Patents
Literature
374 results about "Time derivative" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
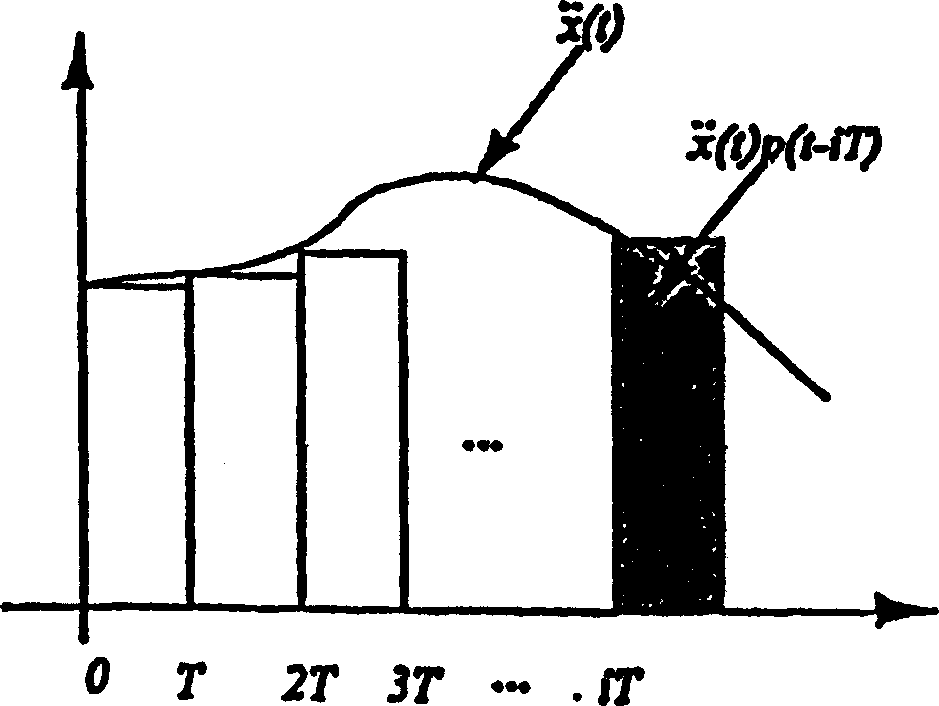
A time derivative is a derivative of a function with respect to time, usually interpreted as the rate of change of the value of the function. The variable denoting time is usually written as t .
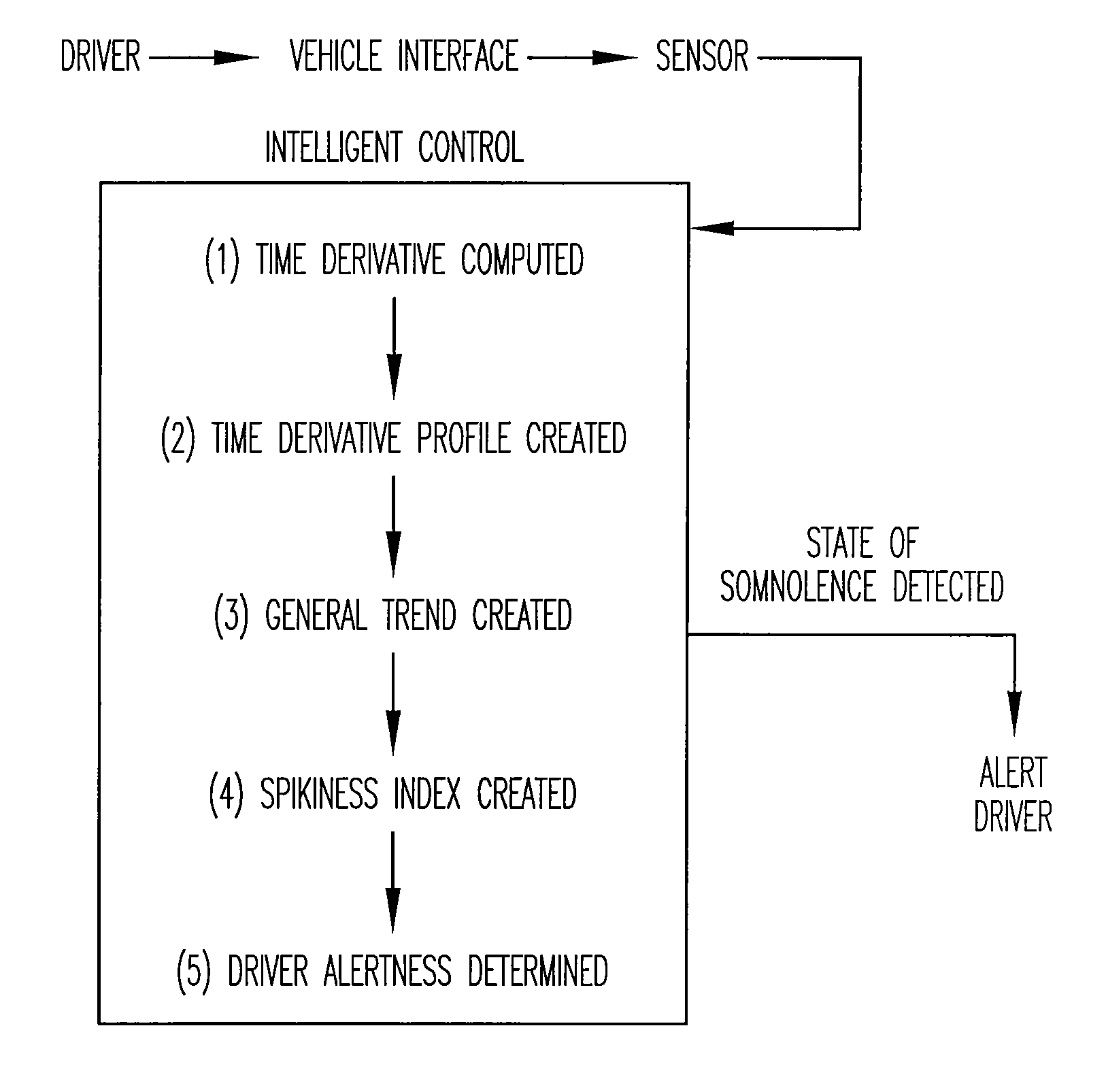
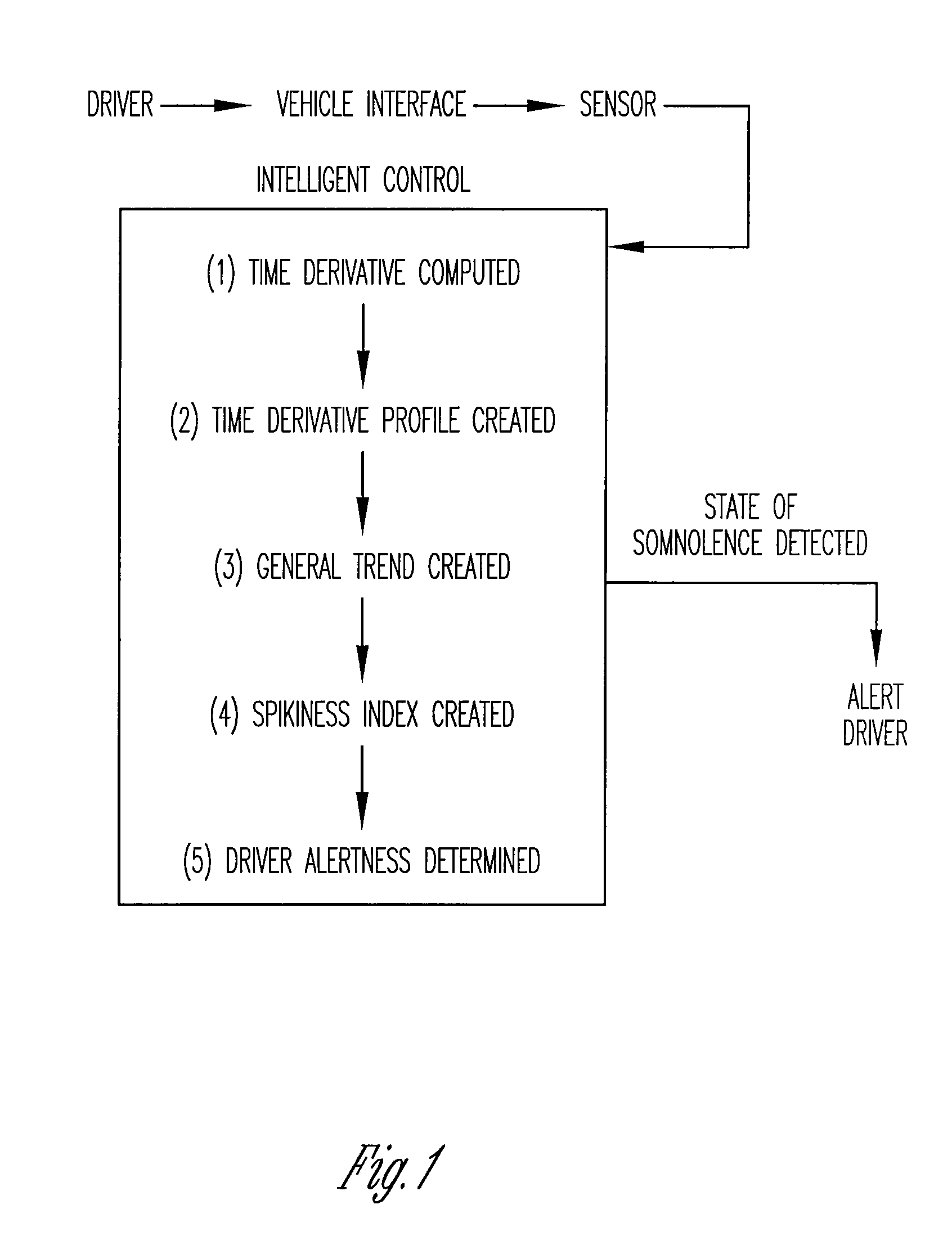
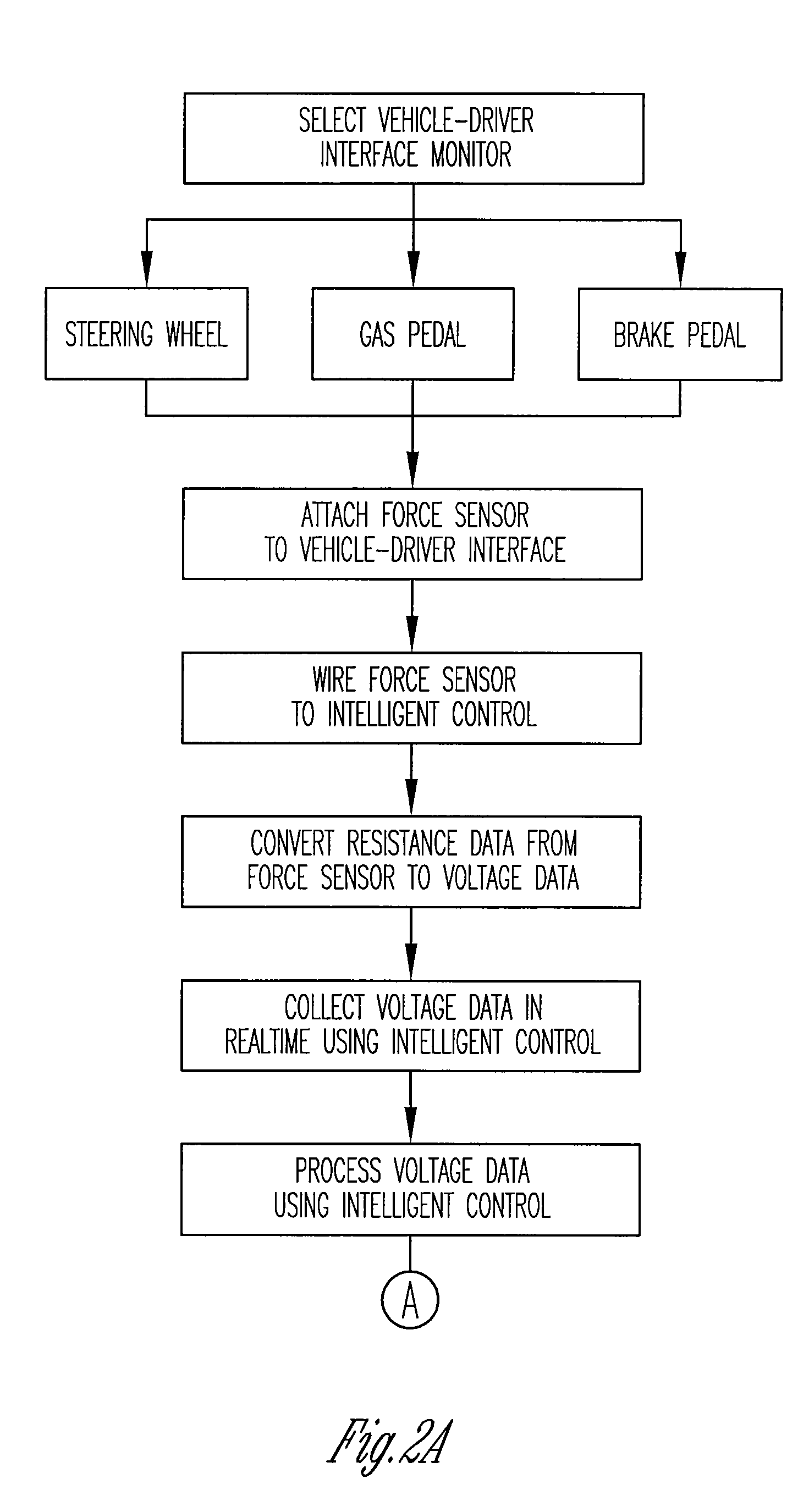
Vigilance monitoring technique for vehicle operators
InactiveUS20070080816A1Increase probabilityDigital data processing detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringMoving averageDriver/operator
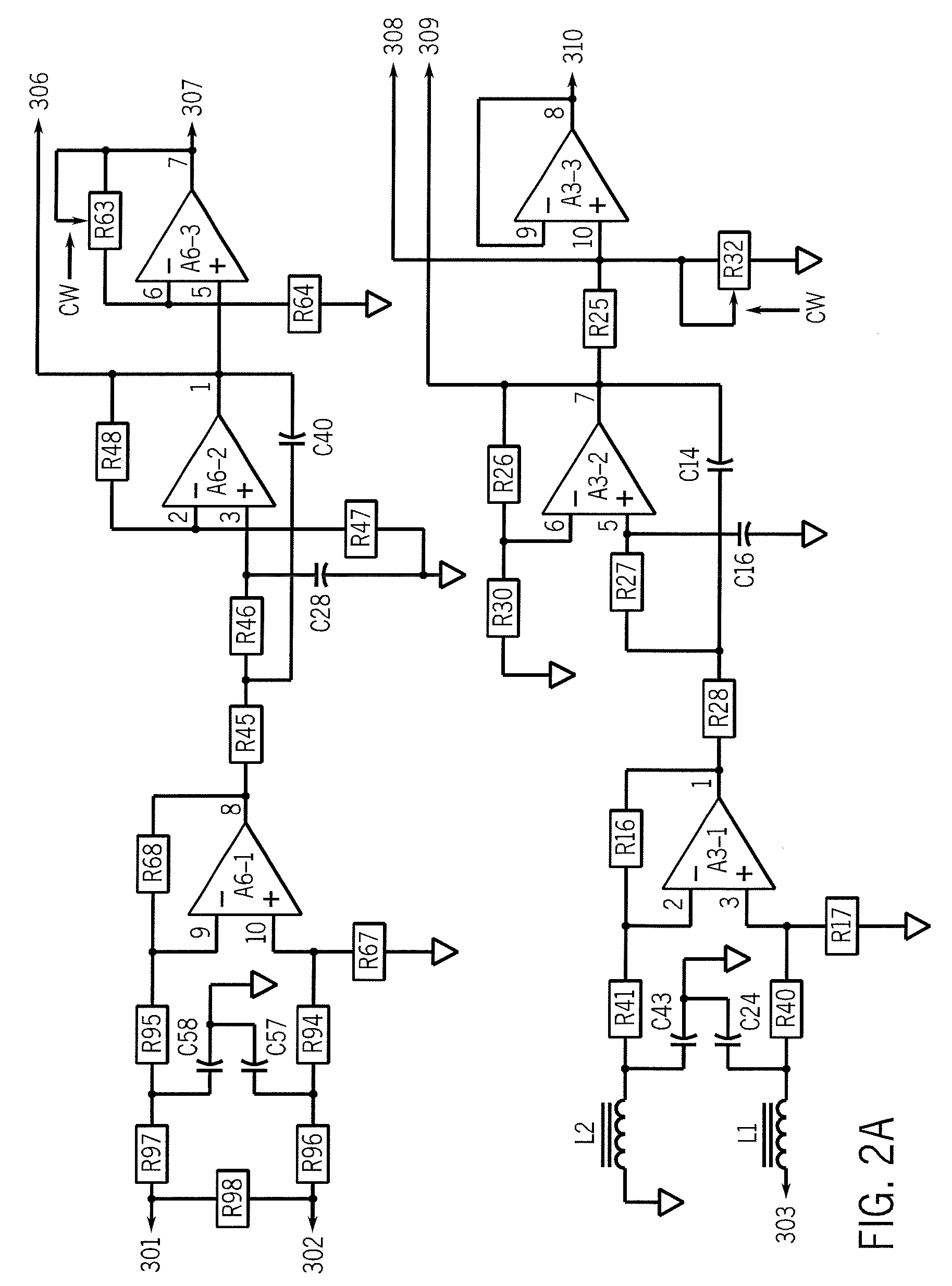
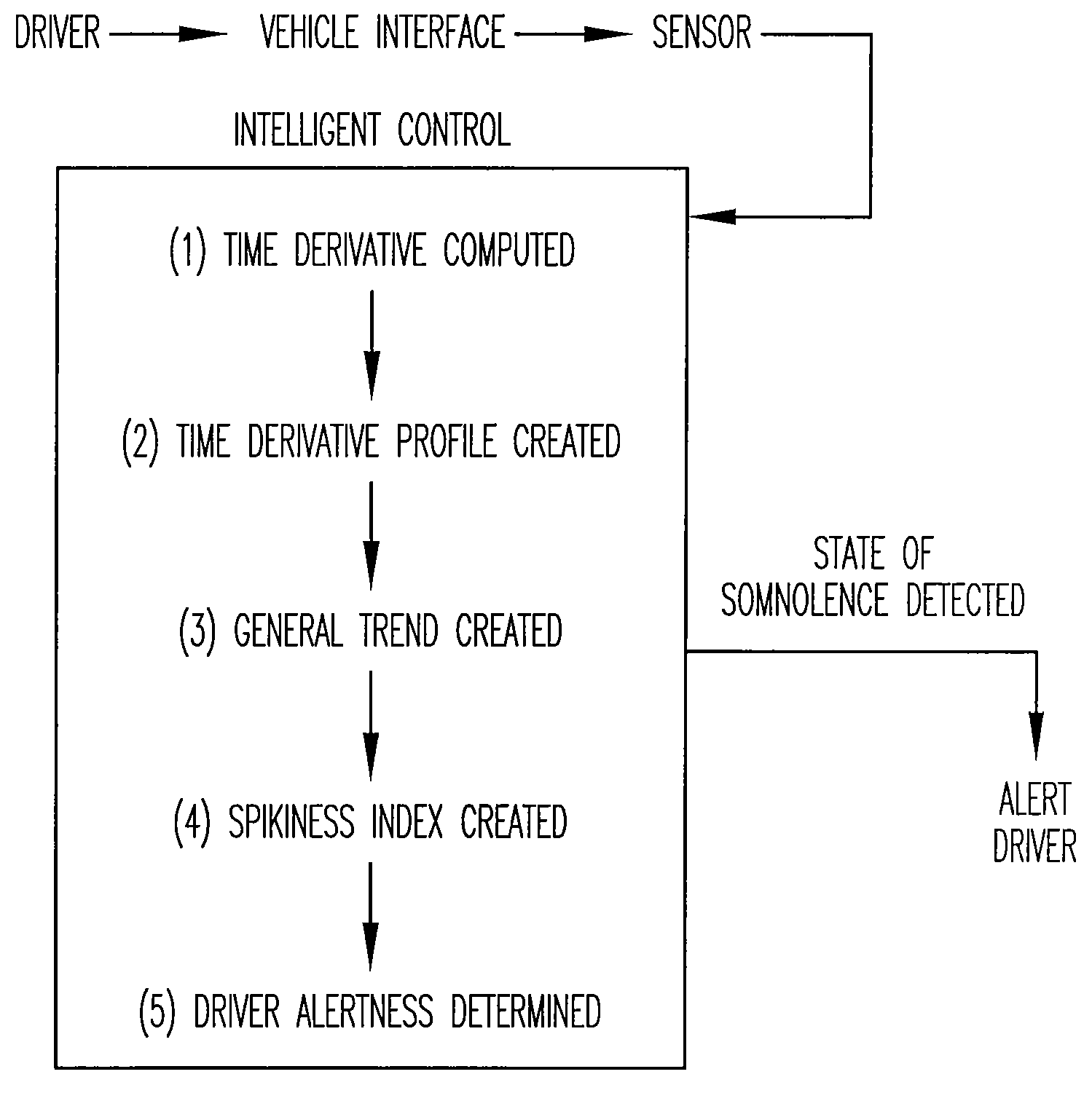
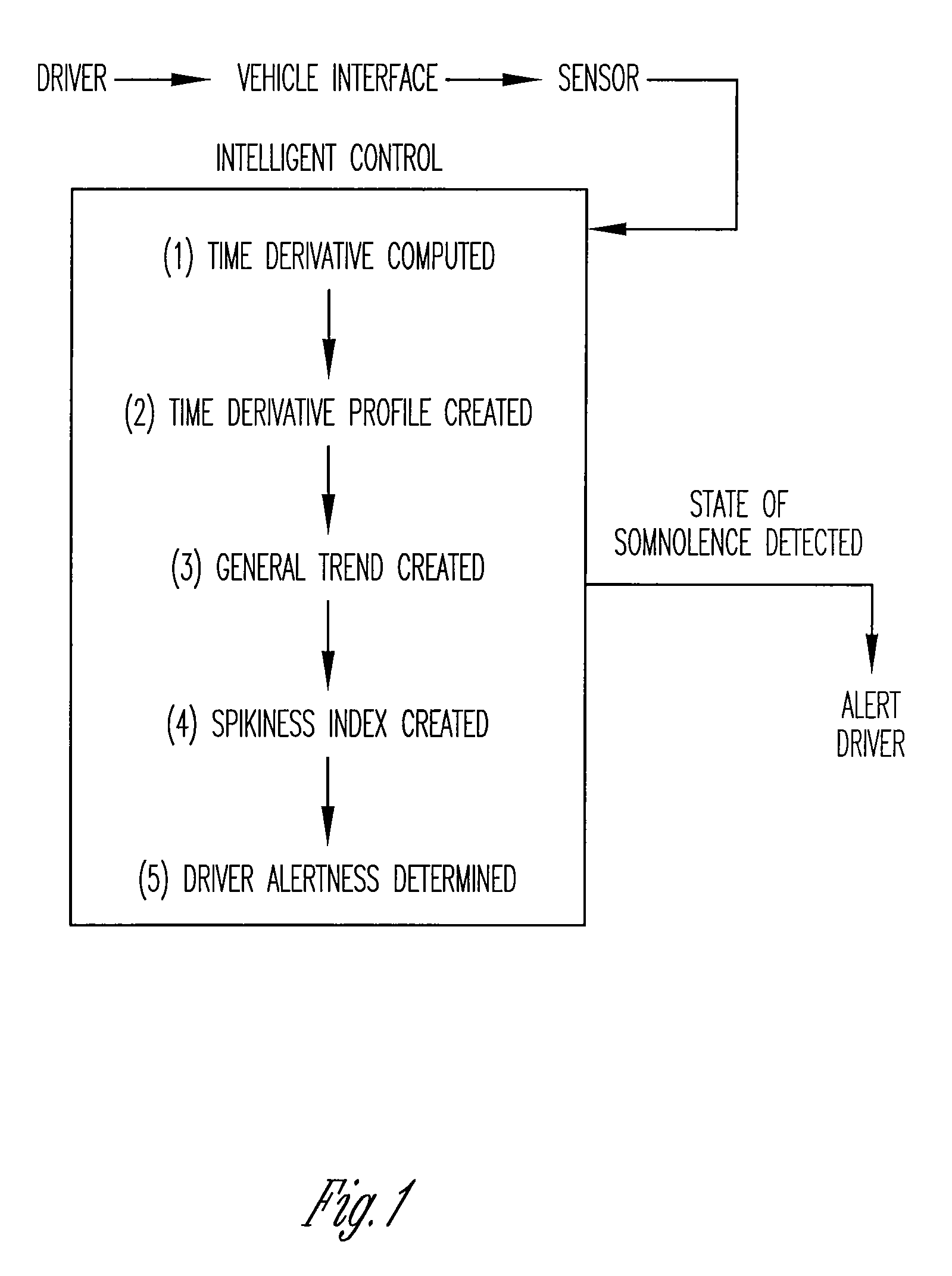
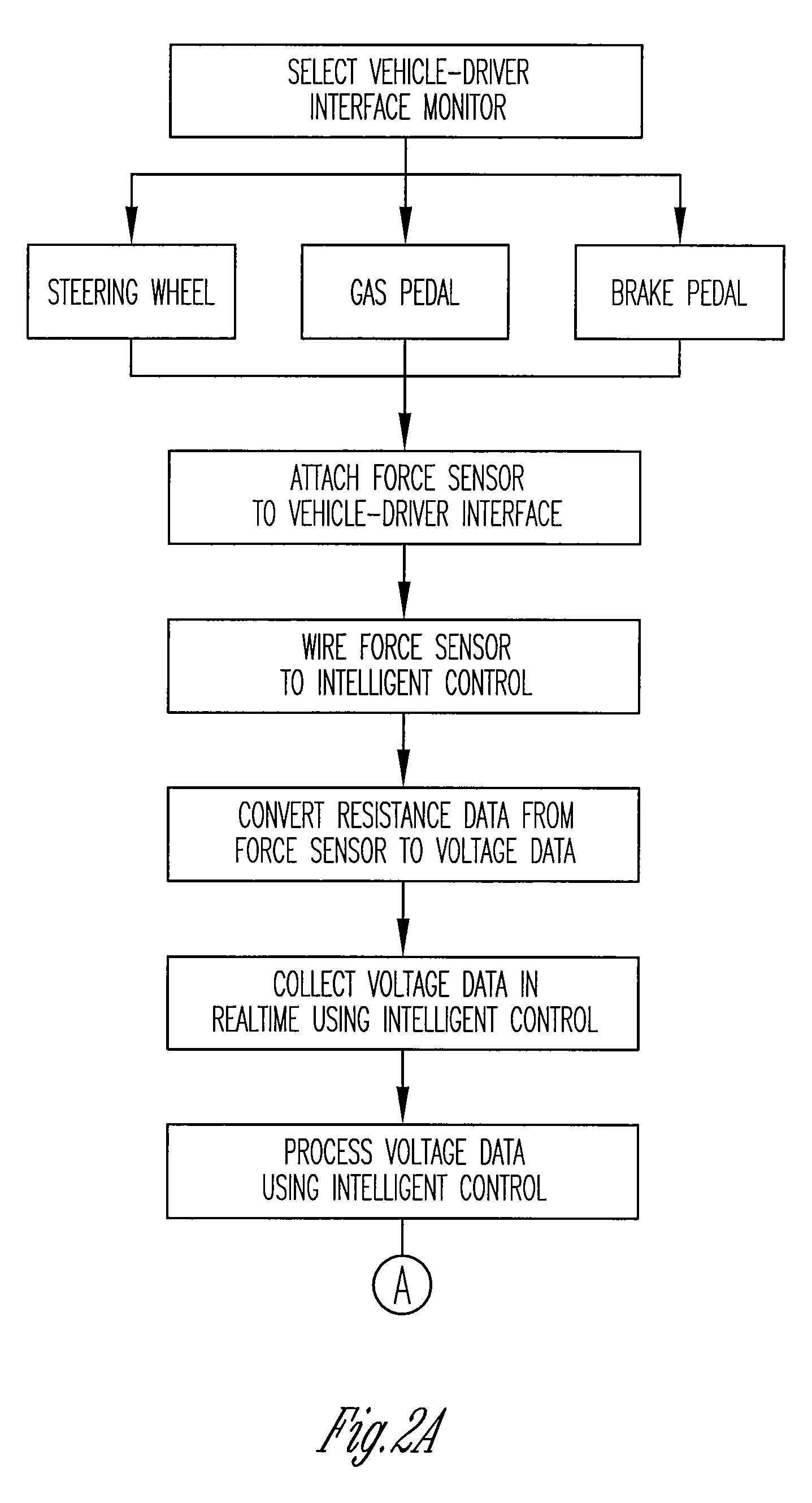
A vigilance monitoring system to determine the alertness of a driver of a vehicle. The system uses one or multiple sensors located at the driver-vehicle interface (steering wheel, accelerator, brakes). The sensor monitors the magnitude and frequency of the force (or displacement) exerted by a driver at the driver interface. A time derivative of the force or displacement profile is created. The variability of the time derivative of the force / displacement data from the general trend of the data as obtained by an optimized moving average of the data. An intelligent control system measures the variability and compares with an alertness rating scale to determine the alertness score of the driver and issue warning signals and actions as appropriate.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
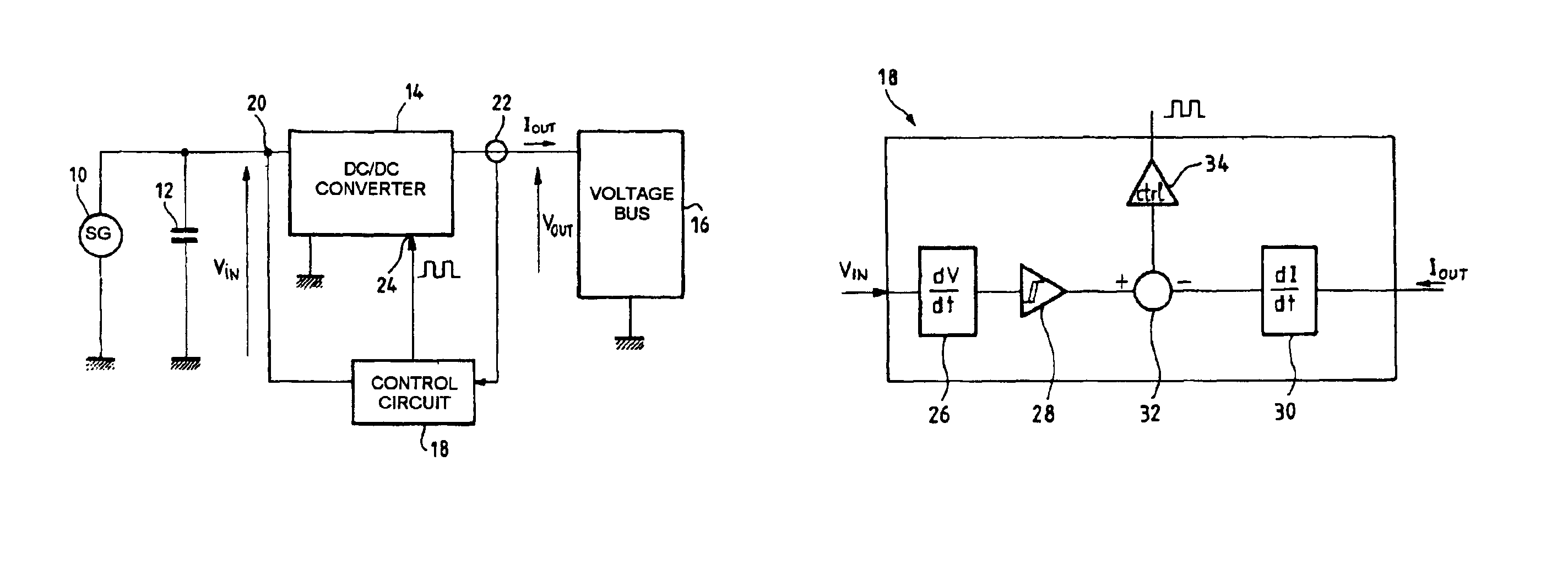
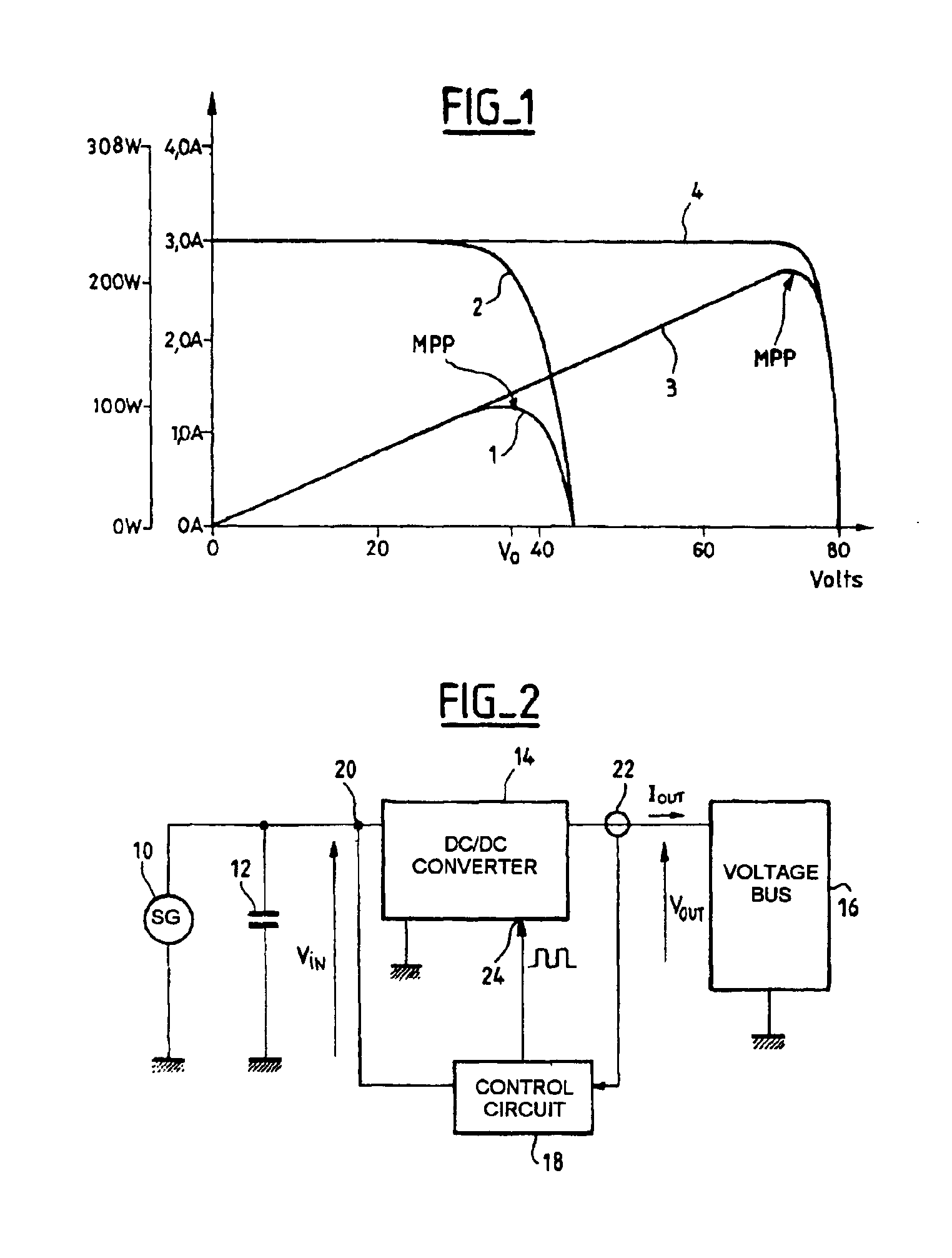
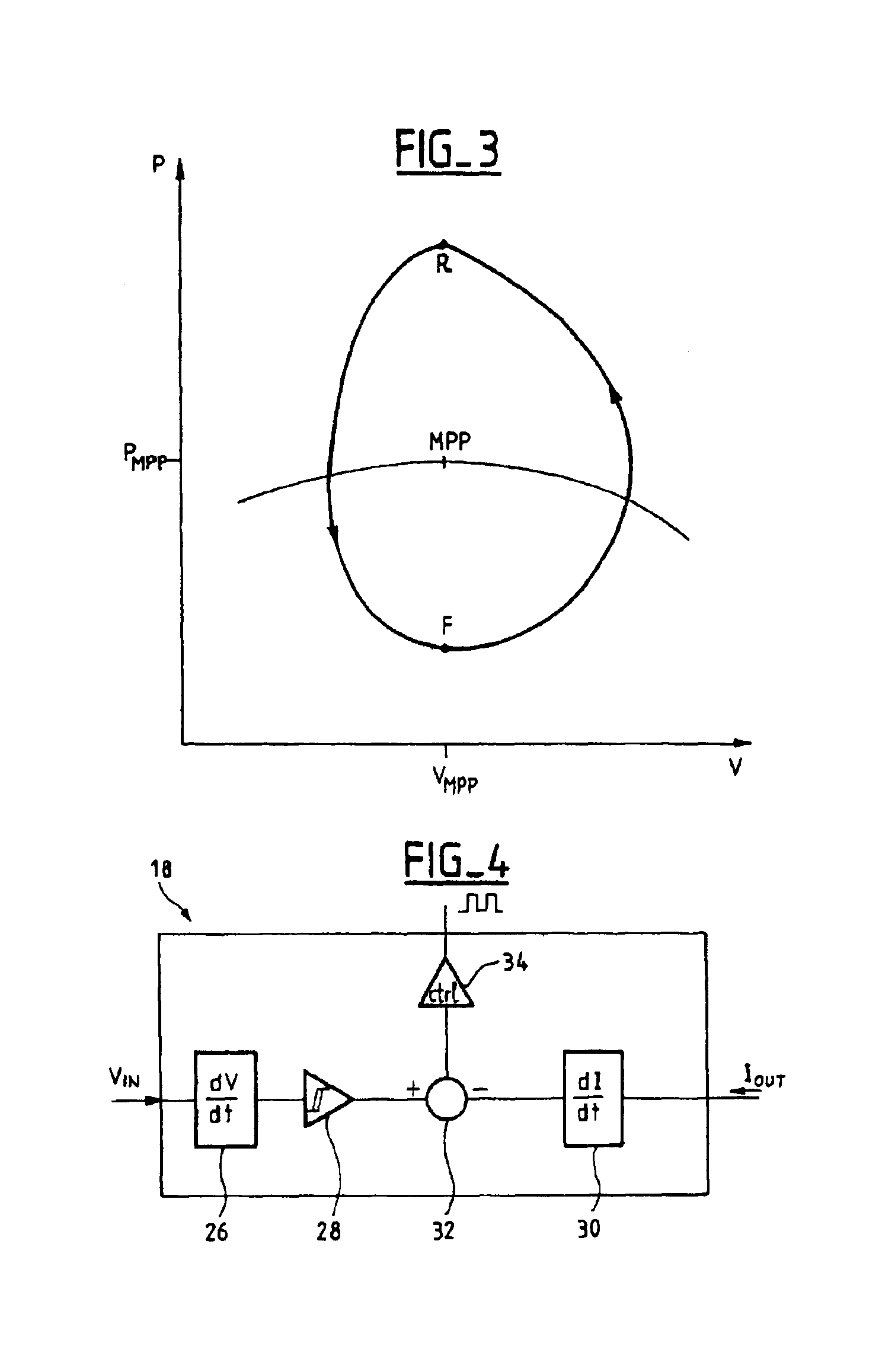
Circuit for conditioning a supply at the maximum power point
InactiveUS6919714B2Vast supplyBatteries circuit arrangementsPower supply linesTransverterControl circuit
A circuit for conditioning a power supply whose graph of the power supplied as a function of the voltage at the terminals of the supply features a maximum comprises a DC / DC converter with an input to which power is supplied by the power supply and an output from which power is supplied to a load. A control circuit controls the converter in accordance with a power set point applied to the converter. The set point is a rising set point when the time derivative of the converter input voltage is higher than a negative first threshold value and a falling set point when the time derivative of the converter input voltage is lower than a positive second threshold voltage. The rate of variation of the average power when the set point is a rising set point is lower than the opposite of the rate of variation of the average power when the set point is a falling set point. The conditioning circuit enables the supply to deliver power at the maximum power point and is simple to implement.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
