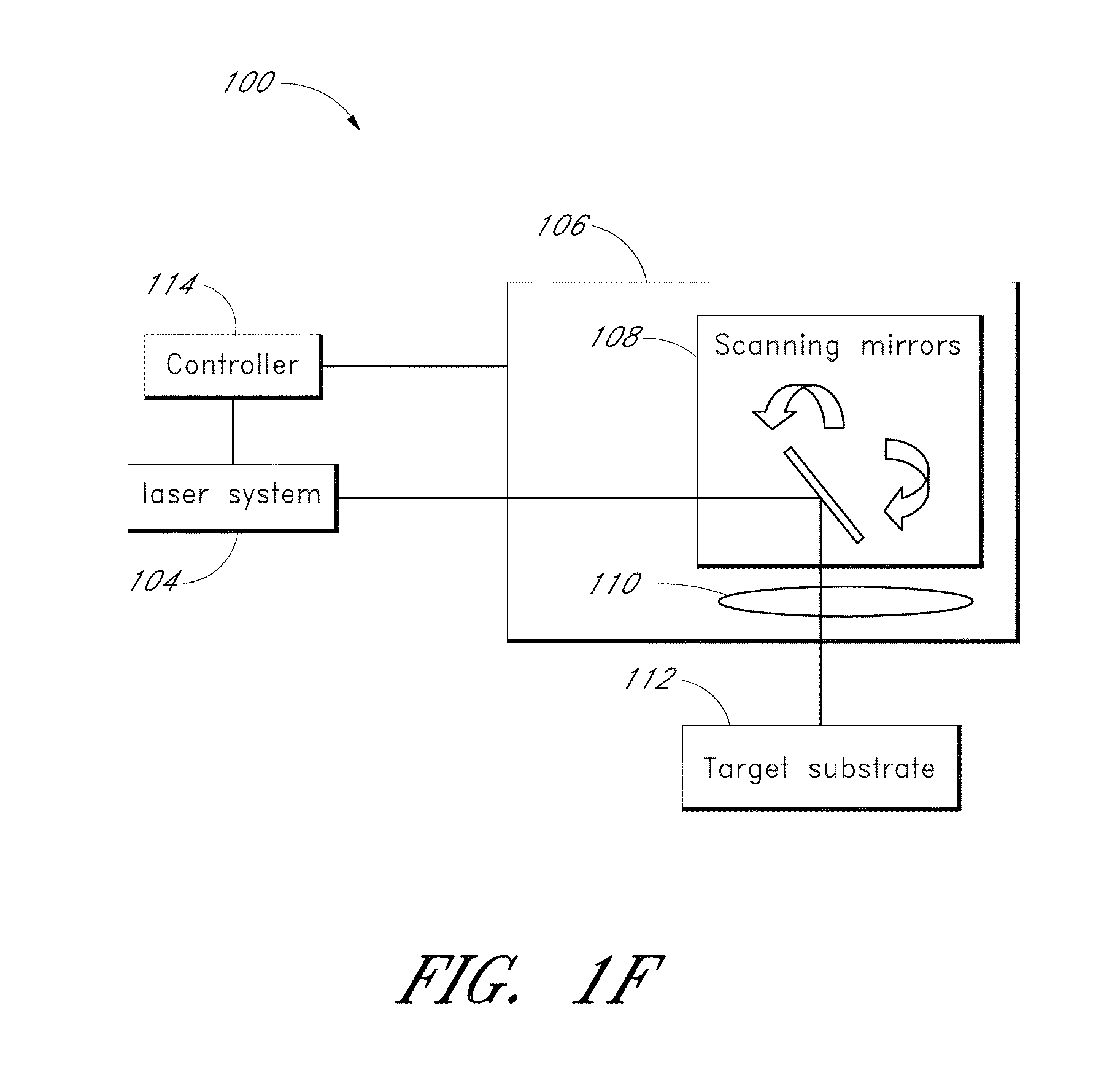
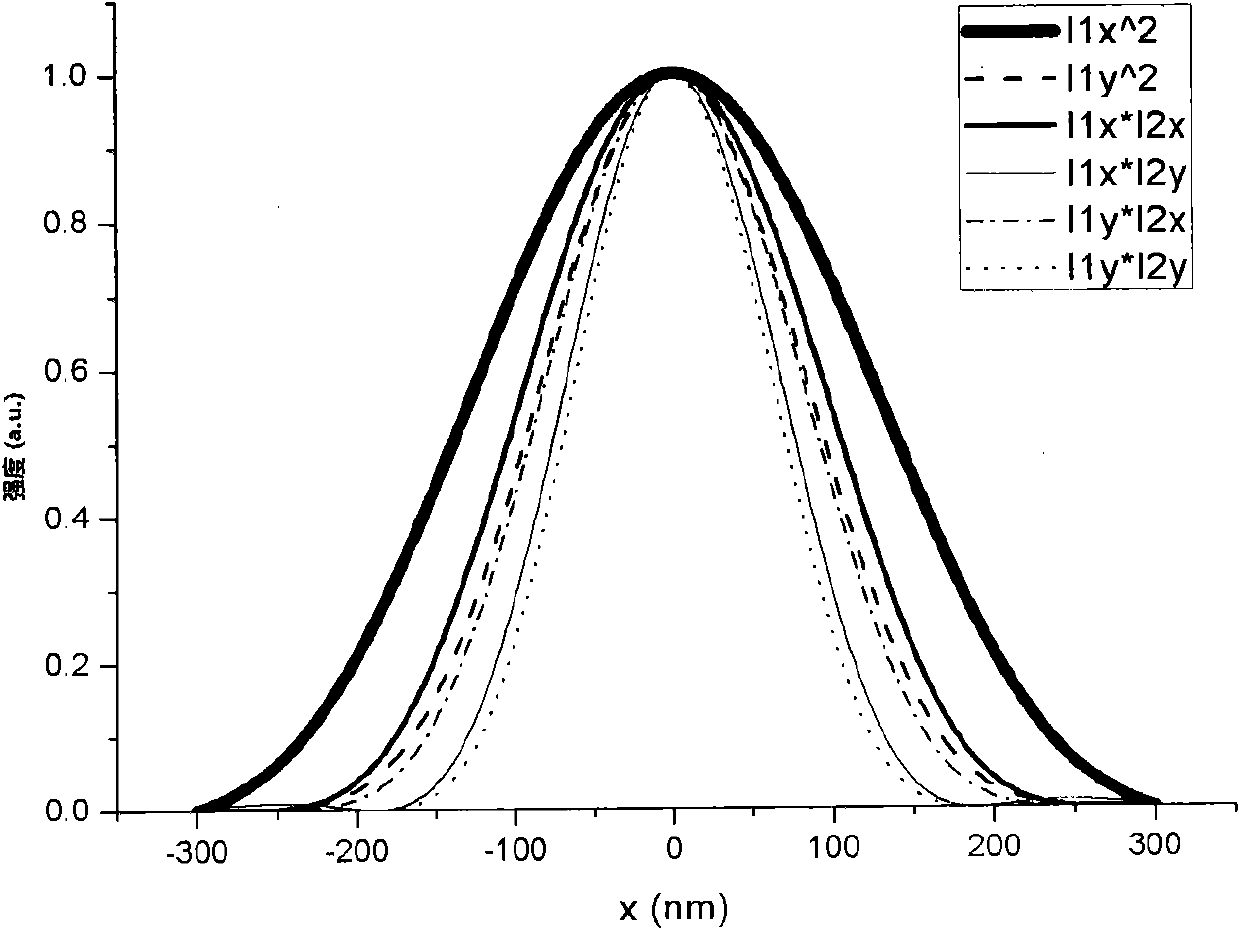
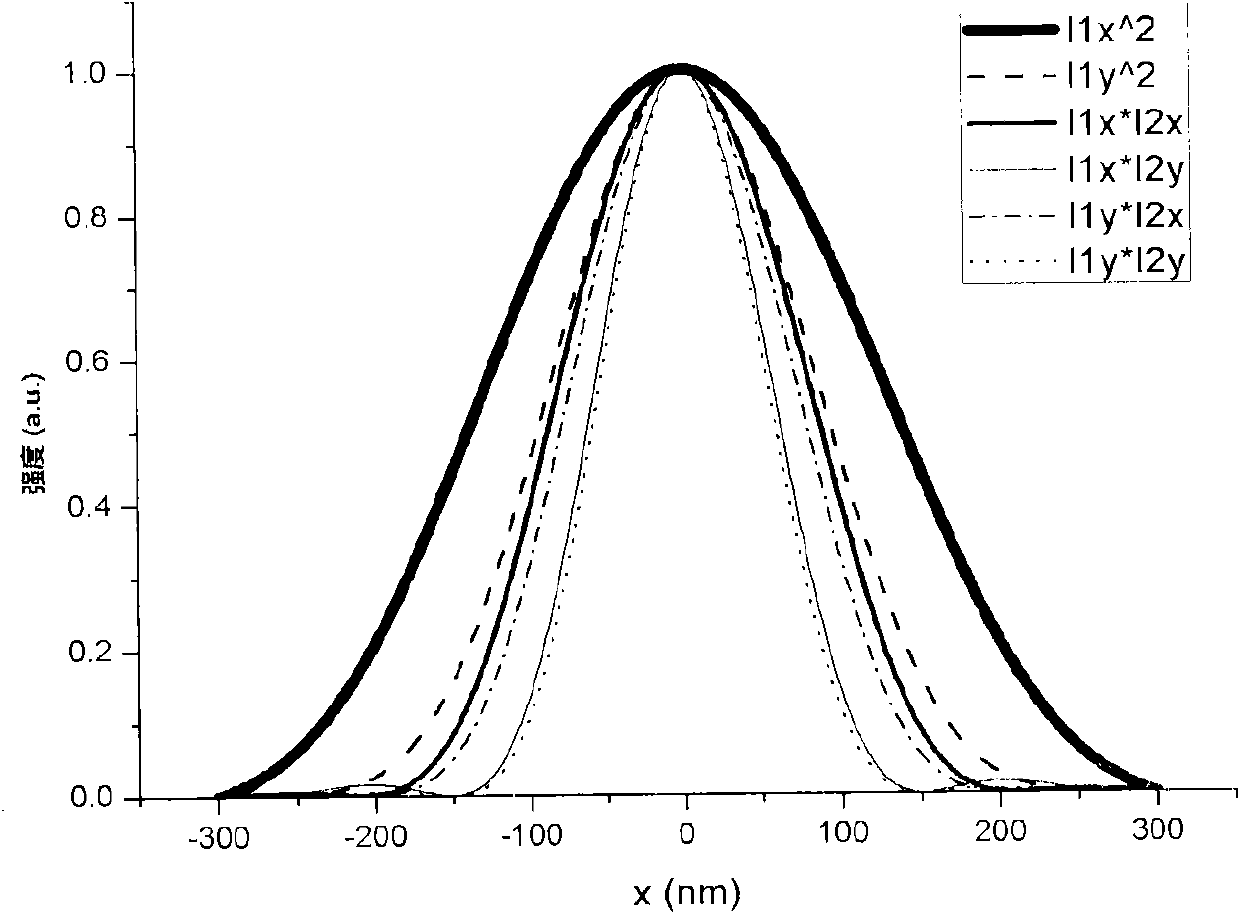
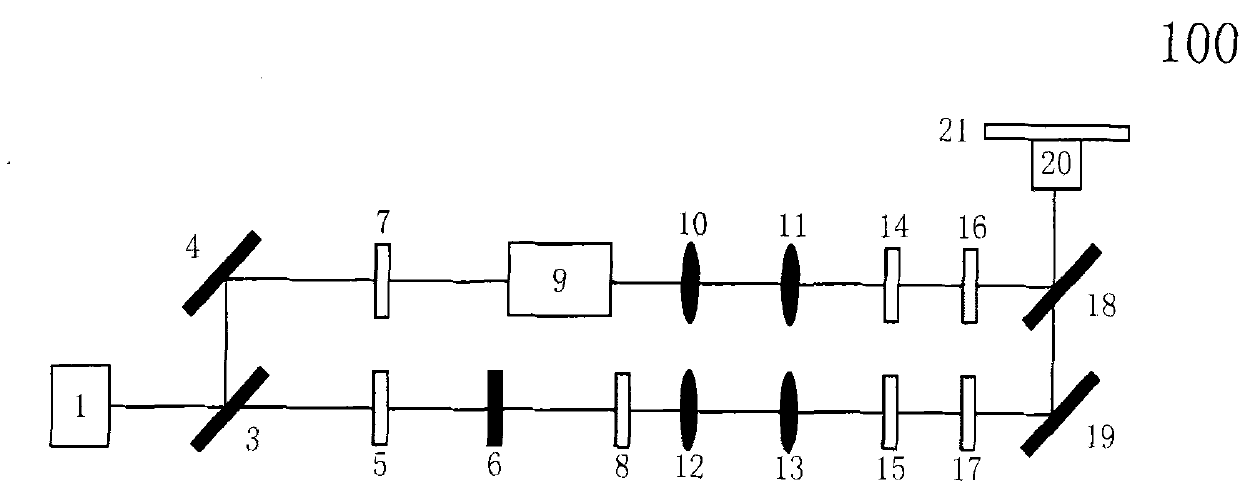
Patents
Literature
1047 results about "Nanosecond" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
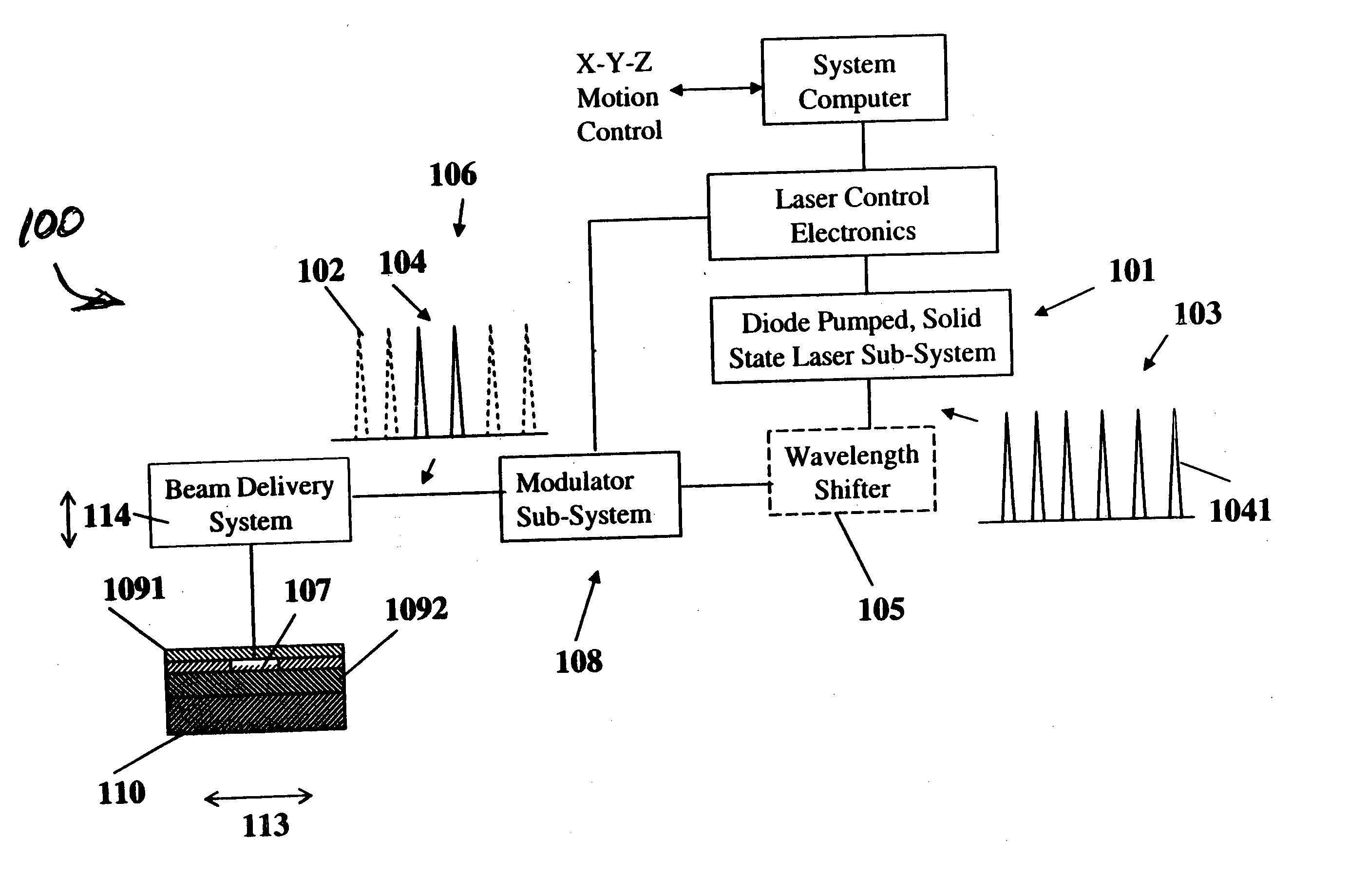
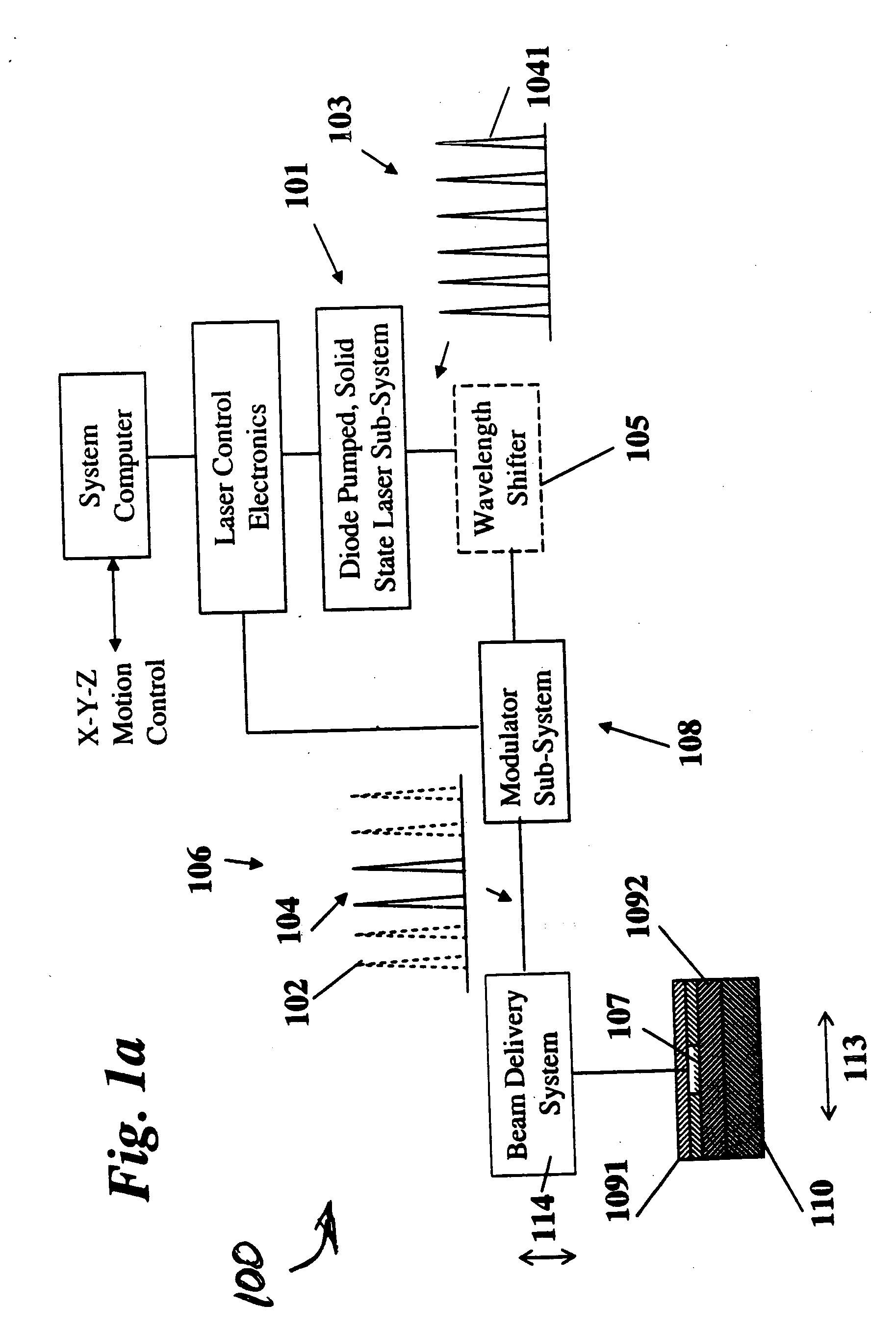
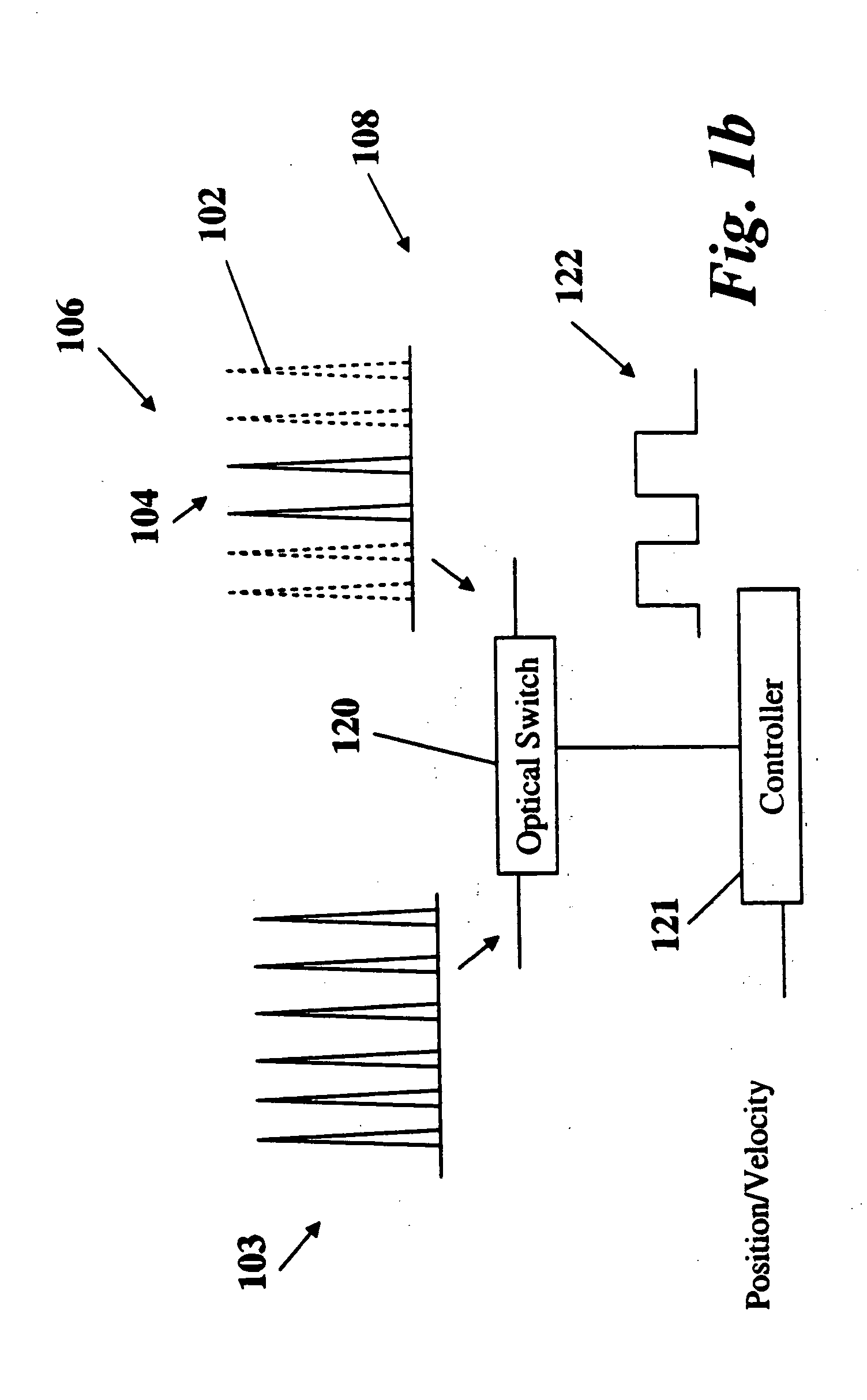
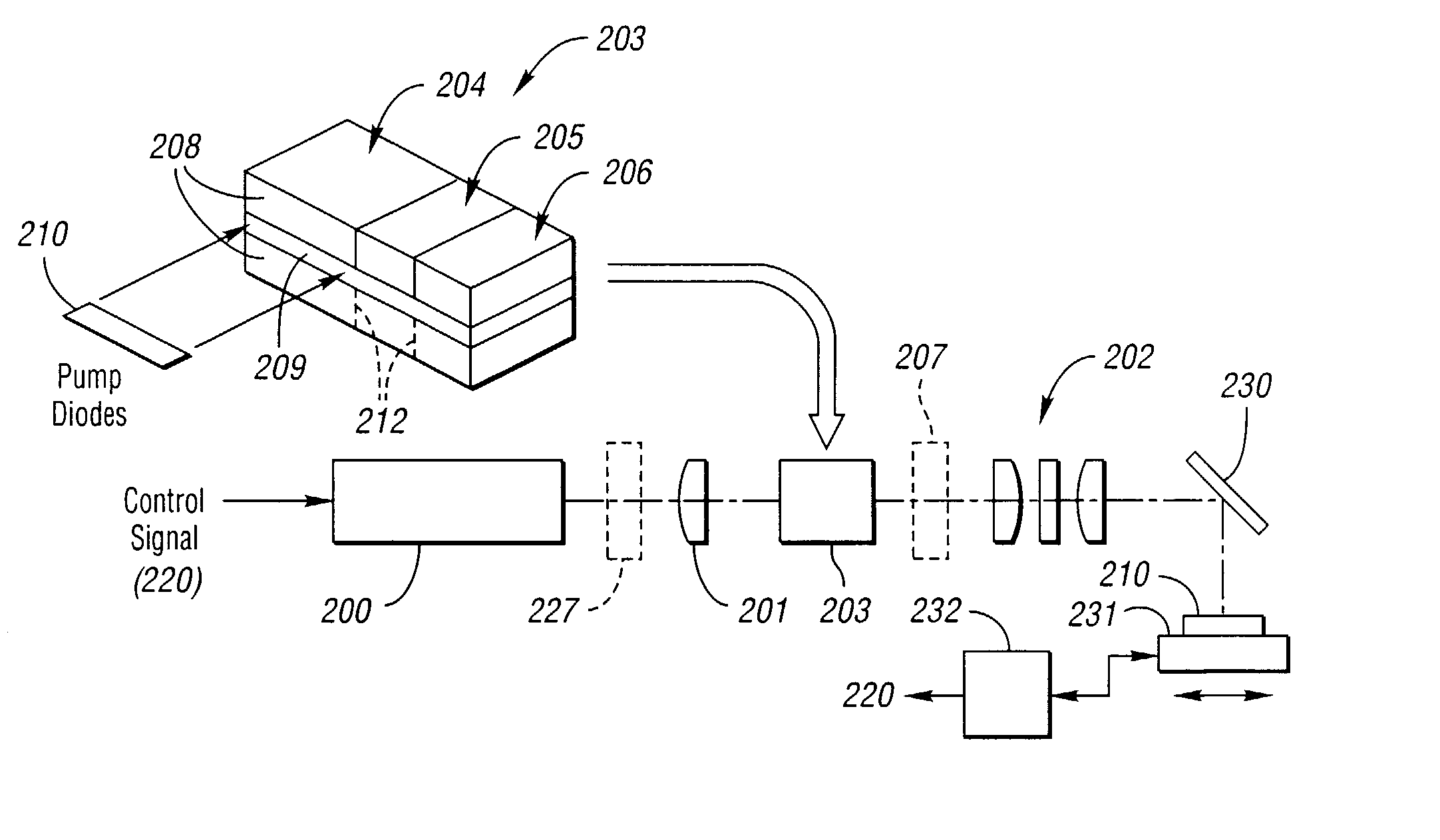
A nanosecond (ns) is an SI unit of time equal to one billionth of a second, that is, /1,000,000,000 of a second, or 10⁻⁹ seconds. The term combines the prefix nano- with the basic unit for one-sixtieth of a minute.
