Patents
Literature
127results about How to "Modulate its function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
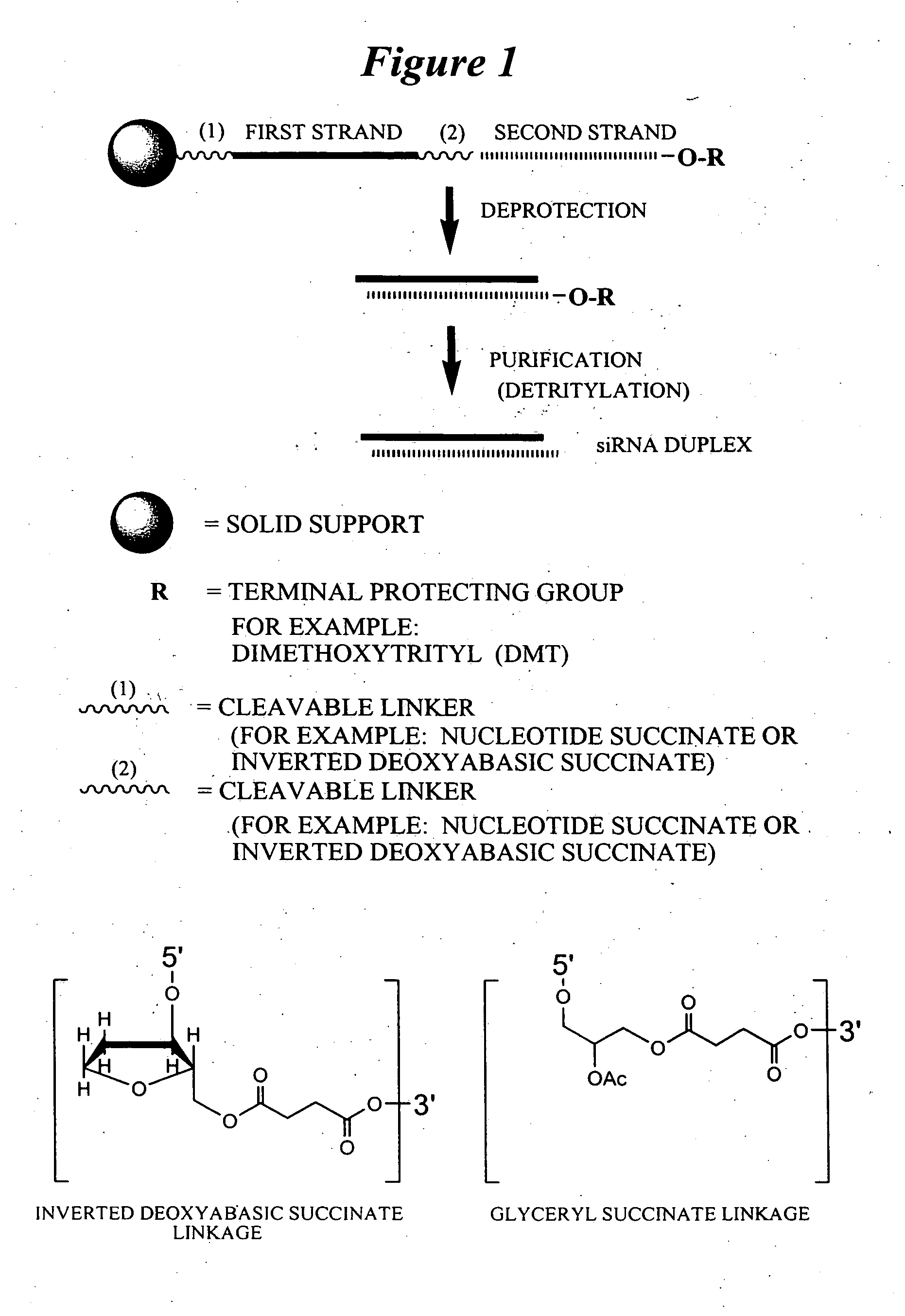
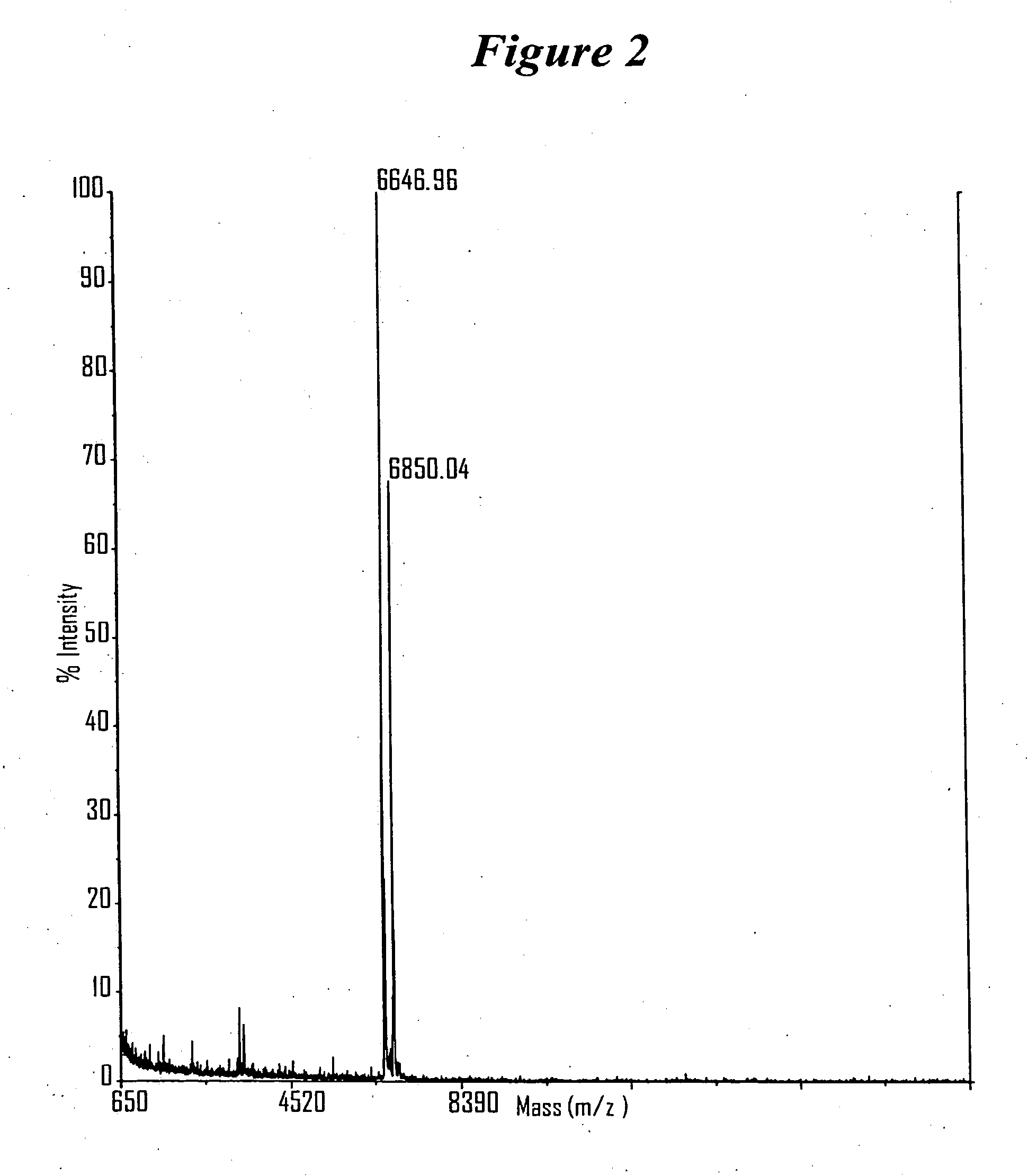
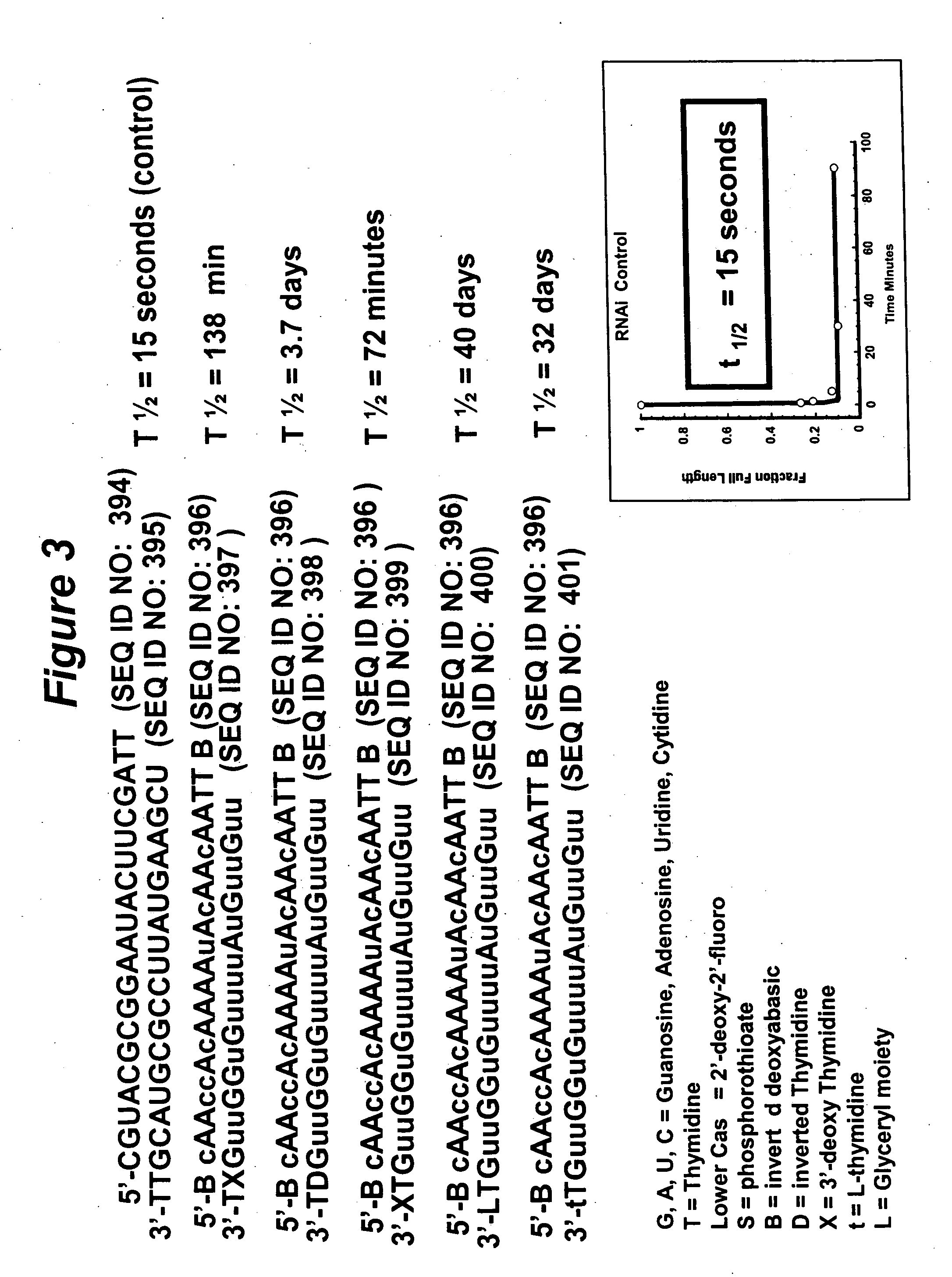
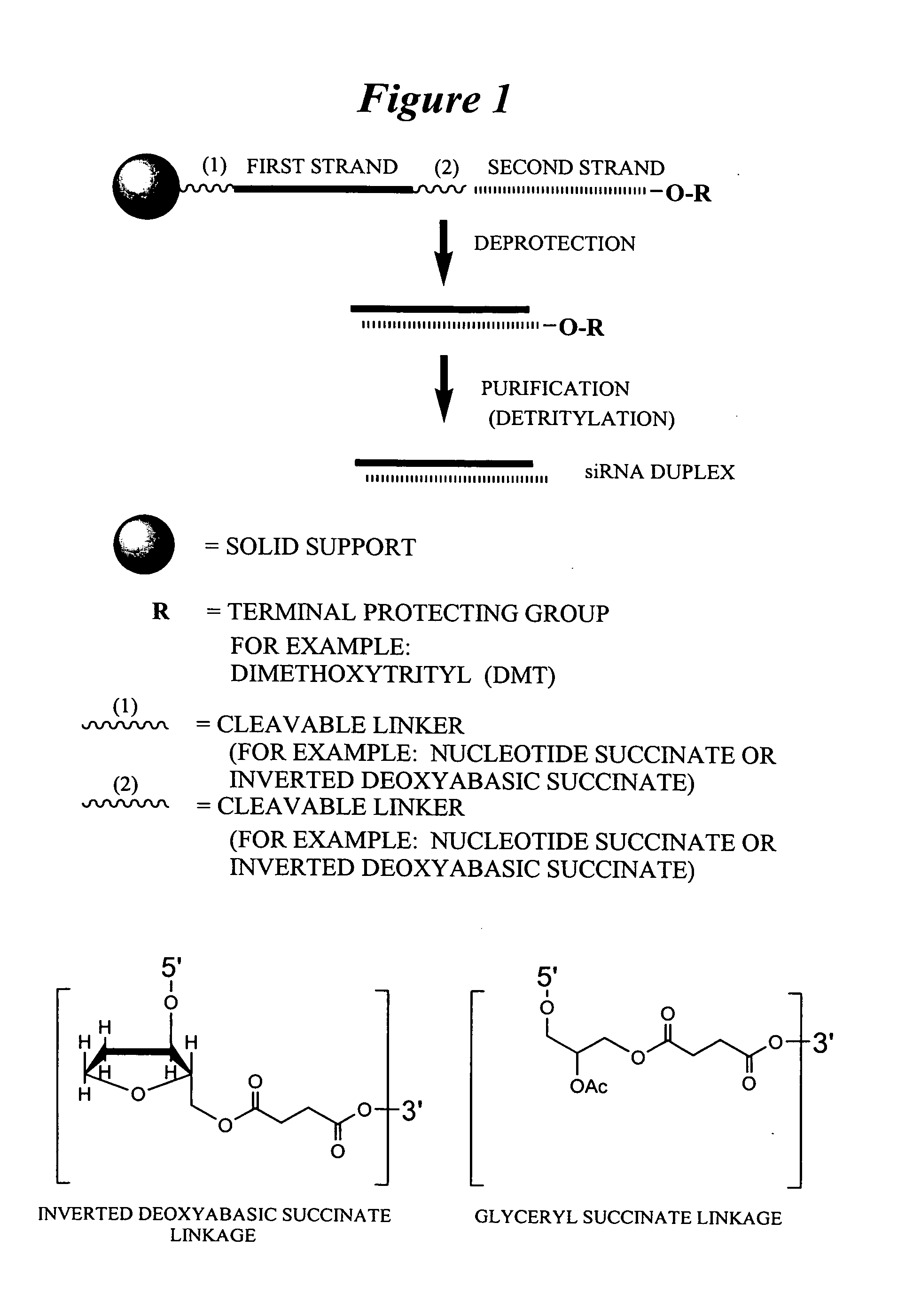
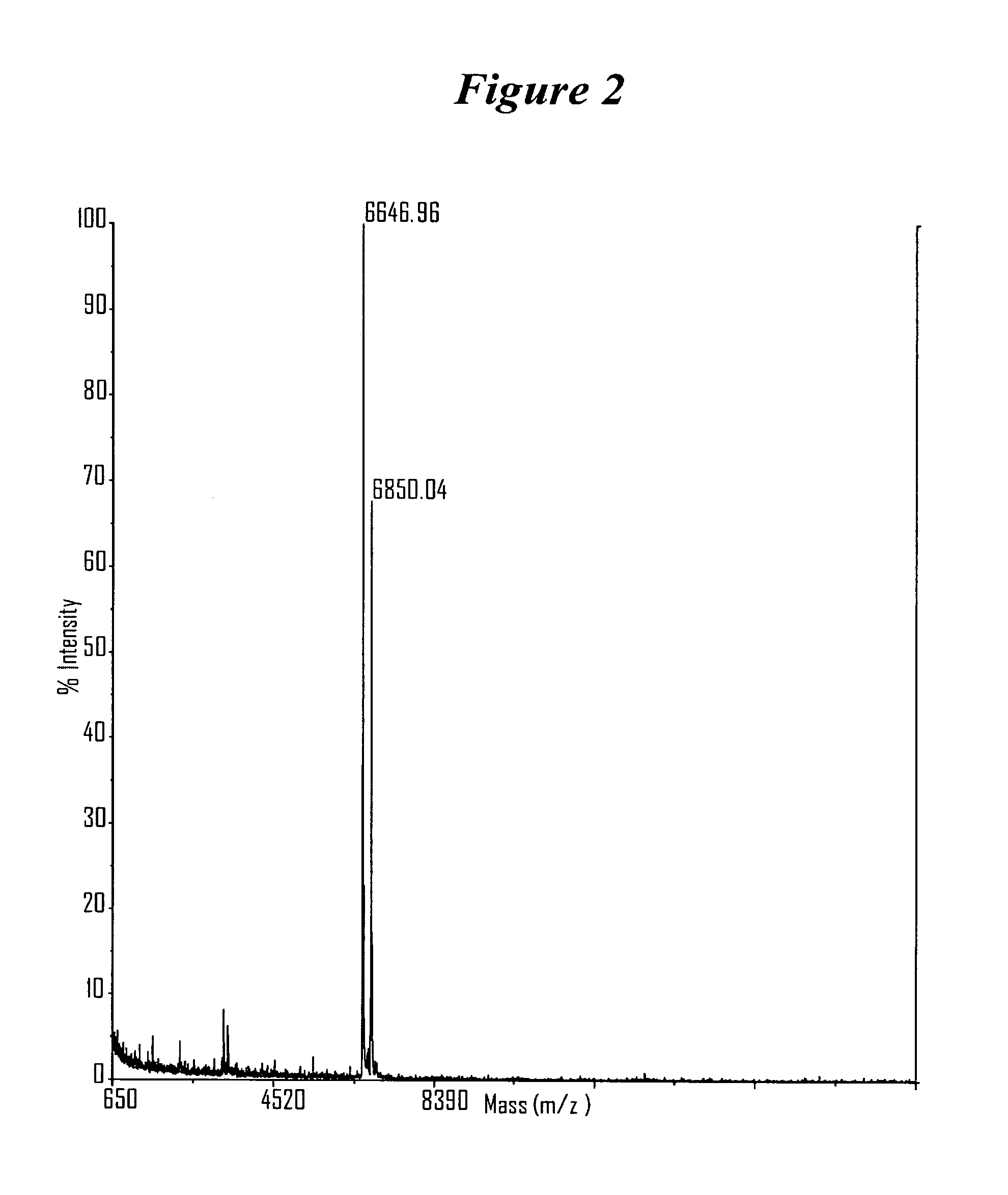
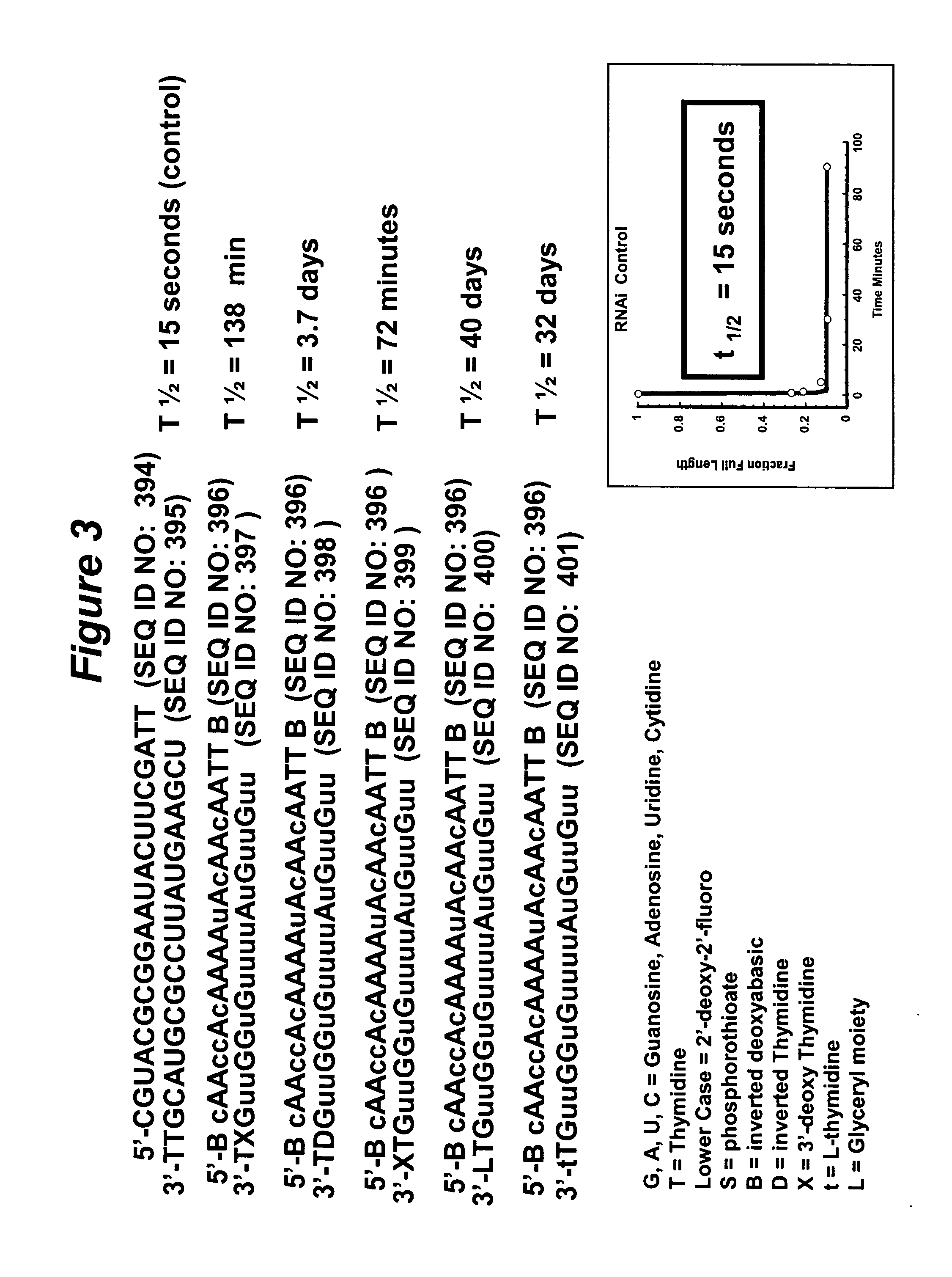
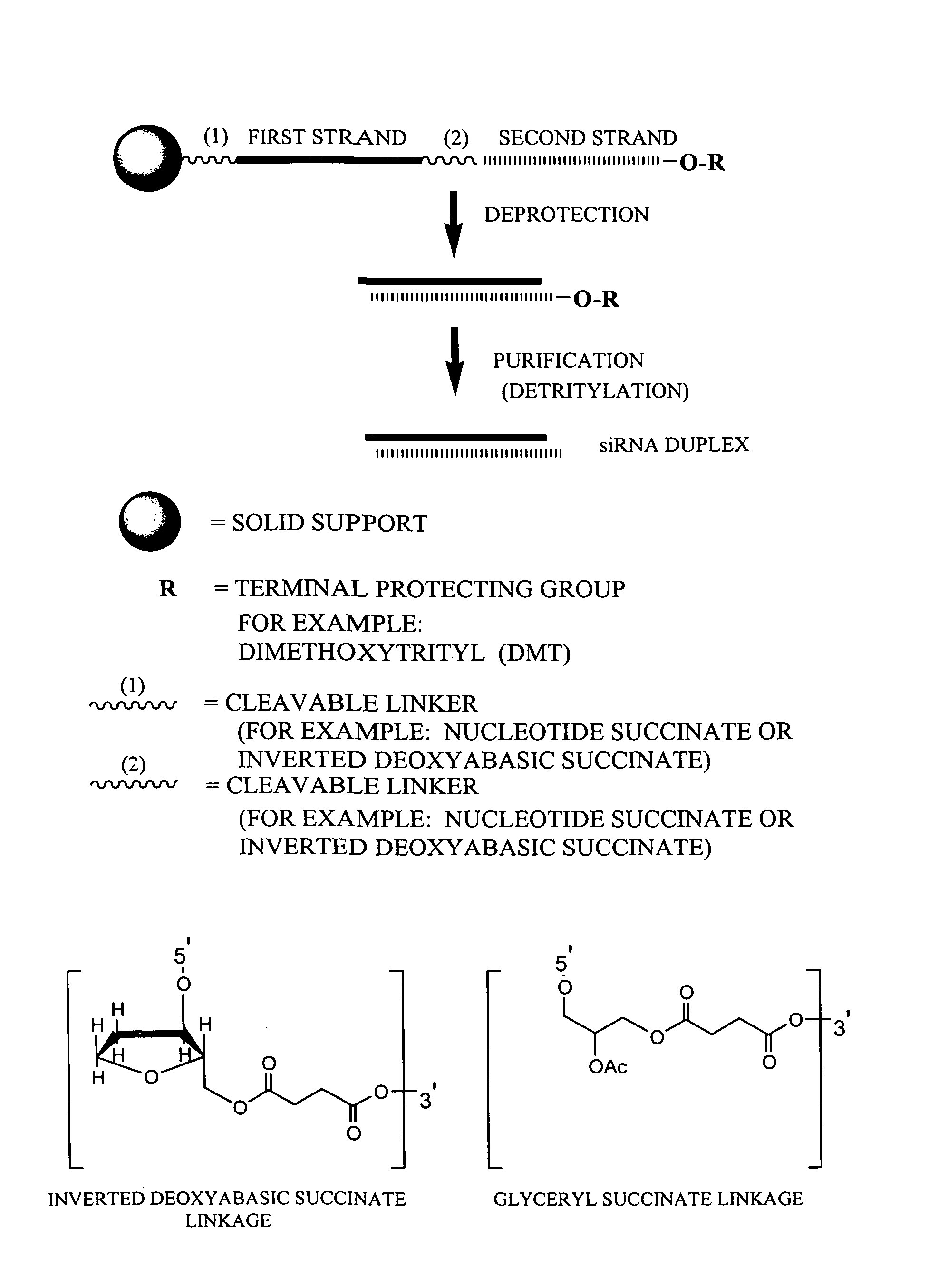
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20050020525A1Improve various propertyModulate its functionCompounds screening/testingSugar derivativesDouble strandOrganism
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIMA THERAPEUTICS ICN
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (SiNA)
InactiveUS20050032733A1Improve various propertyModulate its functionCompounds screening/testingSpecial deliveryBiological bodyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
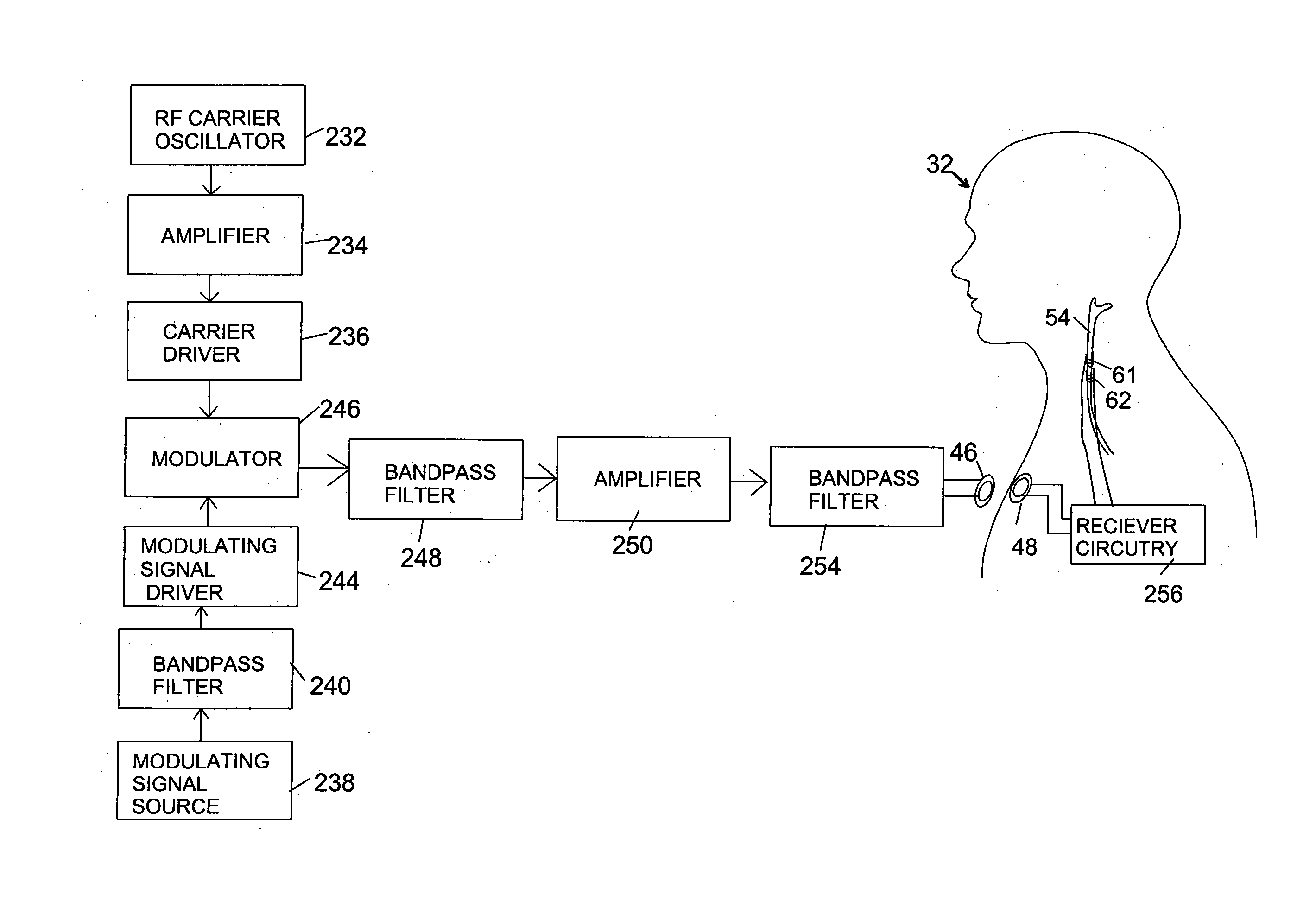
Method and system for providing therapy for autism by providing electrical pulses to the vagus nerve(s)
InactiveUS20050187590A1Modulate its functionSpinal electrodesHead electrodesRechargeable cellImplanted device
A method and system to provide electrical pulses for neuromodulating vagus nerve(s) to provide therapy for autism, comprises implantable and external components. The pulsed electrical stimulation to vagus nerve(s) may be provided using one of the following stimulation systems, such as: a) an implanted stimulus-receiver with an external stimulator; b) an implanted stimulus-receiver comprising a high value capacitor for storing charge, used in conjunction with an external stimulator; c) a programmer-less implantable pulse generator (IPG) which is operable with a magnet; d) a microstimulator; e) a programmable implantable pulse generator; f) a combination implantable device comprising both a stimulus-receiver and a programmable implantable pulse generator (IPG); and g) an implantable pulse generator (IPG) comprising a rechargeable battery. In one embodiment, the external components such as the programmer or external stimulator may comprise a telemetry means for networking. The telemetry means therefore allows for interrogation or programming of implanted device, from a remote location over a wide area network.