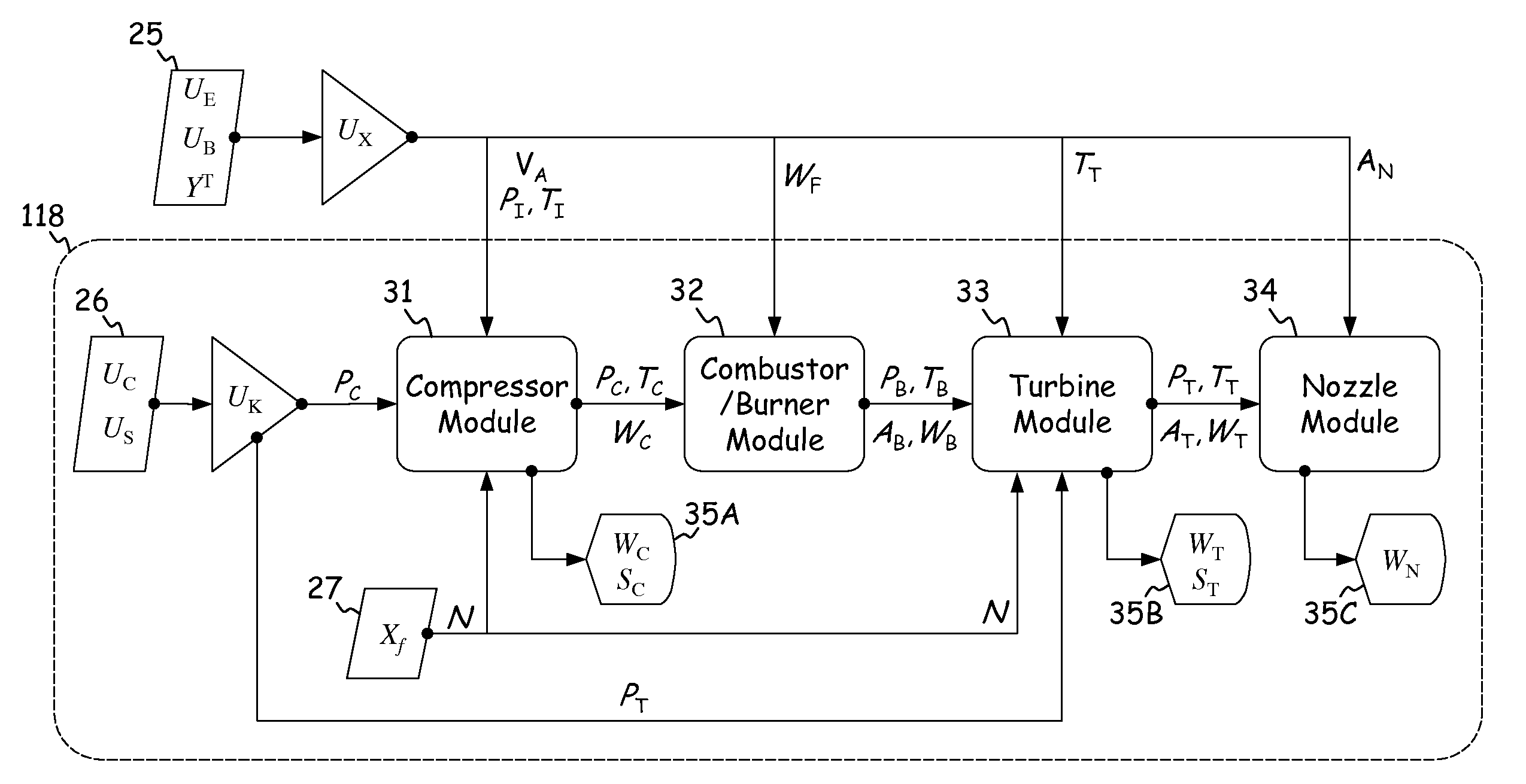
High fidelity integrated heat transfer and clearance in component-level dynamic turbine system control
ActiveUS20110054704A1Turbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsTemperatue controlControl flowEngineering
A system comprises a rotary apparatus, a control law and a processor. The rotary apparatus comprises a rotor and a housing forming a gas path therebetween, and the control law controls flow along the gas path. The processor comprises an output module, a plurality of temperature modules, a thermodynamic module, a comparator and an estimator. The output module generates an output signal as a function of a plurality of rotor and housing temperatures defined along the gas path, and the temperature modules determine time derivatives of the rotor and housing temperatures. The thermodynamic module models boundary conditions for the gas path, and the comparator determines errors in the boundary conditions. The estimator estimates the rotor and housing temperatures based on the time derivatives, such that the errors are minimized and the flow is controlled.
Owner:RTX CORP
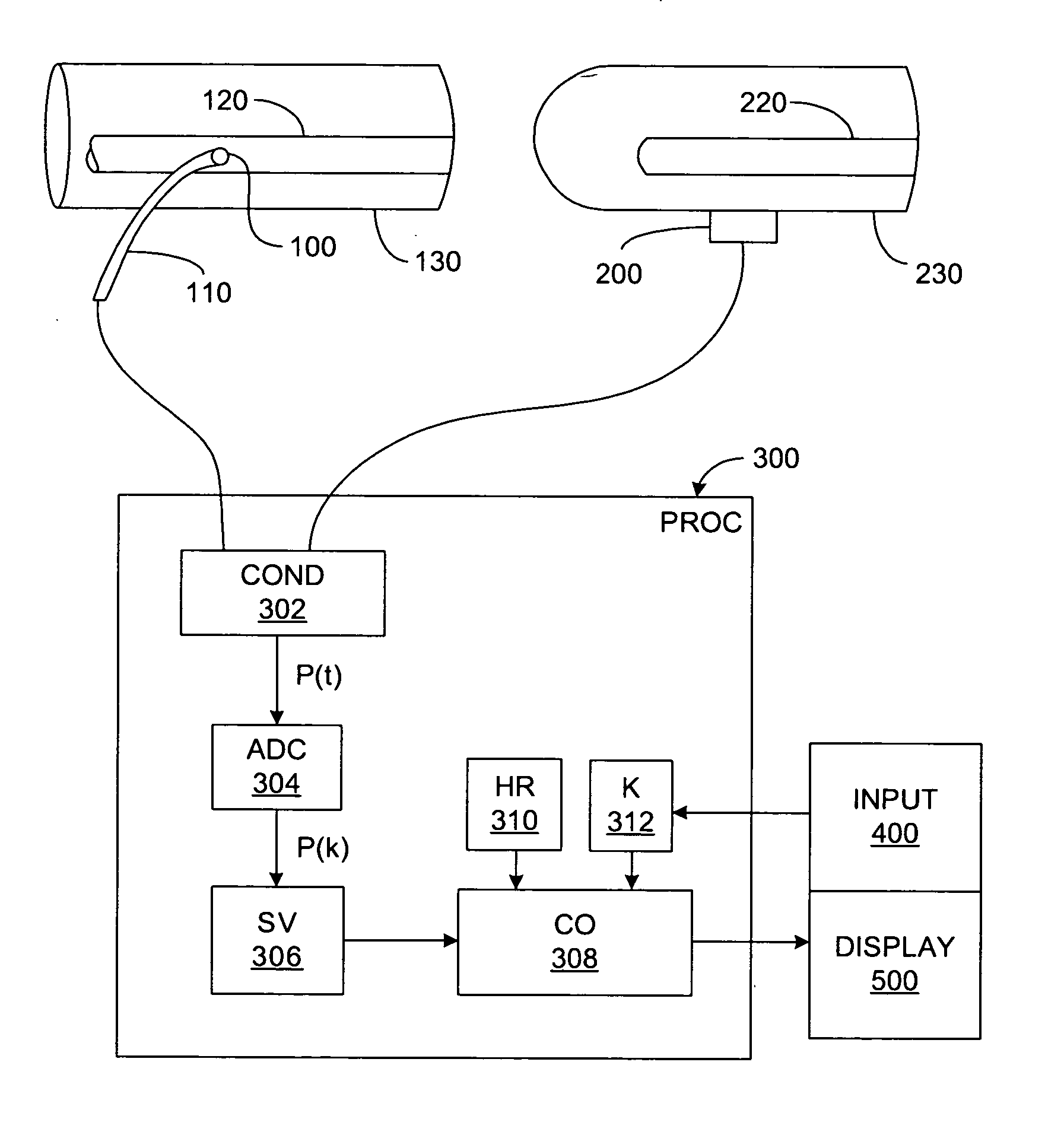
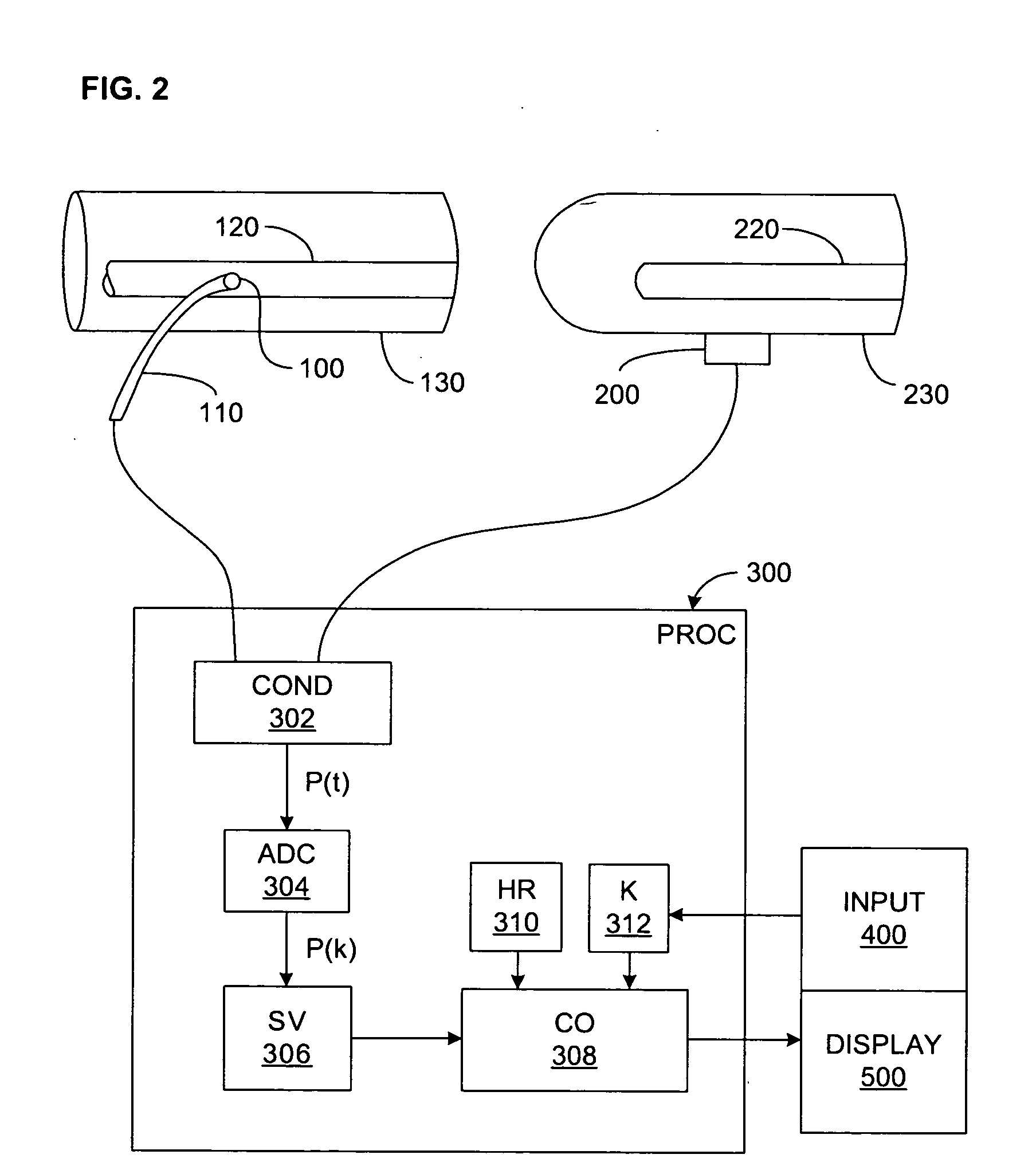
Non-invasive monitoring of hemodynamic parameters using impedance cardiography
InactiveUS6161038AImprove accuracySimple processCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationLeft Ventricular Ejection TimeHarmonic
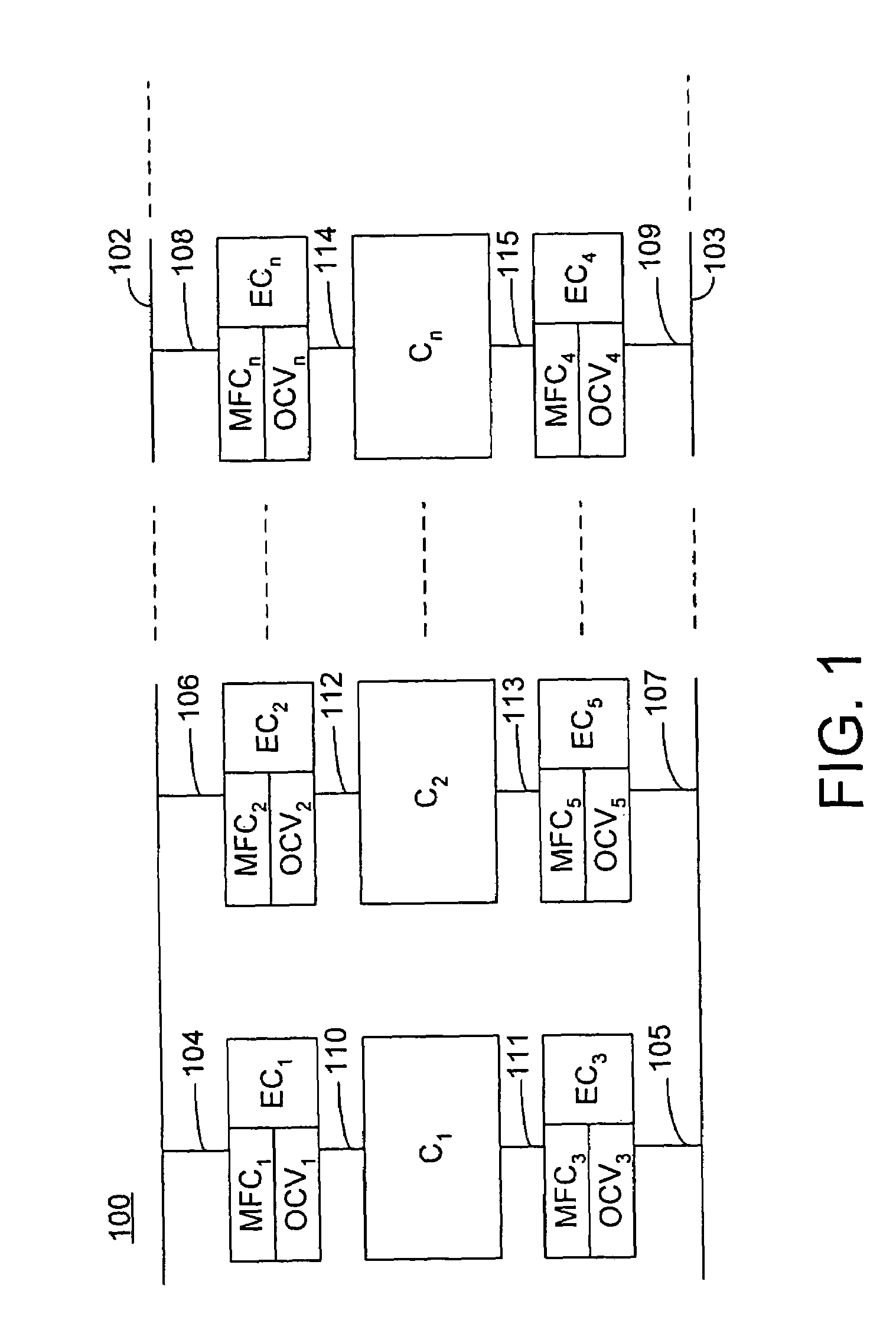
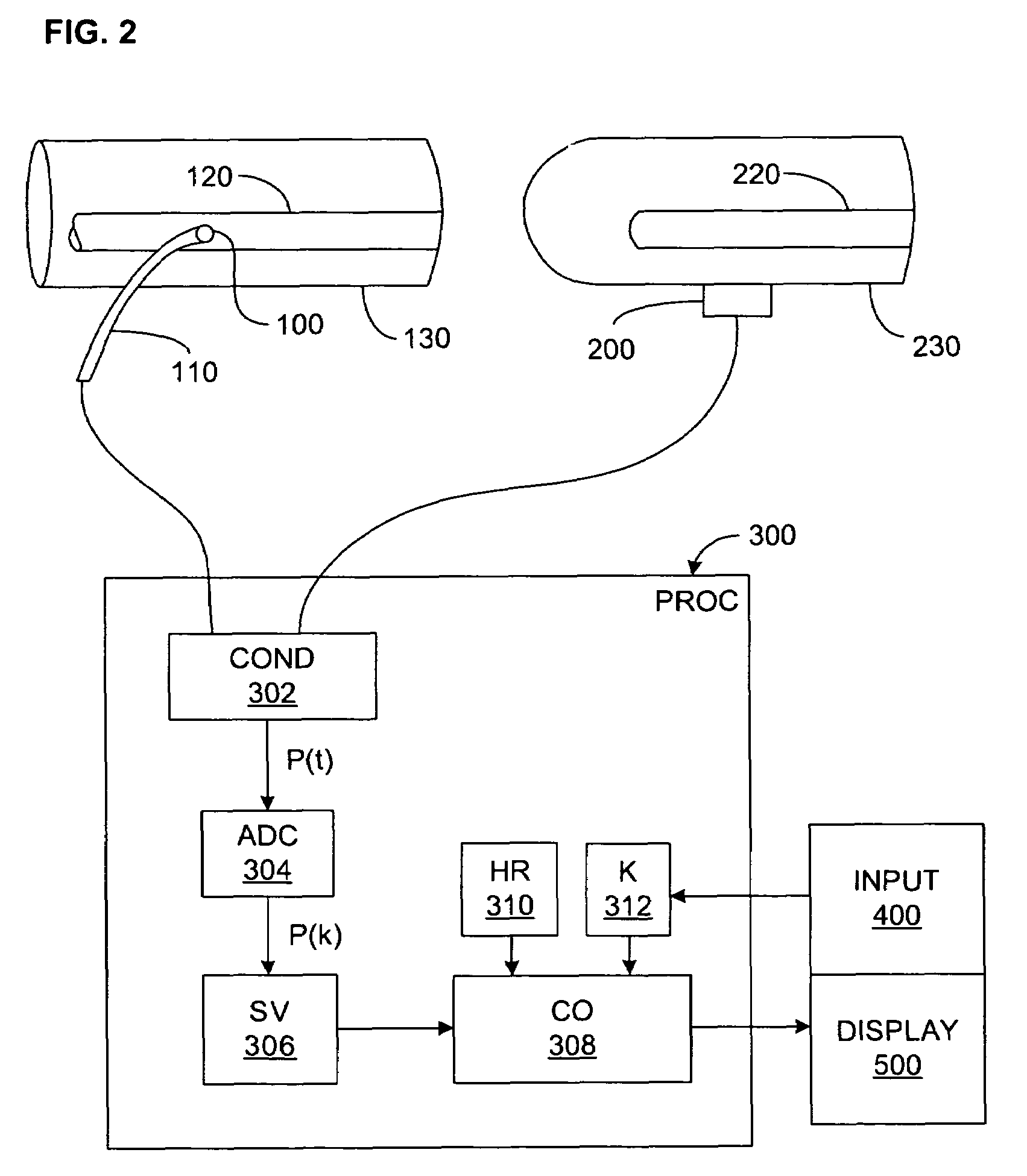
PCT No. PCT / SG97 / 00013 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 8, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 8, 1998 PCT Filed Apr. 7, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 37591 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 16, 1997A method and apparatus for determination of heart rate, heart stroke volume, heart stroke volume, and cardiac output from thoracic bioimpedance signals and electrocardiograms. A unique bioimpedance electrode arrangement is employed, and the bioimpedance signals are corrected for gain-phase-frequency distortion through the use of sinusoidal test signals through the measuring or detection electrodes to identify distortions and correct for same during actual measurements. Time-derivative bioimpedance signals are employed, the power spectrum calculated, and a novel autoconvolution procedure used to emphasize the heart rate harmonic. Breath waves and other signals not indicative of the patient's cardiocycles are removed. Left ventricular ejection time is derived from the bioimpedance signals, and an improved version of Kubicek's equation is employed to derive heart stroke volume and thus cardiac output.
