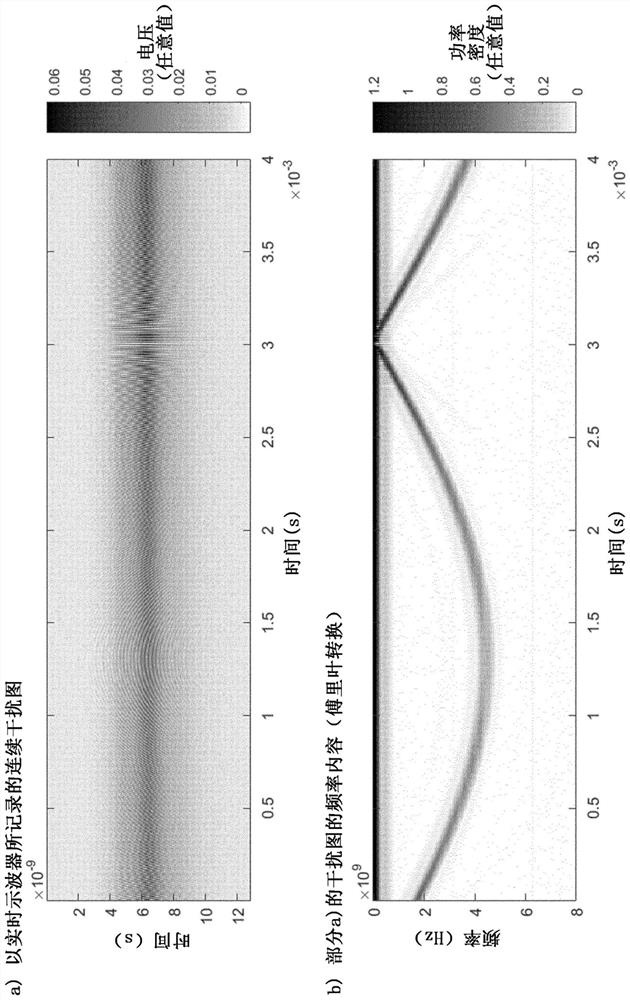
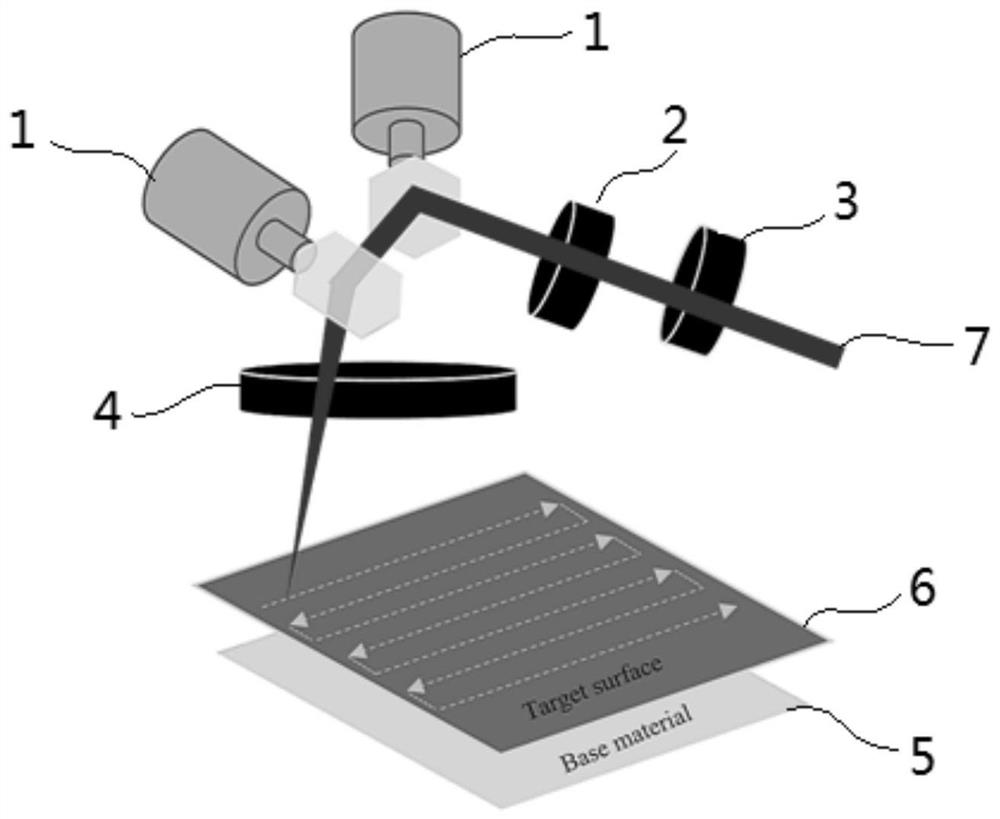
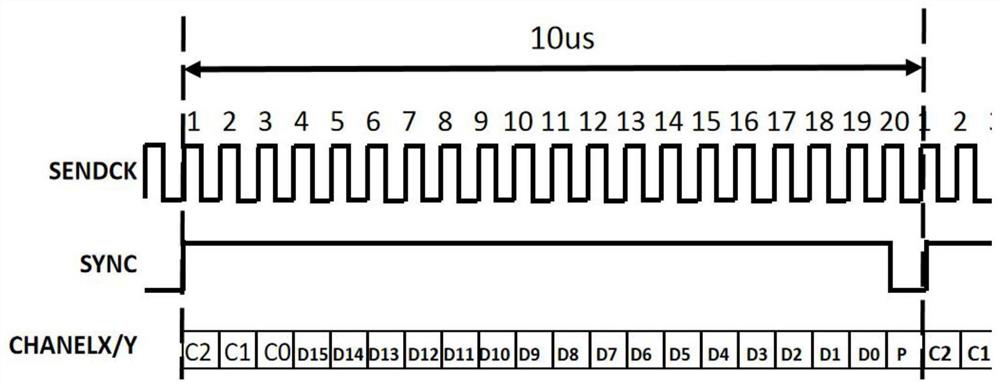
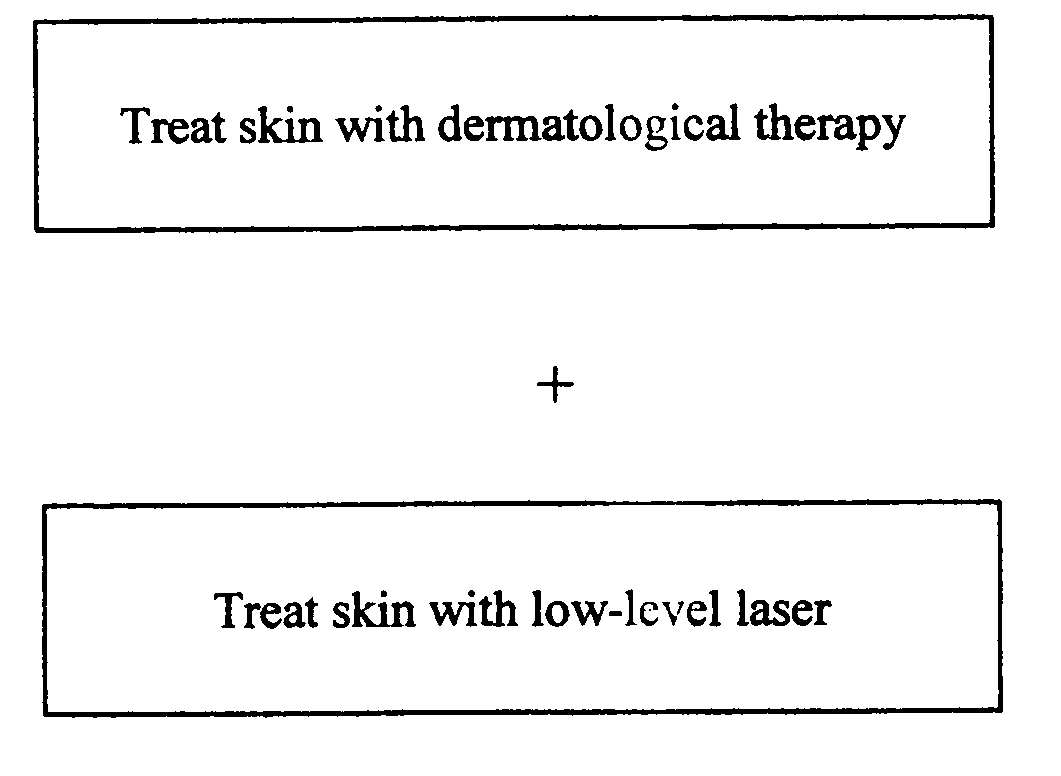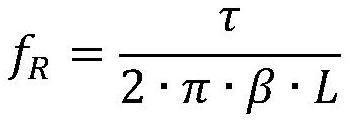Patents
Literature
35 results about "Ablative laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
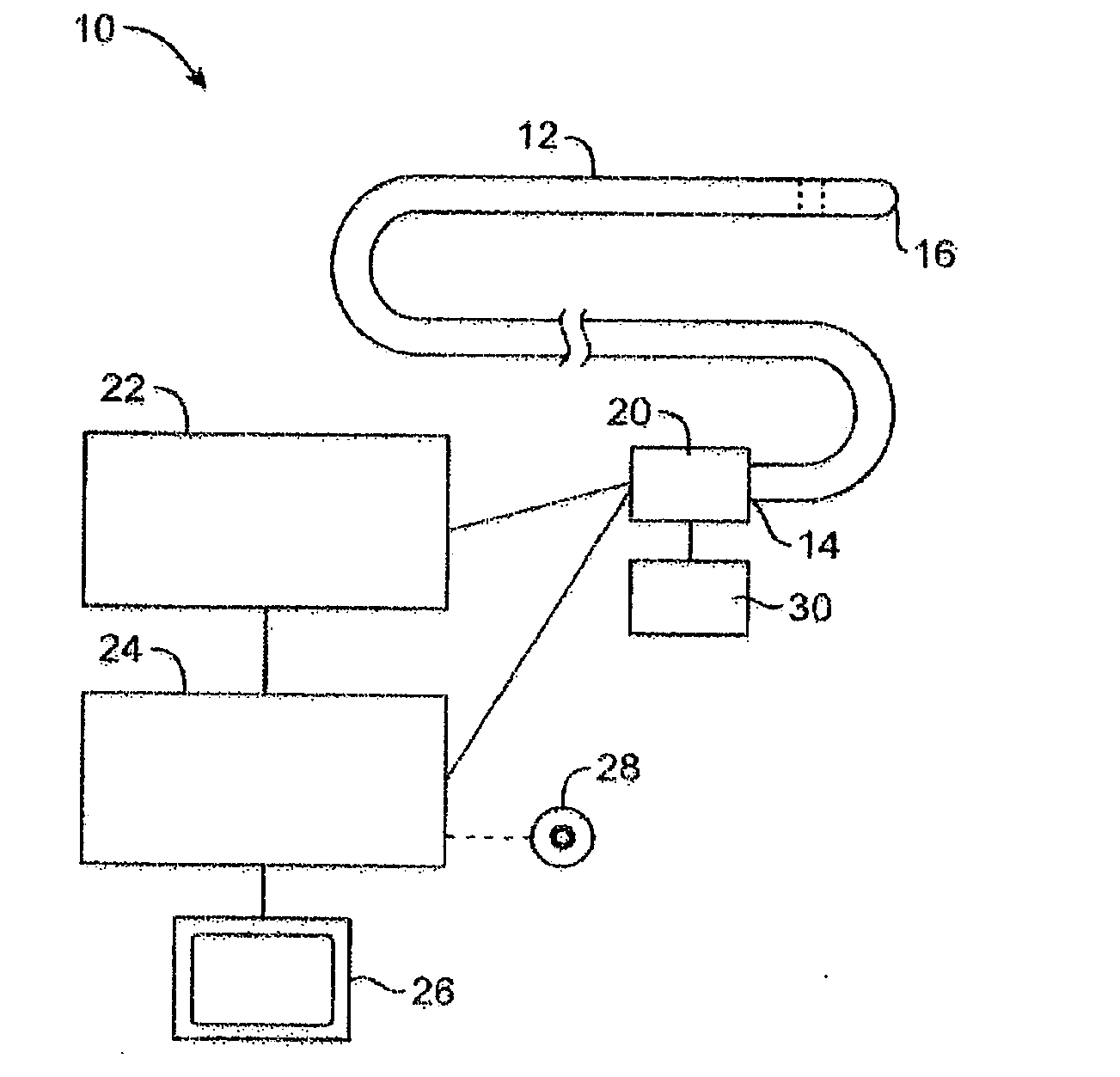
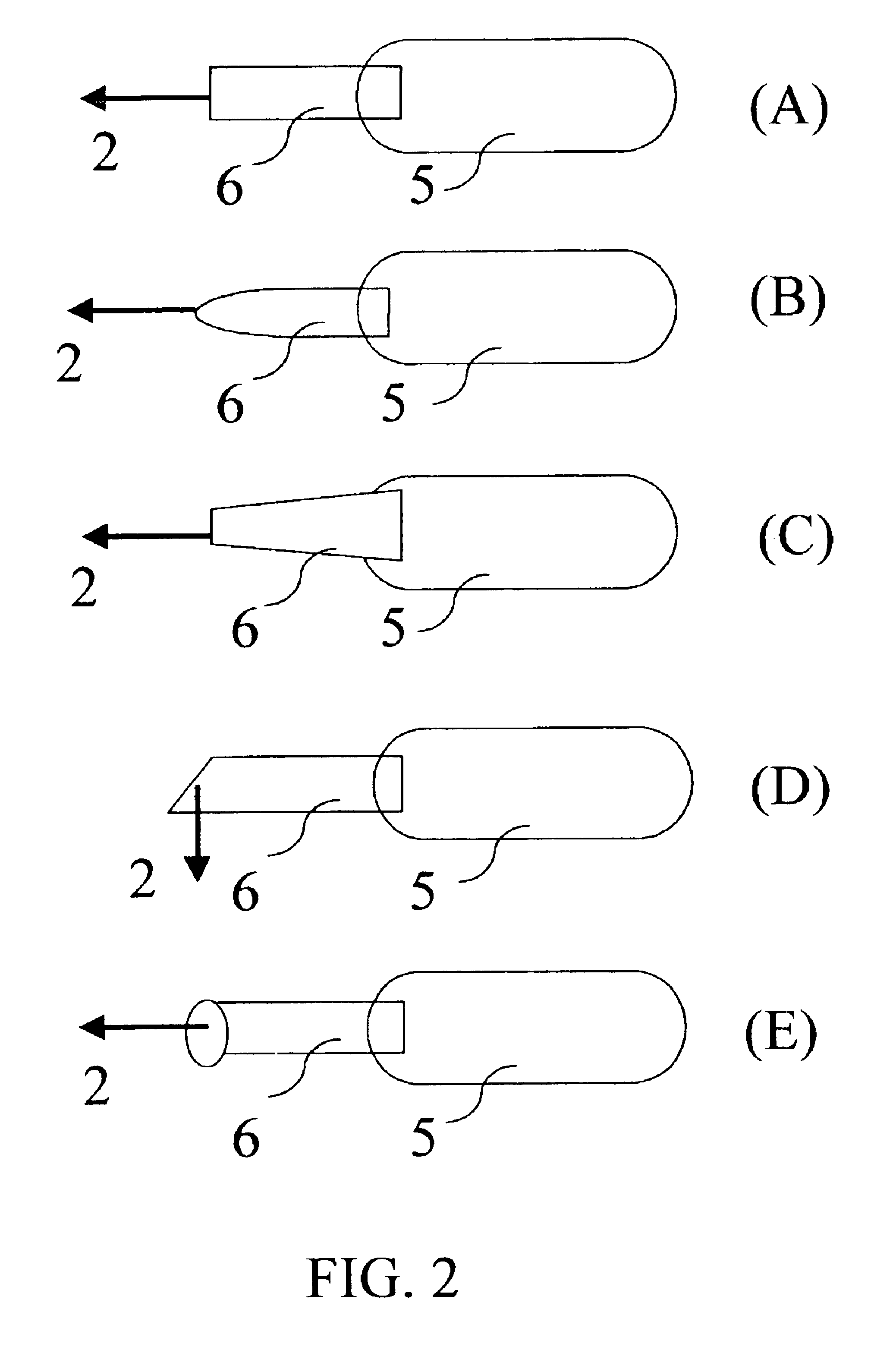
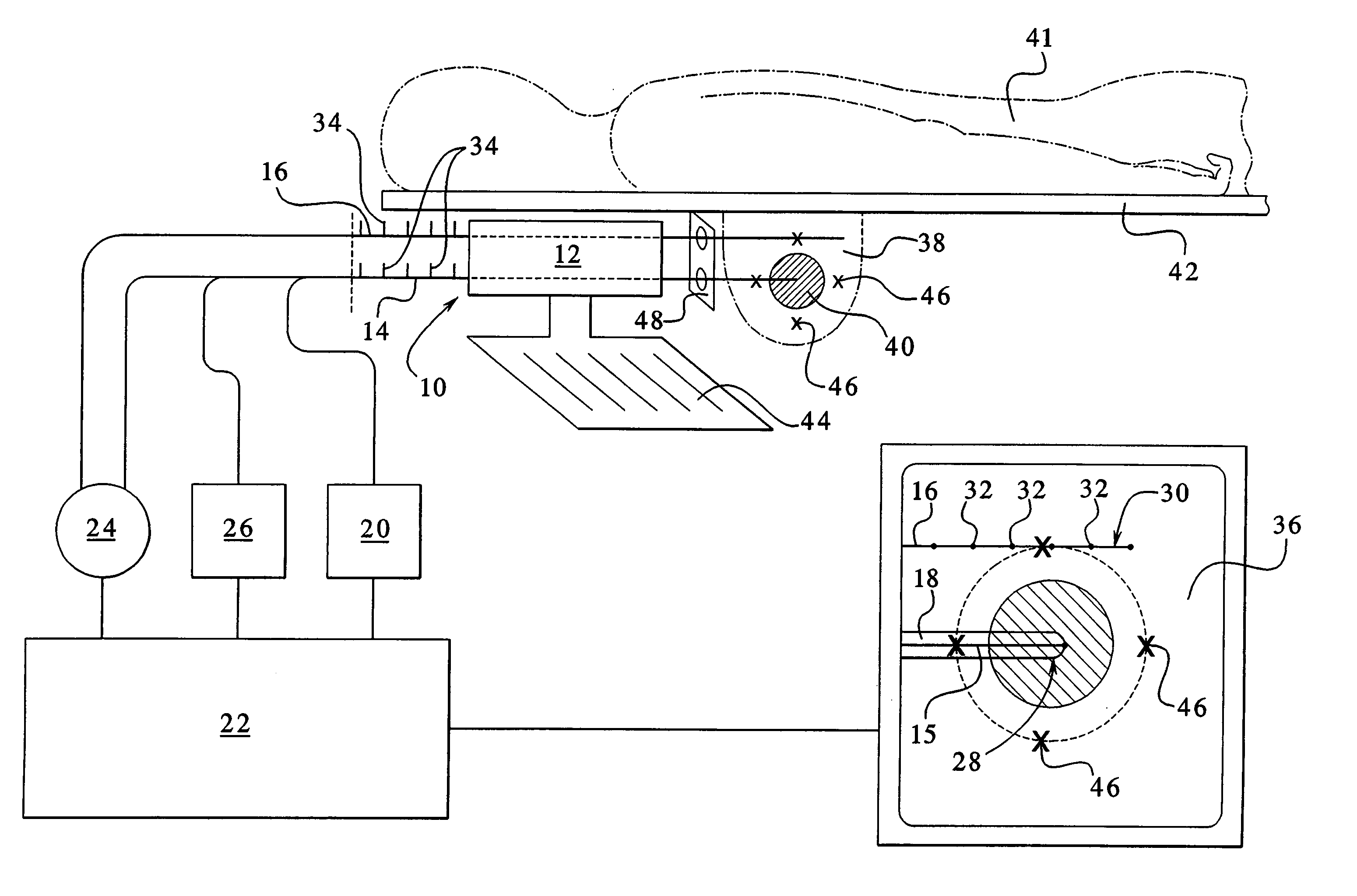
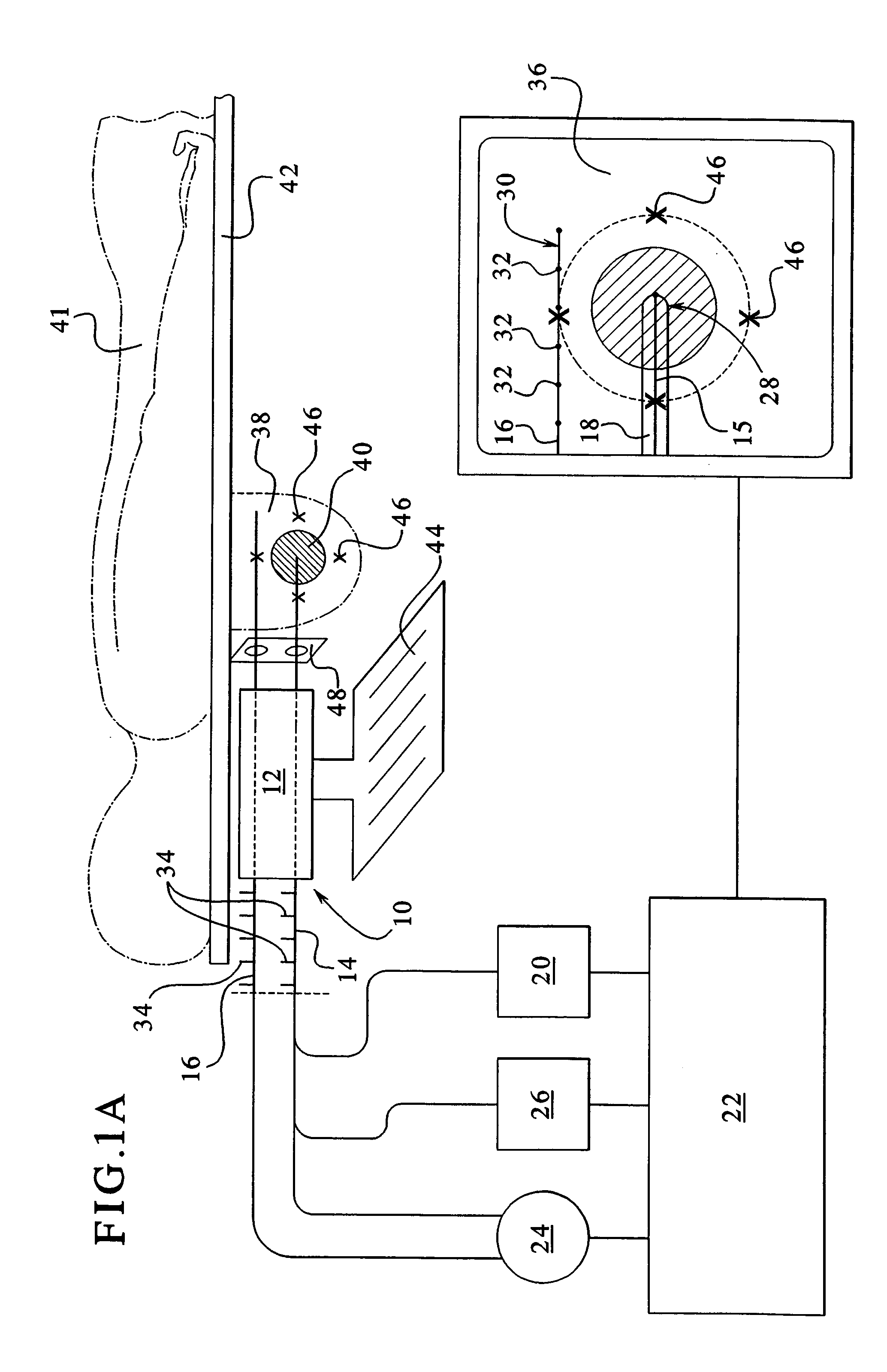
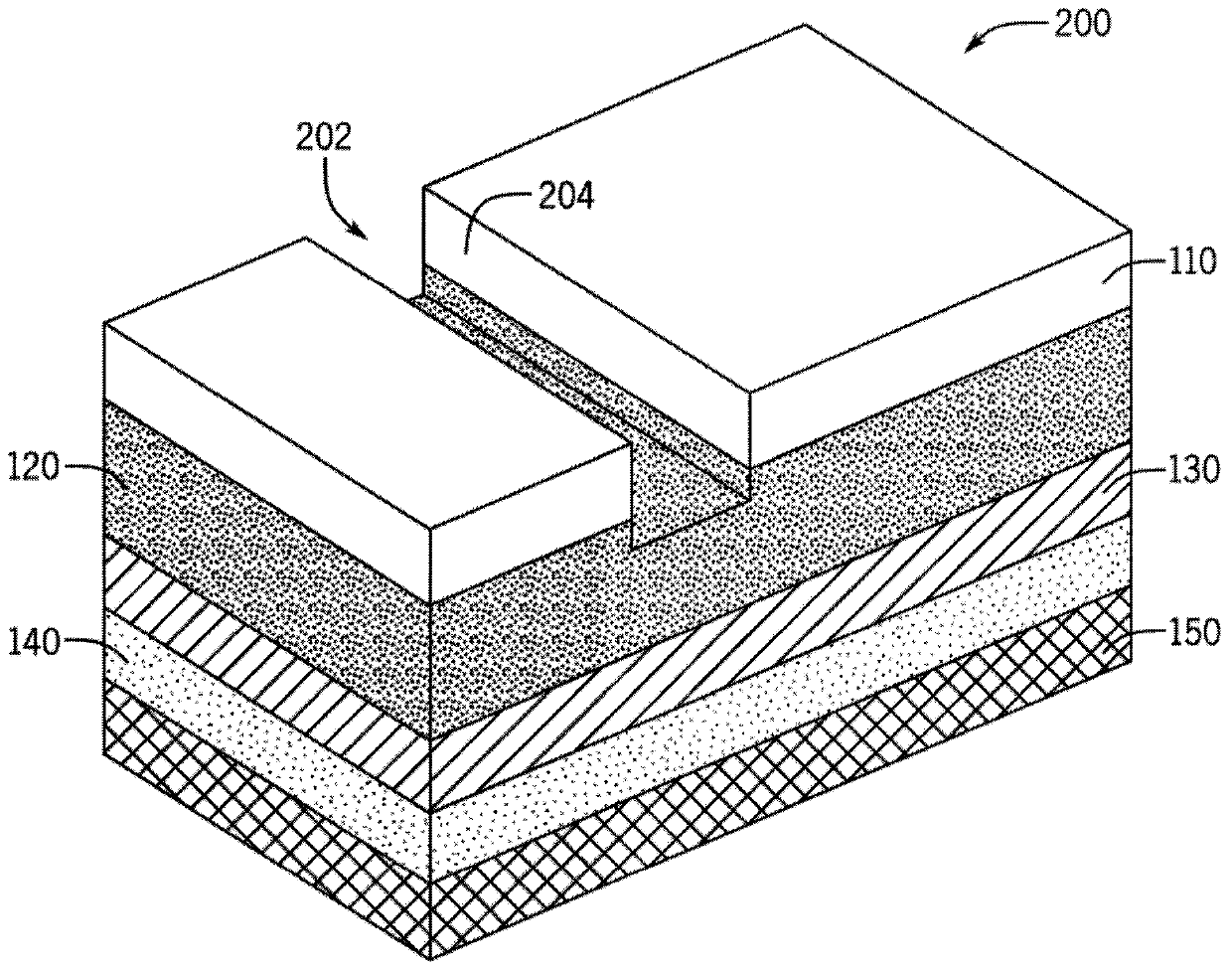
Imaging and eccentric atherosclerotic material laser remodeling and/or ablation catheter
Devices, systems, and methods for treating atherosclerotic lesions and other disease states, particularly for treatment of vulnerable plaques, can incorporate optical coherence tomography or other imaging techniques which allow a structure and location of an eccentric plaque to be characterized. Remodeling and / or ablative laser energy can then be selectively and automatically directed to the appropriate plaque structures, often without imposing mechanical trauma to the entire circumference of the lumen wall.
