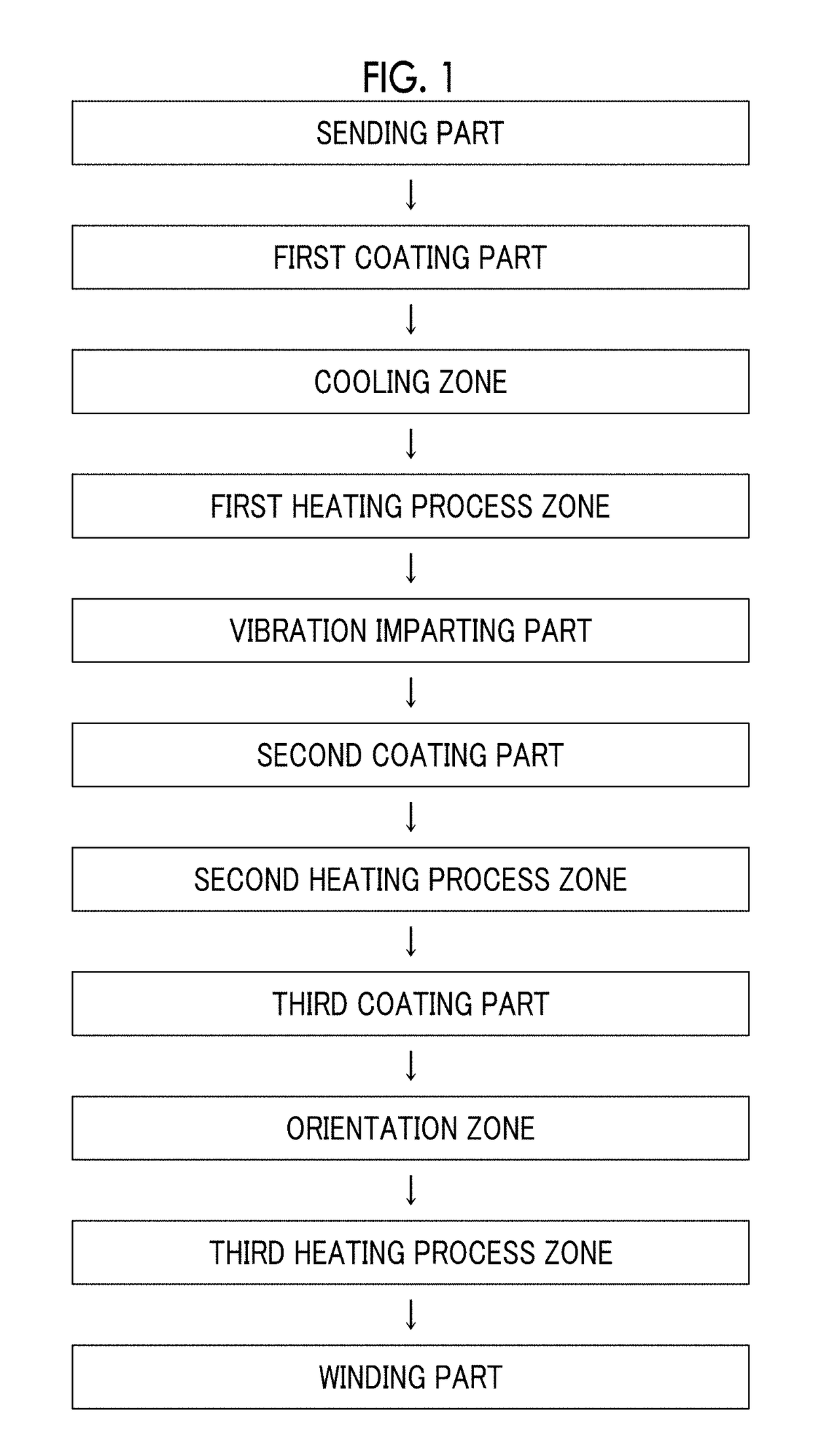
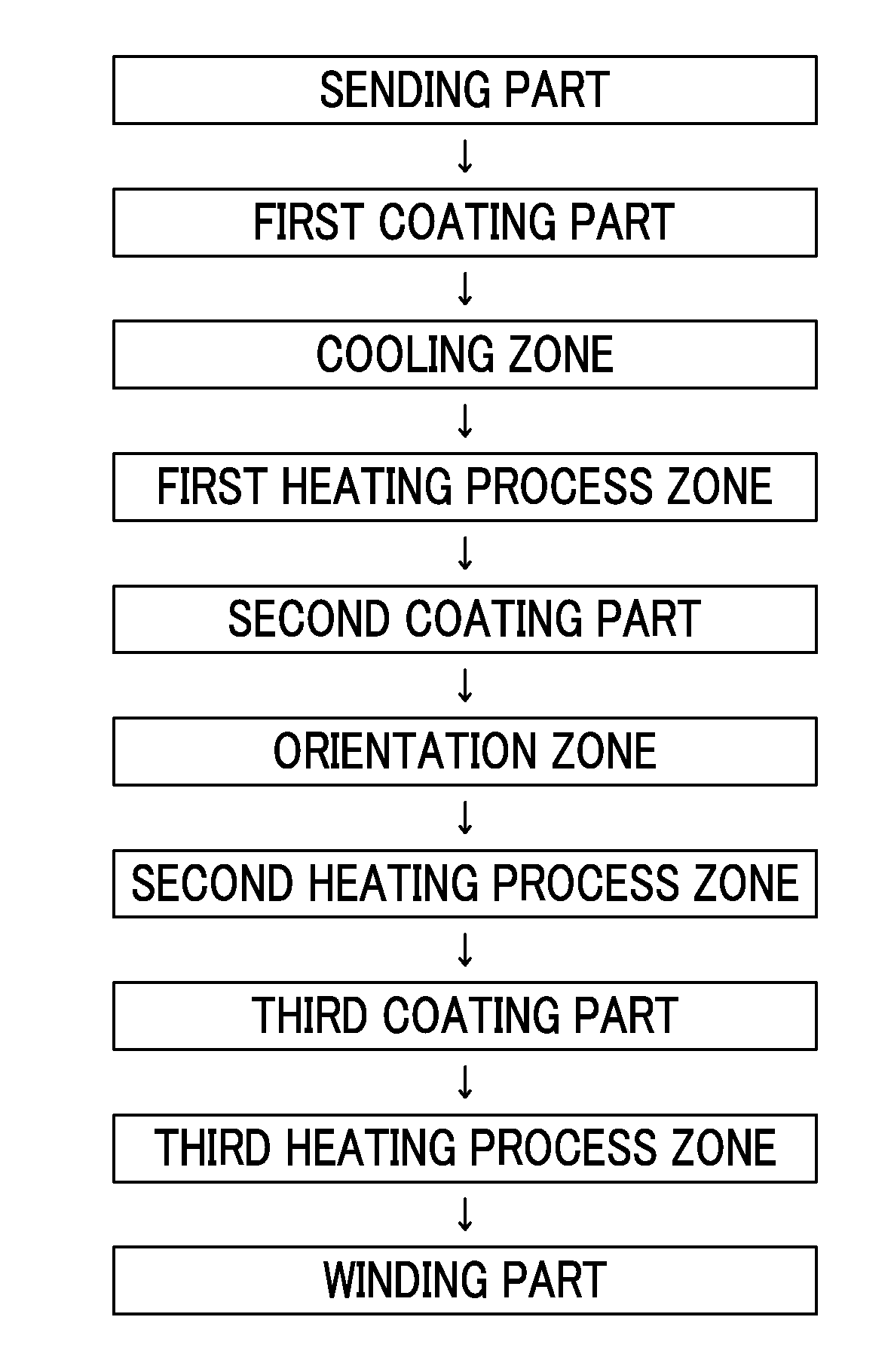
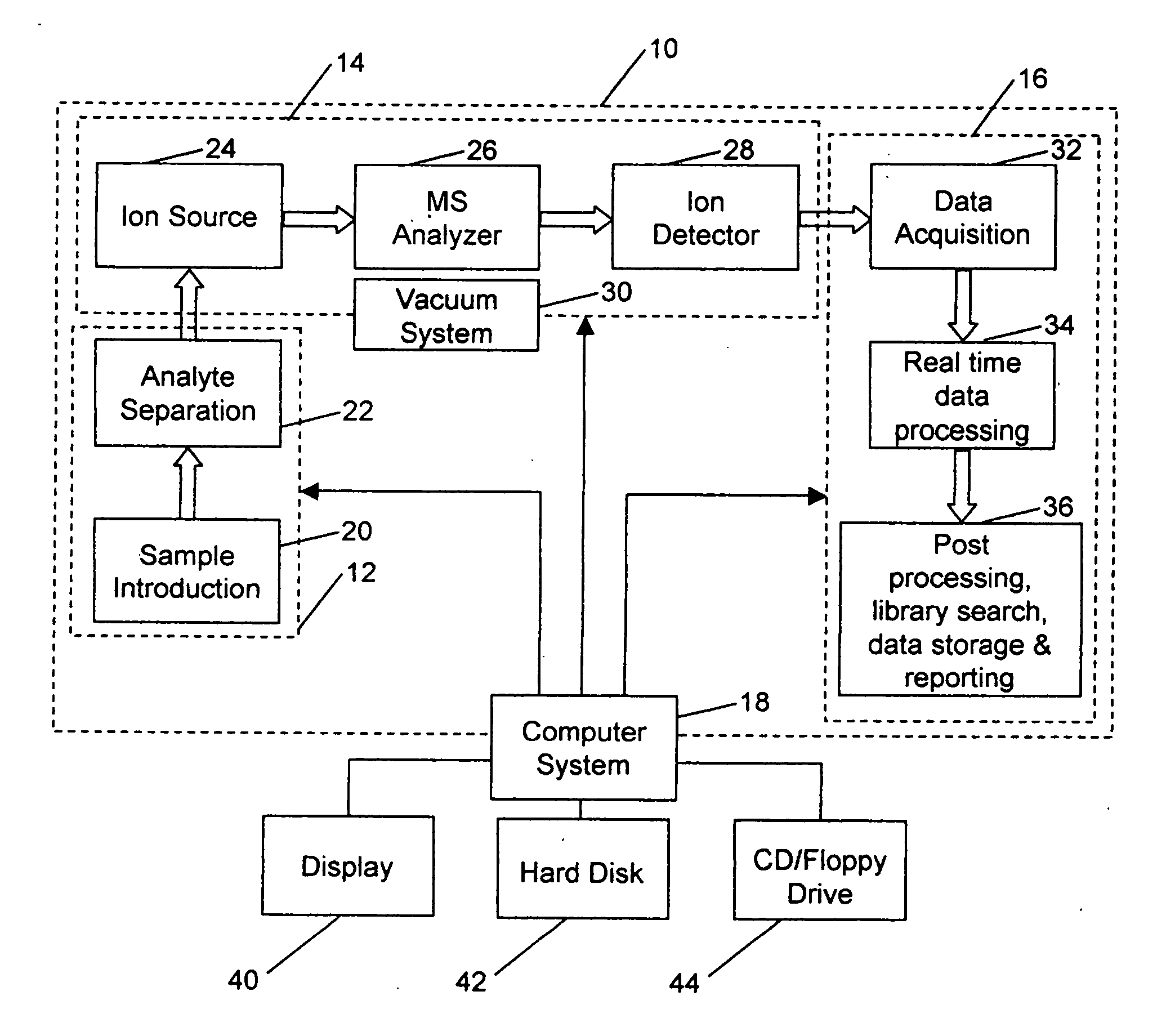
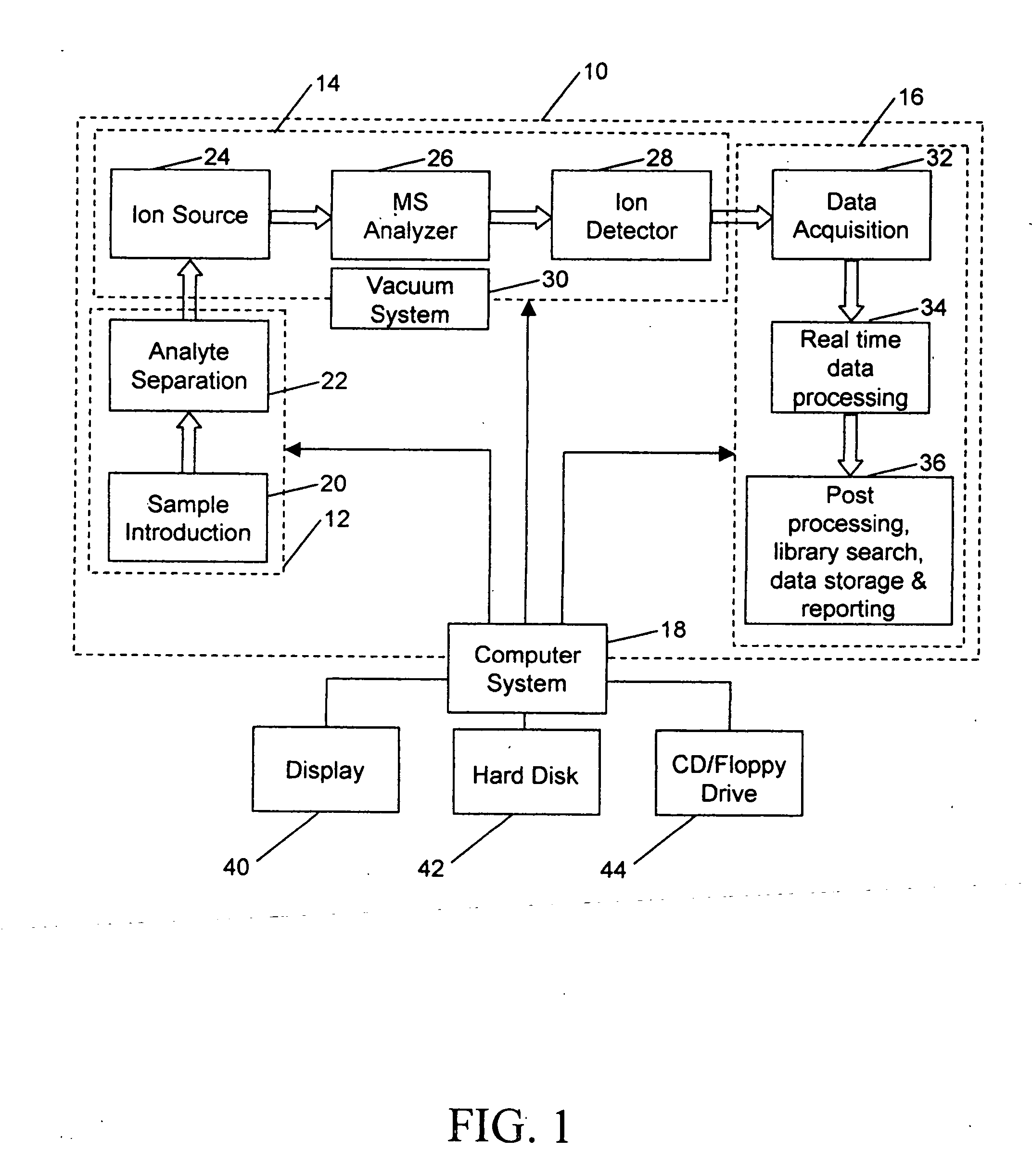
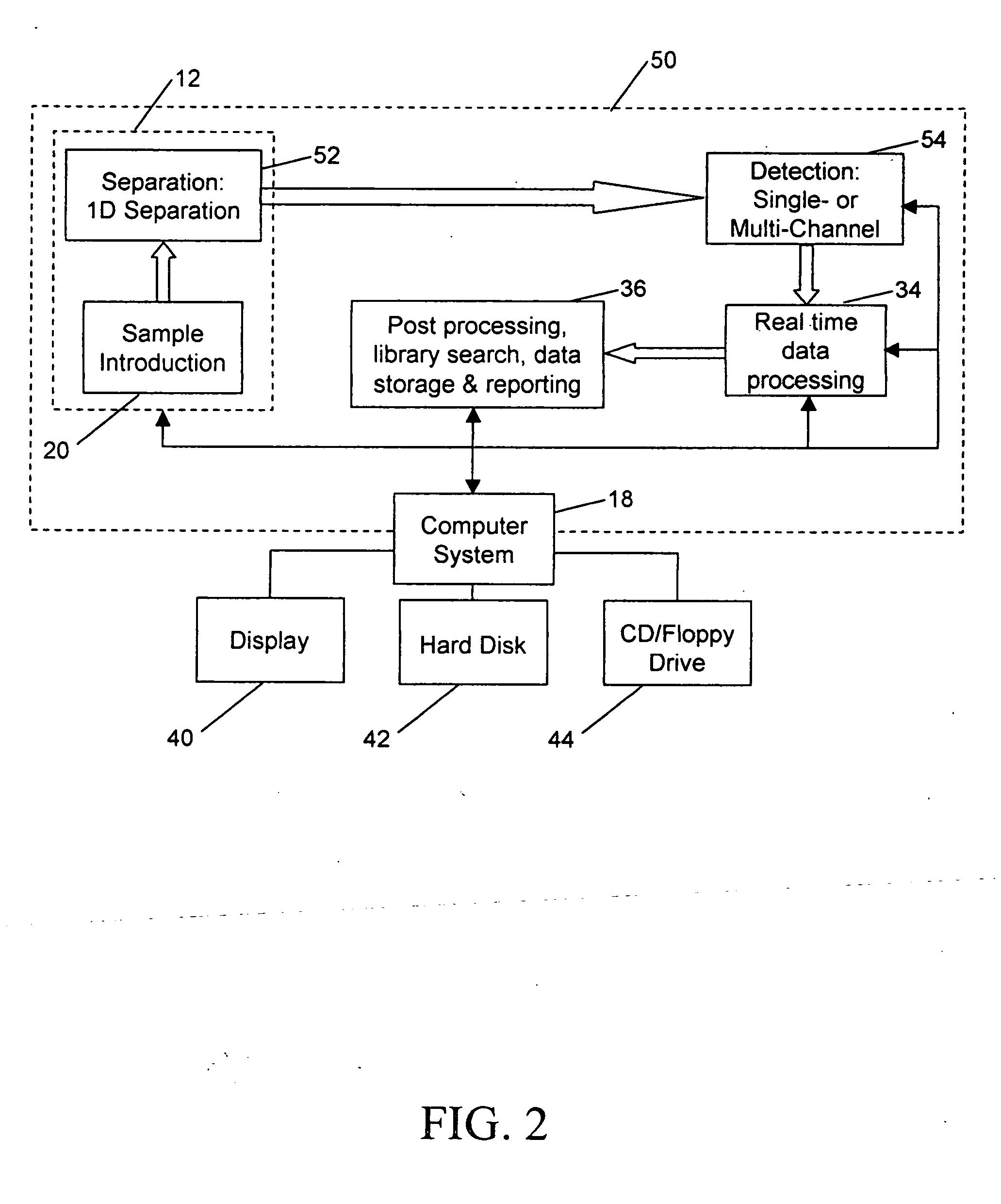
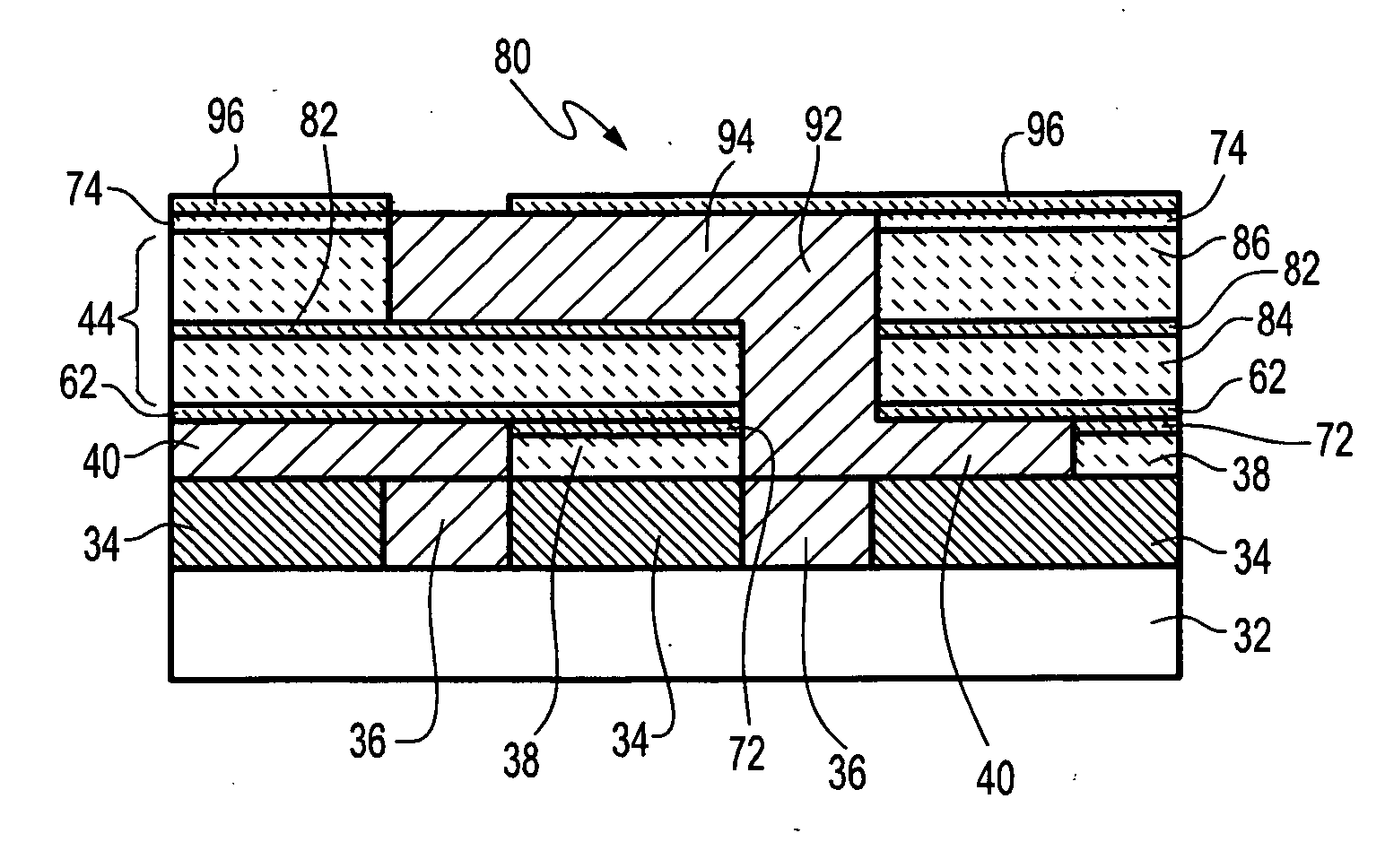
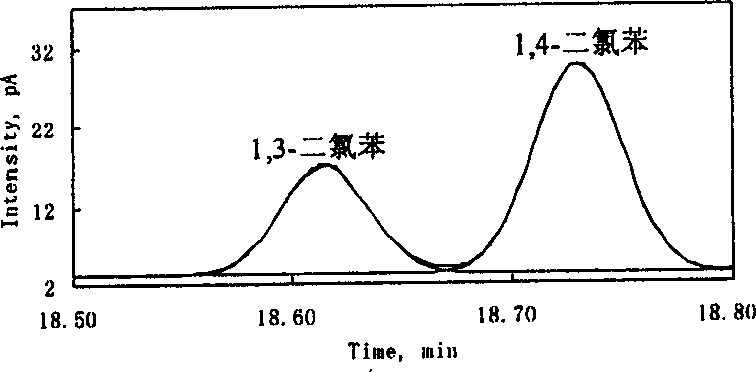
Patents
Literature
2422 results about "Peak area" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
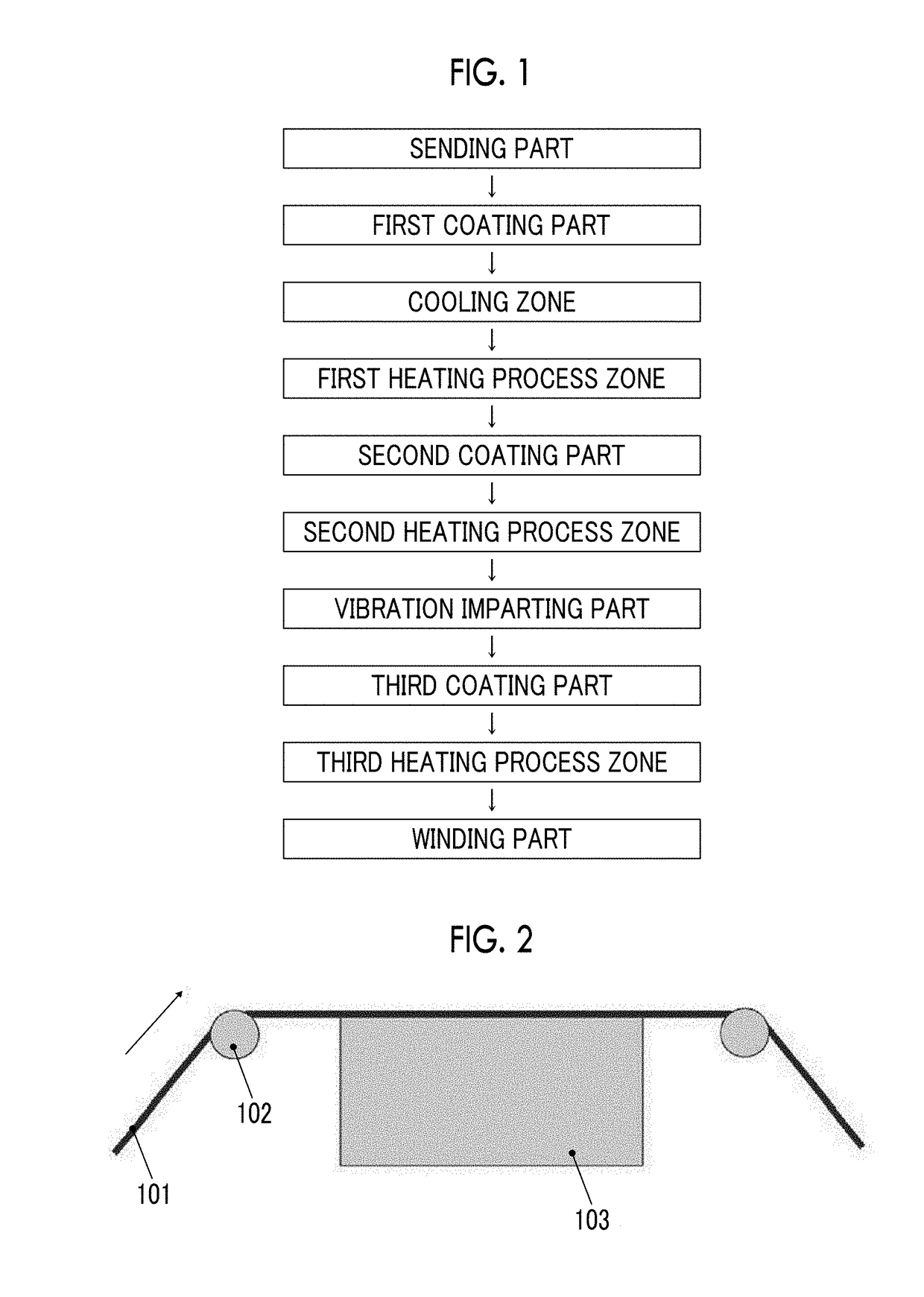
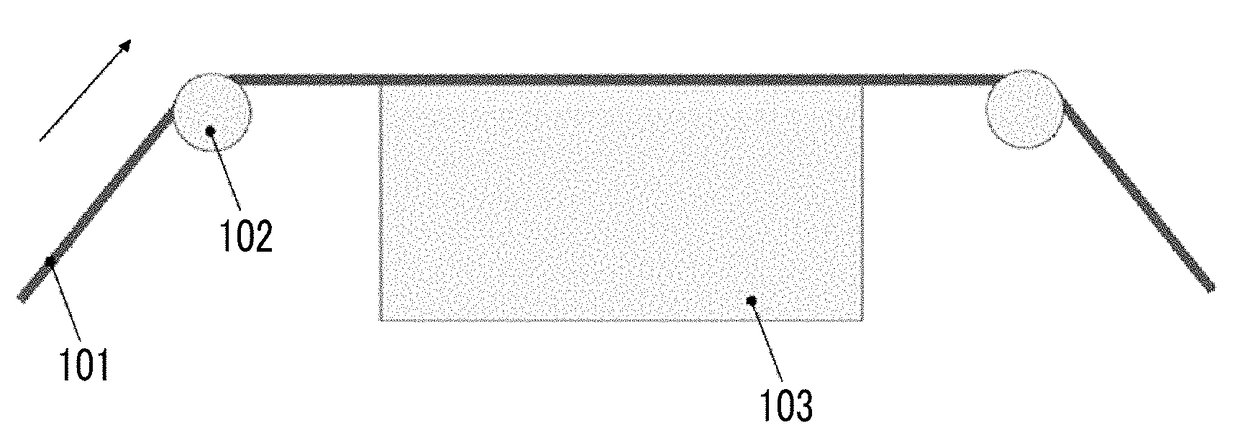
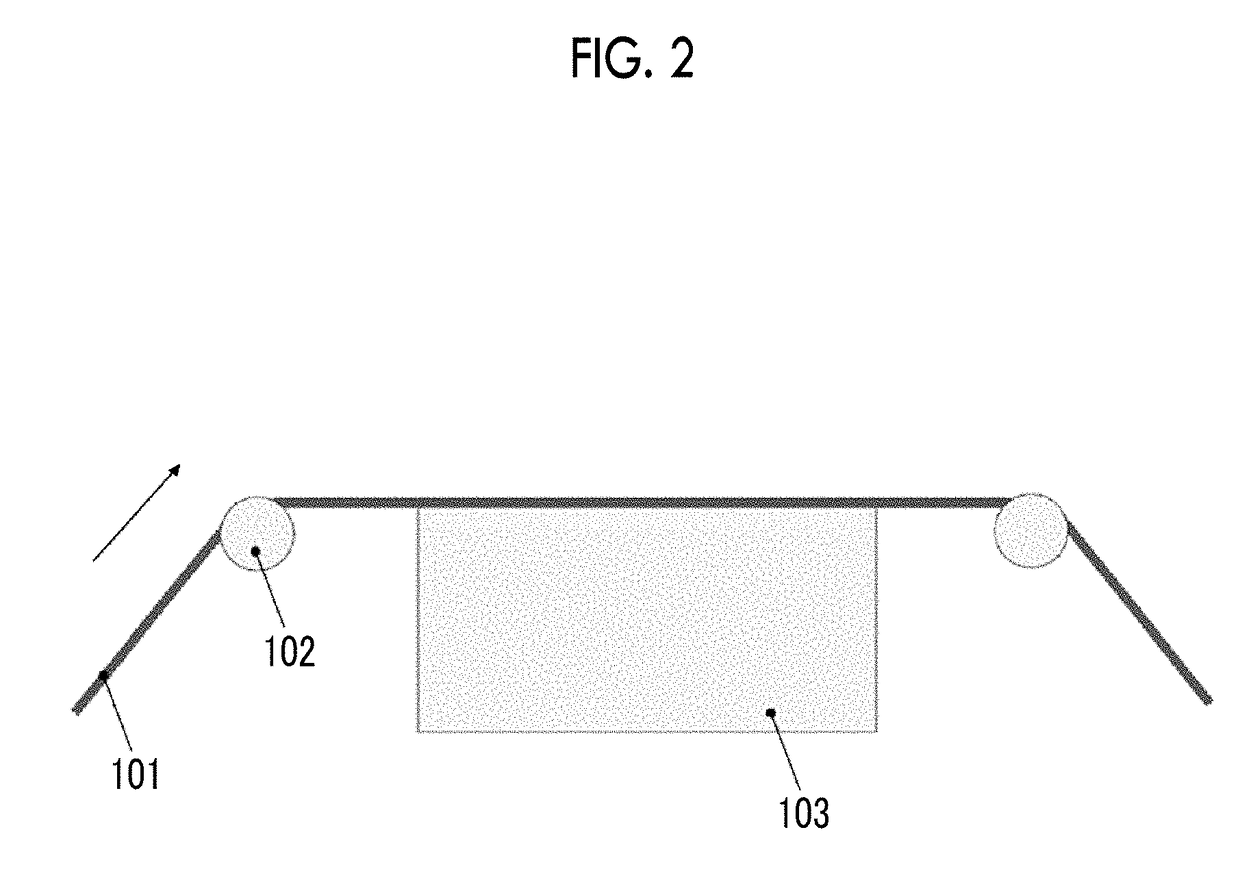
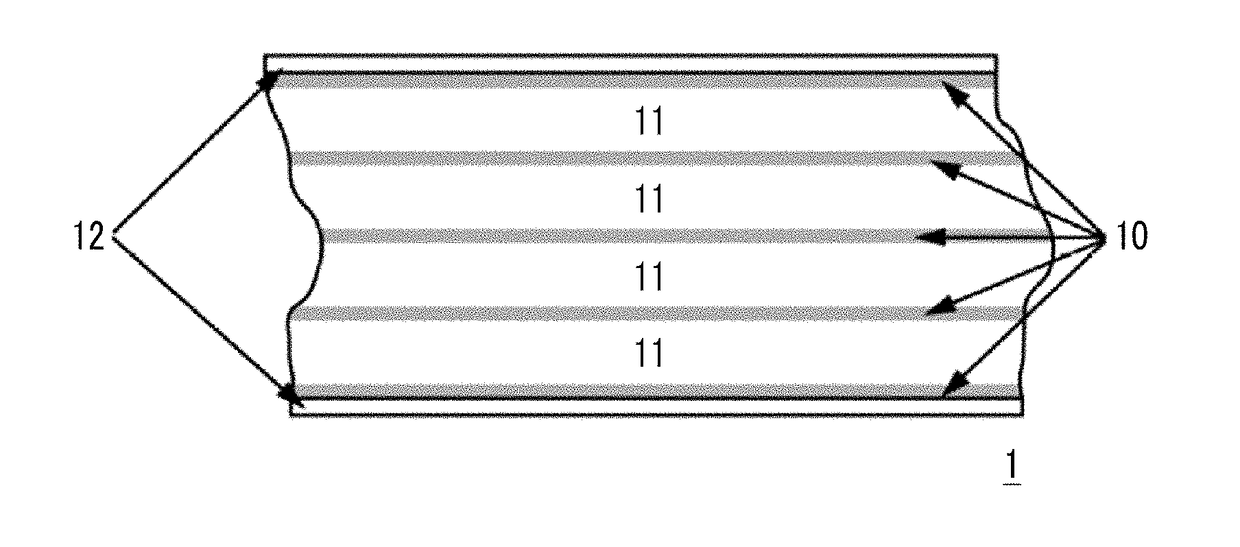
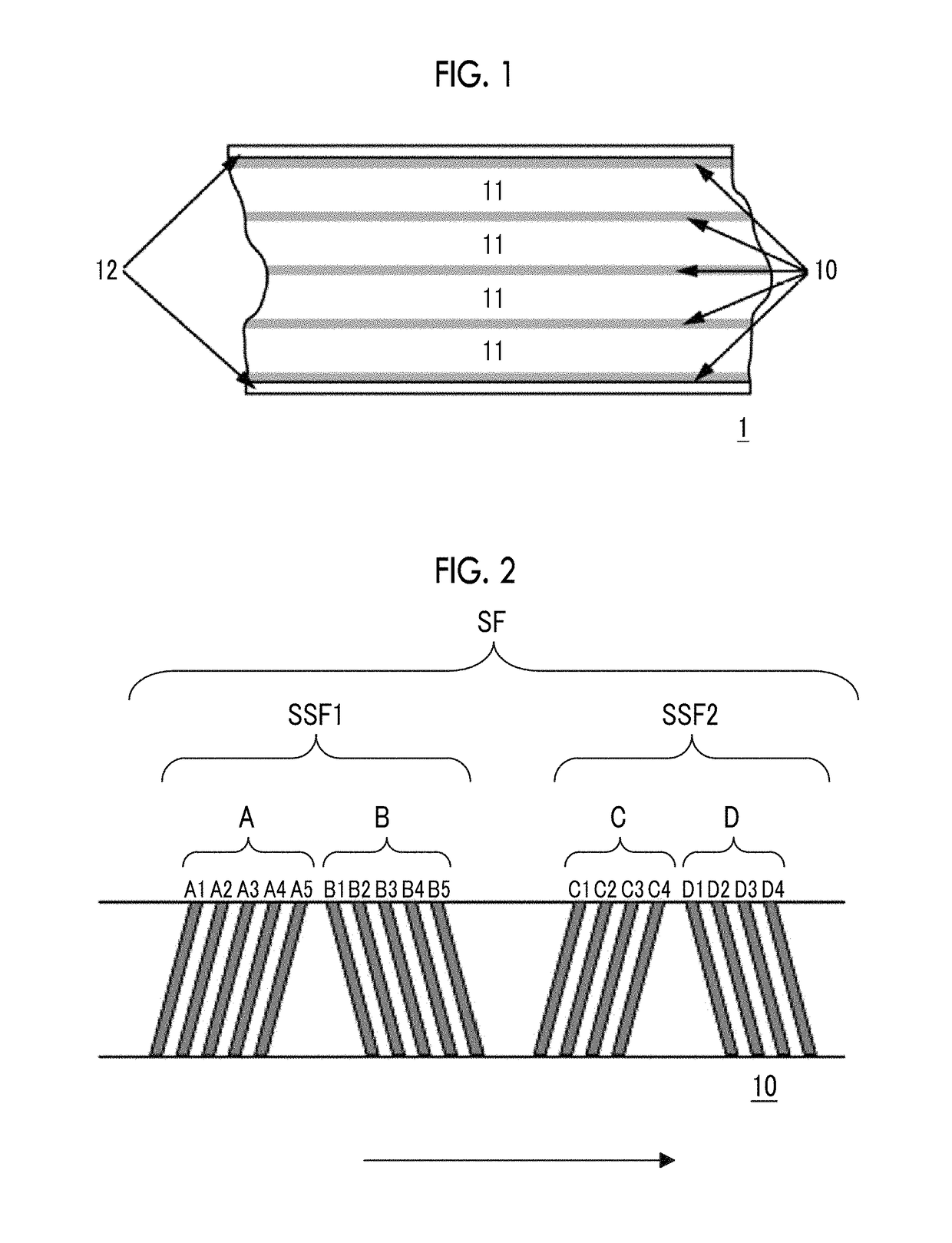
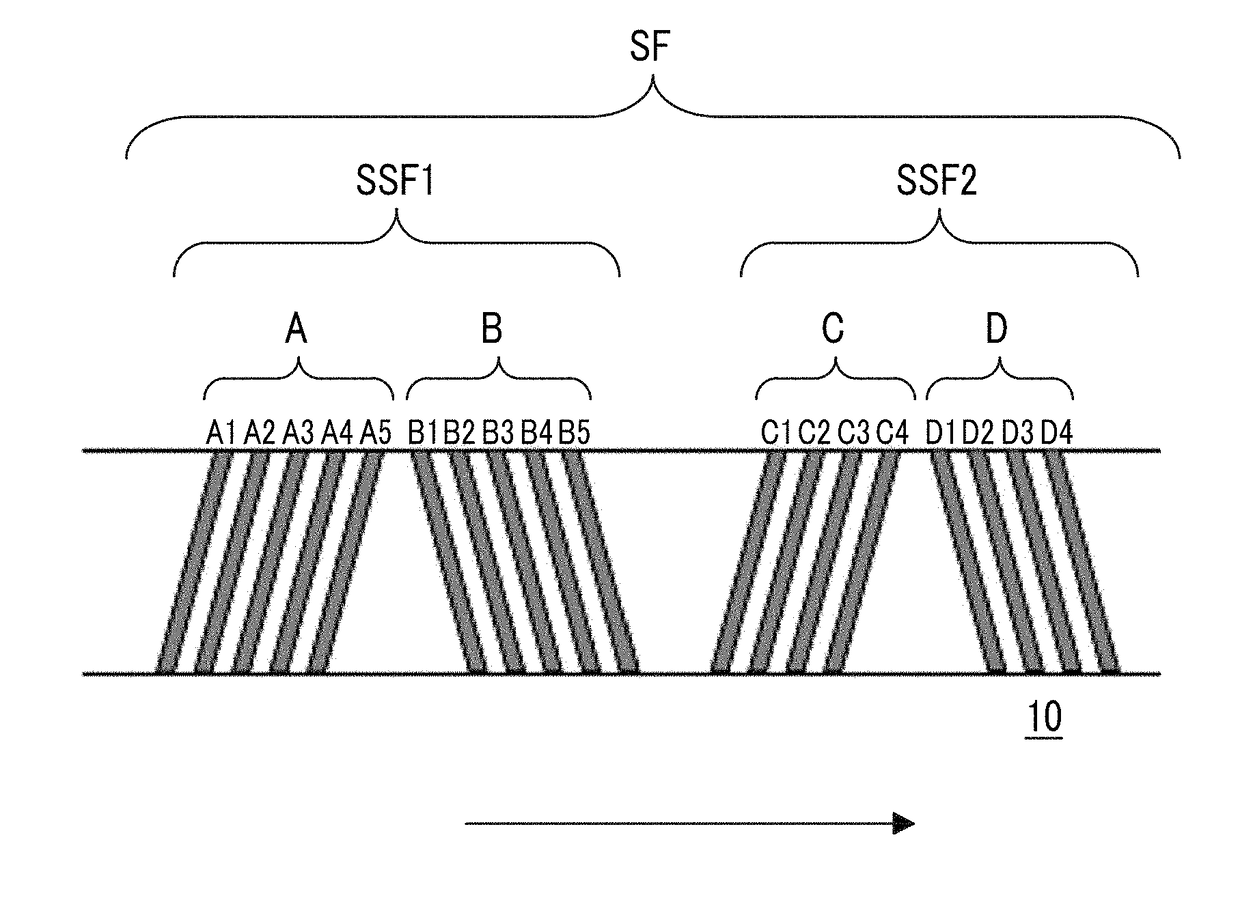
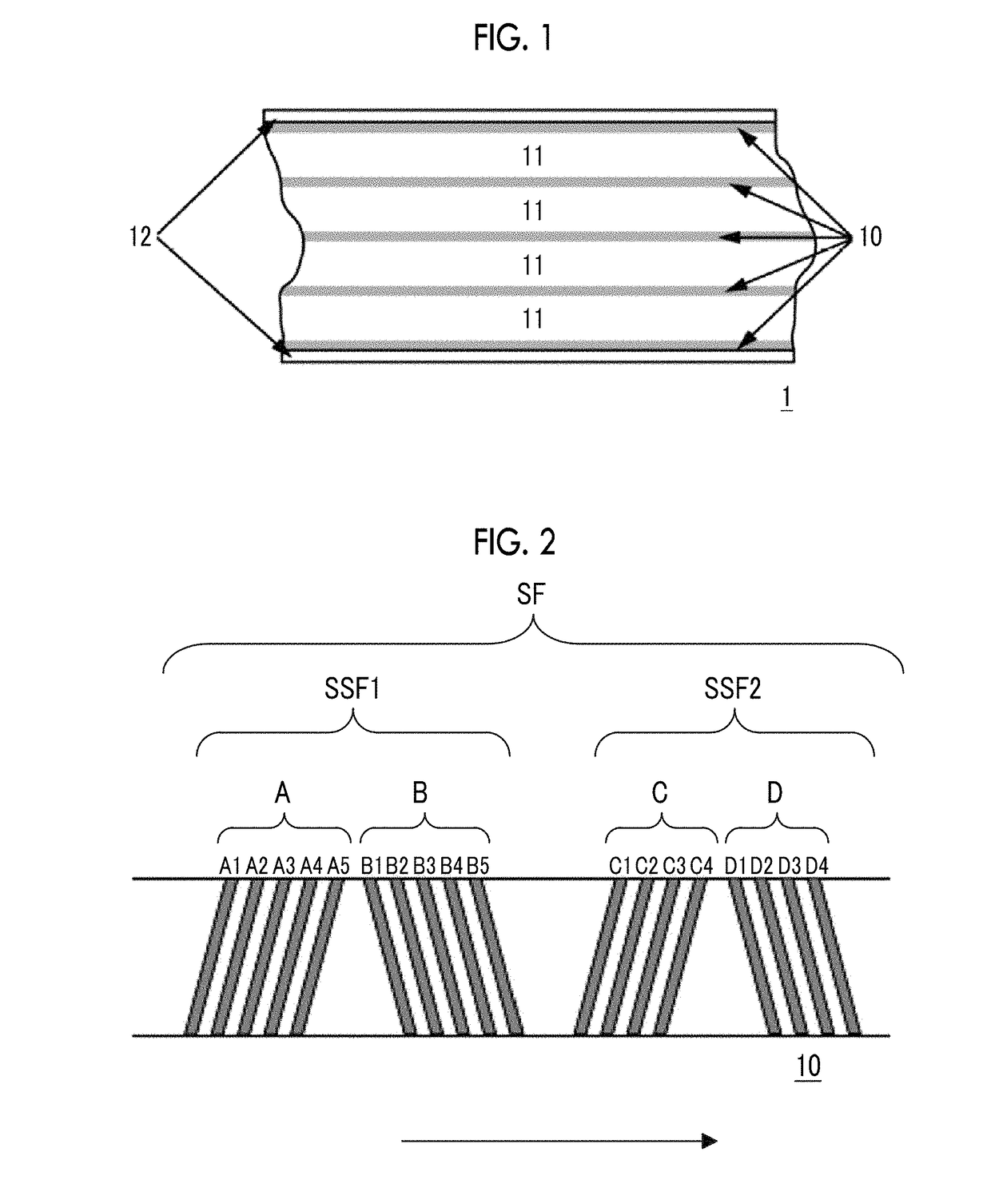
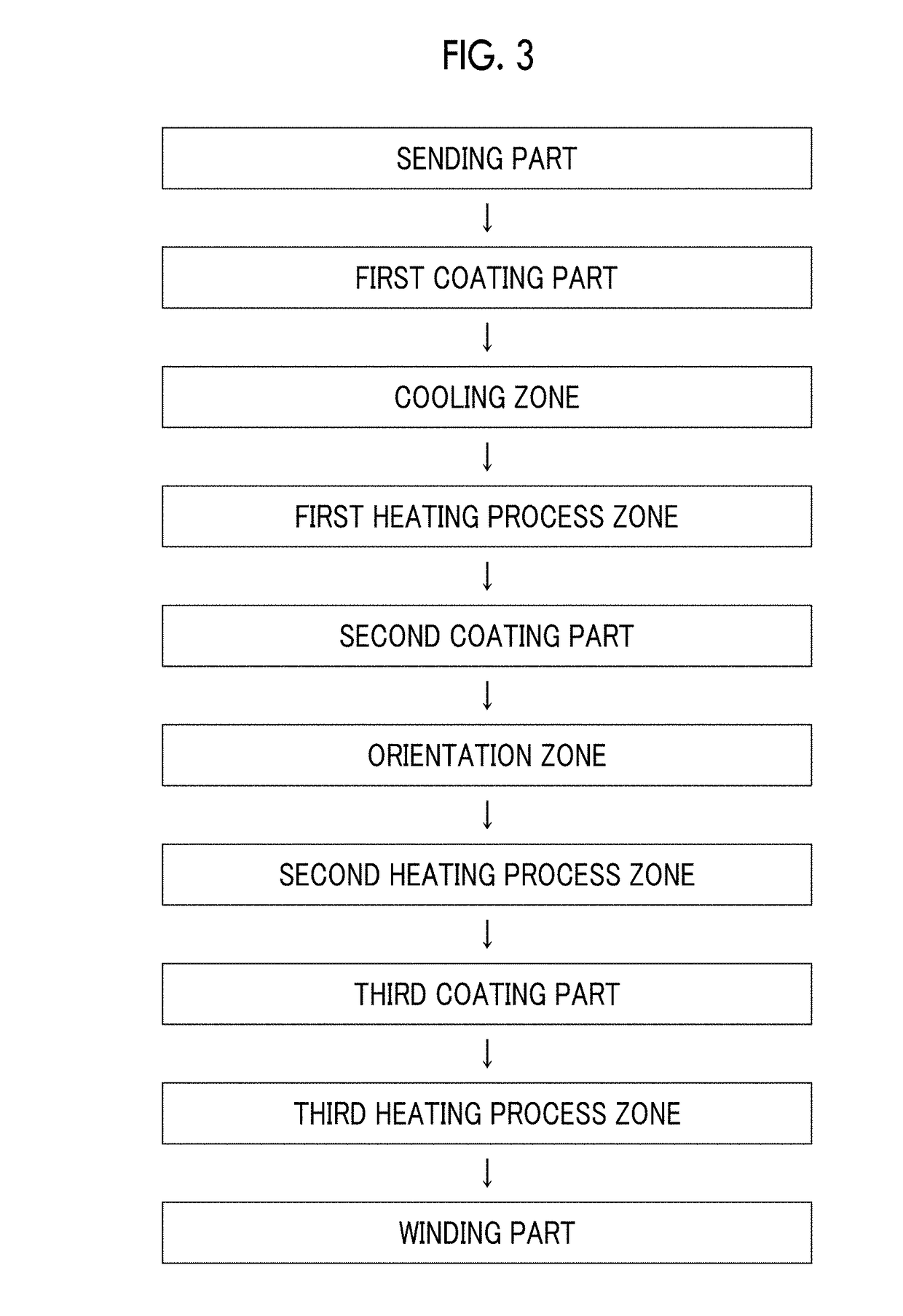
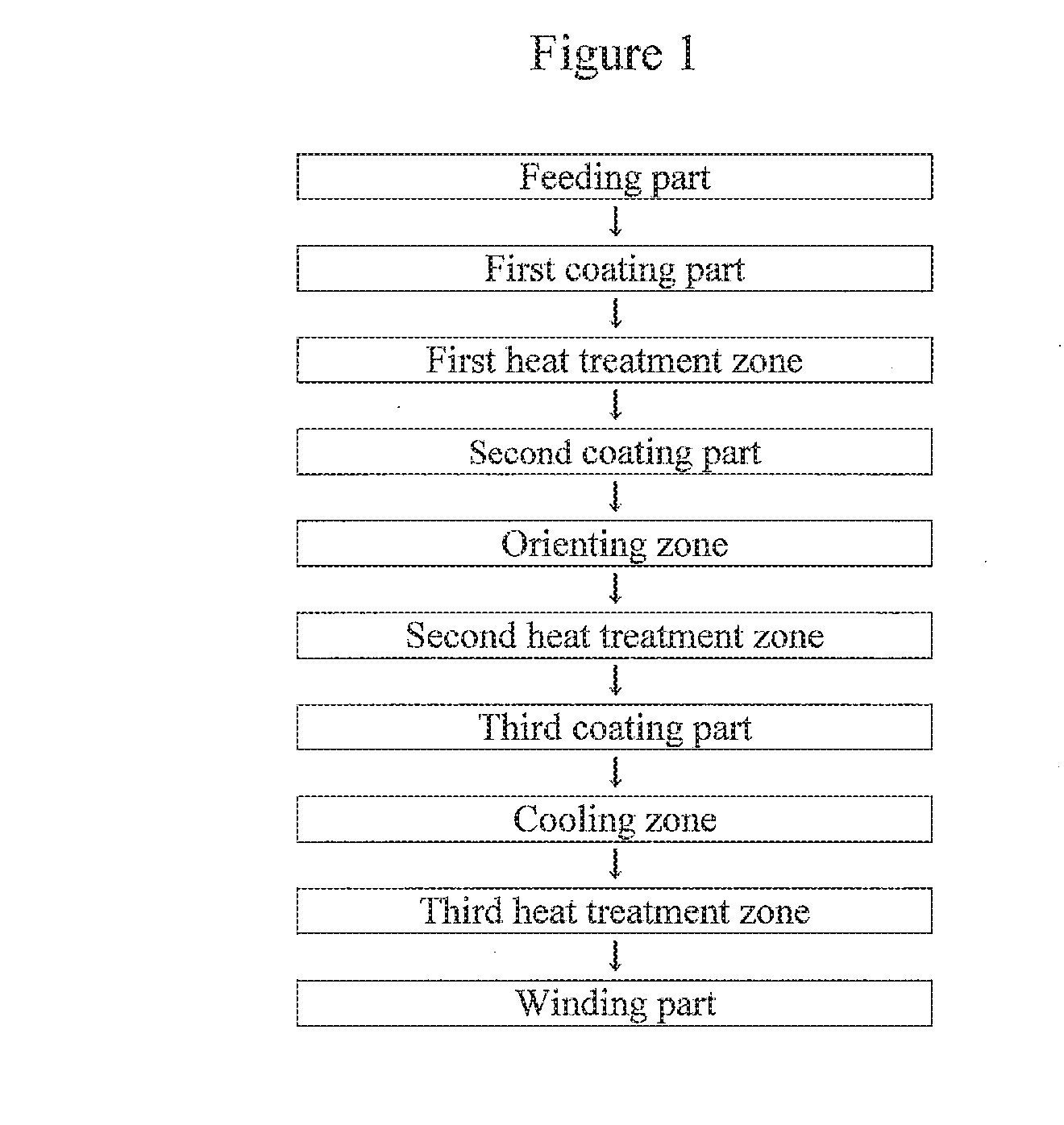
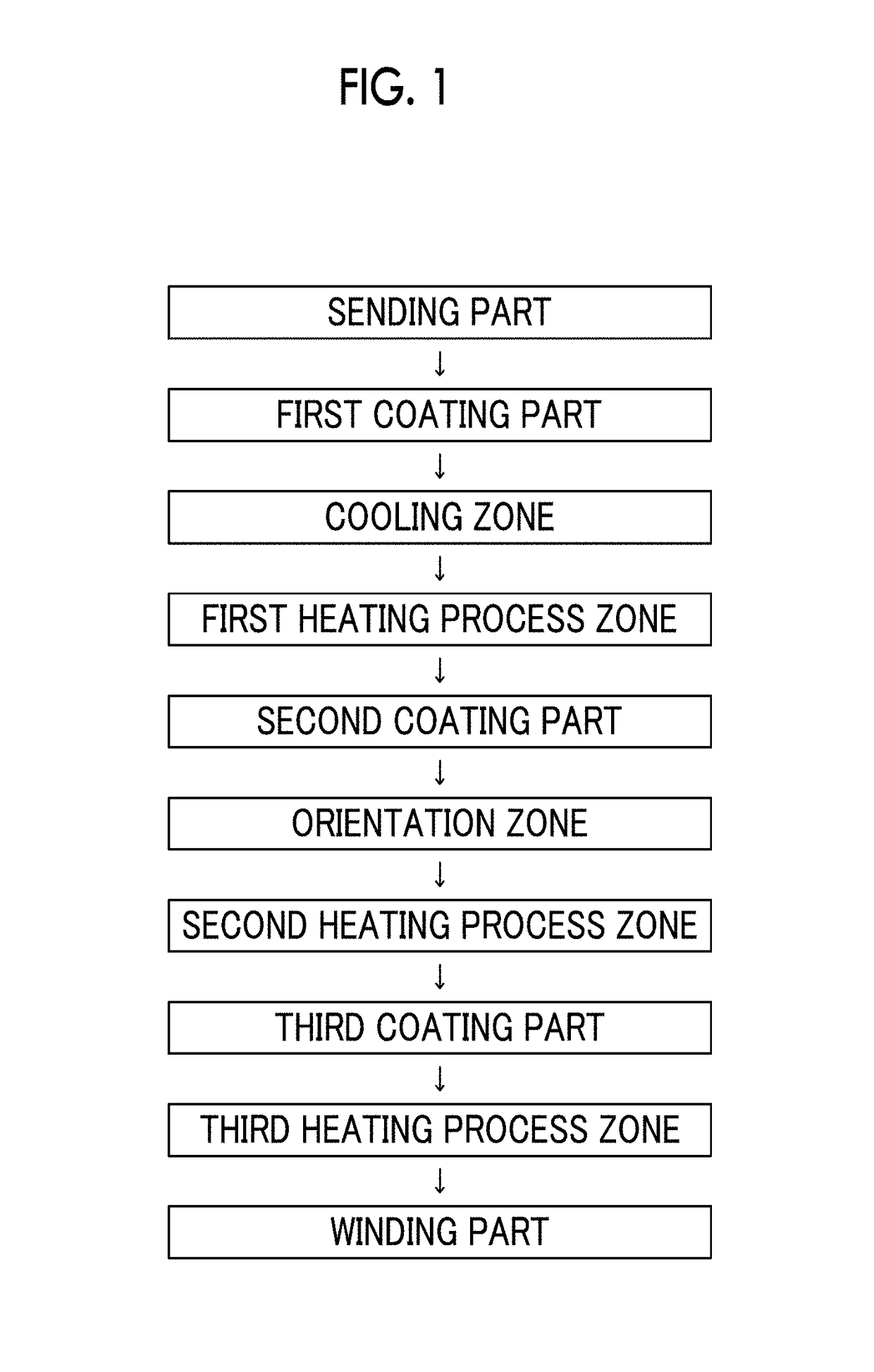
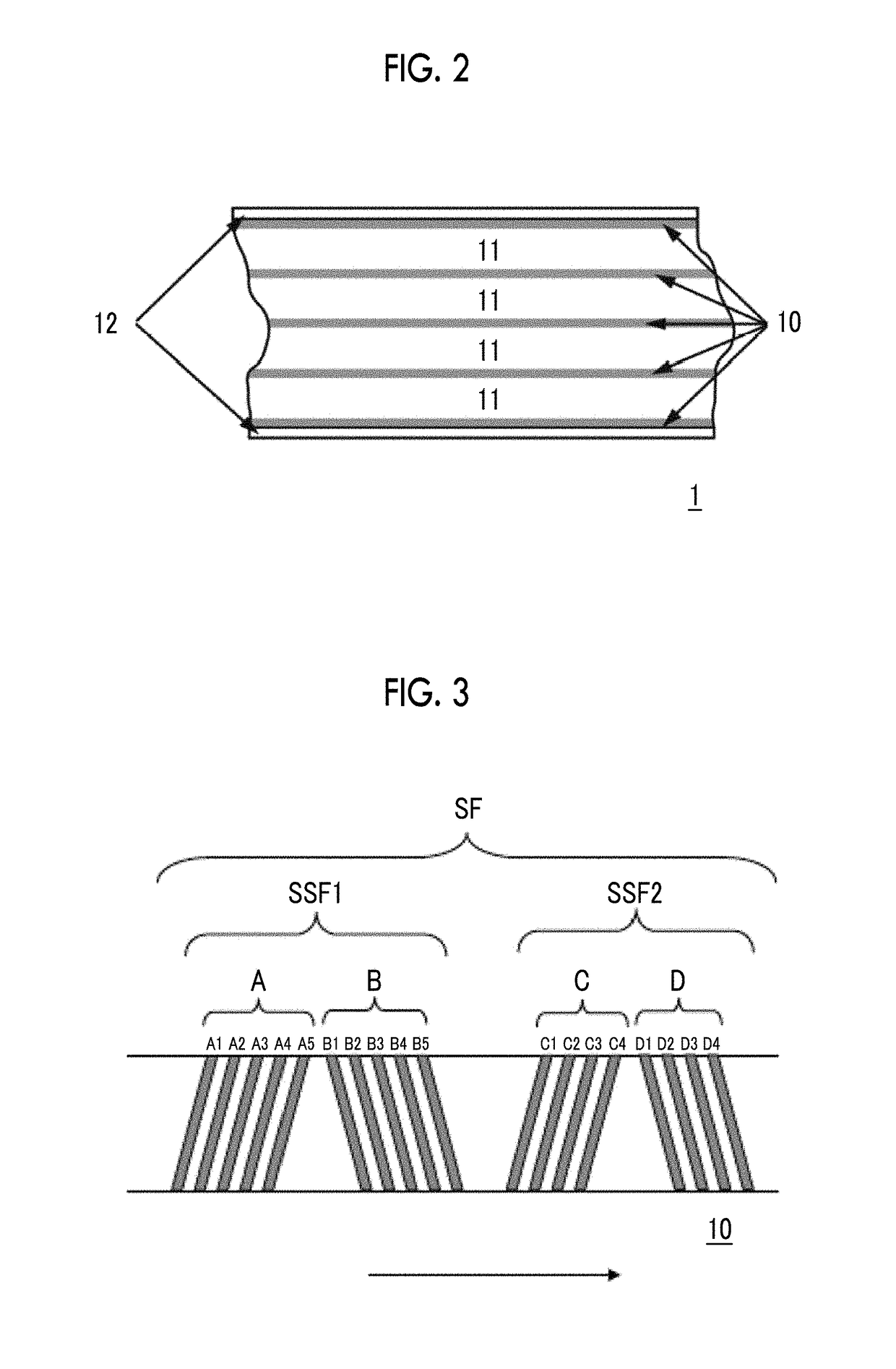
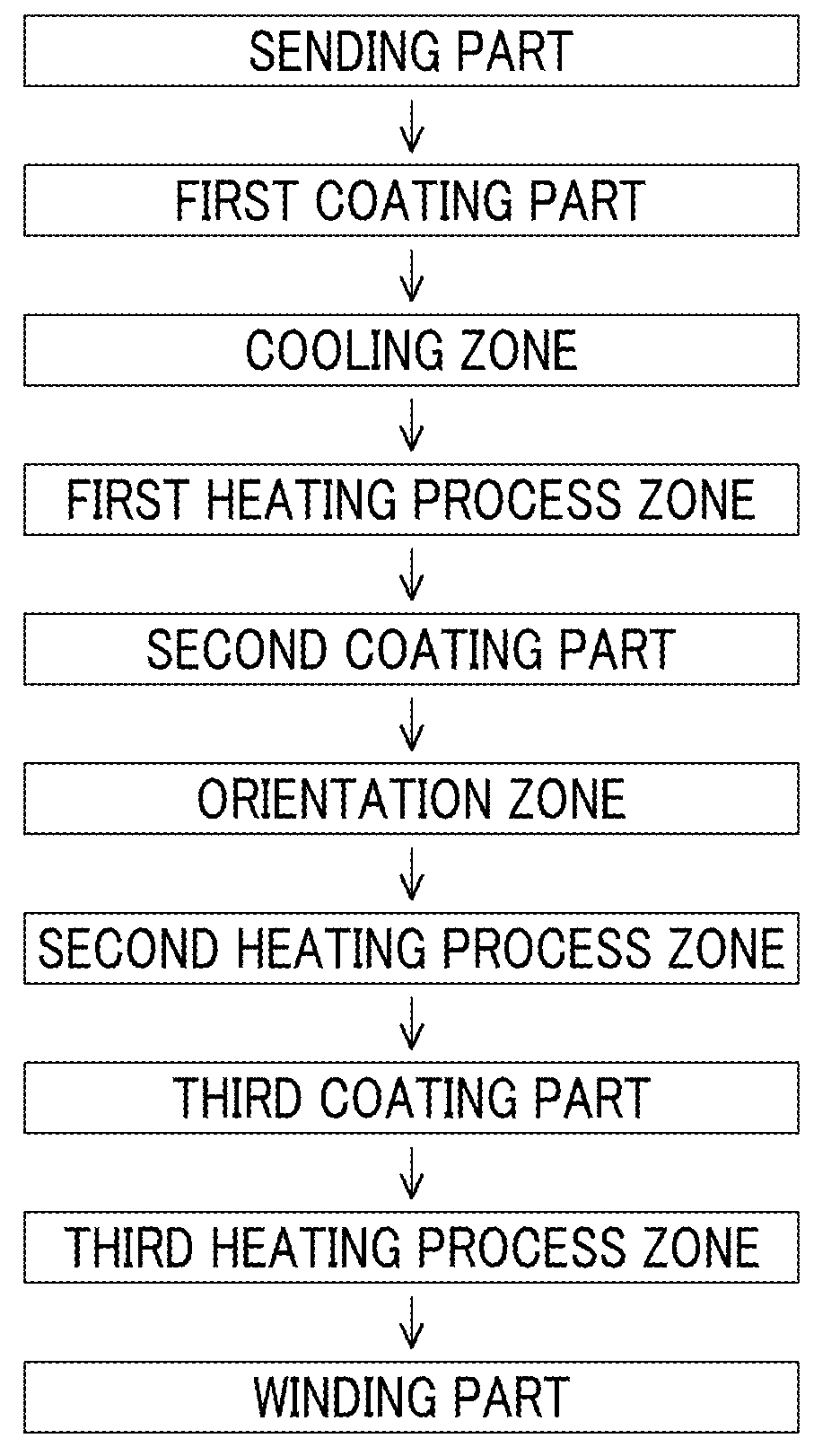
Magnetic tape
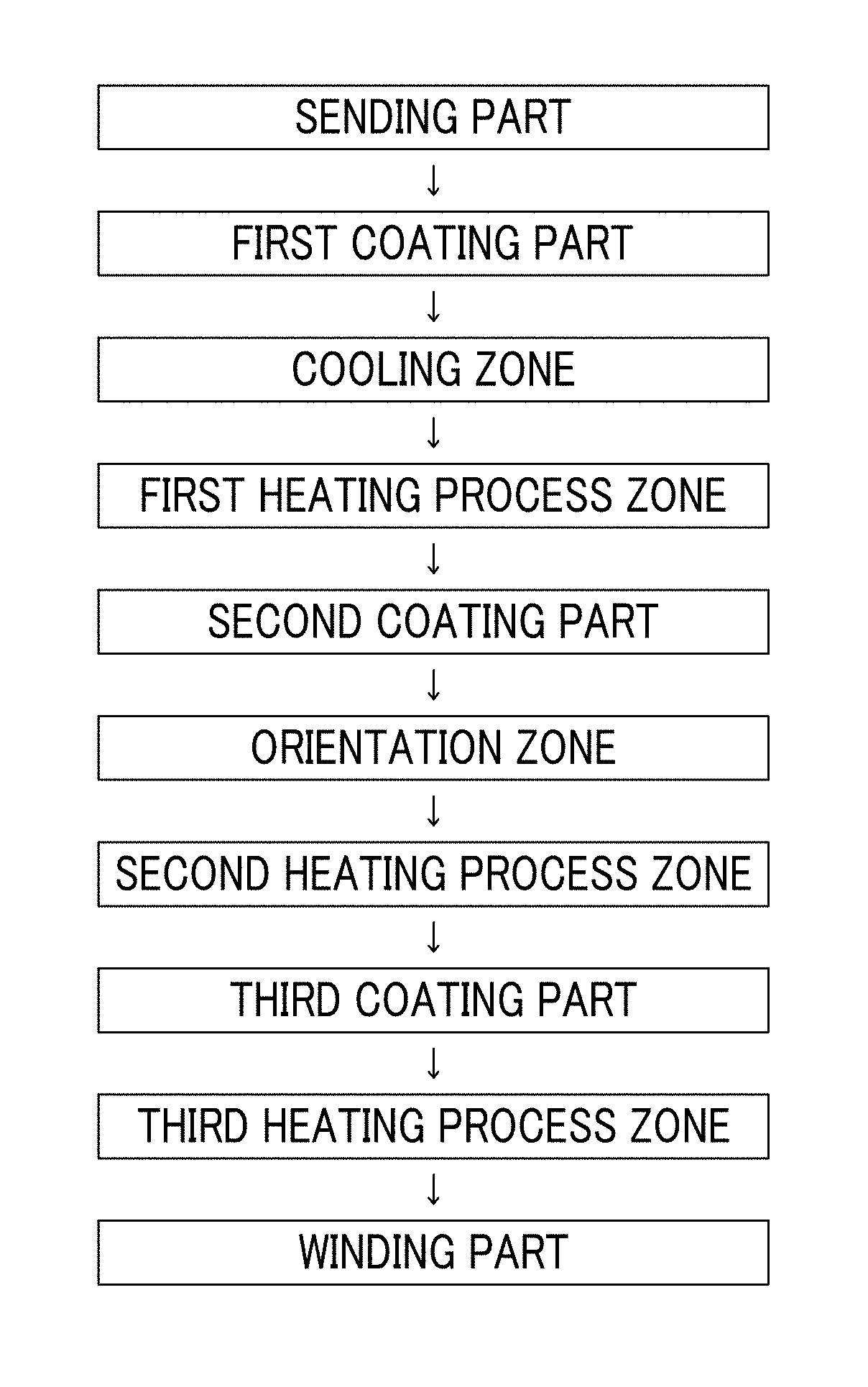
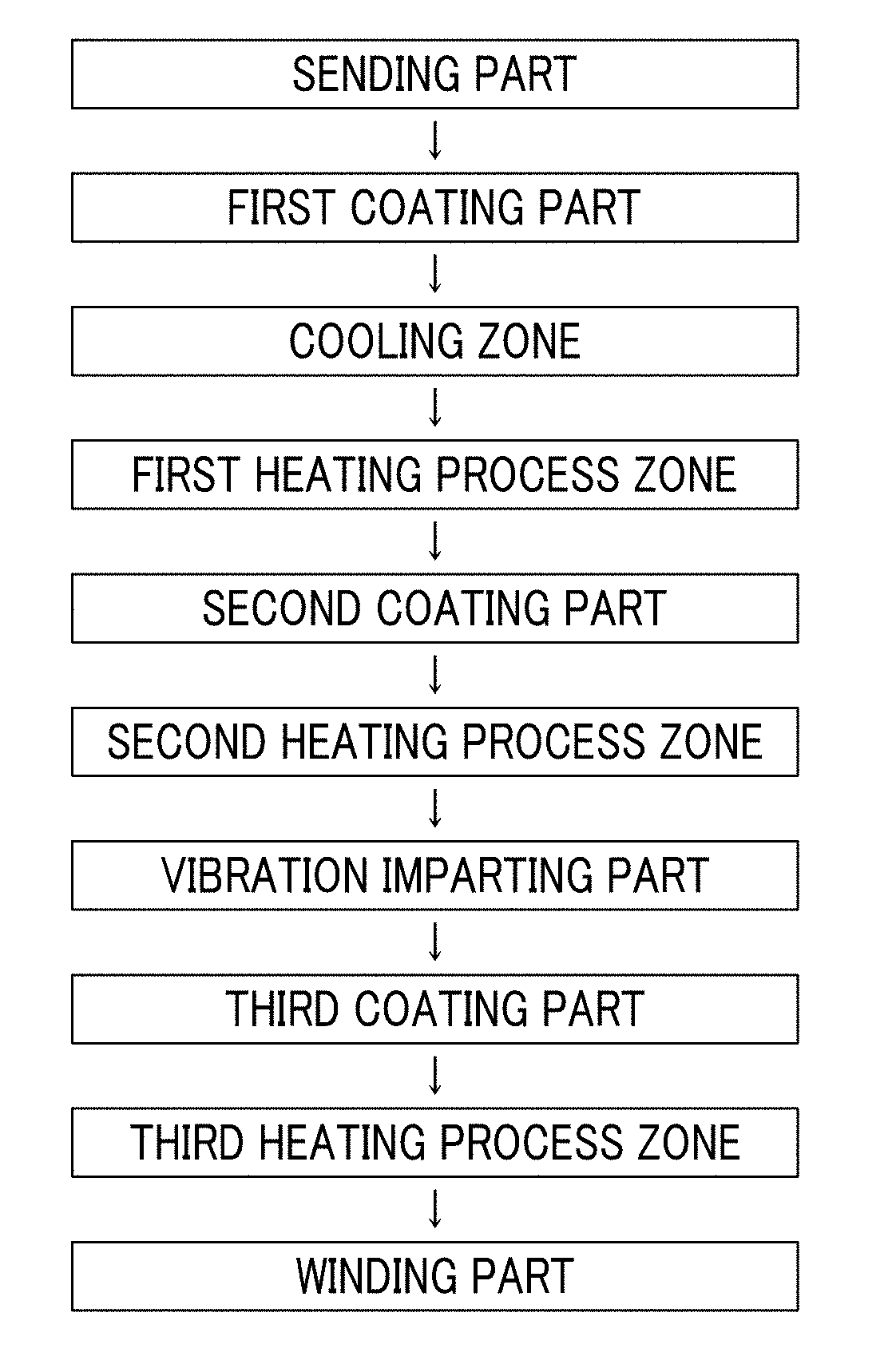
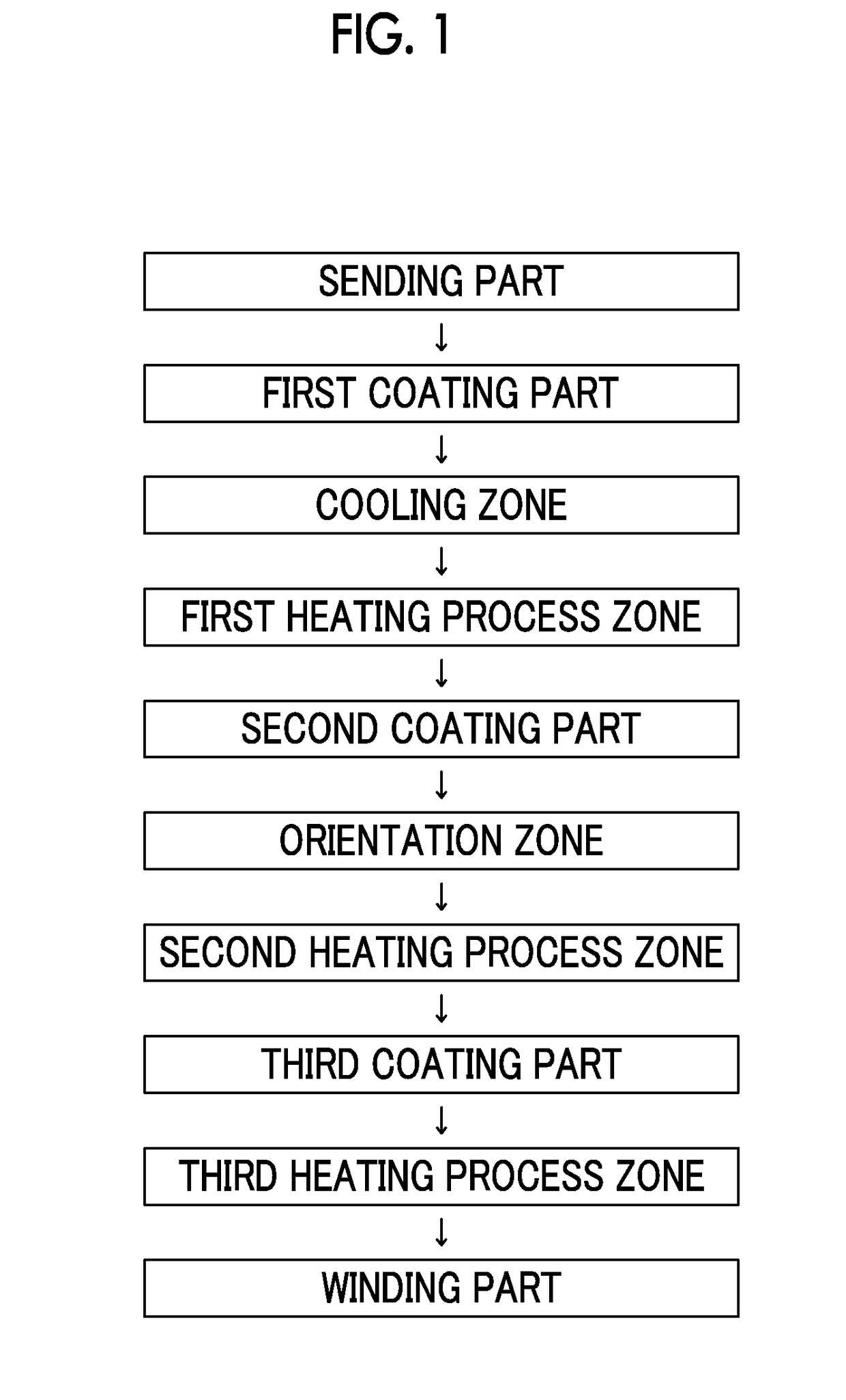
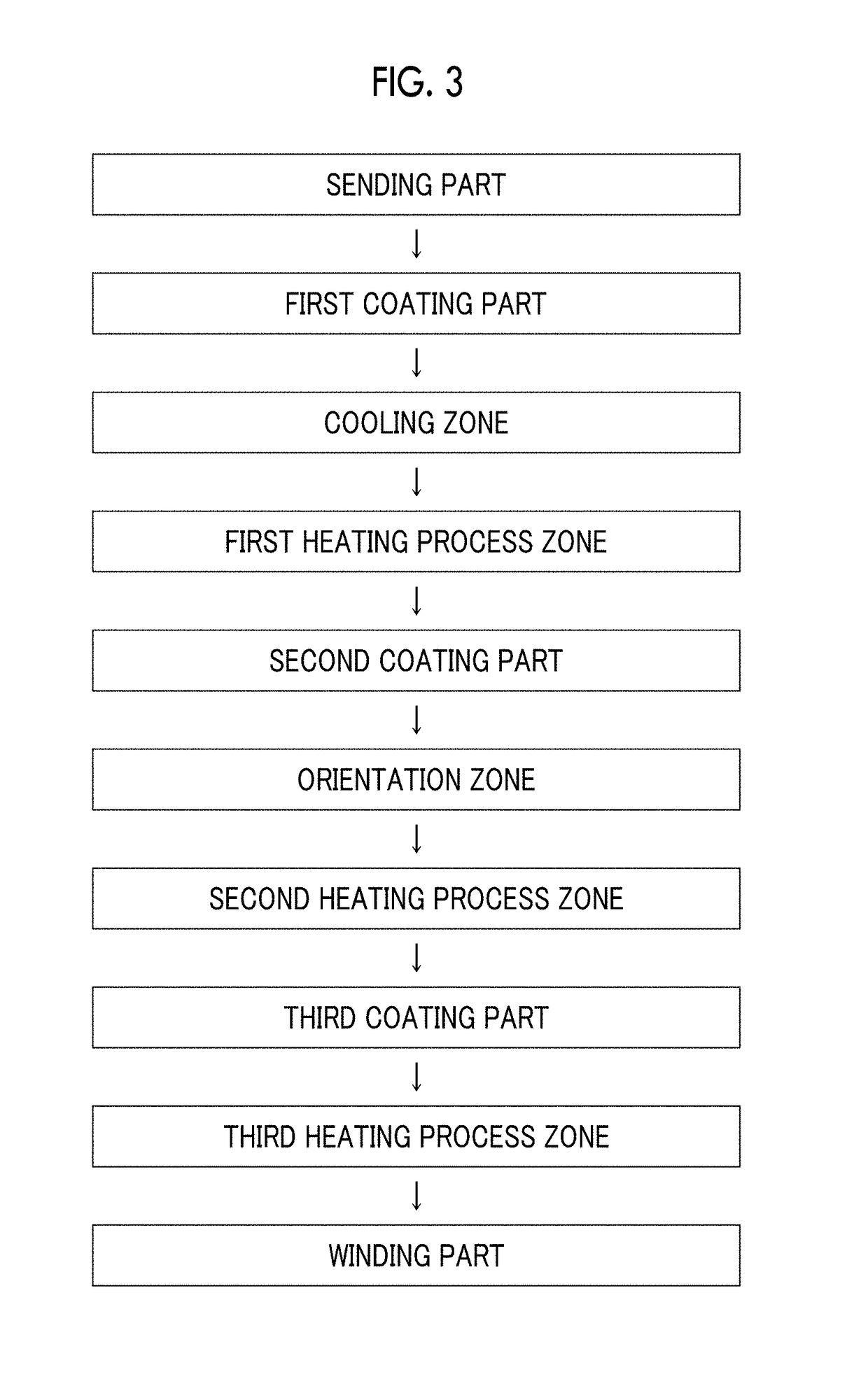
Provided is a magnetic tape in which ferromagnetic powder included in a magnetic layer is ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder having an activation volume equal to or smaller than 1,600 nm3, the magnetic layer includes one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide, and an abrasive, a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 45 atom %, and a tilt cos θ of the ferromagnetic hexagonal ferrite powder with respect to the surface of the magnetic layer acquired by cross section observation performed by using a scanning transmission electron microscope is 0.85 to 1.00.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
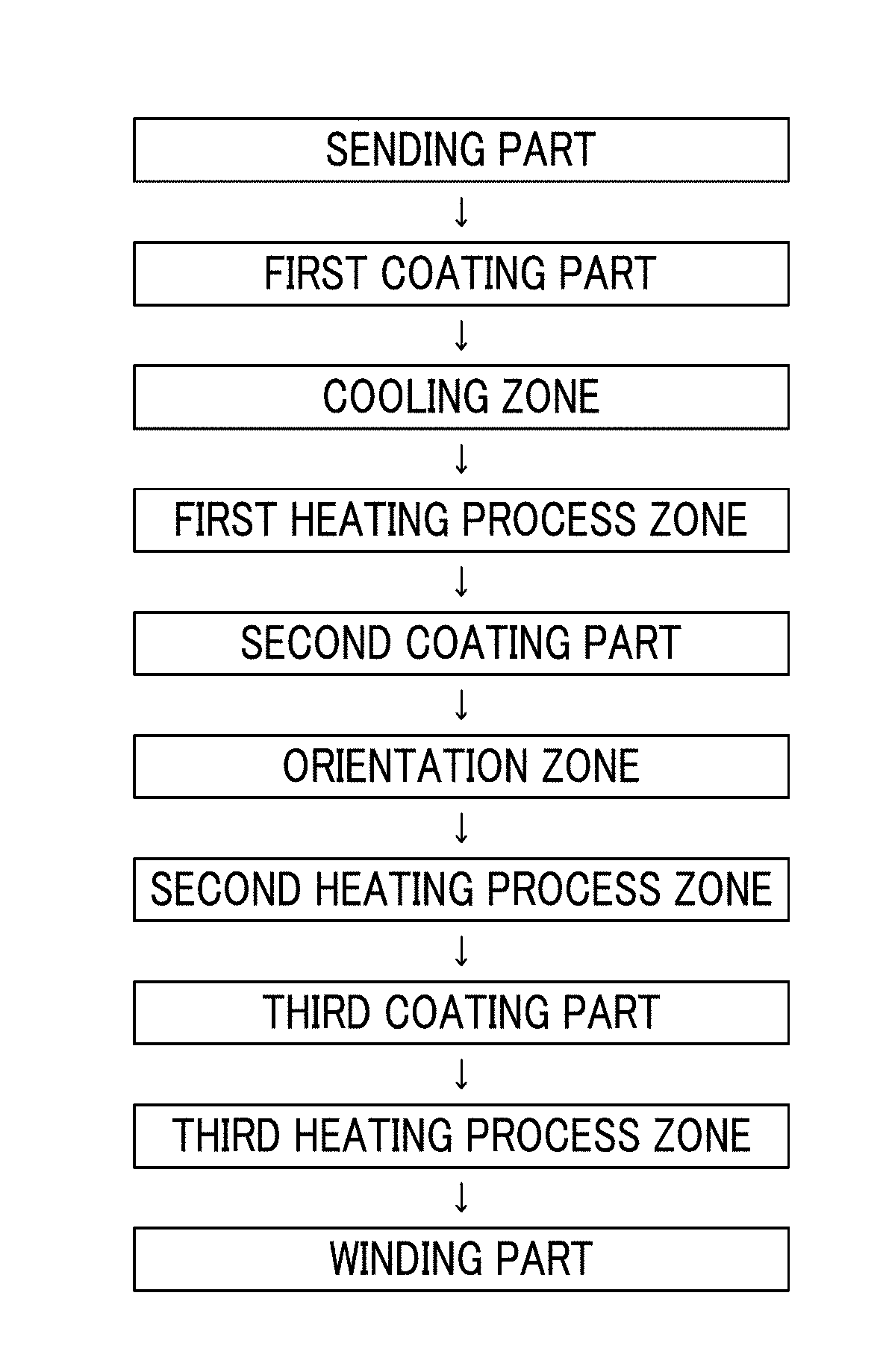
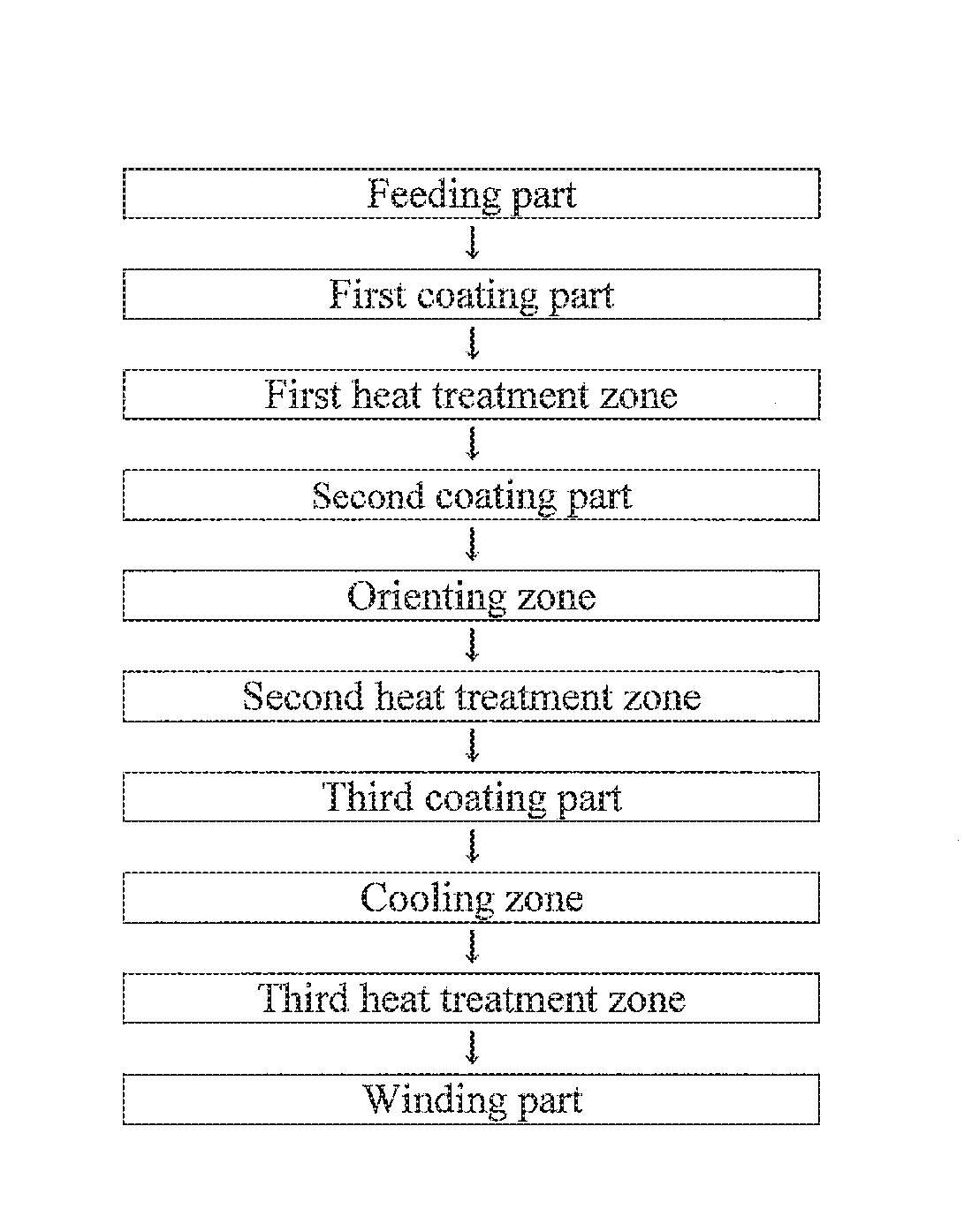
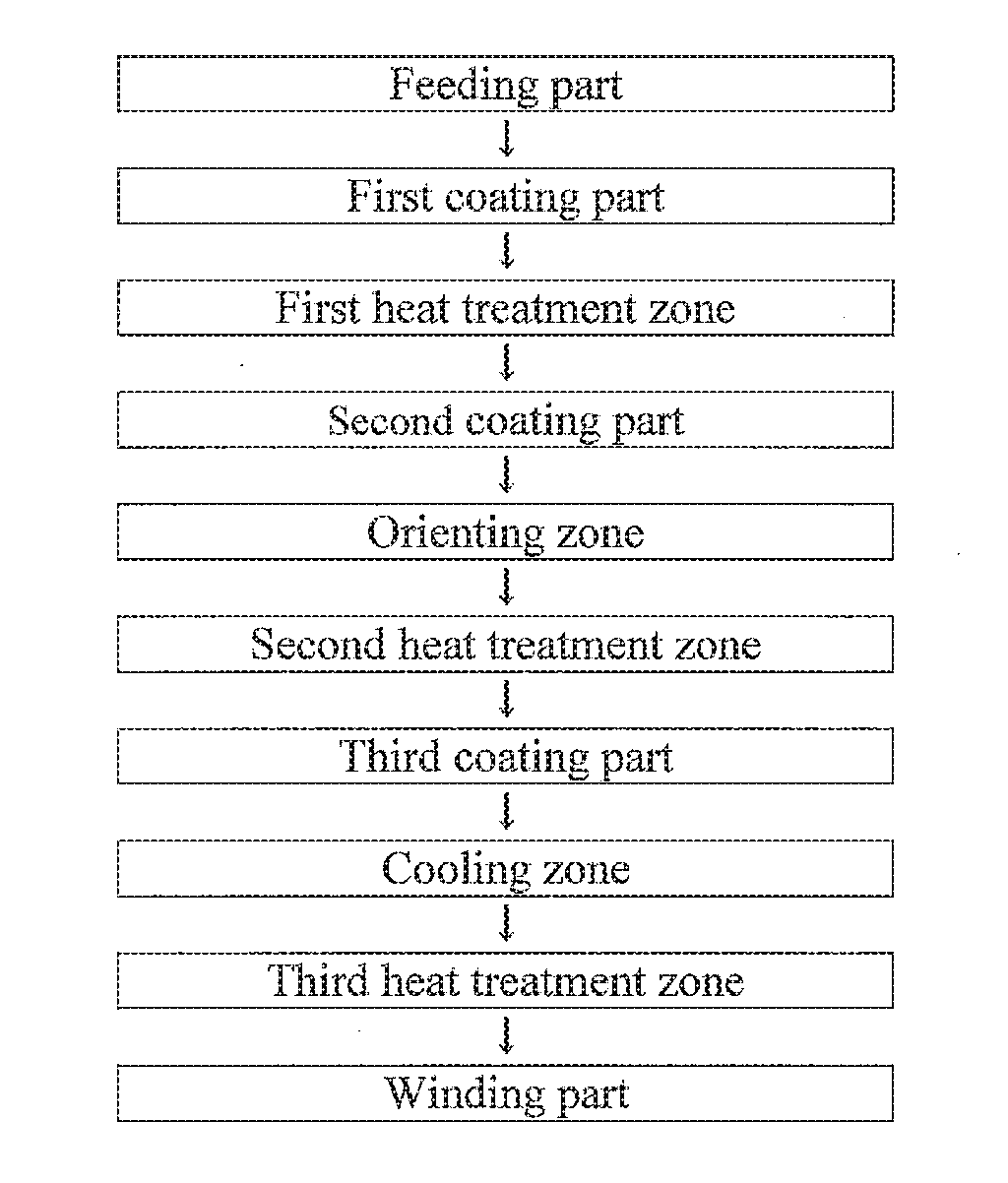
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9711174B2Reduce thicknessIncrease recording capacityBase layers for recording layersTape carriersMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
Provided is a magnetic tape, which comprises, on a nonmagnetic support, a nonmagnetic layer comprising nonmagnetic powder and binder, and on the nonmagnetic layer, a magnetic layer comprising ferromagnetic powder and binder; wherein a total thickness of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 4.80 μm; at least the magnetic layer comprises one or more components selected from the group consisting of a fatty acid and a fatty acid amide; and a C—H derived carbon, C, concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio in a C1s spectrum obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy conducted at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees on a surface on the magnetic layer side of the magnetic tape is greater than or equal to 45 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
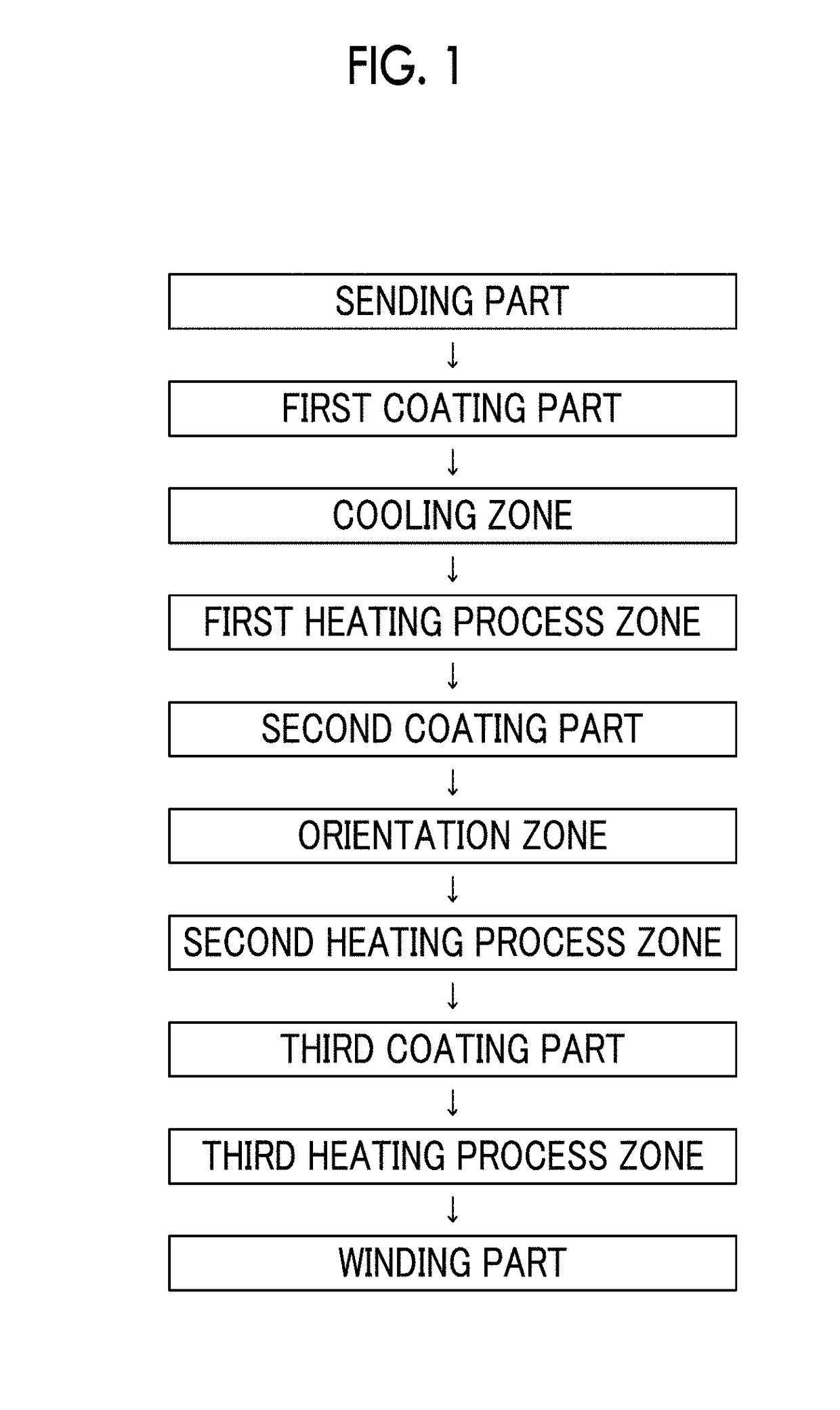
