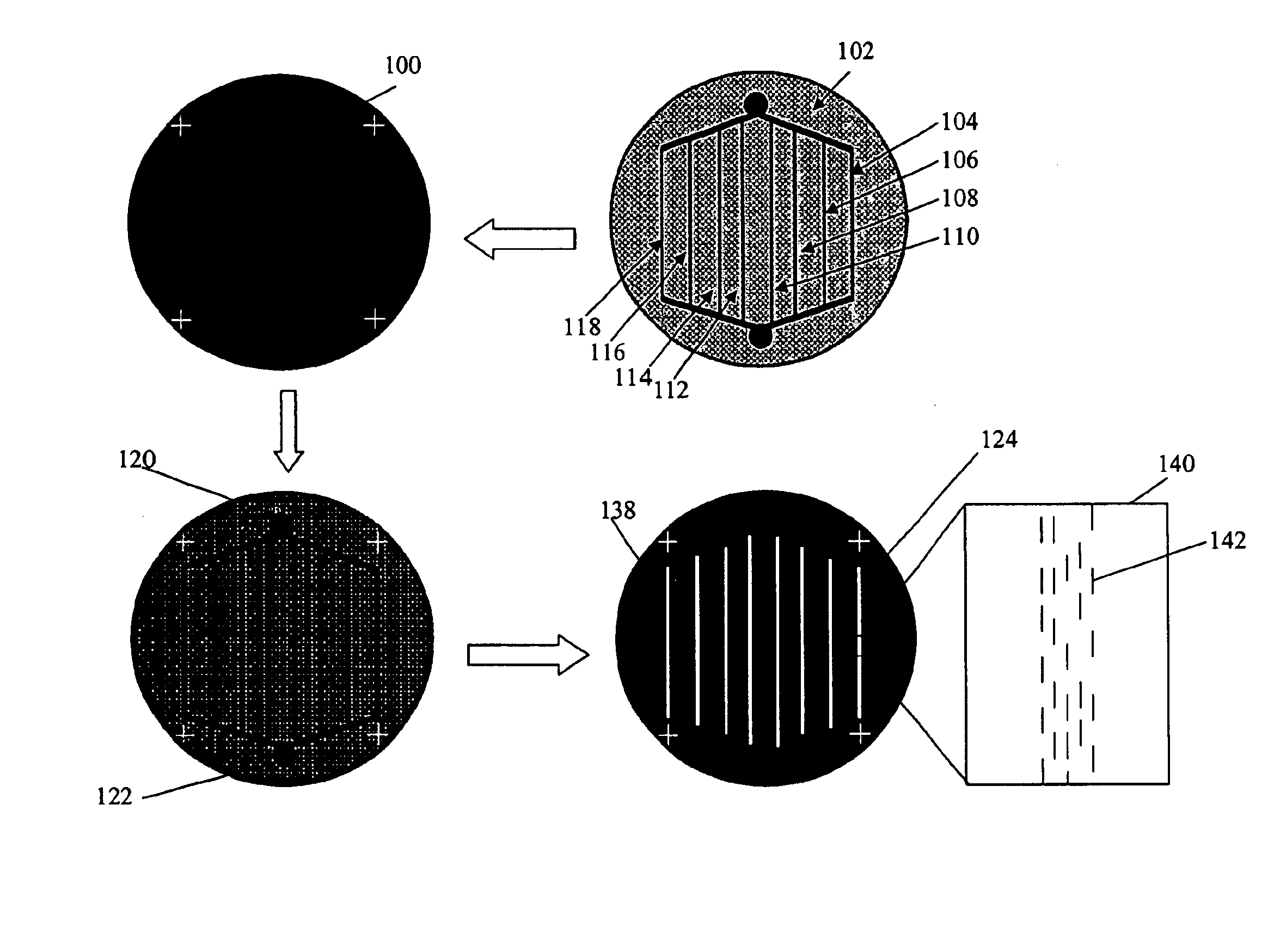
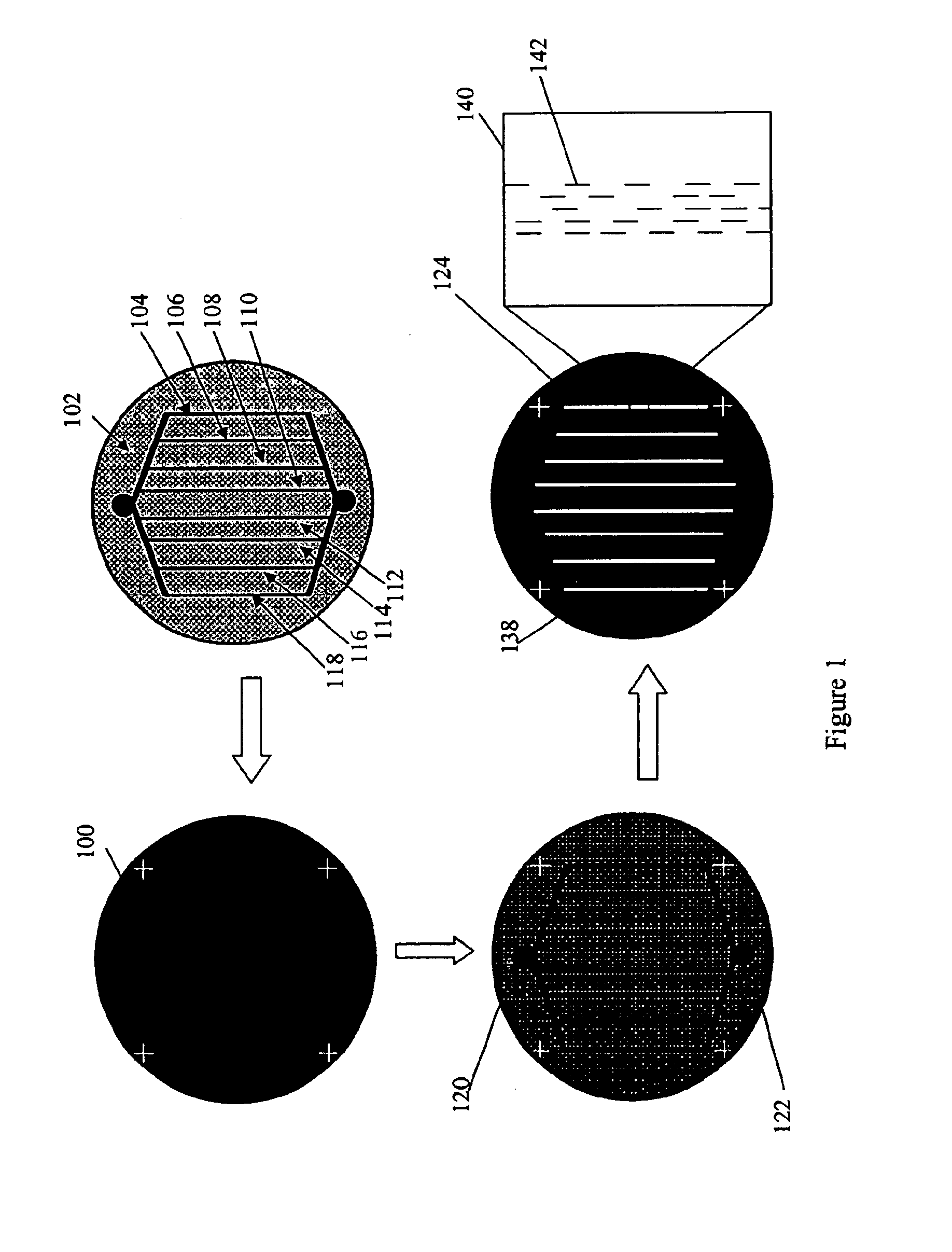
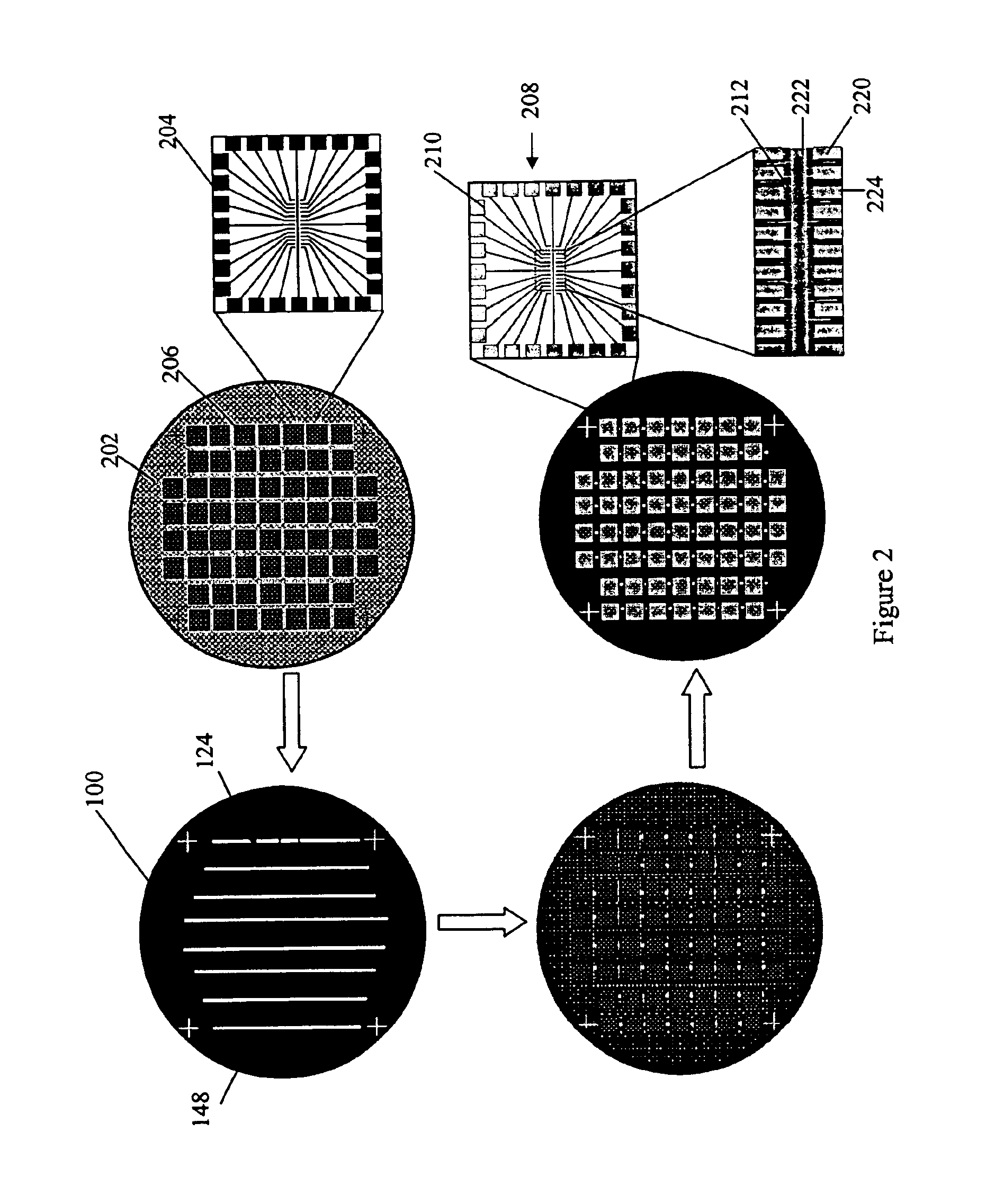
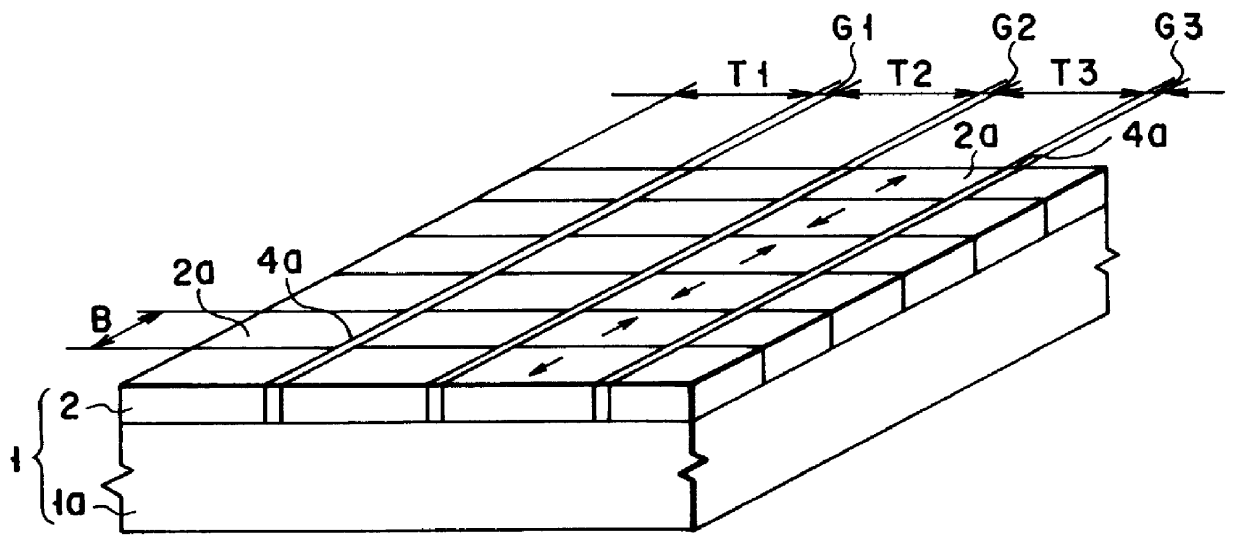
Patents
Literature
961results about "Patterned record carriers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of positioning and/or orienting nanostructures
Methods of positioning and orienting nanostructures, and particularly nanowires, on surfaces for subsequent use or integration. The methods utilize mask based processes alone or in combination with flow based alignment of the nanostructures to provide oriented and positioned nanostructures on surfaces. Also provided are populations of positioned and / or oriented nanostructures, devices that include populations of positioned and / or oriented nanostructures, systems for positioning and / or orienting nanostructures, and related devices, systems and methods.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
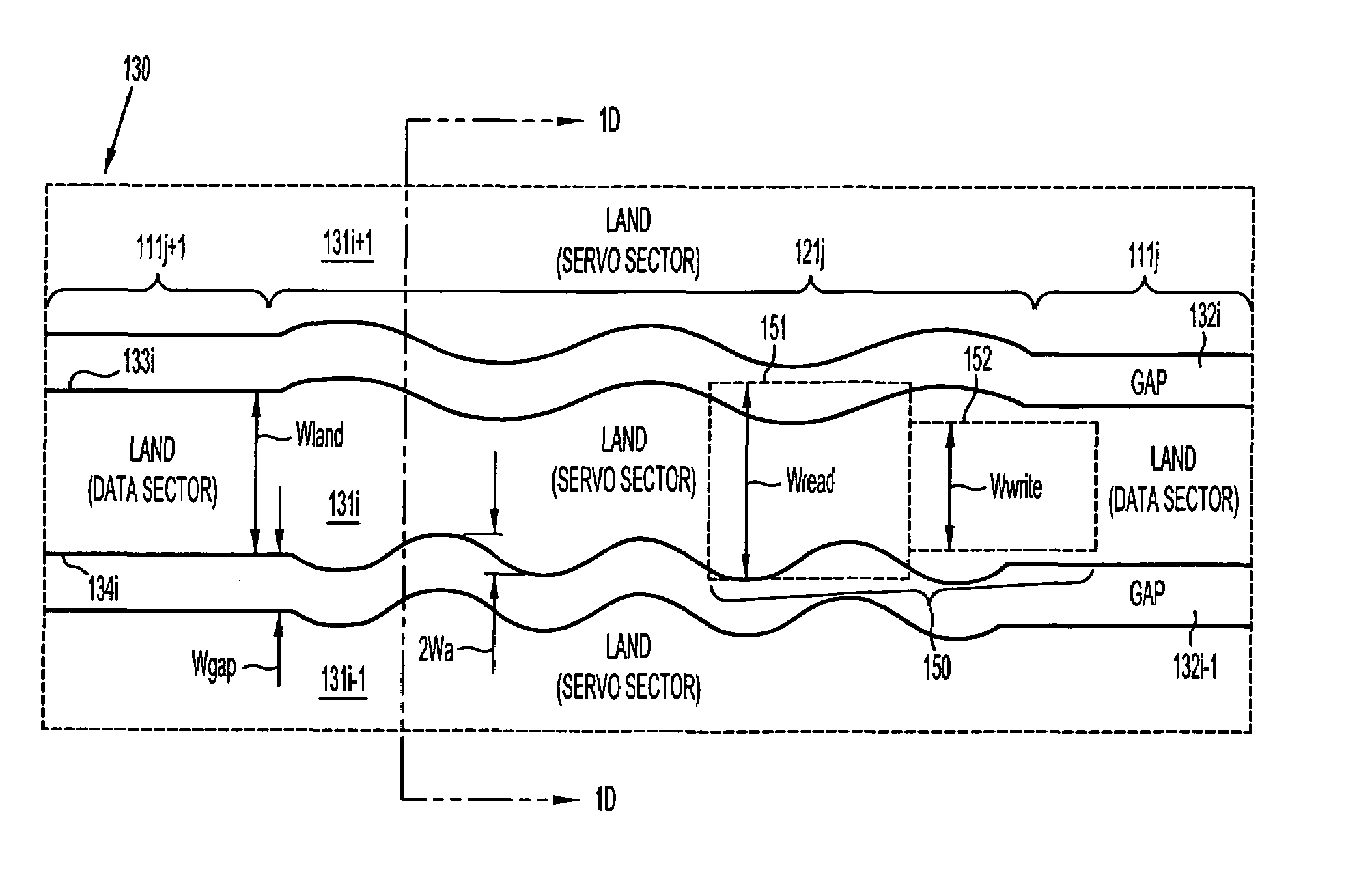
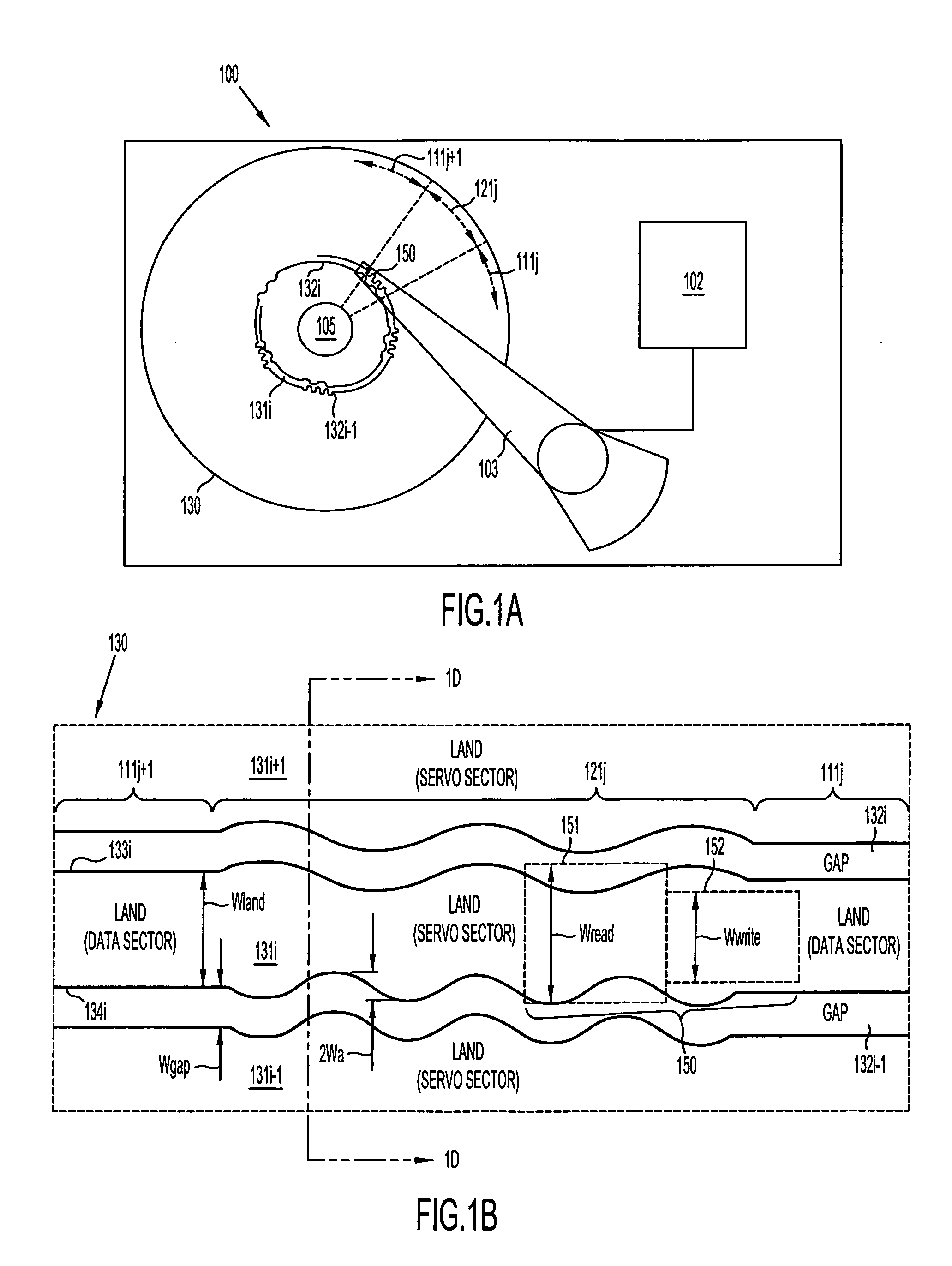
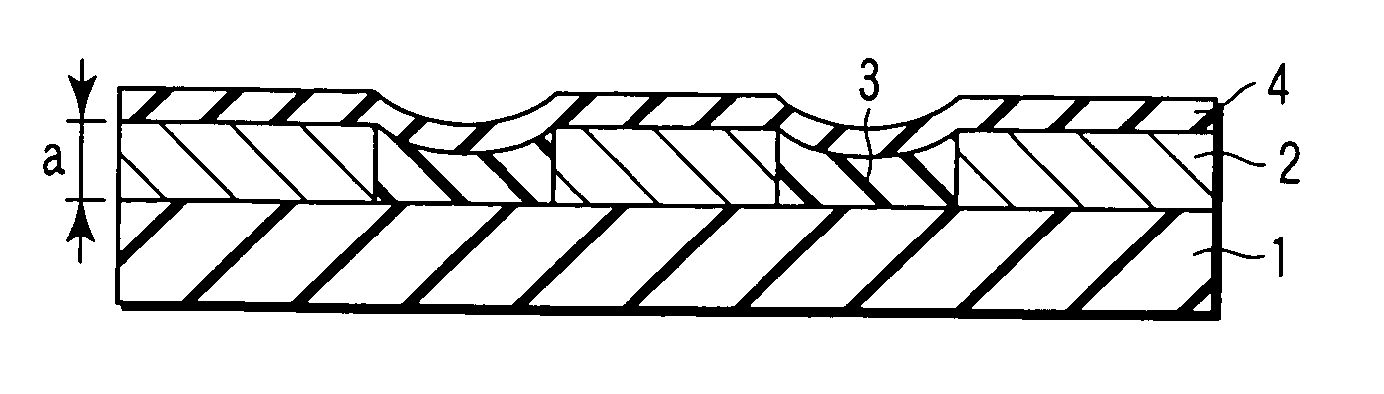
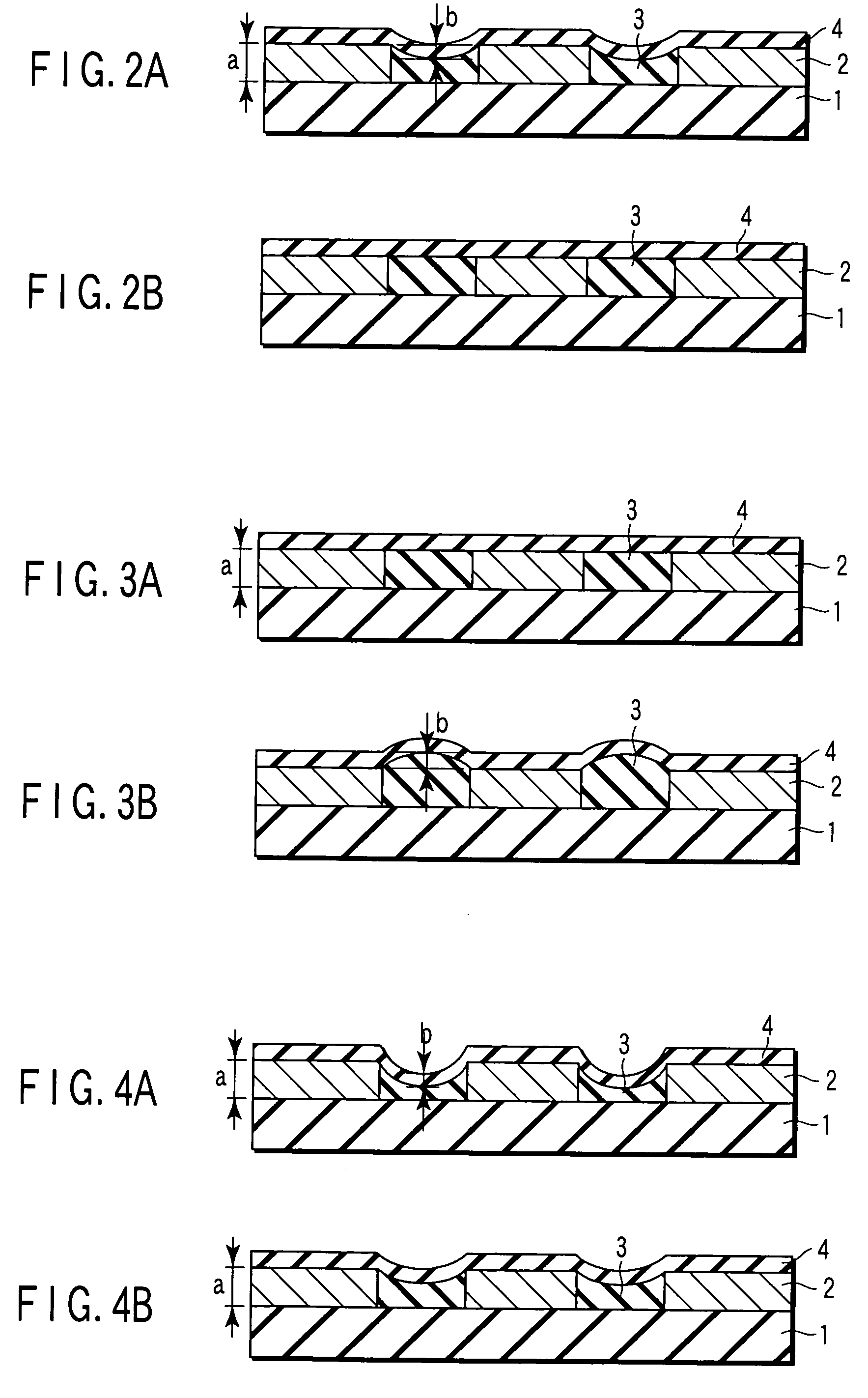
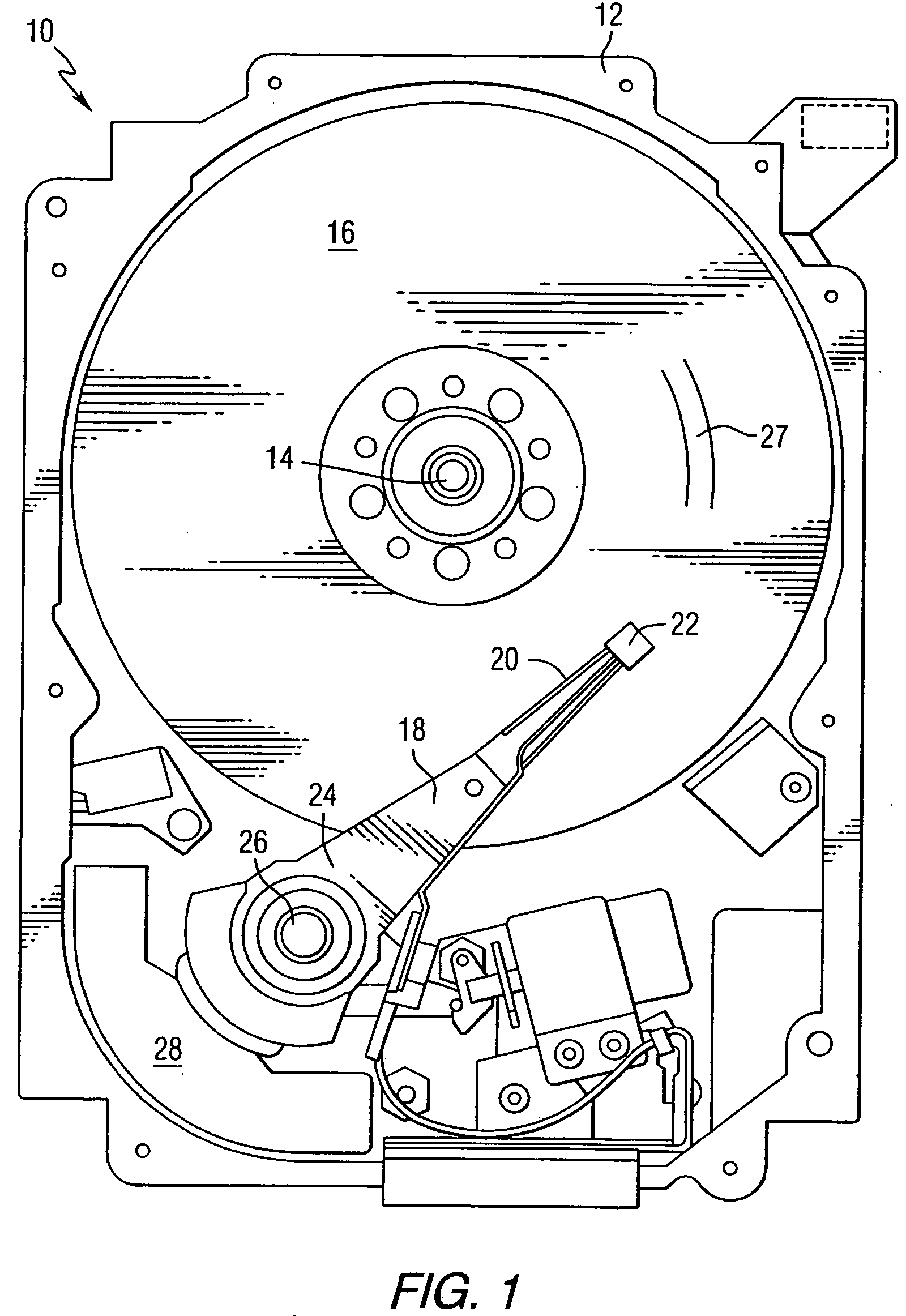
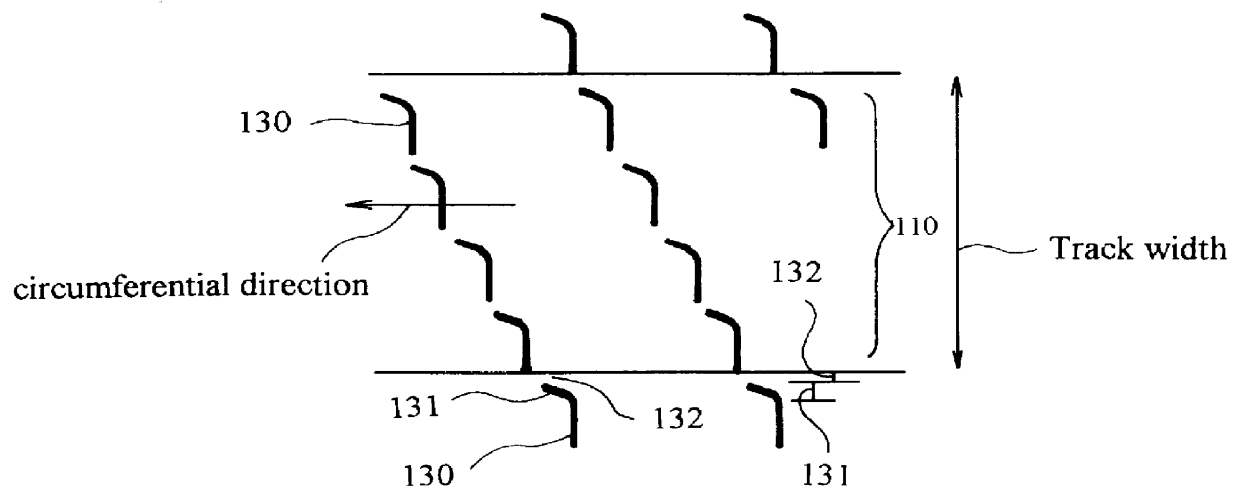
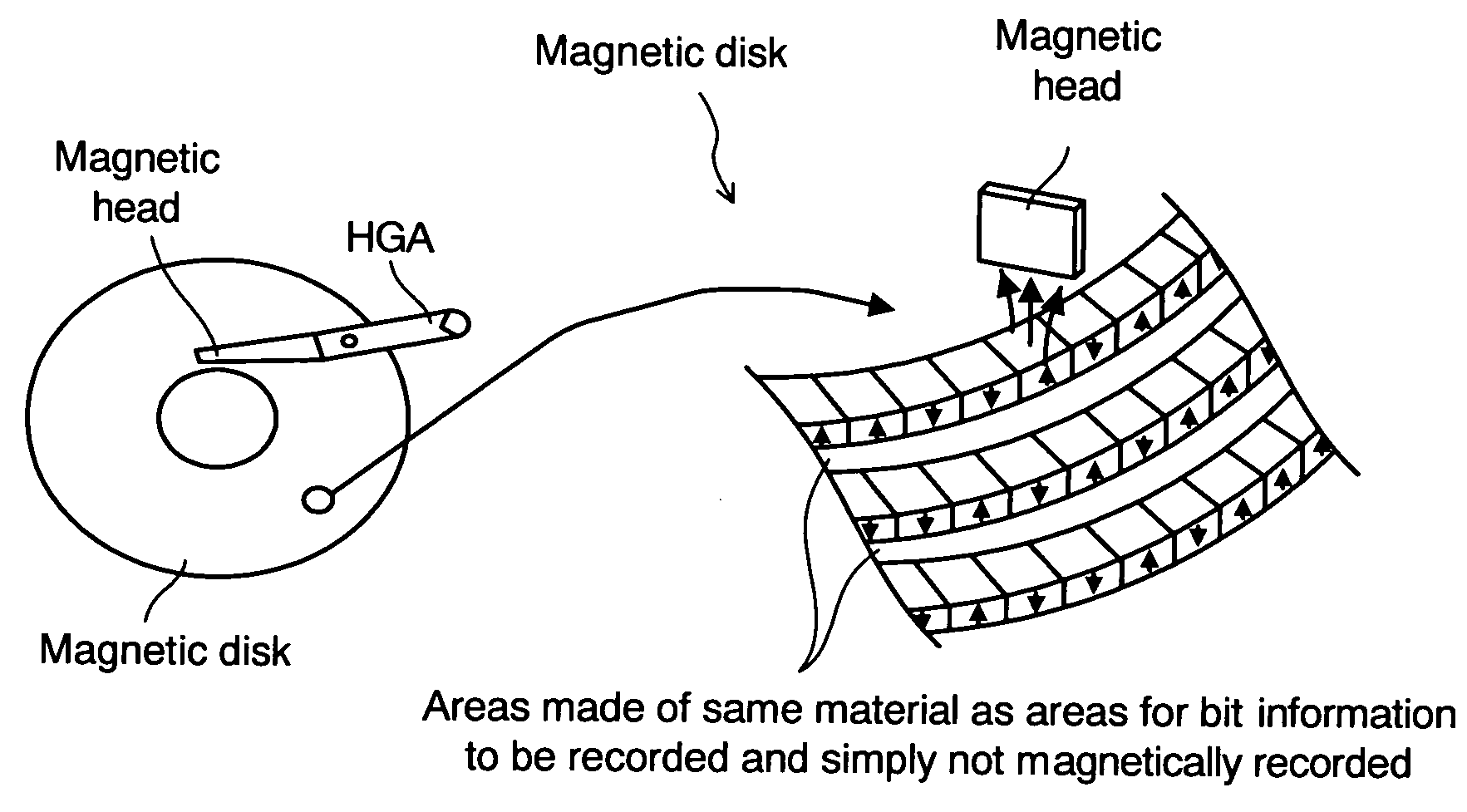
Magnetic disk with a guard band arrangement
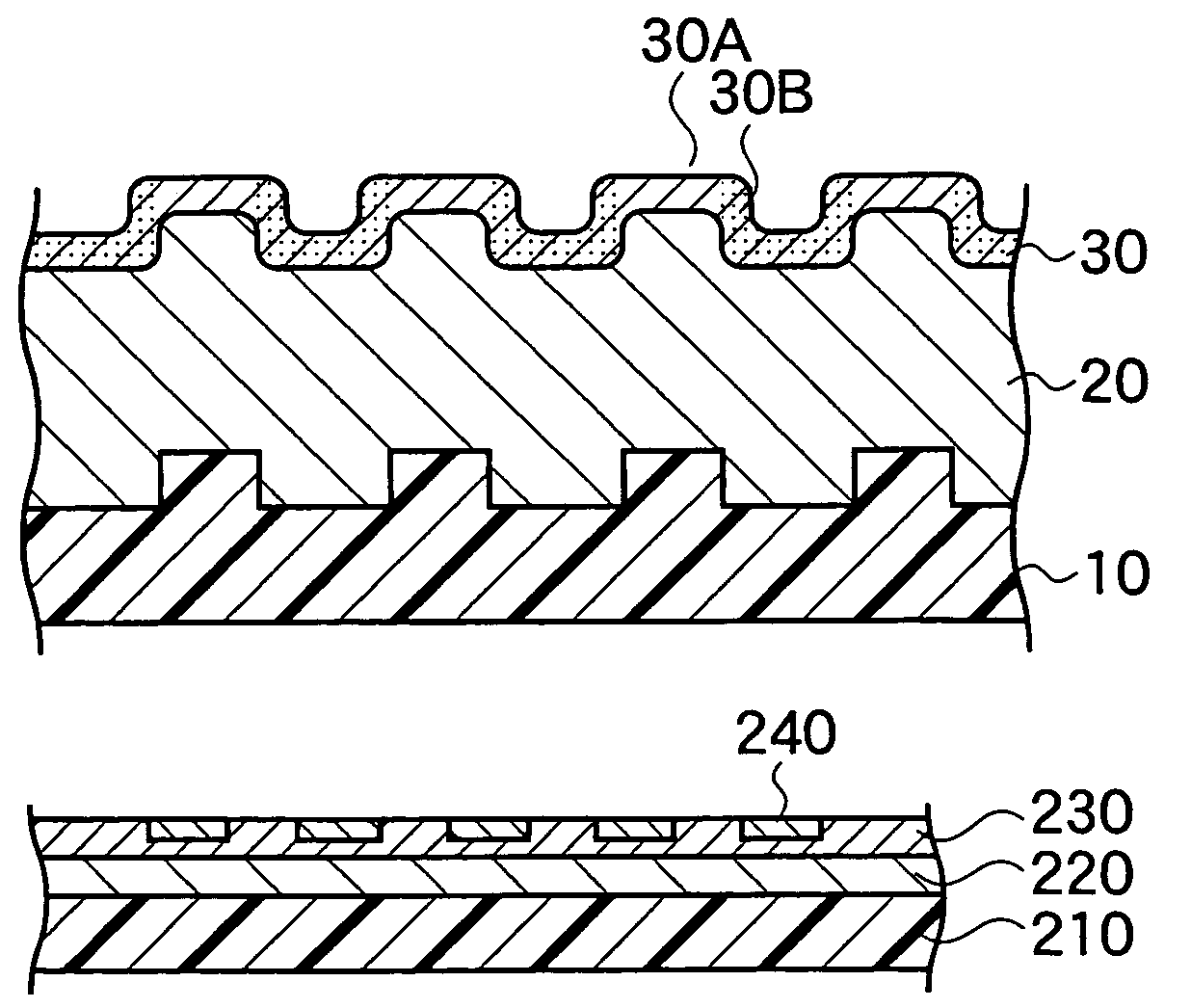
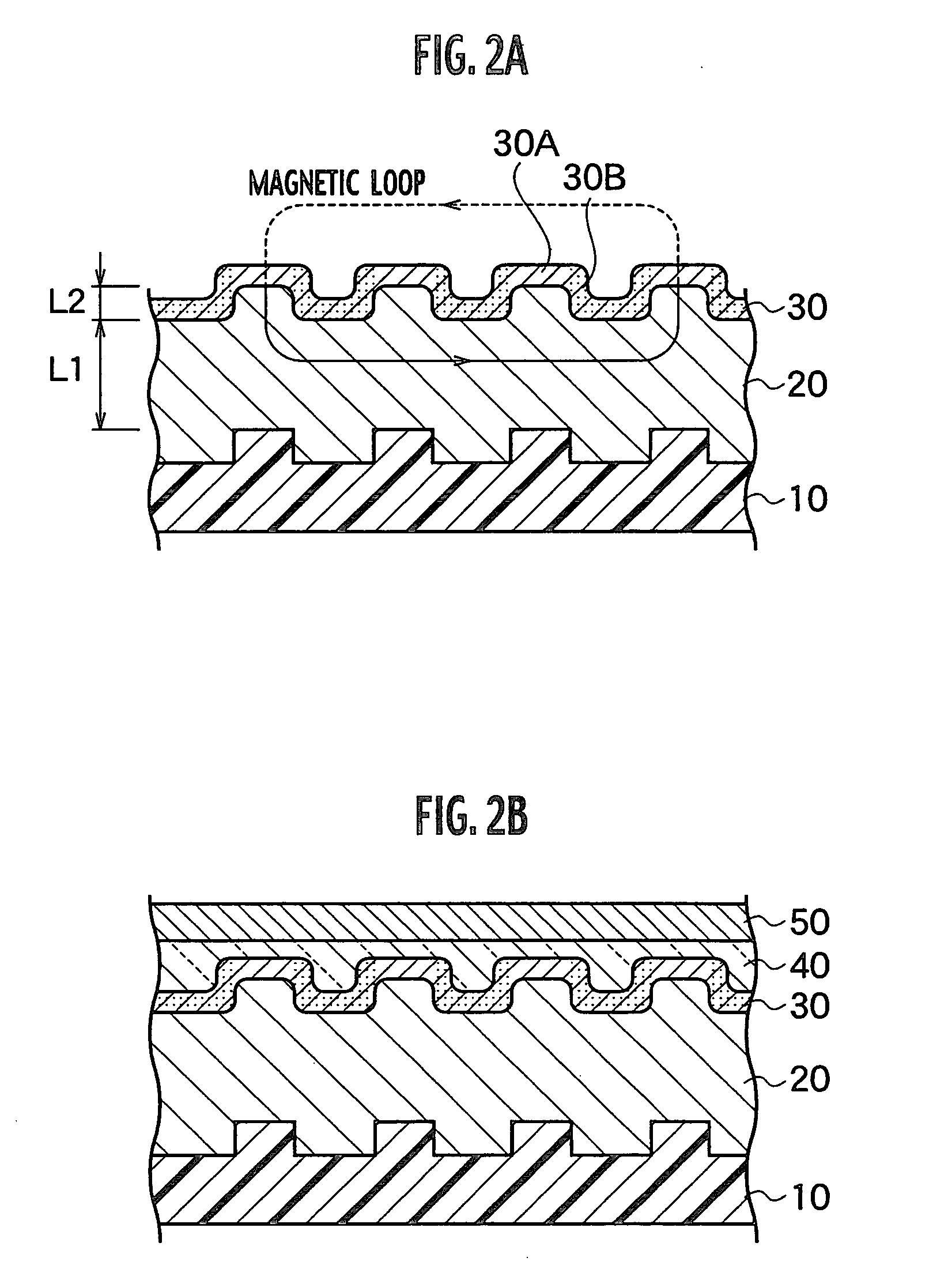
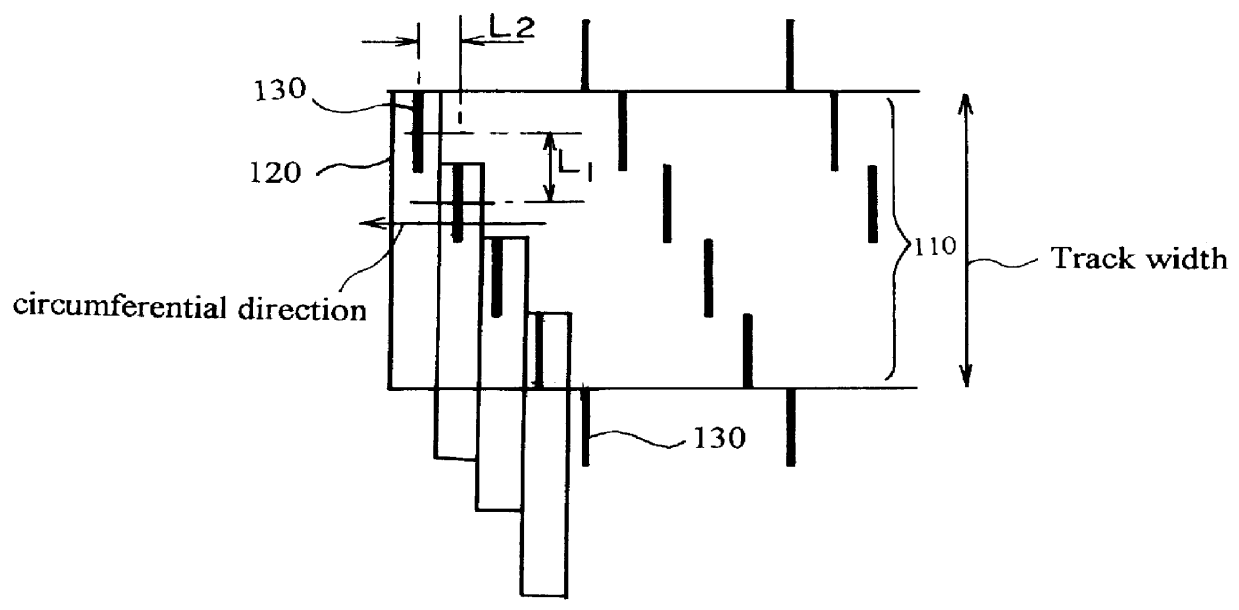
