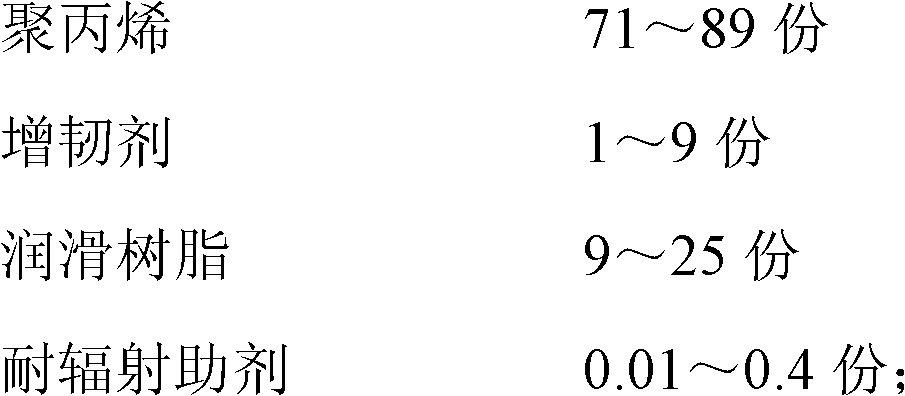Patents
Literature
378 results about "Line radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Line radiation. Electromagnetic radiation from a power line caused mainly by corona pulses; gives rise to radio interference.
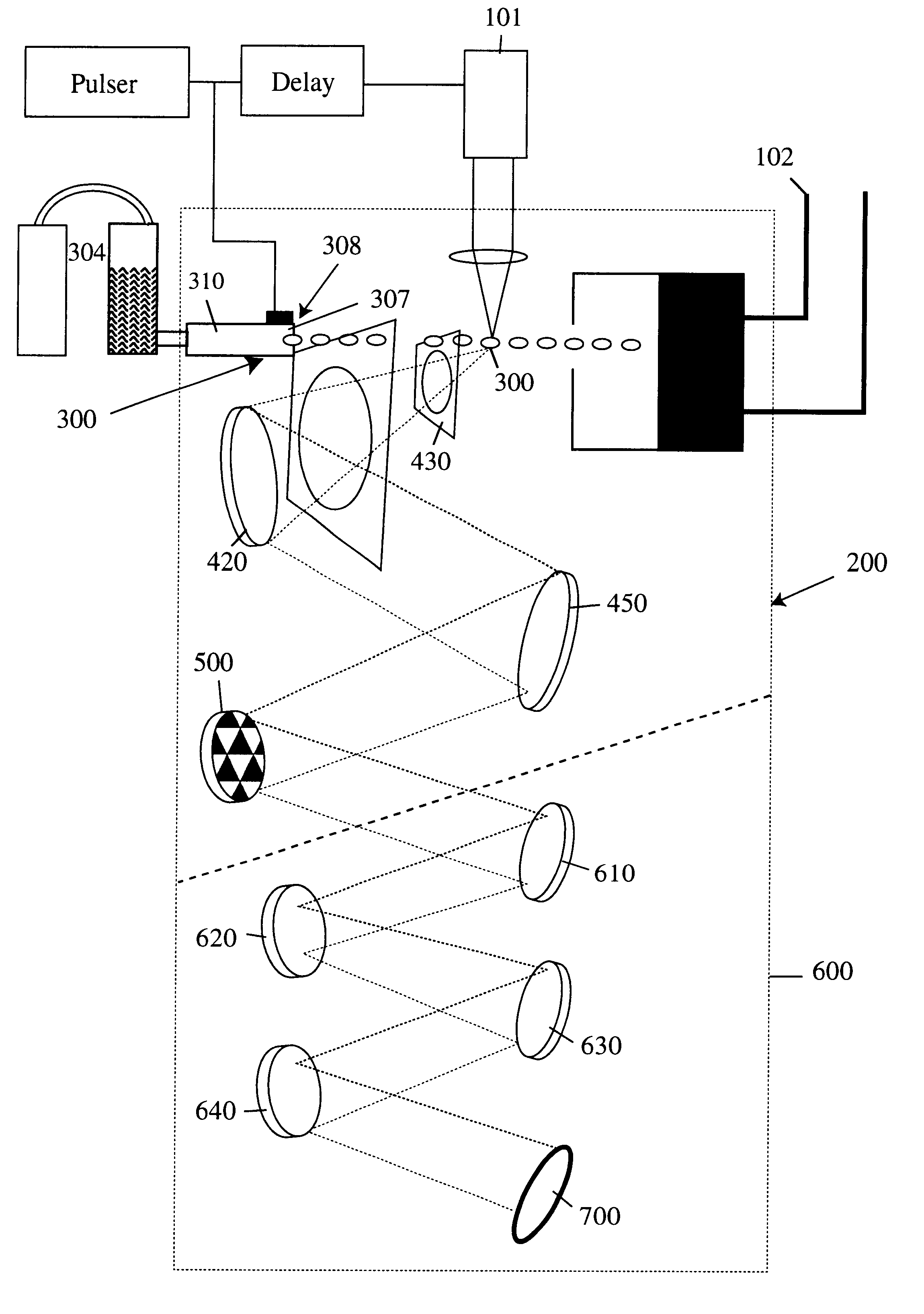
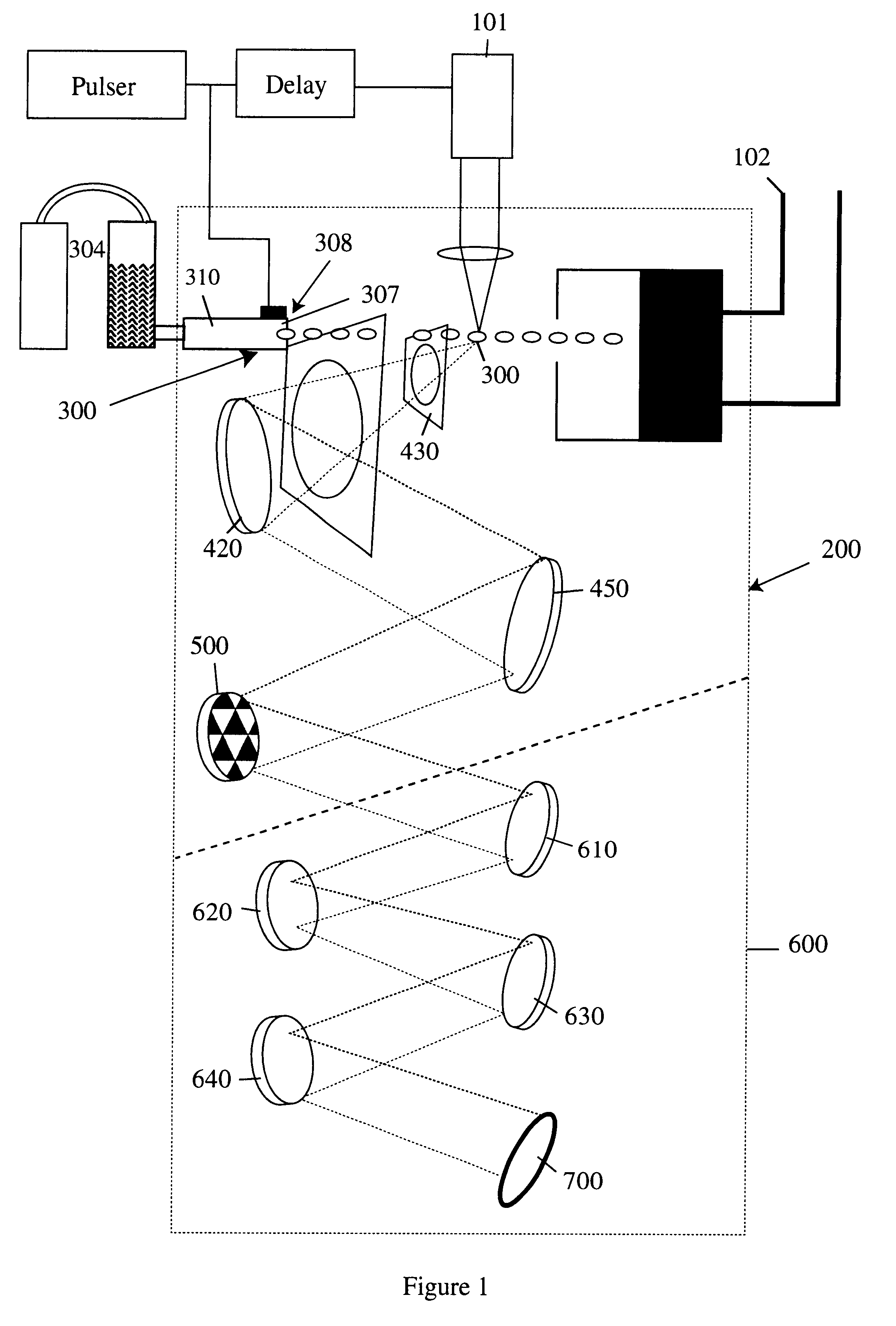
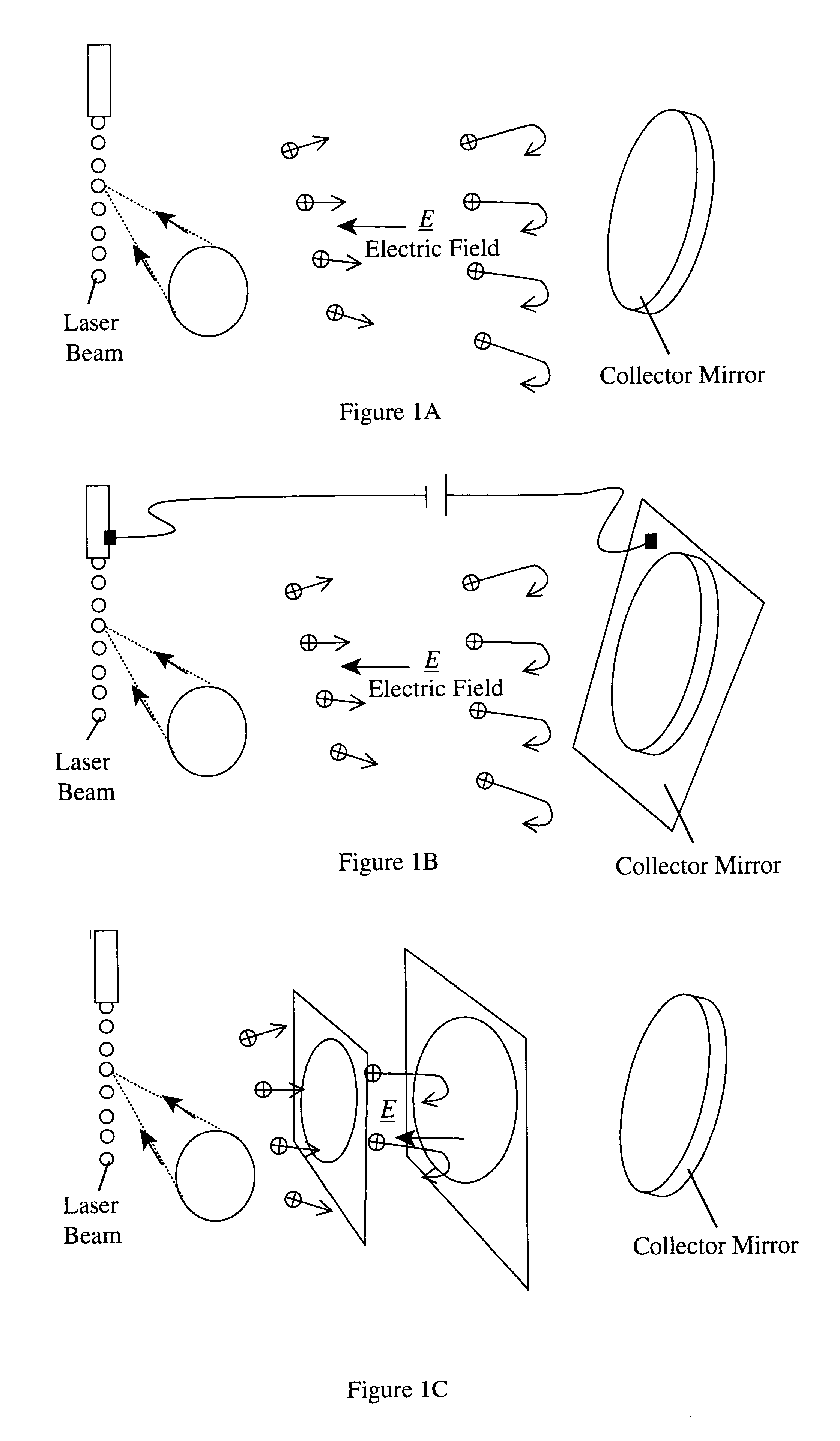
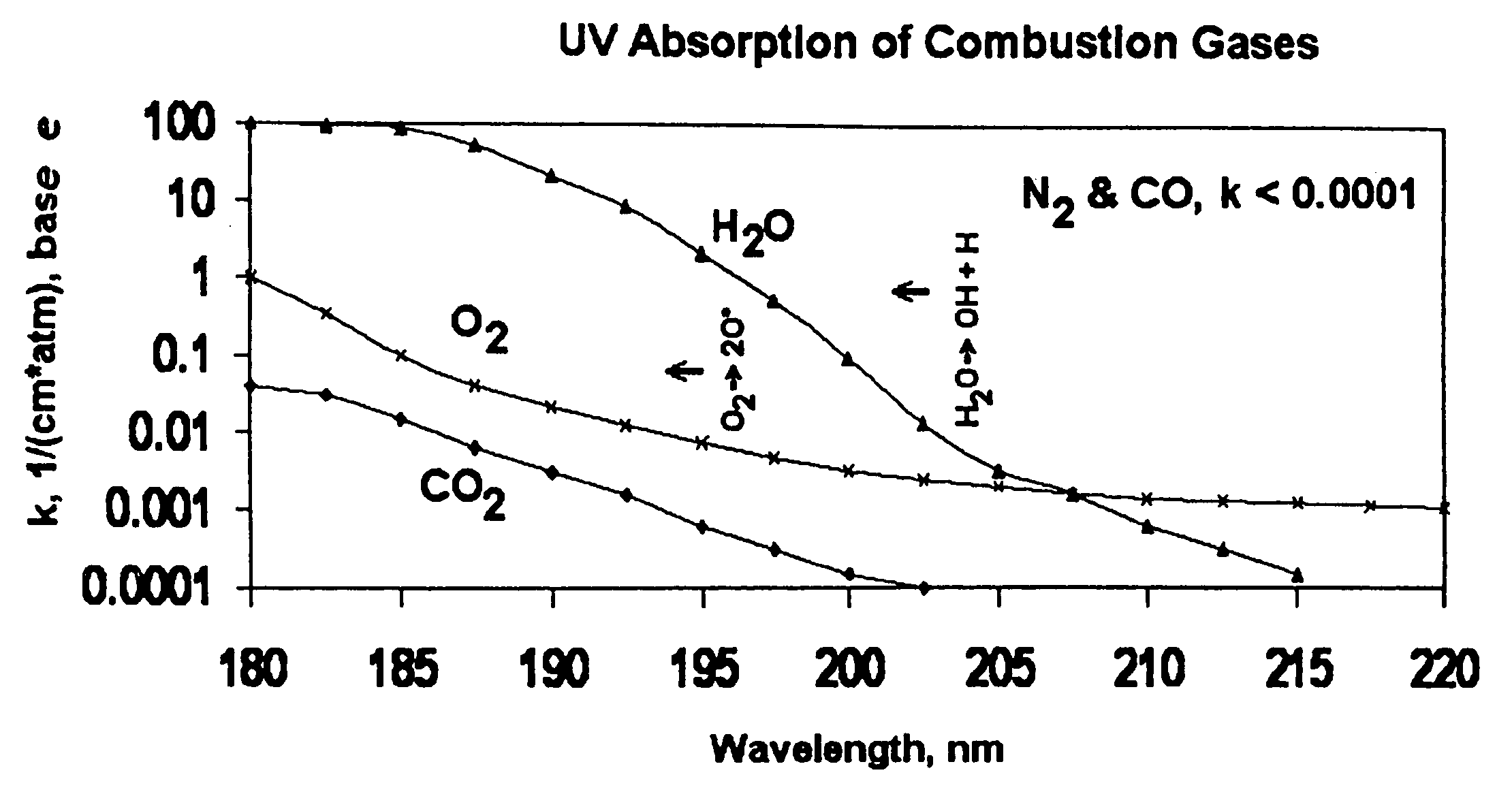
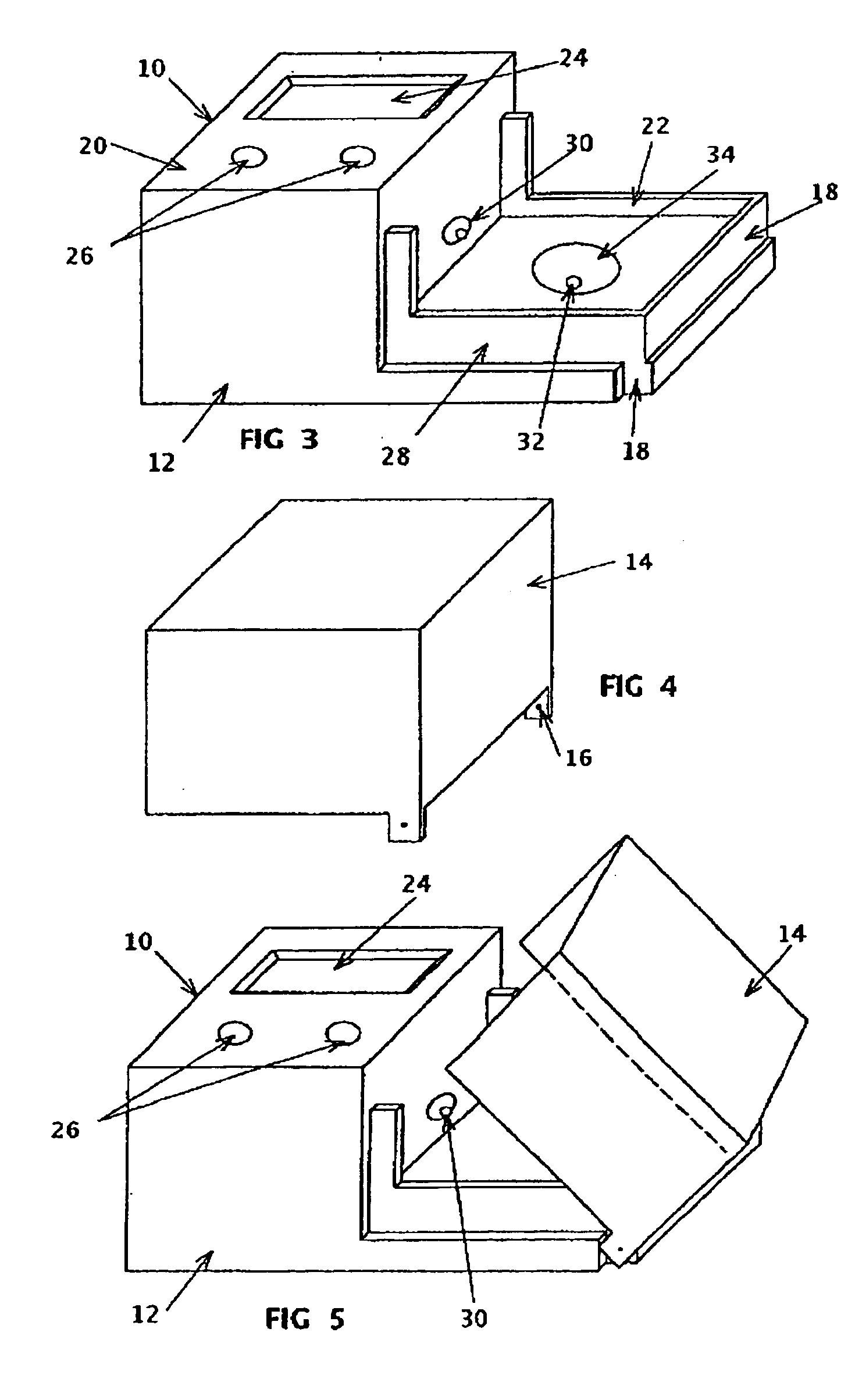
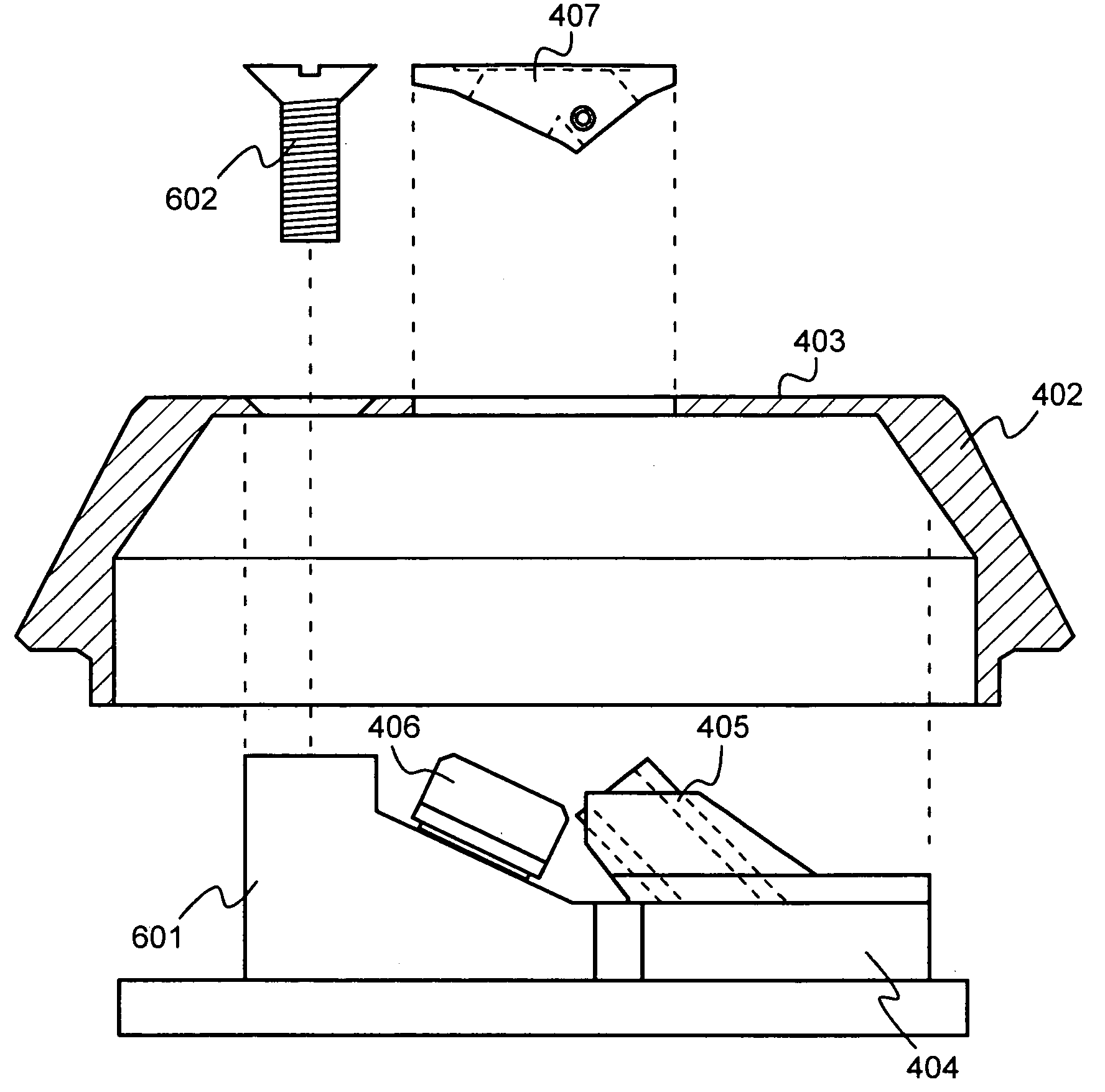
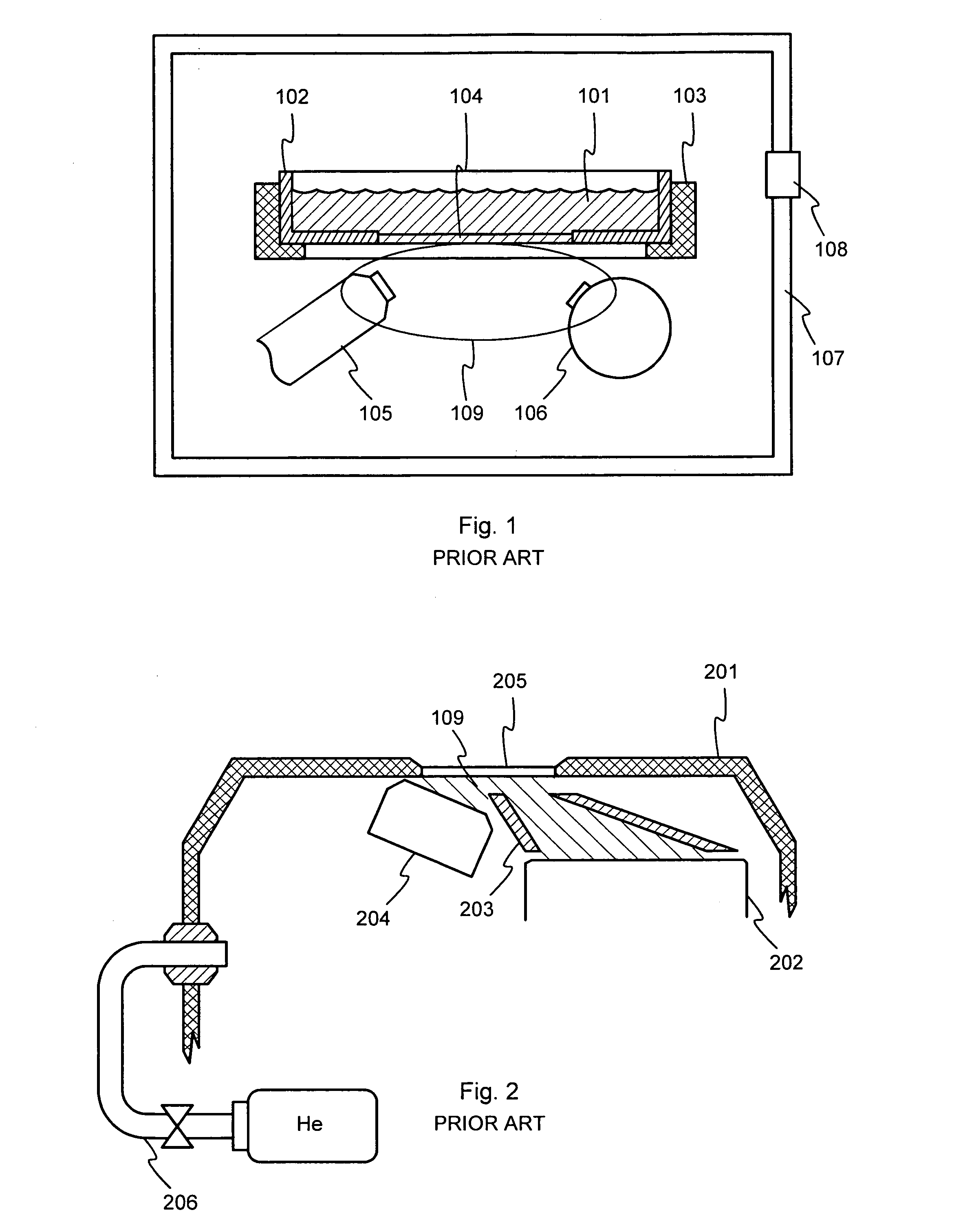
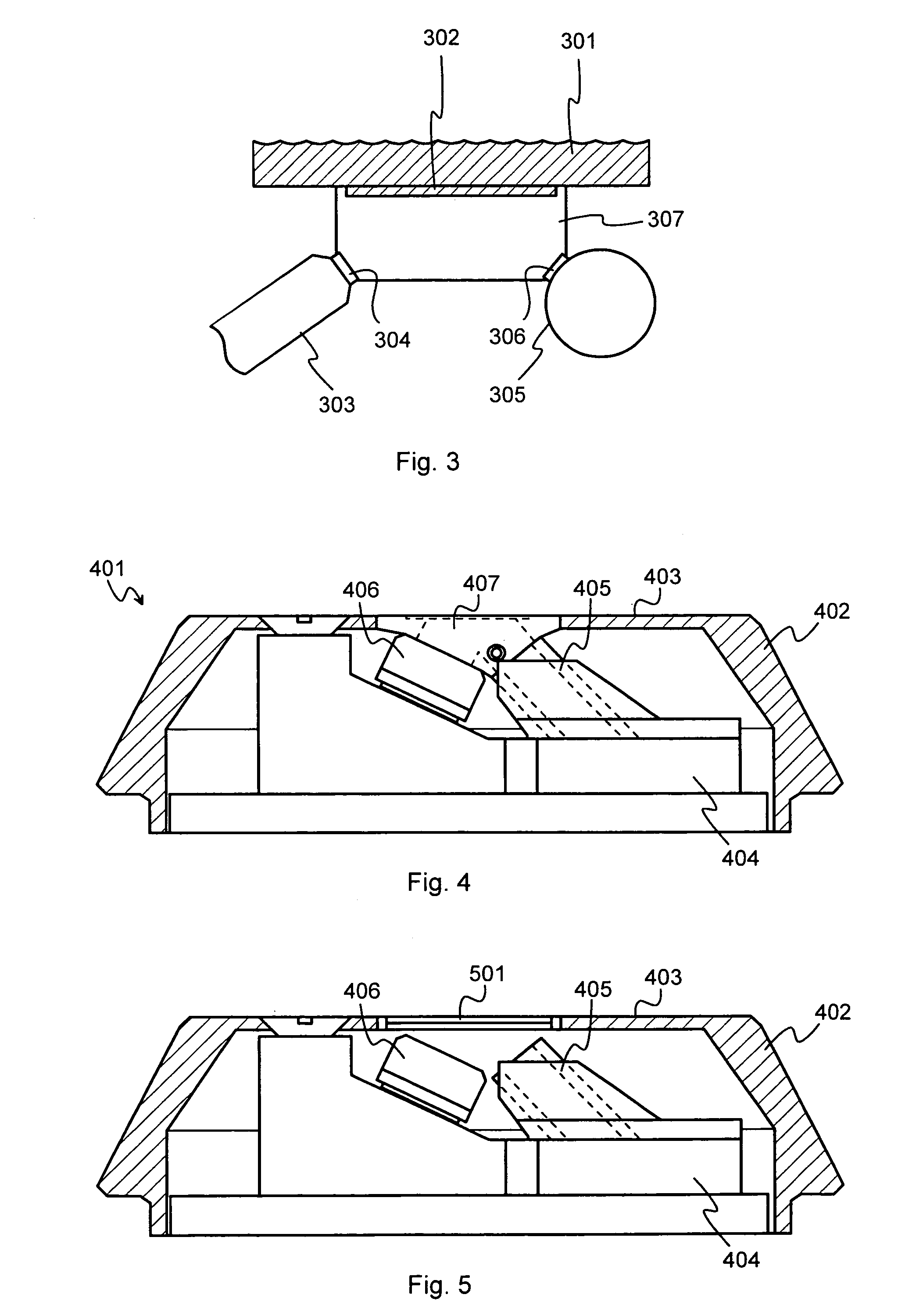
Laser plasma source for extreme ultraviolet lithography using a water droplet target
InactiveUS6377651B1Avoid componentsEasy to operateNanoinformaticsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusAuxiliary electrodeExtreme ultraviolet
A laser produced extreme ultraviolet (EUV) source based on a water droplet target has been implemented an auxiliary electrode system between the source and the first collector mirror. The auxiliary electrode system creates a repeller electric field, possibly a dc voltage imposed on the mirror that slows down and reverses the trajectories of ions from the source before they impact the collection mirror. The source modified according to the invention was evaluated with respect to the demands of EUV lithography and found to have much extended operational lifetimes. The spectral distribution of the generated radiation as well as the conversion efficiency into line radiation