Magnetic tape device and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS9984716B1Avoid it happening againImprove accuracyProtective coatings for layersTape carriersMagnetic tapeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes: a magnetic tape; and a servo head, in which a magnetic tape transportation speed of the magnetic tape device is equal to or lower than 18 m / sec, the servo head is a TMR head, the magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, the magnetic layer includes a servo pattern, the magnetic layer includes one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on a surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
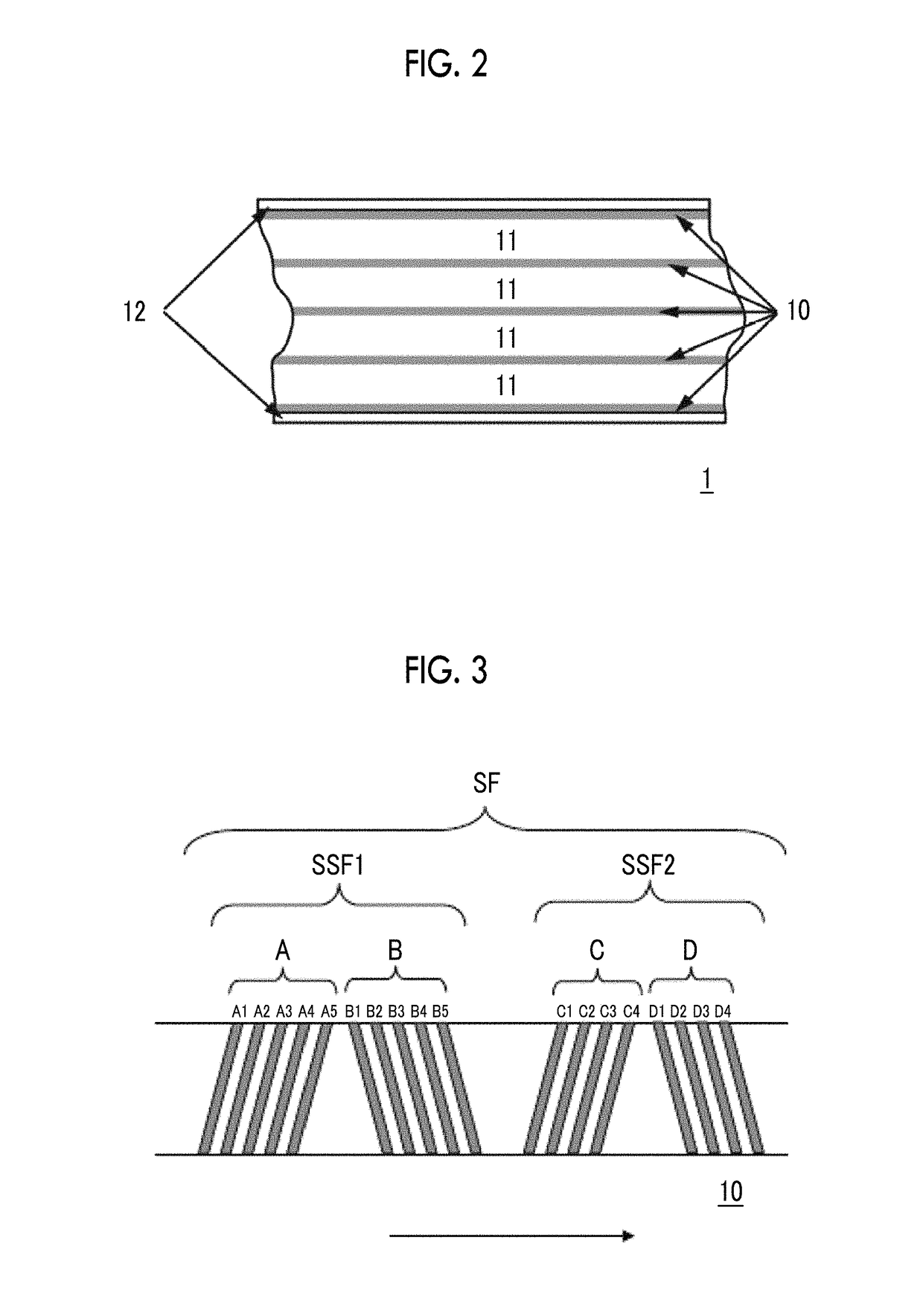
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20170372739A1Improve running stabilityBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeFull width at half maximum
Provided is a magnetic tape with the total thickness of a non-magnetic and magnetic layers is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra by ESCA on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 45 atom %, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the magnetic layer before and after vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are respectively greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 7.0 nm, and a difference between a spacing measured after the vacuum heating and a spacing measured before the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device, magnetic reproducing method, and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS10134433B2Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeX-ray
Provided is a magnetic tape device in which a magnetic tape transportation speed is equal to or lower than 18 m / sec, Ra measured regarding a surface of a magnetic layer of a magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a C-H derived C concentration calculated from a C-H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %, and ΔSFD (=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C.) in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 0.50, with the SFD25° C. being SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−190° C. being SFD measured at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20170372741A1Improve running stabilitySuitable compatibilityProtective coatings for layersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeX-ray
Provided is a magnetic tape in which a thickness of a back coating layer is equal to or smaller than 0.20 μm, a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the back coating layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees, is equal to or greater than 35 atom %, full widths at half maximum of spacing distribution measured by optical interferometry regarding the surface of the back coating layer before and after performing a vacuum heating with respect to the magnetic tape are respectively greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 10.0 nm, and a difference between a spacing measured after performing the vacuum heating and a spacing measured before performing the vacuum heating is greater than 0 nm and equal to or smaller than 8.0 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180286450A1Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessMaterials with ironRecord information storageIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape including a magnetic layer; and a TMR head (reproducing head), in which an intensity ratio of a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (110) plane with respect to a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (114) plane of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170358318A1Improve surface smoothnessImproved head positioning accuracyAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeX-ray
