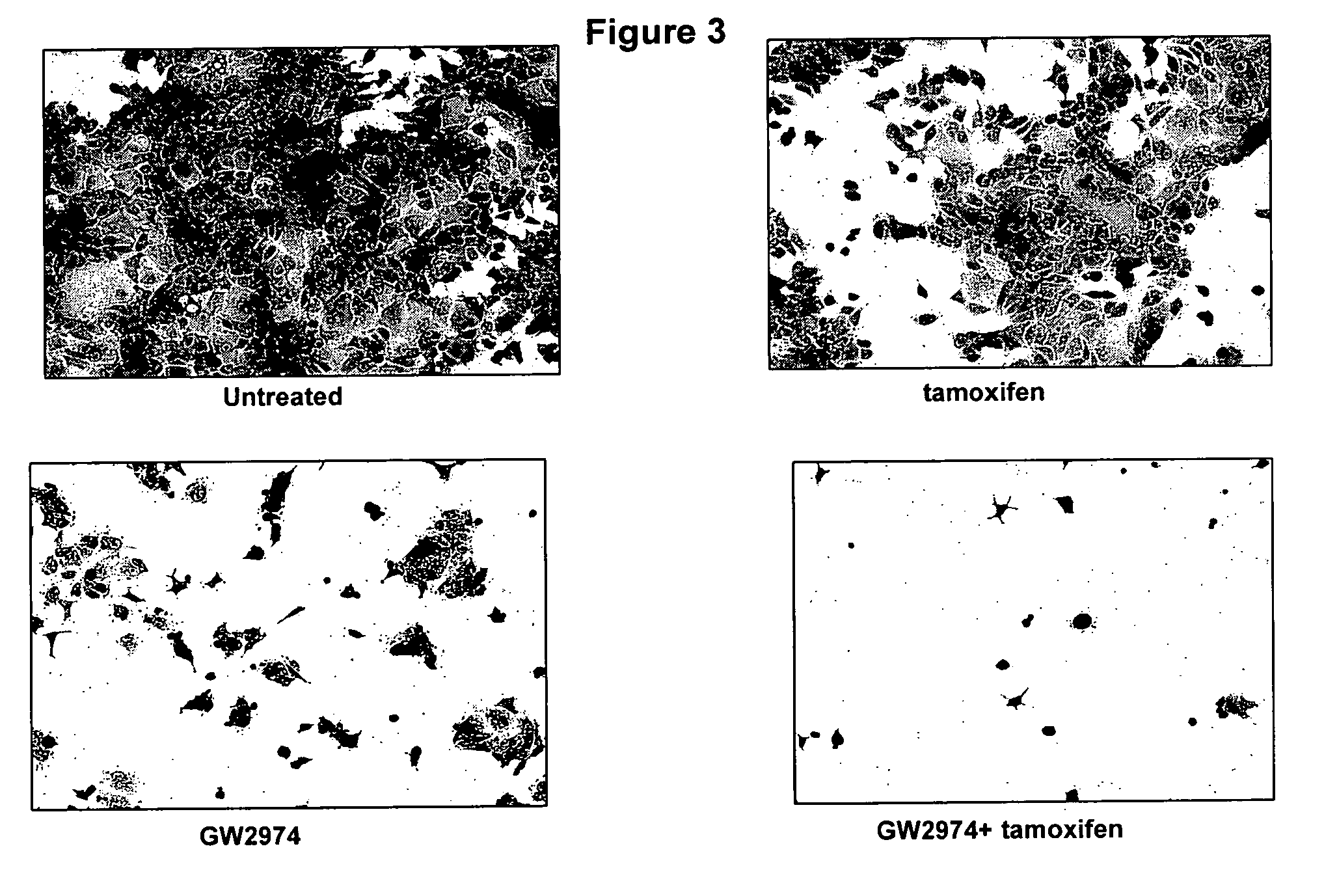
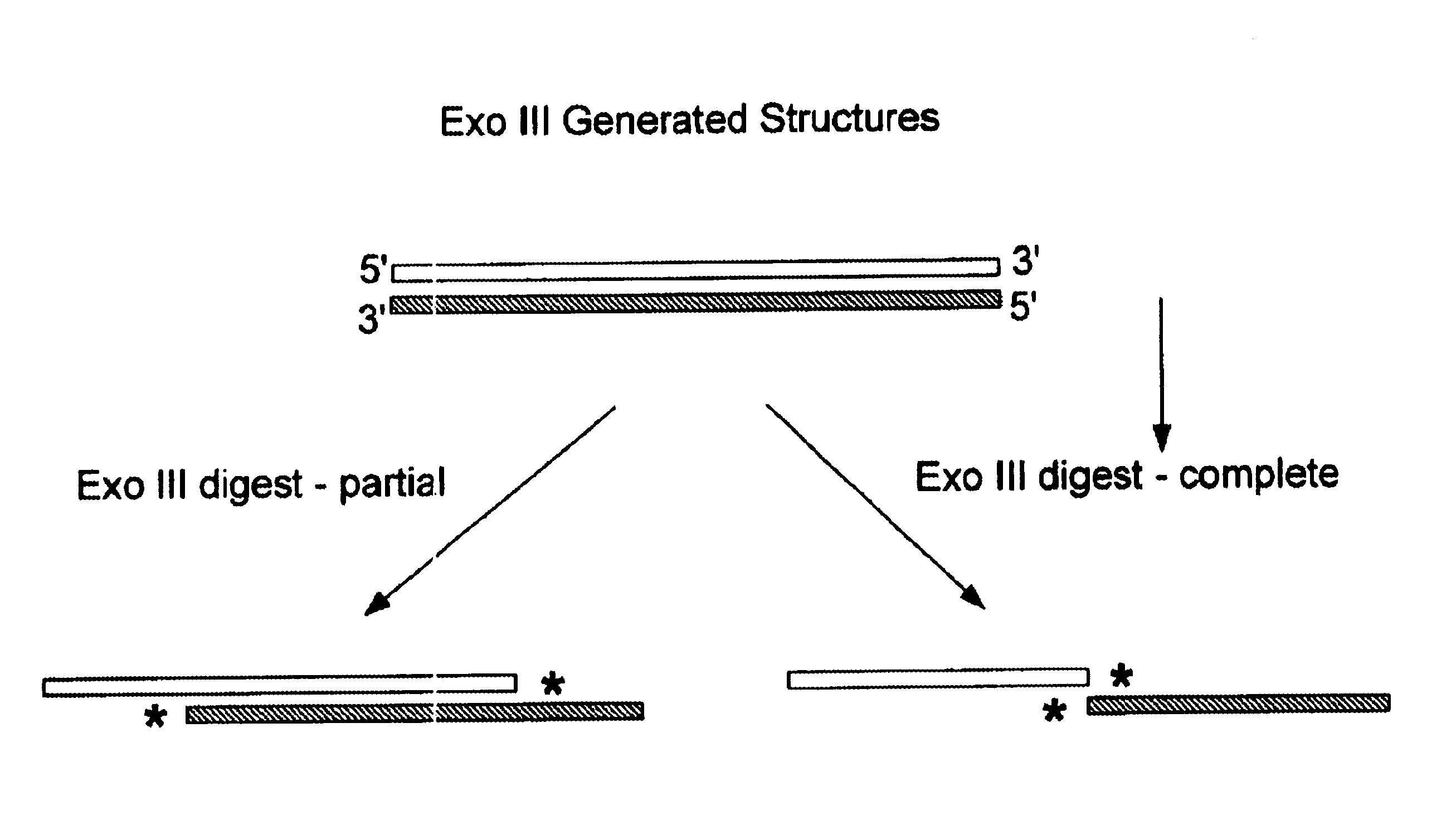
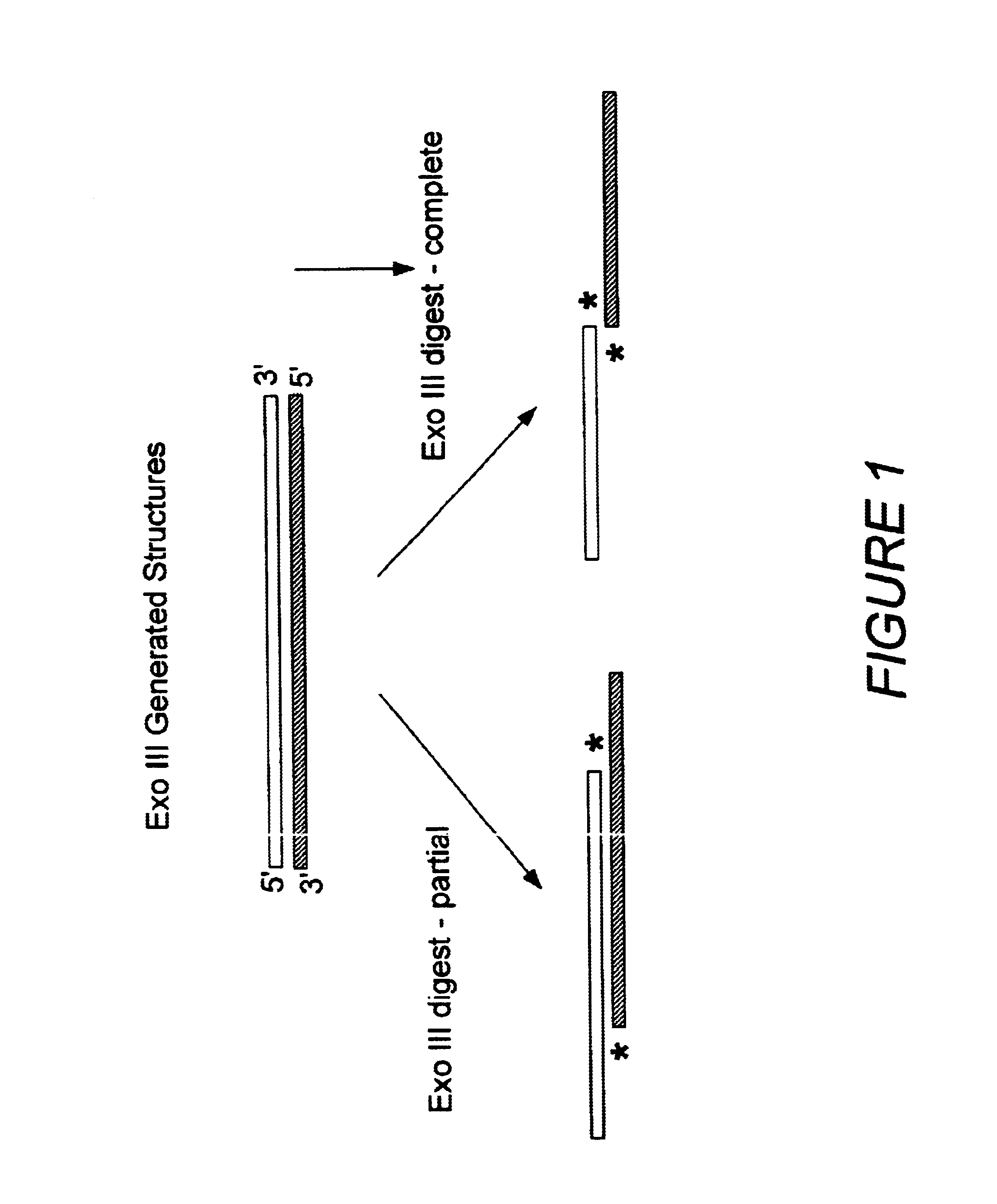
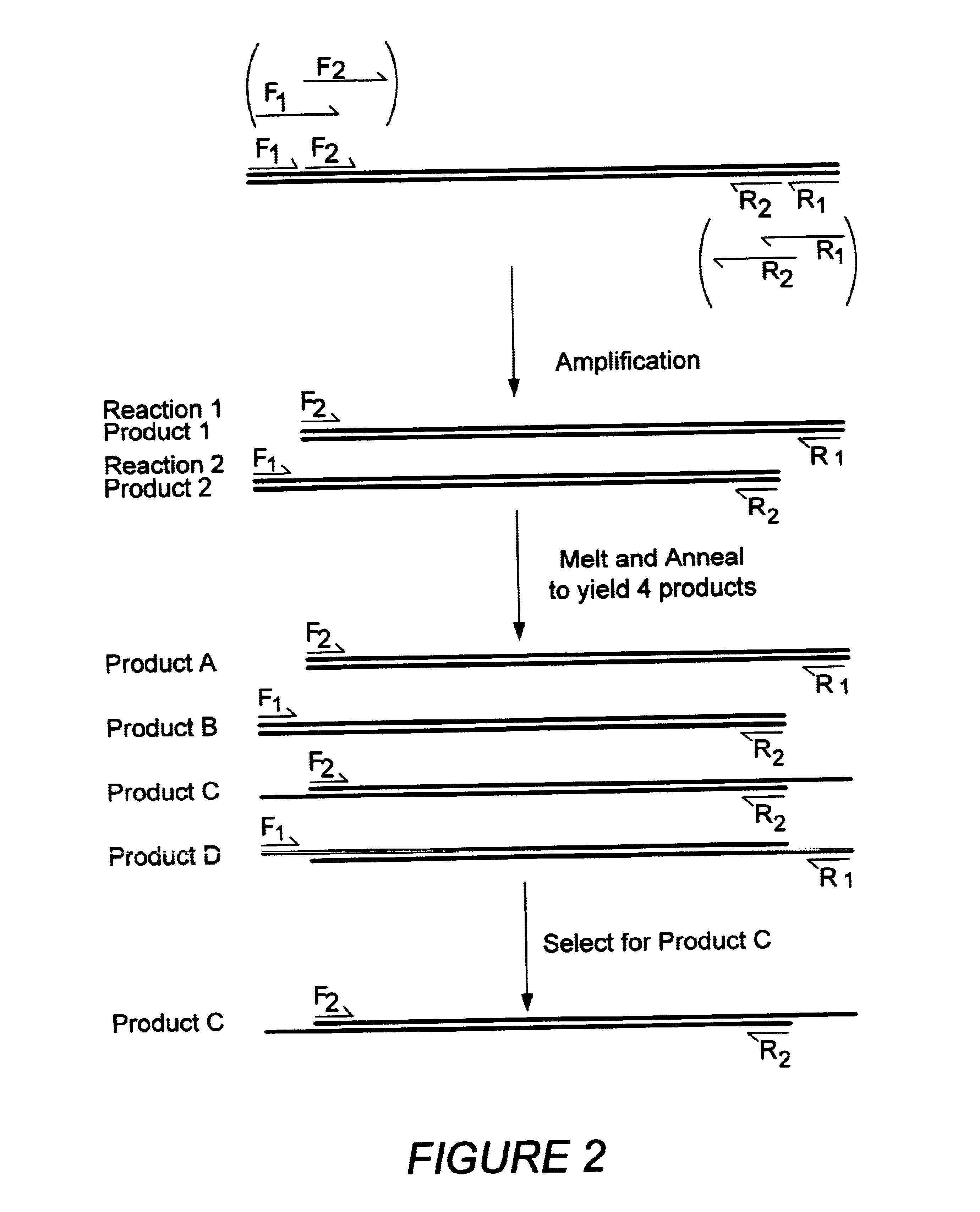
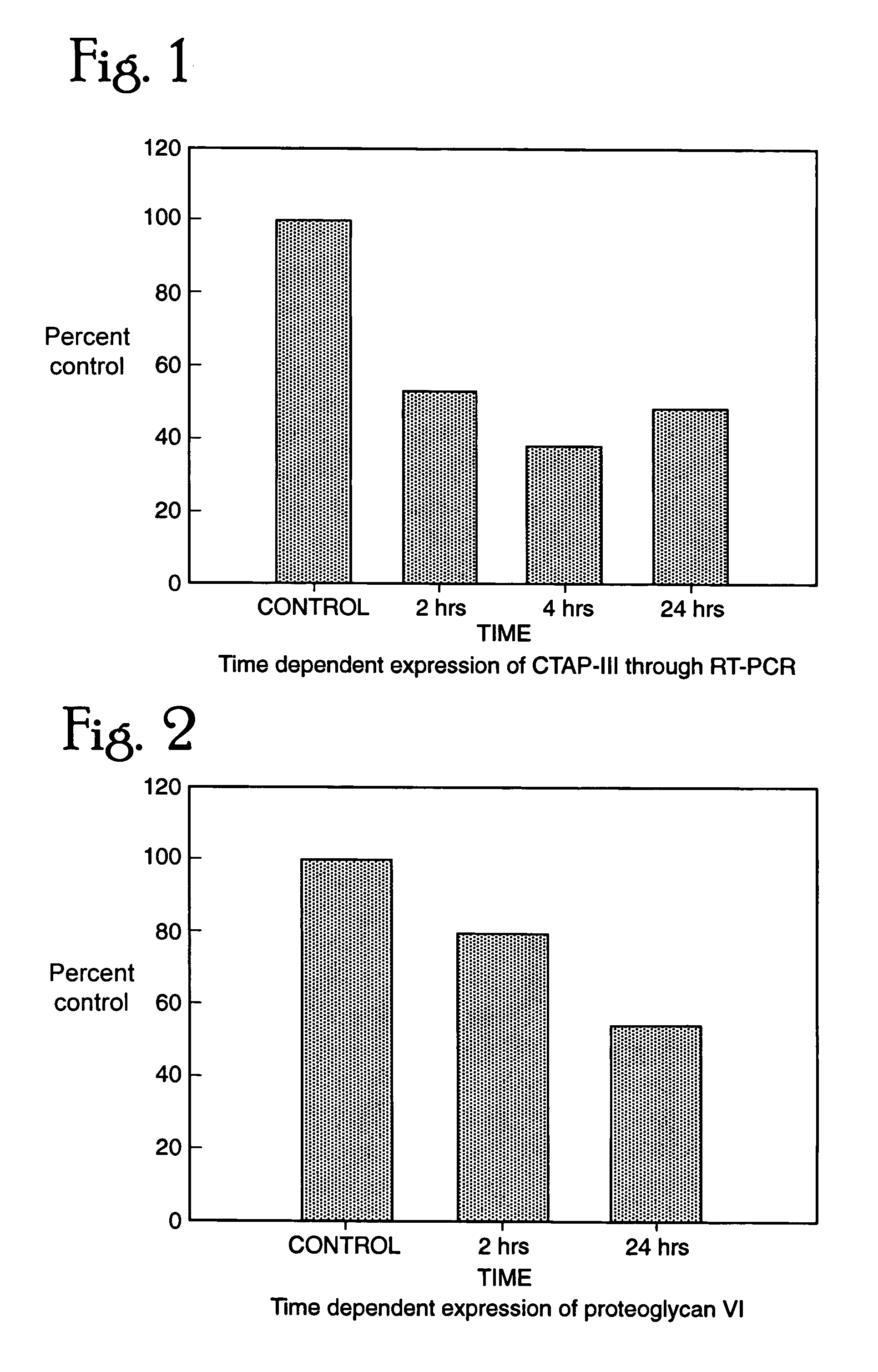
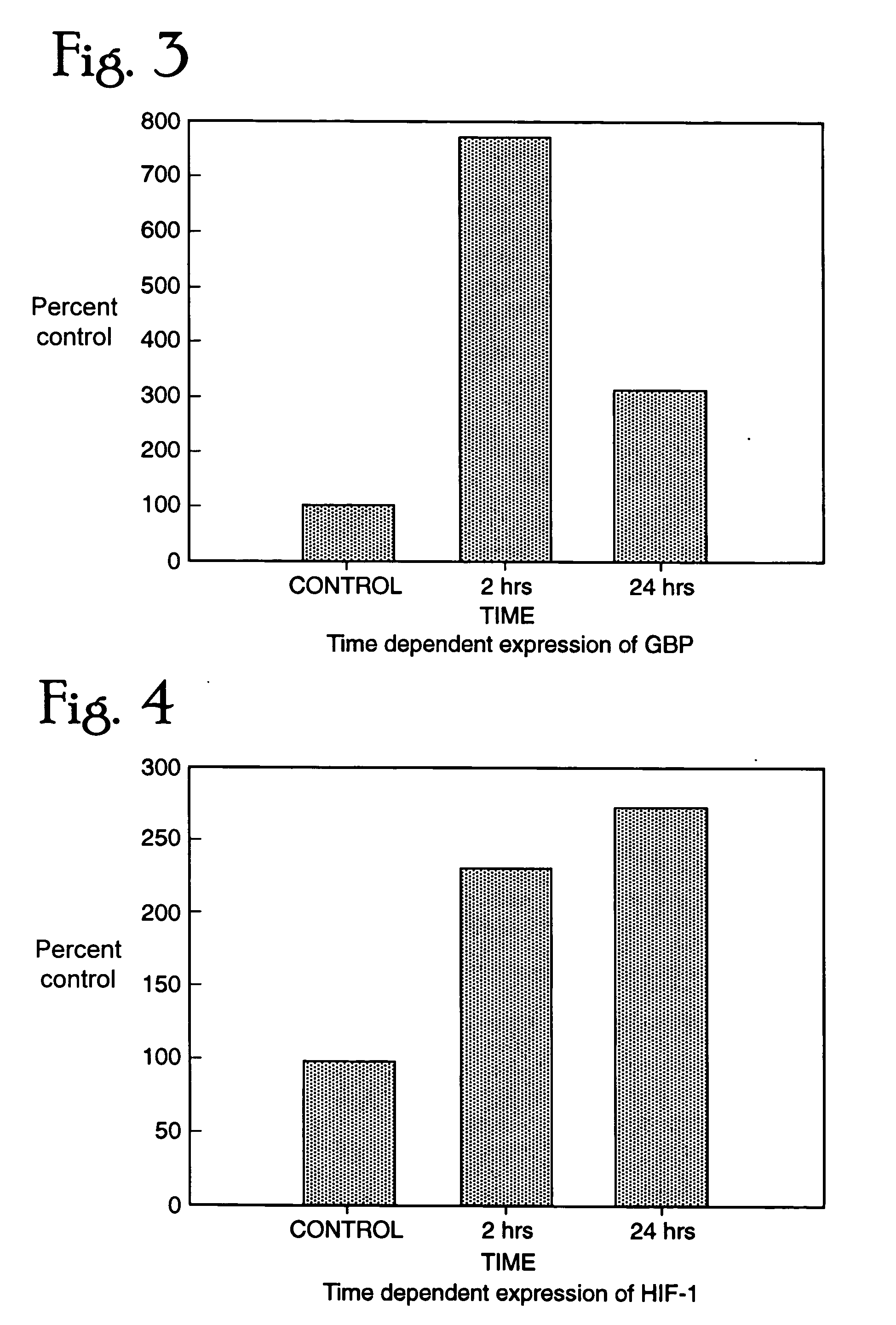
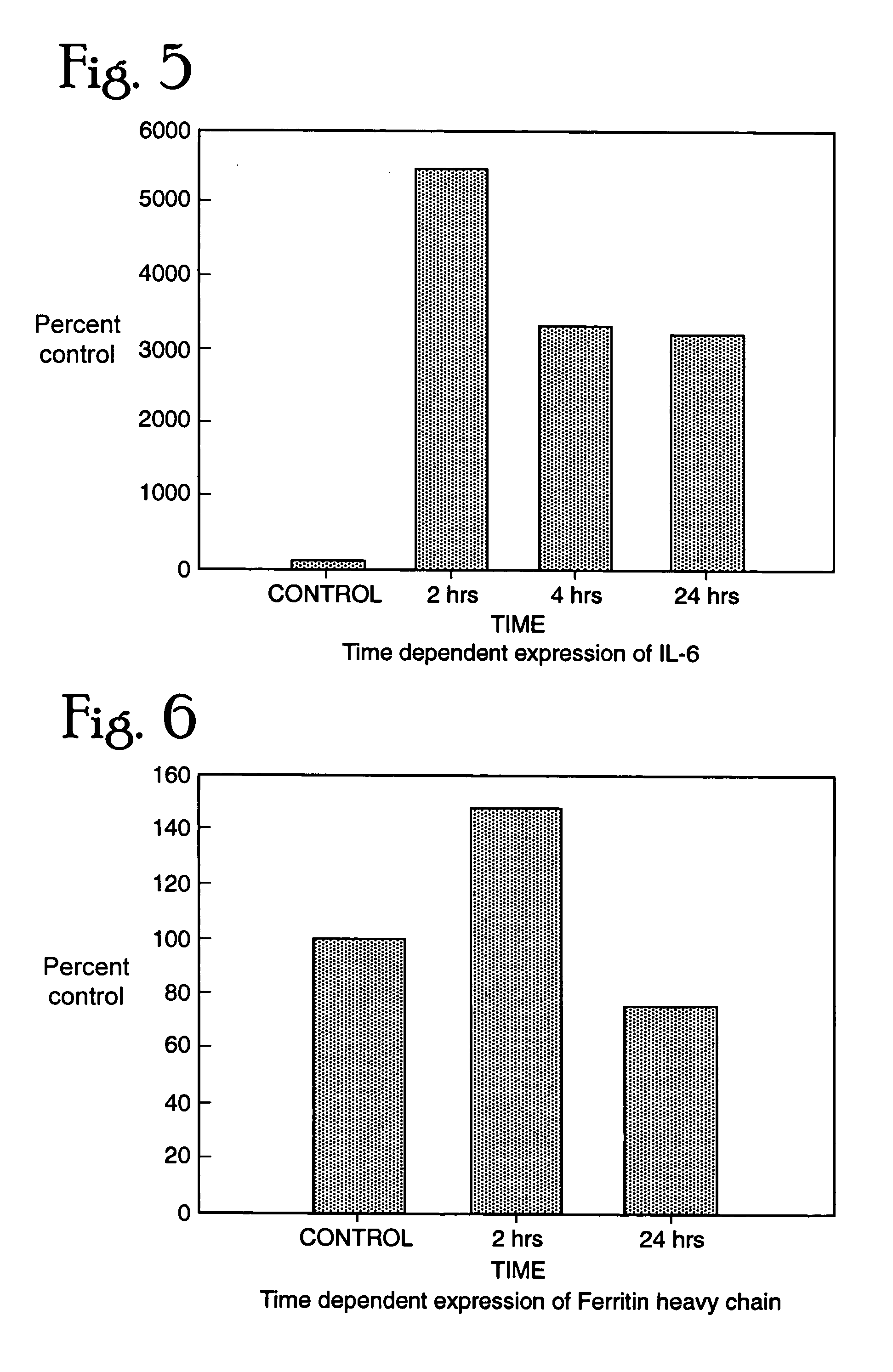
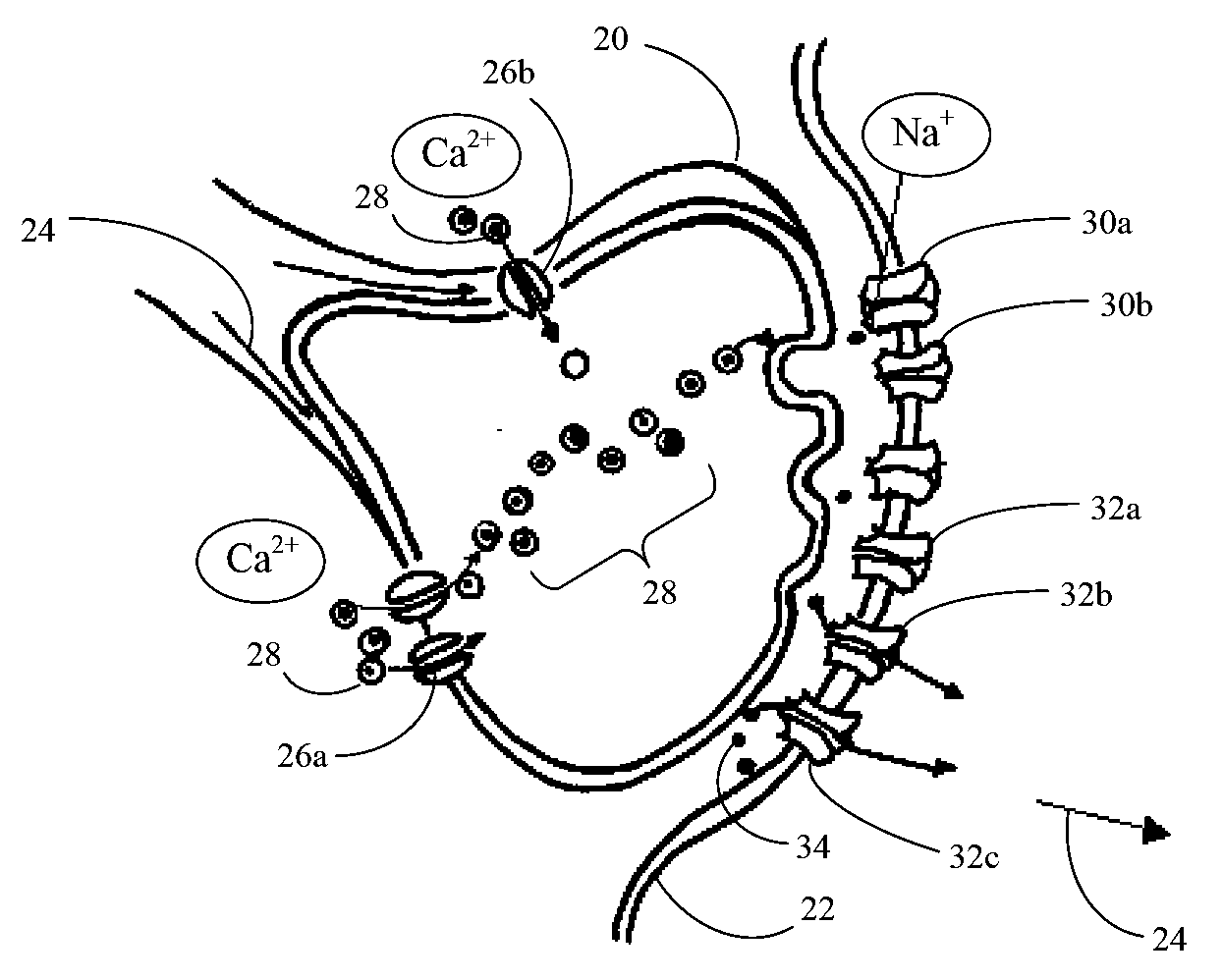
Patents
Literature
143results about How to "Potent effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
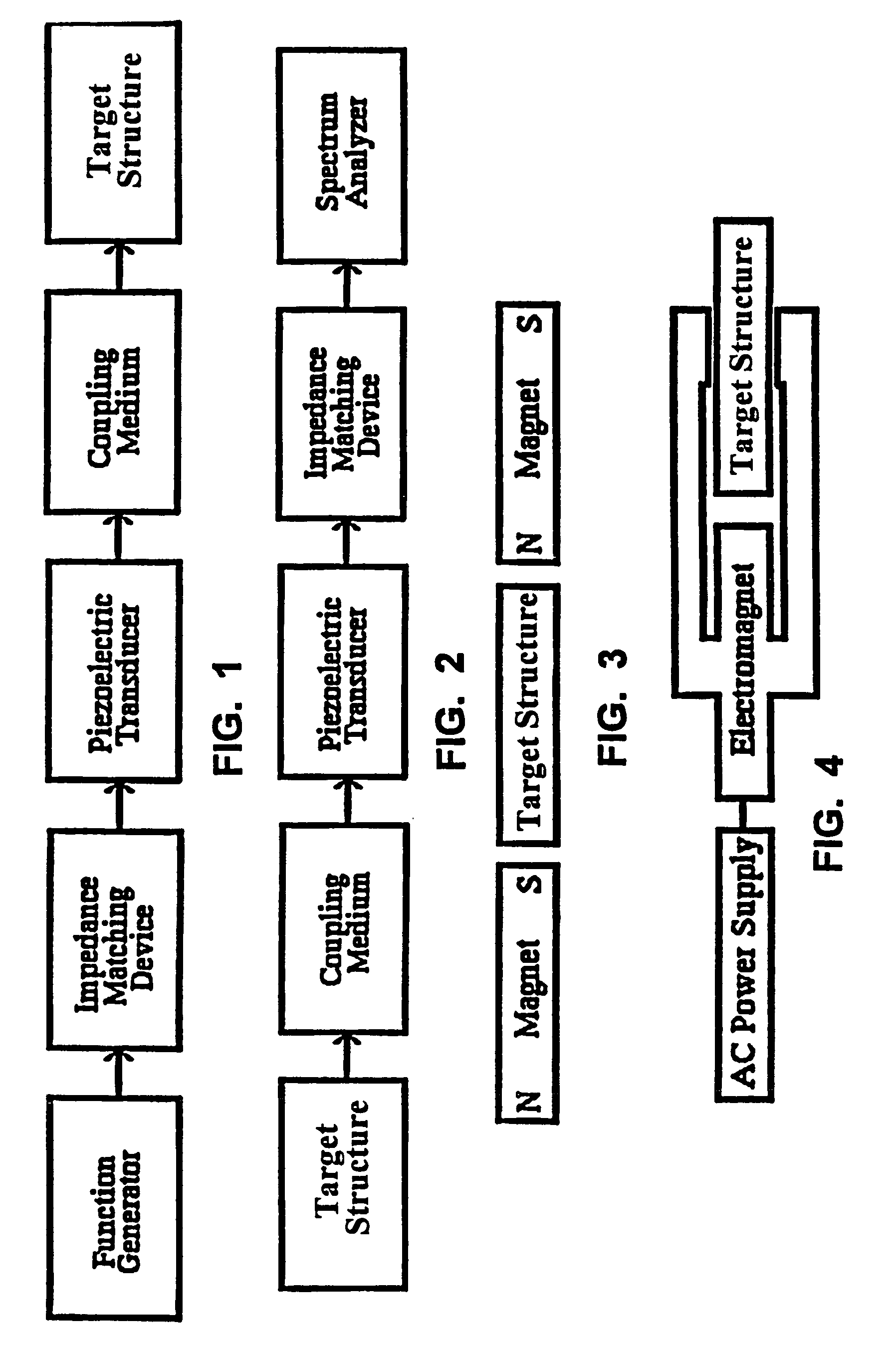
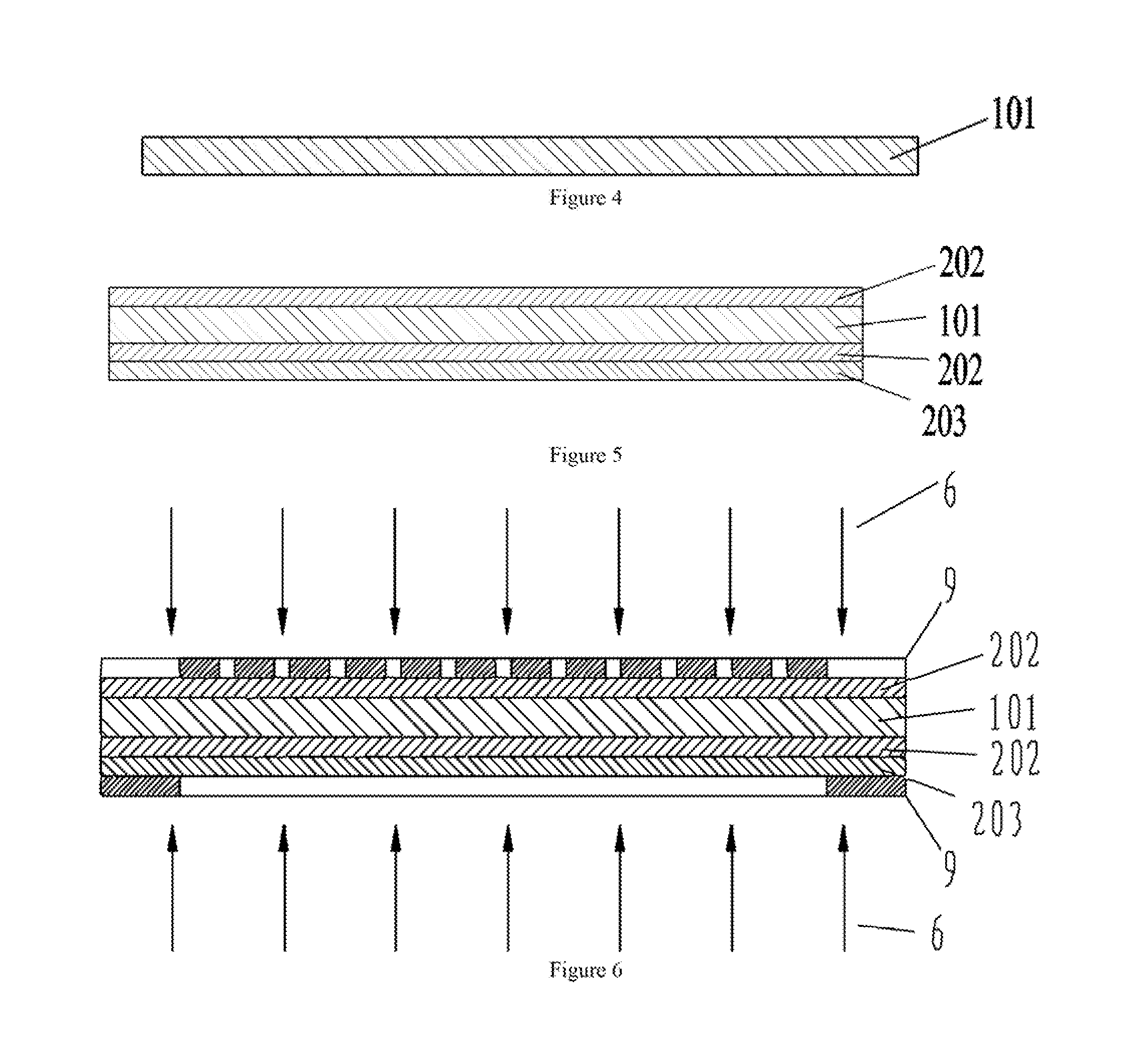
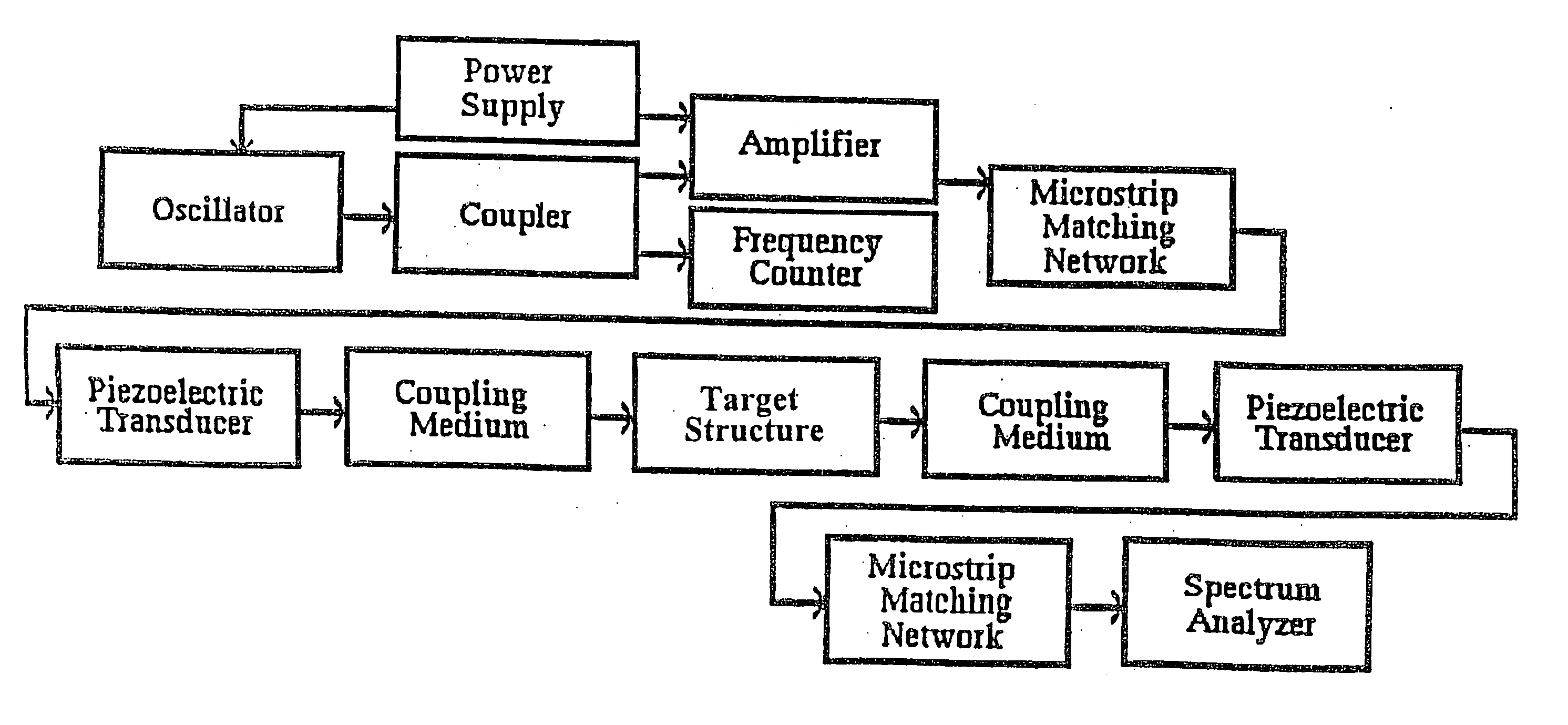
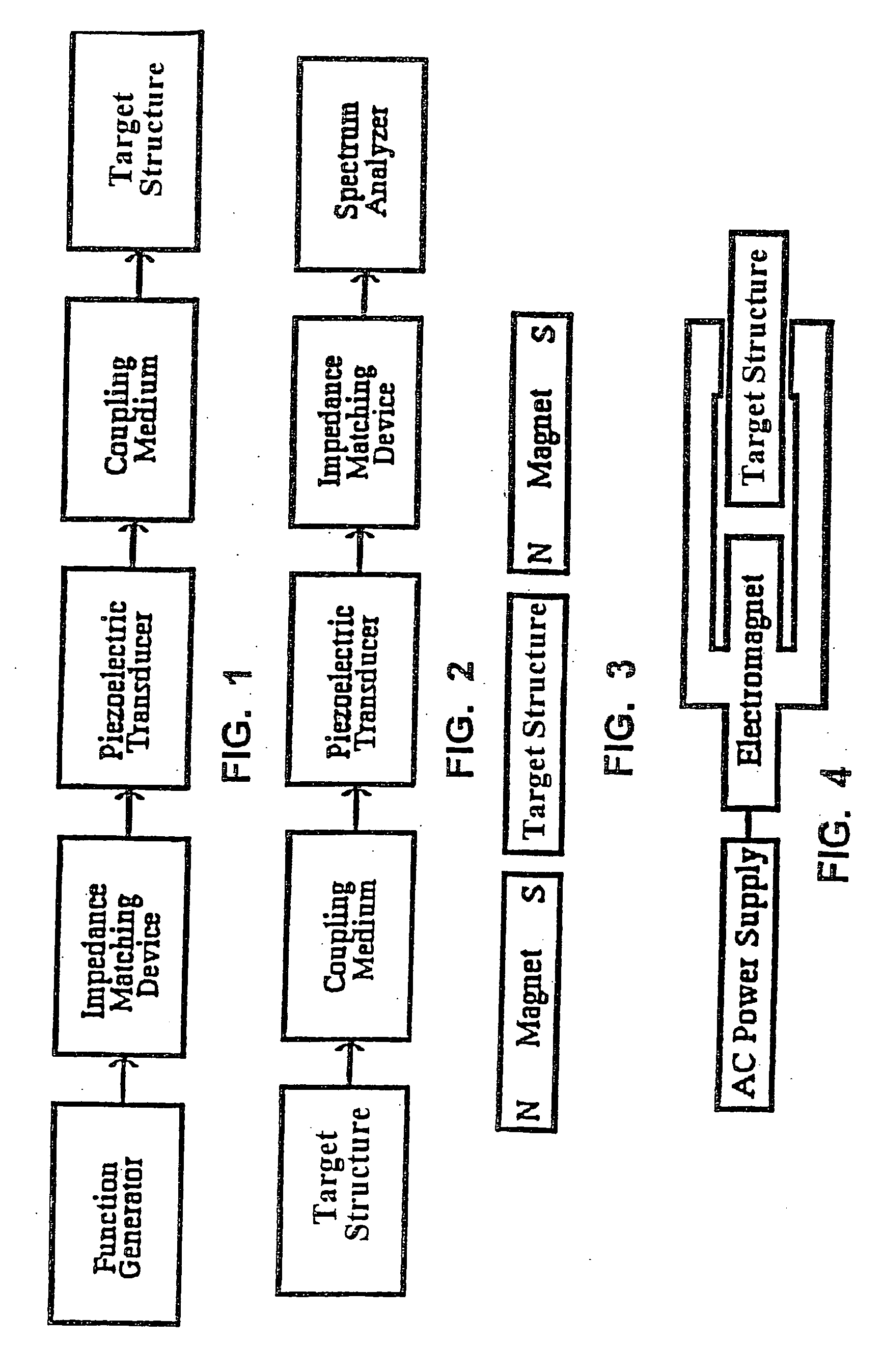
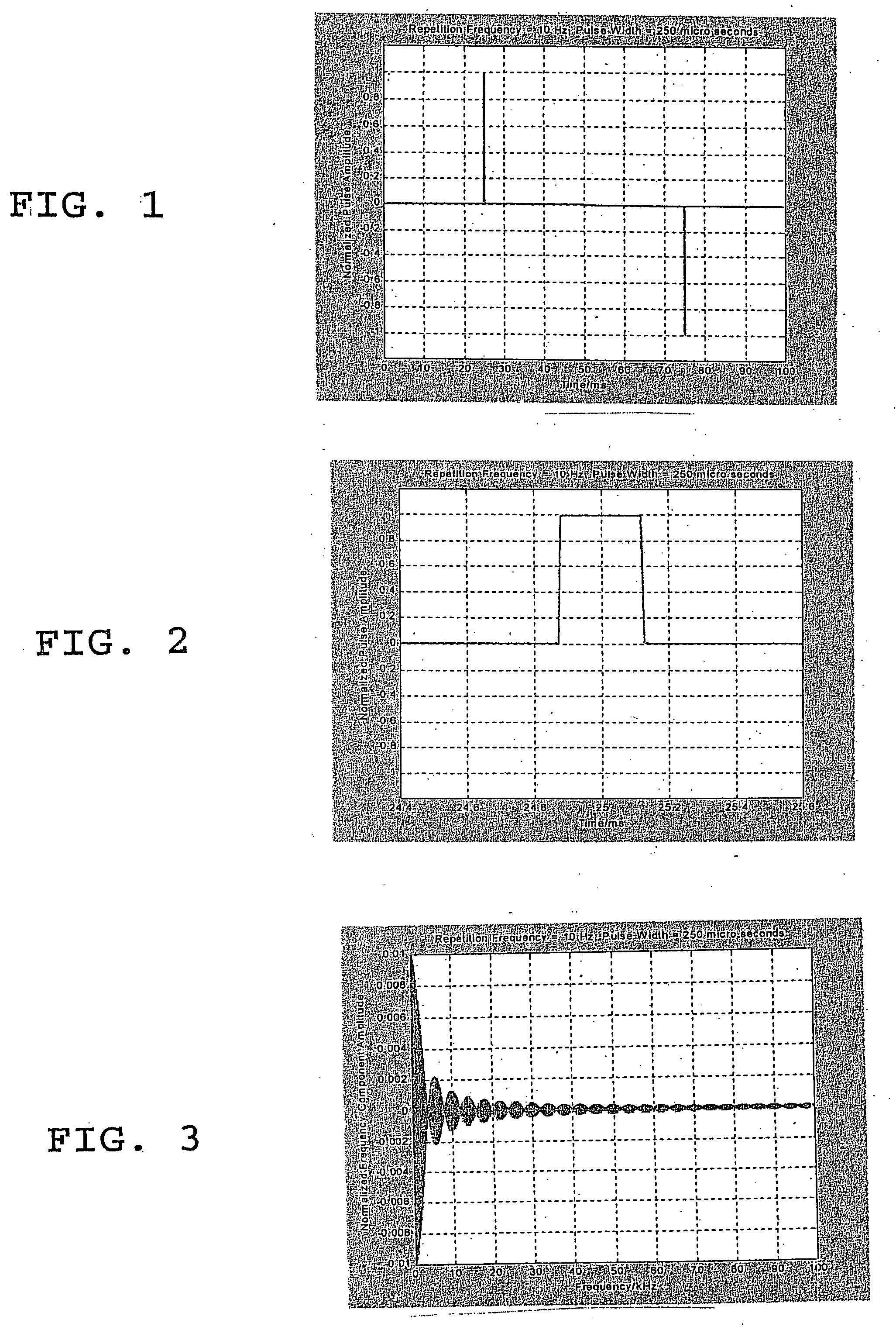
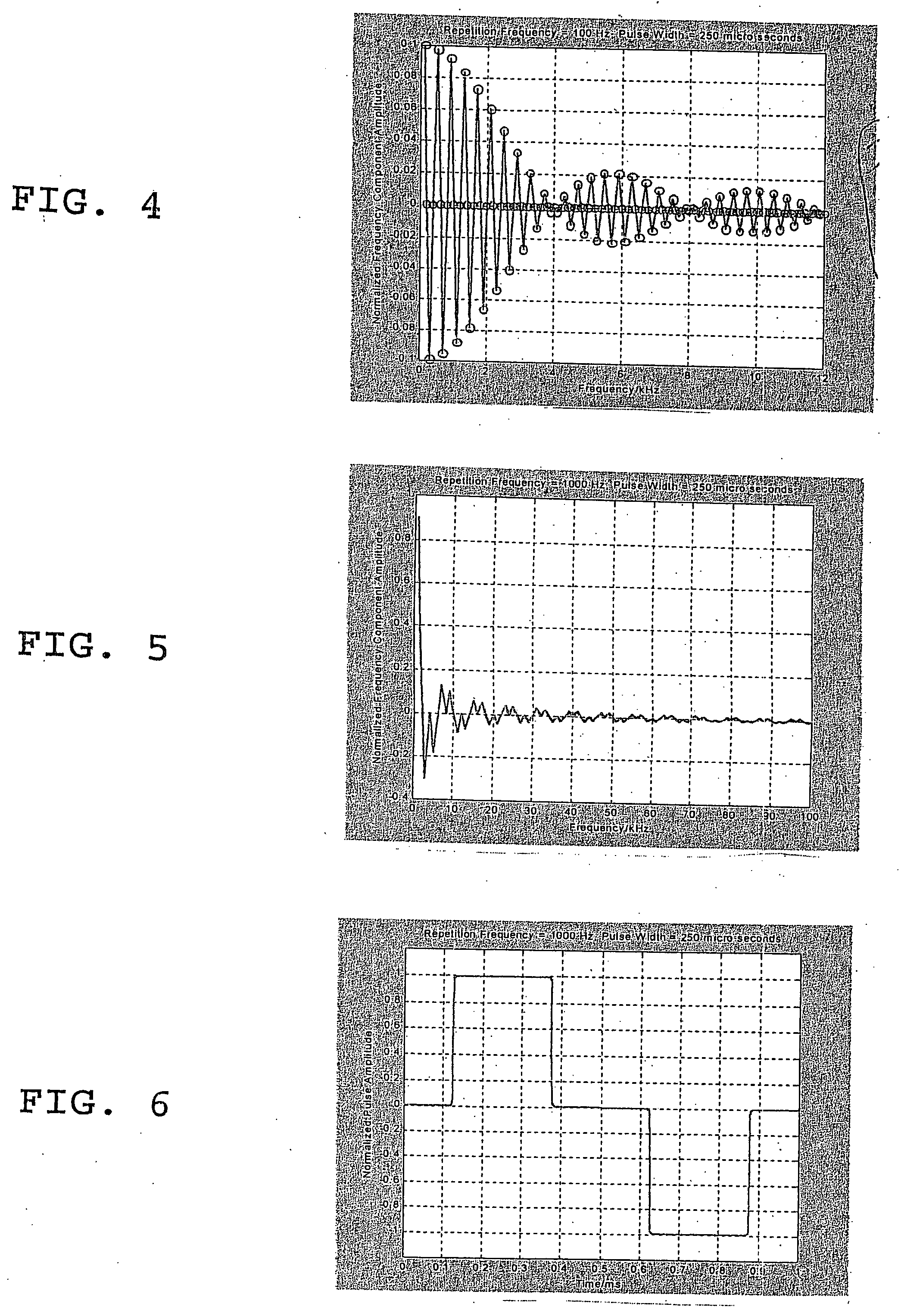
Methods for using resonant acoustic and/or resonant acousto-EM energy to detect and/or effect structures
InactiveUS7165451B1Avoid damageAccurate detectionVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsParticle physicsQuantum electrodynamics
Owner:GR INTELLECTUAL RESERVE LLC
Non-stochastic generation of genetic vaccines
InactiveUS6479258B1Improve abilitiesPotent and direct effect on proliferation and Ig-synthesisHydrolasesLibrary screeningAntigenMutagenic Process