Owner:NEURO & CARDIAC TECH
RNA Interference Mediated Inhibition of Gene Expression Using Chemically Modified Short Interfering Nucleic Acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20100240730A1Improve various propertyModulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseNucleic acid sequencing
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Non-stochastic generation of genetic vaccines
InactiveUS6479258B1Improve abilitiesPotent and direct effect on proliferation and Ig-synthesisHydrolasesLibrary screeningAntigenMutagenic Process
This invention provides methods of obtaining vaccines by use of non-stochastic methods of directed evolution (DirectEvolution(TM)). These methods include non-stochastic polynucleotide site-satuaration mutagenesis (Gene Site Saturation Mutagenesis(TM)) and non-stochastic polynucleotide reassembly (GeneReassembly(TM)). Through use of the claimed methods, vectors can be obtained which exhibit increased efficacy for use as genetic vaccines. Vectors obtained by using the methods can have, for example, enhanced antigen expression, increased uptake into a cell, increased stability in a cell, ability to tailor an immune response, and the like.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Non-stochastic generation of genetic vaccines and enzymes
InactiveUS6713279B1Improve abilitiesPotent and direct effect on proliferation and Ig-synthesisAnimal cellsHydrolasesAntigenBiological property
This invention provides methods of obtaining novel polynucleotides and encoded polypeptides by use of non-stochastic methods of directed evolution (DirectEvolution(TM)). These methods include non-stochastic polynucleotide site-saturation mutagenesis (Gene Site Saturation Mutagenesis(TM)) and non-stochastic polynucleotide reassembly (GeneReassembly(TM)). Through use of the claimed methods, genetic vaccines, enzymes, and other desirable molecules can be evolved towards desirable properties. For example, vaccine vectors can be obtained that exhibit increased efficacy for use as genetic vaccines. Vectors obtained by using the methods can have, for example, enhanced antigen expression, increased uptake into a cell, increased stability in a cell, ability to tailor an immune response, and the like. This invention provides methods of obtaining novel enzymes that have optimized physical & / or biological properties. Furthermore, this invention provides methods of obtaining a variety of novel biologically active molecules, in the fields of antibiotics, pharmacotherapeutics, and transgenic traits.