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic layer including non-magnetic powder and a binder on a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic layer, in which the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide are at least included in the magnetic layer, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 45 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170372743A1Restrain output decreaseImprove accuracyBase layers for recording layersAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeX-ray
The magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic layer including non-magnetic powder and a binder on a non-magnetic support; and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binder on the non-magnetic layer, the total thickness of the non-magnetic layer and the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 0.60 μm, the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide are at least included in the magnetic layer, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 45 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170372726A1Improve surface smoothnessReduce frequencyAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tapeX-ray
The magnetic tape includes a magnetic layer having ferromagnetic powder and a binder on a non-magnetic support, in which a total thickness of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 5.30 μm, the magnetic layer includes a timing-based servo pattern, a center line average surface roughness Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide are included in the magnetic layer, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 45 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS9704527B2Increase coefficient of frictionReduced stabilityRecord information storageMetals or alloysMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20160247530A1Improve running stabilityReduce coefficient of frictionRecord information storageMetals or alloysMagnetic tapeTotal thickness
The magnetic tape has on one surface of a nonmagnetic support a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder, and on the other surface of the nonmagnetic support, a backcoat layer containing nonmagnetic powder and binder, wherein the total thickness of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 4.80 μm, the backcoat layer contains one or more components selected from the group consisting of a fatty acid and a fatty acid amide, and a C—H derived carbon, C, concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio in a C1s spectrum obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy conducted at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees on a surface on the backcoat layer side of the magnetic tape ranges from 35 to 60 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device, magnetic reproducing method, and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20190051325A1Improve accuracyExact reproductionMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeX-ray
