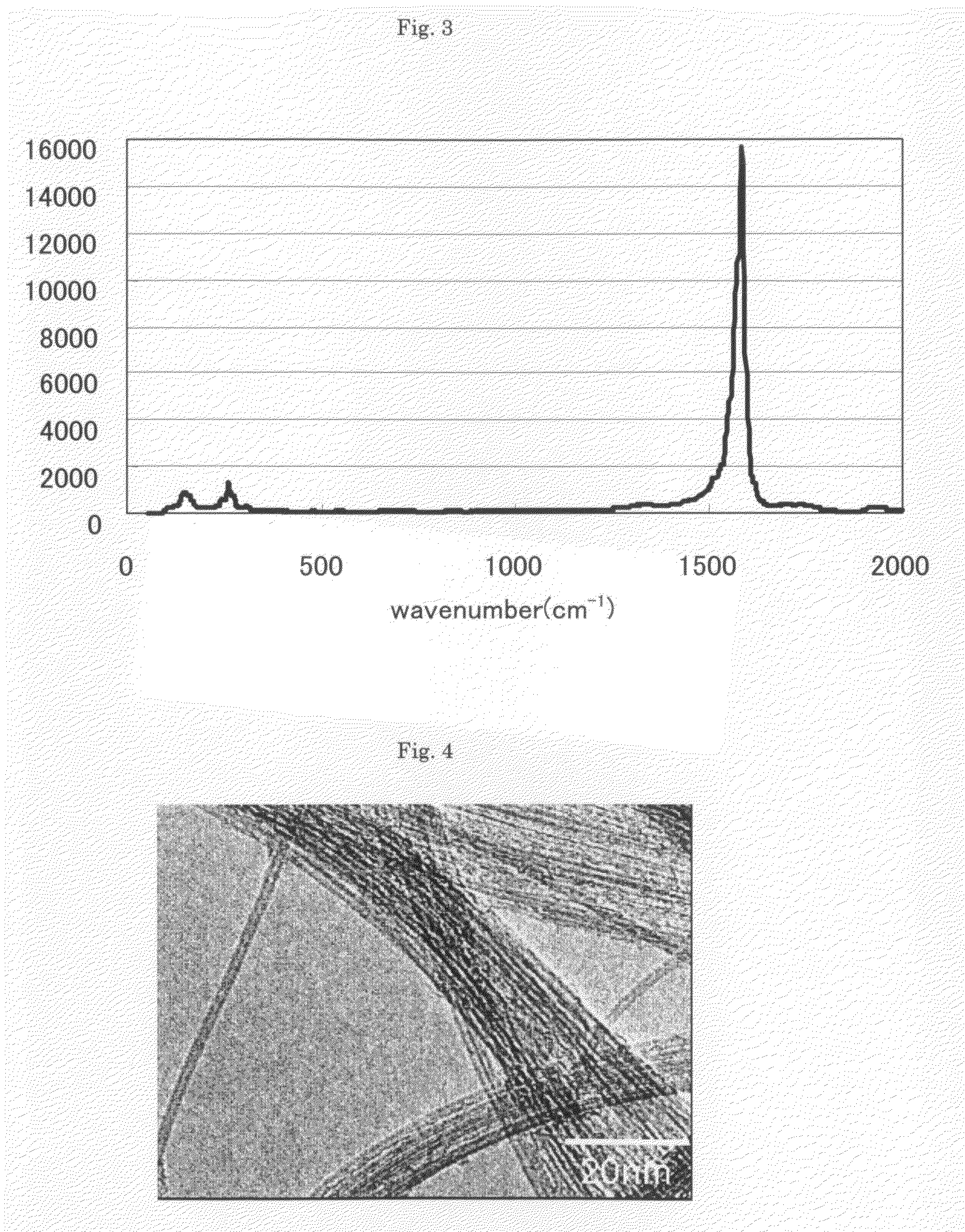
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery negative electrode material, making method, lithium ion secondary battery, and electrochemical capacitor
InactiveUS20090202911A1Improve cycle performanceLarge capacityHybrid capacitor electrodesLiquid electrolytic capacitorsGraphiteCapacitor
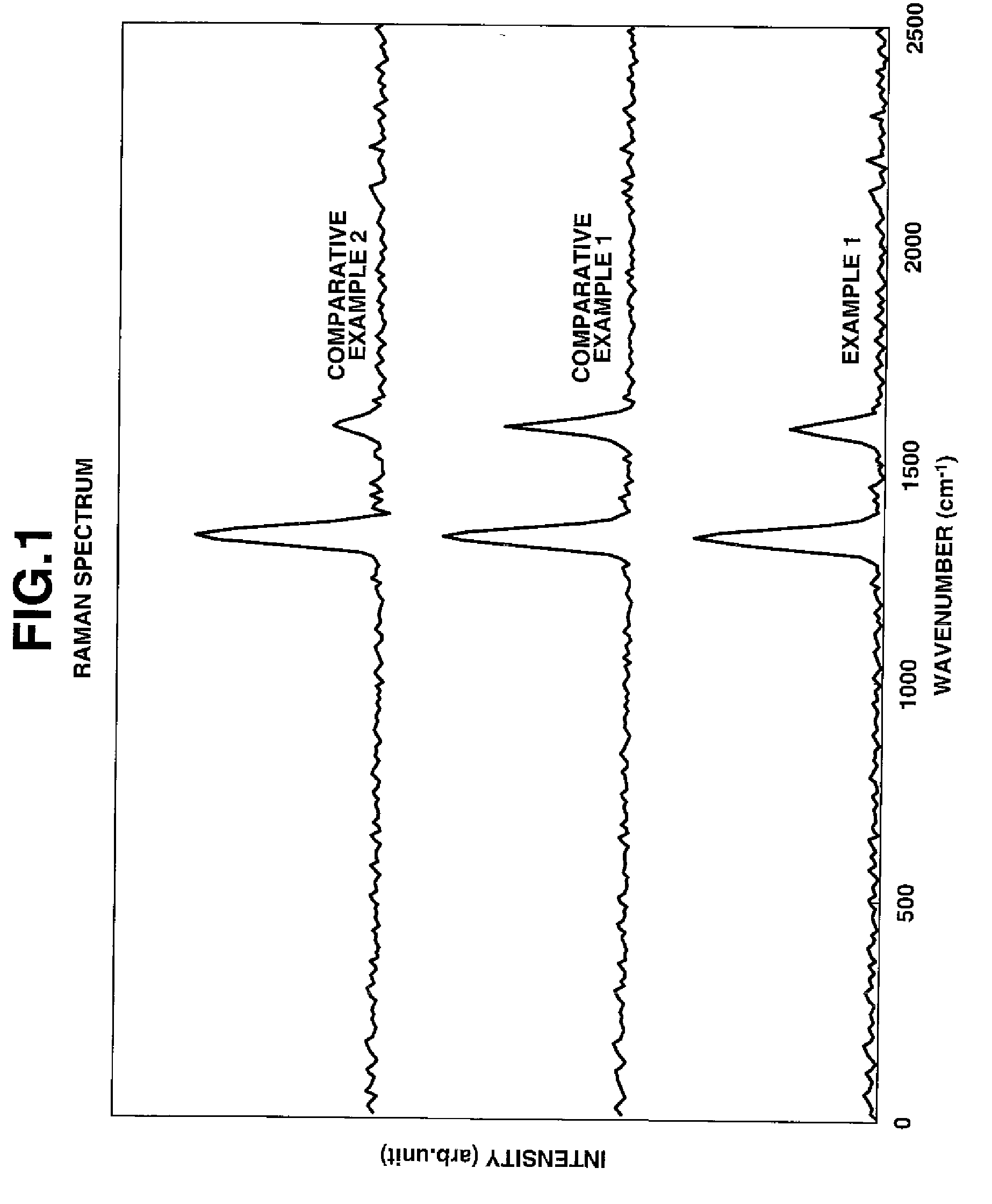
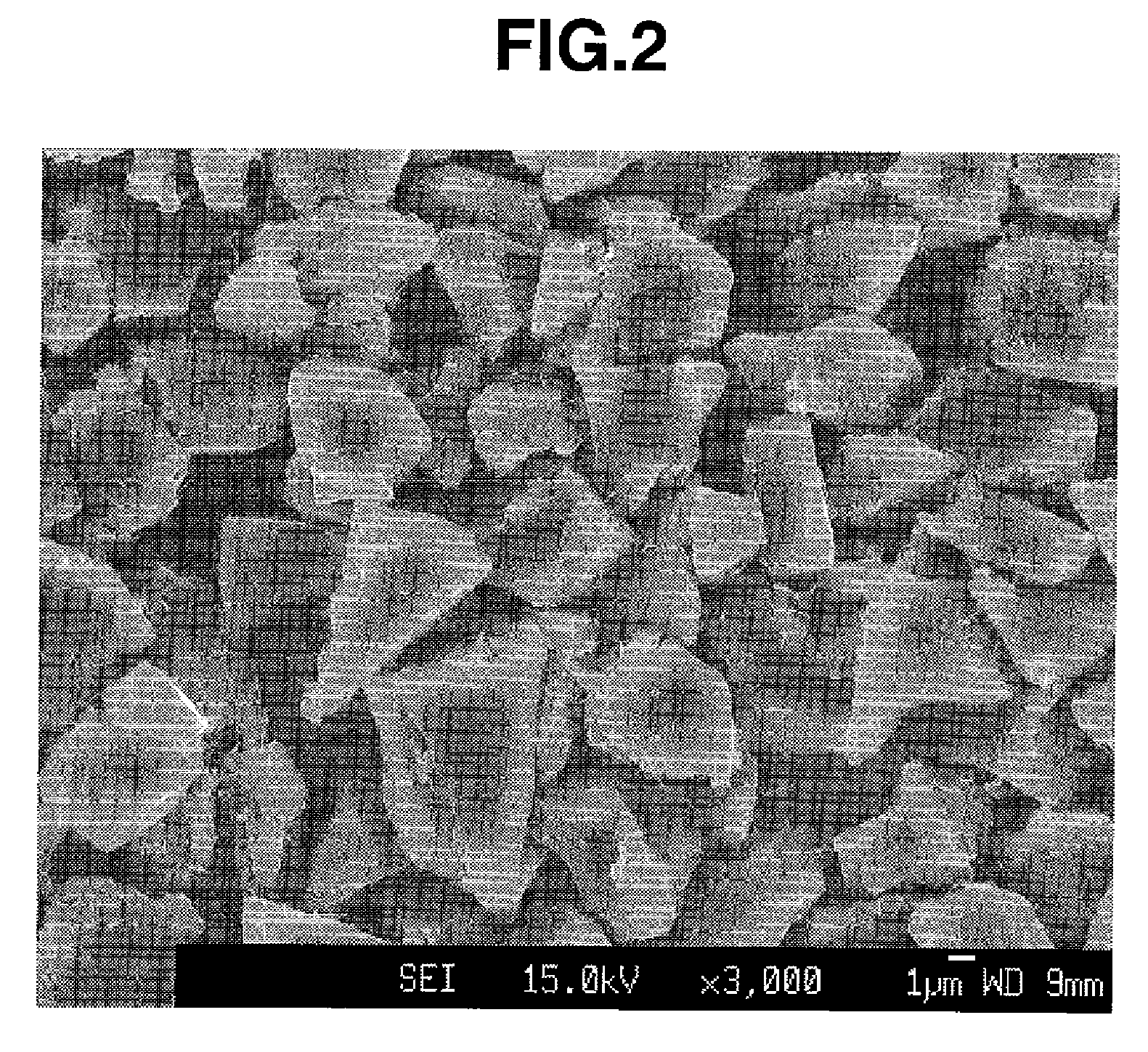
A negative electrode material comprises a conductive powder of particles of a lithium ion-occluding and releasing material coated on their surface with a graphite coating. The graphite coating, on Raman spectroscopy analysis, develops broad peaks having an intensity I1330 and I1580 at 1330 cm−1 and 1580 cm−1 Raman shift, an intensity ratio I1330 / I1580 being 1.5<I1330 / I1580<3.0. Using the negative electrode material, a lithium ion secondary battery having a high capacity and improved cycle performance can be manufactured.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Optical sensor with layered plasmon structure for enhanced detection of chemical groups by SERS
InactiveUS7351588B2Produced in advanceRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementAmplification factorPhysics
An optical sensor and method for use with a visible-light laser excitation beam and a Raman spectroscopy detector, for detecting the presence chemical groups in an analyte applied to the sensor are disclosed. The sensor includes a substrate, a plasmon resonance mirror formed on a sensor surface of the substrate, a plasmon resonance particle layer disposed over the mirror, and an optically transparent dielectric layer about 2-40 nm thick separating the mirror and particle layer. The particle layer is composed of a periodic array of plasmon resonance particles having (i) a coating effective to binding analyte molecules, (ii) substantially uniform particle sizes and shapes in a selected size range between 50-200 nm (ii) a regular periodic particle-to-particle spacing less than the wavelength of the laser excitation beam. The device is capable of detecting analyte with an amplification factor of up to 1012-1014, allowing detection of single analyte molecules.
Owner:POPONIN VLADIMIR
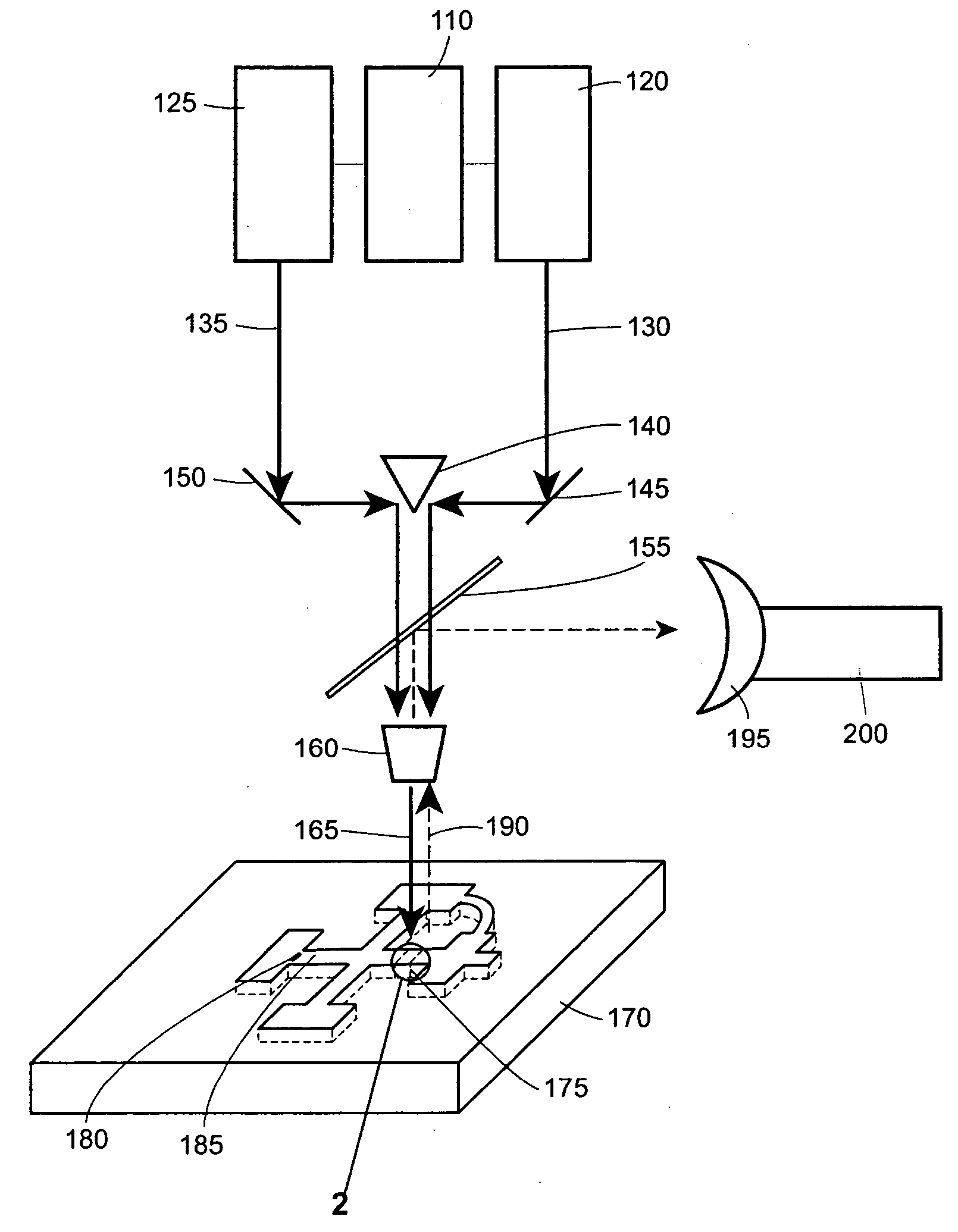
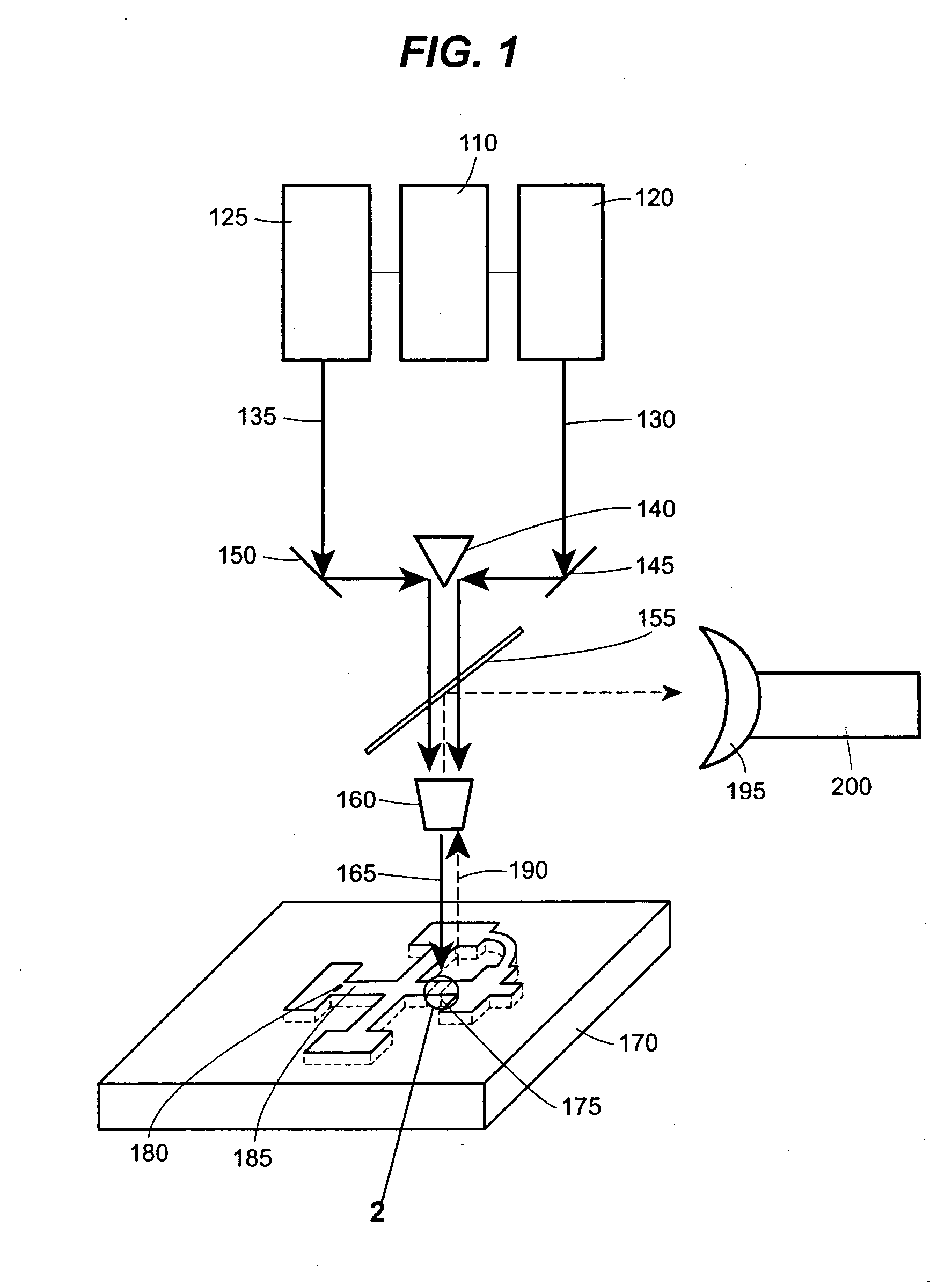
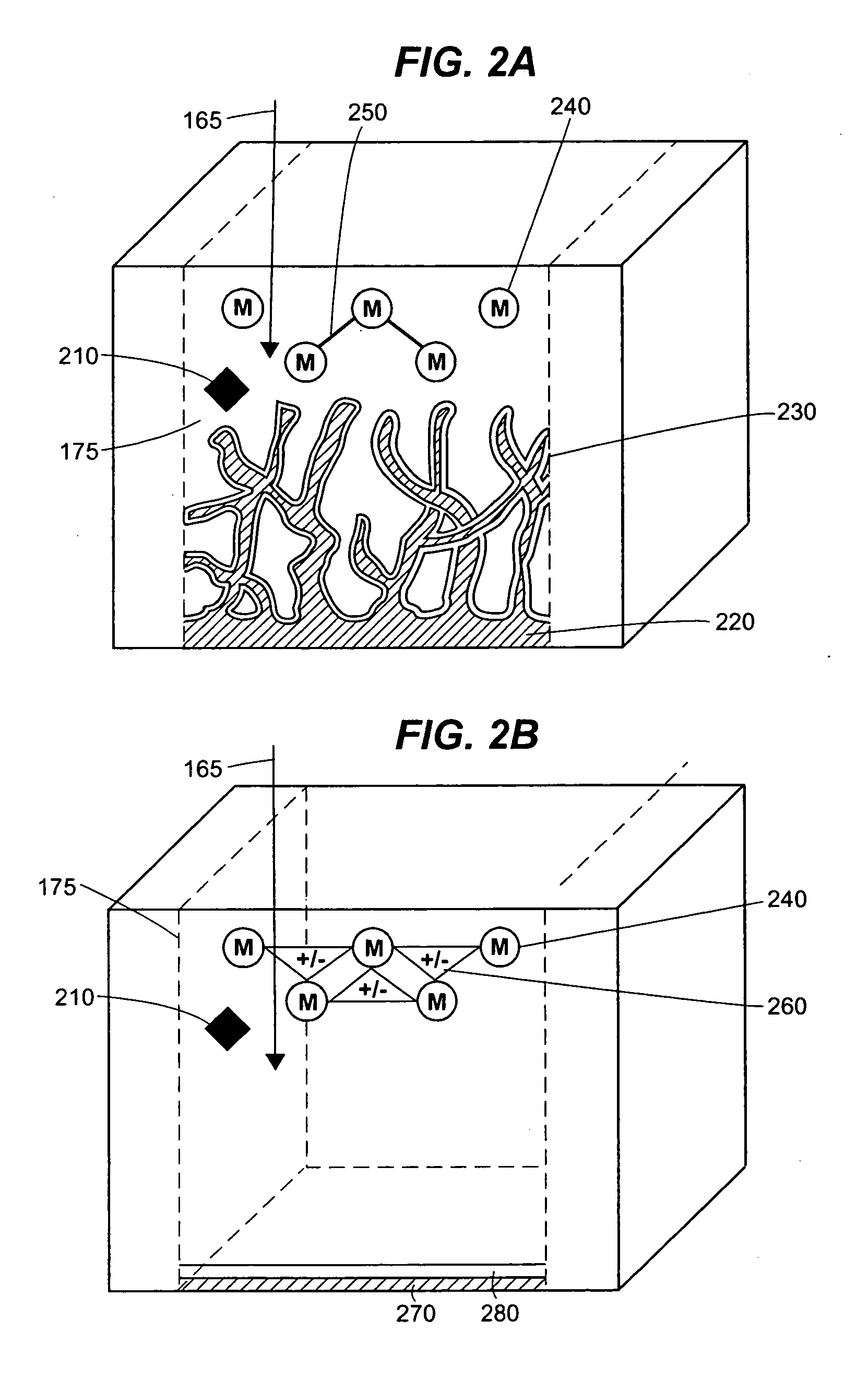
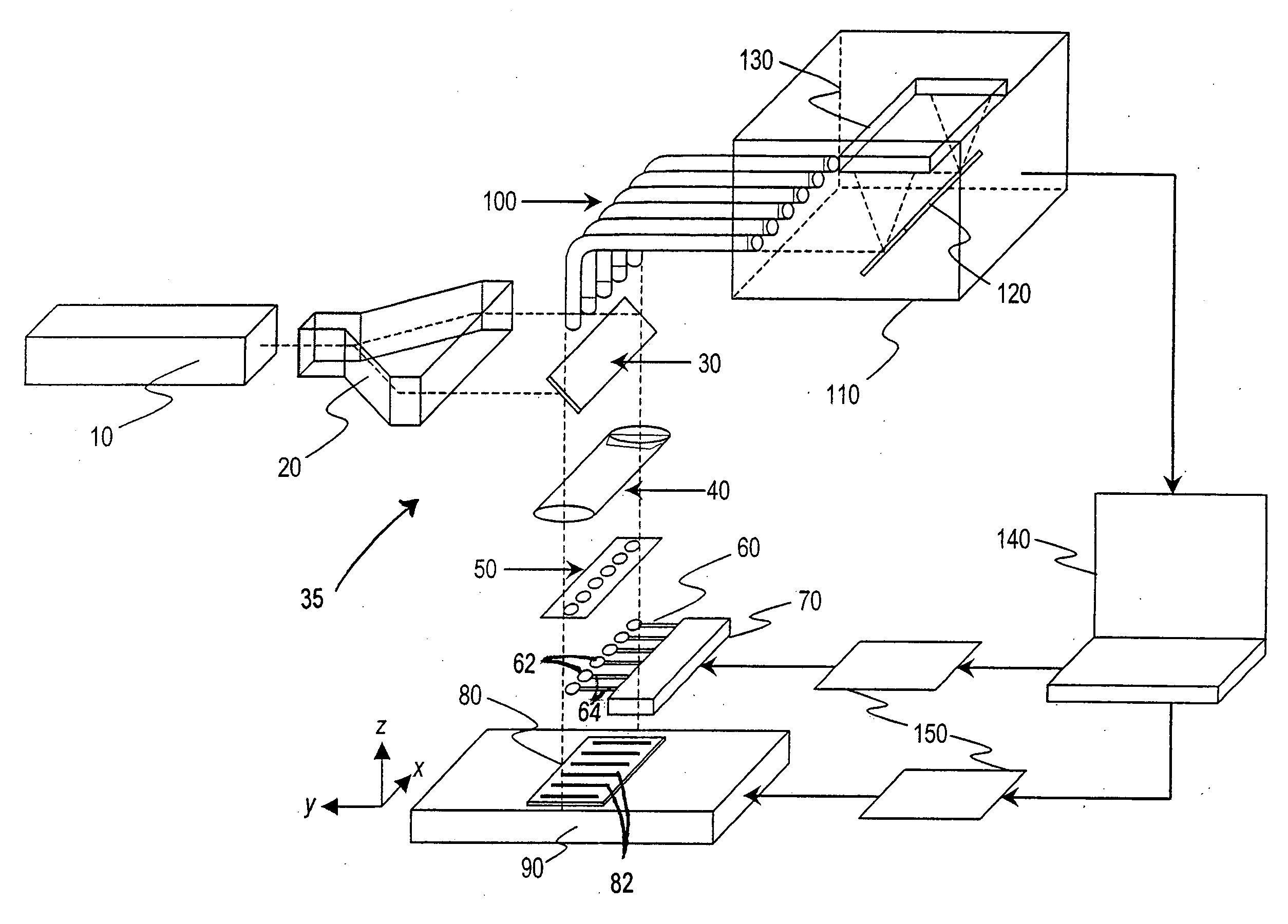
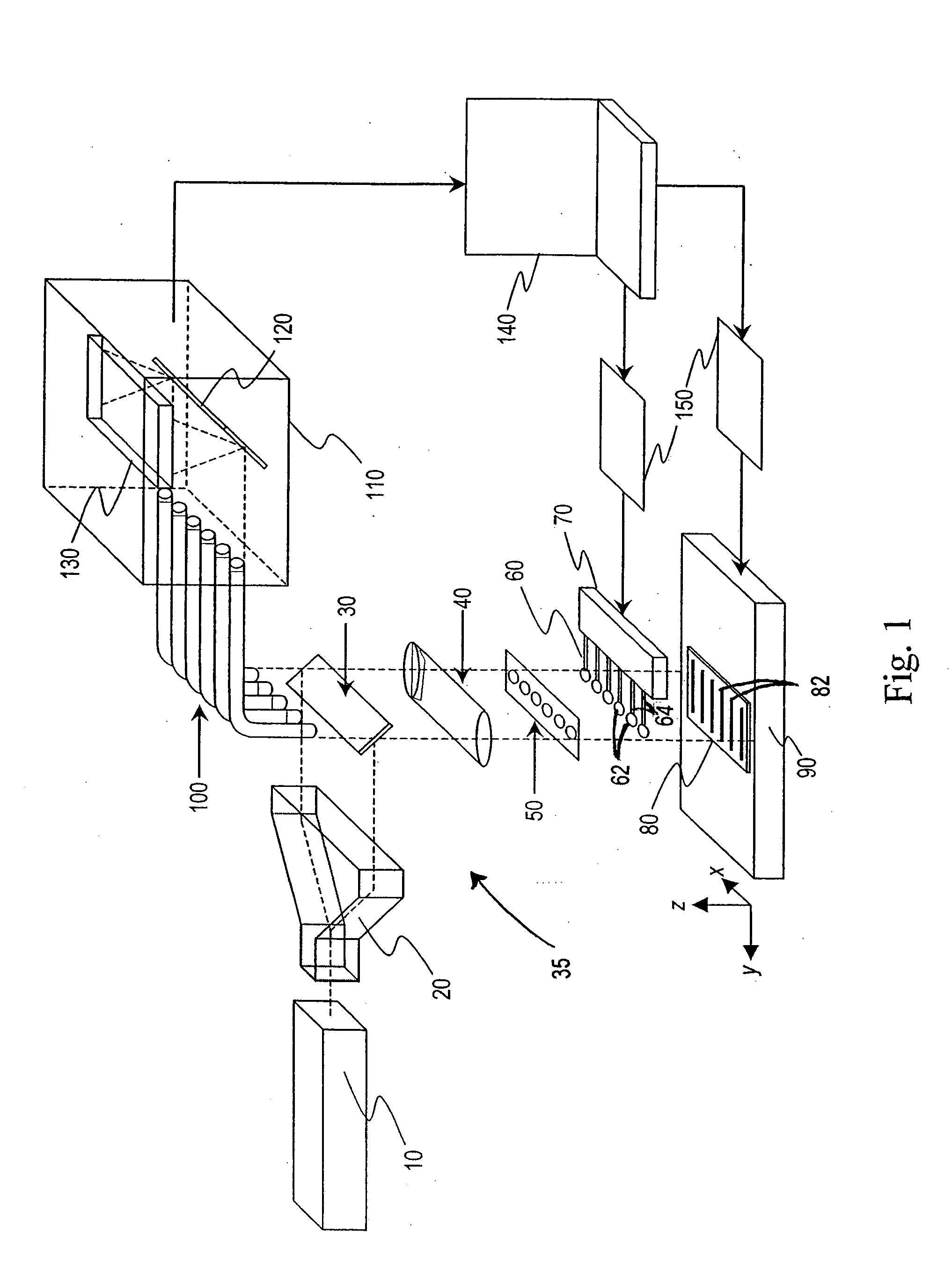
Method and device for detecting a small number of molecules using surface-enhanced coherant anti-stokes raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050084980A1Radiation pyrometryPhase-affecting property measurementsAnalyteCoherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy
