Patents
Literature
1108 results about "Macroscopic scale" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
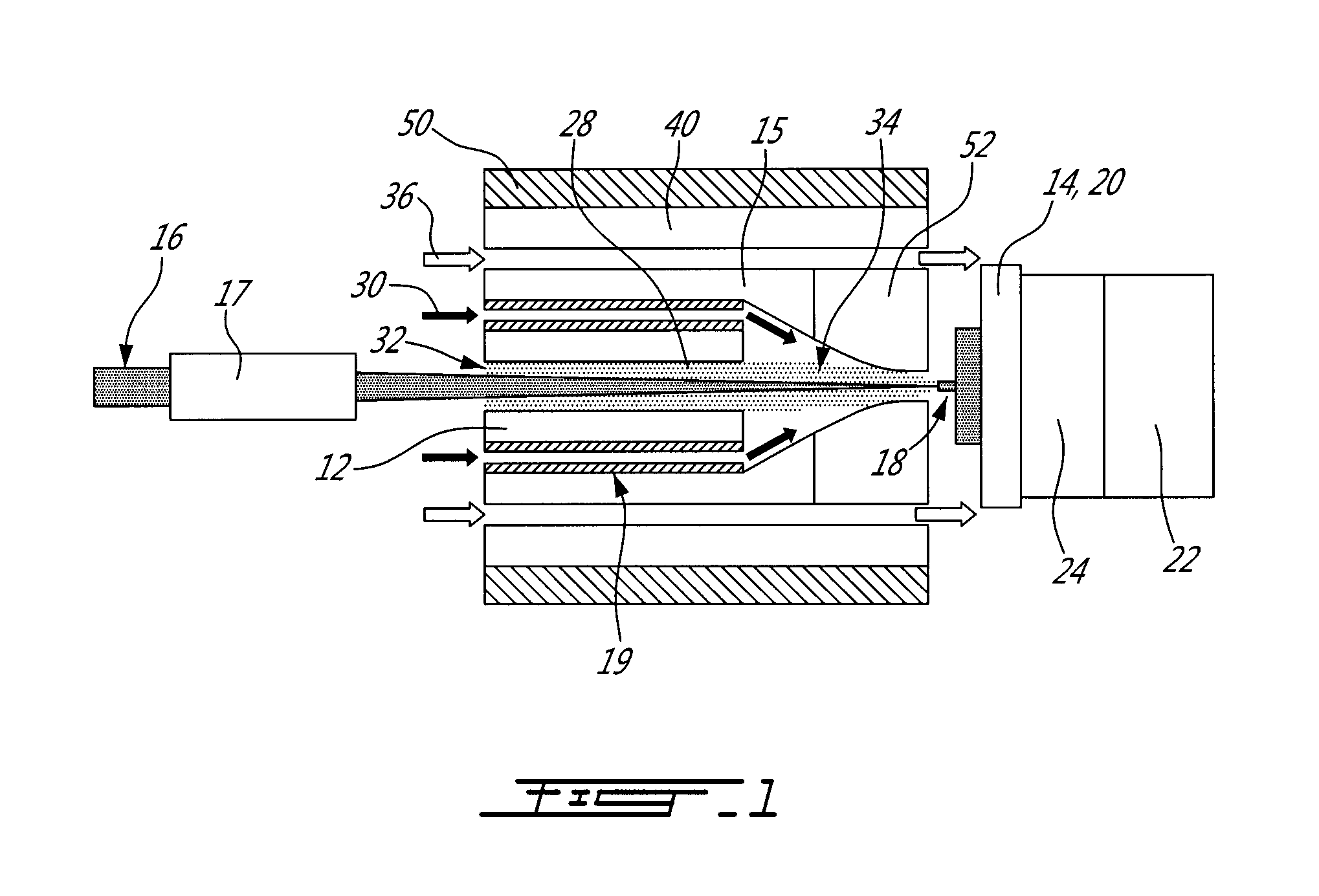
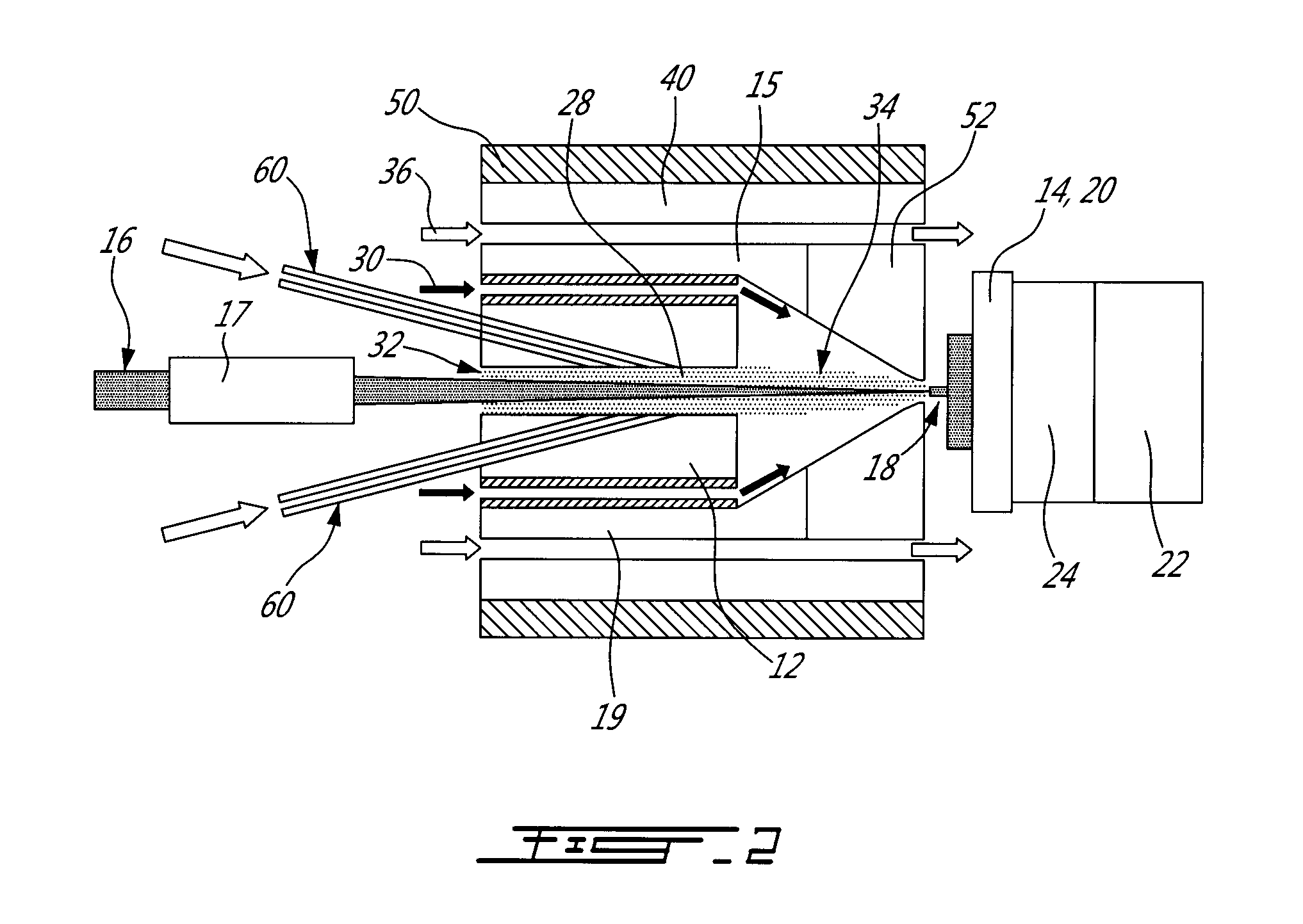
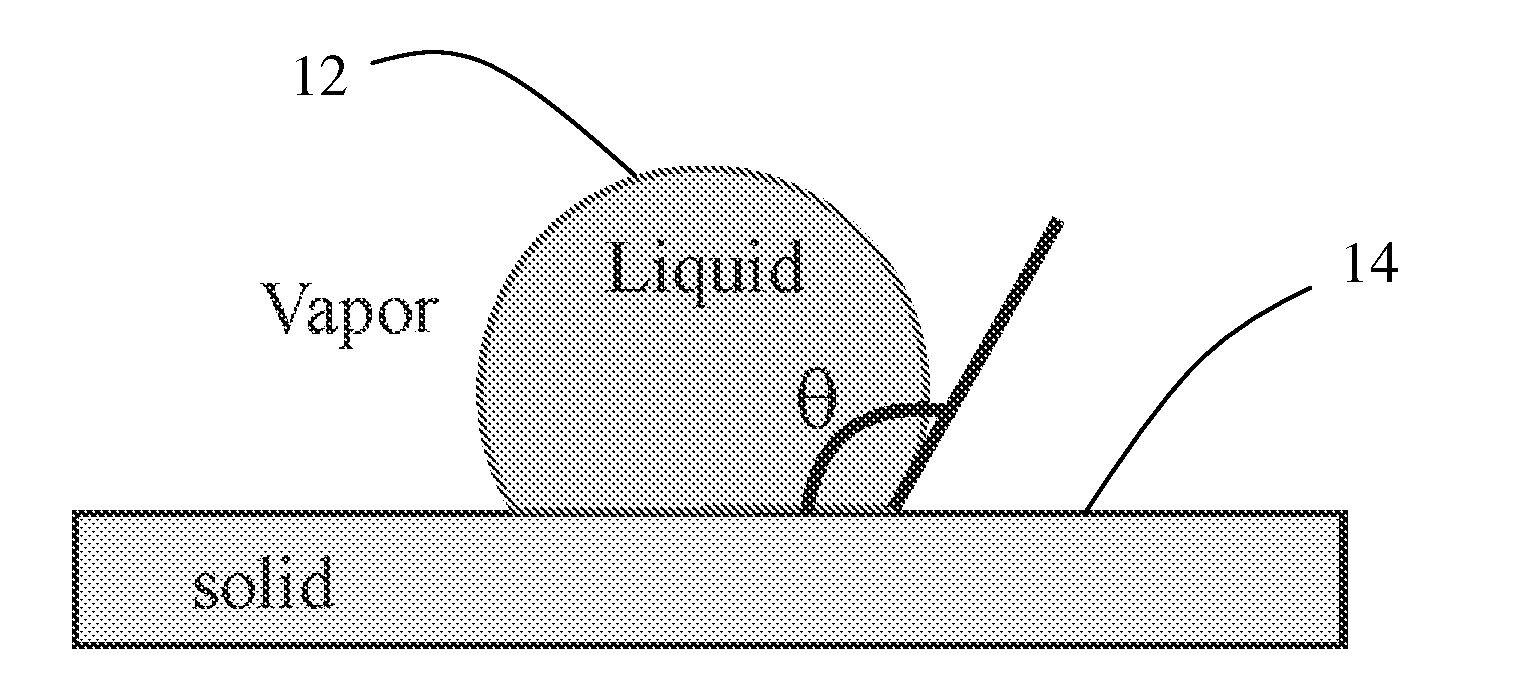
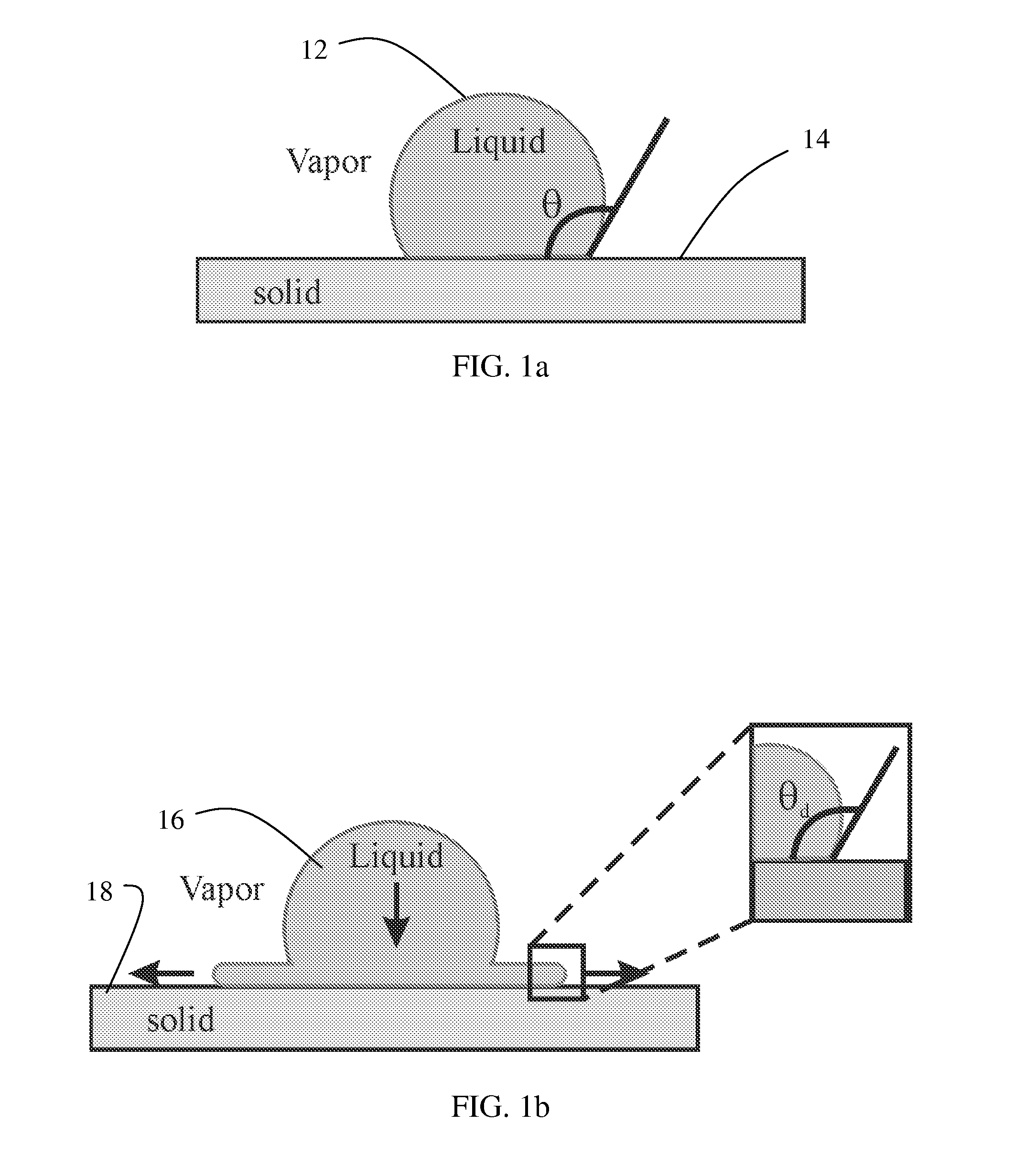
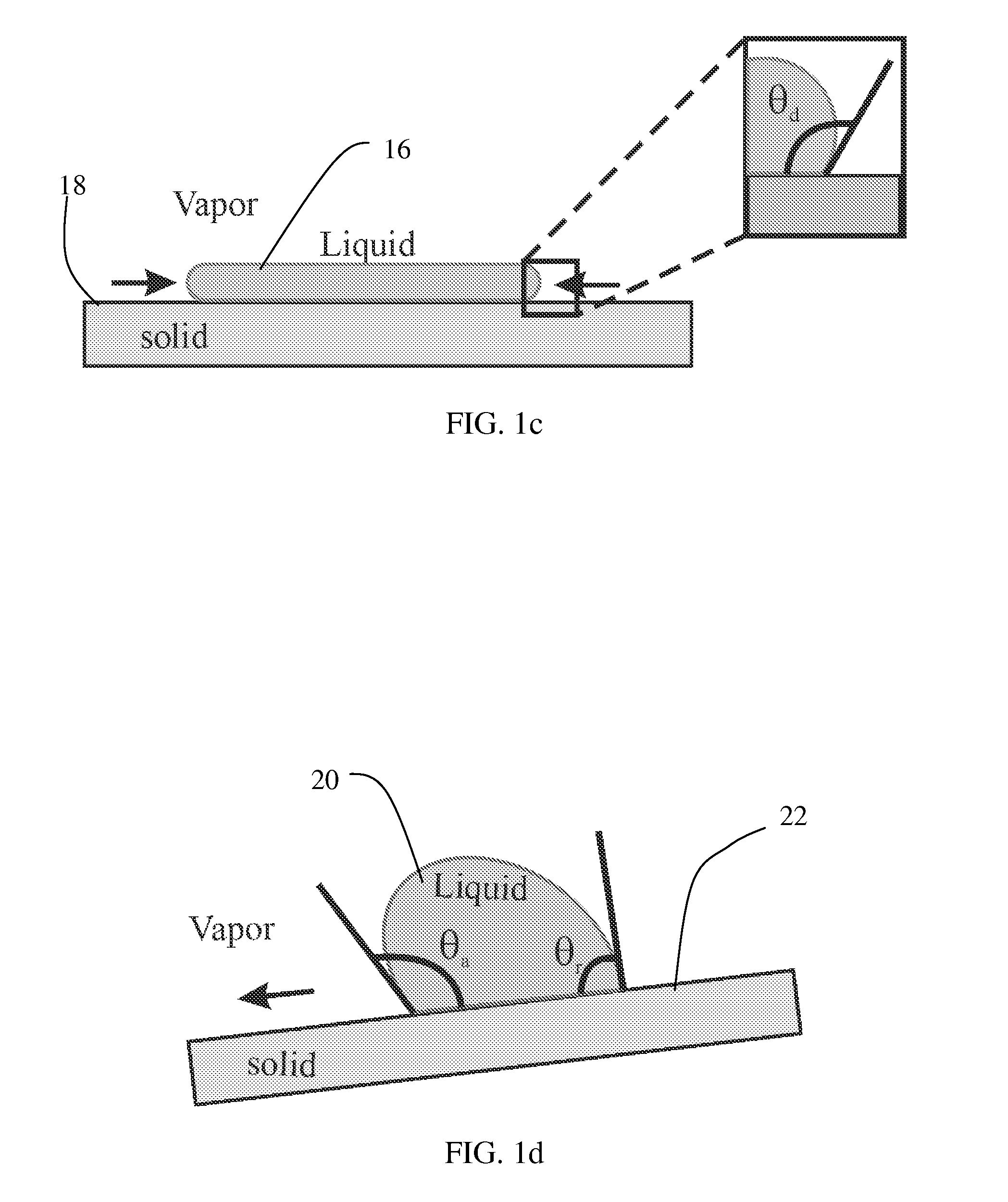
The macroscopic scale is the length scale on which objects or phenomena are large enough to be visible with the naked eye, without magnifying optical instruments.
