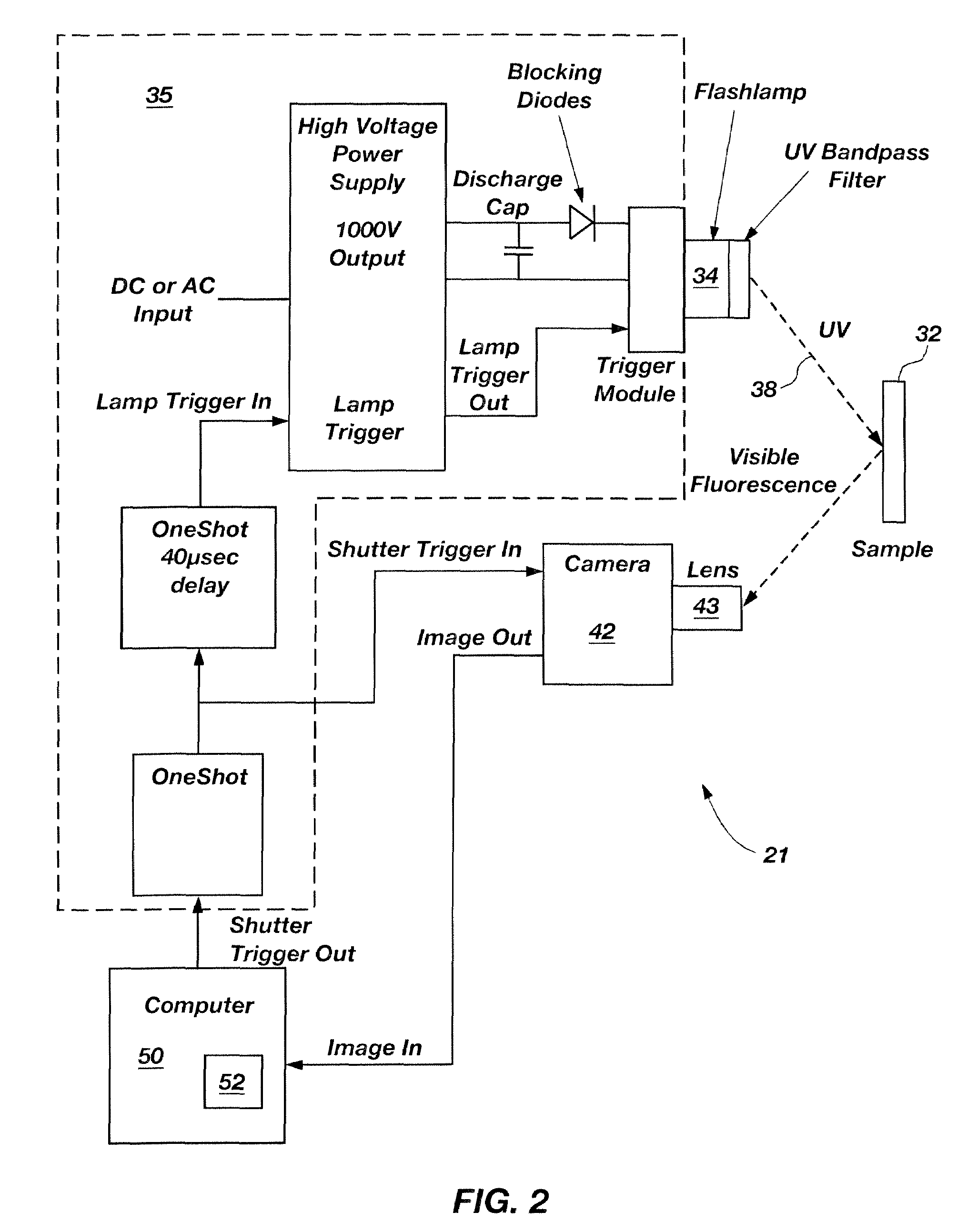
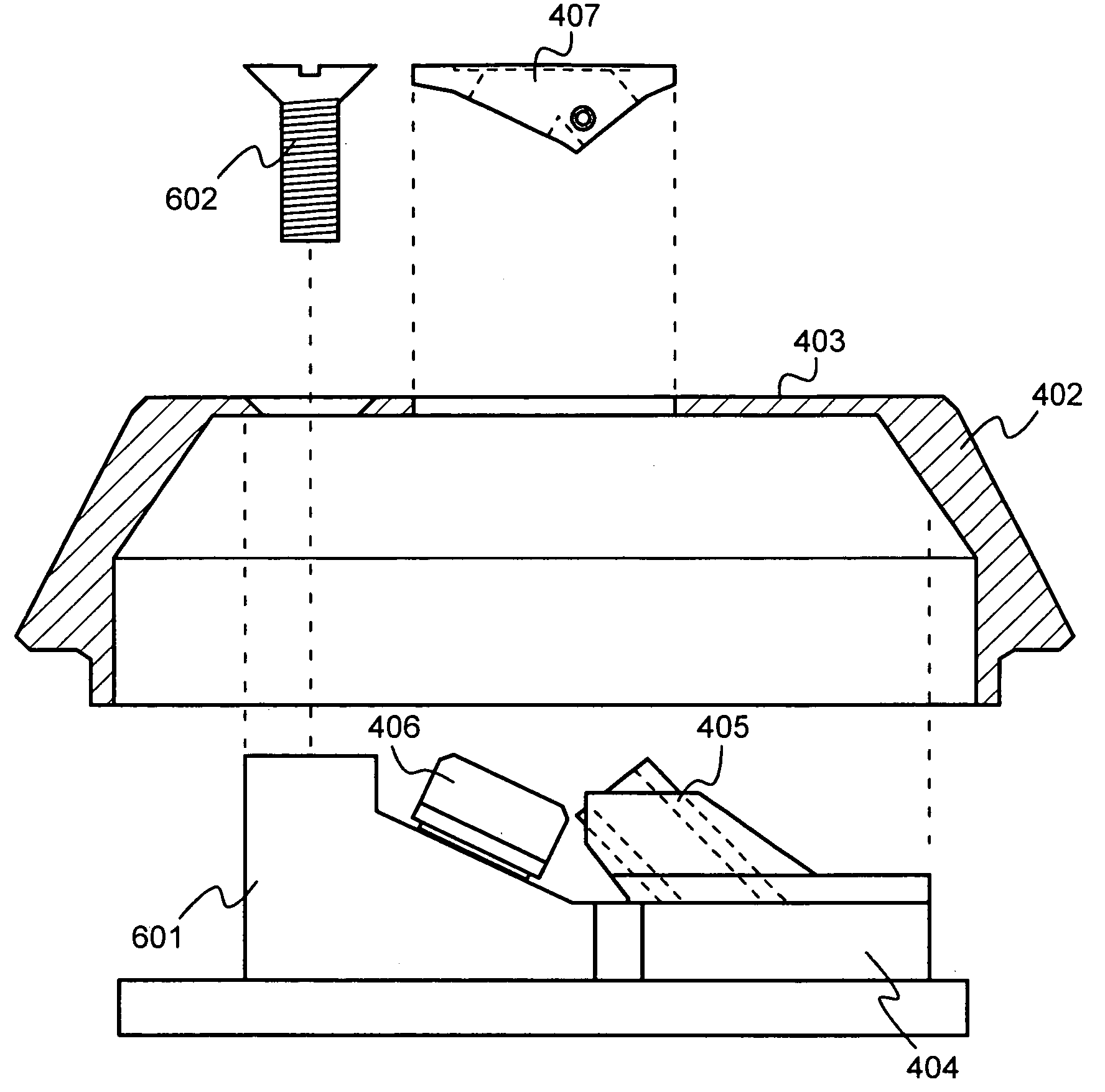
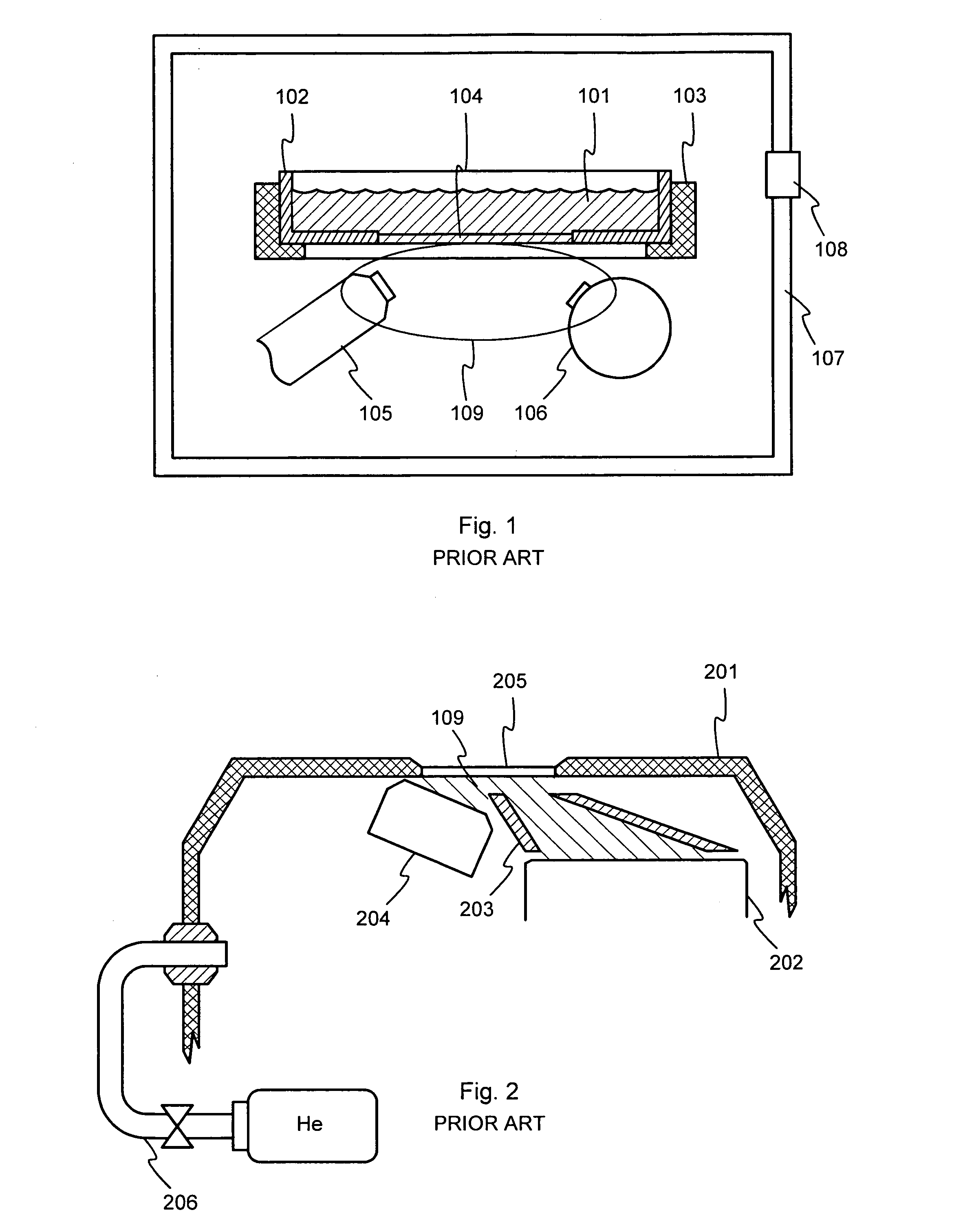
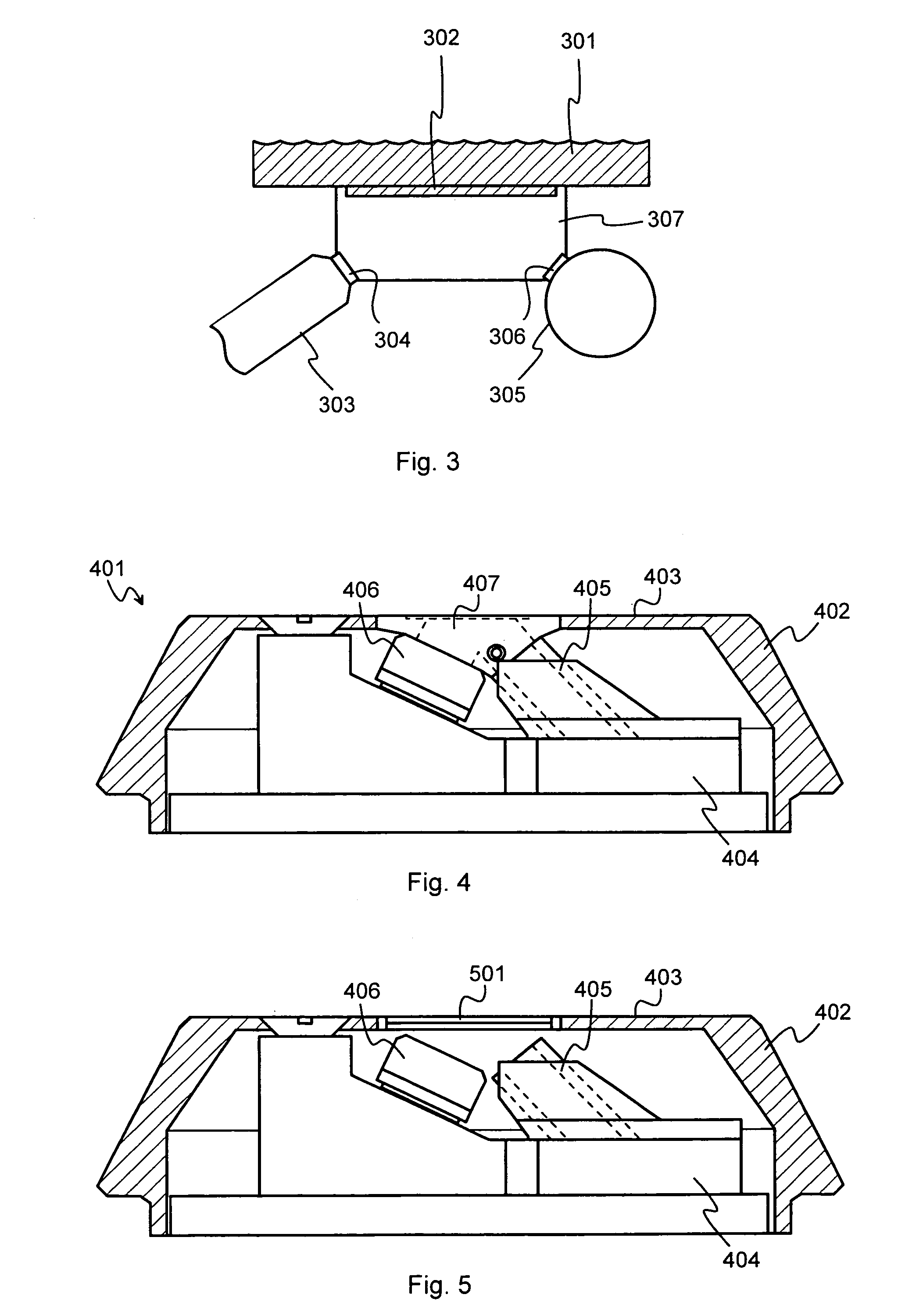
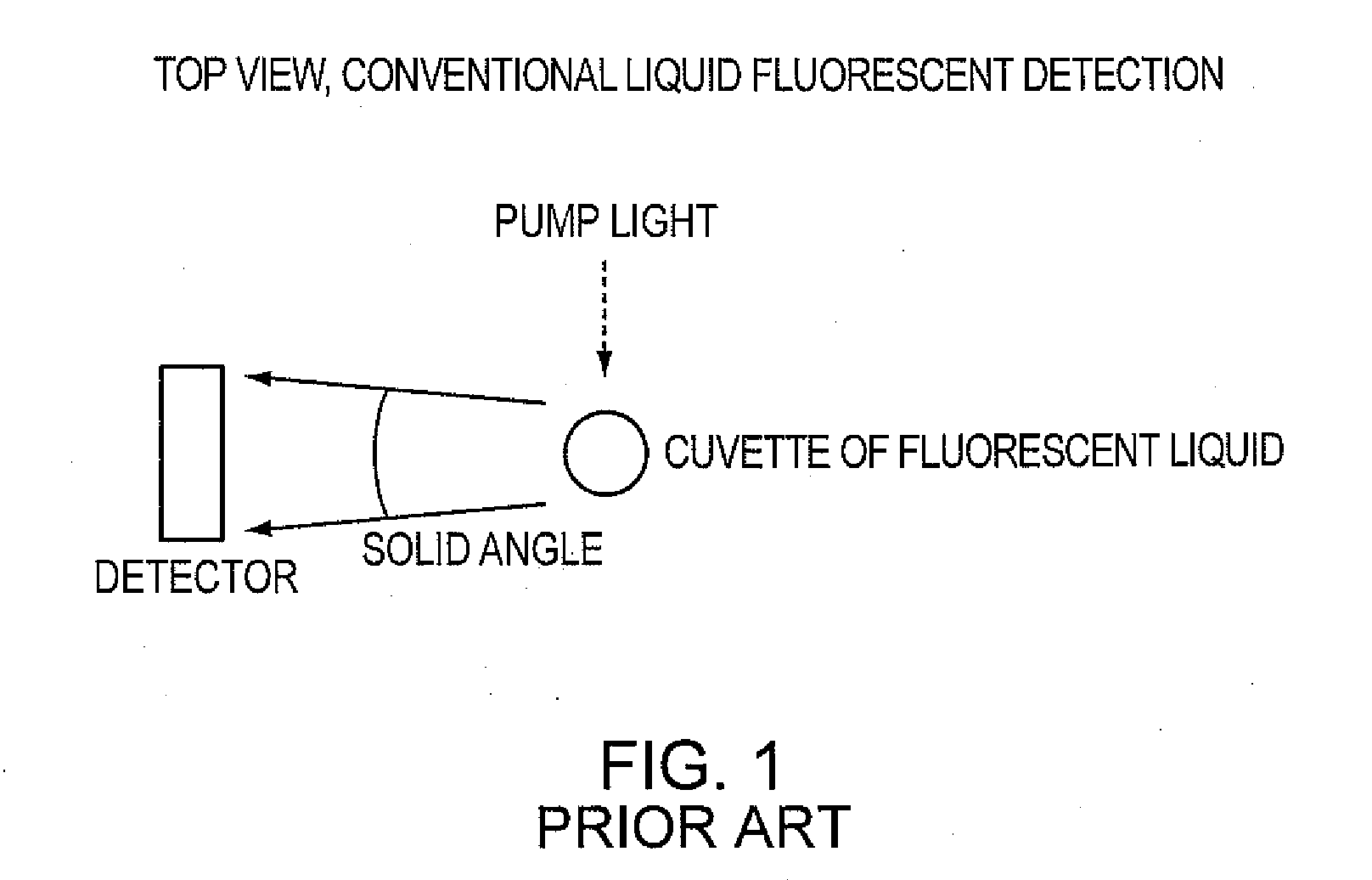
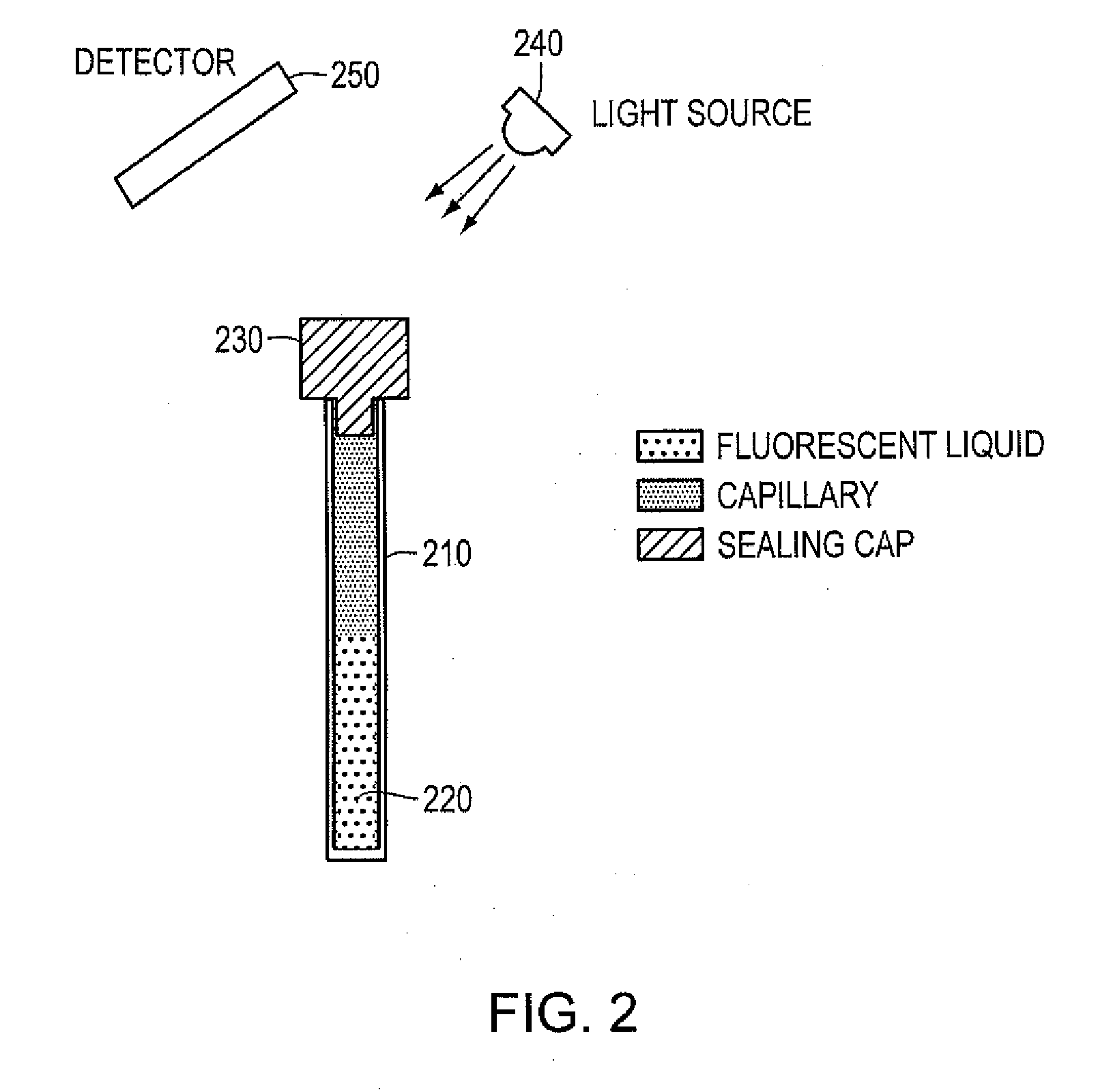
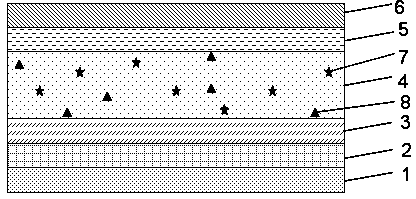
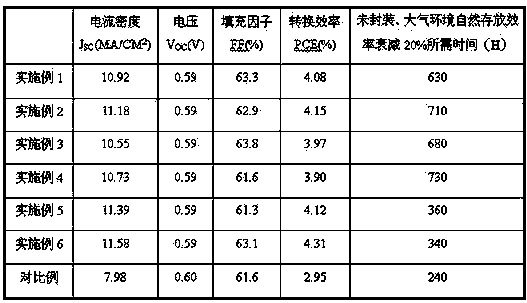
Patents
Literature
163 results about "Fluorescent radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
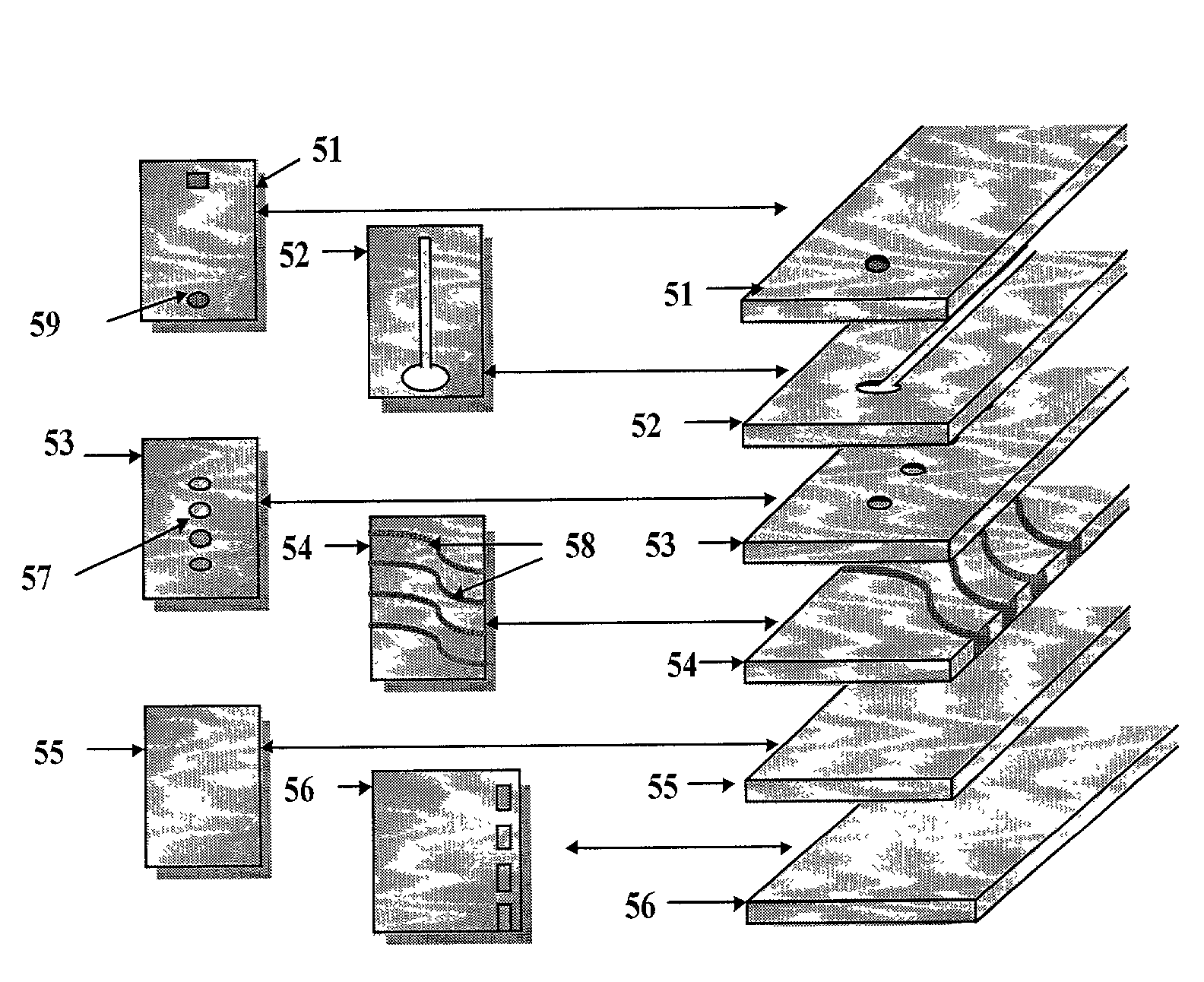
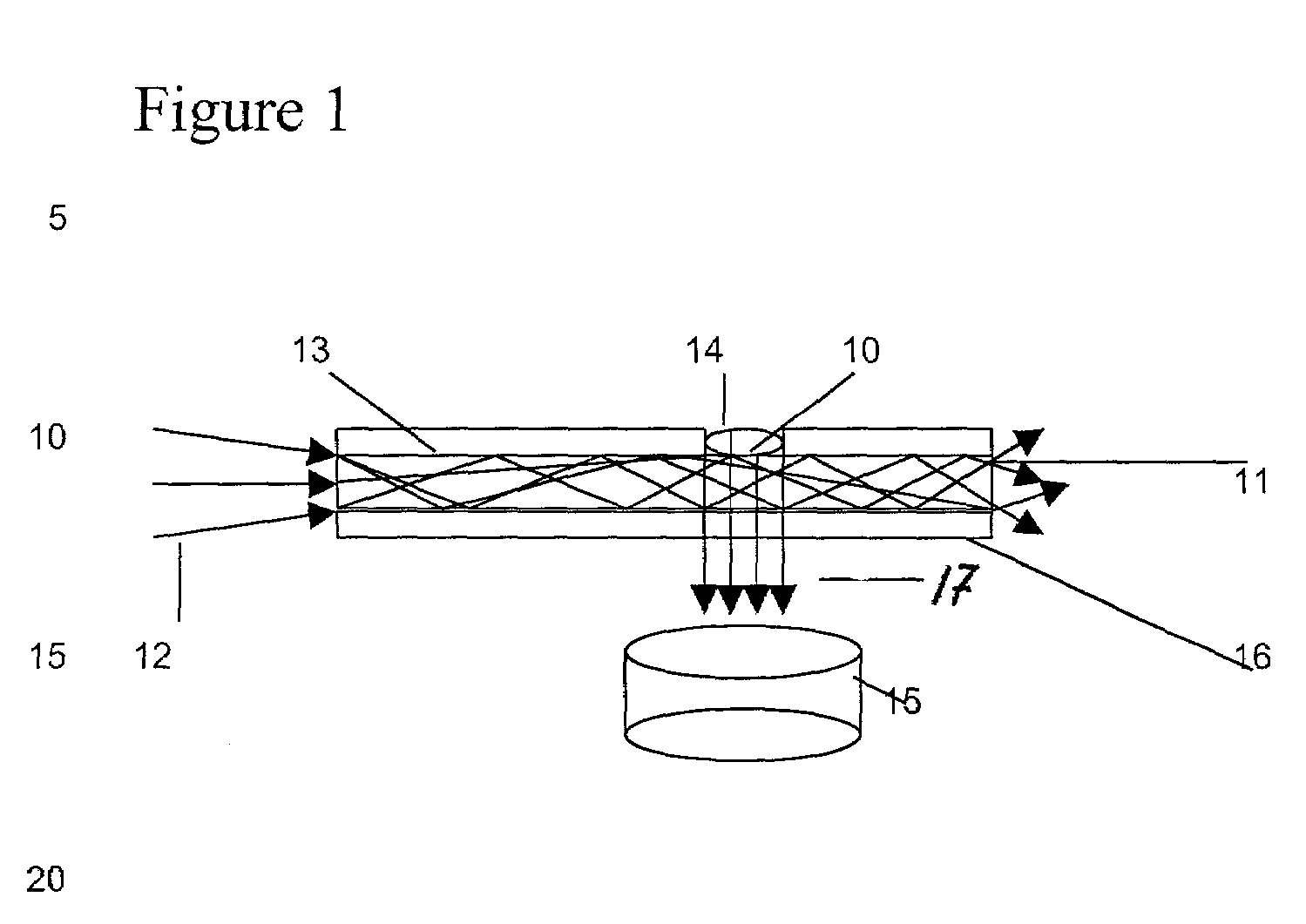
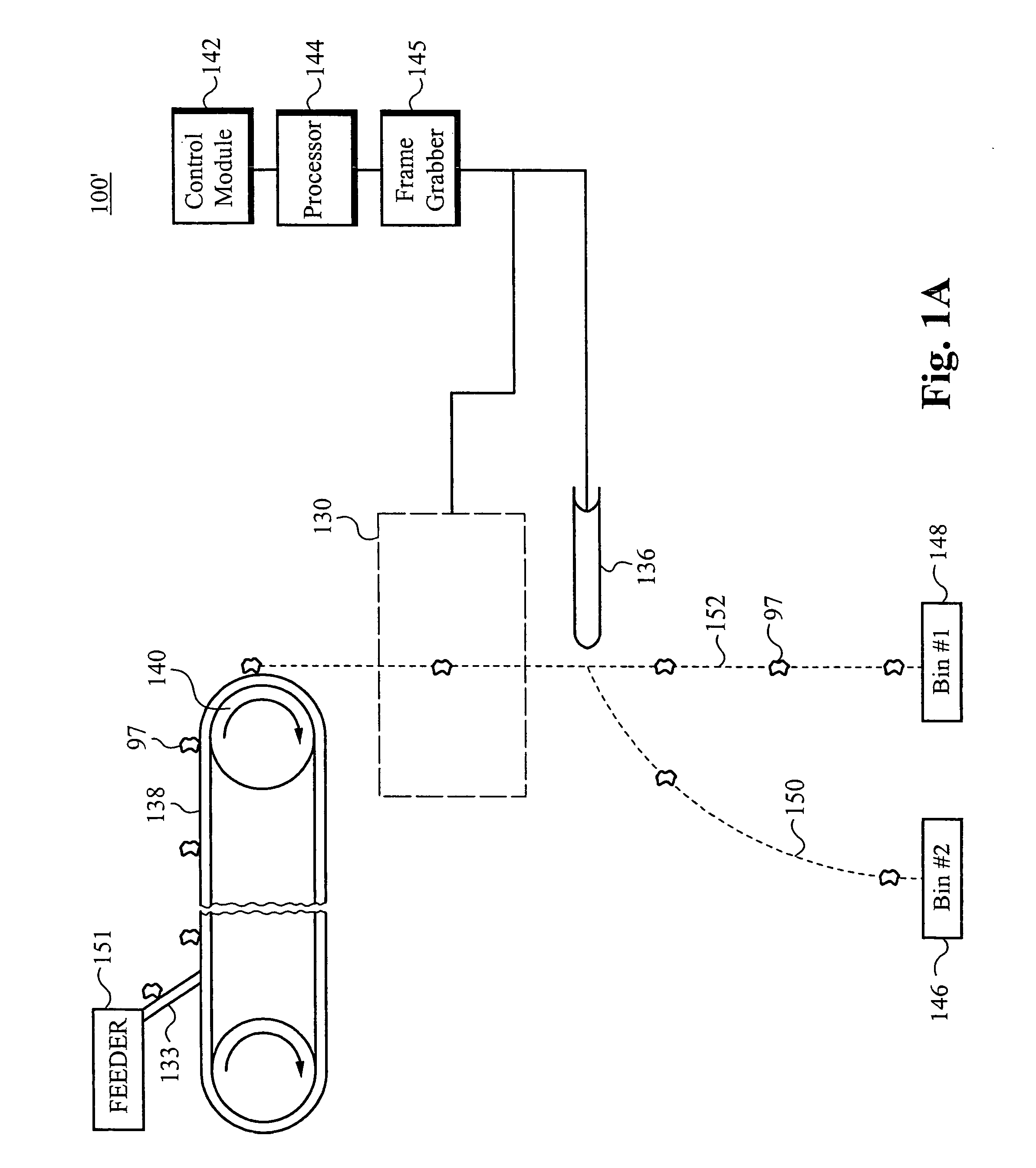
Micro-array evanescent wave fluorescence detection device
InactiveUS7175811B2Quench emissionAvoid disadvantagesOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsWaveguidePolymer
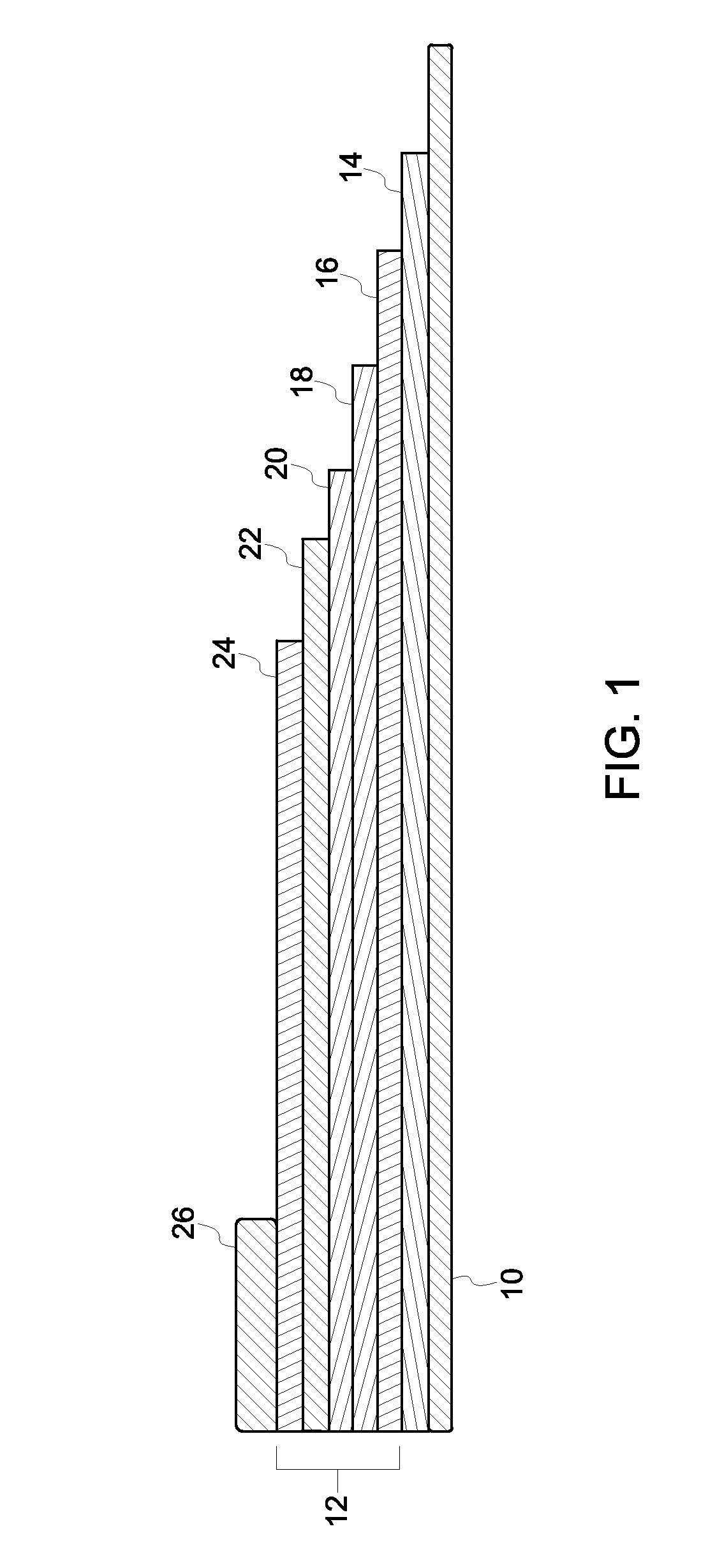
Novel nanowell microarrays are disclosed in optical contact with polymer waveguides wherein evanescent field associated with lightwaves propagated in the waveguide excite target substances in the nanowells either by a common waveguide or by individual waveguides. Fluid samples are conveyed to the nanowells by means of microfluidics. The presence of the target substances in fluid samples is detected by sensing fluorescent radiation generated by fluorescent tag bound to the target substances. The fluorescent tags generate fluorescent radiation as a result of their excitation by the evanescent field. One or more PMT detectors or a CCD detector are located at the side of the waveguide opposite to the nanowells. Fluorescent radiation is detected due to its coupling with the waveguide or its emission through the waveguide.
Owner:EDGELIGHT BIOSCI
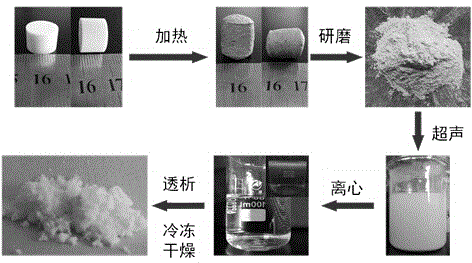
Method for preparing carbon nitride quantum dots
InactiveCN104140084AIncrease useHigh yieldNitrogen and non-metal compoundsFluorescent radiationCarbon nitride