Owner:VESSIX VASCULAR
Treatment of presbyopia and other eye disorders using a scanning laser system
InactiveUS6263879B1Efficient and accurate expansionPreventing of open angle glaucomaLaser surgeryDiagnosticsDiseaseGlaucoma
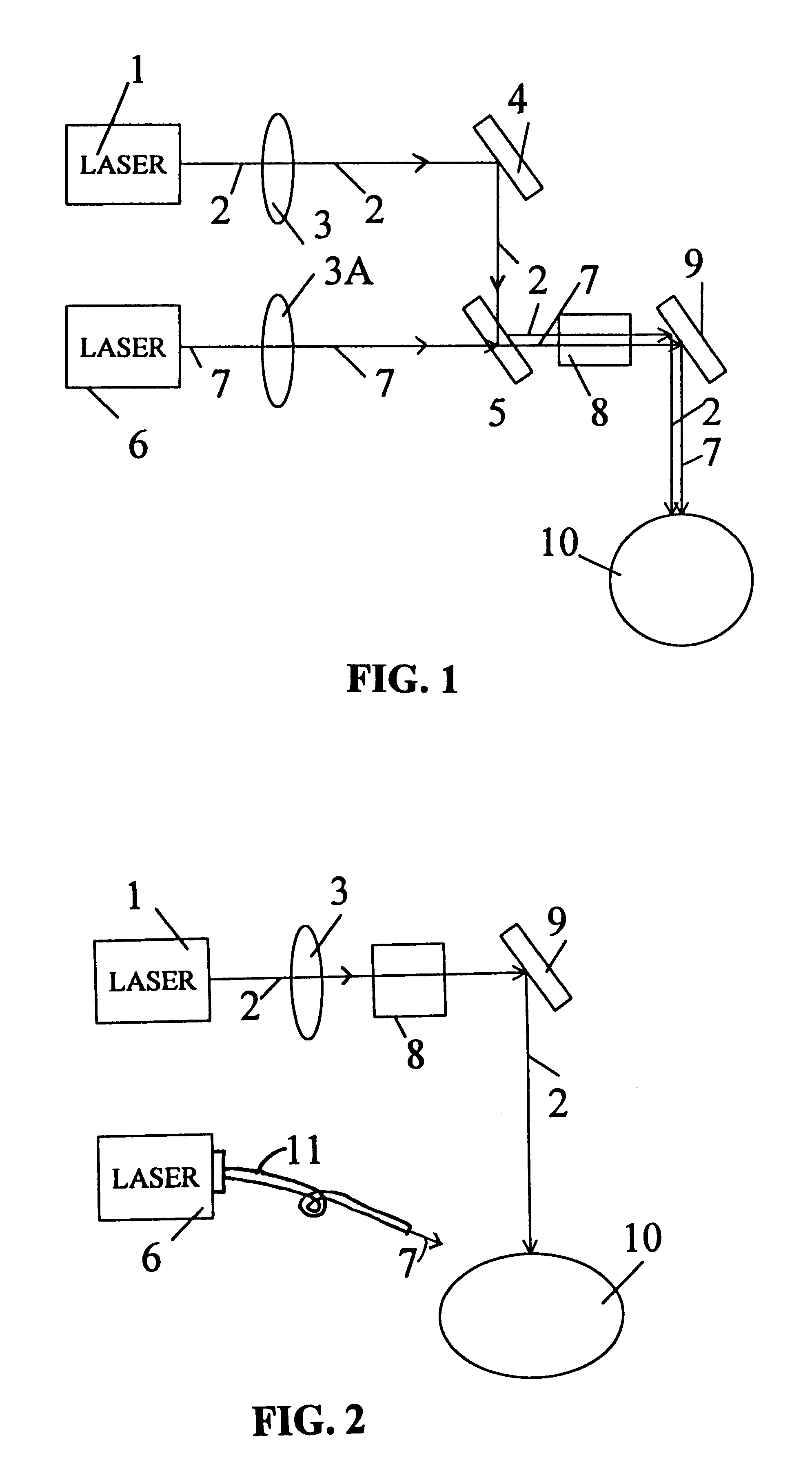
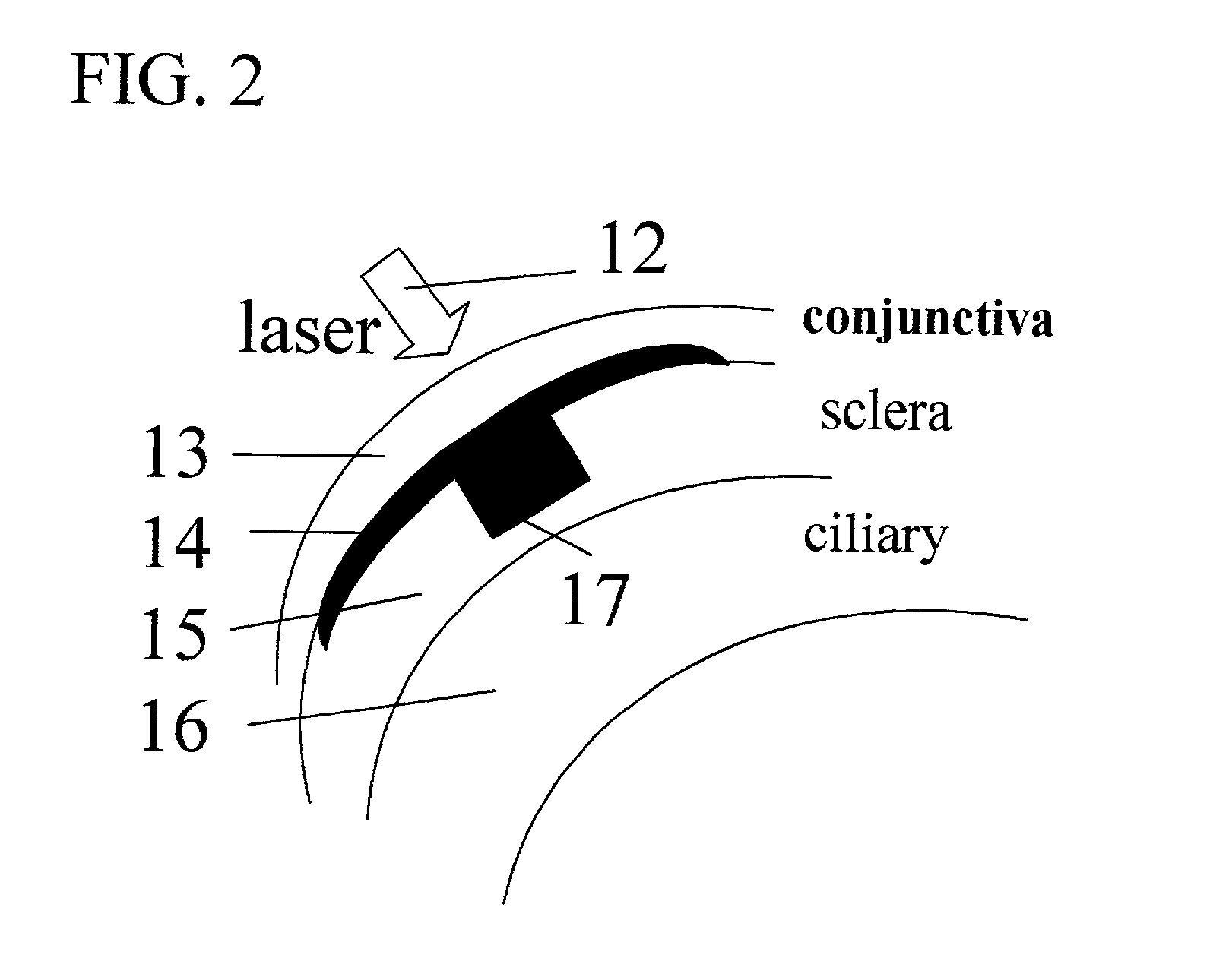
Presbyopia is treated by a method which uses ablative lasers to ablate the sclera tissue and increase the accommodation of the ciliary body. Tissue bleeding is prevented by an ablative laser having a wavelength of between 0.15 and 3.2 micron. A scanning system is proposed to perform various patterns on the sclera area of the cornea to treat presbyopia and to prevent other eye disorder such as glaucoma. Laser parameters are determined for accurate sclera expansion.
Owner:NEOS OCULAR
Apparatus and methods for the treatment of presbyopia using fiber-coupled-lasers
Systems and surgical techniques for presbyopia correction by laser removal of the sclera tissue are disclosed. The disclosed preferred embodiments of the system consists of a beam spot controller, a fiber delivery unit and a fiber tip. The basic laser including UV lasers and infrared lasers having wavelength ranges of (0.15-0.36) microns and (1.9-3.2) microns and diode lasers of about 0.98, 1.5 and 1.9 microns. Presbyopia is treated by a system which uses an ablative laser to ablate the sclera tissue outside the limbus to increase the accommodation of the ciliary body of the eye. The sclera tissue may be ablated by the laser with or without the conjunctiva layer open.
Owner:NEOS OCULAR
Imaging and Eccentric Atherosclerotic Material Laser Remodeling and/or Ablation Catheter
Devices, systems, and methods for treating atherosclerotic lesions and other disease states, particularly for treatment of vulnerable plaques, can incorporate optical coherence tomography or other imaging techniques which allow a structure and location of an eccentric plaque to be characterized. Remodeling and / or ablative laser energy can then be selectively and automatically directed to the appropriate plaque structures, often without imposing mechanical trauma to the entire circumference of the lumen wall.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for tissue expansion
InactiveUS20110251602A1Reduce presenceReduced likelihoodSkin implantsIncision instrumentsMedicineTissue expansion
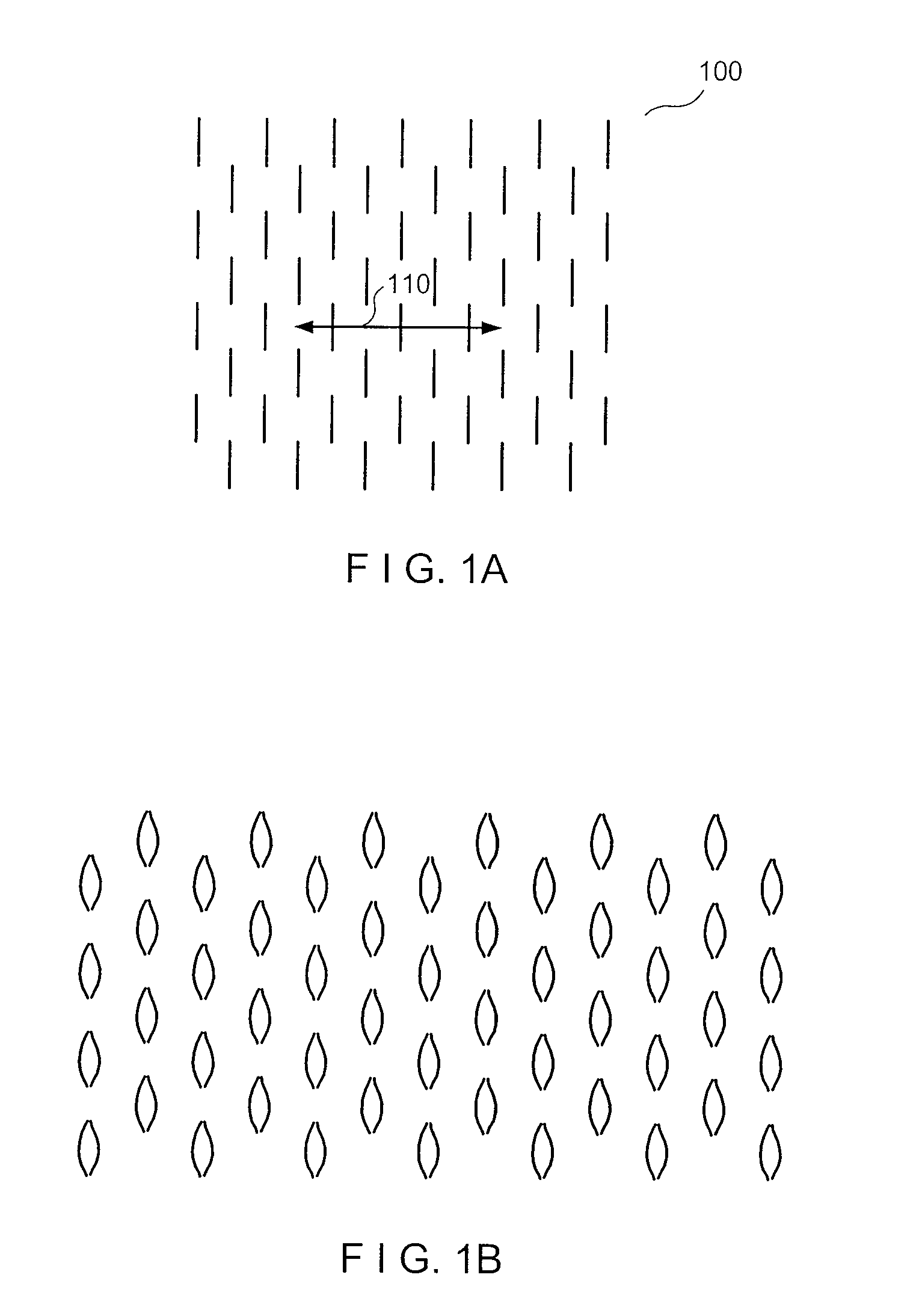
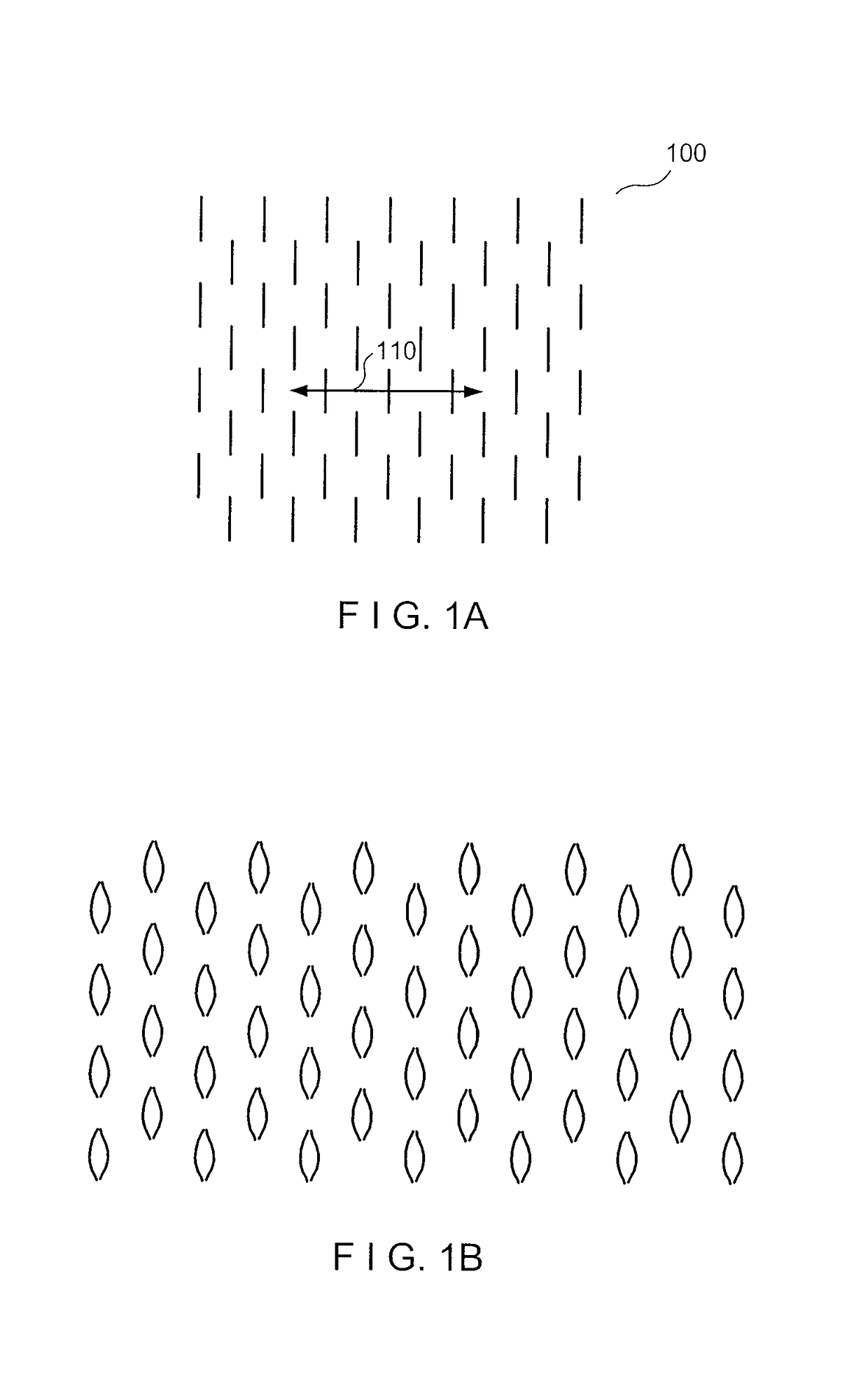
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure provide method and apparatus for facilitating stretching of a bio-logical tissue by forming a plurality of micro-slits in the tissue. Each micro-slit can be less than about 2 mm or less than about 1.5 mm long, or even less than about 1 mm, such that small gaps that can heal quickly can be formed when the tissue is stretched. The micro-slits can be formed using a plurality of cutting arrangements or an ablative laser. The micro-slits can be formed in various patterns, including staggered rows, circular or spiral patterns, or random patterns.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and methods for prevention of age-related macular degeneration and other eye diseases
InactiveUS20030105456A1Minor side effectsIncrease flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instruments for heatingRadio frequencyLaser beams
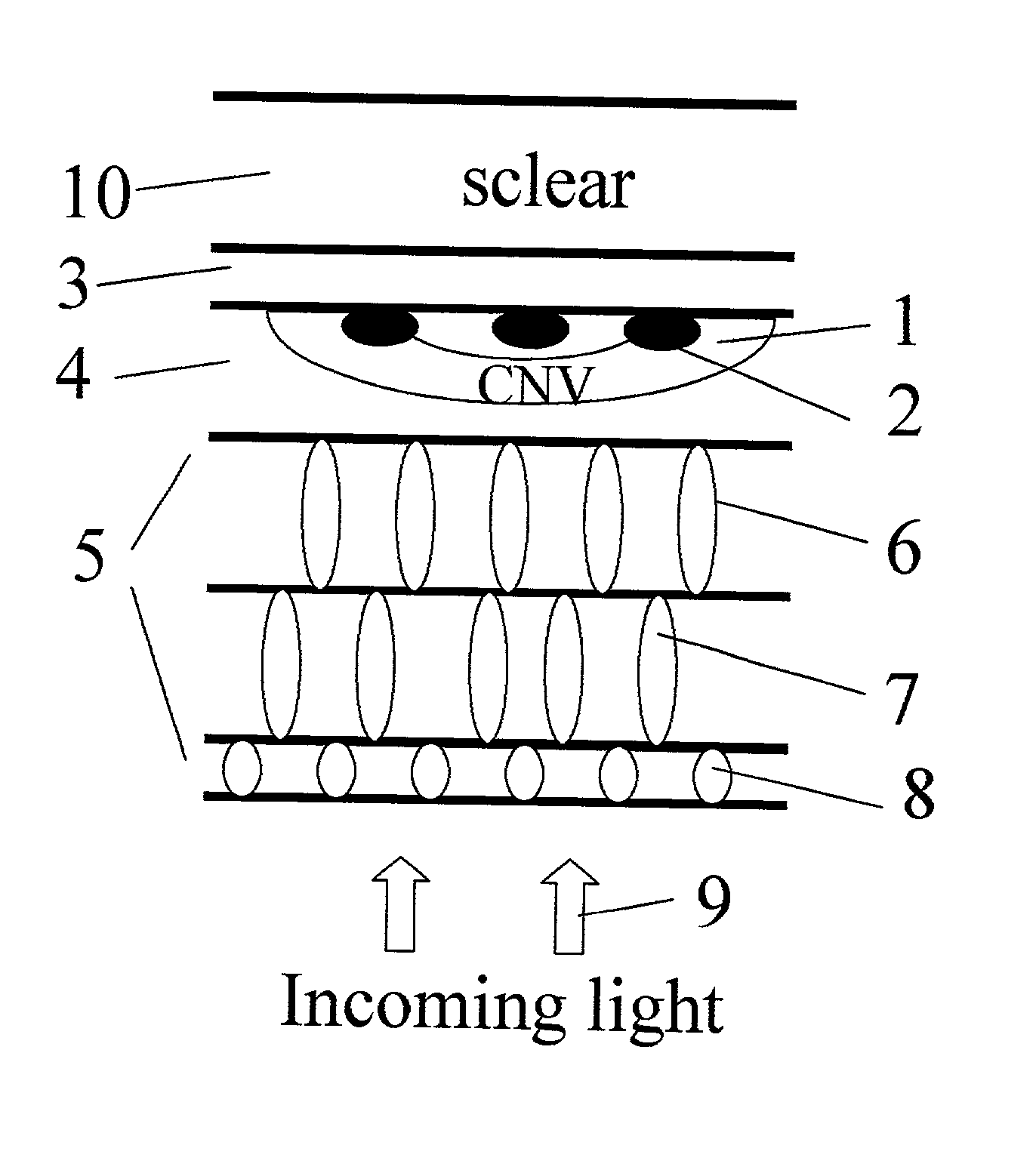
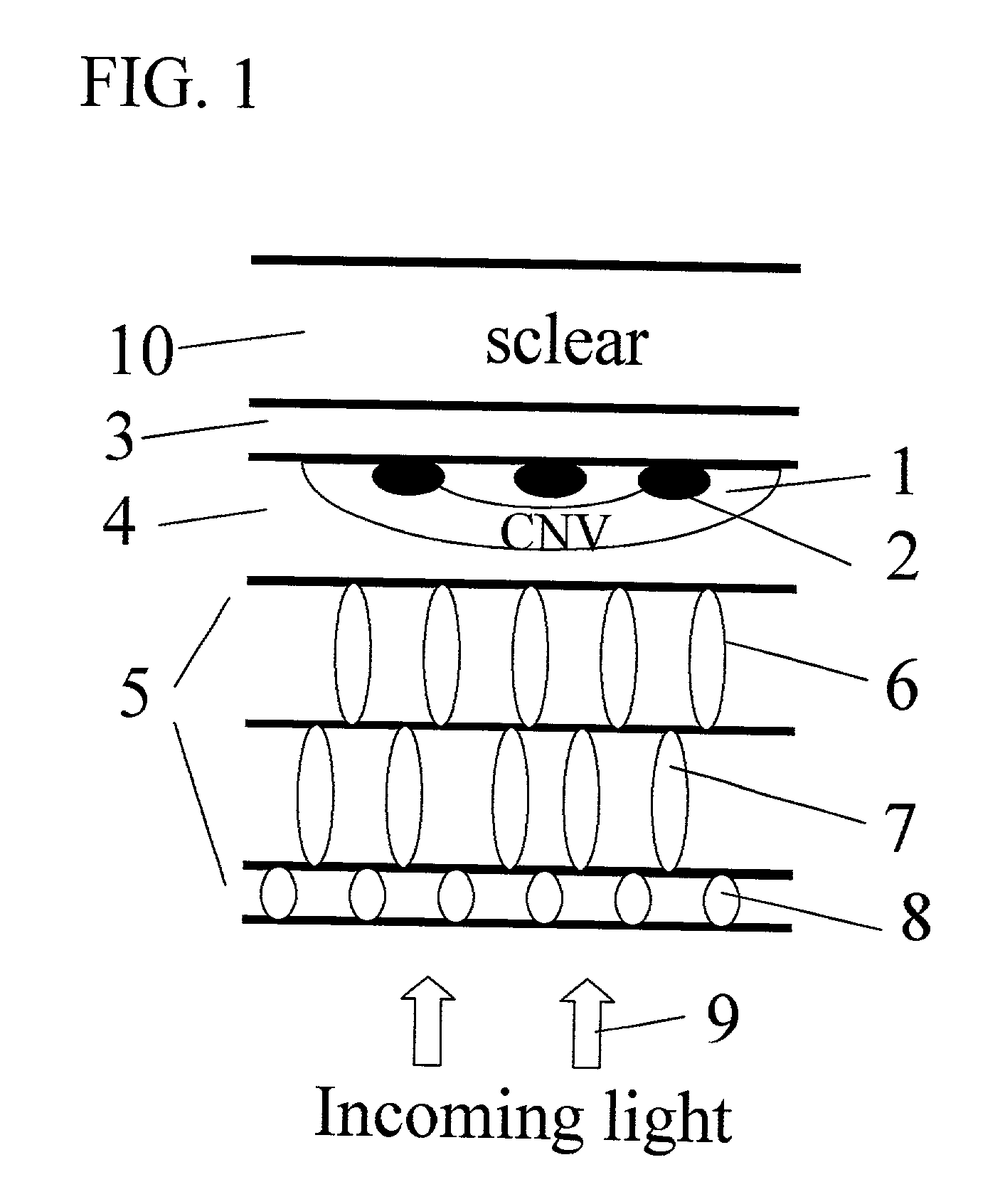
Surgical apparatus and surgical methods are proposed for the prevention of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and choroidal neovascularization (CNV), and other eye diseases such as glaucoma by removal of the sclera tissue to reduce its rigidity and increase the flood flow and decrease pressure in the choriocapillaris. The disclosed preferred embodiments of the system consists of a tissue ablation means and a control means of ablation patterns and a fiber delivery unit. The basic laser beam includes UV lasers and infrared lasers having wavelength ranges of (0.15-0.36) microns and (0.5-3.2) microns and diode lasers of about 0.98, 1.5 and 1.9 microns. AMD and CNV are prevented, delayed or reversed by using an ablative laser to ablate the sclera tissue in a predetermined patterns outside the limbus to increase the elasticity of the sclera tissue surrounding the eye globe The surgery apparatus also includes non-laser device of radio frequency wave, electrode device, bipolar device and plasma assisted device
Owner:LIN J T
Method for dermatology therapies in combination with low level laser treatments