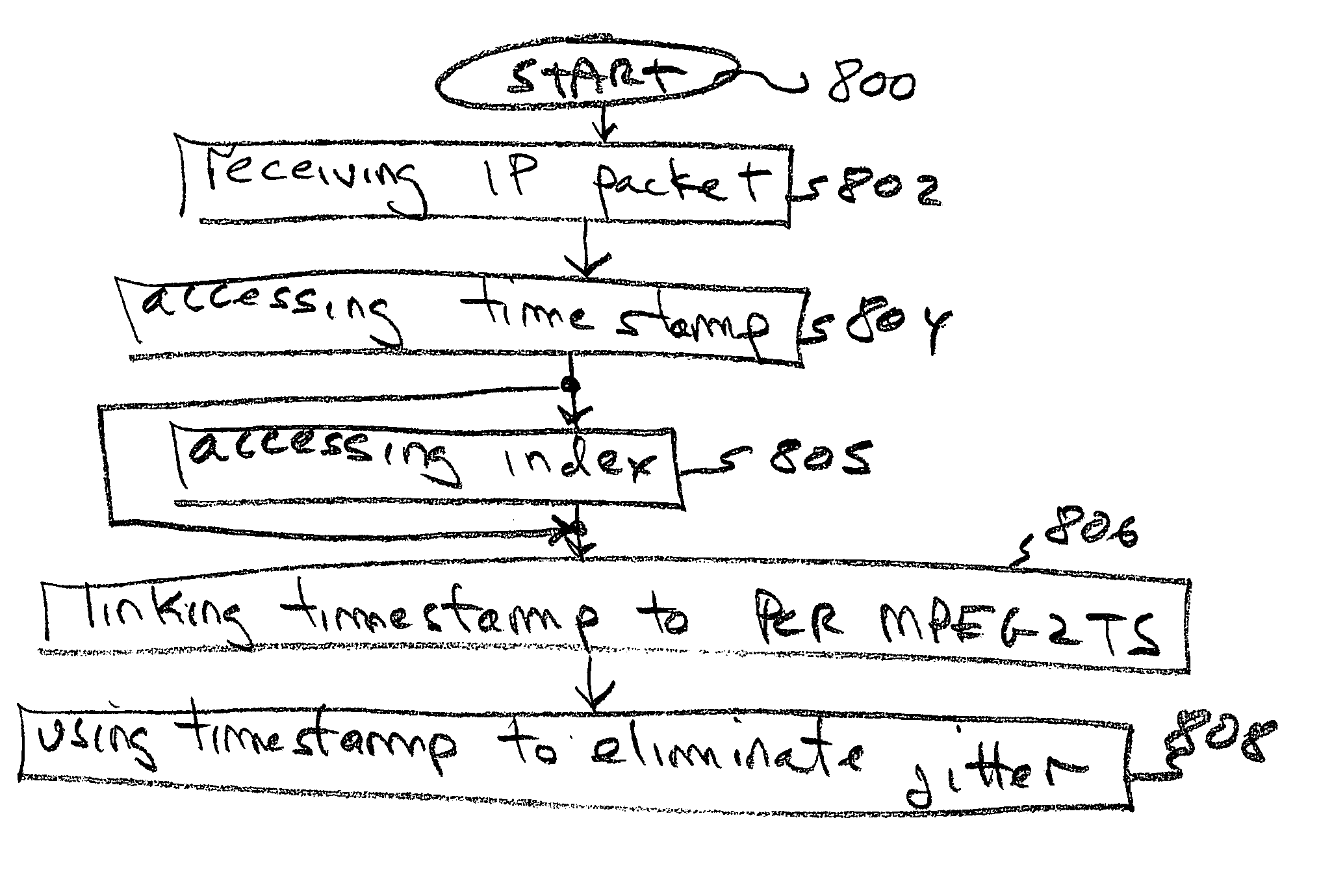
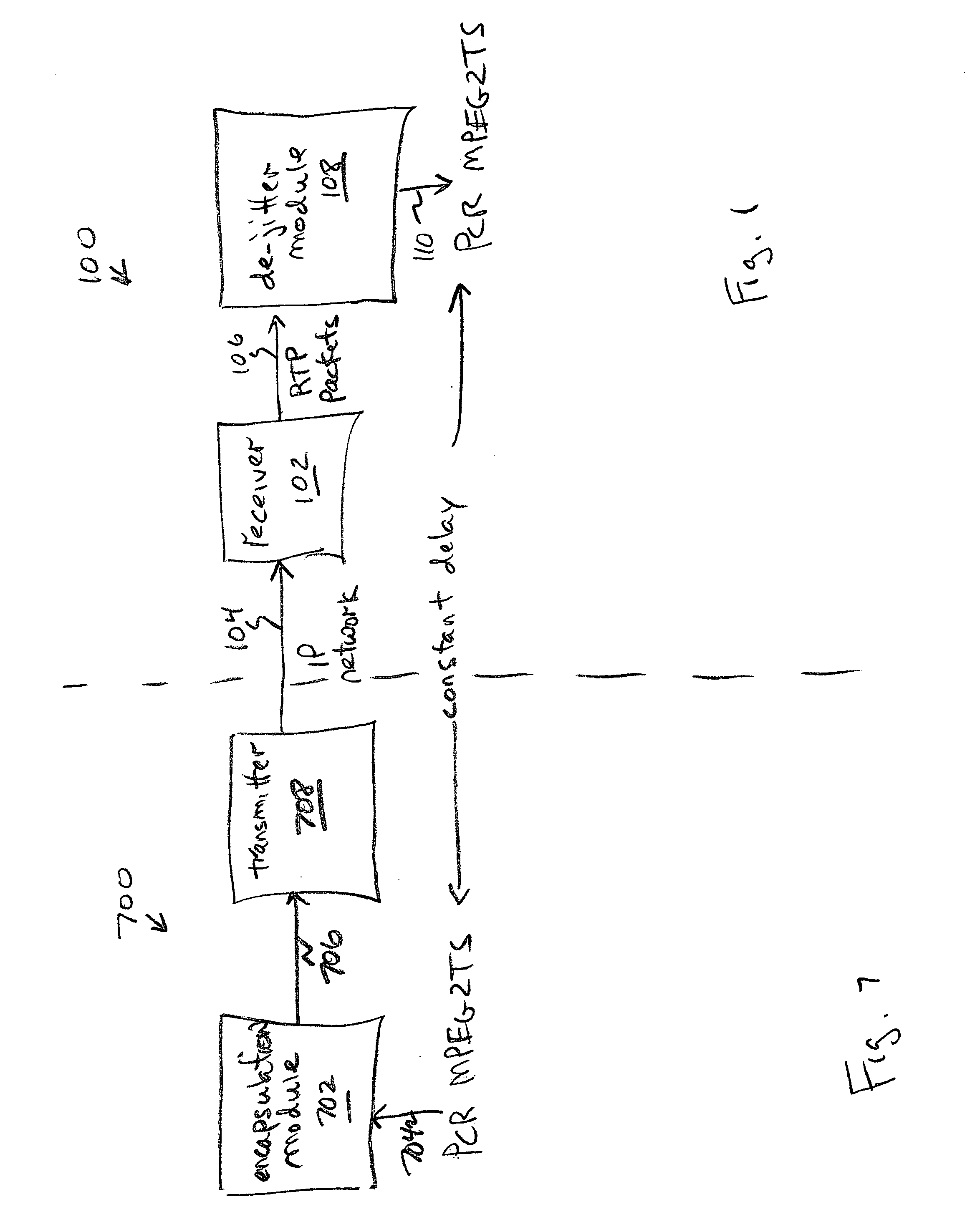
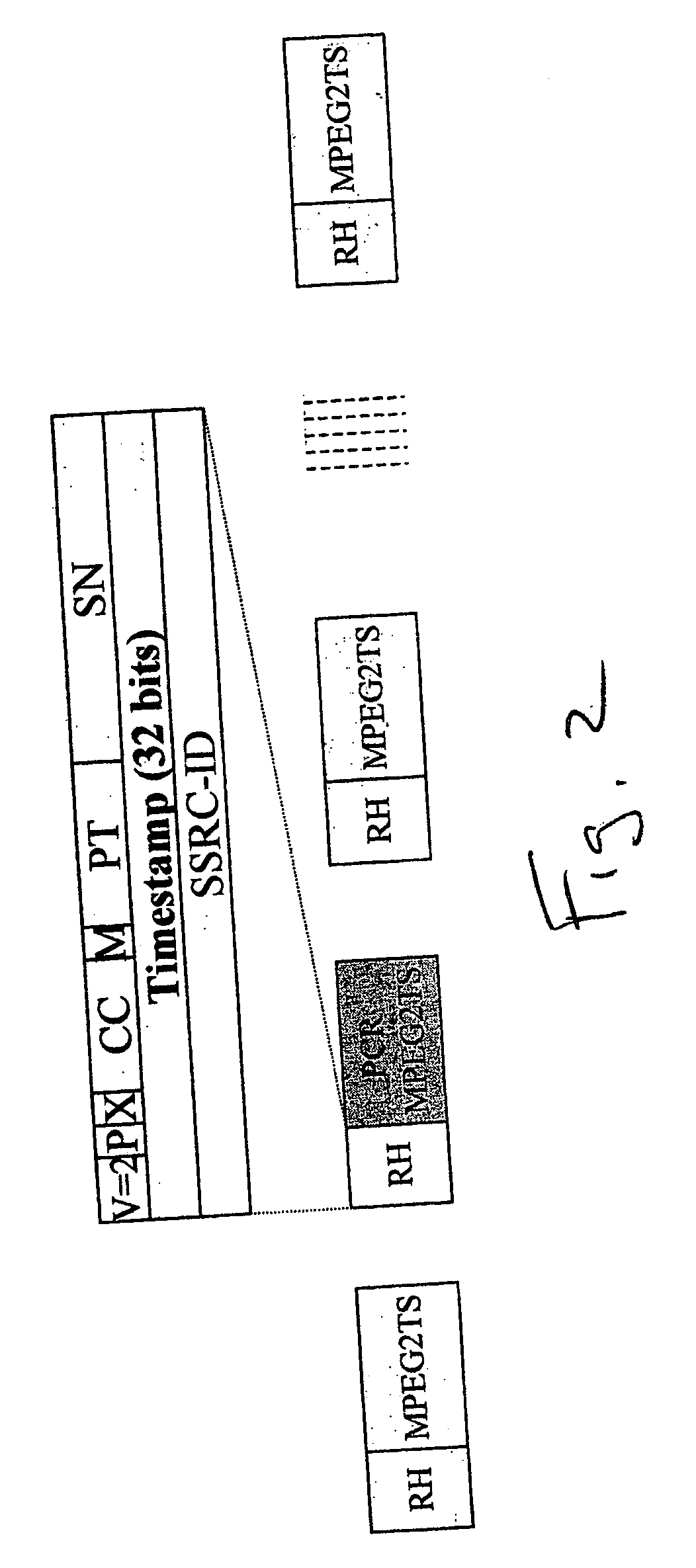
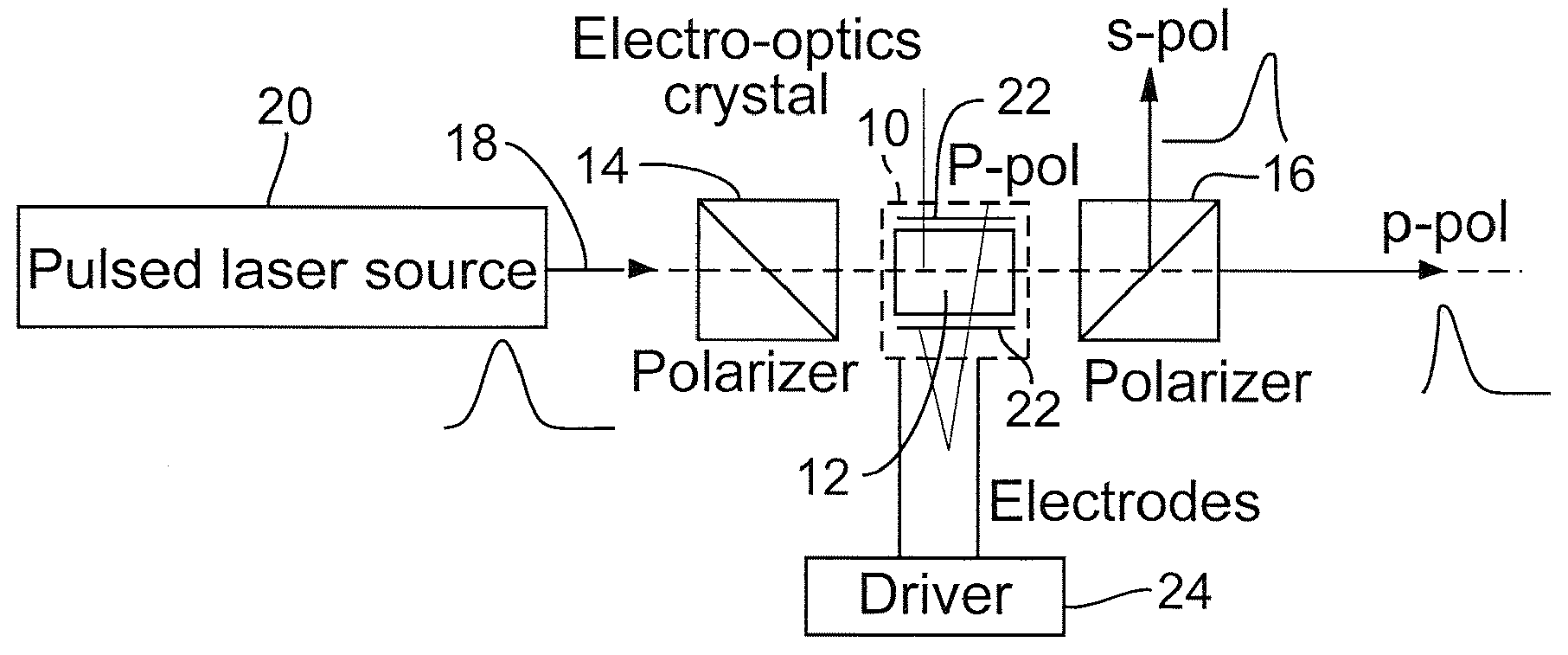
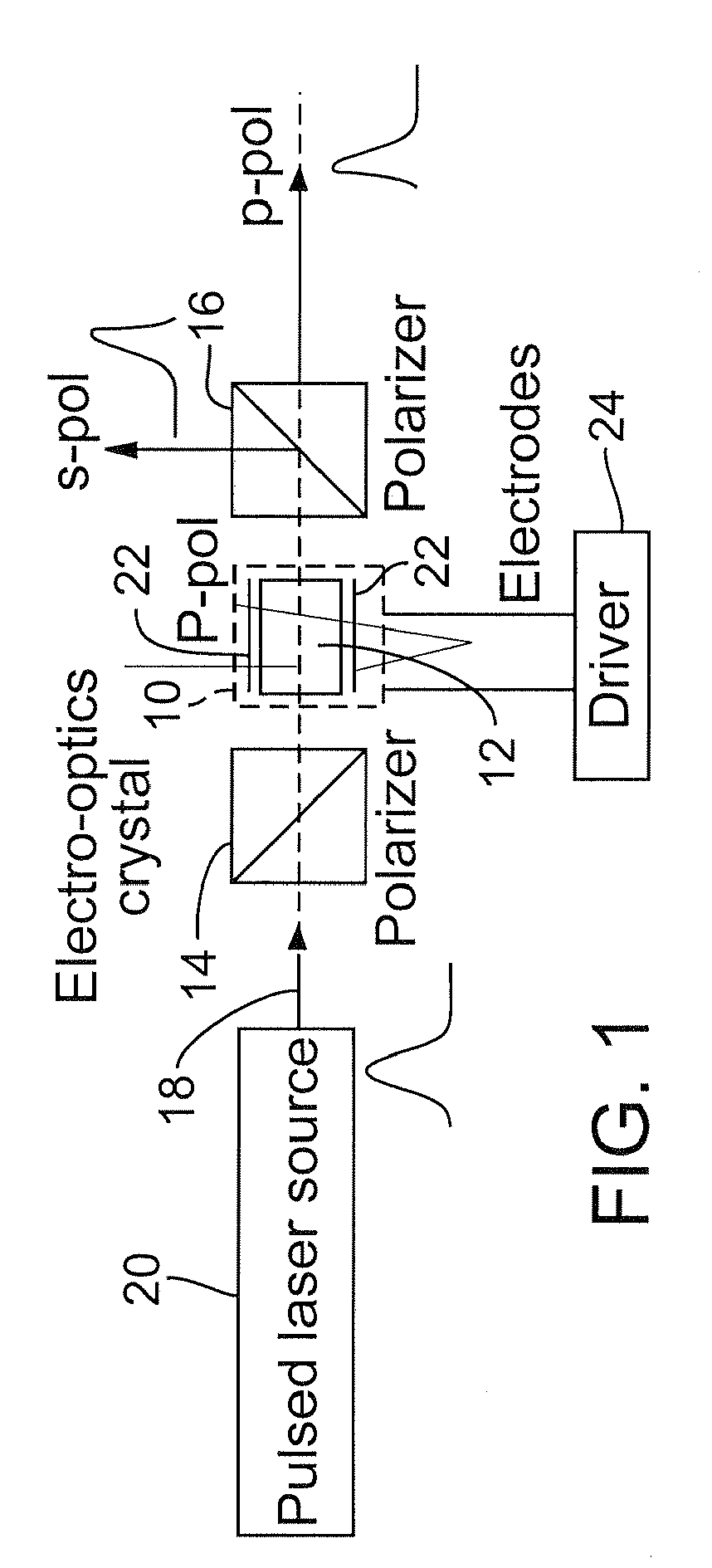
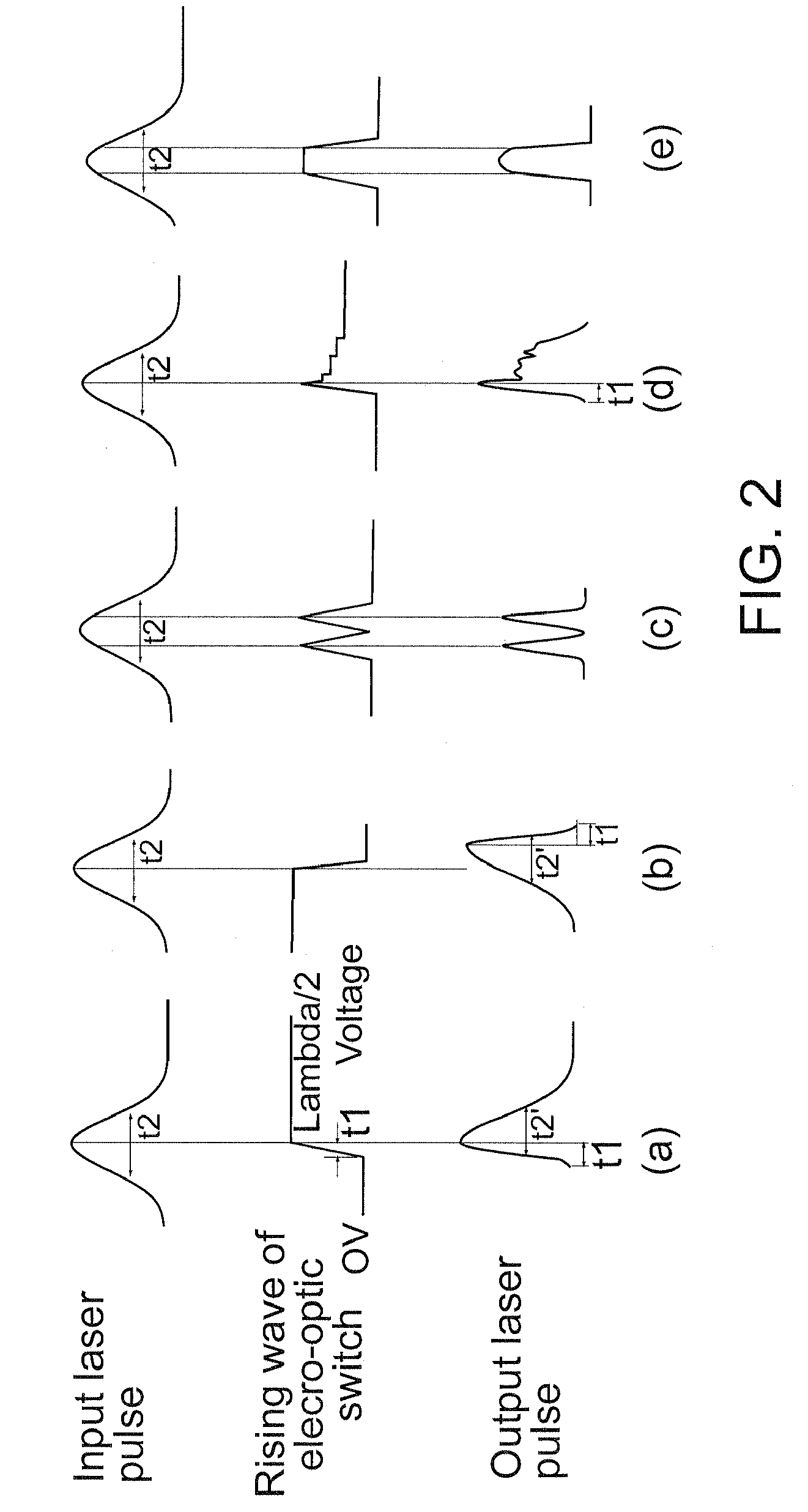
System and method for transporting MPEG2TS in RTP/UDP/IP
InactiveUS20050177643A1Eliminate variable transmission delay jitterError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsProgram clock referenceNanosecond
Systems and methods are provided for receiving and transmitting an MPEG2 transport stream (TS) in a real-time protocol (RTP) / user datagram protocol (UDP) / Internet protocol (IP) packet. The receiving method comprises: receiving an IP packet via an IP network, having a variable transmission delay; accessing a timestamp carried in a RTP packet; linking the timestamp with a program clock reference (PCR) MPEG2TS carried in the RTP packet payload; and, using the timestamp to eliminate variable transmission delay jitter, associated with the PCR MPEG2TS. In one aspect of the method, the timestamp has a resolution of greater than 500 nanoseconds (ns), so that the variable transmission delay jitter, associated with the PCR MPEG2TS can be reduced to a jitter of less than 500 ns.
Owner:SHARP KK
Biosensor and method of making
InactiveUS20050103624A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemical biosensorNanosecond
An electrochemical biosensor with electrode elements that possess smooth, high-quality edges. These smooth edges define gaps between electrodes, electrode traces and contact pads. Due to the remarkable edge smoothness achieved with the present invention, the gaps can be quite small, which provides marked advantages in terms of test accuracy, speed and the number of different functionalities that can be packed into a single biosensor. Further, the present invention provides a novel biosensor production method in which entire electrode patterns for the inventive biosensors can be formed all at one, in nanoseconds—without regard to the complexity of the electrode patterns or the amount of conductive material that must be ablated to form them.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
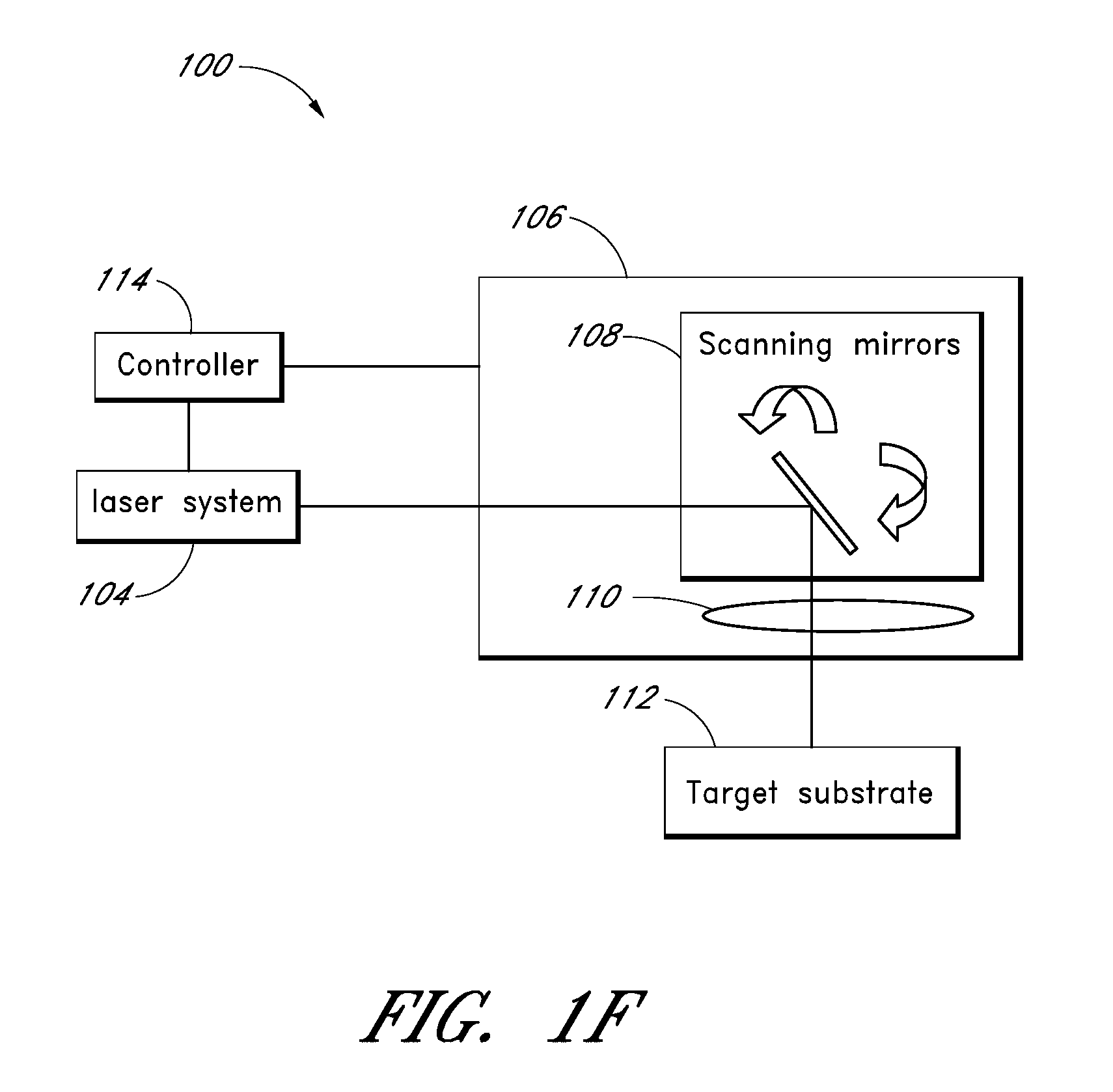
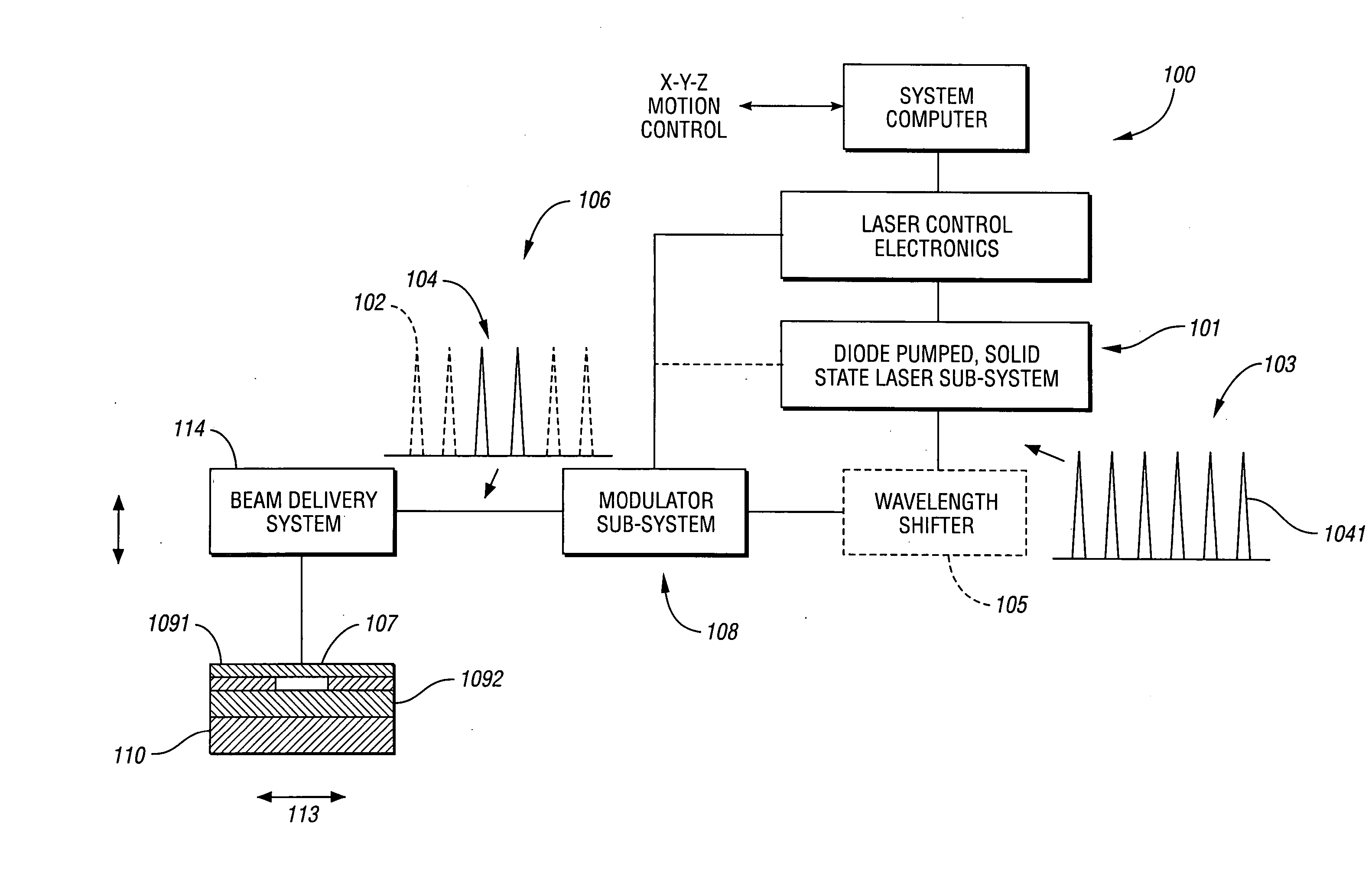
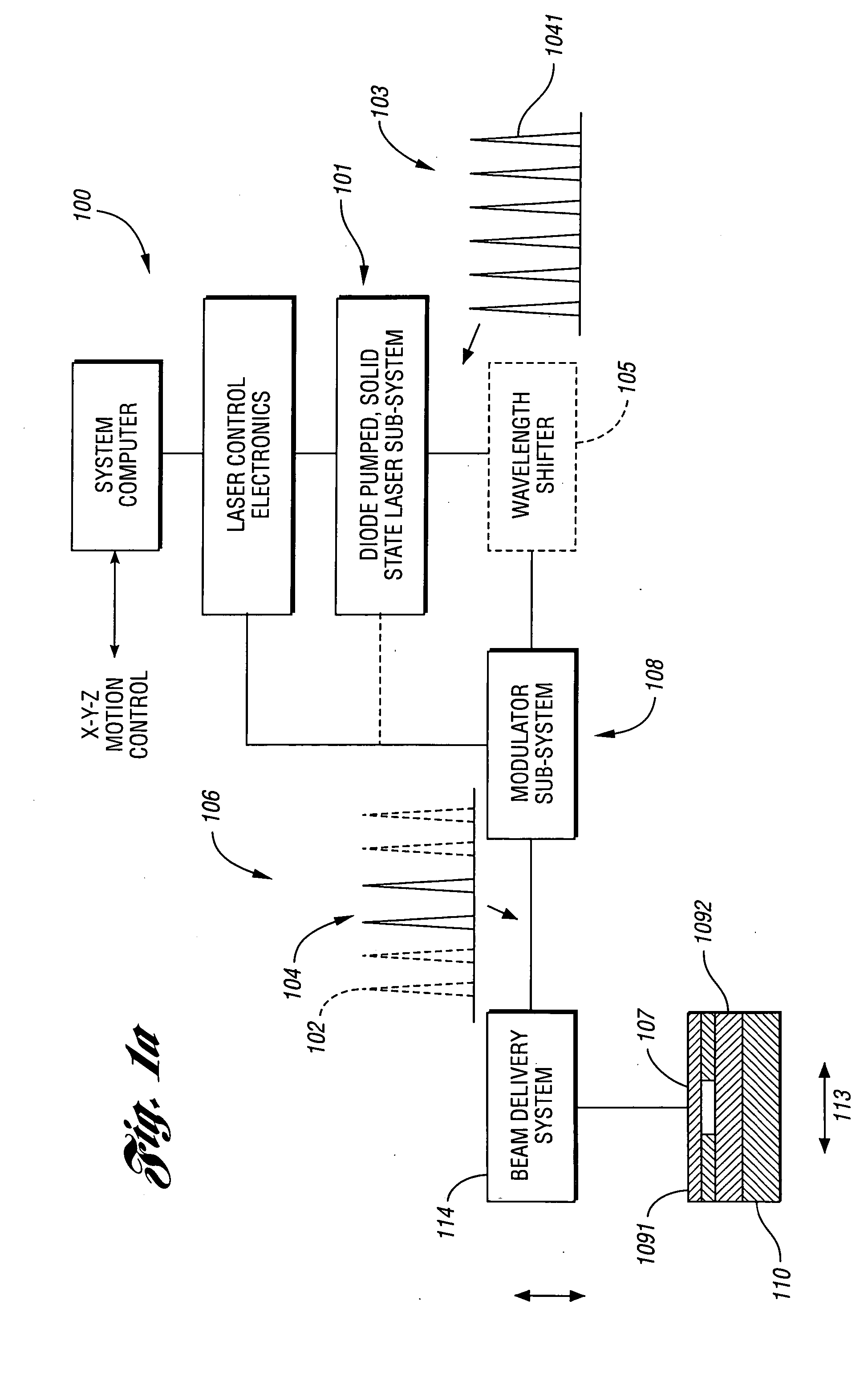
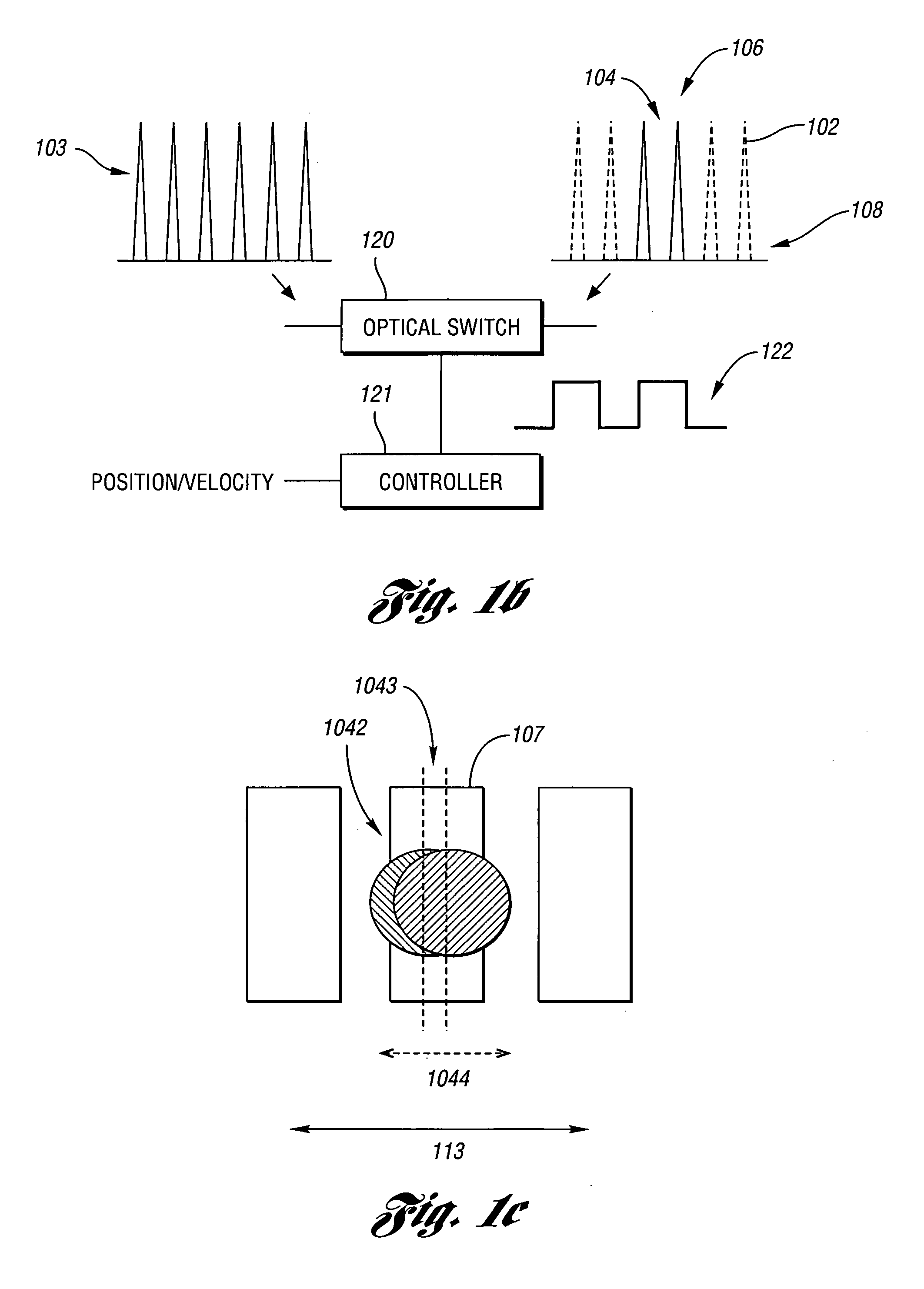
Laser-based material processing methods and systems
ActiveUS20100197116A1Efficient removalAvoid accumulationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesDielectricMaterials processing
Various embodiments may be used for laser-based modification of target material of a workpiece while advantageously achieving improvements in processing throughput and / or quality. Embodiments of a method of processing may include focusing and directing laser pulses to a region of the workpiece at a pulse repetition rate sufficiently high so that material is efficiently removed from the region and a quantity of unwanted material within the region, proximate to the region, or both is reduced relative to a quantity obtainable at a lower repetition rate. In at least one embodiment, an ultrashort pulse laser system may include at least one of a fiber amplifier or fiber laser. Various embodiments are suitable for at least one of dicing, cutting, scribing, and forming features on or within a semiconductor substrate. Workpiece materials may also include metals, inorganic or organic dielectrics, or any material to be micromachined with femtosecond and / or picosecond pulses, and in some embodiments with pulse widths up to a few nanoseconds.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Laser-based system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20040134894A1Quality improvementReduce reflectivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserMicroscopic scale
A laser-based system for processing target material within a microscopic region without causing undesirable changes in electrical or physical characteristics of at least one material surrounding the target material, the system includes a seed laser, an optical amplifier, and a beam delivery system. The seed laser for generating a sequence of laser pulses having a first pre-determined wavelength. The optical amplifier for amplifying at least a portion of the sequence of pulses to obtain an amplified sequence of output pulses. The beam delivery system for delivering and focusing at least one pulse of the amplified sequence of pulses onto the target material. The at least one output pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond. The pulse duration being within a thermal processing range. The at least one focused output pulse having sufficient power density at a location within the target material to reduce the reflectivity of the target material and efficiently couple the focused output into the target material to remove the target material.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS CORP
Method of deposition of thin films of amorphous and crystalline microstructures based on ultrafast pulsed laser deposition
InactiveUS6312768B1Improve surface qualityImprove efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingMacroscopic scaleCarbon nanotube
Powerful nanosecond-range lasers using low repetition rate pulsed laser deposition produce numerous macroscopic size particles and droplets, which embed in thin film coatings. This problem has been addressed by lowering the pulse energy, keeping the laser intensity optional for evaporation, so that significant numbers of the macroscopic particles and droplets are no longer present in the evaporated plume. The result is deposition of evaporated plume on a substrate to form thin film of very high surface quality. Preferably, the laser pulses have a repetition rate to produce a continuous flow of evaporated material at the substrate. Pulse-range is typically picosecond and femtosecond and repetition rate kilohertz to hundreds of megahertz. The process may be carried out in the presence of a buffer gas, which may be inert or reactive, and the increased vapour density and therefore the collision frequency between evaporated atoms leads to the formation of nanostructured materials of increasing interest, because of their peculiar structural, electronic and mechanical properties. One of these is carbon nanotubes, which is a new form of carbon belonging to the fullerene (C60) family. Carbon nanotubes are seamless, single or multishell co-axial cylindrical tubules with or without dome caps at the extremities. Typically diameters range from 1 nm to 50 nm with a length >1 mum. The electronic structure may be either metallic or semiconducting without any change in the chemical bonding or adding of dopant. In addition, the materials have application to a wide range of established thin film applications.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