A method for preparing carbon nitride quantum dots comprises the following steps of (1) material preparation, (2) drying and tabletting, (3) heating, (4) separation and (5) drying. Sodium chloride crystals are used as a template, the preparing process is simple and low in cost, and the sodium chloride crystals can be easily removed through water dissolution; melamine is used as the raw material, and annular carbon nitride basic structural units exist in melamine molecules, so that the yield of preparing the quantum dots is high, and product size uniformity is good; the prepared quantum dots are high in specific area, good in water solubility and good in dispersity, have strong fluorescent radiation visible under naked eyes, and have wide application prospects in the fields of fluorescence detection, light emitting devices, biomarker and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
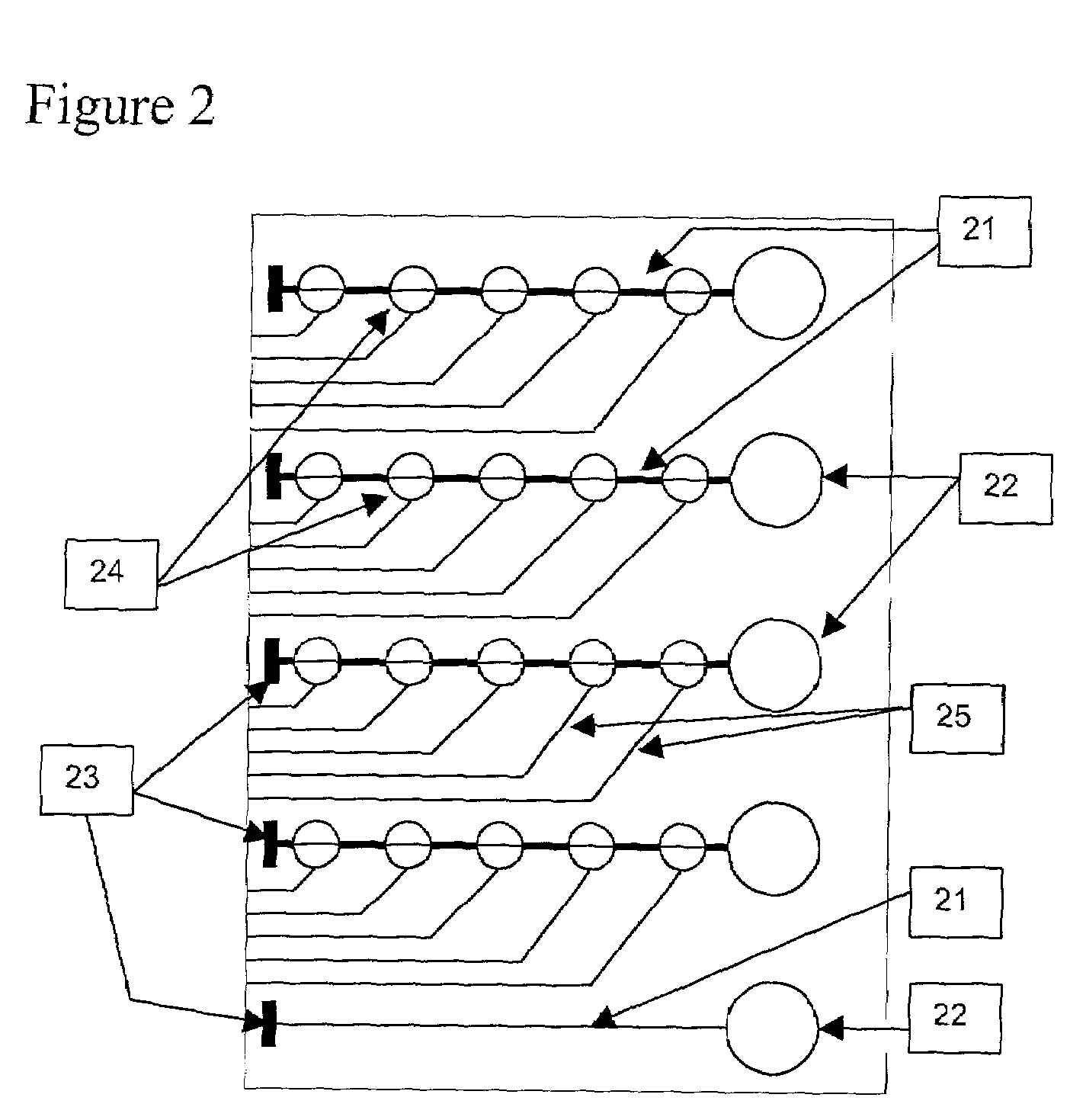
Analysis systems detecting particle size and fluorescence
ActiveUS7057712B2Systems can be simplifiedImprove efficiencyTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrum investigationFluorescent radiationMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
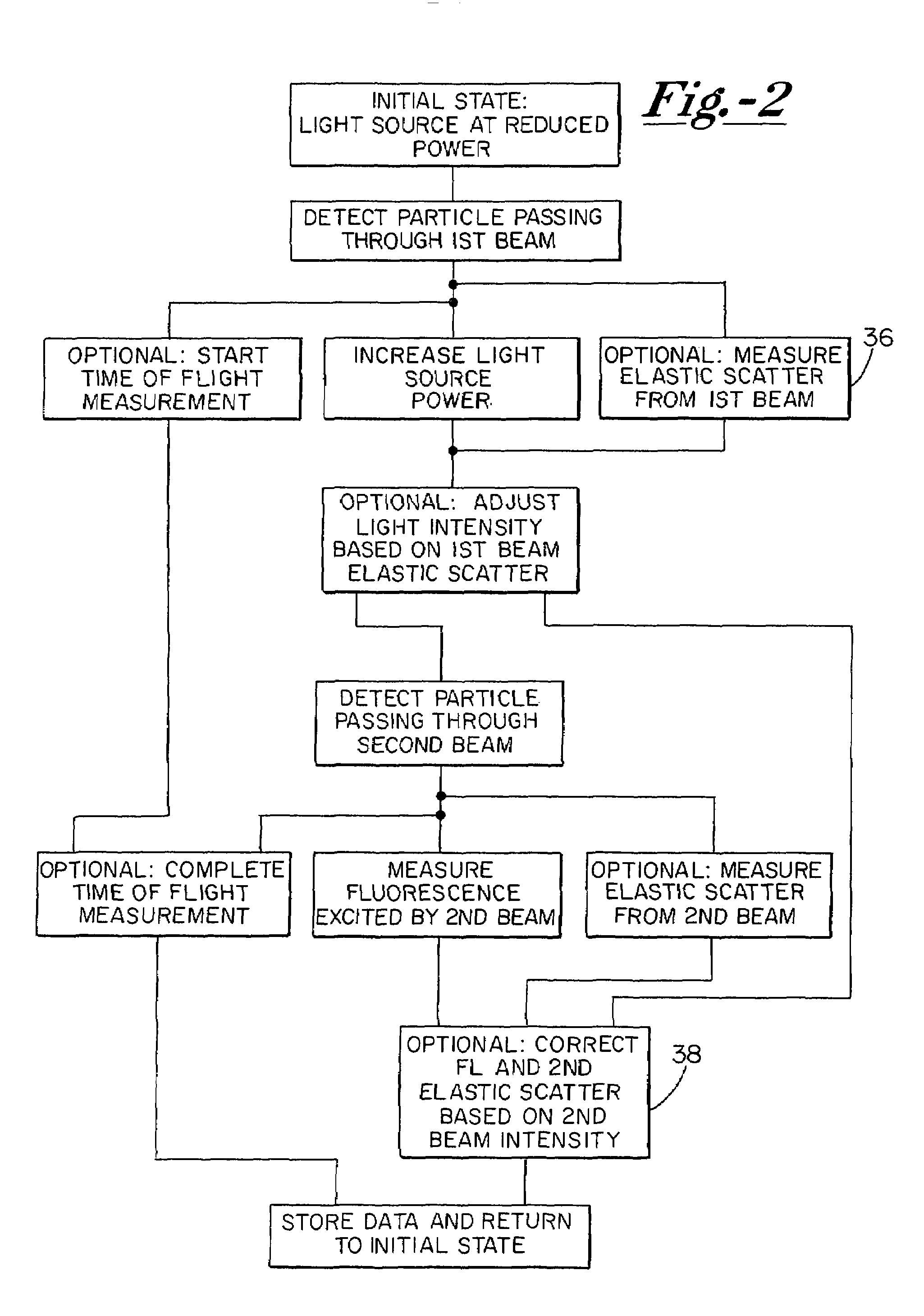
Particle analyzing systems with fluorescence detection are disclosed, primarily in connection with particle sizing based on scattered light intensity or time-of-flight measurement. In one system, emission of fluorescence is used as a threshold for selecting particles for further analysis, e.g. mass spectrometry. In another embodiment, laser beams arranged sequentially along an aerosol path are selectively switched on and off, to increase the useful life of components, and diminish the potential for interference among several signals. Other embodiments advantageously employ color discrimination in aerodynamic particle sizing, single detectors positioned to sense both scattered and emitted fluorescent radiation, and laser beam amplitude or gain control to enhance the range of fluorescence detection.
