Patents
Literature
304 results about "Uv laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
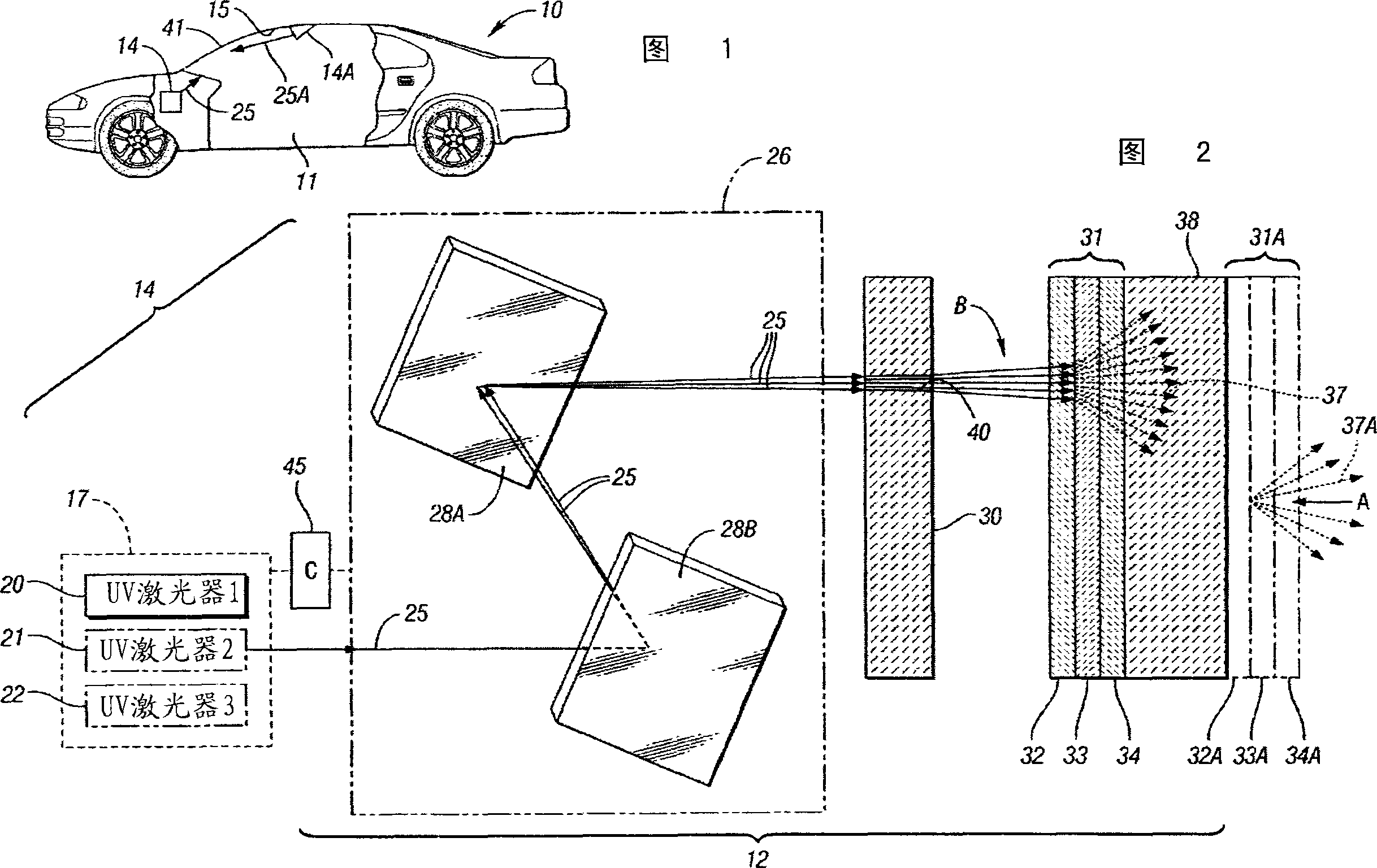
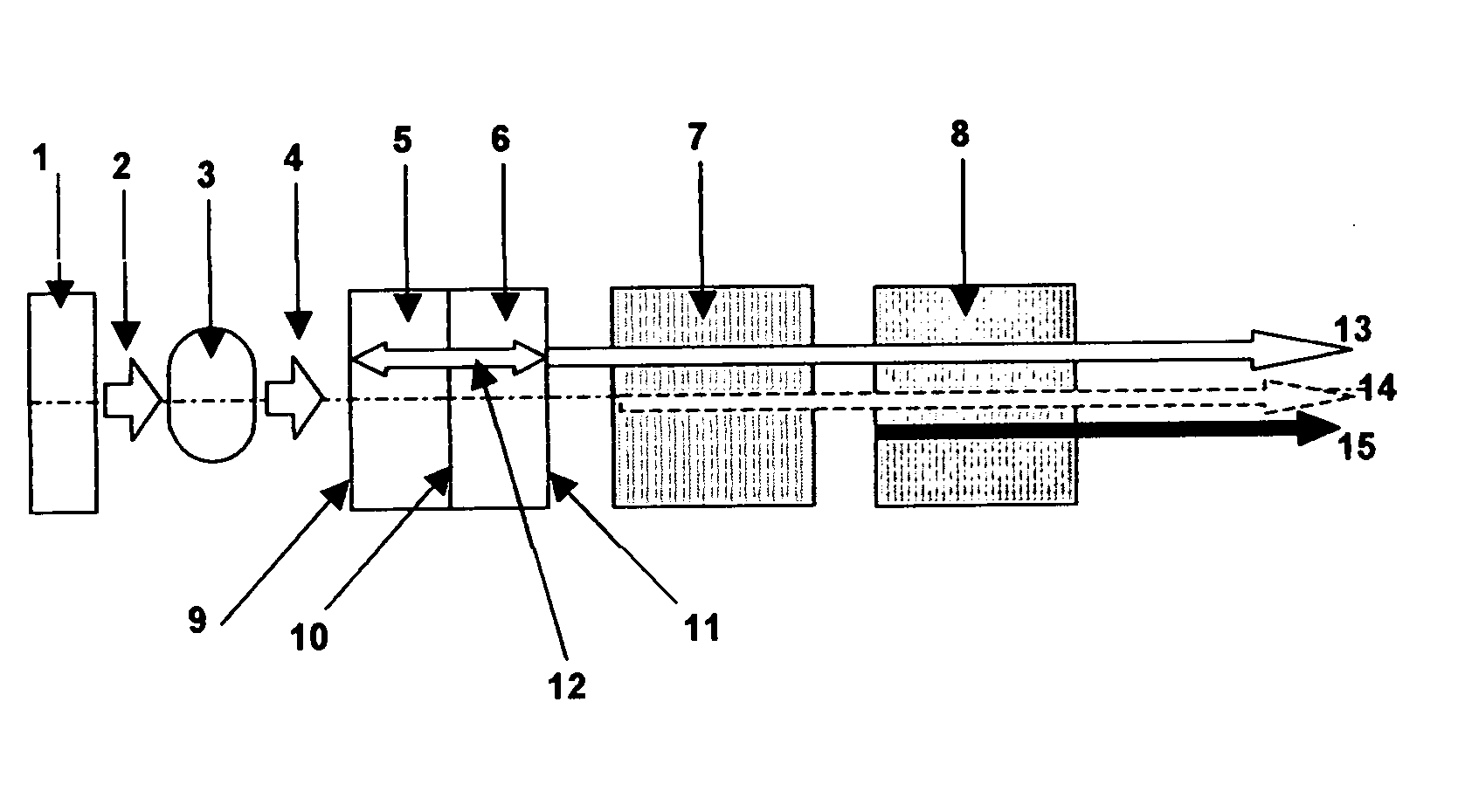
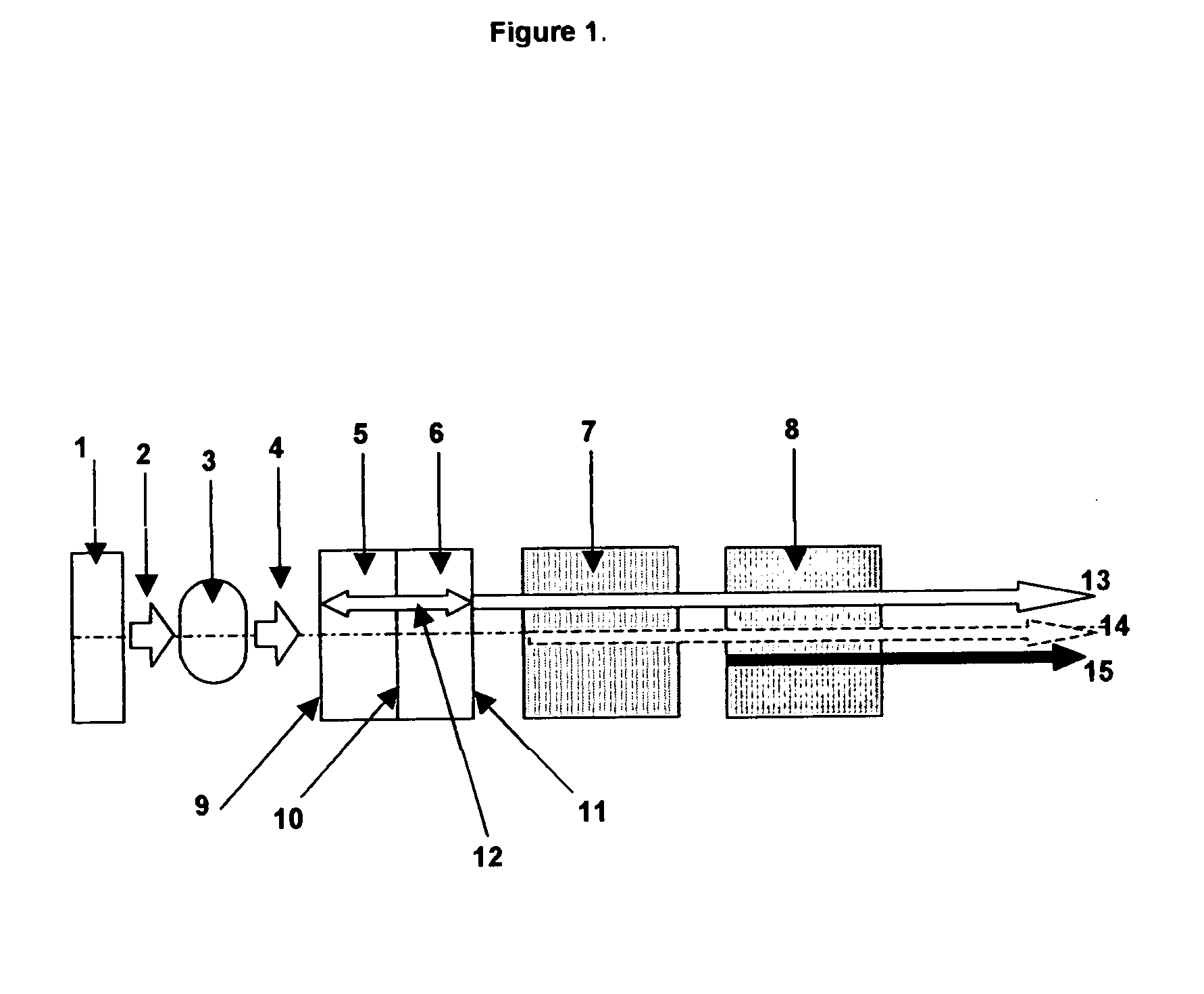
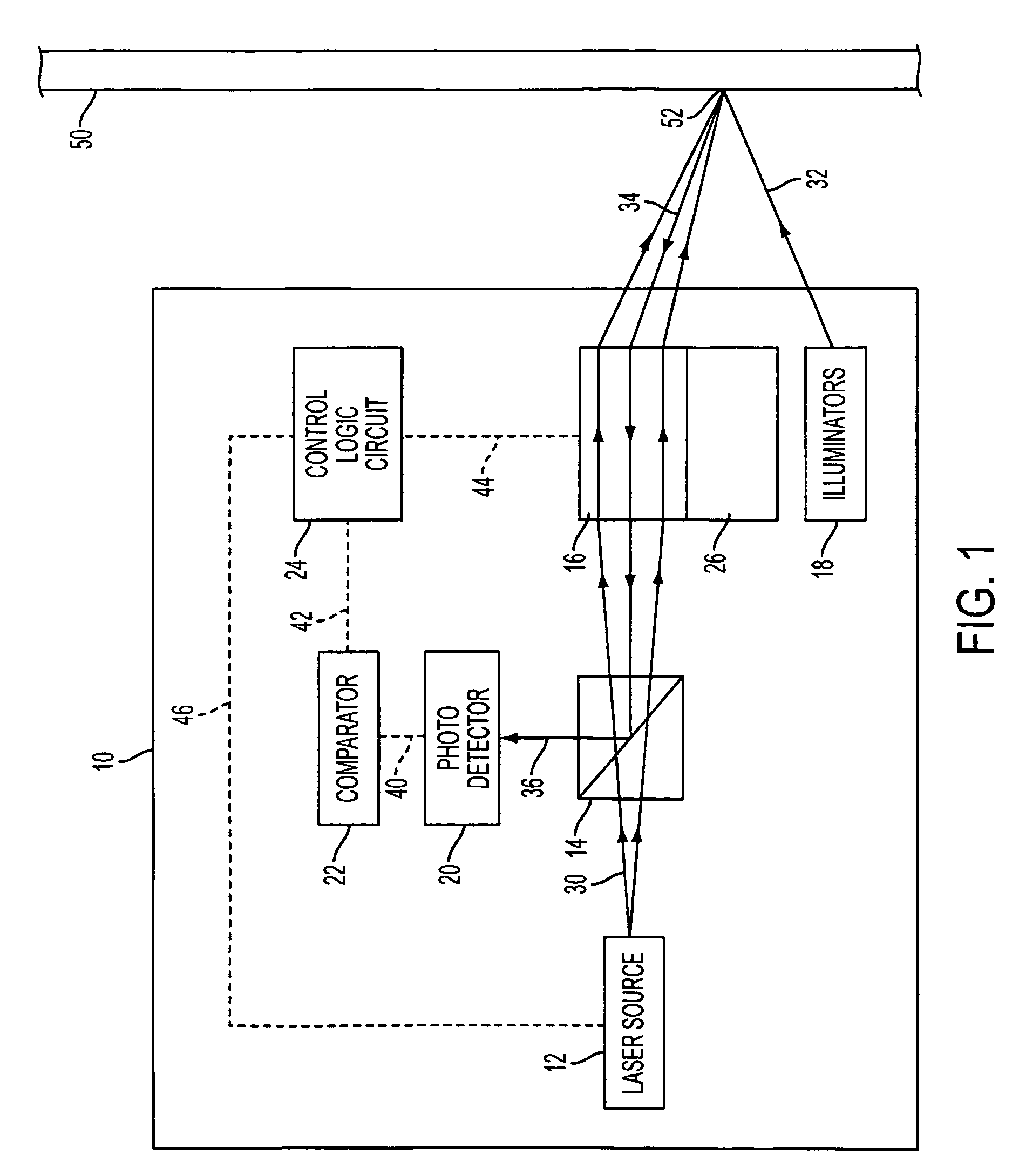
System and method of using fluorescent material to display information on a vehicle window
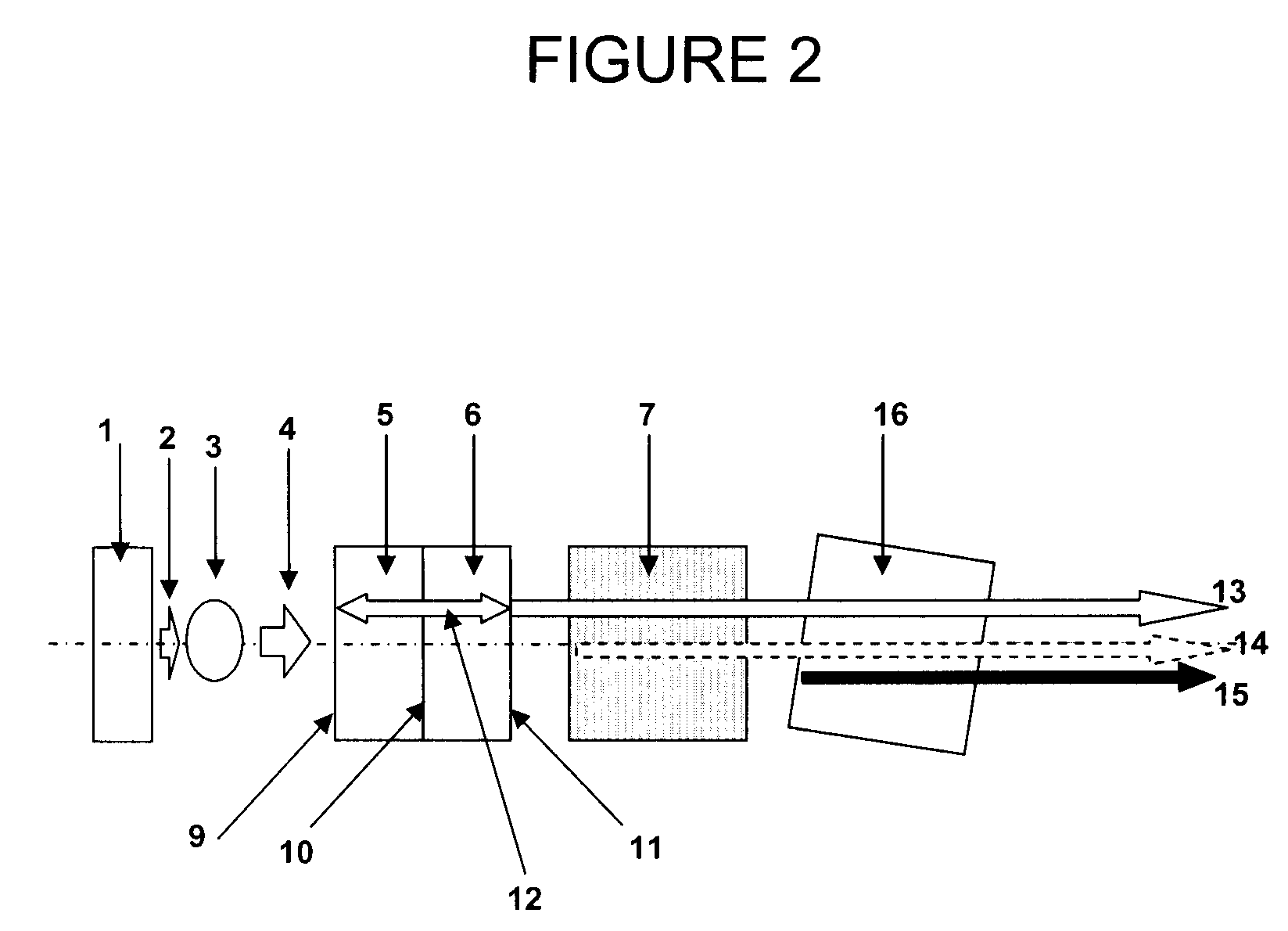
ActiveUS8466438B2Low costEasy to understandInstrument arrangements/adaptationsProjectorsUv laserUltraviolet
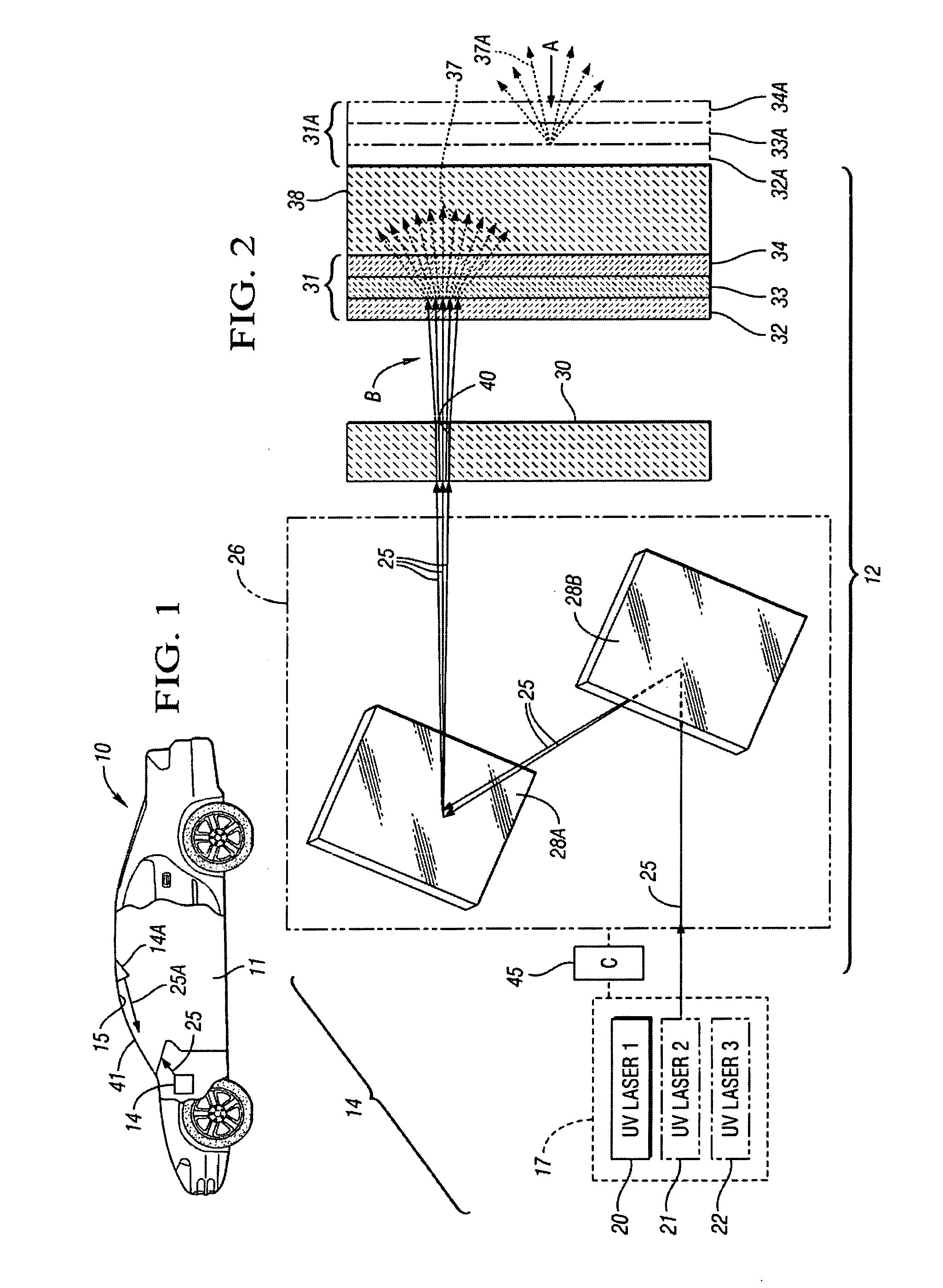
A system to selectively display a symbol at a location on a vehicle window. The system includes an arrangement of a fluorescent material at the location, wherein the fluorescent material: a) is sufficiently transparent in the absence of ultraviolet (UV) light, b) fluoresces when illuminated with UV light, c) and has a shape corresponding to the symbol, and a UV light source configured to illuminate the location with UV light to display the symbol. Such a system may use unfocused UV light sources to illuminate the symbol shaped fluorescent material as opposed to focused UV light sources such as UV lasers.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
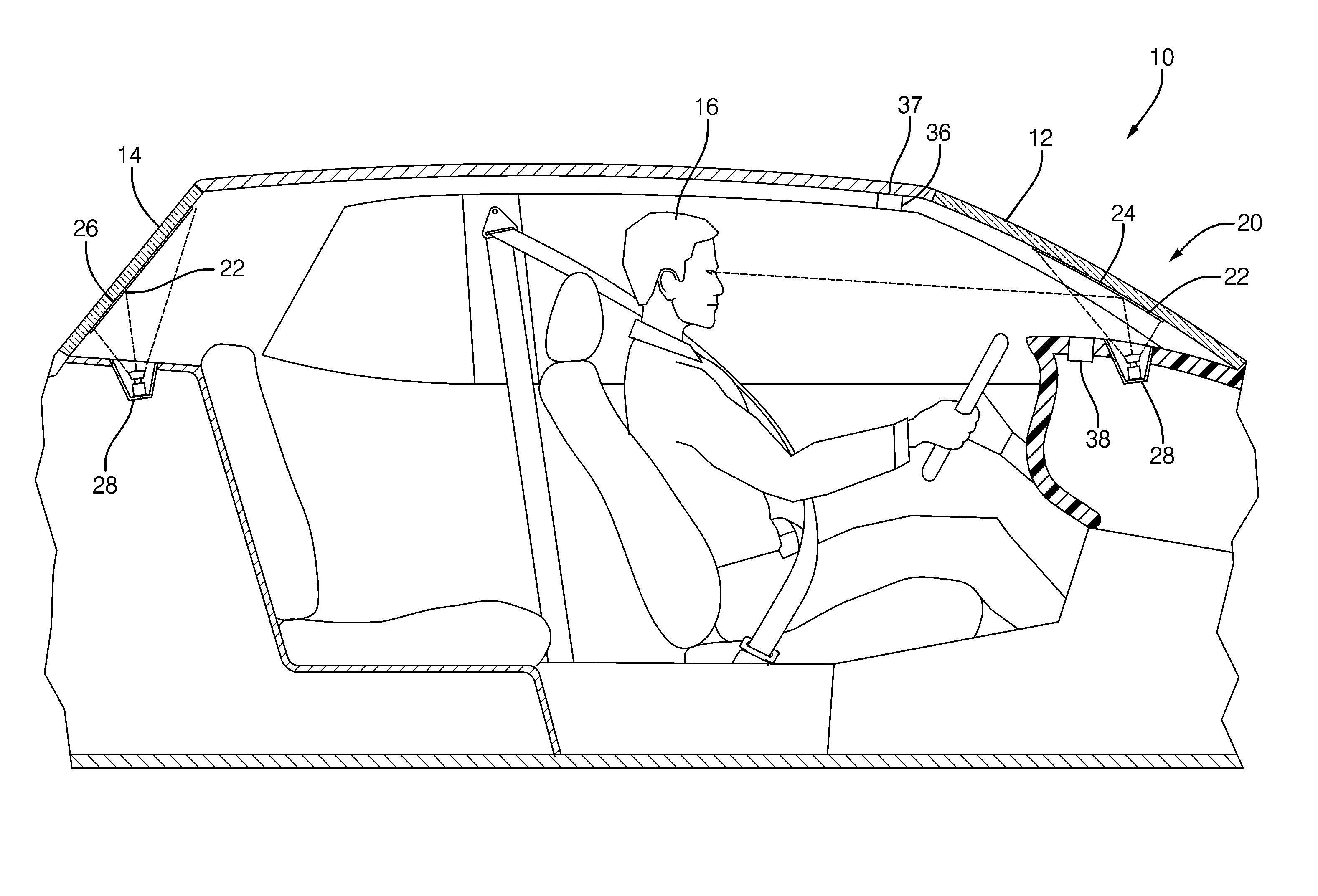
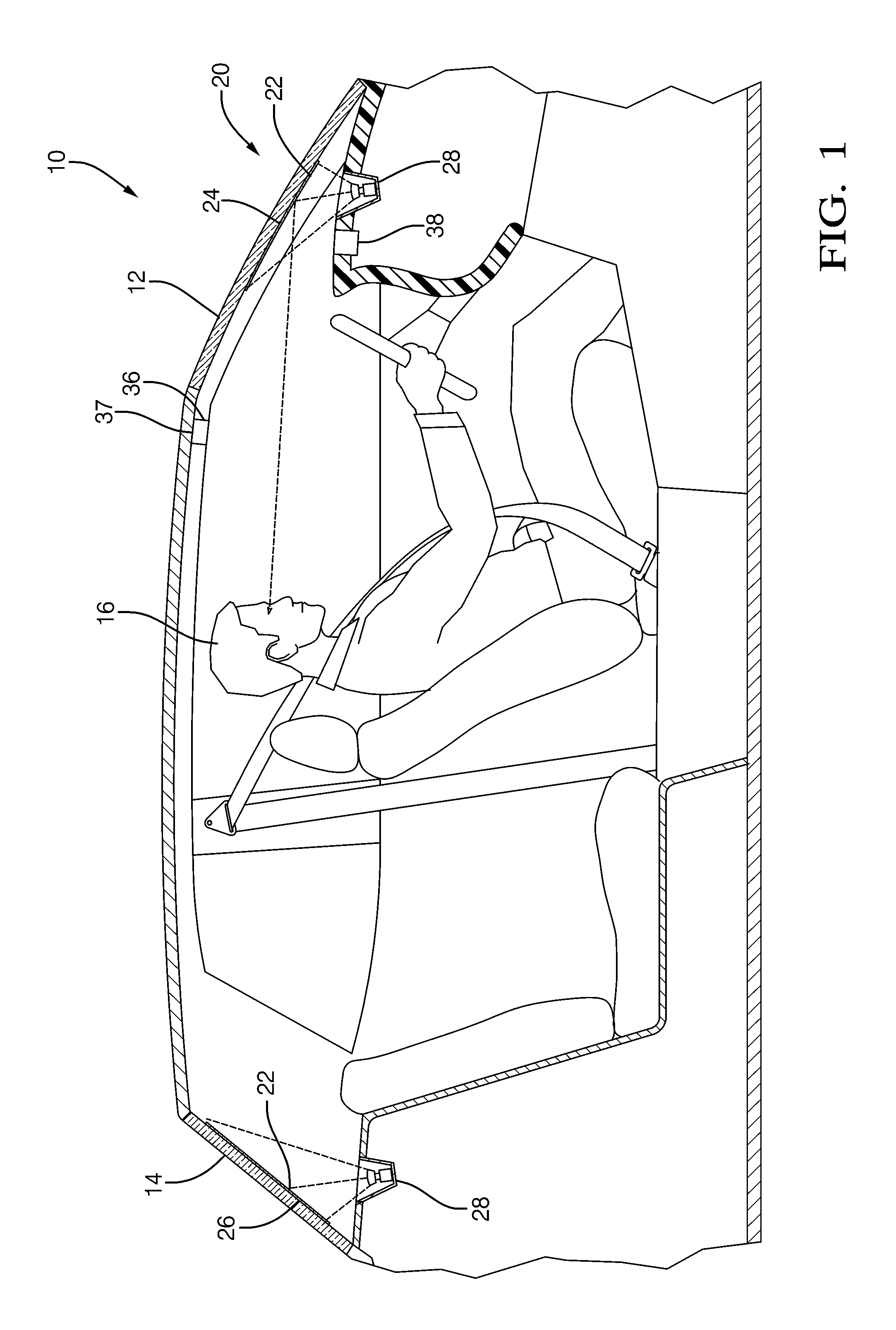
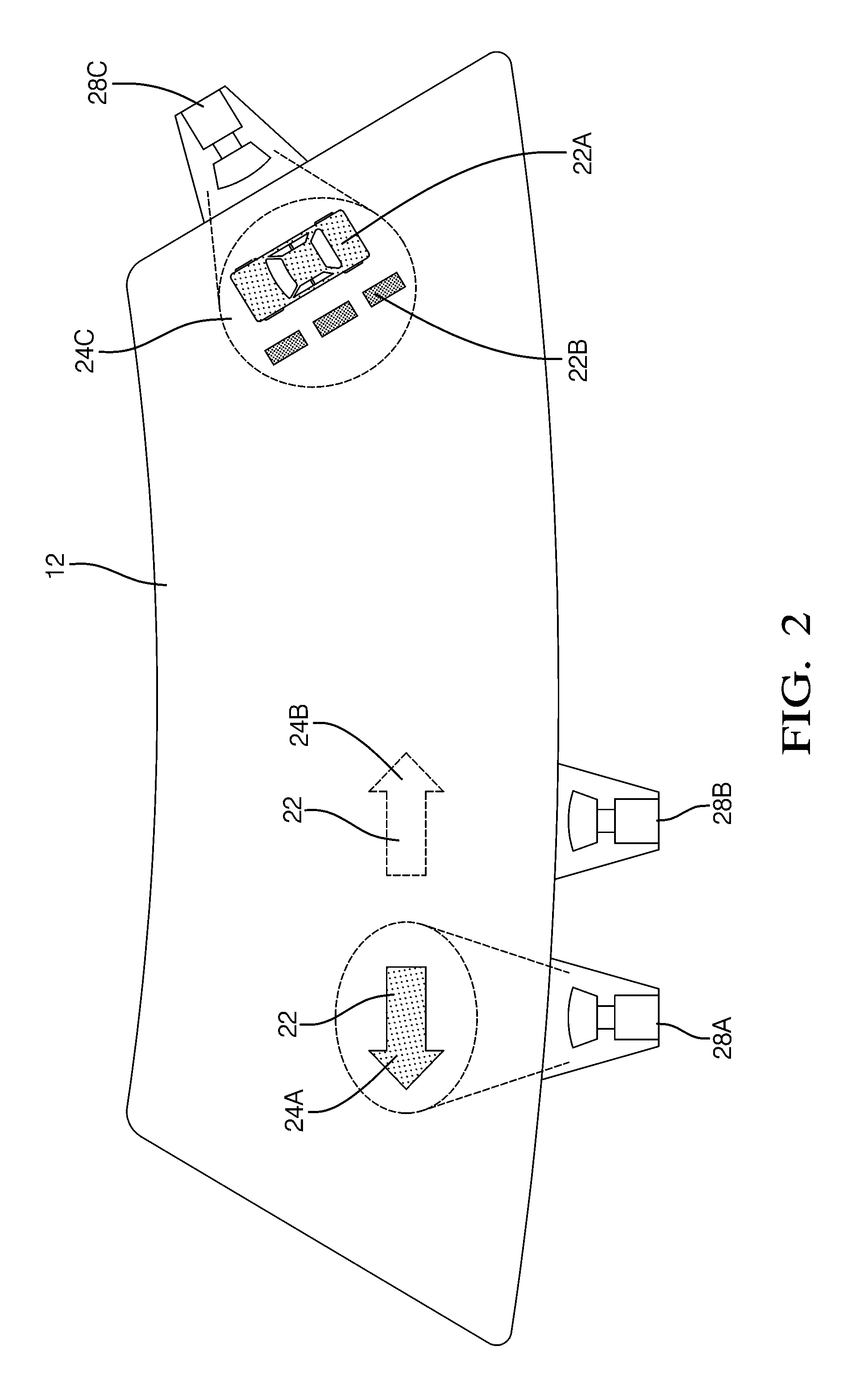
Apparatus And Method For Displaying Information Within A Vehicle Interior
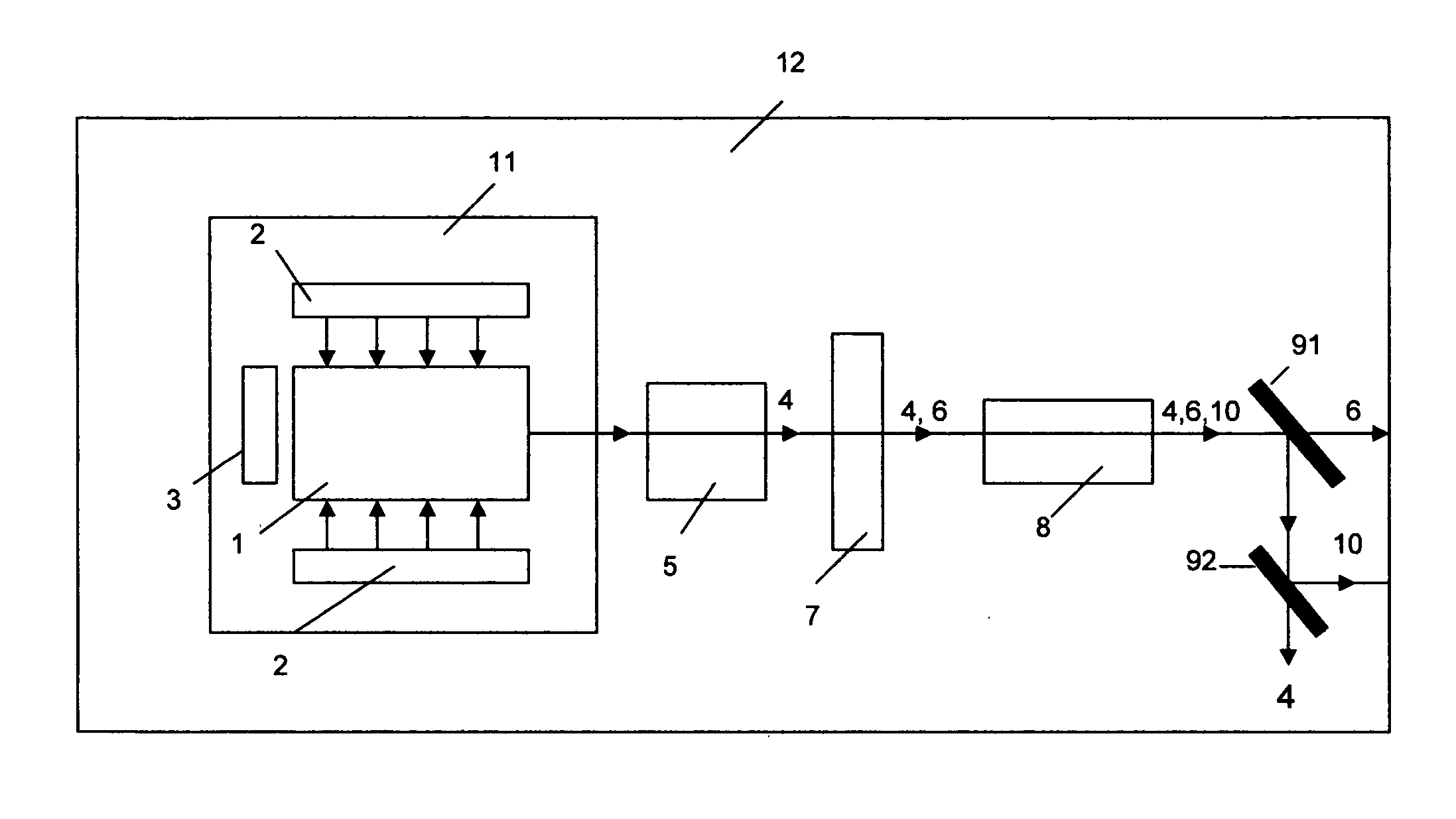
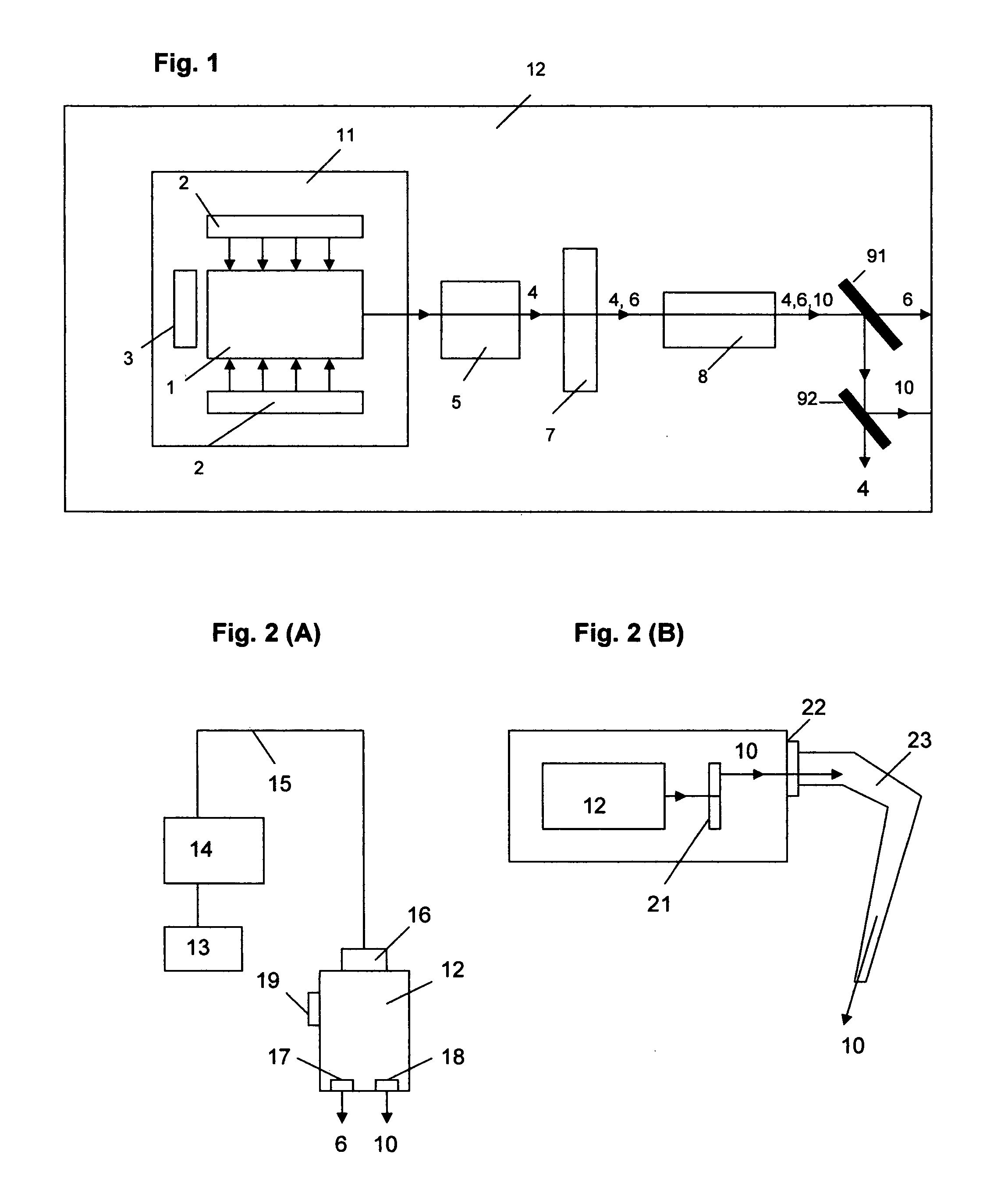
An apparatus for displaying information within a vehicle interior includes a surface having a coating for emitting visible light when excited by an ultraviolet (UV) light beam, and a laser projection device (LPD) for generating and directing the UV light beam onto the coating to display information on the surface. The LPD generates one or more UV laser beams, and the coating has one or more light-emitting layers each excitable by a different UV wavelength. Each layer emits a different color of light when excited. The surface is a transparent windshield or lens, or an opaque surface. A method for displaying information within a vehicle interior includes applying a light-emitting coating to a surface in at least one layer, and generating and projecting a UV light beam onto the coating to present information in at least as many colors as there are layers.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