InactiveUS20050203593A1Promote wound healingRelieve painSurgical instruments for heatingLight therapyDermabrasionRadio frequency
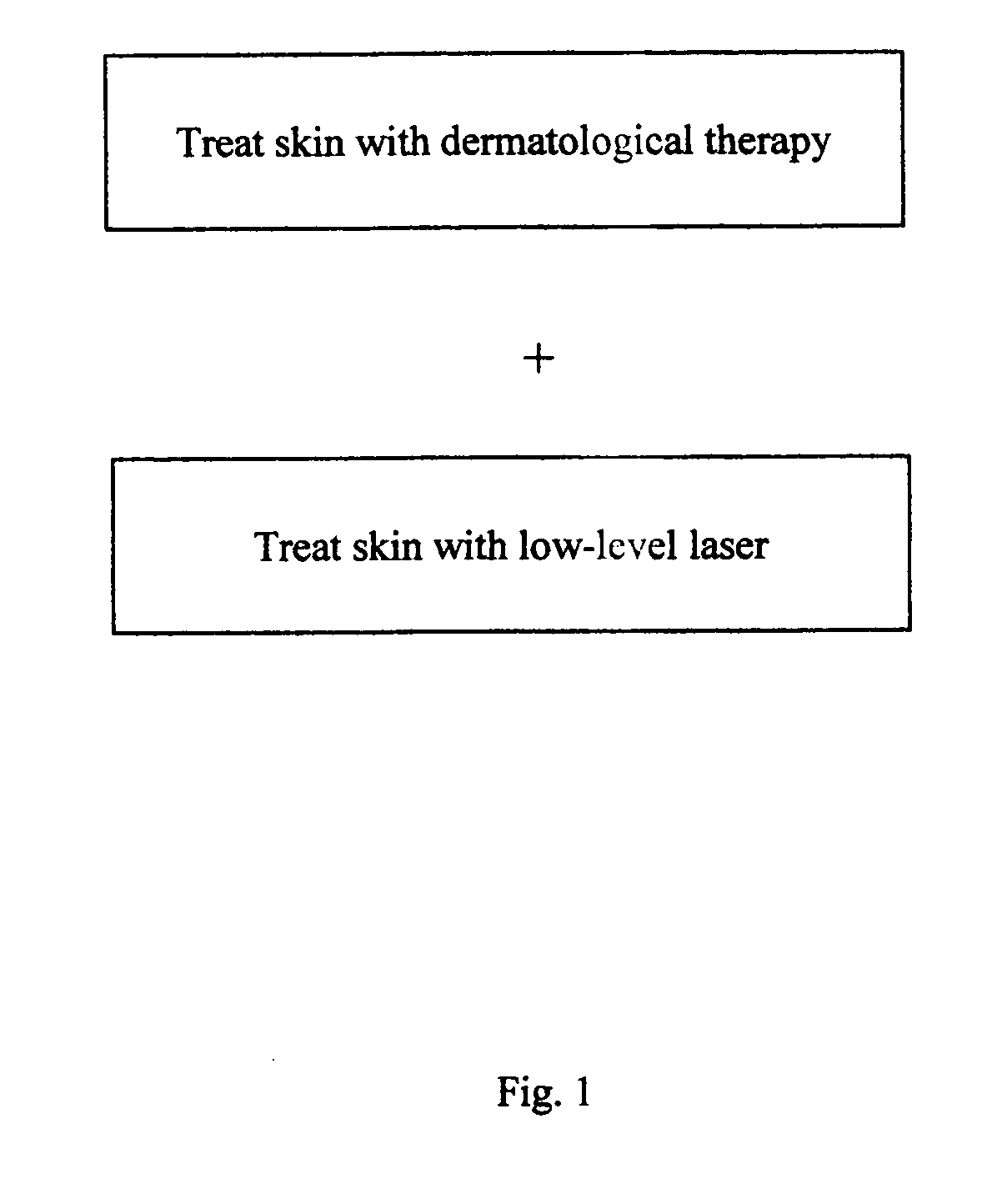
The present invention is a method for promoting faster wound healing and alleviating pain during and after various dermatology-related treatments. The method comprises using low level laser therapy in conjunction with dermatological treatments including intense pulsed light, radio frequency, dermabrasion, microdermabrasion, chemabrasion, chemical peels, ablative lasers, and cryogenics.
Owner:ERCHONIA CORP
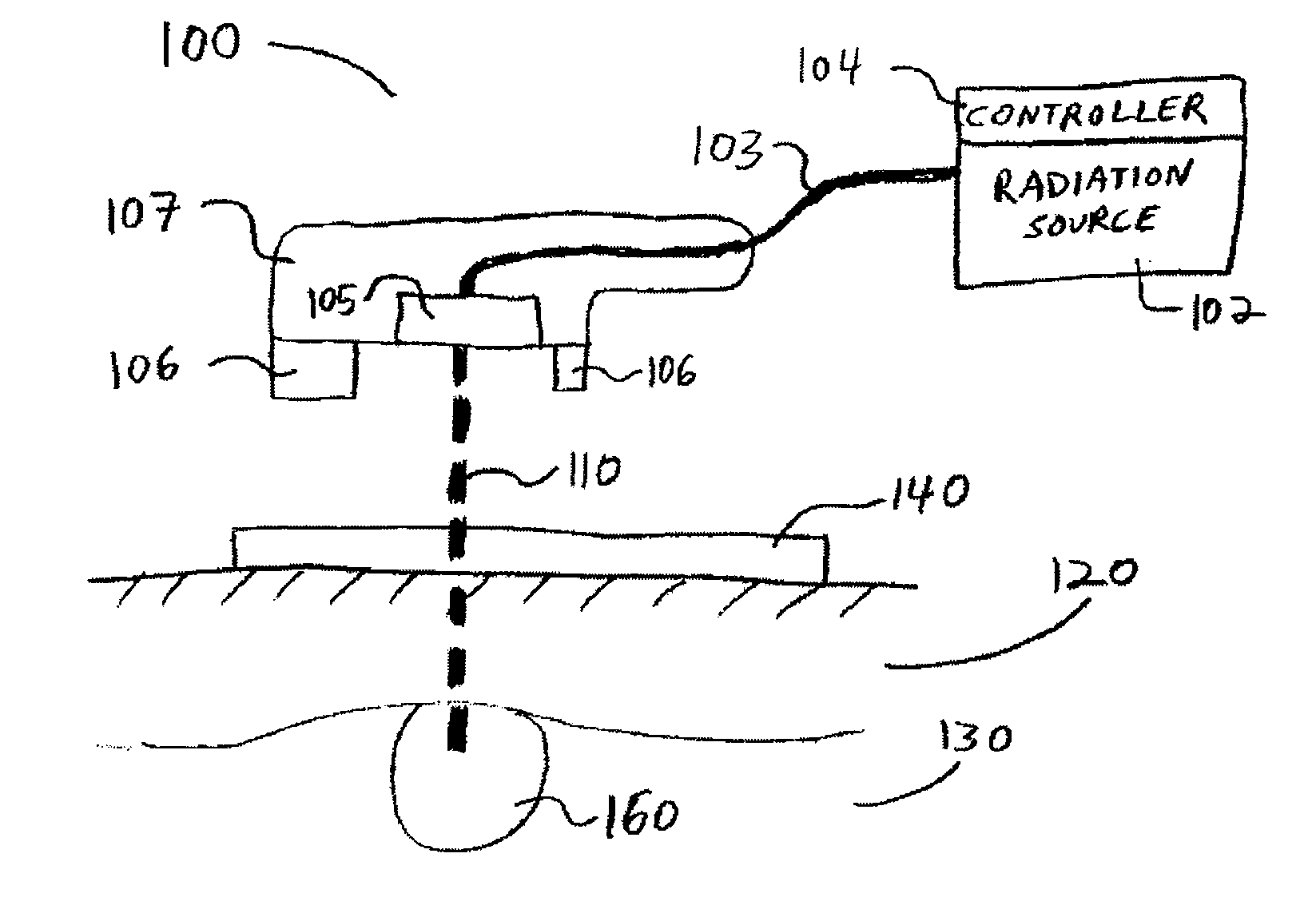
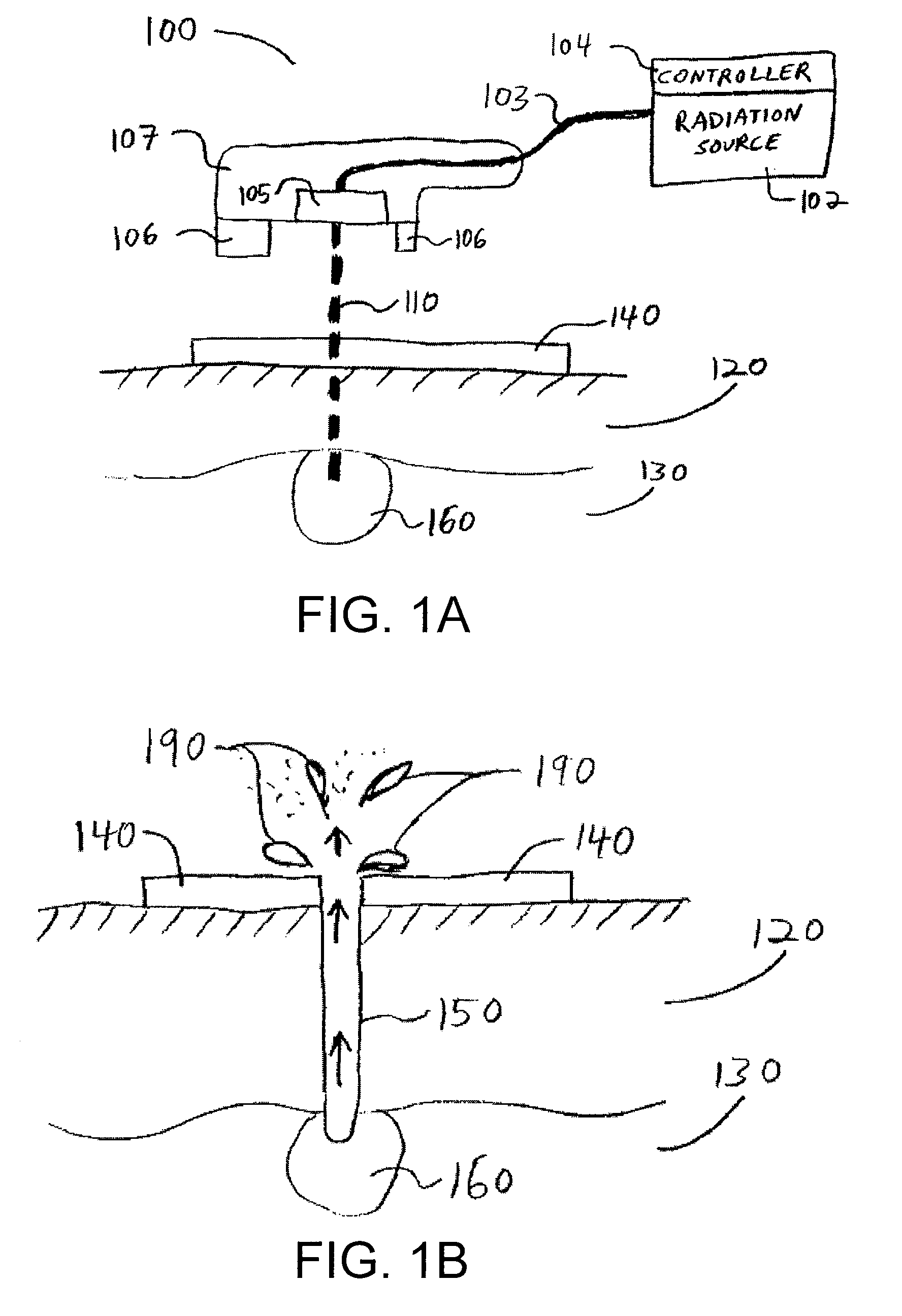
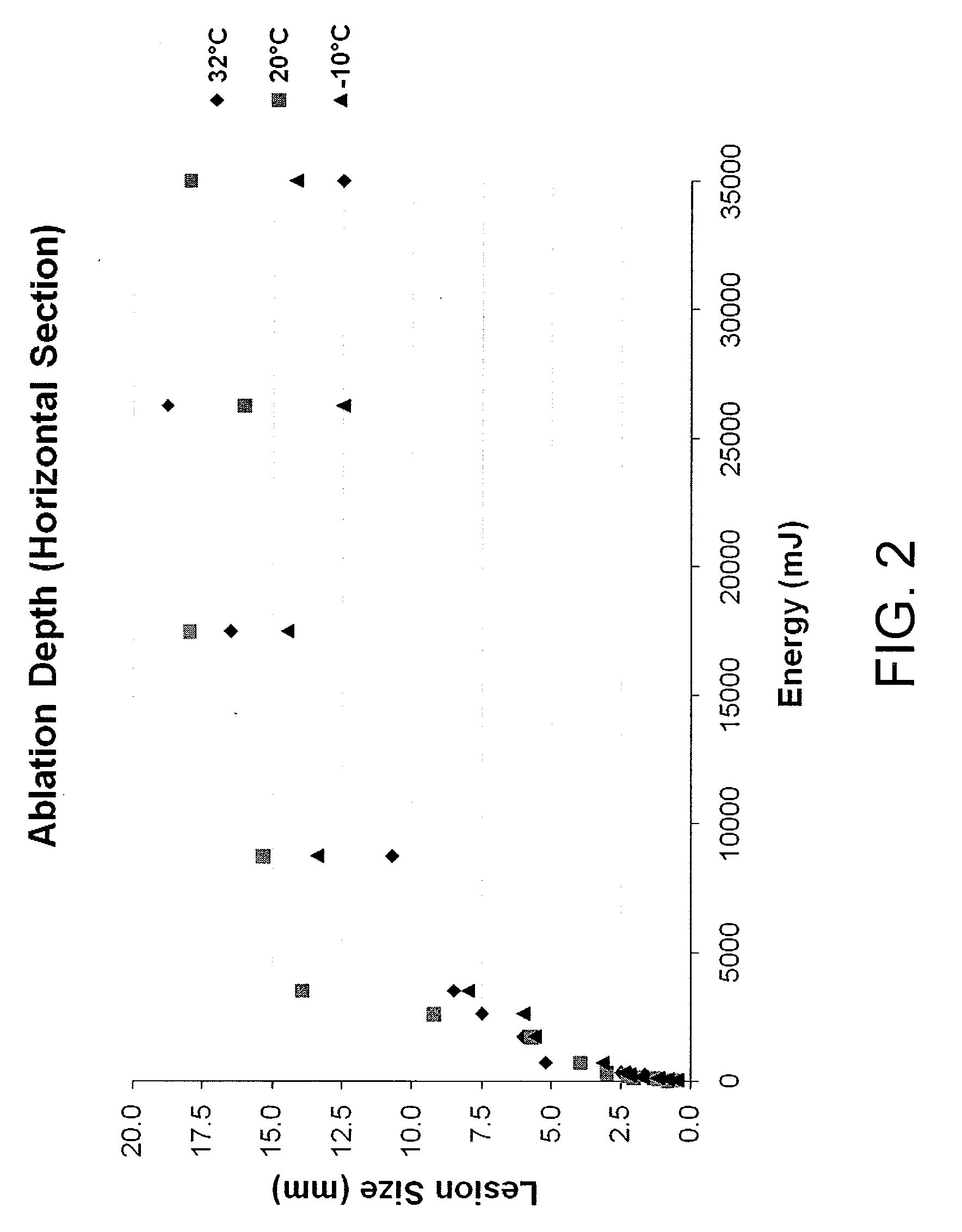
Apparatus and method for delivering ablative laser energy and determining the volume of tumor mass destroyed
InactiveUS7171253B2Complete efficientlyEffective destructionBlood flow measurement devicesSurgical needlesTumour volumeVisual monitoring
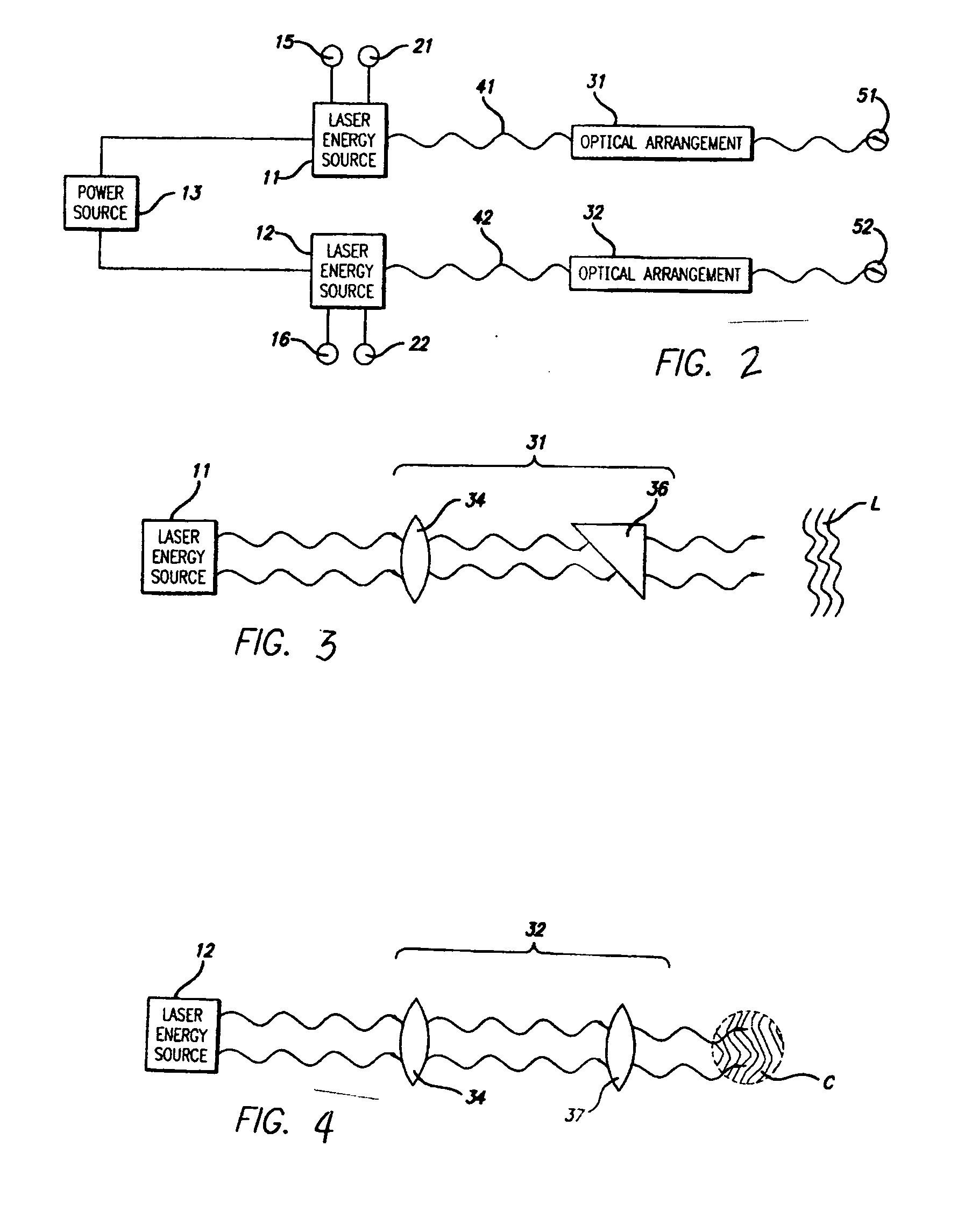
An apparatus and method for determining a volume of tumor mass destroyed. The present invention includes a temperature probe and a laser probe having a temperature sensor. The laser probe and temperature probe are inserted to measure a temperature of the tumor mass and a temperature of tissue mass surrounding the tumor mass. By determining the volume of tumor mass destroyed, a graphical representation of the volume of tumor mass destroyed is provided whereby real-time visual monitoring of the destruction of the tumor mass is achieved.
Owner:NOVIAN HEALTH INC
Method and apparatus for producing thermal damage within the skin
InactiveUS20070239236A1Minor side effectsAccurate locationSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyEr:YAG laserAnalgesics effects
A method and apparatus are provided for treating dermatological conditions, in which a first beam of radiation is used to ablate a hole in skin tissue, and a second beam of radiation is directed into the hole and onto a region of skin tissue adjacent to and / or at the bottom of the hole. The first beam can be provided by an ablative laser such as a CO2 laser or an ER:YAG laser. The second beam can be provided by, e.g., an ablative laser operating at a lower peak power level than the first beam, a non-ablative laser, a flashlamp, a tungsten lamp, a diode or a diode array. A controlled amount of thermal damage can thereby be provided at a desired depth within the skin, using radiation sources that would be absorbed closer to the surface of the skin if an ablated hole were not present. Cooling and / or freezing of the skin prior to ablation can be provided to provide an analgesic effect and / or stabilize the tissue surrounding the ablated hole. The region of skin to be treated can optionally be pulled towards the radiation source using a vacuum to stretch and / or stabilize the skin tissue surrounding the volume to be ablated.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Treatment of presbyopia and other eye disorders using a scanning laser system
Presbyopia is treated by a method which uses ablative lasers to ablate the sclera tissue and increase the accommodation of the ciliary body. Tissue bleeding is prevented by an ablative laser having a wavelength of between 0.15 and 3.2 micron. A scanning system is proposed to perform various patterns on the sclera area of the cornea to treat presbyopia and to prevent other eye disorder such as glaucoma. Laser parameters are determined for accurate sclera expansion.REEXAMINATION RESULTSThe questions raised in reexamination request no. 90 / 006,090, filed Aug. 22, 2001, have been considered and the results thereof are reflected in this reissue patent which constitutes the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 307 as provided in 37 CFR 1.570(e), for ex parte reexaminations, or the reexamination certificate required by 35 U.S.C. 316 as provided in 37 CFR 1.997(e) for inter partes reexaminations.
Owner:SURGILIGHT
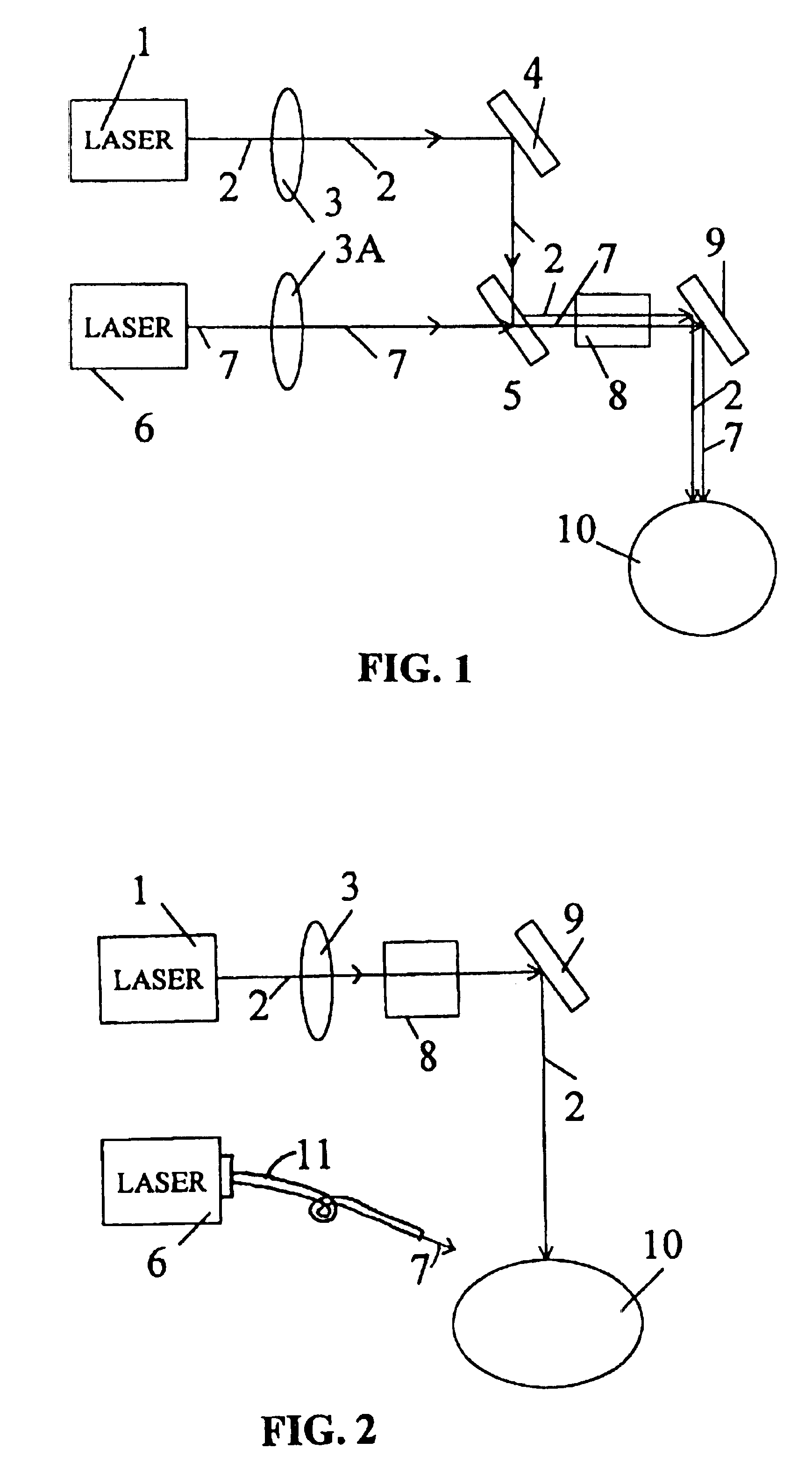
Refractive surgery and presbyopia correction using infrared and ultraviolet lasers
InactiveUSRE40184E1Avoid smooth surfaceImprove distributionLaser surgeryLaser detailsKeratorefractive surgeryFiber
