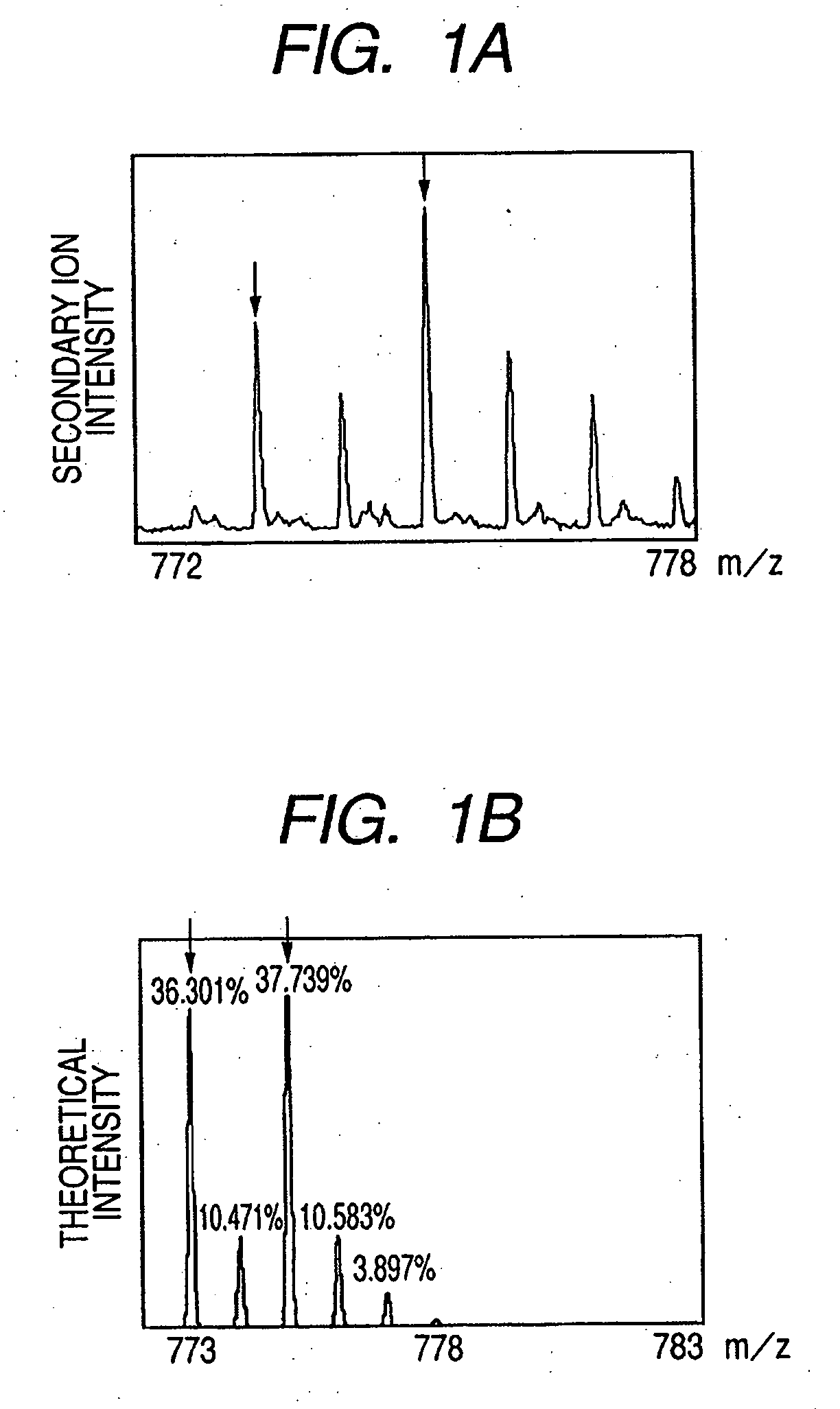
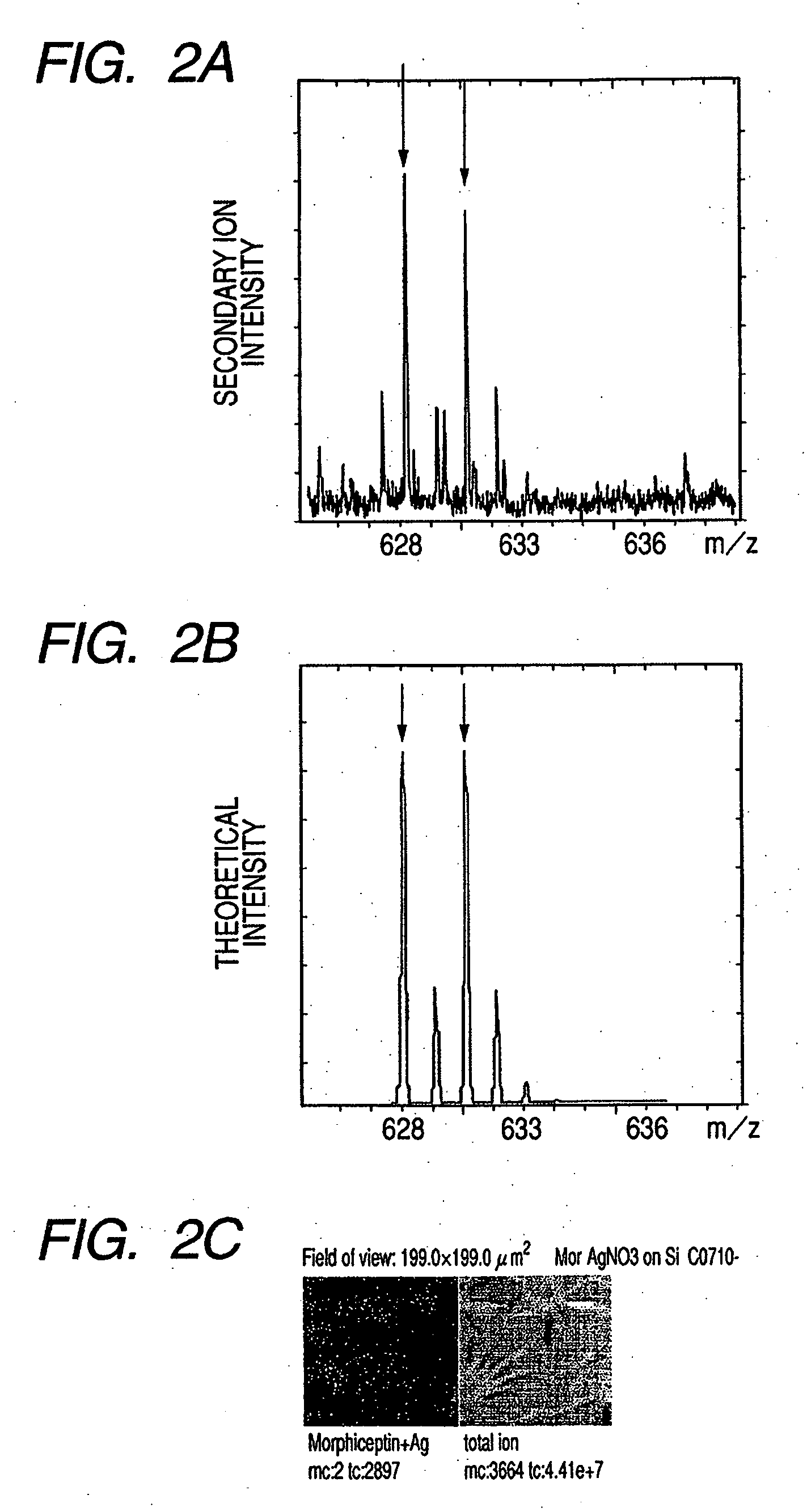
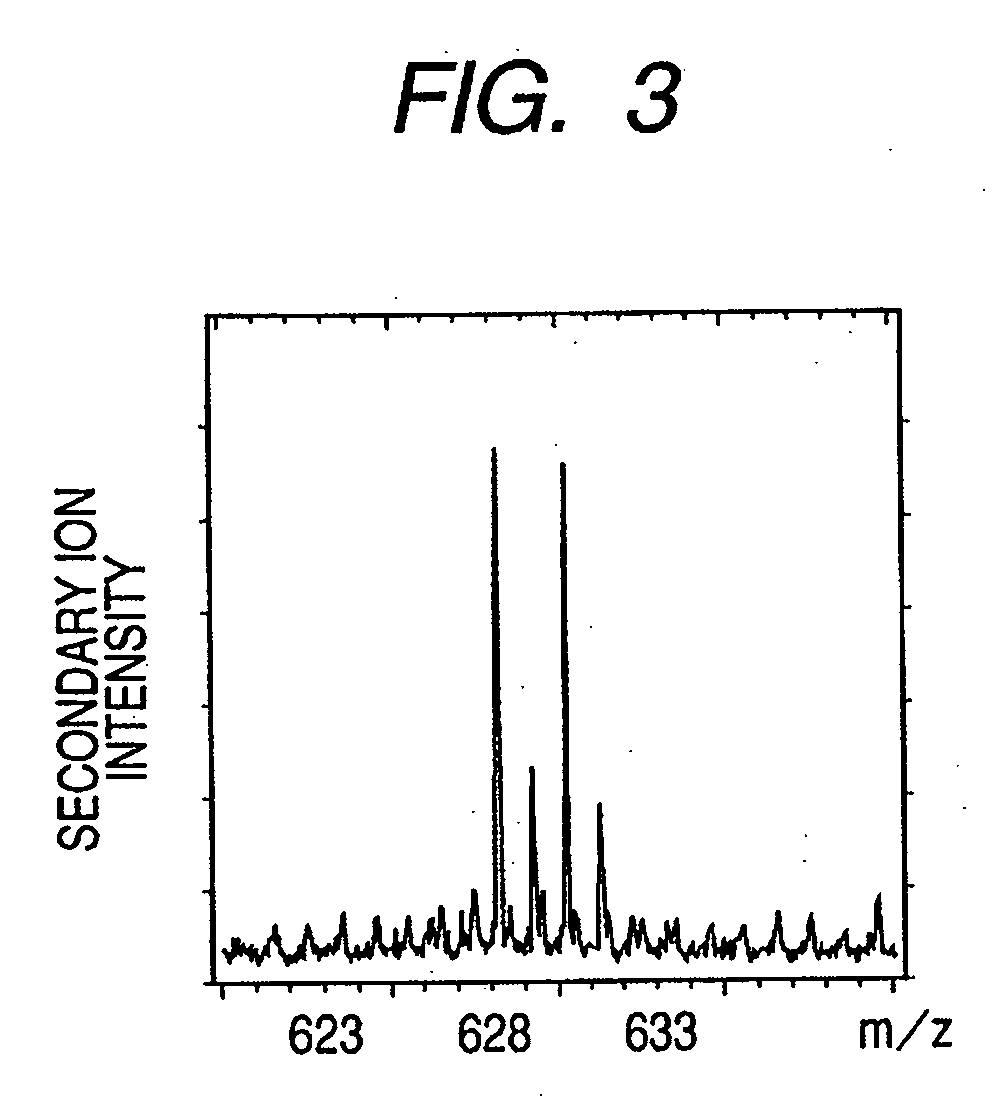
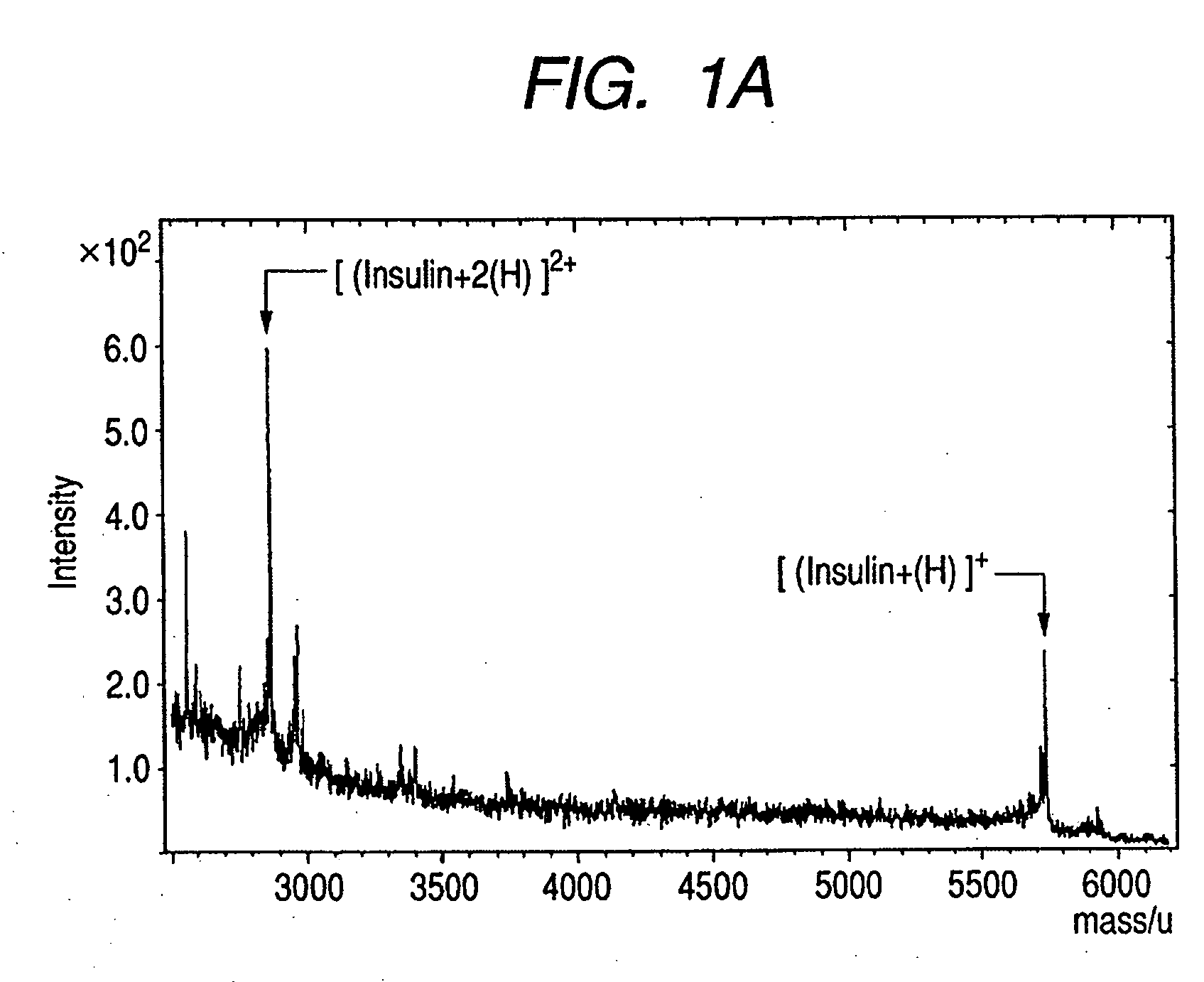
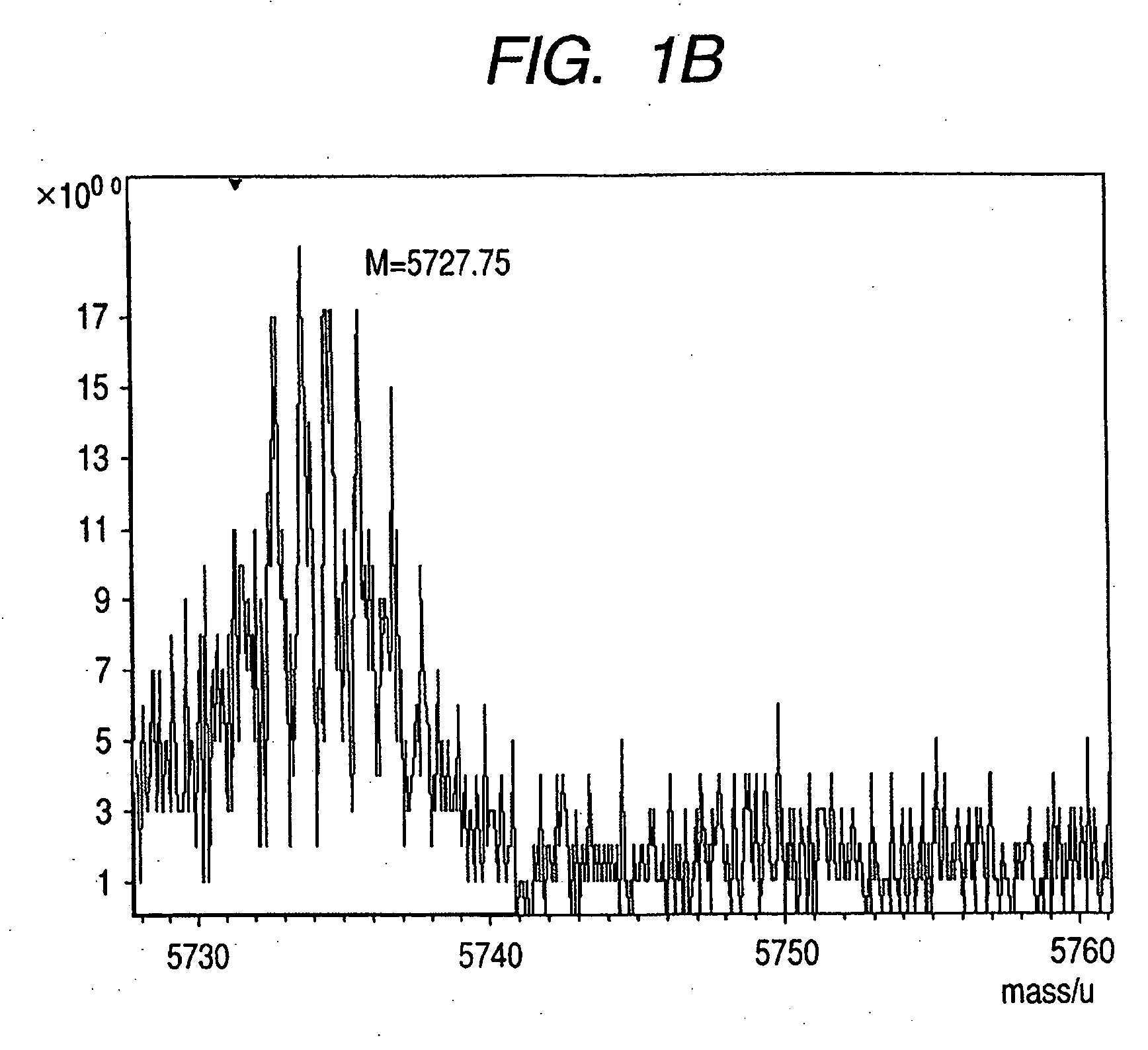
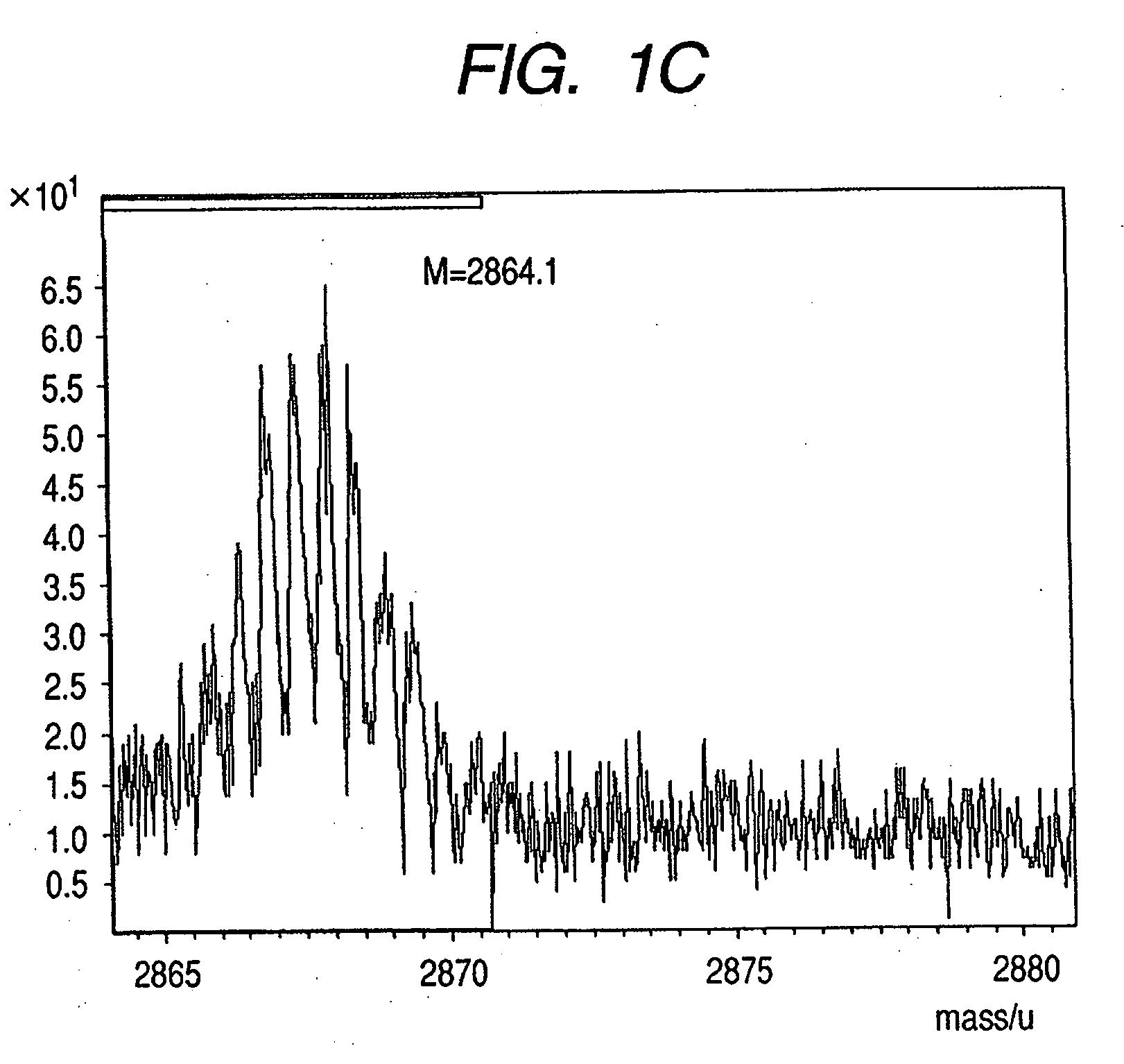
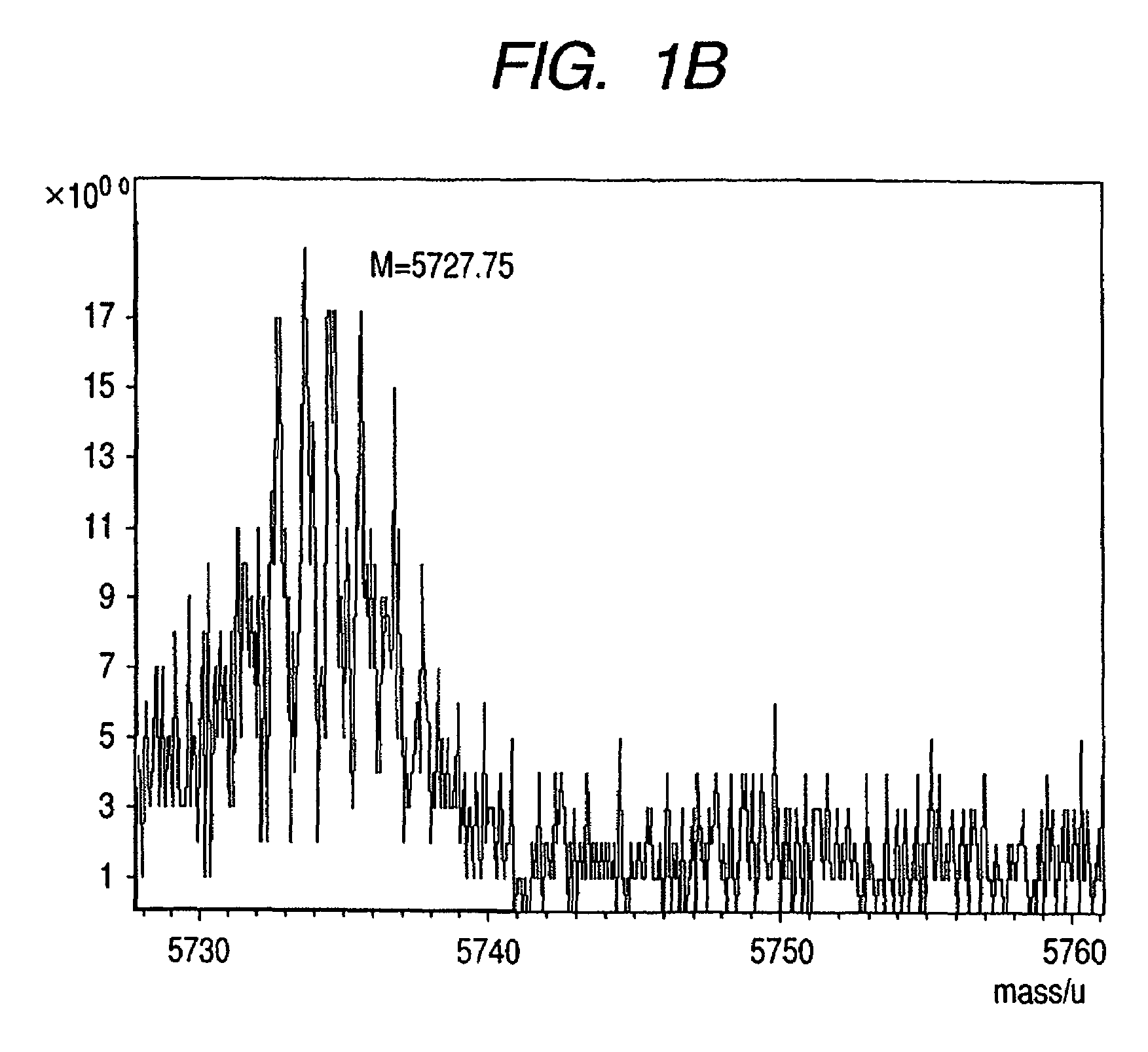
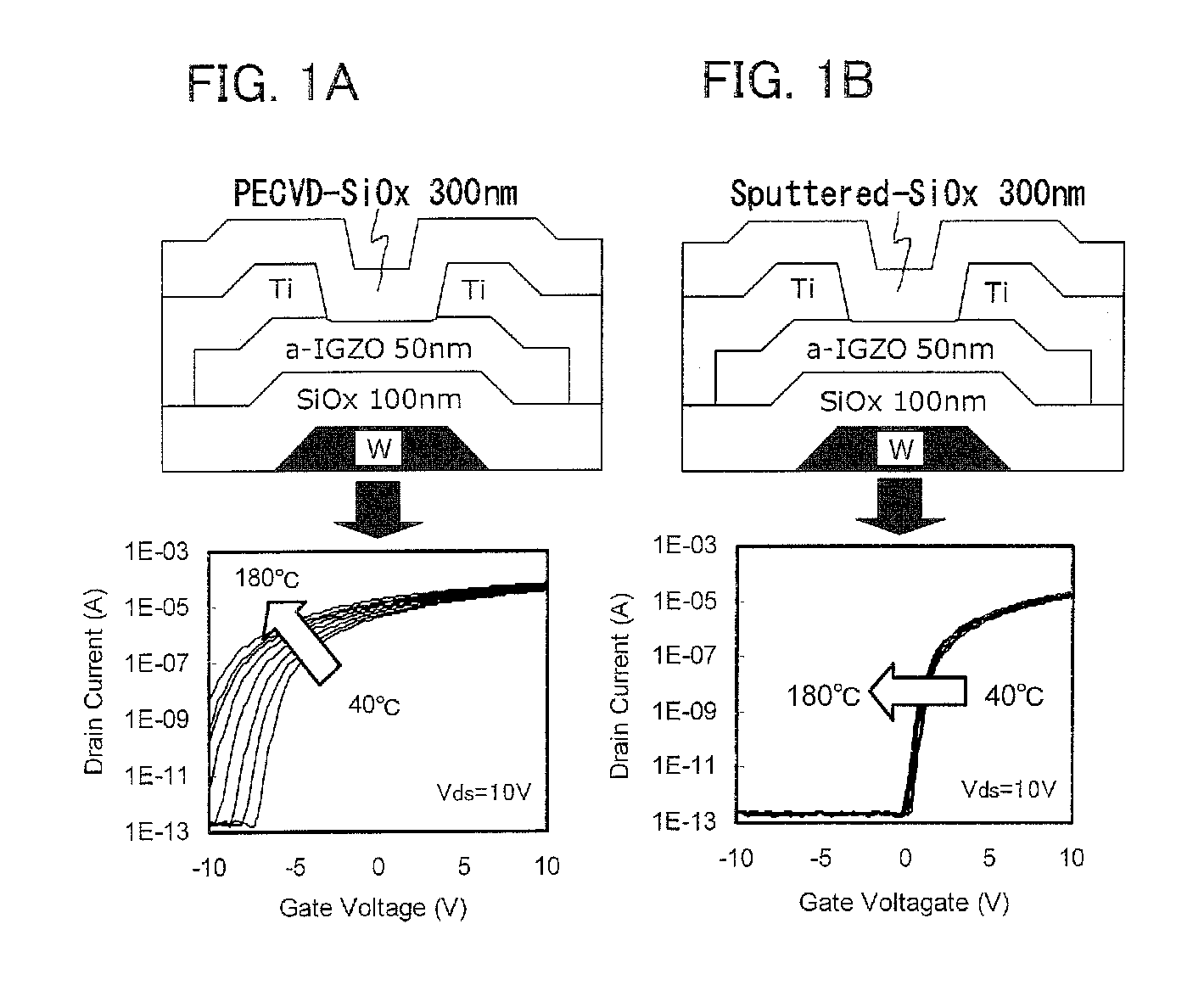
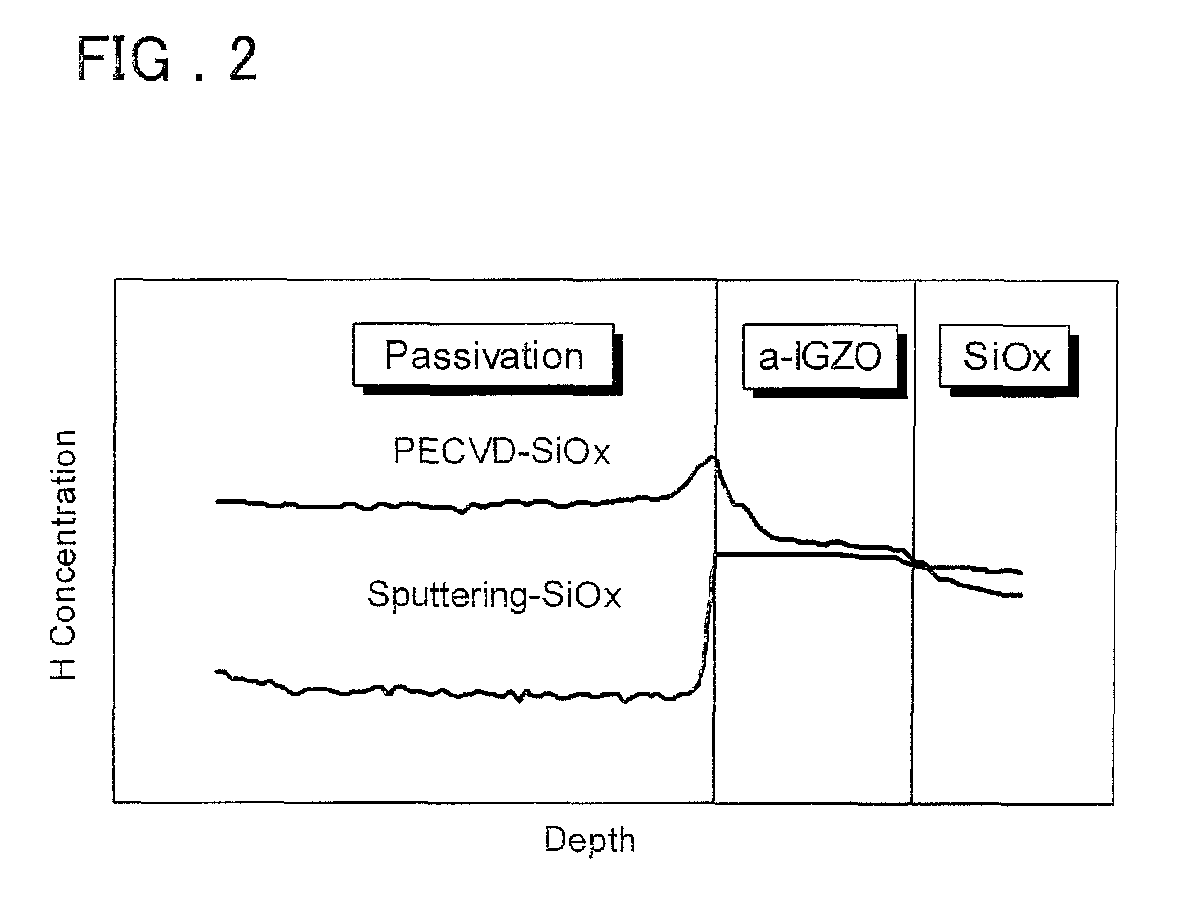
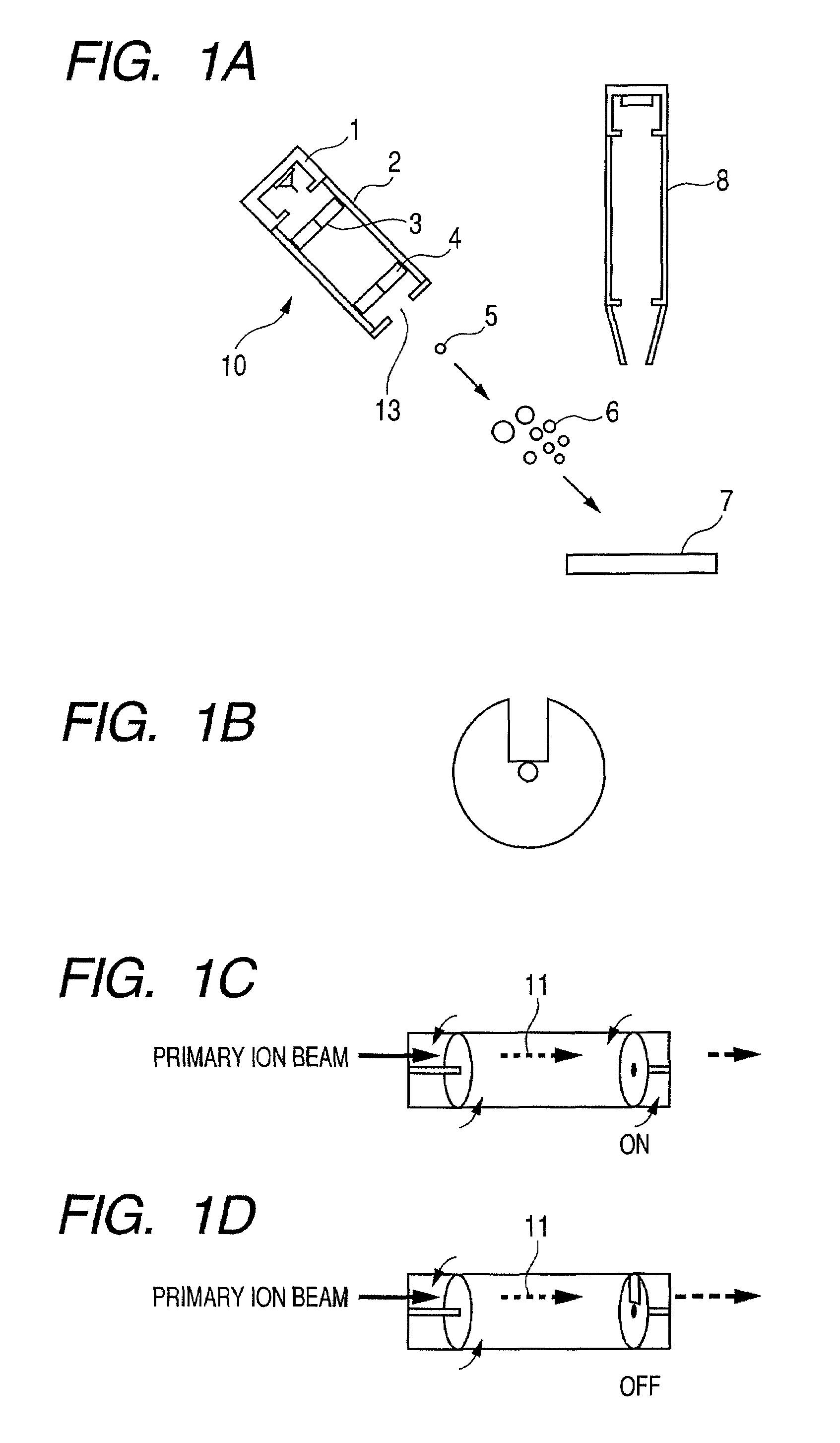
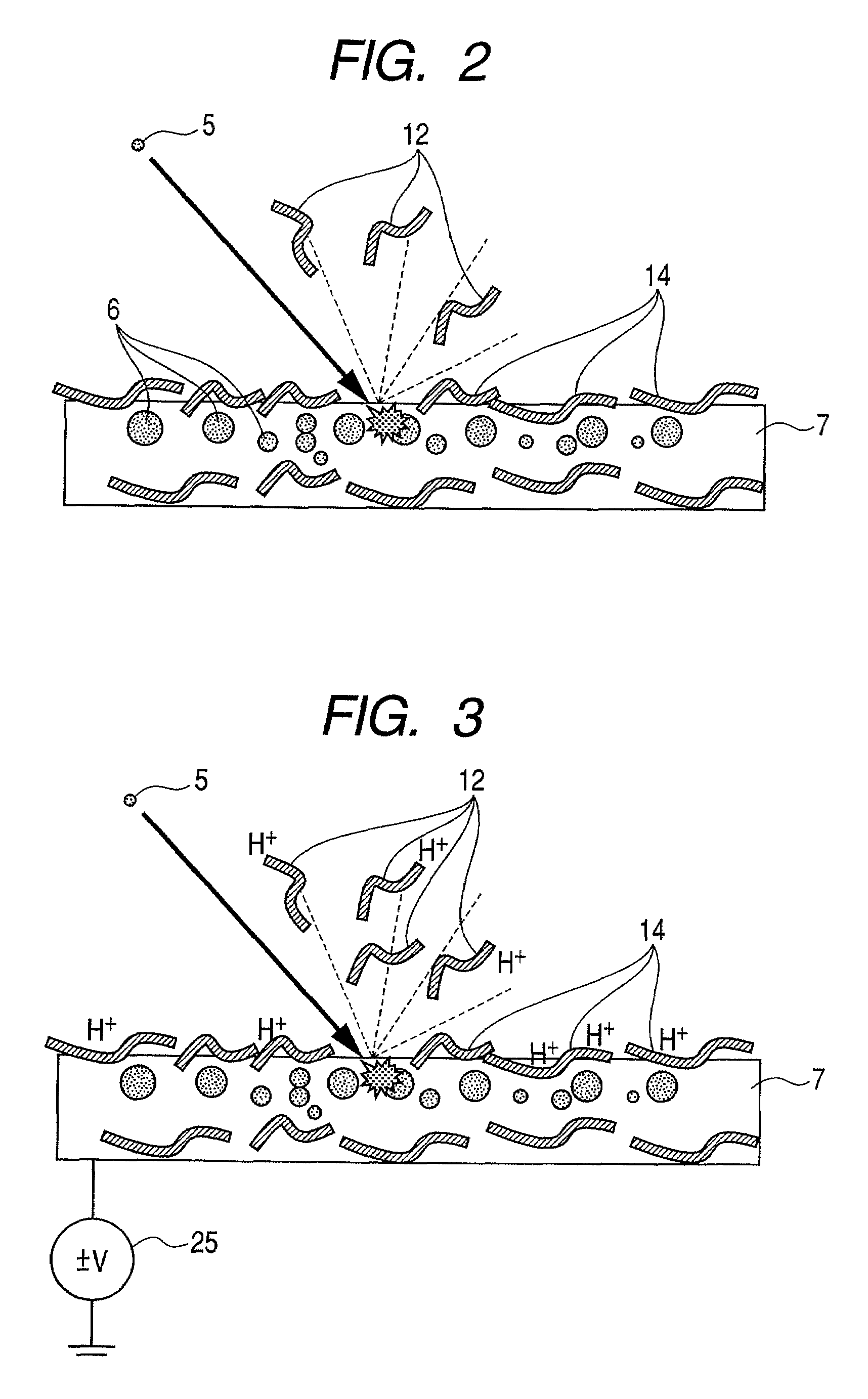
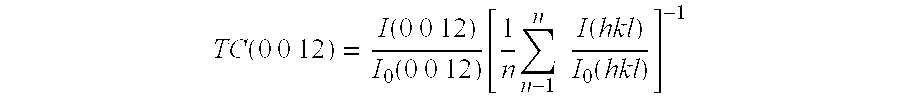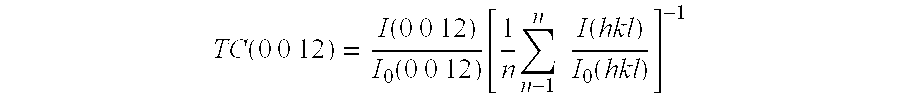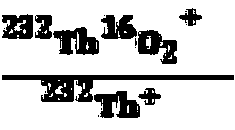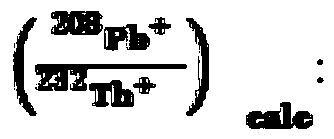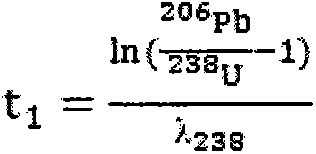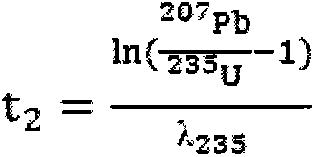Patents
Literature
268 results about "Secondary ion mass spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Secondary-ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) is a technique used to analyze the composition of solid surfaces and thin films by sputtering the surface of the specimen with a focused primary ion beam and collecting and analyzing ejected secondary ions. The mass/charge ratios of these secondary ions are measured with a mass spectrometer to determine the elemental, isotopic, or molecular composition of the surface to a depth of 1 to 2 nm. Due to the large variation in ionization probabilities among different materials, SIMS is generally considered to be a qualitative technique, although quantitation is possible with the use of standards. SIMS is the most sensitive surface analysis technique, with elemental detection limits ranging from parts per million to parts per billion.