This invention provides methods of obtaining vaccines by use of non-stochastic methods of directed evolution (DirectEvolution(TM)). These methods include non-stochastic polynucleotide site-satuaration mutagenesis (Gene Site Saturation Mutagenesis(TM)) and non-stochastic polynucleotide reassembly (GeneReassembly(TM)). Through use of the claimed methods, vectors can be obtained which exhibit increased efficacy for use as genetic vaccines. Vectors obtained by using the methods can have, for example, enhanced antigen expression, increased uptake into a cell, increased stability in a cell, ability to tailor an immune response, and the like.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Targeted therapy marker panels
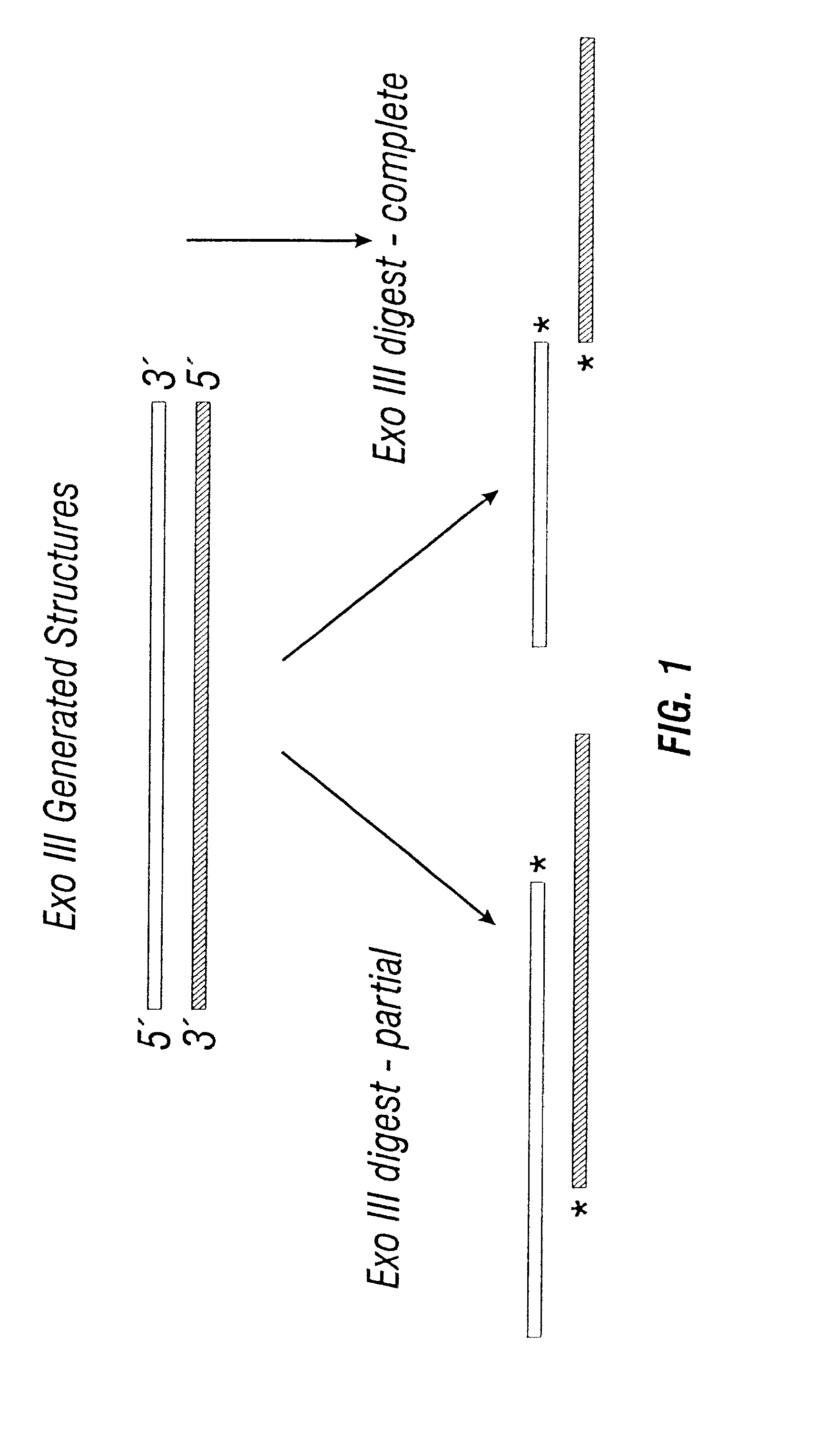
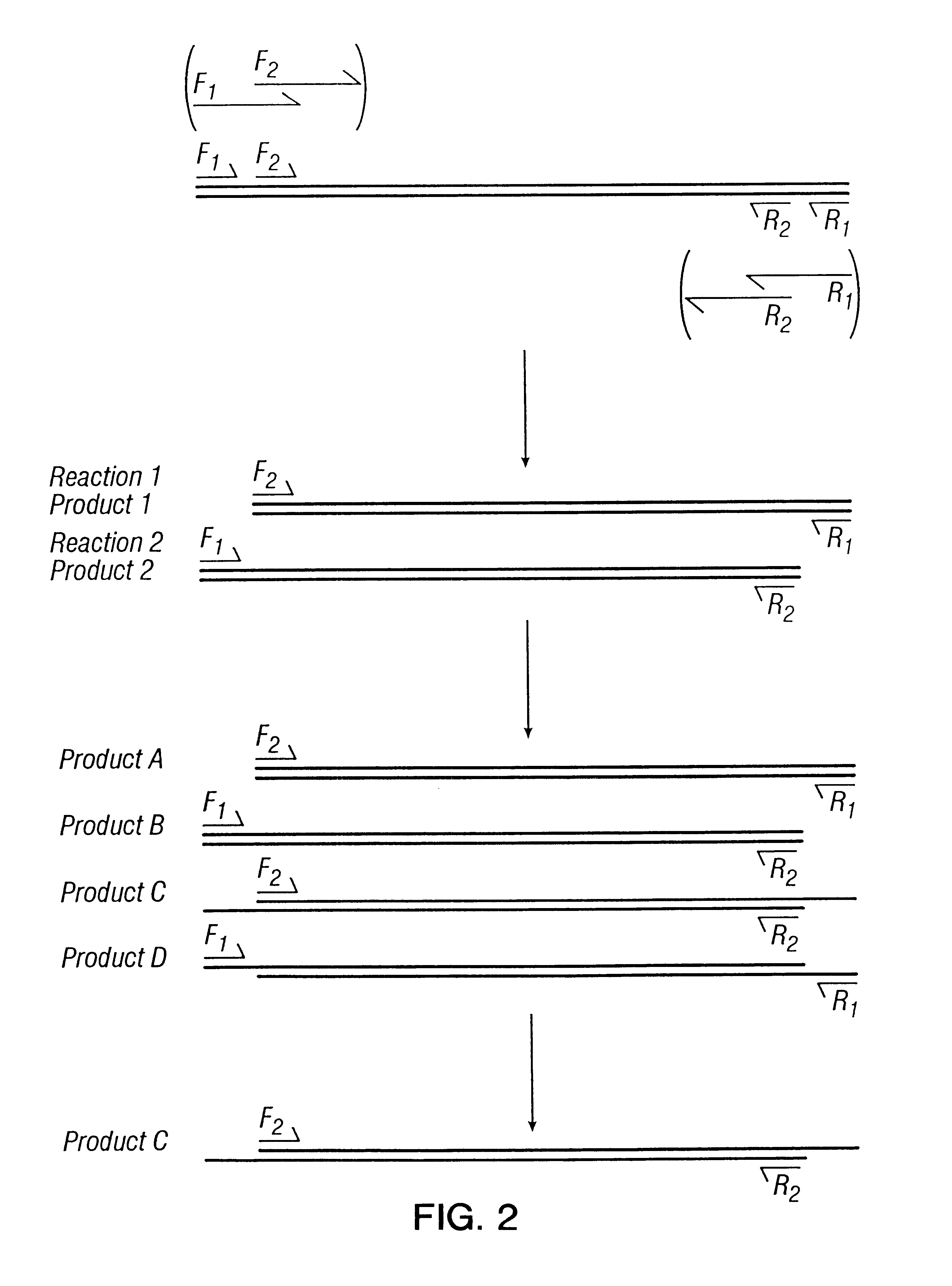
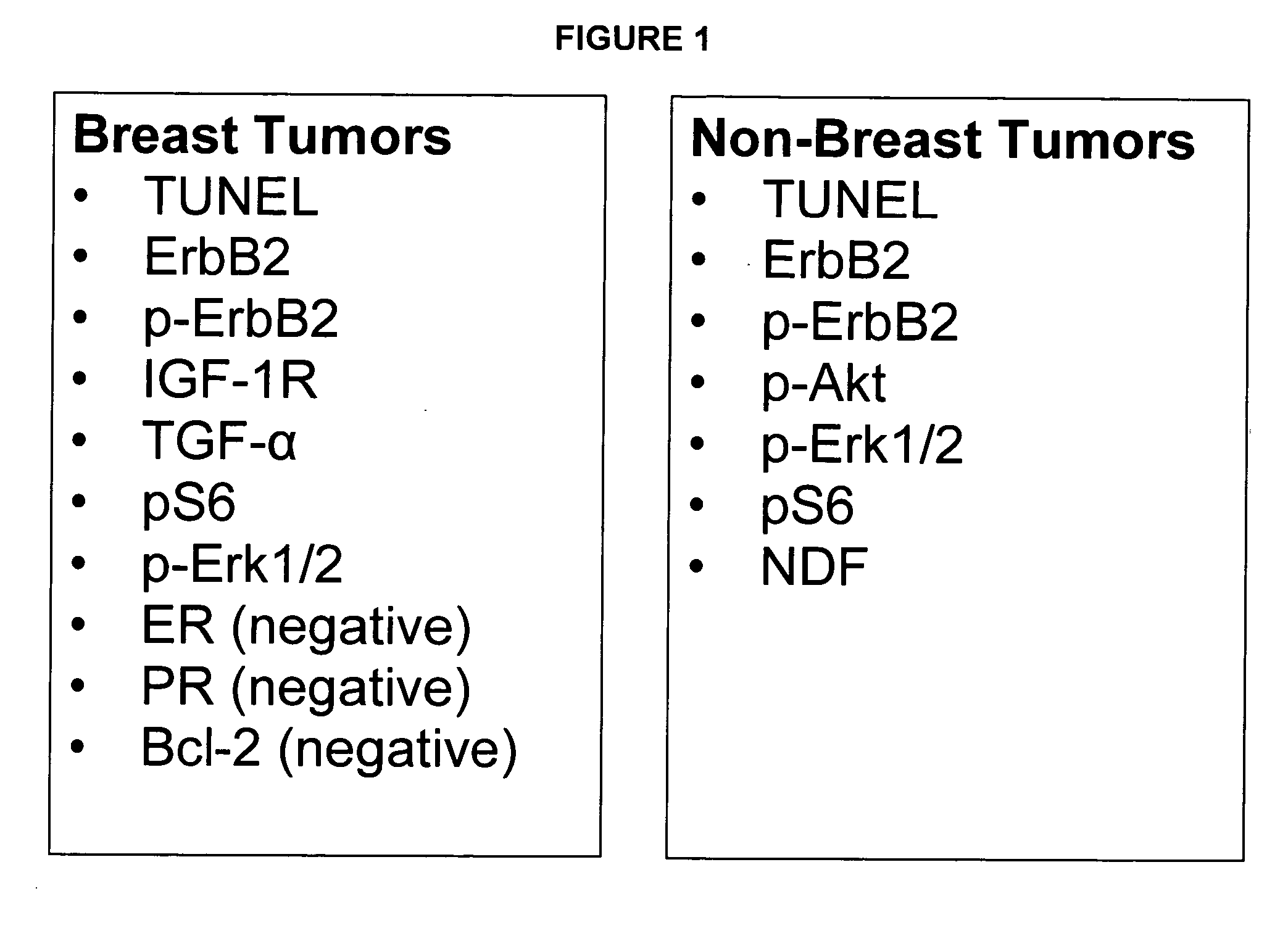
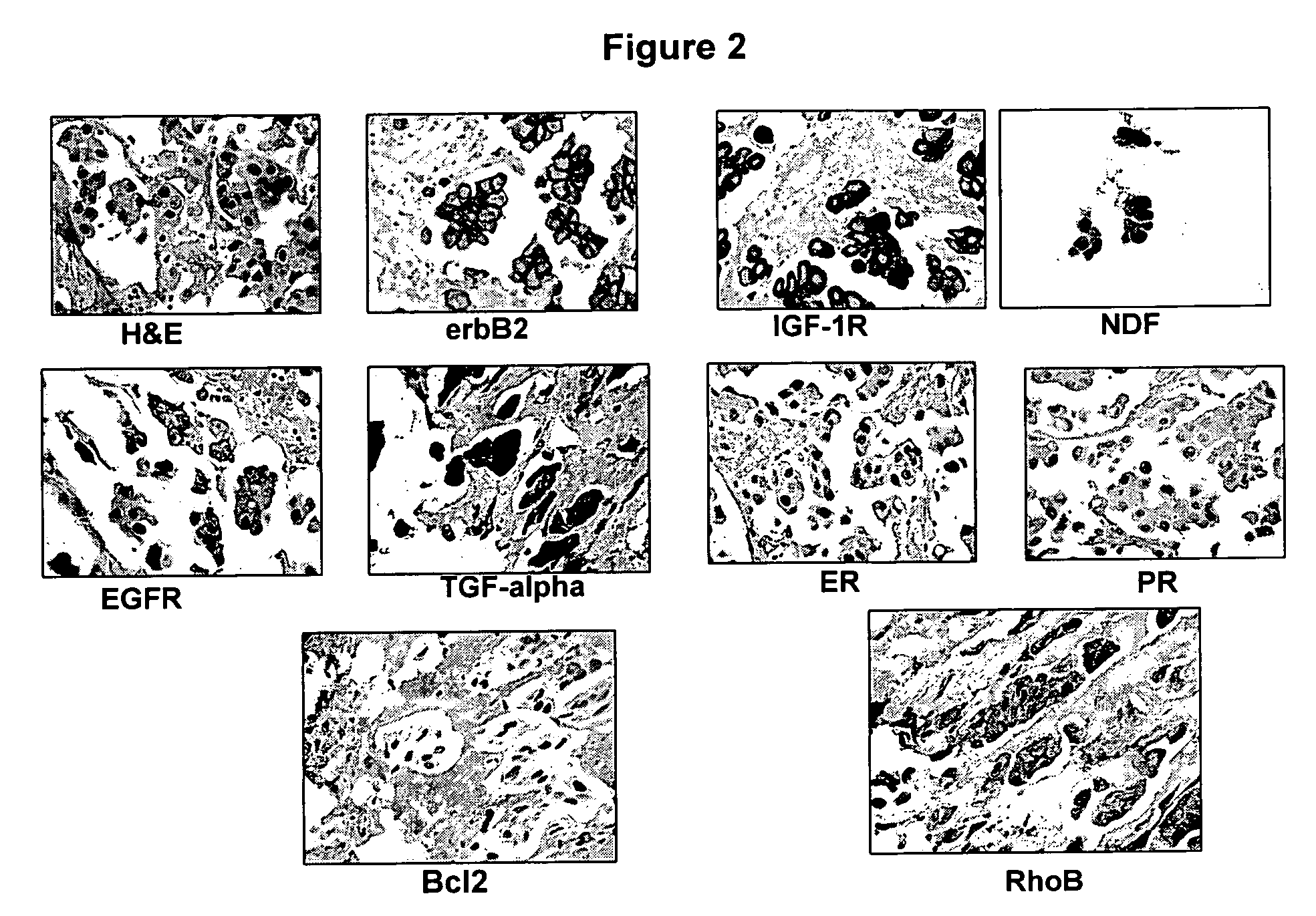
InactiveUS20060127928A1Potent effectDecrease overall survival timePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementTargeted therapyTarget therapy
The present invention relates to a panel of targeted therapy markers that can be used in assessing a particular subject's sensitivity to various therapeutic agents and cancer treatments as a means of prognosticating whether a treatment or use of a particular therapeutic agent will result in a clinically positive outcome. Cellular receptors, ligands to those receptors and molecules involved in the programmed cell death pathway are examples of targeted therapy markers that might be used in the present invention.
