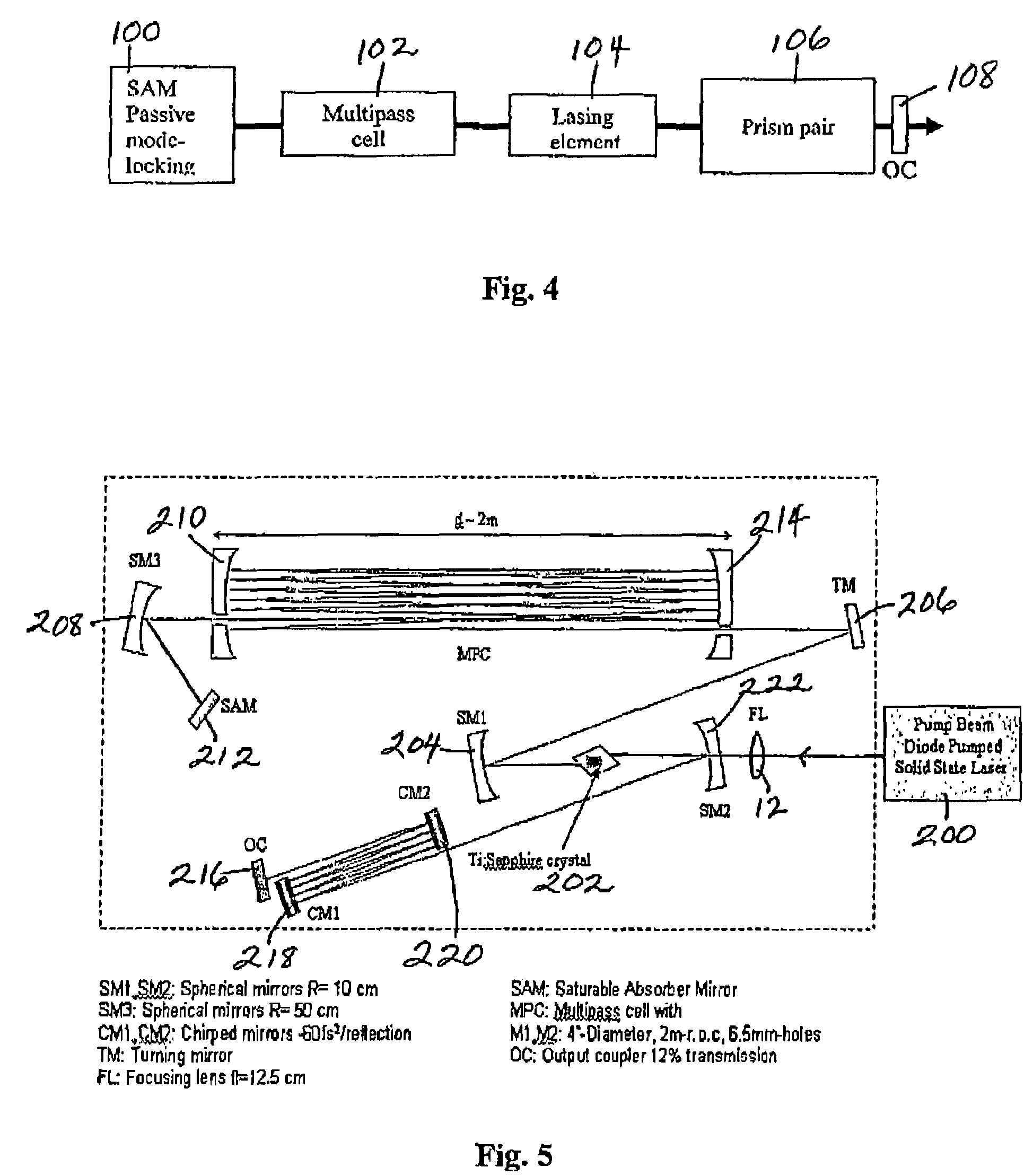
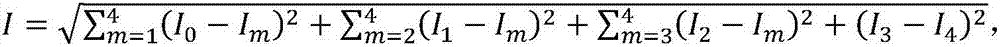Patents
Literature
1655 results about "Femto second laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
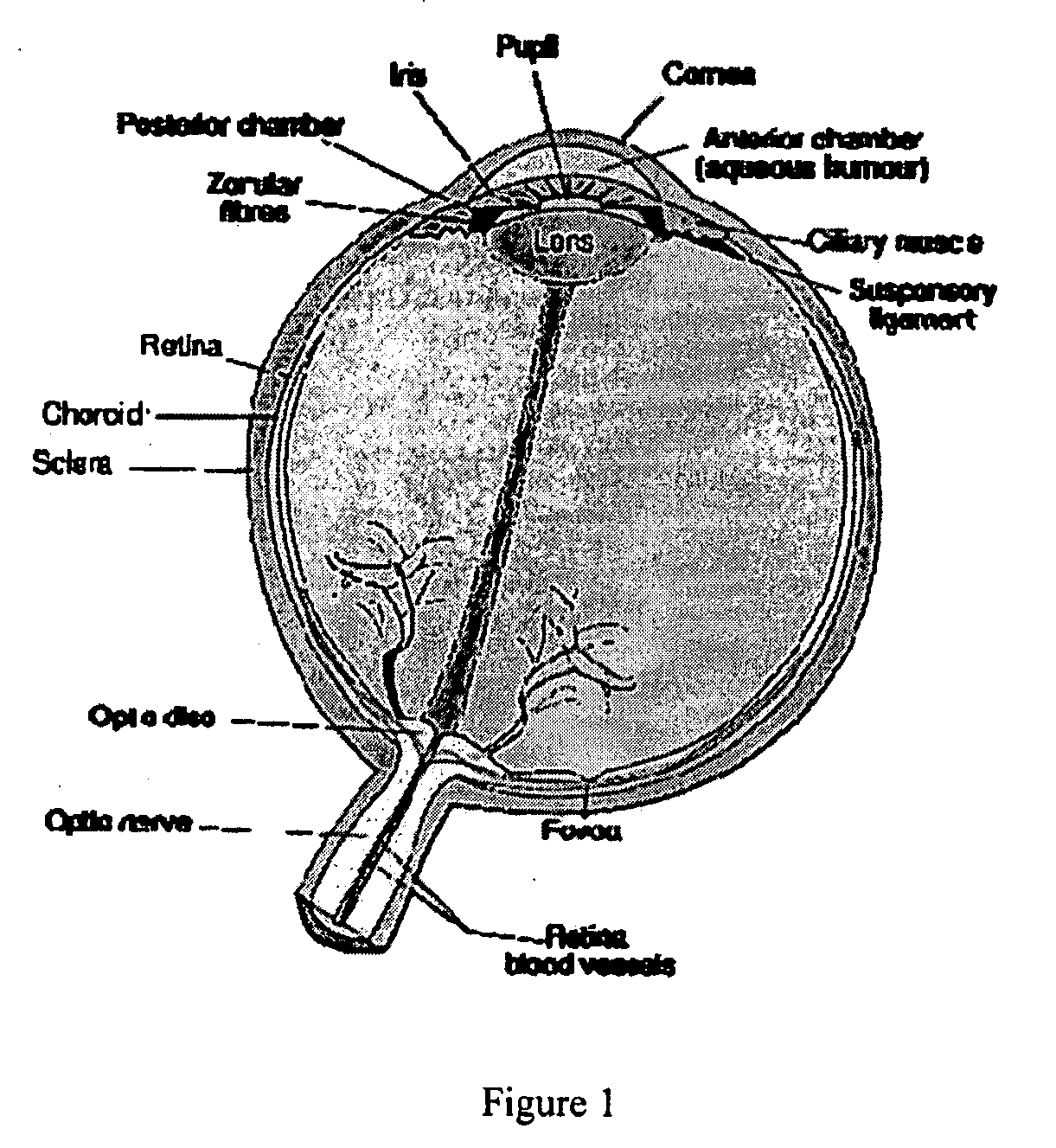
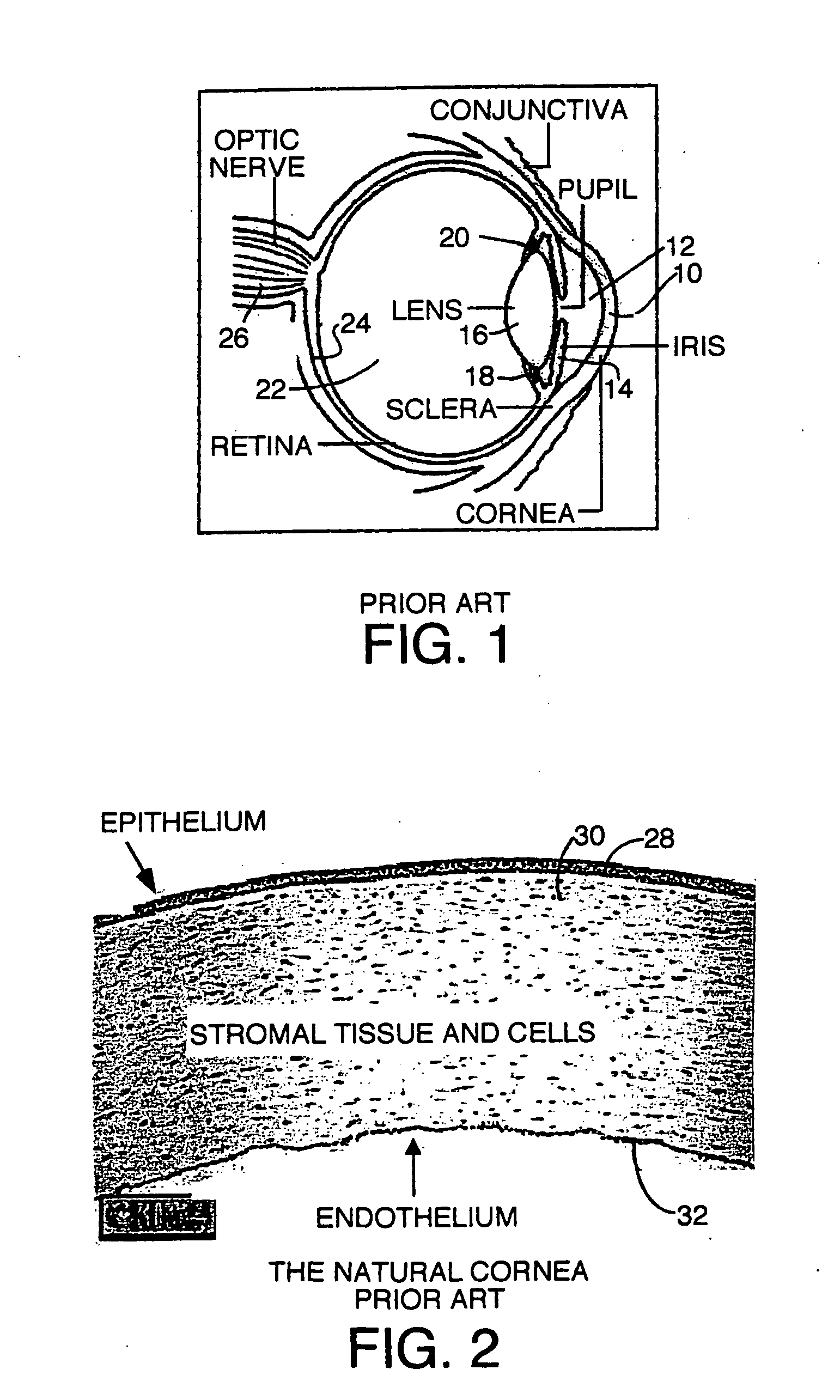
The femtosecond laser is a high-energy optics technology used for eye surgeries and other medical procedures, including all-laser LASIK. During this bladeless procedure, your surgeon uses the femtosecond laser to create a flap in your cornea before altering the shape of the underlying tissue to correct your vision.
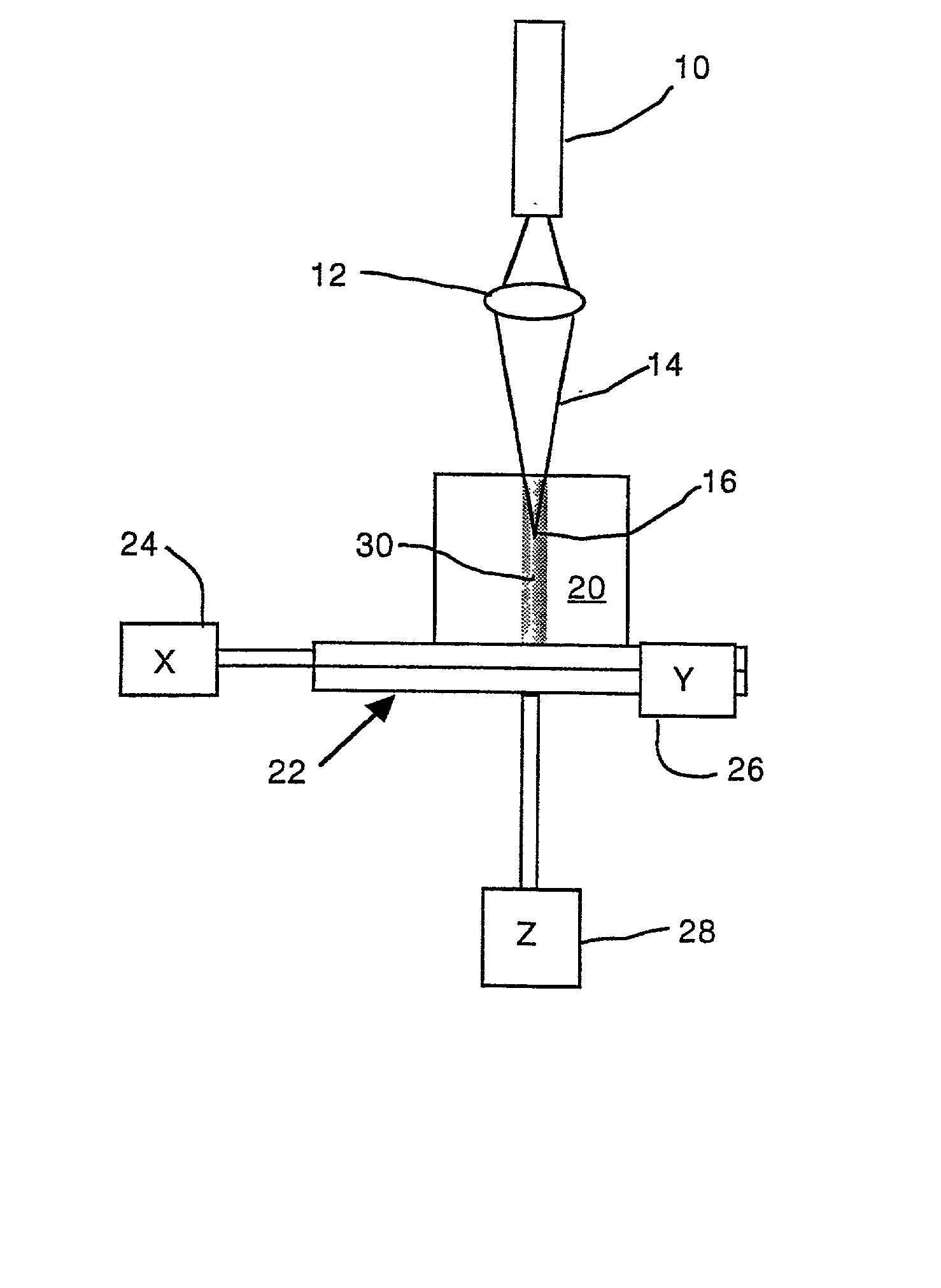
Method and arrangement for high-resolution microscope imaging or cutting in laser endoscopy
ActiveUS20080081950A1Accurate imagingPrecise microcuttingEndoscopesCatheterMicroscopic imageFlexible endoscope
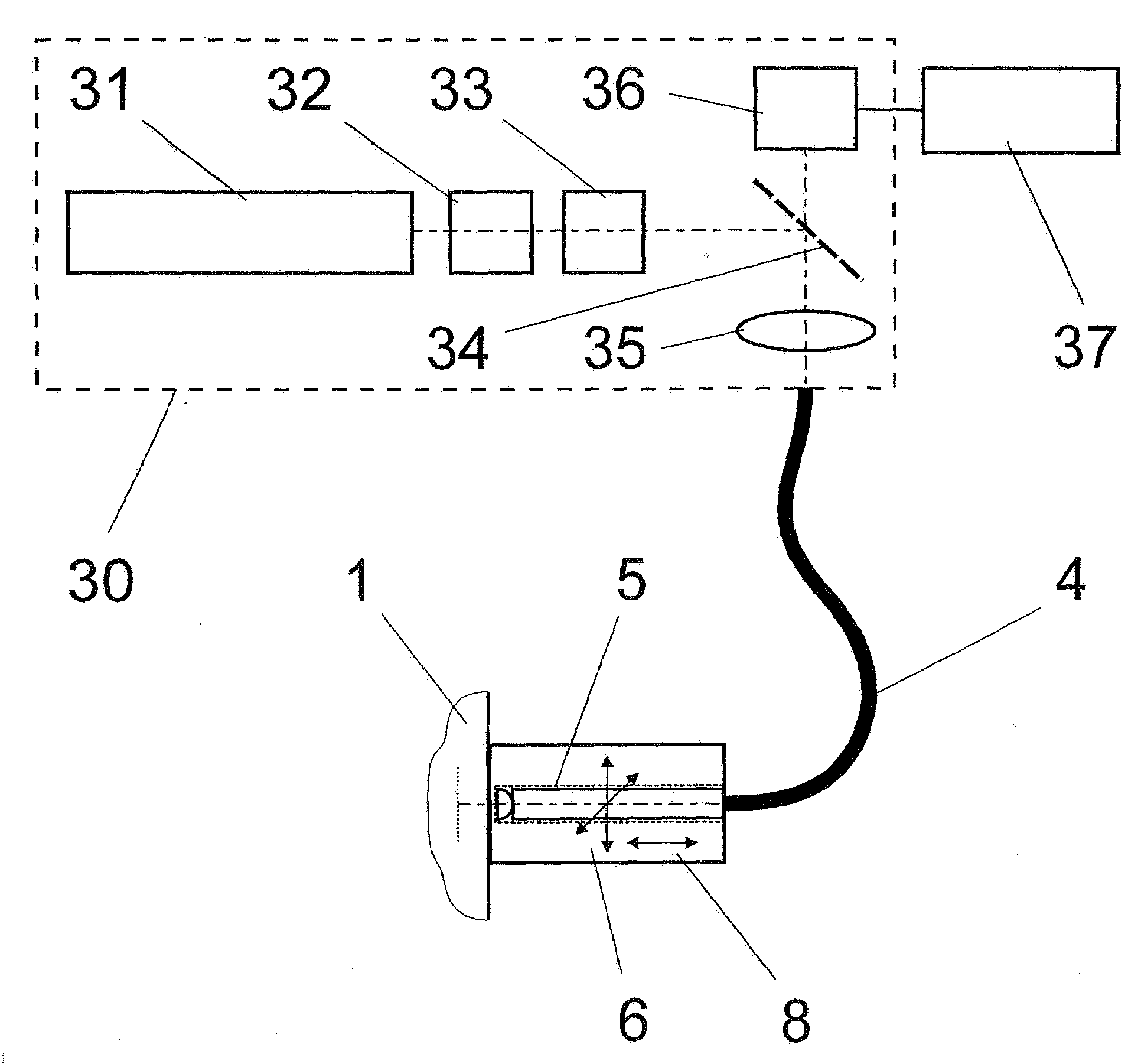
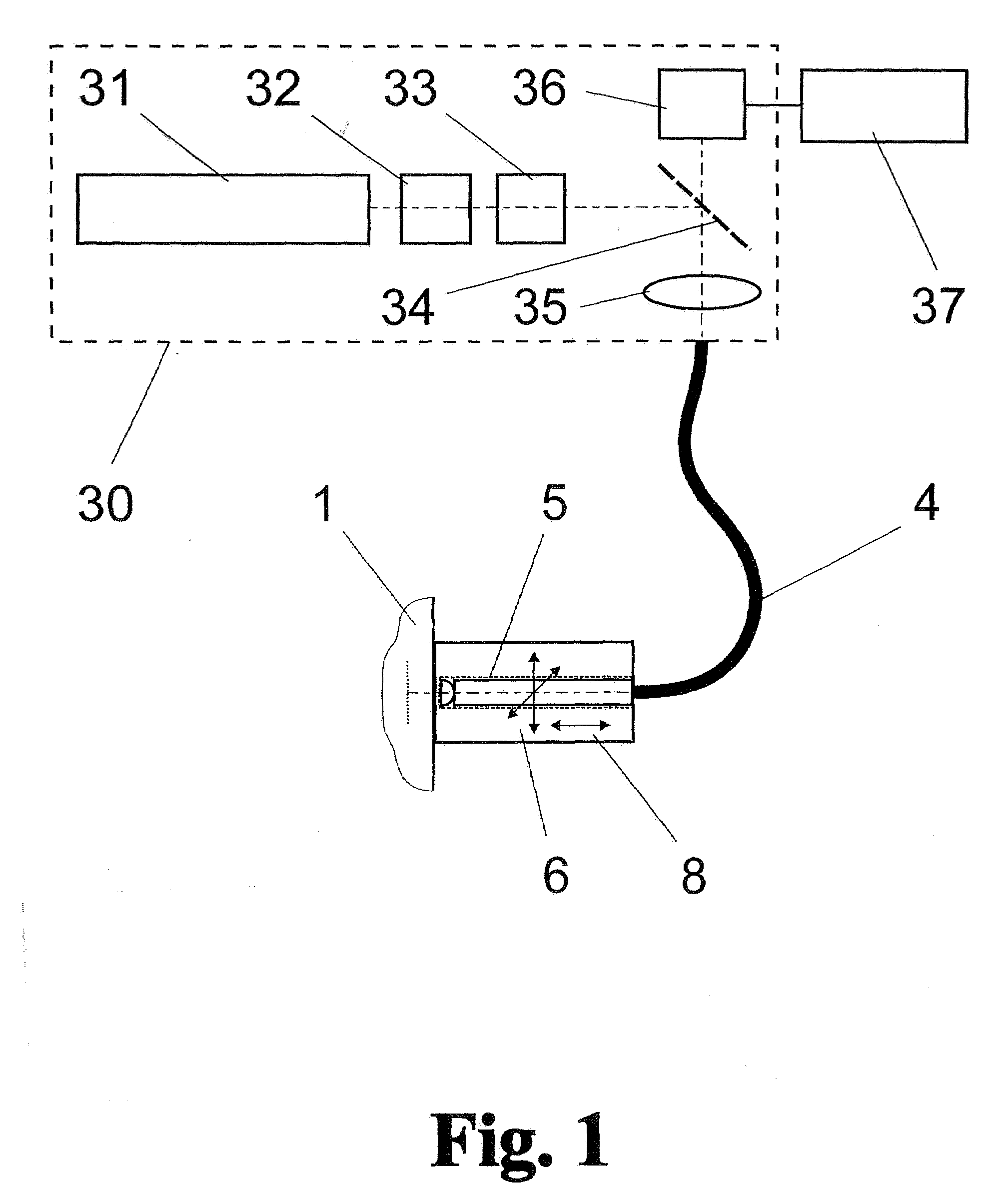
The invention is directed to a method and an arrangement for high-resolution microscopic imaging in laser endoscopy based on laser-induced object reaction radiation and for performing microscopic cuts in biological tissue. In using multiphoton processes for endoscopic applications in biological materials with an accuracy of under one millimeter, radiation of a pulsed femtosecond laser is focused into an object by means of a transmission focusing optics unit comprising a transmission system and miniature focusing optics having a high numerical aperture greater than 0.55 to trigger a local object reaction radiation in the micrometer to nanometer range, and the distal end of the transmission focusing optics unit is moved in at least two dimensions for highly spatially resolved scanning of the object and for transmitting object reaction radiation which is scanned in a locally progressive manner to an image-generating system with a photon detector. In an other embodiment the femtosecond laser radiation is energy enhanced is applied to the same transmission focusing optics unit to perform microendoscopic surgery in biological tissue.