Provided is a magnetic tape device in which a magnetic tape transportation speed is equal to or lower than 18 m / sec, Ra measured regarding a surface of a magnetic layer of a magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %, and ΔSFD (=SFD25°C.−SFD−190° C.) in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 0.50, with the SFD25° C. being SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−190° C. being SFD measured at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS20180182429A1Avoid it happening againAvoiding characteristicMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersMagnetic tapeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes: a magnetic tape; and a reproducing head, in which a magnetic tape transportation speed of the magnetic tape device is equal to or lower than 18 m / sec, the reproducing head is a magnetic head including a tunnel magnetoresistance effect type element as a reproducing element, the magnetic tape includes a non-magnetic support, and a magnetic layer including ferromagnetic powder and a binding agent on the non-magnetic support, the magnetic layer includes one or more components selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape device, magnetic reproducing method, and head tracking servo method
ActiveUS20180286444A1Lower the resistance valueImprove accuracyMaterials with ironAlignment for track following on tapesMagnetic tapeX-ray
Provided is a magnetic tape device in which a magnetic tape transportation speed is equal to or lower than 18 m / sec, Ra measured regarding a surface of a magnetic layer of a magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %, and ΔSFD (=SFD25° C.−SFD−190° C.) in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is equal to or smaller than 0.50, with the SFD25° C. being SFD measured in a longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape at a temperature of 25° C., and the SFD−19° C. being SFD measured at a temperature of −190° C.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
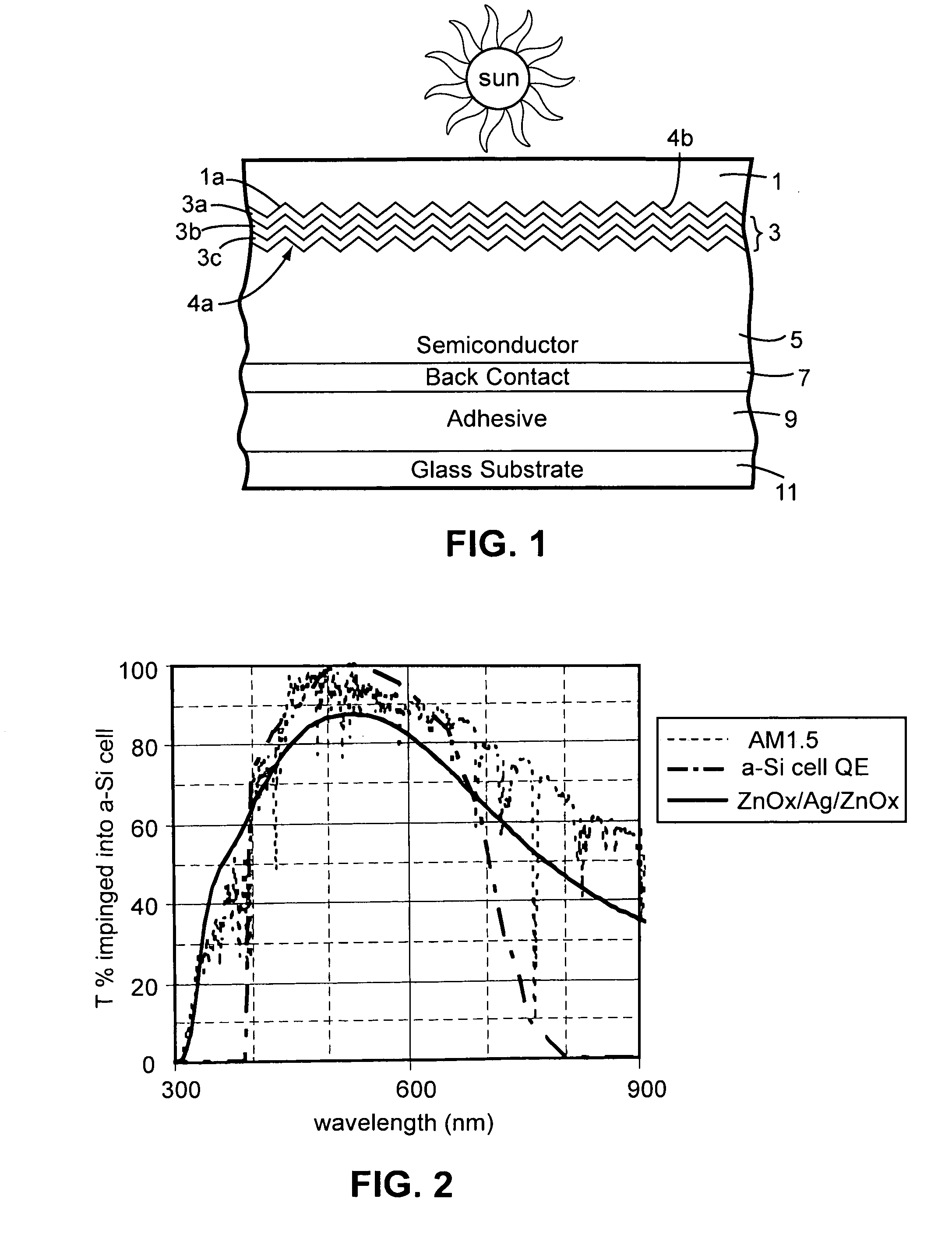
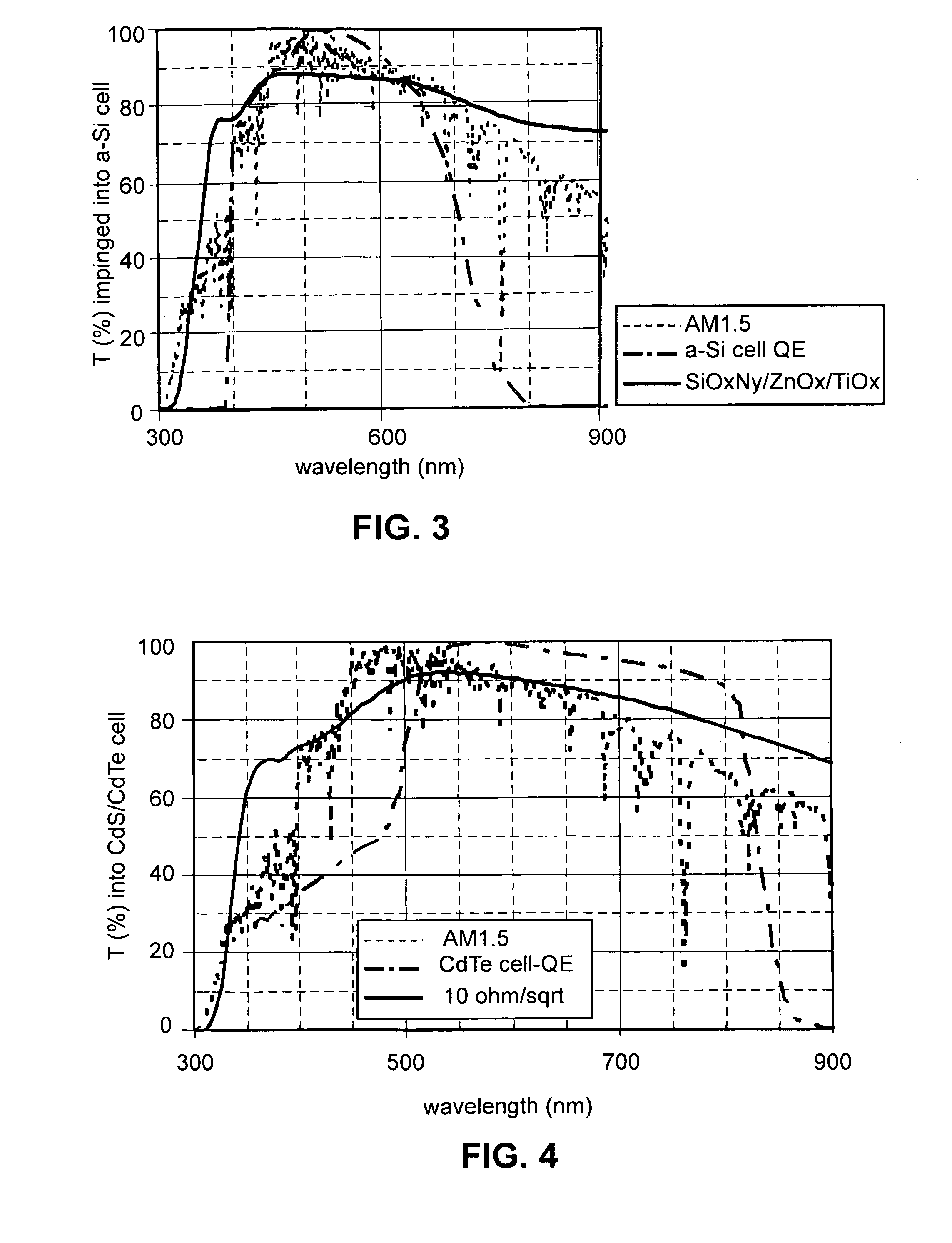
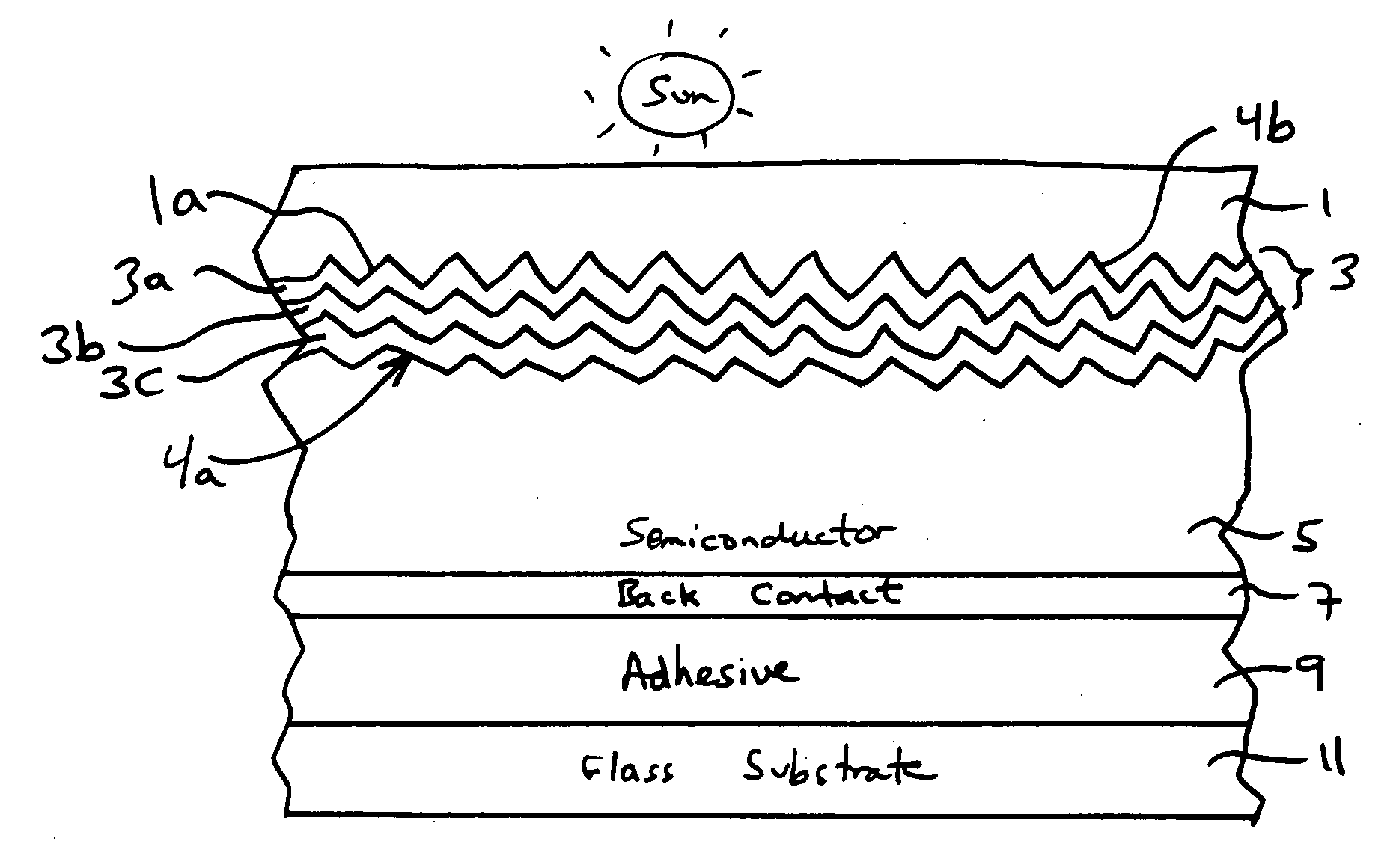
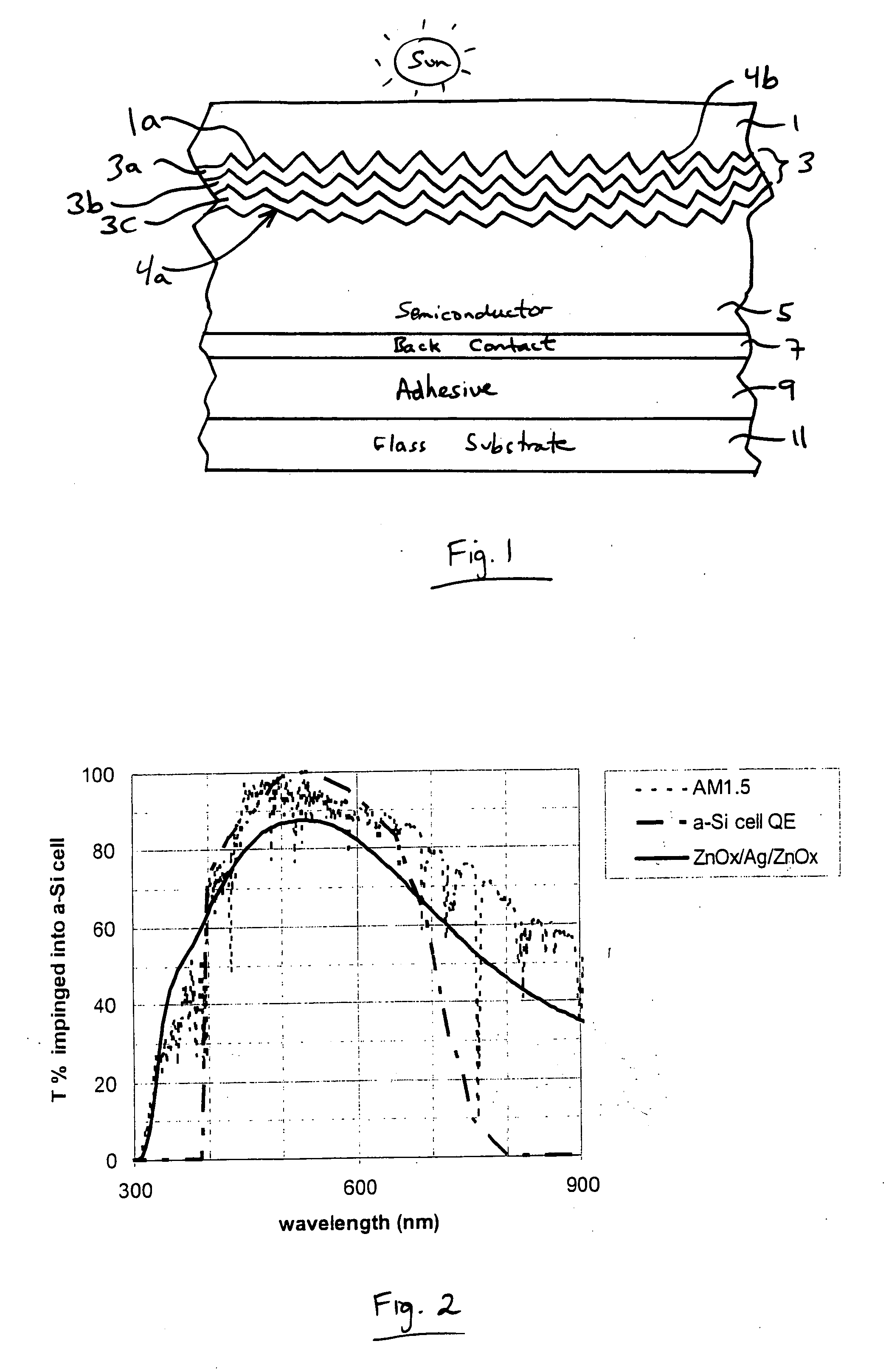
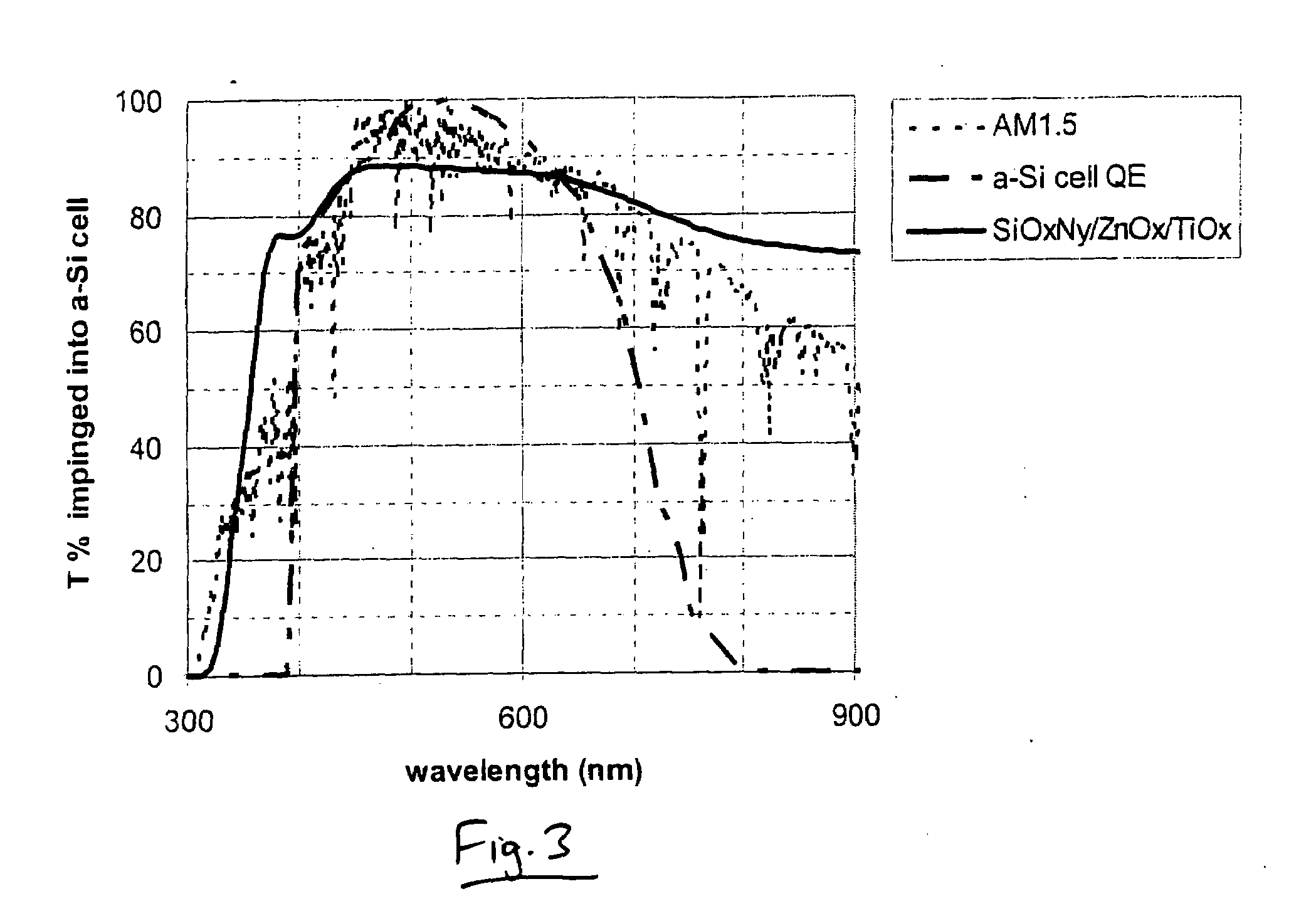
Front electrode including transparent conductive coating on patterned glass substrate for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080178932A1Reduced visible light reflectionImprove conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationPeak valuePeak area
This invention relates to a photovoltaic device including an electrode such as a front electrode / contact. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of the photovoltaic device includes a multi-layered transparent conductive coating which is sputter-deposited on a textured surface of a patterned glass substrate. In certain example embodiments, a maximum transmission area of the substantially transparent conductive front electrode is located under a peak area of a quantum efficiency (QE) and / or QEx (photon flux of solar radiation) curve of the photovoltaic device and a light source spectrum used to power the photovoltaic device. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode includes a transparent conductive layer of or including one or more of (i) titanium zinc oxide doped with aluminum and / or niobium, and / or (ii) titanium niobium oxide.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
