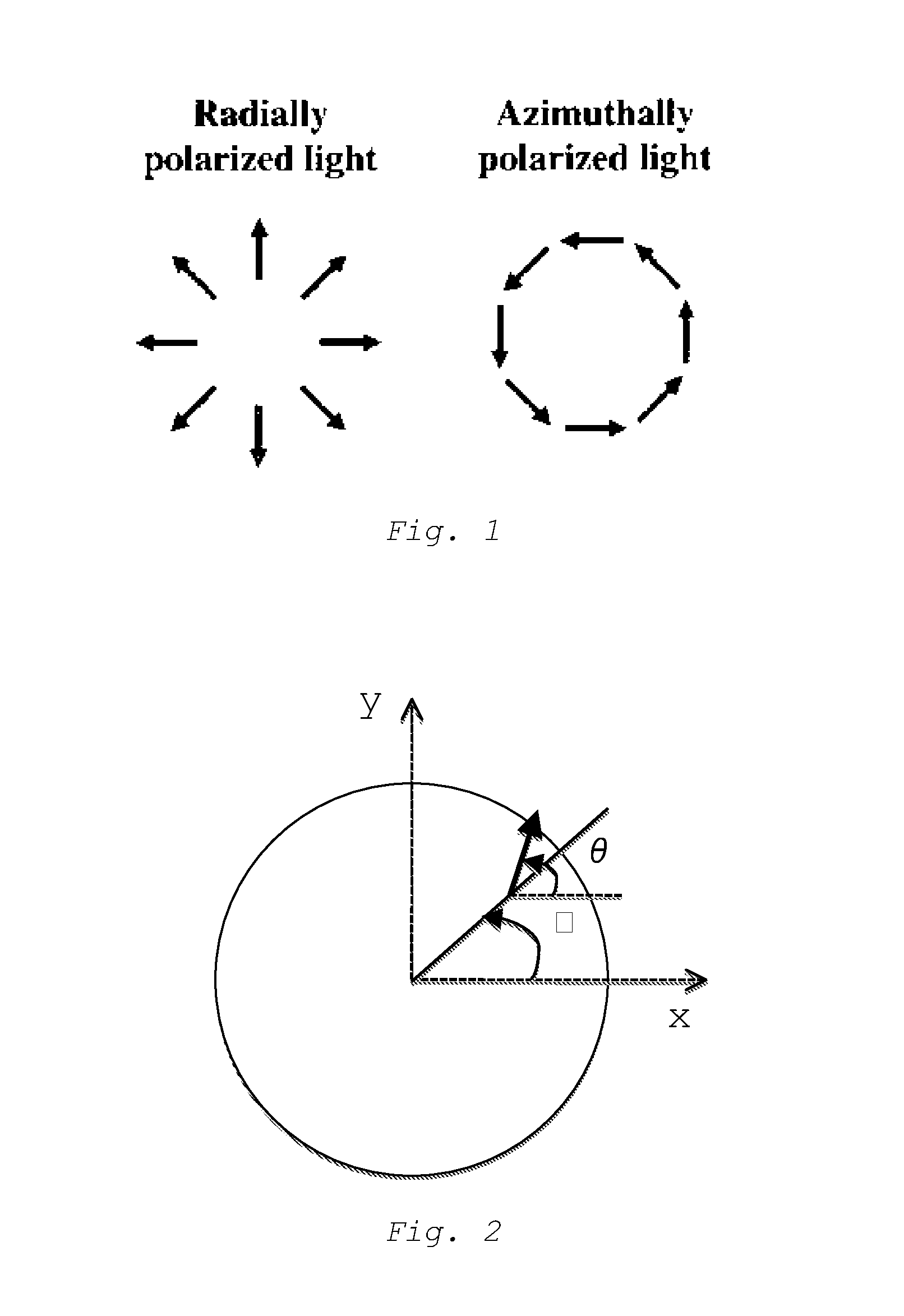
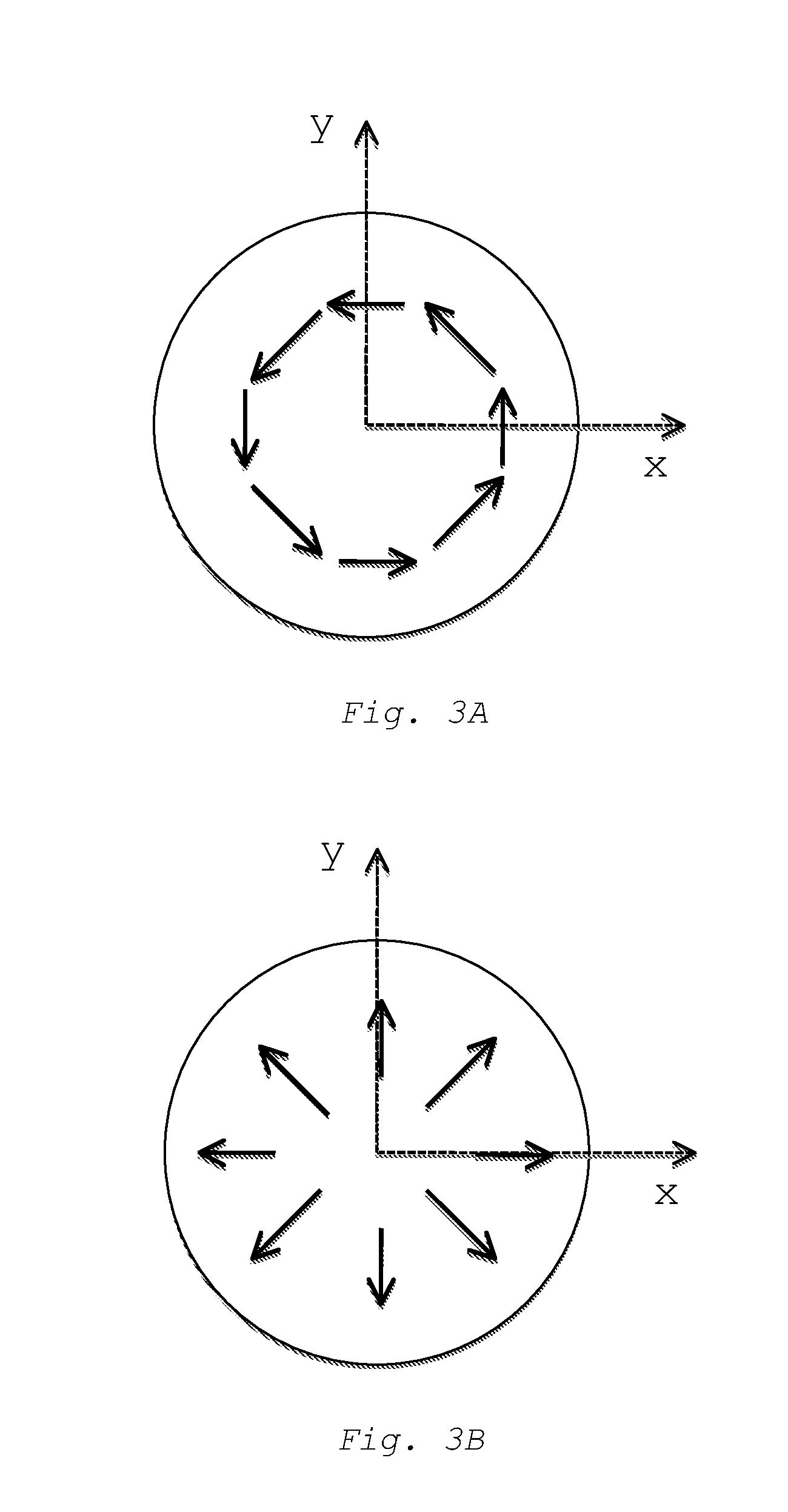
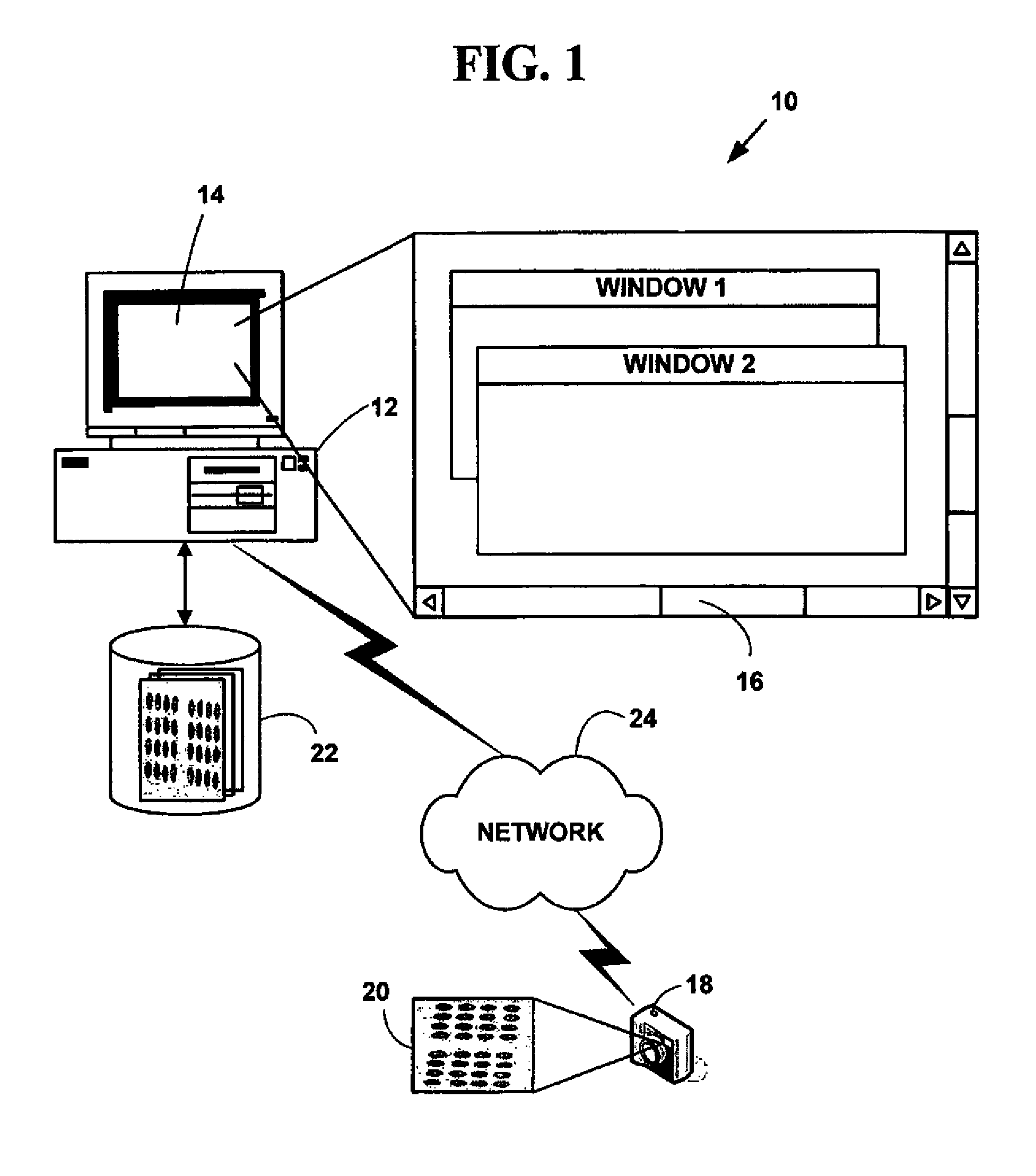
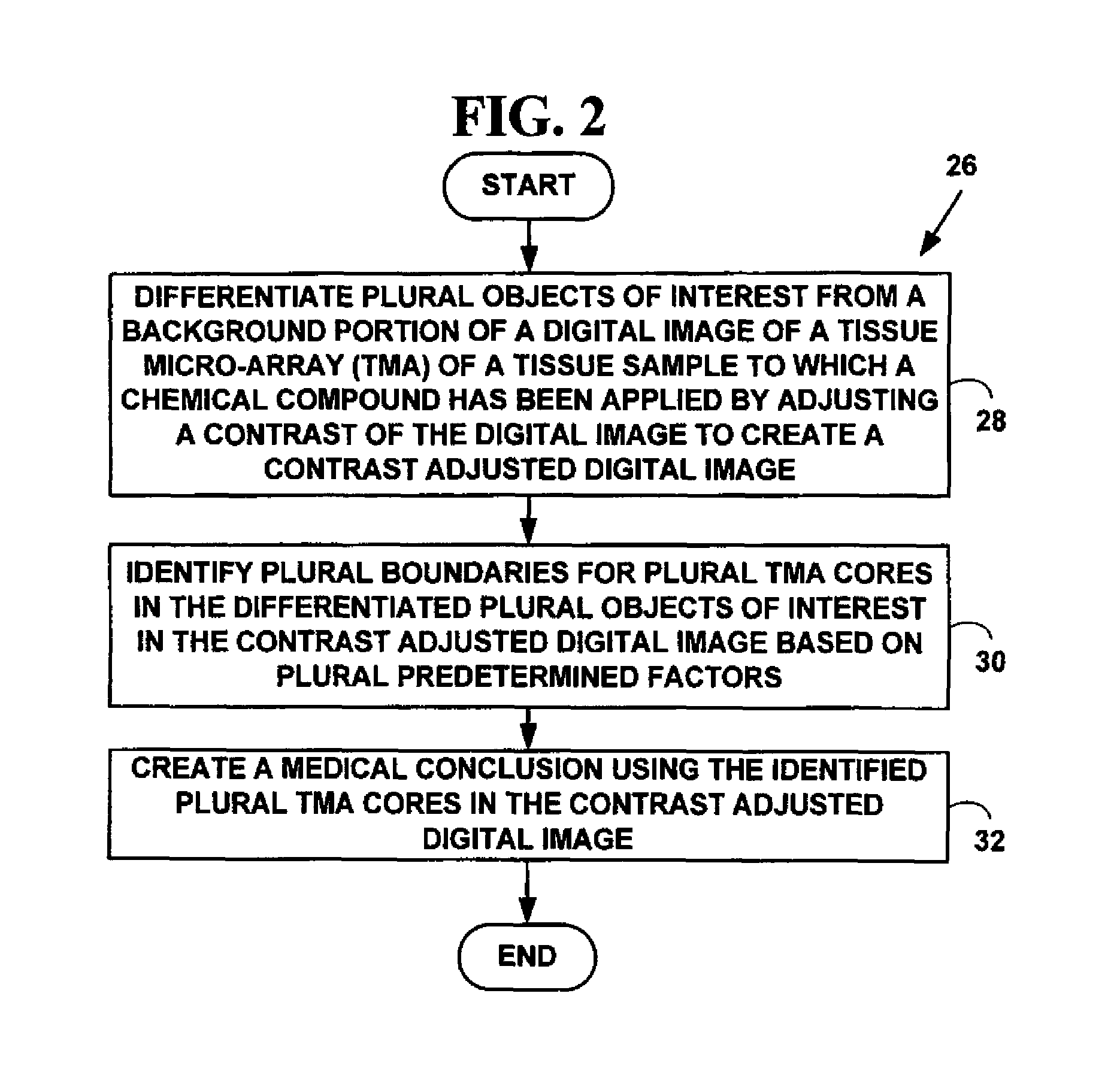
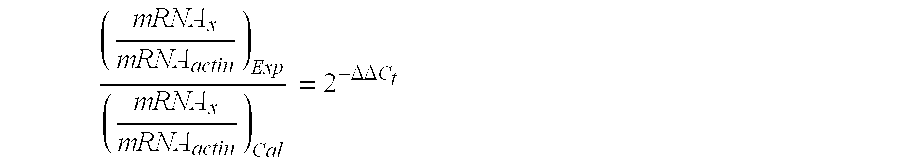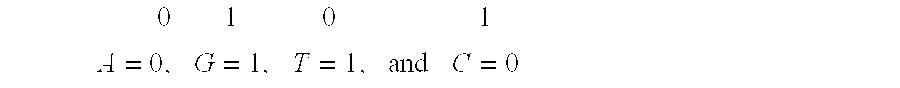Patents
Literature
512 results about "Micro array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Micro array - Computer Definition. A semiconductor device that is used to detect the DNA makeup of a human cell. DNA chains comprise molecules that pair with each other, and micro arrays contain millions of DNA strands designed to mate with their other half as the liquefied human cells are poured over them.
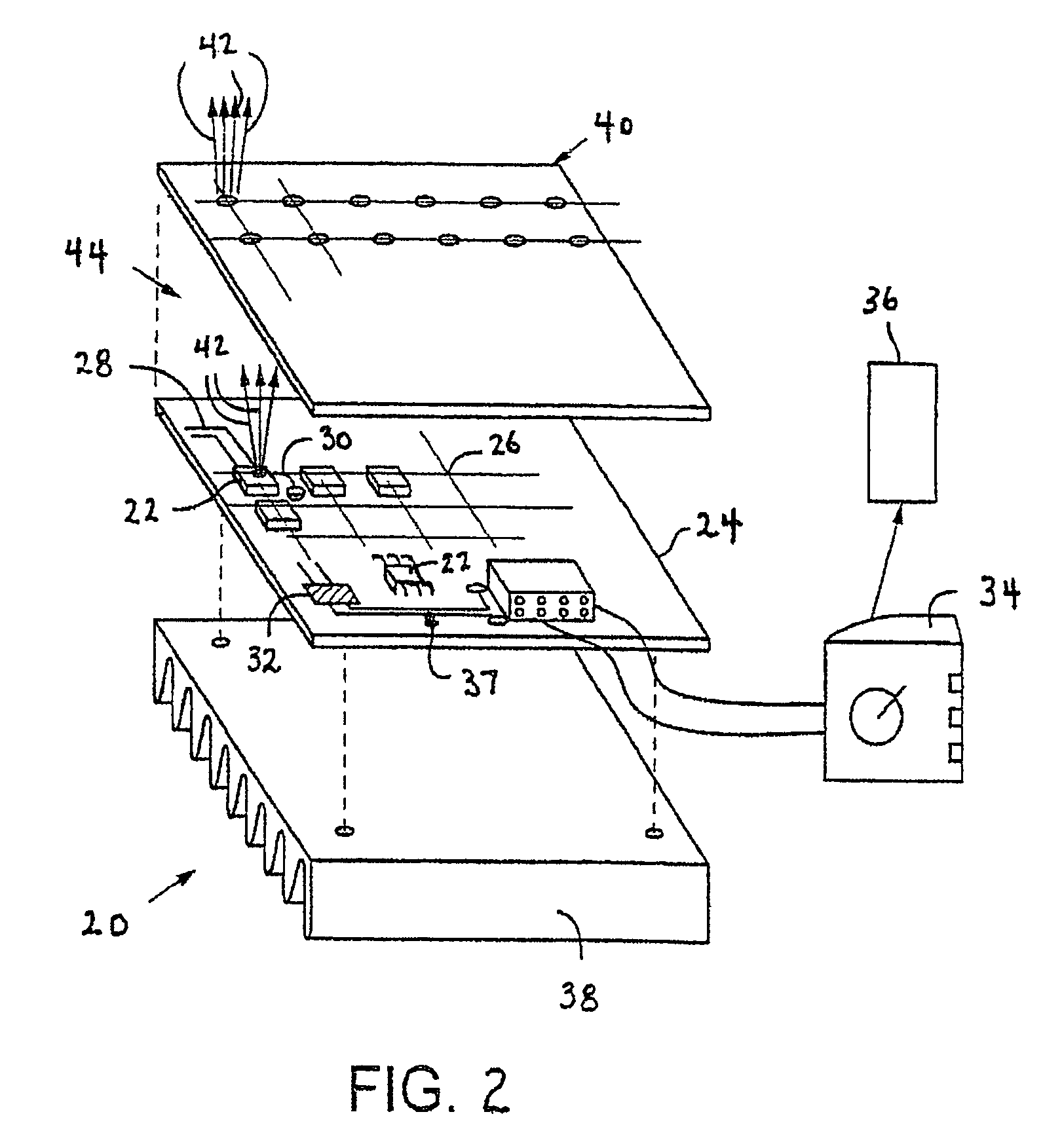
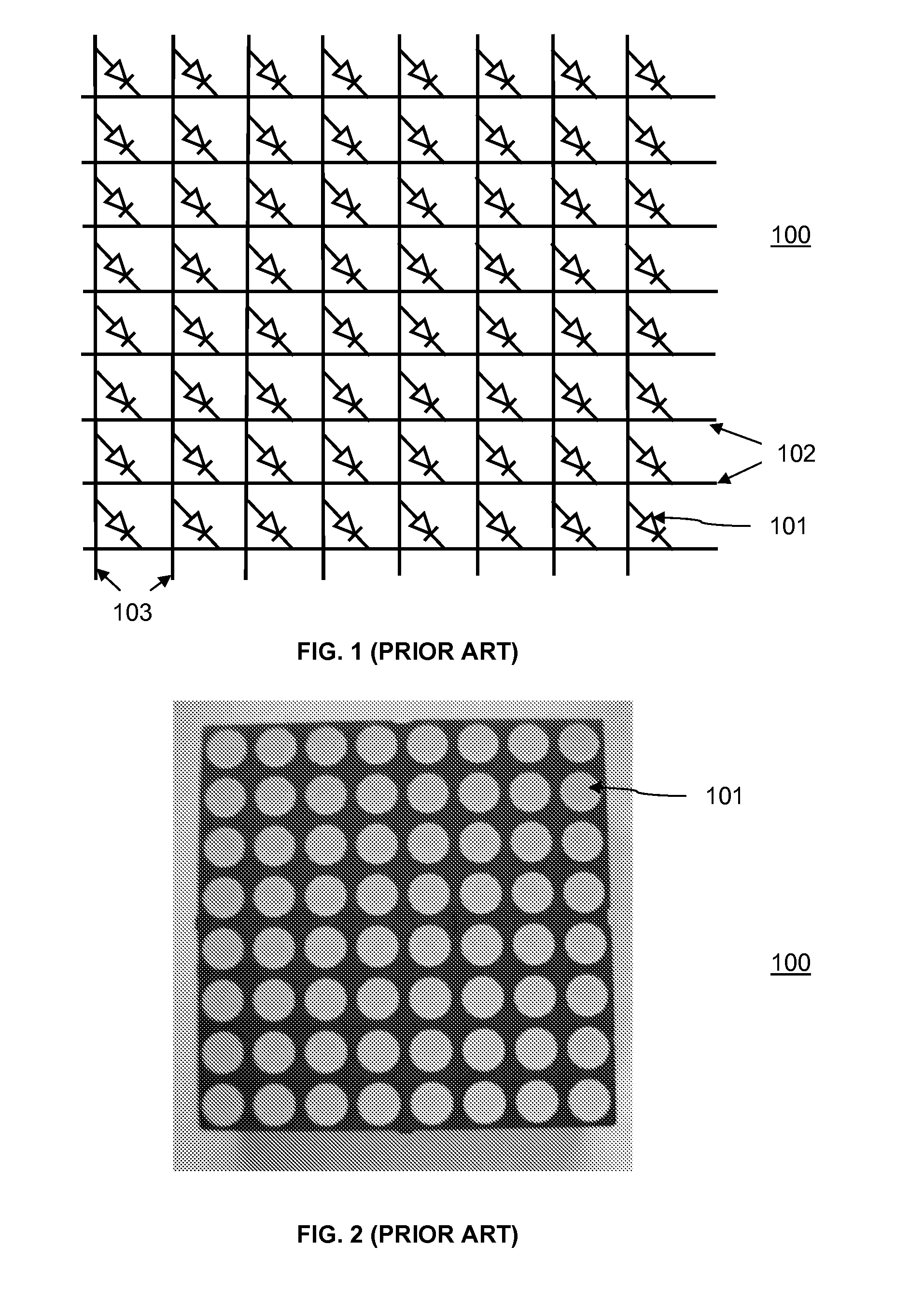
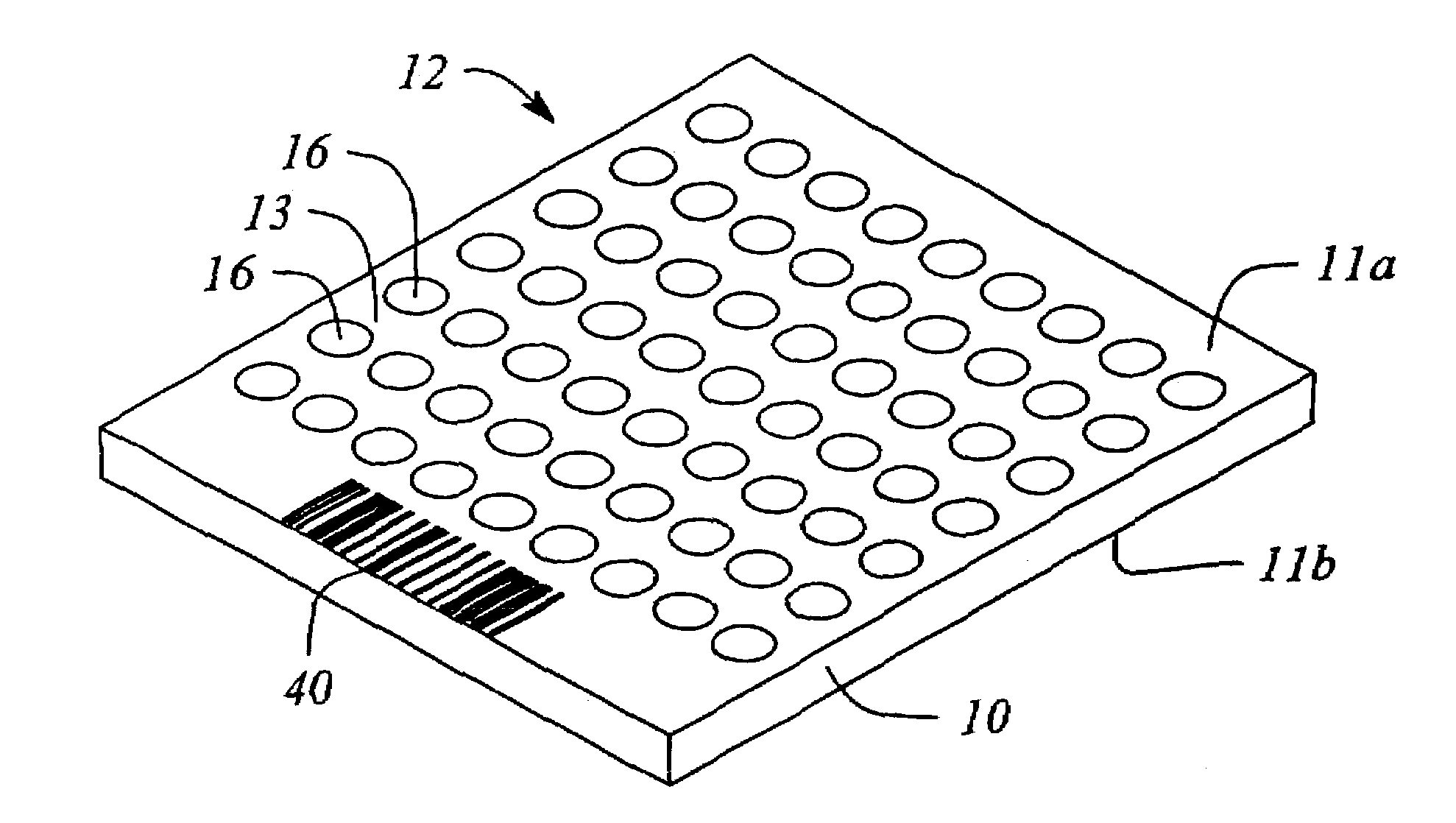
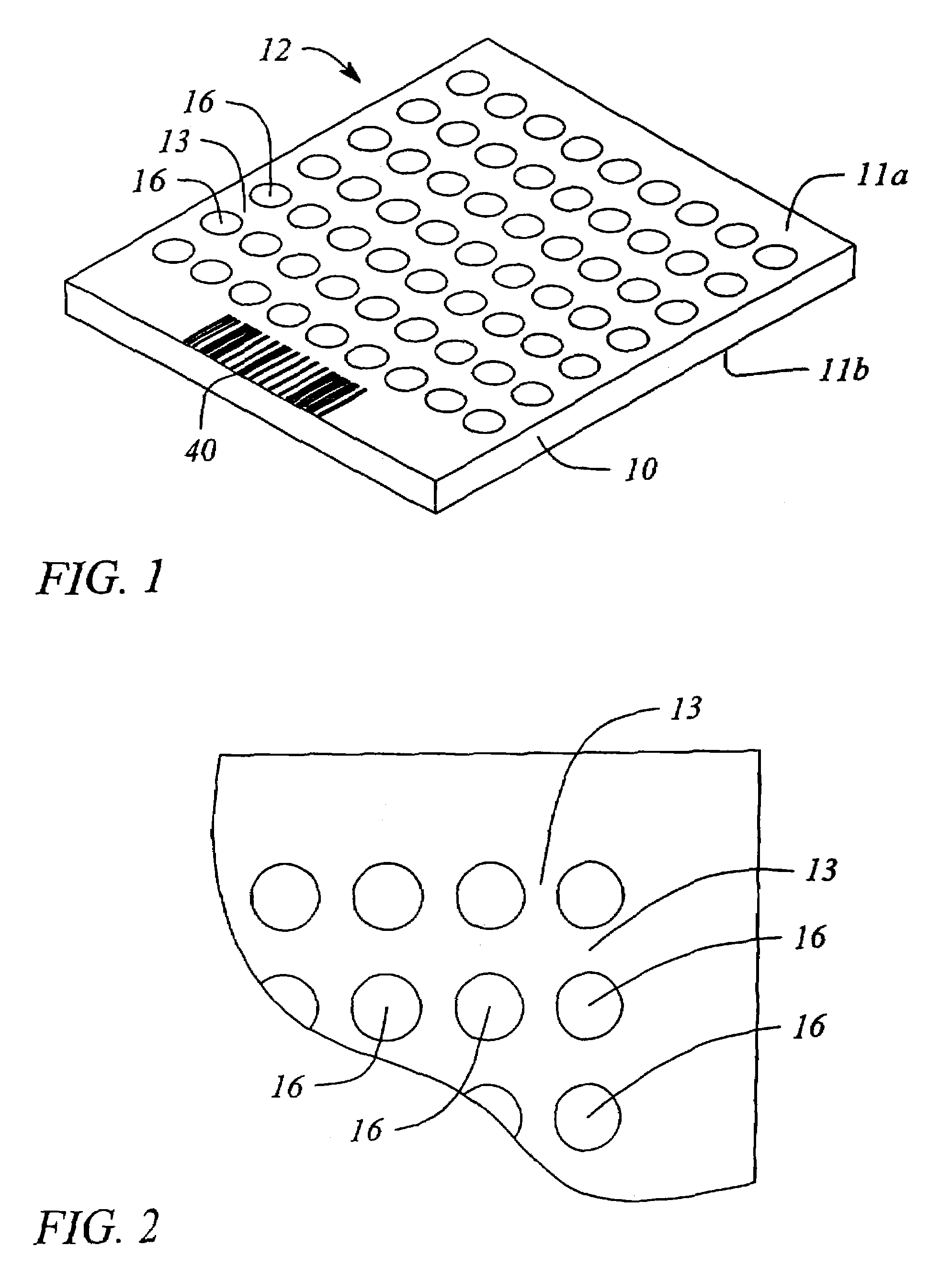
High efficiency solid-state light source and methods of use and manufacture
ActiveUS20050152146A1Eliminate needImprove light outputOptical radiation measurementPoint-like light sourceDevice materialFluorescence
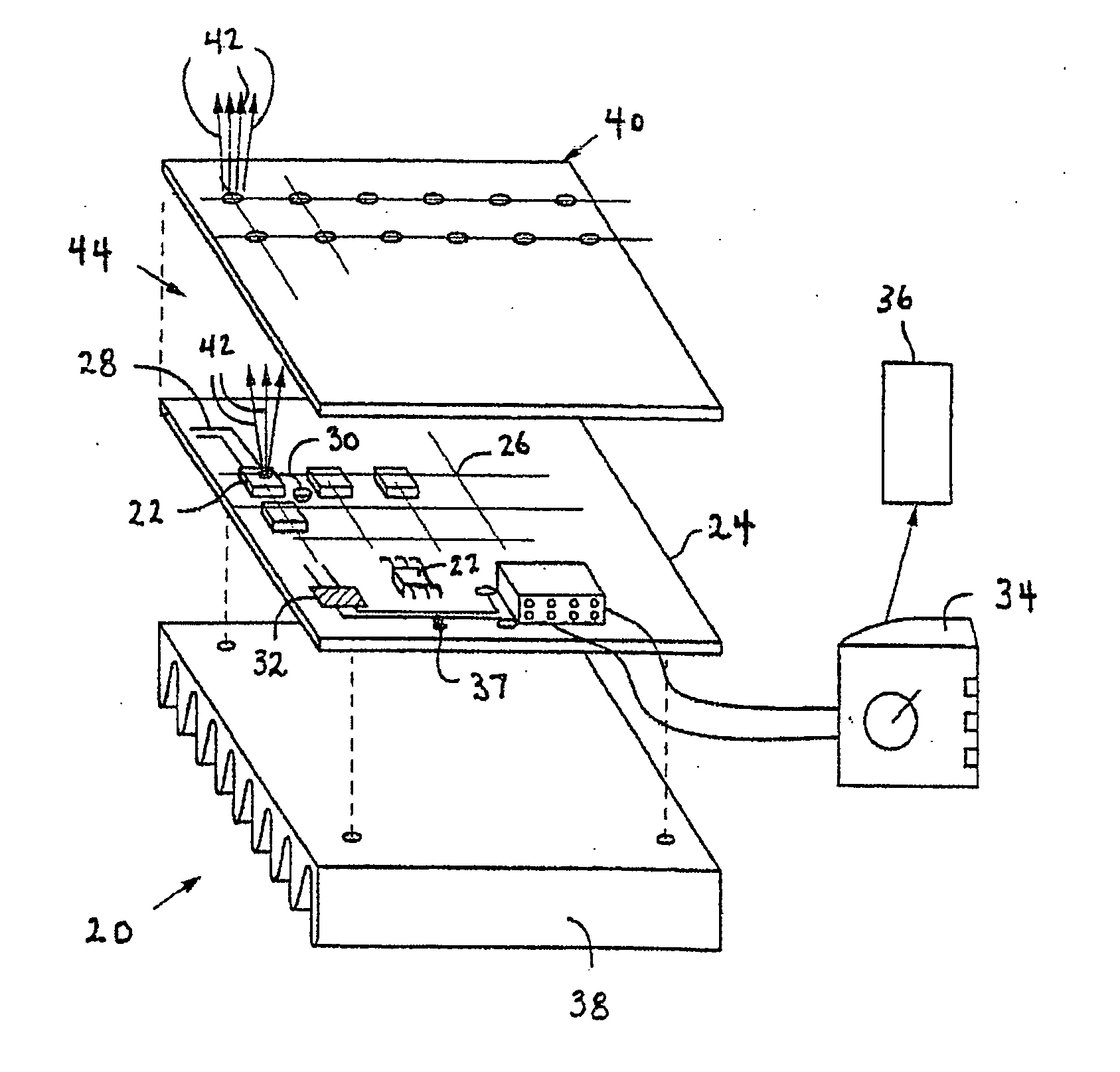
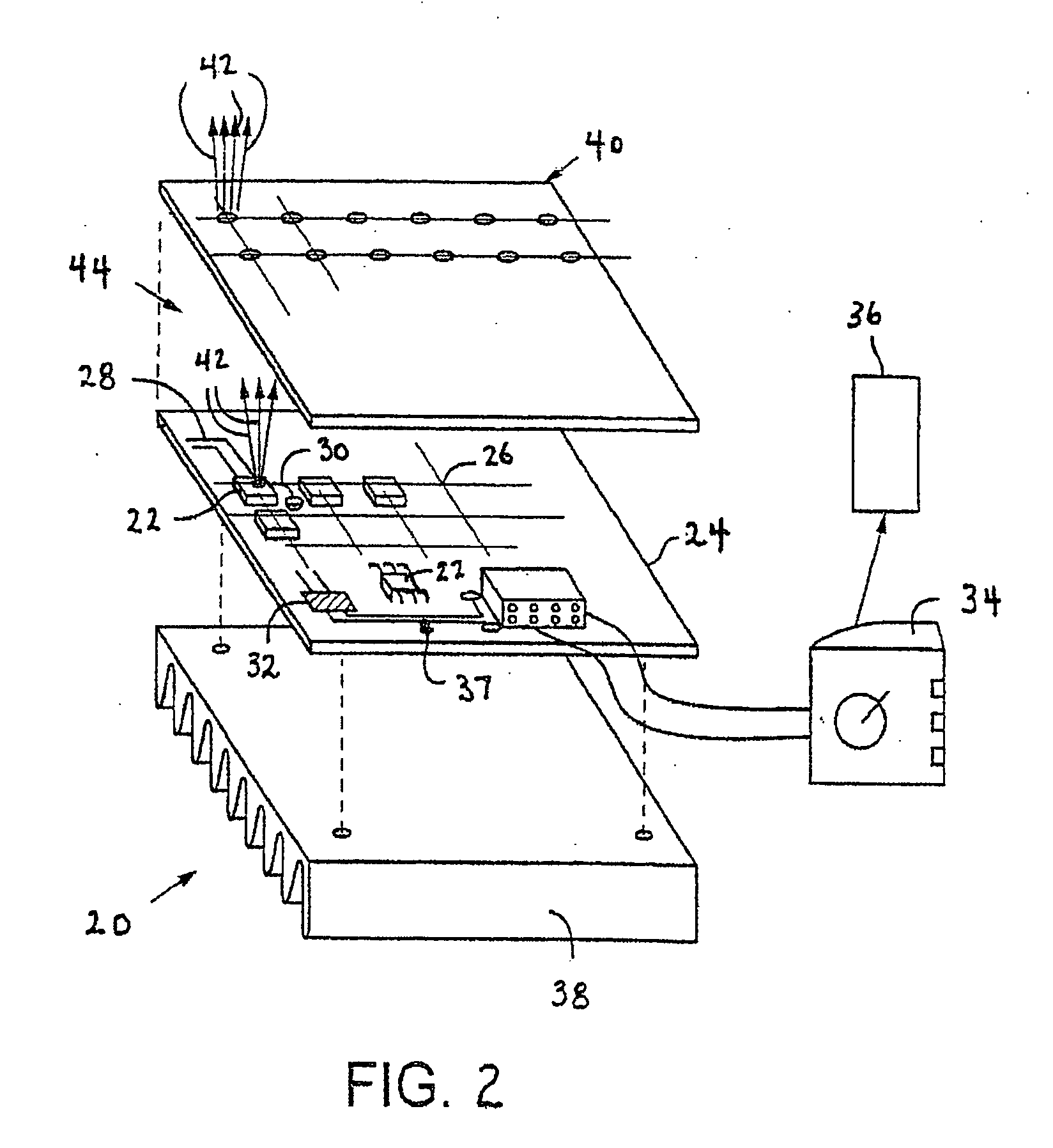
A high-intensity light source is formed by a micro array of a semiconductor light source such as a LEDs, laser diodes, or VCSEL placed densely on a liquid or gas cooled thermally conductive substrate. The semiconductor devices are typically attached by a joining process to electrically conductive patterns on the substrate, and driven by a microprocessor controlled power supply. An optic element is placed over the micro array to achieve