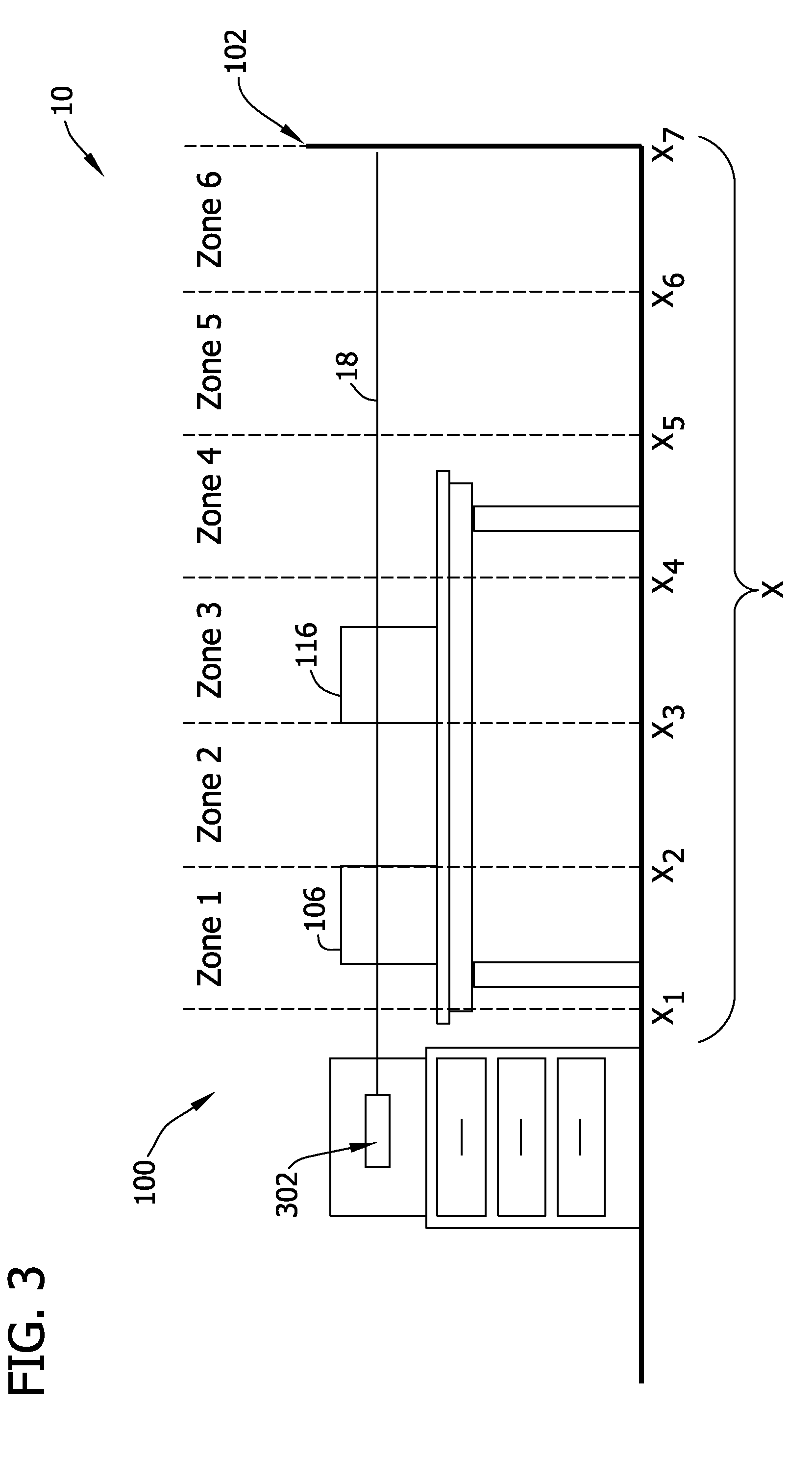
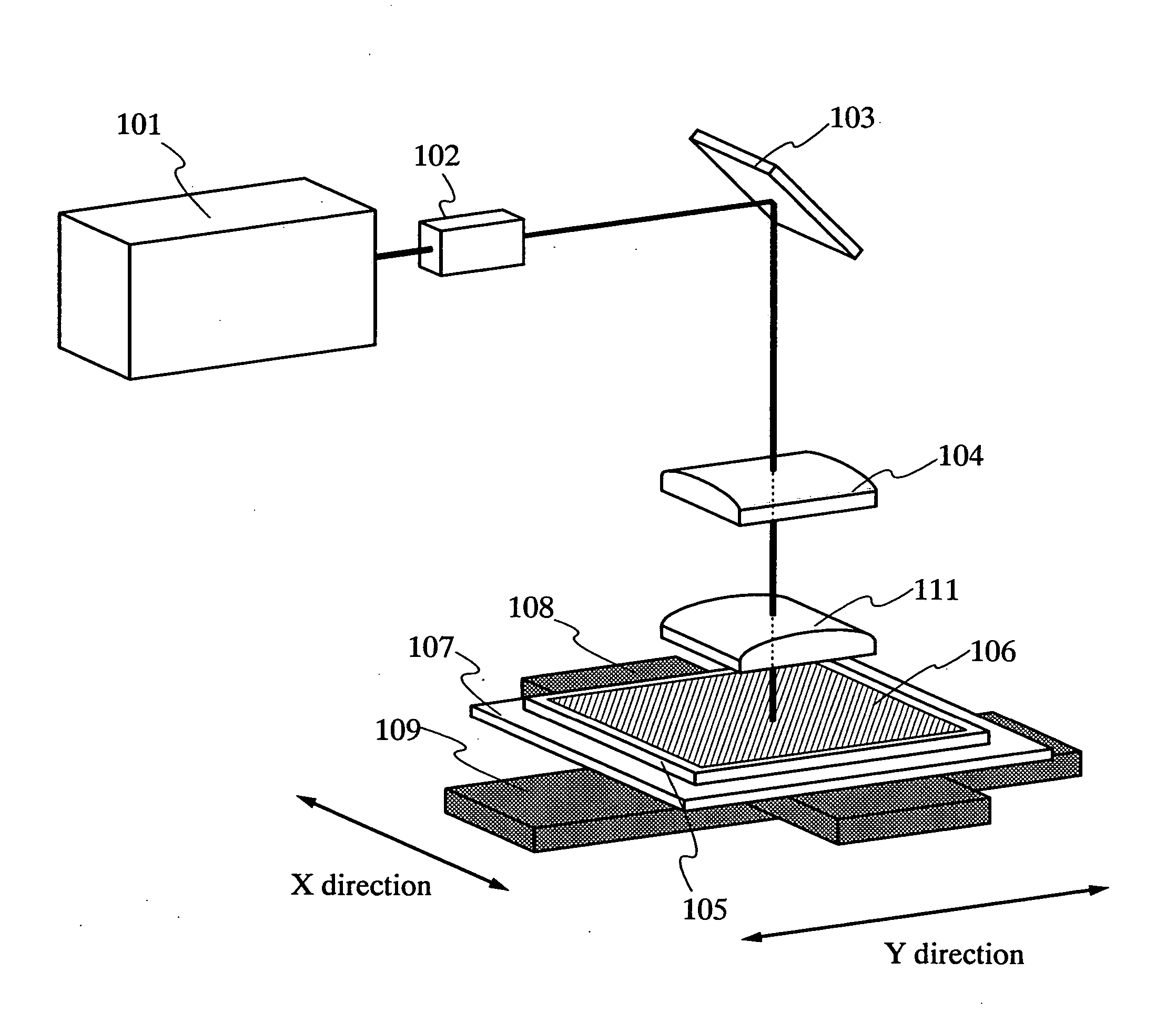
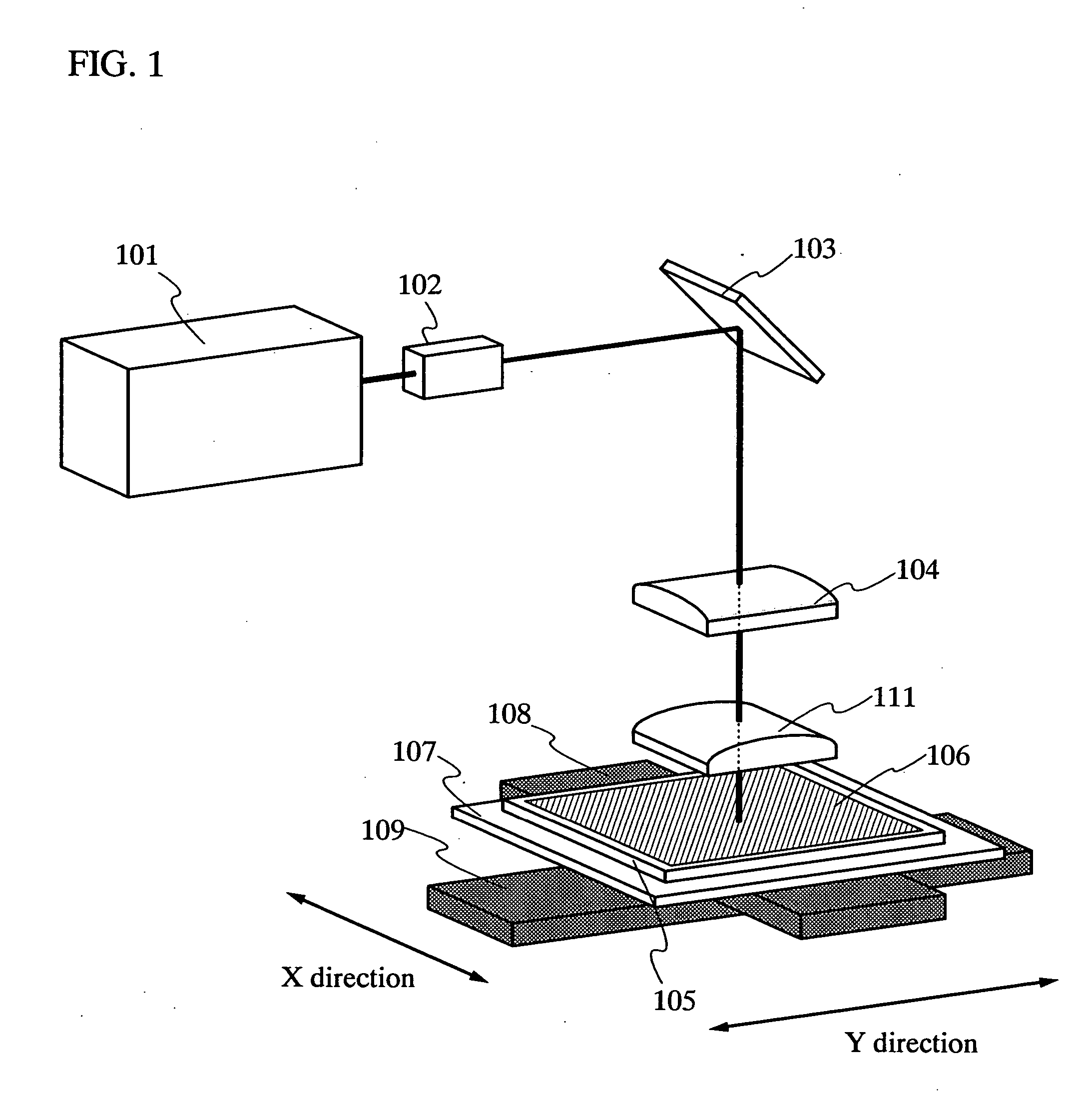
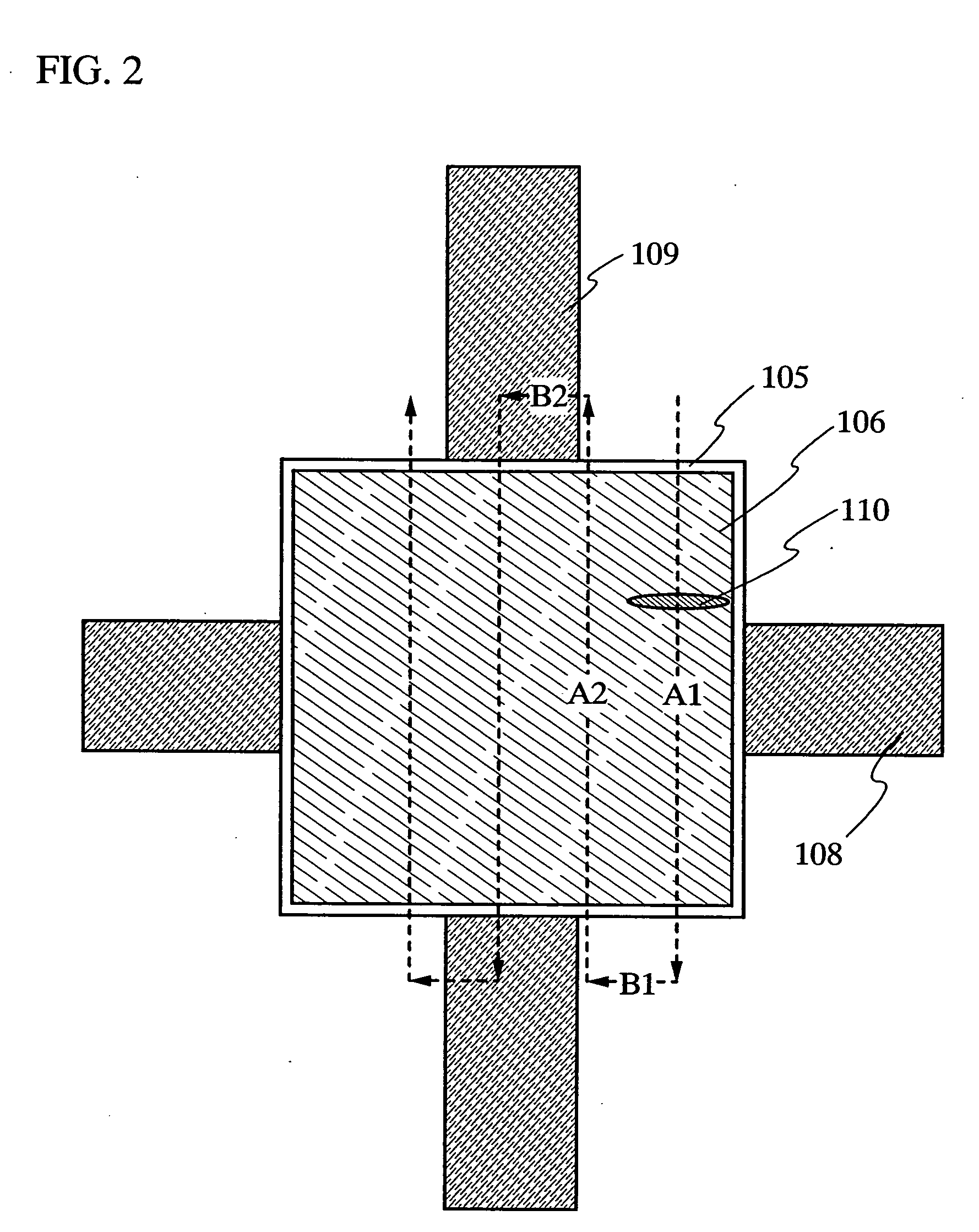
Patents
Literature
604 results about "Picosecond" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A picosecond is an SI unit of time equal to 10⁻¹² or ¹/1,000,000,000,000 (one trillionth) of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000 001 seconds. A picosecond is to one second as one second is to approximately 31,689 years. Multiple technical approaches achieve imaging within single-digit picoseconds: for example, the streak camera or intensified CCD (ICCD) cameras are able to picture the motion of light.
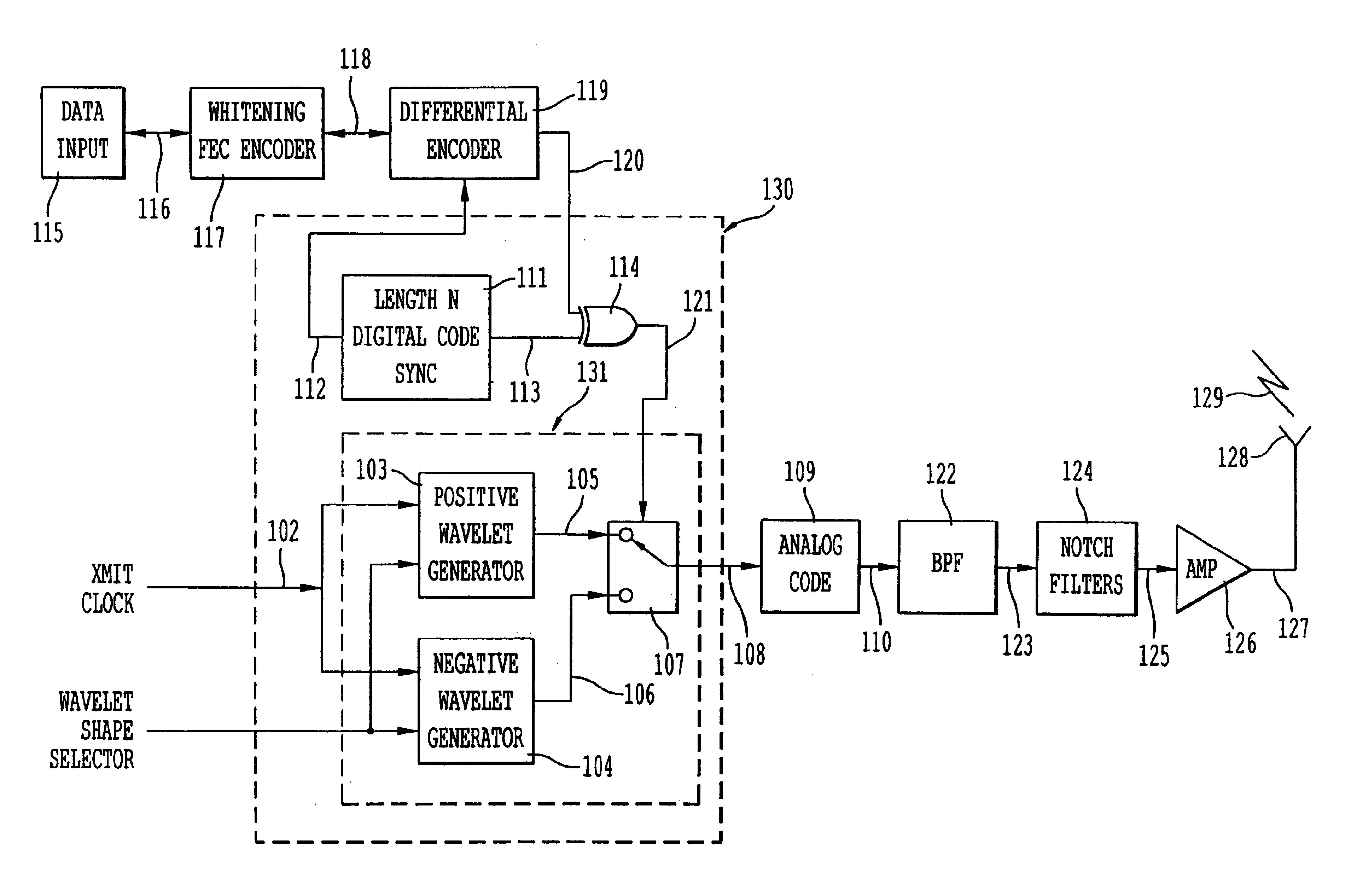
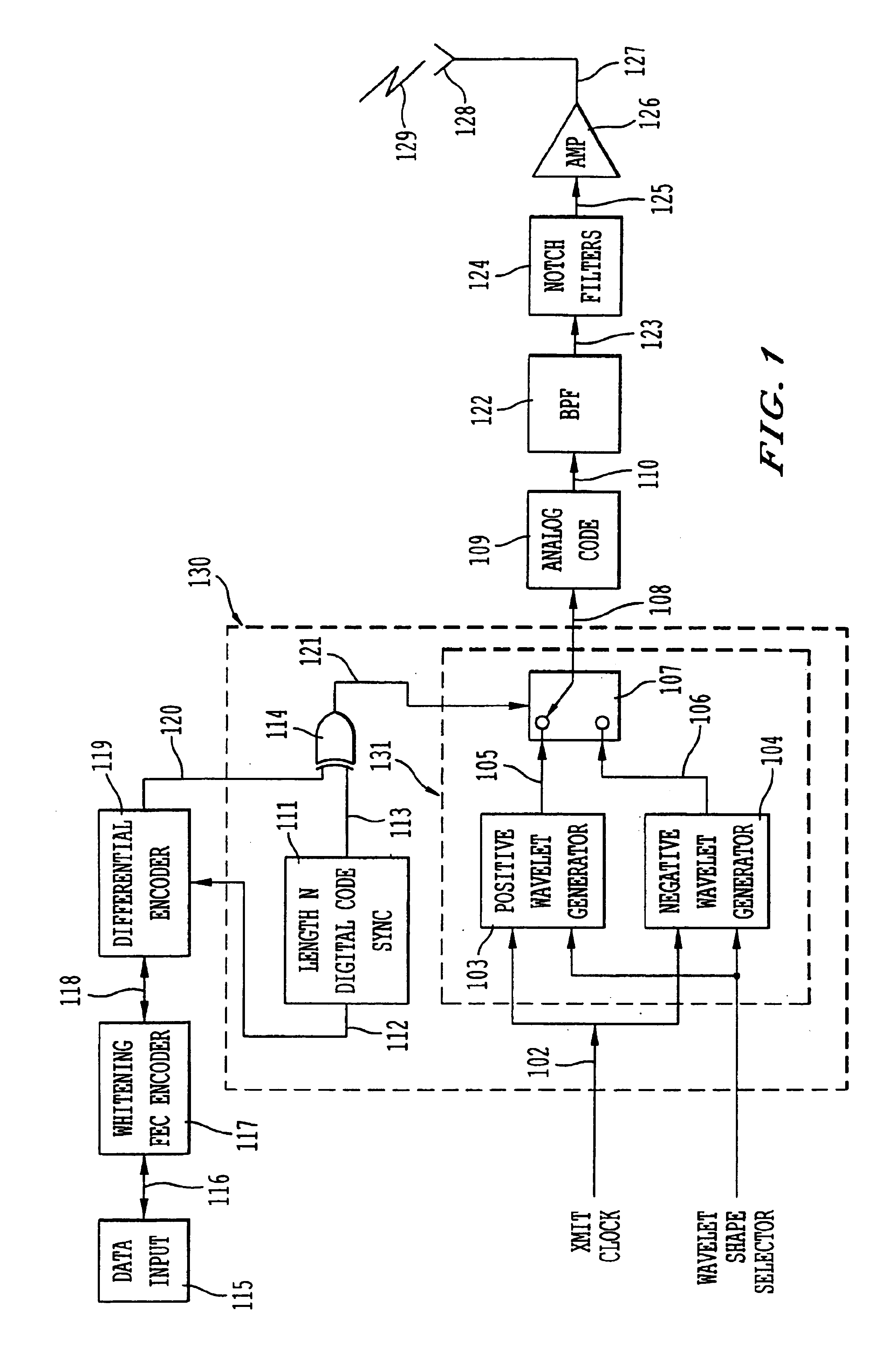
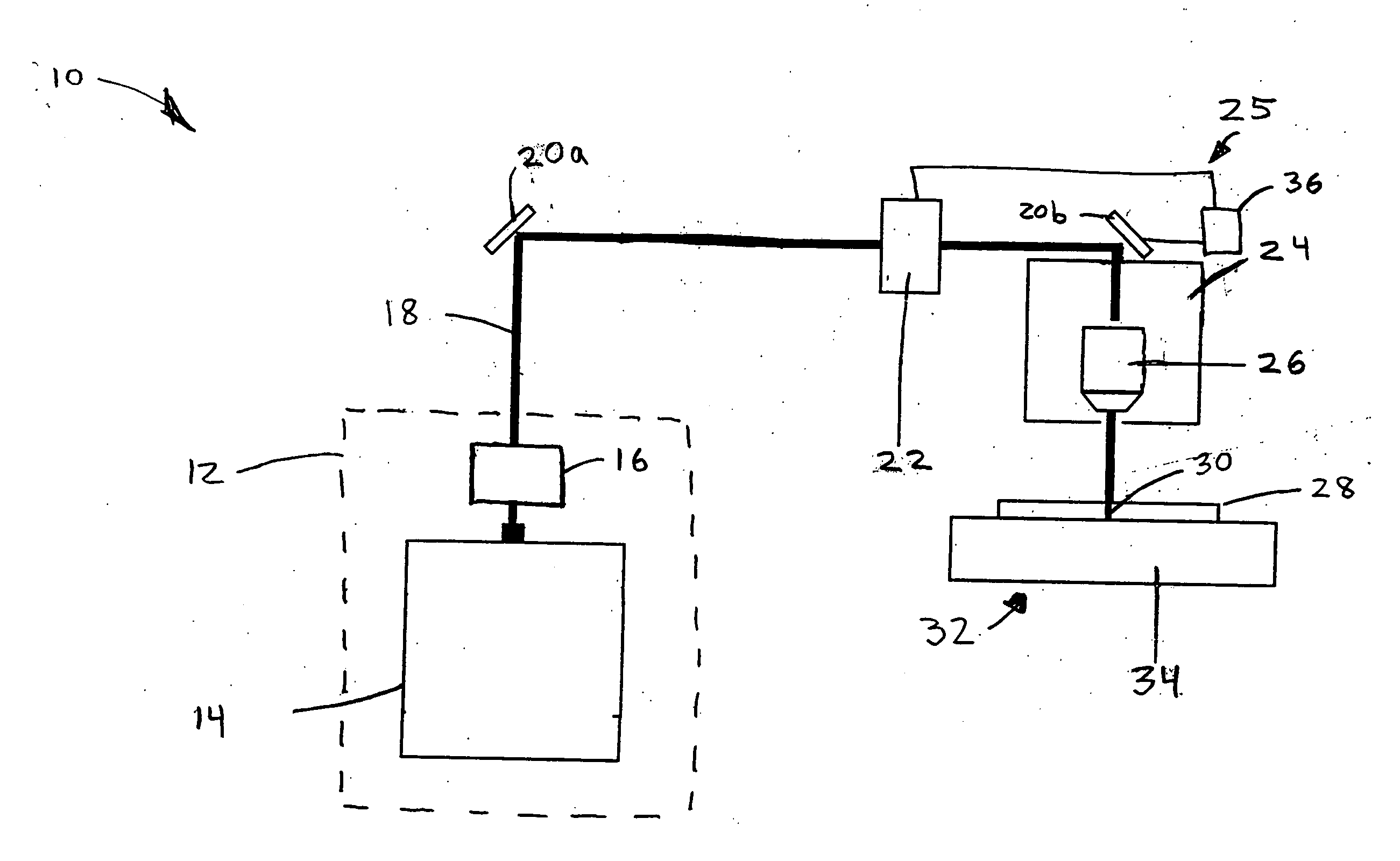
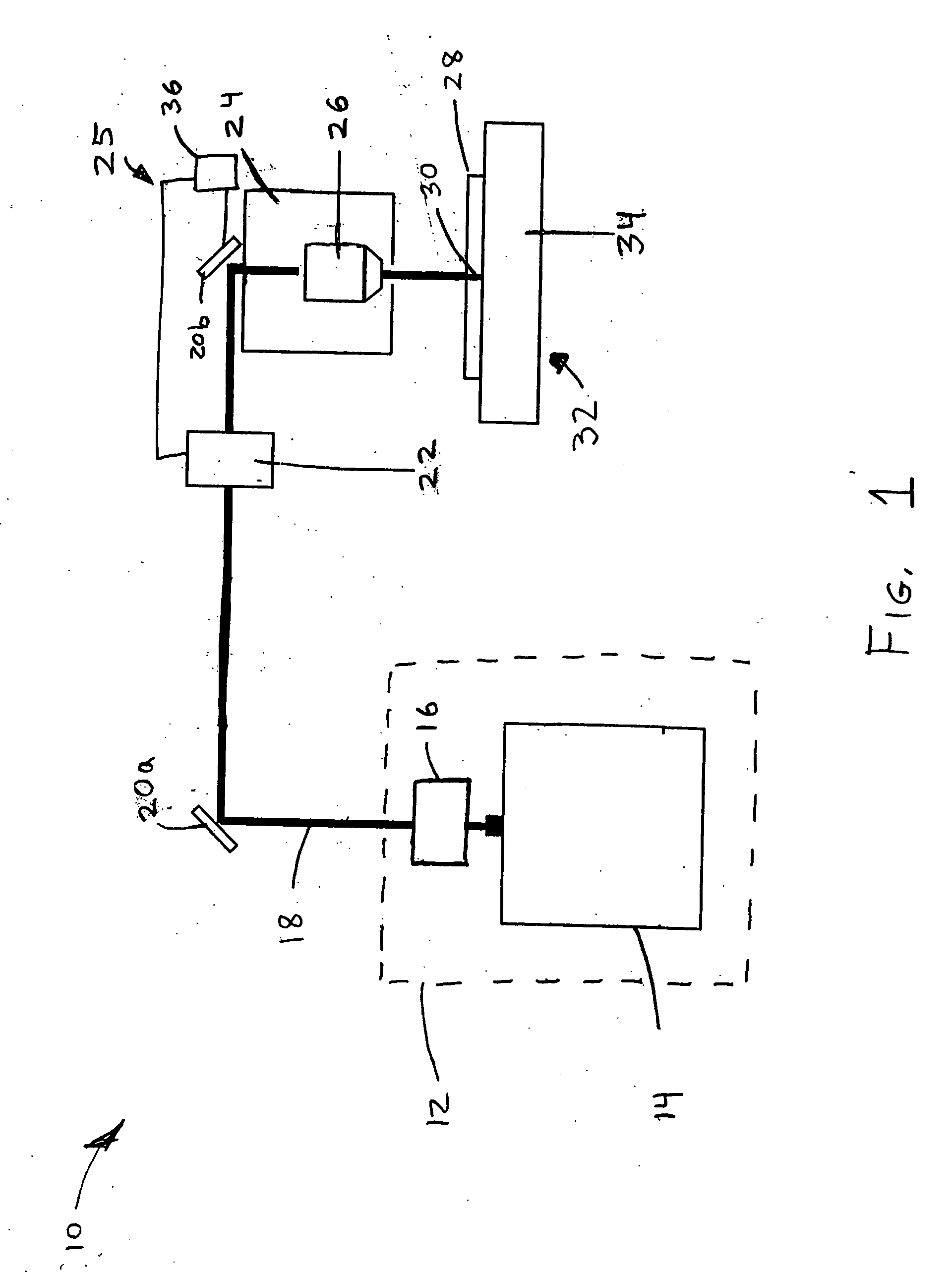
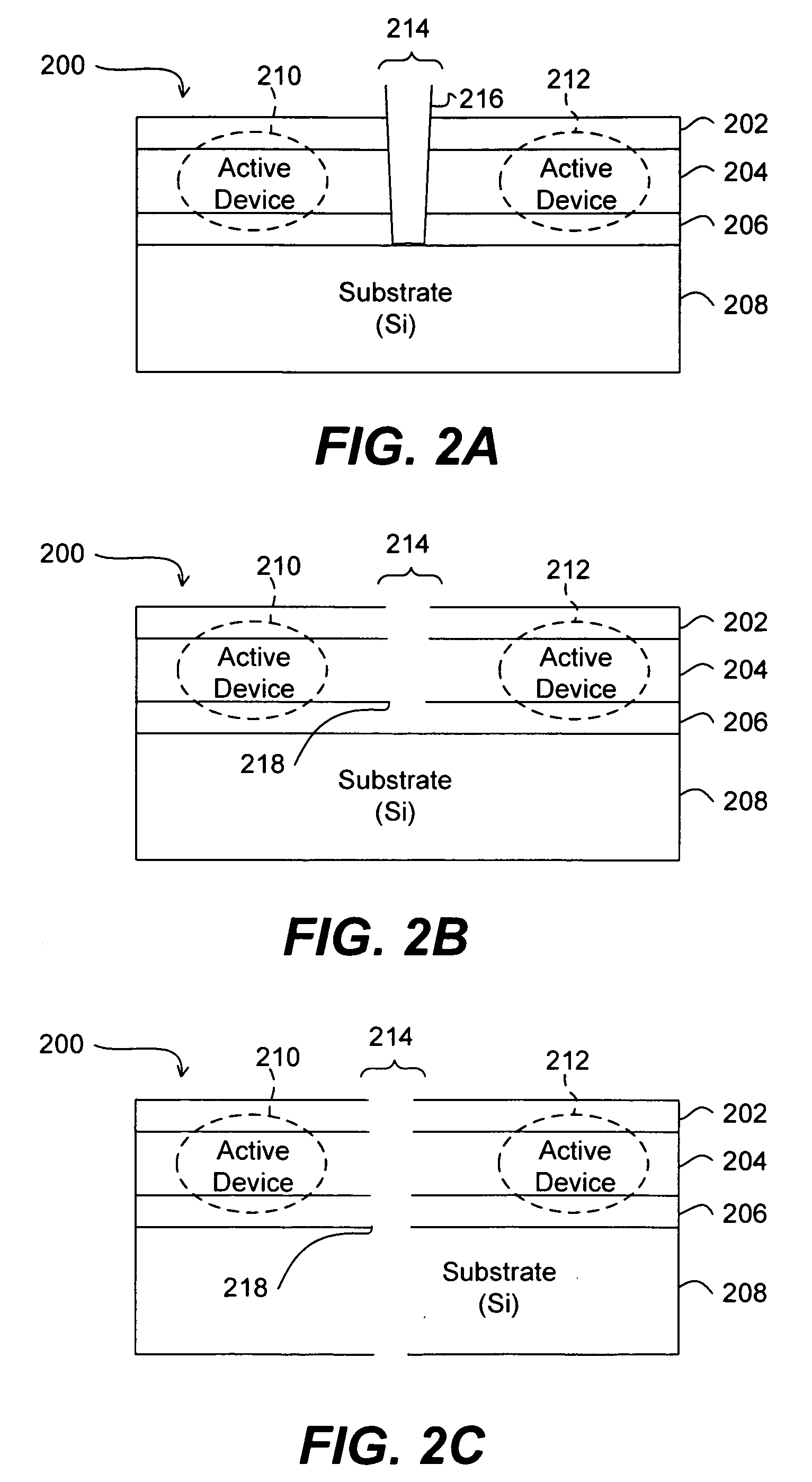
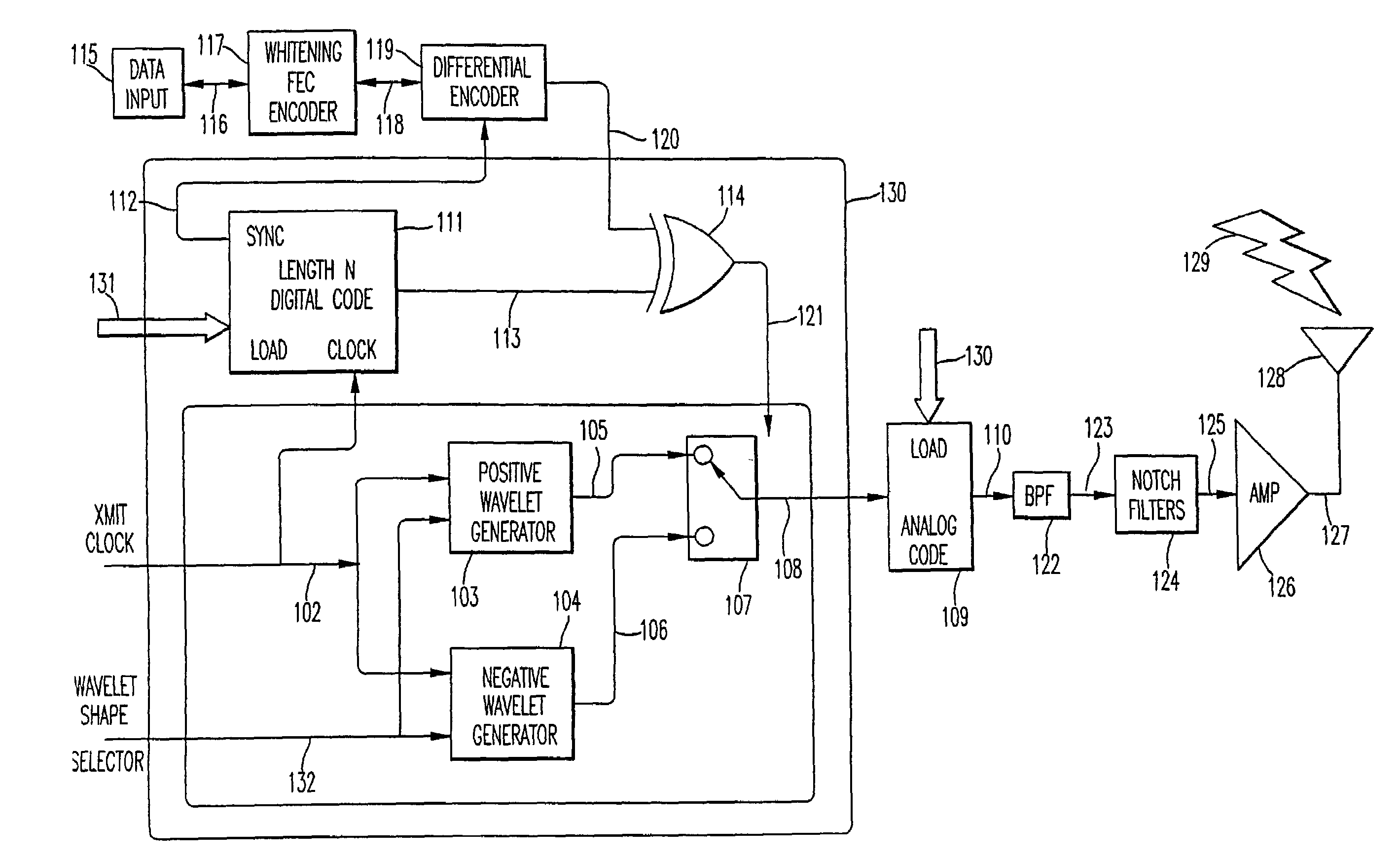
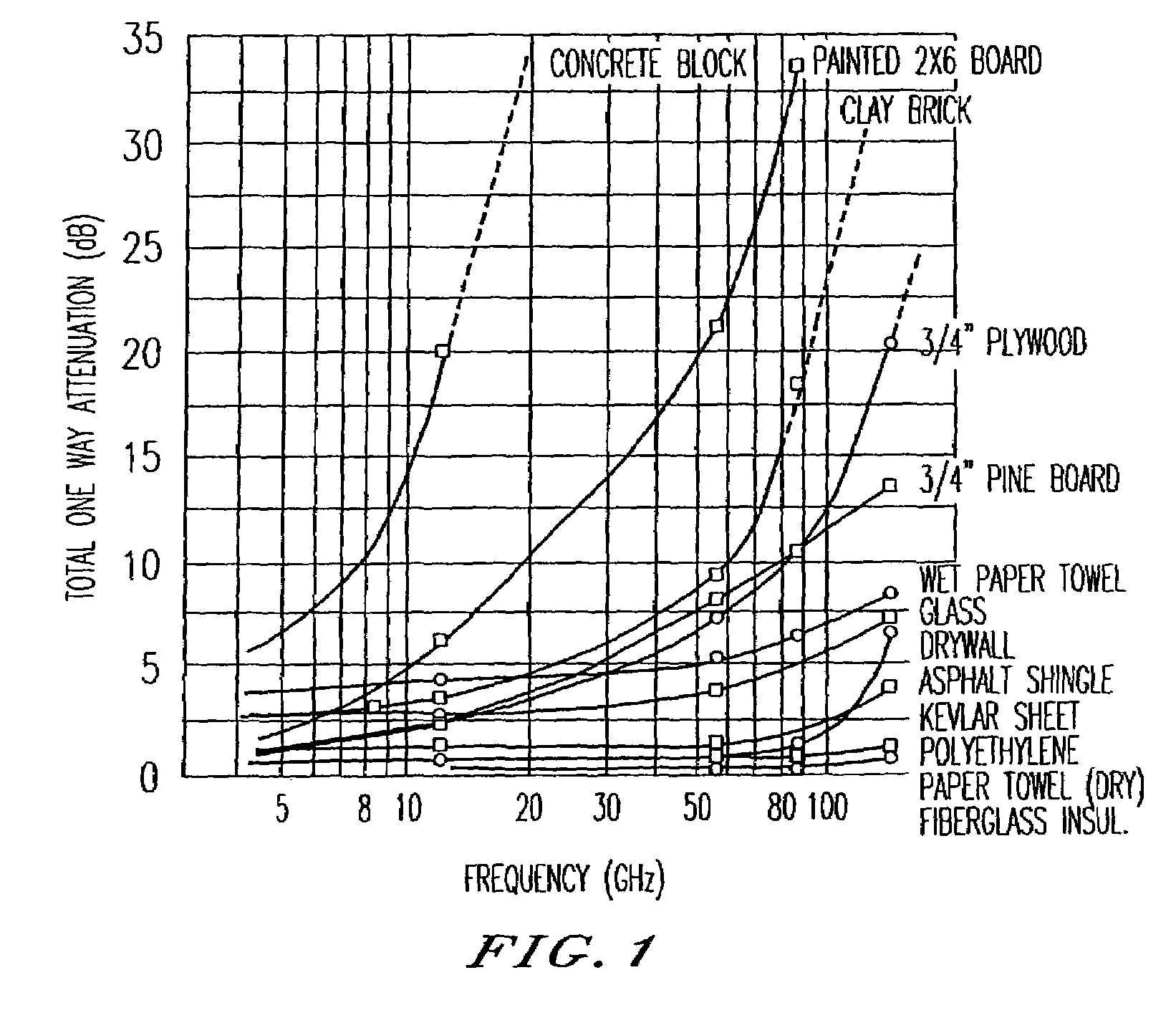
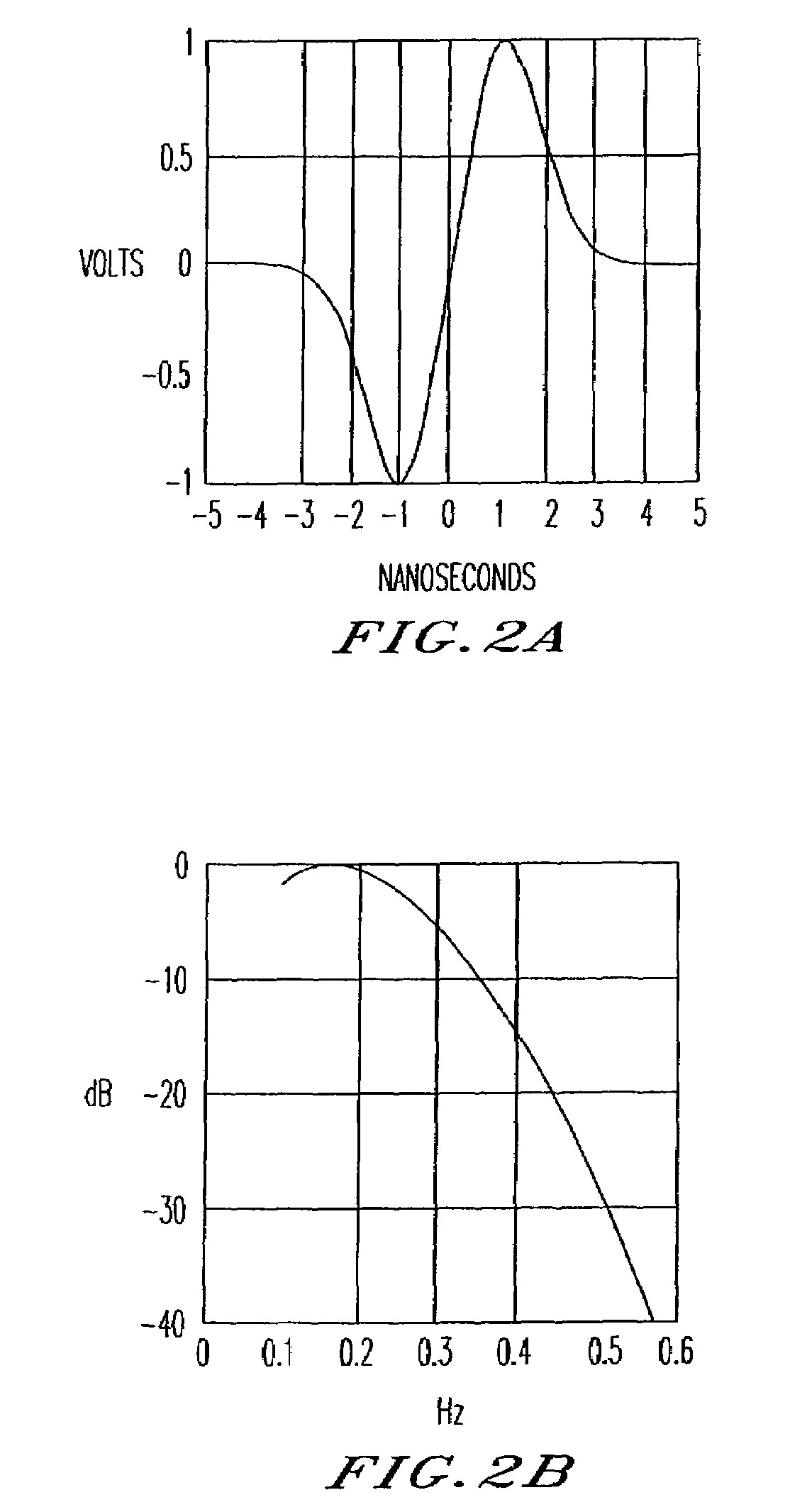
Ultra wide bandwidth spread-spectrum communications system
InactiveUS6901112B2Modulated carrier system with waveletsMultiplex communicationMultipath interferenceEngineering
An ultra wide bandwidth, high speed, spread spectrum communications system uses short wavelets of electromagnetic energy to transmit information through objects such as walls or earth. The communication system uses baseband codes formed from time shifted and inverted wavelets to encode data on a RF signal. Typical wavelet pulse durations are on the order of 100 to 1000 picoseconds with a bandwidth of approximately 8 GHz to 1 GHz, respectively. The combination of short duration wavelets and encoding techniques are used to spread the signal energy over an ultra wide frequency band such that the energy is not concentrated in any particular narrow band (e.g. VHF: 30-300 MHz or UHF: 300-1000 MHz) and is not detected by conventional narrow band receivers so it