Owner:TSI INC
Apparatus for measuring in particular luminescent and/or fluorescent radiation
InactiveUS20030042428A1Compact structureBroad spectrumChemiluminescene/bioluminescencePhotometryFluorescent radiationMeasuring instrument
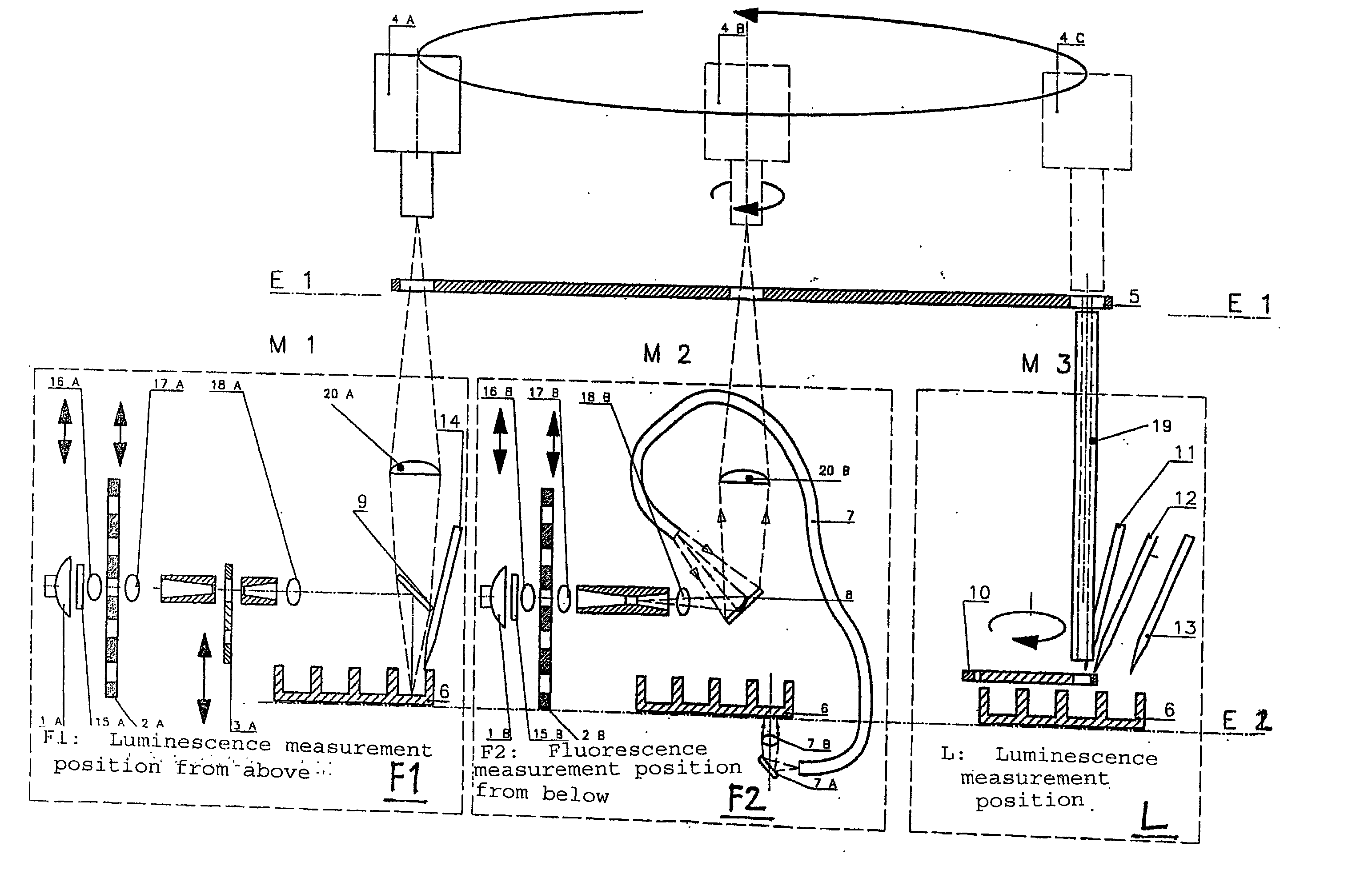
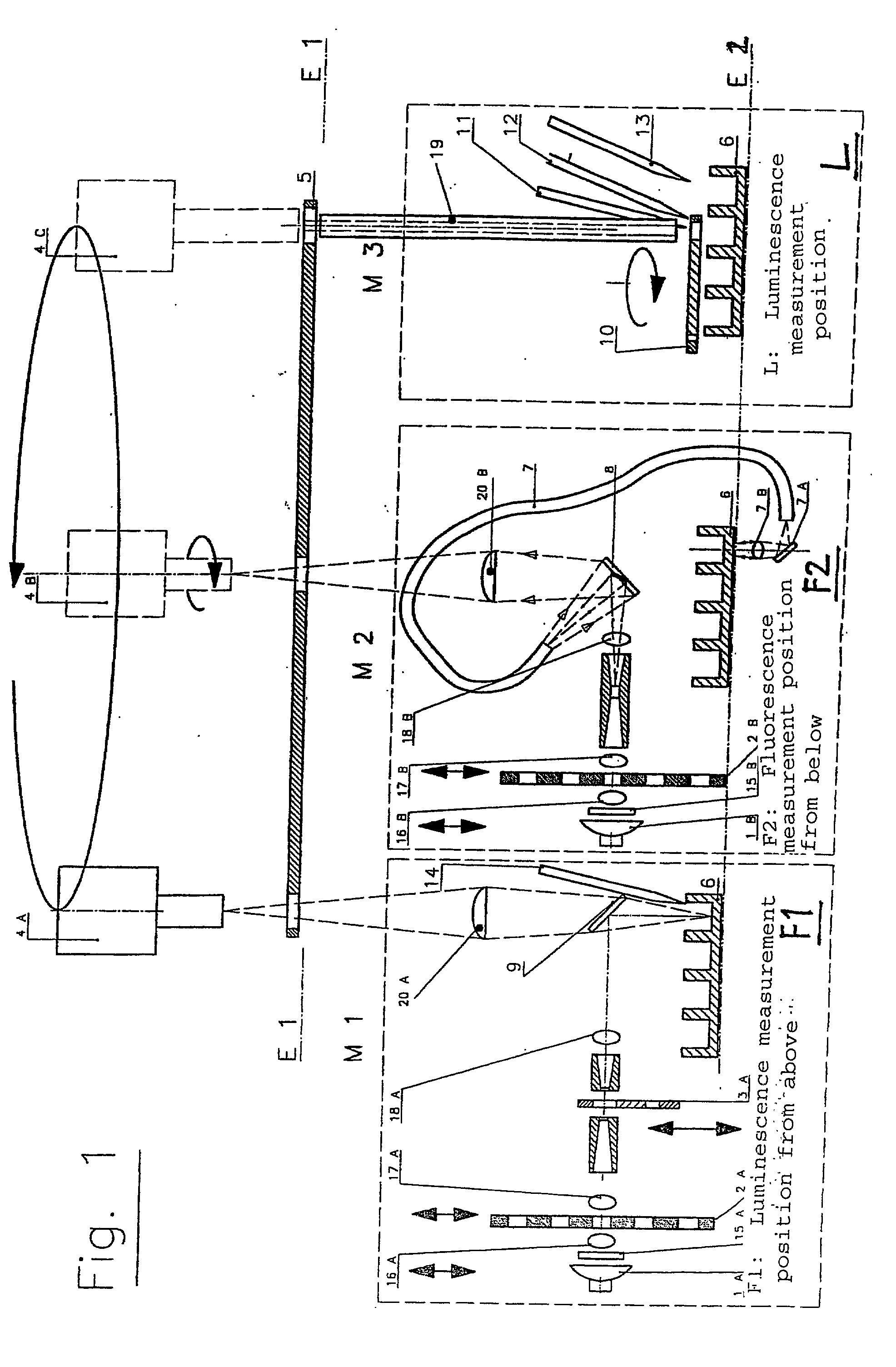
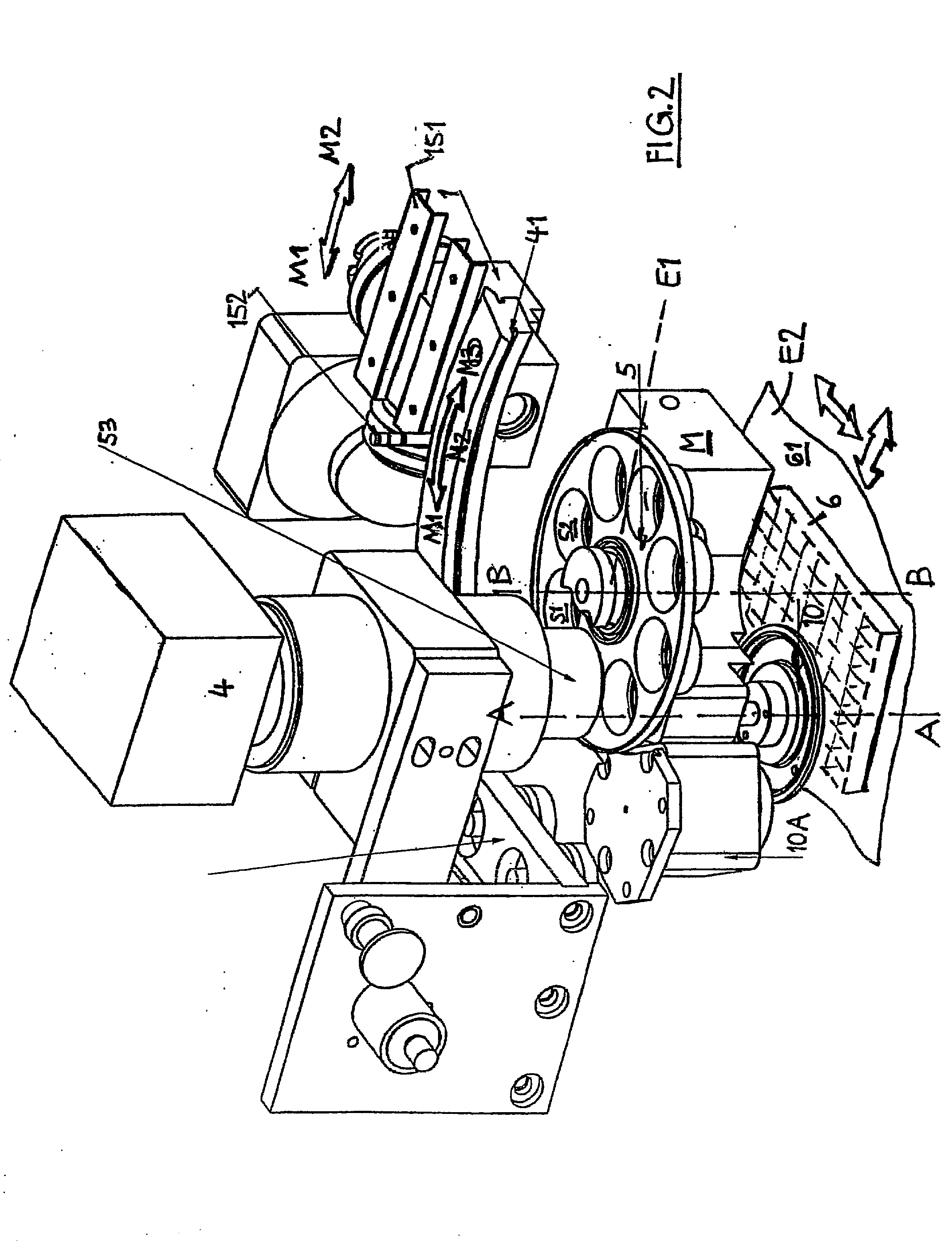
An apparatus for selected measurement of in particular luminescent and / or fluorescent radiation has a plurality of measurement light paths (M1, M2, M3), which each have their own measuring devices optimized for the particular measurement mode. As a common device, a filter holder (5) is used, in which the detector and each of the measuring devices have access to each of the openings of the filter holder, and each of these openings can be equipped with an emissions filter that is expedient for the particular measurement mode involved. The result is an especially compact arrangement of a multipurpose measuring instrument with measurement properties that is largely equivalent to the measurement properties of special individual measuring instruments and that is also suitable in particular as an individual instrument for special luminescence measurements, such as BRET measurements.
Owner:BERTHOLD TECH
Laser cooling apparatus and method
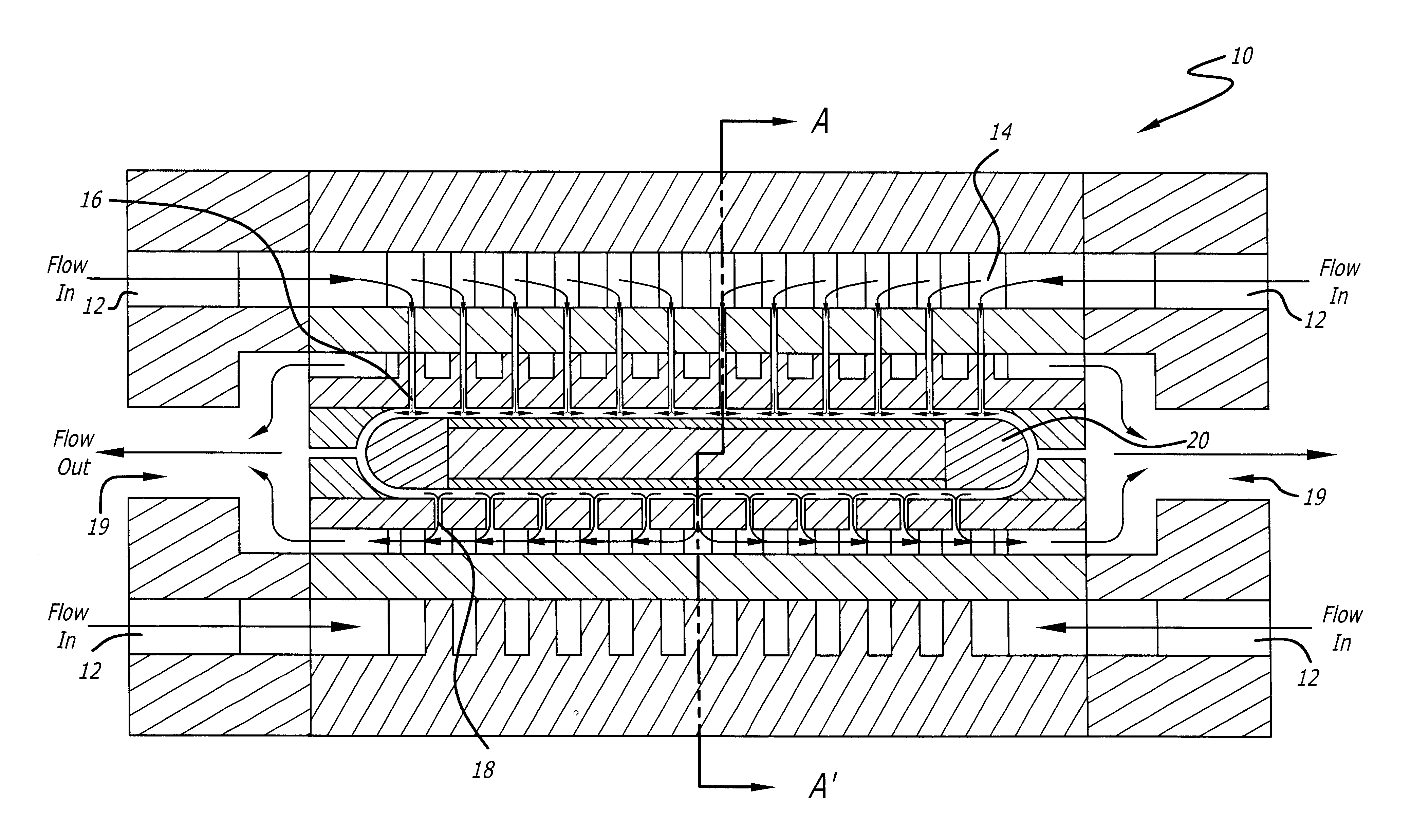
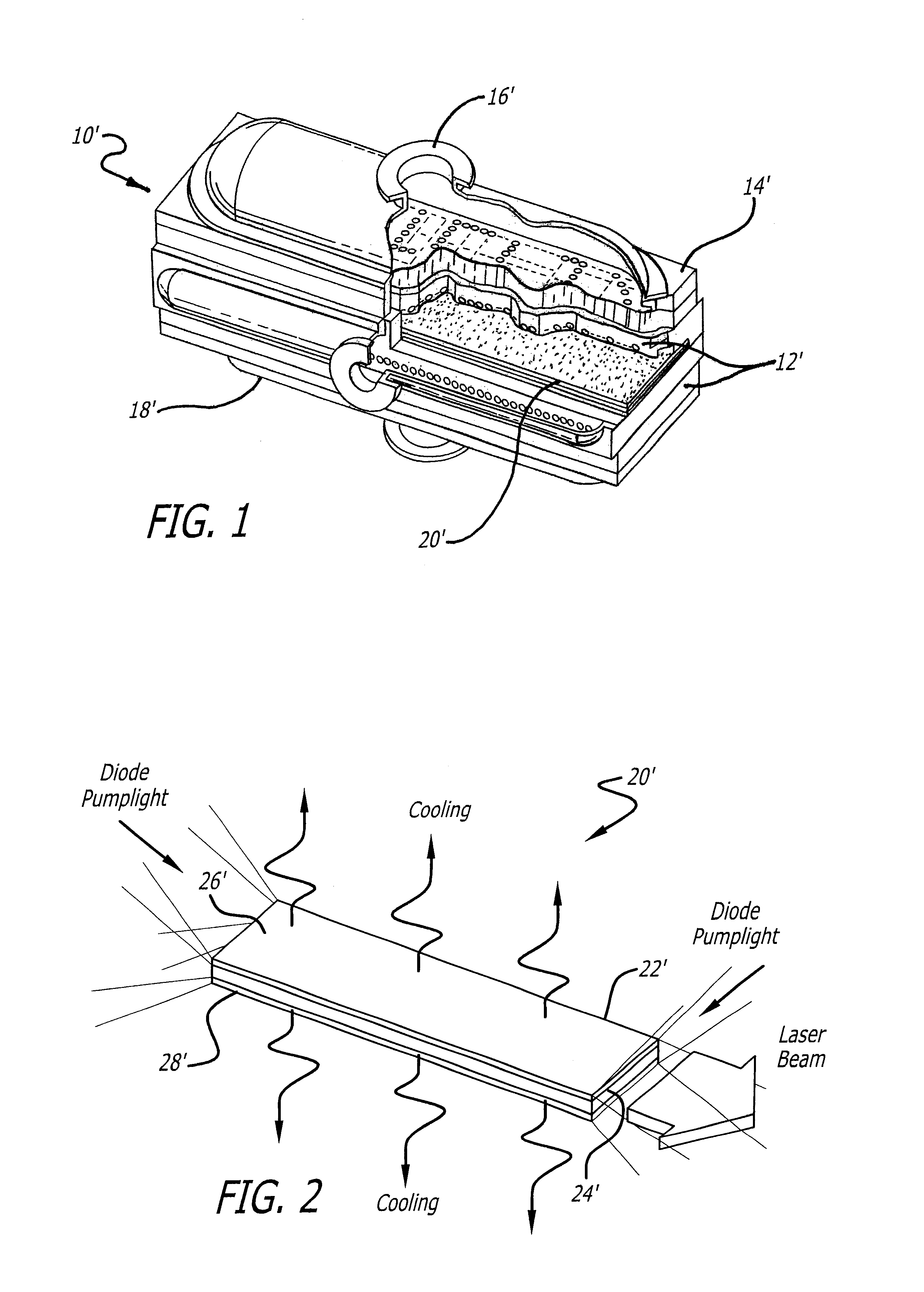
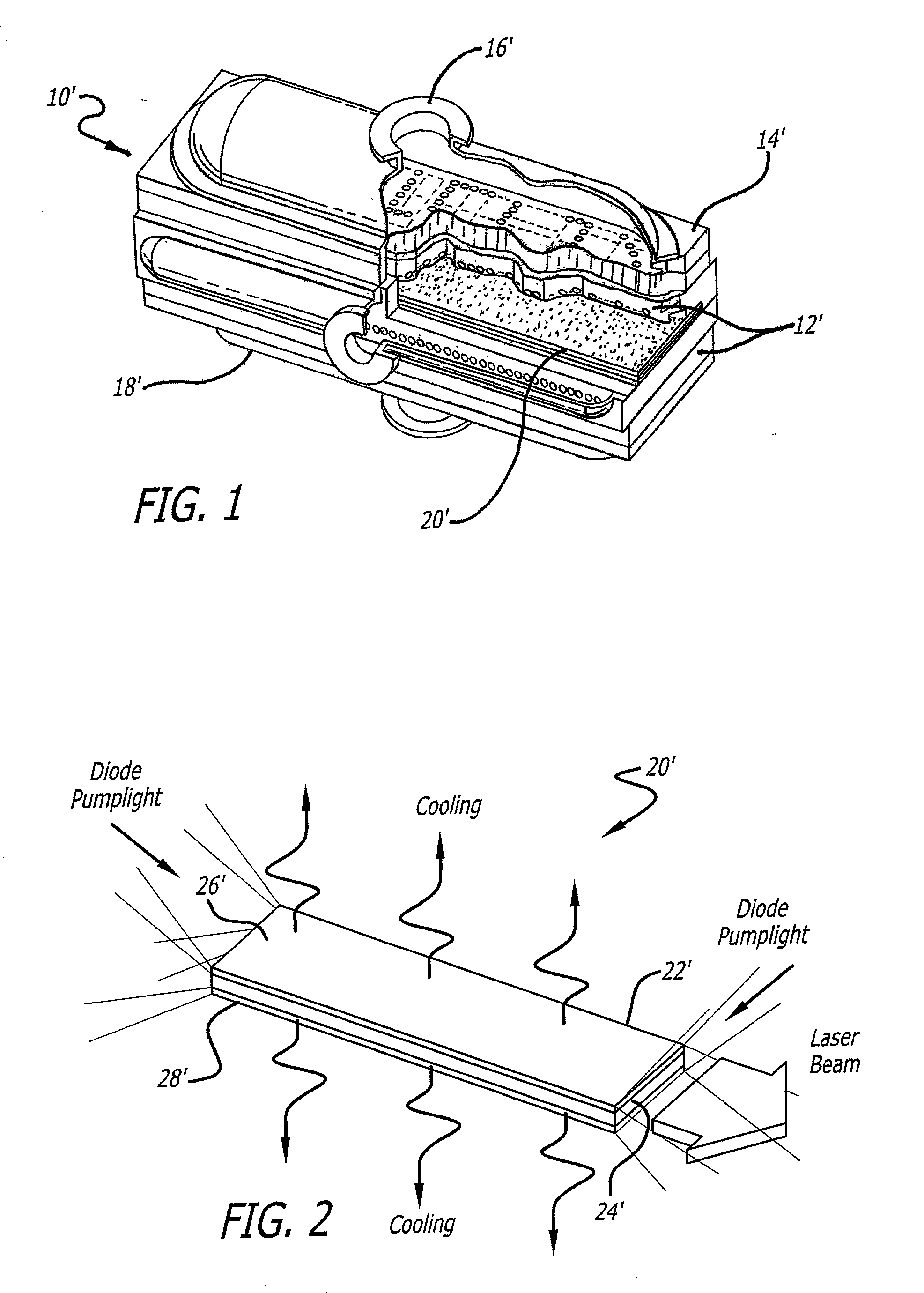
A laser cooling apparatus and method. Generally, the inventive apparatus includes a mechanism for transporting sensible thermal energy from a solid state laser and for communicating waste fluorescent radiation therefrom as well. In the illustrative embodiment, the apparatus includes an optically transparent manifold with an inlet port, an exhaust port and a plurality of spray nozzles therebetween adapted to direct a cooling fluid on the laser medium of a laser. In addition, the optically transparent manifold is used to permit waste fluorescent radiation to escape the confines of the laser and cooling system means such that said fluorescent radiation may be optically directed to an external heat sink such as free space.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Fluorescent nanoscopy method
An analysis of an object dyed with fluorescent coloring agents carried out with the aid of a fluorescent microscope which is modified for improved resolving power and called a nanoscope. The method is carried out with a microscope having an optical system for visualizing and projecting a sample image to a video camera which records and digitizes images of individual fluorescence molecules and nanoparticles at a low noise, a computer for recording and processing images, a sample holder arranged in front of an object lens, a fluorescent radiation exciting source and a set of replaceable suppression filters for separating the sample fluorescent light. Separately fluorescing visible molecules and nanoparticles are periodically formed in different object parts, the laser produces the oscillation thereof which is sufficient for recording the non-overlapping images of the molecules and nanoparticles and for decoloring already recorded fluorescent molecules, wherein tens of thousands of pictures of recorded individual molecule and nanoparticle images, in the form of stains having a diameter on the order of a fluorescent light wavelength multiplied by a microscope amplification, are processed by a computer for searching the coordinates of the stain centers and building the object image according to millions of calculated stain center co-ordinates corresponding to the co-ordinates of the individual fluorescent molecules and nanoparticles. With this invention it is possible to obtain a two-dimensional and a three-dimensional image with a resolving power better than 20 nm and to record a color image by dyeing proteins, nucleic acids and lipids with different coloring agents.