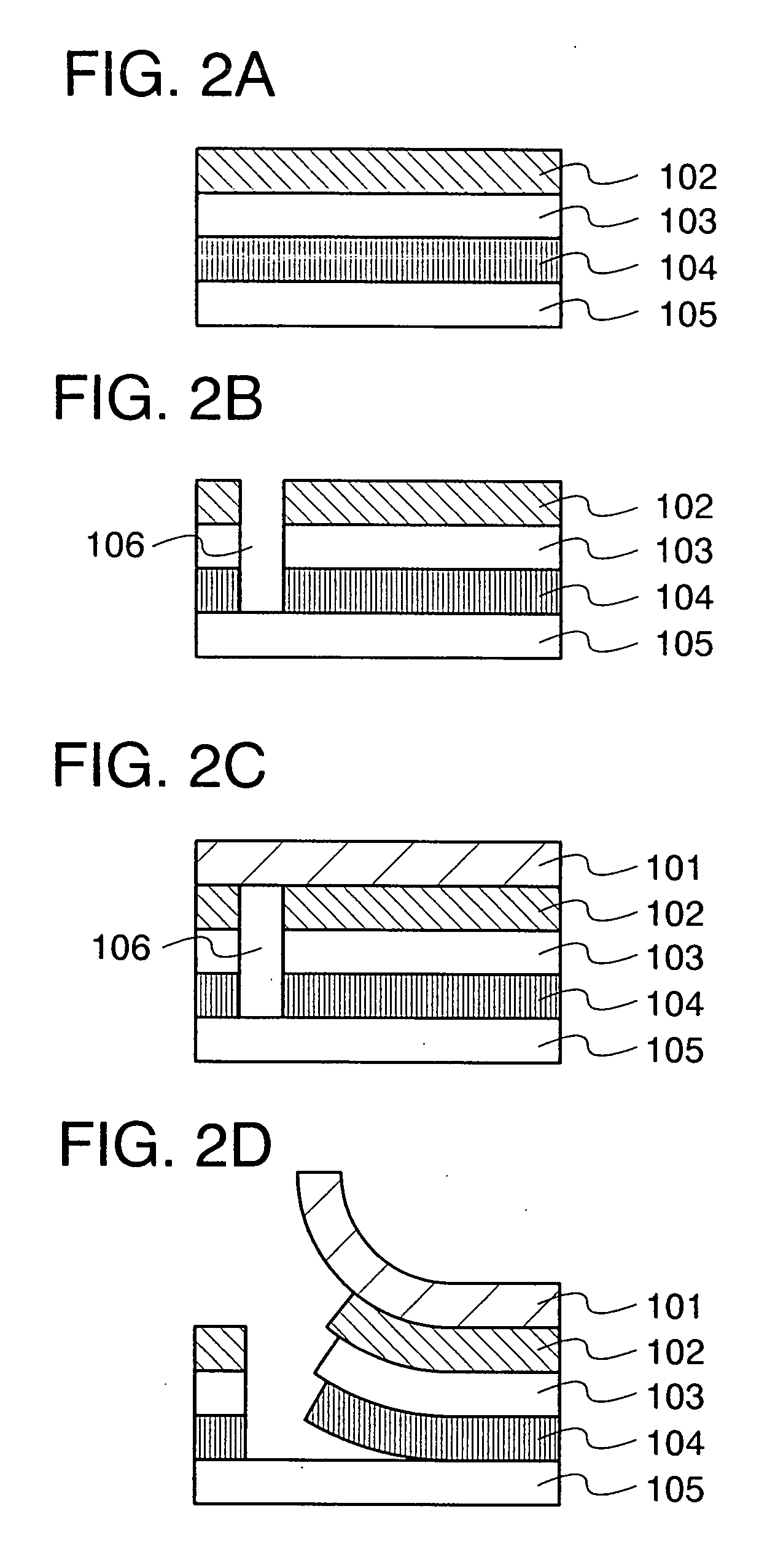
Single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material
ActiveUS20140335339A1Improve optical qualityReduce concentrationPolycrystalline material growthSynthetic resin layered productsPhotoluminescenceSingle crystal
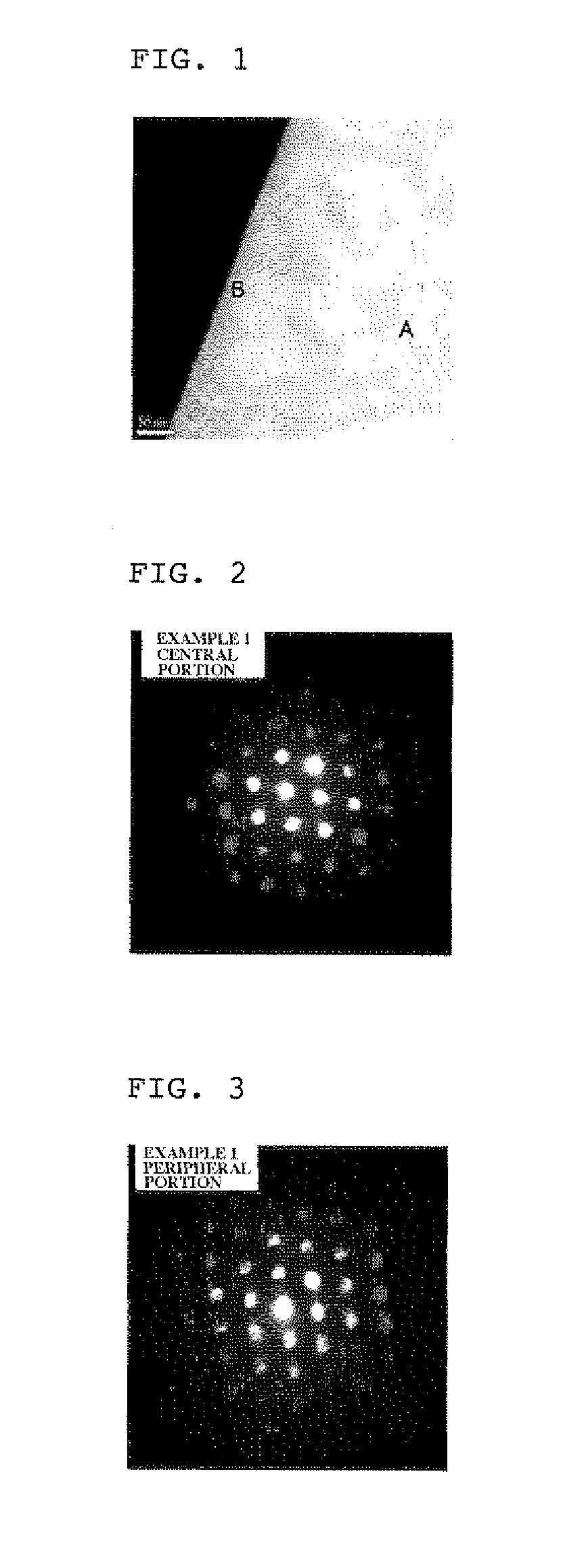
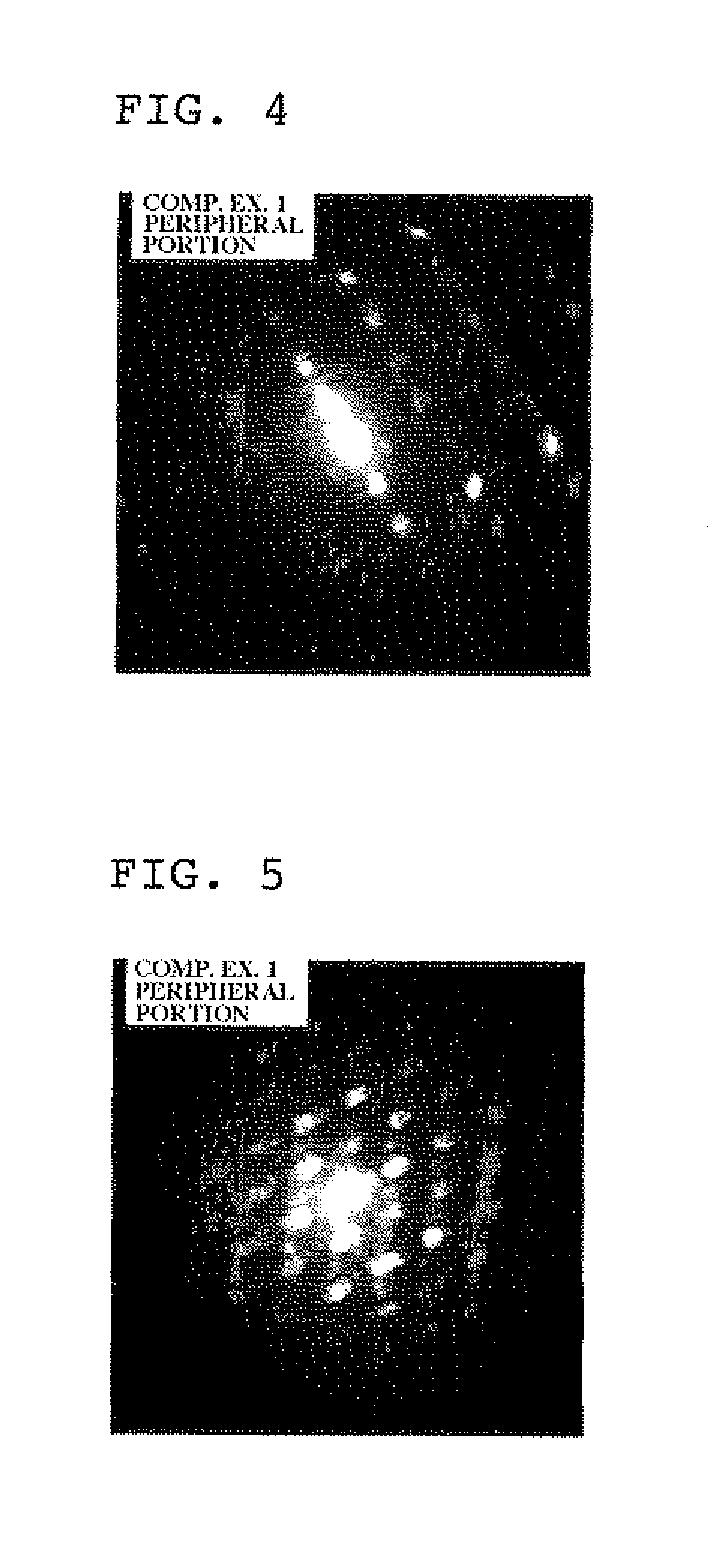
A single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material comprising: a total as-grown nitrogen concentration equal to or greater than 5 ppm, and a uniform distribution of defects, wherein said uniform distribution of defects is defined by one or more of the following characteristics: (i) the total nitrogen concentration, when mapped by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm using an analysis area of 10 μm or less, possesses a point-to-point variation of less than 30% of an average total nitrogen concentration value, or when mapped by SIMS over an area equal to or greater than 200×200 μm using an analysis area of 60 μm or less, possesses a point-to-point variation of less than 30% of an average total nitrogen concentration value; (ii) an as-grown nitrogen-vacancy defect (NV) concentration equal to or greater than 50 ppb as measured using 77K UV-visible absorption measurements, wherein the nitrogen-vacancy defects are uniformly distributed through the synthetic single crystal CVD diamond material such that, when excited using a 514 nm laser excitation source of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at room temperature using a 50 mW 46 continuous wave laser, and mapped over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm with a data interval less than 10 μm there is a low point-to-point variation wherein the intensity area ratio of nitrogen vacancy photoluminescence peaks between regions of high photoluminescent intensity and regions of low photolominescent intensity is <2× for either the 575 nm photoluminescent peak (NV0) or the 637 nm photoluminescent peak (NV); (iii) a variation in Raman intensity such that, when excited using a 514 nm laser excitation source (resulting in a Raman peak at 552.4 nm) of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at room temperature using a 50 mW continuous wave laser, and mapped over an area equal to or greater than 50×50 μm with a data interval less than 10 μm, there is a low point-to-point variation wherein the ratio of Raman peak areas between regions of low Raman intensity and high Raman intensity is <1.25×; (iv) an as-grown nitrogen-vacancy defect (NV) concentration equal to or greater than 50 ppb as measured using 77K UV-visible absorption measurements, wherein, when excited using a 514 nm excitation source of spot size equal to or less than 10 μm at 77K using a 50 mW continuous wave laser, gives an intensity at 575 nm corresponding to NV0 greater than 120 times a Raman intensity at 552.4 nm, and / or an intensity at 637 nm corresponding to NV− greater than 200 times the Raman intensity at 552.4 nm; (v) a single substitutional nitrogen defect (Ns) concentration equal to or greater than 5 ppm, wherein the single substitutional nitrogen defects are uniformly distributed through the synthetic single crystal CVD diamond material such that by using a 1344 cm−1 infrared absorption feature and sampling an area greater than an area of 0.5 mm2, the variation is lower than 80%, as deduced by dividing the standard deviation by the mean value; (vi) a variation in red luminescence intensity, as defined by a standard deviation divided by a mean value, is less than 15%; (vii) a mean standard deviation in neutral single substitutional nitrogen concentration of less than 80%; and (viii) a colour intensity as measured using a histogram from a microscopy image with a mean gray value of greater than 50, wherein the colour intensity is uniform through the single crystal CVD synthetic diamond material such that the variation in gray colour, as characterised by the gray value standard deviation divided by the gray value mean, is less than 40%.
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Display device
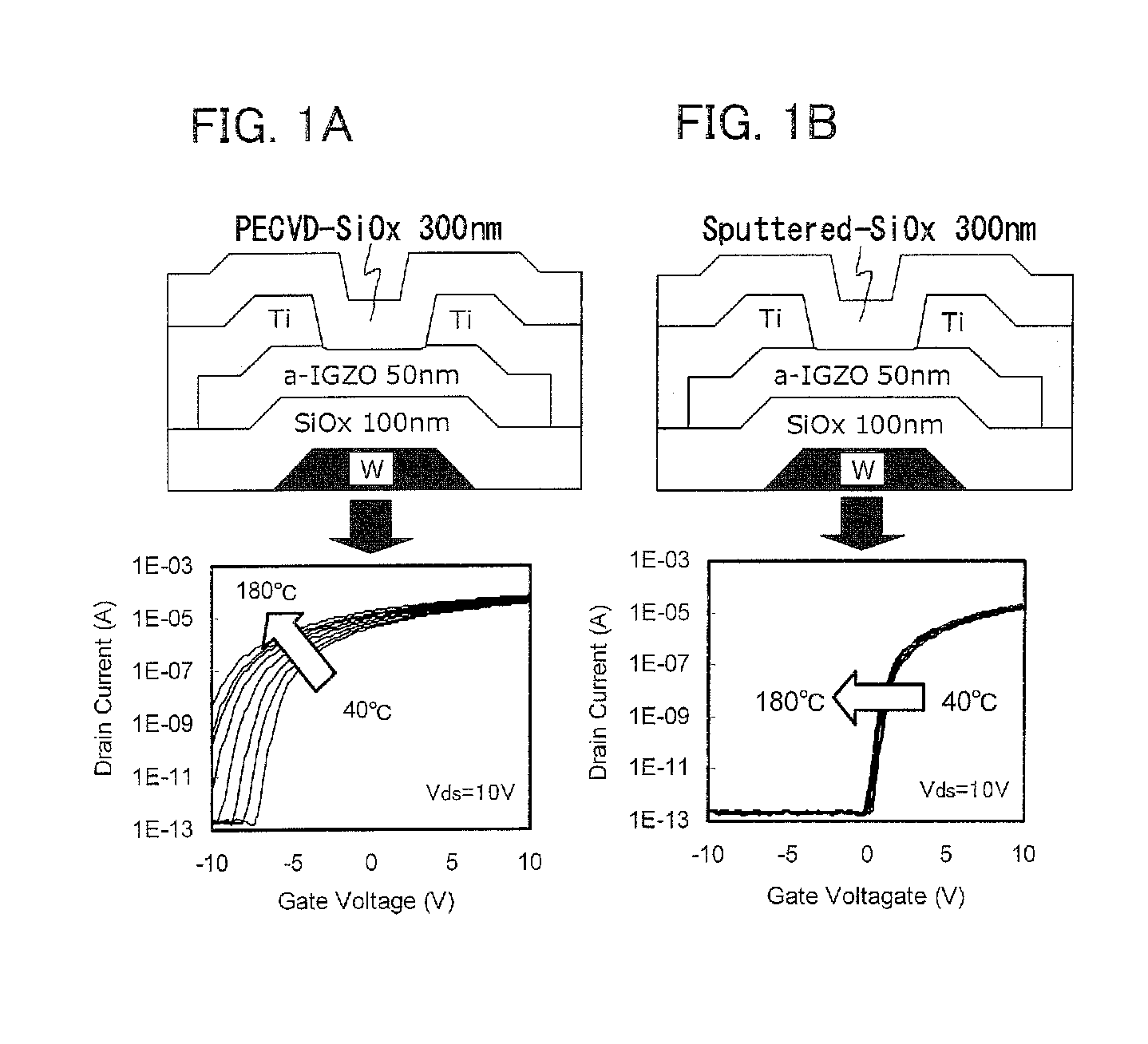
ActiveUS20110133181A1Minimize the numberReduce carrier densityTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesHydrogenHydrogen atom
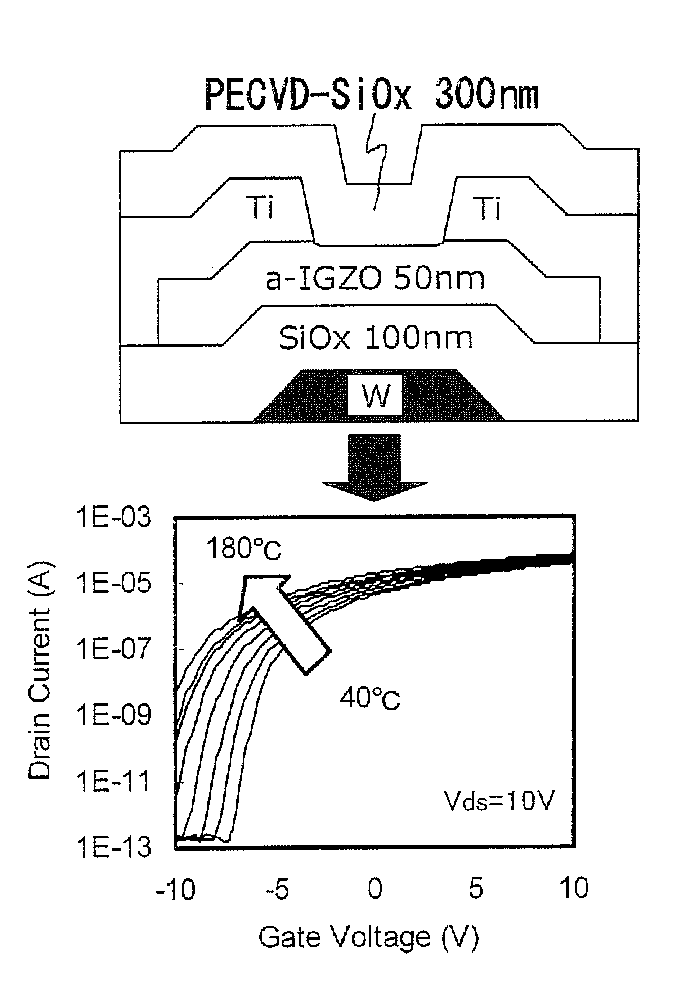
One object is to provide a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film which is used for the pixel portion of a display device and has high reliability. A display device has a first gate electrode; a first gate insulating film over the first gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film over the first gate insulating film; a source electrode and a drain electrode over the oxide semiconductor film; a second gate insulating film over the source electrode, the drain electrode and the oxide semiconductor film; a second gate electrode over the second gate insulating film; an organic resin film having flatness over the second gate insulating film; a pixel electrode over the organic resin film having flatness, wherein the concentration of hydrogen atoms contained in the oxide semiconductor film and measured by secondary ion mass spectrometry is less than 1×1016 cm−3.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
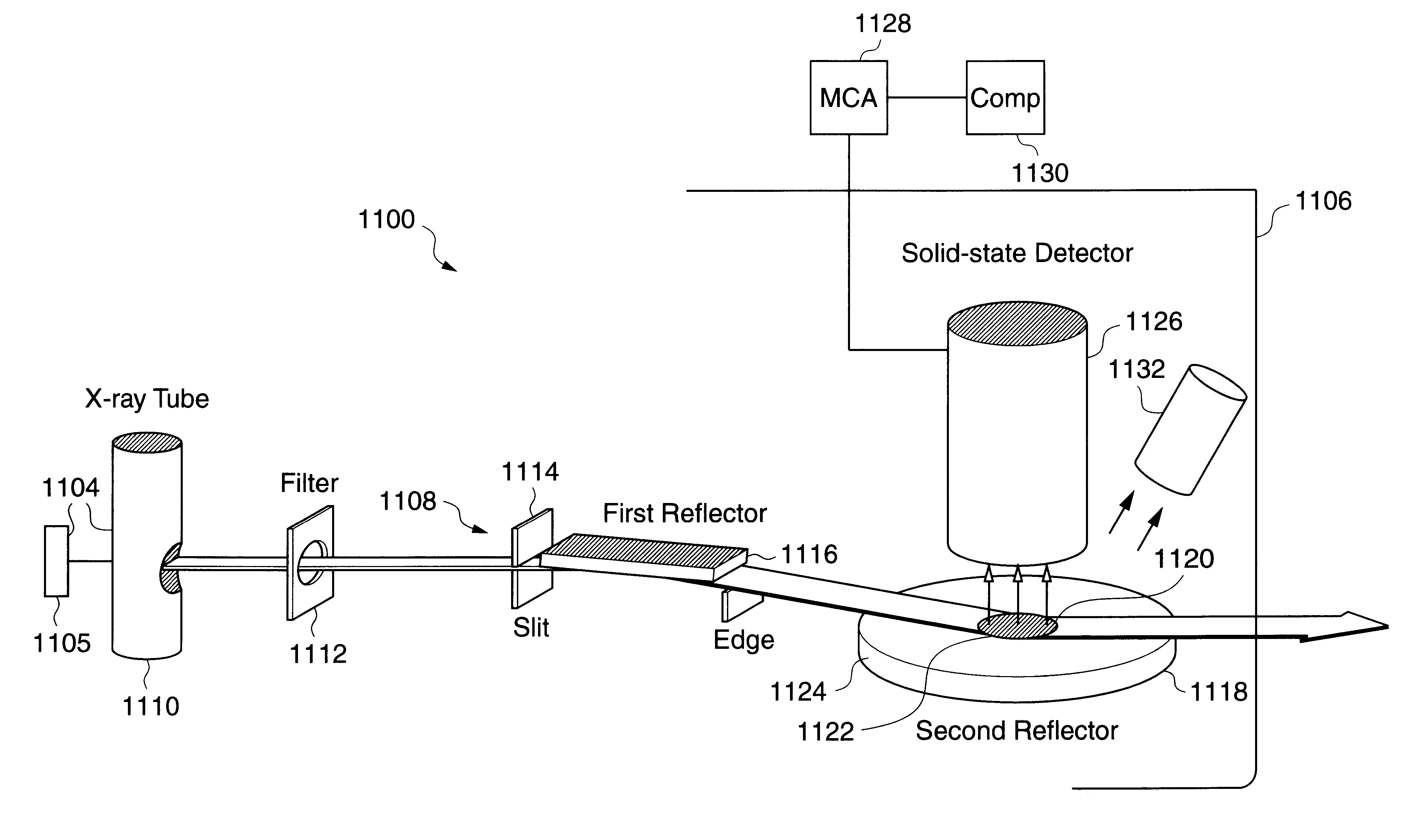
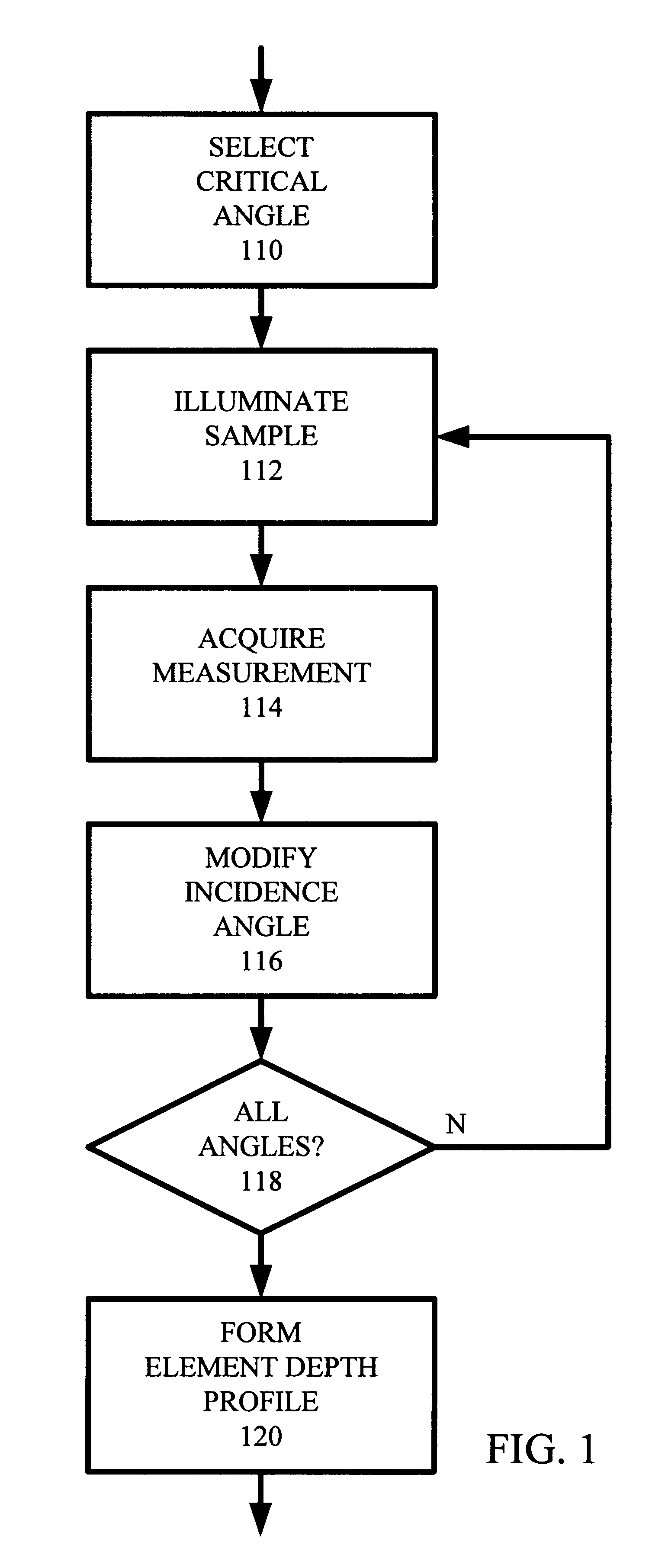
Depth profile metrology using grazing incidence X-ray fluorescence
InactiveUS6173036B1X-ray spectral distribution measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansMetrologyMicro-X-ray fluorescence
For small angles that are near critical angle, a primary incident X-ray beam has excellent depth resolution. A series of X-ray fluorescence measurements are performed at varying small angles and analyzed for depth profiling of elements within a substrate. One highly useful application of the X-ray fluorescence measurements is depth profiling of a dopant used in semiconductor manufacturing such as arsenic, phosphorus, and boron. In one example, angles are be varied from 0.01° to 0.20° and measurements made to profile arsenic distribution within a semiconductor wafer. In one embodiment, measurements are acquired using a total reflection X-ray fluorescence (TXRF) type system for both known and unknown profile distribution samples. The fluorescence measurements are denominated in counts / second terms and formed as ratios comparing the known and unknown sample results. The count ratios are compared to ratios of known to unknown samples that are acquired using a control analytical measurement technique. In one example the control technique is secondary ion mass spectroscopy (SIMS) so that the count ratios from the TXRF-type measurements are compared to ratios of integrals of SIMS profiles. In another example, the TXRF-type measurement ratios are compared to simulation profiles of known samples. Integrals of the SIMS profile that vary as a function of depth into the substrate correspond to the grazing incidence angles of the TXRF-like measurement and respective count rates.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Surface analysis apparatus and method using ion bombardment
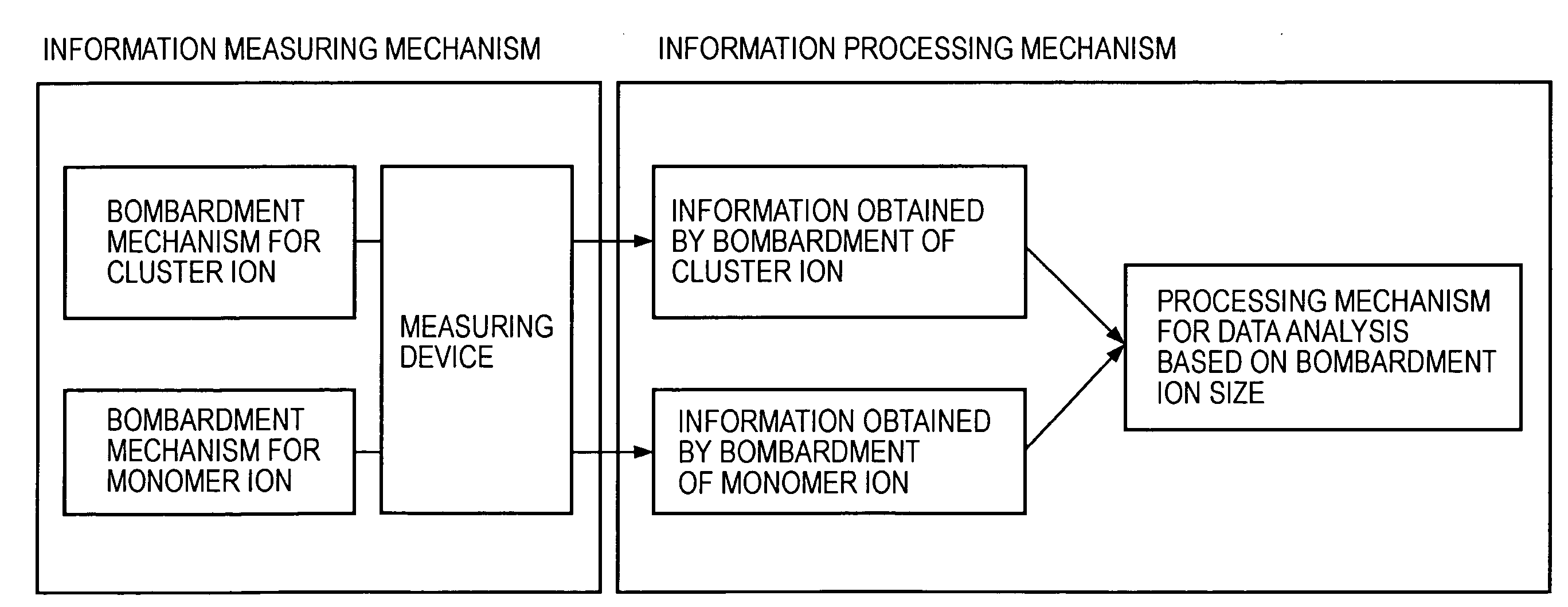
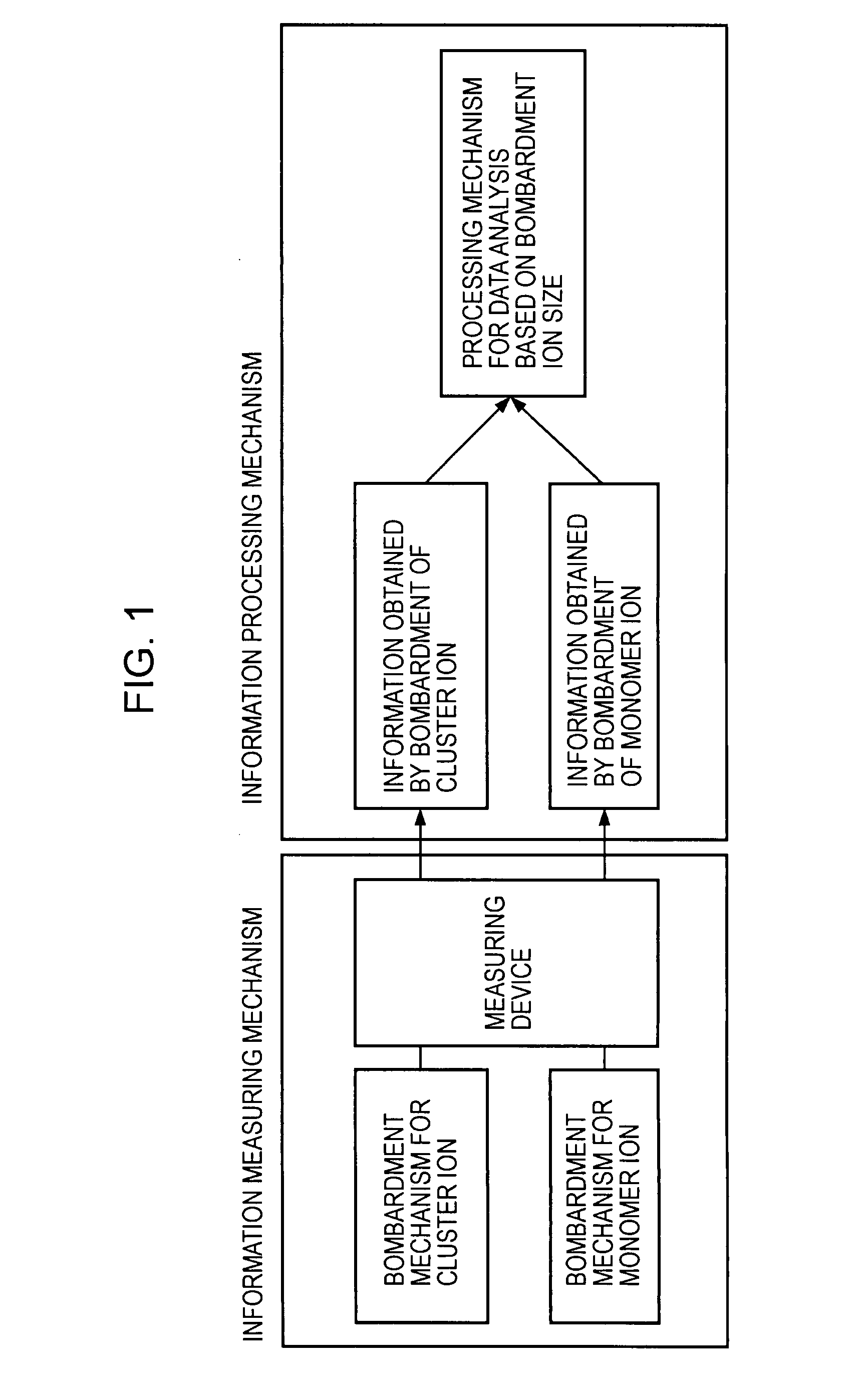
InactiveUS20080001081A1Minimize contaminationReduce harmParticle separator tubesIsotope separationMeasurement deviceIon bombardment
A surface analysis apparatus includes a unit configured to bombard a sample surface with at least two types of ions having different sizes; a measurement device for measuring, with a time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer, a mass spectrum of ions emitted from the sample surface; and an information processor outputting a difference between two mass spectra measured by bombardment of different types of ions.
Owner:CANON KK
Information acquisition method, information acquisition apparatus and disease diagnosis method
InactiveUS20060183235A1Efficient conductionGood quantization propertyBiological testingSolid cathode detailsIonizationTime of flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy
Owner:CANON KK
Lithium composite compound particles and process for producing the same, and non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