Owner:TARGETED MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS
Non-stochastic generation of genetic vaccines and enzymes
InactiveUS6713279B1Improve abilitiesPotent and direct effect on proliferation and Ig-synthesisAnimal cellsHydrolasesAntigenBiological property
This invention provides methods of obtaining novel polynucleotides and encoded polypeptides by use of non-stochastic methods of directed evolution (DirectEvolution(TM)). These methods include non-stochastic polynucleotide site-saturation mutagenesis (Gene Site Saturation Mutagenesis(TM)) and non-stochastic polynucleotide reassembly (GeneReassembly(TM)). Through use of the claimed methods, genetic vaccines, enzymes, and other desirable molecules can be evolved towards desirable properties. For example, vaccine vectors can be obtained that exhibit increased efficacy for use as genetic vaccines. Vectors obtained by using the methods can have, for example, enhanced antigen expression, increased uptake into a cell, increased stability in a cell, ability to tailor an immune response, and the like. This invention provides methods of obtaining novel enzymes that have optimized physical & / or biological properties. Furthermore, this invention provides methods of obtaining a variety of novel biologically active molecules, in the fields of antibiotics, pharmacotherapeutics, and transgenic traits.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
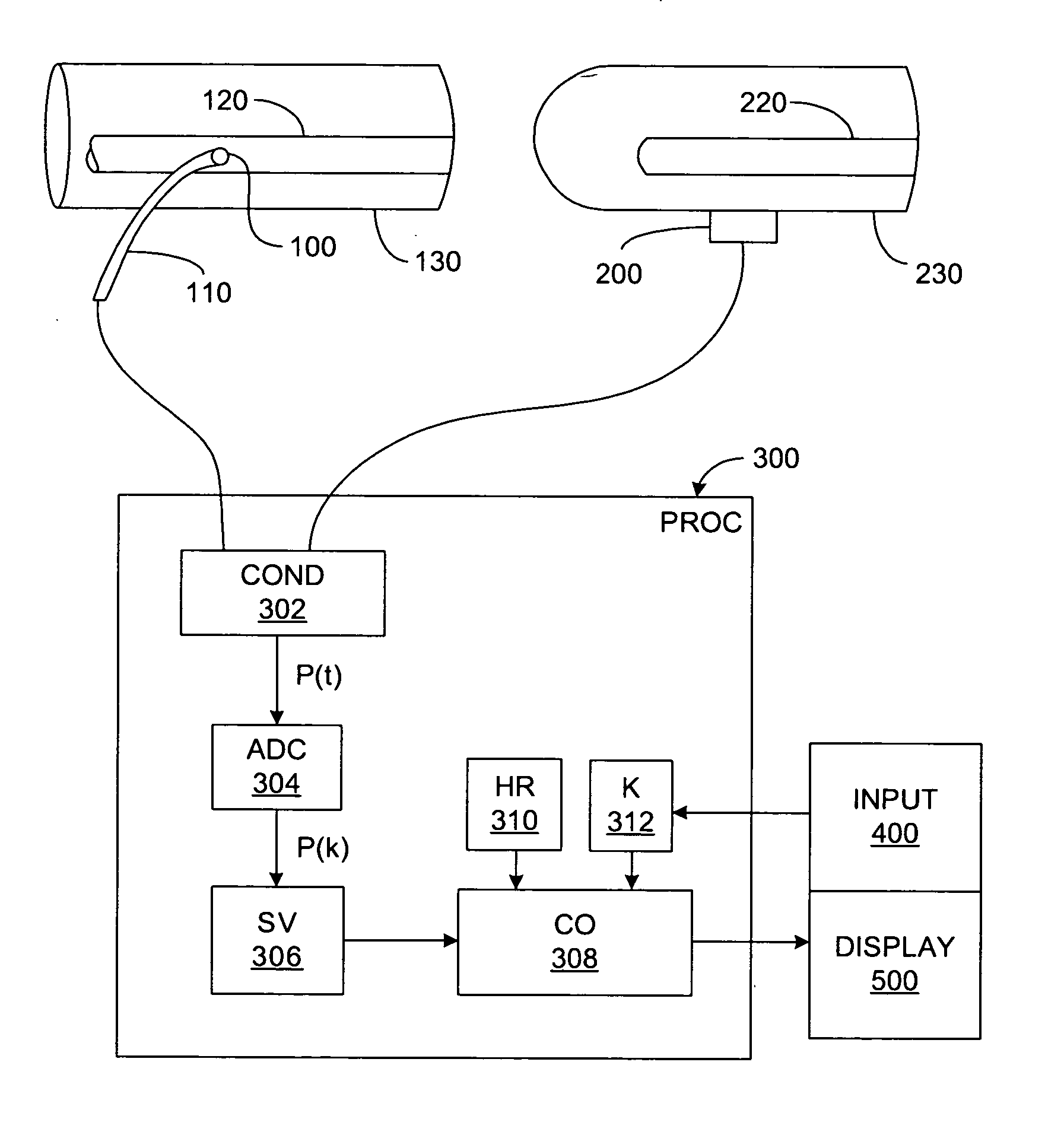
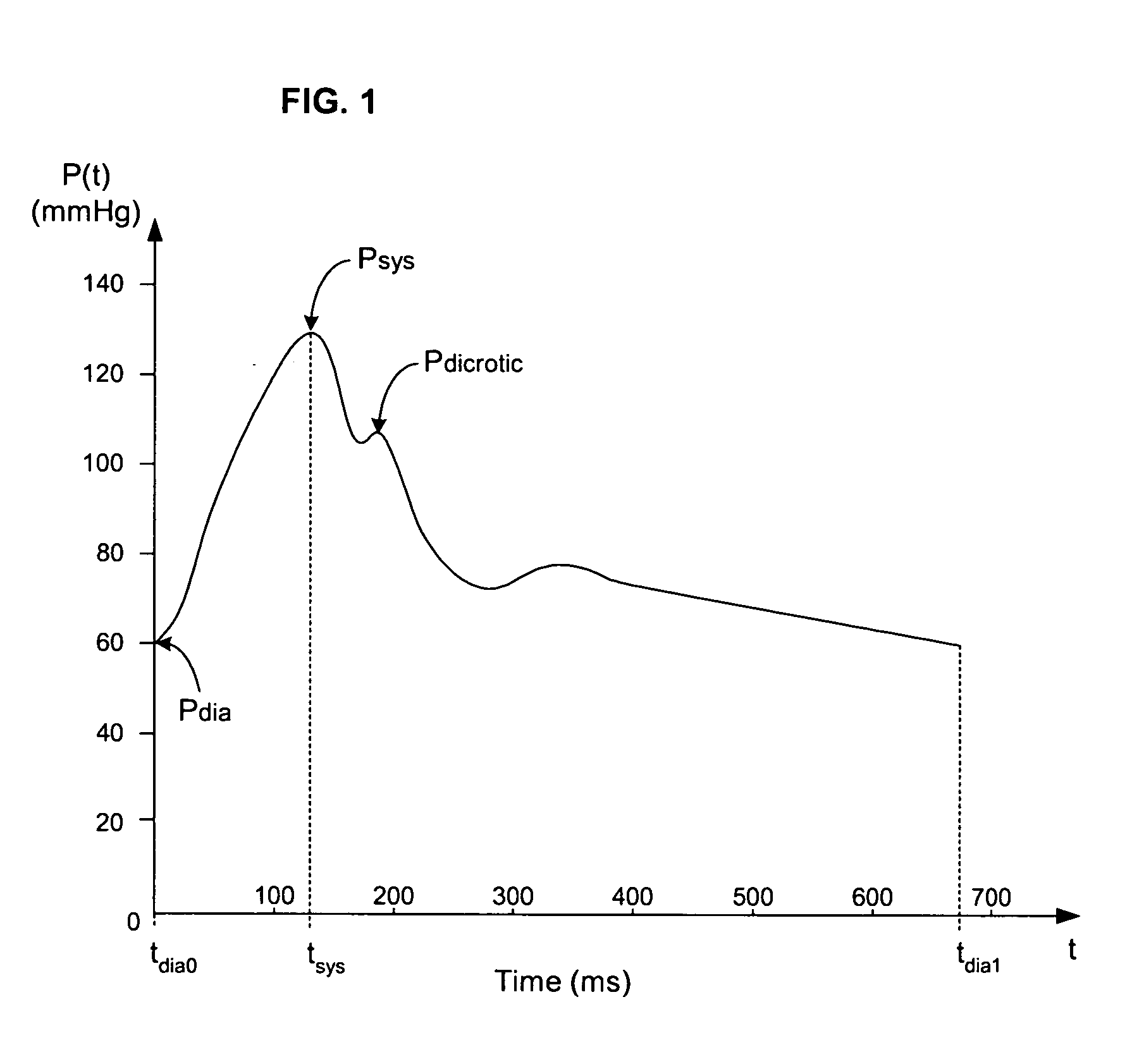
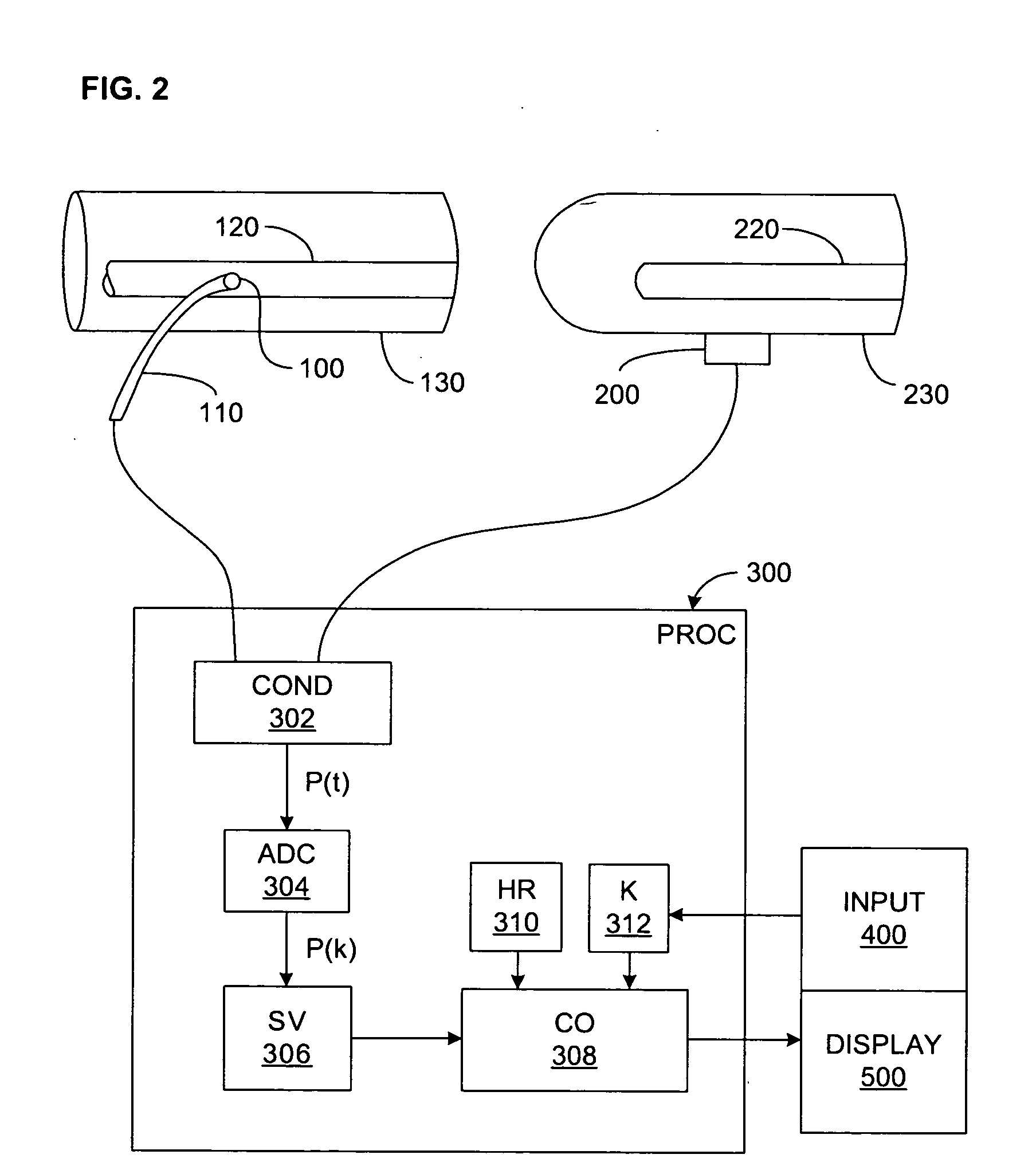
Pressure-based system and method for determining cardiac stroke volume
ActiveUS20050124903A1Potent effectEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterArterial pressure waveformDecreased mean arterial pressure
Cardiac stroke volume (SV) of a subject is estimated as a function of a value derived from a measured arterial pressure waveform. The value may be the standard deviation, or a function of the difference between maximum and minimum pressure values, or a function of either the maximum value of the first time derivative or the absolute value of the minimum of the first time derivative of the pressure waveform, or both, or a function of the magnitude of one or more spectral components of the pressure waveform at a frequency corresponding to the heart rate. Cardiac output is then estimated as the product of the subject's heart rate and SV, scaled by a calibration constant. Arterial pressure may be measured invasively or non-invasively.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
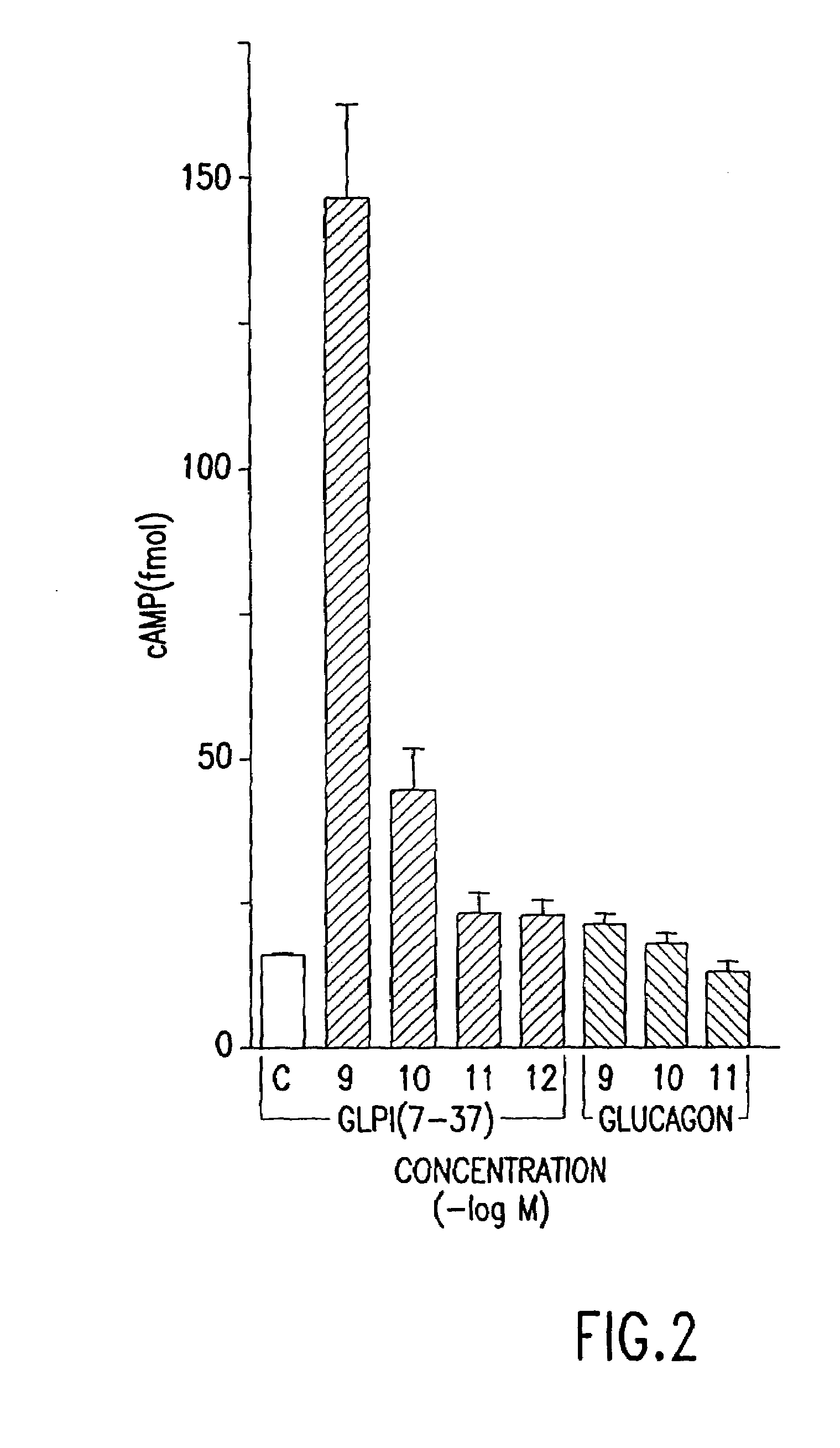
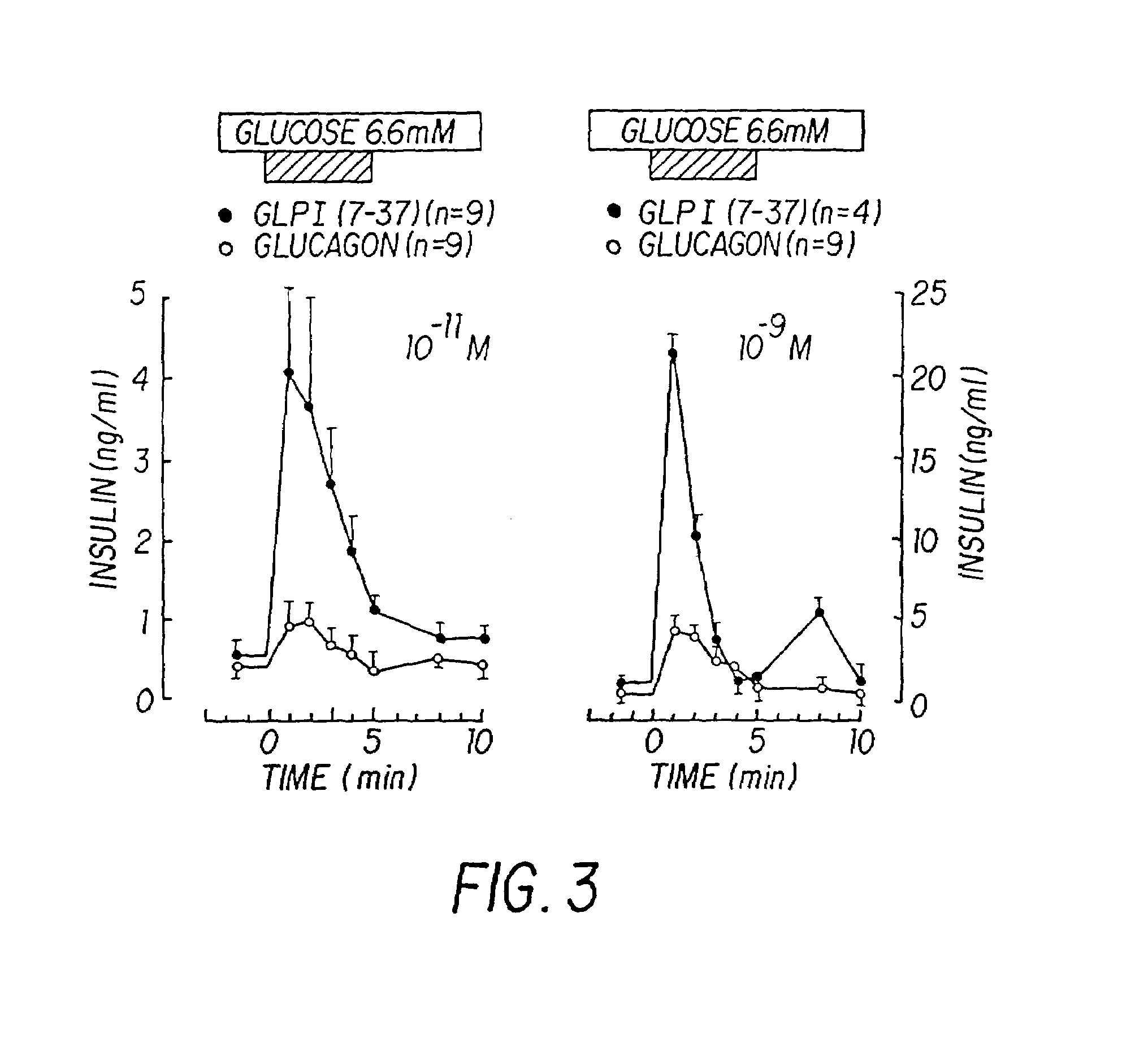
Insulinotropic hormone derivatives and uses thereof
InactiveUS7138486B2Promote insulin secretionIncrease insulin levelsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInsulinotropinPancreatic hormone
Derivatives of glucagon-like peptide I (GLP-1) and especially GLP-1 (7-37) have been found to have insulinotropic activity. The invention pertains to a composition comprising an acid addition salt of GLP-I (7-37) and to a composition comprising a carboxylate salt of GLP-I (7-37). The invention also pertains to method of treating type II diabetes mellitus by providing derivatives of GLP-I (7-37) to the patient.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
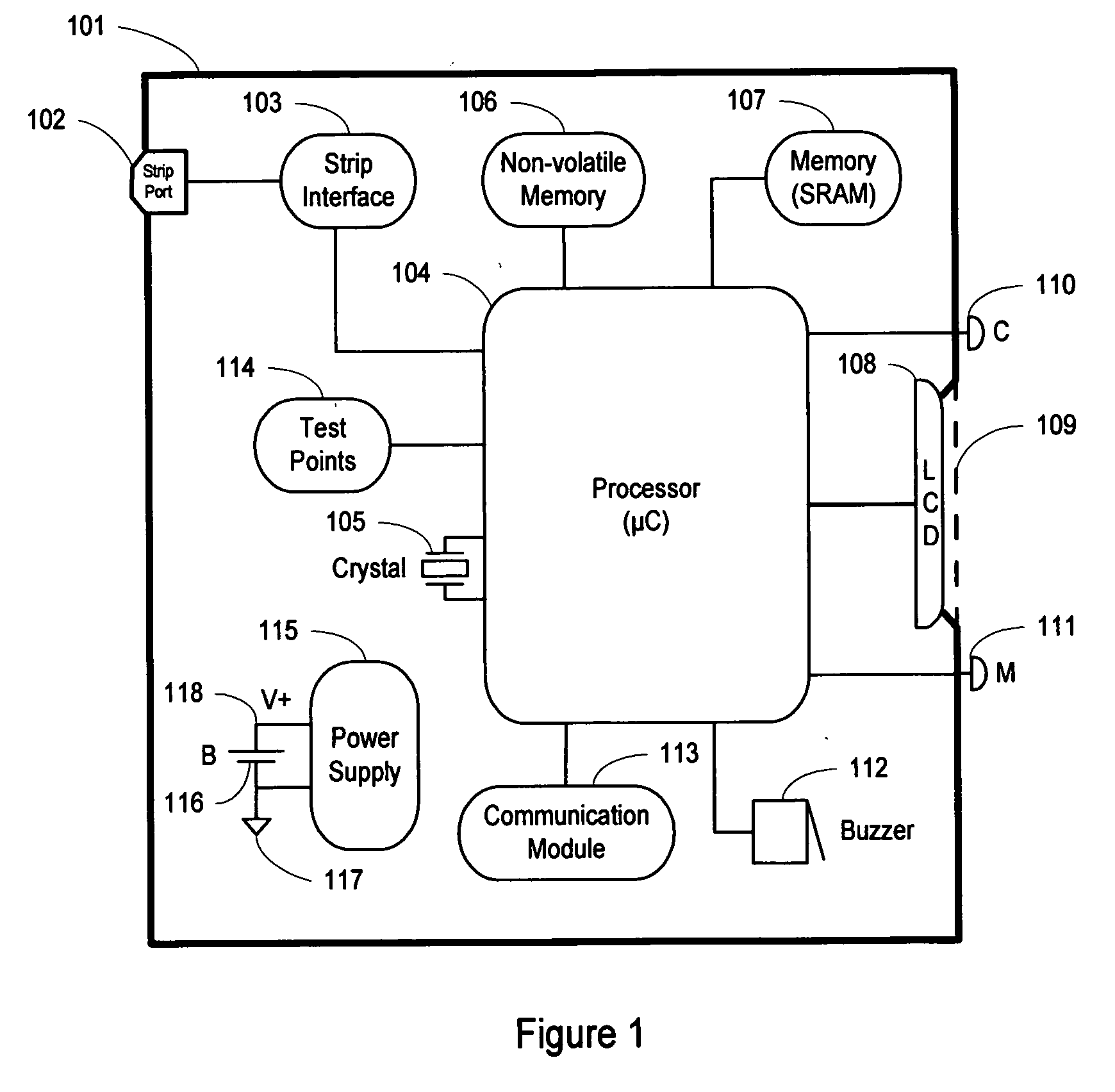
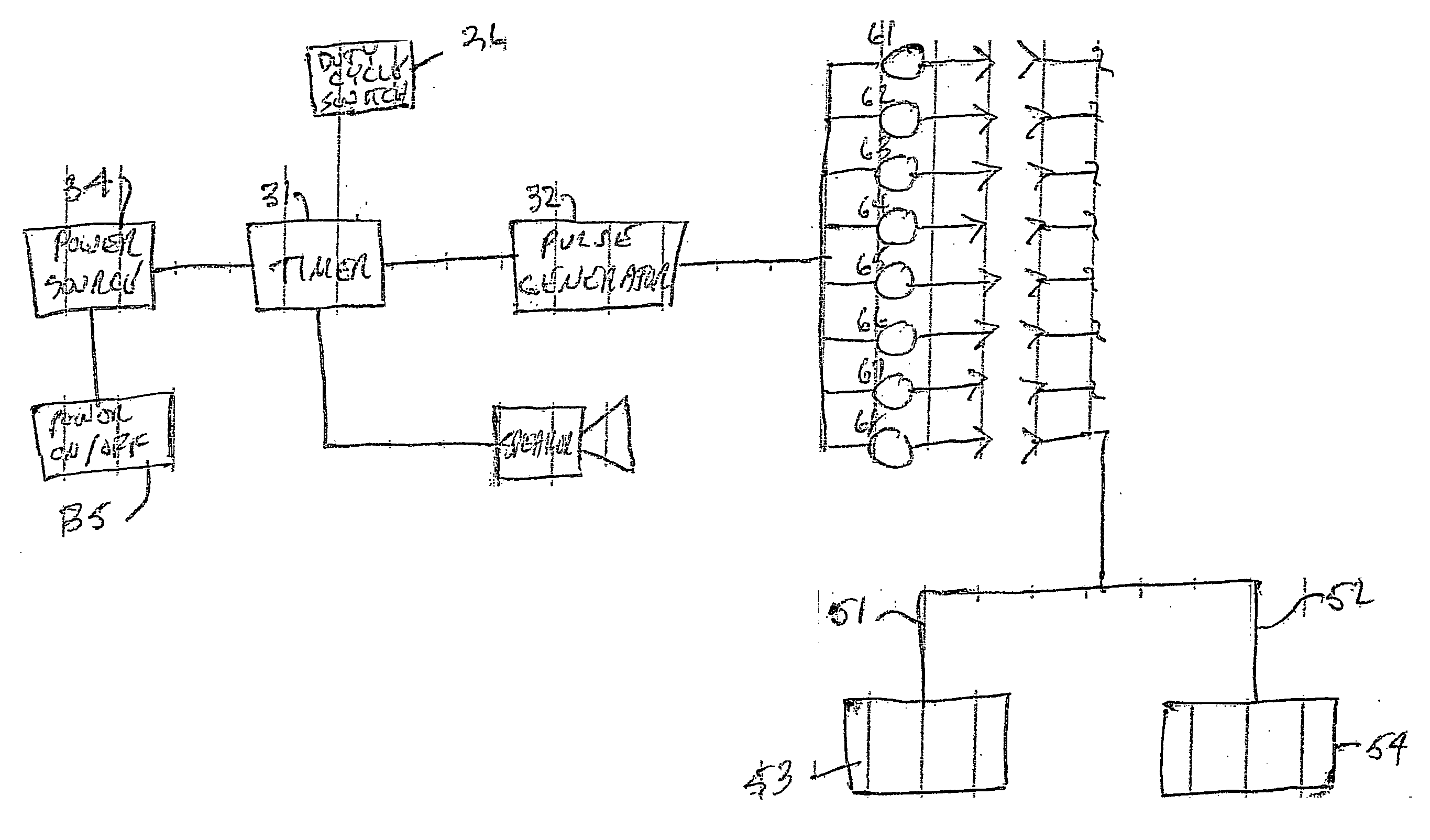
Method and system for providing a fault tolerant display unit in an electronic device
ActiveUS20070176867A1Minimize probabilityReduce effectLocal control/monitoringStatic indicating devicesGlucose meter deviceEngineering
Method and apparatus for providing a fault tolerant display unit for an electronic device such as a glucose meter, including display unit, and a controller unit operatively coupled to the display unit, the controller unit configured to control the display unit to display an information, where when a failure mode of the display unit occurs, the display unit is configured to display a modified information, where the modified information is different from the information for display under the control of the controller unit, is provided.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Method for treating occlusive vascular diseases & wound healing
InactiveUS20050069518A1Restoring cardiac functionIncrease blood flowBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsErectile dysfunctionDisease
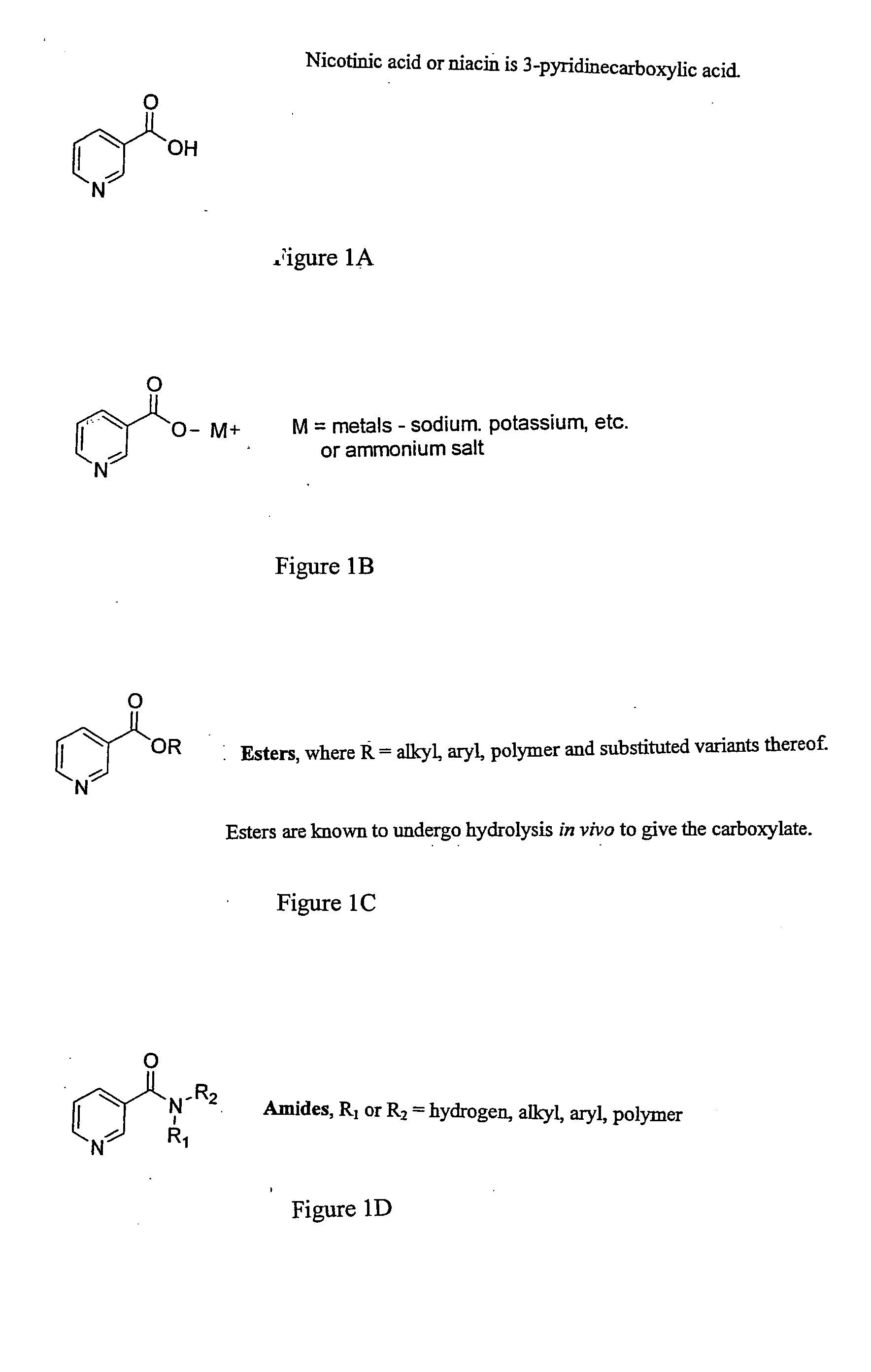
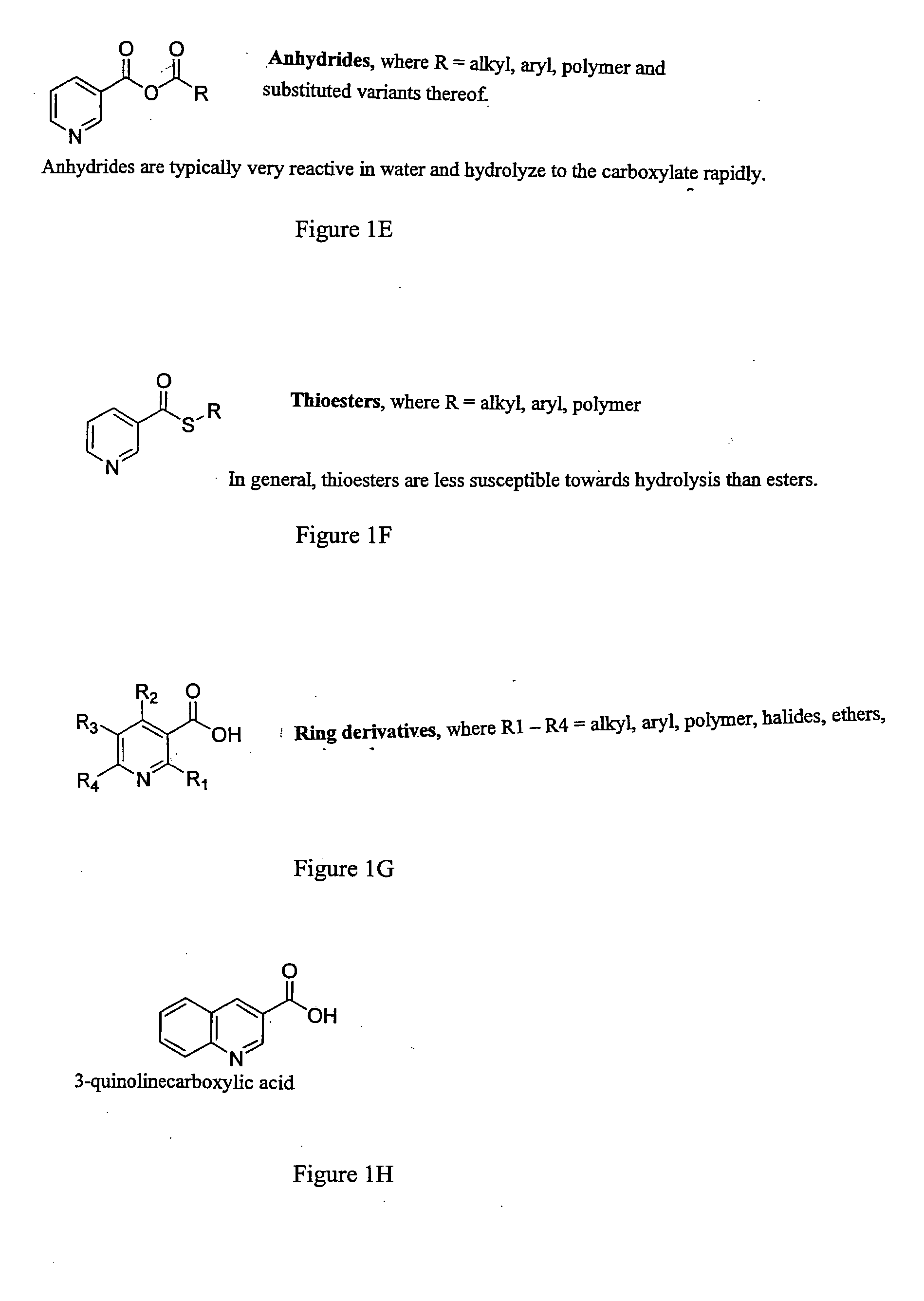
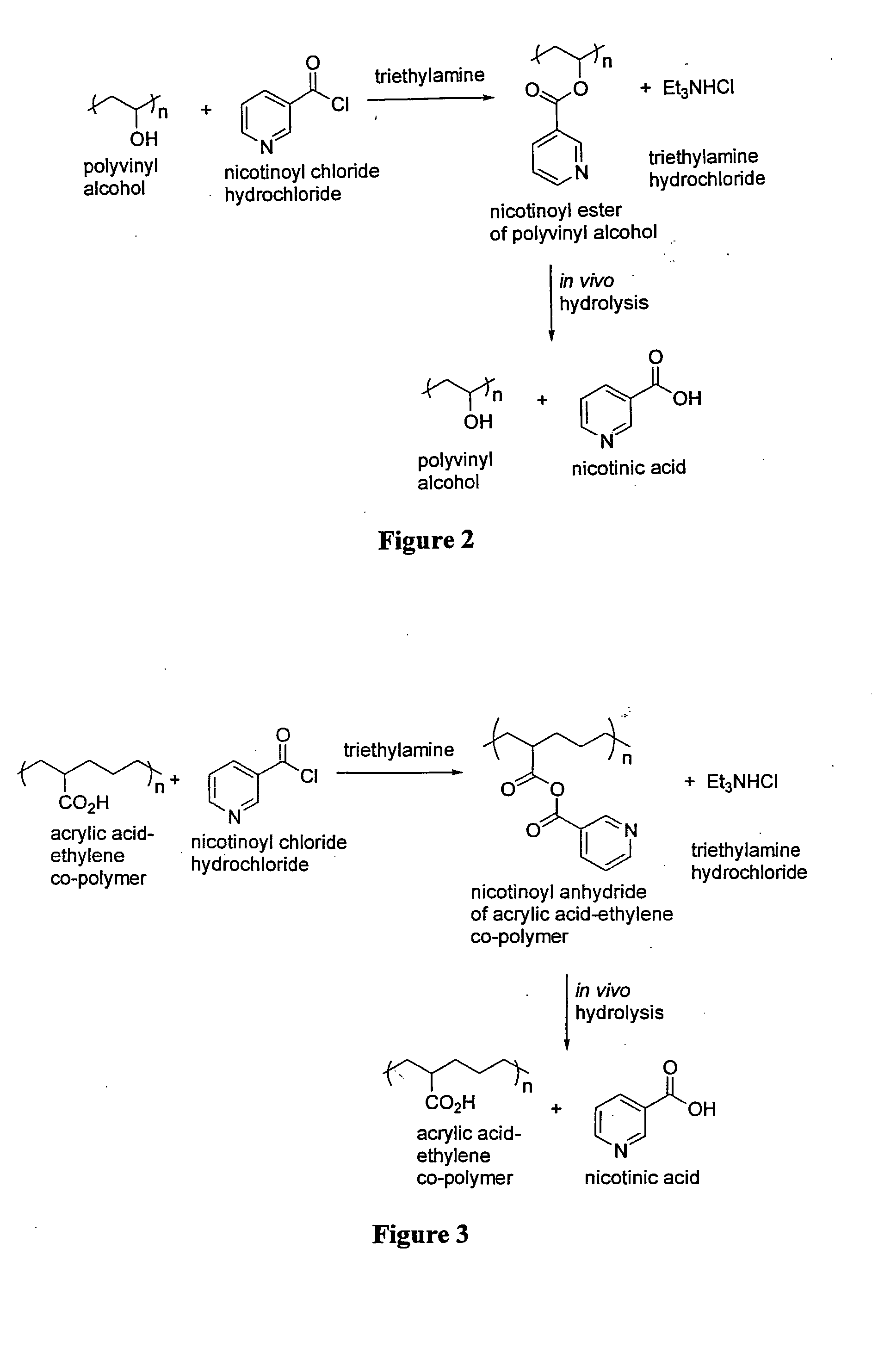
Disclosed are methods of treating subjects having conditions related to angiogenesis including administering an effective amount of a polymeric form of Nicotine, nicotinic acid analogs thereof, their combination with or without other pro-angiogenesis factors, vasodilator, or other therapeutic modalities to promote angiogenesis in the subject. This is composition and combination thereof is applicable to improving wound healing, erectile dysfunction, improving collateral or blood supply in patients with myocardial infarction, stroke, peripheral artery diseases, and other vascular disorders as disclosed.
