Patents
Literature
34results about How to "Decrease thickness)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
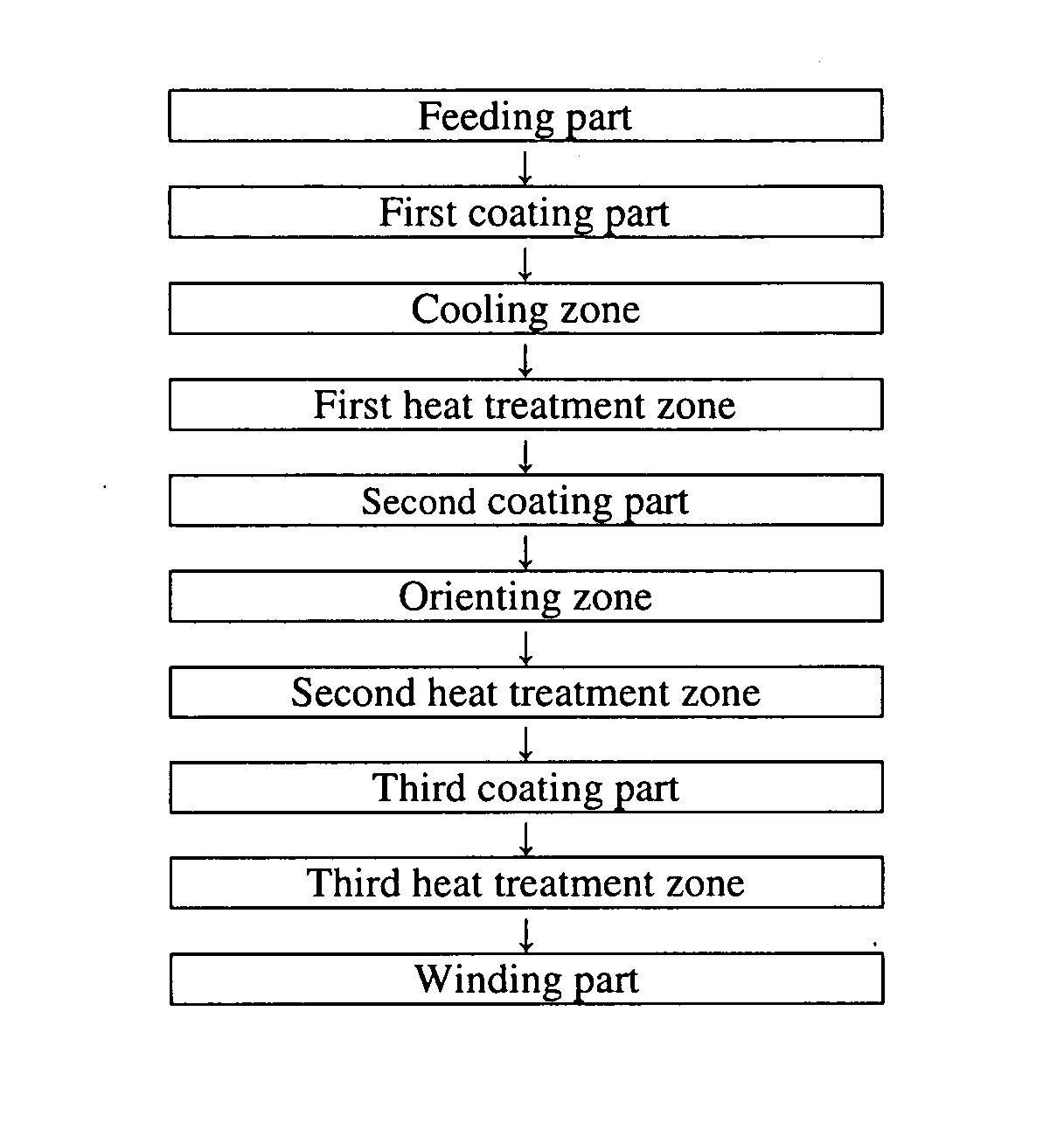
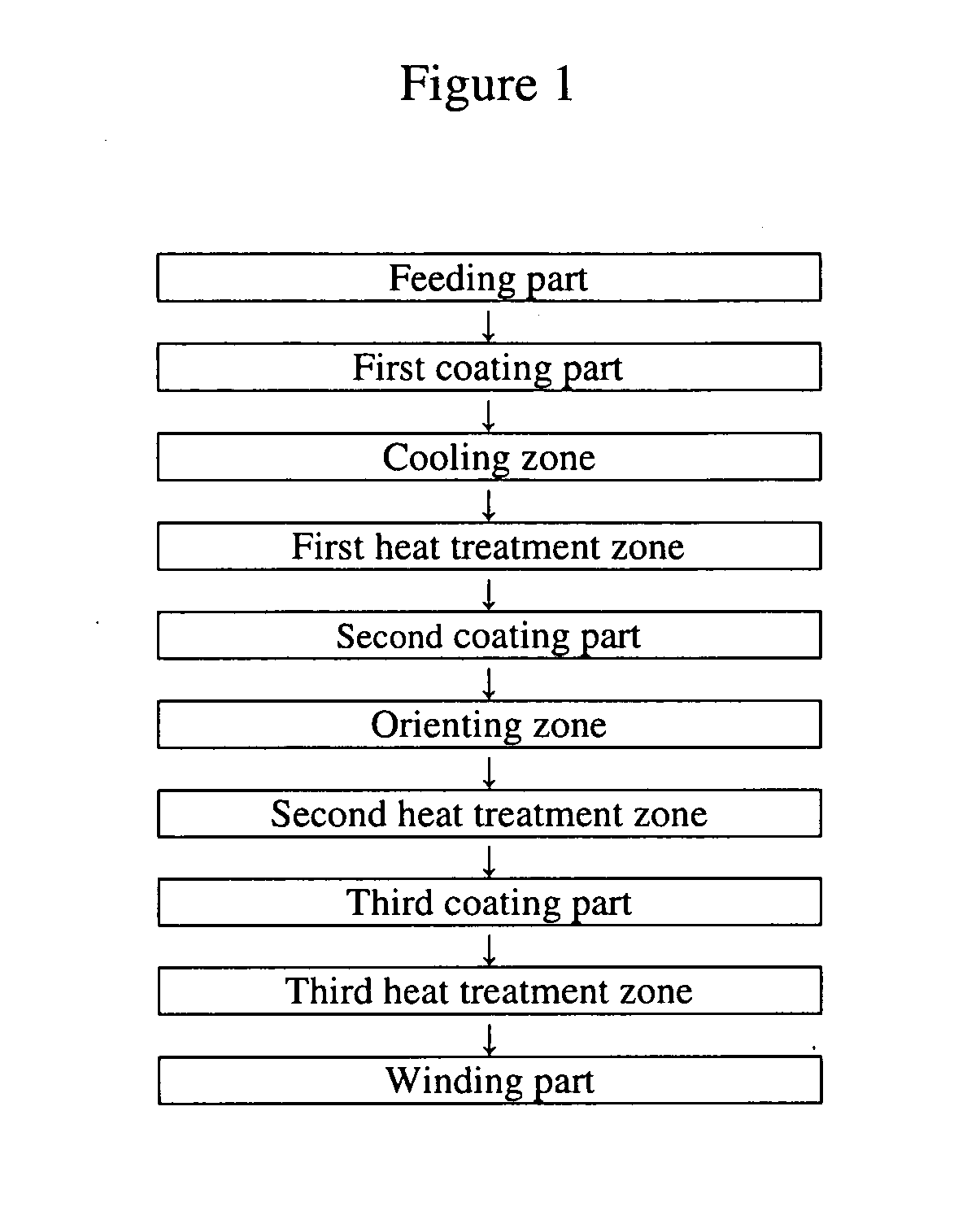
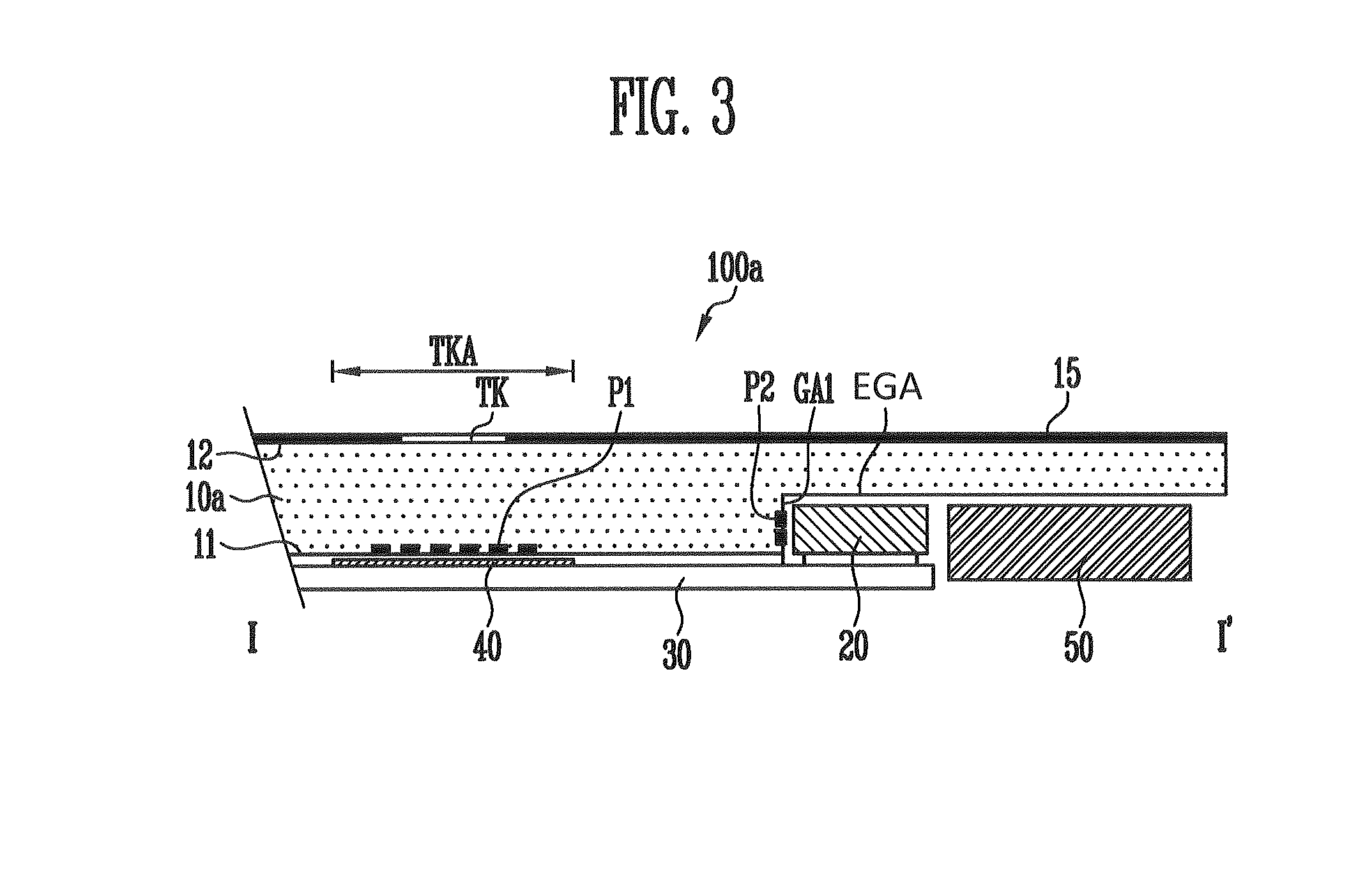
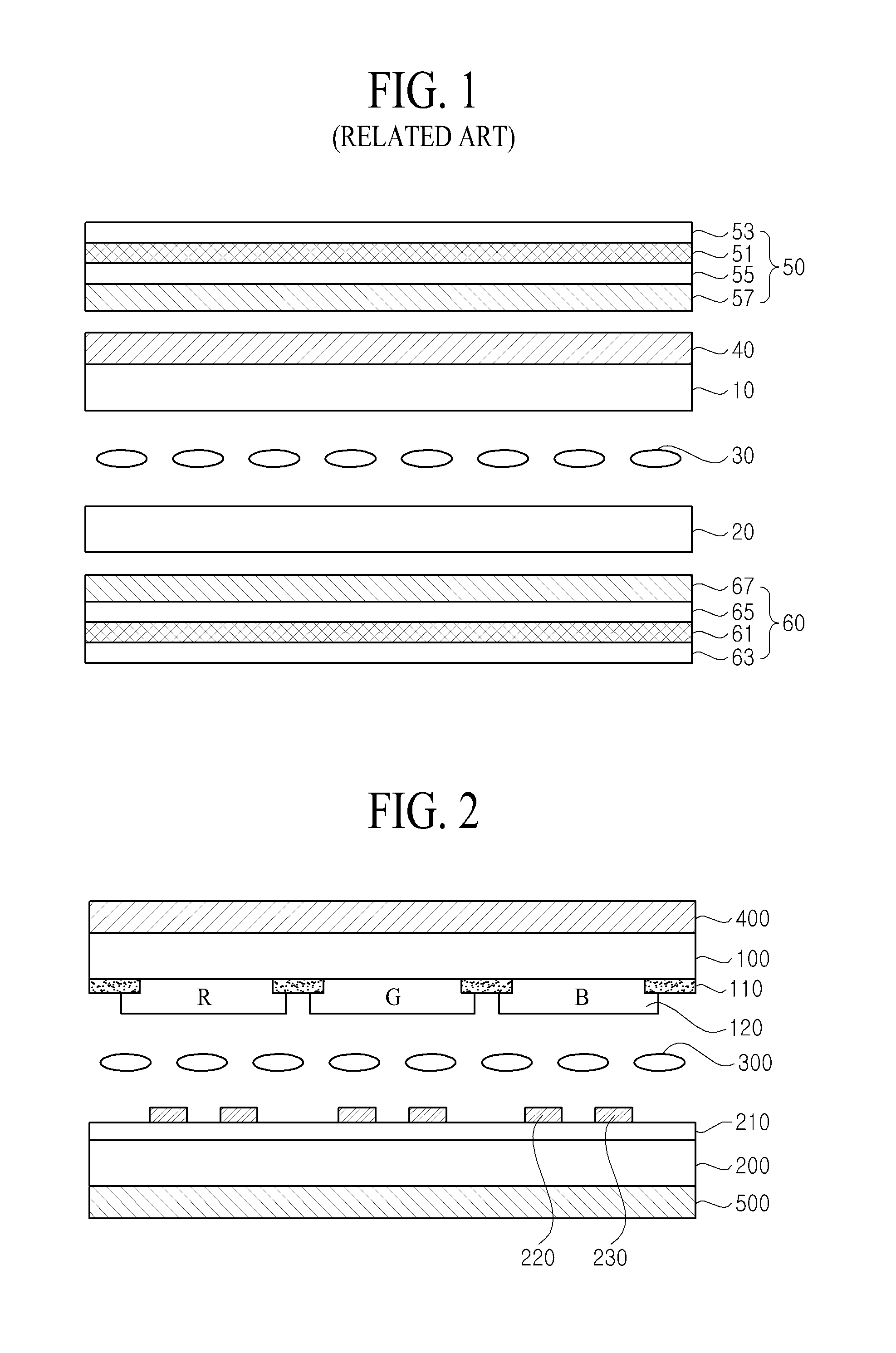
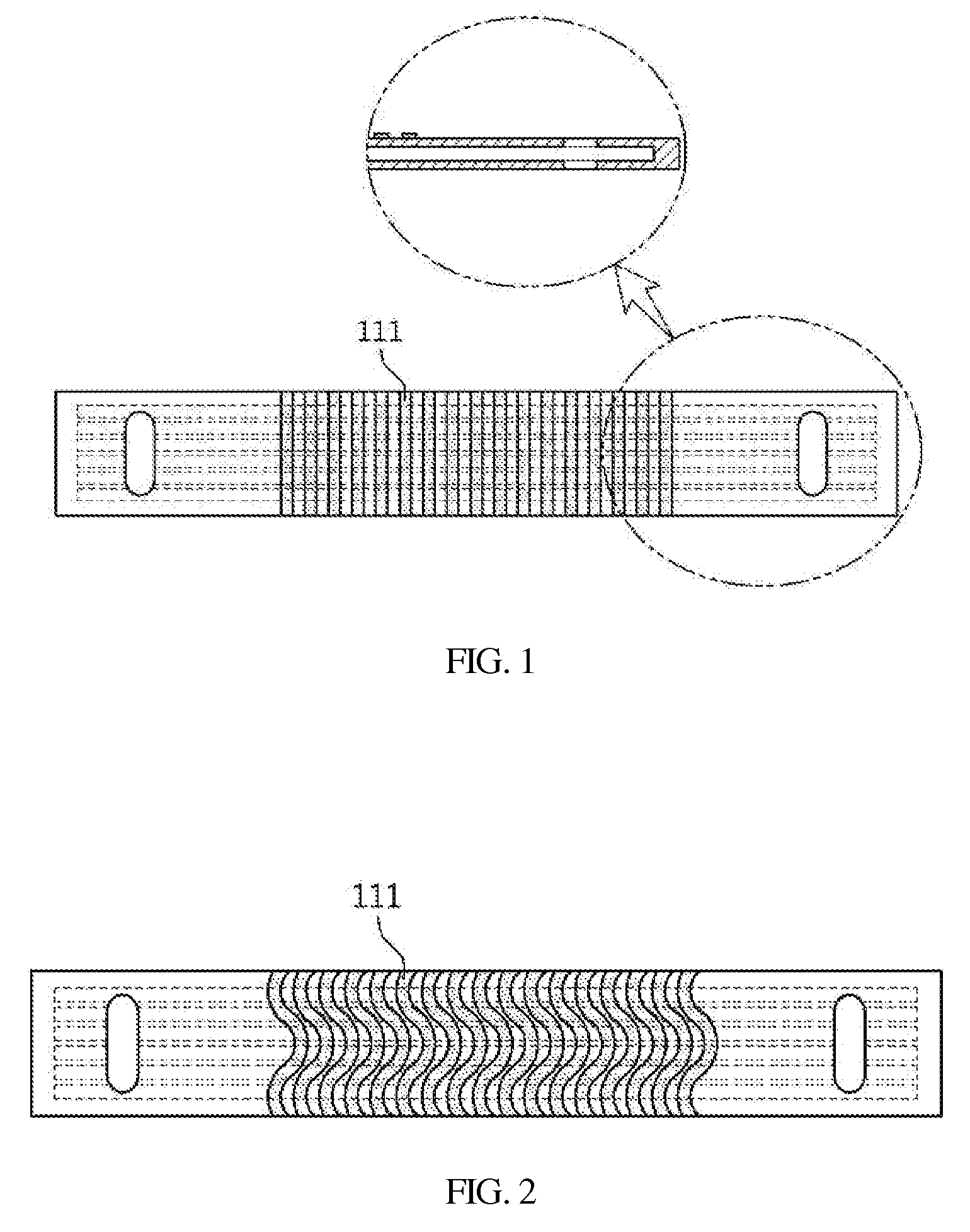
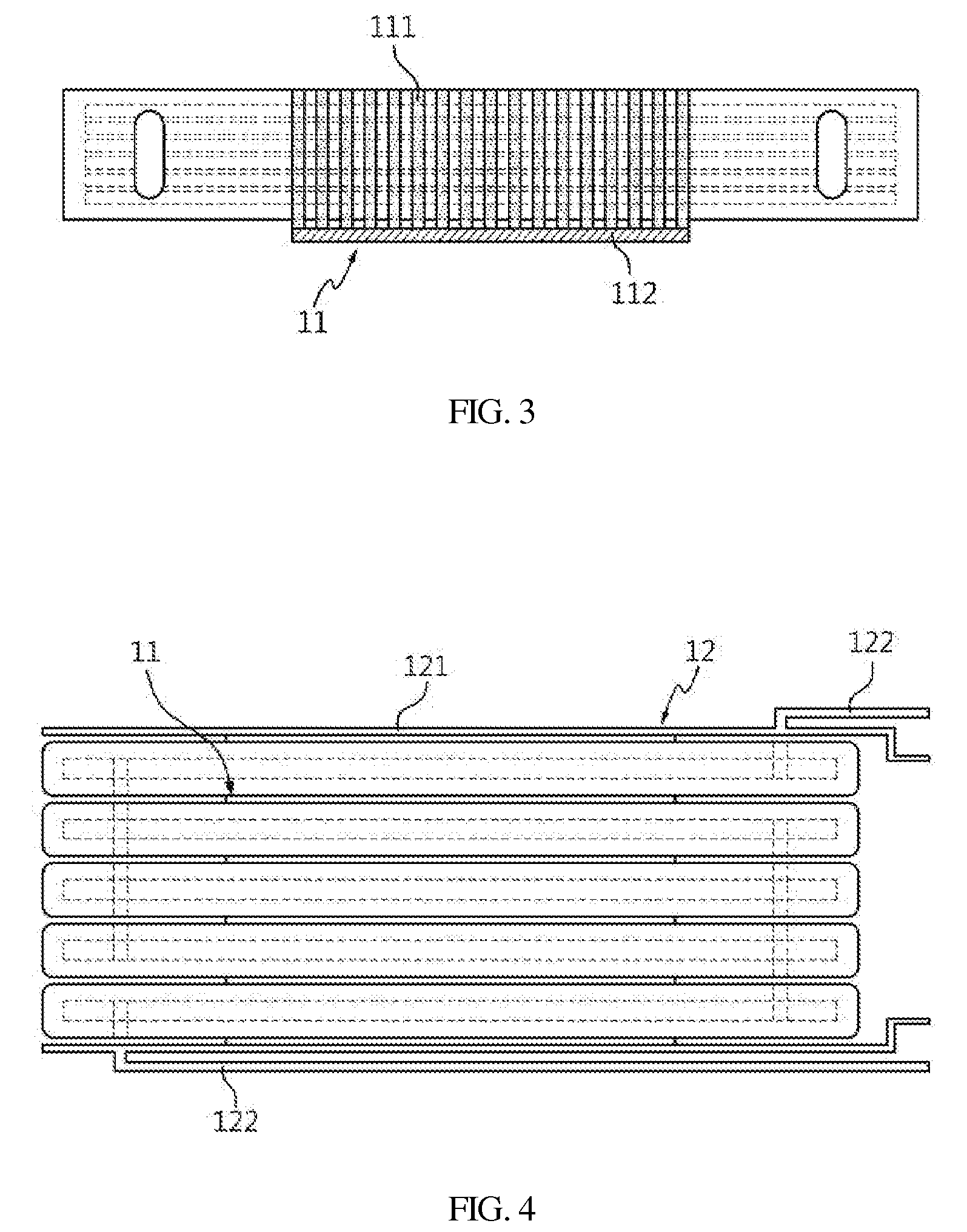
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
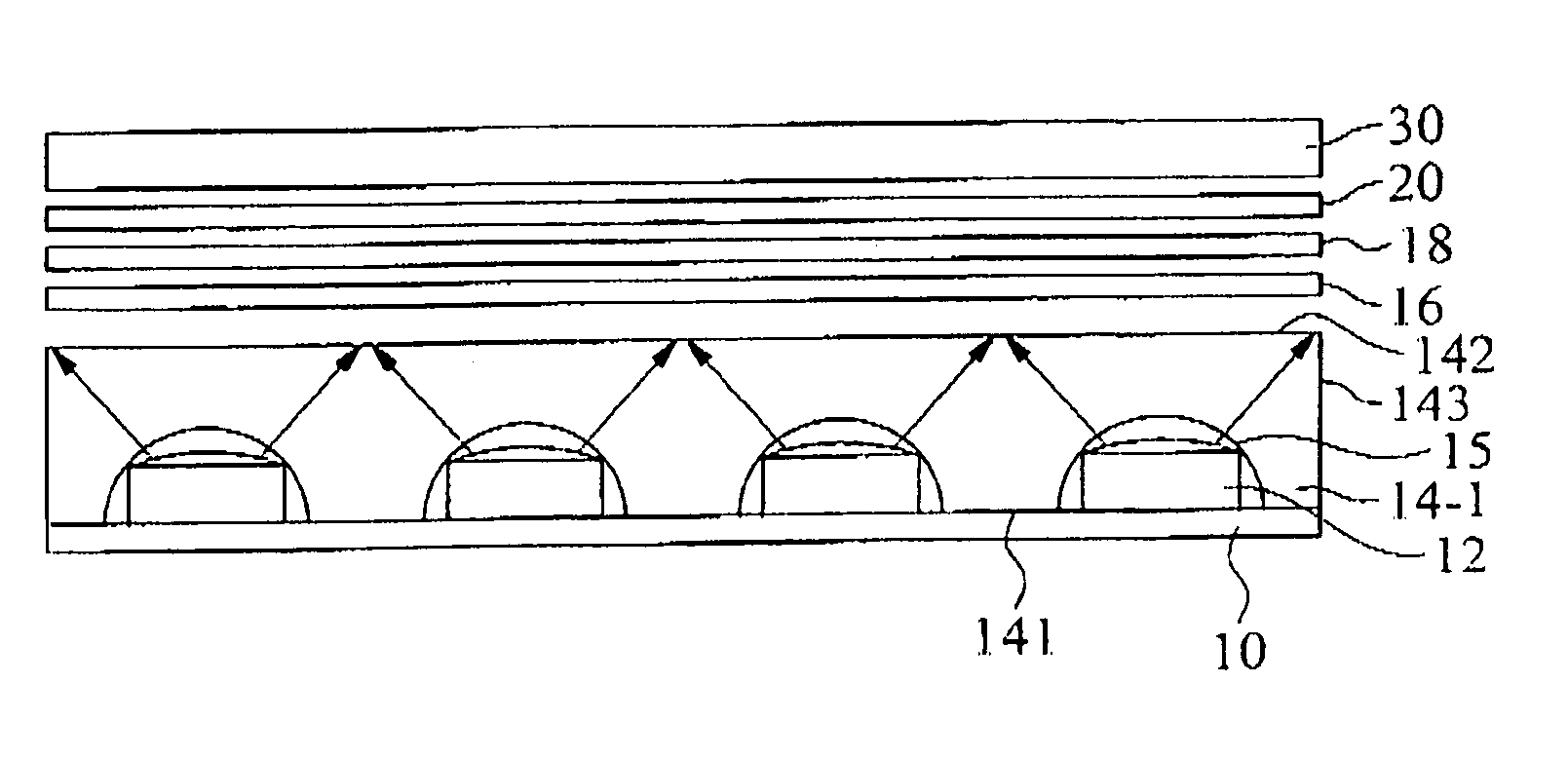
ActiveUS20160189739A1Decrease thicknessIncrease lengthBase layers for recording layersTape carriersTotal thicknessPeak area
Provided is a magnetic tape, which comprises, on a nonmagnetic support, a nonmagnetic layer comprising nonmagnetic powder and binder, and on the nonmagnetic layer, a magnetic layer comprising ferromagnetic powder and binder; wherein a total thickness of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 4.80 μm; at least the magnetic layer comprises one or more components selected from the group consisting of a fatty acid and a fatty acid amide; and a C—H derived carbon, C, concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio in a C1s spectrum obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy conducted at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees on a surface on the magnetic layer side of the magnetic tape is greater than or equal to 45 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
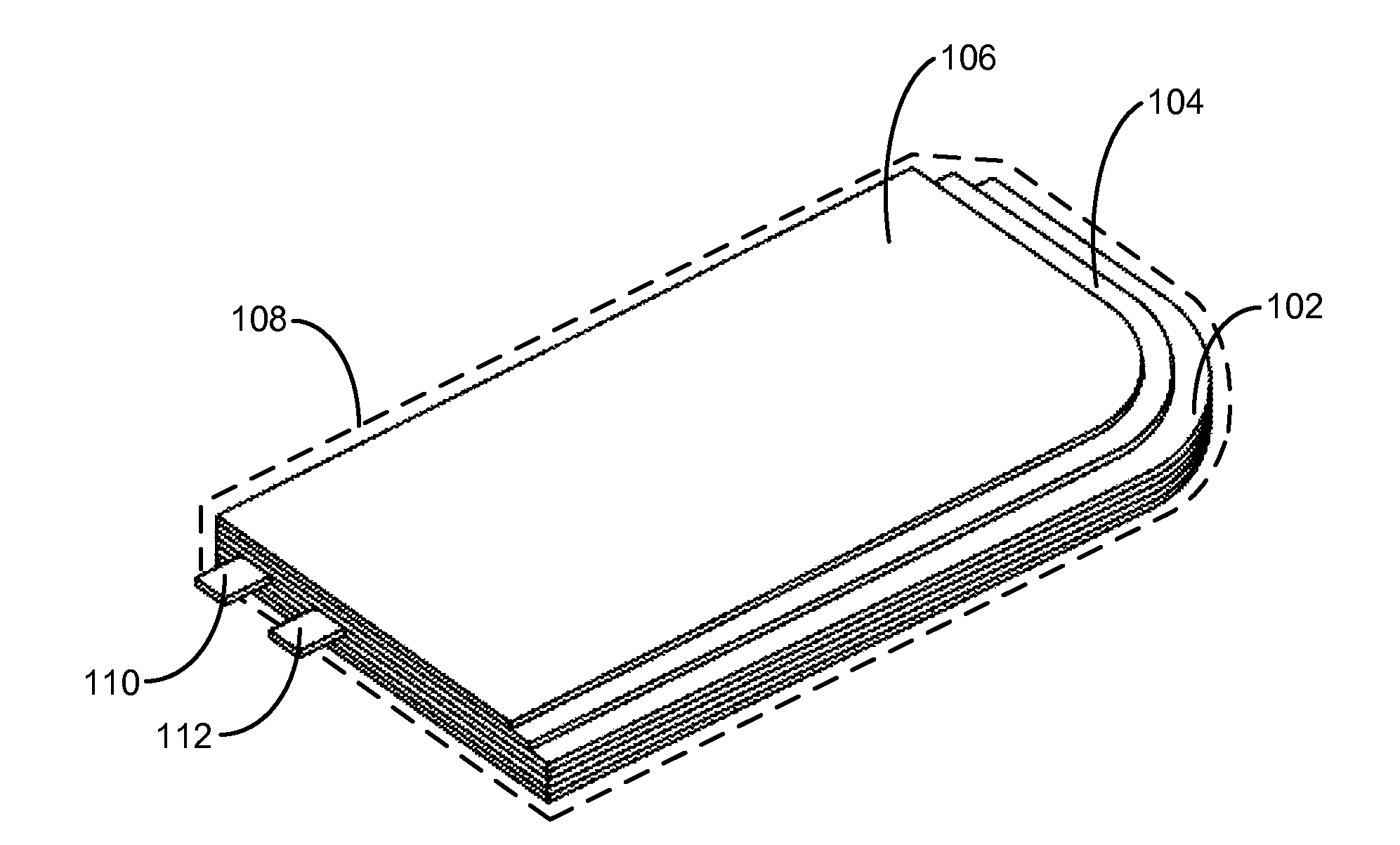
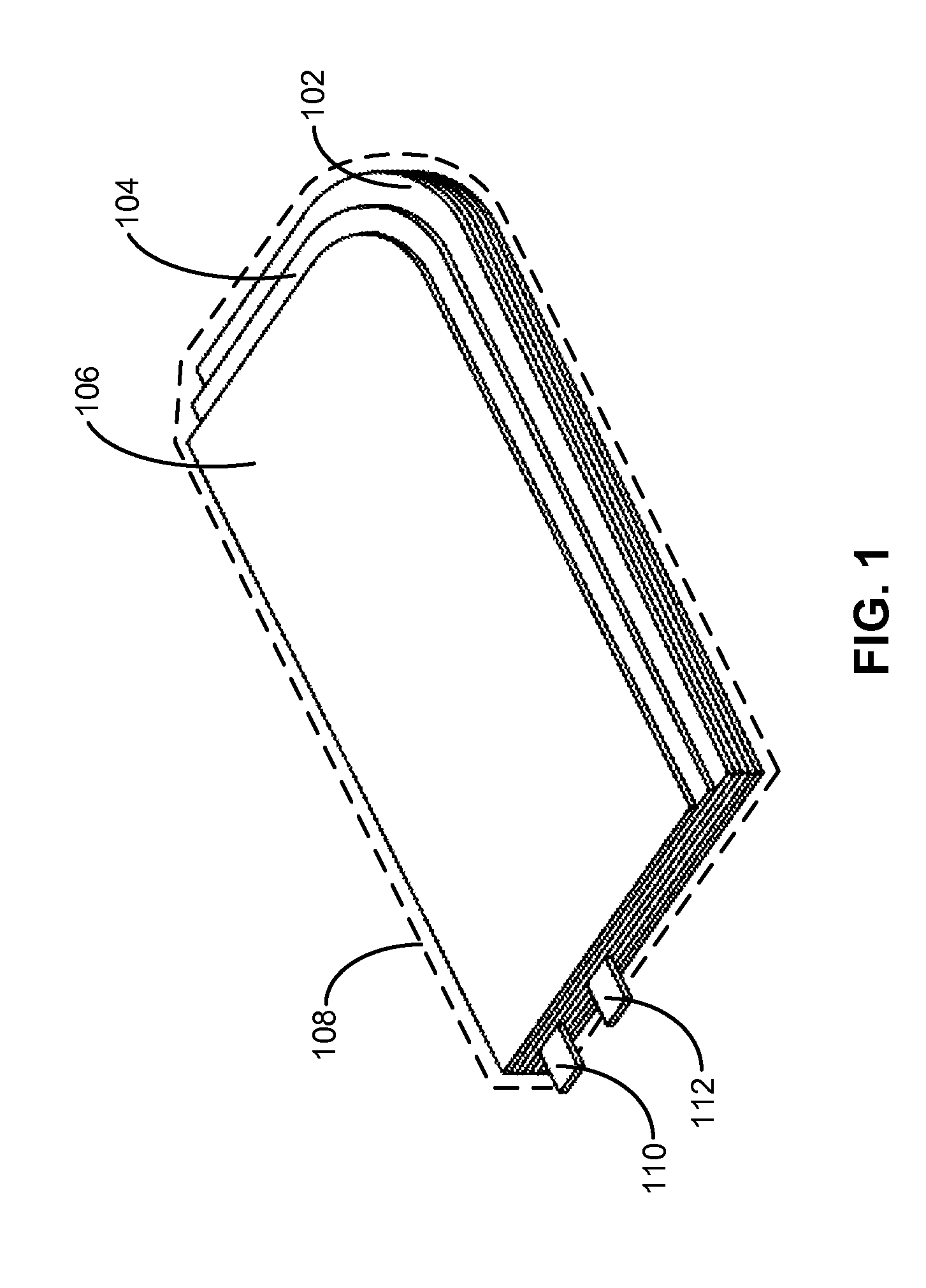
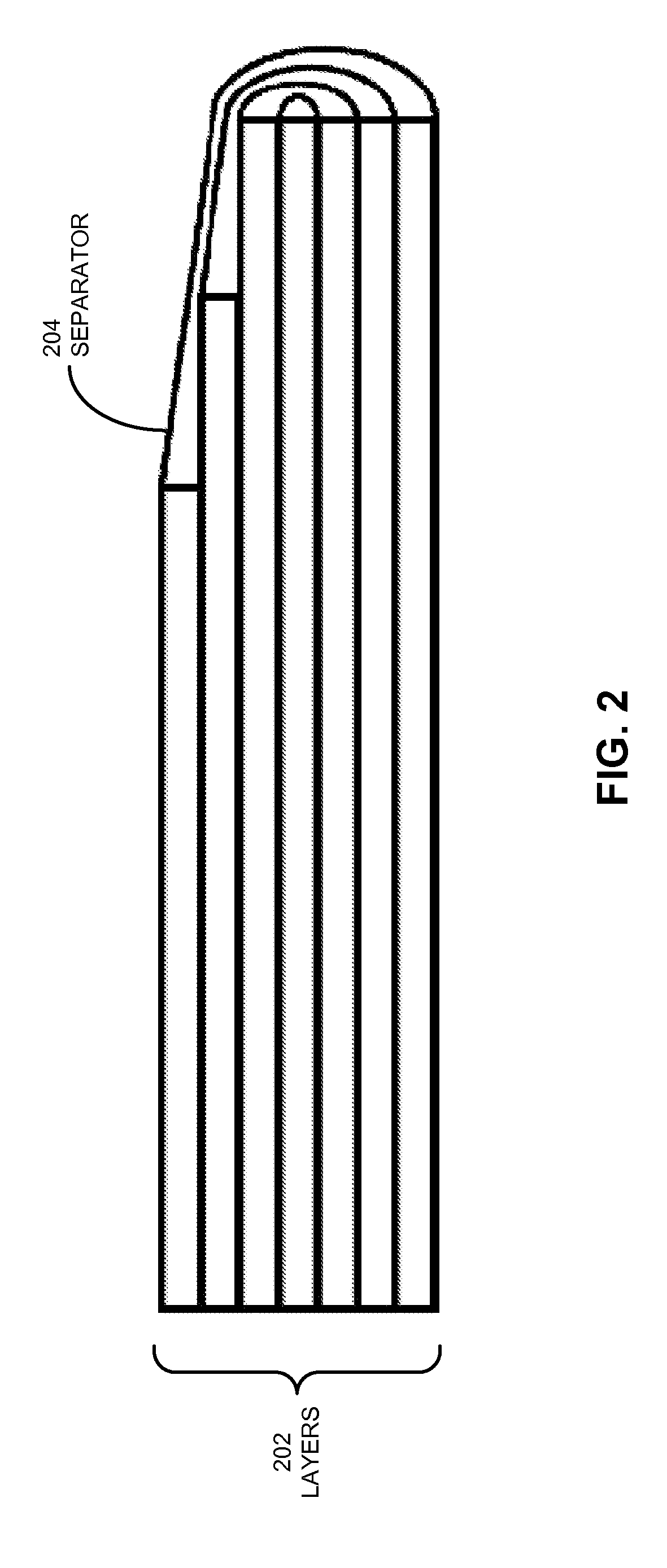
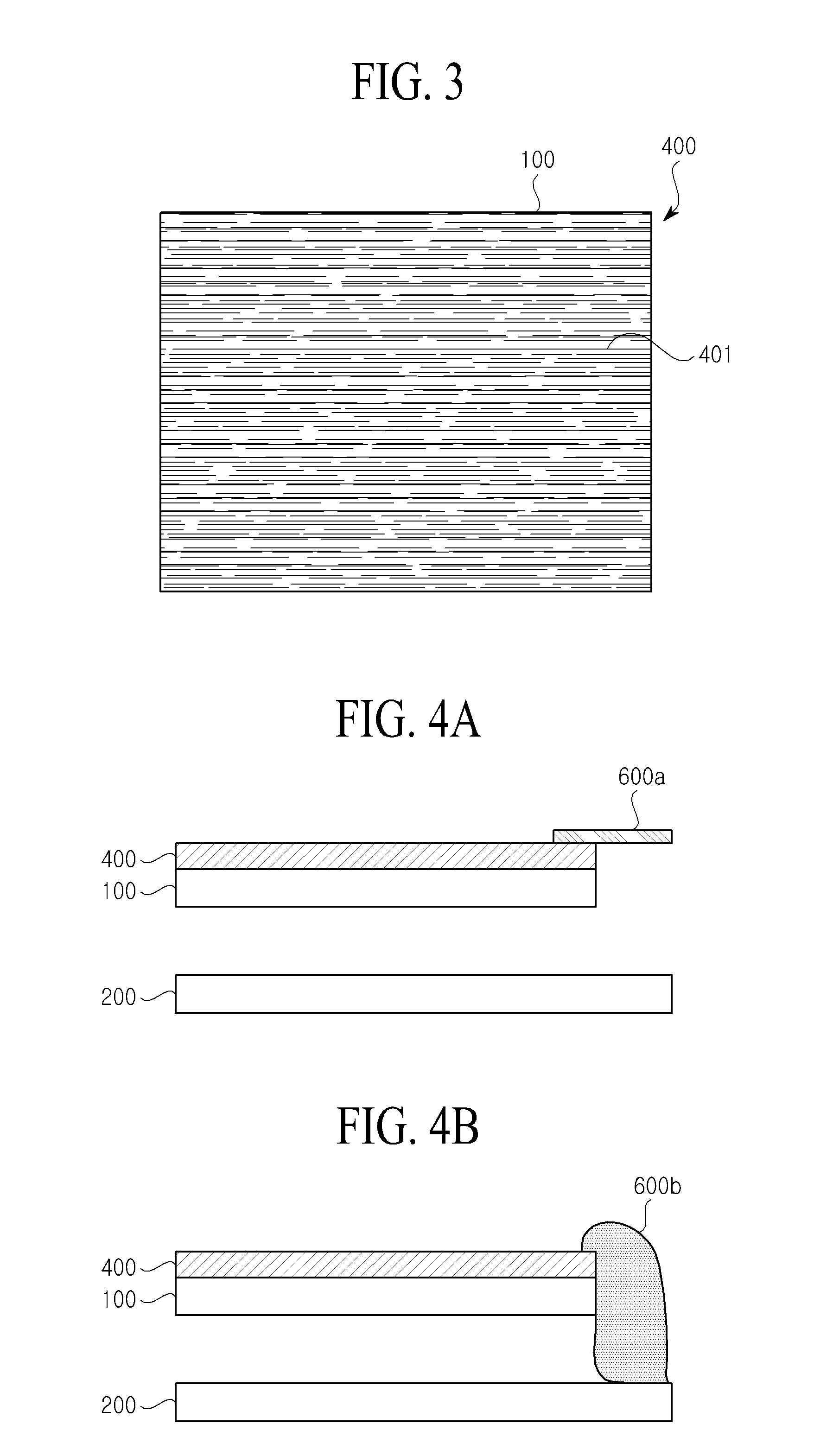
Non-rectangular batteries for portable electronic devices
ActiveUS20130108906A1Decrease thicknessPrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureAnodeElectronic equipment
The disclosed embodiments provide a battery cell. The battery cell includes a set of layers forming a non-rectangular shape, wherein the set of layers comprises a cathode with an active coating, a separator, and an anode with an active coating. The battery cell also includes a first conductive tab coupled to the cathode and a second conductive tab coupled to the anode. The layers are enclosed in a flexible pouch, and the first and second conductive tabs are extended through seals in the pouch to provide terminals for the battery cell. Furthermore, the non-rectangular shape is created by removing material from one or more of the layers.