A method and surgical technique for corneal reshaping and for presbyopia correction are provided. The preferred embodiments of the system consists of a scanner, a beam spot controller and coupling fibers and the basic laser having a wavelength of (190-310) nm, (0.5-3.2) microns and (5.6-6.2) microns and a pulse duration of about (10-150) nanoseconds, (10-500) microseconds and true continuous wave. New mid-infrared gas lasers are provided for the corneal reshaping procedures. Presbyopia is treated by a method which uses ablative laser to ablate the sclera tissue and increase the accommodation of the ciliary body. The tissue bleeding is prevented by a dual-beam system having ablative and coagulation lasers. The preferred embodiments include short pulse ablative lasers (pulse duration less than 200 microseconds) with wavelength range of (0.15-3.2) microns and the long pulse (longer than 200 microseconds) coagulative lasers at (0.5-10.6) microns. Compact diode lasers of (980-2100) nm and diode-pumped solid state laser at about 2.9 microns for radial ablation patterns on the sclera ciliary body of a cornea are also disclosed for presbyopia correction using the mechanism of sclera expansion.
Owner:SURGILIGHT
Apparatus and method for fat removal
InactiveUS20110046616A1Facilitate ablationFacilitate a rapid healing of the tissueSurgical instruments for heatingSubcutaneous fatty tissueRadiation pulse
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure provide methods and apparatus for heating and removing subcutaneous fatty tissue using radiation. For example, an ablative laser or the like can be configured to generate a small hole in skin tissue that passes through the entire layer of dermal tissue. The hole size can be small, e.g., on less than about 1 mm or 0.5 mm in diameter. Continued application of the radiation can heat and / or vaporize subcutaneous fat proximal to the lower portion of the hole. Expansion of the heated or vaporized fatty tissue can facilitate ejection of the fatty tissue from the formed hole. The energy of a radiation pulse used to form a hole and heat the fatty tissue can be, e.g., greater than about 0.5 J, e.g., between about 0.5 J and about 35 J. The skin tissue can be cooled or partially frozen before forming one or more such holes therein, and a stabilizing film or plate may be adhered to the skin surface to help stabilize the ablated holes.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and Apparatus for Tissue Expansion
ActiveUS20180021087A1Reduce presenceReduced likelihoodSkin implantsIncision instrumentsTissue expansionAblative laser
Exemplary embodiments of the present disclosure provide method and apparatus for facilitating stretching of a biological tissue by forming a plurality of micro-slits in the tissue. Each micro-slit can be less than about 2 mm or less than about 1.5 mm long, or even less than about 1 mm, such that small gaps that can heal quickly can be formed when the tissue is stretched. The micro-slits can be formed using a plurality of cutting arrangements or an ablative laser. The micro-slits can be formed in various patterns, including staggered rows, circular or spiral patterns, or random patterns.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Two-dimensional laser spiral cleaning method
ActiveCN110802082AImprove cleaning uniformityImprove cleaning efficiencyCleaning processes and apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusGalvanometerEngineering
Owner:镇江长悦光电科技有限公司
Method and device for the spectral analysis of a metal coating layer deposited on the surface of a steel strip
InactiveCN102428360AImprove performanceHot-dipping/immersion processesAnalysis by thermal excitationSpectral emissionMetal coating
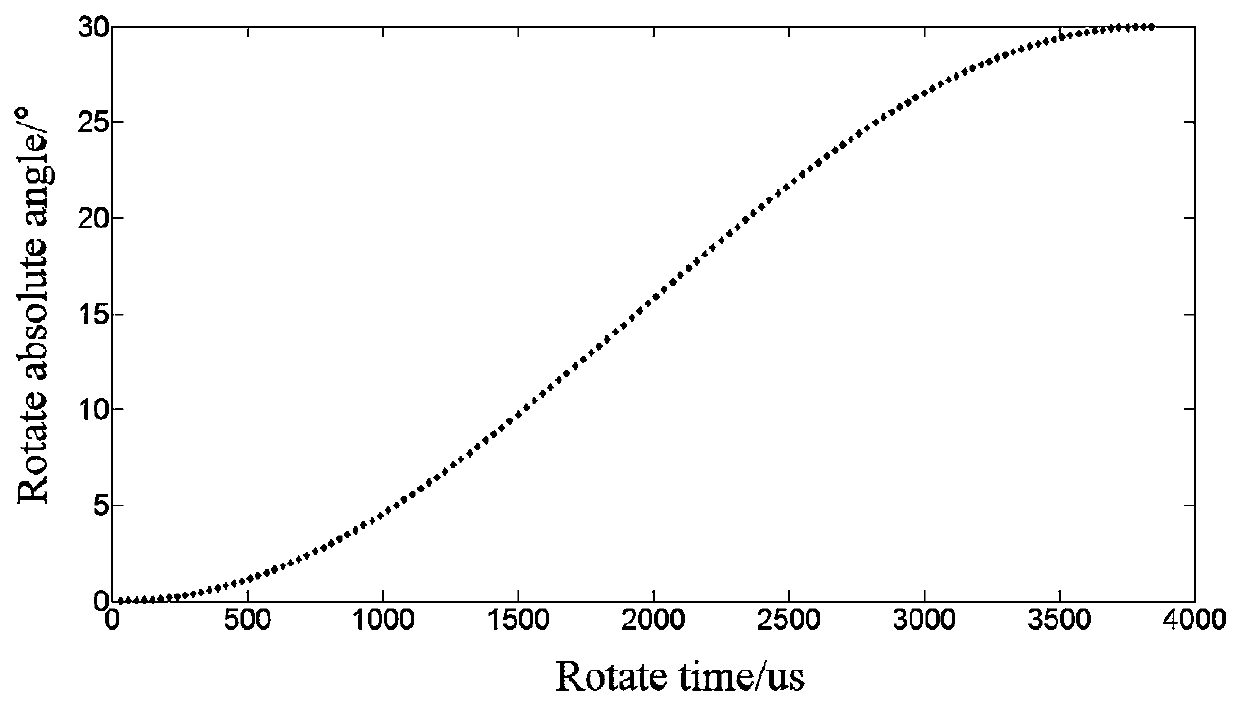
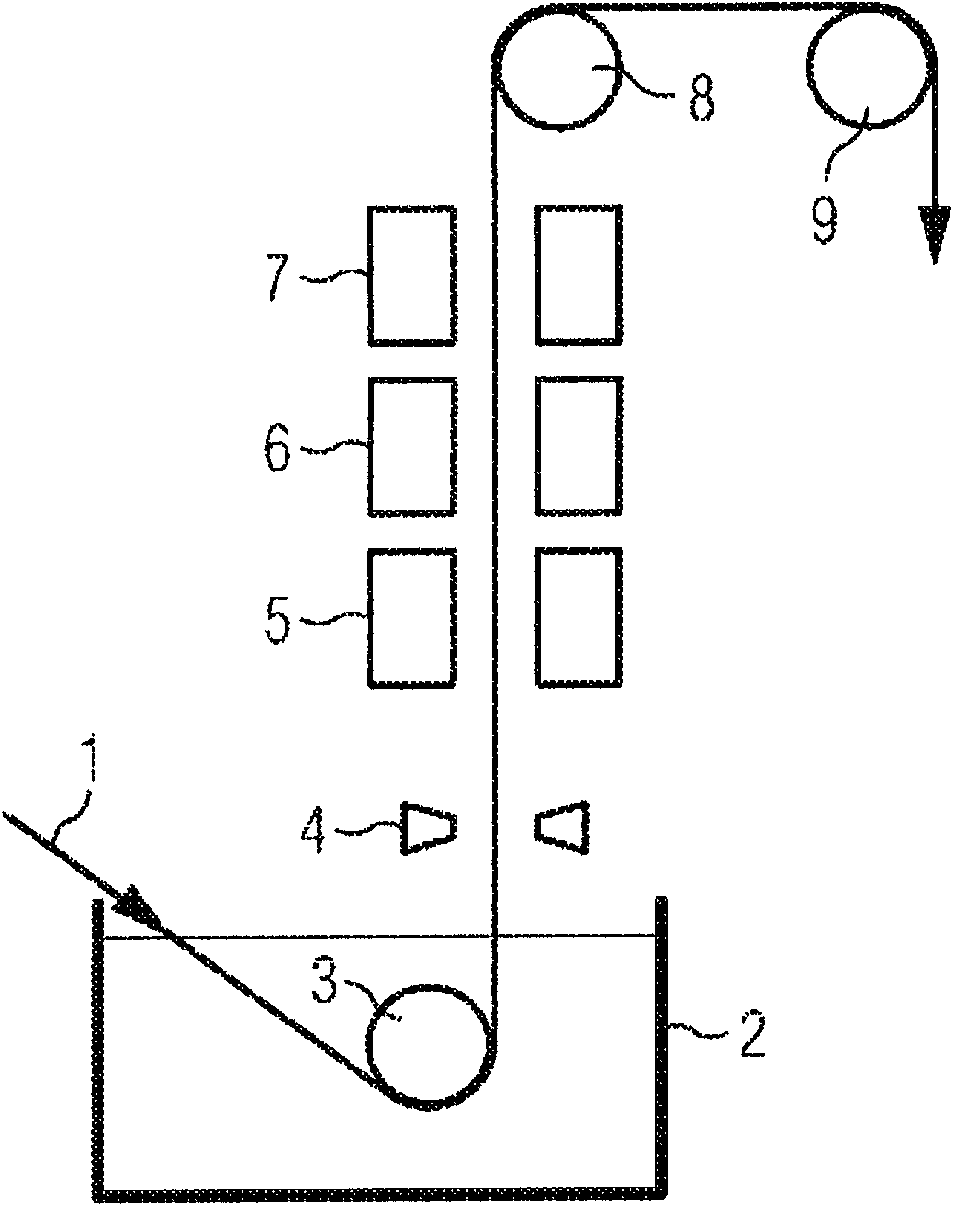
The present invention relates to a method for the spectral analysis of a metal coating layer deposited on the surface of a steel strip (1), characterised by the following steps: said strip is moved along an arc of the outer surface (813) of a rotating roller (8) with a cylindrical wall guiding the strip by contact; a so-called ablation laser beam is guided into an internal cavity of the cylindrical wall in order to be placed in optical incidence under a normal axis (41) on the outer surface of the roller on a targeted contact point (11) of the strip and the roller, said beam passing through the wall via a wall opening (811), which is transparent to the beam; a plasma spectral emission distribution from the laser ablation to the contact point is collected by optical feedback in the direction of the normal axis (41) on the outer surface of the roller and through the opening in order to be guided towards a spectral measurement unit; and the normal axis on the outer surface for the optical incidence and feedback is placed in synchronous rotation with the roller. The invention also relates to a device with a plurality of embodiments for implementing the method of the invention, as well as to the advantageous uses thereof.