Owner:SUPER RESOLUTION TECH
Systems, processes and computer-accessible medium for providing hybrid flourescence and optical coherence tomography imaging
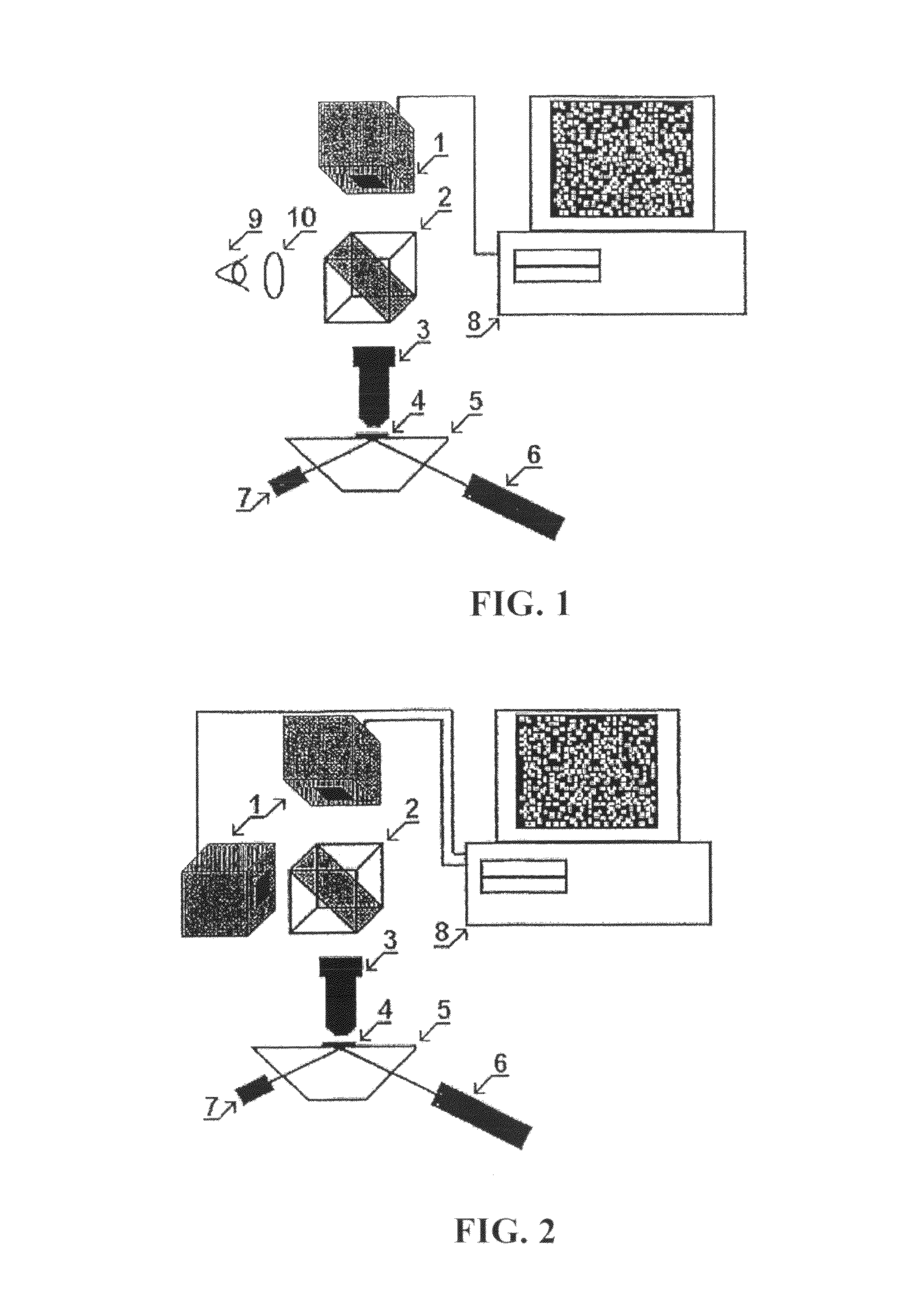
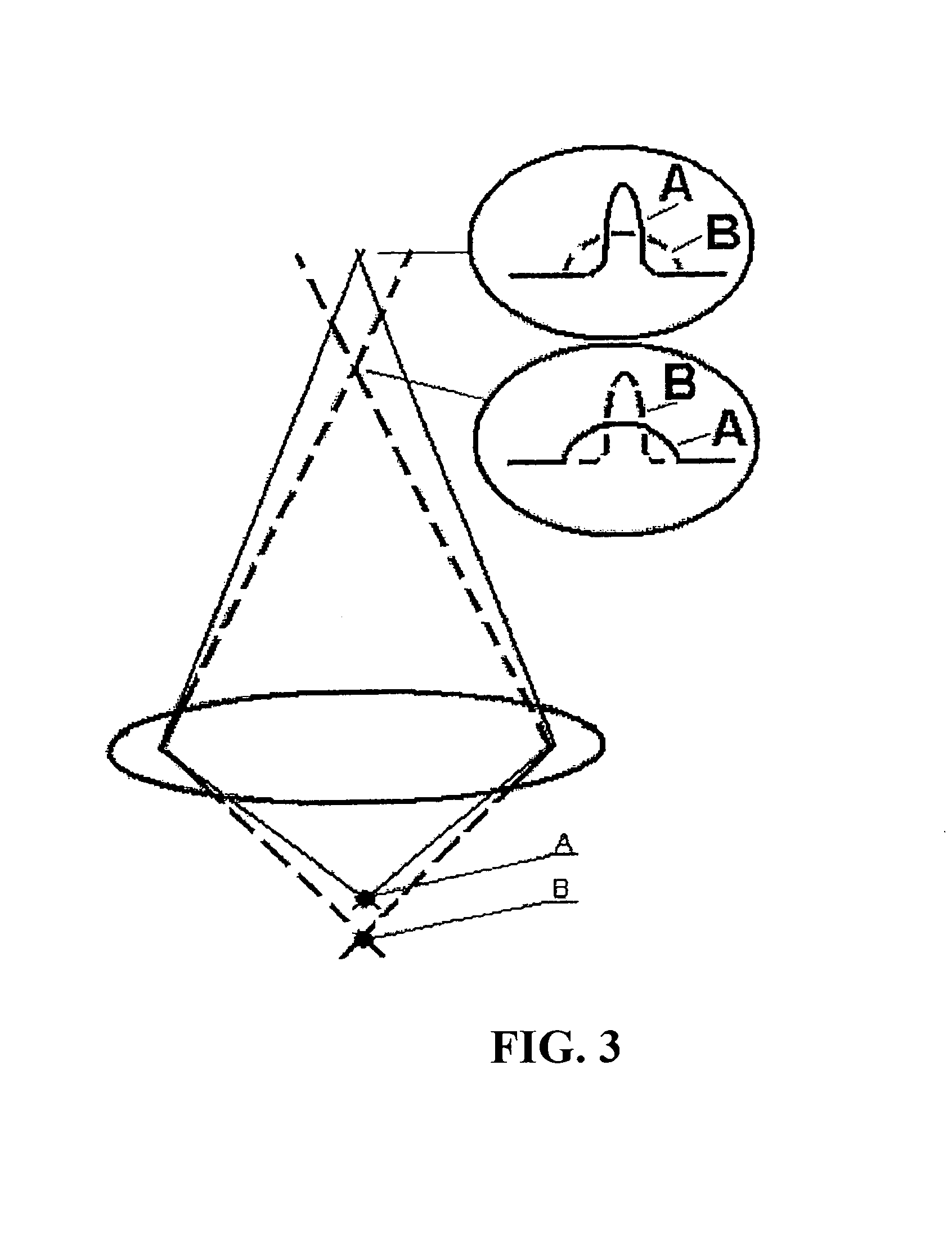
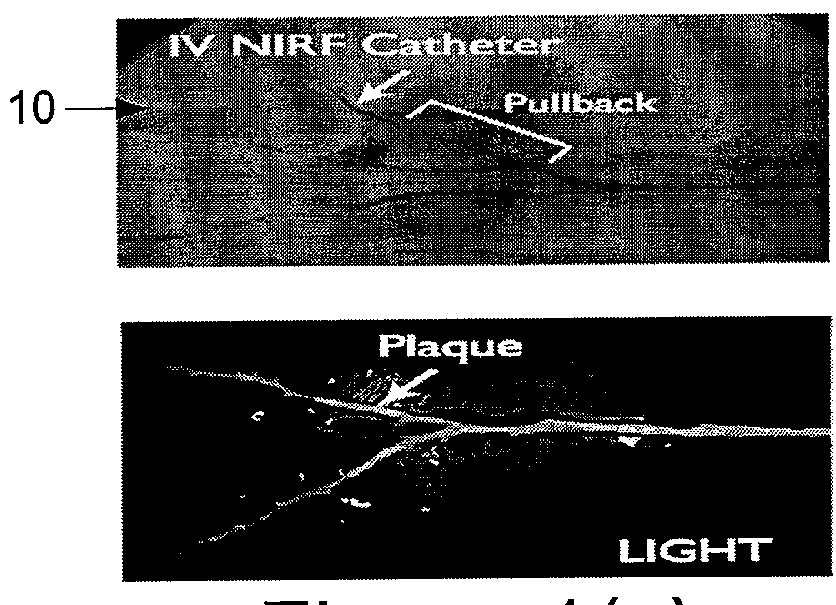
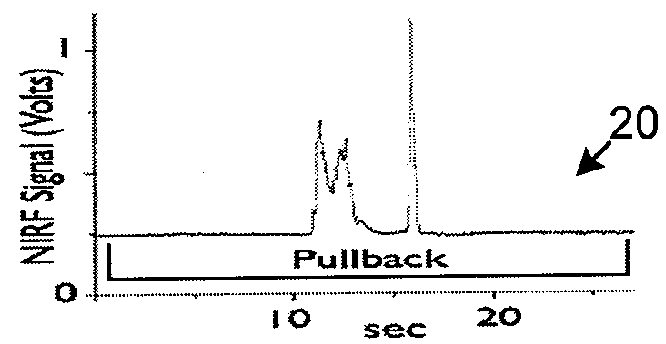
ActiveUS9332942B2Facilitate an accurate co-registrationAccurate imagingSurgeryScattering properties measurementsFluorescent radiationElectromagnetic radiation
Apparatus and method can be provided for obtaining information regarding at least one portion of a biological structure. For example, using a first arrangement, it is possible to generate a first electro-magnetic radiation to be forwarded to the portion and receive, from the portion, a second fluorescent radiation associated with the first electro-magnetic radiation Further, using a second arrangement, it is possible to obtain information associated with the second fluorescent radiation, and generate at least one image of the portion as a function of the second fluorescent radiation. According to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the first arrangement can be inserted into at least one lumen, and the image of the portion may be associated with the at least one lumen.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Special-illumination surgical video stereomicroscope
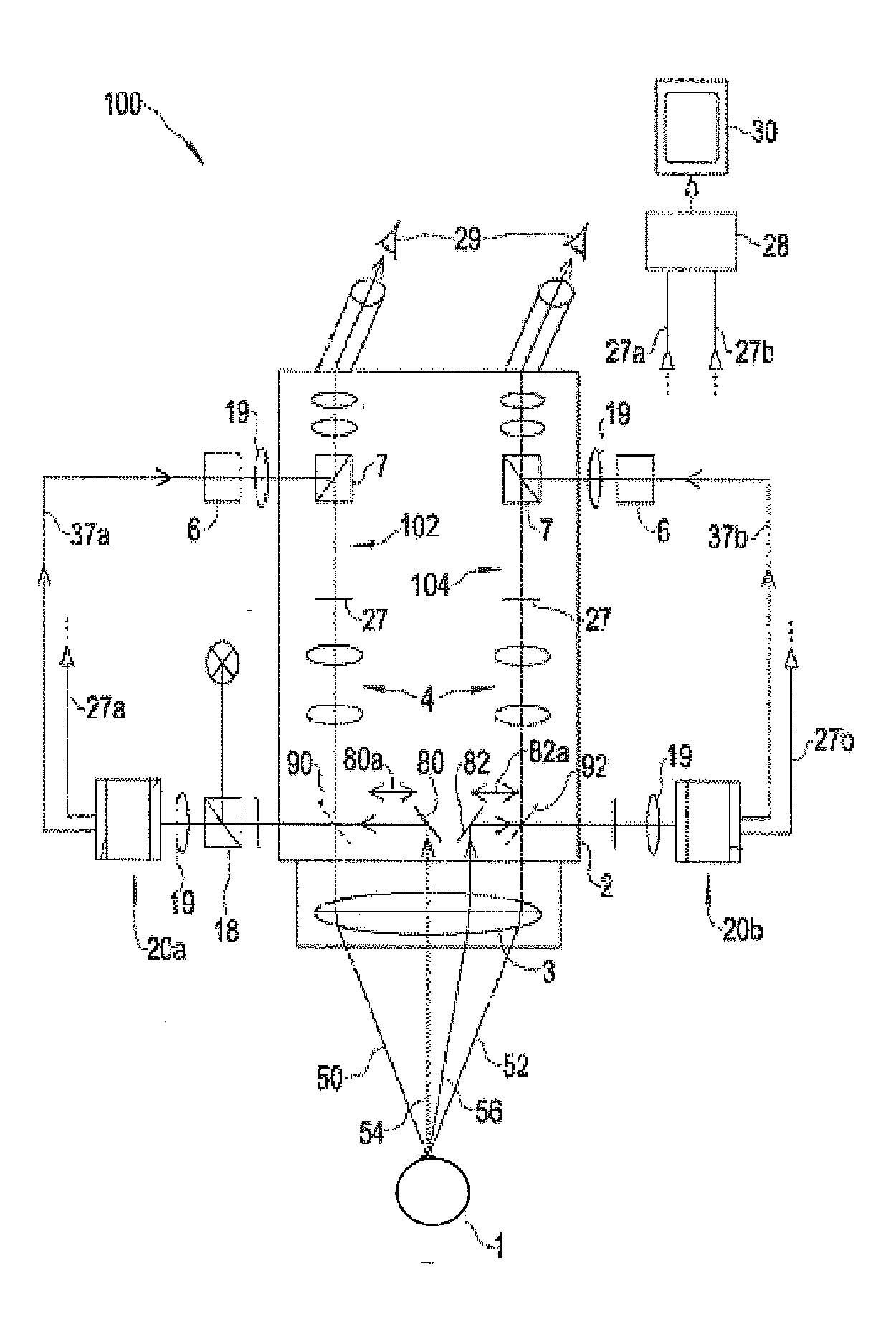
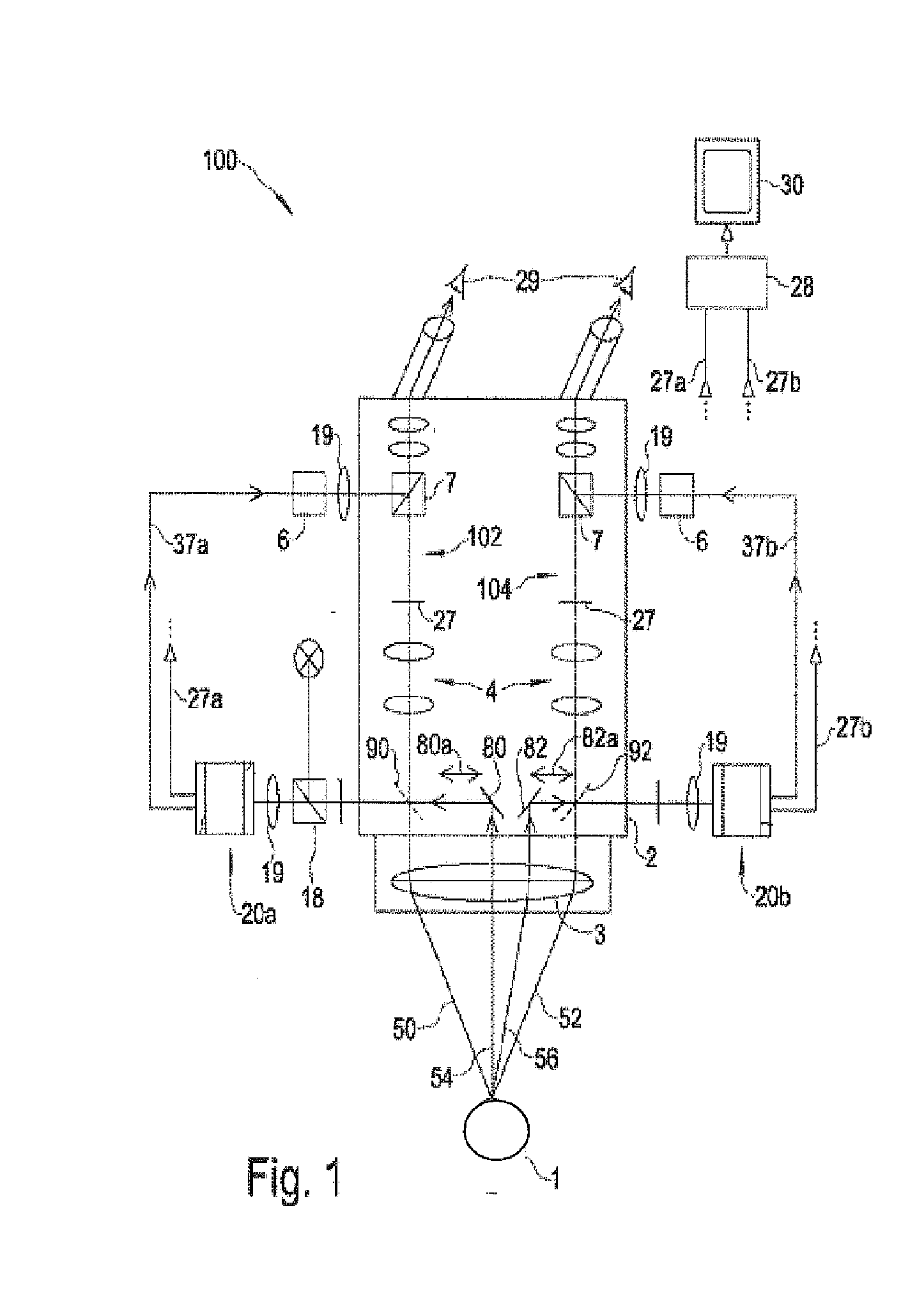
InactiveUS20120056996A1High light efficiencyReduce resolutionDiagnosticsMicroscopesFluorescenceLength wave
A special-illumination surgical video stereomicroscope having at least one light source for illuminating an in-situ specimen, at least one video imaging unit (104a) being provided for acquiring a fluorescence image of the specimen, the spectral sensitivity of the at least one video imaging unit (104a) exhibiting a higher spectral sensitivity in at least one light wavelength region of a special light radiation to be expected, e.g. fluorescence radiation, than in another light wavelength regions.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS (SCHWEIZ) AG
Fluorescent nanoscopy method
ActiveUS20090045353A1High resolutionLow level of background noiseNanotechSamplingColor imageLow noise
Owner:SUPER RESOLUTION TECH
Method and system for wide-area ultraviolet detection of forensic evidence
ActiveUS7545969B2Radiation pyrometryCharacter and pattern recognitionFluorescent radiationUltraviolet lights
The present invention comprises a method for detecting and analyzing forensic evidence. A digital image is taken of background radiation from a suspected-evidence area suspected to contain evidence. The suspected-evidence area is exposed to a high-intensity pulse of ultraviolet radiation. Another digital image is taken of fluorescence within the exposed suspected-evidence area. The digital images are processed to create a composite digital image showing regions of evidence. The composite digital image is analyzed to determine the wavelength of fluorescent radiation emitted by the regions of evidence. Composite evidence image and the analysis results are displayed. The present invention also comprises a forensic evidence detection and analysis system that includes a digital camera, an ultraviolet light source, a computer and display, and a computer program installed on the computer.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
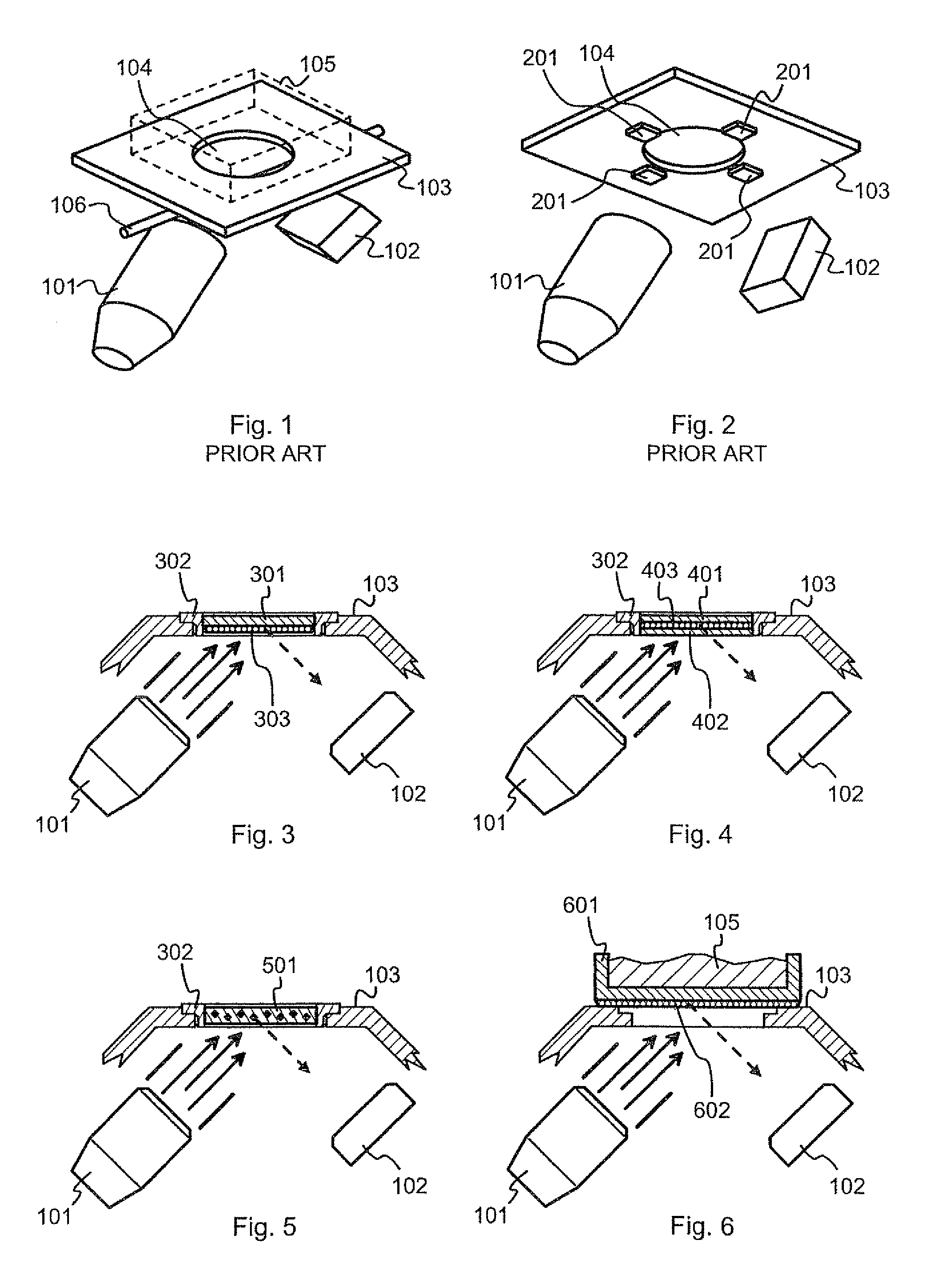
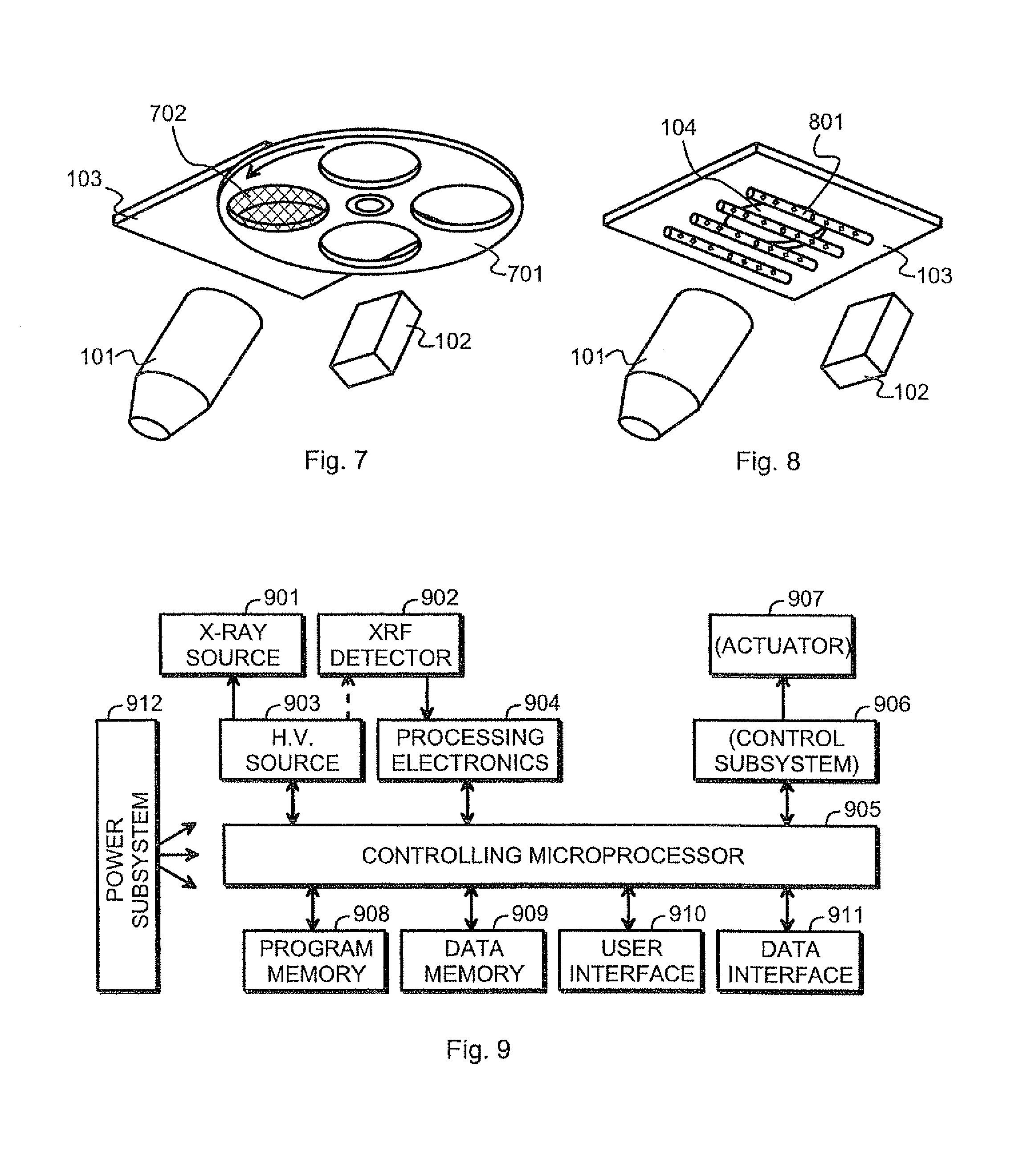
Measurement arrangement for X-ray fluoresence analysis
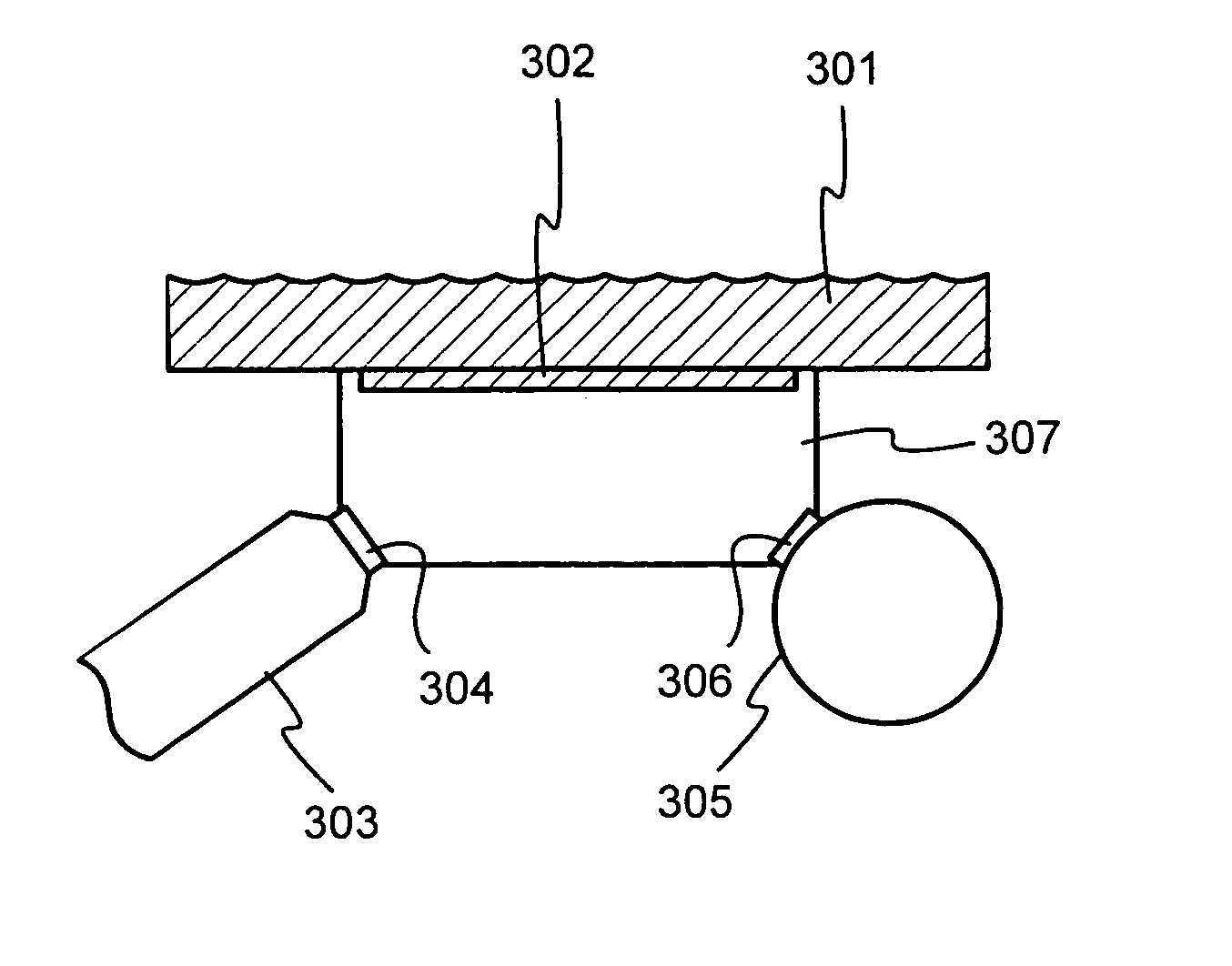
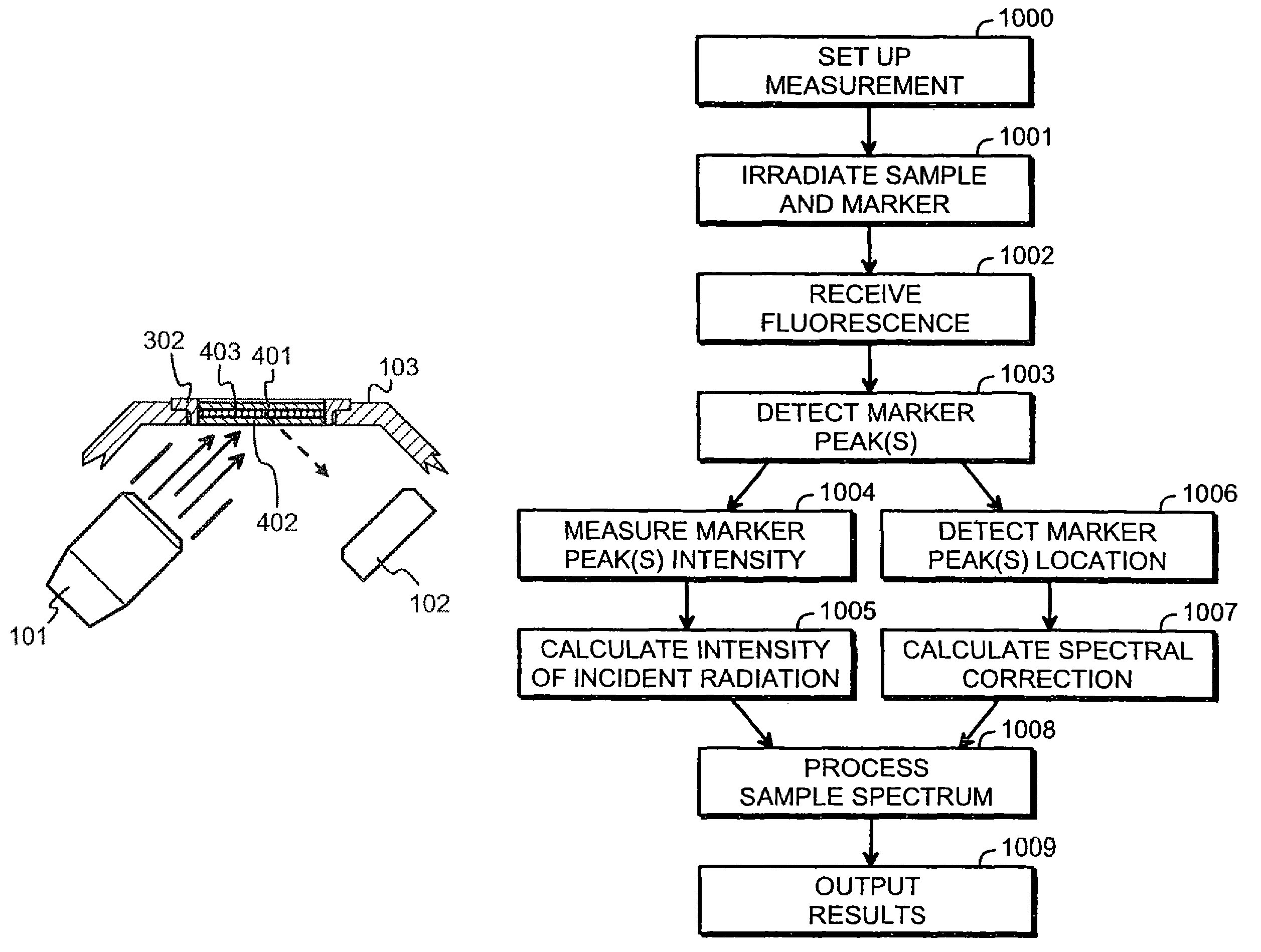
InactiveUS7065174B2Easy maintenanceSmall-sizedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementSoft x rayFluorescent radiation
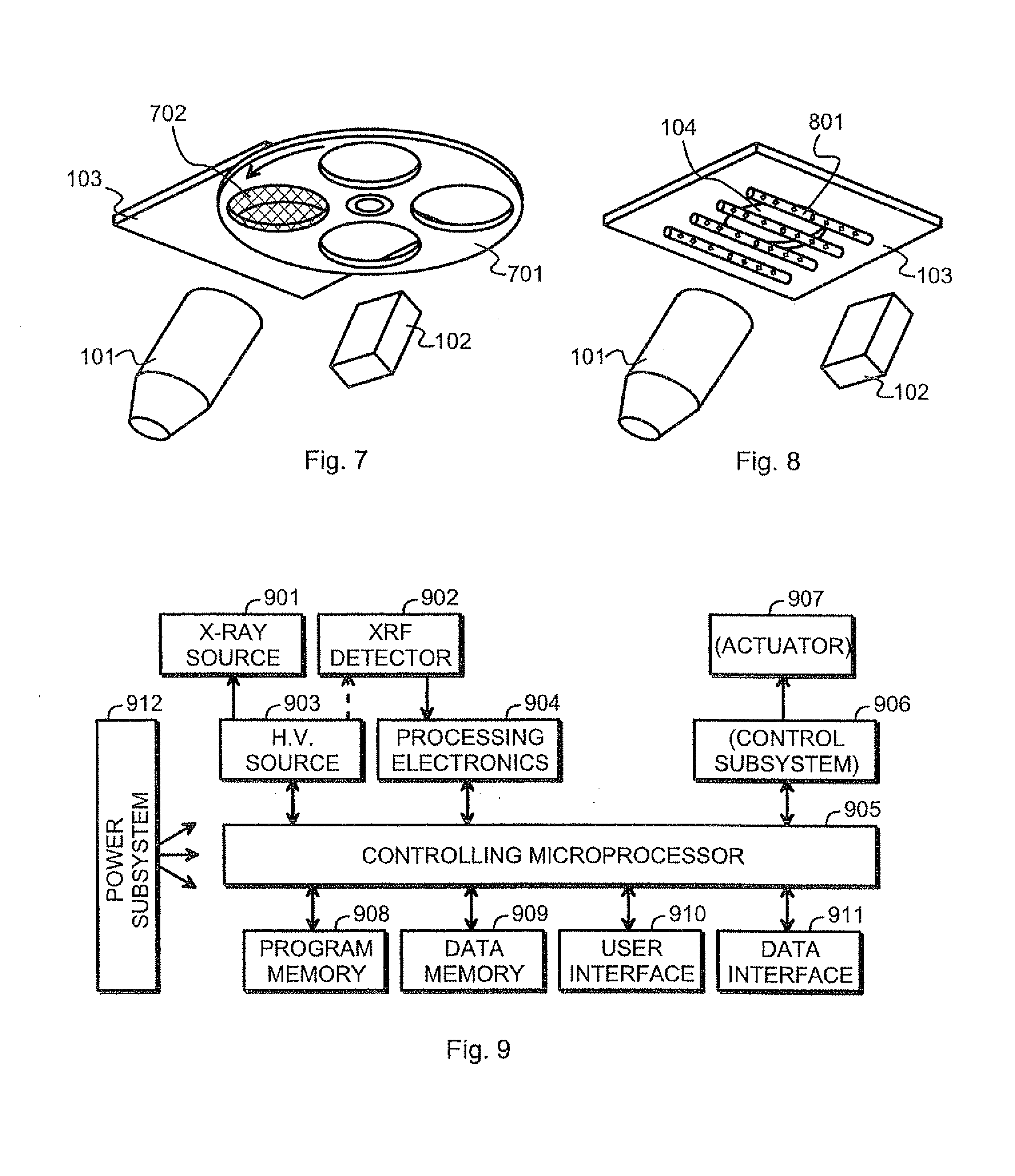
A portable measurement apparatus is presented for inducing and measuring fluorescent X-ray radiation. It comprises an X-ray source (303, 902, 1005, 1105) adapted to controllably irradiate a sample (301, 803) with X-rays, and a detector (305, 406, 1006, 1106) adapted to detect fluorescent radiation emitted by said sample (301, 803). The X-ray source (303, 902, 1005, 1105) is an X-ray tube, an anode of which comprises at least one of silver, rhodium and molybdenium. Consequently said X-ray tube is adapted to controllably emit L-line radiation of at least one of silver, rhodium and molybdenium.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR IND ANALYSIS OY +1
Apparatus for selected measurement of, in particular luminescent and/or fluorescent radiation
InactiveUS20090159803A1Improve optical efficiencyGood effectChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceHandling using diaphragms/collimetersFluorescent radiationOptoelectronics
An apparatus for selected measurement of at least one of luminescent and fluorescent radiation from at least one sample well, the apparatus comprising: means defining an excitation light path for fluorescence measurements; at least one light source in the excitation path; means defining an emission light path; and at least one detector with a wavelength selector in the emission light path, wherein: the apparatus further comprises at least one first reflector element that encompasses a reflection chamber and projects at least a portion of the light emitted from the at least one sample well directionally onto the wavelength selector; the emission light path extends between the at least one sample well and the wavelength selector through the at least one first reflector element; and the excitation light path extends into the reflection chamber and extends to a point above the at least one sample well.