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
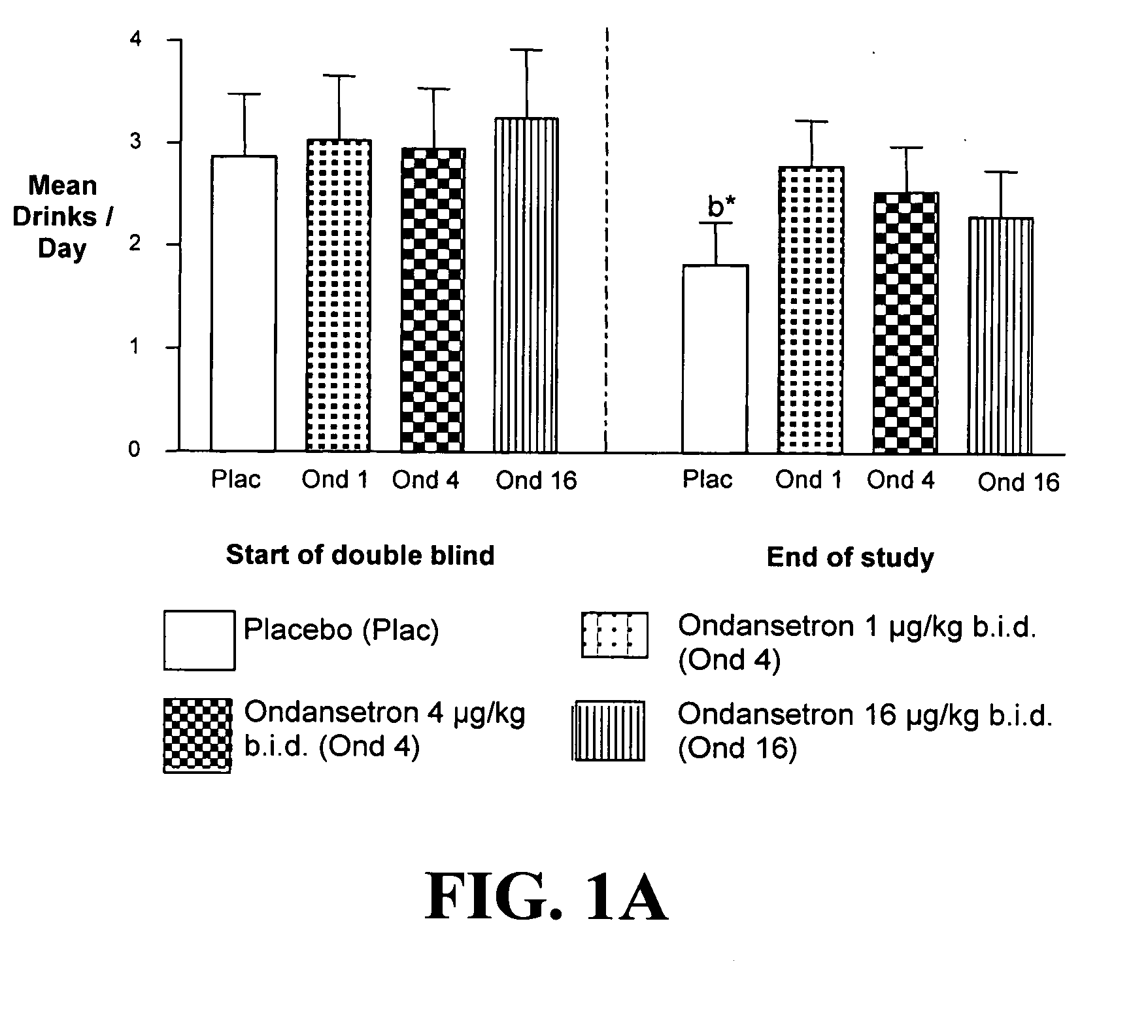
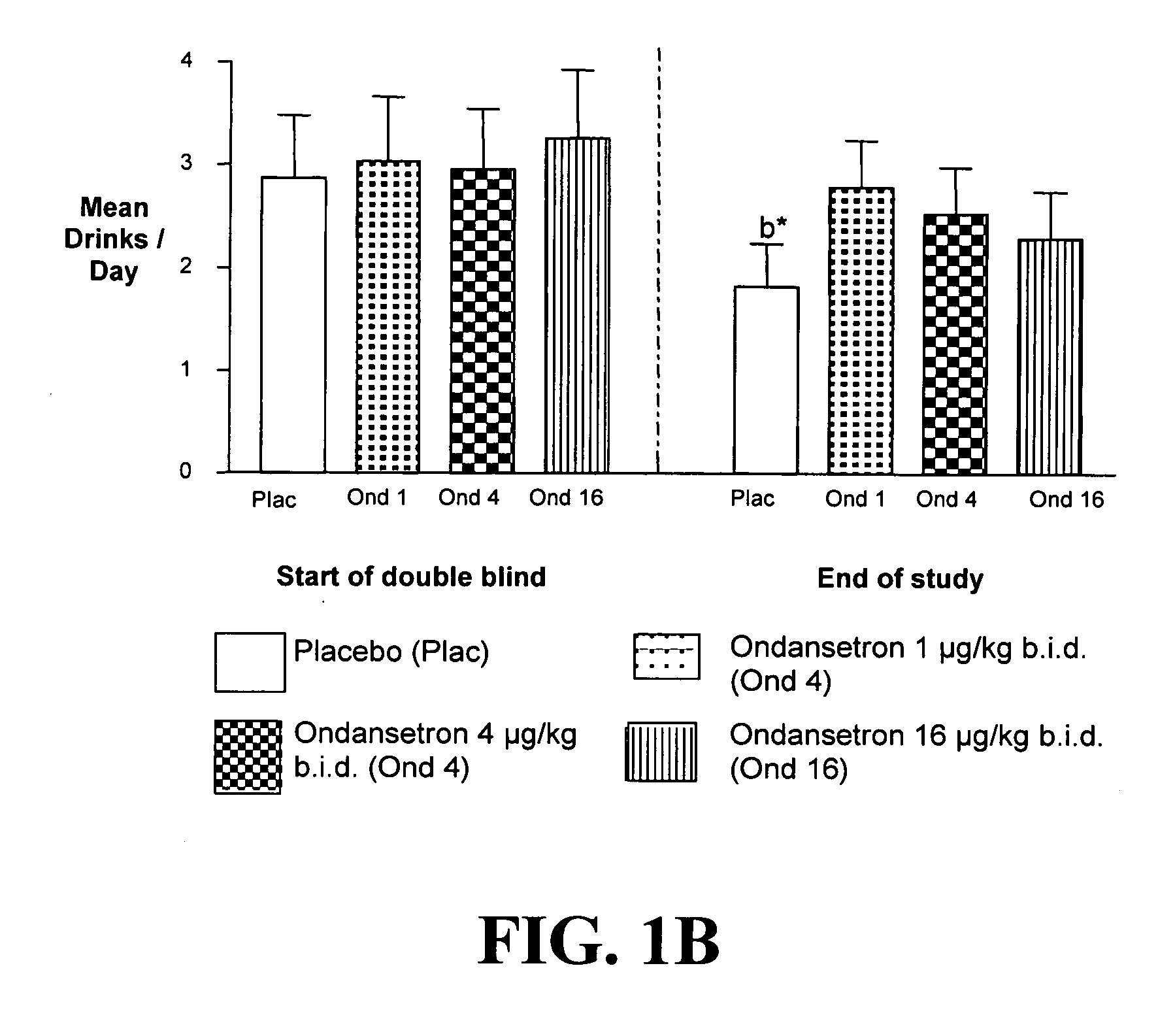
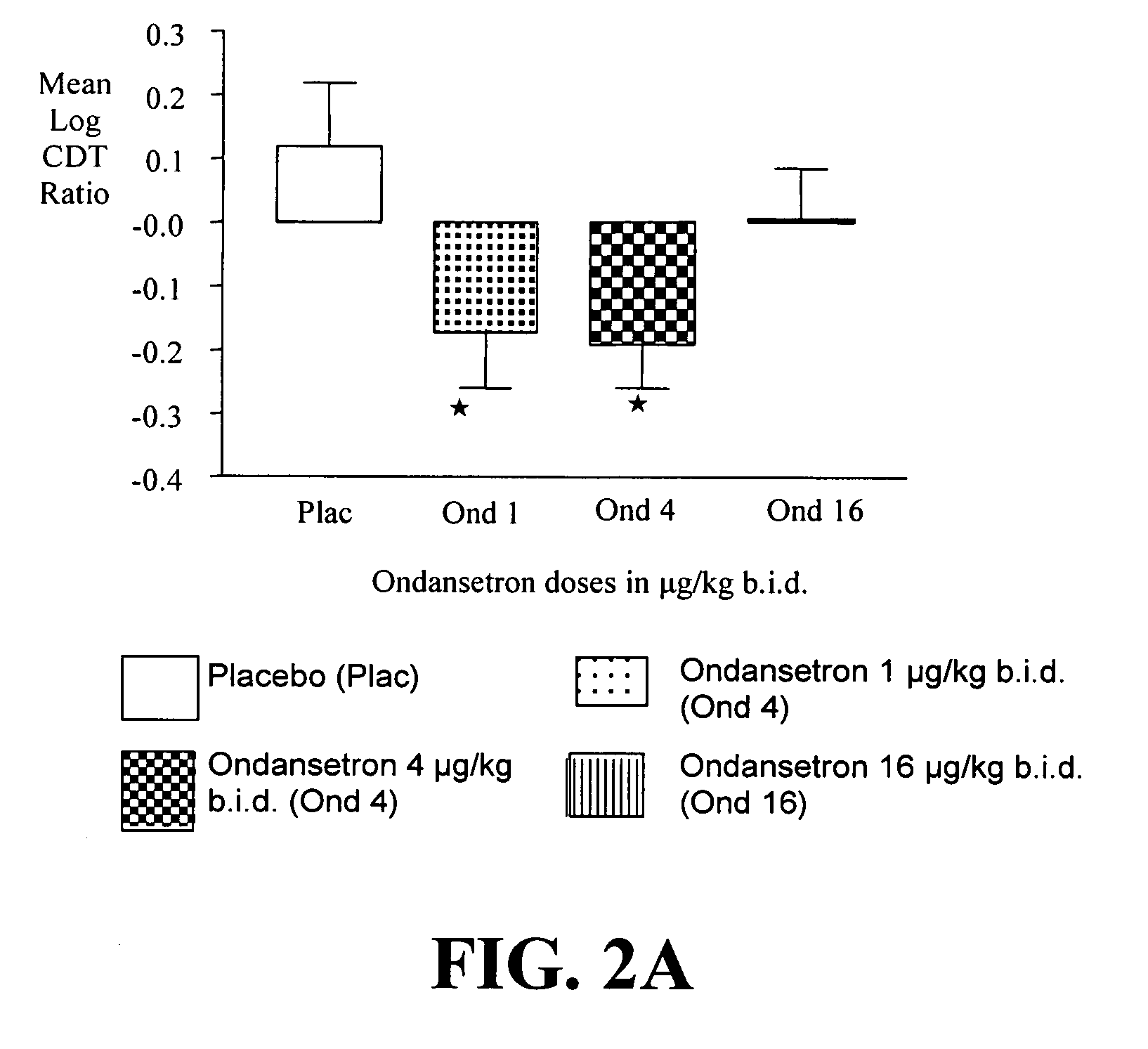
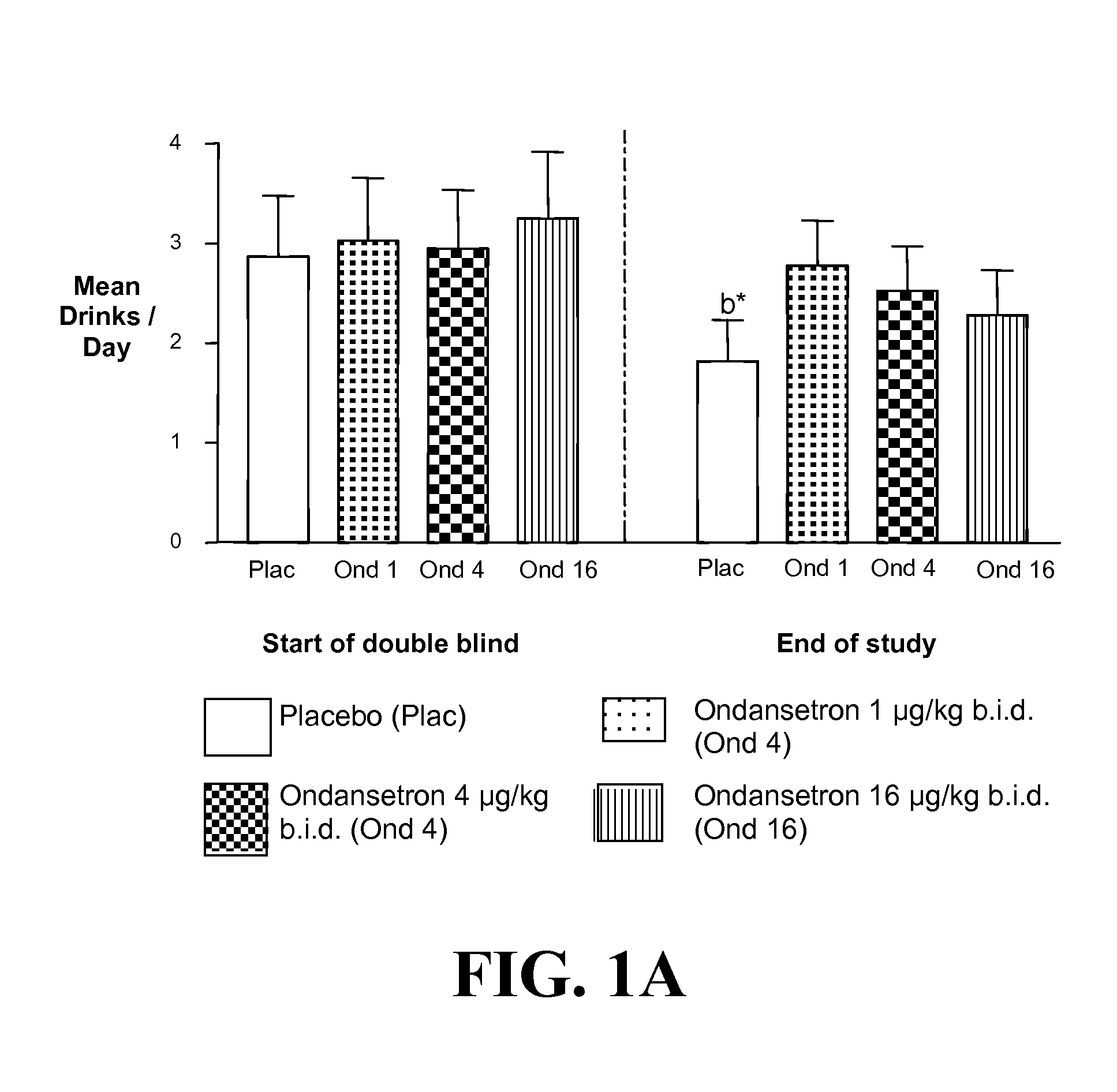
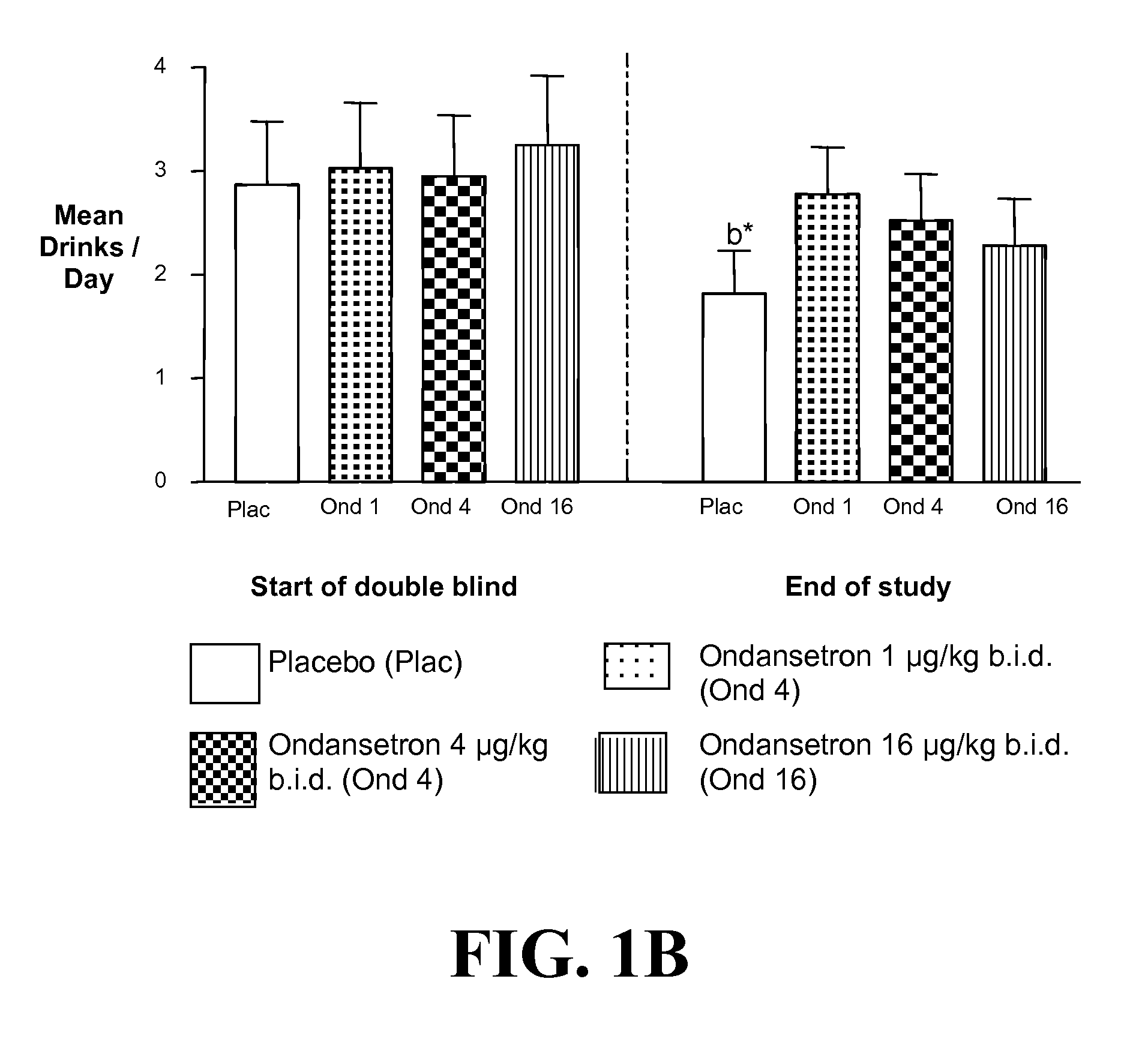
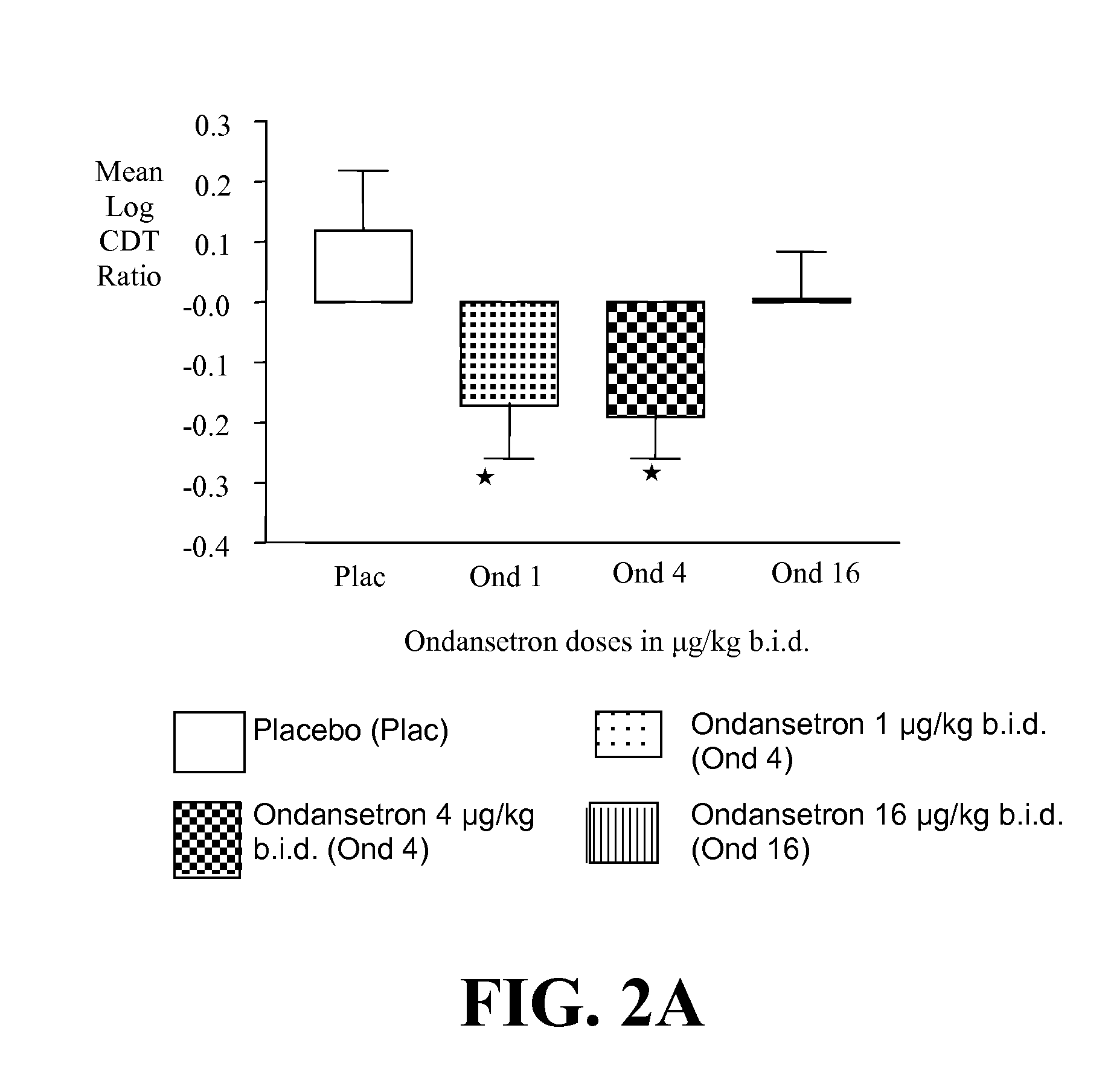
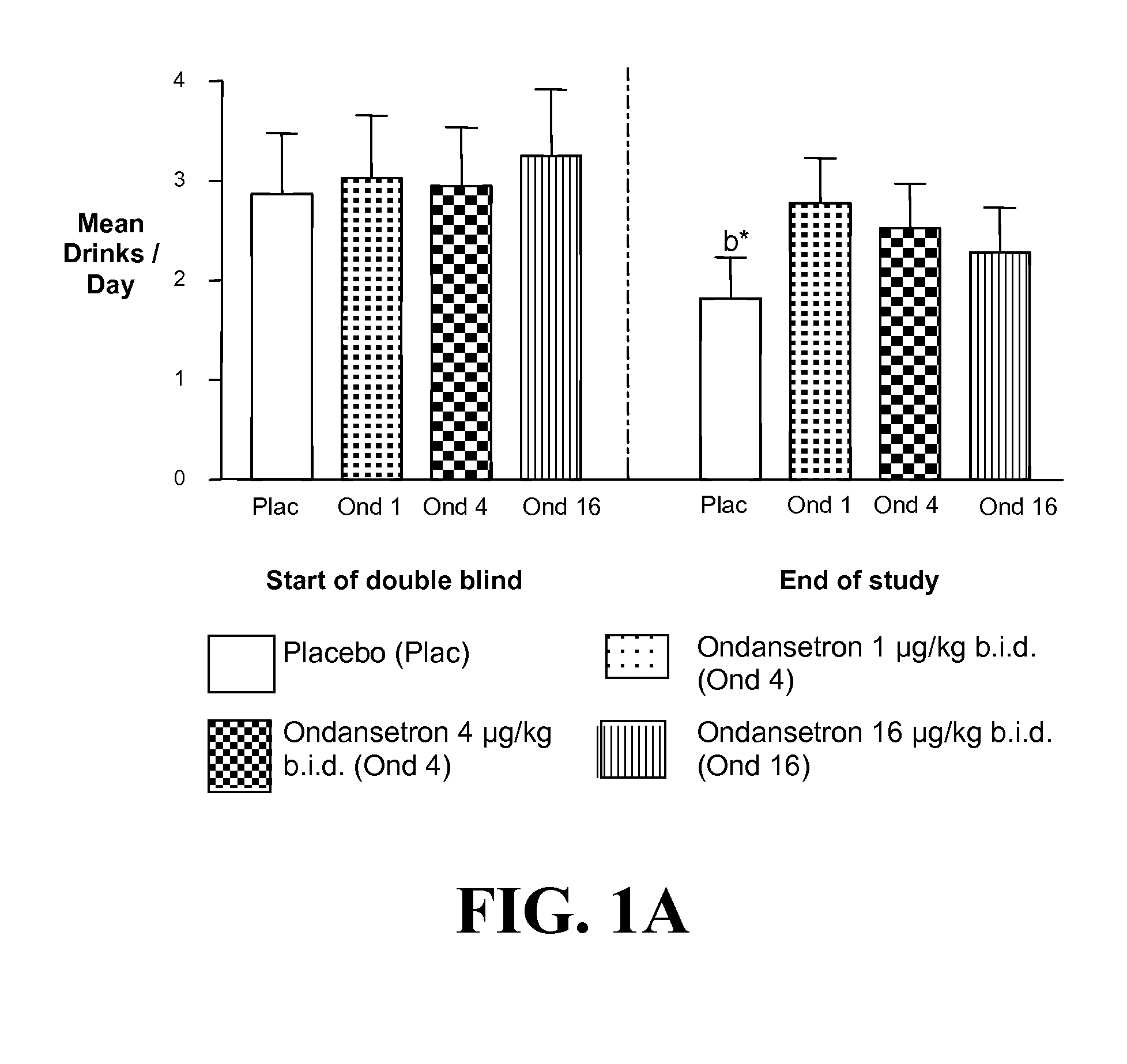
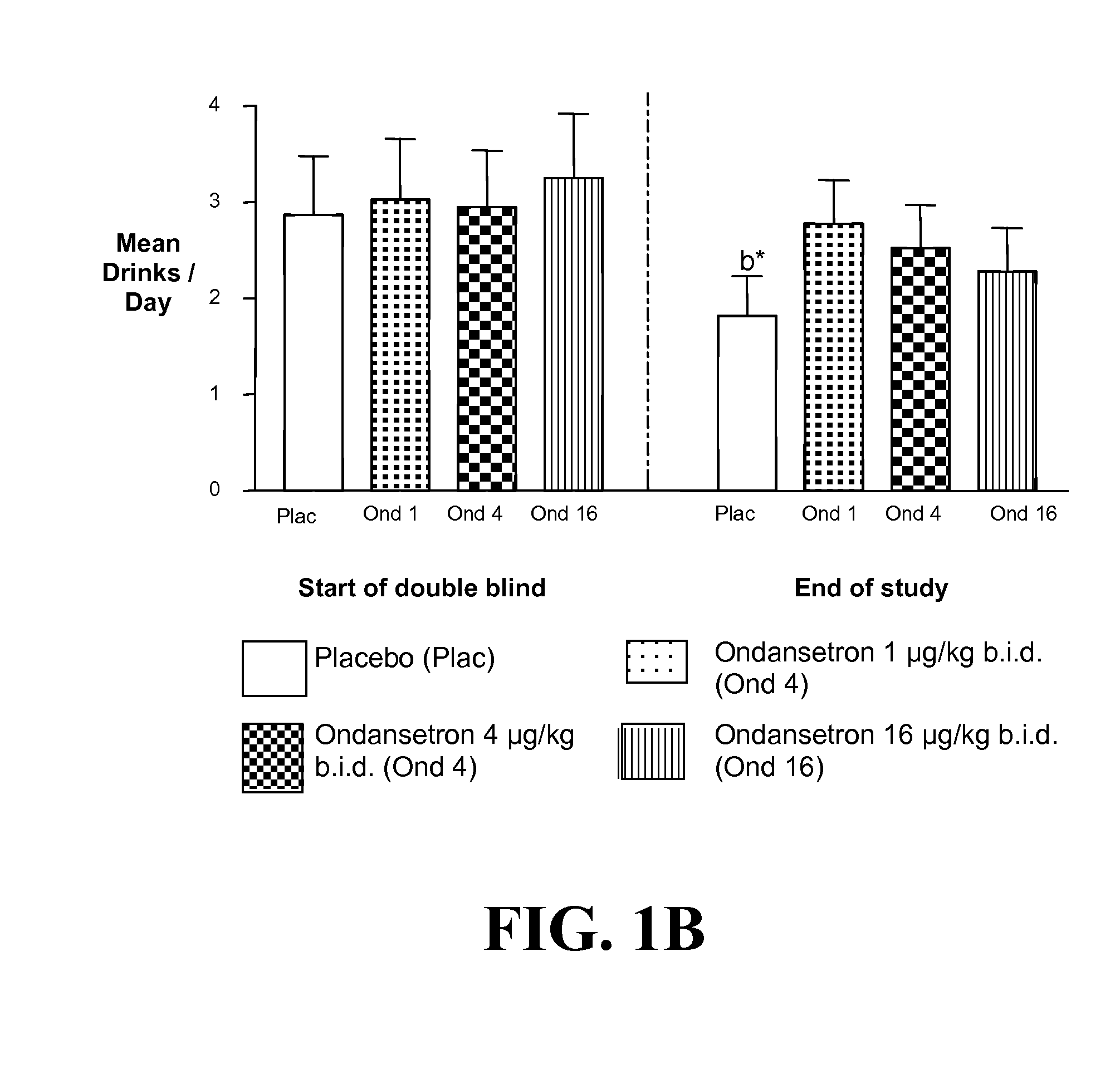
Medication Combinations for the Treatment of Alcoholism and Drug Addiction
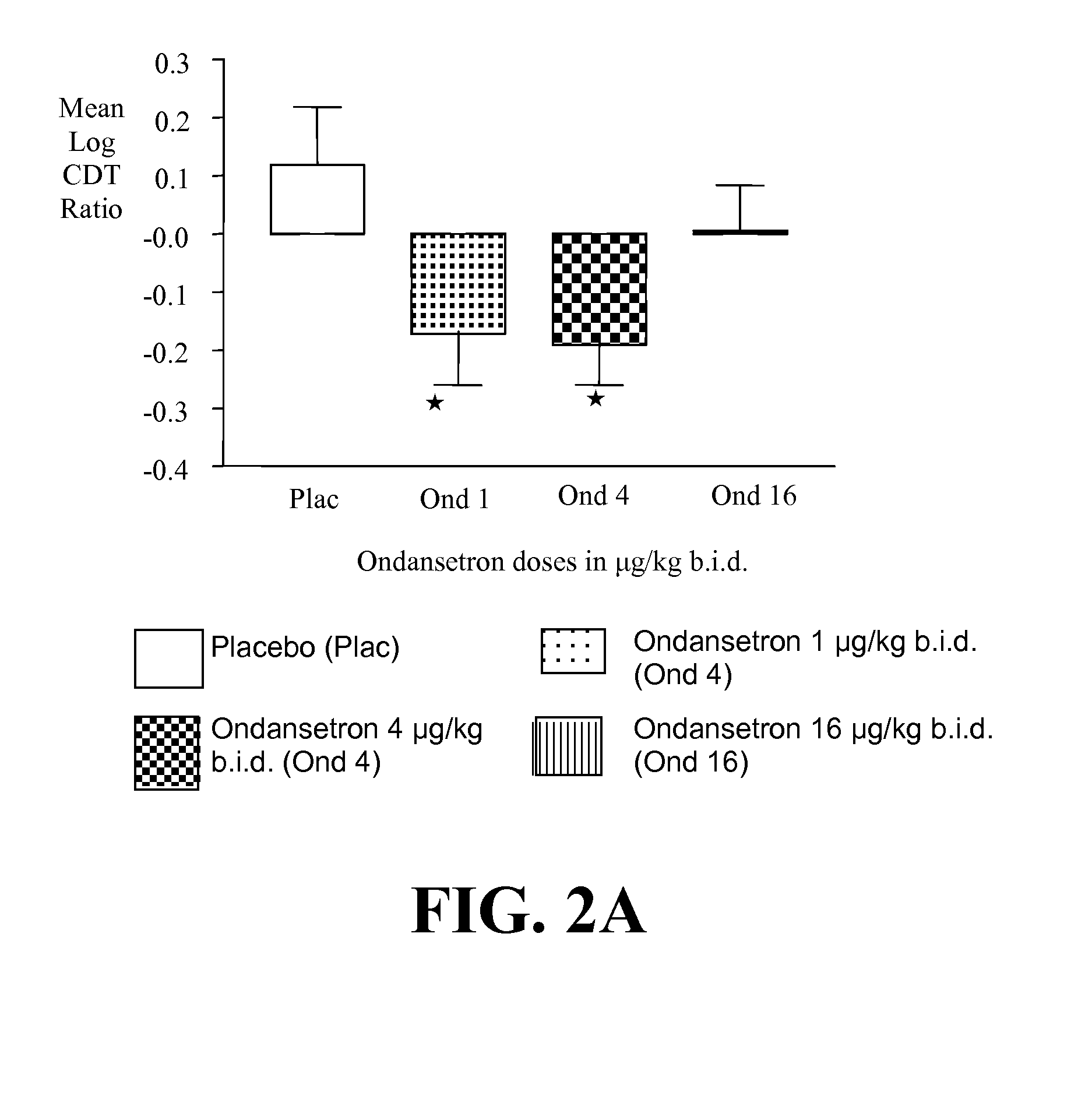
InactiveUS20110065628A1Decrease and cessationReverses effectBiocideNervous disorderAlcoholismsOndansetron
The present invention provides for the use of combinations of drugs to treat addictive disorders. More specifically, the present invention provides compositions and methods for treating disorders using combinations of drugs such as topiramate, ondansetron, and naltrexone.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
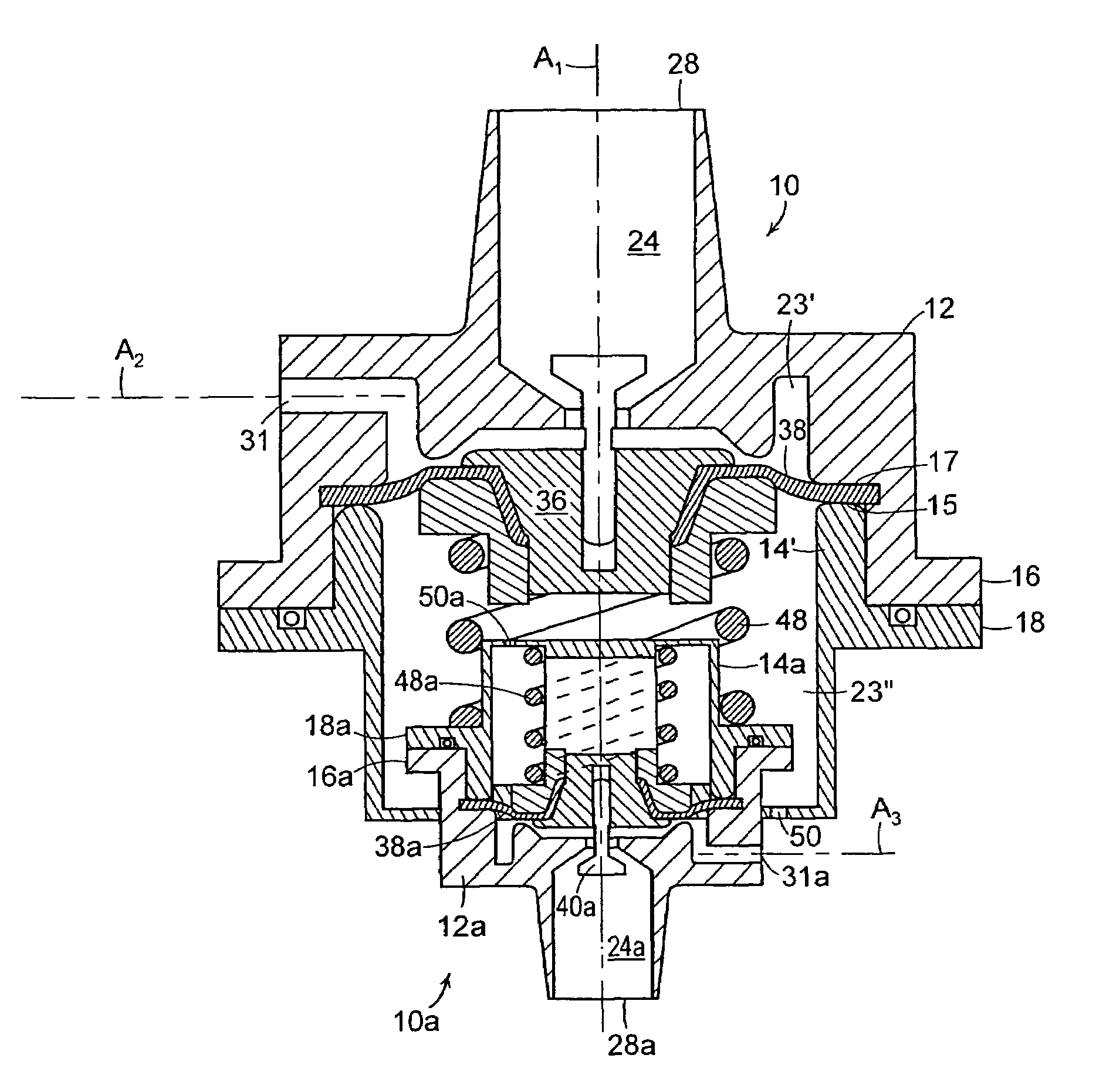
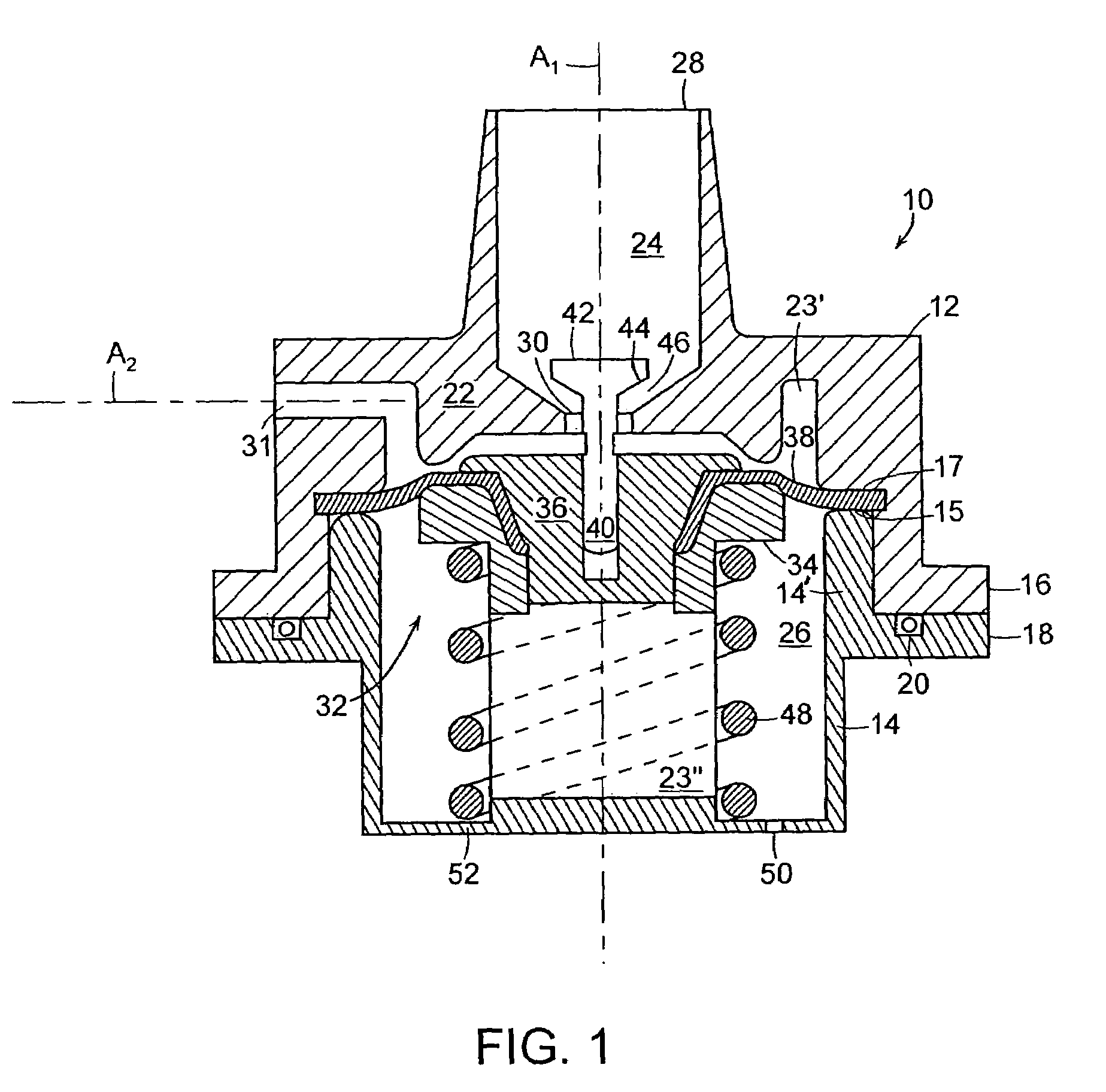
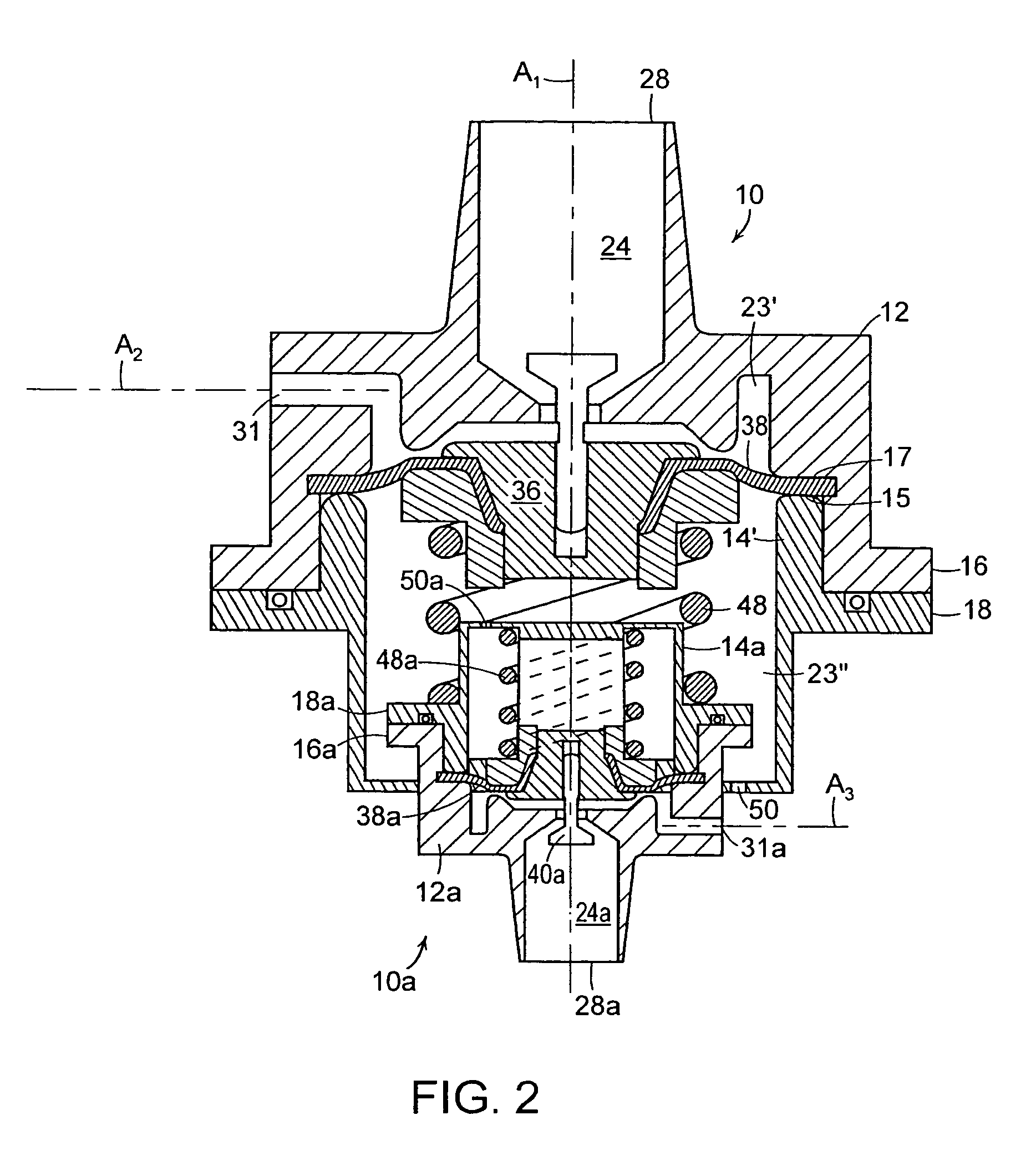
Constant flow valve assembly
InactiveUS7363938B1Avoid flowModulate its functionOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEqualizing valvesVALVE PORTVariable pressure
A dual valve assembly includes two regulating valves. Each valve includes an outer housing comprised of a cap joined to a base. The housing is internally subdivided by a barrier wall into a head section and a base section, the latter being further subdivided by a modulating assembly into a fluid chamber and a spring chamber. An inlet and a 90° outlet in the cap communicate with the fluid chamber. Fluid at a variable pressure is admitted into the fluid chamber via the inlet, with the modulating assembly serving to maintain the fluid exiting the fluid chamber via the outlet at a substantially constant pressure. A smaller one of the valves has its base nested within the spring chamber of the other larger valve.