A magnetic disk including a substrate, a recording track section which is made of a magnetic member for recording and reproducing information magnetically and is provided on the substrate, and a guard band member which is provided between the recording track sections adjacent to each other so that they are substantially continued in a track direction and is harder than the magnetic member and is made of a non-magnetic material. Moreover, the magnetic member is not provided or magnetic members with a different thickness from the magnetic member forming the recording track section is provided on a lower area of the guard band member.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
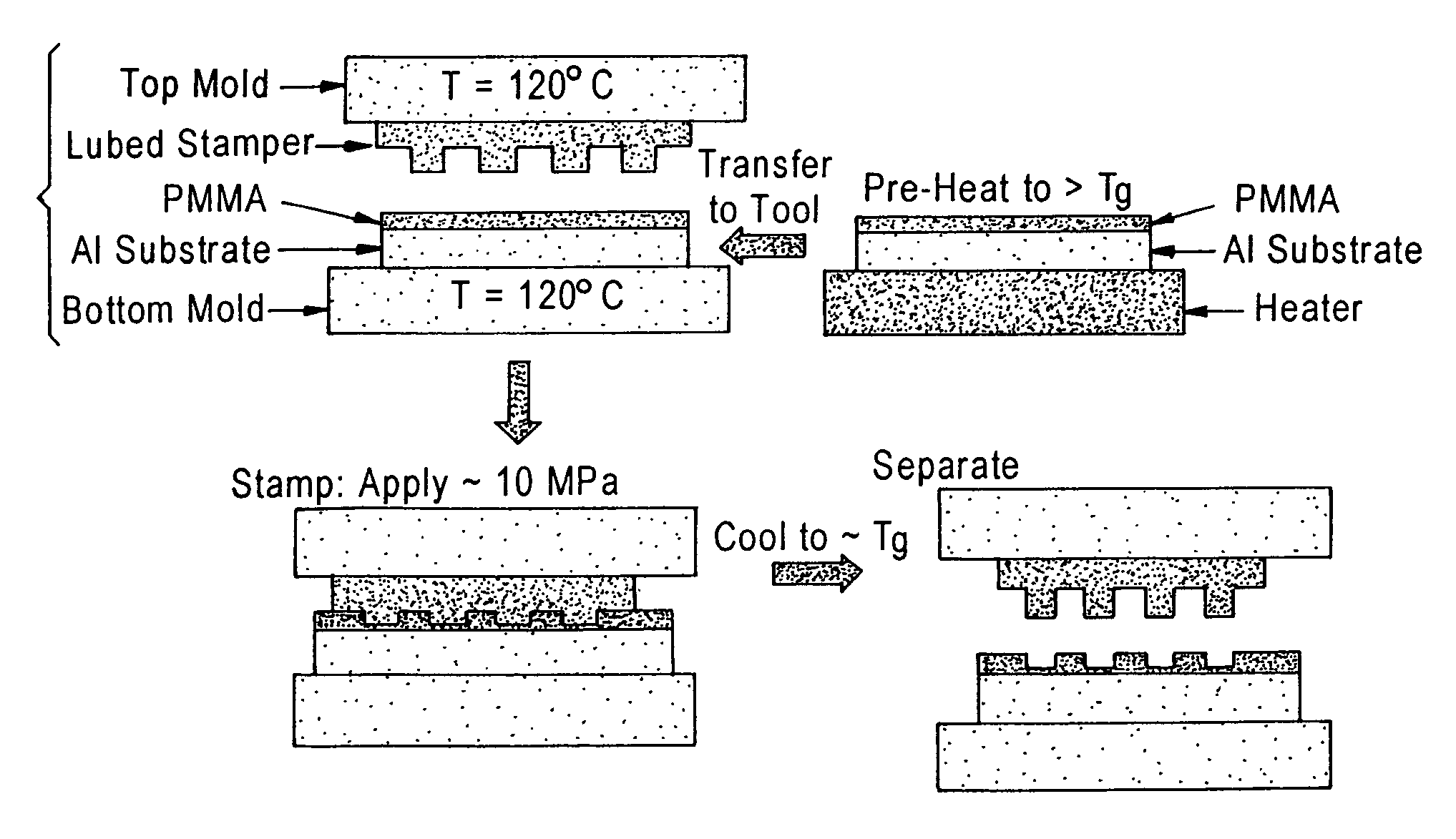
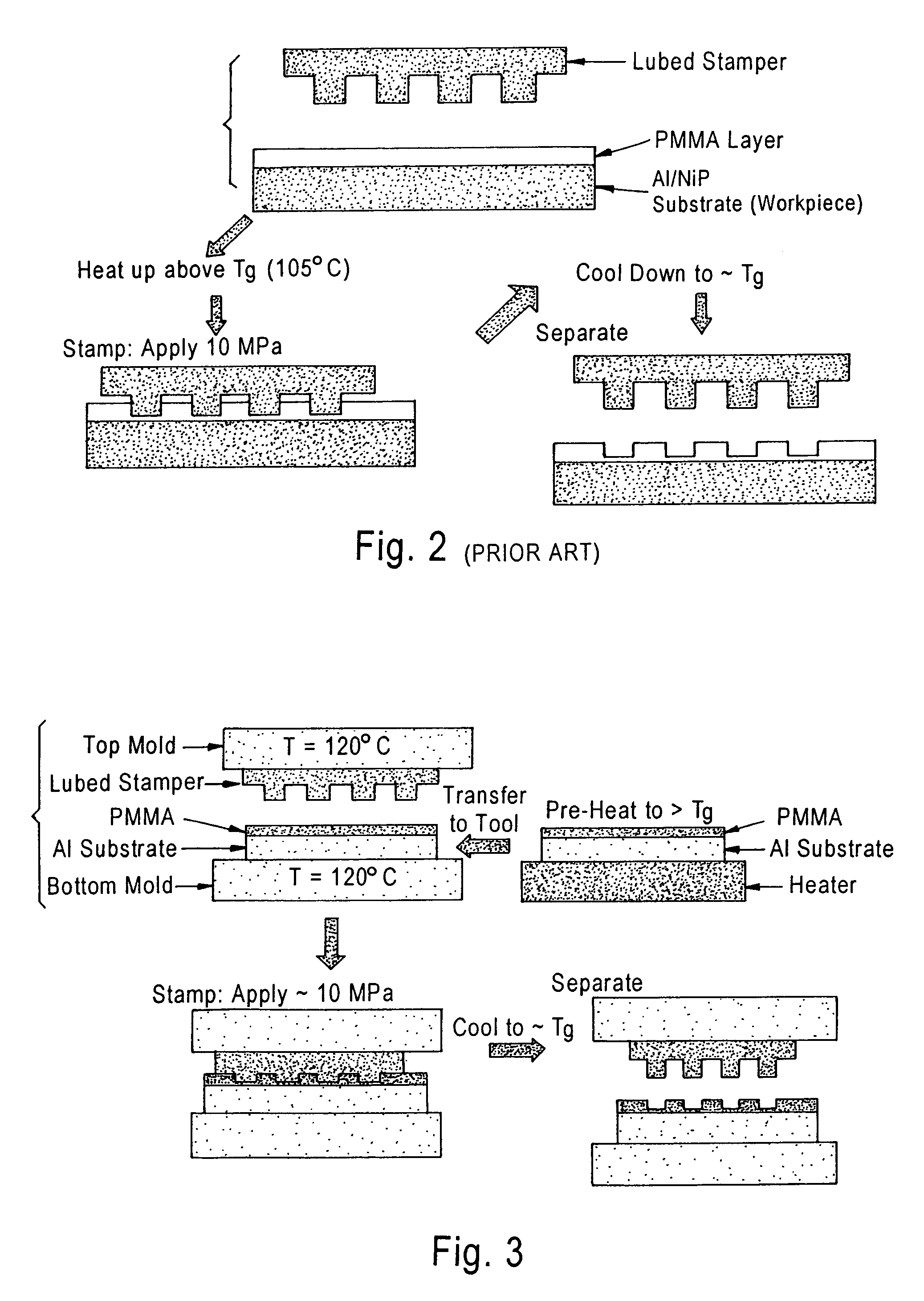
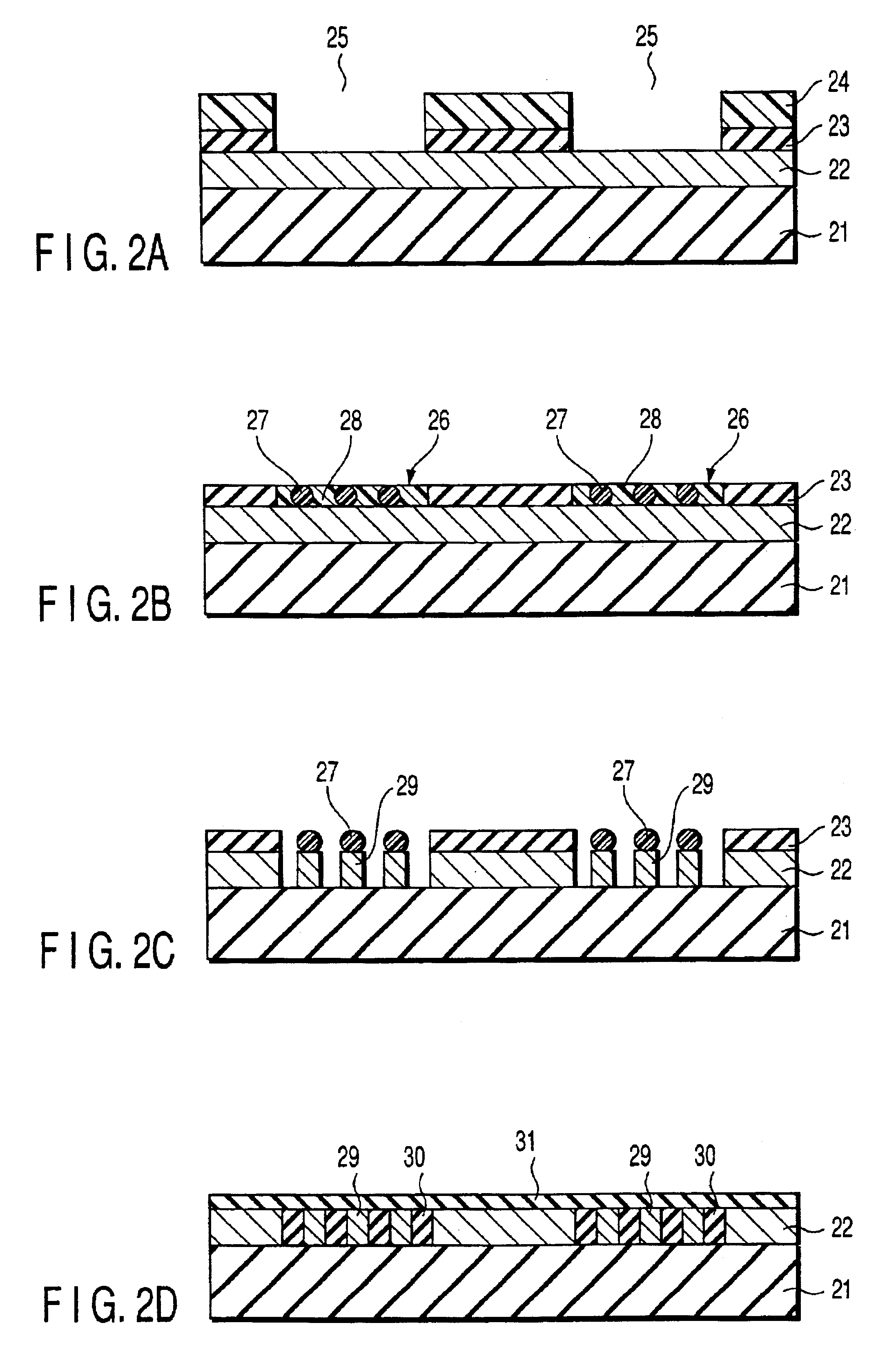
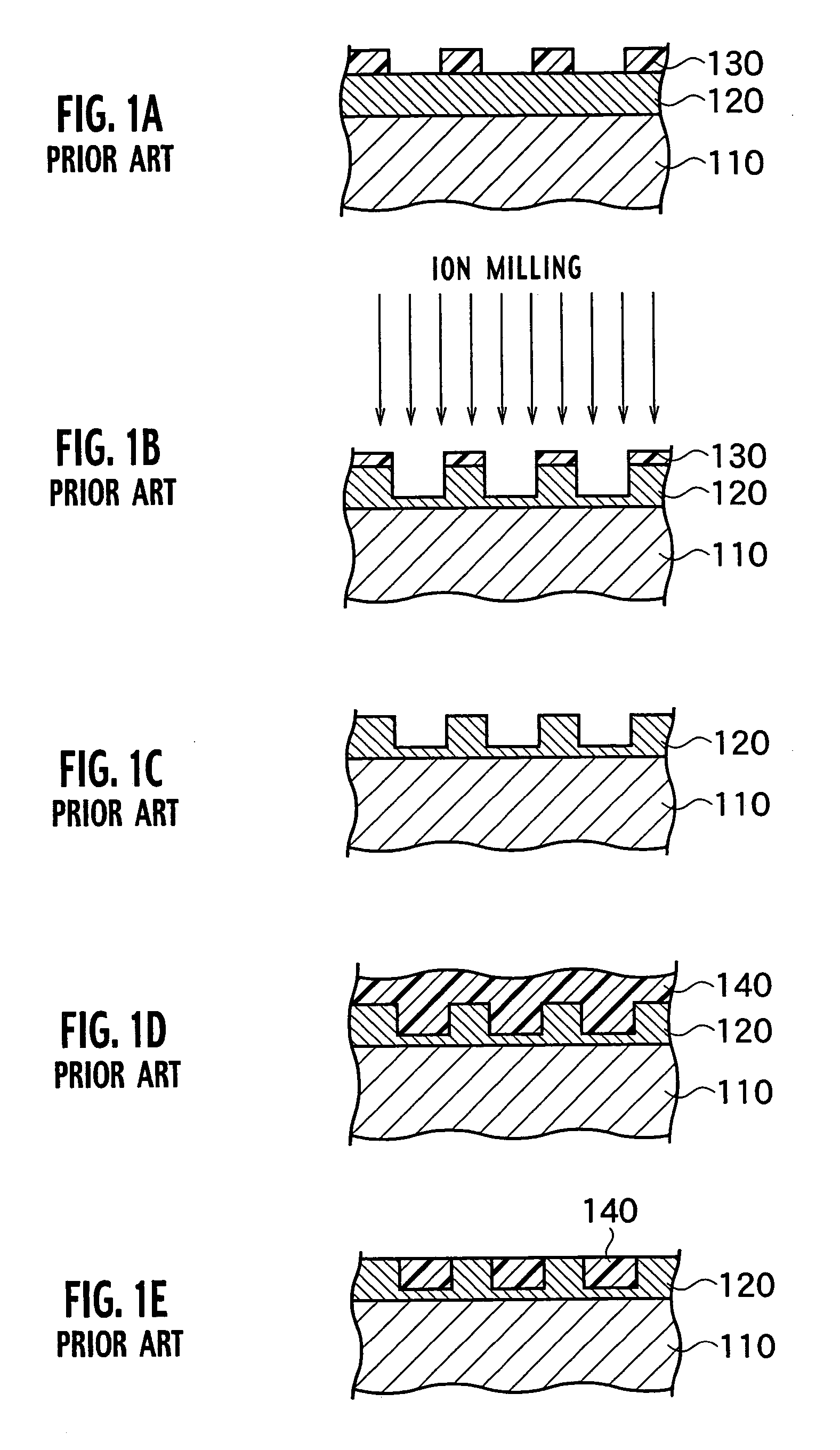
Heat-transfer-stamp process for thermal imprint lithography
InactiveUS6949199B1Eliminate disadvantagesSimple methodNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsStamping processPlanographic printing
A method of performing thermal imprint lithography of a surface of a thermoplastic layer-coated workpiece for forming a pattern therein comprises pre-heating the workpiece to a pre-selected high temperature prior to inserting the workpiece in a stamping / imprinting tool maintained at a predetermined lower temperature, whereby the interval for thermal cycling of the stamping / imprinting tool between higher and lower temperatures is eliminated or at least reduced. Applications of the method include forming servo patterns in disk-shaped substrates for hard disk recording media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Methods of making, positioning and orienting nanostructures, nanostructure arrays and nanostructure devices