at 13 nm was determined. Long time measurements of the reflectivity of silicon / molybdenum multilayer mirrors for up to from 107 to 109 shots show the useful influence of the treatment of ions emitted from the source. Several methods of debris reduction were tested and discussed. Surface analysis of the treated multilayer mirrors of is presented. Long time measurements of the reflectivity of silicon / molybdenum multilayer mirrors for up to 109 shots show the advantage provided by this invention.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Controlled spectrum ultraviolet radiation pollution control process
InactiveUS7498009B2Cost effectiveEasy to adaptCombination devicesOrganic chemistryEnvironmental engineeringNitrogen oxide
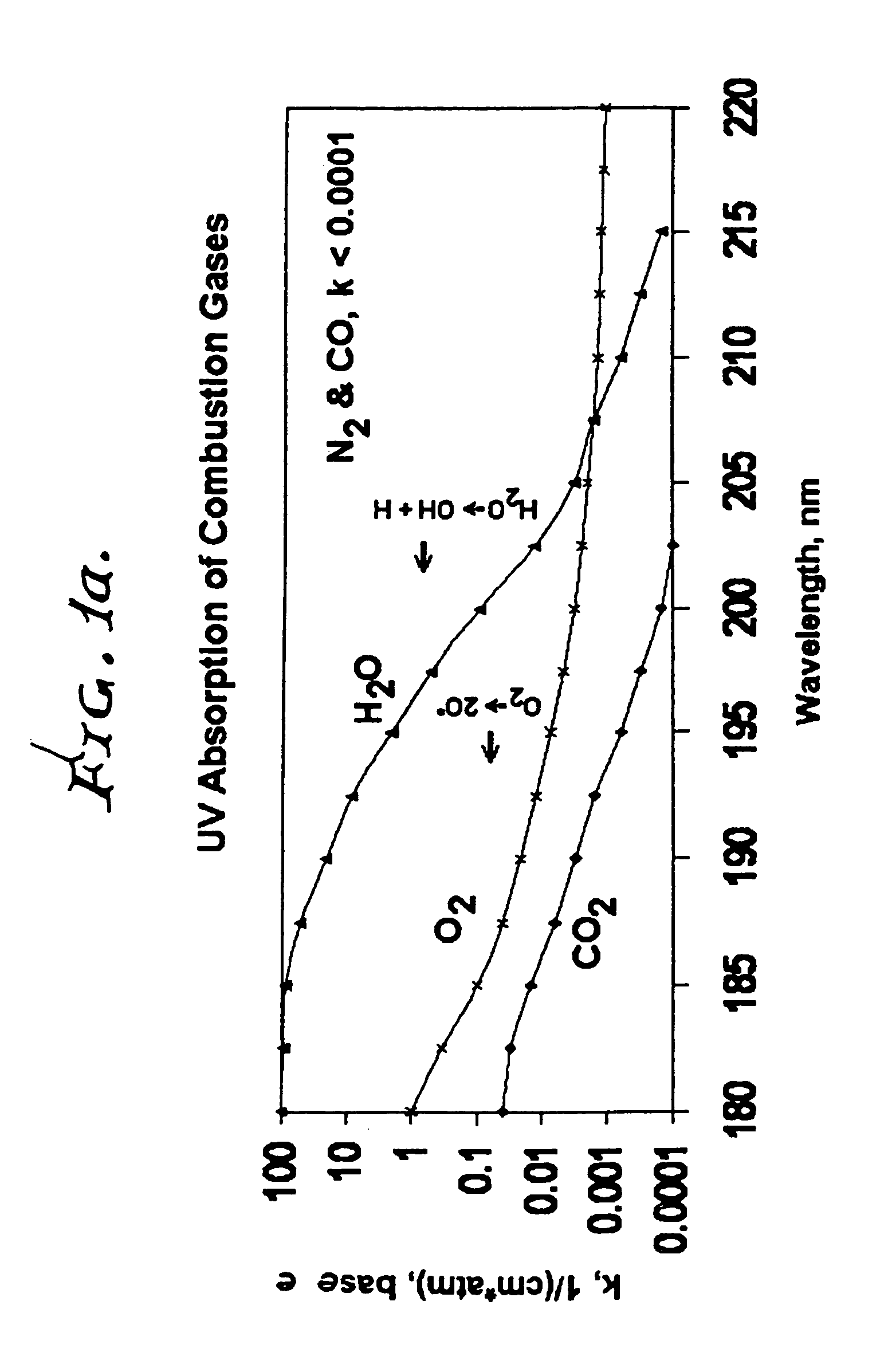
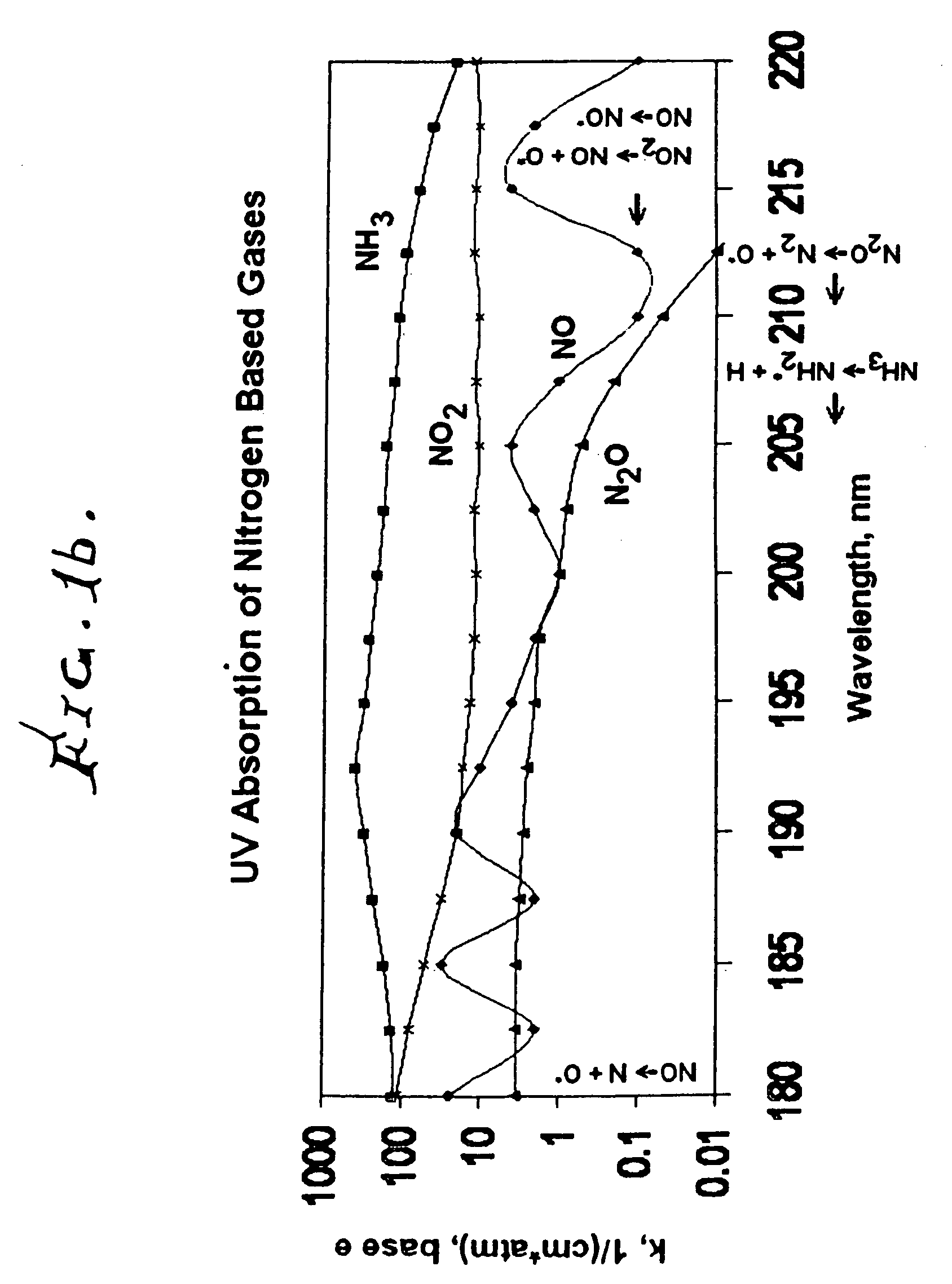
A method for reducing or substantially eliminating oxides of nitrogen from an effluent gas stream, that includes providing a source of ultraviolet radiation with a precise wavelength, adding ammonia or an ammonia based reagent to the effluent stream, upstream of the ultraviolet radiation source, controllably operating the ultraviolet radiation source to irradiate the effluent stream flowing in the duct and substantially reducing or eliminating oxides of nitrogen by promotion a reaction of ammonia with the oxides of nitrogen to produce N2 and H2O, and also thereby destroying any surplus ammonia. This process can also be modified to oxidize carbon monoxide and VOC's to CO2 and H2O.