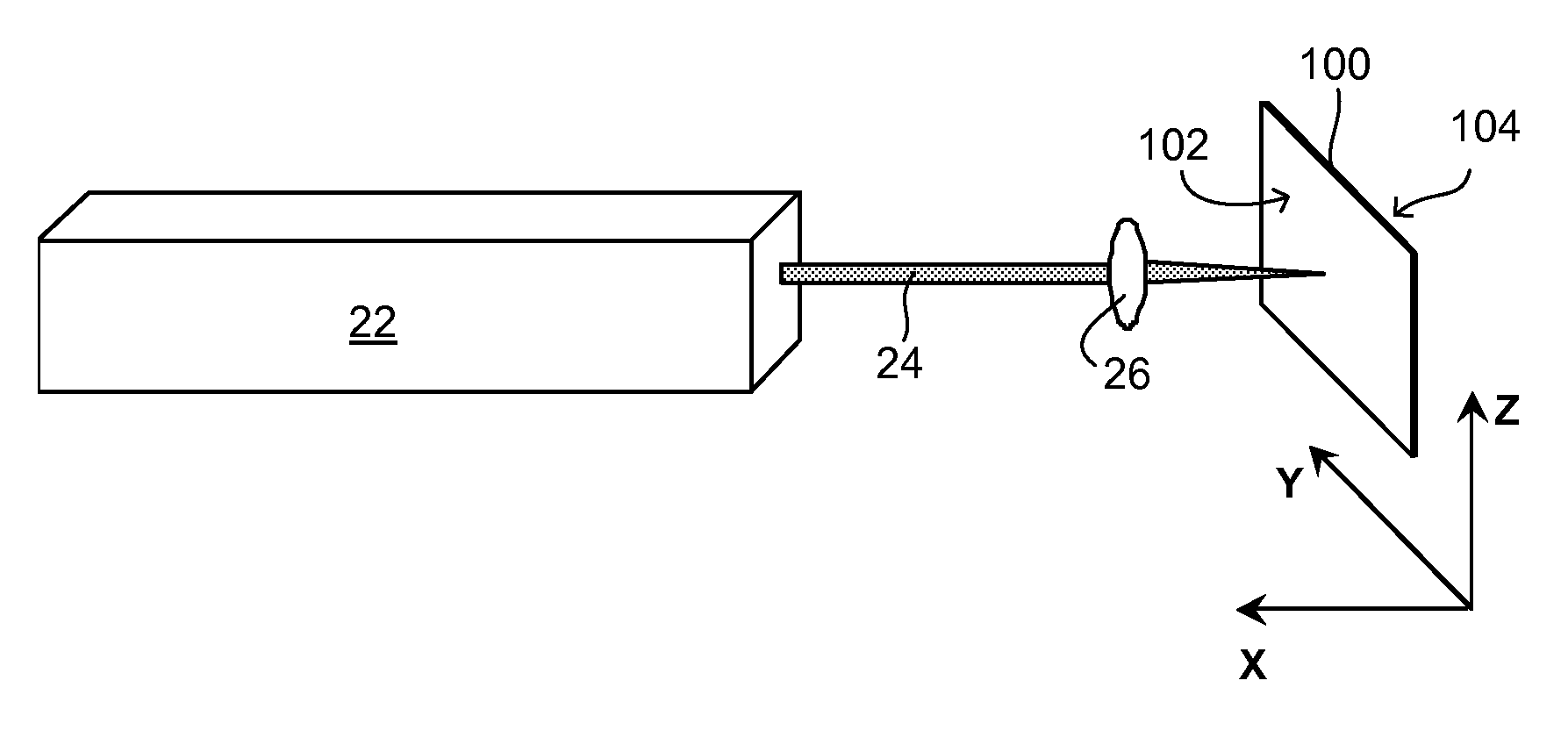
Methods of forming high-density arrays of holes in glass
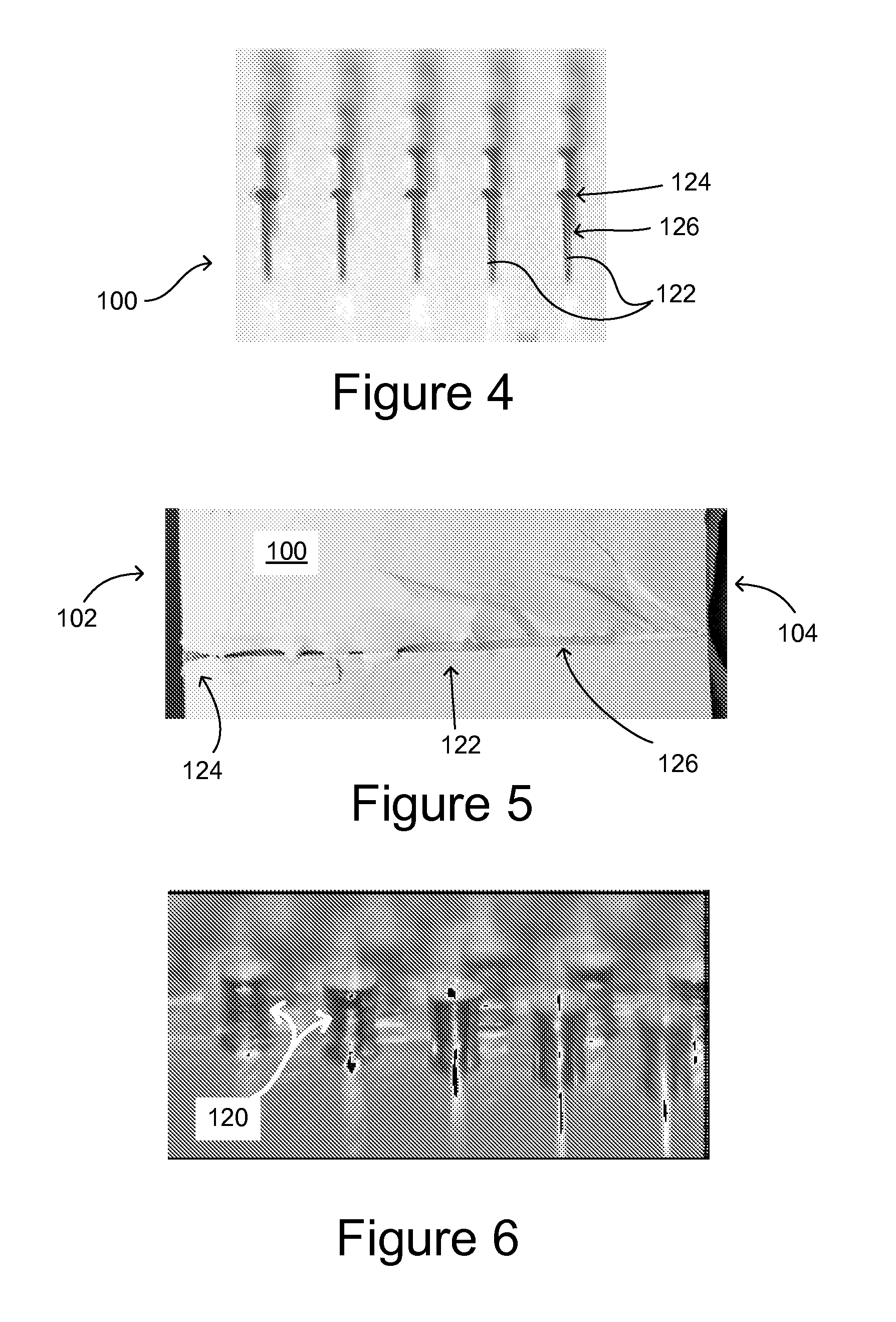
ActiveUS20130247615A1High positioning accuracyReliable and low-costGlass furnace apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsUv laserEtching
A method of fabricating a high-density array of holes in glass is provided, comprising providing a glass piece having a front surface, then irradiating the front surface of the glass piece with a UV laser beam focused to a focal point within + / −100 μm of the front surface of the glass piece most desirably within + / −50 μm of the front surface. The lens focusing the laser has a numerical aperture desirably in the range of from 0.1 to 0.4, more desirably in the range of from 0.1 to 0.15 for glass thickness between 0.3 mm and 0.63 mm, even more desirably in the range of from 0.12 to 0.13, so as to produce open holes extending into the glass piece 100 from the front surface 102 of the glass piece, the holes having an diameter the in range of from 5 to 15 μm, and an aspect ratio of at least 20:1. For thinner glass, in the range of from 0.1-0.3 mm, the numerical aperture is desirably from 0.25 to 0.4, more desirably from 0.25 to 0.3, and the beam is preferably focused to within + / −30 μm of the front surface of the glass. The laser is desirable operated at a repetition rate of about 15 kHz or below. An array of holes thus produced may then be enlarged by etching. The front surface may be polished prior to etching, if desired.
Owner:CORNING INC
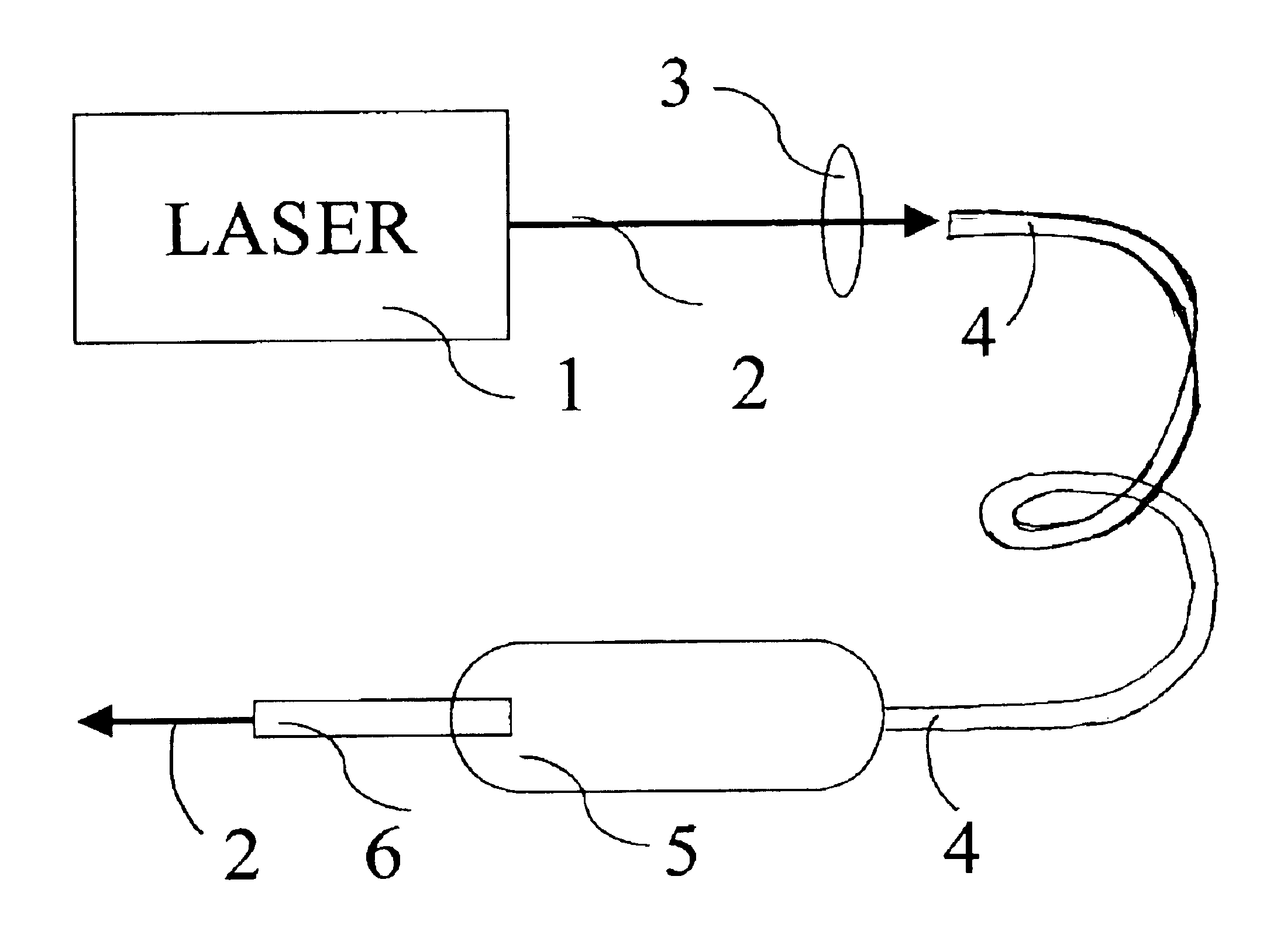
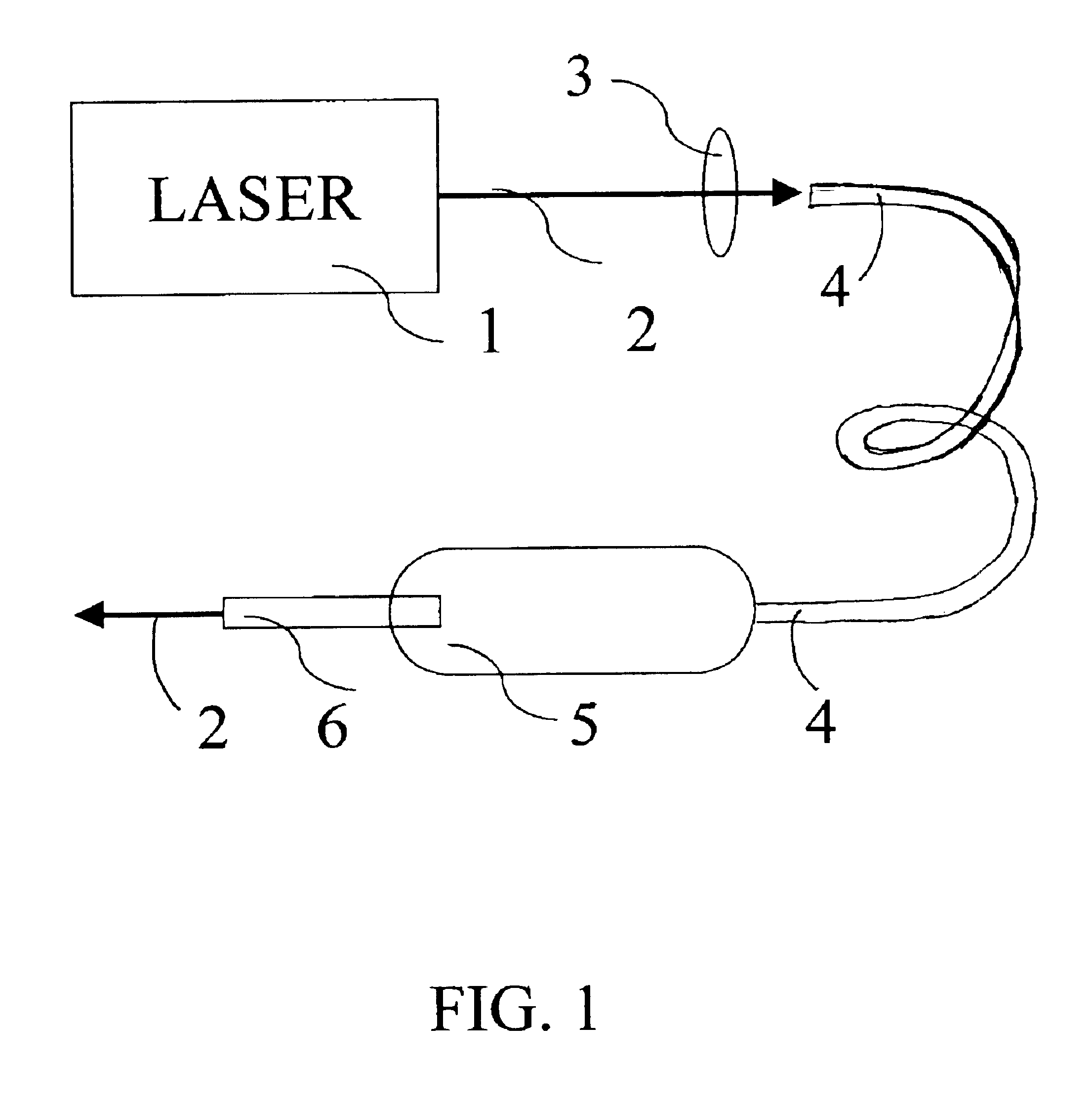
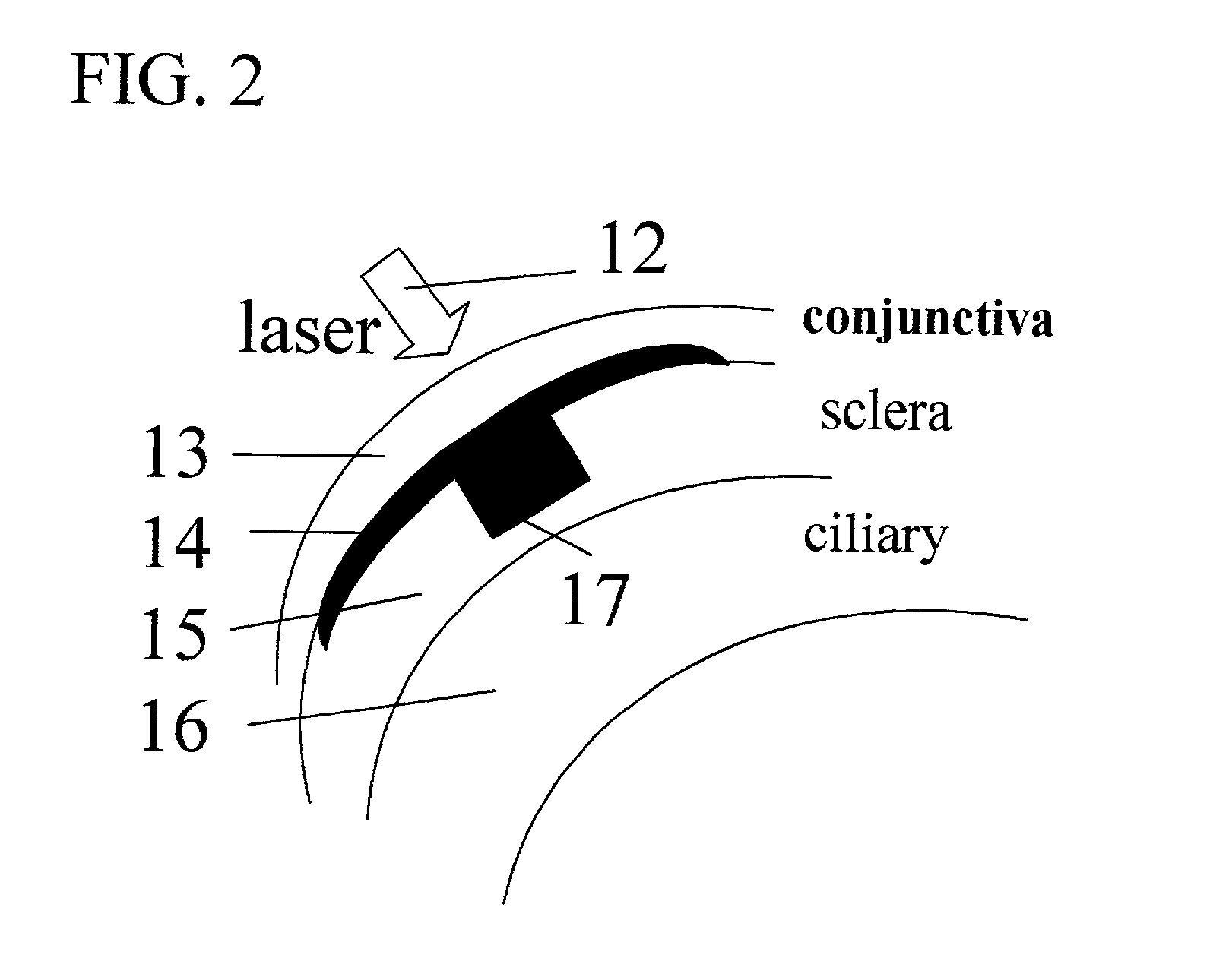
Apparatus and methods for the treatment of presbyopia using fiber-coupled-lasers
Systems and surgical techniques for presbyopia correction by laser removal of the sclera tissue are disclosed. The disclosed preferred embodiments of the system consists of a beam spot controller, a fiber delivery unit and a fiber tip. The basic laser including UV lasers and infrared lasers having wavelength ranges of (0.15-0.36) microns and (1.9-3.2) microns and diode lasers of about 0.98, 1.5 and 1.9 microns. Presbyopia is treated by a system which uses an ablative laser to ablate the sclera tissue outside the limbus to increase the accommodation of the ciliary body of the eye. The sclera tissue may be ablated by the laser with or without the conjunctiva layer open.