improved directionality, intensity, and / or spectral purity of the output beam. The light module may be used for such processes as, for example, fluorescence, inspection and measurement, photopolymerzation, ionization, sterilization, debris removal, and other photochemical processes.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
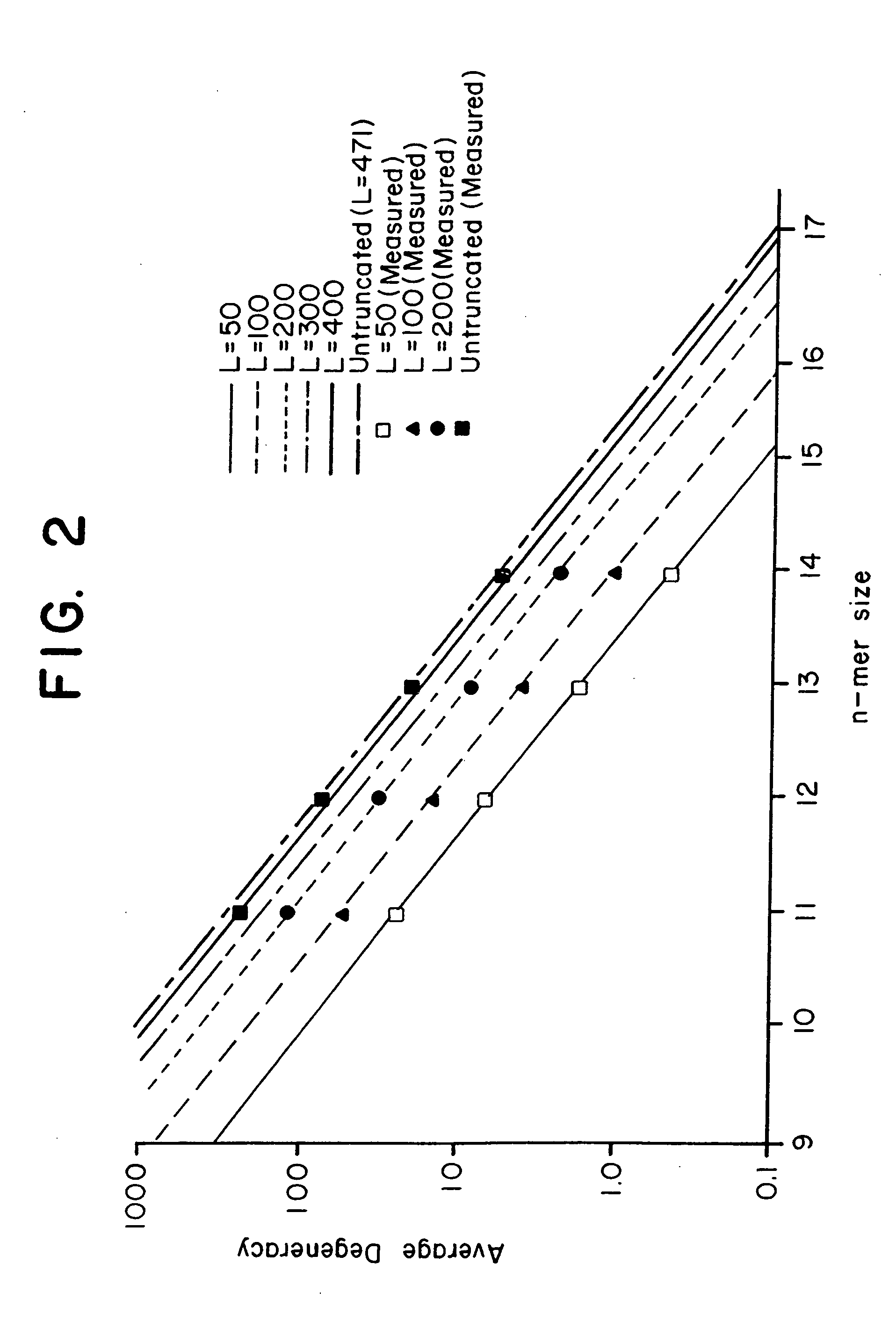
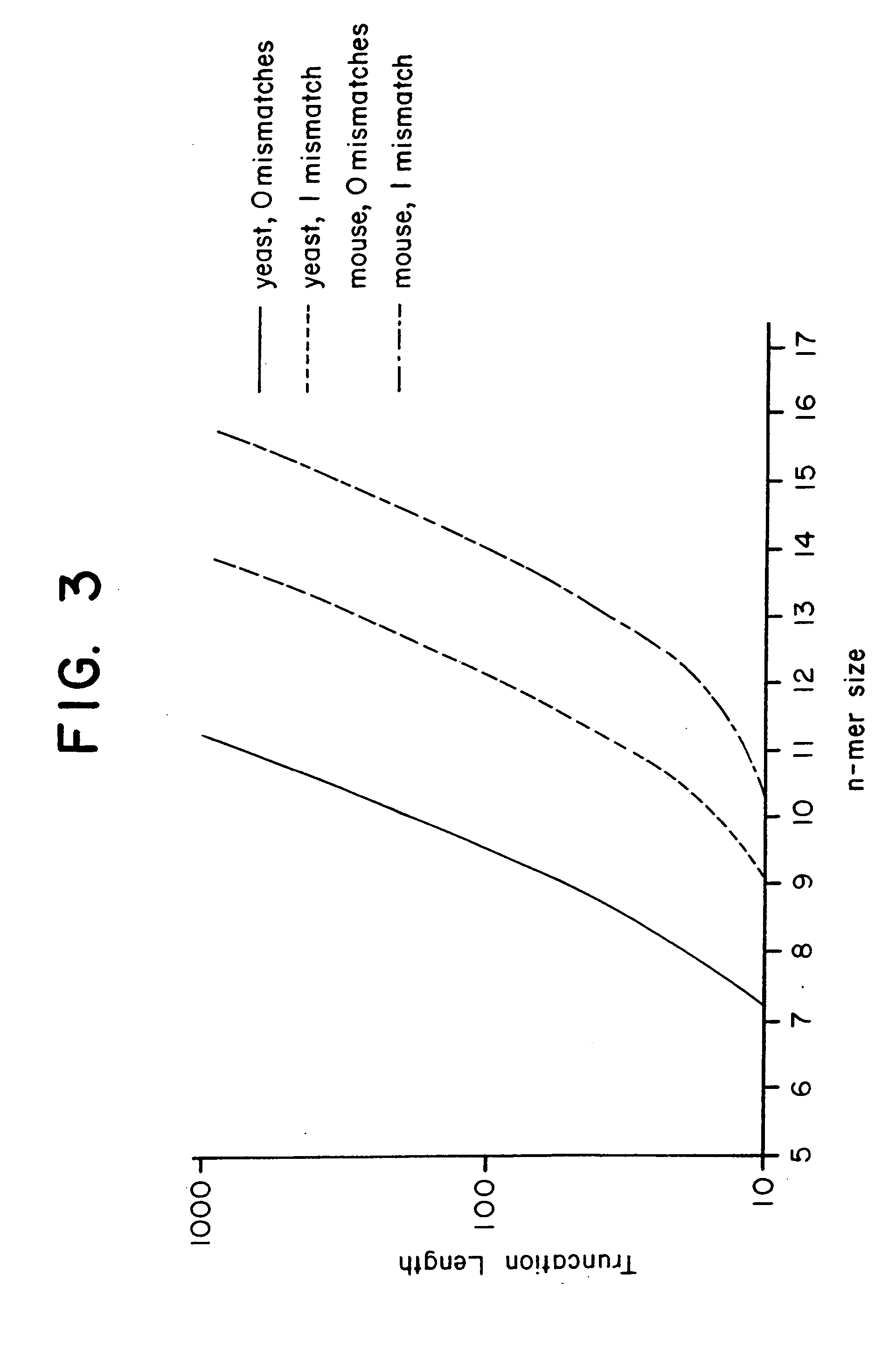
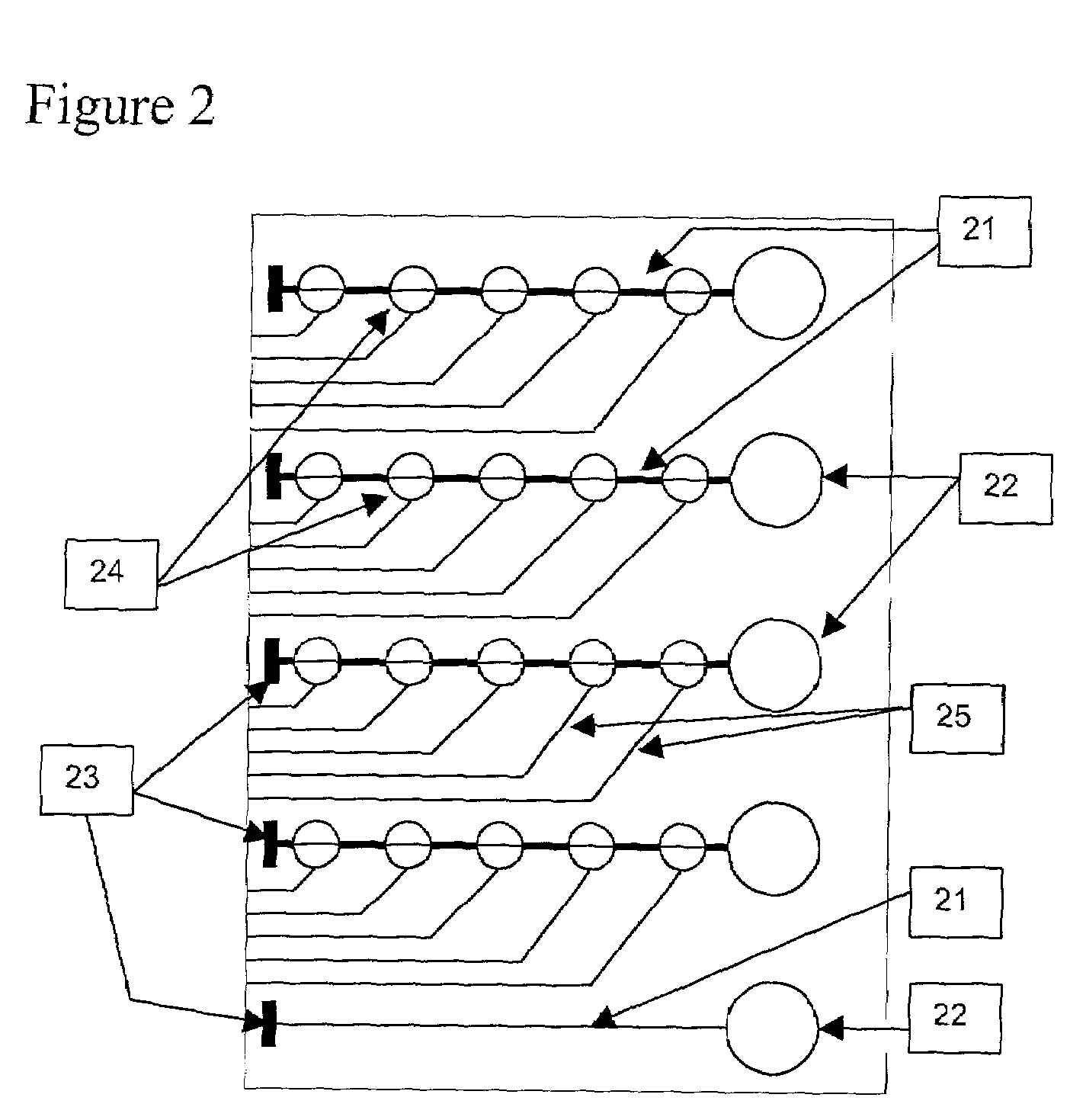
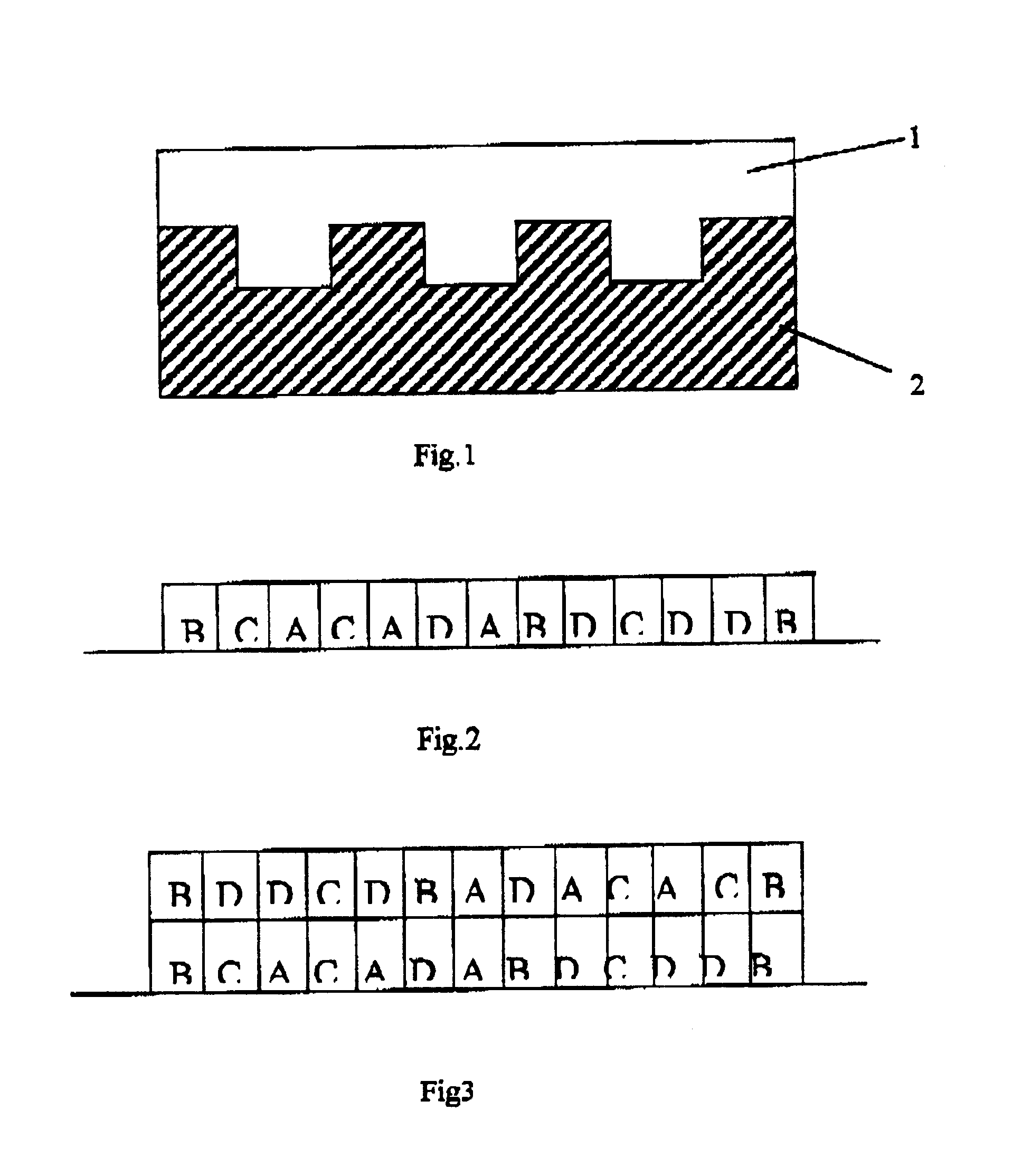
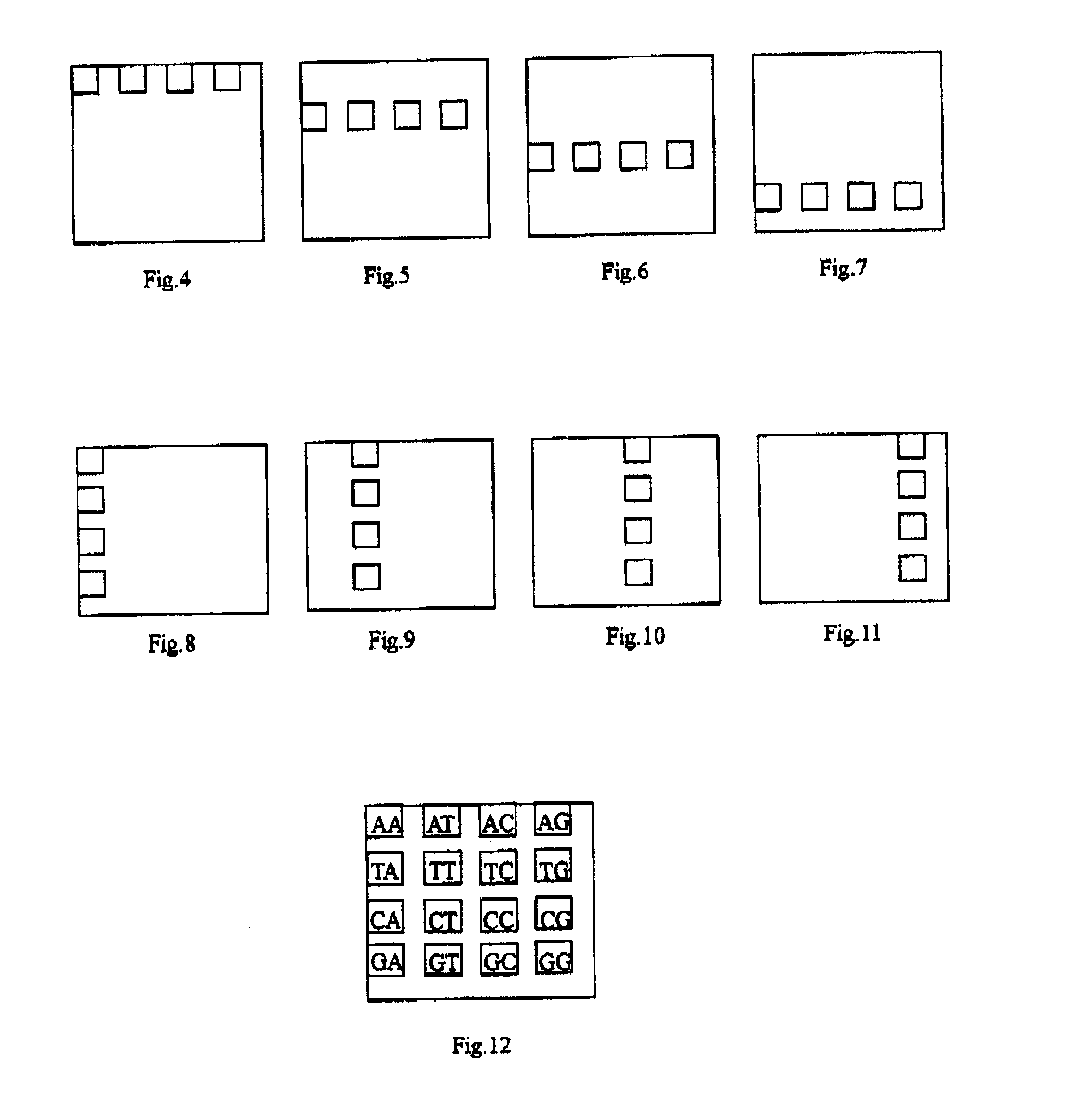
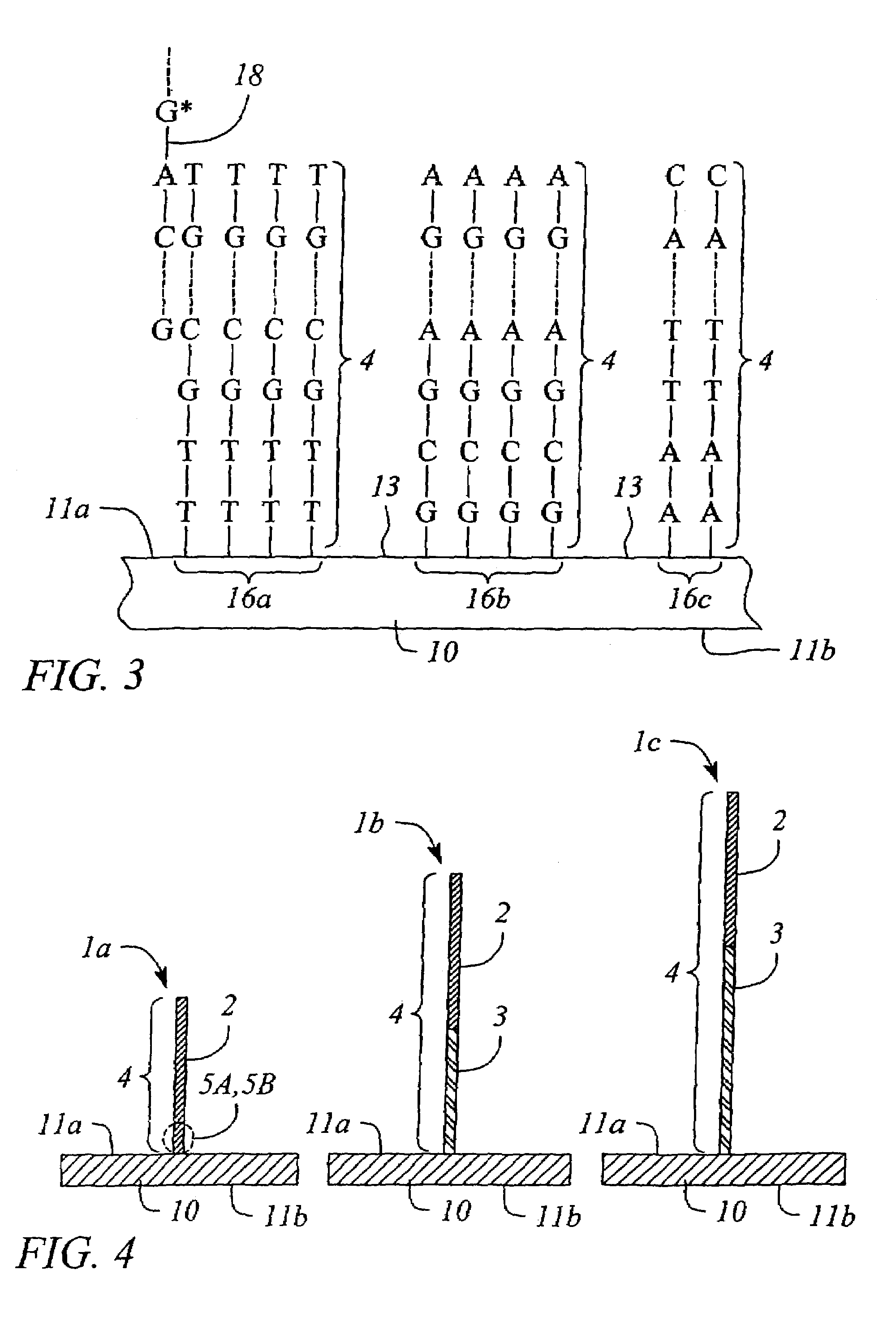
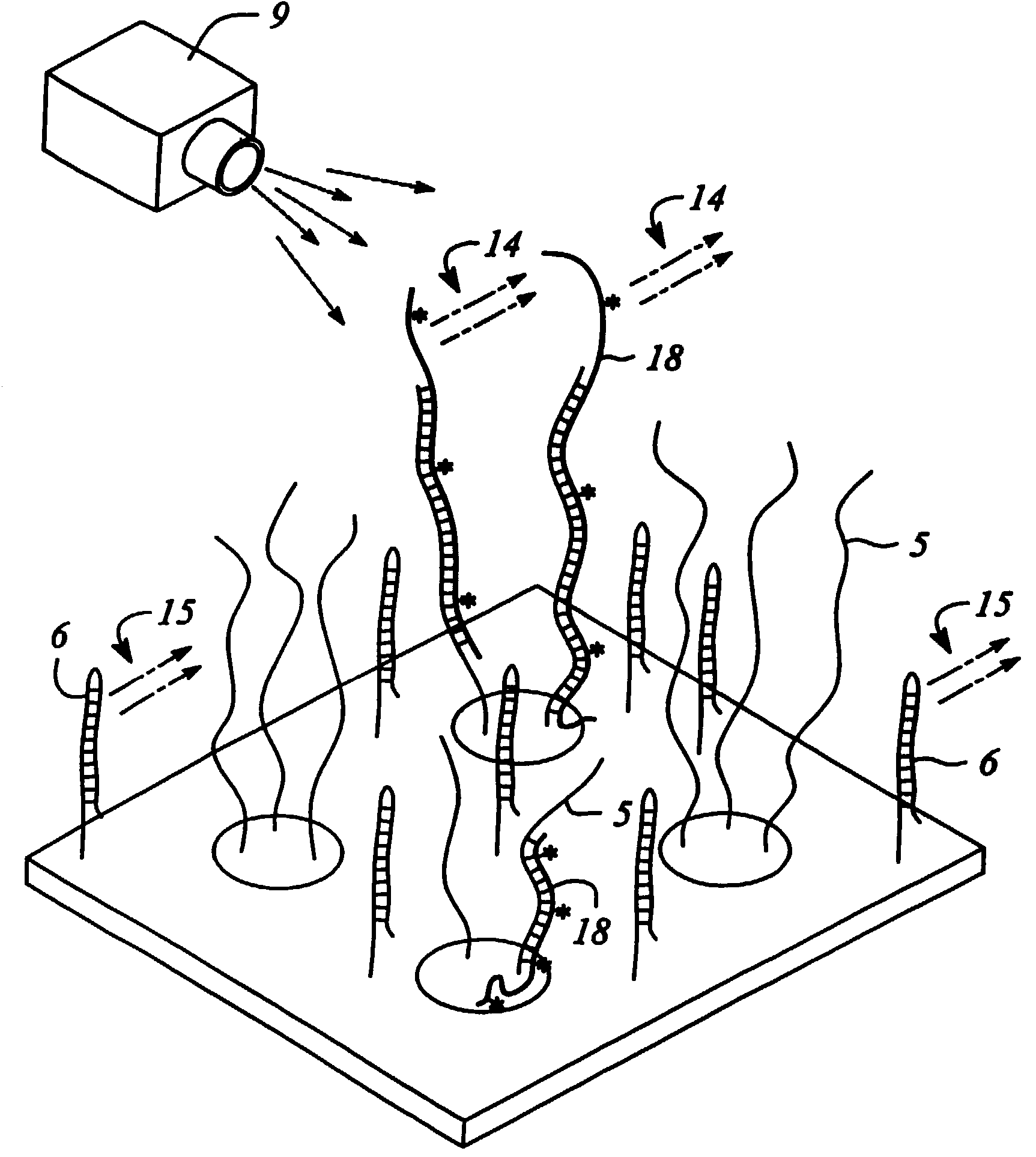
Combinational array for nucleic acid analysis
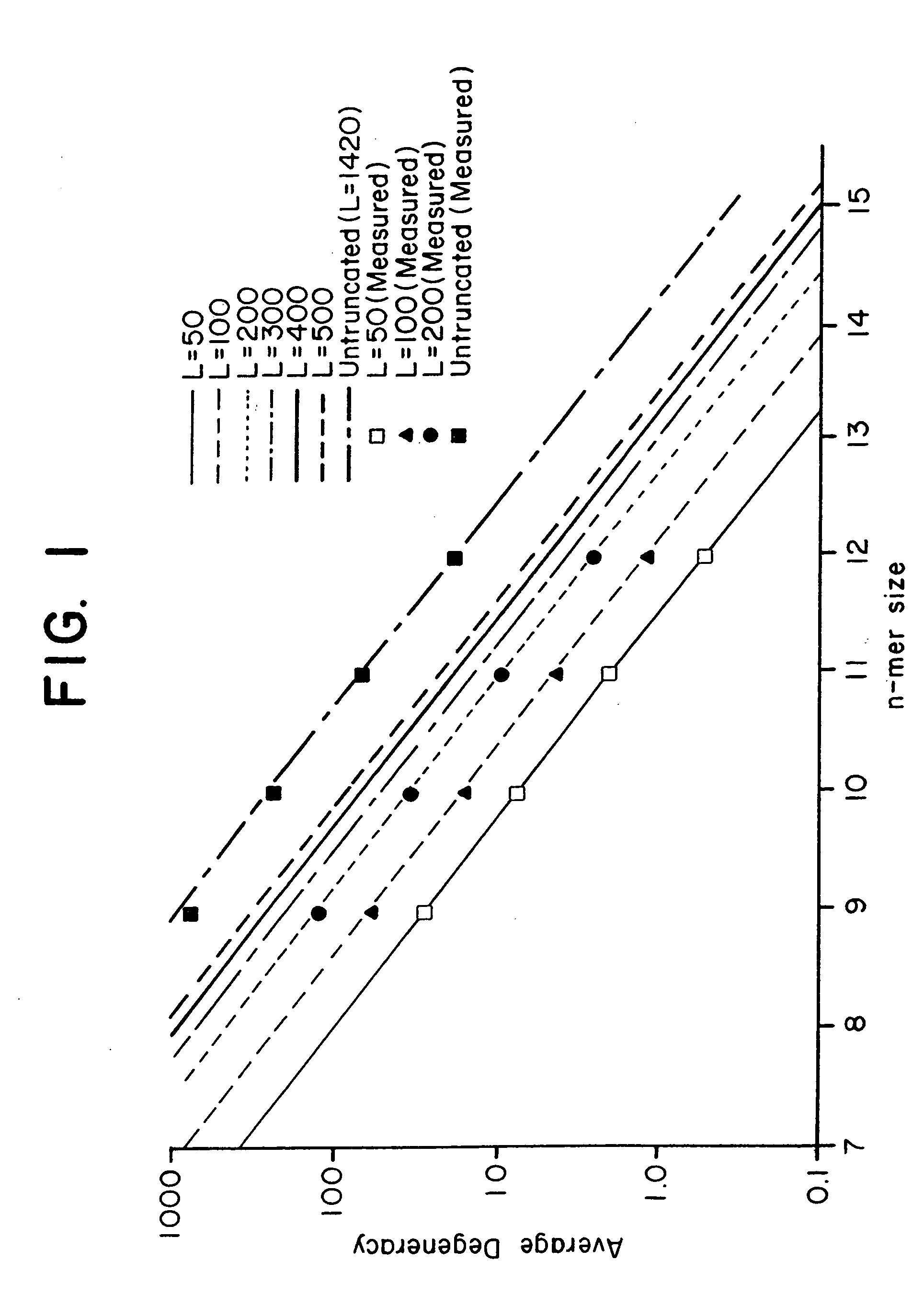
This invention relates to an array, including a universal micro-array, for the analysis of nucleic acids, such as DNA. The devices and methods of the invention can be used for identifying gene expression patterns in any organism. More specifically, all possible oligonucleotides (n-mers) necessary for the identification of gene expression patterns are synthesized. According to the invention, n is large enough to give the specificity to uniquely identify the expression pattern of each gene in an organism of interest, and is small enough that the method and device can be easily and efficiently practiced and made. The invention provides a method of analyzing molecules, such as polynucleotides (e.g., DNA), by measuring the signal of an optically-detectable (e.g., fluorescent, ultraviolet, radioactive or color change) reporter associated with the molecules. In a polynucleotide analysis device according to the invention, levels of gene expression are correlated to a signal from an optically-detectable (e.g. fluorescent) reporter associated with a hybridized polynucleotide. The invention includes an algorithm and method to interpret data derived from a micro-array or other device, including techniques to decode or deconvolve potentially ambiguous signals into unambiguous or reliable gene expression data.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Micro-array evanescent wave fluorescence detection device
InactiveUS7175811B2Quench emissionAvoid disadvantagesOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsWaveguidePolymer
Novel nanowell microarrays are disclosed in optical contact with polymer waveguides wherein evanescent field associated with lightwaves propagated in the waveguide excite target substances in the nanowells either by a common waveguide or by individual waveguides. Fluid samples are conveyed to the nanowells by means of microfluidics. The presence of the target substances in fluid samples is detected by sensing fluorescent radiation generated by fluorescent tag bound to the target substances. The fluorescent tags generate fluorescent radiation as a result of their excitation by the evanescent field. One or more PMT detectors or a CCD detector are located at the side of the waveguide opposite to the nanowells. Fluorescent radiation is detected due to its coupling with the waveguide or its emission through the waveguide.