Owner:DANA UV
Variable wavelength radiation source
An apparatus for selectively producing one or more of a plurality of wavelength distributions of radiation. The apparatus comprises a primary UV radiation source and one or more wavelength transforming materials separated from the primary UV radiation source, that in response to irradiation by the primary UV radiation source, produce transformed radiation having a wavelength distribution that is different from the wavelength distribution of the primary UV radiation source. None, one, or more than one of the various WT materials can be selected by the apparatus, to allow the primary UV radiation, any individual transformed radiation, or any combination of the various radiations to be to be emitted from the apparatus.
Owner:GARDNER III WILLIAM G
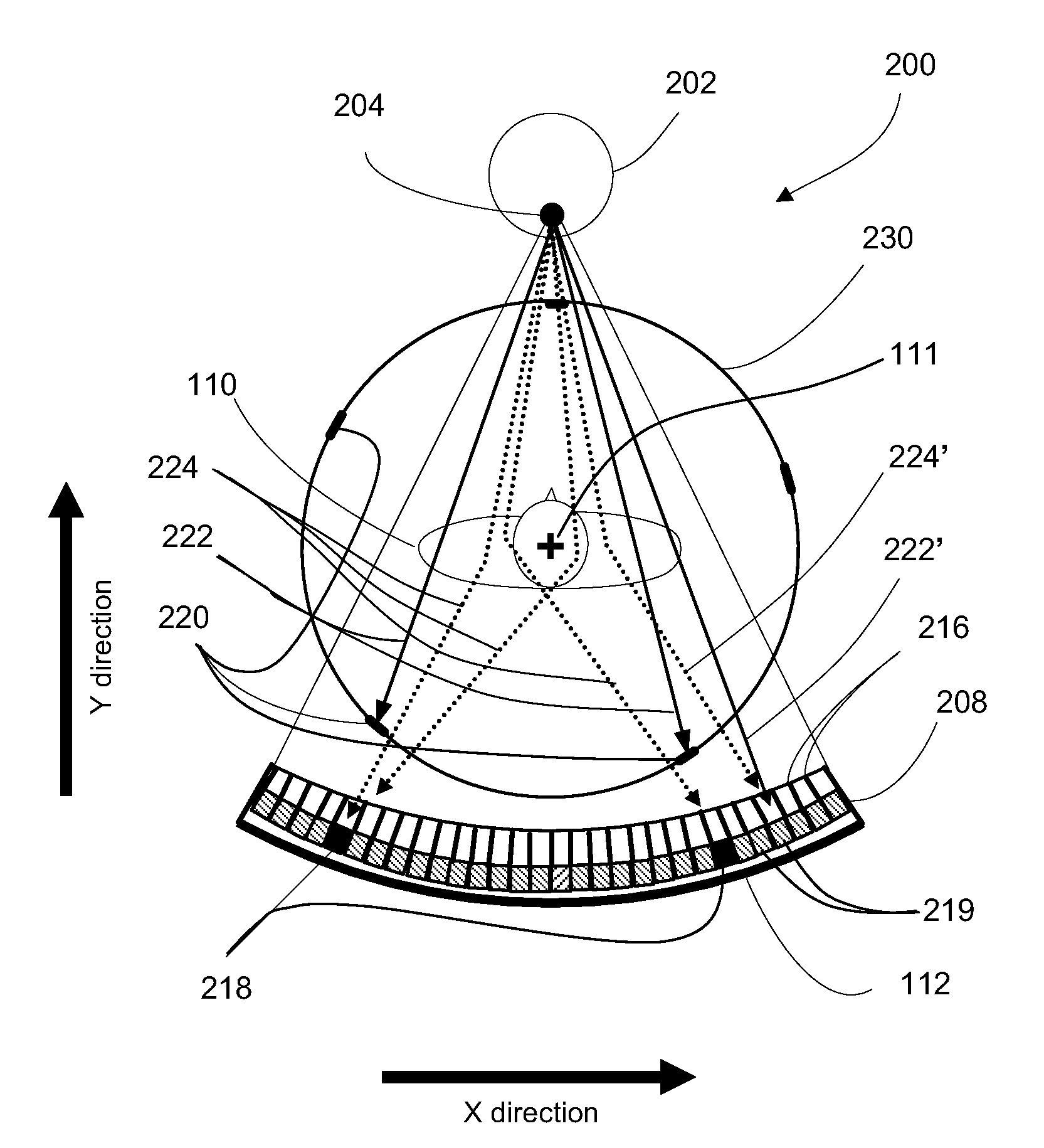
Method, device and computer program product for determining an electromagnetic near-field of a field excitation source of an electrical system
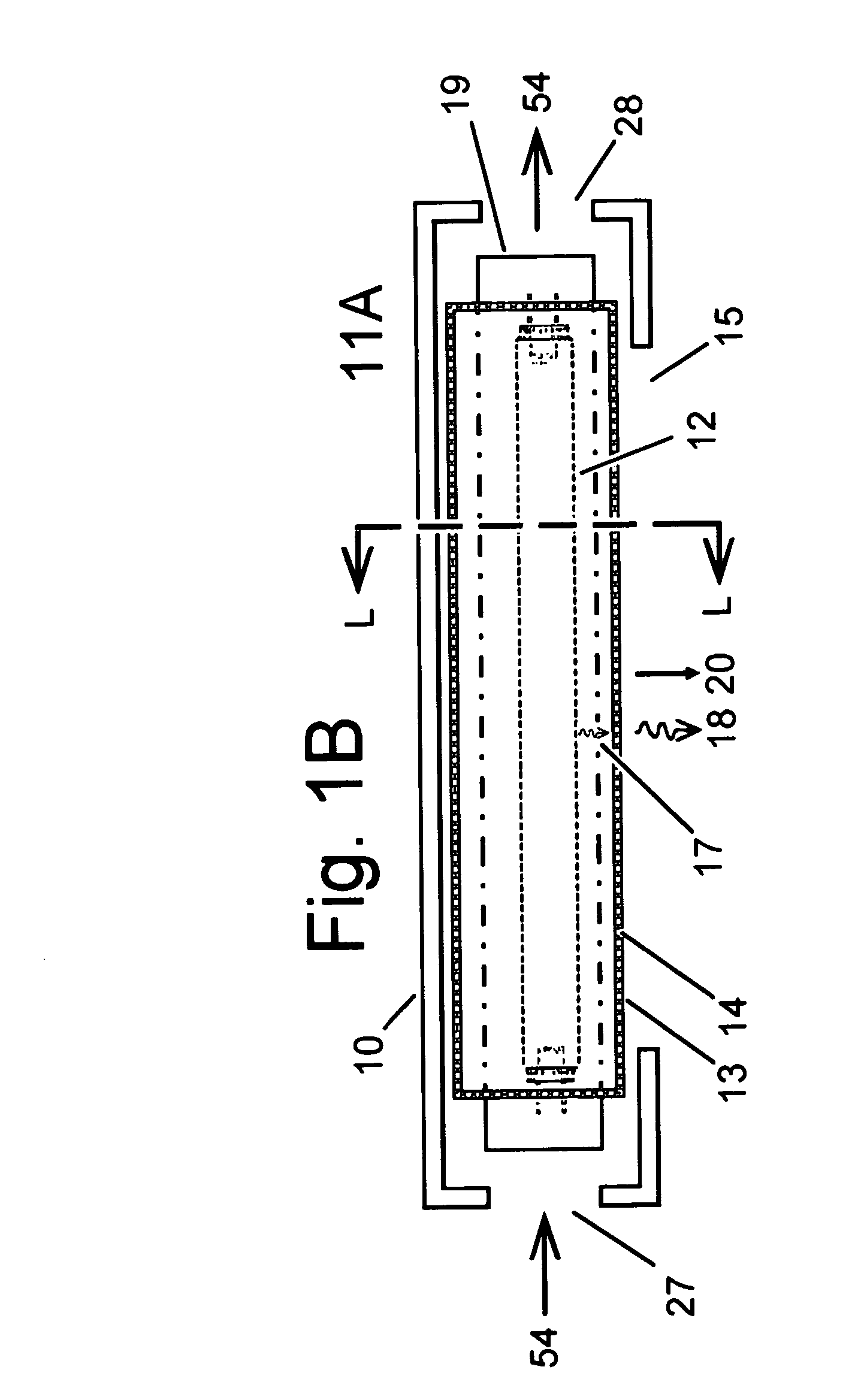
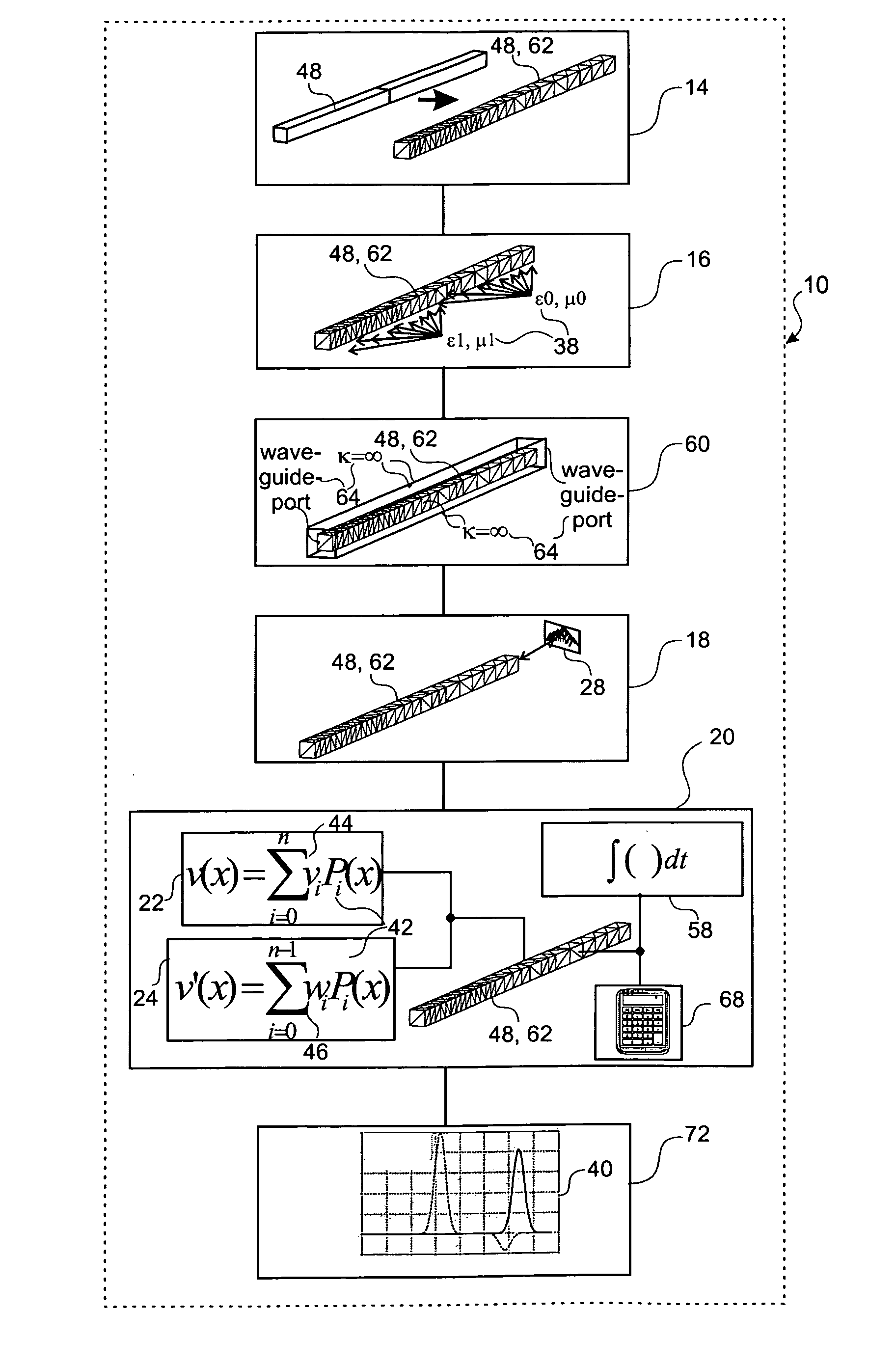
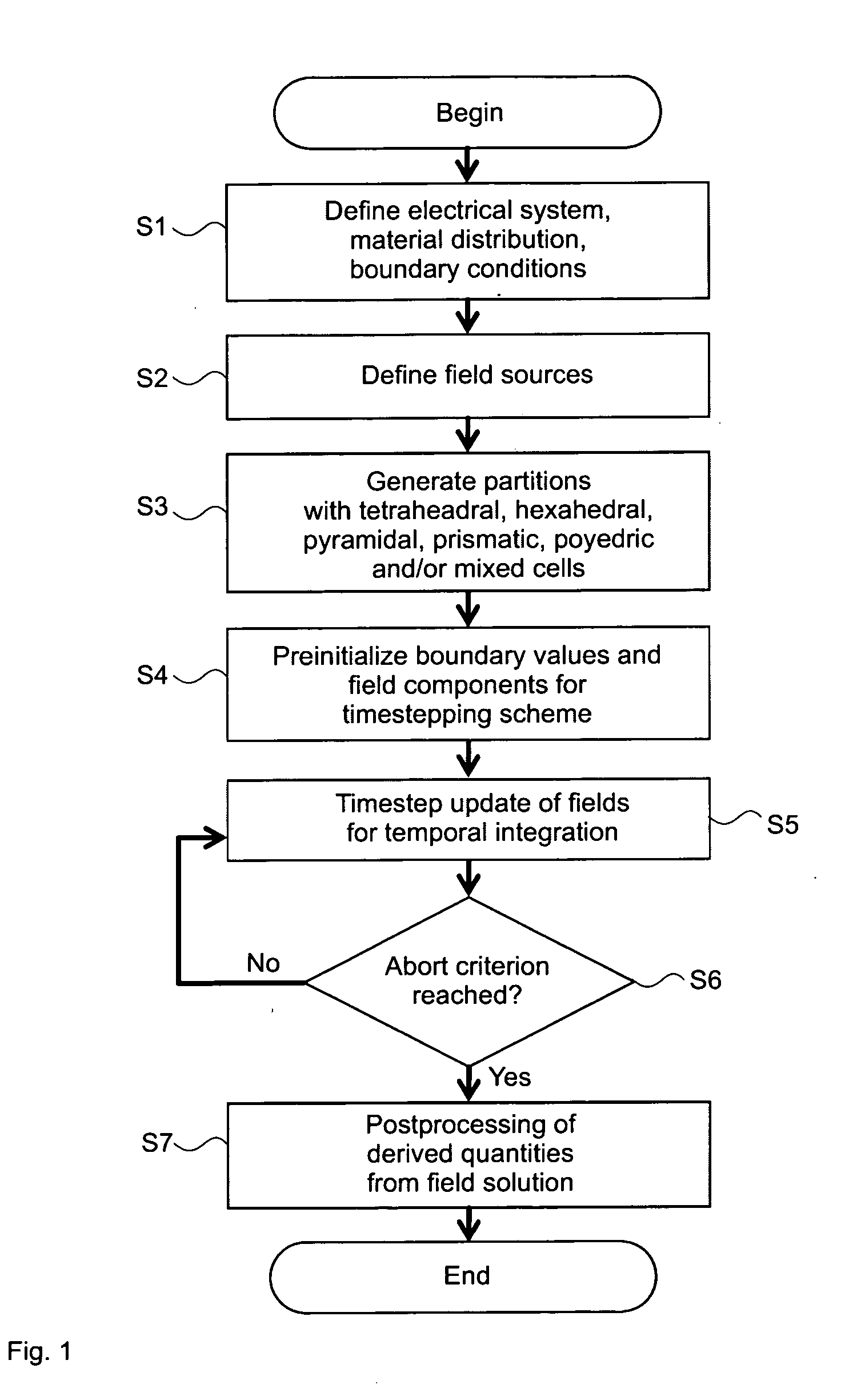
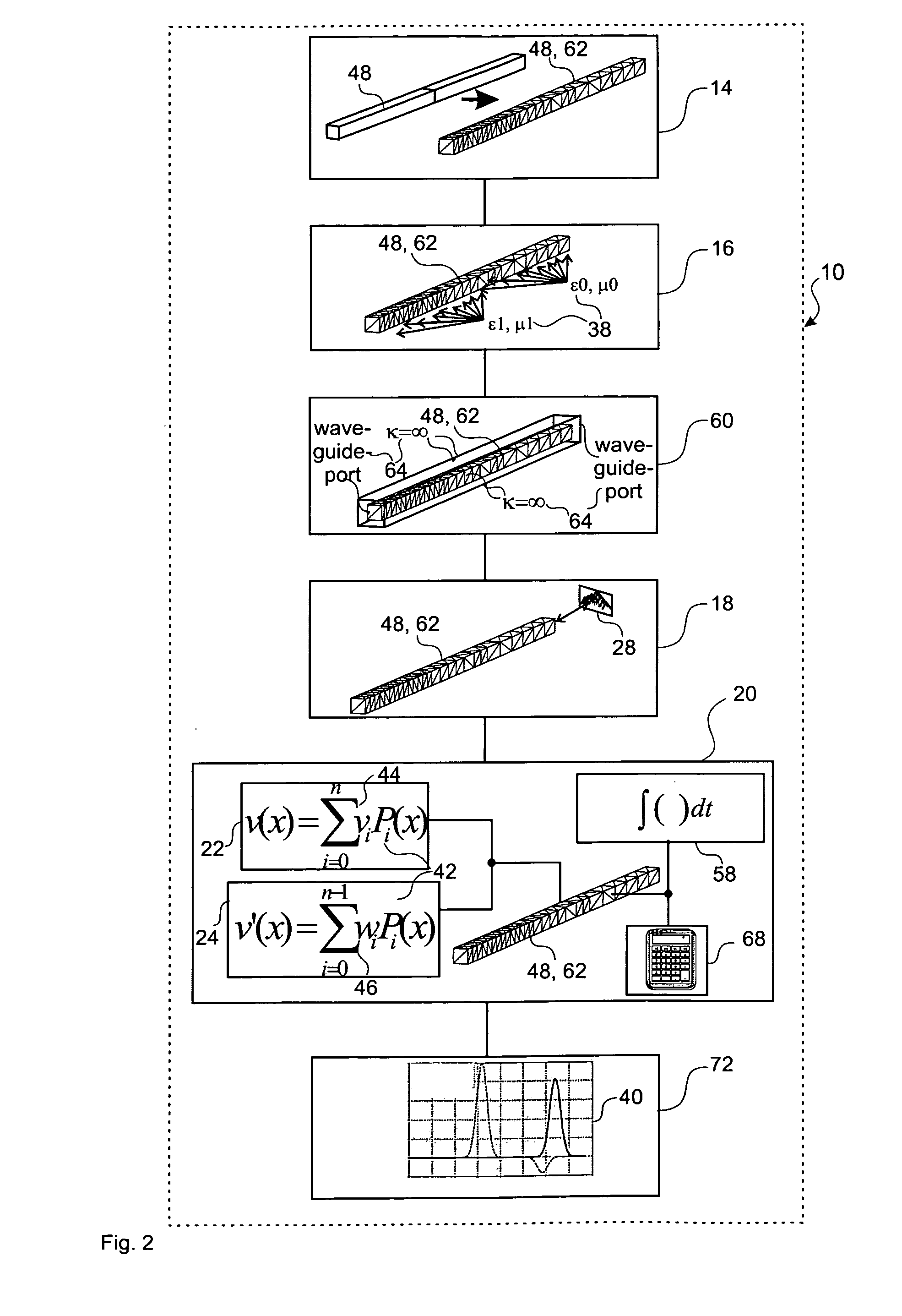
ActiveUS20110251832A1Efficient determinationSimple addressingComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationComputational physicsSignal reflection
A method, a device and a computer program product for determining an electromagnetic near-field of a field excitation source of an electrical system are provided, in particular for analysis and / or optimization of an antenna radiation, of a cross-talk problem, of a signal reflexion / transmission, of a stray field, of an irradiation problem or the like. The method includes defining electrical and magnetic properties of the material distribution of the system, defining at least one field excitation source, and determining the electromagnetic near-field components within at least one and in particular all partitions by solution of the Maxwell's equations of the near-field, where each near-field component of each partition can be represented by a linear position of M predetermined ansatz functions Pi orthogonal to one another with regard to a scalar product and weighted with field coefficients vi, and the spatial and / or time derivative of the near-field component can be determined as a linear position of these ansatz functions Pi weighted with derivative coefficients wi, and where each coefficient wi can be determined from a quantity of previously determined field coefficients vi and derivative coefficients wi, so that the determination effort of the near-field of the system rises in substantially linear manner to the number N of partitions in the domain under consideration and to the number M of ansatz functions Pi used in the linear position.