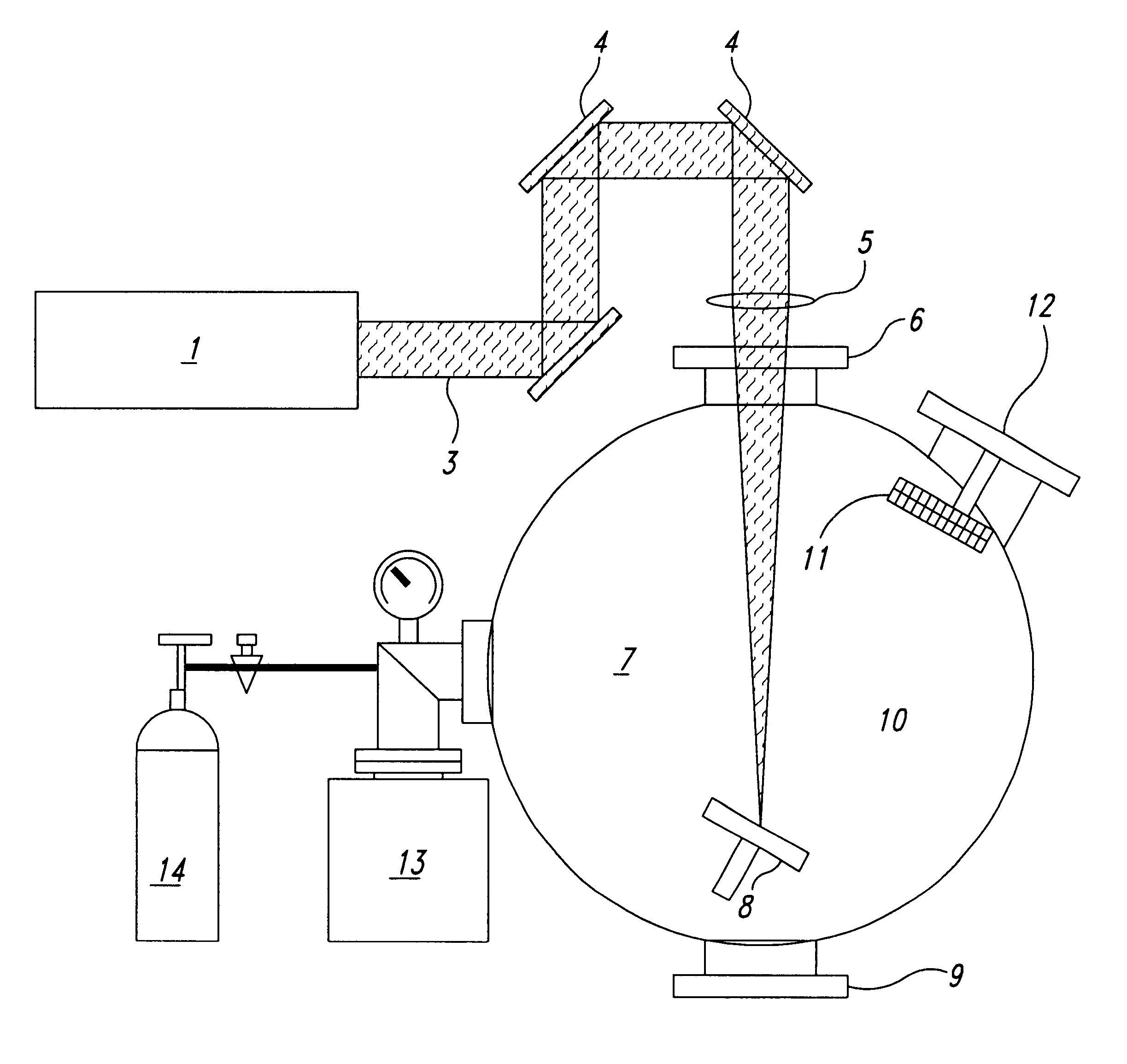
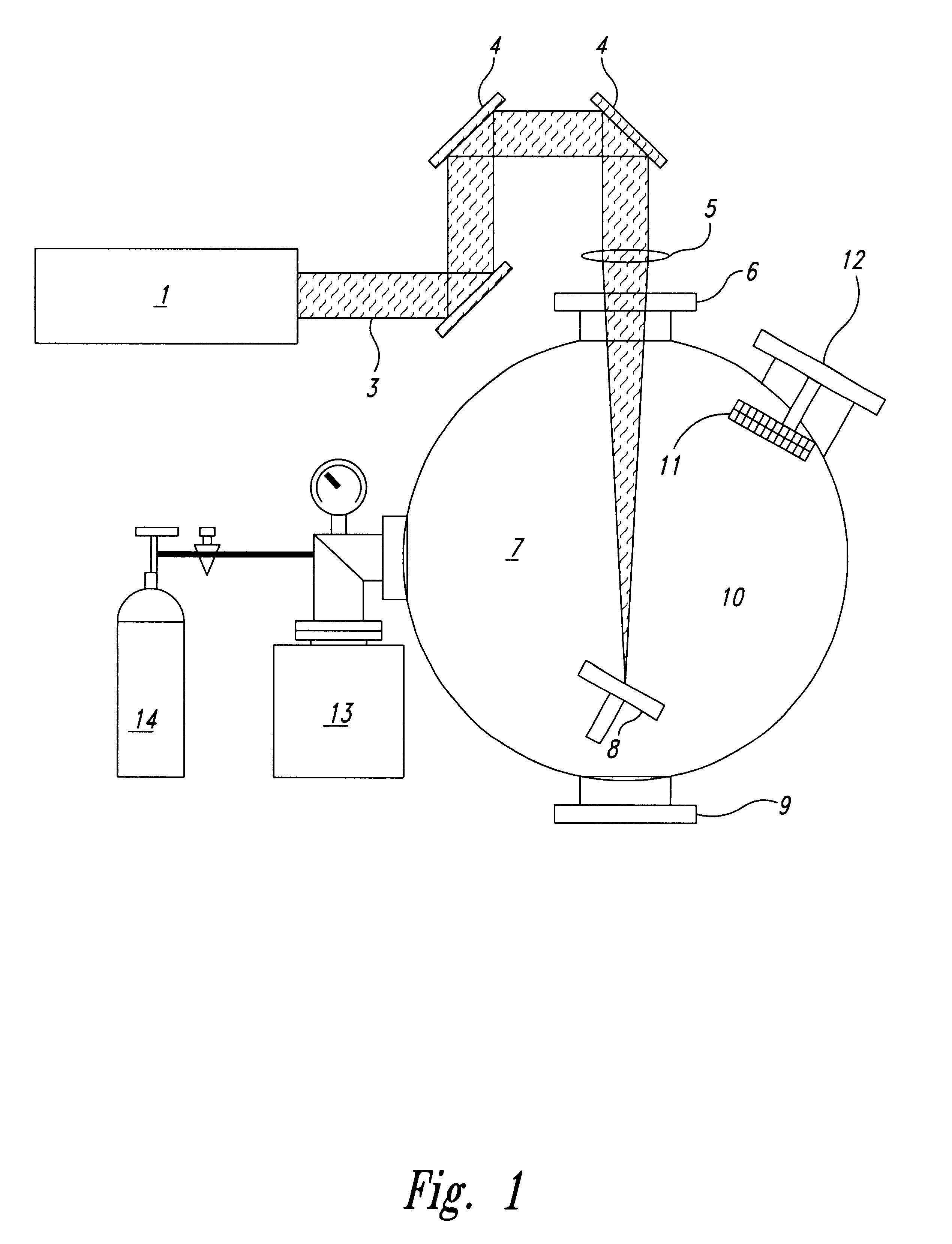
Ophthalmic surgery method using non-contact scanning laser
InactiveUSRE37504E1Low-powerLow-cost and effectiveLaser surgeryDiagnosticsSystem parametersOphthalmic surgery
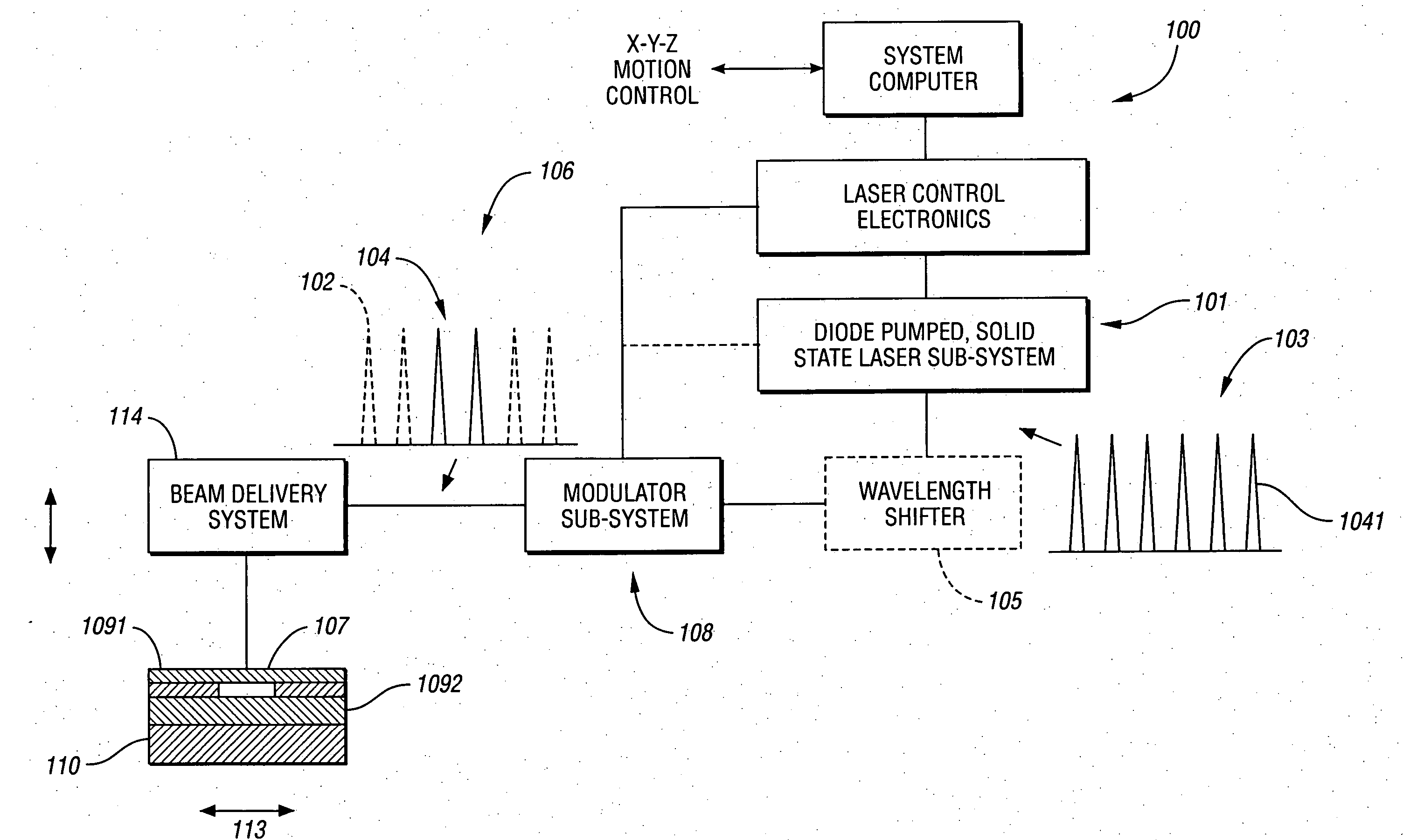
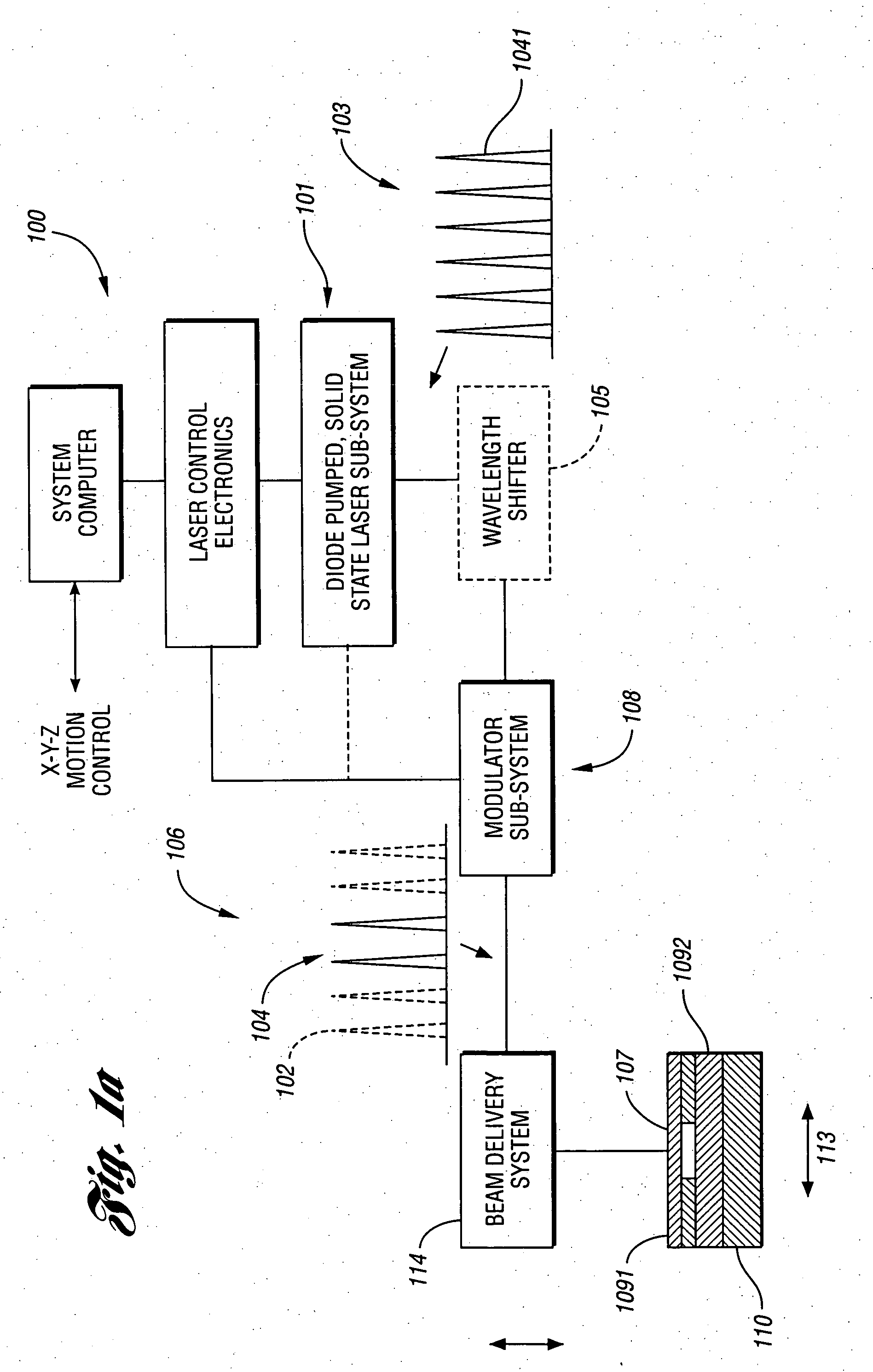
A refractive laser surgery process is disclosed for using compact, low-cost ophthalmic laser systems which have computer-controlled scanning with a non-contact delivery device for both photo-ablation and photo-coagulation in corneal reshaping. The basic laser systems may include flash-lamp and diode pumped UV solid state lasers (193-215 nm), compact excimer laser (193 nm), free-running Er:glass (1.54 microns), Ho:YAG (2.1 microns), Q-switched Er:YAG (2.94 microns), and tunable IR lasers, (750-1100) nm and (2.5-3.2) microns. The advantages of the non-contact, scanning device used in the process over other prior art lasers include being safer, reduced cost, more compact and more precise and with greater flexibility. The theory of beam overlap and of ablation rate and coagulation patterns is also disclosed for system parameters. Lasers are selected with energy of (0.01-10) mJ, repetition rate of (1-10,000), pulse duration of 0.01 nanoseconds to a few hundreds of microseconds, and with spot size of (0.05-2) mm for use with refractive laser surgery.
Owner:LASERSIGHT TECH
Waveguide architecture, waveguide devices for laser processing and beam control, and laser processing applications
InactiveUS20030161375A1Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionEngineeringWaveguide
Methods and systems for laser-based processing of materials are disclosed wherein a scalable laser architecture, based on planar waveguide technology, provides for pulsed laser micromachining applications while supporting higher average power applications like laser welding and cutting. Various embodiments relate to improvements in planar waveguide technology which provide for stable operation at high powers with a reduction in spurious outputs and thermal effects. At least one embodiment provides for micromachining with pulsewidths in the range of femtoseconds to nanoseconds. In another embodiment, 100W or greater average output power operation is provided for with a diode-pumped, planar waveguide architecture.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS LTD
Laser-based method and system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20040134896A1Quality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserNanosecond
A laser-based method of removing a target link structure of a circuit fabricated on a substrate includes generating a pulsed laser output at a pre-determined wavelength less than an absorption edge of the substrate. The laser output includes at least one pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond, the pulse duration being within a thermal laser processing range. The method also includes delivering and focusing the laser output onto the target link structure. The focused laser output has sufficient power density at a location within the target structure to reduce the reflectivity of the target structure and efficiently couple the focused laser output into the target structure to remove the link without damaging the substrate.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
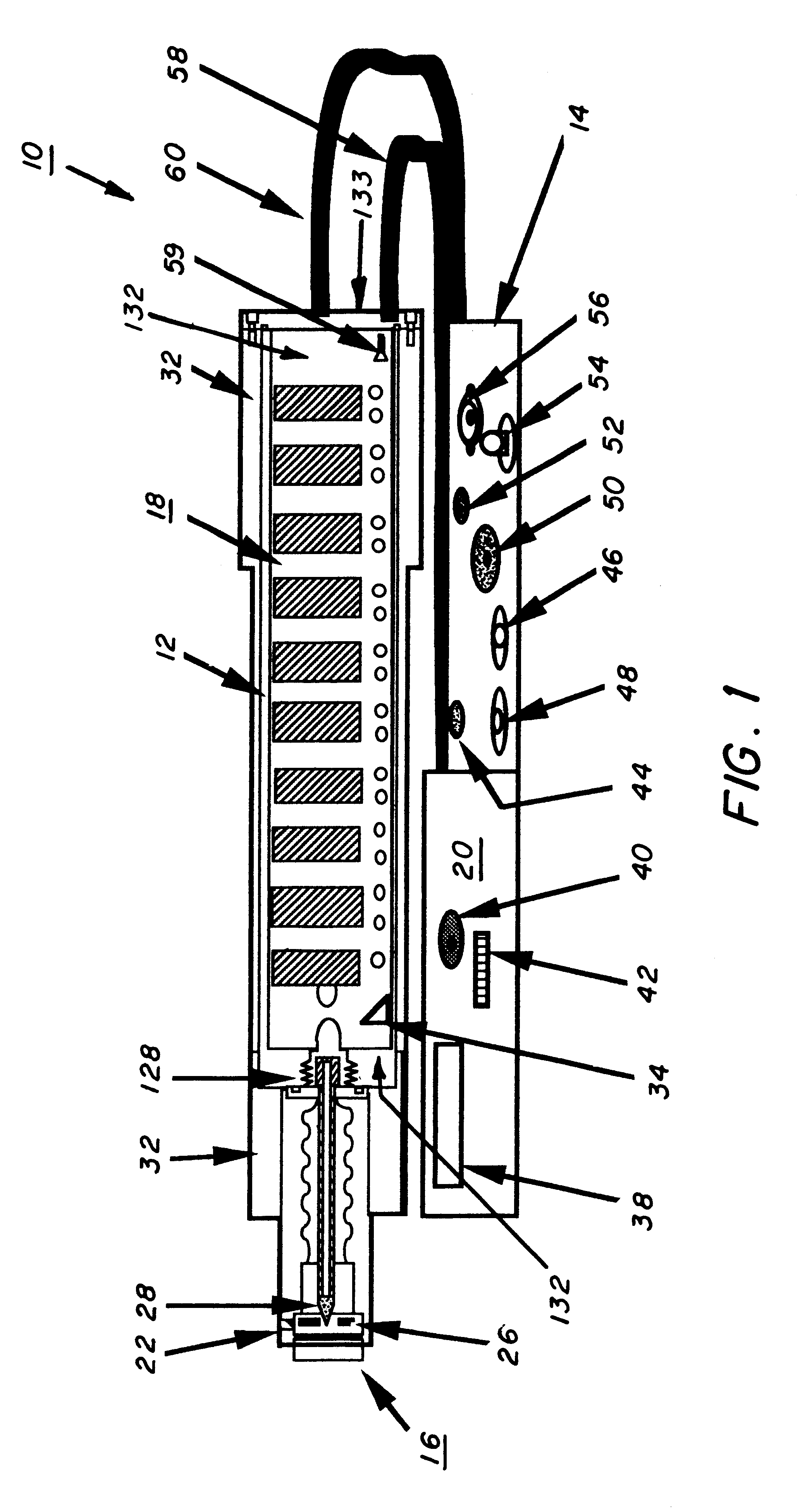
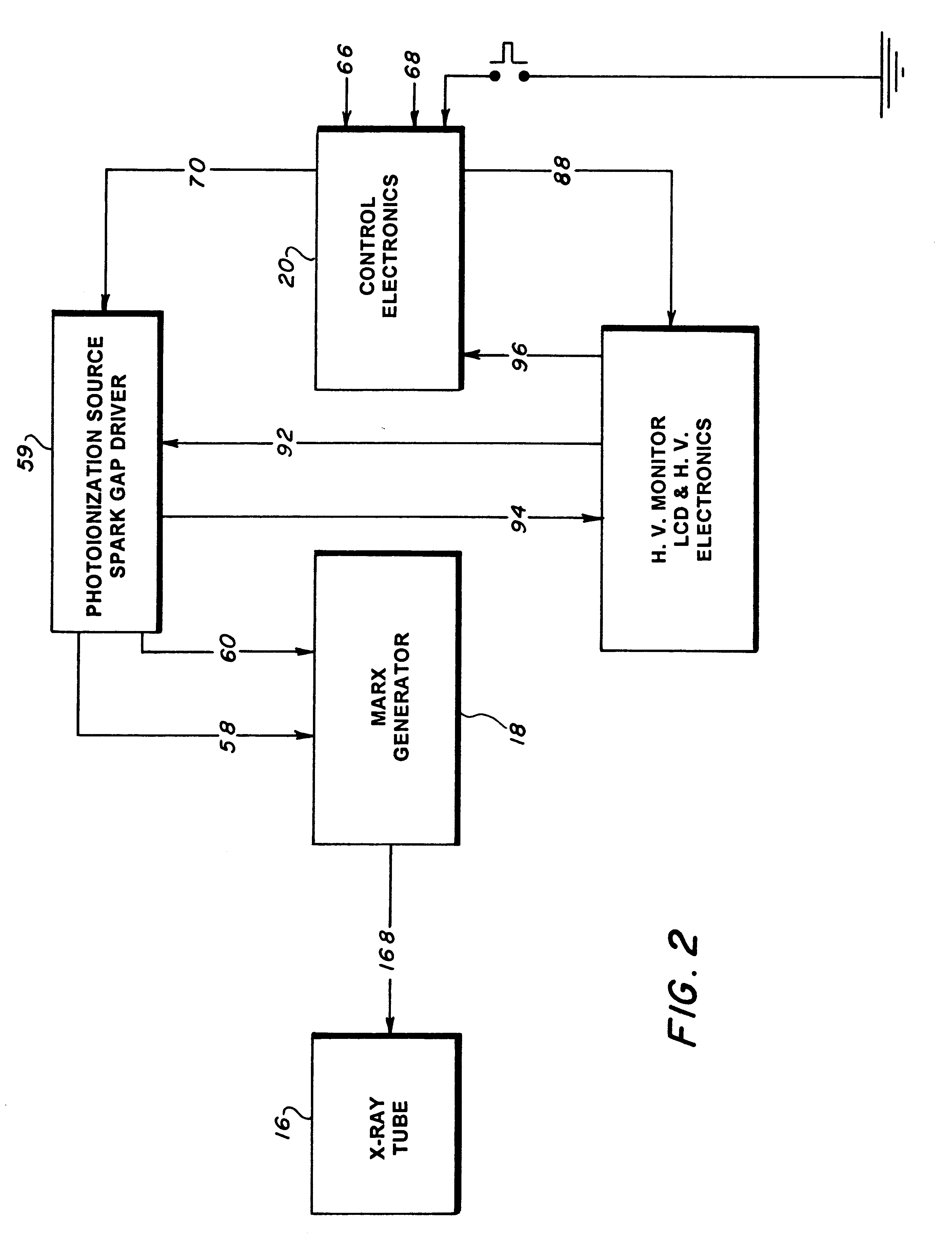
Mobile X-ray unit
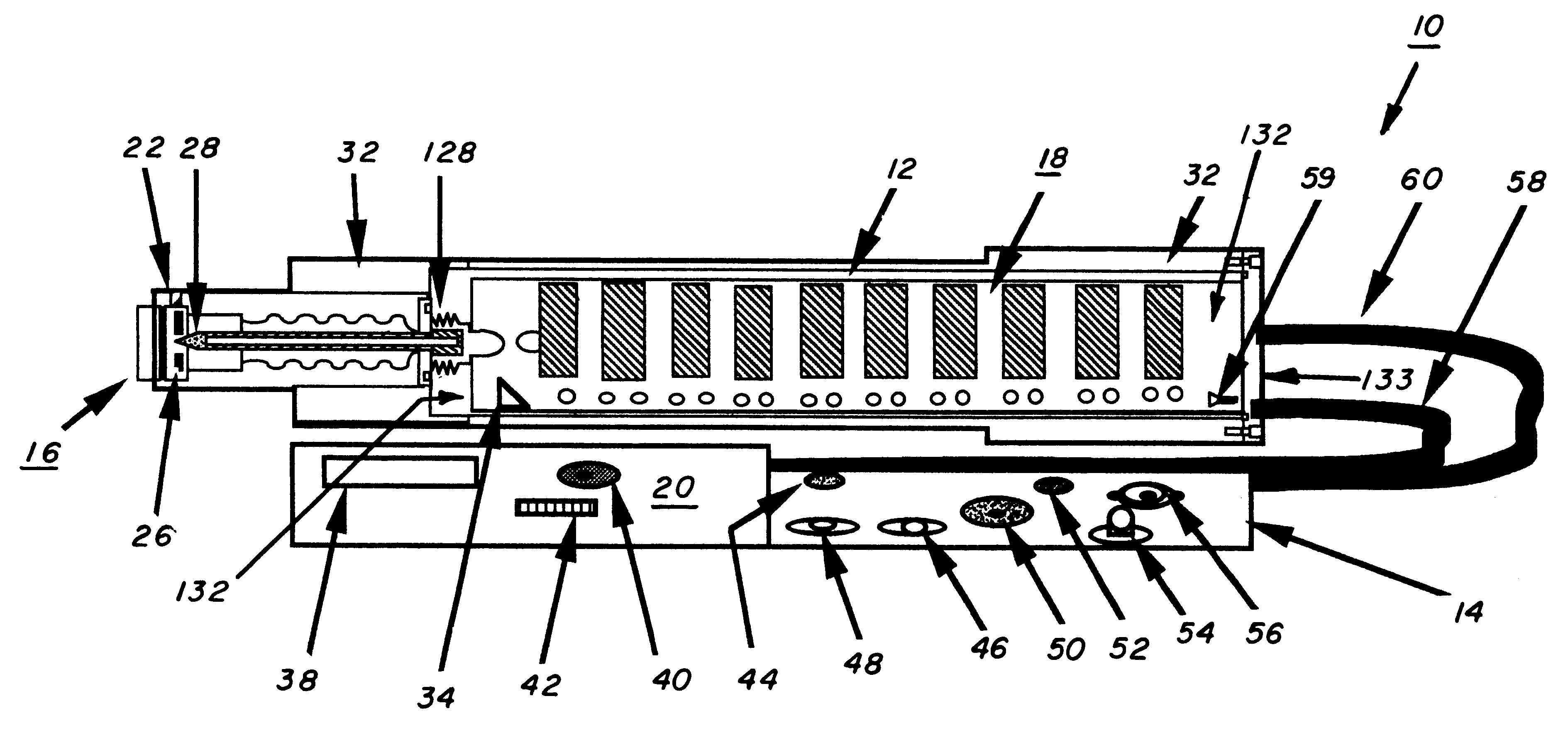
A portable X-ray unit, of a relatively light-weight, occoping a volume of less then one-half a cubic foot containing an x-ray head assembly, a unique Marx generator, a plurality of spark-gap switches and control electronics is disclosed. The Marx generator allows for the development of a relatively high voltage in excess of 100 kV, yet allows for the discharge thereof within the nanosecond range. The Marx generator is enclosed by an acrylic insulator that cooperates with an aluminum enclosure, which functions as a return current path for the capacitors in the Marx generator and also as a shield against the escape of electromagnetic radiation from the pulsed x-ray unit. The Marx generator and spark-gap switches are confined within the pressurized chamber that may contain nitrogen gas to reduce the separation of the gap in the spark-gap switches.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Laser based material processing methods and scalable architecture for material processing
InactiveUS6738396B2Improve stabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionPower applicationNanosecond
Methods and systems for laser-based processing of materials are disclosed wherein a scalable laser architecture, based on planar waveguide technology, provides for pulsed laser micromachining applications while supporting higher average power applications like laser welding and cutting. Various embodiments relate to improvements in planar waveguide technology which provide for stable operation at high powers with a reduction in spurious outputs and thermal effects. At least one embodiment provides for micromachining with pulsewidths in the range of femtoseconds to nanoseconds. In another embodiment, 100W or greater average output power operation is provided for with a diode-pumped, planar waveguide architecture.