Owner:RHEO GRAPHIC PTE
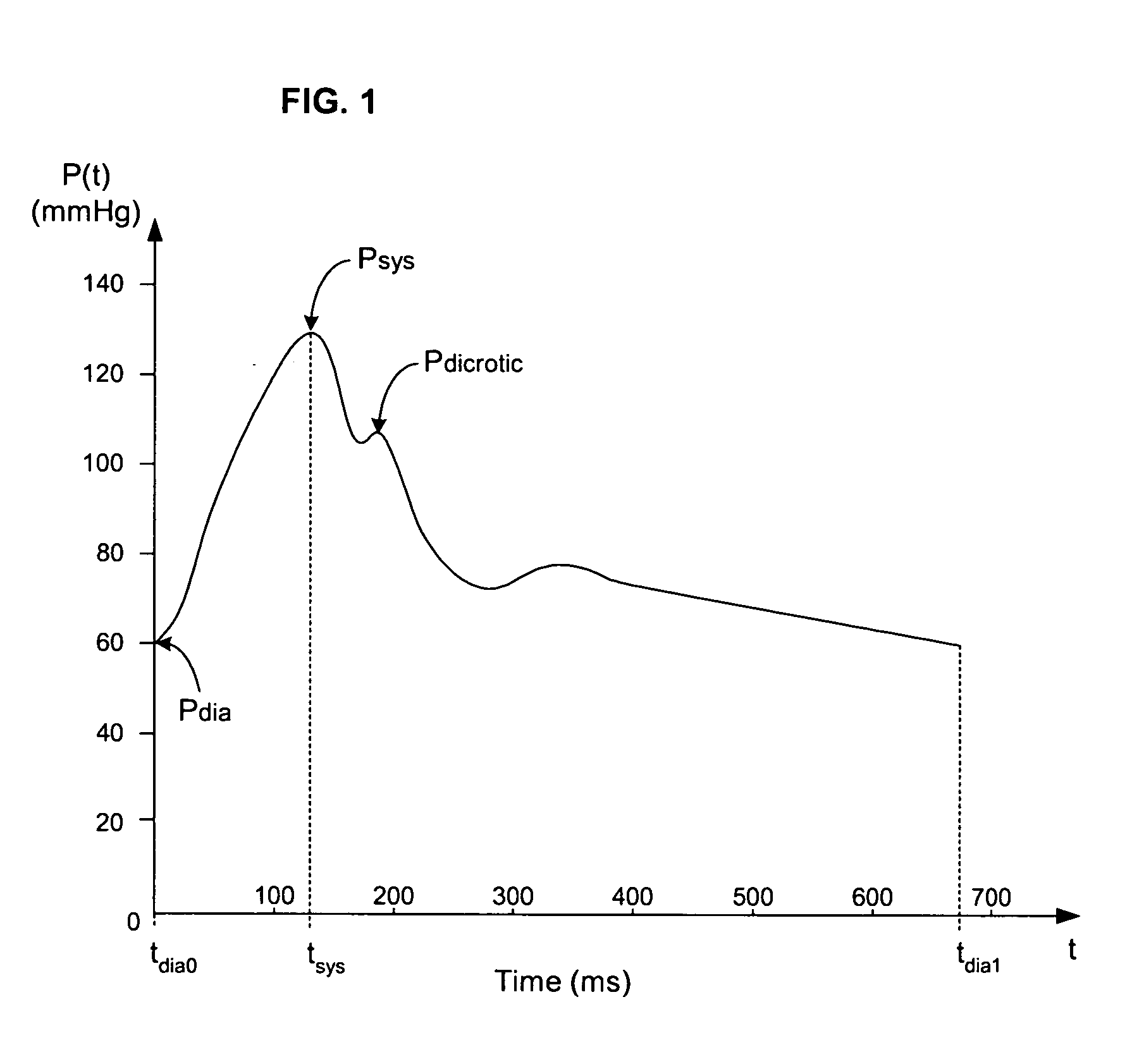
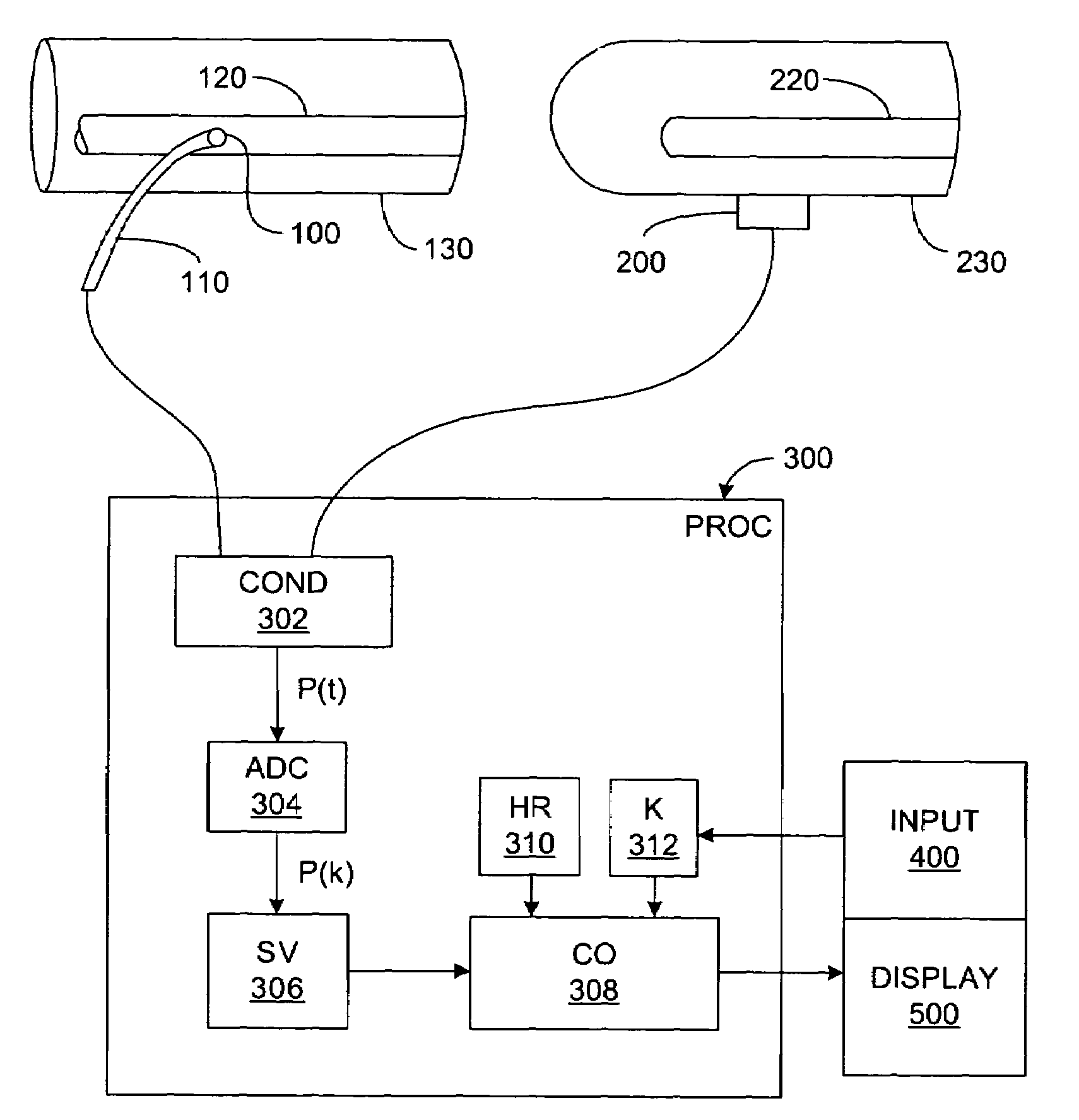
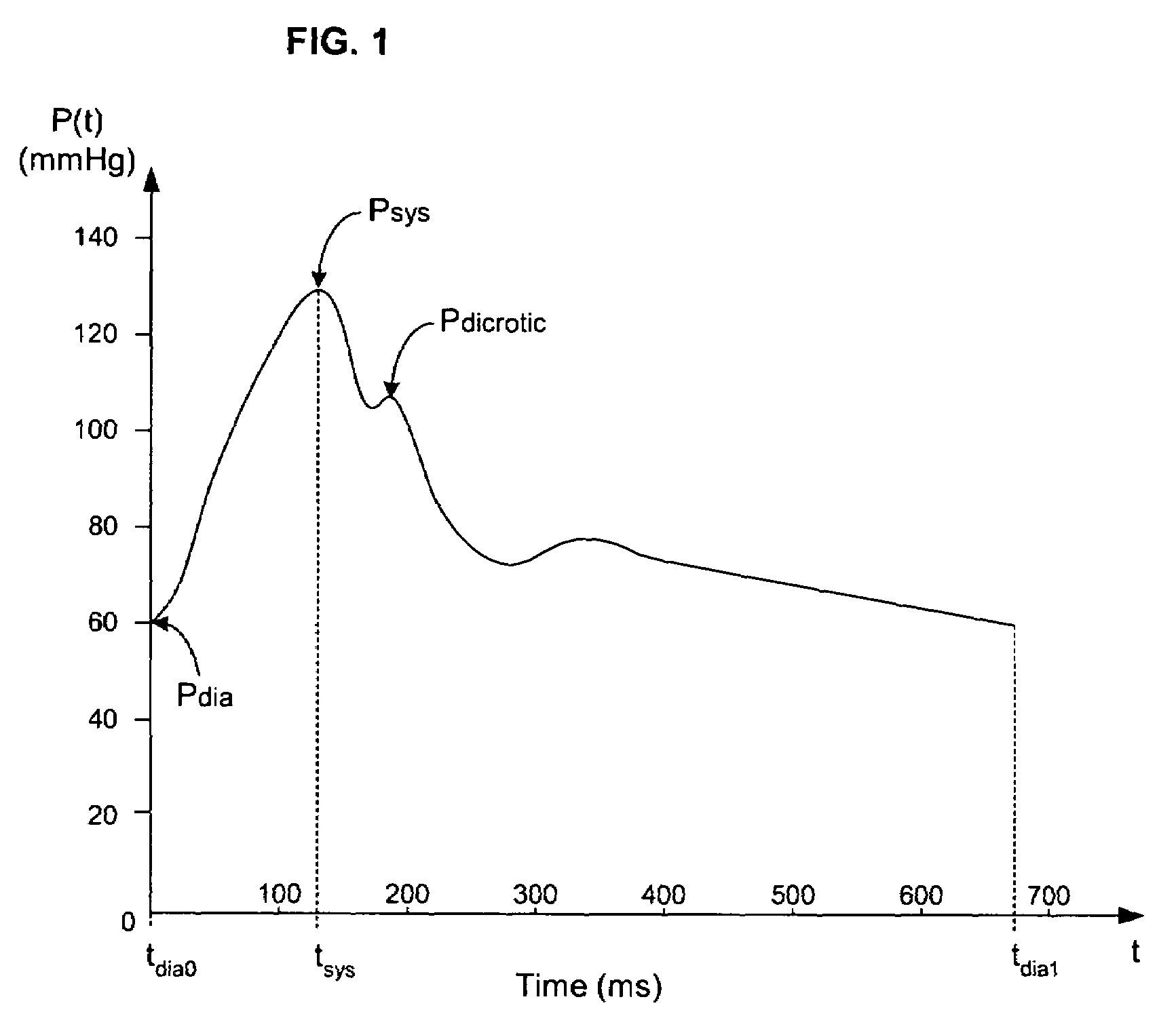
Pressure-based system and method for determining cardiac stroke volume
ActiveUS20050124903A1Potent effectEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterArterial pressure waveformDecreased mean arterial pressure
Cardiac stroke volume (SV) of a subject is estimated as a function of a value derived from a measured arterial pressure waveform. The value may be the standard deviation, or a function of the difference between maximum and minimum pressure values, or a function of either the maximum value of the first time derivative or the absolute value of the minimum of the first time derivative of the pressure waveform, or both, or a function of the magnitude of one or more spectral components of the pressure waveform at a frequency corresponding to the heart rate. Cardiac output is then estimated as the product of the subject's heart rate and SV, scaled by a calibration constant. Arterial pressure may be measured invasively or non-invasively.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
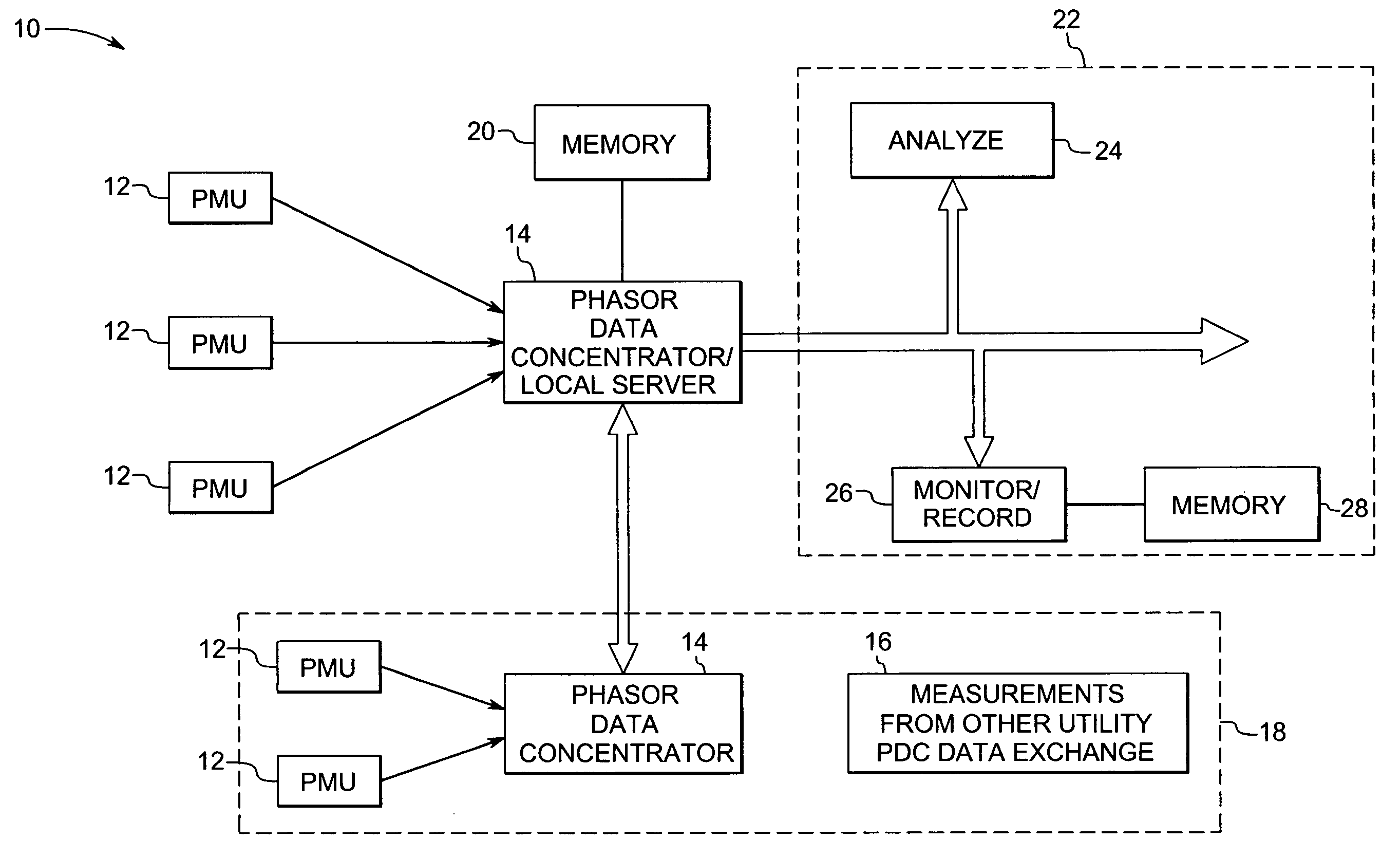
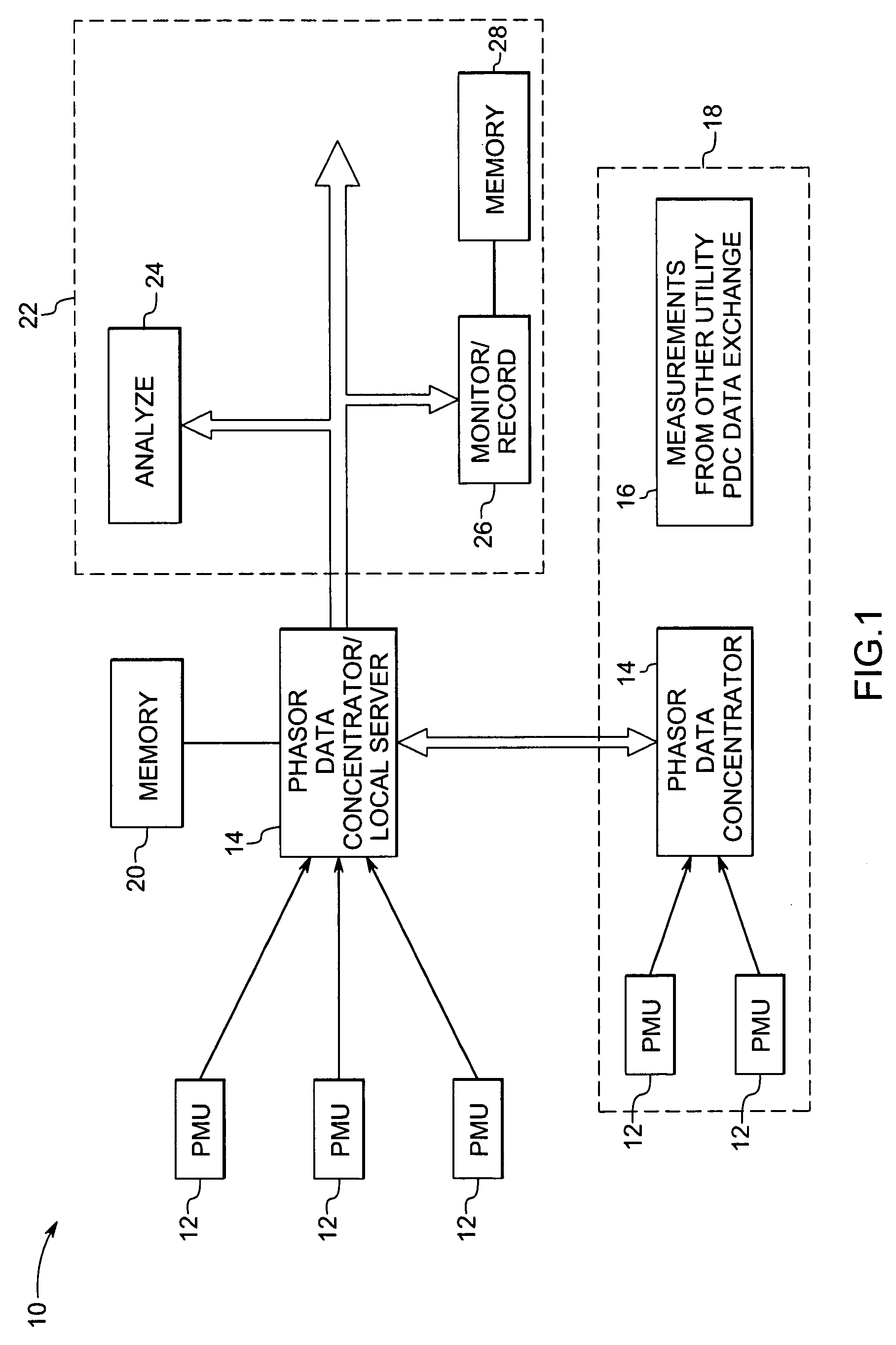
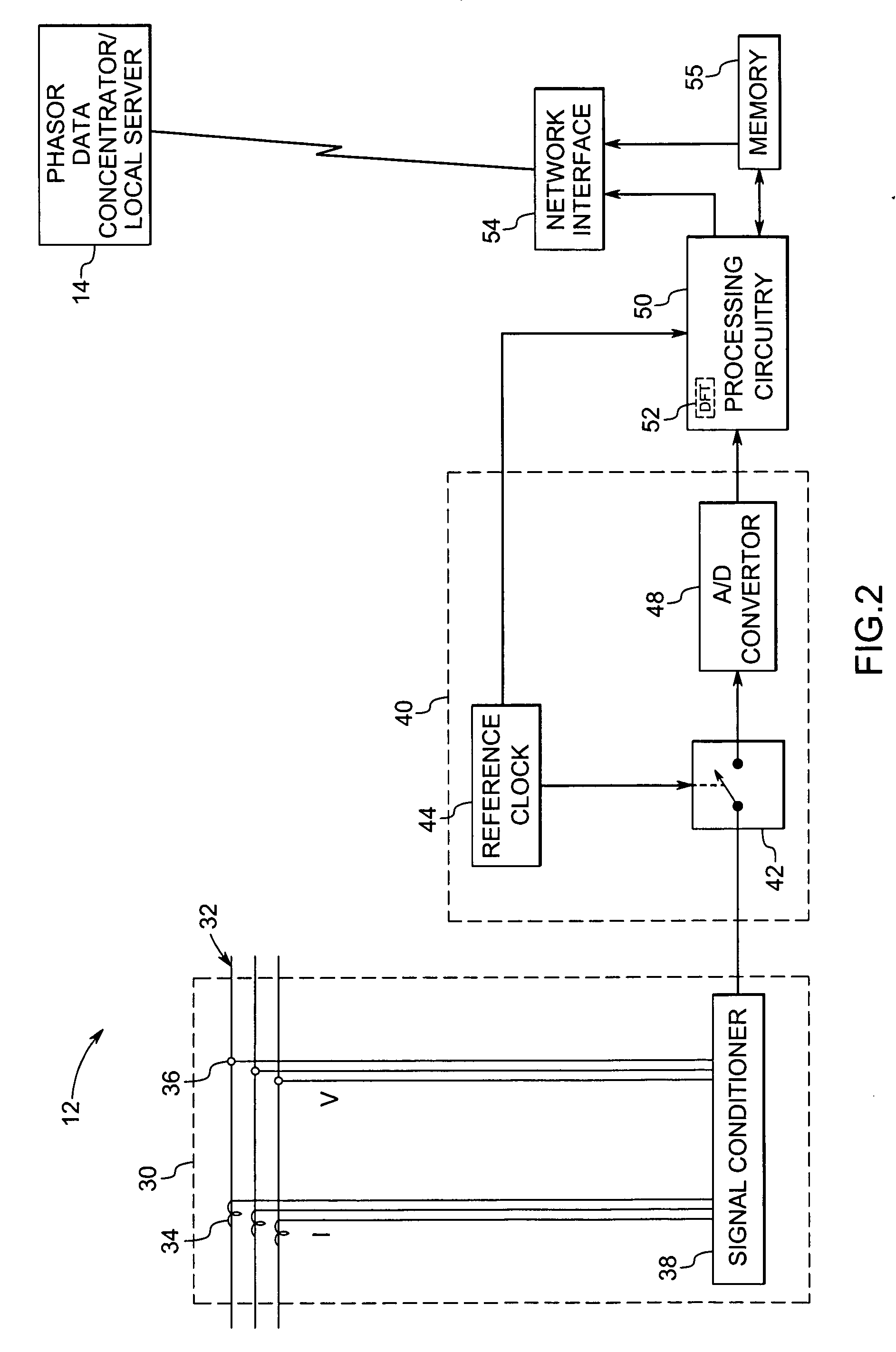
System and method for synchronized phasor measurement
ActiveUS20060247874A1Current/voltage measurementSystems intergating technologiesPhasorTime derivative
A phasor measurement system is provided for computing synchronized phasor measurements. The phasor measurement system includes acquisition circuitry for acquiring voltage or current values from a power line, sampling circuitry for sampling the voltage or current values, and processing circuitry for computing a phasor and at least one time derivative of the phasor based on the sampled voltage or current values and for computing a synchronized phasor value based on the phasor and the at least one time derivative of the phasor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
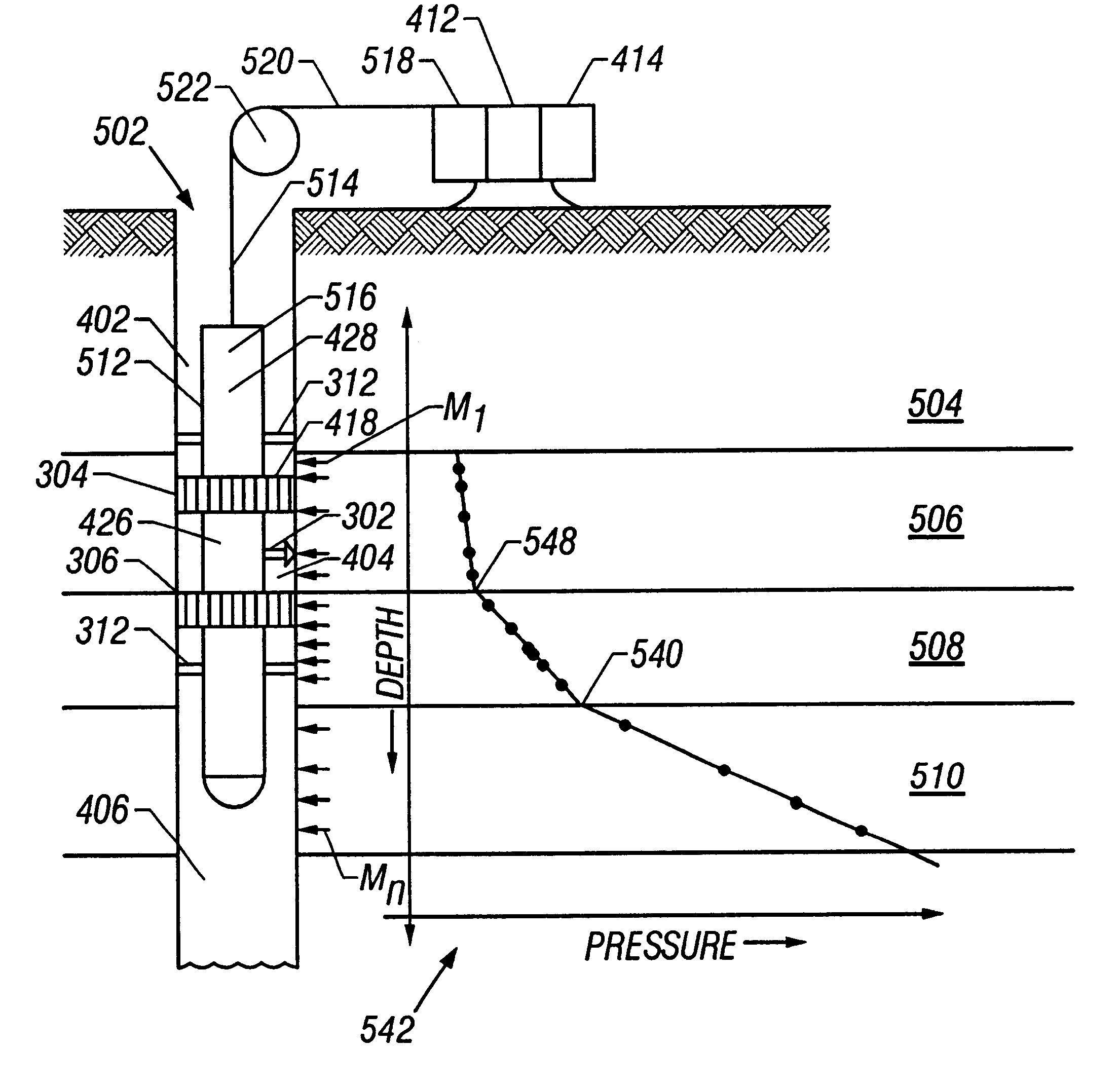
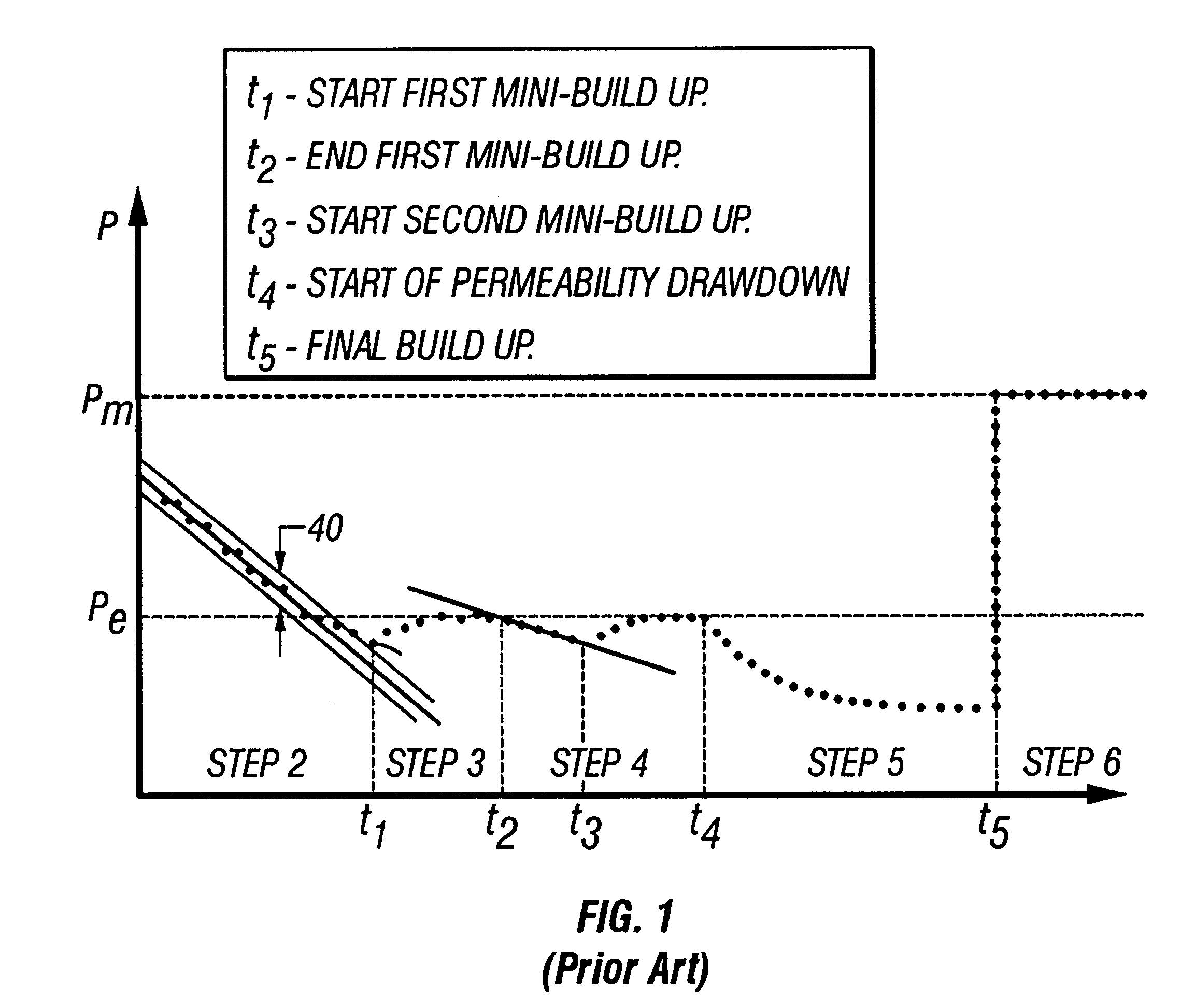
Method for in-situ analysis of formation parameters
A method of performing a formation rate analysis from pressure and formation flow rate data. Pressure and flow rate data are measured as fluid is withdrawn from a formation. Variable system volume is accounted for. The pressure and flow rate data are correlated using a multiple linear regression technique. Time derivative terms related to pressure and flow rate are smoothed using a summation technique, thereby providing better correlations than using the time derivatives directly. Formation parameters comprising formation permeability, formation pressure, and fluid compressibility may be determined from the correlation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
System and method for servo control of nonlinear electromagnetic actuators
InactiveUS20060171091A1Eliminate impactRemove noiseElectrical controlAC motor controlResonance measurementInstability
Servo control using ferromagnetic core material and electrical windings is based on monitoring of winding currents and voltages and inference of magnetic flux, a force indication; and magnetic gap, a position indication. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output; and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target of the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current. Incorporation of permanent magnet material permits the target current to be zero, achieving levitation with low power, including for a monorail deriving propulsion from the levitation magnets. Linear magnetic approximations lead to the simplest controller, but nonlinear analog computation in the log domain yields a better controller with relatively few parts. When servo-controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, electronic LC resonance measurements determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume.