Owner:EDGELIGHT BIOSCI
Combinatorial array for nucleic acid analysis
InactiveUS20020012926A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiological bodyFluorescence
This invention relates to an array, including a universal micro-array, for the analysis of nucleic acids, such as DNA. The devices and methods of the invention can be used for identifying gene expression patterns in any organism. More specifically, all possible oligonucleotides (n-mers) necessary for the identification of gene expression patterns are synthesized. According to the invention, n is large enough to give the specificity to uniquely identify the expression pattern of each gene in an organism of interest, and is small enough that the method and device can be easily and efficiently practiced and made. The invention provides a method of analyzing molecules, such as polynucleotides (e.g., DNA), by measuring the signal of an optically-detectable (e.g., fluorescent, ultraviolet, radioactive or color change) reporter associated with the molecules. In a polynucleotide analysis device according to the invention, levels of gene expression are correlated to a signal from an optically-detectable (e.g. fluorescent) reporter associated with a hybridized polynucleotide. The invention includes an algorithm and method to interpret data derived from a micro-array or other device, including techniques to decode or deconvolve potentially ambiguous signals into unambiguous or reliable gene expression data.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Quantum dot near-to-eye display
A multi-layer optical structure includes a pixel array layer, an addressing matrix layer, and a micro lens array. The pixel array layer includes an array of quantum dot pixels for emitting an image from a first side of the multi-layer optical structure. The addressing matrix layer adjoins the pixel array layer and includes electrically conductive signal lines to individual address and activate the quantum dot pixels to generate the image. The micro lens array includes micro lenses optically aligned with the quantum dot pixels in an emission path of the image to focus the image.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
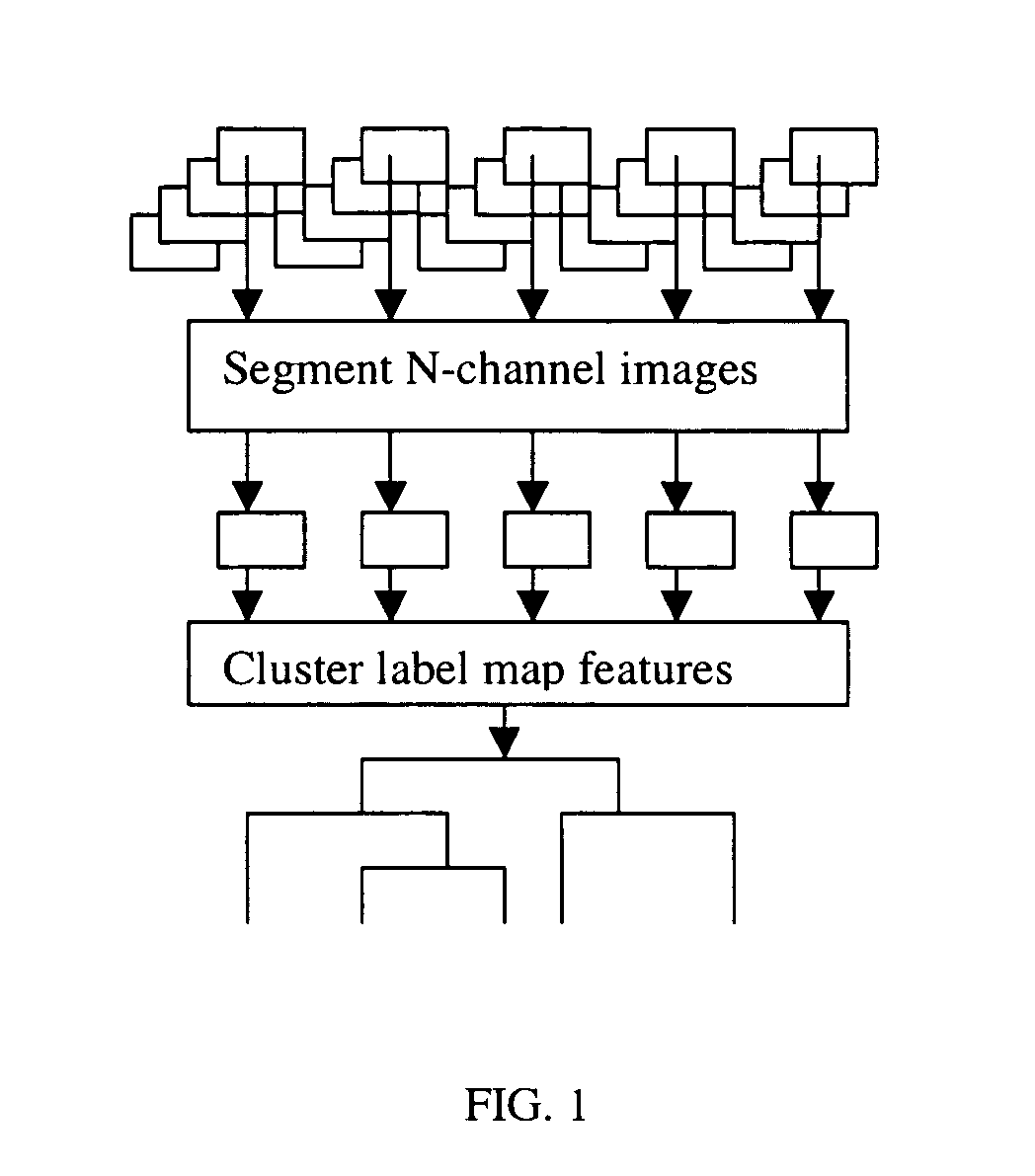
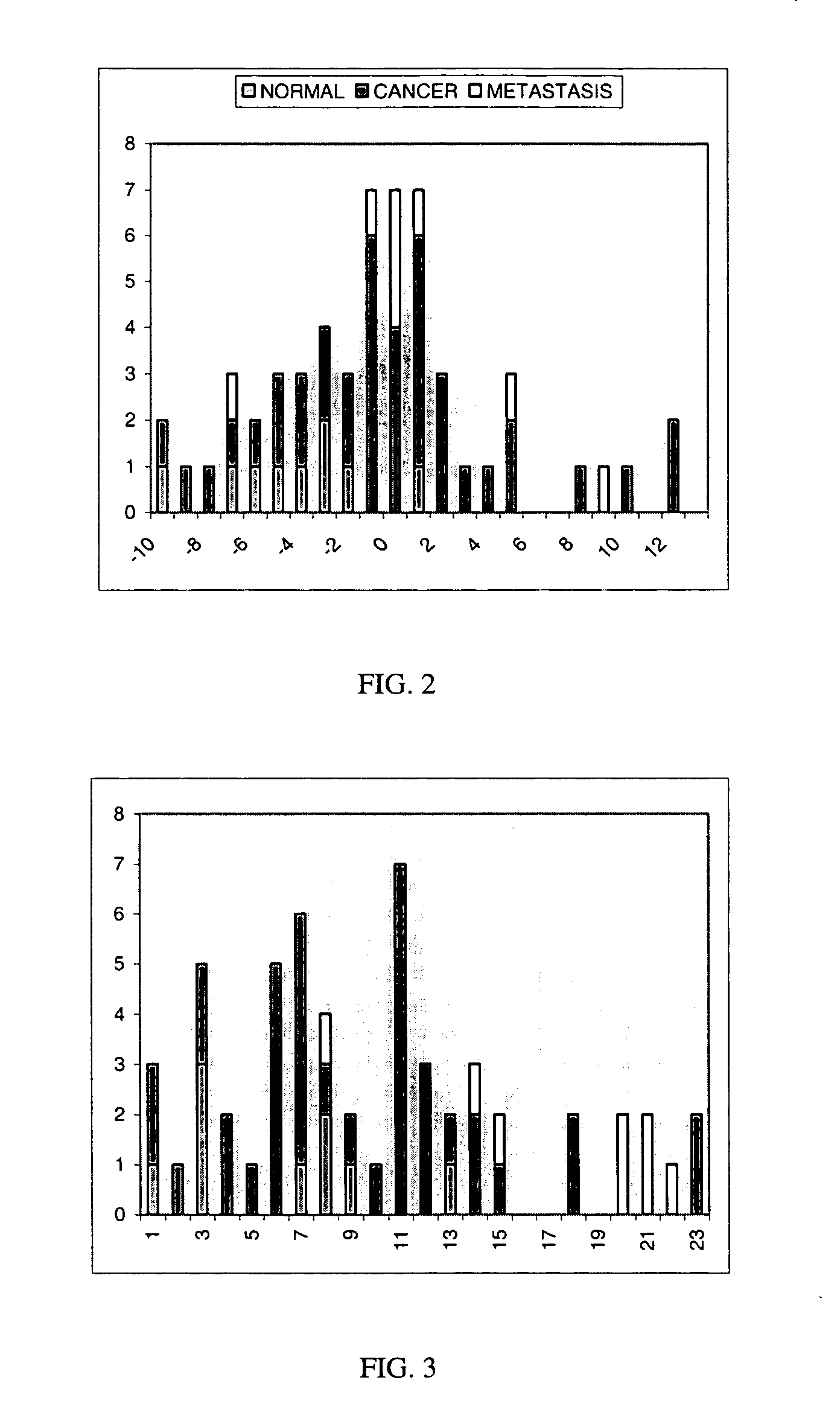
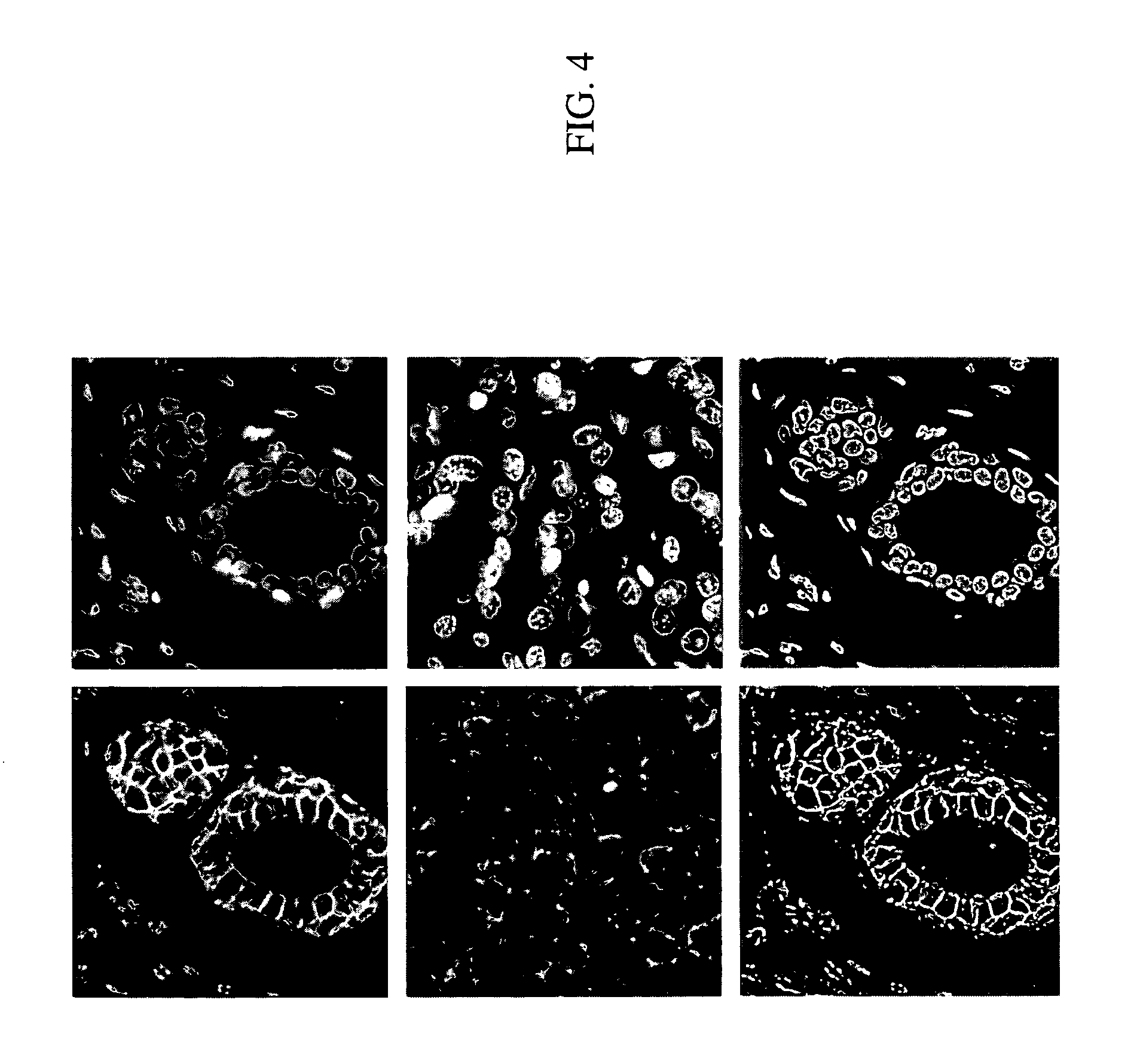
System and method for co-registering multi-channel images of a tissue micro array
ActiveUS20080032328A1Simple technologyIncrease the number ofImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceTissue microarray
A system and methods for co-registering multi-channel images of a tissue micro array, comprising the steps of, providing a biological material on a substrate; applying one or more molecular probes, adapted to provide fluorescent molecular markers, to the biological material; obtaining a first digital image of the biological material and the fluorescent molecular markers; applying a morphological stain to the biological material; obtaining a second digital image of the biological material, computing information common to the first and second images; and co-registering the second image with the first image based on one or more registration metrics.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
High efficiency solid-state light source and methods of use and manufacture
ActiveUS8192053B2Improve efficiencyIncrease powerOptical radiation measurementPoint-like light sourceFluorescenceHigh intensity light
A high-intensity light source is formed by a micro array of a semiconductor light source such as a LEDs, laser diodes, or VCSEL placed densely on a liquid or gas cooled thermally conductive substrate. The semiconductor devices are typically attached by a joining process to electrically conductive patterns on the substrate, and driven by a microprocessor controlled power supply. An optic element is placed over the micro array to achieve improved directionality, intensity, and / or spectral purity of the output beam. The light module may be used for such processes as, for example, fluorescence, inspection and measurement, photopolymerzation, ionization, sterilization, debris removal, and other photochemical processes.