Owner:GLOBAL AGRI TECH & ENG
Methods of modulating immune function
ActiveUS20120219559A1Modulate its functionAdjust immune functionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCTLA-4Autoimmune disease
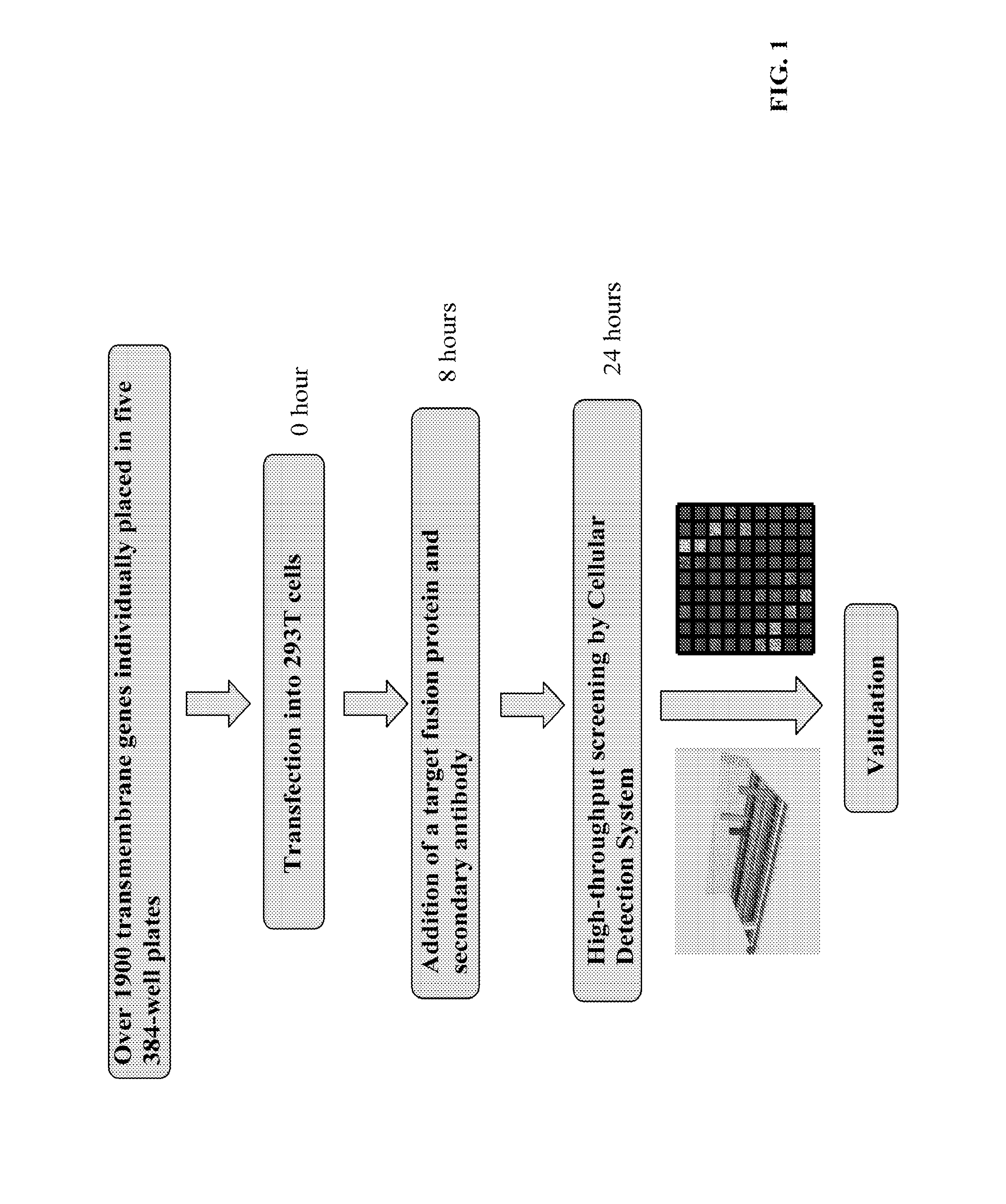
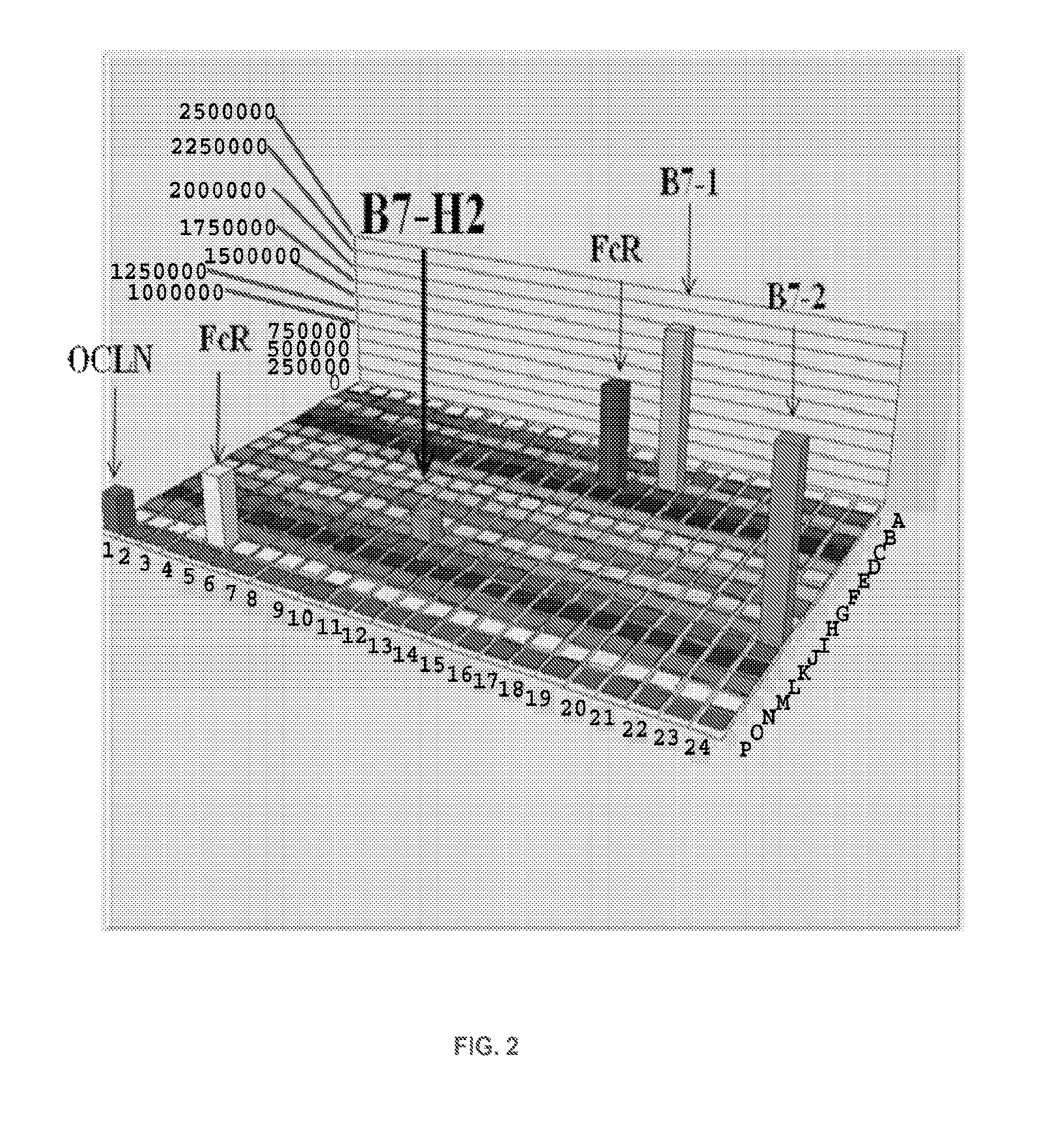
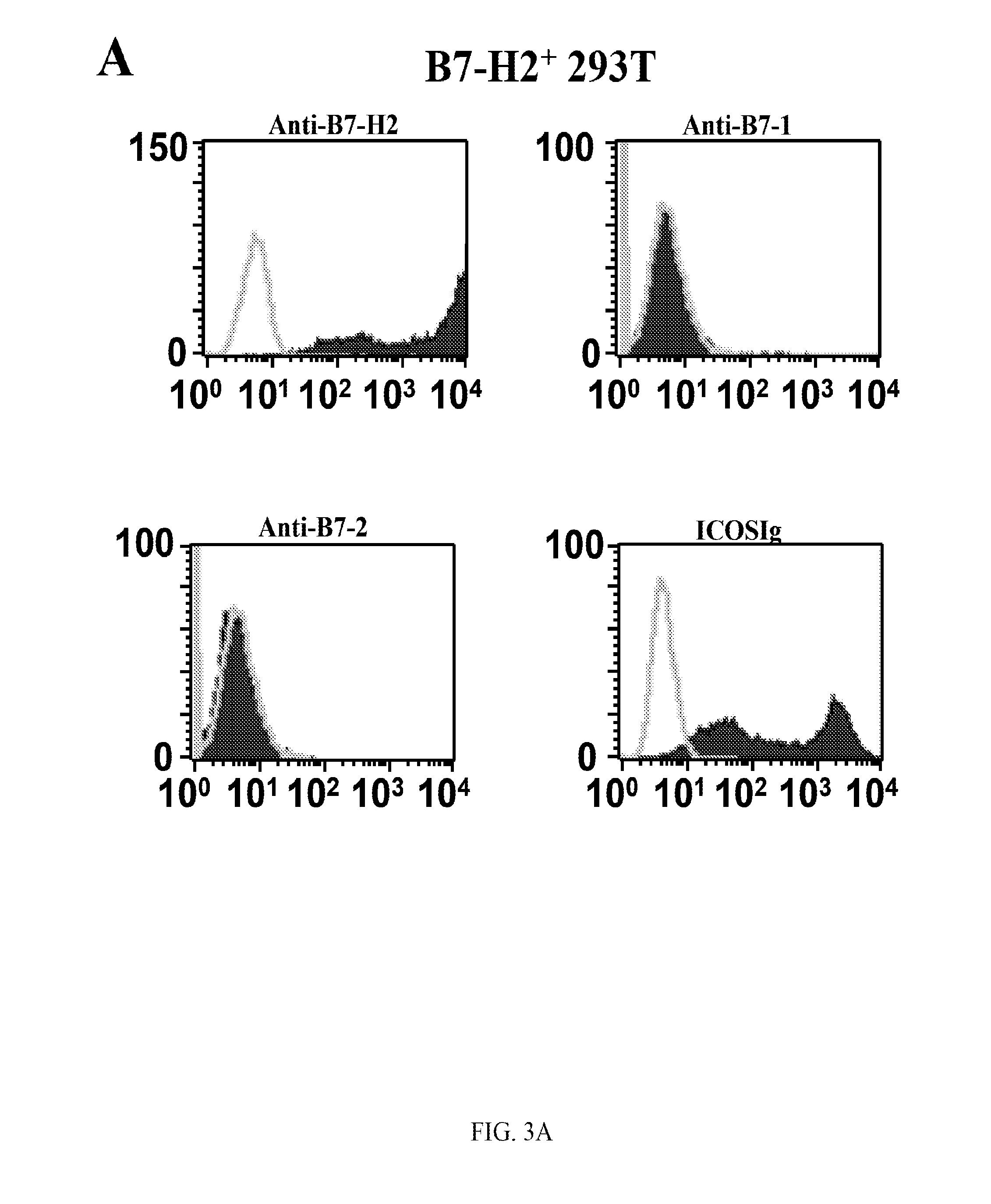
Presented herein are therapeutic agents that modulate one or more immune functions and uses of such therapeutic agents in the prevention, treatment and management of diseases. In one aspect, the therapeutic agents modulate one or more signal transduction pathways induced by the binding of B7-H7 to B7-H7CR, or the binding of B7-H2 to either ICOS, CD28, or CTLA-4. In another aspect, the therapeutic agents modulate the binding of B7-H7 to B7-H7CR, or the binding of B7-H2 to either ICOS, CD28, or CTLA-4. The therapeutic agents can be used in the prevention, treatment and / or management of diseases in which it might be useful to modulate one or more immune functions (e.g., cancer, infectious disease, autoimmune disease, and transplantation rejection). In another aspect, presented herein are methods for identifying receptor-ligand interactions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Treatment of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to tnfr2
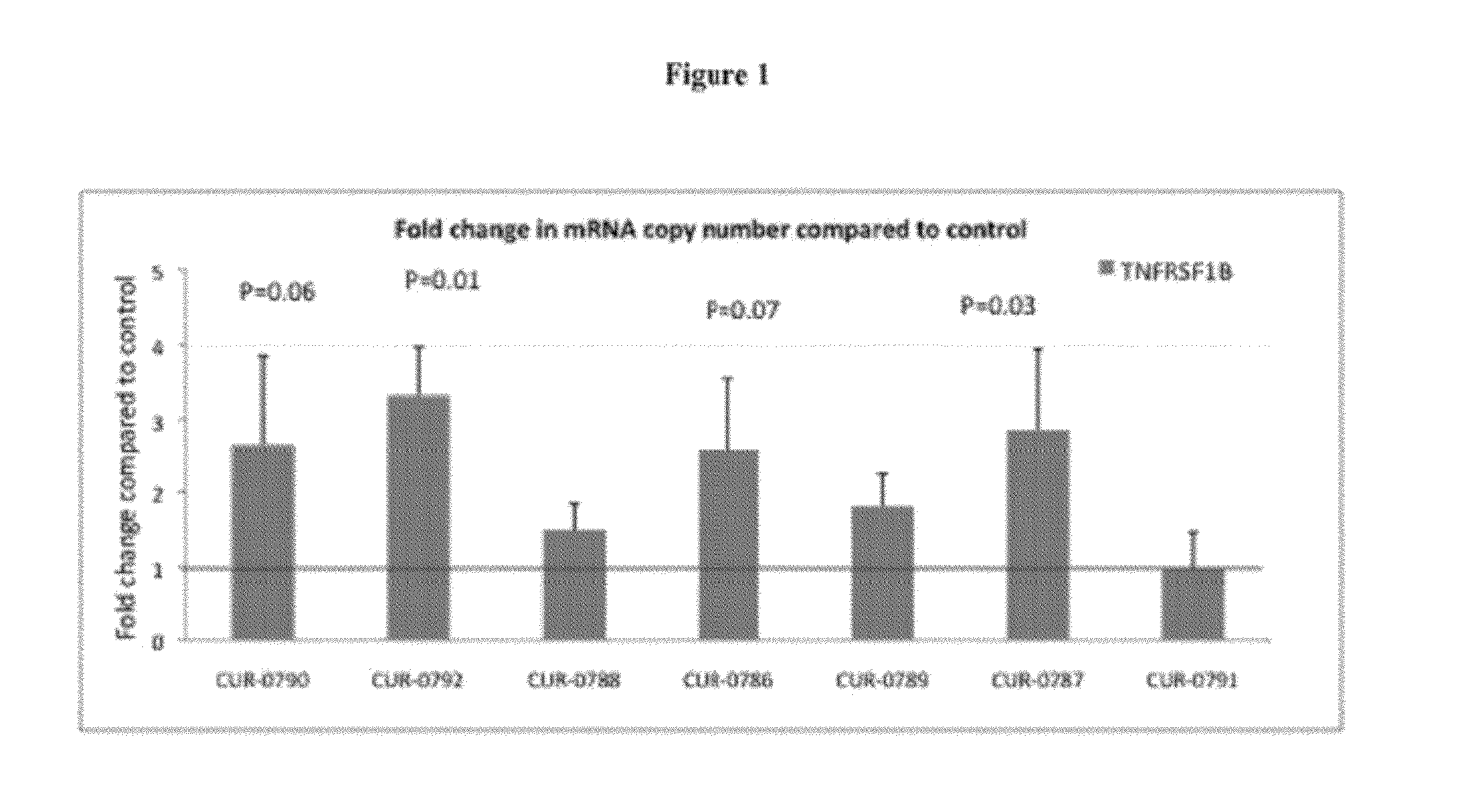
ActiveUS20120094934A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPolynucleotideInhibitory effect
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 2 (TNFR2), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor 2 (TNFR2). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of TNFR2.
Owner:CURNA INC
RNA interference mediated inhibition of gene expression using chemically modified short interfering nucleic acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20080039414A1Improve various propertyModulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesBiological bodyNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention concerns methods and reagents useful in modulating gene expression in a variety of applications, including use in therapeutic, diagnostic, target validation, and genomic discovery applications. Specifically, the invention relates to synthetic chemically modified small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against target nucleic acid sequences. The small nucleic acid molecules are useful in the treatment of any disease or condition that responds to modulation of gene expression or activity in a cell, tissue, or organism.
Owner:SIMA THERAPEUTICS
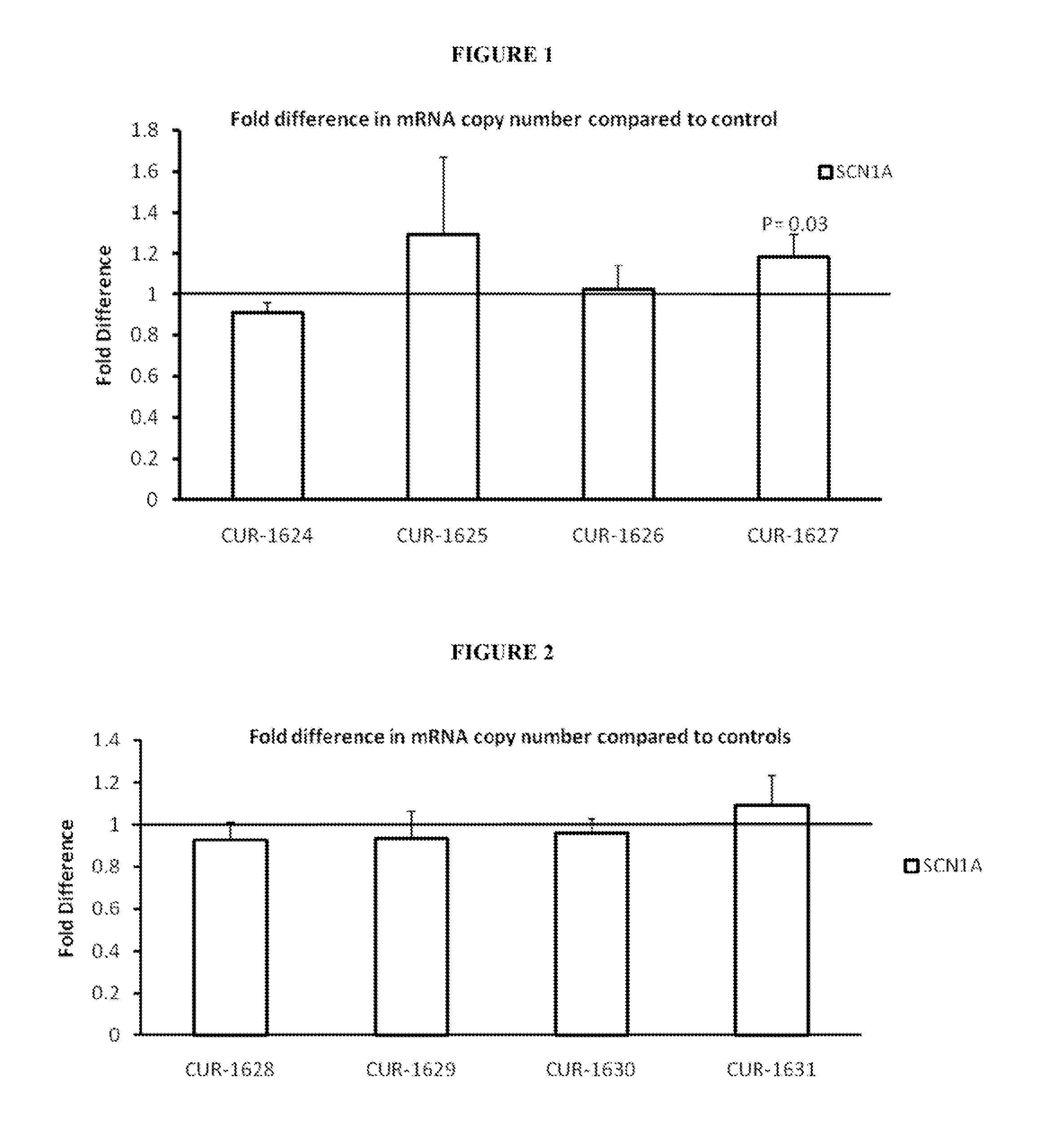
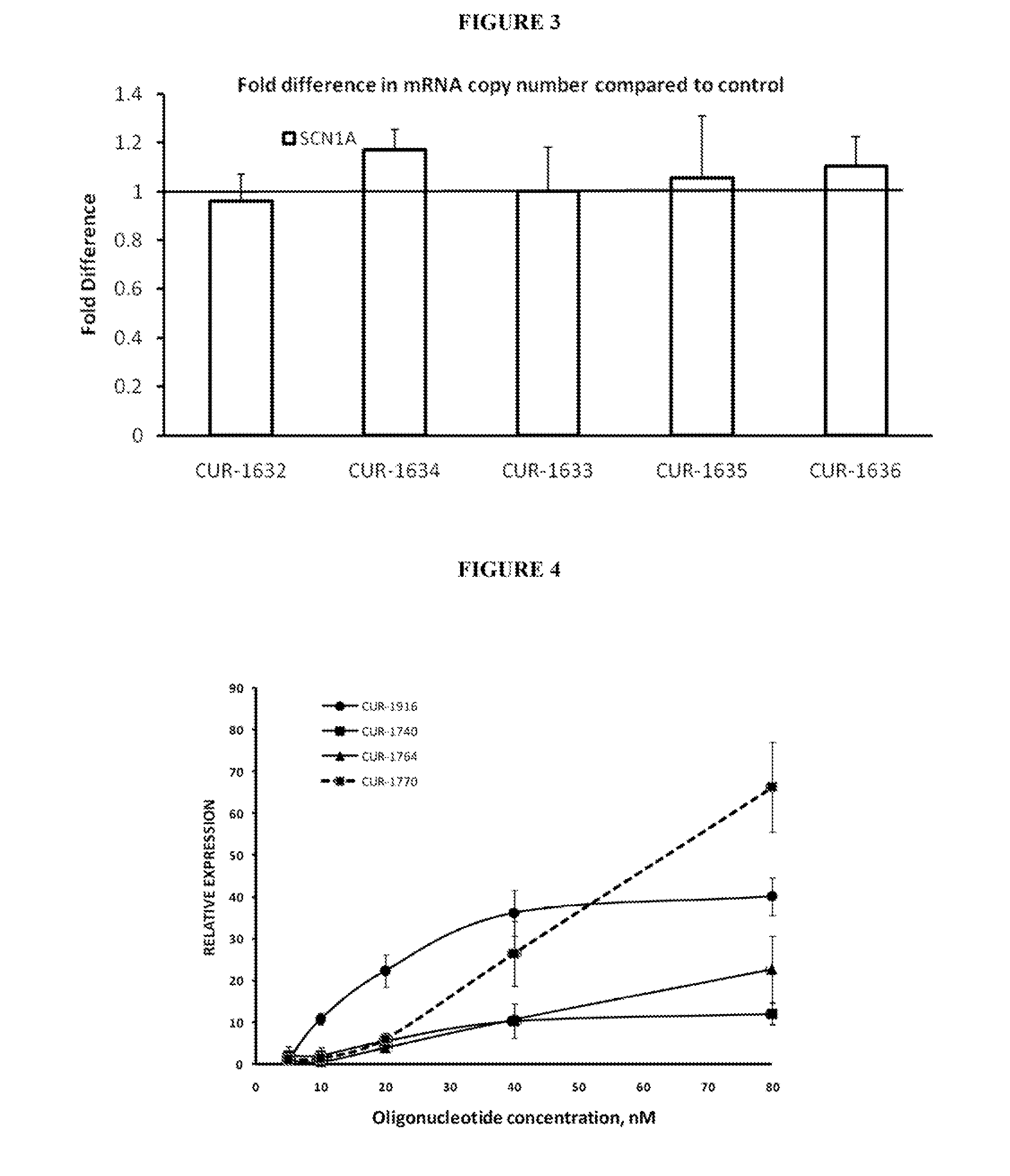
Treatment of sodium channel, voltage-gated, alpha subunit (SCNA) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to scna
ActiveUS20130096183A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPolynucleotideBiology
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Sodium channel, voltage-gated, alpha subunit (SCNA), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Sodium channel, voltage-gated, alpha subunit (SCNA). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of SCNA.
Owner:CURNA INC
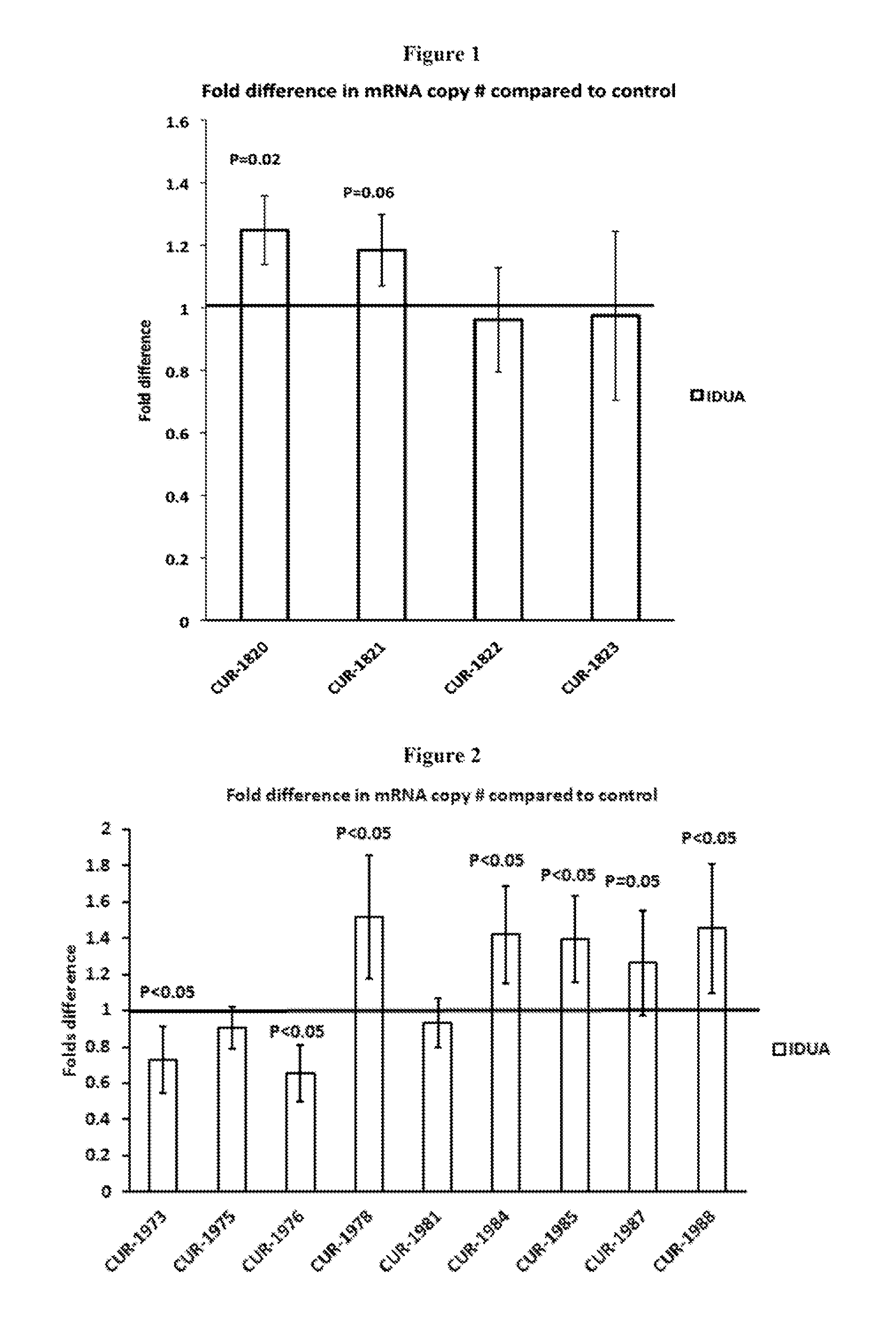
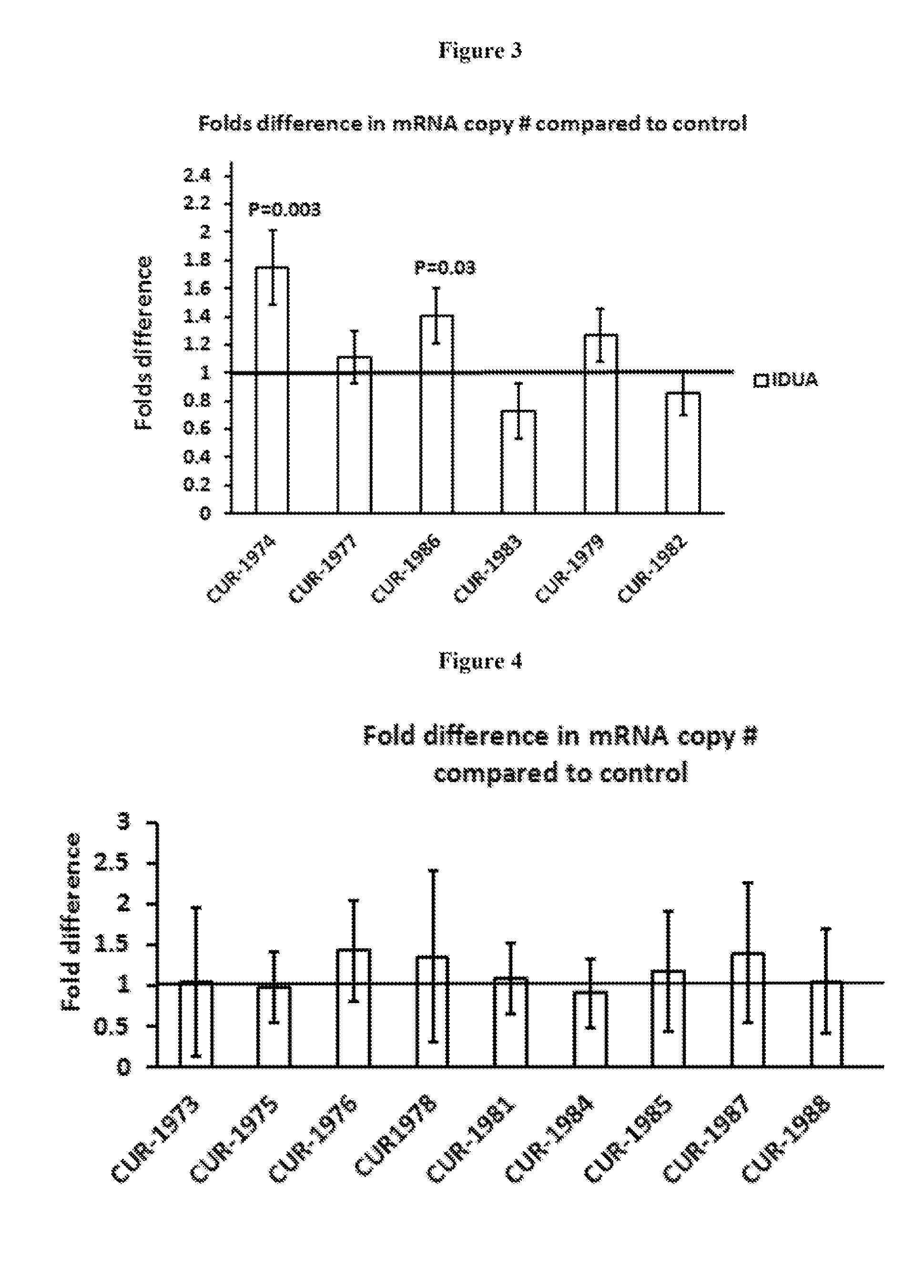
Treatment of alpha-l-iduronidase (IDUA) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to idua
ActiveUS20130253036A1Modulate its functionFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPolynucleotideDisease cause
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Alpha-L-Iduronidase (IDUA), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Alpha-L-Iduronidase (IDUA). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of IDUA.