ActiveUS20110281168A1Excellent cycle characteristicsExcellent in high-temperature storage propertyFinal product manufactureLi-accumulatorsHigh temperature storageIonic strength
The present invention relates to lithium composite compound particles having a composition represented by the formula: Li1+xNi1-y-zCoyMzO2 (M=B or Al), wherein the lithium composite compound particles have an ionic strength ratio A (LiO− / NiO2−) of not more than 0.3 and an ionic strength ratio B (Li3CO3+ / Ni+) of not more than 20 as measured on a surface of the respective lithium composite compound particles using a time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer. The lithium composite compound particles of the present invention can be used as a positive electrode active substance of a secondary battery which has good cycle characteristics and an excellent high-temperature storage property.
Owner:TODA IND
Method for preparing high-resolution emitter tungsten tip and device thereof
InactiveCN101701352AGood repeatabilityGood lookingNanostructure manufactureElectrolysis componentsEngineeringWidth ratio
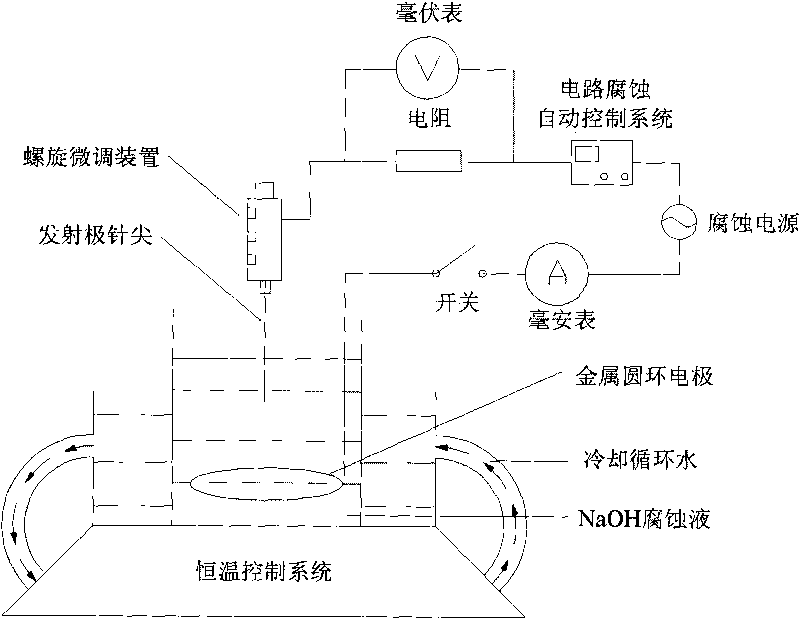
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-resolution emitter tungsten tip and a device thereof, and relates to a liquid metal ion source with high-resolution secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). The invention provides the method for rapidly and safely preparing the emitter tungsten tip with simpleness and high repeatability. The device is provided with an AC voltage signal generating circuit, a corrosion current monitoring circuit, a corrosion voltage monitoring circuit, an automatic corrosion control system, a spiral micro-regulator, a corrosion electrolytic cell and a constant temperature control system. Corrosion solution is placed in a cooler for low-temperature cooling before the manufacture and taken out till a certain temperature, then the cooler with the corrosion solution is horizontally fixed in the constant temperature controller, and the constant temperature control system is regulated for keeping the temperature of the corrosion solution at constant temperature. A clean tungsten wire is taken and annealed by hydrogen flame, one end of the tungsten wire is fixed on the spiral micro-device and used as a pole, and the other pole is a metal annular electrode placed in the NaOH corrosion solution; the metal annular electrode is horizontally placed at the middle and lower part at the bottom of the corrosion electrolytic cell; a central point of the metal annular electrode is taken by the tungsten wire and vertically inserted in the corrosion solution; the tungsten wire is inserted in the corrosion solution, and the insertion depth is kept; the corrosion current is monitored till the corrosion current achieves a threshold; pulse corrosion is continued, and roughening treatment is carried out on the tip, and the length to width ratio of the tip is controlled.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
In-plane distribution measurement method
InactiveUS20060118711A1Generate efficientlyTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIn planeTime of flight
In-plane distribution of a target objectcontained in a sample is measured. The sample dispersedly placed on a substrate is treated to promote ionization of the target object, then the mass and flying amount of an ion containing the target object or a component of the target object is determined by irradiating an ion beam to the sample and performing time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry of the ion that flies from a portion in the sample where the ion beam is irradiated, and the in-plane distribution of the target object is determined from the mass and flying amount data obtained at plural portions by scanning the beam on the sample plane. The step of treating the sample to promote ionization of the target object includes contacting an aqueous solution of an acid that does not crystallize at ordinary temperature with the sample. A high spatial resolution two-dimensional image can be obtained.
Owner:CANON KK
Sulfur Containing Alpha-Alumina Coated Cutting Tool
InactiveUS20140173996A1Reduce frictional contactImprove cutting performancePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesGas phaseSecondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy
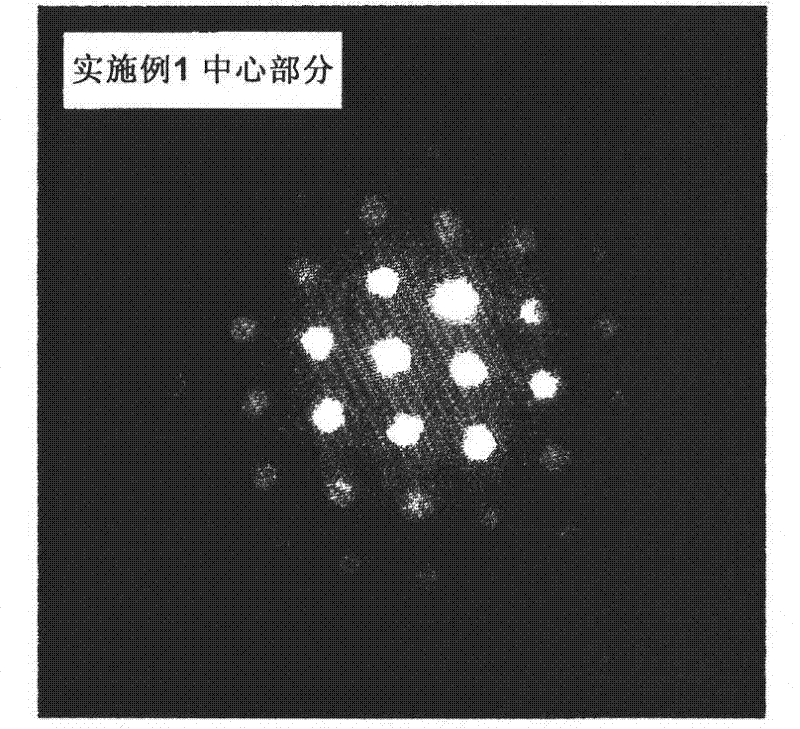
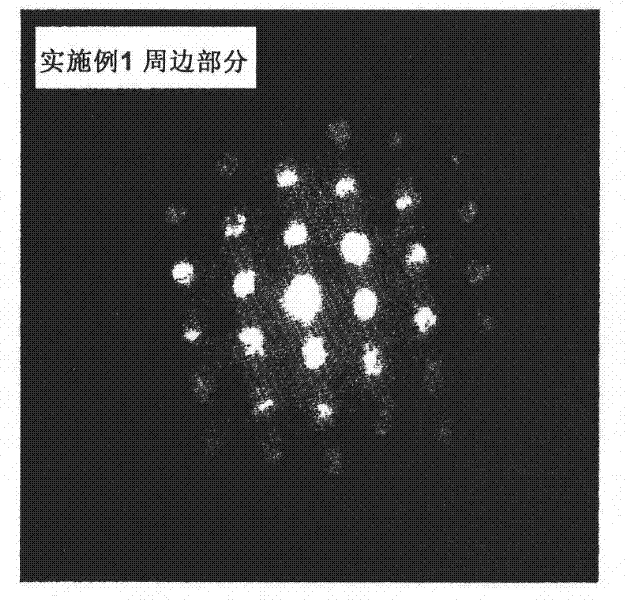
Cutting tool insert has a substrate and a coating of one or more refractory layers of which at least one layer is an α-Al2O3 layer having thickness of 1 to 25 μm, sulphur content of more than 100 ppm analysed by Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy (SIMS), and texture coefficient TC (0 0 12)>4 for the (0 0 12) growth direction.The at least one α-Al2O3 layer is deposited by chemical vapour deposition (CVD) using reaction gases comprising H2, CO2, AlCl3 and X, with X being H2S, SO2, SF6, or combinations thereof, and optional additions of N2 and Ar. The amount of X is at least 1.0 vol-% of the total volume of gases in the reaction chamber. The volume ratio of CO2 and X in the reaction chamber lies within the range of 1≦CO2 / X≦7 during deposition of the at least one α-Al2O3 layer.
Owner:WALTER AG
Powder of lithium complex compound particles, method for producing the same, and nonaqueous electrolyte secondary cell
ActiveCN102239118AExcellent cycle characteristicsExcellent high temperature storage propertiesFinal product manufactureCell electrodesLithiumIonic strength
Provided is a powder of lithium complex compound particles, wherein when the particle surface of the powder of lithium complex compound particles represented byLi1+xNi1-y-zCoyMzO2(M=B, Al)is analyzed using a time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer, the ionic strength ratio A (LiO- / NiO2 -) is 0.3 or less and the ionic strength ratio B (Li3CO3 + / Ni+) is 20 or less. The powder of lithium complex compound particles can be used as the positive electrode active material of a secondary cell having good cycle properties and excellent high-temperature shelf life.
Owner:TODA IND
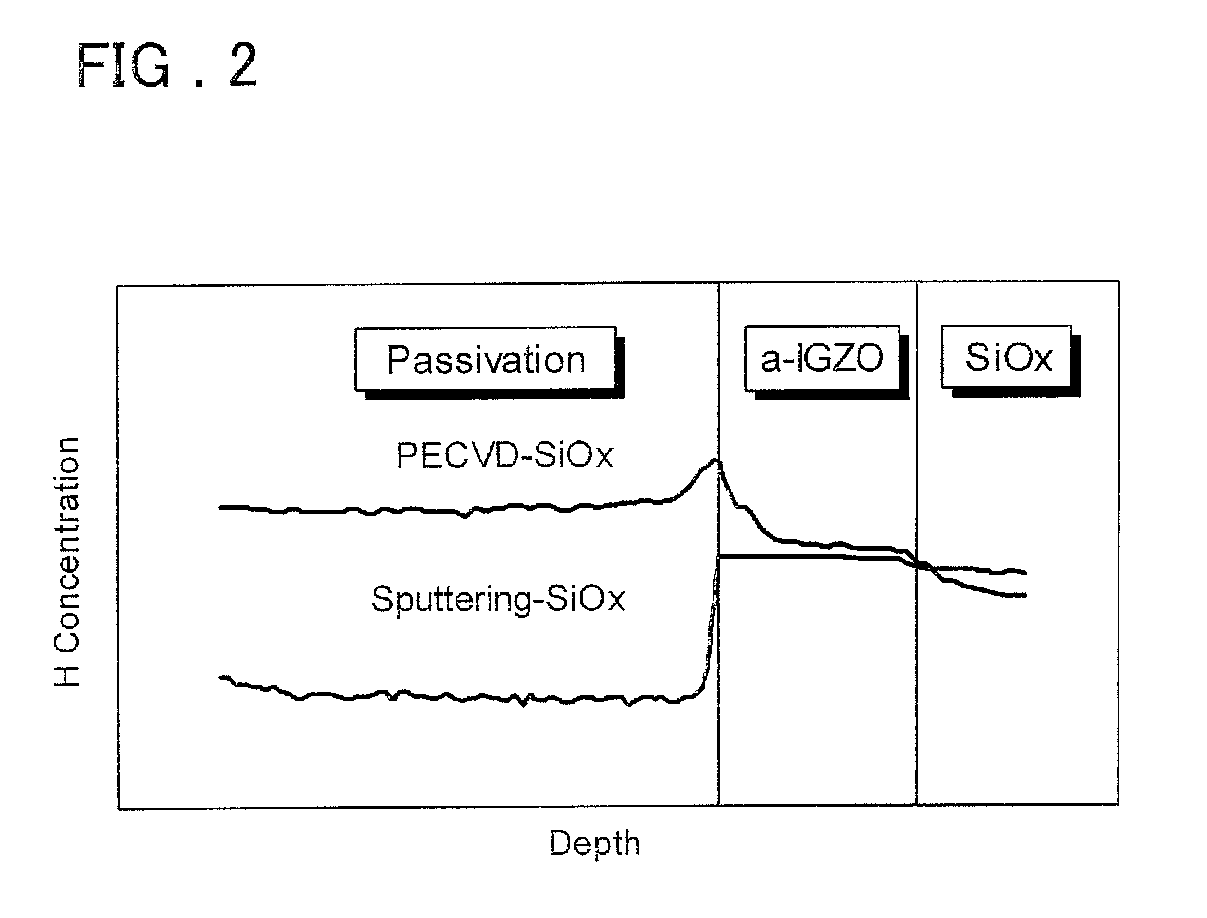
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140030845A1Reduce the amount requiredAvoid changeVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingLower limitNitrogen
The amount of nitrogen that is transferred to an oxide semiconductor film of a transistor including the oxide semiconductor film is reduced. In addition, in a semiconductor device which includes a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film, change in electrical characteristics is suppressed and reliability is improved. After a nitrogen-containing oxide insulating film is formed over a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film where a channel region is formed, nitrogen is released from the nitrogen-containing oxide insulating film by heat treatment. Note that the nitrogen concentration which is obtained by secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) is greater than or equal to the lower limit of detection by SIMS and less than 3×1020 atoms / cm3.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
In-plane distribution measurement method
InactiveUS7446309B2Generate efficientlyTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIn planeTime of flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy
In plane distribution of a target object contained in a sample is measured. The sample dispersedly placed on a substrate is treated to promote ionization of the target object. Then, the mass and flying amount of an ion containing the target object or a component thereof is determined by irradiating an ion beam to the sample and performing time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry of the ion that flies from a portion in the sample where the ion beam is irradiated, and the in-plane distribution of the target object is determined from the mass and flying amount data obtained at plural portions by scanning the beam on the sample plane. The step of treating the sample to promote ionization of the target object includes contacting an aqueous solution of an acid that does not crystallize at ordinary temperature with the sample. A high spatial resolution two-dimensional image can be obtained.