Owner:SILICON VALLEY BANK
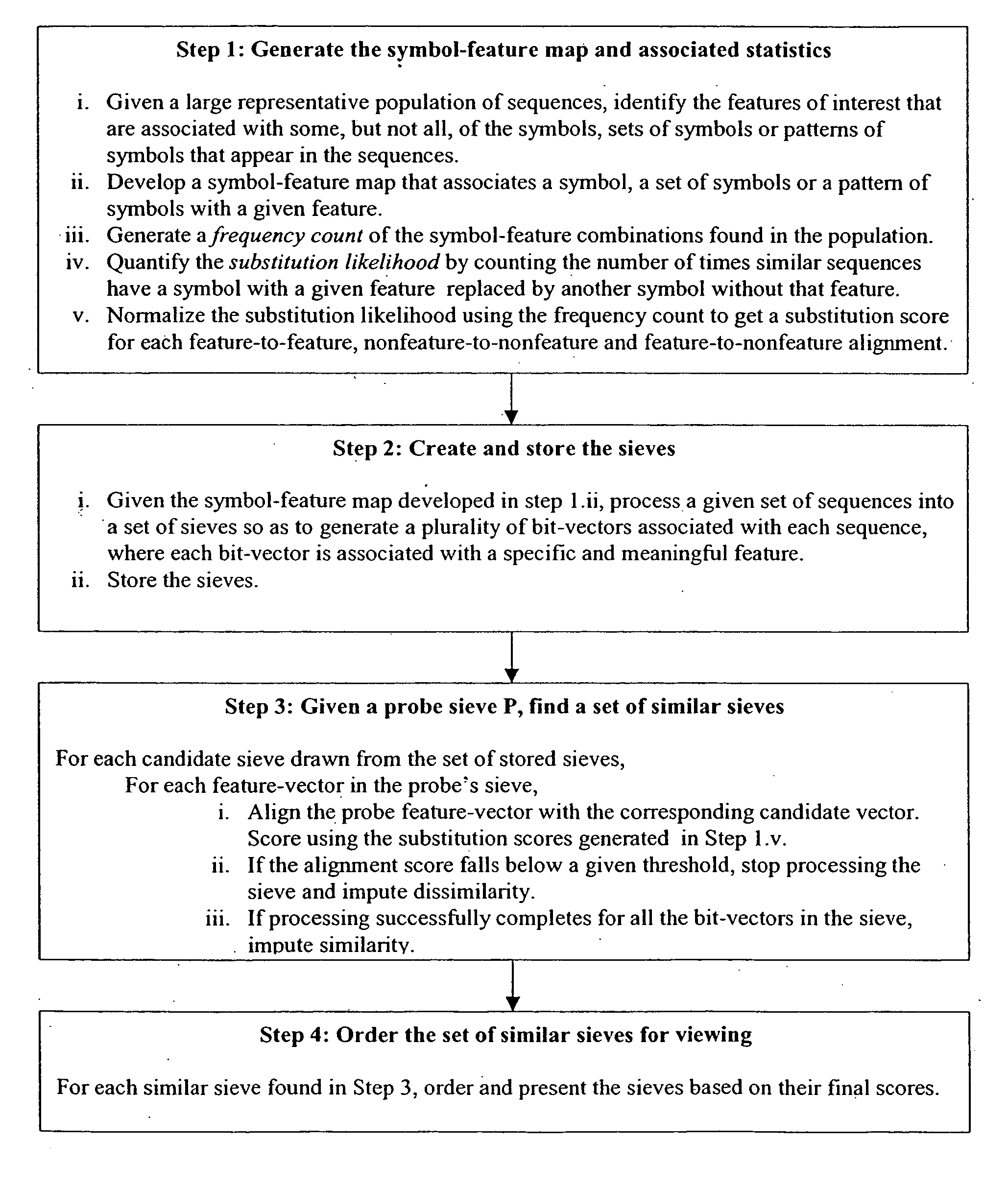
System and method for pattern recognition in sequential data
InactiveUS20050187916A1Easy to useIncrease speedSequence analysisComparison of digital valuesMedical diagnosisSequential data
The present invention is based on the encoding of sequential data or sequences in a novel manner that permits efficient storage and processing of sequential data, as well as methods for searching sequences or databases of sequences. The methods and systems of the current invention may be adapted broadly to various fields of application and to a variety of sequences types. For example, the current invention has broad application including to the fields of bioinformatics, molecular biology, pharmacogenomics, phonetic sequences, lexicographic sequences, signal analysis, game playing, law enforcement, biometrics, medical diagnosis, equipment maintenance and micro-array data analysis.
Owner:ELORET CORP
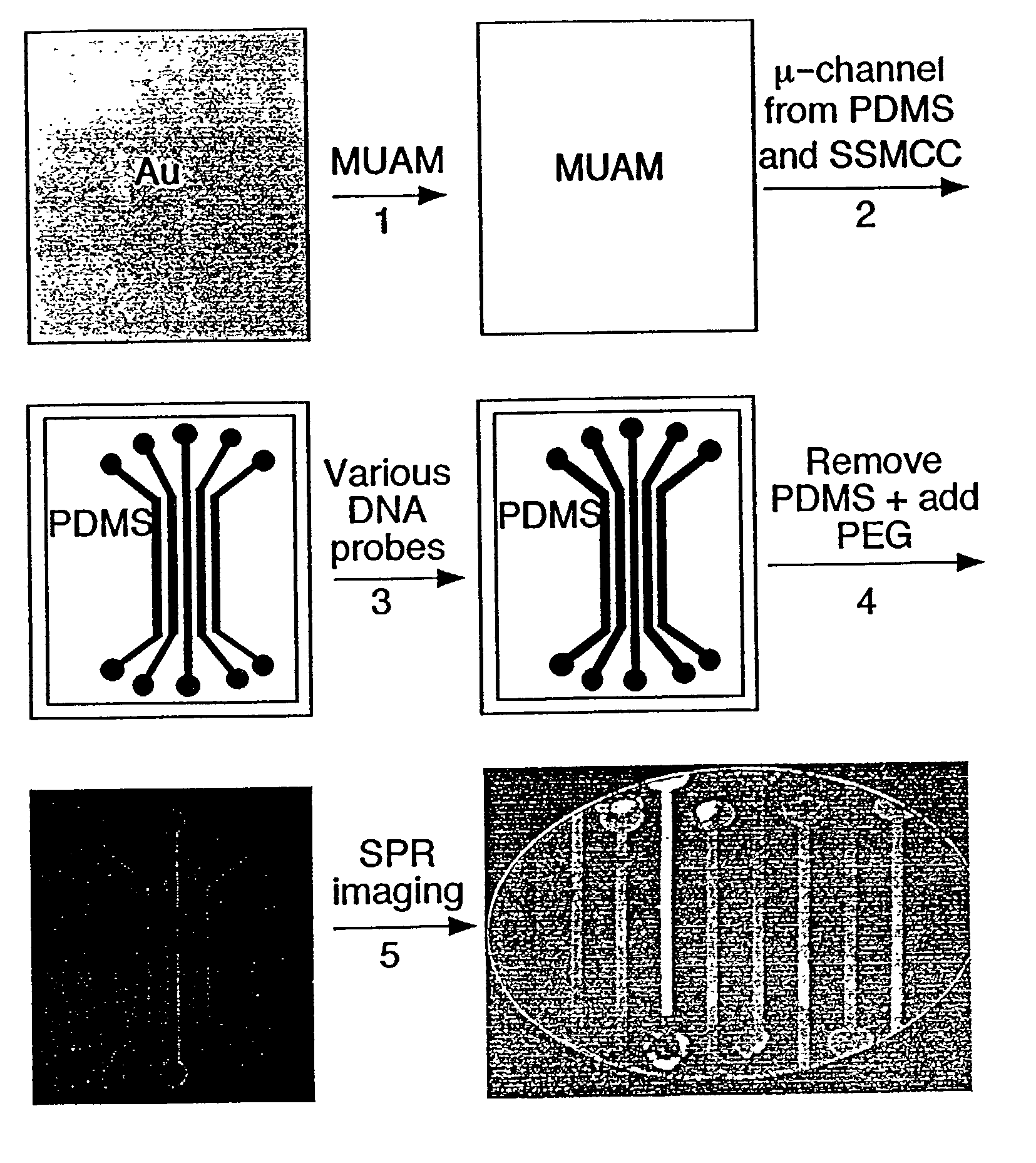
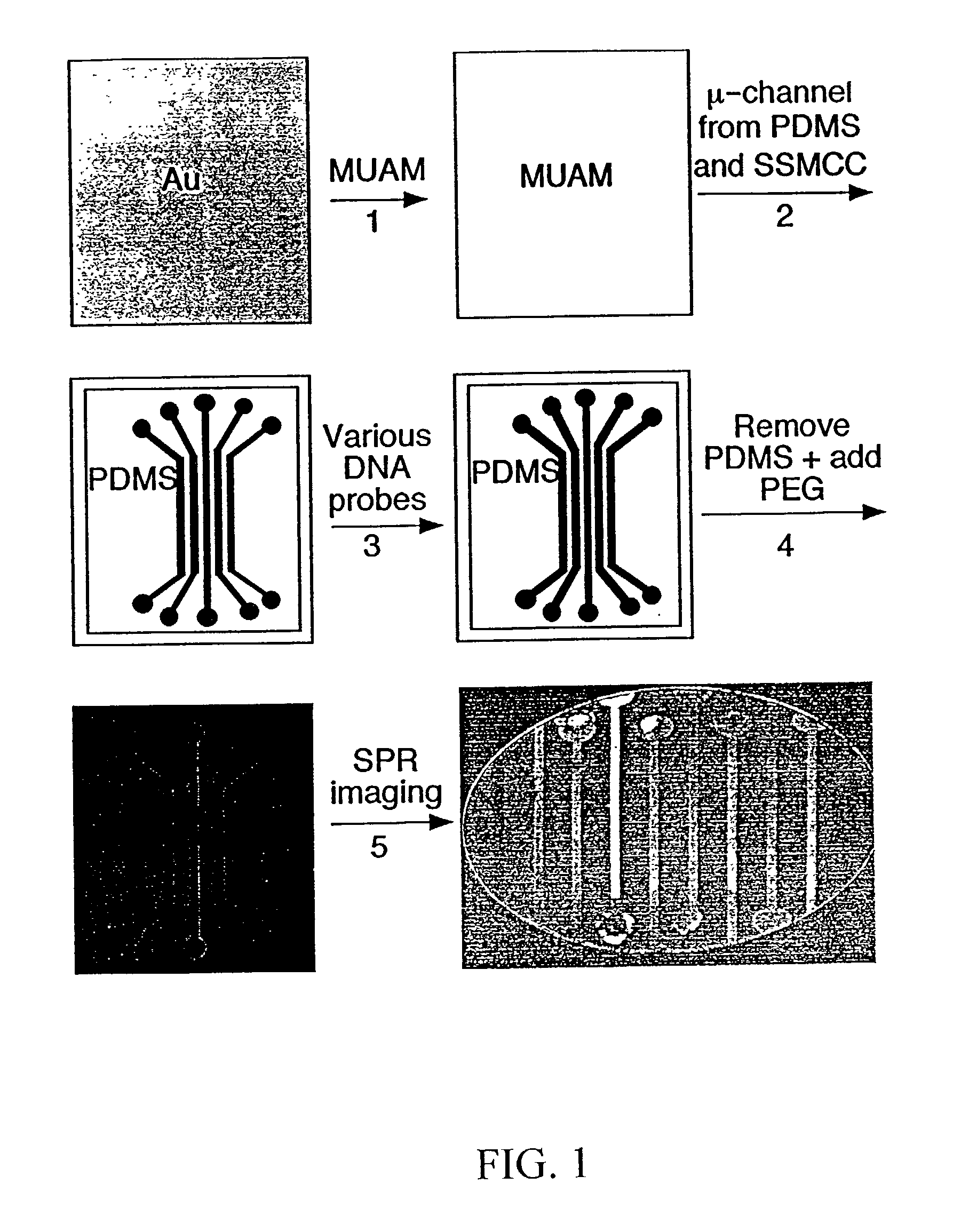
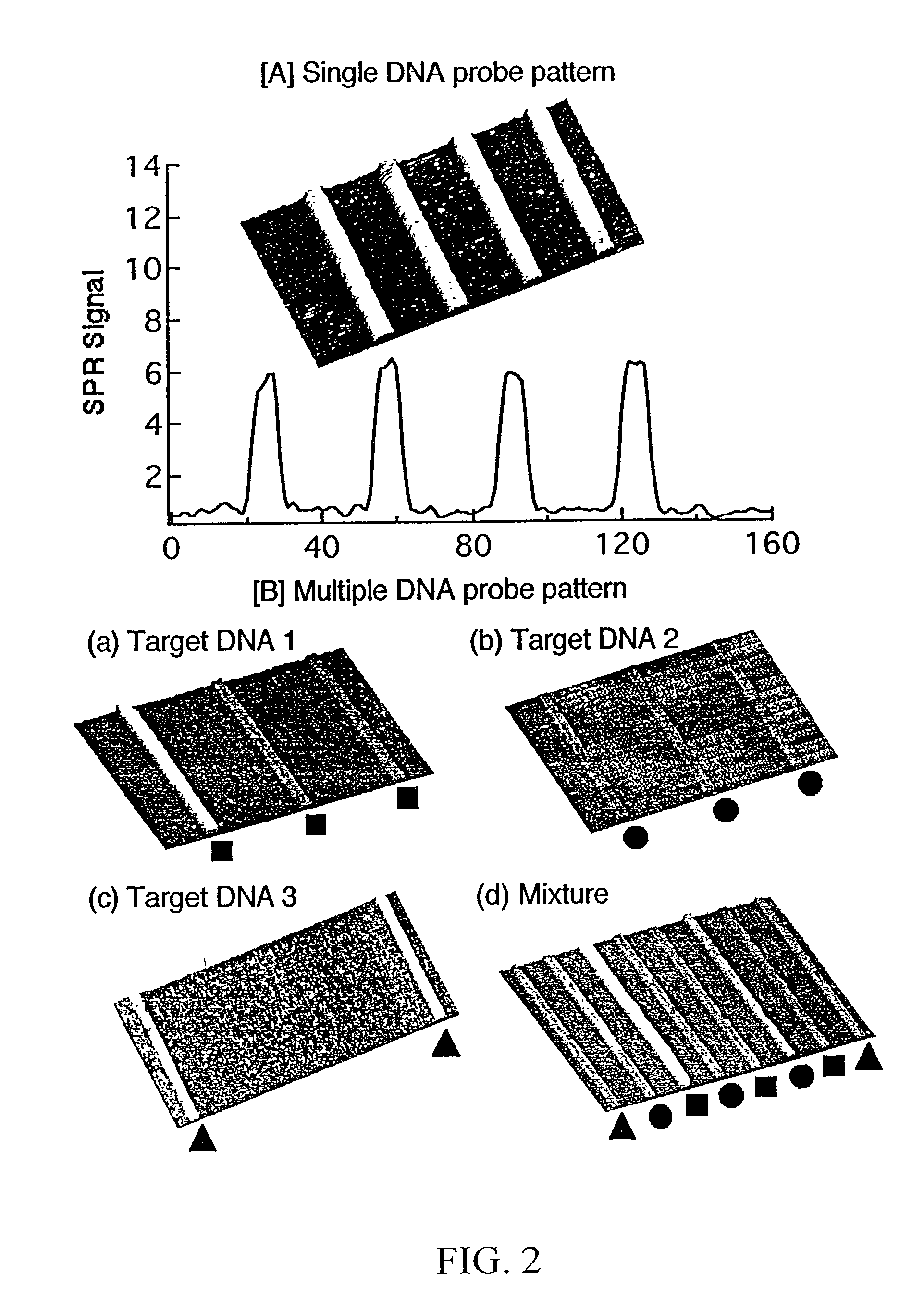
Surface plasmon resonance imaging of micro-arrays
InactiveUS20030017579A1Material nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSpr imagingMicrofluidic channel
Disclosed is a method for fabricating 1-dimensional micro-arrays using parallel micro-fluidic channels on chemically-modified metal, carbon, silicon, and / or germanium surfaces; a muL detection volume method that uses 2-dimensional nucleic acid micro-arrays formed by employing the 1-dimensional DNA micro-arrays in conjunction with a second set of parallel micro-fluidic channels for solution delivery, and the 1-dimensional and 2-dimensional arrays used in the methods. The methodology allows the rapid creation of 1- and 2-dimensional arrays for SPR imaging and fluorescence imaging of DNA-DNA, DNA-RNA, DNA-protein, and protein-protein binding events. The invention enables very small volumes necessary for a variety of bioassay applications to be analyzed by SPR. Target solution volumes as small as 200 pL can be analyzed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
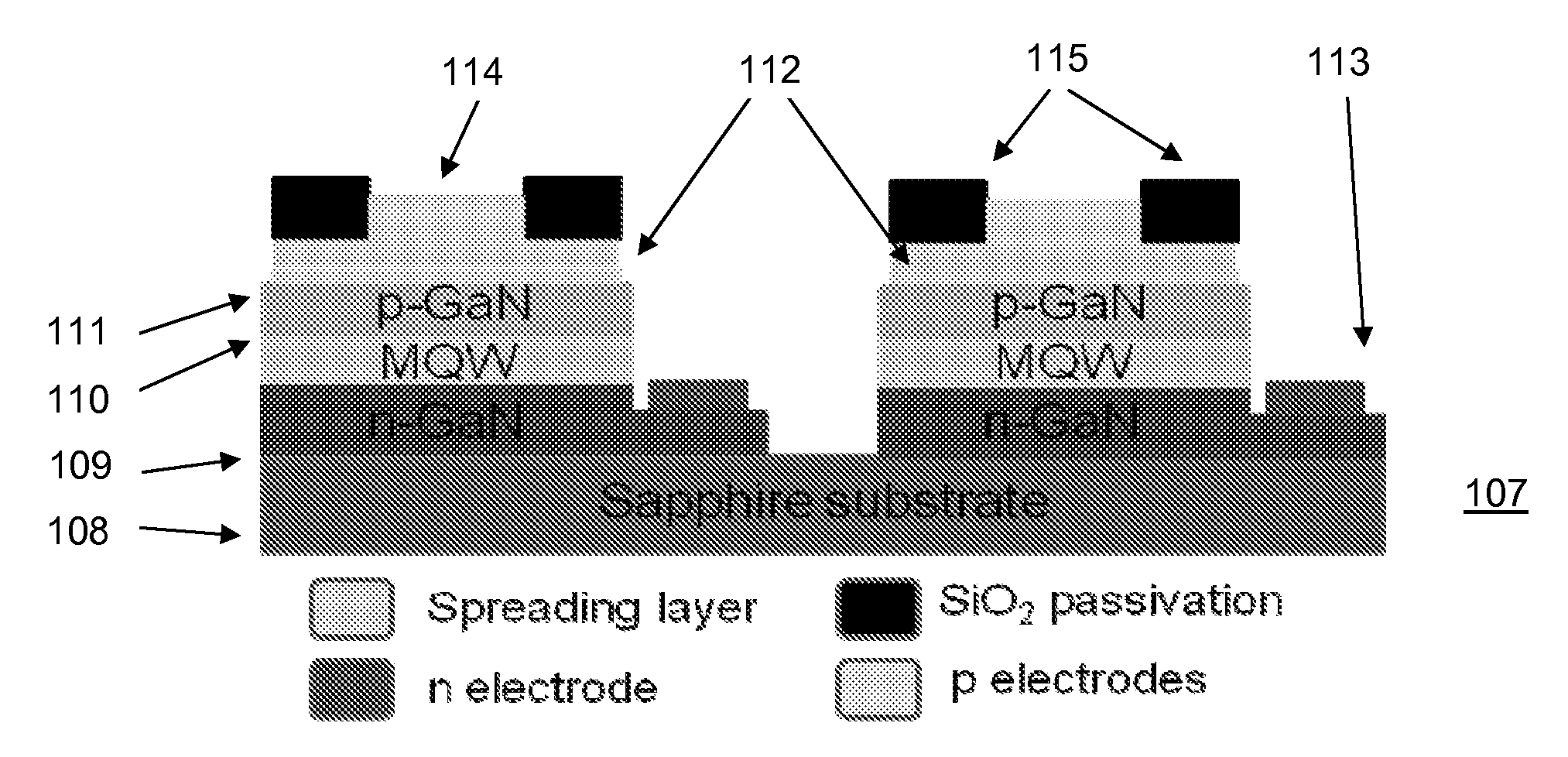
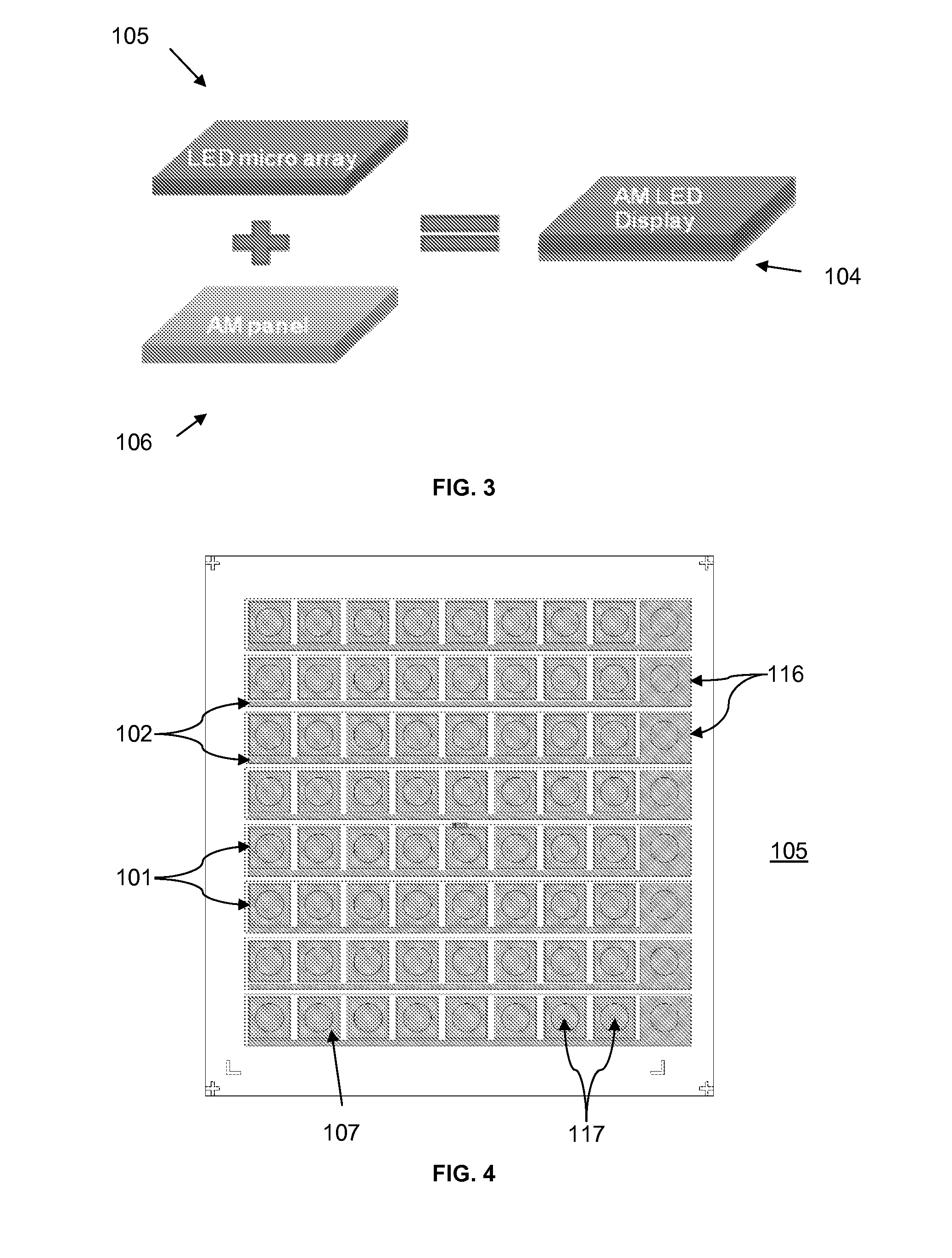
Method for manufacturing a monolithic LED micro-display on an active matrix panel using flip-chip technology and display apparatus having the monolithic LED micro-display
ActiveUS20110309378A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive matrixEngineering
A high-resolution, Active Matrix (AM) programmed monolithic Light Emitting Diode (LED) micro-array is fabricated using flip-chip technology. The fabrication process includes fabrications of an LED micro-array and an AM panel, and combining the resulting LED micro-array and AM panel using the flip-chip technology. The LED micro-array is grown and fabricated on a sapphire substrate and the AM panel can be fabricated using CMOS process. LED pixels in a same row share a common N-bus line that is connected to the ground of AM panel while p-electrodes of the LED pixels are electrically separated such that each p-electrode is independently connected to an output of drive circuits mounted on the AM panel. The LED micro-array is flip-chip bonded to the AM panel so that the AM panel controls the LED pixels individually and the LED pixels exhibit excellent emission uniformity. According to this constitution, incompatibility between the LED process and the CMOS process can be eliminated.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
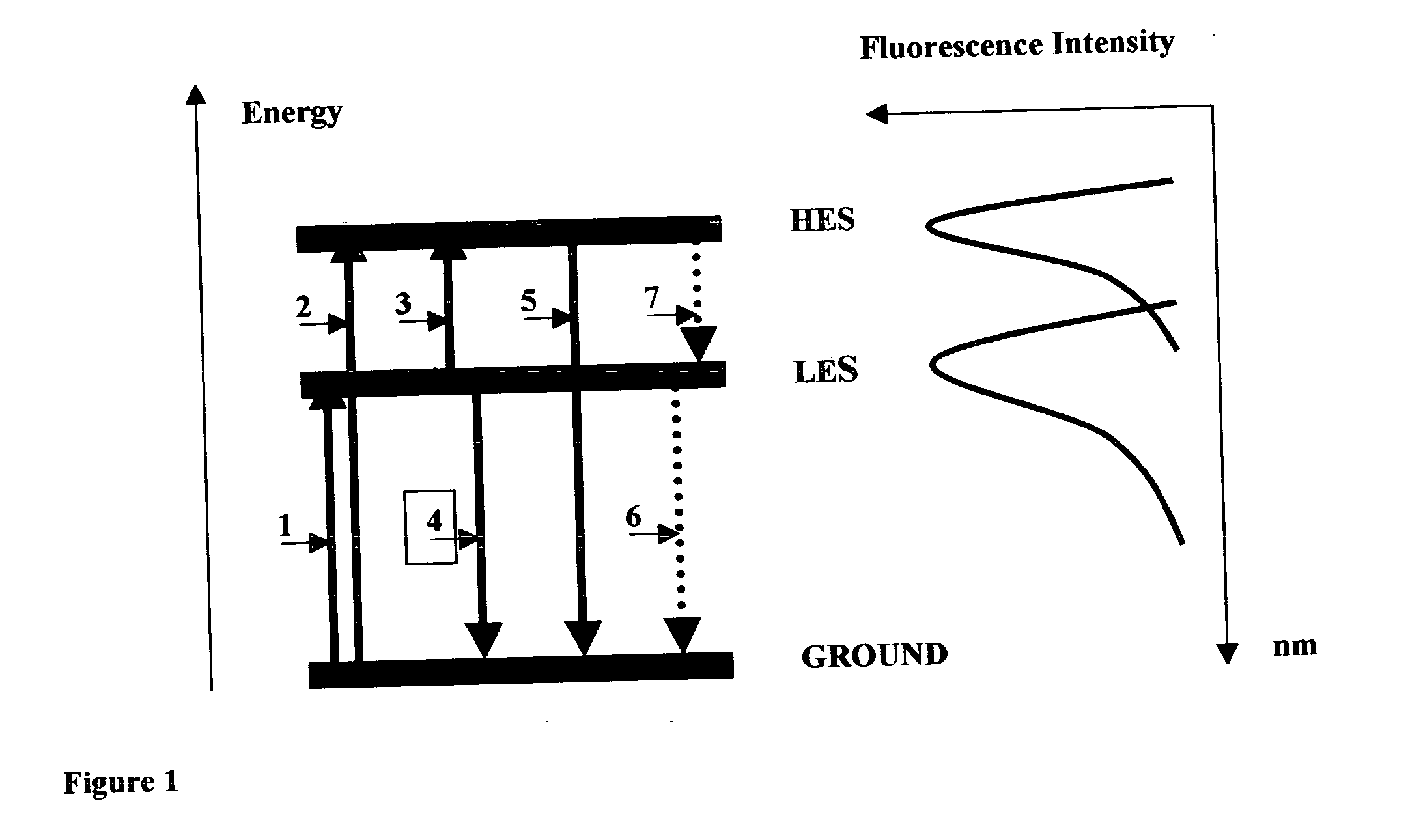
Method and spectral/imaging device for optochemical sensing with plasmon-modified polarization
InactiveUS20050186565A1Low fluorescence quantum yieldHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberFluorescence
The invention discloses a method and spectral-imaging device for optochemical sensing with plasmon-modified multiband fluorescence polarization and with plasmon-modified polarization phase shift changes of a light beam reflected and / or passed through a total internal reflection conducting structure. The optochemical sensing is performed for molecules placed nearby the conducting structure and being excited by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to lower excited state (LES) and / or to higher excited states (HES). The invention also describes the spectral imaging device with an improved sensitivity of several orders of magnitude. The disclosed method and imaging device may find applications in clinical diagnostics, pharmaceutical screening, biomedical research, biochemical-warfare detection and other diagnostic techniques. The device can be used in bio-chip and micro-array technologies, flowcytometer, fiber optic and other types of diagnostic devices.
Owner:AMERICAN ENVIRONMENTAL SYST
Microdissection-based methods for determining genomic features of single chromosomes
InactiveUS20060211001A1Quick fixPromote associationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAChromosome regions
The present provides a microdissection-based method for identifying a genomic feature present within a visible chromosome region. The method includes steps of: (a) micro-dissecting a single copy of a chromosome to obtain a visible chromosome region; (b) amplifying the visible chromosome region to obtain amplified single chromosome DNA; and (c) subjecting the amplified single chromosome DNA to micro-array analysis whereby such analysis identifies at least one genomic feature present within the visible chromosome region. The method is applicable to determining genomic features including, but not limited to, genomic DNA size, gene content, DNA breakpoint, or DNA polymorphism (e.g., single nucleotide polymorphisms).
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method and kit to perform a PCR amplification and micro-array detection in the same medium and/or same chamber
InactiveUS20100273678A1Avoiding and reducing primer-dimers formationFormation is reduced and avoidedNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyReaction chamber
An amplification and micro-array detection method is performed in a same buffer and / or in a same reaction chamber. A kit for an amplification of multiple nucleotide targets, uses low primer concentration.
Owner:EPPENDORF ARRAY TECH SA
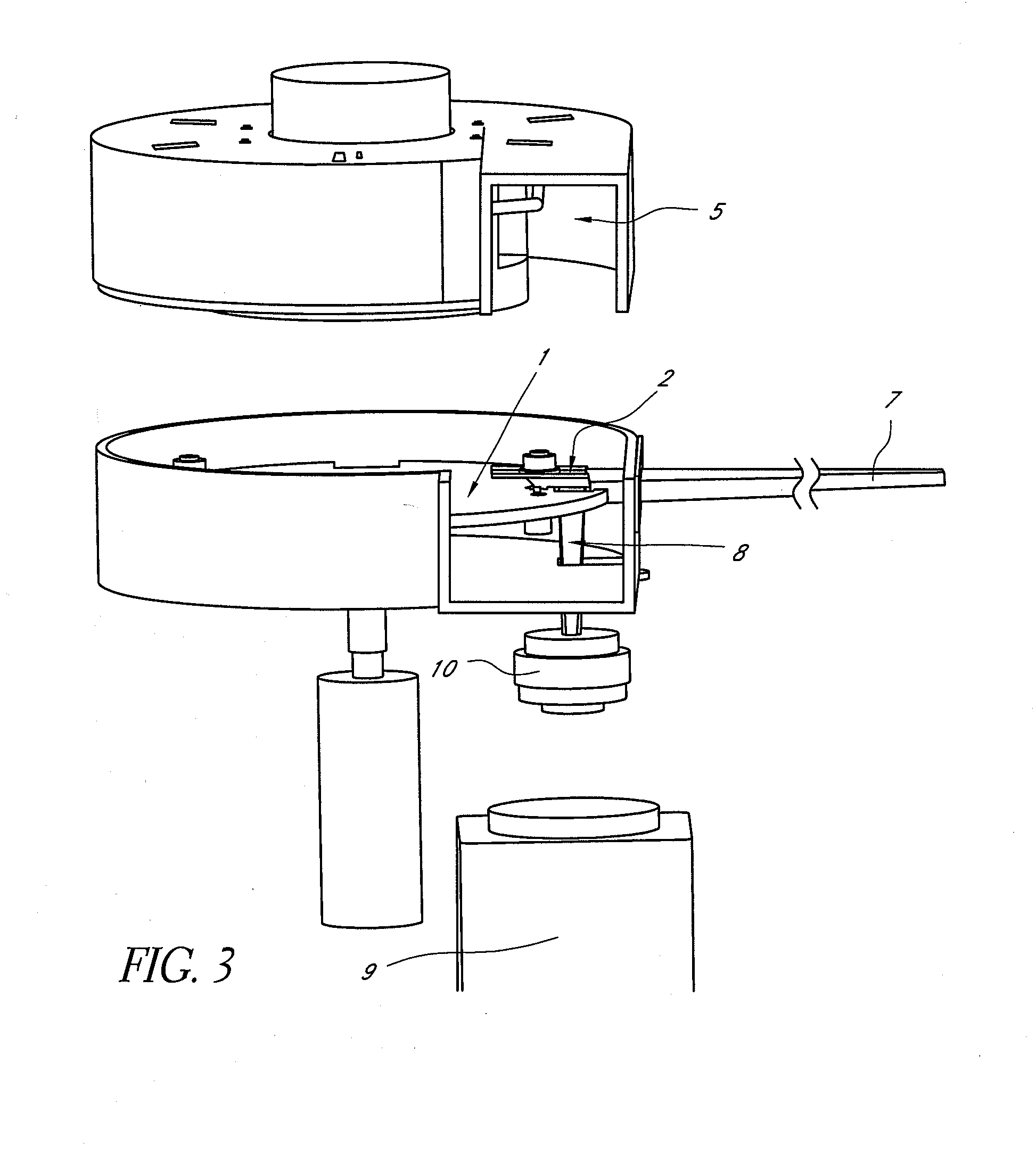
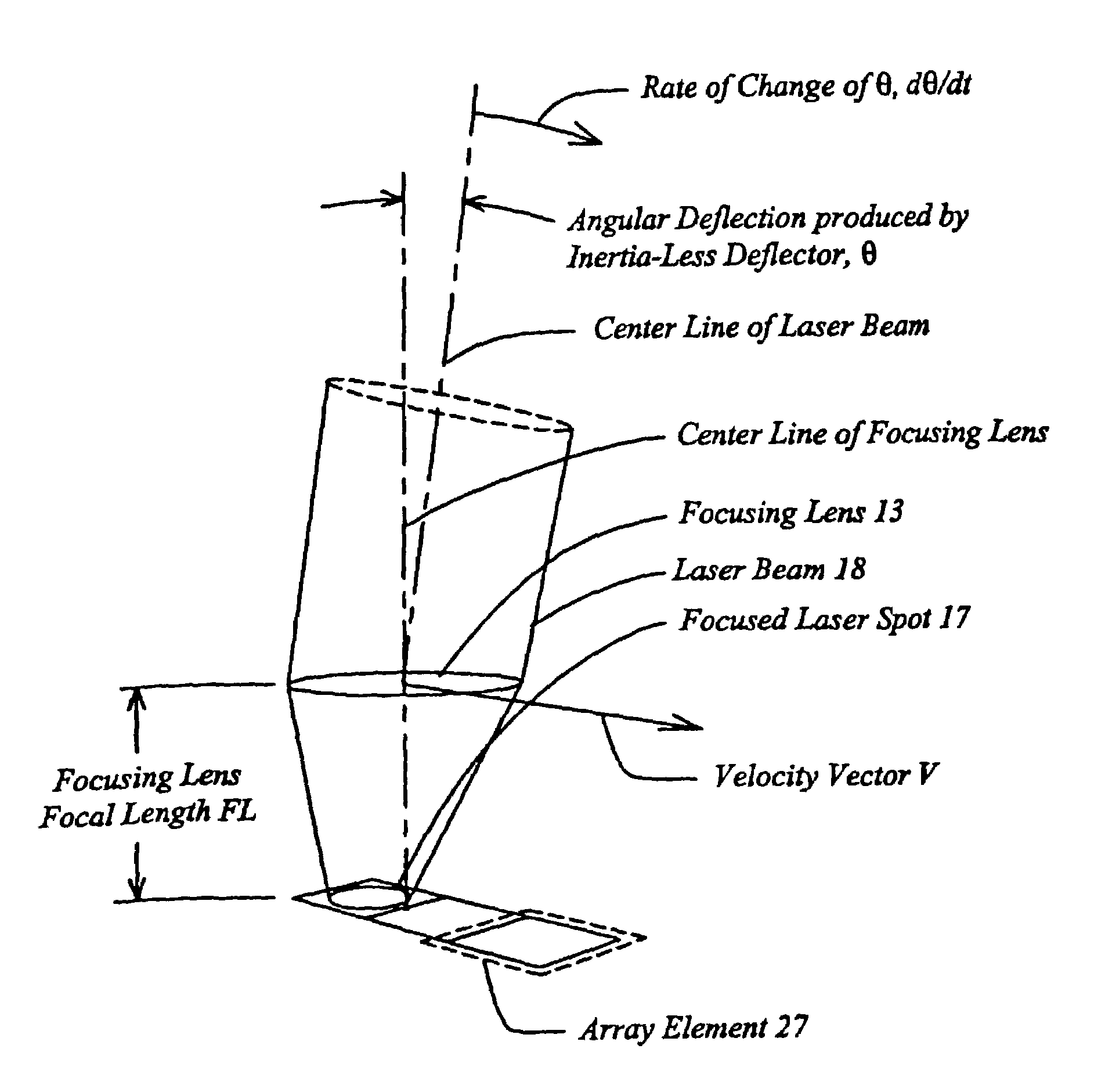
Scanning microscopy, fluorescence detection, and laser beam positioning
InactiveUS20030156323A1Diameter of to varyEnsure high efficiency and accuracyMirrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansWide areaGrating
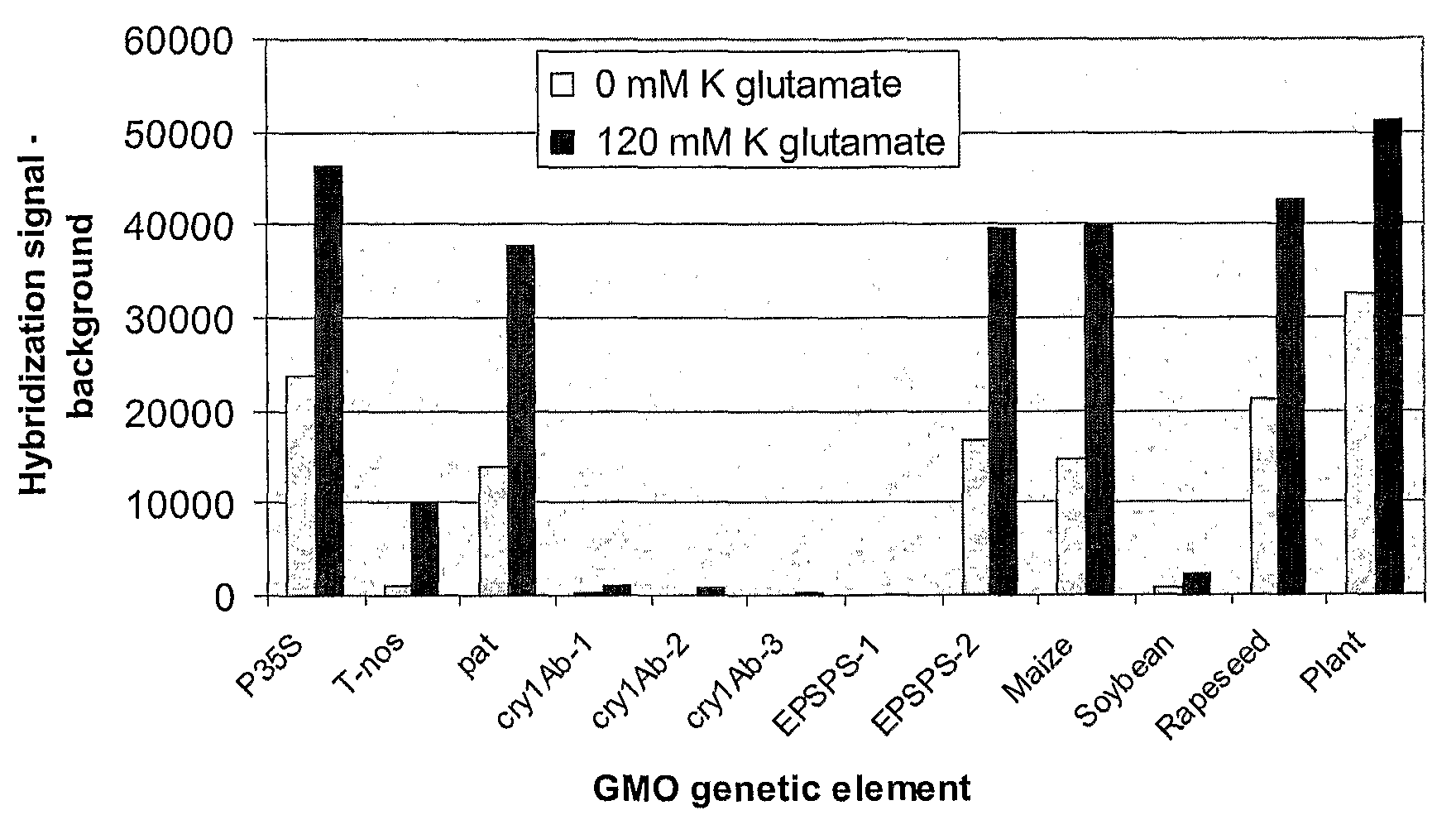
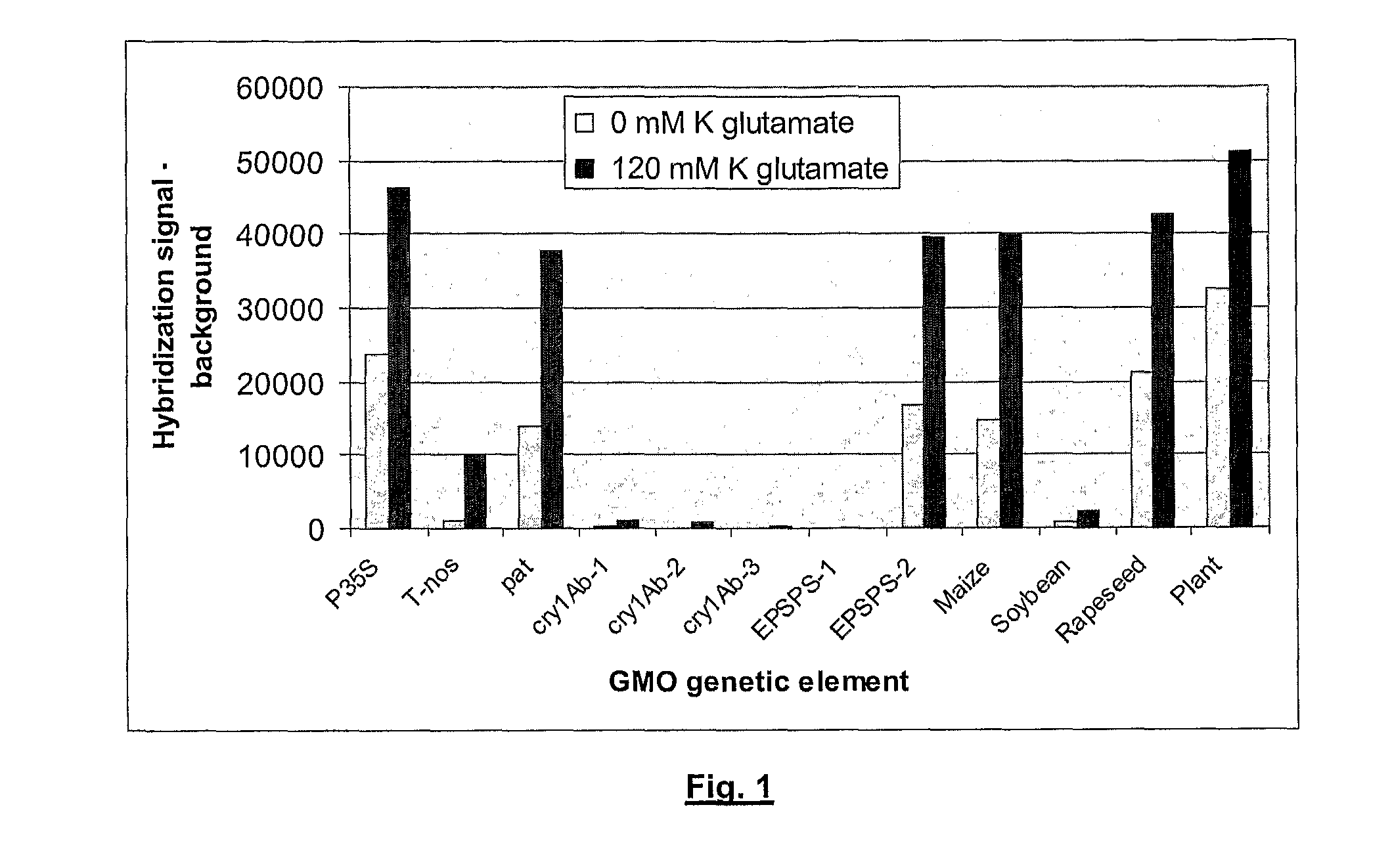
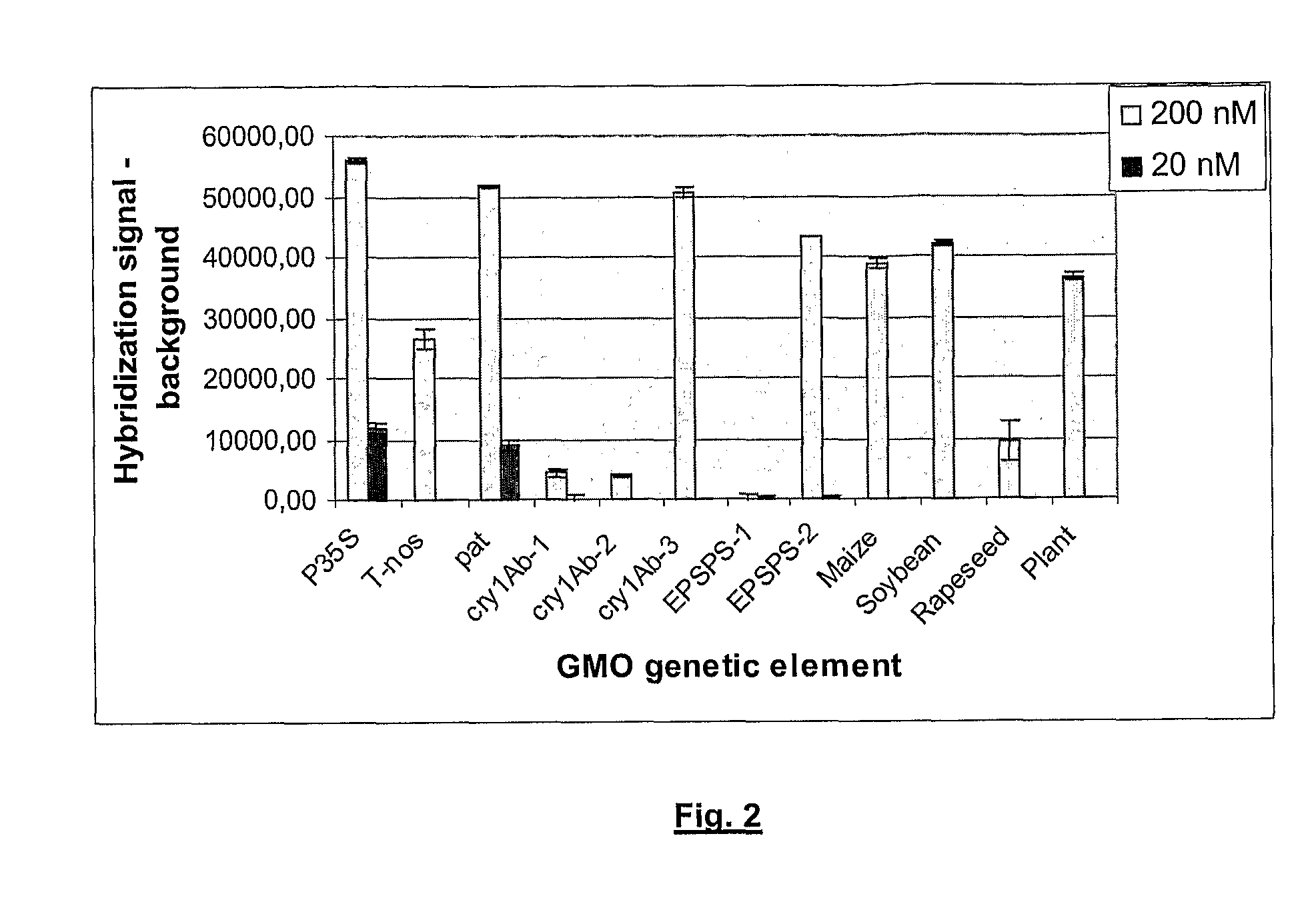
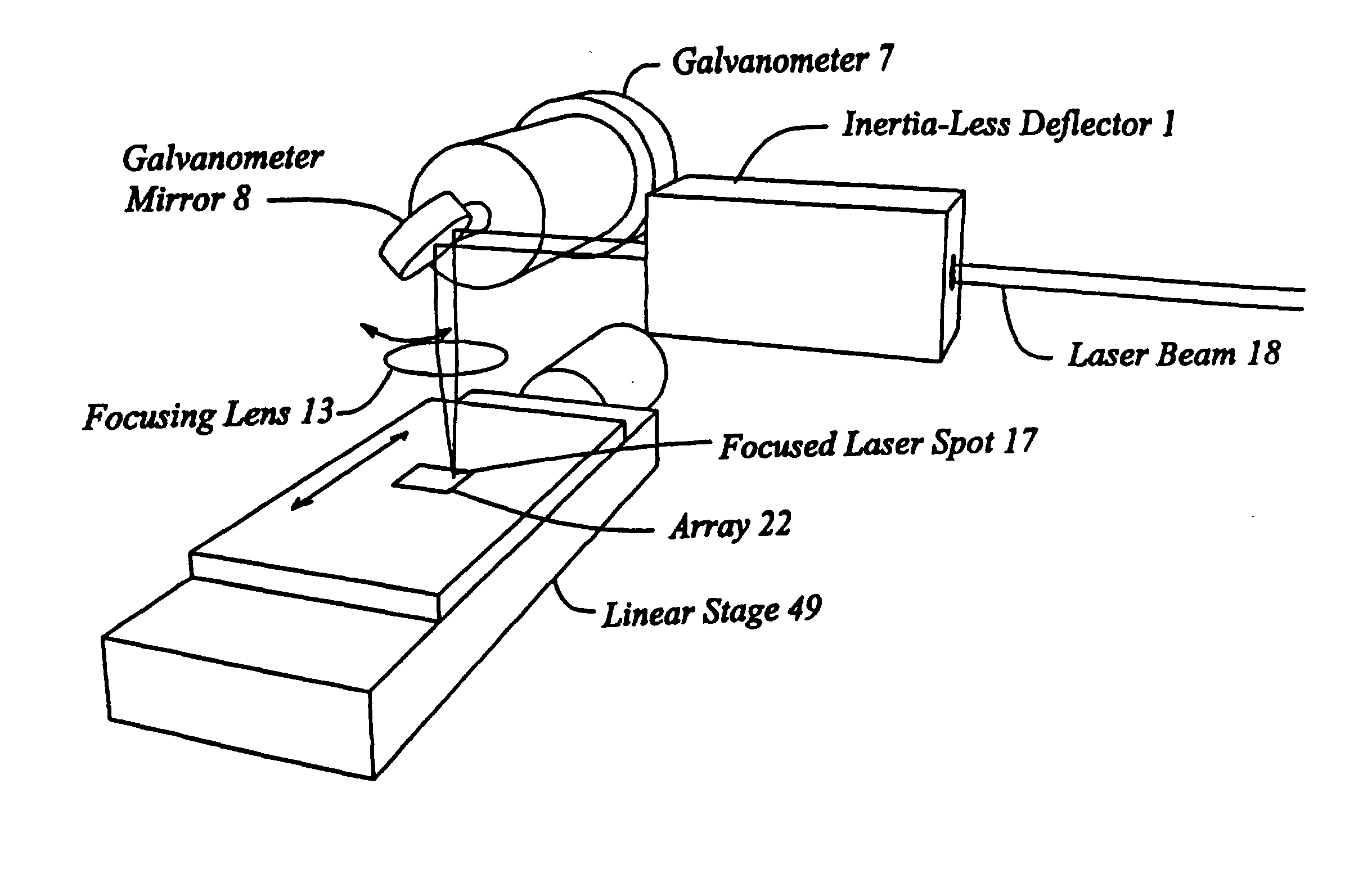
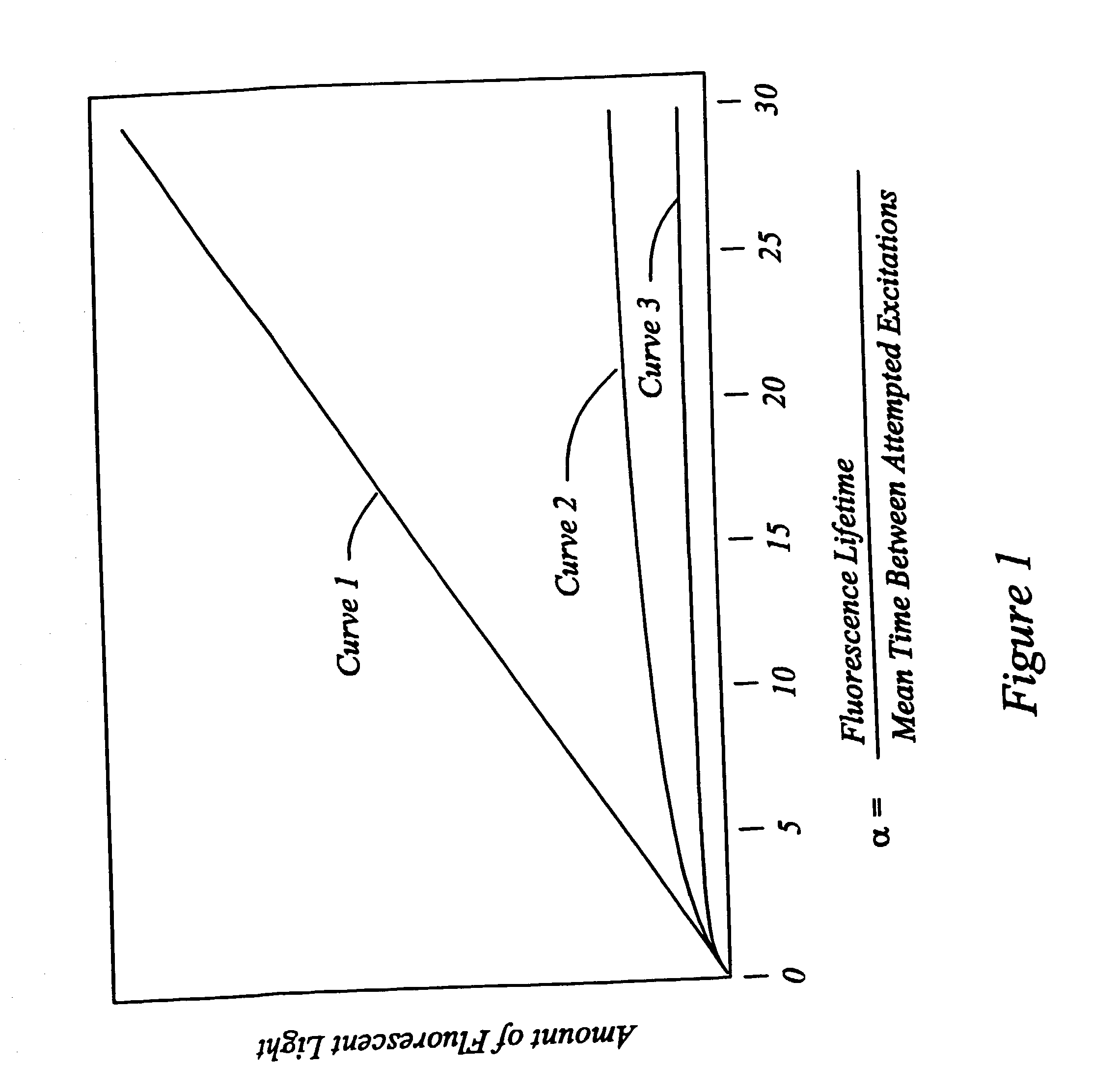
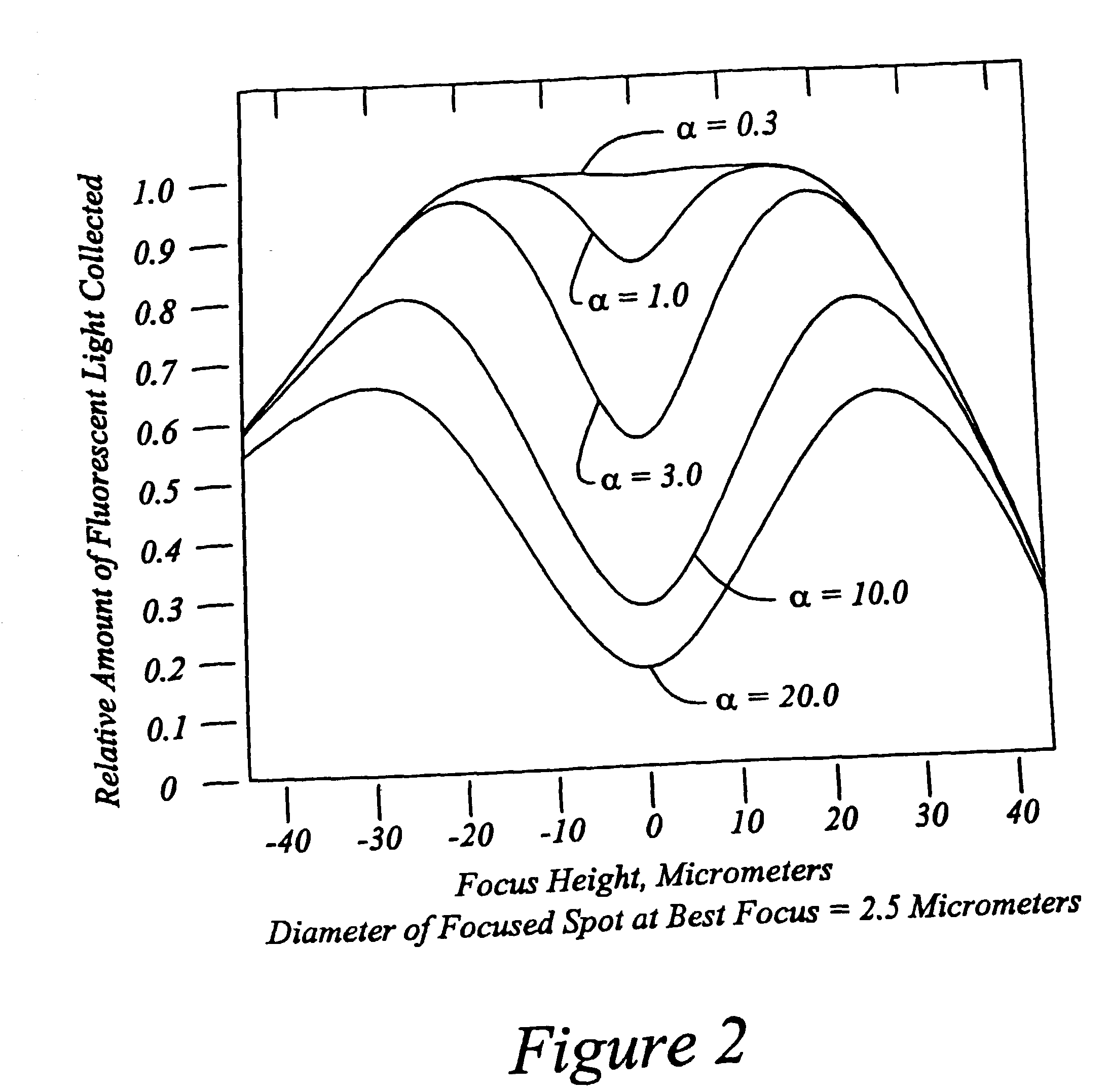
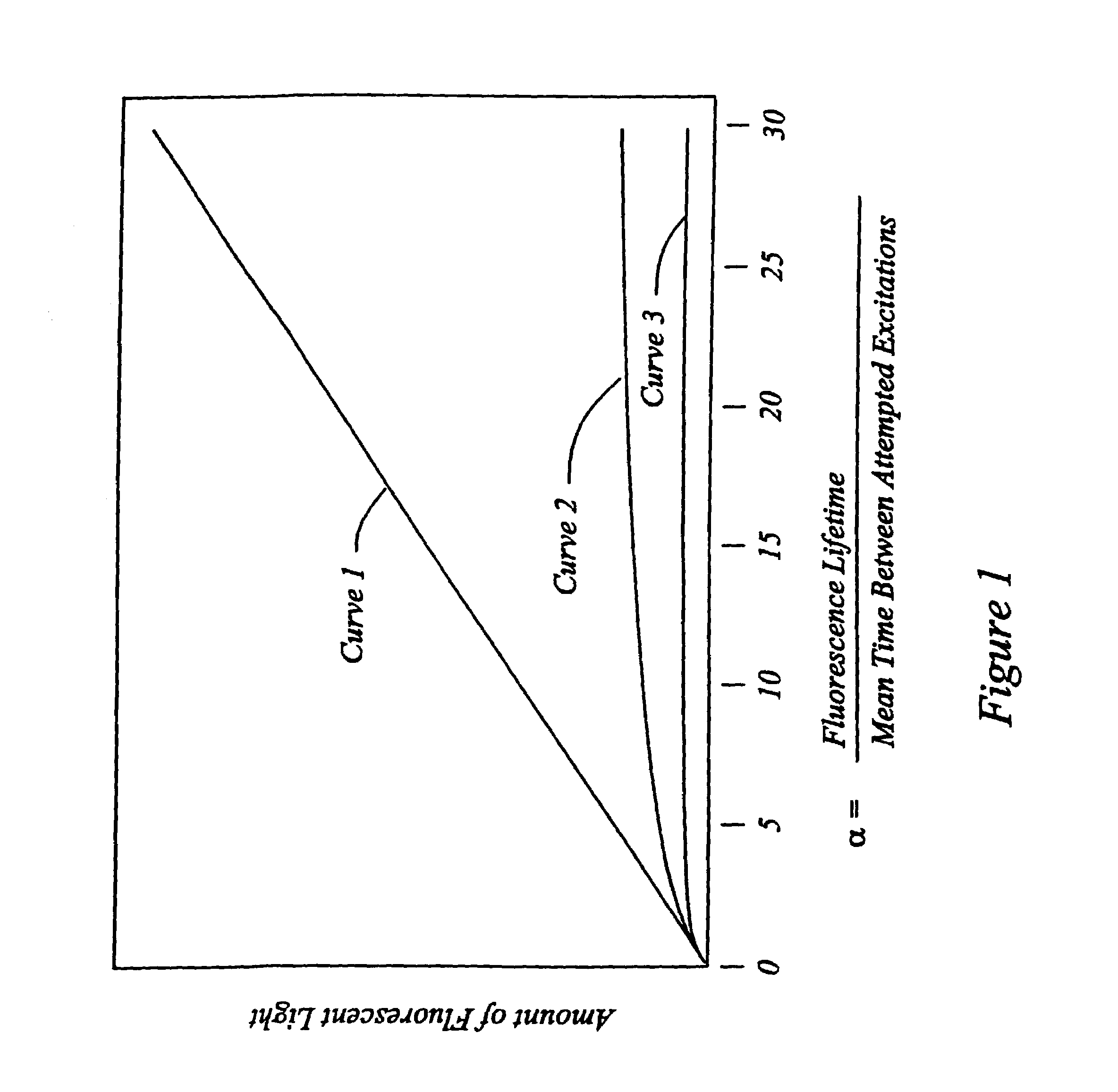
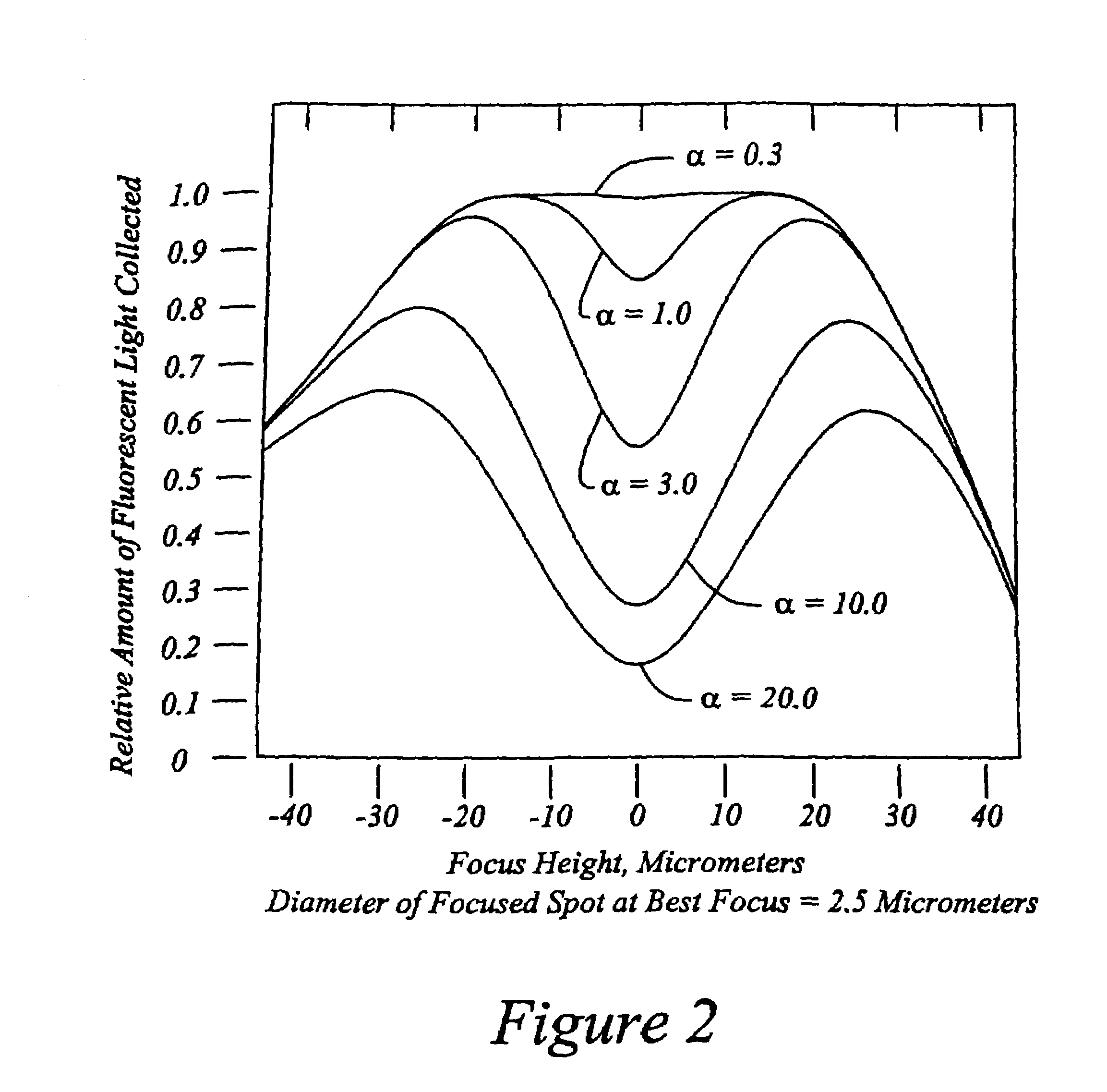
High speed, wide area microscopic scanning or laser positioning is accomplished with an inertia-less deflector (for example an acousto-optic or electro-optic deflector) combined with a high speed wide area microscopic scanning mechanism or laser positioner mechanism that has inertia, the motion of the inertia-less deflector specially controlled to enable a focused spot to stabilize, for example to stop and dwell or be quickly aimed. It leads to improved data acquisition from extremely small objects and higher speed operation. In the case of fluorescence reading of micro-array elements, dwelling of fluorophore-exciting radiation in a spot that is relatively large enables obtaining the most fluorescent photons per array element, per unit time, a winning criterion for reducing fluorophore saturation effects. The same inertia-less deflector performs stop and dwell scanning, edge detection and raster scans. Automated mechanism for changing laser spot size enables selection of spot size optimal for the action being performed.