Owner:MOUSA SHAKER +1
Type of fine metal mask (FFM) used in OLED production and the method of manufacturing it
ActiveUS20150059643A1Overcome deficienciesHigh strengthLiquid surface applicatorsDecorative surface effectsSteel platesMetal substrate
A new type of fine metal mask (FMM) used in OLED production and the method of manufacturing it, wherein the FMM includes a frame made of a metal substrate with a plurality of through holes, a layer of fine mask electroformed on the surface of the frame so that said fine mask and said frame are seamlessly integrated, said fine mask is divided into a pattern area and a border area, and the pattern area corresponds to the through holes on the frame, and the method of manufacturing such an FMM comprising the steps of: A. providing a metal substrate by cutting an invar alloy or stainless steel plate to a desired size; B. providing an fine mask by adding a photoresist layer on the metal substrate, exposing a desired pattern onto said photoresist layer, and electroforming a metal base layer and a metal layer with a low thermal expansion coefficient; and C. etching the metal substrate by etching out a pattern area of the metal substrate that corresponds to the pattern area of said fine mask using a chemical etching method to form a plurality of through holes, and creating an outer border area and internal separation area for support of said fine mask.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN AISCENT TECH
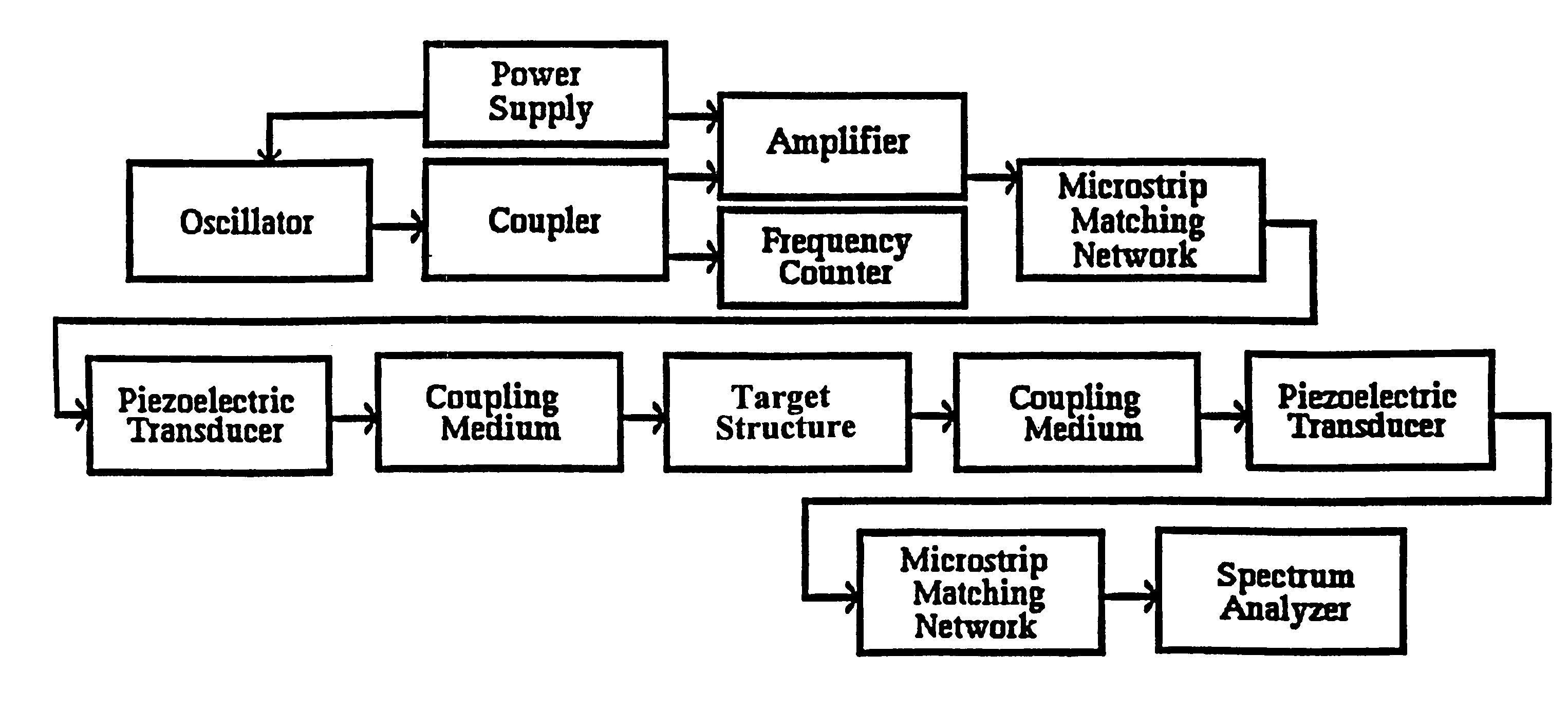
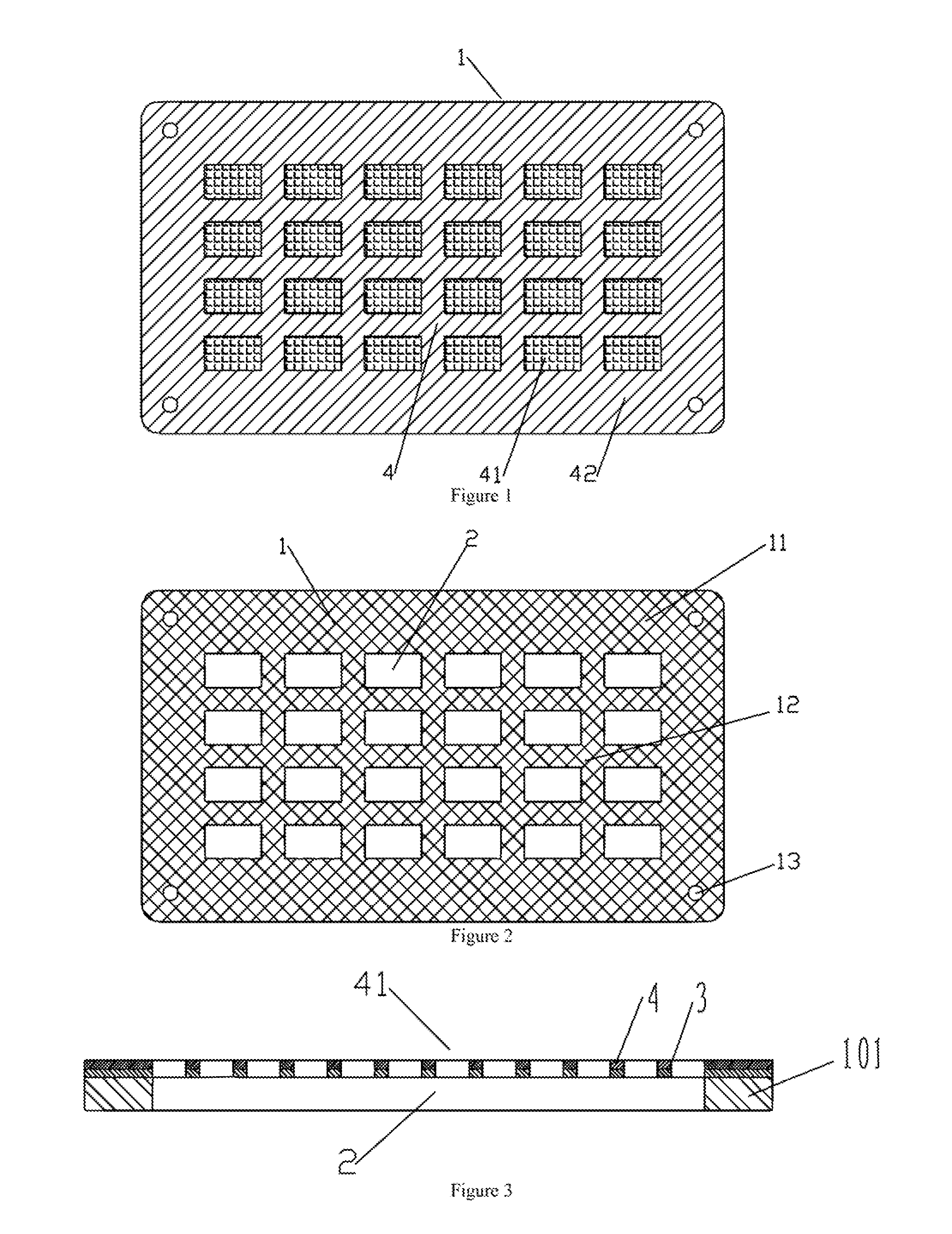
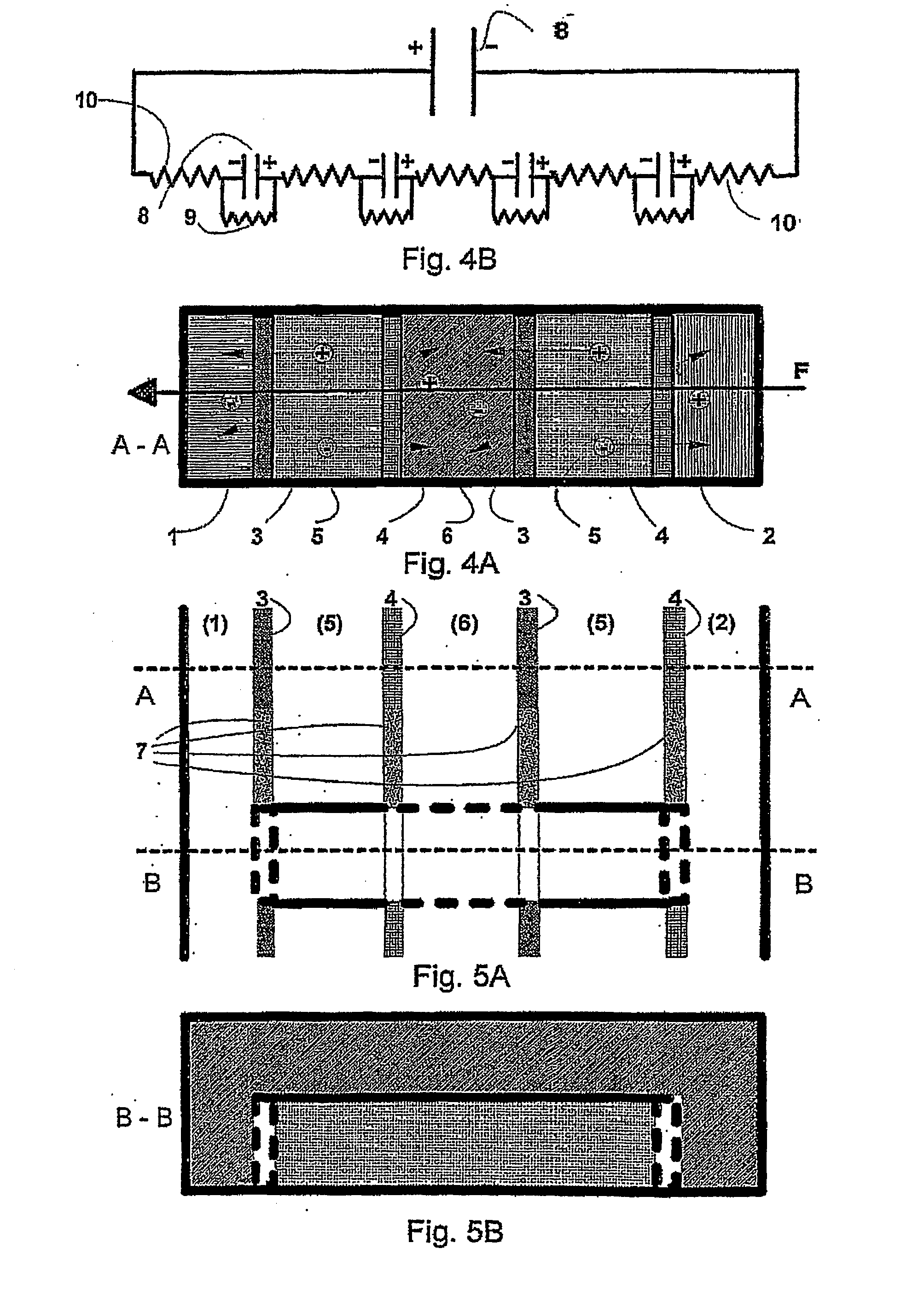
Methods for using resonant acoustic and/or resonant acousto-EM energy to detect and/or effect structures
InactiveUS20070039389A1Avoid damageAccurate detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVibration measurement in solidsEngineeringAcoustics
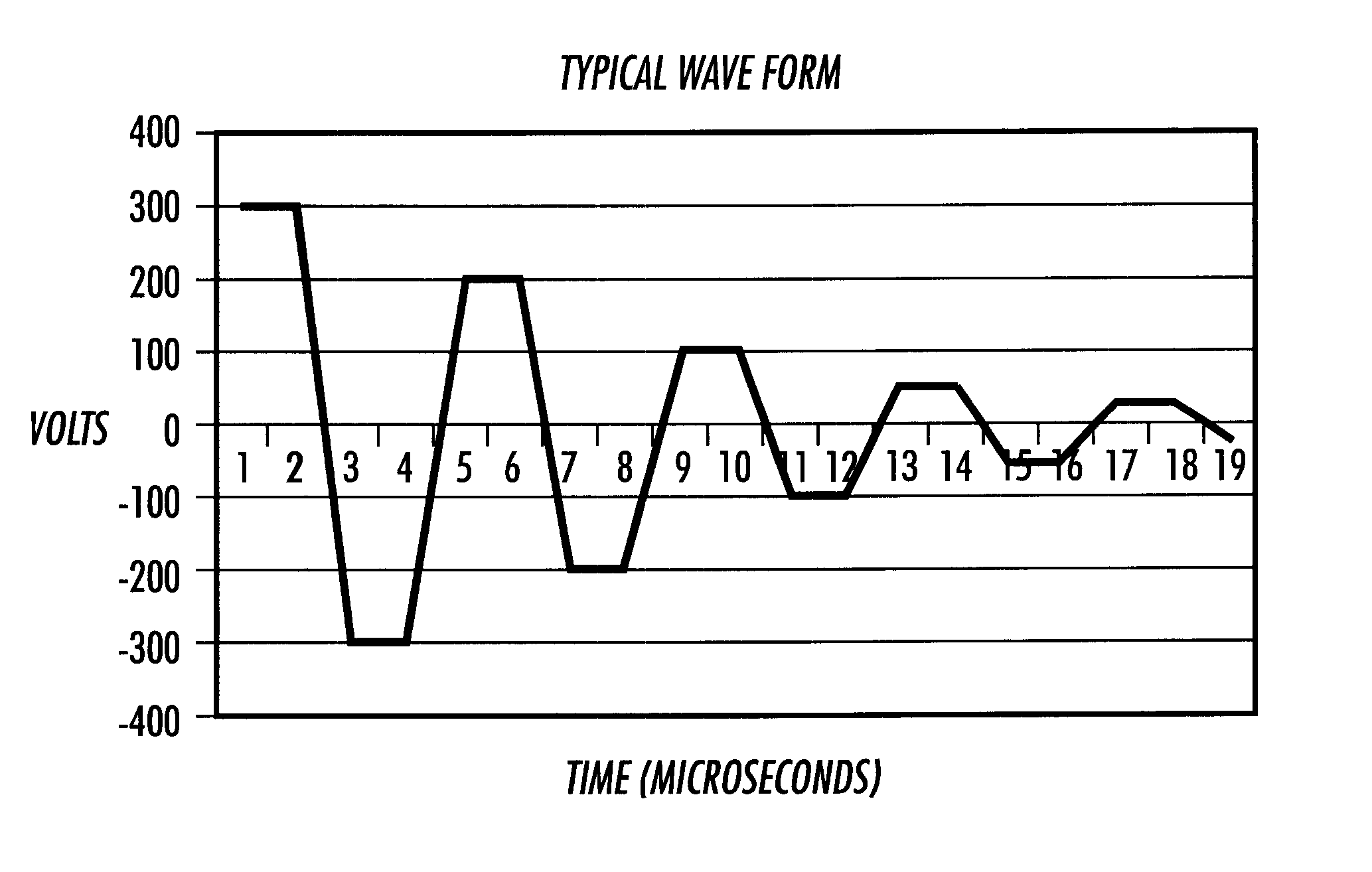
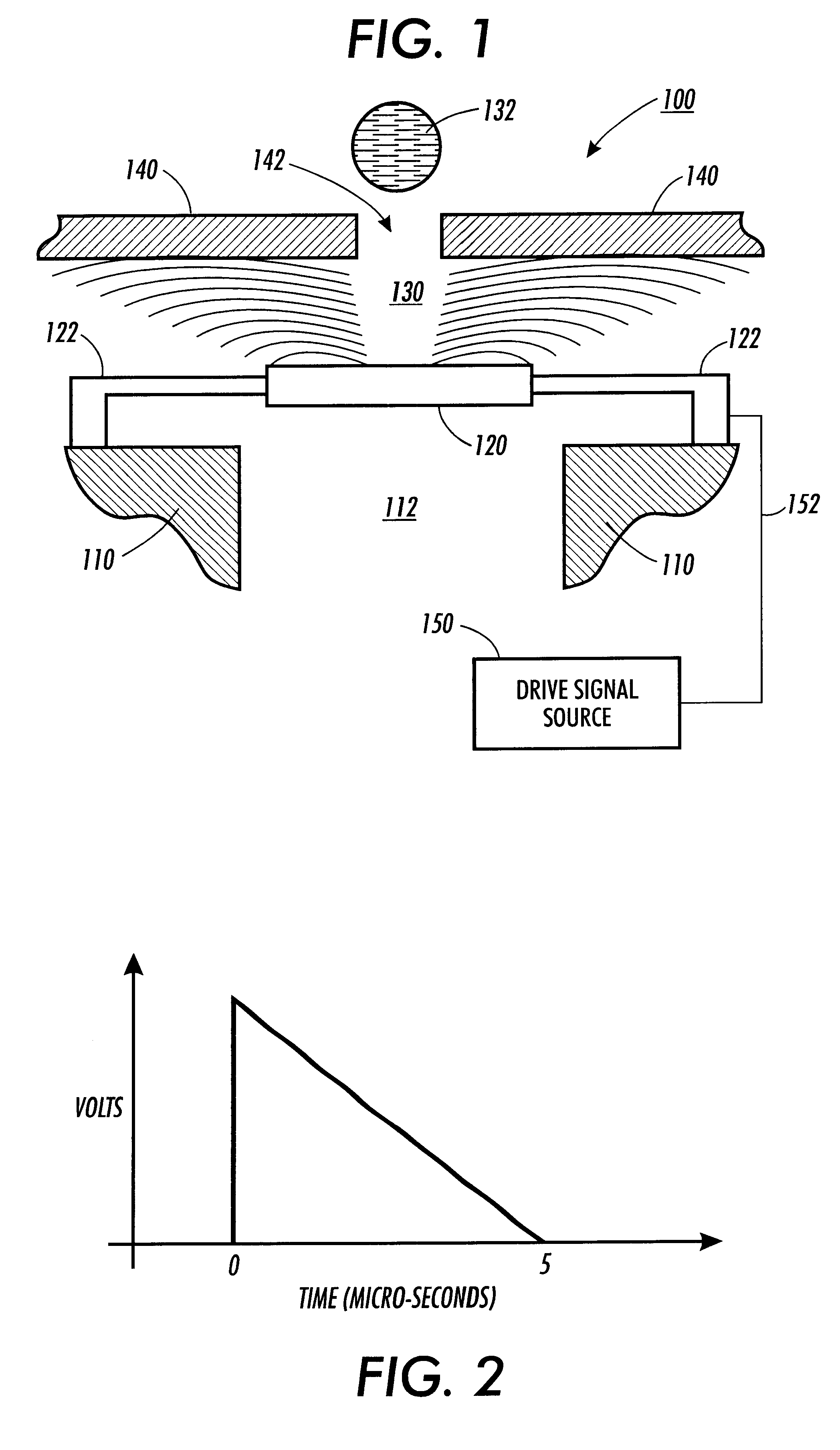
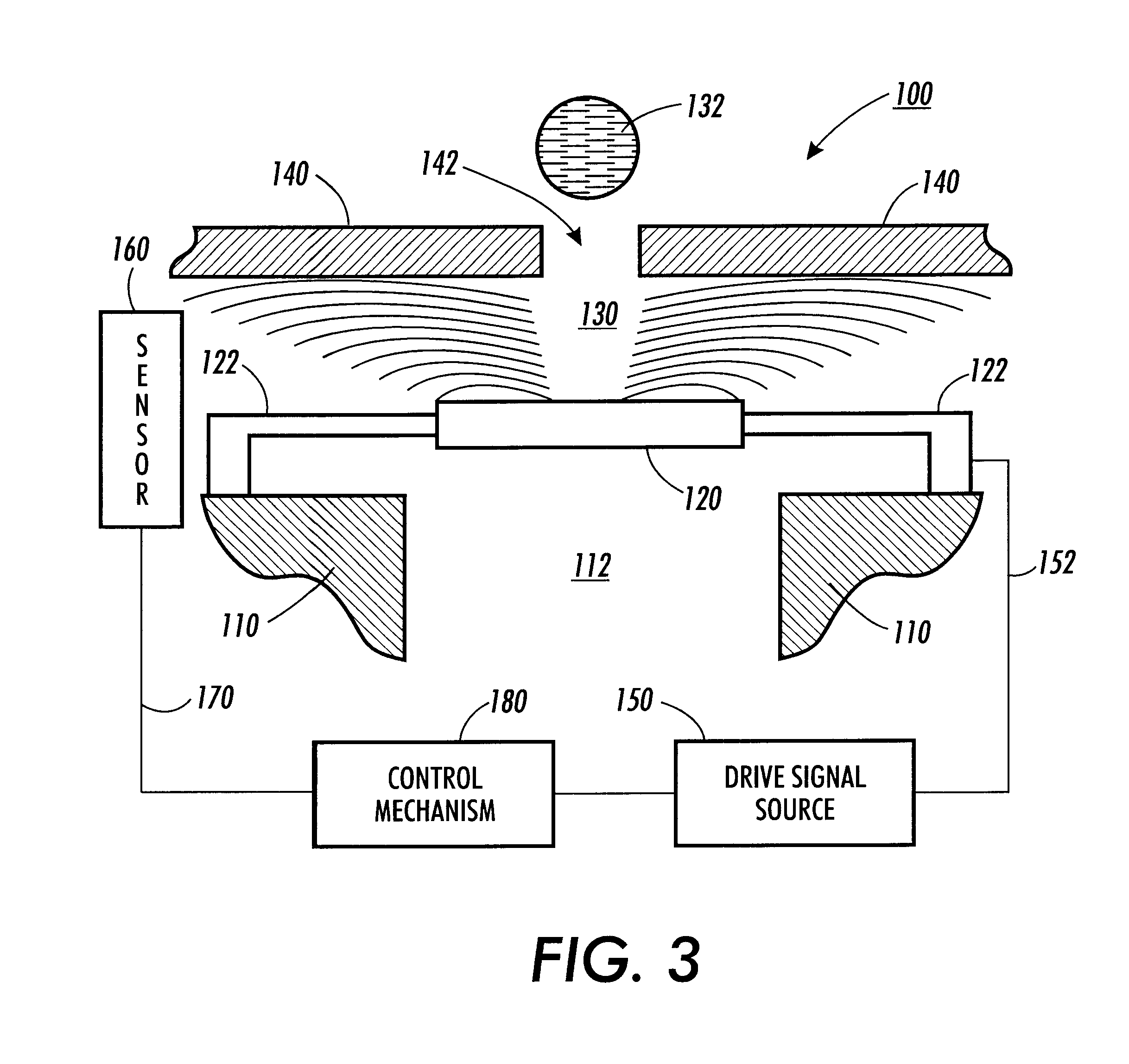
The present invention makes use of resonant acoustic and / or acousto-EM energy applied to inorganic or biologic structures for the detection and / or identification, and for augmentation and / or disruption of function within the biologic structure. In particular, the invention provides a method of generating resonant acoustic and / or acousto-EM energy in biologic structures such as virus, bacteria, fungi, worms and tumors for the detection and disruption of these structures. Moreover, the invention provides a method of augmenting functions of biologic structures such as bone through the generation of resonant acoustic and / or acousto-EM energy in the structure. Systems are also provided for the generation and detection of resonant acoustic and / or resonant acousto-EM energy.
Owner:GR INTELLECTUAL RESERVE LLC
Electronic drive systems and methods
InactiveUS6419335B1Reduce potential impactPotent effectOther printing apparatusElectrochemical responseEngineering
An electronic drive system applies a drive signal to an electrostatically actuated device such that a resulting electric field has a constant force. In various exemplary embodiments, the electronic drive system applies a drive signal to an electrostatically actuated fluid ejector that has a piston and a faceplate including a nozzle hole. A dielectric fluid to be ejected is supplied between the piston and the faceplate. The drive signal is applied to one of the piston and the faceplate. The drive signal generates an electric field across the fluid between the piston and the faceplate. The electric field causes the piston to be electrostatically attracted towards the faceplate so that a jet or drop of fluid is ejected through the nozzle hole of the faceplate. According to exemplary embodiments, the drive signal is from a constant current source or is reduced over the course of its lifetime. Further, according to various exemplary embodiments, the drive signal is of a suitable high frequency to reduce the potential of electrochemical reactions or electrical breakdown, or both. The drive signal may also be a bi-polar drive signal to reduce the possibility of electrochemical reactions.