Owner:NEOS OCULAR
Methods for stripping and modifying surfaces with laser-induced ablation
A coating removal apparatus removes a coating from a surface. The apparatus has a movable scanning head and scanning optics. The scanning head is movable in one dimension, and the scanning optics adjust in two dimensions to compensate for movement of the scanning head to implement long range scanning with a uniform scanning pattern. Further, a surface roughness is determined by measuring specular and scattered reflections at various angles. For composite surfaces, the apparatus utilizes UV laser radiation and a controlled atmosphere to remove coating and alter the chemical characteristics at the surface.
Owner:GEN LASERTRONICS
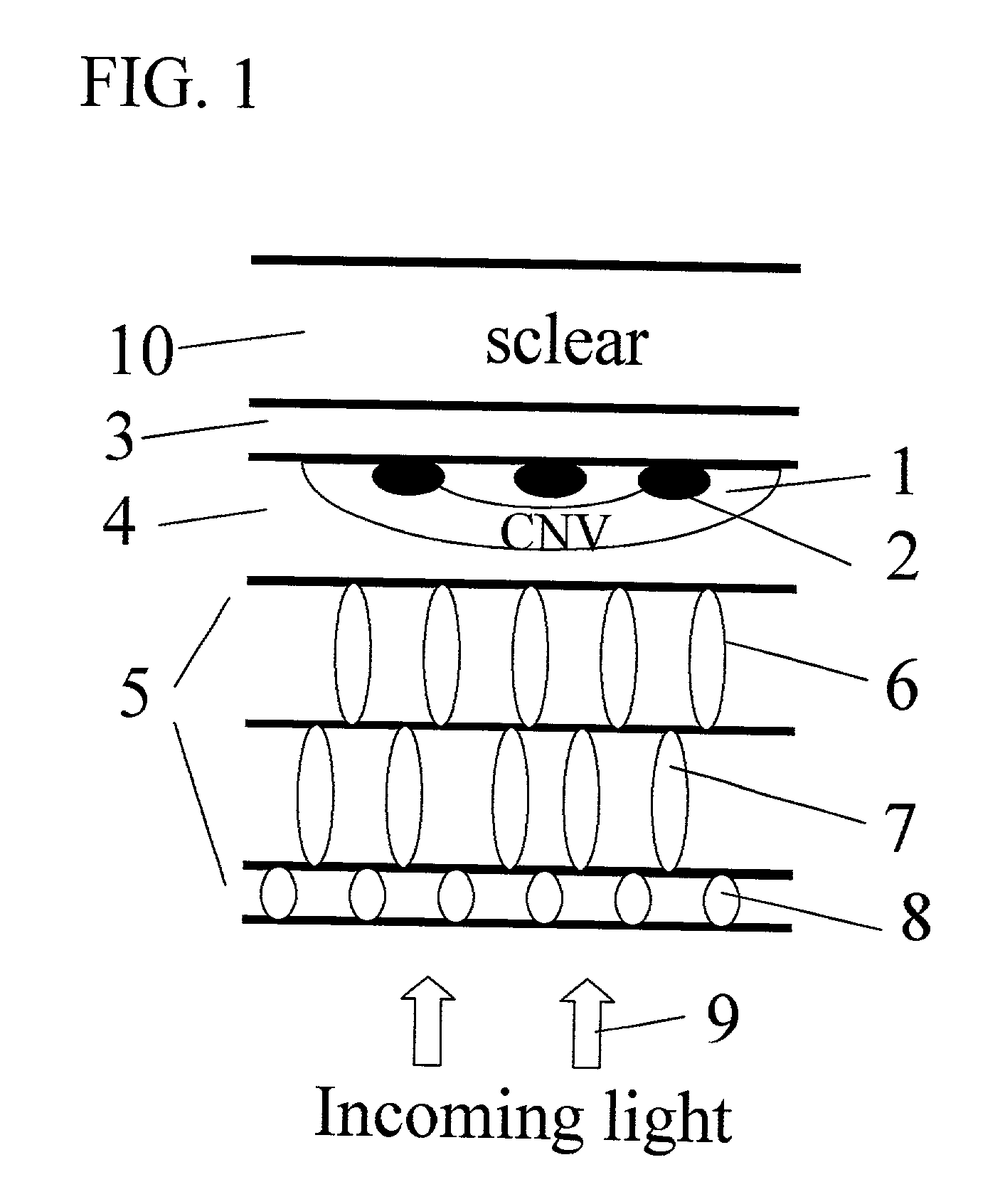
Apparatus and methods for prevention of age-related macular degeneration and other eye diseases
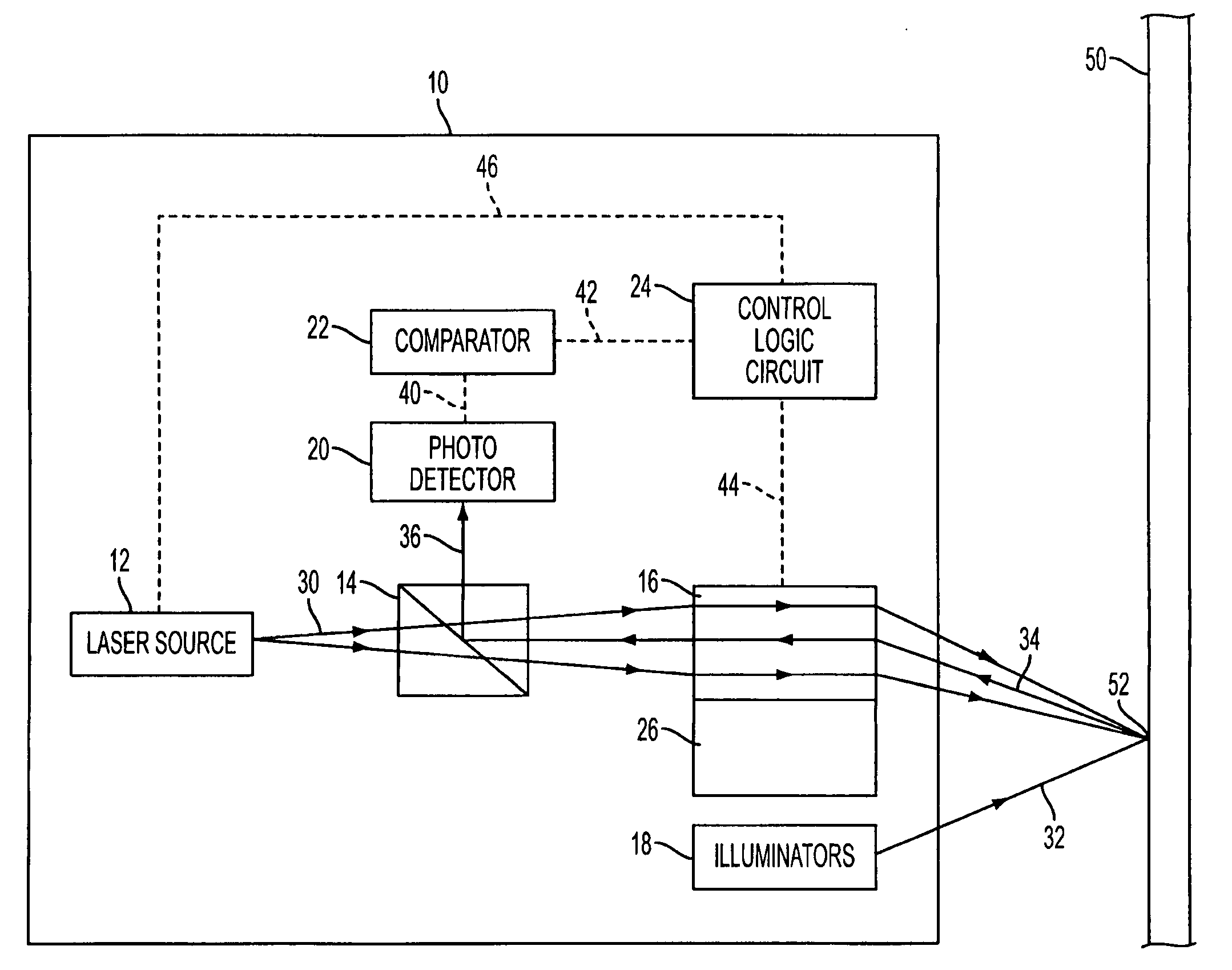
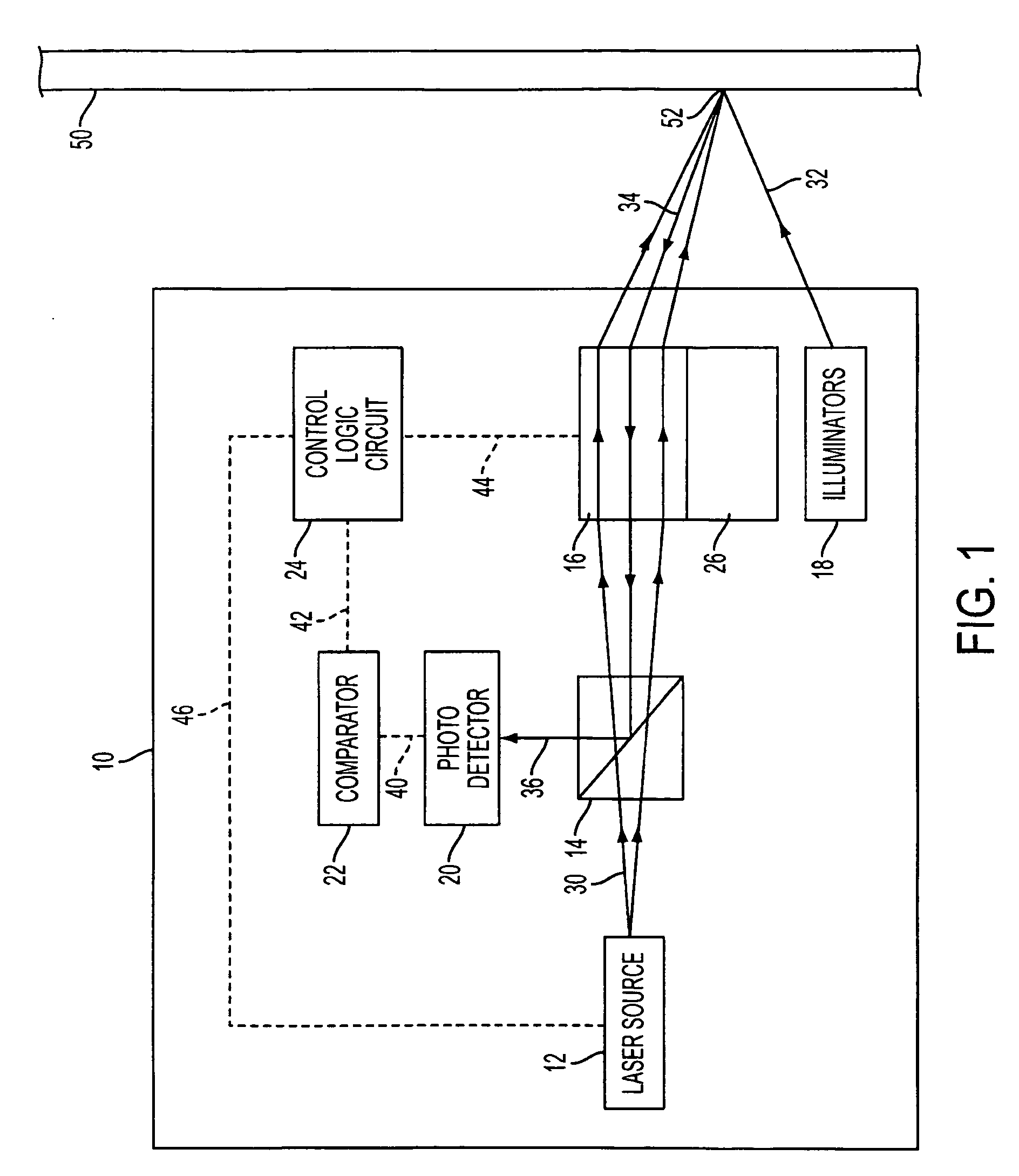
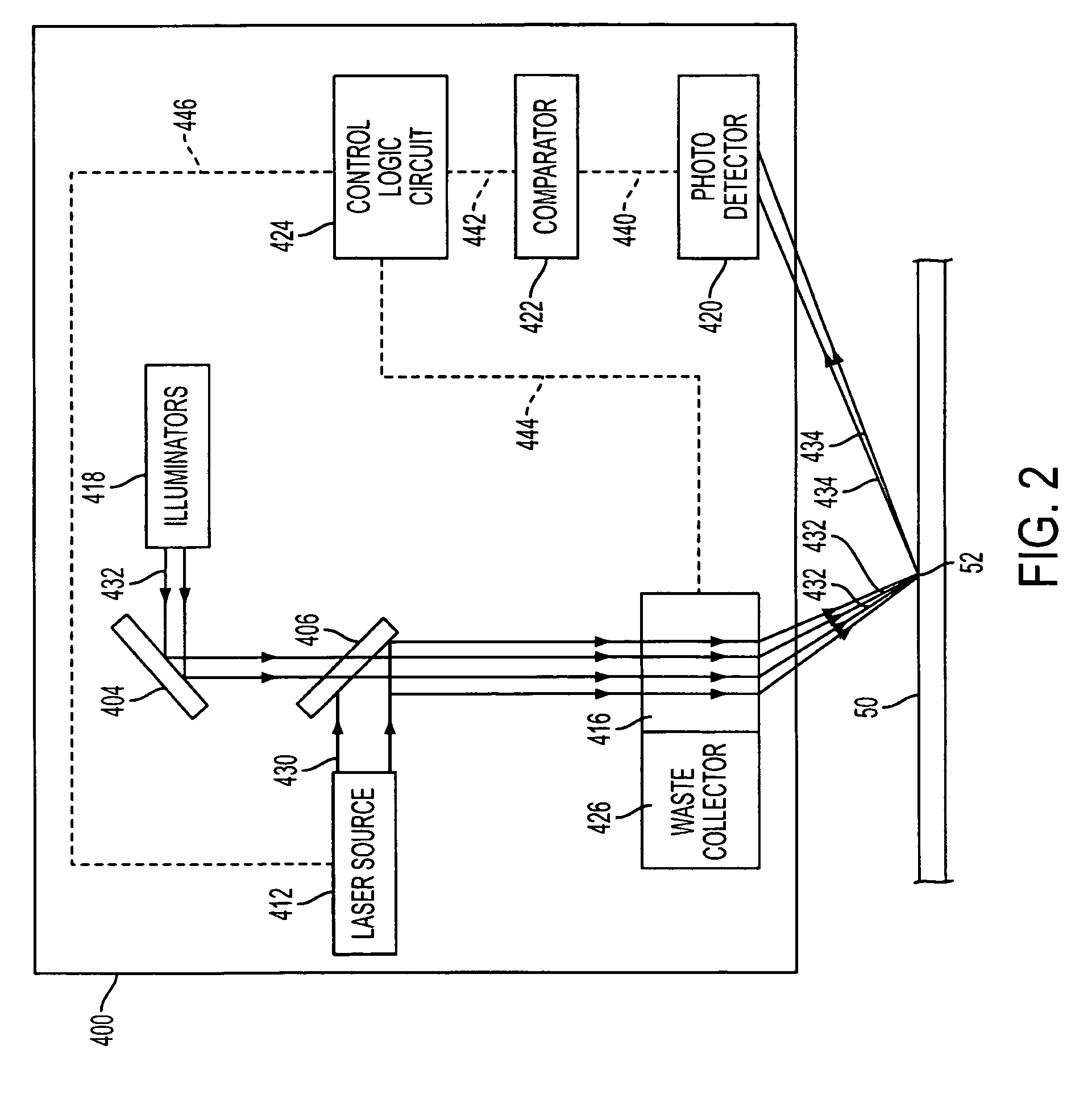
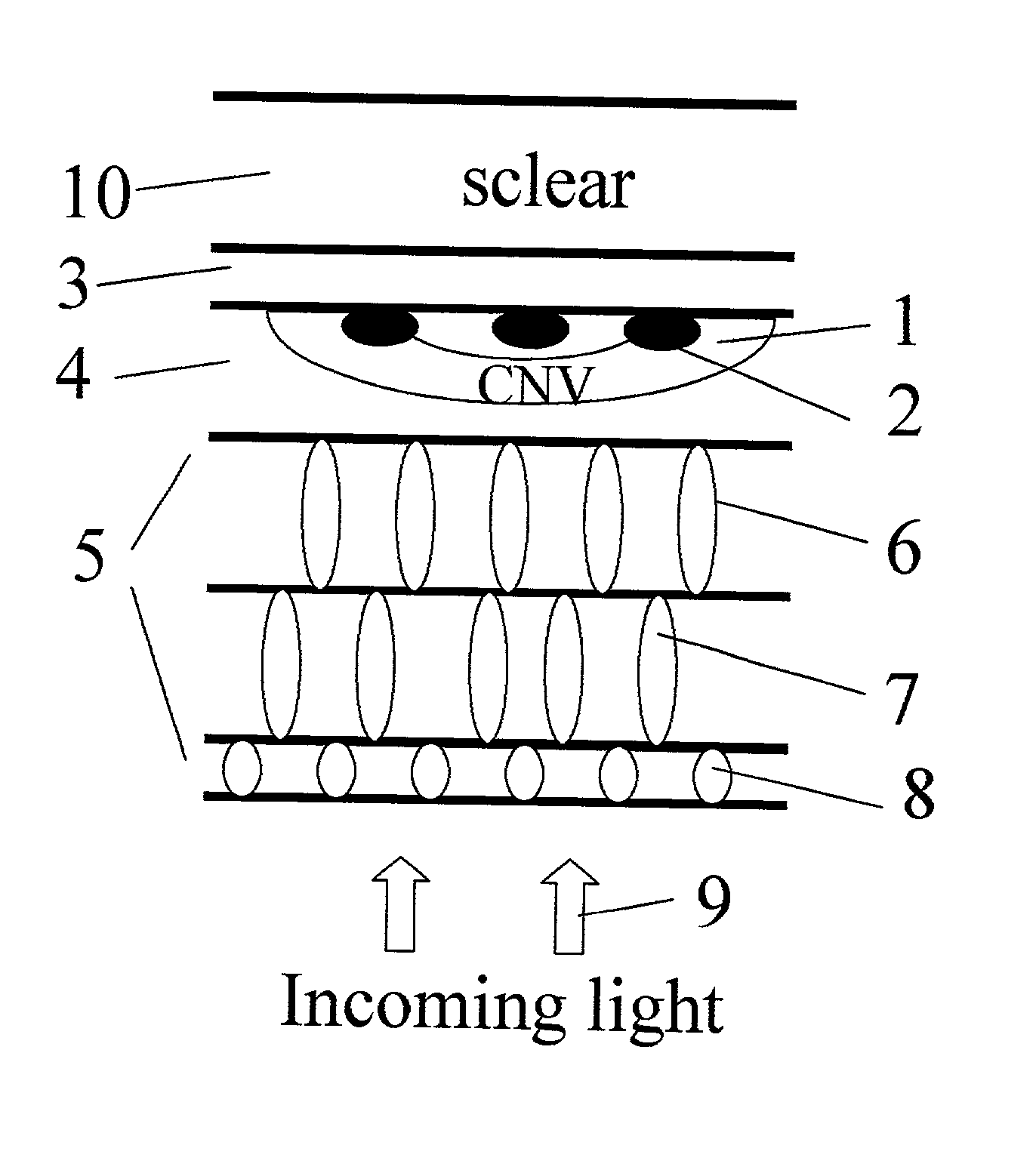
InactiveUS20030105456A1Minor side effectsIncrease flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instruments for heatingRadio frequencyLaser beams
Surgical apparatus and surgical methods are proposed for the prevention of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and choroidal neovascularization (CNV), and other eye diseases such as glaucoma by removal of the sclera tissue to reduce its rigidity and increase the flood flow and decrease pressure in the choriocapillaris. The disclosed preferred embodiments of the system consists of a tissue ablation means and a control means of ablation patterns and a fiber delivery unit. The basic laser beam includes UV lasers and infrared lasers having wavelength ranges of (0.15-0.36) microns and (0.5-3.2) microns and diode lasers of about 0.98, 1.5 and 1.9 microns. AMD and CNV are prevented, delayed or reversed by using an ablative laser to ablate the sclera tissue in a predetermined patterns outside the limbus to increase the elasticity of the sclera tissue surrounding the eye globe The surgery apparatus also includes non-laser device of radio frequency wave, electrode device, bipolar device and plasma assisted device
Owner:LIN J T
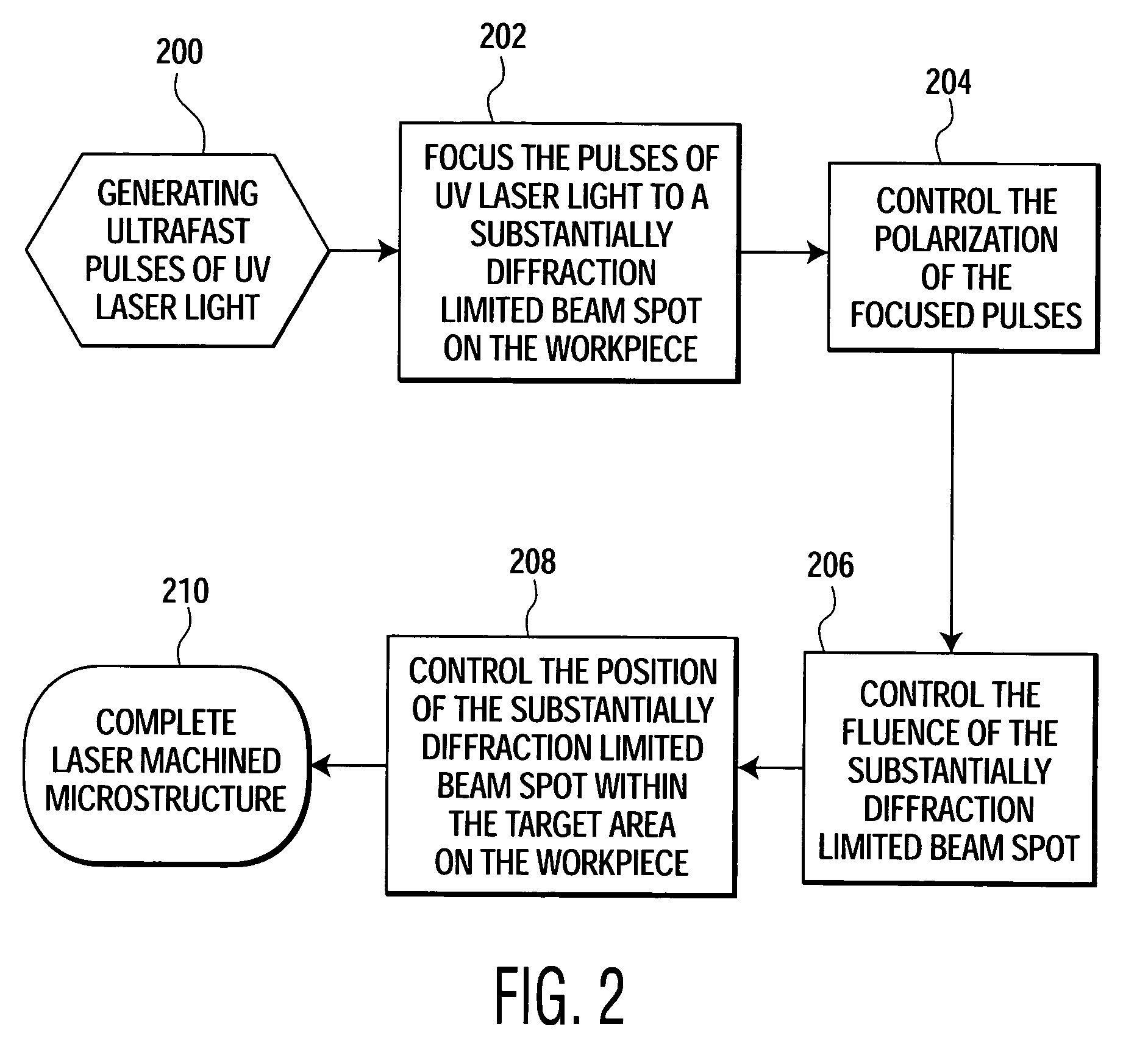
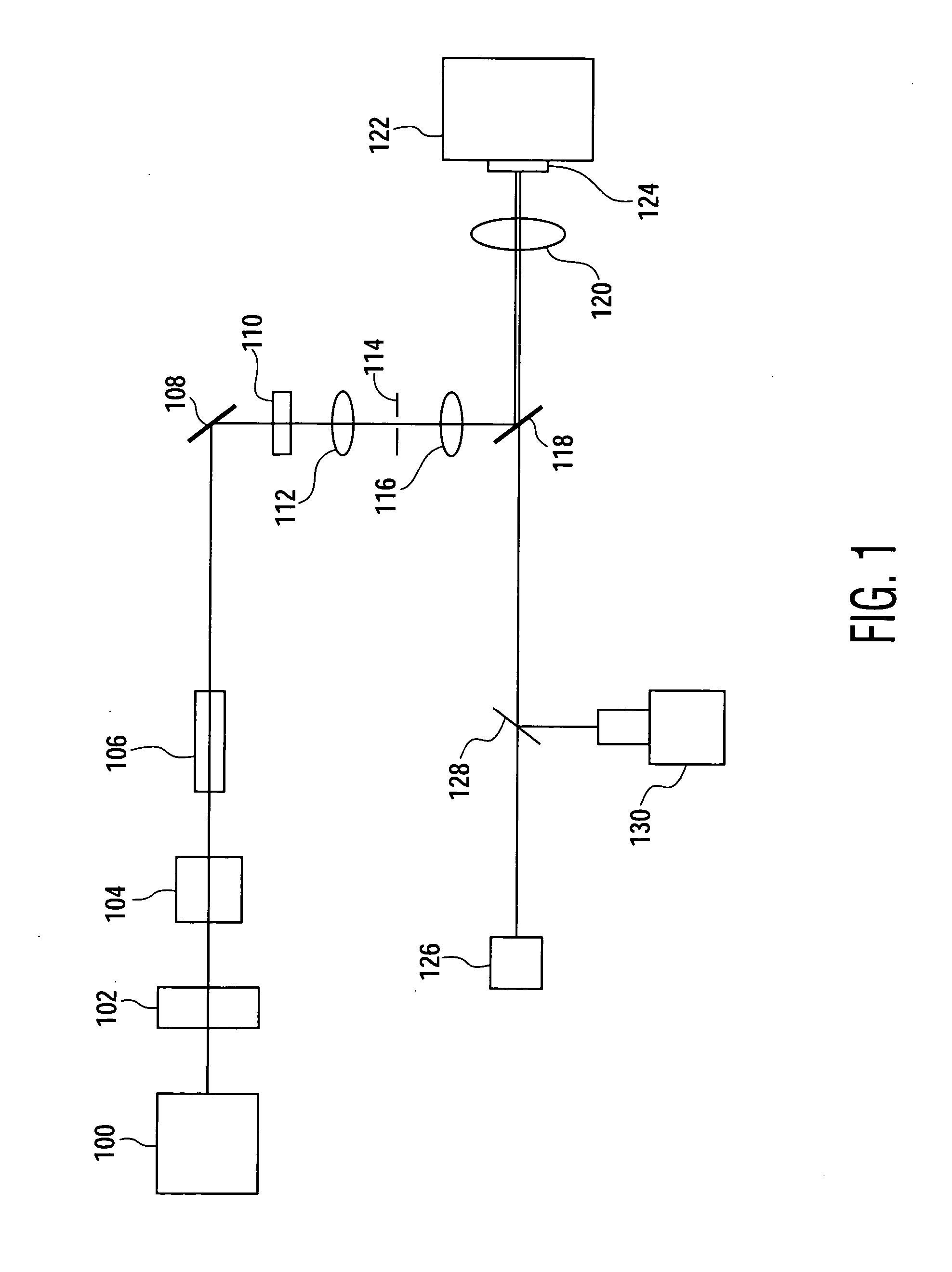
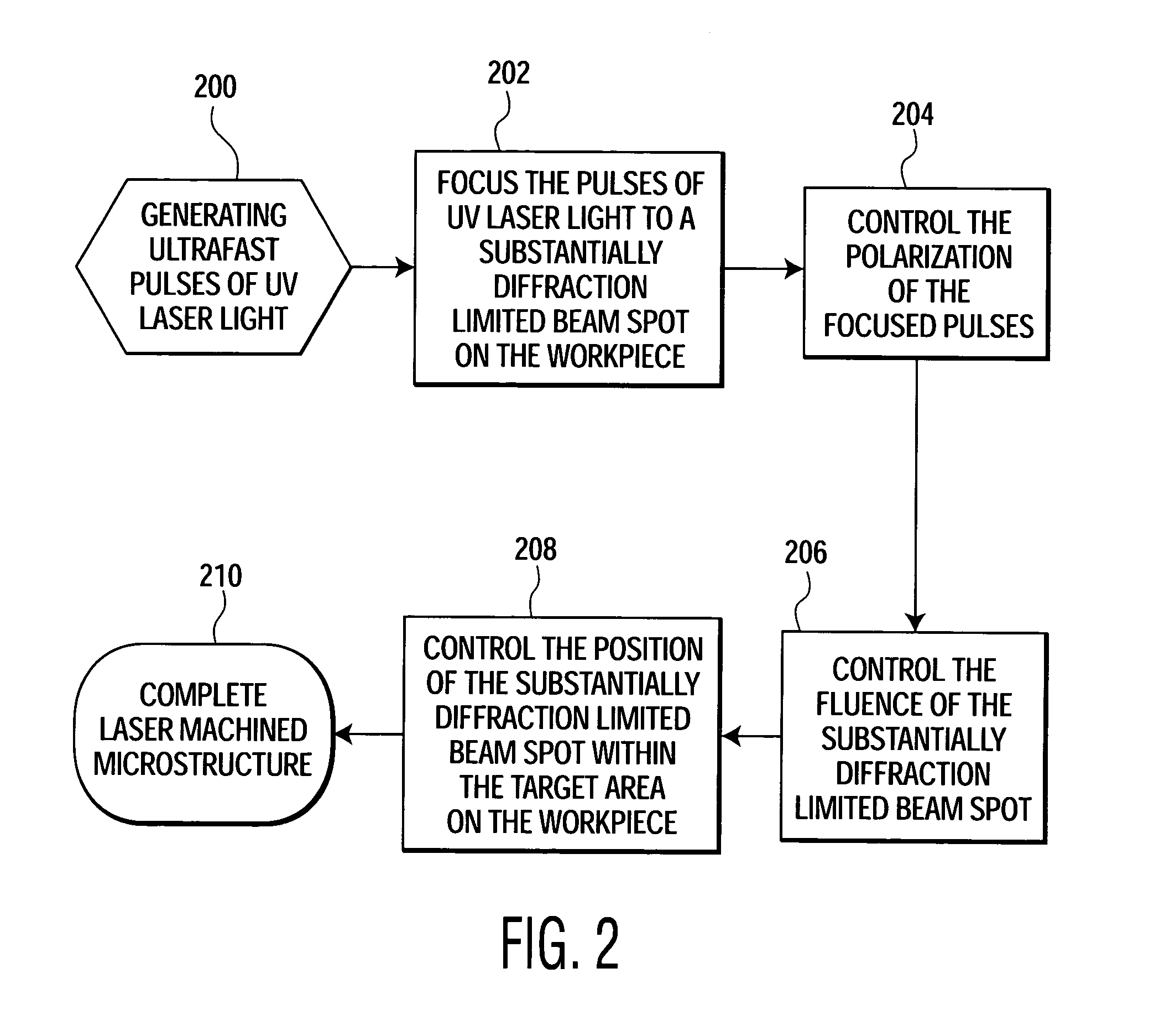
Method of precise laser nanomachining with UV ultrafast laser pulses
A method for manufacturing a microstructure, which includes at least one feature having a dimension less than 200 nm, on a work piece. Pulses of UV laser light having a duration of less than about 1 ps and a peak wavelength of less than about 380 nm are generated. These pulses of UV laser light are focused to a substantially diffraction limited beam spot within a target area of the work piece. The fluence of this substantially diffraction limited beam spot in the target area of the work piece is controlled such that the diameter of the section of the target area machined by one of the pulses of UV laser light is less than 200 nm.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for processing blind hole by laser
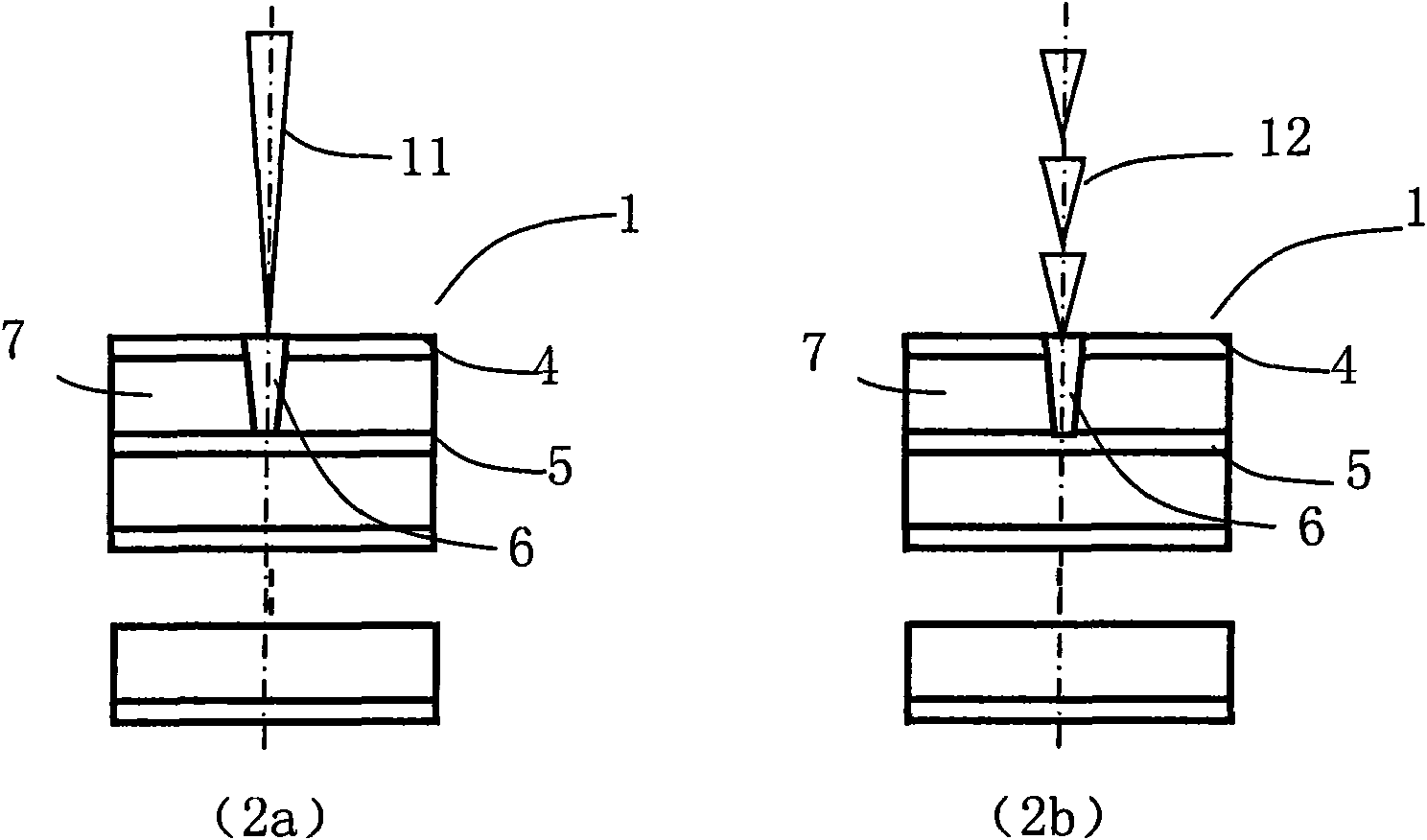
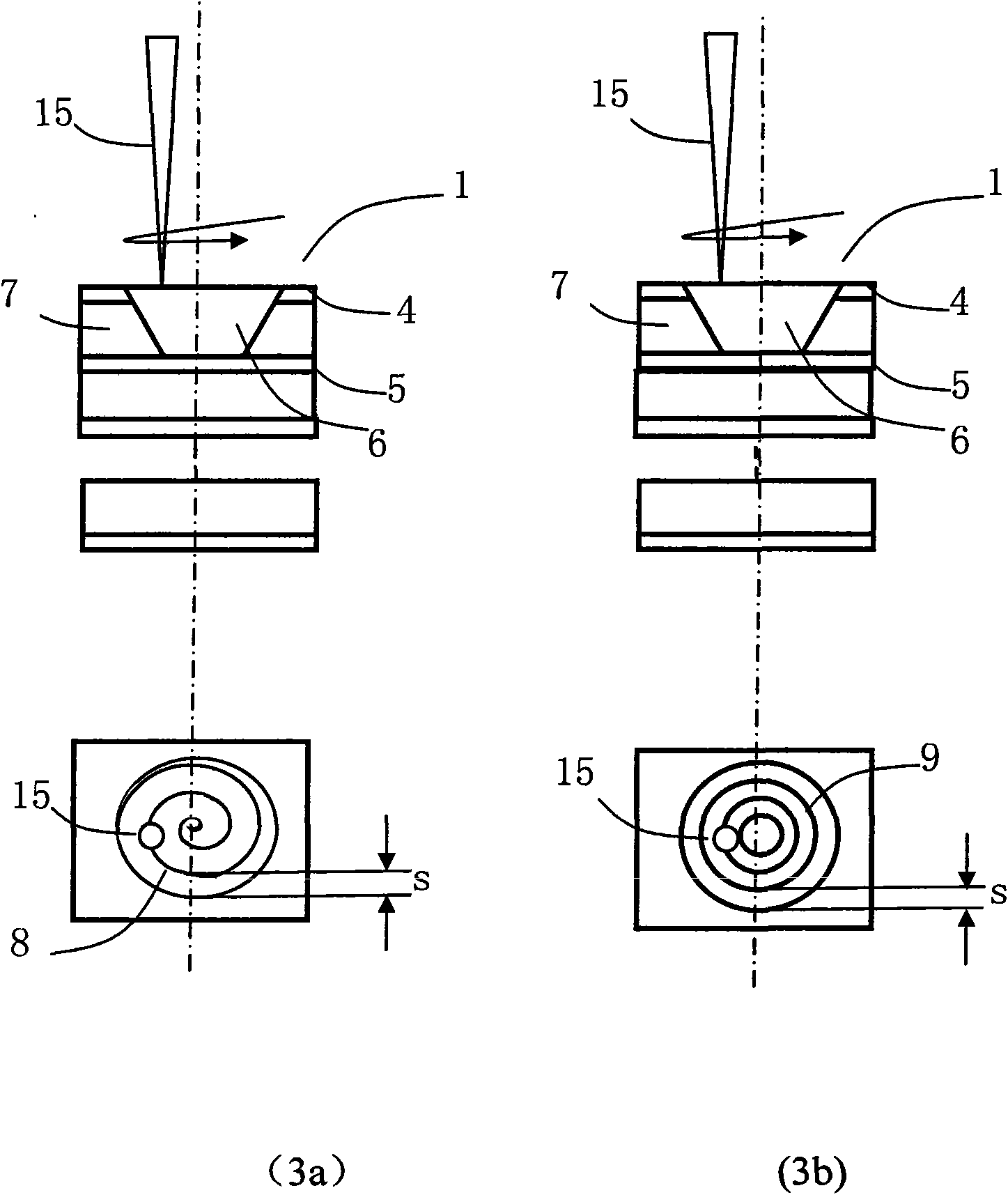
InactiveCN101610643AAvoid Scanning RequirementsRemove distortionConductive material mechanical removalLaser beam welding apparatusUv laserLaser processing
The invention discloses a method for processing a blind hole by laser. The method combines fixed point UV laser impulse and UV laser spiral line or concentric circle scanning and is used for one-step blind hole processing or multi-step blind hole processing on multilayer circuit board. The method divides the UV laser blind hole drilling process into two parts, namely a part with an area near the circle center of the blind hole not more than UV laser spot diameter and a part with an area more than the UV laser spot diameter. Fixed point UV laser impulse is adopted to drill the blind hole, so as to remove material in the region with an area near the circle center not more than UV laser spot diameter; then UV laser spiral line or centric circle scanning method is adopted to move outside, so as to remove the material in the region with an area near the circle center more than UV laser spot diameter until meeting set blind hole size; and one-step blind hole or multi-step blind hole processing is drilled by UV laser through two steps or more steps. The method can ensure processing quality consistency of each blind hole, can greatly reduce bottom unevenness of the blind hole, and also can improve margin quality of blind hole processing.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Treatment of eye disorders using articulated-arm coupled ultraviolet lasers