Owner:CANON KK
Display device
ActiveUS8269218B2Improve featuresImprove reliabilityTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesHydrogenHydrogen atom
One object is to provide a transistor including an oxide semiconductor film which is used for the pixel portion of a display device and has high reliability. A display device has a first gate electrode; a first gate insulating film over the first gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film over the first gate insulating film; a source electrode and a drain electrode over the oxide semiconductor film; a second gate insulating film over the source electrode, the drain electrode and the oxide semiconductor film; a second gate electrode over the second gate insulating film; an organic resin film having flatness over the second gate insulating film; a pixel electrode over the organic resin film having flatness, wherein the concentration of hydrogen atoms contained in the oxide semiconductor film and measured by secondary ion mass spectrometry is less than 1×1016 cm−3.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
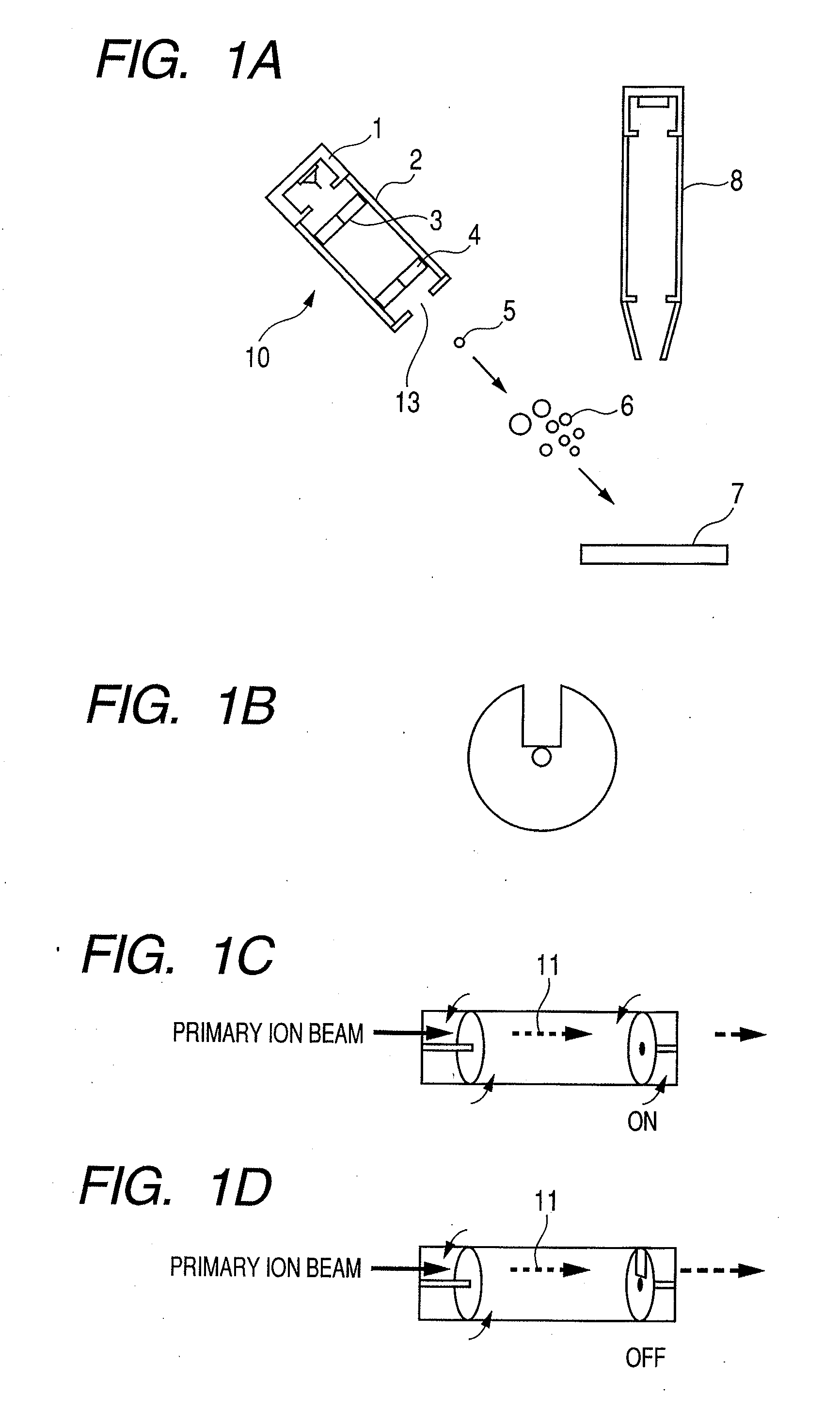
Time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer
InactiveUS20080277576A1High sensitivityGenerate efficientlyParticle separator tubesIsotope separationSpecific massTime of flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy
A time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer comprises an ion source which generates cluster ions each comprised of two or more atoms, a pulsing mechanism which pulses the cluster ions, a selecting mechanism which selects ions having a specific mass number from the pulsed cluster ions and passes the selected ions in an ON state of the selecting mechanism, and, passes the pulsed cluster ions without the selecting in an OFF state of the selecting mechanism, and a time-of-flight mass spectrometric unit which measures a mass spectrum of secondary ions generated from a sample using a difference in time of flight when the sample is irradiated with the ions passed through the selecting mechanism.
Owner:CANON KK
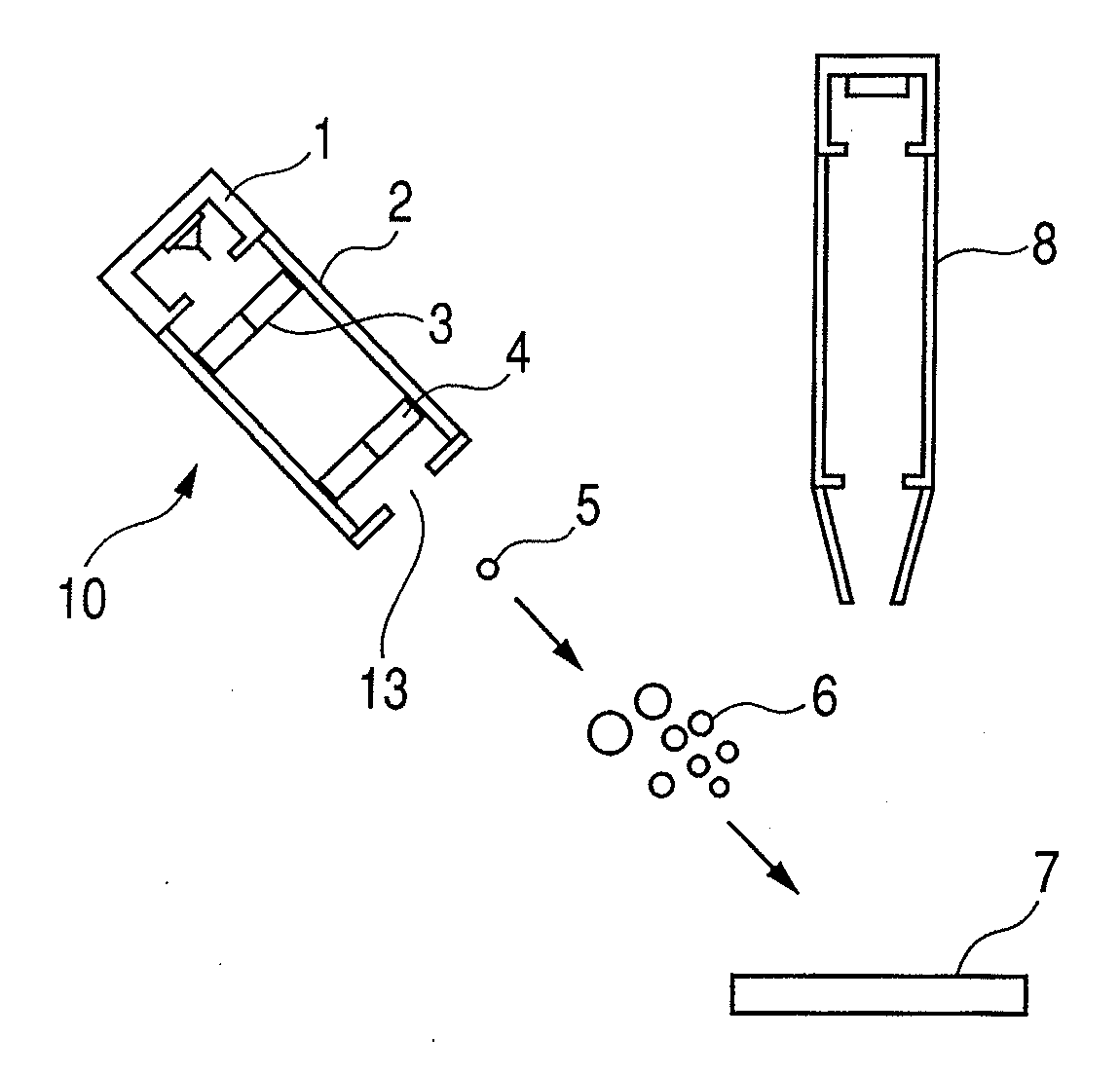
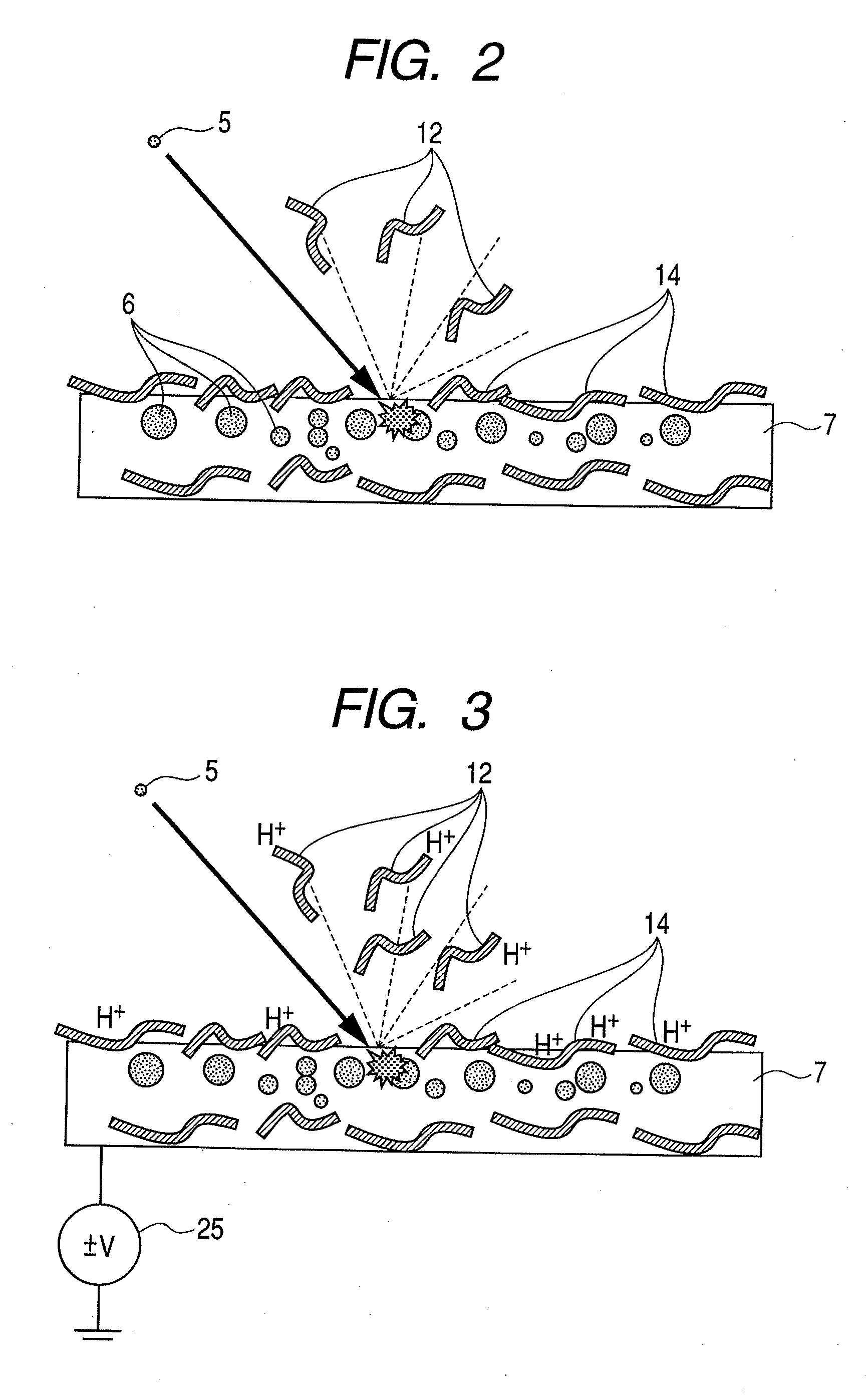
Method for measuring thorium lead age of bastnaesite sample on basis of secondary ion mass spectrometer
ActiveCN105548339AAccurately get the ageReduce mistakesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEpoxyOxygen plasma
The invention discloses a method for measuring the thorium lead age of a bastnaesite sample on the basis of a secondary ion mass spectrometer. The method includes the steps of embedding the bastnaesite sample and a bastnaesite standard substance in epoxy resin to form a sample target, placing the sample target in a sample cavity of the secondary ion mass spectrometer, using an oxygen plasma ion source, focusing the oxygen plasma ion source to the bastnaesite sample on the sample target in the form of parallel light so that secondary ions of the bastnaesite sample can be generated, making the secondary ions of the bastnaesite sample pass through an electric field and a magnetic field in the secondary ion mass spectrometer so that the angle and the speed can both be focused on an ion signal detection system, detecting the original thorium lead ratio in the secondary ions of the bastnaesite sample through the ion signal detection system, correcting the original thorium lead ratio to obtain the corrected thorium lead ratio, and calculating the thorium lead age of the bastnaesite sample through the corrected thorium lead ratio.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for determining age of uranium-lead in zircon by using multi-receive secondary ion mass spectroscopy
InactiveCN103399081AGuaranteed measurement accuracyExtend the effective integration timeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsotopes of leadSecondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy
The method discloses a method for determining the age of a uranium-lead decay system in zircon by using the multi-receive secondary ion mass spectroscopy. In the method described according to the invention, a multi-receiver peak jumping receiving mode is used, so that the age of uranium-lead is measured while the accurate age of lead-lead can be obtained. At least five electron multipliers are required to be used as receivers, wherein three of the receivers simultaneously receive the isotopes of lead, and one of the receivers is used for receiving signals required by calculating the age of uranium-lead. The method is applicable to a situation that the ages of uranium-lead and lead-lead can not be simultaneously and accurately measured by using common methods because of low uranium content or extra-small uranium age.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for acquiring information of a biochip using time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry and an apparatus for acquiring information for the application thereof
InactiveUS20070042496A1Better quantitative-abilityHigh resistivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTime-of-flight spectrometersContinuous scanningHigh resistivity
A measurement method is provided, which enables to obtain a two-dimensional image with better quantitative-ability by suppressing the influence of the charge-up, when the two-dimensional secondary ion image is obtained for a biological material fixed on a substrate having a high resistivity by utilizing a TOF-SIMS method in a certain wide area. A two-dimensional image having considerably high positioning resolution-ability can be obtained by the procedure in which the pulsed primary ion beam is irradiated at a spot, and the pulse-wise spot-applications of the primary ion beam and the simultaneous detection of the secondary ion generated from the irradiated primary ion beam proceed along with a discontinuous scanning pattern, and eventually the results of these secondary ion measurements are reconstructed into a two-dimensional image in line with the aforementioned discontinuous scanning pattern.