The device and method disclosed herein concern detecting, identifying, and or quantifying analytes, such as nucleic acids, with high resolution and fast response times using surface enhanced coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy. In certain embodiments of the invention, a small number molecular sample of the analyte 210 such as a nucleotide, passes through a microfluidic channel, microchannel, or nanochannel 185 and sample cell 175 that contains Raman-active surfaces, and is detected by surface enhanced, coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy (SECARS). Other embodiments of the invention concern an apparatus for analyte detection.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Intrinsic Raman spectroscopy
ActiveUS20070049809A1Reduce errorsSignificant contributionRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringRaman spectroscopyReflectance spectroscopy
The present invention relates to systems and methods for the measurement of analytes such as glucose. Raman and reflectance spectroscopy are used to measure a volume, of material such as a blood sample or tissue within a subject and determine a concentration of a blood analyte based thereon. The present invention further relates to a calibration method, constrained regularization (CR), and demonstrates its use for analyzing spectra including, for example, the measurement glucose concentrations using transcutaneous Raman spectroscopy.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
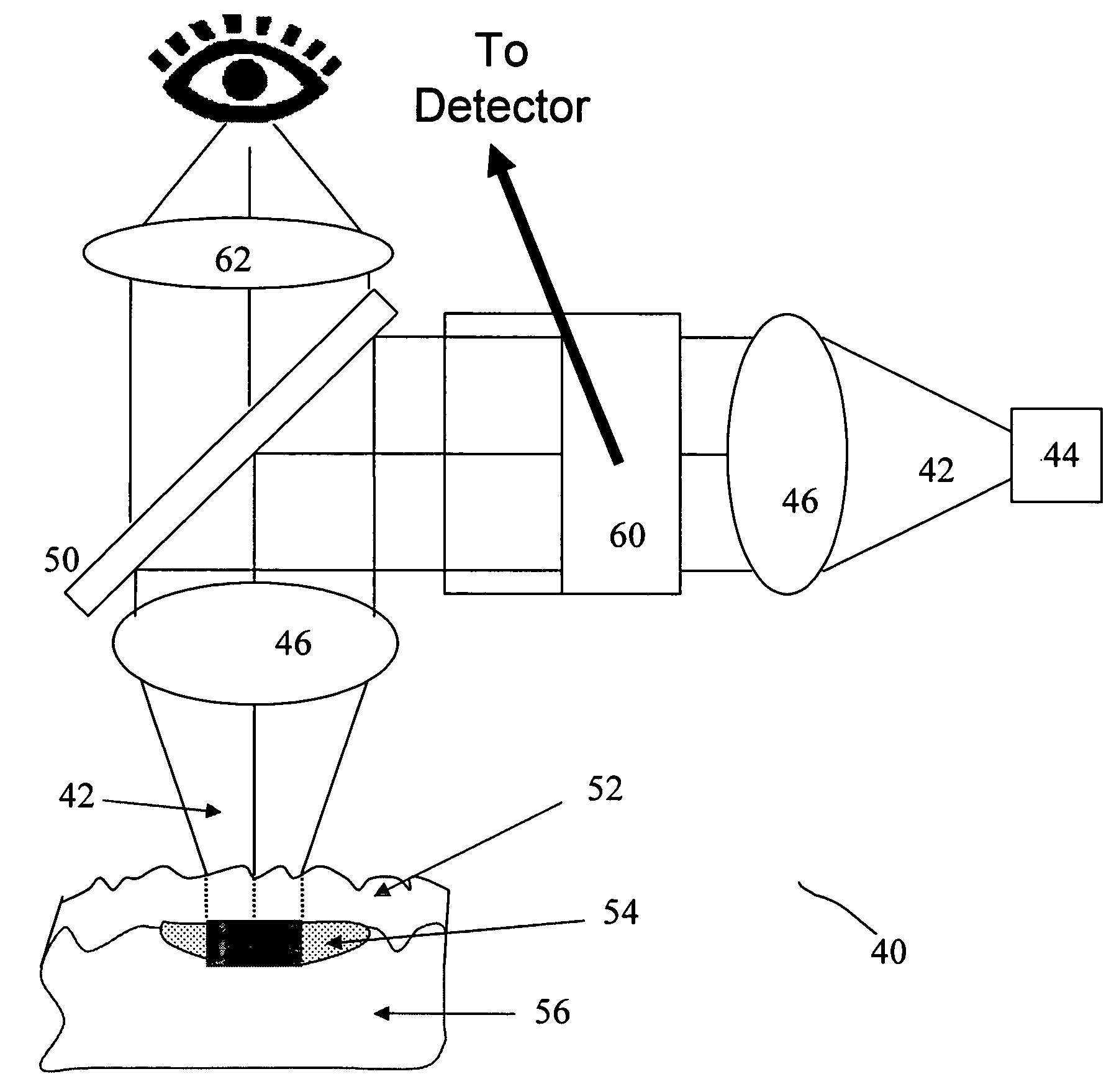
Optical catheter configurations combining raman spectroscopy with optical fiber-based low coherence reflectometry
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods for sample analysis, such as tissue analysis, that integrate high wavenumber (HW) Raman spectroscopy for chemical composition analysis and optical coherence tomography (OCT) to provide depth and morphological information. The invention also provides side-viewing optical probes that are based on a single double clad optical fiber for performing the combined HW Raman spectroscopy and OCT. Intravascular catheter embodiments and related vascular diagnostic methods are also provided.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
Surface enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS) substrates exhibiting uniform high enhancement and stability
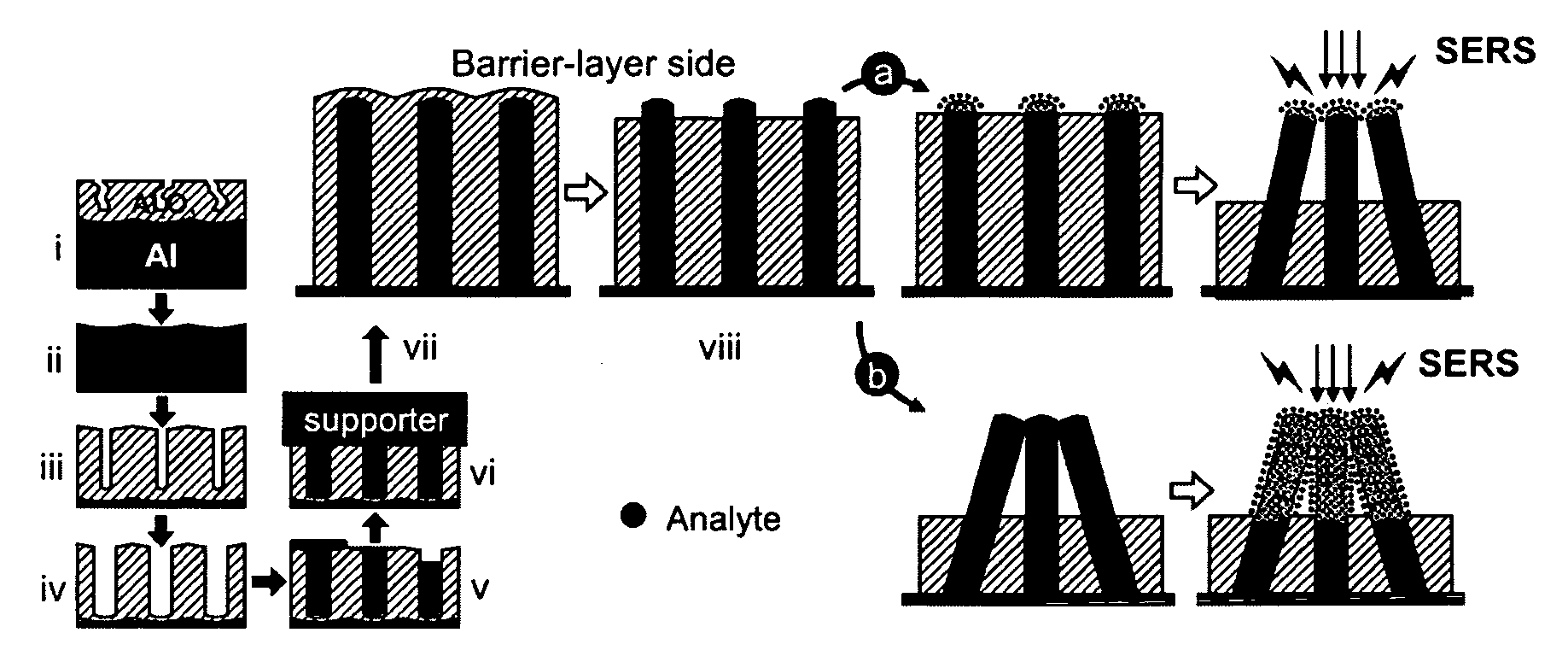
InactiveUS20060061762A1Improve evenlyIncrease valueMaterial nanotechnologyRadiation pyrometryAnalyteSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