Owner:DASSAULT SYST DEUT GMBH
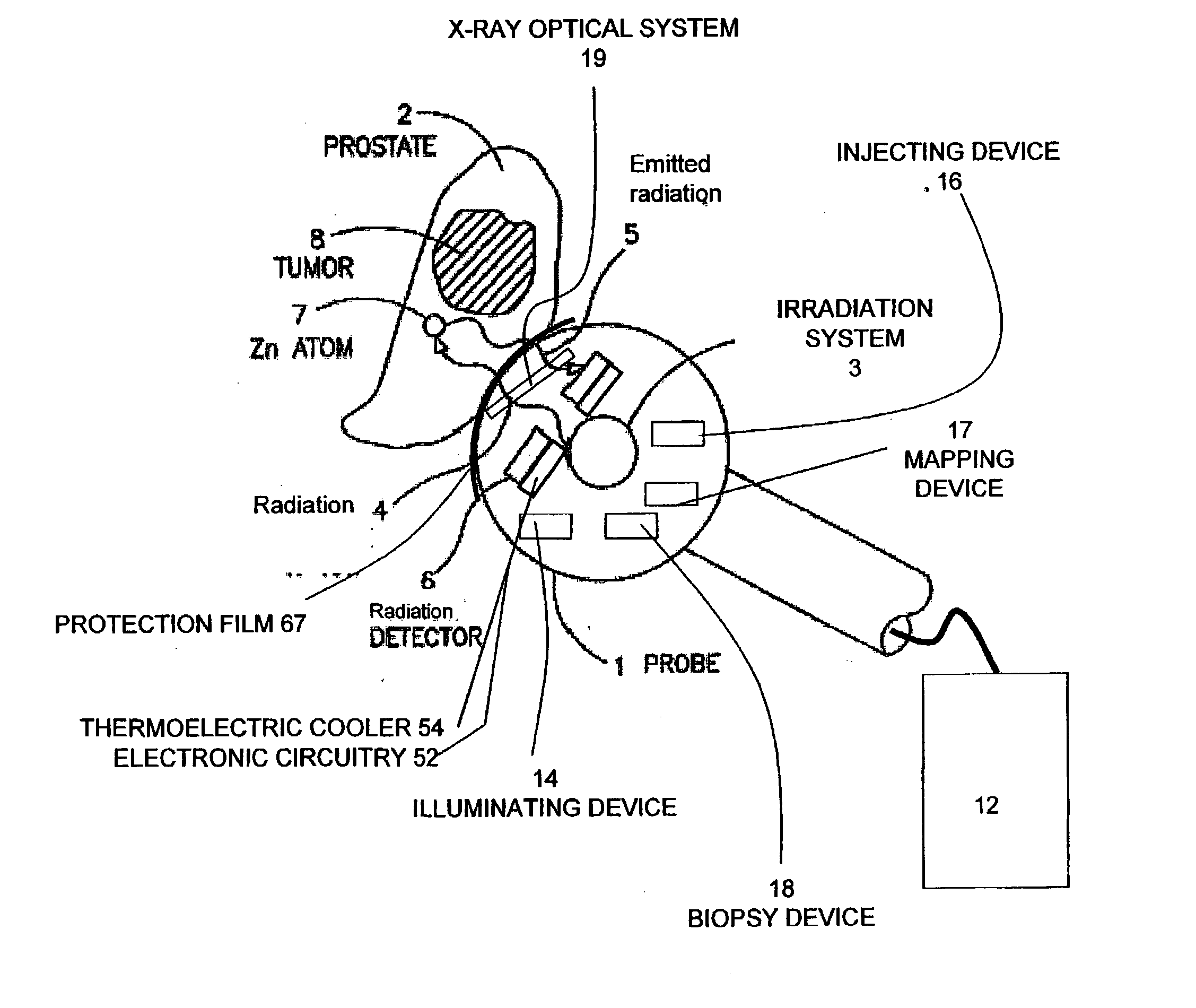
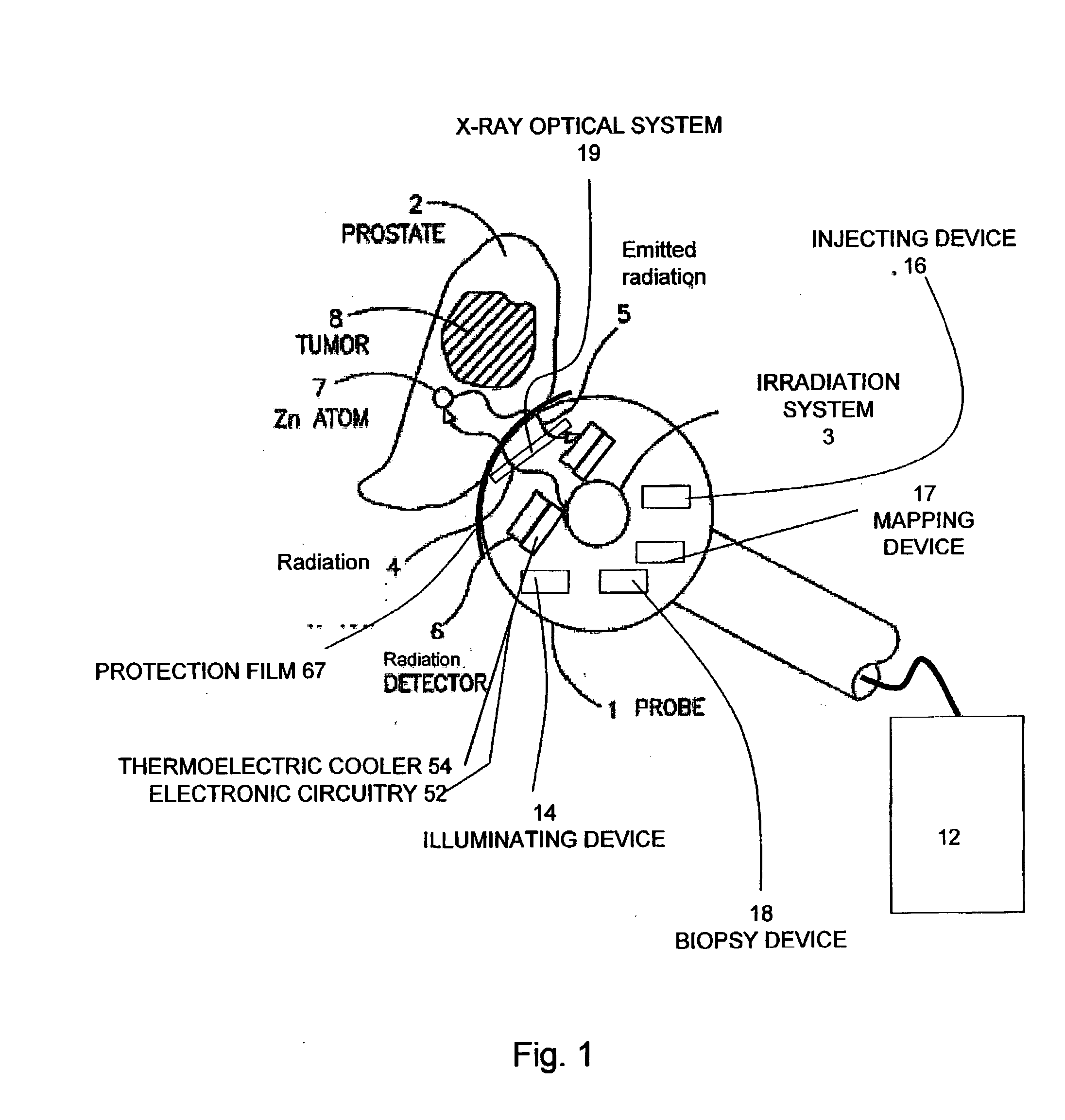
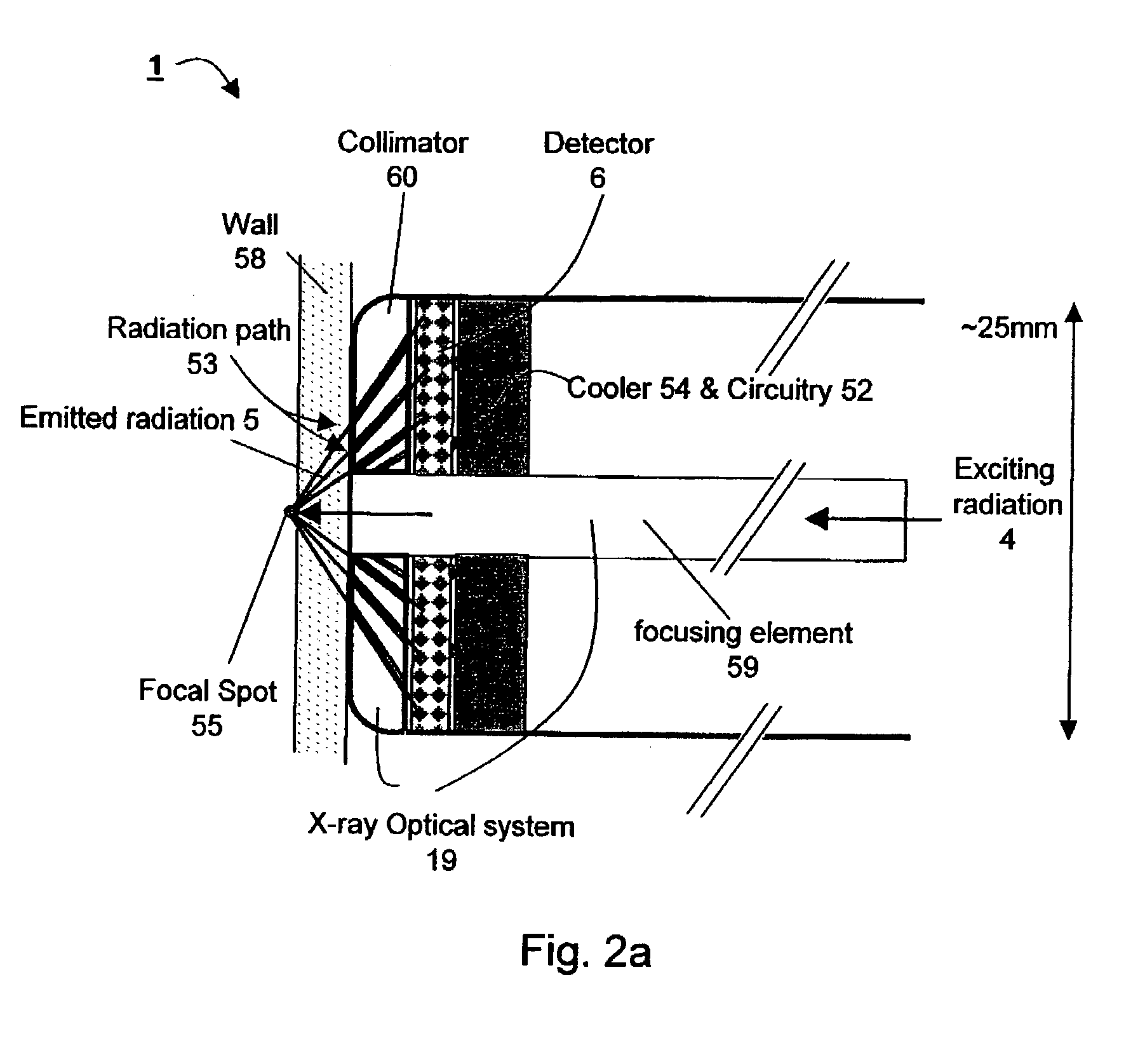
System and method for cancer detection
Apparatus for non-invasive in vivo detection of a chemical element in the prostate of a subject, comprising: (a) a probe adapted for being inserted into at least one of the rectum or the urethra of the subject; (b) an irradiation system capable of exciting the chemical element to emit radiation to form emitted radiation; (c) a radiation detector located within the probe, wherein the radiation detector is capable of detecting the emitted radiation and wherein the radiation detector is suitable for mapping the emitted radiation; and (d) a signal recording, processing and displaying system for mapping the level of tie chemical element in the prostate of the subject at a plurality of different points in the prostate according to the mapping of the emitted radiation. In one embodiment, the irradiation system is capable of delivering exciting radiation through the probe to the prostate; in another embodiment the emitted radiation comprises fluorescent X-ray radiation.