Owner:CURNA INC
Topiramate plus naltrexone for the treatment of addictive disorders
InactiveUS20120302592A1Treatment safetyLess susceptible to neuroadaptationBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseTopiramate
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
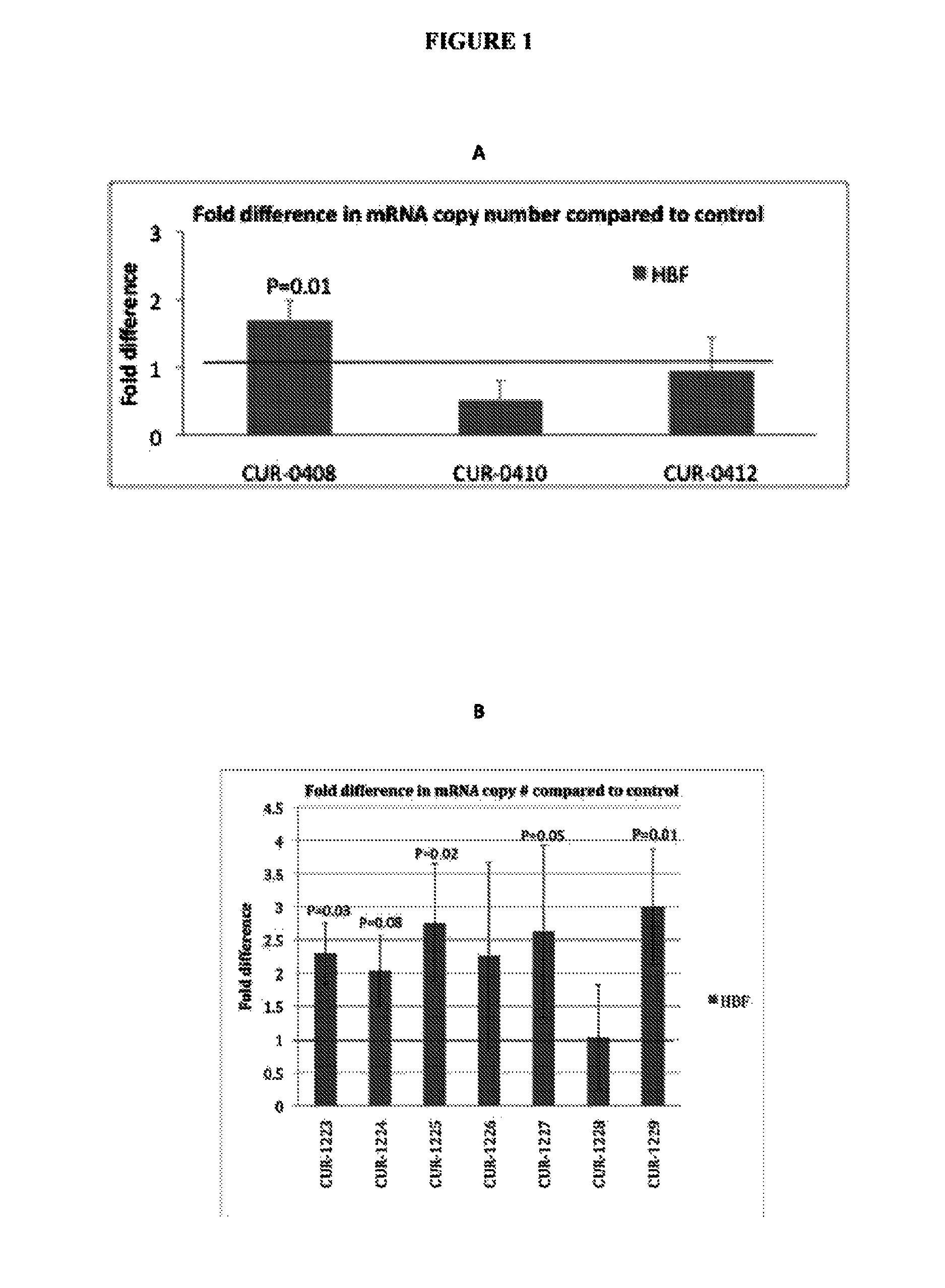
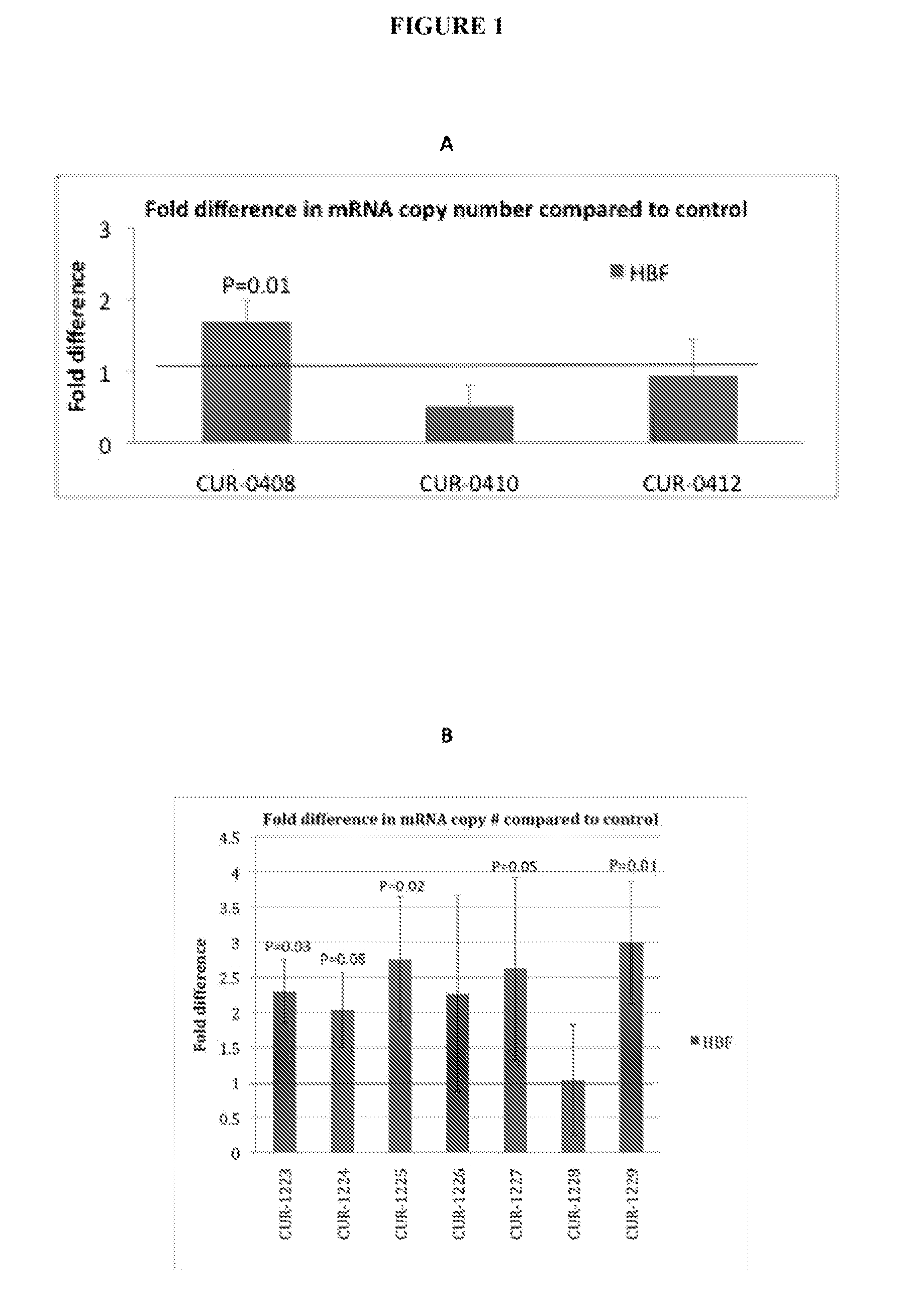
Treatment of hemoglobin (HBF/HBG) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to HBF/HBG
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Hemoglobin (HBF / HBG), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Hemoglobin (HBF / HBG). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of HBF / HBG.
Owner:CURNA INC
Treatment of hemoglobin (hbf/hbg) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to hbf/hbg
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Hemoglobin (HBF / HBG), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Hemoglobin (HBF / HBG). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of HBF / HBG.
Owner:CURNA INC
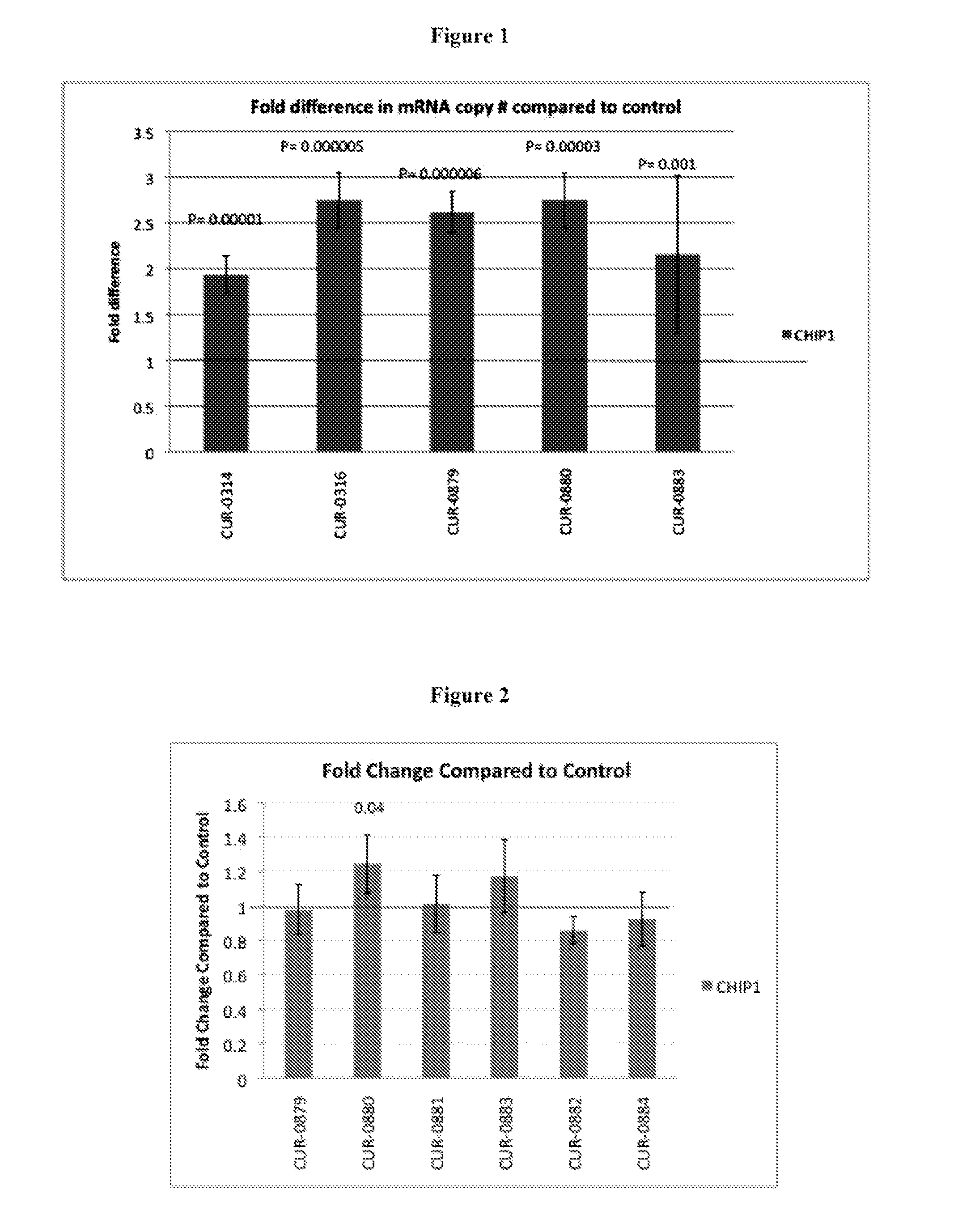
Treatment of 'c terminus of hsp70-interacting protein' (CHIP) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to chip
ActiveUS20120135941A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseasePolynucleotide
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of ‘C terminus of HSP70-Interacting Protein’ (CHIP), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of ‘C terminus of HSP70-Interacting Protein’ (CHIP). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of CHIP.
Owner:CURNA INC
Topiramate Plus Naltrexone for the Treatment of Addictive Disorders
InactiveUS20100076006A1Treatment safetyLess susceptible to neuroadaptationBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseTopiramate
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
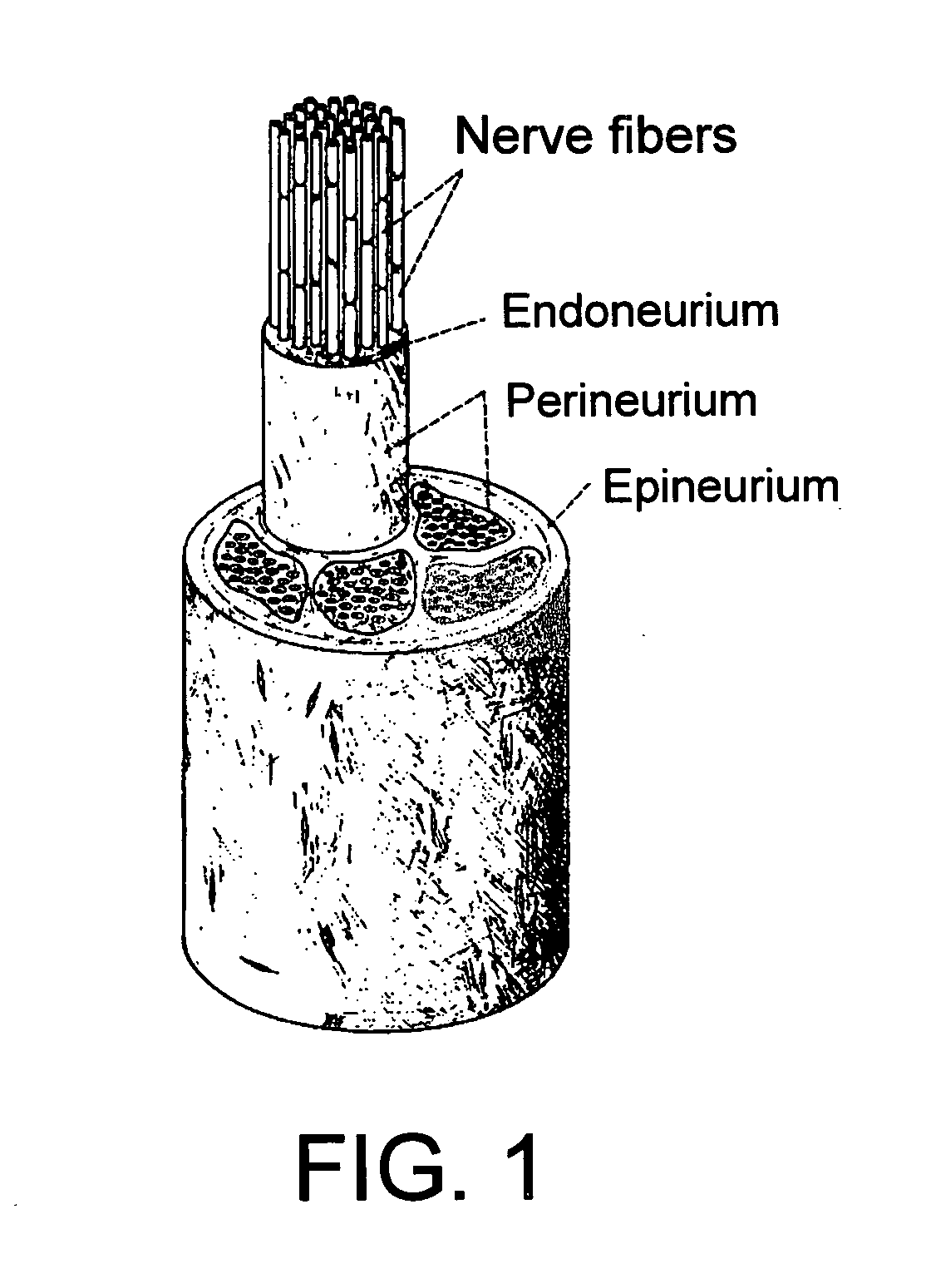
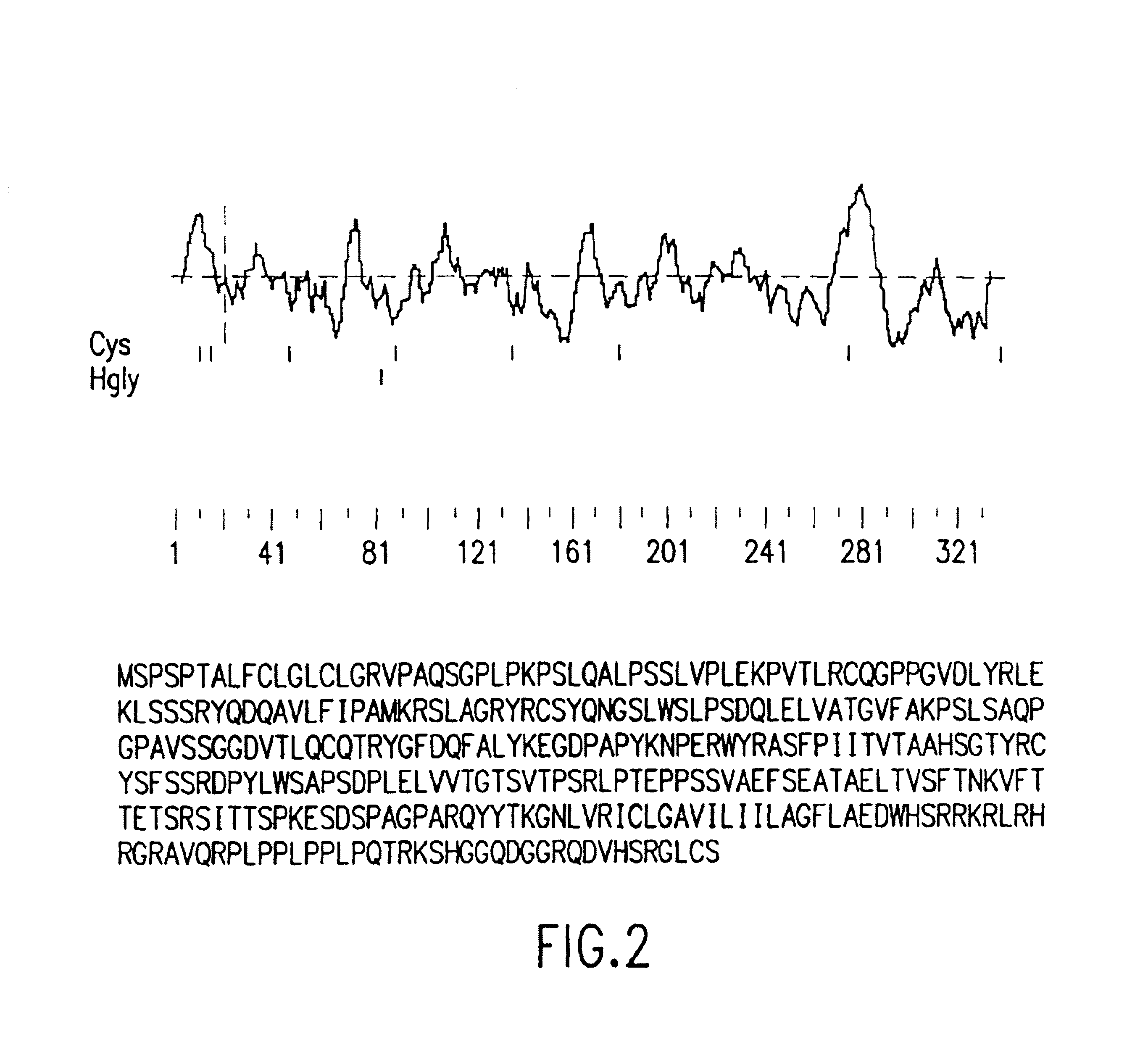
Glycoprotein VI antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS6989144B1Stabilize and promote and inhibit and disrupt protein-protein interactionAbility to modulateCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenAntisense nucleic acid
The invention provides isolated nucleic acid molecules and polypeptide molecules that encode glycoprotein V1, a platelet membrane glycoprotein that is involved platelet-collagen interactions. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, expression vectors containing the nucleic acid molecules of the invention, host cells into which the exposure vectors have been introduced, and non-human transgenic animals in which a nucleic acid molecule of the invention has been introduced or disrupted. The invention still further provides isolated polypeptides, fusion polypeptides, antigenic peptides and antibodies. Diagnostic, screening and therapeutic methods utilizing compositions of the invention are also provided.
Owner:MILLENNIUM PHARMA INC +1
Treatment of tumor suppressor gene related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to the gene
InactiveUS20110294870A1Prevent and treat diseaseModulate its functionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseSuppressor
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Tumor Suppressor genes, in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Tumor Suppressor genes. The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of Tumor Suppressor genes.