InactiveUS20050230356A1Easy to controlHigh resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanostructure fabricationNanostructure
Nanostructure manufacturing methods and methods for assembling nanostructures into functional elements such as junctions, arrays and devices are provided. Systems for practicing the methods are also provided.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
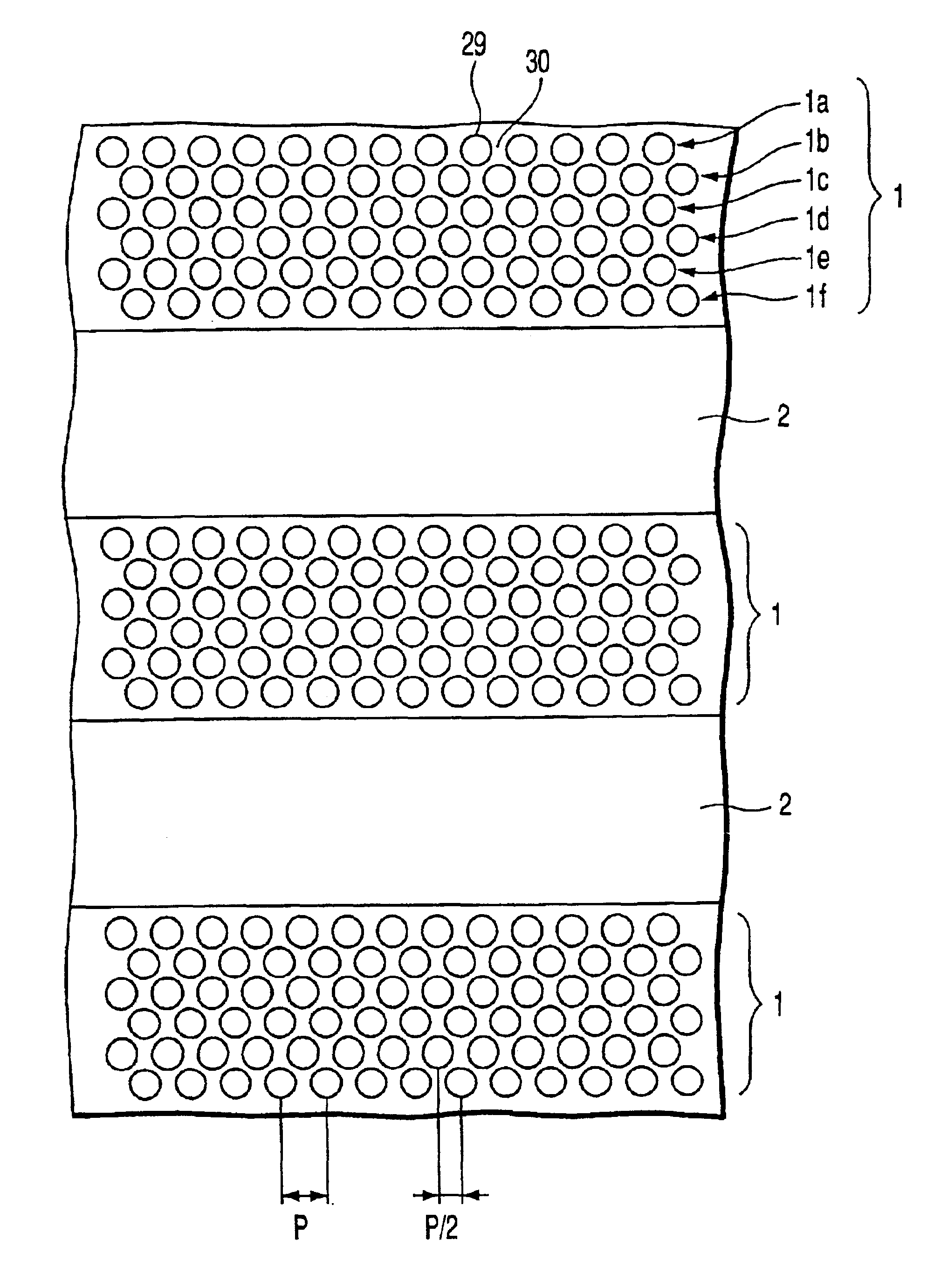
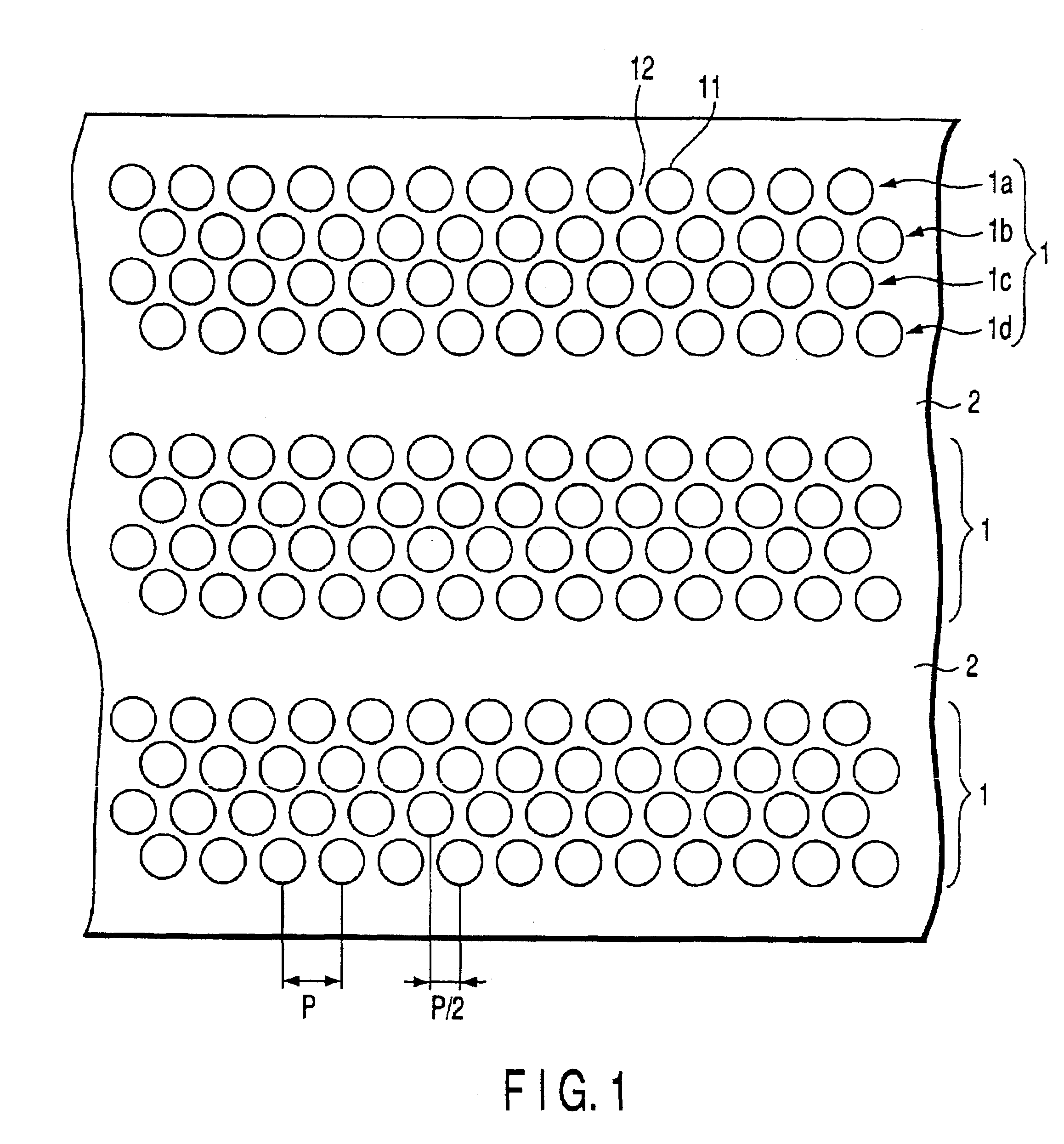
Recording medium including patterned tracks and isolation regions
InactiveUS6977108B2Easy to manufactureIncrease speedTrack finding/aligningMagnetic materials for record carriersEngineeringRecording layer
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
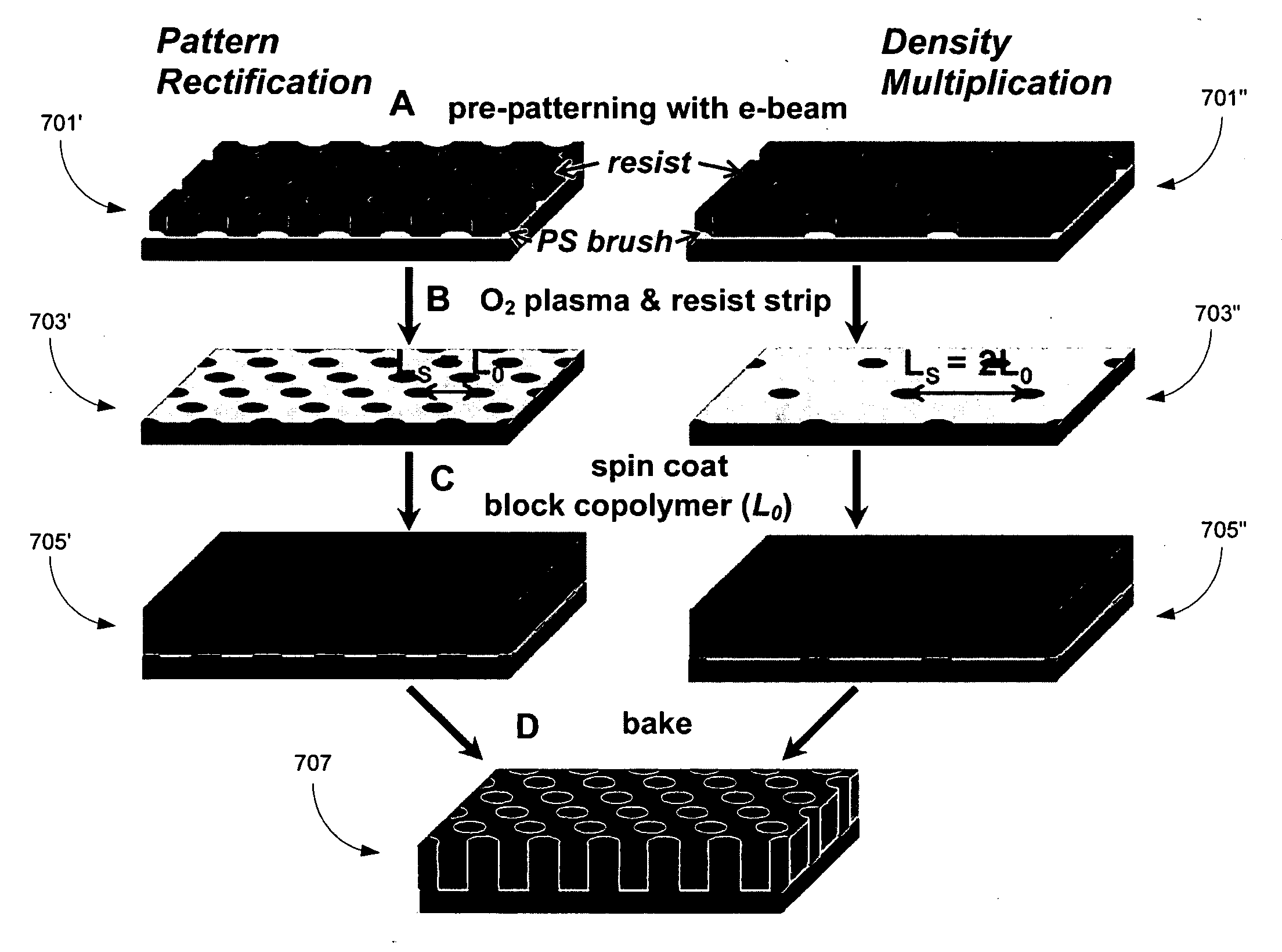
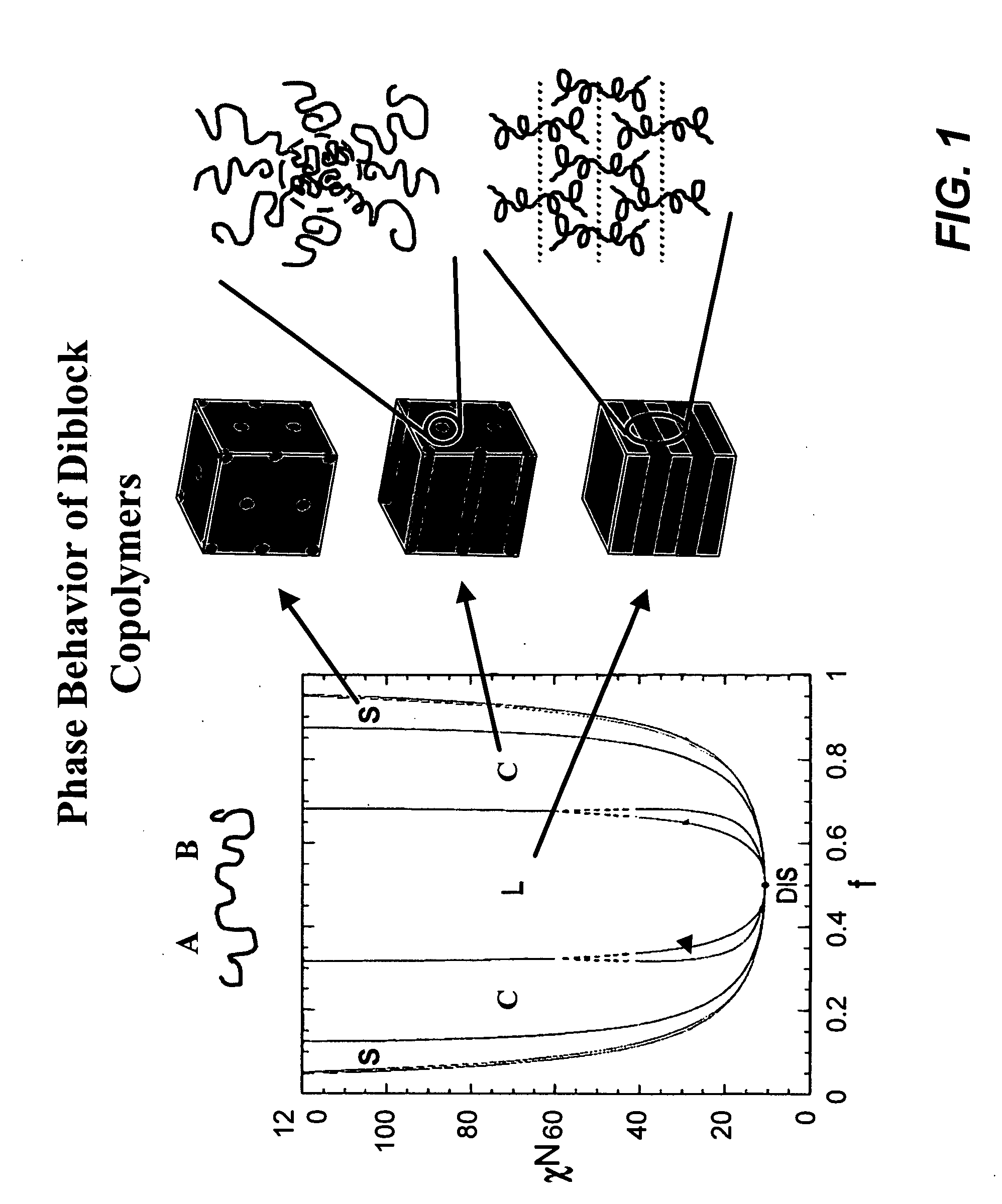
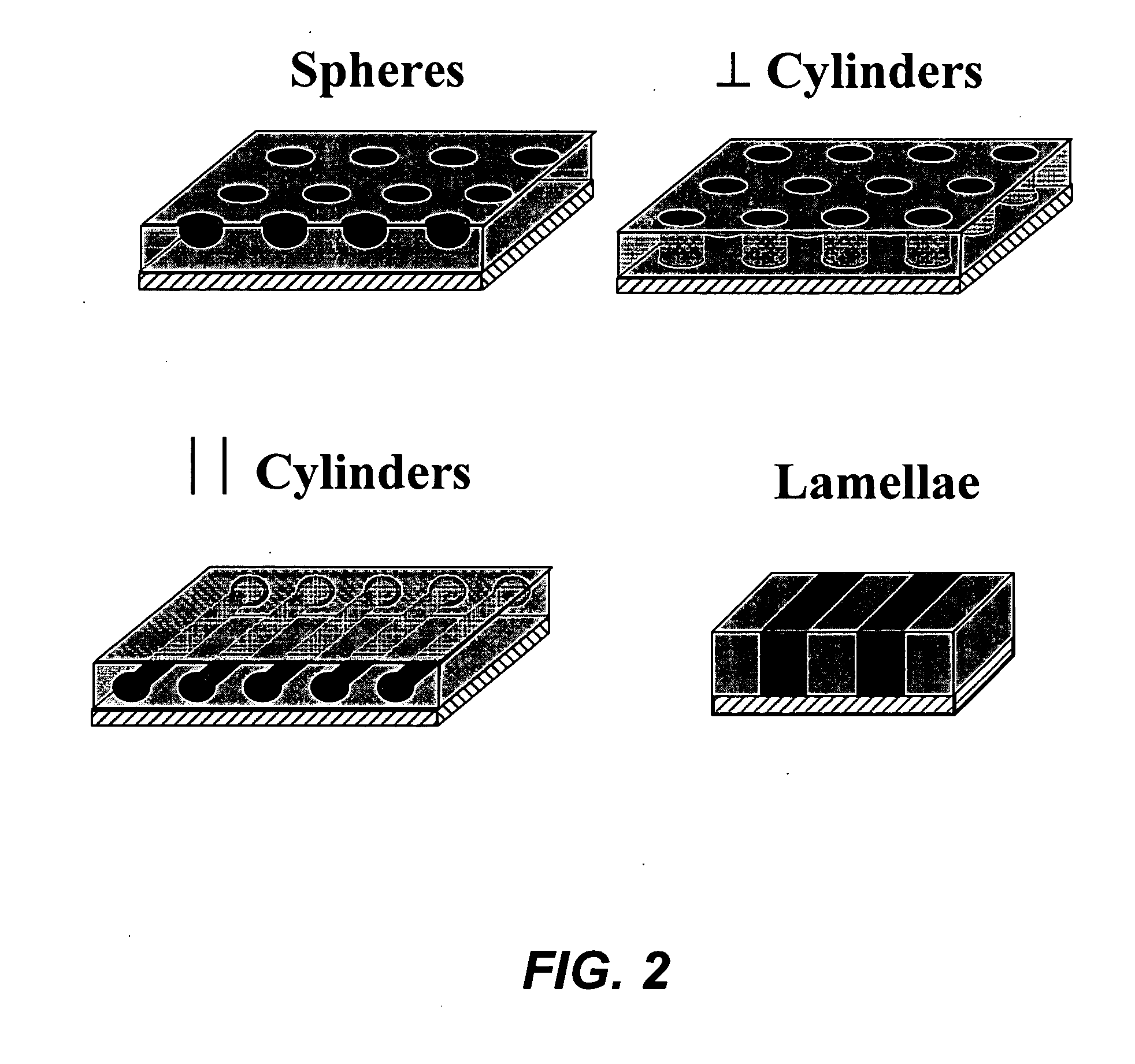
Density multiplication and improved lithography by directed block copolymer assembly
ActiveUS20090196488A1High densityQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyPatterned record carriersHigh densityPeriodic nanostructures
Methods to pattern substrates with dense periodic nanostructures that combine top-down lithographic tools and self-assembling block copolymer materials are provided. According to various embodiments, the methods involve chemically patterning a substrate, depositing a block copolymer film on the chemically patterned imaging layer, and allowing the block copolymer to self-assemble