Owner:BERTHOLD TECH
Laser cooling apparatus and method
A laser cooling apparatus and method. Generally, the inventive apparatus includes a mechanism for transporting sensible thermal energy from a solid state laser and for communicating waste fluorescent radiation therefrom as well. In the illustrative embodiment, the apparatus includes an optically transparent manifold (10) with an inlet port (12), an exhaust port (19) and a plurality of spray nozzles (16) therebetween adapted to direct a cooling fluid on the laser medium (20) of a laser (30). In addition, the optically transparent manifold (10) is used to permit waste fluorescent radiation to escape the confines of the laser and cooling system means such that said fluorescent radiation may be optically directed to an external heat sink such as free space.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Apparatus and method for X-ray fluorescence analysis of a mineral sample
ActiveUS8515008B2Improve reliabilityReduce preparationX-ray spectral distribution measurementPhotometrySingle sampleCost effectiveness
Owner:OREXPLORE
Laser diode pumping full-solid ultraviolet pulse laser
InactiveCN1635670AImprove efficiencyHigh beam qualityOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialFiberLight energy
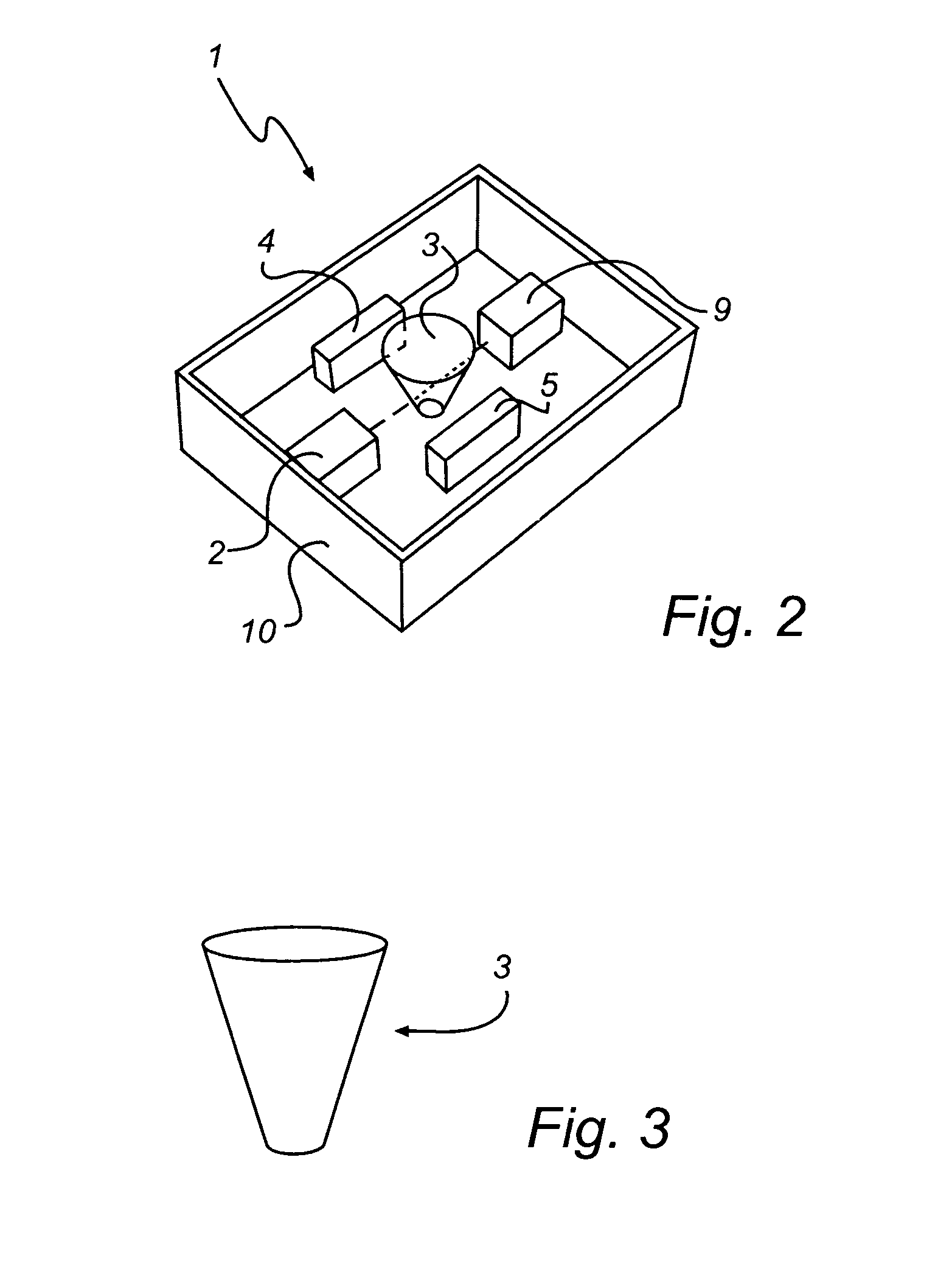
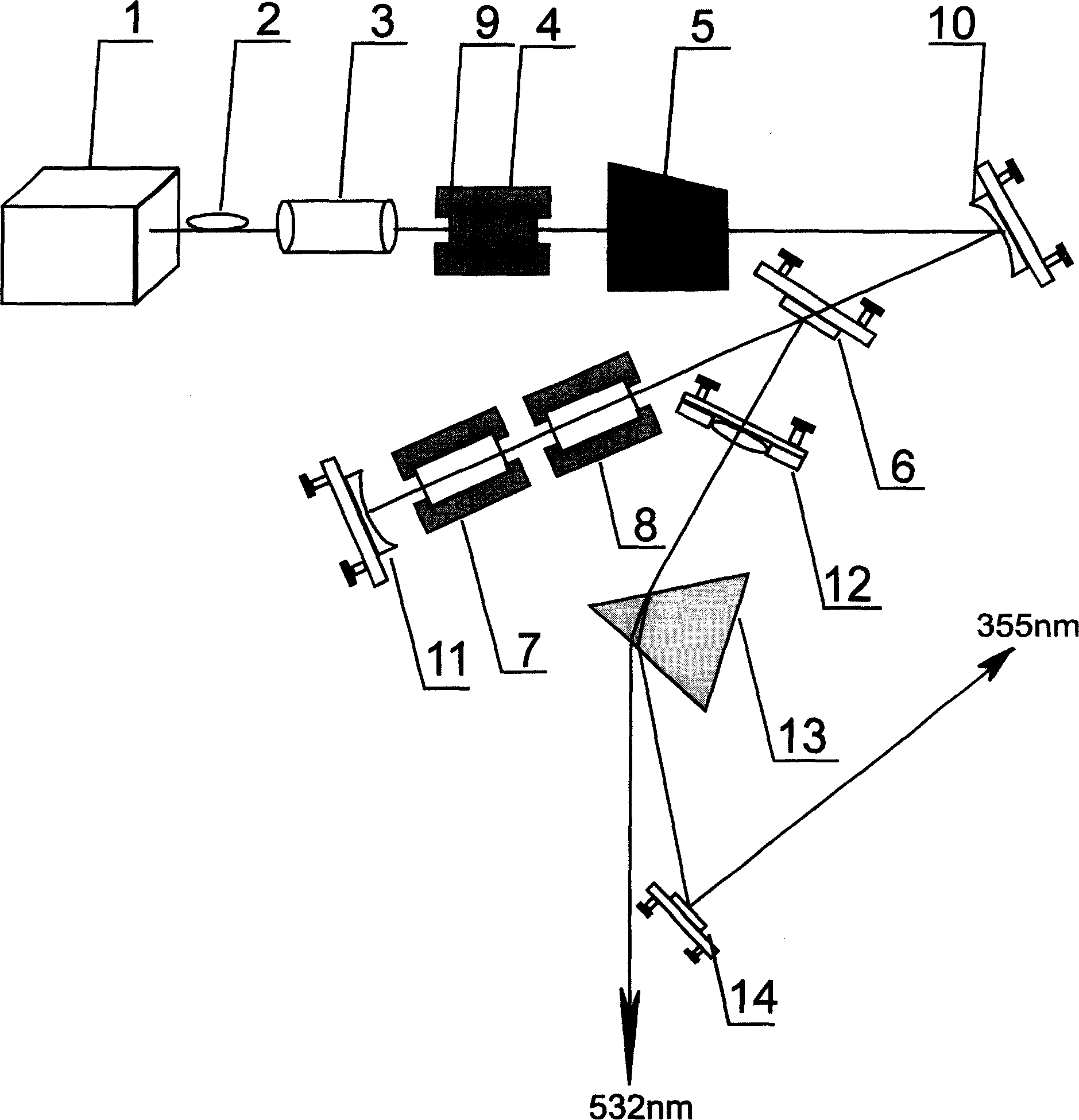
This invention discloses a laser diode pump all solid state ultraviolet pulse laser, the pump light output by coupling optic fiber, the pump light focused the pump end face of laser crystal through pump end face membrane to form plane reflection mirror, the laser crystal generating excited fluorescent radiation after absorbing pump light energy, the fluorescent forming base frequency light beam by oscillation in resonant cavity, laser incident to plane concave mirror by plane reflection mirror through laser crystal, sound and light Q adjusting crystal, plane color separation mirror, sum-frequency crystal and double frequency crystal, the plane color separation mirror leading light from resonant cavity, the focusing by lens, refracting by quartz prism and leading out laser by ultraviolet reflection mirror. Said invention has compact structure, high average output pulse power and large adjustable range of pulse recurrent frequency etc advantages.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN) +1
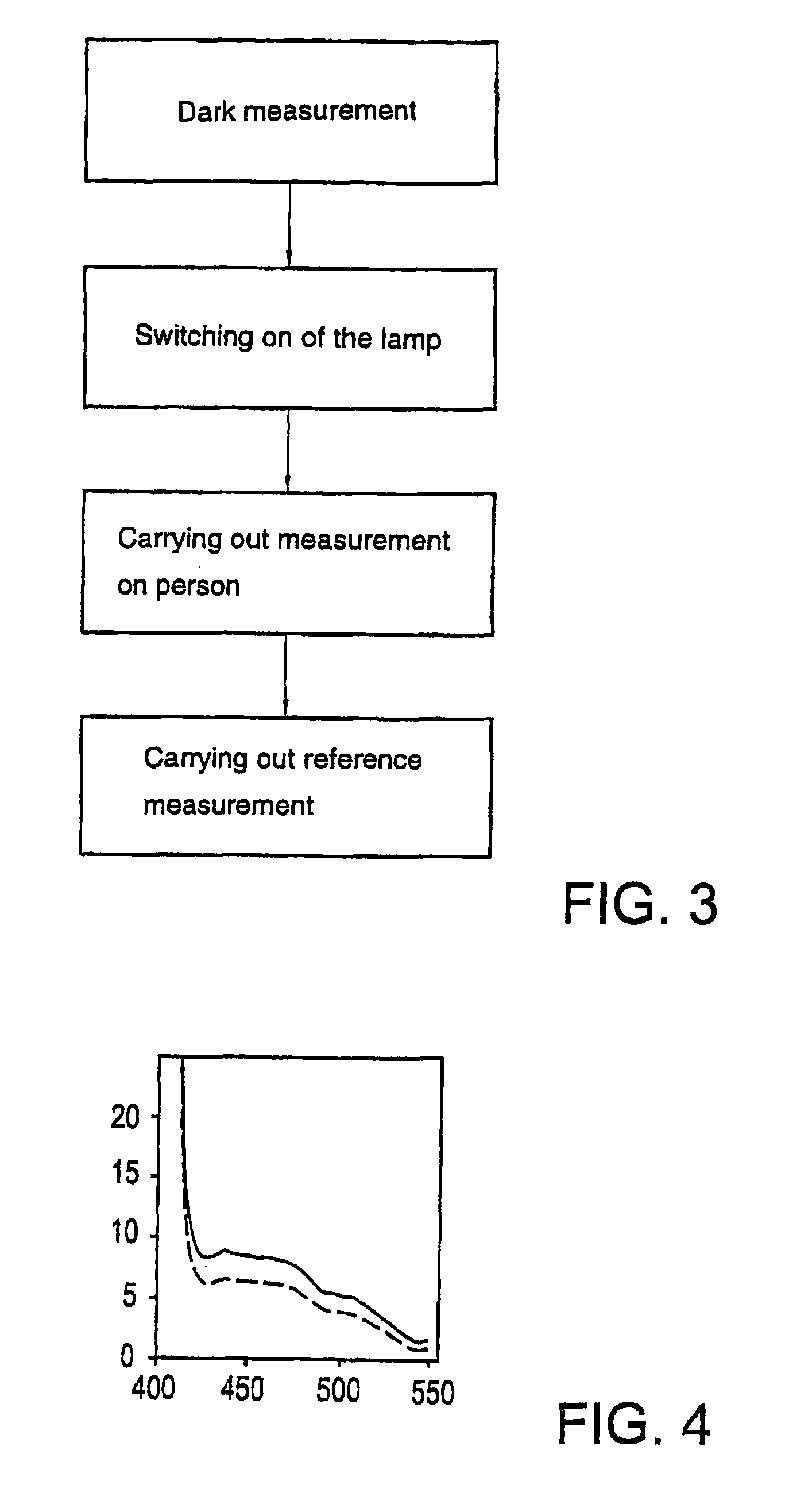
Method and apparatus for determining autofluorescence of skin tissue
InactiveUS7966060B2Diagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionFluorescent radiationNormal skin
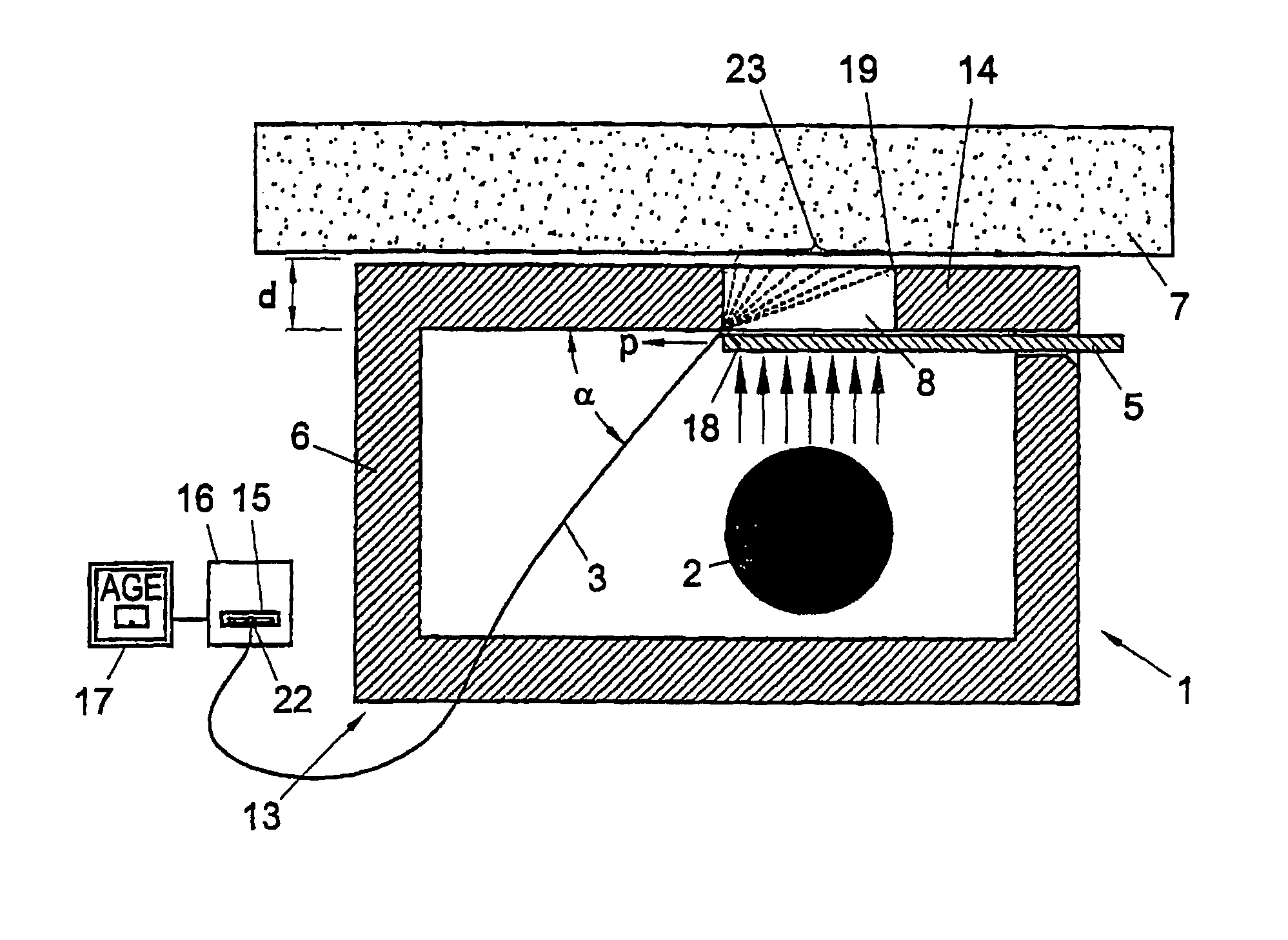
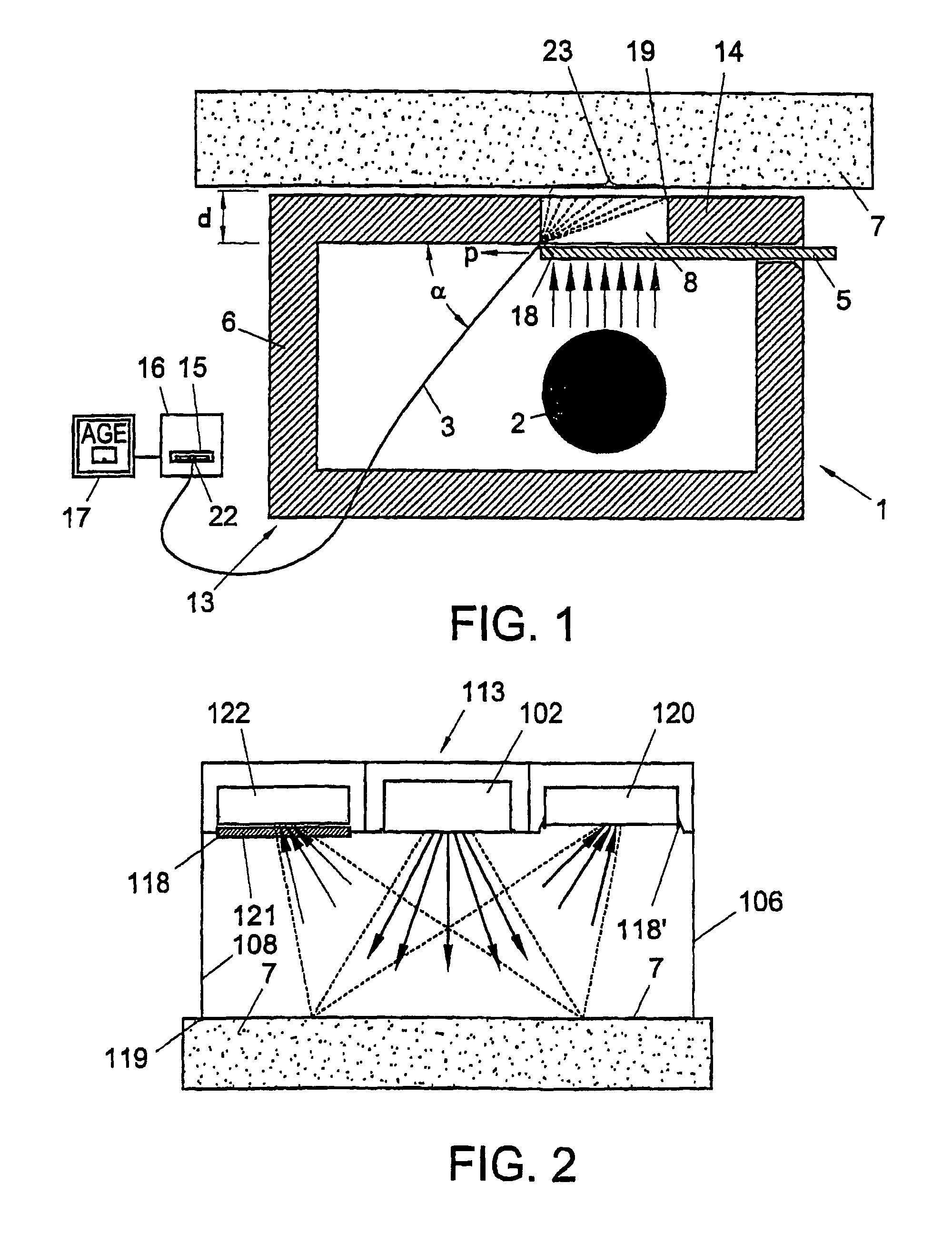
For determining autofluorescence of a clinically normal skin issue (7) of a patient, the tissue (7) is irradiated with electromagnetic radiation. An amount of fluorescent radiation emitted by the tissue (7) in response to the irradiation is measured and, in response thereto, a signal is generated which represents a determined autofluorescence in agreement with the measured amount of electromagnetic radiation. Because the tissue (7) is skin tissue (7) in vivo and irradiation is performed noninvasively, a method which is very simple to apply for determining autofluorescence is obtained. An apparatus especially adapted for use in this method is also described.