Owner:APPLE INC
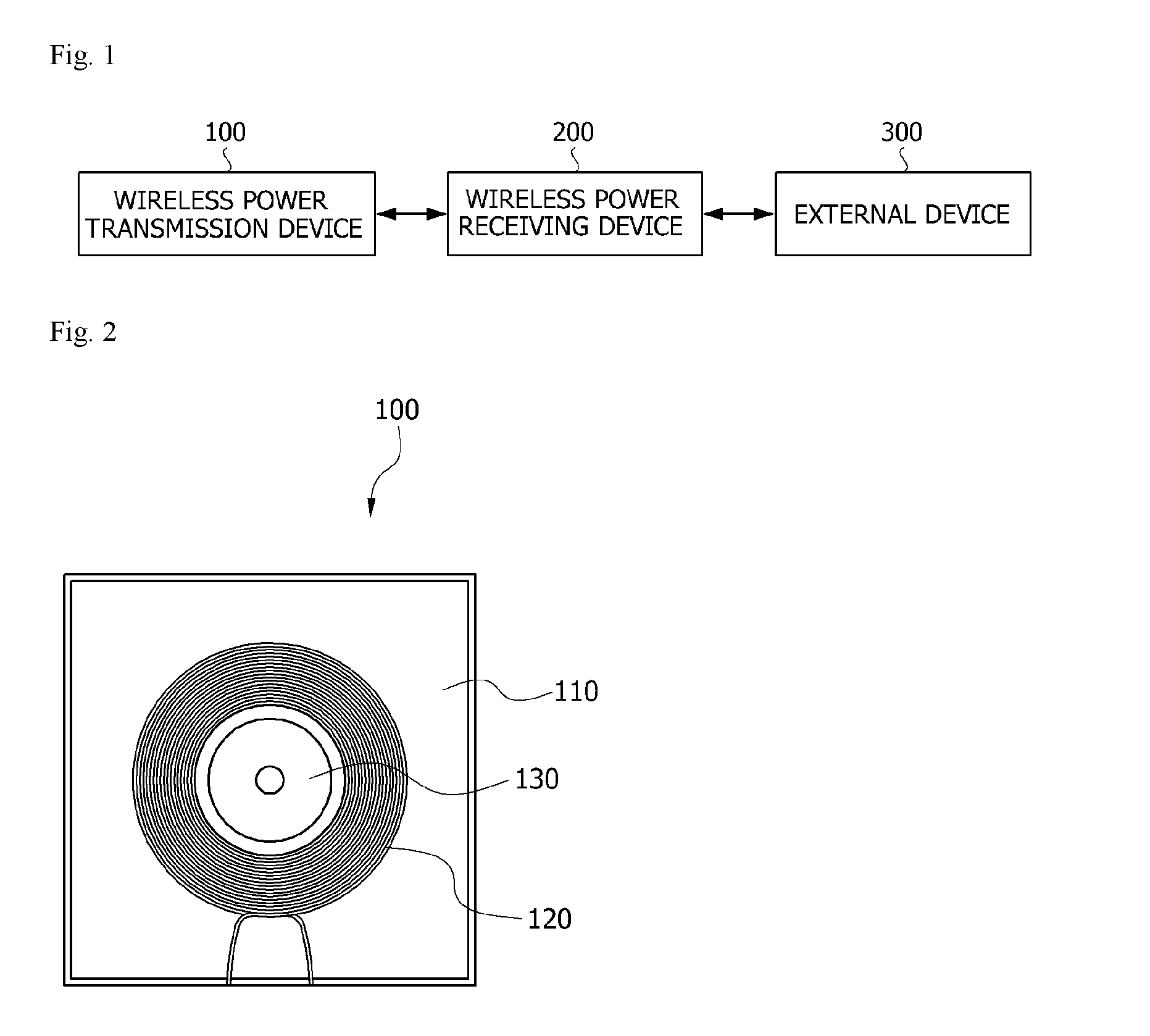
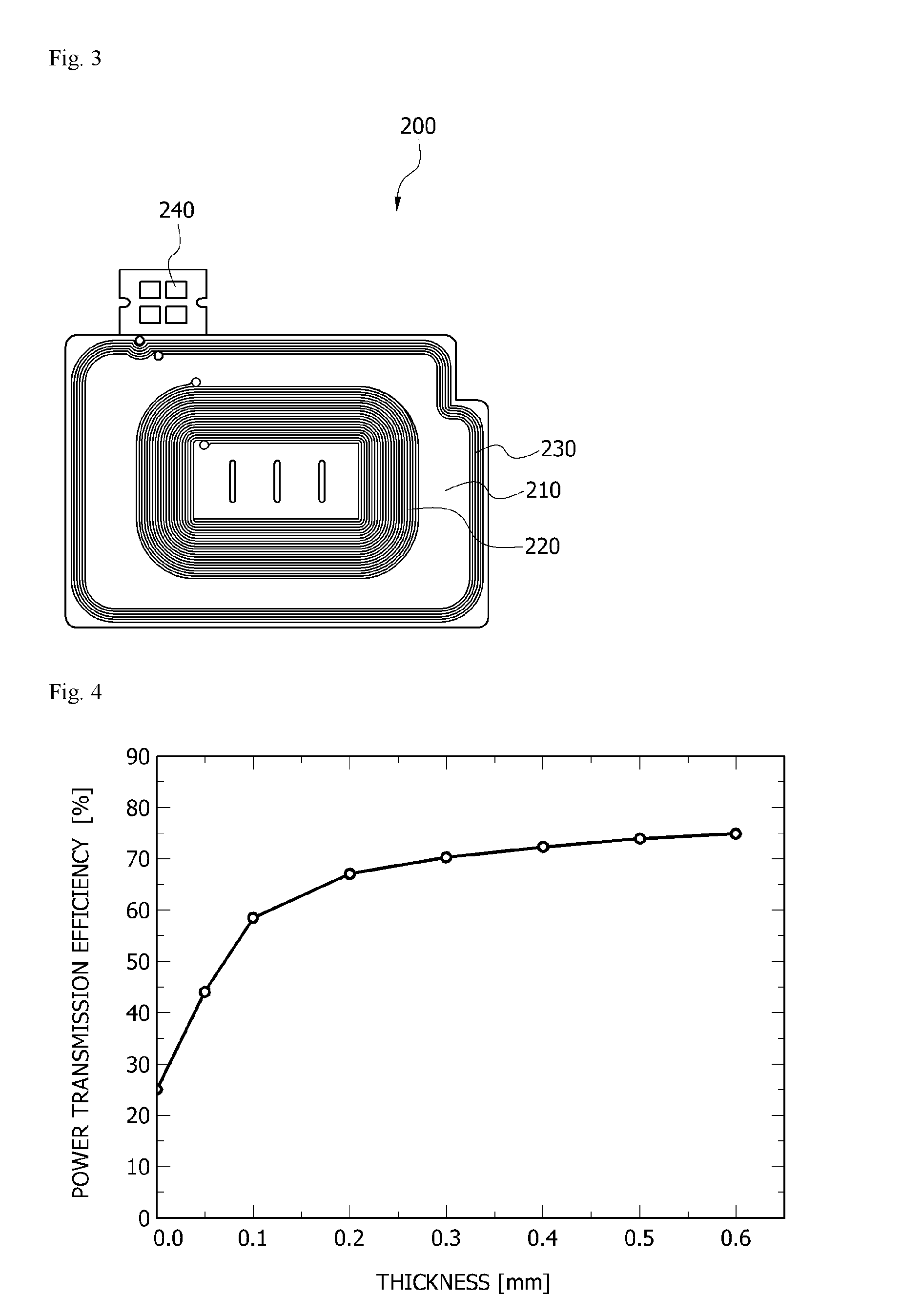
Receiving Antenna and Wireless Power Receiving Device Including the Same
ActiveUS20160156215A1Improved power transmission efficiencyDecrease thicknessLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreNear-field transmissionPhysicsReceiver coil
A receiving antenna of a wireless power receiving device wirelessly charging electric power according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a substrate, a first soft magnetic layer stacked on the substrate, and including a soft magnetic material, and a receiving coil configured to receive electromagnetic energy emitted from a wireless power transmission device, and including a first coil layer wound in parallel with the soft magnetic layer, and a second coil layer electrically connected to the first coil layer and wound in parallel with the first coil layer, and a current direction of the first coil layer is opposite to a current direction of the second coil layer.
Owner:SCRAMOGE TECH LTD
Planar display structure with LED light source
InactiveUS7557781B2Decrease thicknessReduce thicknessMechanical apparatusStatic indicating devicesOptoelectronicsLight guide
A planar display structure with LED light source includes a plane light source constituted by a plurality of LEDs and a light guide plate, wherein the light guide plate has a plurality of recesses that the above LEDs can be put into.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Semiconductor device
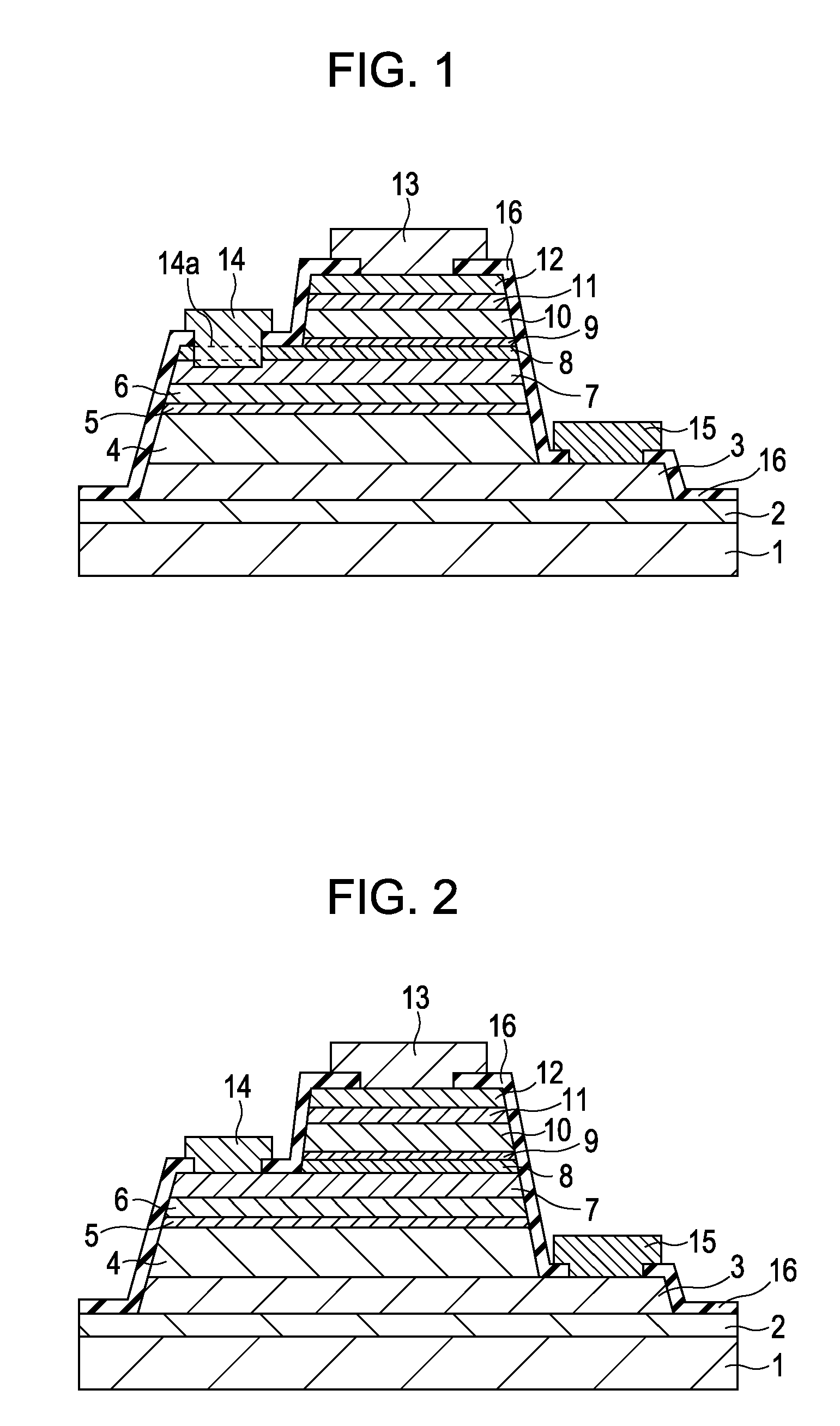
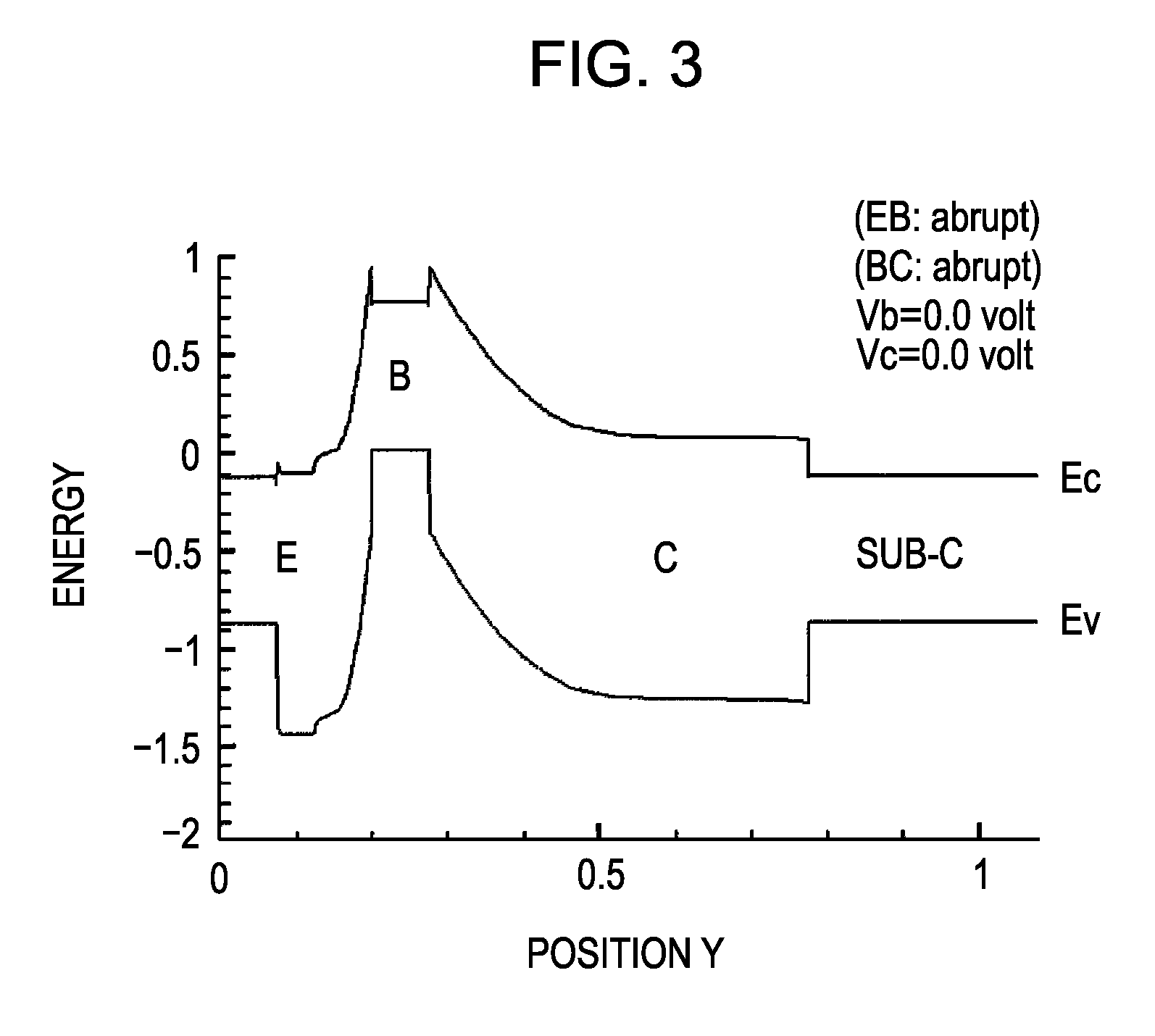
ActiveUS20070023783A1Decrease thicknessEasy to produceSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorDevice material
A semiconductor device includes an emitter layer: a base layer; and a collector layer, wherein the collector layer and the emitter layer each include a heavily doped thin sublayer having a high impurity concentration, and each of the heavily doped thin sublayers has an impurity concentration higher than those of semiconductor layers adjacent to each heavily doped thin sublayer.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
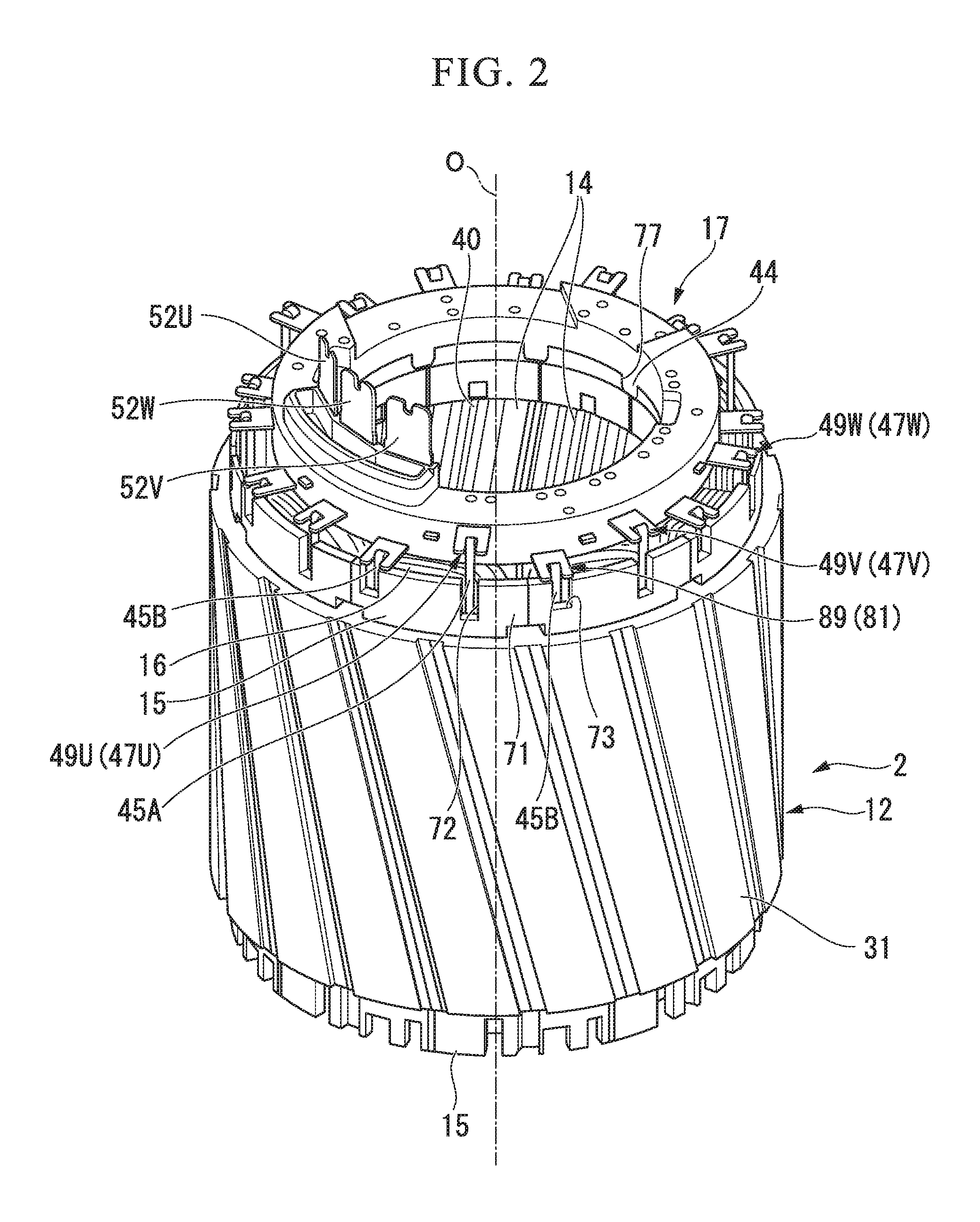
Bus bar unit, method for manufacturing bus bar unit, and brushless motor
InactiveUS20160218578A1Improved yieldDecrease manufacturing costWindings insulation shape/form/constructionManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectrical and Electronics engineeringBrushless motors
A bus bar unit is configured to supply power to coils (16) of a plurality of phases, and includes phase bus bars (47U ), (47V), and (47W) which are provided for each phase and are connected to winding start ends of the coils, and a neutral point bus bar (81) which is connected to winding finish ends of the coils, the neutral point bus bar (81) being formed by bending an elongated plate-shaped member such that a width direction of the elongated plate-shaped member and a radial direction of the bus bar unit coincide with each other, and including a plurality of bus bar pieces (82) and a connection portion (83) which connects the bus bar pieces (82) and (82) adjacent to each other, and a width of a deformation portion (85) of the connection portion (83) being narrower than a width of the bus bar piece (82).