Owner:OVERBECK JAMES W
Real-time PCR of targets on a micro-array
InactiveUS20120053068A1Improve efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningPolynucleotideBiology
The present invention relates to a method, apparatus, cartridge and kit for monitoring on a micro-array a real-time PCR amplification of a polynucleotide molecule being present in a solution.
Owner:EPPENDORF AG
Method for the preparation of compound micro array chips and the compound micro array chips produced according to said method
InactiveUS6423552B1IndexHigh correctnessMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsMicroarray cghReagent
The present invention relates to a method for the preparation of compound of microarray chips, especially the method by repeatedly impressing reagents at fixed locations on a substrate to synthesize said chips; and also realtes to a compound microarray chips produced according to said method.
Owner:ZUHONG LU
Scanning microscopy, fluorescence detection, and laser beam positioning
InactiveUS7050208B2Increase ratingsAdd dimensionMirrorsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringFluorophore
High speed, wide area microscopic scanning or laser positioning is accomplished with an inertia-less deflector (for example an acousto-optic or electro-optic deflector) combined with a high speed wide area microscopic scanning mechanism or laser positioner mechanism that has inertia, the motion of the inertia-less deflector specially controlled to enable a focused spot to stabilize, for example to stop and dwell or be quickly aimed. It leads to improved data acquisition from extremely small objects and higher speed operation. In the case of fluorescence reading of micro-array elements, dwelling of fluorophore-exciting radiation in a spot that is relatively large enables obtaining the most fluorescent photons per array element, per unit time, a winning criterion for reducing fluorophore saturation effects. The same inertia-less deflector performs stop and dwell scanning, edge detection and raster scans. Automated mechanism for changing laser spot size enables selection of spot size optimal for the action being performed.
Owner:OVERBECK JAMES W
Tape stripping methods for analysis of skin disease and pathological skin state
ActiveUS20050221334A1Less traumaticEfficient methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAdhesiveNon invasive
The present invention provides non-invasive methods for detecting, monitoring, and diagnosing skin disease and pathological skin states such as irritated skin and psoriasis. The methods include using tape stripping to analyze expression in epidermal samples, of one or more skin markers. In illustrative examples, the tape stripping is performed using pliable tape that has a rubber adhesive. Furthermore, the present invention provides methods for predicting and monitoring response to therapy for a skin disease, such as psoriasis or dermatitis. Finally, the methods can include the use of a micro array.
Owner:DERMTECH INT
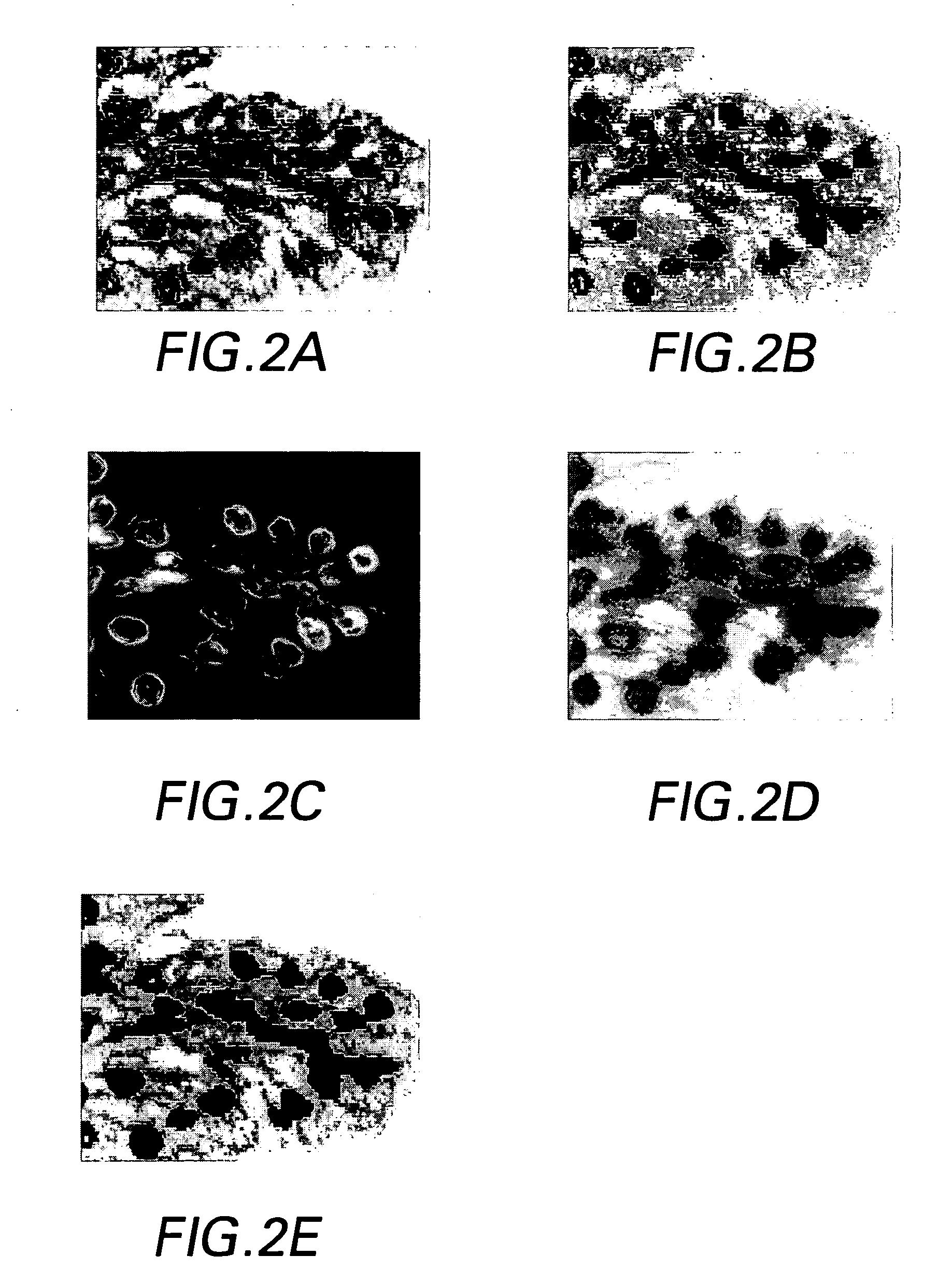
System and methods for scoring images of a tissue micro array
A system for analyzing tissue samples, that generally comprises, a storage device for at least temporarily storing one or more images of one or more cells, wherein the images comprise a plurality of channels; and a processor that is adapted to determine the extent to which a biomarker may have translocated from at least one subcellular region to another subcellular region; and then to generate a score corresponding to the extent of translocation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for microarray fabrication
InactiveUS7247337B1Added fabricationReduce defective rateMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsEngineeringMicro array
The invention provides a method and apparatus for micro array fabrication exclusive from the impact of a gas. A housing with a gas free chamber provides for improved micro array fabrication with a lower defect rate. The invention provides a housing that excludes a gas such as ozone to prevent interaction with probe construction or attachment. A method of fabricating a micro array in an ozone free environment is also disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Micro arrays with structured and unstructured probes
InactiveUS7094537B2Reduce background noiseImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMicro arrayPhysics
The invention provides an apparatus and method for determining a signal produced by a micro array device. The apparatus provides an unstructured probe and structured probe. The unstructured probe binds to a target and provides a first signal that can be compared to a second signal produced by a structured probe. A more accurate level of intensity of the first signal can be determined by comparing to the second signal produced by the structured probe. A method for determining a more accurate level of signal intensity produced from the unstructured probes bound to the target is also disclosed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Pre-processed feature ranking for a support vector machine
InactiveUS7475048B2Reduce in quantityMinimize the numberKernel methodsDigital computer detailsDiseaseData set
A computer-implemented method is provided for ranking features within a large dataset containing a large number of features according to each feature's ability to separate data into classes. For each feature, a support vector machine separates the dataset into two classes and determines the margins between extremal points in the two classes. The margins for all of the features are compared and the features are ranked based upon the size of the margin, with the highest ranked features corresponding to the largest margins. A subset of features for classifying the dataset is selected from a group of the highest ranked features. In one embodiment, the method is used to identify the best genes for disease prediction and diagnosis using gene expression data from micro-arrays.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
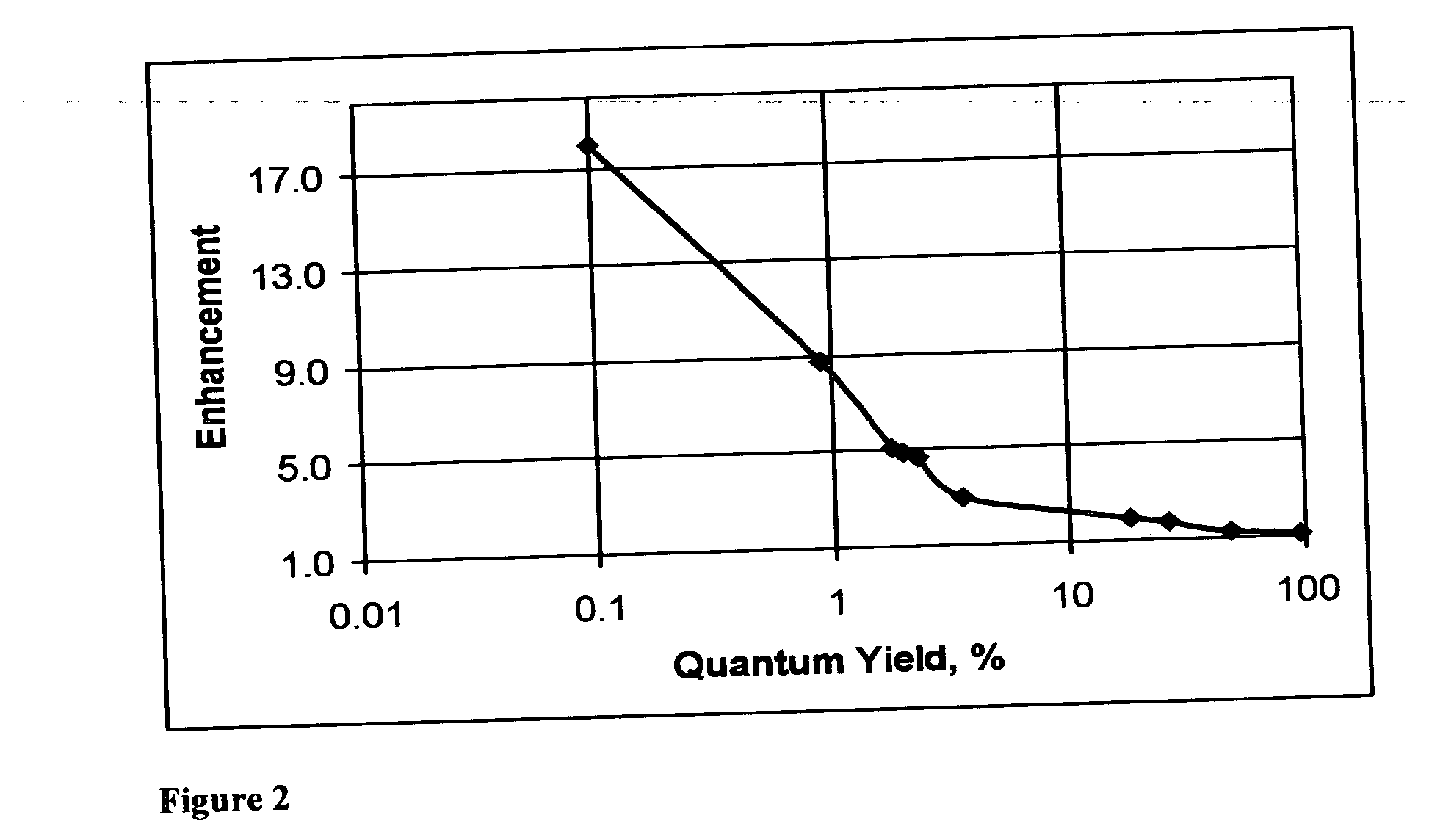
Carbon dots with high fluorescent quantum yield, and application thereof in fluorescent color development
InactiveCN103395771AHigh fluorescence quantum yieldMaterial nanotechnologyNano-carbonEthylenediamineQuantum yield
The invention relates to carbon dots with high fluorescent quantum yield, and an application thereof in fluorescent color development, and belongs to the application field of fluorescent carbon nanomaterials. Specifically, the invention relates to the carbon dots with the high fluorescent quantum yield which are synthesized by using citric acid and ethene diamine as raw materials as a fluorescent ink for writing or fluorescent printing, and further broadens the application thereof in fluorescent electrospining, fluorescent micro arrays and fluorescent composites. The carbon dots with the high fluorescent quantum yield are obtained by blending 1-100 mmol of citric acid and 1-100 mmol of ethene diamine in 5-100 mL of deionized water and transferring the mixture into a reaction kettle; carrying out a hydrothermal reaction for 2-10 hours at a temperature of 100-500 DEG C; cooling the reaction kettle to a room temperature after the reaction is finished to obtain a water solution of the carbon dots with the high fluorescent quantum yield; pouring the water solution of the carbon dots in a dialysis bag with a molecular weight of 3,500; dialyzing for 48-60 h; spin drying a dialysis outer solution and vacuum drying.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