does not interfere with those communication systems. The use of pulse codes composed of time shifted and inverted wavelets gives the system according to the present invention has a spatial resolution on the order of 1 foot which is sufficient to minimize the negative effects of multipath interference and permit time domain rake processing.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
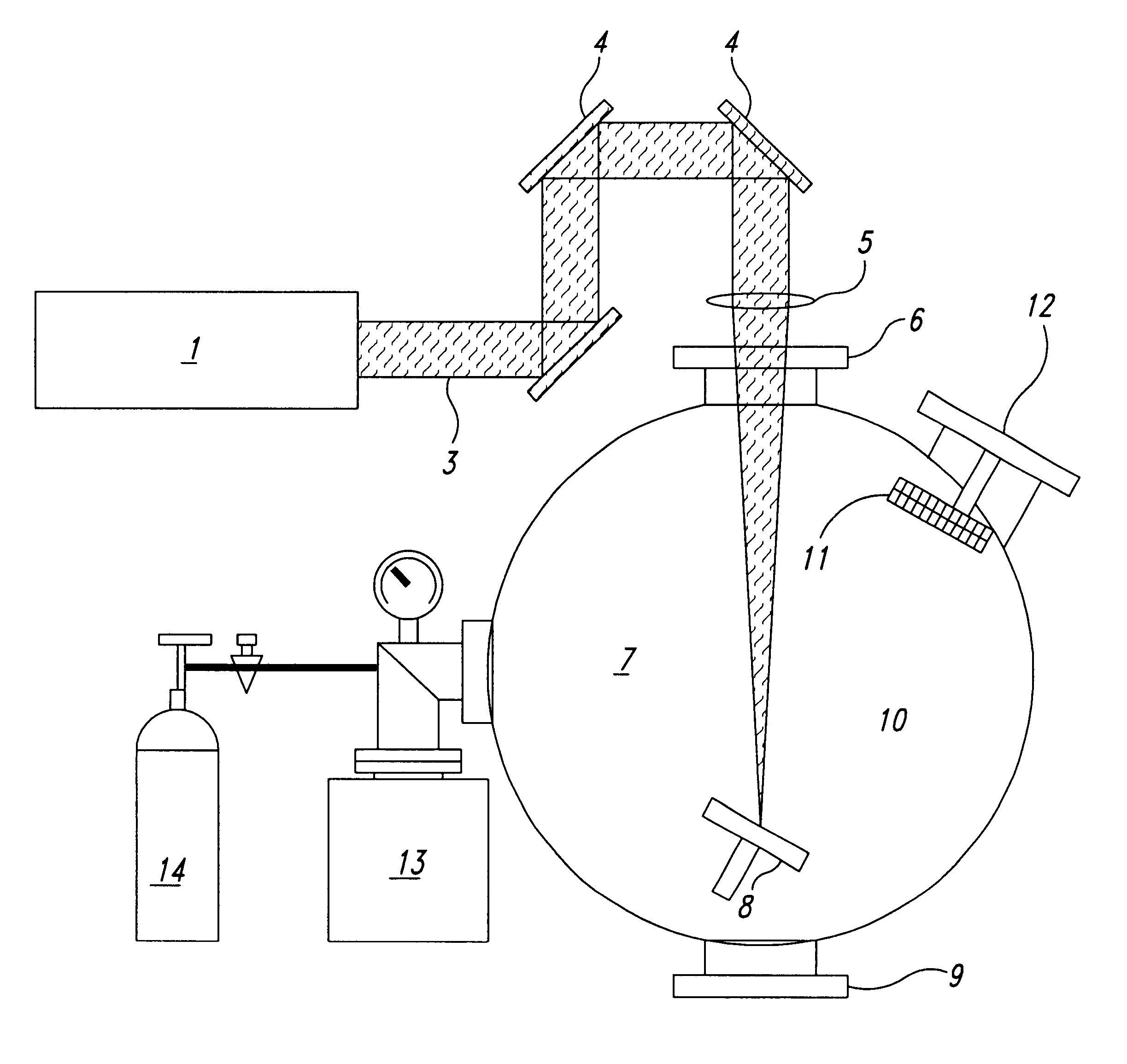
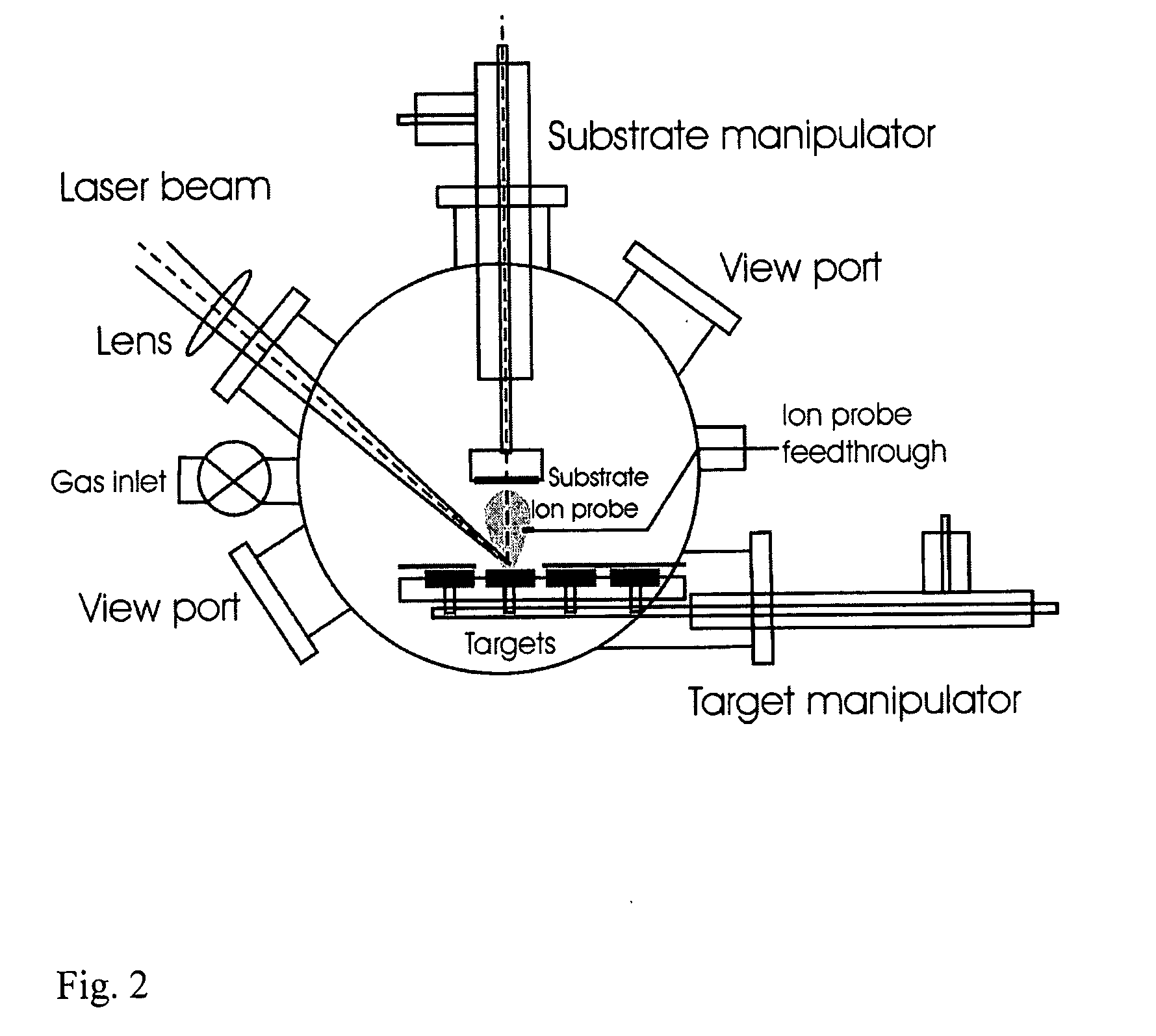
Method of deposition of thin films of amorphous and crystalline microstructures based on ultrafast pulsed laser deposition
InactiveUS6312768B1Improve surface qualityImprove efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingMacroscopic scaleCarbon nanotube
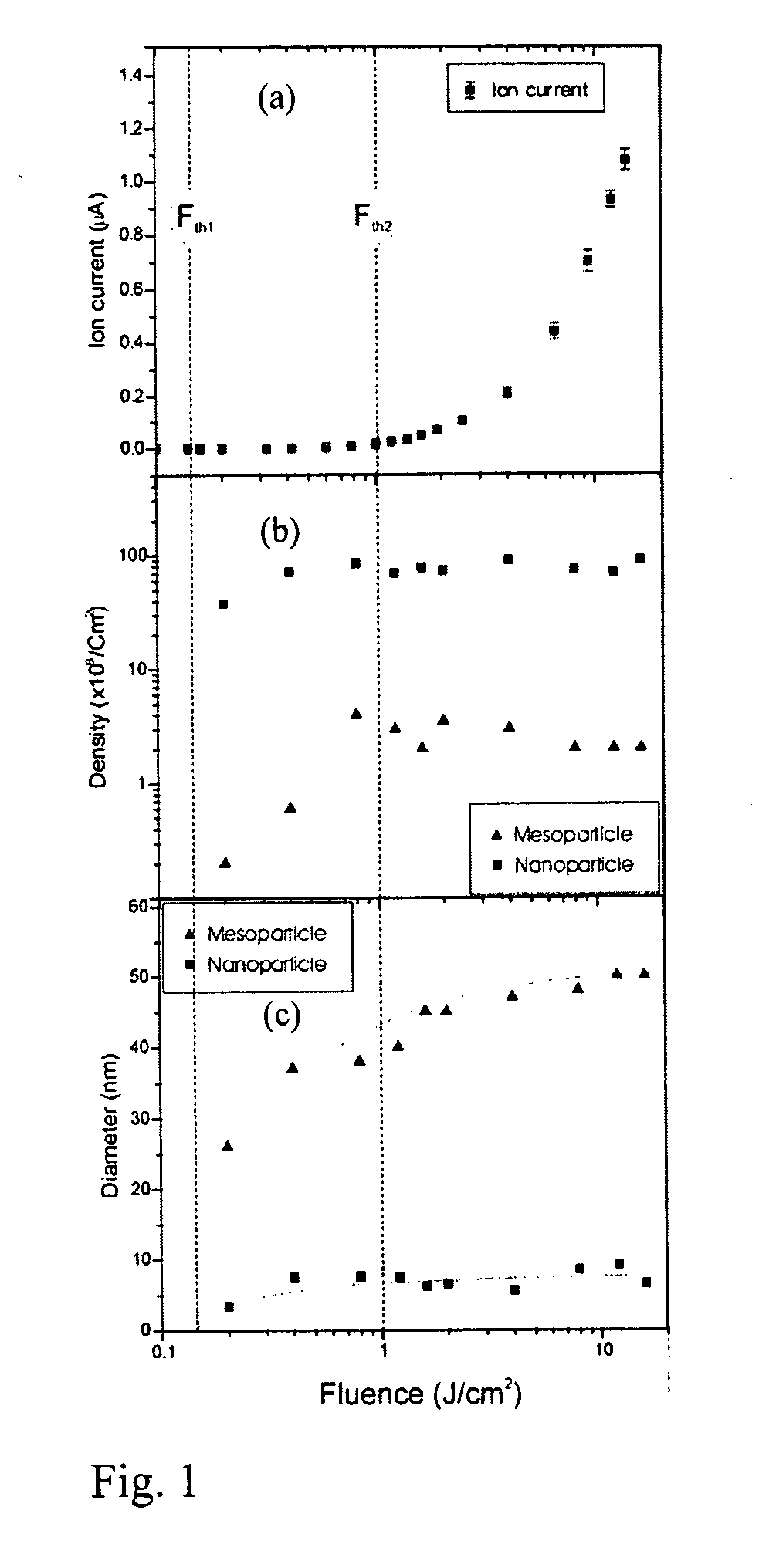
Powerful nanosecond-range lasers using low repetition rate pulsed laser deposition produce numerous macroscopic size particles and droplets, which embed in thin film coatings. This problem has been addressed by lowering the pulse energy, keeping the laser intensity optional for evaporation, so that significant numbers of the macroscopic particles and droplets are no longer present in the evaporated plume. The result is deposition of evaporated plume on a substrate to form thin film of very high surface quality. Preferably, the laser pulses have a repetition rate to produce a continuous flow of evaporated material at the substrate. Pulse-range is typically picosecond and femtosecond and repetition rate kilohertz to hundreds of megahertz. The process may be carried out in the presence of a buffer gas, which may be inert or reactive, and the increased vapour density and therefore the collision frequency between evaporated atoms leads to the formation of nanostructured materials of increasing interest, because of their peculiar structural, electronic and mechanical properties. One of these is carbon nanotubes, which is a new form of carbon belonging to the