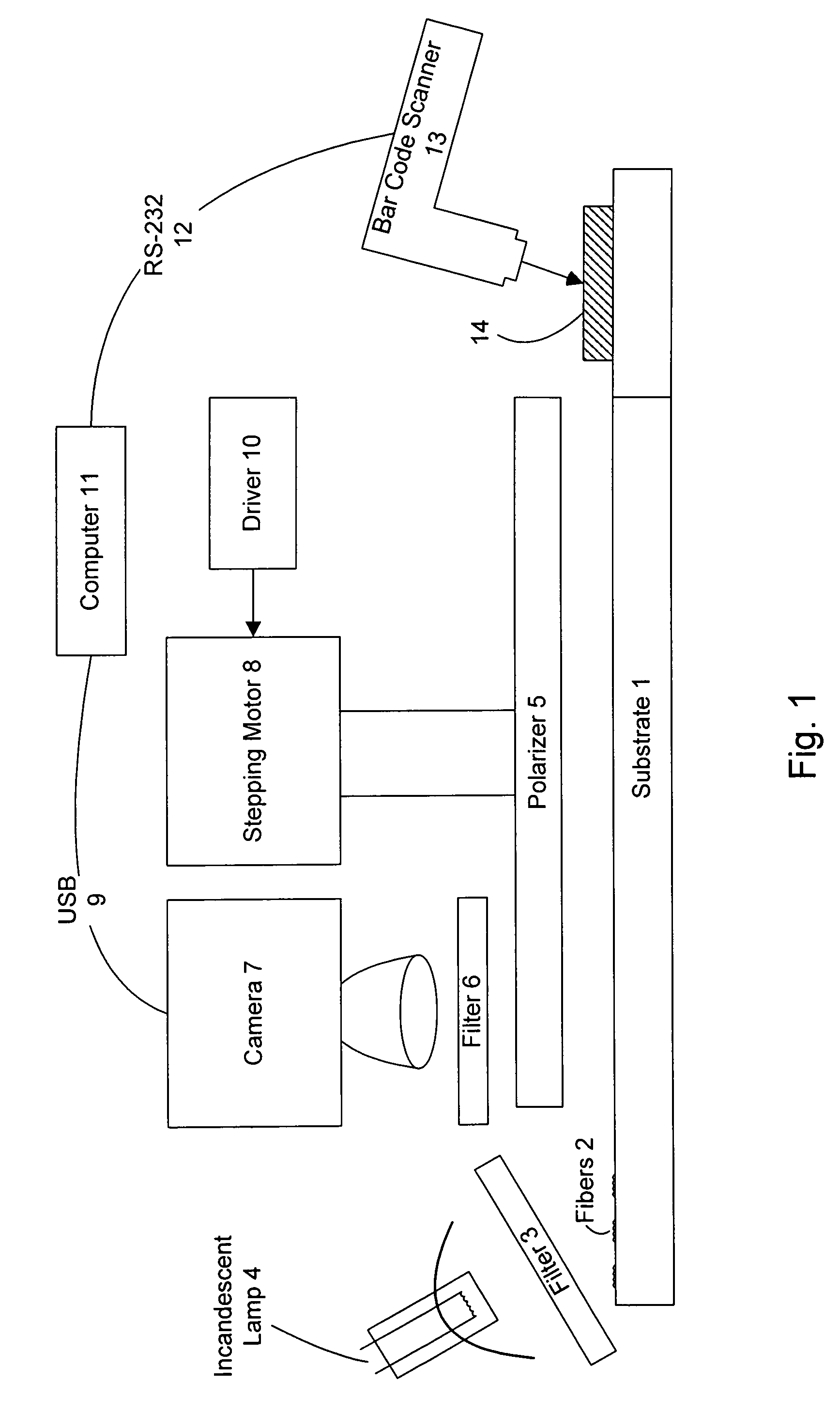
Authentication method and system
InactiveUS7089420B1Great difficultyEfficient codingOther printing matterUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareOptical property
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the production and labeling of objects in a manner suitable for the prevention and detection of counterfeiting. Thus, the system incorporates a variety of features that make unauthorized reproduction difficult. In addition, the present invention provides an efficient means for the production of labels and verification of authenticity, whereby a recording apparatus which includes a recording medium, having anisotrophic optical domains, along with a means for transferring a portion of the recording medium to a carrier, wherein a bulk portion of the recording medium has macroscopically detectable anisotrophic optical properties and the detecting apparatus thereon.
Owner:COPILOT VENTURES FUND III
Authentication method and system
InactiveUS7162035B1Great difficultyEfficient codingUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsComputer hardwareOptical property
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the production and labeling of objects in a manner suitable for the prevention and detection of counterfeiting. Thus, the system incorporates a variety of features that make unauthorized reproduction difficult. In addition, the present invention provides an efficient means for the production of labels and verification of authenticity, whereby a recording apparatus which includes a recording medium, having anisotrophic optical domains, along with a means for transferring a portion of the recording medium to a carrier, wherein a bulk portion of the recording medium has macroscopically detectable anisotrophic optical properties and the detecting apparatus thereon.
Owner:COPILOT VENTURES FUND III
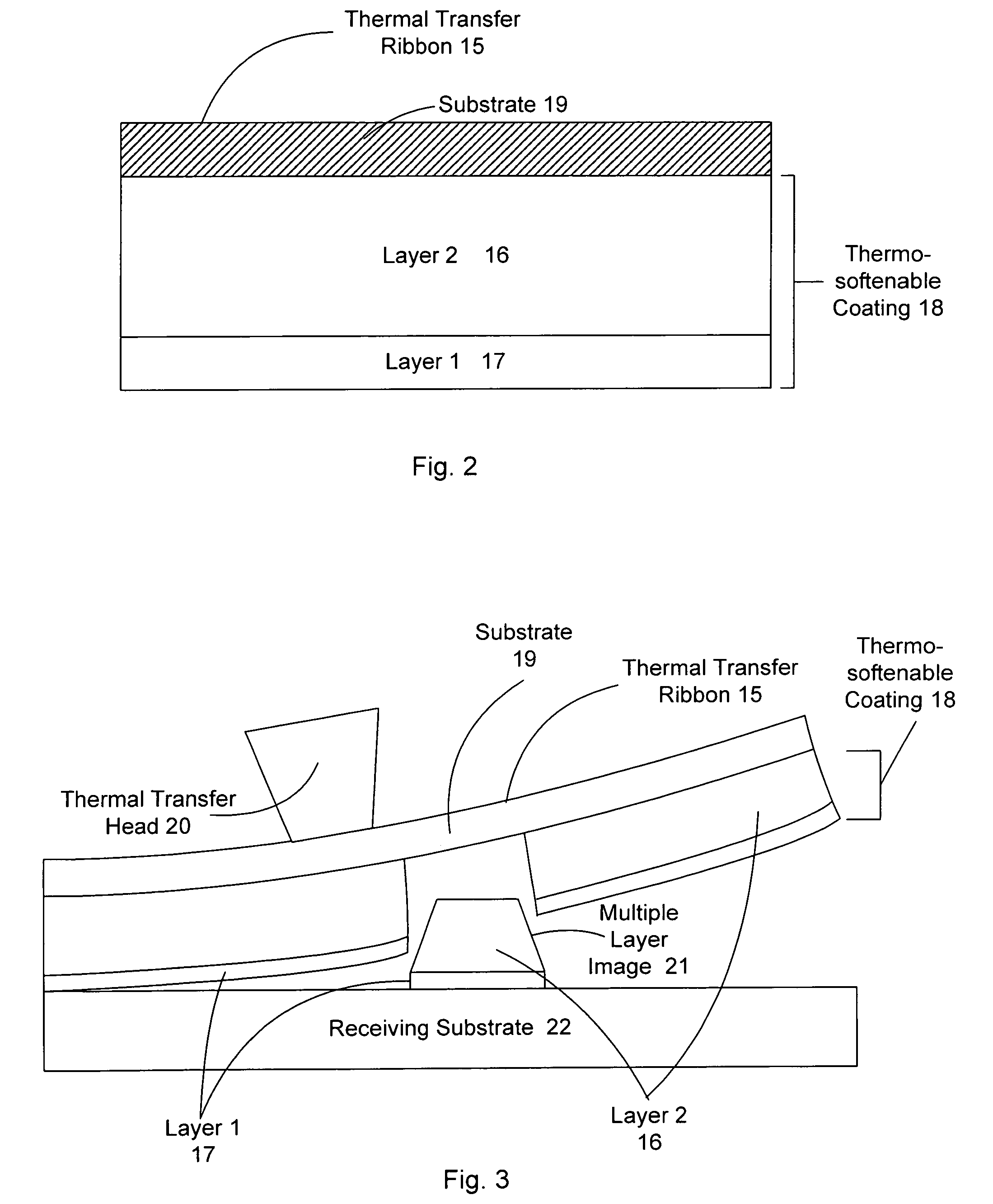
Self-calibrating, digital, large format camera with single or mulitiple detector arrays and single or multiple optical systems
InactiveUS20020163582A1High resolutionTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationDigital signal processingAccelerometer
Large format, digital camera systems (10, 100, 150, 250, 310) expose single detector arrays 20 with multiple lens systems (12, 14, 16, 18) or multiple detector arrays (104, 106, 108, 110, 112, 114, 116, 118, 120, 152, 162, 172, 182, 252, 262, 272, 282, 322, 324) with one or more single lens systems (156, 166, 176, 186) to acquire sub-images of overlapping sub-areas of large area objects. The sub-images are stitched together to form a large format, digital, macro-image (80, 230'', 236'', 238'', 240''), which can be colored. Dampened camera carrier (400) and accelerometer (404) signals with double-rate digital signal processing (306, 308) are used.
Owner:VEXCEL IMAGING US INC
Method of deposition of thin films of amorphous and crystalline microstructures based on ultrafast pulsed laser deposition
InactiveUS6312768B1Improve surface qualityImprove efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingMacroscopic scaleCarbon nanotube
Powerful nanosecond-range lasers using low repetition rate pulsed laser deposition produce numerous macroscopic size particles and droplets, which embed in thin film coatings. This problem has been addressed by lowering the pulse energy, keeping the laser intensity optional for evaporation, so that significant numbers of the macroscopic particles and droplets are no longer present in the evaporated plume. The result is deposition of evaporated plume on a substrate to form thin film of very high surface quality. Preferably, the laser pulses have a repetition rate to produce a continuous flow of evaporated material at the substrate. Pulse-range is typically picosecond and femtosecond and repetition rate kilohertz to hundreds of megahertz. The process may be carried out in the presence of a buffer gas, which may be inert or reactive, and the increased vapour density and therefore the collision frequency between evaporated atoms leads to the formation of nanostructured materials of increasing interest, because of their peculiar structural, electronic and mechanical properties. One of these is carbon nanotubes, which is a new form of carbon belonging to the fullerene (C60) family. Carbon nanotubes are seamless, single or multishell co-axial cylindrical tubules with or without dome caps at the extremities. Typically diameters range from 1 nm to 50 nm with a length >1 mum. The electronic structure may be either metallic or semiconducting without any change in the chemical bonding or adding of dopant. In addition, the materials have application to a wide range of established thin film applications.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
Ophthalmic lens synthesized from its specification
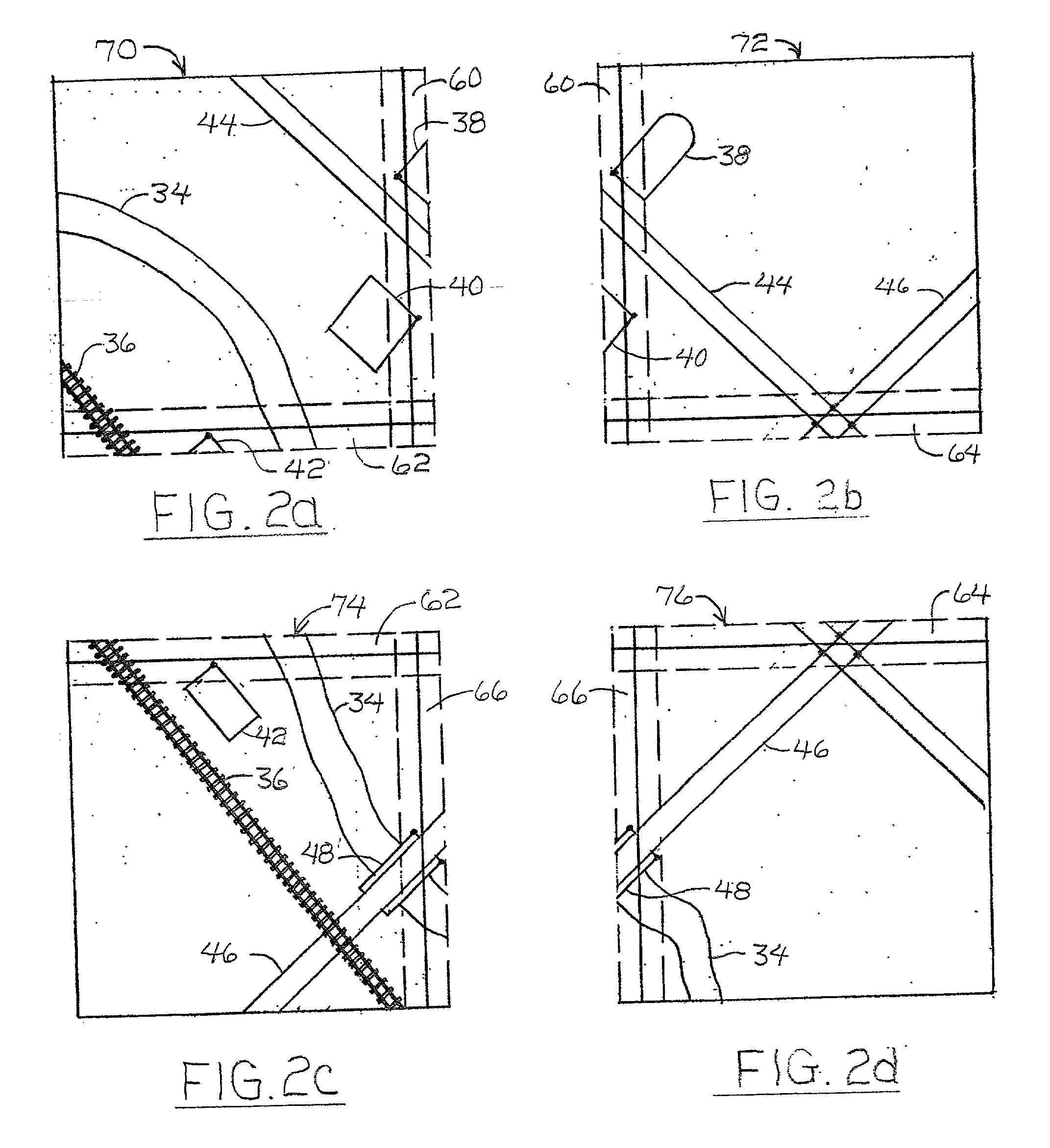
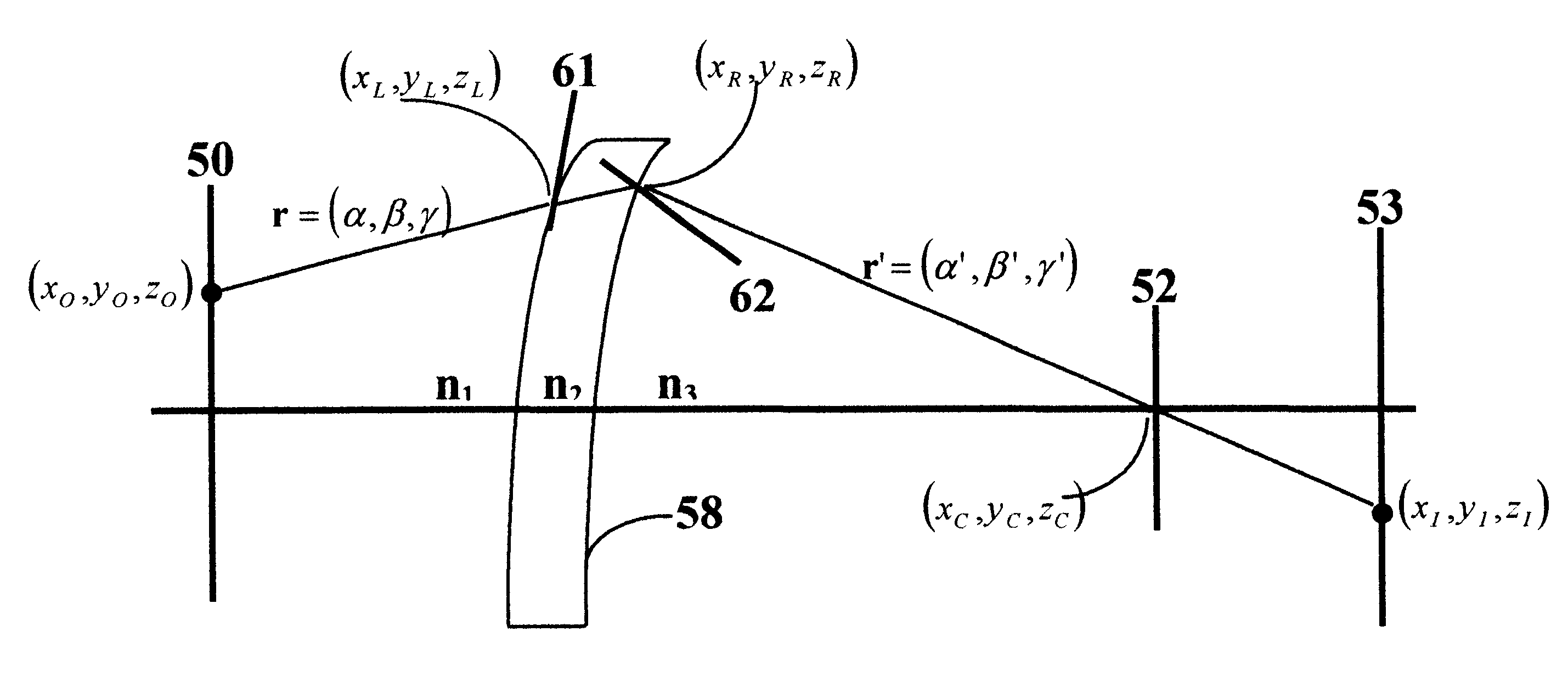
InactiveUS6464355B1Less aberrationImprove optical qualityEye diagnosticsOptical partsRough surfaceMicroscopic scale
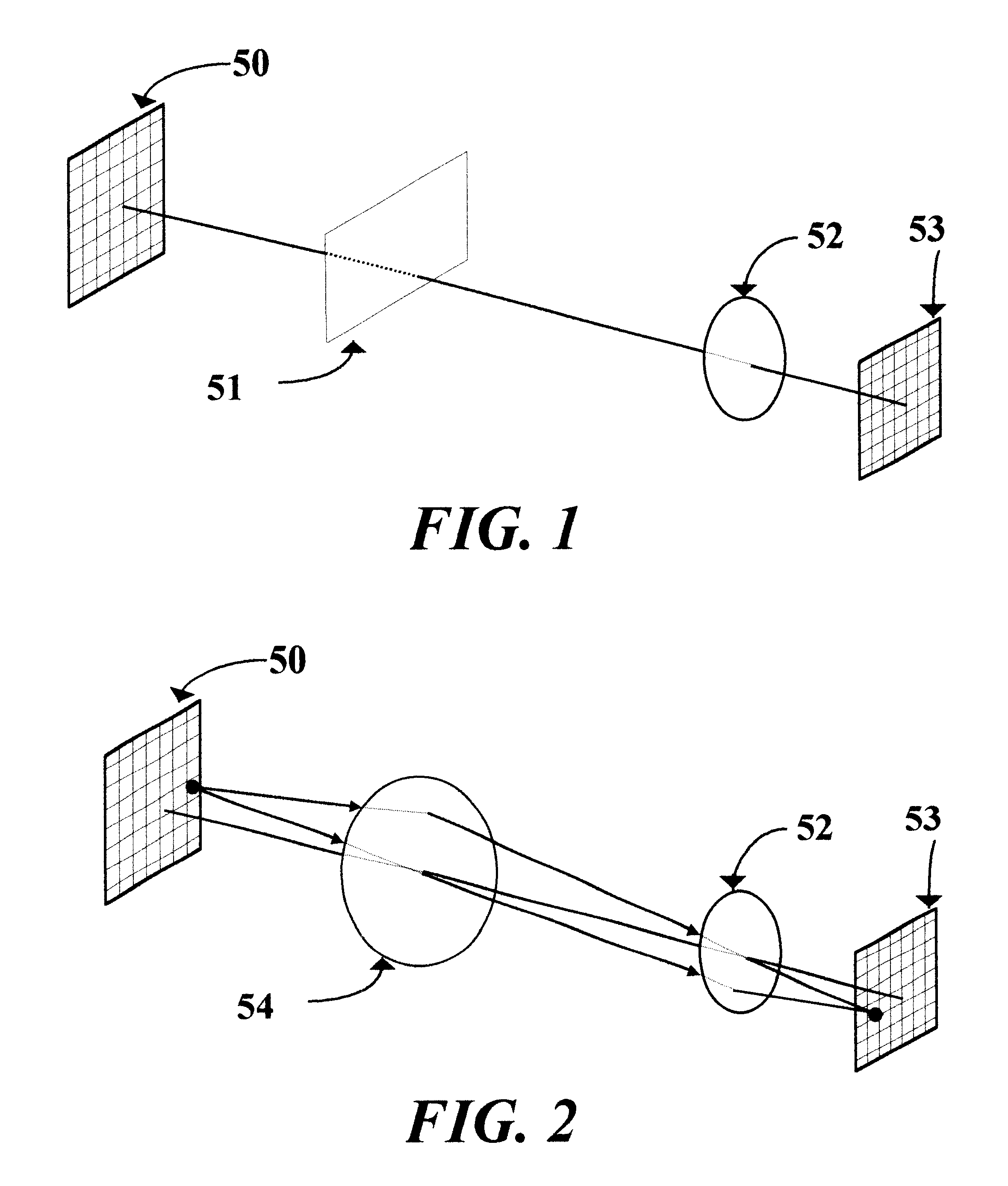
This invention relates to a novel prescription lens (58), mainly suited for ophthalmic applications. The lens designer defines the macroscopic surfaces of the lens (59, 60) as desired. The design process assumes that the location of the object (50), the lens (51), and the required image (53) are known. By using Ray-tracing technique we calculate the microscopic normals to the lens that will form the required image. From those microscopic normals we calculate microscopic surface by a process of summation the slopes with geometric pattern conditions. The final surface is not smooth but contains plenty of dense microscopic shapes that look like saw-teeth. That rough surface enables the lens to have almost any desired shape and thickness.