Owner:JACKSON BRAD
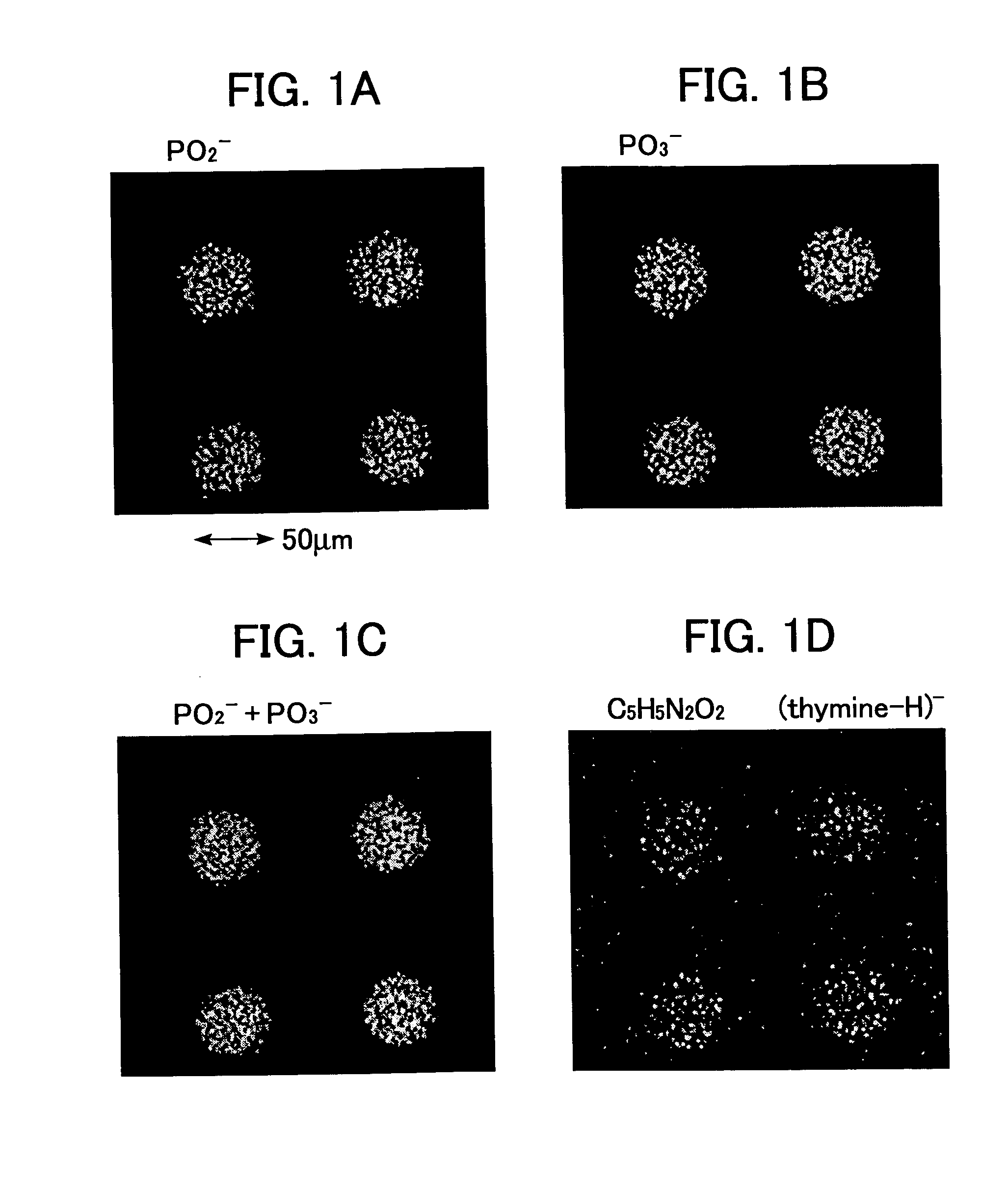
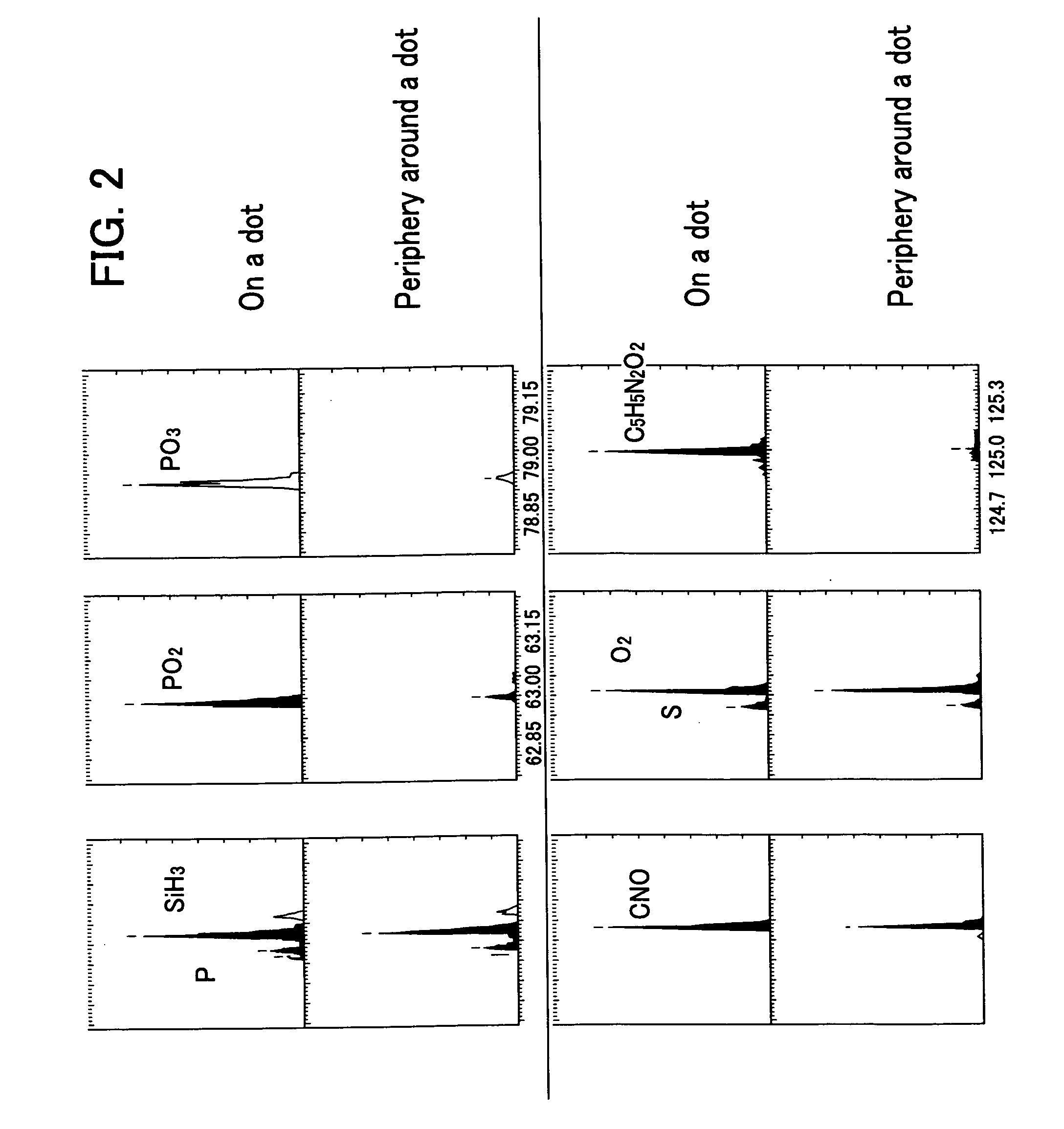
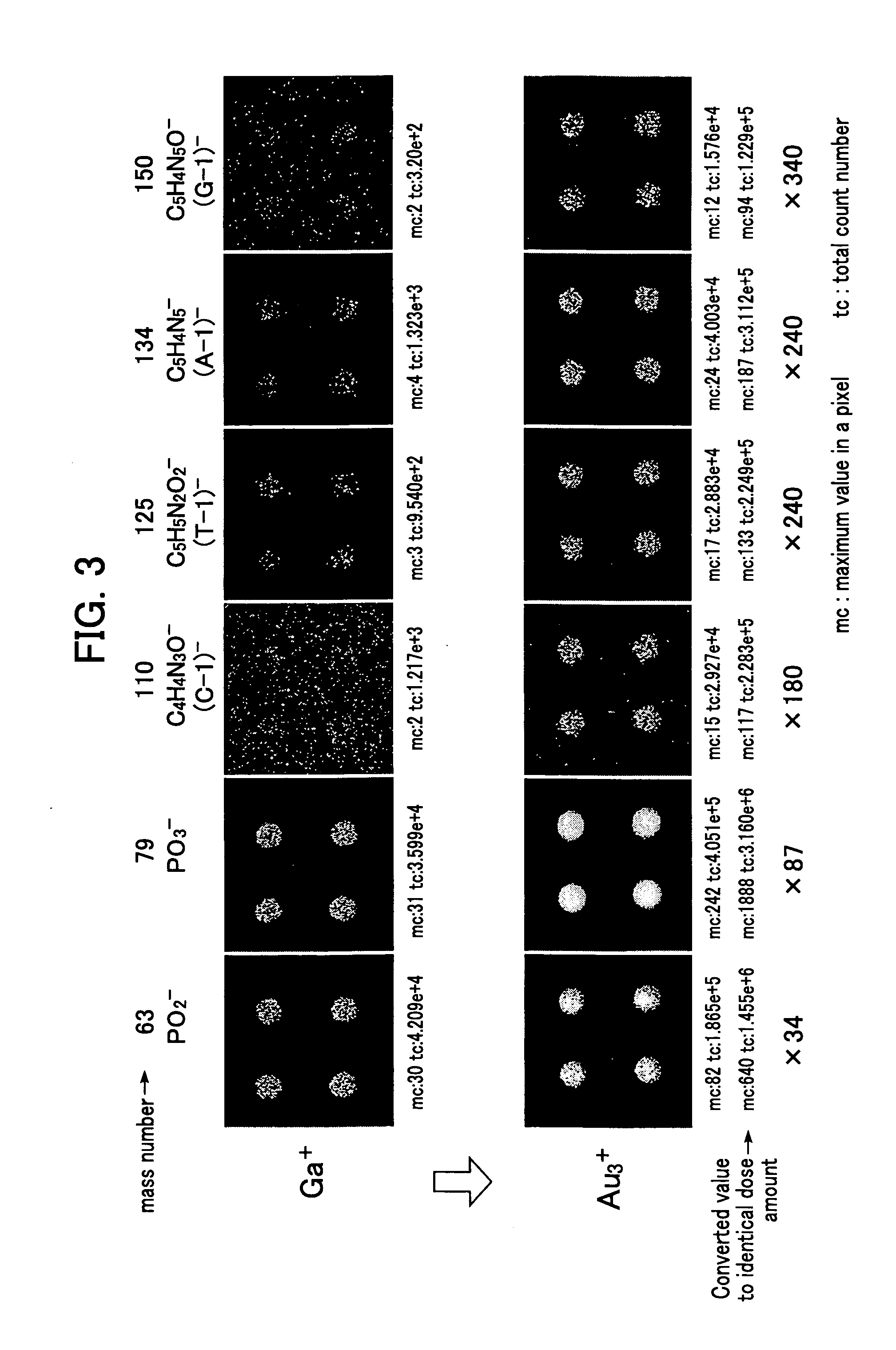
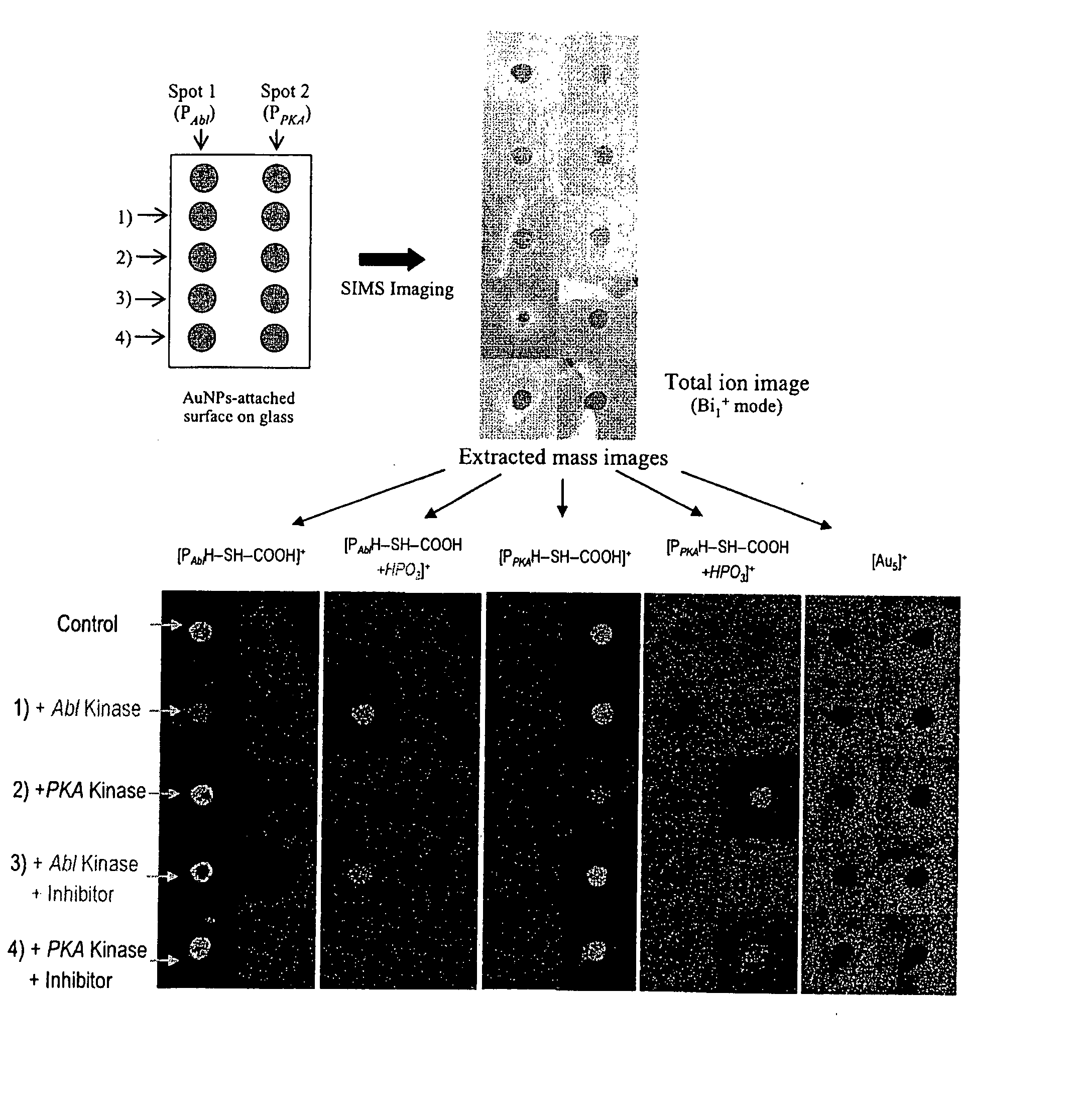
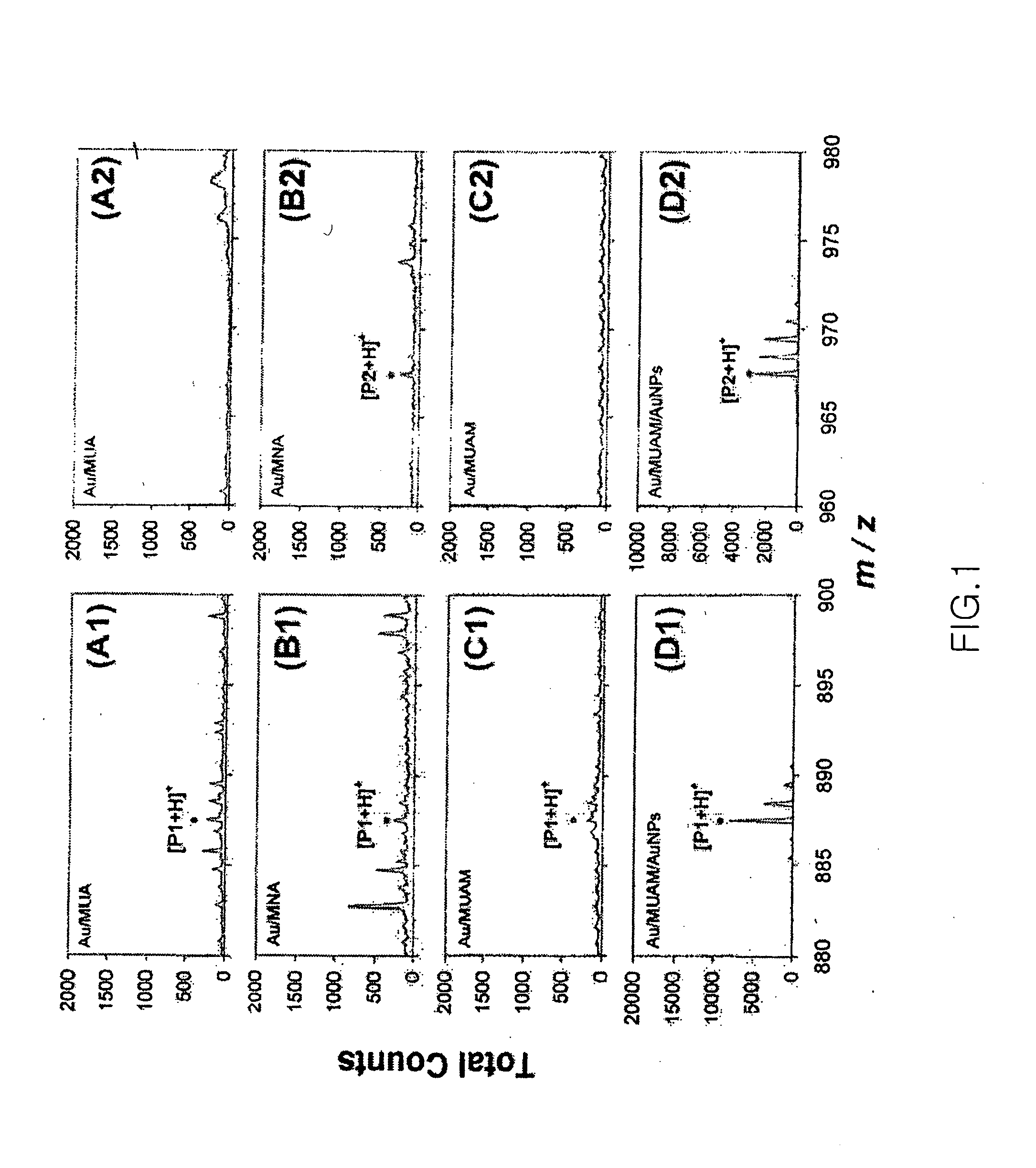
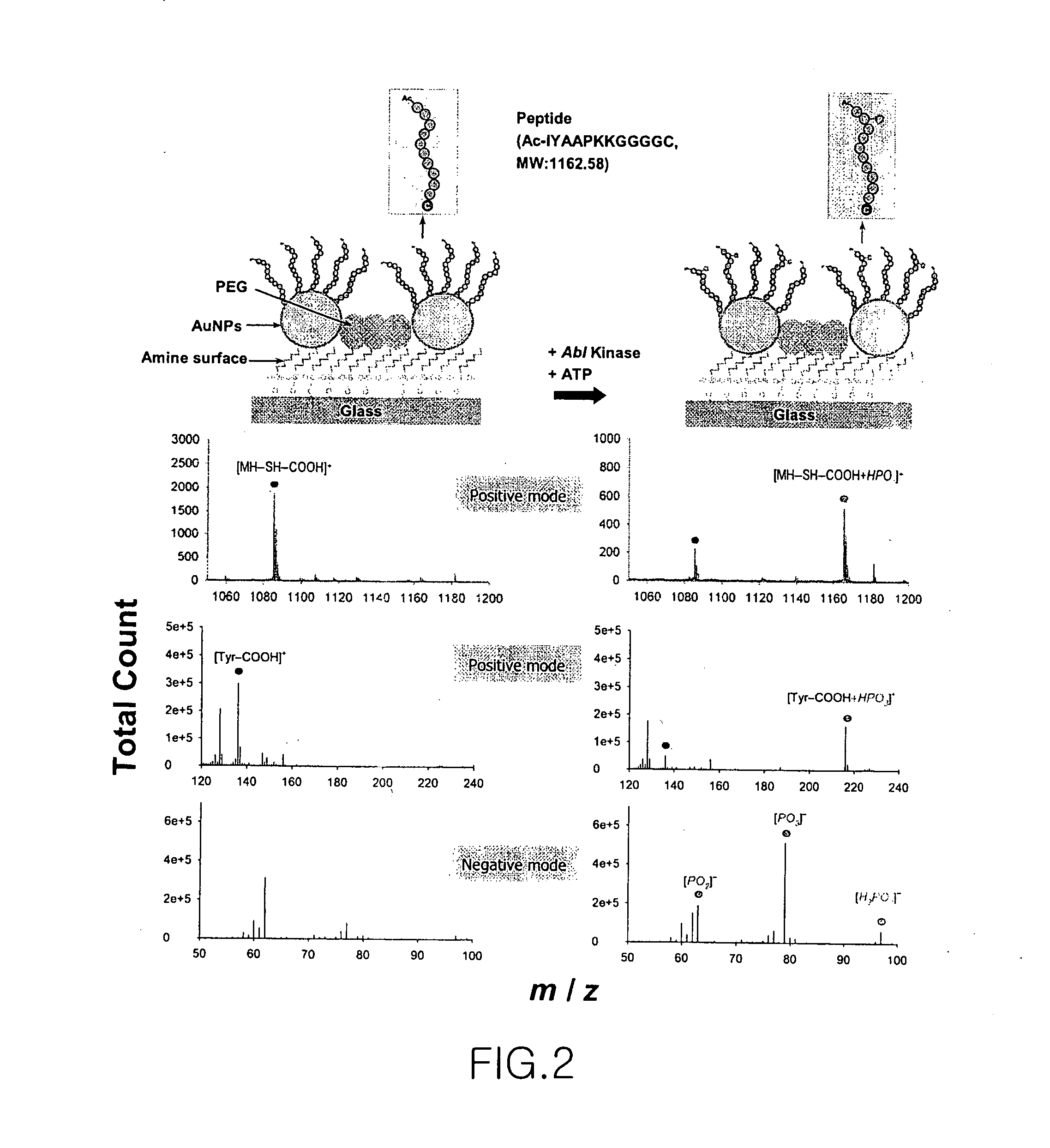
Novel construction of gold nanoparticle-based peptide chip, and assaying enzyme activity and inhibitor effect using secondary ion mass spectrometric analysis thereof
ActiveUS20080076676A1Effectively amplifying the mass signal of peptideAccurately measuring massCompound screeningPeptide librariesDiseaseSelf-assembled monolayer
Disclosed herein is a gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-based peptide chip prepared by forming a monolayer of AuNPs onto a self-assembled monolayer constructed on a solid support, and then immobilizing a peptide on the AuNPs. The AuNPs can effectively amplify the mass signal of the peptide, thus making it possible to measure the mass change of the peptide in a simple and accurate manner. Also, when secondary ion mass spectrometric analysis (spectrum or imaging) is performed on the AuNP-based peptide chip, the activities of enzymes and related inhibitors can be effectively quantified. The disclosed invention enables various enzyme activities to be analyzed rapidly and accurately, and thus can provide an important method for disease diagnosis and new drug development through the elucidation of signaling and interaction mechanisms.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
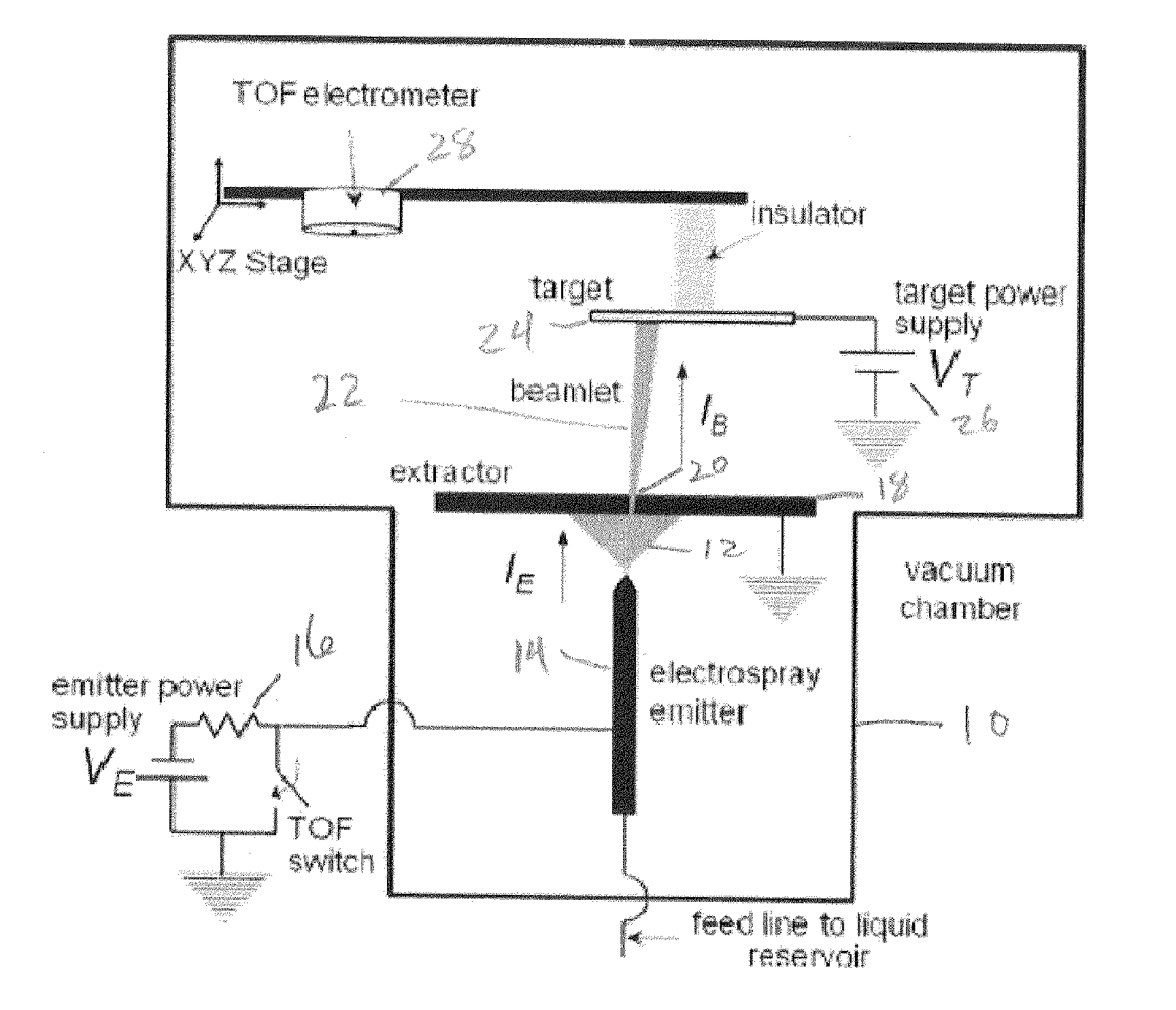
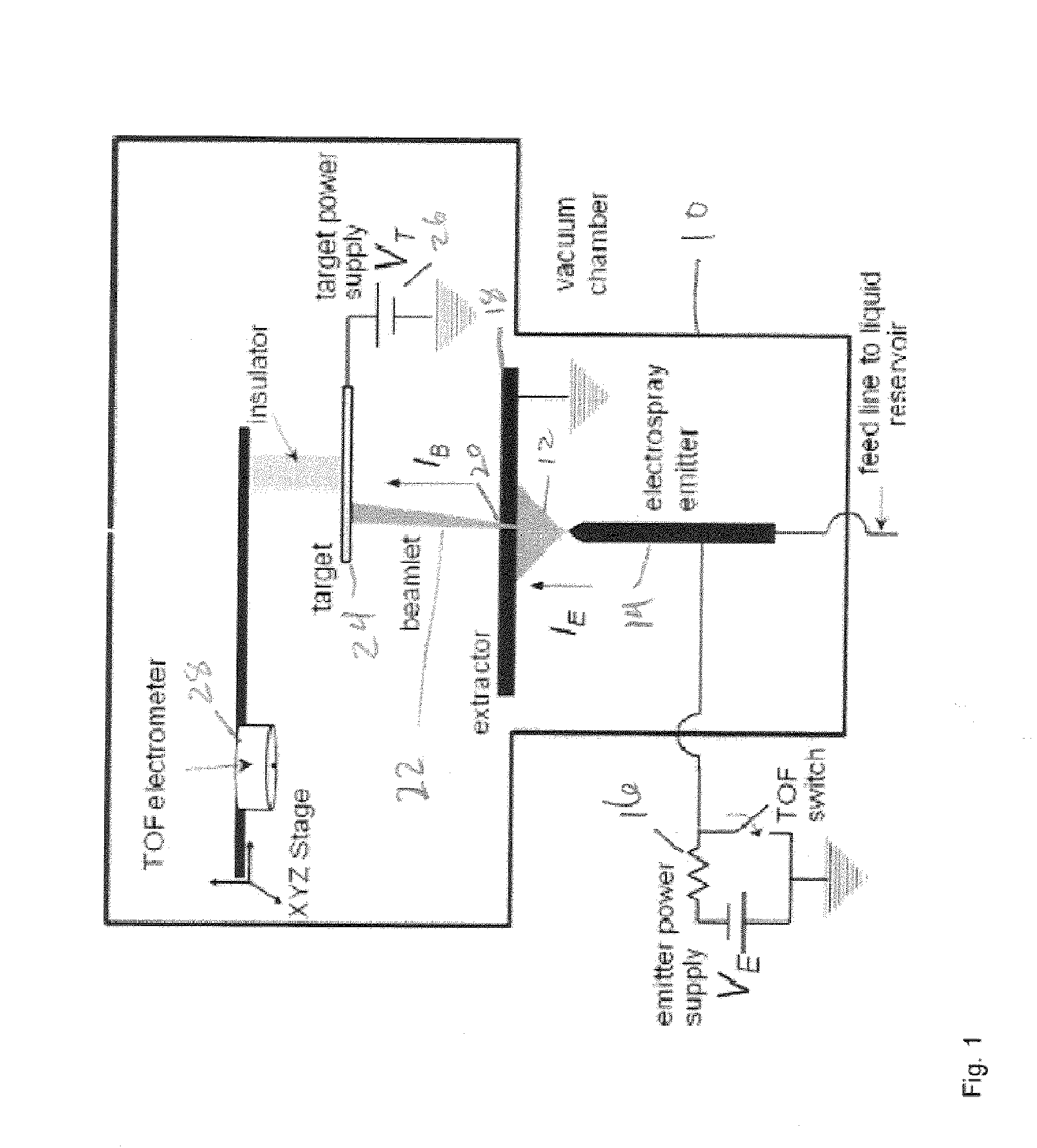
Method and apparatus for providing beams of nanodroplets for high sputtering rate of inert materials
InactiveUS20110290639A1Increase sputtering rateHigh yieldCellsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSputteringAcceleration voltage
A method for milling of a workpiece of inert material by nanodroplet beam sputtering includes the steps of providing a liquid; electrohydrodynamically atomizing the liquid to form charged nanodroplets; and directing the atomized charged nanodroplets onto the workpiece to selectively remove material. The method is used for broad-beam milling the workpiece of inert material, for precision micromachining and / or for three dimensionally profiling organic samples via secondary ion mass spectrometry. The liquid is electrosprayed in a cone-jet mode in a vacuum and average nanodroplet diameter, nanodroplet velocity, and molecular energy of the nanodroplets is adjusted by changing liquid flow rate and the acceleration voltage applied to the ionic liquid as it is atomized. Apparatus for performing the method are also included embodiments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Direct detection method for products of cellular metabolism using ToF-SIMS
InactiveUS20060188868A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationComponent separationMultivariate statisticsScreening method
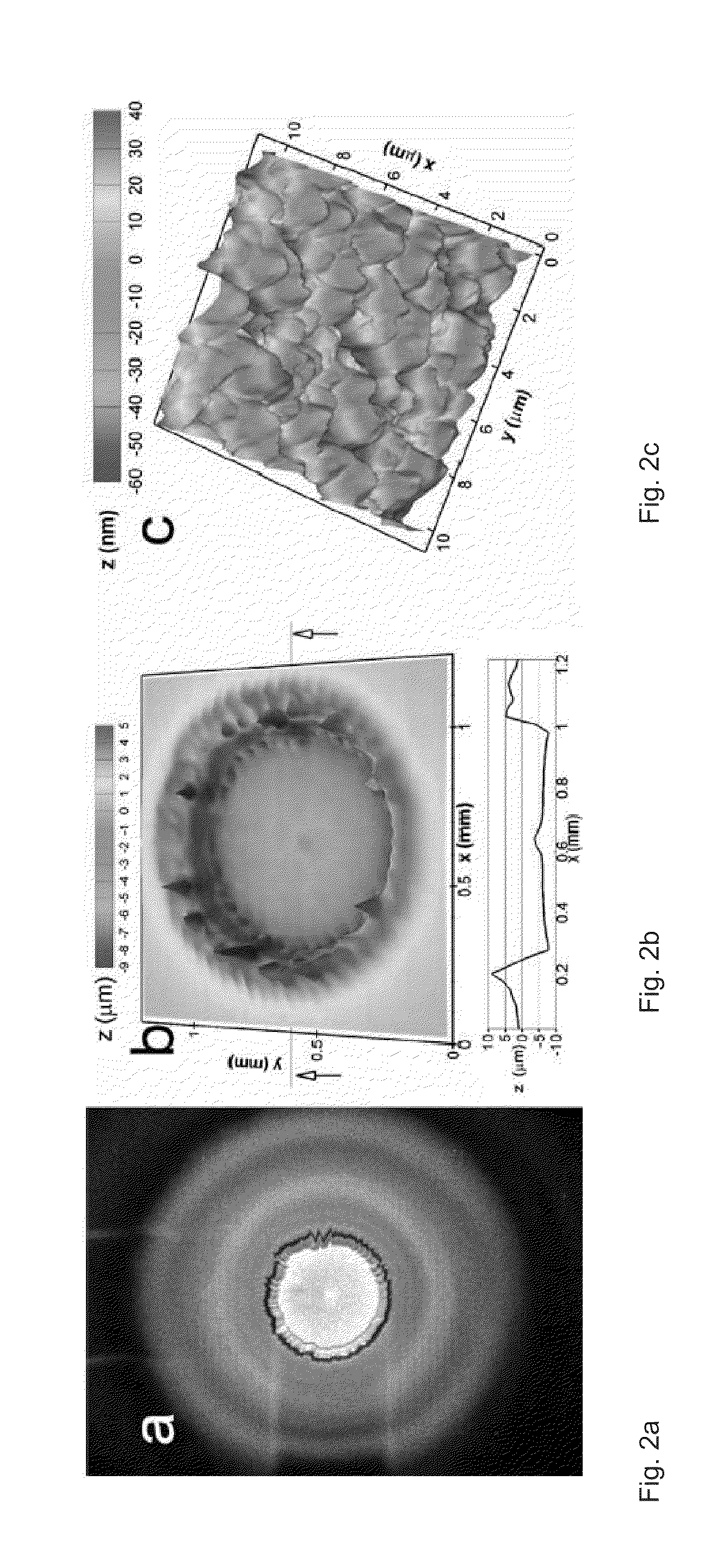
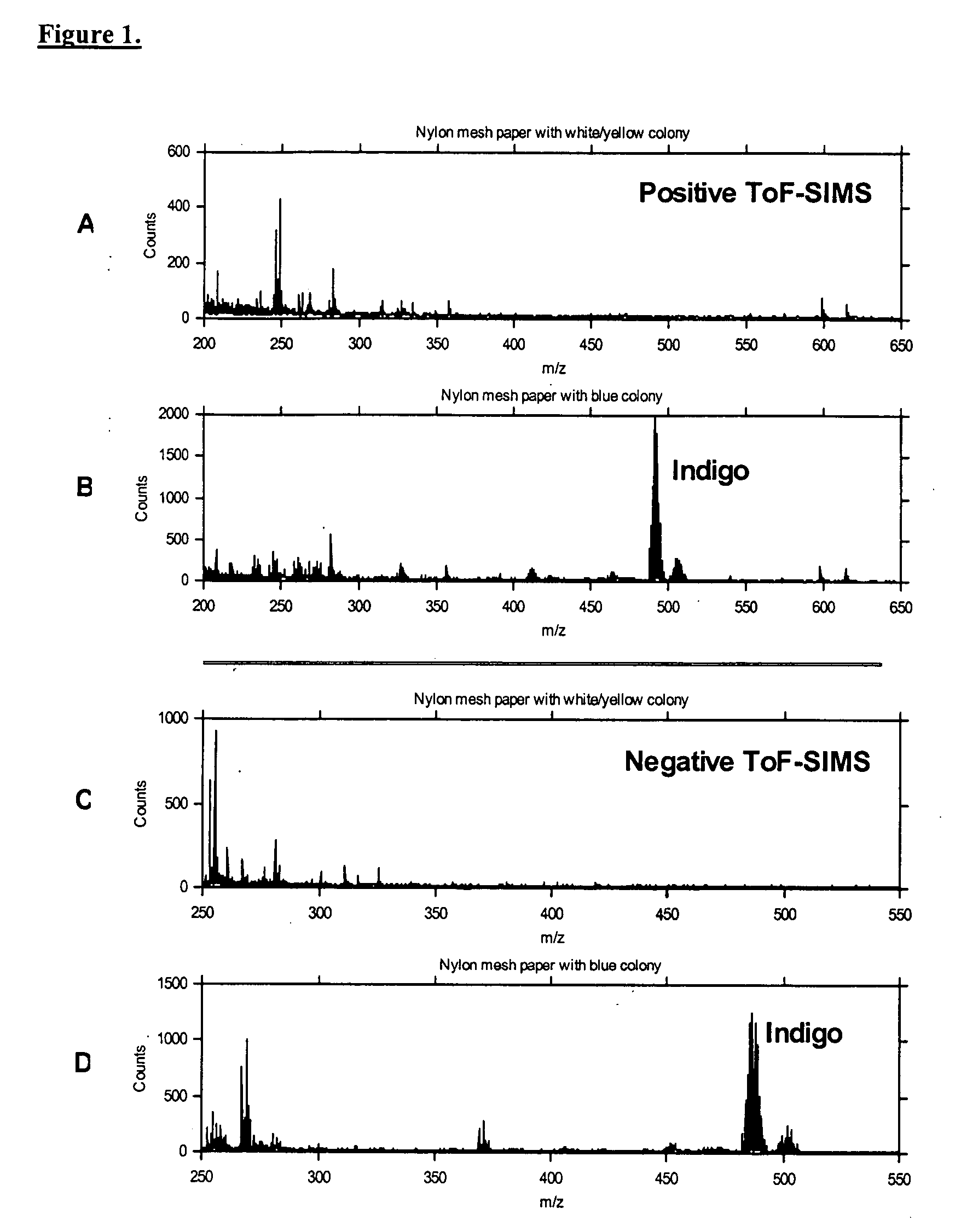
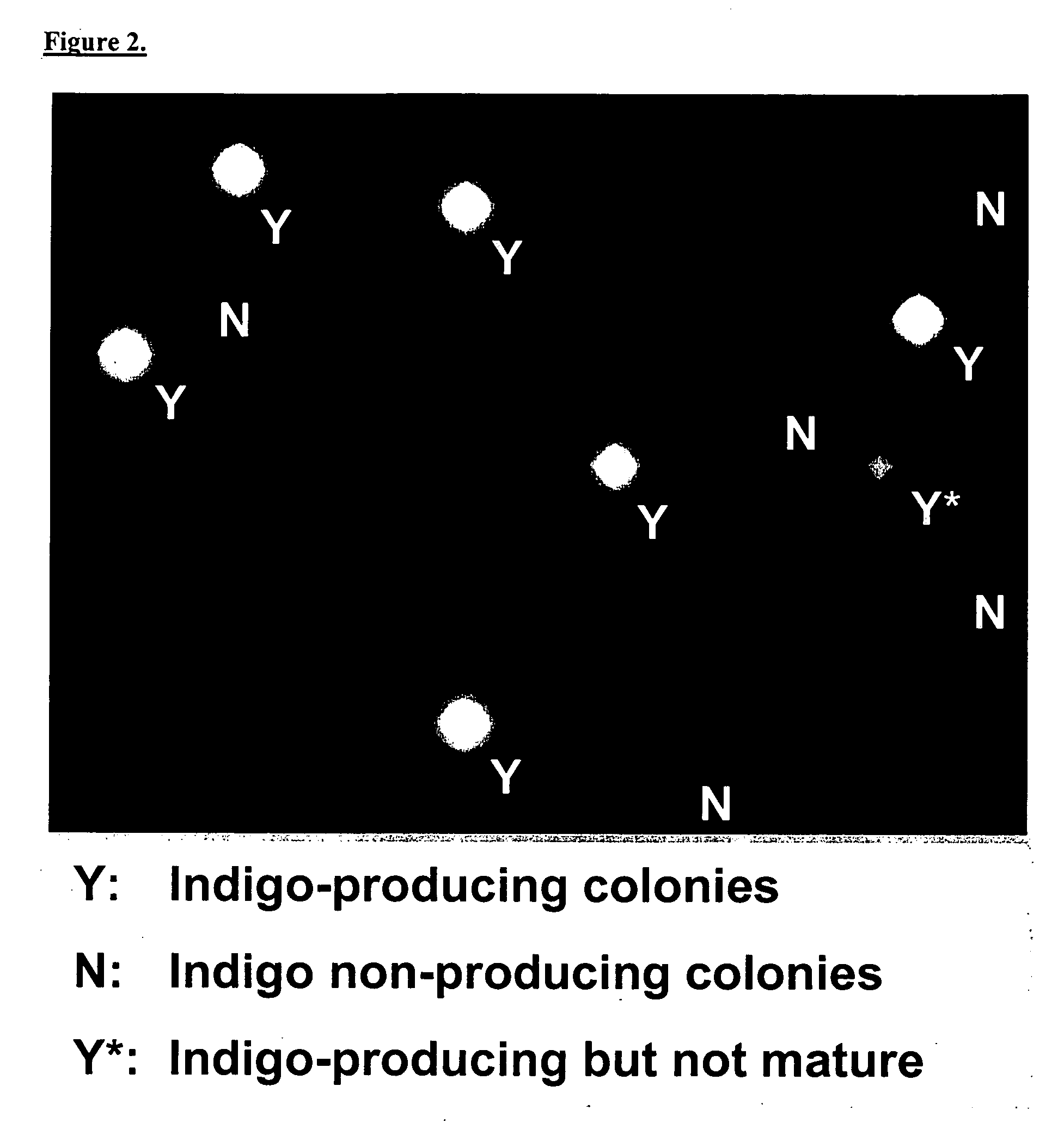
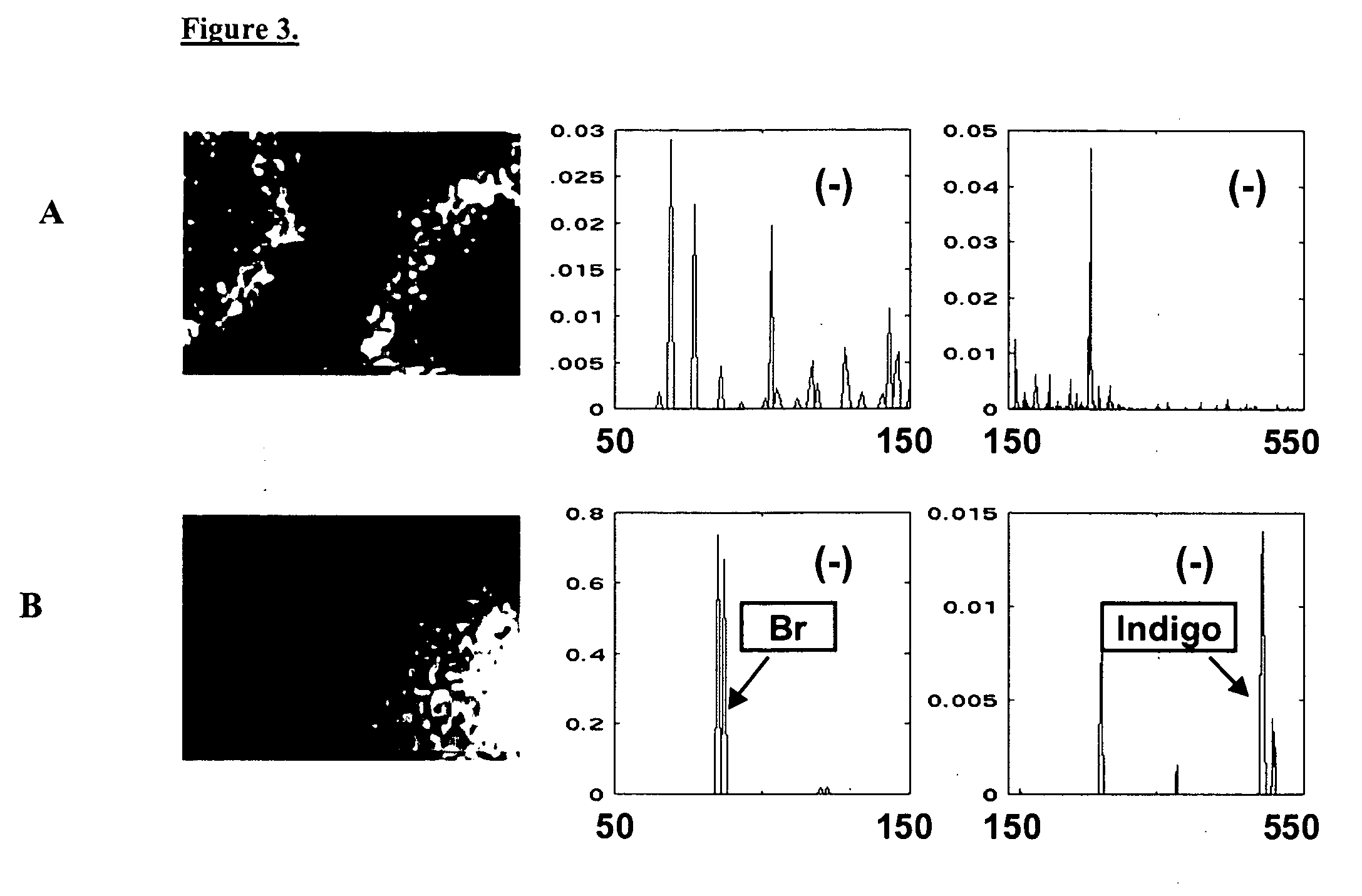