in the presence of the chemically patterned substrate, thereby producing a pattern in the block copolymer film that is improved over the substrate pattern in terms feature size, shape, and uniformity, as well as regular spacing between arrays of features and between the features within each array compared to the substrate pattern. In certain embodiments, the density and total number of pattern features in the block copolymer film is also increased. High density and quality nanoimprint templates and other nanopatterned structures are also provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Modulation of sidewalls of servo sectors of a magnetic disk and the resultant disk
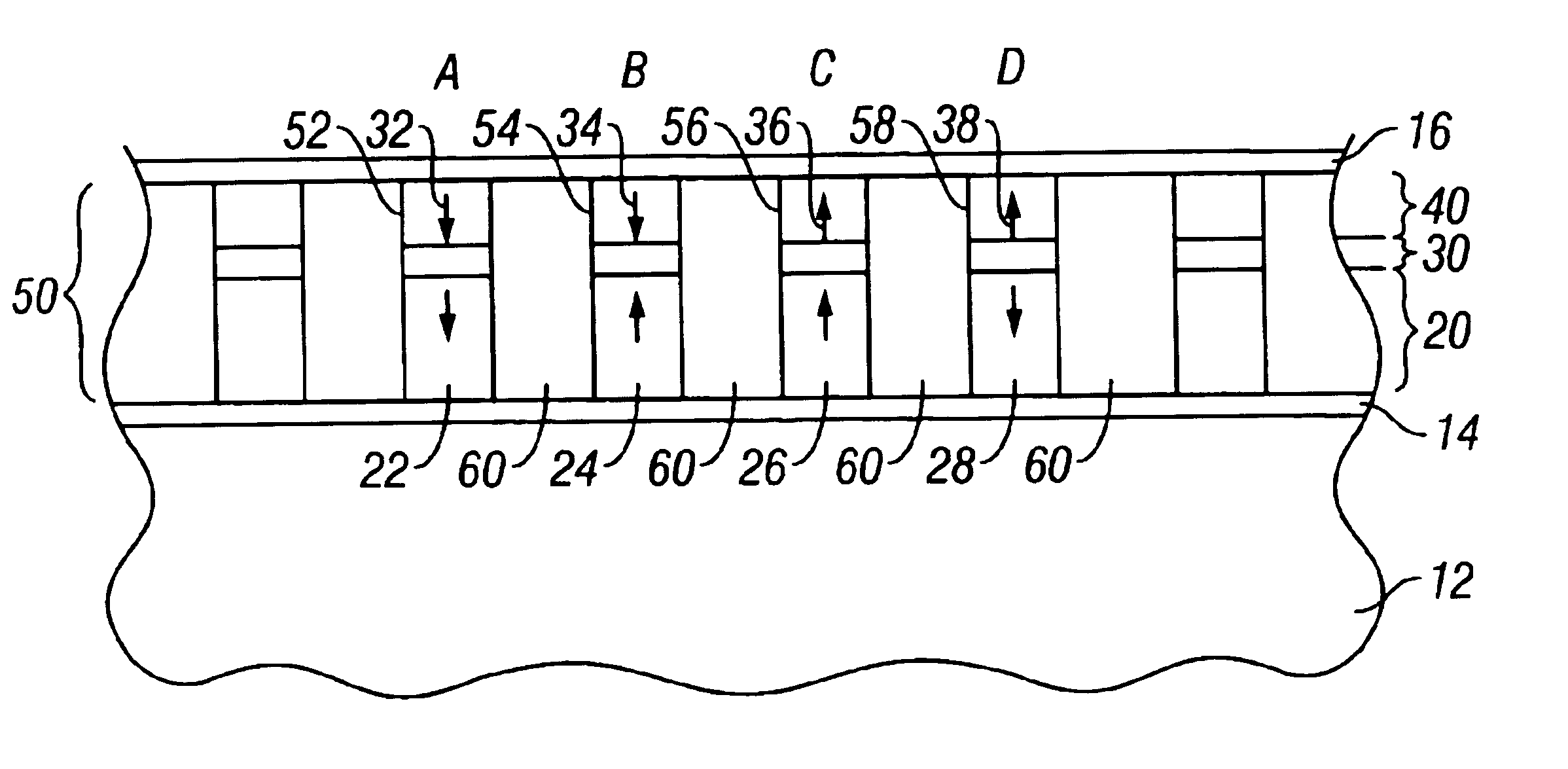
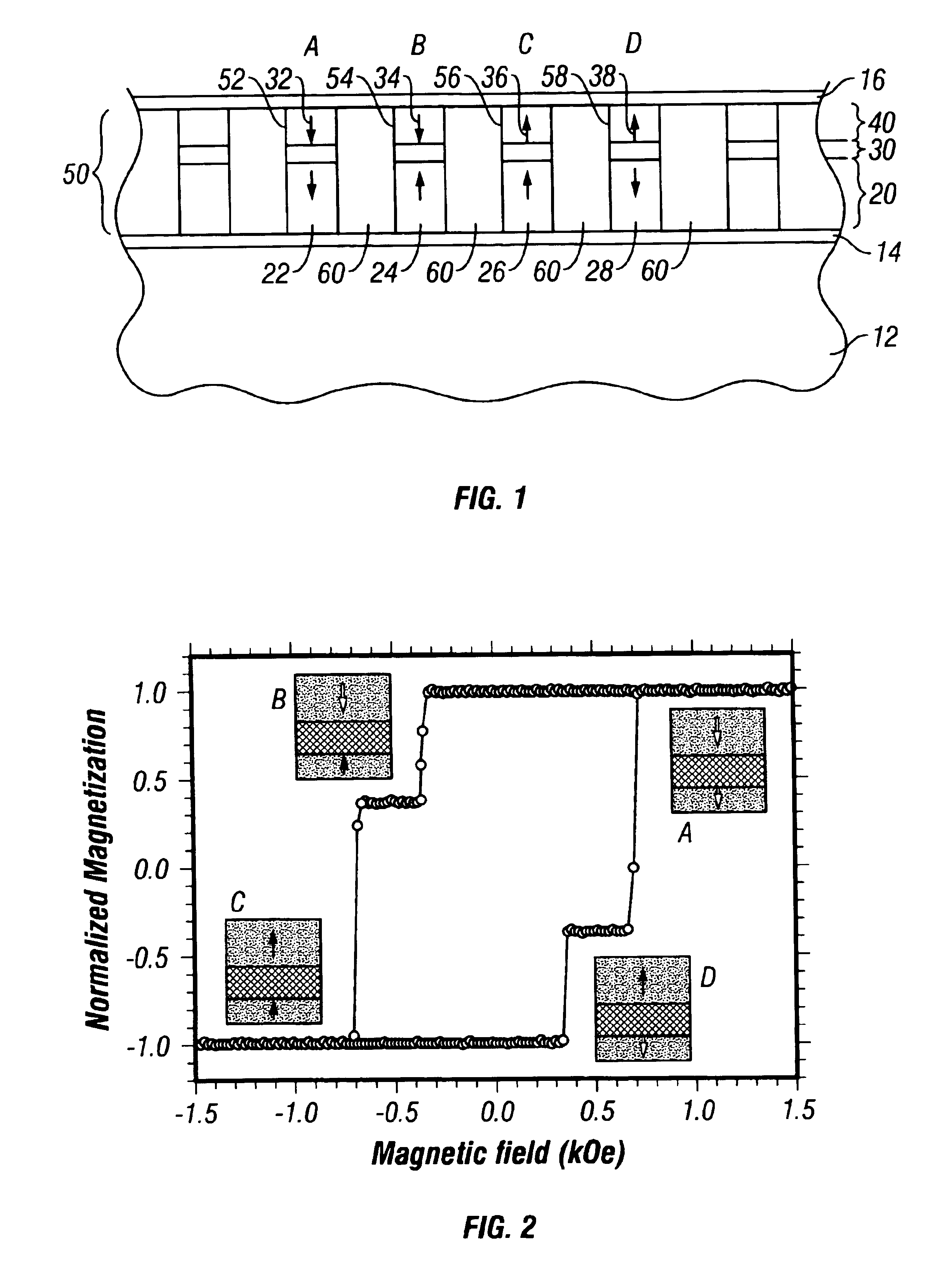
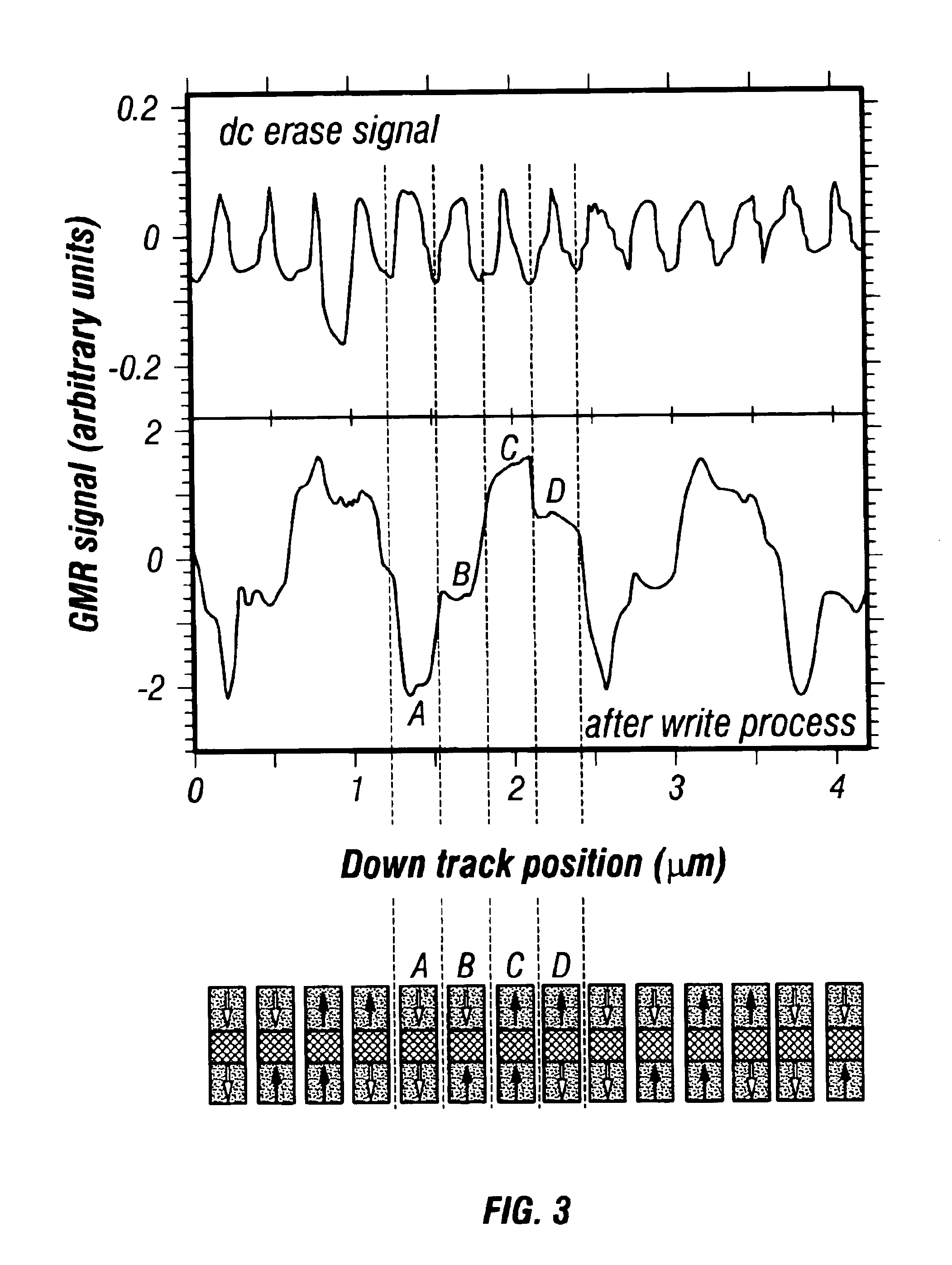
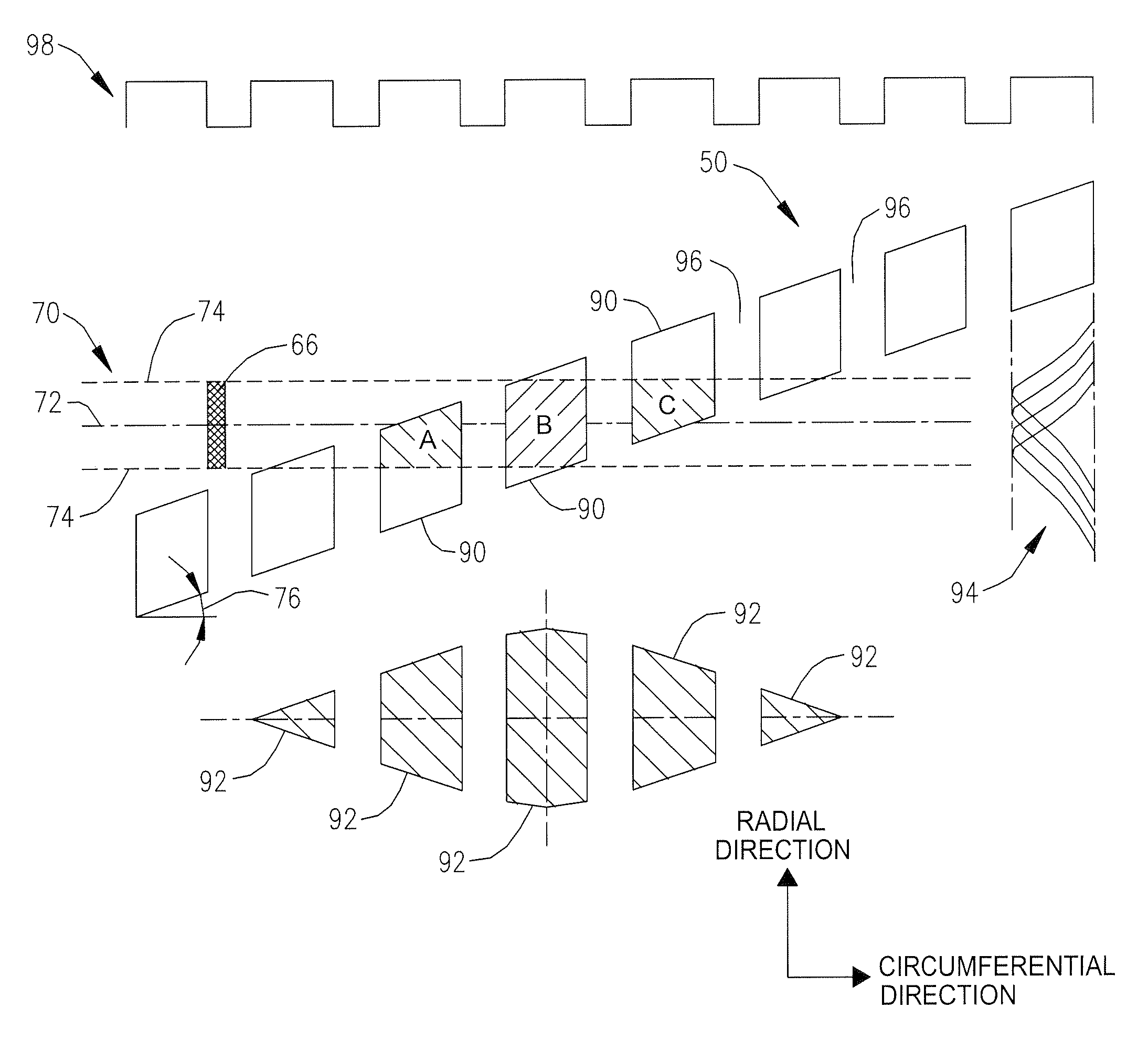
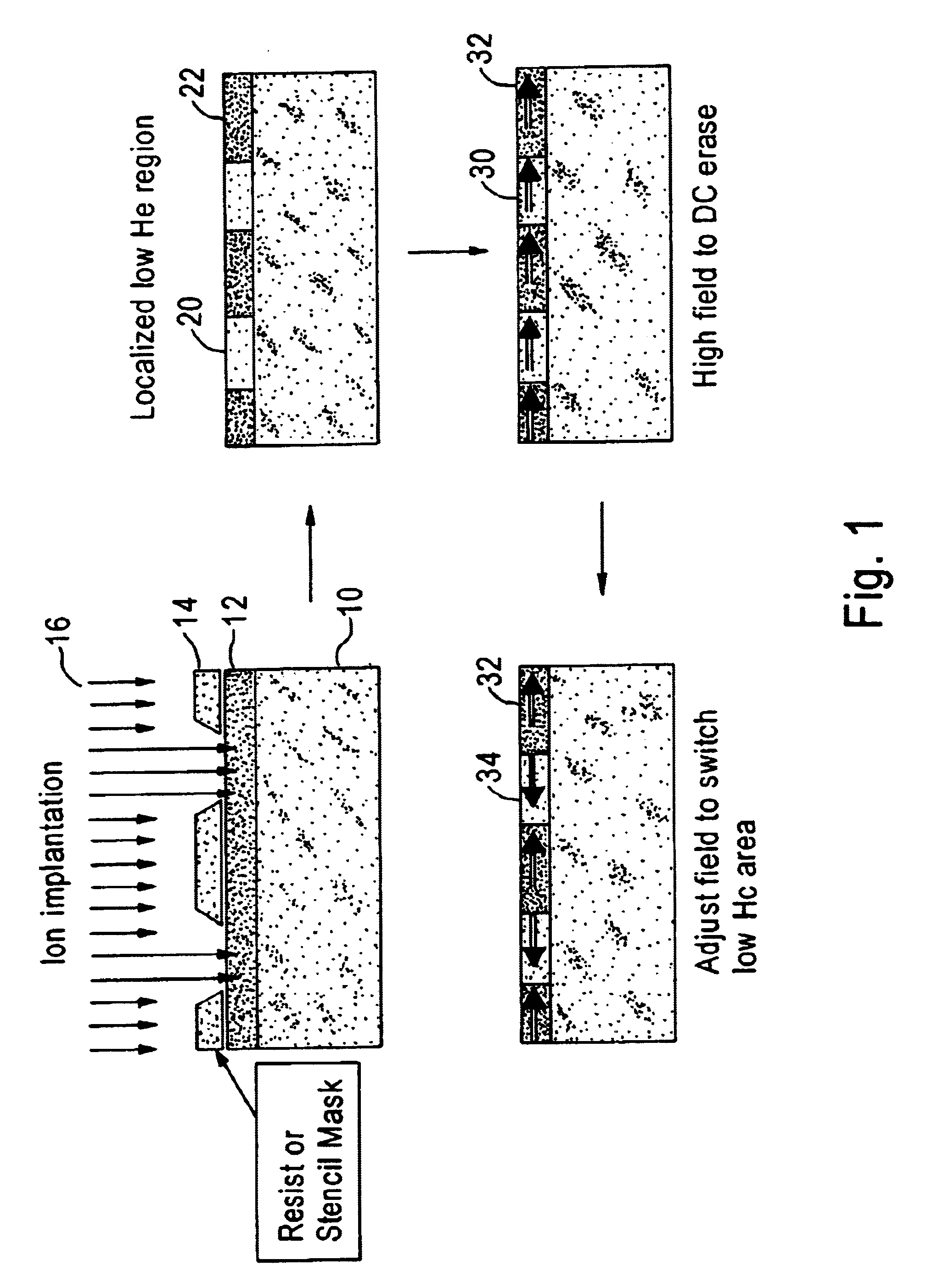
A discrete-track-recording (DTR) disk (also called “patterned” disk) has a sectored servo formed by modulation of its sidewalls in a predetermined manner, whereas sidewalls of data sectors are not modulated in this manner. Each servo sector has two side walls that are each respectively modulated in two different ways. Hence, a readback signal from a given servo sector contains components of each of the two different modulations, even in case of “DC” erase initiation. Therefore, the just-described modulated servo sectors eliminate servowriting. Moreover, data signals are read without filtering the modulation, because data sector sidewalls are not modulated.
