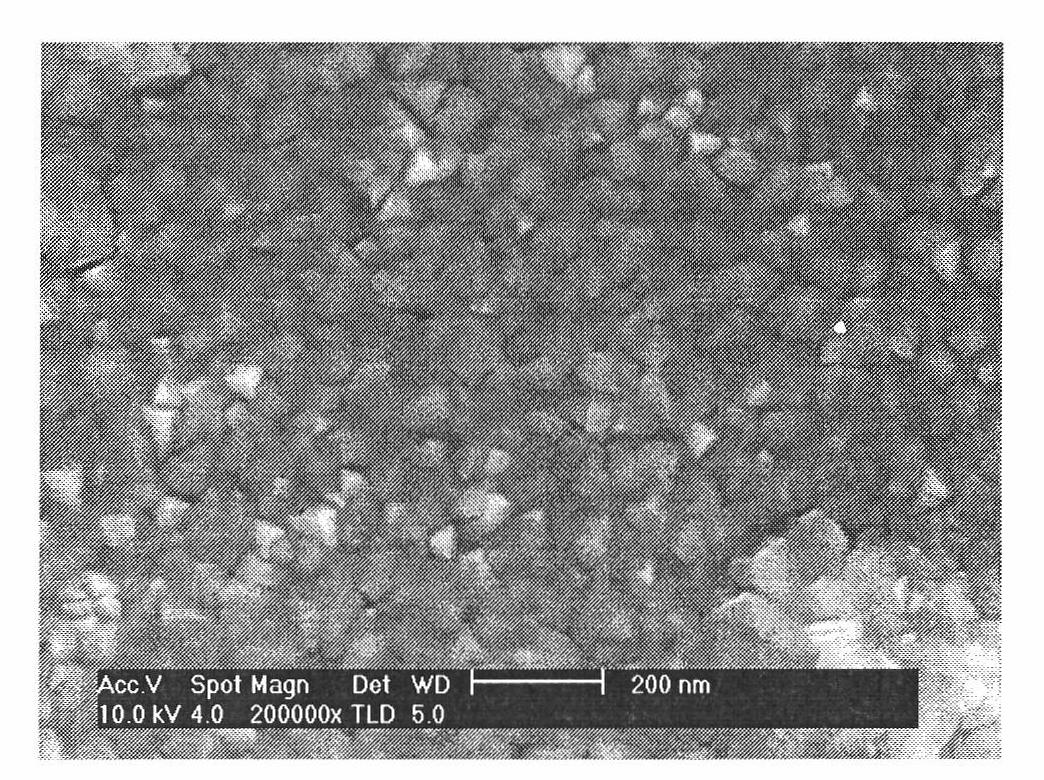
Patents
Literature
781 results about "Ion bombardment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ion bombardment. noun. Physics Chemistry. The fact of being struck by a beam of ions; specifically the process of bombarding a surface with ions (usually ions of an inert gas) as a means of removing impurities.
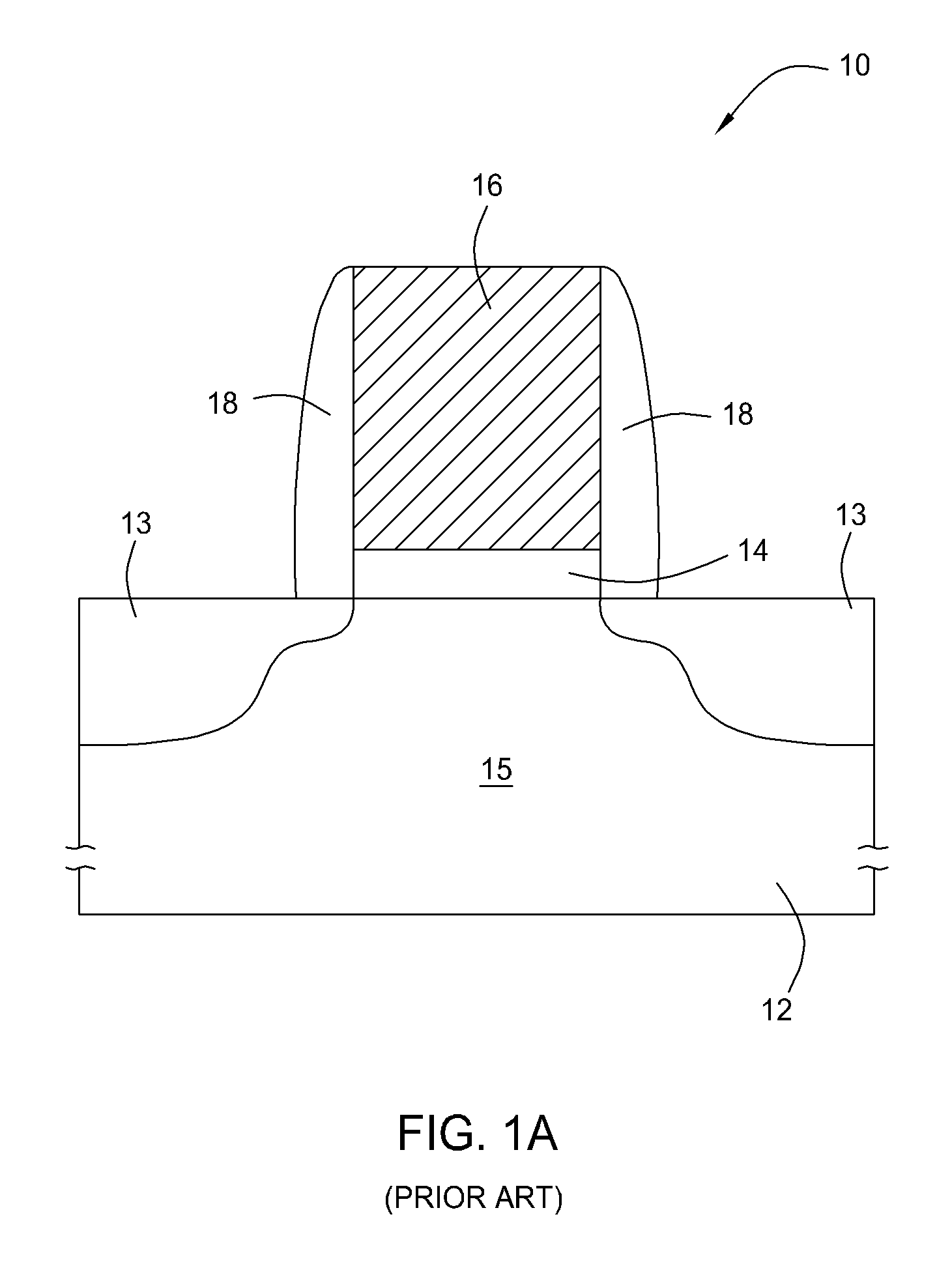
Methods of removing silicon oxide and gaseous mixtures for achieving same
ActiveUS20090275205A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical treatmentPartial oxidation
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
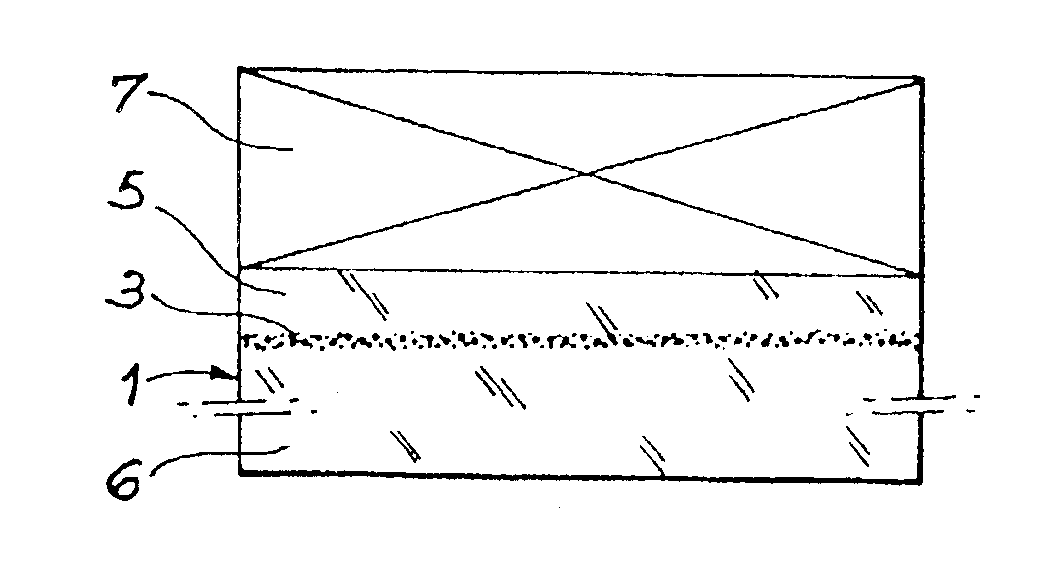
Process for the production of thin semiconductor material films
InactiveUSRE39484E1Uniform and controlled thicknessHigh implantationFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsSolid-state devicesIon bombardmentMicrobubbles
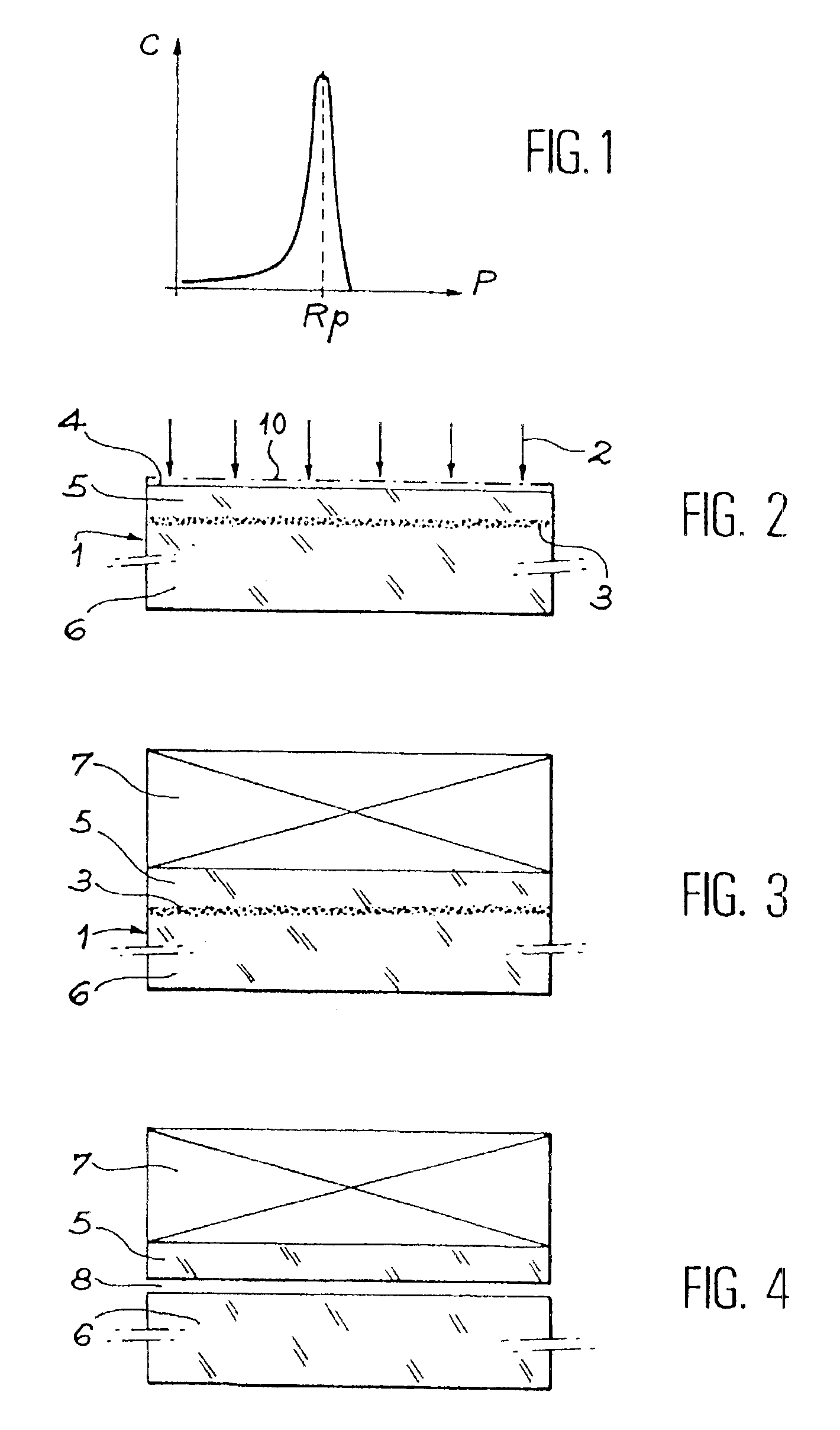
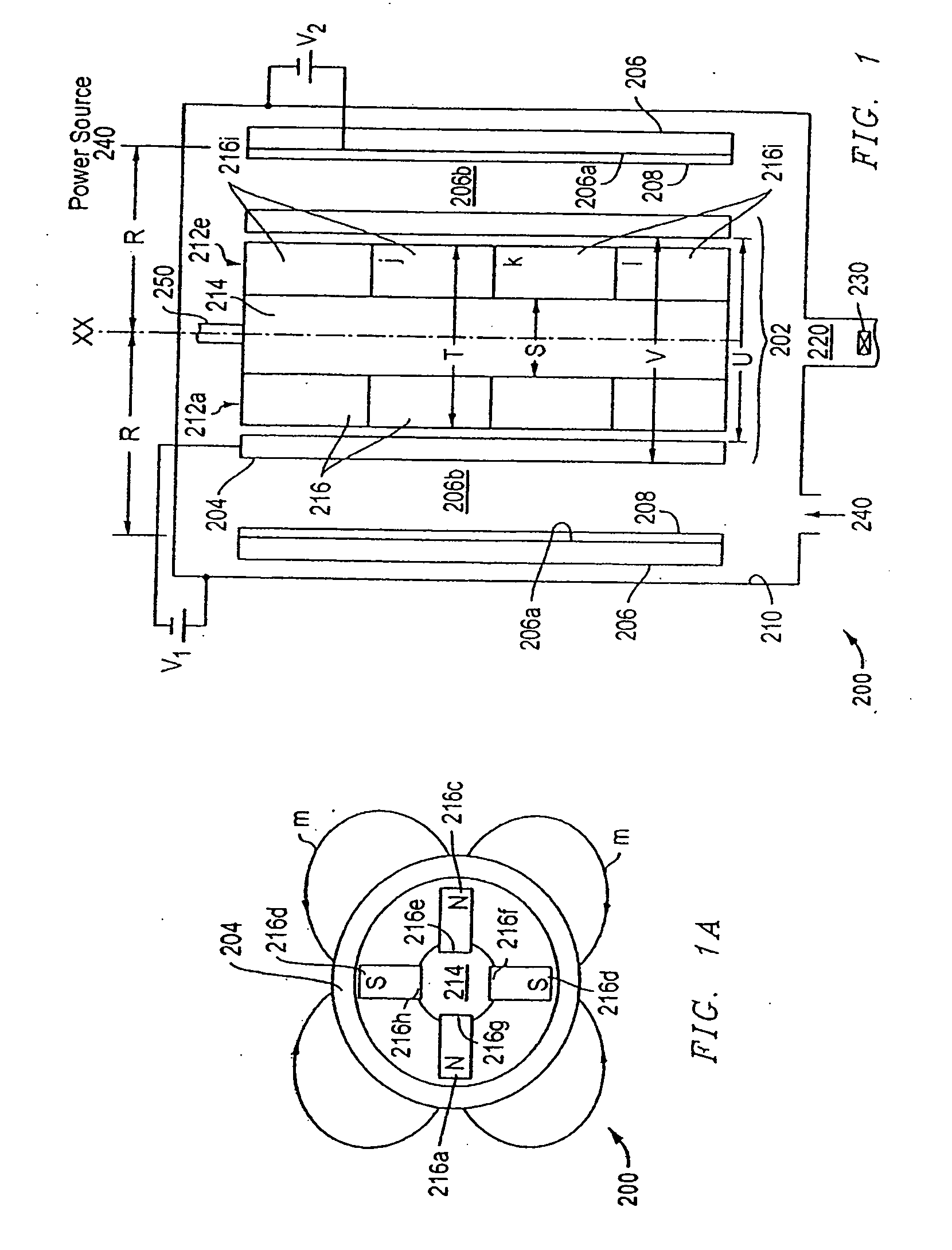
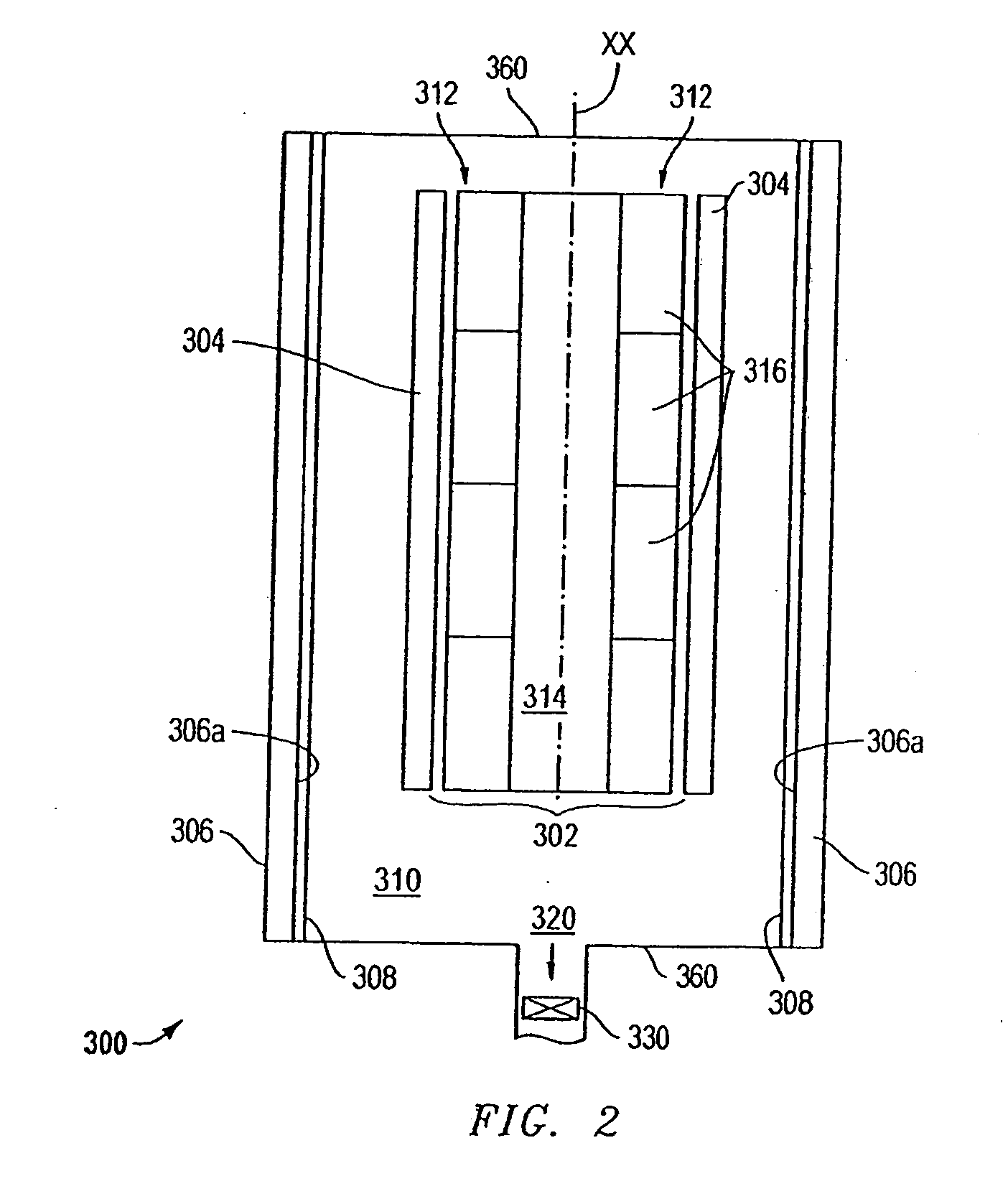
Process for the preparation of thin monocrystalline or polycrystalline semiconductor material films, characterized in that it comprises subjecting a semiconductor material wafer having a planar face to the three following stages: a first stage of implantation by bombardment (2) of the face (4) of the said wafer (1) by means of ions creating in the volume of said wafer a layer (3) of gaseous microbubbles defining in the volume of said wafer a lower region (6) constituting the mass of the substrate and an upper region (5) constituting the thin film, a second stage of intimately contacting the planar face (4) of said wafer with a stiffener (7) constituted by at least one rigid material layer, a third stage of heat treating the assembly of said wafer (1) and said stiffener (7) at a temperature above that at which the ion bombardment (2) was carried out and sufficient to create by a crystalline rearrangement effect in said wafer (1) and a pressure effect in the said microbubbles, a separation between the thin film (5) and the mass of the substrate (6).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method for surface corona/ozone making, devices utilizing the same and methods for corona and ozone applications
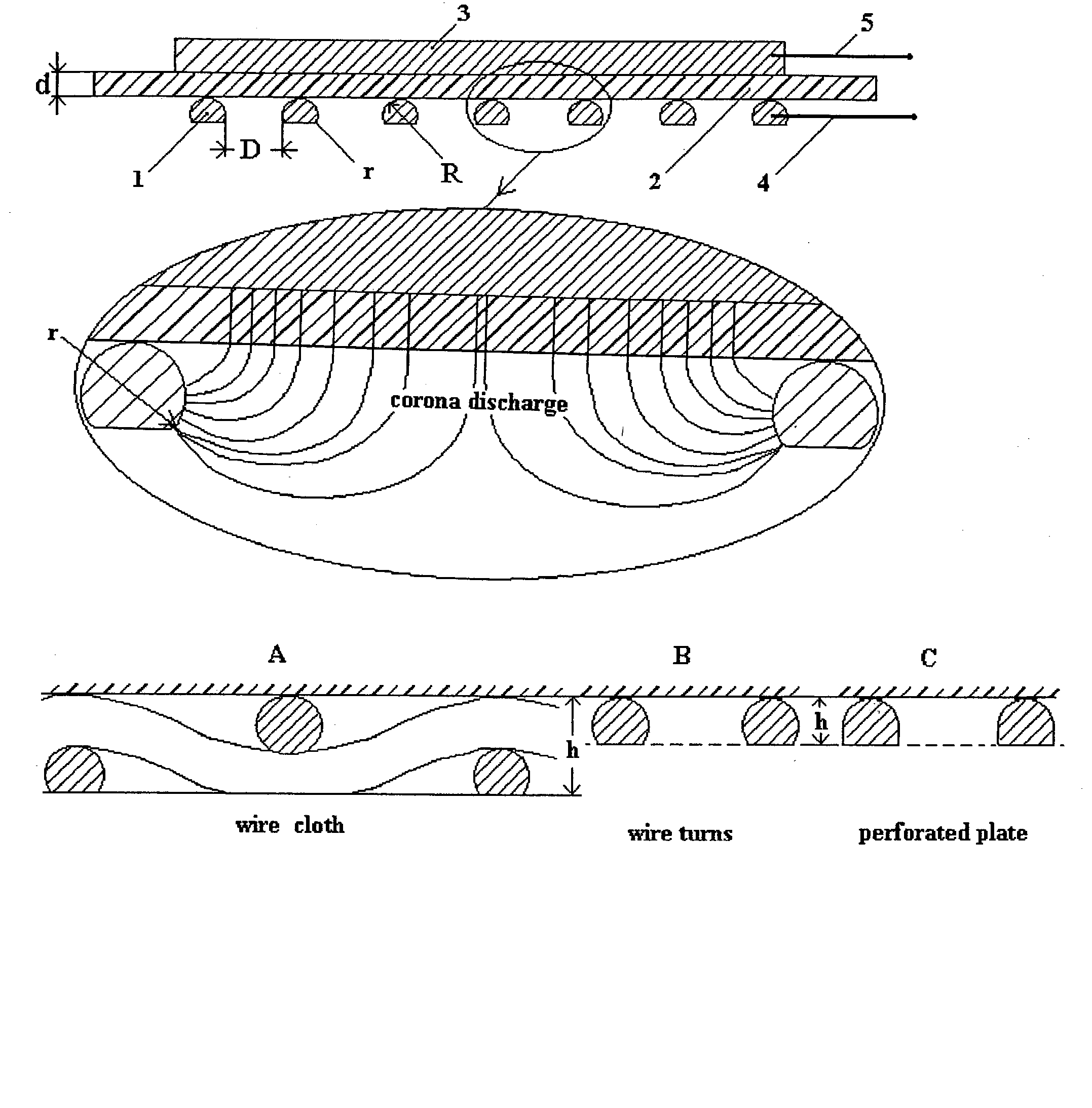
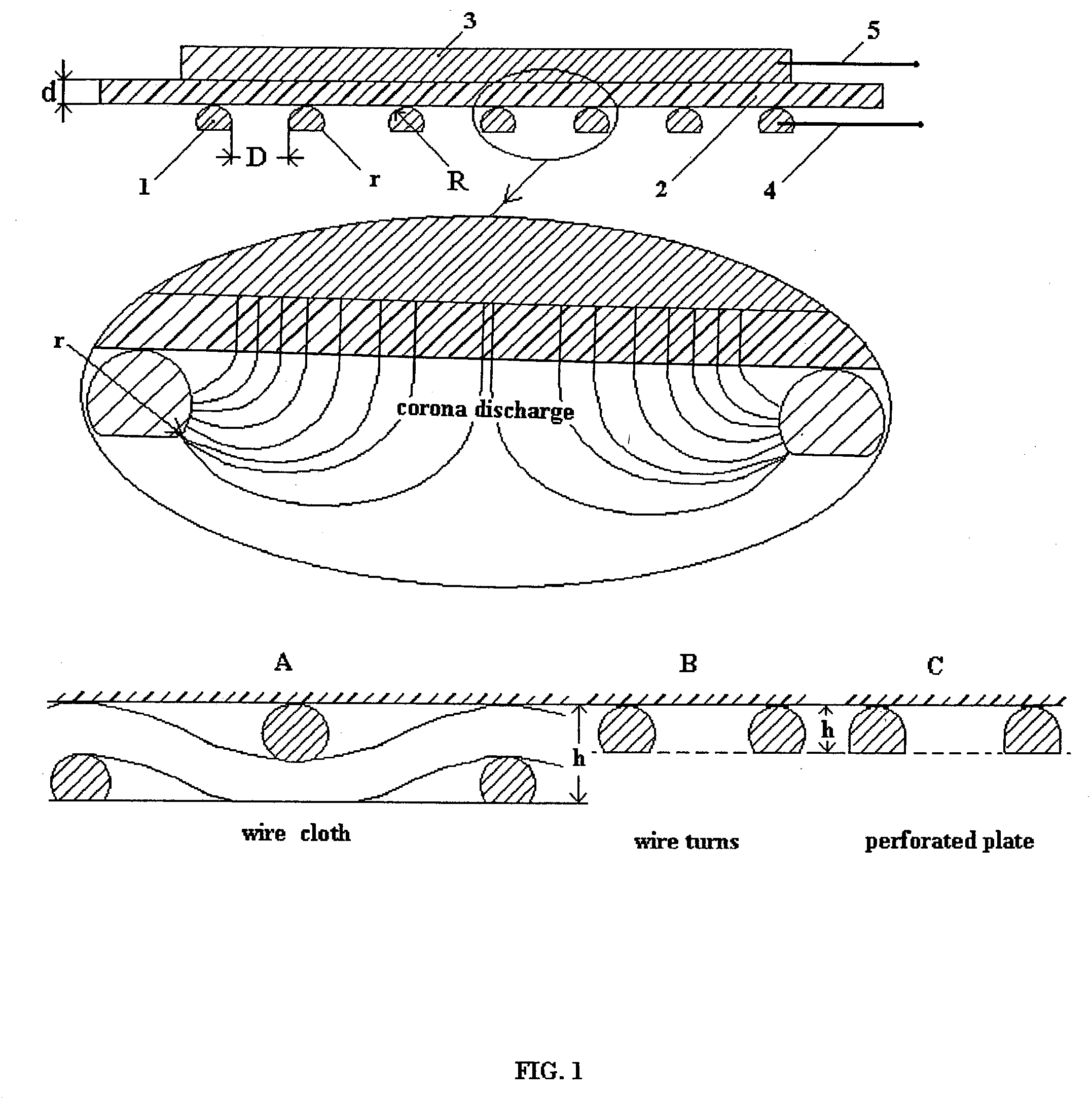
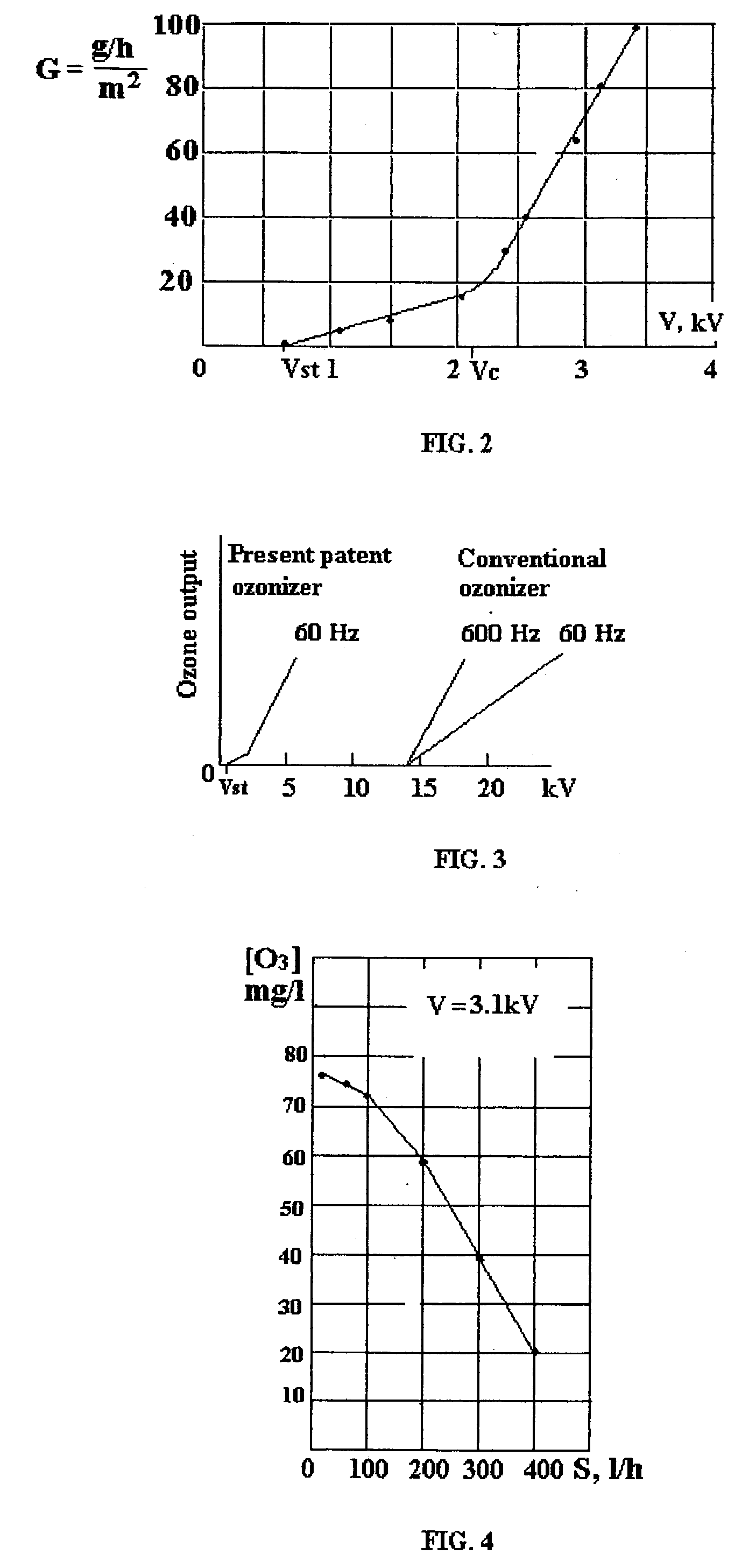
A method for making surface corona discharge, which produces ozone gas and apparatus for producing the same are disclosed, in which a dielectric spacer / film having a specific capacity C' equal to or more than 200 nanofarad per square meter positioned between the base electrode and the net electrode. Said net electrode is a wire net or a perforated metal or a wire winding having an open area not less than about 70%, and a size of hole D equals to or less than about 0.7V / P, where V is a voltage in kilovolts and P is pressure of an ambient air or an oxygen in atmospheres. Net electrode has radius R of wire or radius of an edge of openings in the perforated metal equal to or more than about 1.6d, where d is the thickness of the said dielectric spacer / film, which is determined by a fundamental formula d=9k / C', where d is in millimeters, C' is in nF / m2, and k is dimensionless dielectric constant k of given material. Under disclosed parameters said surface corona is safe for human contact if said net electrode is grounded. Start voltage Vst of ozone production is determined by experimental formula Vst=0.7+60 / C', kV, here C' in nF / m2. The even and high intensity corona surface and high ozone output takes place if the operating voltage is more than about 3Vst. AC power supply is applied to produce ozone gas at "home" voltage 0.7-1.0 kV and produces ozone gas more effectively at 2,5-3.6 kV. A method for disinfection and decontamination of objects by using the direct corona contact and apparatus for making the same is disclosed, in which safe corona surface is placed on said object and is acting by ozone, ultraviolet and ion bombing simultaneously in the unique environment, which takes place inside of the safe corona. A method for ozone disinfection and decontamination and devices for making the same is disclosed, in which said ozone generating element is placed in a closed container / room with or without treated objects and produce a high ozone concentration due to effective ozone dispersion from corona surface without blowing of air / oxygen through said container / room.