Owner:JENLAB
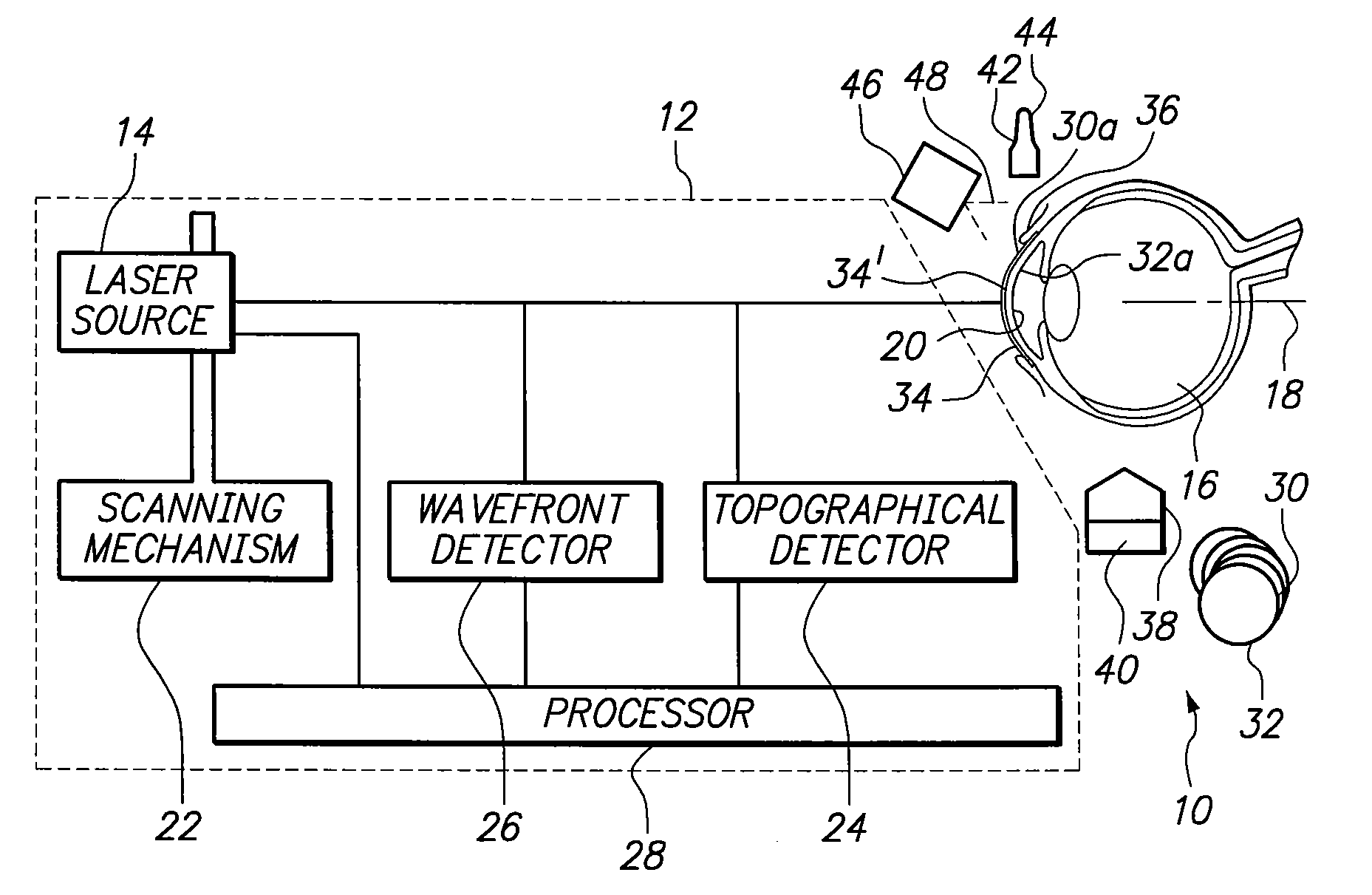
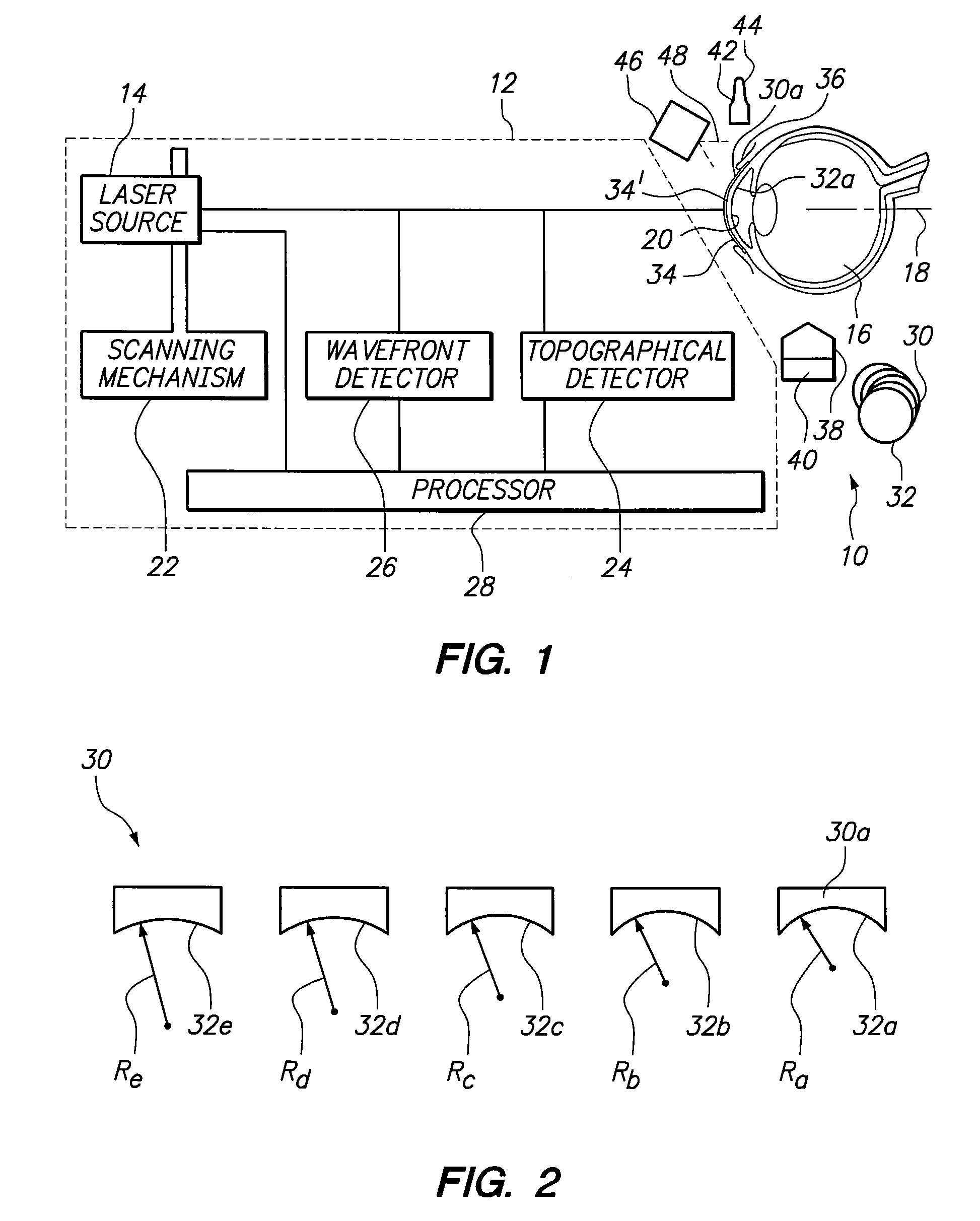
Method and apparatus to guide laser corneal surgery with optical measurement
InactiveUS20070282313A1Faster visual recoveryLess invasiveLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorPhototherapeutic keratectomy
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is used to map the surface elevation and thickness of the cornea. The OCT maps are used to plan laser procedures for the treatment of an irregular, opacified or weakened cornea, and in the treatment of refractive errors. In the excimer laser phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) procedure, the OCT data is used to plan a map of ablation depth needed to restore a smooth optical surface. In the excimer laser photorefractive keratectomy procedure, OCT mapping of epithelial thickness is used to achieve clean laser epithelial removal. In femtosecond laser anterior keratoplasty procedure, OCT data is used to plan the depth of femtosecond laser dissection to remove an anterior layer of the cornea, leaving a smooth recipient bed of uniform thickness to receive a disk of donated corneal tissue. The linkage of an OCT system to a precise laser surgical system enables the performance of new procedures that are safer, less invasive and produce faster visual recovery than conventional surgical procedures.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
Methods and Apparatuses for the Treatment of Glaucoma using visible and infrared ultrashort laser pulses
InactiveUS20120283557A1Short pulse durationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsDiseaseFemto second laser
Transcorneal and fiberoptic laser delivery systems and methods for the treatment of eye diseases wherein energy is delivered by wavelengths transparent to the cornea to effect target tissues in the eye for the control of intraocular pressure in diseases such as glaucoma by delivery systems both external to and within ocular tissues. External delivery may be effected under gonioscopic control. Internal delivery may he controlled endoscopically or fiberoptically, both systems utilizing femtosecond laser energy to excise ocular tissue. The femtosecond light energy is delivered to the target tissues to be treated to effect precisely controlled photodisruption to enable portals for the outflow of aqueous fluid in the case of glaucoma in a manner which minimizes target tissue healing responses, inflammation and scarring.
Owner:BERLIN MICHAEL S
Laser and environmental monitoring system