A rapid and efficient method for novel biological substance screening by surface analysis has been developed using Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (ToF-SIMS). This method relies on the surface screening of an array of micro-organisms grown on porous membranes, which had previously been in contact with a solid growth medium. TOF-SIMS analysis differentiates among organisms producing different substances, either directly as molecular product, or indirectly through the use of multivariate statistical data reduction techniques. This method has many advantages over traditional microbial screening methods, which require sample preparation and time for assay development.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Liquid-repellent member, nozzle plate, liquid-jet head using the same, and liquid-jet apparatus
To provide a liquid-repellent member such as a nozzle plate having high liquid repellency and liquid-repellent durability, a liquid-jet head using the same, and a liquid-jet apparatus.A liquid-repellent member includes: an underlayer film which is provided on a surface of a base and contains silicon; and a liquid-repellent film which is provided on the underlayer film and is made of a silane coupling agent having a fluorocarbon group. In the liquid-repellent member, a intensity ratio of ions highest detected in fluorocarbon-based fragment ions to silicon ions is greater than or equal to 10 when the fluorocarbon-based fragment ions and the silicon ions are detected through measurement by a Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometer.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer
InactiveUS7714280B2High sensitivityGenerate efficientlyEnergy spectrometersIsotope separationSpecific massTime of flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy
A time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer comprises an ion source which generates cluster ions each comprised of two or more atoms, a pulsing mechanism which pulses the cluster ions, a selecting mechanism which selects ions having a specific mass number from the pulsed cluster ions and passes the selected ions in an ON state of the selecting mechanism, and, passes the pulsed cluster ions without the selecting in an OFF state of the selecting mechanism, and a time-of-flight mass spectrometric unit which measures a mass spectrum of secondary ions generated from a sample using a difference in time of flight when the sample is irradiated with the ions passed through the selecting mechanism.
Owner:CANON KK
Lithium composite compound particles and process for producing the same, and non-awueous electrolyte secondary battery
ActiveUS20130119307A1Excellent cycle characteristicsExcellent in high-temperature storage propertyFinal product manufactureLithium compoundsHigh temperature storageLithium
The present invention aims to provide lithium composite compound particles which can exhibit good cycle characteristics and an excellent high-temperature storage property when used as a positive electrode active substance of a secondary battery, and a secondary battery using the lithium composite compound particles. The present invention relates to lithium composite compound particles having a composition represented by the compositional formula: Li1+xNi1−y−z−aCoyMnzMaO2, in which the lithium composite compound particles have an ionic strength ratio A (LiO− / NiO2−) of not more than 0.5 and an ionic strength ratio B (Li3CO3+ / Ni+) of not more than 20 as measured on a surface of the respective lithium composite compound particles using a time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer.