Owner:THE GSI GRP LLC
High power optical apparatus employing large-mode-area, multimode, gain-producing optical fibers
ActiveUS20080180787A1Promote absorptionIncrease brightnessExcitation process/apparatusCoupling light guidesFiberNanosecond
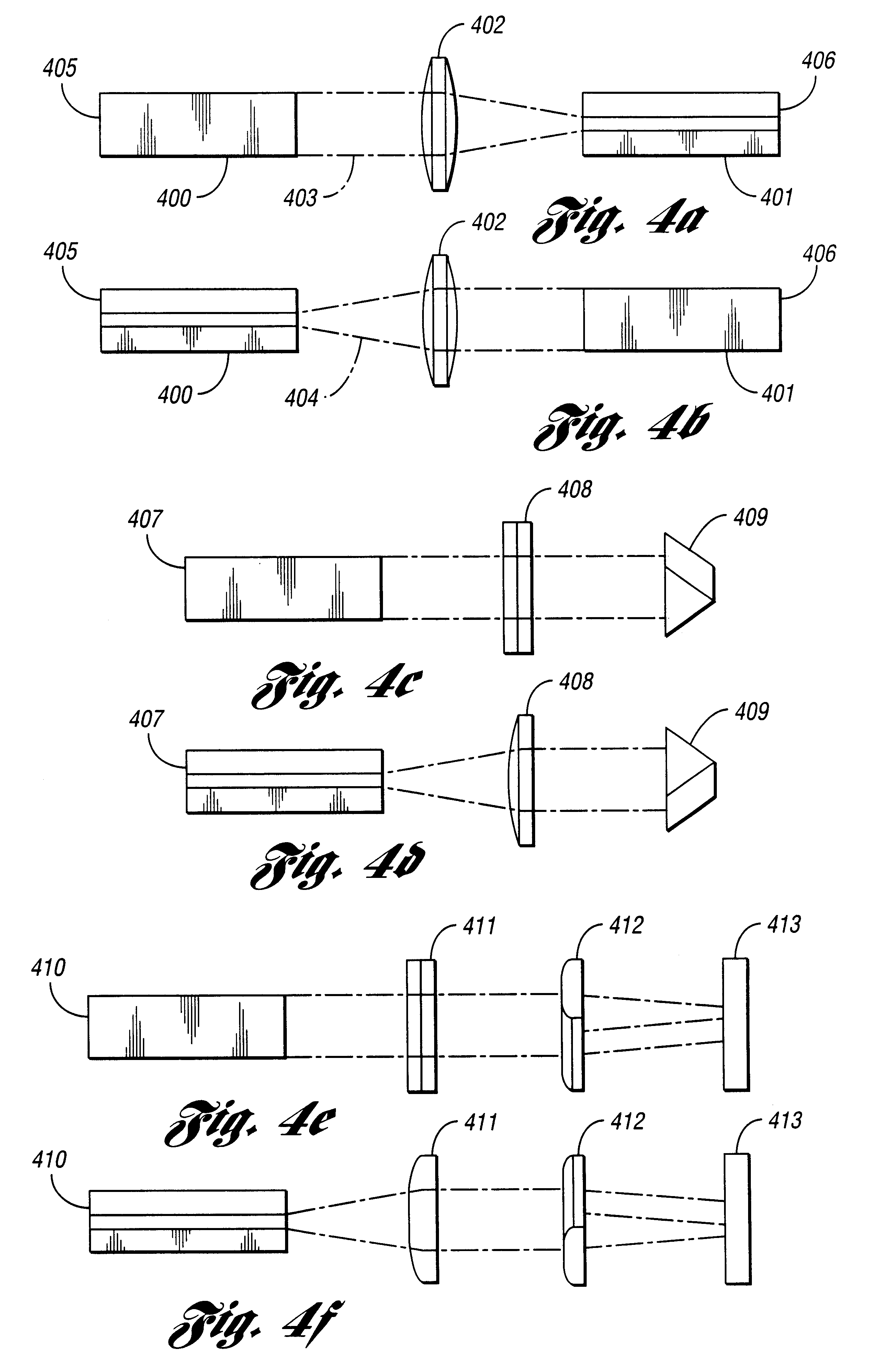
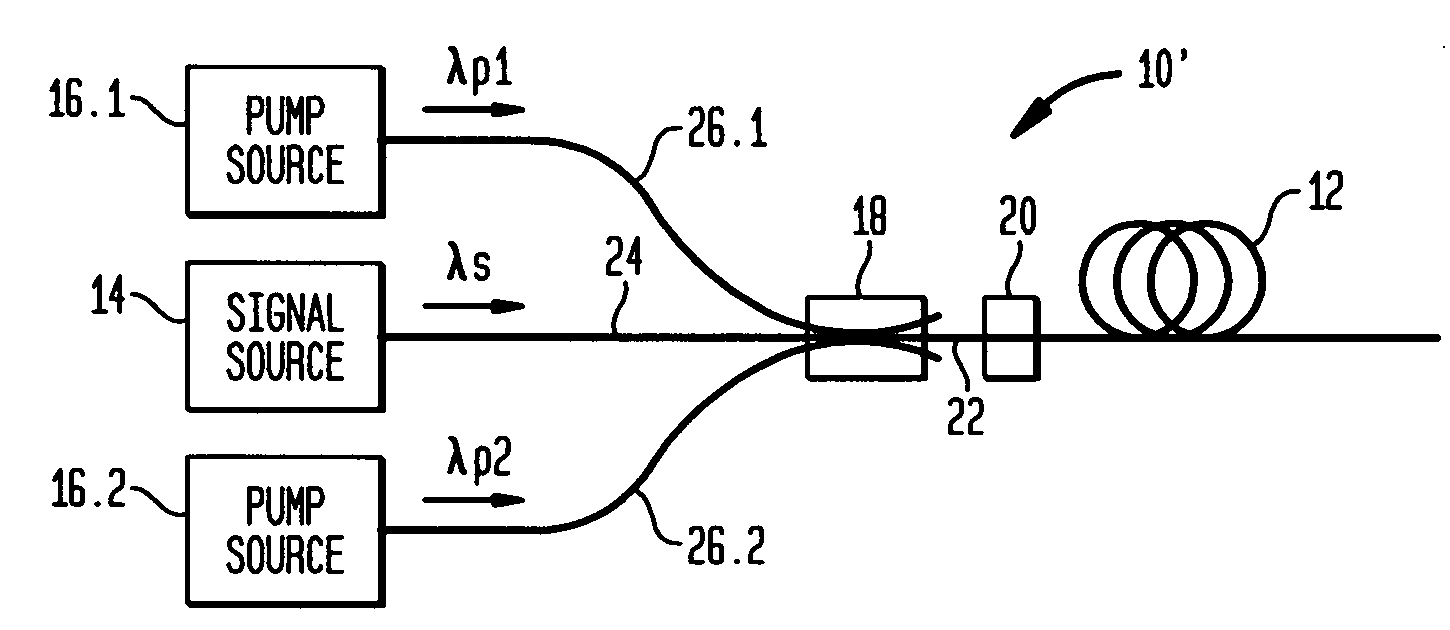
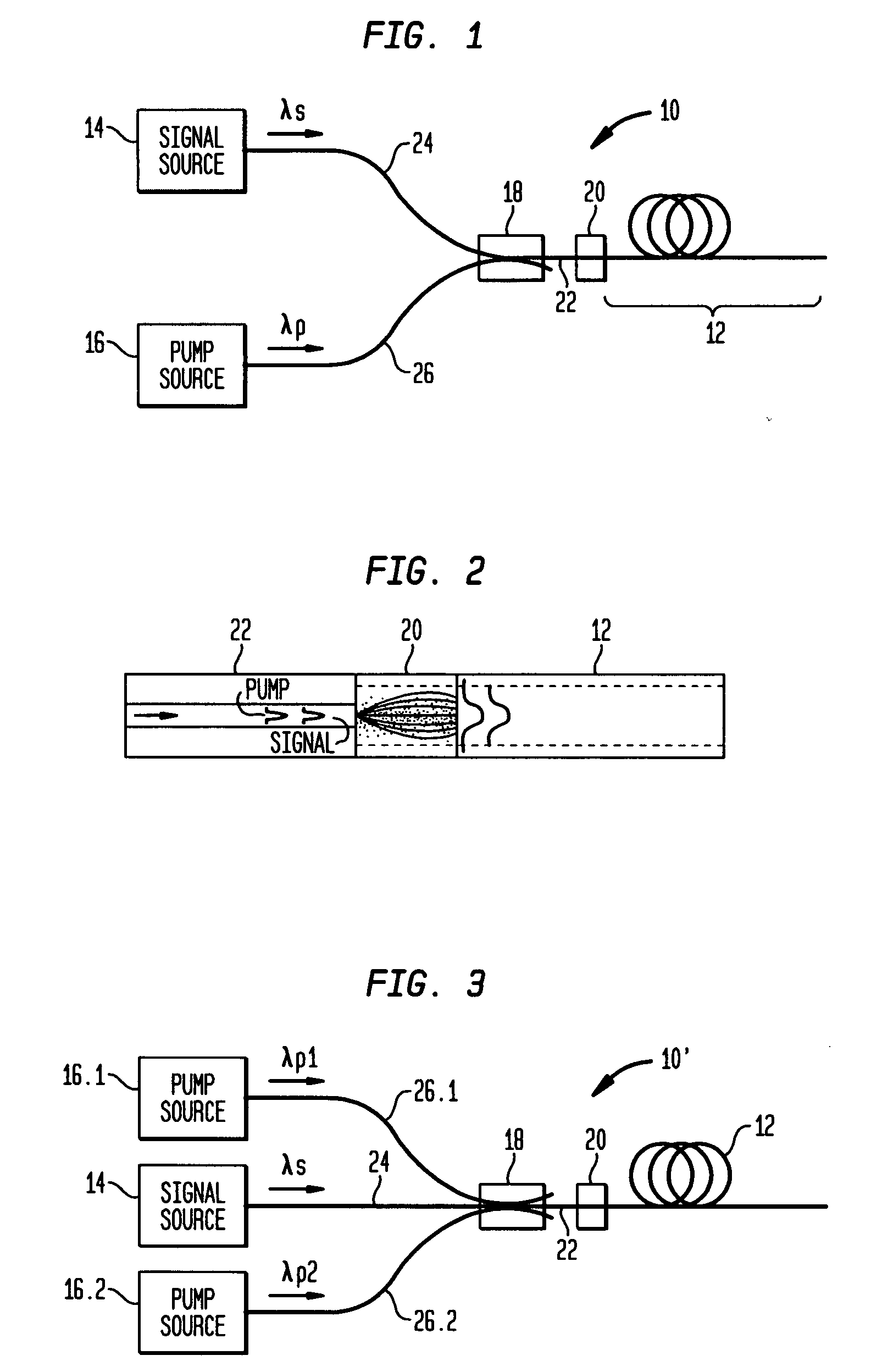
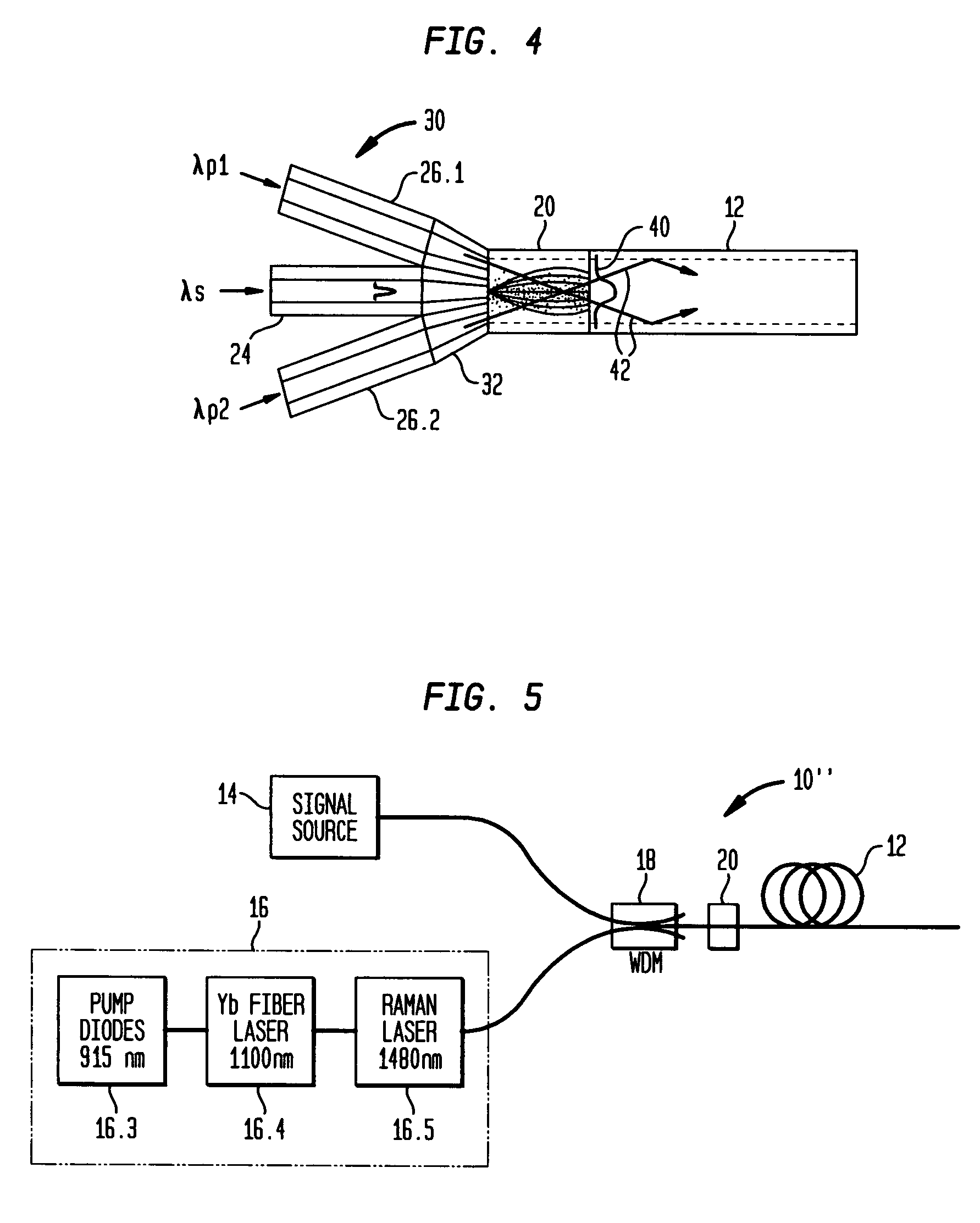
Optical apparatus includes a multimode, gain-producing fiber for providing gain to signal light propagating in the core of the fiber, and a pump source for providing pump light that is absorbed in the core, characterized in that (i) the pump source illustratively comprises a low brightness array of laser diodes and a converter for increasing the brightness of the pump light, (ii) the pump light is coupled directly into the core, and (iii) the area of the core exceeds approximately 350 μm2. In one embodiment, the signal light propagates in a single mode, and the pump light co-propagates in at least the same, single mode, both in a standard input fiber before entering the gain-producing fiber, and a mode expander is disposed between the input fiber and the gain-producing fiber. In another embodiment, multiple pumps are coupled into the core of the gain-producing fiber. The pumps may generate light of the same wavelength or of different wavelengths. In accordance with a particular embodiment of our invention, we have demonstrated amplification of nanosecond optical pulses at 1545 nm in a single clad Er-doped fiber having a core area of 875 μm2; the core was pumped by a high brightness Raman laser at 1480 nm; and the pulses had a record peak power of several hundred kW.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
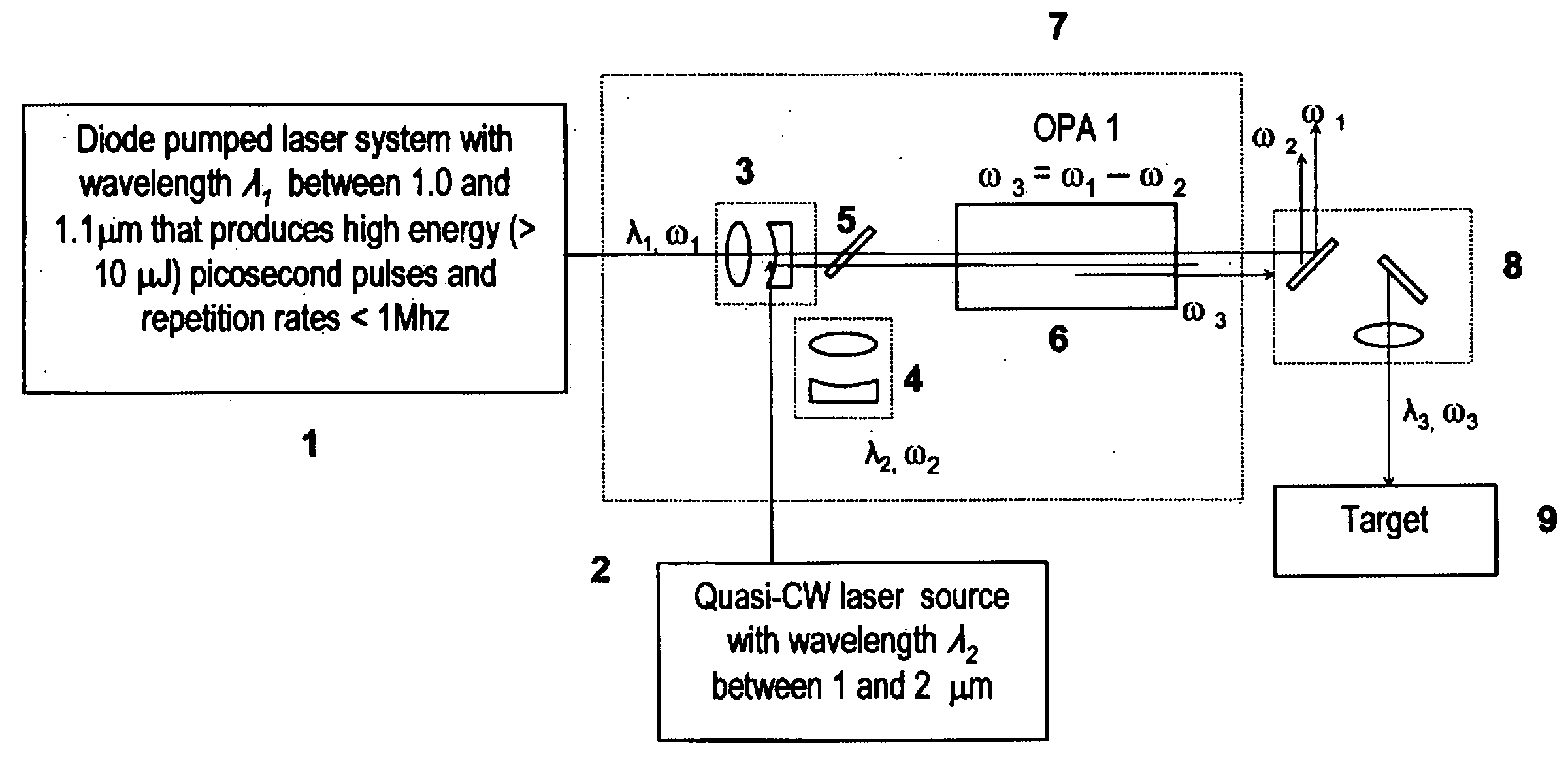
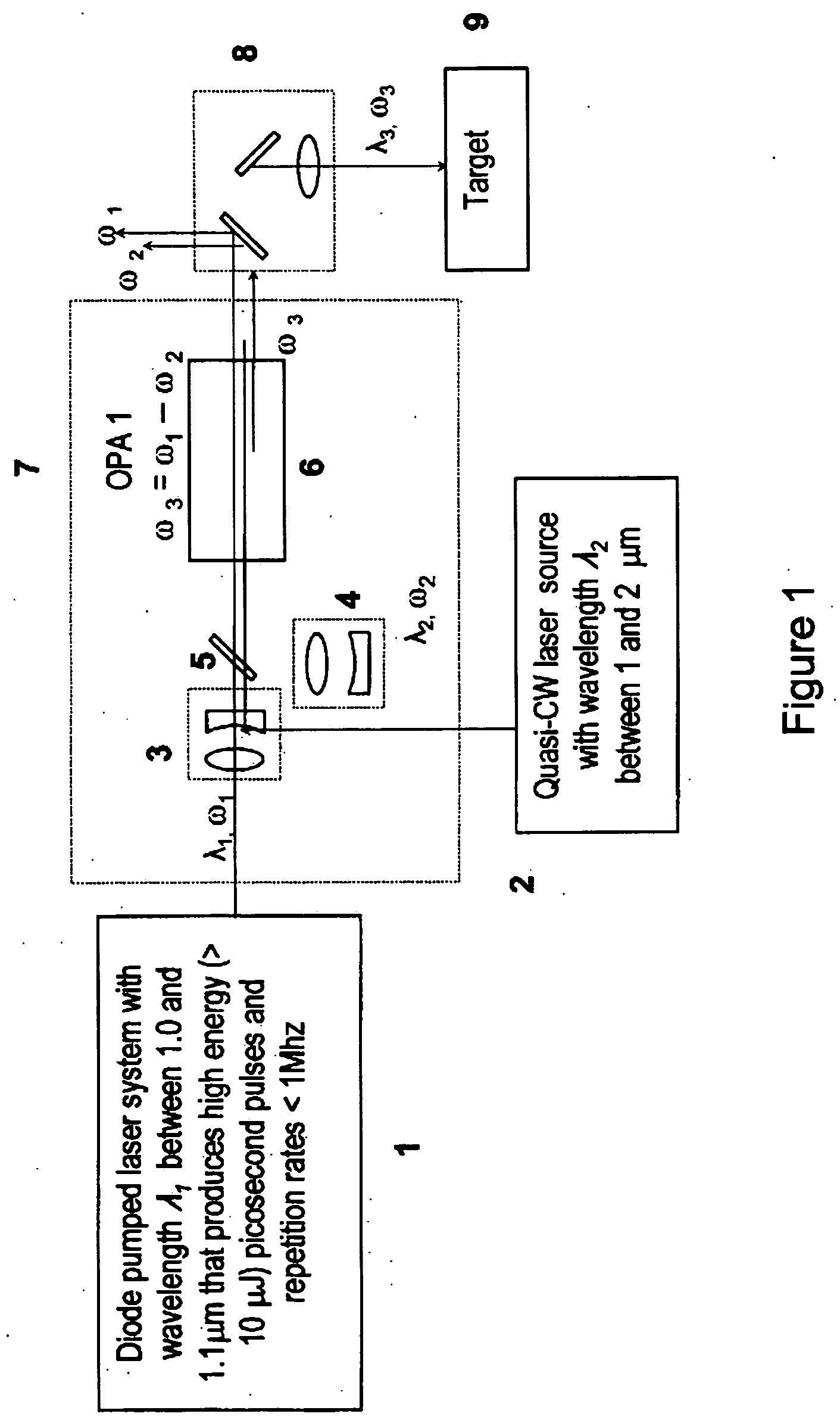
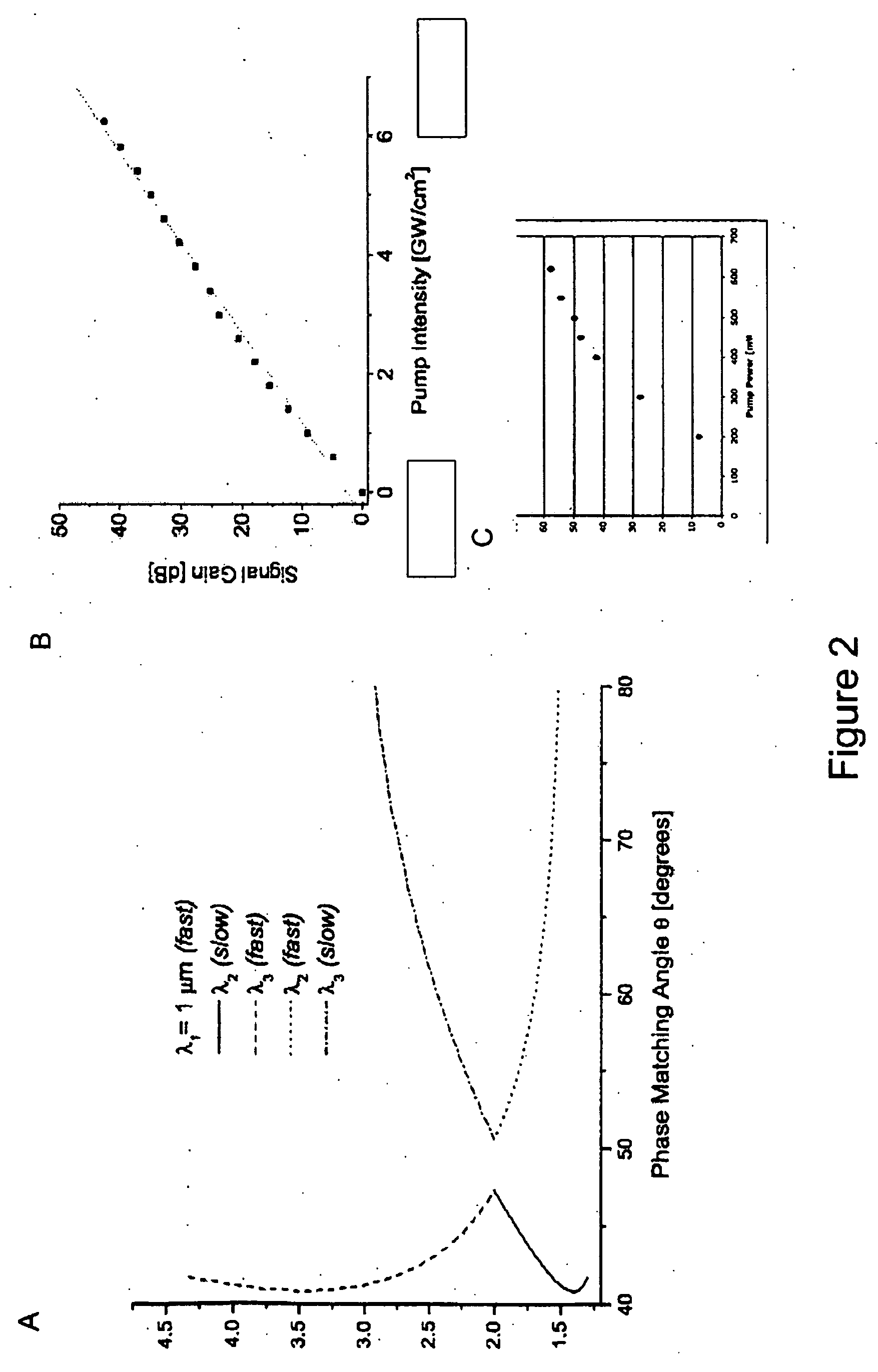
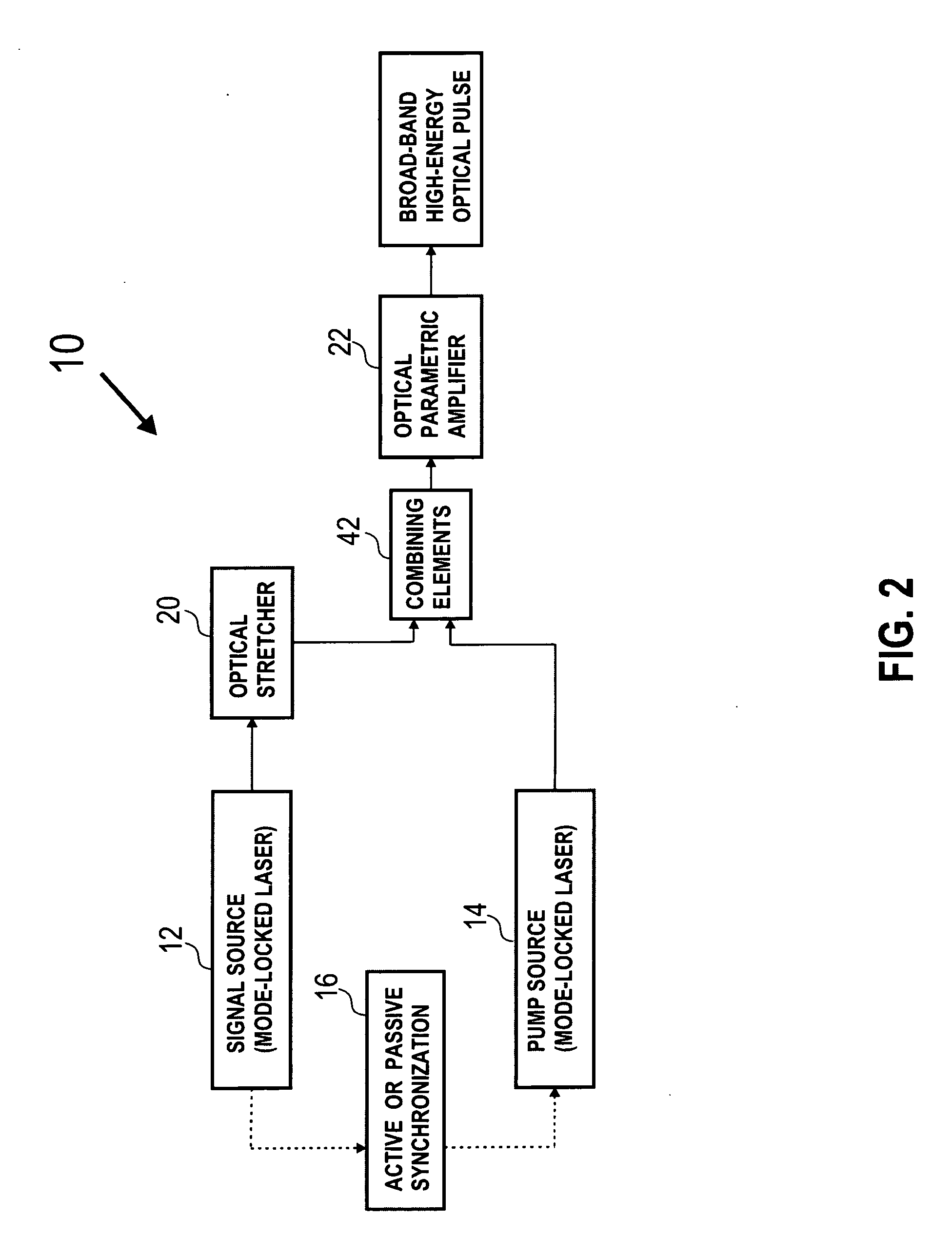
Laser system for generation of high-power sub-nanosecond pulses with controlable wavelengths in 2-15 mum region
ActiveUS20060153254A1Big spaceSubstantial temporal overlapLaser using scattering effectsSurgical instrument detailsSystems designHigh energy
A laser system capable of efficient production of high energy sub-nanosecond pulses in the 2-15 μm spectral region is disclosed. Diode pumped solid state lasers are used as pump sources. The system design is simple, reliable and compact allowing for easy integration. The laser system includes a combination of compact solid-state ˜1 micron laser sources, producing high power picosecond pulses, with optical parametric amplification and a quasi-continuous wave laser for seeding the amplification process that enables the efficient conversion of the high power ˜1 micron laser radiation to tuneable mid-infrared sub-ns pulses. New parametric processes are presented for achieving high gains in bulk nonlinear crystals. Furthermore, a method of exceeding the fundamental conversion efficiency limit of direct three wave mixing is presented. The compact and robust nature of this novel laser system opens up the use of high power and high peak power mid-infrared laser pulses to a wide variety of important medical and dental applications.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION
Laser based material processing methods and scalable architecture for material processing
InactiveUS20030160034A1Improve stabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionPower applicationNanosecond
Methods and systems for laser-based processing of materials are disclosed wherein a scalable laser architecture, based on planar waveguide technology, provides for pulsed laser micromachining applications while supporting higher average power applications like laser welding and cutting. Various embodiments relate to improvements in planar waveguide technology which provide for stable operation at high powers with a reduction in spurious outputs and thermal effects. At least one embodiment provides for micromachining with pulsewidths in the range of femtoseconds to nanoseconds. In another embodiment, 100W or greater average output power operation is provided for with a diode-pumped, planar waveguide architecture.