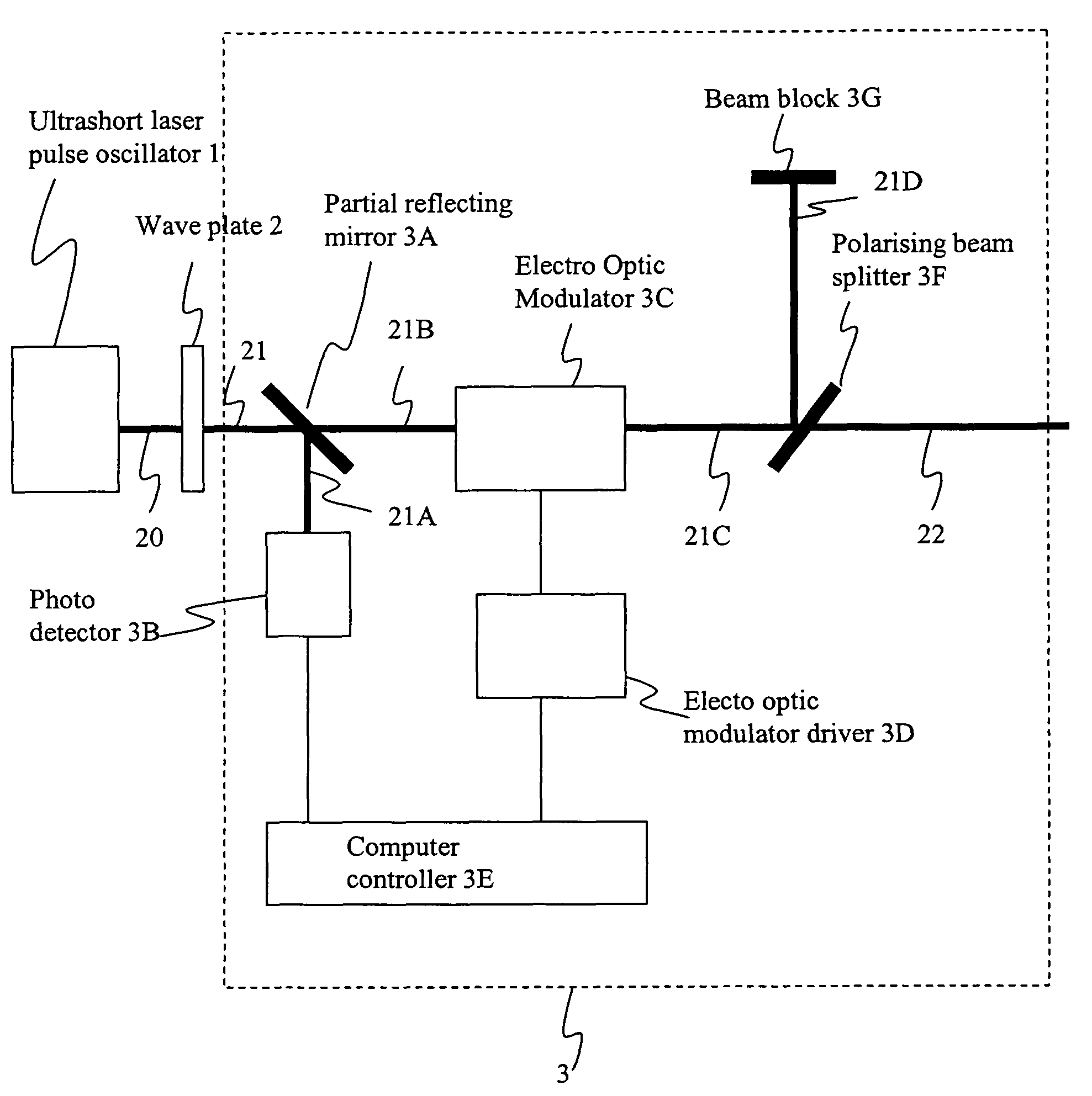
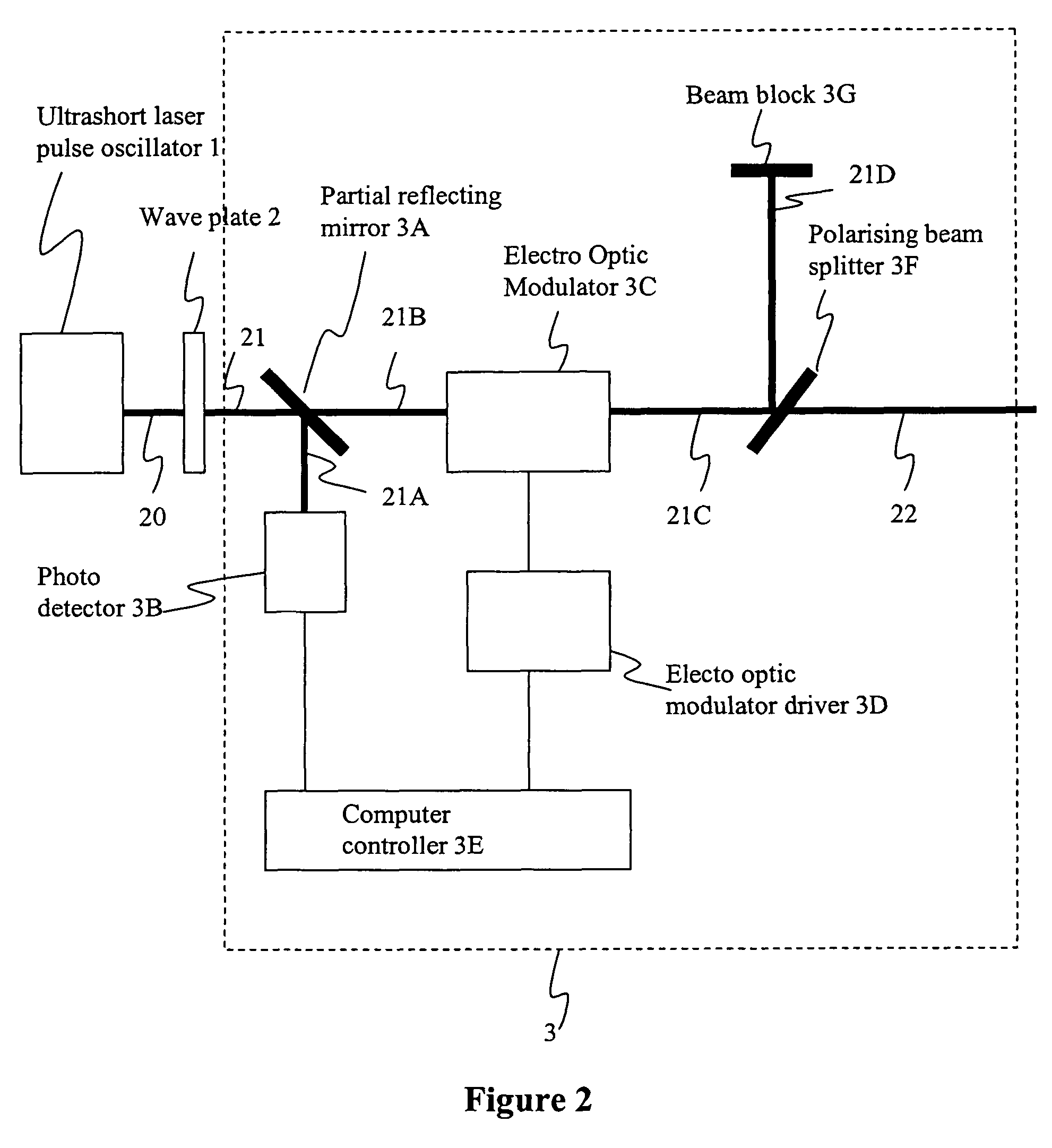
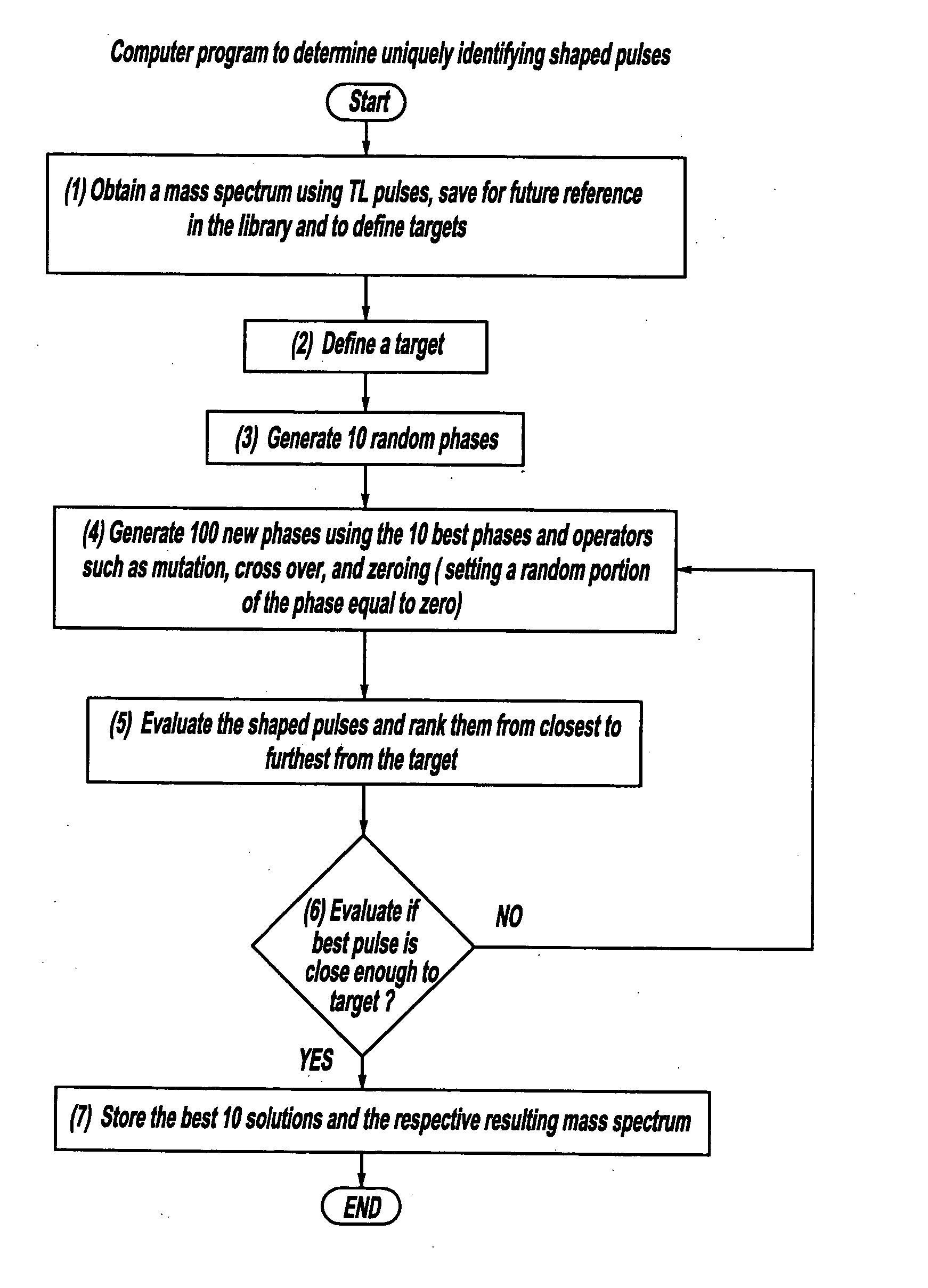
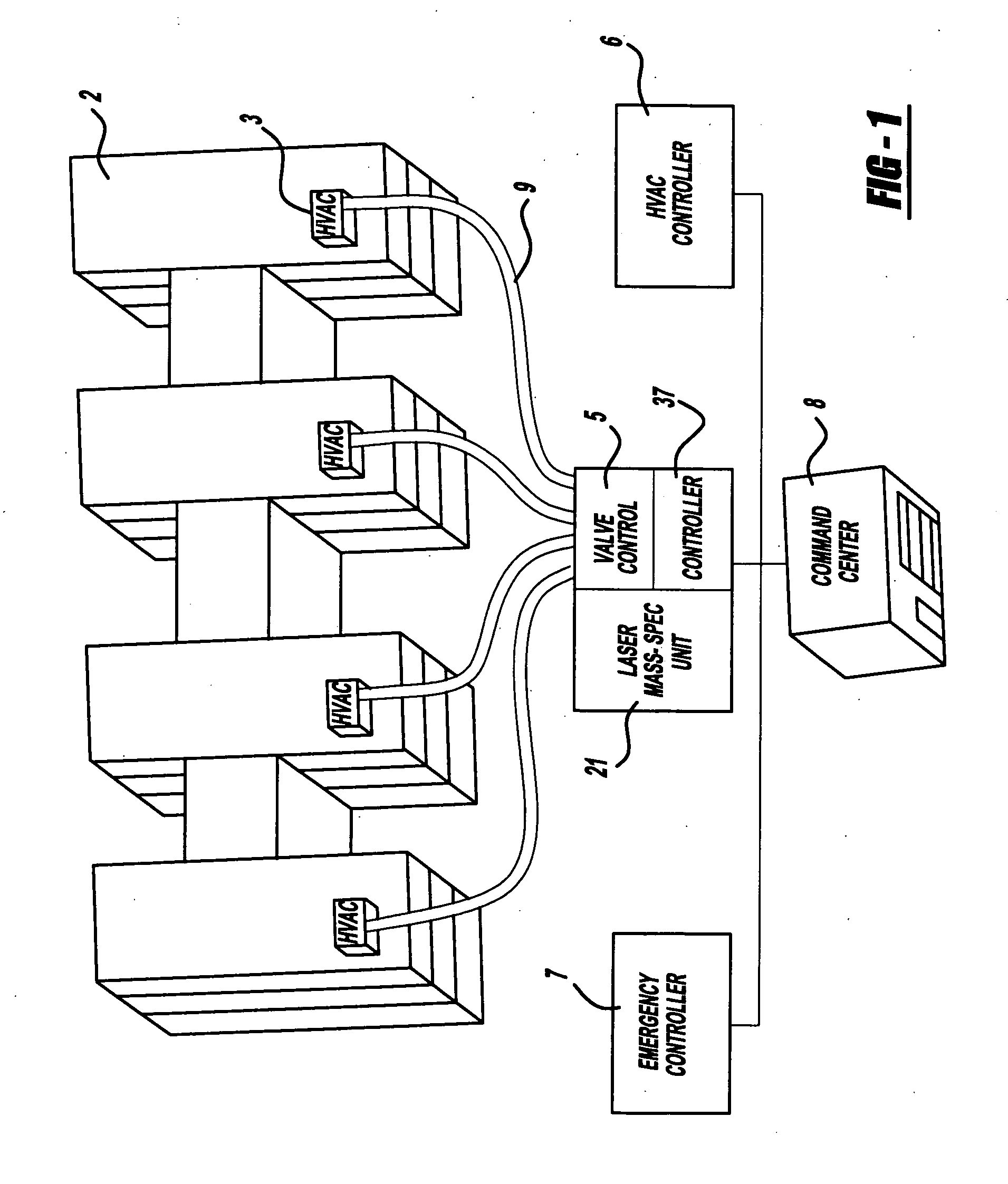
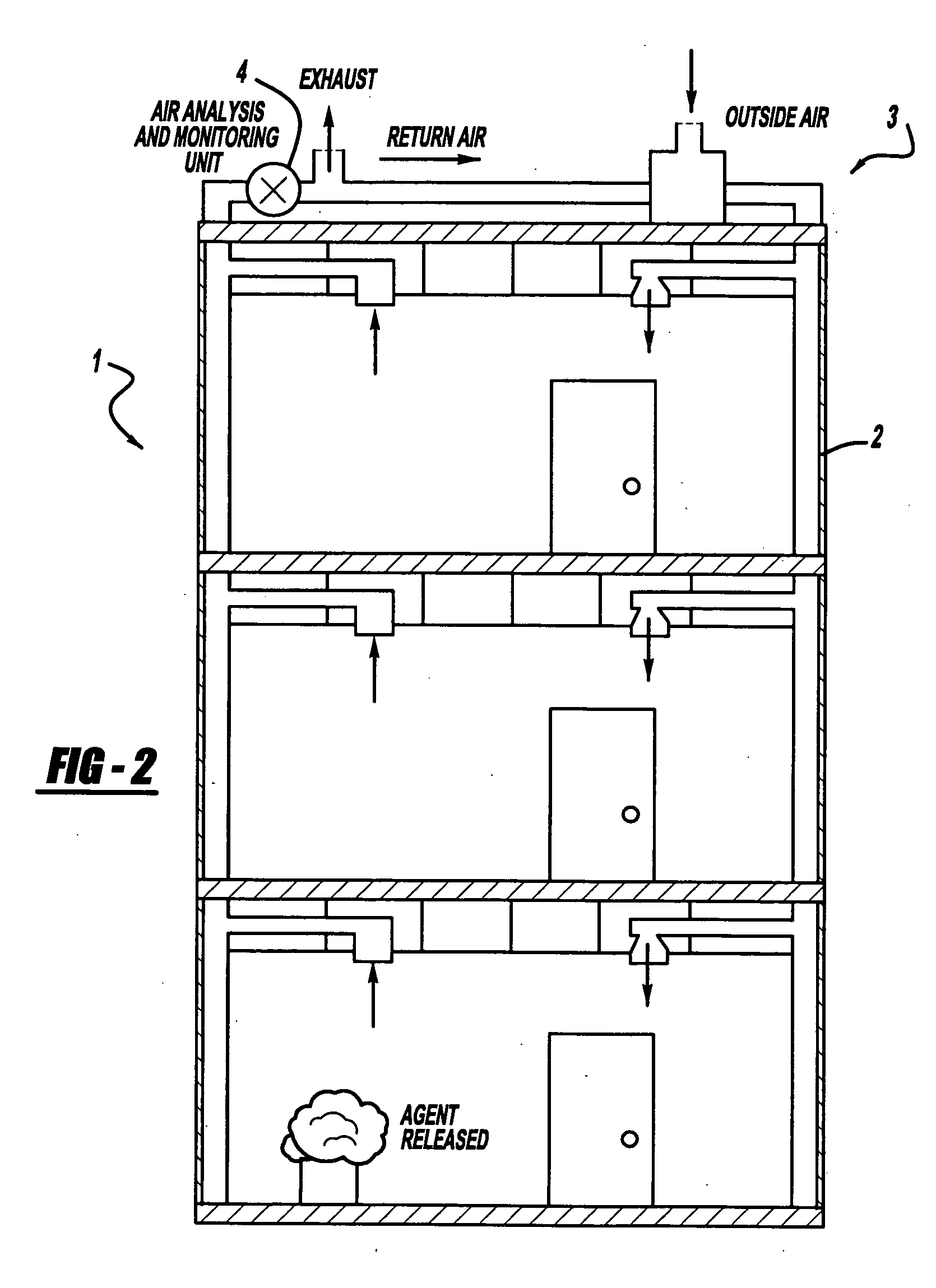
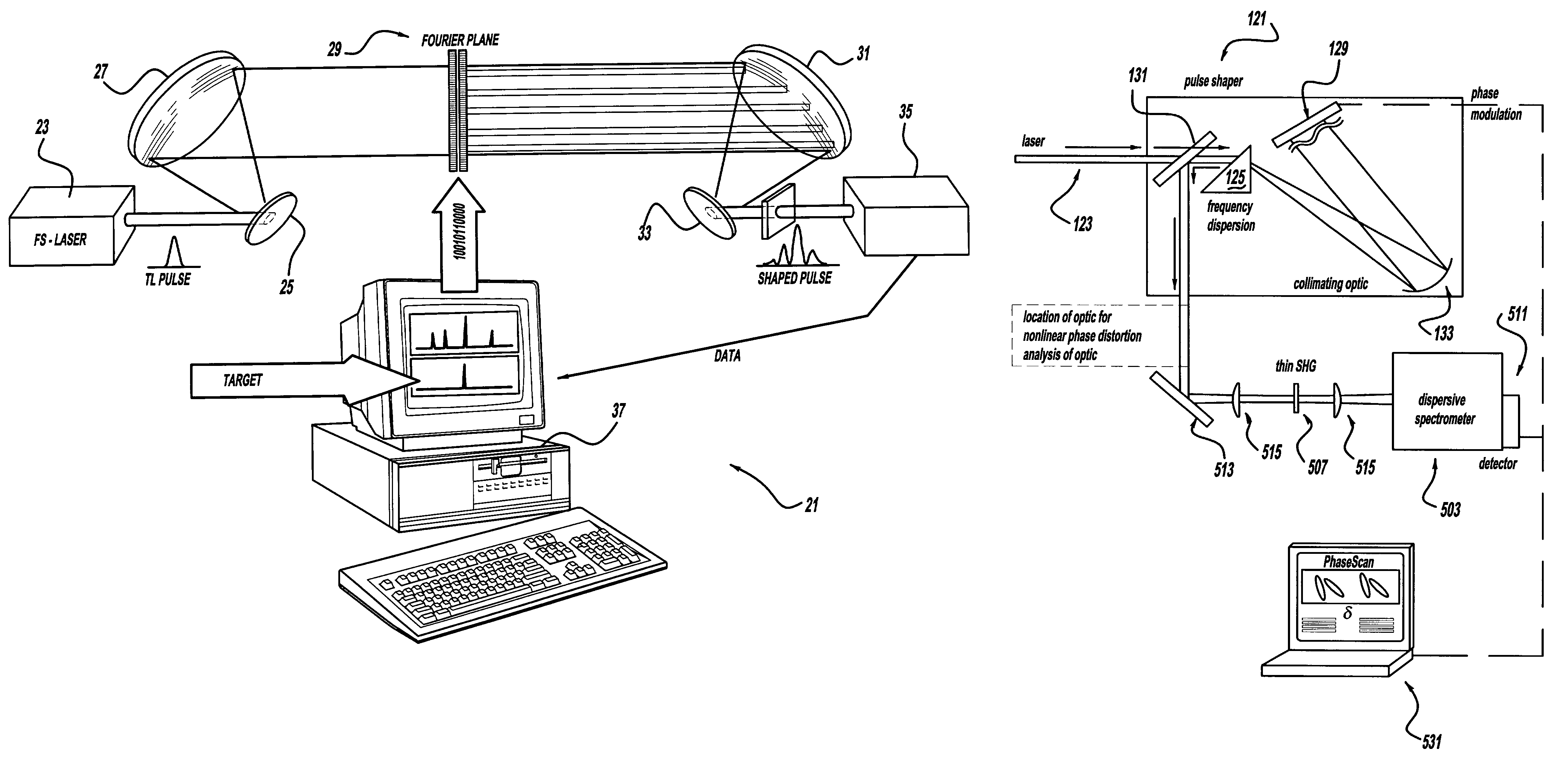
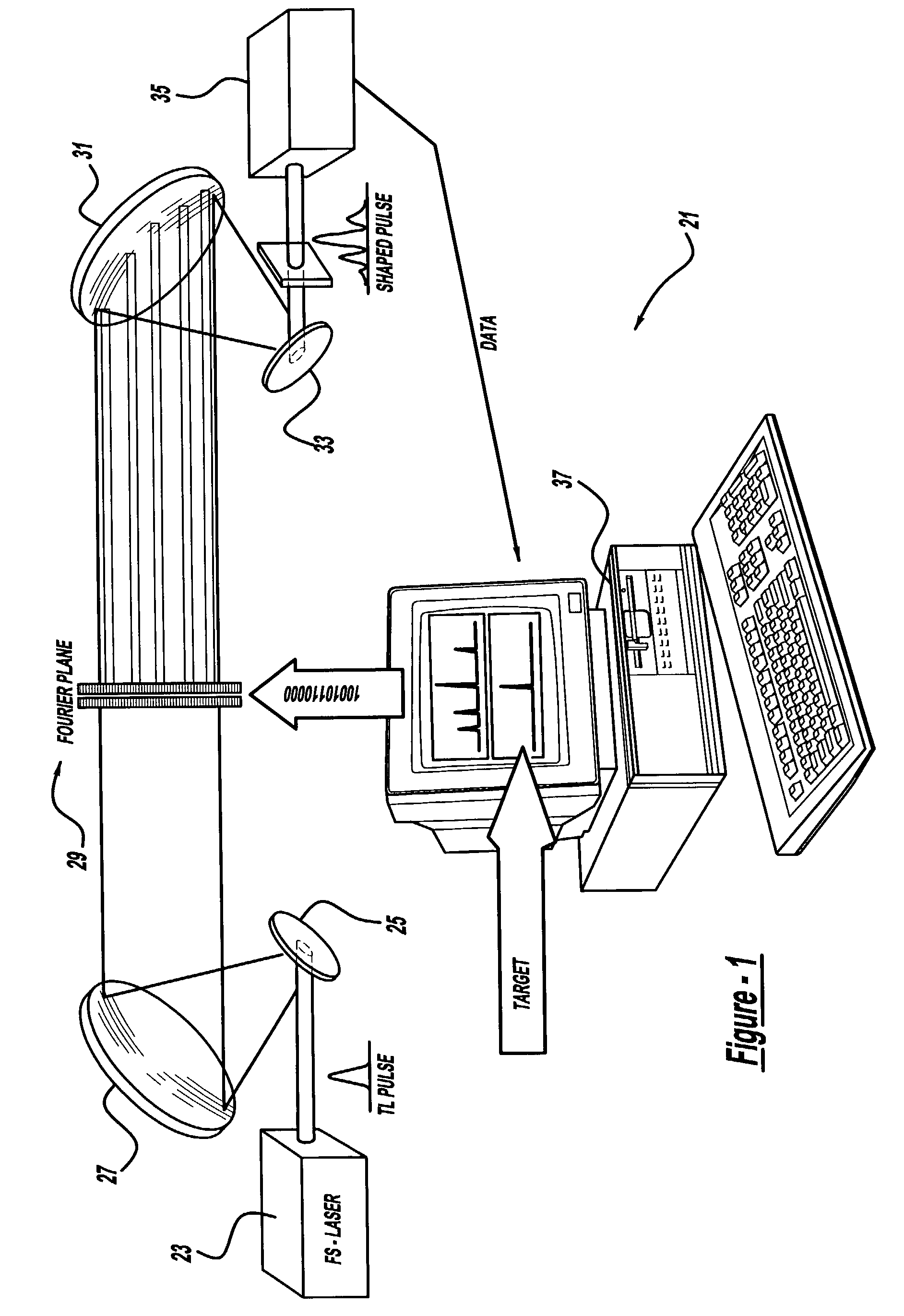
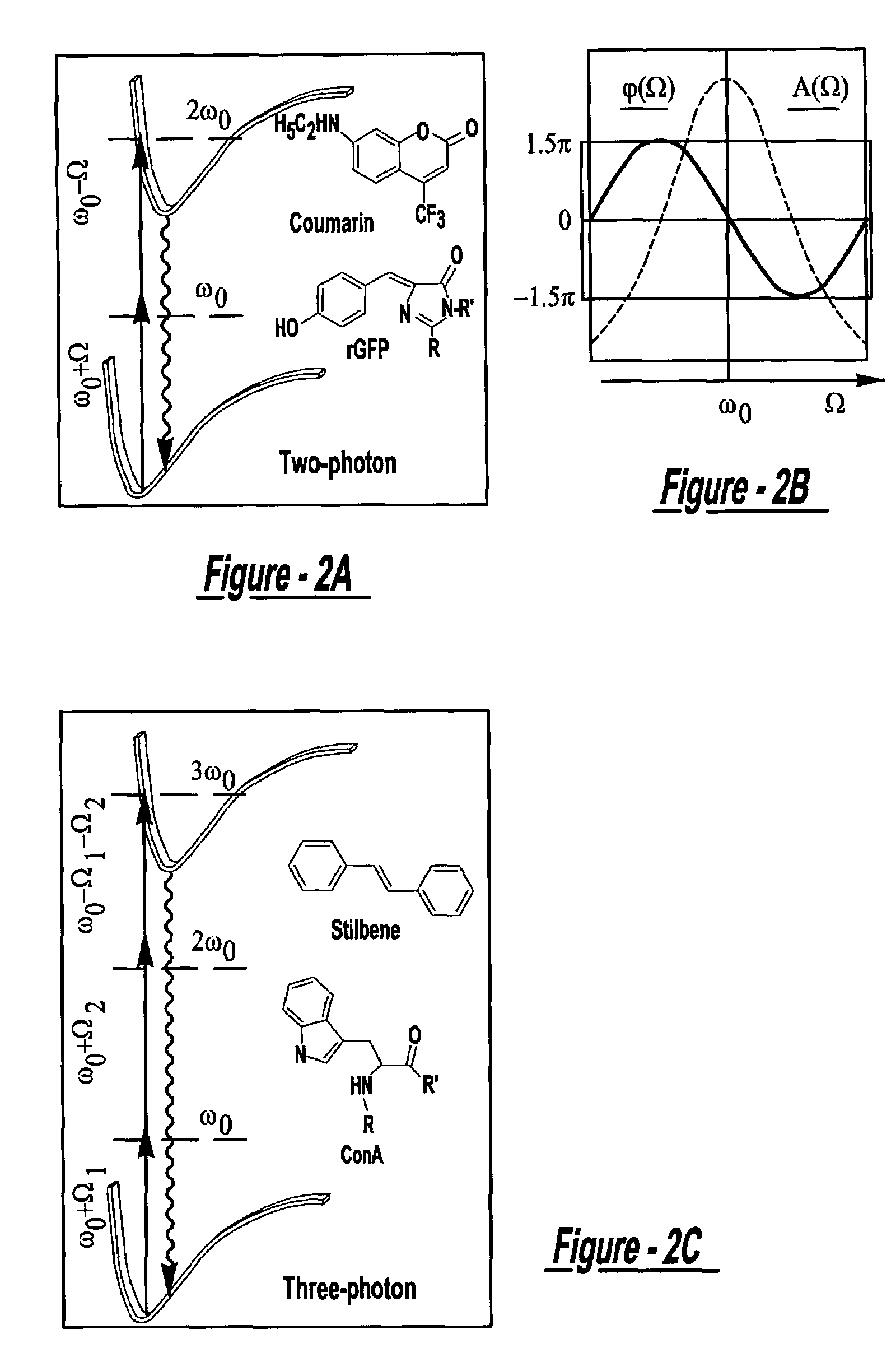
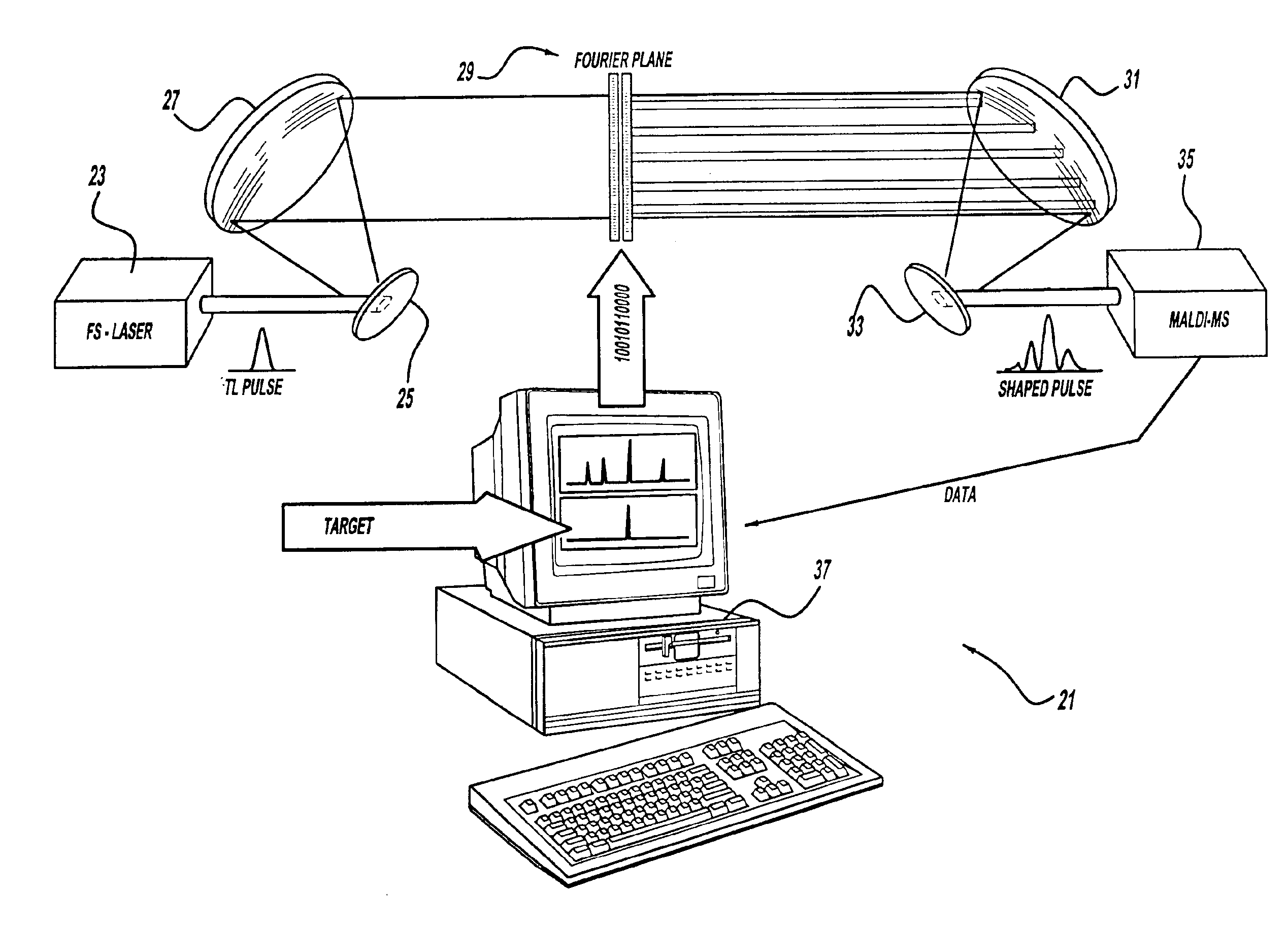
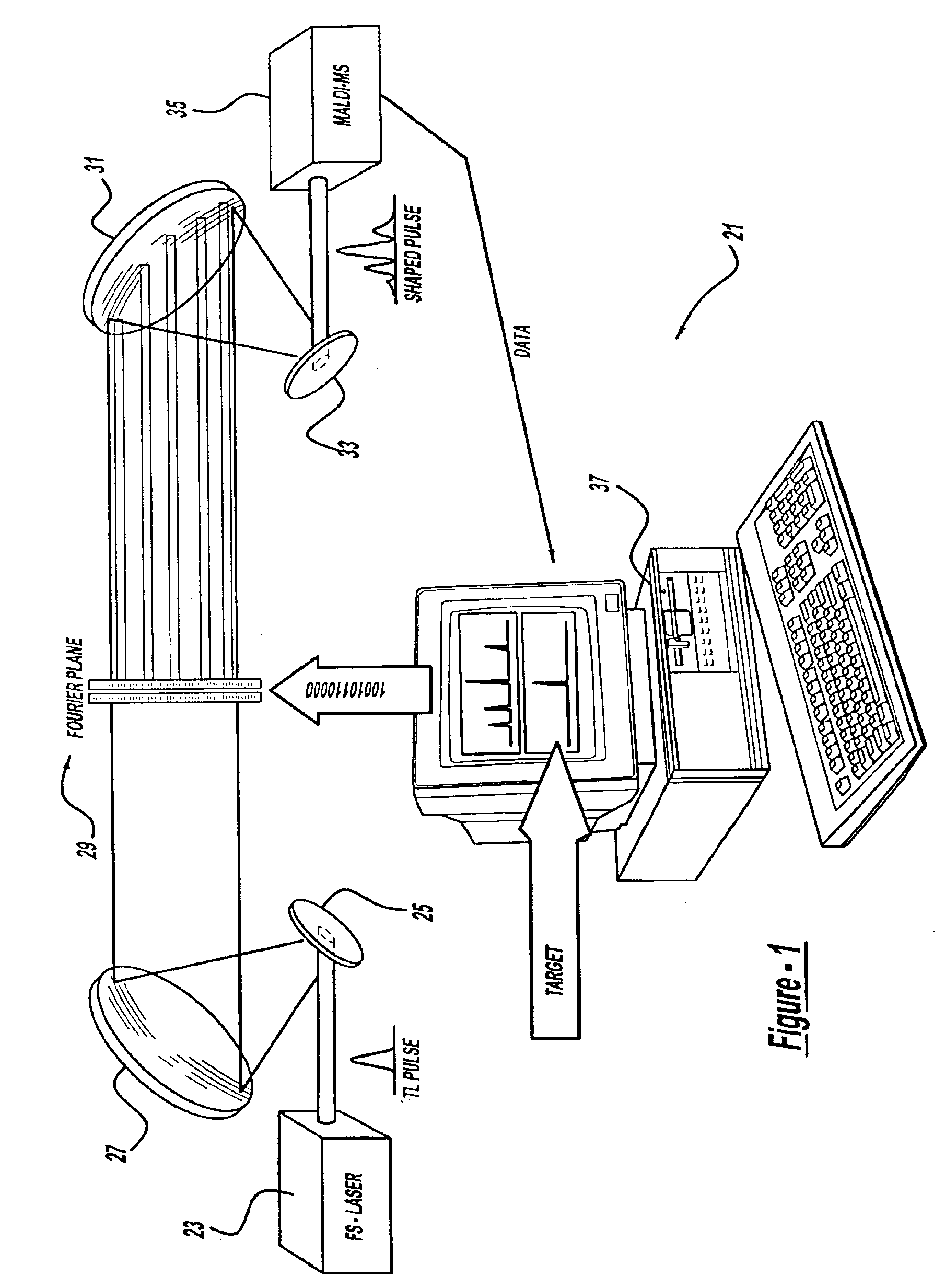
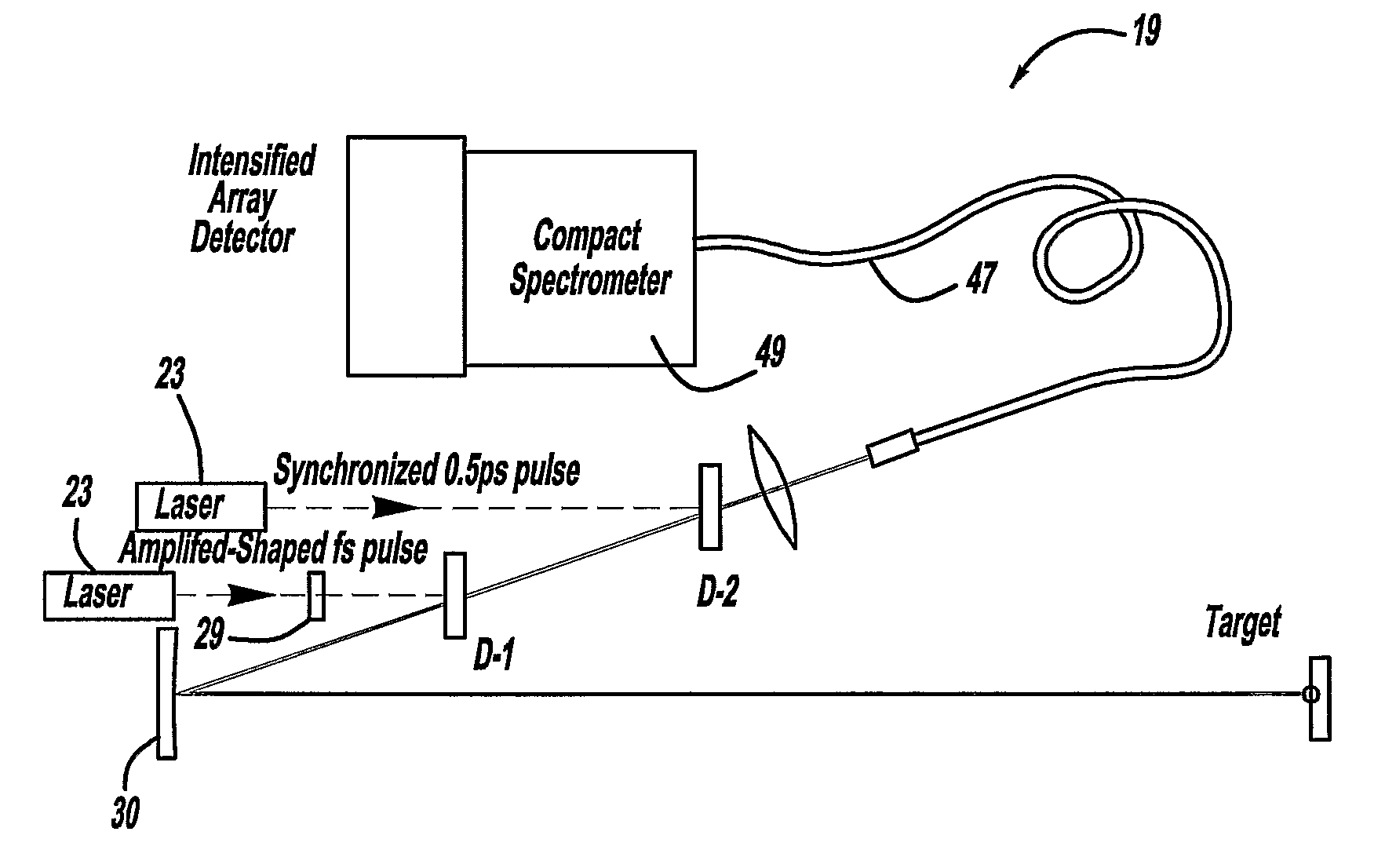
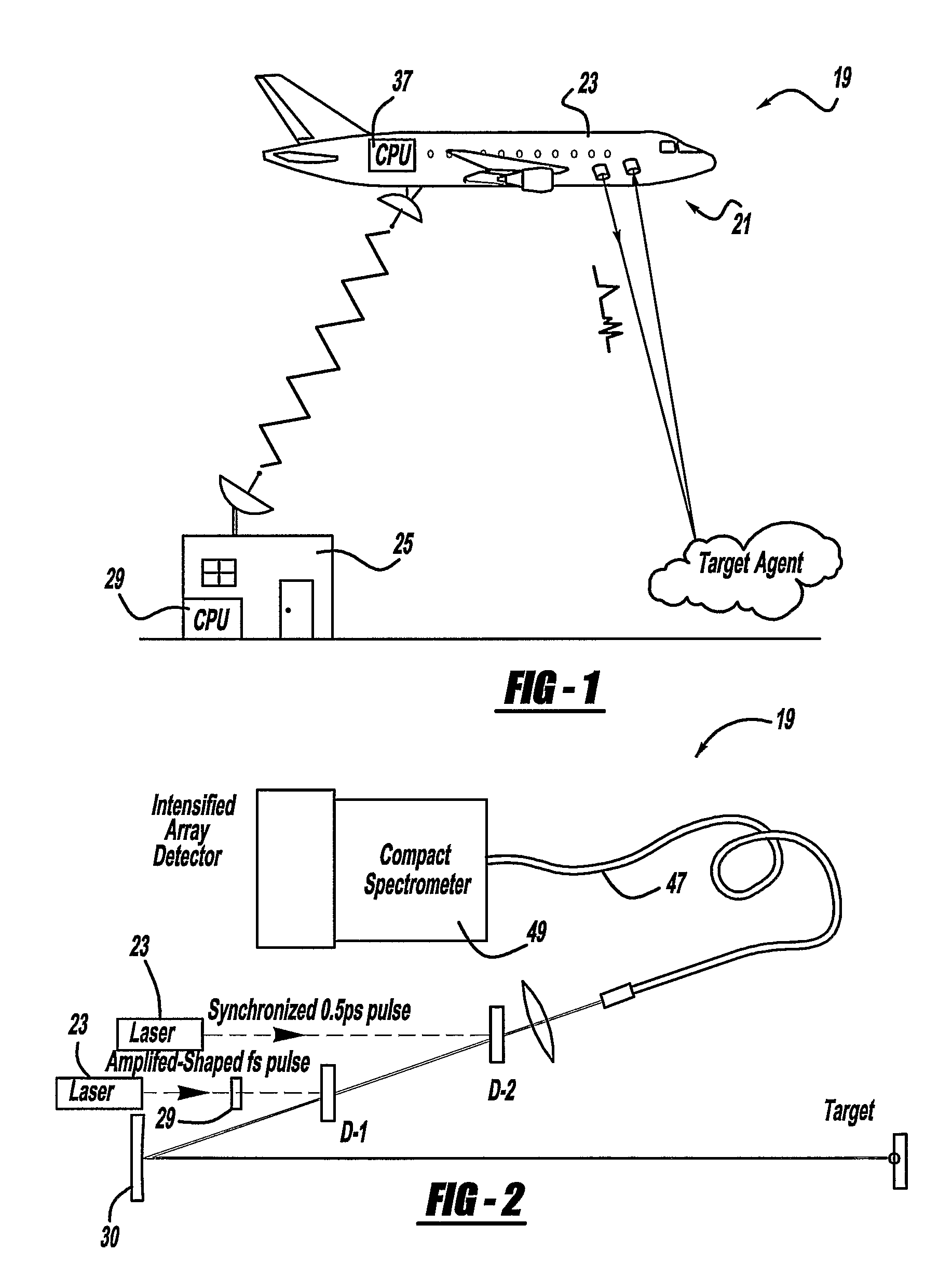
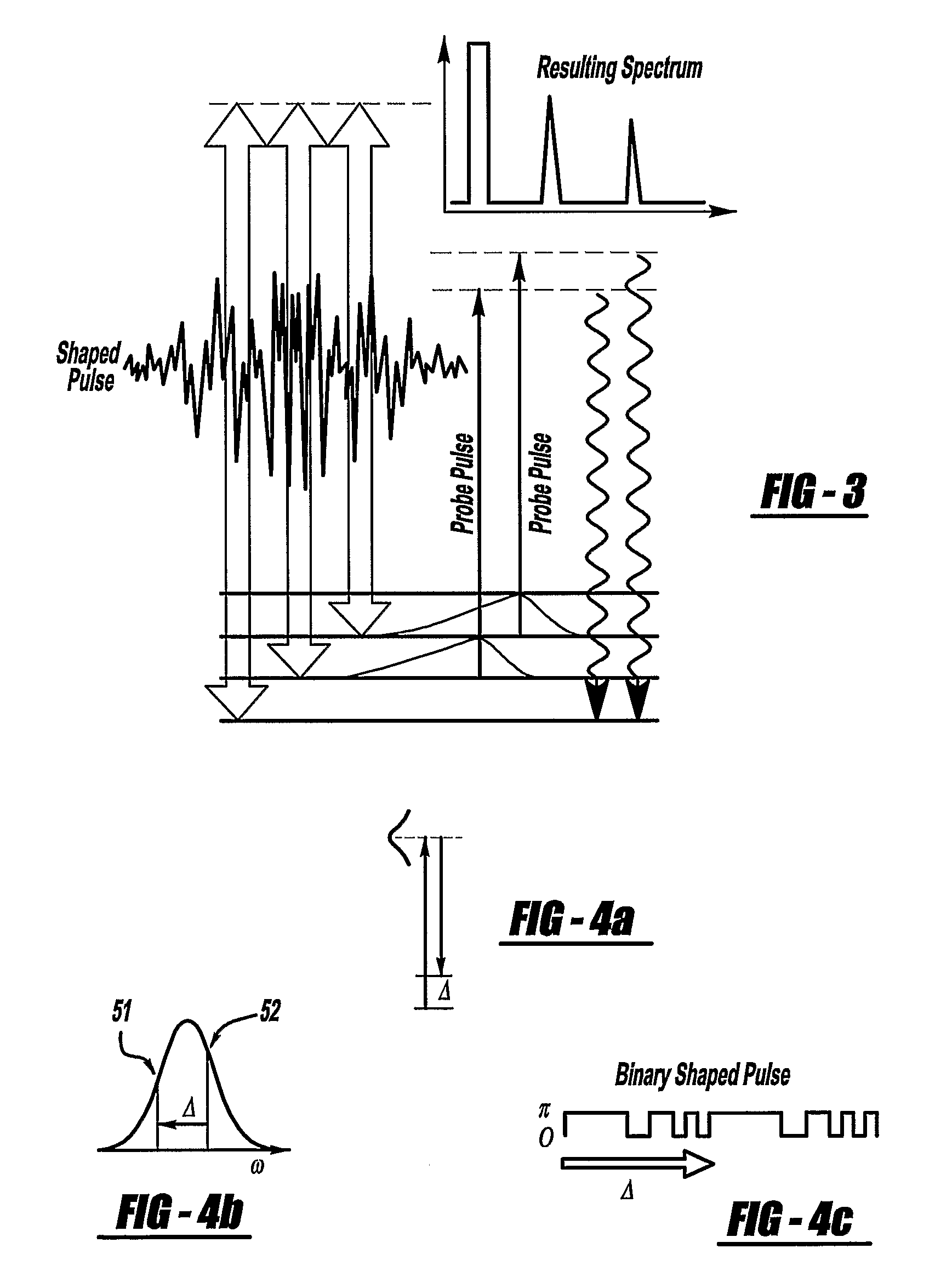
A laser and monitoring system is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the system includes a laser, pulse shaper and detection device. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and binary pulse shaping (BPS). Still another aspect of the present invention uses a laser beam pulse, a pulse shaper and a SHG crystal. In yet another aspect of the present invention, a multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan (hereinafter “MIIPS”) method is used to characterize the spectral phase of femtosecond laser pulses and to correct them. A further aspect of the system of the present invention is employed to monitor environmental chemicals and biological agents, including toxins, explosives, and diseases.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Laser system using ultrashort laser pulses
ActiveUS7450618B2Easy to set upEasy to useLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansFemto second laserCharacterization test
A laser system using ultrashort laser pulses is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the system includes a laser, pulse shaper and detection device. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and a spectrometer. Still another aspect of the present invention uses a laser beam pulse, a pulse shaper and a SHG crystal. In yet another aspect of the present invention, a multiphoton intrapulse interference phase scan system and method characterize the spectral phase of femtosecond laser pulses. Fiber optic communication systems, photodynamic therapy and pulse characterization tests use the laser system with additional aspects of the present invention.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
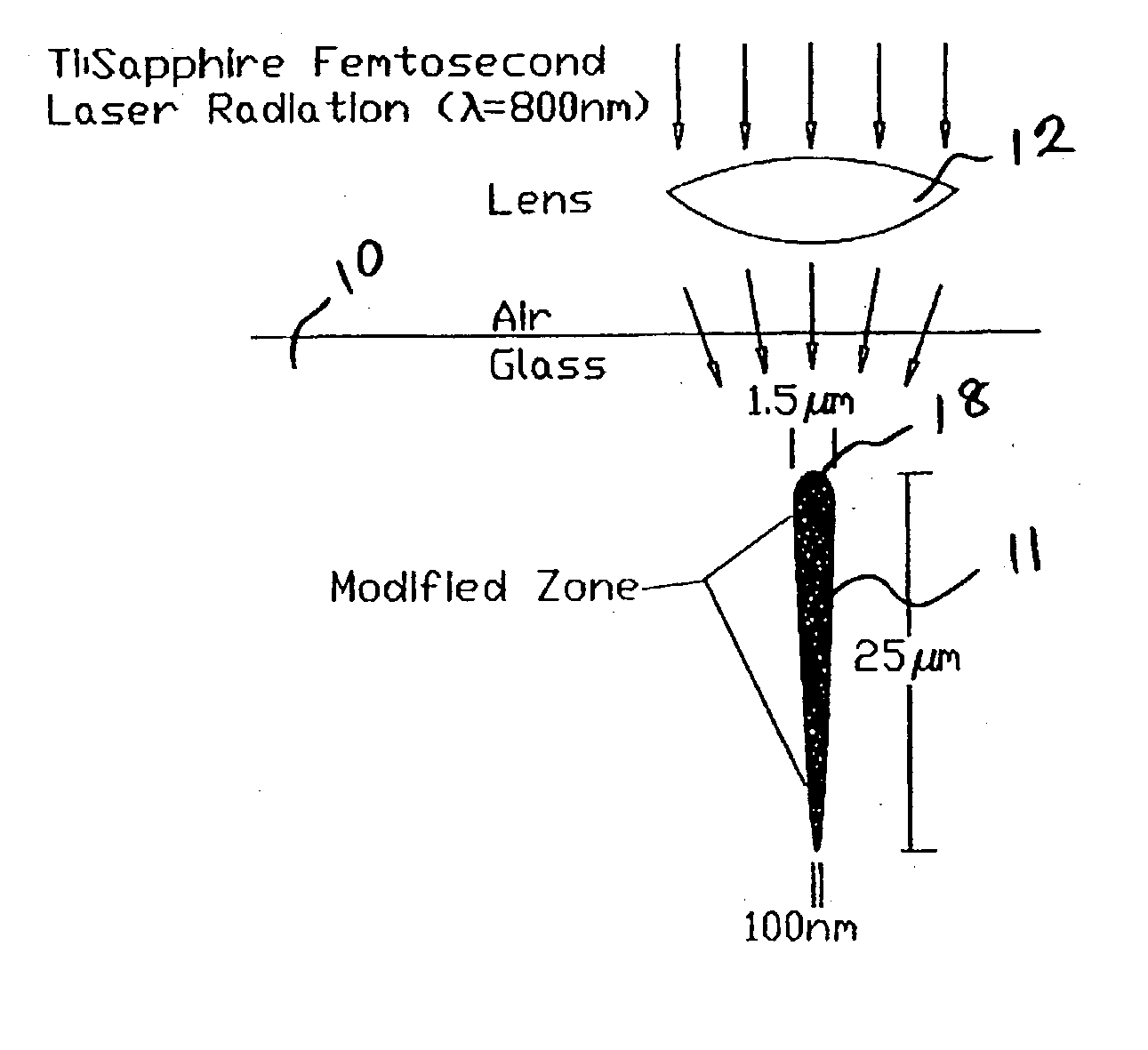
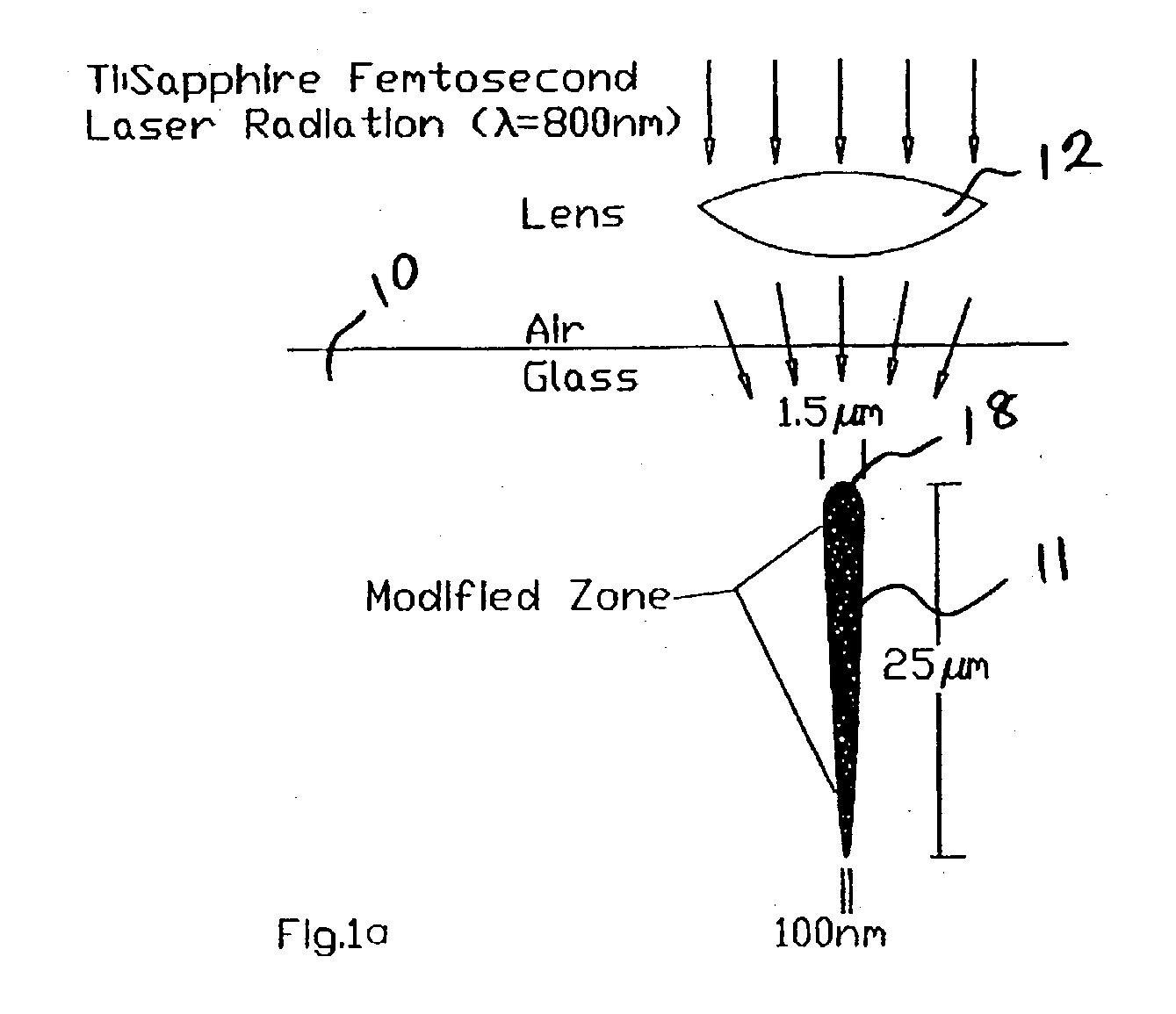
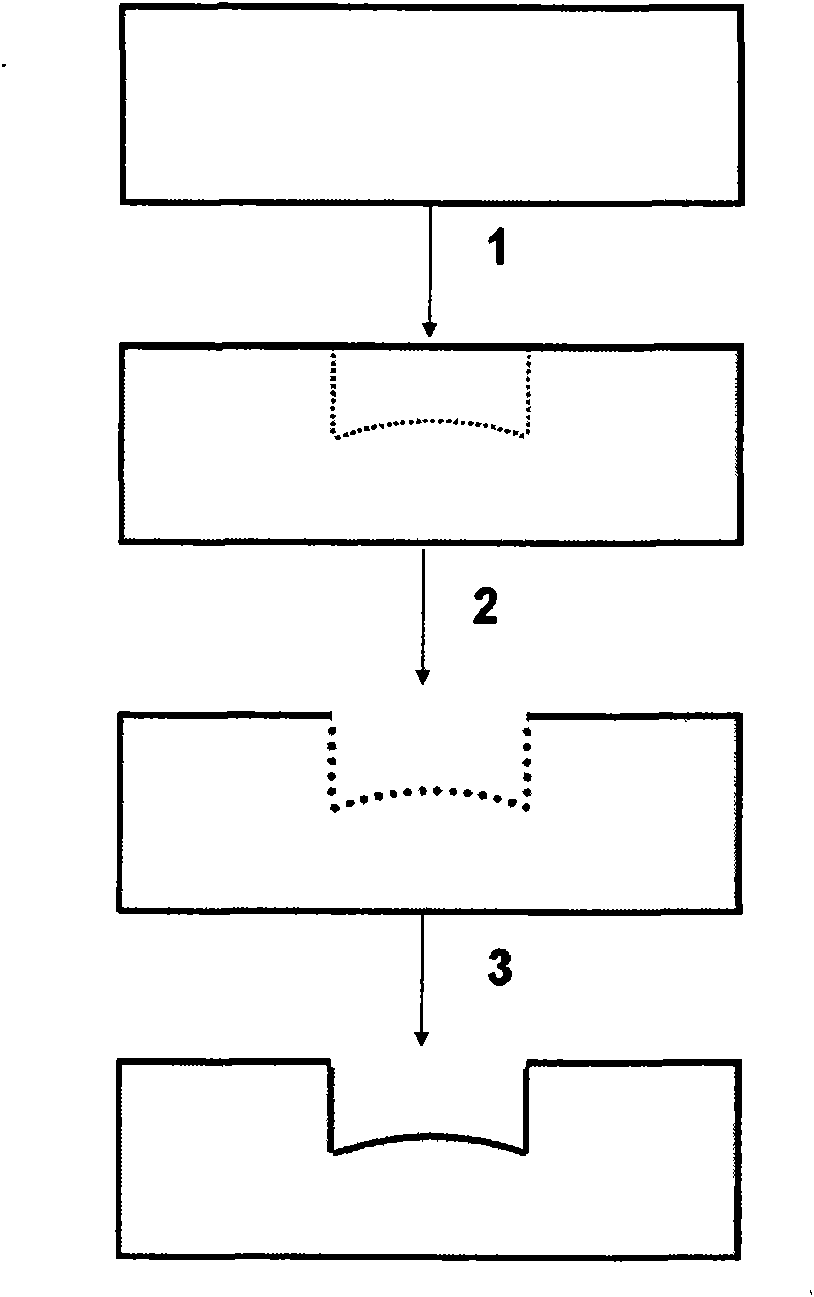
Method of fabricating sub-micron structures in transparent dielectric materials