Owner:TODA IND
Method for testing blocking capacity of photoresist layer to ion implantation
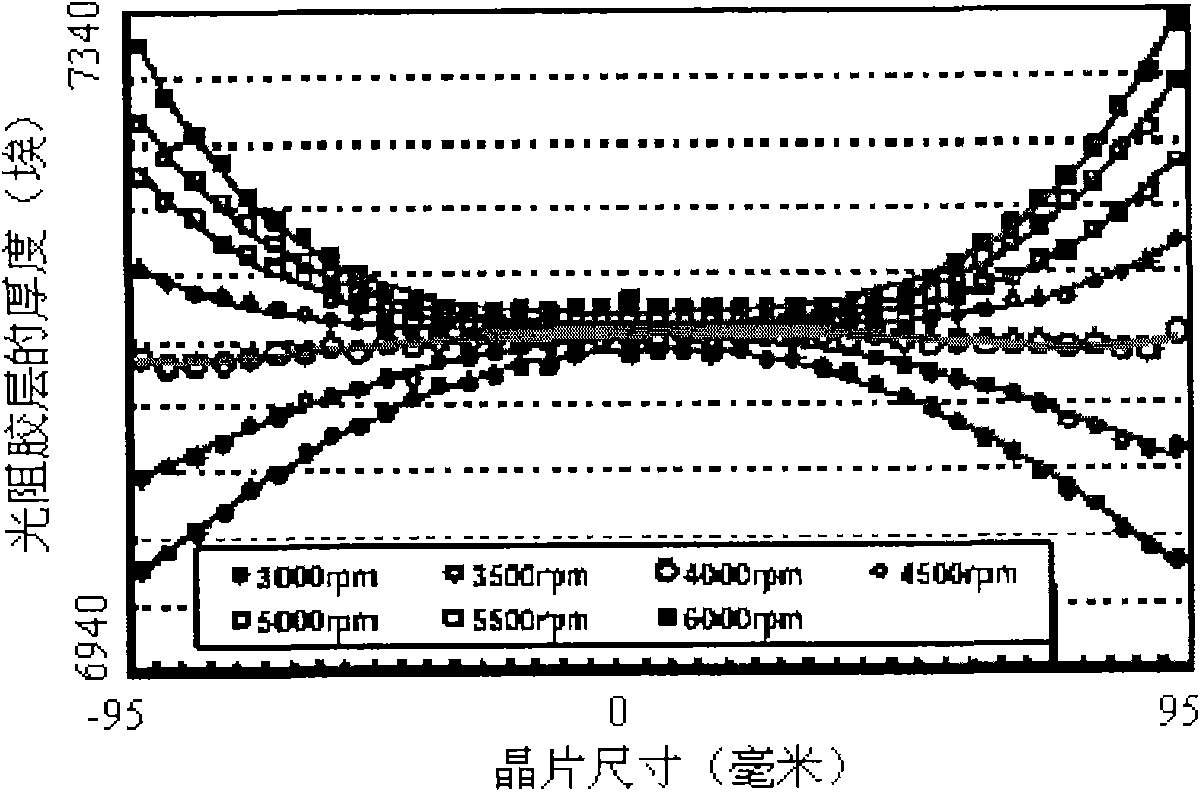
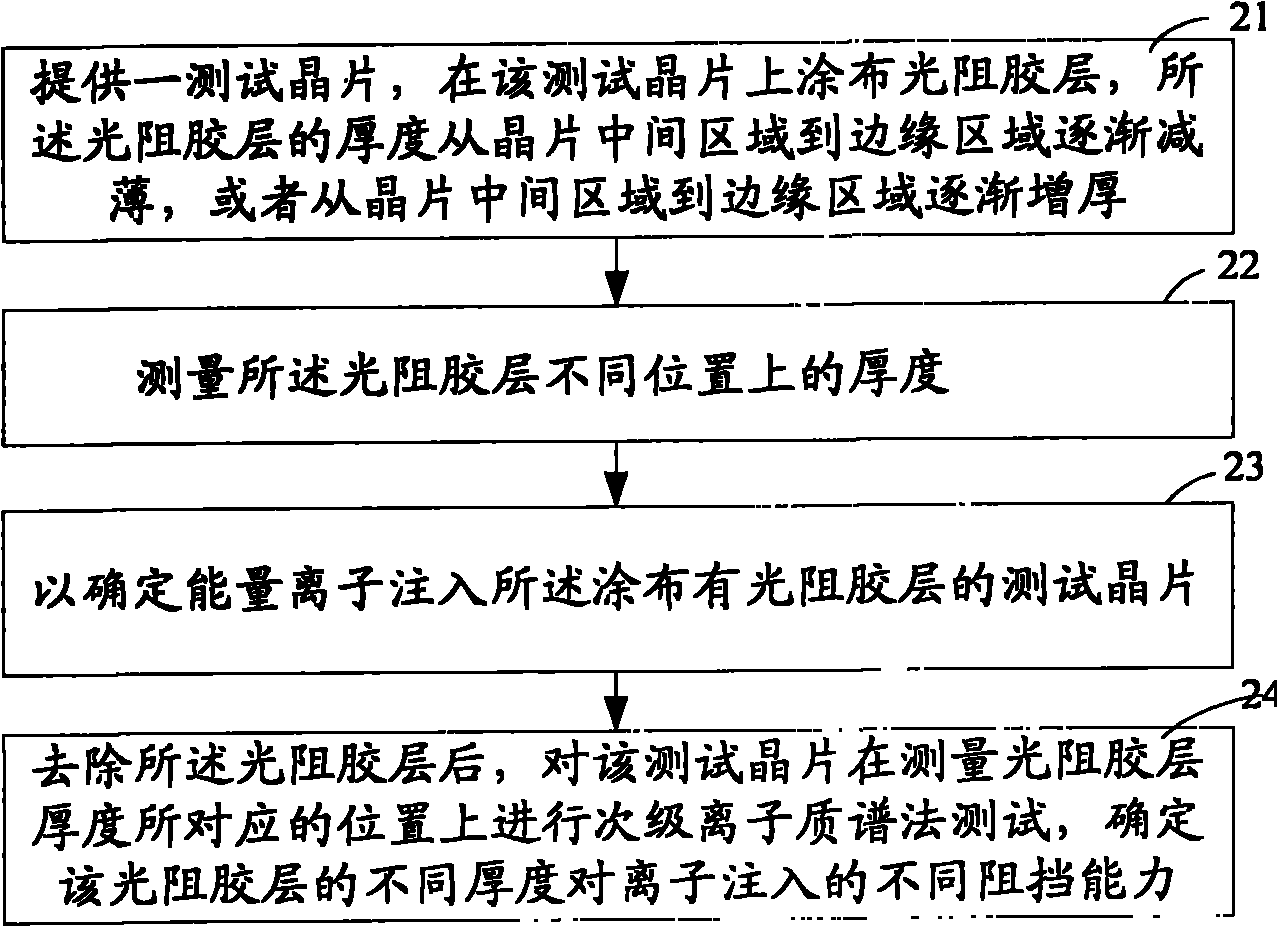
InactiveCN102403245AReduce in quantityReduce testing costsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputational physicsLayer thickness
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
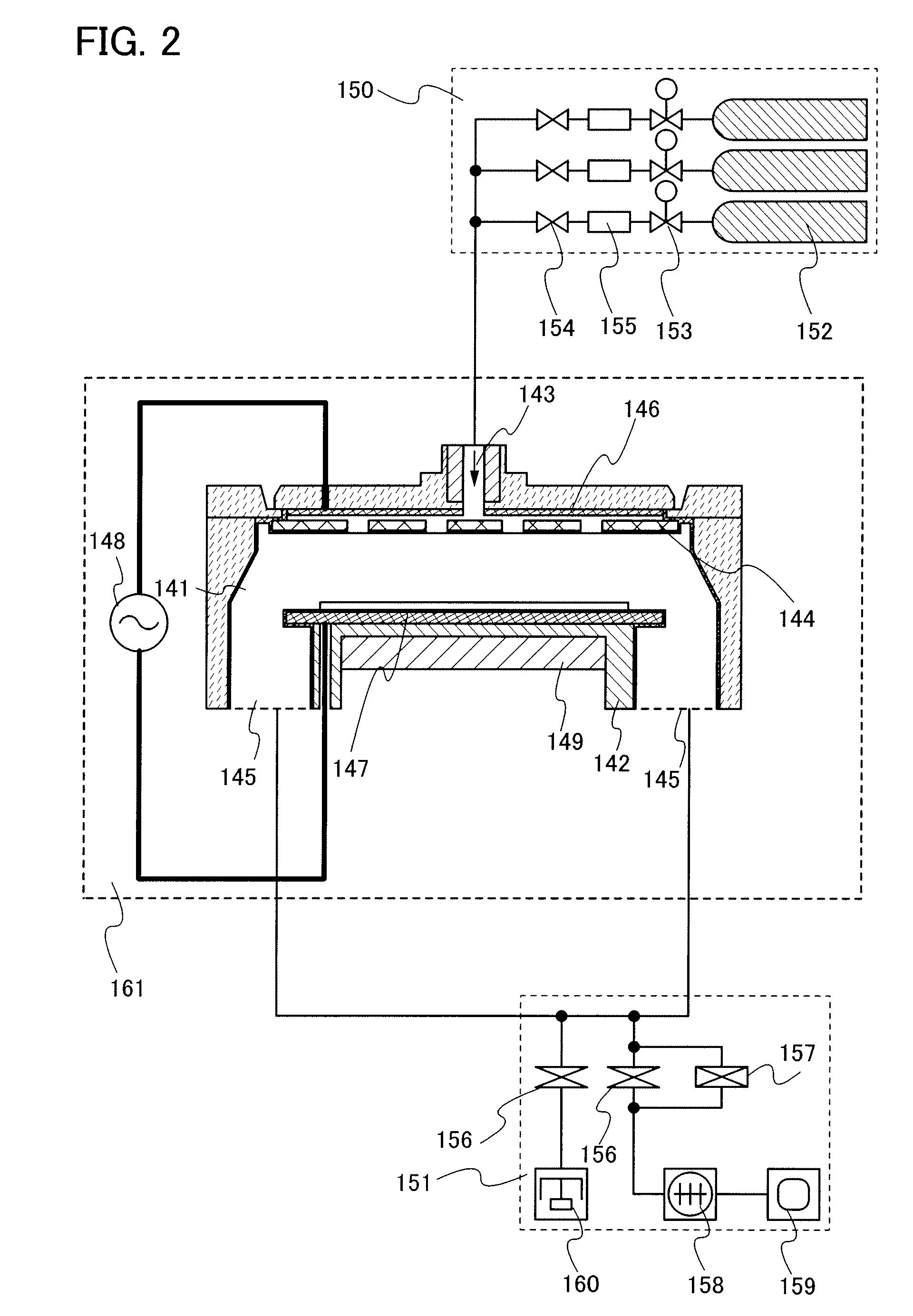
Method of manufacturing an analytical sample and method of analyzing an analytical sample
InactiveUS20080102536A1High precision analysisCostSilicon organic compoundsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPellicle membraneSecondary ion mass spectrometry
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
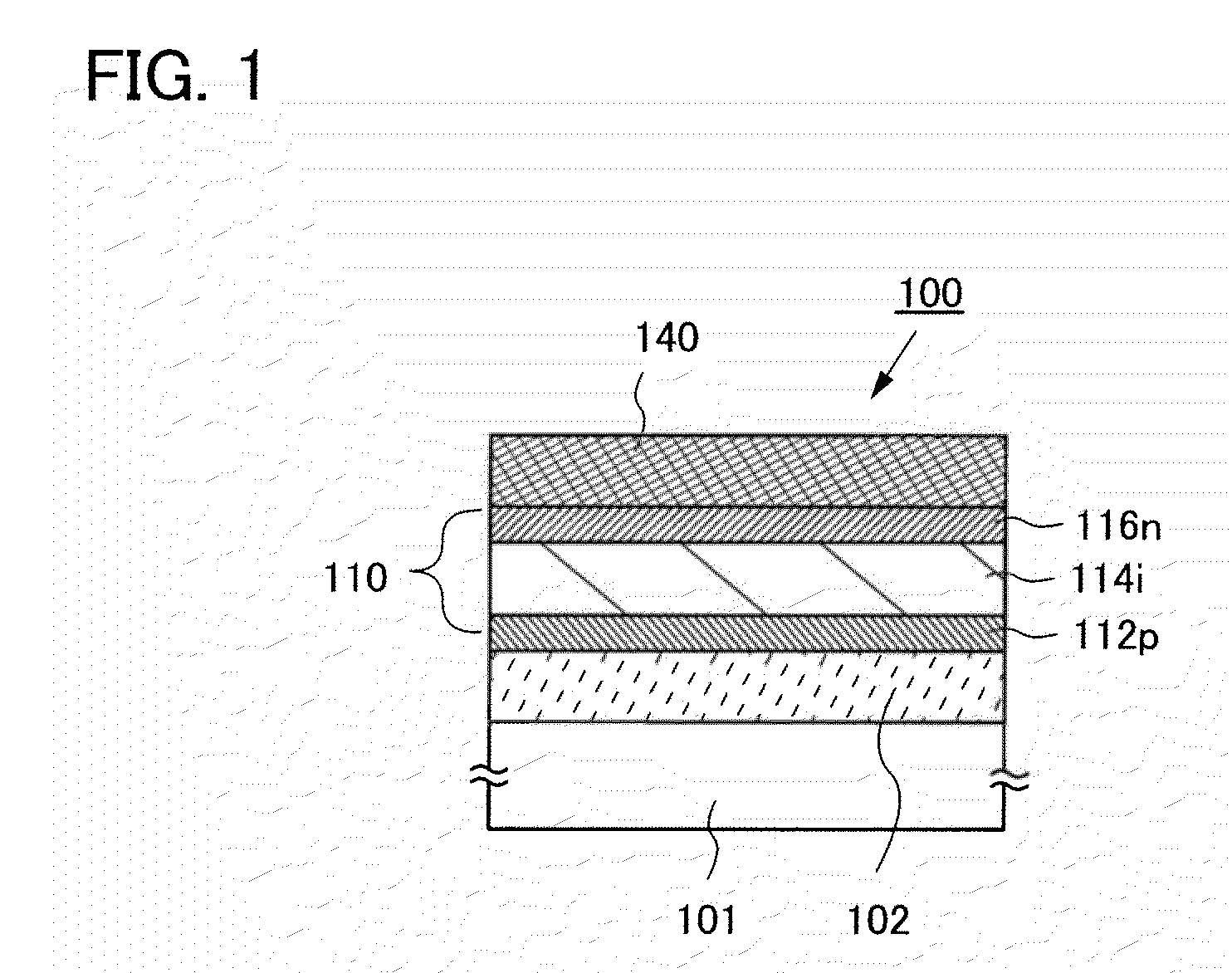
Photoelectric conversion device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100078071A1Reduce defectsImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenSingle crystal
A photoelectric conversion device includes one or more unit cells between a first electrode and a second electrode, in which a semiconductor junction is formed by sequentially stacking: a first impurity semiconductor layer of one conductivity type; an intrinsic non-single-crystal semiconductor layer including an NH group or an NH2 group; and a second impurity semiconductor layer of opposite conductivity type to the first impurity semiconductor layer. In the non-single-crystal semiconductor layer of a unit cell on a light incident side, the nitrogen concentration measured by secondary ion mass spectrometry is 5×1018 / cm3 or more and 5×1020 / cm3 or less and oxygen and carbon concentrations measured by secondary ion mass spectrometry are less than 5×1018 / cm3.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for detecting micro space debris
ActiveCN102042820AImplement detectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionX-rayElectron
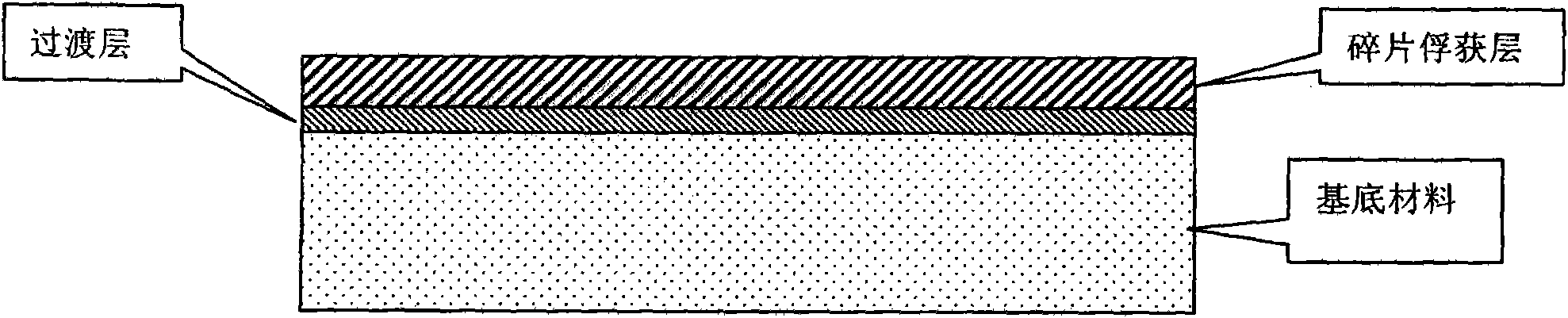
The invention relates to a method for detecting micro space debris and belongs to the technical field of micro space debris. A detection thin film comprises a debris capturing layer material, a transitional layer material and a base material from top down, wherein the micro space debris layer material is 1to 4 micrometer-thick Au; the base material is 1 to 3-millimeter-thick quartz glass, and the transitional layer material is 50 to 100 nanometer-thick Ir; the detection thin film is carried by the windward side or leeside of spacecraft, and after being exposed in space, the detection thin film is brought back to the ground; ground analysis is performed by secondary ion mass spectroscopic analysis or X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic analysis under ion gun analysis to obtain the correspondence between the data after the analysis of the detection thin film and the related data of the space debris; and thus, the chemical composition of the captured debris is obtained. In the invention, a low-weight power-free detection thin film is used to realize the detection of the space micro debris, and the space debris that can be captured and analyzed by the debris capturing layer is of mg order.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
Photocured product and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20150004790A1High pattern accuracyImprovement in pattern defectNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingUltimate tensile strengthSURFACTANT BLEND
It is intended to provide a photocured product that is prepared using the photo-imprint method and has favorable pattern precision and improvement in pattern defects. The present invention provides a photocured product obtained by irradiating a coating film in contact with a mold with light, the photocured product containing a fluorine atom-containing surfactant, wherein of secondary ion signals obtained by the surface analysis of the photocured product based on time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometry, the intensity of a C2H5O+ ion signal is higher than that of a C3H7O+ ion signal.
Owner:CANON KK
Glass sheet capable of being inhibited from warping through chemical strengthening
ActiveCN104203858AReduce warpageInhibition of differences in the extent to which chemical strengthening proceedsThin material handlingDepth directionUltimate tensile strength
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a glass sheet which can be effectively inhibited from warping through chemical strengthening and which enables polishing, etc., as treatments to be conducted before chemical strengthening, to be omitted or simplified. The invention relates to a glass sheet which, when analyzed with a secondary-ion mass spectrometer (SIMS), gives depth-direction profiles in which the abscissa is depth and the ordinate is F / Si intensity ratio, wherein the average value of the depth-direction profile in the depth range of 0-20 µm of one surface is larger than the average value of the depth-direction profile in the depth range of 0-20 µm of the other surface, the ratio of the two values being higher than 1.4.
Owner:AGC INC
Combined system of super-resolution confocal optical microscope and secondary ion mass spectroscopy
ActiveCN103616355ARealize Optical ImagingRealize SIMS imagingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceKinetic energy
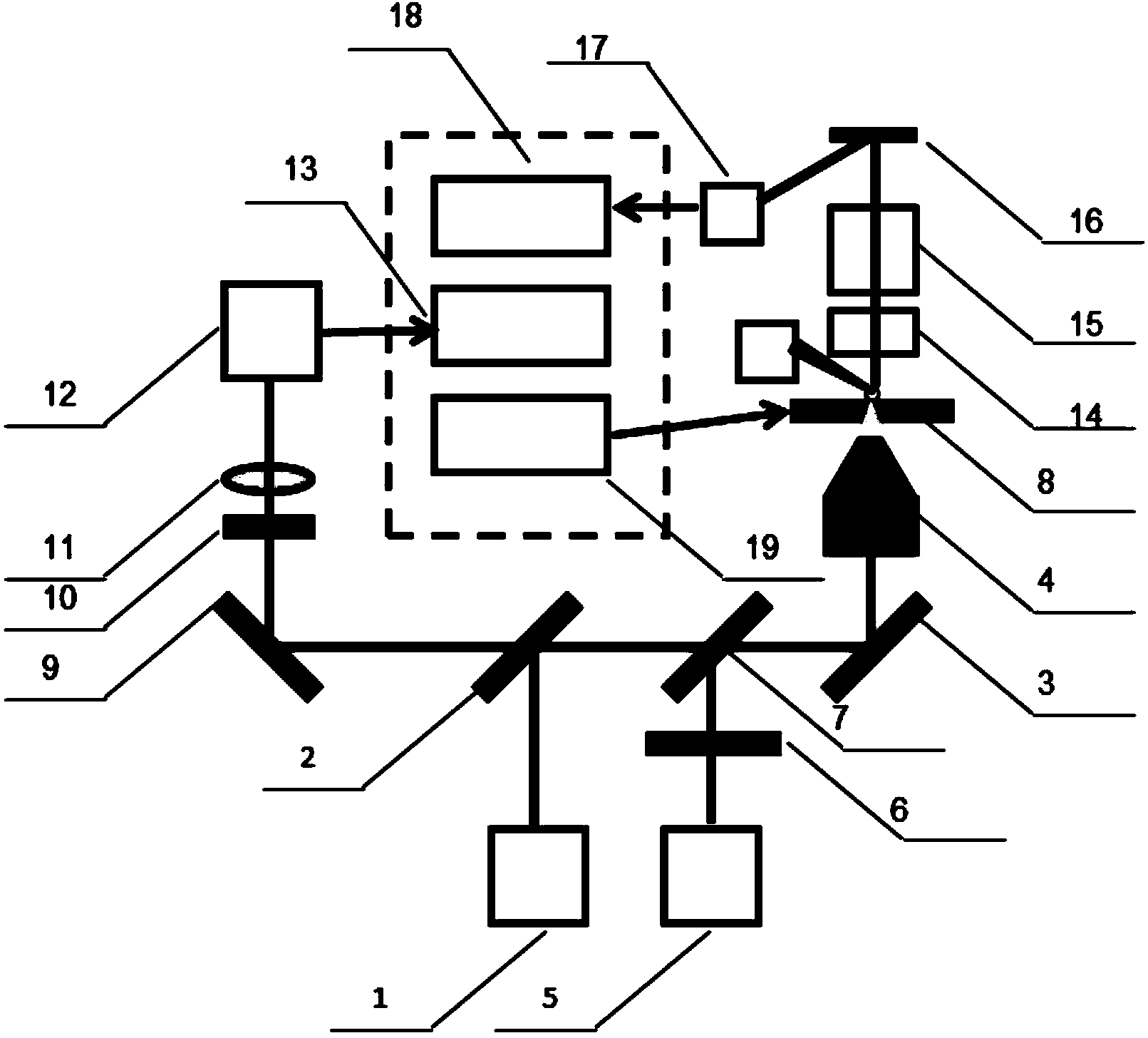
The invention discloses a combined system of a super-resolution confocal optical microscope and a secondary ion mass spectroscopy. According to the combined system, laser output by a laser device a is filtered by a dichroic optical filter a and is converged to a microscope objective; laser output by a laser device b is filtered by a phase plate and a dichroic optical filter b in sequence and then is converged to the microscope objective; the laser converged by the microscope objective irradiates a sample platform to obtain a fluorescence signal of a sample to be detected; the laser is converged by the microscope objective, is collected by a collection lens a, and then is emitted into a photoelectric detector; a photoelectric signal output by the photoelectric detector is input to an optical signal acquisition device; the sample to be detected is bombarded by an ion beam generator to obtain secondary ions; after passing through a pull-out electrode to obtain kinetic energy, the secondary ions are screened by an ion gate and are detected by a reflection detector; a signal output by the reflection detector is input into an SIMS (Secondary Ion Mass Spectroscopy) signal acquisition device; the ion beam generator and the sample platform are connected with a displacement controller. According to the combined system, SIMS imaging and analysis are guided by super-resolution optical imaging; the resolution of the super-resolution confocal optical microscope can be close to that of the SIMS so that the high-precision target spot positioning can be realized.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SEMICON SUBSTRATE TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com