Owner:DIAGNOPTICS HLDG
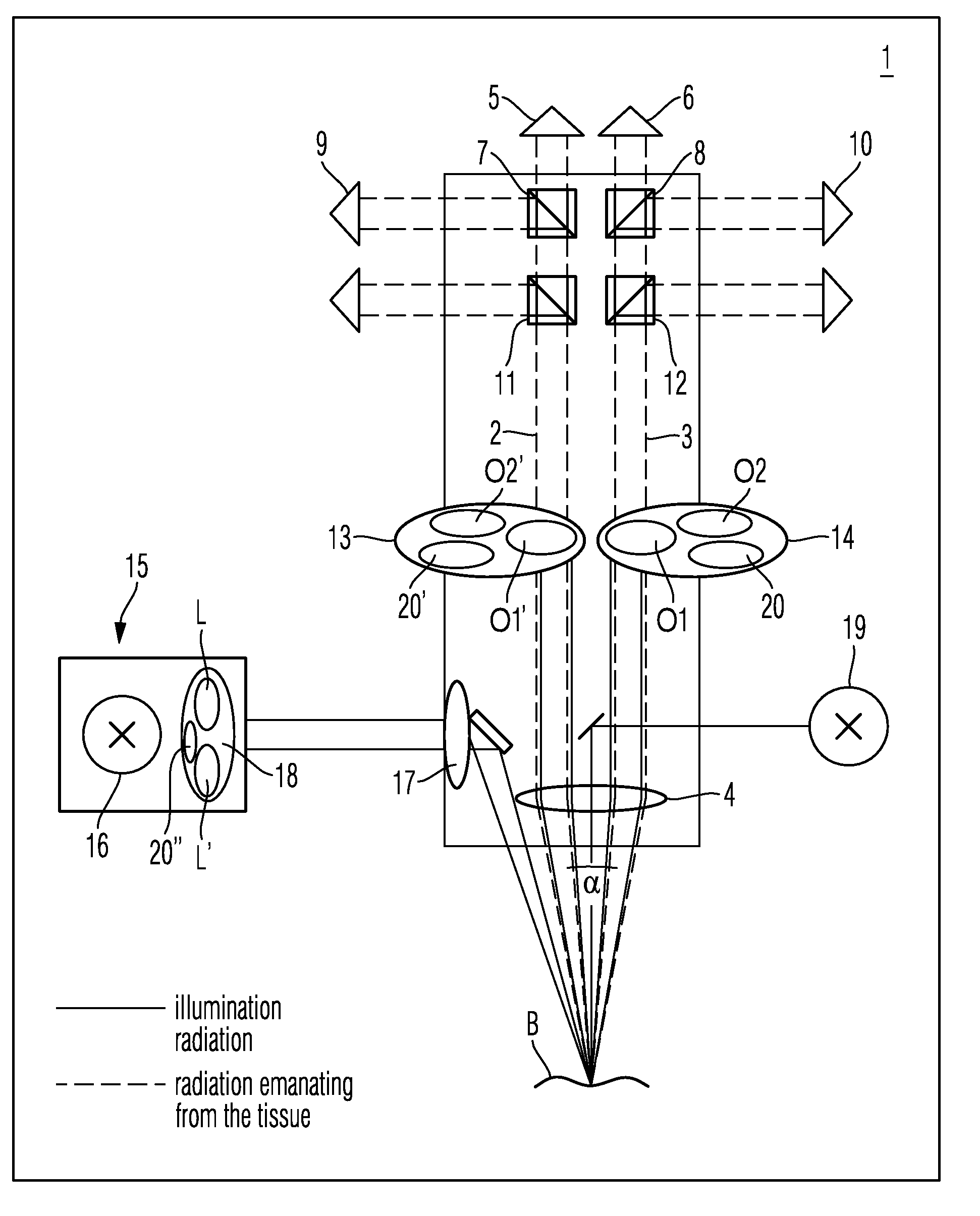
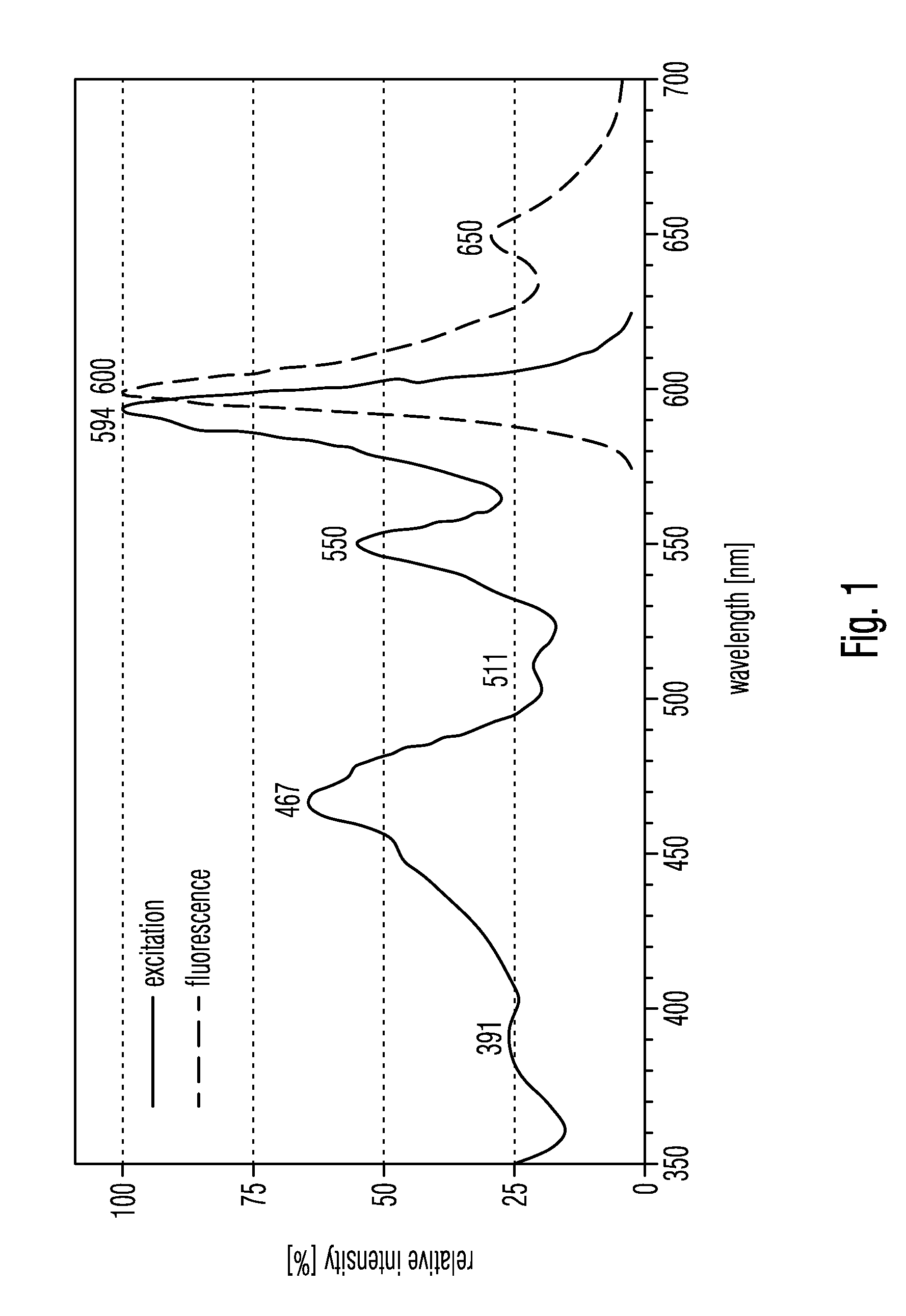
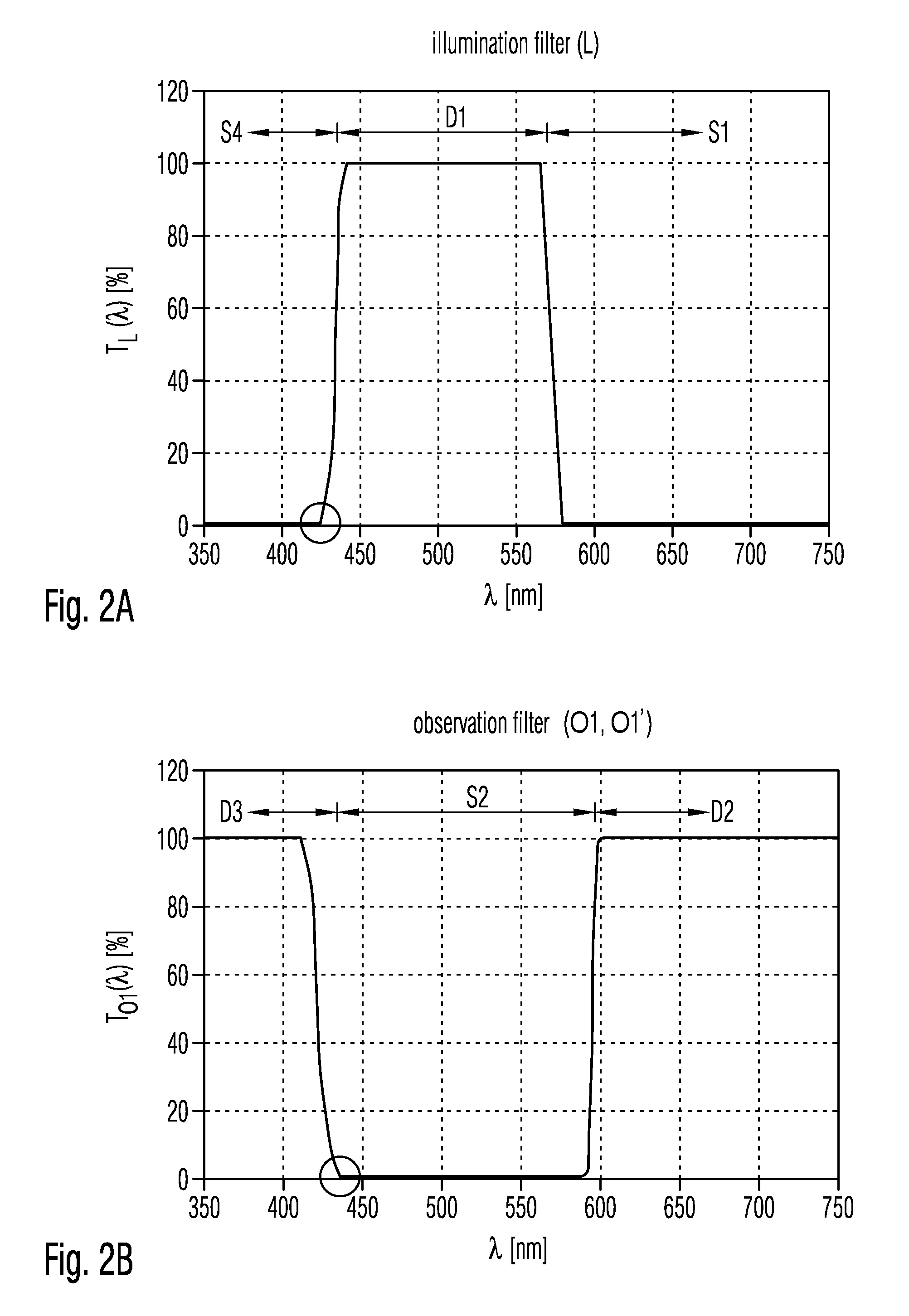
Filter set for observing fluorescence radiation in biological tissue
ActiveUS20100044583A1Easy to adaptRaman/scattering spectroscopyOptical filtersFluorescent radiationLighting system
A filter set for observing fluorescent radiation in biological tissue includes at least one illumination filter and at least one observation filter. The at least one illumination filter is arrangeable in an illumination system of an optical system. The at least one least one observation filter is arrangeable in an imaging system of the optical system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Measurement arrangement for X-ray fluoresence analysis
InactiveUS20050129174A1Easy maintenanceSmall-sizedX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorescent radiationX-ray
A portable measurement apparatus is presented for inducing and measuring fluorescent X-ray radiation. It comprises an X-ray source (303, 902, 1005, 1105) adapted to controllably irradiate a sample (301, 803) with X-rays, and a detector (305, 406, 1006, 1106) adapted to detect fluorescent radiation emitted by said sample (301, 803). The X-ray source (303, 902, 1005, 1105) is an X-ray tube, an anode of which comprises at least one of silver, rhodium and molybdenium. Consequently said X-ray tube is adapted to controllably emit L-line radiation of at least one of silver, rhodium and molybdenium.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR IND ANALYSIS OY +1
Compensation for fluctuations over time in the radiation characteristics of the X-ray source in an XRF analyser
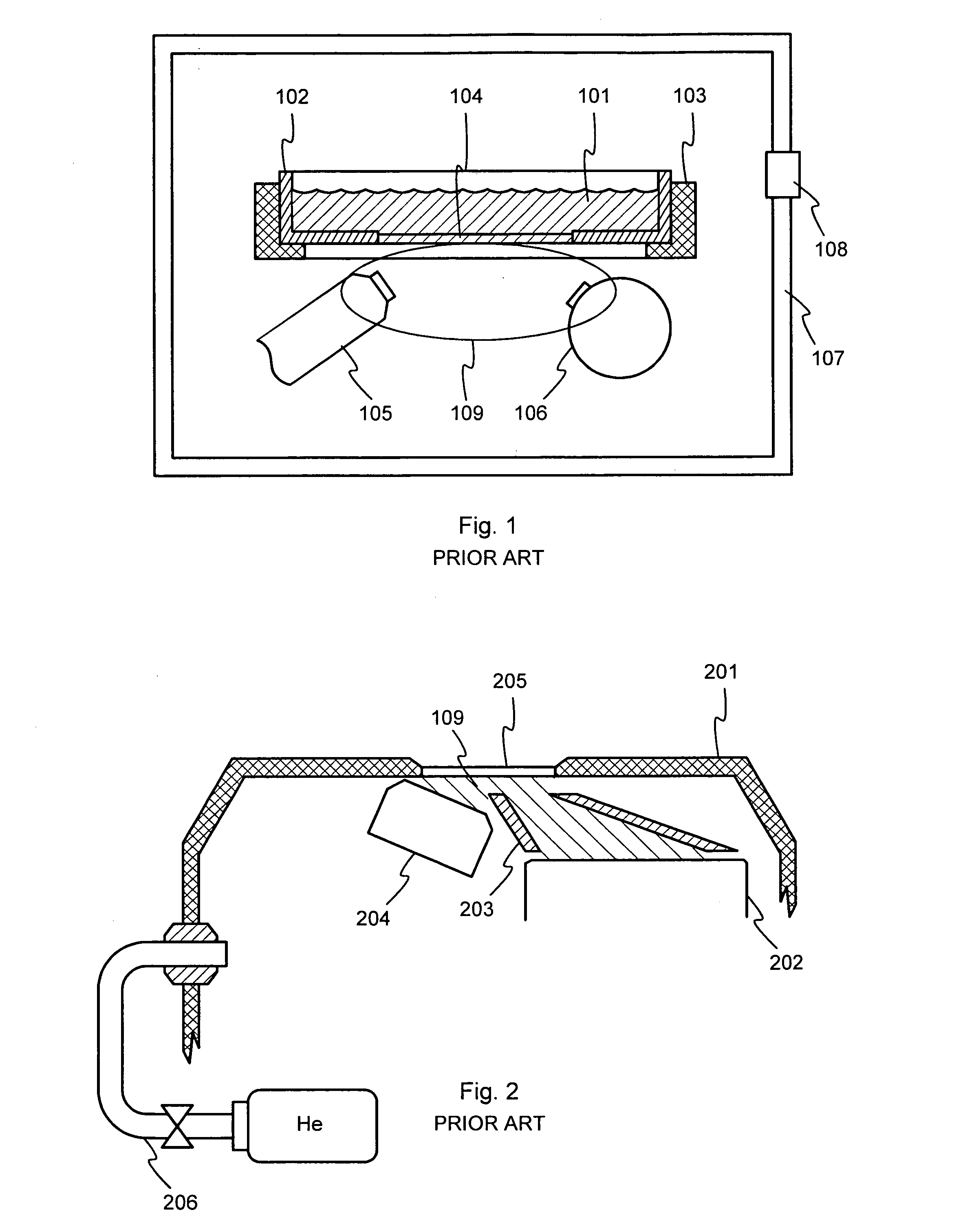
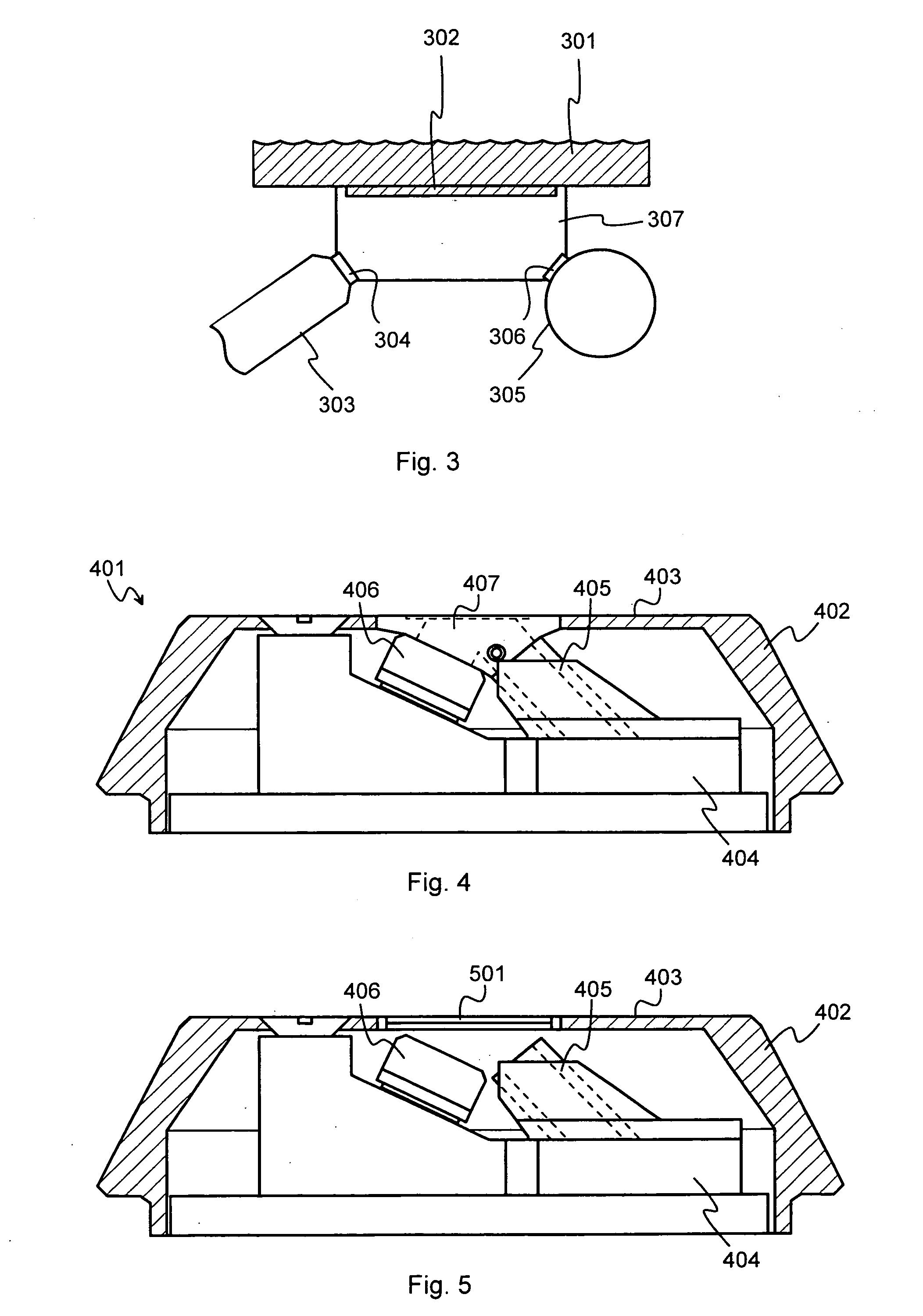
InactiveUS7474730B2X-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorescent radiationX-ray
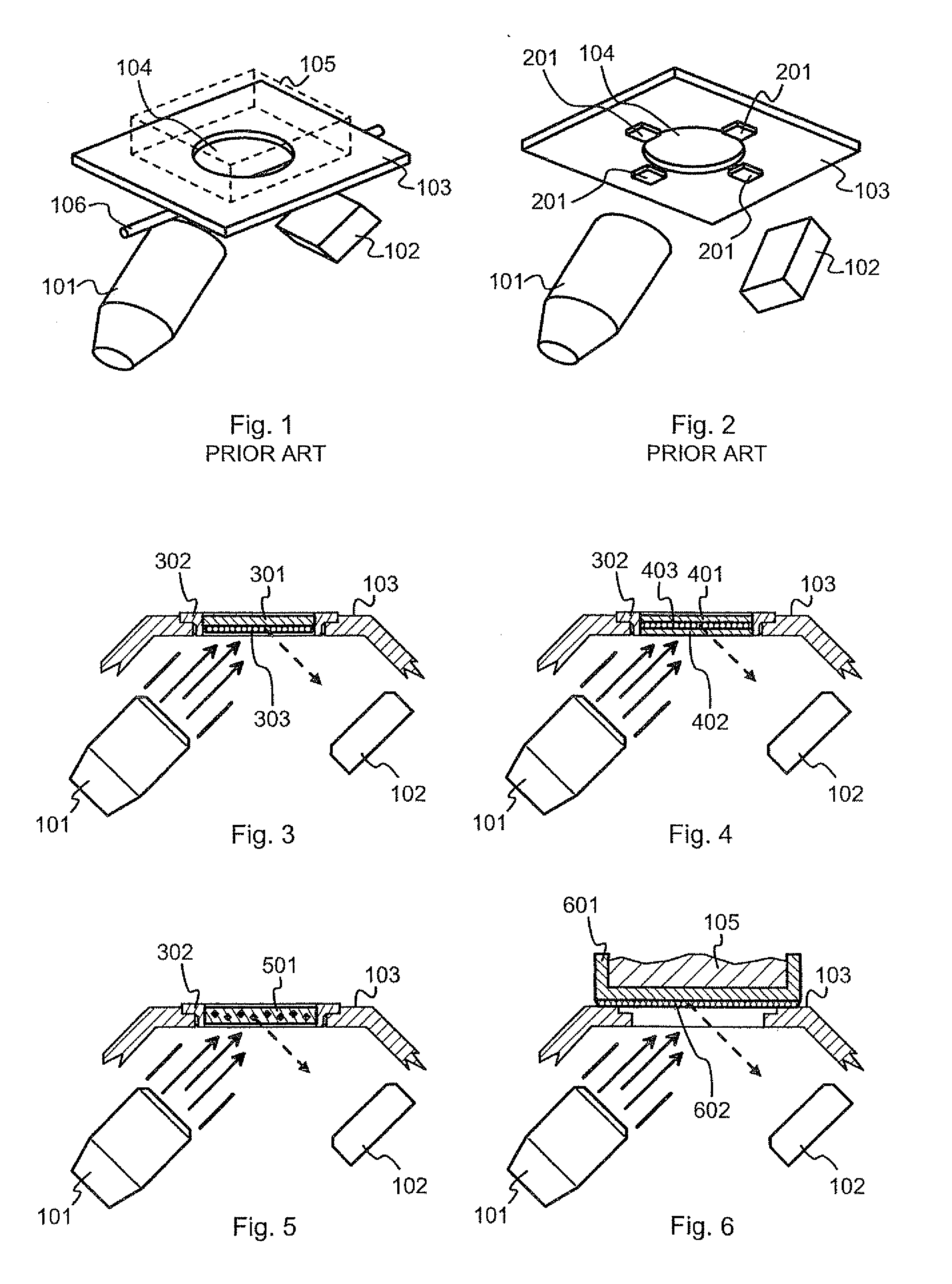
An X-ray source (101) is configured to controllably irradiate a sample (105) with incident X-rays through a sample window (104) that has a two-dimensional area. A detector (102) is configured to detect fluorescent radiation coming from the irradiated sample. A carrier (301, 401, 402, 501, 601) is essentially transparent to X-rays and disposed to spatially coincide with a substantial part of the two-dimensional area of the sample window (104). Marker material (303, 403, 602), which is responsive to X-rays by emitting fluorescent radiation, is mechanically supported by said carrier and essentially evenly distributed across at least that part of the carrier that spatially coincides with said two-dimensional area of the sample window.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH ANALYTICAL SCI FINLAND OY
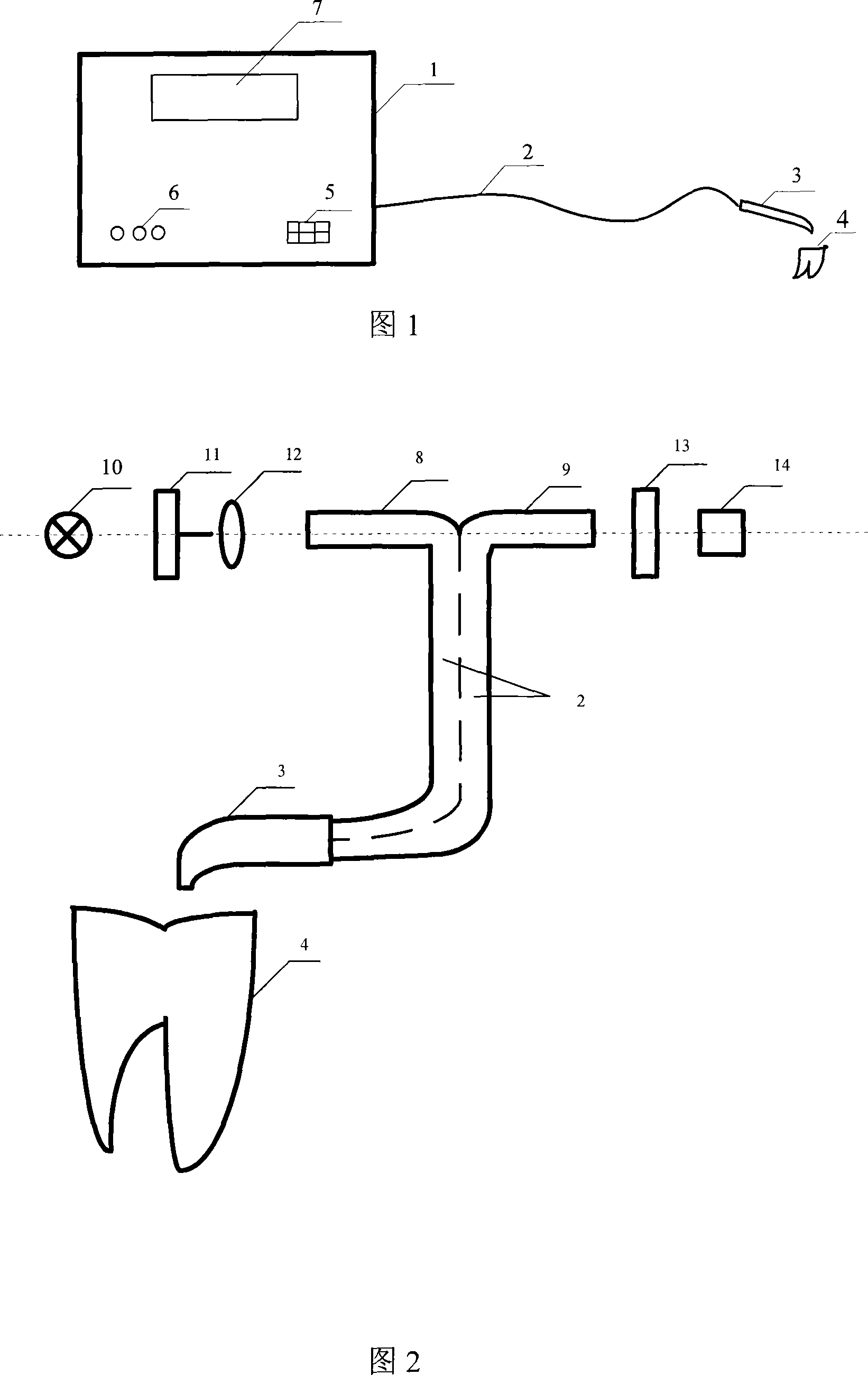
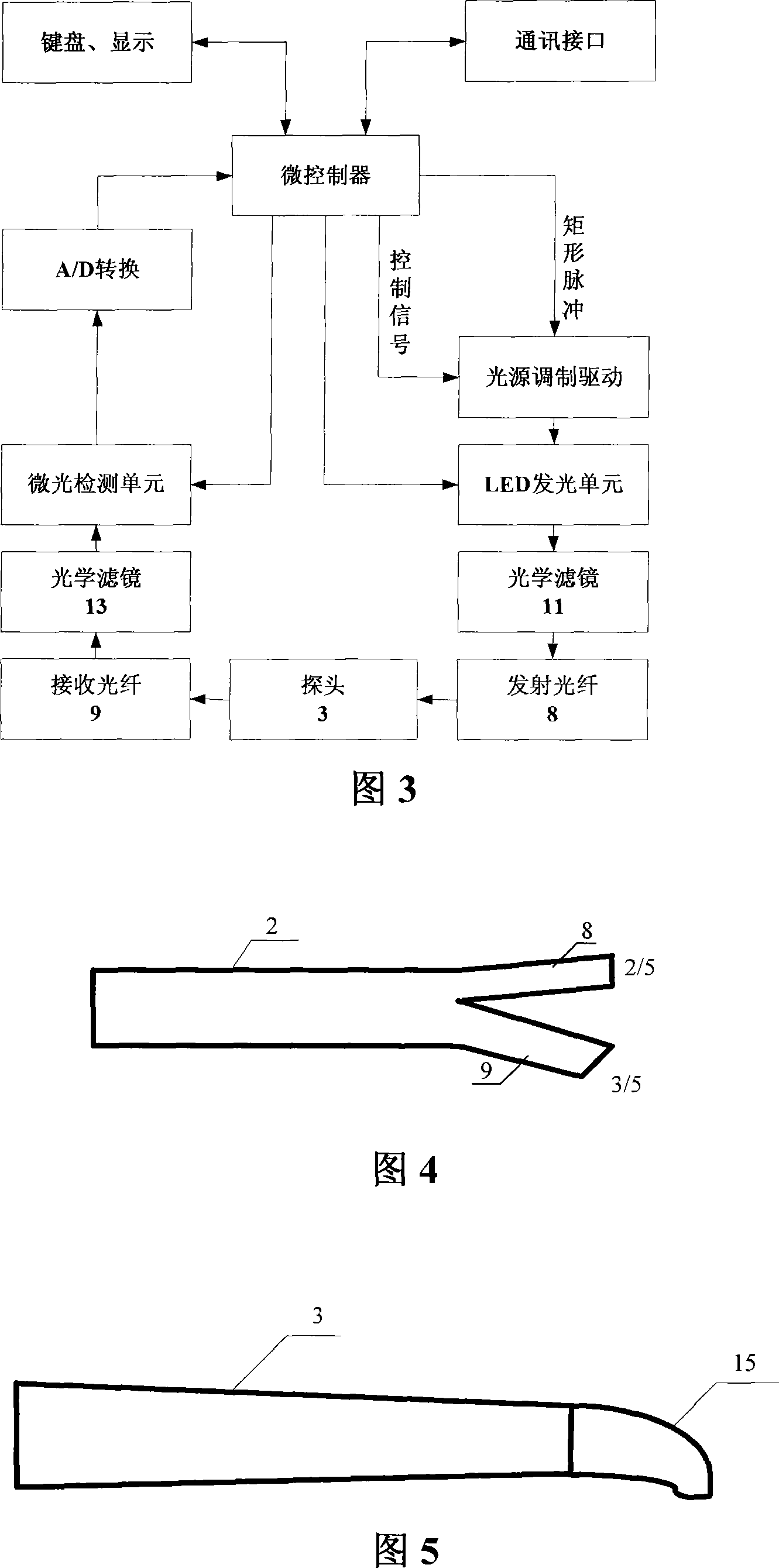
Pulp active fluorescent detecting device and detecting method
InactiveCN101167647AAvoid interferenceReduce volumeDentistryDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseFiber
The invention provides a pulp-vitality fluorescence detection device and a detection method, by employing fluorescence for detection, the modulated exciting light after passing through a filter is transmitted by a transmitting fiber, and irradiates the surface of a detected tooth via a probe window and drives the tooth to produce fluorescent radiation, then the modulated exciting light is received and transmitted by a receiving fiber in the probe window, and is transferred to a glimmer detection unit via a receiving filter, and then the modulated exciting light enters into a data processing and control circuit for being controlled and processed. The invention resolves professional difficult problems which include painless detection of dental diseases and particularly the fast synthetic detection of pulp vitality, tooth decalcification and carious dentin, the detection is accurate, and the corresponding data can be directly displayed. By applying the invention, the detection is flexible because one point detection and multi-point detection can be chosen, the detection procedure is capable of rejecting operation mistakes, the detection is rapid, visual and accurate, the detection range is large, and the structure is simple. The invention can be used in places such as stomatological hospitals, dental clinics, etc., in which dental diseases are detected.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Fluorescence biosensor
ActiveUS7541176B2Improve fluorescence sensitivityHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotovoltaic detectorsIntegrator
A fluorescence detector includes a light source being positioned so that in use, radiation emitted therefrom falls on one or more fluorescing species, and a photodetector being switchably connectable between a charge integrator device and a charge disposal device. The photodetector is positionable to detect fluorescent radiation from the fluorescing species. A controller communicates with the light source and the photodetector, and is operable in a cyclic manner to activate the light source to emit radiation and connect the photodetector to the charge disposal device for a first period of time, and connect the photodetector to the charge integrator device for a second period of time after the first period. The charge integrator device is not reset from one cycle to the next.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD
High efficiency coupling optics for pumping and detection of fluorescence
InactiveUS20080151249A1Avoid soakingWithdrawing sample devicesScattering properties measurementsCuvetteOptical radiation
The invention provides a high efficiency coupling structure for extracting illumination such as fluorescent radiation from a chemical reaction vessel such as a cuvette. The cuvette is provided with a mirrored surface. An end cap for the cuvette includes a probe portion that exhibits total internal reflection. Lenses are provided in various embodiments that improve the light collection and directing properties of the end cap. A fast optical system for free space coupling of optical radiation emanating from a chemical processing cuvette that uses the end cap as an element is also described.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Organic solar cell