Owner:SEALE JOSEPH B +1
Contactless respiration monitoring of a patient
ActiveUS20110112425A1Easy to handleReliable of direction changeRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsPhase shiftedRadar
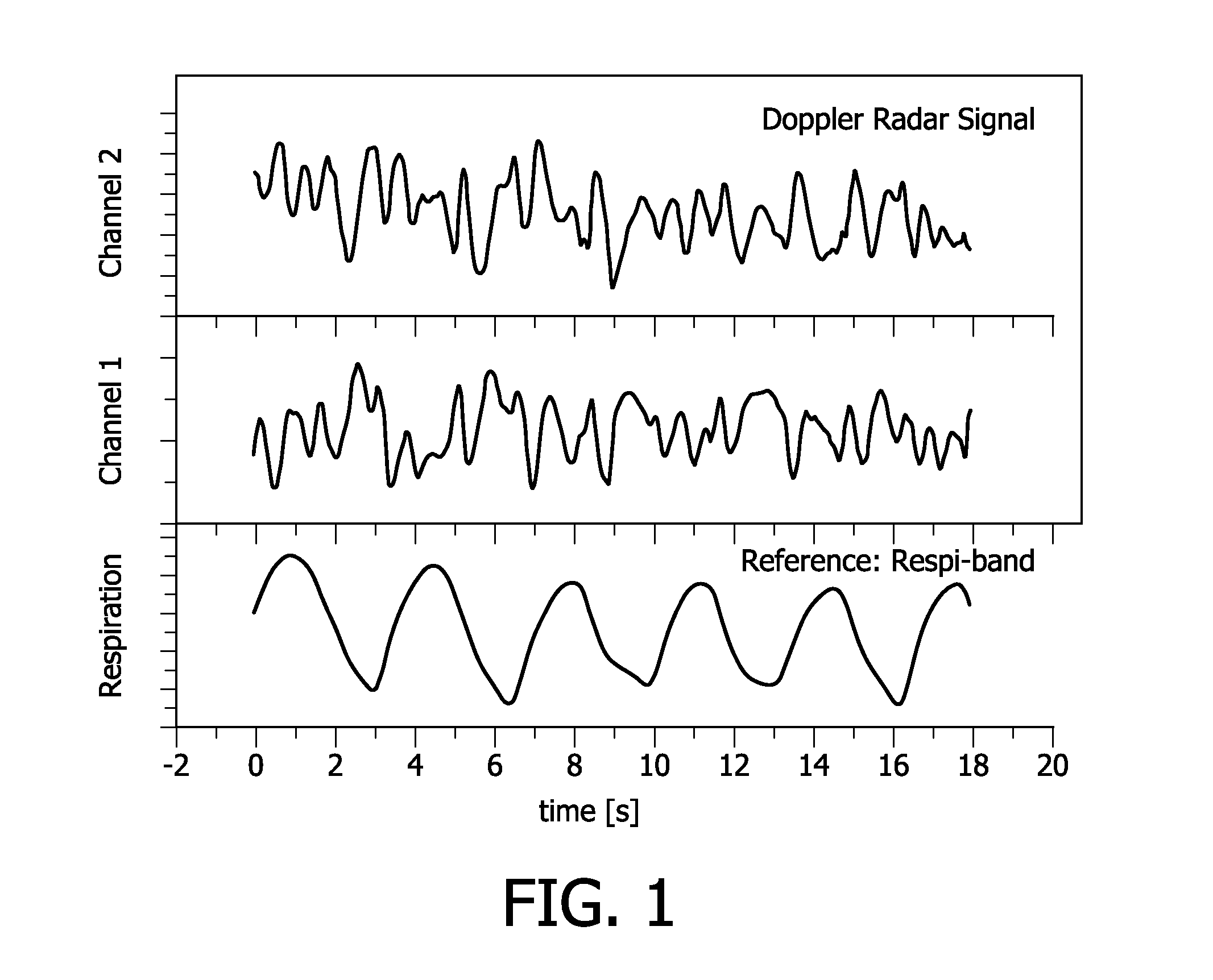
The invention relates to a method for detection of respiration of a patient comprising the following steps: emitting an electromagnetic signal towards the patient; receiving a reflected electromagnetic signal reflected from the patient; converting the reflected electromagnetic signal, yielding a first signal; phase-shifting the reflected electromagnetic signal and converting the phase-shifted reflected electromagnetic signal, yielding a second signal; determining a first vector being defined by the time derivatives of the first signal and the second signal, for a common first point in time; determining a second and vector being defined by the time derivatives of the first signal and the second signal, for a common second point in time; and calculating the scalar product of the normalized first vector and the normalized second vector as an indicator value for a change from expiration to inspiration of the patient or vice versa. A change from expiration to inspiration of the patient or vice versa is preferably indicated if the indicator value is below a threshold value, preferably below a value of 0. In this way, a possibility for contactless remote respiration monitoring of a patient based on the Doppler radar principle is provided which is reliable and easy to handle.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
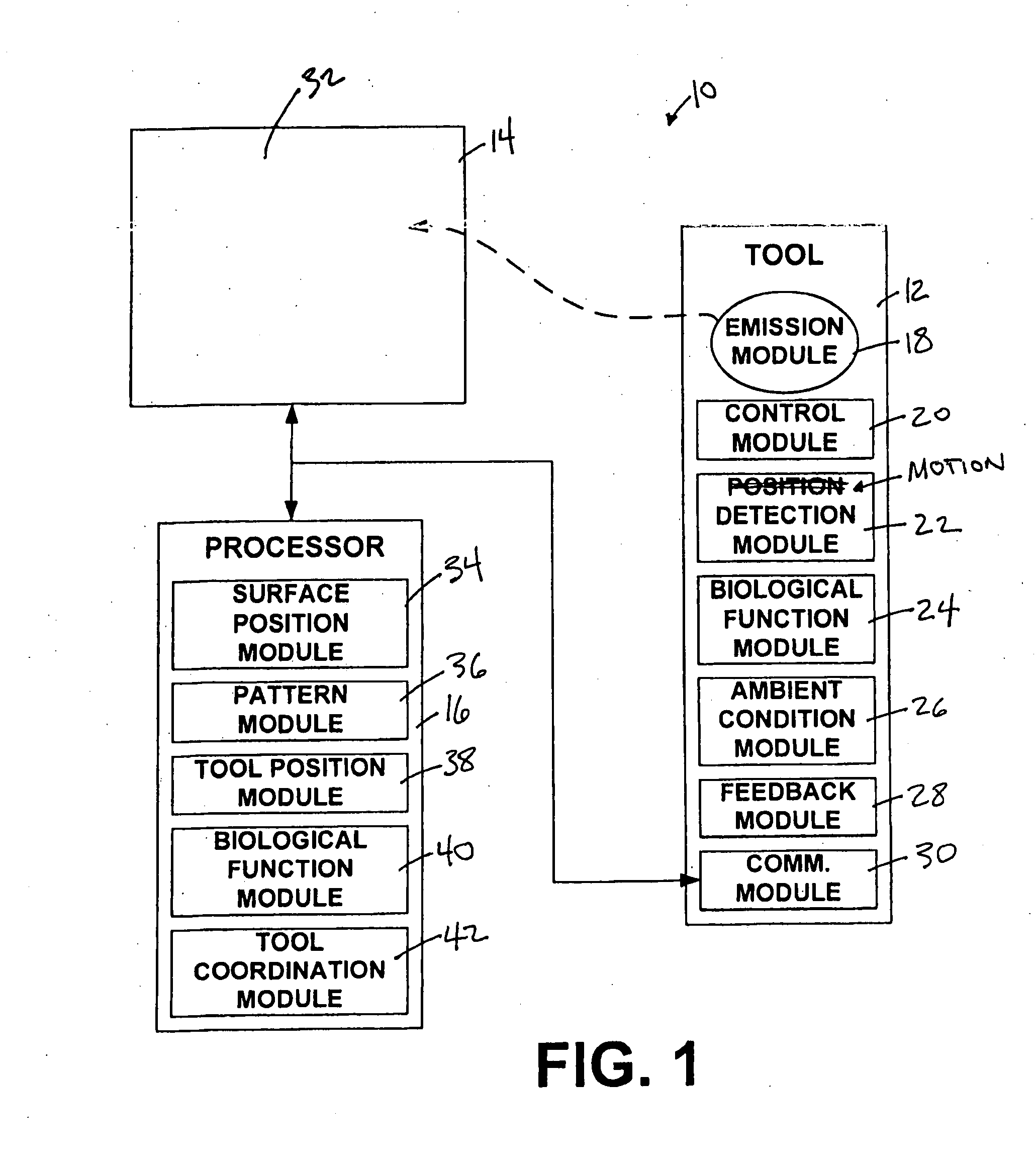
Optical tool with dynamic electromagnetic radiation and a system and method for determining the position and/or motion of an optical tool
InactiveUS20080189046A1Strong specificityDigital computer detailsAcceleration measurementTime changesRotational degrees of freedom
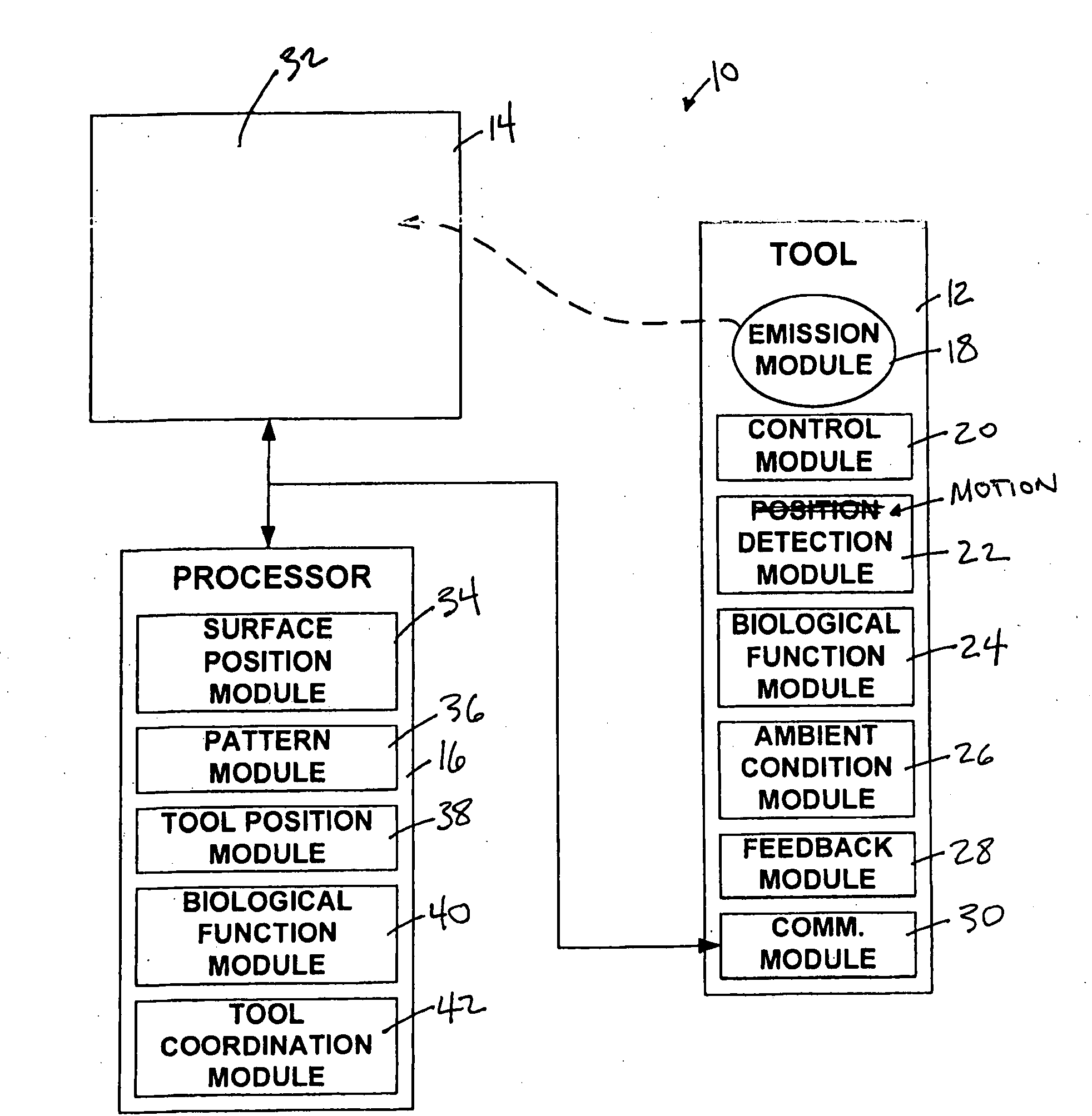
A tool configured to emit electromagnetic radiation therefrom such that one or more aspects of the emission of the electromagnetic radiation may be varied as a function of time. By varying the emission of the electromagnetic radiation as a function of time, the tool may enable information related to its position and / or motion to be determined with an enhanced specificity based on detection of the emitted electromagnetic radiation. For example, the varying emission of the electromagnetic radiation may enable a three dimensional position of the tool to be determined, may enable the position of the tool to be determined in three rotational degrees of freedom, and / or may enable time derivatives of these (and other) position information to be determined to quantify motion of the tool. In some implementations, the emission of the electromagnetic radiation may be varied such that position and / or motion information related to a plurality of tools may be determined simultaneously (or substantially simultaneously).
Owner:FLATFROG LAB
Method and apparatus for welding
A short circuit arc welding system is disposed. The control scheme uses a current command signal to drive the output current. The command signal is comprised of a long-term current command that sets the long-term current command level and a real-time or short-by-short current command. Arc voltage feedback is used to determine if the desired arc length is present and to adjust the long-term command. The short-by-short current command is derived from real-time arc current feedback and is used to control the burn-off rate by an instantaneous, or short-by-short, adjustment of the current command. A function of the time derivative of arc power, less the time derivative of arc current, is used to detect, in real time, when the short is about to clear. A stop algorithm is employed that monitors the arc on a short-by-short basis. When the process is ending a very low current level is provided to avoid forming a ball. However, if a short is created, (indicated by a drop in arc voltage) after the low current level, a burst of energy is provided to clear of burn off the short. After the short is cleared, very low current is again provided to avoid forming a large ball. This is repeated until the wire stops and the process ends.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Vigilance monitoring technique for vehicle operators
InactiveUS7663495B2Increase probabilityDigital data processing detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringMoving averageSteering wheel
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
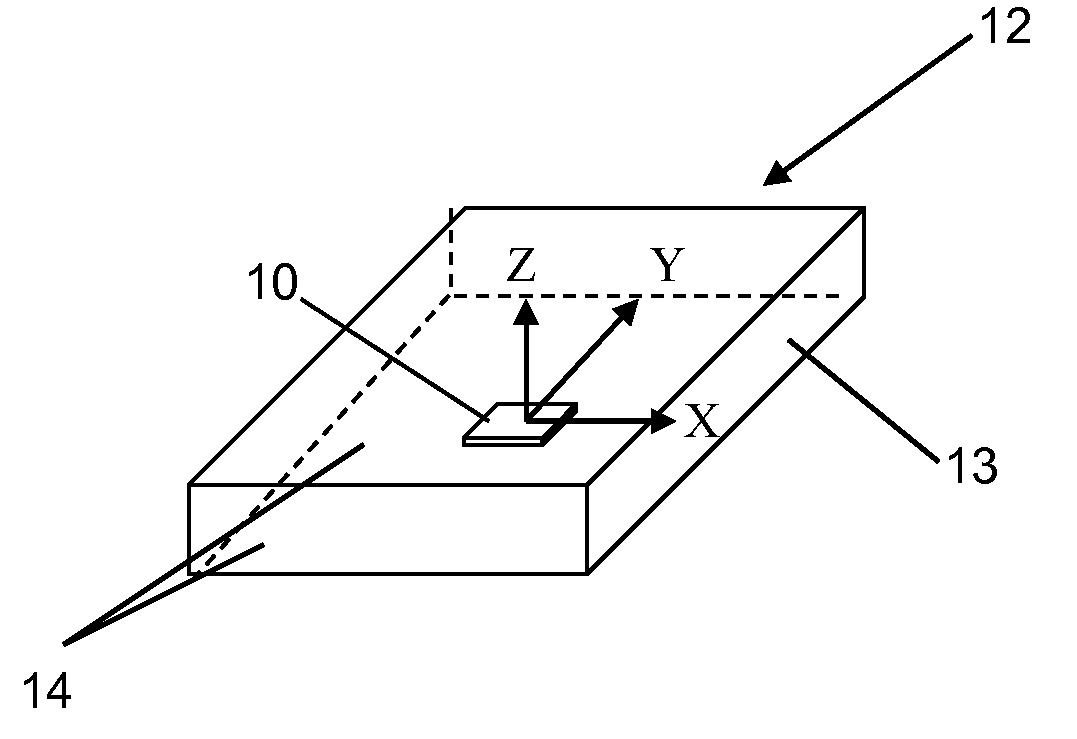
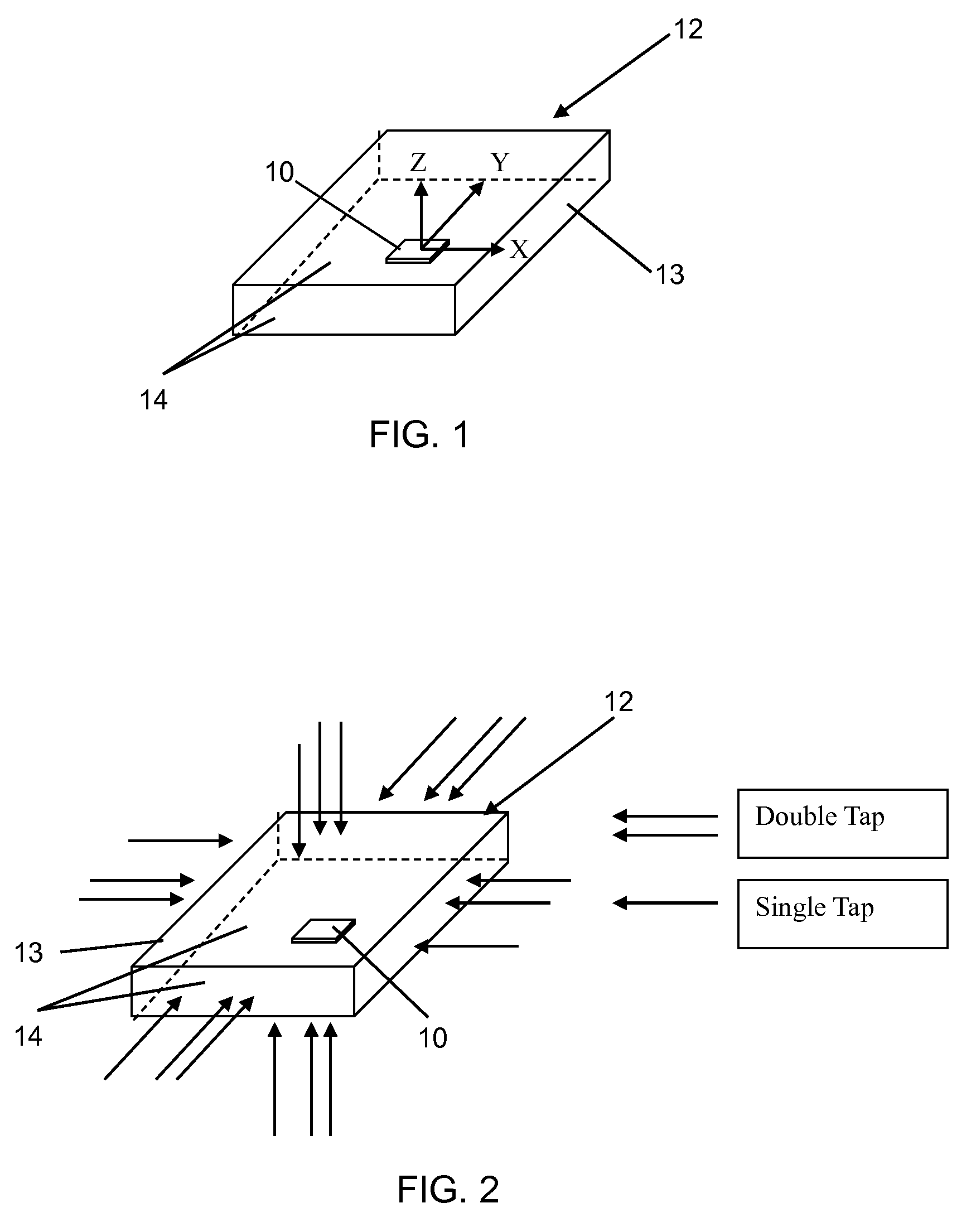
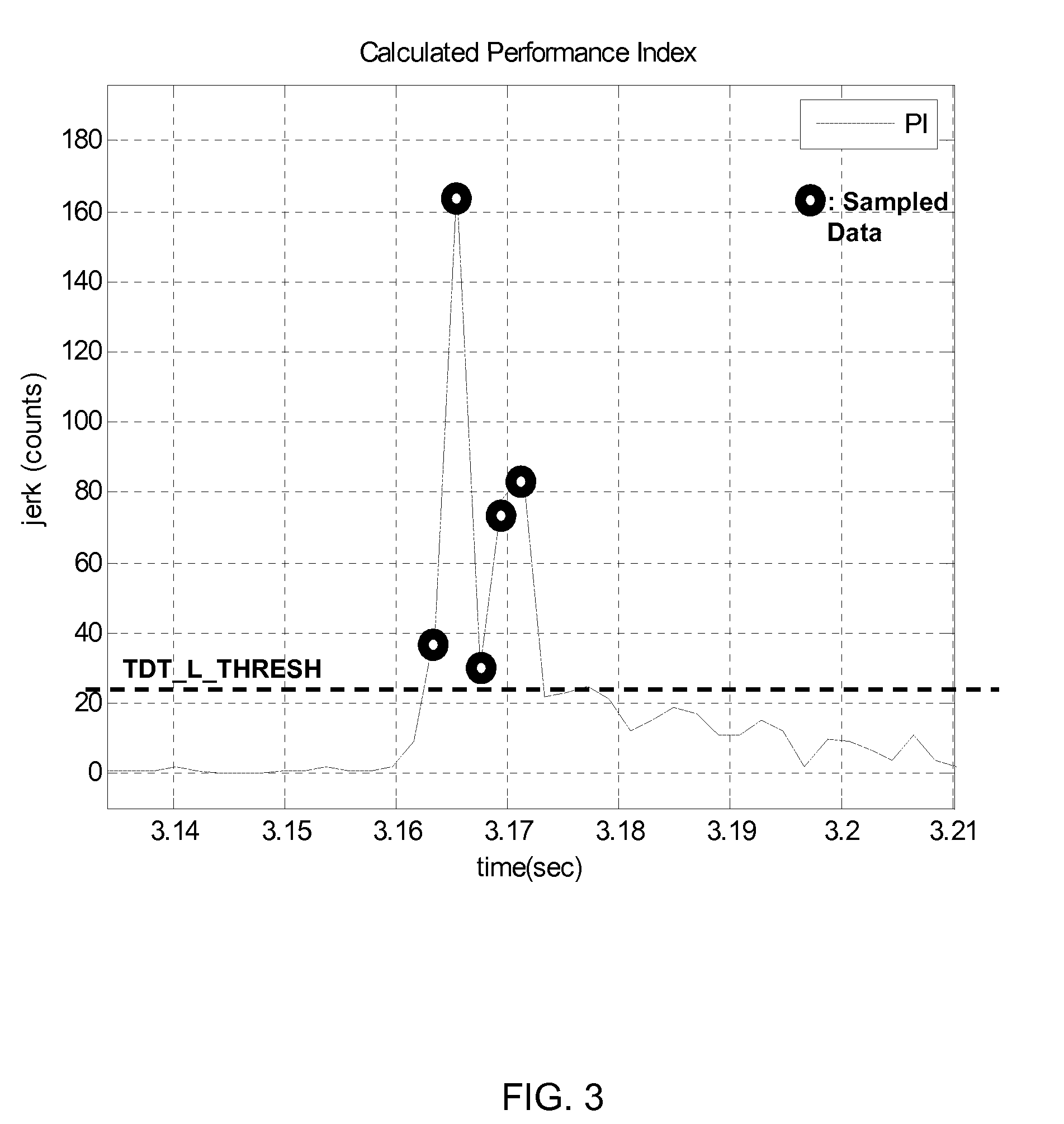
Directional tap detection algorithm using an accelerometer
ActiveUS20100256947A1Increase the number ofForce measurementAcceleration measurementTriaxial accelerometerPerformance index
A directional tap detection algorithm and a single tri-axis accelerometer (10) are employed to extend the number of unique button less input commands available for a small mobile electronic device (12) such as a cell phone or a MP3 player. The algorithm analyzes acceleration data from the tri-axis accelerometer (10) to detect the direction and number of taps imparted to any of the six sides (14) of a housing (13) of the device (12), yielding 12 unique inputs. The algorithm employs a parameter referred to as the performance index (PI) to identify tap induced movements. The PI is determined by calculating the time derivative of each acceleration signal for each axis and then calculating the sum of the absolute values of the calculated acceleration derivatives. A tap is determined to have occurred if the sum exceeds a threshold value for a predetermined amount of time. If a second tap is detected within a predetermined time after the first tap, then a double tap is determined to have occurred.
Owner:KIONIX CORP
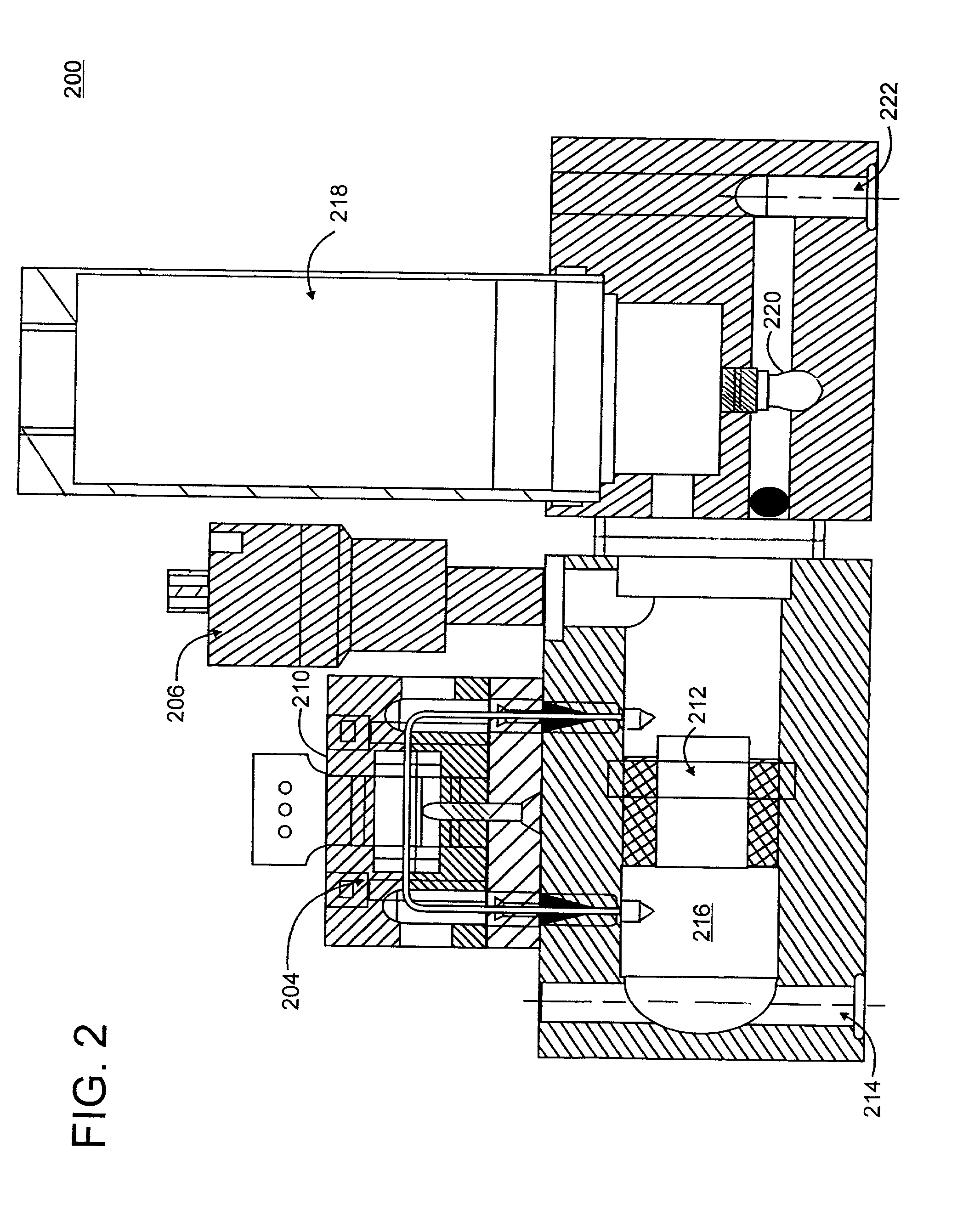
Apparatus and method for calibration of mass flow controller
InactiveUS7136767B2Testing/calibration apparatusVolume flow proportion measurementDifferentiatorEngineering
A mass flow sensor calibrator employs a variable-flow fluid source, a receptacle of known volume, and a pressure differentiator. The variable-flow fluid source supplies gas at varying rates to the mass flow sensor being calibrated and at proportional rates to a receptacle of known volume. A pressure differentiator computes the time derivative of gas flow into the receptacle of known volume and, from that, the actual flow into the receptacle. Given the actual flow, the proportionate flow into the mass flow sensor may be determined and the flow signal from the mass flow sensor correlated to the actual flow.
Owner:MKS INSTR INC
Pressure-based system and method for determining cardiac stroke volume
ActiveUS7220230B2Evaluation of blood vesselsCatheterArterial pressure waveformDecreased mean arterial pressure
Cardiac stroke volume (SV) of a subject is estimated as a function of a value derived from a measured arterial pressure waveform. The value may be the standard deviation, or a function of the difference between maximum and minimum pressure values, or a function of either the maximum value of the first time derivative or the absolute value of the minimum of the first time derivative of the pressure waveform, or both, or a function of the magnitude of one or more spectral components of the pressure waveform at a frequency corresponding to the heart rate. Cardiac output is then estimated as the product of the subject's heart rate and SV, scaled by a calibration constant. Arterial pressure may be measured invasively or non-invasively.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Solenoid cassette pump with servo controlled volume detection
InactiveUS6942469B2Eliminate closure impactEliminate associated noiseAC motor controlElectrical controlResonance measurementDriving current
Servo controlled solenoids provide actuation of a pump piston and valves, and electronic LC resonance measurements to determine liquid volume and gas bubble volume. Third order nonlinear servo control is split into nested control loops: a fast nonlinear first-order inner loop causing flux to track a target by varying a voltage output, and a slower almost linear second-order outer loop causing magnetic gap to track a target by controlling the flux target or the inner loop. The inner loop uses efficient switching regulation, preferably based on controlled feedback instabilities, to control voltage output. The outer loop achieves damping and accurate convergence using proportional, time-integral, and time-derivative gain terms. The time-integral feedback may be based on measured and target solenoid drive currents, adjusting the magnetic gap for force balance at the target current.