fullerene (C60) family. Carbon nanotubes are seamless, single or multishell co-axial cylindrical tubules with or without dome caps at the extremities. Typically diameters range from 1 nm to 50 nm with a length >1 mum. The electronic structure may be either metallic or semiconducting without any change in the chemical bonding or adding of dopant. In addition, the materials have application to a wide range of established thin film applications.
Owner:AUSTRALIEN NAT UNIV
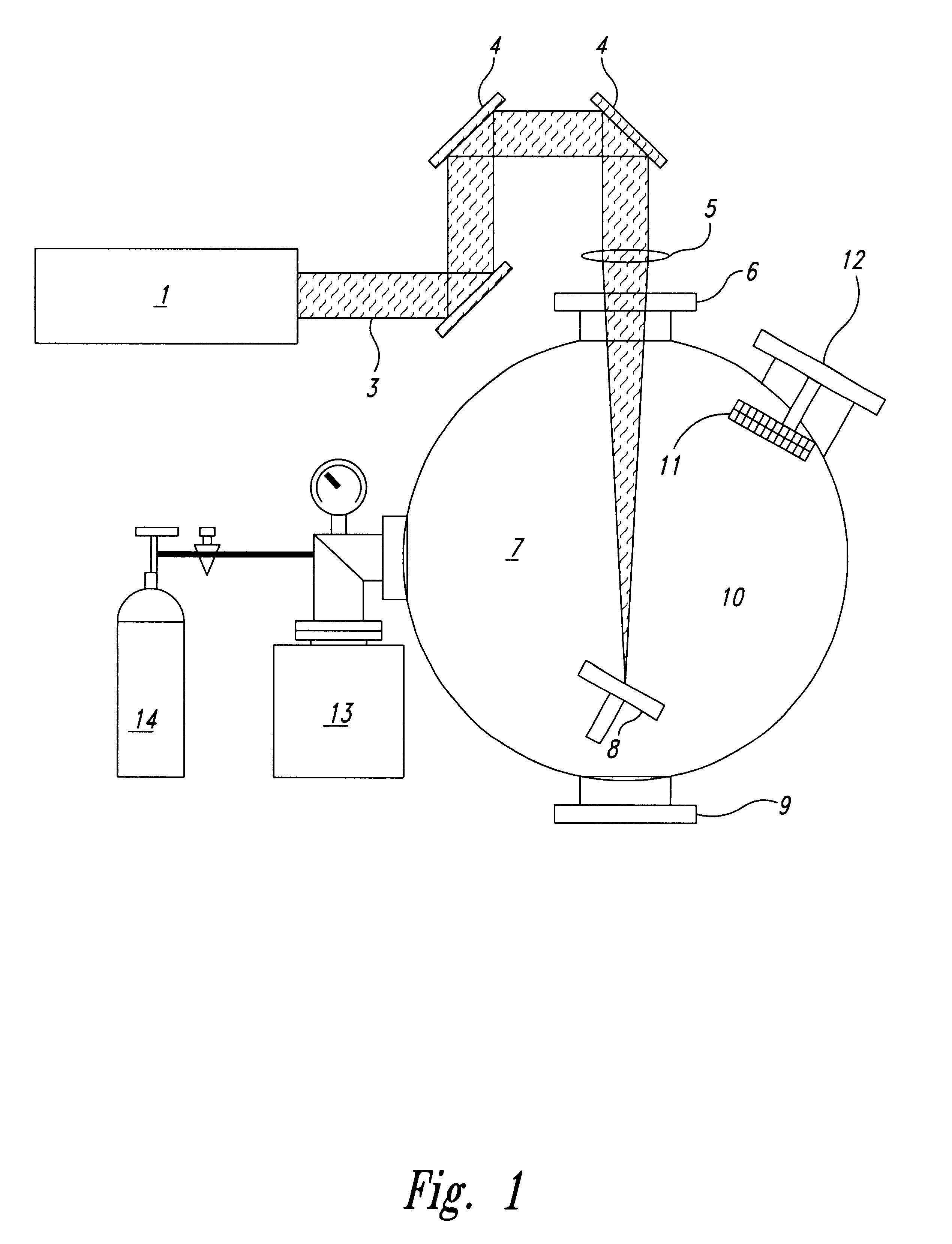
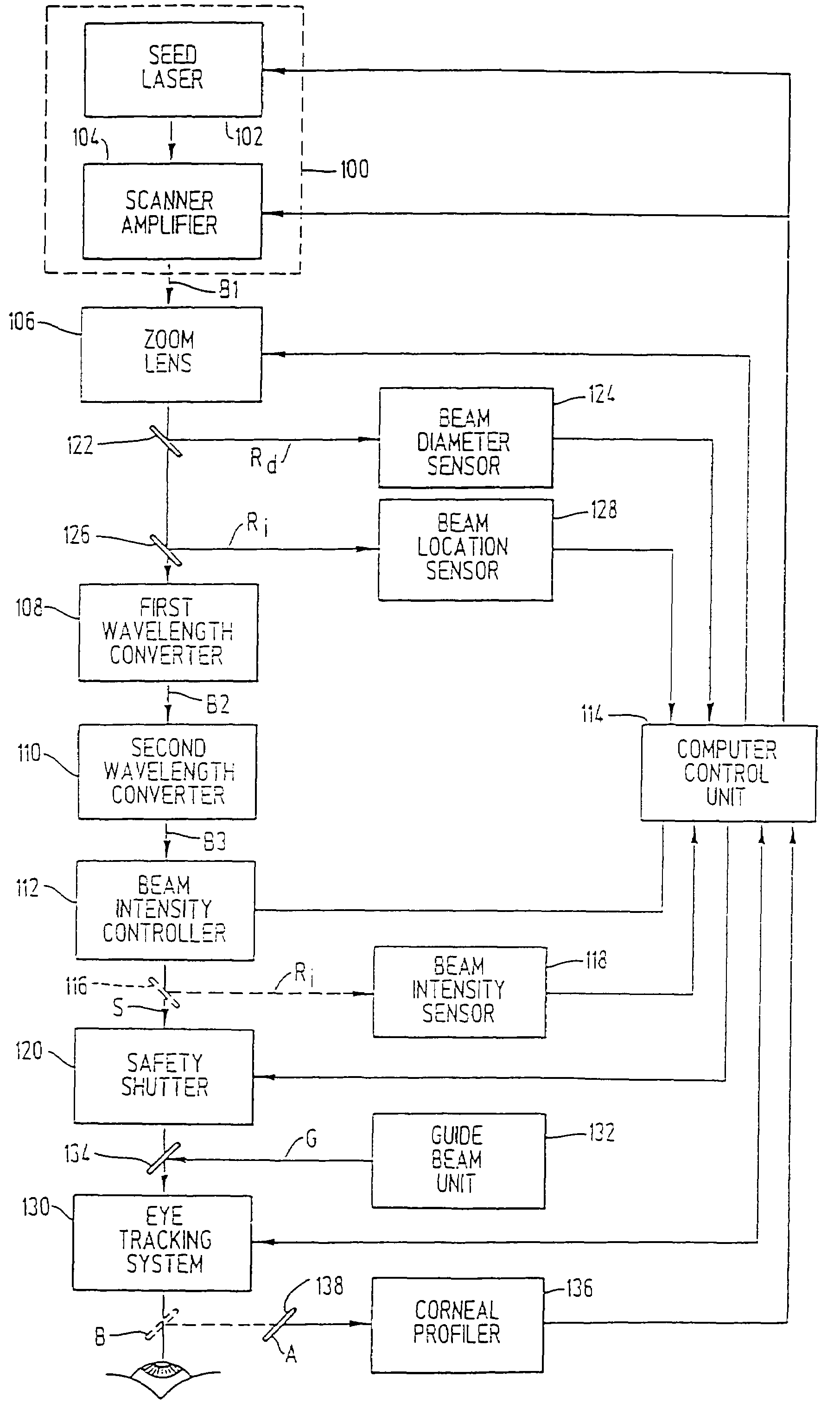
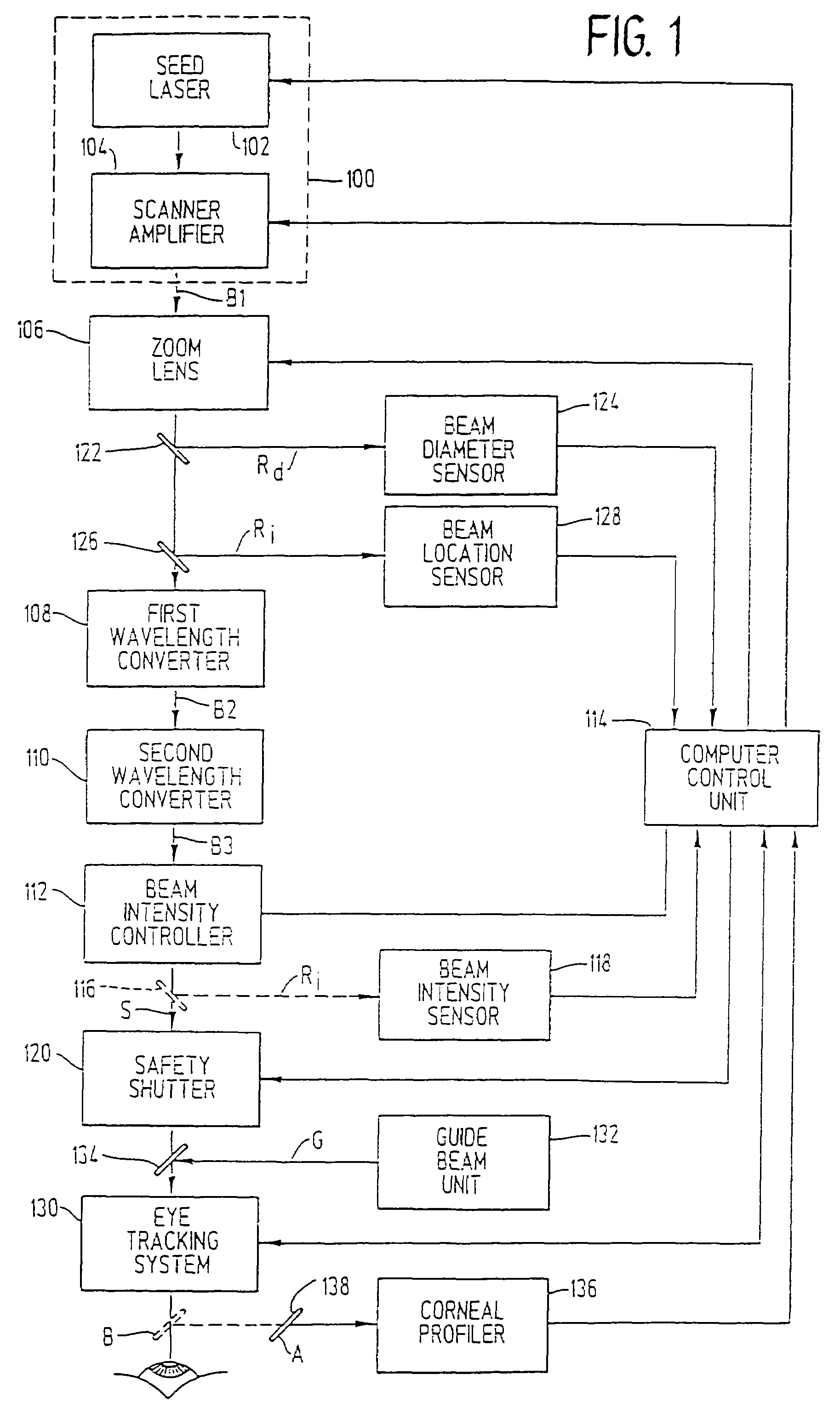
Method and apparatus for laser surgery of the cornea
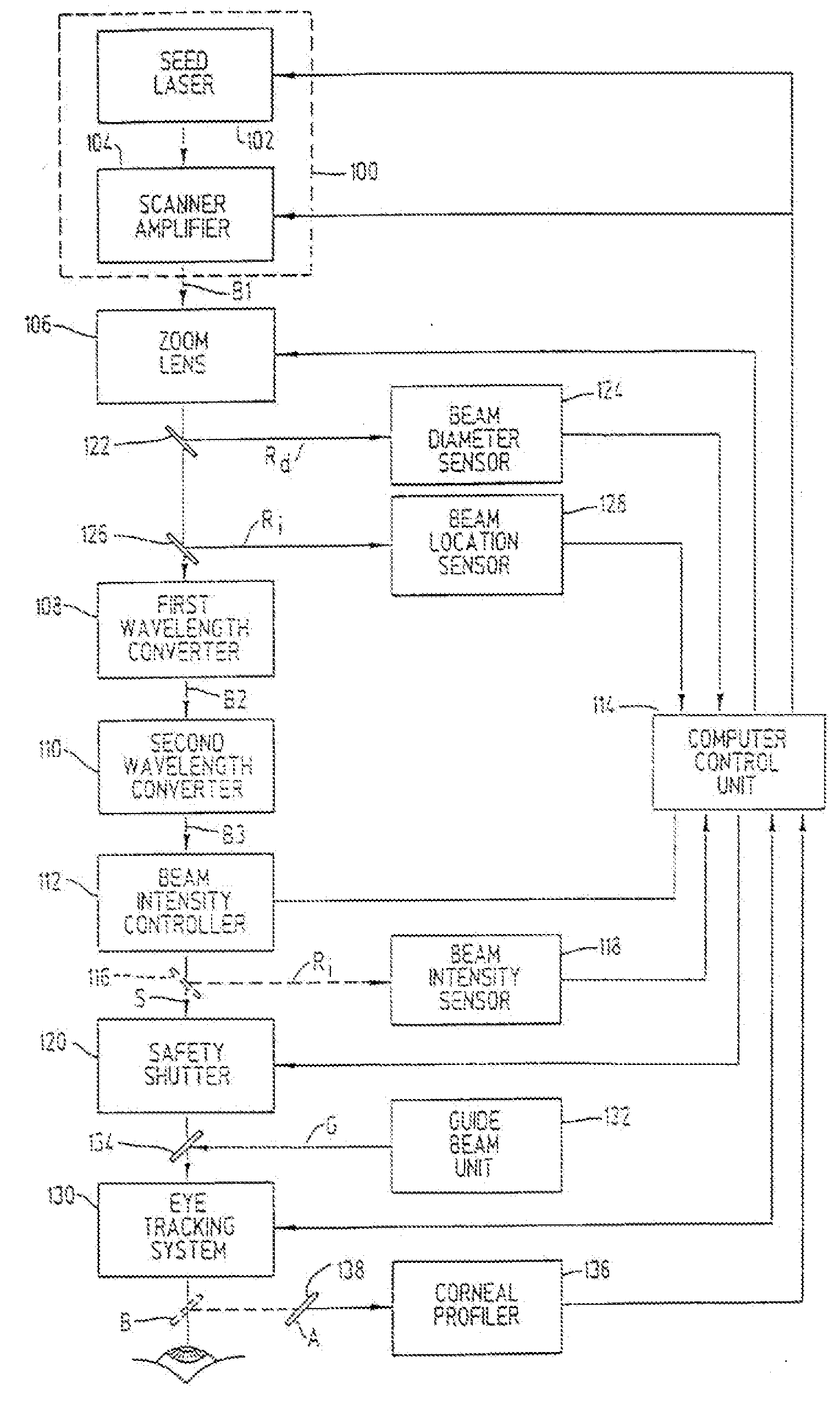
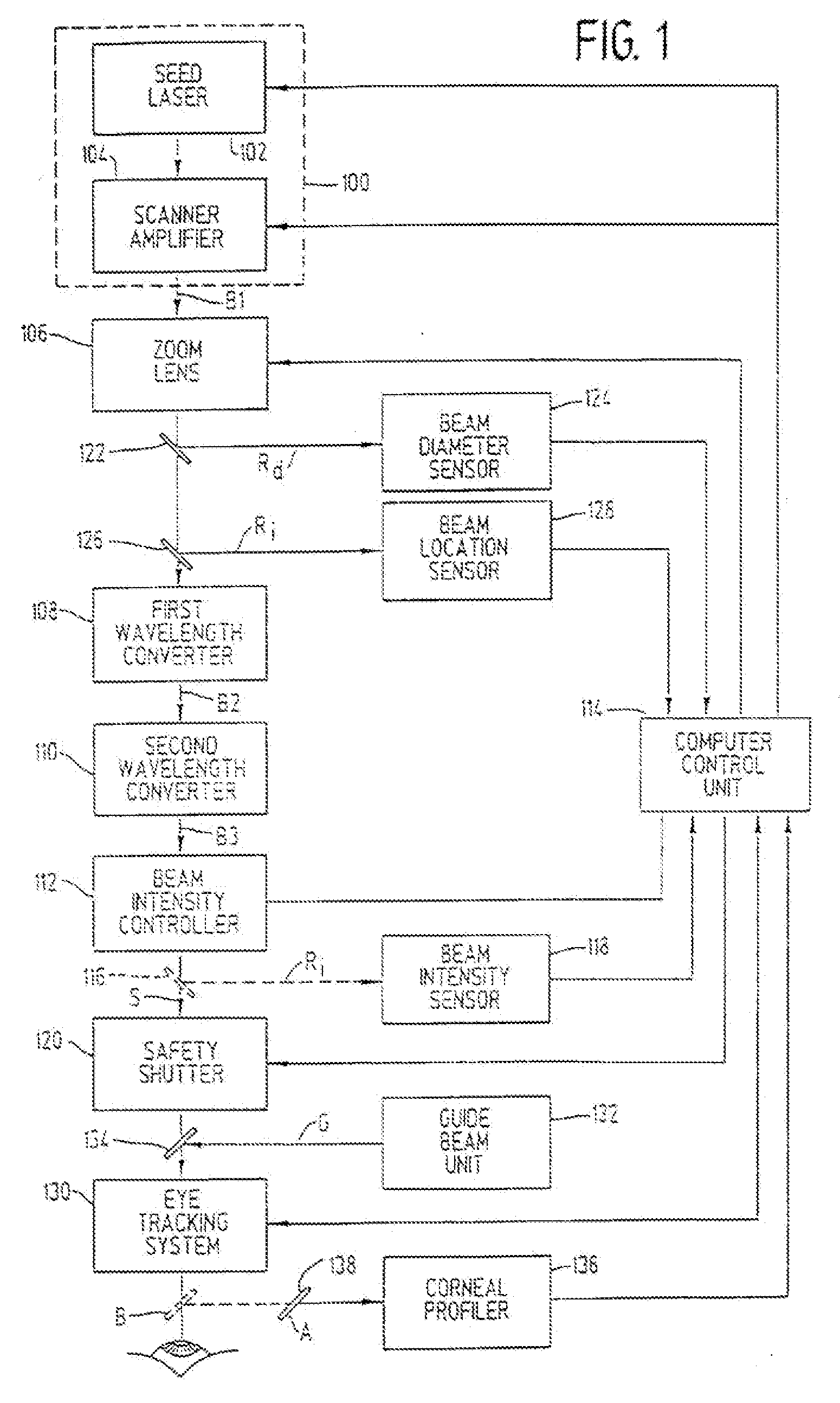
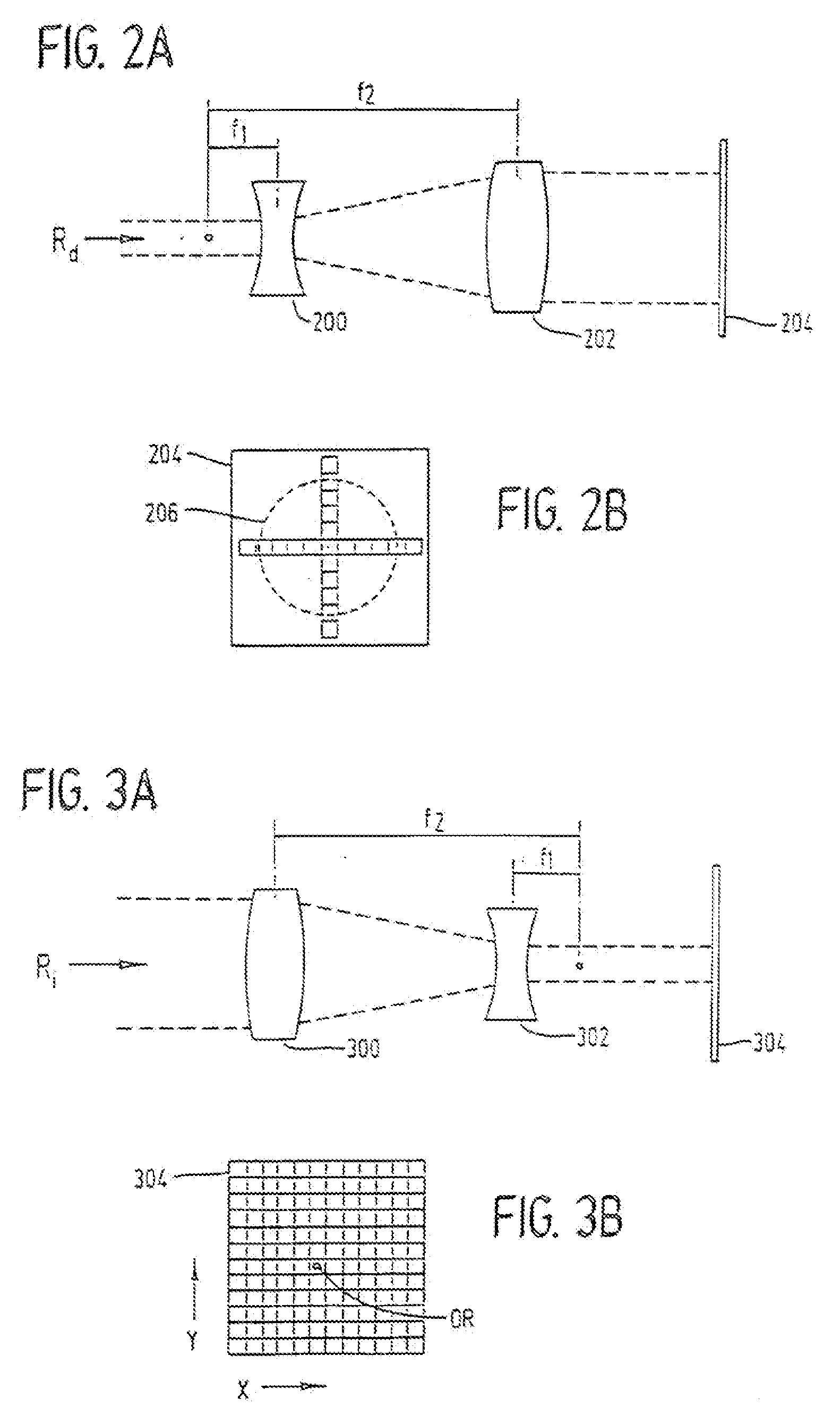
InactiveUS7220255B2Easy to controlIncrease powerLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100–50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198–300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1–5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
Laser material micromachining with green femtosecond pulses
Various embodiments of a system described herein relate to micromachining materials using ultrashort visible laser pulses. The ultrashort laser pulses may be green and have a wavelength between about 500 to 550 nanometers in some embodiments. Additionally, the pulses may have a pulse duration of less than one picosecond in certain embodiments.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
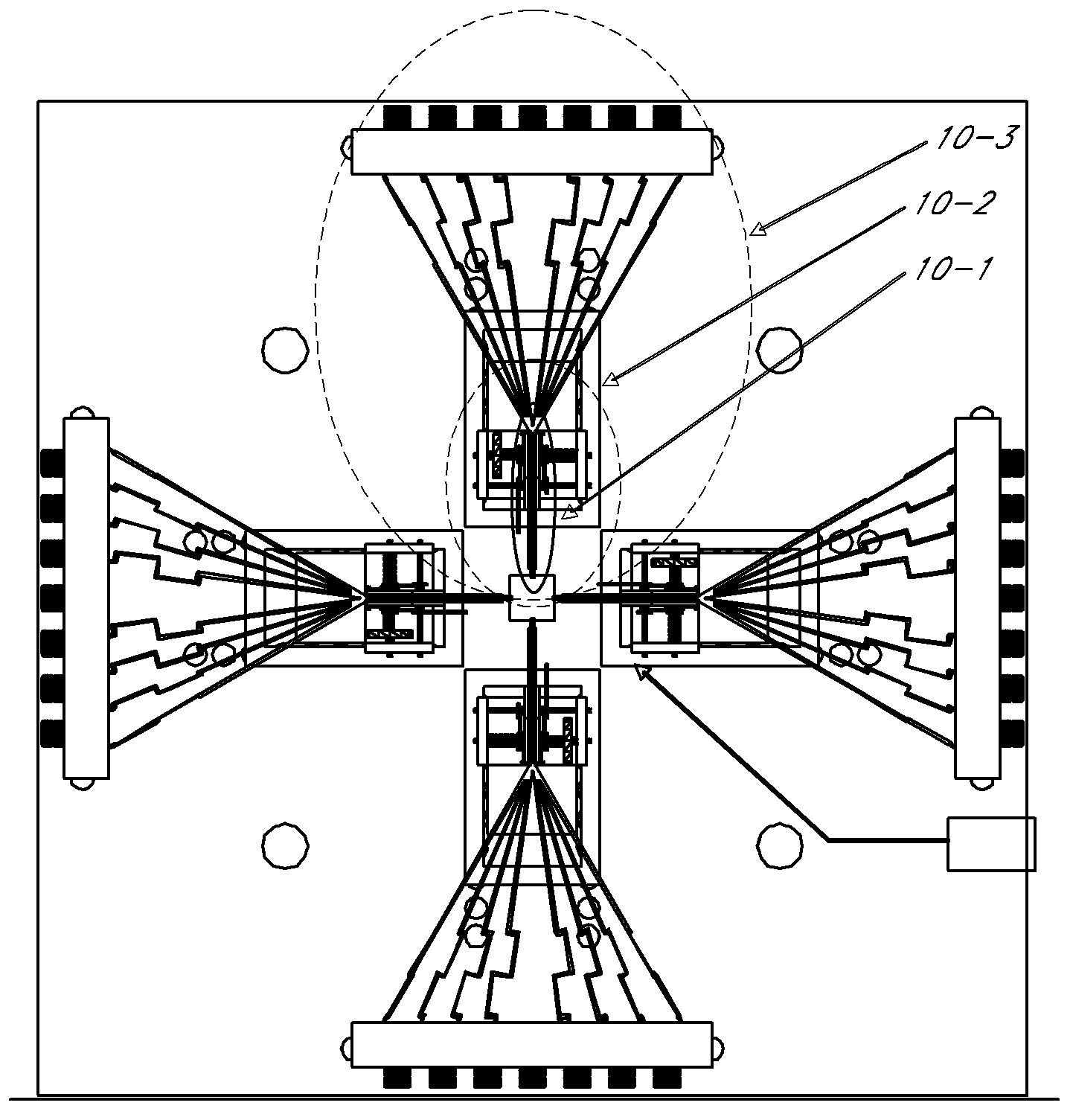
Scalable wideband probes, fixtures, and sockets for high speed IC testing and interconnects
ActiveUS20080265919A1Reducing cross talk and prasiticsIncrease speedElectrical measurement instrument detailsSolid-state devicesRadiation lossPicosecond
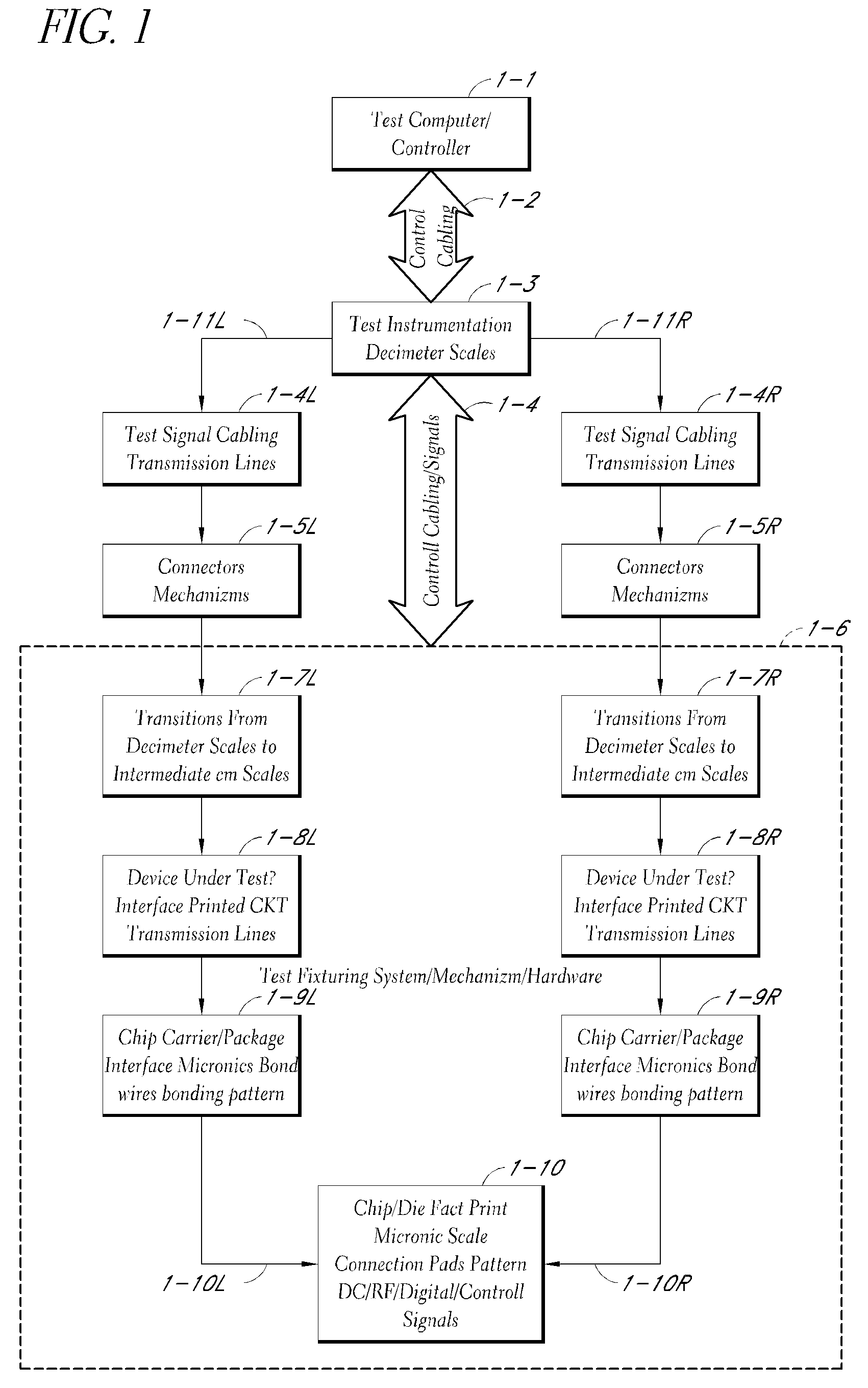
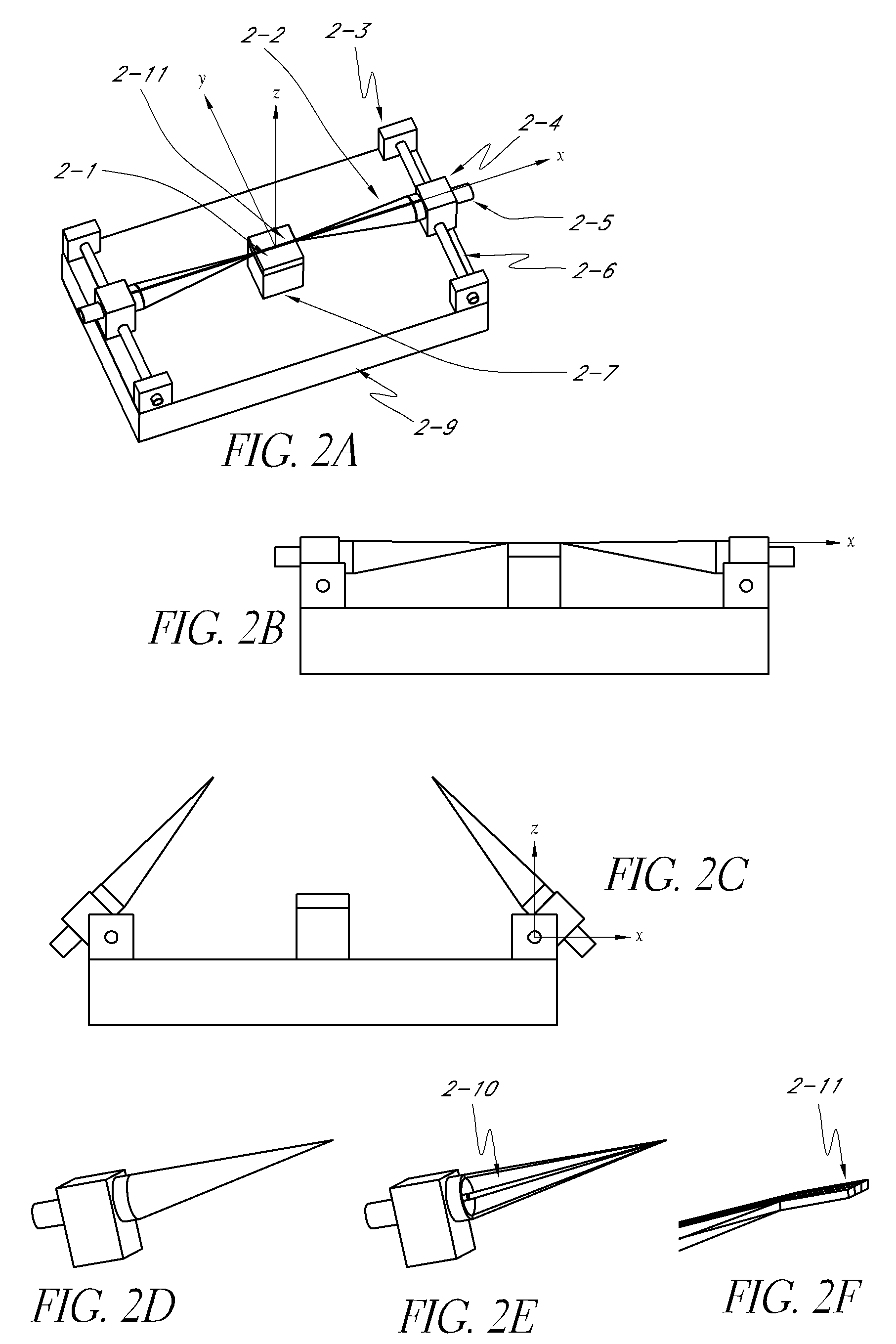