A sub-micron structure is fabricated in a transparent dielectric material by focusing femtosecond laser pulses into the dielectric to create a highly tapered modified zone with modified etch properties. The dielectric material is then selectively etched into the modified zone from the direction of the narrow end of the tapered zone so that as the selective etching proceeds longitudinally into the modified zone, the progressively increasing width of the modified zone compensates for lateral etching occurring closer to the narrow end so as to produce steep-walled holes. The unetched portion of the modified zone produced by translating the laser beam close to and parallel to the bottom surface of the dielectric can serve as an optical waveguide to collect light from or deliver light to the etched channel which can contain various biological, optical, or chemical materials for sensing applications.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
System and method of performing femtosecond laser accomodative capsulotomy
Disclosed is a system and method for making a first incision in an anterior capsule of a capsular bag, the first incision being less than or equal to approximately 3.5 mm in diameter and making a second incision in the anterior capsule, the second incision being less than or equal to approximately 3.0 mm in diameter. The first incision and the second incision are positioned off-center from a center portion of the anterior capsule. The method includes performing lens fragmentation of a lens in the capsular bag to yield lens material, inserting a first instrument into the first incision, inserting a second first instrument into the second incision and removing the lens material via one of the first instrument and the second instrument and through one of the first incision and the second incision. The tensile structure of the anterior portion of the capsular bag is maintained such that accommodation exists within the eye after insertion of the intraocular lens.
Owner:IANCHULEV PRAVOSLAVA
Manipulating the size of waveguides written into substrates using femtosecond laser pulses
InactiveUS20030099452A1Control over the refractive index profile of the waveguidesPhotomechanical apparatusCoupling light guidesFemto second laserLight beam
Waveguides produced in bulk glass using femtosecond pulsed lasers have diameters and refractive index profiles that are manipulated by additional motions or beams. For example, spot focuses of the femtosecond pulsed lasers trace overlapping or widened tracks by superimposing additional relative motions between the spot focuses and the bulk glass. Additional femtosecond pulsed beams can also be used to produced widened waveguides.