Owner:THE GSI GRP LLC
Method and apparatus for high power optical amplification in the infrared wavelength range (0.7-20 mum)
InactiveUS20050271094A1Laser detailsNon-linear opticsAcousto-optic programmable dispersive filterAdemetionine
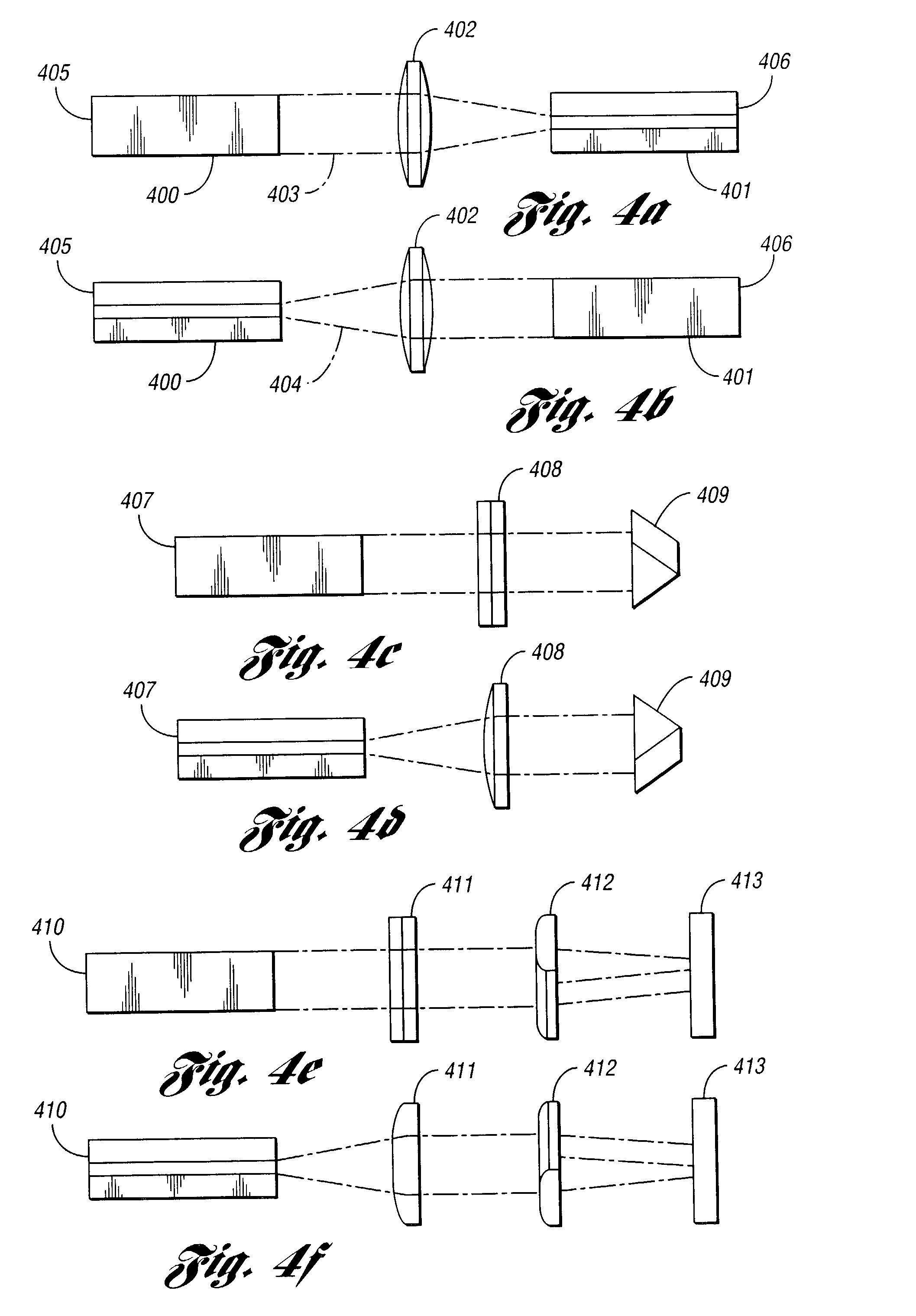
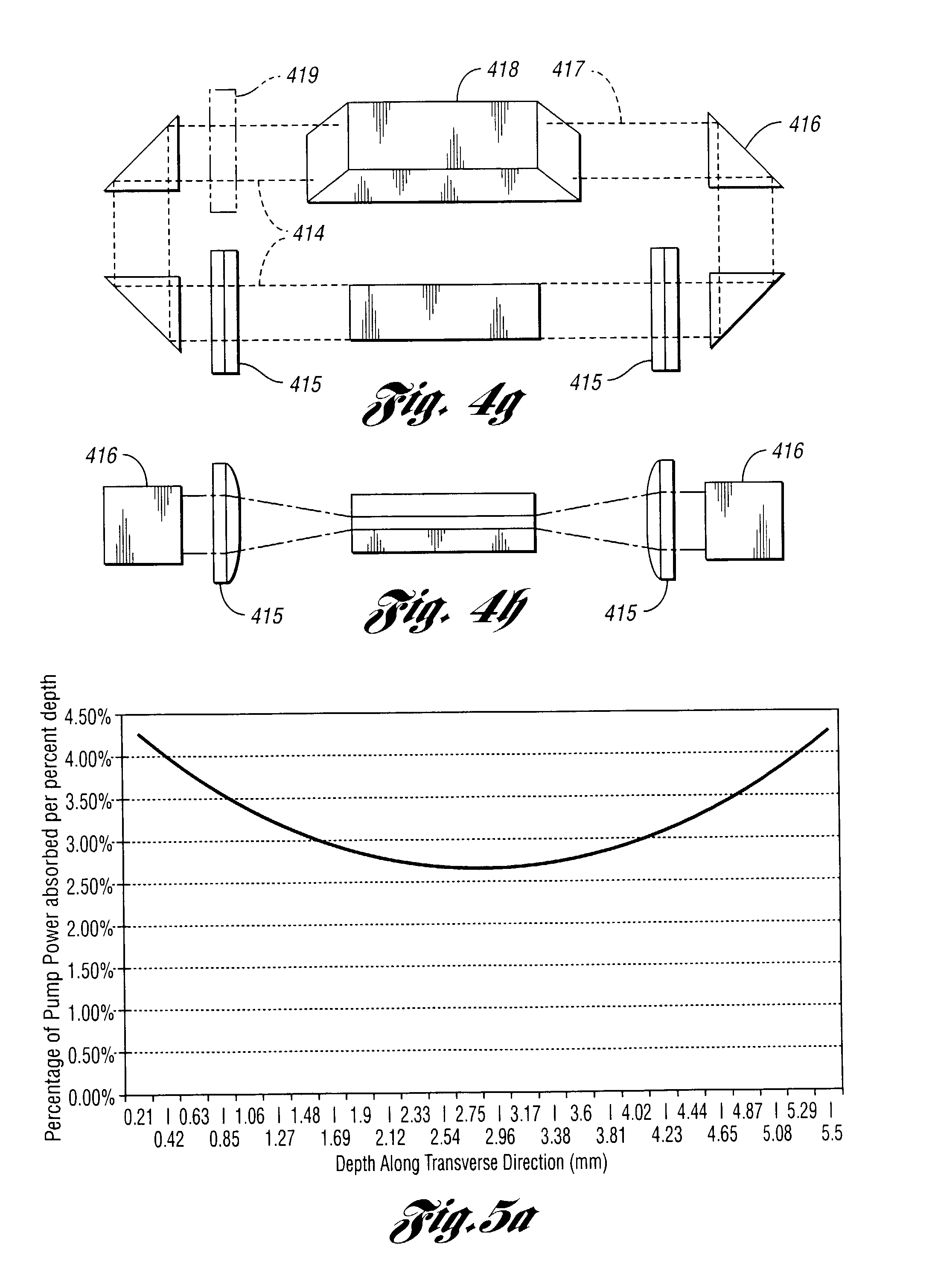
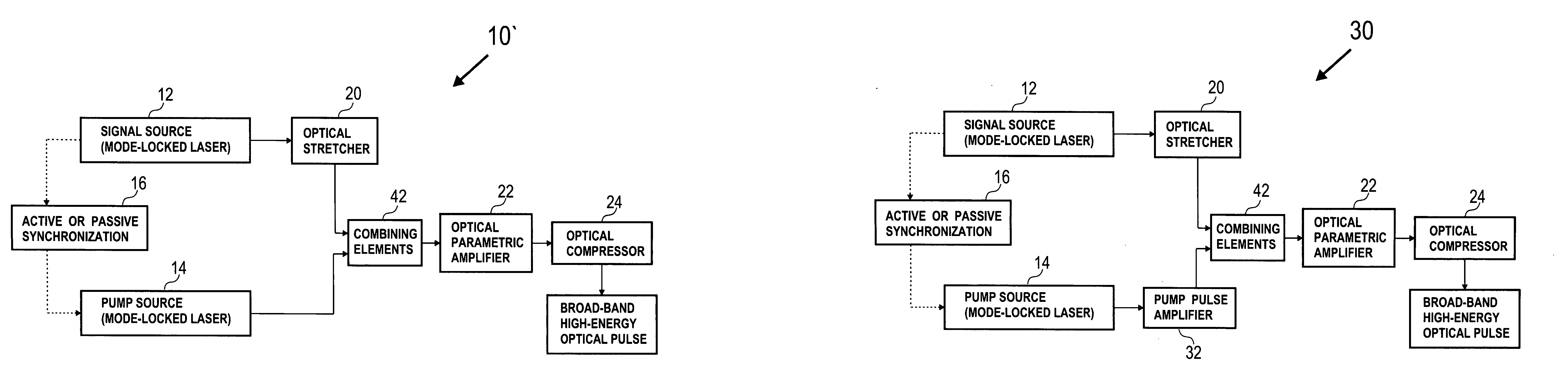
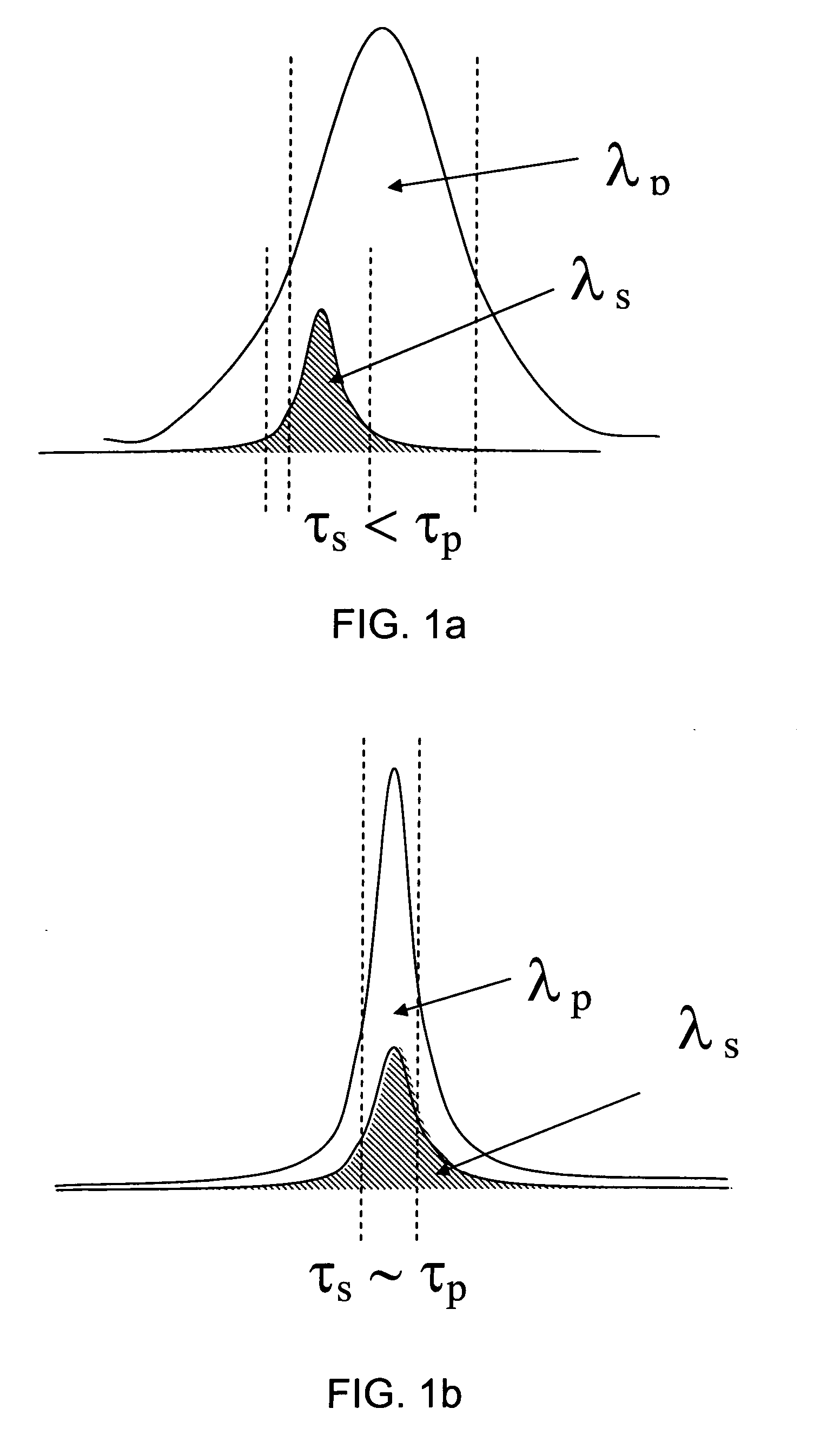
A novel method for high power optical amplification of ultrashort pulses in IR wavelength range (0.7-20 Ãm) is disclosed. The method is based on the optical parametric chirp pulse amplification (OPCPA) technique where a picosecond or nanosecond mode locked laser system synchronized to a signal laser oscillator is used as a pump source or alternatively the pump pulse is created from the signal pulse by using certain types of optical nonlinear processes described later in the document. This significantly increases stability, extraction efficiency and bandwidth of the amplified signal pulse. Further, we disclose five new practical methods of shaping the temporal and spatial profiles of the signal and pump pulses in the OPCPA interaction which significantly increases its efficiency. In the first, passive preshaping of the pump pulses has been made by a three wave mixing process separate from the one occurring in the OPCPA. In the second, passive pre-shaping of the pump pulses has been made by spectral filtering in the pump mode-locked laser or in its amplifier. In the third, the temporal shape of the signal pulse optimized for OPCPA interaction has been actively processed by using an acousto-optic programmable dispersive filter (Dazzler) or liquid crystal light modulators. In the fourth alternative method, the signal pulse intensity envelope is optimized by using passive spectral filtering. Finally, we disclose a method of using pump pulses which interact with the seed pulses with different time delays and different angular orientations allowing the amplification bandwidth to be increased. In addition we describe a new technique for high power IR optical beam delivery systems based on the microstructure fibres made of silica, fluoride or chalcogenide glasses as well as ceramics. Also we disclose a new optical system for achieving phase matching geometries in the optical parametric interactions based on diffractive optics. All novel methods of the ultrashort optical pulse amplification described in this disclosure can be easily generalized to other wavelength ranges.
Owner:MILLER ROBERT JOHN DWAYNE +3
Biosensor and method of making
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC +1
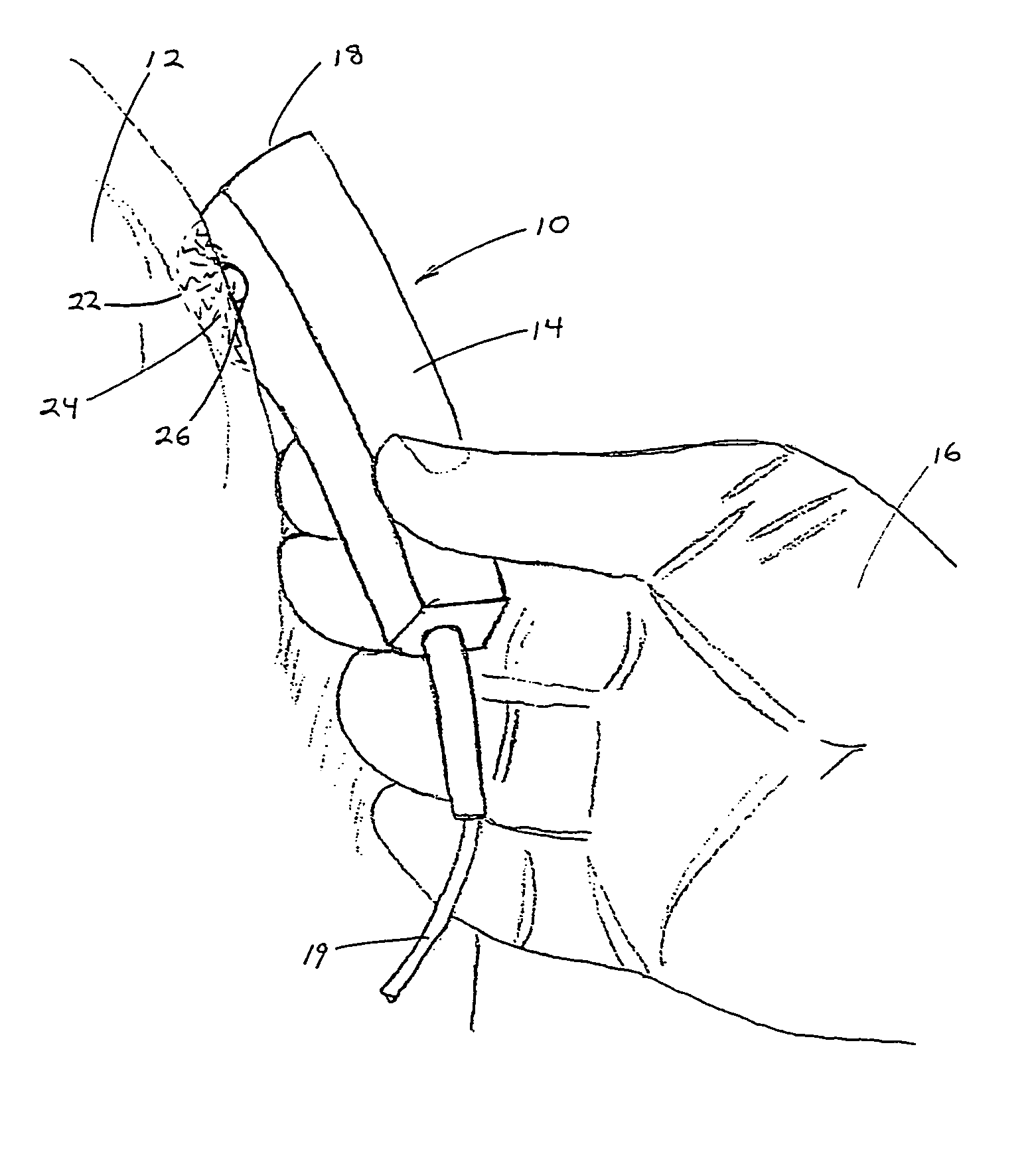
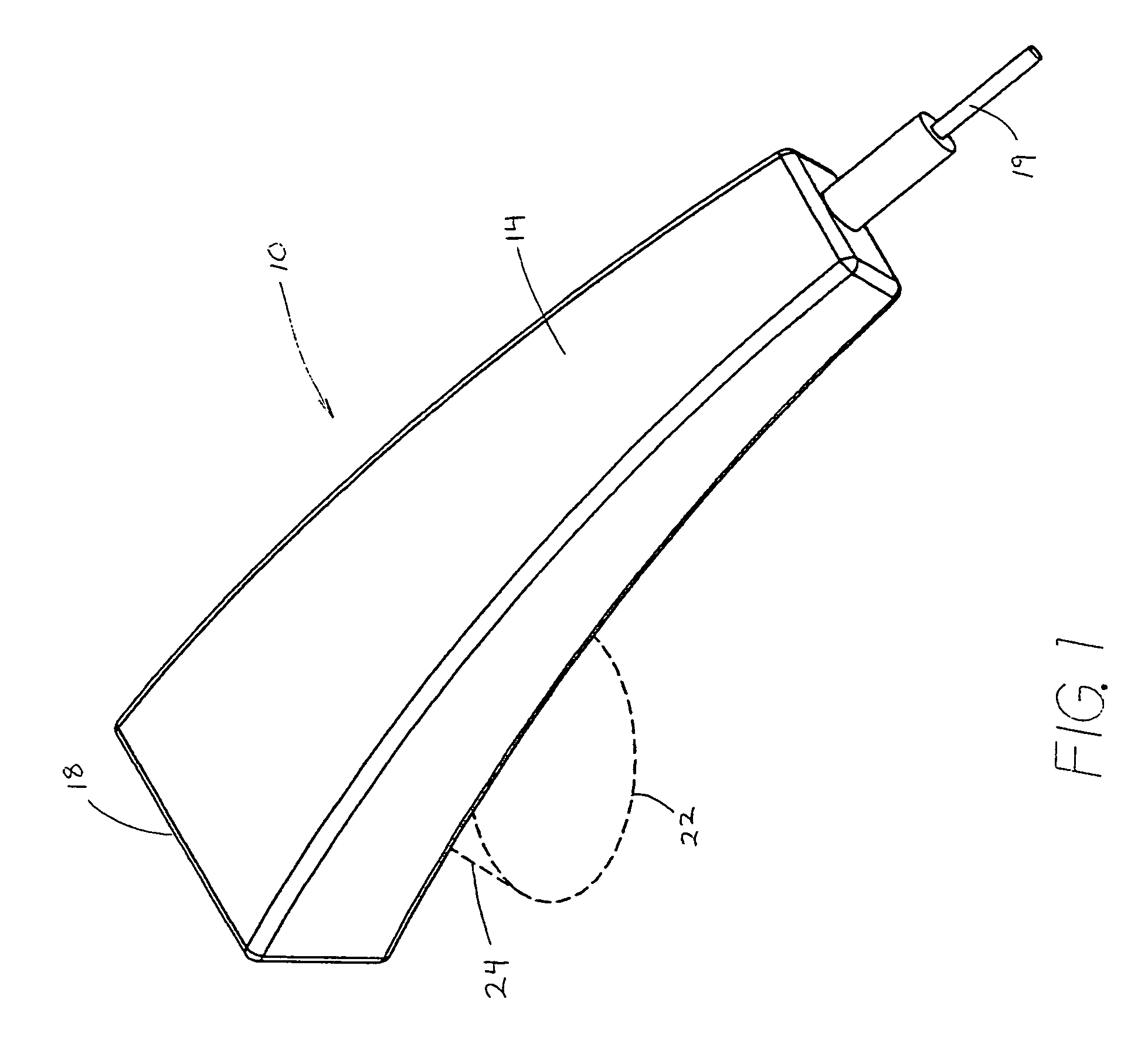
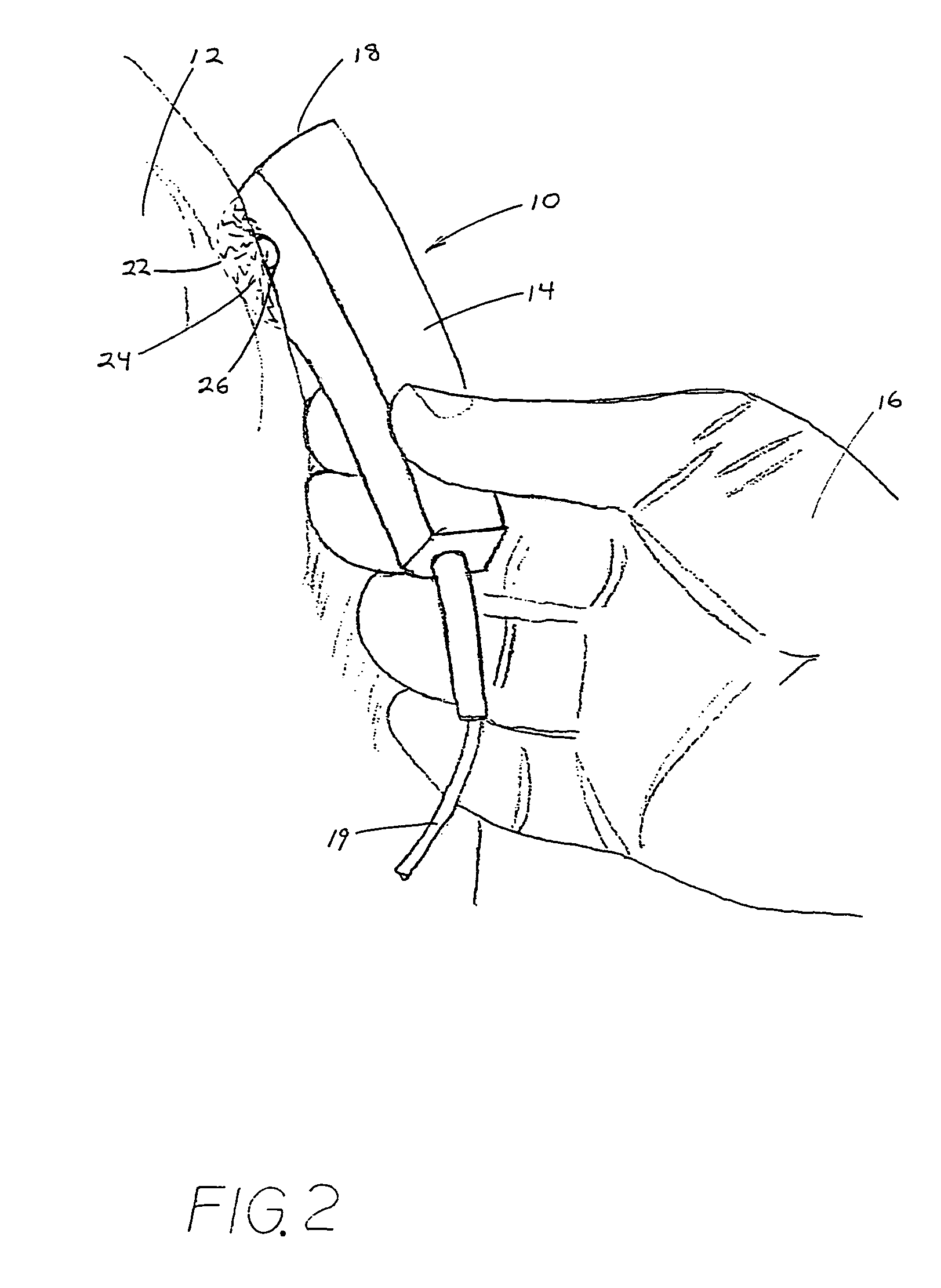
Method and apparatus for pulsed electromagnetic therapy
An apparatus and method for applying pulsed electromagnetic therapy to humans and animals. A straight wire element is employed to generate the magnetic field. A power and timer circuit supplies current pulses that approximate square pulses in form, so that the straight wire element generates magnetic pulses having rapid rise and fall times. Peak field strength is approximately 2 gauss at a 1 cm distance from the straight wire element, and the duration of peak field strength is approximately 200 nanoseconds. The pulses are repeated at a frequency of about 70 Hz. The straight wire element and circuit may be housed in a hand-held probe, with an LED illuminating the skin area to provide a visual indication of effective range, or a plurality of the straight wire elements and associated circuits may be embedded in a conformable pad that is placed over the affected area of the body.