ActiveCN103531712ABroad absorption spectrumImprove utilization efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic solar cellFluorescent radiation
An organic solar cell comprises a transparent substrate, a cathode, an electron transport layer, an optical activity layer, a hole transport layer and an anode, wherein the optical activity layer comprises a donor material, an acceptor material and two or more dyes with different absorption wavelengths. According to the organic solar cell, the absorption of the organic solar cell for near ultraviolet and near infrared regions in sunlight is increased through the addition of dye combination, the absorption spectrum of the organic solar cell for the sunlight is broadened, the fluorescent radiation loss is reduced, the utilization efficiency of the sunlight is reinforced, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the organic solar cell is further improved. Meanwhile, the crystallinity of the optical activity layer is also improved due to the addition of the dyes, and the stability of the organic solar cell is improved.
Owner:CHINA LUCKY FILM CORP
Tapered monocapillary-optics for point source applications
InactiveUS6126844APaper/cardboard articlesDecorative surface effectsElectron probe microanalysisElectron
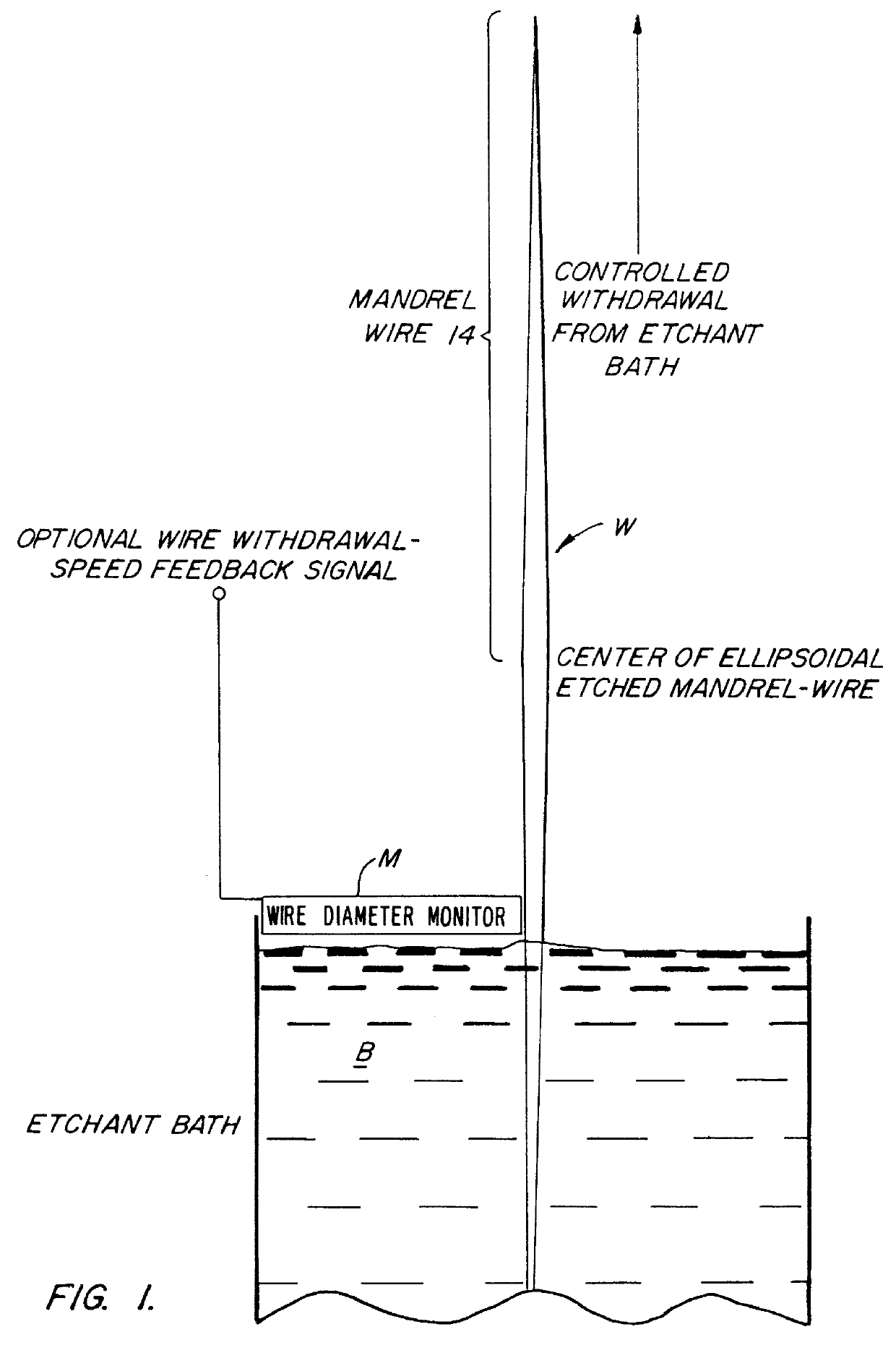
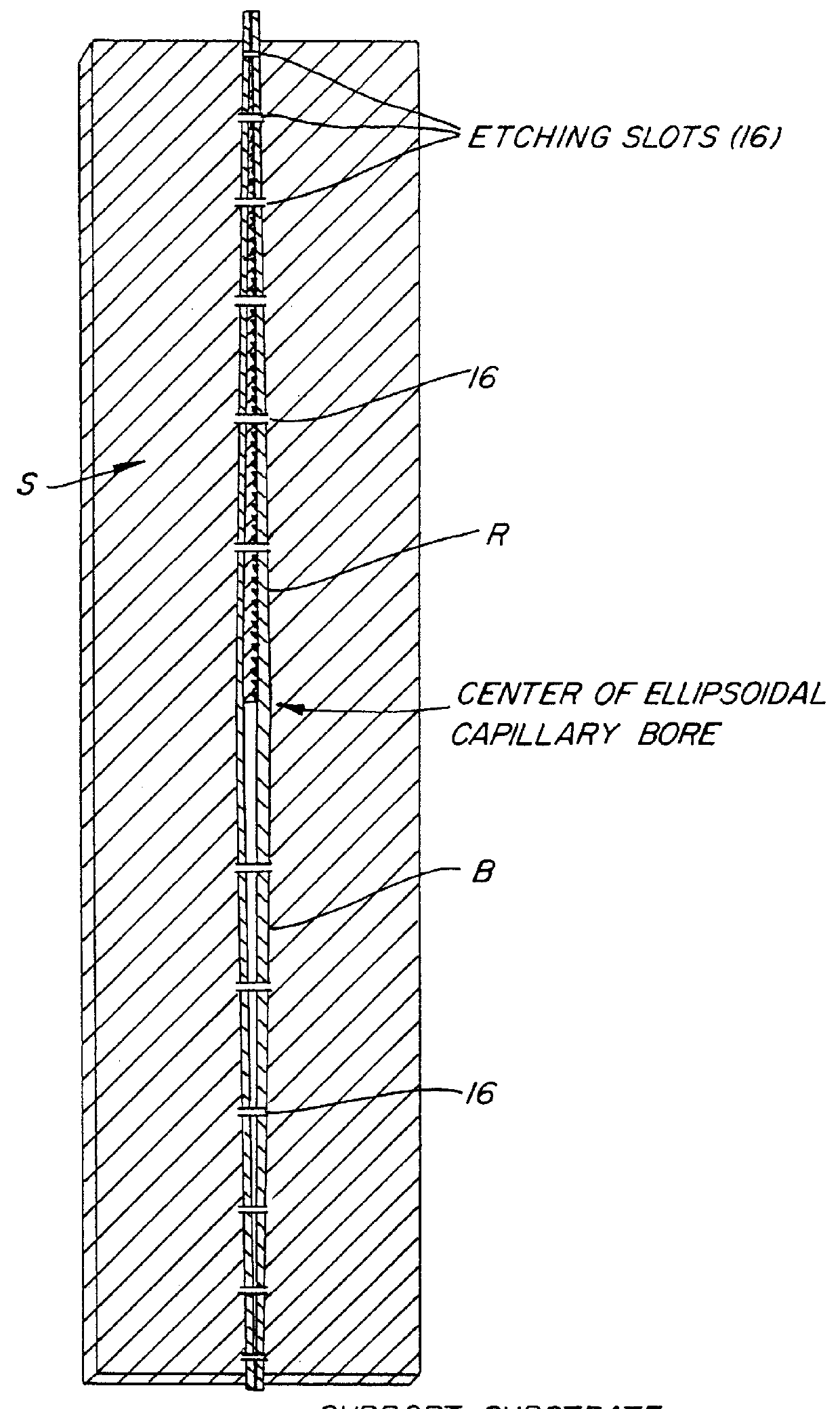
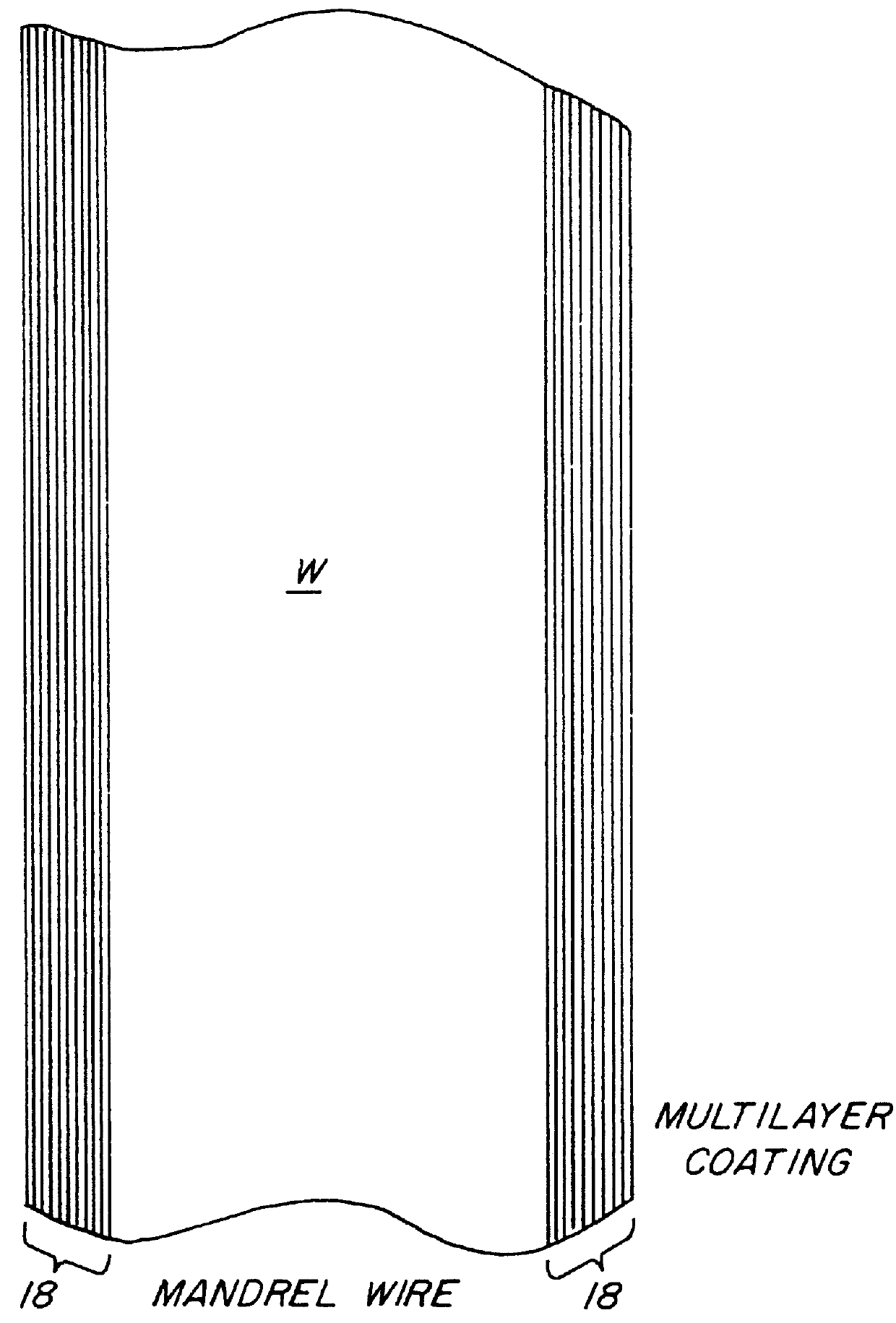
A glass or metal wire is precisely etched to form the paraboloidal or ellipsoidal shape of the final desired capillary optic. This shape is created by carefully controlling the withdrawal speed of the wire from an etchant bath. In the case of a complete ellipsoidal capillary, the etching operation is performed twice in opposite directions on adjacent wire segments. The etched wire undergoes a subsequent operation to create an extremely smooth surface. This surface is coated with a layer of material which is selected to maximize the reflectivity of the radiation. This reflective surface may be a single layer for wideband reflectivity, or a multilayer coating for optimizing the reflectivity in a narrower wavelength interval. The coated wire is built up with a reinforcing layer, typically by a plating operation. The initial wire is removed by either an etching procedure or mechanical force. Prior to removing the wire, the capillary is typically bonded to a support substrate. One option for attaching the wire to the substrate produces a monolithic structure by essentially burying it under a layer of plating which covers both the wire and the substrate. The capillary optic is used for efficiently collecting and redirecting the divergent radiation from a source which could be the anode of an x-ray tube, a plasma source, the fluorescent radiation from an electron microprobe, or some other source of radiation.
Owner:HIRSCH GREGORY
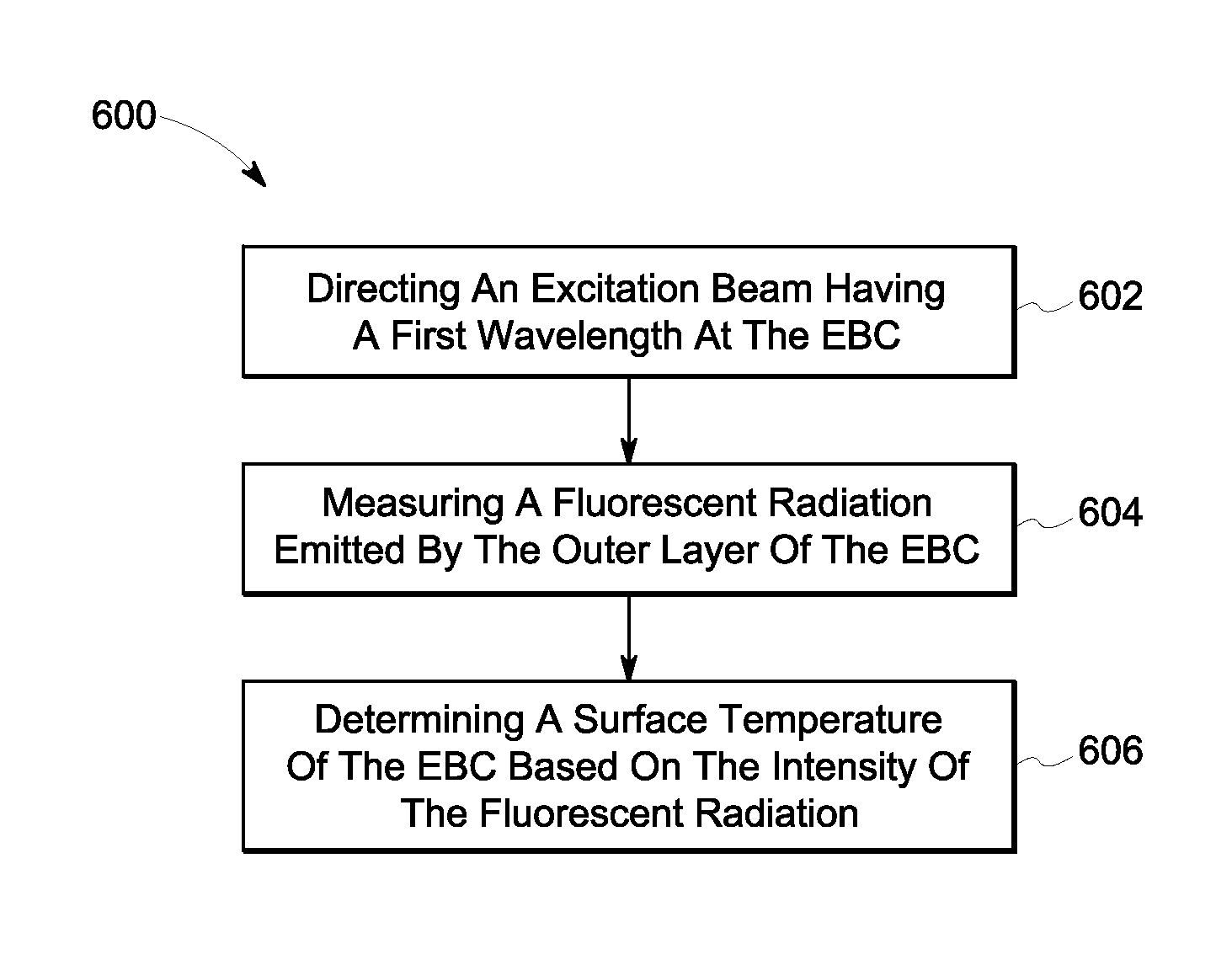
Methods for monitoring environmental barrier coatings
A method of monitoring a surface temperature of an environmental barrier coating (EBC) of a hot gas component includes directing an excitation beam having a first wavelength at a layer of a temperature indicator formed on the hot gas component. The method also includes measuring a fluorescent radiation emitted by the temperature indicator. The fluorescent radiation has a second wavelength and an intensity. In addition, the method includes determining a surface temperature of the EBC based on the intensity of the second wavelength of the fluorescent radiation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Compensation for fluctuations over time in the radiation characteristics of the X-ray source in an XRF analyser
InactiveUS20080095309A1Equally distributedX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorescent radiationX-ray
An X-ray source (101) is configured to controllably irradiate a sample (105) with incident X-rays through a sample window (104) that has a two-dimensional area. A detector (102) is configured to detect fluorescent radiation coming from the irradiated sample. A carrier (301, 401, 402, 501, 601) is essentially transparent to X-rays and disposed to spatially coincide with a substantial part of the two-dimensional area of the sample window (104). Marker material (303, 403, 602), which is responsive to X-rays by emitting fluorescent radiation, is mechanically supported by said carrier and essentially evenly distributed across at least that part of the carrier that spatially coincides with said two-dimensional area of the sample window.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH ANALYTICAL SCI FINLAND OY
Pyrene-containing organic compound and application in OLED
PendingCN111662258AImprove current efficiencyExtend your lifeOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesHigh current densityOrganic compound
The invention relates to a pyrene-containing organic compound and application in OLED, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductors, wherein the structure of the compound is represented by a general formula (1). The compound provided by the invention has relatively strong hole transport capability, and the hole injection and transport performance is improved under a proper HOMO energy level; under the proper LUMO energy level, the electron blocking effect is achieved, and the recombination efficiency of excitons in the light-emitting layer is improved; and when the compound is used asa functional layer material of an OLED light-emitting device, exciton utilization rate and high fluorescence radiation efficiency can be effectively improved, efficiency roll-off under high current density is reduced, device voltage is reduced, current efficiency of the device is improved, and service life of the device is prolonged.