Owner:ANDREEV SERGEY I +1
Method and system for coating internal surfaces of prefabricated process piping in the field
ActiveUS7300684B2Improve adhesionIncreases magnitudeLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingHydrocarbon mixturesDiamond-like carbon
The coating of internal surfaces of a workpiece is achieved by connecting a bias voltage such that the workpiece functions as a cathode and by connecting an anode at each opening of the workpiece. A source gas is introduced at an entrance opening, while a vacuum source is connected at an exit opening. Pressure within the workpiece is monitored and the resulting pressure information is used for maintaining a condition that exhibits the hollow cathode effect. Optionally, a pre-cleaning may be provided by introducing a hydrocarbon mixture and applying a negative bias to the workpiece, so as to sputter contaminants from the workpiece using argon gas. Argon gas may also be introduced during the coating processing to re-sputter the coating, thereby improving uniformity along the length of the workpiece. The coating may be a diamond-like carbon material having properties which are determined by controlling ion bombardment energy.
Owner:AGM CONTAINER CONTROLS
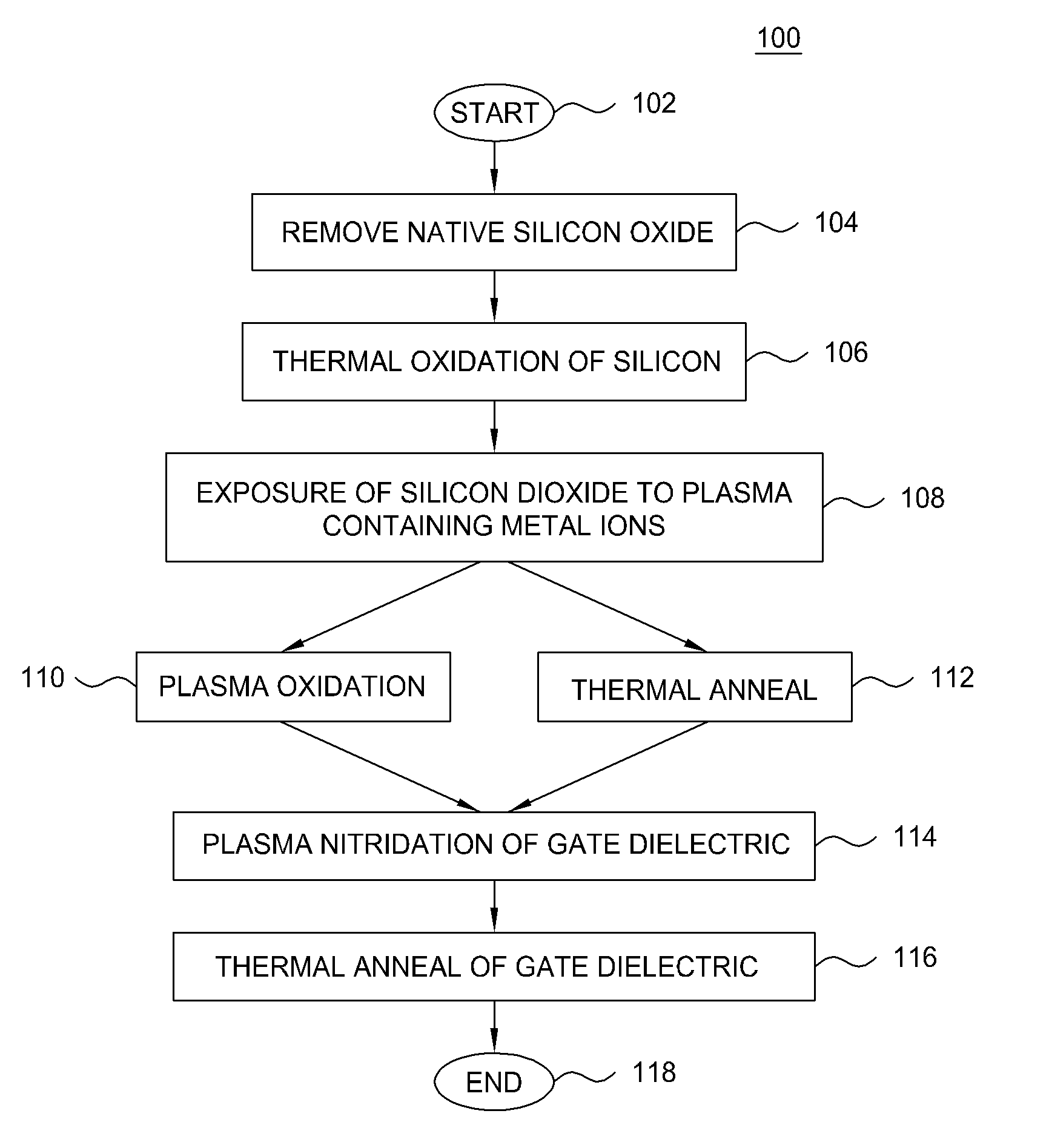
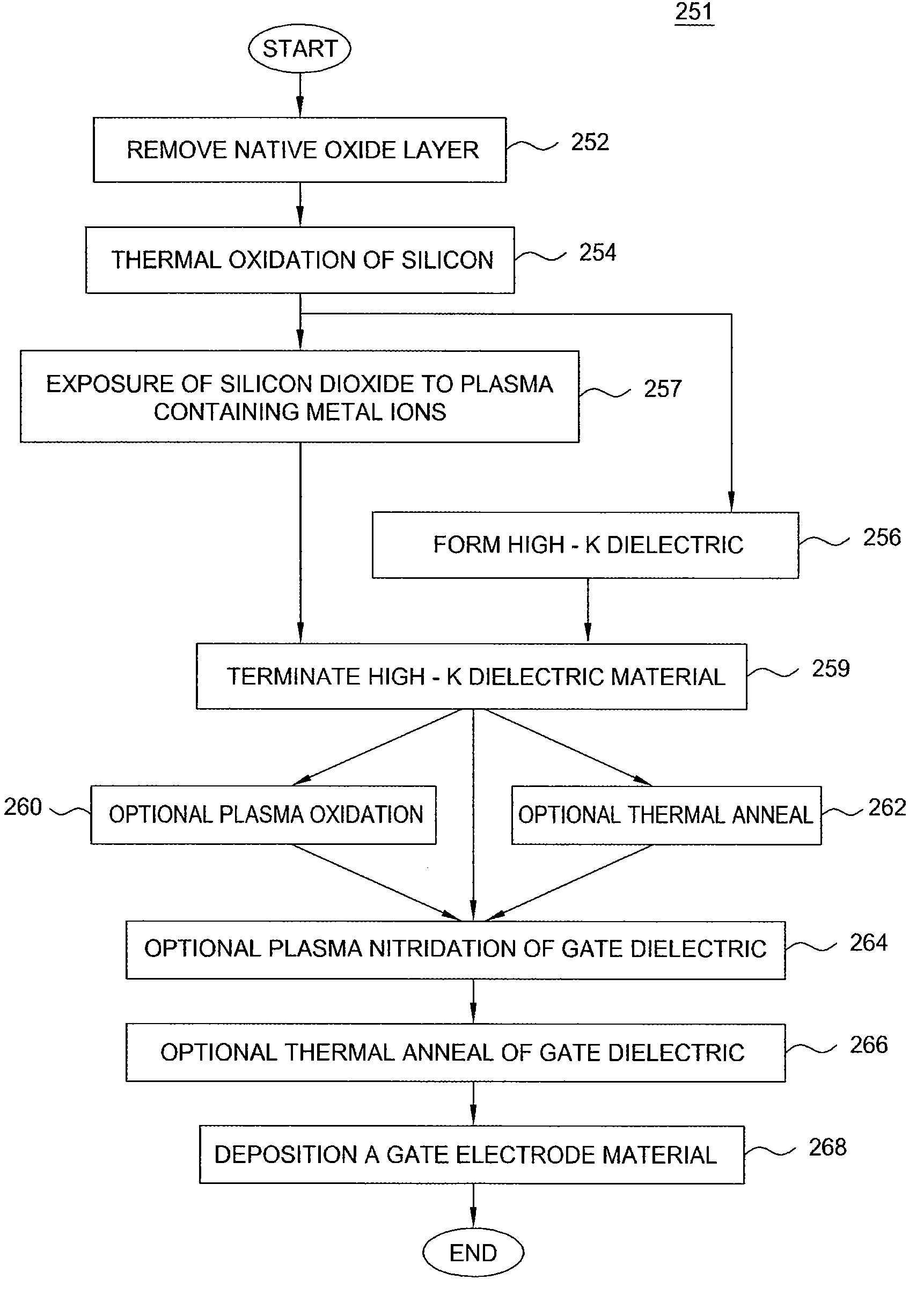
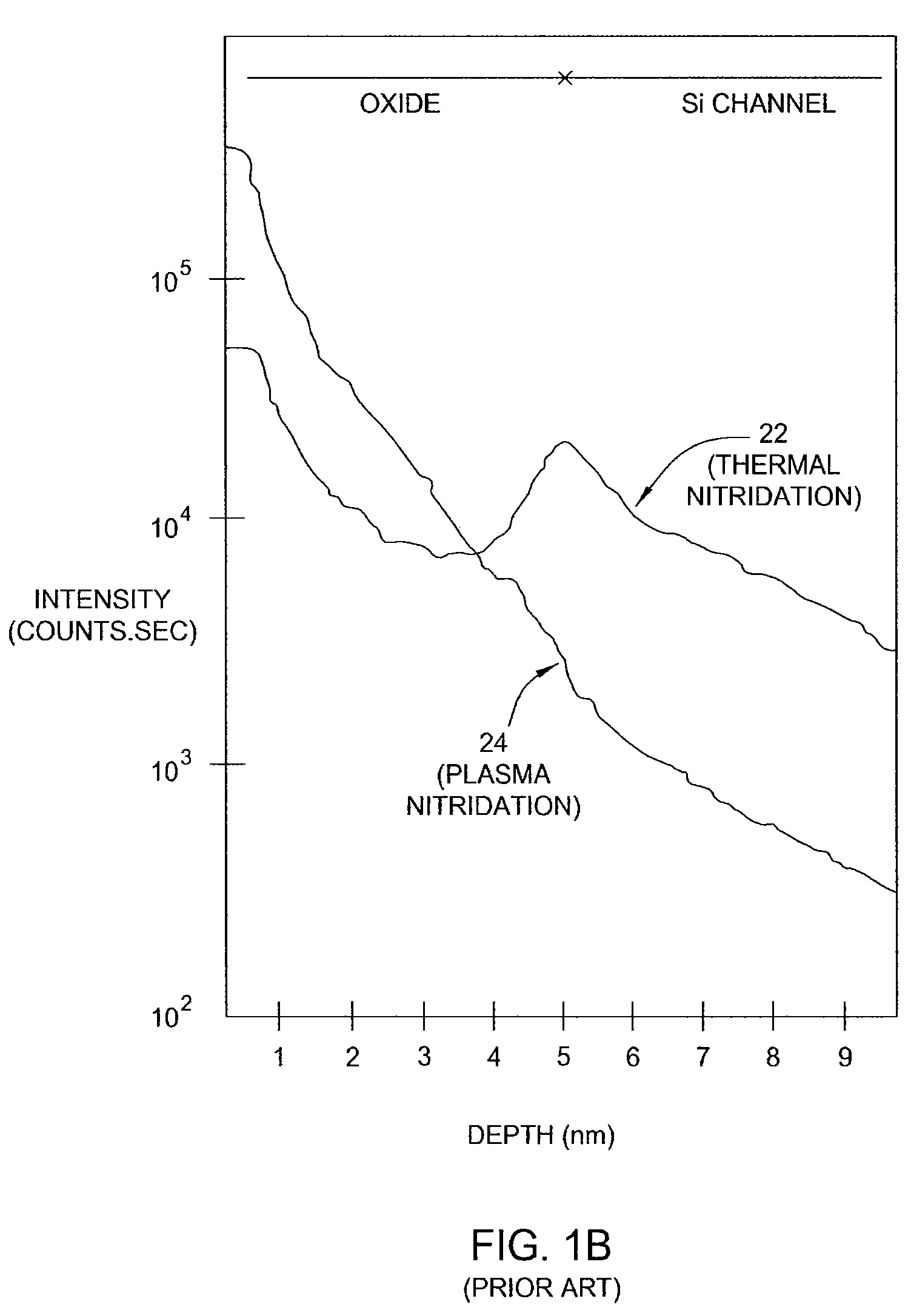
Method of fabricating a high dielectric constant transistor gate using a low energy plasma apparatus
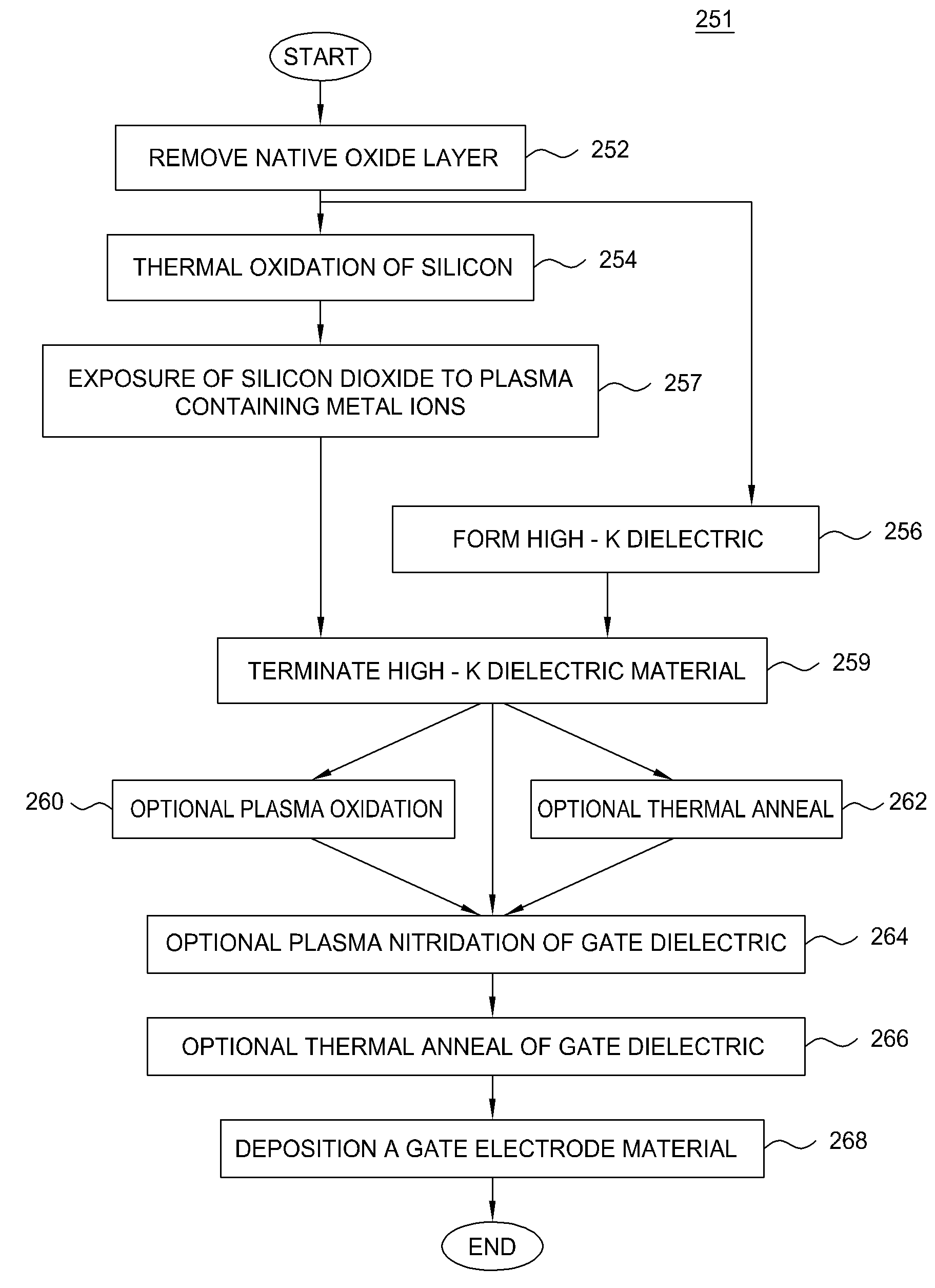
The present invention generally provides methods and apparatuses that are adapted to form a high quality dielectric gate layer on a substrate. Embodiments contemplate a method wherein a metal plasma treatment process is used in lieu of a standard nitridization process to form a high dielectric constant layer on a substrate. Embodiments further contemplate an apparatus adapted to “implant” metal ions of relatively low energy in order to reduce ion bombardment damage to the gate dielectric layer, such as a silicon dioxide layer and to avoid incorporation of the metal atoms into the underlying silicon. In general, the process includes the steps of forming a high-k dielectric and then terminating the surface of the deposited high-k material to form a good interface between the gate electrode and the high-k dielectric material. Embodiments of the invention also provide a cluster tool that is adapted to form a high-k dielectric material, terminate the surface of the high-k dielectric material, perform any desirable post treatment steps, and form the polysilicon and / or metal gate layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
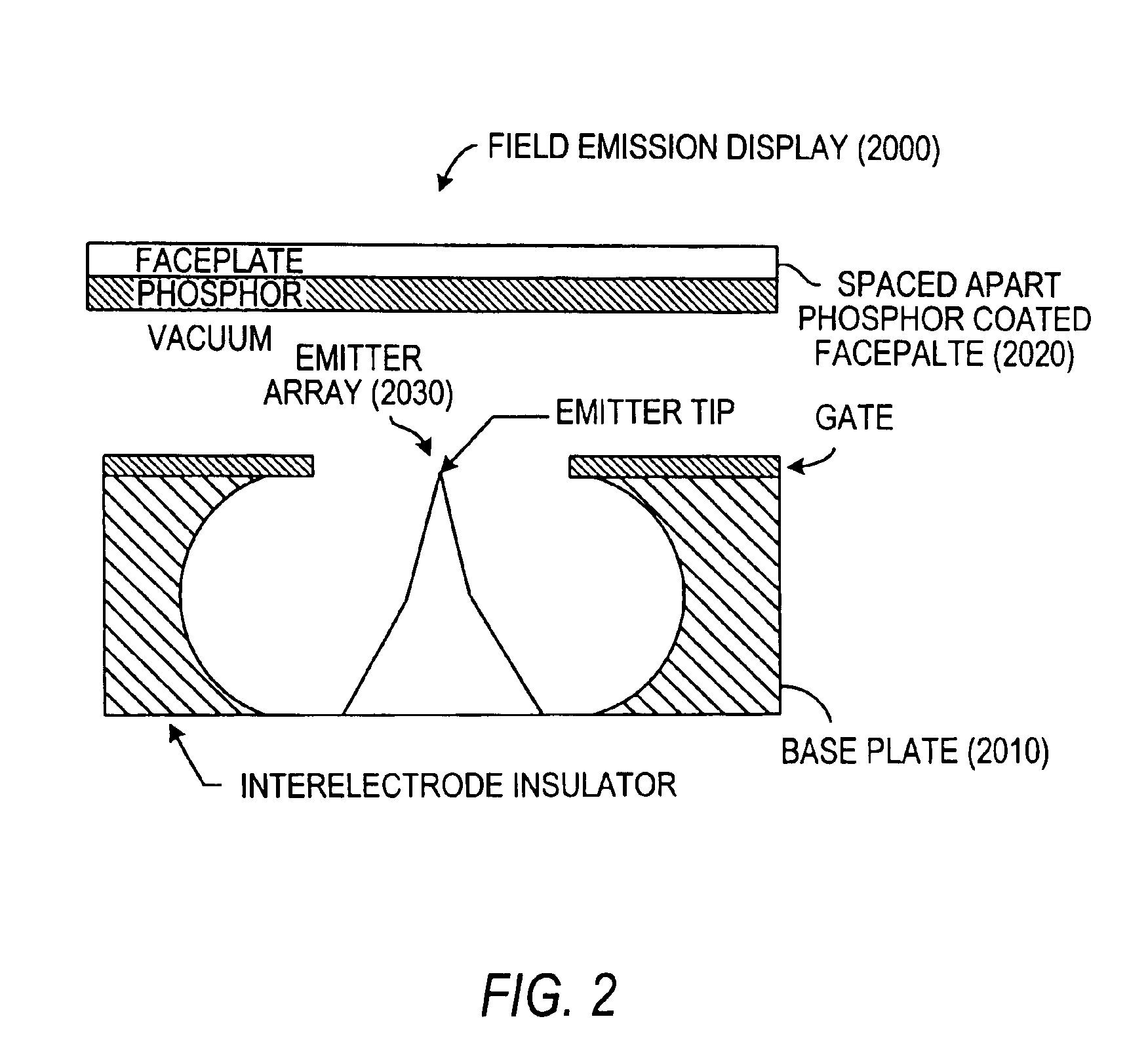