Owner:MITSUBA CORP
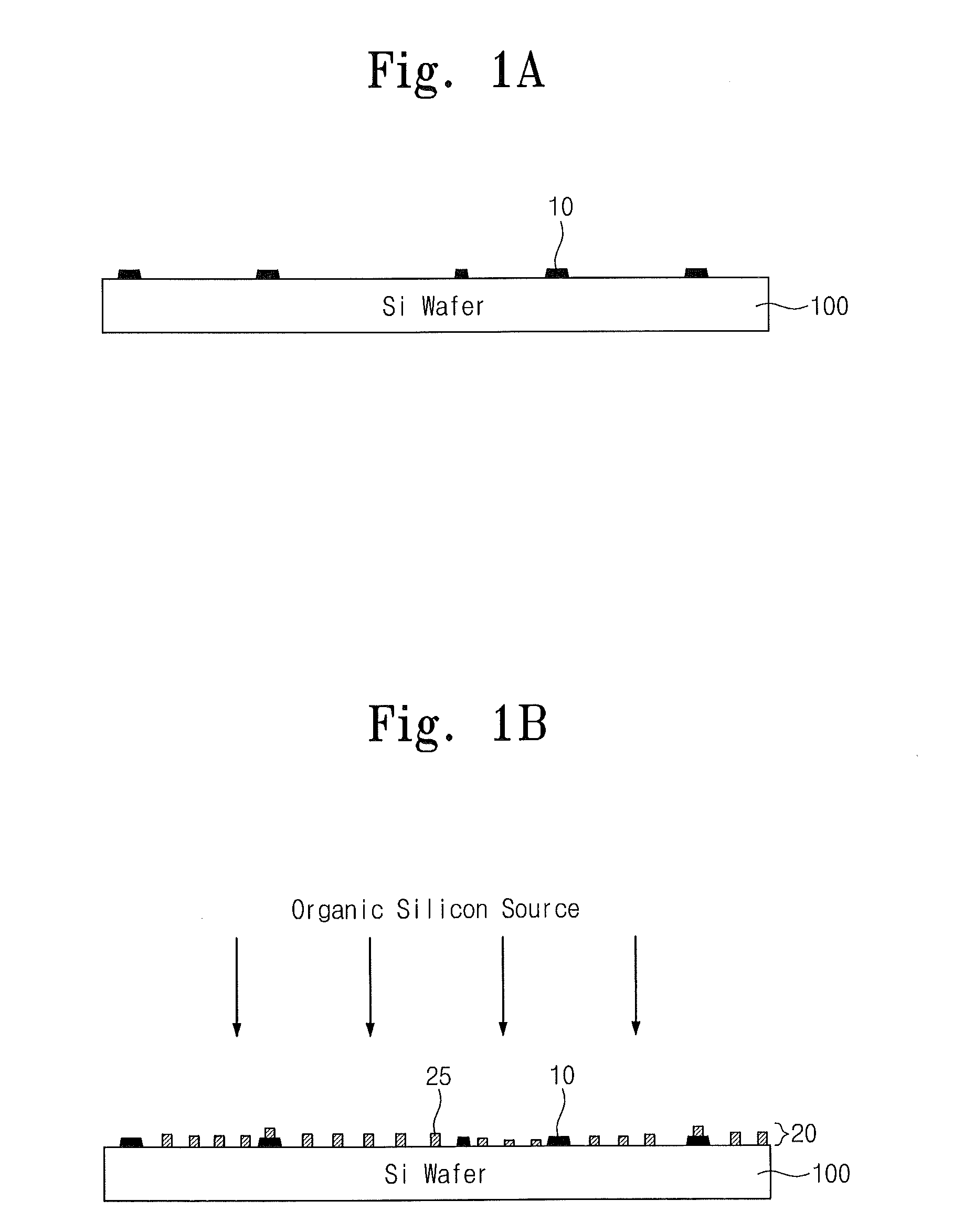
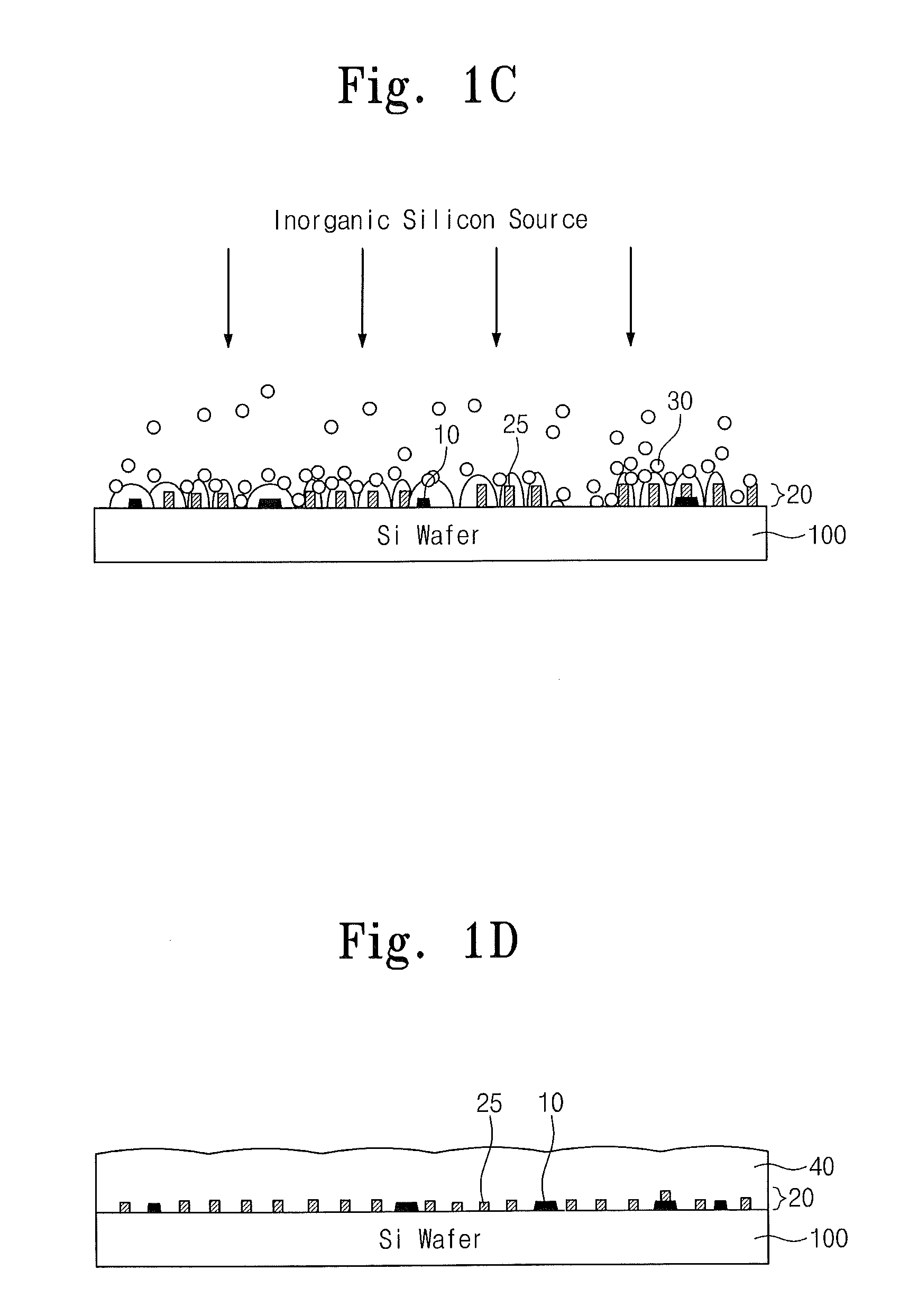
Methods of forming a thin film and methods of fabricating a semiconductor device including using the same
ActiveUS20130164907A1Decrease thicknessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor deviceSemiconductor device modeling
Provided are methods of forming a thin film and methods of fabricating a semiconductor device including the same. The thin film forming methods may include supplying an organic silicon source to form a silicon seed layer on a lower layer, the silicon seed layer including silicon seed particles adsorbed on the lower layer, and supplying an inorganic silicon source to deposit a silicon film on the lower layer adsorbed with the silicon atoms.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Lever switch
InactiveUS6172311B1Decrease thicknessEasily assembleContact operating partsOptical signallingEngineeringMechanical engineering
In a lever switch assembly, a sliding portion is formed on a bracket at an area located inside a first unit case. The sliding portion is constructed so as to slide along a face inside the first unit case which is directed facing away from a second unit case. With this arrangement, a projection conventionally provided at a tip end of the bracket has become unnecessary, and an overall thickness of the assembly can be decreased. During assembly, the sliding portion is blocked by the face inside the first unit case which is directed facing away from the second unit case and therefore, the bracket will be prevented from being disengaged at a stage before the second unit case is assembled.
Owner:KK TOKAI RIKA DENKI SEISAKUSHO
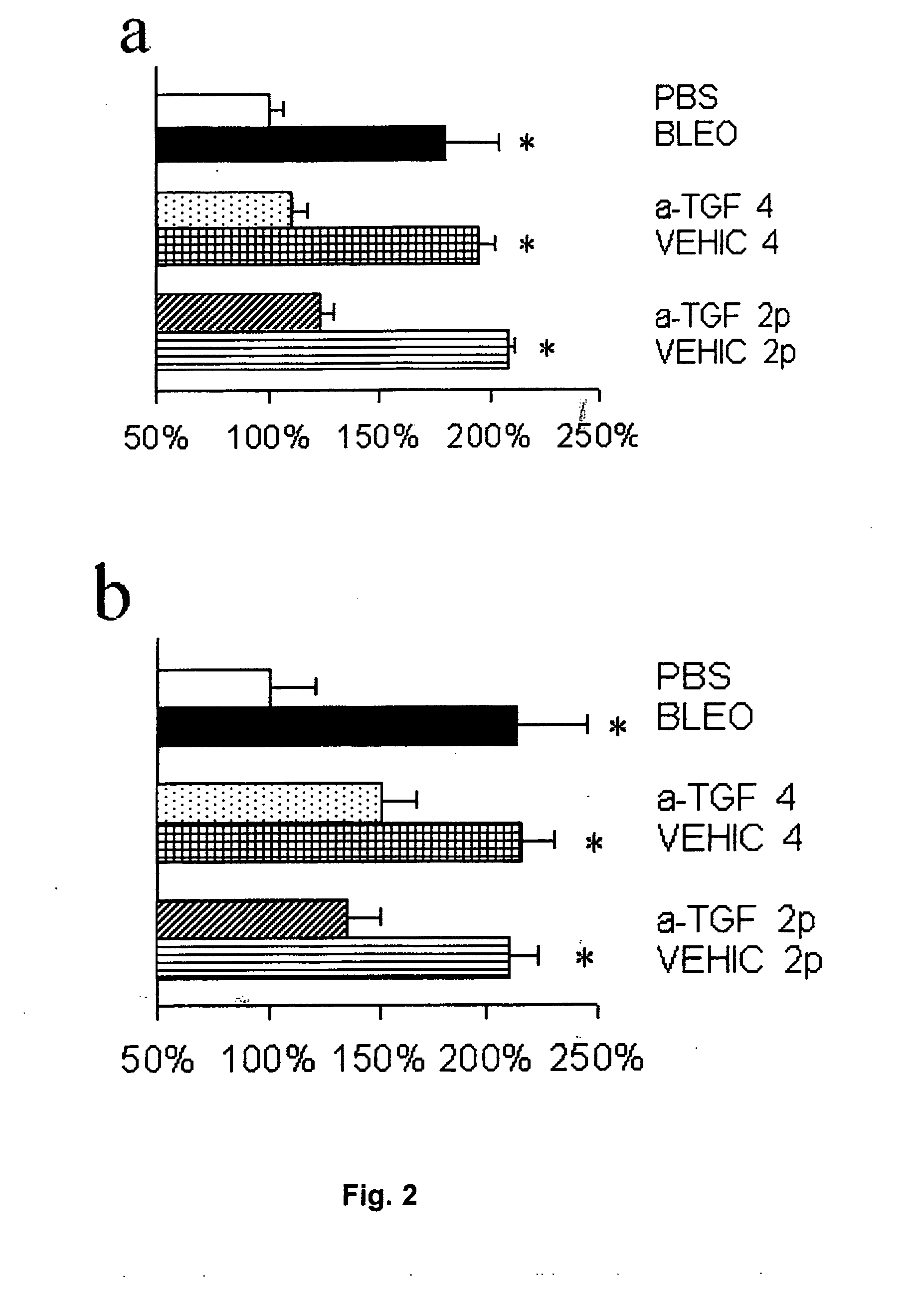
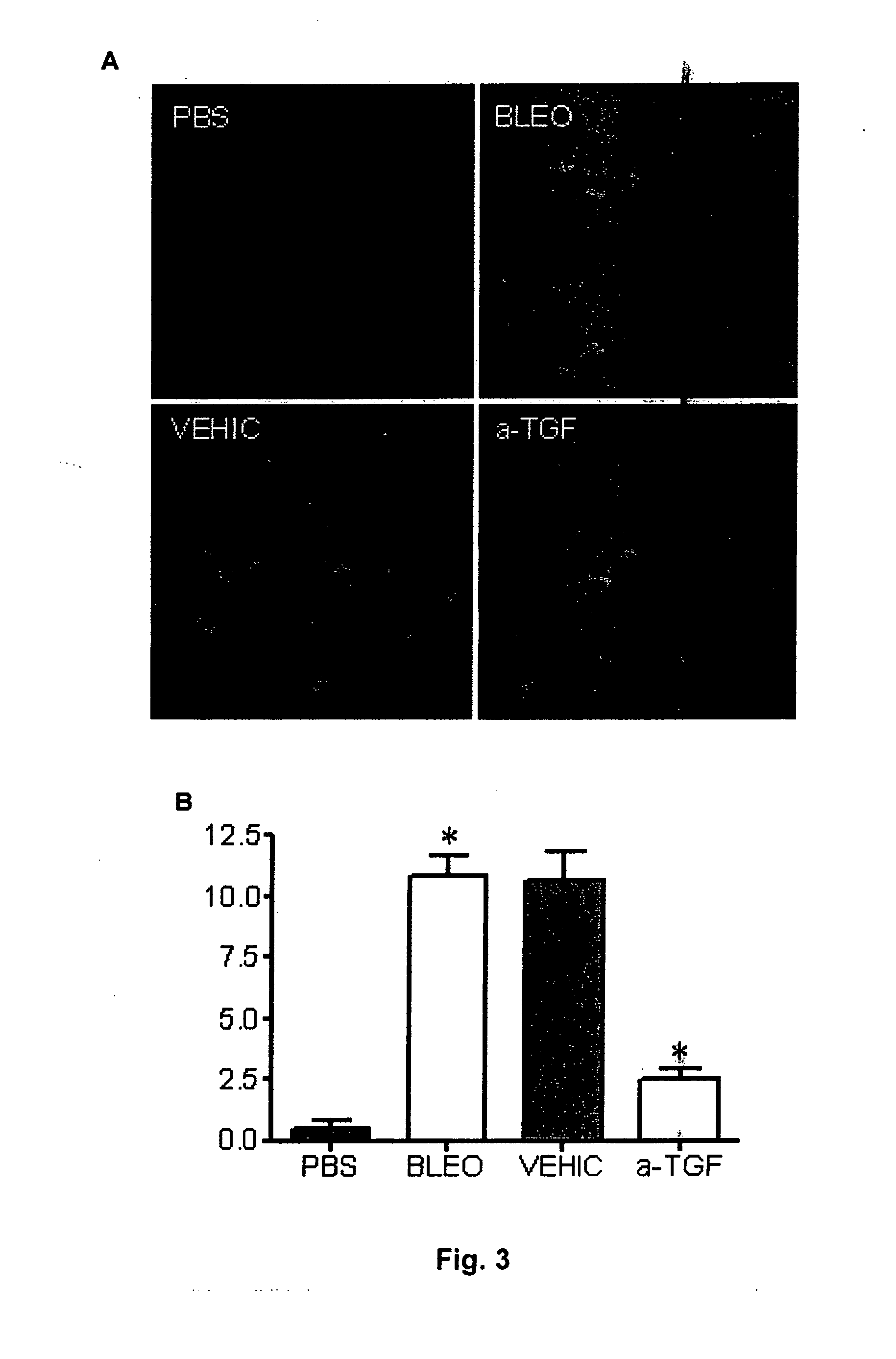
Method for the treatment of skin fibrosis and suitable compositions for such treatment
InactiveUS20070207965A1Reduction in potential effectDecrease thicknessPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesPeptideDisease
A Method for the treatment of skin fibrosis with a peptide that inhibits TGF-β, and suitable compositions for its administration. The method includes in particular, the use of peptide P144, a compound that is a known inhibitor of TGF-β, for the treatment of skin fibrosis by topical application. The method is shown effective in an animal model of bleomycin-induced skin sclerosis, to a reduction both of the skin fibrosis and of the content of soluble collagen, without any signs of systemic toxicity being detected. This shows that P144 is effective for topical application in mammals for treating fibrotic skin diseases and pathological scarring of the skin. For the administration of this peptide, stable compositions are also supplied, with pleasant appearance without being greasy, with good spreading characteristics and with a viscosity that permits it to be processed easily in industrial plant, and which are suitable for administering the peptide to humans.