Owner:GIL THIEBERGER
System and method for manipulating illumination created by an array of light emitting devices
ActiveUS7182480B2Desired effectNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceDiffusionMacroscopic scale
The present invention provides an illumination optical system that enables the direction and mixing of light from light emitting devices. The optical system comprises a plurality of light emitting devices that are spatially arranged in an array, wherein this array comprises one or more sections, such that the light emitting devices in a particular section emit light within a predetermined wavelength range. Through the use of a combination of macroscopic and microscopic optical systems, the illumination created by the array can be manipulated such that a desired illumination distribution is created. The macroscopic optical system provides a means for redirecting the illumination in one or more desired directions, wherein this redirection is provided by a collection of appropriately shaped and positioned reflective optics. Subsequent to its interaction with the macroscopic optical system, the illumination is manipulated by a microscopic optical system that enables the diffusion of the illumination in a predetermined manner, while retaining the desired angular distribution of the illumination created by the macroscopic optical system. Through the appropriate design and orientation of both the macroscopic and microscopic optical systems, a desired illumination effect can be created.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Structures useful as cleaning sheets
InactiveUS6645604B1Organic detergent compounding agentsKitchenware cleanersMacroscopic scaleStructural engineering
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Endoscope having microscopic and macroscopic magnification
InactiveUS6530882B1Resolving structureHigh resolutionSurgeryEndoscopesMacroscopic scaleMicroscopic exam
An endoscope assembly is disclosed having a housing adapted to be manipulated by medical personnel, such as a surgeon. An elongated lens tube has one end secured to the housing while an elongated stage is removably secured to the housing so that the stage encompasses and is coaxial with the tube. The stage together with the lens tube are adapted for insertion into the cavity of a body. A lens assembly provided within the lens tube relays the optical image from the free end of the stage to the housing. A lens assembly within the housing, furthermore, varies the magnification of the image between macroscopic magnification and microscopic magnification in which tissue may be examined on a cellular level. For macroscopic magnification, white light is transmitted through the lens tube as well as reflected back from the target tissue through the lens tube and to the housing. For microscopic examination, laser radiation is utilized in lieu of the white light illumination. A line scanning confocal assembly contained within the housing enables microscopic examination of the target tissue at varying levels into the tissue from the end of the stage.
Owner:INNER VISION IMAGING
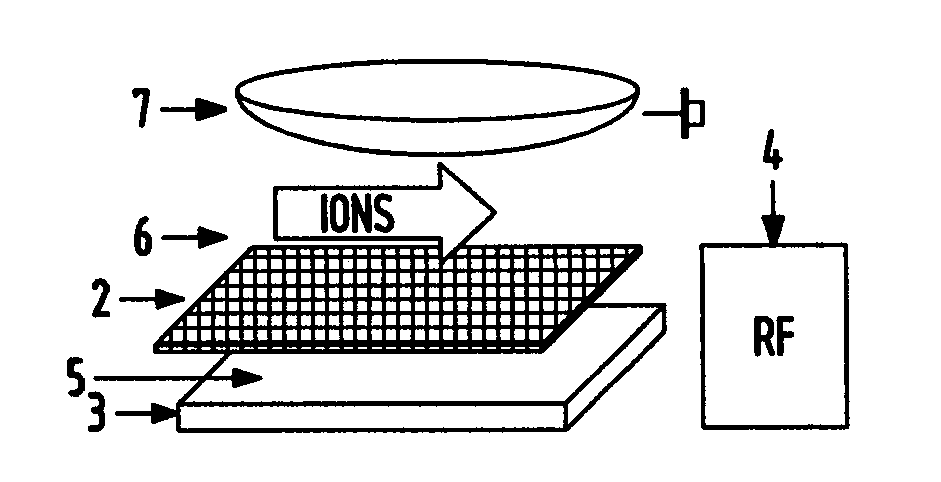
Method and apparatus for ion manipulation using mesh in a radio frequency field
ActiveUS20110192969A1Better wayEasy to buildTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationIon chromatographyDesorption
Ion manipulation systems include ion repulsion by an RF field penetrating through a mesh. Another comprises trapping ions in a symmetric RF field around a mesh. The system uses macroscopic parts, or readily available fine meshes, or miniaturized devices made by MEMS, or flexible PCB methods. One application is ion transfer from gaseous ion sources with focusing at intermediate and elevated gas pressures. Another application is the formation of pulsed ion packets for TOF MS within trap array. Such trapping is preferably accompanied by pulsed switching of RF field and by gas pulses, preferably formed by pulsed vapor desorption. Ion guidance, ion flow manipulation, trapping, preparation of pulsed ion packets, confining ions during fragmentation or exposure to ion to particle reactions and for mass separation are disclosed. Ion chromatography employs an ion passage within a gas flow and through a set of multiple traps with a mass dependent well depth.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Method for producing alloy deposits and controlling the nanostructure thereof using negative current pulsing electro-deposition, and articles incorporating such deposits