InactiveUS20060129141A1Increase flexibilityIncrease spacingLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsIntra ocular pressureDisease
Surgical method and apparatus for presbyopia correction and glaucoma by laser removal a portion of the sclera and / or ciliary tissue are disclosed. The disclosed preferred embodiments of the system consists of a beam spot controller, an articulated arm and an attached end-piece. The basic laser beam includes UV laser having wavelength ranges of (0.19-0.36) microns, generated from UV excimer lasers of ArF, XeCl or solid state lasers of Nd:YLF, Nd:YAG, Ti:sapphire with harmonic generation using nonlinear crystals. Presbyopia is treated by ablation of the treated surface tissue in predetermined patterns outside the limbus to increase the accommodation of the eye. Glaucoma is treated by decreasing of intra ocular pressure of the laser surgery.
Owner:NEW VISION
Method of precise laser nanomachining with UV ultrafast laser pulses
A method for manufacturing a microstructure, which includes at least one feature having a dimension less than 200 nm, on a work piece. Pulses of UV laser light having a duration of less than about 1 ps and a peak wavelength of less than about 380 nm are generated. These pulses of UV laser light are focused to a substantially diffraction limited beam spot within a target area of the work piece. The fluence of this substantially diffraction limited beam spot in the target area of the work piece is controlled such that the diameter of the section of the target area machined by one of the pulses of UV laser light is less than 200 nm.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
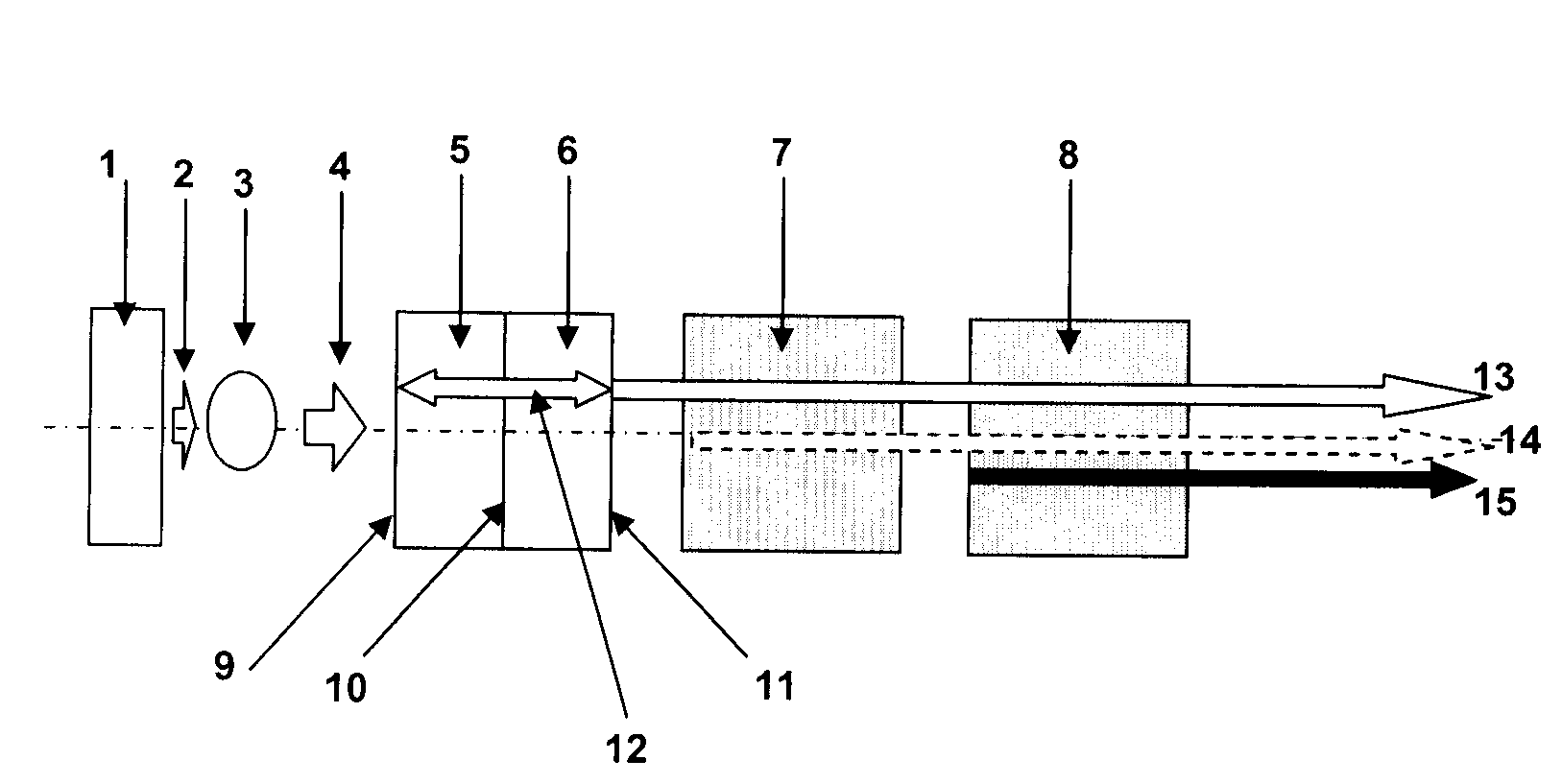
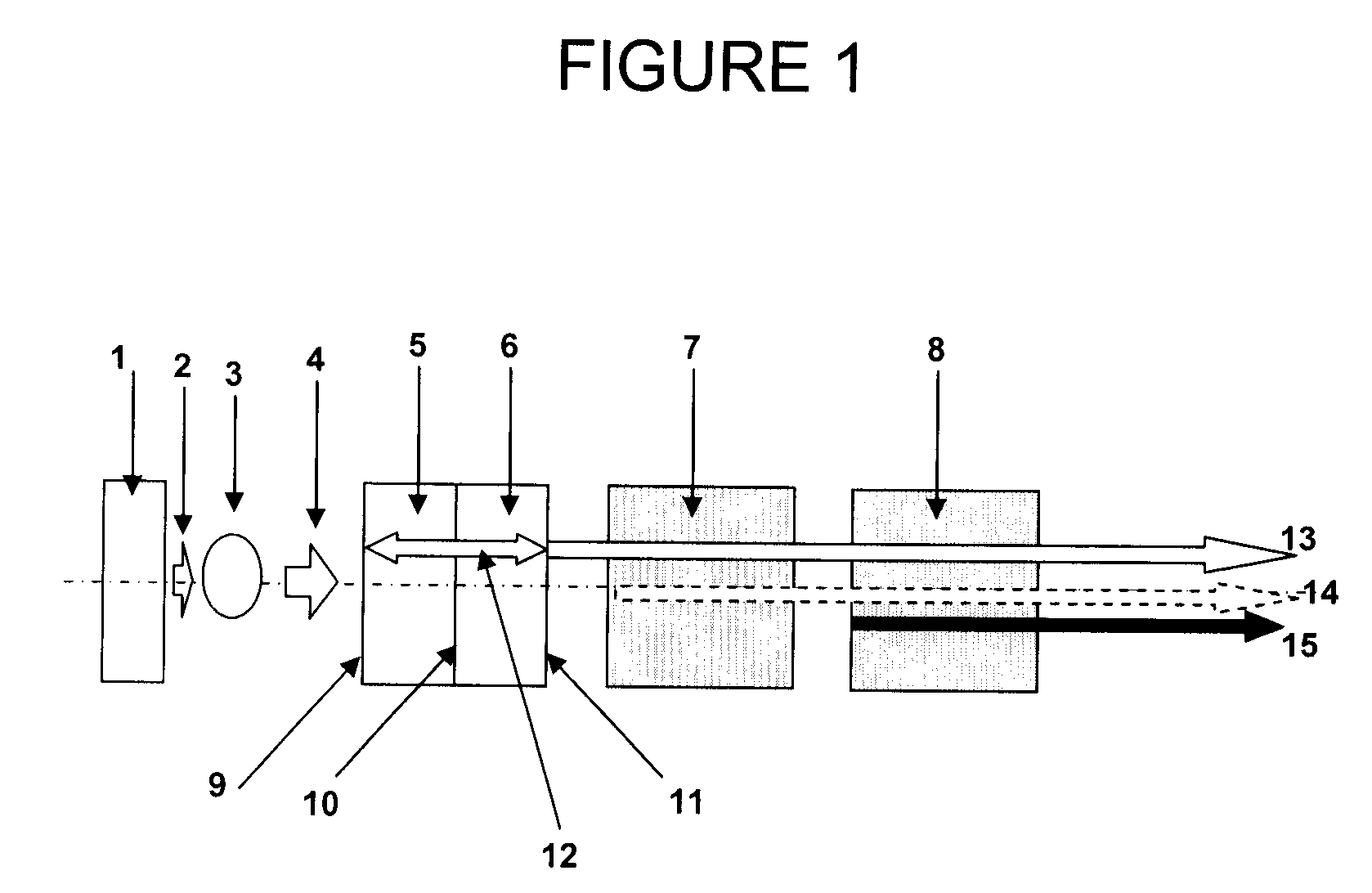
Compact efficient and robust ultraviolet solid-state laser sources based on nonlinear frequency conversion in periodically poled materials
InactiveUS7570676B2Low costHigh peak powerOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsNonlinear crystalsLight source
A compact and efficient ultraviolet laser source based on a optically-pumped solid-state or fiber laser that produces near-infrared output light suitable for nonlinear frequency conversion. The infrared laser output is frequency tripled or quadrupled to produce light in the ultraviolet wavelength range (200 nm to 400 nm). The novel technology is the use of highly efficient periodically poled nonlinear crystals, such as stoichiometric and MgO-doped lithium tantalate and lithium niobate. As opposed to conventional frequency-converted UV laser sources, which have high power consumption, high cost, and low efficiency, the laser sources of this invention utilize high efficiency nonlinear conversion provided by periodically poled materials and allow lower-cost architectures without additional focusing lenses, high power pump diodes, etc.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Diode-laser-pumped ultraviolet and infrared lasers for ablation and coagulation of soft tissue
Method and systems for eye surgery for the treatment of presbyopia, ocular hypertension and glaucoma and other soft tissue surgeries are disclosed. System design parameters of lasing crystals (Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, Er:YAG and Er:YSGG), nonlinear crystals (KTP, BBO, LBO), laser cavity configuration and energy delivery means are disclosed for diode-laser-pumped lasers with output wavelength at UV (263 or 266 nm), green (527 or 523 nm), and mid-IR (2.78 or 2.94 microns). Dual function of ablation and coagulation is proposed by a mode control means. The preferred diode-laser includes a wavelength at about 0.75 to 0.98 microns with power about 15 to 40 W and used in a side-pumping configuration to generate UV or IR having an energy per pulse about 3 to 30 mJ, power of about 0.1 to 1.5 W and operated at free running mode (IR laser) or pulsed mode (UV laser).