An improved substrate for Raman spectroscopy of an analyte comprises a porous metal film. Enhancement factors and uniformity of the substrate can be enhanced by electrochemical roughening of the film. Improved sensors and spectrometers using such substrates are also described.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
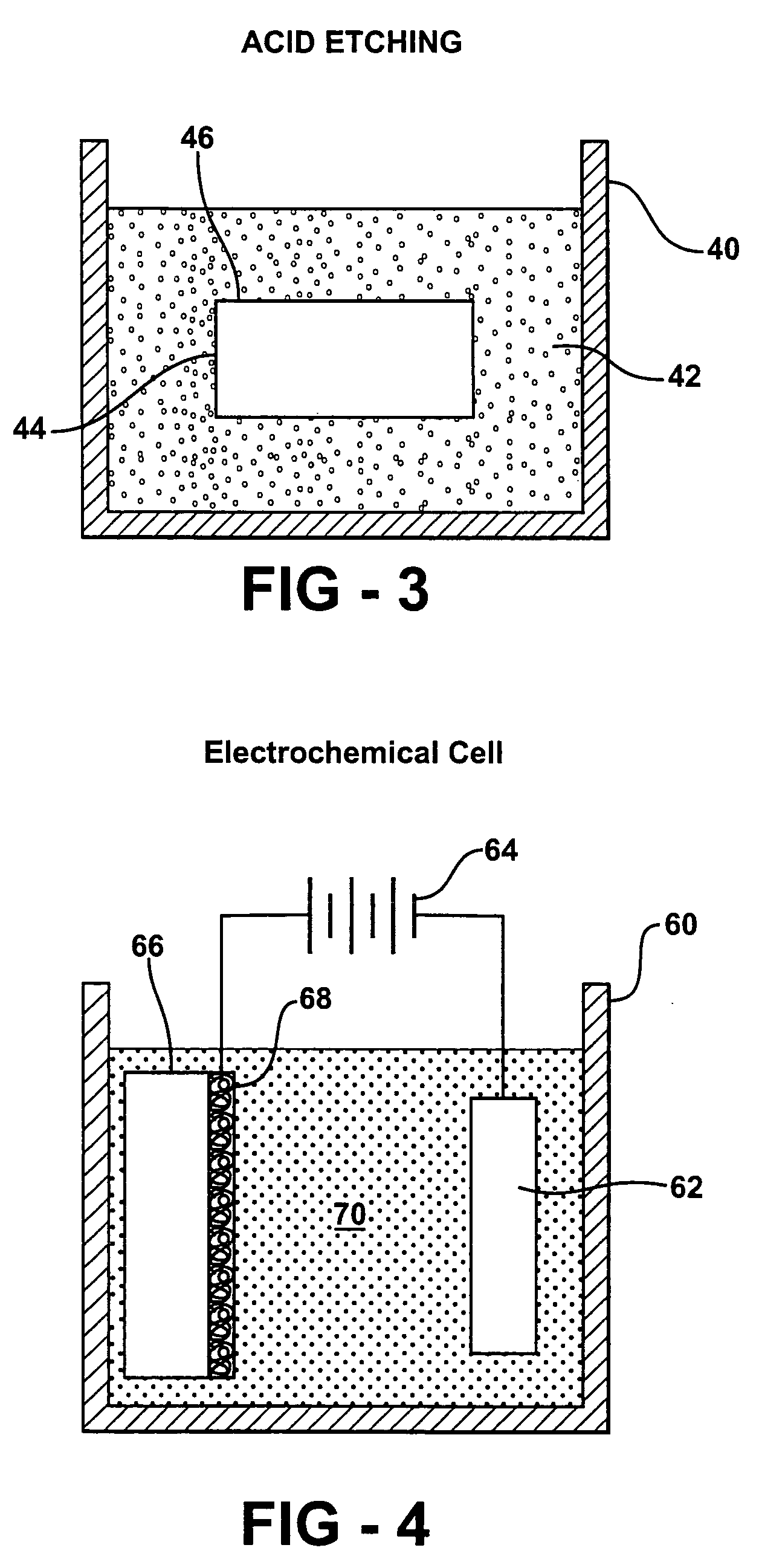
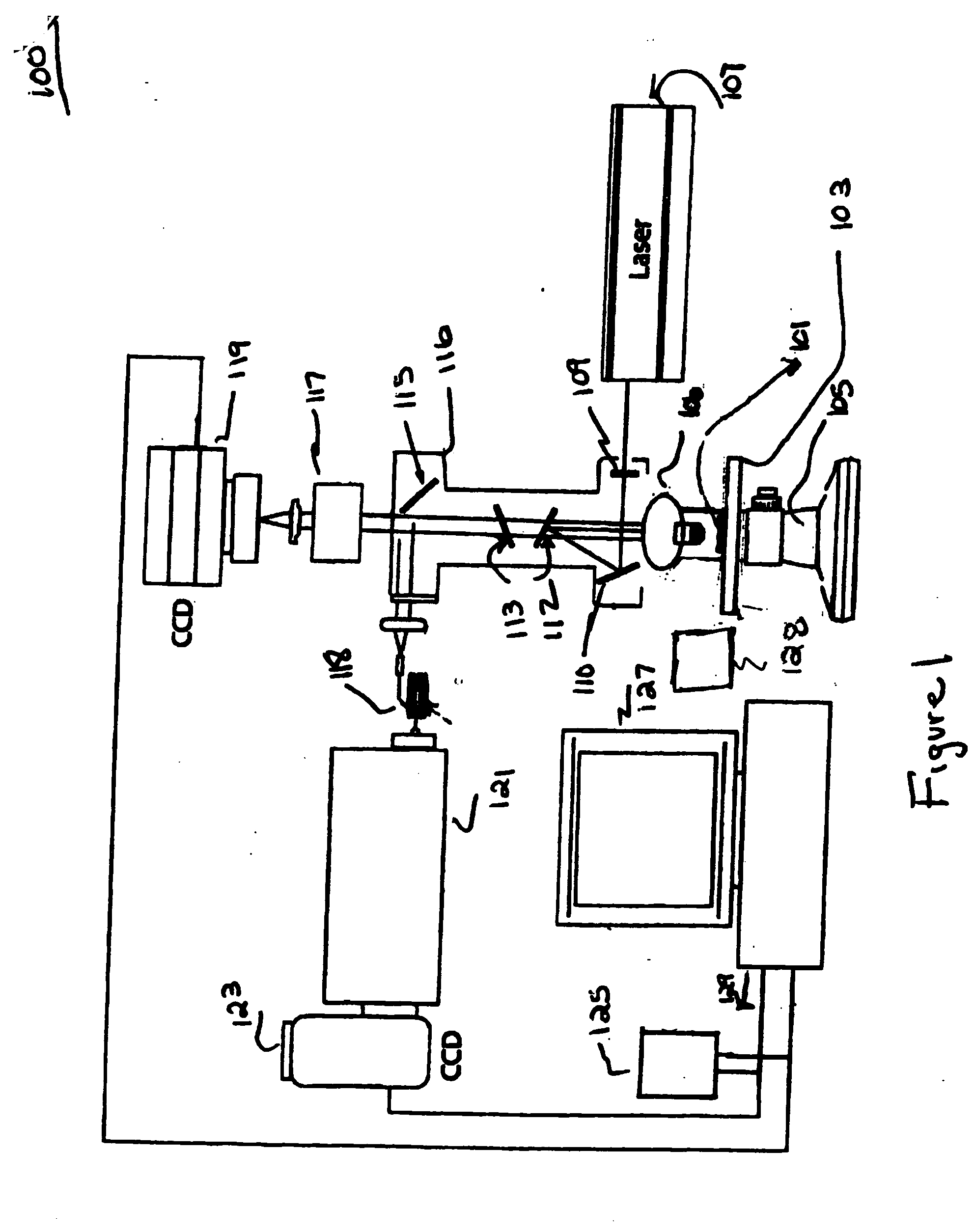
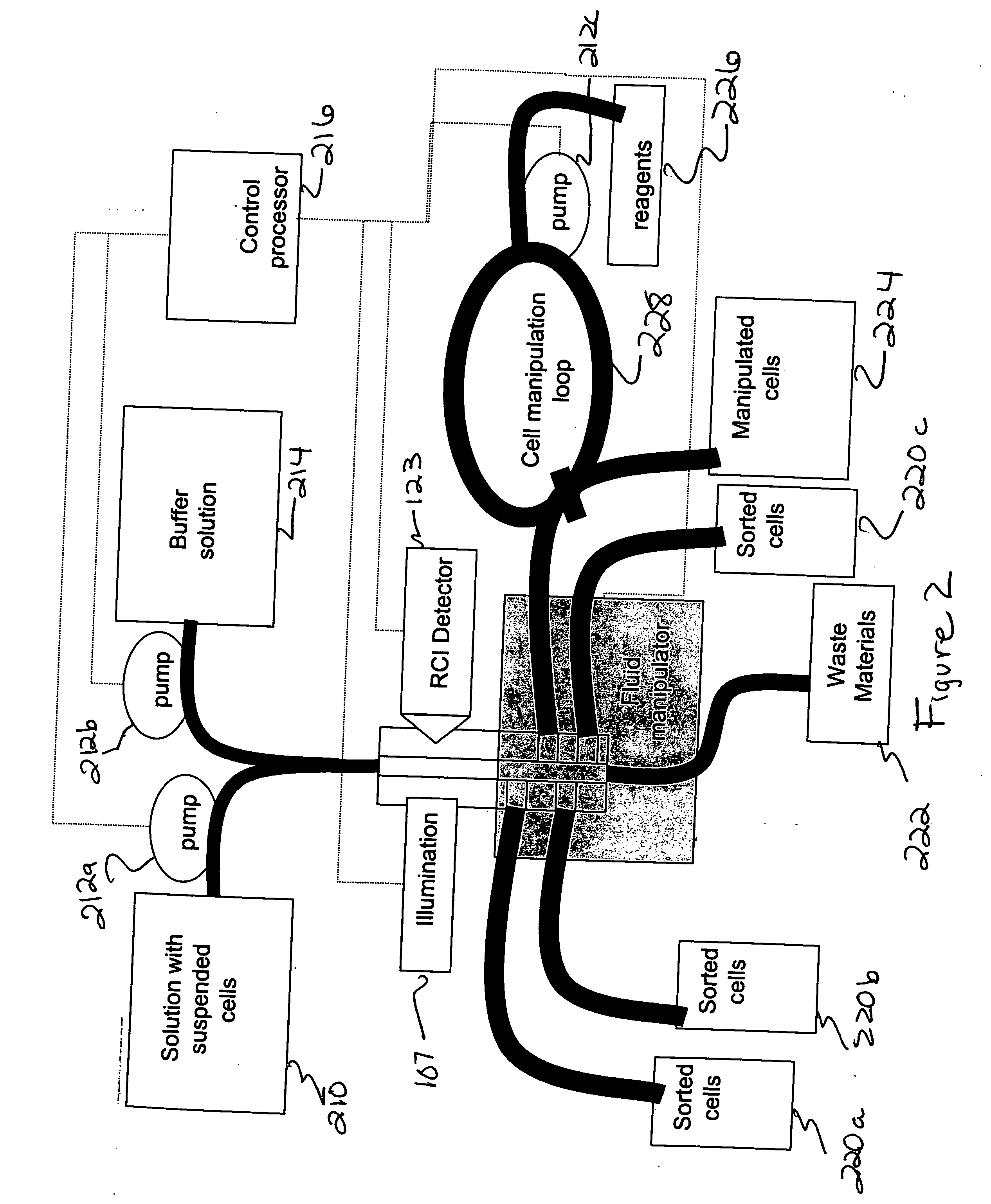
System and method for cytological analysis by raman spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS20070178067A1Superior resolution and intensitySensitive assessmentBiocideGenetic material ingredientsBiological StressData set
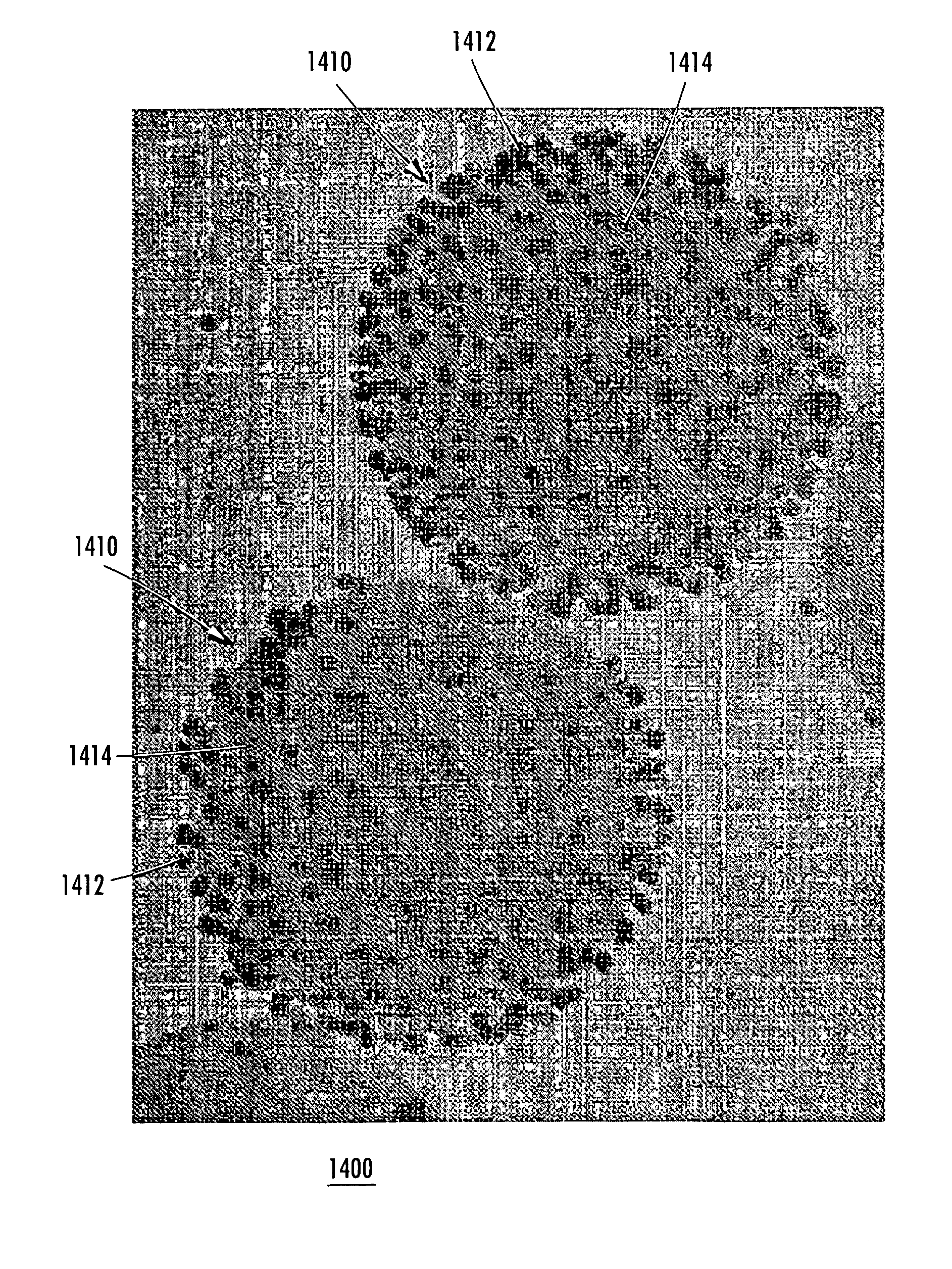
A method and system of differentially manipulating cells where the cells, suspended in a fluid, are irradiated with substantially monochromatic light. A Raman data set is obtained from the irradiated cells and where the data set is characteristic of a disease status. The data set is assessed to identify diseased cells. A Raman chemical image of the irradiated cells is also obtained. Based on the assessment and the Raman chemical image, the fluid in which the cells are suspended is differentially manipulated. The diseased cells are directed to a first location and other non-diseased cells are directed to a second location as part of the differential manipulation. The diseased cells may be treated with a physical stress, a chemical stress, and a biological stress and then returned to a patient from whom the diseased cells were obtained prior to the irradiation.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE
Assays using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy (SERS)-active particles
ActiveUS20110275061A1Enhanced signalImprove detection limitComponent separationGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsChemical physicsAssay
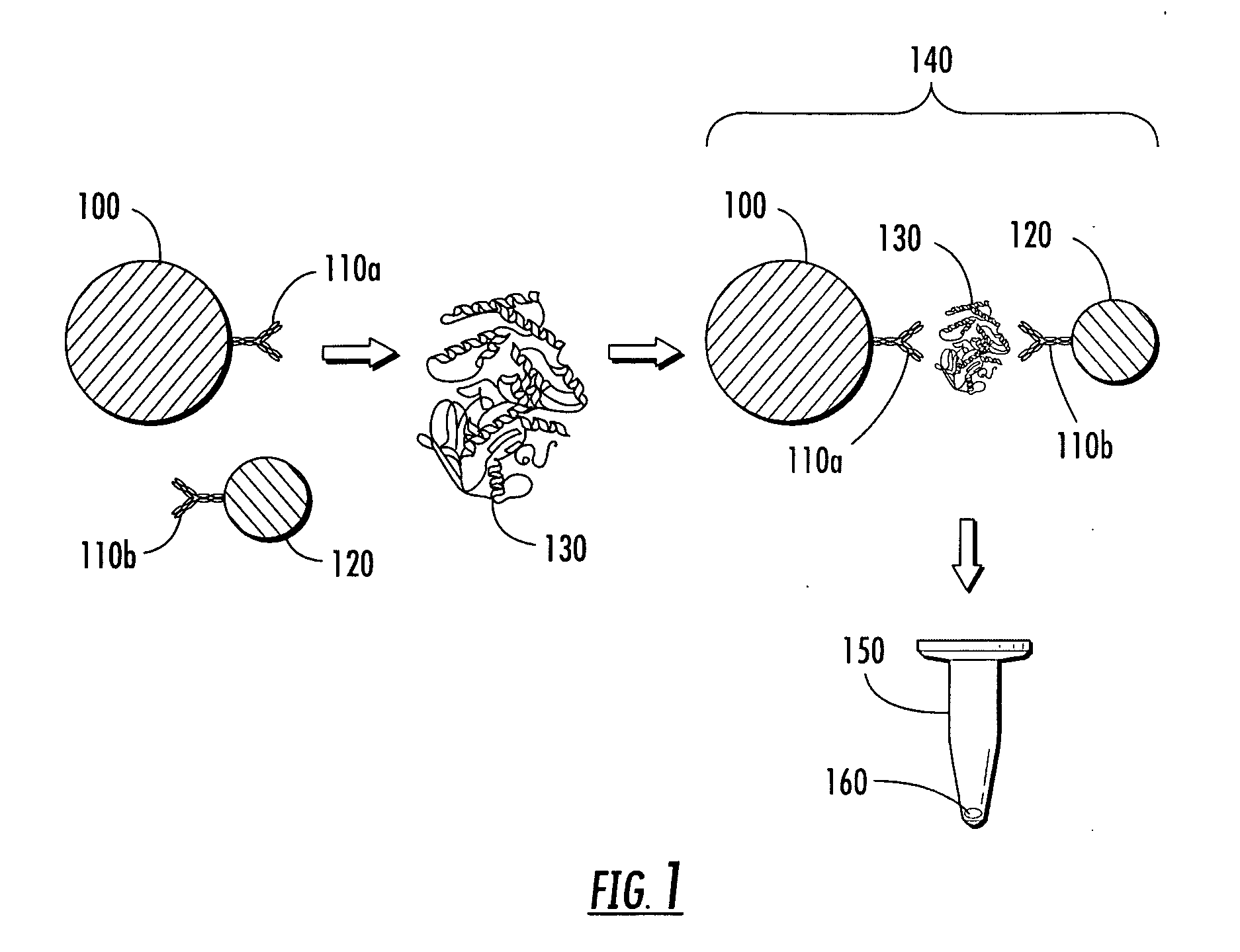
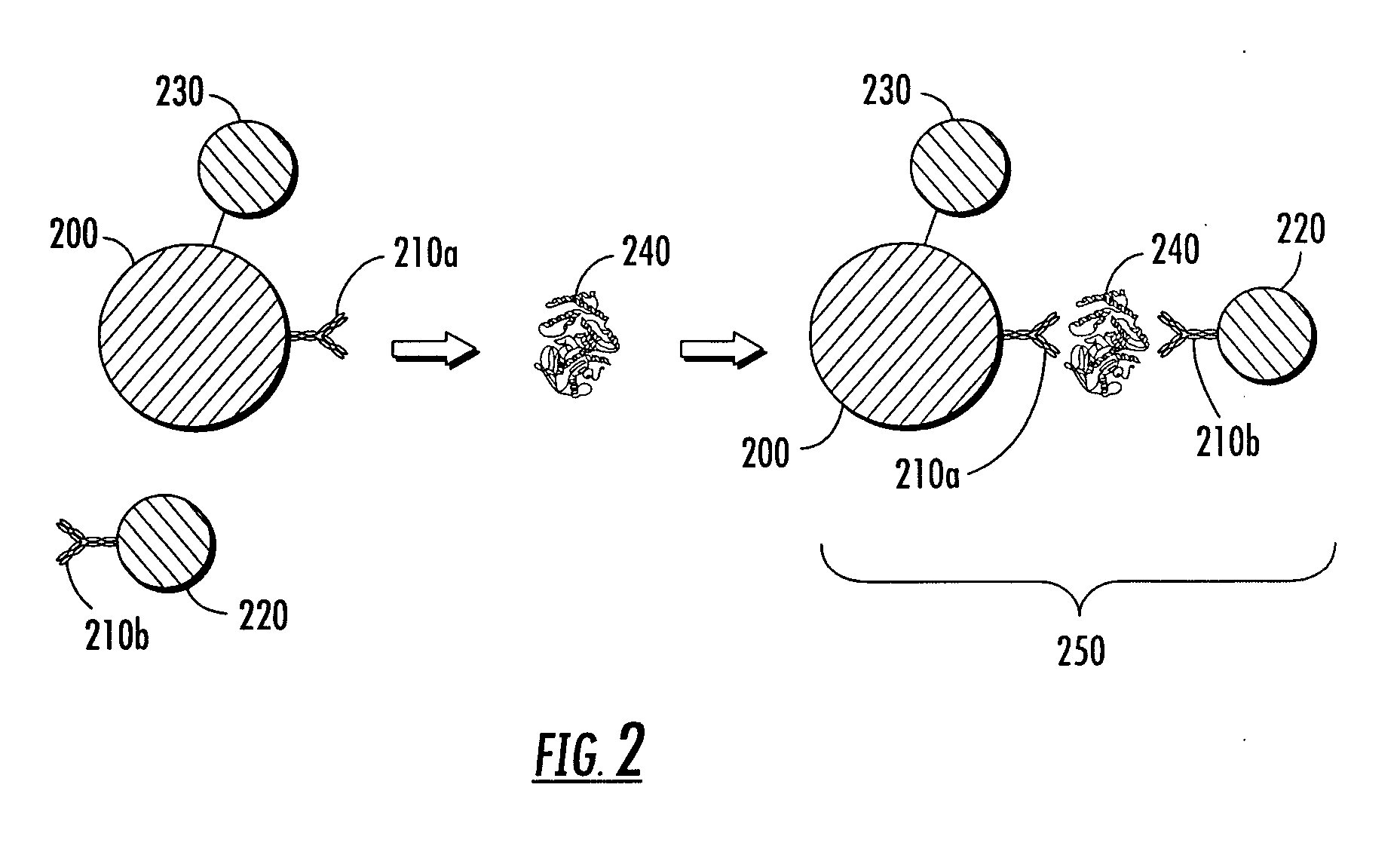
Disclosed herein are diagnostic assays using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)-active particles, including liquid-based assays; magnetic capture assays; microparticle-nanoparticle satellite structures for signal amplification in an assay; composite SERS-active particles useful for enhanced detection of targets; and sample tubes and processes for using the same.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Platform for chemical and biological sensing by surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy
InactiveUS20080174775A1High strengthWell formedRadiation pyrometryPaper/cardboard articlesAnalyteSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Methods of analysis, and compositions relating to such, to determine the presence or absence of an analyte in a sample utilizing a composite substrate which facilitates surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy through the use of ‘hot spots’ of the form ‘metal / analyte / metal’ are presented. Additionally, substrates which contain ‘hot spots’ of the form ‘metal / analyte / metal’ and substrates which facilitate the formation of ‘hot spots’ of the form ‘metal / analyte / metal’ are presented as well as methods for making these substrates.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
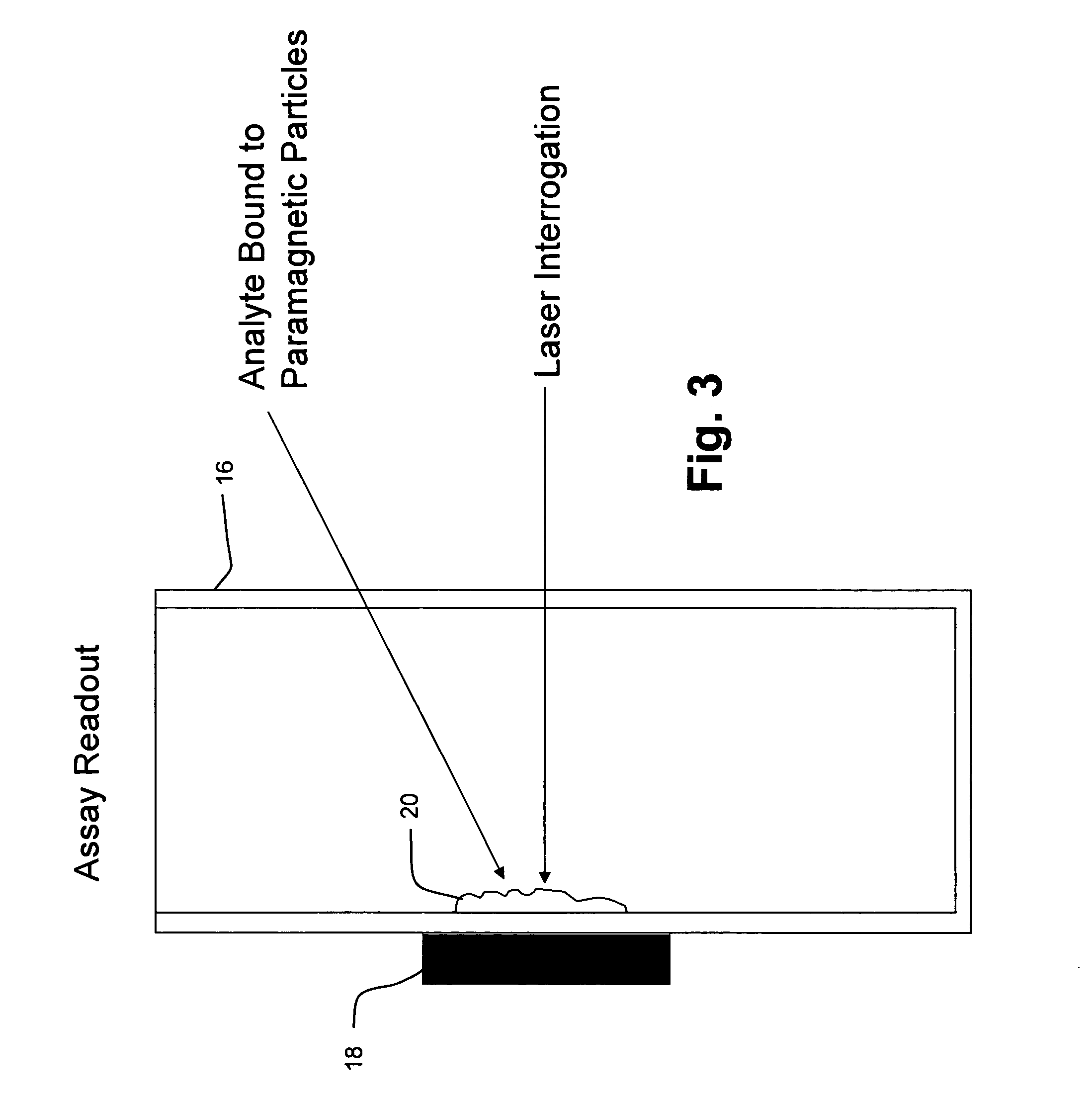
System and method for Raman spectroscopy assay using paramagnetic particles
ActiveUS20060240572A1Easy to measureRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteCompound (substance)
A Raman spectroscopy technique allows an analyte, a paramagnetic particle, and a spectral enhancement particle to combine in solution and for the combination product to be localized by a magnetic field for analysis. The spectral enhancement particle may be comprised of an active SERS metal particle with or without a material coating. The spectral enhancement particle may function as a reporter for the presence of the analyte or merely increase the magnitude of the Raman spectrum of the analyte. The technique is applicable to both immunoassays and chemical assays. Multiple spectral enhancement particle reporters may be measured in a single assay that can detect multiple analytes using the SERS effect.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Fibers of aligned single-wall carbon nanotubes and process for making the same
ActiveUS7125502B2Good dispersionEasy to incorporatePigmenting treatmentNanosensorsFiberCarbon nanotube
The present invention involves fibers of highly aligned single-wall carbon nanotubes and a process for making the same. The present invention provides a method for effectively dispersing single-wall carbon nanotubes. The process for dispersing the single-wall carbon nanotubes comprises mixing single-wall carbon nanotubes with 100% sulfuric acid or a superacid, heating and stirring under an inert, oxygen-free environment. The single-wall carbon nanotube / acid mixture is wet spun into a coagulant to form the single-wall carbon nanotube fibers. The fibers are recovered, washed and dried. The single-wall carbon nanotubes were highly aligned in the fibers, as determined by Raman spectroscopy analysis.