Owner:DIGNA BIOTECH
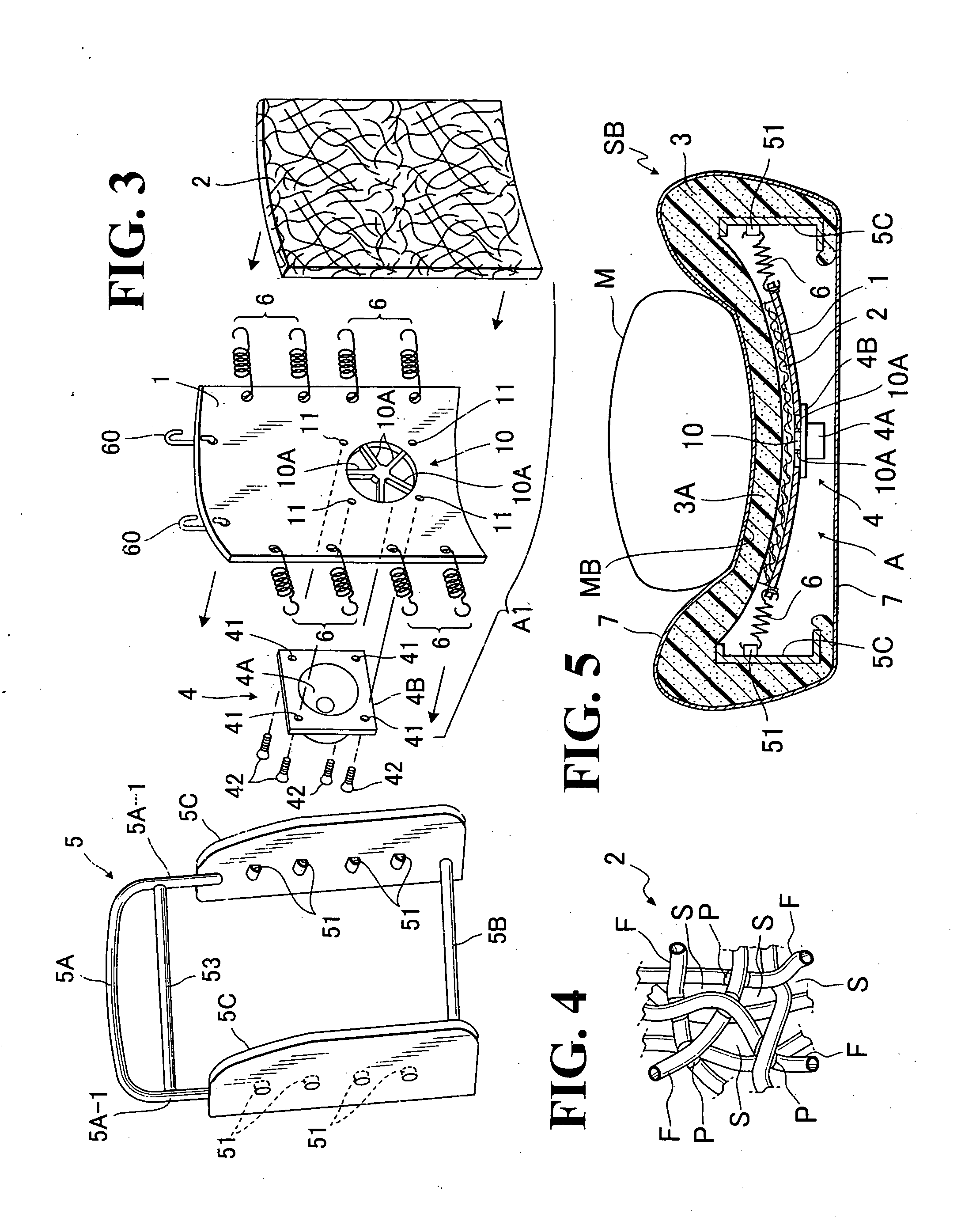
Acoustic structure of seat back
An acoustic structure of seat back includes a suspension board element provided therein. The suspension board element, which has a speaker unit provided to a backward surface thereof, is resiliently provided in a seat back frame of the seat back. A sound-conductive cushion element of a flat plate configuration is juxtaposed on a forward surface of the suspension board element. Those seat back frame and sound-conductive cushion element are covered with a foam padding and a trim cover assembly to thereby form such an acoustic seat back structure wherein all the suspension board element, speaker unit and sound-conductive cushion element are resiliently supported within the seat back, as an acoustic and vibration generator unit effective for imparting sound and vibration directly to a back portion of seat occupant.
Owner:TACHI S CO LTD
Liquid Crystal Display Device
InactiveUS20120176325A1Manufacturing cost be increaseDecrease thicknessStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsPolarizerTouch panel
A liquid crystal display device includes a touch panel constructed from a single substrate plate and disposed over a liquid crystal display panel. A color filter is disposed over a TFT substrate, and the touch panel is bonded onto the color filter substrate by way of a first adhesion layer. An upper polarizing plate is bonded over the touch panel, and a front window is bonded over the upper polarizing plate via a second adhesion layer. The front window covers a terminal portion which is a portion where only the TFT substrate exists so as to physically protect the portion. Since the upper polarizing plate is disposed over the touch panel, the connection portion of the flexible wiring substrate for the touch panel does not contact with the front window. Thus, the touch panel can be prevented from being strained.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Superior slim type of speaker slim high-powered amplifier
InactiveUS20080253590A1Shorten in lengthDecrease thicknessTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsDeaf-aid setsLoudspeakerEngineering
A superior slim type of speaker comprises: a baffle, a hole being disposed at a center of the baffle, an vibrating system being disposed at an inner edge of the hole; a voice coil, a periphery of a bottom surface of the vibrating system being connected to a top edge of the voice coil, an outer edge of the voice coil being set a coil, the voice coil being adjacent to two sides of an outer edge of the coil, and the two sides being connected to two lead wires respectively; and a U-type iron member, a loop groove is disposed at a top periphery of the U-type iron member, two sides of the U-type iron member has two gaps respectively, and at least one side of each of the two gaps has an isolating portion; wherein when the U-type iron member is disposed at a bottom of the baffle, the voice coil is elongated to the loop groove in order to let the lead wires outwardly pass through the gaps and be upwardly fastened at a bottom surface of the baffle. As a conclusion, the distance between the lead wires and the U-type iron member are not necessarily considered, so that the length of the voice coil is shortened and the thickness of the whole speaker is decreased as well.
Owner:SUN SZU WEI
Loudspeakers
InactiveUS20050084131A1High complianceDecrease thicknessPlane diaphragmsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsMass distributionFlexural rigidity
A method of making an acoustic member for a loudspeaker having an operative frequency range and acoustic output which depends on the values of parameters of geometry, bending stiffness, areal mass distribution, damping, tension modulus, compression modulus and shear modulus of the member, the method comprising providing an acoustic member having at least one frequency dependent parameter with a variation which depends on frequency, selecting the variation which depends on frequency, selecting the variation of the frequency dependent parameter to effect a desired acoustic output from the loudspeaker and making the member having said selected variation. The method may comprise selecting an acoustic member having a component made from a frequency dependent material which has a glass to rubber transition Tg in the operative frequency range of the speaker.
Owner:NEW TRANSDUCERS LTD
Touch screen panel
InactiveUS20140125610A1Decrease thicknessEasy to performDigital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingLight sourceTouchscreen
A touch screen panel includes a window, a light source portion, a touch key circuit board and a touch sensing portion. The window has a touch key area on which a touch key icon is displayed, and has a recessed portion formed adjacent to the touch key area in a first surface thereof. The light source portion is disposed inside the recessed portion so as to emit light. The touch key circuit board has the light source portion mounted thereon. The touch sensing portion is formed between the window and the touch key circuit board, geometrically corresponding to the touch key area.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Stimulus Indicating Device Employing Polymer Gels