Owner:CURNA INC
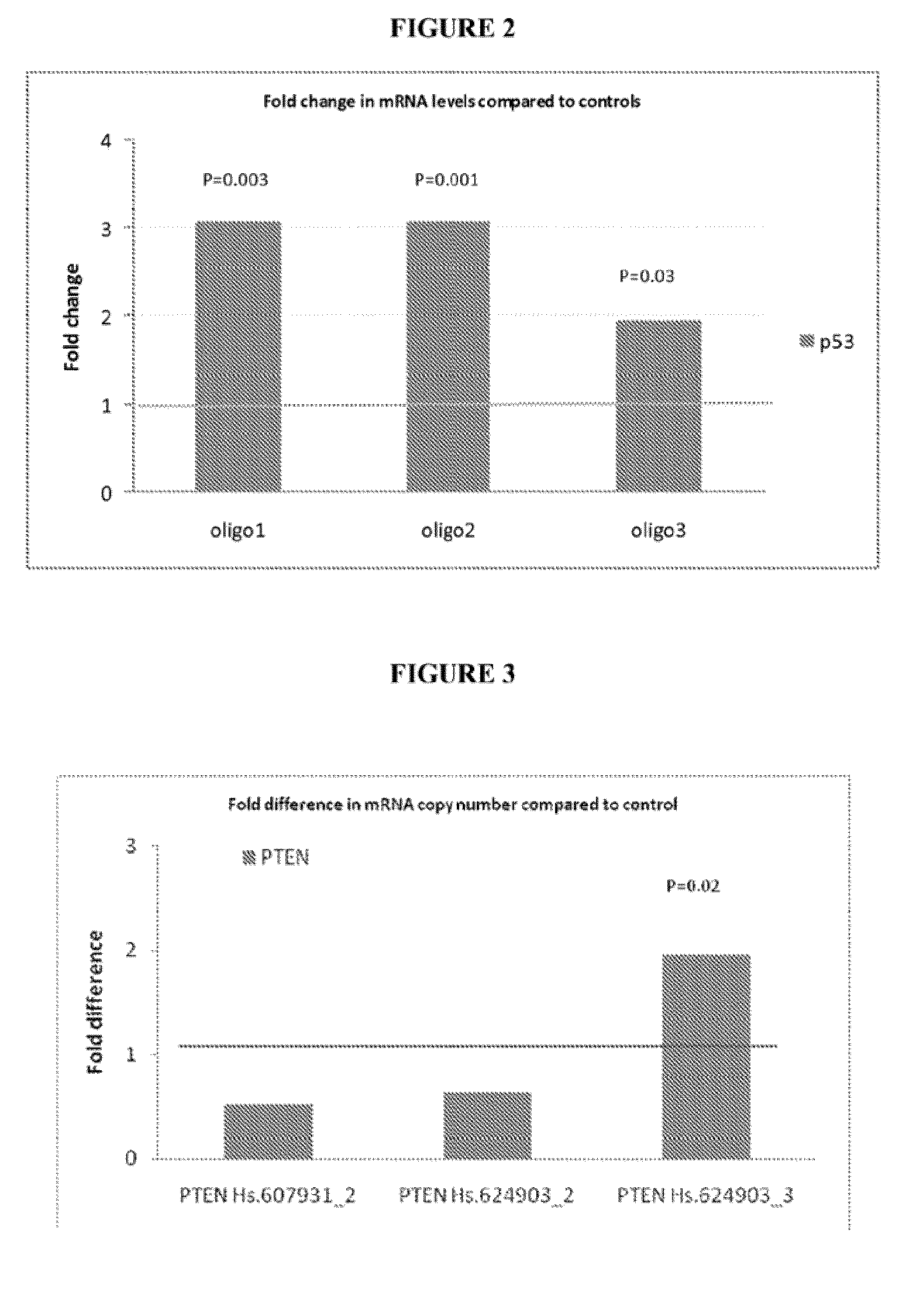
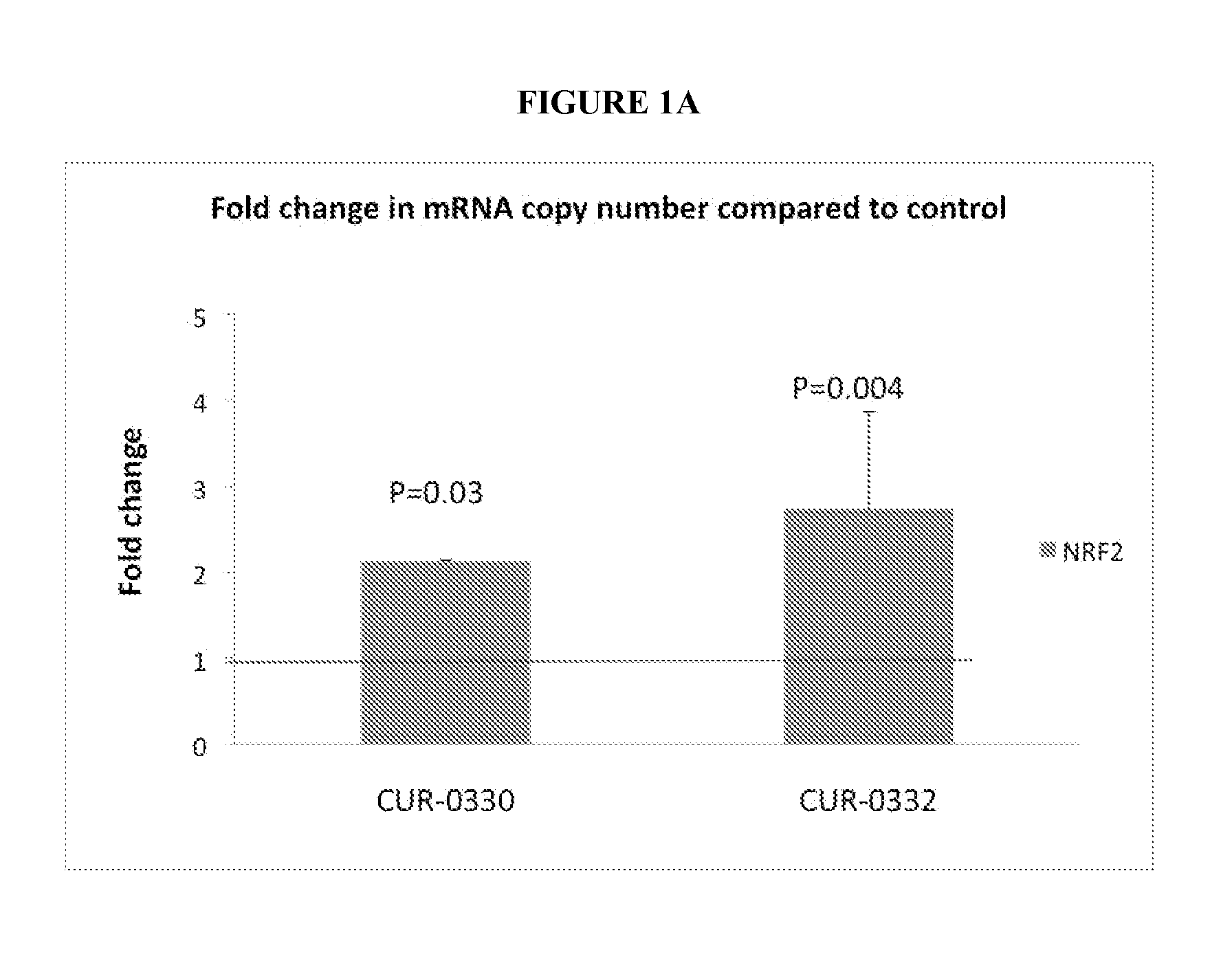
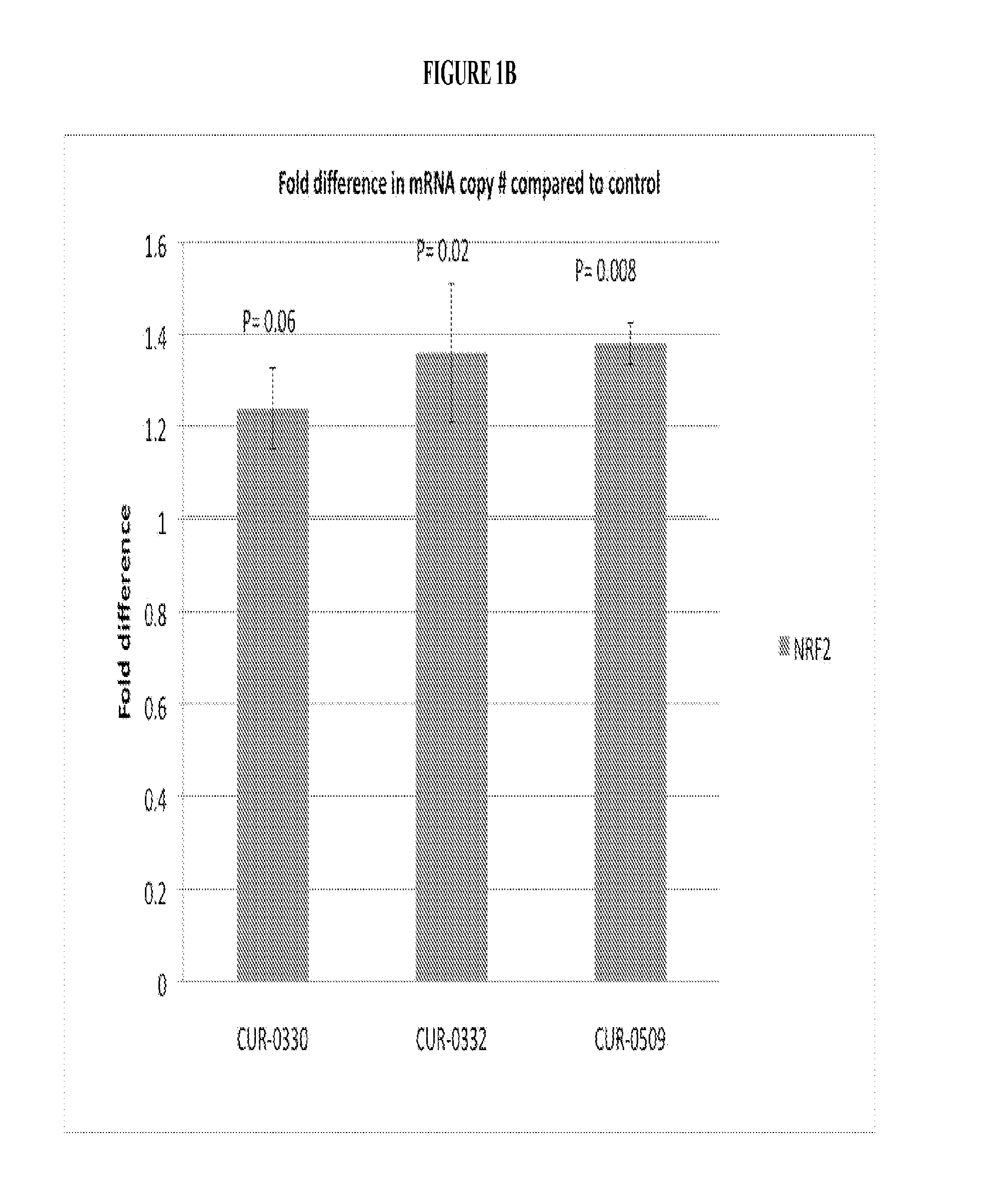
Treatment of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to nrf2
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Nu-clear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of NRF2.
Owner:CURNA INC
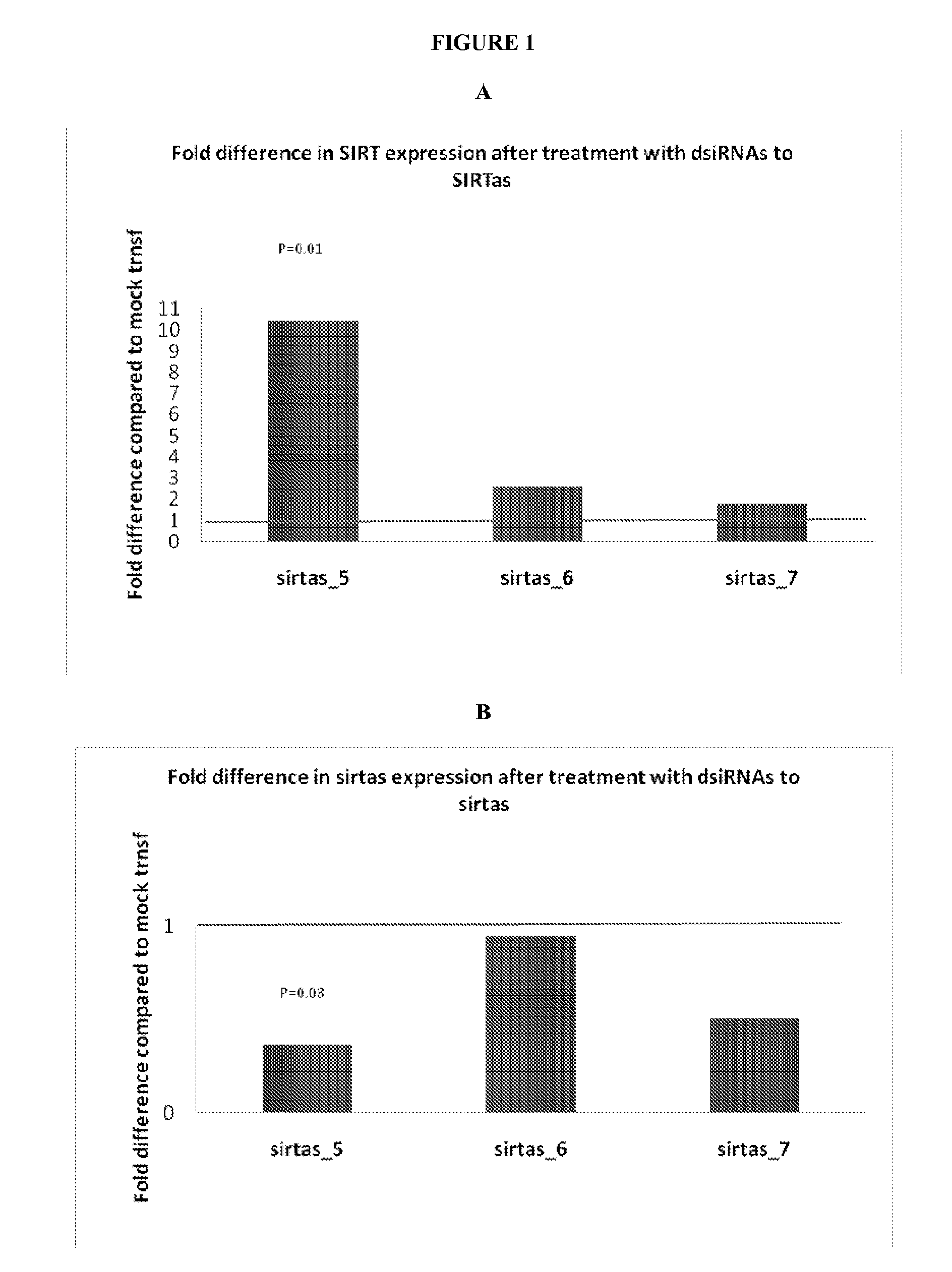
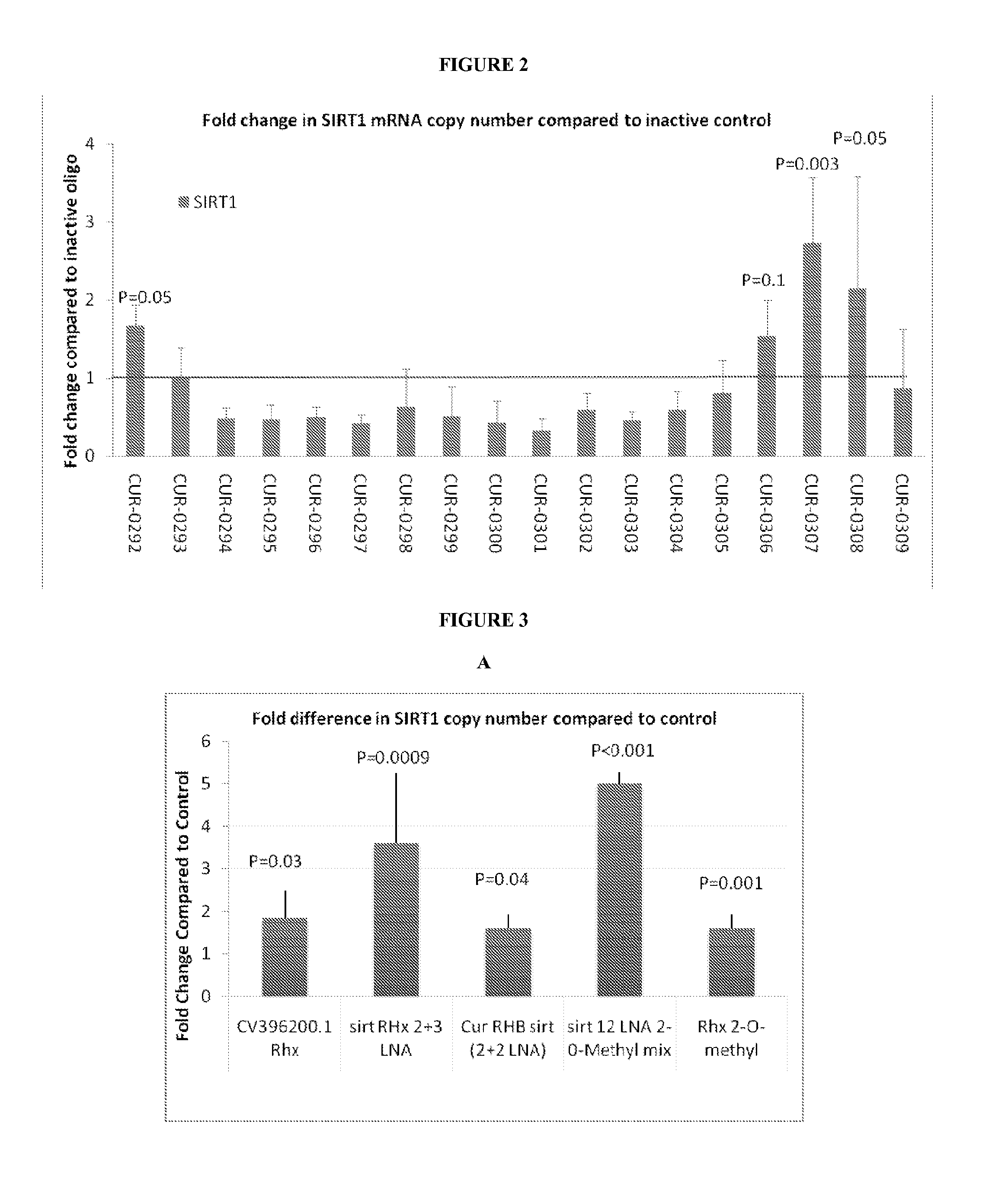
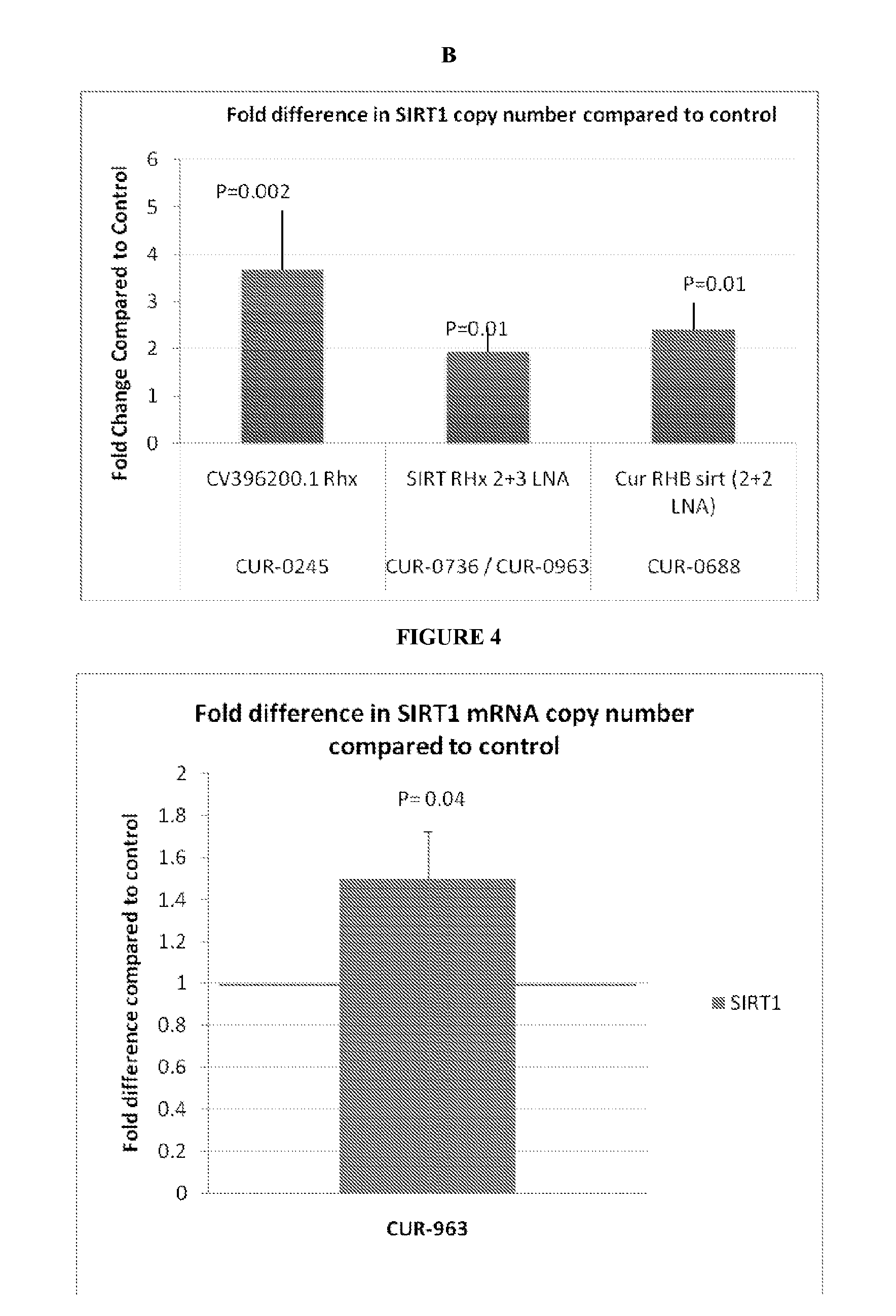
Treatment of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to sirt1
InactiveUS20110319317A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseSirtuin 1
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of SIRT 1.
Owner:CURNA INC
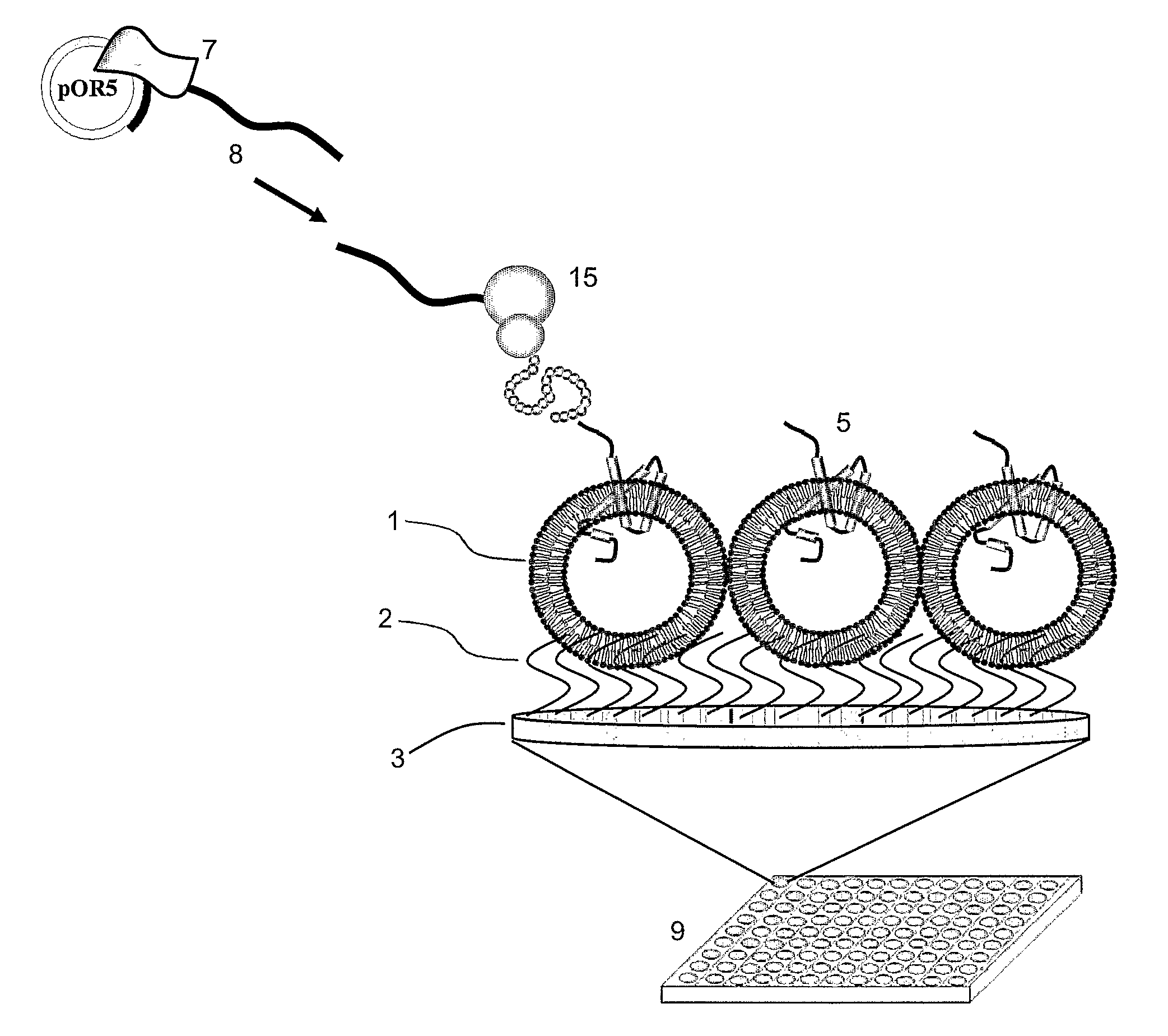
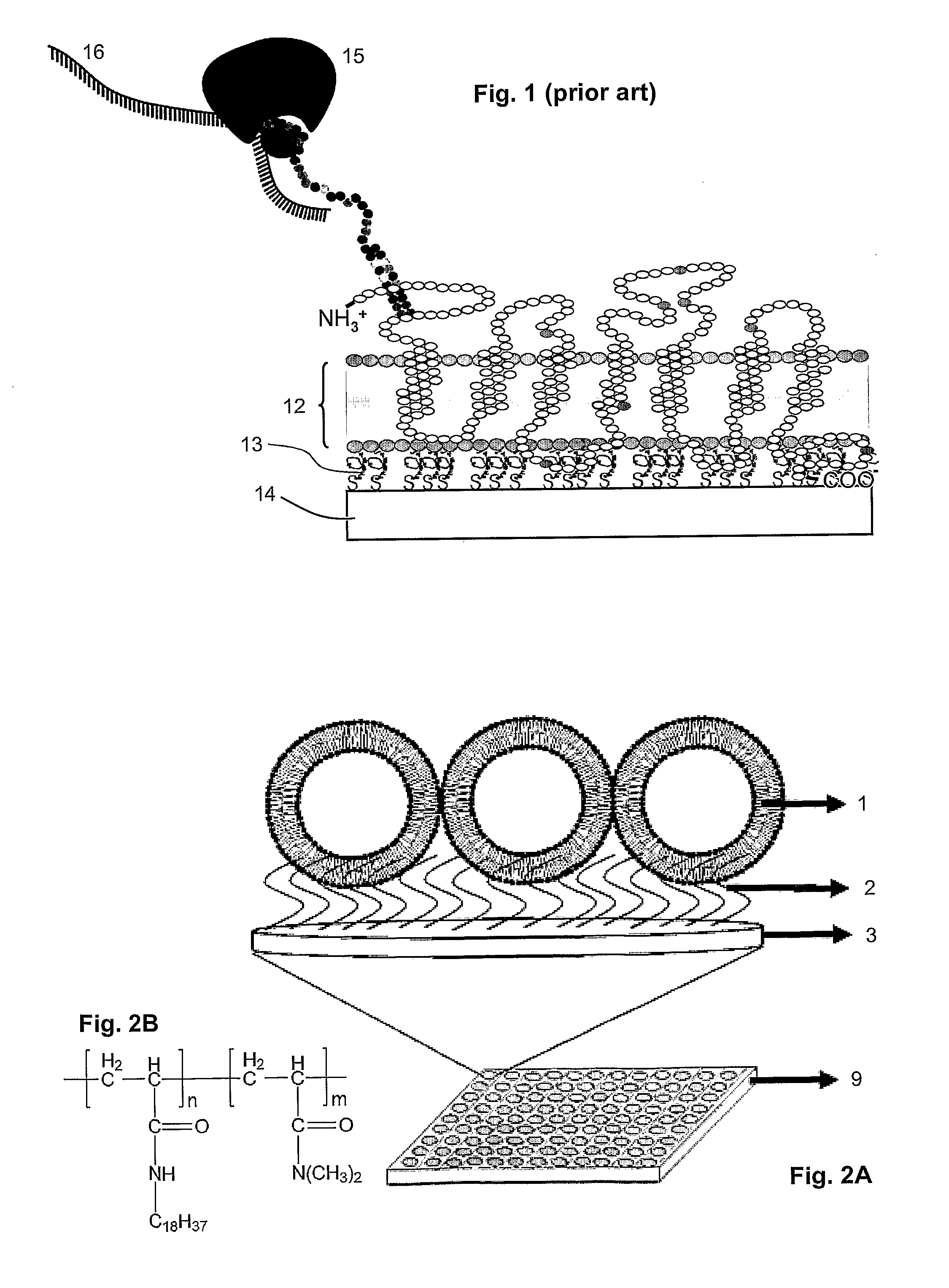
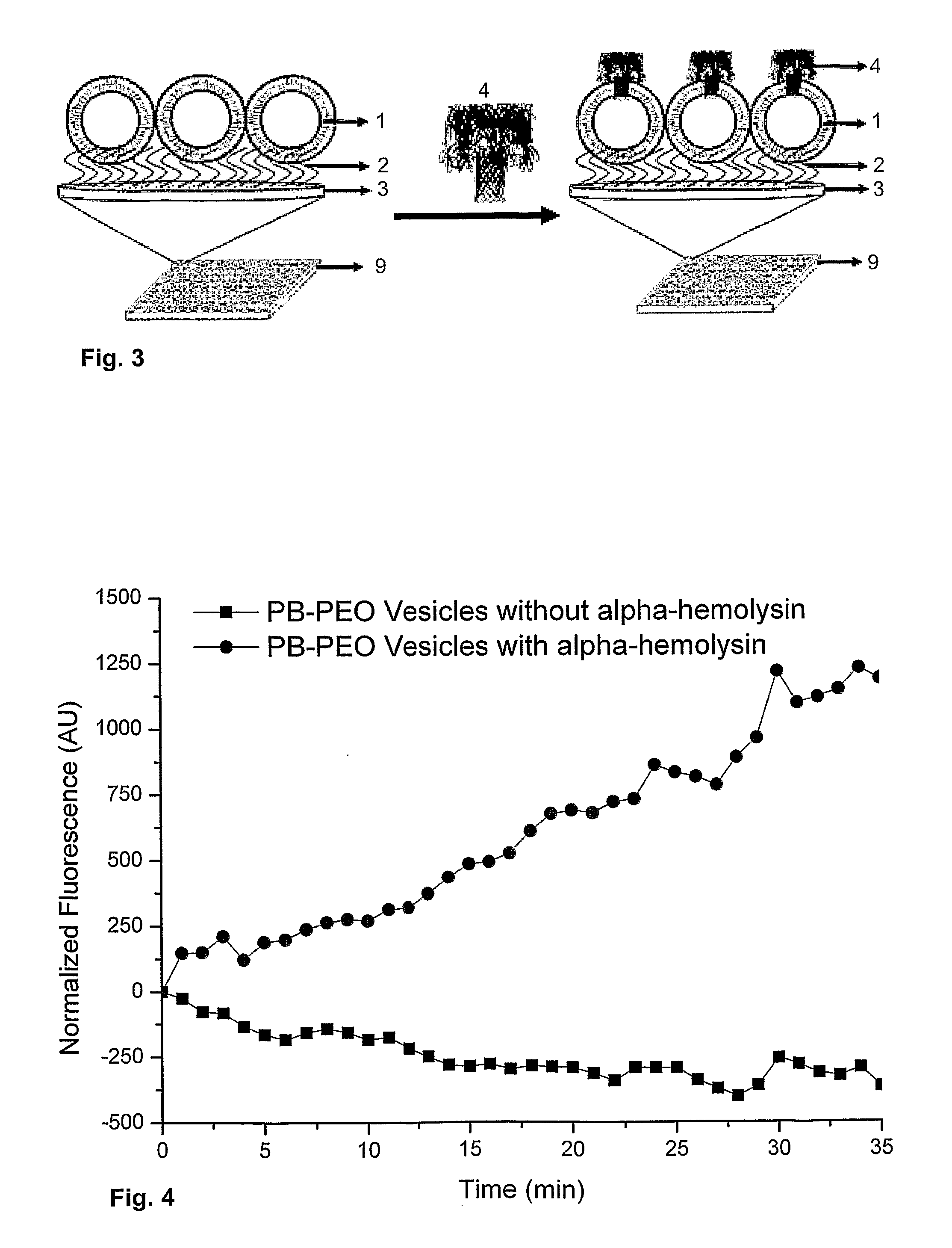
Vesicular system and uses thereof
ActiveUS20120129270A1Overcome difficultiesModulate its functionPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMaterial analysisHeteroatomBackbone chain
Disclosed is a vesicular system comprising a surface with a vesicle immobilized thereon. The immobilized vesicle has a circumferential membrane of an amphiphilic polymer. The vesicle is coupled to a surface by means of a molecule with a non-polar moiety. The non-polar moiety comprises a main chain of 3 to about 30 carbon atoms and 0 to about 12 heteroatoms selected from Si, O, S, and Se. The molecule with the non-polar moiety is coupled to the surface via a covalent or non-covalent bond. A portion of the non-polar moiety is integrated in the circumferential membrane.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Treatment of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to hgf
ActiveUS20130184325A9Modulate its functionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseHepatocyte growth factor
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of HGF.