Owner:DEXMAT INC
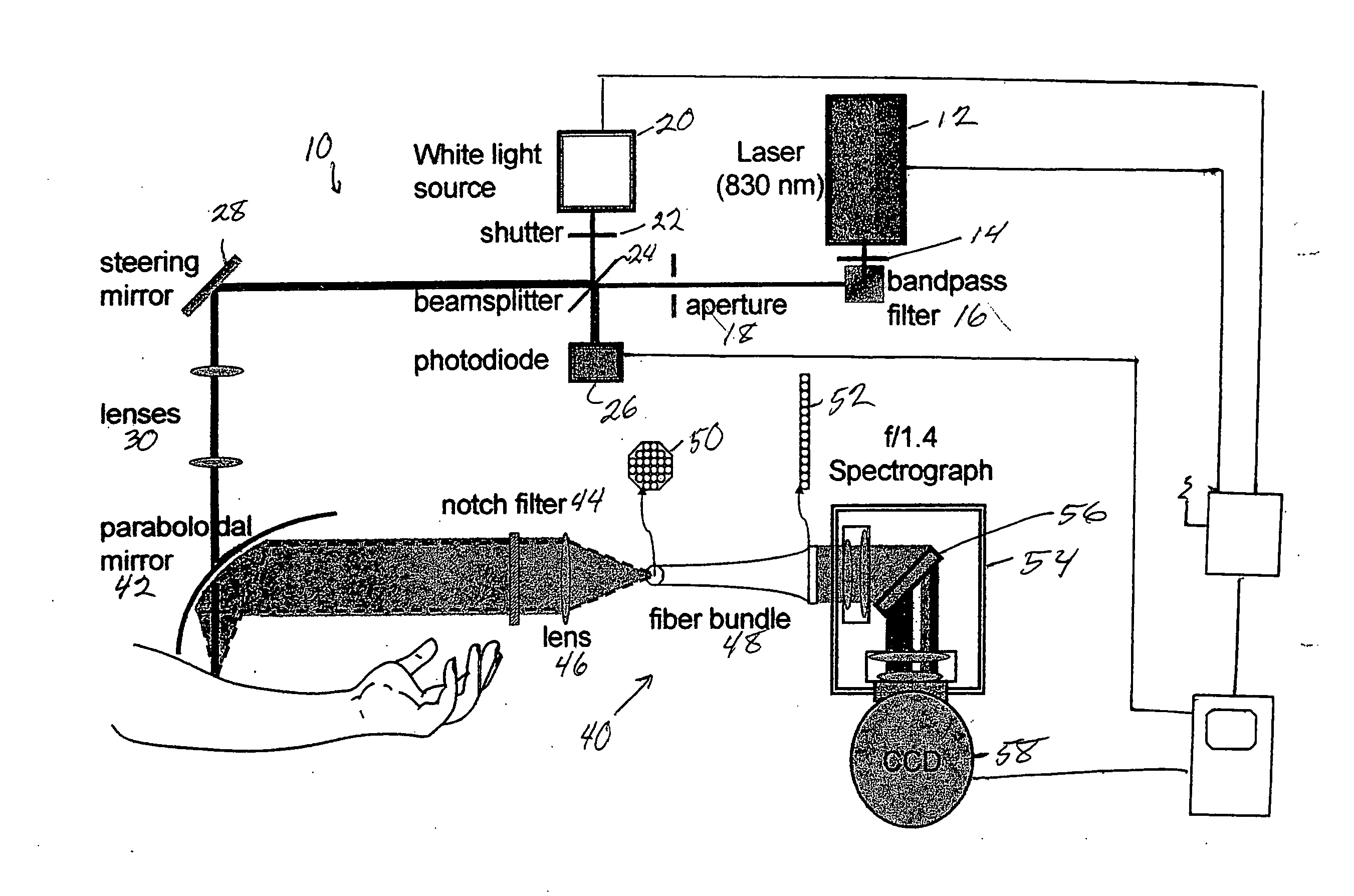
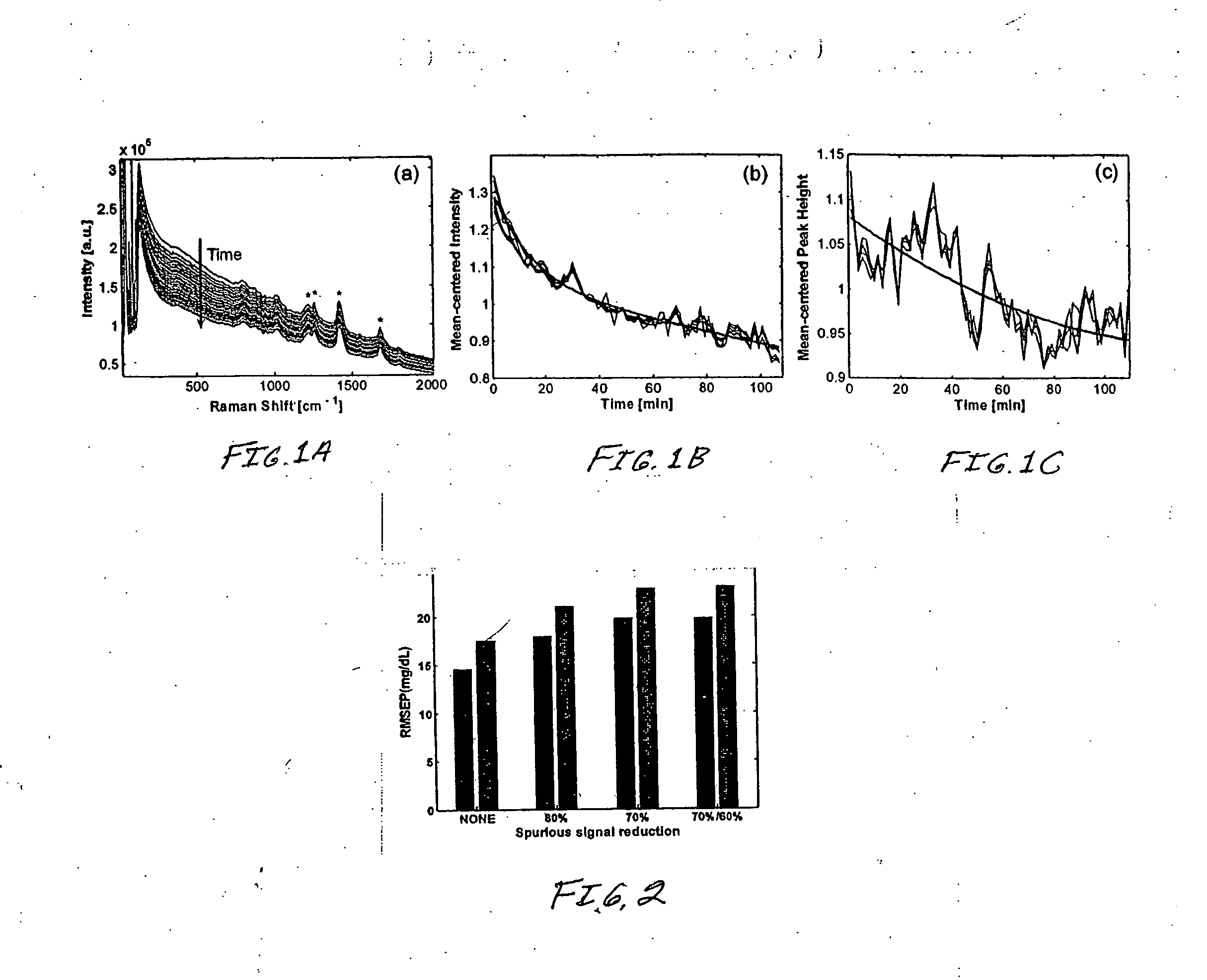
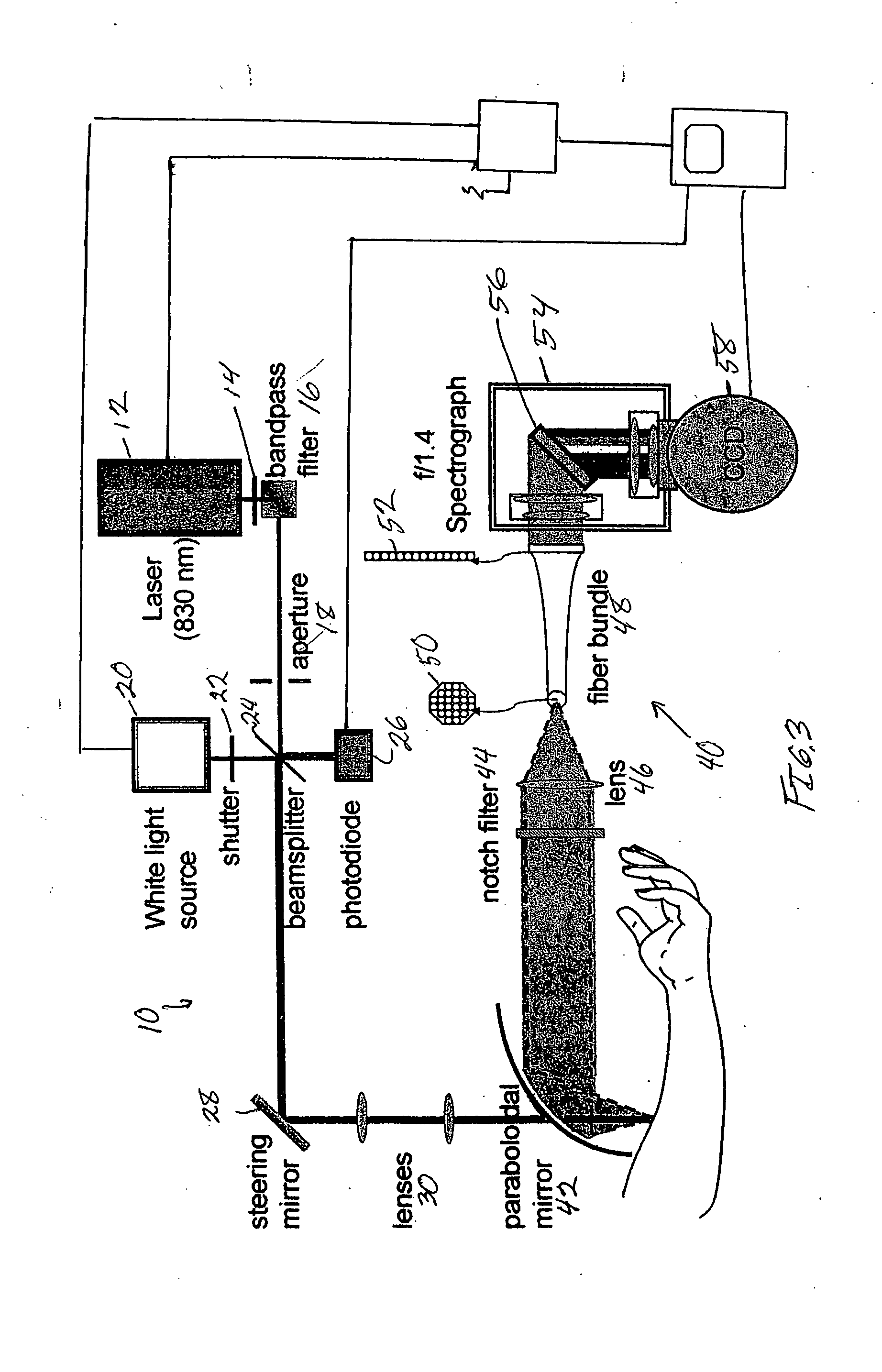
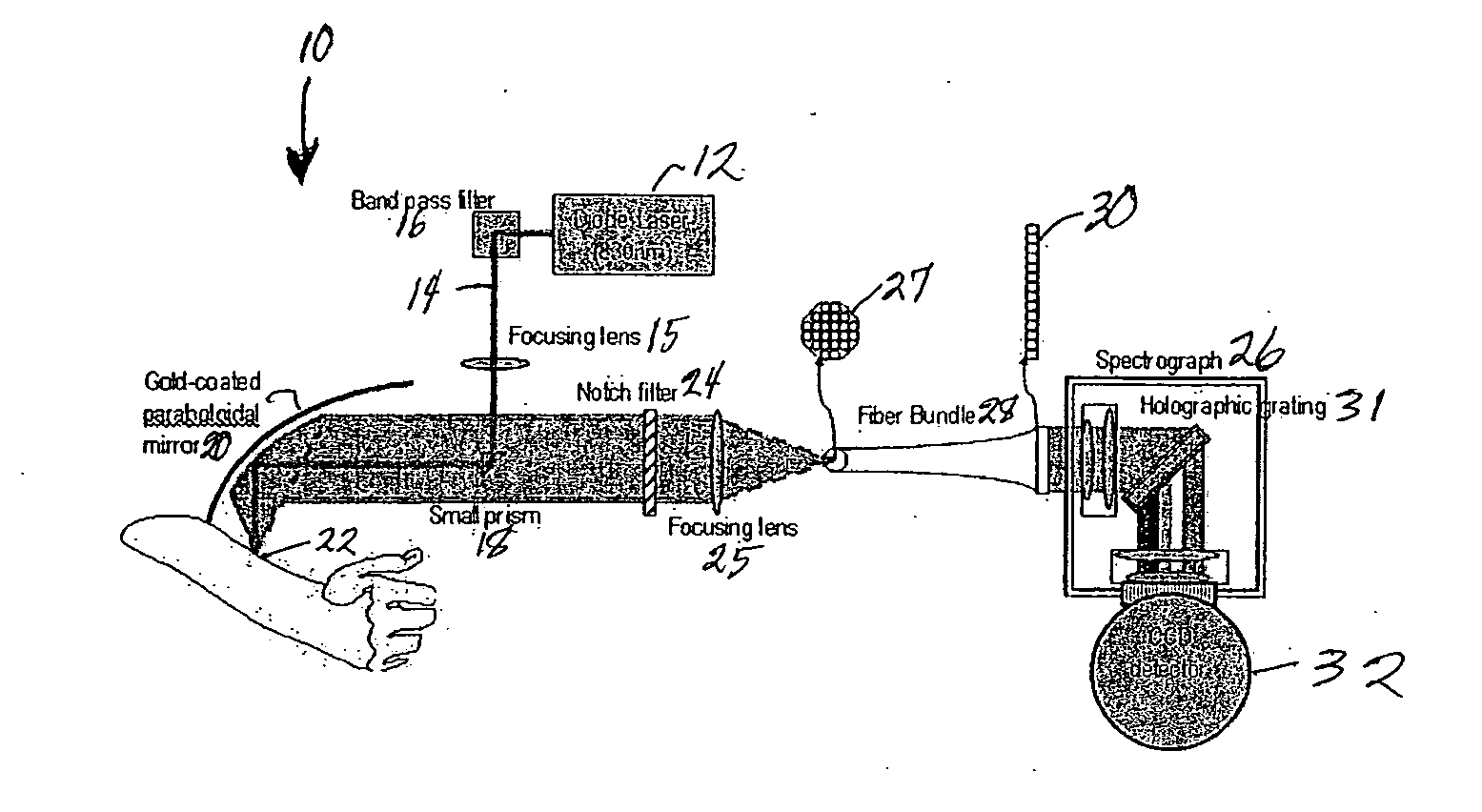
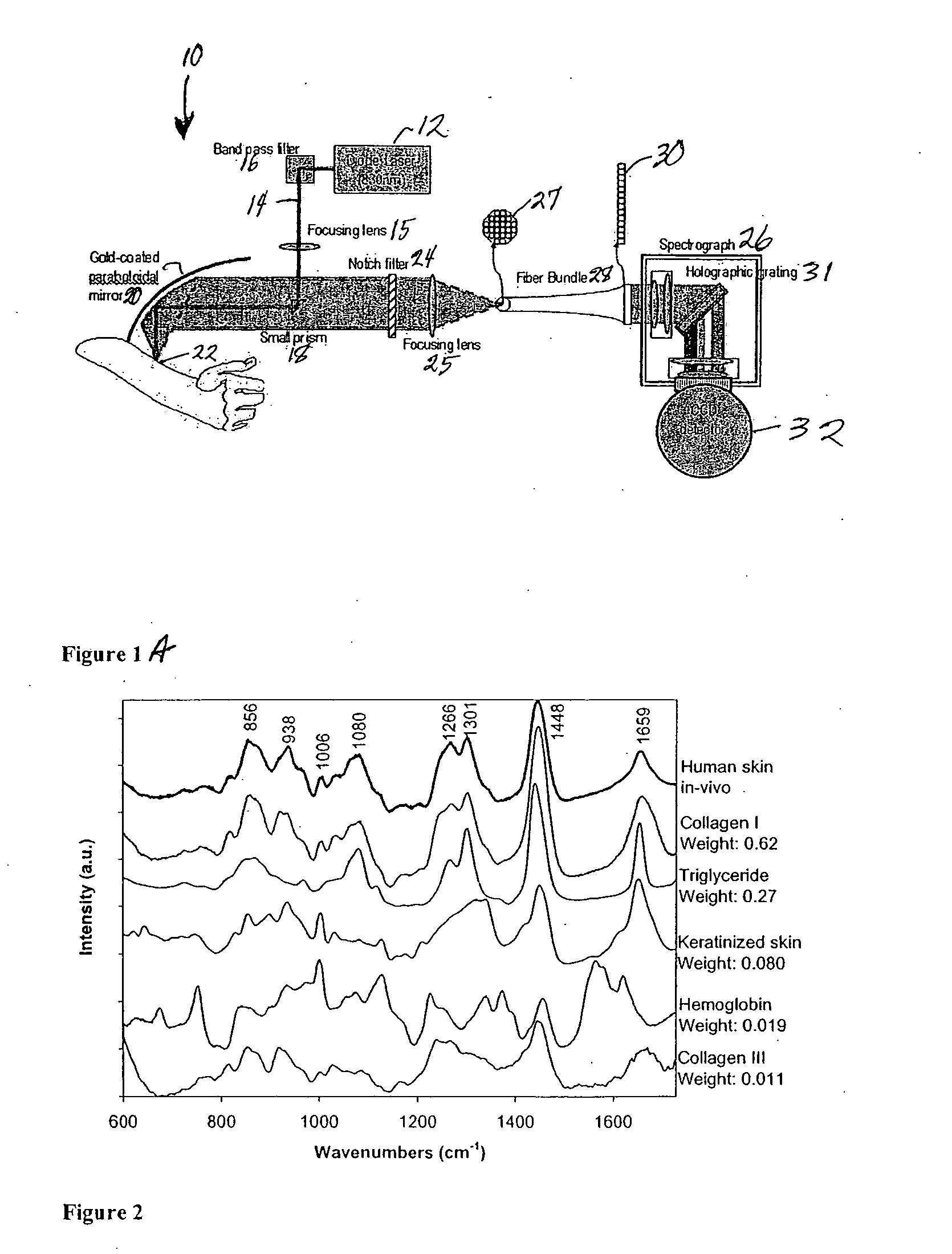
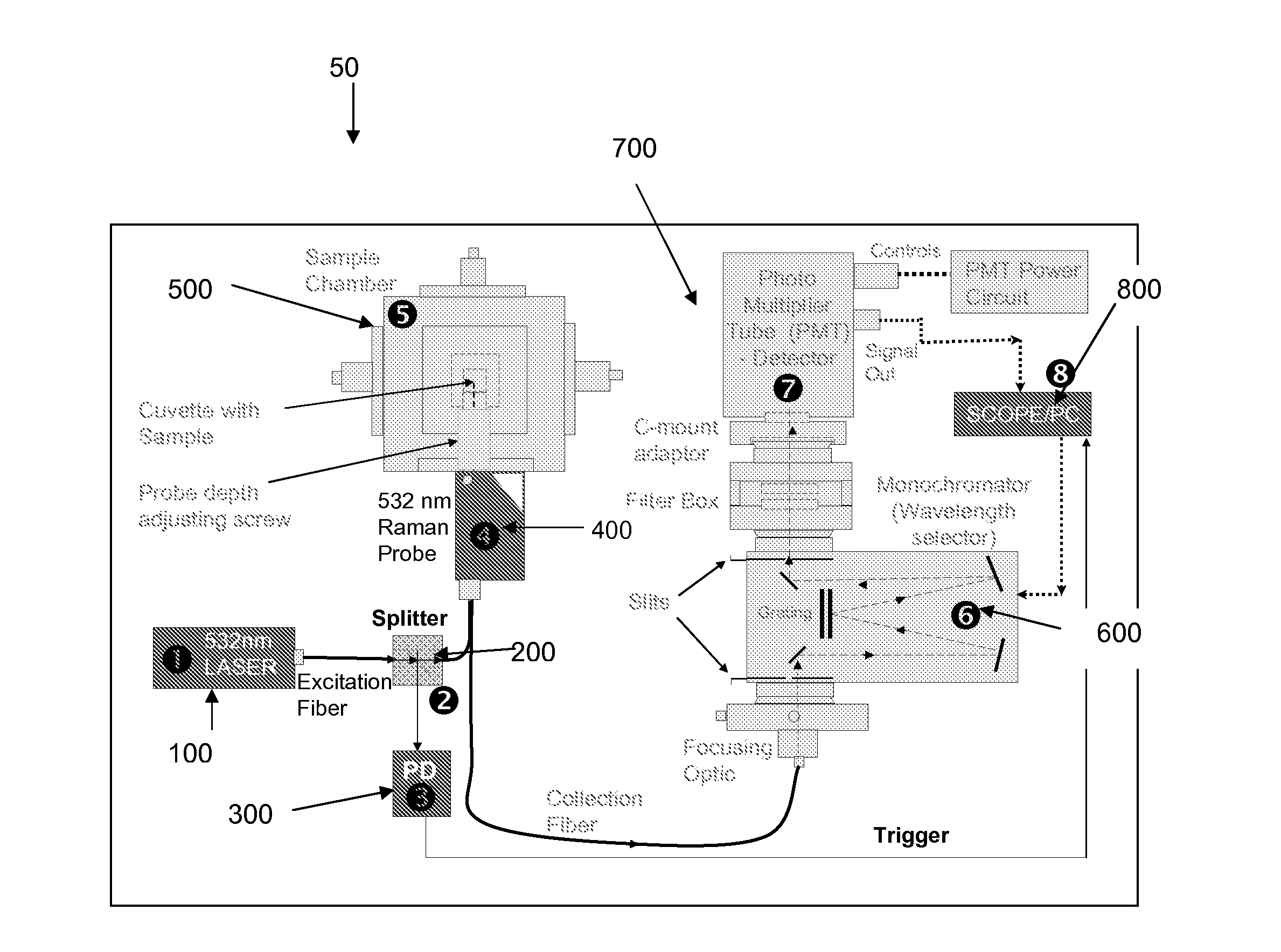
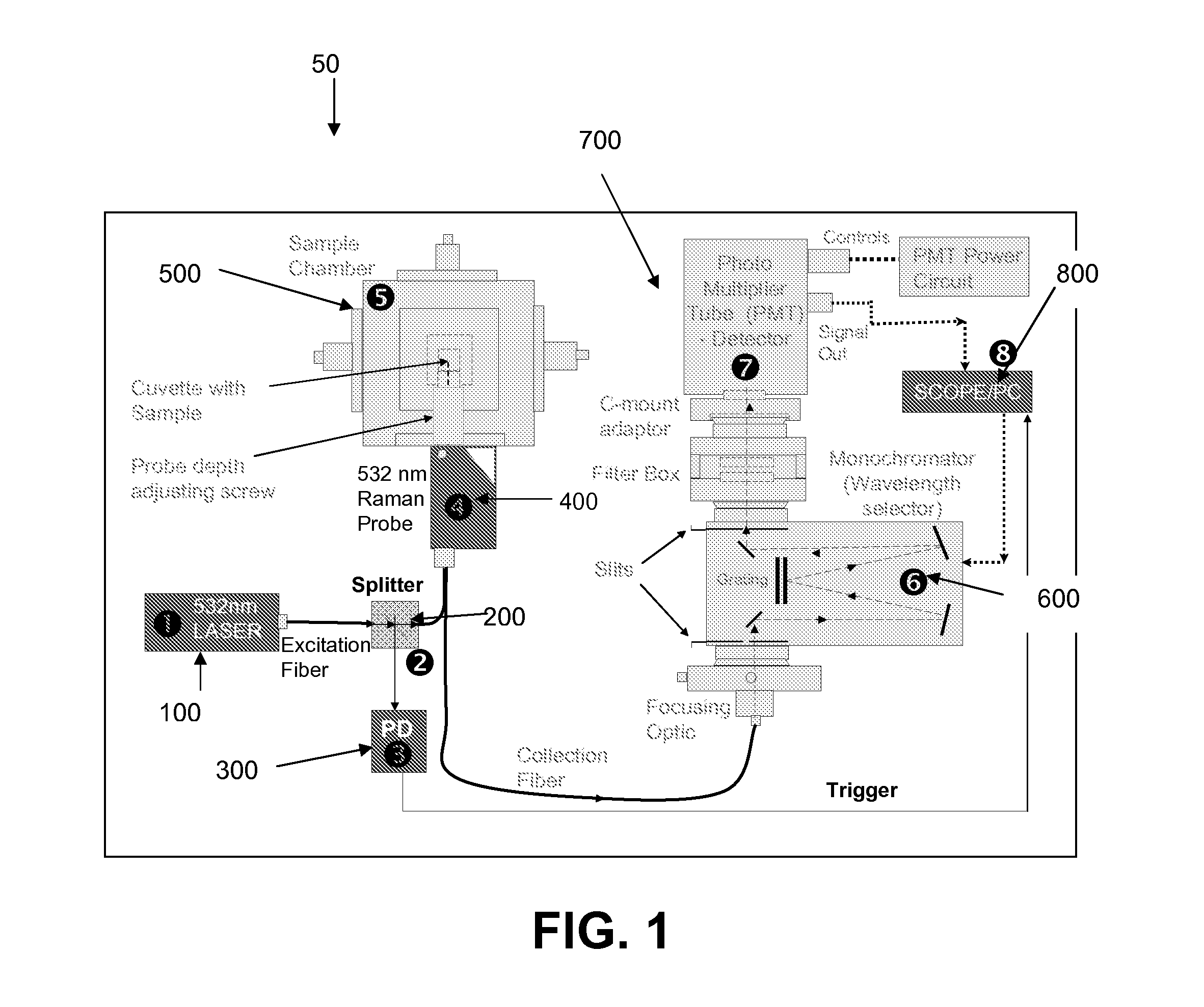
Raman spectroscopy for non-invasive glucose measurements
ActiveUS20070060806A1Error minimizationIncreased signal noiseRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringMonitor glucoseGlucose Measurement
The present invention relates to the use of Raman spectroscopy for quantitative, non-invasive transcutaneous measurement of blood analytes, such as glucose. Raman spectroscopy is used to measure glucose transcutaneously, in patients whose blood glucose levels were monitored. Raman spectra were collected transcutaneously along with glucose reference values provided by standard capillary blood analysis. A partial least squares calibration was created from the data from each subject and validated using leave-one-out cross validation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
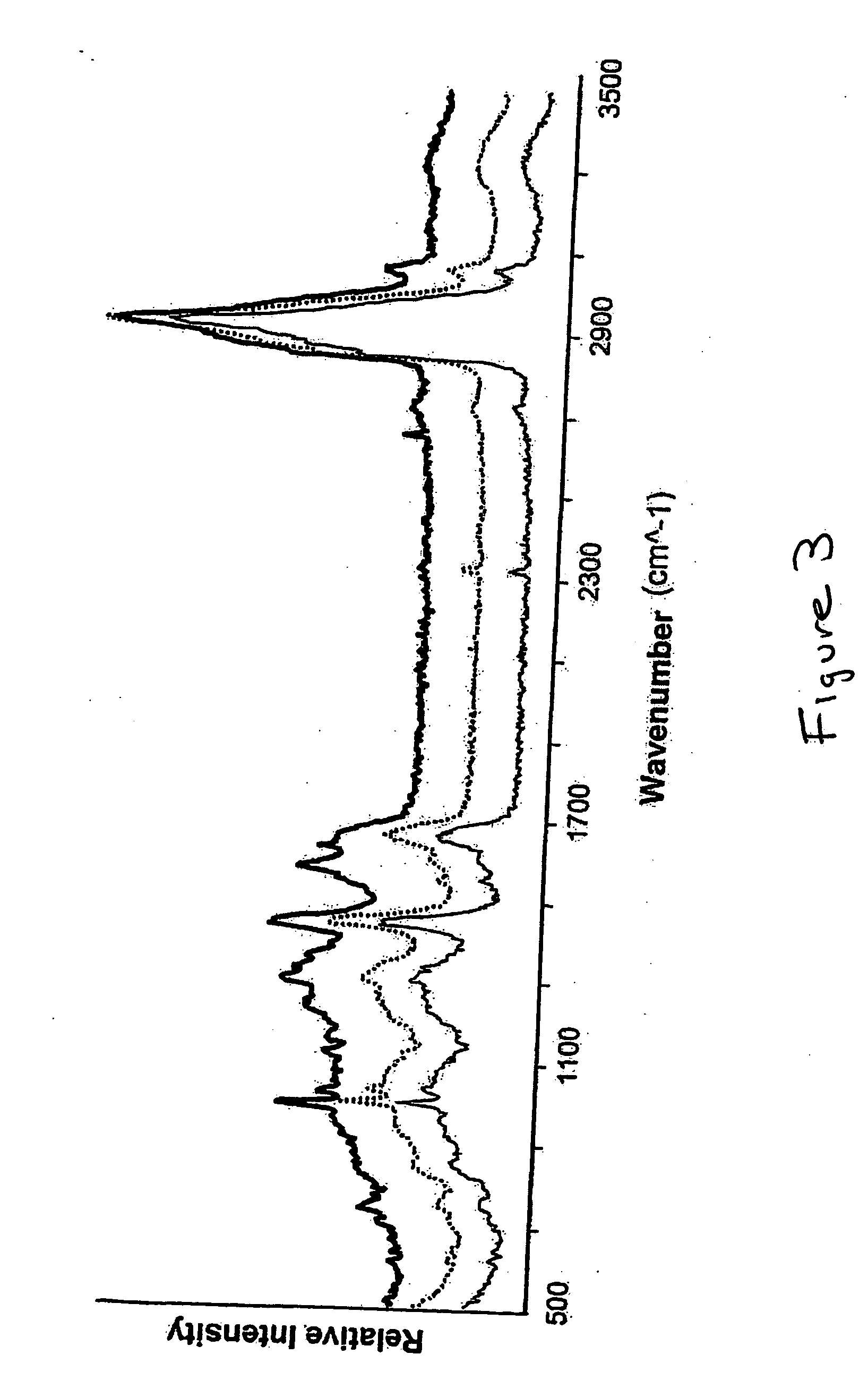
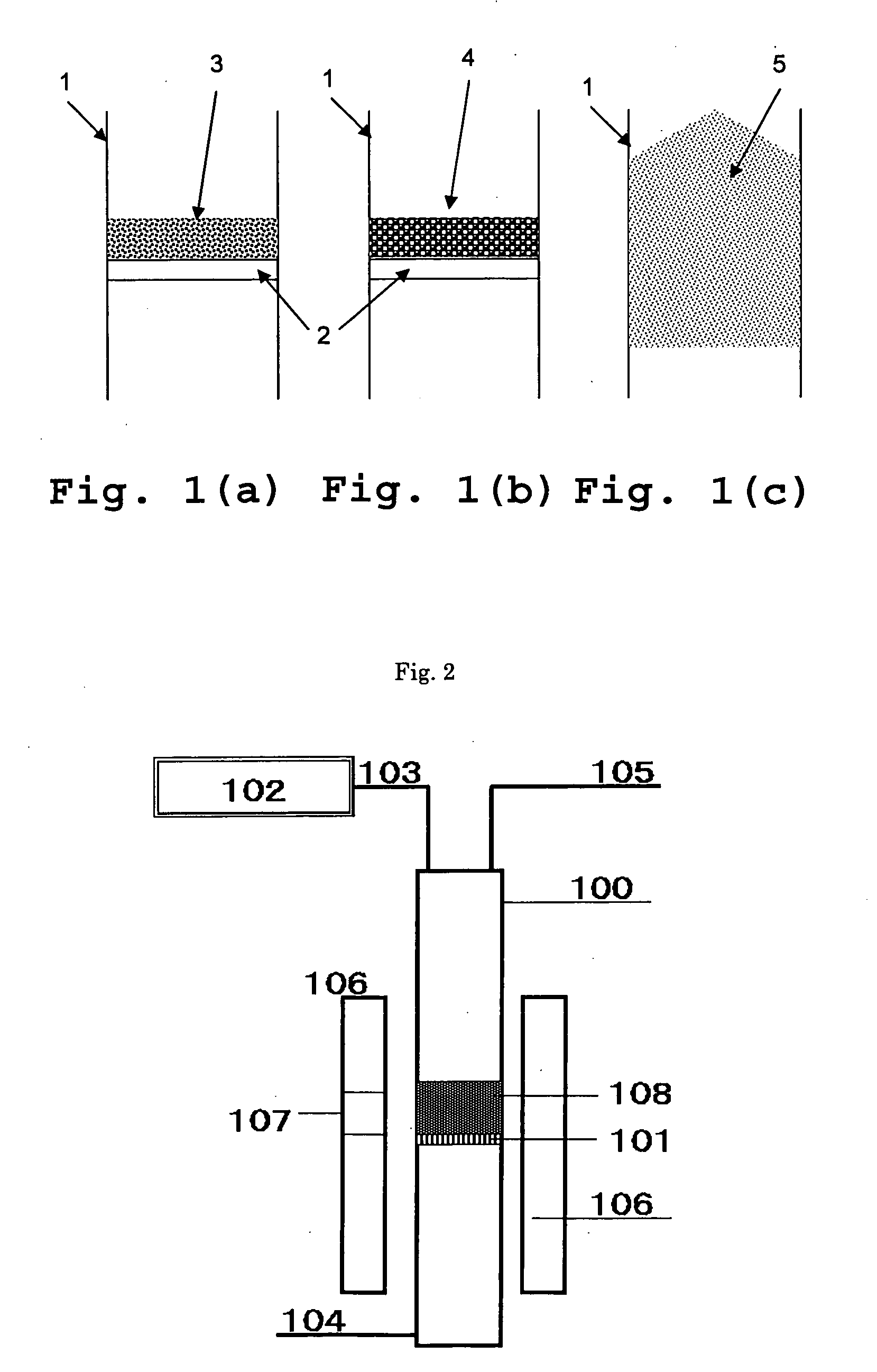
Raman spectroscopy crystallization analysis method
A method of monitoring sample crystallization from a solution. The method includes the collection of multiple Raman spectra from a sample dissolved in a solvent as a function of time and under conditions promoting crystallization. Within each of the multiple Raman spectra, a first signal is identified corresponding to the sample associated with the solvent. A second signal corresponding to the sample in a microcrystallite state is also identified. Thereafter, the intensity of the multiple Raman spectra are measured for an increase relating to formation of the sample in a microcrystallite state. A method of monitoring sample crystallization from a solution as a function of turbidity is also disclosed. The method includes the collection of multiple Raman spectra from a sample dissolved in a solvent as a function of time under conditions promoting crystallization. A decrease in intensity is measured across the multiple Raman spectrum over time, the intensity decrease associated with macroscopic crystallization opacity. The decrease in intensity is finely correlated with the onset of macroscopic crystallization of the sample from the solvent.
Owner:KAISER OPTICAL SYST INC
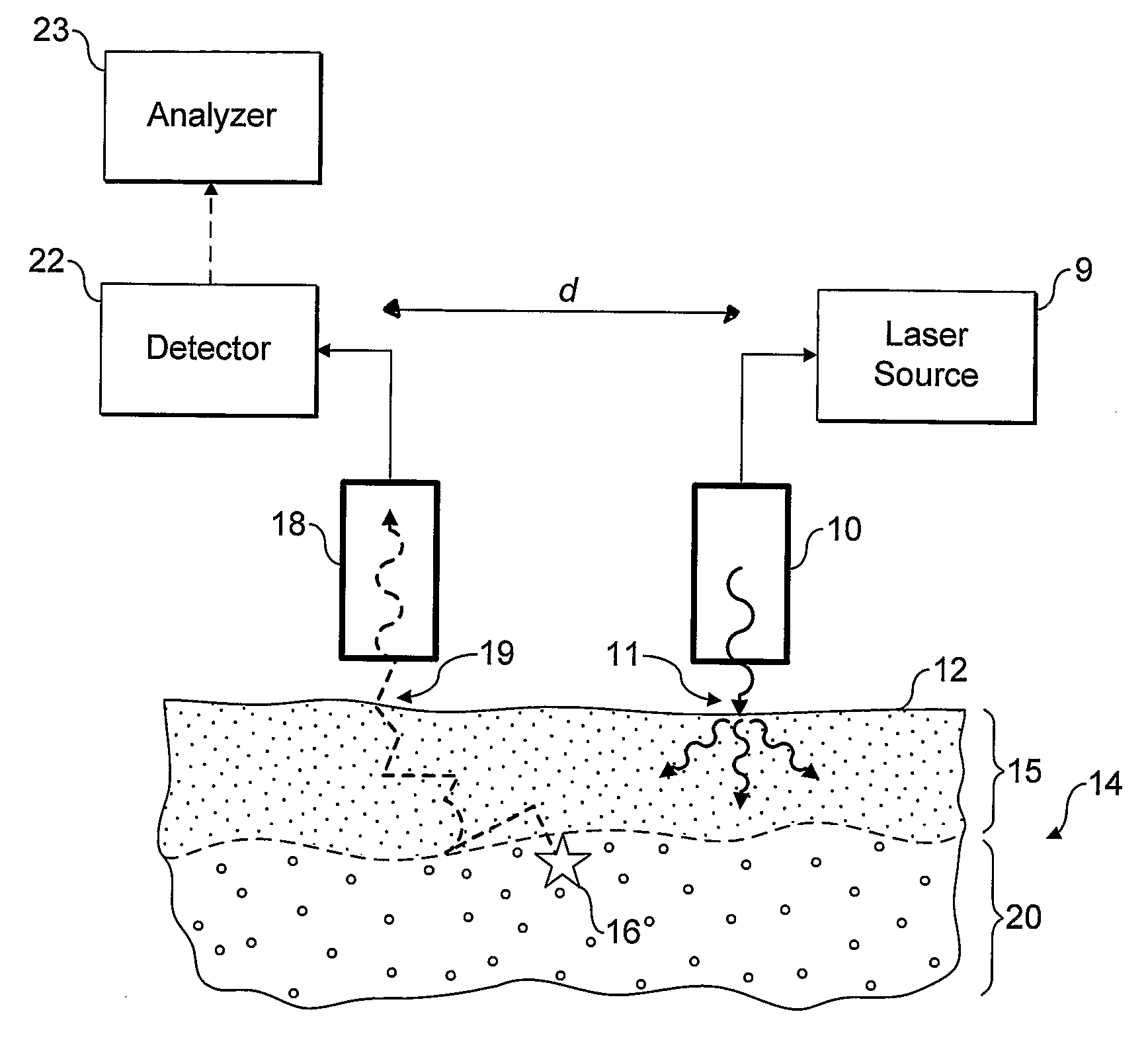
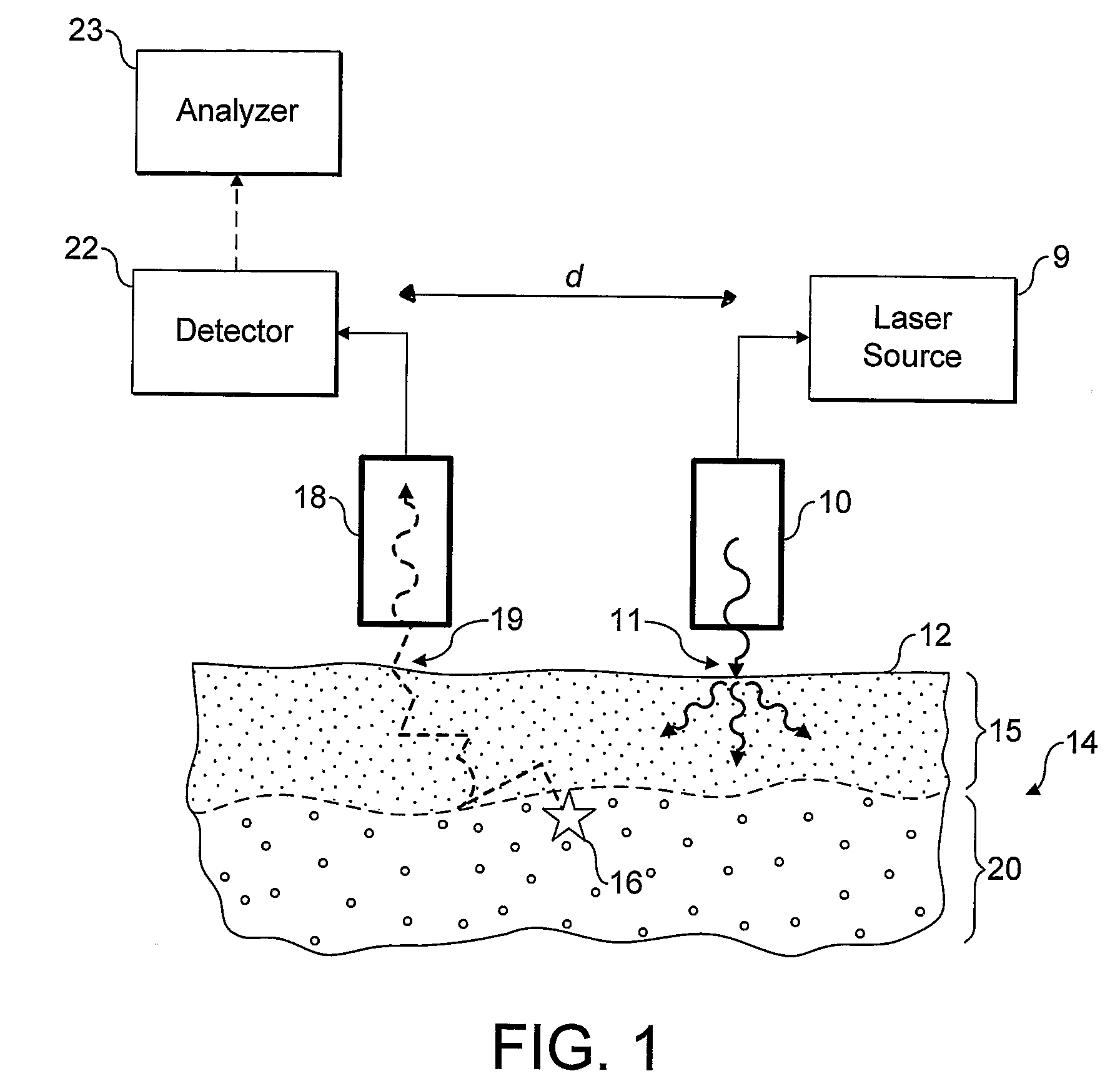
Raman Spectral Analysis Of Sub-Surface Tissues And Fluids
ActiveUS20080076985A1Extraction of informationThe surface is moreRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightRaman microspectroscopyIn vivo
Apparatus and methods for determining, in-vivo, characteristics of sub-surface tissues or fluids in the human or animal body are disclosed. Incident radiation is supplied at one or more entry regions on a surface, and light is collected from one or more collection regions spaced from the entry regions. Raman features are detected in the collected light and depth related information derived therefrom.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
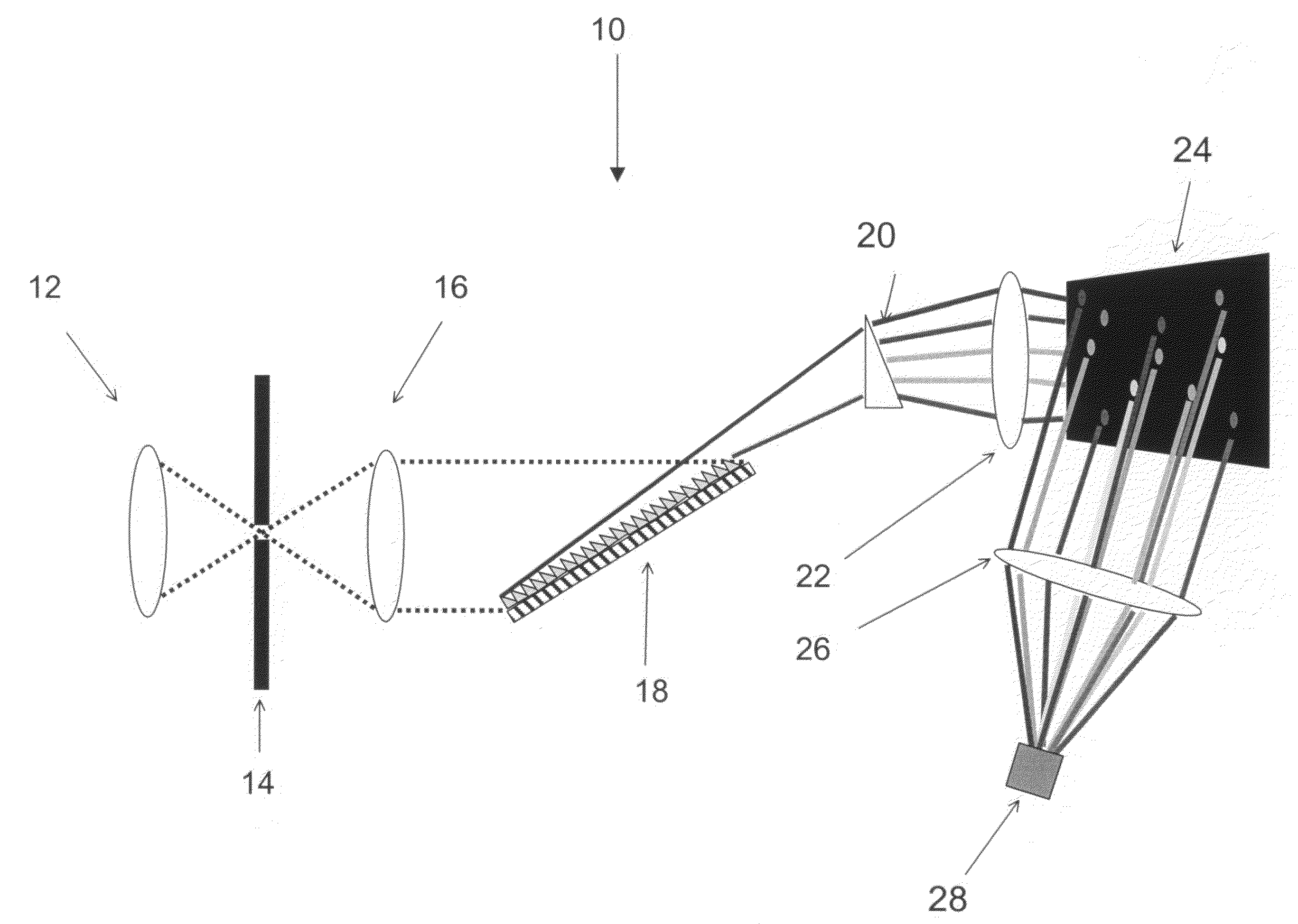
Spectrometers using 2-dimensional microelectromechanical digital micromirror devices
InactiveUS20080174777A1Low costSpeed up the time required for analysisEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryGratingSpectroscopy
Echelle gratings and microelectromechanical system (MEMS) digital micromirror device (DMD) detectors are used to provide rapid, small, and highly sensitive spectrometers. The new spectrometers are particularly useful for laser induced breakdown and Raman spectroscopy, but could generally be used with any form of emission spectroscopy. The new spectrometers have particular applicability in the detection of improvised explosive devices.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Aggregate of carbon nanotubes, dispersion thereof and conductive film using the same
InactiveUS20090001326A1Good dispersionQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyNon-metal conductorsCombustionX-ray
Provided is an aggregate of carbon nanotubes satisfying (1) there is a 2θ peak at 24°±2° by X-ray powder diffraction analysis; (2) a height ratio (G / D ratio) of G band to D band by Raman spectroscopic analysis of wavelength 532 nm is 30 or more; and (3) a combustion peak temperature is 550° C. or more, and 700° C. or less. The present invention provides an aggregate of carbon nanotubes excellent in dispersibility while high quality, giving a film, molded article, membrane or the like having excellent characteristics
Owner:TORAY IND INC
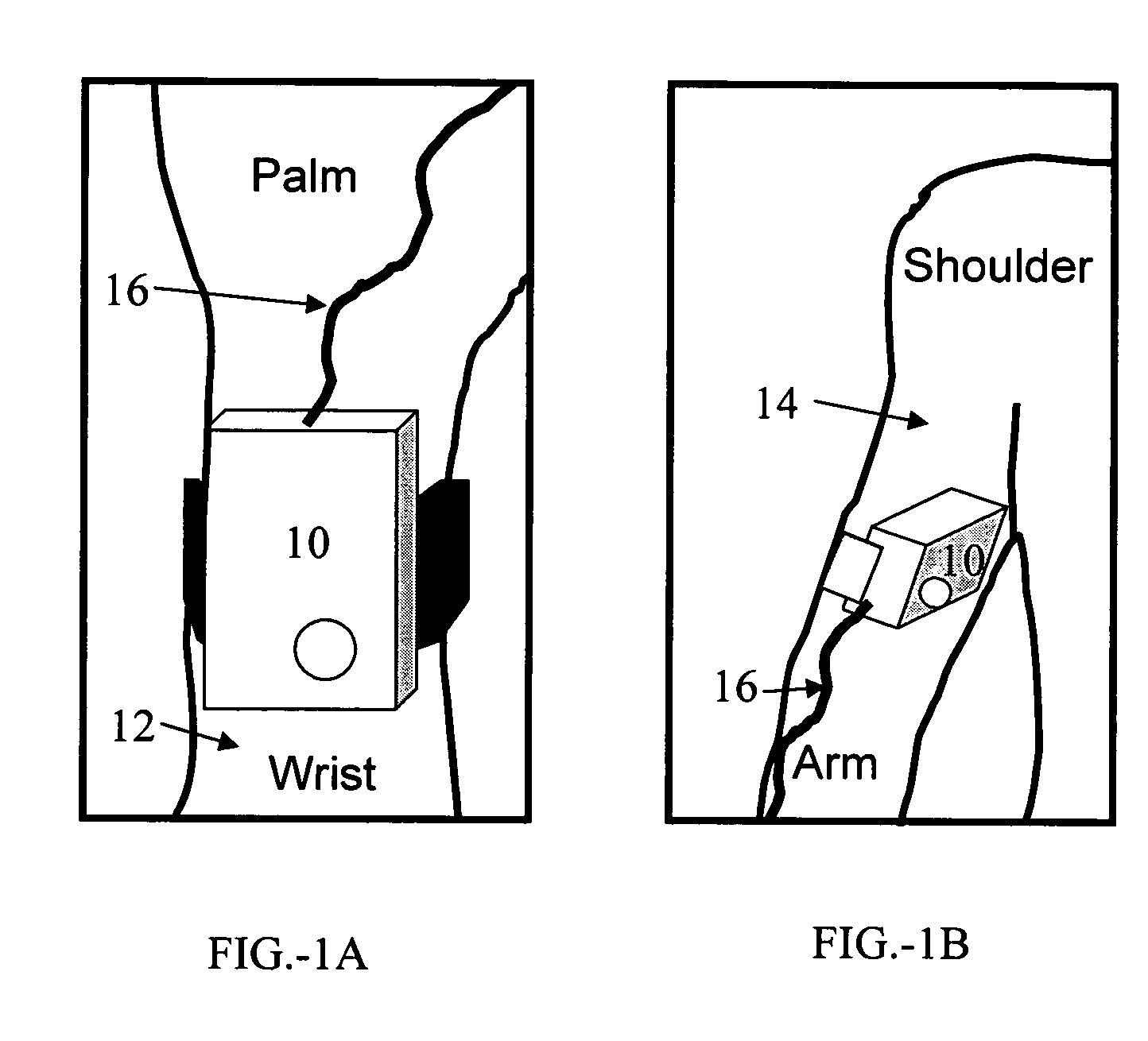
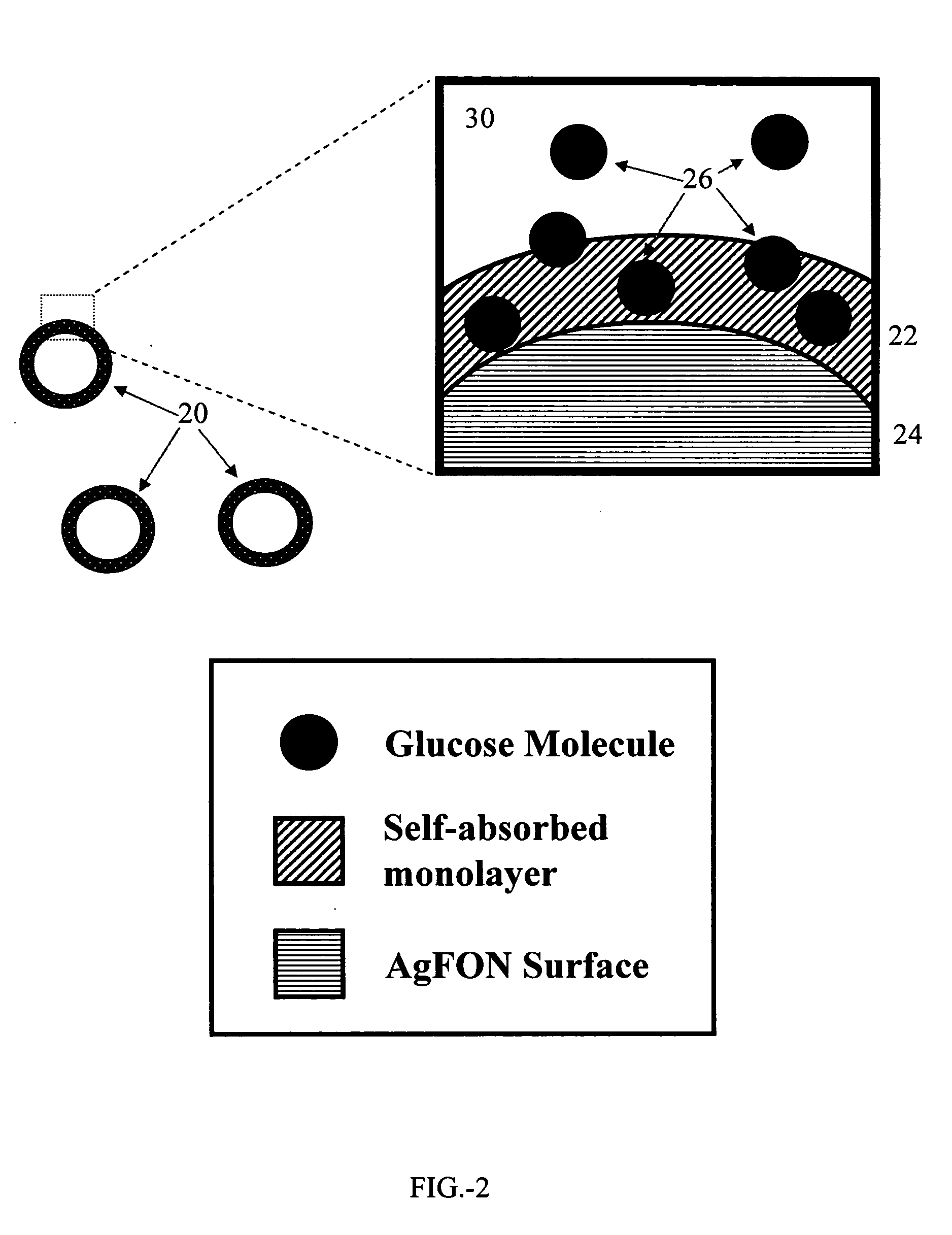
Optical in vivo analyte probe using embedded intradermal particles
A system and method of in vivo detection and quantification of one or more analytes. Small particles comprising a surface-active monolayer coating are embedded in the dermis. The surface-active monolayer acts to pre-concentrate the analyte by adsorbing the analyte from bulk solution. The concentrated analyte is more readily detected and quantified by one or more spectroscopic methods such as Raman spectroscopy
Owner:MARBLIA LTD +1
Time resolved raman spectroscopy
ActiveUS20110261354A1Low costHigh resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPhotometry using reference valueComputer control systemInelastic scattering
System, method, and apparatus for determining the composition of a sample of material. In one embodiment, the method pertains to the counting of photons that were inelastically scattered by the sample, and for minimizing the effects of fluorescent or phosphorescent photons. In yet another embodiment of the invention, a sample is illuminated by a repetitive pulse of monochromatic light, and the resultant scattered photons from the samples are collected and counted during a predetermined integration period. Yet other embodiments pertain to a low-cost, computer-controlled system for repetitively counting inelastically scattered photons so as to create a Raman histogram and a Raman spectrogram of the photons.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Method and catalyst for producing a crude product with minimal hydrogen uptake
A catalyst that one or more metals from Column 5 of the Periodic Table and / or one or more compounds of one or more metals from Column 5 of the Periodic Table is described. The catalyst exhibits one or more bands in a range from 650 cm−1 to 1000 cm−1, as determined by Raman Spectroscopy. Methods of contacting a crude feed with hydrogen with the catalyst to produce a crude product with minimal hydrogen uptake are also described.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Detection of biomolecules using porous biosensors and Raman spectroscopy
ActiveUS20050196876A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsRadiation pyrometryProtein profilingFluorescence