Owner:CLECIM SAS
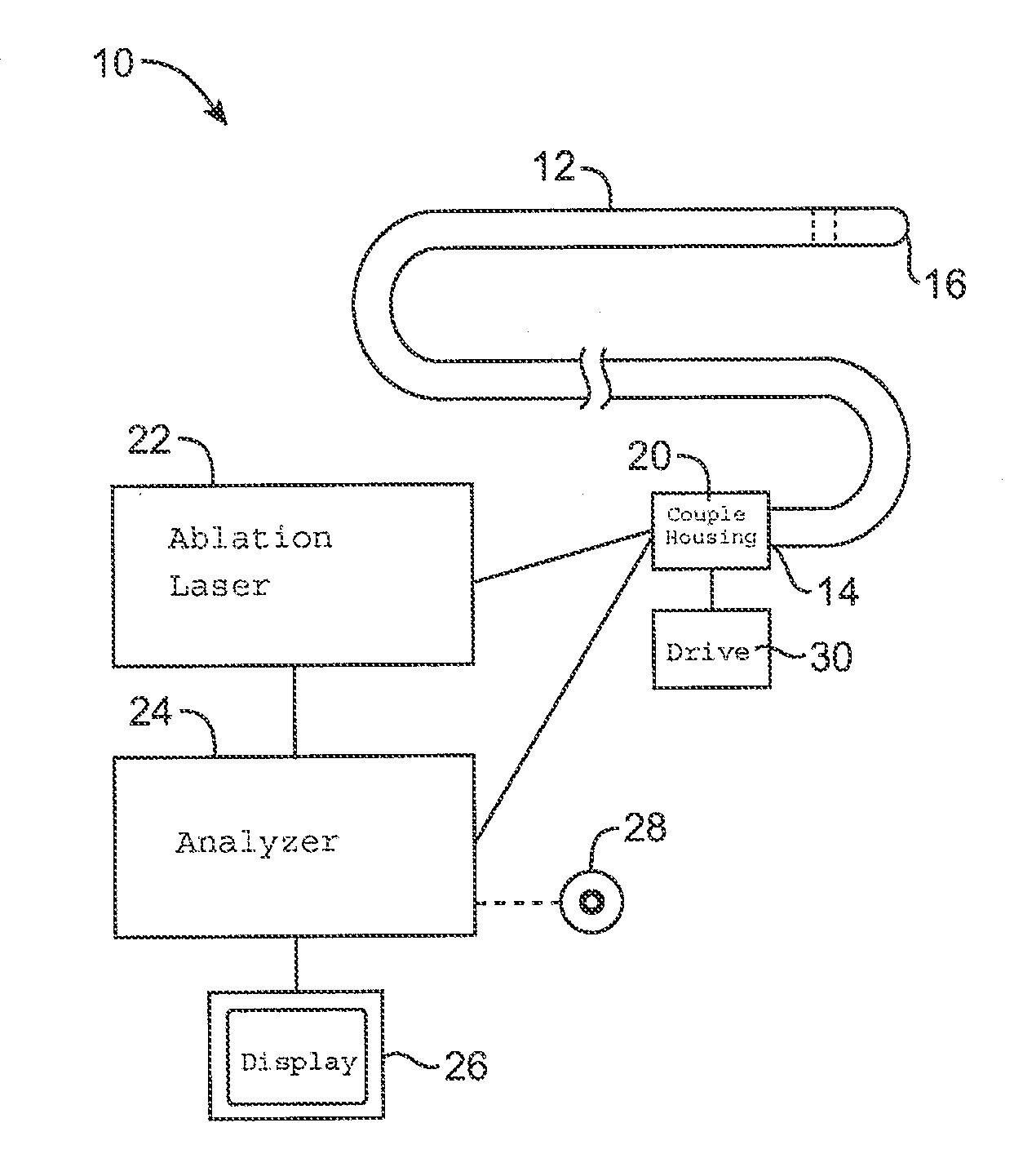
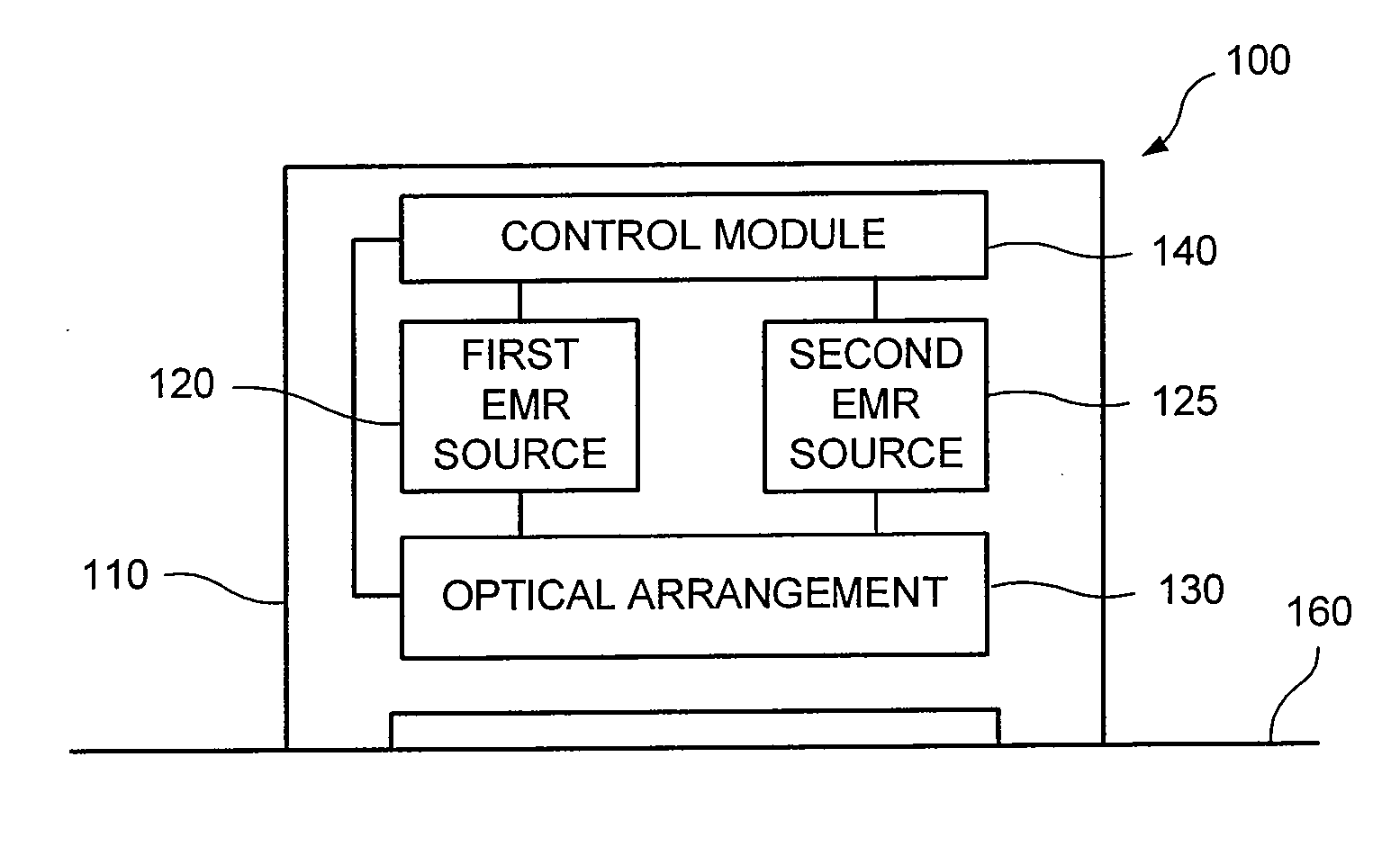
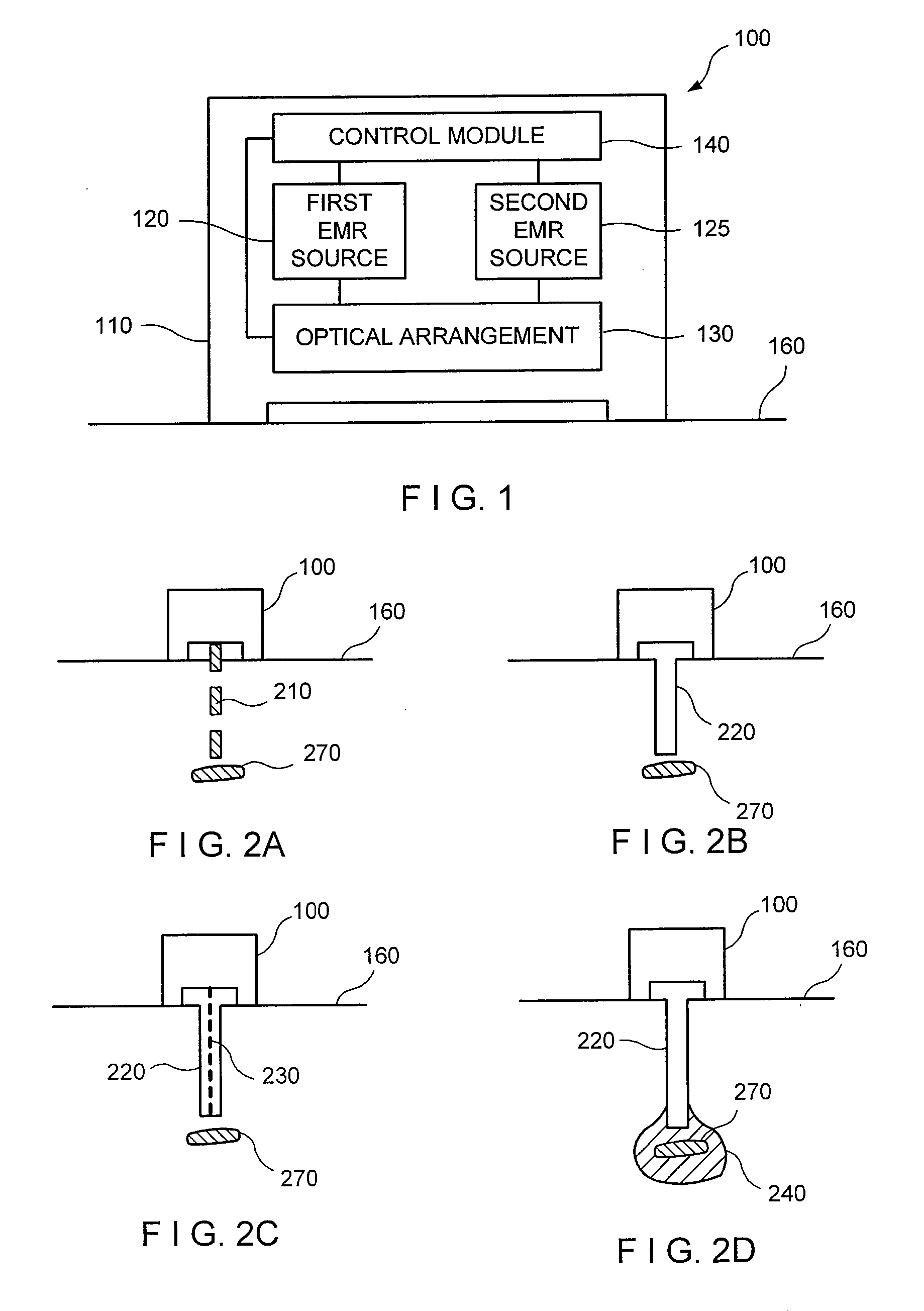
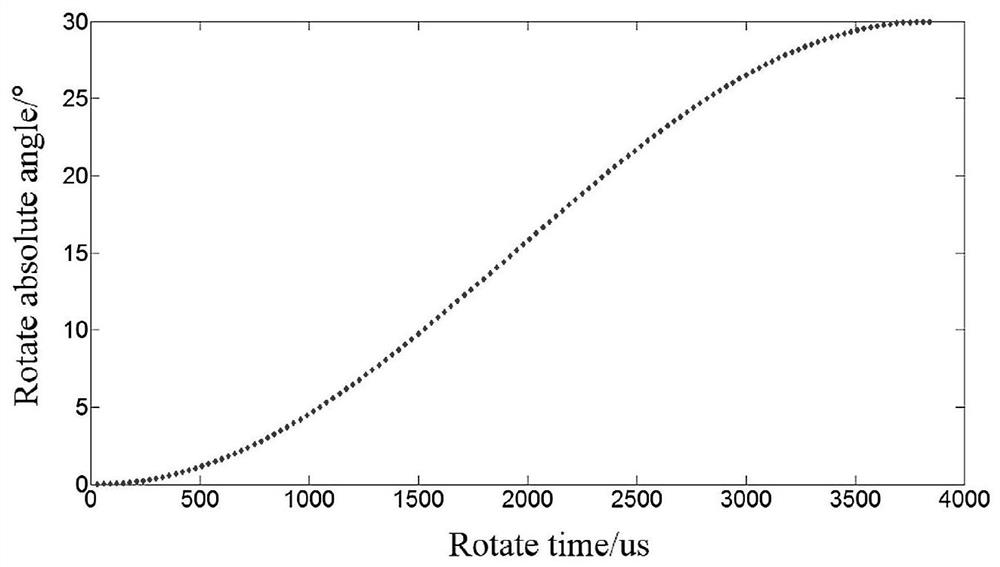
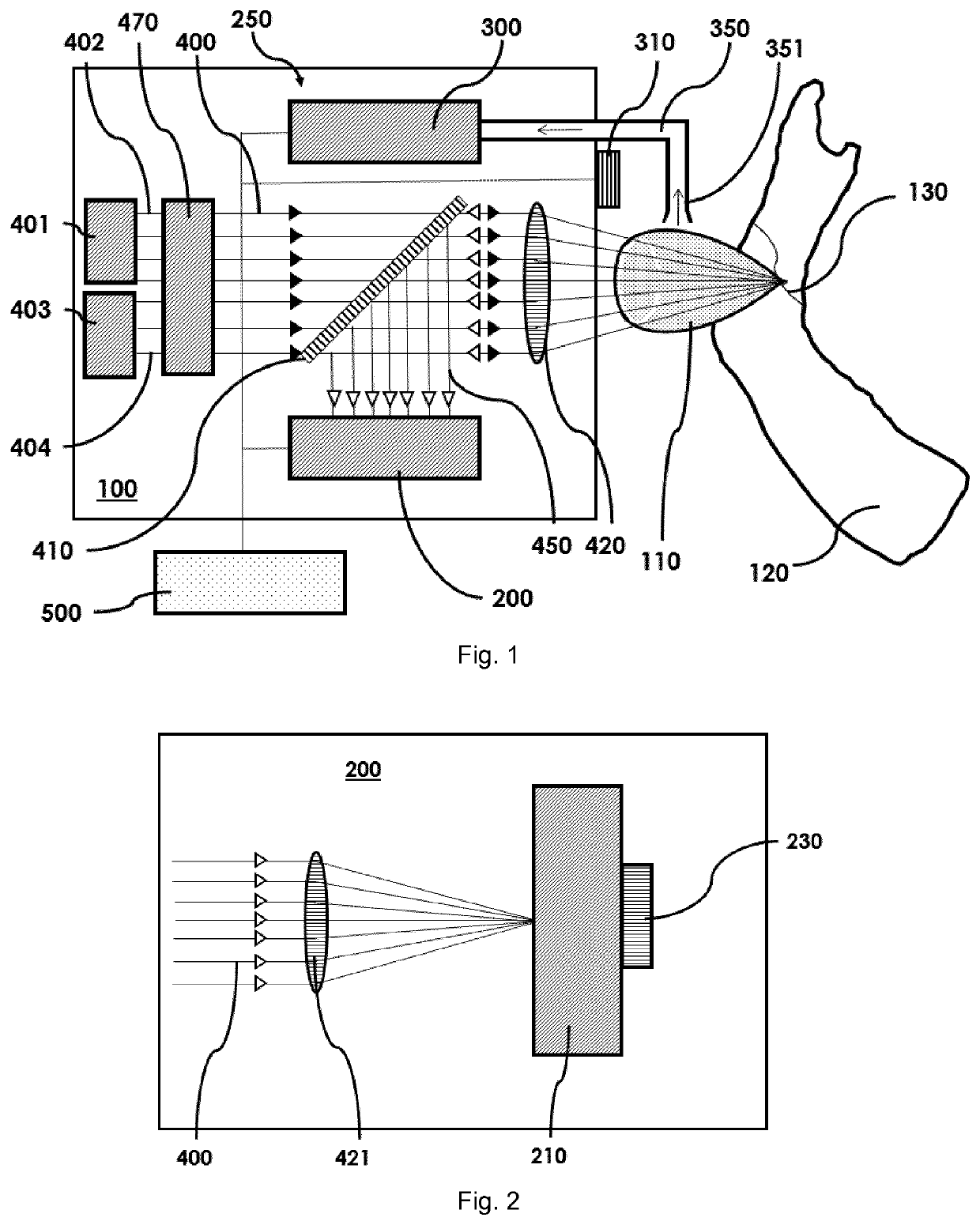
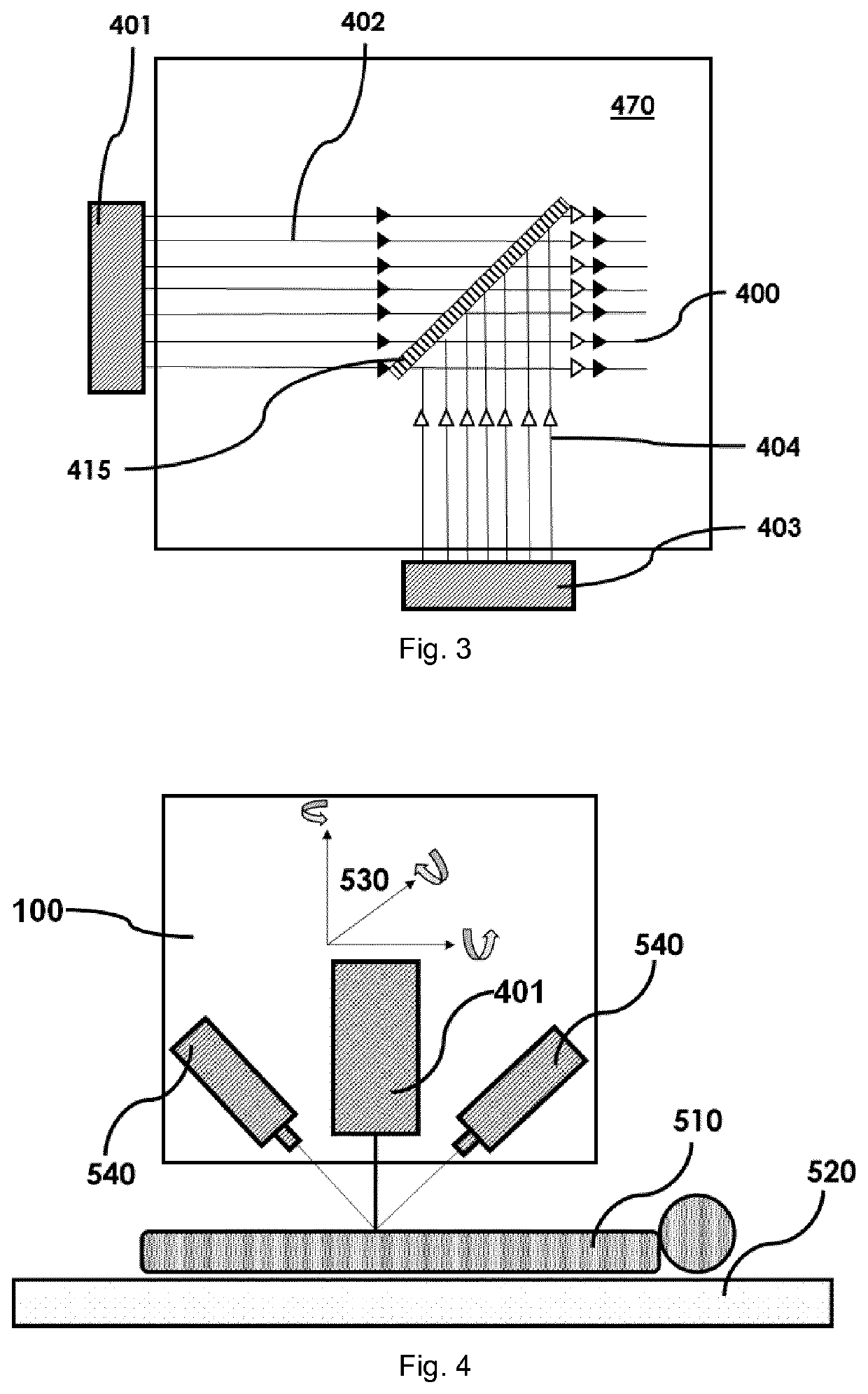
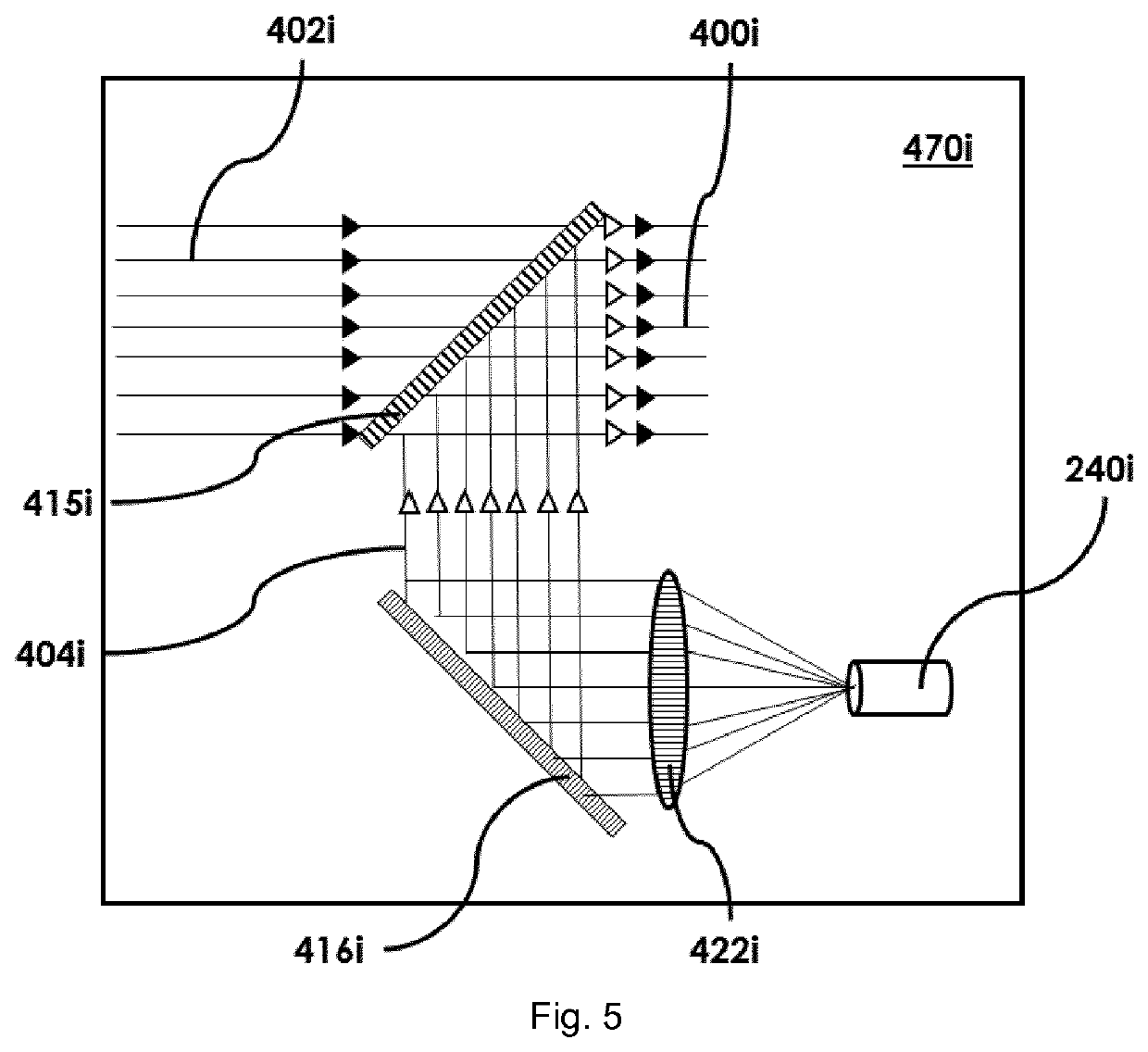
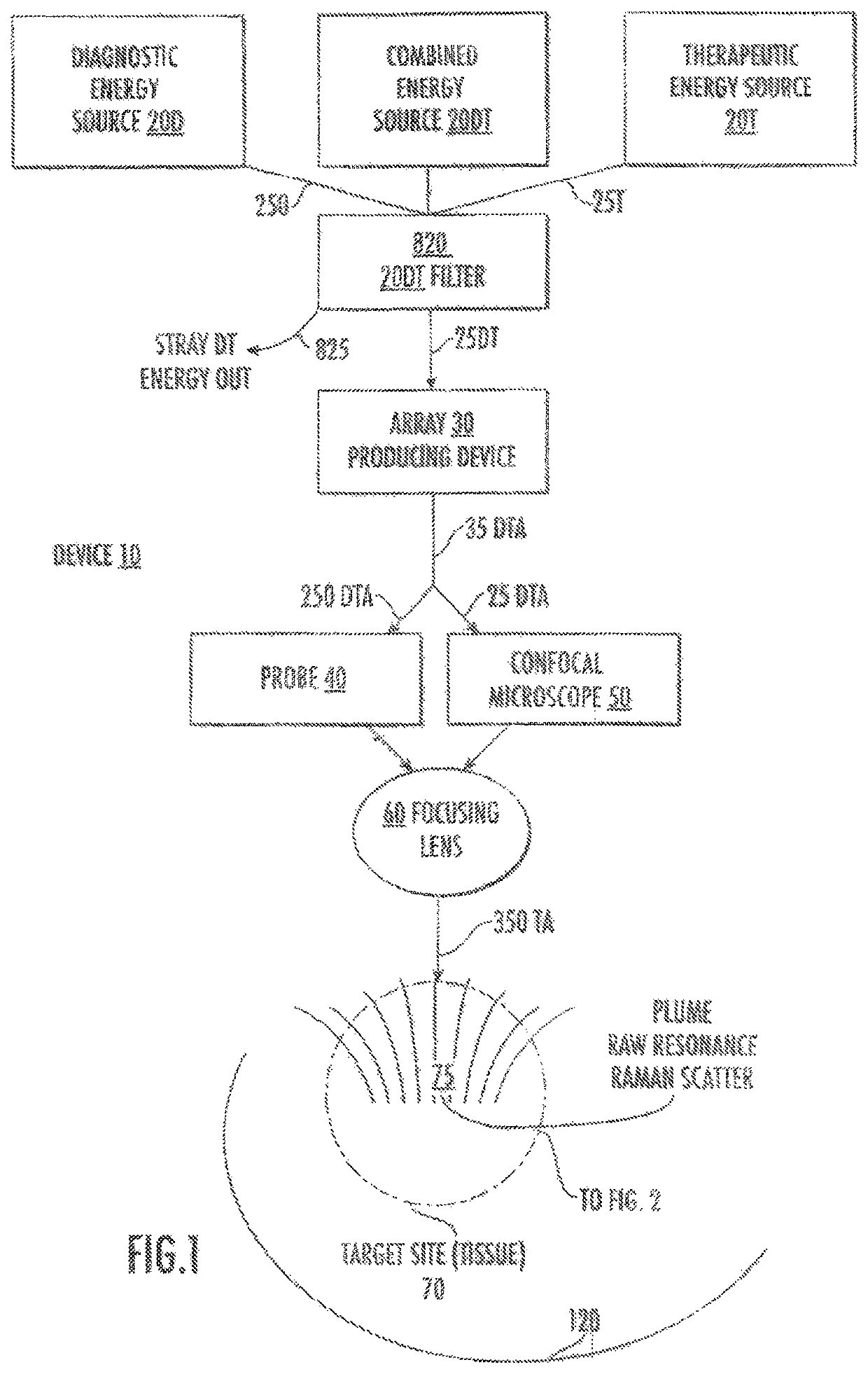
Laser device and tissue characterizing method
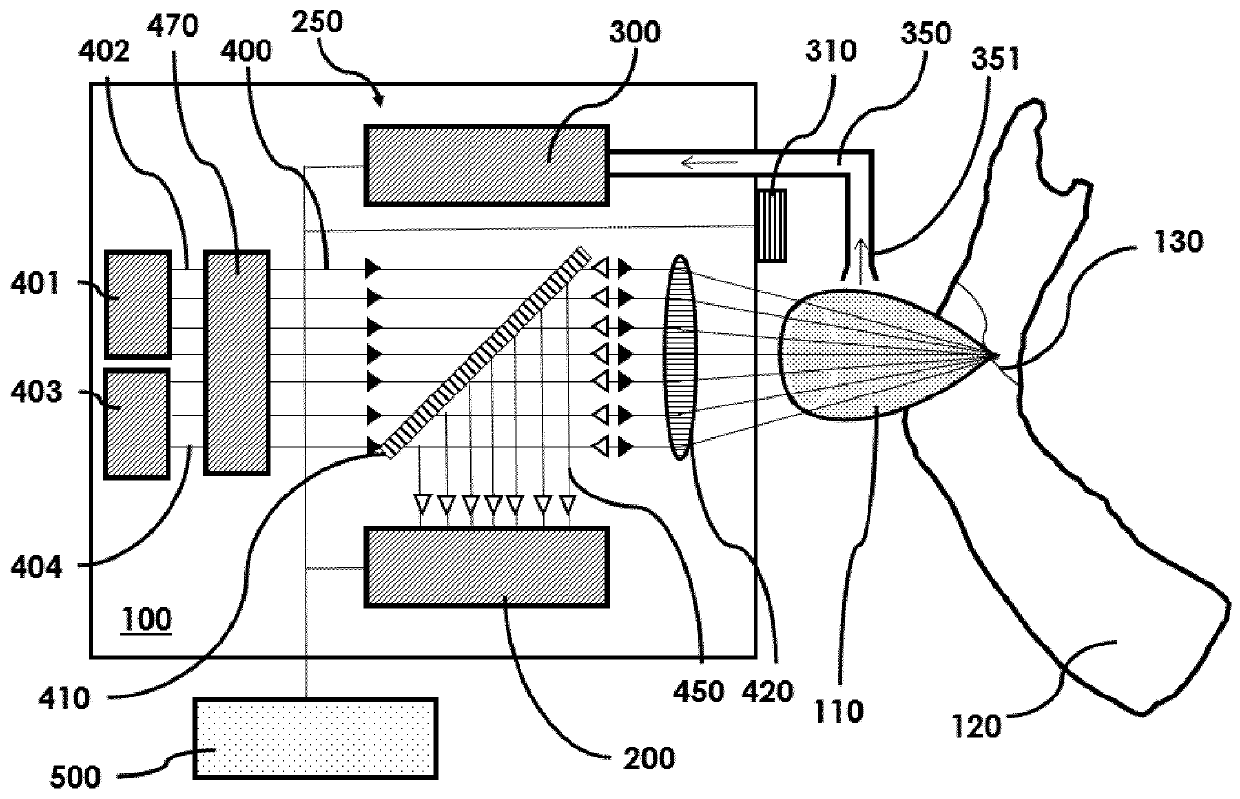
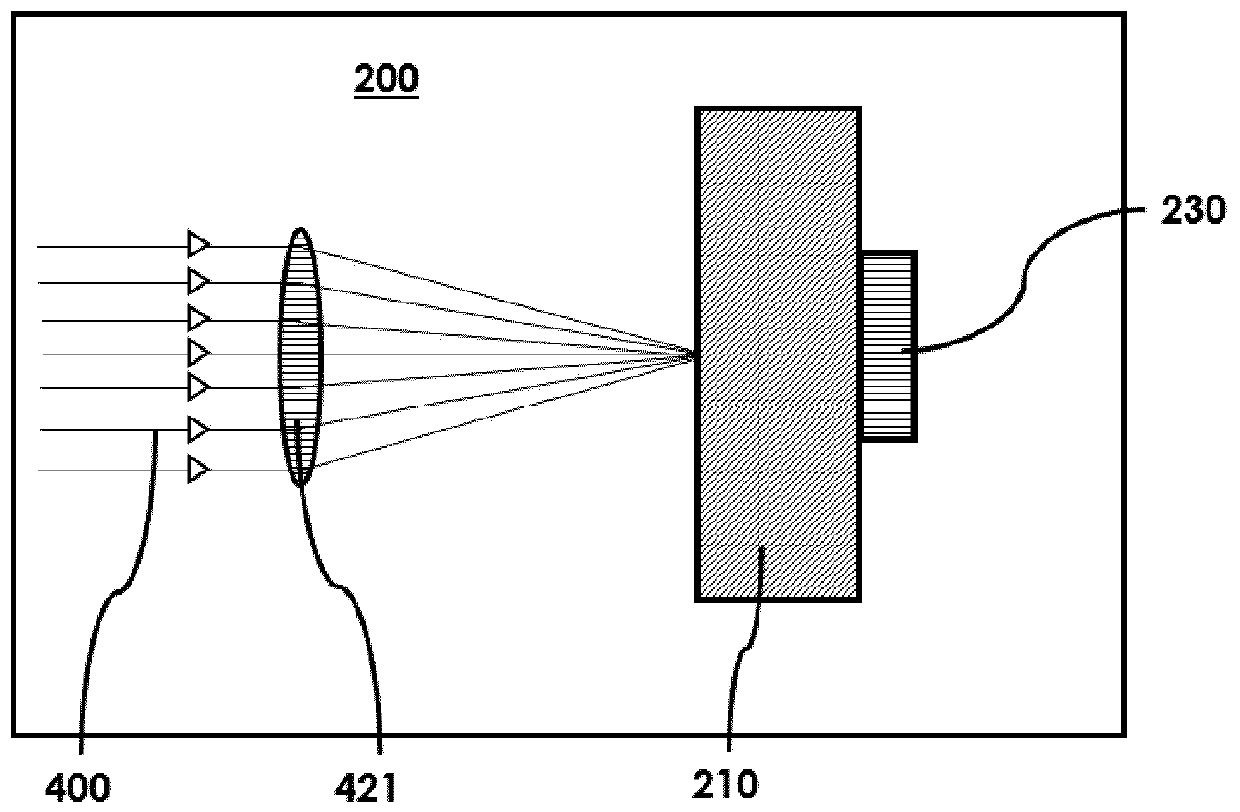
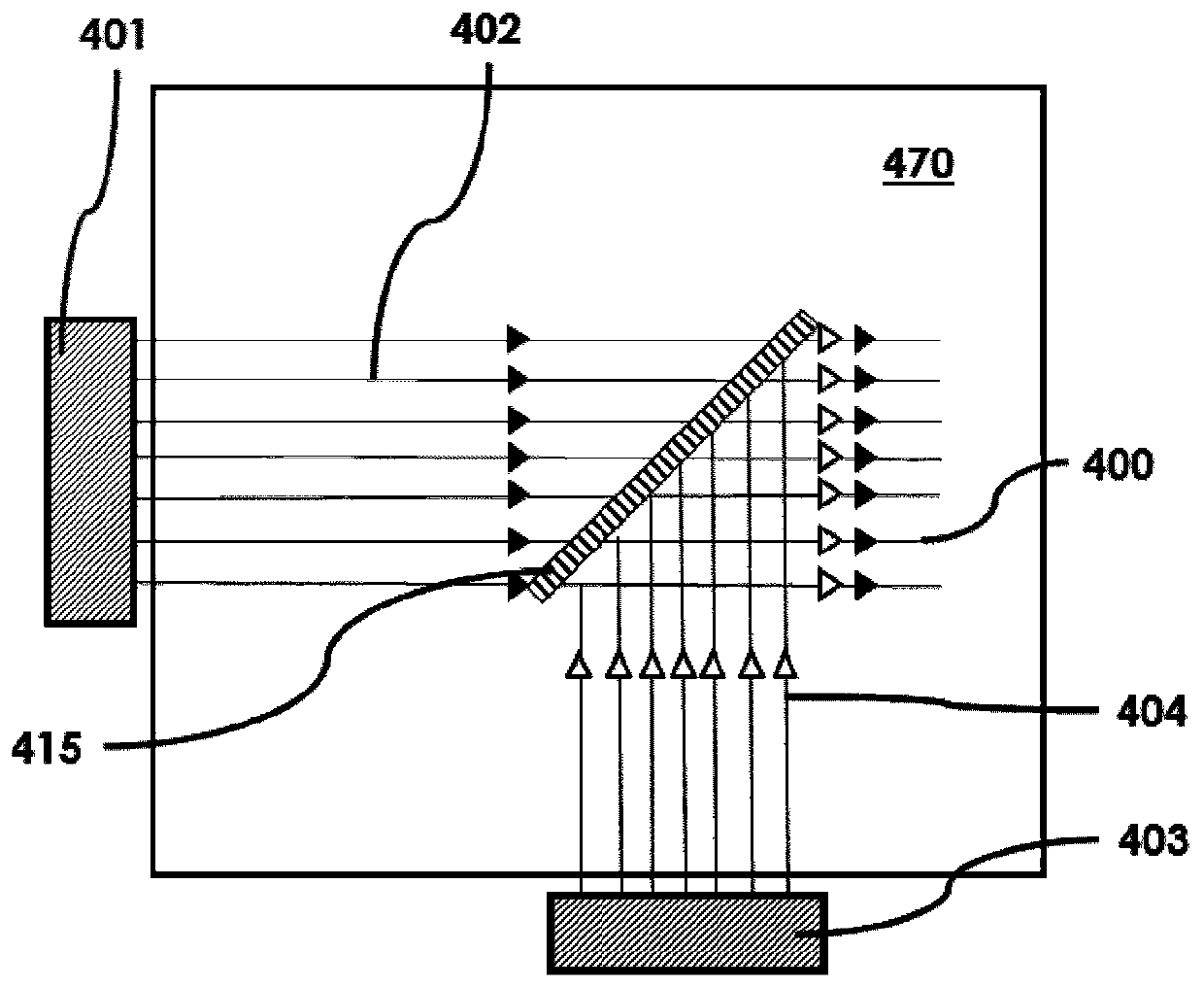
A laser device (100) has an ablation laser source (401) adapted to provide an ablating laser beam (402; 402i) for ablating a target tissue (120). It further comprises a plume analyzing arrangement (250) adapted to identify and / or quantify substances in the debris of the plume (110) generated by the ablating laser beam (402) ablating the target tissue (120) particularly substances being biomarkersof the ablated target tissue (120).
Owner:ADVANCED OSTEOTOMY TOOLS - AOT
Method and apparatus for directional skin tightening
A cosmetic method of directionally tightening human skin tissue includes providing an ablative laser source and a non-ablative laser source, then using the ablative laser source to form one or more overlapping circular shaped microchannels in the skin tissue; the overlapping microchannels formed have a longitudinal dimension larger than their cross dimension; then, using the non-ablative laser source to weld the microchannels, whereby the welding causes the skin tissue to tighten.