Owner:XEROX CORP +1
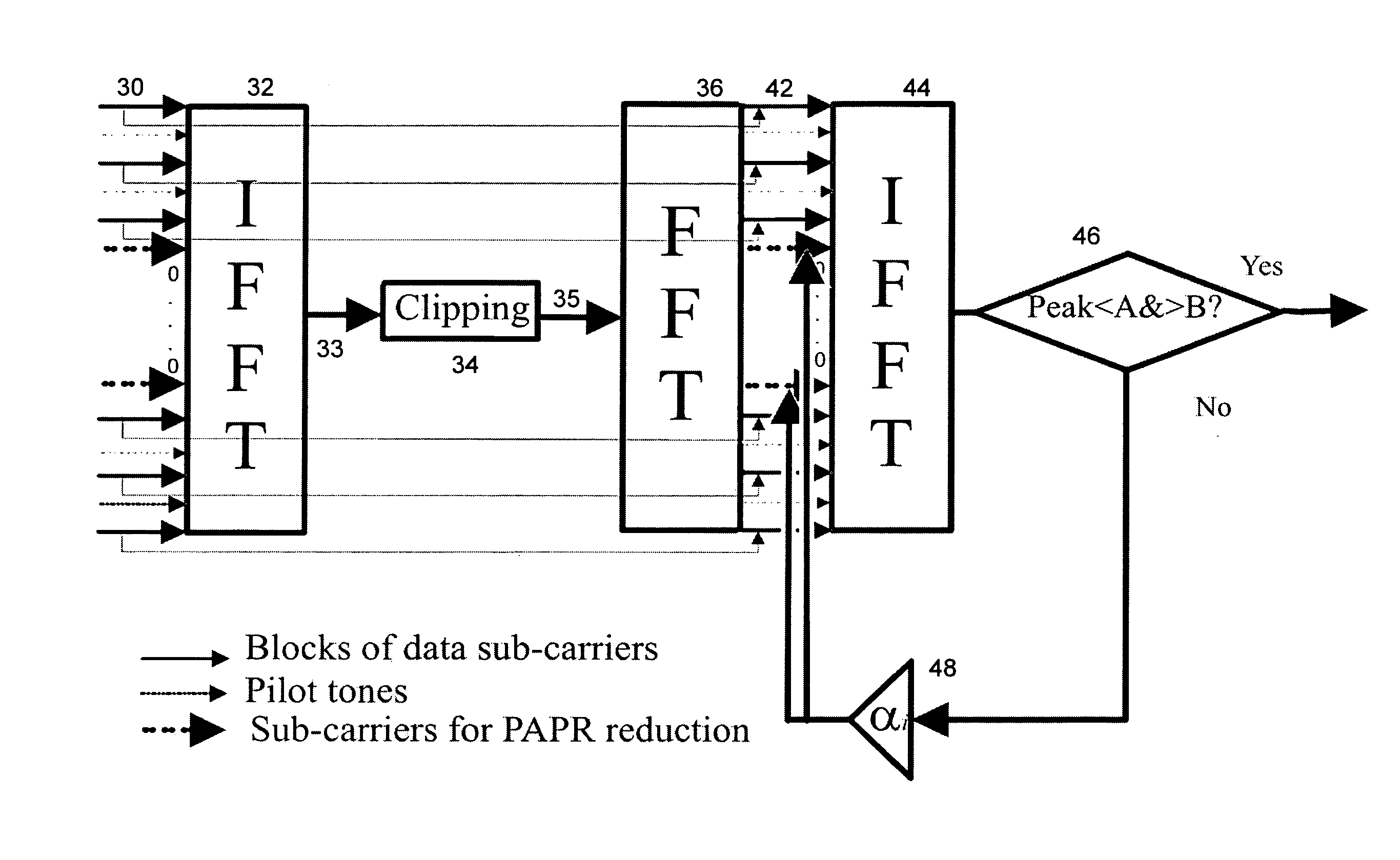
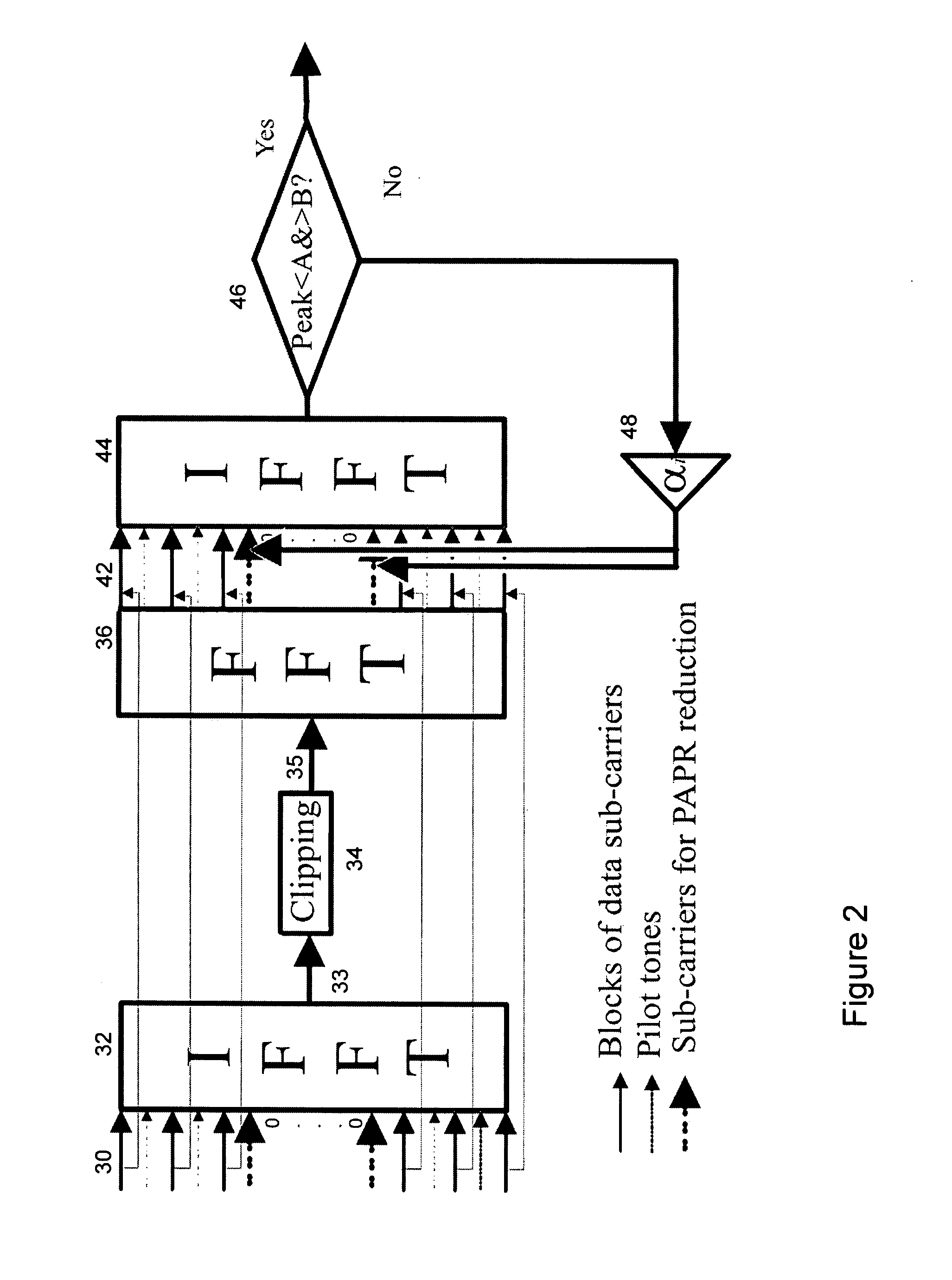
Peak-to-average-power reduction of OFDM signals
InactiveUS20080112496A1Improvement in Peak-to-Average-Power ratioEffect of clipping is minimisedAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersTime domainAudio power amplifier
A method of processing an Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplex (OFDM) signal having a plurality of data carriers and a plurality of unused carriers is disclosed. The method comprises transforming an original frequency-domain OFDM signal into a time domain signal and simulating the effect of a non-linear amplifier on the time-domain signal to provide a potentially distorted time domain signal. The potentially distorted time domain signal is transformed into a potentially distorted frequency domain signal and at least some of any values of the data carriers in the potentially distorted frequency domain signal are restored with corresponding values from the original frequency domain signal. At least some of the unused carriers in the at least partially restored frequency domain signal are scaled with a scaling factor. The scaled frequency domain signal is transformed into a temporary time domain signal and the temporary time domain signal is analysed for the presence of a peak or near zero amplitude value that would lead to distortion by said amplifier. If the signal includes such a peak or near zero value, the scaling, transforming and analysing are repeated with an increased scaling factor.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE DUBLIN NAT UNIV OF IRELAND DUBLIN
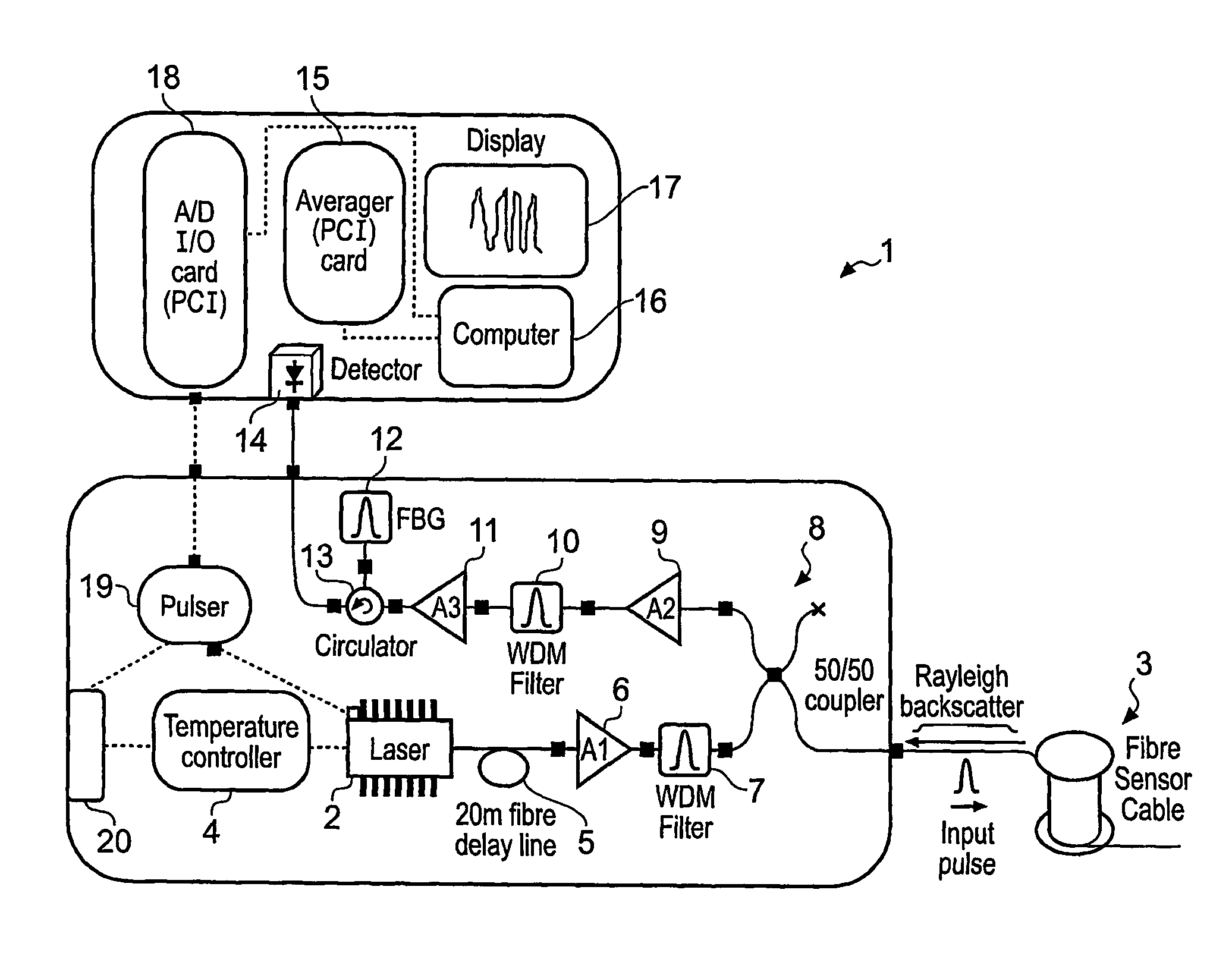
Detecting a disturbance in the phase of light propagating in an optical waveguide
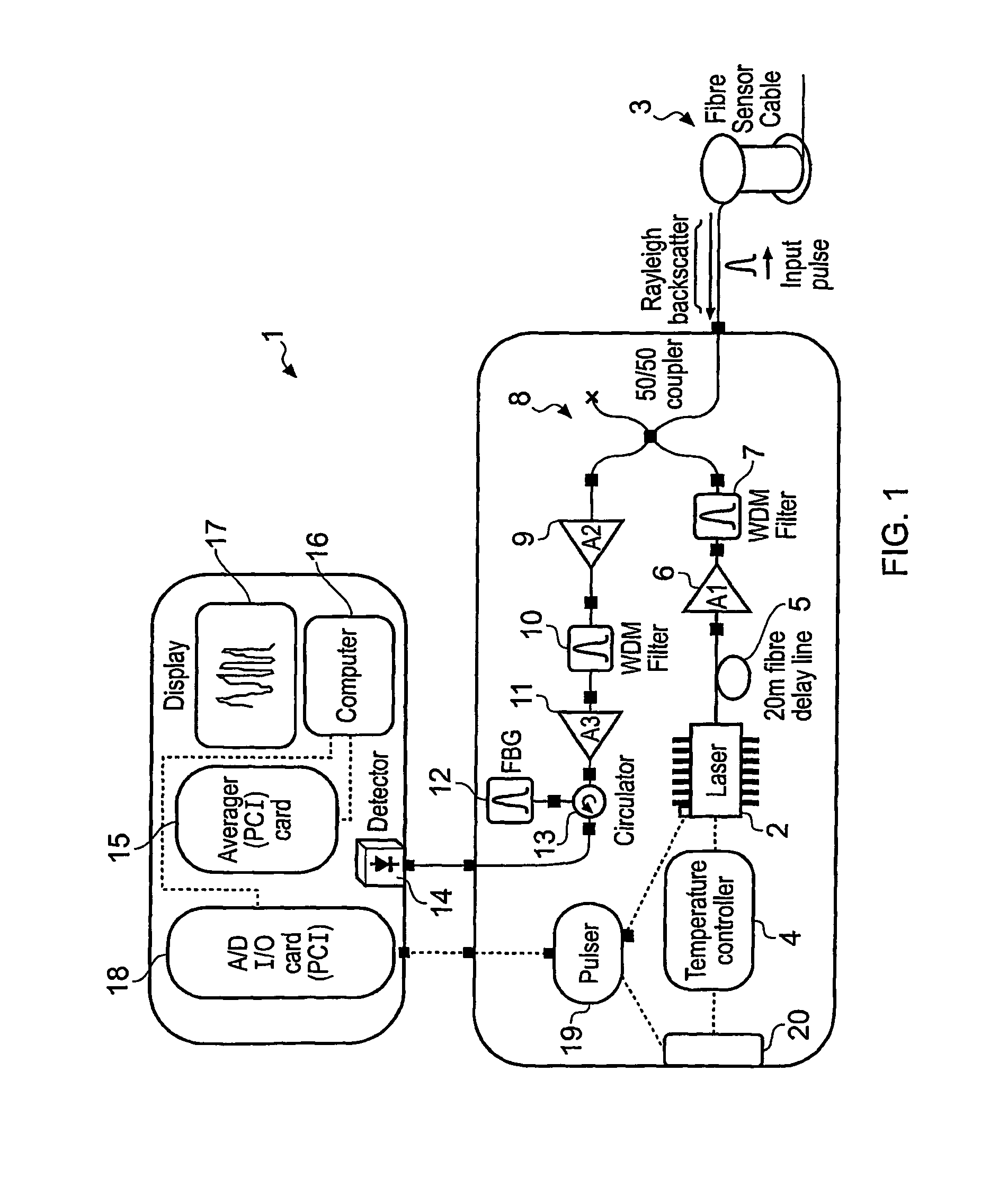
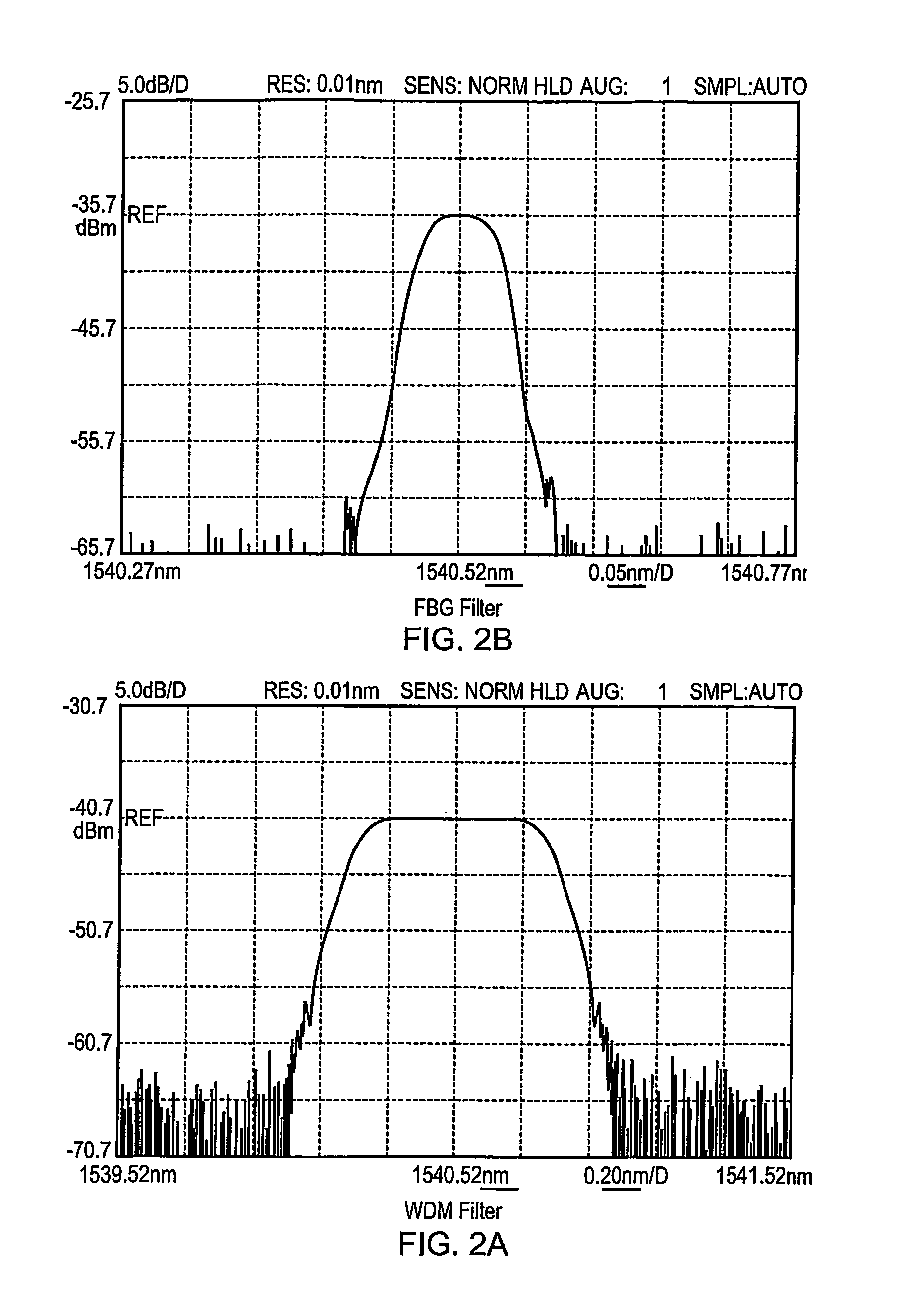
ActiveUS8264676B2Raise the ratioImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansGratingPhotodetector
A partially coherent Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR) apparatus has a light source comprising a directly modulated semiconductor Distributed FeedBack (DFB) laser diode for transmitting partially coherent light pulses along a monomode optical fibre. Light Rayleigh backscattered from the light pulses as they travel along the optical fibre is output from the end of the fibre into which the light pulses are transmitted to a Fibre Bragg Grating (FBG) filter. The FBG filter reduces the supectral width of light received at a photodetector. In one embodiment, the supectral width of the FBG filter is around one fifth of the supectral width of the light pulse after it has travelled around 1 km along the optical fibre. As a consequence of reducing the supectral width of the light received at the photodetector, the FBG filter increases the temporal coherence of the light. So, the FBG filter can ensure that the detected light is sufficiently coherent that a temporal supeckle pattern can be detected at the photodetector. At the same time, the light traveling in the optical fibre can be relatively supectrally broad so that non-linear effects in the optical fibre, such as Brillouin scattering, can be reduced.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Image processing device and printing apparatus for performing bidirectional printing
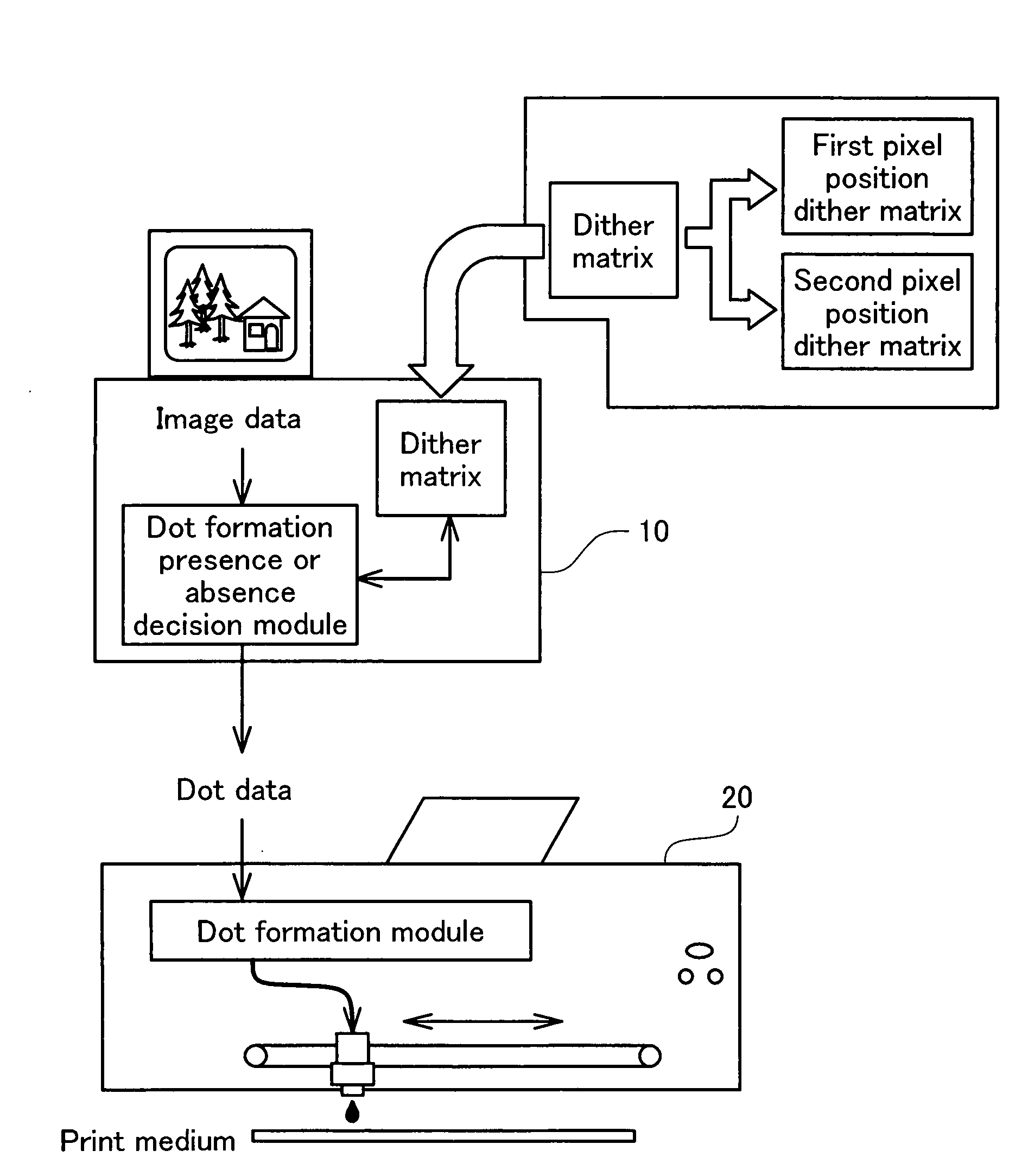
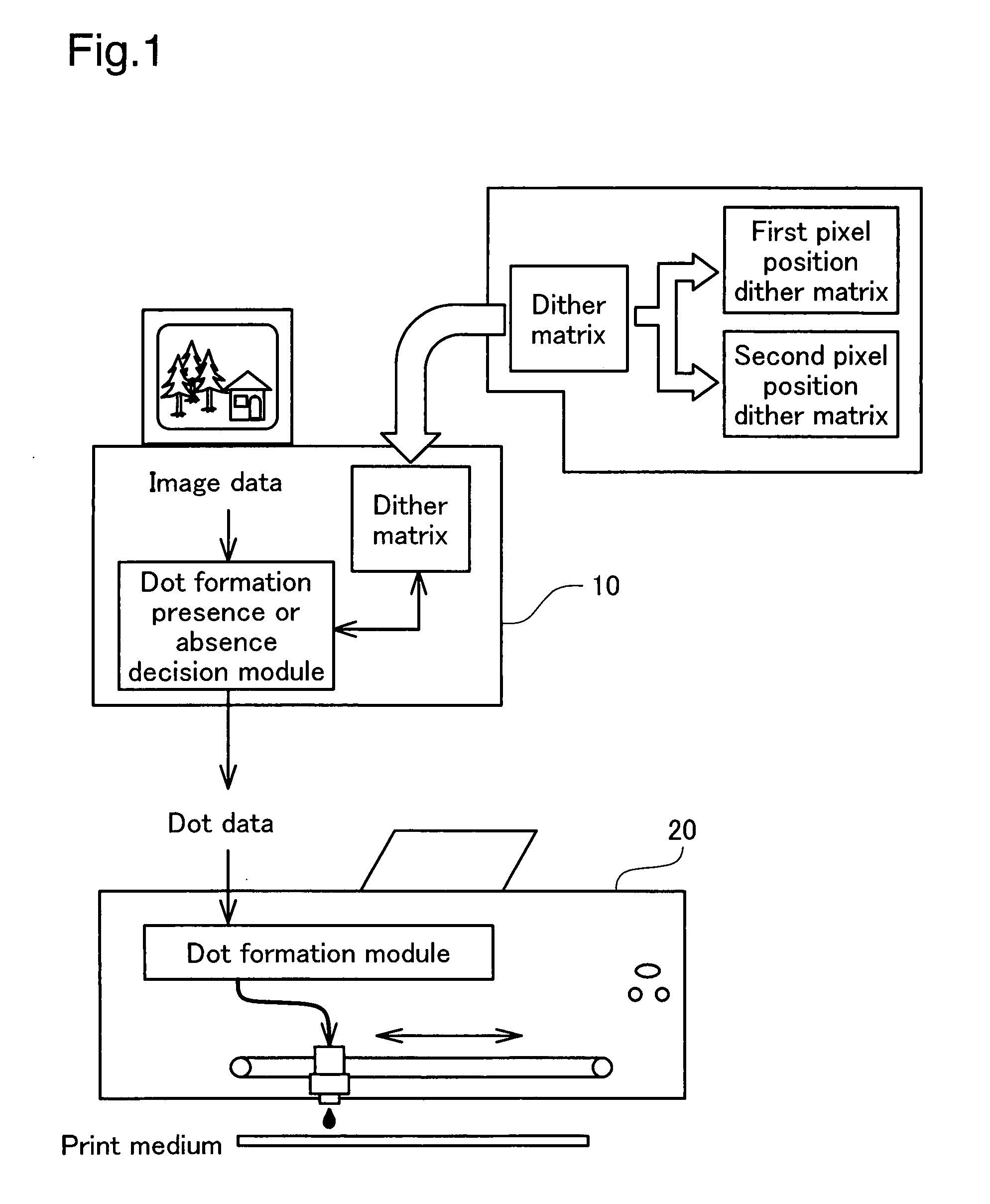
InactiveUS20080266608A1Potent effectReduce potential deterioration of picture qualitySpacing mechanismsPower drive mechanismsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
The invention provides a printing method of performing printing on a print medium. The method includes: generating dot data representing a status of dot formation on each of print pixels of a print image to be formed on the print medium, by performing a halftone process on image data representing a input tone value of each of pixels constituting an original image; providing a print head and a platen; setting a platen gap as a distance between the print head and the platen to a single fixed value that is commonly applied to plural printing environments; and performing a main scan of the print head to form a dot in each of the print pixels on the print medium supported by the platen according to the dot data in each of a forward pass and a backward pass of the print head, for generating the print image. The performing includes combining dots formed on a first pixel position group with dots formed on a second pixel position group in a common print area to generate the print image, the first pixel position group including multiple print pixels as objects of dot formation in the forward pass of the print head, the second pixel position group including multiple print pixels as objects of dot formation in the backward pass of the print head. The generating dot data includes setting a condition of the halftone process to reduce potential deterioration of picture quality due to a positional misalignment between the dots formed on the first pixel position group and the dots formed on the second pixel position group.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Treatment of Cancer with Dopamine Receptor Antagonists