Owner:SOREQ NUCLEAR RES CENT ISRAEL ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION +1
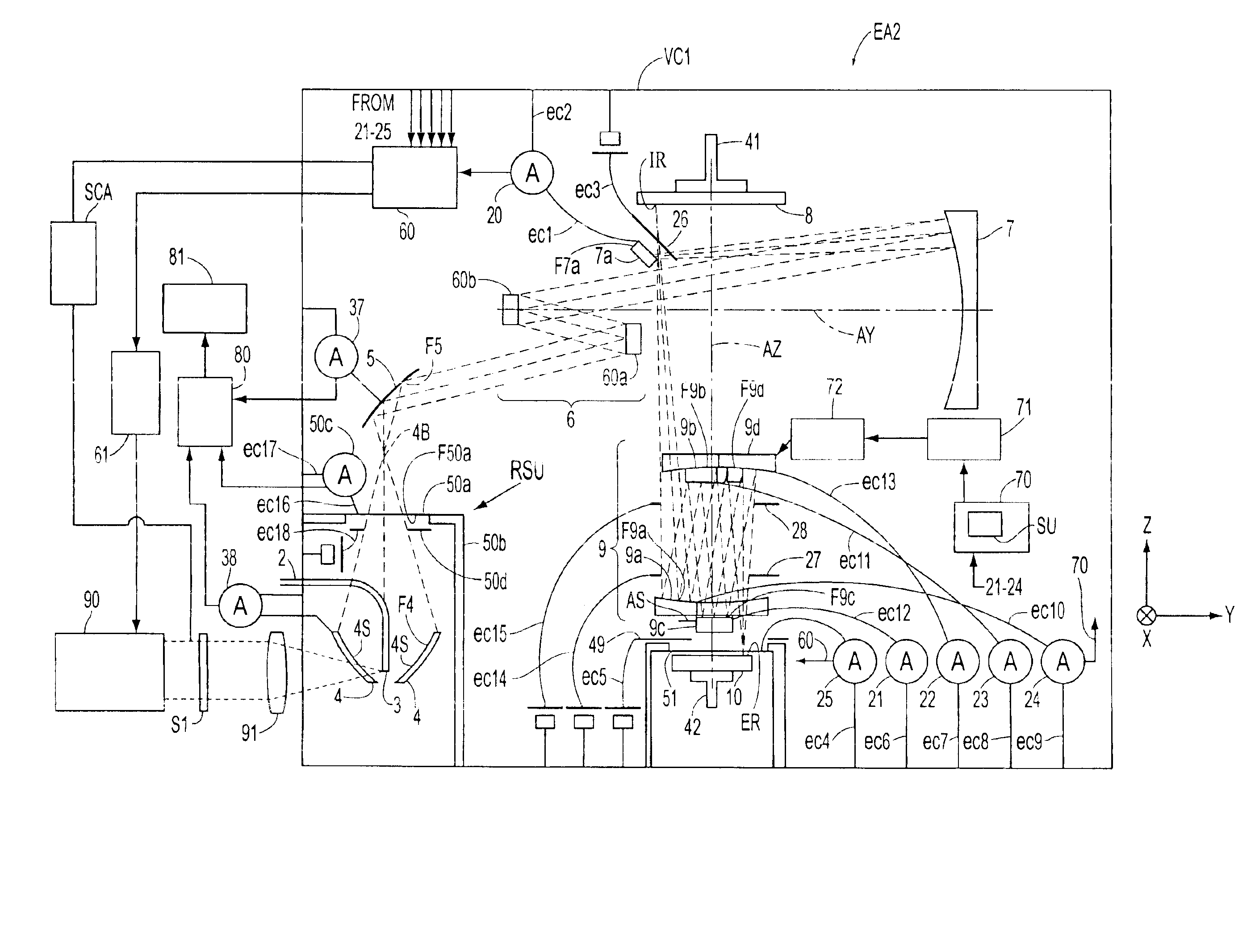
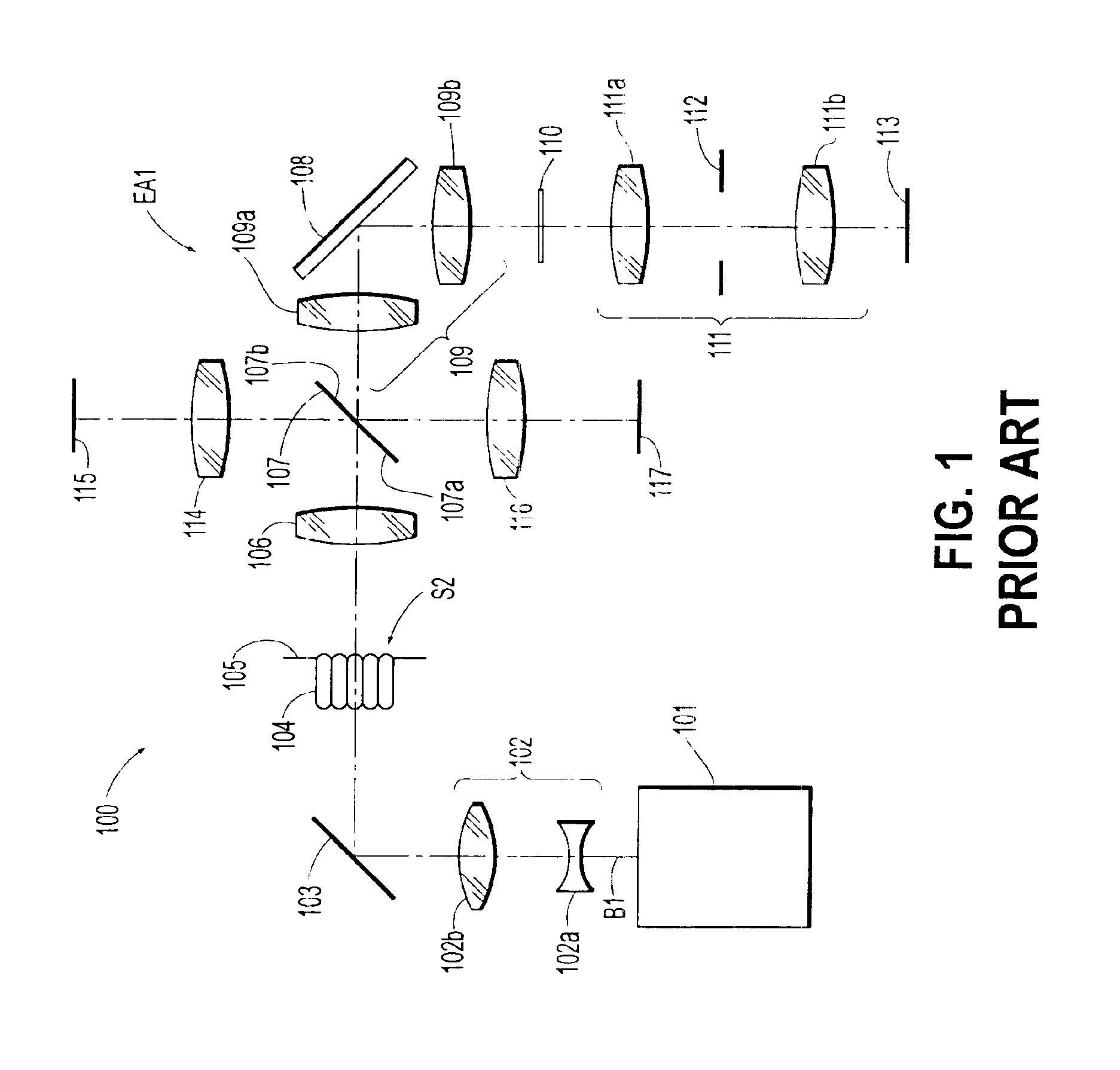
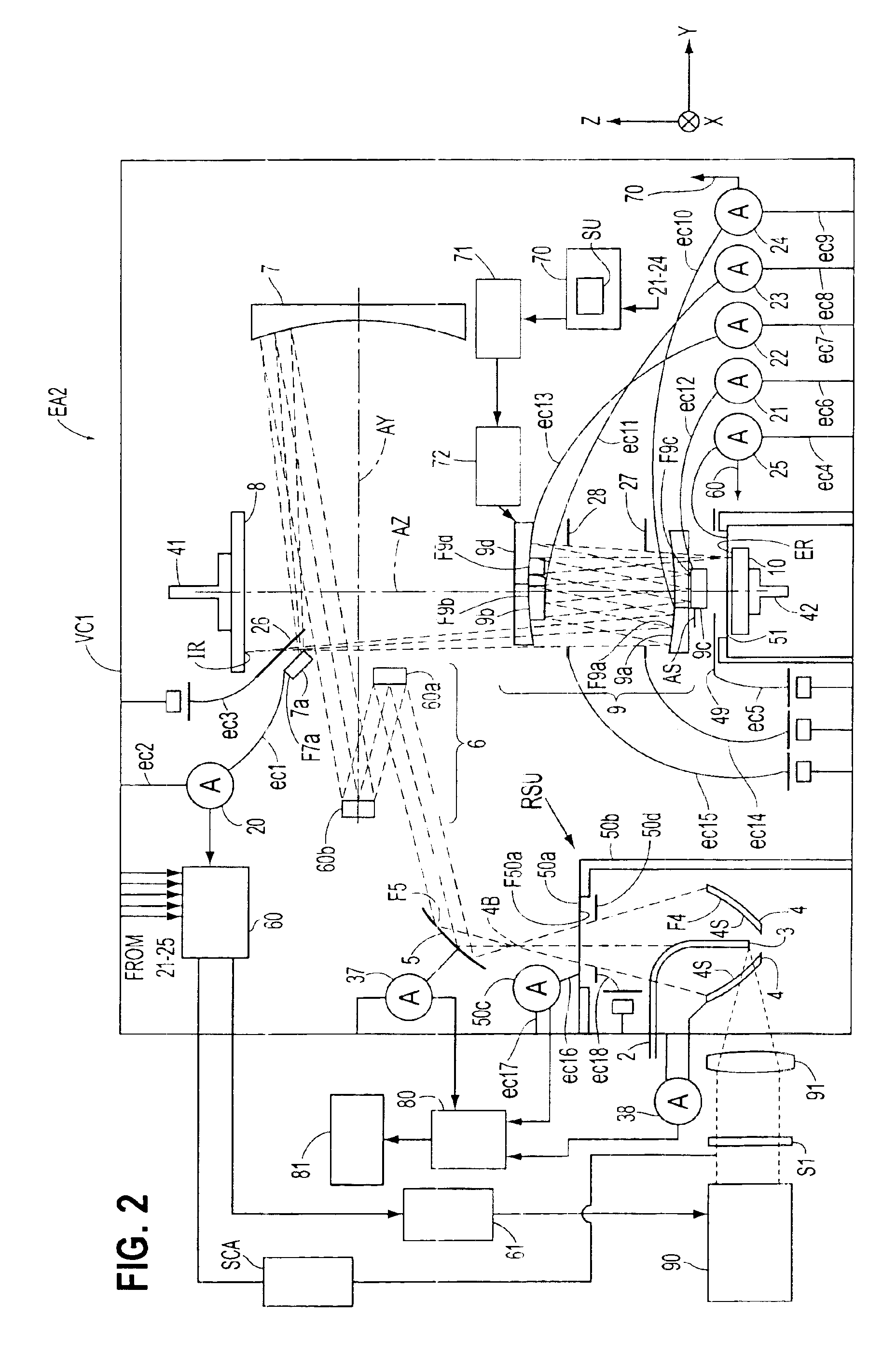
Exposure apparatus and exposure method using same
InactiveUS6842500B1Reduced strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusX-rayPhotoelectric effect
An exposure apparatus (EA2) that uses X-ray radiation in a photolithographic process and can obtain various measurements regarding the X-ray radiation used, by obtaining and analyzing readings of the photoelectric effect on various reflective surfaces (5, 60a, 60b, 7, 7a, 9a, 9b, 9c and 9d) or optical elements (50a and 51). With the measurements of the X-ray radiation, the exposure apparatus can control the exposure dose during the mask (8) and wafer (10) illumination process. The exposure system also has the ability to detect deformation in the mirrors (9a, 9b, 9c and 9d) of the projection optical system caused by heat generated by absorption of the X-ray radiation. This is accomplished by analyzing the photoelectric effect occurring on the mirror surfaces and correcting the deformation of the mirrors based on this analysis.
Owner:NIKON CORP
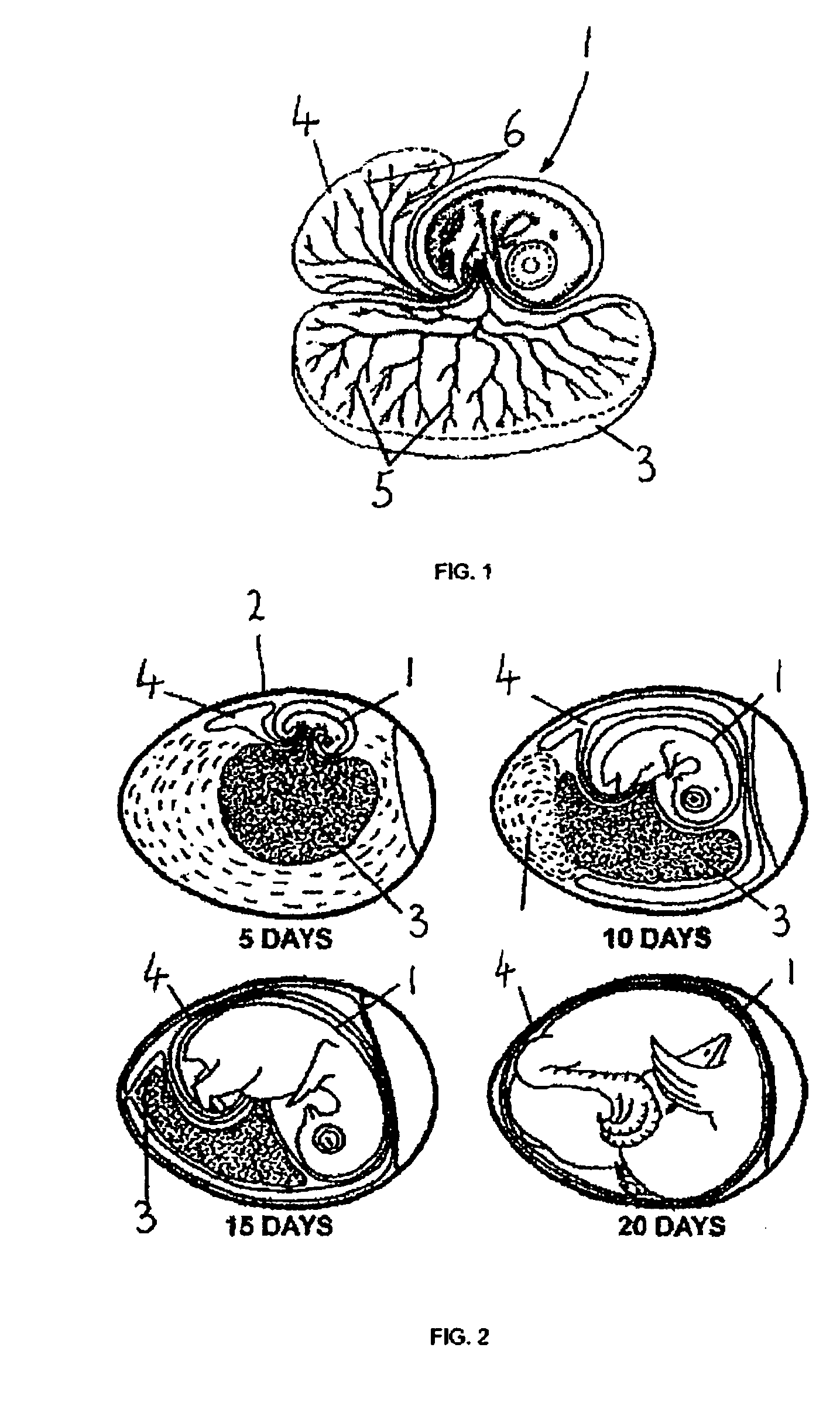
Method and apparatus for determining the viability of eggs
InactiveUS20050206876A1Determine viabilityViability can be determinedTesting eggsScattering properties measurementsAnimal scienceEggs per gram
A method of determining the viability of an egg at least approximately 50% through its incubation period, which method comprises the steps of: (a) causing electromagnetic radiation to impinge upon the egg, the electromagnetic radiation having one or more wavelengths in the infra-red part of the spectrum; (b) receiving at least a part of the infra-red radiation that has passed through the egg and generating an output signal representative of the received infra-red radiation; and (c) processing said output signal to determine whether there is a cyclical variation in the intensity of the infra-red radiation leaving the egg corresponding to action of a heart, the existence of said cyclical variation indicating that the egg is viable; wherein step (a) is performed by directing infra-red radiation so that it passes through the shell for reflection from an outer surface of a vascular structure adjacent an inner surface of said shell, and step (b) is performed by receiving any infra-red radiation so reflected.
Owner:VISCON BV
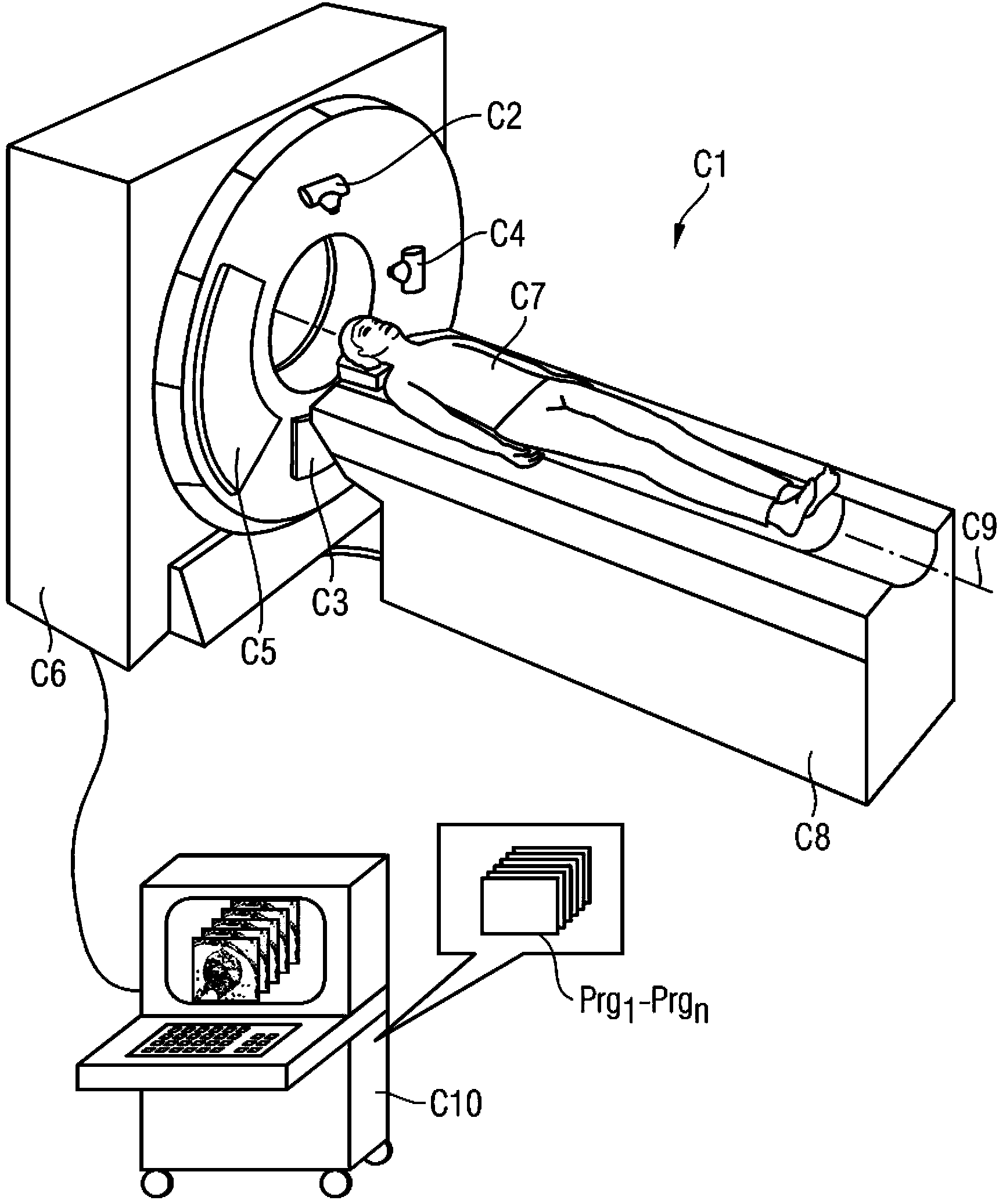
Ct scanner with scatter radiation correction and method of using same
ActiveUS20090304142A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCt scannersX-ray
A CT scanner with scatter correction device and a method for scatter correction are provided. The method of correcting CT images from artifacts caused by scattered radiation comprises affixing to the non-rotating frame of the CT gantry a plurality of shields for shielding some of the CT detector elements from direct X ray radiation, while allowing scattered radiation to arrive at said shielded elements; measuring scatter signals from said shielded elements, indicative of scattered radiation intensity; and correcting for scatter by subtracting scatter intensity values estimated from said measured scatter signals from signals measured by unshielded detector elements.