Owner:GORDON GLEN A
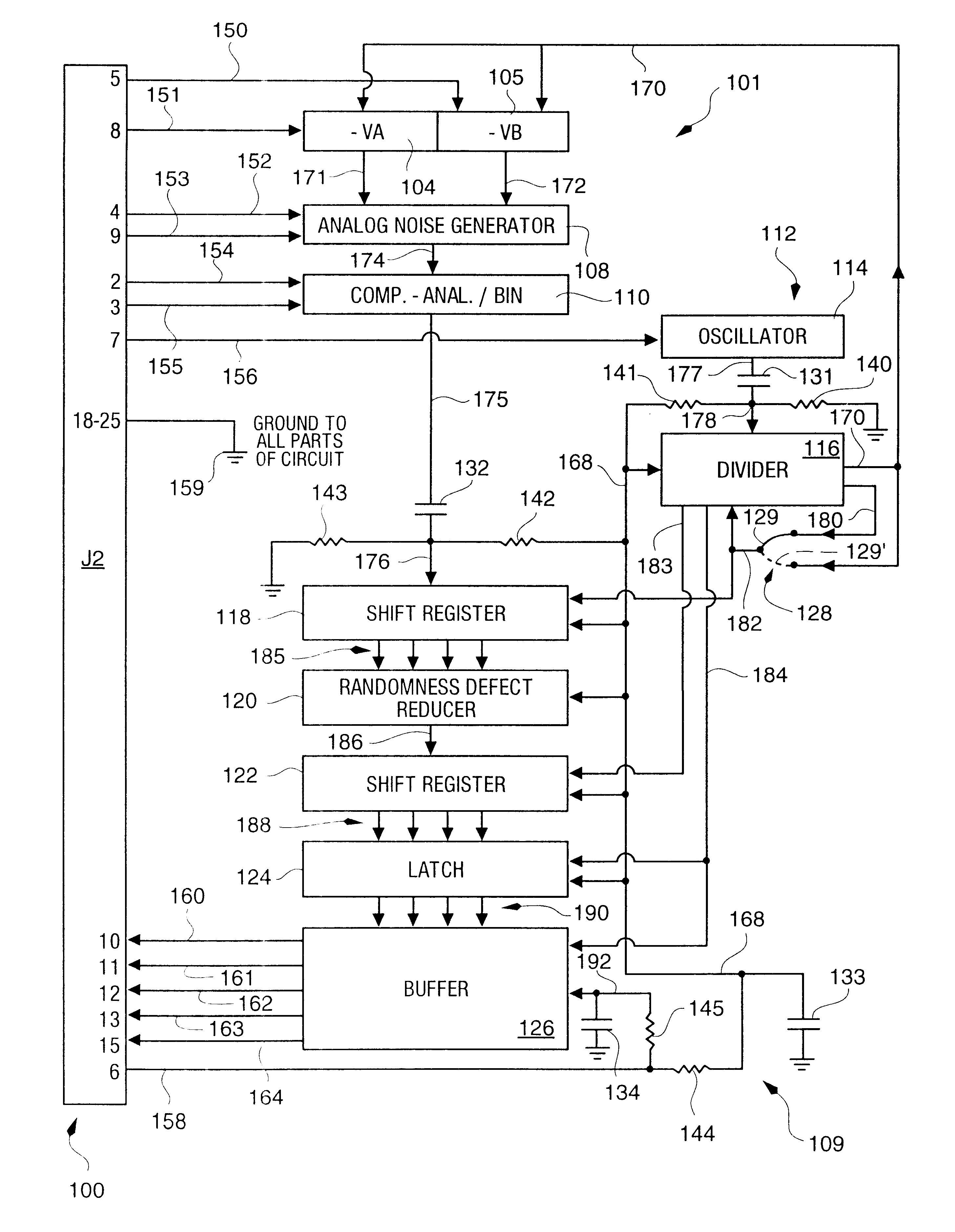
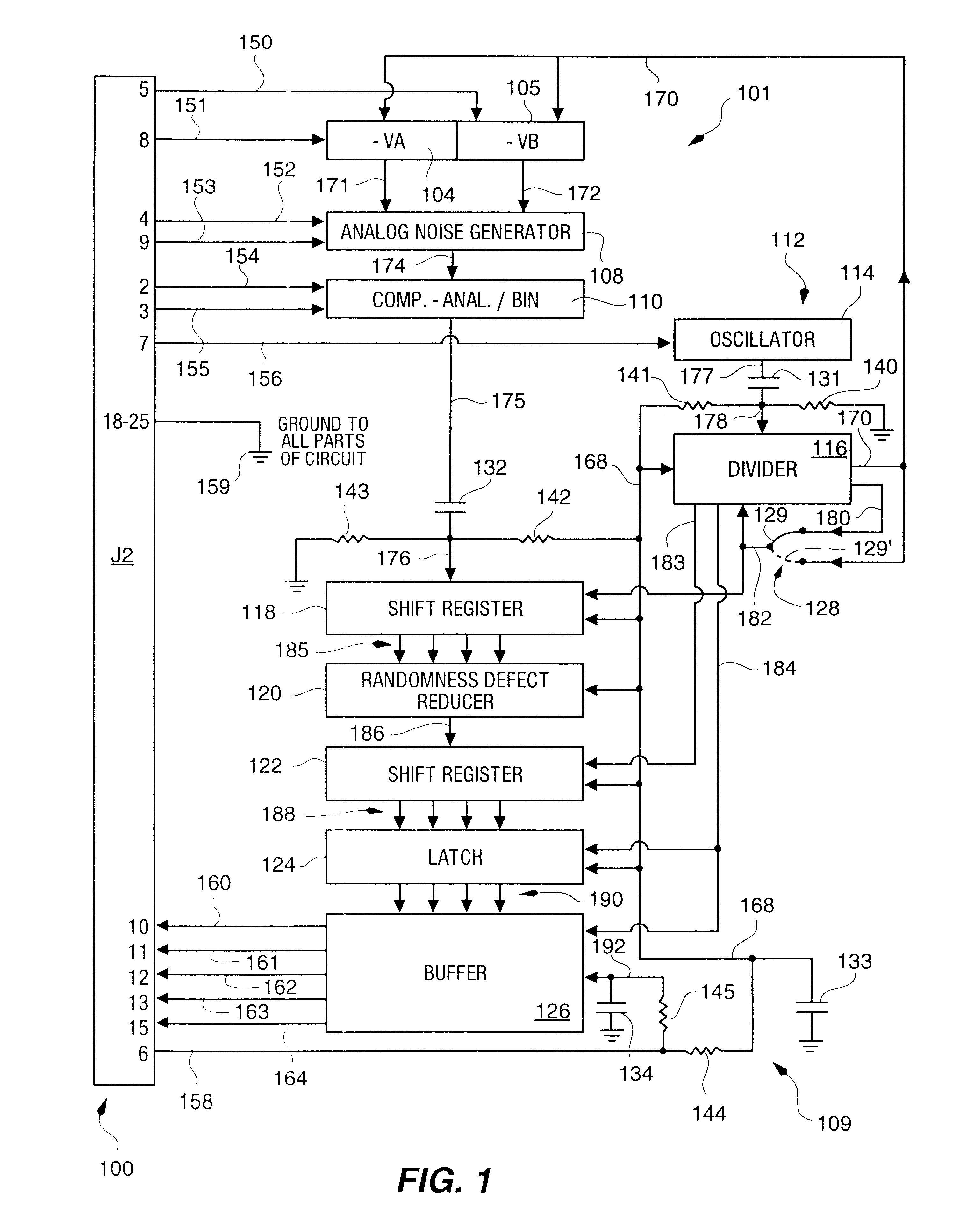
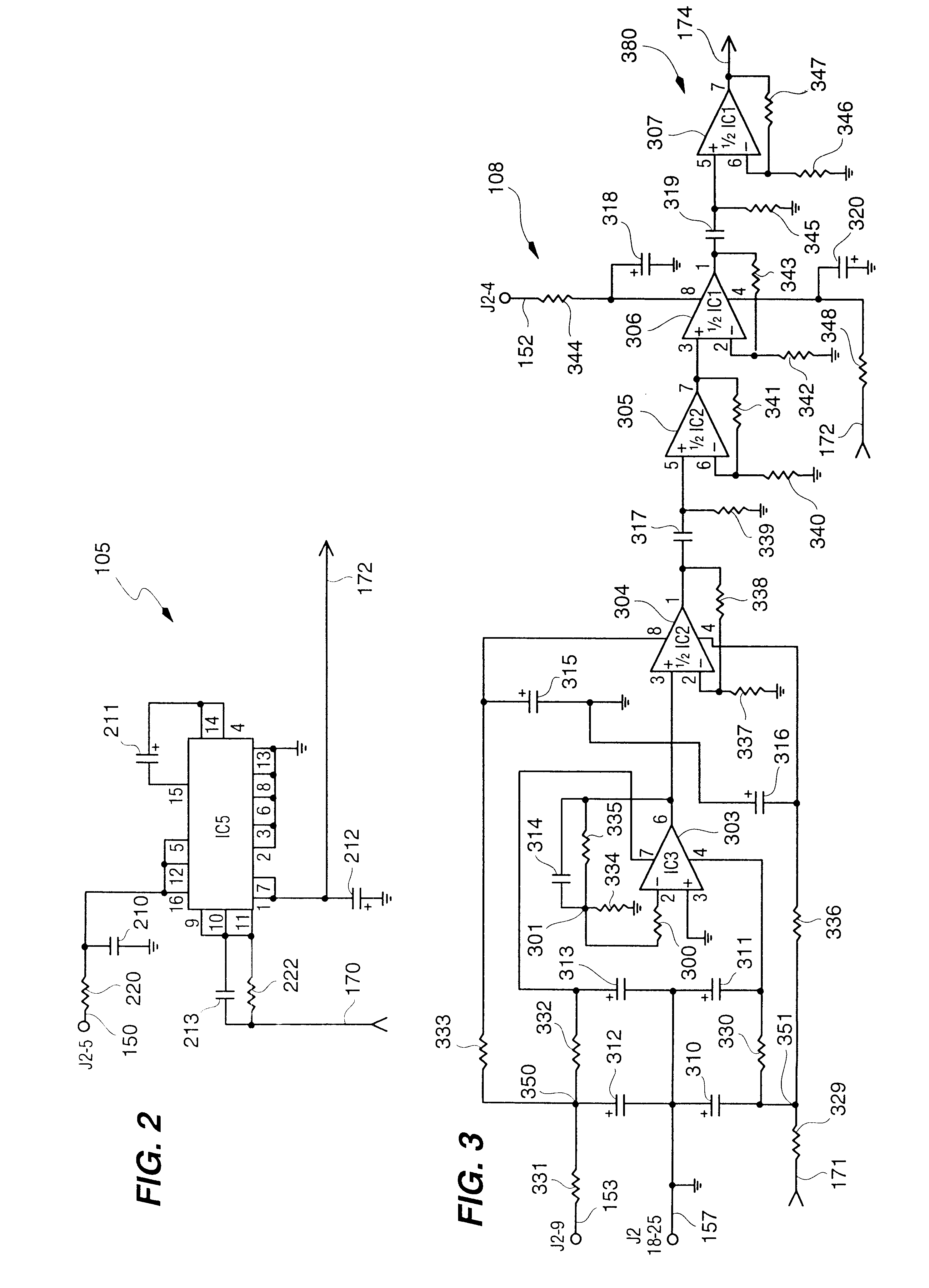
Random number generator and generation method
InactiveUS6324558B1Improve its ability to generateReduce defectsRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsCmos comparatorShift register
An RNG circuit is connected to the parallel port of a computer. The circuit includes a flat source of white noise and a CMOS amplifier circuit compensated in the high frequency range. A low-frequency cut-off is selected to maintain high band-width yet eliminate the 1 / f amplifier noise tail. A CMOS comparator with a 10 nanosecond rise time converts the analog signal to a binary one. A shift register converts the serial signal to a 4-bit parallel one at a sample rate selected at the knee of the serial dependence curve. Two levels of XOR defect correction produce a BRS at 20 kHZ, which is converted to a 4-bit parallel word, latched and buffered. The entire circuit is powered from the data pins of the parallel port. A device driver interface in the computer operates the RNG. The randomness defects with various levels of correction and sample rates are calculated and the RNG is optimized before manufacture.
Owner:QUANTUM WORLD
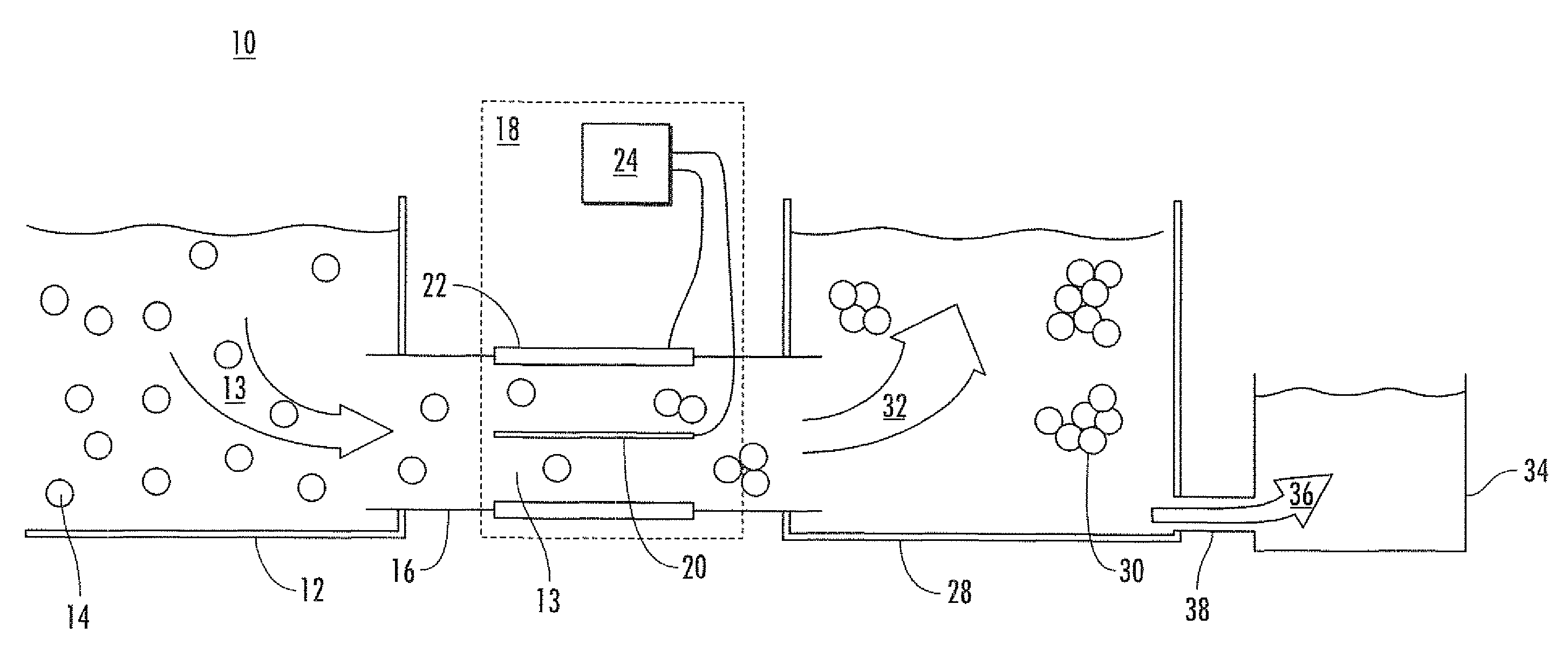
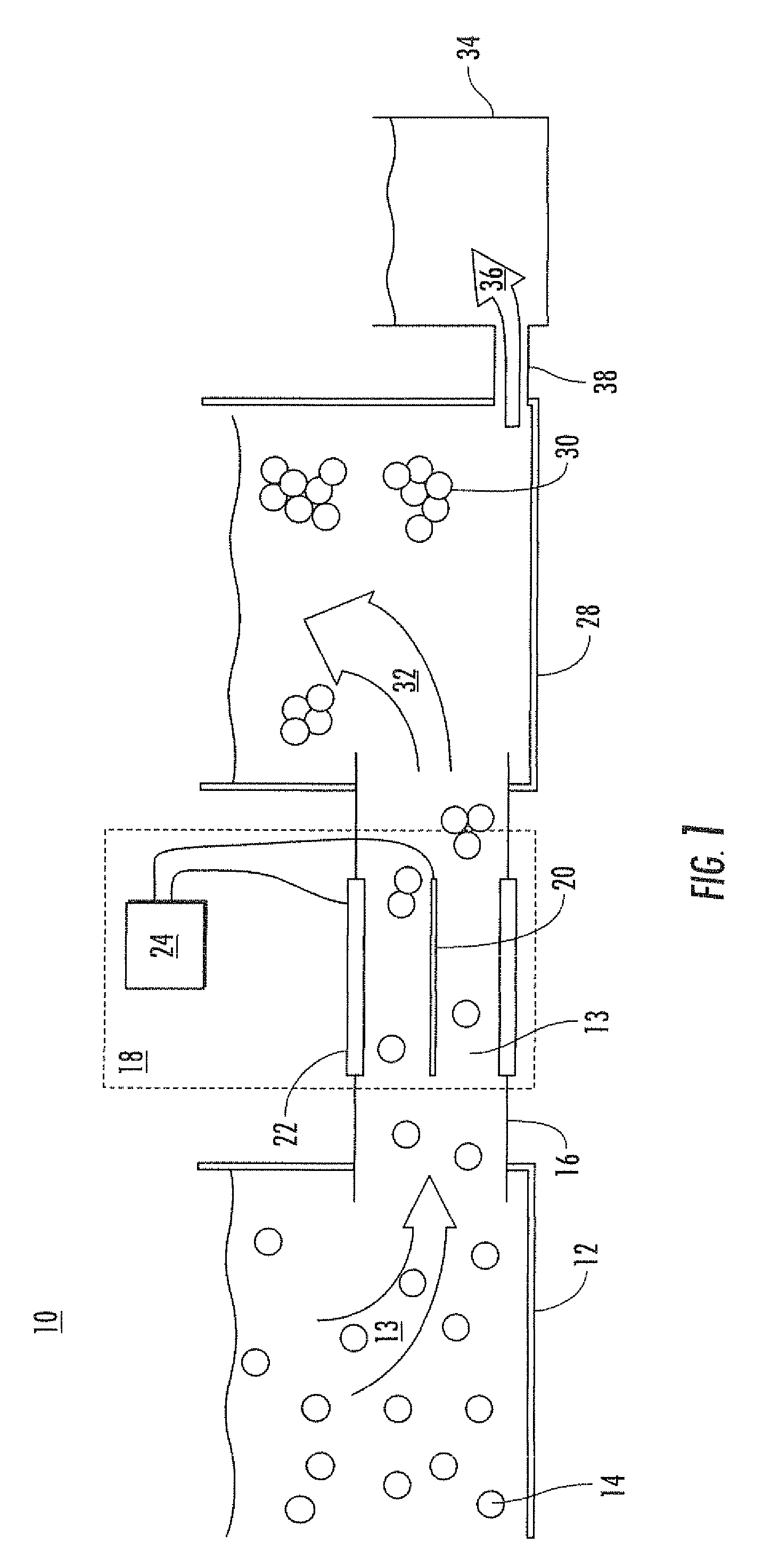
System and method for high-voltage pulse assisted aggregation of algae
ActiveUS20110003350A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanosecondNanosecond pulse
A method and device for aggregating algae in an aqueous solution is disclosed. The method can include providing an algae feed comprising a liquid and algae dispersed therein. The algae feed can be aggregated by applying a nanosecond pulsed electric field to the algae feed. The nanosecond pulsed electric field can include a plurality of electric pulses having a pulse duration ranging from 1 to 1,000 nanoseconds. The method can also include separating an aggregated algae stream from the algae feed and feeding the aggregated algae stream to a lipid extraction operation.
Owner:OLD DOMINION UNIVERSITY RESEARCH FOUNDATION
System and method for treating tumors
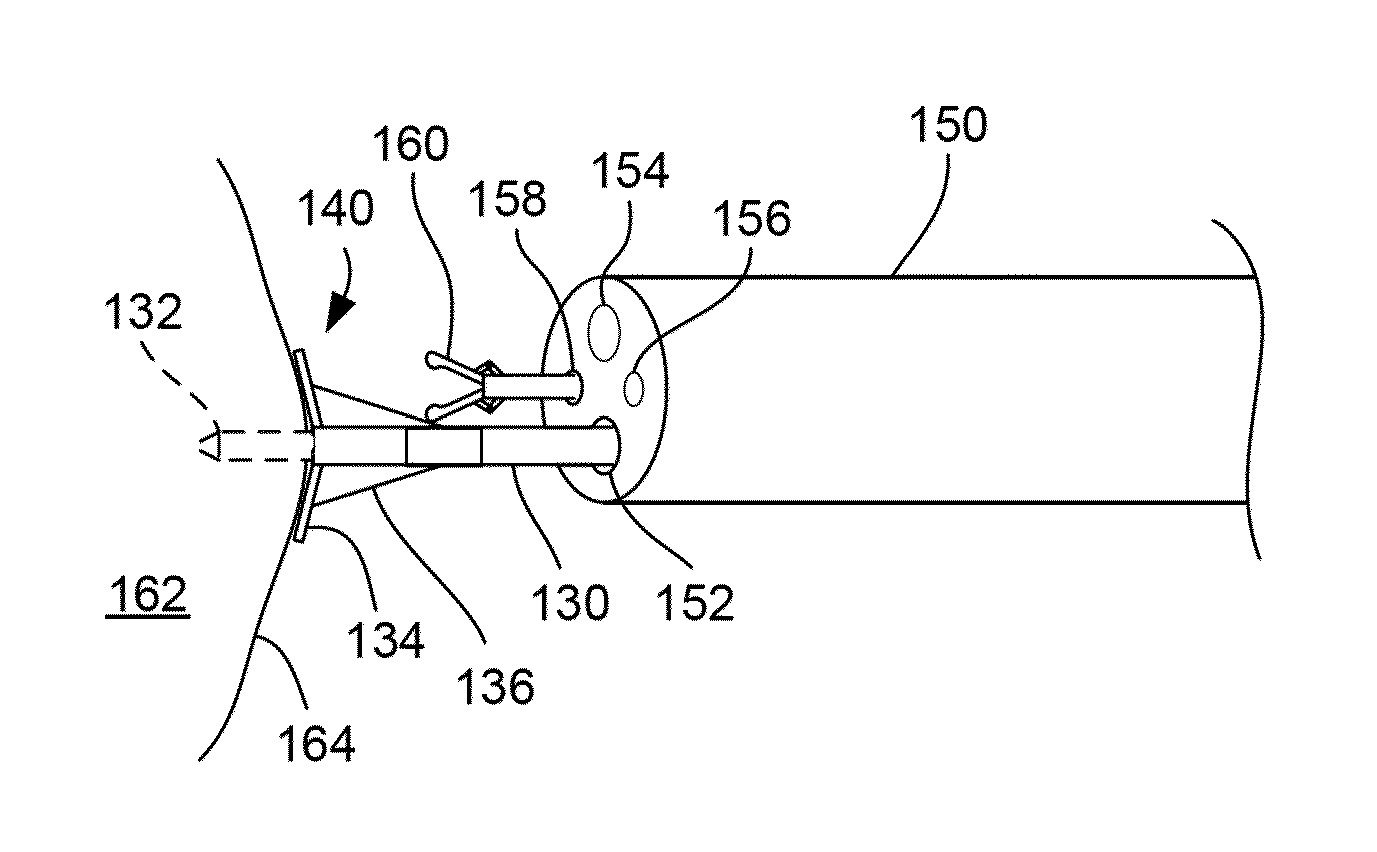
InactiveUS20100240995A1Easy to controlAvoid damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesIntestinal structureAbnormal tissue growth
Systems and methods for treating tumors on or within internal organs of mammals that have been imaged with endoscopic ultrasound are described. The system uses an expandable bipolar electrode assembly that can be imaged by ultrasound and can penetrate, e.g., the stomach, intestine or bowel wall, etc. and be positioned in or around the tumor on an internal organ while being guided by an operator who visualizes its position with ultrasound imaging. It utilizes an electrode assembly that extends down an internal cavity in the endoscope to allow the operator to spread the electrodes for pulse delivery of a nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF) to the tumor.