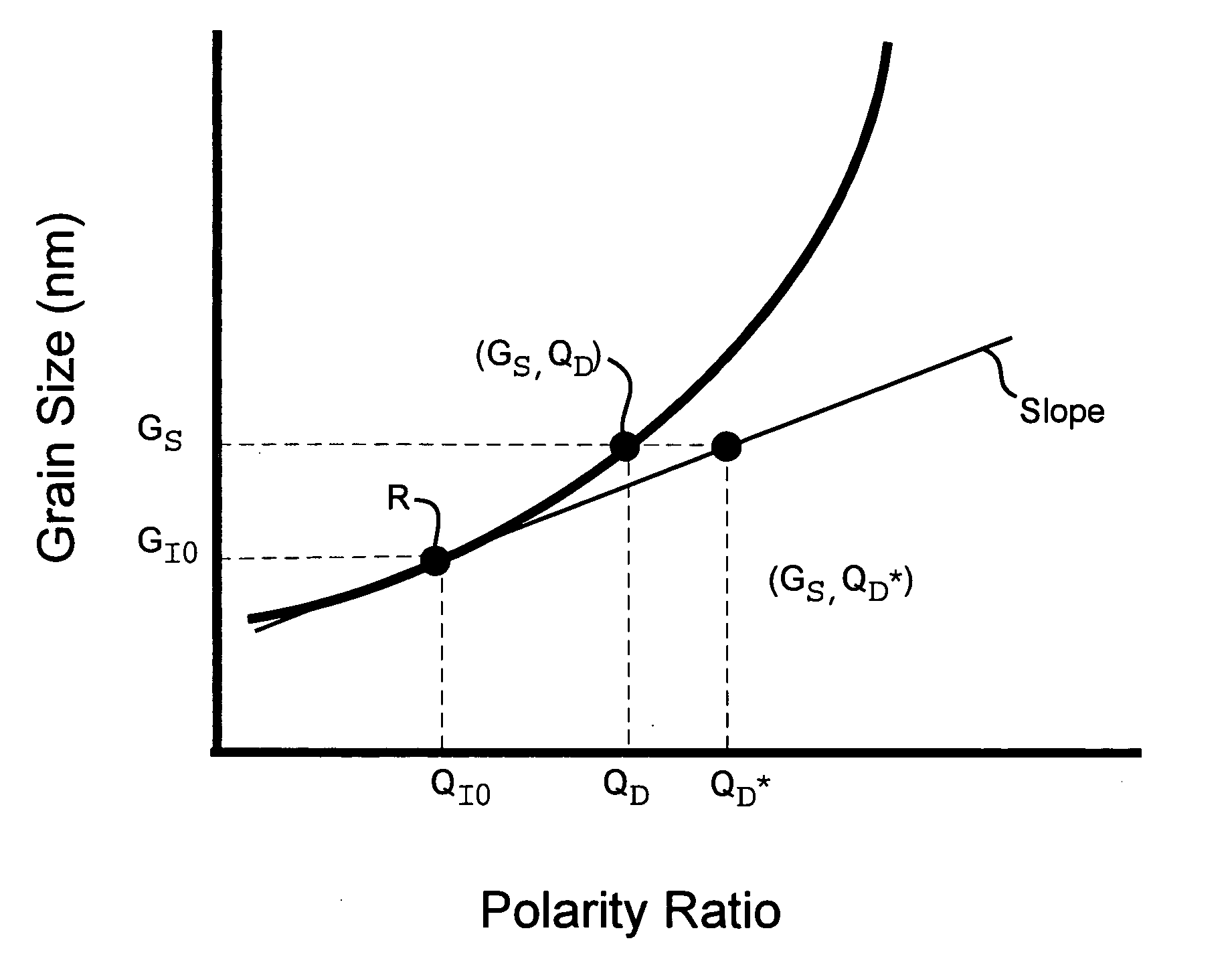
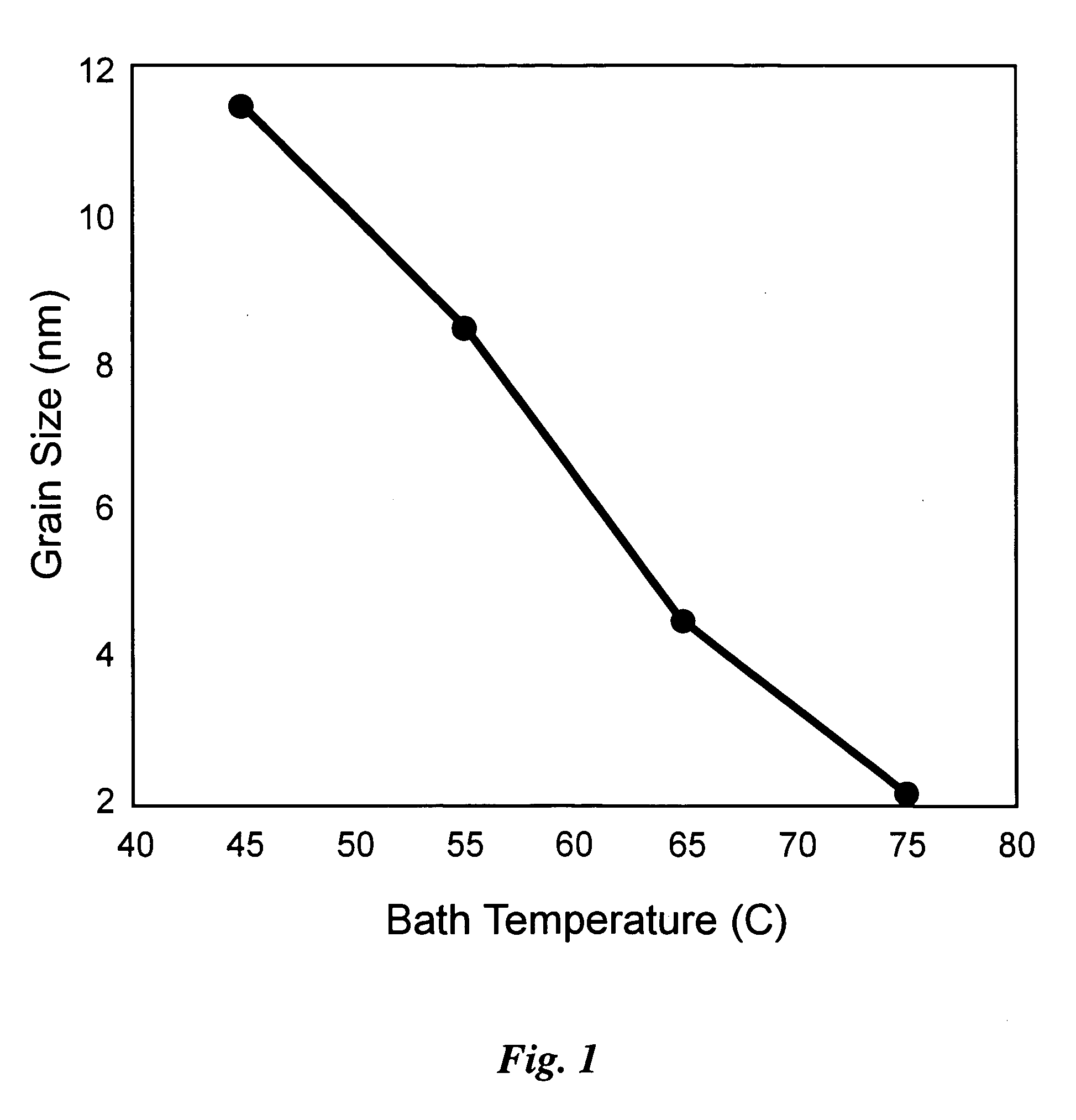
Bipolar wave current, with both positive and negative current portions, is used to electrodeposit a nanocrystalline grain size deposit. Polarity Ratio is the ratio of the absolute value of the time integrated amplitude of negative polarity current and positive polarity current. Grain size can be precisely controlled in alloys of two or more chemical components, at least one of which is a metal, and at least one of which is most electro-active. Typically, although not always, the amount of the more electro-active material is preferentially lessened in the deposit during times of negative current. The deposit also exhibits superior macroscopic quality, being relatively crack and void free. Parameters of current density, duration of pulse portions, and composition of the bath are determined with reference to constitutive relations showing grain size as a function of deposit composition, and deposit composition as a function of Polarity Ratio, or, perhaps, a single relation showing grain size as a function of Polarity ratio. A specified grain size can be achieved by selecting a corresponding Polarity Ratio, based on these relations. Coatings can be in layers, each having an average grain size, which can vary layer to layer and also in a region in a graded fashion. Coatings can be chosen for environmental protection (corrosion, abrasion), decorative properties, and for the same uses as a hard chrome coating. A finished article may be built upon a substrate of electro-conductive plastic, or metal, including steels, aluminum, brass. The substrate may remain, or be removed.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Community division method in complex network
InactiveCN101383748AEmbody the essential characteristicsReflect the interactionStar/tree networksSpecial data processing applicationsMacroscopic scaleGranularity
The invention provides a community classification method in complex network, a plurality of different nodes having partial influences are taken as the cores, the influences of the nodes are caused to evenly diffuse from the core outwards layer by layer, finally the node having the greatest influence becomes the core, the influences of the nodes in layer-by-layer expansion continuously attenuate, the interconnection of the nodes form a local region which expands until the method stops, the influences of the nodes are slight and can reach the edge of the network of the local region. For a large-scale unordered complex network, the positions of the nodes having different importance degrees can be rapidly located, a great deal of more fine-granularity information is dug out, simultaneously the original structural character of the network is kept unchanged, and the original large-scale complex network is simplified and downsized, so that not only the efficiency of search can be improved, but also the structure of the large-scale network from macroscopic view can be more clearly analyzed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
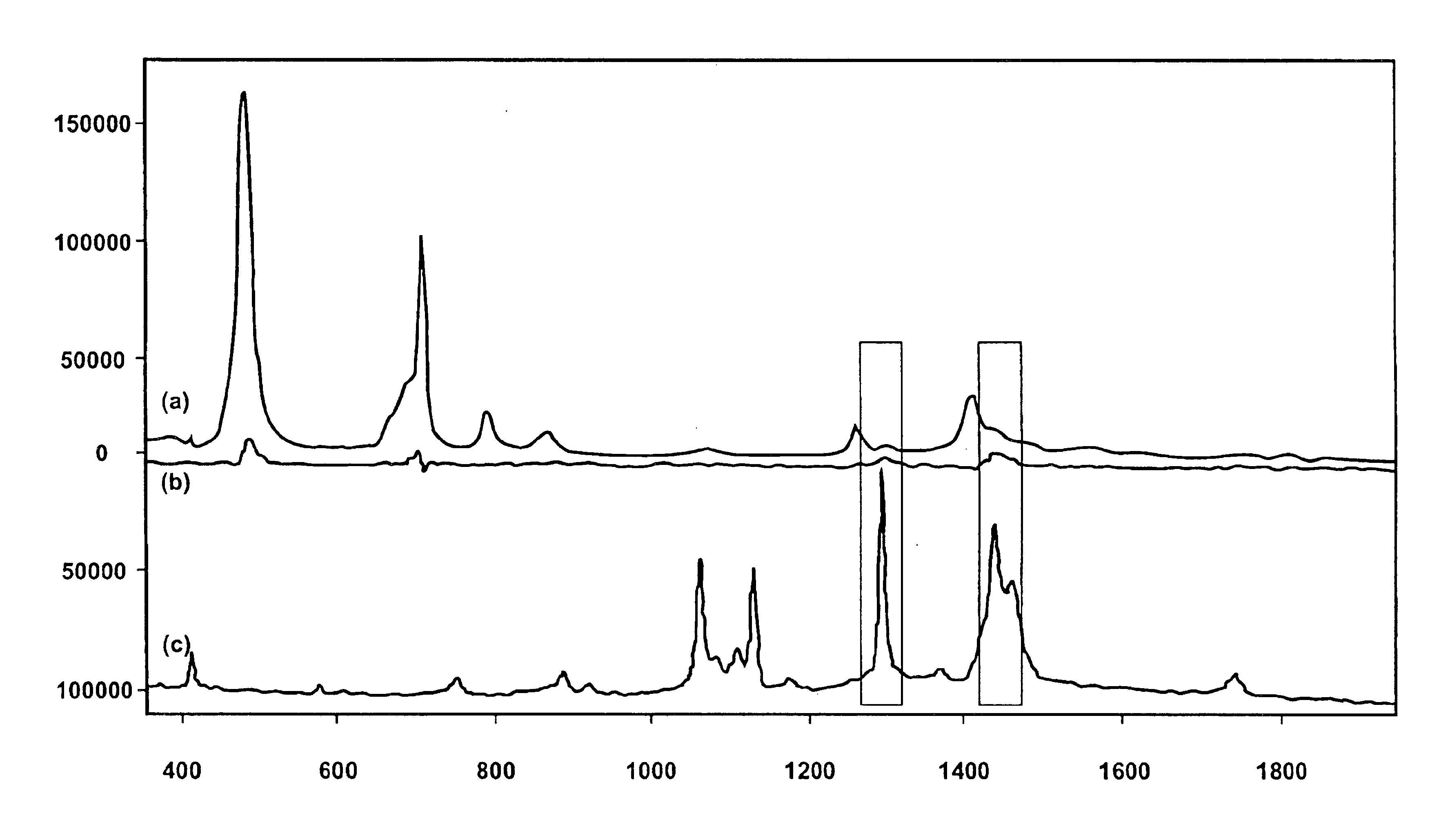
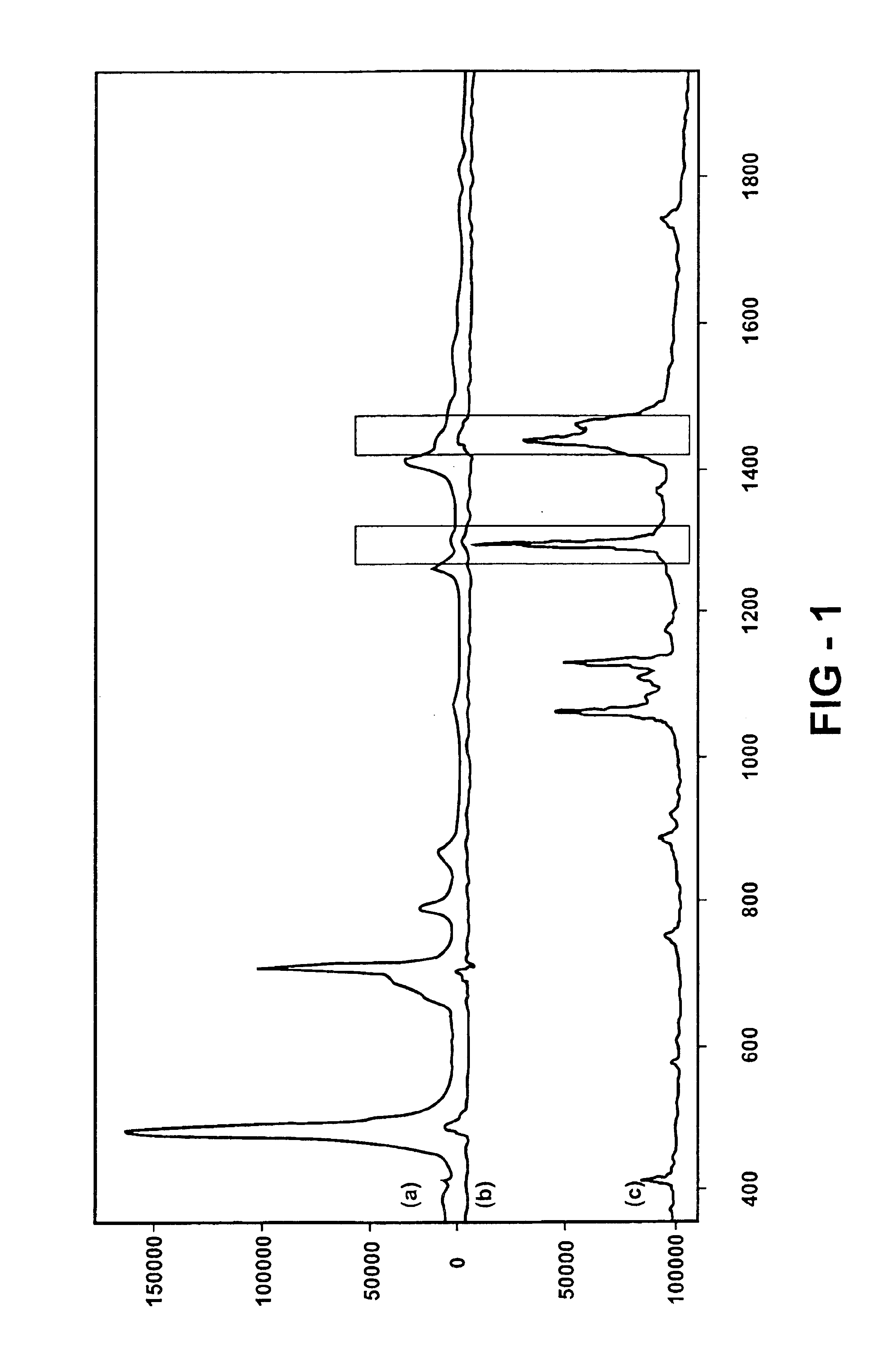
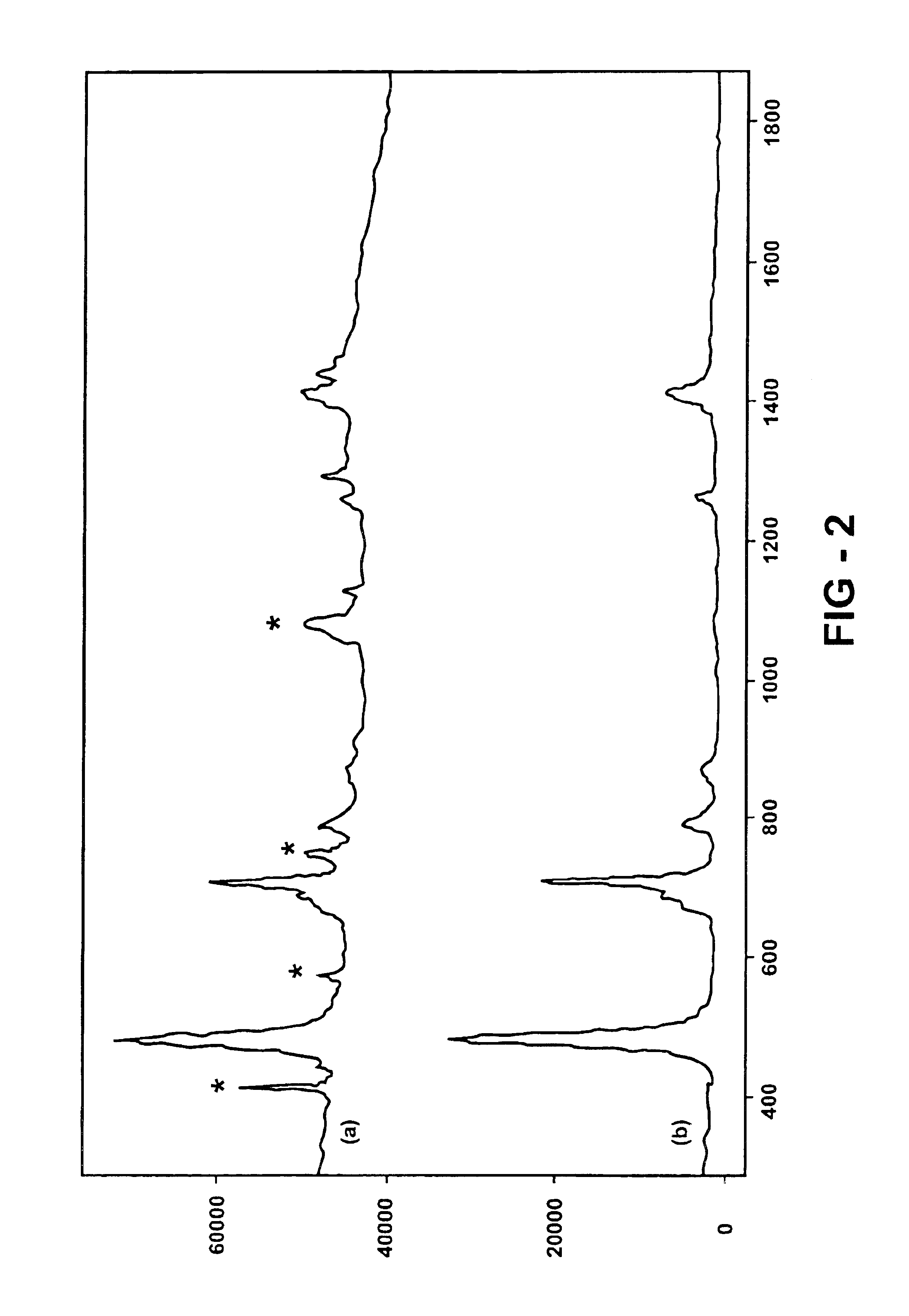
Raman spectroscopy crystallization analysis method
A method of monitoring sample crystallization from a solution. The method includes the collection of multiple Raman spectra from a sample dissolved in a solvent as a function of time and under conditions promoting crystallization. Within each of the multiple Raman spectra, a first signal is identified corresponding to the sample associated with the solvent. A second signal corresponding to the sample in a microcrystallite state is also identified. Thereafter, the intensity of the multiple Raman spectra are measured for an increase relating to formation of the sample in a microcrystallite state. A method of monitoring sample crystallization from a solution as a function of turbidity is also disclosed. The method includes the collection of multiple Raman spectra from a sample dissolved in a solvent as a function of time under conditions promoting crystallization. A decrease in intensity is measured across the multiple Raman spectrum over time, the intensity decrease associated with macroscopic crystallization opacity. The decrease in intensity is finely correlated with the onset of macroscopic crystallization of the sample from the solvent.