Owner:ARINETA
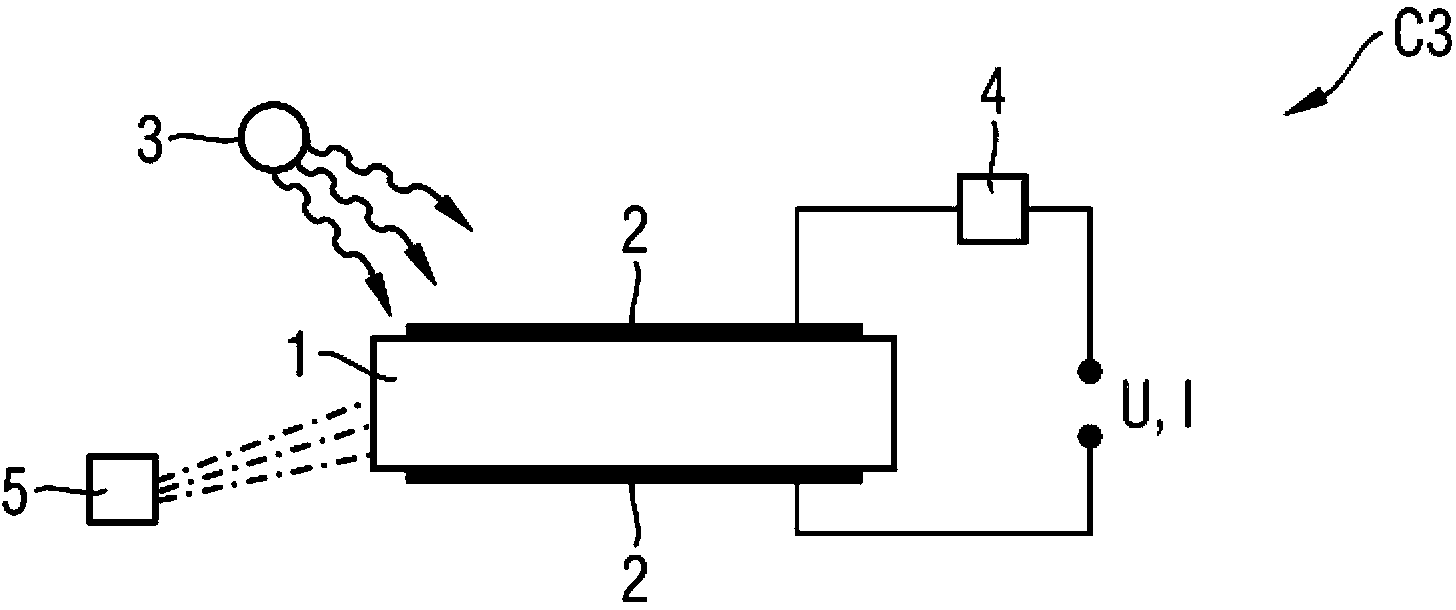
Measurement arrangement for X-ray fluoresence analysis
InactiveUS7065174B2Easy maintenanceSmall-sizedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementSoft x rayFluorescent radiation
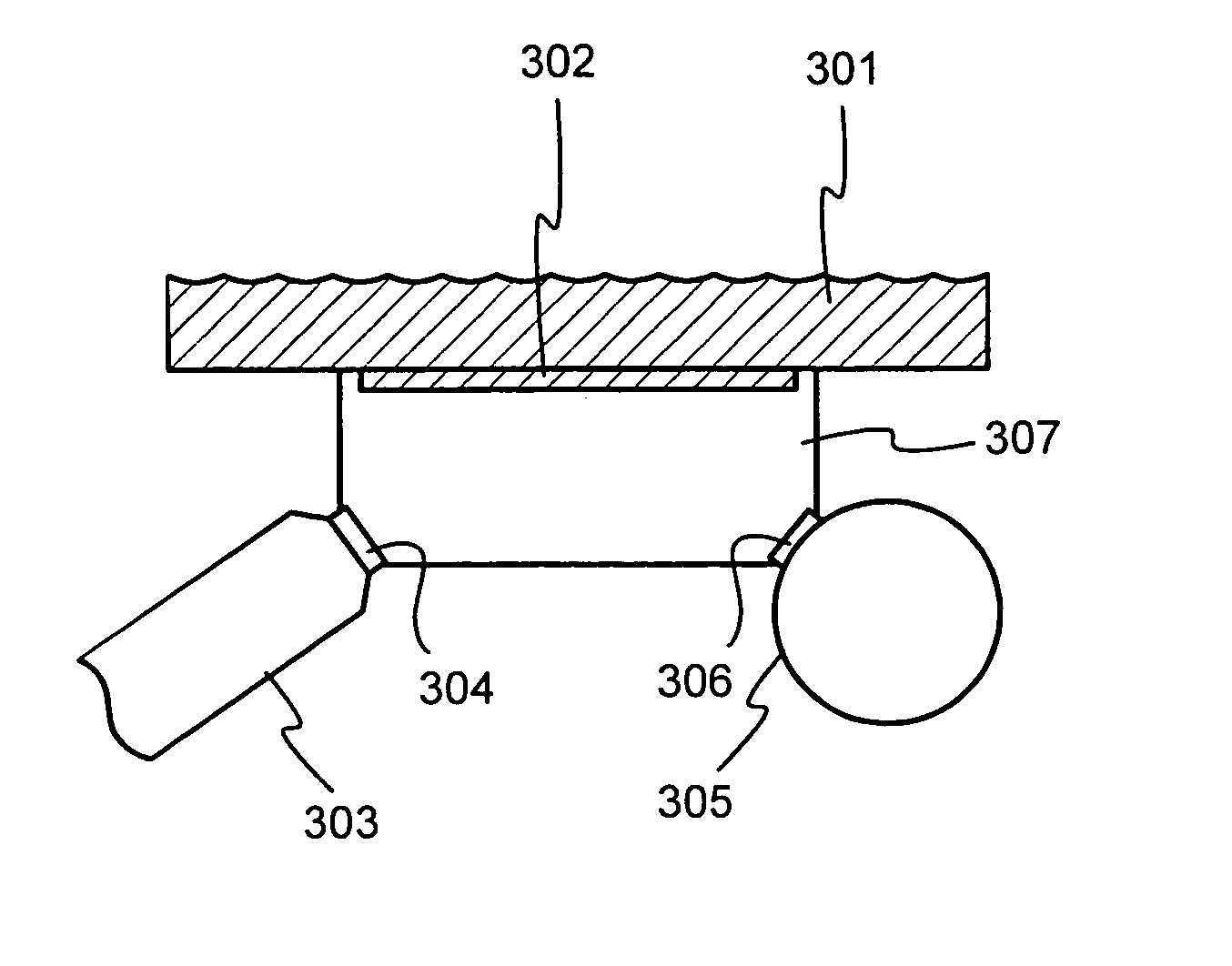
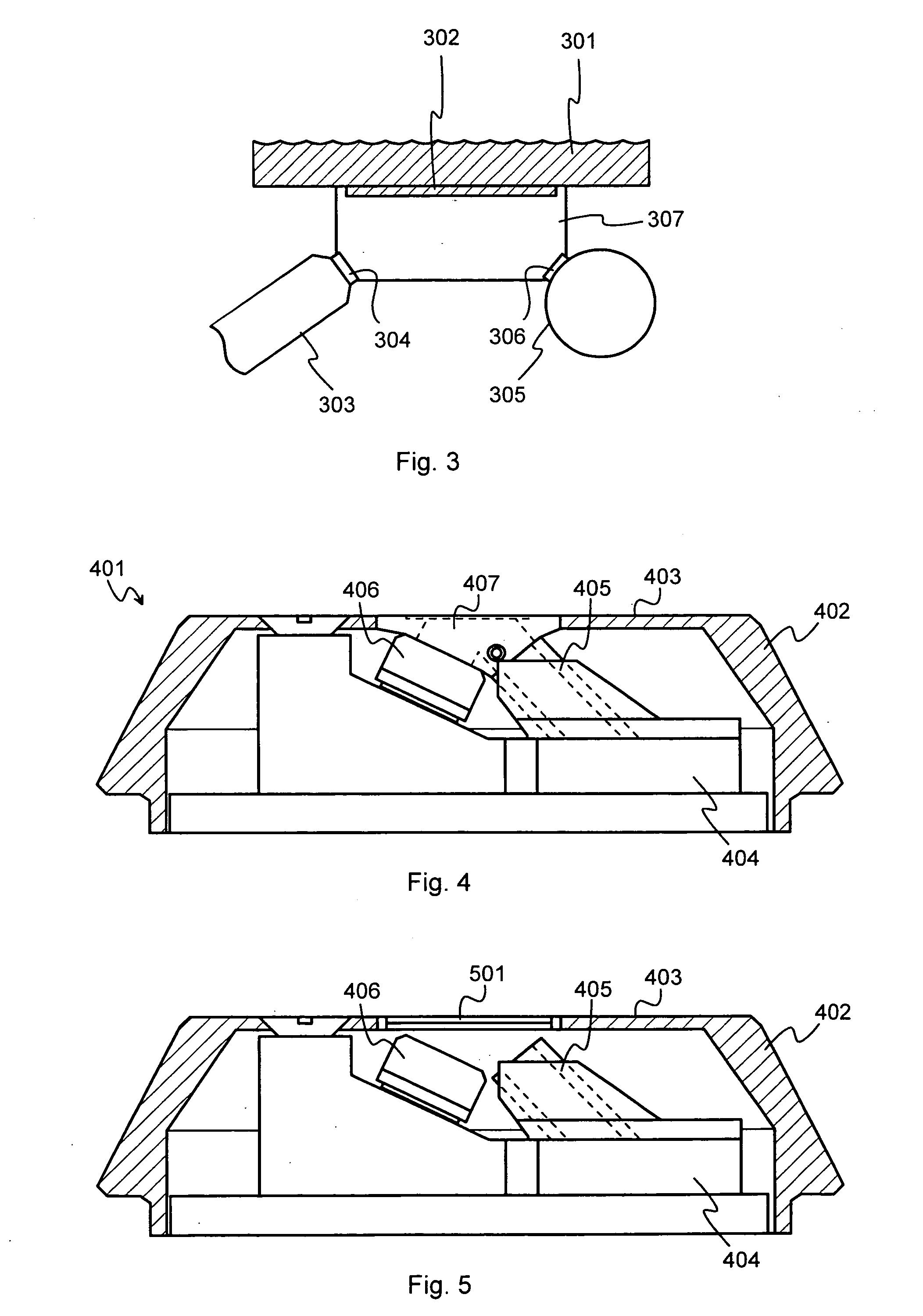
A portable measurement apparatus is presented for inducing and measuring fluorescent X-ray radiation. It comprises an X-ray source (303, 902, 1005, 1105) adapted to controllably irradiate a sample (301, 803) with X-rays, and a detector (305, 406, 1006, 1106) adapted to detect fluorescent radiation emitted by said sample (301, 803). The X-ray source (303, 902, 1005, 1105) is an X-ray tube, an anode of which comprises at least one of silver, rhodium and molybdenium. Consequently said X-ray tube is adapted to controllably emit L-line radiation of at least one of silver, rhodium and molybdenium.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR IND ANALYSIS OY +1
Functionalization of carbon nanotubes
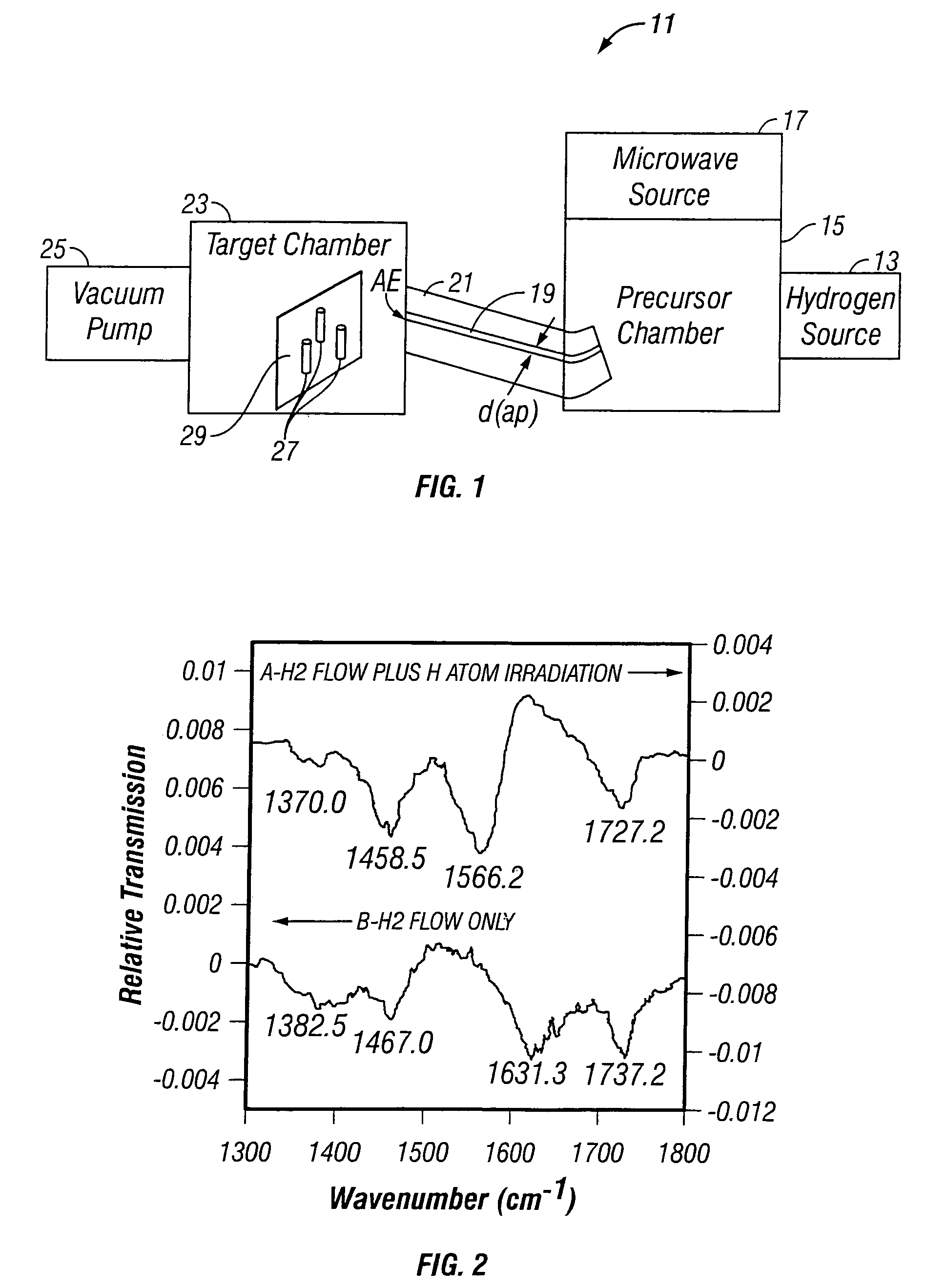
Method and system for functionalizing a collection of carbon nanotubes (CNTs). A selected precursor gas (e.g., H2 or F2 or CnHm) is irradiated to provide a cold plasma of selected target particles, such as atomic H or F, in a first chamber. The target particles are directed toward an array of CNTs located in a second chamber while suppressing transport of ultraviolet radiation to the second chamber. A CNT array is functionalized with the target particles, at or below room temperature, to a point of saturation, in an exposure time interval no longer than about 30 sec.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE
Differential phase-contrast imaging
ActiveUS10028716B2Handling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPhase gratingDifferential phase
The present invention relates to differential phase-contrast imaging, in particular to a structure of a diffraction grating, e.g. an analyzer grating and a phase grating, for X-ray differential phase-contrast imaging. In order to make better use of the X-ray radiation passing the object, a diffraction grating (14) for X-ray differential phase-contrast imaging is provided with at least one portion (24) of a first sub-area (26) and at least one portion (28) of a second sub-area (30). The first sub-area comprises a grating structure (54) with a plurality of bars (34) and gaps (36) being arranged periodically with a first grating pitch P G (38), wherein the bars are arranged such that thy change the phase and / or amplitude of an X-ray radiation and wherein the gaps are X-ray transparent. The second sub-area is X-ray transparent and wherein the at least one portion of the second sub-area provides an X-ray 1 transparent aperture (40) in the grating. Portions of the first and second sub-areas are arranged in an alternating manner in at least one direction (42).