We introduce a new Periodic micro coaxial transmission line (PMTL) that is capable of sustaining a TEM propagation mode up to THz band. The PMTL can be manufactured using the current photolithographic processes. This transmission line can be embedded in microscopic layers that allow many new applications. We use the PMTL to develop a wideband highly scalable connector that is then used in a Probe that can be used for connecting to microscopic scale Integrated Circuits with picoseconds High Speed Digital and near THz Analogue performance in various stages of development from R&D to production testing. These probes, in one embodiment, provide a thin pen-like vertical probe tip that matches the die pad pattern precisely that can be as agile as a high speed plotter pen, connecting on the fly to any die pattern on a wafer. This approach allows the most valuable part of the test, namely the wafer to remain stationary and safe, and the least costly part of the test, namely the probe to take most of the wear and tear. We further use the embedded PMTL to develop a modular, scaleable and fully automated Universal Test Fixture for testing chips in various stages of development mainly for digital IC chips that can be utilized in production lines with pick and place of chips on tape to test every chip before insertion into circuits. One embodiment includes a low profile wideband Signal Launcher and an alligator type RF Clip that can be used at the edge of PCB's directly for validation broads. The Signal Launcher is used to develop a new versatile Flush Top Test Fixtures for individual device testing in various stages of development from die, to packaged, to Module, to Circuit Boards. The PMTL can also provide Confined Field Interconnects (CFI) between various elements on semiconductor wafers to reduce parasitic and radiation losses and practically eliminating cross talk, thus, increasing the speed of digital IC's. The PMTL is also used to develop a Universal Test Socket, and a Hand Probe with performance up to 220 GHz.