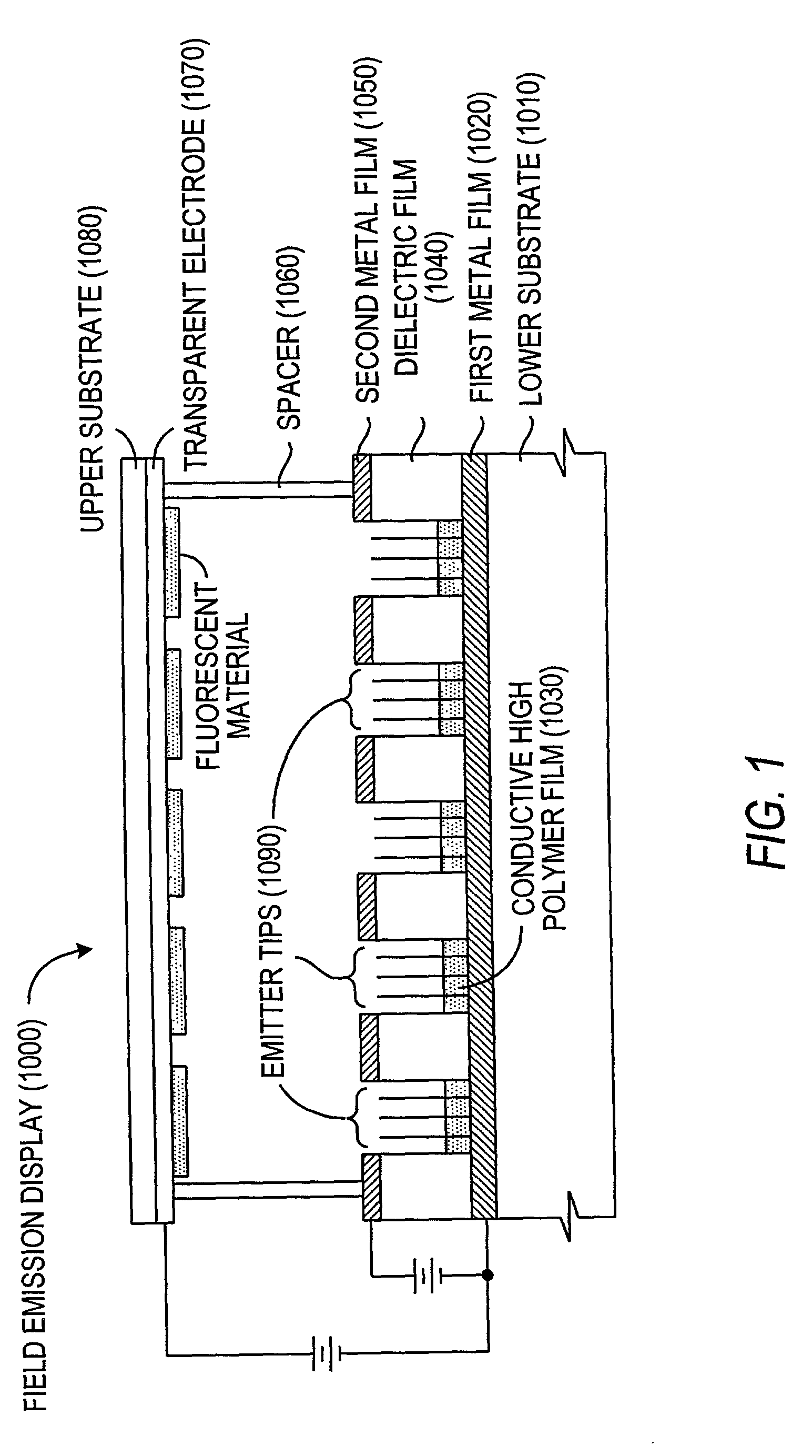
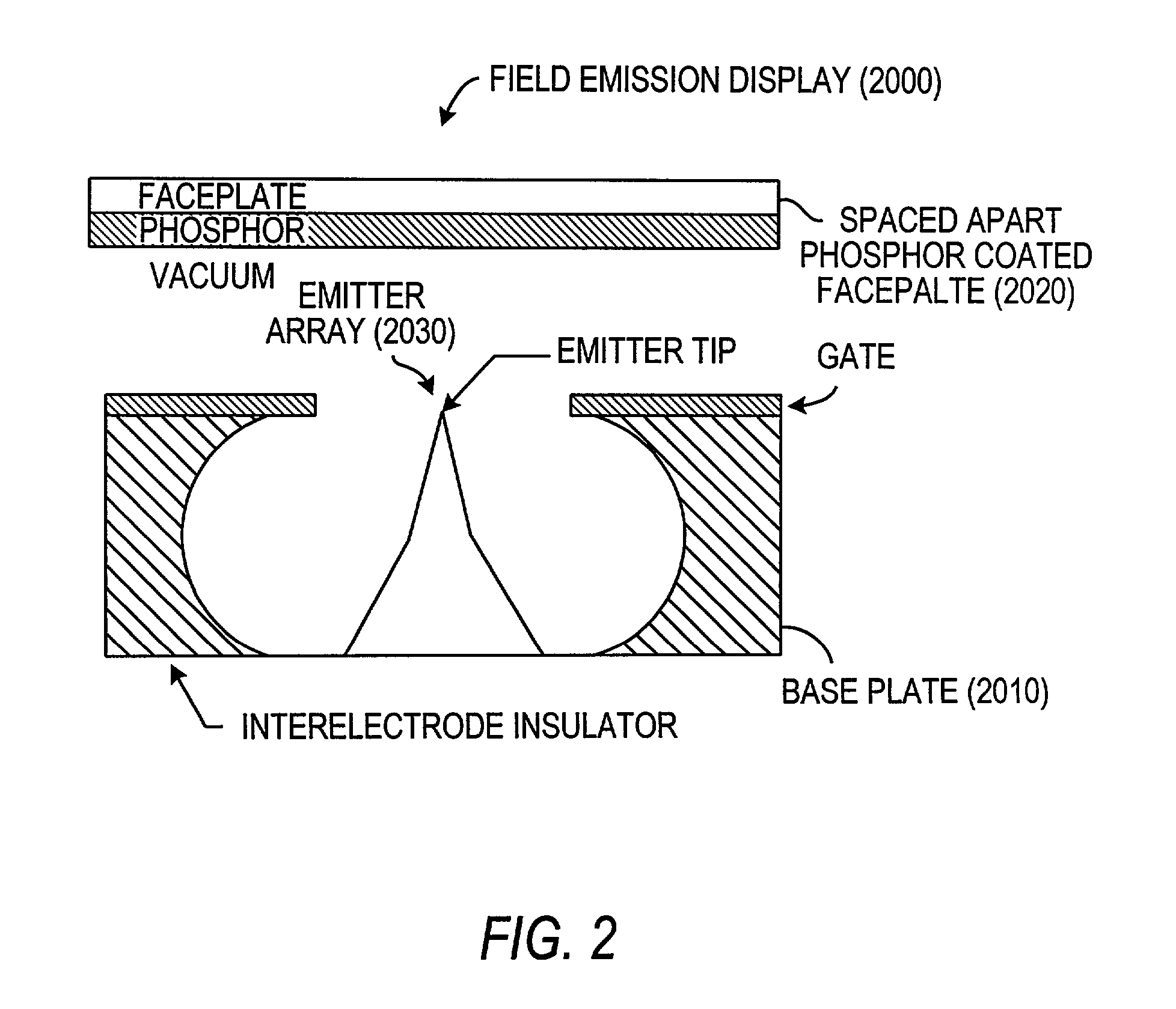
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6911767B2Reduce voltageAccelerate emissionsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Method and apparatus for fabricating a high dielectric constant transistor gate using a low energy plasma system
InactiveUS20070212896A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricGate dielectric
The present invention generally provides methods and apparatuses that are adapted to form a high quality dielectric gate layer on a substrate. Embodiments contemplate a method wherein a metal plasma treatment process is used in lieu of a standard nitridization process to form a high dielectric constant layer on a substrate. Embodiments further contemplate an apparatus adapted to “implant” metal ions of relatively low energy in order to reduce ion bombardment damage to the gate dielectric layer, such as a silicon dioxide layer and to avoid incorporation of the metal atoms into the underlying silicon. In general, the process includes the steps of forming a high-k dielectric and then terminating the surface of the deposited high-k material to form a good interface between the gate electrode and the high-k dielectric material.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
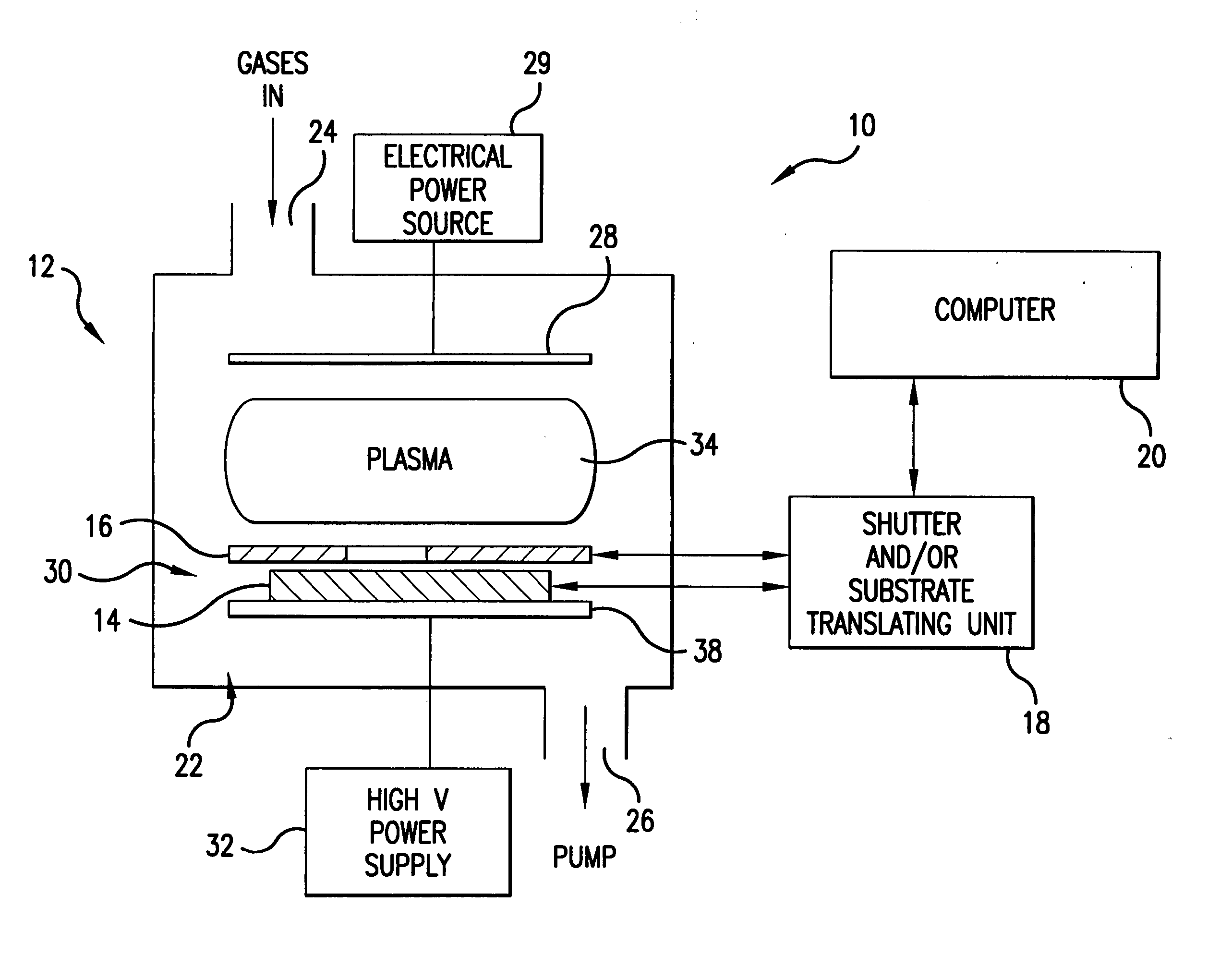
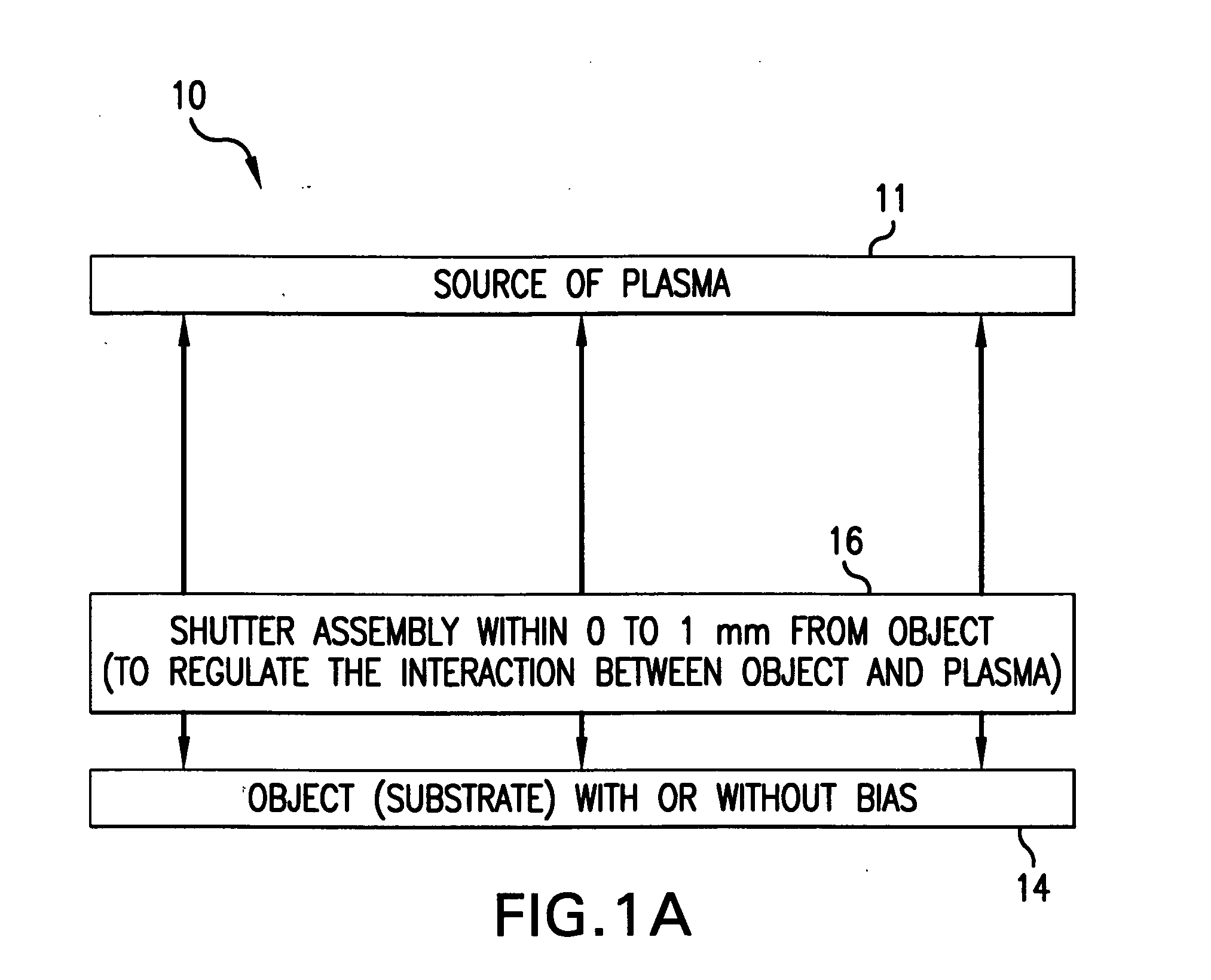
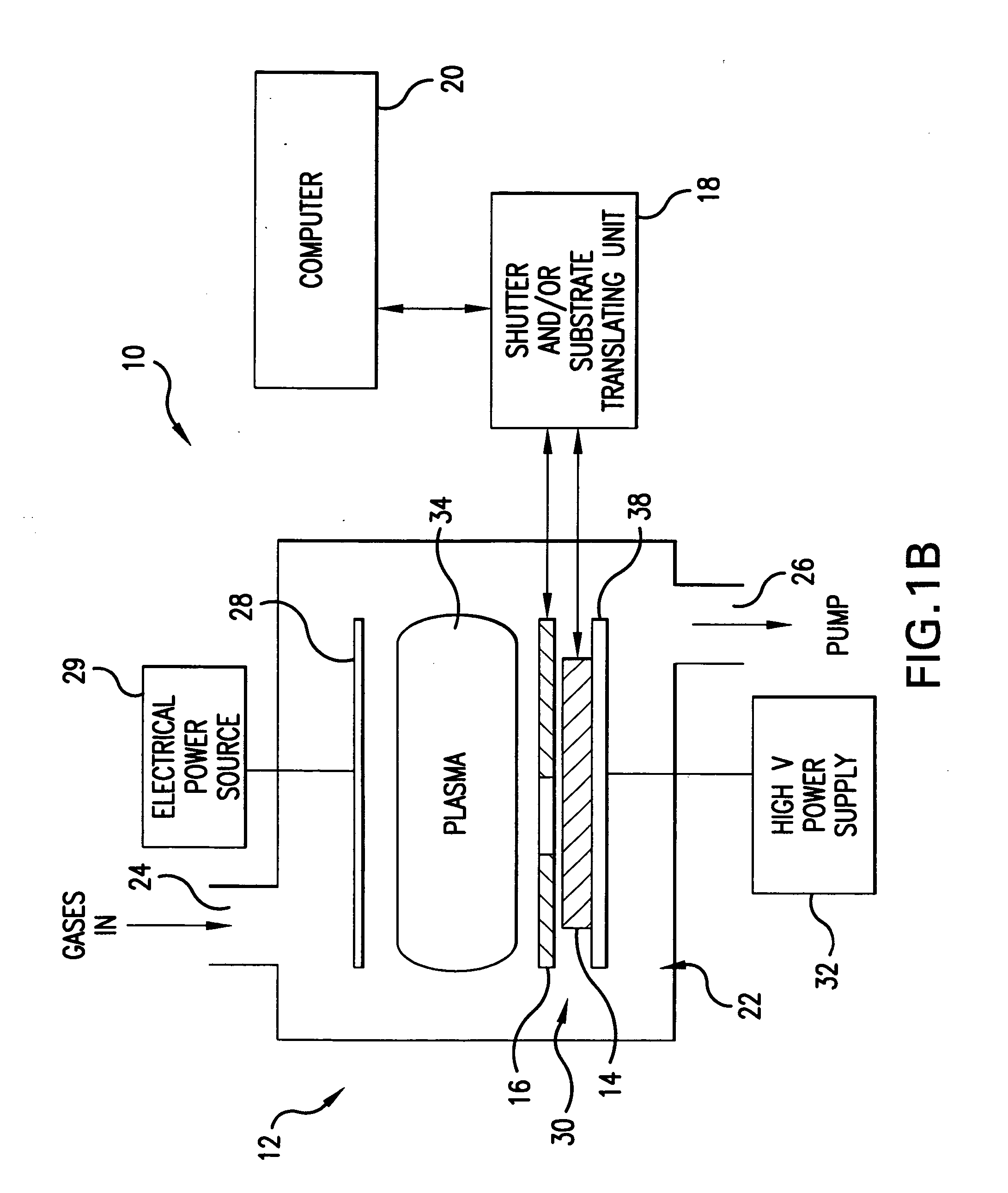
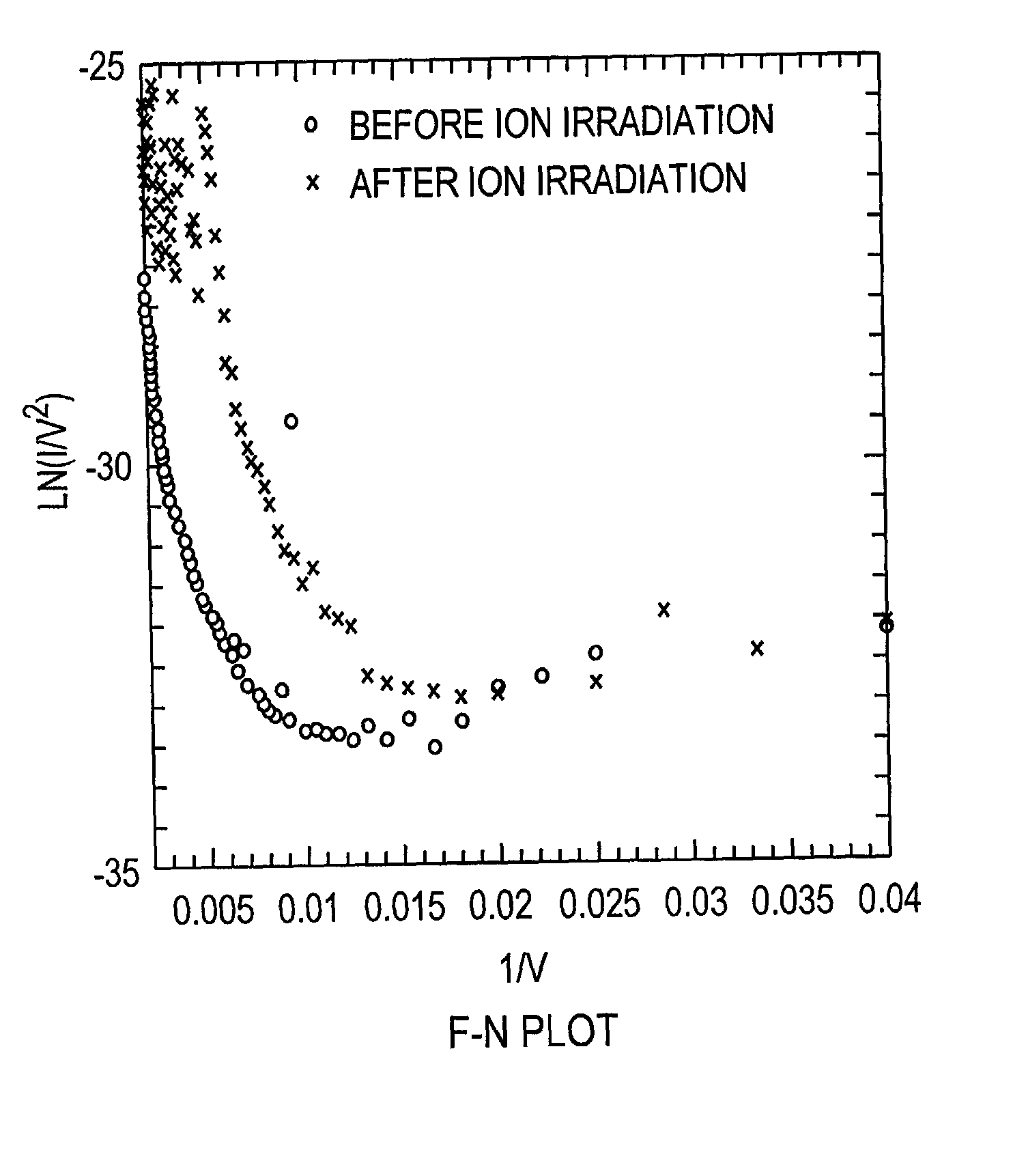
Method and system for nanoscale plasma processing of objects
InactiveUS20050051517A1Permit control of interactionPrecise, short time, nanoscale plasma processingCellsElectric discharge tubesInteraction timeDebye
A plasma processing system includes a source of plasma, a substrate and a shutter positioned in close proximity to the substrate. The substrate / shutter relative disposition is changed for precise control of substrate / plasma interaction. This way, the substrate interacts only with a fully established, stable plasma for short times required for nanoscale processing of materials. The shutter includes an opening of a predetermined width, and preferably is patterned to form an array of slits with dimensions that are smaller than the Debye screening length. This enables control of the substrate / plasma interaction time while avoiding the ion bombardment of the substrate in an undesirable fashion. The relative disposition between the shutter and the substrate can be made either by moving the shutter or by moving the substrate.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS20030044519A1Easy to disassembleReduce voltageCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
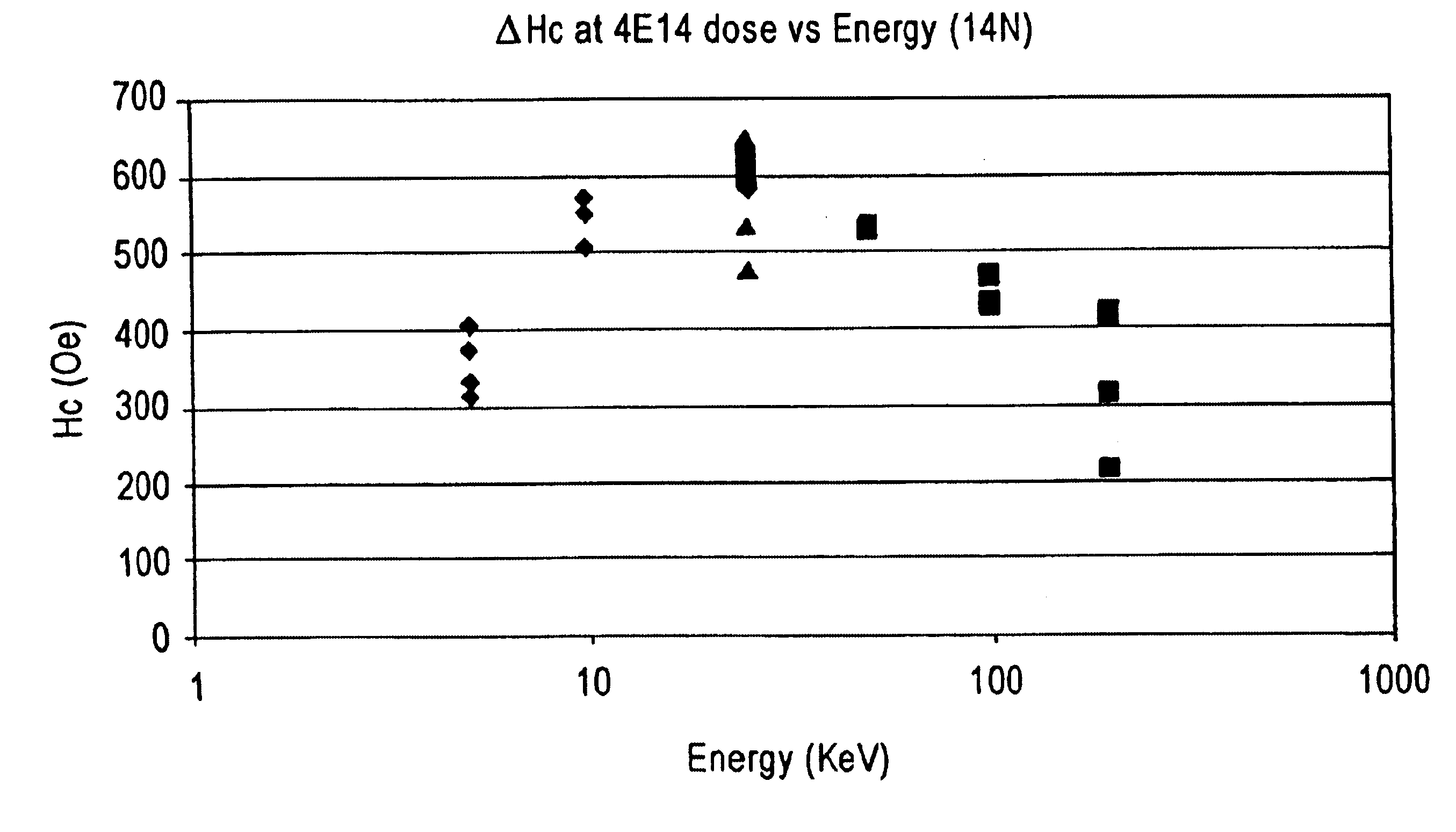