Owner:THISTLE ADVISORS
Method of processing seismic data
InactiveUS7068568B2Reduce the impactAccurate de-ghostingSeismic signal processingSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic surveyTime derivative
A method of de-ghosting seismic data acquired in a marine seismic survey comprises estimating ∂zp (where p is the fluid pressure) from a time-derivative of p and a derivative of p in a horizontal direction such as the x-direction. The time-derivative of p and the derivative of p in the horizontal direction can be readily obtained from the acquired seismic data, and are used to provide an improved estimate of ∂zp which, in general, cannot be directly determined from the acquired seismic data.Once ∂zp has been estimated it can be used to de-ghost the acquired seismic data.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
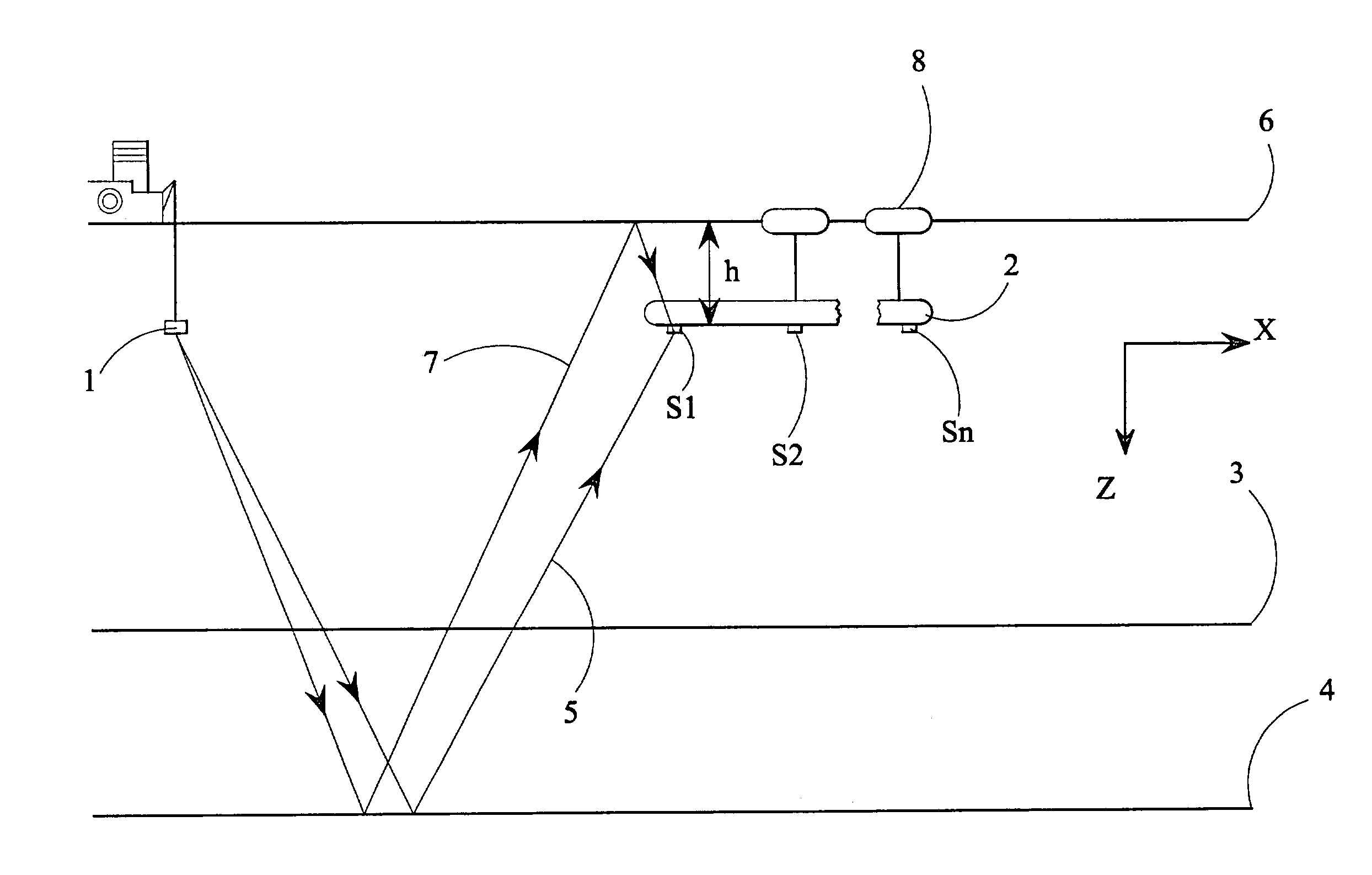
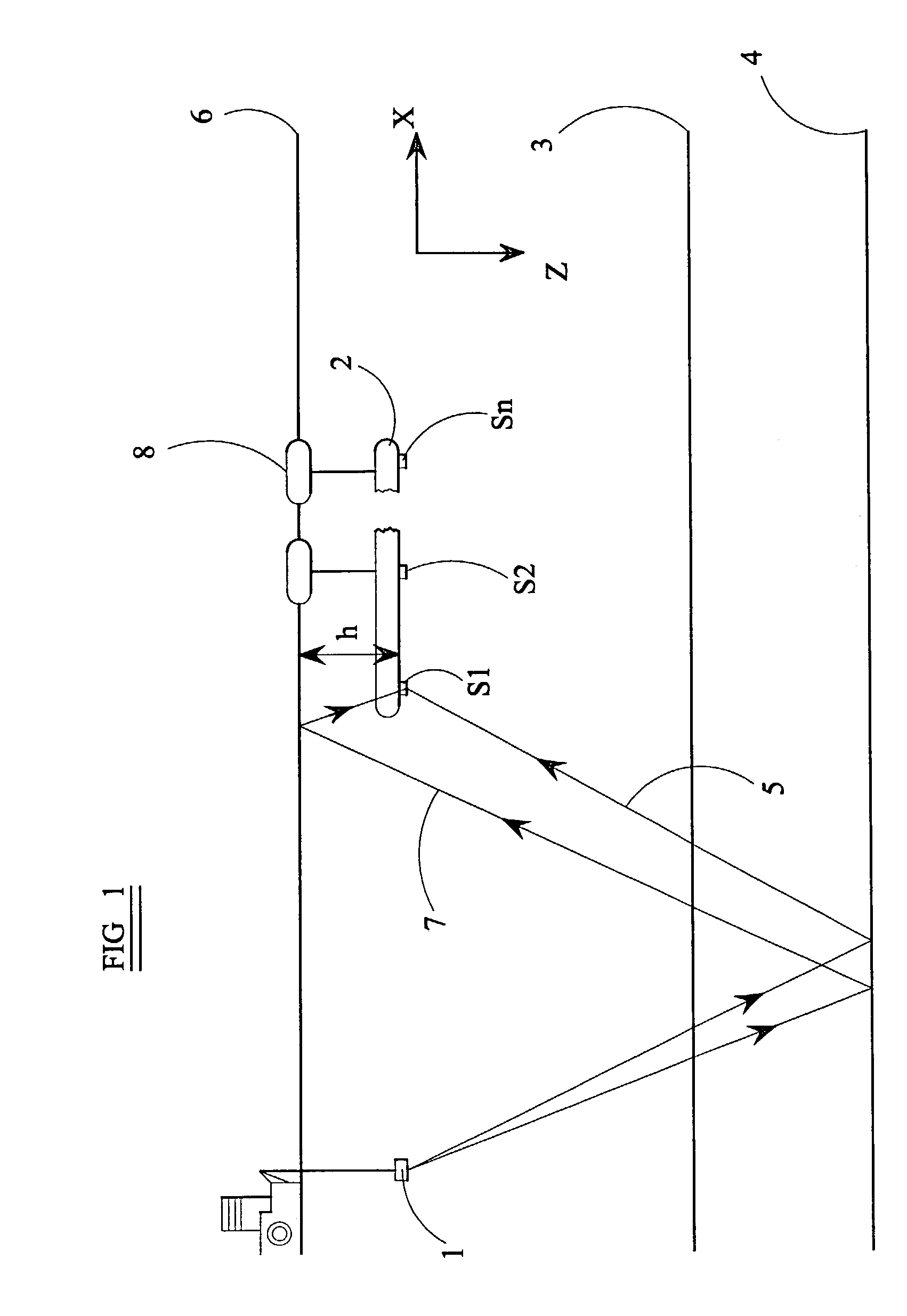
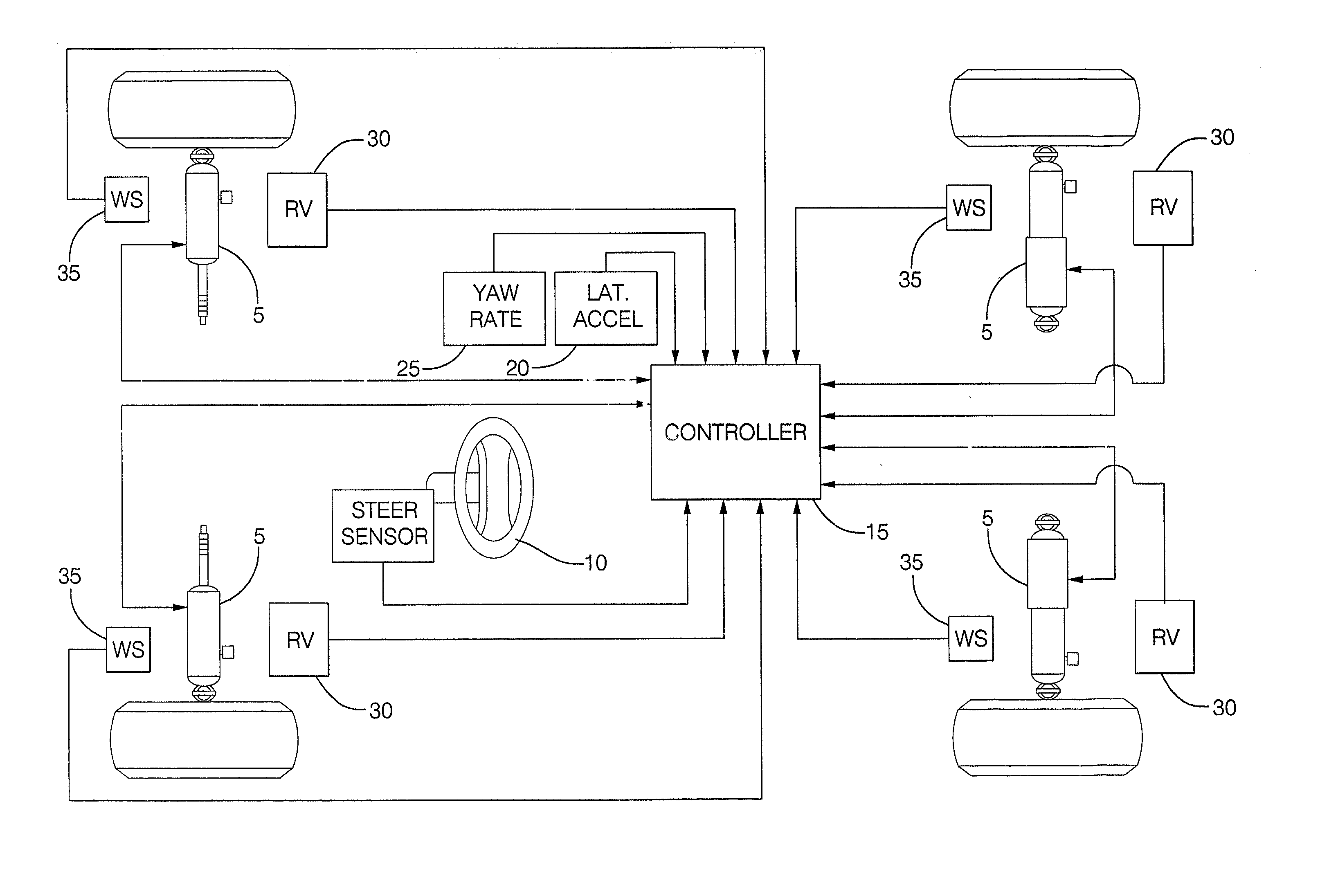
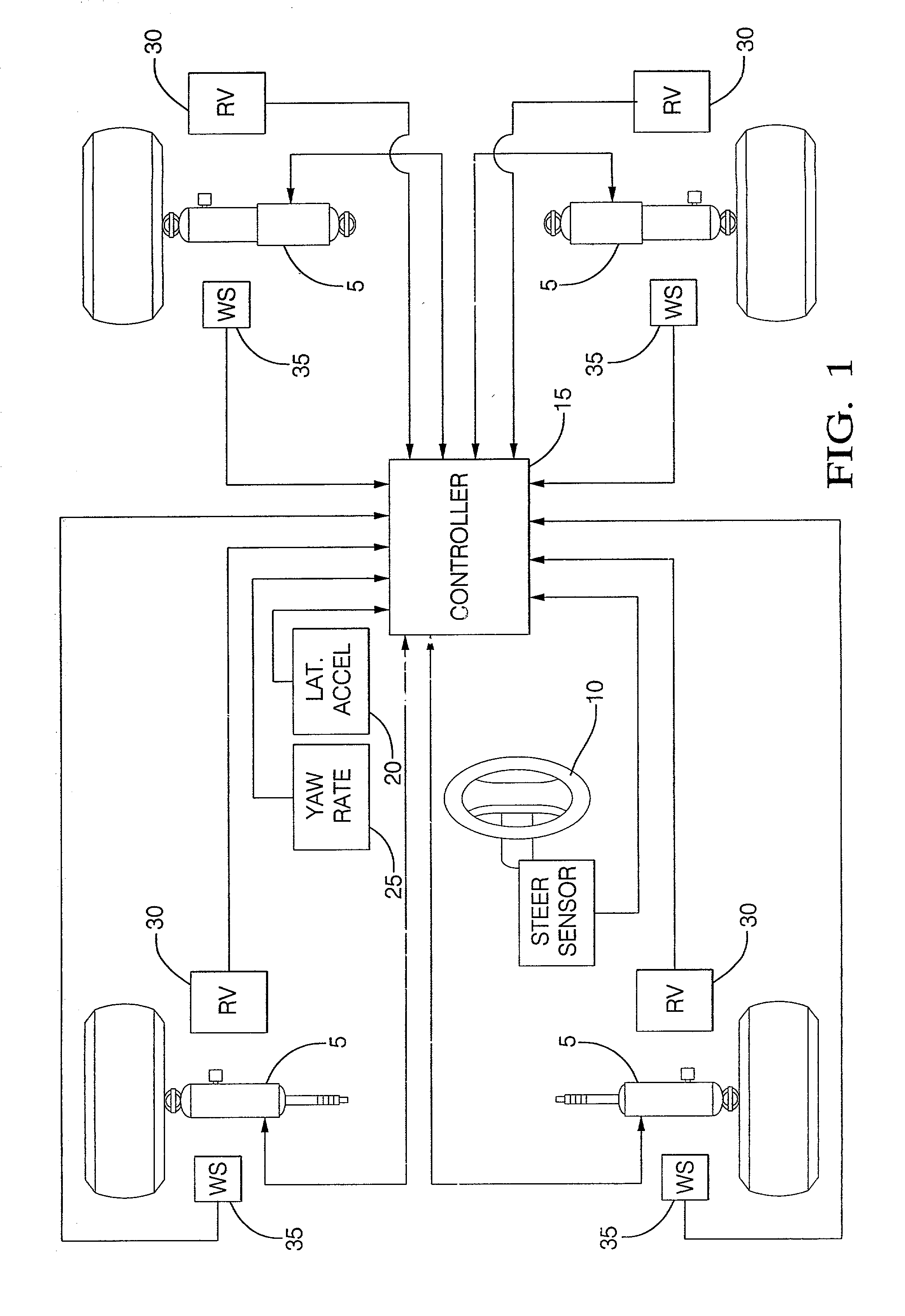
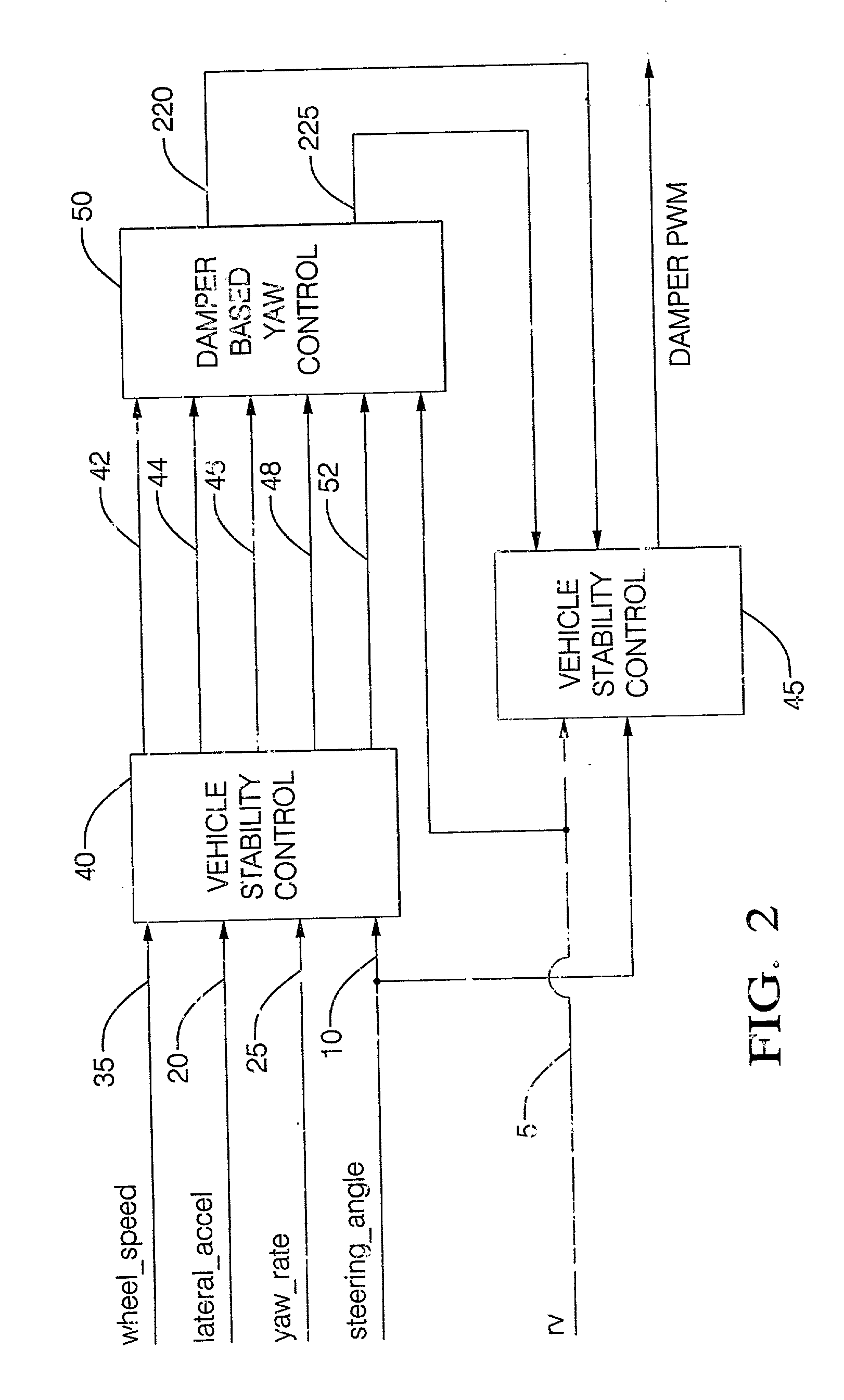
Damper based vehicle yaw control
InactiveUS20020128760A1Improve vehicle responseImprove stabilityDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesTime derivativeYaw control
Controllable dampers are used to improve vehicle responses and stability during severe vehicle handling maneuvers. A total handling damping value for the vehicle is derived, preferably from the greatest of a yaw rate error value, a lateral acceleration value and a time derivative of lateral acceleration value. In addition, a control ratio of front axle roll damping to total roll damping is derived, preferably from the yaw rate error value, an oversteer / understeer indication and possibly vehicle speed. From these values, handling damping values are derived for each wheel of the vehicle and blended with damping values for the same wheels derived from suspension component movement to determine a corner damping command for each controllable damper. Preferably, the damping values derived from suspension component movement are shifted away from damping control of the vehicle body toward handling damping control when yaw rate error is large in magnitude.
Owner:BWI +1
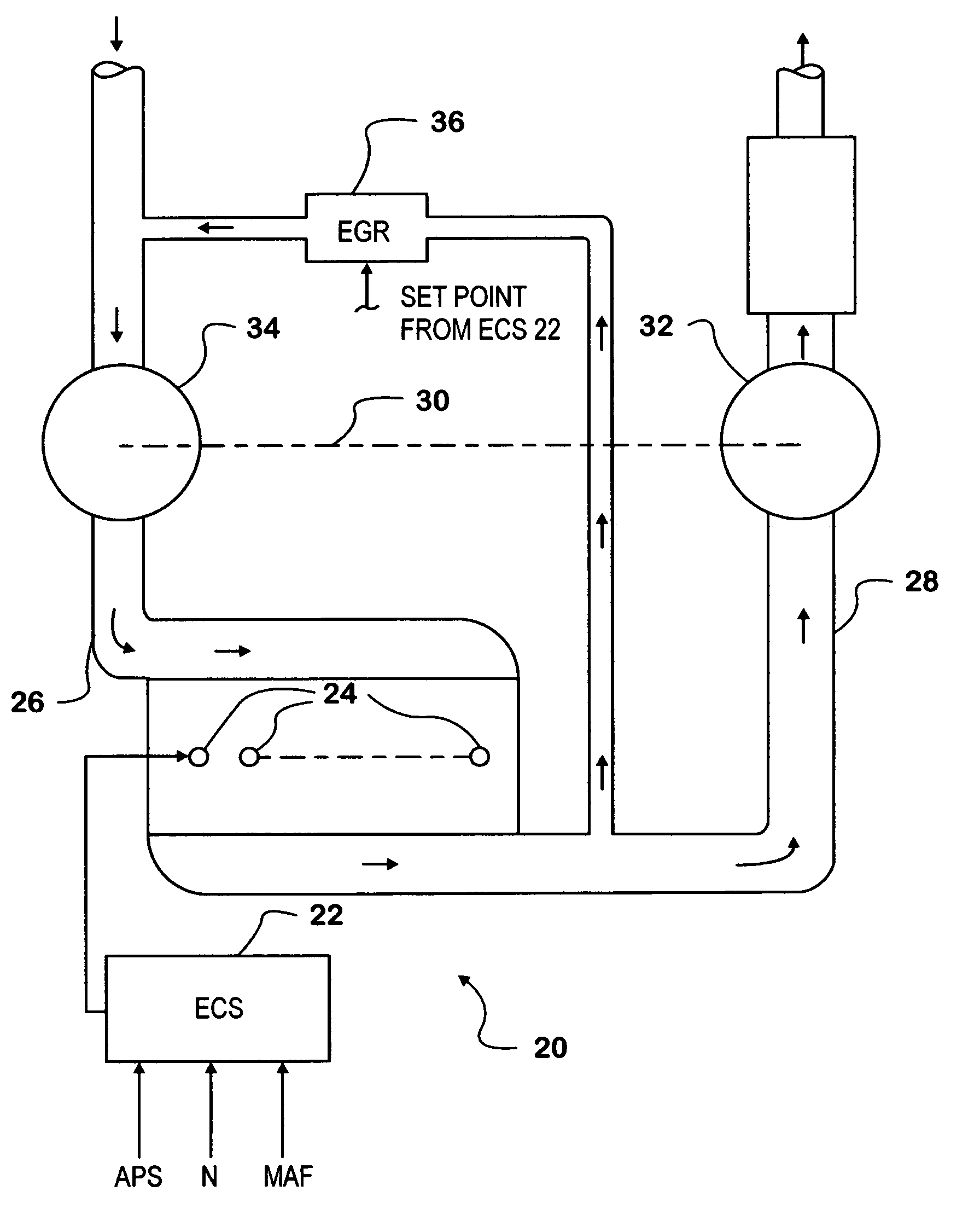
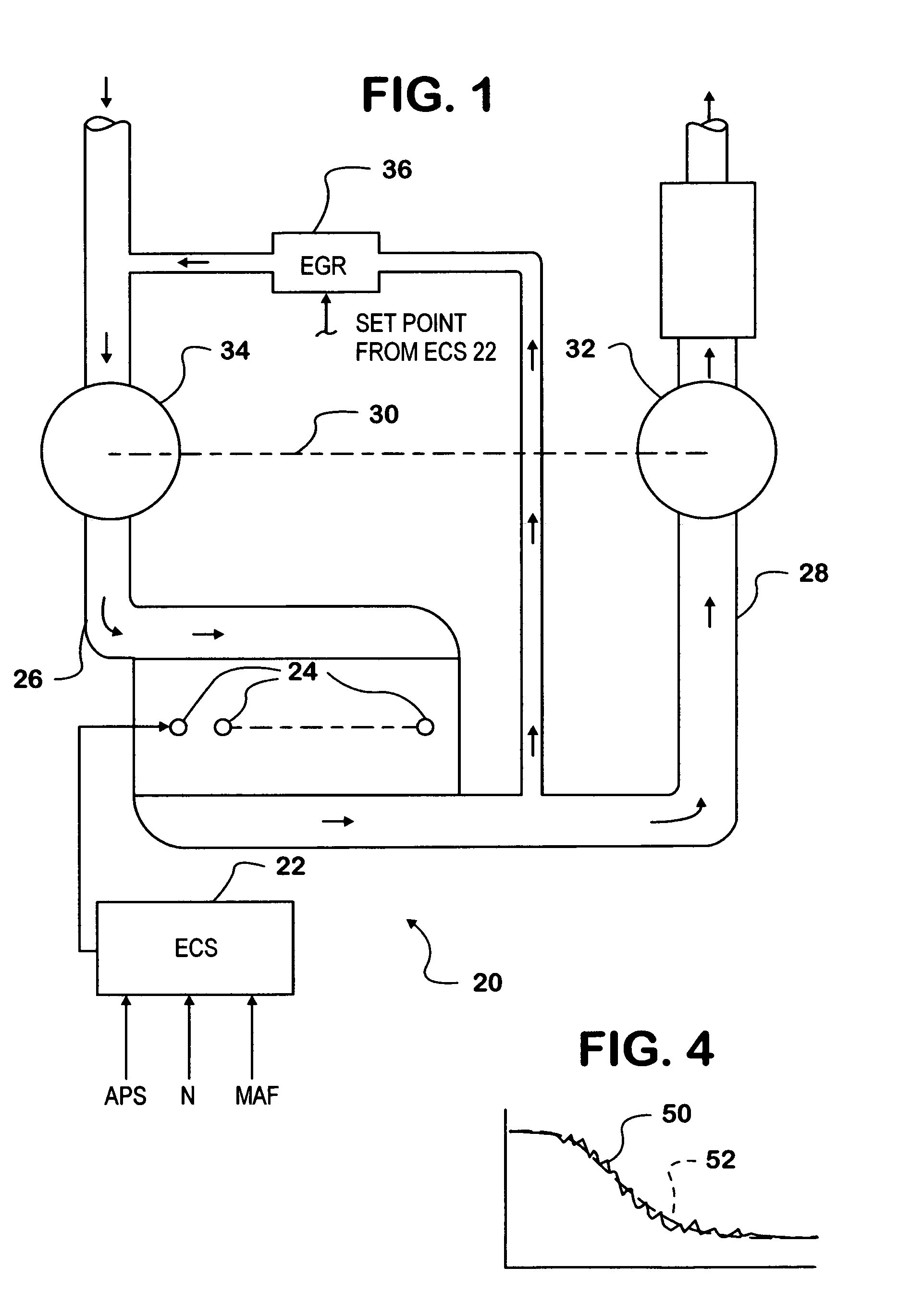
Controlling an engine operating parameter during transients in a control data input by selection of the time interval for calculating the derivative of the control data input
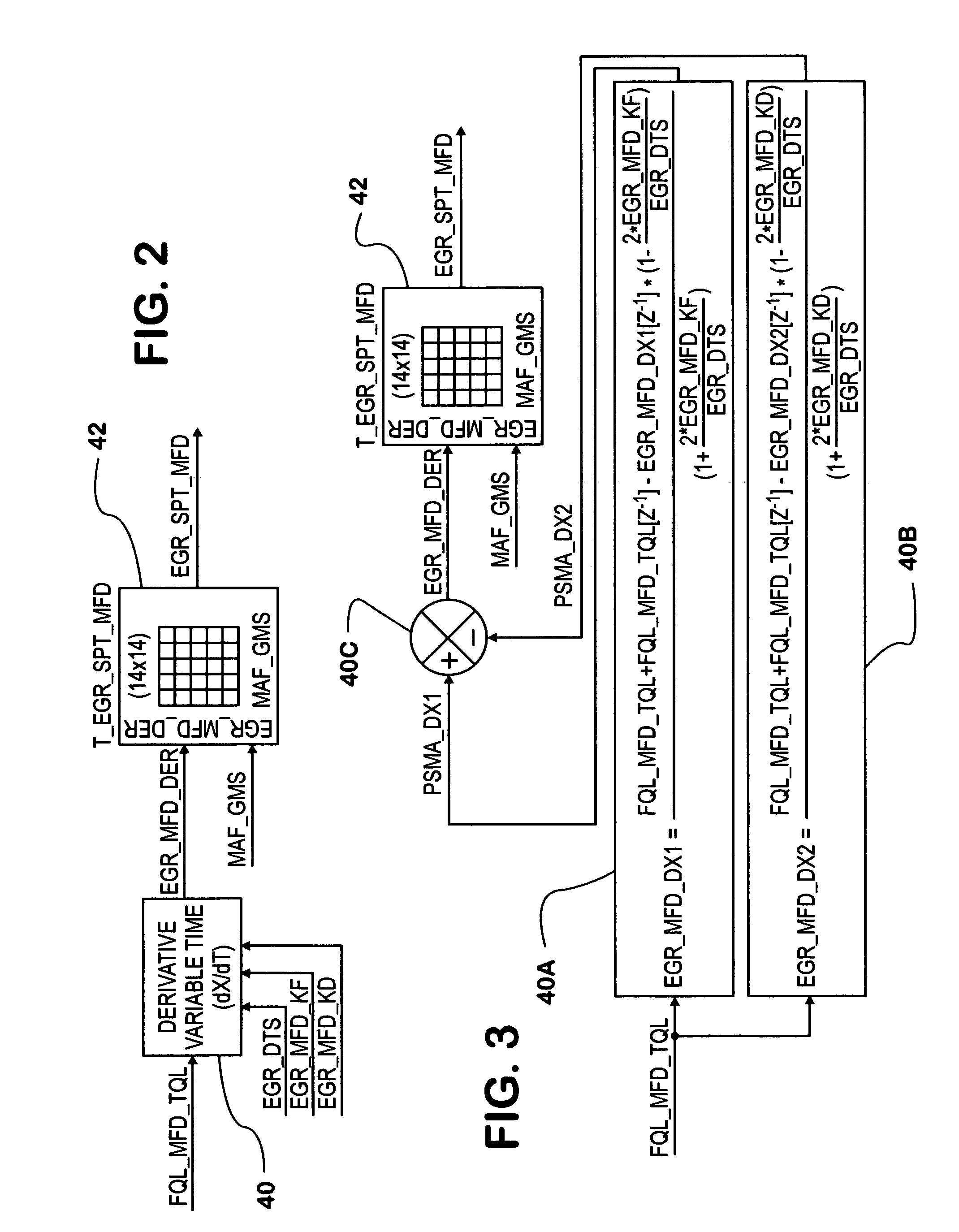
Desired engine fueling data FQL—MFD—TQL is processed by a derivative variable time function (40) embodied in an algorithm to develop a data value EGR—MFD—DER representing the time derivative of desired fueling. The algorithm comprises certain selectable parameters (EGR—DTS, EGR—MFD—KF, EGR—MFD—KD). An iteration of the algorithm includes processing FQL—MFD—TQL according to a first function (40A) to yield a first data value and according to a second function (40B) to yield a second data value. A third function (40C) subtracts the second data value from the first to yield a data value for the time derivative that forms one input to a map (42). A second input to the map is a data value for mass airflow (MAF—GMS). The map provides data for calculating the set point of an EGR valve (36). The invention provides improved control of EGR during fueling transients.