Owner:CORNING INC
Multifunctional optical micro-control device
InactiveCN101216414AOvercome singleOvercome deficienciesSurface/boundary effectMaterial analysis by optical meansFemto second laserCcd camera
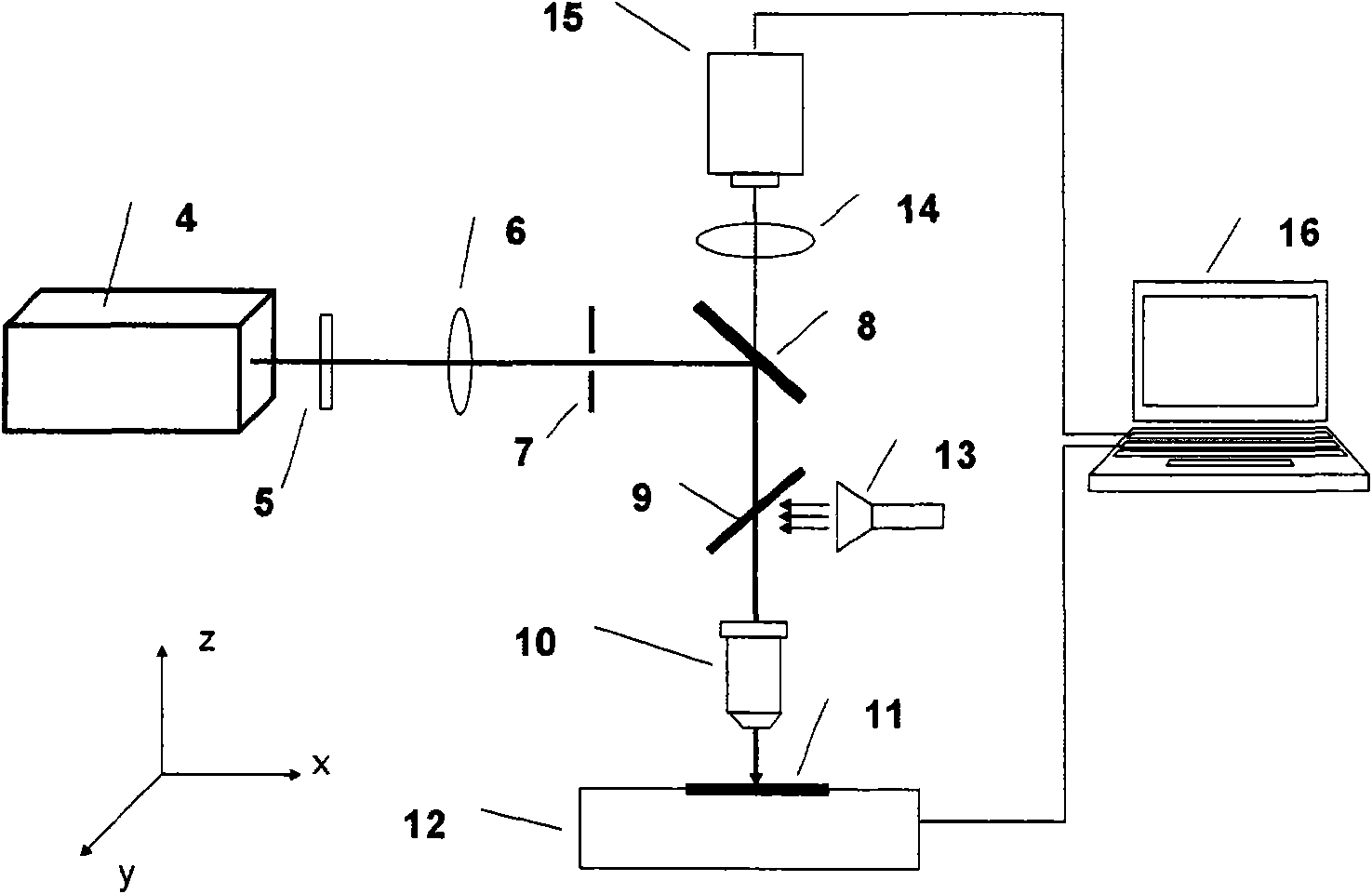
A multifunctional optical micro-manipulation device comprises a femtosecond laser, an optical tweezers laser, an optical system, a stage, a light source system, an imaging system, a spectral measurement system and a computer, wherein the optical system comprises a shutter, an attenuator, a focusing lens, a near IR reflector and a microscopic objective lens; the light source system comprises an illumination light source and a condenser lens; the microscopic objective lens is arranged on the stage for condensing a laser beam emitted by a laser generator onto a sample; the condenser lens is arranged below the stage for condensing a visible light emitted by the illumination light source onto the sample; and the imaging system includes an IR filter and CCD camera sequentially disposed on the projection light path of the near IR reflector. By integrating three functions of laser tweezers, femtosecond laser scissors and microspectrometer in one system, the invention can overcome the singleness and the disadvantages of the prior laser micro-beam technology and can be widely used for studying in biological, medical, biophysical, material chemistry and nano-technology fields.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for Modifying the Refractive Index of an Optical Material and Resulting Optical Vision Component
ActiveUS20120310340A1Little and no scattering lossSpectales/gogglesLaser surgeryOptical polymersOptical axis
A method for modifying the refractive index of an optical polymeric material. The method comprises continuously irradiating predetermined regions of an optical, polymeric material with femtosecond laser pulses to form a gradient index refractive structure within the material. An optical device includes an optical, polymeric lens material having an anterior surface and posterior surface and an optical axis intersecting the surfaces and at least one laser-modified, GRIN layer disposed between the anterior surface and the posterior surface and arranged along a first axis 45° to 90° to the optical axis, and further characterized by a variation in index of refraction across at least one of at least a portion of the adjacent segments and along each segment.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
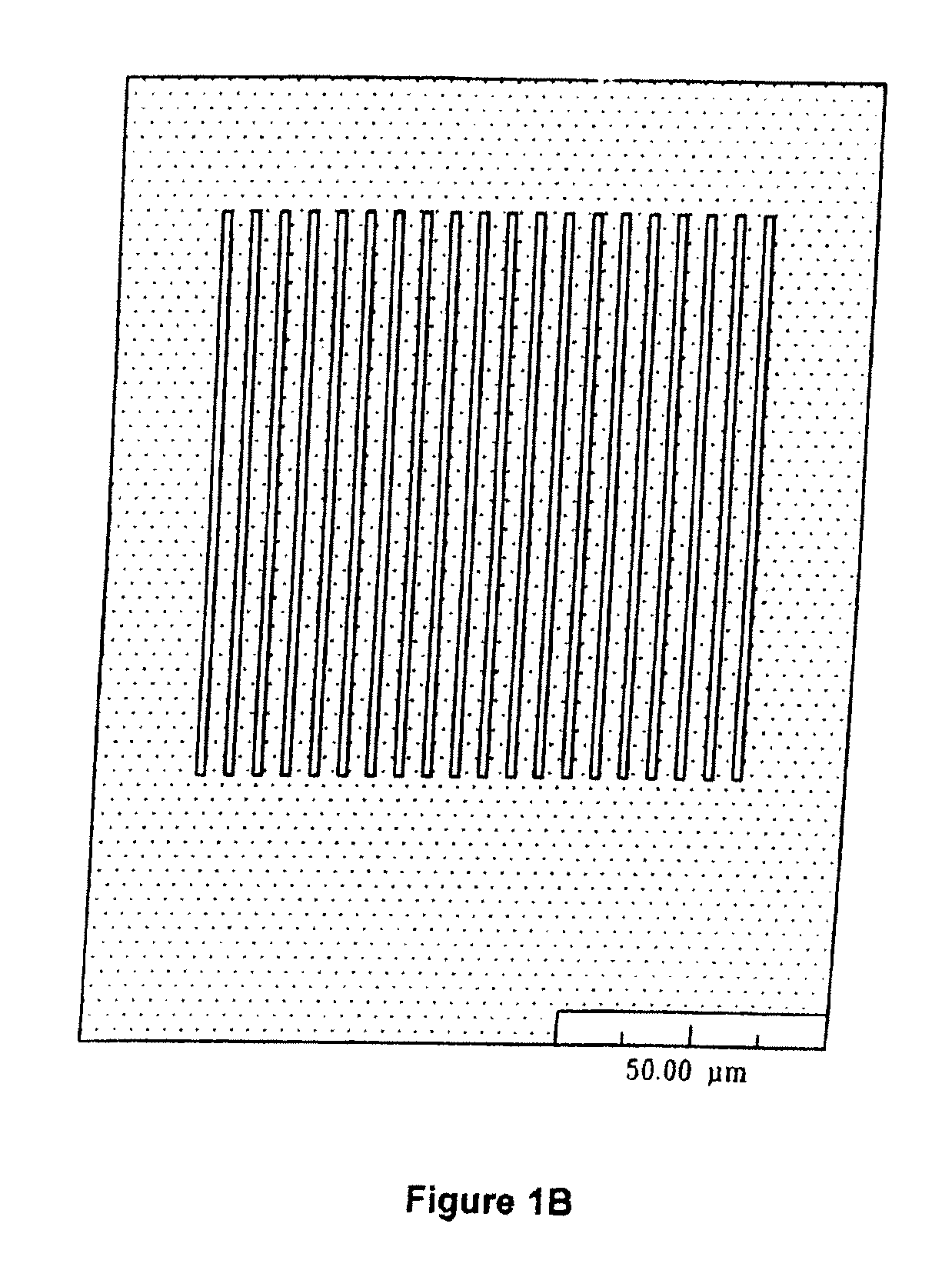
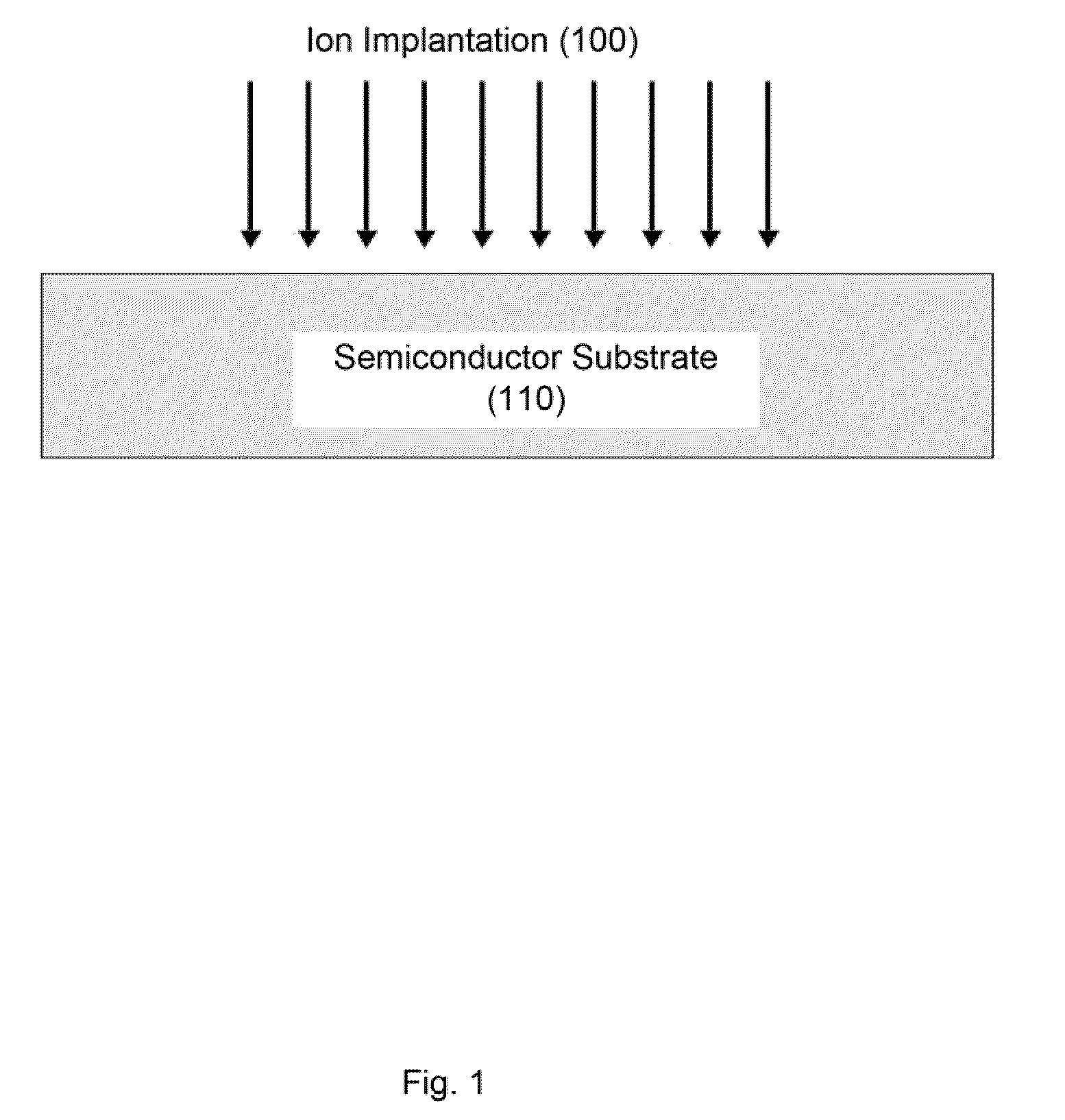
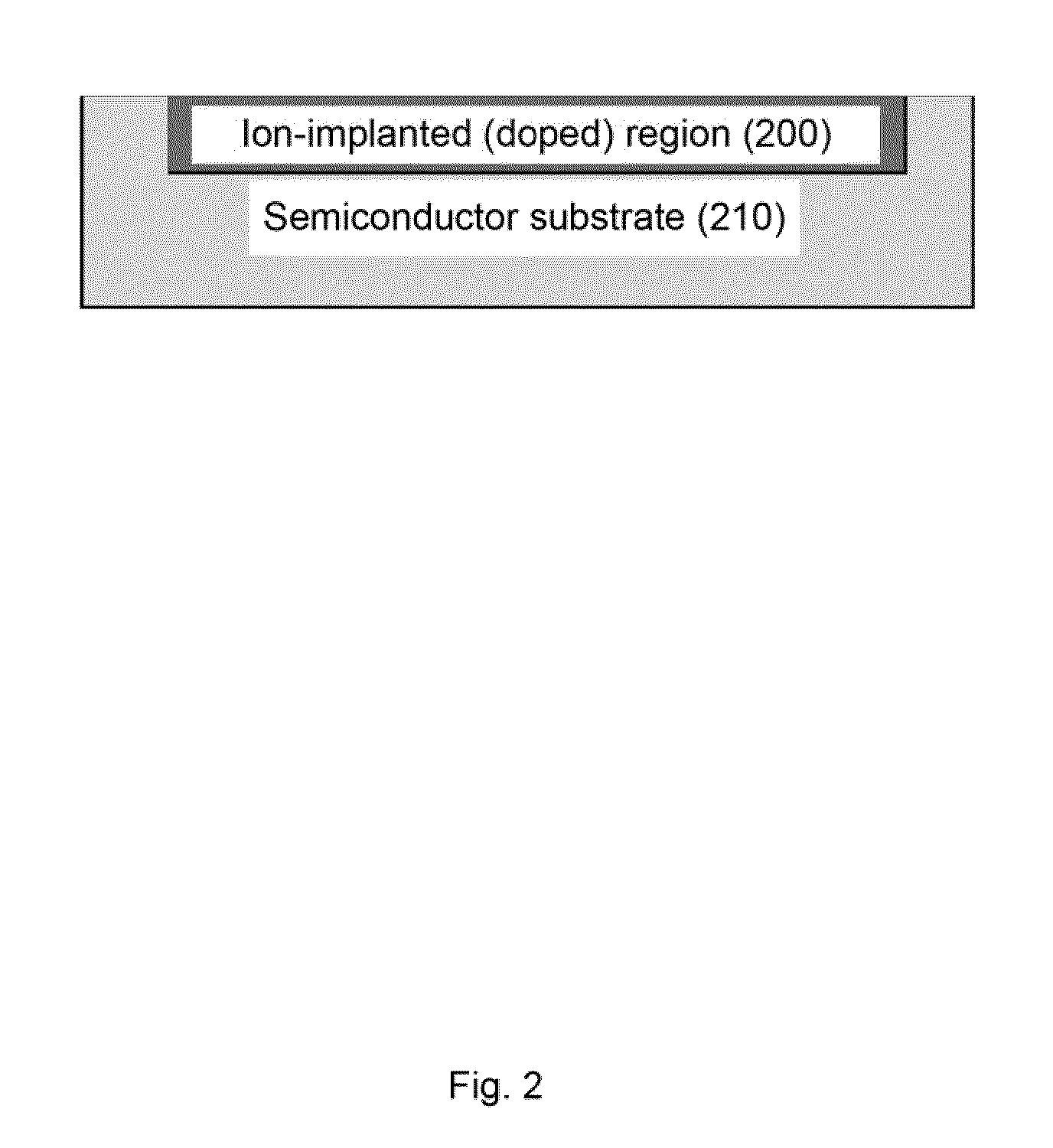
High sensitivity photodetectors, imaging arrays, and high efficiency photovoltaic devices produced using ion implantation and femtosecond laser irradiation
ActiveUS20100052088A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
The present invention relates generally to methods for high throughput and controllable creation of high performance semiconductor substrates for use in devices such as high sensitivity photodetectors, imaging arrays, high efficiency solar cells and the like, to semiconductor substrates prepared according to the methods, and to an apparatus for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:SIONYX
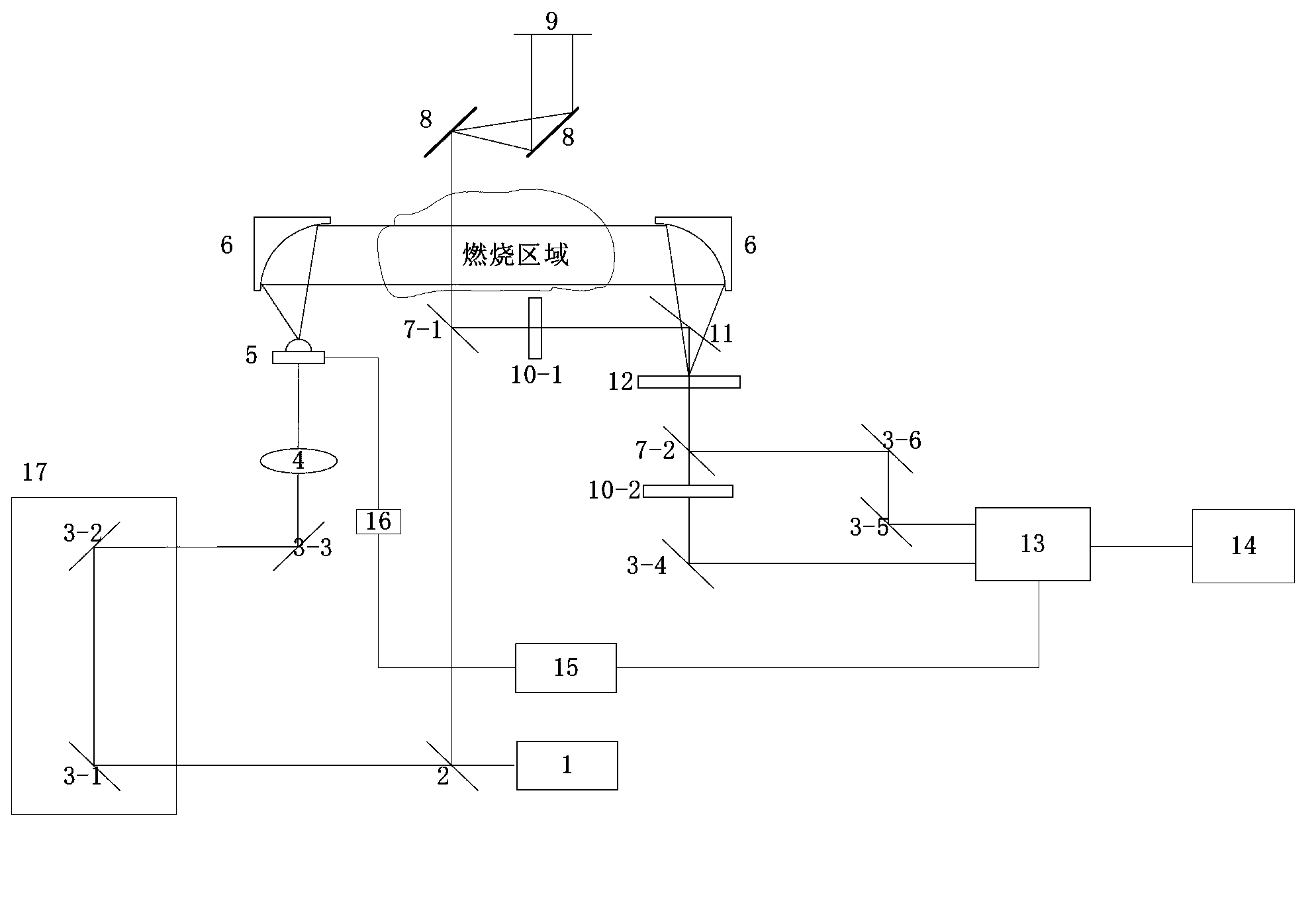
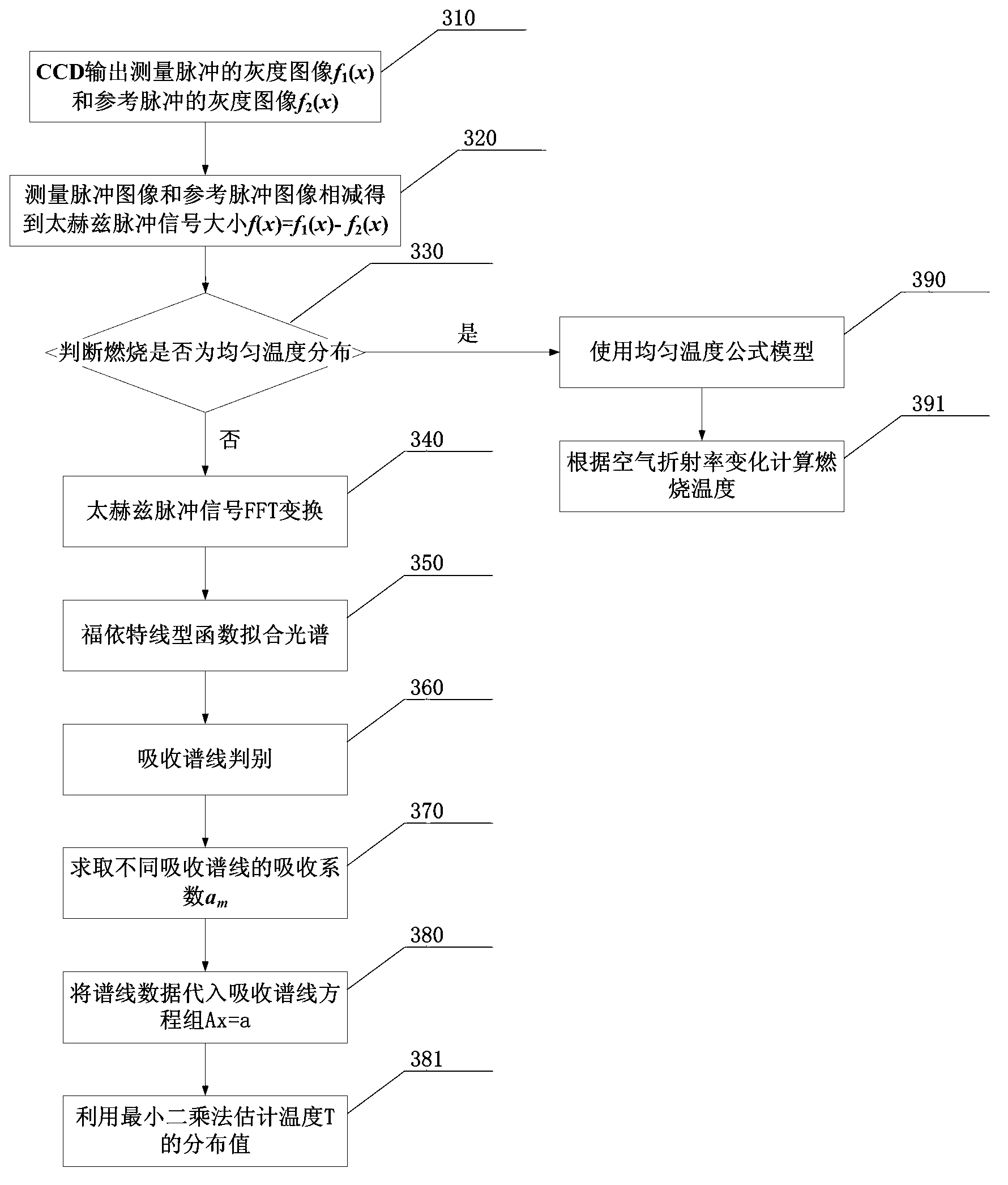
Terahertz pulse measurement-based burning temperature sensing device and method
ActiveCN103076107AAchieving Wavelength Division Electro-Optic SamplingEasy accessThermometers using physical/chemical changesBeam splitterGrating