Owner:WD MEDIA
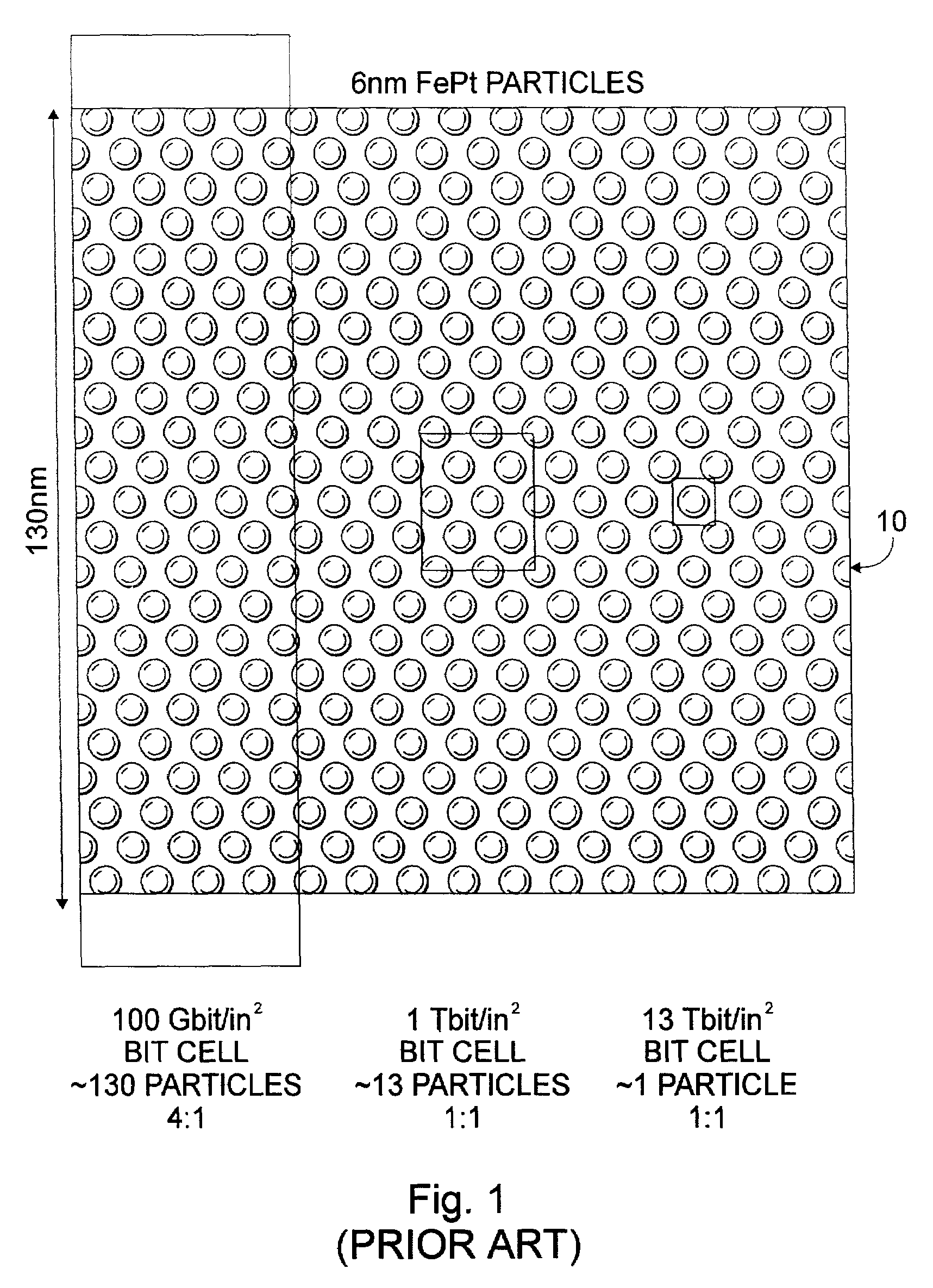
Optimized media grain packing fraction for bit patterned magnetic recording media
InactiveUS20050157597A1Optimizes optical coupling efficiencyOptimizes medium grain packing fractionCombination recordingNanoinformaticsEngineeringOptical coupling
A bit patterned magnetic recording medium for use in HAMR, which is optimized for optical coupling efficiencies and improved magnetic read-back coupling. The medium comprises bit-patterned magnetic recording elements, each corresponding to a magnetic data bit, and each comprising a cluster of discrete and separated magnetic grains. The desired packing fraction may be obtained by defining the number of grains within a bit, while bit-patterning provides efficient optical transmission. The grains have an effective packing fraction that enhances magnetic read-back signals, and the bits are distributed in a pattern having a packing fraction that enhances the optical coupling efficiency. The bits and / or the grains may be substantially thermally and optically isolated.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic recording medium having a patterned soft magnetic layer
InactiveUS7067207B2Reduce noiseMagnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersNon magneticFerromagnetism
A magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic substrate; a soft magnetic layer which is formed on the non-magnetic substrate and which includes projected parts arranged on the surface thereof and recessed parts surrounding each of the projected part; and a ferromagnetic layer which is formed on the soft magnetic layer and which includes projected parts and recessed parts reflecting the projected parts and the recessed parts of the soft magnetic layer. Further the magnetic recording medium includes recording areas which have perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and ferromagnetism, and which are formed of the projected parts of the ferromagnetic layer and separated magnetically from their surroundings. A method for manufacture of the magnetic recording medium includes forming a soft magnetic layer including of projected parts arranged regularly on the surface thereof and recessed parts surrounding each projected part; and forming a ferromagnetic layer having perpendicular magnetic anisotropy on the soft magnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
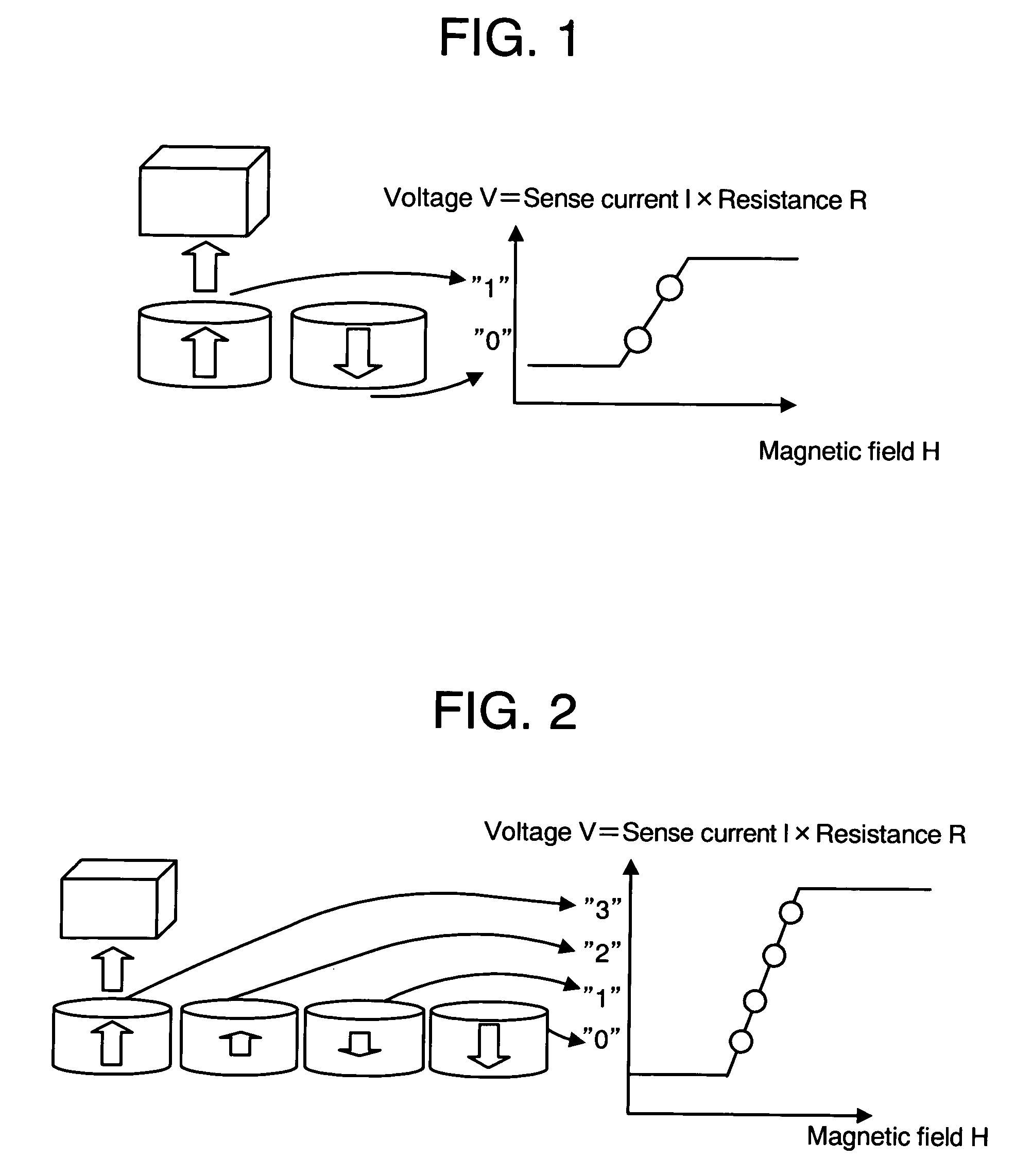
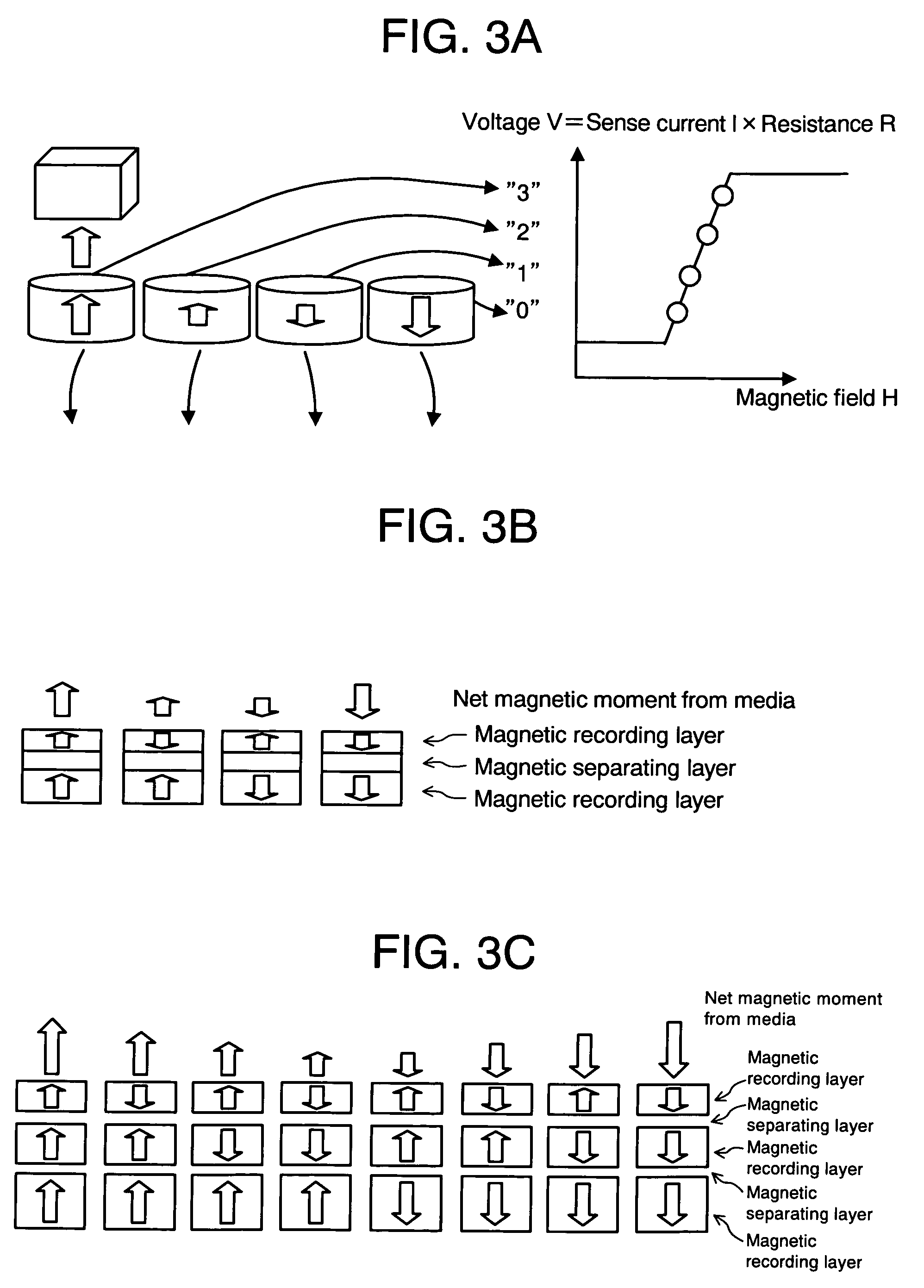
Patterned multilevel perpendicular magnetic recording media
InactiveUS6947235B2Improve noiseImprove recording densityBase layers for recording layersPatterned record carriersMaterials scienceMagnetic moment
A patterned perpendicular magnetic recording medium has magnetic islands that contain stacks of individual magnetic cells to provide multilevel recording. Each cell in an island is formed of a material or set of materials to provide the cell with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and is a single magnetic domain. Each cell is magnetically decoupled from the other cells in its island by nonmagnetic spacer layers. Thus each cell can have a magnetization (magnetic moment) in one of two directions (into or out of the plane of the layer making up the cell), and this magnetization is independent of the magnetization of the other cells in its island. This permits multiple magnetic levels or states to be recorded in each magnetic island.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