InactiveUS20130065887A1High throughput testHigh levelCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDopamine receptor antagonistD2 dopamine receptors
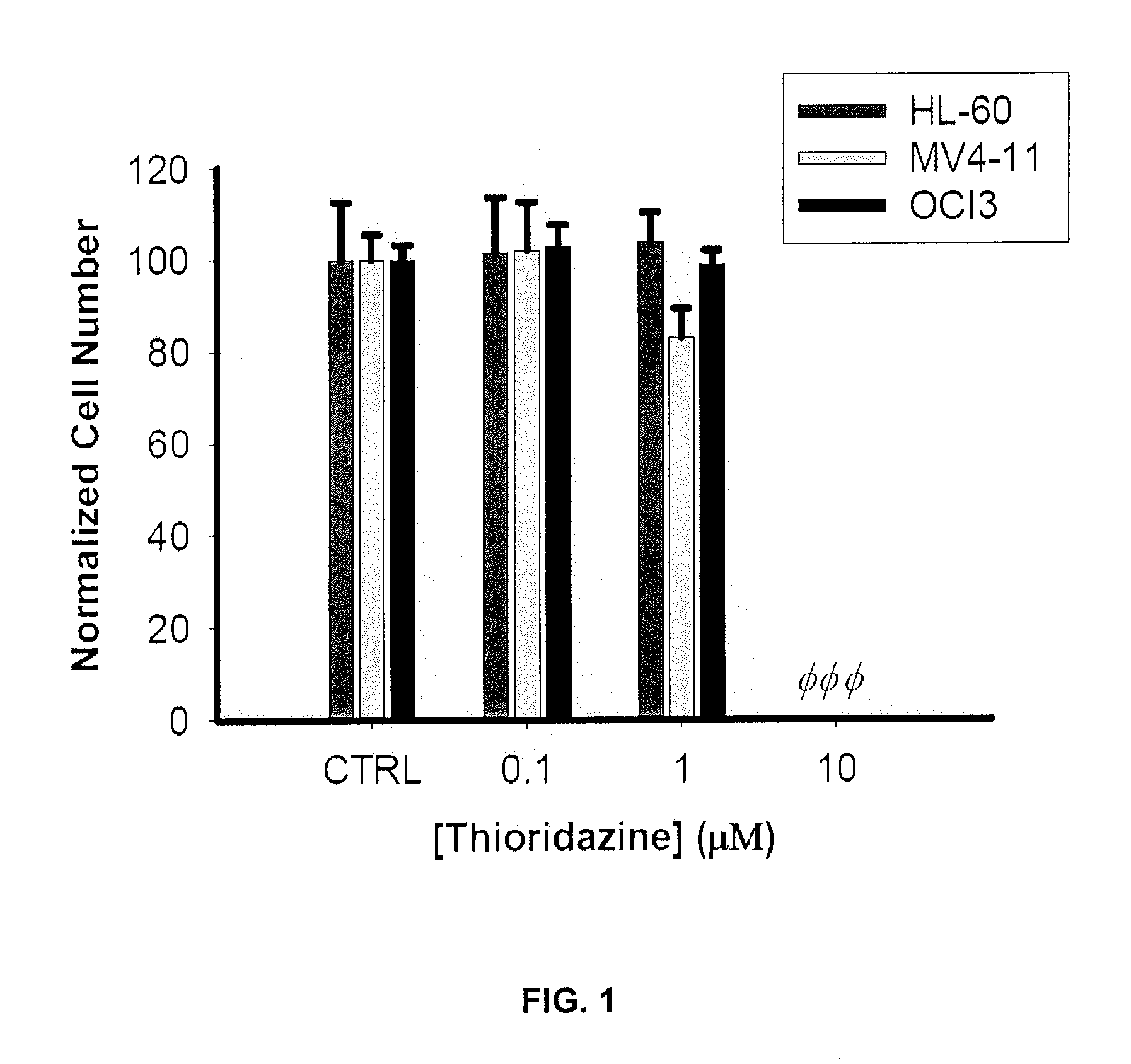
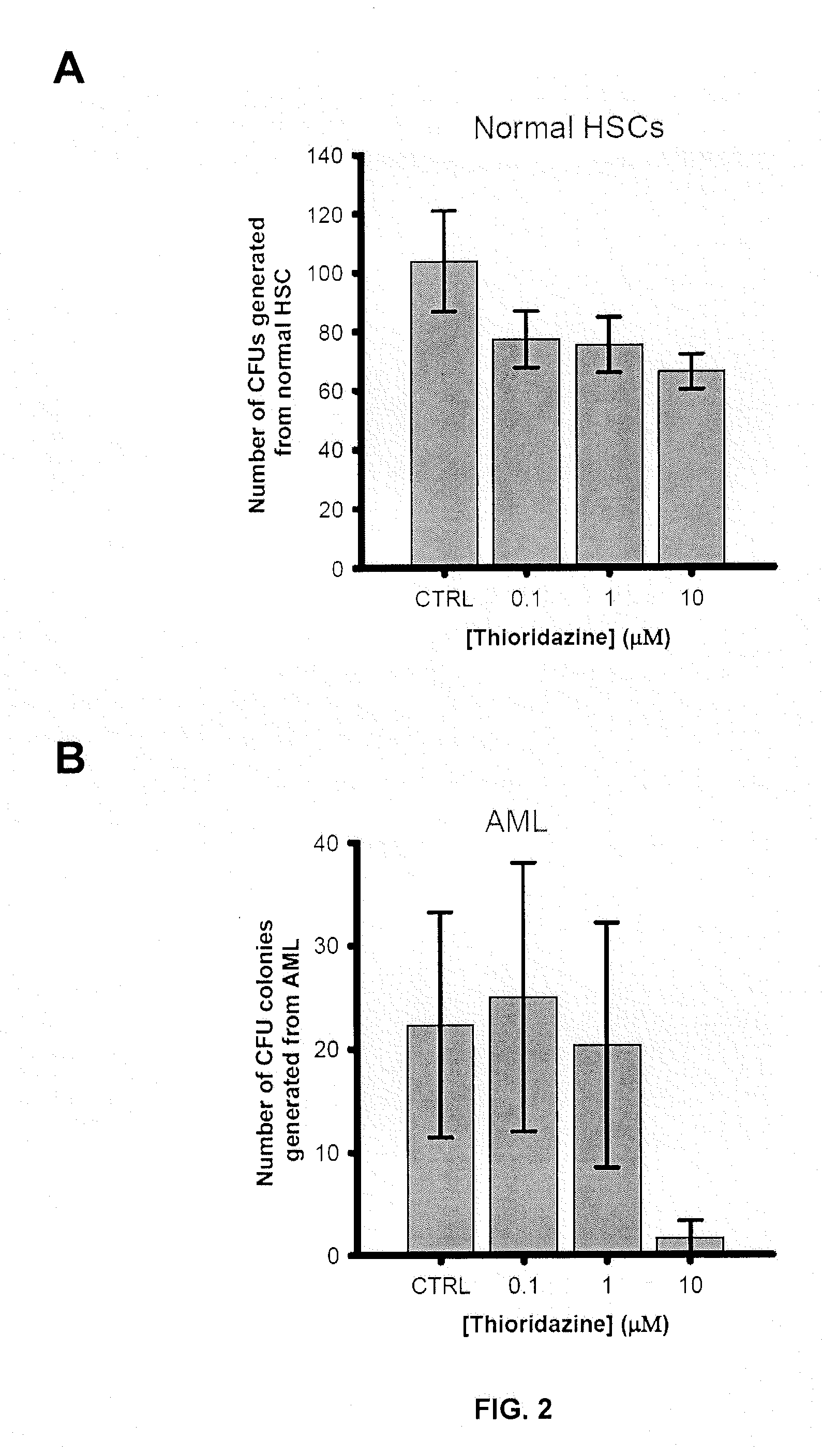
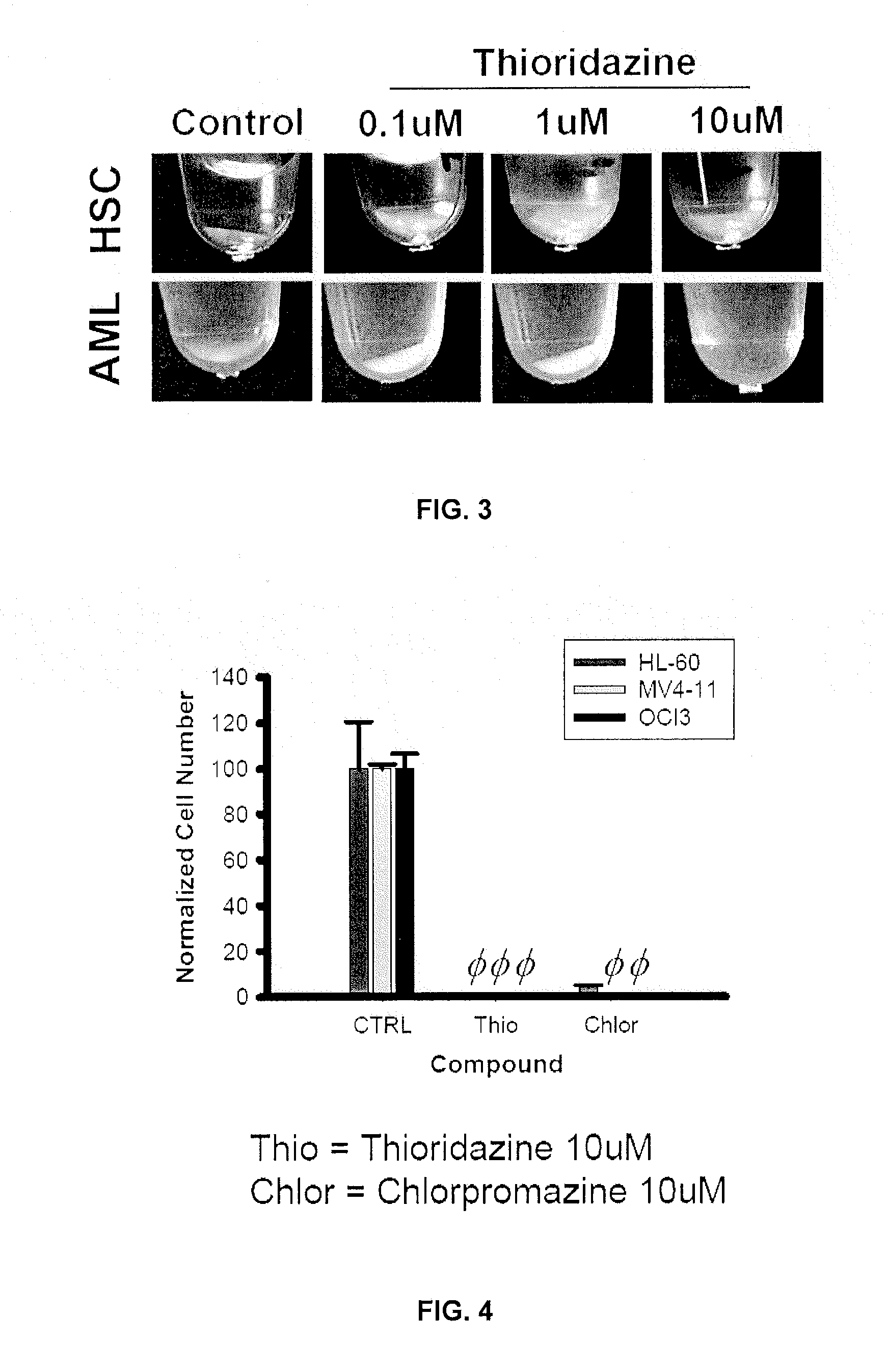
Described are methods of treating a cancer comprising administering to a subject in need thereof an effective amount of a dopamine receptor (DR) antagonist. The DR antagonist may be a phenothiazine derivative, such as thioridazine or chlorpromazine. Optionally, the cancer is acute myeloid leukemia. Also described are methods for identifying subjects with cancer, methods for providing a prognosis for a subjects with cancer and methods for identifying subjects likely to be responsive to therapy with DR receptor antagonists. Methods for identifying cancer stem cells and chemotherapeutic compounds that are DR receptor antagonists as also provided. Also described are methods for the identification and validation of agents that target cancer stem cells.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
Method for the treatment of skin fibrosis and suitable compositions for such treatment
InactiveUS20070207965A1Reduction in potential effectDecrease thicknessPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesPeptideDisease
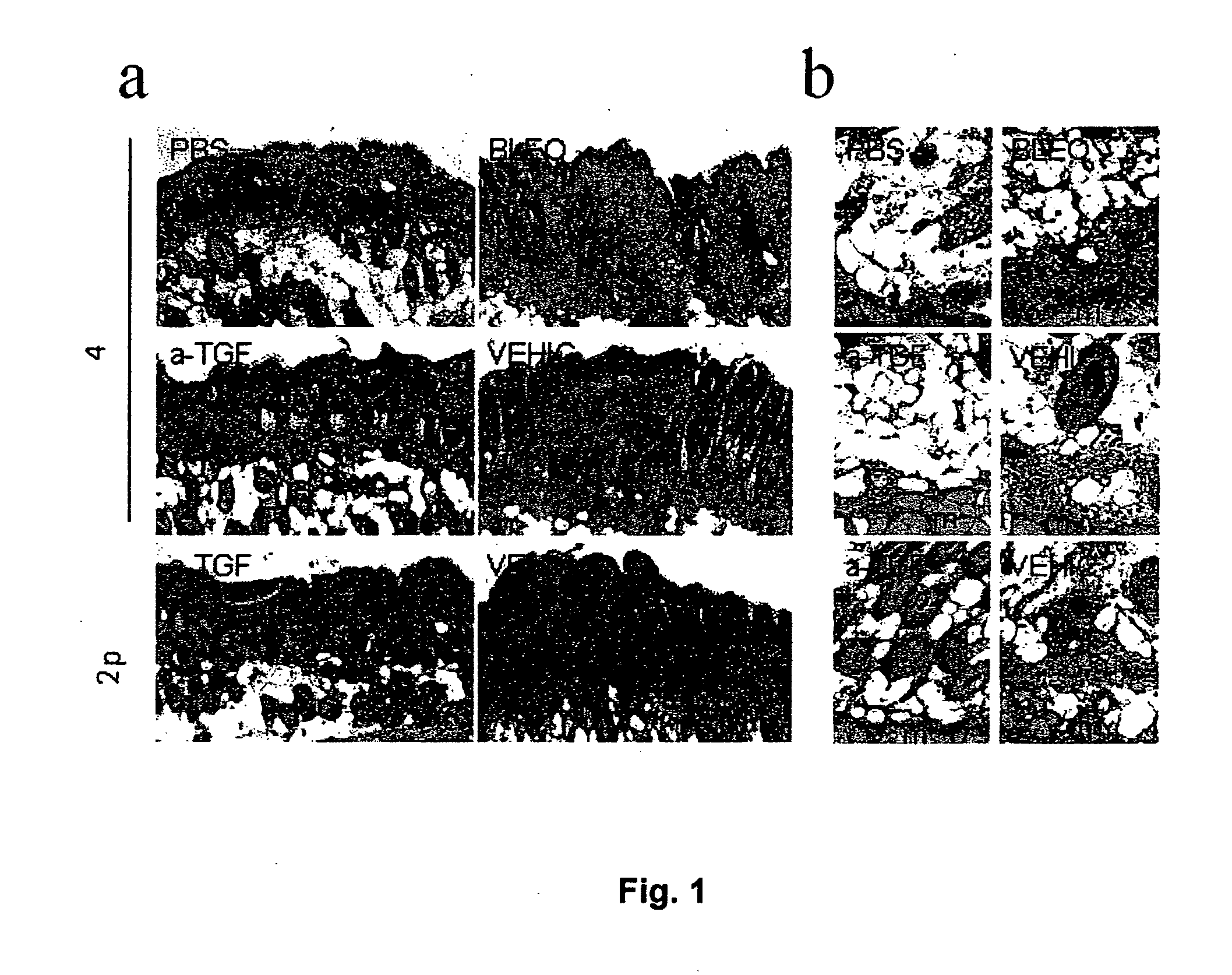
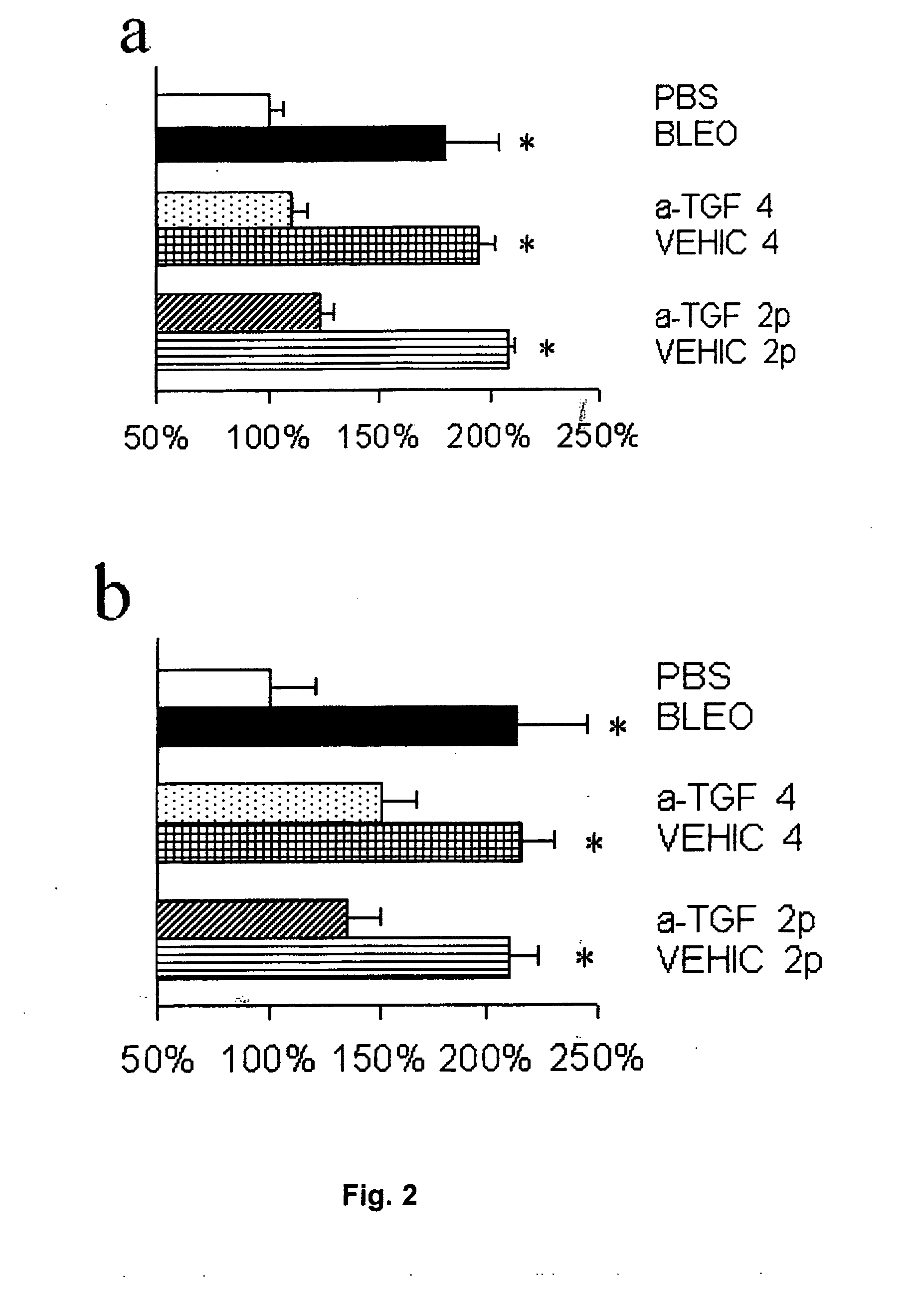
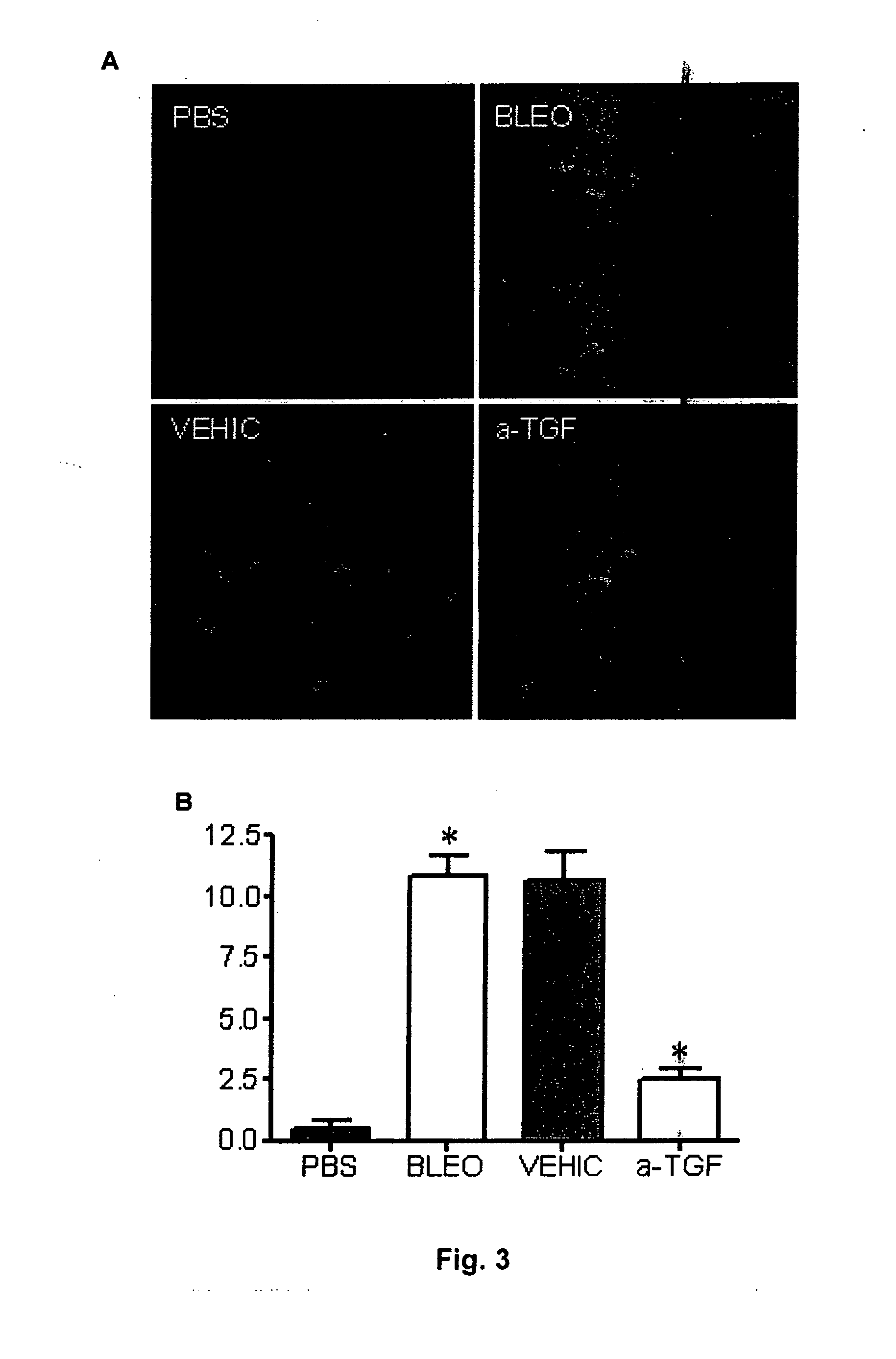
A Method for the treatment of skin fibrosis with a peptide that inhibits TGF-β, and suitable compositions for its administration. The method includes in particular, the use of peptide P144, a compound that is a known inhibitor of TGF-β, for the treatment of skin fibrosis by topical application. The method is shown effective in an animal model of bleomycin-induced skin sclerosis, to a reduction both of the skin fibrosis and of the content of soluble collagen, without any signs of systemic toxicity being detected. This shows that P144 is effective for topical application in mammals for treating fibrotic skin diseases and pathological scarring of the skin. For the administration of this peptide, stable compositions are also supplied, with pleasant appearance without being greasy, with good spreading characteristics and with a viscosity that permits it to be processed easily in industrial plant, and which are suitable for administering the peptide to humans.
Owner:DIGNA BIOTECH
Preventive or remedy for glaucoma
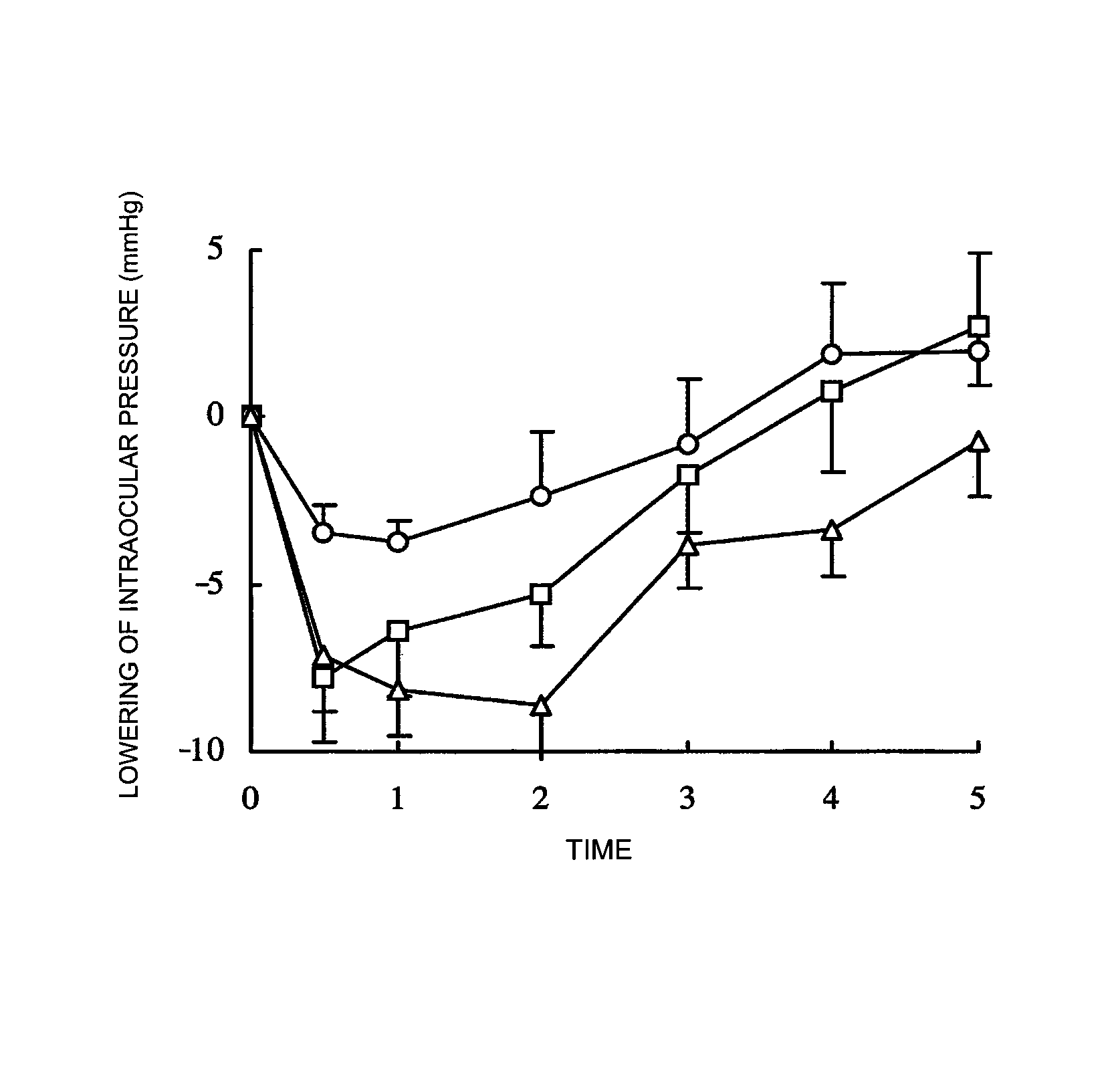
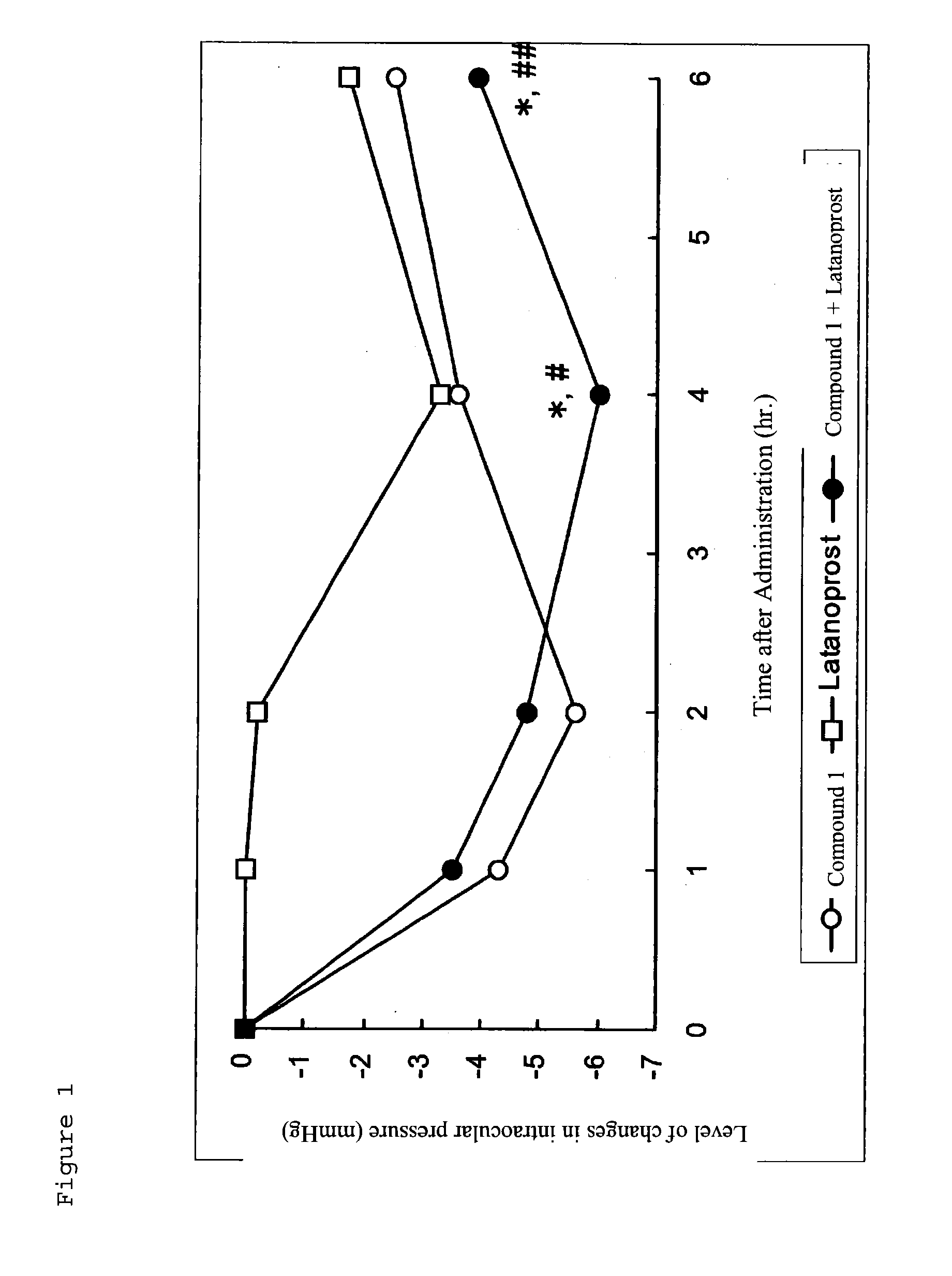
InactiveUS8629161B2Potent effectProlong the action timeBiocideSenses disorderAlpha-adrenergic blockersRho kinase inhibitor
There is provided a preventive for glaucoma or a preventive or a remedy for ocular hypertension, with a potent ocular hypotensive effect and prolonged duration thereof. A preventive or a remedy for glaucoma comprising a Rho kinase inhibitor and an α1 blocker in combination.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
Gastro-esophageal reflux control system and pump
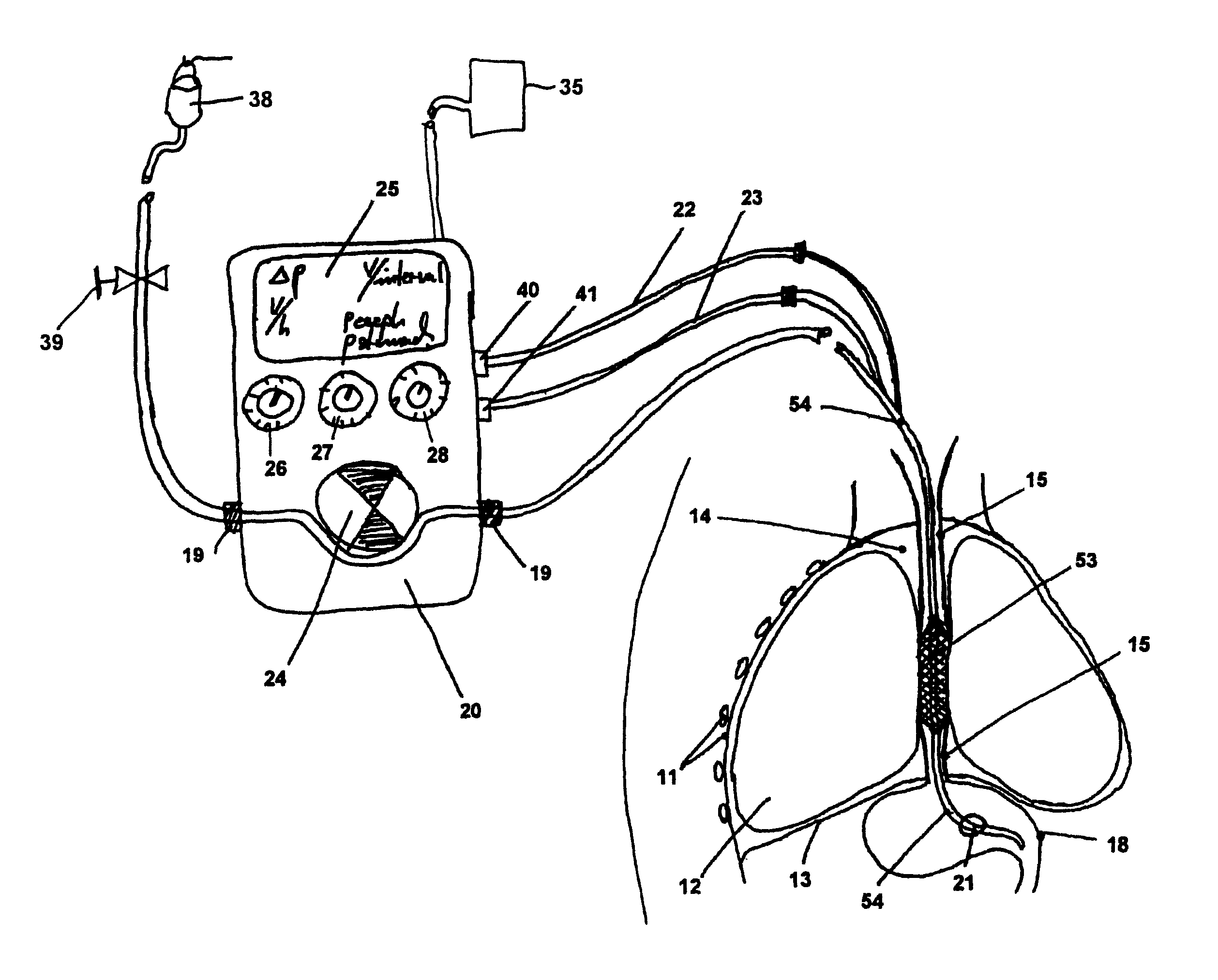
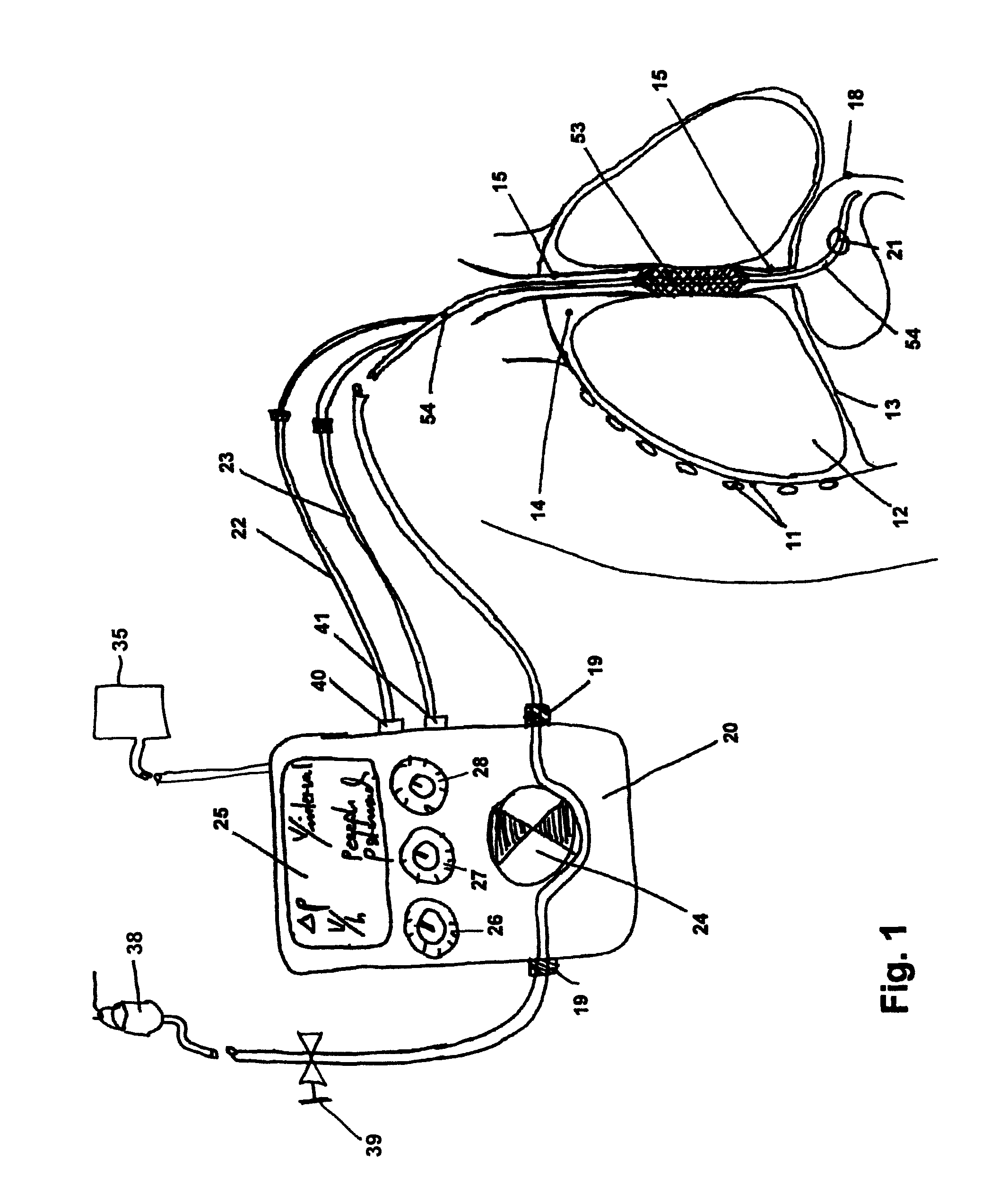
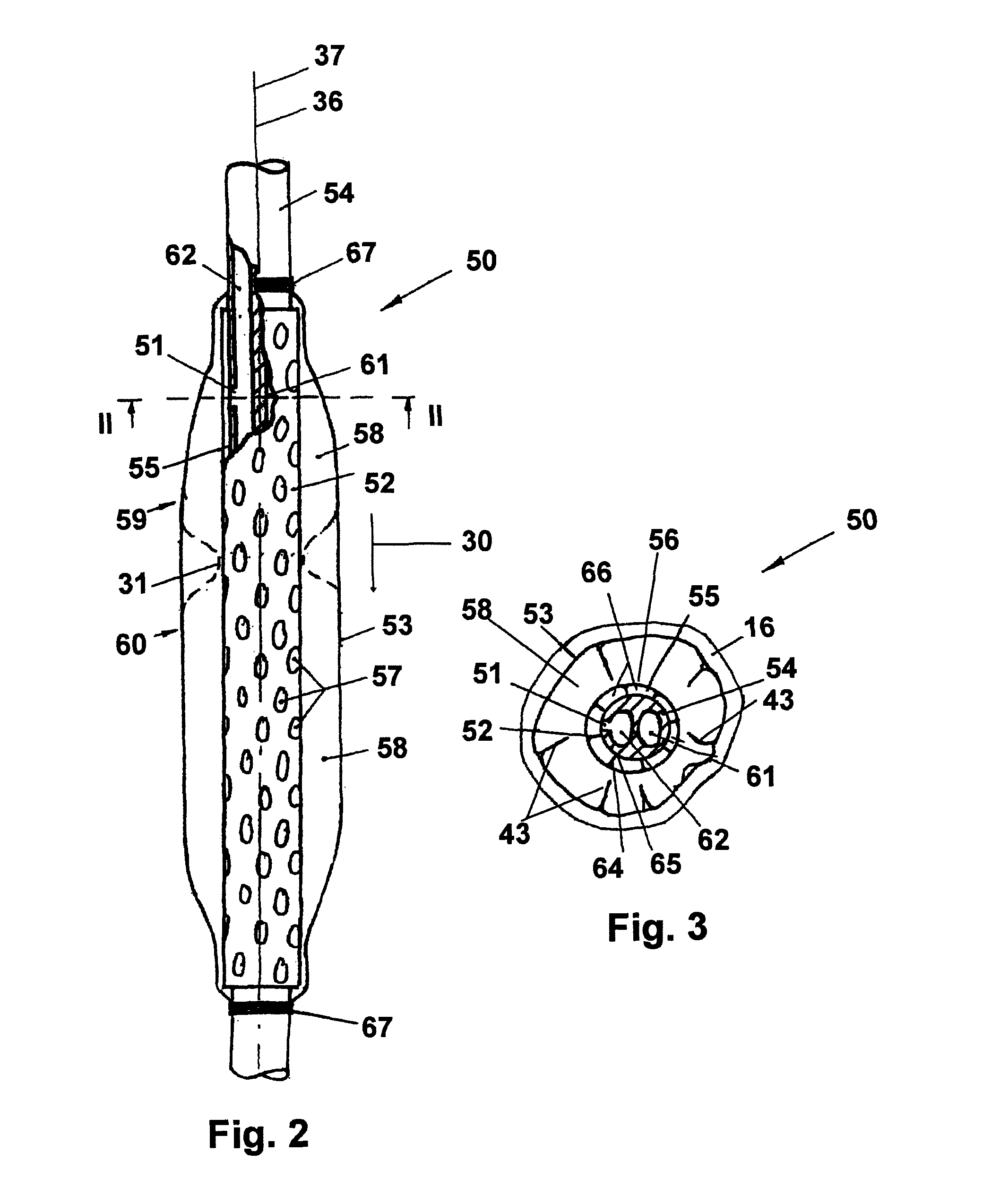
ActiveUS7967780B2Without causing deleterious effects on the esophageal structuresReduce contentSurgeryDilatorsOesophageal tubeLiquid medium
An enteral feeding unit that reduces the occurrence of gastro-esophogeal-pharynegal reflux during feeding includes an automatable feeding pump with a feedback sensor for sensing a relative pressure in a patient's stomach and esophagus, and a regulator system for controlling and monitoring feeding rate to the patient as a function of the relative gastro-esophageal pressure. The system includes a stomach probe that provides a fluid-tight closure of the esophagus. The stomach probe includes a tampon-bladder for watertight closure of the esophagus, in which the tampon-bladder is formed of flexible and / or elastic material. At least an inner cavity of the bladder is provided for the reception of a fluid medium. A prescribed pressure for the medium in the tampon-bladder (53) is maintained by an inner lumen forming the stomach probe, from which an outer hose-like lumen (62) extending to the tampon-bladder (53) is so arranged that between the outer lumen (62) and the inner lumen (61) a channel is formed connected to the inner cavity of the tampon-bladder (53) arranged on the outer lumen (62) by a number of openings (57). The inner cavity (58) of the tampon-bladder (53) is connected via a canal formed between the inner and outer lumina (62) with a suitably graded reservoir or equalizing vessel for the liquid medium situated above the tampon-bladder and outside the patient.