System and method for pattern recognition in sequential data
InactiveUS8280640B2Easy to useIncrease speedBiological testingComparison of digital valuesSequential dataMedical diagnosis
The present invention is based on the encoding of sequential data or sequences in a novel manner that permits efficient storage and processing of sequential data, as well as methods for searching sequences or databases of sequences. The methods and systems of the current invention may be adapted broadly to various fields of application and to a variety of sequences types. For example, the current invention has broad application including to the fields of bioinformatics, molecular biology, pharmacogenomics, phonetic sequences, lexicographic sequences, signal analysis, game playing, law enforcement, biometrics, medical diagnosis, equipment maintenance and micro-array data analysis.
Owner:ELORET CORP
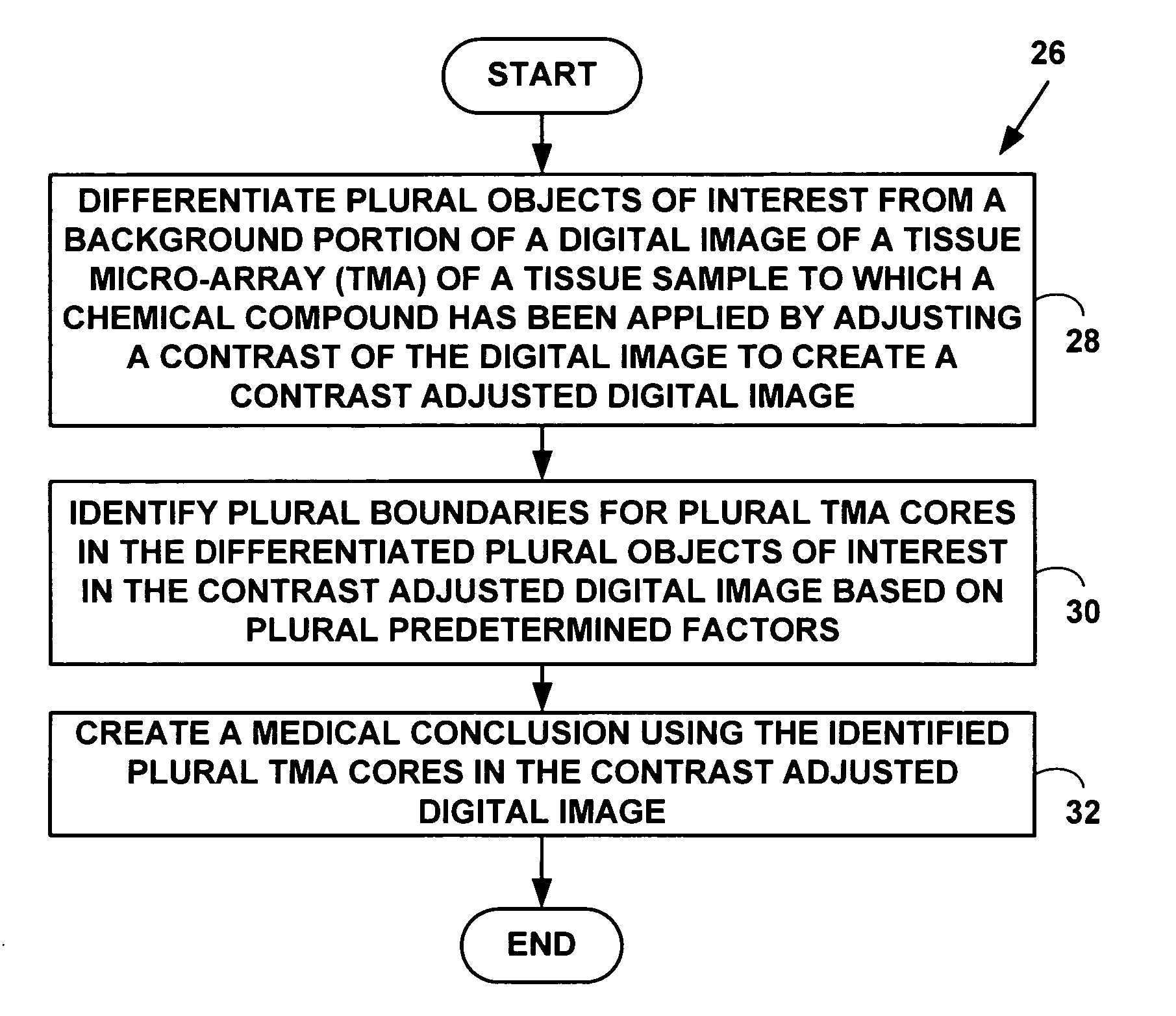
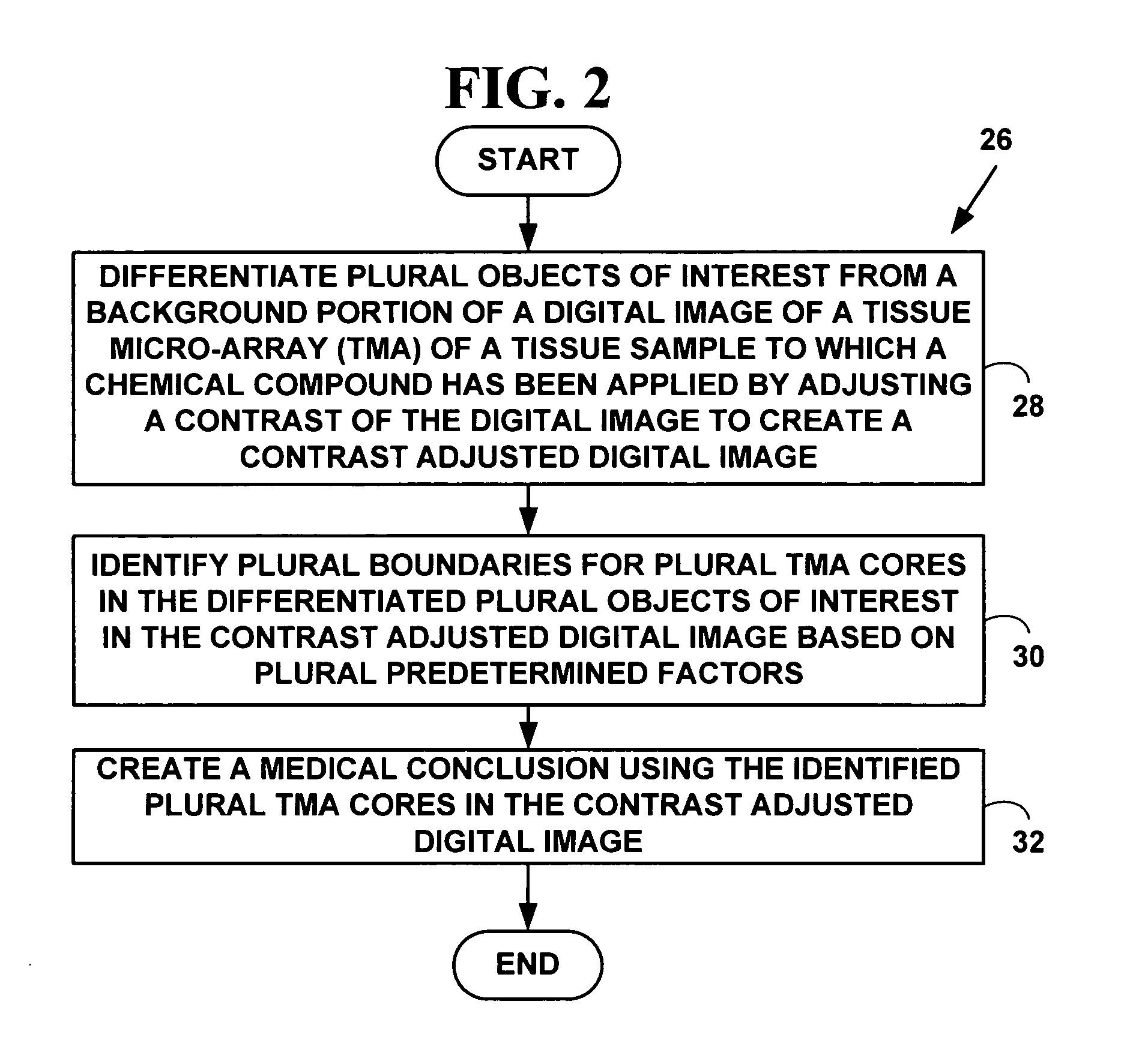
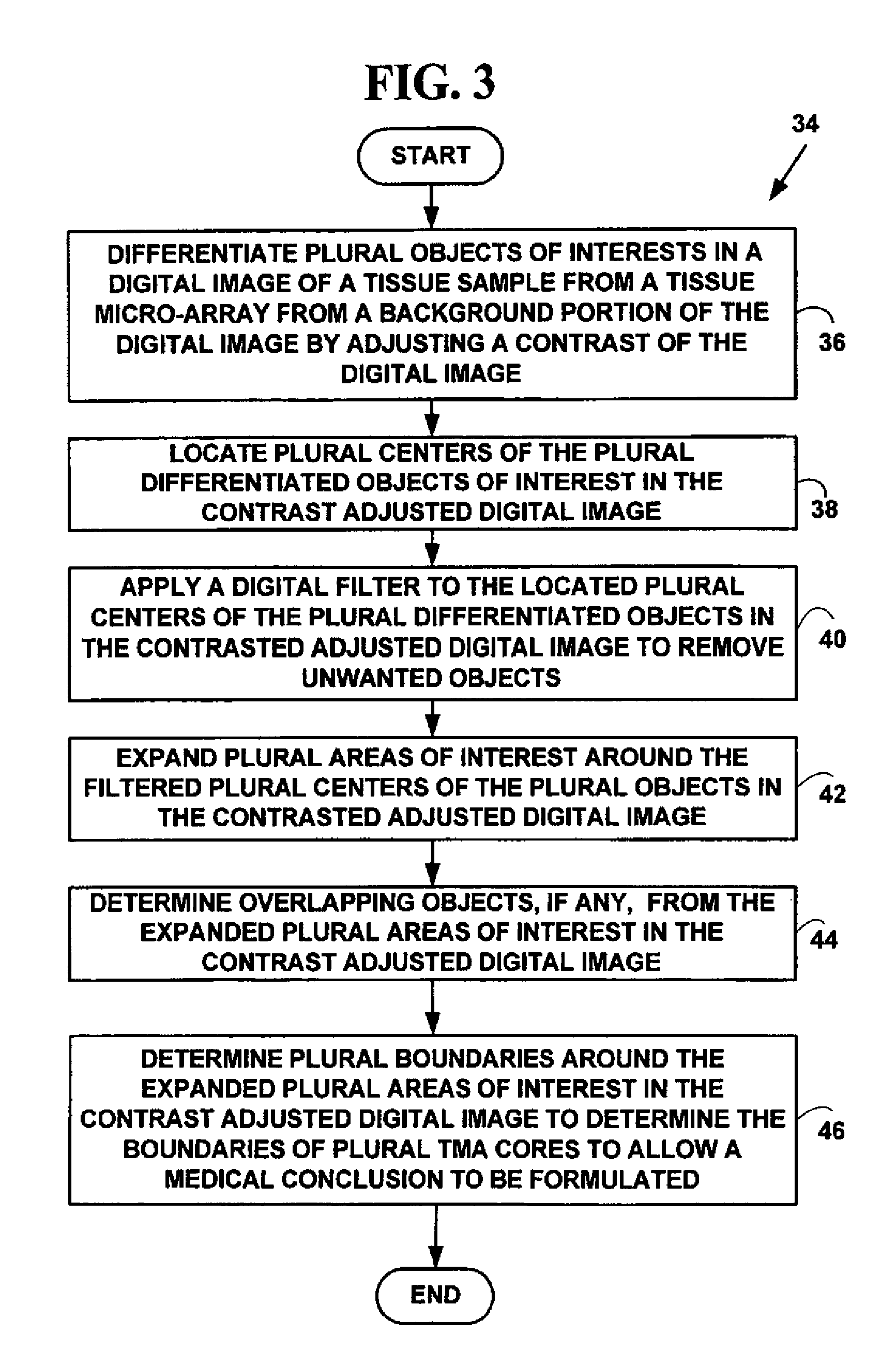
Method and system for automated quantitation of tissue micro-array (TMA) digital image analysis
ActiveUS20060015262A1Facilitates automated analysisAuxiliary diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsHuman cancerTissue microarray
A method and system for automated quantitation of tissue micro-array image (TMA) digital analysis. The method and system automatically analyze a digital image of a TMA with plural TMA cores created using a needle to biopsy or other techniques to create standard histologic sections and placing the resulting needle cores into TMA. The automated analysis allows a medical conclusion such as a medical diagnosis or medical prognosis (e.g., for a human cancer) to be automatically determined. The method and system provides reliable automatic TMA core gridding and automated TMA core boundary detection including detection of overlapping or touching TMA cores on a grid.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Apparatus for and methods of handling biological sample containers
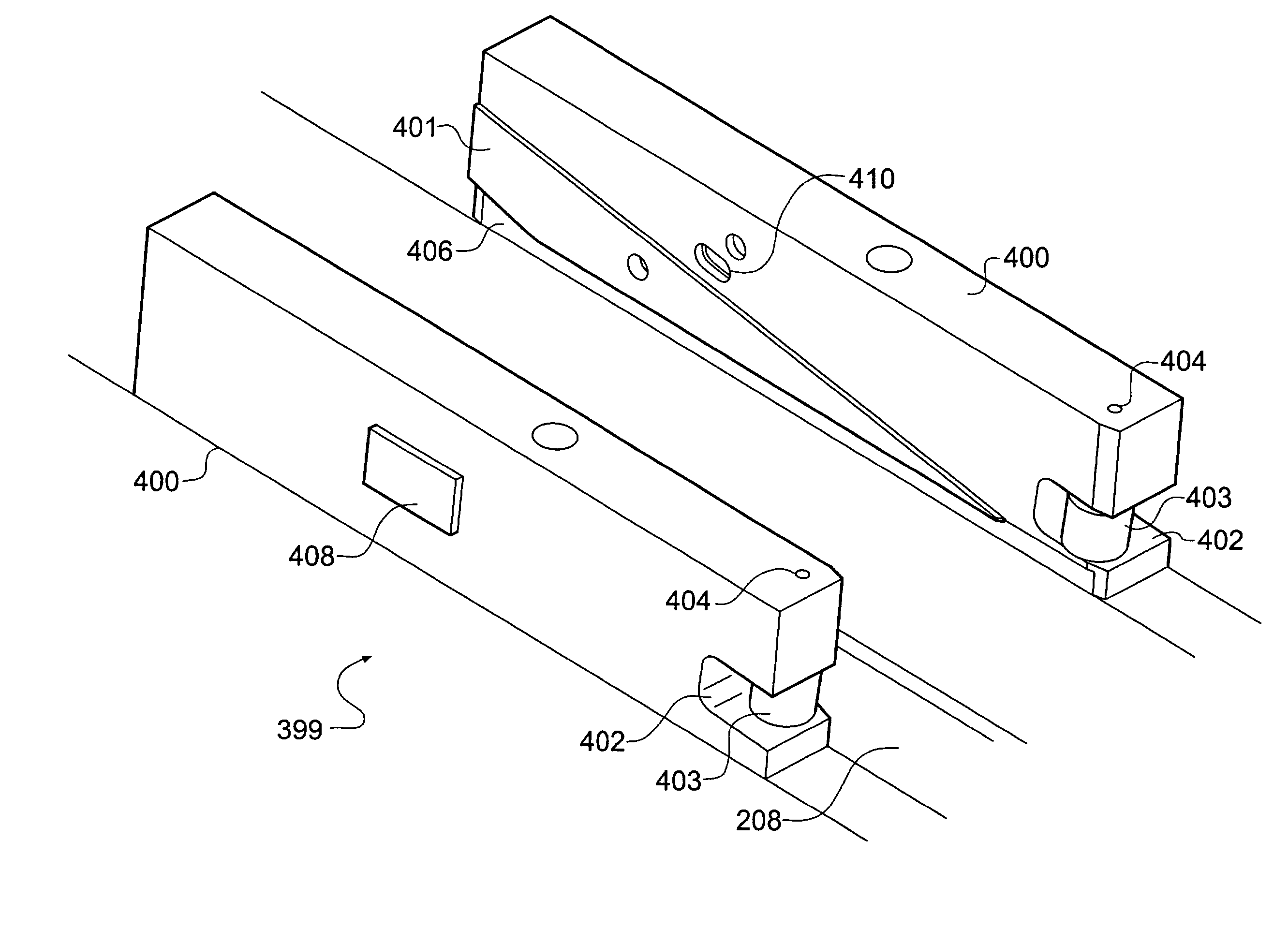
InactiveUS6998094B2Reduce complexity and costAutomationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
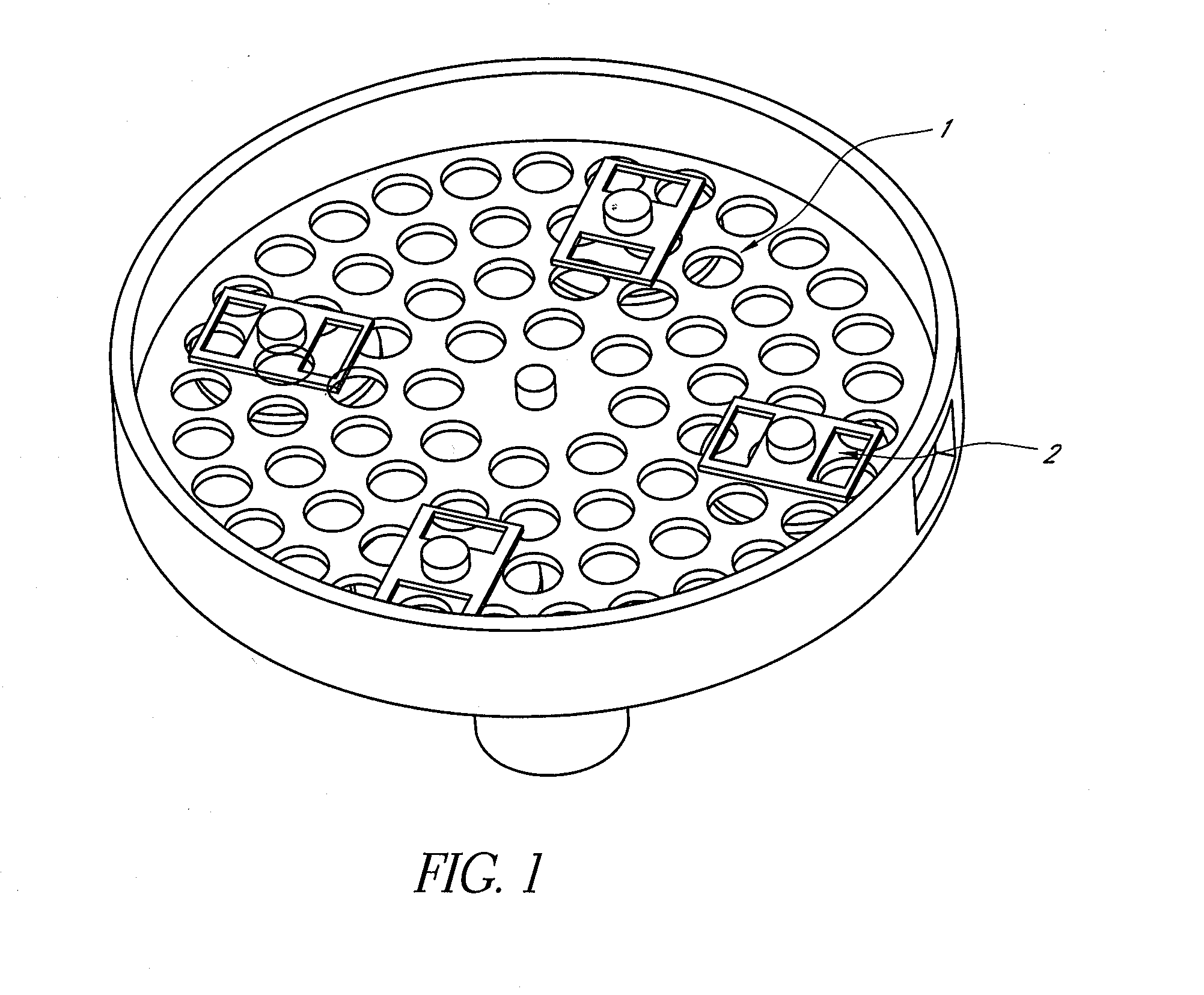
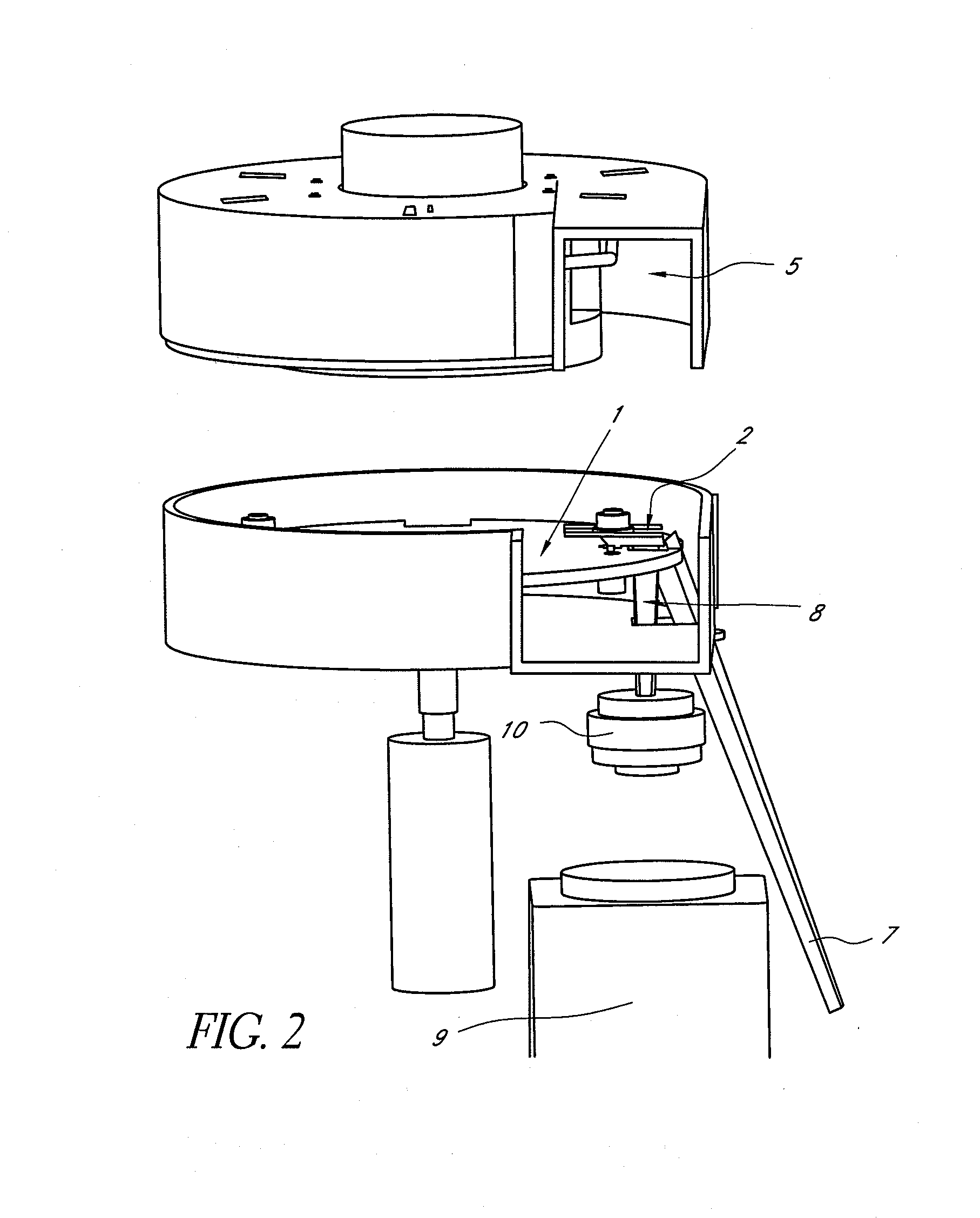
Apparatus for handling biological sample containers comprises a conveyor assembly for conveying containers and a lid handling assembly operable to remove lids from and replace lids onto containers while the containers are in motion on the conveyor assembly. The lid handling assembly comprises a pair of ramps onto which a lid is lifted by a lifting mechanism configured to handle overhanging lids or non-overhanging lids as required. The lid handling assembly may be configured to handle lids of containers of various sizes by altering the ramp spacing. A conveyor assembly comprises a pair of converging rails which carry a pair of jaws operable to carry a container. The convergence of the rails makes the jaws clamp the container so that it is held tightly in position for micro-arraying to be carried out. The conveyor assembly may be adapted to handle different sizes of container by the provision of holders to hold various container types.
Owner:GENETIX LTD
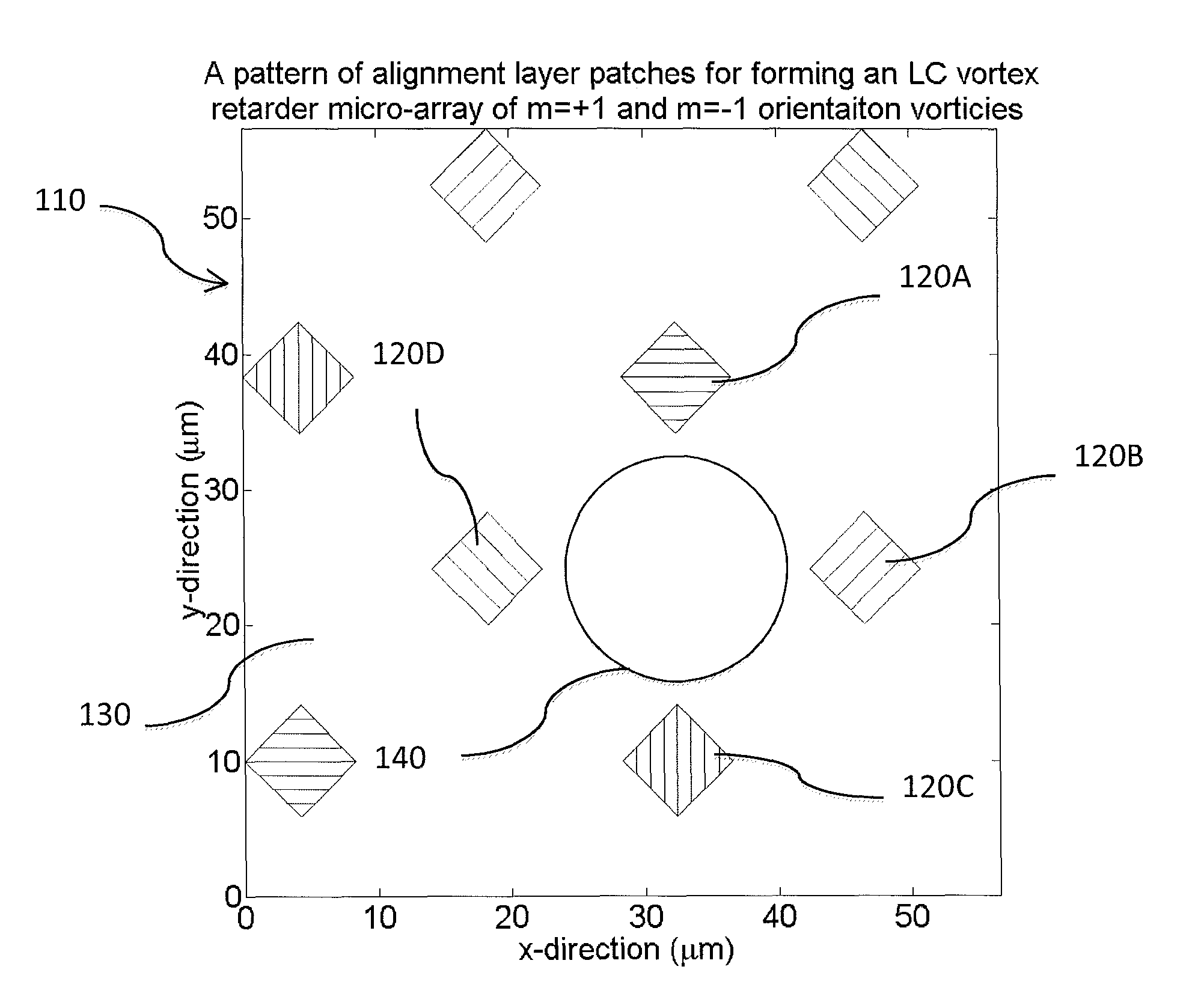
Optical vortex retarder micro-array
InactiveUS20100066929A1Liquid crystal compositionsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid crystalPolymer
A micro-array of optical vortex retarders is provided by forming an alignment layer having a plurality of discrete alignment patches with different orientations. A layer of birefringent material, including one of a liquid crystal and a liquid crystal polymer precursor material, is provided adjacent to the alignment layer. The aligning orientation and position of each discrete alignment patch in the plurality of discrete alignment patches is selected to induce the layer of birefringent material to form at least one optical vortex retarder adjacent to a substantially non-oriented region of the alignment layer.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Method for automated processing of digital images of tissue micro-arrays (TMA)
ActiveUS8068988B2Facilitates automated analysisAuxiliary diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsHuman cancerTissue microarray
A method and system for automated quantitation of tissue micro-array image (TMA) digital analysis. The method and system automatically analyze a digital image of a TMA with plural TMA cores created using a needle to biopsy or other techniques to create standard histologic sections and placing the resulting needle cores into TMA. The automated analysis allows a medical conclusion such as a medical diagnosis or medical prognosis (e.g., for a human cancer) to be automatically determined. The method and system provides reliable automatic TMA core gridding and automated TMA core boundary detection including detection of overlapping or touching TMA cores on a grid.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Apparatus for and methods of handling biological sample containers
InactiveUS6843962B2Reduce complexity and costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Apparatus for handling biological sample containers comprises a conveyor assembly for conveying containers and a lid handing assembly operable to remove lids from and replace lids onto containers while the containers are in motion on the conveyor assembly. The lid handling assembly comprises a pair of ramps onto which a lid is lifted by a lifting mechanism configured to handle overhanging lids or non-overhanging lids as required. The lid handling assembly may be configured to handle lids of containers of various sizes by altering the ramp spacing. A conveyor assembly comprises a pair of converging rails which carry a pair of jaws operable to carry a container. The convergence of the rails rakes the jaws clamp the container so that it is held tightly in position for micro-arraying to be cared out. The conveyor assembly may be adapted to handle different sizes of container by the provision of holders to hold various container types.
Owner:GENETIX LTD
Method for processing micro array on glass surface via femtosecond laser pulse sequence
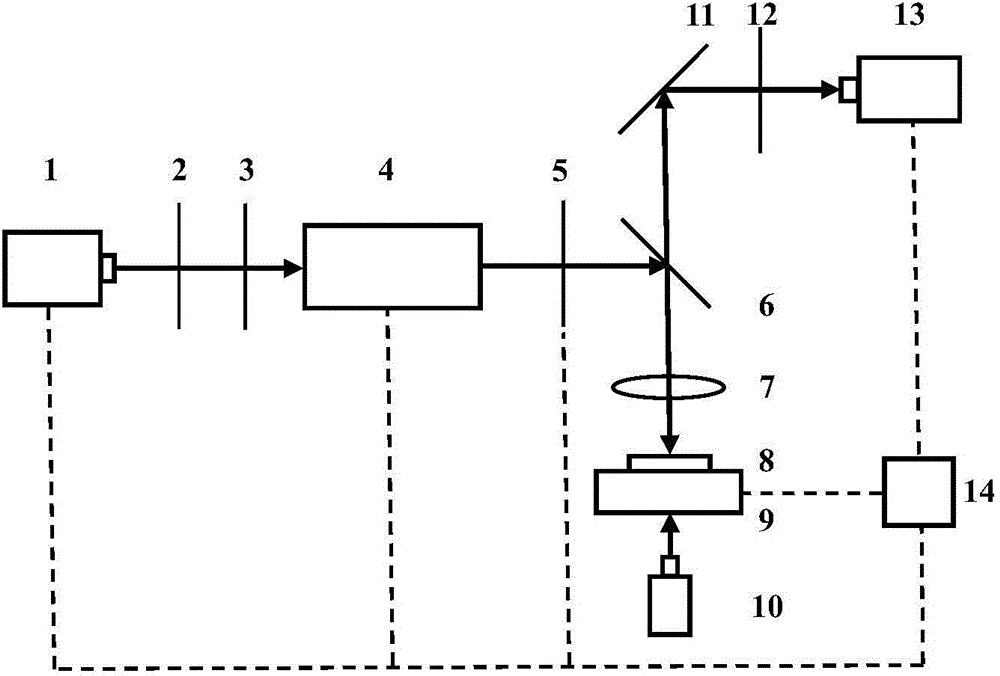
The invention relates to a method for processing a micro array on glass surface via femtosecond laser pulse sequence belonging to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. The method comprises the following steps: (1) modulating the conventional femtosecond laser into the femtosecond laser pulse sequence including two sub-pulses on a time domain via a pulse shaping method, wherein the time interval range of two sub-pulses is 50fs-2ps, and the energy ratio range of two sub-pulses is 0.2-5; (2) focusing the femtosecond laser pulse sequence on the surface of glass material, scanning the required micro array configuration pattern on the glass surface according to the relative movement between the glass material and the laser focal point; (3) immersing the glass material with micro array configuration pattern obtained in the step (2) in a hydrofluoric acid solution with the concentration being 1-10%, carrying out reaction on the micro array configuration pattern region and the hydrofluoric acid solution so as to from a concave micro array structure. The modification degree of the femtosecond laser irradiation region is increased and the etching efficiency of the irradiation region is finally improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com