Owner:KAISER OPTICAL SYST INC
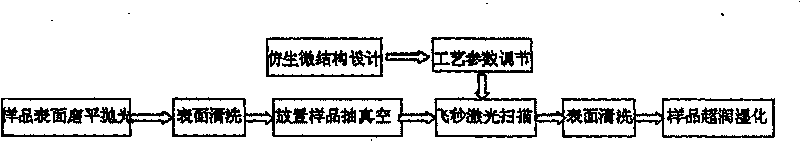
Bionic metal ultra-wetting trans-scale structure design method and preparation method
InactiveCN101712102AEasy to analyze and calculateIdeal wettability structureLaser beam welding apparatusMacroscopic scaleScale structure
The invention relates to the technical field of laser microprocessing, in particular to a method for obtaining a metal-based ultra-wetting surface by designing the trans-scale structure of a metal surface, preparing a laser microstructure on the metal surface and carrying out necessary ultra-wetting decoration to the metal surface. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, designing a macroscopical large-area superficial periodical mastoid structure which simulates a locus leaf surface; constructing a micronano periodical structure on the microstructure of the mastoid structure to obtain a macroscopical-micronano trans-scale geometric model; adjusting laser parameters and a laser scanning path according to geometric parameters acquired after the bionic metal ultra-wetting trans-scale structure is designed; scanning the plane first time; rotating a sample 90 degrees; and scanning the plane again with low-energy laser. The trans-scale microstructure approaches to the surface appearance of a natural organism, is easy to calculate and analyze a contact angle and has a simple and controllable preparation process.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Imaging system having a fine focus
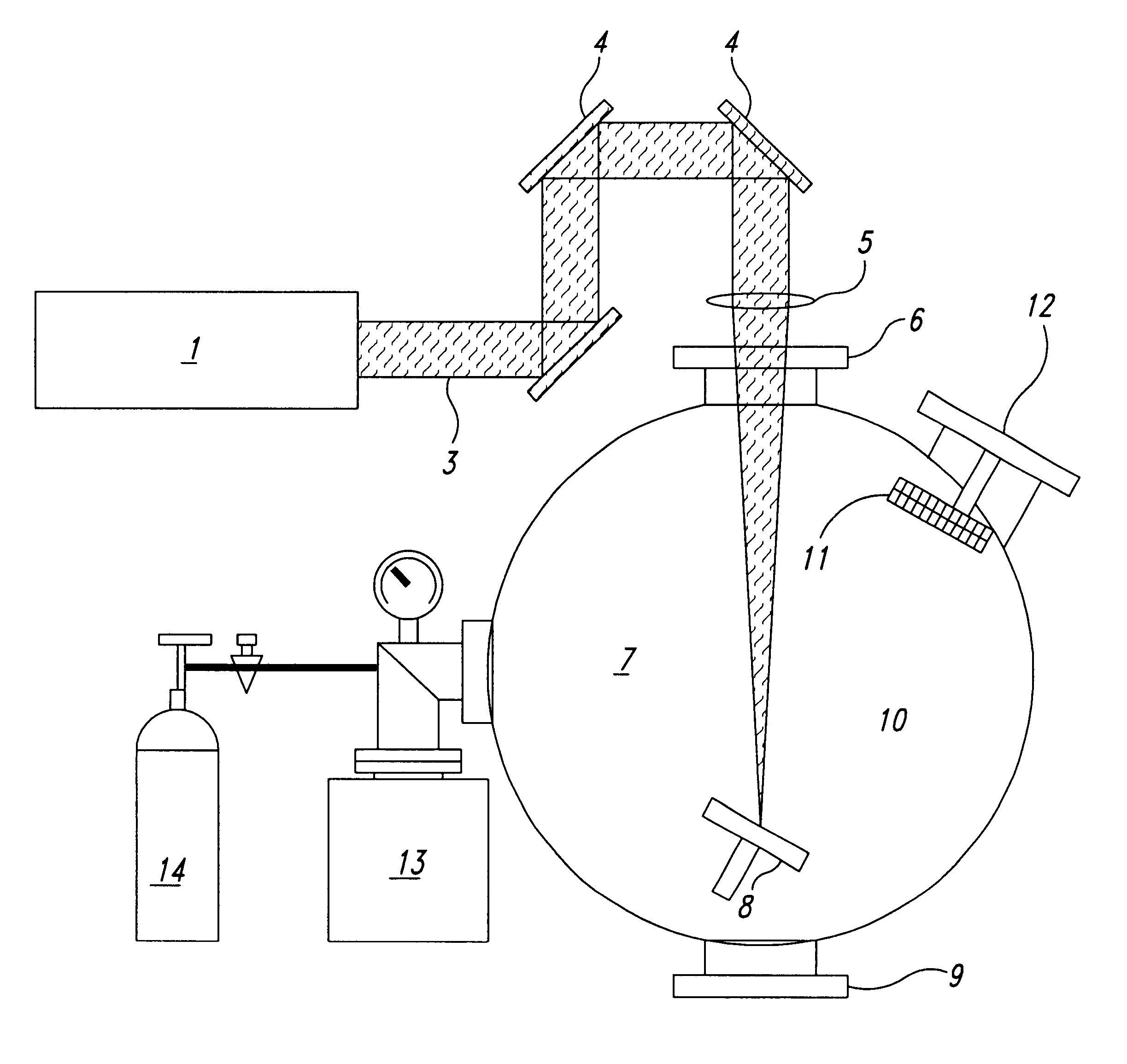
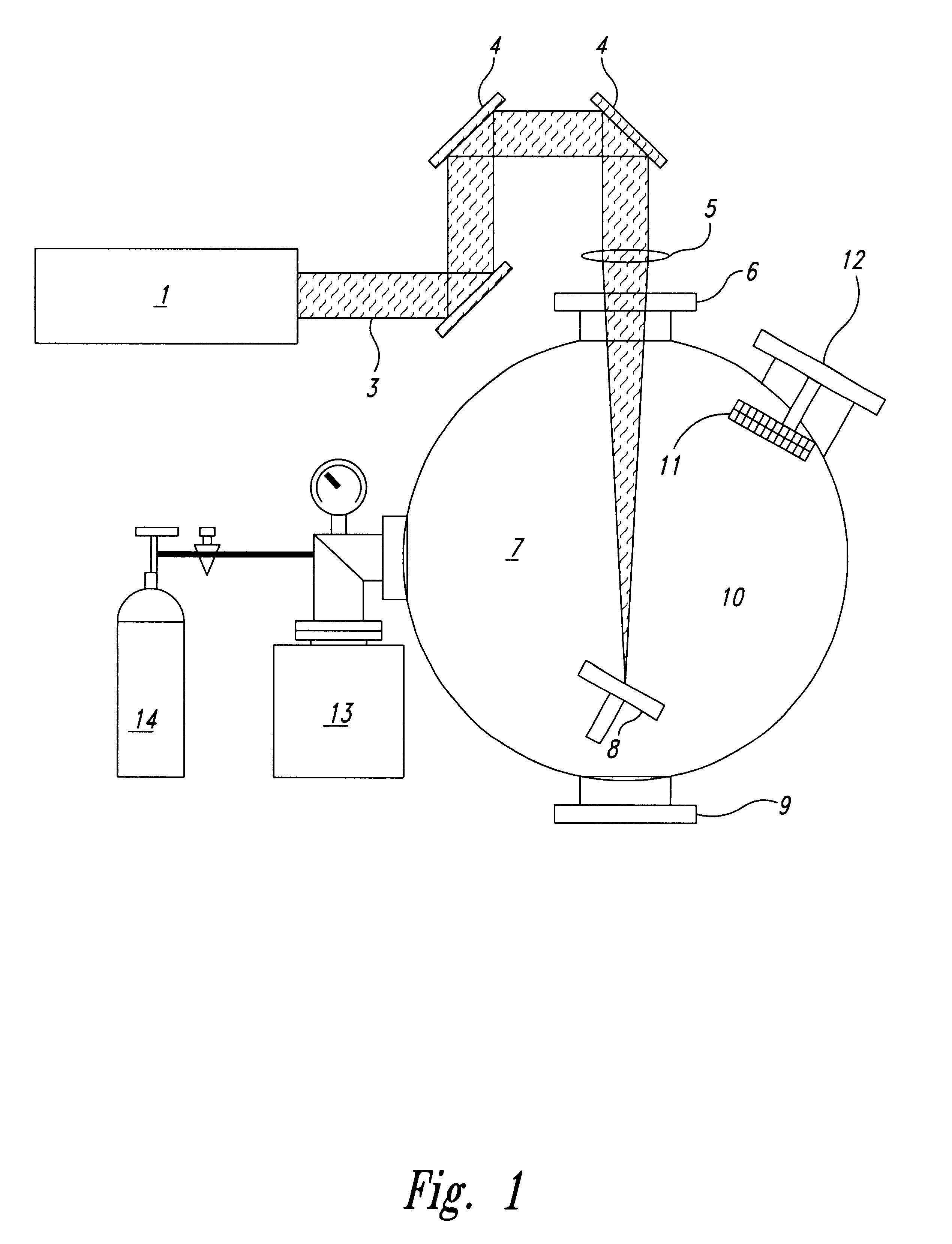
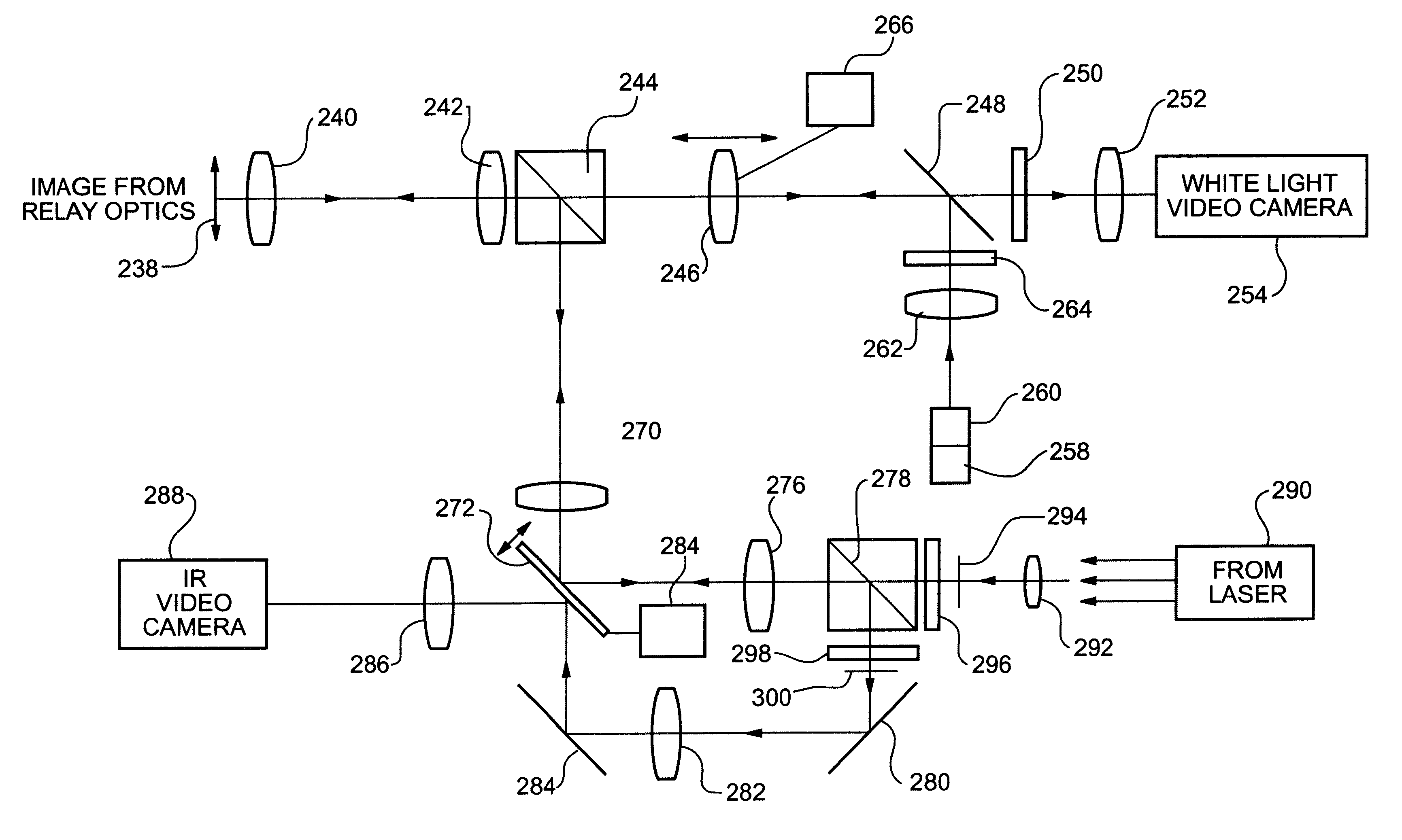
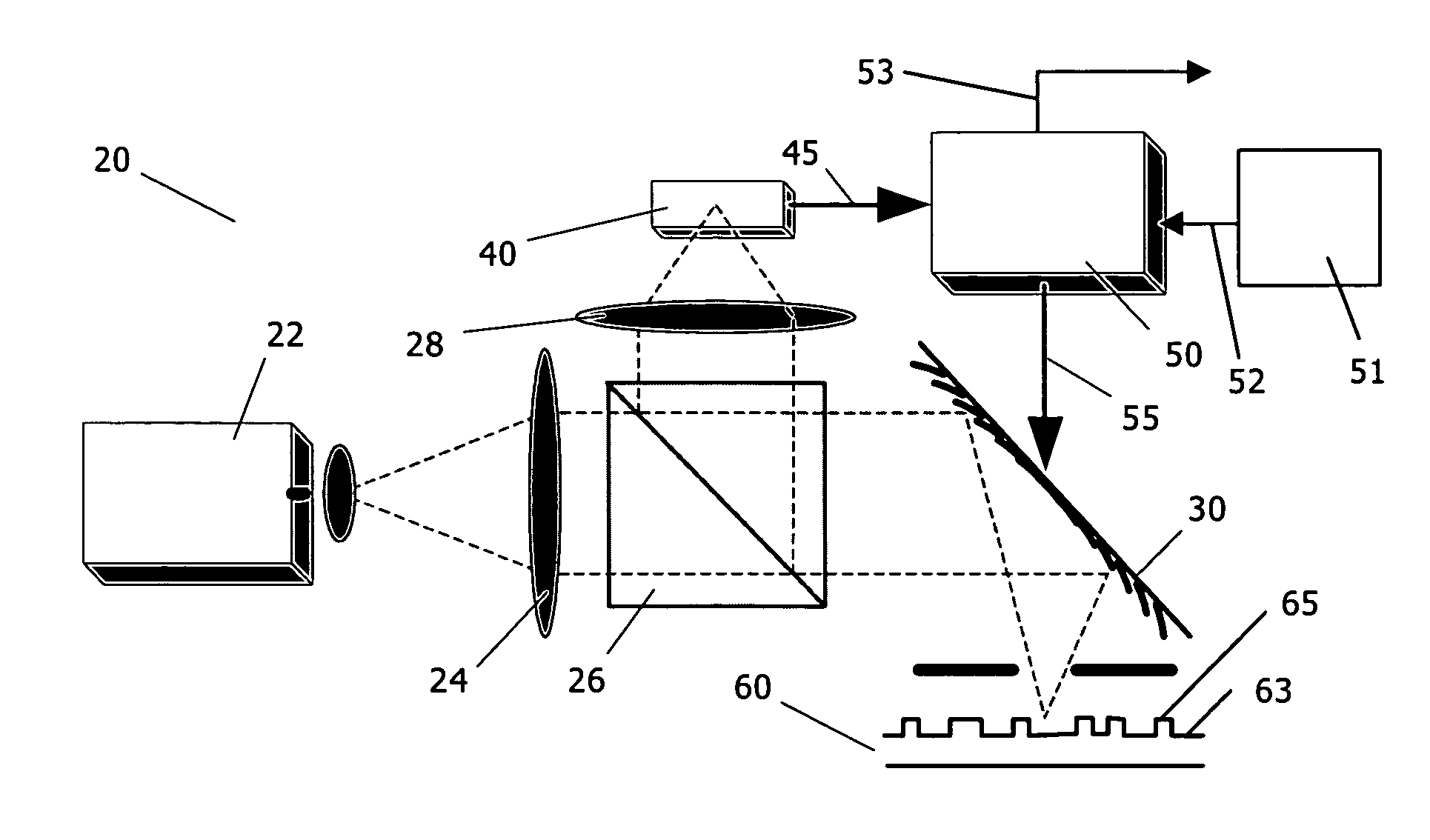
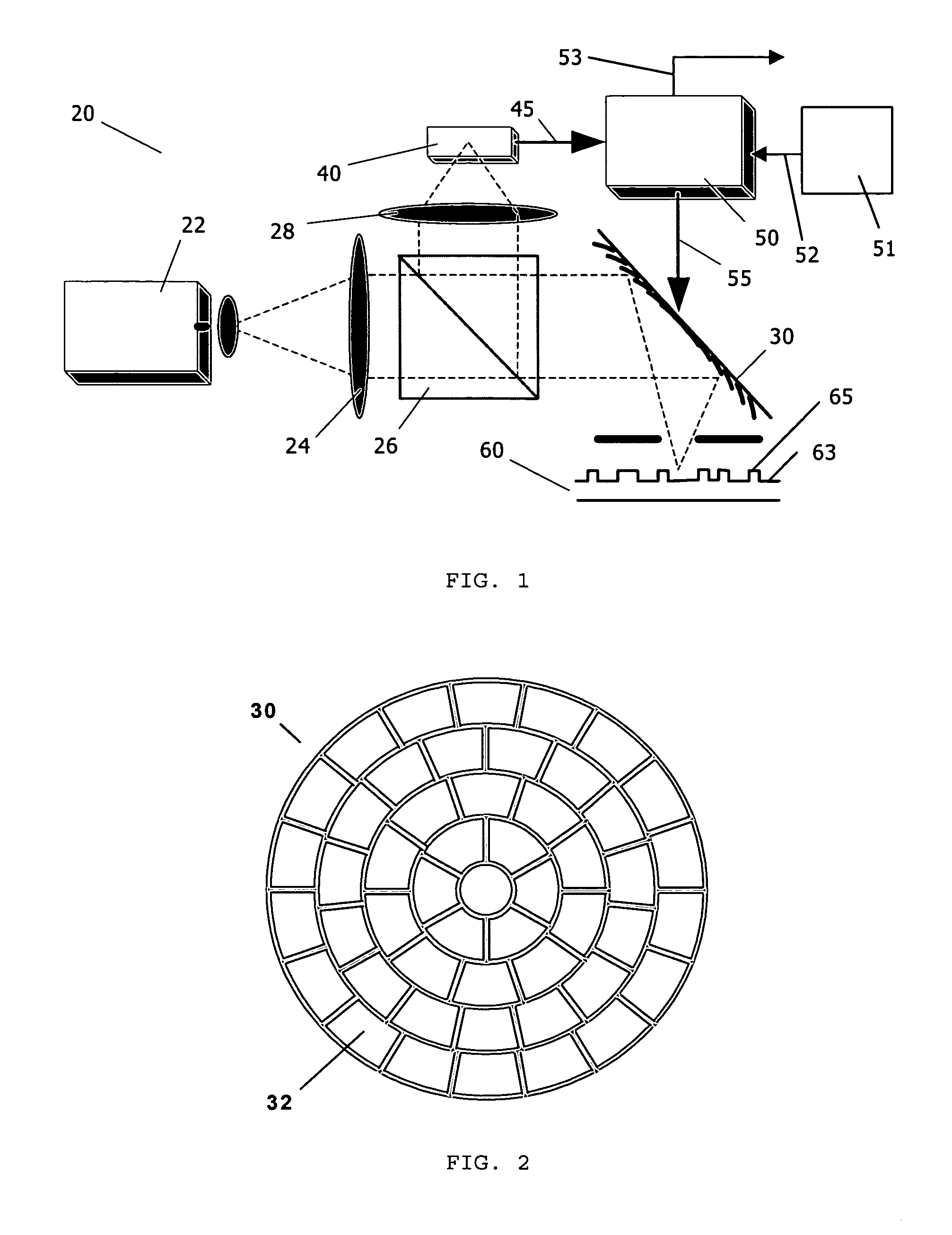
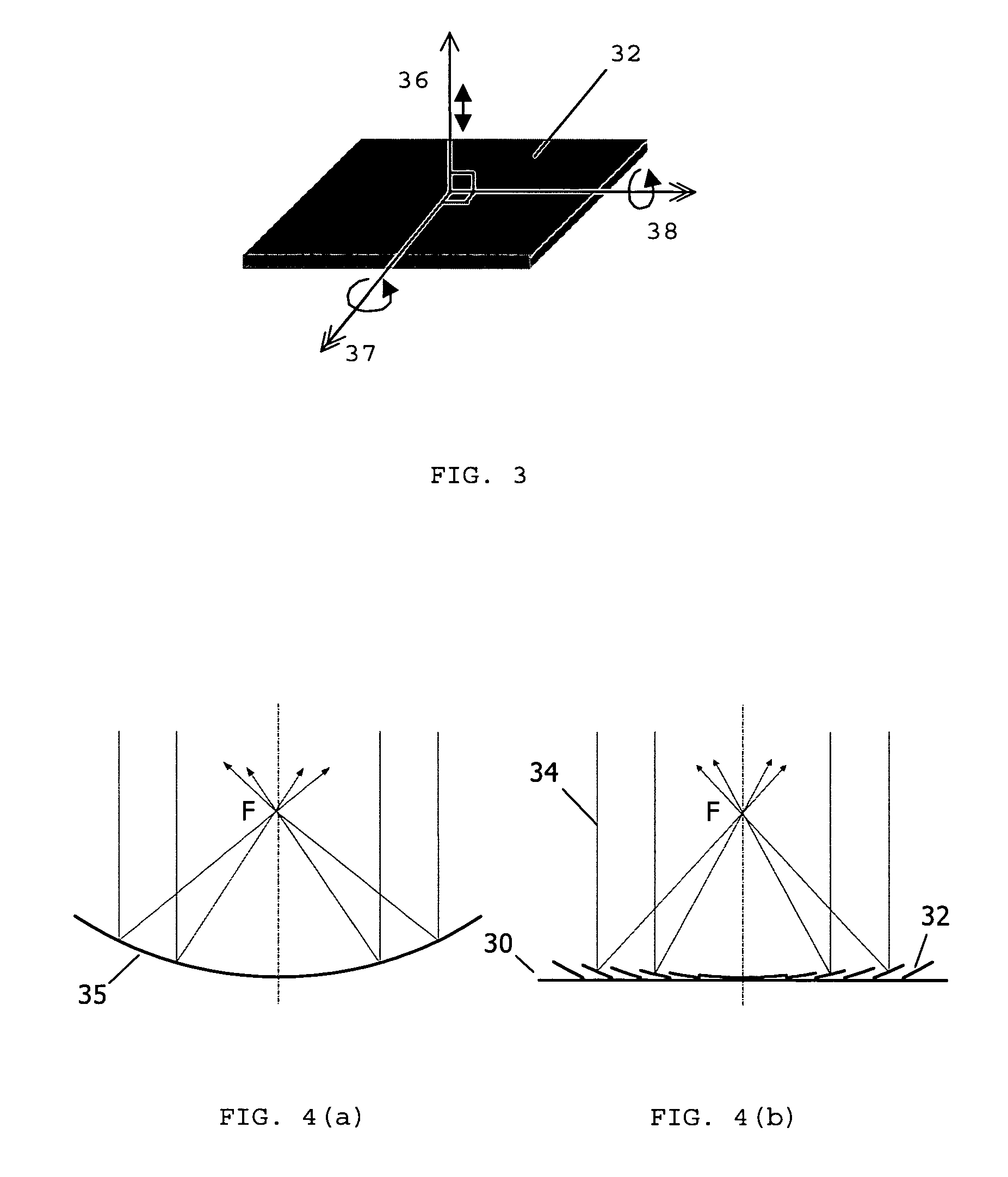
A new high resolution confocal and non-confocal scanning laser macroscope is disclosed which achieves fine focus and control of focus position by moving a lens in the intermediate optics. This arrangement is particularly useful for imaging specimens where it is difficult to focus by changing the distance between the scan lens and the specimen, for example for in-vivo imaging, photodynamic therapy, and image-guided surgery. It is also important to keep the lens-to-specimen distance constant when a liquid-immersion scan lens is used, in order to maintain a constant thickness of liquid between the lens and the specimen. In addition to being useful for confocal slicing, motion of the intermediate lens under computer control also enables dynamic focus and the ability to move the focal spot along a general path inside the specimen. Several applications of the imaging system are described. The macroscope images macroscopic specimens in reflected light, transmitted light, fluorescence, photoluminescence and multi-photon fluorescence.