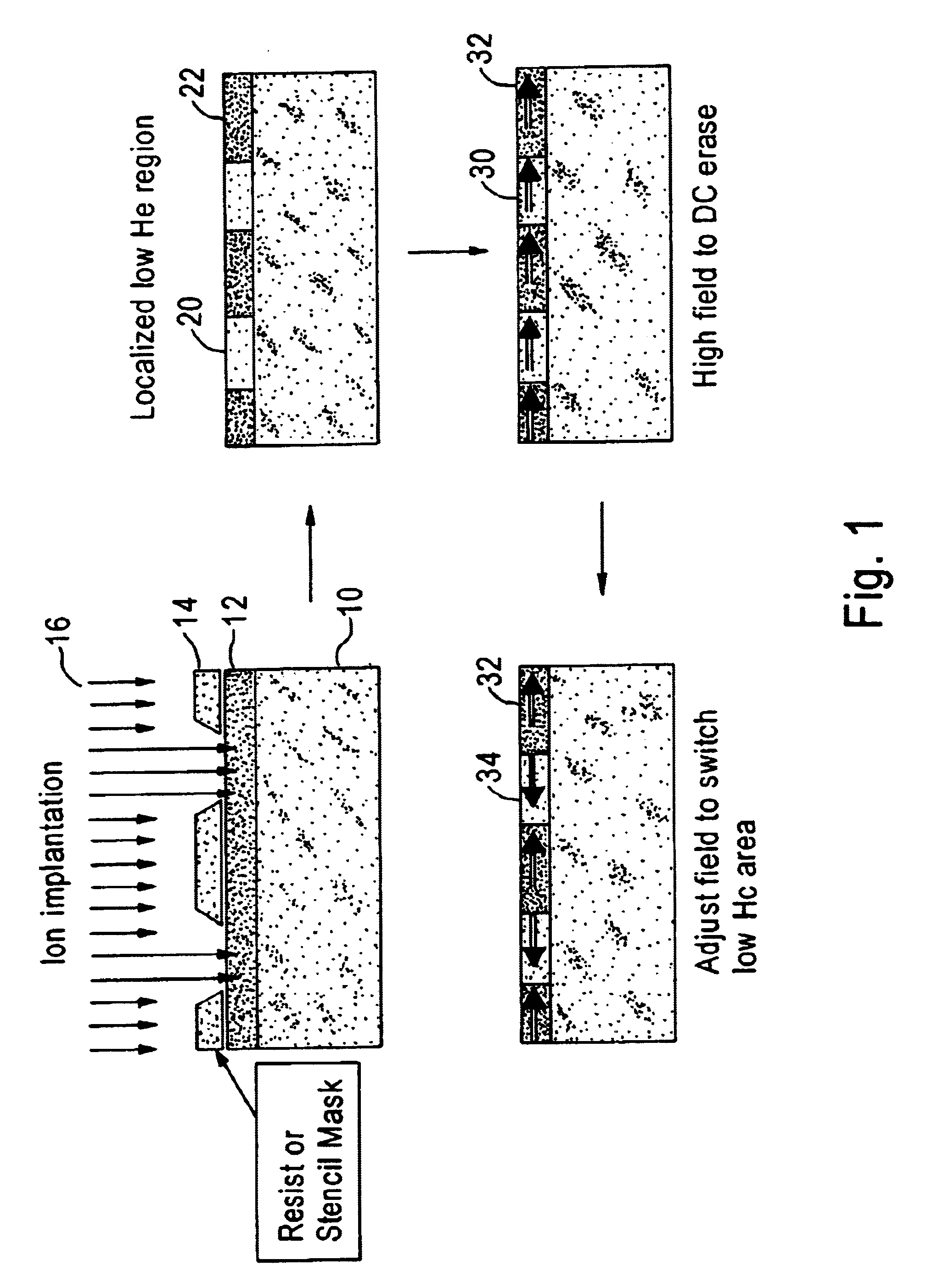
Patterning longitudinal magnetic recording media with ion implantation
InactiveUS6864042B1Increased areal recording densityUniform surfaceNanoinformaticsPatterned record carriersIon bombardmentTopography
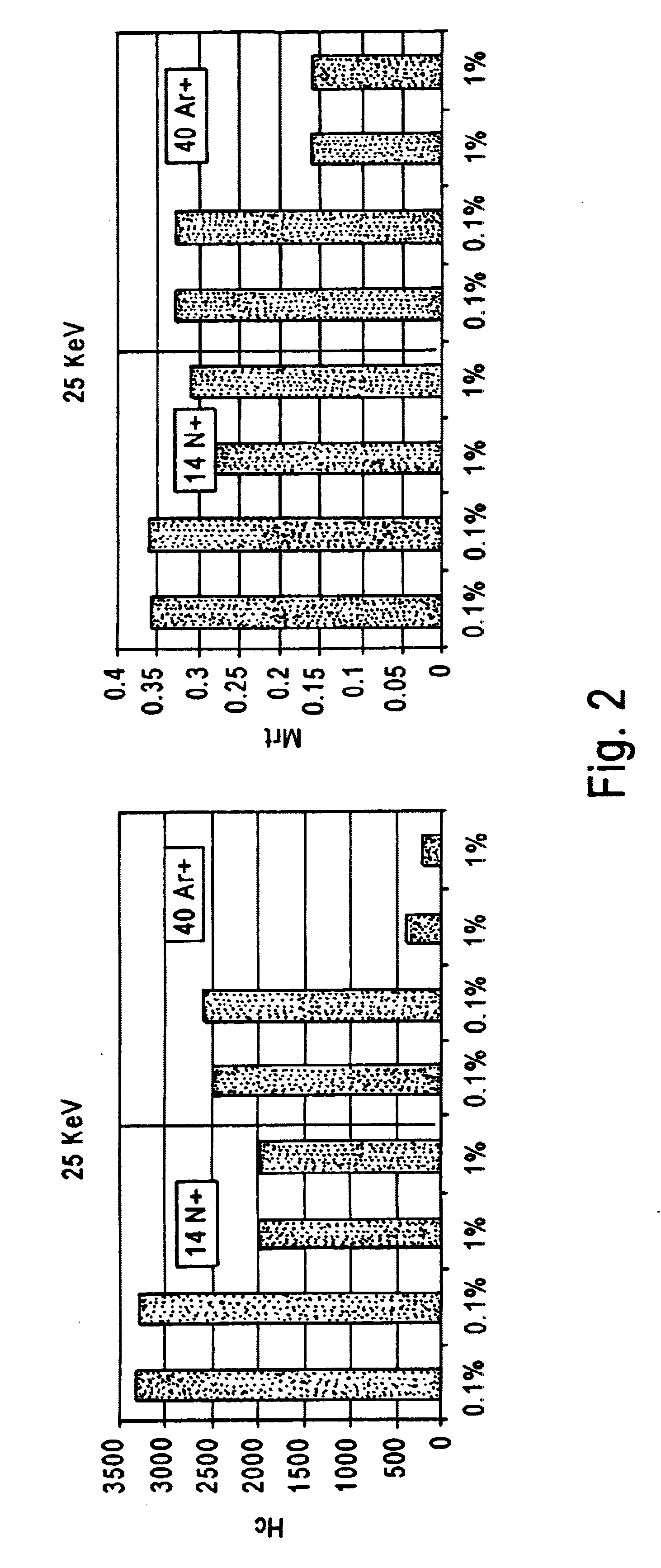
A magnetic recording medium is formed with a distribution of low coercivity regions functioning as a transition pattern for servo information capable of being sensed by a read / write head by exposing a masked magnetic layer to ions to change the coercivity of the exposed magnetic layer without substantially affecting the topography of the magnetic layer.Embodiments of the present invention include forming a series of substantially radially extending low coercivity regions used to divide the magnetic layer into a plurality of sectors comprising substantially concentric circumferentially extending data tracks by exposing a masked magnetic layer having a high coercivity, i.e. from about 2000 Oe to about 10000 Oe, to one or more heavy atom ion bombardments of gaseous ions, e.g. argon ions, at a dose of about 1×1013 atoms / cm2 to about 9×1015 atoms / cm2 having an implantation energy of about 10 KeV to about 50 KeV.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Biological functionalisation of substrates
InactiveUS20100227372A1Improve surface stabilityMaintaining conformationLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkPolymeric surface
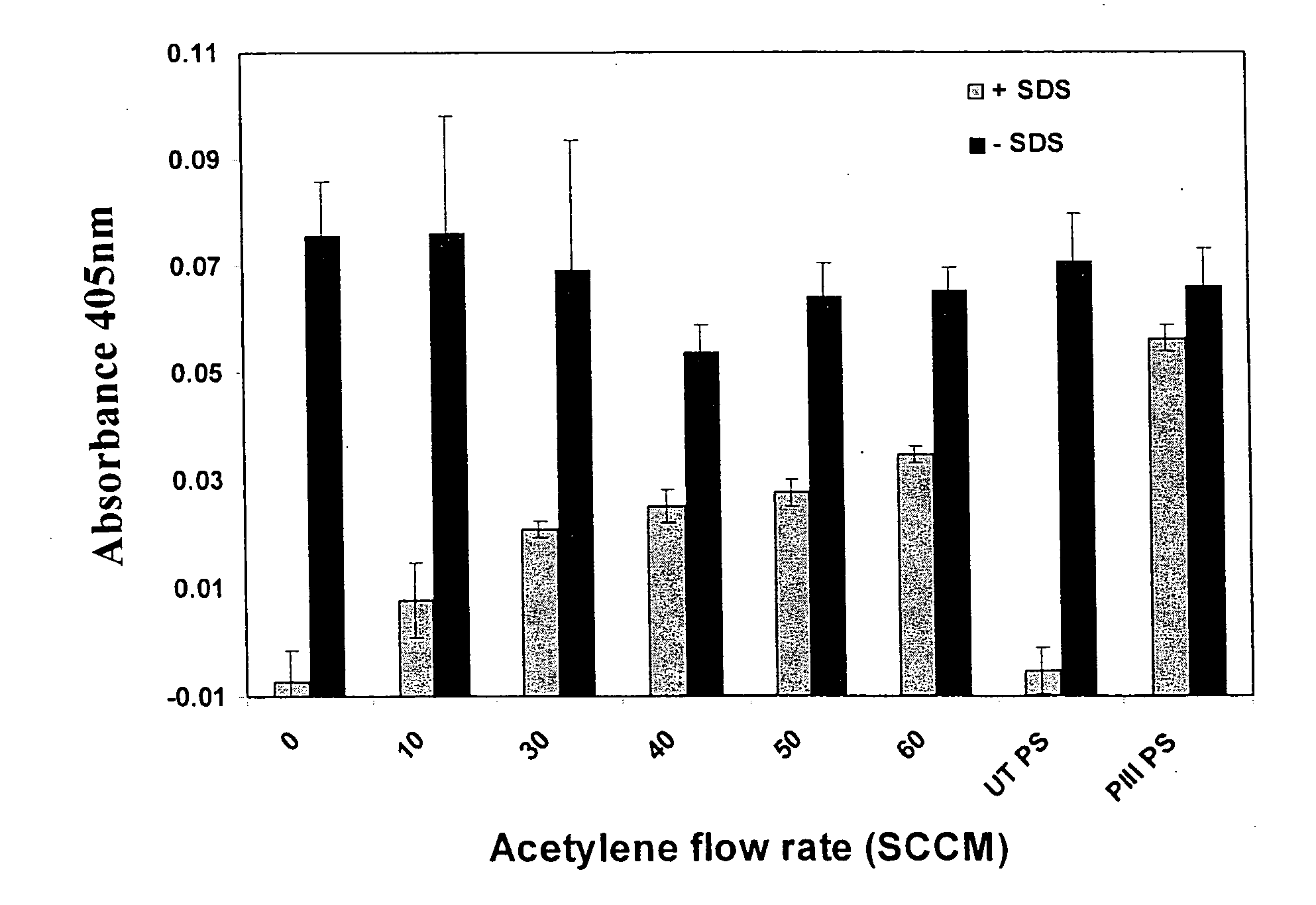
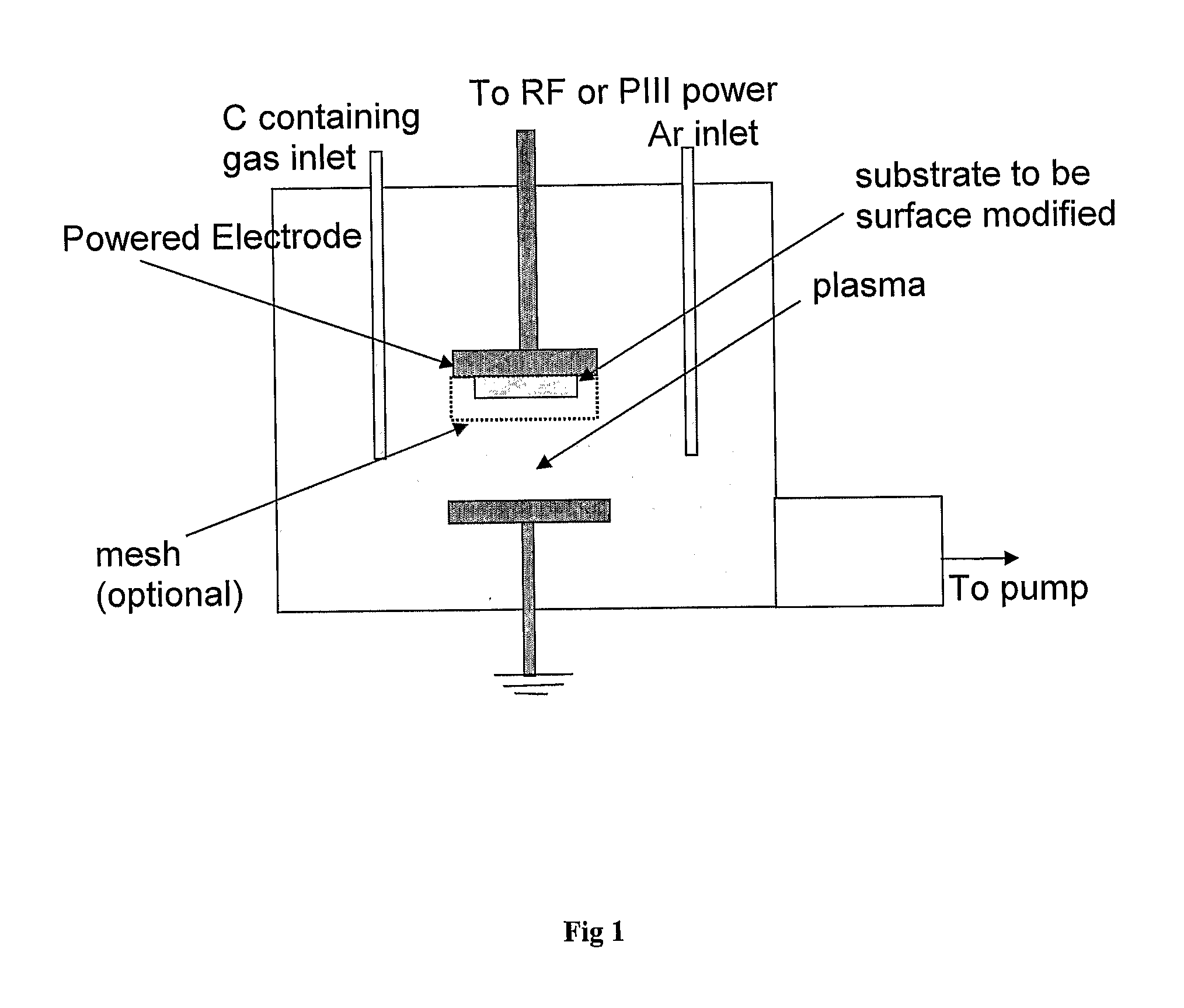
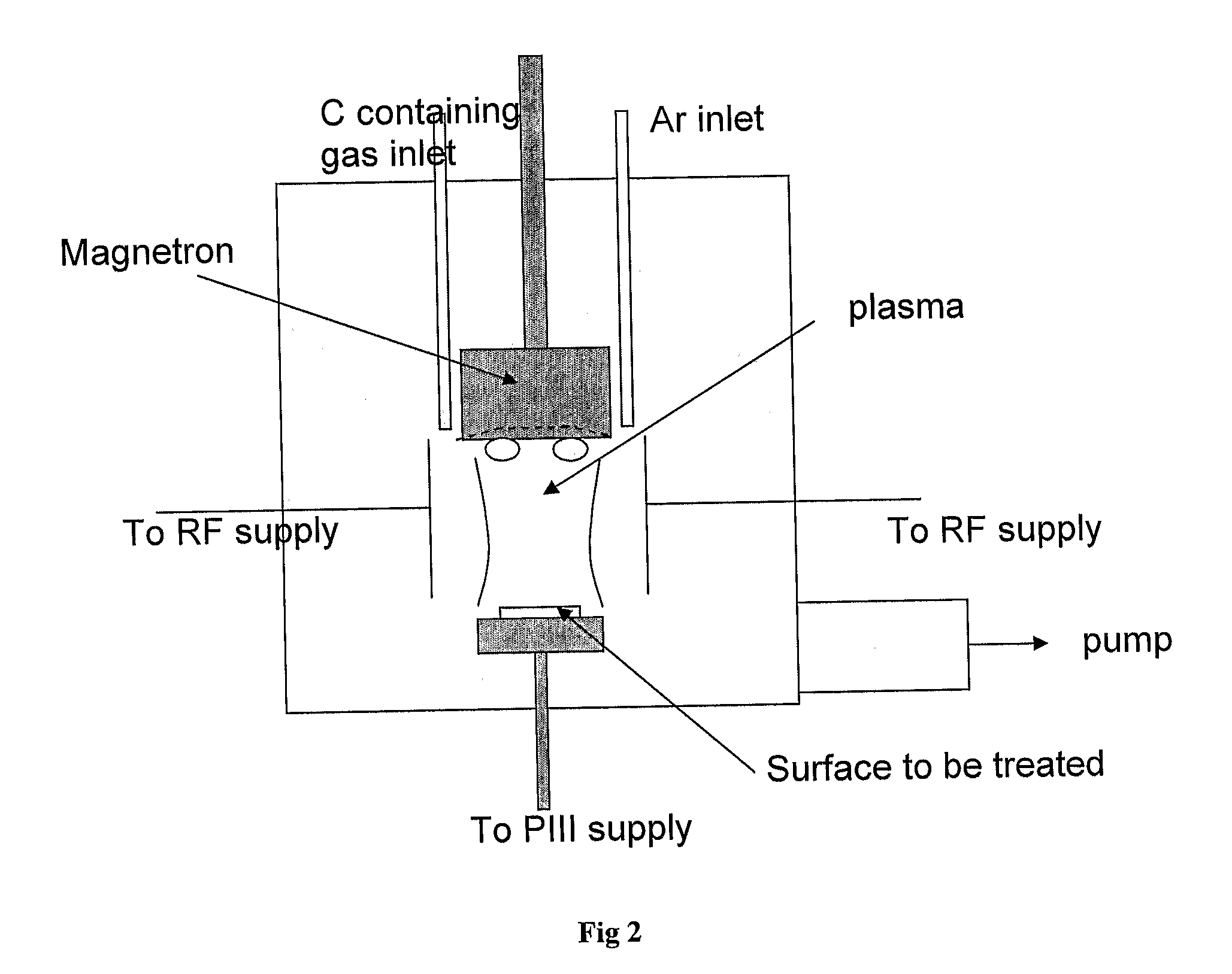
The invention relates to an activated metallic, semiconductor, polymer, composite and / or ceramic substrate, the substrate being bound through a mixed or graded interface to a hydrophilic polymer surface that is activated to enable direct covalent binding to a functional biological molecule, the polymer surface comprising a sub-surface that includes a plurality of cross-linked regions, as well as to such activated substrates that have been functionalised with a biological molecule and to devices comprising such functionalised substrates. Such substrates can be produced by a method comprising steps of: a. exposing a surface of the substrate to any or more of (i) to (iii): (i) plasma ion implantation with carbon containing species; (ii) co-deposition under conditions in which substrate material is deposited with carbon containing species while gradually reducing substrate material proportion and increasing carbon containing species proportion; (iii) deposition of a plasma polymer surface layer with energetic ion bombardment; incubating the surface treated according to step (a) with a desired biological molecule.