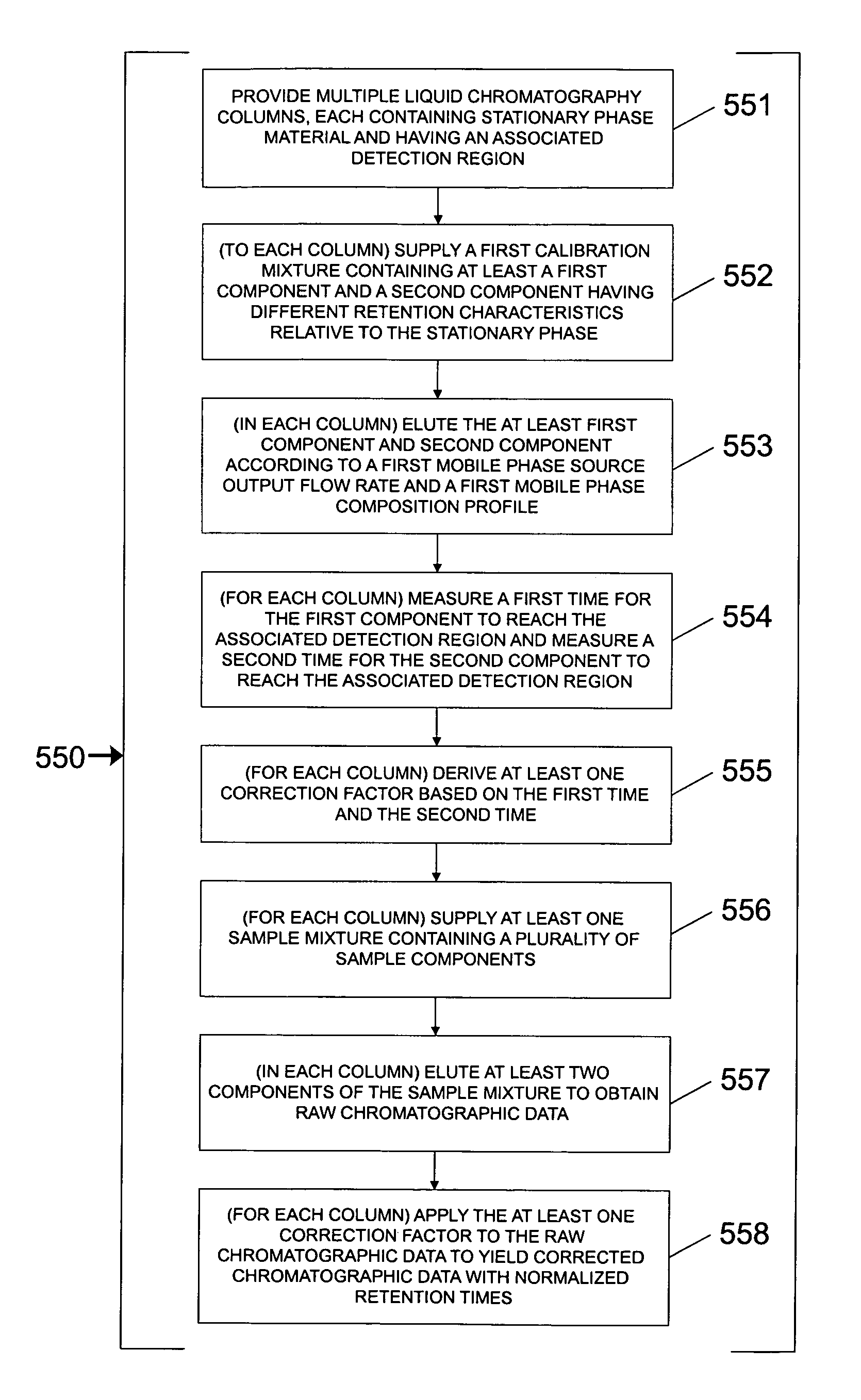
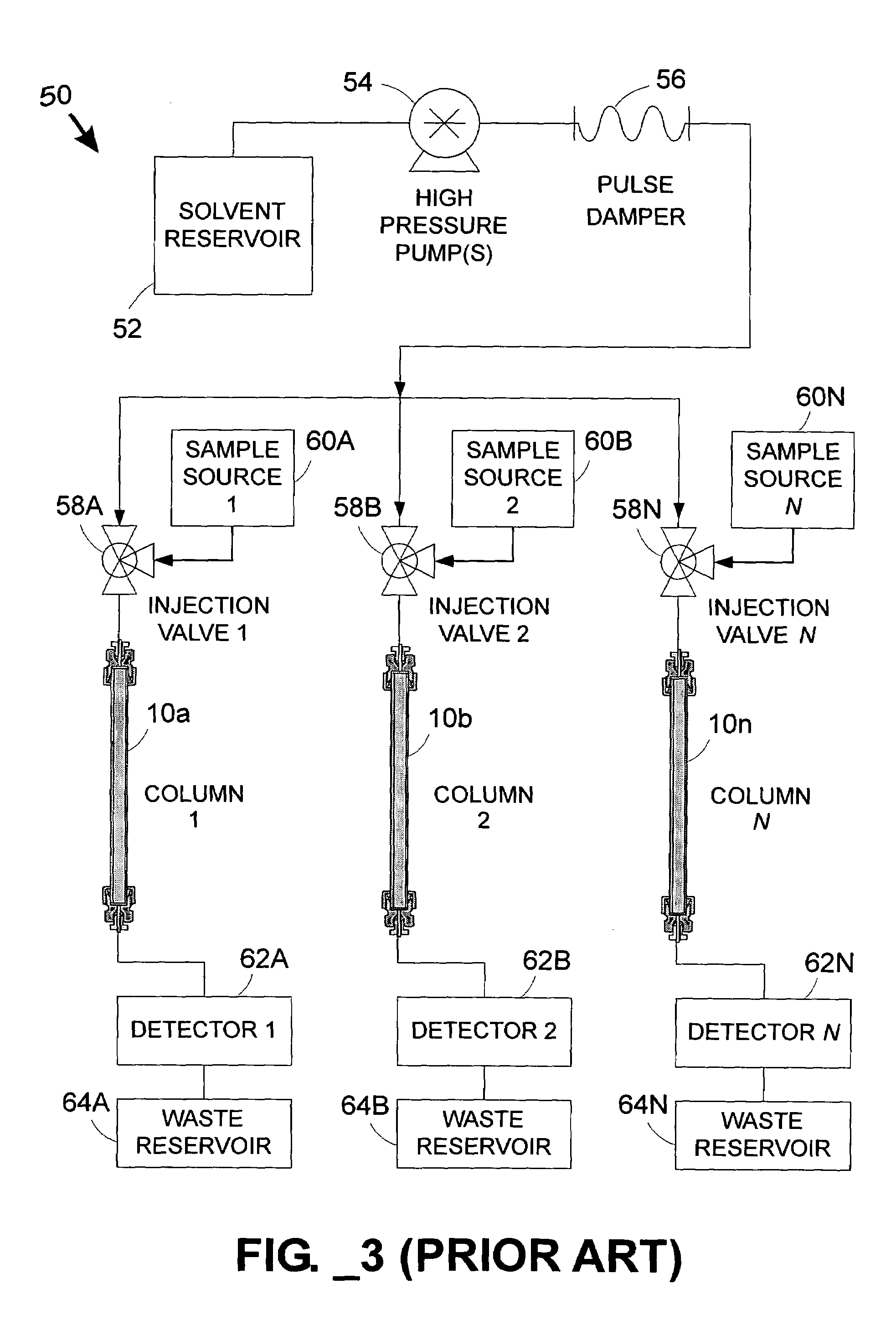
Parallel fluid processing systems and methods
ActiveUS7178386B1Ion-exchange process apparatusWave based measurement systemsFactor baseRetention time
A parallel fluid processing system including multiple fluid process regions containing solid material in fluid communication with a common first fluid source may be used to conduct analyses and / or synthesis in parallel. A parallel fluid processing data correction method includes supplying and processing a calibrant in each fluid process region, measuring a first physical parameter and deriving at least one correction factor based on the parameter, supplying and processing at least one second fluid in each fluid process region, and then applying the correction factor to yield corrected process data. Retention time correction, peak area correction, and other useful data corrections may be performed. Parallel fluid processing may be performed with microfluidic devices and systems. A system for correcting retention times in parallel liquid chromatography is further provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Magnetic tape
ActiveUS20190027174A1Improve surface smoothnessAvoid it happening againRecord information storageTape carriersIn planeX-ray
Provided is a magnetic tape in which an Ra measured regarding a surface of a magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 1.8 nm, Int(110) / Int(114) of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, the back coating layer includes one or more kinds of component selected from the group consisting of fatty acid and fatty acid amide, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the back coating layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is equal to or greater than 35 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Electrophotographic photoreceptor, process cartridge and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS20040086794A1Improve stain resistanceViscosity control of solutionElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargePeak areaSilicon
An electrophotographic photoreceptor comprising a conductive support and a photosensitive layer disposed on the conductive support, wherein the photosensitive layer comprises a silicon compound-containing layer containing a silicon compound, and the silicon compound-containing layer further contains a resin, and wherein the photosensitive layer has a peak area in the region of -40 to 0 ppm (S1) and a peak area in the region of -100 to -50 ppm (S2) in a <29>Si-NMR spectrum satisfying the following equation (1): S1 / (S1+S2)>=0.5 (1).
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Front electrode including transparent conductive coating on patterned glass substrate for use in photovoltaic device and method of making same