Owner:AVENT INC
Method of treating lethal shock induced by toxic agents and diagnosing exposure to toxic agents by measuring distinct pattern in the levels of expression of specific genes
InactiveUS20050272055A1Reduce expressionPotent effectMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsGene expression levelToxicology
Owner:DAS RINA +3
Topical Eutectic Anesthetic Composition for Oral or Dermal Tissue
A pharmaceutical anesthetic composition for topical administration for dental, emergency and general medical use is described. The composition is a eutectic composition of anesthetic agents, sugar alcohol, and menthol for the purpose of numbing oral or dermal tissue. Methods of making and of using the composition are described.
Owner:DENTON MARCIA MARYE +1
High density trench MOSFET with reduced on-resistance
InactiveUS7687851B2Reduce resistanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesInsulation layerBody contact
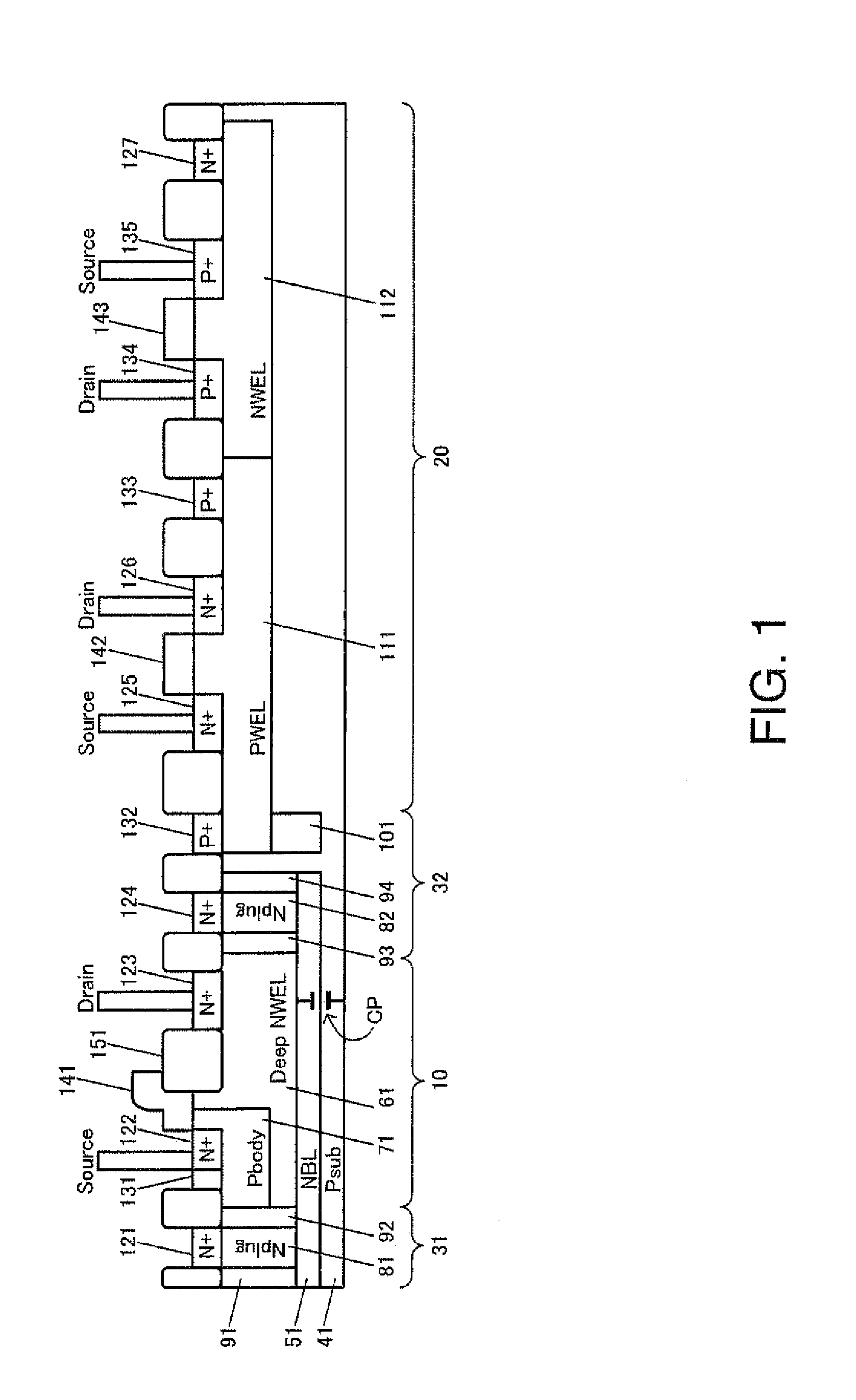
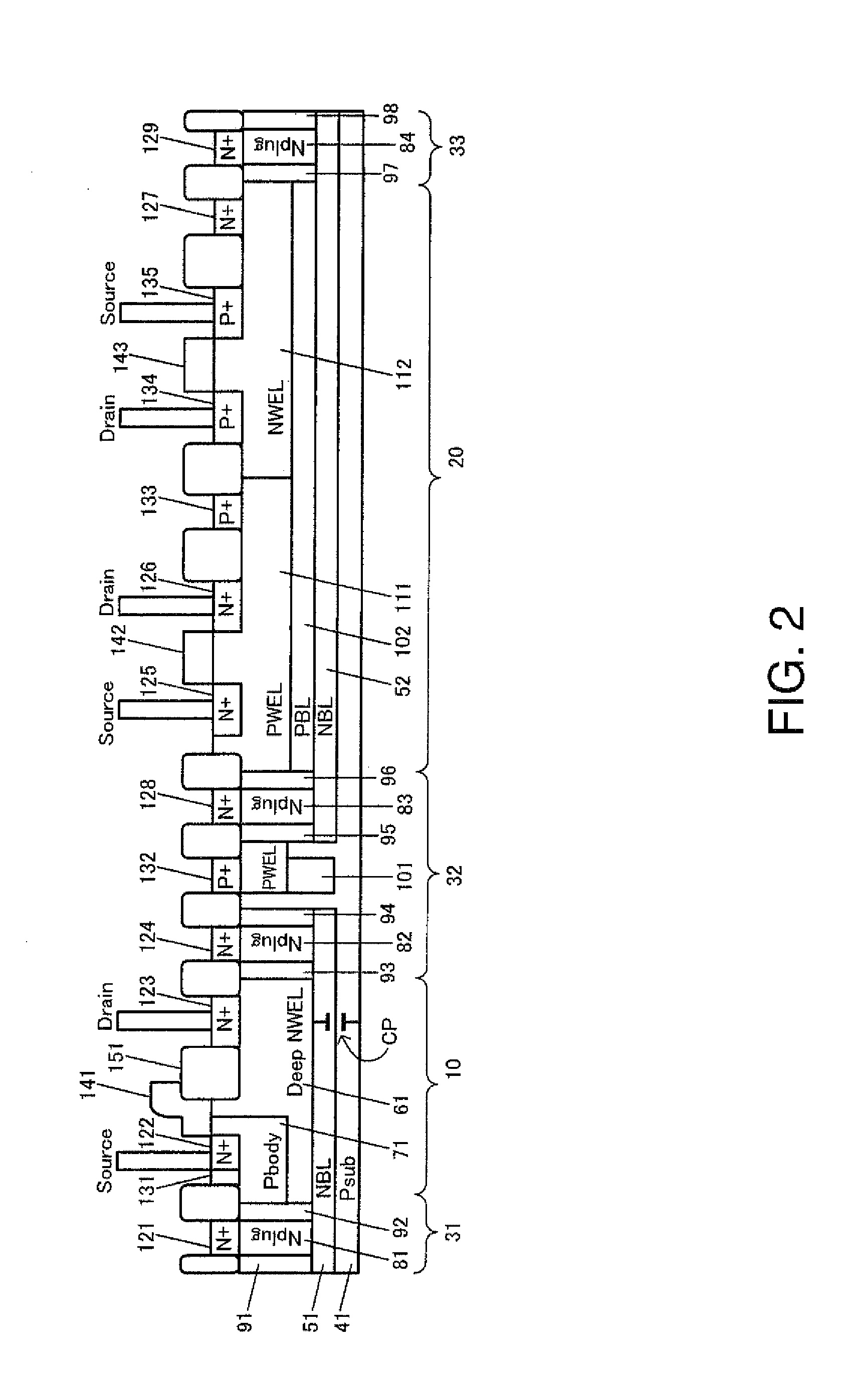
A method for manufacturing a trenched metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) cell includes the steps of opening a gate trench in a semiconductor substrate and implanting ions of a first conductivity type same as a conductivity type of a source region with at least two levels of implanting energies to form a column of drain-to-source resistance reduction regions below the gate trench. The method further includes steps of forming a gate in the gate trench and forming body and source regions in the substrate surrounding the gate trench. Then the MOSFET cell is covered with an insulation layer and proceeds with applying a contact mask for opening a source-body contact trench with sidewalls substantially perpendicular to a top surface of the insulation layer into the source and body regions. The method further includes a step of implanting ions of a second conductivity type opposite the first conductivity type with at least two levels of implanting energies to form a column of electrical field reduction regions below the source-body contact trench next to the column of drain-to-source resistance reduction regions to function as charge balance regions to the drain-to-source resistance reduction regions.
Owner:M MOS SEMICON
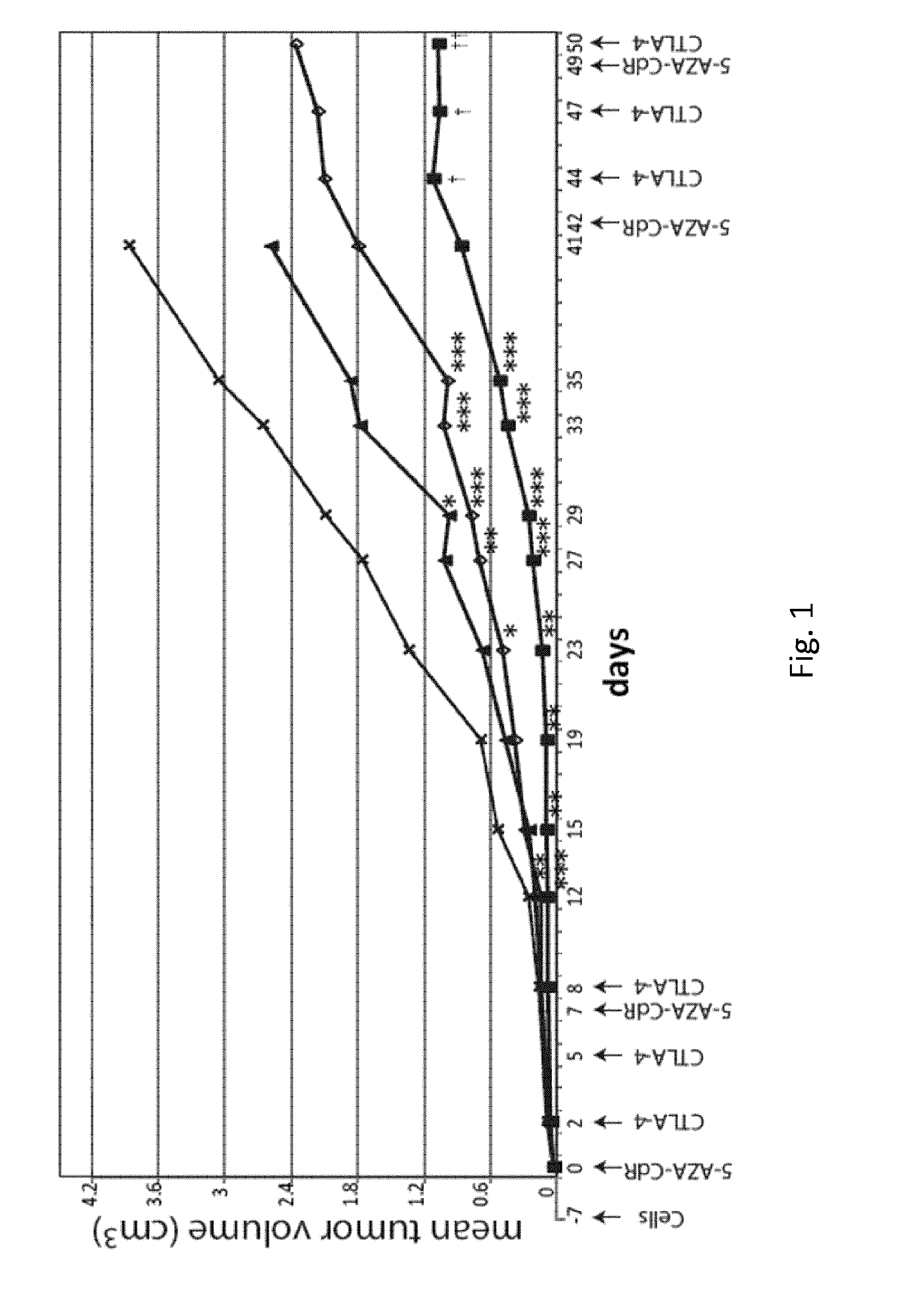
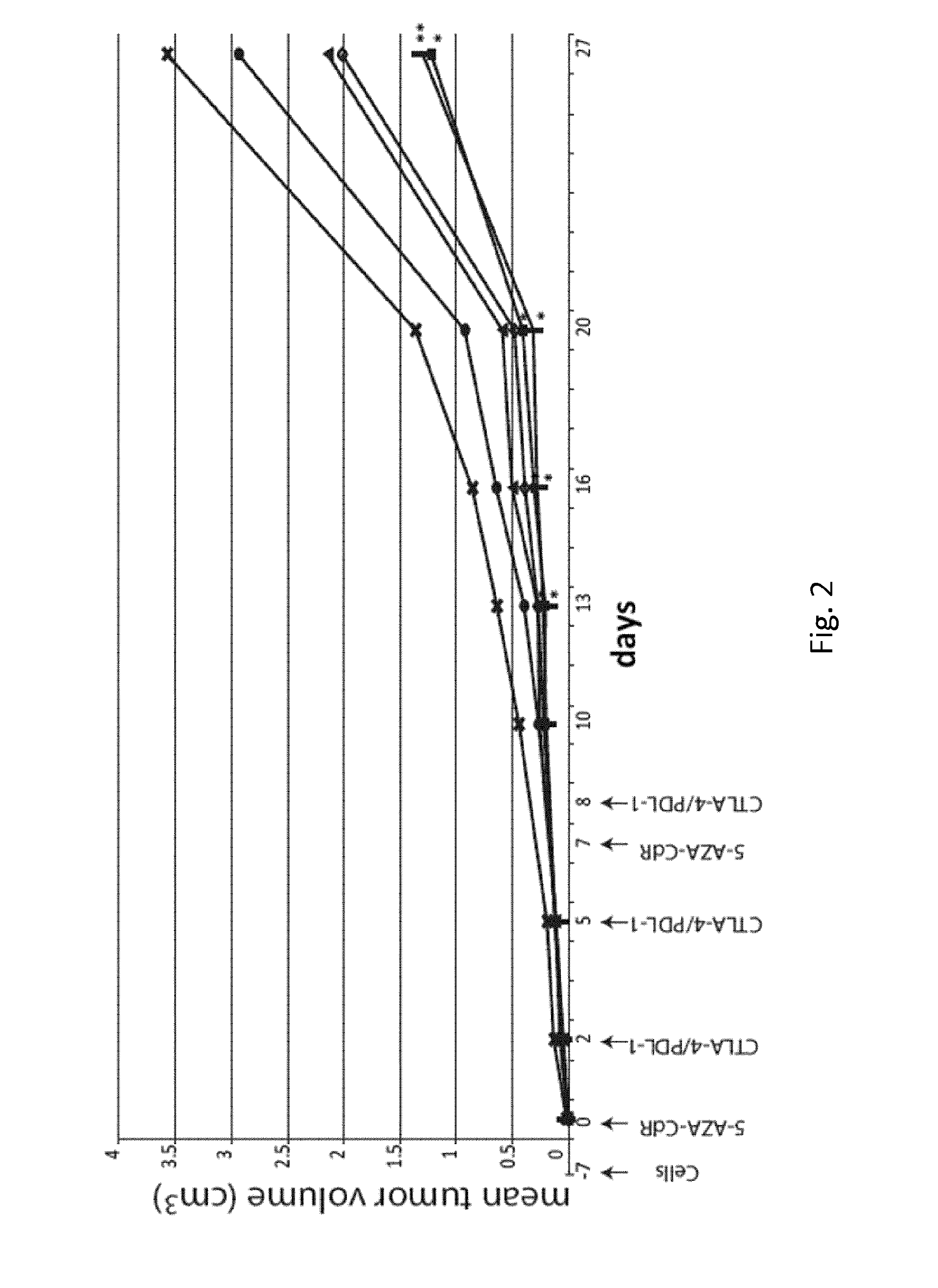
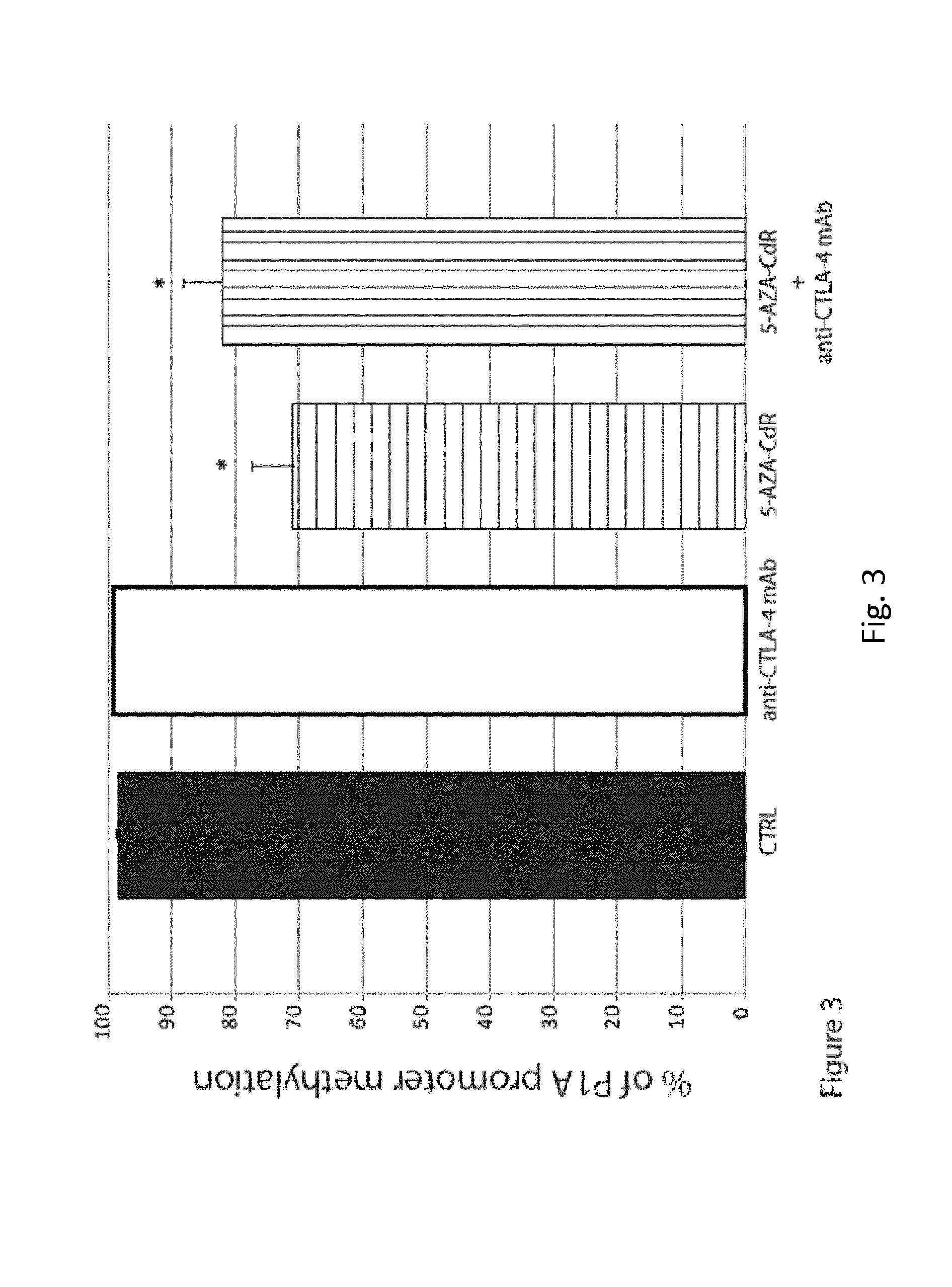
DNA hypomethylating agents for cancer therapy
ActiveUS20150374731A1Improve anti-tumor activityStrong anti-tumor effectOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsCancer preventionMolecular Targeted Therapies
The present invention relates to a method of treating and / or preventing cancer comprising administering a combination of an effective amount of a DNA hypomethylating agent and an effective amount of at least one immunomodulatory agent and / or optionally an effective amount of at least one targeted therapy agent.
Owner:MAIO MICHELE +2
Biological materials and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090053247A1Reduce managementHighly preventive effectAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderCoupling ratioSolvent
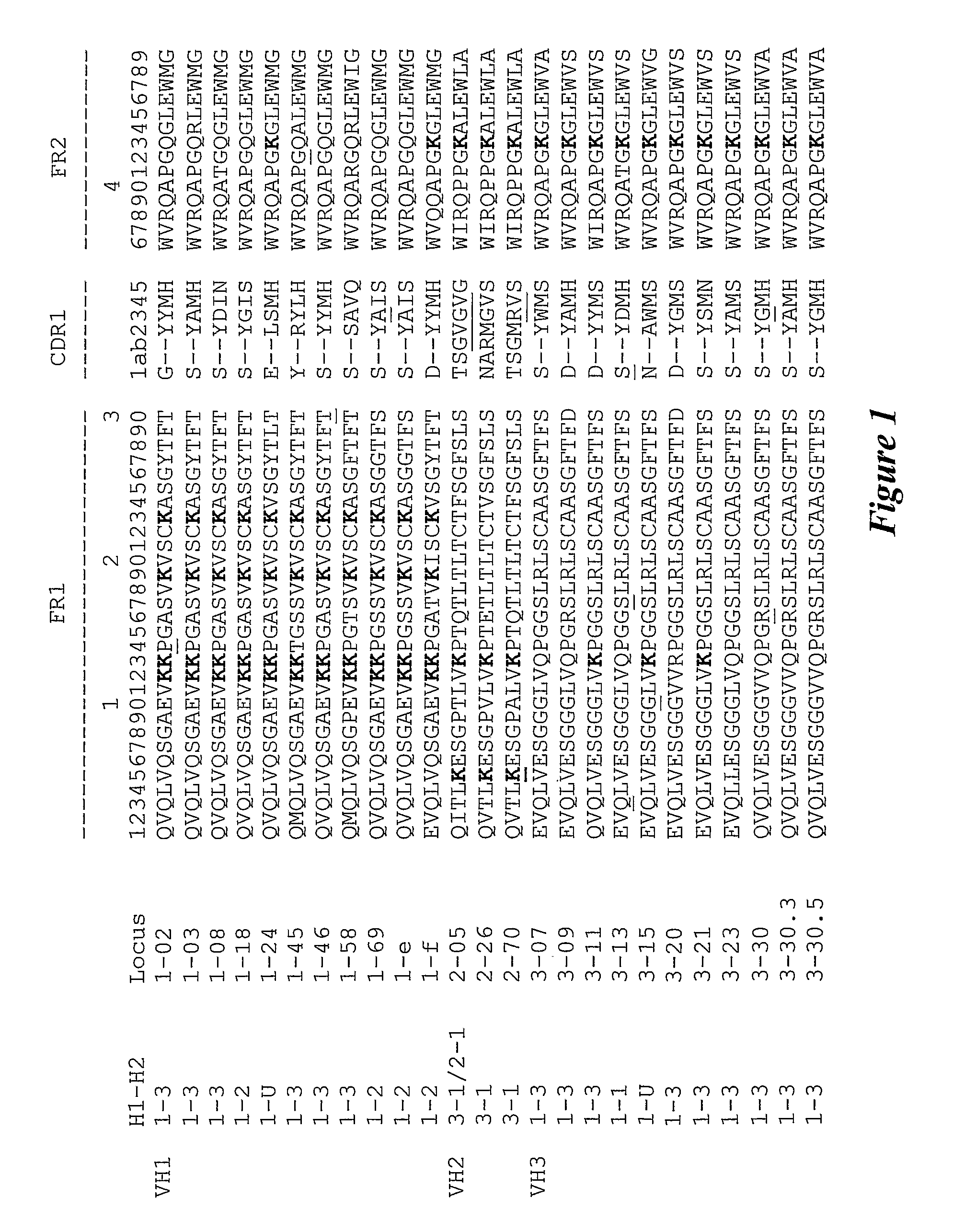
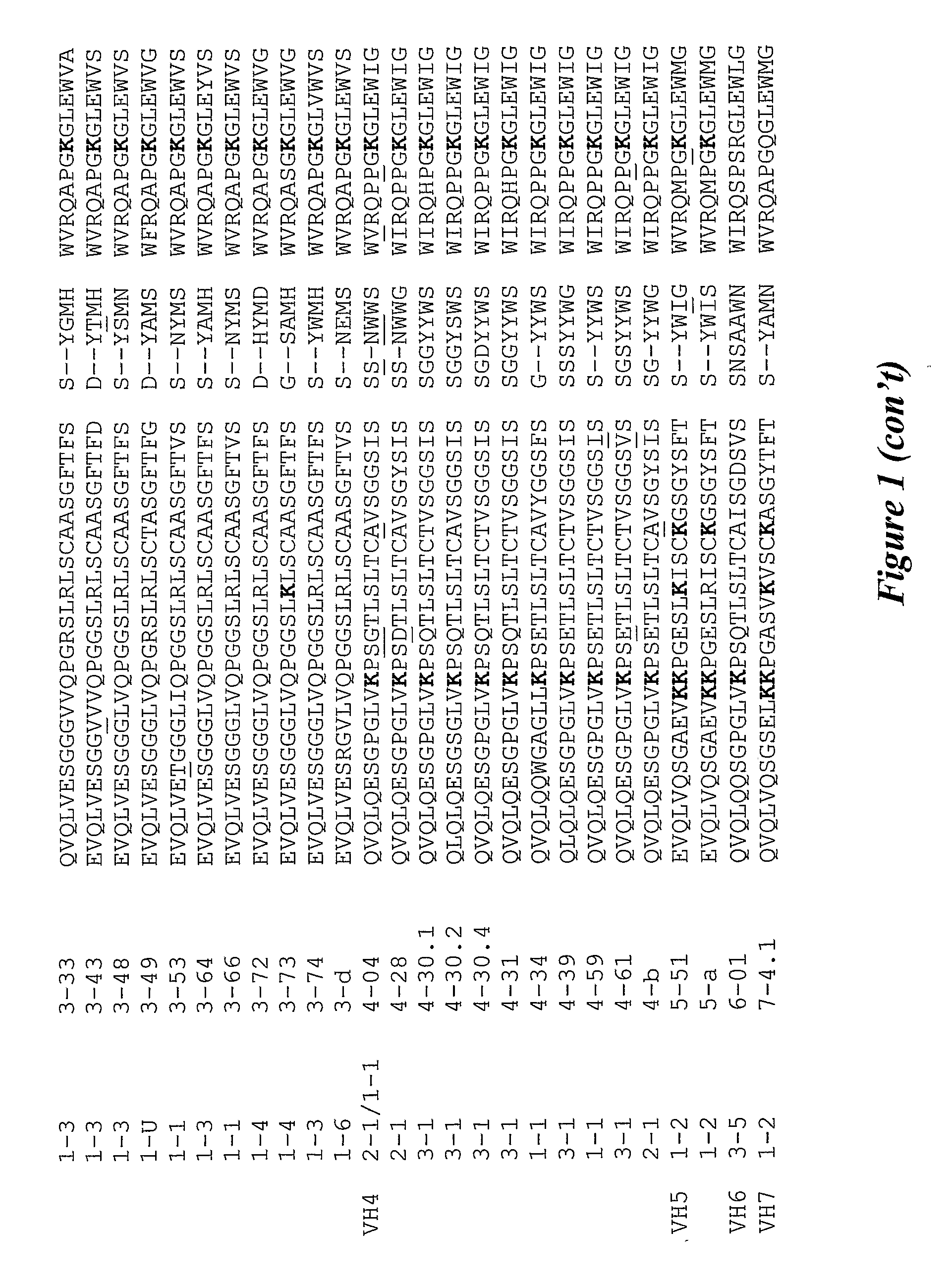
FR1 1 2 3H1-H2Locus123456789012345678901234567890VH11-31-02QVQLVQSGAEVKKPGASVKVSCKASGYTFT1-31-03QVQLVQSGAEVKKPGASVKVSCKASGYTFT1-31-08QVQLVQSGAEVKKPGASVKVSCKASGYTFT1-21-18QVQLVQSGAEVKKPGASVKVSCKASGYTFT1-U1-24QVQLVQSGAEVKKPGASVKVSCKVSGYTLT1-31-45QMQLVQSGAEVKKTGSSVKVSCKASGYTFT1-31-46QVQLVQSGAEVKKPGASVKVSCKASGYTFT1-31-58QMQLVQSGPEVKKPGTSVKVSCKASGFTFT1-21-69QVQLVQSGAEVKKPGSSVKVSCKASGGTFS1-21-eQVQLVQSGAEVKKPGSSVKVSCKASGGTFS1-21-fEVQLVQSGAEVKKPGATVKISCKVSGYTFTVH23-1 / 2-12-05QITLKESGPTLVKPTQTLTLTCTFSGFSLS3-12-26QVTLKESGPVLVKPTETLTLTCTVSGFSLS3-12-70QVTLKESGPALVKPTQTLTLTCTFSCFSLSVH31-33-07EVQLVESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFS1-33-09EVQLVESGGGLVQPGRSLRLSCAASGFTFD1-33-11QVQLVESGGGLVKPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFS1-13-13EVQLVESGGSLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFS1-U3-15EVQLVESGGGLVKPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFS1-33-20EVQLVFSGGSVVRPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFD1-33-21EVQLVESGGGLVKPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFS1-33-23EVQLLESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFTFS1-33-30QVQLVESSGGVVQPGRSLRLSCAASGFTFS1-33-30.3QVQLVESGGGVVQPGRSLRLSCAASGFTFS1-33-30.5QVQLVESGGGVVQPGRSLRLSCAASGFTFSFR2CDR1 4H1-H2Locus1ab234567890123456789VH11-31-02G--YYMHWVRQAPGQGLEWMG1-31-03S--YAMHWVRQAPGQRLEWMG1-31-08S--YDINWVRQATGQGLEWMG1-21-18S--YGISWVRQAPGQGLEWMG1-U1-24E--LSMHWVRQAPGKGLEWMG1-31-45Y--RYLHWVRQAPGQALEWMG1-31-46S--YYMHWVRQAPGQGLEWMG1-31-58S--SAVQWVRQARGQRLEWIG1-21-69S--YAISWVRQAPGQGLEWMG1-21-eS--YAISWVRQAPGQGLEWMG1-21-fD--YYMHWVQQAPGKGLEWMGVH23-1 / 2-12-05TSGVGVGWIRQPPGKALEWLA3-12-26NARMGVSWIRQPPGKALEWLA3-12-70TSGMRVSWIRQPPGKALEWLAVH31-33-07S--YWMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVA1-33-09D--YAMHWVRQAPGKGLEWVS1-33-11D--YYMSWIRQAPGKGLEWVS1-13-13S--YDMHWVRQATGKGLEWVS1-U3-15N--AWMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVG1-33-20D--YGMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVS1-33-21S--YSMNWVRQAPGKGLEWVS1-33-23S--YAMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVS1-33-30S--YGMHWVRQAPGKGLEWVA1-33-30.3S--YAMHWVRQAPGKGLEWVA1-33-30.5S--YGMHWVRQAPGKGLEWVAThe invention provides a compound comprising a photosensitising agent coupled to a carrier molecule with a minimum coupling ratio of 3:1 wherein the carrier molecule has a binding specificity for a target cell. There is also provided a process of conjugation comprising the use of a first and second aprotic solvent and uses of the conjugated compounds.