Owner:SYDNEY THE UNIV OF
Method for preparing multi-metal element doped diamond film
InactiveCN101787512AImprove performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCathodic arc depositionIon bombardment
The invention discloses a method for preparing a multi-metal element doped diamond film, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: removing a pollution layer on matrix surface by using the ultrasonic cleaning technology, carrying out ion beam bombardment cleaning on the matrix surface by using inert gas ion beam produced by an ion source, carrying out metal ion bombardment cleaning on the matrix surface by using metal ions produced by a cathodic arc source under a condition of high workpiece negative bias, preparing a gradient transition layer by using a cathodic arc deposition or ion beam assisted magnetron sputtering (IBAMS), and synthesizing a multi-metal element doped DLC film on the transition layer by using ion beam deposition and mosaic composite target magnetron sputtering, wherein the ion beam deposition is realized by introducing carbon gas in the ion source; and the mosaic composite target doped multiple metal are used, and the main body material of the mosaic composite target can be any one of Ti, Cr, W, Zr, Nb and Ta, and the mosaic block material is one or more of other metals except the above main body materials.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
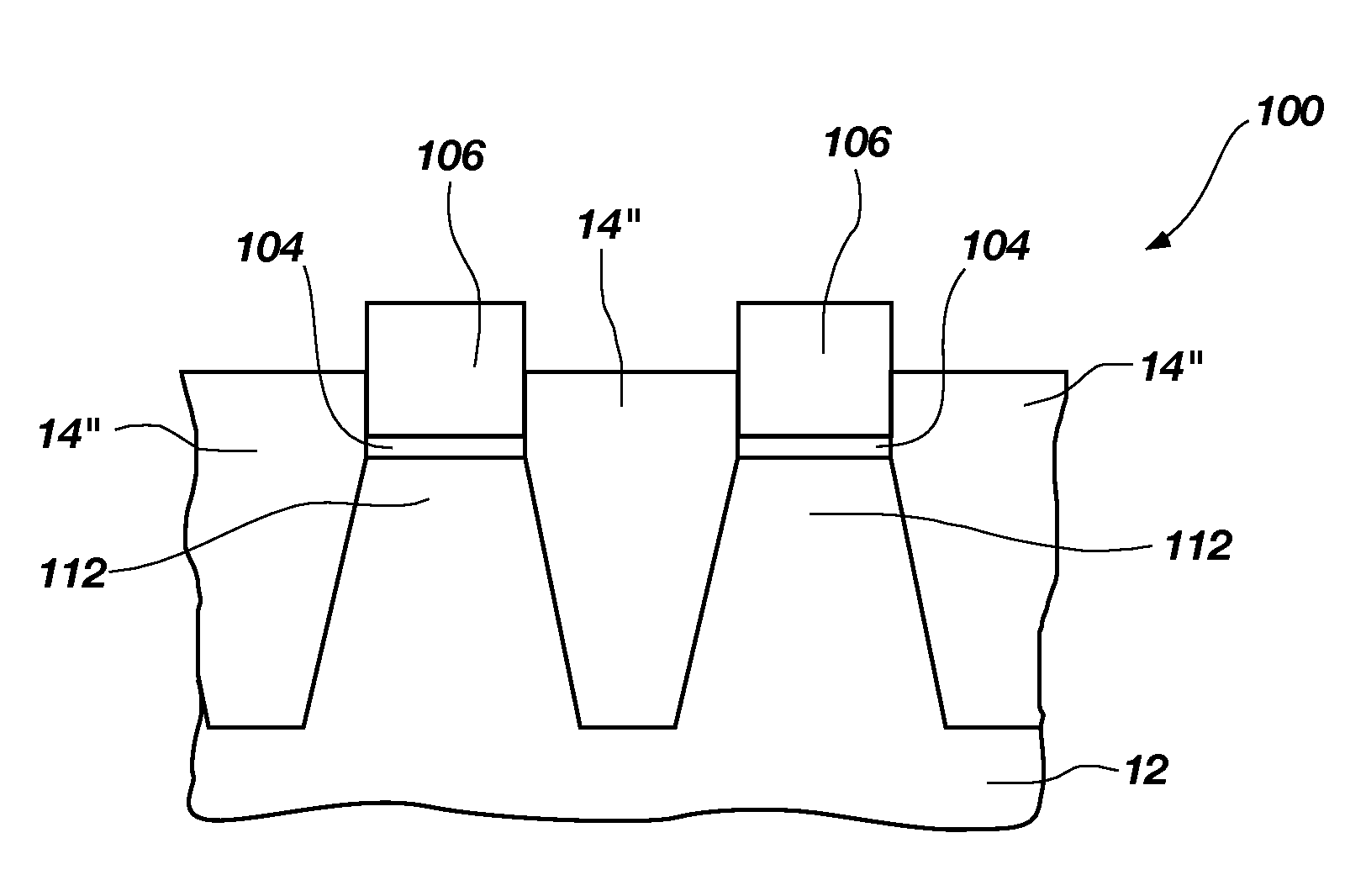
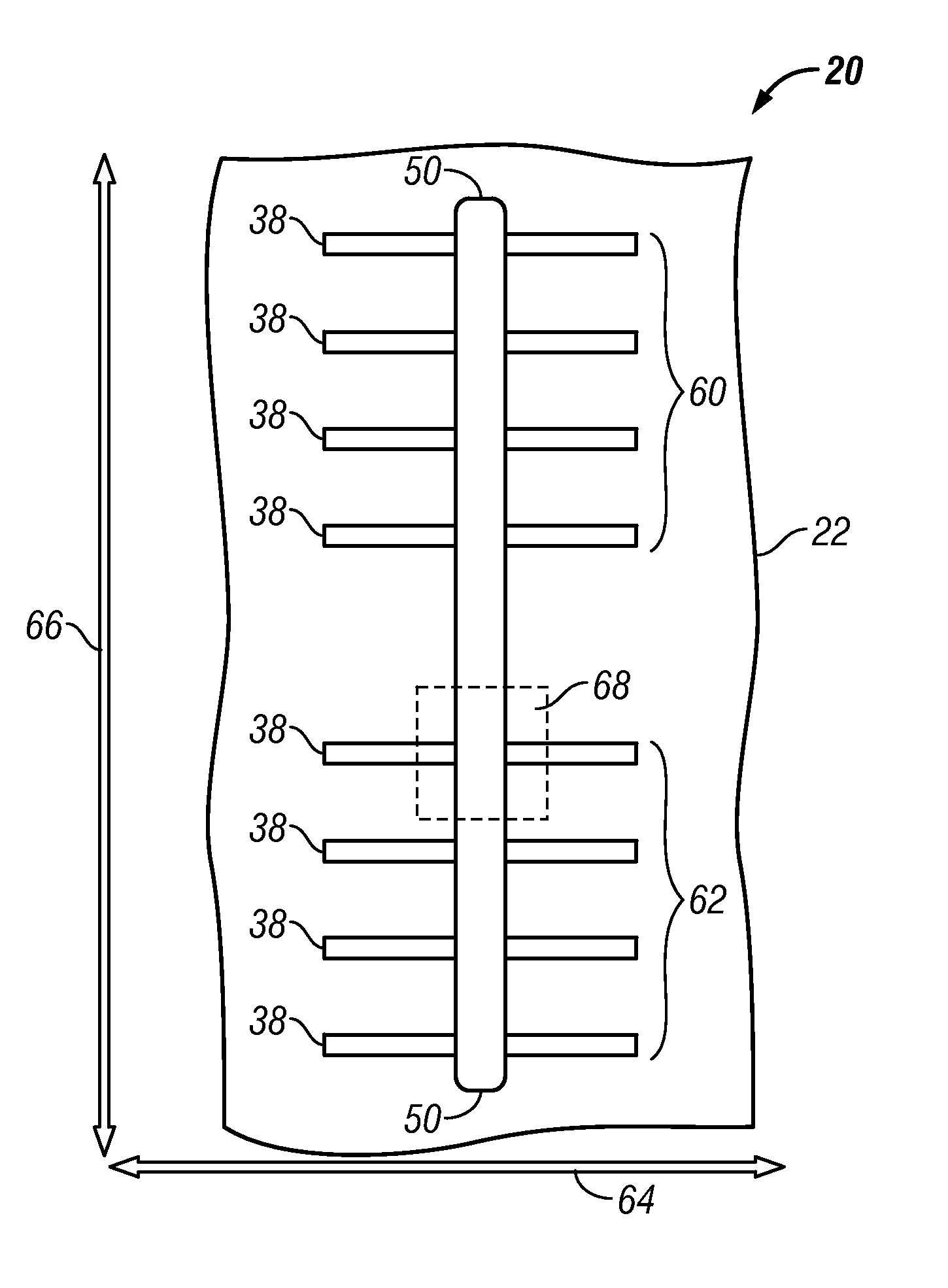
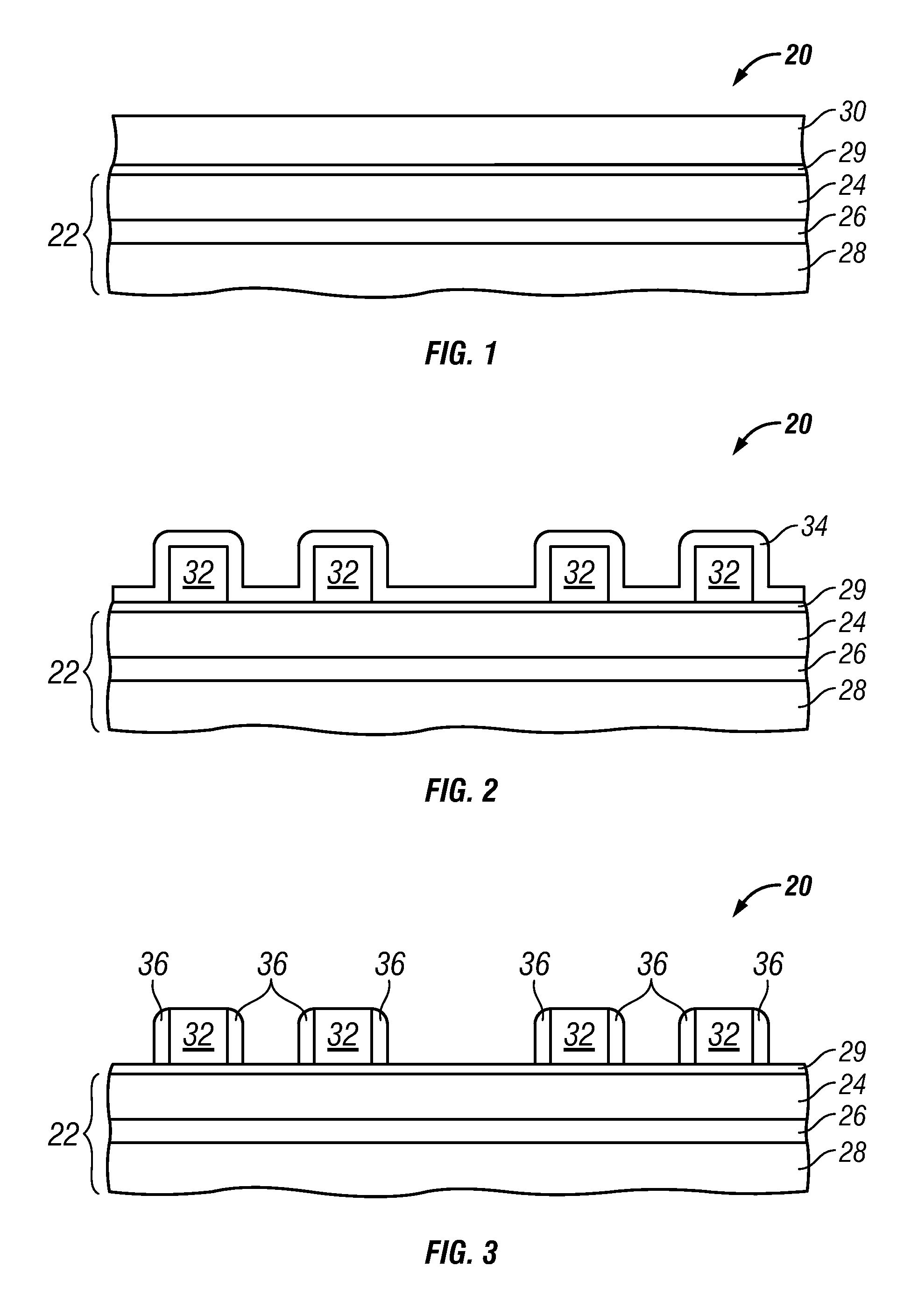
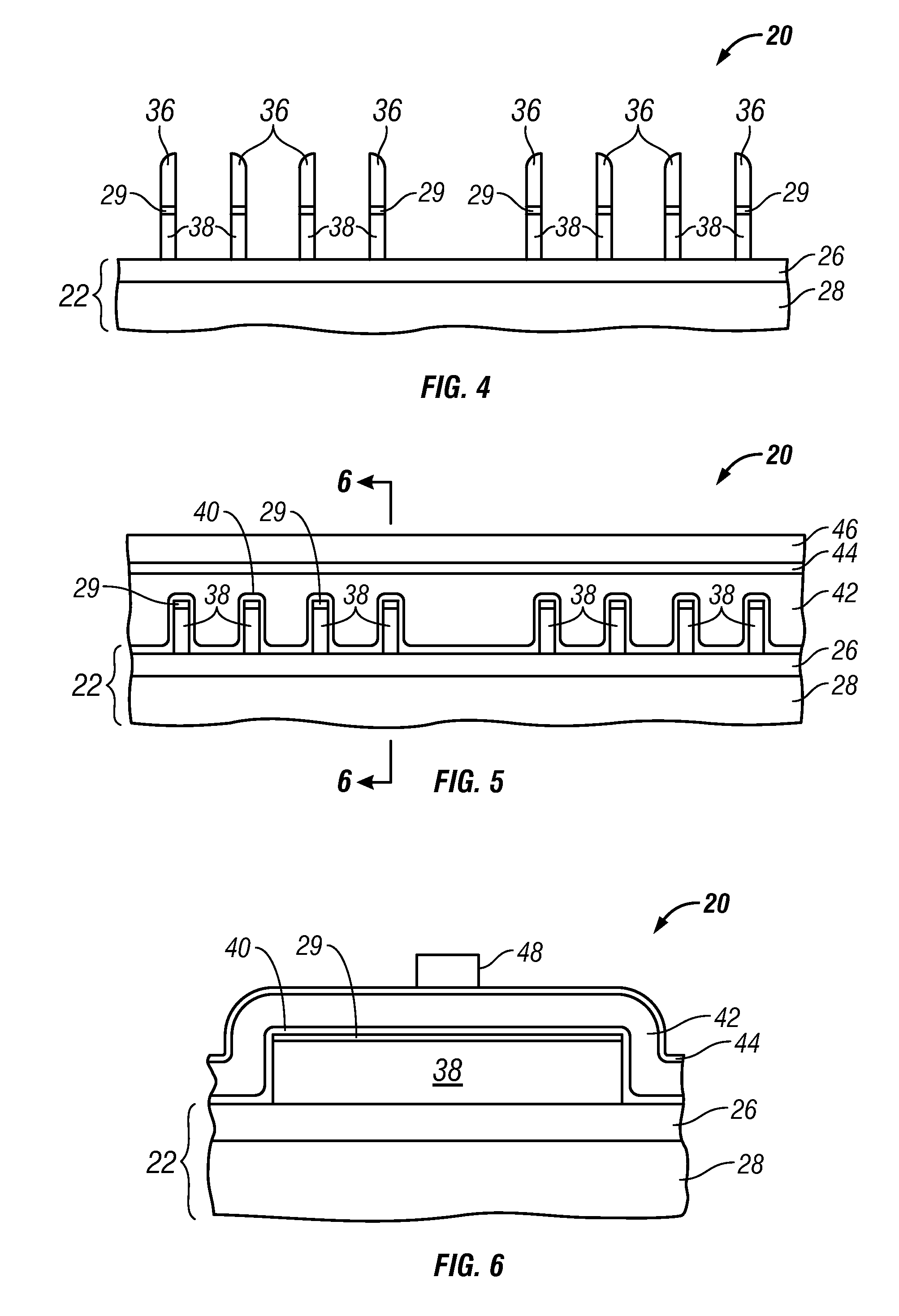
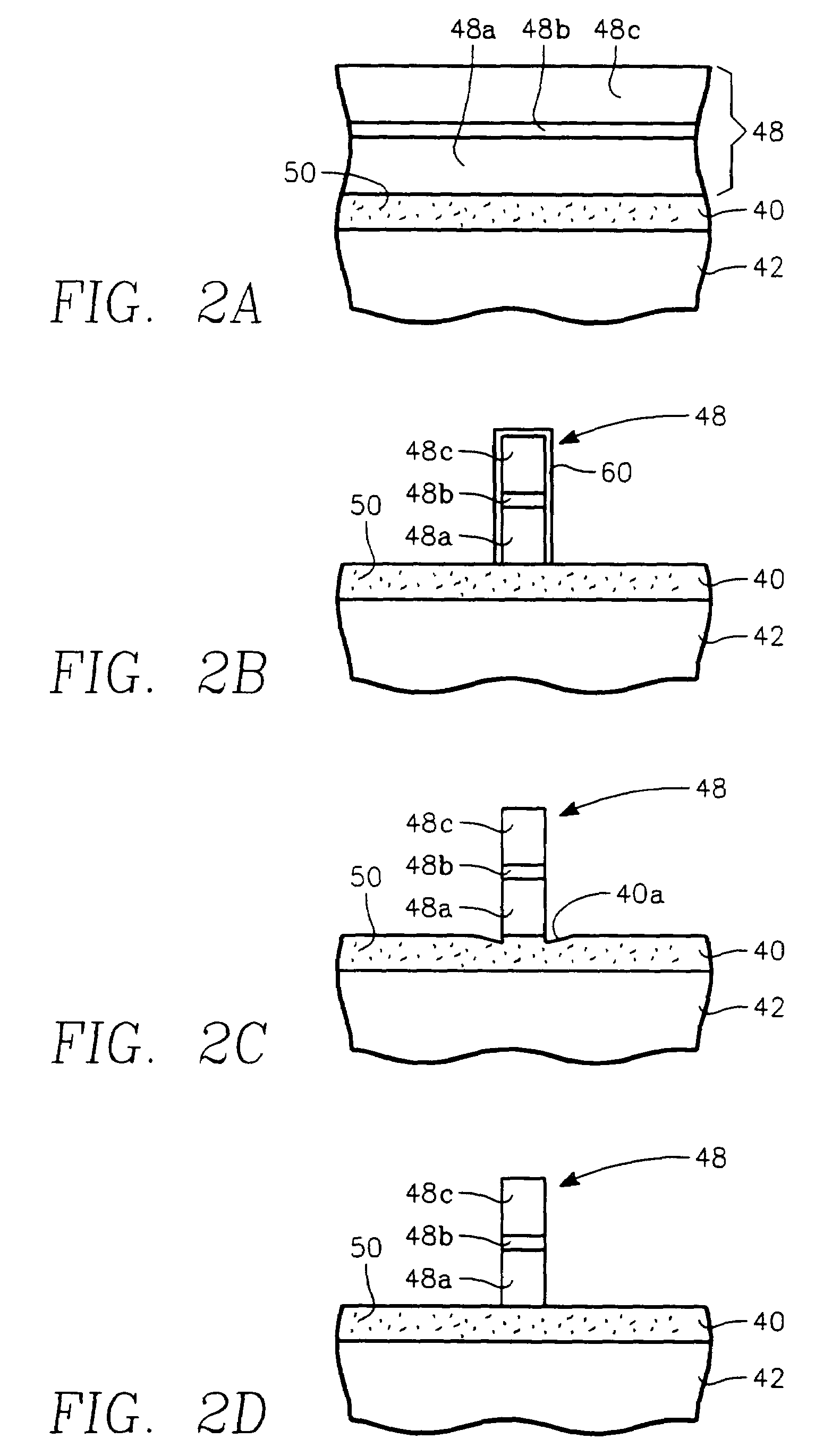
Methods for fabricating non-planar electronic devices having sidewall spacers formed adjacent selected surfaces
InactiveUS20110021027A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIon bombardmentEngineering
Methods are provided for fabricating an electronic device having at least one sidewall spacer formed adjacent a selected surface. In one embodiment, the method includes the step of depositing spacer material adjacent first and second raised structures formed on the substrate and extending along substantially perpendicular axes. The method further includes the step of selectively removing spacer material laterally adjacent one of the first raised structure and the second raised structure. During the step of selectively removing, the electronic device is bombarded with ions from a first predetermined direction forming a first predetermined grazing angle with the substrate such that the spacer material adjacent a first sidewall of the first raised structure is substantially exposed to the ion bombardment while the spacer material adjacent opposing sidewalls of the second raised structure is substantially shielded therefrom.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Method and system for coating internal surfaces of prefabricated process piping in the field
ActiveUS20060011468A1Improve adhesionIncreases magnitudeCellsLiquid surface applicatorsDiamond-like carbonHydrocarbon mixtures
The coating of internal surfaces of a workpiece is achieved by connecting a bias voltage such that the workpiece functions as a cathode and by connecting an anode at each opening of the workpiece. A source gas is introduced at an entrance opening, while a vacuum source is connected at an exit opening. Pressure within the workpiece is monitored and the resulting pressure information is used for maintaining a condition that exhibits the hollow cathode effect. Optionally, a pre-cleaning may be provided by introducing a hydrocarbon mixture and applying a negative bias to the workpiece, so as to sputter contaminants from the workpiece using argon gas. Argon gas may also be introduced during the coating processing to re-sputter the coating, thereby improving uniformity along the length of the workpiece. The coating may be a diamond-like carbon material having properties which are determined by controlling ion bombardment energy.
Owner:AGM CONTAINER CONTROLS
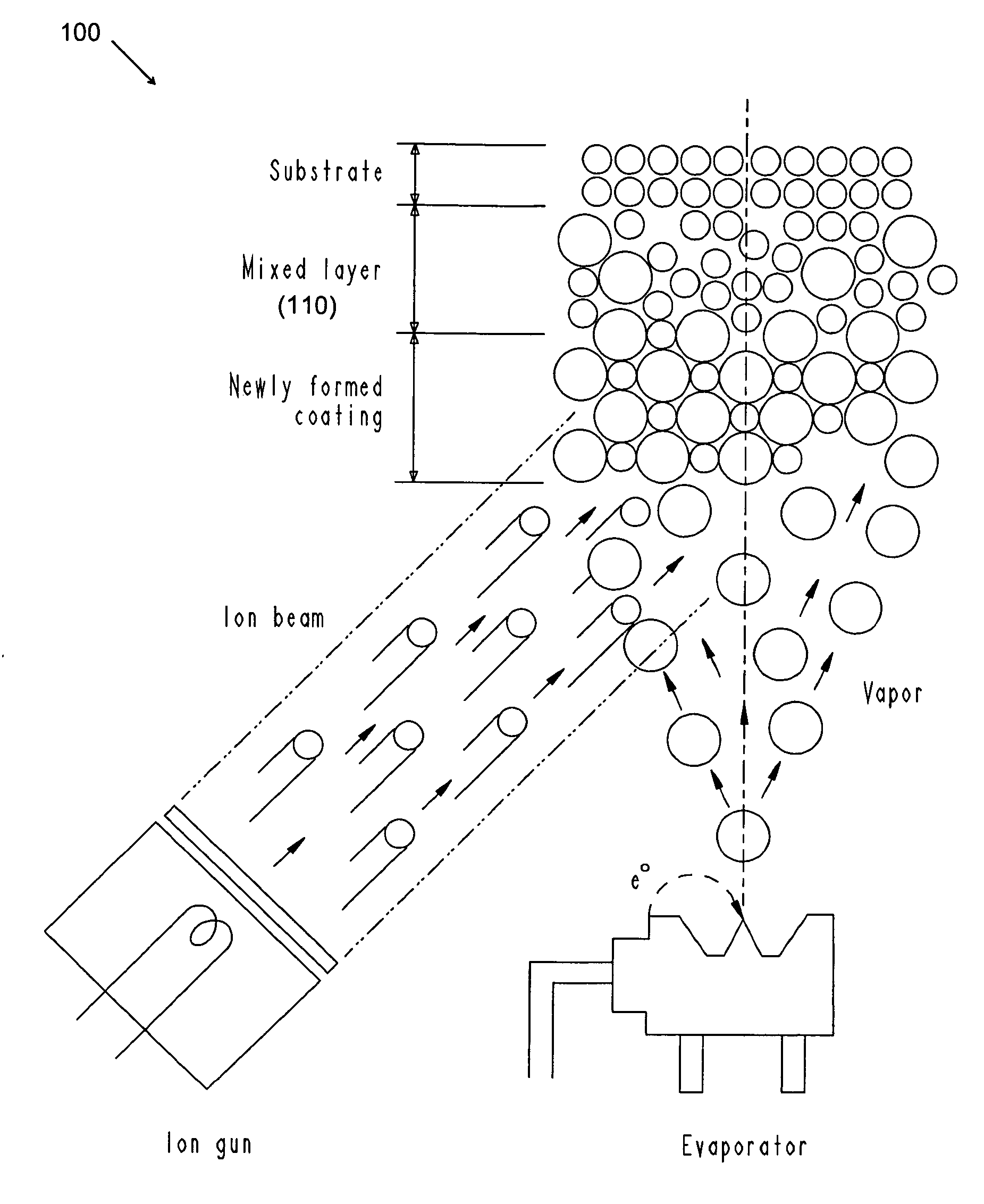
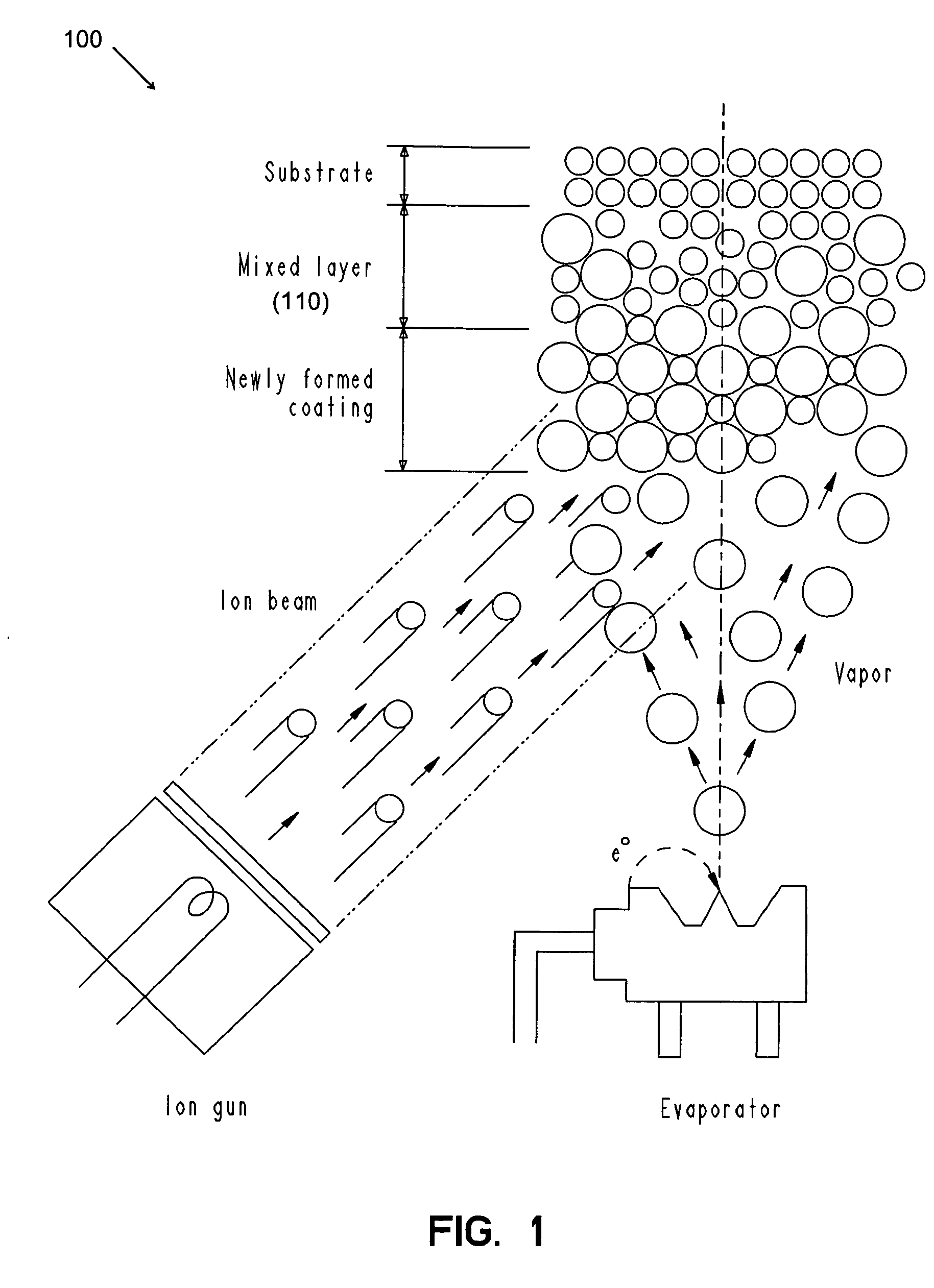
Method for deposition of high-performance coatings and encapsulated electronic devices
A method is disclosed for forming multi-layered structures on polymeric or other materials that provide optical functions or protect underlying layers from exposure to oxygen and water vapor. Novel devices are also disclosed that may include both multi-layered protective structures and AMOLED display, OLED lighting or photovoltaic devices. The protective multi-layer structure itself may be made by depositing successively on a substrate at least three very thin layers of material with different density or composition. In some methods for deposition of such film, the layers are deposited by varying the energy of ion bombardment per unit thickness of the film Any layer of the structure may include one or more of the materials: silicon nitride, silicon oxide, silicon oxynitride, or metallic nitride or oxide. Specific commercial applications that benefit from this include manufacturing of photovoltaic devices or organic light emitting diode devices (OLED) including lighting and displays.