Owner:PULSE BIOSCI INC
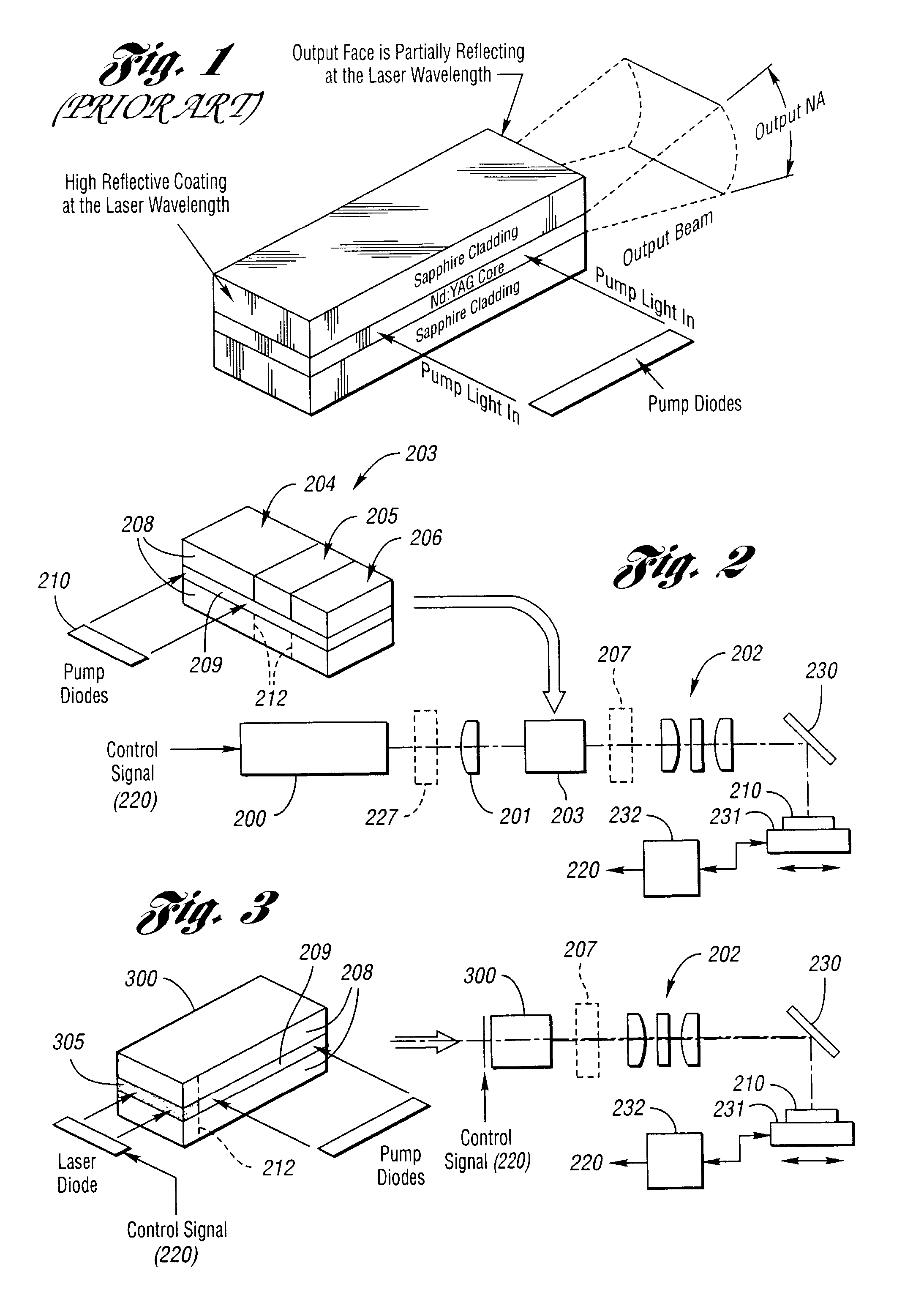
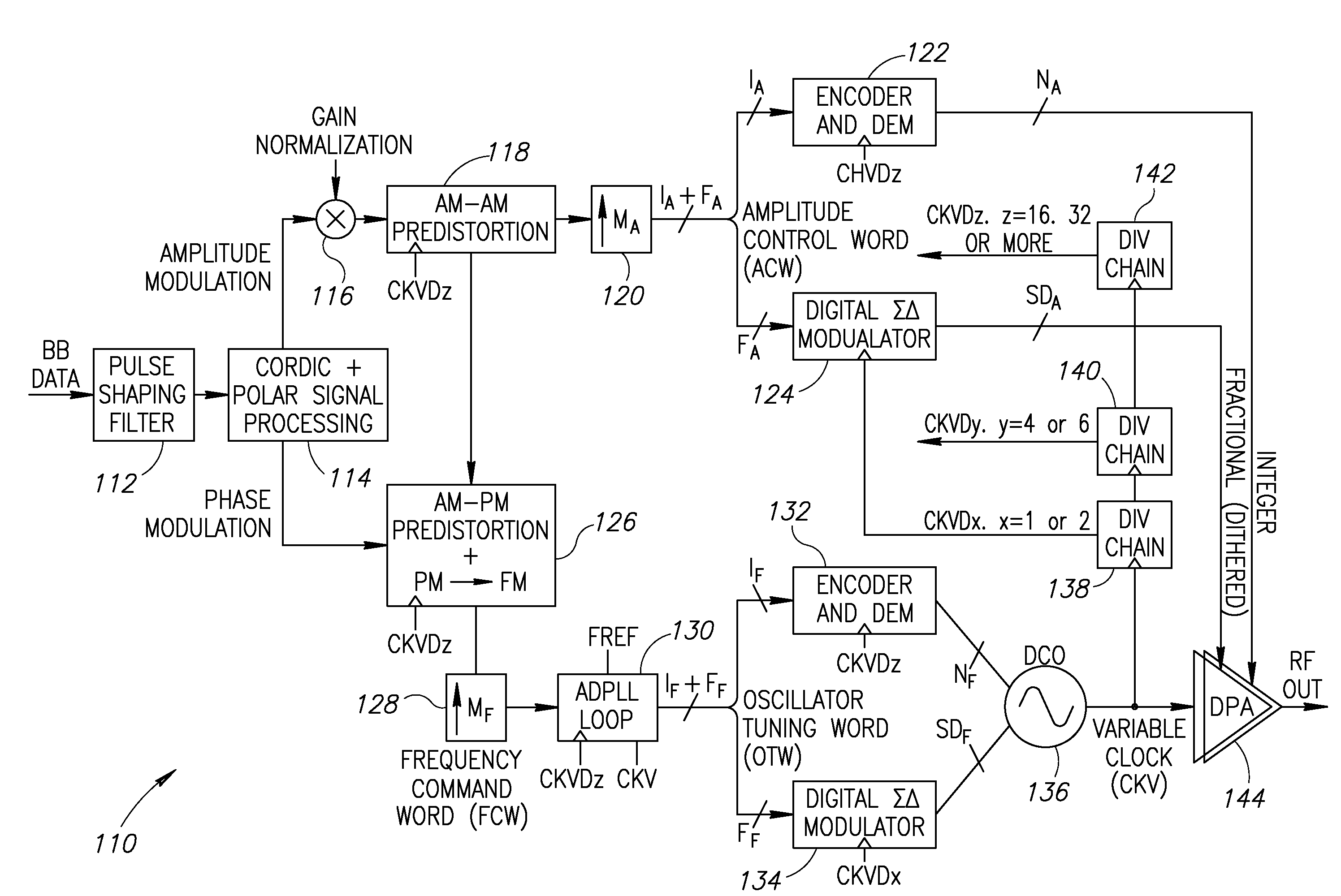
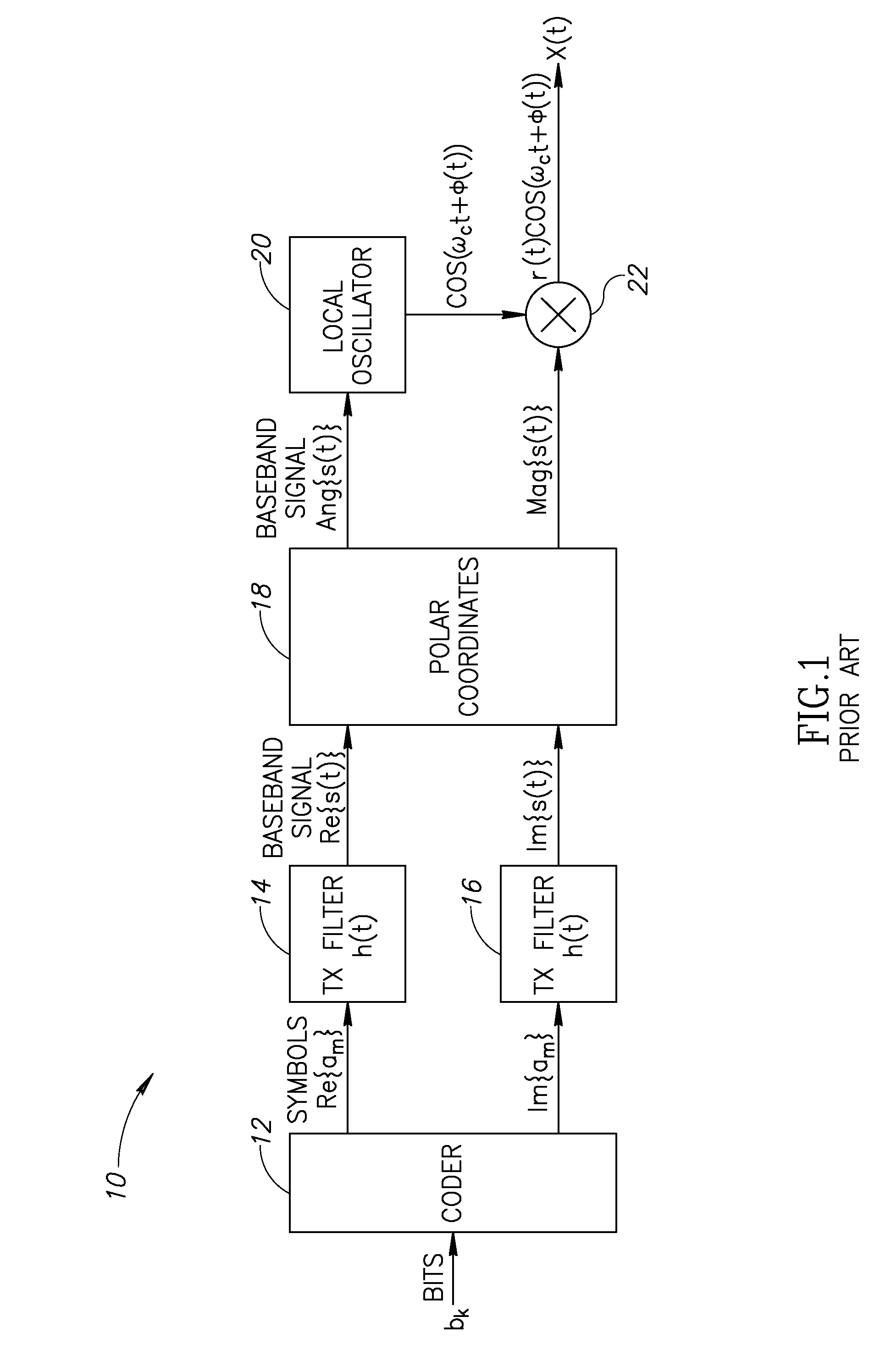
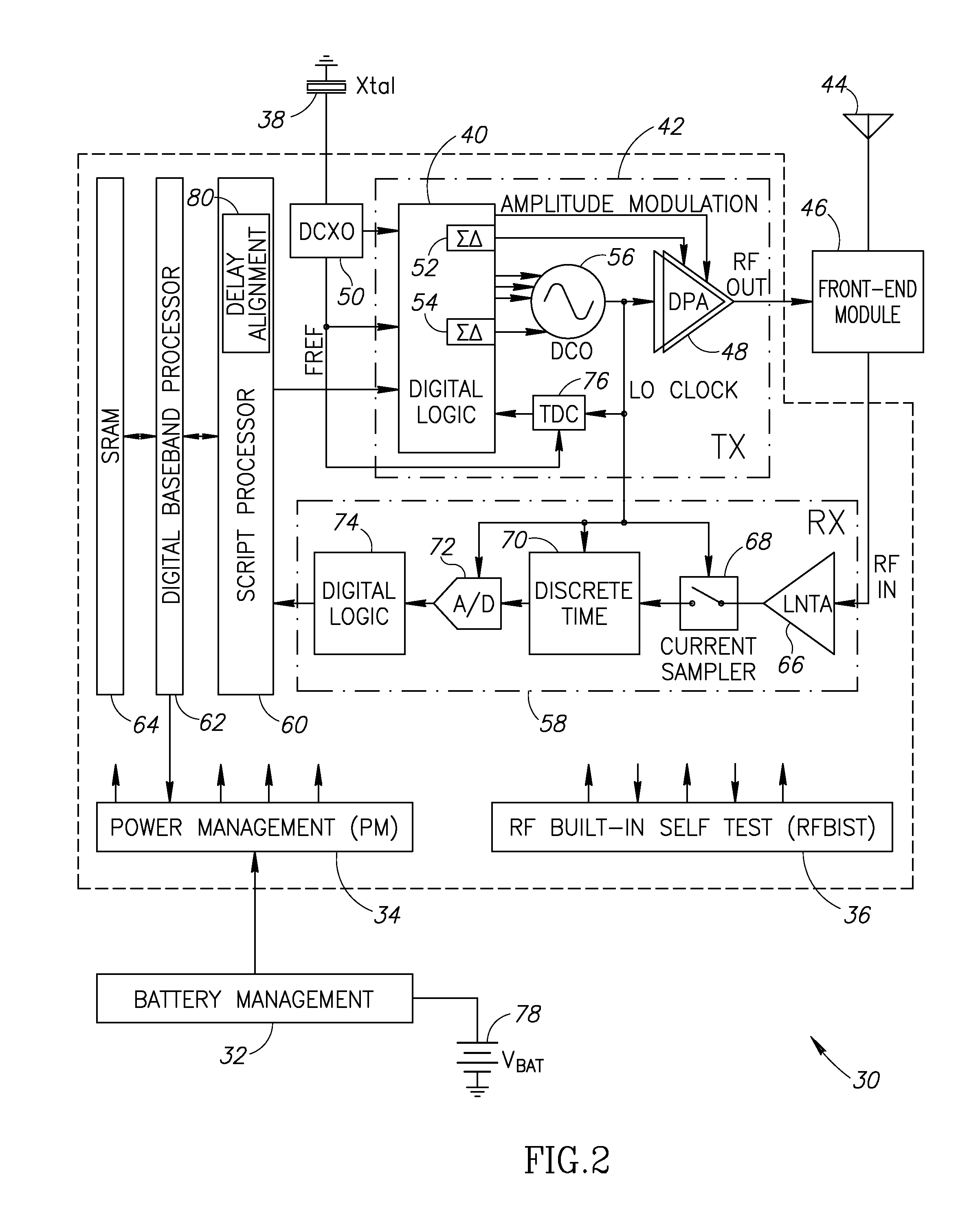
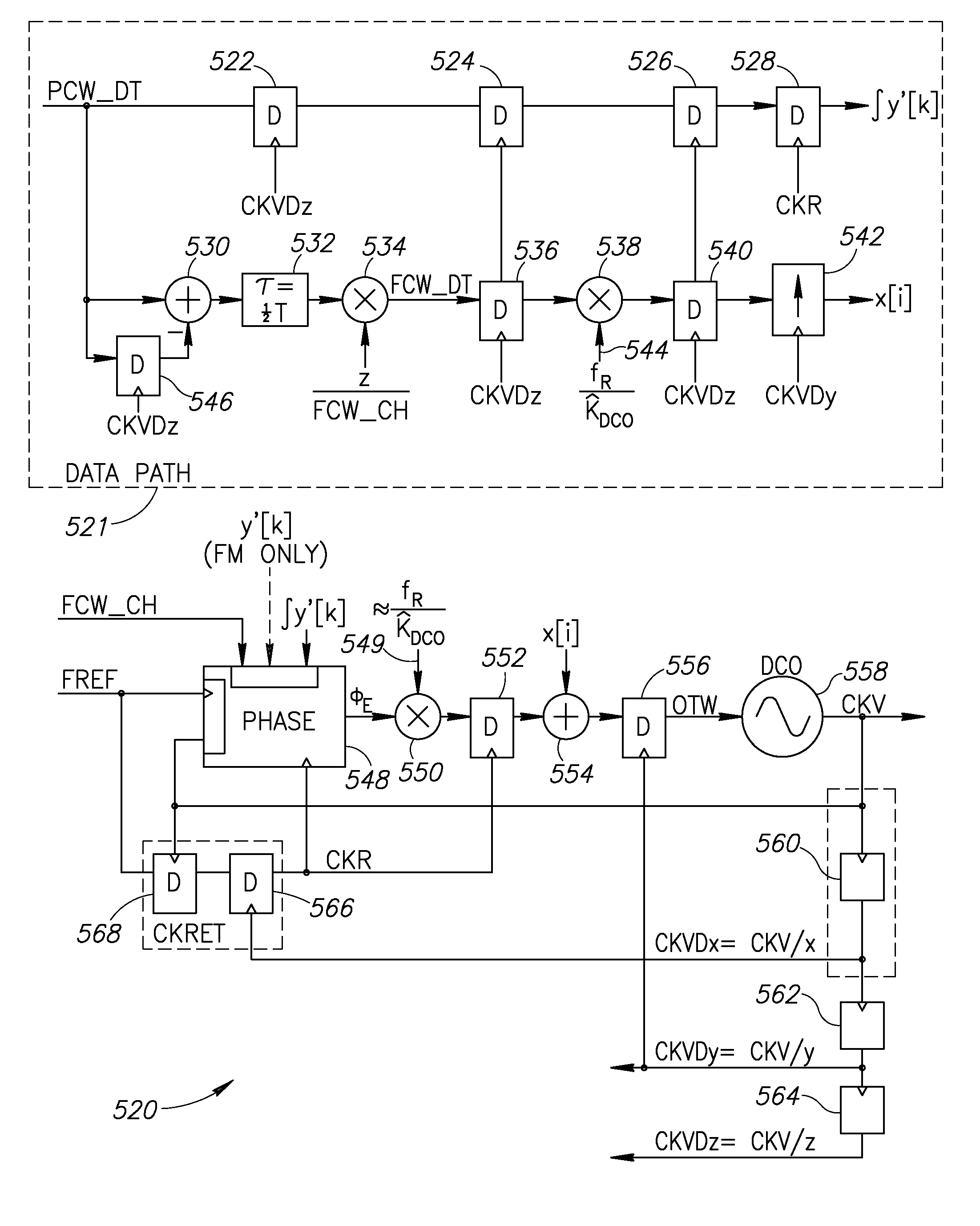
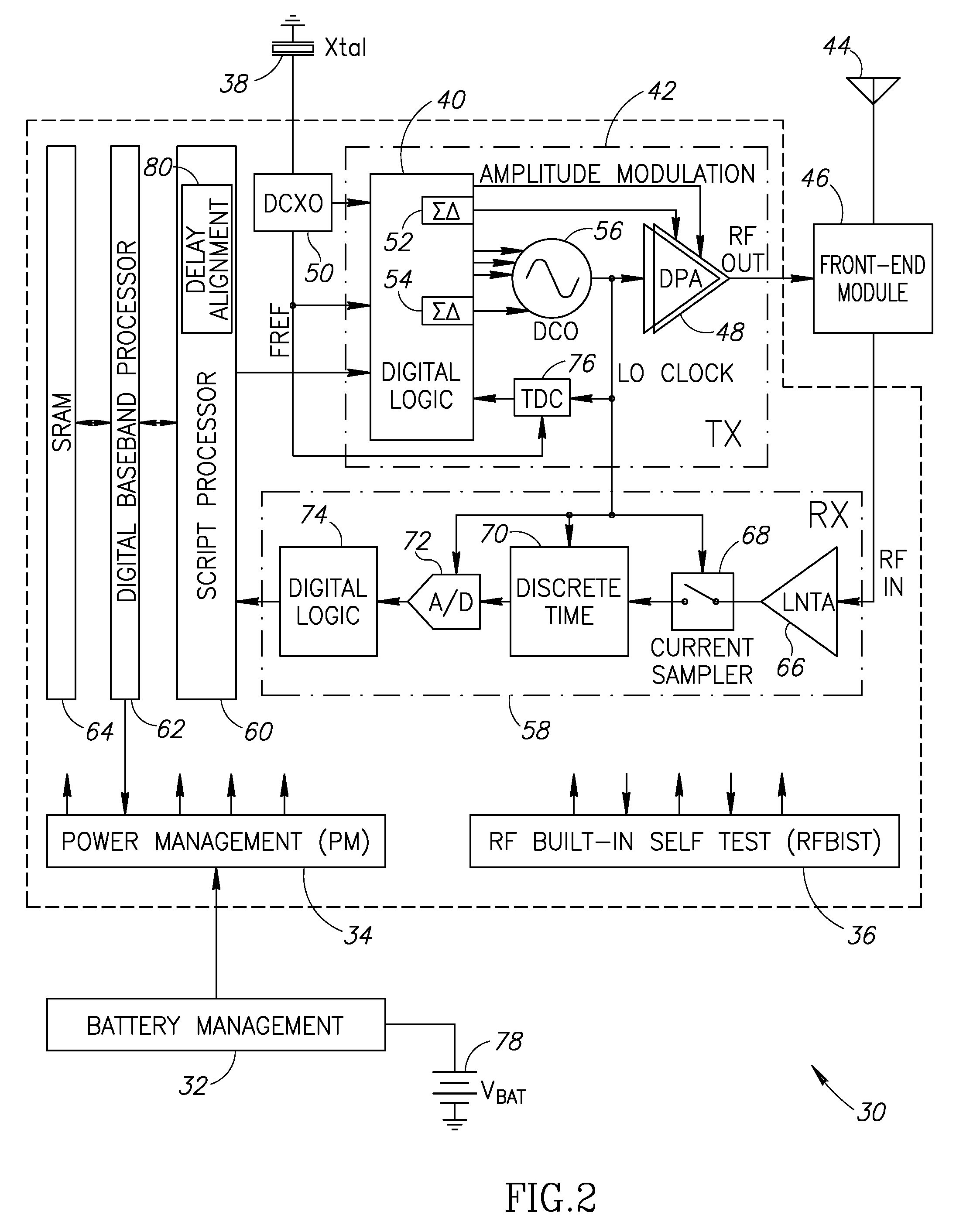
Precise delay alignment between amplitude and phase/frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter
ActiveUS20070189417A1Achieve alignmentHigh phase modulation accuracy requirementSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulation with suppressed carrierAudio power amplifierNanosecond
A novel apparatus for and method of delay alignment between amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths in a digital polar transmitter. The invention provides a fully digital delay alignment mechanism where better than nanosecond alignment is achieved by accounting for processing delays in the digital circuit modules of the transmitter and by the use of programmable delay elements spread across several clock domains. Tapped delay lines compensate for propagation and settling delays in analog elements such as the DCO, dividers, quad switch, buffers, level shifters and digital pre-power amplifier (DPA). A signal correlative mechanism is provided whereby data from the amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths to be matched is first interpolated and then cross-correlated to achieve accuracy better than the clock domain of comparison. Within the ADPLL portion of the transmitter, precise alignment of reference and direct point injection points in the ADPLL is provded using multiple clock domains, tapped delay lines and clock adjustment circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Laser-based material processing methods and systems
ActiveUS8158493B2Avoid insufficient heatingAvoid layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesDielectricPicosecond
Various embodiments may be used for laser-based modification of target material of a workpiece while advantageously achieving improvements in processing throughput and / or quality. Embodiments of a method of processing may include focusing and directing laser pulses to a region of the workpiece at a pulse repetition rate sufficiently high so that material is efficiently removed from the region and a quantity of unwanted material within the region, proximate to the region, or both is reduced relative to a quantity obtainable at a lower repetition rate. Embodiments of an ultrashort pulse laser system may include at least one of a fiber amplifier or fiber laser. Various embodiments are suitable for at least one of dicing, cutting, scribing, and forming features on or within a semiconductor substrate. Workpiece materials may also include metals, inorganic or organic dielectrics, or any material to be micromachined with femtosecond, picosecond, and / or nanosecond pulses.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Laser micro/nano processing system and method
ActiveCN102000912AHigh processing resolutionPrecise Control of ResolutionNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsLaser lightMobile station
The invention provides a laser micro / nano processing system and a laser micro / nano processing method. The system of the invention comprises a laser light source, an optical retardation component, an optical focusing component and a computer-controlled micro mobile station, wherein the laser light source is used for providing a first laser beam having a first wavelength and a second laser beam having a second wavelength, the pulse widths of the first laser beam and the second laser beam range from femtosecond to nanosecond and the first wavelength is different from the second wavelength; the optical retardation component is used for regulating the optical path of the first laser beam or the second laser beam so that the difference between the arrival times of the first laser beam and the second laser beam at a focus is not greater than the level life time for a photochromic material to be processed to be excited to an excited state; the optical focusing component is used for focusing the first laser beam and the second laser beam onto the same focus; and the computer-controlled micro mobile station is used for regulating a photochromic material on the computer-controlled micro mobile station to the focus.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser-based method and system for memory link processing with picosecond lasers
InactiveUS20050092720A1Quality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPicosecond laserLaser processing
A laser-based method of removing a target link structure of a circuit fabricated on a substrate includes generating a pulsed laser output at a pre-determined wavelength less than an absorption edge of the substrate. The laser output includes at least one pulse having a pulse duration in the range of about 10 picoseconds to less than 1 nanosecond, the pulse duration being within a thermal laser processing range. The method also includes delivering and focusing the laser output onto the target link structure. The focused laser output has sufficient power density at a location within the target structure to reduce the reflectivity of the target structure and efficiently couple the focused laser output into the target structure to remove the link without damaging the substrate.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS CORP
Waveguide architecture, waveguide devices for laser processing and beam control, and laser processing applications
InactiveUS7065121B2Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionWaveguideBeam control
Methods and systems for laser-based processing of materials are disclosed wherein a scalable laser architecture, based on planar waveguide technology, provides for pulsed laser micromachining applications while supporting higher average power applications like laser welding and cutting. Various embodiments relate to improvements in planar waveguide technology which provide for stable operation at high powers with a reduction in spurious outputs and thermal effects. At least one embodiment provides for micromachining with pulsewidths in the range of femtoseconds to nanoseconds. In another embodiment, 100 W or greater average output power operation is provided for with a diode-pumped, planar waveguide architecture.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS LTD
Delay alignment in a closed loop two-point modulation all digital phase locked loop