ActiveUS20090010803A1Decrease thicknessDecreased surface areaAnalysis using chemical indicatorsThermometers using mean/integrated valuesPolymer gelBiomedical engineering
Owner:PRASIDIUX
Stereoscopic image control module and stereoscopic display device
InactiveUS20140009819A1Cost reductionDecrease thicknessNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceElectrical polarity
A stereoscopic image control module that can be disposed on a display module to form a stereoscopic image display module is provided. The stereoscopic image control module includes a first substrate, a touch composite layer, and a grating composite layer. The first substrate has a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface, and the touch composite layer is disposed on at least one of the first surface and the second surface and includes a plurality of touch electrodes. The grating composite layer is disposed on the second surface and includes a plurality of grating control electrodes and a grating layer, wherein the grating control electrodes change a polarity of the grating layer to determine a display mode.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Liquid crystal display device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150124186A1Manufacturing process be facilitateDecrease thicknessPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsCarbon nanotubeLiquid-crystal display
Disclosed is a liquid crystal display device and a method of manufacturing the same. The liquid crystal display device includes first and second substrates, a liquid crystal layer between the first and second substrates, and a first polarizing layer on the first substrate, wherein the first polarizing layer includes a plurality of carbon nanotubes aligned in a first direction.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Liquid crystal lens and 3D display device
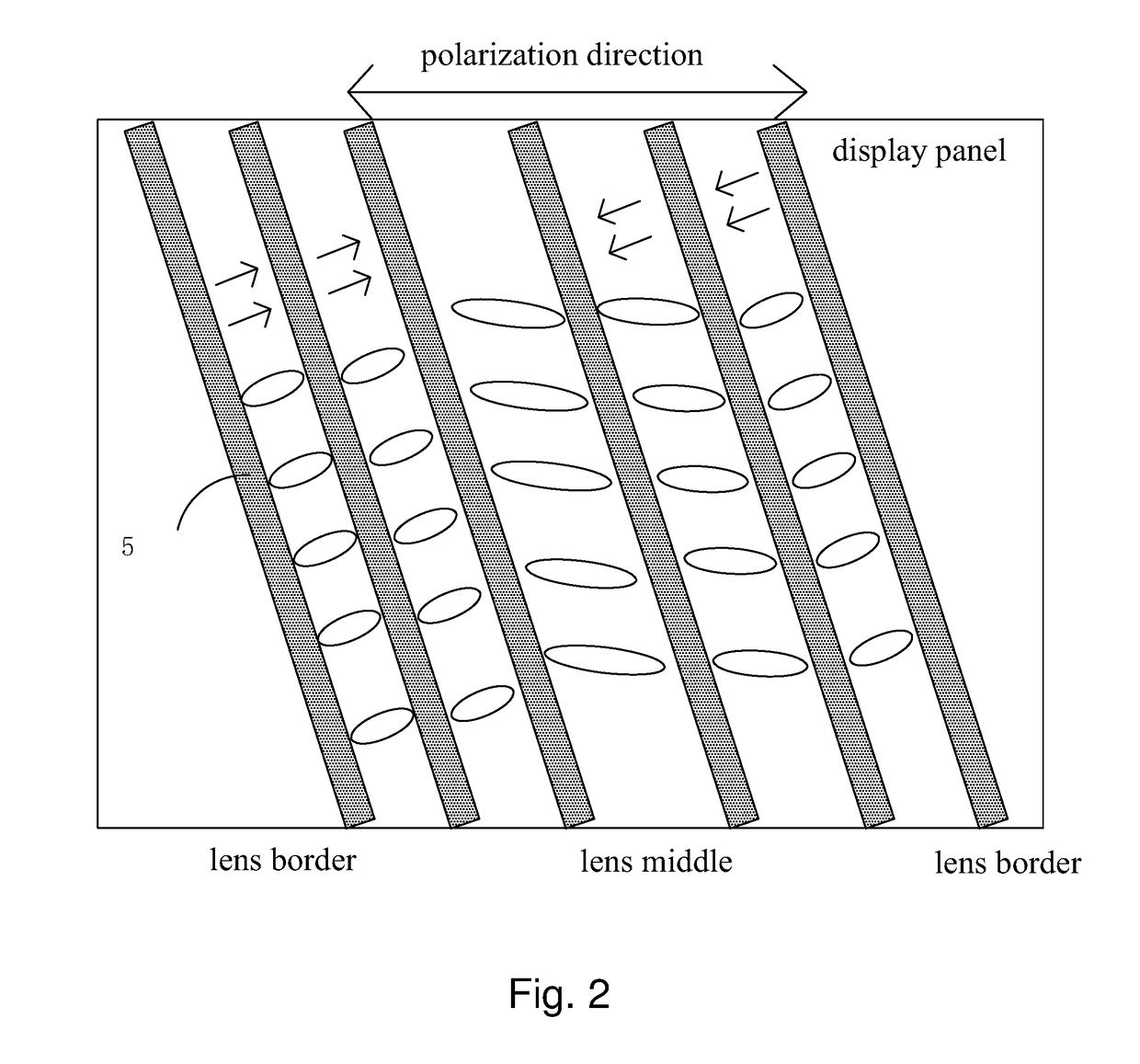
ActiveUS20180101054A1High qualityDecrease thicknessNon-linear opticsOptical elementsLiquid crystal3d image
The present invention provides a liquid crystal lens and a 3D display device. By utilizing the metal wire grid (20) to realize the functions of electrode and polarizer at the same time, and the polarizer filters the o light to solve the display degradation issue due to the o light leakage, and corresponding high quality 3D image display is realized. By combining function of the polarizer and the electrode in the metal wire grid (20), the additional polarizer adhesion is no longer required, which can effectively decrease the thickness of the liquid crystal lens. The present invention further provides a 3D display device, which can decrease the thickness of the 3D display device to realize the high quality 3D image display.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Method of forming a color filter layer on an array substrate and device thereof
InactiveUS6933993B2Decrease thicknessSimplify produce processOriginals for photomechanical treatmentNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayScan line
The present invention provides a color liquid crystal display device in which a color filter layer is formed on an array substrate. The array substrate includes a scan line and a data line forming a pixel, on which a thin film transistor is formed, and a pixel electrode is connected to the thin film transistor. A black matrix layer is formed on the array substrate. A black matrix frame is formed around the periphery of the black matrix layer. A color filter layer is formed on the array substrate and the black matrix layer, and extends to cover the black matrix frame.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Extruded products for aeroplane floors made of an aluminium-copper-lithium alloy
The invention relates in particular to an unprocessed extruded product for manufacturing a machined extruded product for the aeronautical industry, made of an Al—Cu—Li alloy. The invention also relates to the method for manufacturing a machined extruded product and to the corresponding machined extruded product. The products according to the invention are useful in particular for manufacturing floor beams and girders.
Owner:CONSTELLIUM ISSOIRE
Unit cell for flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell or solid oxide electrolyzer, and flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell and flat-tubular solid oxide electrolyzer using the same
ActiveUS20130266884A1Decrease thicknessReduce thicknessCellsElectrolyte moving arrangementsTubular solid oxide fuel cellOxide
This invention relates to a unit cell for a flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell or solid oxide electrolyzer, and a flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell and a flat-tubular solid oxide electrolyzer using the same, and more particularly to a unit cell for a flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell or solid oxide electrolyzer, wherein the unit cell includes a connector including connection parts, thus decreasing the thickness of the unit cell and reducing the size of a cell stack, and to a flat-tubular solid oxide fuel cell and a flat-tubular solid oxide electrolyzer using the same.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ENERGY RES