Owner:INT ENGINE INTPROP CO LLC
Transformer inrush current detector
ActiveUS20090147412A1Reduce inductanceImprove responseEmergency protective arrangement detailsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionCurrent sensorEngineering
A differential protection system for power transformers using Rogowski coils as current sensors can support an inrush current detection method based on sensing lows in the derivative of the sensed current. Effective detection of power transformer inrush conditions can enable blocking of a protection relay during inrush where the differential current may exceed a differential threshold value indicative of a fault without the presence of an actual fault. The outputs of the Rogowski coils, being proportional to the first time derivative of the sensed current, may be useful in the inrush detection method. Also, with reduced saturation concerns, the Rogowski coil protection system may employ a single slope response with increased sensitivity. A discrete time sampling technique for identifying low di / dt portions within the sensed current also may be useful in detecting power transformer inrush conditions.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Adaptive controller for d-statcom in the stationary reference frame to compensate for reactive and harmonic distortion under unbalanced conditions
InactiveUS6862199B2Flexible AC transmissionActive power filteringLoop controlTotal harmonic distortion
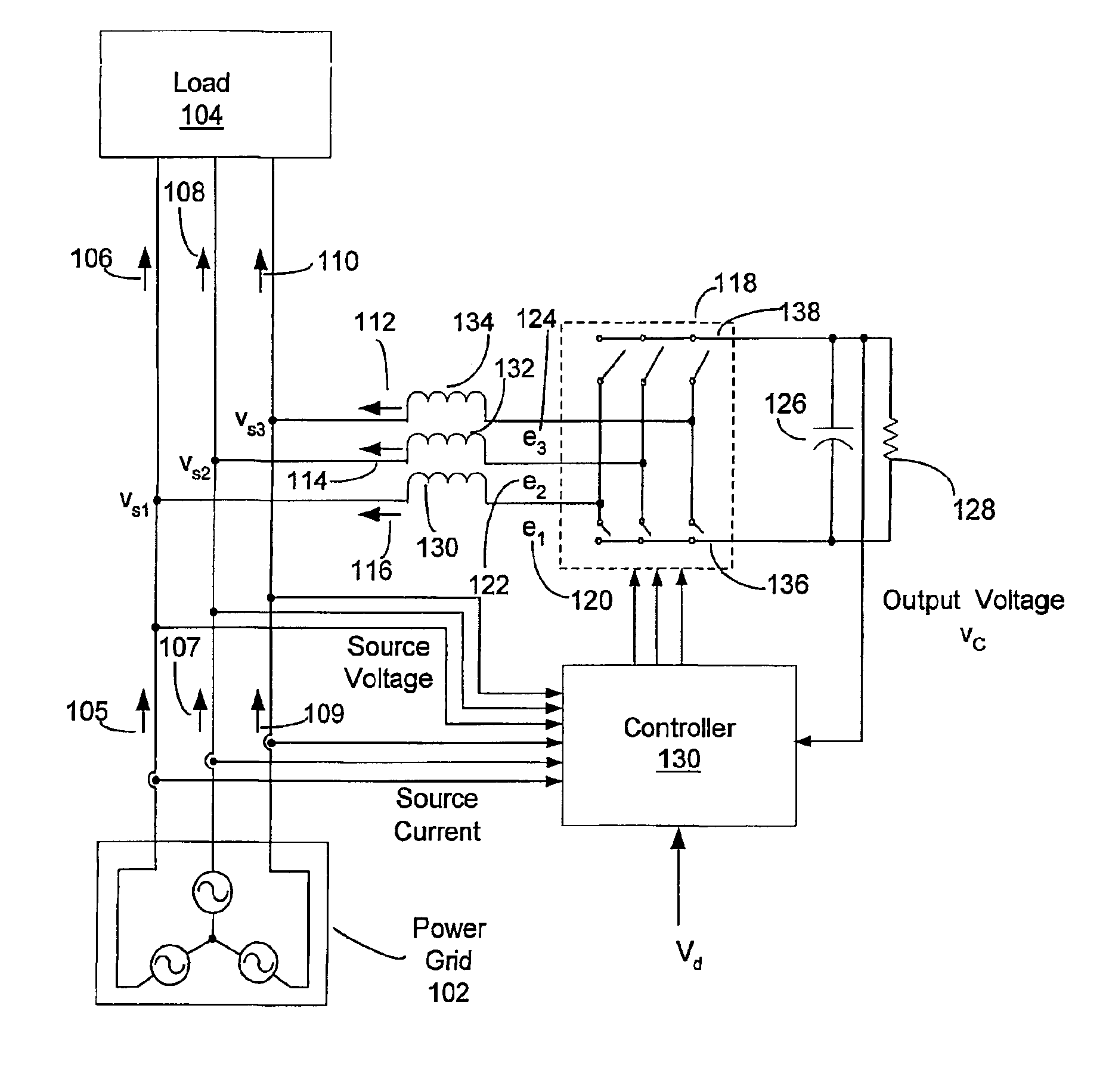
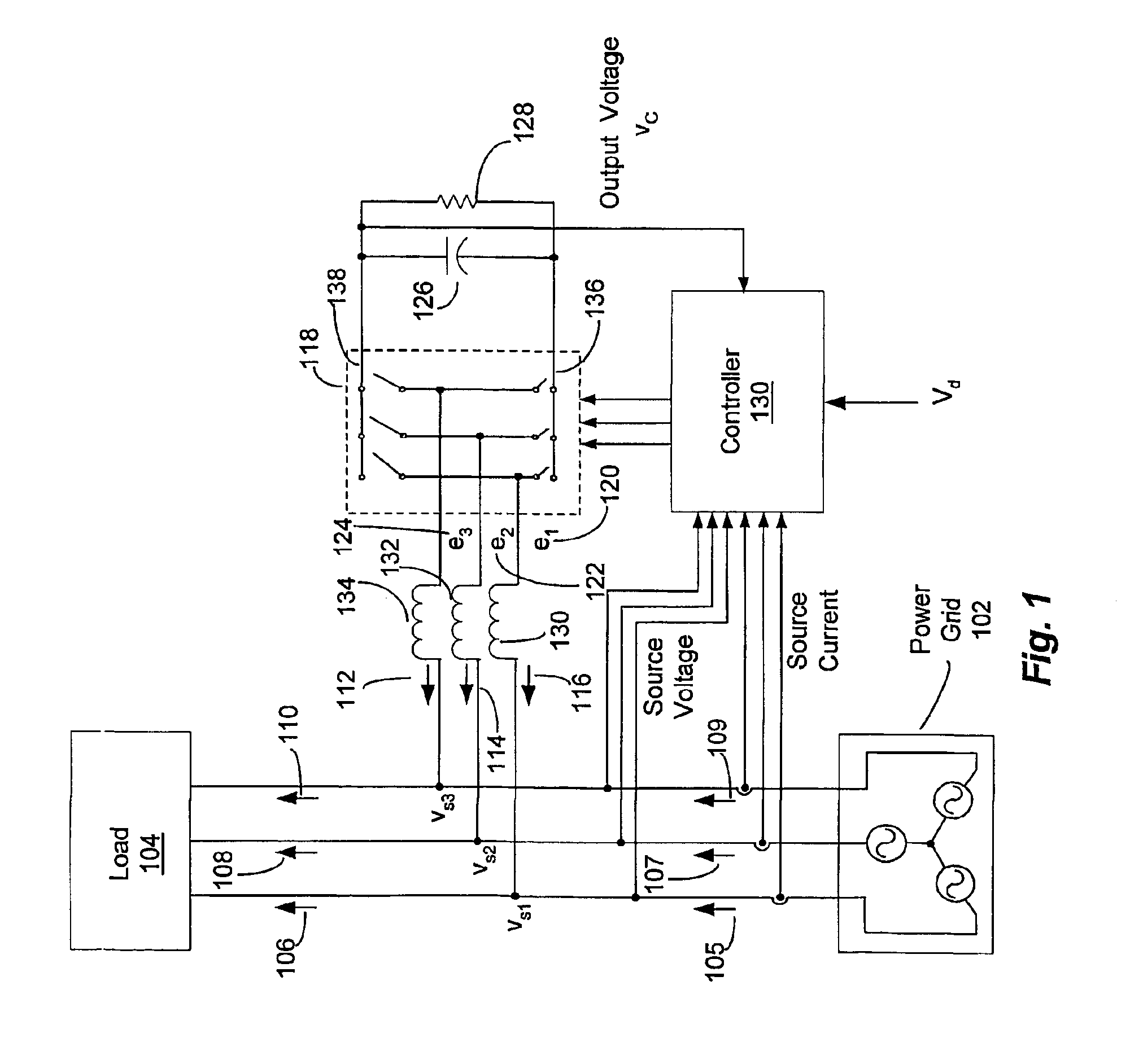
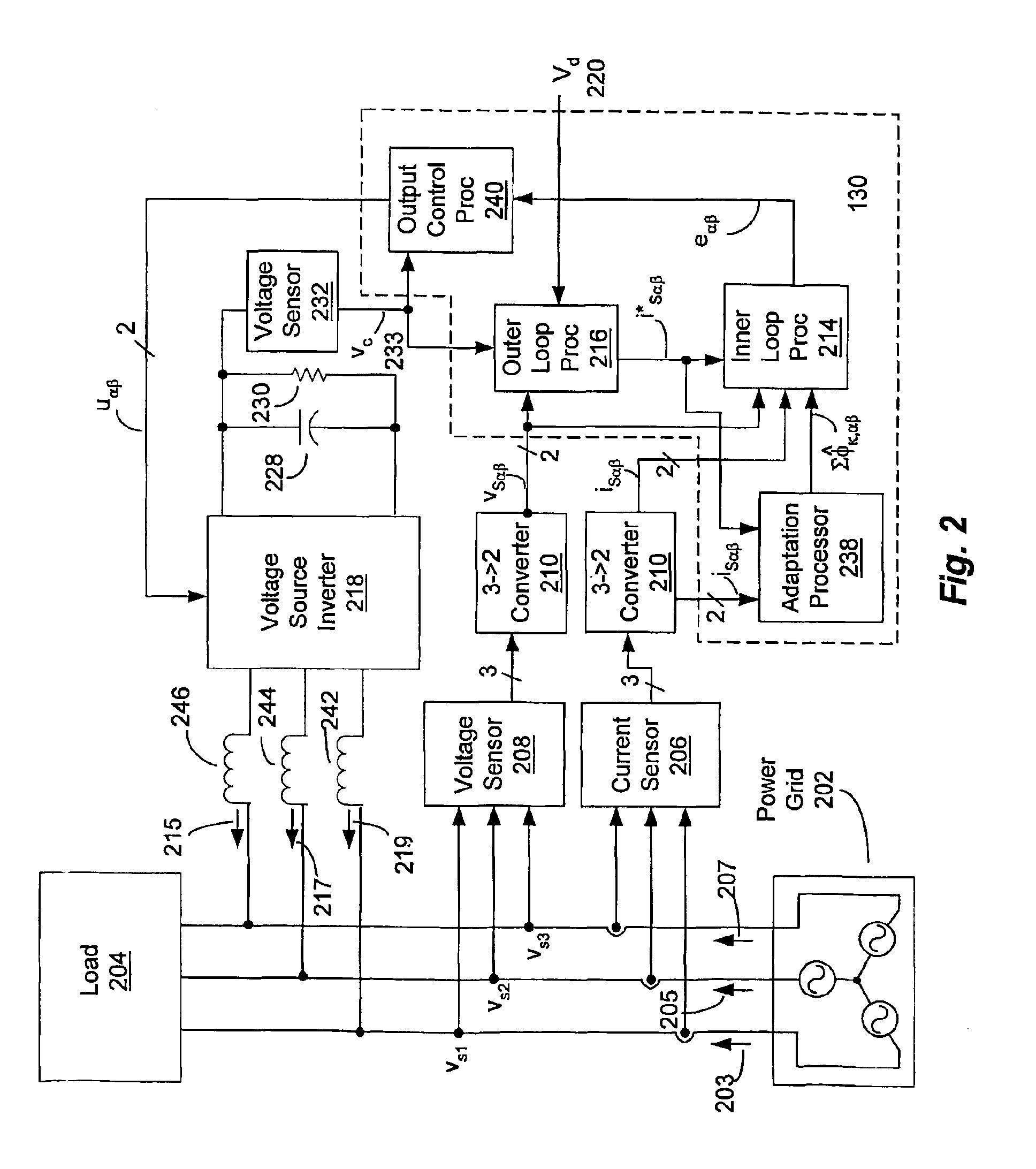
A controller (130) for compensating reactive power and selected current load harmonics in an unbalanced multi-phase power distribution system. Control current is injected from a multi-phase voltage source inverter (118) into the multi-phase power distribution system as a function of the voltage and current provided by the source inverter 118. The injected current is operative to balance the load seen by the power distribution system including non-linear / distorted and unbalanced loads in each phase. The controller includes an inner loop control processor (216), an outer loop control processor, and an adaptation processor. The adaptation processor (238) is operative to estimate a selected set of predetermined harmonic components in the periodic disturbance which is a function of the unknown system parameters, the source current, the source voltage, and their time derivatives in stationary coordinates.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Harvester with fuzzy control system for detecting steady crop processing state
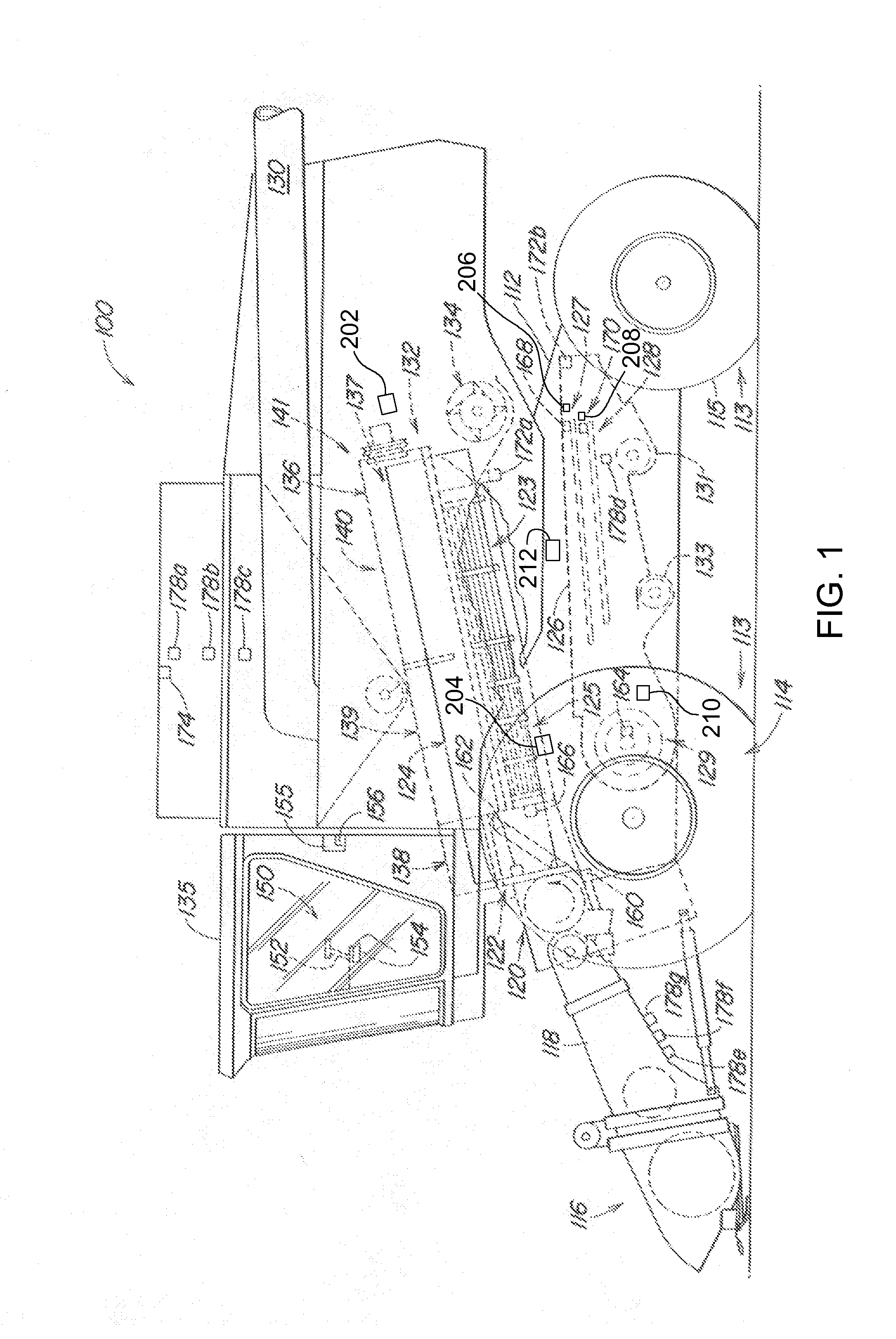
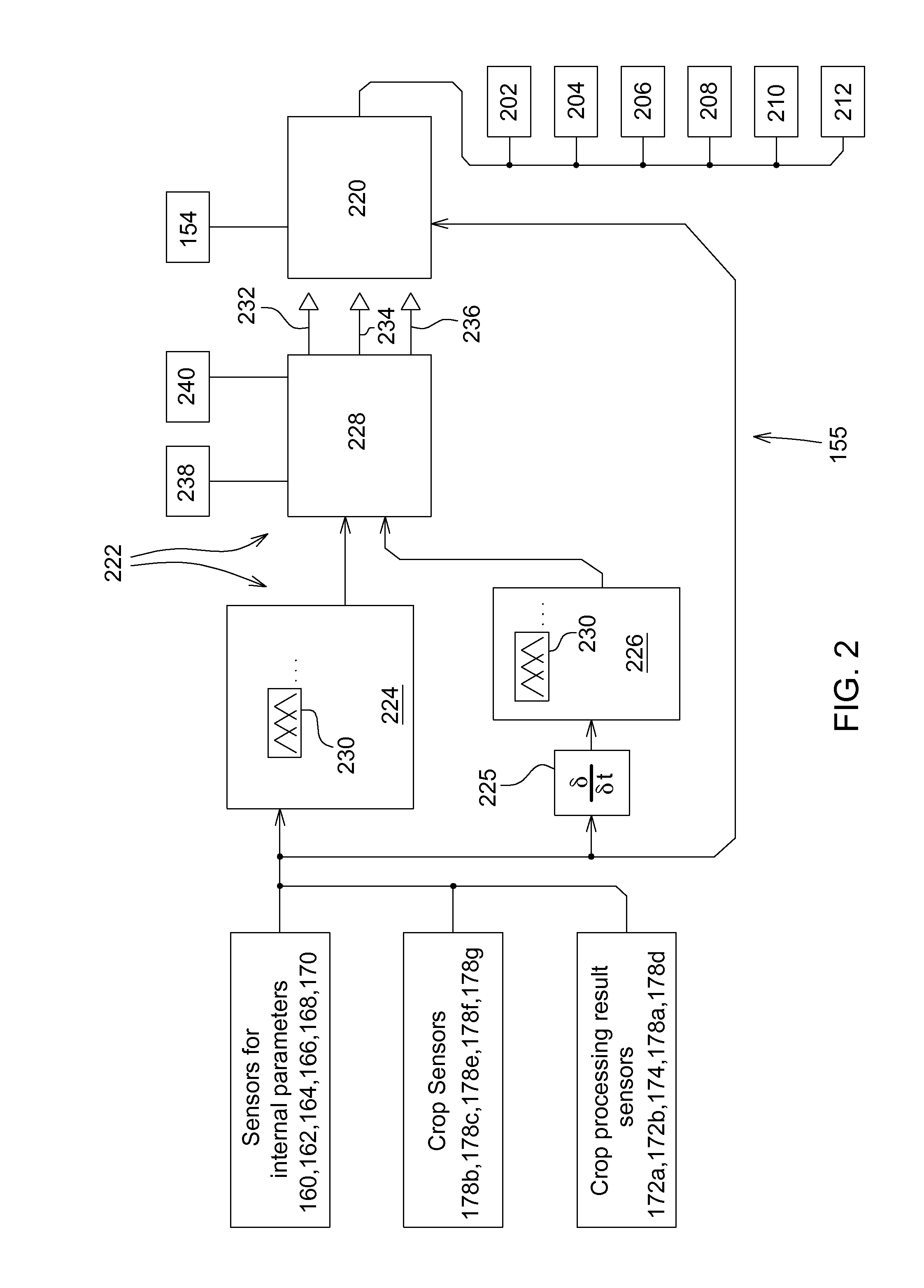
InactiveUS20140277960A1Simple control systemOvercome problemsVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficFuzzy control systemEngineering
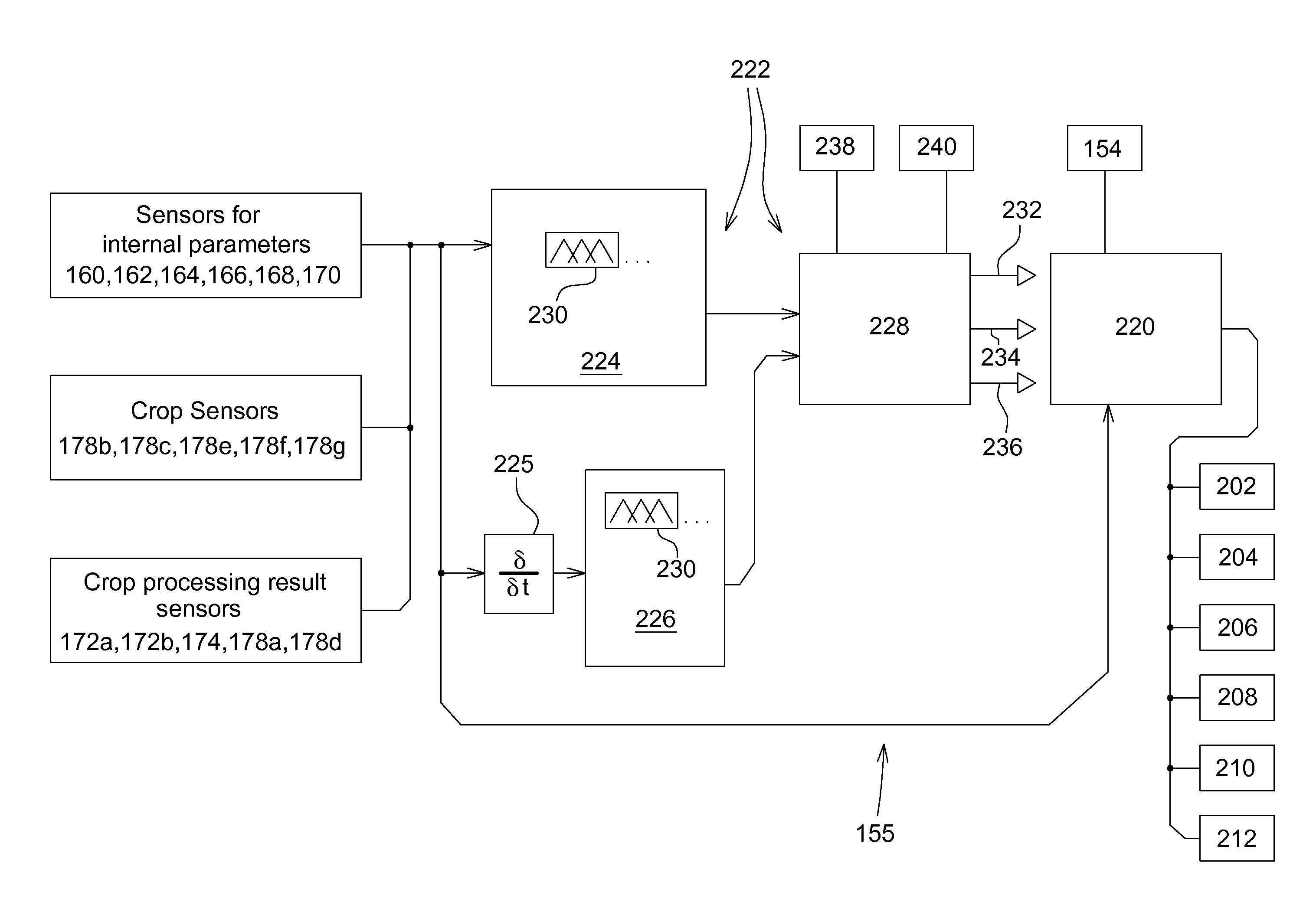
A method, a system and a harvester (100) are arranged to detect a steady operating state of the harvester (100). A crop sensor (178b, 178c, 178e, 178f, 178g) senses a crop parameter. A processing result sensor (172a, 172b, 174, 178a, 178d) senses at least one processing result parameter. The crop parameter, the processing result parameter and time derivatives of the crop parameter and the processing result parameter are submitted as input signals to a fuzzy logic circuit (222). The fuzzy logic circuit (222) is configured to generate a binary steady state signal value indicating a steady state of the crop processing in the harvesting machine based upon the input signals.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Digital processing method and system for determination of optical flow
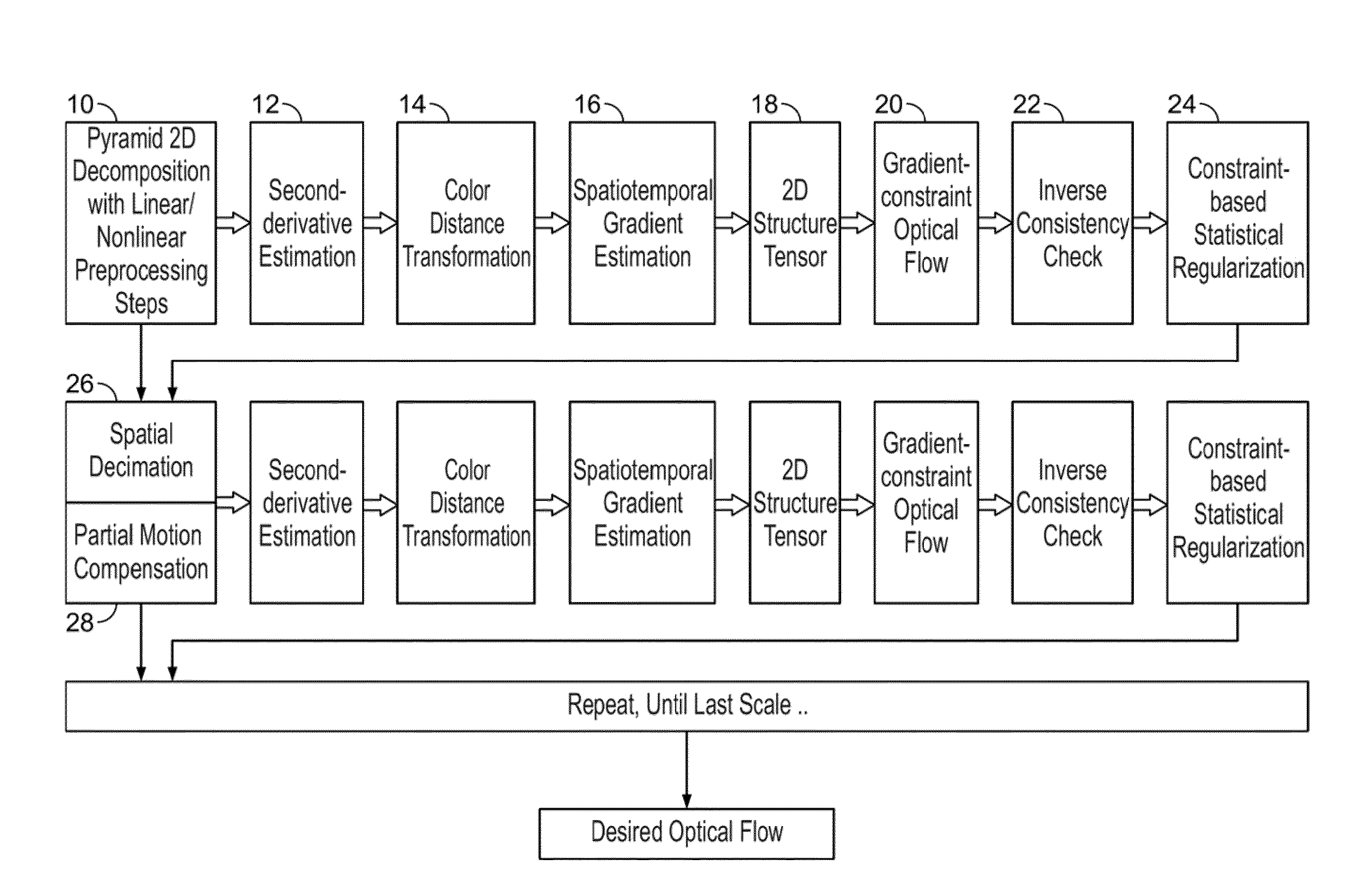
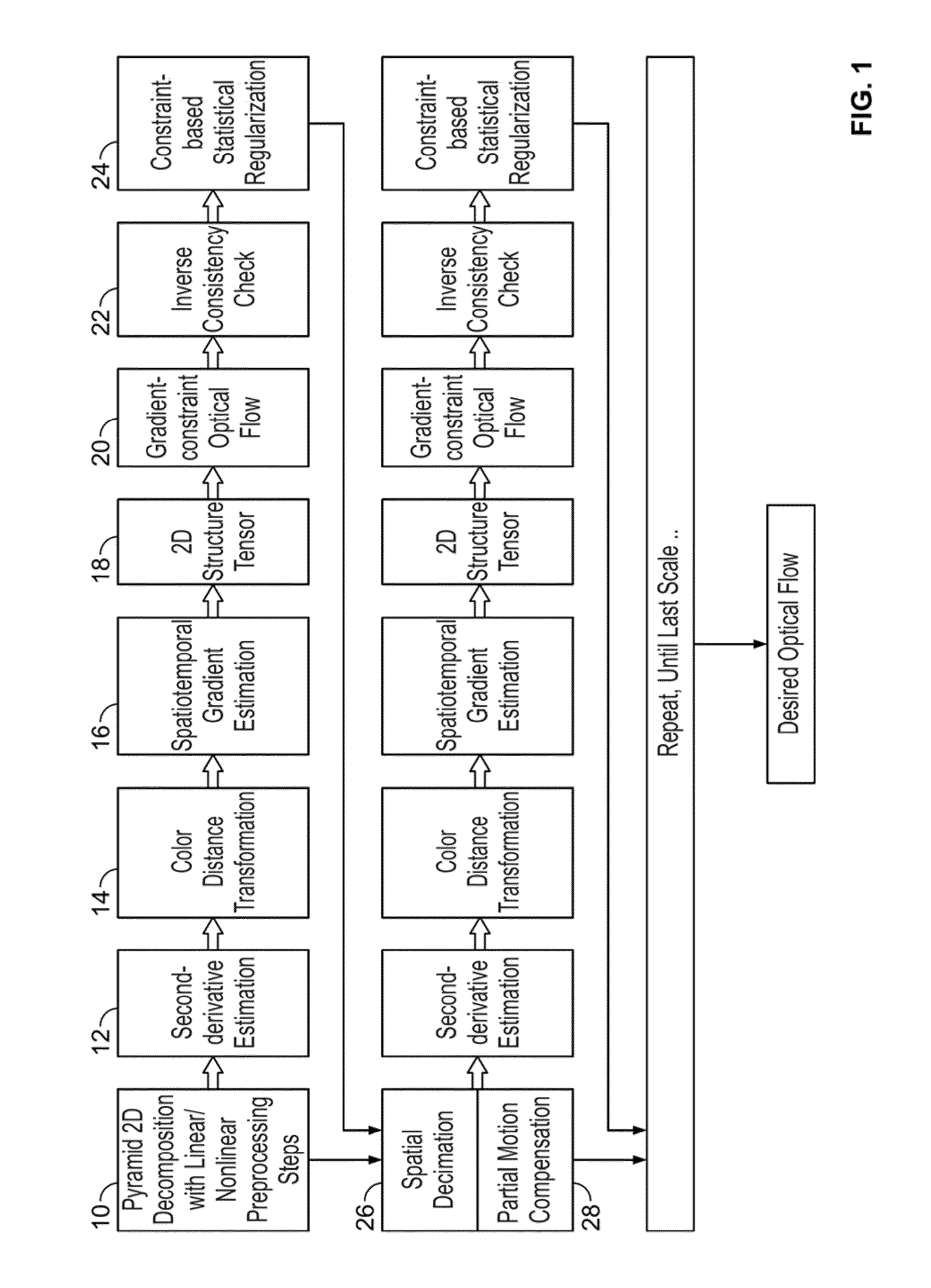
InactiveUS20100124361A1Reduce resolutionHigh resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisOctaveGradient estimation
A method and system for determining an optical flow field between a pair of images is disclosed. Each of the pair of images is decomposed into image pyramids using a non-octave pyramid factor. The pair of decomposed images is transformed at a first pyramid scale to second derivative representations under an assumption that a brightness gradient of pixels in the pair of decomposed images is constant. Discrete-time derivatives of the second derivative image representations are estimated. An optical flow estimation process is applied to the discrete-time derivatives to produce a raw optical flow field. The raw optical flow field is scaled by the non-octave pyramid factor. The above-cited steps are repeated for the pair of images at another pyramid scale until all pyramid scales have been visited to produce a final optical flow field, wherein spatiotemporal gradient estimations are warped by a previous raw optical flow estimation.