Owner:HURON TECH INT
Large caliber aspheric surface measuring apparatus and method based on ultra-precise revolving scanning
InactiveCN101377410AGood effectRealize measurementUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceMacroscopic scale
The invention provides a large diameter aspheric measuring device based on ultra-precision rotary scan and a method, belongs to the macroscopic measuring technology. The device comprises an ultra-precision air flotation turntable, a precision angle and angle measuring system, an ultra-precision linear air flotation guide, a length-measuring device and a gradient measurement system. The gradient measurement system comprises a linear polarization He-Ne laser or a semiconductor laser, a diffraction element, a scanning head and an image receiving unit. The linear polarization He-Ne laser or the semiconductor laser and the image receiving unit are separately fixed on the two sides of the base beam. The scanning head is fixed on the ultra-precision linear air flotation guide. The scanning head comprises a radial gradient measurement sub-scanning head and a tangential gradient measurement sub-scanning head, both of which comprise an error compensation light path. The working platforms of the two sub-scanning heads are orthogonal to each other. The invention discloses a large diameter aspheric measuring method based on ultra-precision rotary scan.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for controlling self-adaption code rate based on space-time shielding effect
InactiveCN101325711AReasonable adjustmentGood subjective visual qualityError preventionTelevision systemsPattern recognitionMathematical model
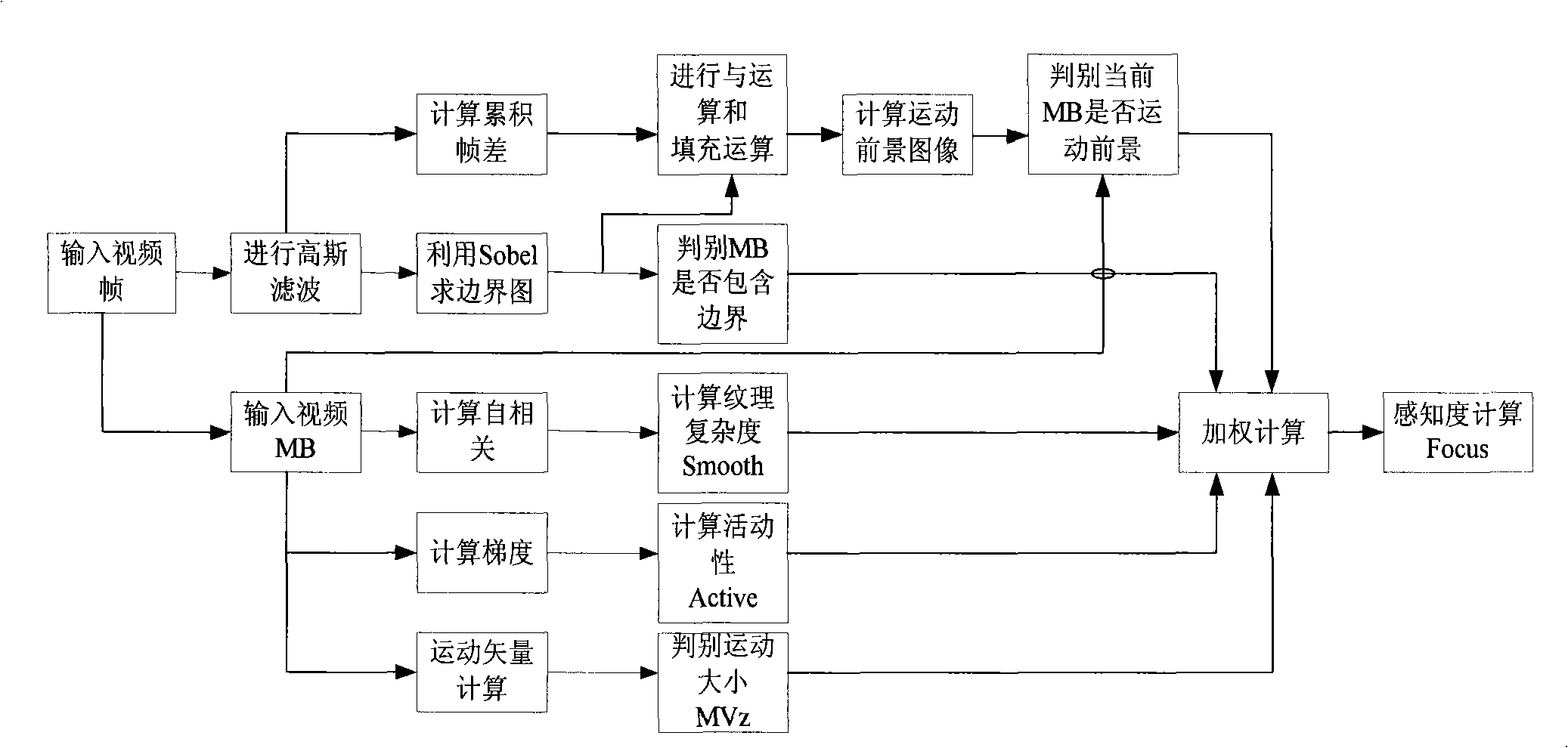
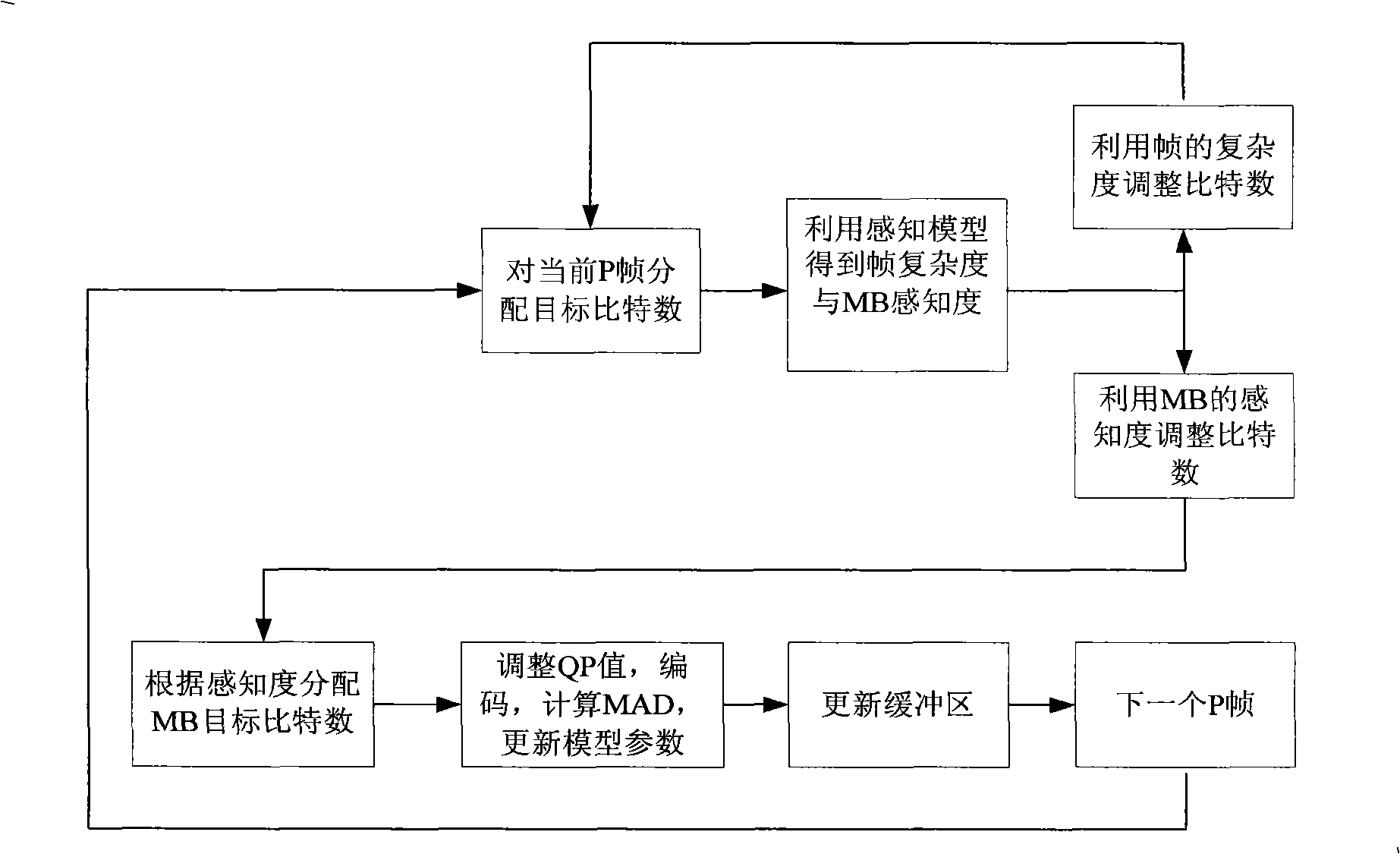
The invention relates to a control method of self-adapted code rate based on time-space masking effect. The method unifies a macroscopic description that reflects features in some part of a visual sensing system, especially merging the perceiving property of eye about motion information with other sensing features, which includes: preprocessing the original sequence of video code; then calculating frame level complexity and degrees of perception of each macro-block using time-space masking effect; the self-adapted code rate control algorithm distributes frame bit number according to frame complexity; finally determining the quantization parameter of macro-block according to the degree of perception of the macro-block. The method obtains a better object visual quality under the condition of identical or less bit number in comparison with the code rate control algorithm on the JM10.2 edition of H.264 check model.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Multi-dimensional parameter assessment method of aging degree of running composite insulator
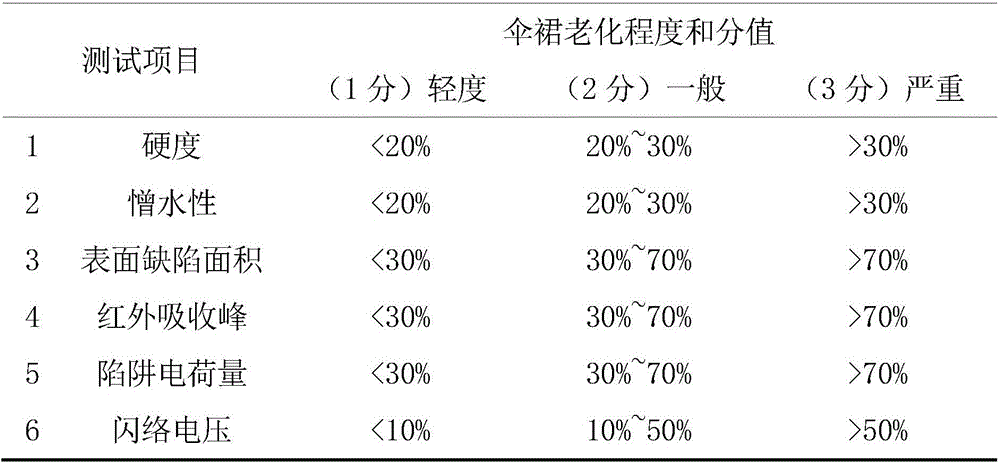
InactiveCN106771765ARealize evaluationAvoid one-sidednessTesting dielectric strengthMaterial analysisElectricityComposite insulators
The invention provides a multi-dimensional parameter assessment method of an aging degree of a running composite insulator. The method comprises the following steps: firstly measuring hardness, hydrophobicity, a surface defect area, an infrared absorption peak corresponding to a Si-O-Si group, a trap charge amount and a flashover voltage of a high-temperature vulcanized silicone rubber test sample of an umbrella skirt of a target composite insulator; then performing quantitative processing on the measured data, and scoring the aging degrees of the processed feature parameters; performing weighted summation on the scores of the feature parameters to obtain a comprehensive feature parameter characterizing the aging degree of the composite insulator; and finally determining the aging degree of the insulator according to a corresponding relation between the size of the comprehensive feature parameter and the grade of the aging degree. According to the multi-dimensional parameter assessment method provided by the invention, the microscopic electrical characteristics and microscopic physical and chemical characteristics of the umbrella skirt material of the composite insulator are combined with macroscopic characteristics to realize the comprehensive assessment of the aging degree of the composite insulator. By adoption of the method, the one-sidedness of the traditional assessment method is avoided, and thus the accuracy of an assessment result is guaranteed.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Imaging system with dynamic range maximization
ActiveUS20110064296A1Small rangeMaximize dynamic rangeMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer scienceImage system
A method of operating an instrument that is a macroscope, microscope, or slide scanner is provided where the instrument has a larger dynamic range for measurement than a dynamic range required in the final image of a specimen. In the method, data is measured from a specimen using the instrument, and the dynamic range of the measured data is contracted in the final image file during scanning.