Owner:WAYMO LLC
Ultrashort laser pulse wafer scribing
InactiveUS20070272668A1Improve mechanical stressImprove thermal stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamOptoelectronics
Systems and methods are provided for scribing wafers with short laser pulses so as to reduce the ablation threshold of target material. In a stack of material layers, a minimum laser ablation threshold based on laser pulse width is determined for each of the layers. The highest of the minimum laser ablation thresholds is selected and a beam of one or more laser pulses is generated having a fluence in a range between the selected laser ablation threshold and approximately ten times the selected laser ablation threshold. In one embodiment, a laser pulse width in a range of approximately 0.1 picosecond to approximately 1000 picoseconds is used. In addition, or in other embodiments, a high pulse repetition frequency is selected to increase the scribing speed. In one embodiment, the pulse repetition frequency is in a range between approximately 100 kHz and approximately 100 MHz.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
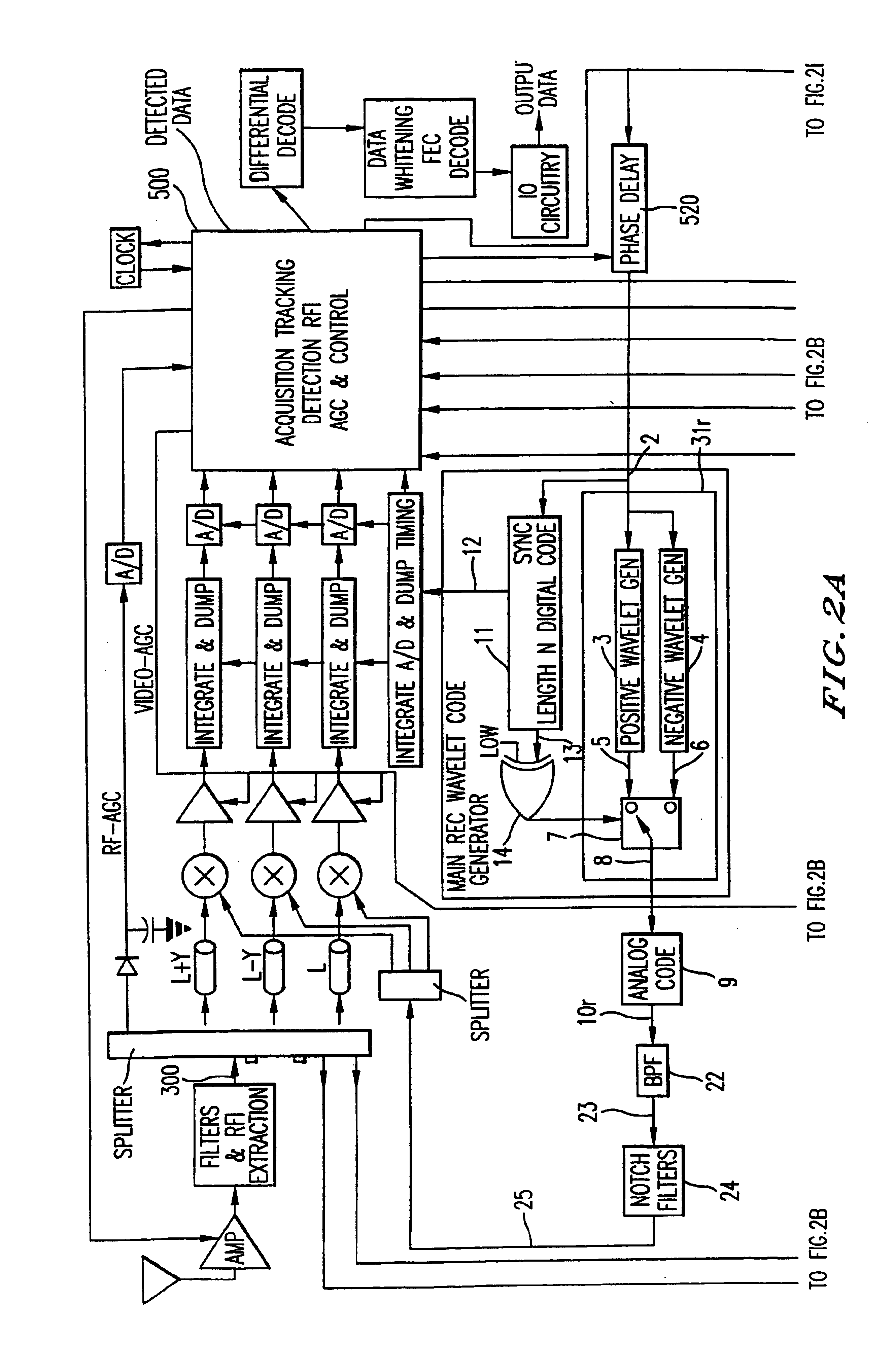
Ultra wide bandwidth communications method and system
InactiveUS7280607B2For signal receptionImprove communication efficiencyModulated carrier system with waveletsCode conversionMultipath interferencePicosecond
An ultra wide bandwidth, high speed, spread spectrum communications system uses short wavelets of electromagnetic energy to transmit information through objects such as walls or earth. The communication system uses baseband codes formed from time shifted and inverted wavelets to encode data on a RF signal. Typical wavelet pulse durations are on the order of 100 to 1000 picoseconds with a bandwidth of approximately 8 GHz to 1 GHz, respectively. The combination of short duration wavelets and encoding techniques are used to spread the signal energy over a an ultra wide frequency band such that the energy is not concentrated in any particular narrow band (e.g. VHF: 30-300 MHz or UHF: 300-1000 MHz) and is not detected by conventional narrow band receivers so it does not interfere with those communication systems. The use of pulse codes composed of time shifted and inverted wavelets gives the system according to the present invention has a spatial resolution on the order of 1 foot which is sufficient to minimize the negative effects of multipath interference and permit time domain rake processing.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
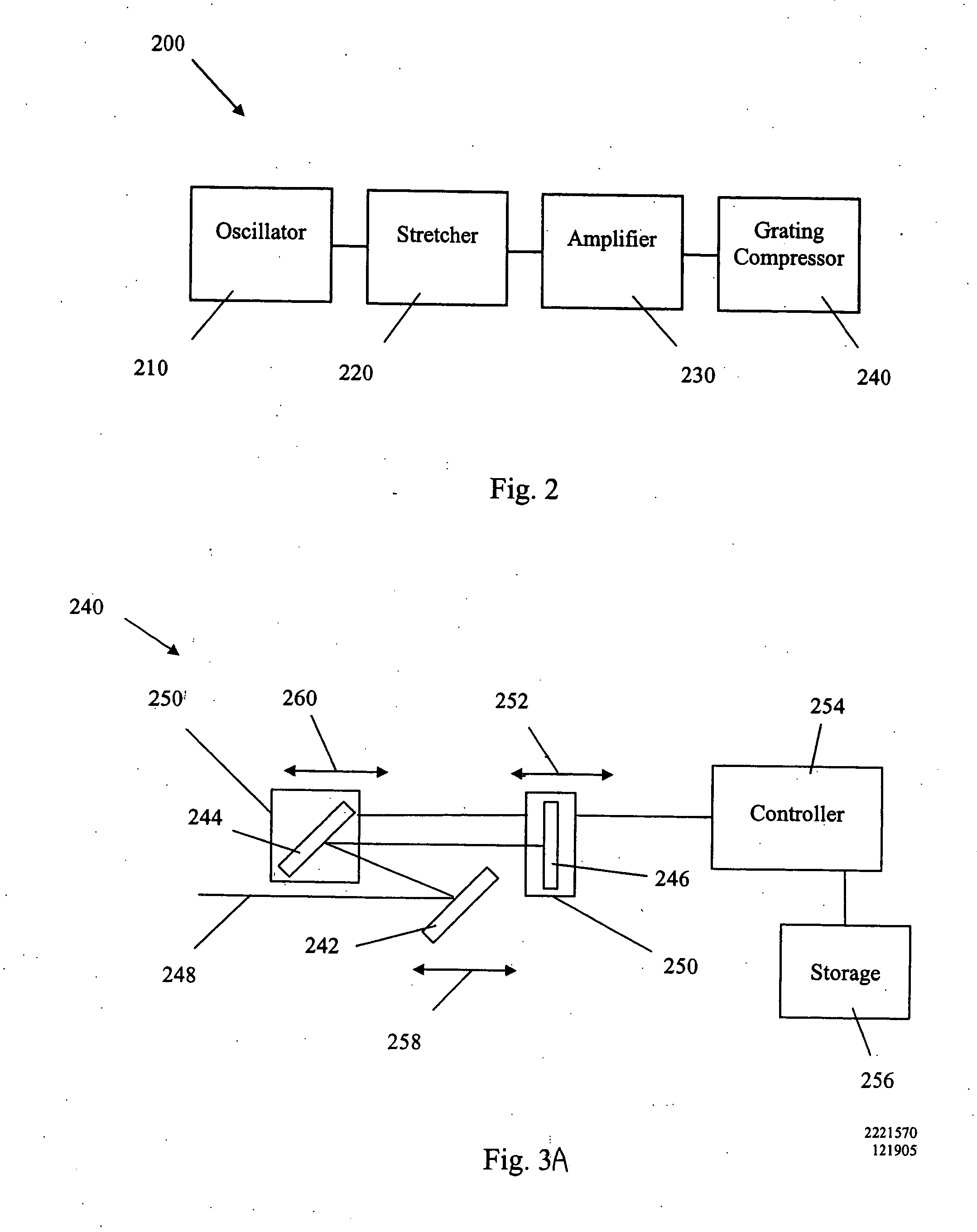
Method and apparatus for high power optical amplification in the infrared wavelength range (0.7-20 mum)
InactiveUS20050271094A1Laser detailsNon-linear opticsAcousto-optic programmable dispersive filterAdemetionine
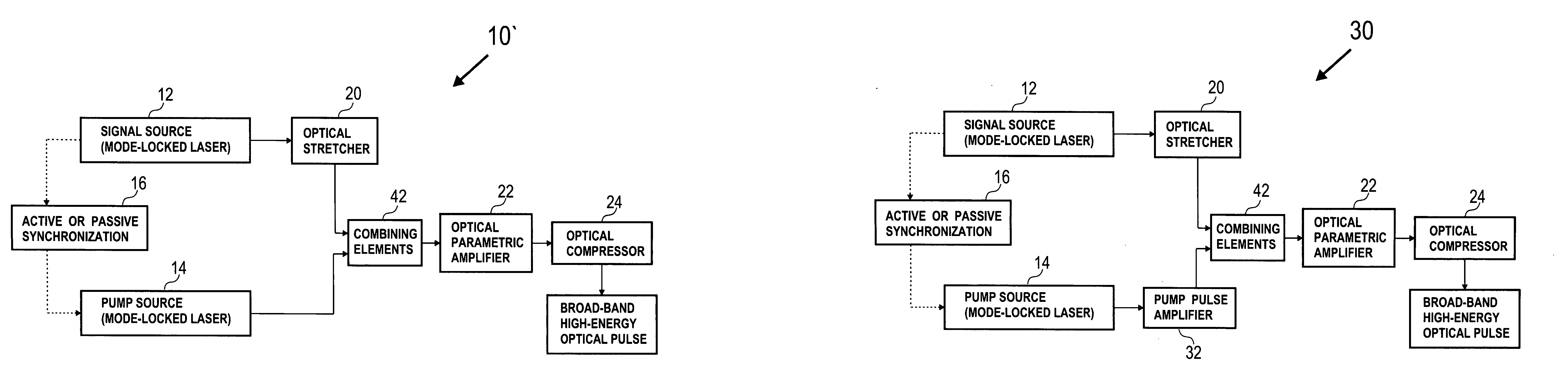
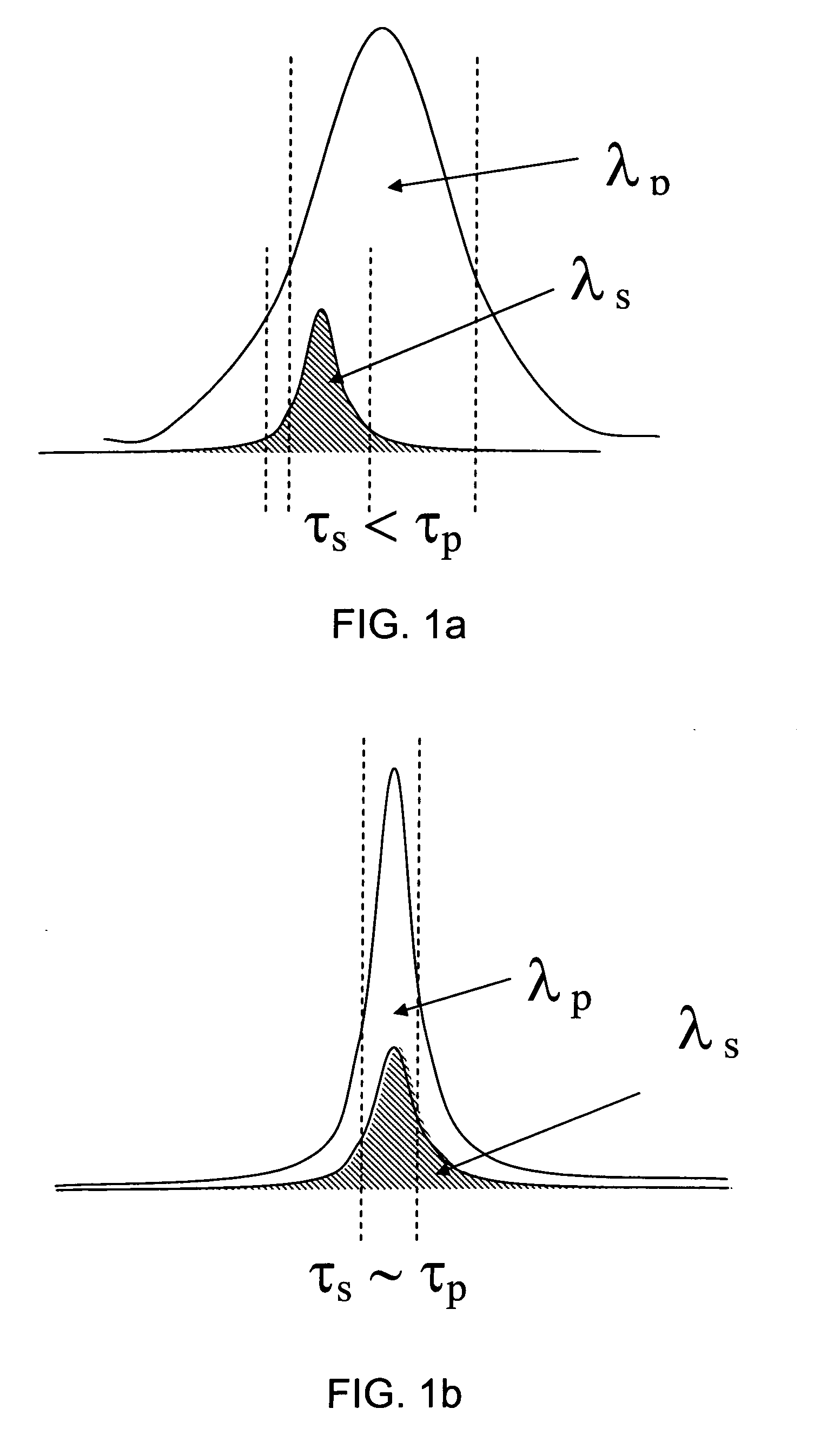
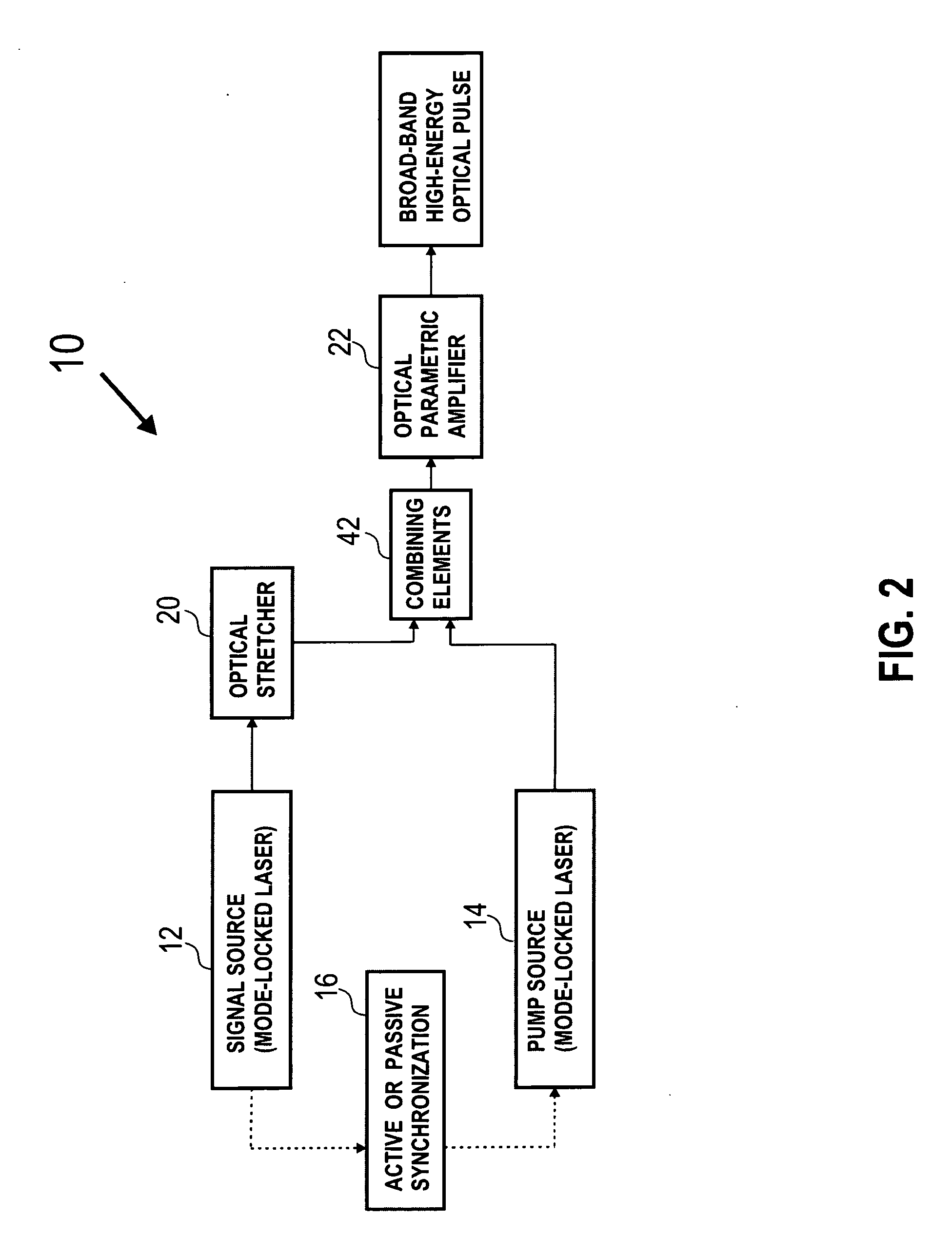
A novel method for high power optical amplification of ultrashort pulses in IR wavelength range (0.7-20 Ãm) is disclosed. The method is based on the optical parametric chirp pulse amplification (OPCPA) technique where a picosecond or nanosecond mode locked laser system synchronized to a signal laser oscillator is used as a pump source or alternatively the pump pulse is created from the signal pulse by using certain types of optical nonlinear processes described later in the document. This significantly increases stability, extraction efficiency and bandwidth of the amplified signal pulse. Further, we disclose five new practical methods of shaping the temporal and spatial profiles of the signal and pump pulses in the OPCPA interaction which significantly increases its efficiency. In the first, passive preshaping of the pump pulses has been made by a three wave mixing process separate from the one occurring in the OPCPA. In the second, passive pre-shaping of the pump pulses has been made by spectral filtering in the pump mode-locked laser or in its amplifier. In the third, the temporal shape of the signal pulse optimized for OPCPA interaction has been actively processed by using an acousto-optic programmable dispersive filter (Dazzler) or liquid crystal light modulators. In the fourth alternative method, the signal pulse intensity envelope is optimized by using passive spectral filtering. Finally, we disclose a method of using pump pulses which interact with the seed pulses with different time delays and different angular orientations allowing the amplification bandwidth to be increased. In addition we describe a new technique for high power IR optical beam delivery systems based on the microstructure fibres made of silica, fluoride or chalcogenide glasses as well as ceramics. Also we disclose a new optical system for achieving phase matching geometries in the optical parametric interactions based on diffractive optics. All novel methods of the ultrashort optical pulse amplification described in this disclosure can be easily generalized to other wavelength ranges.
Owner:MILLER ROBERT JOHN DWAYNE +3
Fast faraday cup with high bandwidth
InactiveUS20050212503A1High bandwidthGood dispersionThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTime structureHigh bandwidth
A circuit card stripline Fast Faraday cup quantitatively measures the picosecond time structure of a charged particle beam. The stripline configuration maintains signal integrity, and stitching of the stripline increases the bandwidth. A calibration procedure ensures the measurement of the absolute charge and time structure of the charged particle beam.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method and apparatus for optimally laser marking articles
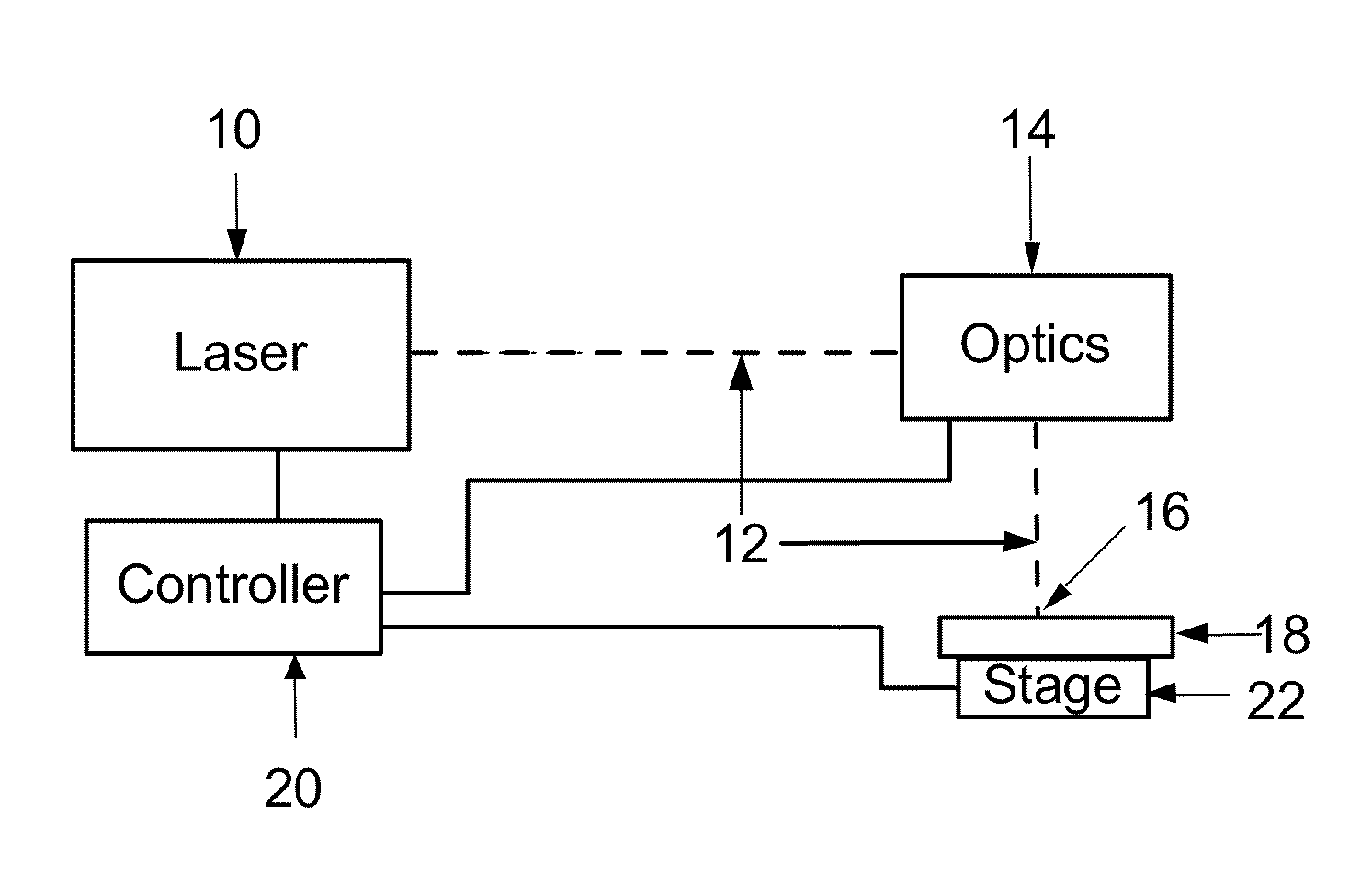
InactiveUS8604380B2Solve the lack of precisionQuick switchThermographyMetal working apparatusLaser processingPulse parameter
The invention is a method and apparatus for laser marking a stainless steel specimen with commercially desirable marks. The method includes providing a laser processing system having a laser, laser optics and a controller with pre-determined laser pulse parameters, selecting the pre-determined laser pulse parameters associated with the desired mark, and directing the laser marking system to produce laser pulses having laser pulse parameters associated with the desired marks including temporal pulse widths greater than about 1 and less than about 1000 picoseconds.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser-based material processing methods and systems
ActiveUS8158493B2Avoid insufficient heatingAvoid layeringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesDielectricPicosecond
Various embodiments may be used for laser-based modification of target material of a workpiece while advantageously achieving improvements in processing throughput and / or quality. Embodiments of a method of processing may include focusing and directing laser pulses to a region of the workpiece at a pulse repetition rate sufficiently high so that material is efficiently removed from the region and a quantity of unwanted material within the region, proximate to the region, or both is reduced relative to a quantity obtainable at a lower repetition rate. Embodiments of an ultrashort pulse laser system may include at least one of a fiber amplifier or fiber laser. Various embodiments are suitable for at least one of dicing, cutting, scribing, and forming features on or within a semiconductor substrate. Workpiece materials may also include metals, inorganic or organic dielectrics, or any material to be micromachined with femtosecond, picosecond, and / or nanosecond pulses.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Method and Apparatus for Laser Surgery of the Cornea
InactiveUS20060217688A1Correction of myopiaCorrected astigmatismLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal ablationSurgical lasers
A laser-based method and apparatus for corneal surgery. The present invention is intended to be applied primarily to ablate organic materials, and human cornea in particular. The invention uses a laser source which has the characteristics of providing a shallow ablation depth (0.2 microns or less per laser pulse), and a low ablation energy density threshold (less than or equal to about 10 mJ / cm.sup.2), to achieve optically smooth ablated corneal surfaces. The preferred laser includes a laser emitting approximately 100-50,000 laser pulses per second, with a wavelength of about 198-300 nm and a pulse duration of about 1-5,000 picoseconds. Each laser pulse is directed by a highly controllable laser scanning system. Described is a method of distributing laser pulses and the energy deposited on a target surface such that surface roughness is controlled within a specific range. Included is a laser beam intensity monitor and a beam intensity adjustment means, such that constant energy level is maintained throughout an operation. Eye movement during an operation is corrected for by a corresponding compensation in the location of the surgical beam. Beam operation is terminated if the laser parameters or the eye positioning is outside of a predetermined tolerable range. The surgical system can be used to perform surgical procedures including removal of corneal scar, making incisions, cornea transplants, and to correct myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, and other corneal surface profile defects.