Owner:CHEYTEC TECH LLC
Apparatus and method for controlling excitation frequency of magnetostrictive transducer
InactiveUS20060188841A1Simple and inexpensive circuitrySimple and inexpensive and componentTooth pluggers/hammersRelaysSonificationTransformer
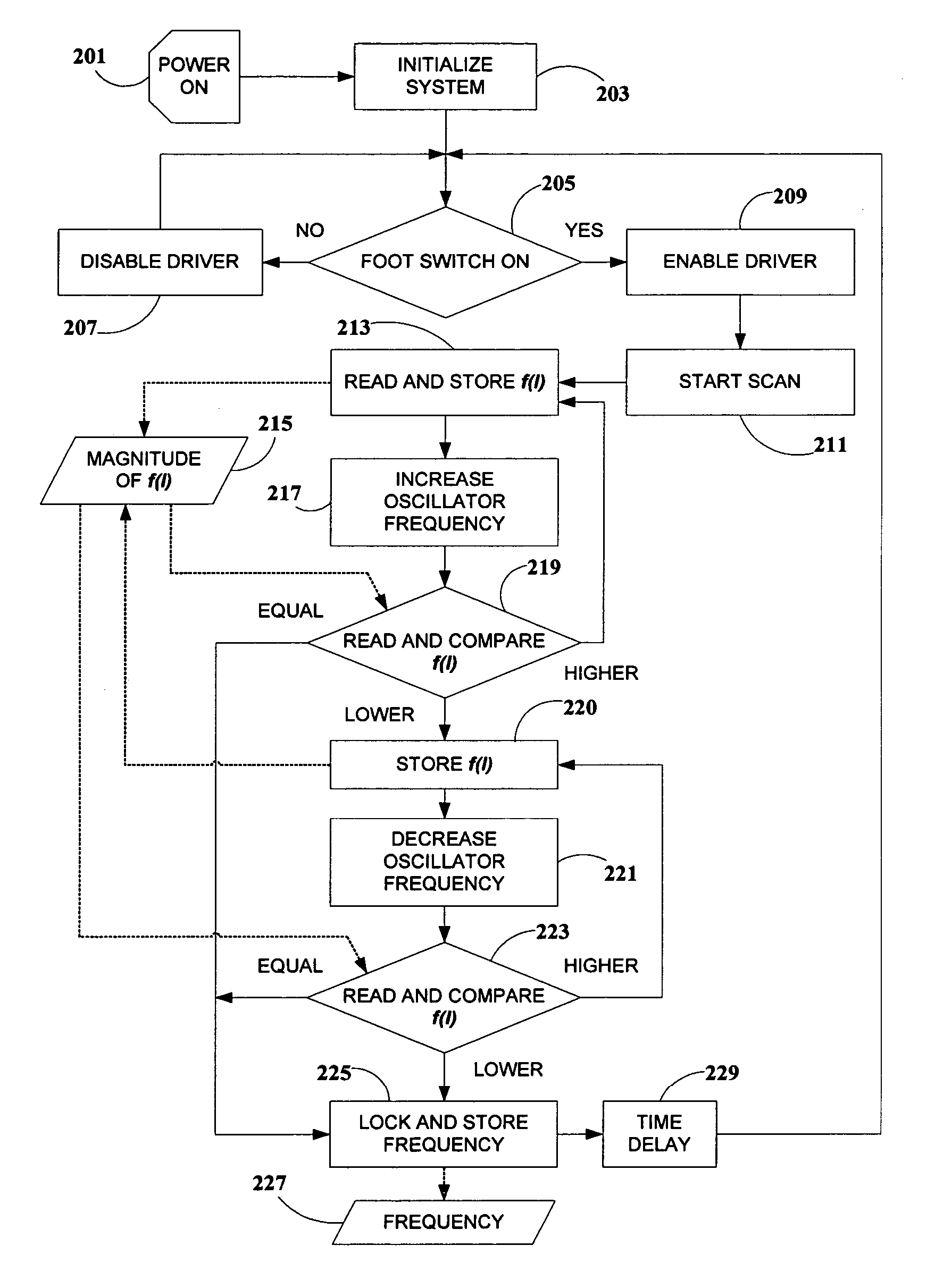
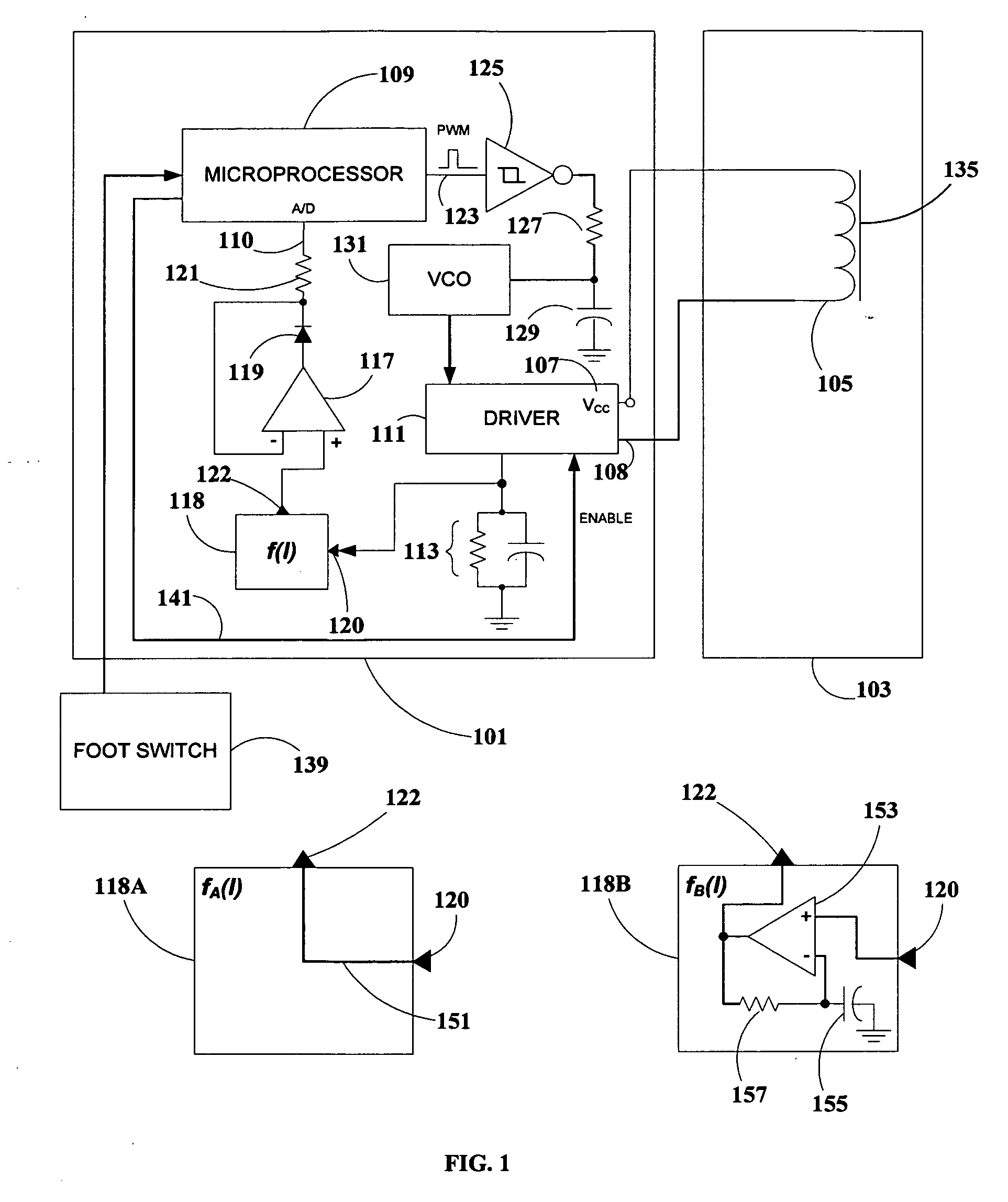
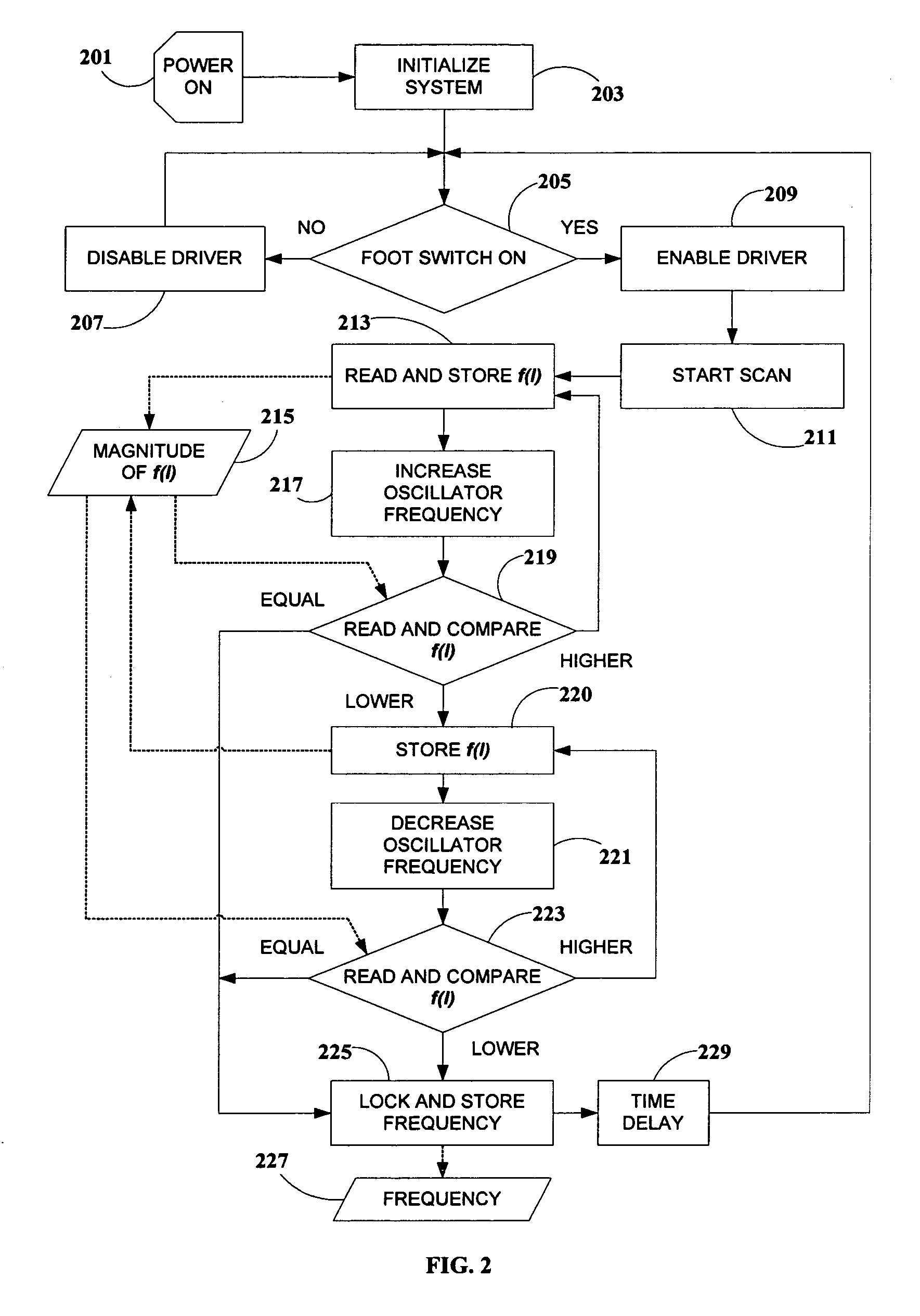
Apparatus and method for controlling the frequency of the current in the excitation coil of the handpiece of a dental magnetostrictive ultrasonic scaling unit, or similar transducer. A microprocessor continually samples a predetermined function of the current through the excitation coil, and adjusts the frequency for a function maximum, performing coarse and fine frequency adjustments. The function can be proportional to the current, its time-derivative, or combination thereof A voltage-controlled oscillator is employed, controlled by pulse-width modulation from the microprocessor. The base frequency scan is performed each time the handpiece is energized by the practitioner, assuring automatic optimal frequency adjustment at all times and under all conditions. Apparatus according to the invention does not require transformers, sensing coils, or complex power- or impedance-sensing circuitry, and covers a wide range of resonant frequencies for different insert types. A configuration with multiple handpieces is supported.
Owner:EDEL ALAN +2
Mobile unit and control method of mobile unit
InactiveUS8050837B2Smooth changeSpeed controllerAnalogue computers for trafficStabilization controlGravity center
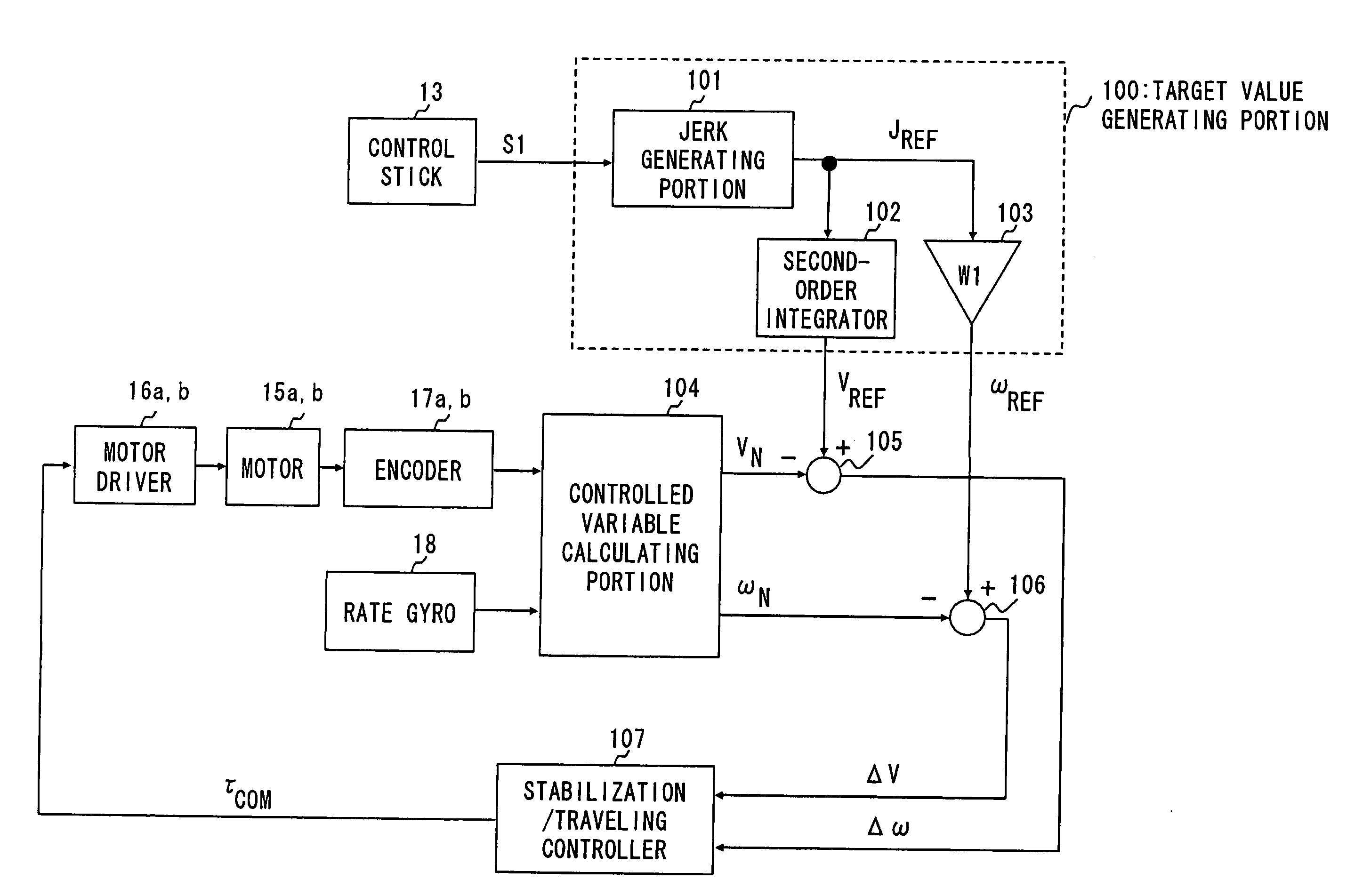
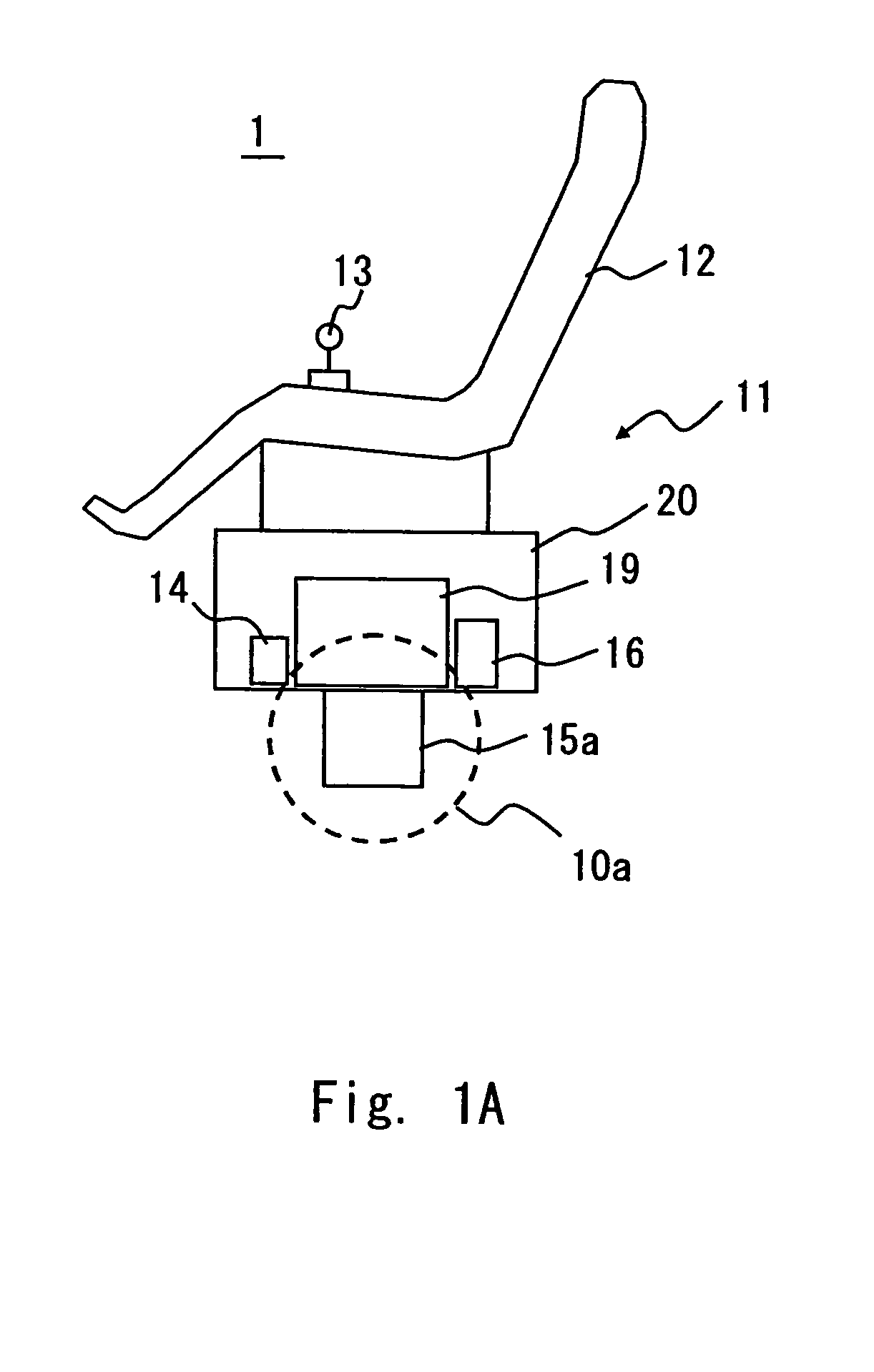
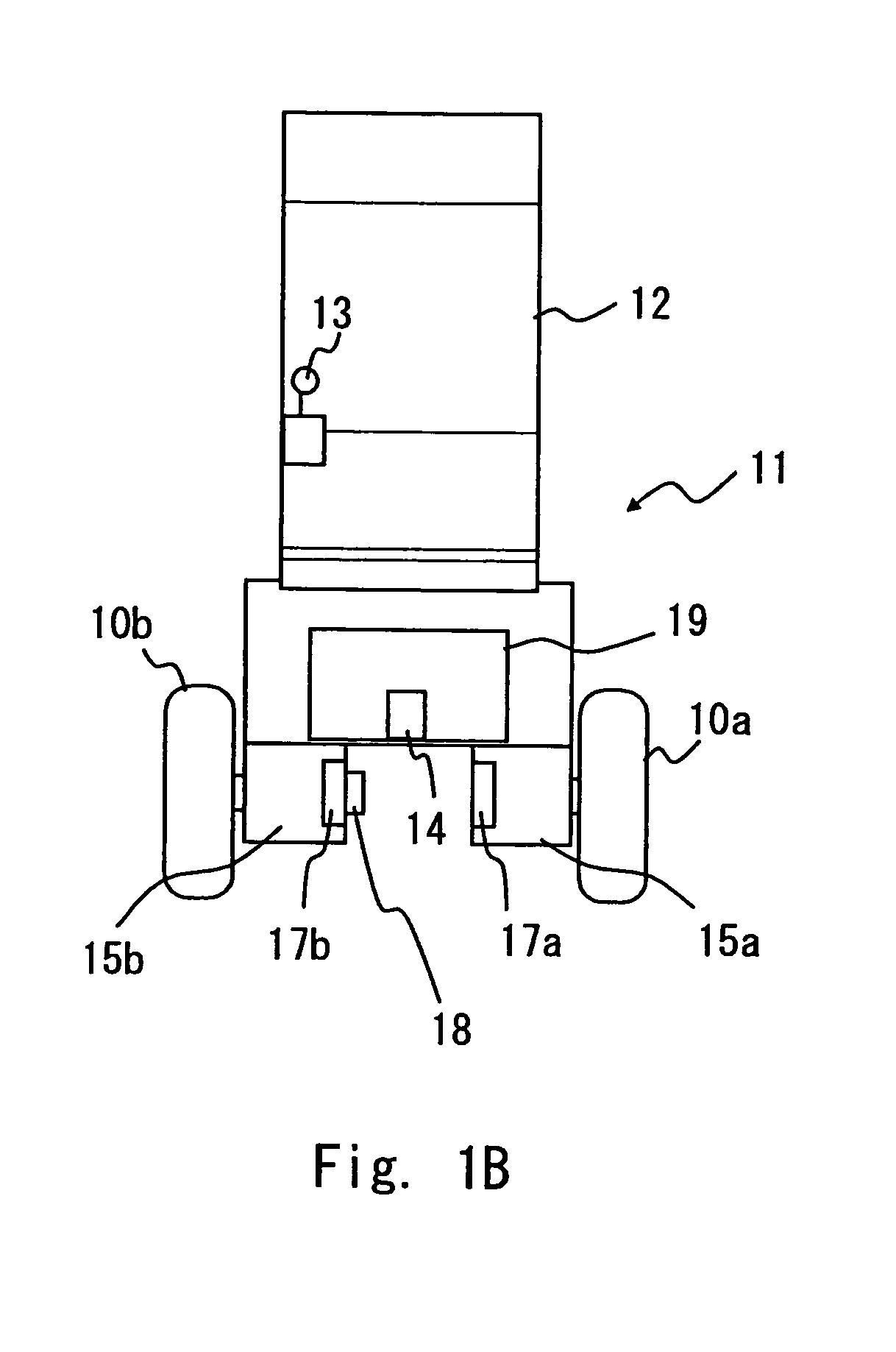
In an inverted pendulum type mobile unit that performs inverted pendulum stabilization control and traveling control based on a velocity target value as an input variable, a change in tilt angle of a vehicle body occurring during traveling is smoothed. The target value generating portion in the inverted pendulum type mobile unit generates the velocity target value VREF of the mobile unit and the tilt angular rate target value ωREF of the vehicle body so that a second-order time derivative of VREF is continuous and ωREF is continuous with respect to time. The controller in the inverted pendulum type mobile unit calculates a torque command value Tcom for the motor drivers using VREF and ωREF as a control target to allow the mobile unit to travel at VREF while maintaining the state where the gravity center of the vehicle body or the gravity center of total mass of the vehicle body and a subject supported on the vehicle body is located above the rotation center of the wheels.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
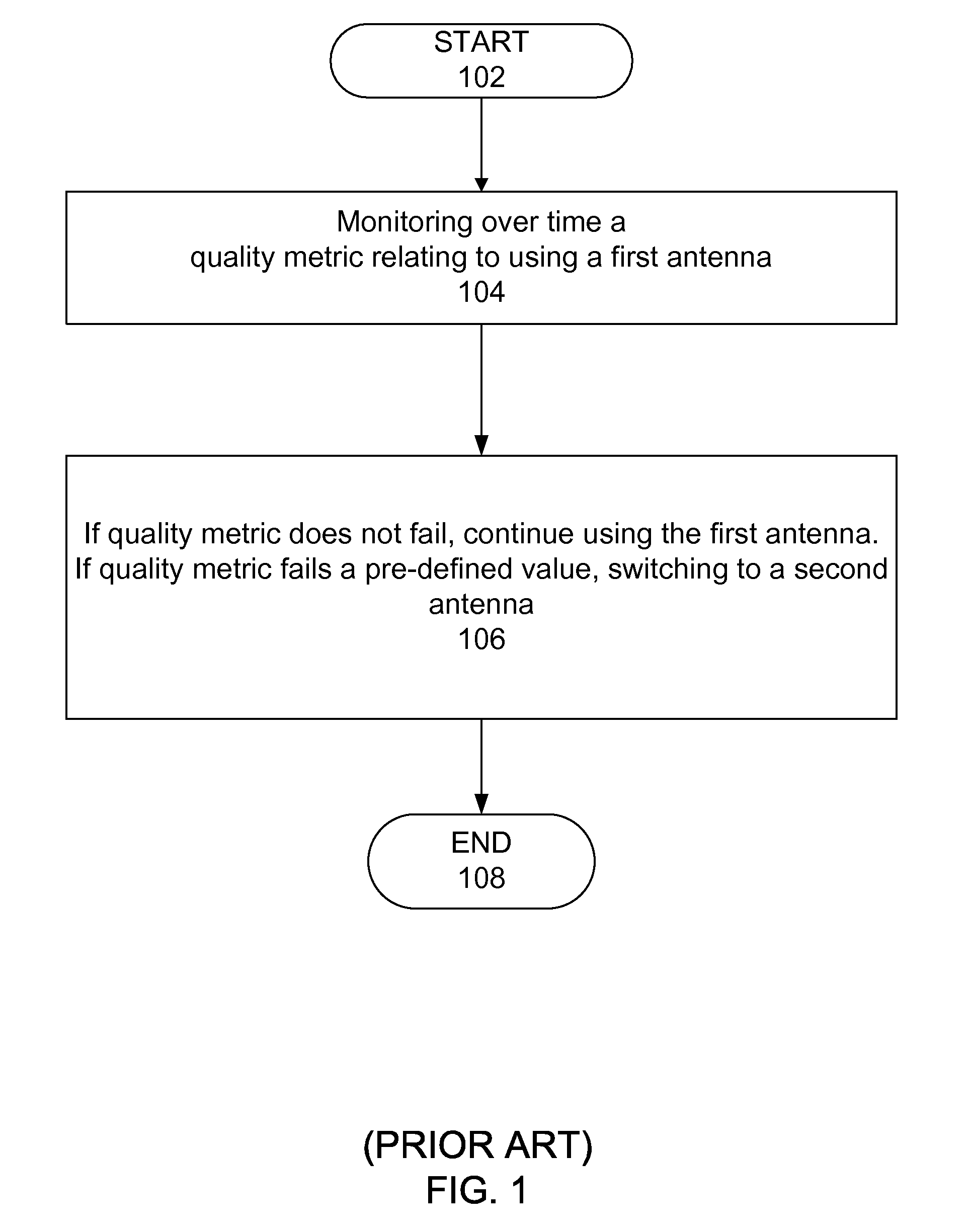
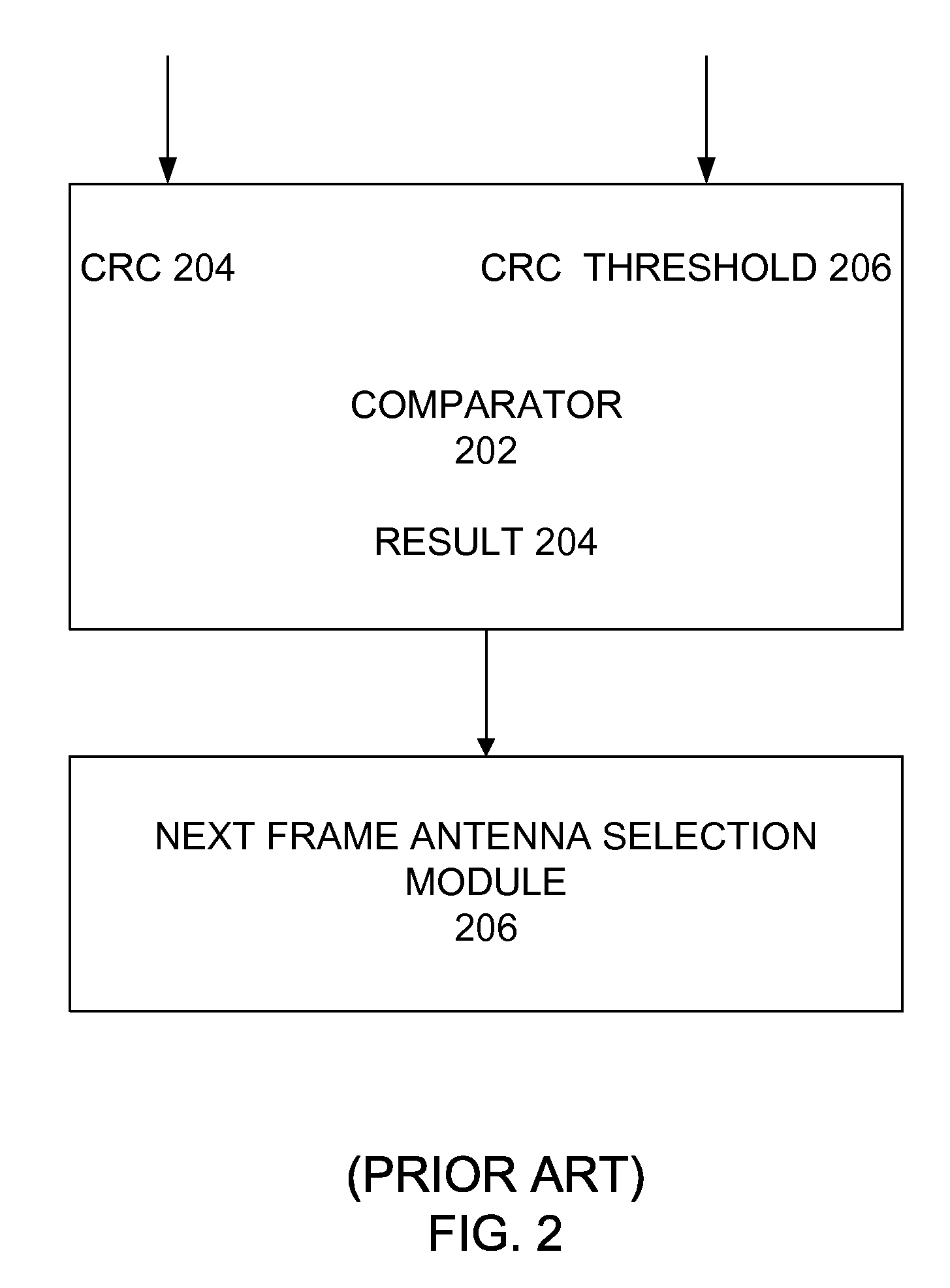
Intelligent Iterative Switch Diversity
InactiveUS20080240280A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionDiversity schemeComputer science
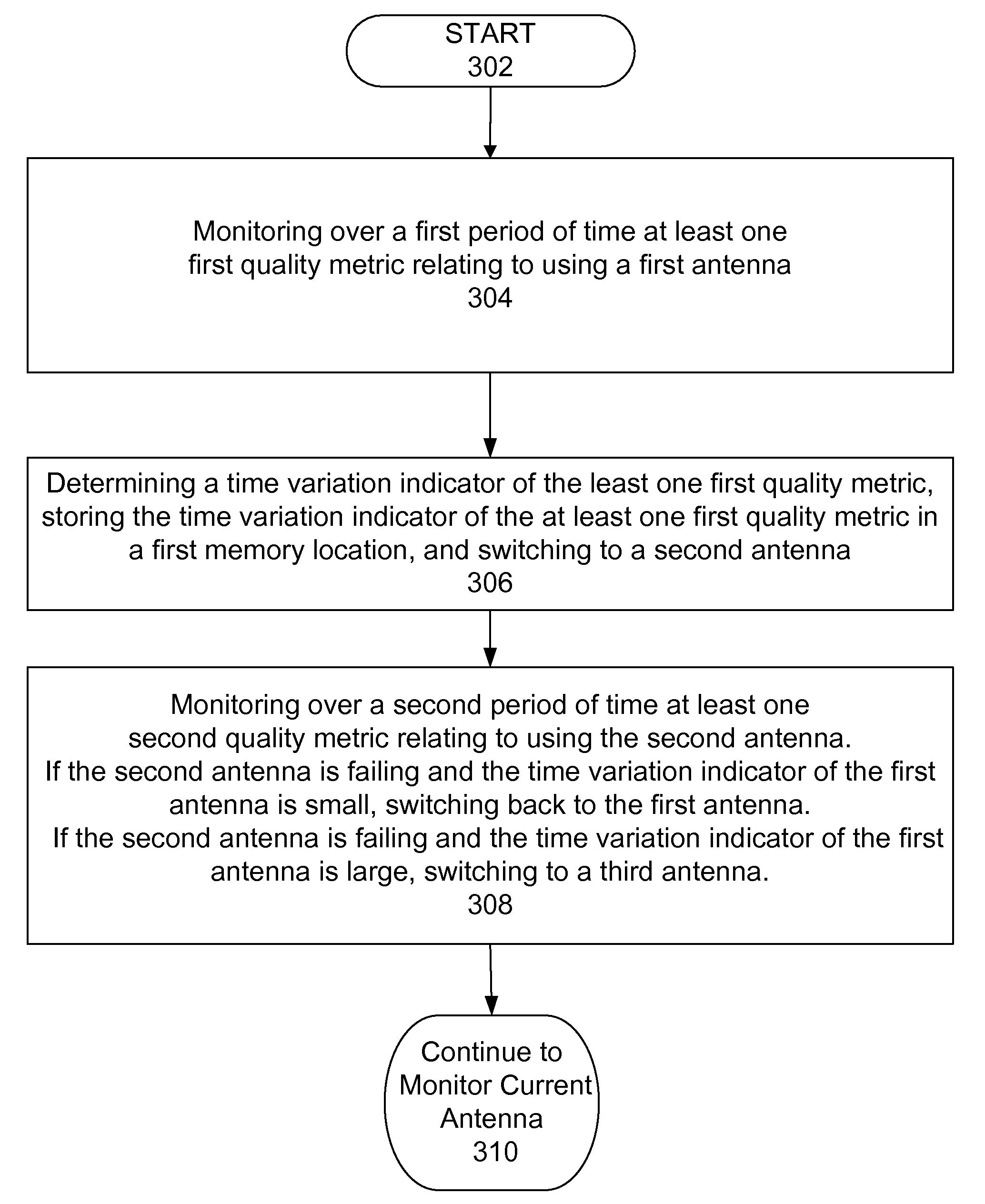
A method and system to switch among a plurality of antennae used for wireless communications. A first embodiment is a method for using at least one quality metric and at least one time variation indicator of at least one quality metric to selectively switch among a plurality of antennae to maintain wireless communications. A second embodiment is a method using at least one quality metric and at least one time derivative slope of at least one quality metric to selectively switch among a plurality of antennae to maintain wireless communications. These embodiments can be applied in several wireless communication applications using multiple antennae including, but not limited to, WiMAX applications.