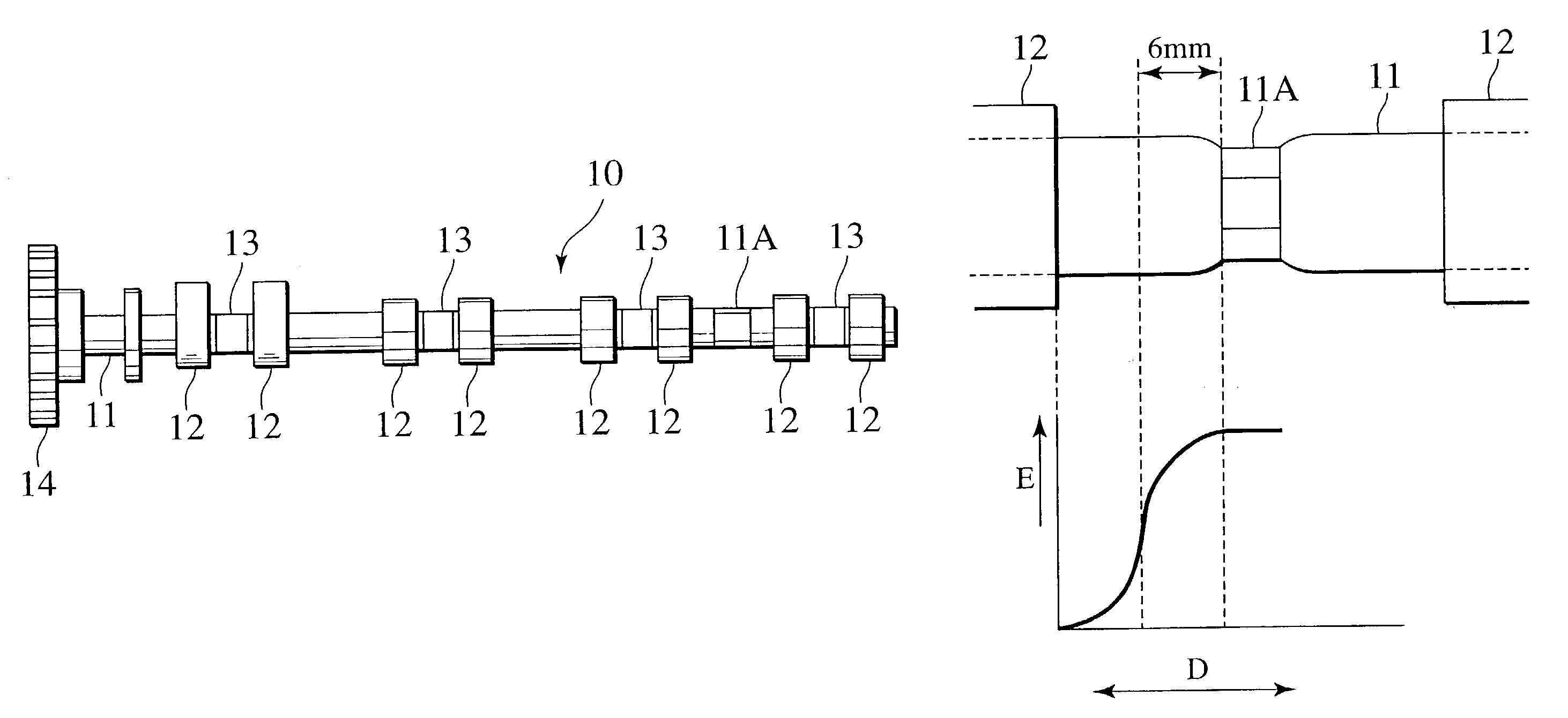
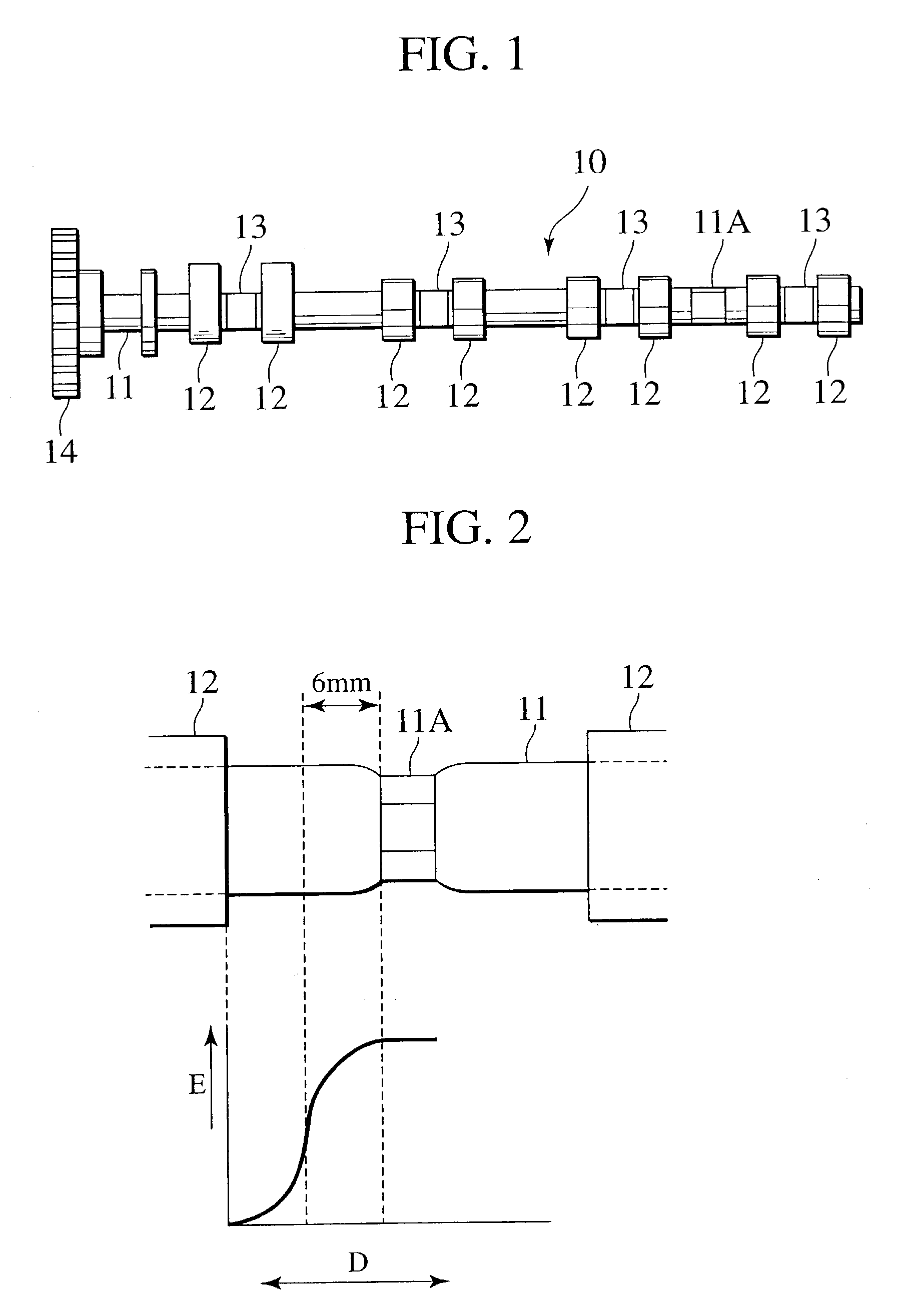
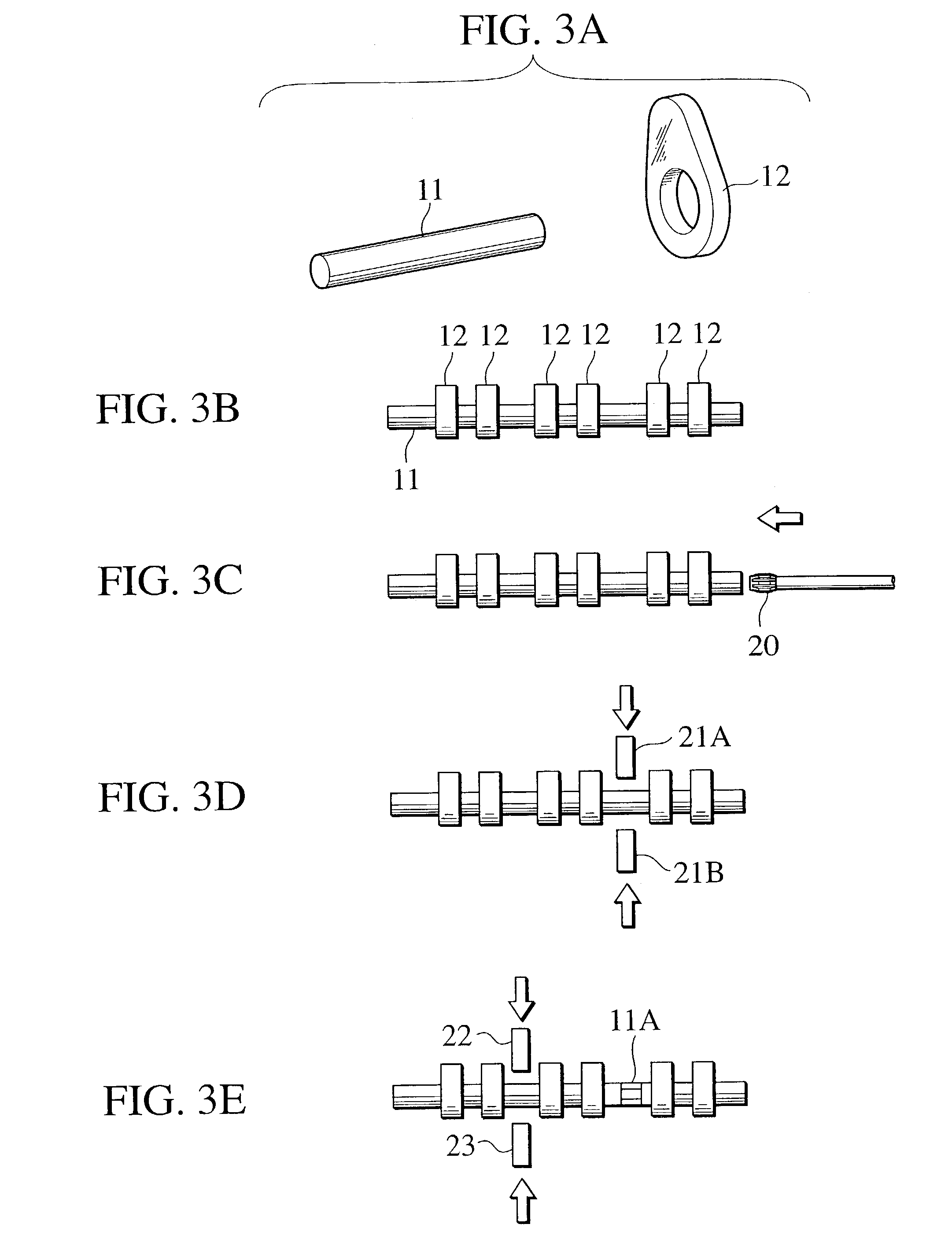
Assembled camshaft for engine and production method thereof
An assembled camshaft (10) for engine includes: a cam lobe piece (12); and a hollow shaft member (11) having at least two shaft fixing surfaces (11A) formed by plasticity process on a portion of the hollow shaft member (11) corresponding to a position between cylinders of the engine.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Separator supporting structure
ActiveUS20180241050A1Decrease thicknessLow costMotive system fuel cellsCollectors/separatorsEngineeringMetal
A separator supporting structure includes a metal lug provided on a separator, a set of protrusions that protrude from an inner surface of a metal casing toward the separator to form a recess into which the lug is inserted, a first insulating portion covering the lug at least in the recess, and a second insulating portion extending from the first insulating portion and between the separator and each of the protrusions.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Light source assembly, display apparatus having the same, and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150003107A1Improve light efficiencyDecrease thicknessMechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFirst lightEngineering
A light source assembly includes a base substrate, a resin layer disposed on the base substrate, and exposing a portion of the base substrate, and a first light source disposed on the portion of the base substrate which is exposed by the resin layer. The first light source has a hexahedron shape. The first light source has a face in parallel with the base substrate and having a height smaller than length or width of the face.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
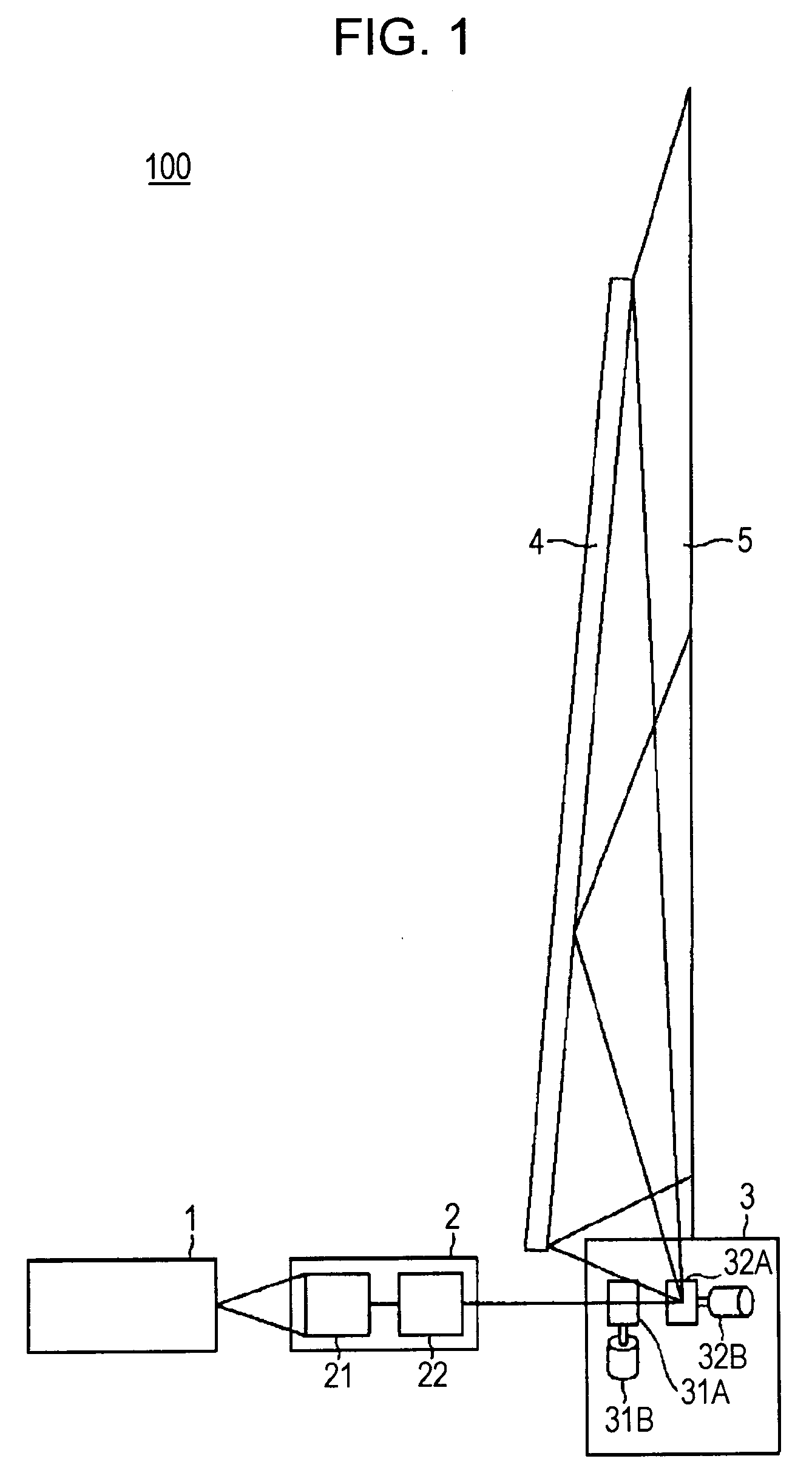
Rear projection display device
InactiveUS20080024737A1Increase in sizeDecrease thicknessProjectorsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsCollimated light
A rear projection display device that projects an image on a rear side of a screen includes a light source, an optical element, a scanning unit, and a reflecting plate. The light source emits a light beam. The optical element converts the light beam emitted from the light source into a substantially collimated light beam. The scanning unit performs scanning with the substantially collimated light beam converted by the optical element so as to allow the substantially collimated light beam to be incident on the screen. The reflecting plate has a height which is at least ½ of a height of the screen. The reflecting plate reflects the light beam from the scanning unit so that the light beam is incident on the screen.
Owner:SONY CORP
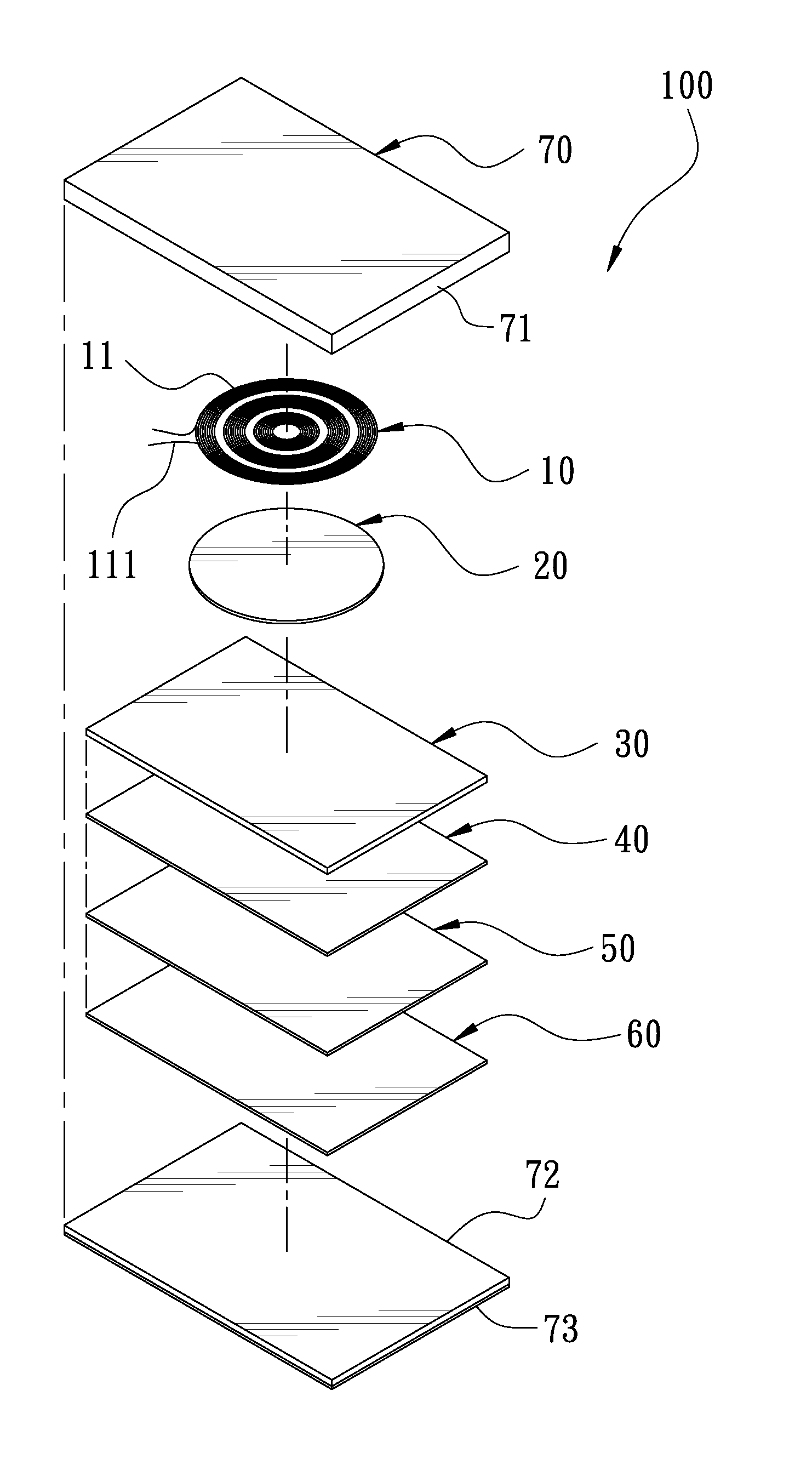
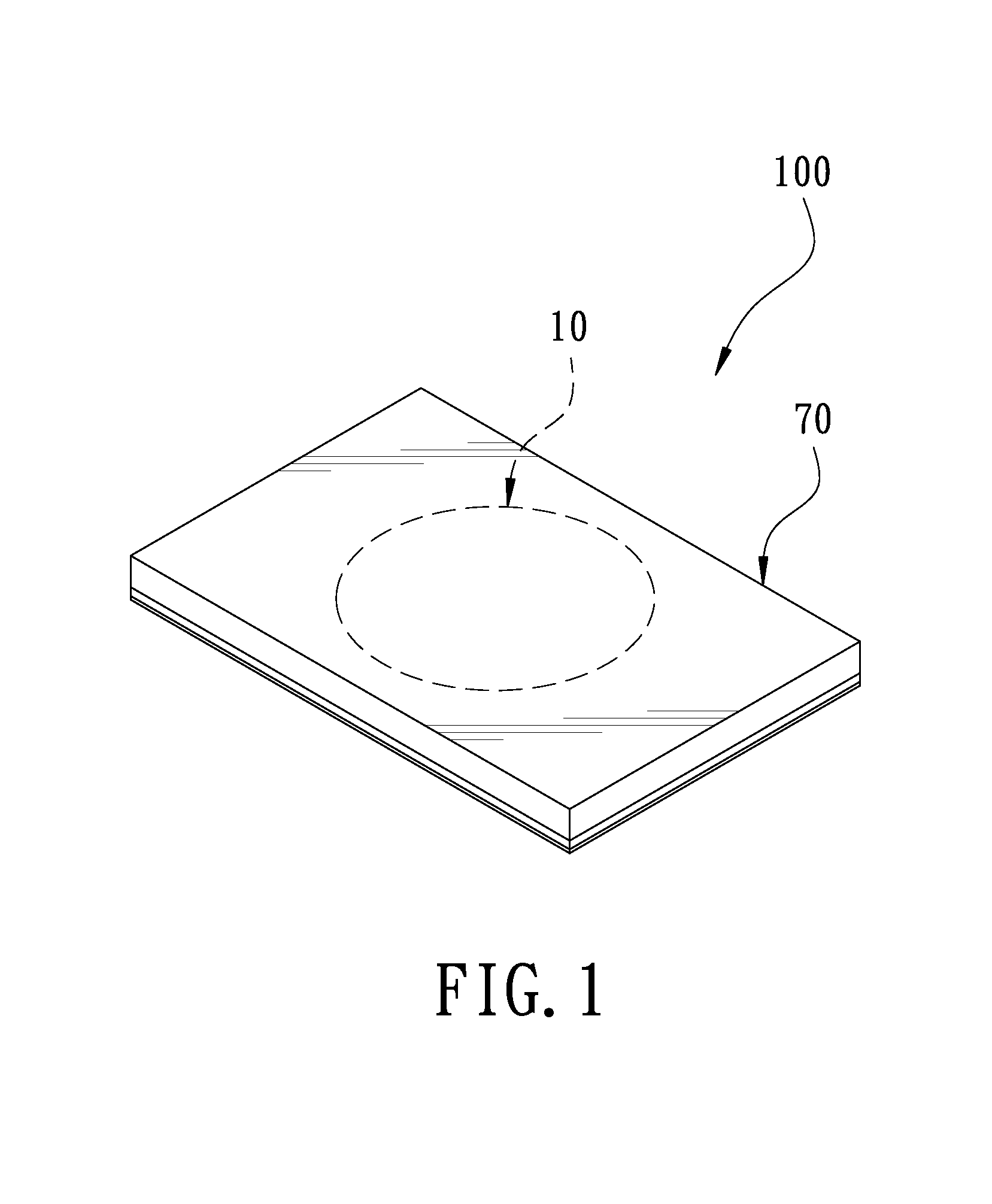
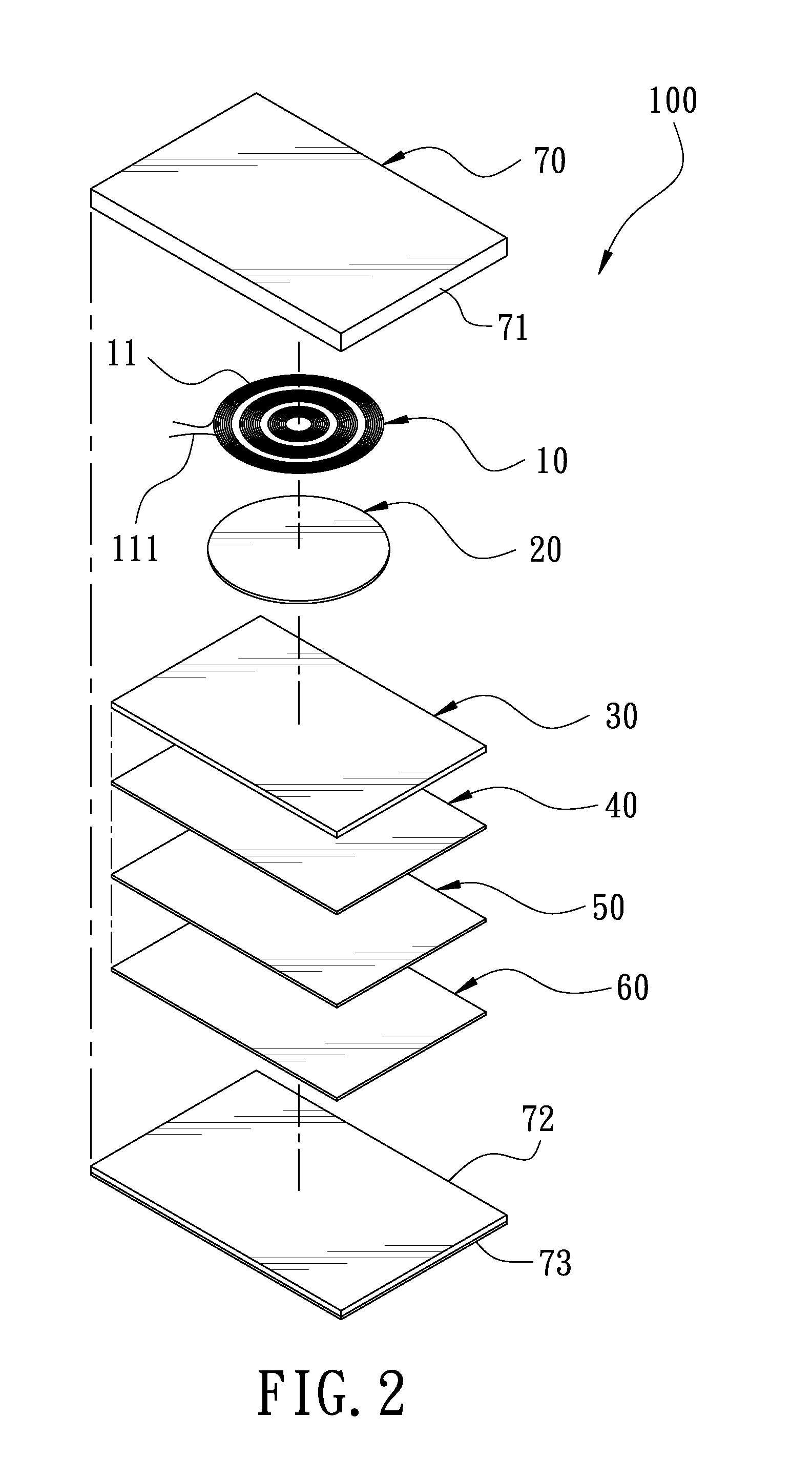
Soft power wireless transmission induction plate
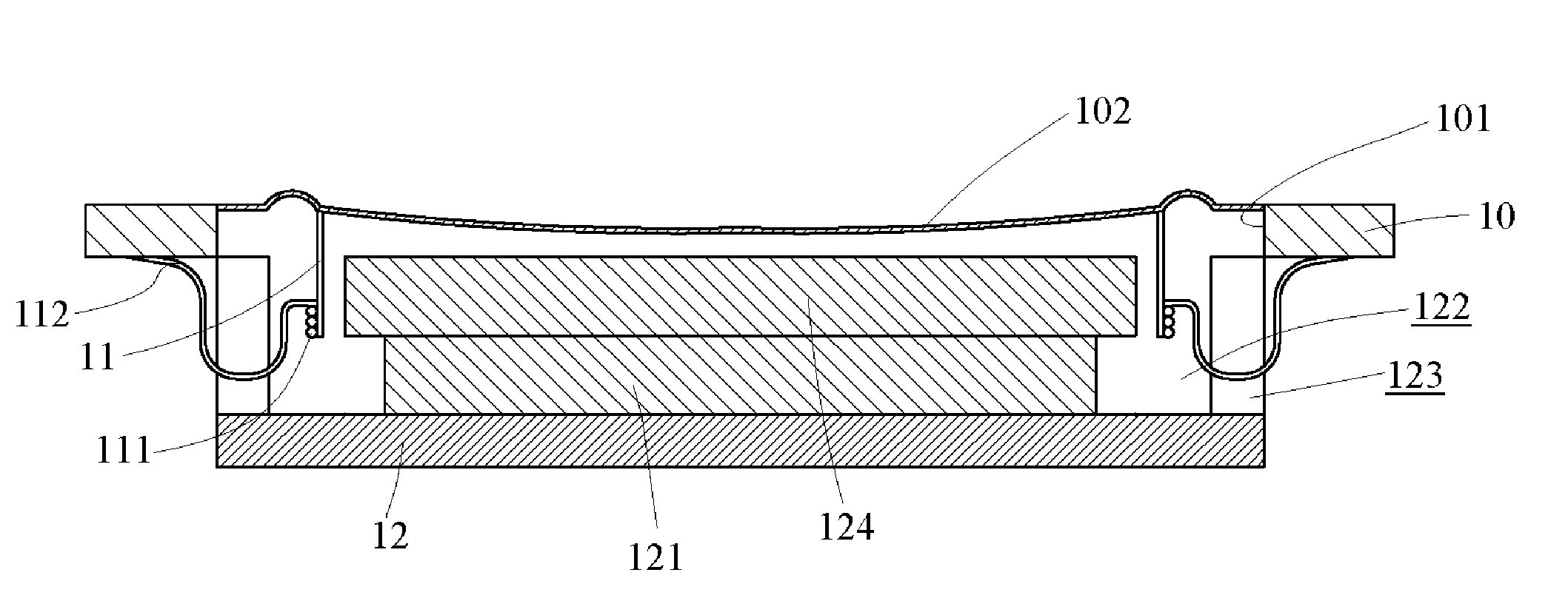
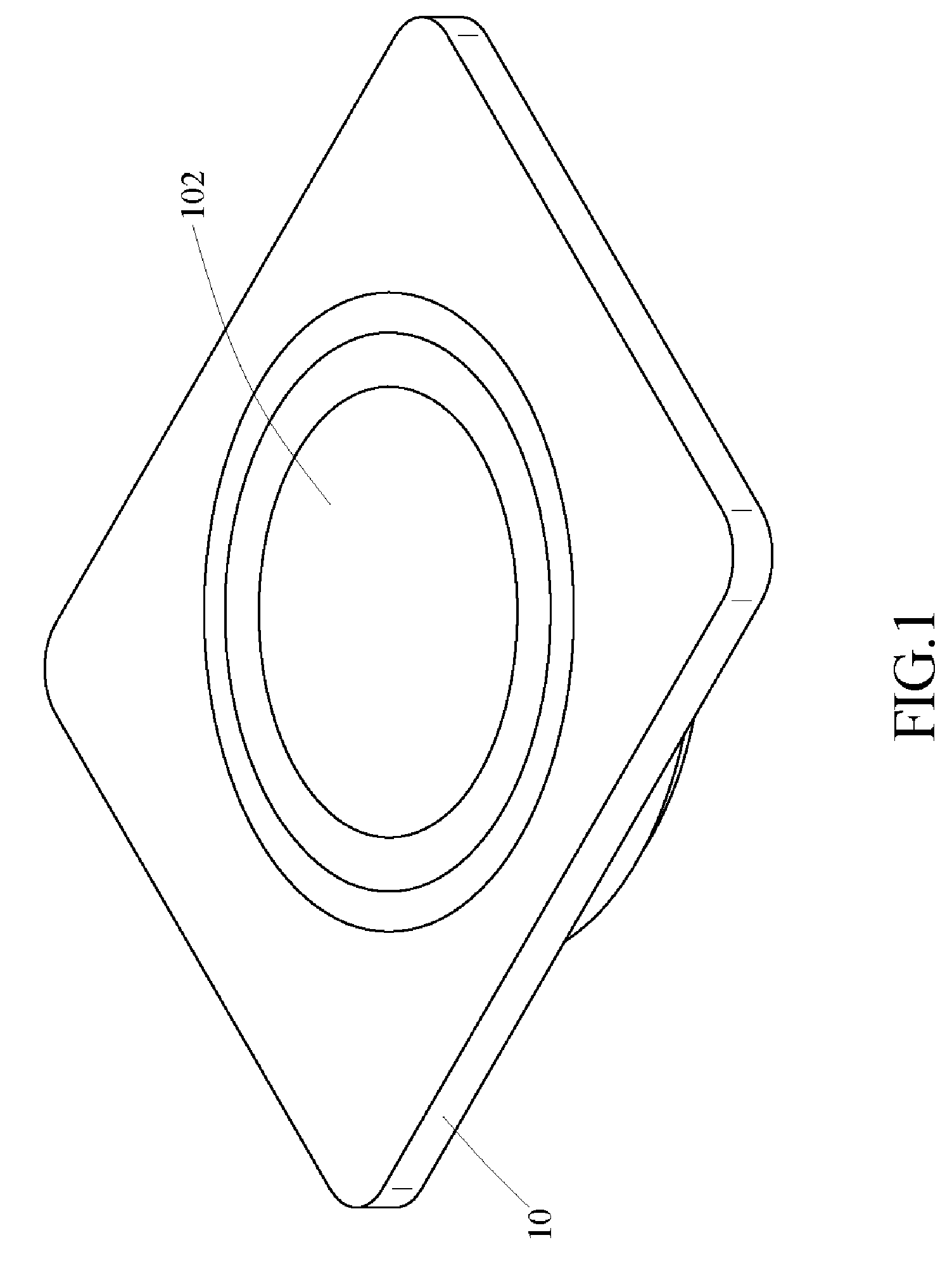
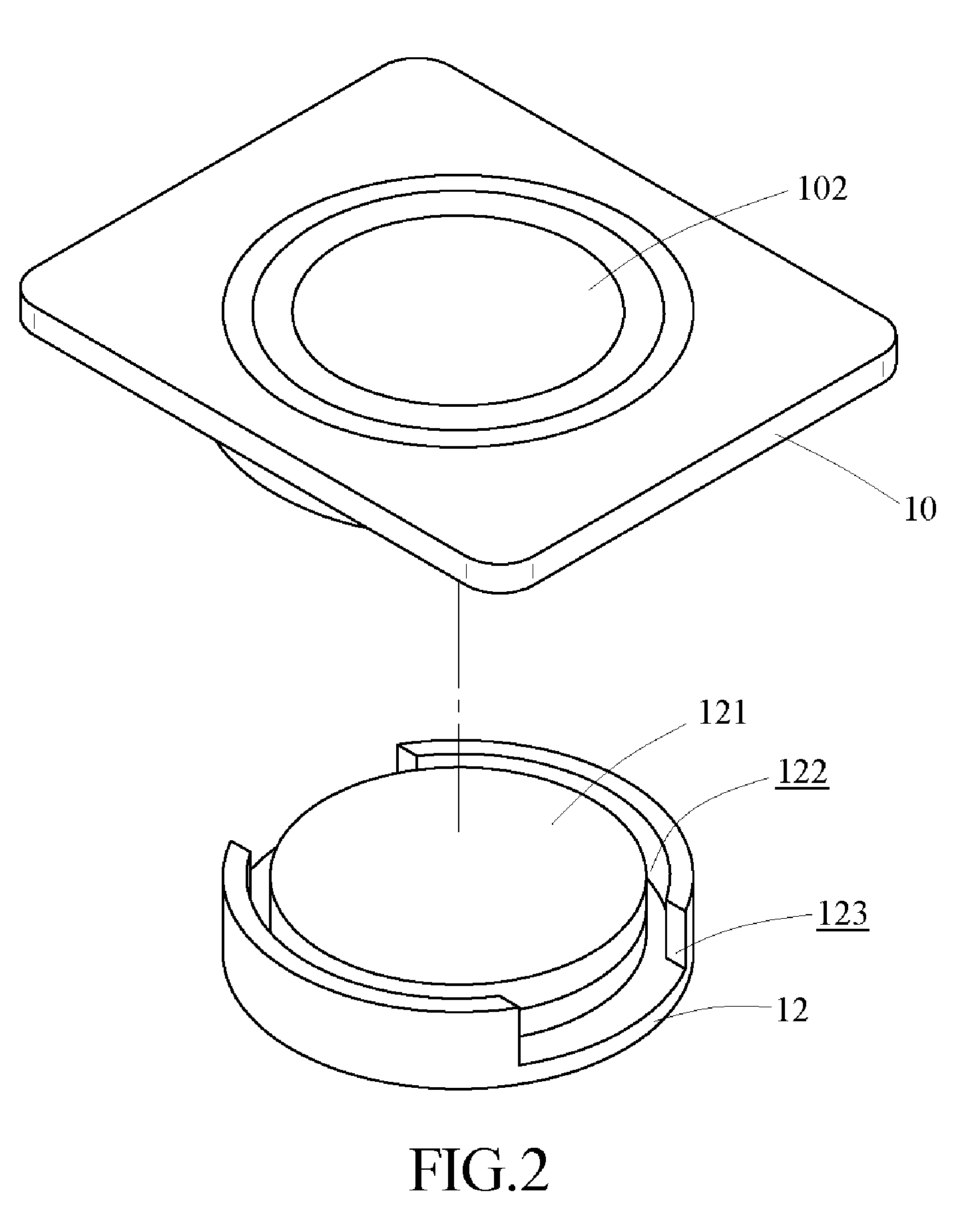
InactiveUS20150102682A1Decrease thicknessReduce thicknessTransformersCircuit arrangementsWireless power supplyInduction coil
A soft power wireless transmission induction plate includes a gap adjustment sheet, a shielding sheet and a separation sheet. The gap adjustment sheet includes a power induction module, an LED indication light and an LED indication light bar thereon. Through the power induction module, the present invention can supply power to an external electric appliance having induction coils in a wireless transmission way, achieving the object of wireless power supply. The present invention can decrease its entire thickness effectively to achieve an ultra-thin effect, and uses soft materials, without worrying about cracks and magnetic leakage. The LED indication light is to indicate the charging position and the LED indication light bar is to show the charging state.
Owner:COREMATE TECH CO LTD
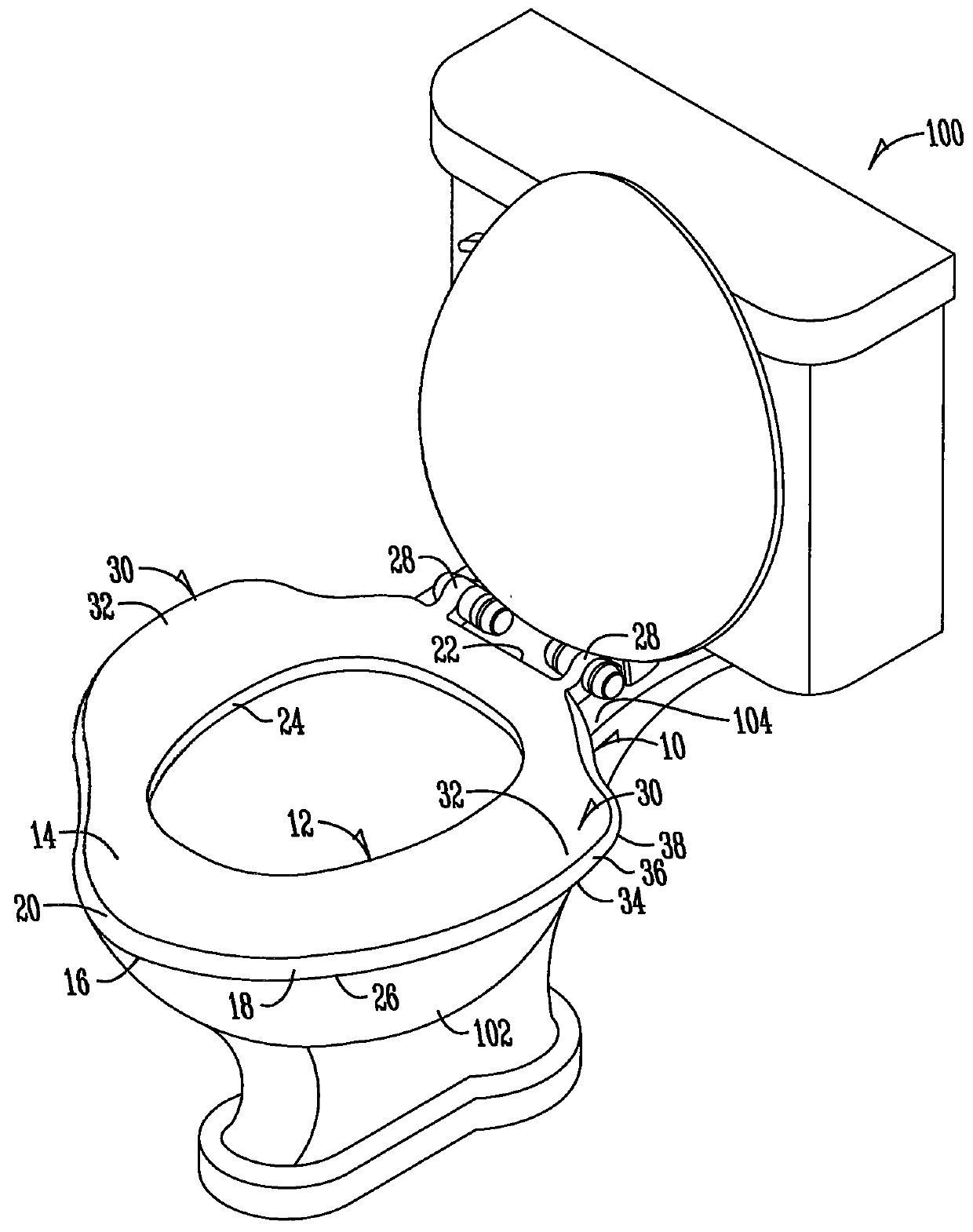
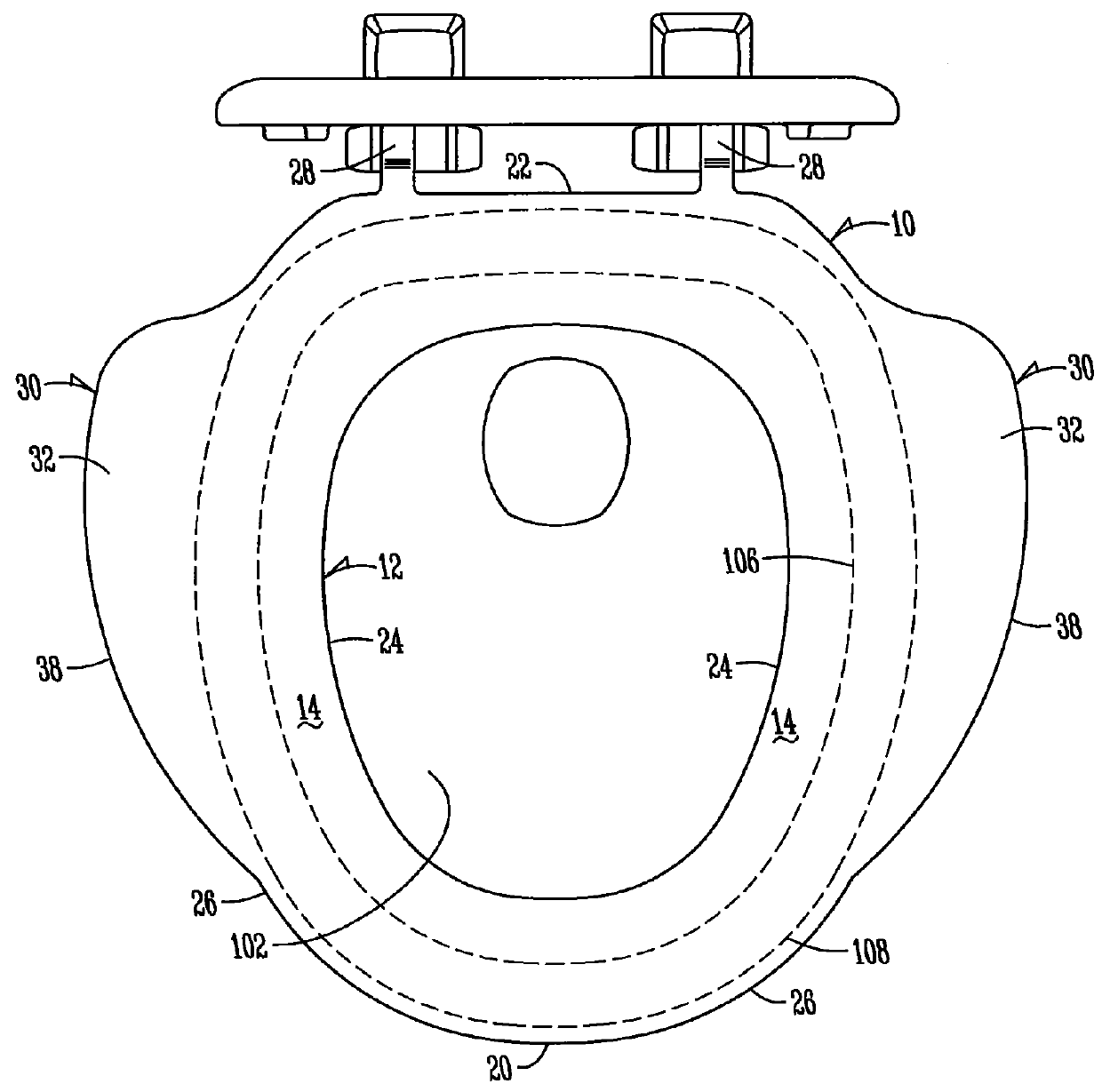
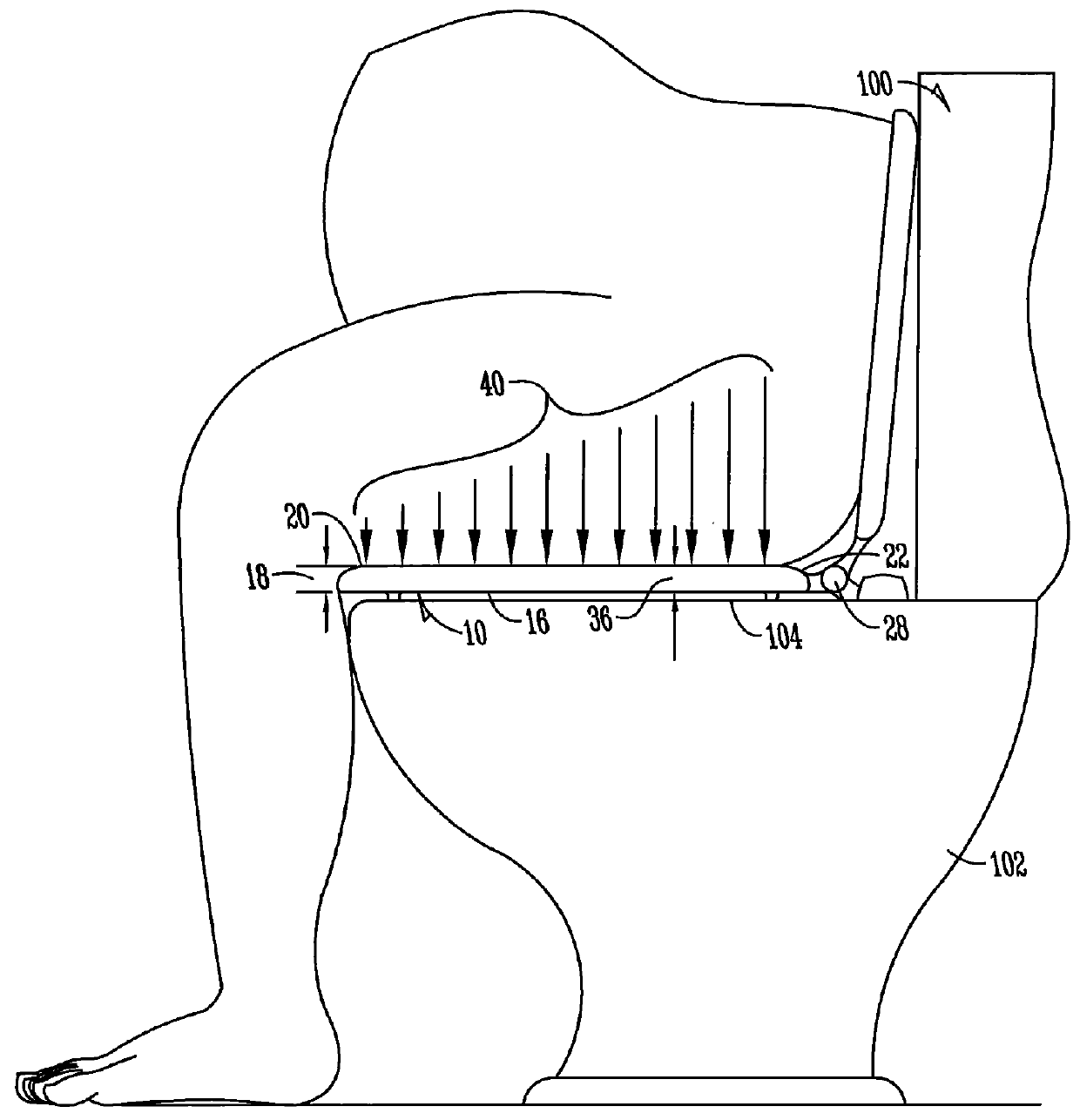
Toilet seat
InactiveUS20160029860A1Decrease thicknessReduce thicknessBathroom coversEngineeringSkeletal structures
A toilet seat and method for supporting an individual atop a toilet is disclosed. The toilet seat may be configured with a first portion generally for supporting skeletal structure of an individual and a second portion generally for supporting lateral fat of the individual. The second portion may be configured to extend outwardly from the first portion generally between the back and the front of the toilet bowl. The second portion is cantilevered outward relative to the toilet bowl. The moment of pressure between the first portion and a forward portion of the individual's legs remains unchanged by approximating the second portion relative to the front end of the toilet bowl to not inhibit the individual from being able to lean forward and stand from a seated position.