The invention discloses a terahertz pulse measurement-based burning temperature sensing device and a terahertz pulse measurement-based burning temperature sensing method. Laser is emitted from a femtosecond laser device, and is divided into reference laser and detection laser through a beam splitter, the detection laser is focused on a photoconduction antenna type terahertz emitter, terahertz pulses emitted by the terahertz emitter are focused on a ZnTe crystal through an off-axis paraboloid lens group; and the reference layer is collimated and is coincident with terahertz waves focused on the ZnTe crystal after passing through a semi-transmission and self-reflection mirror, parallel grating groups and a polarizing film, the terahertz waves are modulated by using Pockels effect of the ZnTe crystal, and image signals corresponding to collected first reference layer carrying terahertz pulse strength information and second reference laser not carrying the terahertz pulse strength information are input into a computer by a CCD (Charge Coupling Device) detector for subsequence processing. According to the invention, the precision and speed of the non-contact combustion measurement method are increased, and the non-contact measurement of combustion object temperature and temperature distribution is realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Femtosecond laser micromachining of a contact lens and a contact lens manufactured thereby
InactiveUS20060285071A1Minimal heat related damageEye diagnosticsLaser beam welding apparatusFemto second laserLight beam
A method of providing a feature on a contact lens including applying a femtosecond laser beam to ablate at least a portion of the contact lens to provide the feature on the contact lens. In one embodiment, the femtosecond laser beam has a pulse width between 10×10−15 seconds and 200×10−15 seconds, and has a wavelength between 100 nm and 1500 nm. A contact lens is also provided including at least one fenestration fluidically connecting the anterior surface and the posterior surface, the fenestration being formed using a femtosecond laser in a manner that areas surrounding the fenestration are substantially free of heat damage.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
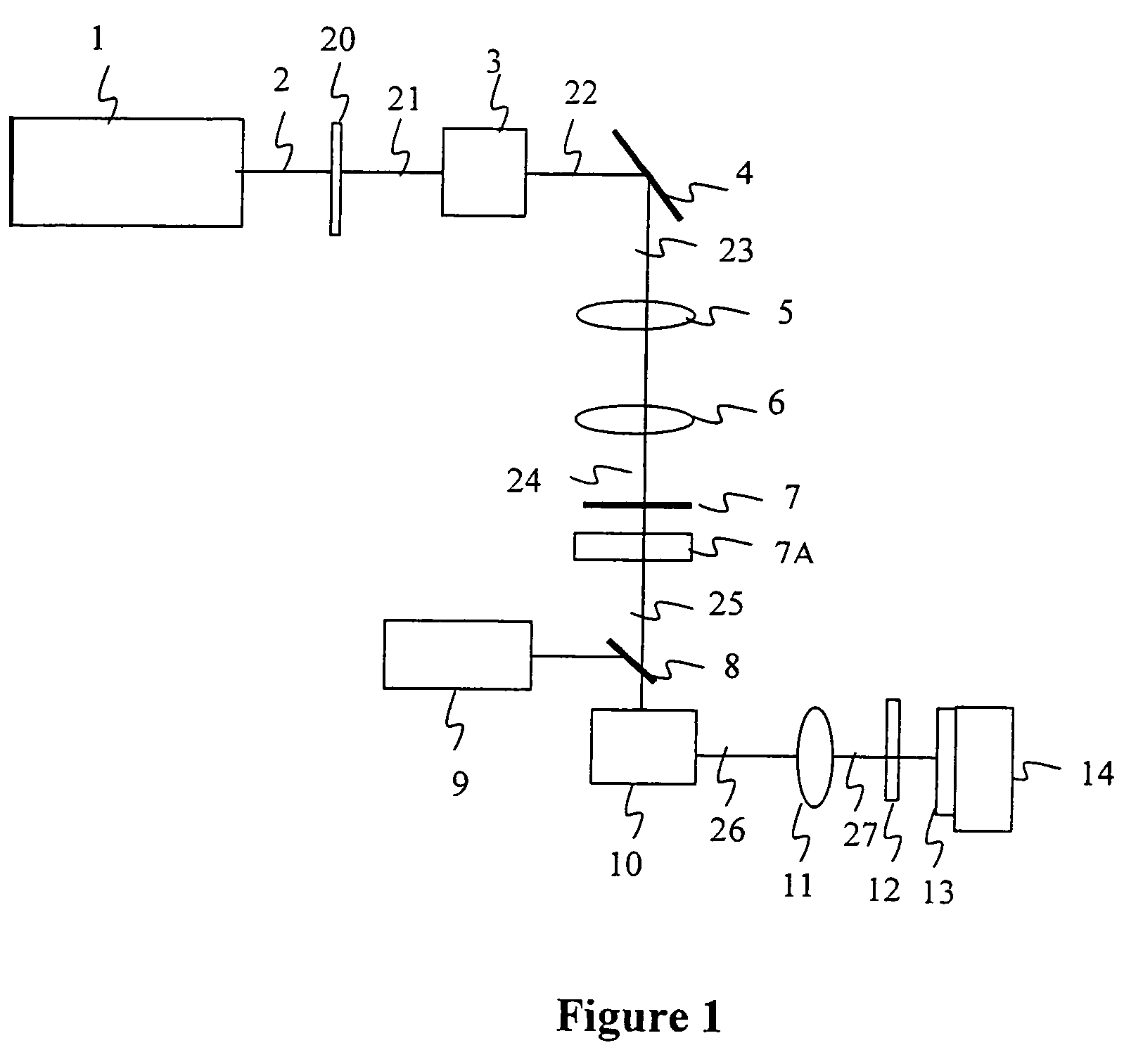
Control system and apparatus for use with laser excitation or ionization
InactiveUS7105811B2Way fastMaximize sensitivityLaser detailsIon sources/gunsPhotodynamic therapyControl system
A control system and apparatus for use with laser ionization is provided. In another aspect of the present invention, the apparatus includes a laser, pulse shaper, detection device and control system. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and a mass spectrometer. In yet other aspects of the present invention, the control system and apparatus are used in MALDI, chemical bond cleaving, protein sequencing, photodynamic therapy, optical coherence tomography and optical communications processes.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Surgical procedure and instrumentation for intrastromal implants of lens or strengthening materials
InactiveUS20070219542A1Improve permeabilityIncrease elasticityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal surfaceFemto second laser
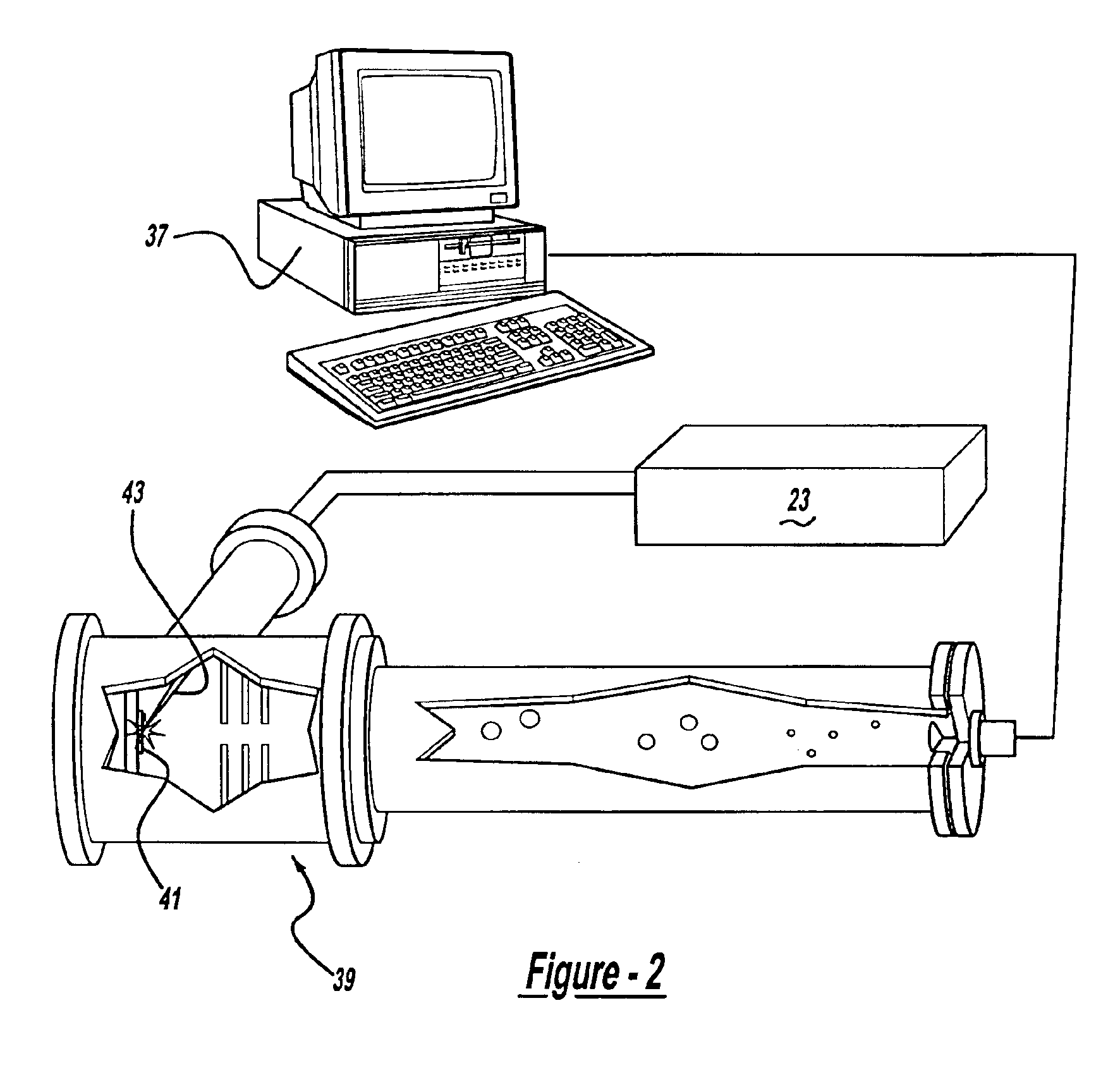
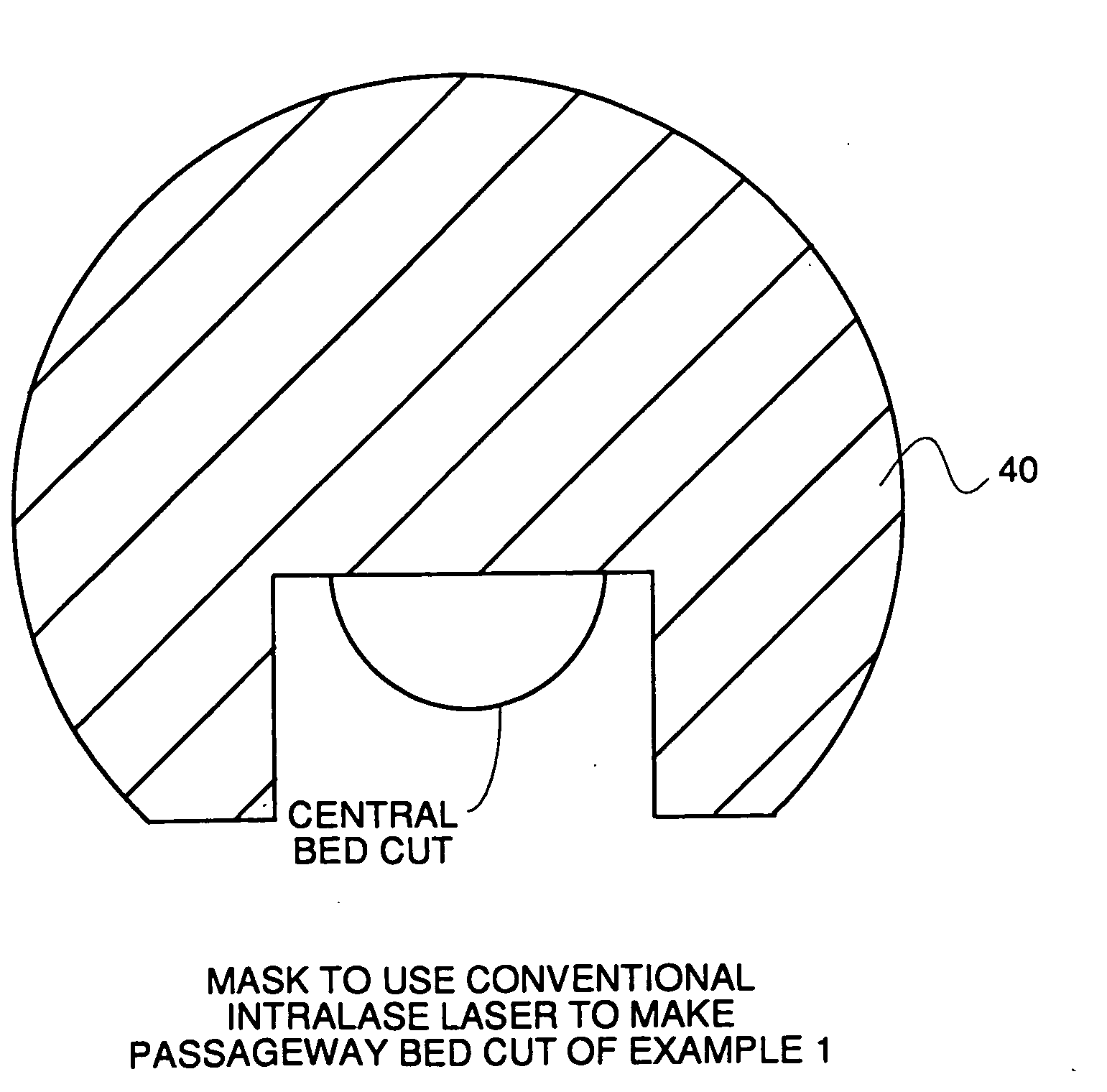
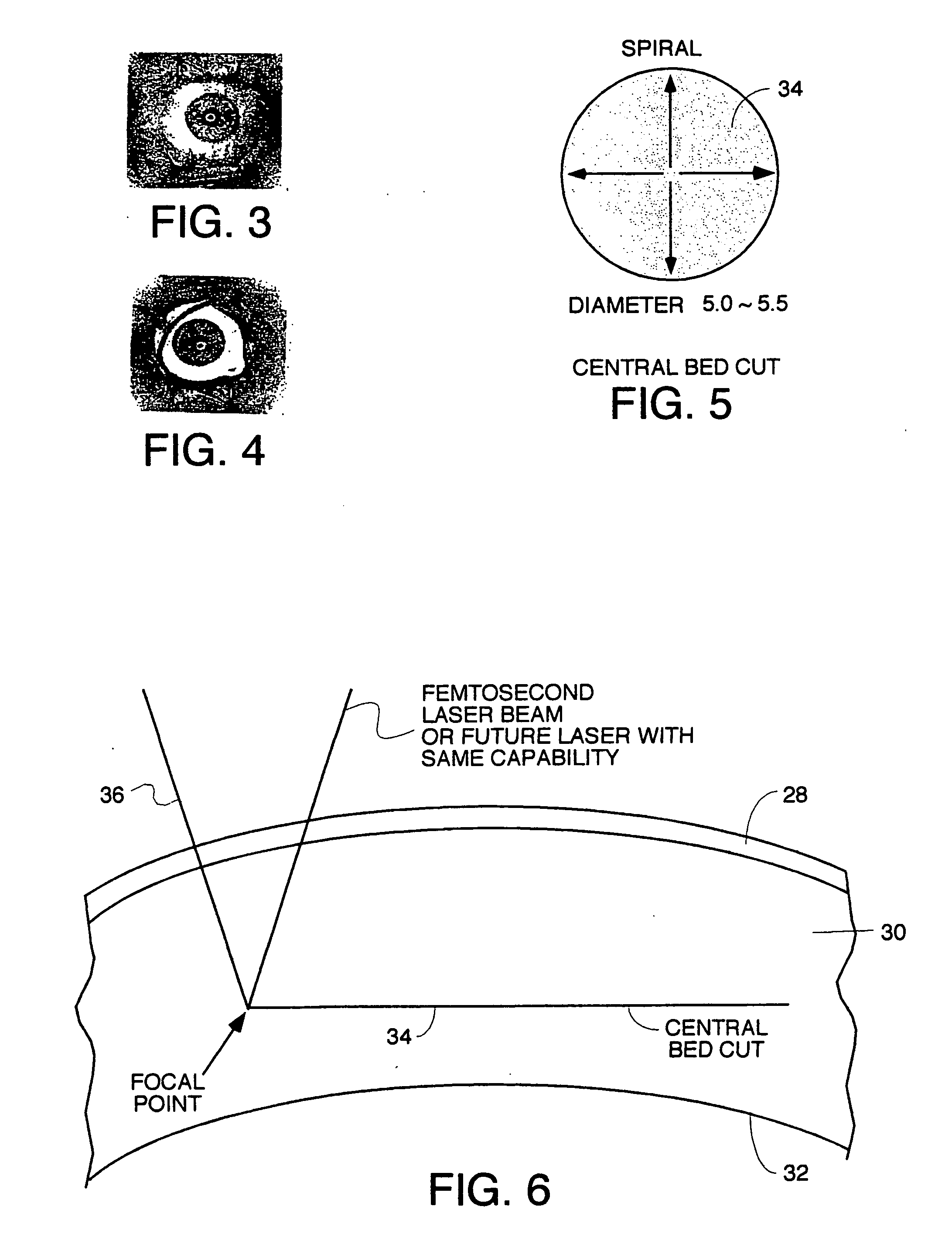
A surgical procedure for implanting a lens or strengthening material in a cornea without making a flap as is done in Lasik procedures. A femtosecond laser or some future developed laser which has the same ability is modified to cut a pocket in the stroma layer of a cornea with no side cuts and only an opening at the surface of a cornea. Alternatively, a modified microkeratome shaped and sized to form the desired shape for a passageway bed cut which is cut to join a central bed cut. Alternatively, the passageway bed cut can be done using a femtosecond laser or some future developed laser which has the same ability. The passageway bed cut is smaller in dimension than a central bed cut of a pocket in which the lens will be implanted in procedures where an expandable lens or strengthening material is used. A modified microkeratome having a web, a central blade shaped to form the passageway bed cut and sled runner on either side of the blade and separated therefrom is also disclosed. A patient interface with a mask is also disclosed to allow a femtosecond laser or some future developed laser which has the same ability may also be used to form both the central bed cut and a passageway bed cut or only a single bed cut with an opening at the surface of the cornea to form the pocket is also disclosed.