Owner:CURNA INC
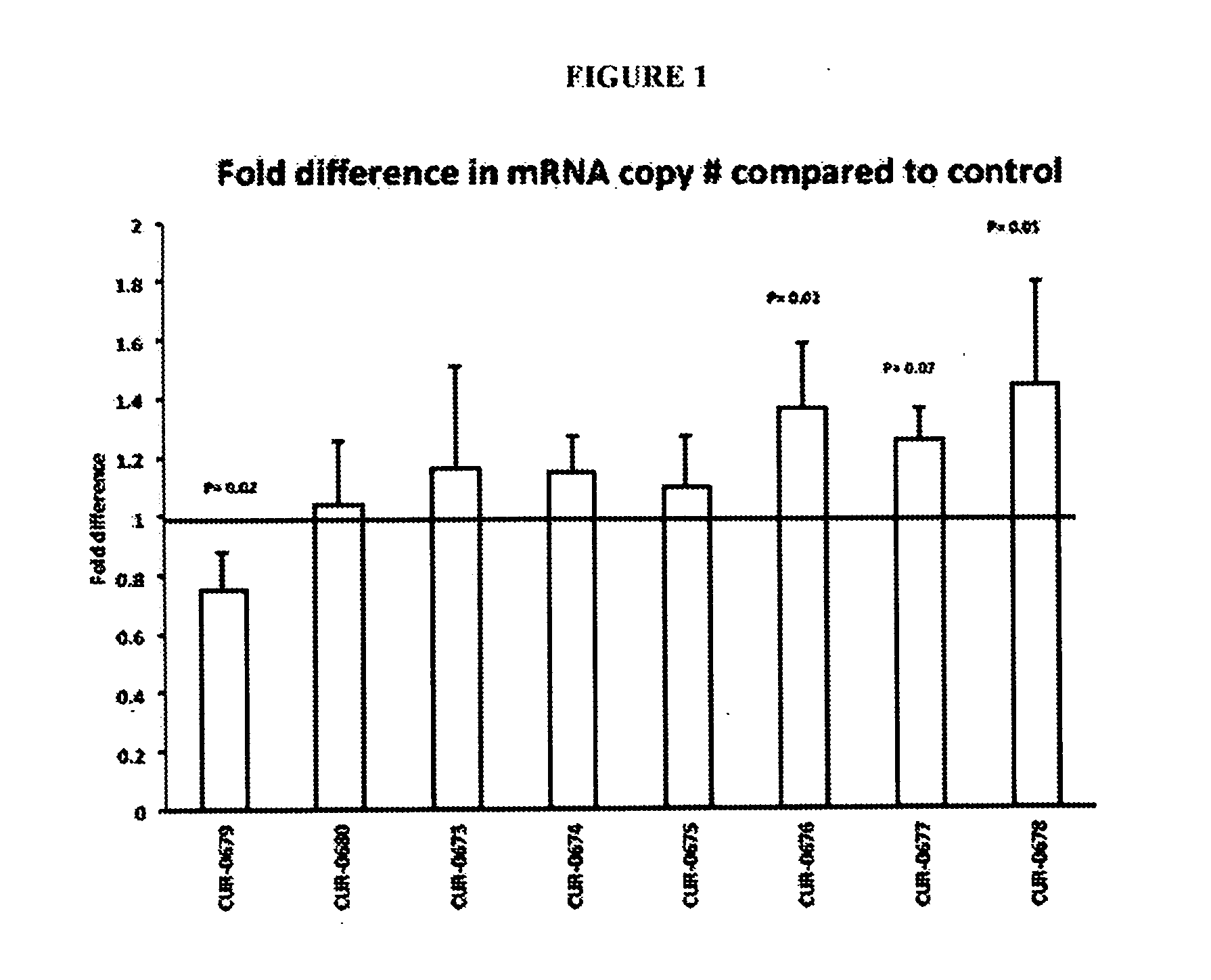
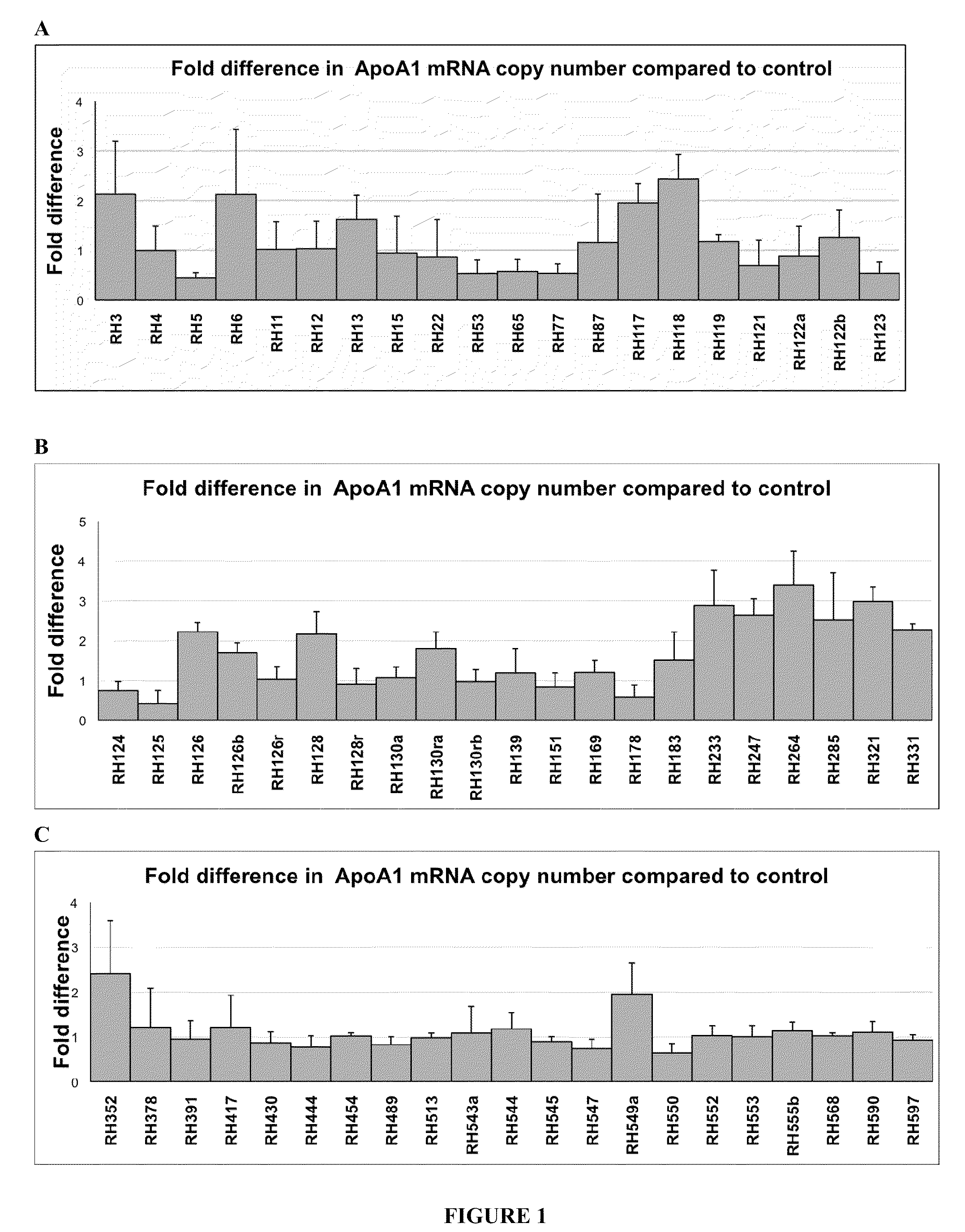
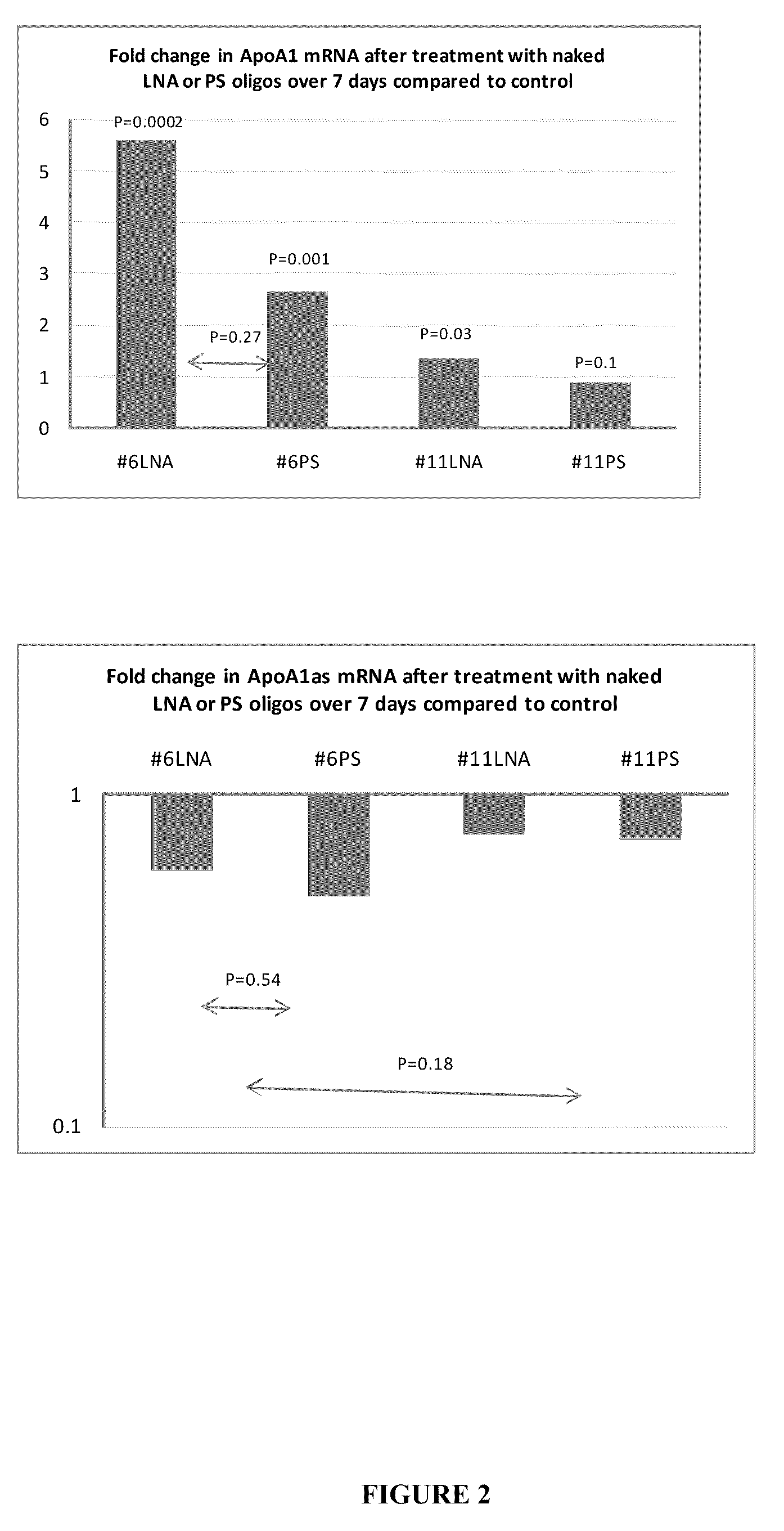
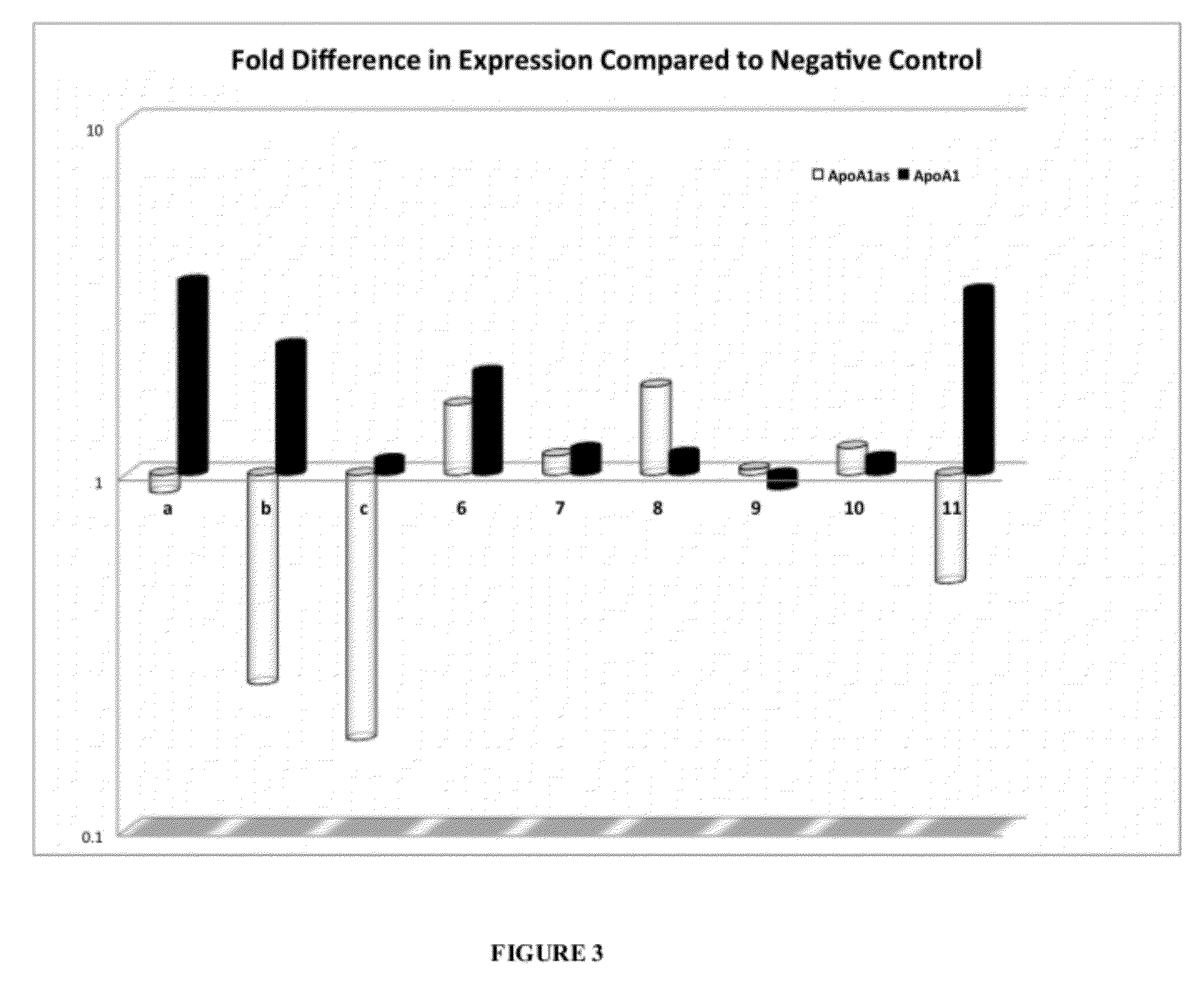
Treatment of apolipoprotein-A1 related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to apolipoprotein-A1
Oligonucleotide compounds modulate expression and / or function of an apolipoprotein (ApoA1) polynucleotides and encoded products thereof. Methods for treating diseases associated with apolipoprotein-A1 (ApoA1) comprise administering one or more Oligonucleotide compounds designed to inhibit the Apo-A1 natural antisense transcript to patients.
Owner:CURNA INC
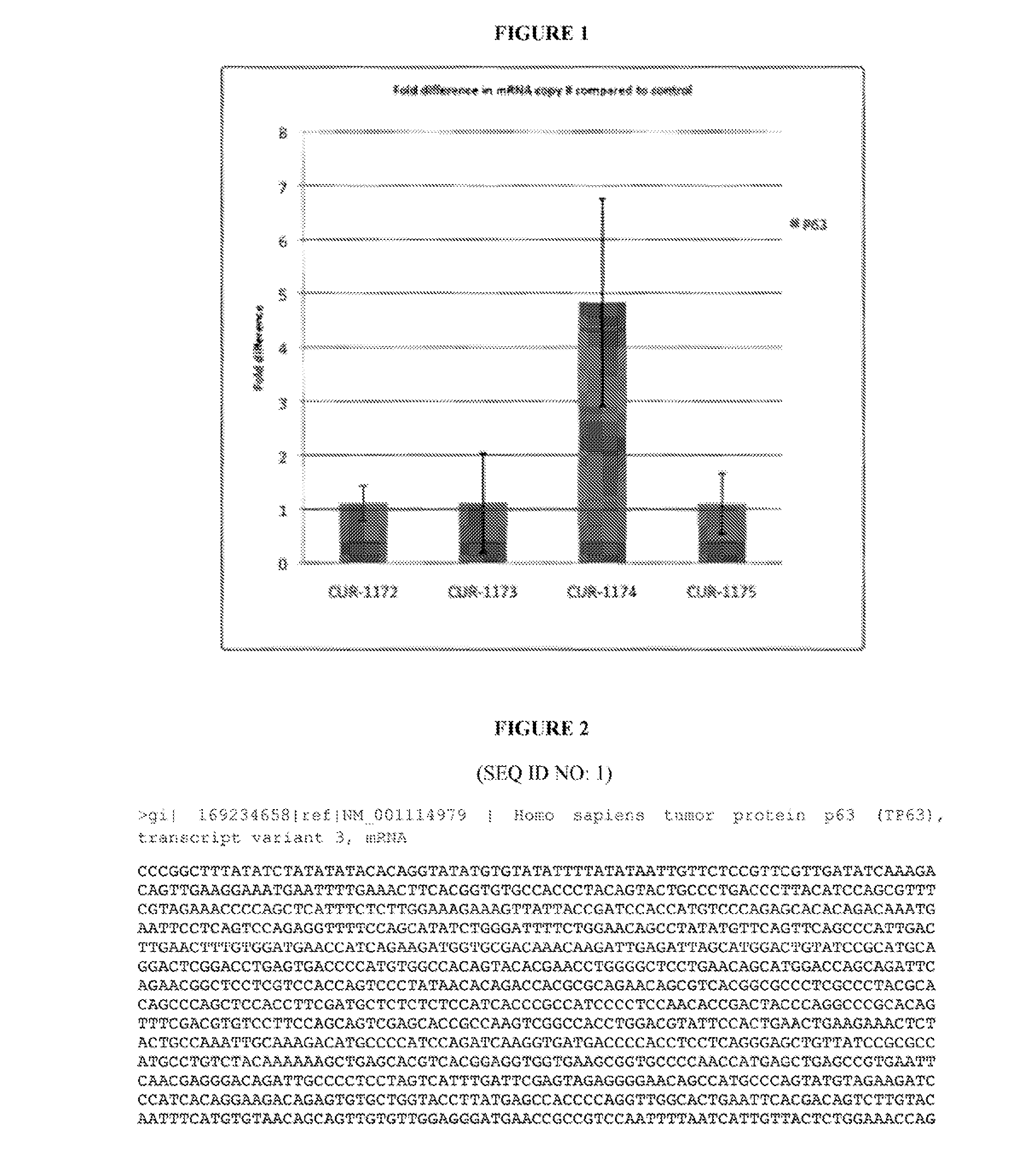
Treatment of tumor protein 63 (P63) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to p63
InactiveUS20120295953A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseasePolynucleotide
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Tumor Protein 63 (p63), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Tumor Protein 63 (p63). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of p63.
Owner:CURNA INC
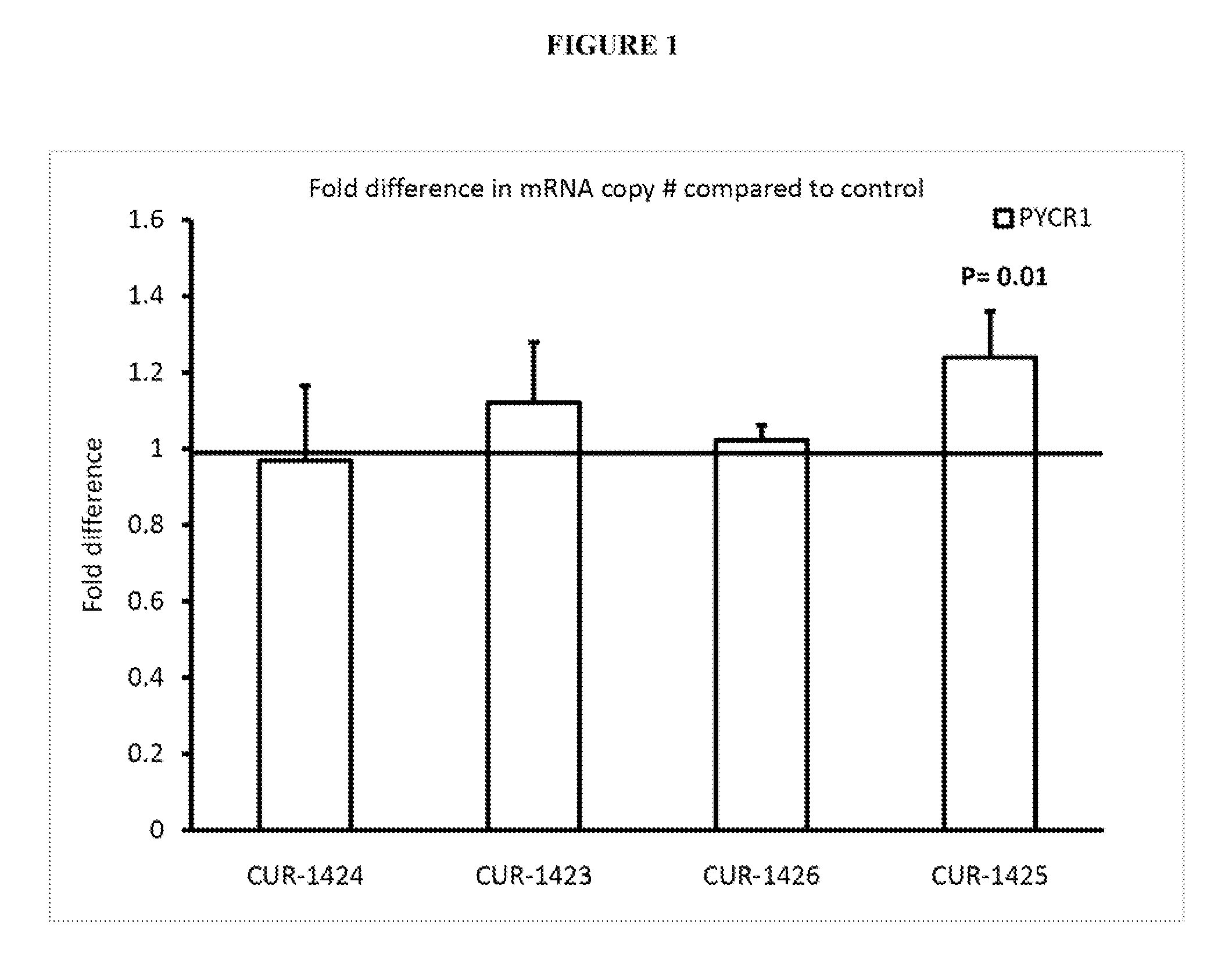
Treatment of pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 (PYCR1) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to pycr1
ActiveUS20120309814A1Modulate function and expressionModulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderPyrroline 5 carboxylate reductaseCarboxylic acid reductase
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 (PYCR1), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1 (PYCR1). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of PYCR1.