Owner:NEW VISION
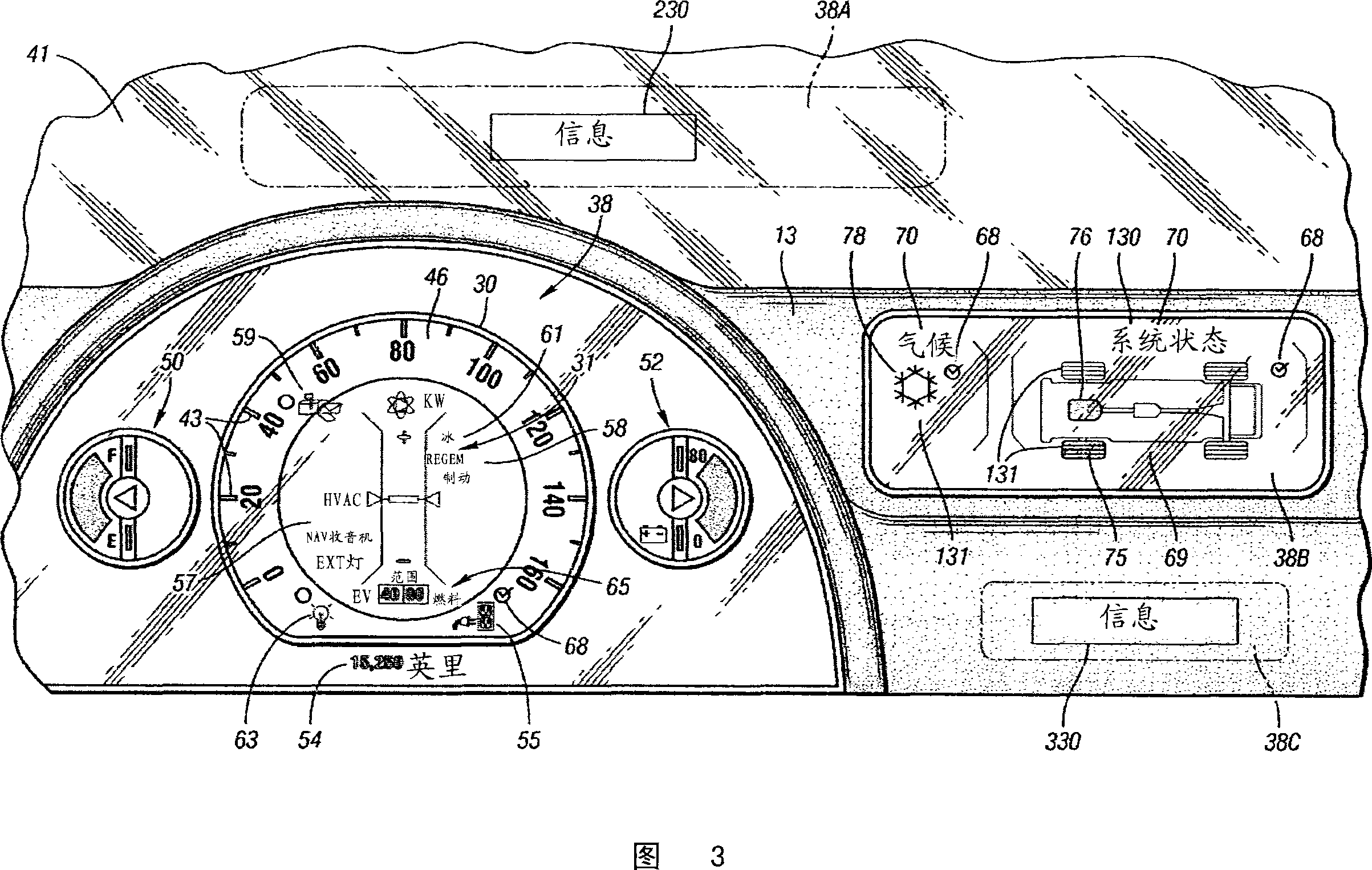
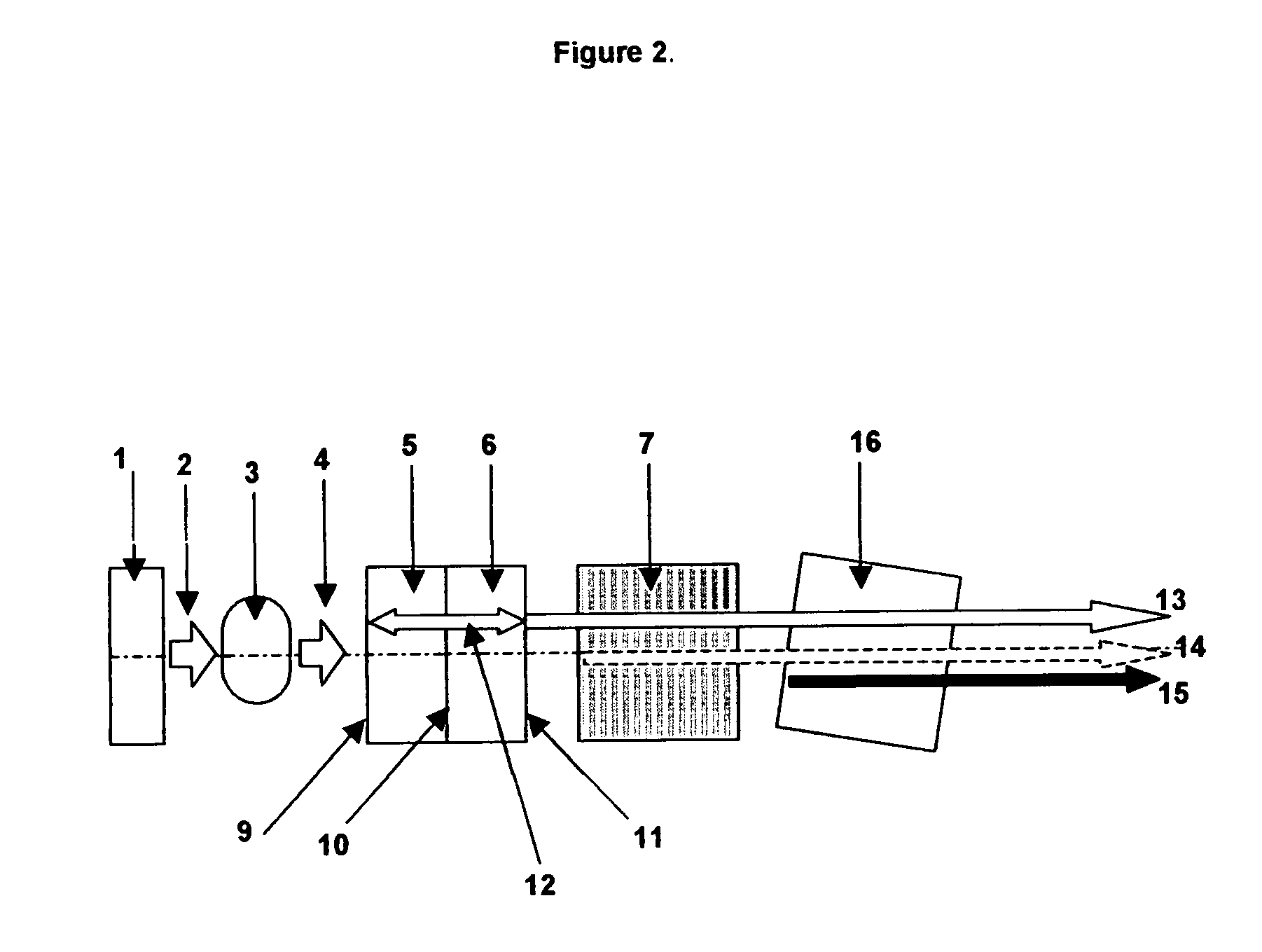
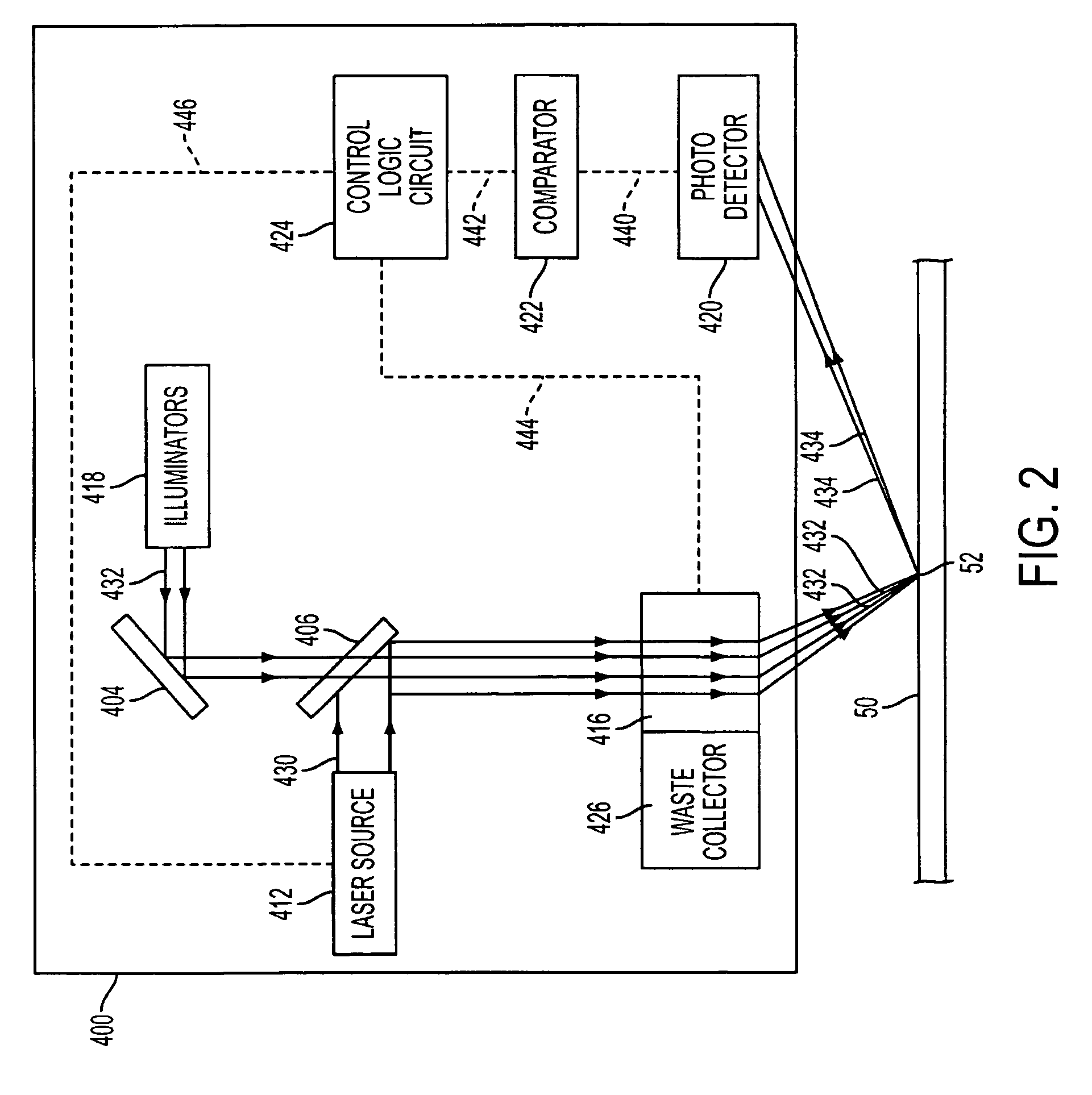
Apparatus and method for displaying information within a vehicle interior
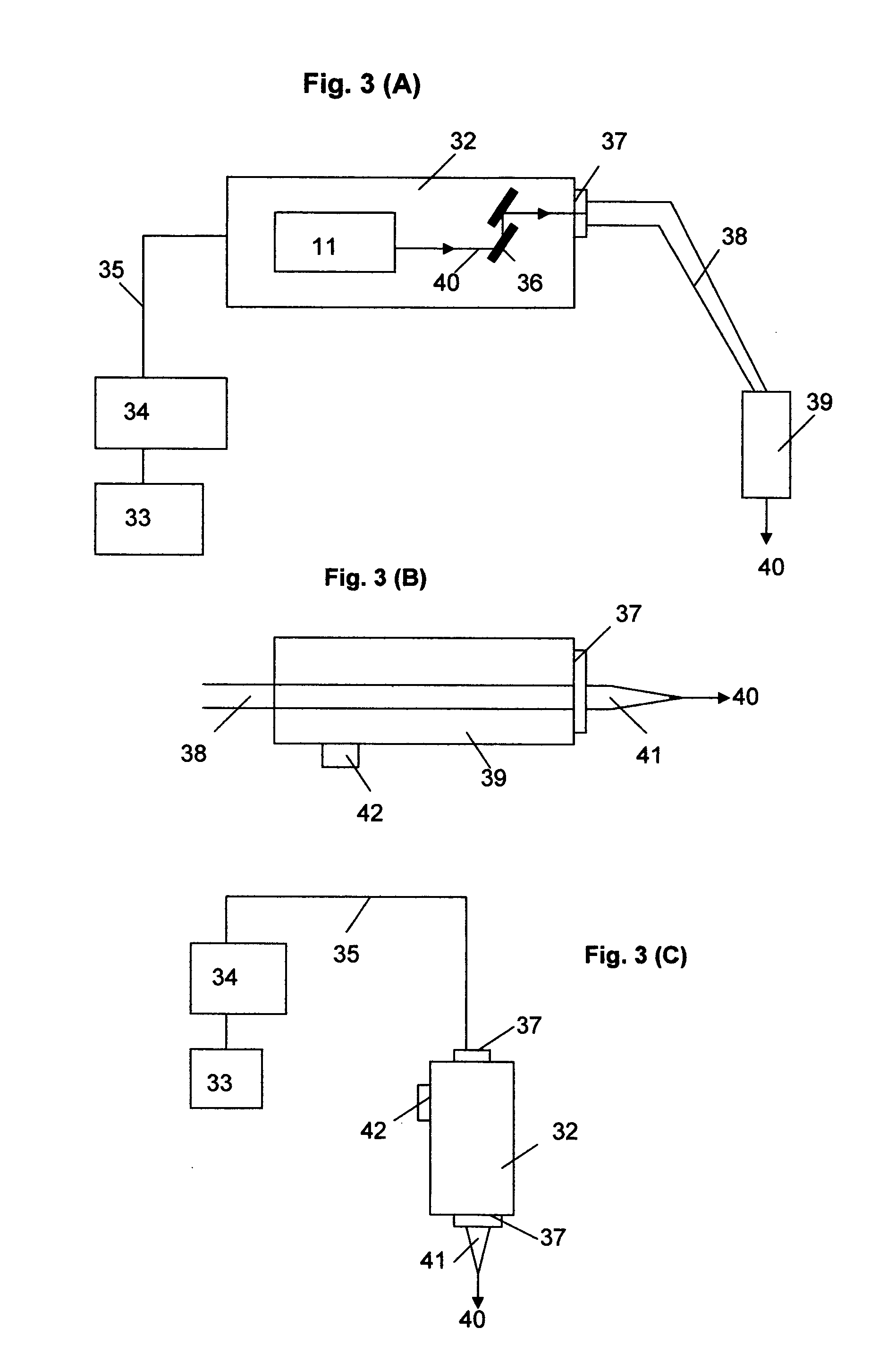
The invention relates to a device and a method for displaying information inside a vehicle. An apparatus for displaying information inside a vehicle comprising a surface having a coating that emits visible light when excited by an ultraviolet (UV) beam, and a laser for generating and directing the UV beam to the coating to display information on the surface Projection device (LPD). The LPD produces one or more UV laser beams, and the coating has one or more light emitting layers, each of which can be excited by different UV wavelengths. Each layer emits light of a different color when excited. The surface is a transparent windshield or lens, or an opaque surface. A method for displaying information in a vehicle interior includes applying a luminescent coating to a surface in at least one layer, and generating and projecting a UV beam onto the coating to present information in at least as many colors as the coating.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Laser architectures for coherent short-wavelength light generation
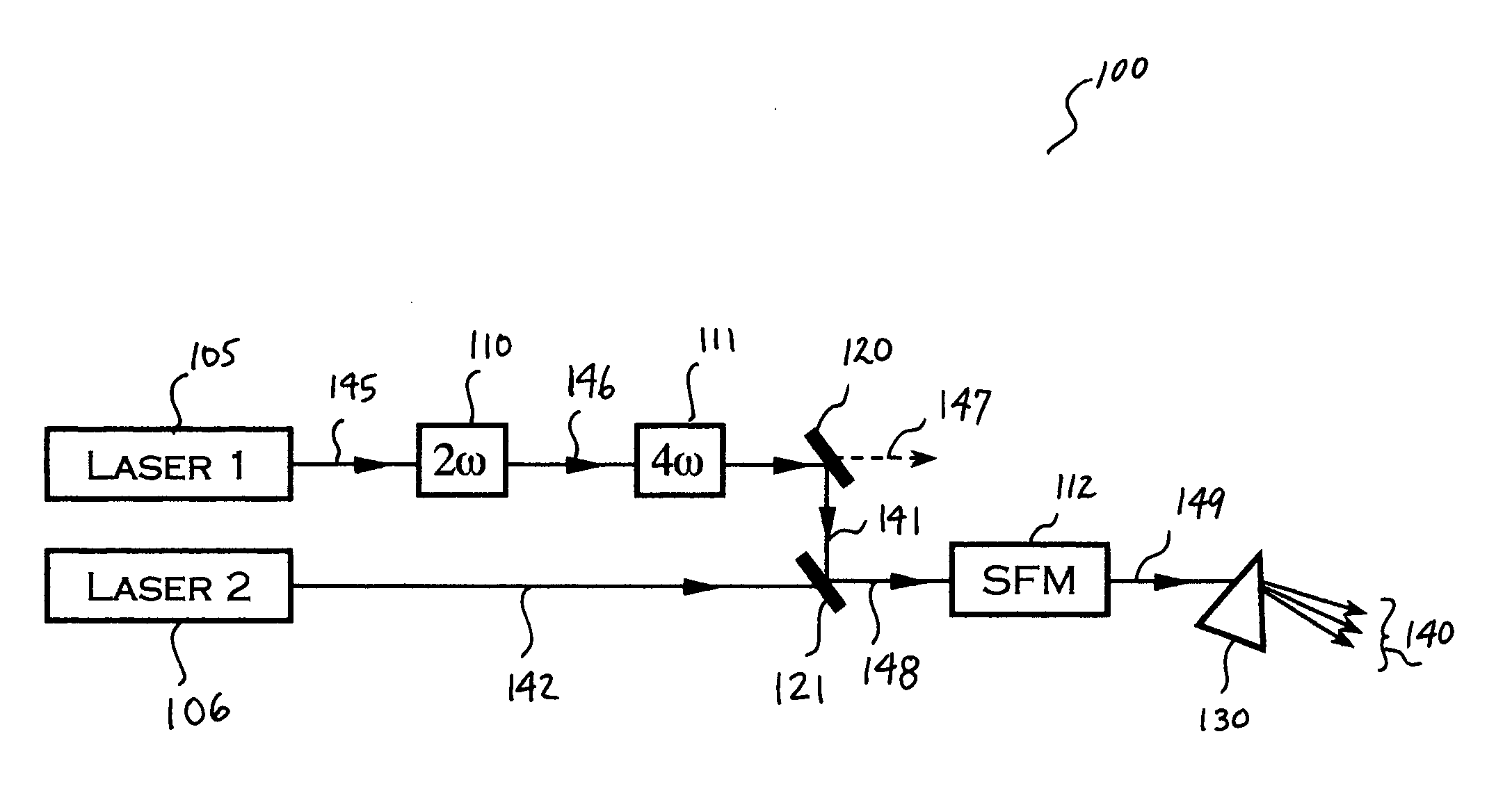
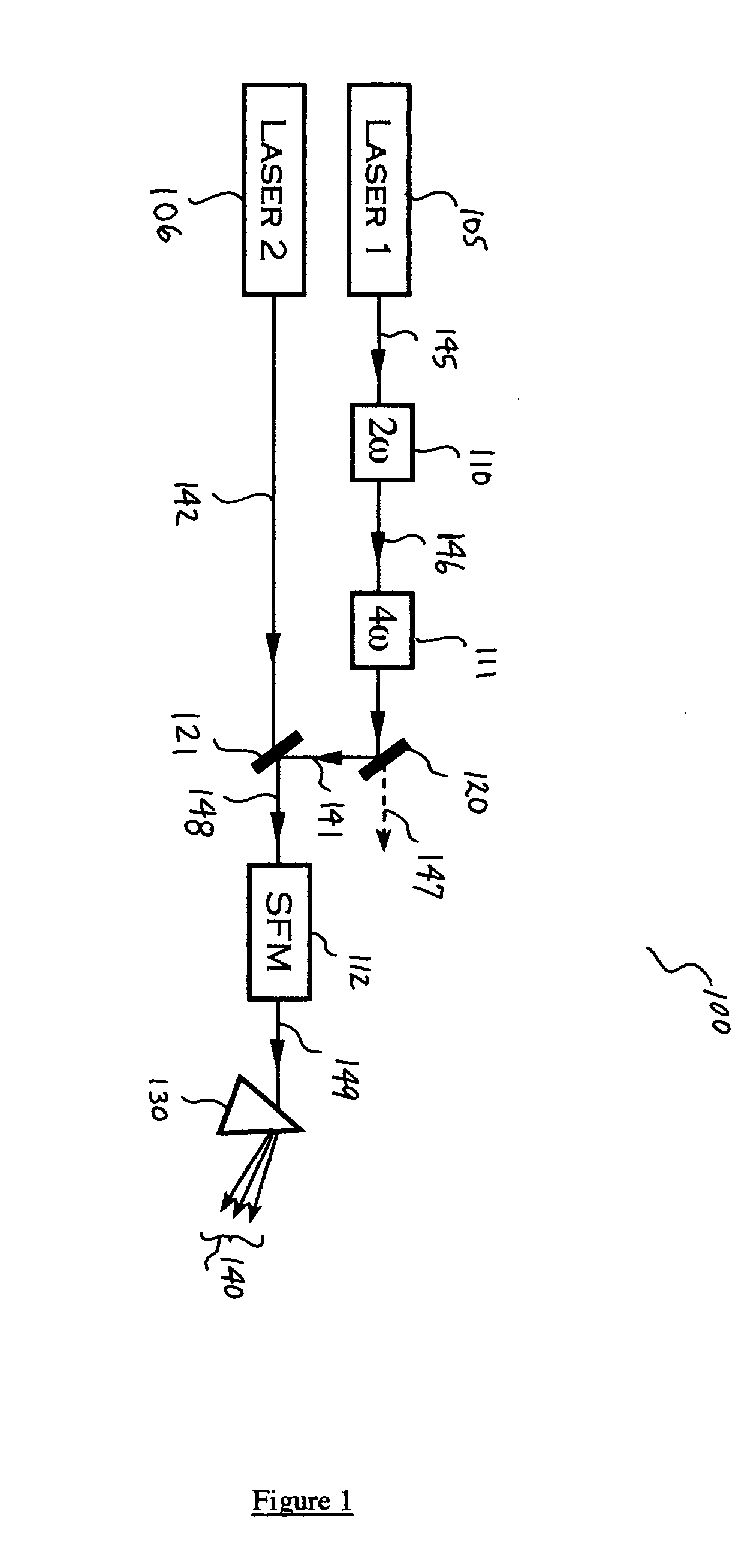
InactiveUS20050169326A1Increase power levelMaximize efficiencyLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsPoynting vectorRare earth
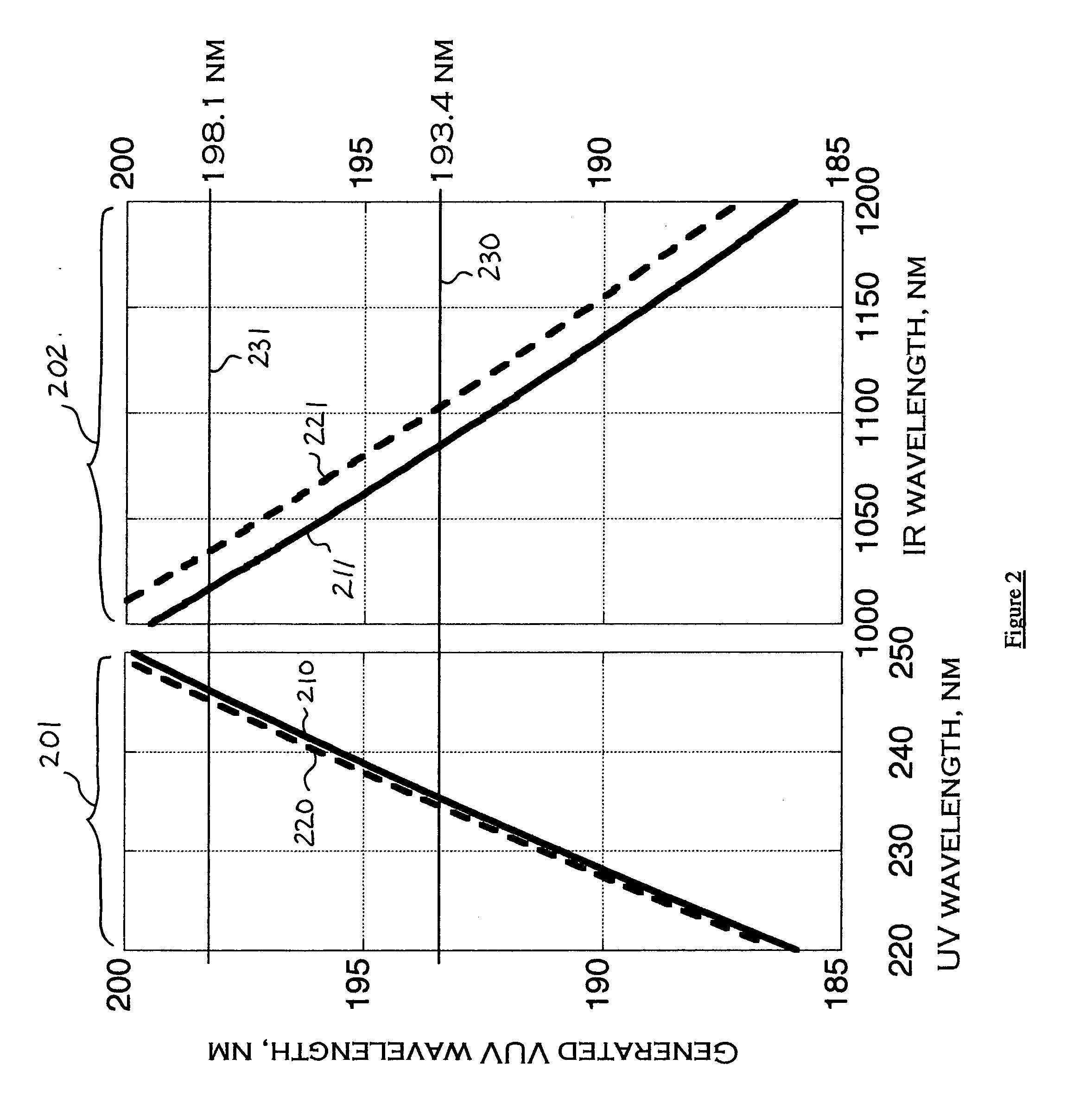
Several methods are disclosed for the generation of coherent short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation through optical nonlinear frequency mixing means. The invention involves several stages of efficient nonlinear frequency conversion to shift the output of high-power infra-red fiber-lasers into the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV). The described laser source architecture is designed around non-critically phase-matched (NCPM) sum-frequency mixing (SFM) interactions in the nonlinear crystal CLBO. The NCPM interaction is an optimum condition for bulk frequency conversion of cw radiation because it allows tight focusing of the input laser radiation without Poynting vector walk-off, thereby increasing the non-linear drive significantly. The sub-200-nm output wave is generated from SFM of a long-wave IR laser field and a short-wave UV laser field. The long-wave laser beam may be derived directly from a rare-earth-doped fiber laser, whereas the short-wavelength UV beam is provided as the fourth frequency harmonic of a second rare-earth-doped fiber laser system.