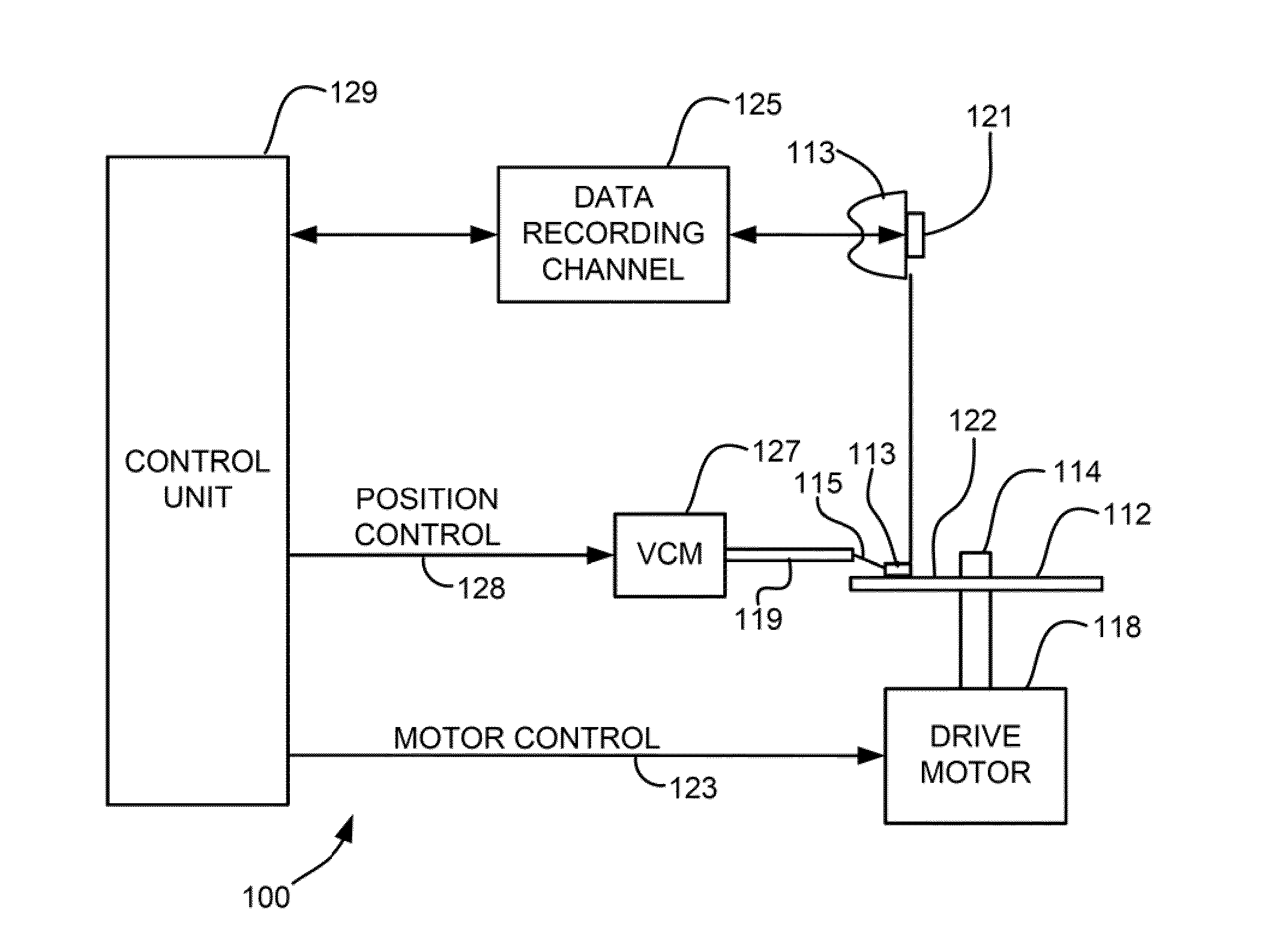
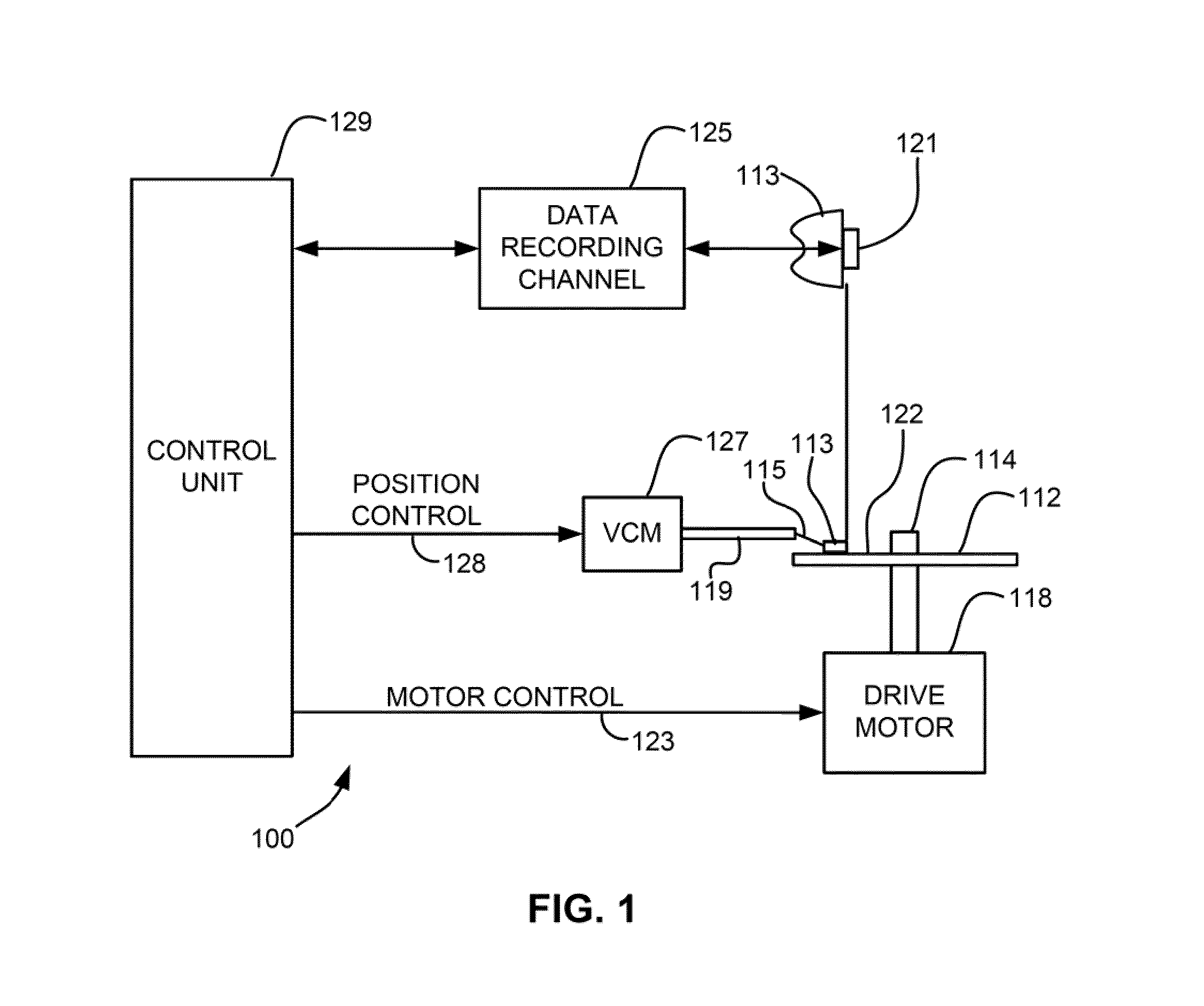
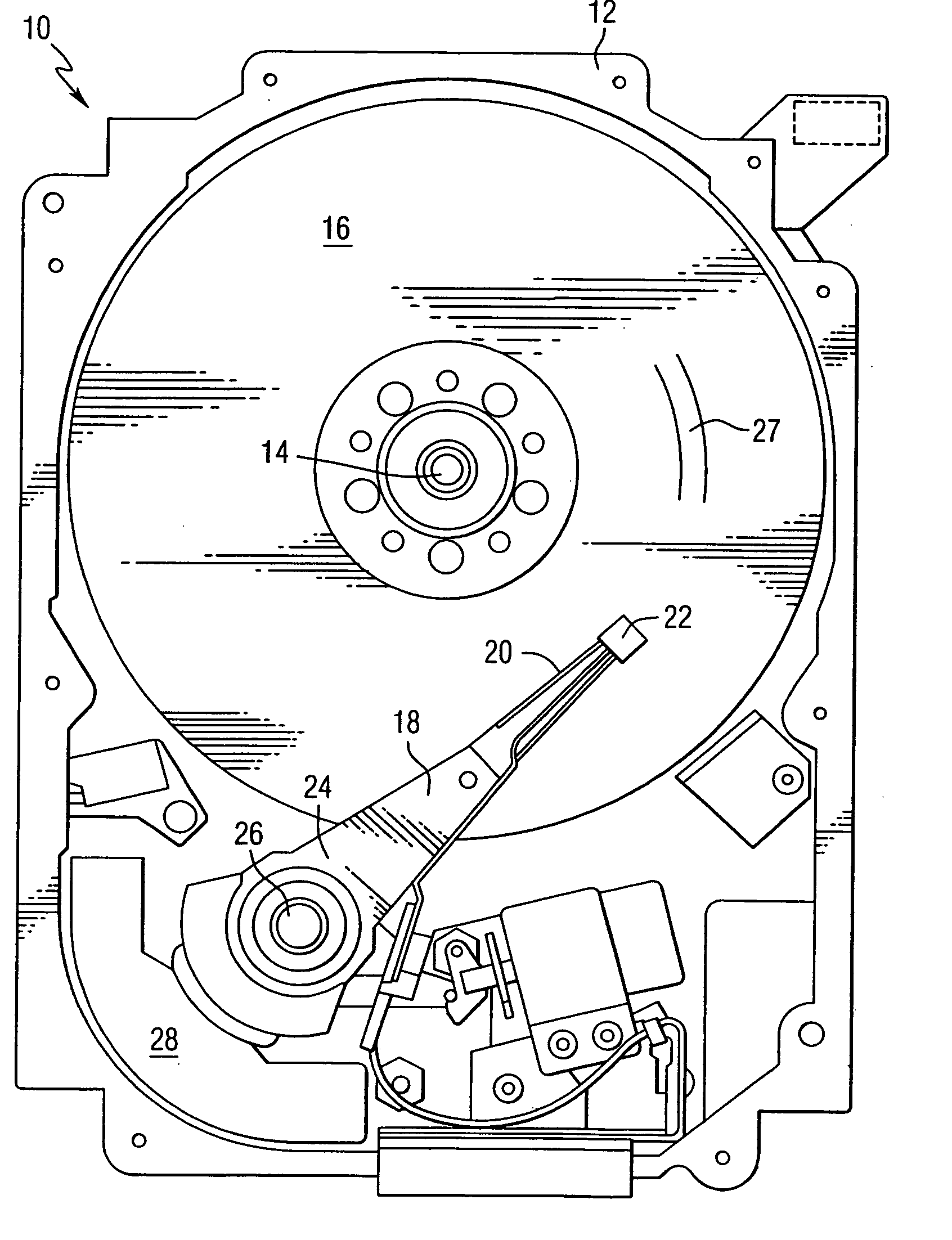
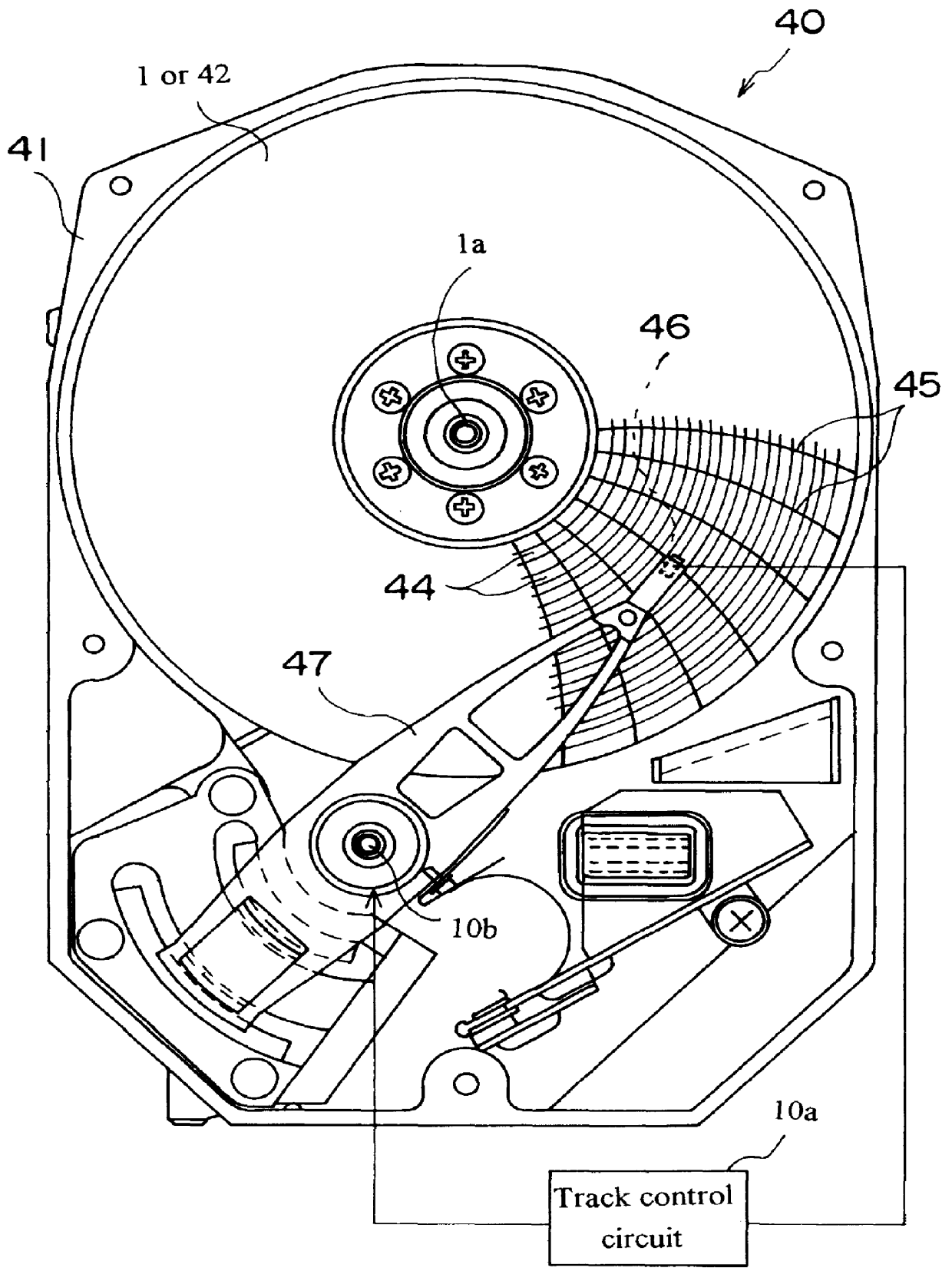
Method of self-servo writing in a disk drive using multiple timing windows
A disk drive includes a head and a disk, spiral patterns are located on the disk, and the disk drive self-writes servo patterns on the disk using the spiral patterns as a reference for servoing the head. In an embodiment, the disk drive uses preliminary servo patterns to determine repeatable runout of the spiral patterns. In another embodiment, the disk drive reads each spiral pattern with multiple timing windows.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH HDD HLDG +3
Magnetic recording medium and method for manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20040091748A1Magnetic materials for record carriersBase layers for recording layersEngineeringNon magnetic
A magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic substrate; a soft magnetic layer which is formed on the non-magnetic substrate and which includes projected parts arranged on the surface thereof and recessed parts surrounding each of the projected part; and a ferromagnetic layer which is formed on the soft magnetic layer and which includes projected parts and recessed parts reflecting the projected parts and the recessed parts of the soft magnetic layer. Further the magnetic recording medium includes recording areas which have perpendicular magnetic anisotropy and ferromagnetism, and which are formed of the projected parts of the ferromagnetic layer and separated magnetically from their surroundings. A method for manufacture of the magnetic recording medium includes forming a soft magnetic layer including of projected parts arranged regularly on the surface thereof and recessed parts surrounding each projected part; and forming a ferromagnetic layer having perpendicular magnetic anisotropy on the soft magnetic layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Magnetic recording medium and method for manufacturing magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS7833639B2Delay transitionImprove thermal stabilityPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsGrain boundaryCrystallite
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic recording medium manufacturing method
InactiveUS20120170152A1Reduced durabilityPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsIn planeRecording layer
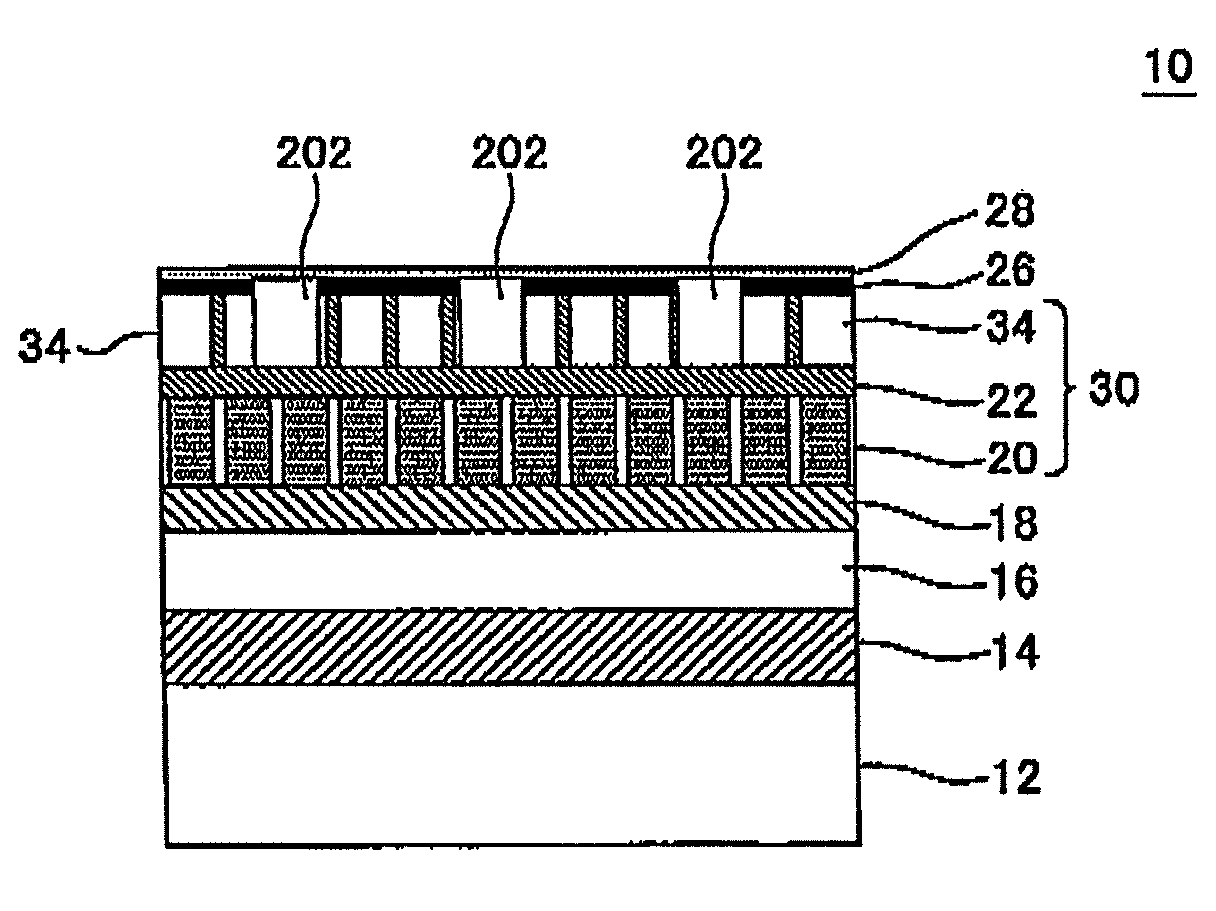
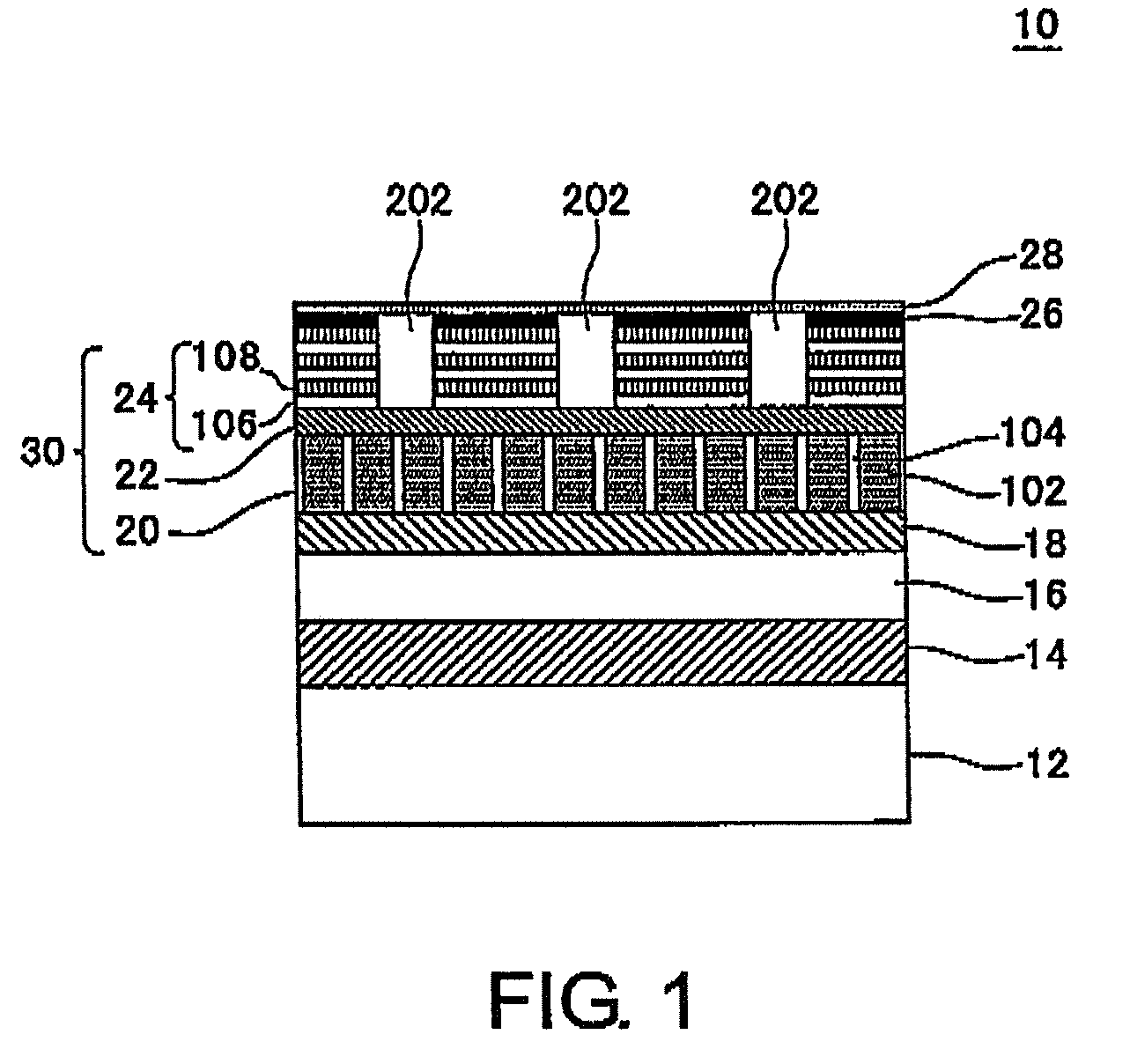
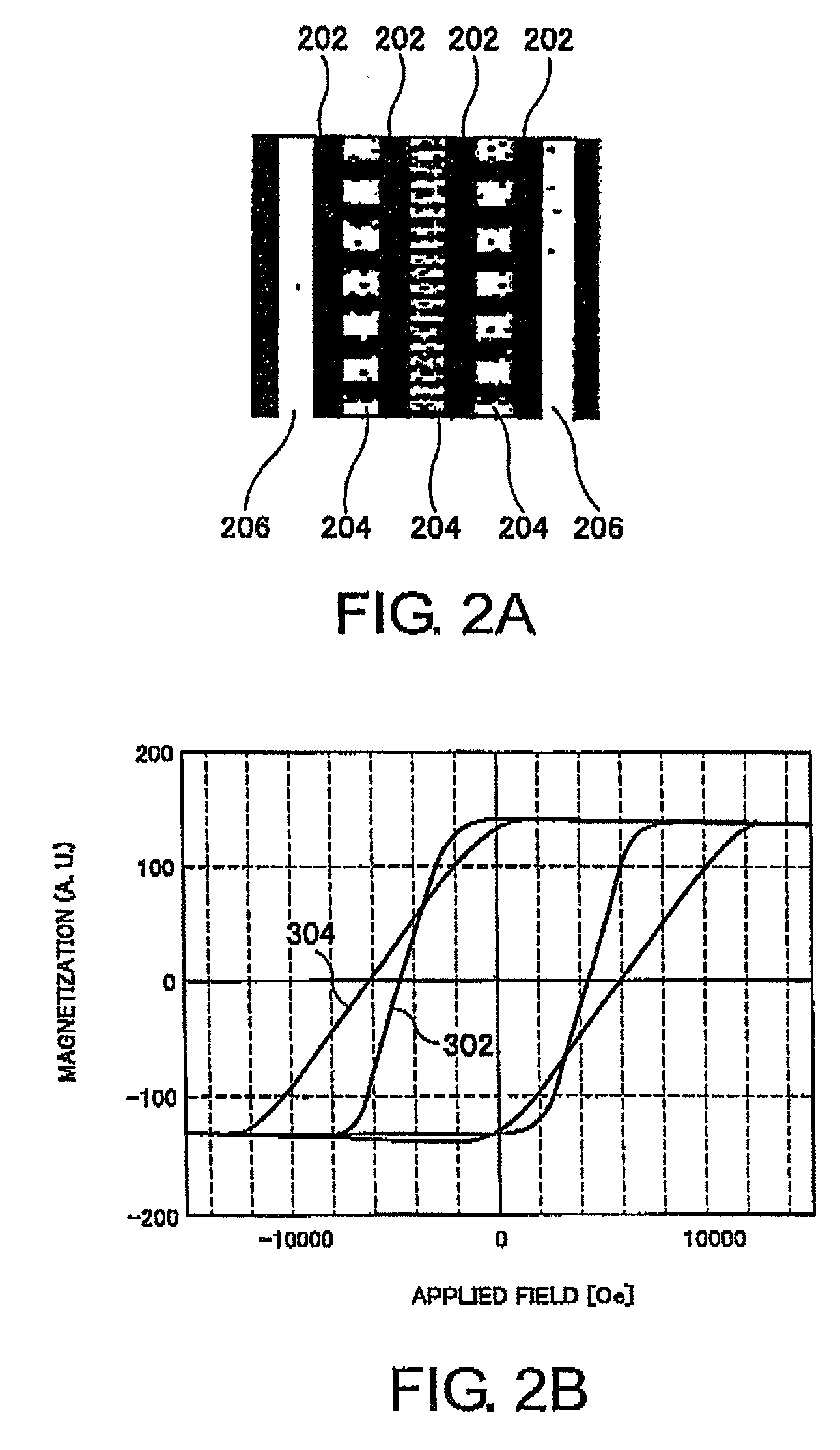
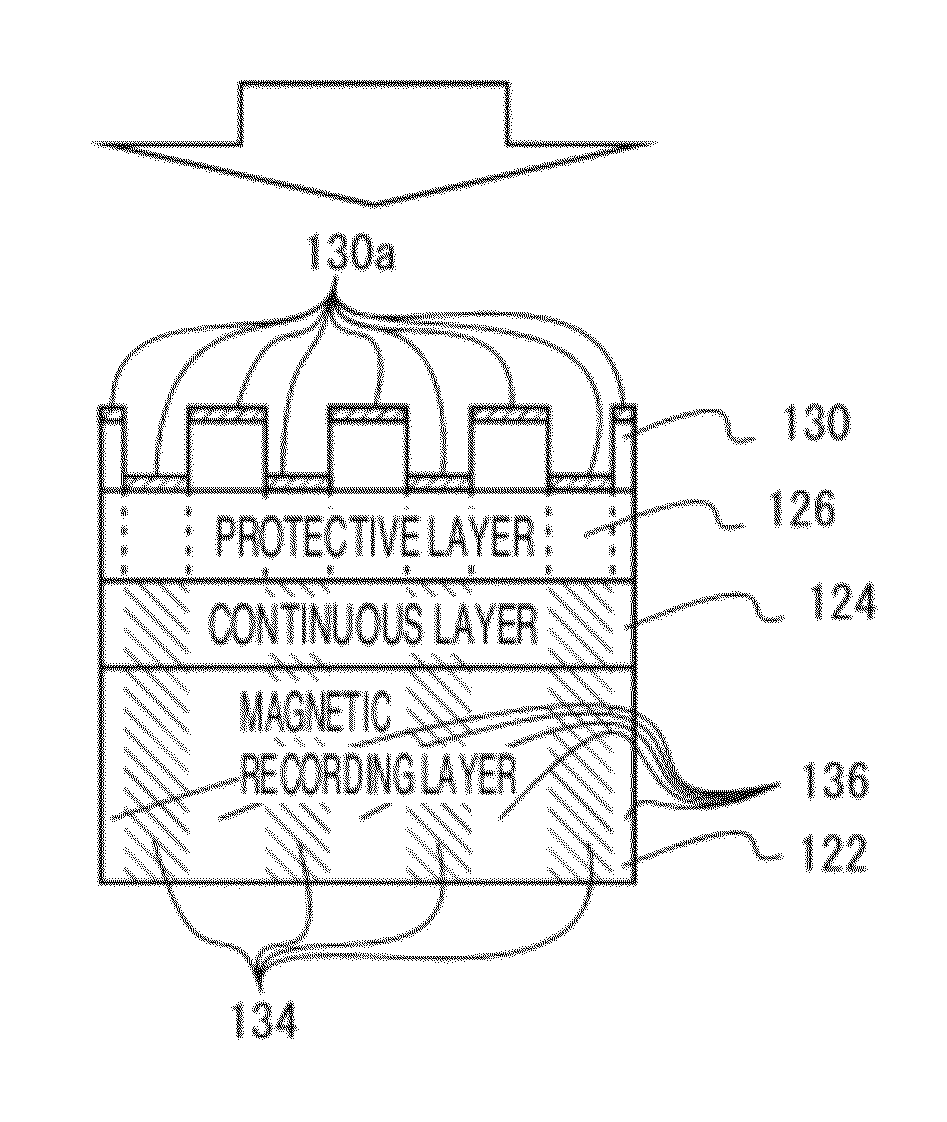
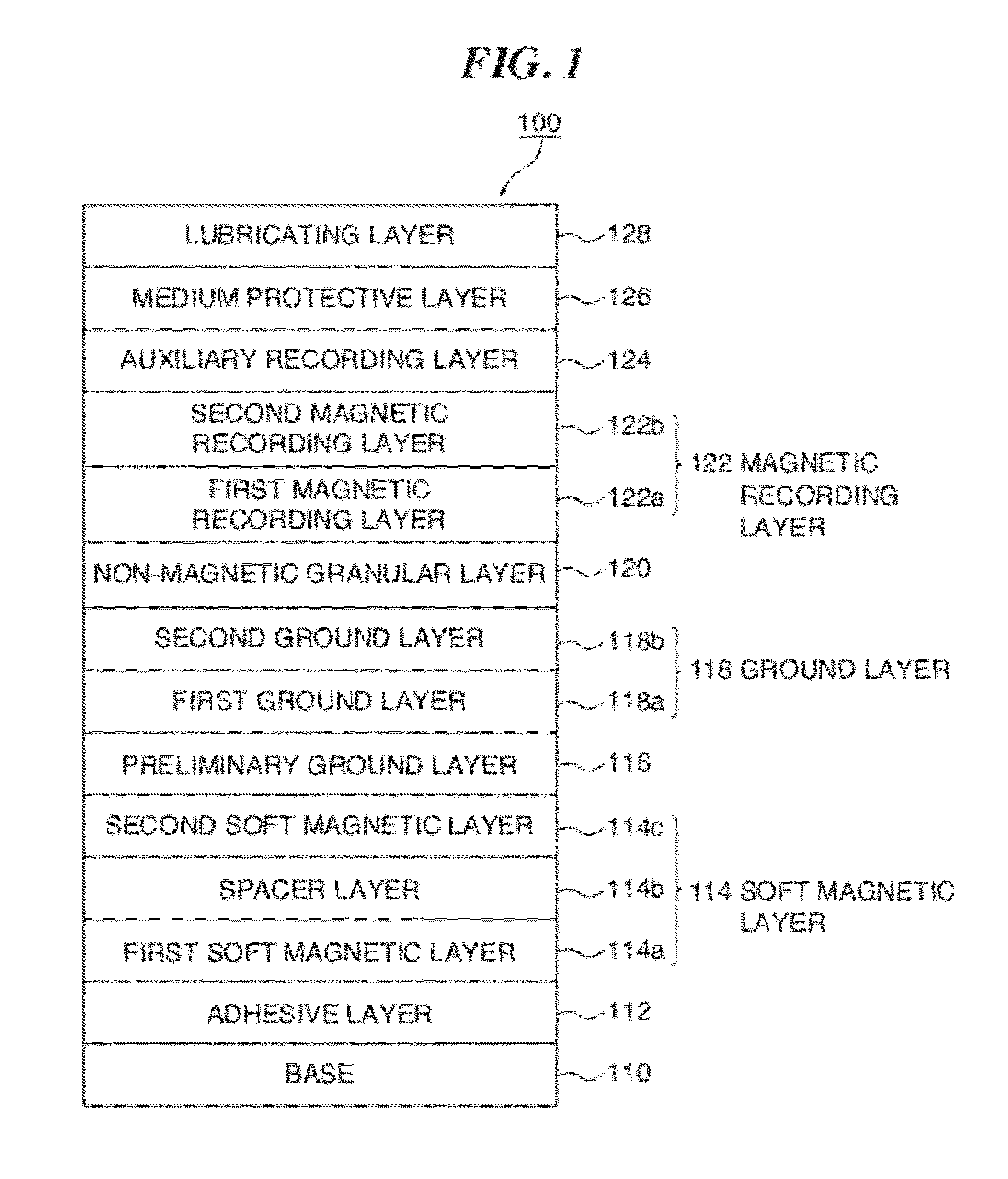
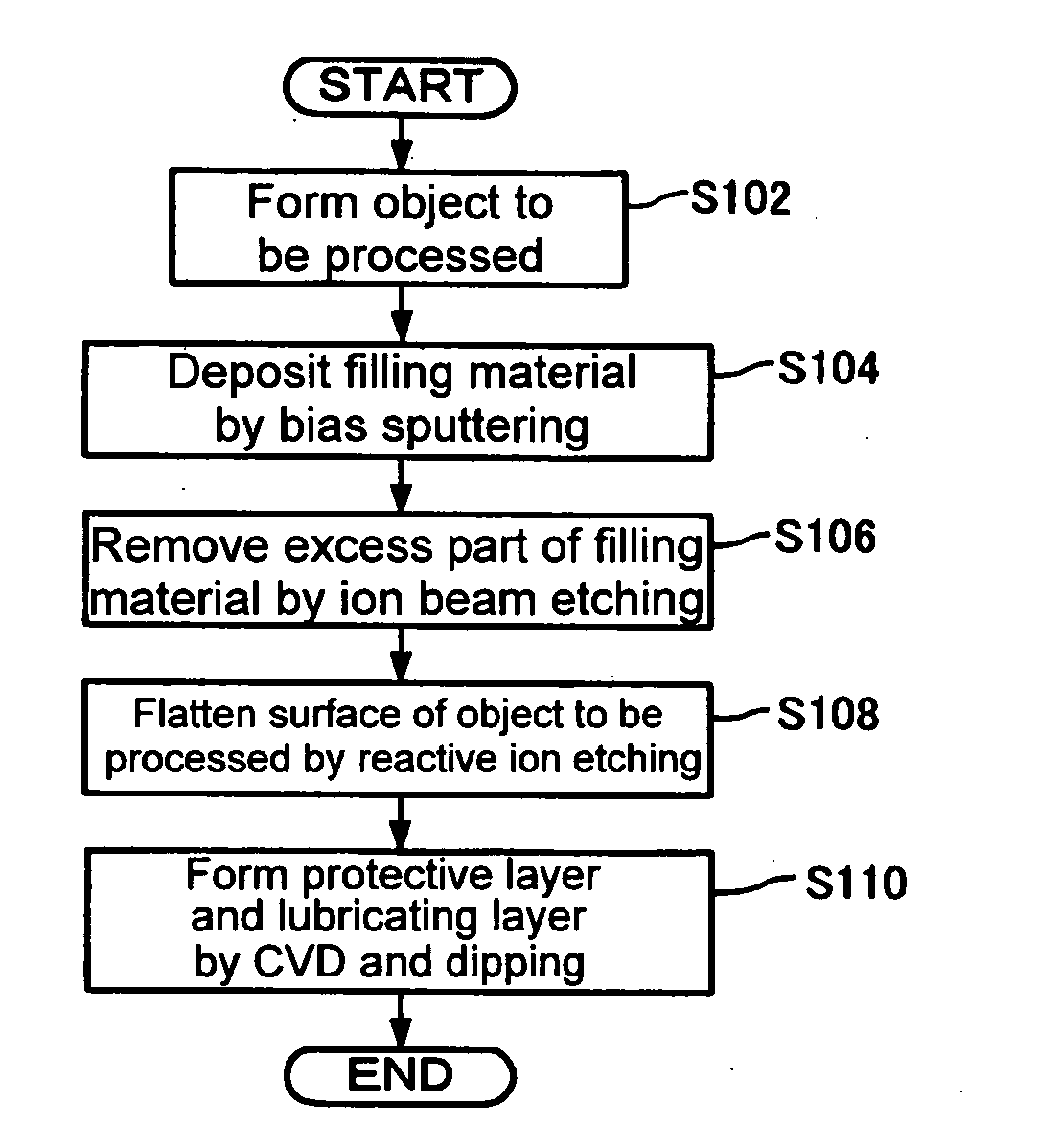
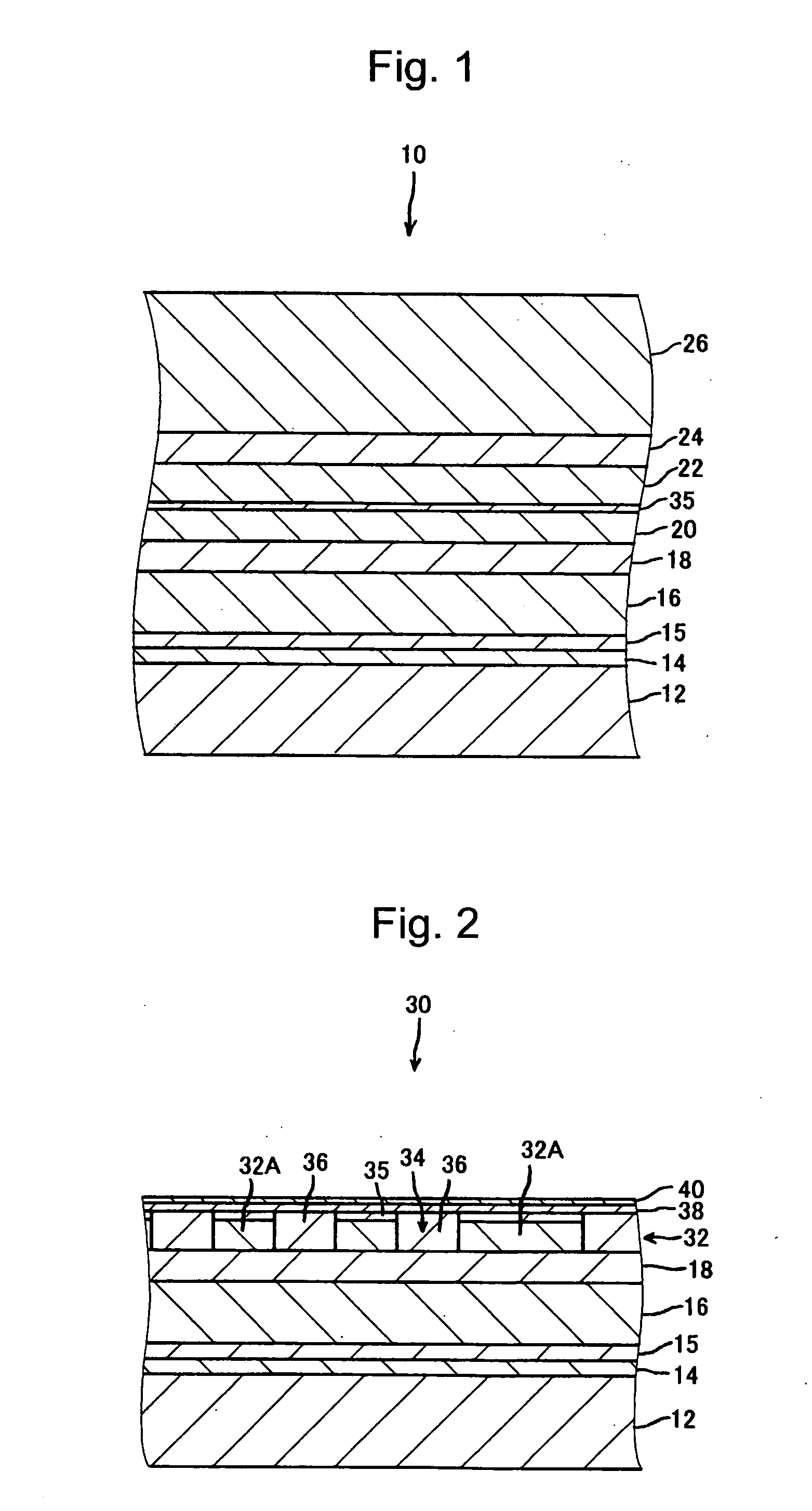
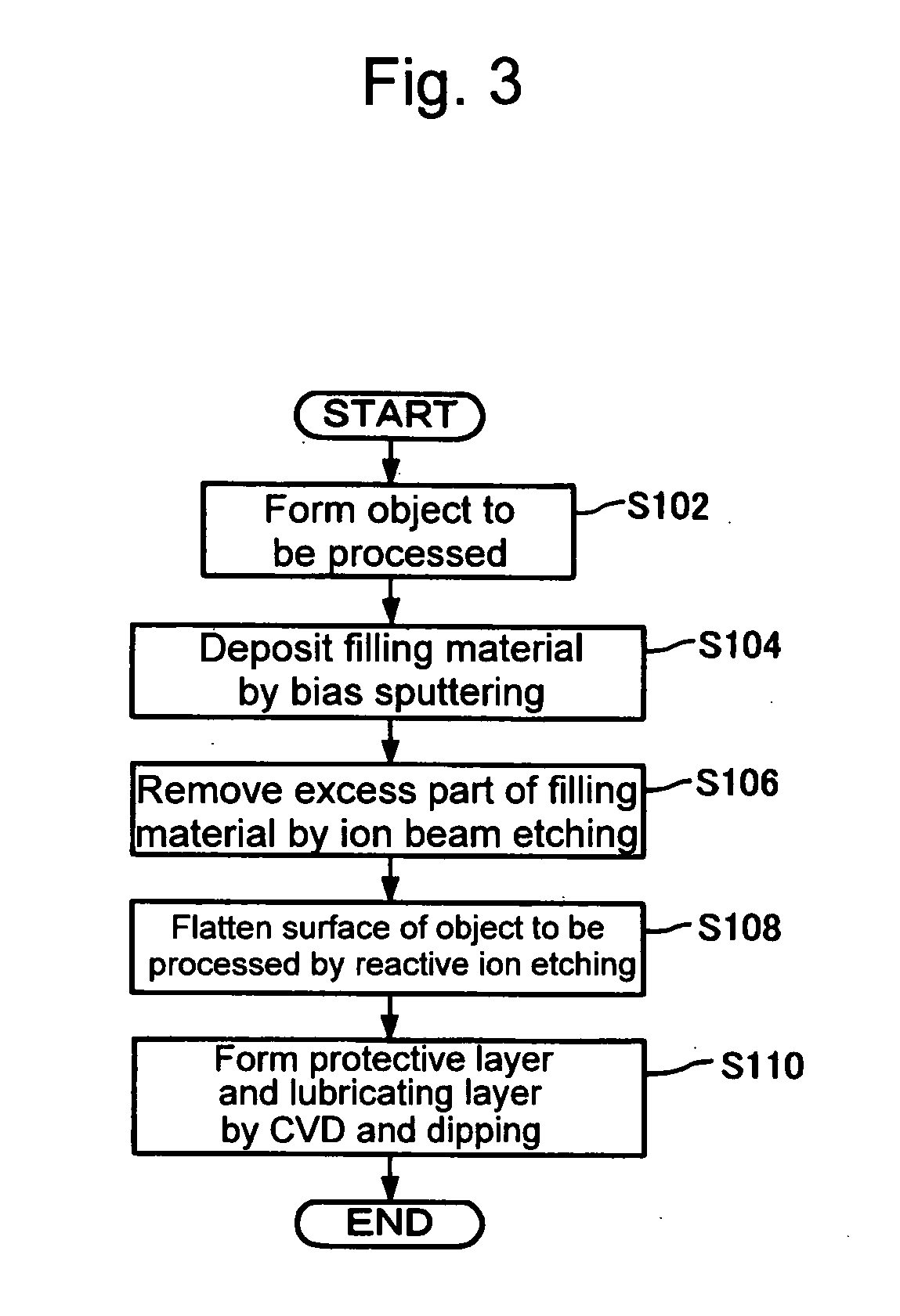
[Problem] An object is to provide a magnetic recording medium with improved HDI characteristics, such as impact resistance, and its manufacturing method.[Solution] A typical structure of a magnetic recording medium 100 according to the present invention includes, on a base, at least a magnetic recording layer 122, a protective layer 126, and a lubricating layer 128, wherein the magnetic recording layer 122 includes, in an in-plane direction, a magnetic recording part 136 configured of a magnetic material and a non-recording part 134 magnetically separating the magnetic recording part 136, and a surface corresponding to the non-recording part 134 protuberates more than a surface corresponding to the magnetic recording part 136.