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Low temperature process for making radiopac materials utilizing industrial/agricultural waste as raw material
ActiveUS20060066013A1Saving on accountConsiderable heat energyCeramic shaping apparatusNon-woven fabricsPyrophyllitePhosphate binder
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
A kind of pull-tab outer cover material for infusion bottle or bag and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102276932AGuaranteed melting temperatureGuaranteed welding strengthPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingRadiation resistantSize change
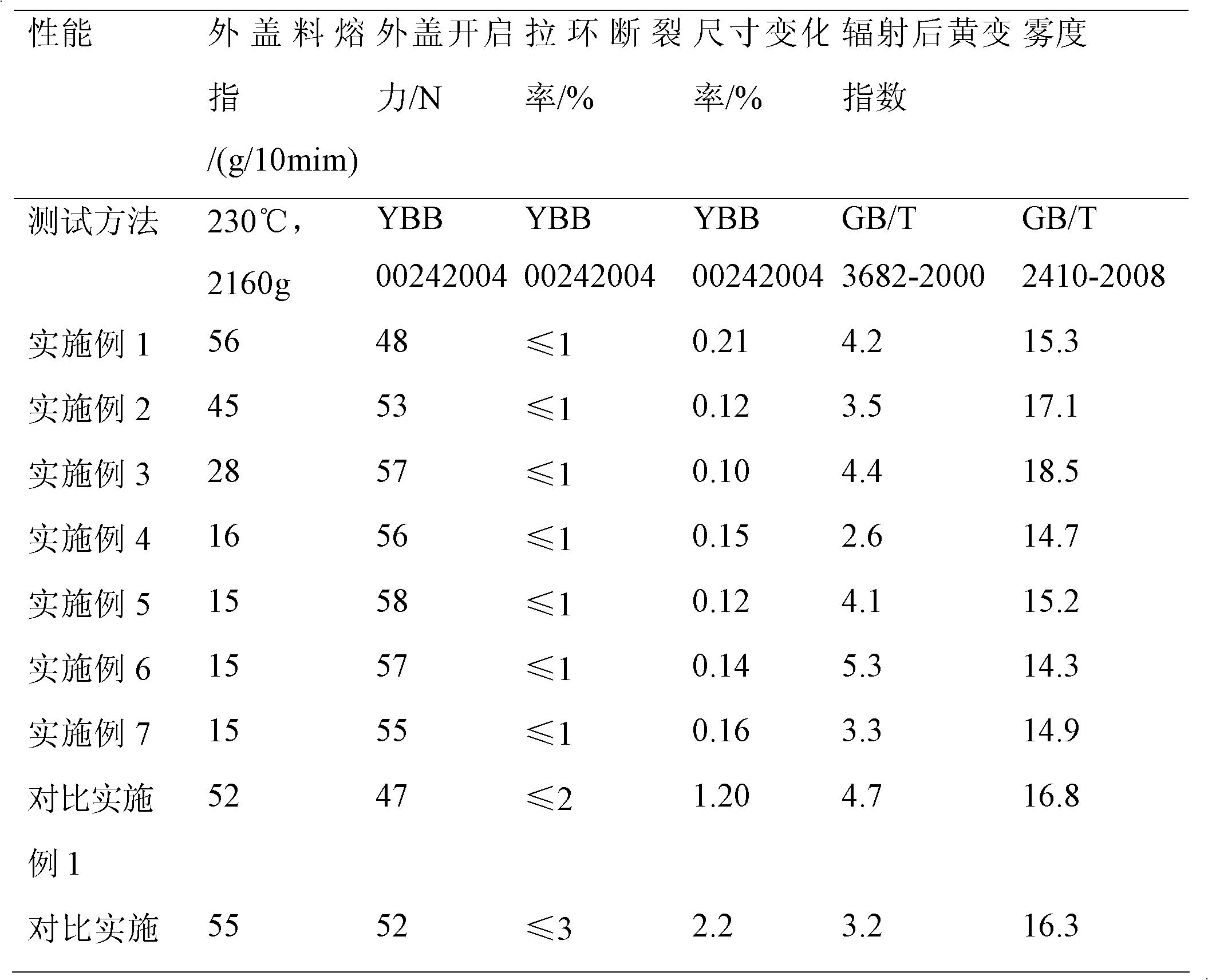
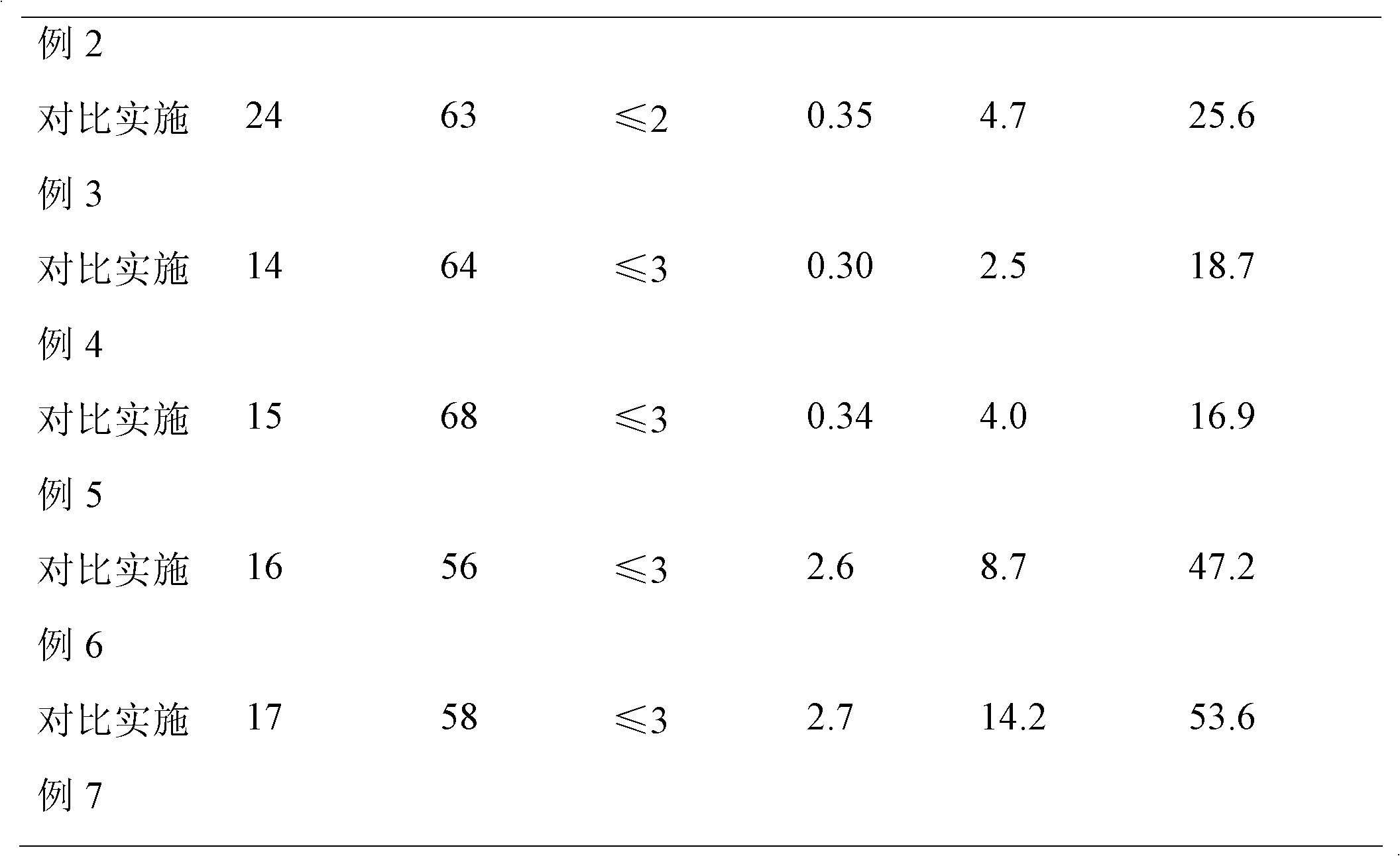
The invention discloses a pull-tab outer cover material used for infusion bottles or bags, and the material provided by the invention comprises the following components in parts by weight: 71-89 parts of polypropylene, 1-9 parts of flexibilizer, 9-25 parts of lubrication resin and 0.01-0.4 part of radiation-resistant accessory ingredient. The melting index of the pull-tab outer cover material used for infusion bottles or bags is 9-60g / min under the condition of 230DEG C and 2160g, and the outer cover material can be directly injected to prepare the pull-tab outer cover material used for infusion bottles or bags. A cover body and the infusion bottles or bags have high welding strength, a pull tab is easy to open, an opening edge is tidy, and the opening force is less than or equal to 60N; the pull tab has small possibility of being ruptured, and the fracture rate of the pull tab is less than or equal to 1%; no low-molecule ingredients are separated out, the size stability is good, and the size change rate of the outer cover is less than or equal to 0.5% before and after disinfection; and the radiation-resistant performance is good, the yellow index is less than or equal to 7 after the material is radiated by 60Co-gamma ray of 25kGy dose, and the material haze is less than or equal to 20.
Owner:合诚技术股份有限公司
Method and apparatus for determining the viability of eggs
InactiveUS7289196B2Determine viabilityViability can be determinedTesting eggsScattering properties measurementsElectromagnetic radiationLength wave
Determining the viability of an egg by:(a) causing electromagnetic radiation, having one or more wavelengths in the infra-red part of the spectrum, to impinge upon the egg;(b) receiving at least a part of the infra-red radiation that has passed through the egg and generating an output signal representative of the received infra-red radiation; and(c) processing said output signal to determine whether there is a cyclical variation in the intensity of the infra-red radiation leaving the egg corresponding to action of a heart, the existence of said cyclical variation indicating that the egg is viable;wherein step (a) is performed by directing infra-red radiation so that it passes through the shell for reflection from an outer surface of a vascular structure adjacent an inner surface of said shell, and step (b) is performed by receiving any infra-red radiation so reflected.
Owner:VISCON BV
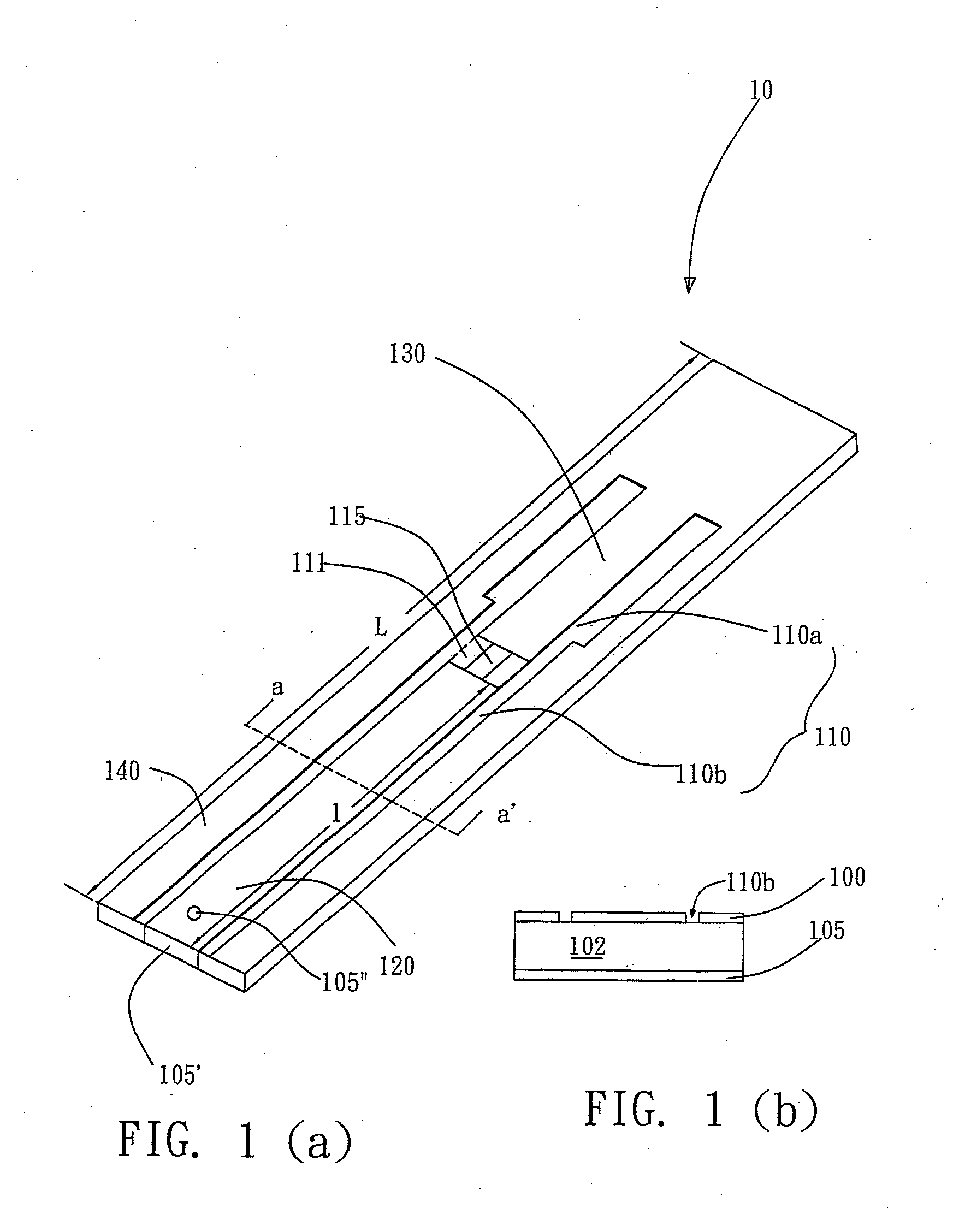
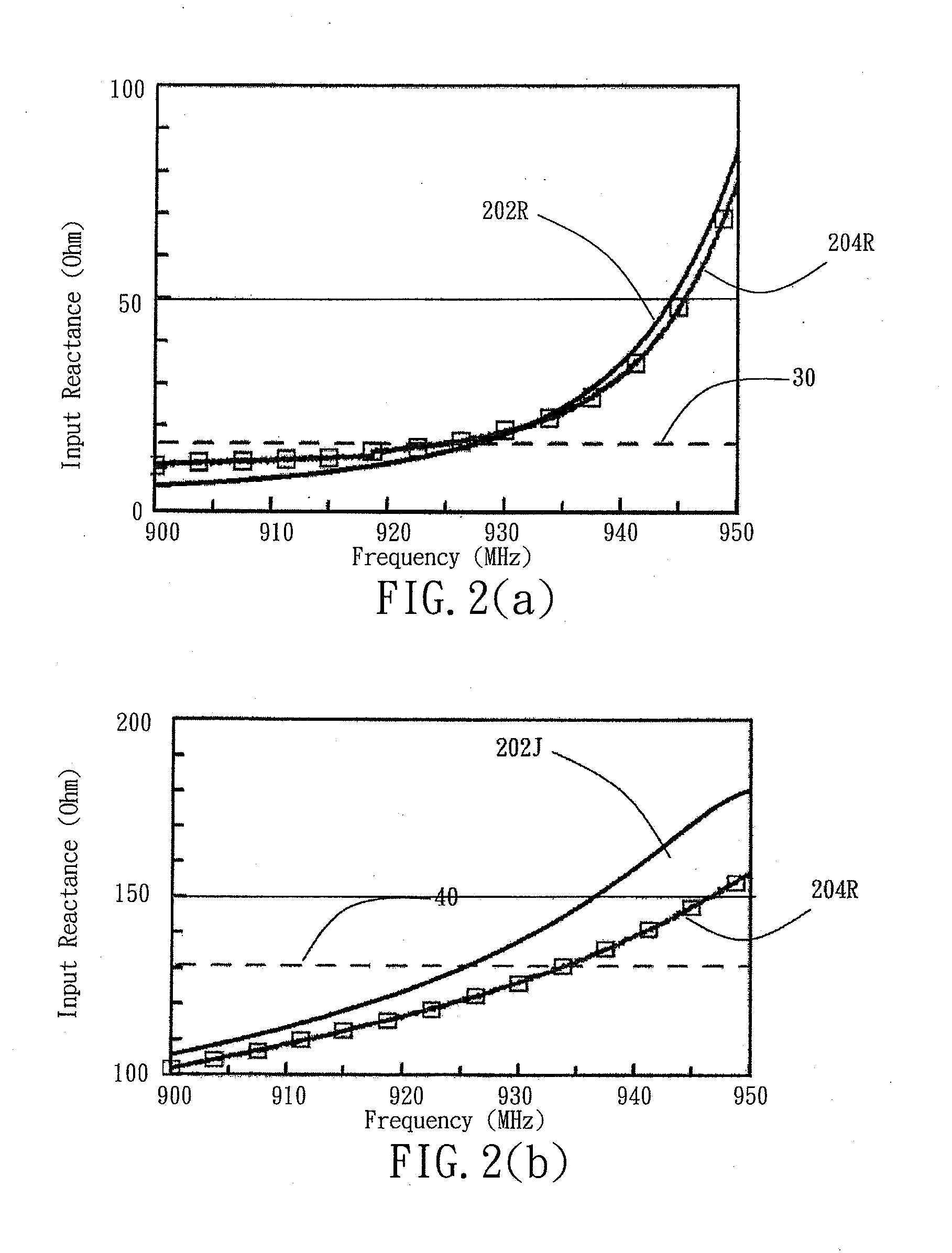
Trapped wave controllable ultra-wide-band antenna
PendingCN107706523AImproving Impedance BandwidthImproving Impedance MatchingSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric substrateGround plate
The invention belongs to the technical field of an antenna in a communication system, and specifically relates to a trapped wave controllable ultra-wide-band antenna. The trapped wave controllable ultra-wide-band antenna comprises a microstrip feeder line, a radiation unit, a dielectric substrate and a grounding plate; the microstrip feeder line and the radiation unit are arranged on the upper layer, the dielectric substrate is arranged in the middle layer and positioned below the microstrip feeder line and the radiation unit, and the grounding plate is arranged on the lower layer and positioned below the dielectric substrate; an open circuit gap and an opening resonance ring are arranged on the radiation unit, and the open circuit gap extends from the right side edge of the radiation unitto the interior of the radiation unit; a first opening resonance ring and a second opening resonance ring are arranged on the grounding plate; the open circuit gap and the opening resonance ring areloaded with a first PIN diode and a second PIN diode respectively; and the first opening resonance ring and the second opening resonance ring are loaded with a third PIN diode and a fourth PIN diode respectively. The trapped wave controllable ultra-wide-band antenna can realize ultra wide band, single band wave trapping, dual band wave trapping and triple band wave trapping, and is simple in structure and suitable for the ultra-wide-band wireless communication system.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Radiography system and method for recording X-rays in phosphor layers
ActiveUS20060180773A1High possible picture quality of X-rayElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesX-rayRoentgen rays
The invention relates to a radiography system with a recording device and to a corresponding method for recording X-rays in storage phosphor layers. In order to improve a picture quality of an X-ray, a recording control is provided for controlling the recording device such that in a first phosphor layer having a first thickness, an X-ray with a first energy limit of the X-ray radiation is recorded, and in a second phosphor layer, having a second thickness which is greater than the first thickness, an X-ray with a second energy limit of the X-ray radiation is recorded, the second energy limit of the X-ray radiation being greater than the first energy limit of the X-ray radiation.
Owner:AGFA NV
Vivaldi antenna array with symmetrical directional diagrams
InactiveCN104659482AFunctionalReduced lateral radiationAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsTransition lineVivaldi antenna
The invention provides a vivaldi antenna array with symmetrical directional diagrams. The vivaldi antenna array comprises array feeding and array antenna radiation arm design and array mounting and feeding mode design, wherein an array feeding part comprises a multi-stage transition line power divider, and width and length of each cascaded power division line are adjusted through software to realize impedance matching; an array antenna radiation arm part adopts a coplanar exponential line radiation arm; an array mounting and feeding mode is as follows: an antenna array is rotated by 180 degrees, and two feed ports are opposite in the leftward and rightward direction and subjected to constant-amplitude inverse feeding through magic T. With adoption of asymmetric design of unit radiation arms, the disadvantage is turned into the advantage, and a feeding network is simple and easy and convenient to design; after rotation and inverse feeding are adopted, radiation of higher-order modes with symmetrical structures cancels, and effective energy concentration radiation is facilitated; due to polarization cancellation of electrical fields in other directions, lateral radiation of the rotated arrays is remarkably reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Mobile terminal
ActiveCN109728412AImprove Radiation PerformanceHigh bandwidthSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna radiationPhysics
The present invention provides a mobile terminal. A first housing includes a first conductive body and a first antenna radiation branch which are arranged at intervals, the first antenna radiation branch is provided with a feed point and is connected with a matching circuit; a first insulation region is arranged between the first end of the first antenna radiation branch and the first conductive body, a second insulation region is arranged between the second end of the first antenna radiation branch and the first conductive body, and a third insulation region is arranged between the first sideof the first antenna radiation branch and the first conductive body; a second housing comprises a second conductive body and a second antenna radiation branch which are arranged at intervals, the second antenna radiation branch is provided with a first grounding point; a fourth insulation region is arranged between the first end of the second antenna radiation branch and the second conductive body, a fifth insulation region is arranged between the second end of the second antenna radiation branch and the second conductive body, and a sixth insulation region is arranged between the first sideof the second antenna radiation branch and the second conductive body; and when the first housing and the second housing are closed, the first insulation region and the fourth insulation region, the second insulation region and the fifth insulation region, the third insulation region and the sixth insulation region are at least partially opposite, and the first antenna radiation branch and the second radiation branch are subjected to capacity coupling. The radiation capacity of the antenna is improved, and the antenna bandwidth is increased.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Method for laser sealing glass and kovar alloy
InactiveCN103212812AOptimizing Process ParametersControl pulse widthLaser beam welding apparatusRoom temperatureLight beam
The invention discloses a method for laser sealing glass and kovar alloy. The method includes that (a) clean treatment is carried out on the glass, and derosination treatment and deoiling treatment are carried out on the kovar alloy; (b), the glass is placed on the kovar alloy and is contacted with the kovar alloy tightly; (c) straight-line radiation is carried out with a laser device, the focus of a laser beam is positioned in the junction of the glass and the kovar alloy to obtain a sealing body; and (d) the sealing body is moved to a heating furnace of 100-300 DEG C, stress relief annealing is carried out, and after cooled to room temperature along with the furnace, the sealing body of the glass and the kovar alloy can be obtained. According to the method, due to the fact that technological parameters are optimized, a heat action area and temperature distribution in the area are accurately controlled, and the pulse width, frequency, scanning speed and the temperature of the stress relief annealing are controlled, so that the low-stress and large-size sealing body of the glass and the kovar alloy is obtained, the sealing body can be applied to the construction industry, and the service life of a product is improved substantially.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Measurement arrangement for X-ray fluoresence analysis
InactiveUS20050129174A1Easy maintenanceSmall-sizedX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorescent radiationX-ray
A portable measurement apparatus is presented for inducing and measuring fluorescent X-ray radiation. It comprises an X-ray source (303, 902, 1005, 1105) adapted to controllably irradiate a sample (301, 803) with X-rays, and a detector (305, 406, 1006, 1106) adapted to detect fluorescent radiation emitted by said sample (301, 803). The X-ray source (303, 902, 1005, 1105) is an X-ray tube, an anode of which comprises at least one of silver, rhodium and molybdenium. Consequently said X-ray tube is adapted to controllably emit L-line radiation of at least one of silver, rhodium and molybdenium.