Owner:AIXTRON AG
Non-vacuum solar spectrum selective absorption coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102121757ASolve high temperature oxidationImprove absorption rateSolar heat devicesLayered productsIr reflectionLow emissivity
The invention relates to a non-vacuum solar spectrum selective absorption coating and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting copper or stainless steel with low infrared emissivity as a base material; (2) selecting oxide resistant to high-temperature oxidation, nitride and complex or doped oxide as a film material, wherein a metal or an alloy serves as a bonding force increased layer, metal nitride or pure metal serves as a high infrared reflecting layer, an absorption layer is composed of two conducting particle ceramic layers with different metal nitride conducting particle volume fractions, and aluminium nitride and aluminium oxide serve as an antireflection layer; (3) controlling the components and contents of different film materials by controlling gas flow and sputtering power; (4) cleaning the base material before the base material is placed into a vacuum chamber, and carrying out argon ion bombarding on the surface of the base material before sputtering is carried out; and (5) obtaining a multilayer coating, wherein the thickness of the coating is less than 500nm, and the coating has high absorption rate alpha (0.9-0.97) in the solar spectrum range (0.3-2.5microns) and has extremely low emissivity epsilon (0.02-0.18) in the infrared region (2.5-50microns).
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Process for fabricating a monolayer or multilayer metal structure in LIGA technology, and structure obtained
ActiveCN101038440AImprove qualityEasy thickness controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical coating apparatusResistIon bombardment
The invention relates to a process for fabricating a monolayer or multilayer metal structure in LIGA technology, in which a photoresist layer is deposited on a flat metal substrate, a photoresist mold is created by irradiation or electron or ion bombardment, a metal or alloy is electroplated in this mold, the electroformed metal structure is detached from the substrate and the photoresist is separated from this metal structure, wherein the metal substrate is used as an agent involved in the forming of at least one surface of the metal structure other than that formed by the plane surface of the substrate.
Owner:ROLEX SA
Ion beam process for deposition of highly abrasion-resistant coatings
InactiveUSRE37294E1High hardnessReduce coefficient of frictionLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingEye lensVacuum chamber
An ion beam deposition method is provided for manufacturing a coated substrate with improved abrasion resistance, and improved lifetime. According to the method, the substrate is first chemically cleaned to remove contaminants. In the second step, the substrate is inserted into a vacuum chamber, and the air in said chamber is evacuated. In the third step, the substrate surface is bombarded with energetic ions to assist in the removal of residual hydrocarbons and surface oxides, and to activate the surface. <DEL-S DATE="20010724" ID="DEL-S-00001">Alter<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00001"> <INS-S DATE="20010724" ID="INS-S-00001">After <INS-E ID="INS-S-00001">the substrate surface has been sputter-etched, a protective, abrasion-resistant coating is deposited by ion beam deposition. The ion beam-deposited coating may contain one or more layers. Once the chosen thickness of the coating has been achieved, the deposition process on the substrates is terminated, the vacuum chamber pressure is increased to atmospheric pressure, and the coated substrate products having improved abrasion-resistance are removed from the vacuum chamber. The coated products of this invention have utility as plastic sunglass lenses, ophthalmic lenses, bar codes scanner windows, and industrial wear parts that must be protected from scratches and abrasion.
Owner:MORGAN ADVANCED CERAMICS
Surface analysis apparatus and method using ion bombardment
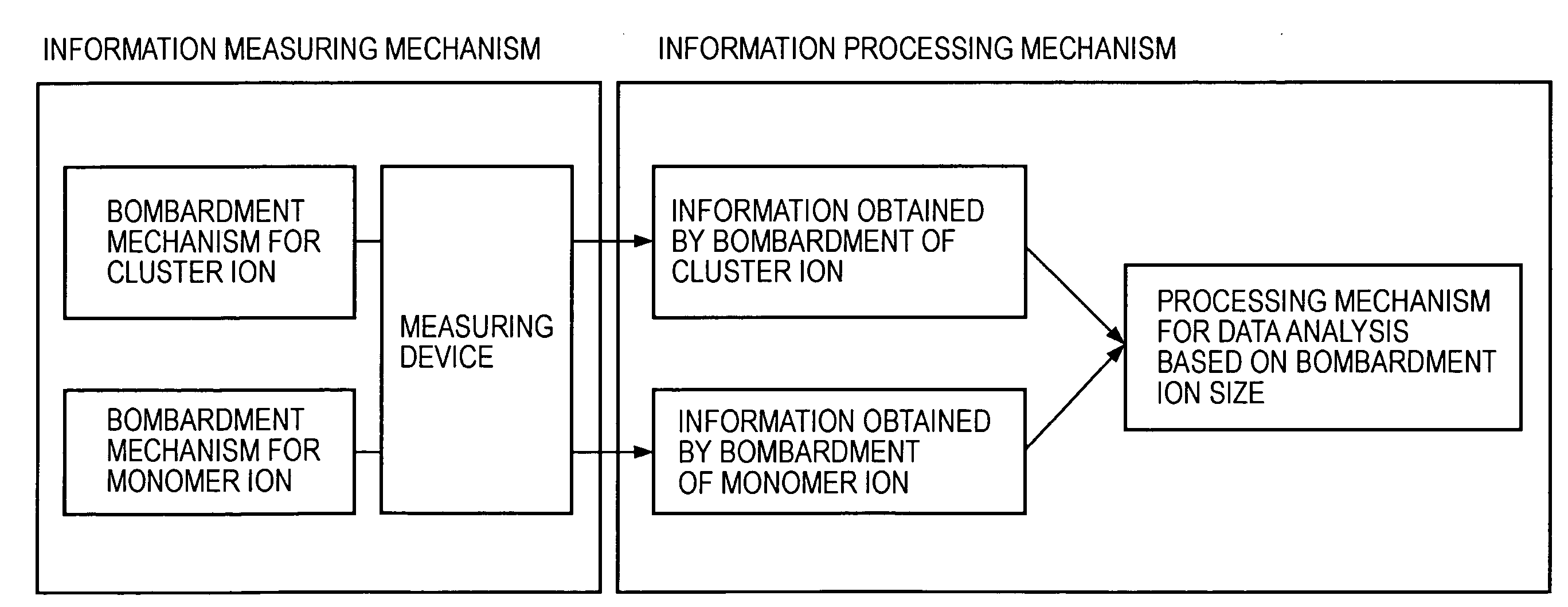
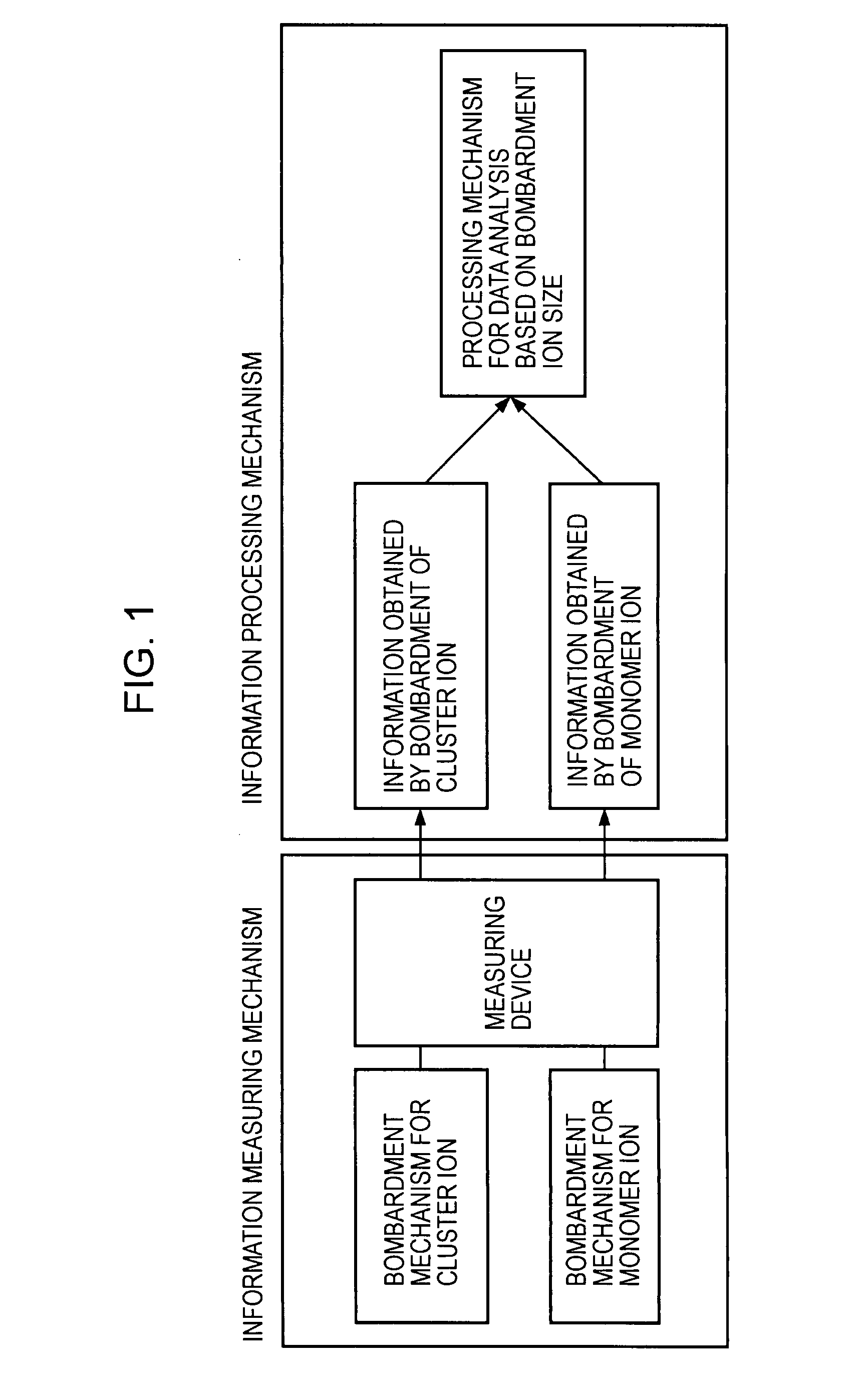
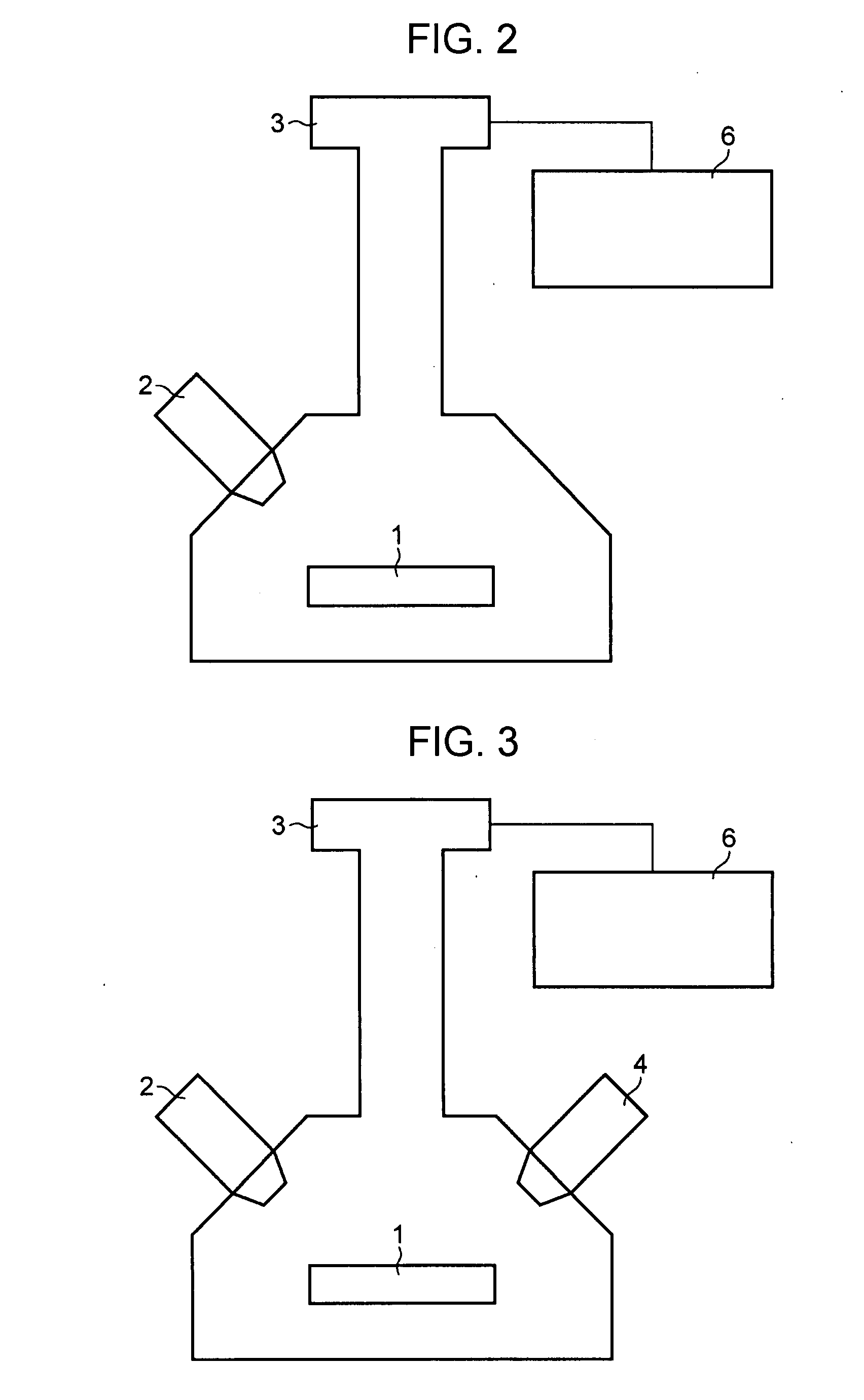
InactiveUS20080001081A1Minimize contaminationReduce harmParticle separator tubesIsotope separationMeasurement deviceIon bombardment
A surface analysis apparatus includes a unit configured to bombard a sample surface with at least two types of ions having different sizes; a measurement device for measuring, with a time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer, a mass spectrum of ions emitted from the sample surface; and an information processor outputting a difference between two mass spectra measured by bombardment of different types of ions.
Owner:CANON KK
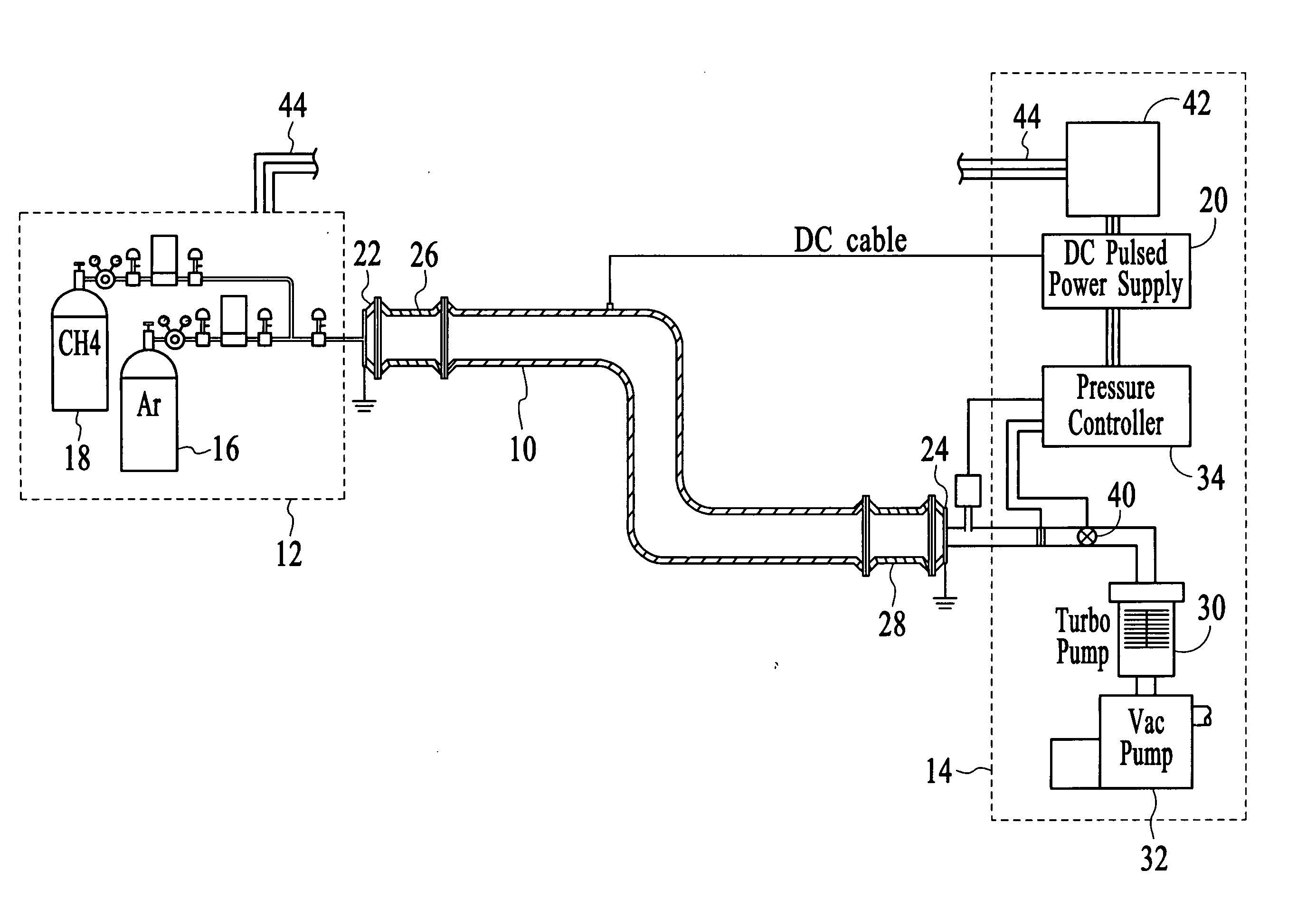
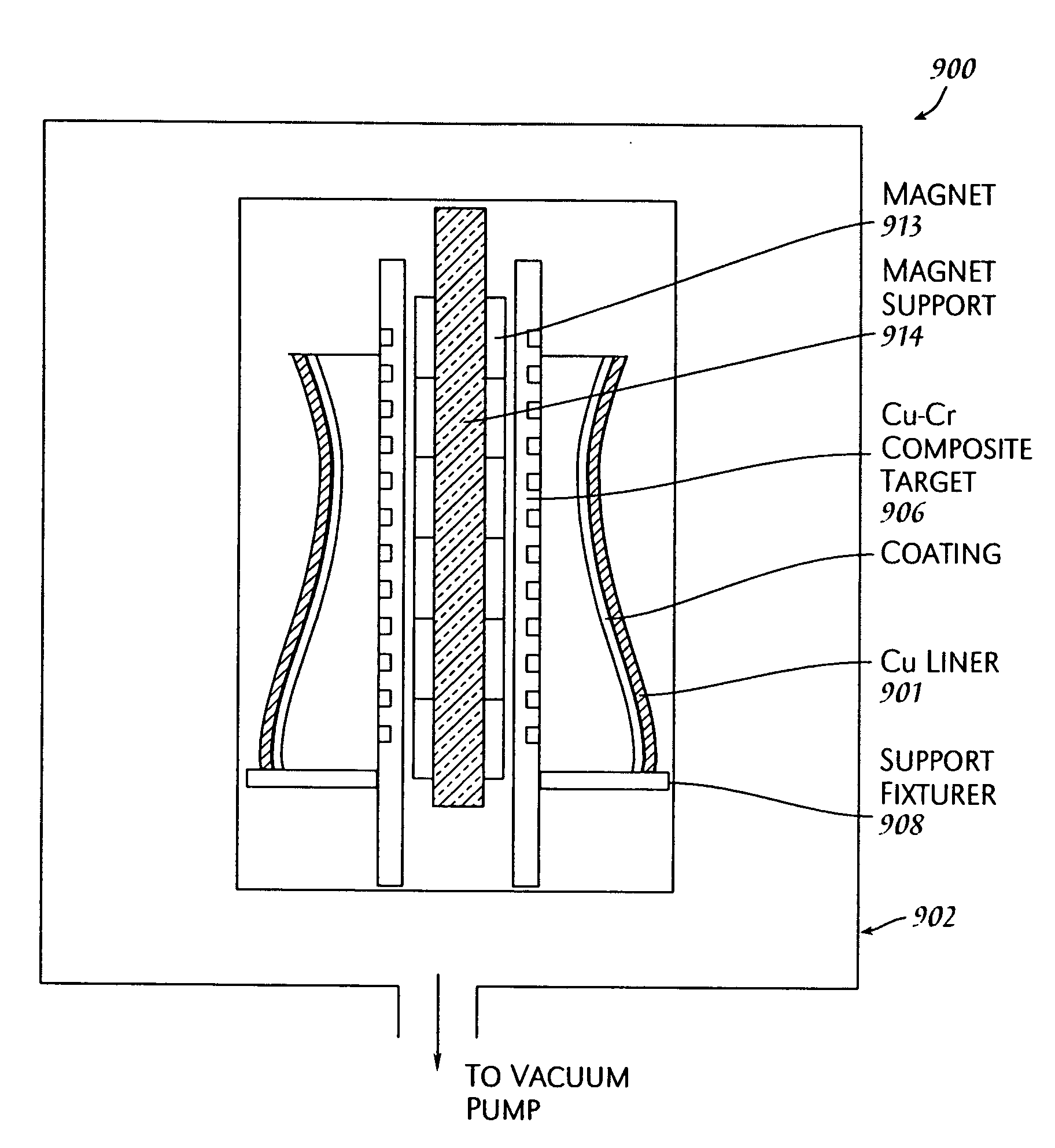
Method for magnetron sputter deposition
ActiveUS20060251917A1Reduce pressureElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingIon bombardmentJet engine
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Deterioration resistant chambers for inductively coupled plasma production
InactiveUS6946063B1Improved wall resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingElectricityIon bombardment
In one aspect of the invention is a method to construct plasma chambers with improved wall resistance to deterioration. In one embodiment of the invention, a chamber is made of an aluminum alloy having low concentrations of elements that form non-soluble, intermetallic particles to address coating / substrate issues, has swaged-in cooling tubes to reduce thermal stress by improving thermal resistance, and has a plurality of dielectric gaps to decrease ion bombardment.