Owner:LAI SHUI T
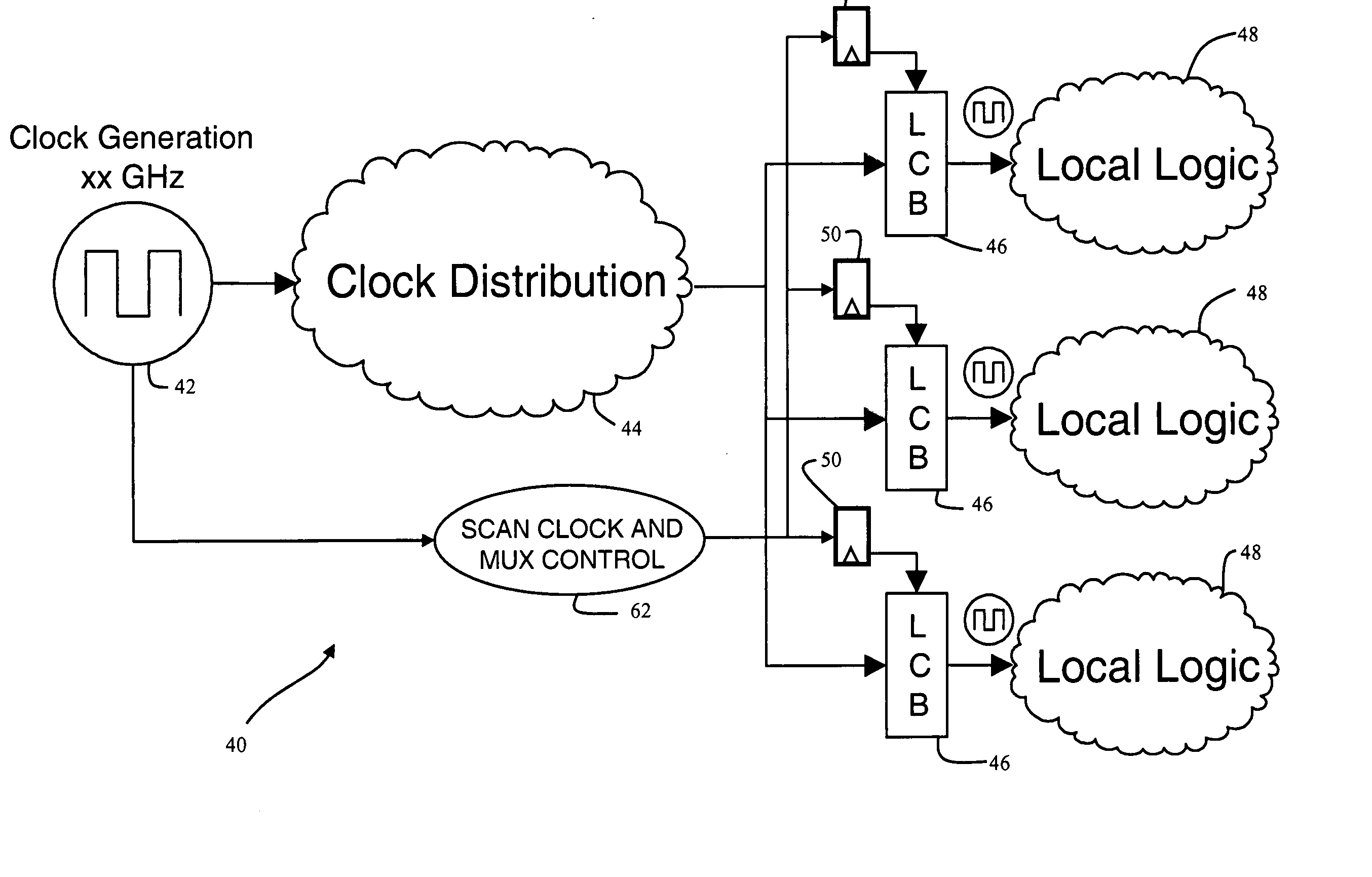
Self-resetting, self-correcting latches
ActiveUS20070028157A1Efficient designElectronic circuit testingRedundant data error correctionControl systemMultiplexer
A latch circuit having three latch stages generates a majority output value from the stages, senses when the latch stage outputs are not all equal, and feeds the majority output value back to inputs of the latch stages to reload the latch stages. The latch circuit uses a not-equal gate whose output is an error signal that can be monitored to determine when a single-event upset has occurred. A master stage is controlled by a first multiplexer which receives one system clock signal, while a slave stage is controlled by a second multiplexer which receives another system clock signal, and the latch stage outputs are connected to respective inputs of the not-equal gate, whose output is connected to second inputs of the multiplexers. The latch circuit is part of a latch control system, and reloading of the latch stages takes less than one cycle of the system clock (less than 500 picoseconds).
Owner:IBM CORP
Composite cutting with optical ablation technique
InactiveUS20050077275A1Avoid delaminationAvoid thermal effectsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusAudio power amplifierAblation Techniques
The present invention relates to methods and systems for dynamically controlled laser amplifier configuration for composite cutting includes the steps of generating an initial wavelength-swept-with-time optical pulse in an optical pulse generator, amplifying the initial optical pulse, compressing the amplified optical pulse to a duration of less than 10 picoseconds and applying the compressed optical pulse on the composite with an ablating energy density, to controllably remove a slice of material from the composite.
Owner:RAYDIANCE
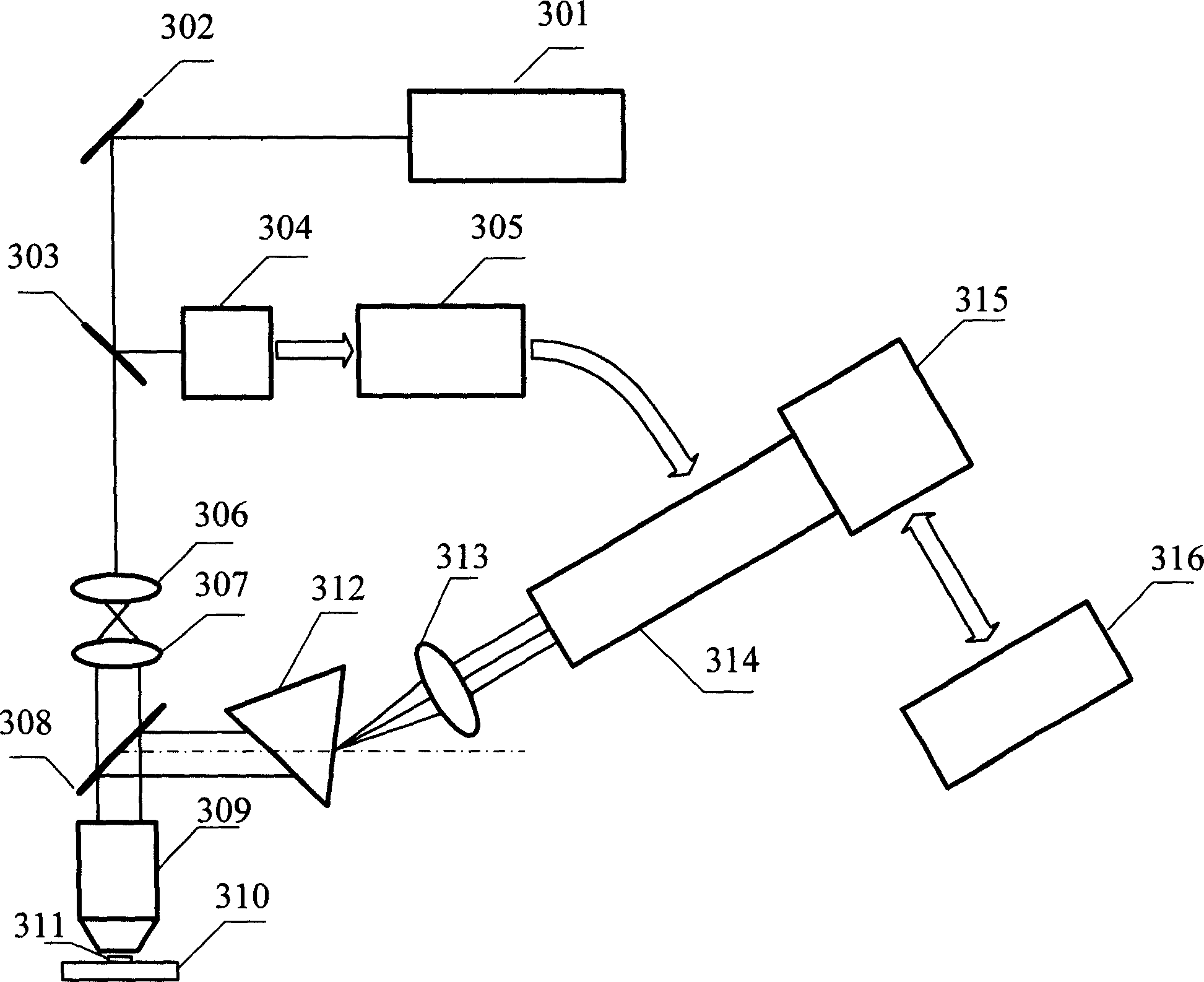
Time resolution fluorescence spectral measuring and image forming method and its device
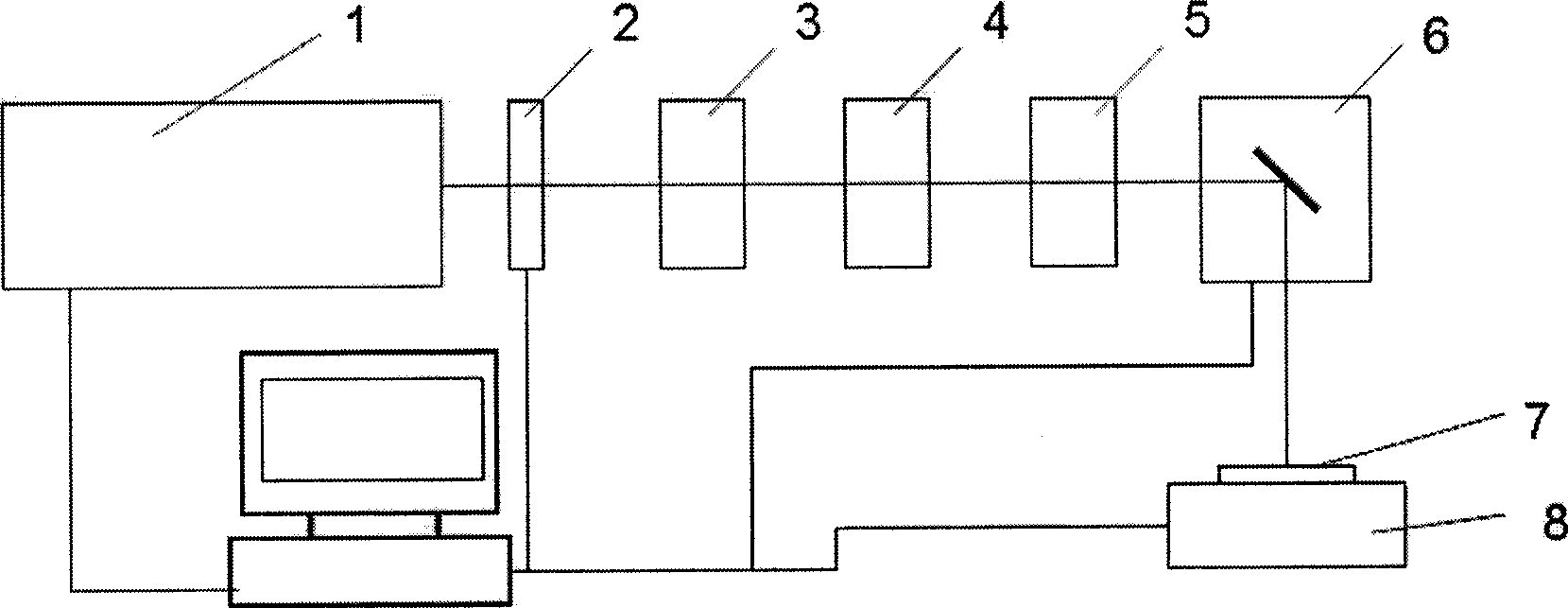
InactiveCN1912587ADifferent temporal resolutionsAchieving high-sensitivity detectionFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotocathodePicosecond
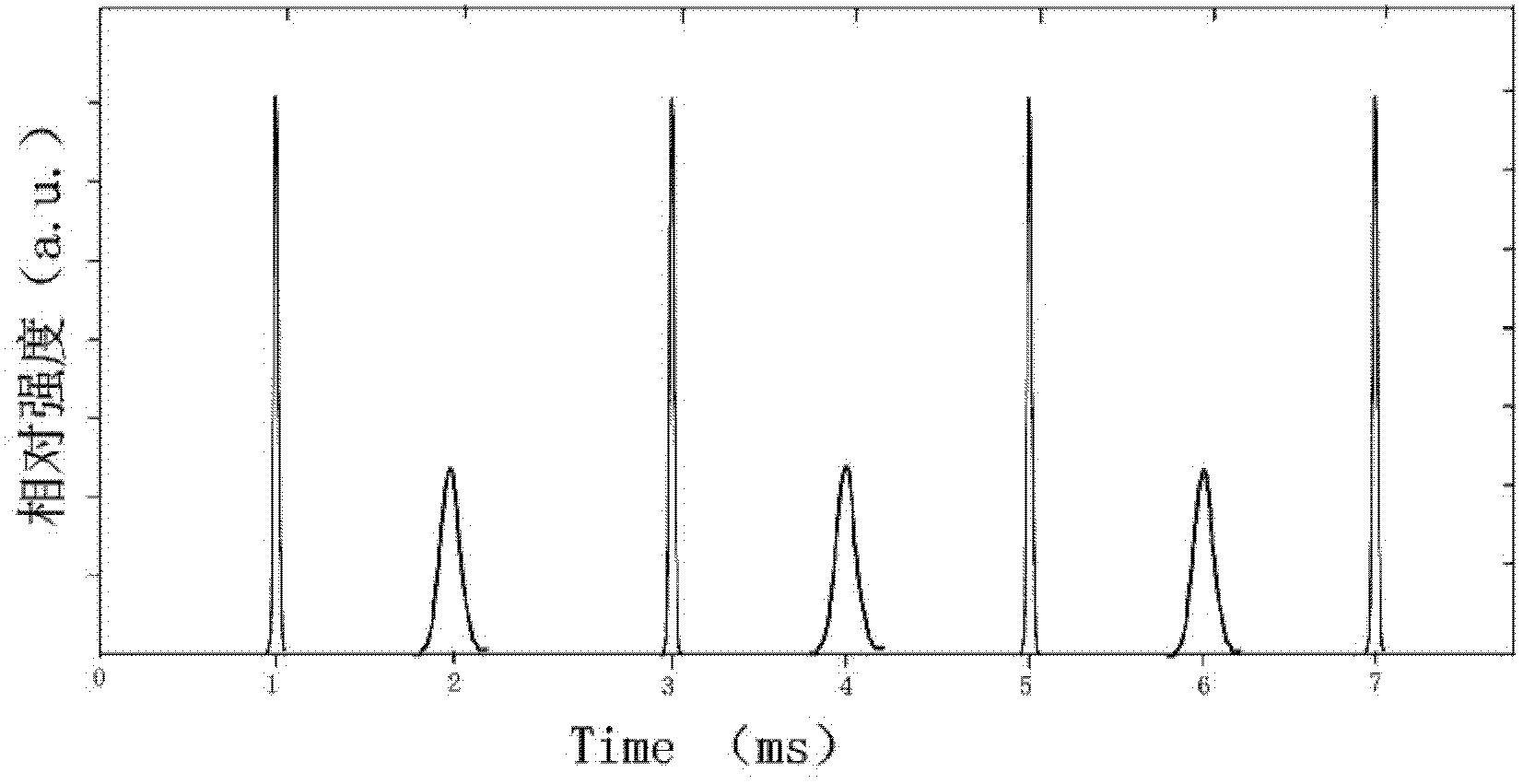
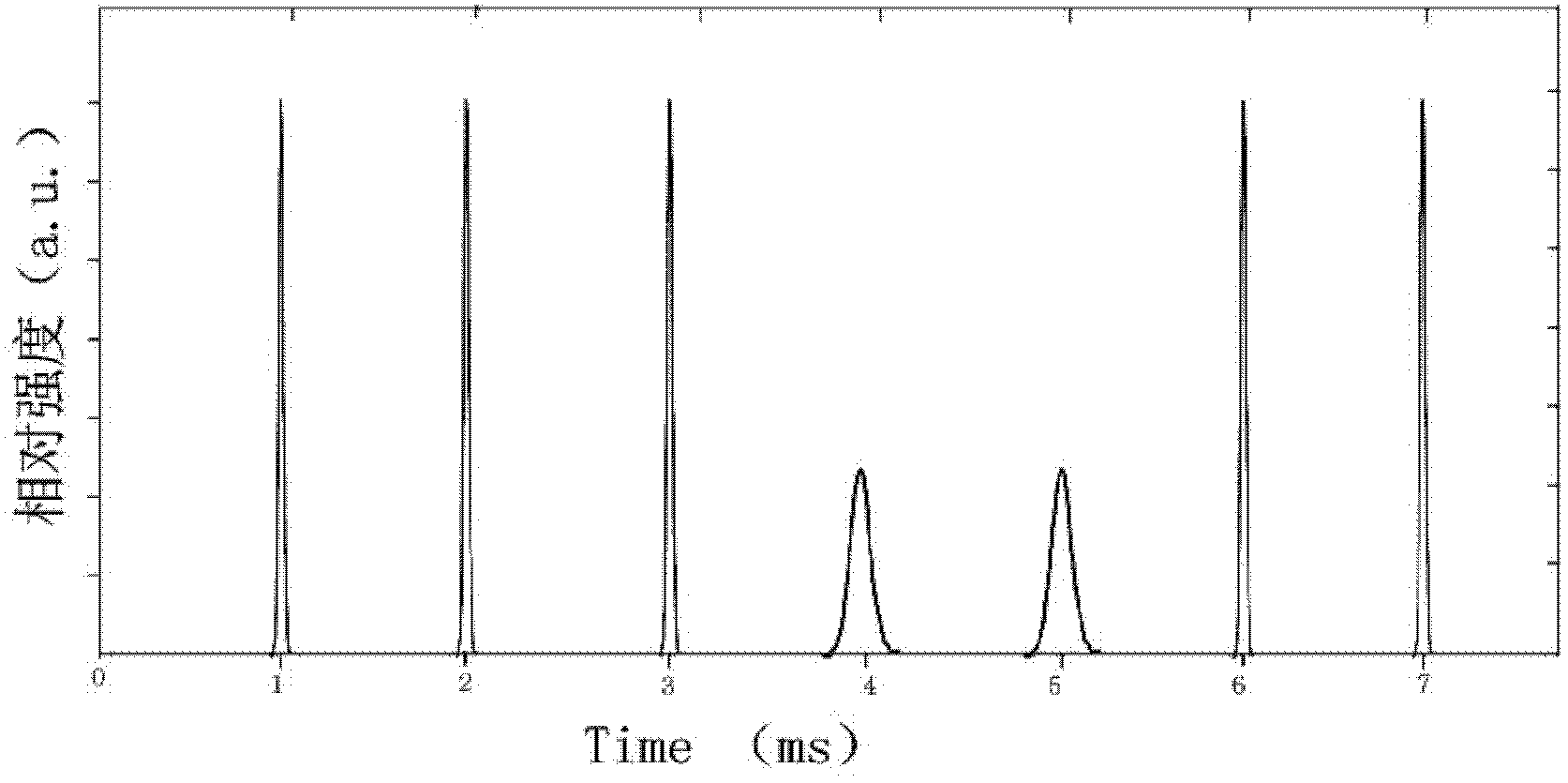
A method of using picosecond scan camera to simultaneously obtain fluorescent light spectrum and fluorescent lifetime of sample includes focusing blue violet light emitted by laser on sample by objective to excite sample single photon, collecting fluorescent from sample then splitting it and focusing it to be image on photoelectric cathode of picosecond scan camera, setting dispersion direction of fluorescent to be the same as slit direction of said camera but to be vertical to scan direction in order to measure out fluorescent lifetime of different light spectrum simultaneously under coaction of scan circuit and image intensifier deflection system.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method and apparatus for reliably laser marking articles
InactiveUS20110194574A1Desirable appearanceMarking is durableRecording apparatusLaser detailsPulse parameterPicosecond
The invention is a method and apparatus for creating a color and optical density selectable visible mark on an anodized aluminum specimen. The method includes providing a laser marking system having a laser, laser optics and a controller operatively connected to said laser to control laser pulse parameters and a controller with stored laser pulse parameters, selecting the stored laser pulse parameters associated with the desired color and optical density, directing the laser marking system to produce laser pulses having laser pulse parameters associated with the desired color and optical density including temporal pulse widths greater than about 1 and less than about 1000 picoseconds to impinge upon said anodized aluminum.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
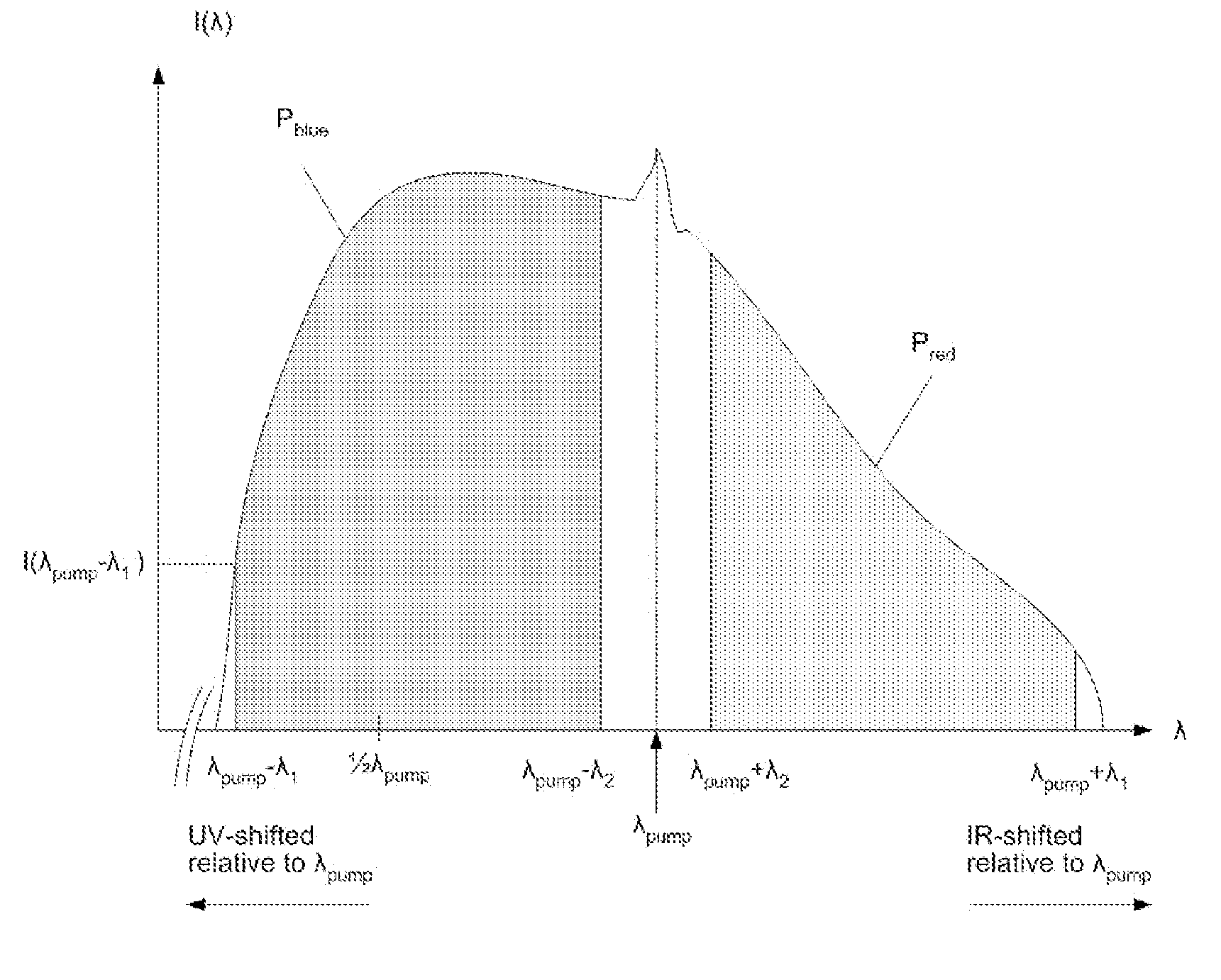
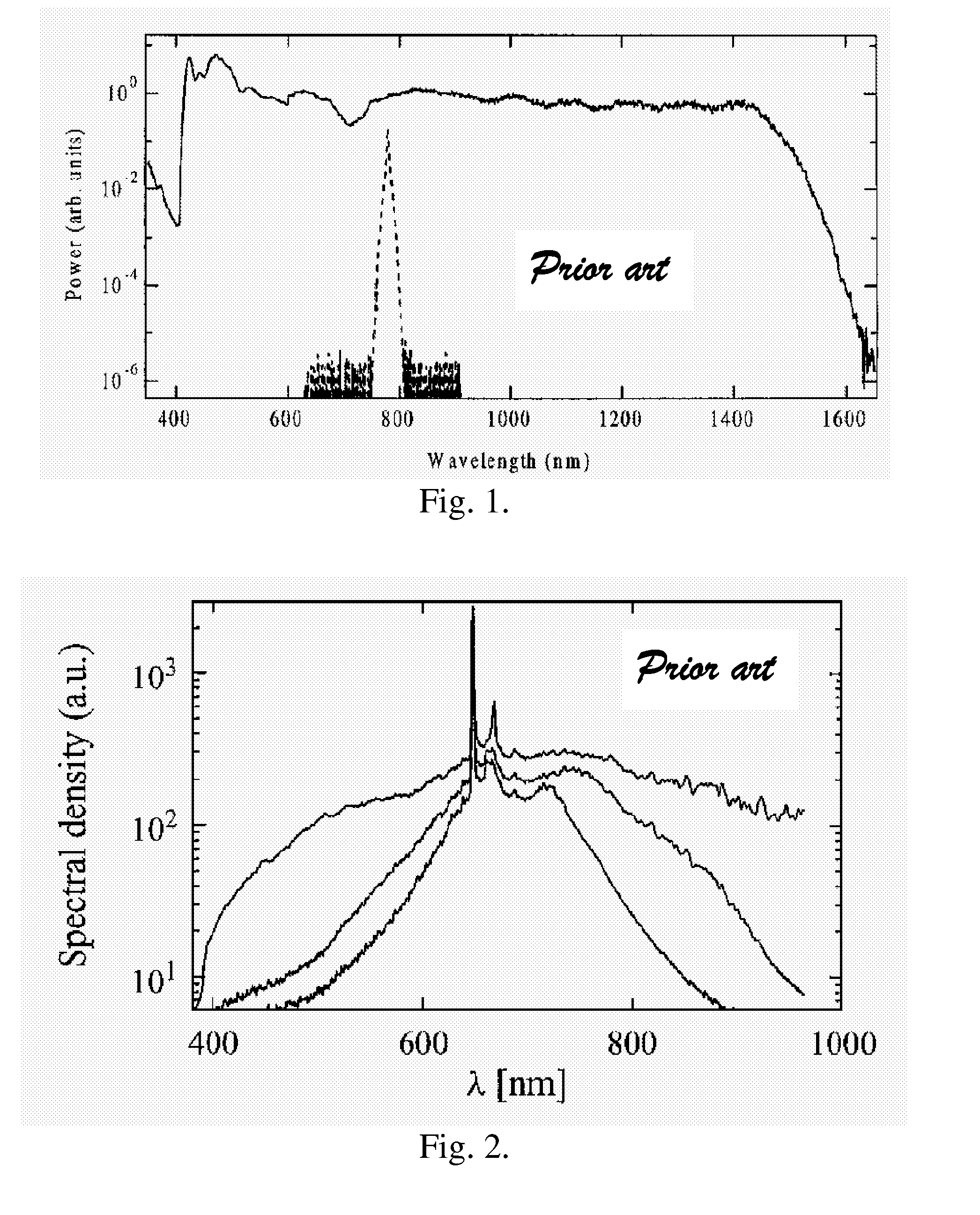
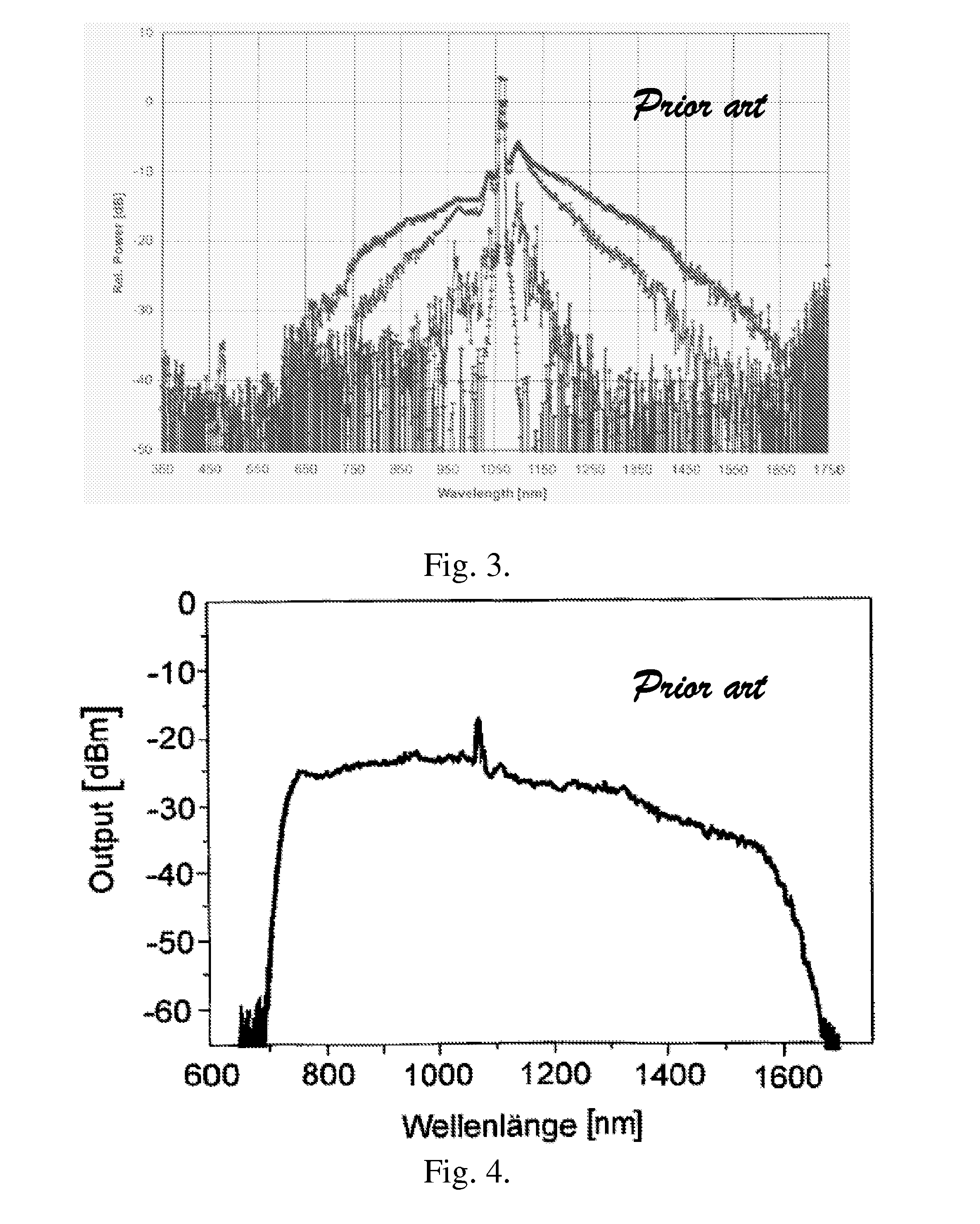
Blue extended super continuum light source
InactiveUS7800818B2Increase powerLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInstabilityRefractive index
In a blue extended super continuum light source, when pulses of partly coherent monochromatic “pump” radiation of essentially constant amplitude are propagating through a microstructure fiber medium within a region of anomalous dispersion of the medium, then, provided the medium has a finite nonlinear coefficient of the index of refraction, the pump pulse is subject to a modulation instability. This results in formation of a train of narrow pulses with Tera Hertz repetition rate. Phase match between red shifted Raman solitons generated by the pump pulse and energy shed by the pump pulse at all frequencies with a group velocity below the pump pulse group velocity may lead to the formation of Cherenkov radiation. The solitons may seed Cherenkov radiation at different wavelengths depending on the actual fiber parameters. This allows extension of generated super continuum light beyond the four wave mixing limit when applying picosecond or nanosecond pump pulses.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
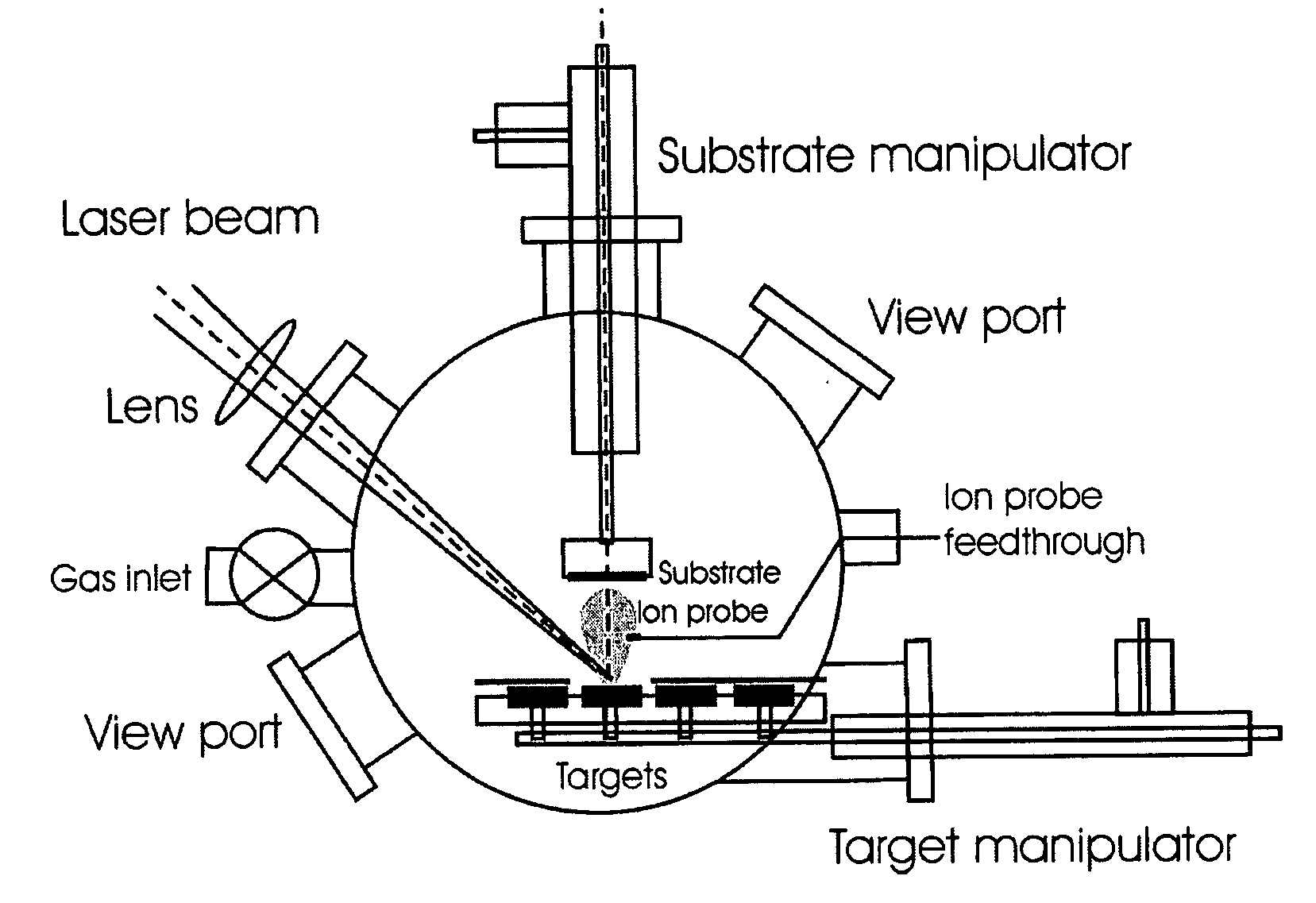
Method for producing and depositing nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080006524A1Increase influenceIncrease rangeCellsTransportation and packagingPicosecondVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention provides a one-step process for producing and depositing size-selected nanoparticles onto a substrate surface using ultrafast pulsed laser ablation of solid target materials. The system includes a pulsed laser with a pulse duration ranging from a few femtoseconds to a few tens of picoseconds, an optical setup for processing the laser beam such that the beam is focused onto the target surface with an appropriate average energy density and an appropriate energy density distribution, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and the background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Particle detection system and method of detecting particles