Owner:YAHAGI TORU
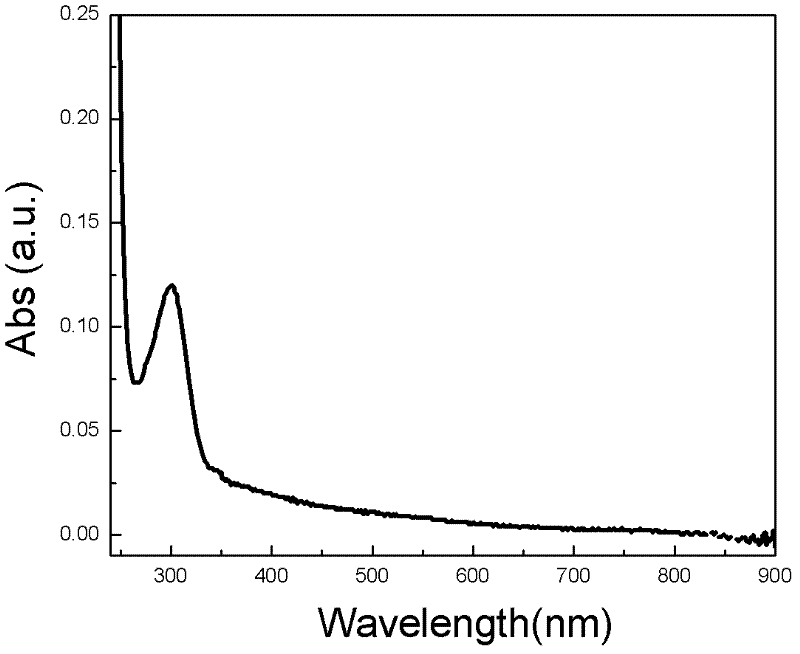
Preparation method of super-hydrophobic micro-nano structure on titanium alloy surface
The invention provides a preparation method of a super-hydrophobic micro-nano structure on a titanium alloy surface. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing ultrasonic cleaning on a titanium alloy sample respectively with acetone and anhydrous alcohol, to obtain a titanium alloy sample with a clean surface; performing femtosecond laser photoetching processing on the surface of the titanium alloy sample with the clean surface, to obtain the titanium alloy sample with the surface having the super-hydrophobic micro-nano structure in one step, wherein a femtosecond laser beam is fixed and perpendicular to the surface of a processed material, the single pulse energy of the femtosecond laser beam is 100mu J-800mu J, the pulse width is 100fs-500fs, the central wavelength is 500nm-1000nm, the repetition frequency is 500Hz-2kHz, and the size of the etched facula of the femtosecond laser beam is 0.5mum-300mum; the surface of the titanium alloy sample moves relative to the etched facula of the femtosecond laser beam along the three-dimensional directions x, y and z, the motion positioning precision in x and y directions is 50nm-100nm, and the motion positioning precision in z direction is 5nm-10nm.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING AERONAUTICAL MFG TECH RES INST
Method for preparing multistage metal micro-nanostructures inside micro fluidic chip
InactiveCN102311095ADecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMicro nanoSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention relates to a method for selectively preparing or integrating multistage silver micro-nanostructures inside various plane substrates and micro fluidic chip channels by the utilization of the femtosecond laser inducing metallic silver reduction technology. In addition, the silver multistage micro-nanostructure substrate prepared by the method is used as a reinforced substrate for surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy SERS. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: preparing a silver plating solution for femtosecond laser micro-nano machining, establishing a femtosecond laser micro-nano machining system for realizing multi-point scan in the silver plating solution, placing the silver plating solution and the substrate into the femtosecond laser micro-nano machining system and preparing the multistage silver micro-nanostructures on the substrate. According to the invention, a laser beam scans in the silver plating solution along a track designed in advance by a program. The preparation method is independent of the smoothness of the substrate. In particular, the preparation of silver multistage structure SERS substrate can be accomplished on the bottom of the micro fluidic chip channels, thus realizing catalysis and surface-enhanced raman test application.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
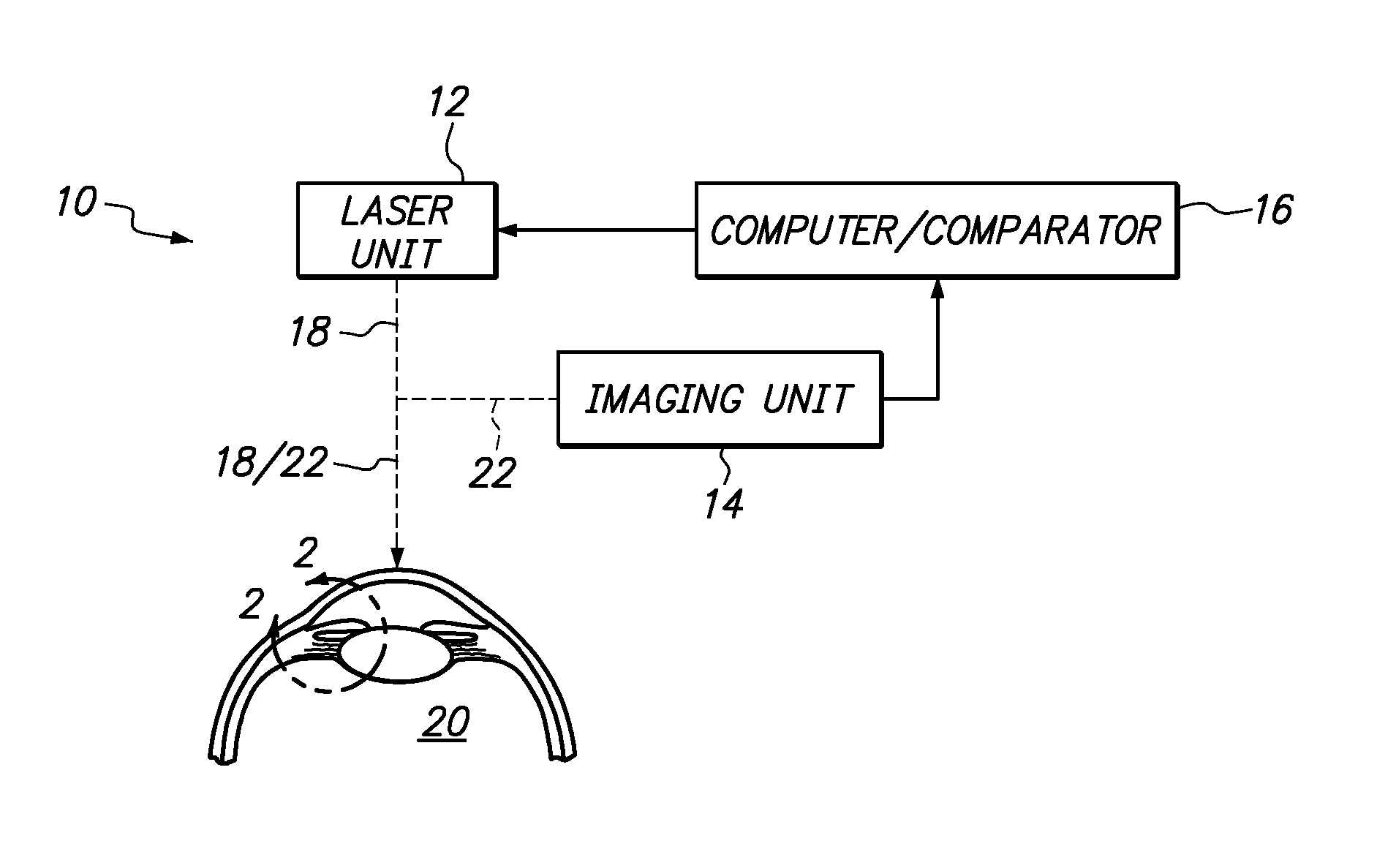
Method and system for reshaping the cornea
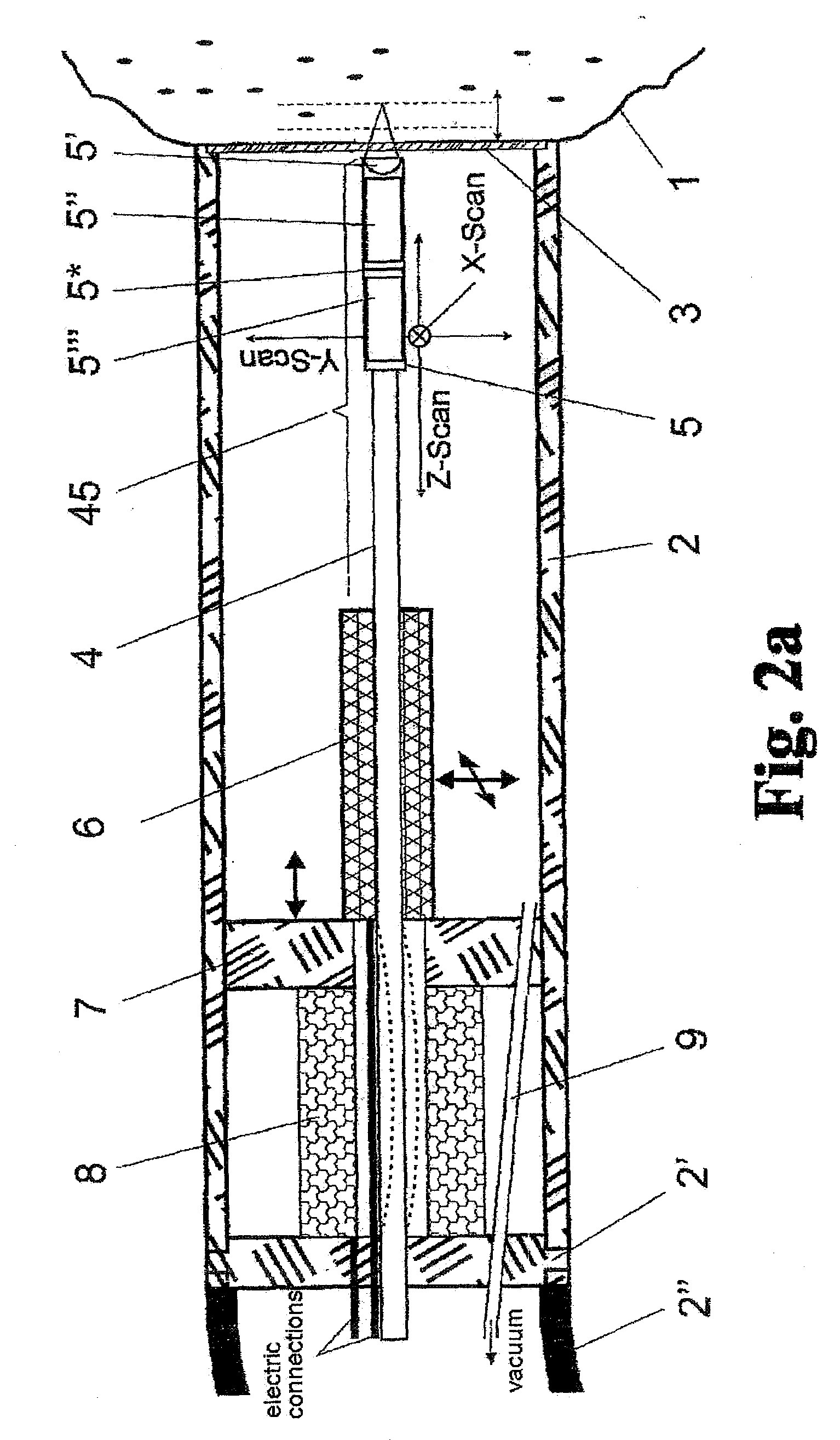
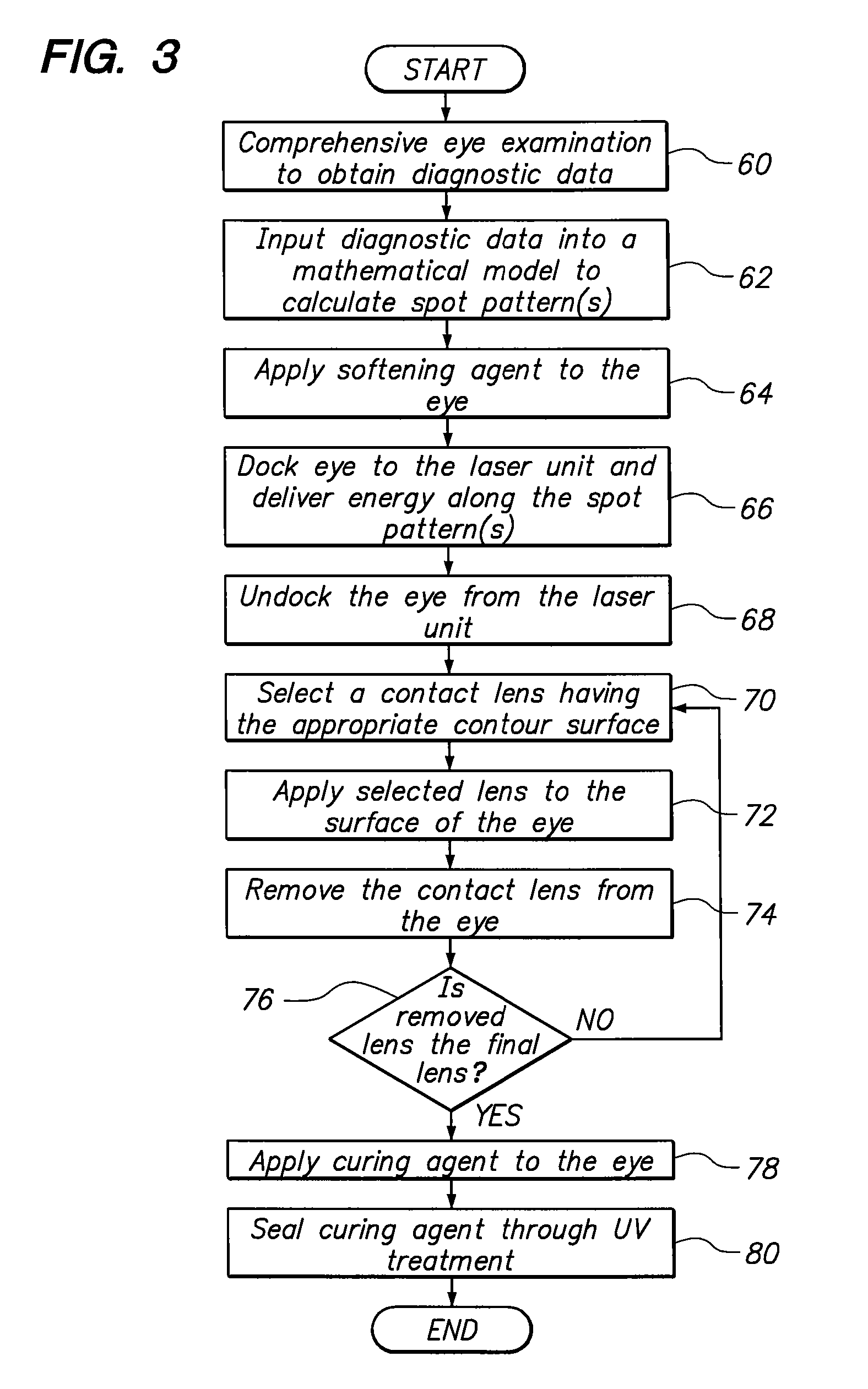
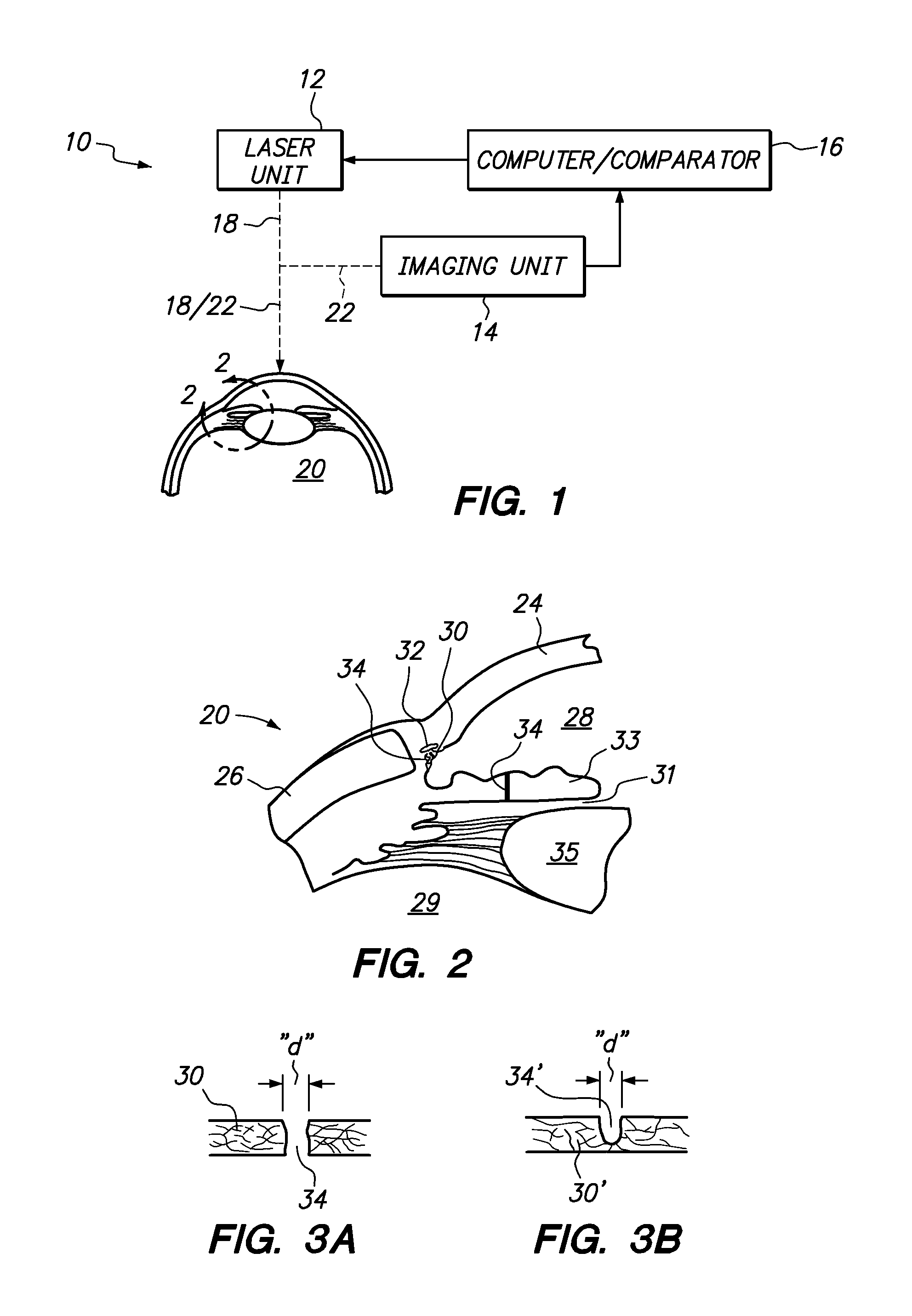
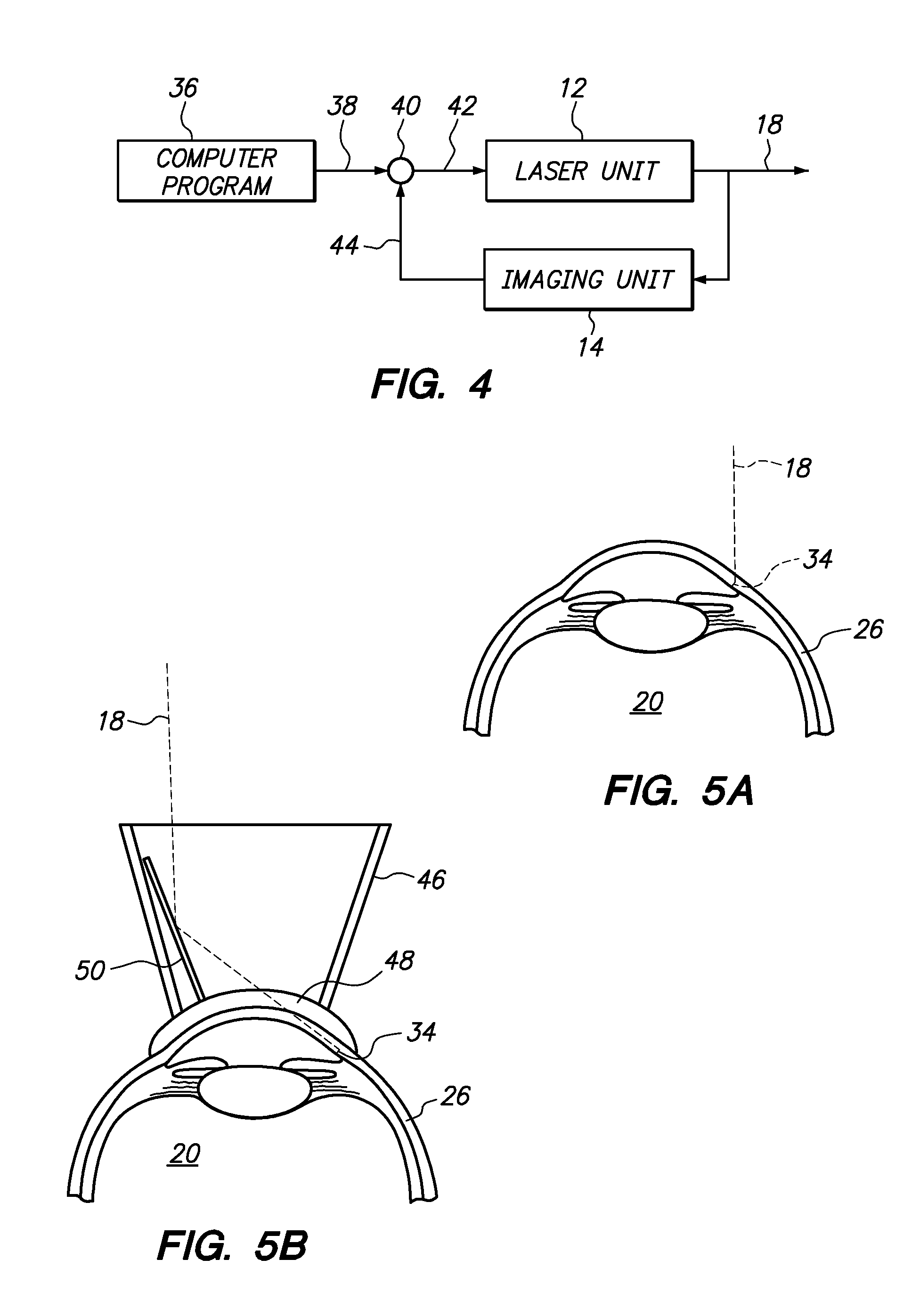
A system and method are provided for reshaping the surface of a resilient transparent material such as a cornea. In the system, a laser unit generates a femto-second laser beam to deliver focused energy inside the material. Specifically, the energy is focused over a defined spot pattern to weaken the material. Further, the system includes a contact element that forms a contour surface. In order to reshape the material, the system provides for holding the contour surface of the contact element against the surface of the weakened material. After holding the contour surface against the material for a pre-determined time duration, the surface of the material is reshaped with a desired configuration that substantially mimics the contour surface of the contact element.