InactiveUS20080107799A1Reduced visible light reflectionImprove conductivityPV power plantsVacuum evaporation coatingQuantum efficiencyConductive coating
This invention relates to a photovoltaic device including an electrode such as a front electrode / contact. In certain example embodiments, the front electrode of the photovoltaic device includes a multi-layered transparent conductive coating which is sputter-deposited on a textured surface of a patterned glass substrate. In certain example embodiments, a maximum transmission area of the substantially transparent conductive front electrode is located under a peak area of a quantum efficiency (QE) curve of the photovoltaic device and a light source spectrum used to power the photovoltaic device.
Owner:GUARDIAN GLASS LLC
Chromatographic and mass spectral date analysis
InactiveUS20060255258A1Improve accuracyEasy to quantifyParticle separator tubesComponent separationAnalyteRegression analysis
Apparatus, methods, and computer readable media having computer code for calibrating chromatograms to achieve chromatographic peak shape correction, noise filtering, peak detection, retention time determination, baseline correction, and peak area integration. A method for processing a chromatogram, comprises obtaining at least one actual chromatographic peak shape function from one of an internal standard, an external standard, or an analyte represented in the chromatogram; performing chromatographic peak detection using known peak shape functions with regression analysis; reporting regression coefficients from the regression analysis as one of peak area and peak location; and constructing a calibration curve to relate peak area to known concentrations in the chromatogram. A method for constructing an extracted ion chromatogram, comprises calibrating a low resolution mass spectrometer for both mass and peak shape in profile mode; performing mass spectral peak analysis and reporting both mass locations and integrated peak areas; specifying a mass defect window of interest; summing up all detected peaks with mass defects falling within the specified mass defect window to derive summed intensities; and plotting the summed intensities against time to generate a mass defect filtered chromatogram.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
Advanced low dielectric constant organosilicon plasma chemical vapor deposition films
ActiveUS20060183345A1Increase Si-O-Si bondingImprove propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPorosityNetwork structure
A porous low k or ultra low k dielectric film comprising atoms of Si, C, O and H (hereinafter “SiCOH”) in a covalently bonded tri-dimensional network structure having a dielectric constant of less than about 3.0, a higher degree of crystalline bonding interactions, more carbon as methyl termination groups and fewer methylene, —CH2— crosslinking groups than prior art SiCOH dielectrics is provided. The SiCOH dielectric is characterized as having a FTIR spectrum comprising a peak area for CH3+CH2 stretching of less than about 1.40, a peak area for SiH stretching of less than about 0.20, a peak area for SiCH3 bonding of greater than about 2.0, and a peak area for Si—O—Si bonding of greater than about 60%, and a porosity of greater than about 20%.