InactiveUS20100194574A1Early detectionScattering properties measurementsFire alarmsNanosecondLight beam
A method for detecting an aerosol plume includes emitting a light beam from a light source, the light beam having at least one light pulse, wherein the light pulse having a pulse width of between about 10 picoseconds (ps) and about 75 nanoseconds (ns), detecting backscattered light produced by the at least one light pulse interacting with particles in the aerosol plume, determining a presence of the aerosol plume based on the detected backscattered light, and outputting a signal indicating the presence of the aerosol plume.
Owner:UTC FIRE & SECURITY AMERICAS CORPORATION INC
Laser irradiation method and method for manufacturing crystalline semiconductor film
ActiveUS20050139786A1Suppression of inhomogeneityHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid statePicosecondCrystallinity
Even when the laser irradiation is performed under the same condition with the energy distribution of the beam spot shaped as appropriate, the energy given to the irradiated surface is not yet homogeneous. When a semiconductor film is crystallized to form a crystalline semiconductor film using such inhomogeneous irradiation energy, the crystallinity becomes inhomogeneous in this film, and the characteristic of semiconductor elements manufactured using this film varies. In the present invention, an irradiated object formed over a substrate is irradiated with a laser beam having the pulse width that is an order of picosecond (10−12 second) or less.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for machining glass substrate
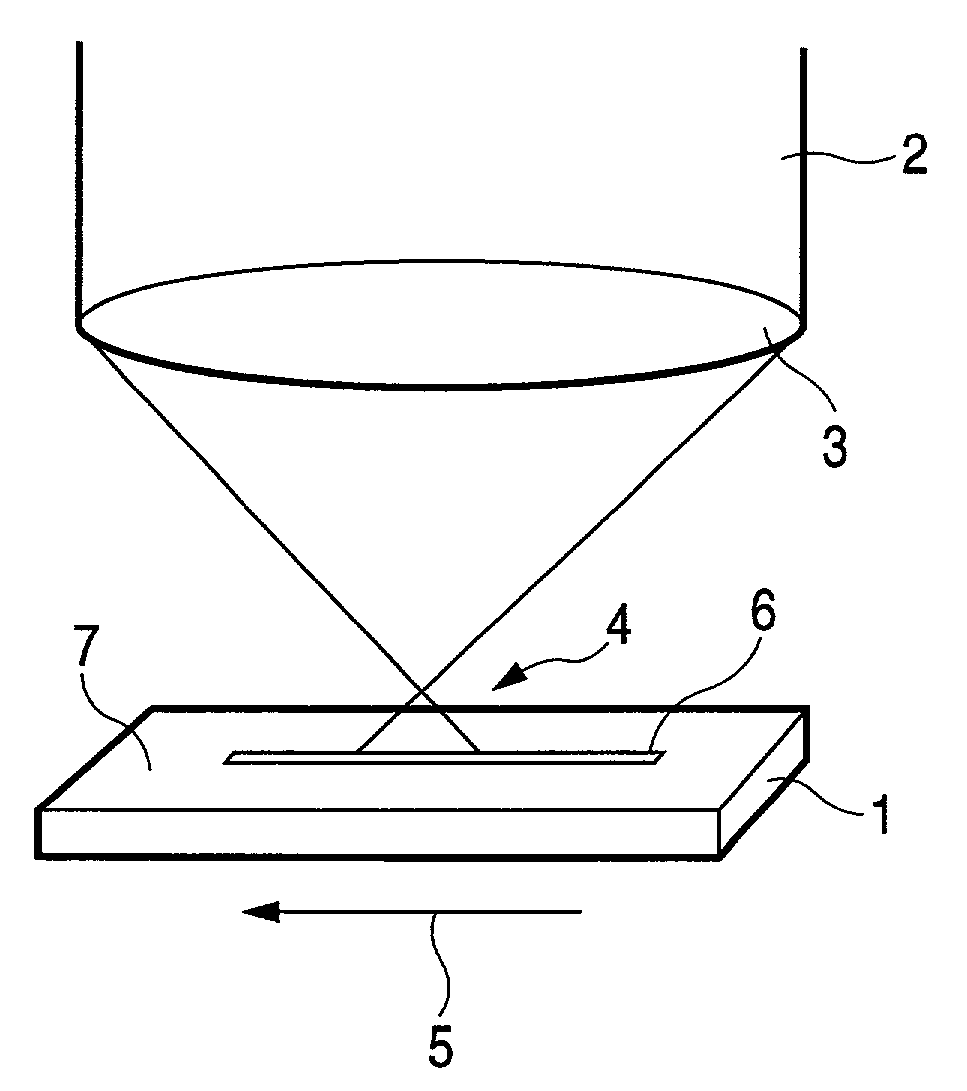
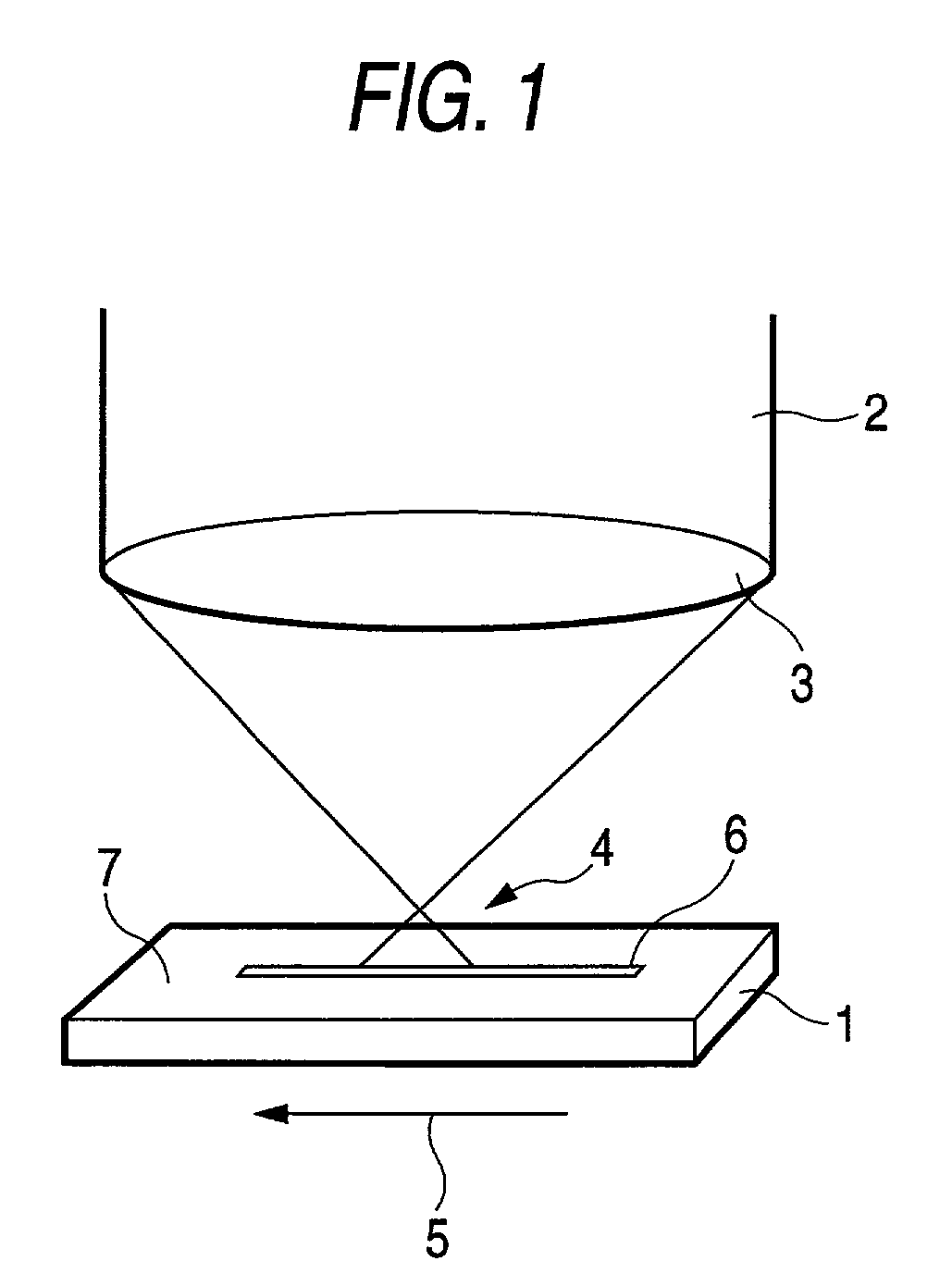
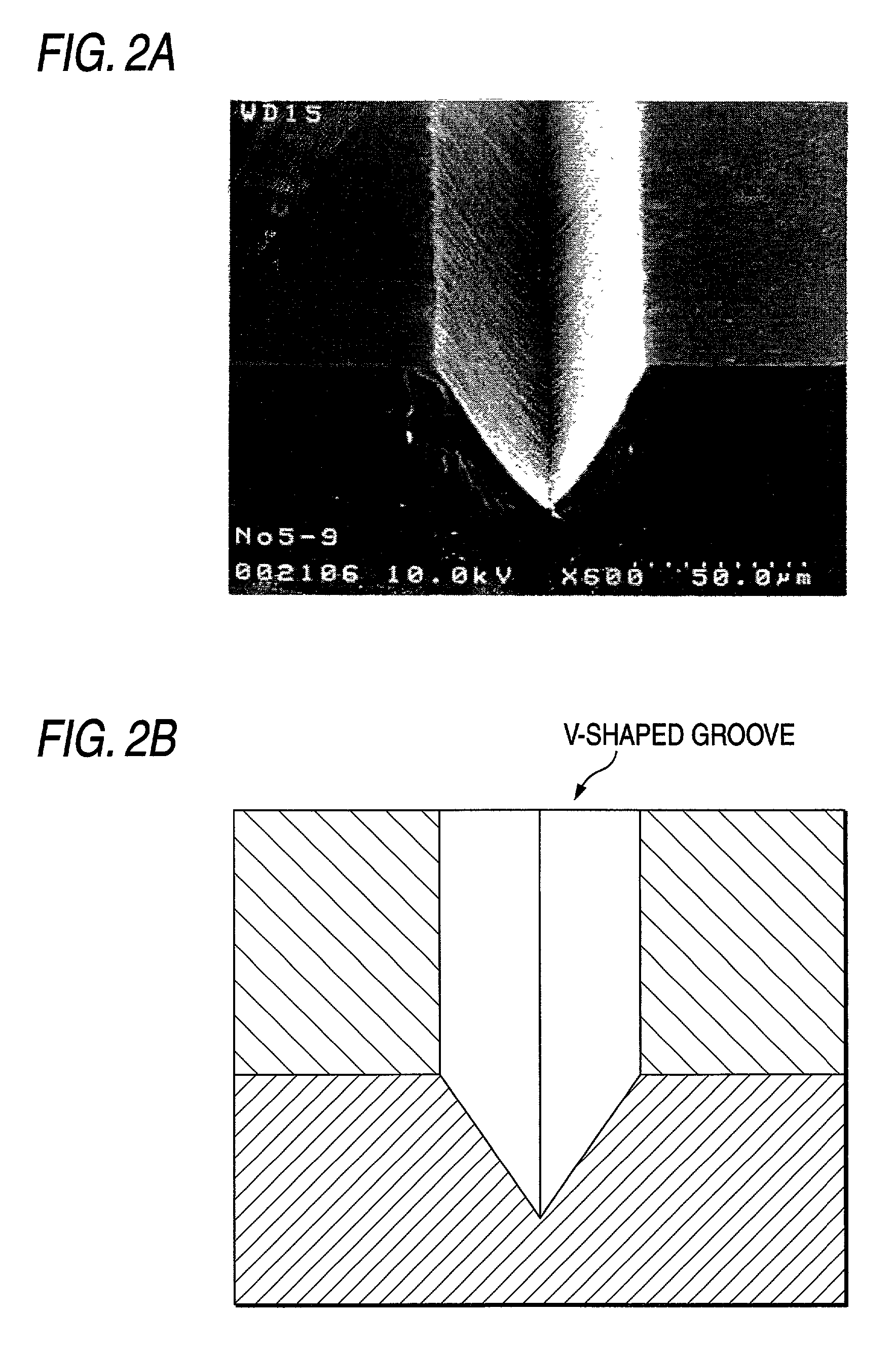
InactiveUS7007512B2Accuracy in intervalContinuous processingDecorative surface effectsLayered productsLight beamOptoelectronics
In the present invention, a surface 7 of a glass substrate 1 is irradiated with a laser beam 2 to thereby form a V-shaped groove 6. At that time, the laser beam 2 is condensed outside and above the glass substrate 1. The distance between a beam-condensing point 4 of the laser beam 2 and the surface 7 of the glass substrate 1 is changed to thereby make it possible to change the angle between opposite side surfaces of the V-shaped groove. The angle is in a range of from 30 degrees to 120 degrees. Further, the laser beam used in the present invention is pulsed light, preferably with a pulse width not larger than 10 picoseconds.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Method and apparatus for reliably laser marking articles
InactiveUS8379679B2Desirable appearanceRecording apparatusLaser detailsPulse parameterOptoelectronics
The invention is a method and apparatus for creating a color and optical density selectable visible mark on an anodized aluminum specimen. The method includes providing a laser marking system having a laser, laser optics and a controller operatively connected to said laser to control laser pulse parameters and a controller with stored laser pulse parameters, selecting the stored laser pulse parameters associated with the desired color and optical density, directing the laser marking system to produce laser pulses having laser pulse parameters associated with the desired color and optical density including temporal pulse widths greater than about 1 and less than about 1000 picoseconds to impinge upon said anodized aluminum.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Initiation and Control of Nanothermal Plasmonic Engineering
InactiveUS20080154431A1Sampled-variable control systemsRadiation pyrometryChemical synthesisChemical reaction
The present disclosure concerns a means to use at least a form of electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interaction, including solar or laser energy to generate localized conditions that enable initiation and spatial and temporal control of catalysis, chemical reactions, deposition, synthesis, photocatalysis, electrocatalysis and catalytic processes. Initiation and spatial and temporal control may be obtained by restricting and directing the electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions to specific objects or features embedded or located in or on a host matrix material or substrate. In some implementations this provides a means to use electromagnetic excitation to initiate and control chemical synthesis or reactions without entirely or partially heating any of or all of the reaction chamber, reactor mass, reaction precursors and products, or reactor substrate. It may further provide for the use of temperature sensitive elements or substrates. The method of use could include initiation and control of light-matter interactions addressed at optical and other frequencies to generate controlled localized thermal conditions. A further implementation concerns a means to employ electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions to generate localized thermal conditions to initiate or control or cause the combination, separation, reformation or reclamation of a gas, a combination of gasses, a material or a combination of materials in the form of a gas, plasma, solid or liquid. The method of use disclosed could provide a means to initiate and control chemical reactions for the generation, use, transfer and output of controlled localized thermal heat or energy. The method of use disclosed could provide a means to realize and control local thermal conditions down to or below the length scale of a single nanometer and down to or below the timescale of a single picosecond. In some implementations surface plasmon excitations may be used to realize and control local thermal conditions down to or below the length scale of a single nanometer and down to or below the timescale of a single picosecond.