Owner:LUMENIS BE LTD
Element isotope analysis system and method based on laser-induced plasma
ActiveCN113970540AAvoid harmEasy to operateNuclear energy generationAnalysis by thermal excitationLaser lightIsotope
The invention discloses an element isotope analysis system and method based on laser-induced plasma. The system comprises an ablation laser light source, a detection laser light source, a mobile platform, a spectrum acquisition assembly, an optical fiber, a photodiode and an oscilloscope; after the pulse of the ablation laser light source acts on the sample, the surface of the sample is heated, evaporated and expanded, so that a small amount of substances are ejected out, a gaseous substance is formed above the sample, plasma is generated under the collision of free electrons and the subsequent action of the laser pulse, and after the plasma is subjected to 1-2 microseconds, when the plasma in the excited state jumps back to the ground state or the number of thelow-energy-level particlesreaches the maximum, at the moment, the detection laser light source emits a laser pulse, the specific wavelength part of the pulse is absorbed by the ground state or low-energy-level particles, and the intensity of the absorption peak can reflect the abundance of the specific isotope in the sample. The detection process is non-contact, the operation is simple, the process is controllable, and the analysis result is rapid and accurate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Inert gas-assisted laser machining of ceramic-containing articles
ActiveUS20200230747A1Reduce contact areaReduce frictionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingMachined surface
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Novel uranium isotope ratio measuring device and method
PendingCN113295675APortable and fastHigh sensitivityAnalysis by thermal excitationColor/spectral properties measurementsBeam splitterPhotovoltaic detectors
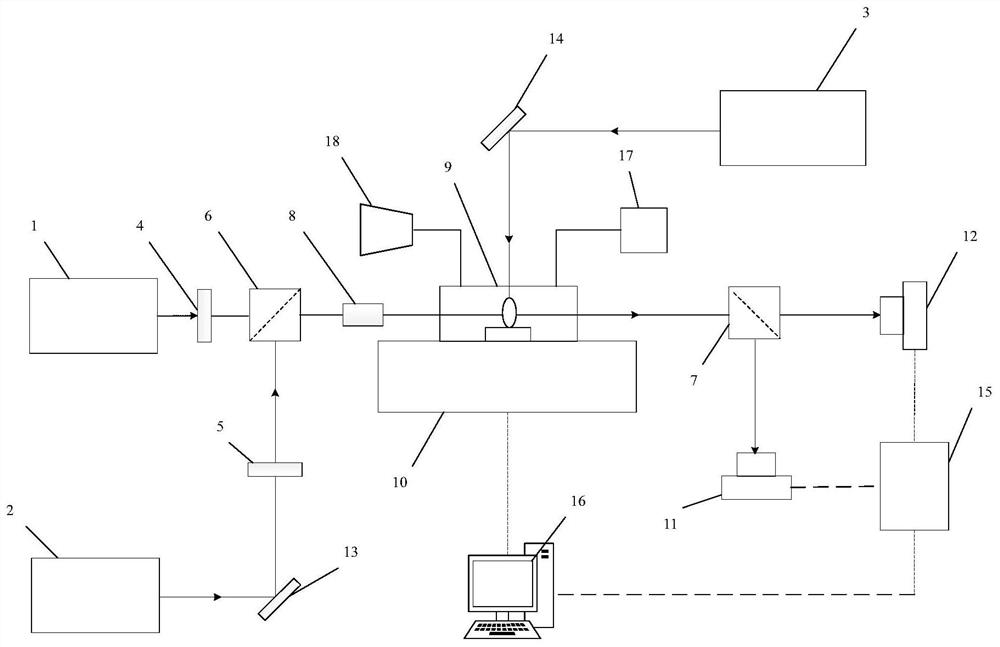
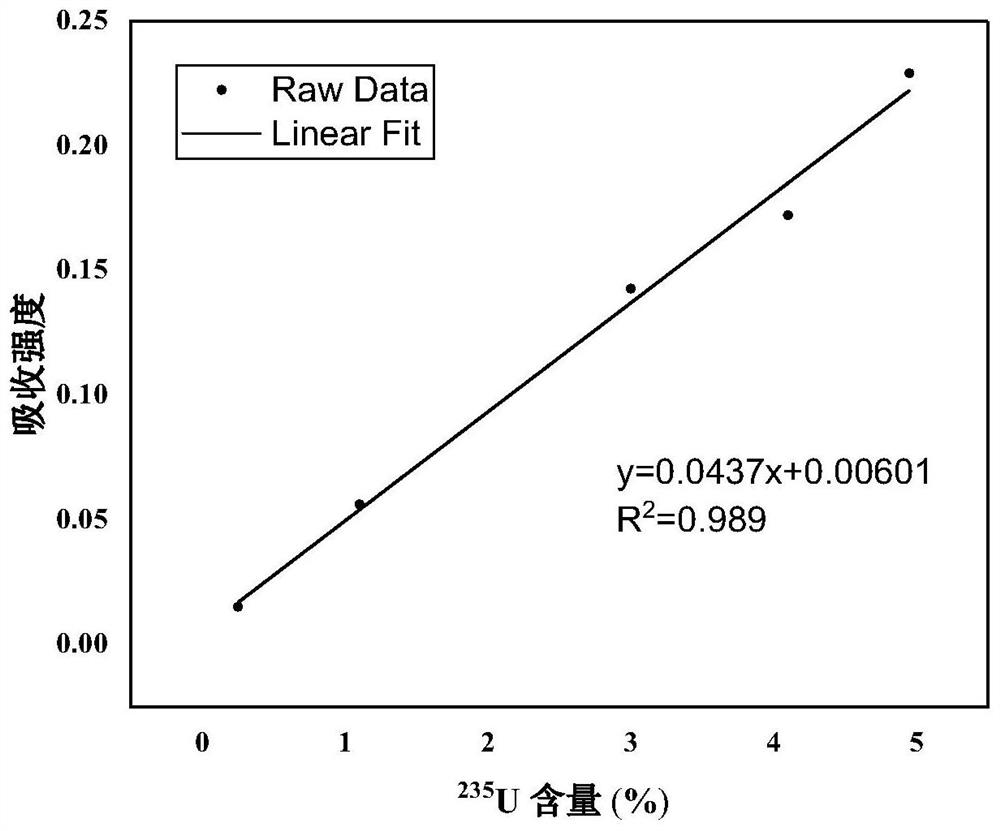
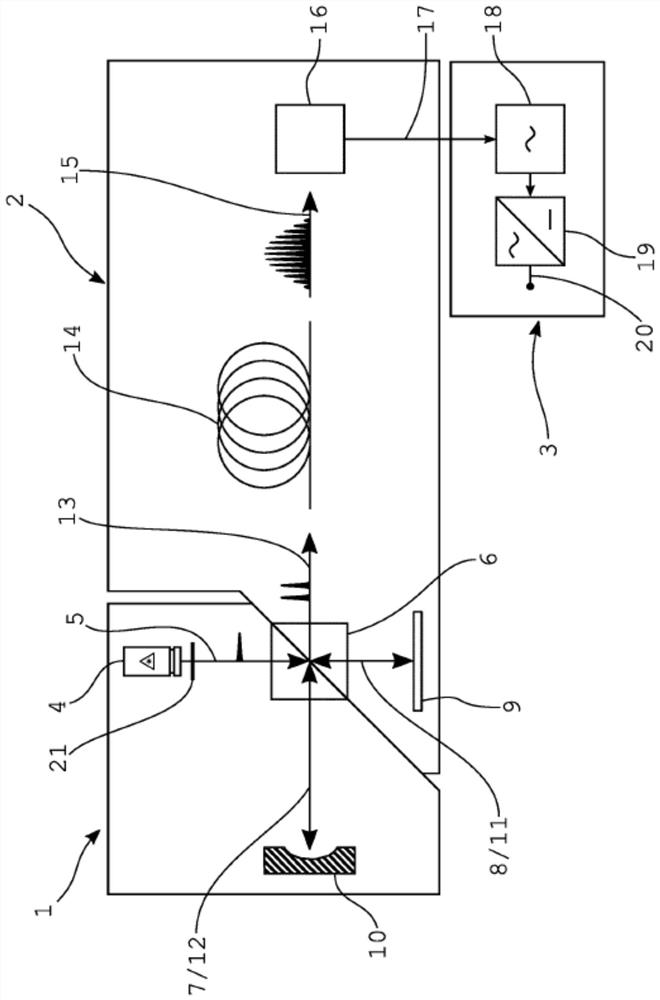
The invention discloses a novel uranium isotope ratio measuring device which mainly comprises a first detection laser, a second detection laser, a beam combiner, an ablation laser, a beam splitter, a first photoelectric detector, a second photoelectric detector, a data acquisition card and an industrial personal computer. Ablating laser emitted by the ablating laser irradiates a sample in the ablating chamber through the second reflecting mirror to excite plasma, laser emitted by the first detecting laser passes through the first polarizing film, laser emitted by the second detecting laser passes through the first reflecting mirror and the polarizing film in sequence, the two beams of laser are combined by the beam combiner and then pass through the plasma, the beam splitter re-splits to the first photoelectric detector and the second photoelectric detector, and the data acquisition card acquires signals of the first photoelectric detector and the second photoelectric detector and transmits the signals to the industrial personal computer. The invention further discloses a novel uranium isotope ratio measuring method. The invention provides a technology which is portable, rapid, high in sensitivity and capable of measuring the uranium isotope ratio in a non-contact mode.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for in situ process monitoring
PendingCN113056650AEasy to handleUsing optical meansLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingRefractive index
Owner:UNIV OF BAYREUTH
A two-dimensional laser spiral cleaning method
ActiveCN110802082BLaser beam welding apparatusCleaning processes and apparatusProgressive scanGalvanometer
The invention discloses a two-dimensional laser spiral cleaning method. The laser cleaning system includes two orthogonally deflected digital vibrating mirror motors. On the mirror on the shaft of the digital galvanometer motor, after secondary reflection, the field lens is constrained to focus on the surface stains on the ablation target substrate in a two-dimensional plane; the interface protocol of the two digital galvanometer motors is XY2‑ 100; The two digital vibrating mirror motors are independently controlled. The two-dimensional laser spiral cleaning method of the present invention, for any point in the cleaning area, compared with line-by-line ablation, the laser returns to the vicinity of the point after completing the outer ring according to the spiral filling path, and the point area obtains cooling time, The heat accumulation effect of the laser is weakened; the progressive scanning speed is the speed of a single vibrating mirror motor, and the helical scanning speed is the vector sum of the two motor speeds. Therefore, compared with the progressive scanning method, the laser spiral cleaning effect is more uniform and the cleaning efficiency is higher. high.
Owner:镇江长悦光电科技有限公司
Laser device and tissue characterizing method
PendingUS20210128237A1Improve image captureAccurately knowDiagnostics using spectroscopyEndoscopesExAblateTarget tissue
A laser device (100) has an ablation laser source (401) adapted to provide an ablating laser beam (402; 402i) for ablating a target tissue (120). It further comprises a plume analyzing arrangement (250) adapted to identify and / or quantify substances in the debris of the plume (110) generated by the ablating laser beam (402) ablating the target tissue (120) particularly substances being biomarkers of the ablated target tissue (120).
Owner:ADVANCED OSTEOTOMY TOOLS - AOT
Apparatus and method for delivering ablative laser energy and determining the volume of tumor mass destroyed
InactiveUS20050137467A1Complete efficientlyEffective destructionBlood flow measurement devicesSurgical needlesAbnormal tissue growthTumour volume
An apparatus and method for determining a volume of tumor mass destroyed. The present invention includes a temperature probe and a laser probe having a temperature sensor. The laser probe and temperature probe are inserted to measure a temperature of the tumor mass and a temperature of tissue mass surrounding the tumor mass. By determining the volume of tumor mass destroyed, a graphical representation of the volume of tumor mass destroyed is provided whereby real-time visual monitoring of the destruction of the tumor mass is achieved.
Owner:NOVIAN HEALTH INC
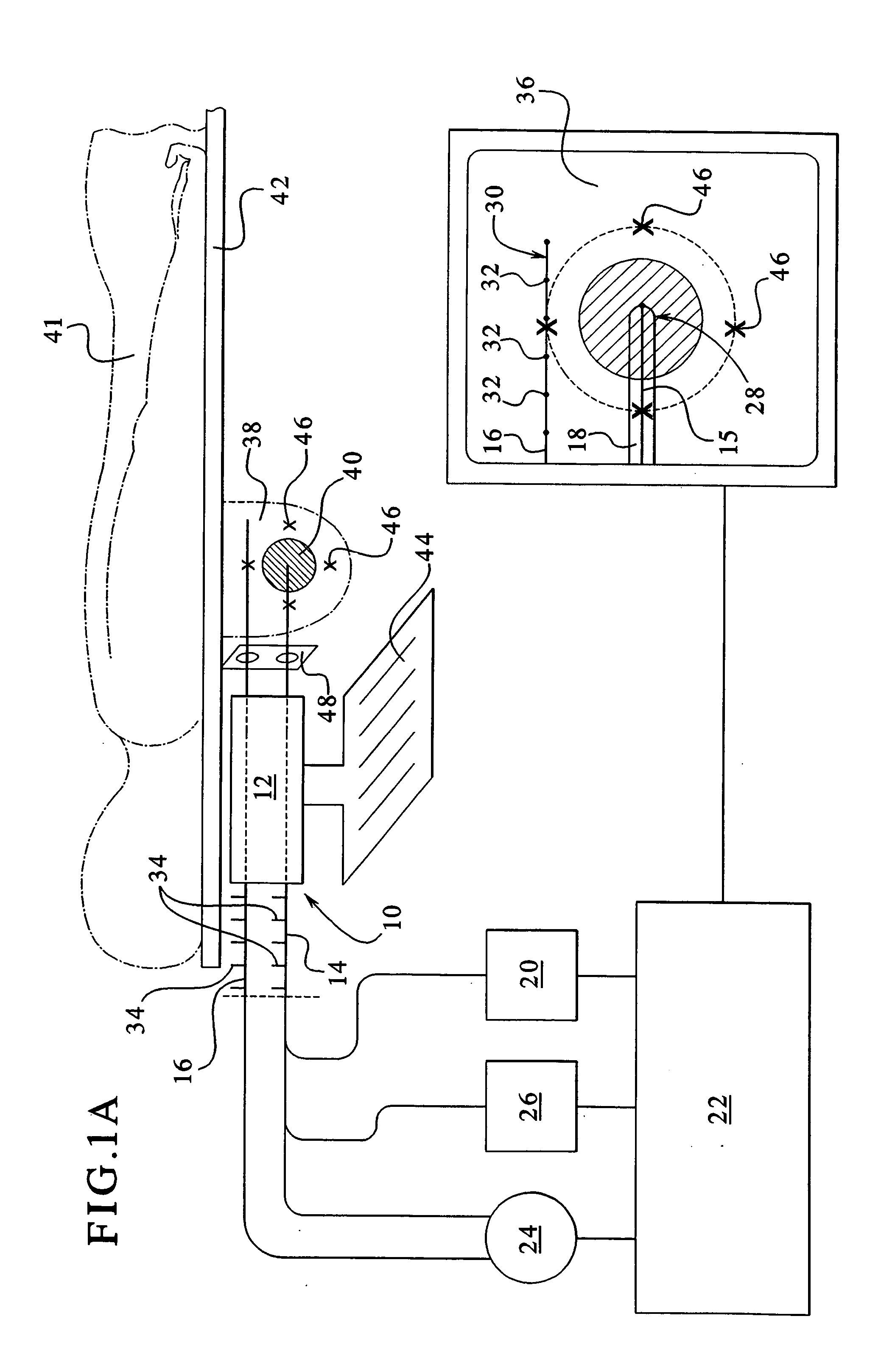
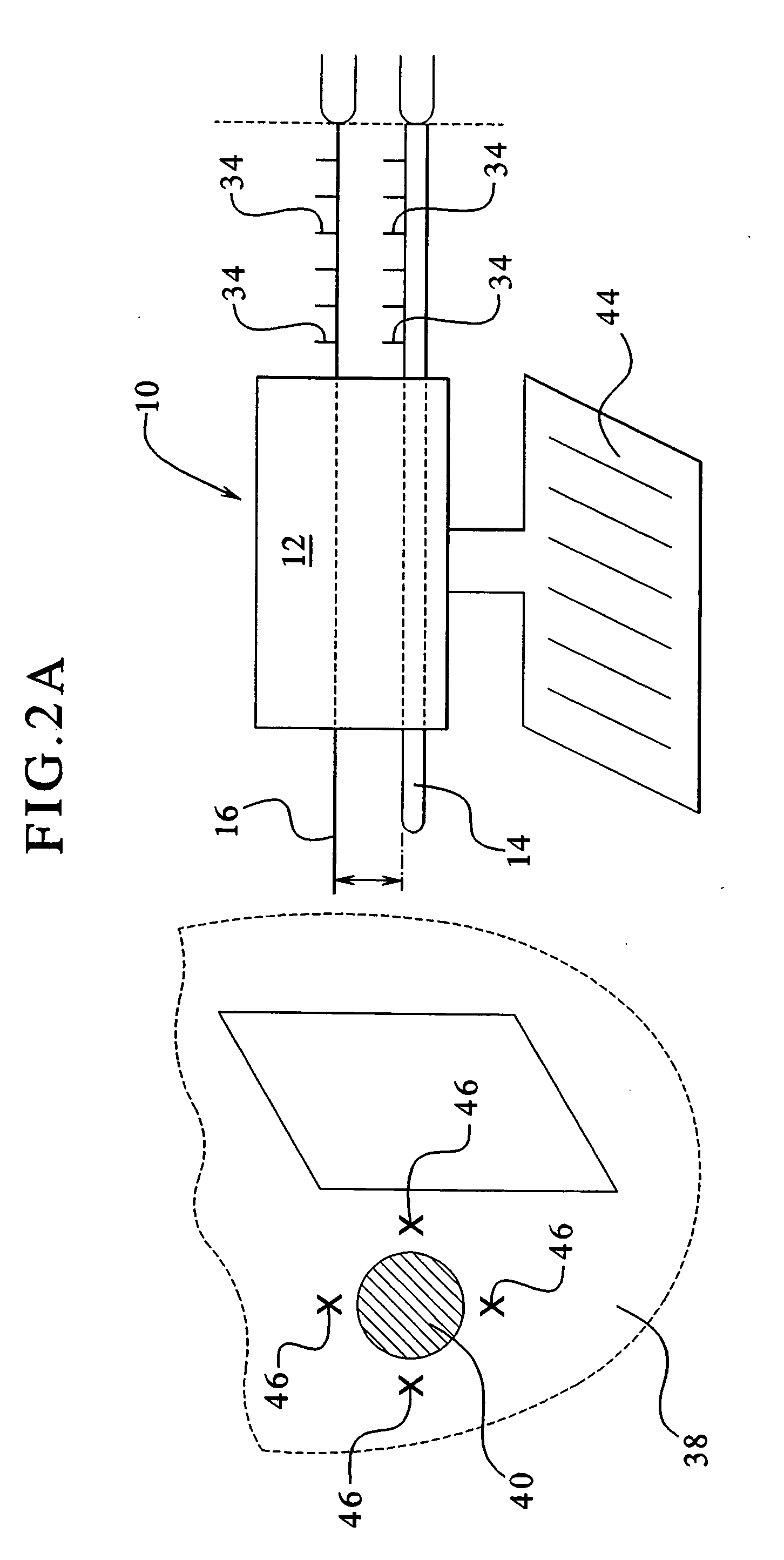
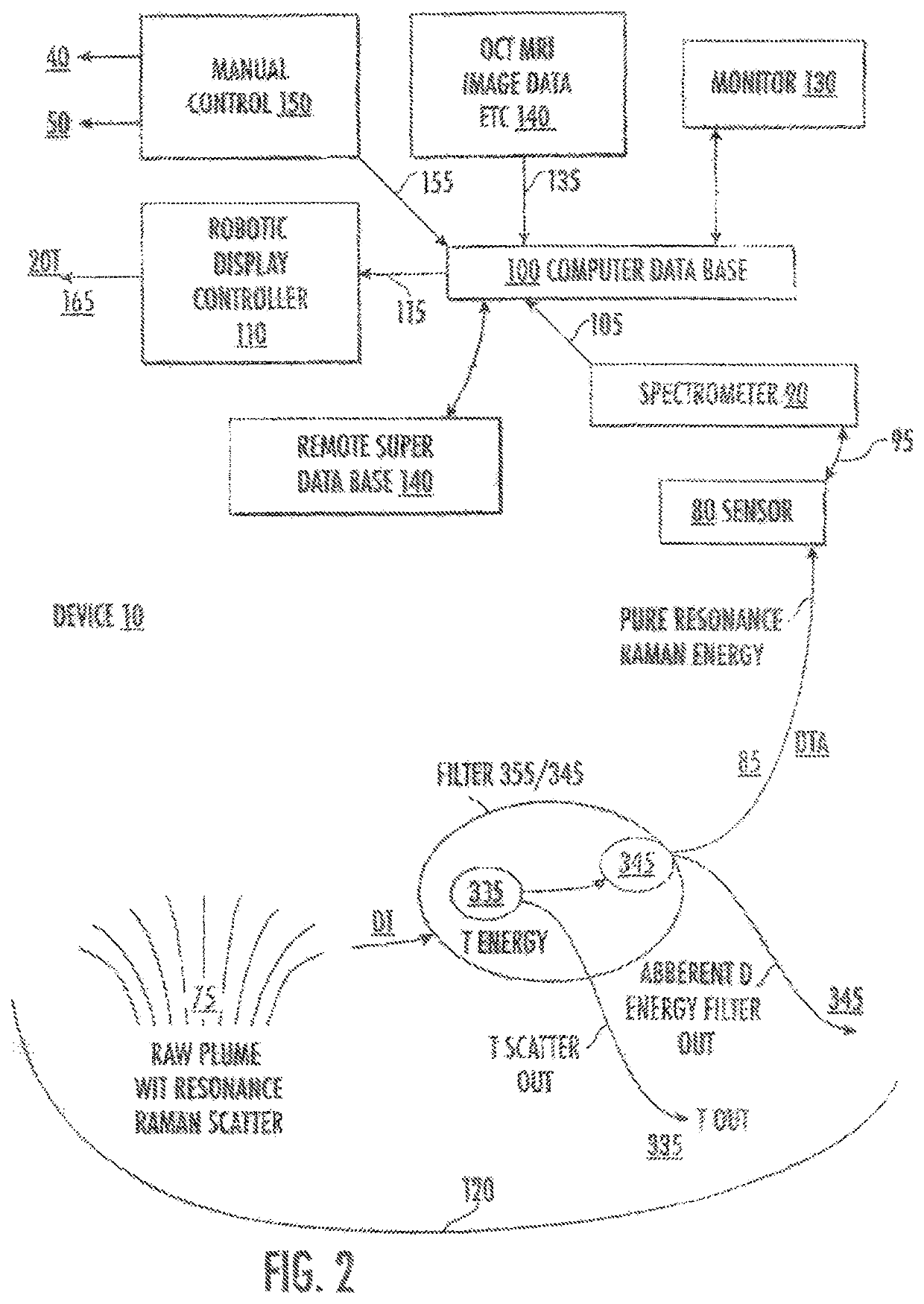
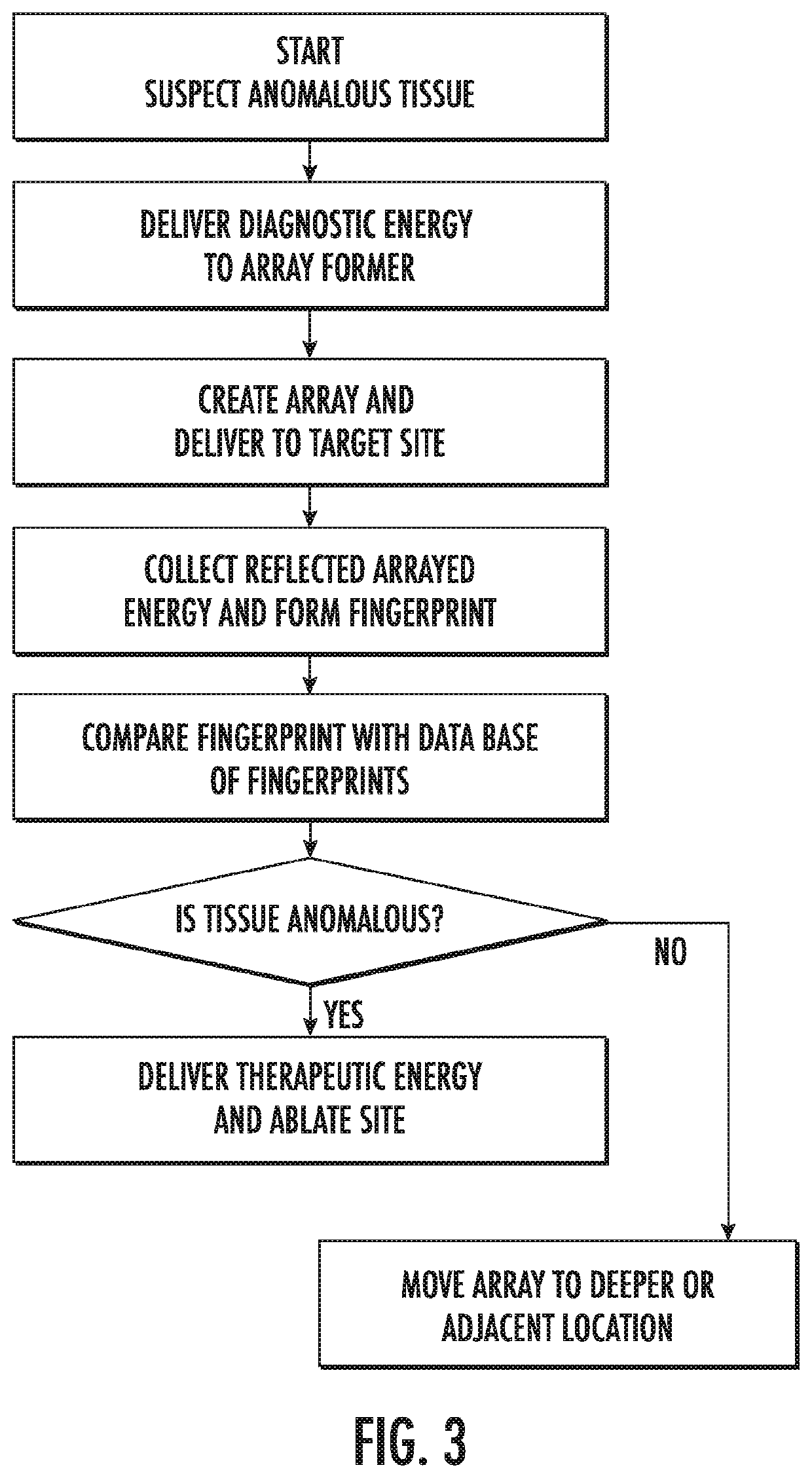
System and method of using ultrafast Raman spectroscopy and an ablative laser for quasi-real time removal of skin cancer and other anomalous tissues with clear tissue margins formed by array created displays
ActiveUS11185234B2Reduce threatMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDiagnostics using spectroscopyDisplay deviceTarget tissue
Resonance Raman scatter is used to differentiate in quasi-real time (QRT) anomalous tissue from adjacent normal tissue. The fingerprint generated from the tissue by a 1 second pulse of 532 nm emission for approximately one second is collected and is relayed by fiber-optic to a computerized controller that determines whether the target tissue is anomalous or normal. If anomalous it is ablated. This is performed by a pattern of Resonance Raman diagnostic emission and diagnostic sensor fibers. This diagnostic / therapeutic pattern of fibers can be moved by a joystick or robotically controlled. The data received by the computer is examined instantly, and should the site be diagnosed as anomalous, the optical biopsy / ablation is repeated immediately and repeated until the site is read as normal. Novel arrays of the diagnostic and therapeutic energies ensure a 3D anomalous tissue free zone around the removal site.