Owner:JACOB JAMES JEFFREY +1
Method of forming a scribe line on a passive electronic component substrate
InactiveUS20050042805A1Facilitates high precision fractureFacilitates cleaner fractureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingStress concentrationUv laser
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Compact efficient and robust ultraviolet
InactiveUS20070263693A1Low costHigh peak powerOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsUltravioletLaser source
A compact and efficient ultraviolet laser source based on a optically-pumped solid-state or fiber laser that produces near-infrared output light suitable for nonlinear frequency conversion. The infrared laser output is frequency tripled or quadrupled to produce light in the ultraviolet wavelength range (200 nm to 400 nm). The novel technology is the use of highly efficient periodically poled nonlinear crystals, such as stoichiometric and MgO-doped lithium tantalate and lithium niobate. As opposed to conventional frequency-converted UV laser sources, which have high power consumption, high cost, and low efficiency, the laser sources of this invention utilize high efficiency nonlinear conversion provided by periodically poled materials and allow lower-cost architectures without additional focusing lenses, high power pump diodes, etc.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Methods of forming high-density arrays of holes in glass
ActiveUS9278886B2High positioning accuracyVariation in diameterGlass furnace apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsUv laserHigh density
A method of fabricating a high-density array of holes in glass is provided, comprising providing a glass piece having a front surface, then irradiating the front surface of the glass piece with a UV laser beam focused to a focal point within + / −100 μm of the front surface of the glass piece most desirably within + / −50 μm of the front surface. The lens focusing the laser has a numerical aperture desirably in the range of from 0.1 to 0.4, more desirably in the range of from 0.1 to 0.15 for glass thickness between 0.3 mm and 0.63 mm, even more desirably in the range of from 0.12 to 0.13, so as to produce open holes extending into the glass piece 100 from the front surface 102 of the glass piece, the holes having an diameter the in range of from 5 to 15 μm, and an aspect ratio of at least 20:1. For thinner glass, in the range of from 0.1-0.3 mm, the numerical aperture is desirably from 0.25 to 0.4, more desirably from 0.25 to 0.3, and the beam is preferably focused to within + / −30 μm of the front surface of the glass. The laser is desirable operated at a repetition rate of about 15 kHz or below. An array of holes thus produced may then be enlarged by etching. The front surface may be polished prior to etching, if desired.
Owner:CORNING INC
Micromachining with short-pulsed, solid-state UV laser
ActiveUS7605343B2Reduce the numberReduce in quantityLaser detailsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesUv laserPicosecond
In some embodiments, laser output including at least one laser pulse having a wavelength shorter than 400 microns and having a pulsewidth shorter than 1,000 picoseconds permits the number of pulses used to clean a bottom surface of a via or the surface of a solder pad to increase process throughput. An oscillator module in cooperation with an amplification module may be used to generate the laser output.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Laser assisted direct imprint lithography
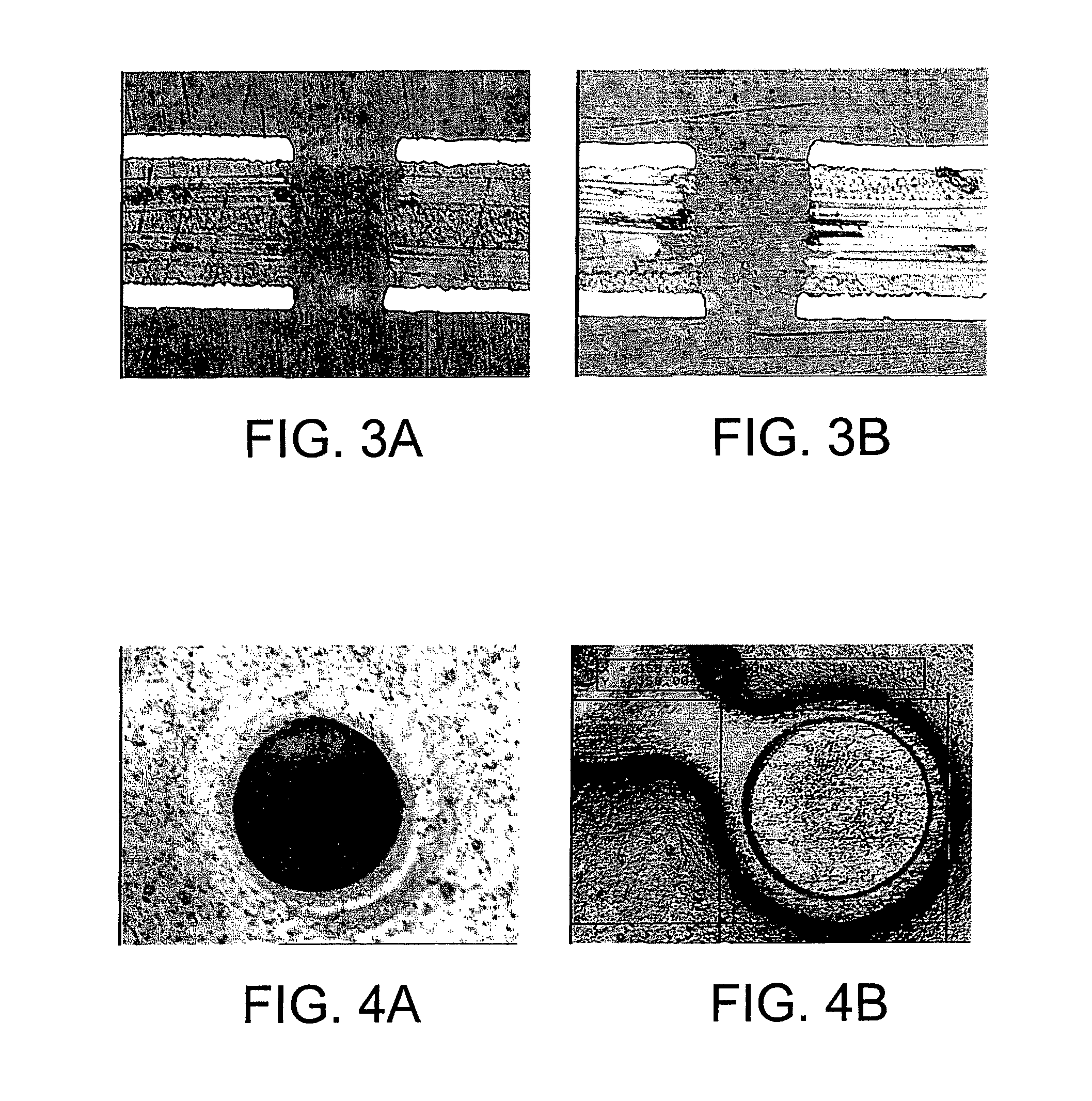
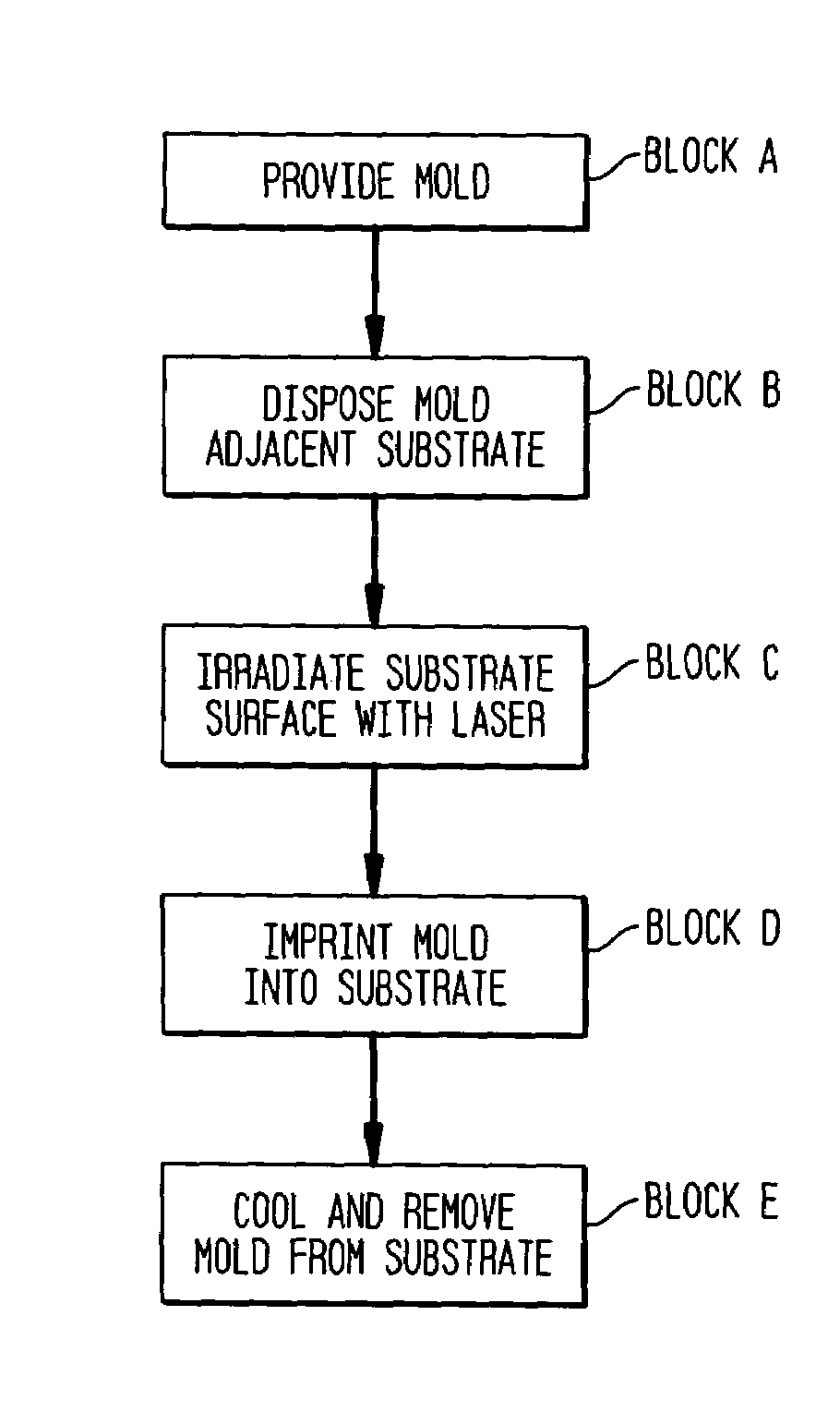
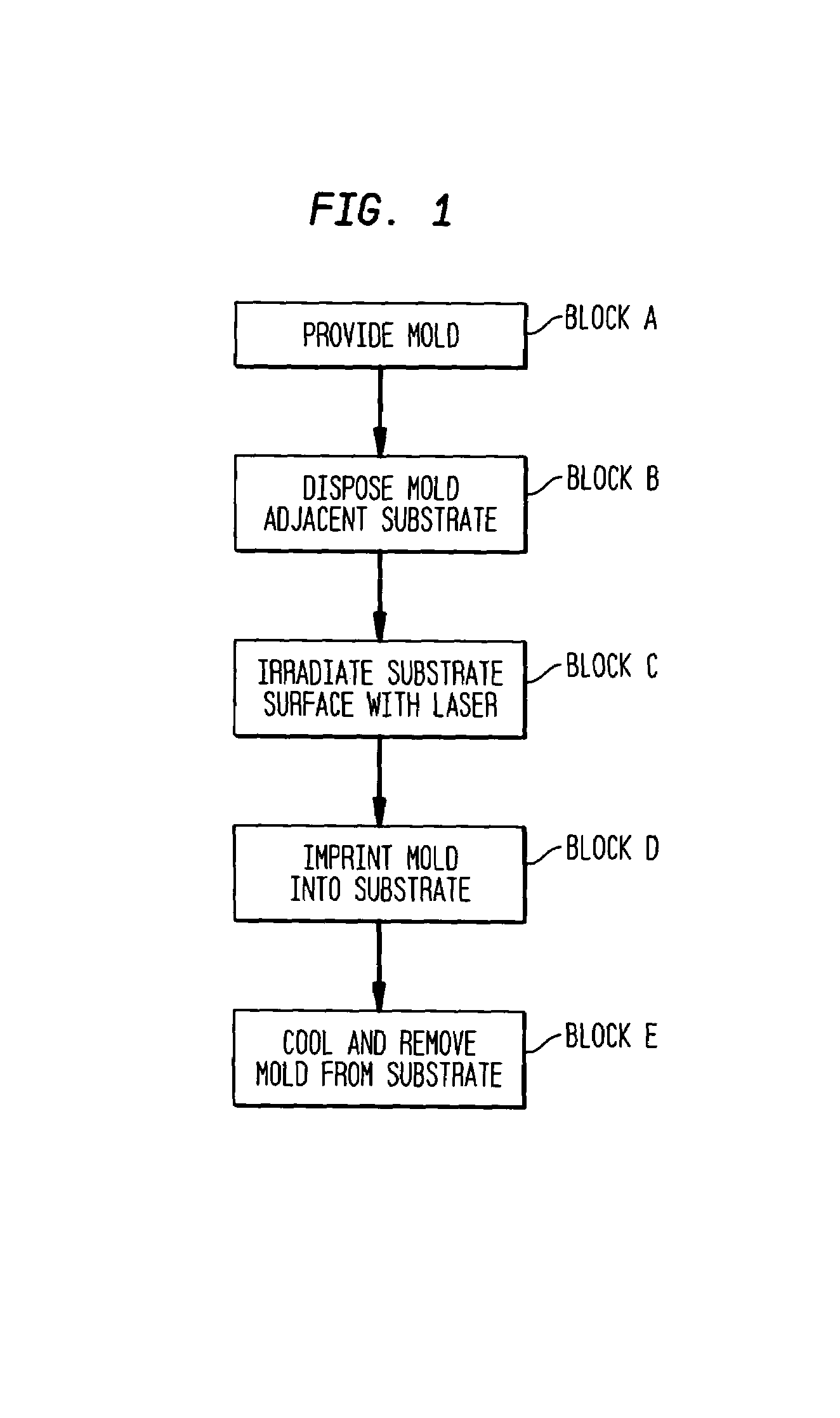
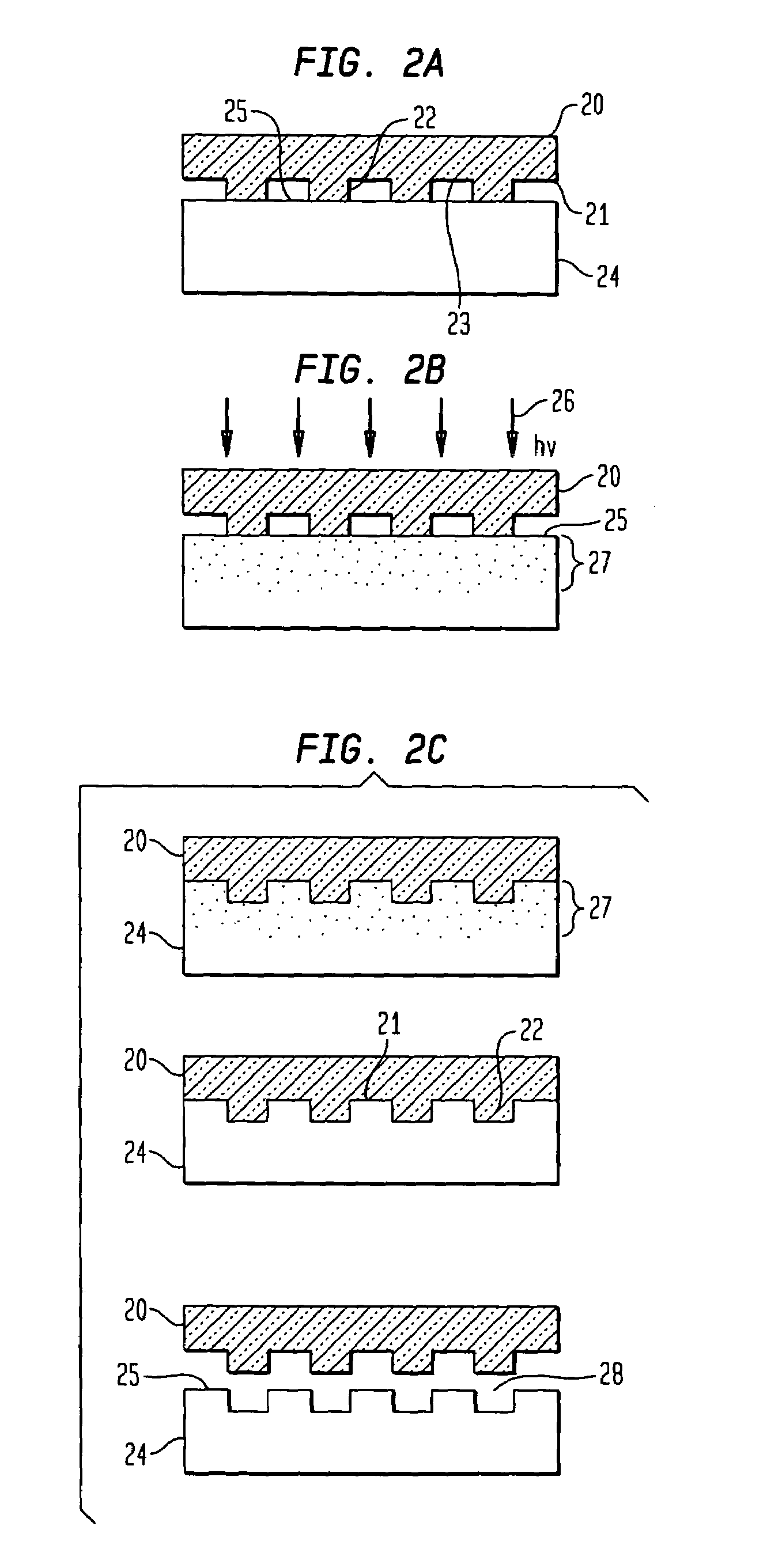