The invention provides methods used to analyze the contents of a biological sample, such as blood serum, with cascade Raman sensing. A fluorescence producing nanoporous biosensor having probes that bind specifically to known analytes is contacted with a biological sample and one or more bound complexes coupled to the porous semiconductor structure are formed. The bound complexes are contacted with a Raman-active probe that binds specifically to the bound complexes and the biosensor is illuminated to generate fluorescent emissions from the biosensor. These fluorescent emissions generate Raman signals from the bound complexes. The Raman signals produced by the bound complexes are detected and the Raman signal associated with a bound protein-containing analyte is indicative of the presence of the protein-containing compound in the sample. The invention methods are useful to provide a protein profile of a patient sample. The invention also provides detection systems useful to practice the invention methods.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multimodal method for identifying hazardous agents
ActiveUS20080192246A1Shorten the timeRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyOptical propertySpectral analysis
The invention relates to apparatus and methods for assessing occurrence of a hazardous agent in a sample by performing multimodal spectral analysis of the sample. Methods of employing Raman spectroscopy for entities in a sample which exhibit one or more optical properties characteristic of a hazardous agent are disclosed. Devices and systems suitable for performing such methods are also disclosed.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Portable optical fiber probe-based spectroscopic scanner for rapid cancer diagnosis
InactiveUS20120302892A1Overcoming distortionImprove accuracyDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiseaseReflectance spectroscopy
A multimodal probe system for spectroscopic scanning of tissue for disease diagnosis. The system can use diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy for the detection of cancerous tissue, such as tissue margin assessment.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
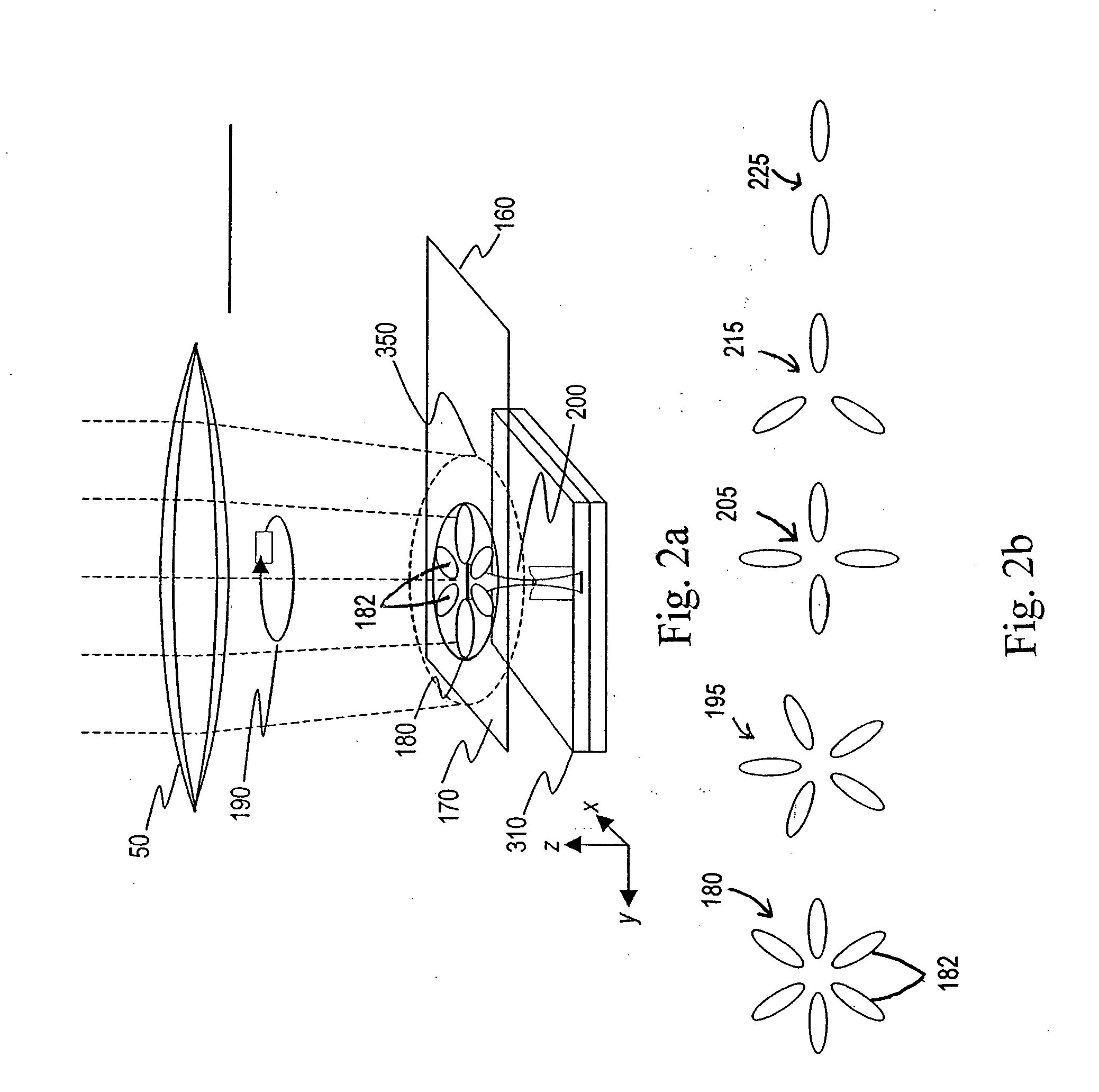
Method and apparatus for enhanced nano-spectroscopic scanning
InactiveUS20050084912A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsResonanceLight beam
Apparatus and method for examining the identity of chemical groups in a sample are disclosed. The apparatus has a substrate having a plasmon resonant surface on which the sample is supported, a source of a beam of light, and a lens assembly having a tip region and a nanolens composed of one or more plasmon resonance particles (PRPs) on the tip region. The PRPs are arranged to produce near-field electromagnetic gap modes in a space between the nanolens and a confronting detection region on the substrate surface when the gap between the nanolens and substrate is 30 nm or less. A focusing mechanism in the apparatus operates to move the lens assembly toward and away from the substrate surface, with a gap of less than 30 nm, to produce electromagnetic gap modes that enhance the Raman spectroscopy signals produced by the sample in the detection region. The apparatus and method are useful, for example, in identifying successive bases in a single DNA strand, for direct DNA sequencing. In one embodiment, the nanolens is positioned adjacent a nanopore opening for use in identifying successive bases of DNA, as the individual DNA bases are translocated through the nanopore.