Owner:HURON TECH INT
Optical pick-up device using micromirror array lens
ActiveUS7315503B2Reduce signalingQuality improvementRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansMacroscopic scaleMicromirror array
Owner:STEREO DISPLAY
Cross-scale micro-nano-scale in-situ composite load mechanical performance testing platform
ActiveCN102262016ARealize acquisitionEasy to controlMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesNanotechnologyMicro nanoElectromechanics
The invention relates to a cross-scale micro nanometer grade in-situ composite load mechanical property testing platform, belonging to electromechanics. The cross-scale micro nanometer grade in-situ composite load mechanical property testing platform is composed of a precision drive and transmission unit, a signal detection and control unit and a clamping, connecting and supporting unit, wherein,in the precision drive and transmission unit, a DC servo motor provides power output, and a two-stage worm and gear mechanism with large reduction ratio and a precision ball screw mechanism transmit power; the signal detection and control unit is composed of a precision displacement sensor, a precision pull pressure sensor and a coder in coaxial rigid connection with the DC servo motor; and the clamping, connecting and supporting unit comprises a clamper component for locating and mounting a standard test specimen, and the like. The cross-scale micro nanometer grade in-situ composite load mechanical property testing platform can be compatible with imaging instruments, and performs a cross-scale in-situ micro nanometer composite load test on a macroscopic test specimen through observation via the imaging instruments, so as to perform in-situ monitoring on processes of microscopic deformation, injury and fracture of materials, so that a new testing method for revealing the mechanical properties and the injury mechanism of the materials at the micro nanometer grade is provided.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
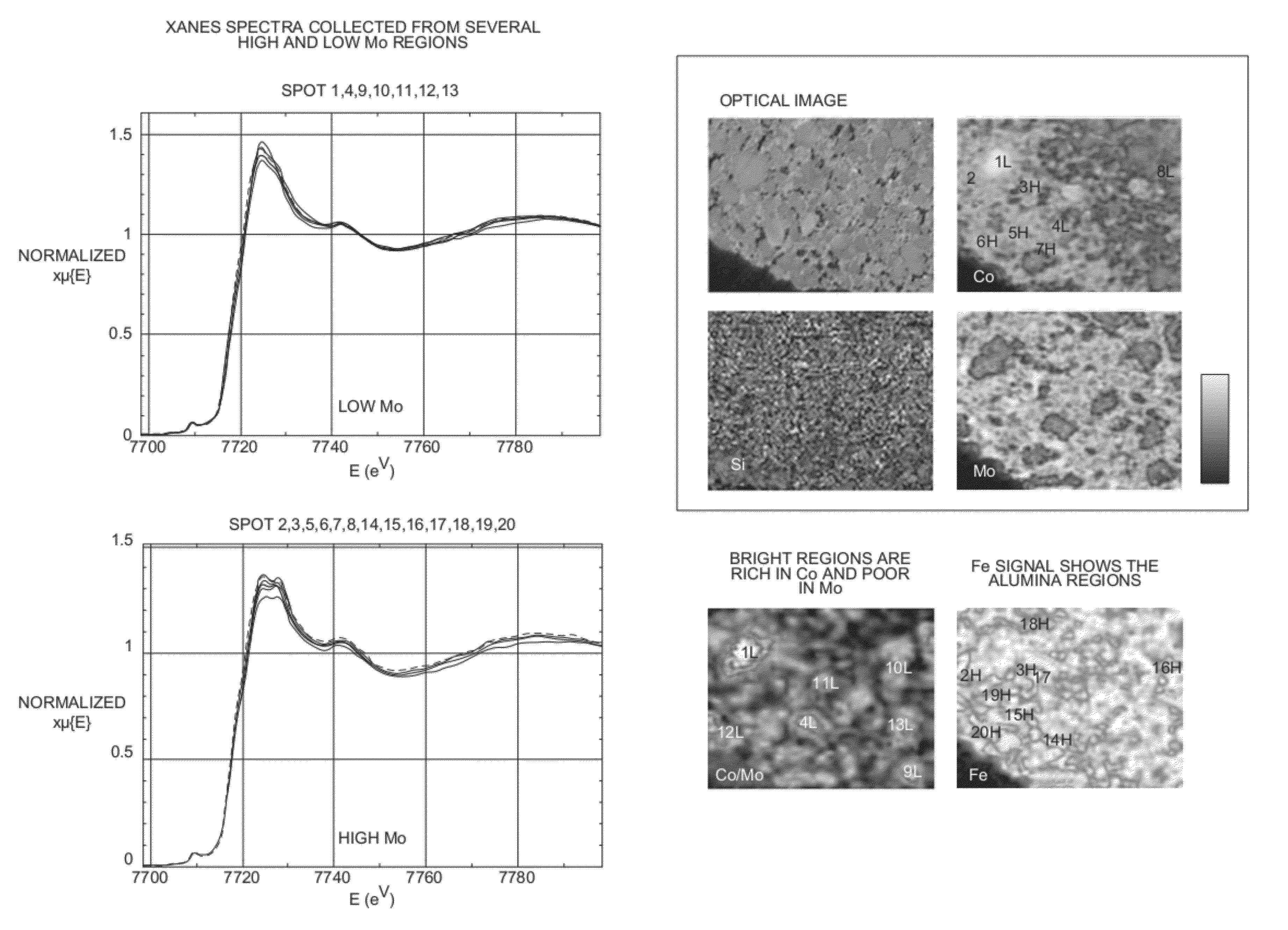
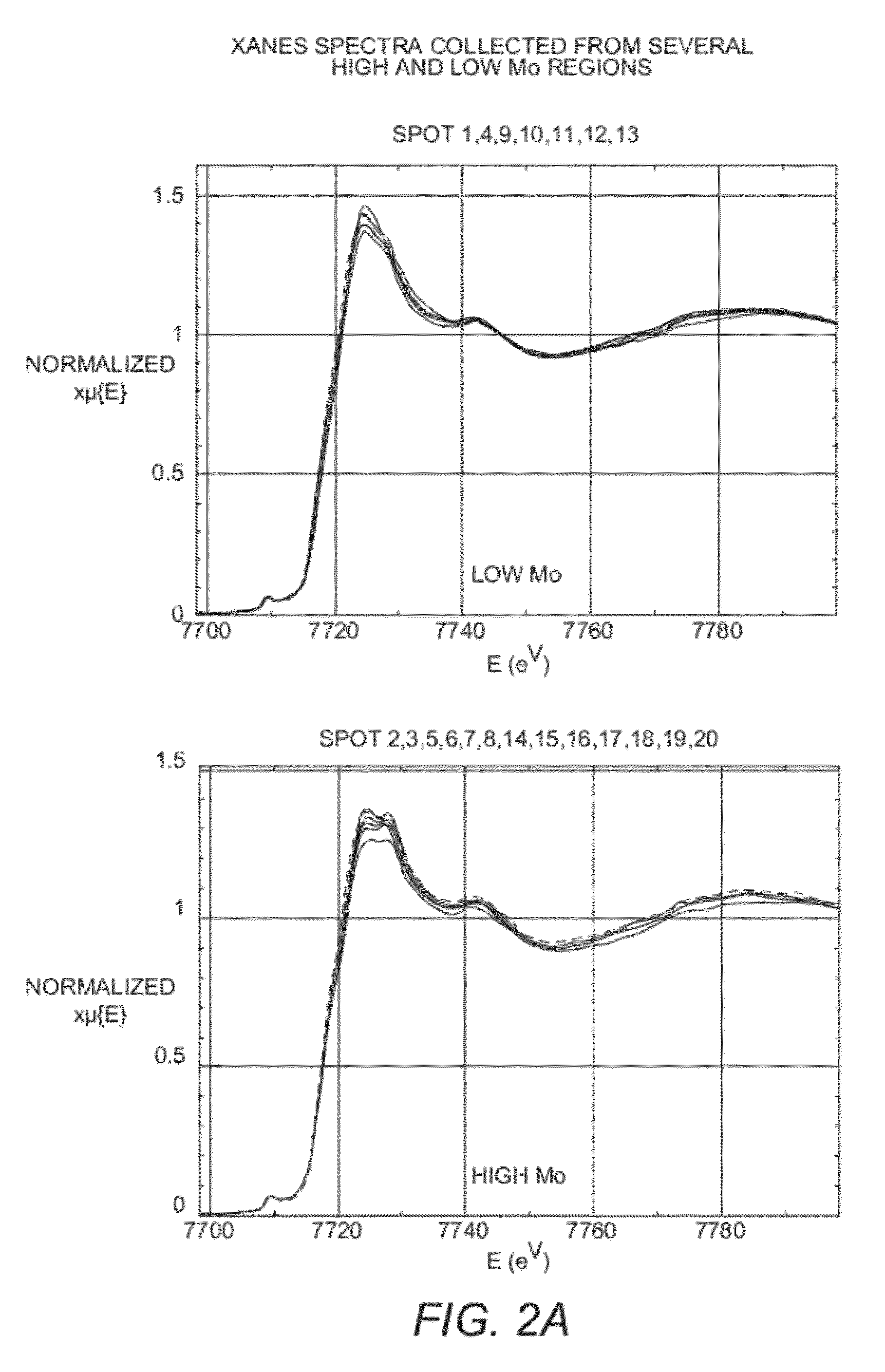
Solid material characterization with x-ray spectra in both transmission and fluoresence modes
InactiveUS20120321039A1Efficient analysisGood mechanical integrityX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSoft x rayX-ray absorption spectroscopy
Methods are disclosed utilizing synchrotron X-ray microscopy including x-ray fluorescence and x-ray absorption spectra to probe elemental distribution and elemental speciation within a material, and particularly a solid that may have one or more elements distributed on a solid substrate. Representative materials are relatively homogeneous in composition on the macroscale but relatively heterogeneous on the microscale. The analysis of such materials, particularly on a macroscale at which their heterogeneous nature can be observed, provides valuable insights into the relationships or correlations between localized concentrations of elements and / or their species, and concentrations of other components of the materials. Sample preparation methods, involving the use of a reinforcing agent, which are advantageously used in such methods are also disclosed.
Owner:UOP LLC
Atomic layer deposition process for manufacture of battery electrodes, capacitors, resistors, and catalyzers
InactiveUS20100123993A1No leaksReduced series resistancePorous dielectricsSolid electrolytic capacitorsMulti materialMacroscopic scale
The present disclosure relates generally to the field of sequential surface chemistry. More specifically, it relates to products and methods for manufacturing products using Atomic Layer Deposition (“ALD”) to depose one or more materials onto a surface. ALD is an emerging variant of Chemical Vapor Deposition (“CVD”) technology with capability for high-quality film deposition at low pressures and temperatures, which may produce defect-free films, on a macroscopic scale, at any given thickness. The present disclosure includes, in varying embodiments, methods of manufacturing microelectronic assemblies and components such as battery electrodes, capacitors, resistors, catalyzers and PCB assemblies by ALD, and the products manufactured by those methods.
Owner:LAOR CONSULTING +1
System and method for fabricating macroscopic objects, and nano-assembled objects obtained therewith
ActiveUS20110095198A1Stability-of-path spectrometersAdditive manufacturing apparatusMacroscopic scaleParticle physics
A method and a system for fabricating a macroscopic object, comprising, in an environment at least one energy source; at least one hollow cathode separated from an anode by a bias potential; and a support; a flow of gas through the hollow cathode generating a hollow cathode discharge, particles emitted by the hollow cathode being assembled on the support under action of energy from the energy source.
Owner:FABLAB
Camouflage U.S. Marine Corps combat utility uniform: pattern, fabric, and design
InactiveUS20090313740A1Accelerated destructionImprove concealmentDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsFiberInfrared
A camouflage system to be used for both military uniforms and equipment. The system includes specialized means of printing the camouflage system unto fabric. The system can also be used for civilian applications, particularly with sportsman hunters. The system provides camouflage in both the human visible light range and the infrared. The system depends on the use of a macro-pattern resulting from a repeat of a micro-pattern. When applied to fabric, a polyamide-cotton fiber blend has a macro pattern resulting from a repeat of a micro pattern printed on at least one surface. The coloring system used comprises at least four colorings from dyes that in combination produce a percent reflectance value comparable to the negative space of the surroundings near the camouflaged subject. The system functions by a macro pattern being disruptive of the shape of the subject and a micro pattern comprising sharp edge units of a size capable of blending the subject into the background. The relative lightness values and percentages of total pattern are sufficient to produce a percent reflectance of acceptable colors, wet or dry in terms of lightness values compared to current military four-color camouflage. On fabric, the results are achieved by printing A macro pattern that disrupts the sensed shape and a micro pattern with a repeat size that produces the macro pattern. The reflectance of the material is comparable to the negative space surrounding a subject so the subject does not appear too dark or too light (out of place). The variation in the lightness between wet and dry is not greater than 17-28%, achieved during the printing process.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
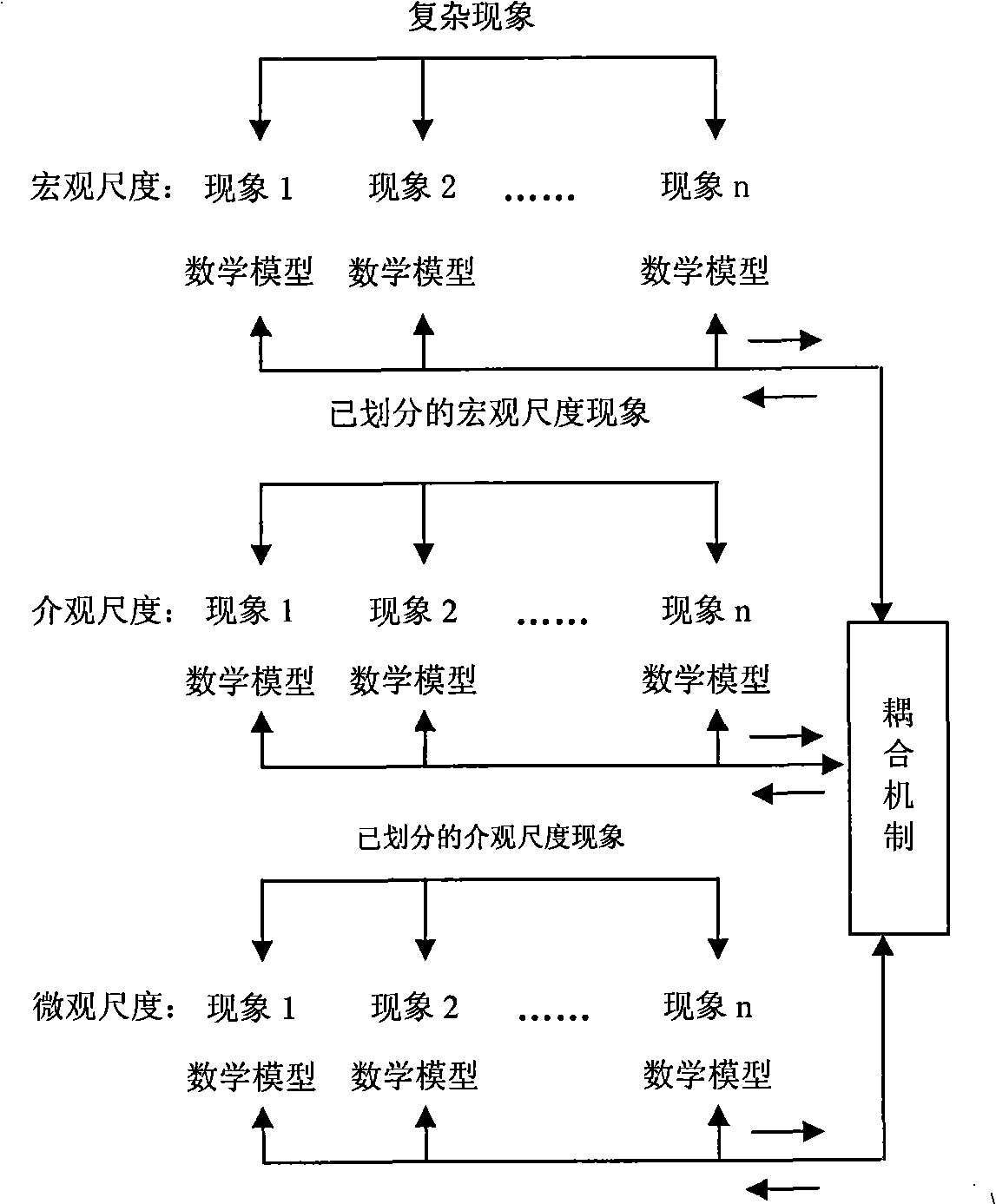
Numerical modeling method of rock mass mechanics considering macroscopic and microscopic defect coupling
ActiveCN108629126AReasonableUniversalDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNODALMacroscopic scale