Owner:CURNA INC
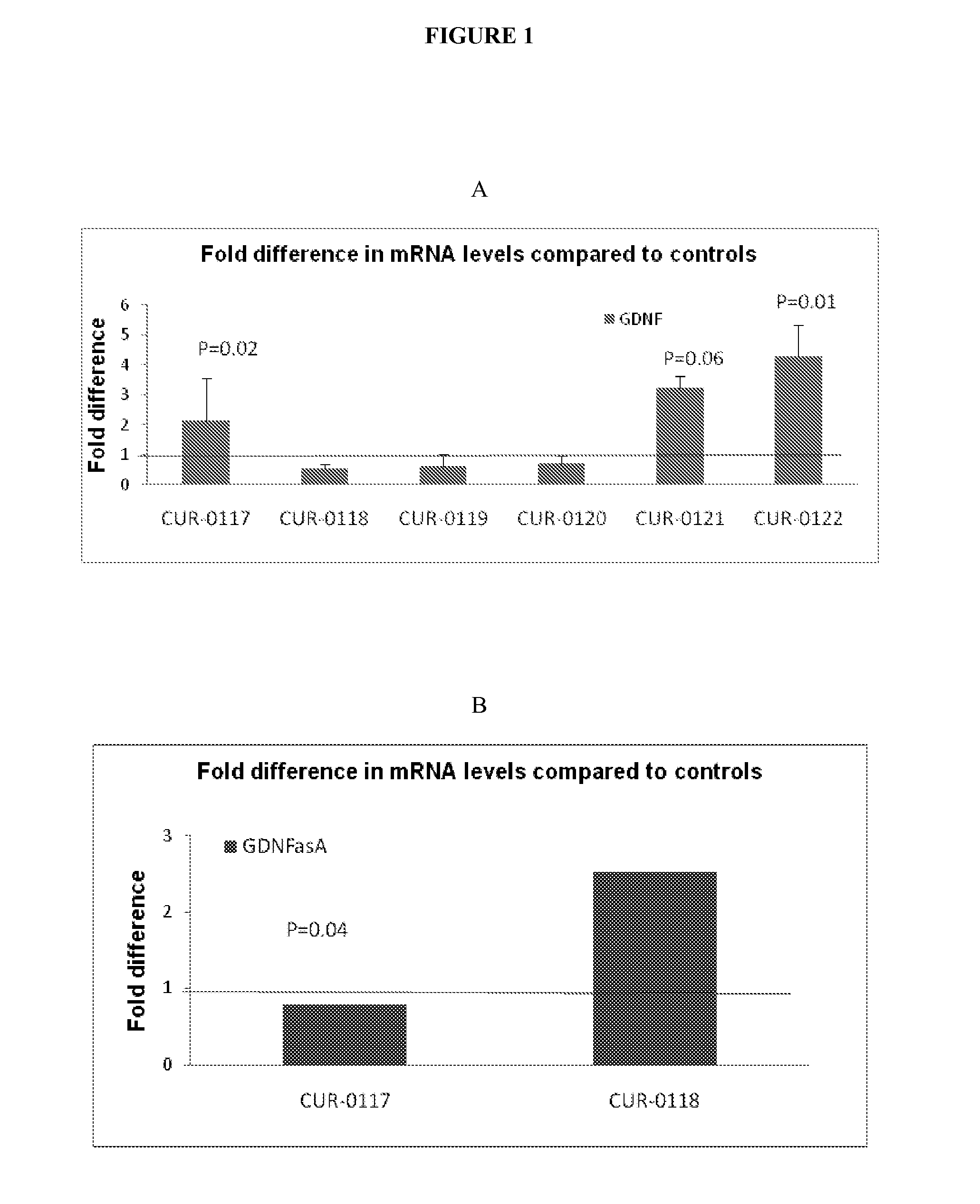
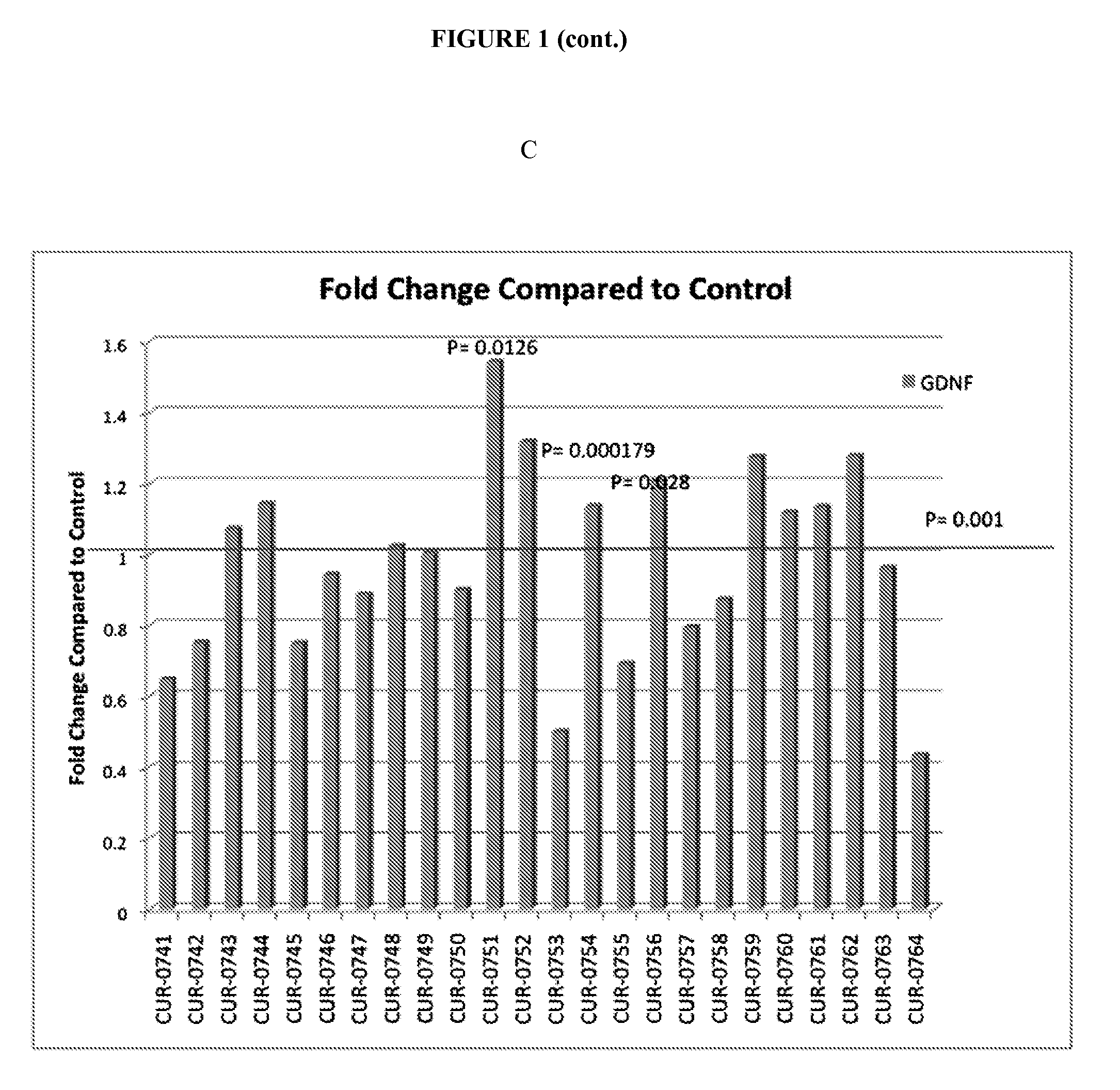
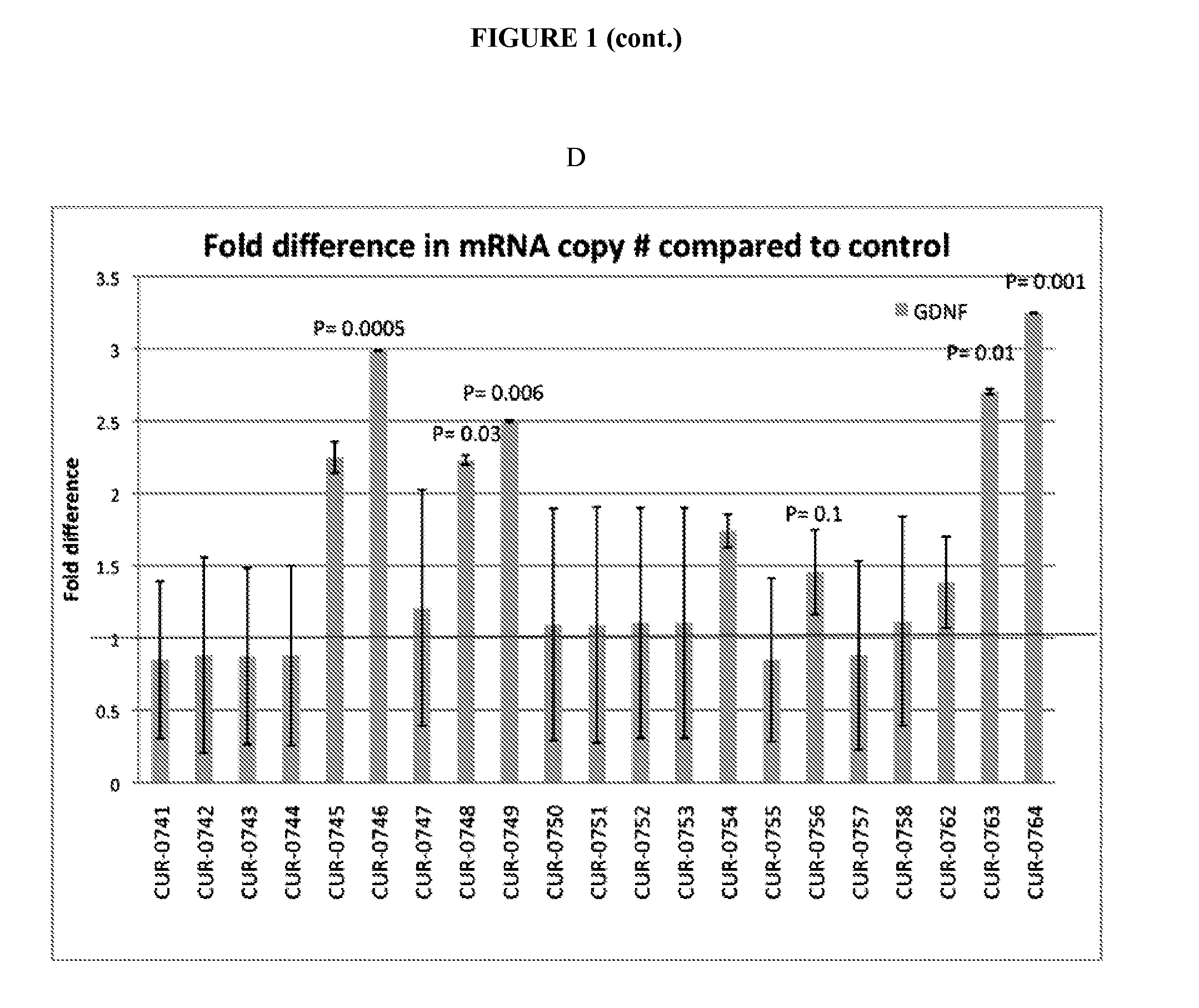
Treatment of glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to gdnf
InactiveUS20110319476A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseCiliary neurotrophic factor
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of GDNF.
Owner:CURNA INC
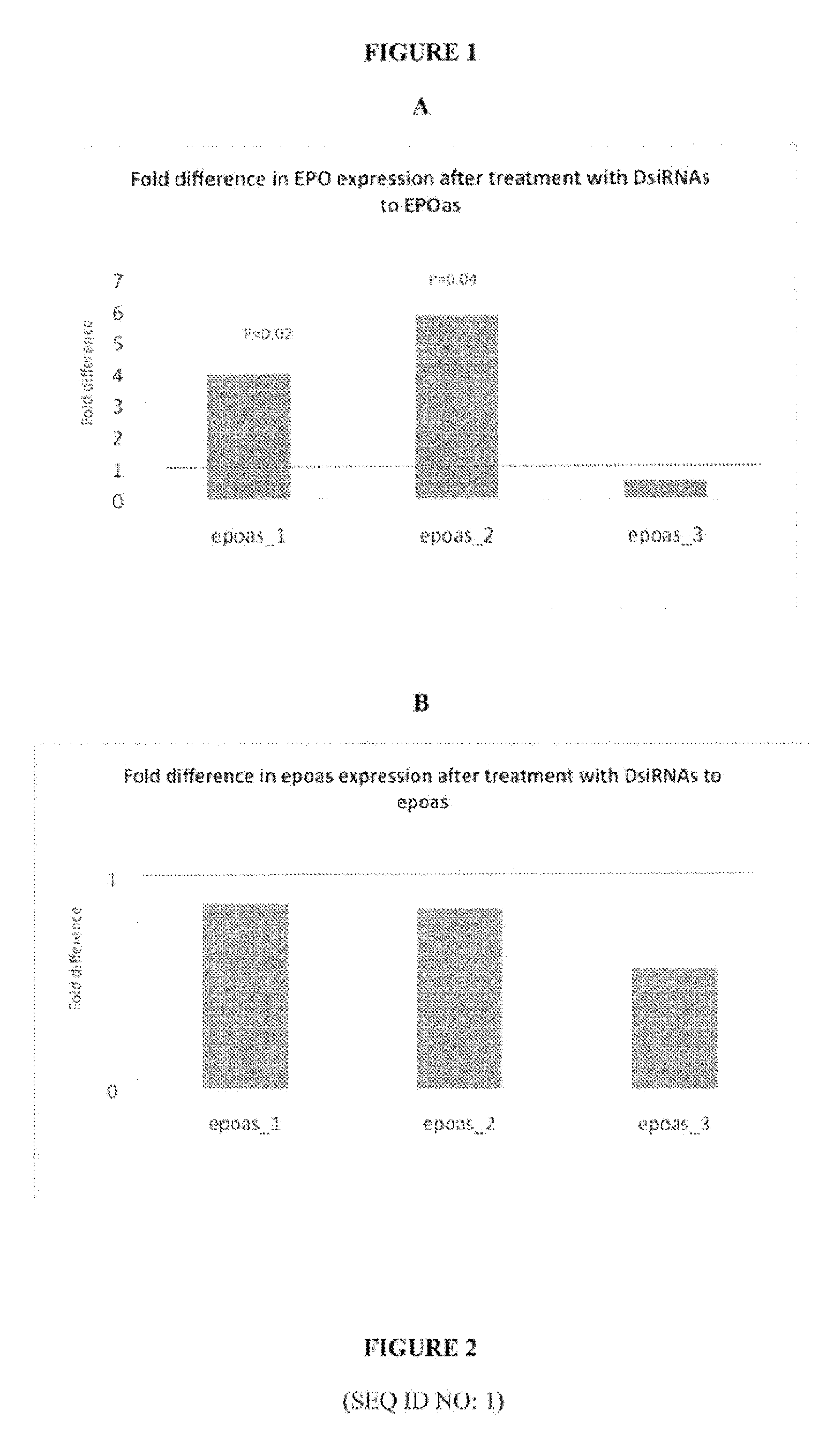
Treatment of erythropoietin (EPO) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to epo
ActiveUS20110237651A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseRed blood cell
Oligonucleotide compounds modulate expression and / or function of Erythropoietin (EPO) polynucleotides and encoded products thereof. Methods for treating diseases associated with Erythropoietin (EPO) comprise administering one or more oligonucleotide compounds designed to inhibit the EPO natural antisense transcript to patients.
Owner:CURNA INC
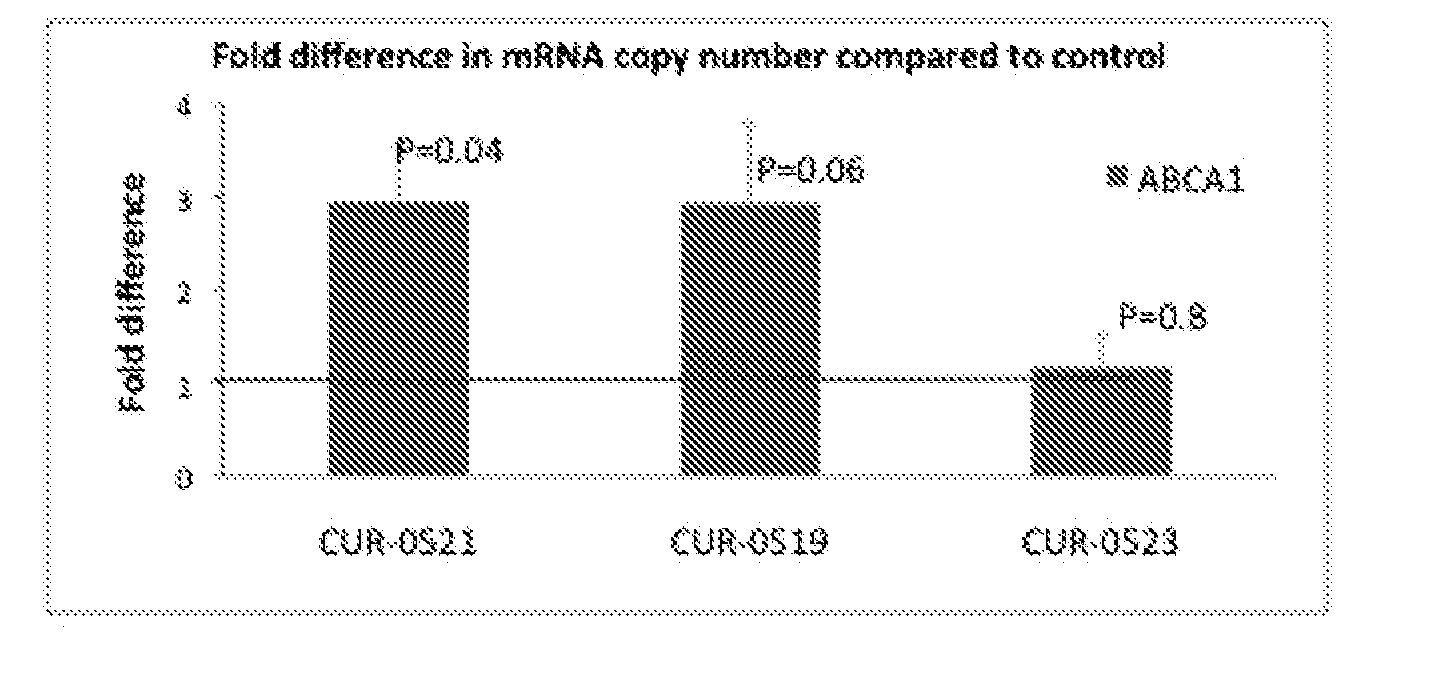
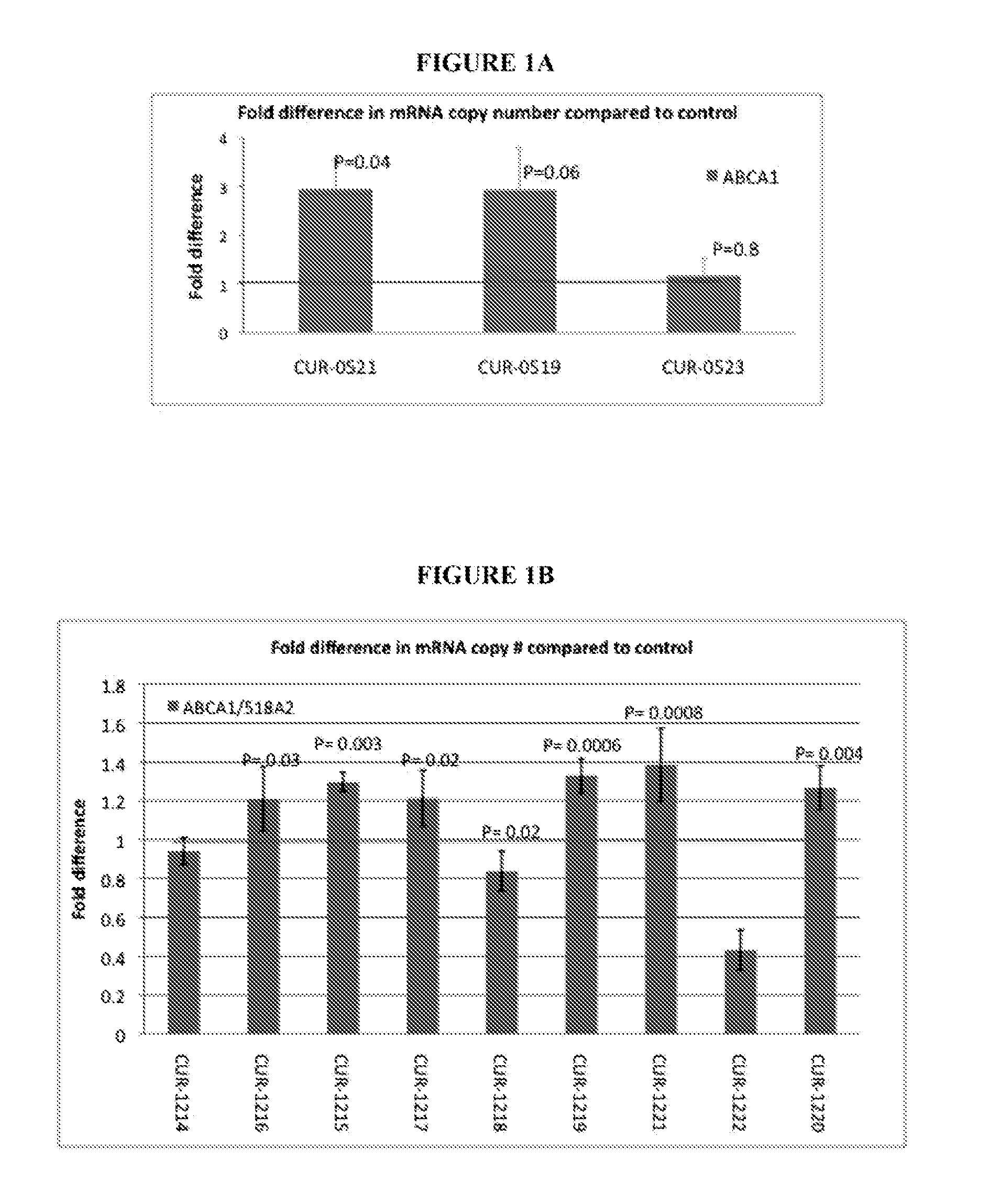
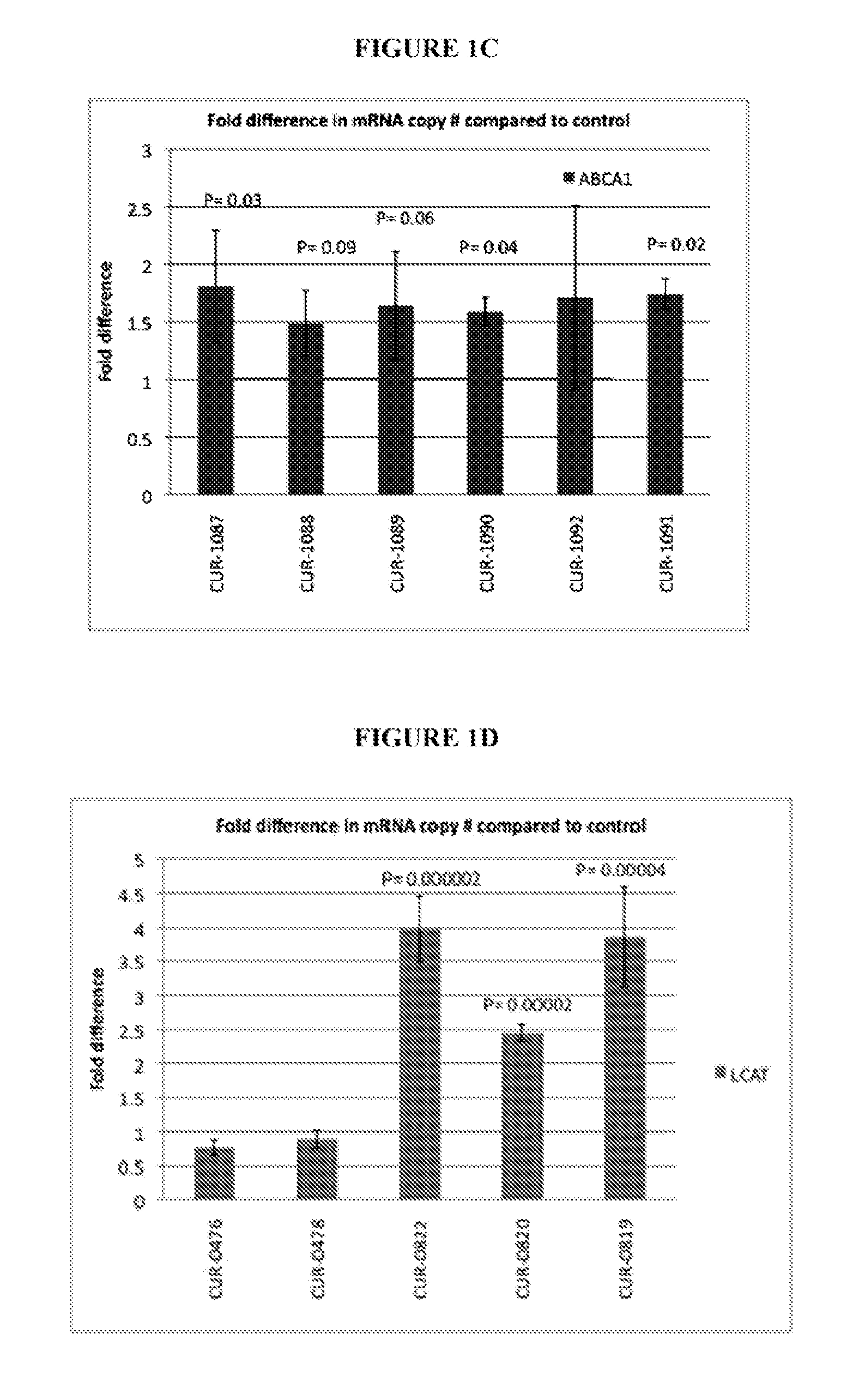
Treatment of lipid transport and metabolism gene related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to a lipid transport and metabolism gene
ActiveUS20120046344A1Modulate its functionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseLipid Transport
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of a Lipid transport and metabolism gene, in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of a Lipid transport and metabolism gene. The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of a Lipid transport and metabolism genes.
Owner:CURNA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com