Owner:ADVANCED ENERGY IND INC
Method and apparatus for fabricating a high dielectric constant transistor gate using a low energy plasma system
InactiveUS20070212895A1Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricGate dielectric
The present invention generally provides methods and apparatuses that are adapted to form a high quality dielectric gate layer on a substrate. Embodiments contemplate a method wherein a metal plasma treatment process is used in lieu of a standard nitridization process to form a high dielectric constant layer on a substrate. Embodiments further contemplate an apparatus adapted to “implant” metal ions of relatively low energy in order to reduce ion bombardment damage to the gate dielectric layer, such as a silicon dioxide layer and to avoid incorporation of the metal atoms into the underlying silicon. In general, the process includes the steps of forming a high-k dielectric and then terminating the surface of the deposited high-k material to form a good interface between the gate electrode and the high-k dielectric material. Embodiments of the invention also provide a cluster tool that is adapted to form a high-k dielectric material, terminate the surface of the high-k dielectric material, perform any desirable post treatment steps, and form the polysilicon and / or metal gate layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
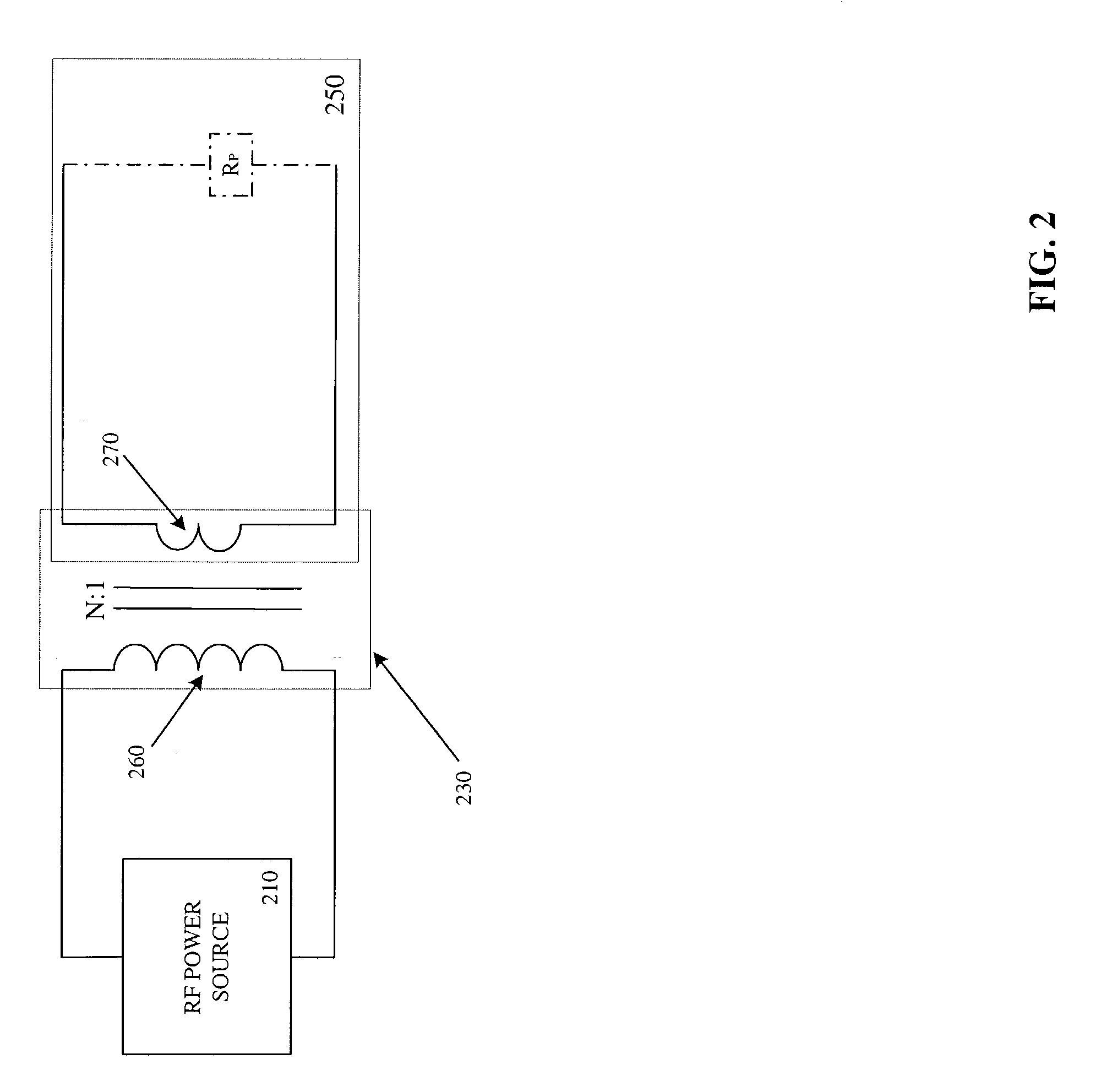
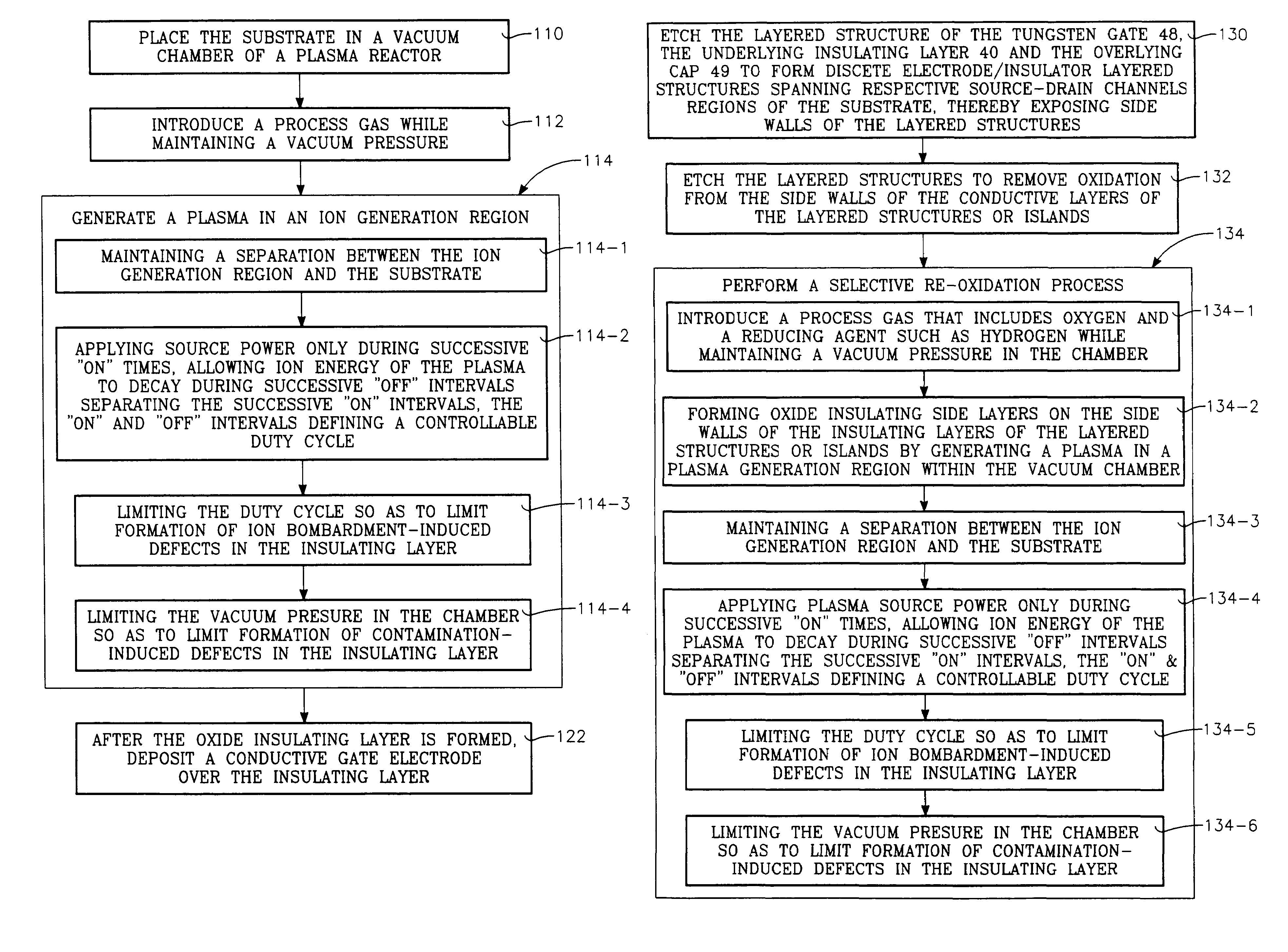
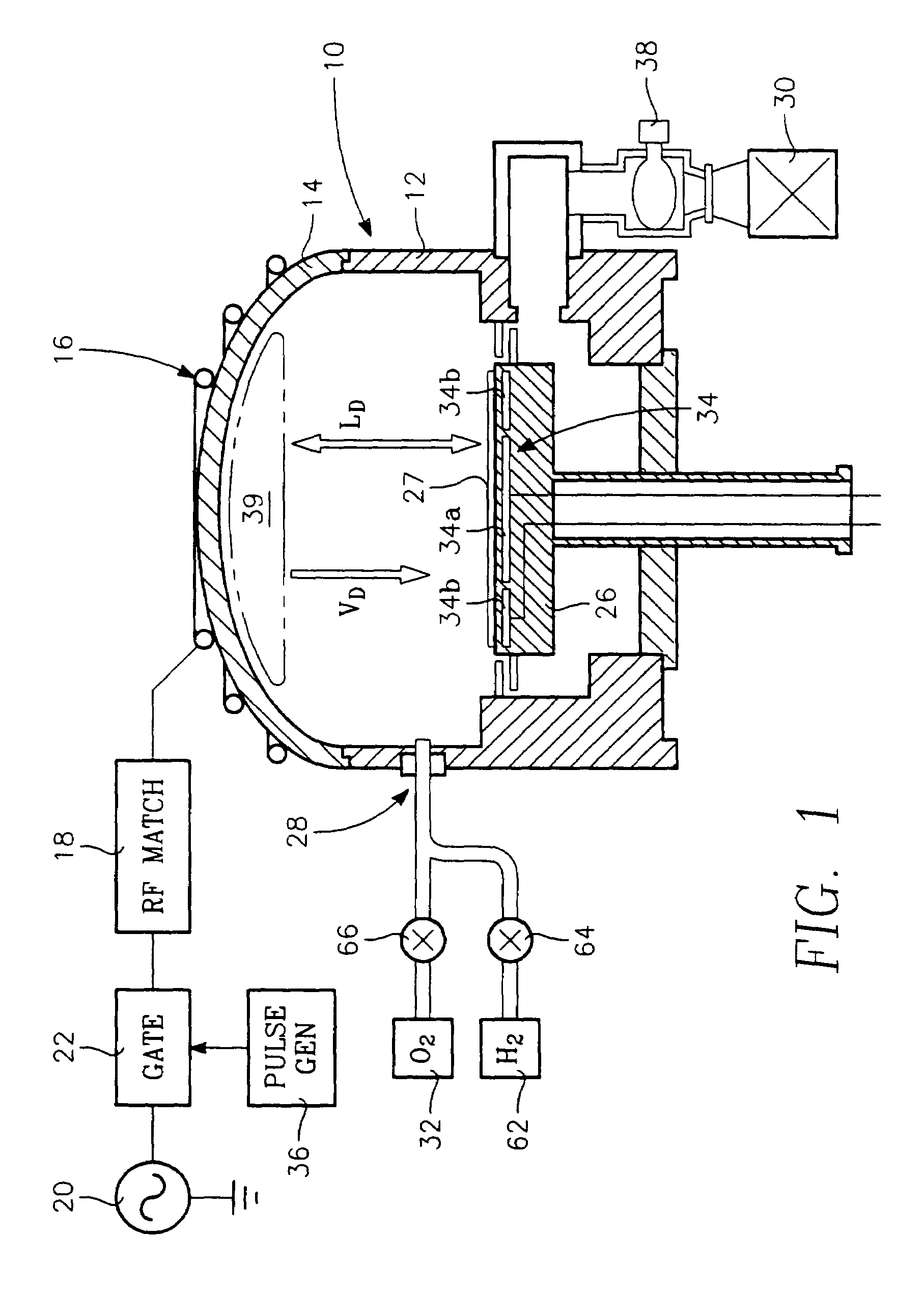
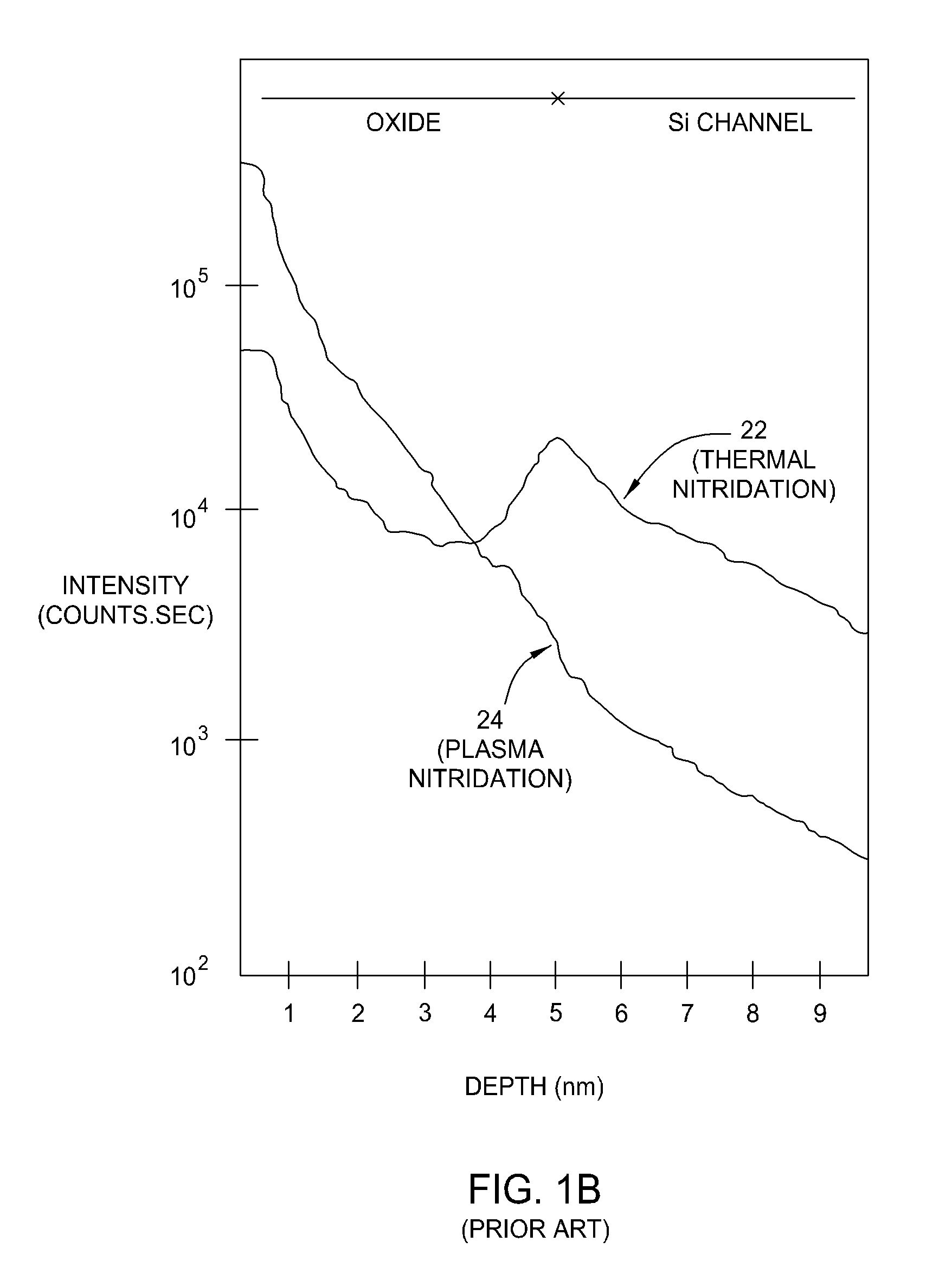
Plasma gate oxidation process using pulsed RF source power
ActiveUS7214628B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygenVacuum chamber
A method of fabricating a gate of a transistor device on a semiconductor substrate, includes the steps of placing the substrate in a vacuum chamber of a plasma reactor and introducing into the chamber a process gas that includes oxygen while maintaining a vacuum pressure in the chamber. An oxide insulating layer on the order of several Angstroms in thickness is formed at the surface of the substrate by generating a plasma in a plasma generation region within the vacuum chamber during successive “on” times, and allowing ion energy of the plasma to decay during successive “off” intervals separating the successive “on” intervals, the “on” and “off” intervals defining a controllable duty cycle. During formation of the oxide insulating layer, the duty cycle is limited so as to limit formation of ion bombardment-induced defects in the insulating layer, while the vacuum pressure is limited so as to limit formation of contamination-induced defects in the insulating layer. A conductive gate electrode is formed over the insulating layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
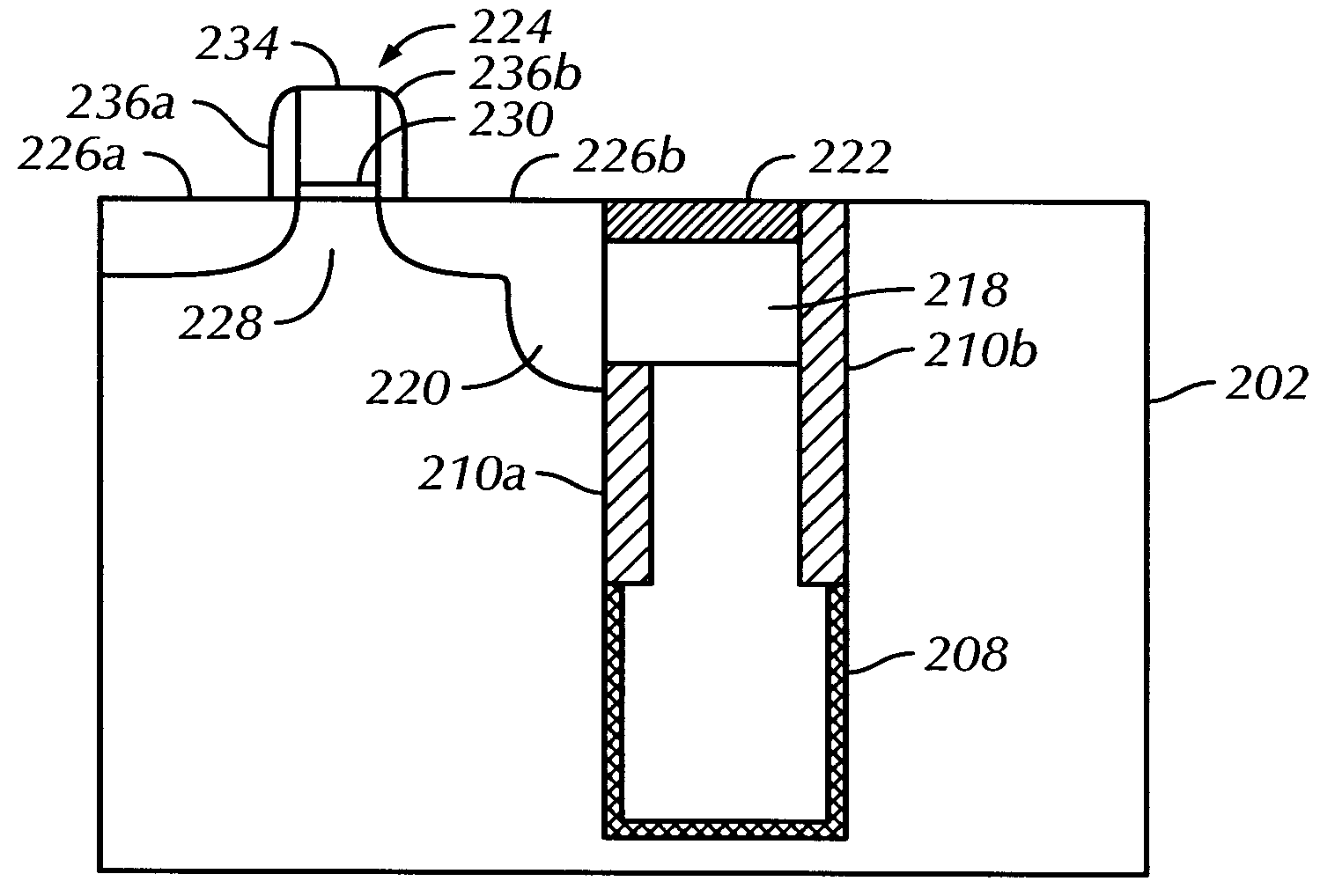
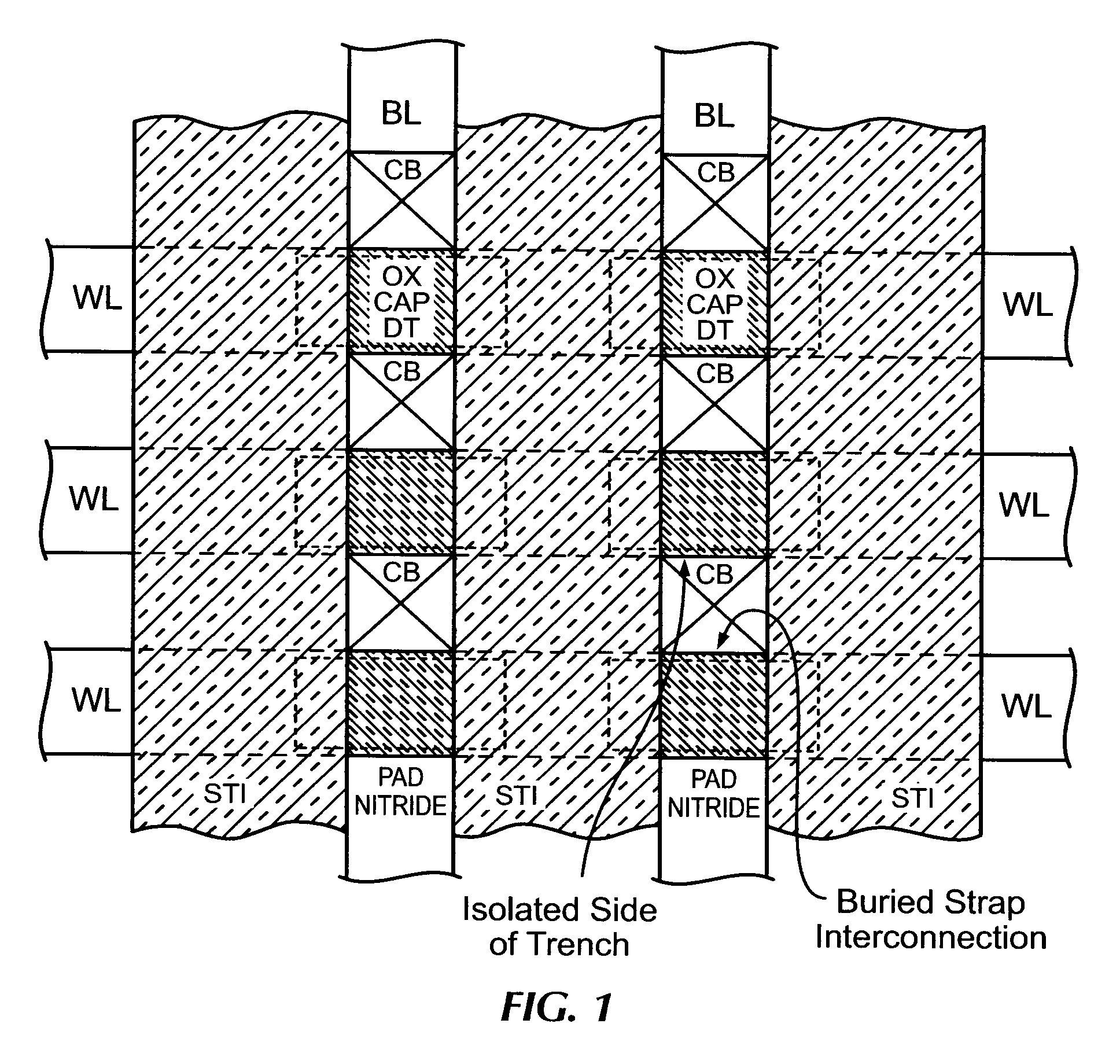
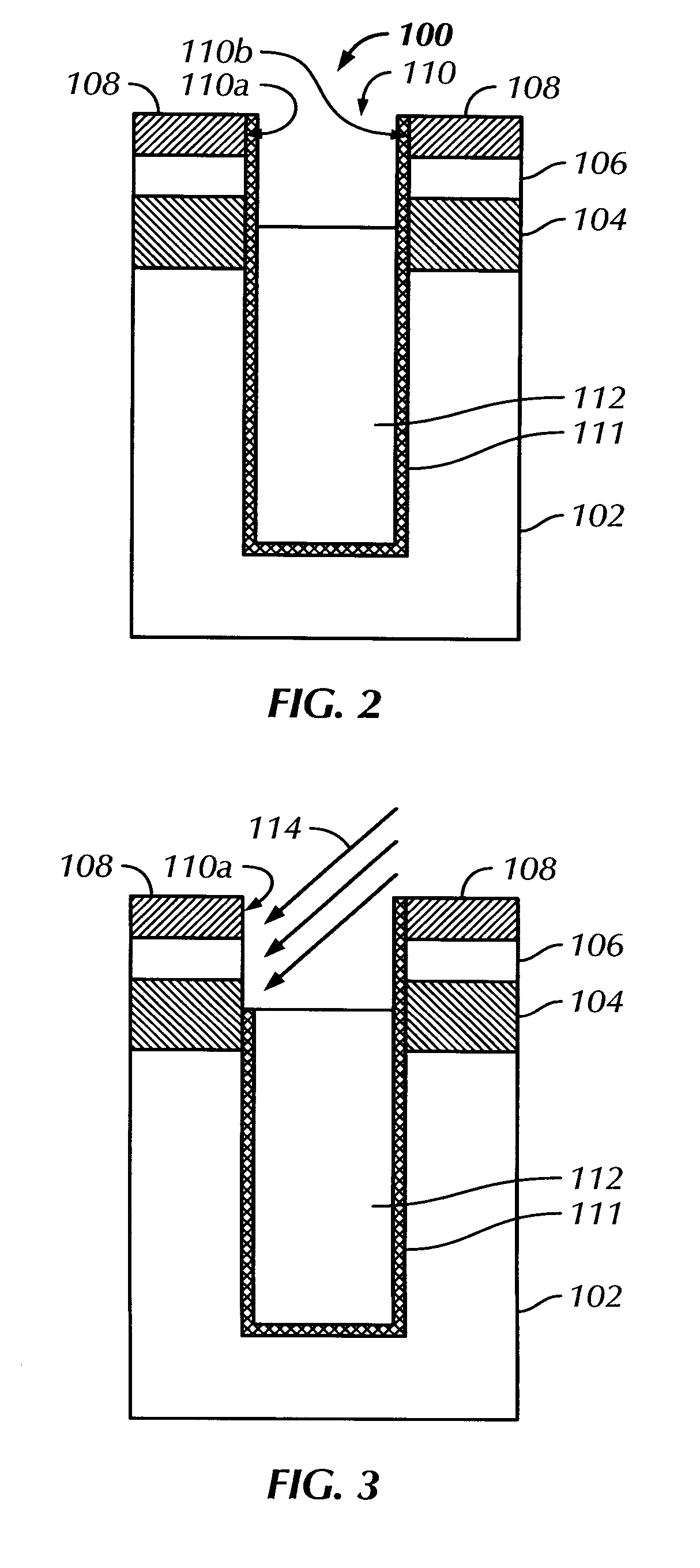
Method and structure for forming trench dram with asymmetric strap
InactiveUS20090184392A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricIon bombardment
A method of forming a trench device structure having a single-side buried strap is provided. The method includes forming a deep trench in a semiconductor substrate, said deep trench having a first side portion and a second side portion; depositing a node dielectric on said deep trench, wherein said node dielectric covers said first side portion and said second side portion; depositing a first conductive layer over said node dielectric; performing an ion implantation or ion bombardment at an angle into a portion of said node dielectric, thereby removing said portion of said node dielectric from said first side portion of said deep trench; and depositing a second conductive layer over said first conductive layer, wherein said second conductive layer outdiffuses into a portion of said semiconductor substrate. A trench device structure having a single-side buried strap is also provided. The device structure includes a semiconductor substrate having a deep trench therein; and a first conductive layer and a second conductive layer sequentially disposed on said deep trench, wherein said second conductive layer outdiffuses into a portion of said semiconductor substrate.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
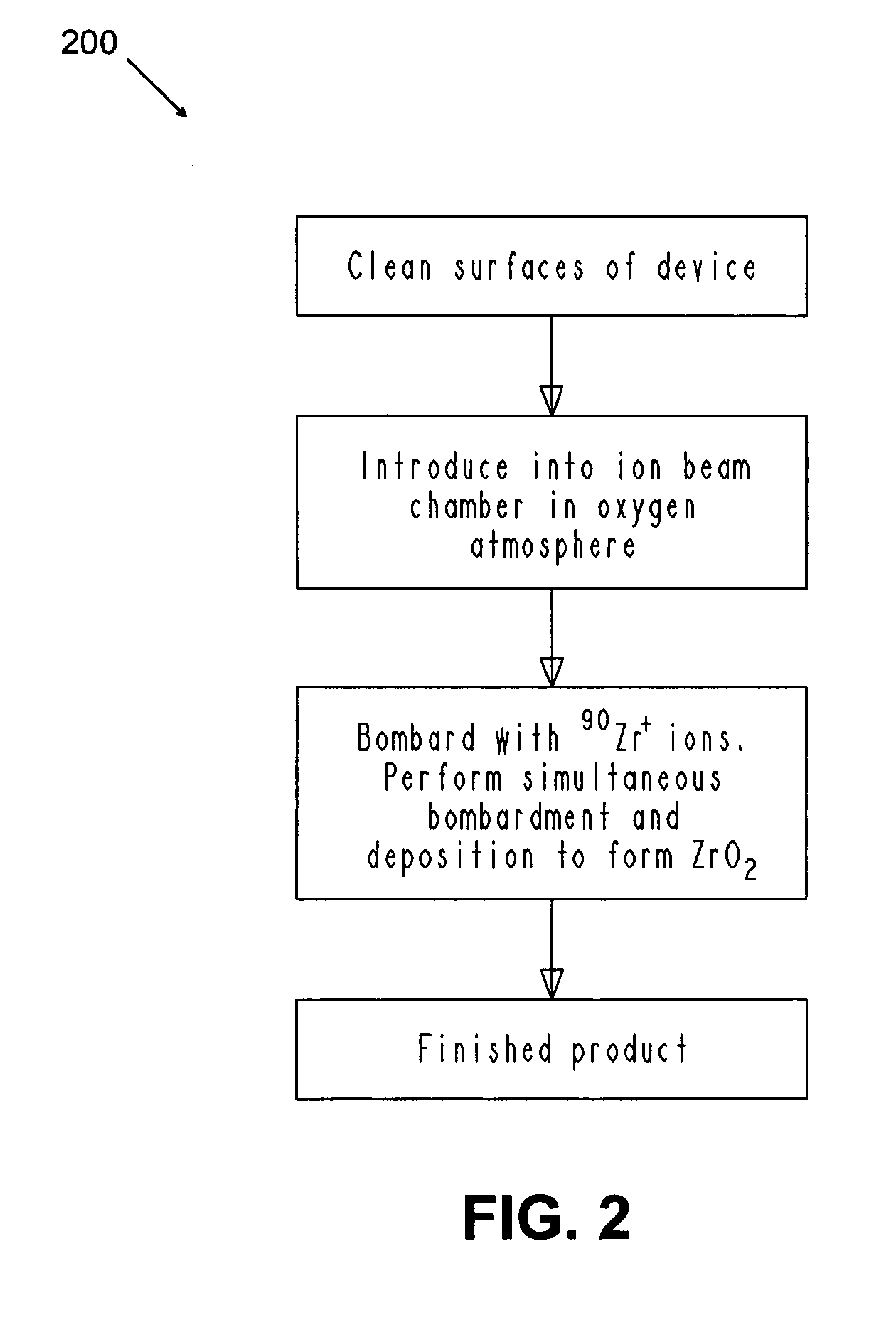
Method for producing a zirconia-layered orthopedic implant component
A method for producing a zirconia-layered orthopedic implant component includes depositing zirconium onto the orthopedic implant component, thereby forming a zirconium-layered component, and converting at least a portion of the zirconium into a substantially monoclinic zirconia surface layer unaccompanied by a substantial underlying α-phase. A method for producing a zirconia-layered orthopedic implant component includes depositing zirconium onto the orthopedic implant component by ion bombardment and deposition in a vacuum to form a zirconium-layered component including an intermix zone at least 1000 Å thick and a zirconium layer about 3-5 μm thick, and heat treating the zirconium-layered component at a temperature of about 500-600° C. in an atmosphere containing oxygen.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Material for aneurysm curing
InactiveUS20110196415A1Reduce riskPrevent leakageOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryIon bombardmentIon beam
It is an object of the present invention to provide a polymer material, the histocompatibility of which has been improved by irradiation of ion beam, which prevents an aneurysm having a risk of rupture from actually rupturing. The present invention provides a material for treating aneurysms, which is composed of a polymer material containing carbon as a constitutional element, and which is produced by modifying at least a portion of the surface thereof by ion bombardment.