Owner:DEFRIES ANTHONY +1
Method and apparatus for reliably laser marking articles
The invention is a method and apparatus for laser marking a stainless steel specimen with commercially desirable marks. The method includes providing a laser processing system having a laser, and laser optics and a controller with pre-determined laser pulse parameters, selecting the pre-determined laser pulse parameters associated with the desired mark, and directing the laser marking system to produce laser pulses having laser pulse parameters associated with the desired marks including temporal pulse widths greater than about 1 and less than about 1000 picoseconds.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser-induced plasma micromachining
A method and system for laser ablating a target material in an ambient atmosphere are disclosed. The method includes generating one or more laser pulses, each of the laser pulses having a pulse width of 1 picosecond (ps) or less and a pulse energy of 50 micro joules (μJ) or more. The laser pulses are directed towards the target material such that the laser pulses interact with a gas to form a plasma. The plasma removes a portion of the target material by interaction of the plasma with the target material.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Micromachining with short-pulsed, solid-state UV laser
ActiveUS7605343B2Reduce the numberReduce in quantityLaser detailsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesUv laserPicosecond
In some embodiments, laser output including at least one laser pulse having a wavelength shorter than 400 microns and having a pulsewidth shorter than 1,000 picoseconds permits the number of pulses used to clean a bottom surface of a via or the surface of a solder pad to increase process throughput. An oscillator module in cooperation with an amplification module may be used to generate the laser output.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser capable of simultaneously outputting nanosecond pulses and pico-second pulses
ActiveCN102709801AImprove utilization efficiencyAvoid complexityLaser detailsChemical reactionHigh energy
The invention discloses a laser capable of simultaneously outputting nanosecond pulses and pico-second pulses. The laser comprises a signal source, a signal isolation system and an amplifier. According to the invention, with an electric light control technology of combining an extra-cavity Pockels cell and intra-cavity Pockels cell, a regenerative amplification process is realized in case of signal light importing so as to obtain high-energy pico-second laser output, and cavity empty process is also realized in case of no signal light importing so as to obtain nanosecond pulse output; and thefree combination of the two processes can be realized according to practical application demand, and as a result, free combination of numbers of the nanosecond pulses and the pico-second pulses in a single laser is realized and is output in an alternative way. The laser provided by the invention has an important application in high-precision high-efficiency fine processing field, as well as basicresearch fields such as plasma excitation, excited state control, chemical reaction control, special radiation excitation and the like.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and apparatus for optimally laser marking articles
InactiveUS20120043306A1Nice appearanceSolve the lack of precisionThermographyMetal working apparatusLaser processingPulse parameter
The invention is a method and apparatus for laser marking a stainless steel specimen with commercially desirable marks. The method includes providing a laser processing system having a laser, laser optics and a controller with pre-determined laser pulse parameters, selecting the pre-determined laser pulse parameters associated with the desired mark, and directing the laser marking system to produce laser pulses having laser pulse parameters associated with the desired marks including temporal pulse widths greater than about 1 and less than about 1000 picoseconds.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Carrier phase detection system for radar sensors
ActiveUS7379016B1Improve accuracyImprove dynamic rangeOptical rangefindersResistance/reactance/impedenceRadarPicosecond
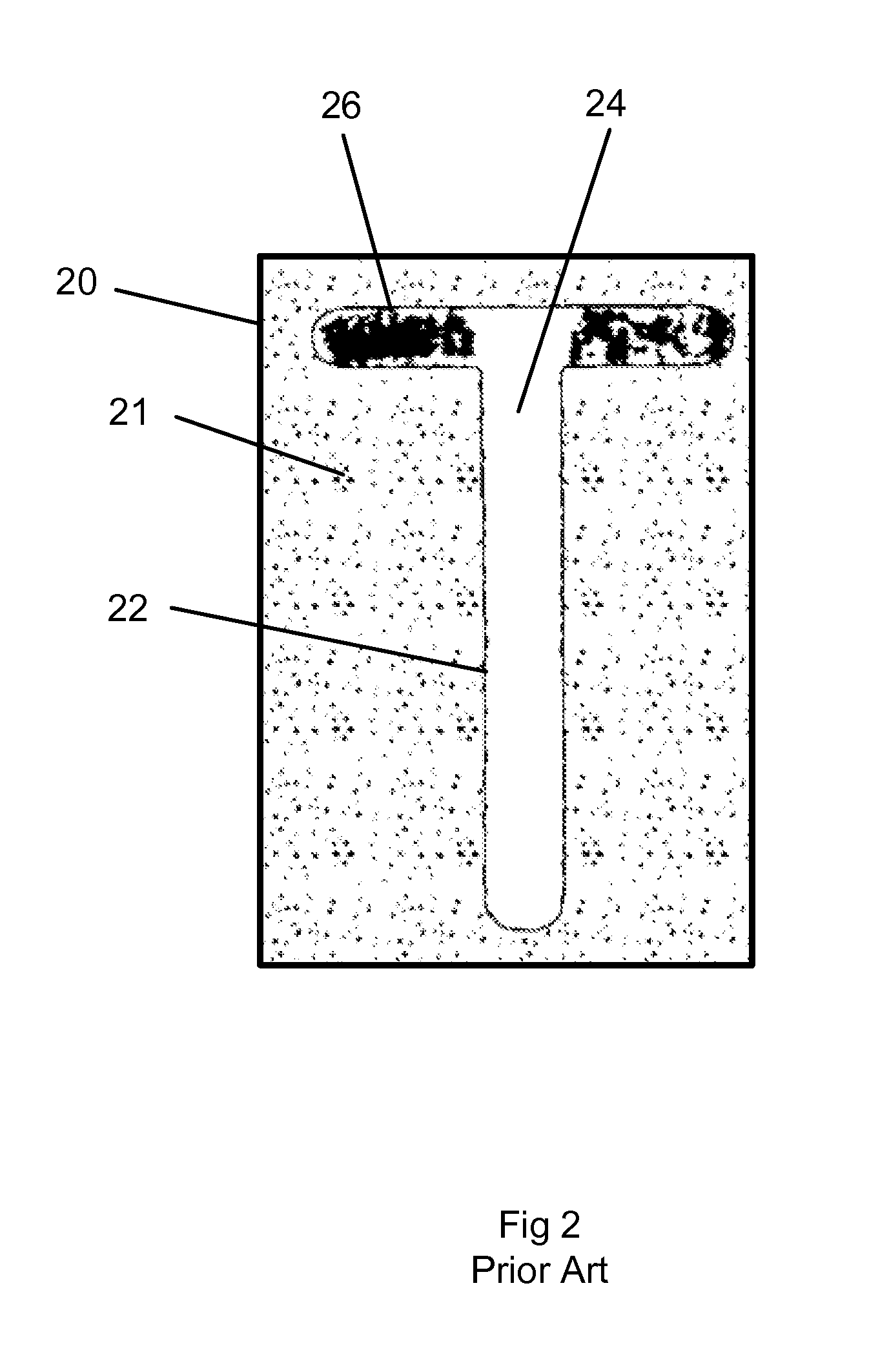
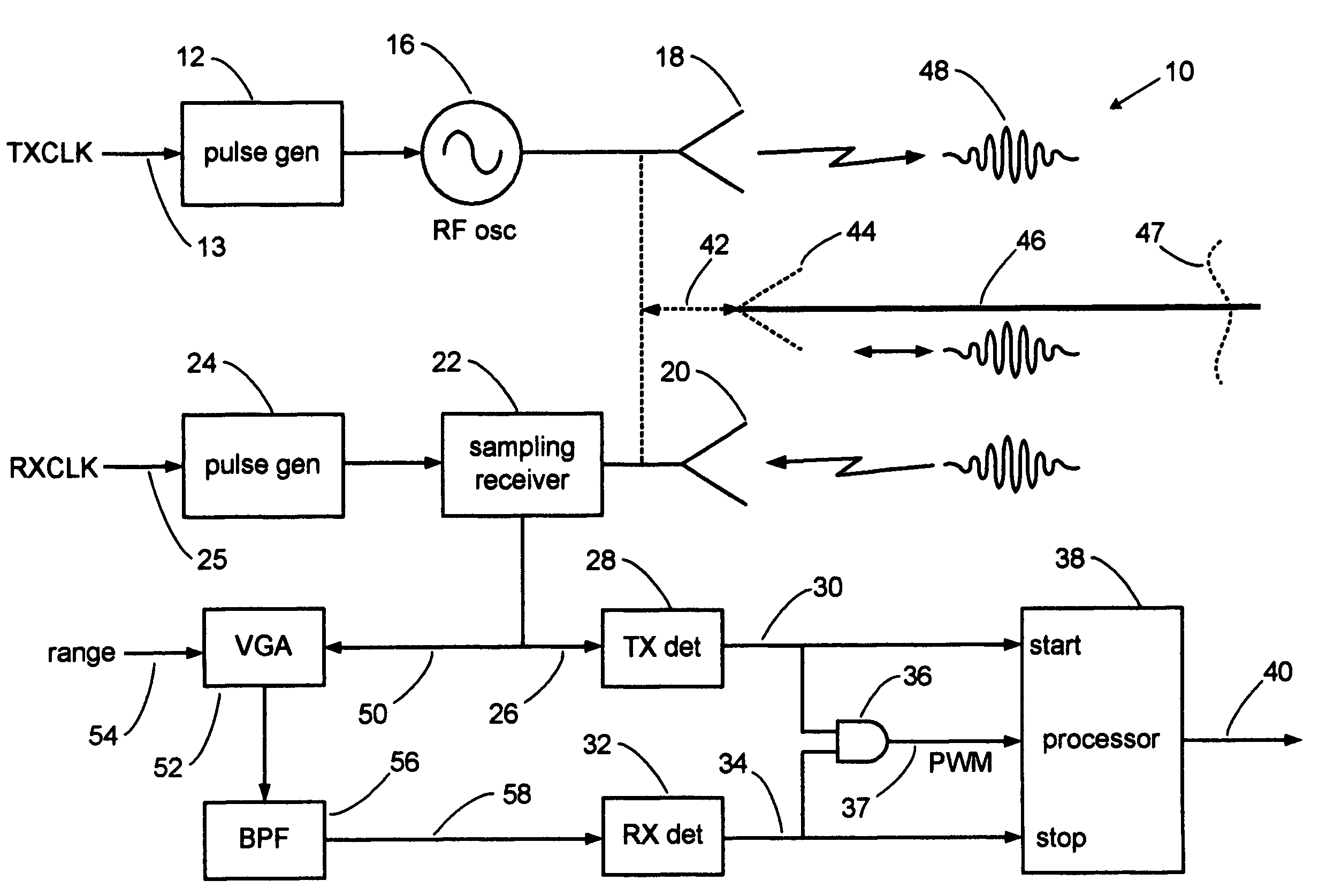
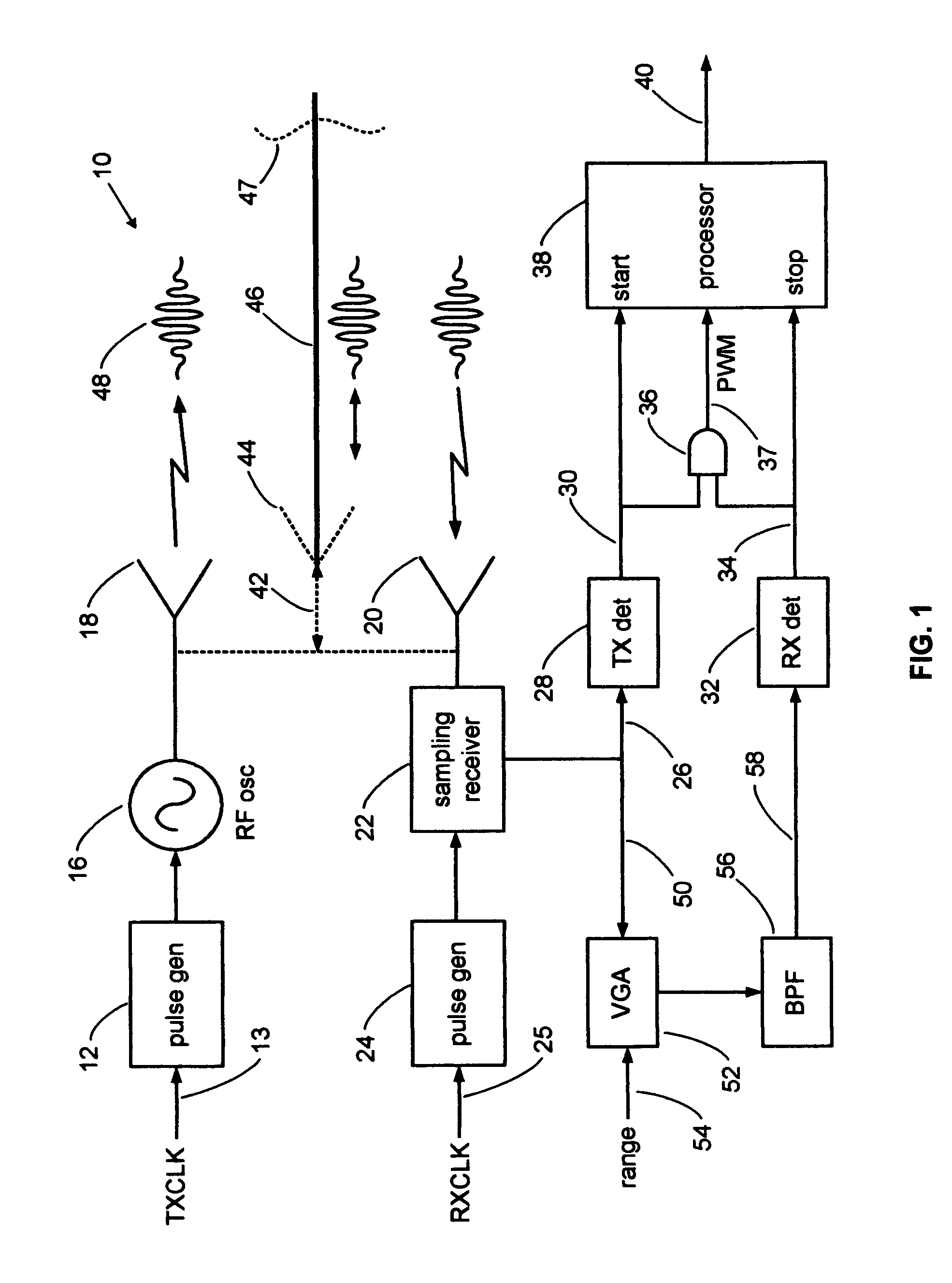
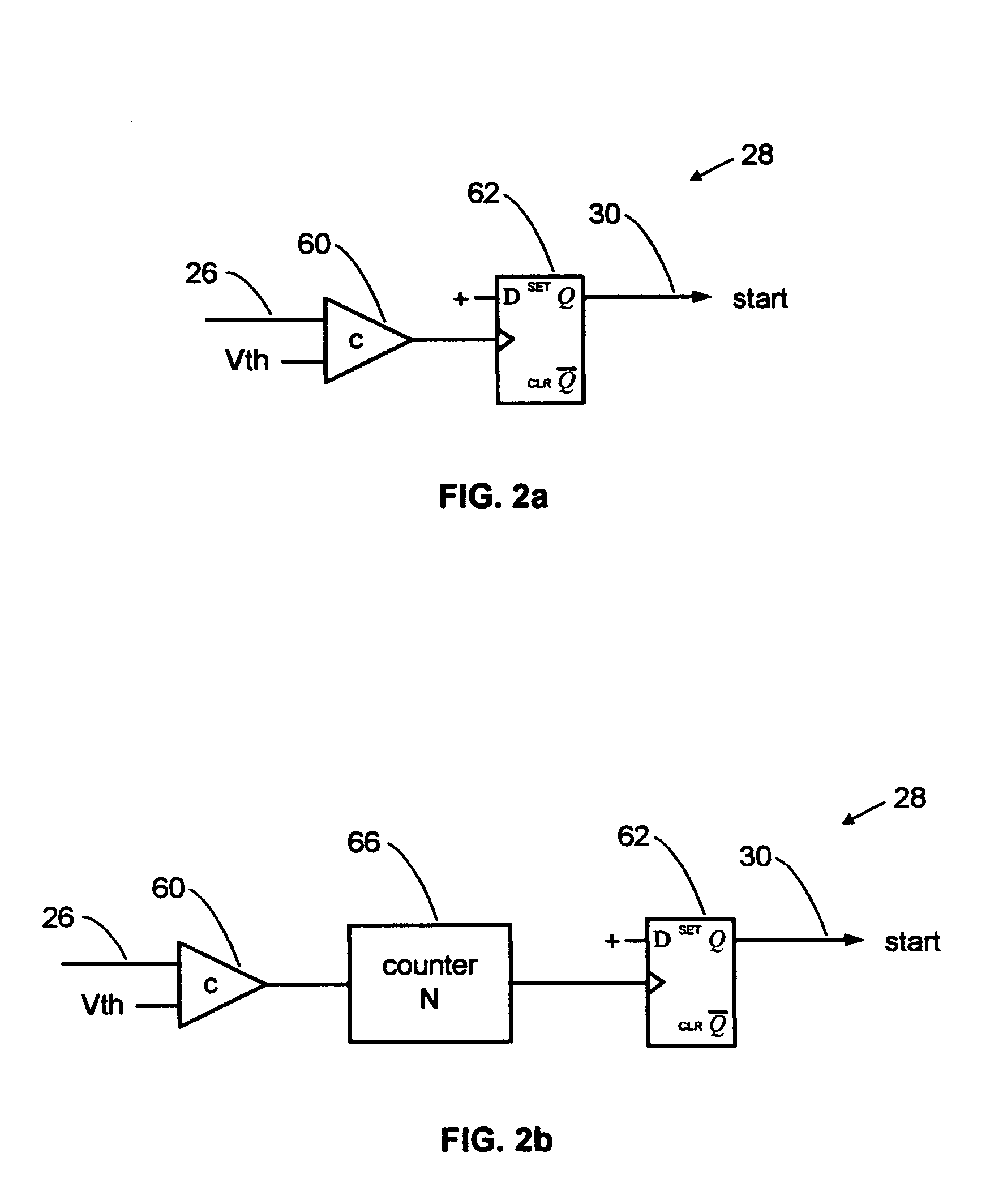
A pulse detection system for expanded time radar, laser and TDR sensors detects specific cycles within bursts of cycles. A sensor transmits and receives short bursts of RF cycles. A transmit pulse detector triggers on a selected cycle of the detected transmit burst and starts a range counter. A receive detector triggers on a selected cycle within a received echo burst to stop the range counter, thereby indicating range. Cycle selection is enabled by an analysis window of time. The detection system can provide accuracies on the order of one picosecond and is well-suited to accurate ranging along an electromagnetic guide wire.
Owner:MCEWAN TECH
Method for altering metal surface color with ultra-short pulse laser
InactiveCN101368256ANanostructure manufactureSolid state diffusion coatingSelective reflectionLight beam
The invention discloses a method for changing the color and lustre on a metal surface by an ultra-short pulse laser, which relates to the field of processing the surface of metal material. In the invention, an ultra-short pulse laser beam with a pulse width between 2 femtosecond and 100 picosecond is used to directly radiate the metal surface; different micron and even nanometer structures are formed on the metal surface through controlling the parameters like energy and polarization of the pulse laser; the forming of the nanometers makes the metal surface realize selective reflection phenomenon on the light at different angles and lead the metal surface to be seen to have a plurality of different metal colors. The technology can be applied for the manufactures like the color changing and anti-fake brands on the surfaces of metal jewelleries and can obtain polychrome colors like the wings of butterflies.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com