Owner:OXFORD INSTR IND ANALYSIS OY +1
Ultra-wideband dual-polarization radiating unit and array antenna
ActiveCN103151603AImproving Impedance BandwidthSimple structureAntenna supports/mountingsRadiating elements structural formsUltra-widebandWide band
The invention relates to the technical field of dual-polarization radiating units and discloses an ultra-wideband dual-polarization radiating unit and an array antenna comprising the radiating unit. The radiating unit comprises a first dipole, a second dipole and a balance-unbalance connector, wherein the first dipole comprises two first half dipoles, the second dipole comprises two second half dipoles, the first half dipoles comprise first radiating plates, the second half dipoles comprise second radiating plates, the first radiating plates and the second radiating plates are in a shape that two ends are contracted, and two sides in the middle outwards extend, in addition, the middle is in a hollow shape, and the upper ends of the two first radiating plates and the two second radiating plates are jointly in insulation connection with a loading sheet. The radiating unit and the array antenna have the advantages that two ends of a first radiating body and a second radiating body are contracted, two sides in the middle outwards extend, the middle is in a hollow shape, the upper ends of the first radiating plate and the second radiating plate are provided with loading sheets, the impedance bandwidth of the radiating unit can be greatly improved, in addition, through the use of the loading sheets, the convergence of the radiation pattern of the radiating unit can be improved, and the structure is also very simple.
Owner:MOBI TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD +3
Broadband high-isolation dual polarization antenna and radiating unit thereof
ActiveCN103066376AAdjust Radiation PerformanceThe effect of radiation characteristics is smallRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationBroadbandHeight difference
The invention discloses a broadband high-isolation dual polarization antenna and a radiating unit of the broadband high-isolation dual polarization antenna. The radiating unit comprises a reflecting plate, a first feed part, a second feed part, a first radiating body, a second radiating body and four supporting parts. The first radiating body and the second radiating body are composed of diagonal radiating bodies. The four radiating bodies are respectively fixed on the four supporting parts which are fixed on the reflecting plate. Tops of the first feed part and the second feet part are crossed in an orthogonality mode and a height difference exists. The first feed part is a feed structure of the first radiating body and the second feed part is a feed structure of the second radiating body. A cross-shaped seam is formed among the four radiating bodies. A rectangle-shaped branch knot which is longer than the radiating body and faces the rim direction of an outer side of the radiating body is arranged in the middle of each radiating body face. A branch knot is arranged at the rim of the outer side of each radiating body. The dual polarization antenna radiating unit and an antenna array composed of the dual polarization antenna radiating unit have the advantages of being high in isolation , high in radiation characteristic, wide in frequency band and the like.
Owner:杭州平治信息技术股份有限公司
Cross feed broad-band omnidirectional antenna
InactiveCN1832252AHigh gainEasy to processSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsOmnidirectional antennaMicrowave
This invention discloses a cross feed broadband all-around antenna, which applies dual face copper coat to print on a microwave dielectric plate to form an upper antenna unit and a lower antenna unit with metal through holes, in which, the upper antenna unit is composed of a connecting line, radiation unit A and radiation unit B, a feed port is set on the connecting line, the lower antenna unit is composed of a connecting line, radiation unit A and radiation unit B and a feed port is set on the connecting line, radiation unit A of the upper layer antenna unit and that of the lower antenna constitute a symmetric element antenna radiation device A of a capacitive load and radiation unit B of the upper layer antenna unit and that of the lower layer antenna unit make up of a capacitive loaded symmetric element antenna radiation device B, the connecting lines of the two layer antenna units make up of a parallel wide edge couple crewel to crossly feed devices A and B.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Low-profile broadband circularly polarized antenna for 5G communication and design method thereof
ActiveCN111864368AIncrease electrical sizeWide Impedance BandwidthRadiating elements structural formsAntennas earthing switches associationCircularly polarized antennaMicrowave
The invention provides a low-profile broadband circularly polarized antenna for 5G communication and a design method thereof and belong to the technical field of microwave passive devices and the antenna comprise an antenna radiation assembly, a reflector assembly and an antenna feed assembly. The antenna radiation assembly is used for signal radiation, and the reflector assembly is used for reflecting radiation signals of the antenna radiation assembly. The antenna radiation assembly comprises an upper layer microwave dielectric substrate and first and second irregular slotted rectangular patch antennas etched on the upper and lower surfaces of the upper layer microwave dielectric substrate. The reflector assembly comprises a lower layer microwave dielectric substrate and a plurality of AMC reflectors distributed on the upper surface of the lower layer microwave dielectric substrate at equal intervals. The AMC reflectors are loaded below the first irregular slotted rectangular patch antenna and the second irregular slotted rectangular patch antenna; and the antenna feed assembly provides feed for the first irregular slotted rectangular patch antenna and the second irregular slotted rectangular patch antenna. L-shaped grooves are respectively etched in the first irregular slotted rectangular patch antenna and the second irregular slotted rectangular patch antenna; and the antenna is low in profile and small in size, contains 5G, is compatible with a 4G frequency band, and is wide in bandwidth after being loaded with an artificial magnetic conductor.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
A method and system for projecting a visible representation of infrared radiation
ActiveCN104254869AImprove experienceEasy to analyzeTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationThermographyVisible spectrum
A method for enabling easier interpretation and analysis of an observed real world scene by presenting a visible representation of infrared (IR) radiation information, based on infrared (IR) radiation emitted from said real world scene, and additional information onto said observed real world scene, using a thermography arrangement (10) comprising an infrared (IR) imaging system (18), a visible light imaging system (14) and a visible light projecting system (22).
Owner:FLIR SYST AB
Novel reforming furnace for preparing reducing gas
PendingCN110578027ALess investmentSmall footprintCombustible gas catalytic treatmentEnergy inputEngineeringRaw material
The invention provides a novel reforming furnace for preparing reducing gas, and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy and petrifaction. The reforming furnace comprises a lining radiation chamber, a reforming furnace pipe, a reforming gas port pipe system, a transition section, a convection section and an air and flue gas system. The reforming furnace pipe adopts a large caliber to reduce the furnace pipe number, so that the investment is reduced; a reforming gas inlet pipe is connected with the reforming furnace pipe by adopting a flexible pipe, so that the axial and radial heat displacements of the furnace pipe are conveniently absorbed, and the heat stress of a furnace pipe system is reduced; an elastic bracket is arranged at the bottom of the reforming furnace pipe for bearing part weight of the furnace pipe and facilitating recovery of the furnace pipe after heat expansion under the working condition of parking; a radiation chamber furnace top inclined tee joint replaces atraditional heat pipe wall, and a short tail box is canceled, so that materials are saved, and the investment is reduced; and high-temperature smoke is guided to the transition section from multiple channels at the upper parts of the two sides of the radiation chamber, and is fed in the convection section for preheating air and reforming raw material gas and fuel gas to generate high-quality vapor, so that the smoke discharge heat loss is reduced, and the heat efficiency of the reforming furnace is improved.
Owner:SINOPEC NANJING ENG & CONSTR +1
RFID tag antenna for attached on high conductive object
InactiveUS20130120197A1Simultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsGlass fiberTag antenna
An UHF RFID antenna for attached on any high conductive object is disclosed. The antenna radiation body has a first copper foil mounted thereon a backside surface of a FR4 glass fiber served as a ground plane, a second copper foil mounted thereon a front surface of the FR4 glass fiber as a main radiation plane. The main radiation plane contains two etched slits spaced each other. Each etched slit has a shape like a blade with a long handle. The two etched slits are mirror symmetry and a trench formed to connect the two etched slits for a RFID tag seated thereon so that There are short circuit microstrip and a feed-in microstrip are generated.
Owner:NAT TAIPEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for temperature stabilization, X-ray detector and CT system
ActiveCN103576179ASimple structureSimplify your cooling solutionX-ray apparatusRadiation intensity measurementEnergy regulationX-ray
A method is disclosed for the temperature stabilization of a direct-converting X-ray detector, including a detector surface having a semiconductor and being divided into a plurality of partial detector surfaces. During the irradiation of the detector surface, heat is generated in the semiconductor by electric power. Electric power generated in the semiconductor is kept constant for each partial detector surface at least during a heterogeneous and / or temporally variable irradiation of the detector surface by feeding-in power-adjusted additional radiation for each partial detector surface. A direct-converting X-ray detector is disclosed for the detection of X-rays. At least one control loop with at least one reference variable is embodied for the energy regulation of the additional radiation, which keeps the temperature in the semiconductor constant for each partial detector surface by keeping the electric power in the semiconductor constant by changing the energy of the additional radiation. A CT system is disclosed.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
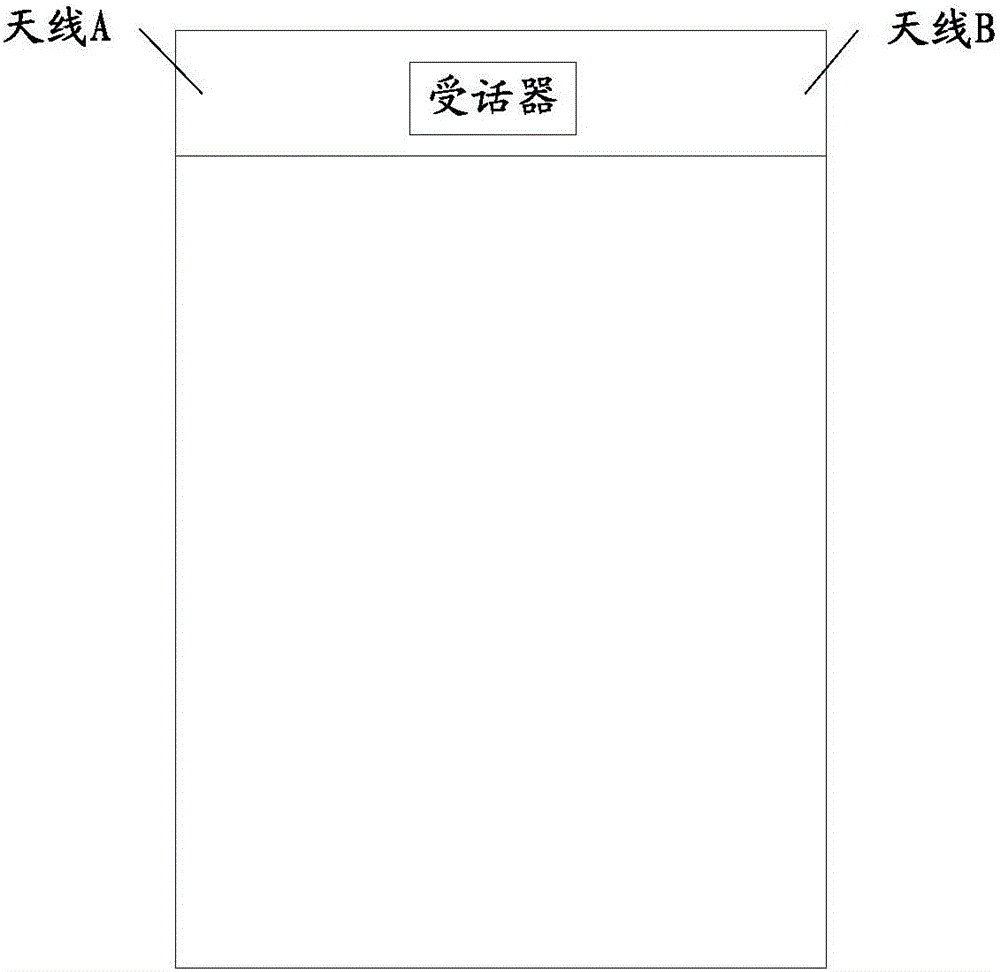
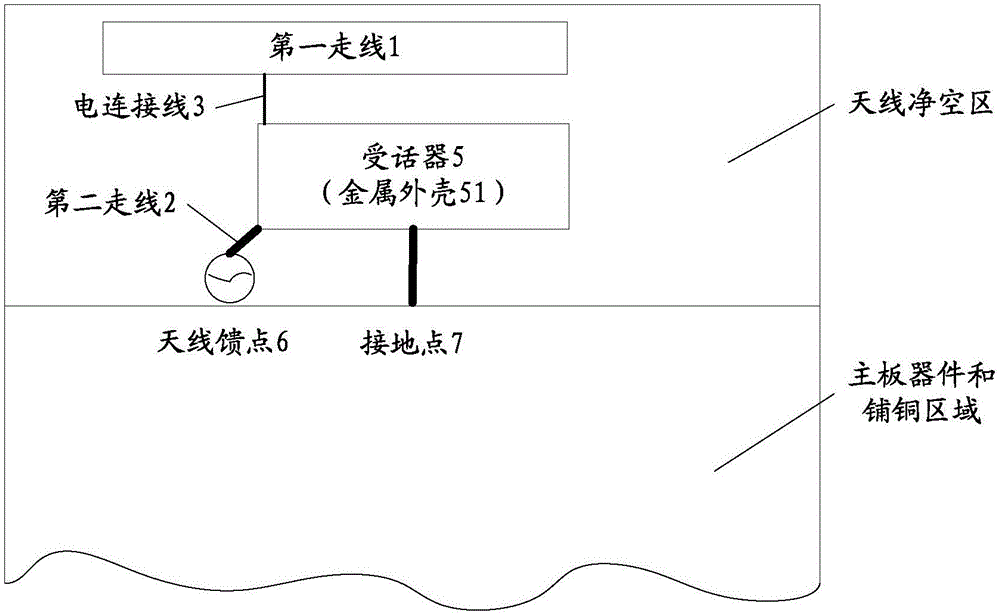
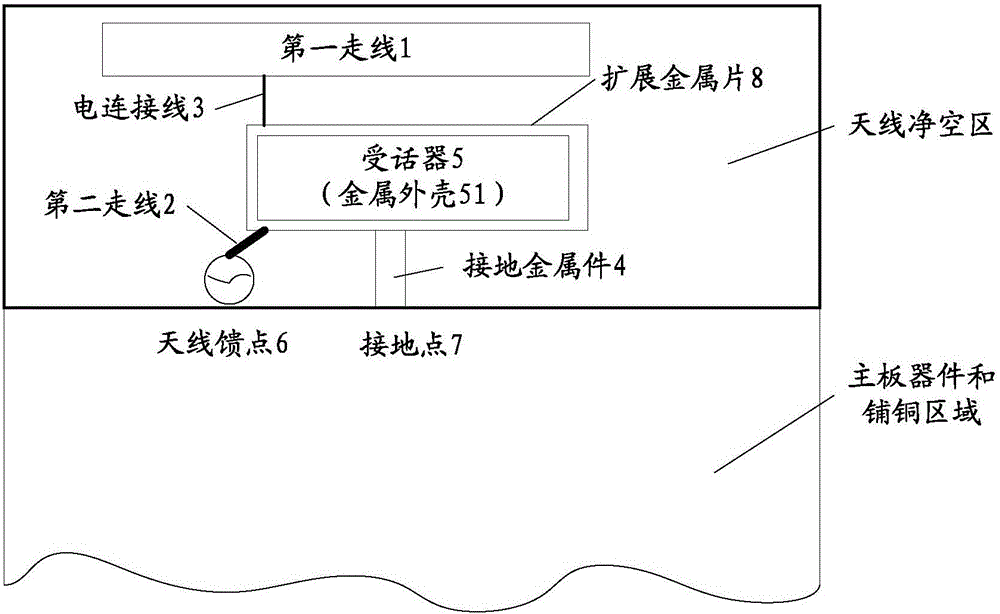
Antenna, carrier radio frequency circuit, terminal and carrier aggregation method
InactiveCN106252845AImplementation settingsIncrease profitRadiating elements structural formsAntenna equipments with additional functionsElectricityCarrier signal
The embodiment of the invention provides an antenna, a carrier radio frequency circuit, a terminal and a carrier aggregation method. The antenna comprises an antenna body and a radiation body, wherein the antenna body comprises a first wire arranged on a printed circuit board, the radiation body comprises a metal shell of a receiver, and the metal shell of the receiver is grounded; and the first wire is connected with the metal shell of the receiver through an electric connecting wire, and the metal shell of the receiver is connected to an antenna feed point through a second wire arranged on the printed circuit board. According to the invention, the metal shell of the receiver in the terminal is used as the antenna radiation body of the antenna, and an additional antenna radiation body is not required to be arranged, so that setting of the antenna is well realized by effectively utilizing the metal shell of the receiver of the terminal. In addition, the space of an area in which the receiver in the terminal is sufficiently utilized, and the utilization rate of the terminal space is improved.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
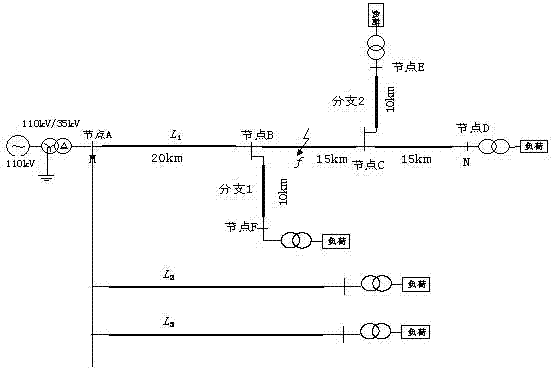
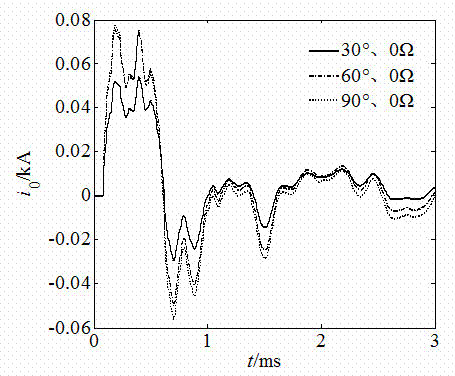
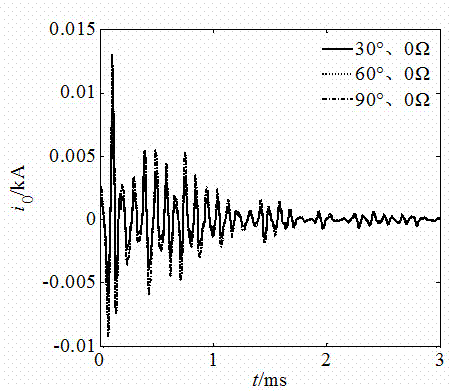
Multi-outgoing-line radiation network fault distance measuring method for k-NN algorithm based on waveform similarity
The invention relates to a multi-outgoing-line radiation network fault distance measuring method for a k-NN algorithm based on waveform similarity, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. Zero-mode current data of a measuring side at different fault positions and under different fault conditions are acquired through simulation, wavelet decomposition is carried out on the data, and wavelet coefficient organization historical sample data under a sixth scale are obtained. When a single-phase grounding fault occurs, the k-NN algorithm is utilized, similarity matching is carried out on a wavelet coefficient waveform of measured zero-mode current waveforms after wavelet decomposition and wavelet coefficient waveforms in a simulated historical sample under the different fault conditions through correlation analysis, fault distances corresponding to the first three waveform data with the highest similarity are obtained, and the fault distance is obtained through the different application regression methods of weights. A large amount of simulation shows that the method is reliable and high in precision for the single-phase grounding fault.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com