InactiveUS20070189431A1Easy to adjustAchieve alignmentSimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationPulse automatic controlNanosecondAudio power amplifier
A novel apparatus for and method of delay alignment in a closed loop two-point modulation all digital phase locked loop (ADPLL). The invention provides a fully digital delay alignment mechanism where better than nanosecond alignment is achieved by accounting for processing delays in the digital circuit modules of the transmitter and by the use of programmable delay elements spread across several clock domains. Tapped delay lines compensate for propagation and settling delays in analog elements such as the DCO, dividers, quad switch, buffers, level shifters and digital pre-power amplifier (DPA). A signal correlative mechanism is provided whereby data from the amplitude and phase / frequency modulation paths to be matched is first interpolated and then cross-correlated to achieve accuracy better than the clock domain of comparison. Within the ADPLL portion of the transmitter, precise alignment of reference and direct point injection points in the ADPLL is provided using multiple clock domains, tapped delay lines and clock adjustment circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
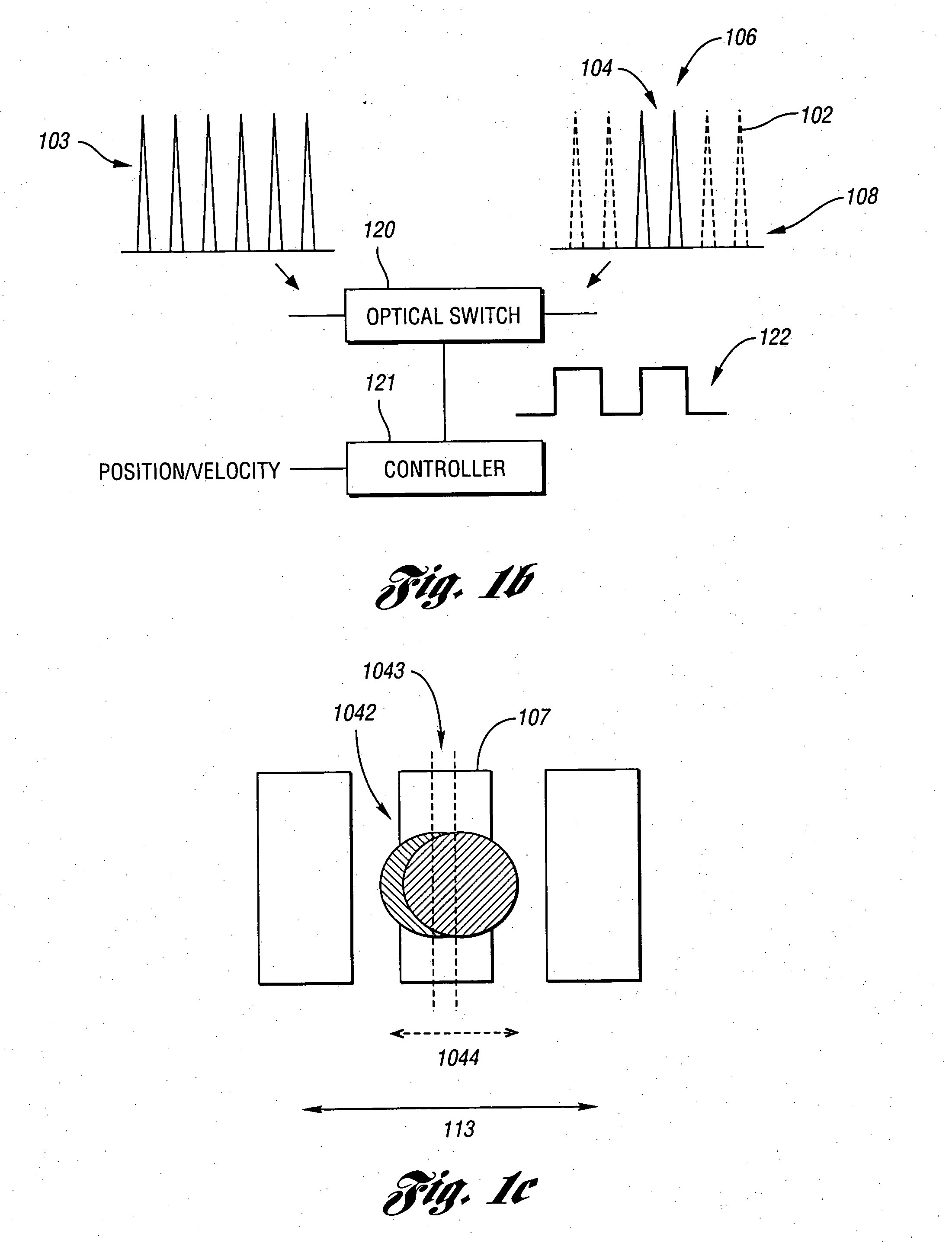
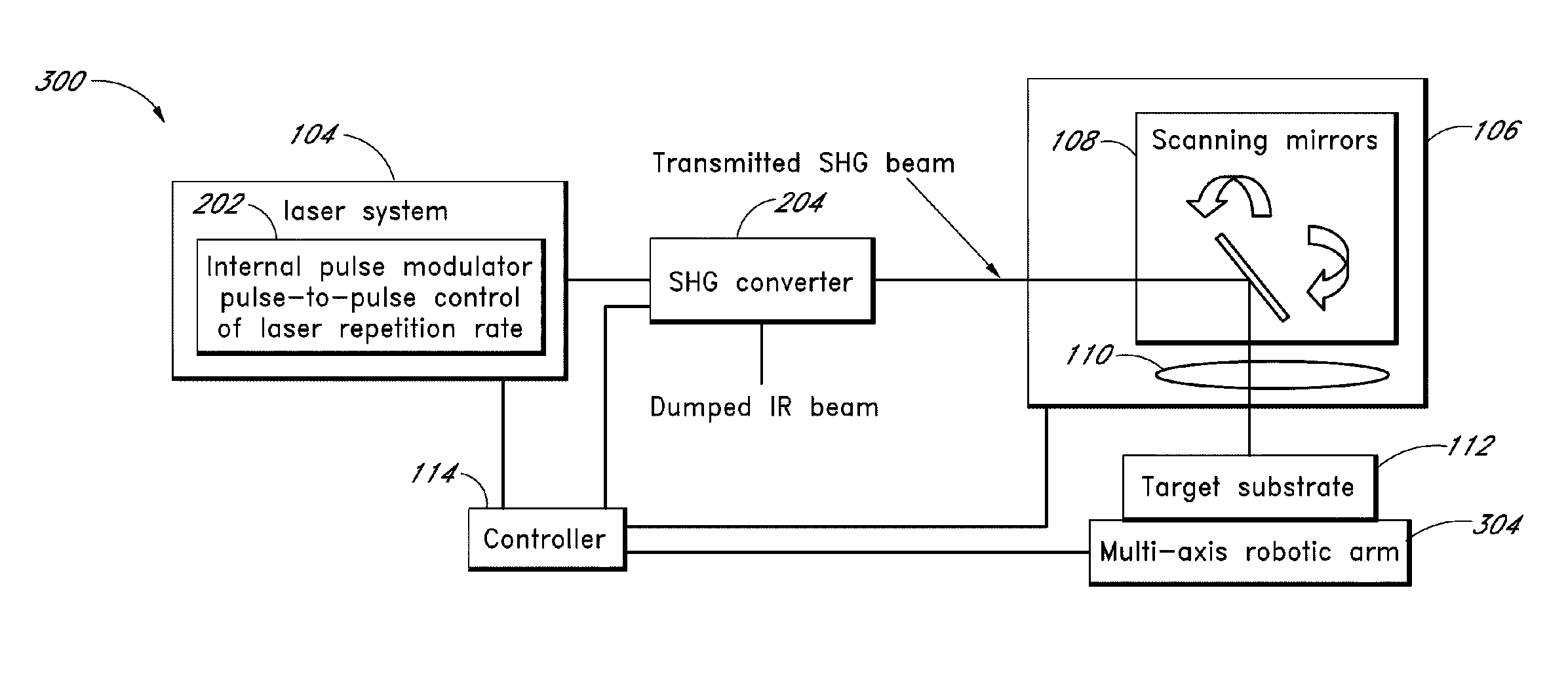
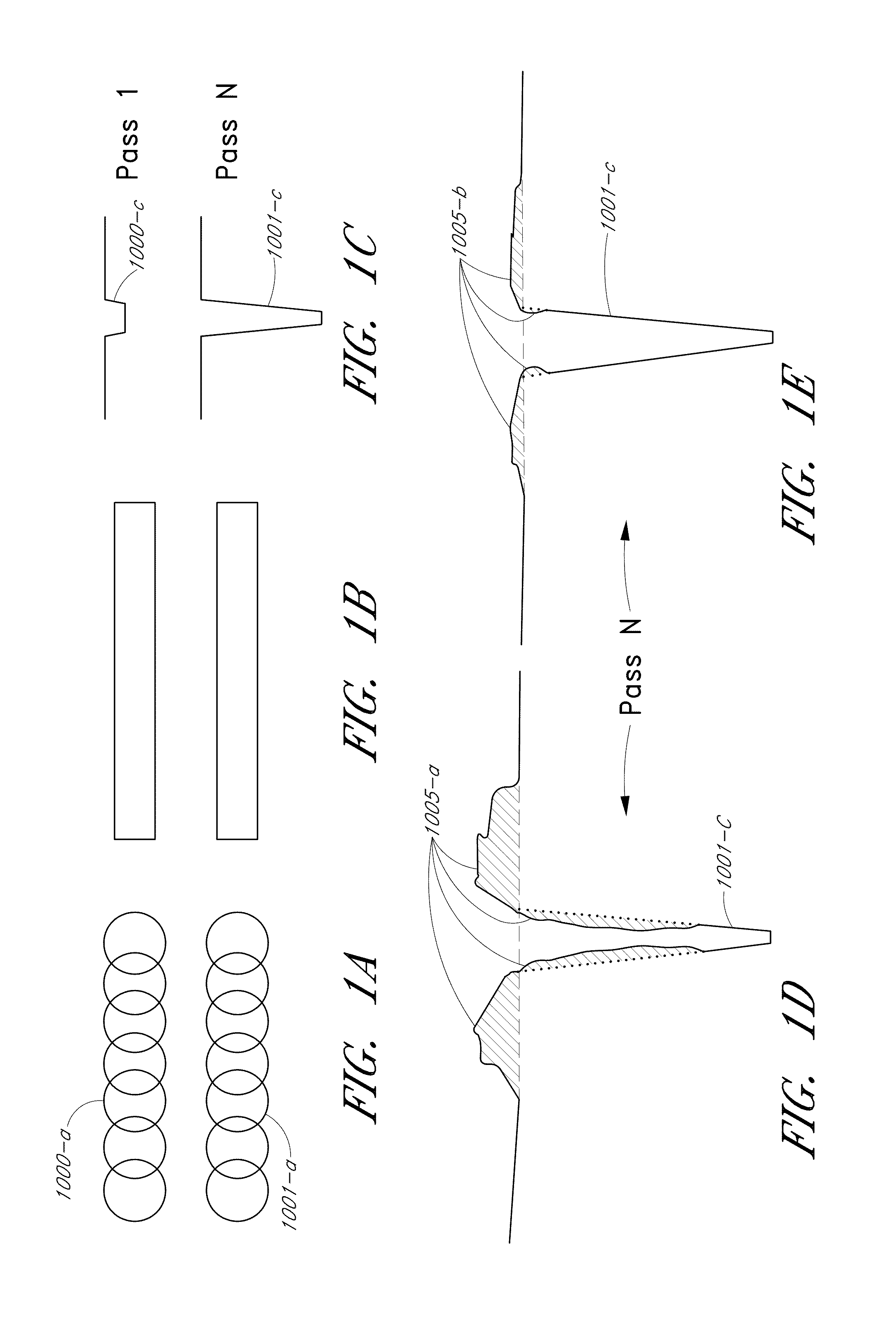
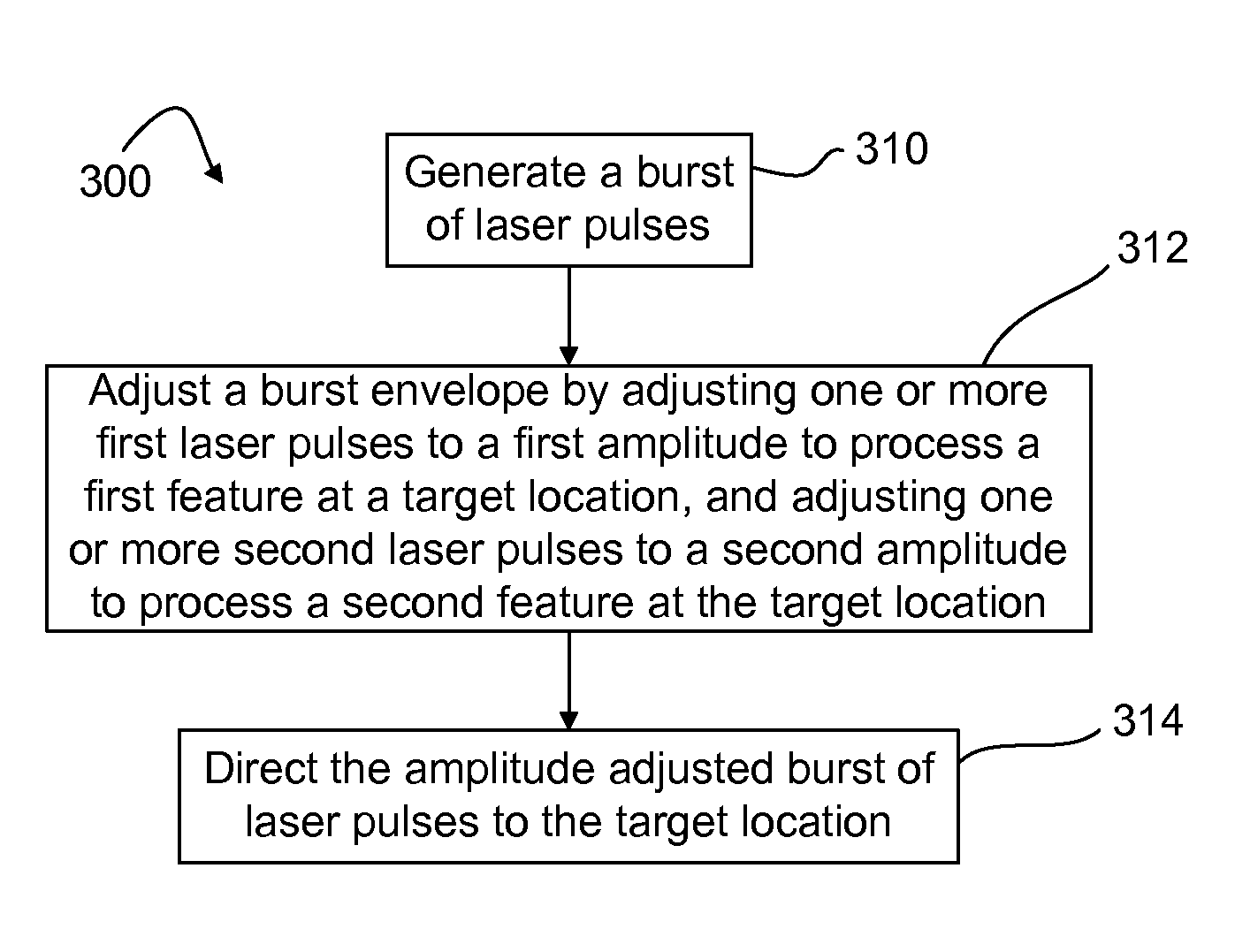
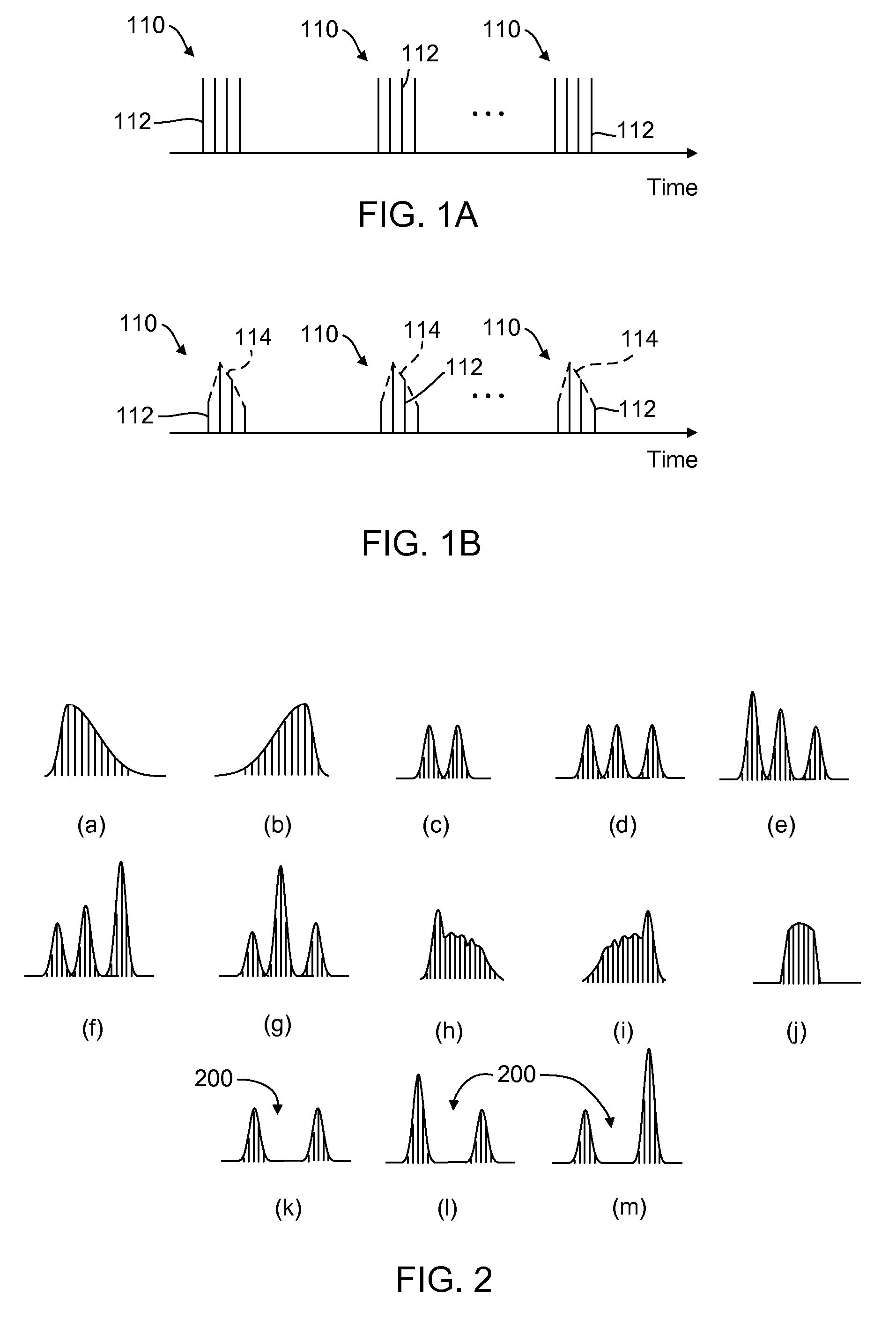
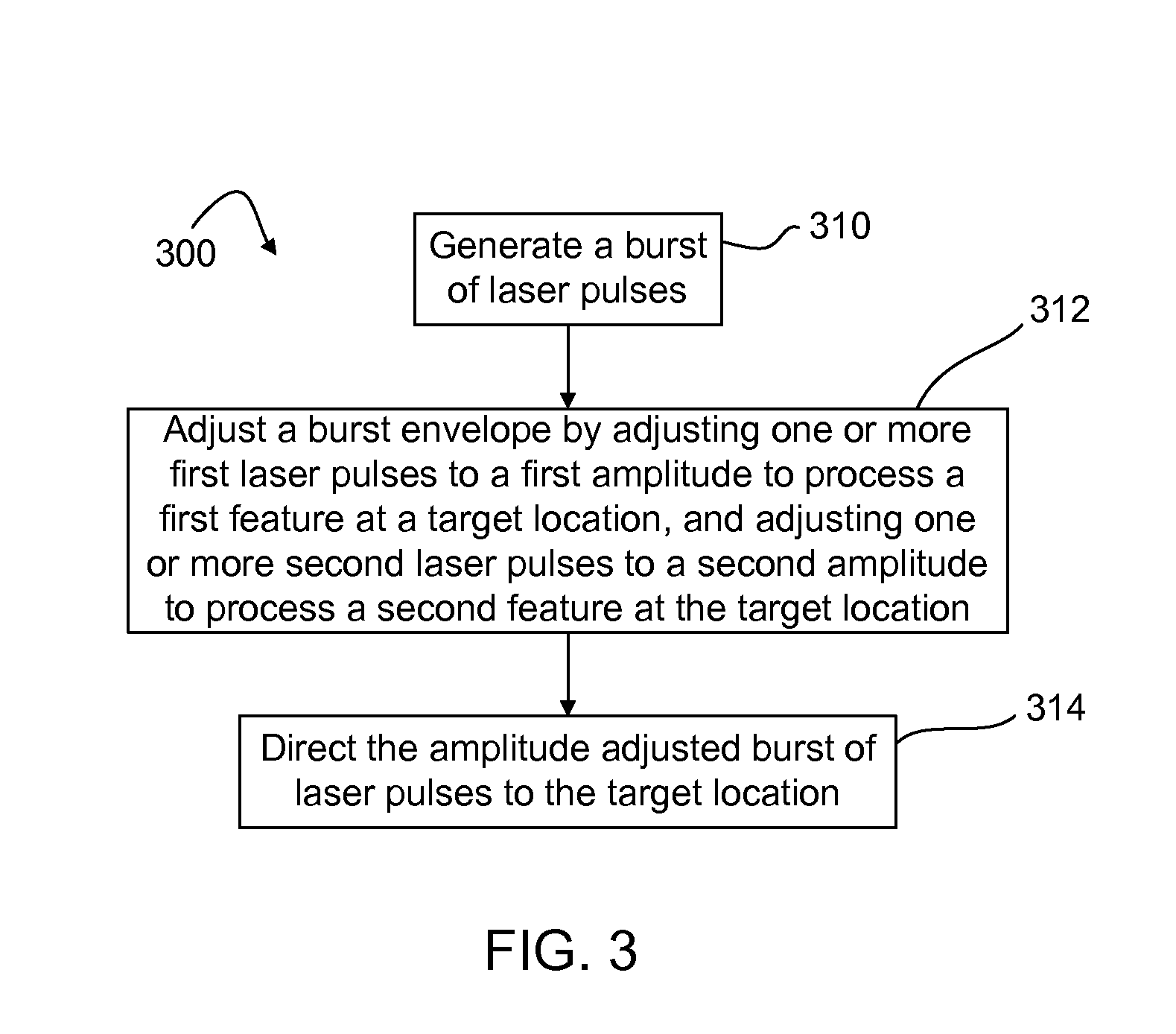
Laser micromachining with tailored bursts of short laser pulses
A series of laser pulse bundles or bursts are used for micromachining target structures. Each burst includes short laser pulses with temporal pulse widths that are less than approximately 1 nanosecond. A laser micromachining method includes generating a burst of laser pulses and adjusting an envelope of the burst of laser pulses for processing target locations. The method includes adjusting the burst envelope by selectively adjusting one or more first laser pulses within the burst to a first amplitude based on processing characteristics of a first feature at a target location, and selectively adjusting one or more second laser pulses within the burst to a second amplitude based on processing characteristics of a second feature at the target location. The method further includes directing the amplitude adjusted burst of laser pulses to the target location.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser micromachining using programmable pulse shapes
InactiveUS20090245301A1Improve throughputAvoid damageLaser detailsNon-linear opticsLeading edgeNanosecond
Laser pulse shaping techniques produce tailored laser pulse spectral output. The laser pulses can be programmed to have desired pulse widths and pulse shapes (such as sub-nanosecond to 10 ns-20 ns pulse widths with 1 ns to several nanoseconds leading edge rise times). Preferred embodiments are implemented with one or more electro-optical modulators receiving drive signals that selectively change the amount of incident pulsed laser emission to form a tailored pulse output. Triggering the drive signal from the pulsed laser emission suppresses jitter associated with other stages of the link processing system and substantially removes jitter associated with pulsed laser emission build-up time.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
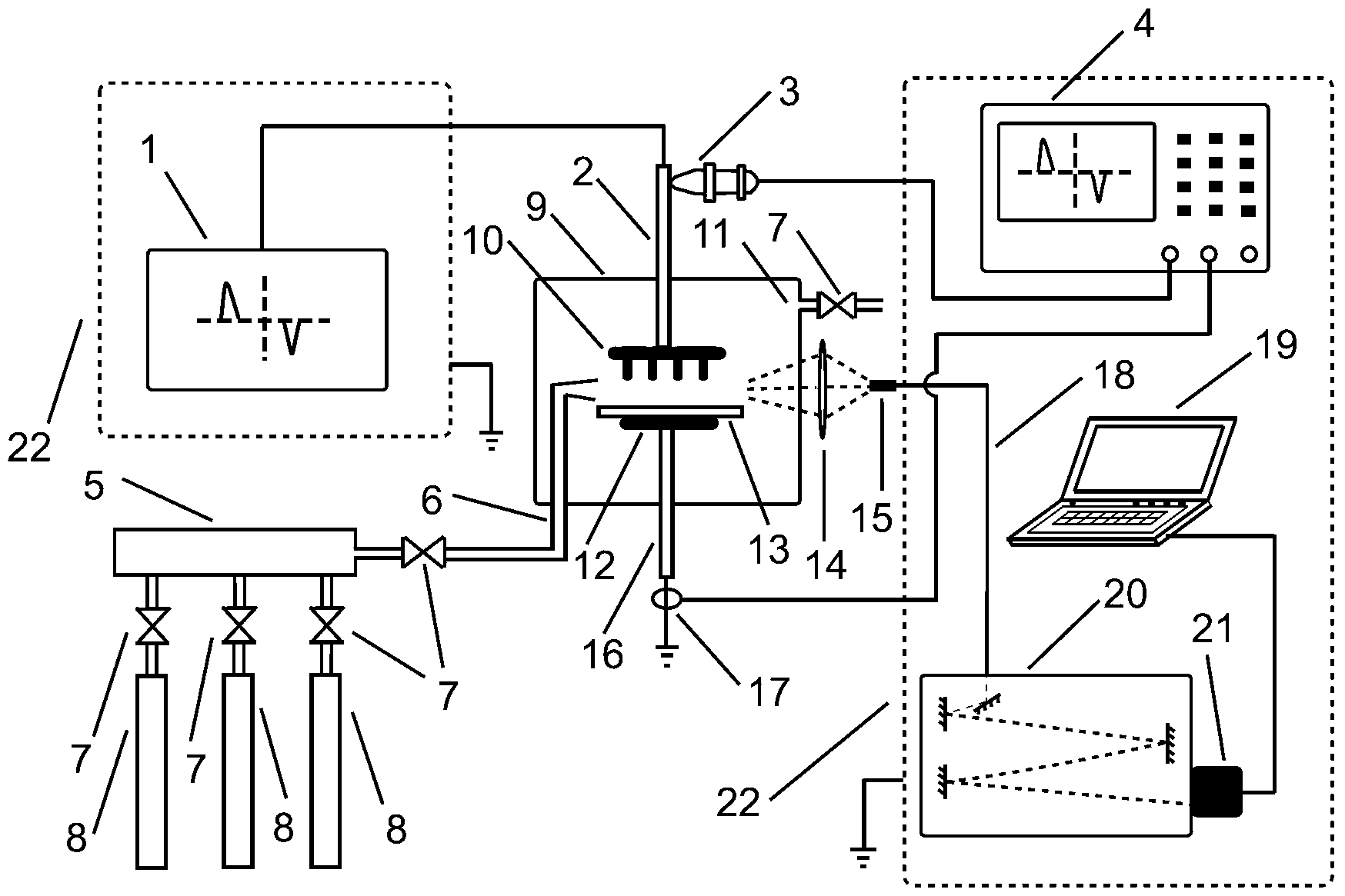
Experimental apparatus for acquiring large-area uniform discharge plasmas
InactiveCN103245655AIncrease electron densityImprove energy utilizationAnalysis by thermal excitationPlasma techniqueDischarge measurementsElectron density
The invention relates to an experimental apparatus for acquiring large-area uniform discharge plasmas, which belongs to the technical field of plasmas. The experimental apparatus comprises a bipolar nanosecond pulse power supply, a reactor, multi-needle-to-plate electrodes, a gas distribution system, a spectral measurement system and a discharge measurement system, wherein the bipolar nanosecond pulse power supply drives dielectric barrier discharge of air and other gas mixtures among the multi-needle-to-plate electrodes in the reactor, and the gas mixtures are input to the reactor through the gas distribution system; the spectral measurement system collects photonic information of plasma discharge in real time and inputs the photonic information to a computer for spectral analysis; and the discharge measurement system collects discharge voltage and current of the high-voltage nanosecond pulse power supply in real time, and the discharge voltage and current are displayed through a digital oscilloscope. By virtue of the bipolar nanosecond narrow-pulse power supply, the large-area discharge plasmas are generated without a magnetic field; and the generated plasmas are uniform, diffusive, high in electron density, high in energy utilization ratio, low in energy consumption and easy to control in a discharge process.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Probes with high current carrying capability and laser machining methods
ActiveUS20120286816A1High strengthElectrical measurement instrument detailsManufacture of electrical instrumentsPicosecond laserNanosecond
The present invention is a probe having a distal end made of one material, a tip and a portion disposed between the distal end and the tip that is a different second material. The probe is laser machined manufactured using a nanosecond or picosecond laser.
Owner:MICRO PROBE
Fiber mopa system without stimulated brillouin scattering
ActiveUS20090010288A1Shorten fiber lengthIncreasing mode areaLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionNanosecondSeeds source
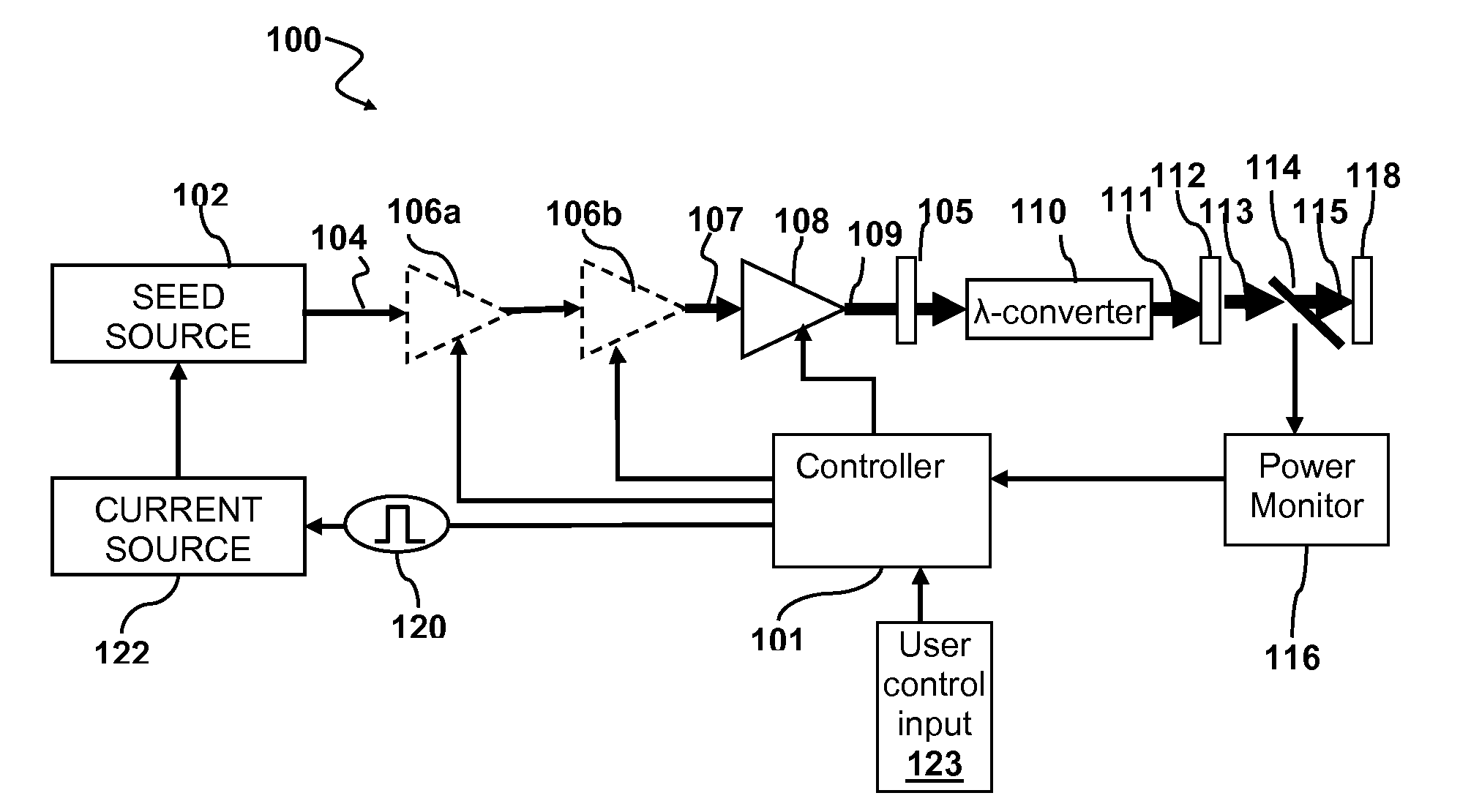
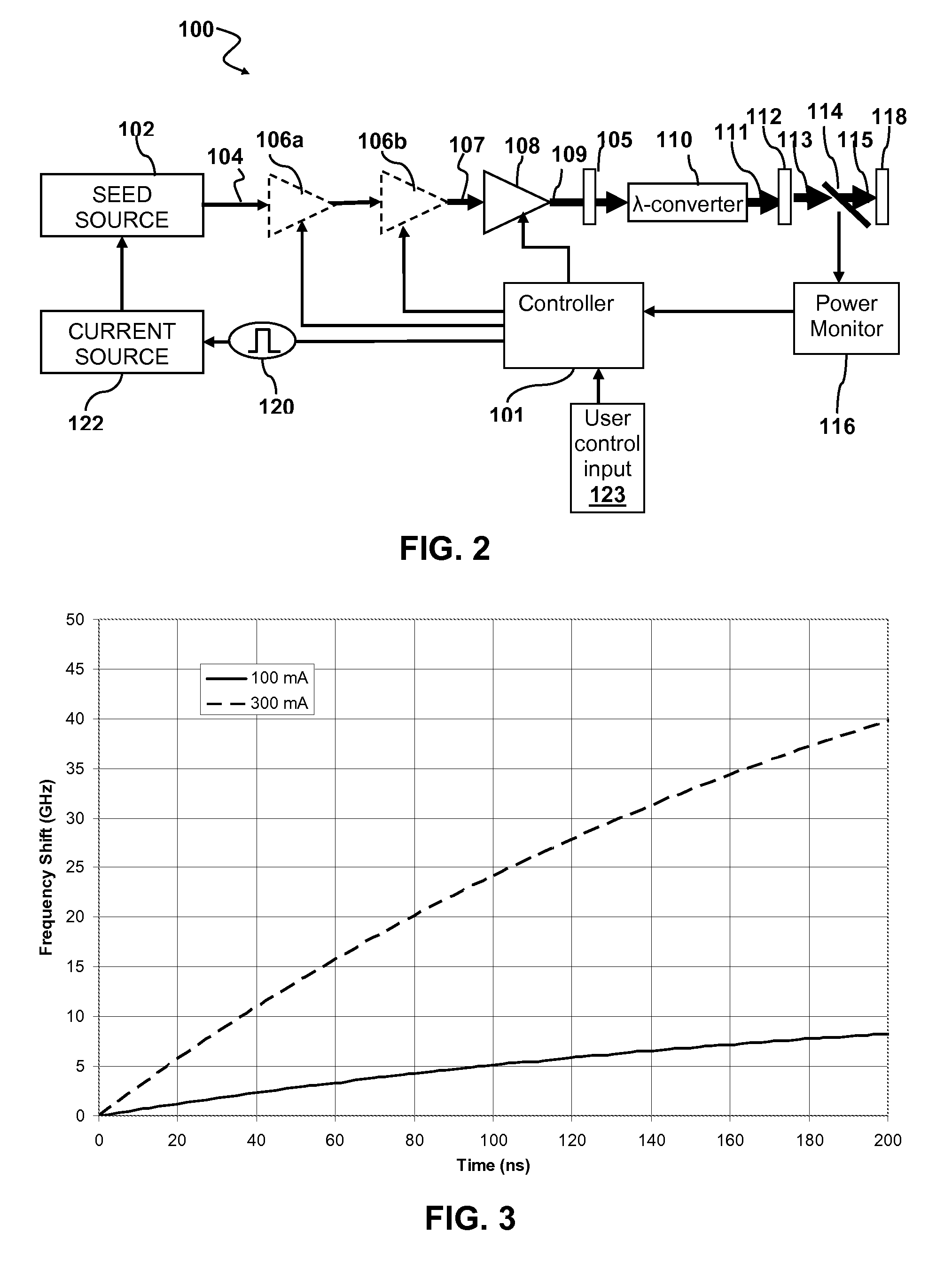
Methods and systems for increasing the threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering are described. A seed source may generate one or more chirped seed pulses characterized by a pulse duration τ, and a frequency chirp. The pulse duration τ may be greater than about 2 nanoseconds. A photonic crystal amplifier amplifies the seed pulses to produce one or more amplified pulses characterized by a peak power P greater than about 1 kilowatt. The pulse duration τ, frequency chirp, and the photonic crystal fiber may be selected such that a threshold for stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in the photonic crystal fiber is greater than the peak power P.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com