Owner:BECKMAN HUGH
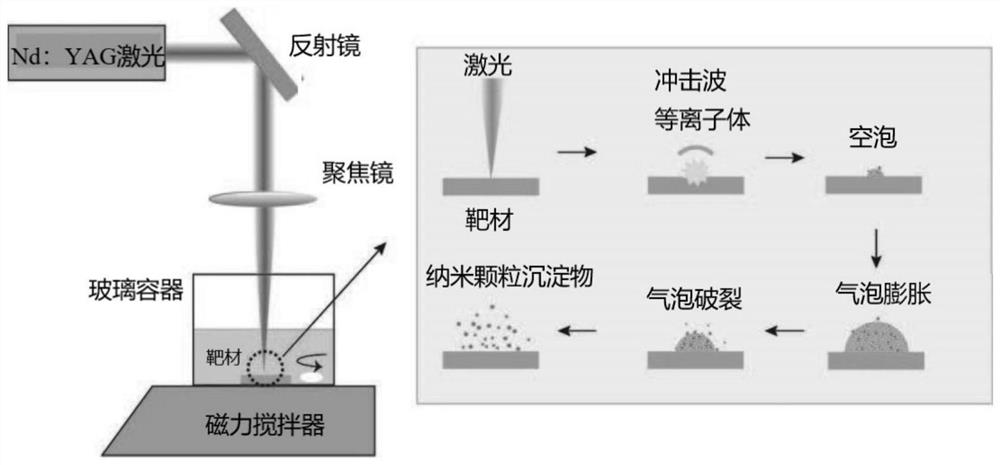
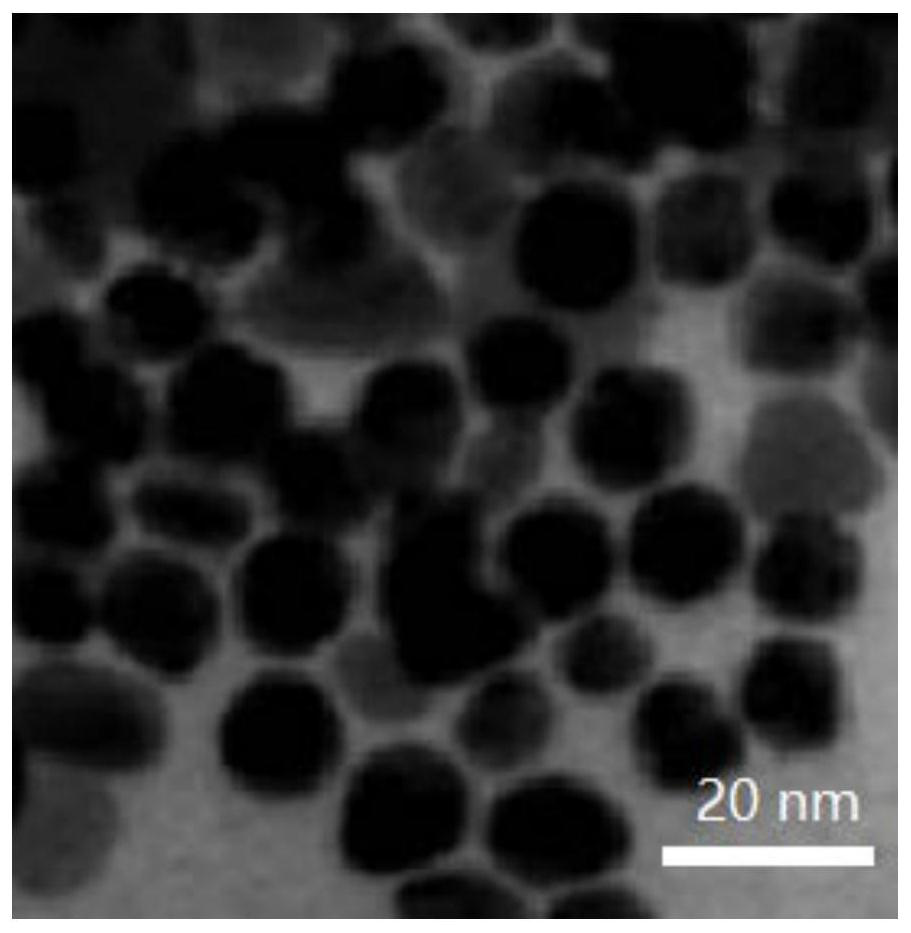
Method for preparing nanoscale high-performance Nd2Fe14B/MnBi composite magnet material
PendingCN113593878AImprove cooling effectRapid coolingInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsPulse beamLaser light
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nanoscale high-performance Nd2Fe14B / MnBi composite magnet material. The method comprises the following steps: weighing raw materials according to a certain stoichiometric ratio, grinding and mixing, and pressing powder into blocks; presintering the pressed block under a certain temperature condition to form a precursor; cleaning and drying a precursor, putting the precursor as a target on a target bracket of a beaker, filling an isopropyl-ketone solution to submerge the precursor by 5-10 mm, putting the beaker on a rotating platform, and focusing a laser pulse beam on the surface of the precursor by adopting third harmonic of an Nd: YAG laser as an ablation laser light source to ablate so as to generate a mixed solution containing a nanoscale particle precipitate; and filtering the precipitate of the mixed solution, and repeatedly cleaning and drying to obtain the nanoscale high-performance composite permanent magnet material. The prepared composite nanocrystalline permanent magnet is clean in surface and good in chemical activity, meanwhile, structural deformity is effectively inhibited, and the magnetic performance of the nanocrystalline magnet is improved.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Processing method for cutting silicon wafer by utilizing time-resolved shadow imaging technology to assist laser liquid phase ablation
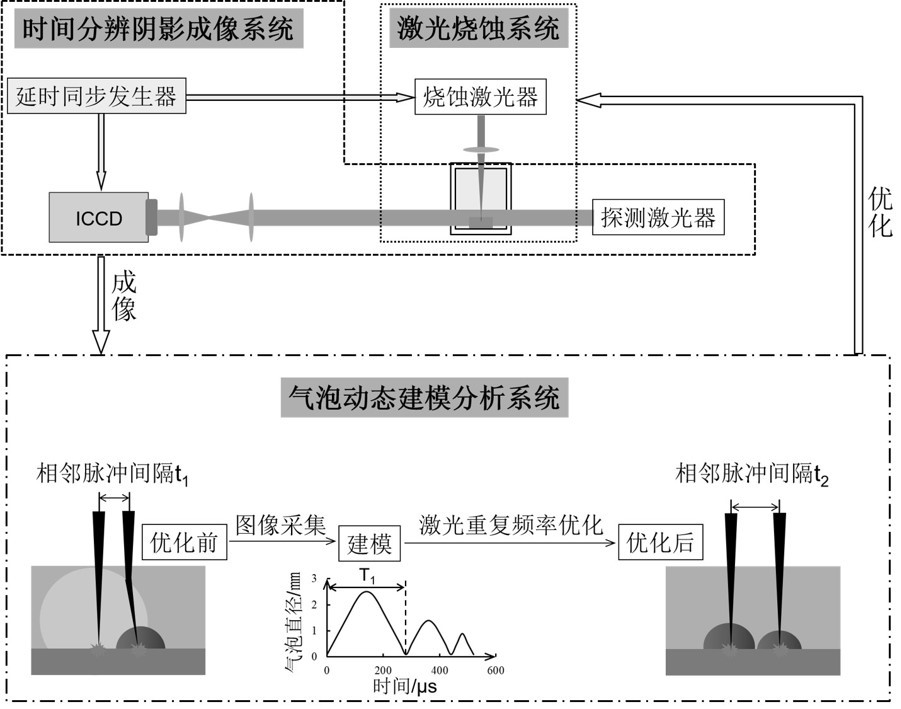
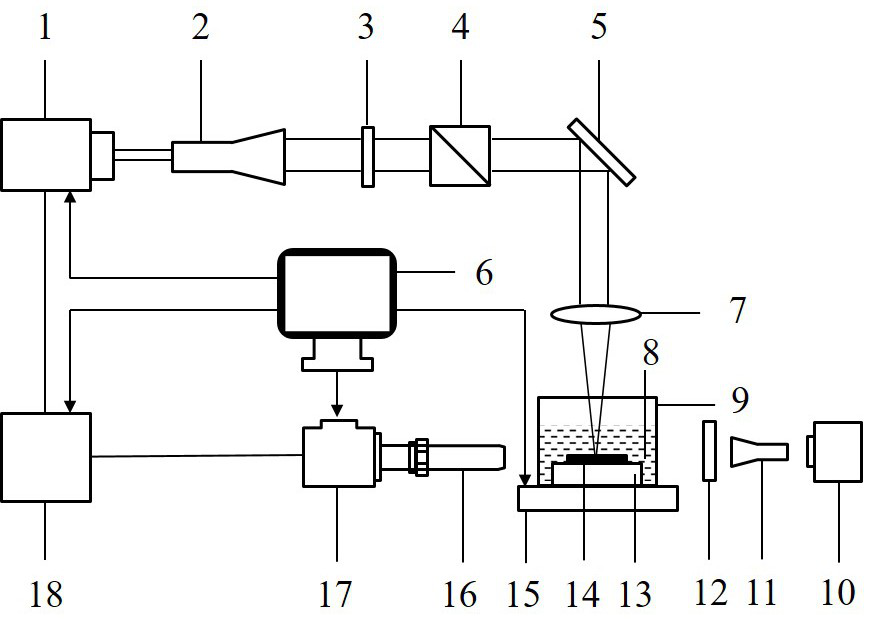
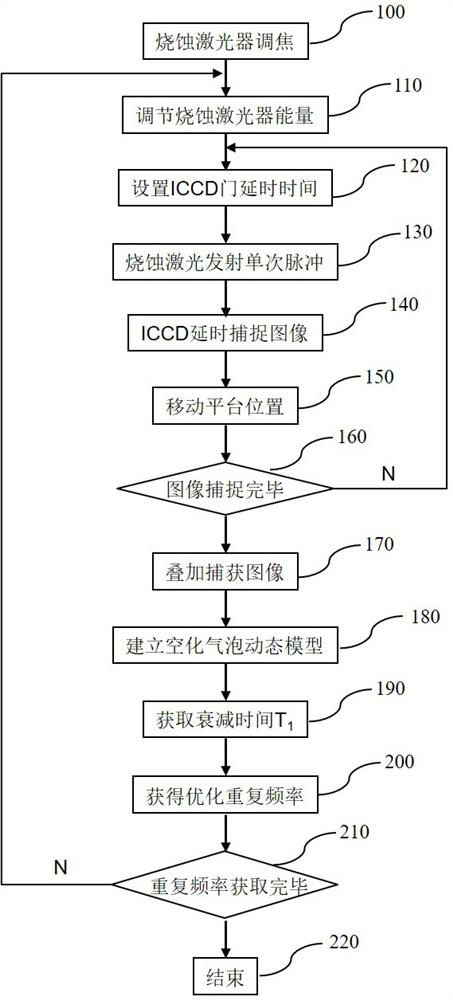
PendingCN113909702AContact establishmentReduce adverse effectsWorking accessoriesFine working devicesLaser technologyLiquid medium
The invention discloses a processing method for cutting a silicon wafer by utilizing a time-resolved shadow imaging technology to assist laser liquid phase ablation in the technical field of laser,. Shadow images of cavitation bubbles and persistent bubbles are captured through an established time-resolved shadow imaging system, and dynamic models of the cavitation bubbles and the persistent bubbles are established; according to the dynamic model of the cavitation bubbles, the repetition frequency of the ablation laser is optimized, and the adverse effect of cavitation bubble refraction on the surface of the silicon wafer is reduced; the type and concentration of a liquid medium are optimized according to the dynamic model of the persistent bubbles, the residence time of the persistent bubbles is regulated and controlled, the persistent bubbles staying on the surface of the silicon wafer for a long time are prevented from reacting with subsequent laser pulses, and the adverse effect of the rupture impact effect of the persistent bubbles on the surface of the silicon wafer is relieved; and the processing method provided by the invention is utilized to process the silicon wafer, the obtained kerf is narrow, the heat affected zone is small, the sputter deposition range of the micro-nano particles is small, and the negative influence of induced bubbles is small.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing microstructural target by using laser to improve laser propulsion impulse coupling coefficient
InactiveCN102179622BEasy to manufactureMake fastLaser beam welding apparatusLight energyFemto second laser
The invention discloses a method for preparing a microstructural target by using laser to improve a laser propulsion impulse coupling coefficient. In the method, preprocessing treatment is performed on a solid target in an ablation laser propulsion technology by a focused near-infrared femtosecond laser pulse, so that microstructures in various shapes can be generated on the surface of the solid target to effectively enhance the impulse coupling coefficient. The microstructural solid target prepared by the femtosecond laser pulse comprises a plurality of types of protruding structures and groove structures which contribute to enhancing light absorption. By a high-sensitivity torsion balance precision measurement device established by experiments, the impulse coupling coefficient of the microstructural solid target is improved by about 170 percent compared with that of a common plane target which is not preprocessed by femtosecond laser within a laser flux variation range of 0.6 to 100joules / square centimeter. The new method for effectively enhancing the conversion from light energy to mechanical energy in the laser ablation process is potentially and importantly applied in the technical field of laser propulsion.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
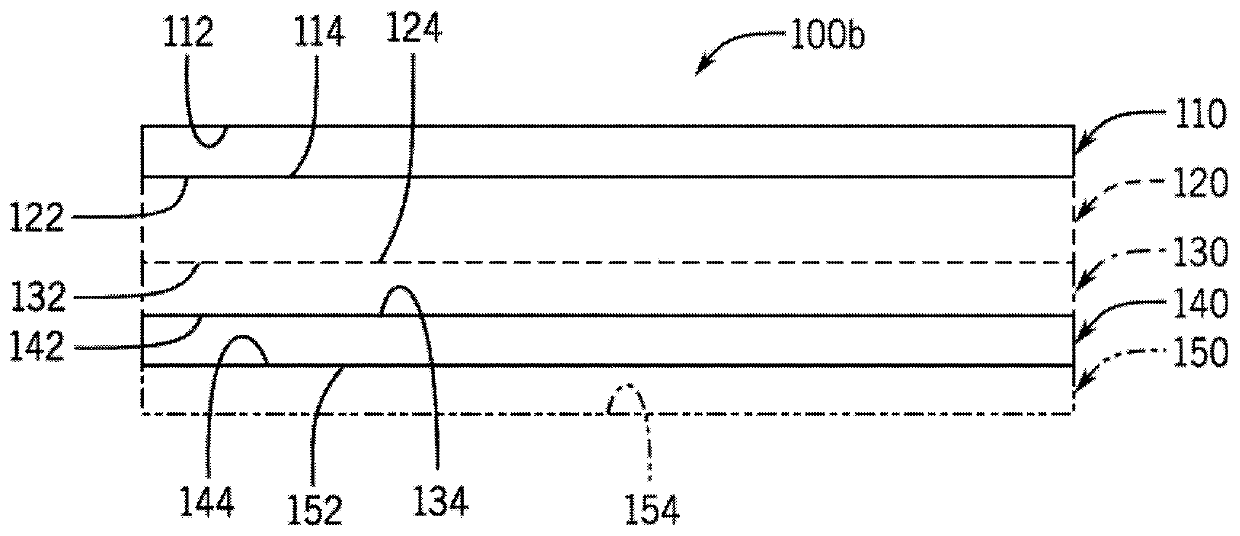
Label construction for ablative laser marking
A label has a topcoat layer and a sacrificial layer. The topcoat layer has a first color having a first L-value and the sacrificial layer has a second color having a second L-value. The topcoat layercomprises at least one reflective pigment and a polymeric binder and the sacrificial layer comprises at least one infrared (IR) absorbing material and a polymeric binder. The first L-value is greaterthan the second L-value, and the total amount of the at least one reflective pigment is from 40 wt% to 80 wt%, based on the weight of the topcoat layer.
Owner:BRADY WORLDWIDE INC
Method and apparatus for directional skin tightening
A cosmetic method of directionally tightening human skin tissue includes providing an ablative laser source and a non-ablative laser source, then using the ablative laser source to form one or more overlapping circular shaped microchannels in the skin tissue; the overlapping microchannels formed have a longitudinal dimension larger than their cross dimension; then, using the non-ablative laser source to weld the microchannels, whereby the welding causes the skin tissue to tighten.
Owner:LUMENIS BE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com