Owner:POPONIN VLADIMIR
Metal nano-void photonic crystal for enhanced raman spectroscopy
InactiveCN101057132AInjection is simpleSimple and more reproducible injectionMaterial nanotechnologyScattering properties measurementsOptical radiationAnalyte
A planar optical platform for generating a Raman signal from a foreign object comprises an input region and an output region, for receiving and extracting optical radiation, optically coupled to a plasmonic band structure region. The plasmonic band structure region comprises a layer of a first material, having a first refractive index, patterned with an array of sub-regions of a second material, having a second refractive index, wherein a side-wall of each sub-region is coated with a metallodielectric layer. The array of sub-regions gives rise to a plasmonic band structure and, in use, each sub-region confines a plasmon resonance excited by optical radiation coupled into the plasmonic band structure region, which gives rise to a Raman signal from a foreign object placed proximate the plasmonic band structure region. The platform may be incorporated into a spectroscopic measurement system and is particularly useful for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of analyte molecules.
Owner:D3 TECH
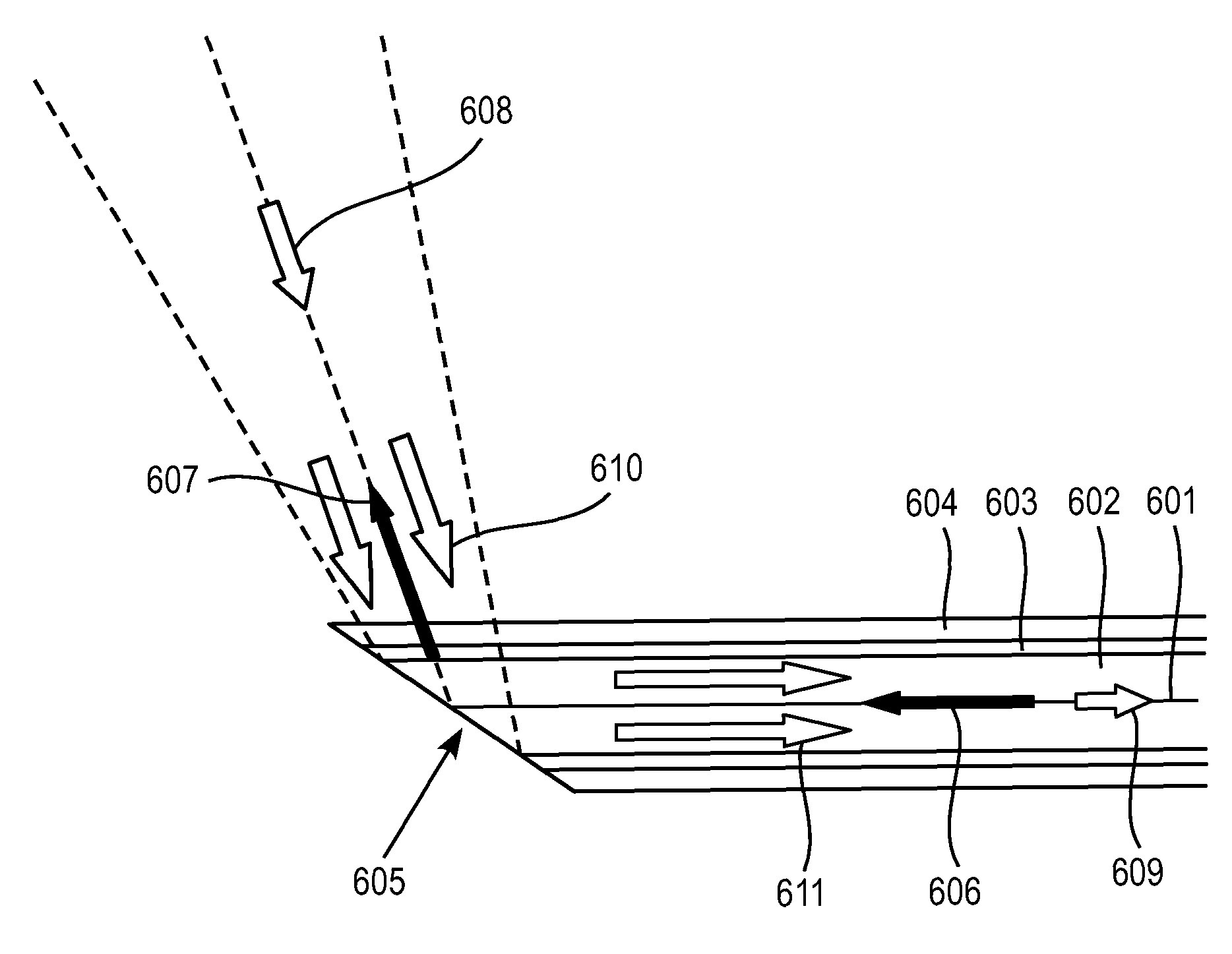
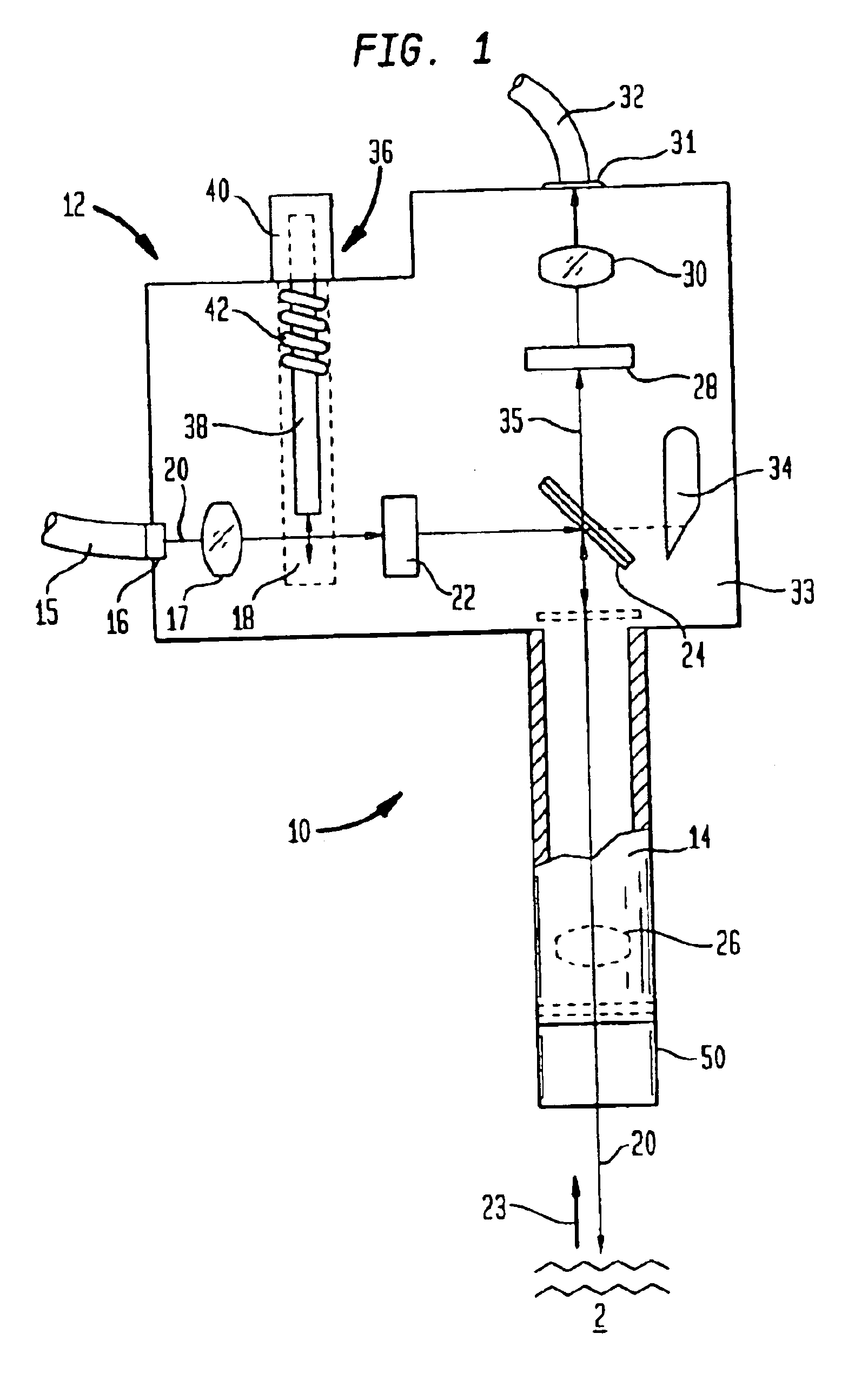
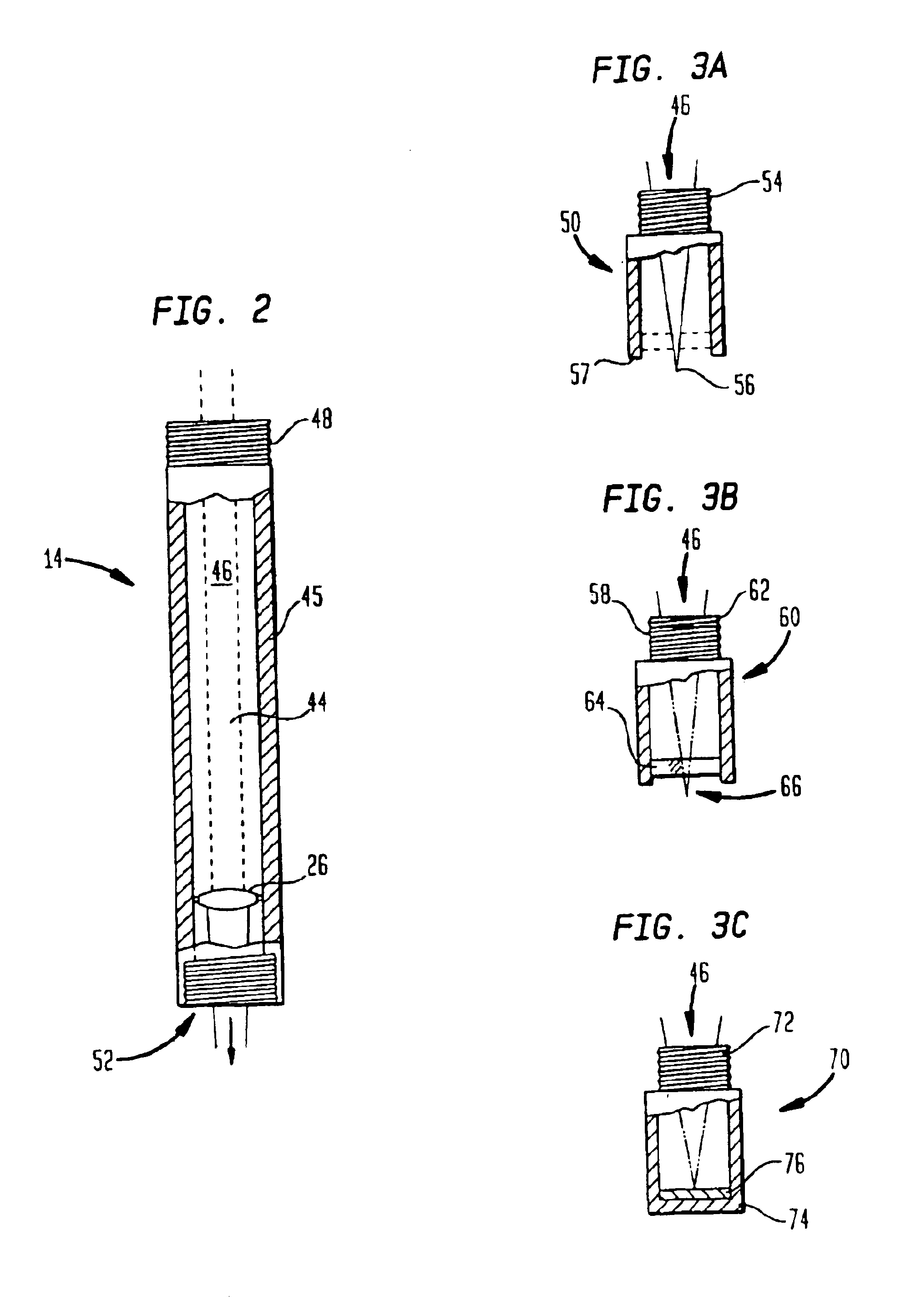
Probe assemblies for Raman spectroscopy
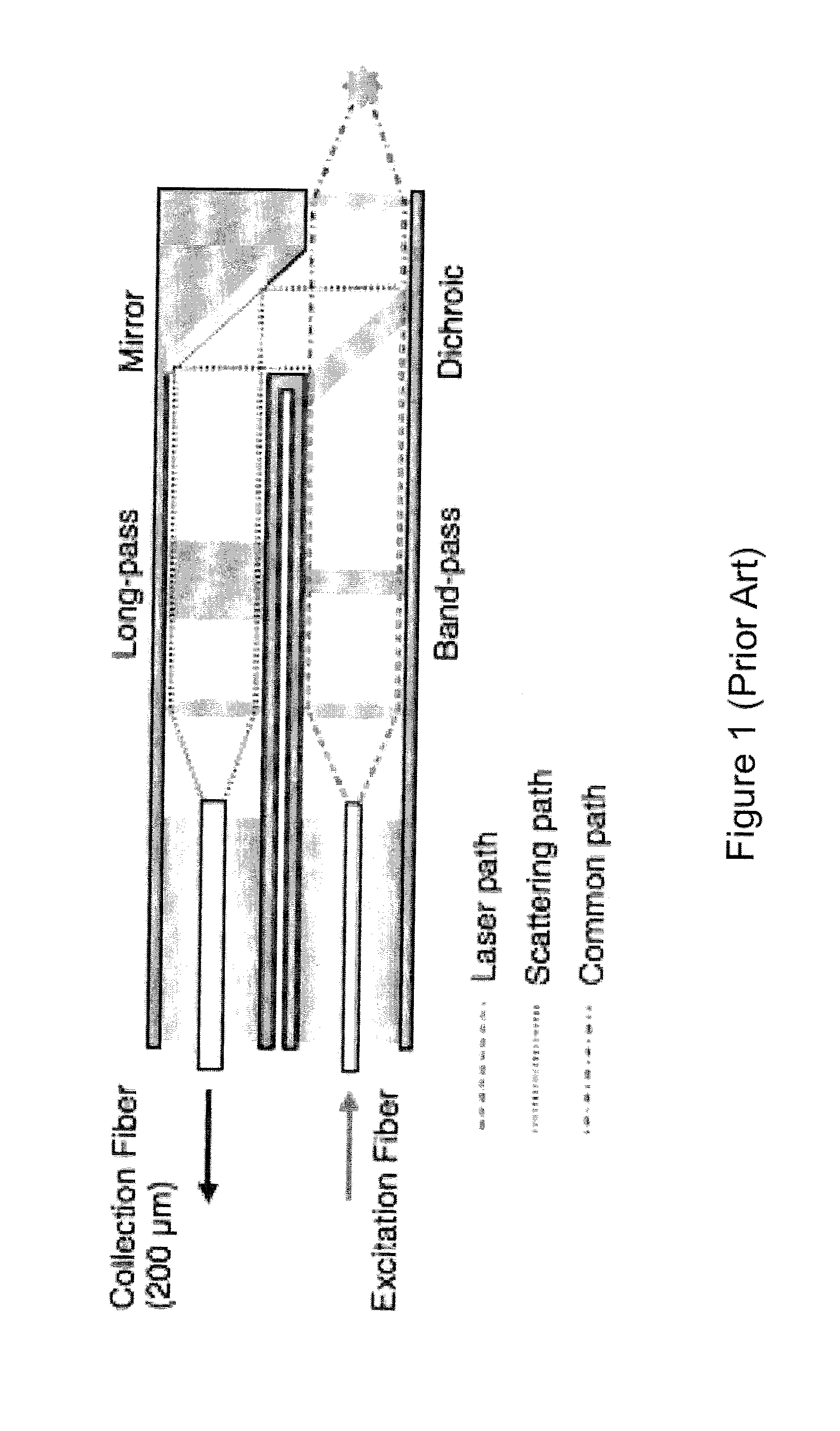
InactiveUS6897951B2Easy to manufactureSuitable for useRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringEngineeringLight spectrum
Raman spectroscopy probe assemblies are disclosed for use with portable and / or handheld analyzers. The probes are also adaptable to sample liquids, and / or powders, tablets and / or other solids and are capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions. The probes include an optical head assembly, associated optical fibers and replaceable sampling tubes. In one aspect of the invention, a simple orthogonal optical head assembly is disclosed that does not require collinear optical paths. The orthogonal arrangement of input and captured light paths also reduces the need for precise alignment of the optical components. The orthogonal optical head assemblies of the present invention are well suited to accommodate the shutoff mechanisms of the present invention. In another aspect of the invention, sampling tubes, and replaceable end caps for such tubes, are disclosed that facilitate hand measurements of substances.
Owner:RAMAN SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com