Owner:JIANGSU SUNERA TECH CO LTD
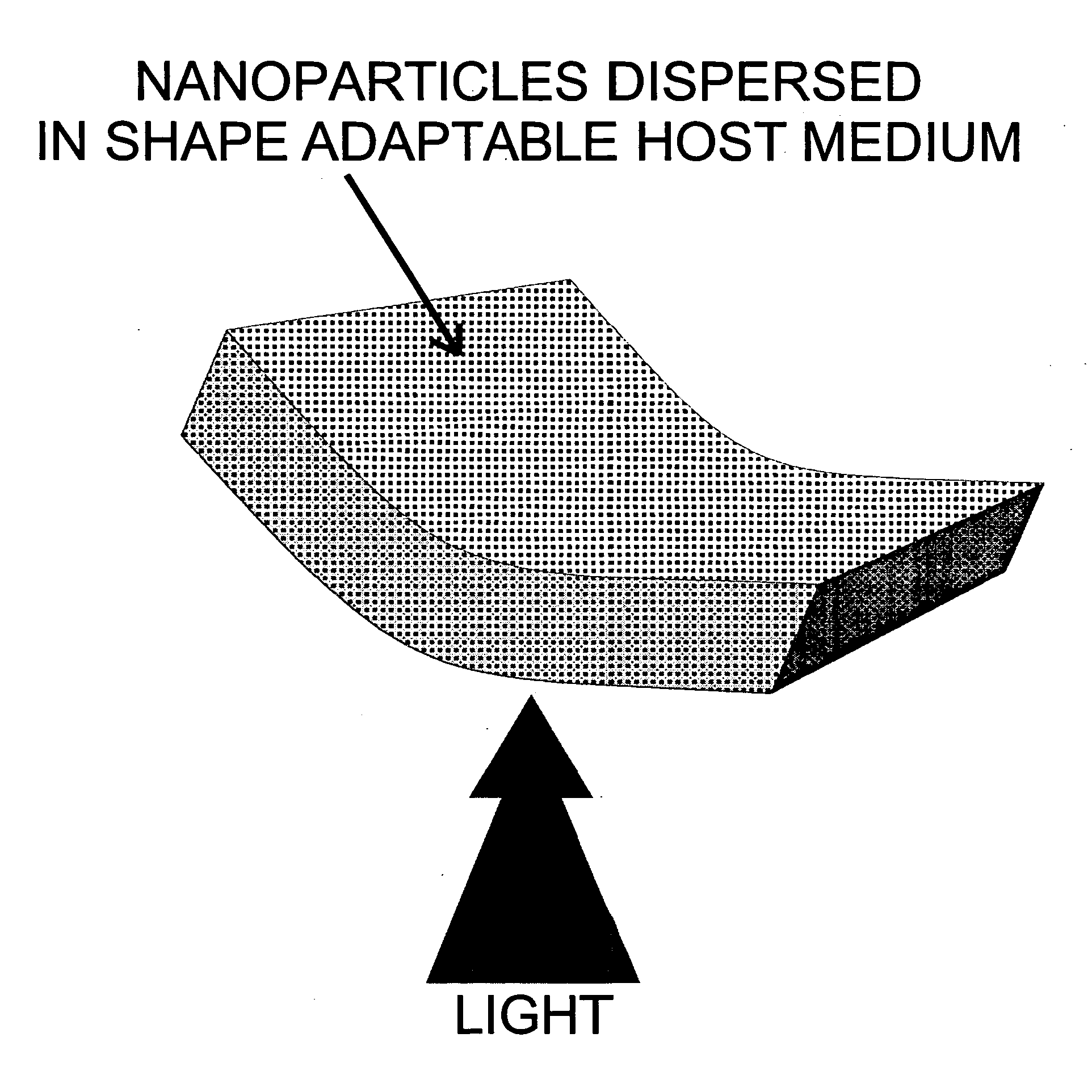
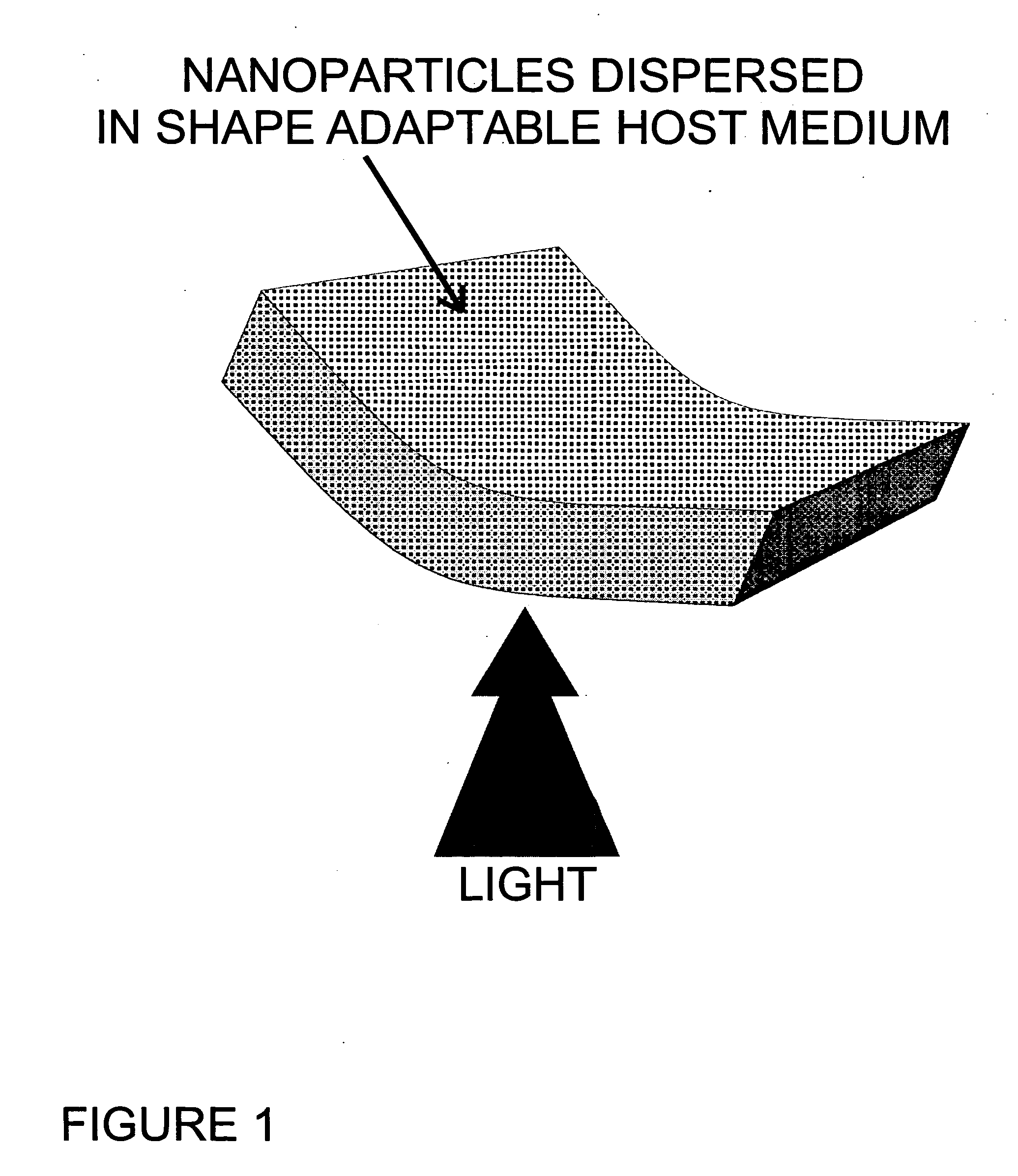
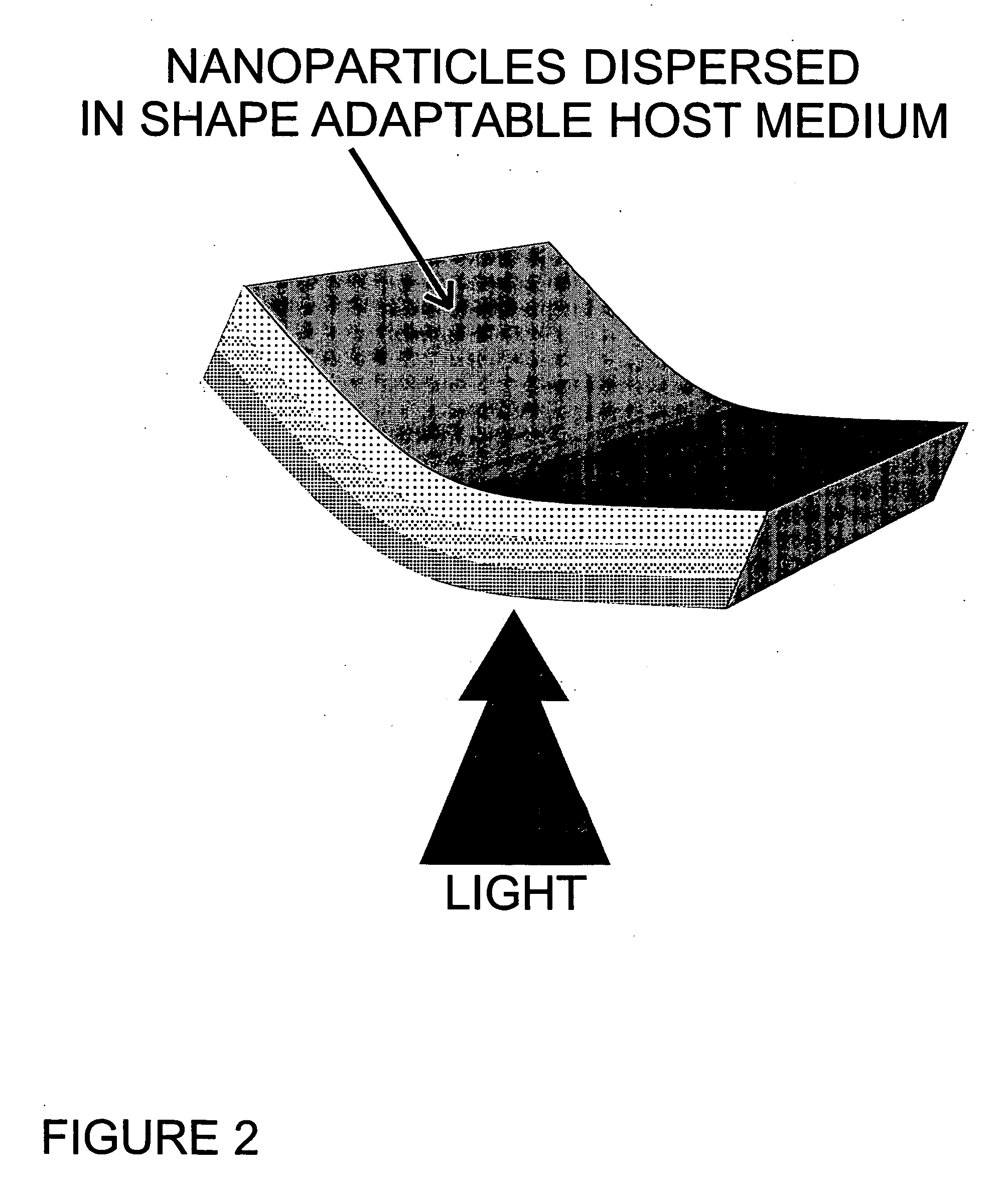
Shape-adaptable and spectral-selective distributed light sources using passive host medium
ActiveUS20050182461A1Soft deliveryWide response rangeEnergy modified materialsDiagnosticsOptical radiationFluorescent radiation
A method of making shape-adaptable and spectral-selective distributed optical radiation sources, in the wavelength range between UV and mid-infrared, for therapeutic treatment using passive host medium containing nanocrystals is disclosed. The spectral output of the distributed optical radiation source is controlled by the nanocrystal size distribution that determines the spectral output of fluorescence radiation originating from these nanocrystals from within the said host medium, which contains the said nanocrystals, under excitation by an external source. The size of nanocrystals, or the size distribution of nanocrystals, incorporated in the host medium is selected based on the radiation spectral output required for therapeutic requirements. The passive host medium, incorporating the said nanocrystals, is made of adaptable, geometrically configurable, material that conforms to any desired shape.
Owner:MEDX HEALTH
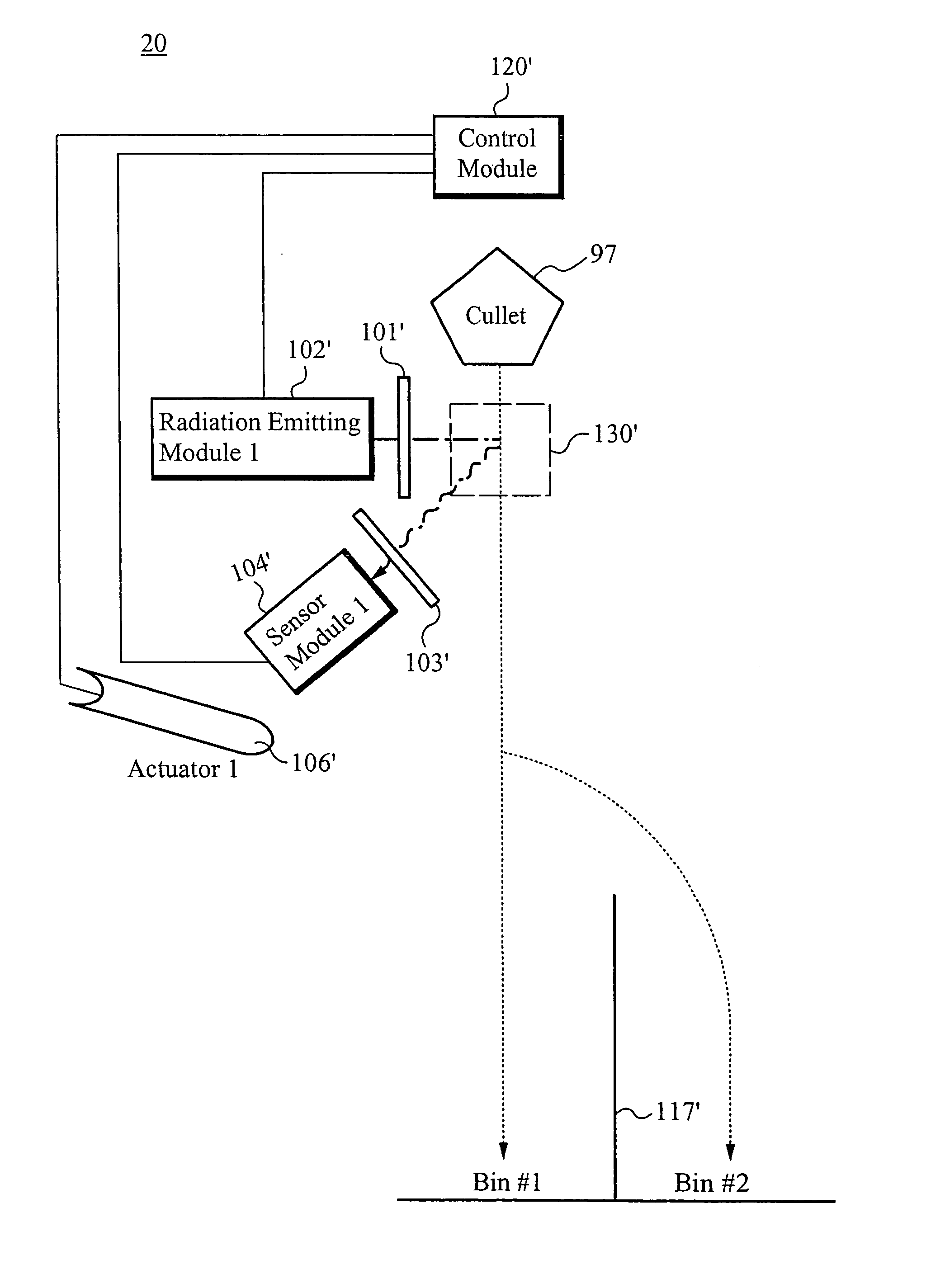
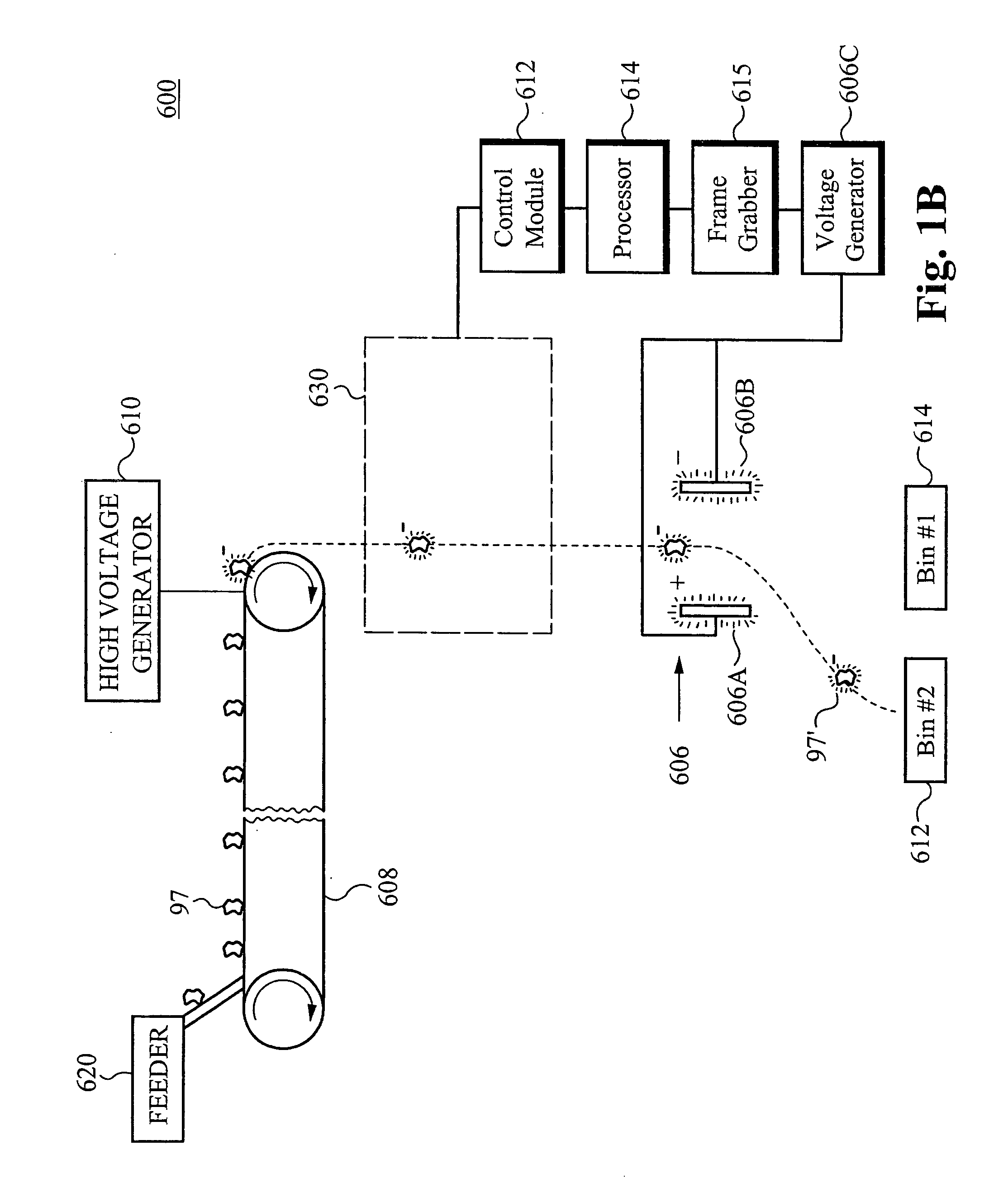
Method of and apparatus for type and color sorting of cullet
A system for sorting a mixed stream of colors and types of cullet into separate groups of cullet with similar color and type includes a source for transmitting light through a cullet, and a camera having a plurality of pixels for receiving light transmitted through the cullet or detecting the absence of light blocked by an opaque contaminant, the camera providing at least one value from the light received, wherein the cullet moves along a designated path based in part on the at least one value. The system further includes a radiation source for irradiating a cullet with selected spectral ranges of radiation, and a sensor for determining characteristics of one or more selected spectral ranges of fluorescent radiation emitted by the cullet, wherein the cullet moves along a designated path based in part on the characteristics of the one or more selected spectral ranges of fluorescent radiation. The camera and the sensor collect the received light at desired sampling intervals and a circuit converts the output of the camera and the sensor into digital representation values. The circuit calculates a non-linear function from the digital representation values. An electrostatic or fluid driving actuator directs the cullet along a deflected path based on a value of the non-linear function. A vibratory feeder provides the cullet onto a conveyer belt having an exit roller of a desired diameter.
Owner:STRATEGIC MATERIALS INC
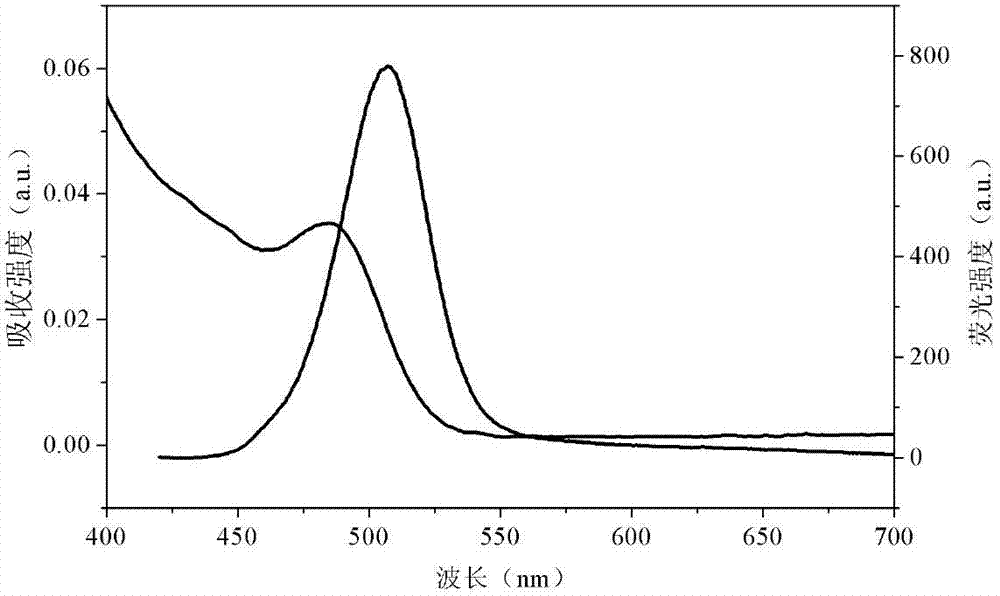
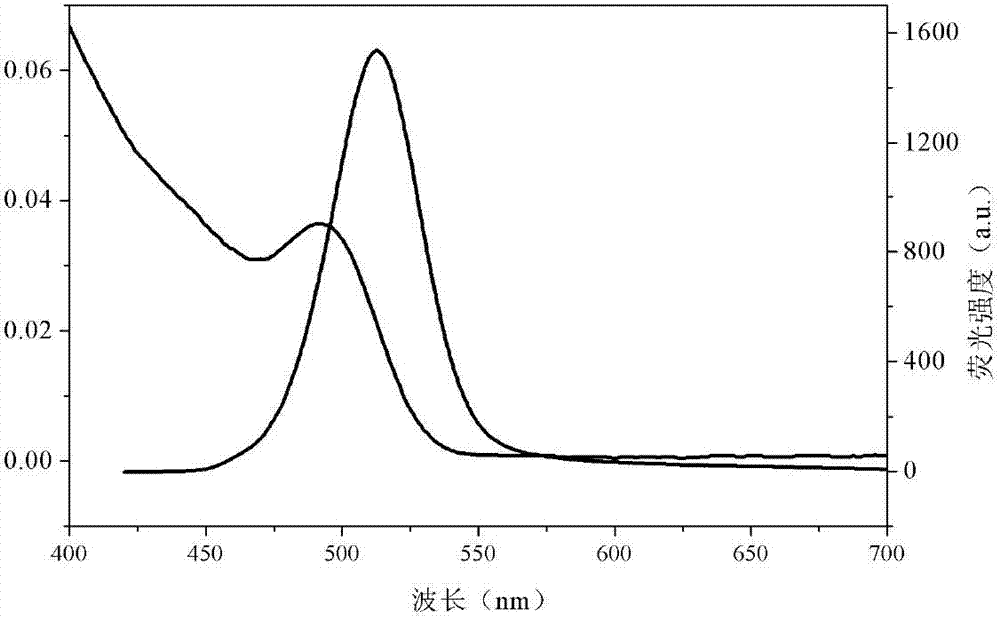
Preparation method of water-soluble CdSe quantum dots
ActiveCN102766463AGood water solubilityImprove stabilityLuminescent compositionsFluorescent radiationWater soluble
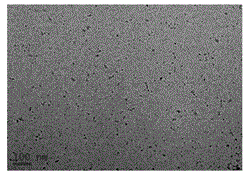
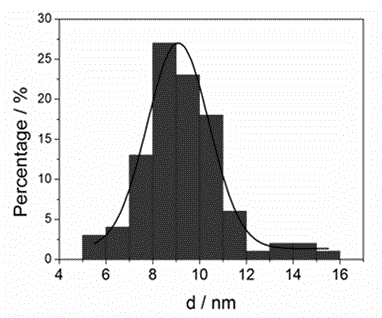
The invention discloses a preparation method of water-soluble CdSe quantum dots and belongs to the field of nanotechnology preparation. According to the method, sodium selenite is used as a selenium source, cadmium chloride is used as a cadmium source, mercaptopropionic acid and sodium hexametaphosphate are used as double complexing agents, and hydrazine hydrate deoxidizes the sodium selenite in an aqueous solution to prepare the water-soluble CdSe quantum dots in a one-step mode. The preparation method of the water-soluble CdSe quantum dots is simple and easy to operate, mild in conditions and suitable for batch preparation and large-scale synthesis. The prepared CdSe quantum dots are strong in fluorescent radiation in green light areas, and the radiation intensity can be controlled by controlling reaction time.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com