The invention relates to a numerical modeling method of rock mass mechanics considering macroscopic and microscopic defect coupling. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, generation ofa numerical calculation model, wherein an FLAC3D program is adopted for numerical modeling, the planar size, thickness and boundary conditions of the calculation model are set, a three-node triangularunit is adopted for conducting superfine mesh division on the model, during the superfine mesh division, divided mesh units are cubes, and the side length of each cube is not greater than 1 mm; constitutive models and parameters of rock masses or rocky slopes are set, and the numerical calculation model is established; secondly, generation of macroscopic defects; thirdly, generation of microscopic defects. According to the method, the macroscopic defects represent macroscopic joints, cracks and the like, and the microscopic defects represent micro-cracks and the like; by means of the method,the macroscopic and microscopic defects existing in the rock masses are simultaneously considered, and the rock masses obtained through modeling is closer to actual rock masses.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
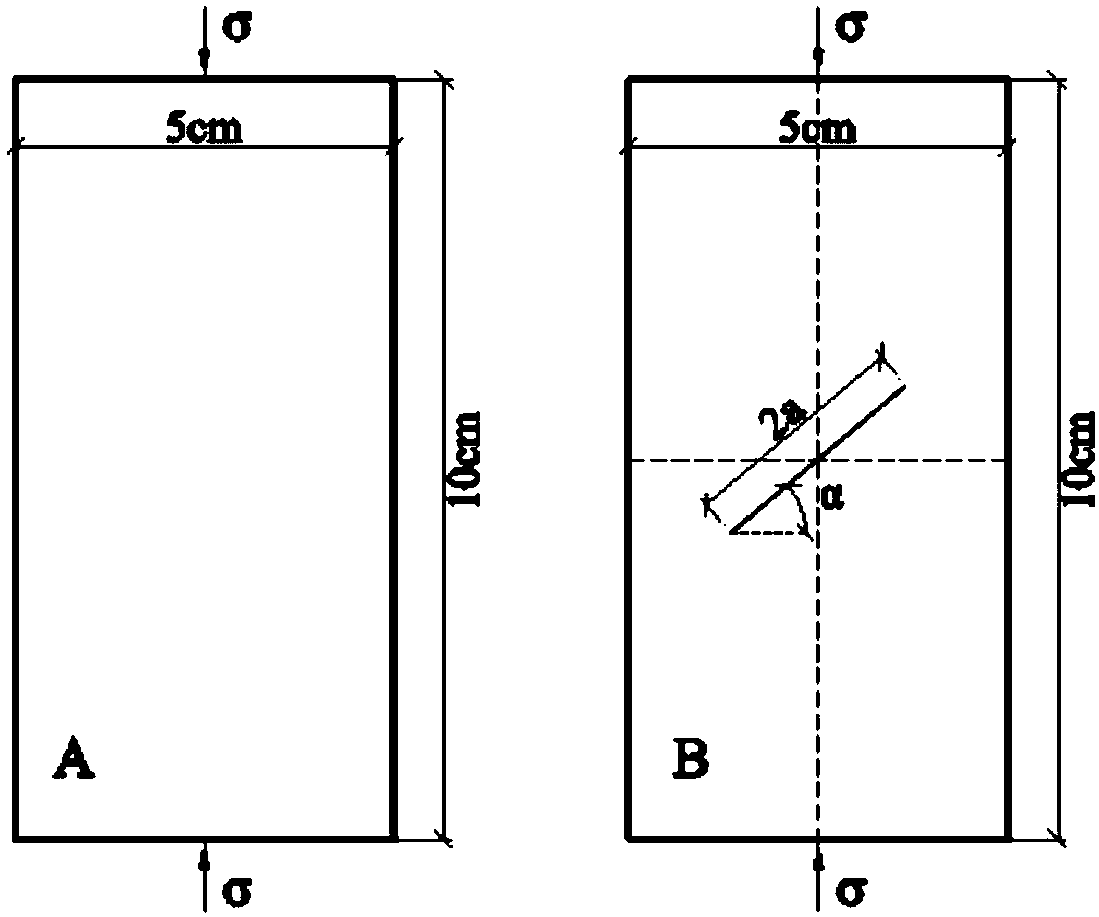
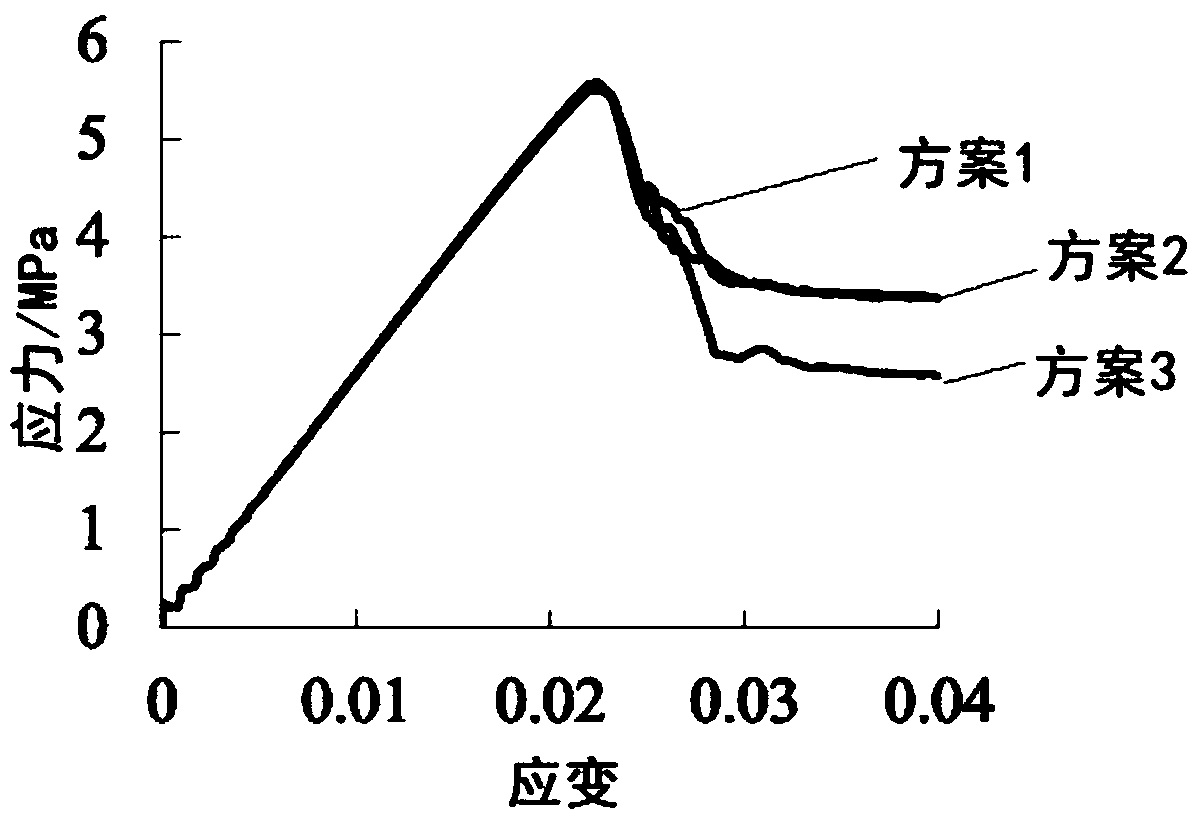
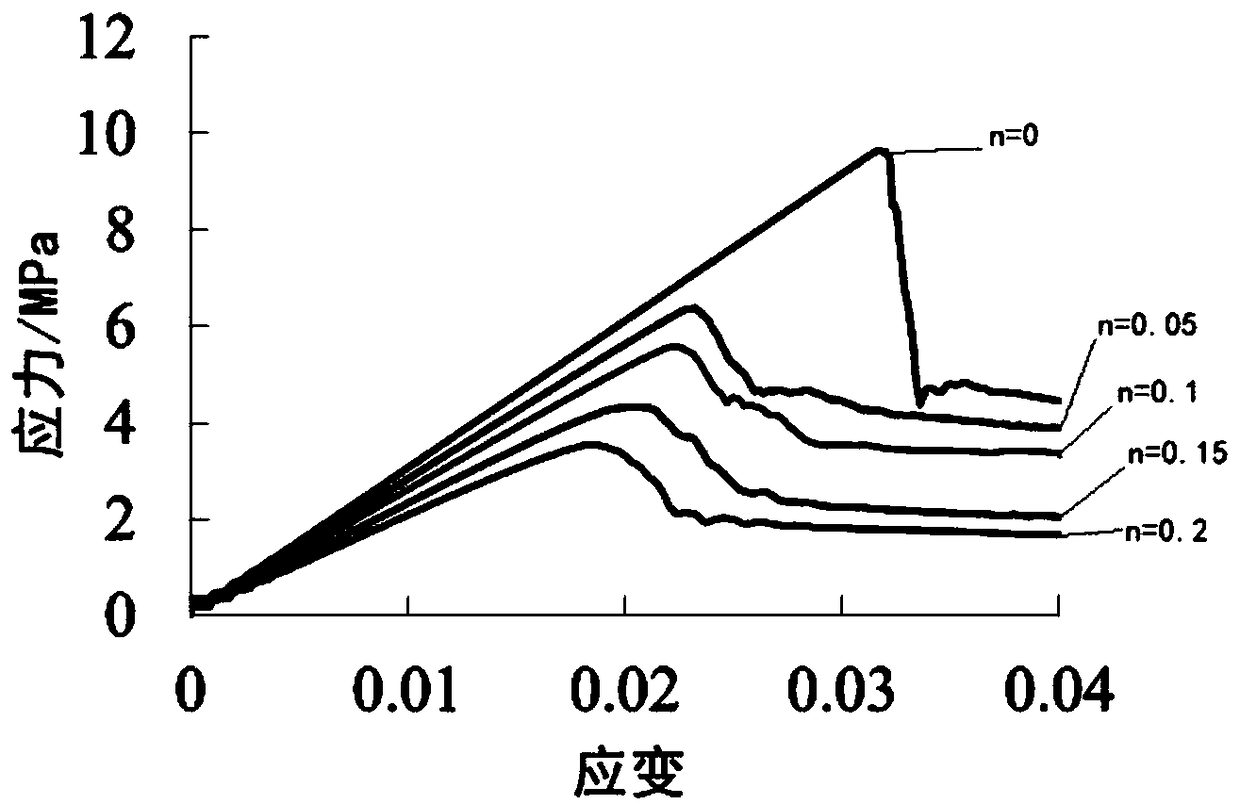
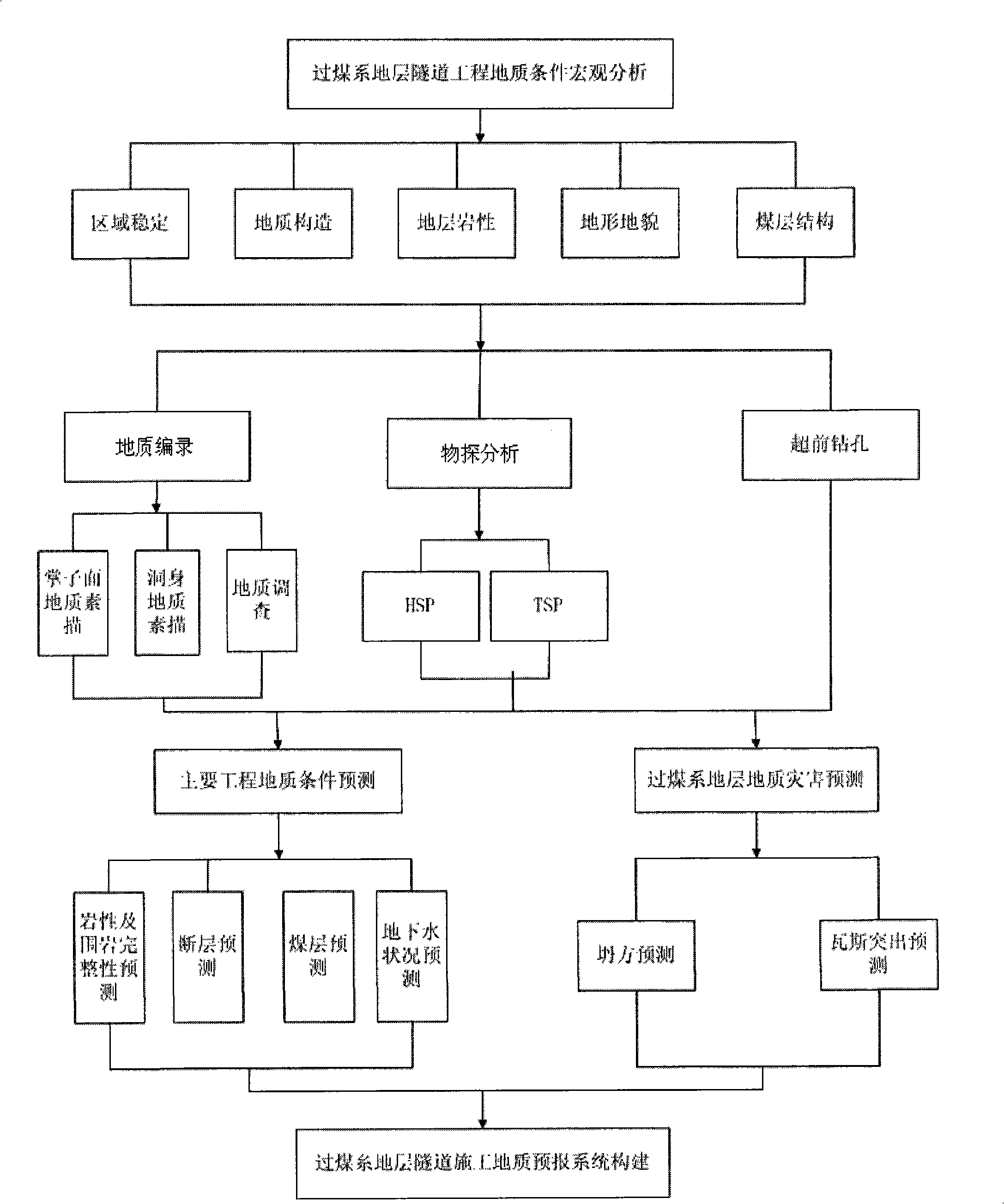
Geological prediction system for constructing tunnel passing through coal measure strata
ActiveCN101526629ADetection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationCoal measuresGeomorphology
The invention discloses a geological prediction system for constructing a tunnel passing through coal measure strata. The condition of the tunnel passing through the coal measure strata is specifically analyzed in a way of geological record, geophysical prospecting analysis or advance borehole according to specific condition based on macroscopic analysis which is adopted in sequence; the obtained information is classified so as to predict the geological condition of a main job and the geologic hazard of the coal measure strata; and the correlative information and data are used for completing the construction of the geological prediction system for constructing tunnel passing through coal measure strata. The invention provides a system for perfectly and exactly predicting the geology for constructing the tunnel passing through coal measure strata.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY NO 2 ENG GRP CO LTD
Tension-compression and fatigue loading testing machine based on laser confocal microscope
InactiveCN101592573AAchieve stretchImplement compressed loadingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansTension compressionFatigue loading
The invention relates to a tension-compression and fatigue loading testing machine based on a laser confocal microscope, and in particular provides a loading testing machine applicable to a laser confocal microscope platform. The testing machine comprises a fixed base plate, a tension-compression loading device driven by a motor, a fatigue loading device driven by a piezoelectric ceramic, a force sensor, a holding device, a phase-shifting device and the like. The testing machine can perform tension-compression and fatigue loading tests on a typical sample and a film of a metal or non-metal material under macroscopic scale uniaxial stress, and designs the phase-shifting device for an optical testing method for improving the test accuracy and the automation degree. The testing machine has a compact structure, and a test piece is abutted on the lower bottom surface of the testing machine so that the loading under the laser confocal microscope platform can be achieved; besides, the testing machine uses the microscope to collect loading images, and process the images by an optical method to obtain mechanical parameters of a test piece material. The testing machine has the advantages of high system measurement sensitivity, reliable result and wide application range.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Multi-dimension analogy method of solid-oxide fuel battery
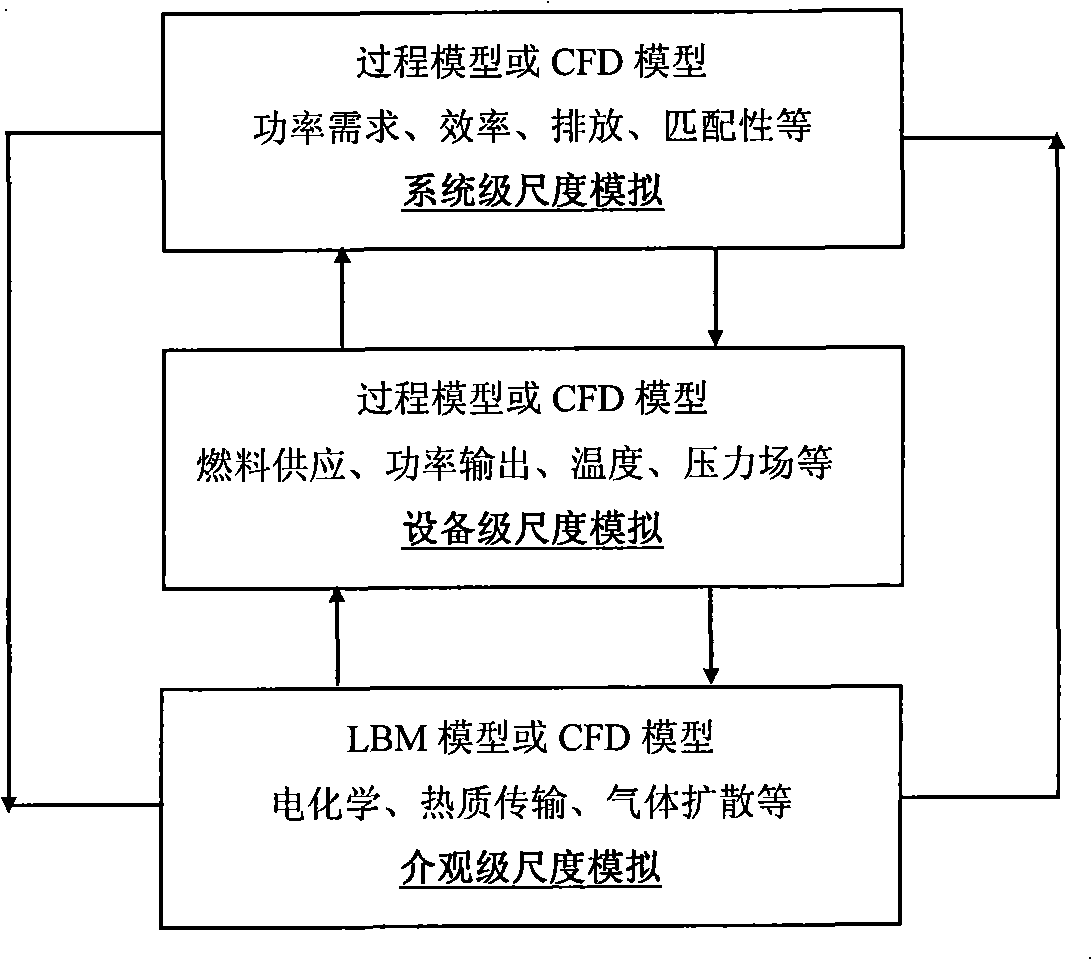
InactiveCN101324908AEnable multiscale simulationsImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsElectrochemical responseScale model
The invention relates to a multi-scale simulation method for solid oxide fuel cells, and is characterized in that the method conducts multi-scale simulation from the mesoscopic scale to the macro equipment scale for complex physical and chemical phenomenon, such as coupled heat calorie transmission, electrochemical reaction in the solid oxide fuel cells, etc. The invention further relates to an integration and co-simulation method of a multi-scale model. Because a modeling method provided by the invention adopts the modeling method by mechanism from the macro-scale based on the phenomenon, the model has the advantages of clear physical meaning, high accuracy and strong adaptability. A simulation method is adopted between the mesoscopic scale and the macro equipment scale based on molecules or molecular clusters, thereby compensating for a deficiency of traditional single scale simulation. Layered method and the method of different scales are combined to study the complex system, so as to be conducive to disclosing the nature of complex systems, such the solid oxide fuel cells and provide a novel means for studying complex the systems.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Articles for manipulating impinging liquids and methods of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20130032646A1Improve performanceMore practicalMaterial nanotechnologyLayered productsNon wettingMacroscopic scale
This invention relates generally to an article that includes a non-wetting surface having a dynamic contact angle of at least about 90°. The surface is patterned with macro-scale features configured to induce controlled asymmetry in a liquid film produced by impingement of a droplet onto the surface, thereby reducing time of contact between the droplet and the surface.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Air-ground-space integrated hyperspectral water quality monitoring and analyzing method
PendingCN110865040AMeet the needs of large-scale water quality monitoringIncrease dynamicsArtificial lifeColor/spectral properties measurementsMacroscopic scaleData acquisition
The invention provides an air-ground-space integrated hyperspectral water quality monitoring and analyzing method. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, acquiring of water quality monitoring data: including hyperspectral data acquisition and water body sample data acquisition; S2, water quality monitoring data processing: performing data processing on the acquired multi-source water quality monitoring data; S3, establishment of a water quality parameter inversion model: establishing a water quality parameter inversion model according to the multi-source hyperspectral monitoring data, and modeling the water quality parameters through the inversion model based on artificial intelligence; and S4, water quality parameter inversion analysis. The beneficial effects of the air-ground-space integrated hyperspectral water quality monitoring and analyzing method are that: the method can meet the requirement of large-range water quality monitoring, can reflect the distribution and change conditions of the water quality in space and time, can make up defects that water surface sampling is singly adopted, can find pollution source distribution and migration characteristics and influence ranges of pollutants which are difficult to reveal by some conventional methods, can provide a basis for scientifically monitoring the water environment, and has the remarkable characteristics ofhigh dynamic, low cost and macroscopicity.
Owner:深圳航天智慧城市系统技术研究院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com