Owner:PHOTOBIOTICS
Drug therapy for preventing or treating glaucoma
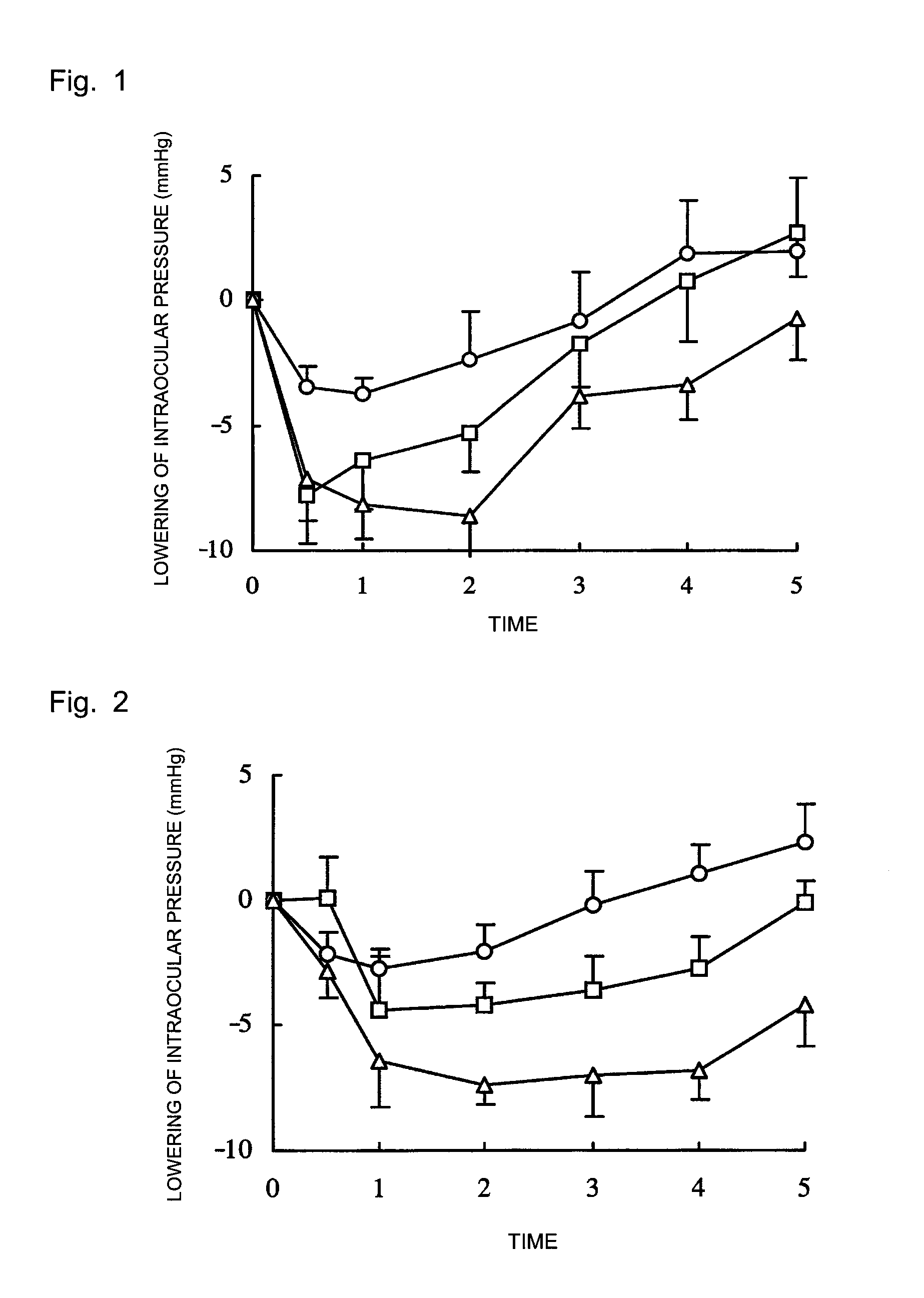
InactiveUS20130310370A1Potent intraocular pressure lowering effectProlong the action timeBiocideSenses disorderOcular hypertensionTreatment glaucoma
There is provided a drug therapy for prevention of glaucoma or prevention or treatment of ocular hypertension, with a potent ocular hypotensive effect and prolonged duration thereof. Disclosed is a combination of (S)-(−)-1-(4-fluoro-5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-2-methyl-1,4-homopiperazine or a salt thereof, or a solvate thereof, and a prostaglandin for prevention or treatment of glaucoma.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
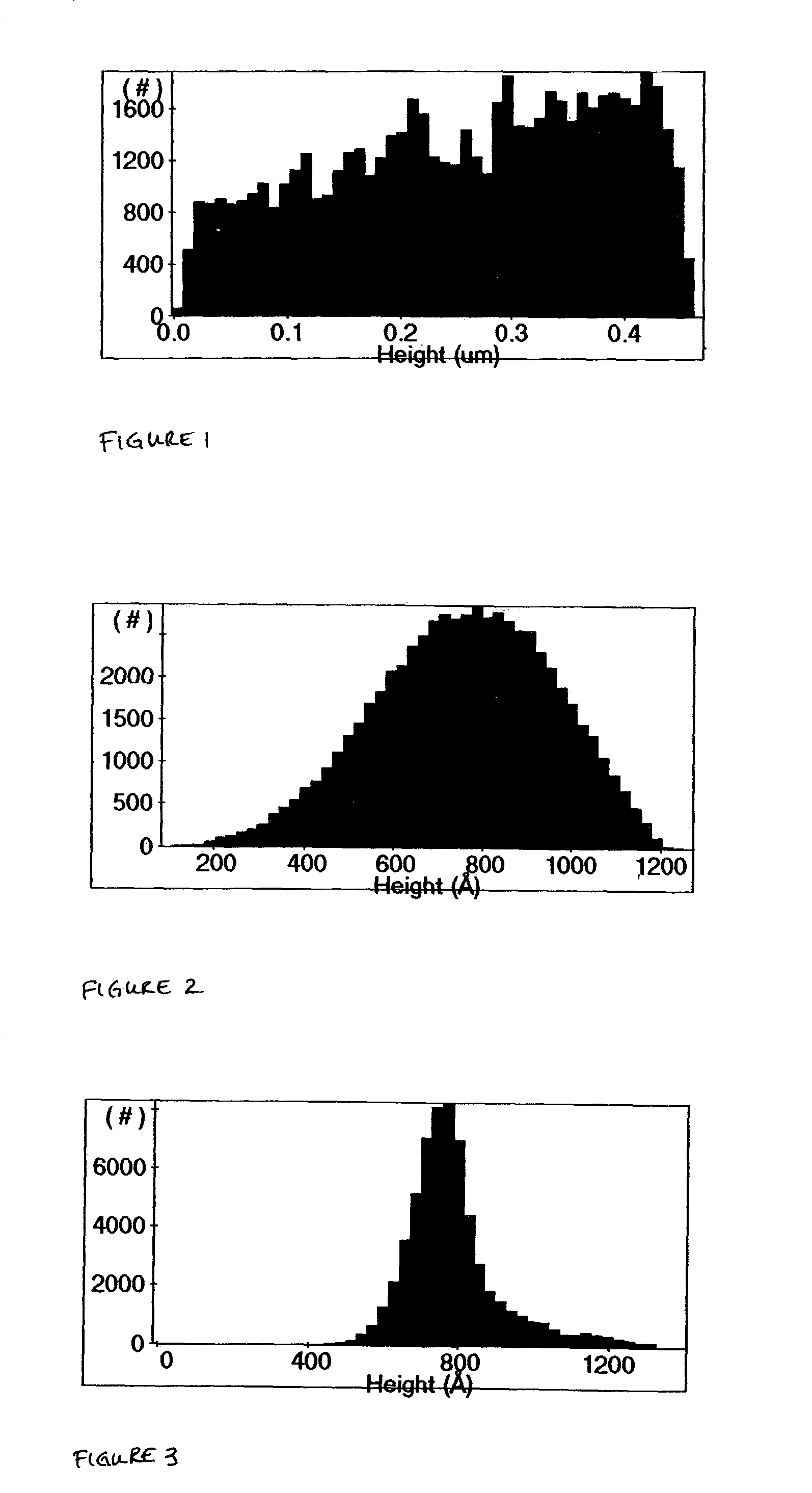
Composition for chemical-mechanical polishing and method of using same
ActiveUS7037350B2Evenly distributedDesirable sizeFireproof paintsOther chemical processesCompound (substance)Aqueous solution
A composition for chemical-mechanical polishing, comprising an aqueous solution and an abrasive that comprises polymer particles, is described. The polymer particles carry an electrical charge, such that nearby particles repel one another. Accordingly, aggregation of polymer particles may be reduced, minimized or eliminated. The composition may additionally comprise an oxidizing agent. A method of using the composition to polish a substrate surface, such as a substrate surface having a metal surface feature or layer, is also described. A substrate so polished may exhibit good surface characteristics, such as a relatively smooth surface or a reduced number of, or a lack of, microscratches on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Composition for chemical-mechanical polishing and method of using same
ActiveUS20050014890A1Flat surfaceDesirable surface characteristicFireproof paintsOther chemical processesCompound (substance)Aqueous solution
A composition for chemical-mechanical polishing, comprising an aqueous solution and an abrasive that comprises polymer particles, is described. The polymer particles carry an electrical charge, such that nearby particles repel one another. Accordingly, aggregation of polymer particles may be reduced, minimized or eliminated. The composition may additionally comprise an oxidizing agent. A method of using the composition to polish a substrate surface, such as a substrate surface having a metal surface feature or layer, is also described. A substrate so polished may exhibit good surface characteristics, such as a relatively smooth surface or a reduced number of, or a lack of, microscratches on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Oncogenic ras-specific cytotoxic compound and methods of use thereof
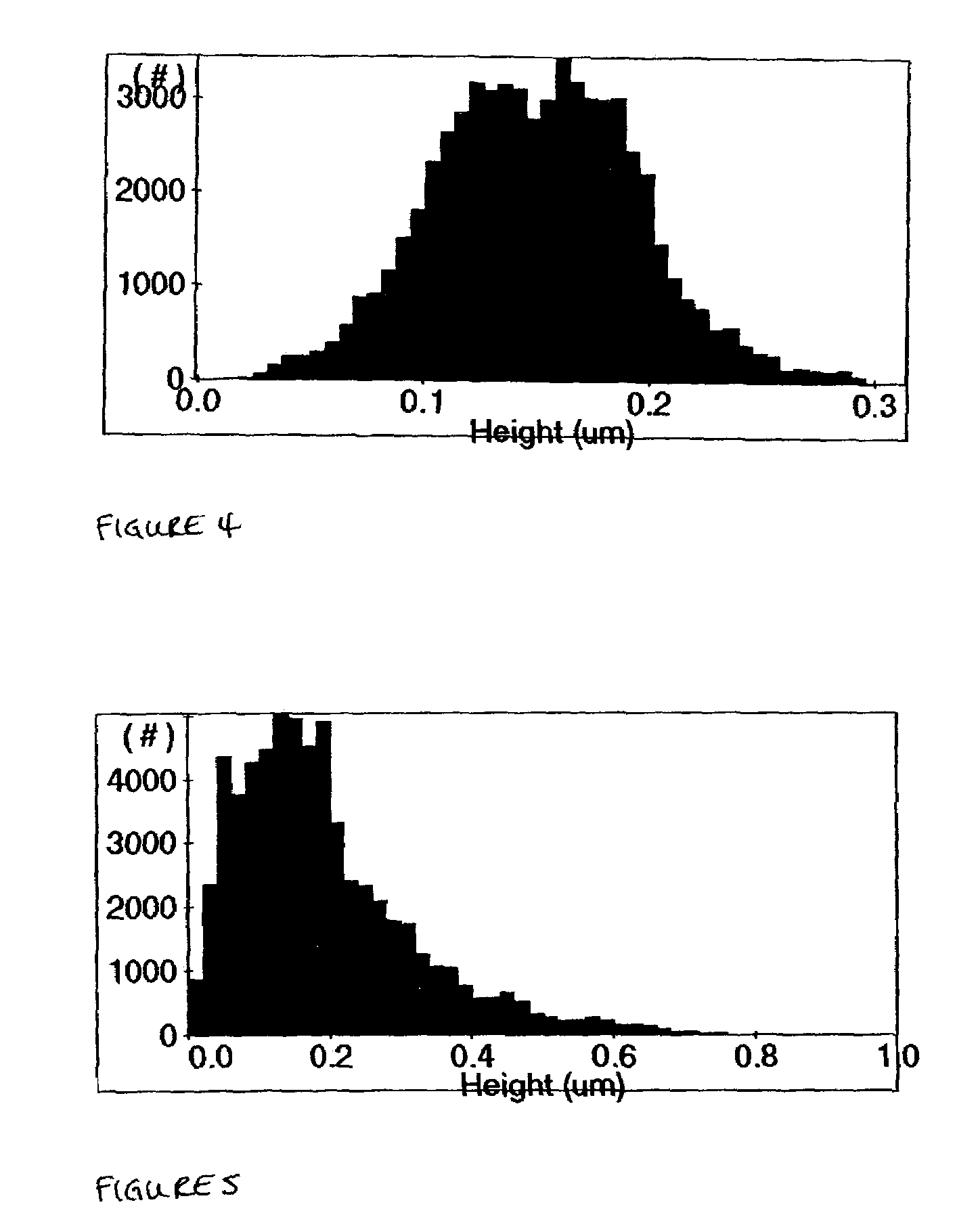
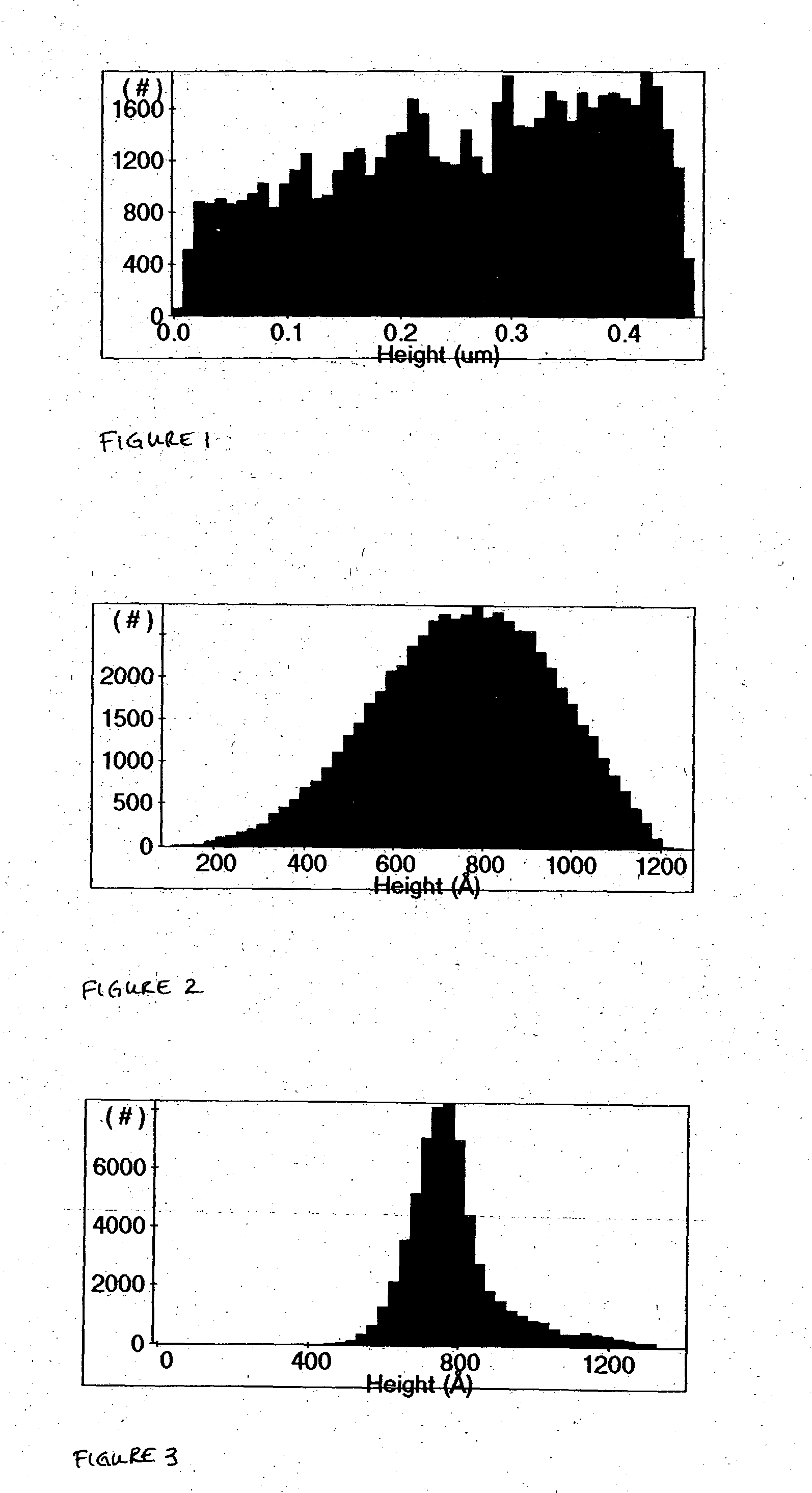
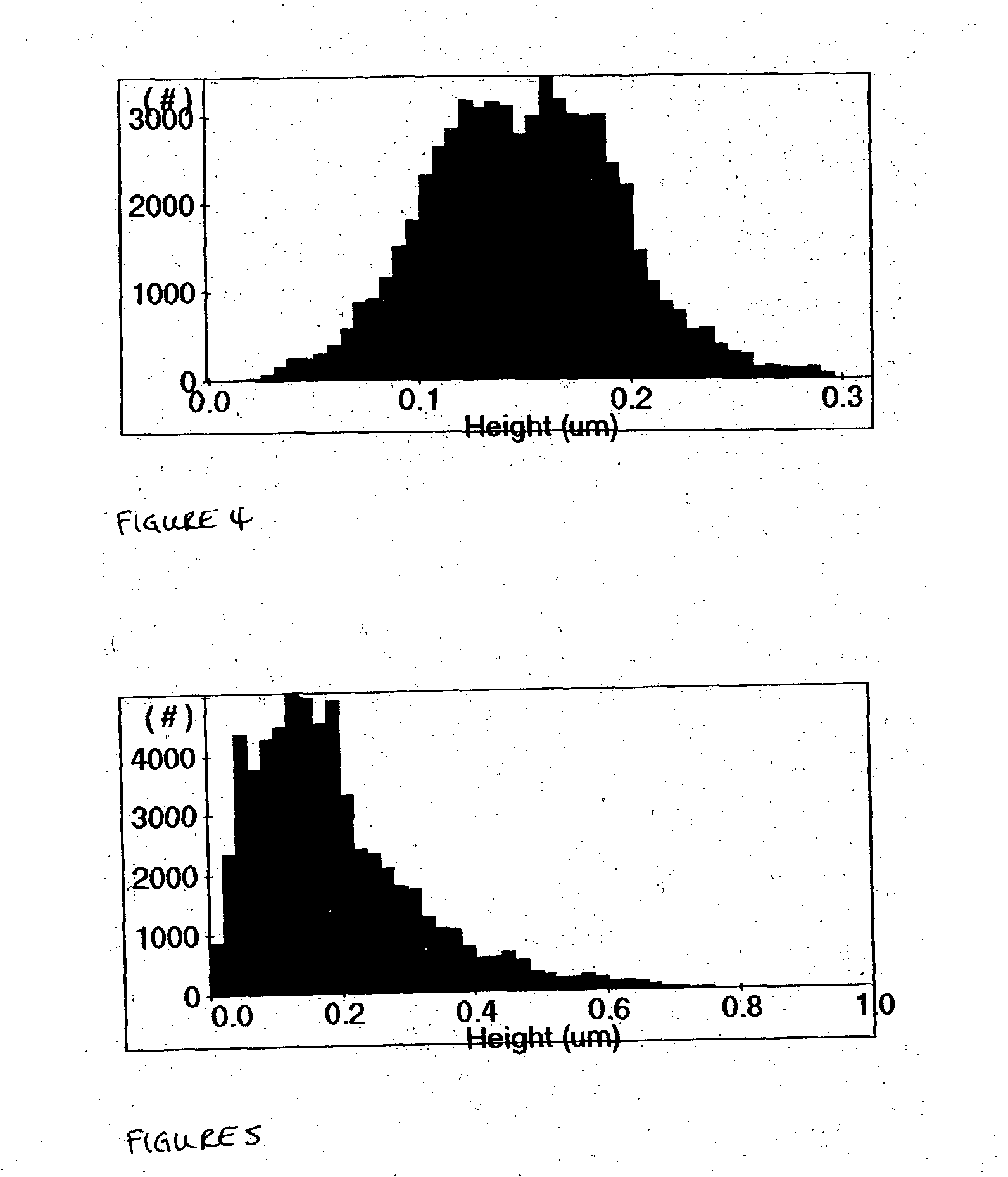
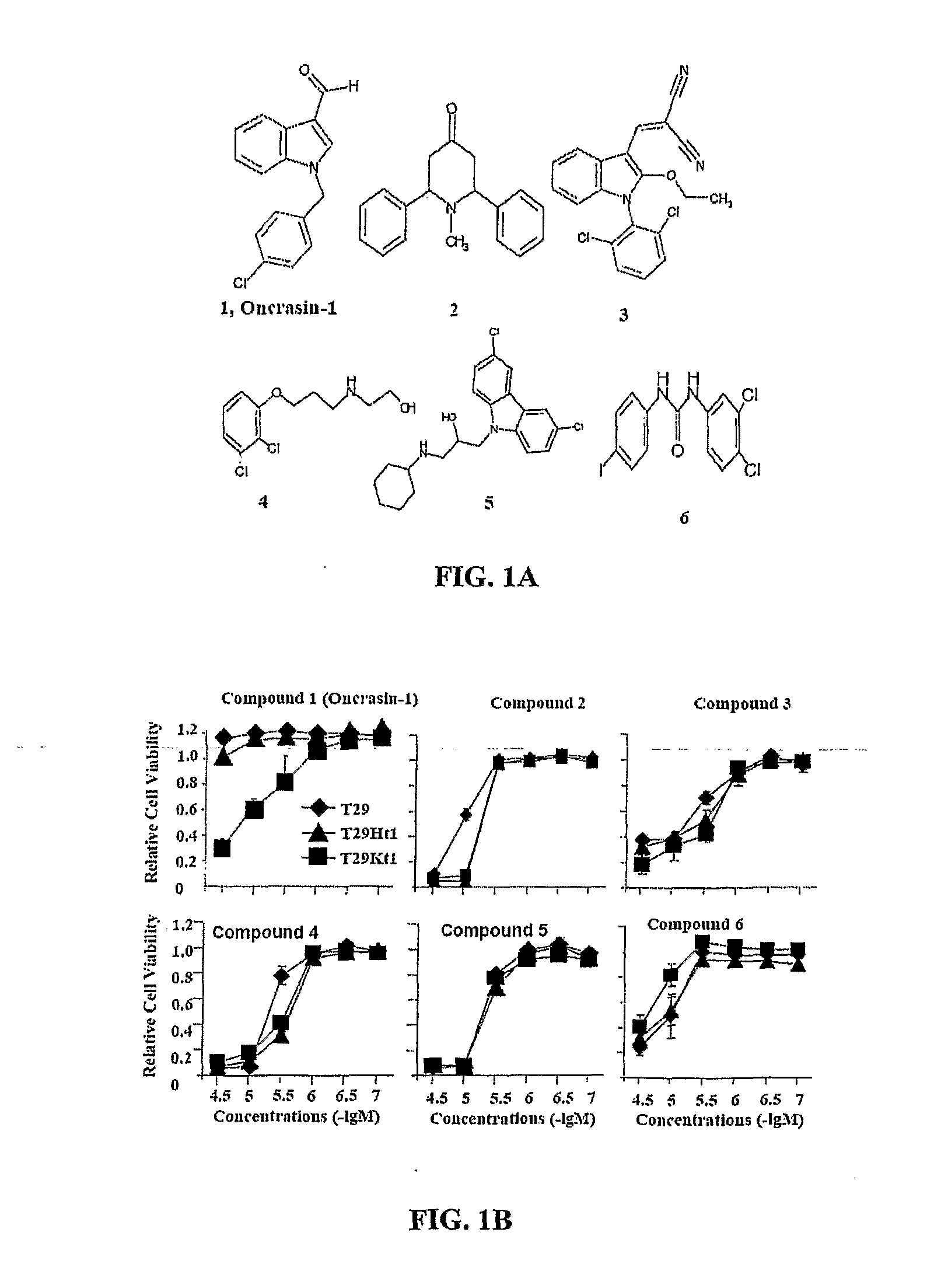
ActiveUS20090286847A1Reduce phosphorylationGrowth inhibitionBiocideOrganic active ingredients1H-indole-3-carboxaldehydePharmacology
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Device for deionizing saline solutions
InactiveUS20070034514A1Avoid problemsContinuous operationSludge treatmentGeneral water supply conservationElectricityEngineering
The invention relates to a device comprising a Laplace power generator acting on a deionizing cell provided with at least one deionizing cell comprising a first element provided with an alternate pile of membranes which are selectively ion-permeable and define concentrating chambers, deionizing chambers and a chamber on each end of the pile, a second element comprising a pile having a number of membranes equal to the first element but said membranes are electrically insulated and extend the chambers of the first element, and a third element provided with two chambers, one of them combining all concentrating chambers and end chambers, the other combining all deionizing chambers.
Owner:R CUBE PROJET
Procedure and machine for electro-inducing/stimulating deep layered muscle contractions using a biphasic faradic pulse sequence
InactiveUS20050033387A1High speedIncrease perfusionExternal electrodesArtificial respirationMuscle contractionLymphatic vessel
A procedure and machine promotes healing by causing muscle fasciculation and contraction relaxation cycles that effectively pump blood through the microcirculation, draining the venous beds and raising the tissue oxygen levels. A high phase charged system is electronically pulsed and adjusted to induce deep-layered muscle contractions, causing greatly increased flow rates of both blood and lymphatics, patency of vessels permitting, and forcing blood into the microcirculation of the treated tissue. The machine electrical waveform stimulates angiogenesis, facilitating new tissue growth and repair in the healing process and raises the metabolic rate in the treated tissues.
Owner:MICROVAS TECH
Circuit device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20140247001A1Reduce impactReduce stepsTransistorElectronic commutation motor controlEngineeringLogic circuitry
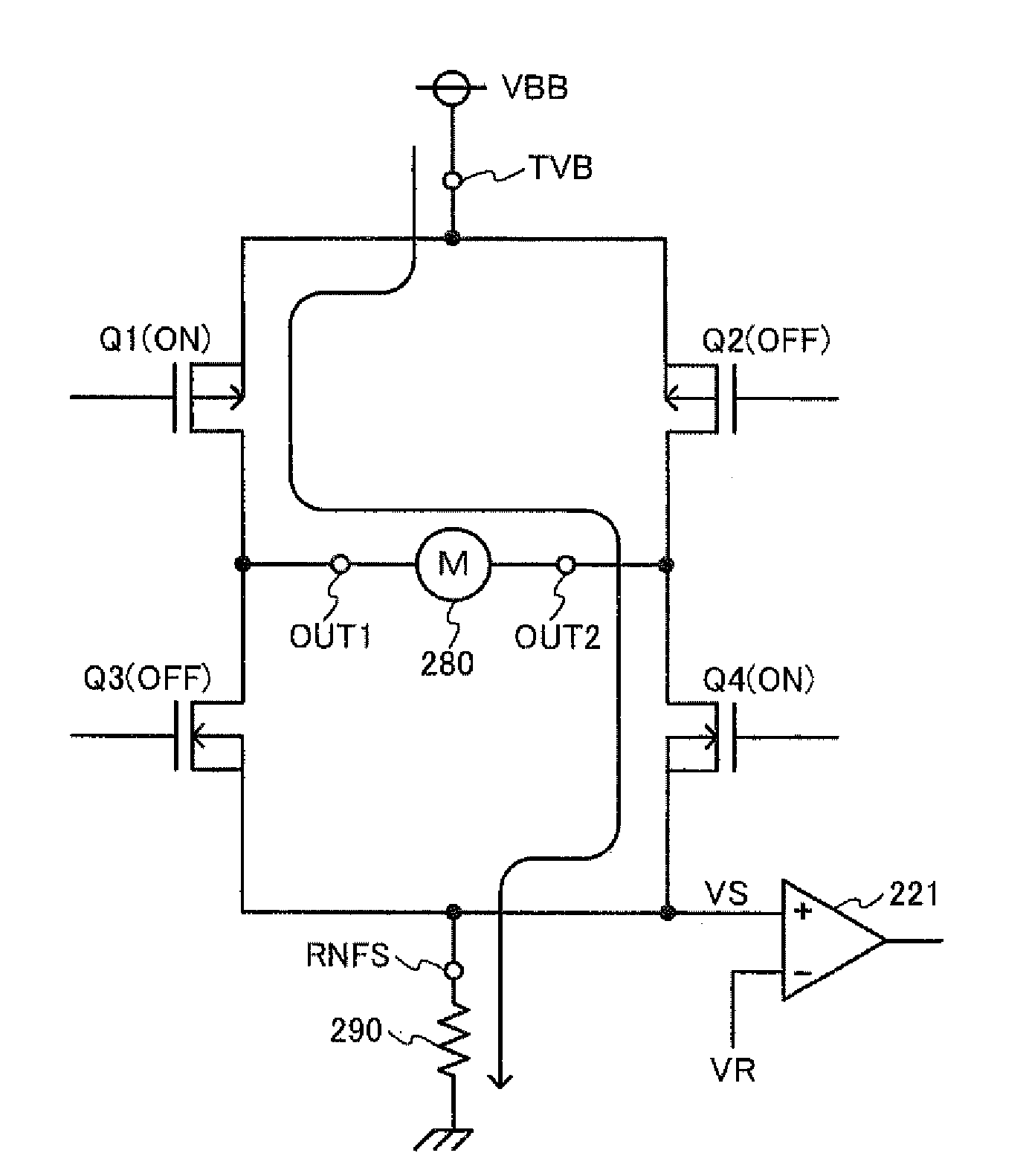
An electronic circuit includes a noise source and an analog circuit and a logic circuit that may be adversely affected by noise. At least a portion of the analog circuit and the logic circuit is formed on a buried impurity layer whose conductivity is different from that of a substrate, and at least a portion of the periphery of that portion is surrounded by an impurity layer that is different from the substrate. Thus, propagation of the noise from the noise source is prevented.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com