In accordance with the invention, features can be directly imprinted into the surface of a solid substrate. Specifically, a substrate is directly imprinted with a desired pattern by the steps of providing a mold having a molding surface to imprint the pattern, disposing the molding surface adjacent or against the substrate surface to be imprinted, and irradiating the substrate surface with radiation to soften or liquefy the surface. The molding surface is pressed into the softened or liquefied surface to directly imprint the substrate. The substrate can be any one of a wide variety of solid materials such as semiconductors, metals, or polymers. In a preferred embodiment the substrate is silicon, the laser is a UV laser, and the mold is transparent to the UV radiation to permit irradiation of the silicon workpiece through the transparent mold. Using this method, applicants have directly imprinted into silicon large area patterns with sub-10 nanometer resolution in sub-250 nanosecond processing time. The method can also be used with a flat molding surface to planarize the substrate.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
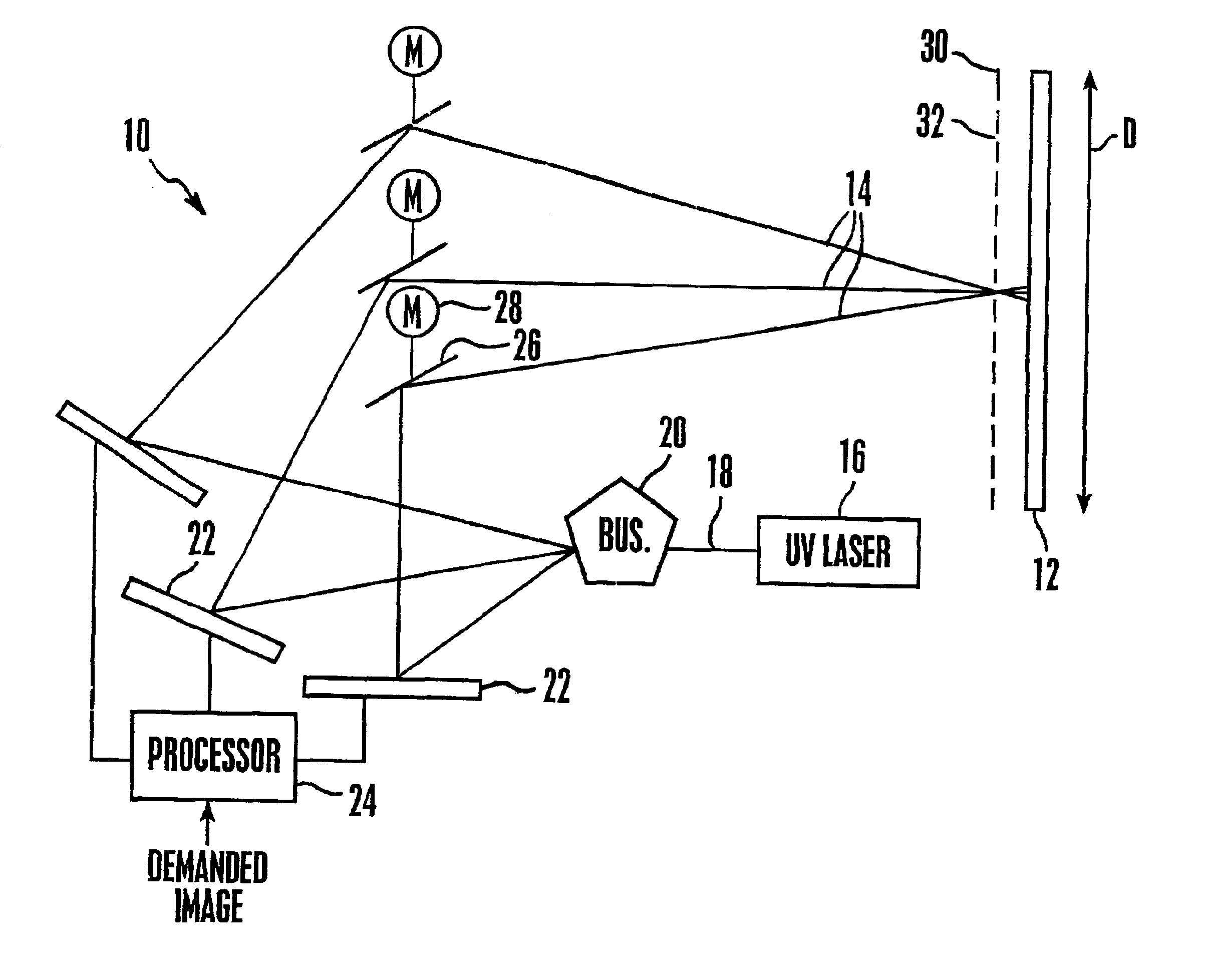
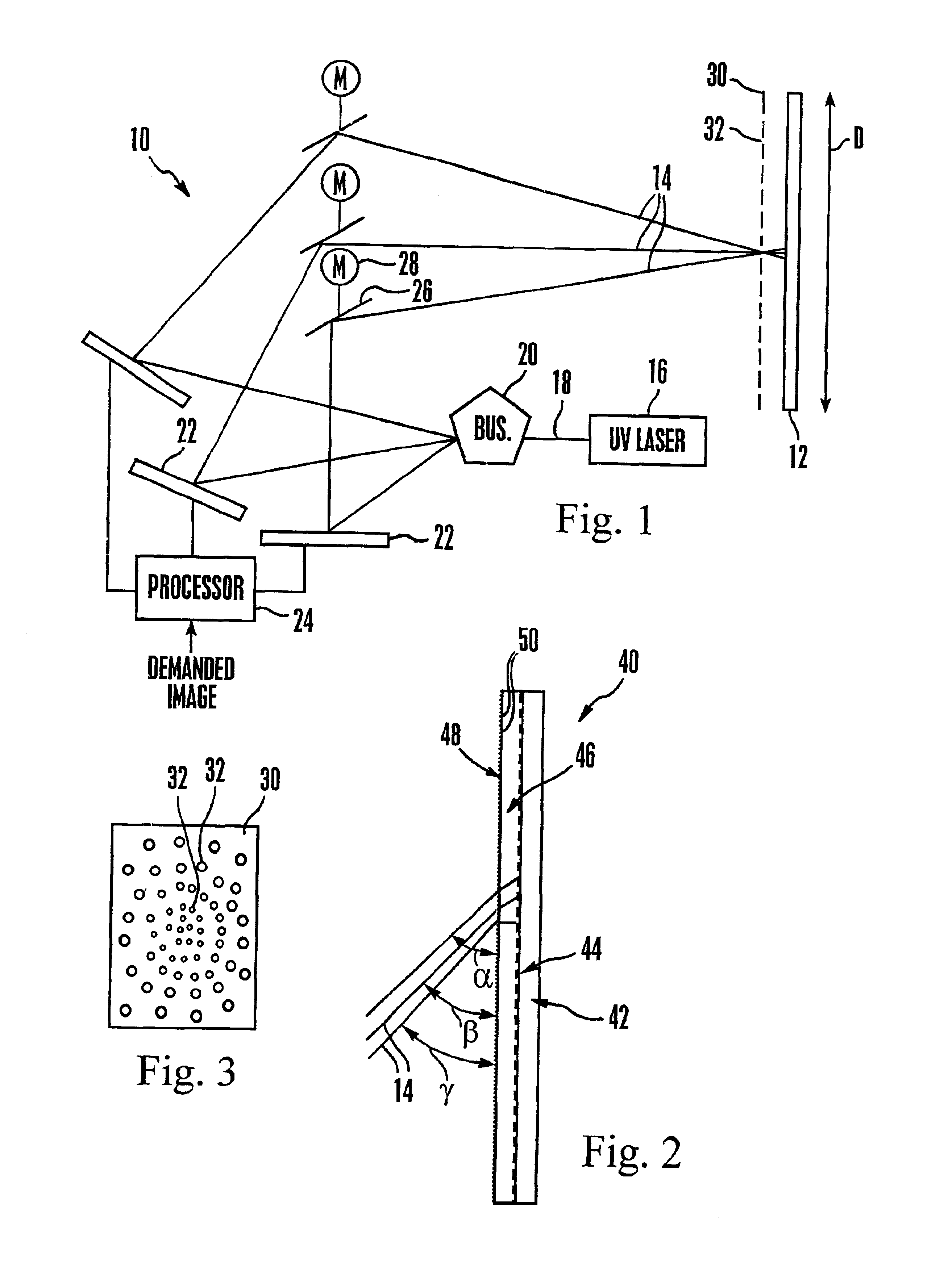
Emissive image display apparatus
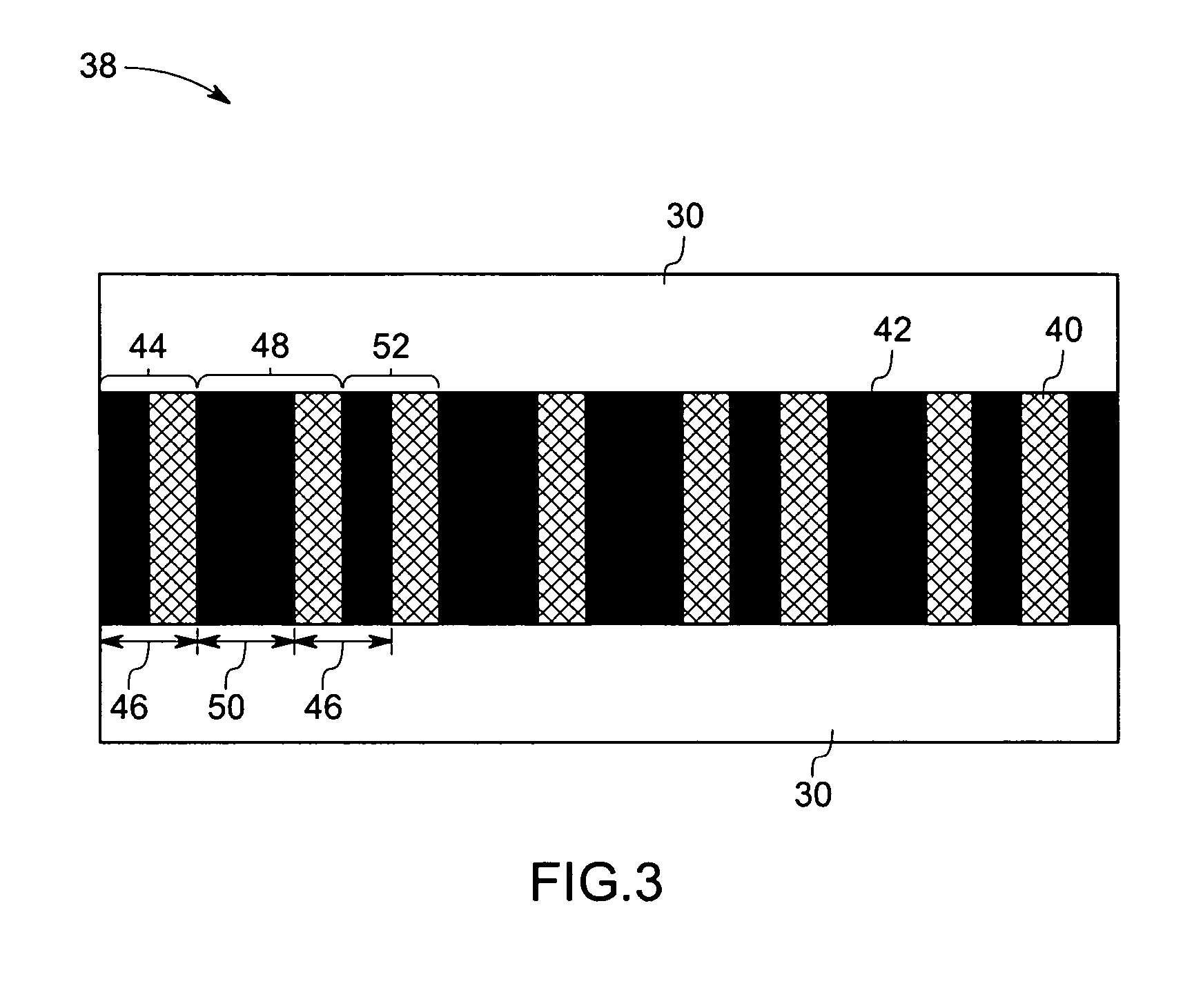
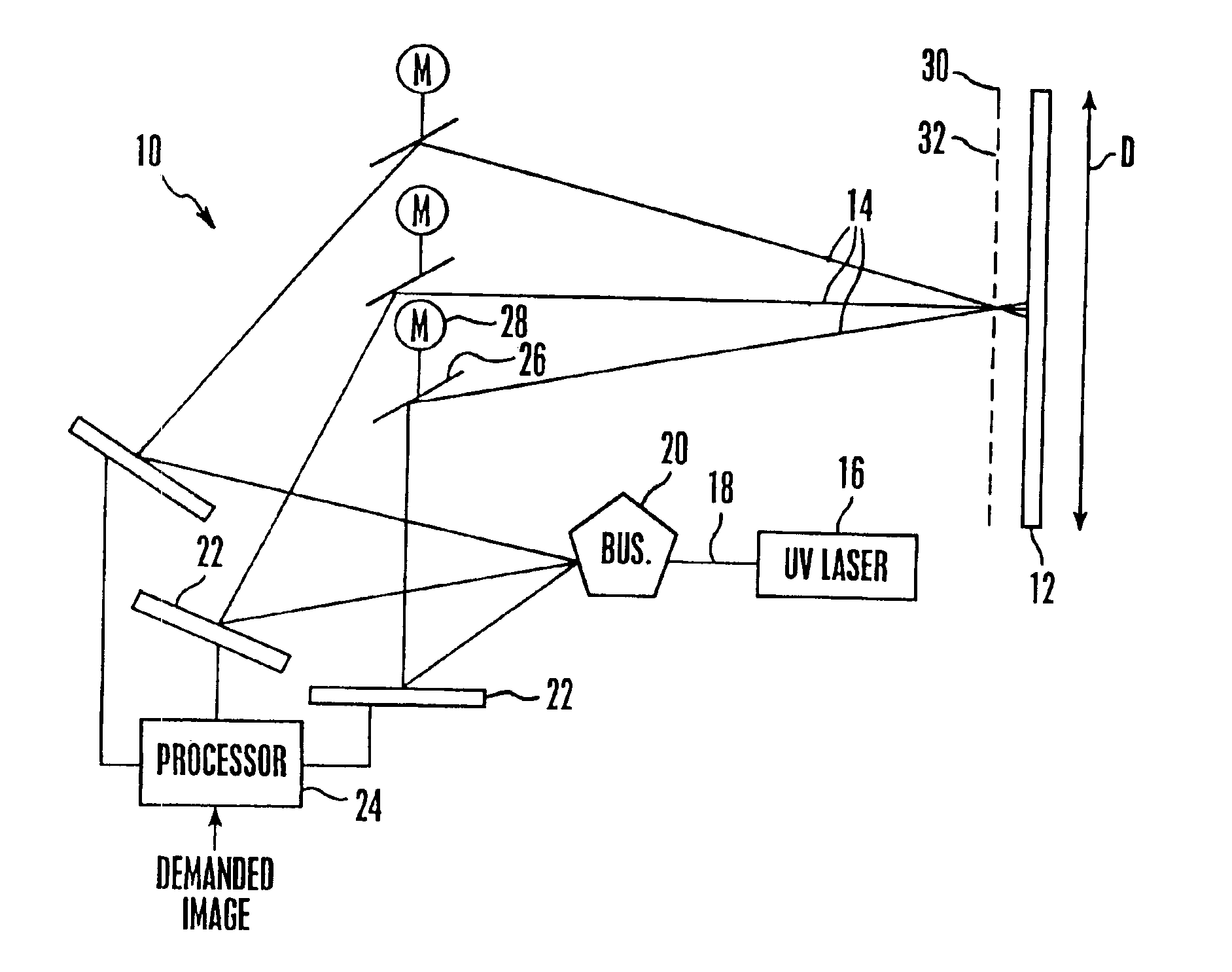
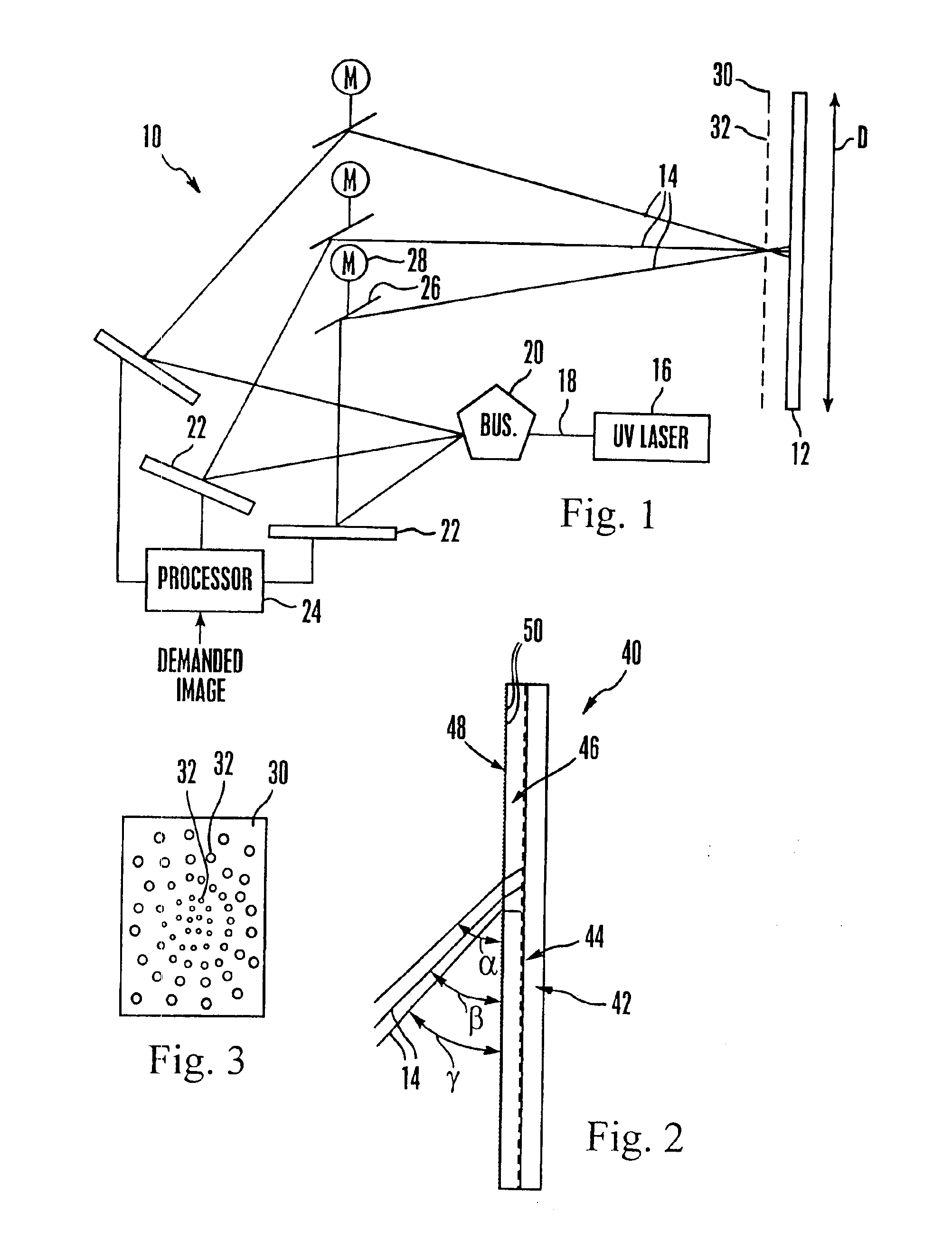
A large screen emissive display operating at atmospheric pressure includes pixels, the red, green, and blue subpixels of which are excited by UV laser light scanned onto the subpixels by a pixel activation mechanism. The pixel activation mechanism includes three grating light valves (GLVs) that are controlled by a processor in response to a demanded image to modulate the UV light as appropriate to produce the demanded image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Fiber optic sensing device and method of making and operating the same
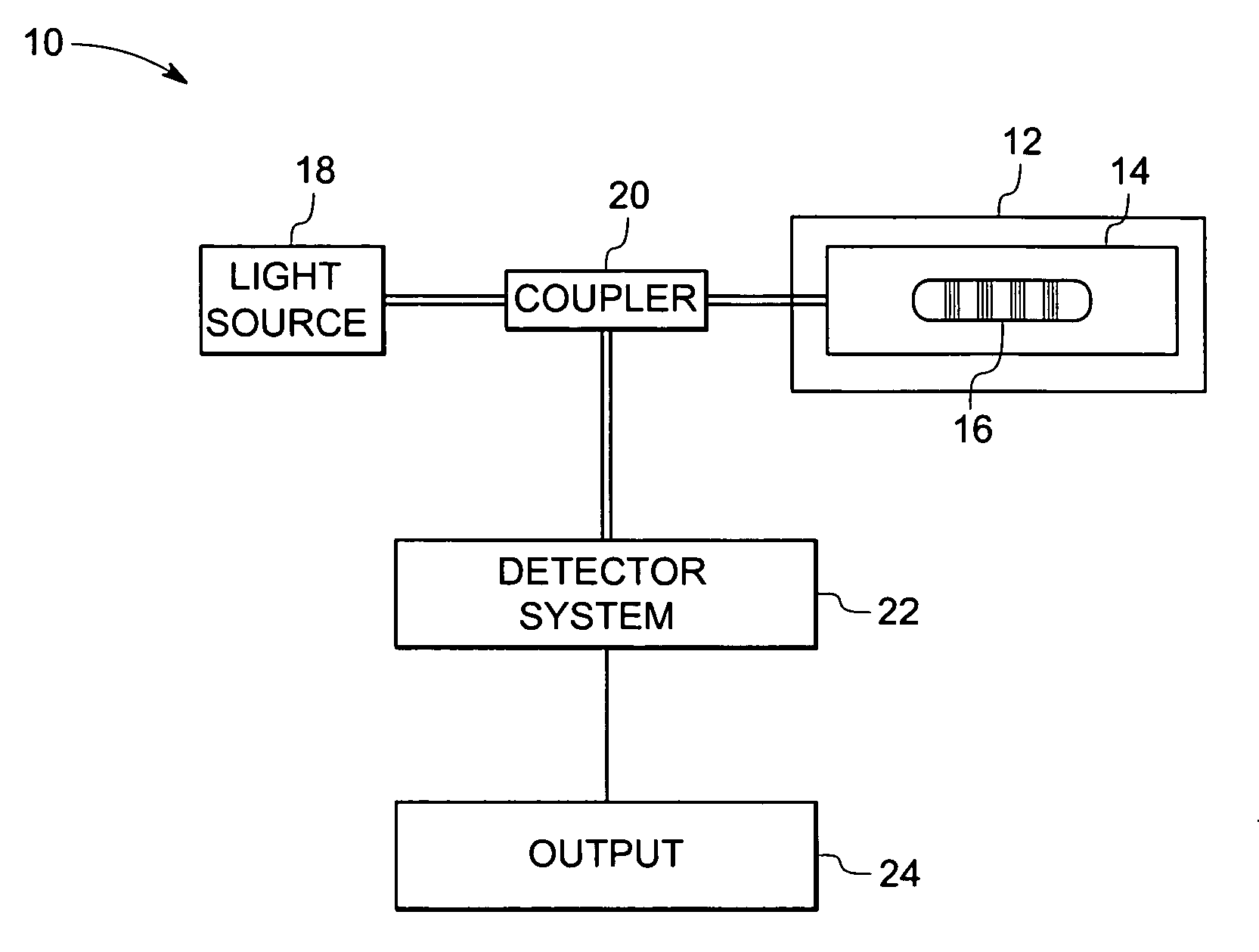
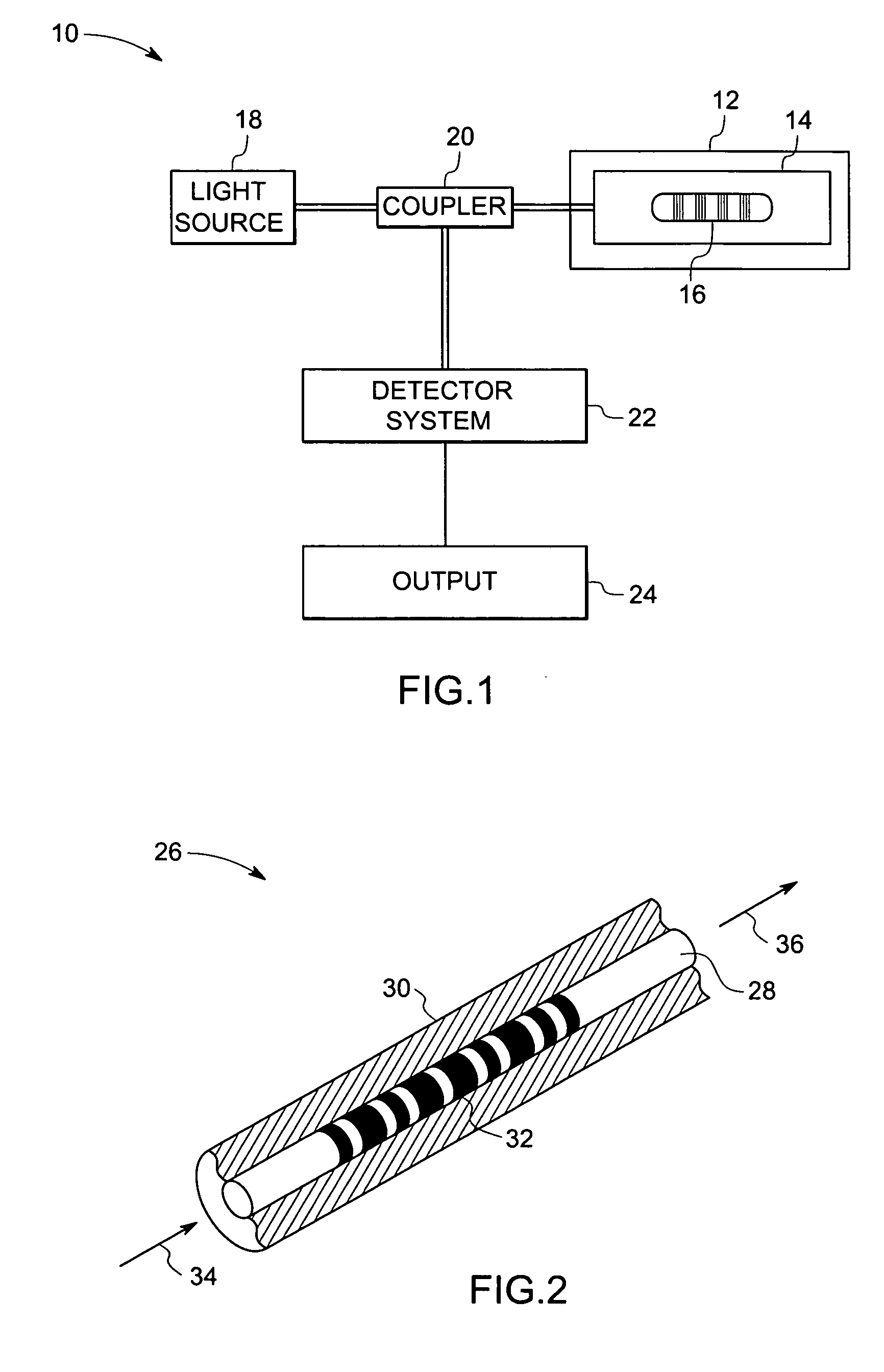
In accordance with one exemplary embodiment the invention provides a multi-parameter fiber optic sensing system with an aperiodic sapphire fiber grating as sensing element for simultaneous temperature, strain, NOx, CO, O2 and H2 gas detection. The exemplary sensing system includes an aperiodic fiber grating with an alternative refractive index modulation for such multi-function sensing and determination. Fabrication of such quasiperiodic grating structures can be made with point-by-point UV laser inscribing, diamond saw micromachining, and phase mask-based coating and chemical etching methods. In the exemplary embodiment, simultaneous detections on multi-parameter can be distributed, but not limited, in gas / steam turbine exhaust, in combustion and compressor, and in coal fired boilers etc. Advantageously, the mapping of multiple parameters such as temperature, strain, and gas using sapphire aperiodic gratings improves control and optimization of such systems directed to improve efficiency and output and reduce emissions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Emissive image display apparatus
A large screen emissive display operating at atmospheric pressure includes pixels, the red, green, and blue subpixels of which are excited by UV laser light scanned onto the subpixels by a pixel activation mechanism. The pixel activation mechanism includes three grating light valves (GLVs) that are controlled by a processor in response to a demanded image to modulate the UV light as appropriate to produce the demanded image.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
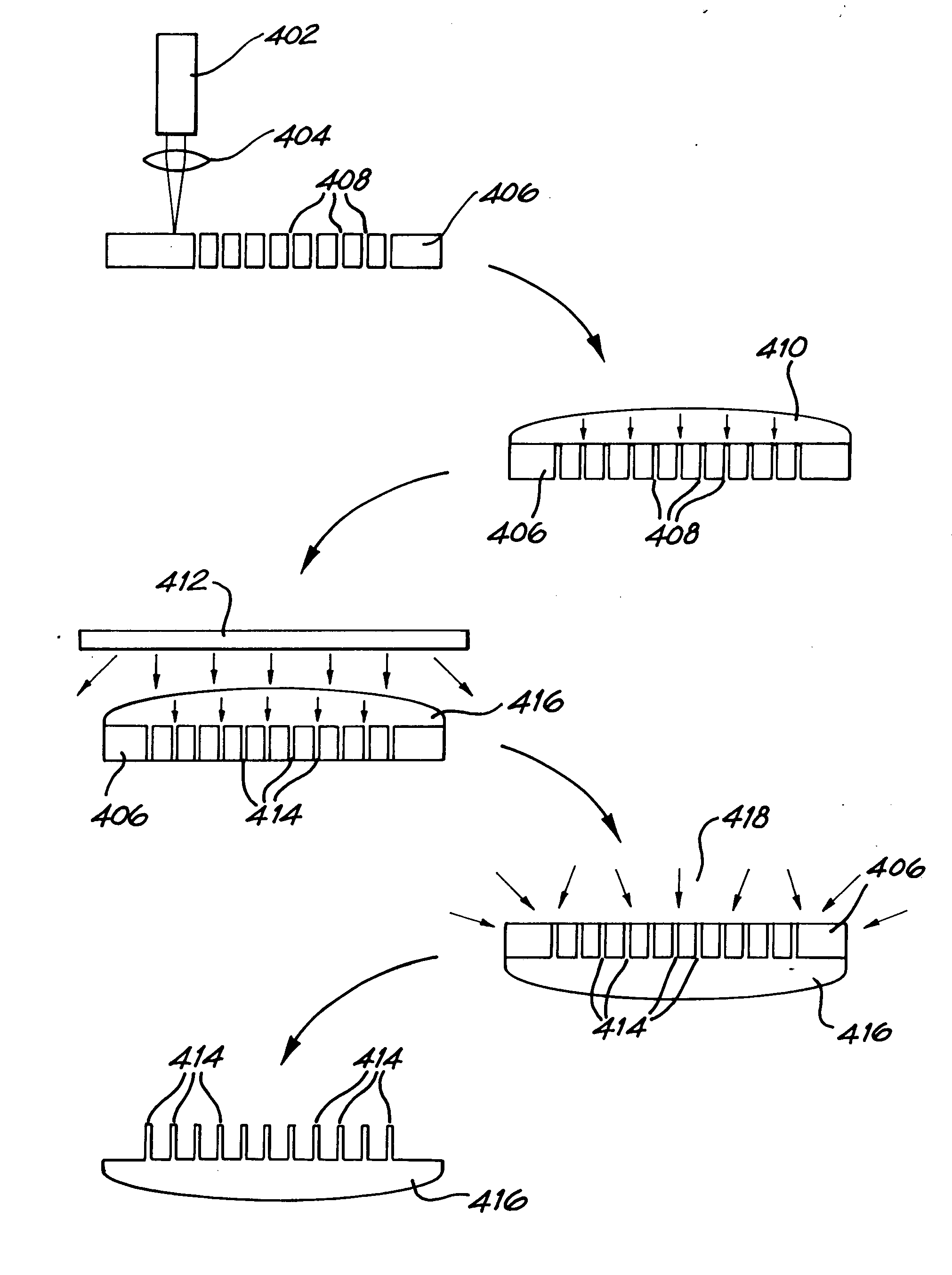
Microstructures and methods of fabricating
A process of making a microstructure, is described. The process comprises the steps of forming a plurality of fillable features in a first material, to form a template; and applying a second material to the template so that the second material at least partially fills at least some of the fillable features in the template so as to form the microstructure, said second material being different from the first material. The process of forming a template uses a laser selected from a picosecond laser, a femtosecond laser and a nanosecond UV laser. The invention includes a photonic crytal made by this process.