Owner:SONY CORP +2
Single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material
ActiveUS20140335339A1Improve optical qualityReduce concentrationPolycrystalline material growthSynthetic resin layered productsPhotoluminescenceSingle crystal
A single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material comprising: a total as-grown nitrogen concentration equal to or greater than 5 ppm, and a uniform distribution of defects, wherein said uniform distribution of defects is defined by one or more of the following characteristics: (i) the total nitrogen concentration, when mapped by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm using an analysis area of 10 μm or less, possesses a point-to-point variation of less than 30% of an average total nitrogen concentration value, or when mapped by SIMS over an area equal to or greater than 200×200 μm using an analysis area of 60 μm or less, possesses a point-to-point variation of less than 30% of an average total nitrogen concentration value; (ii) an as-grown nitrogen-vacancy defect (NV) concentration equal to or greater than 50 ppb as measured using 77K UV-visible absorption measurements, wherein the nitrogen-vacancy defects are uniformly distributed through the synthetic single crystal CVD diamond material such that, when excited using a 514 nm laser excitation source of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at room temperature using a 50 mW 46 continuous wave laser, and mapped over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm with a data interval less than 10 μm there is a low point-to-point variation wherein the intensity area ratio of nitrogen vacancy photoluminescence peaks between regions of high photoluminescent intensity and regions of low photolominescent intensity is <2× for either the 575 nm photoluminescent peak (NV0) or the 637 nm photoluminescent peak (NV); (iii) a variation in Raman intensity such that, when excited using a 514 nm laser excitation source (resulting in a Raman peak at 552.4 nm) of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at room temperature using a 50 mW continuous wave laser, and mapped over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm with a data interval less than 10 μm, there is a low point-to-point variation wherein the ratio of Raman peak areas between regions of low Raman intensity and high Raman intensity is <1.25×; (iv) an as-grown nitrogen-vacancy defect (NV) concentration equal to or greater than 50 ppb as measured using 77K UV-visible absorption measurements, wherein, when excited using a 514 nm excitation source of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at 77K using a 50 mW continuous wave laser, gives an intensity at 575 nm corresponding to NV0 greater than 120 times a Raman intensity at 552.4 nm, and / or an intensity at 637 nm corresponding to NV− greater than 200 times the Raman intensity at 552.4 nm; (v) a single substitutional nitrogen defect (Ns) concentration equal to or greater than 5 ppm, wherein the single substitutional nitrogen defects are uniformly distributed through the synthetic single crystal CVD diamond material such that by using a 1344 cm−1 infrared absorption feature and sampling an area greater than an area of 0.5 mm2, the variation is lower than 80%, as deduced by dividing the standard deviation by the mean value; (vi) a variation in red luminescence intensity, as defined by a standard deviation divided by a mean value, is less than 15%; (vii) a mean standard deviation in neutral single substitutional nitrogen concentration of less than 80%; and (viii) a colour intensity as measured using a histogram from a microscopy image with a mean gray value of greater than 50, wherein the colour intensity is uniform through the single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material such that the variation in gray colour, as characterised by the gray value standard deviation divided by the gray value mean, is less than 40%.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Magnetic tape device and magnetic reproducing method
ActiveUS10410666B2Improve smoothnessImprove surface smoothnessMaterials with ironRecord information storageIn planeX-ray
The magnetic tape device includes a magnetic tape including a magnetic layer; and a TMR head (reproducing head), in which an intensity ratio of a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (110) plane with respect to a peak intensity of a diffraction peak of a (114) plane of a hexagonal ferrite crystal structure obtained by an X-ray diffraction analysis of the magnetic layer by using an In-Plane method is 0.5 to 4.0, a vertical direction squareness ratio of the magnetic tape is 0.65 to 1.00, Ra measured regarding a surface of the magnetic layer is equal to or smaller than 2.0 nm, and a C—H derived C concentration calculated from a C—H peak area ratio of C1s spectra obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis performed on the surface of the magnetic layer at a photoelectron take-off angle of 10 degrees is 45 to 65 atom %.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method for screening traditional Chinese medicine effect related ingredients and model building method