Owner:EXACTA DATA DEV LIMITED LIABILITY
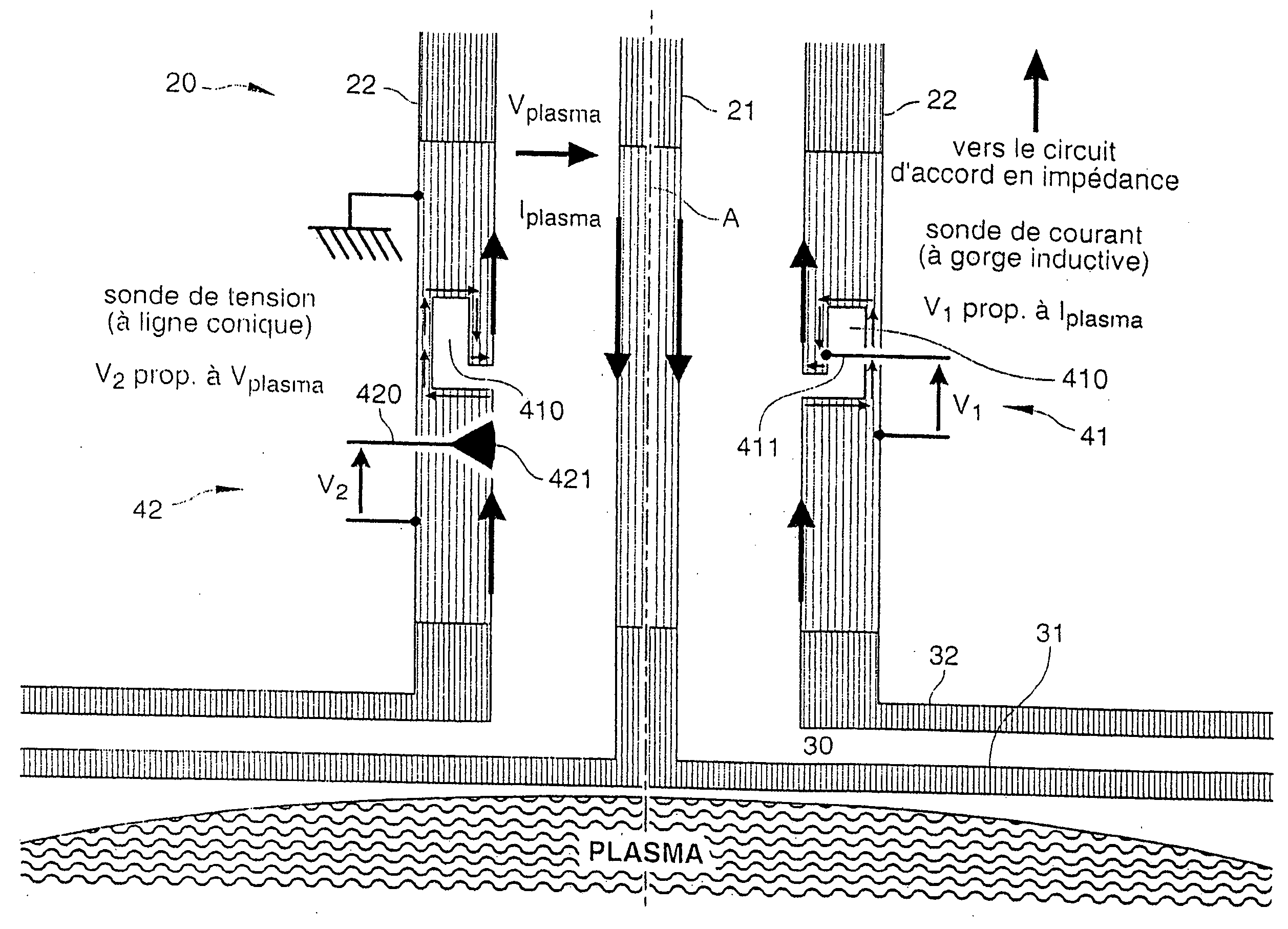
Probe for Measuring Characteristics of an Excitation Current of a Plasma, and Associated Plasma Reactor
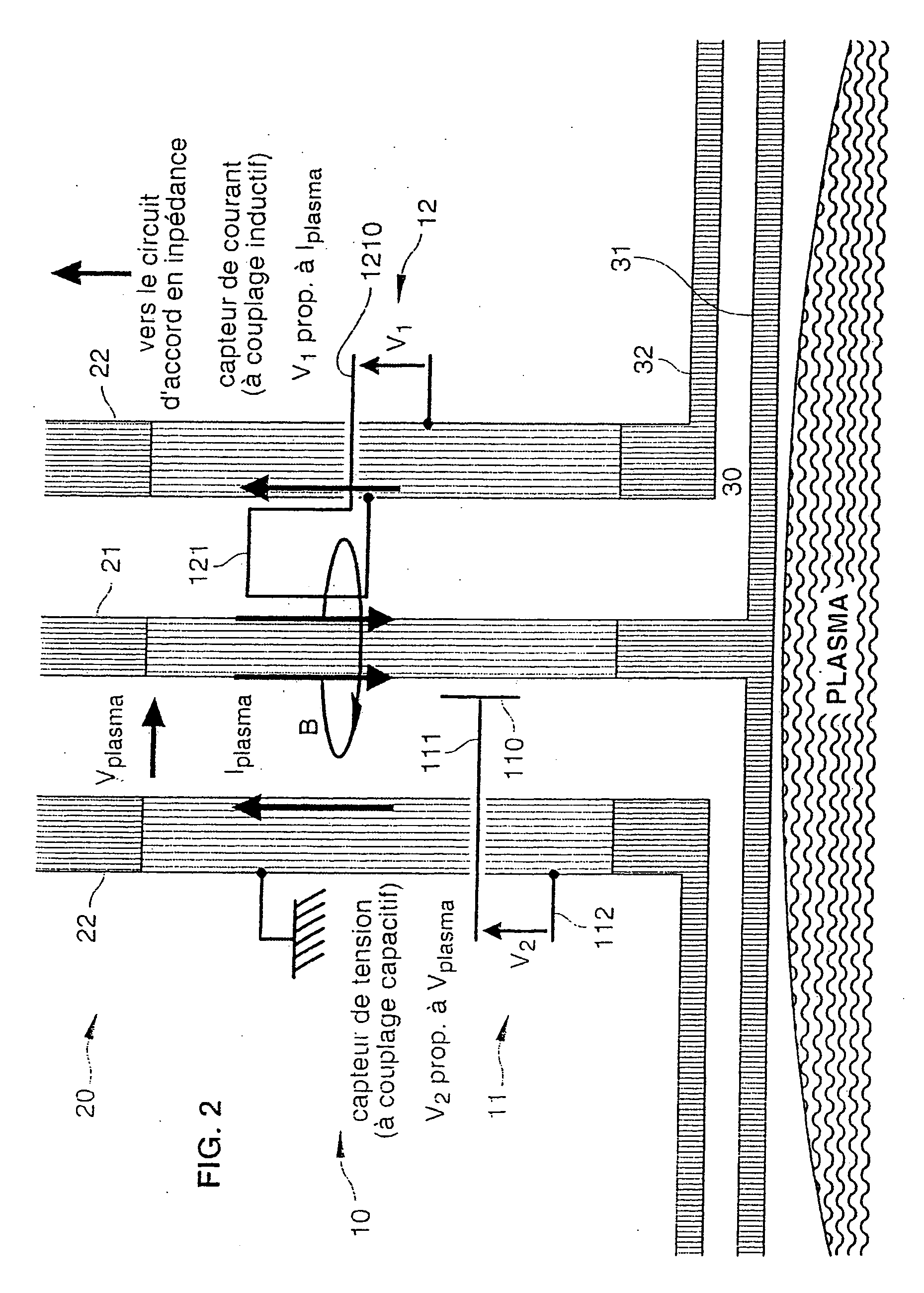
InactiveUS20070252580A1Current/voltage measurementElectrical testingElectrical conductorExcitation current
A probe for measuring electrical characteristics of an excitation current of a plasma is provided. The probe is mounted on a conductive line that includes an inner conductor and an outer conductor. The probe includes a current sensor and a voltage sensor. The current sensor includes a grove formed in the ground of one of the conductors in order to form a detour for the current flowing through the conductor, and a point for measuring electric voltage between a ground connected to the conductor and a point of the groove. The current sensor thus is able to measure a voltage proportional to the first time derivative of intensity (Iplasma) of the excitation current. The voltage sensor is a shunt sensor capable of measuring a voltage proportional to the first time derivative of the voltage (Vplasma) of the excitation current. A plasma reactor including a probe of the aforementioned type is also provided.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE +1
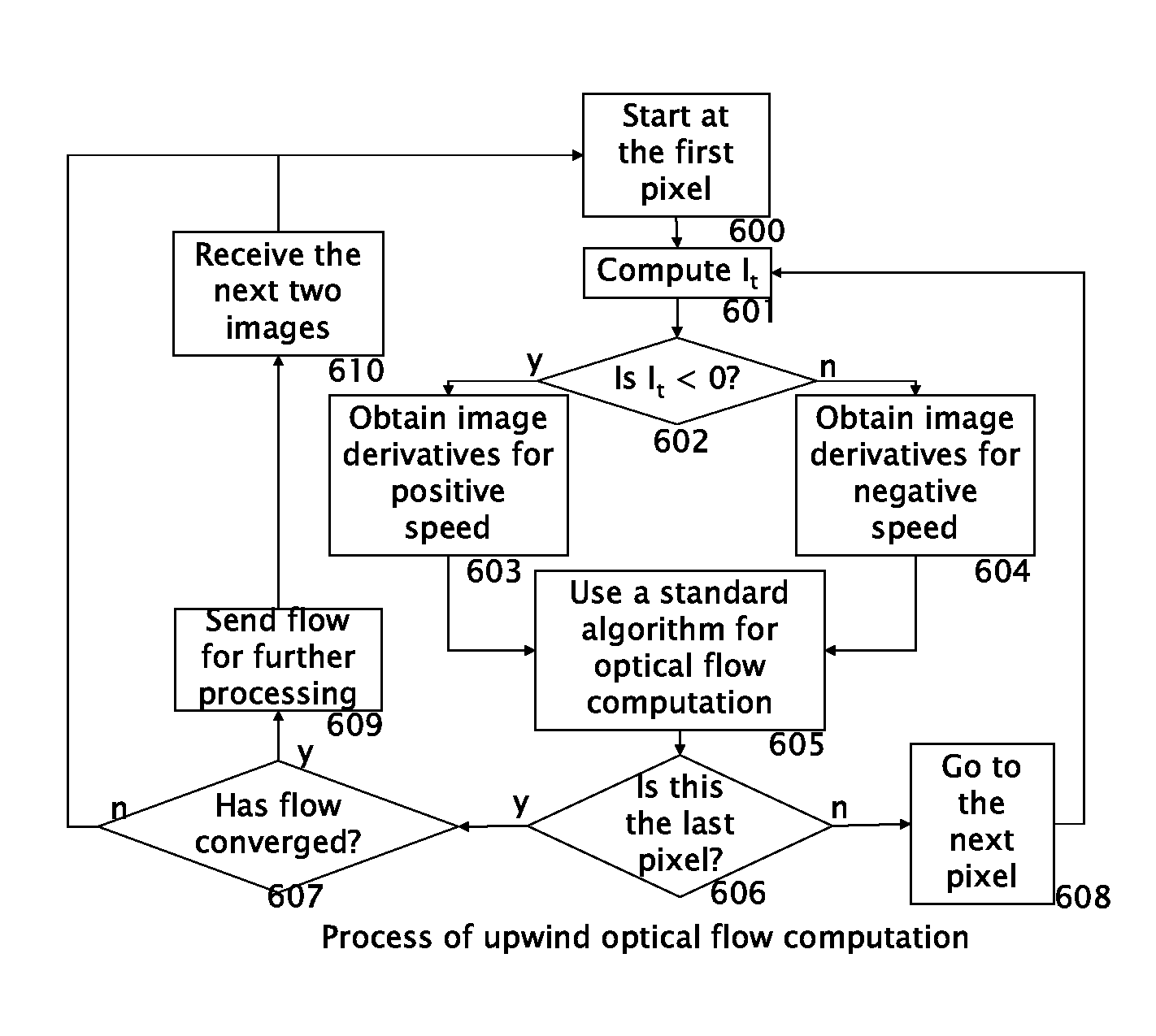
Apparatus and Upwind Methods for Optical Flow Velocity Estimation
Apparatus and methods for estimating the optical flow velocity components using an upwind discretization are presented. In prior art, the knowledge of the signs of the optical flow velocity components is needed for using upwind discretization. But in optical flow computations the velocity components are precisely the unknowns and thus their sign information is not available. This invention discloses apparatus and methods in which upwinding is done based on the sign of the local time derivative instead of the signs of the optical flow velocity components.
Owner:MURALI BEDDHU
Anti-sway control of a crane under operator's command
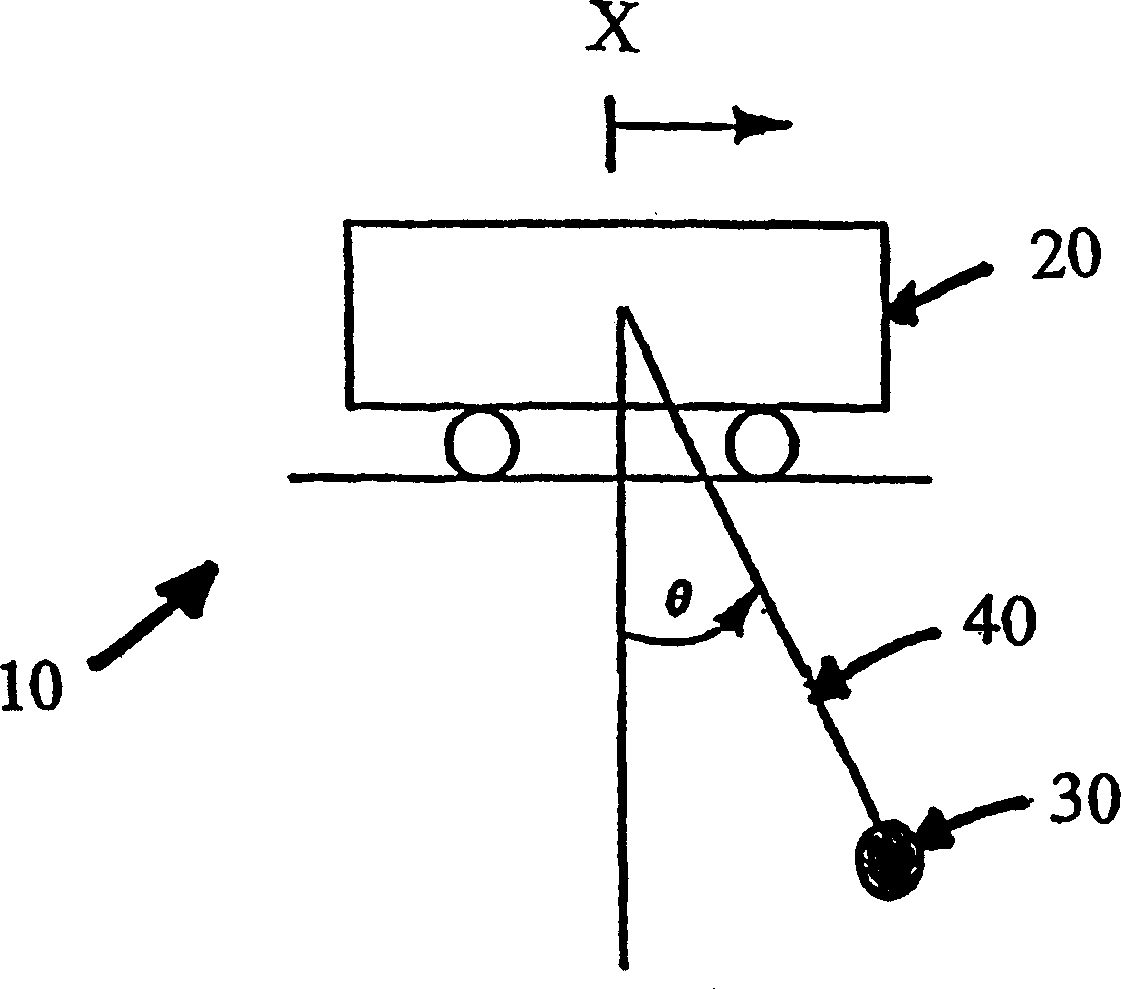
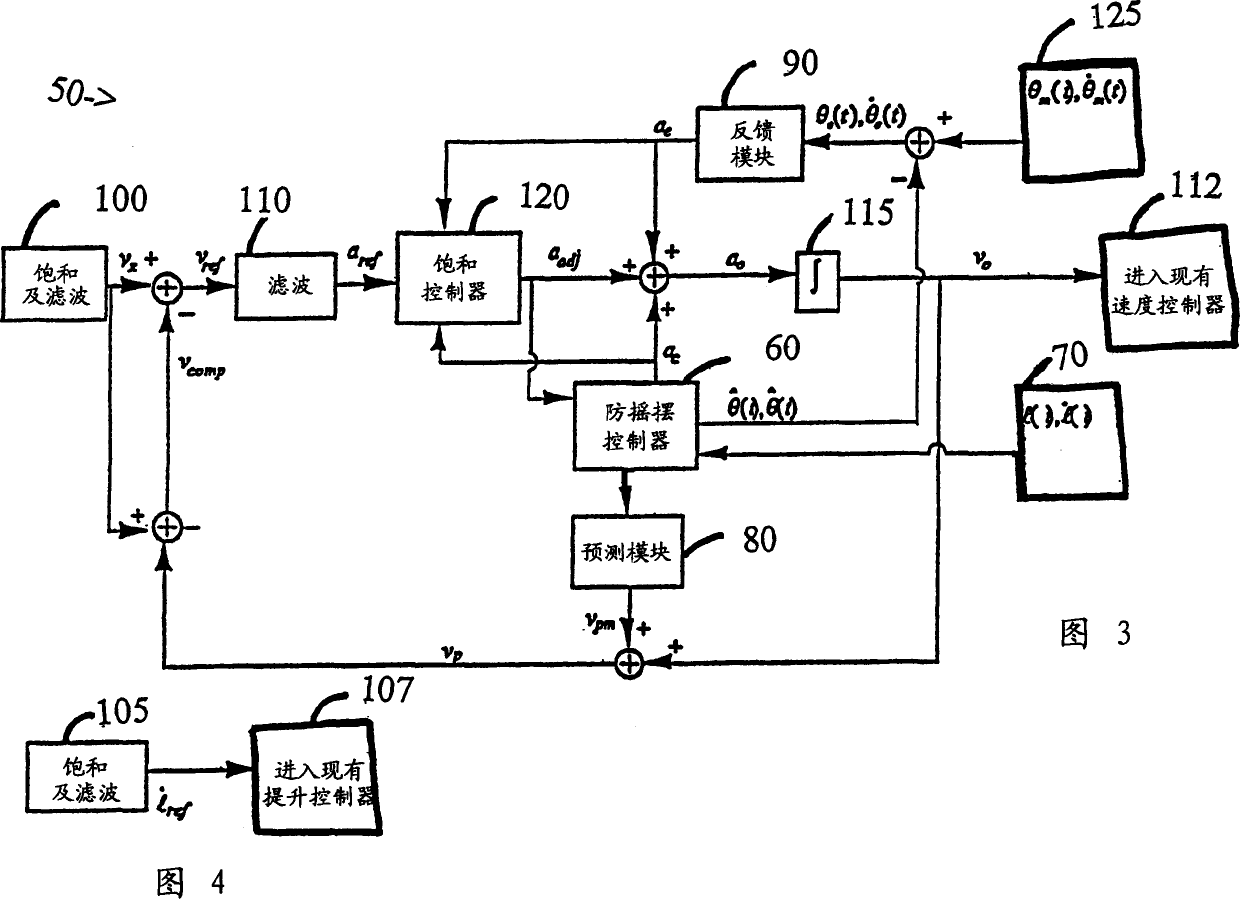
InactiveCN1505590AMake sure it works correctlyResidual Swing EliminationTrolley cranesLoad-engaging elementsEngineeringKey factors
A system (10) is disclosed for eliminating sway of a load (30) in a crane or crane-like system subject to operator's command. The load is suspended by a cable (40) from a horizontally movable trolley (20) and can be hoisted vertically. The system uses the principle of cancellation to eliminate sway even when the crane has simultaneous trolley and hoisting motions. The system takes into account the full dynamical effect in computing cancellation signals. The use of a family of ordinary differential equations for the computation of the cancellation controls is a key component of the invention. In computing these controls, the differential equations are solved in real time using sensory measurement of the cable length and its time derivative. The cancellation controls handle the sway induced by the operator's command. Sway can also be induced by other factors, like wind load and external disturbances. This system also includes a feedback mechanism for eliminating sway due to such factors. The system ensures saturation limits, corresponding to the velocity and acceleration limits of the drive system of the trolley are not exceeded for proper functioning of the system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
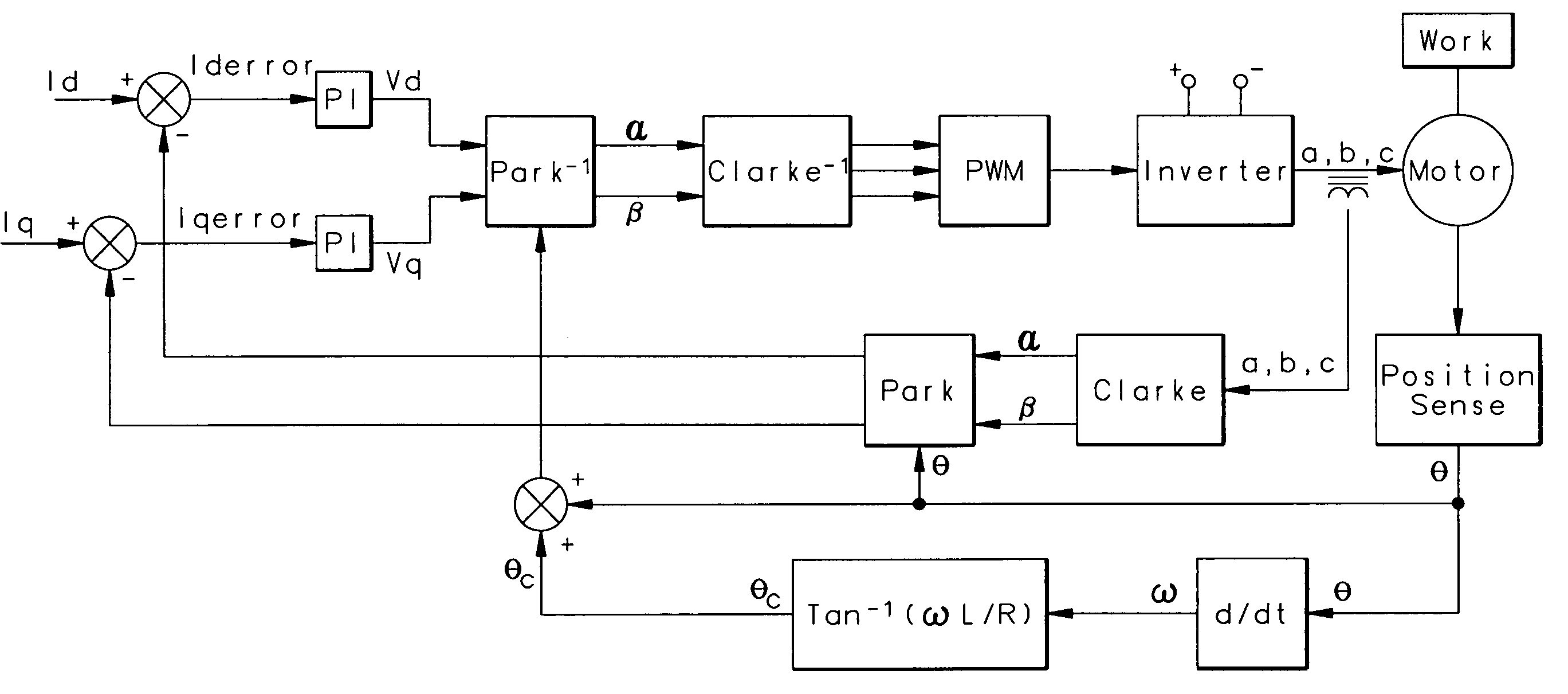
Performance enhancement for motor field oriented control system
InactiveUS20060043923A1Improve phase marginImprove stabilityDC motor speed/torque controlAC motor controlState of artPerformance enhancement
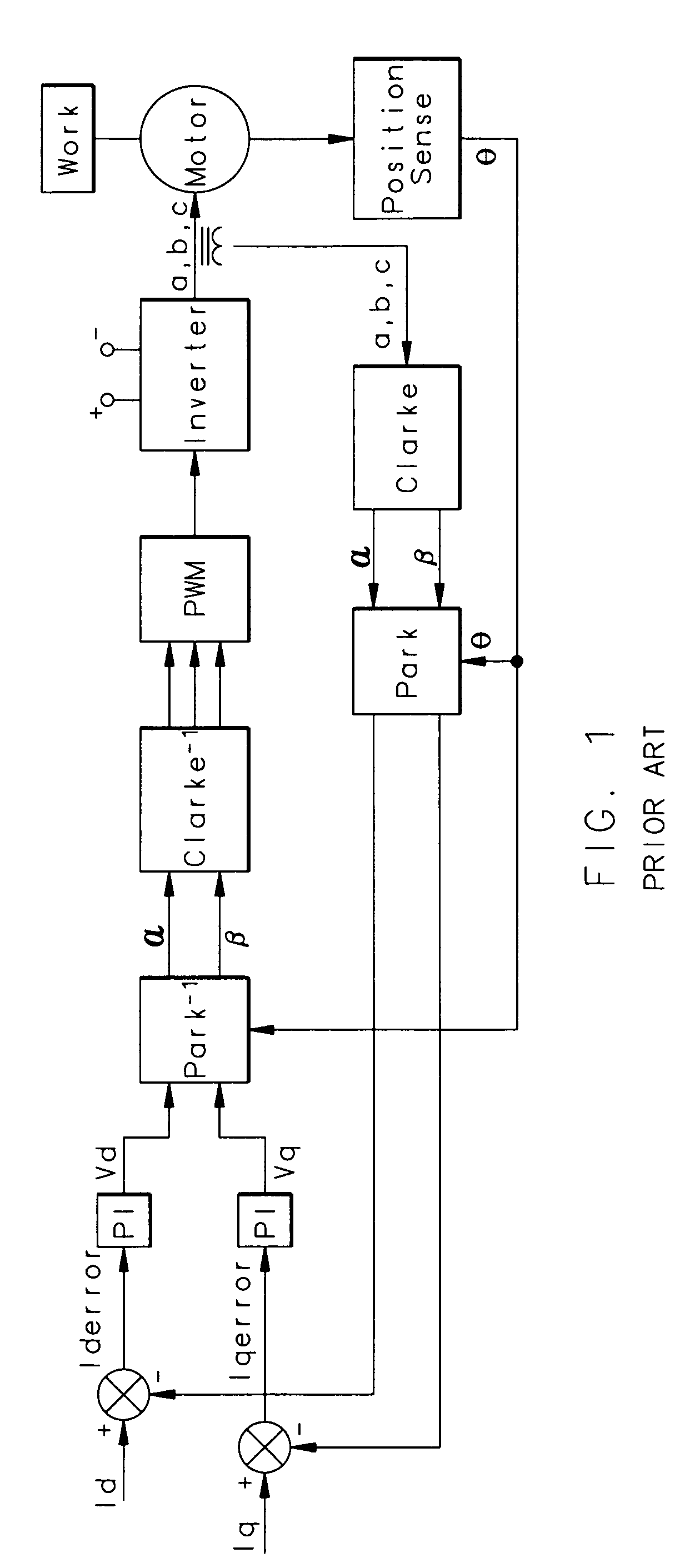
A motor controller of the sort having both a transformation function for transforming three-phase feedback information into two components, and then changing an error signal for each of the two components back into three-phase correction numbers is provided with an ARCTAN correction function. The ARCTAN correction function takes in the time derivative of the changing angular position of the motor rotor, and creates a correction factor that is supplied back to the transformation function for changing the two error signals back into three. By supplying this correction ARCTAN function, the control eliminates a disturbance that may have occurred in the prior art at higher frequencies wherein both of the control loops for the two components needed to come into play to correct an error on either of the two loops.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com