Owner:RANFT DONALD
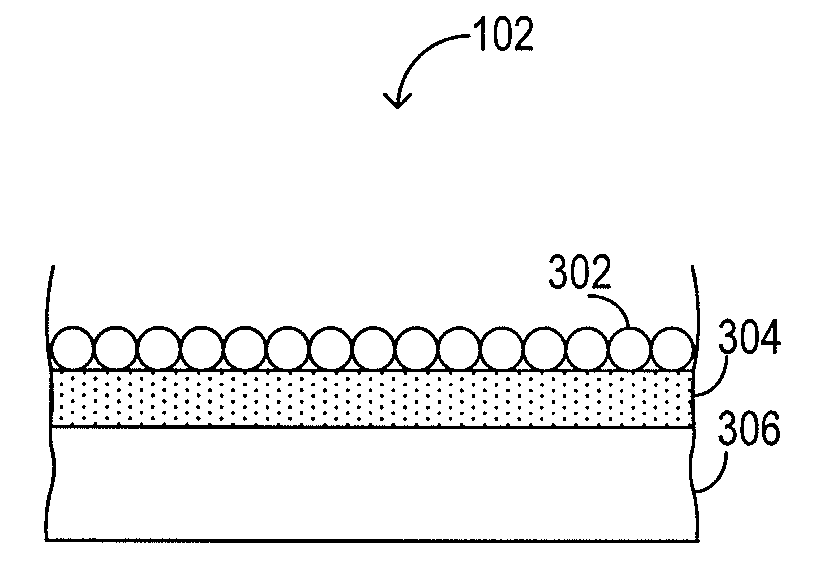
Air-cooled thermal management for a fuel cell stack
ActiveUS8168344B2Decrease thicknessLimit scopeFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesAirflowAir cooling
The air-cooled thermal management of a fuel cell stack is disclosed. One disclosed embodiment comprises a cooling plate apparatus for an air-cooled fuel cell stack, where the cooling plate comprises a body configured to receive heat from one or more fuel cells in thermal communication with the body, and airflow channels formed in the body and configured to allow a flow of a cooling air to pass across the body. An insulating structure is disposed in the airflow channels, wherein the insulating structure has decreasing thickness from a cooling air inlet toward a cooling air outlet.
Owner:HYAXIOM INC
Method of processing a substrate
InactiveUS20150086708A1Improve qualityDecrease thicknessAdhesive processesEster polymer adhesivesEngineeringSurface plate
A method of processing a substrate or panel is disclosed. A substrate having thereon an array of chips is provided. A mask layer is laminated on the substrate. The mask layer has a plurality of openings to reveal active areas of the chips respectively. A spray-coating process is then performed to form an adhesive film in the active areas. The mask layer is then stripped off.
Owner:INTERFACE OPTOELECTRONICS SHENZHEN +1
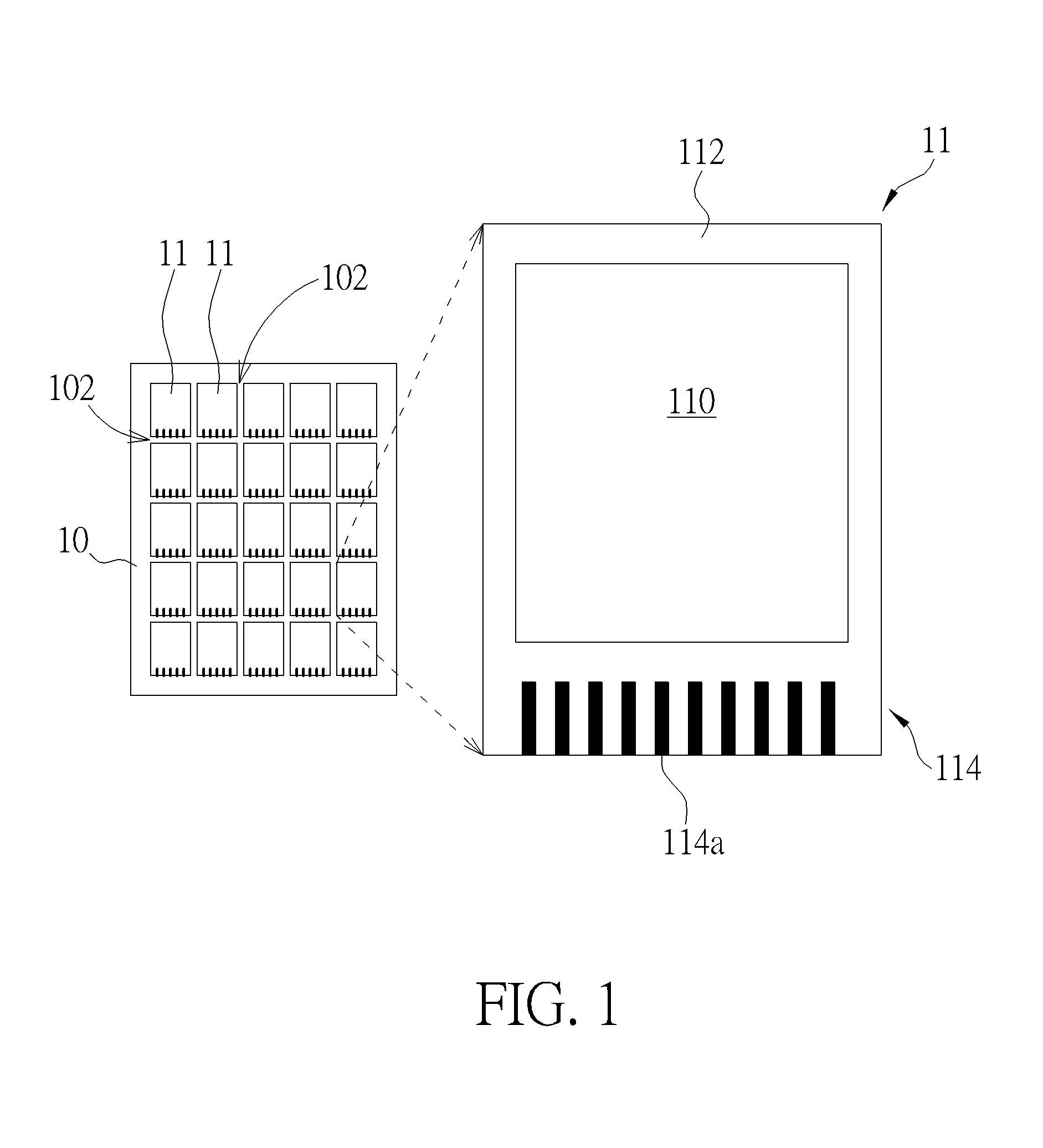
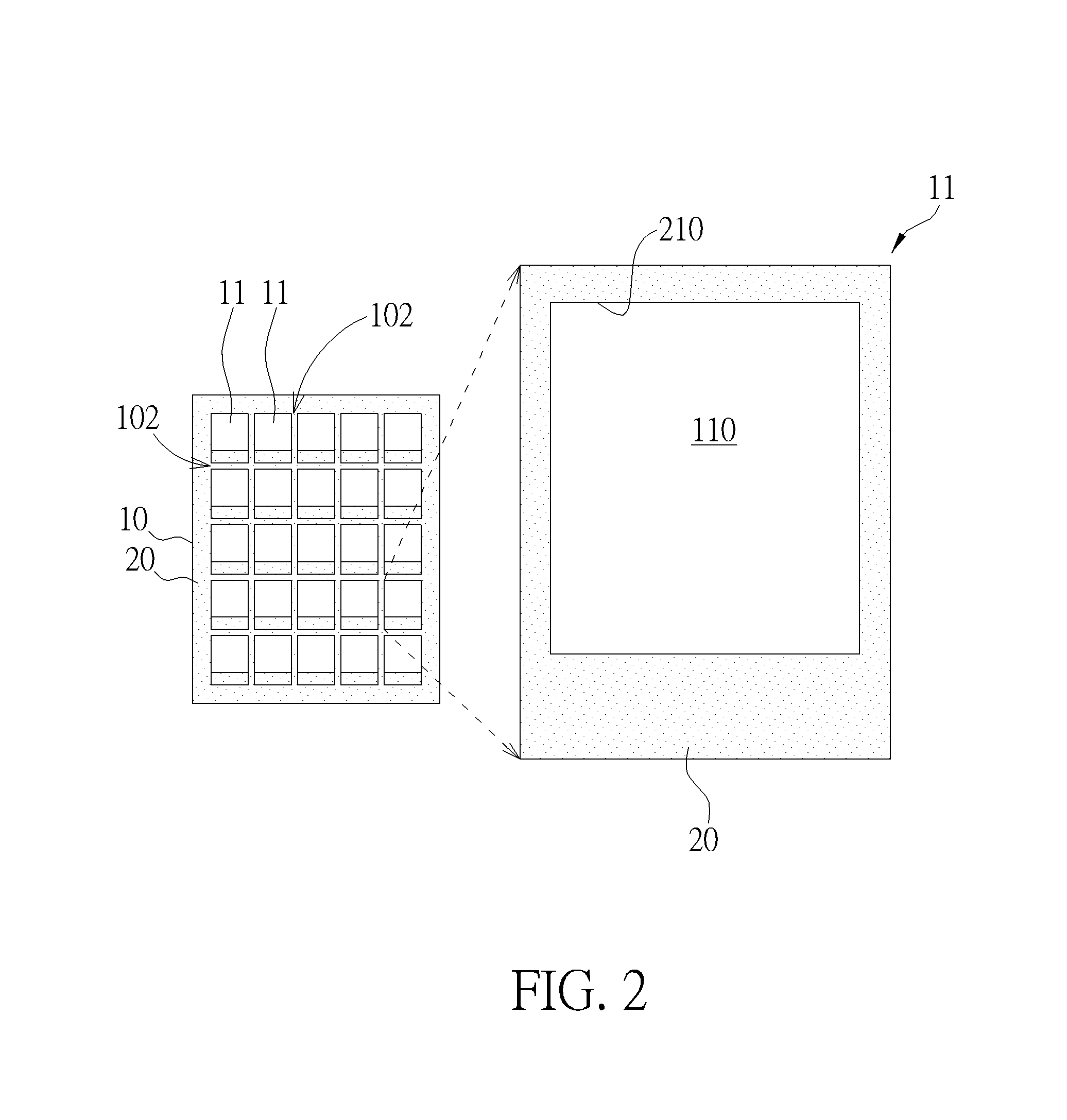
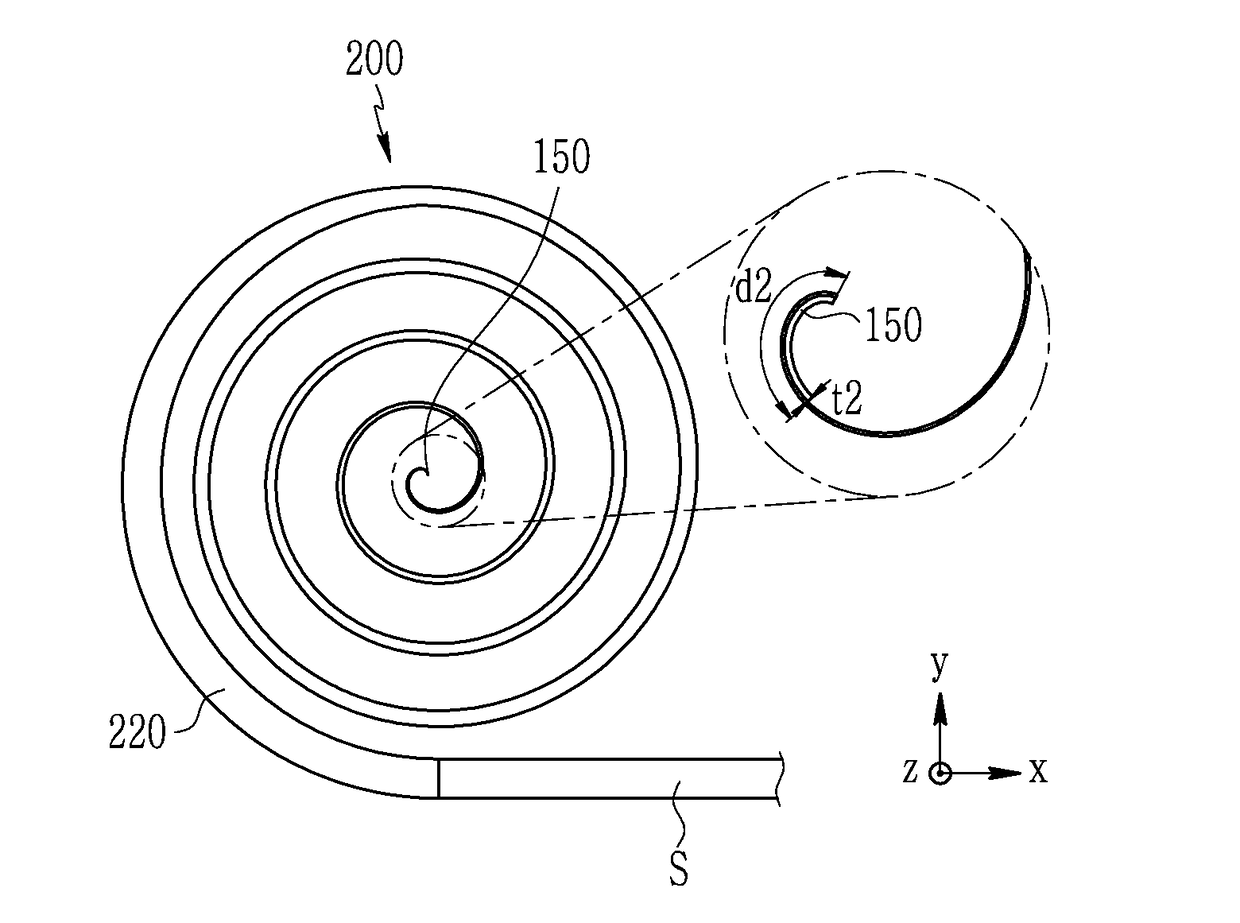
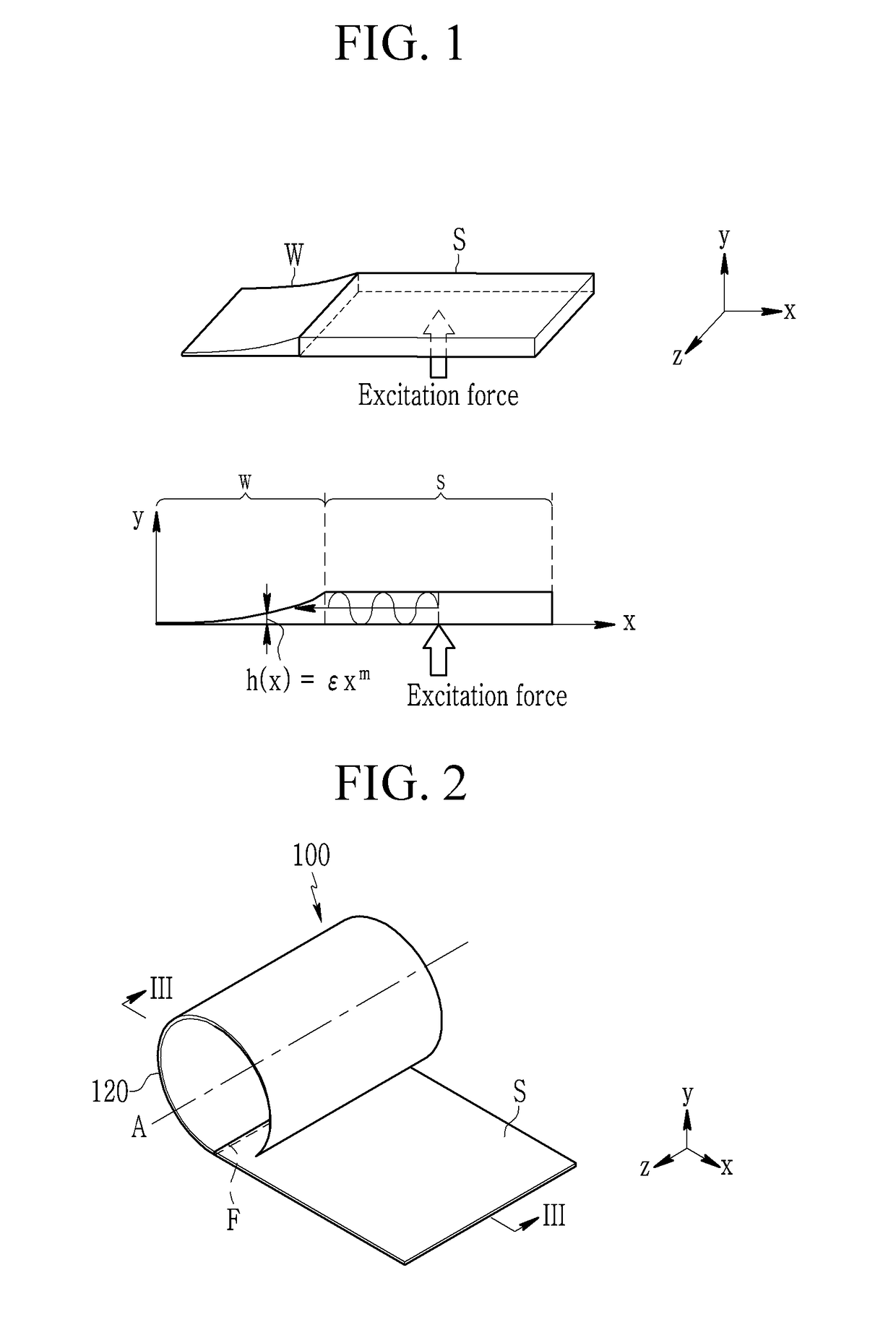
Apparatus for damping vibration
ActiveUS20180187734A1Decrease thicknessOptimize vibration and noise damp effectNon-rotating vibration suppressionShock absorbersEngineering
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com