Owner:TECHNOLAS PERFECT VISION
Laser modeling method for semiconductor material micro-nano multi-scale function surface
InactiveCN101219770AEasy to operateLow costNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsMicro nanoMaterials preparation
The invention relates to a laser shaping method of a multi-scale functional surface of micronano for semiconductor material, relating to micronano material preparation and laser micromachining technical field; the invention aims at providing a method and a device for preparing femtosecond laser of super-hydrophobic functionalization for microstructural surface based on the semiconductor material and through the systematically technical design of multi-scale surface micro-shaping and microstructural surface processing, and realizing optional and controllable preparation of semiconductor material surface having multi-scale microstructure such as micron, submicron and nano. The invention solves the technical problems such as high cost, low efficiency and difficult operation in traditional preparation methods of microstructural surface with super-hydrophobic function.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
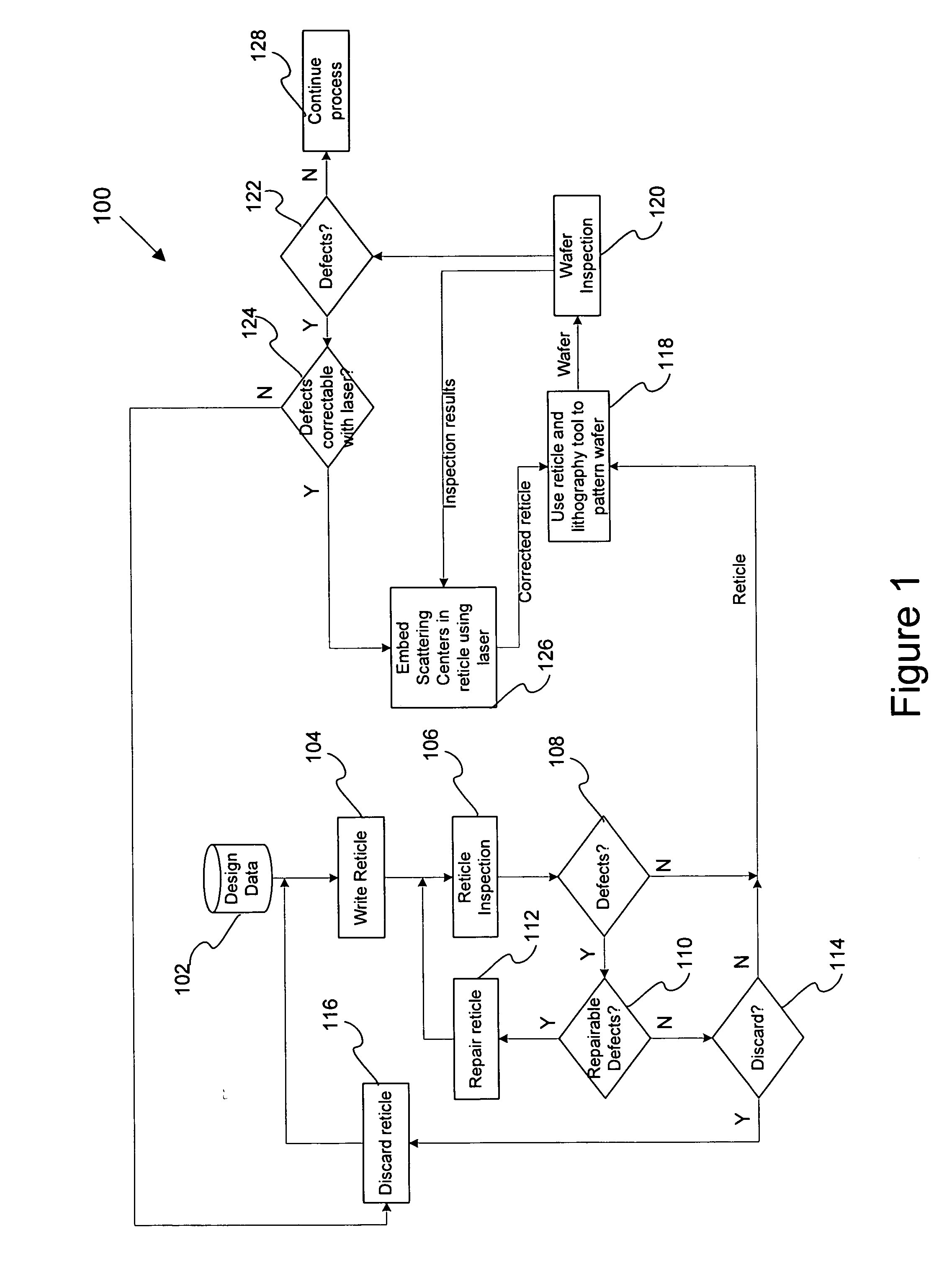
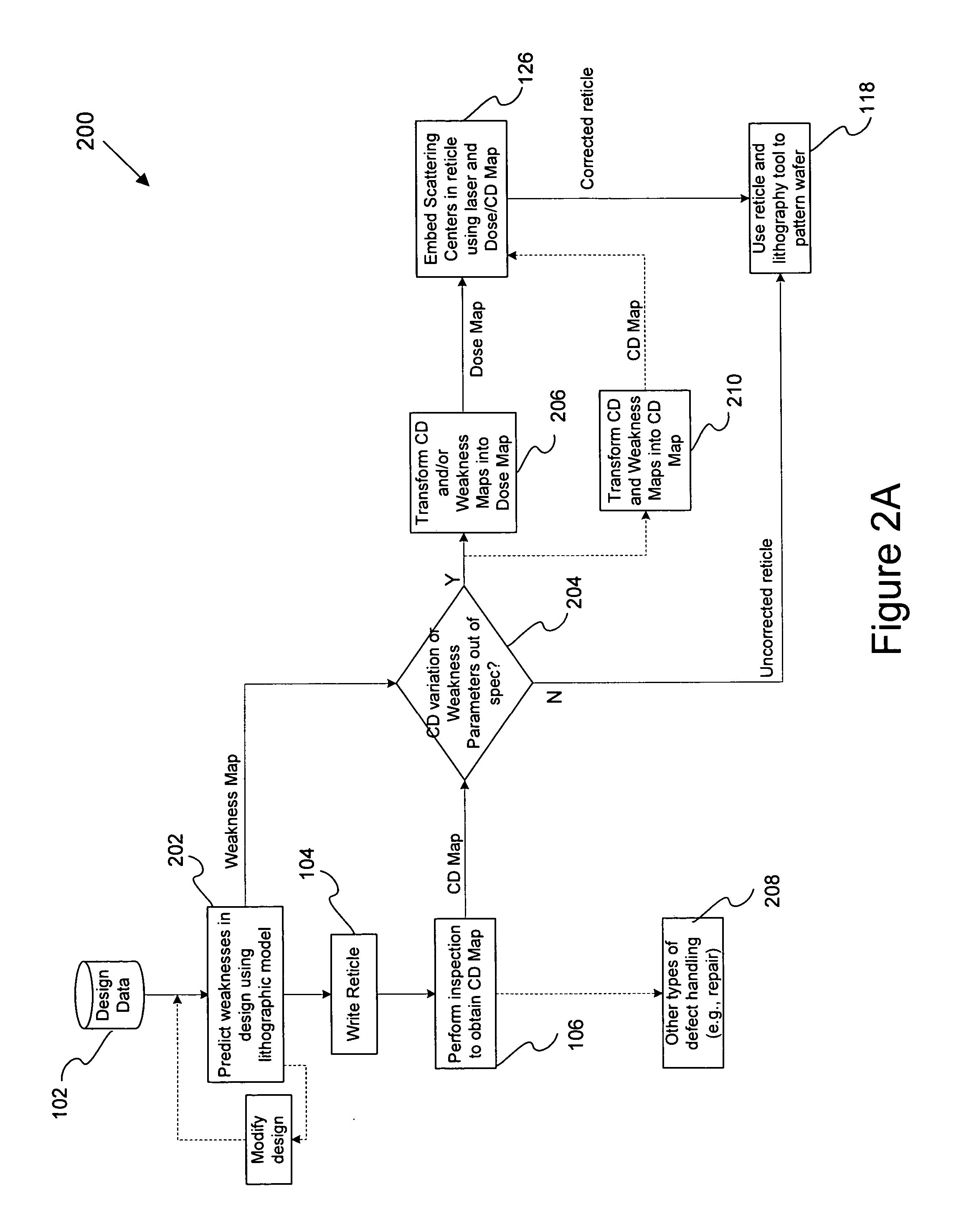
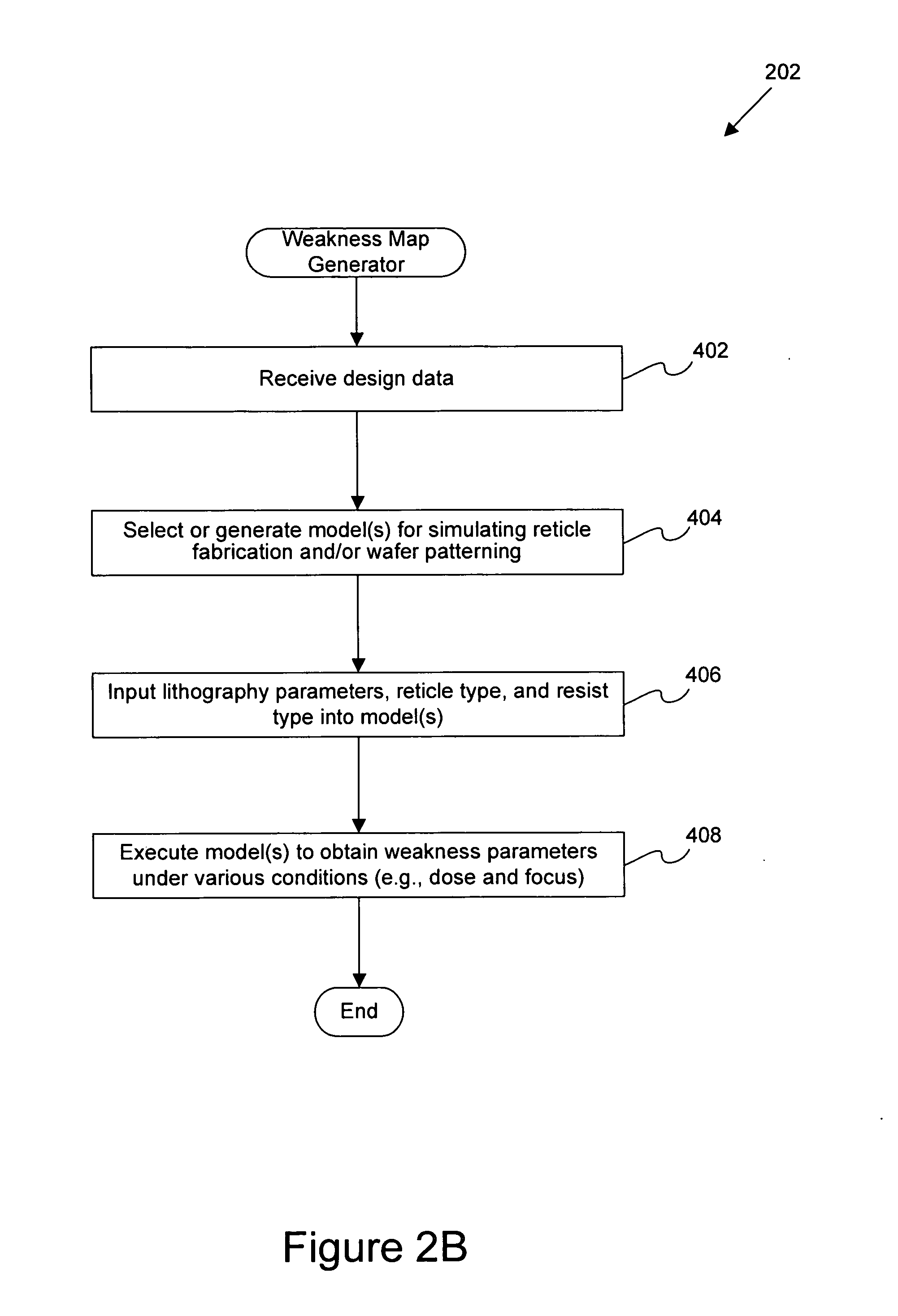
Systems and methods for modifying a reticle's optical properties
InactiveUS20060234139A1Maximum flexibilityMany deviationRadiation applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical propertyFemto second laser
Disclosed are systems and methods for modifying a reticle. In general, inspection results from a plurality of wafers or prediction results from a lithographic model are used to individually decrease the dose or any other optical property at specific locations of the reticle. In one embodiment, any suitable optical property of the reticle is modified by an optical beam, such as a femto-second laser, at specific locations on the reticle so as to widen the process window for such optical property. Examples of optical properties include dose, phase, illumination angle, and birefringence. Techniques for adjusting optical properties at specific locations on a reticle using an optical beam may be practiced for other purposes besides widening the process window.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
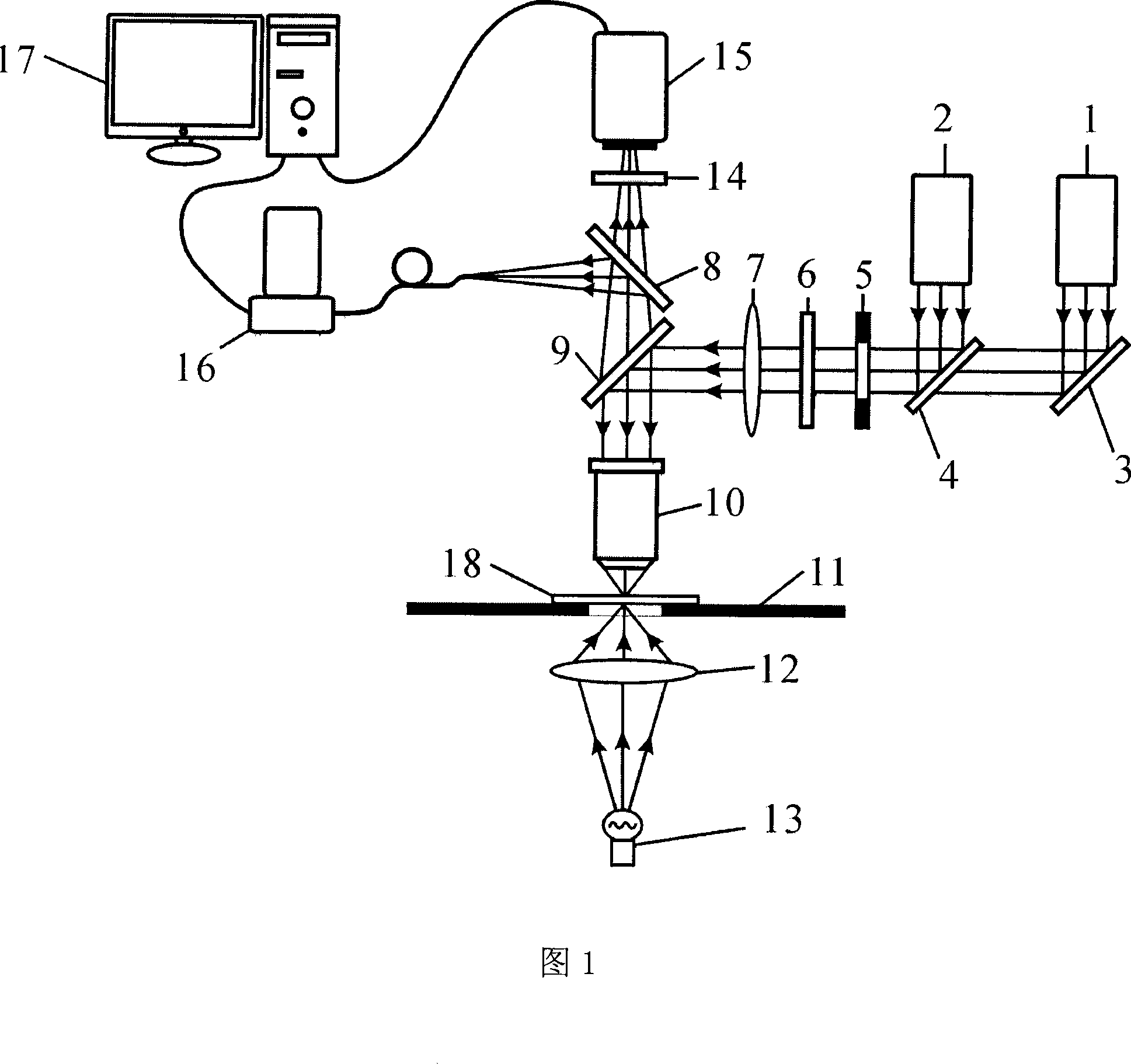
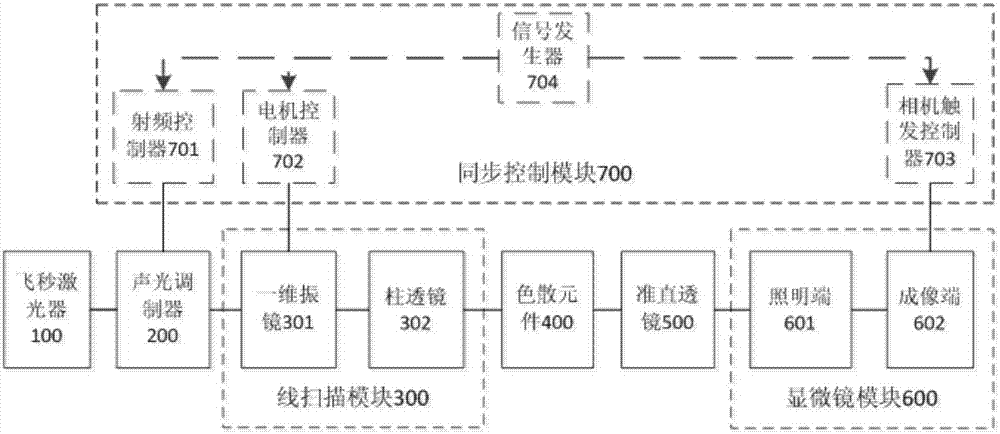
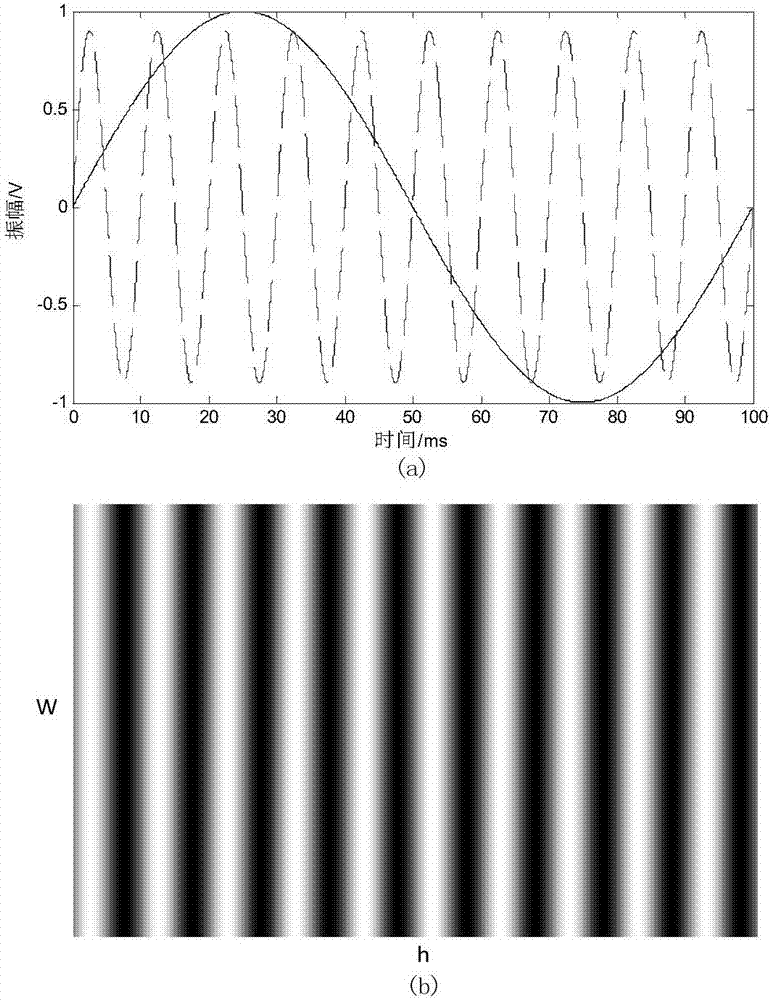
Structural light microscopic imaging system based on line scanning time-space focusing
InactiveCN107144955AHigh resolutionIncrease contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesGratingLight spot
The invention discloses a structural light microscopic imaging system based on line scanning time-space focusing. The system comprises the components of a femto second laser device; an acousto-optical modulator which is used for periodically modulating light source strength according to a sine function; a line scanning module which is used for scanning in a linear focusing light spot direction and a vertical linear light spot function; a dispersion element which is used for generating a spatial chirp; a collimating lens which is used for focusing different frequency components after grating dispersion to a parallel transmission direction; a microscope module; and a synchronous control module which is used for performing synchronous controlling on the acousto-optical modulator, the line scanning module and the microscope module, thereby obtaining a reconstructed image. According to the structural light microscopic imaging system, the reconstructed image can be obtained through strength-modulated line scanning structural light illumination in a line scanning time-space focused scanning mode and strength change of synchronously modulated excited light, thereby improving resolution and contrast in line scanning time-space focusing and reducing excitation outside a focal plane caused by medium scattering.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Laser and environmental monitoring system
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Ultra-fast laser system
ActiveUS8633437B2Accurate and redundant identificationCost effectiveRadiation pyrometryLaser using scattering effectsPulse shaperUltra fast
A laser system is provided which selectively excites Raman active vibrations in molecules. In another aspect of the present invention, the system includes a laser, pulse shaper and detection device. A further aspect of the present invention employs a femtosecond laser and binary pulse shaping (BPS). Still another aspect of the present invention uses a laser beam pulse, a pulse shaper and remote sensing.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
System and Method for Lowering IOP by Creation of Microchannels in Trabecular Meshwork Using a Femtosecond Laser
InactiveUS20130103011A1Function increaseIncrease outflowLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsFemto second laserOptoelectronics
A system and its method for creating a microchannel in the trabecular meshwork of an eye include a laser unit for generating a laser beam, and an imaging unit for creating an image of the trabecular meshwork. The system also includes a computer which defines the microchannel. A comparator that is connected with the computer then controls the laser unit to move the focal point of the laser beam. This focal point movement is accomplished to create the microchannel, while minimizing deviations of the focal point from the defined microchannel.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Method for preparing micro optical element on quartz glass substrate by applying femto-second laser
InactiveCN101571603AReduce thermal effectsAchieve high precision machiningPhotomechanical apparatusCleaning using liquidsChemical reactionEtching
The invention relates to a method for preparing a micro optical element on a quartz glass substrate by applying femto-second laser, which is characterized by comprising three steps of femto-second laser irradiation, chemical etching and hydrogen-oxygen flame polishing. The method can achieve processing of any surface types including a plane, a standard spherical surface, a non-spherical surface and the like; and the step of the hydrogen-oxygen flame polishing only has a generated product of water, thus the method is environment-friendly, has quick polishing, avoids physical contacts and chemical reactions at the same time, and solves the difficulty which cannot be solved by a common polishing wheel because the high temperature of the flame can repair lattice damages caused by micro-machining.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for processing micro array on glass surface via femtosecond laser pulse sequence
The invention relates to a method for processing a micro array on glass surface via femtosecond laser pulse sequence belonging to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The method comprises the following steps: (1) modulating the conventional femtosecond laser into the femtosecond laser pulse sequence including two sub-pulses on a time domain via a pulse shaping method, wherein the time interval range of two sub-pulses is 50fs-2ps, and the energy ratio range of two sub-pulses is 0.2-5; (2) focusing the femtosecond laser pulse sequence on the surface of glass material, scanning the required micro array configuration pattern on the glass surface according to the relative movement between the glass material and the laser focal point; (3) immersing the glass material with micro array configuration pattern obtained in the step (2) in a hydrofluoric acid solution with the concentration being 1-10%, carrying out reaction on the micro array configuration pattern region and the hydrofluoric acid solution so as to from a concave micro array structure. The modification degree of the femtosecond laser irradiation region is increased and the etching efficiency of the irradiation region is finally improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
High intensity MHz mode-locked laser
ActiveUS7590156B1Low costHigh peak powerOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersChemical reactionTerahertz radiation
Systems, configurations and methods of using an ultrafast, self-starting, mode-locked laser are provided. The systems, devices and methods of using stable, self-starting mode-locked lasers, can be compact, use fewer optical elements and have energies sufficient for most micro-processing and micro-structuring applications. The large spectral bandwidth of ultra-short (femtosecond) laser pulses can be used in laser sensing applications, micro-machining, time-resolved experiments, where short-lived transient species can be observed in biological or chemical reactions. Terahertz radiation can be generated using ultrashort pulses and used for imaging applications.
Owner:RES FOUNDATIN OF THE UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA INC
Fiber micro-nano Fabry-Perot interference type pressure sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104880267AHigh temperature resistantWith anti-electromagnetic interferenceForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMicro structureMicro nano
The invention relates to a fiber micro-nano Fabry-Perot interference type pressure sensor and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the fiber sensor technical field; the pressure sensor is formed by fusing a fiber (1) with a fiber film (2), wherein an end face of the fiber is provided with a micropore, and an end face of the fiber film (2) is complete; a fuse surface and the micropore form an embedded Fabry-Perot micro-cavity; the manufacturing method comprises the following steps: using a femto second laser to process the micropore on the end face fo the fiber; fusing the fiber with the other fiber having the complete end face so as to form the Fabry-Perot micro-cavity; cutting and grinding the fiber length on one end to several micrometers so as to form a fiber thin film, and forming the pressure sensor with a micro-nano structure. Compared with the prior art, a sensor head is in micro-nano size, so temperature has small intersect influence for pressure measurement; the sensor is made of quartz material with same performance, so thermal expansion coefficient is consistent, and structure is stable; considering material and a making process, the pressure sensor is high temperature resistant, has micro structure, is anti-electromagnetic interference, anti pollution, high in reliability, and high in precision.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
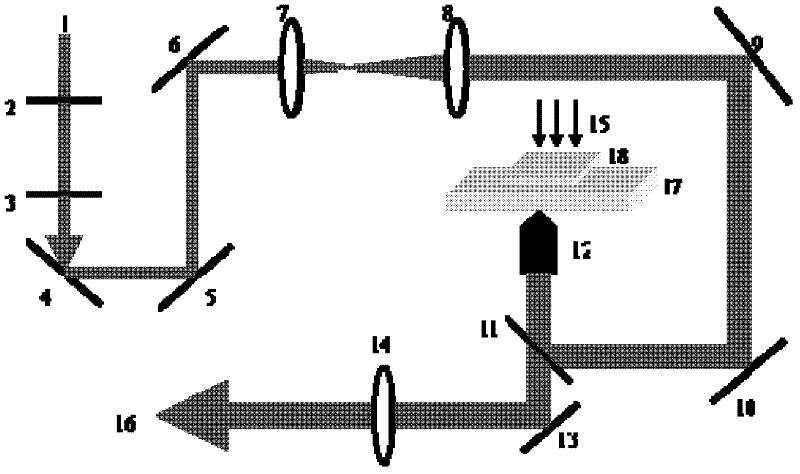
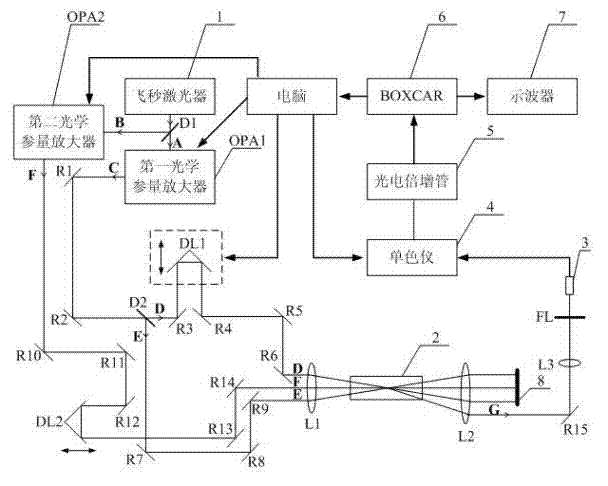
Normal-temperature normal-pressure femto-second CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Spectroscopy) time-resolved spectrum measuring system
InactiveCN101819064ASimple and fast operationImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringNonlinear opticsFemto second laser
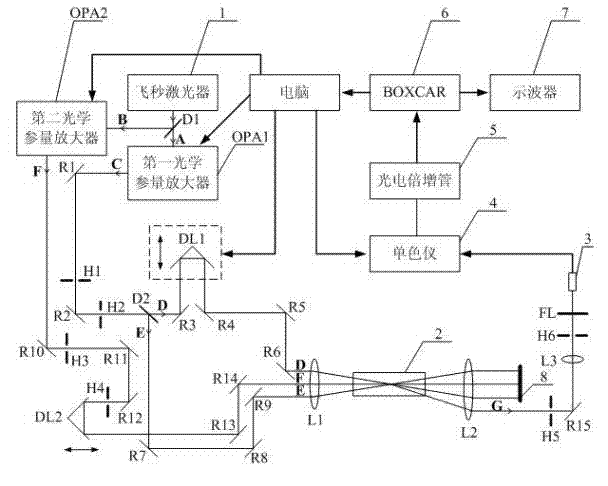
The invention relates to a normal-temperature normal-pressure femto-second CARS (Coherent Anti-stokes Raman Spectroscopy) time-resolved spectrum measuring system which relates to the technical field of nonlinear optics and solves the problem of multiple limiting factors of traditional femto-second CARS time-resolved spectrum measuring experiment. Beams output by a femto-second laser are adjusted through a series of reflectors and optical delay lines by the system to form three bundles of beams which have approximate energy and are respectively positioned on three peaks of a square on the vertical direction of the beams, the beams are focused to a sample pool and then emit a new beam along a specific angle, i.e. a CARS signal, the CARS signal is filtered through a filter plate, then received by a probe and input to a monochromator, the data acquisition of an electrical signal converted by a photomultiplier is carried out by utilizing BOCCAR, and the data are input to a computer for data processing. The invention can carry out femto-second CARS time-resolved spectrum measurement under the experimental conditions of normal temperature and normal pressure and is applicable for the femto-second CARS spectrum measurement of gas samples and liquid samples in a static sample pool.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com