Owner:MACQUARIE UNIV
Dim-out method for organic EL panel
InactiveUS20030214248A1Effectively dimming out a defective pixelImprove the immunityStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesUv laserLight beam
A UV laser beam is selectively irradiated on an active layer (semiconductor layer) of a second TFT in a pixel, so as to degrade crystallinity of the active layer and thereby execute electrical disconnection. According to this method, dimming out of pixels can be performed without generating undesirable influences in other components. By directing the laser beam to a portion of the active layer located beneath the gate electrode, the laser beam can be reflected by the gate electrode, allowing execution of a more efficient laser irradiation.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
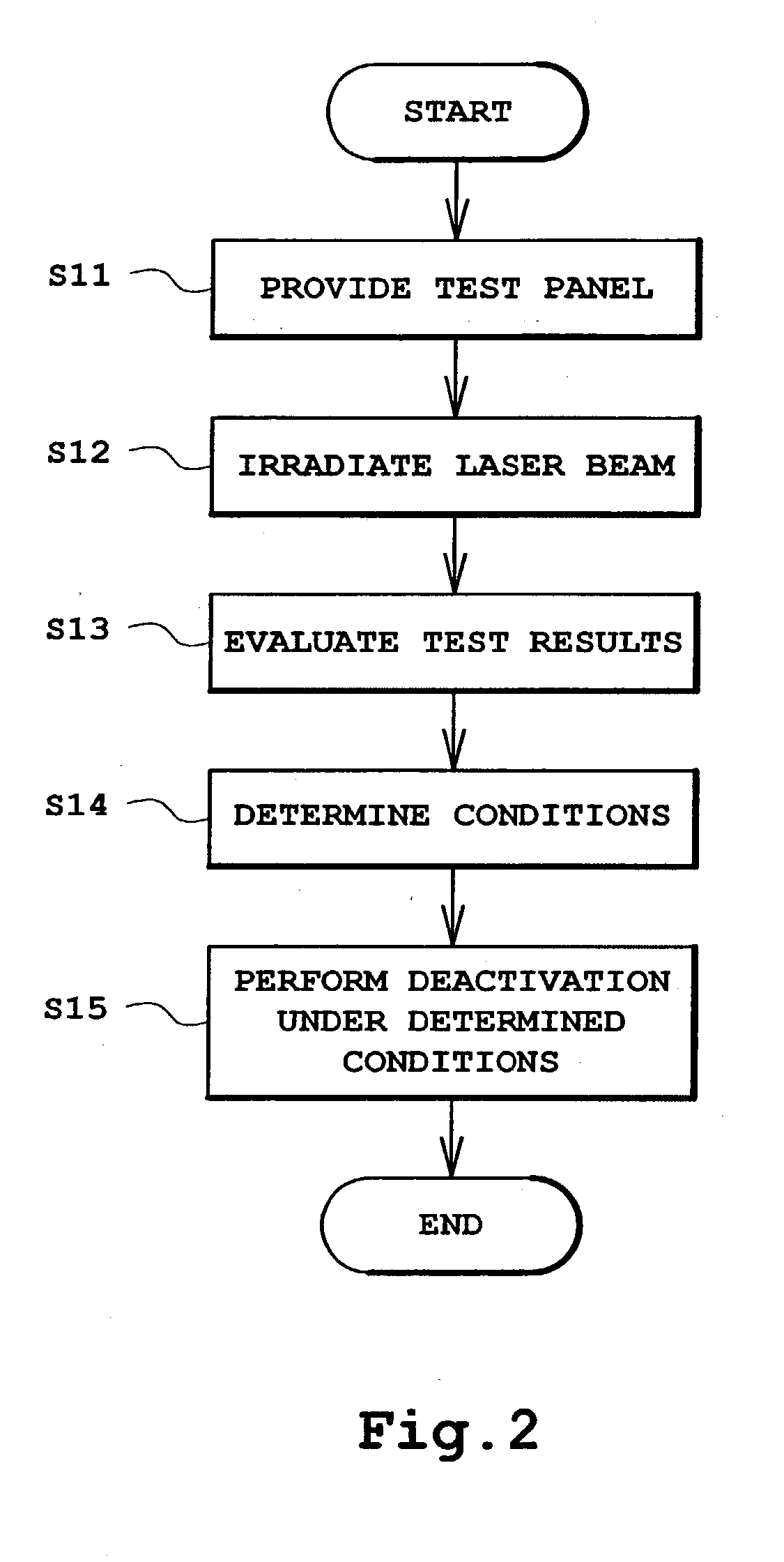
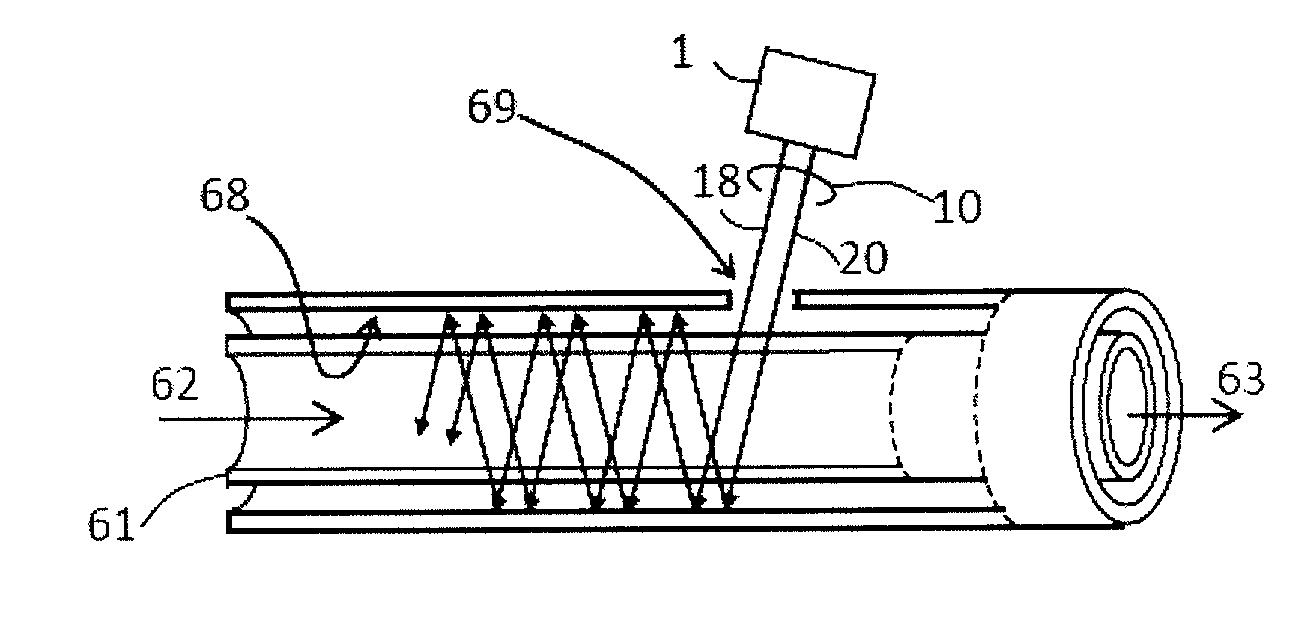
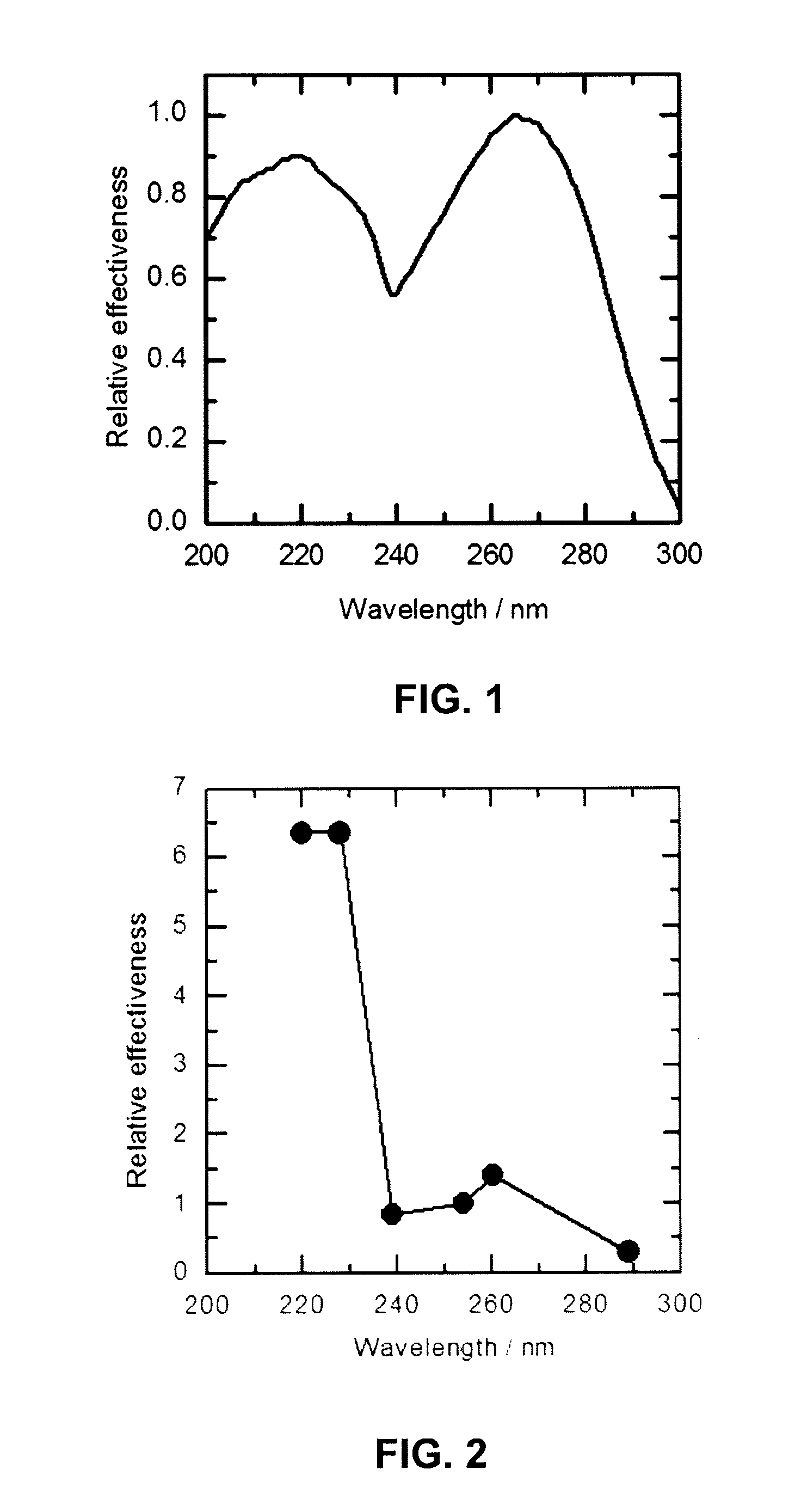
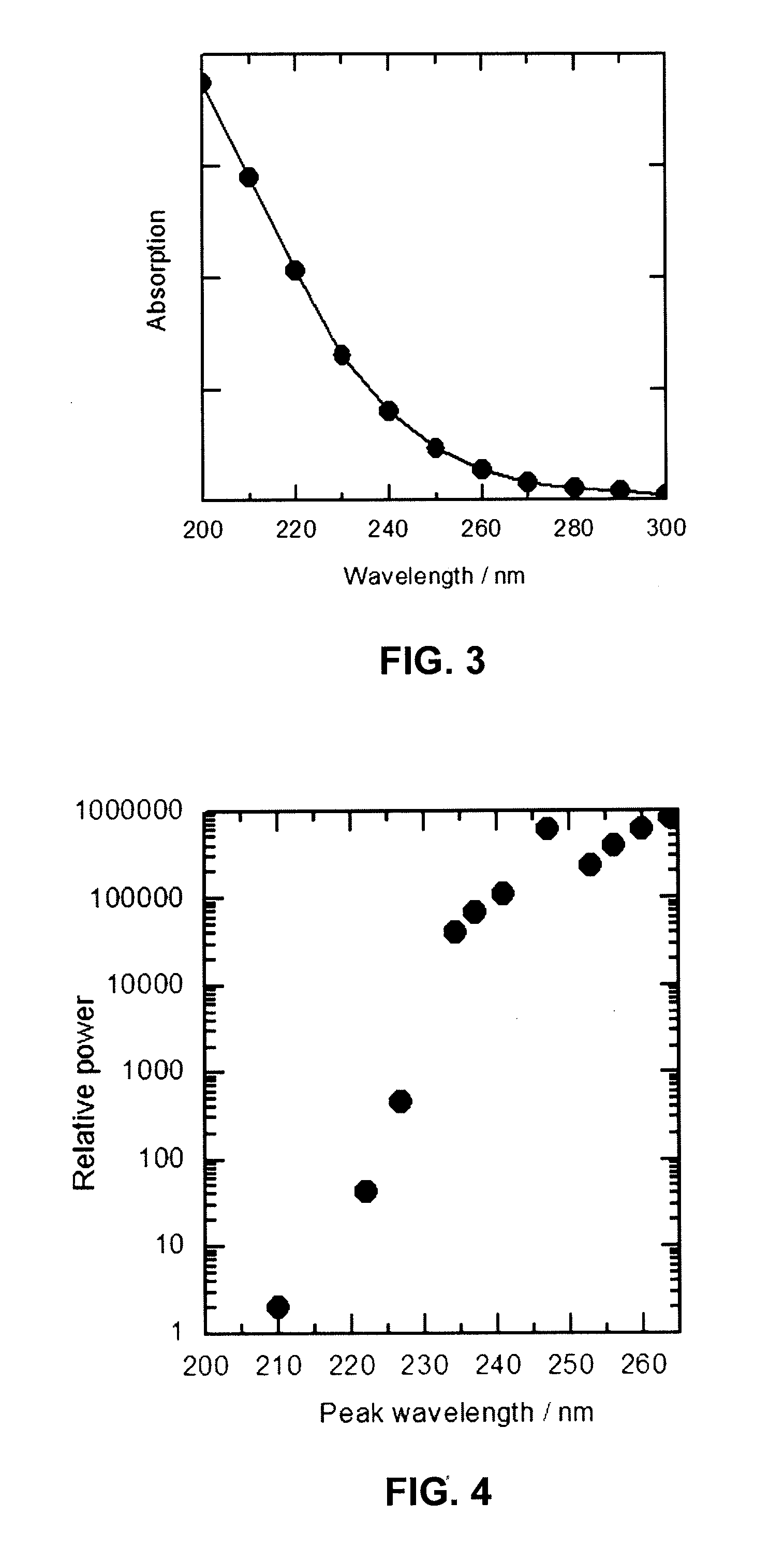
Ultraviolet treatment device
A light source is provided for use in a treatment device for treating a fluid, solid or surface. The light source includes a light emitting diode that emits a first component of ultraviolet (UV) light, and a UV laser light source that emits a second component of UV light having a peak wavelength different from a peak wavelength of the first component of UV light. The first component of UV light and the second component of UV light are applied to treat the fluid or surface. The UV laser light source may include a laser light source and a frequency doubling component that receives light from the laser light source and converts the light to the second component of UV light. A treatment device includes the described light source and a container containing the fluid, or a solid surface, to be treated.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method and apparatus for producing UV laser from all-solid-state system
ActiveUS20090201952A1Improve efficiencyLow costLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusAll solid stateUv laser
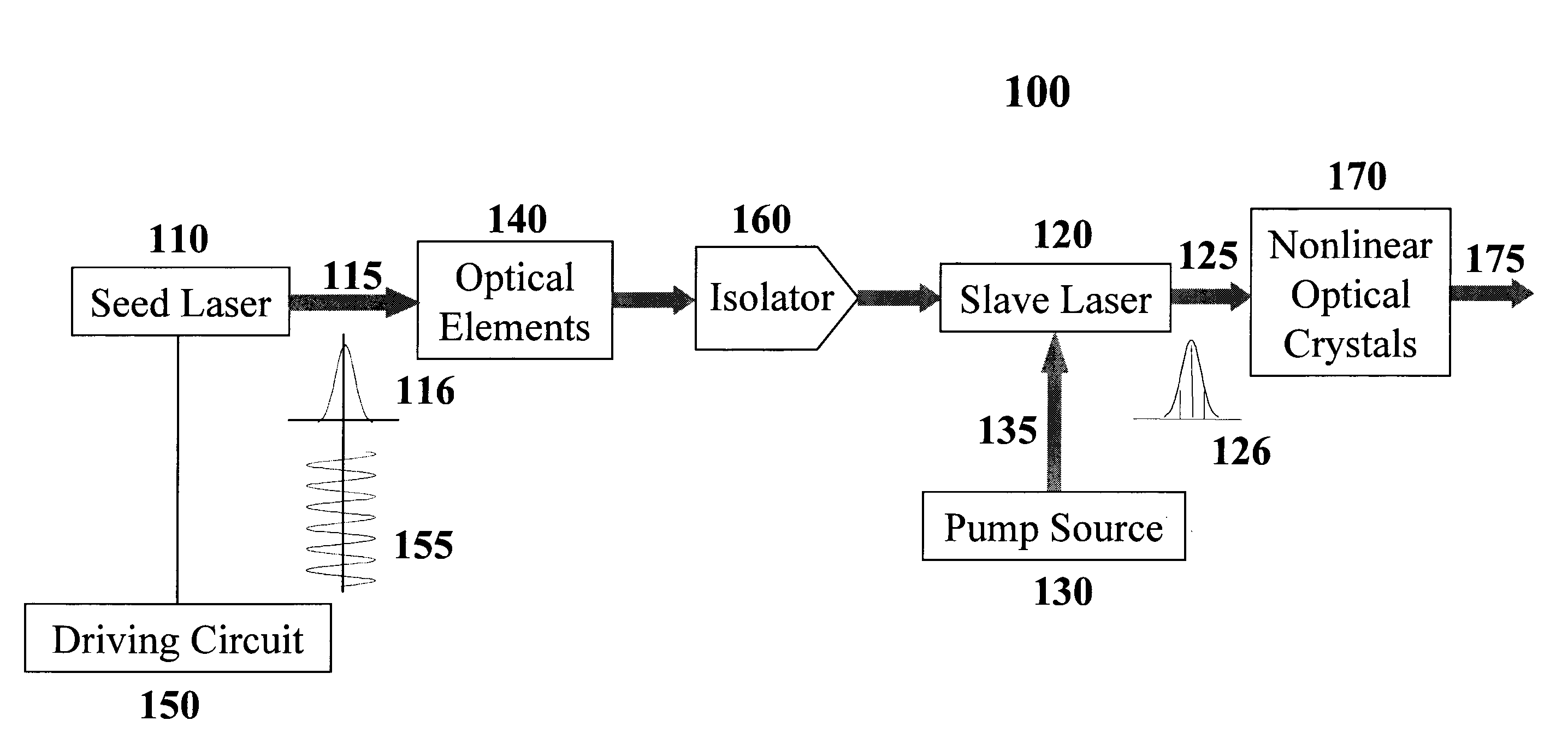
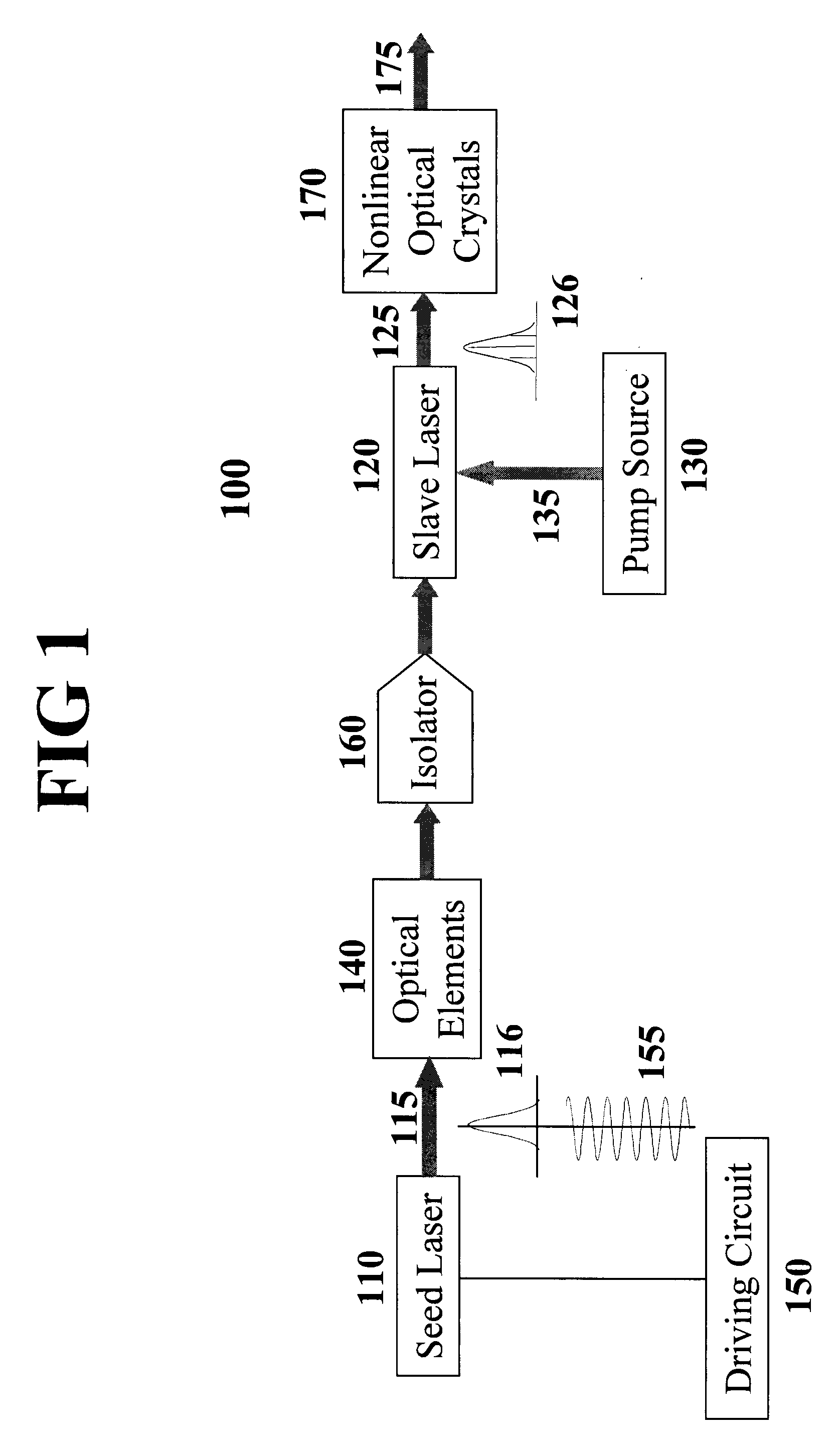
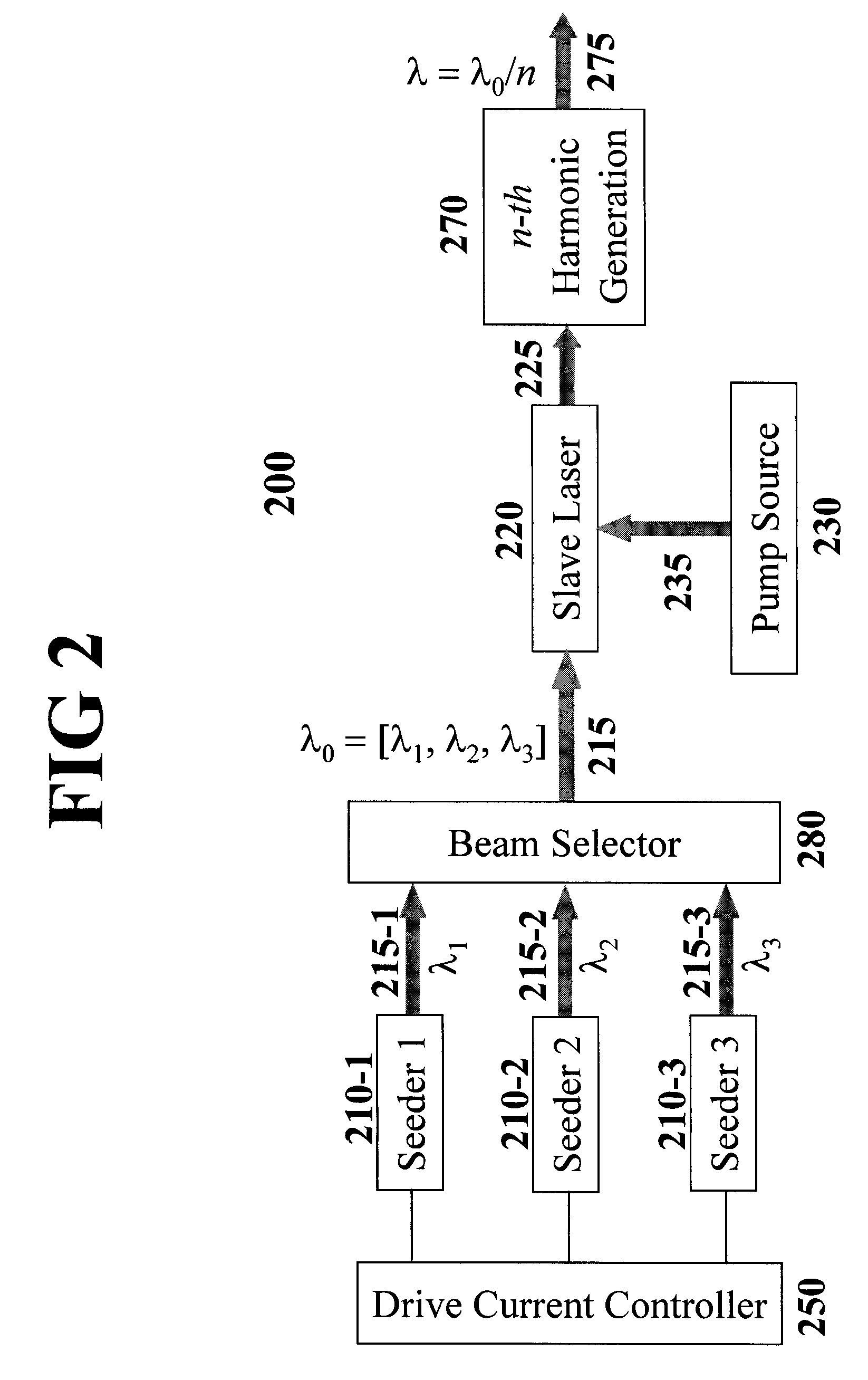
An all-solid-state laser system produces coherent DUV radiation through a third or fourth harmonic generation. The fundamental wavelength is generated by a slave laser optically pumped by one or more light source(s) of high density array(s) and is stabilized by injecting optical seeds whose wavelength is rapidly swept to cover the fundamental wavelength. The pump effects are enhanced by a pump chamber that recycles unabsorbed pump light. The present invention enables DUV pulses with a width shorter than 1 ns and a repetition rate higher than 100 kHz. The output DUV wavelength is adjustable by selecting an appropriate seeder.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Methods for stripping and modifying surfaces with laser-induced ablation
A coating removal apparatus removes a coating from a surface. The apparatus has a movable scanning head and scanning optics. The scanning head is movable in one dimension, and the scanning optics adjust in two dimensions to compensate for movement of the scanning head to implement long range scanning with a uniform scanning pattern. Further, a surface roughness is determined by measuring specular and scattered reflections at various angles. For composite surfaces, the apparatus utilizes UV laser radiation and a controlled atmosphere to remove coating and alter the chemical characteristics at the surface.
Owner:GEN LASERTRONICS
Portable three-channel near-deep-UV Raman spectrometer
ActiveCN105258800ASo as not to damageFast and non-destructive measurementRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsLaser transmitterBeam splitter
The invention discloses a portable three-channel near-deep-UV Raman spectrometer. The spectrometer comprises a near-deep-UV laser emitter, a laser spot shaping device, a first beam splitter, a zooming or non-zooming lens, a second beam splitter, a third beam splitter, a relay optical system, a point-to-line optical system, a spectrum forming system, an optical or mechanical sample scanning system and a data processing and wirelessly transmitting-receiving system. After Raman, fluorescent and visible / laser channels are fused in the point-to-point manner in real time, the whole sample is scanned, and data processing such as spectral separation, peak positioning, spectral library establishment and substance identification is carried out. The portable three-channel near-deep-UV Raman spectrometer has the advantages including that the flexibility and resolution are high, illumination points are large, the detection distance is long, rapid onsite non-contact measurement can be implement in the sun, and the spectrometer is relatively safe for the eyes.
Owner:CSR HANGZHOU RAIL TRANSIT
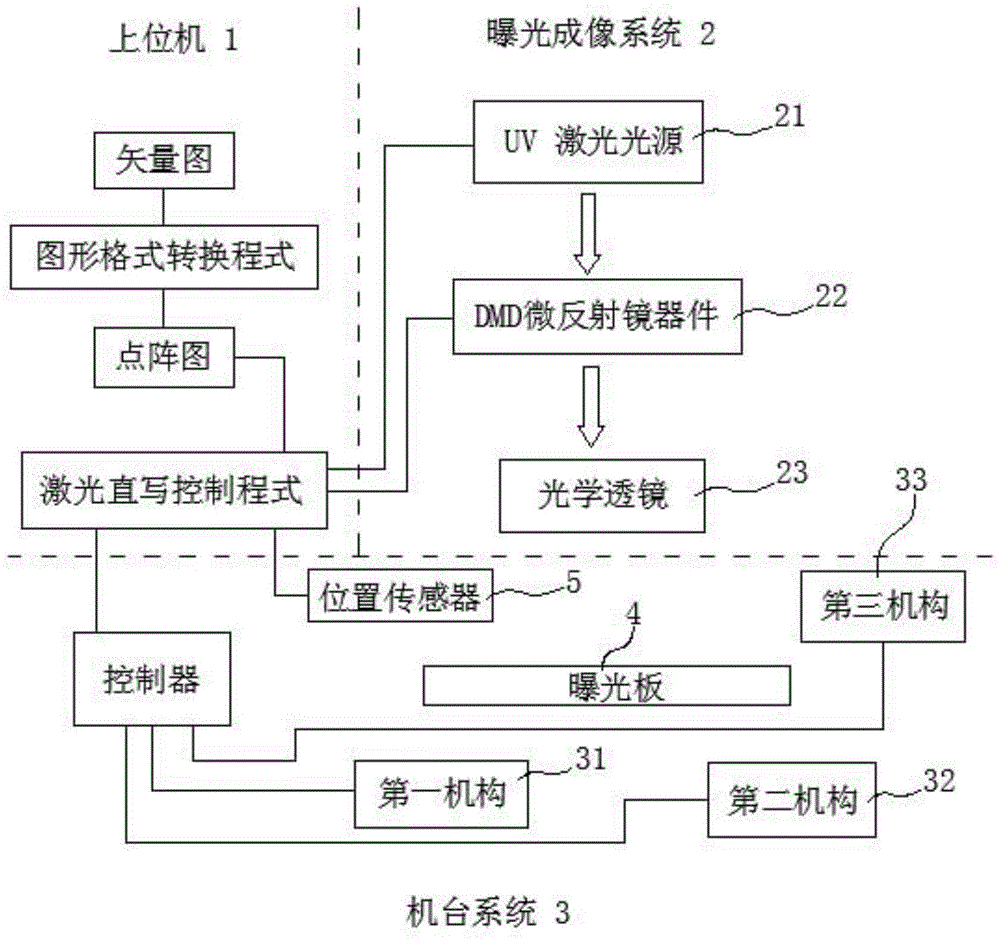
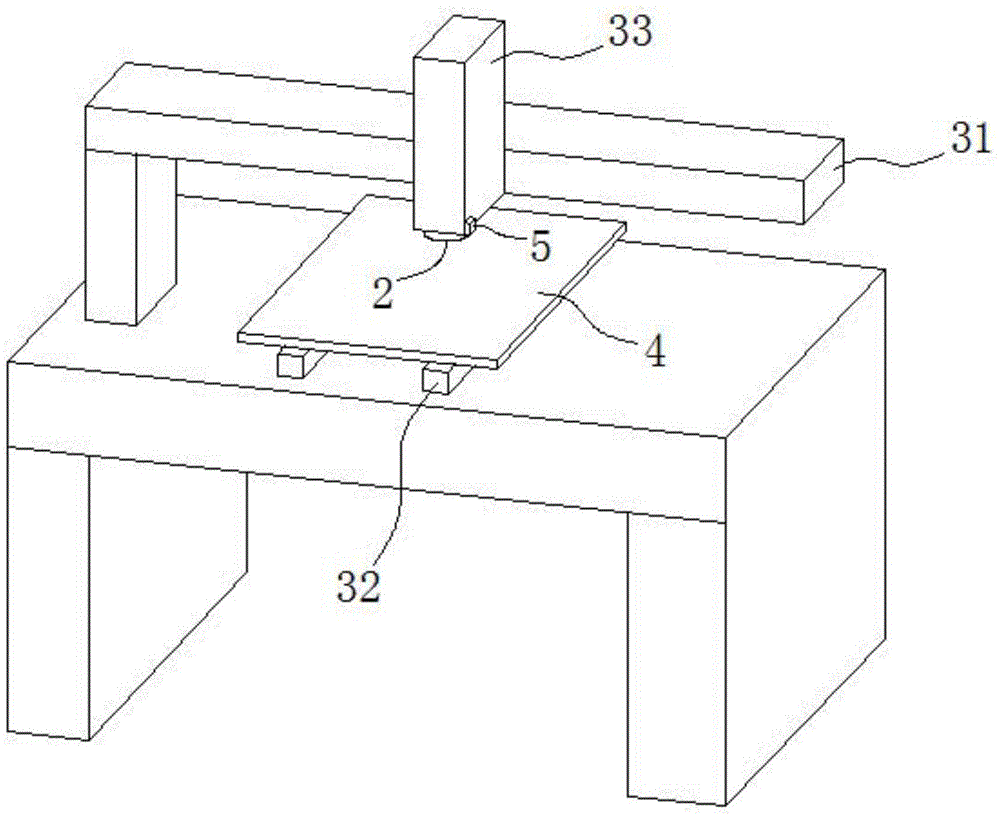
Synchronous pulse exposure method for maskless lithography equipment and digital laser direct-writing system
InactiveCN104865800AExtend effective lifeImprove and increase contrastPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusUv laserDigital micro mirror device
The invention provides a synchronous pulse exposure method for maskless lithography equipment. The maskless lithography equipment adopts an exposure imaging system consisting of a UV (ultraviolet) laser or UV LED light source, a DMD (digital micro-mirror device) and an optical lens; the synchronous pulse exposure method is characterized in that a series of pulse synchronization signals are generated, the DMD and the UV laser or UV LED light source are triggered to synchronously work, and the pulse interval of the pulse synchronization signals depends on the replacement or refreshing cycle of the DMD to graphs; a digital laser direct-writing system comprises an upper computer in charge of outputting digital lattice patterns and the series of pulse synchronization signals to the exposure imaging systems, and one or more exposure imaging systems arranged side by side. According to the method, a synchronous control problem of parts of the lithography equipment is solved, more effective and reasonable exposure and refreshing time is convenient to design, and the shortcomings of low production capacity and poor system adaptability of a conventional exposure machine are overcome.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN AISCENT TECH
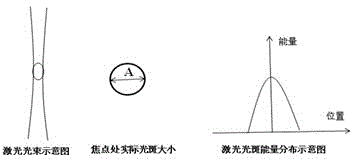
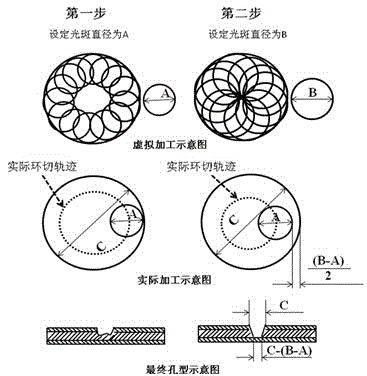
UV laser drilling method for preparing blind holes controllable in taper
The invention provides a UV laser drilling method for preparing blind holes controllable in taper in a printed circuit board. A laser beam scans needed micro-guide through holes in the surface of a workpiece within the set aperture range along a certain track. Each micro-guide through hole is molded through two steps, the blind holes controllable in taper are prepared by adjusting the energy, defocusing amount and light spots of each step of parameters, and the problem that the taper and quality of the blind holes can not be easily controlled through an existing preparation method is effectively solved.
Owner:AKM ELECTRONICS TECH SUZHOU
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com