Owner:JURIDICAL FOUND THE CHEMO SERO THERAPEUTIC RES INST
Stress tunable tantalum and tantalum nitride films
InactiveUS6488823B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIon bombardmentHigh density
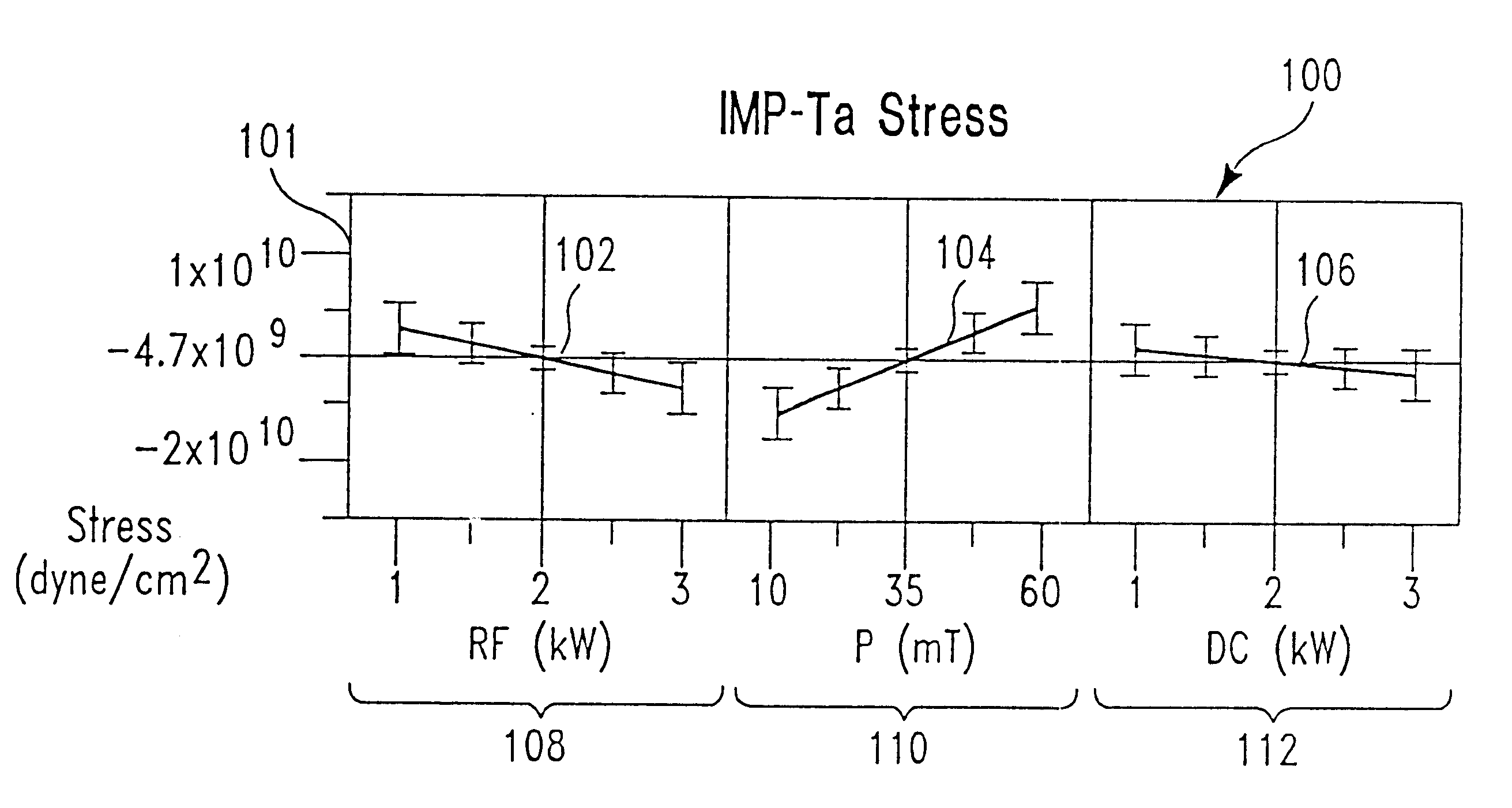
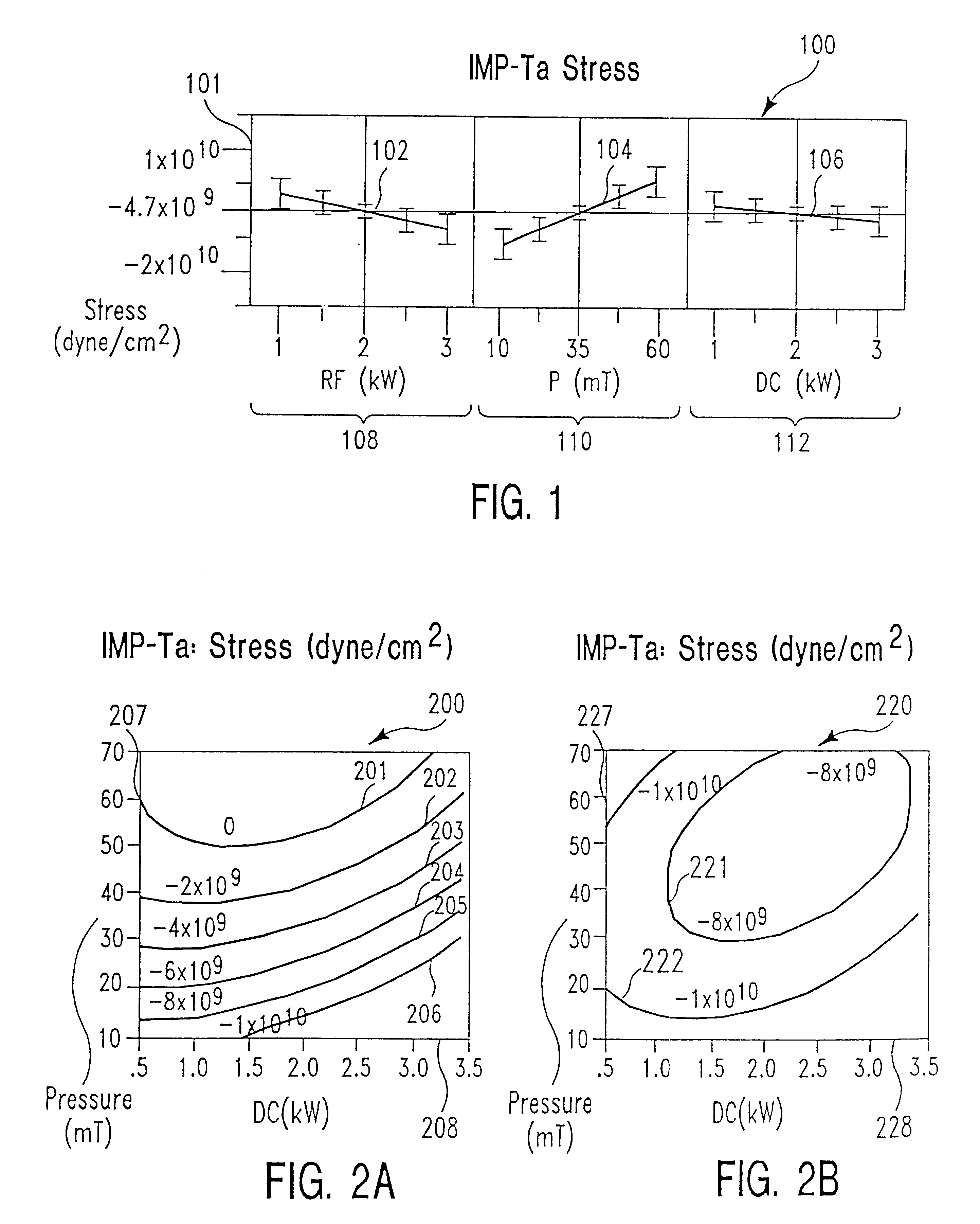
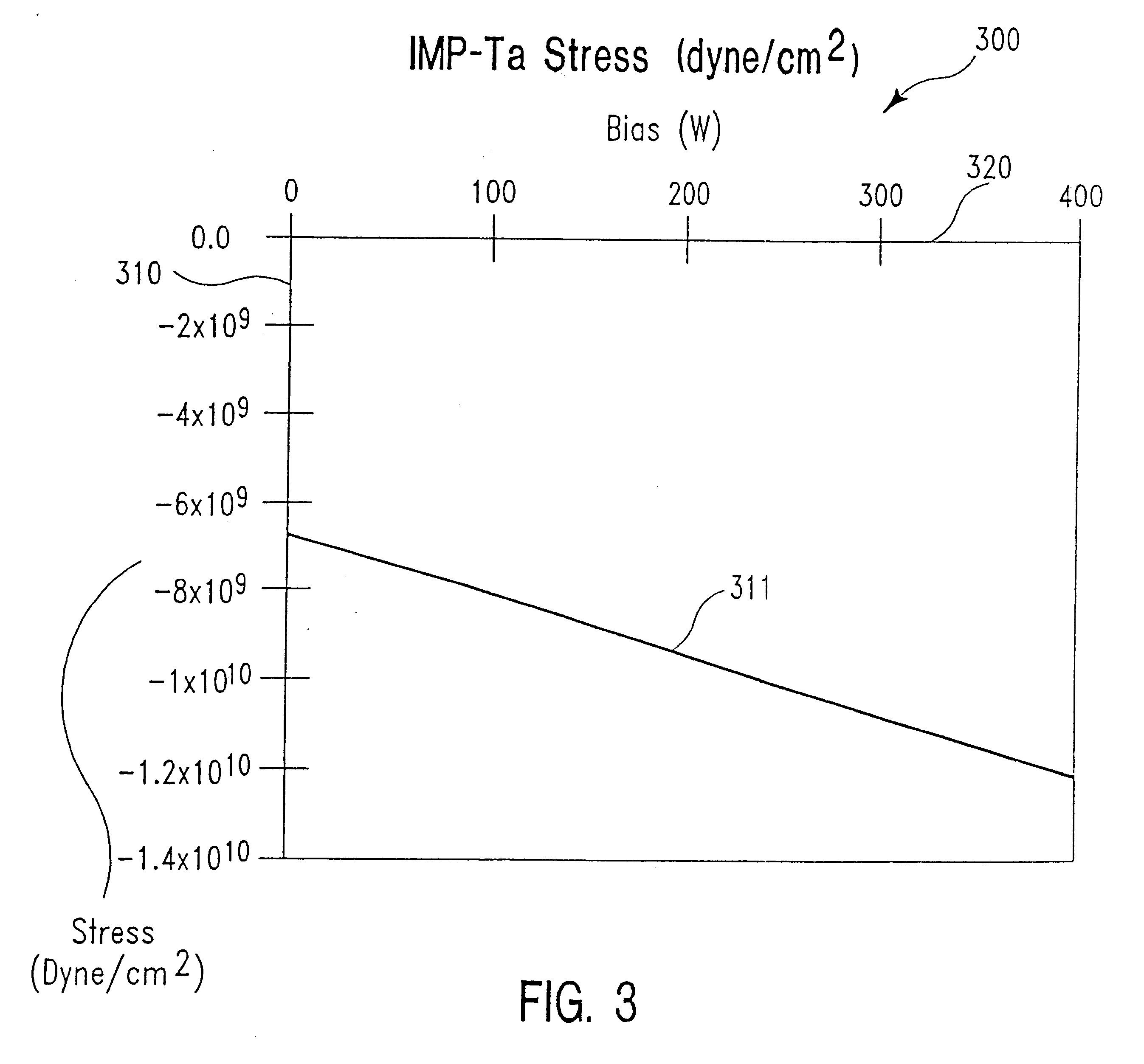
The present disclosure pertains to our discovery that residual stress residing in a tantalum film or tantalum nitride film can be controlled (tuned) during deposition by adjusting at least two particular process variables which have counteracting effects on the residual film stress. By tuning individual film stresses within a film stack, it is possible to balance stresses within the stack. Process variables of particular interest include: power to the sputtering target process chamber pressure (i.e., the concentration of various gases and ions present in the chamber); substrate DC offset bias voltage (typically an increase in the AC applied substrate bias power); power to an ionization source (typically a coil); and temperature of the substrate upon which the film is deposited. The process chamber pressure and the substrate offset bias most significantly affect the film tensile and compressive stress components, respectively. The most advantageous tuning of a sputtered film is achieved using high density plasma sputter deposition, which provides for particular control over the ion bombardment of the depositing film surface. When the tantalum or tantalum nitride film is deposited using high density plasma sputtering, power to the ionization source can be varied for stress tuning of the film. We have been able to reduce the residual stress in tantalum or tantalum nitride films deposited using high density plasma sputtering to between about 6x10+9 dynes / cm2 and about -6x10+9 dynes / cm2 using techniques described herein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus for fabricating a high dielectric constant transistor gate using a low energy plasma system
The present invention generally provides methods and apparatuses that are adapted to form a high quality dielectric gate layer on a substrate. Embodiments contemplate a method wherein a metal plasma treatment process is used in lieu of a standard nitridization process to form a high dielectric constant layer on a substrate. Embodiments further contemplate an apparatus adapted to “implant” metal ions of relatively low energy in order to reduce ion bombardment damage to the gate dielectric layer, such as a silicon dioxide layer and to avoid incorporation of the metal atoms into the underlying silicon. In general, the process includes the steps of forming a high-k dielectric and then terminating the surface of the deposited high-k material to form a good interface between the gate electrode and the high-k dielectric material. Embodiments of the invention also provide a cluster tool that is adapted to form a high-k dielectric material, terminate the surface of the high-k dielectric material, perform any desirable post treatment steps, and form the polysilicon and / or metal gate layers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
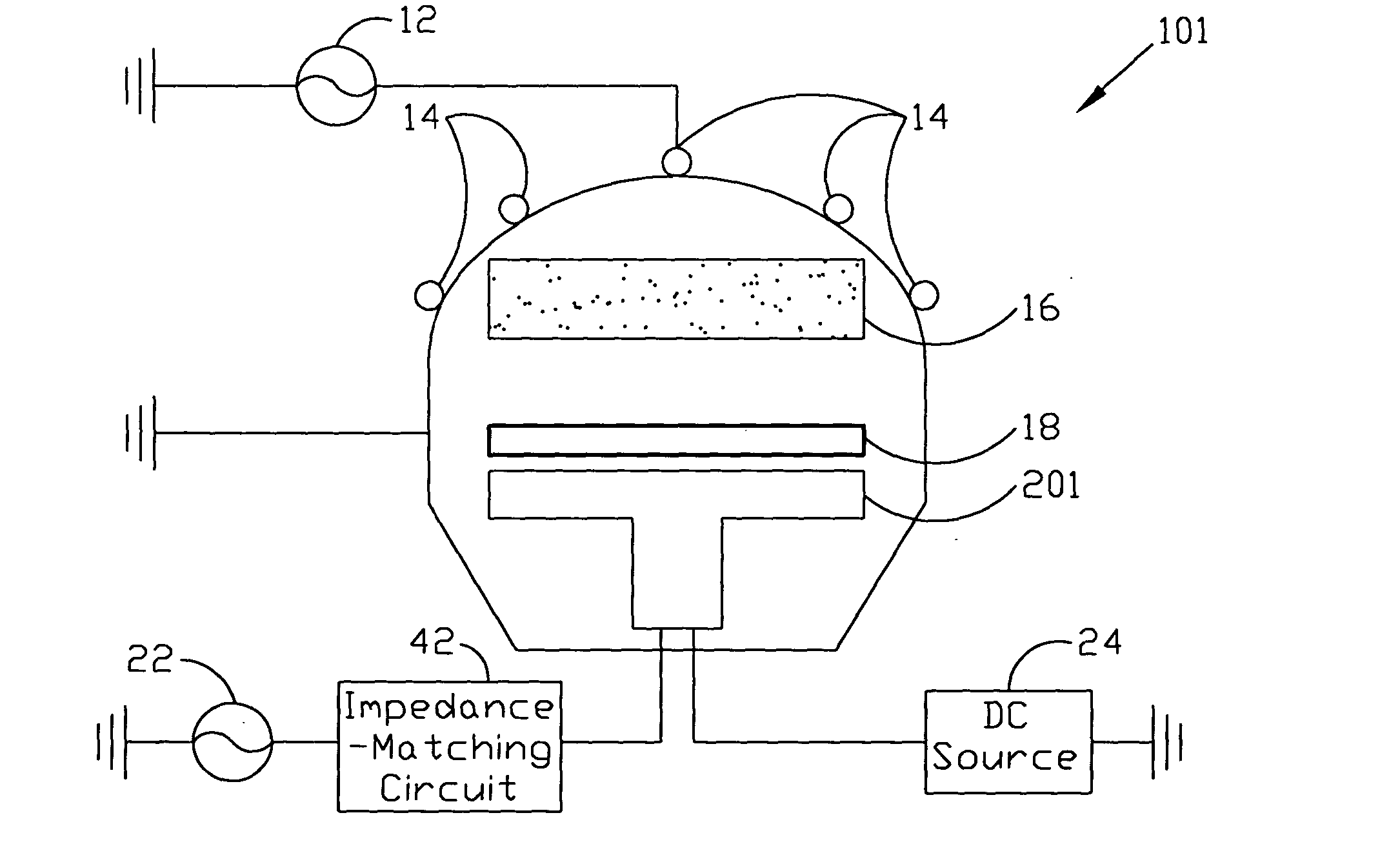
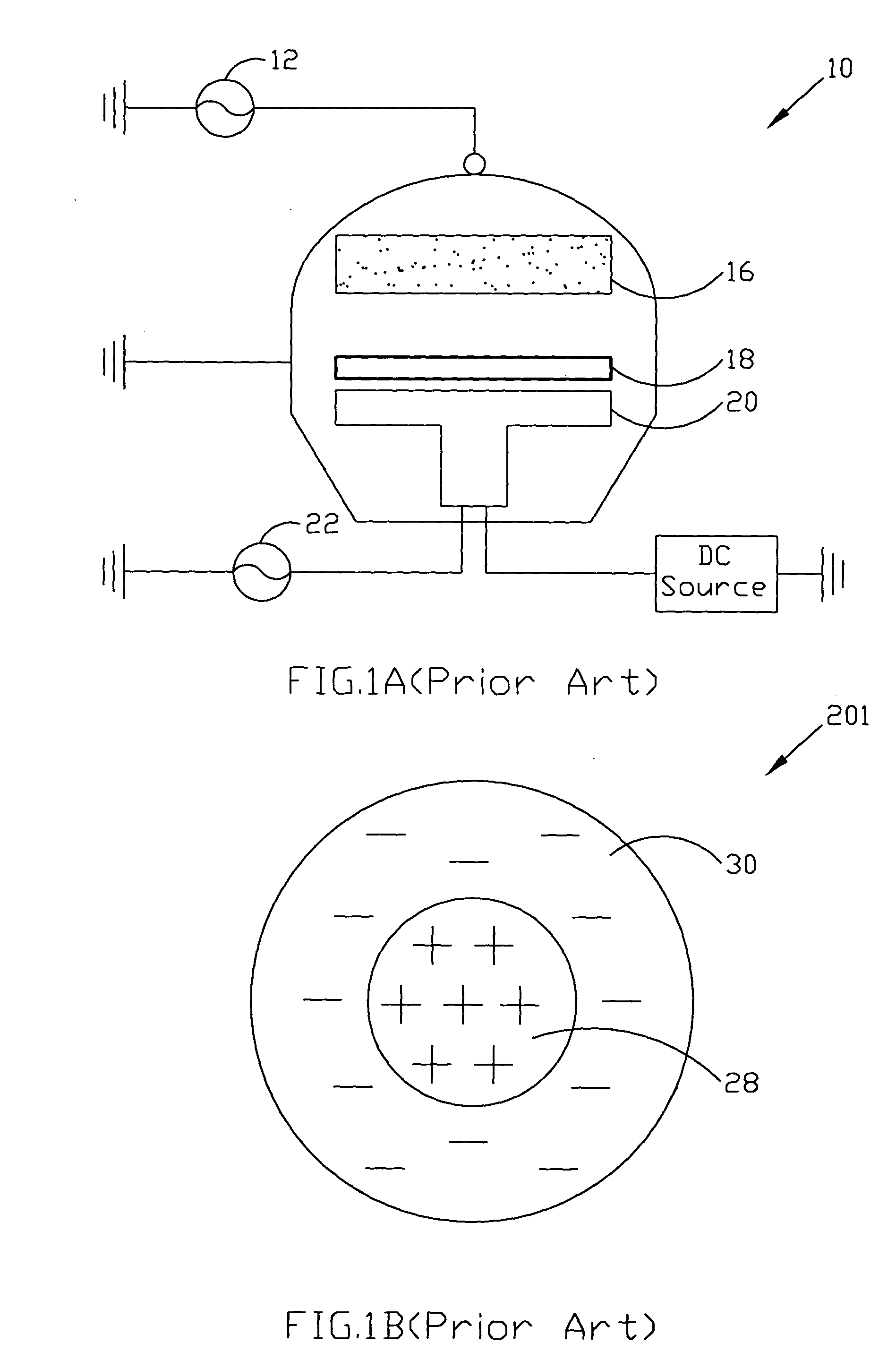
Plasma apparatus and method capable of adaptive impedance matching
ActiveUS20050056369A1Low failure rateSleeve/socket jointsElectric discharge tubesIon bombardmentGas phase
A plasma apparatus capable of adaptive impedance matching comprises a plasma reactor which can produce plasma to proceed with CVD (chemical vapor deposition) process, a bi-polar electrostatic chuck which locates inside the plasma reactor and is used to support and secure a wafer, an alternating current bias power supply which connects to the bi-polar electrostatic chuck supplies the voltage potential bias for ion-bombardment from plasma, and an impedance-matching circuit which connects the alternating current bias power supply to the bi-polar electrostatic chuck is used to balance the inner electrode power output and the outer electrode power output of the bi-polar electrostatic chuck.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Methods of changing threshold voltages of semiconductor transistors by ion implantation
InactiveUS20090124069A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantIon bombardment
A method for forming a semiconductor structure. The method includes providing a semiconductor structure including a semiconductor substrate. The semiconductor substrate includes (i) a top substrate surface which defines a reference direction perpendicular to the top substrate surface and (ii) a semiconductor body region. The method further includes implanting an adjustment dose of dopants of a first doping polarity into the semiconductor body region by an adjustment implantation process. Ion bombardment of the adjustment implantation process is in the reference direction. The method further includes (i) patterning the semiconductor substrate resulting in side walls of the semiconductor body region being exposed to a surrounding ambient and then (ii) implanting a base dose of dopants of a second doping polarity into the semiconductor body region by a base implantation process. Ion bombardment of the base implantation process is in a direction which makes a non-zero angle with the reference direction.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com