Owner:WD MEDIA SINGAPORE PTE +1
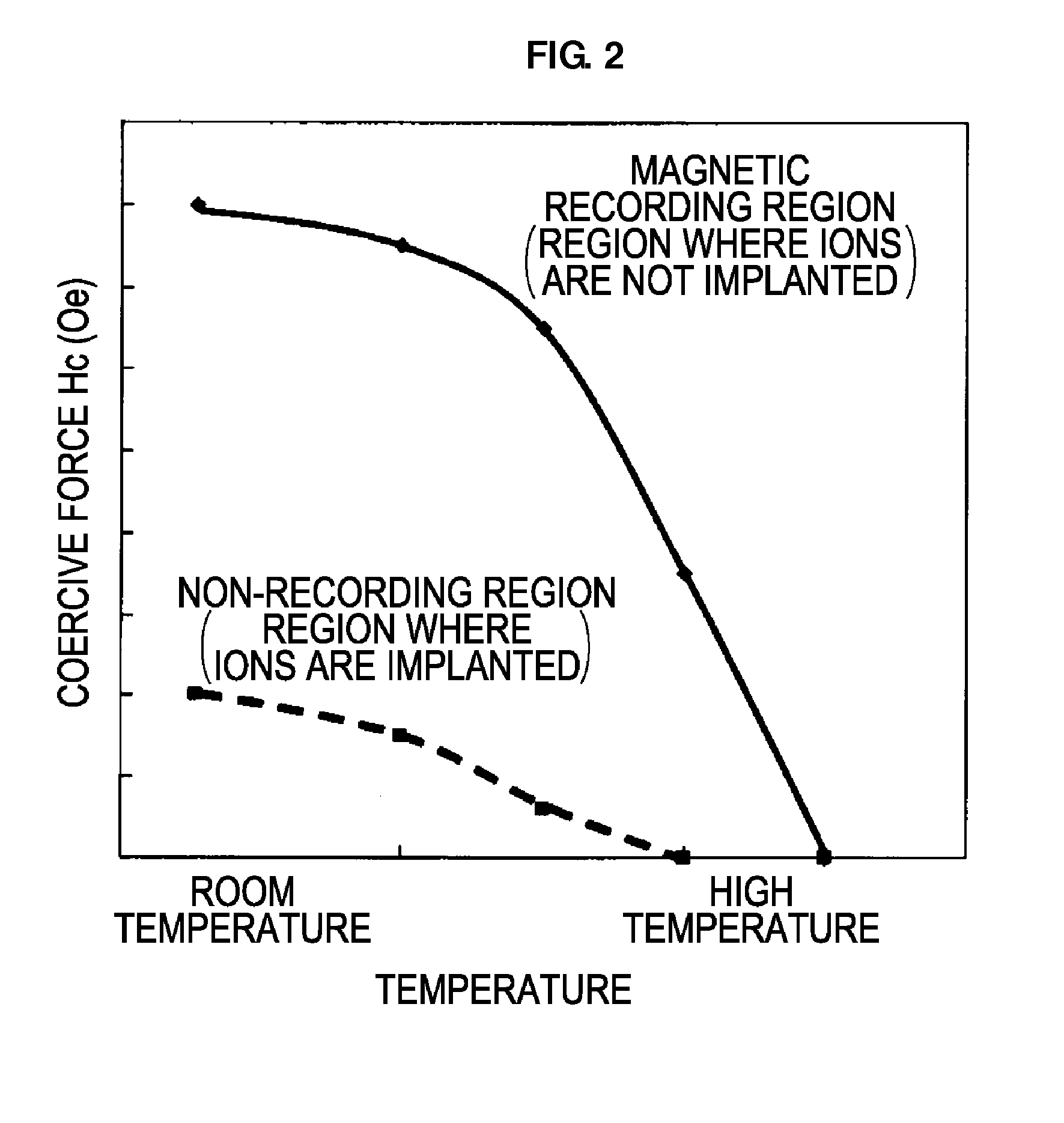
Thermally assisted magnetic recording disk with ion-implant facilitated non-magnetic regions, manufacturing method thereof, and magnetic recording method
ActiveUS8634155B2Low coercivityPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingThermal expansion
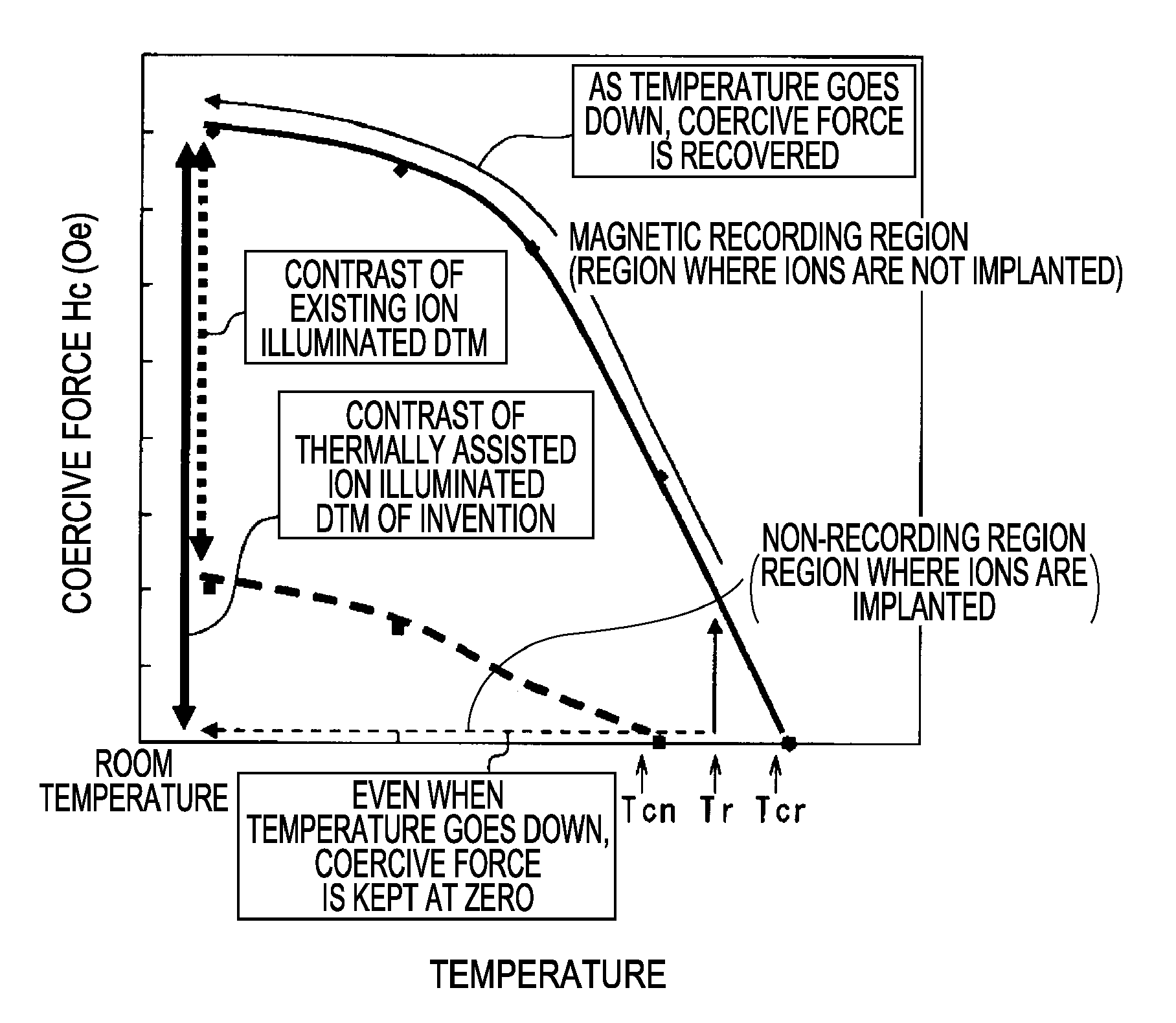
The invention provides a magnetic disk that solves (1) a problem of cross-talk that cannot be solved even by an existing thermally assisted recording method or a discrete method (DTM or the like), (2) a problem of surface flatness, which an existing embedding type DTM or the like has, and (3) a problem of a difference in thermal expansion coefficient between materials when a thermally assisted method is applied to the DTM, and that (4) does not necessitate a special medium structure, and is excellent in a surface flatness and economically and functionally high in realizability. A DTM manufactured by ion implantation is excellent in the surface flatness, and can solve the cross-talk problem by conducting the thermally assisted recording at a temperature between a Curie temperature (Tcn) of a portion where ions are implanted (non-recording region) and a Curie temperature (Tcr) of a portion where ions are not implanted (recording region).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Joint design of thermally-assisted magnetic recording head and patterned media for high optical efficiency
ActiveUS20110096431A1Combination recordingPatterned record carriersHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
A system according to one embodiment includes a magnetic recording medium having a magnetic layer with features in a discrete track configuration or a bit patterned configuration and an underlayer adjacent the magnetic layer, the underlayer comprising a material capable of forming surface plasmon resonance; and a magnetic head having: a writer for writing to the medium; and a near-field transducer for heating the medium for thermally assisted recording. Additional systems and methods are also presented.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
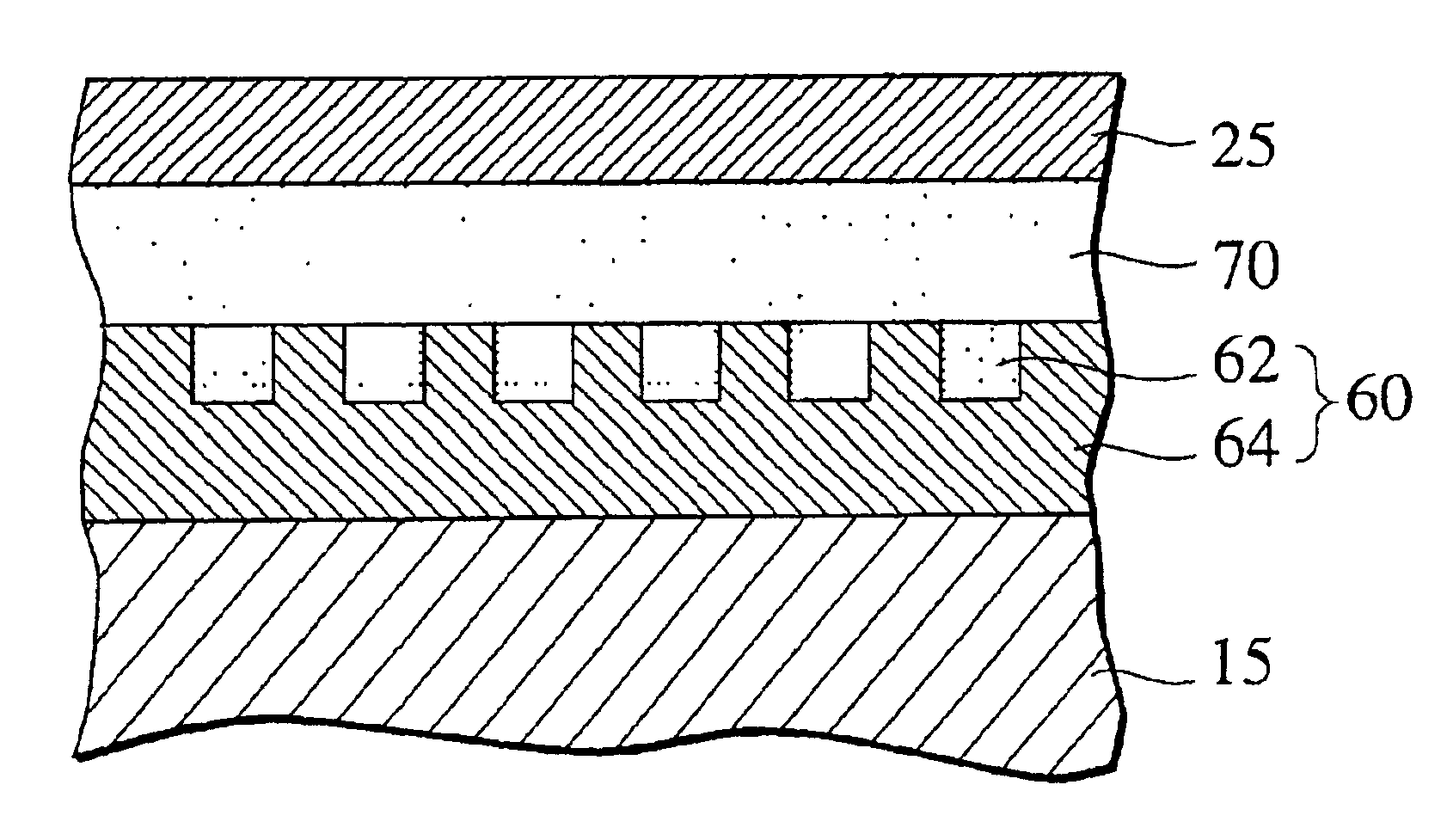
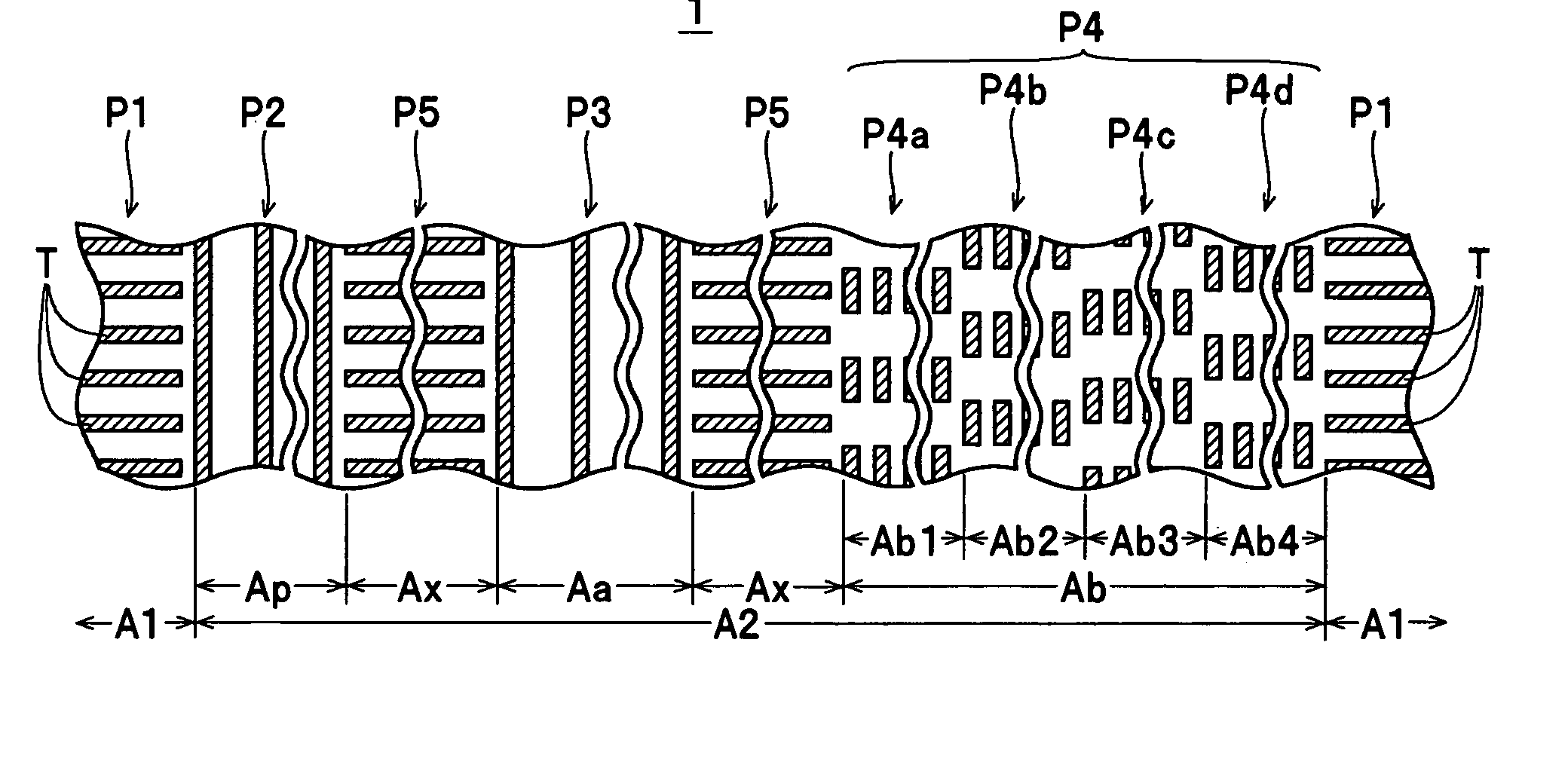
Discrete track media and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060222897A1Reduce thicknessPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsEngineeringRecording layer
A discrete track media has a nonmagnetic substrate, and a magnetic recording layer provided on the nonmagnetic substrate and having a data region including a recording track and a servo region including a preamble zone, an address zone and a burst zone, the data region and the servo region include patterns of a ferromagnetic layer forming protrusions and a nonmagnetic material filled into recesses between the patterns of the ferromagnetic layer, in which a height of the nonmagnetic material filled into the recesses in the data region is lower than that in the burst zone.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
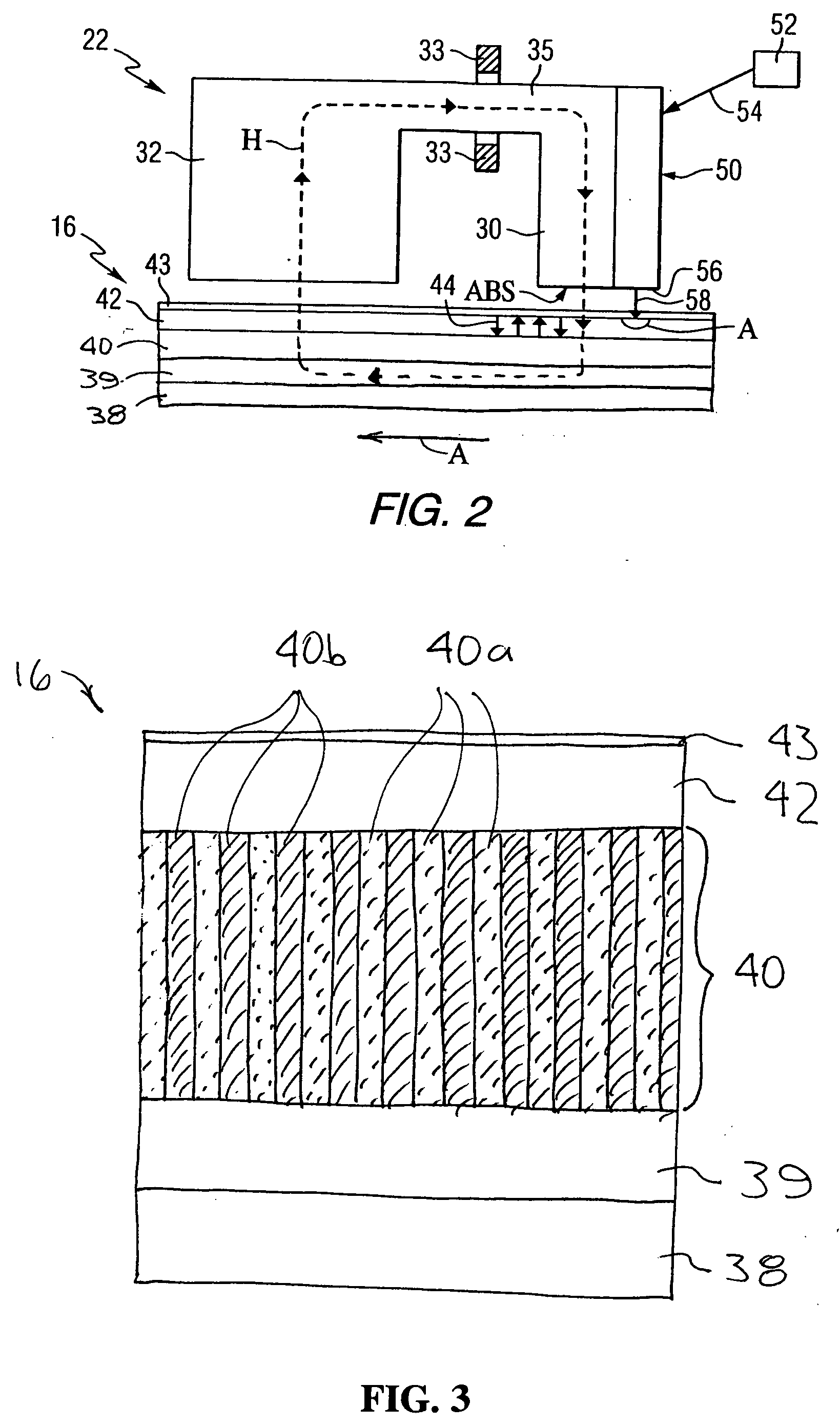