ActiveCN102879486ASimple methodReliable methodComponent separationHplc fingerprintAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for screening traditional Chinese medicine effect related ingredients and a model building method. The method comprises the steps as follows: taking the researched traditional Chinese medicines as objects for preparing multiple sets of sample solutions containing chemical components with different concentrations; selecting part of the chemical components for HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) analysis, and investigating linear relations between the peak areas and the concentrations; selecting the multiple sets of sample solutions in the linear range, and determining the respective HPLC fingerprint spectrums and the medicine effect indexes of the sample solutions; and obtaining relations between the peak areas and the medicine effect indexes of the ingredients by adopting a linear regression analysis method in the linear relation range, and confirming the actions of the medicine effect related ingredients on the medicine effect indexes according to the positive value and the negative value of the standard regression coefficients and / or the t check results of the ingredients so as to screen out the traditional Chinese medicine effect related ingredients. The method is simple, convenient, easy to implement, reliable and good in commonality, can embody the characteristics of comprehensive actions of the multiple ingredients on the medicine effect indexes, is suitable for screening the traditional Chinese medicine effect related ingredients, and provides a technical data support for discovering and screening traditional Chinese medicine active ingredients.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
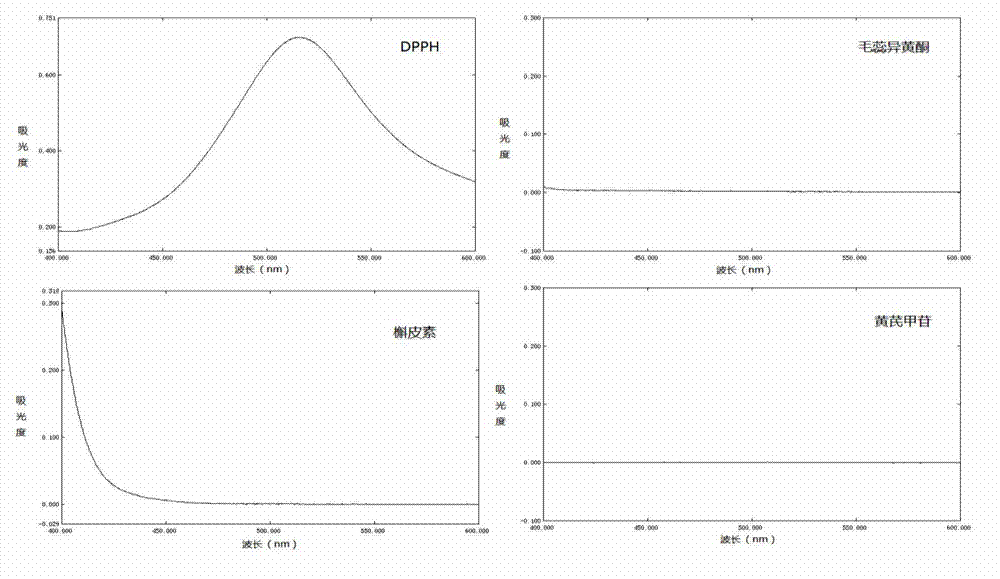
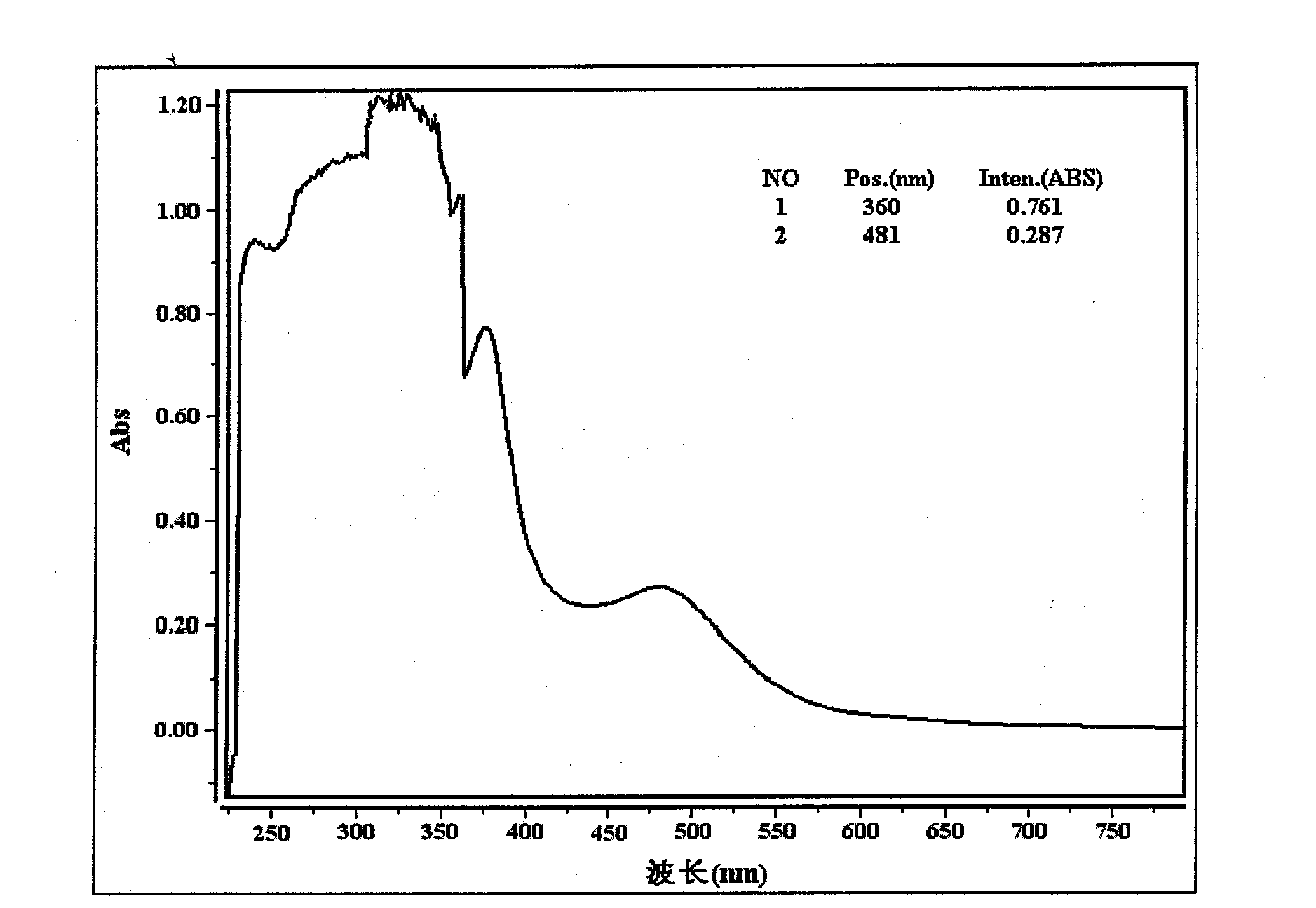
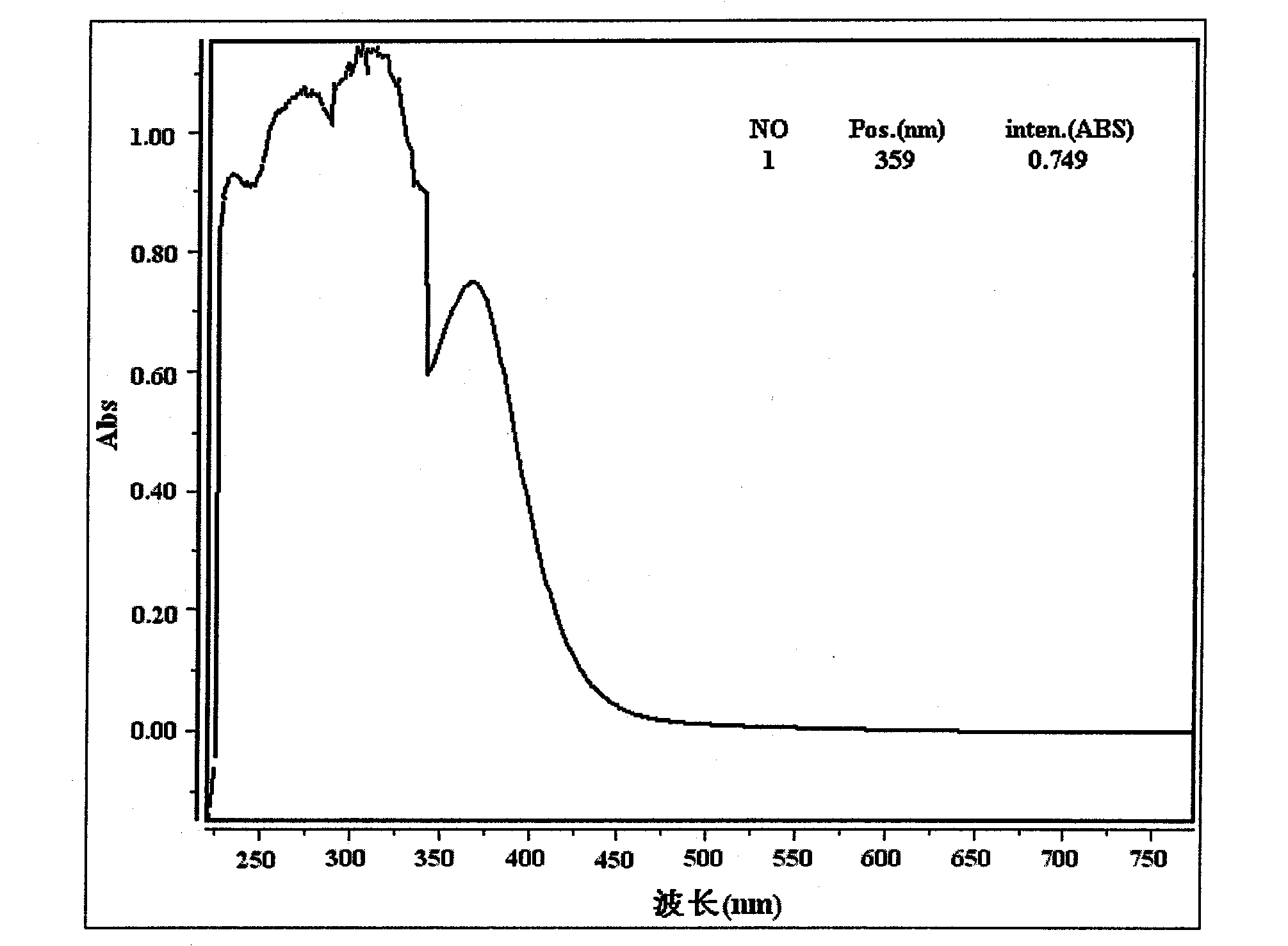
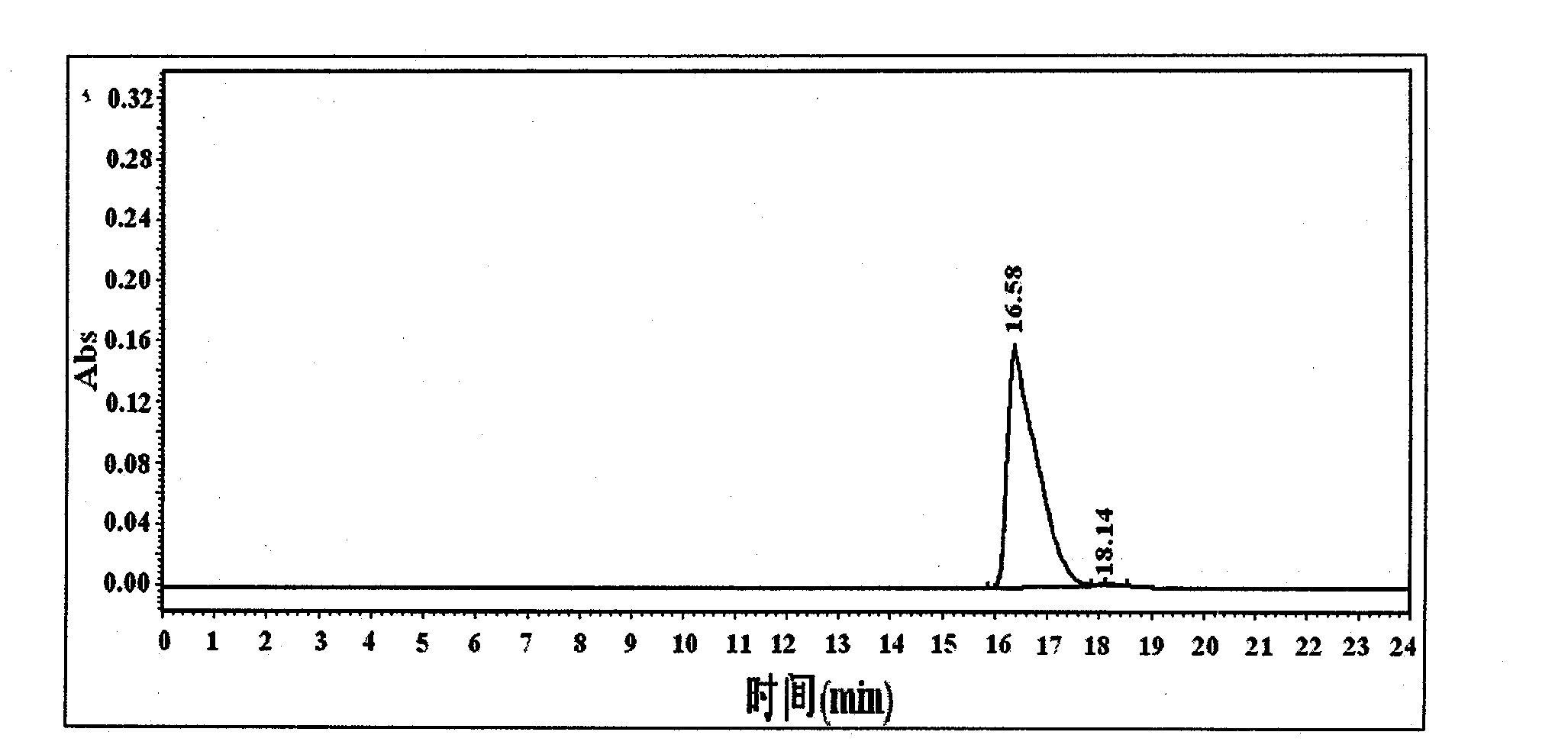
Method for extracting suaeda salsa flavone and measuring content of flavones in suaeda salsa
InactiveCN103027962AImprove production rateIncrease profitAntipyreticComponent separationConcentration gradientSolvent
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF IND TECH
Sleep state estimating device and program product
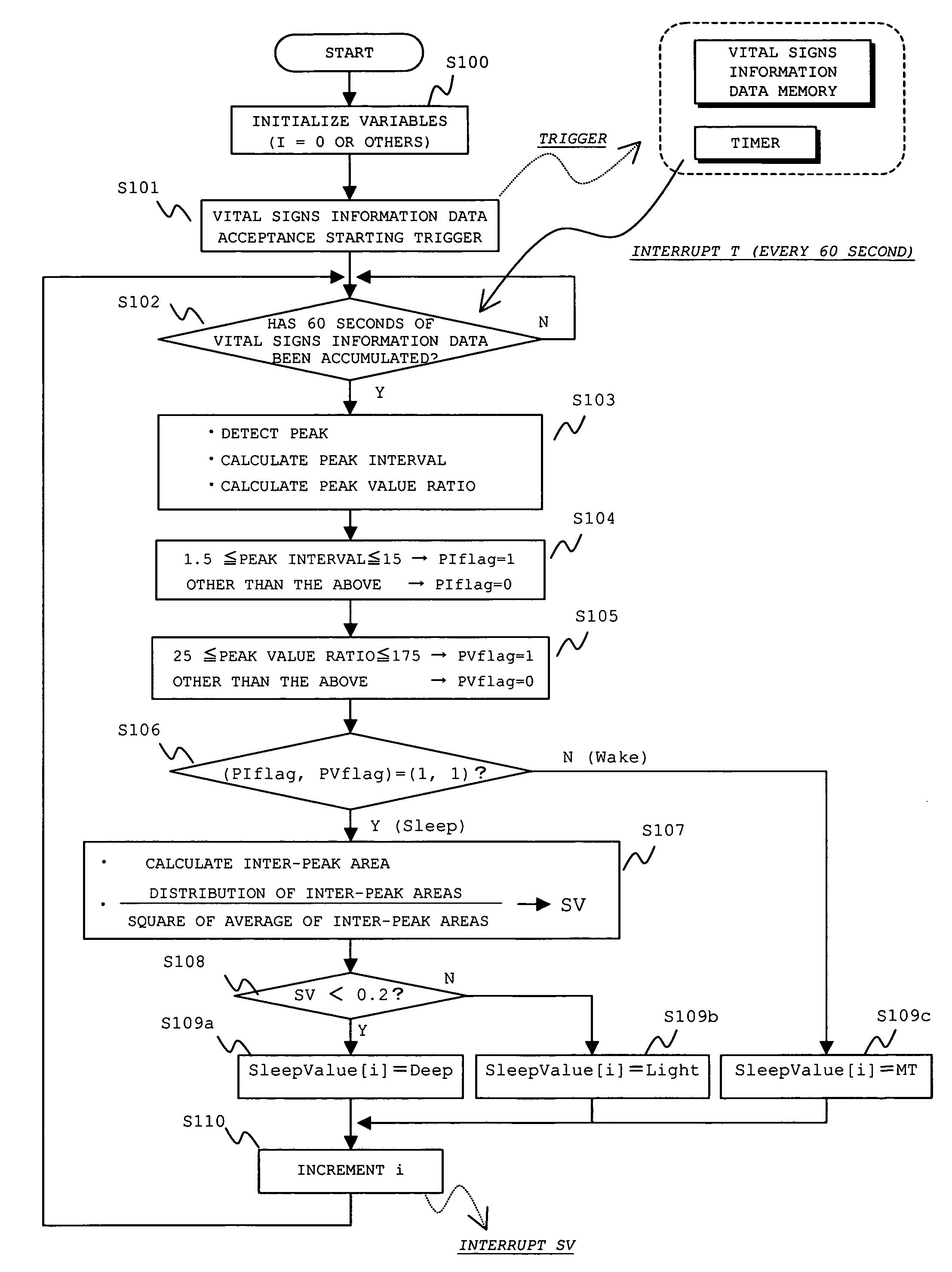
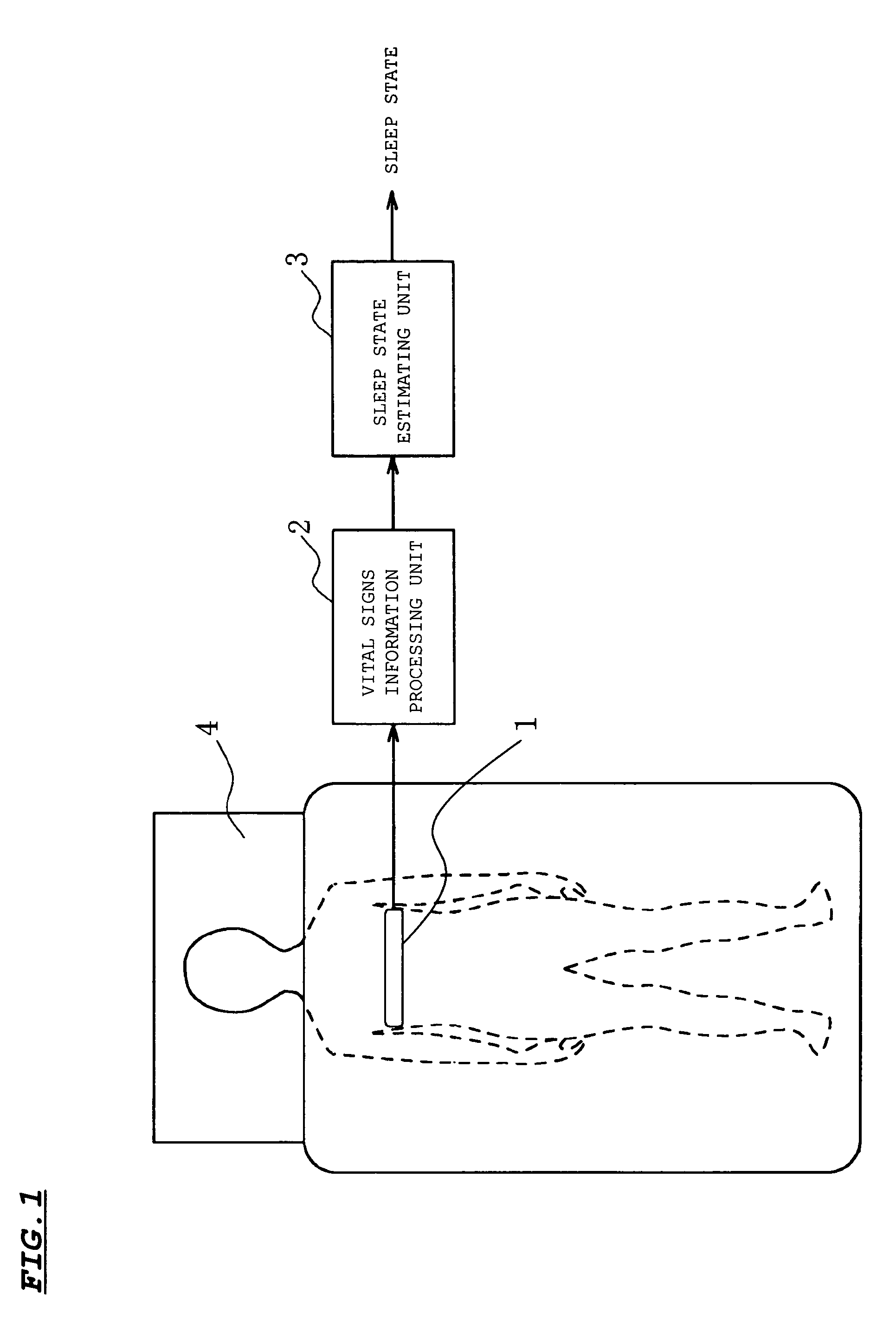
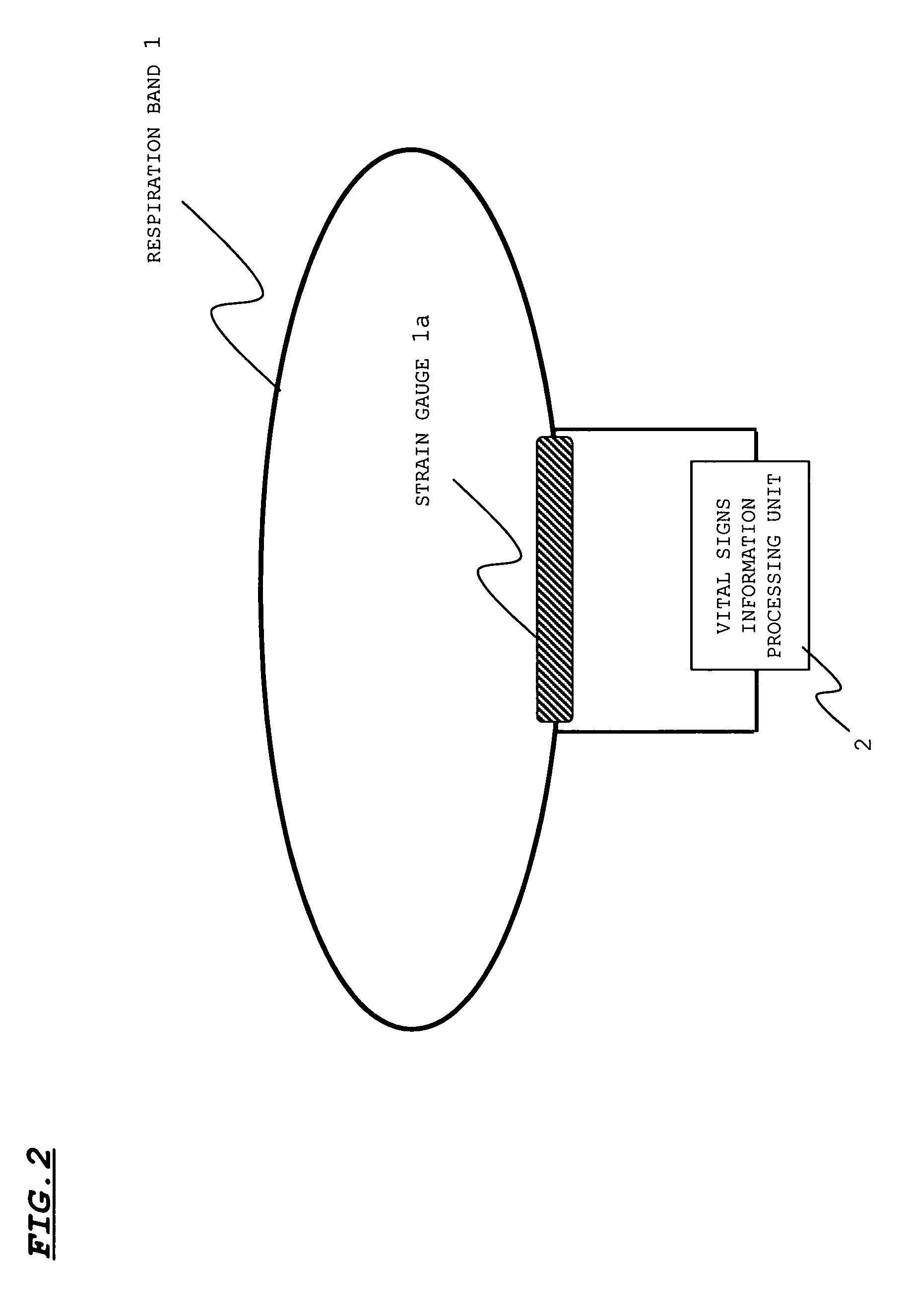
InactiveUS7429247B2Easy to detectGood estimateRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsSleep stateMedicine
A sleep state of a subject is estimated from respiration signals that are readily detected without restraining the subject. From a voltage waveform based on respiratory movement of a person, positive peak values and the (time) interval between adjacent peaks are calculated. Also obtained is the area of a region that is enclosed by the voltage waveform and a time axis between peaks, and the average value and dispersion value of the obtained inter-peak areas are calculated. The calculated values are used to set a preliminary sleep state value for a given period, and sleep state values over plural periods are factored in to estimate a sleep state at a given time point.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Formulations of bendamustine
InactiveUS20130210879A1Improve long-term stabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAntioxidantMedicine
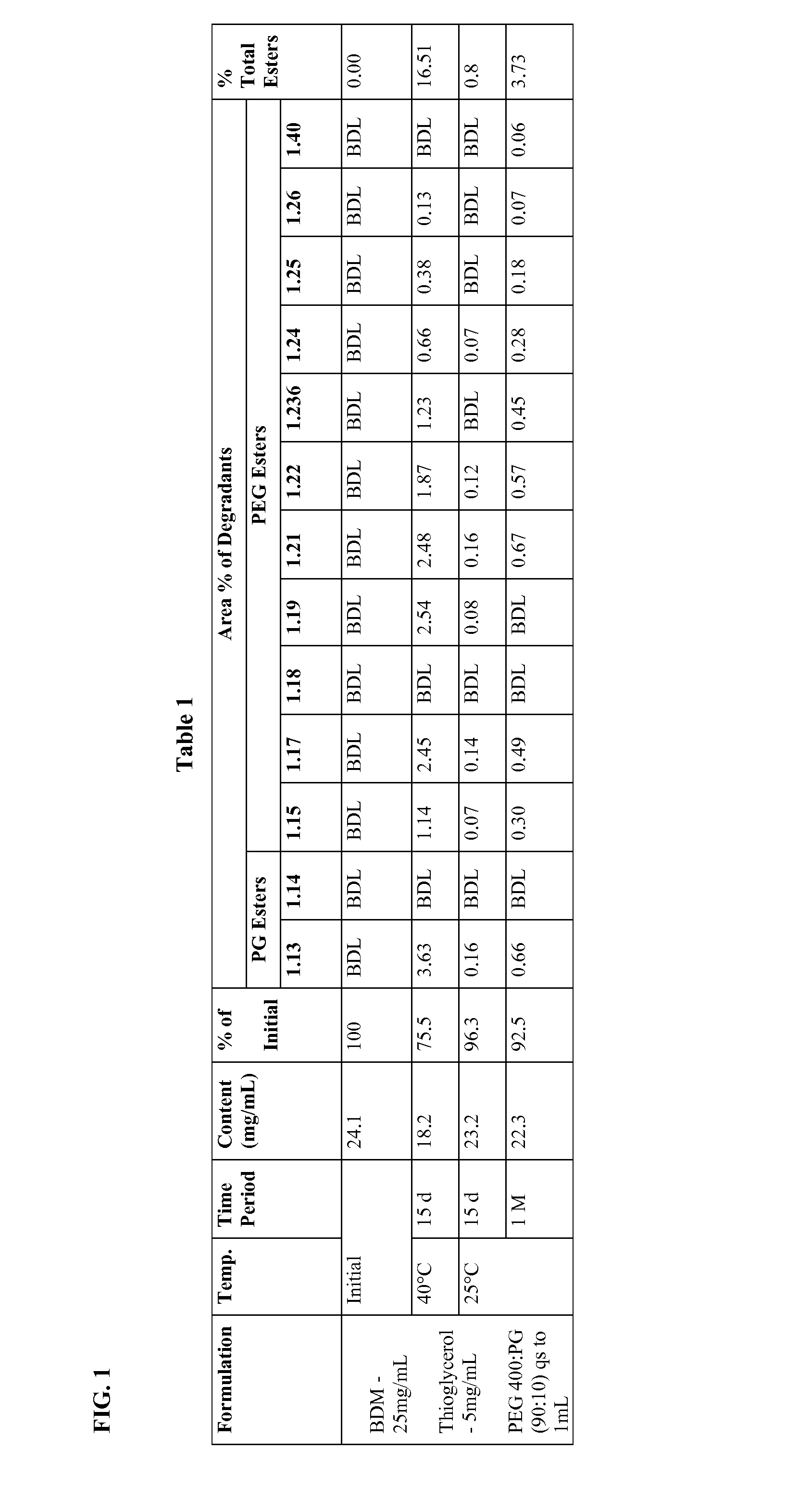
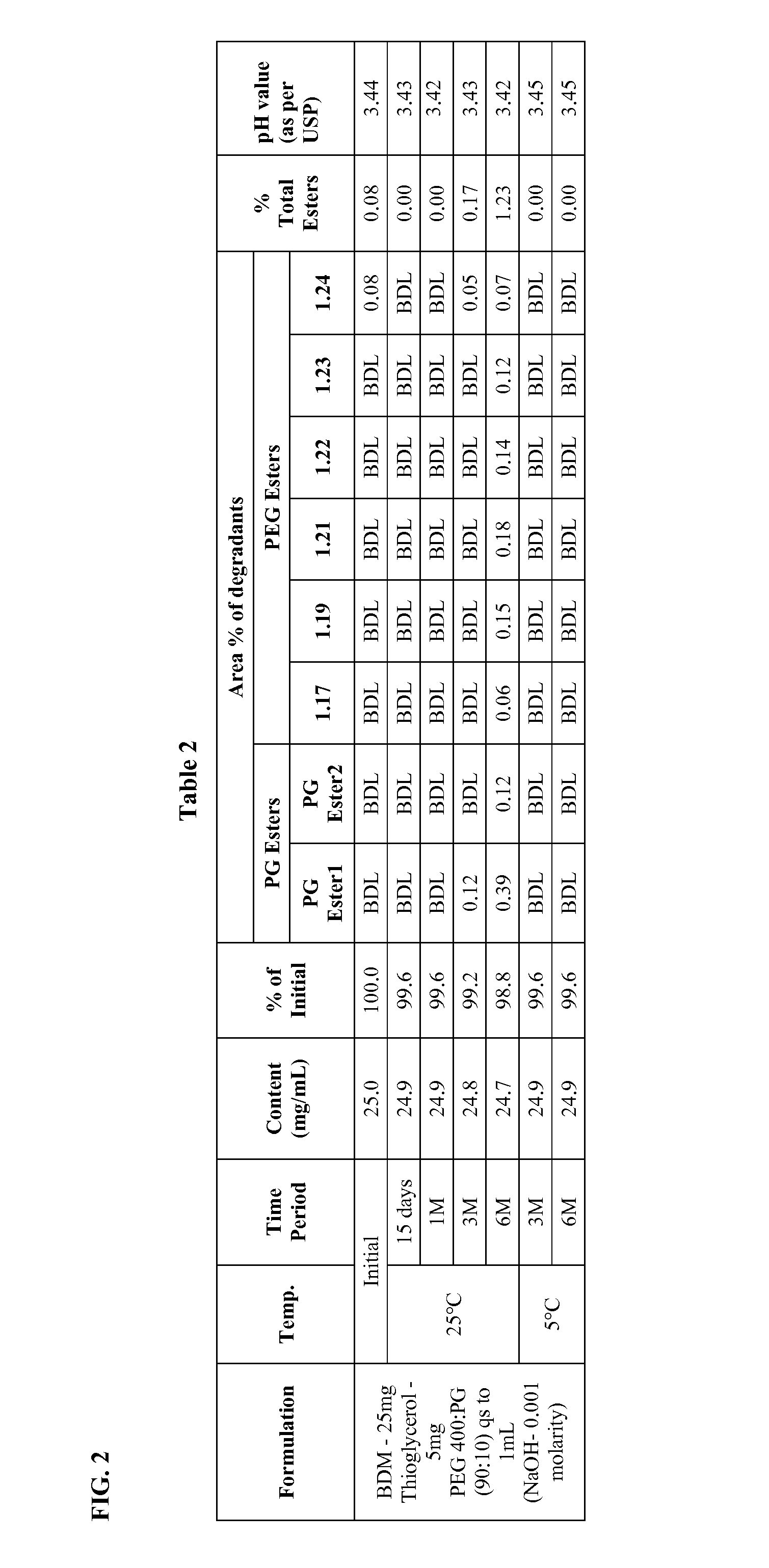
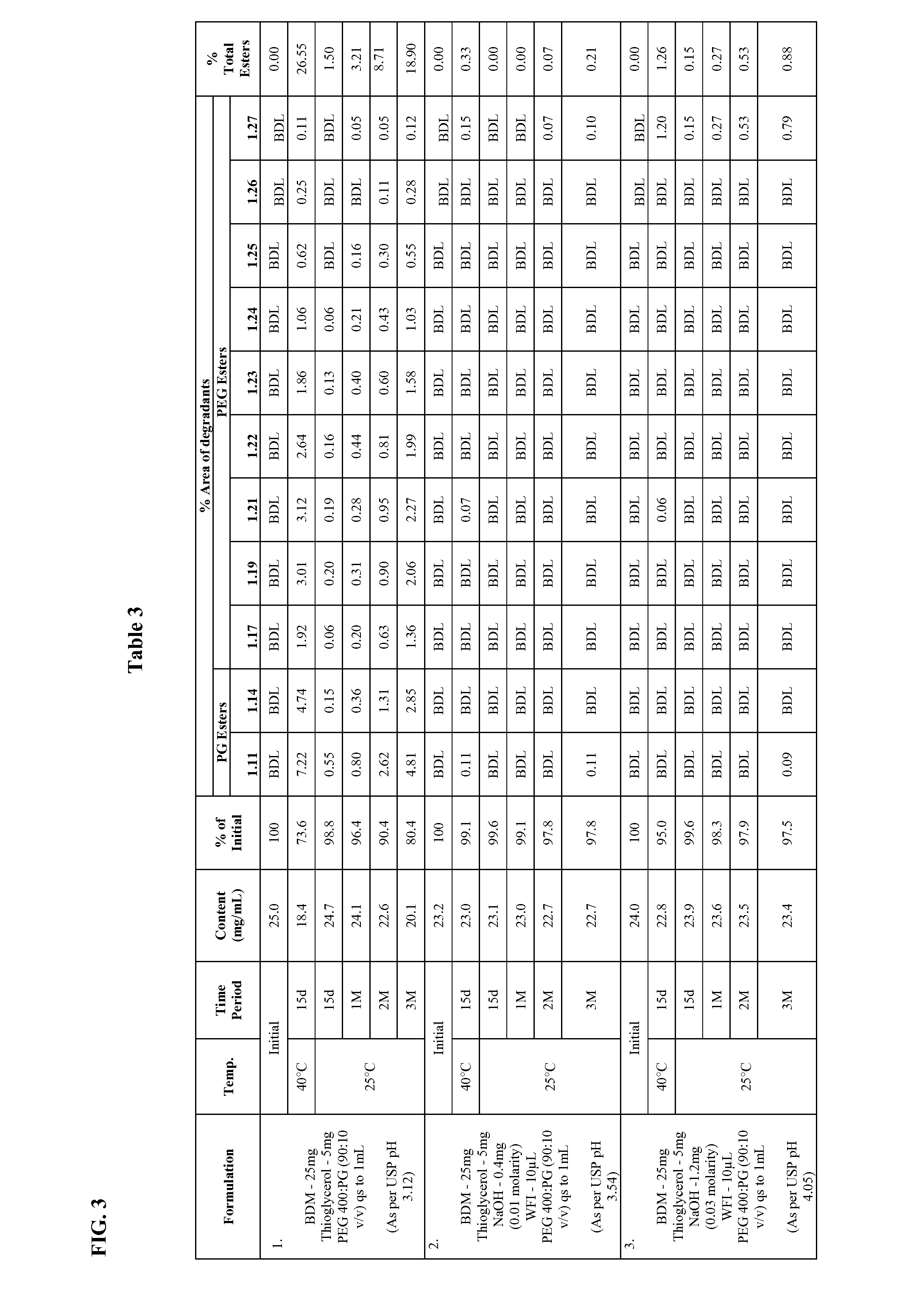
Long term storage stable bendamustine-containing compositions are disclosed. The compositions can include bendamustine or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and a pharmaceutically acceptable fluid contains a mixture of PEG and PG; an organic or inorganic compound in an amount sufficient to obtain a pH of from about 6.0 to about 11 for the polyethylene glycol, as measured using USP monograph for polyethylene glycol; and optionally an antioxidant. The bendamustine-containing compositions have less than about 5% total esters, on a normalized peak area response (“PAR”) basis as determined by high performance liquid chromatography (“HPLC”) at a wavelength of 223 nm, after at least about 15 months of storage at a temperature of from about 5° C. to about 25° C.
Owner:EAGLE PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Precisive measurement for parameter of chromatography spike and area of overlapped peak
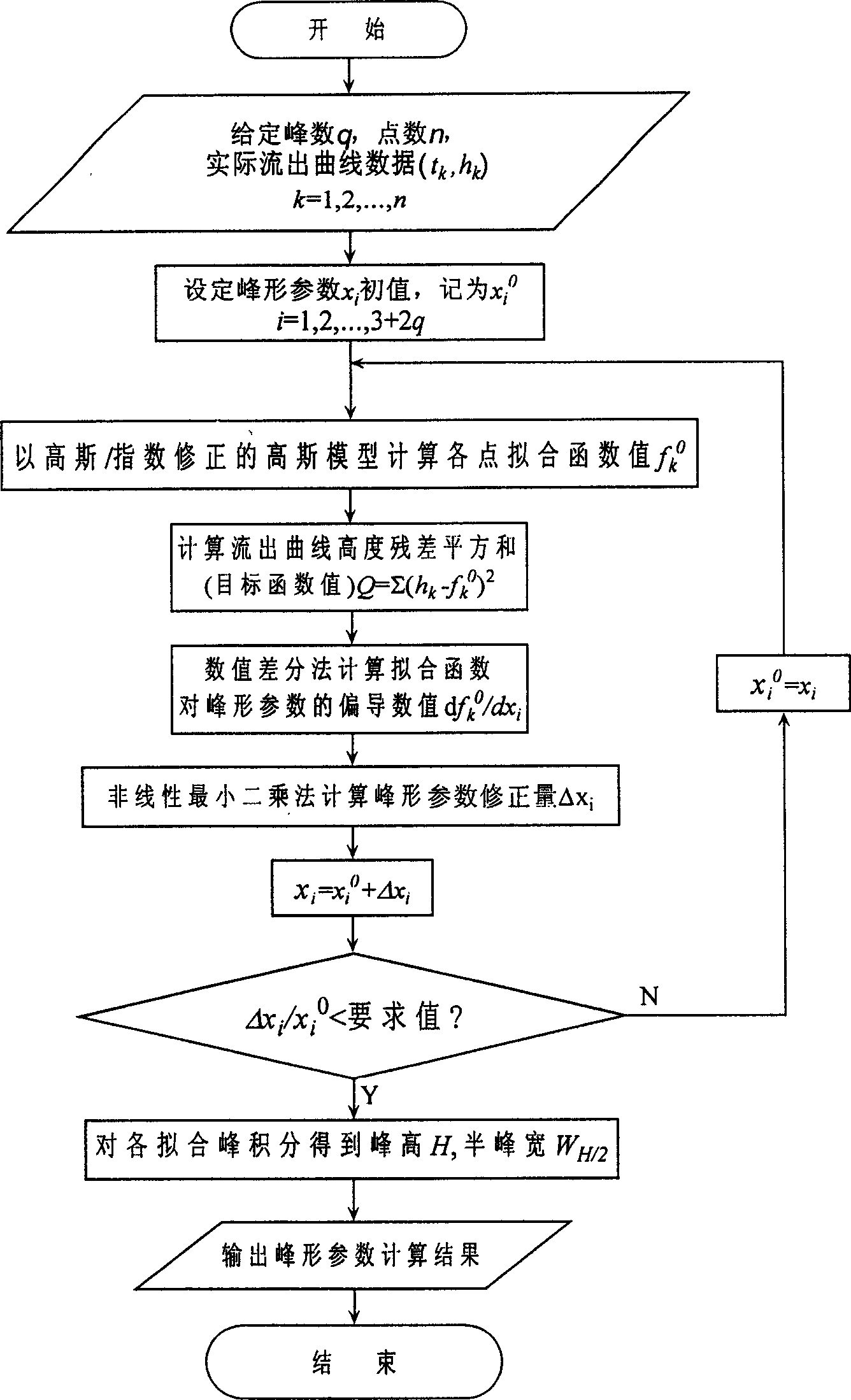
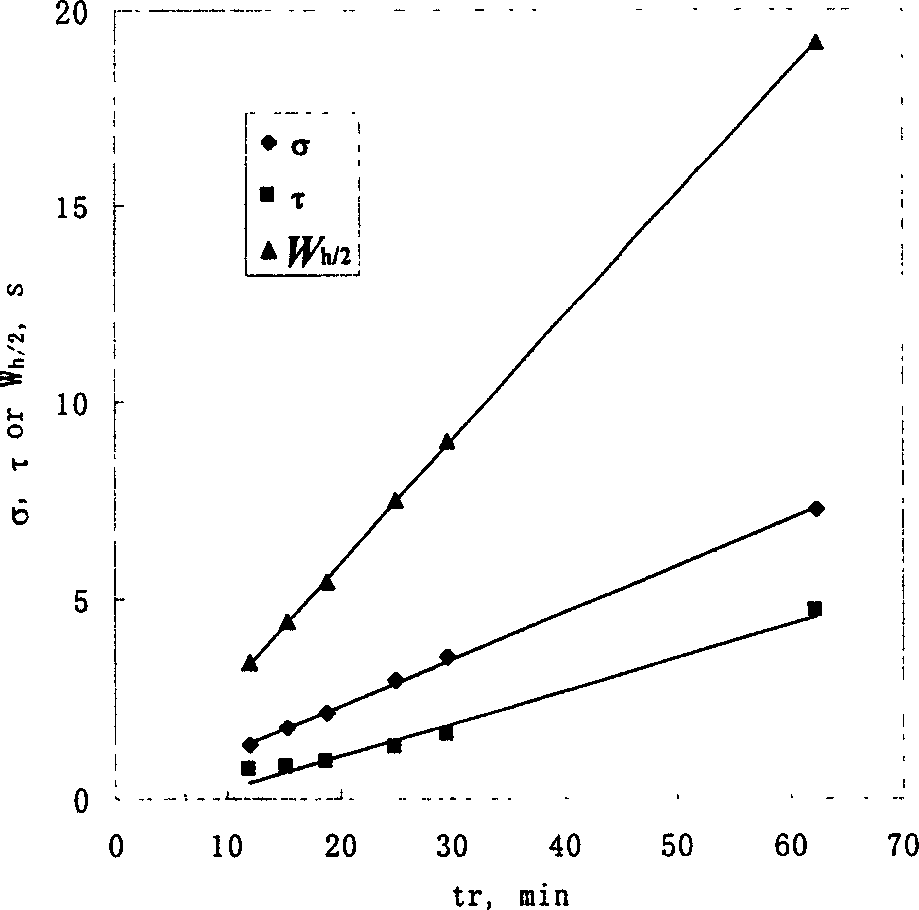
A method for determining chromatograph peak form parameter and overlapped peak area includes setting time value and chromatographic signal value at point for chromatographic elution curve and peak number, using n as total number for point, using Gauss model as objective function to fit said elution curve to be determined, utilizing nonlinear least square method to solve out optimum parameter and using the corresponding relation of fitting elution curve to elution curve to be determined to work out peak form parameter and overlapped peak area of chromatograph .
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inkjet ink, and ink cartridge, inkjet recording method, inkjet recording apparatus and ink record using the same
ActiveUS20090047431A1Improve discharge stabilityAvoid fixationMeasurement apparatus componentsInksWater insolublePeak area
The present invention provides an inkjet ink containing at least a colorant, water, a water insoluble resin, a fluorine surfactant, and a polyether-modified silicone oil, wherein the polyether-modified silicone oil has a hydrophobic value of 0.40 to 1.5, and the hydrophobic value is expressed by Equation 1:Hydrophobic value=A / B Equation 1where “A” represents an integration value of a peak area from 0 ppm to 0.3 ppm in a 1H-NMR spectrum of the polyether-modified silicone oil using tetramethylsilane as a reference substance; and “B” represents an integration value of a peak area from 3.5 ppm to 4.0 ppm in the 1H-NMR spectrum.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com