Patterned thin films and use of such films as thermal control layers in heat assisted magnetic recording media
ActiveUS20060154110A1Reduce heat transferImprove heat transfer performanceRecording by magnetic meansNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingOptoelectronics
Patterned thin films comprise regions of relatively low thermal conductivity material separated by regions of relatively high thermal conductivity material. The low thermal conductivity regions may be provided in the form of cylinders or cuboids which are arranged in a continuous matrix of the high thermal conductivity material. The thin film may be used as thermal control layers in data recording media such as heat assisted magnetic recording media.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic recording medium and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20050069732A1High-density recordingIncreased durabilityProtective coatings for layersLayered productsCarbon filmHigh density
A magnetic recording medium which allows high density recording and has excellent durability can be obtained. A magnetic recording medium includes: a plurality of ferromagnetic material dots arranged on a soft magnetic layer formed on a non-magnetic substrate so as to be separated from one another; and carbon films which are formed on the respective ferromagnetic material dots, each carbon film having a smooth film face shape in a section passing through the center of each ferromagnetic material dot and a film thickness gradually decreasing from the center of the ferromagnetic material dot toward an outer edge thereof.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Electron beam irradiating method and manufacturing method of magnetic recording medium
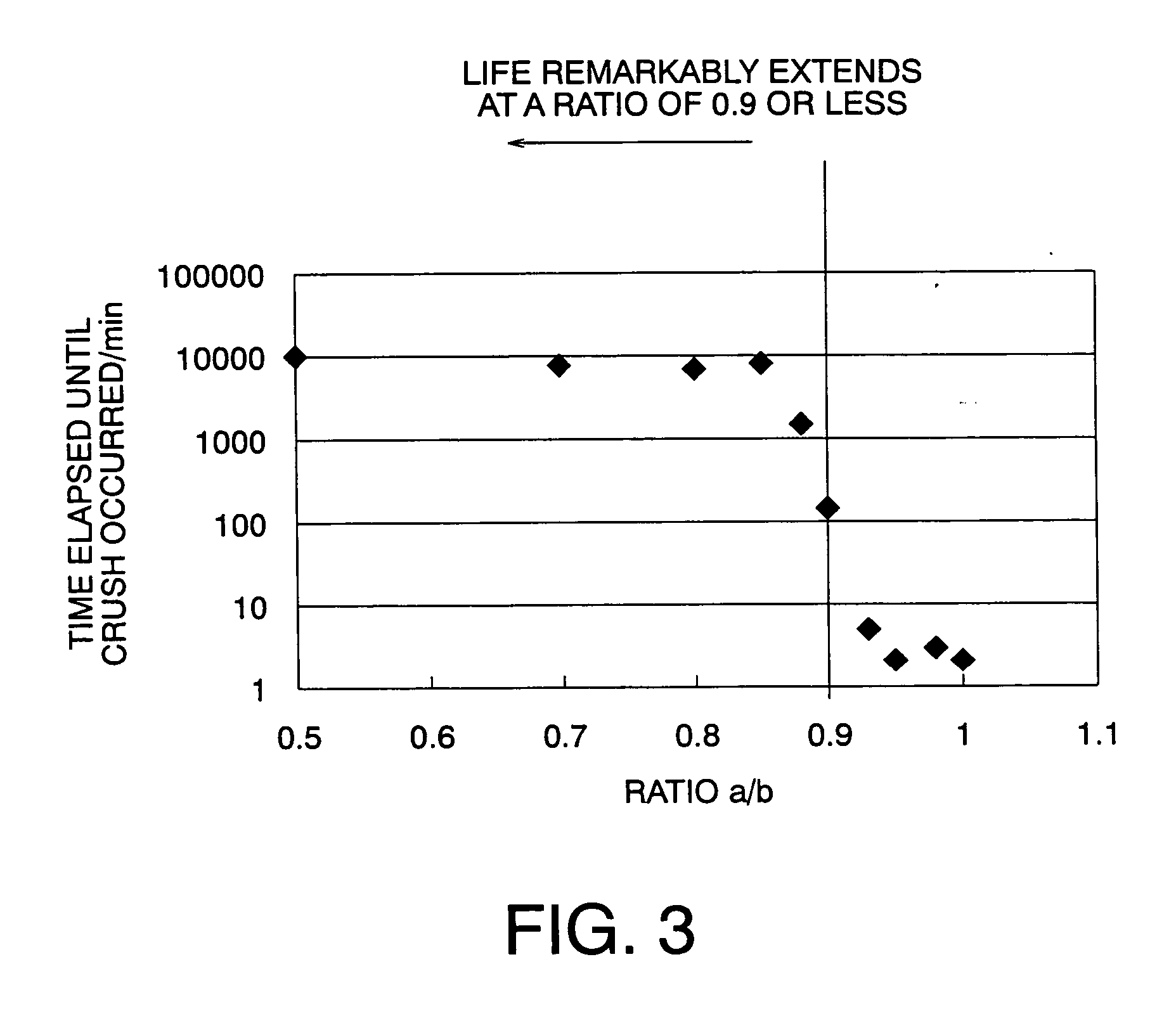
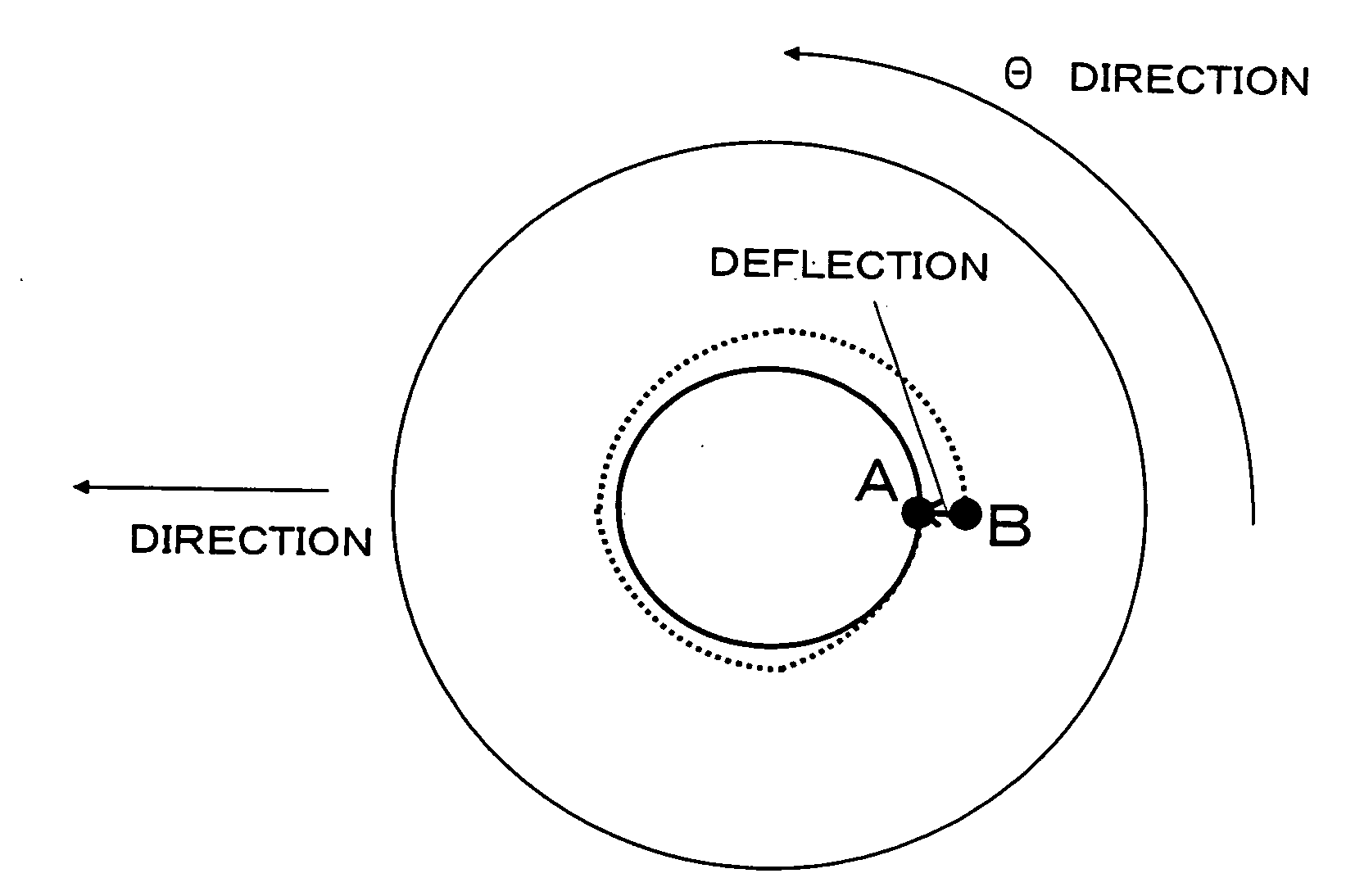
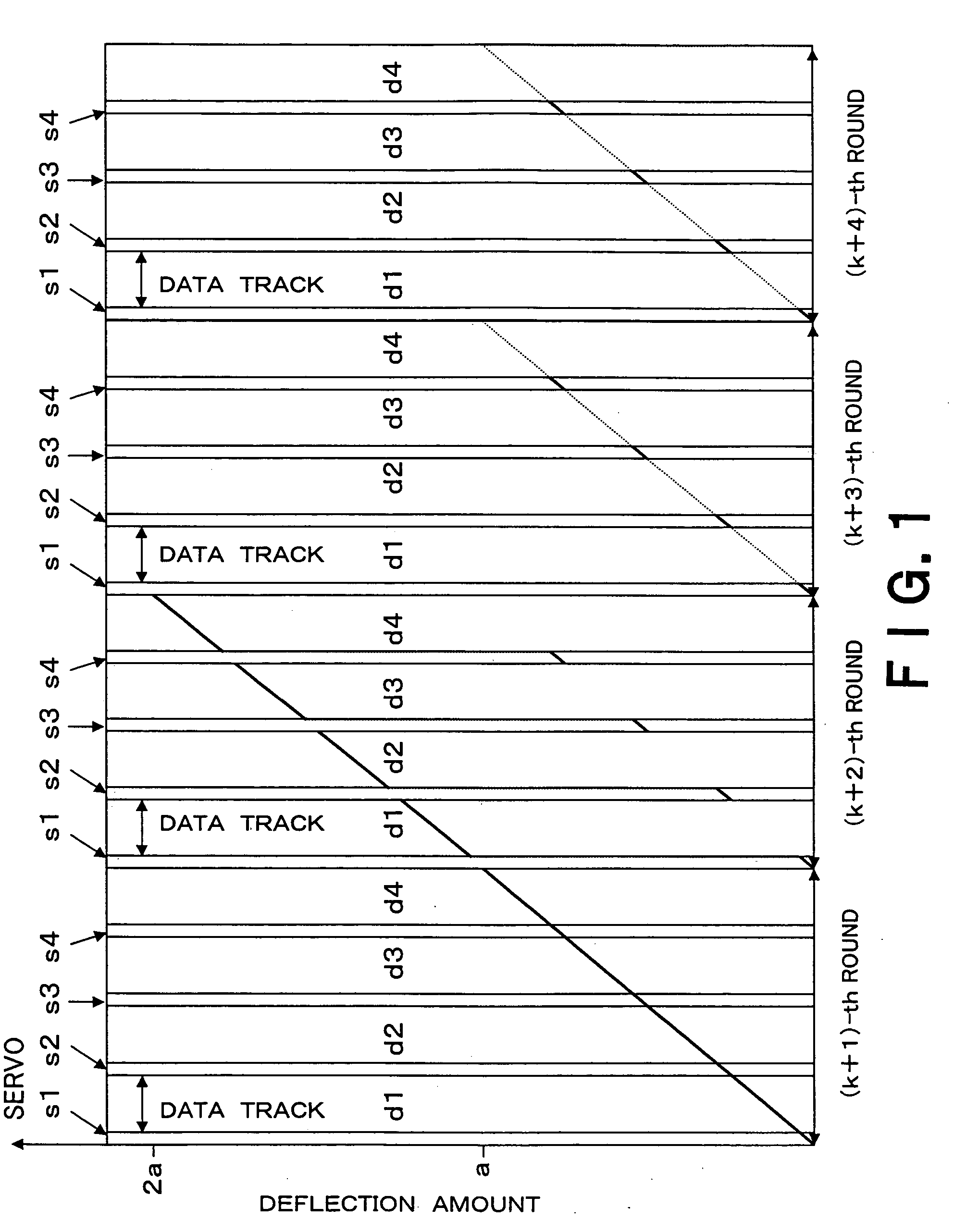
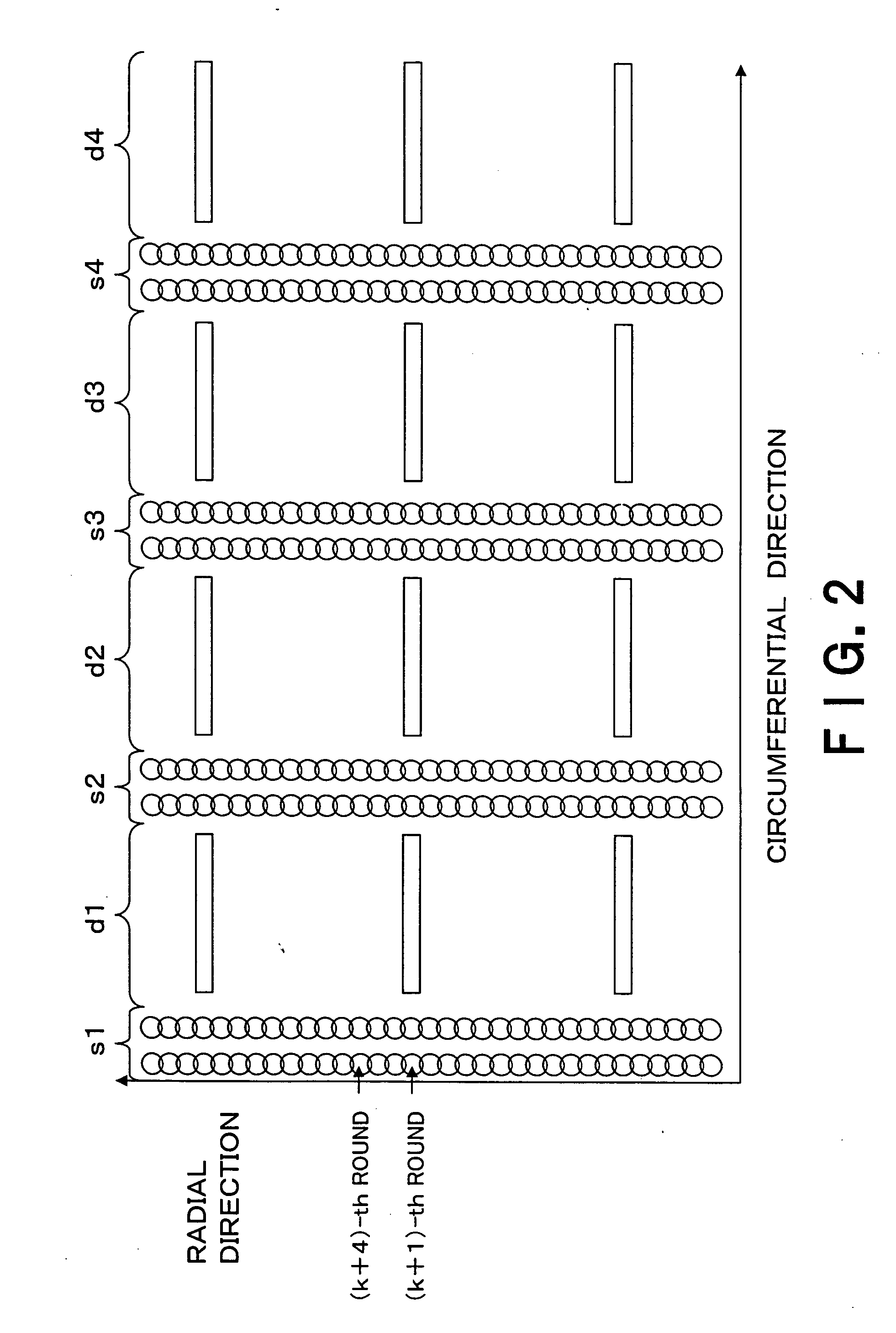
The present invention is to make it possible to form a fine pattern, and improve a recording density on a magnetic recording medium and increase signal intensity. There is provided an electron beam irradiating method which irradiates an electron beam on a resist to perform irradiating using an electron beam irradiating apparatus provided with a moving mechanism which moves a state on which a substrate applied with the resist is put in one horizontal direction, and a rotating mechanism which rotates the stage. The electron beam irradiating method includes: exposing a portion once exposed while changing a deflection amount of the electron beam at least one time in the next round and rounds subsequent thereto, when exposure is performed while a deflection amount of an electron beam is being gradually changed so as to draw a concentric circle for each round.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
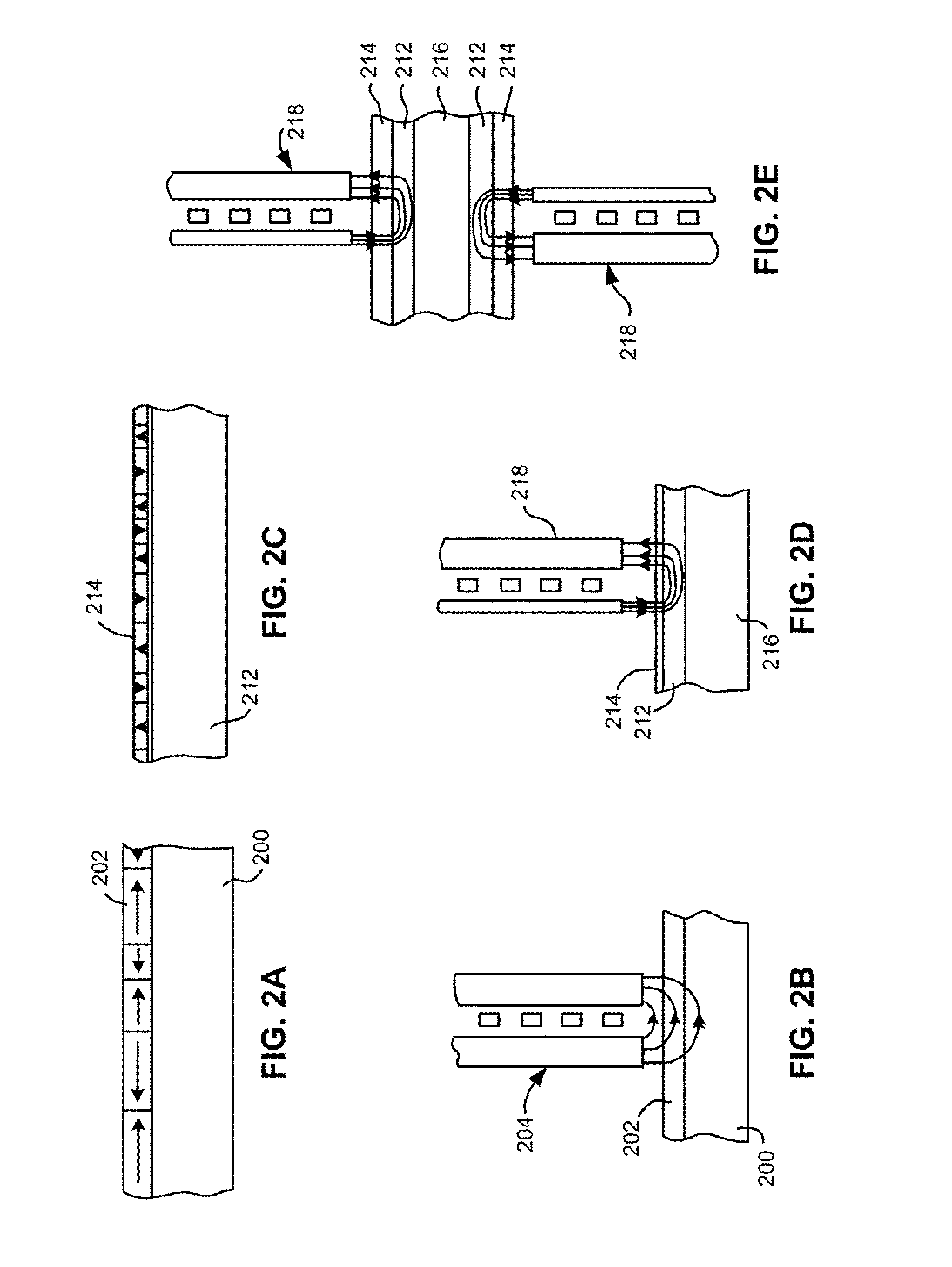
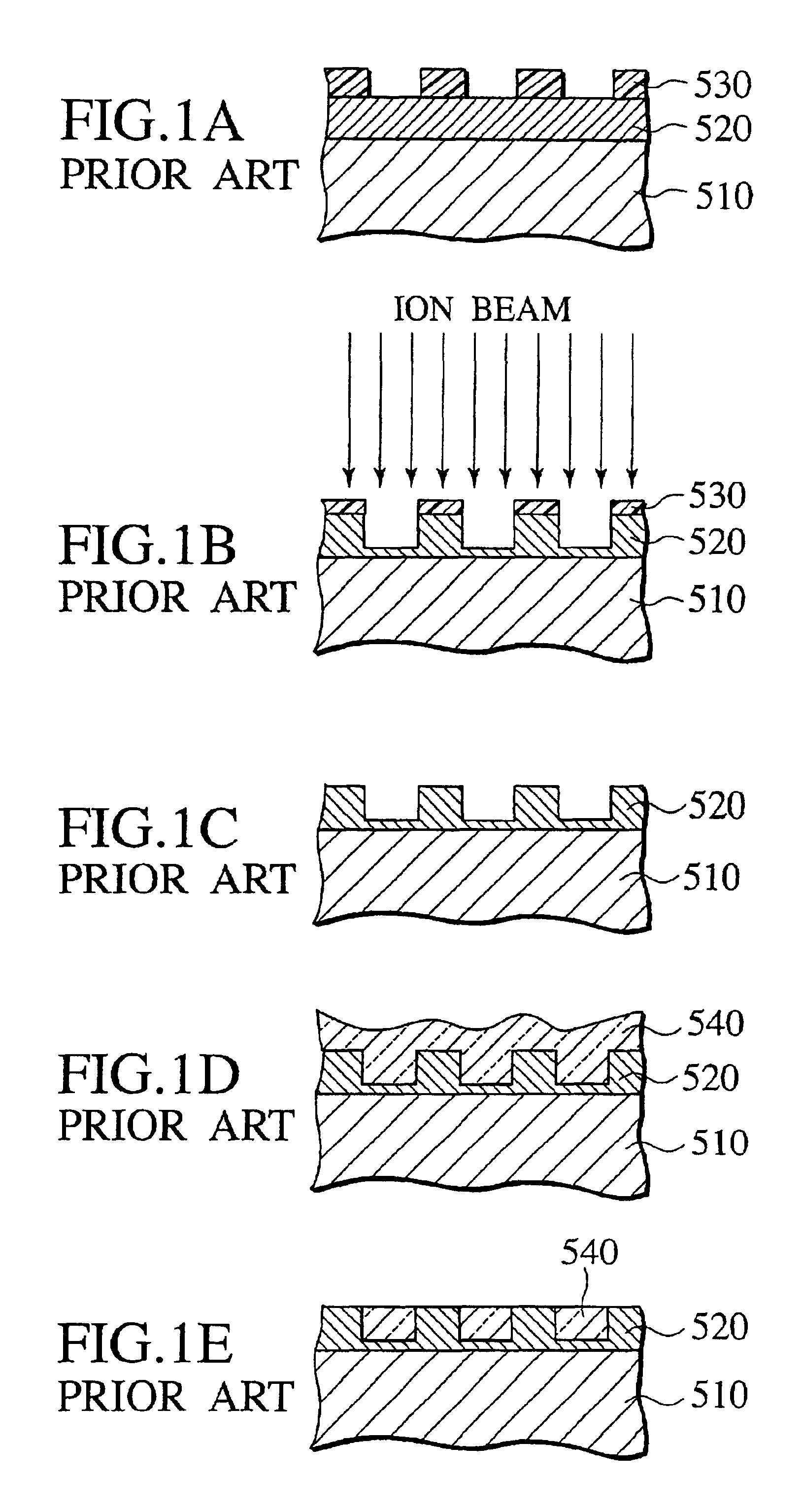
Patterning longitudinal magnetic recording media with ion implantation
InactiveUS6864042B1Increased areal recording densityUniform surfaceNanoinformaticsPatterned record carriersIon bombardmentTopography
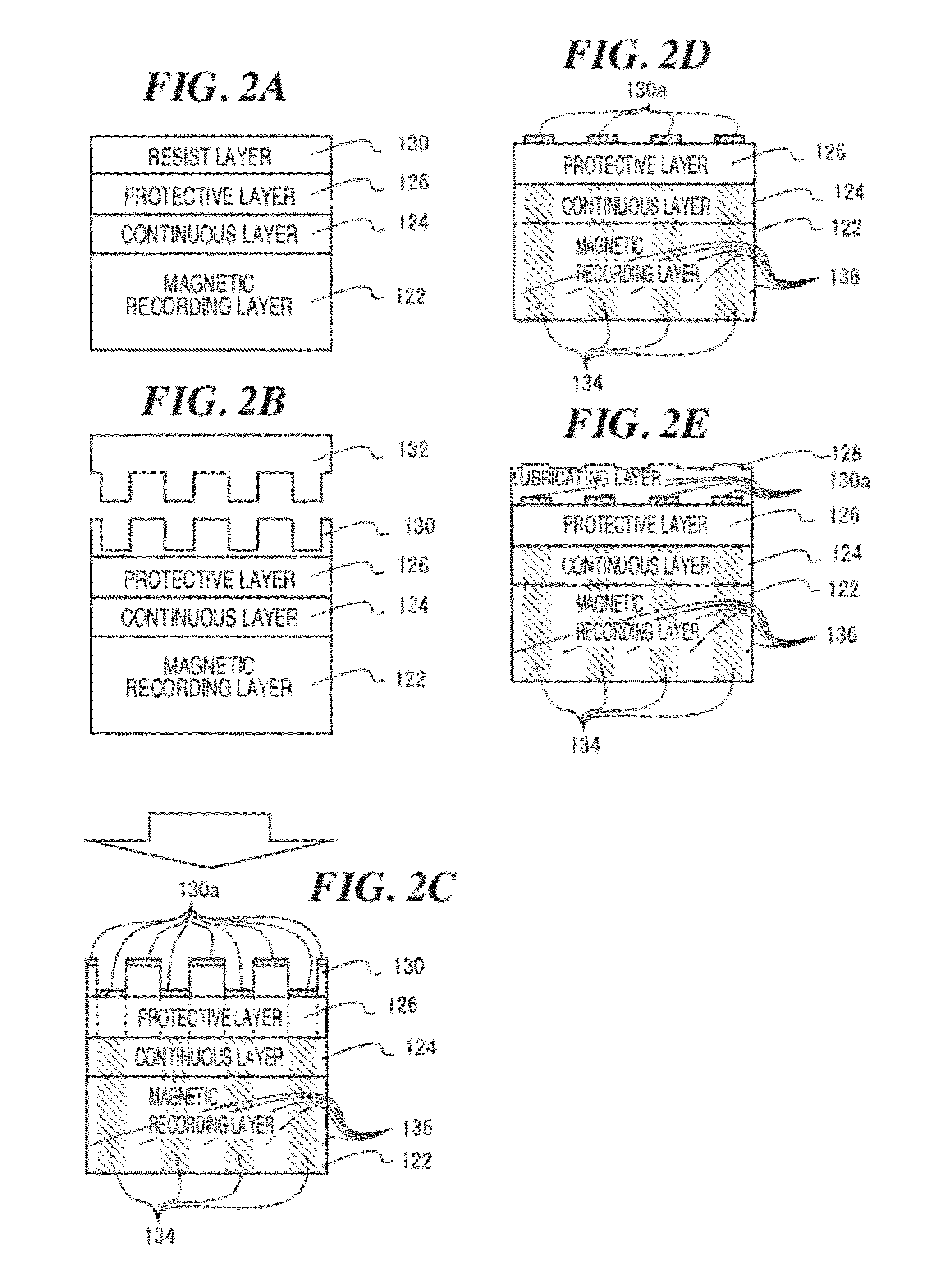
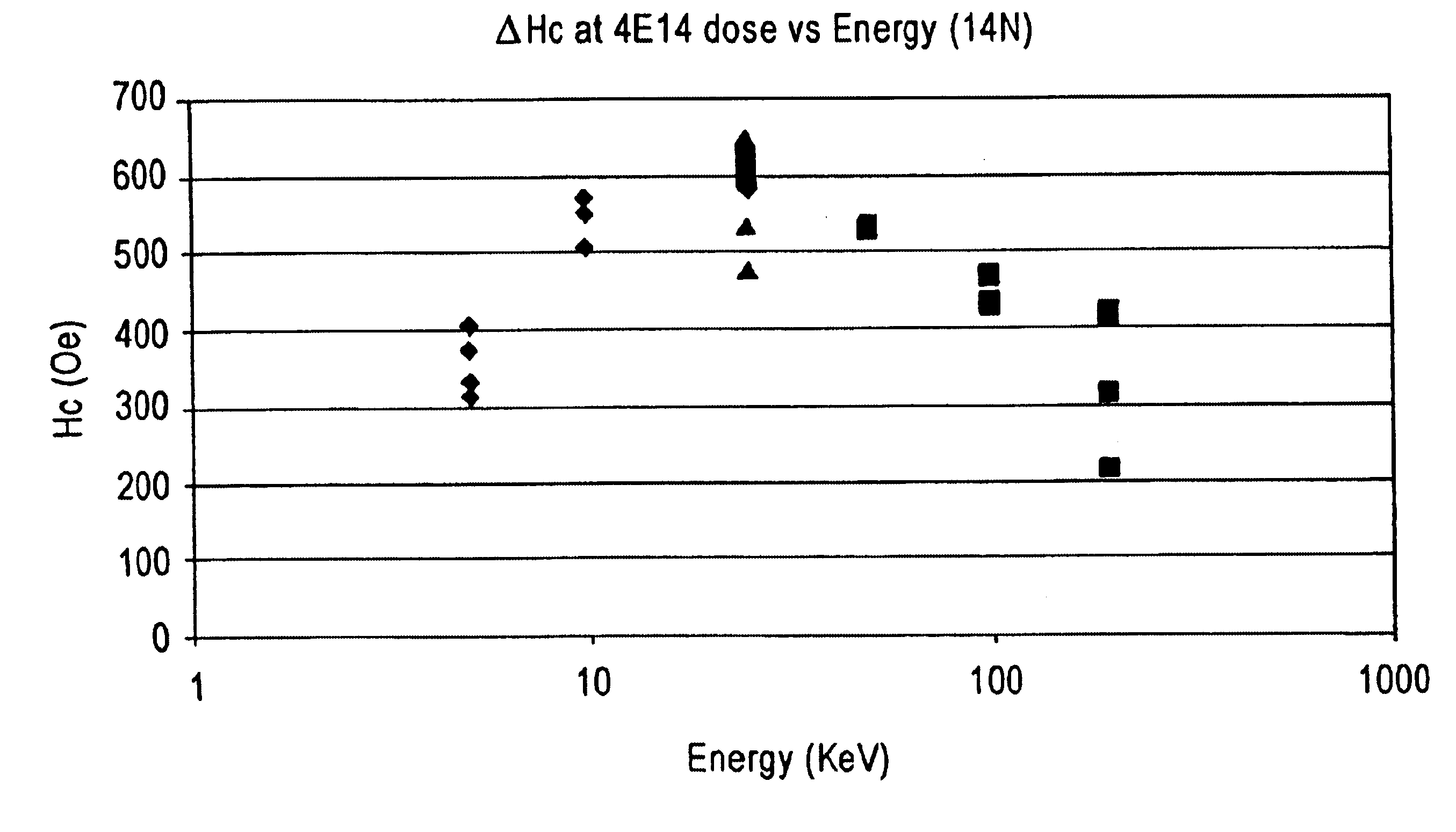
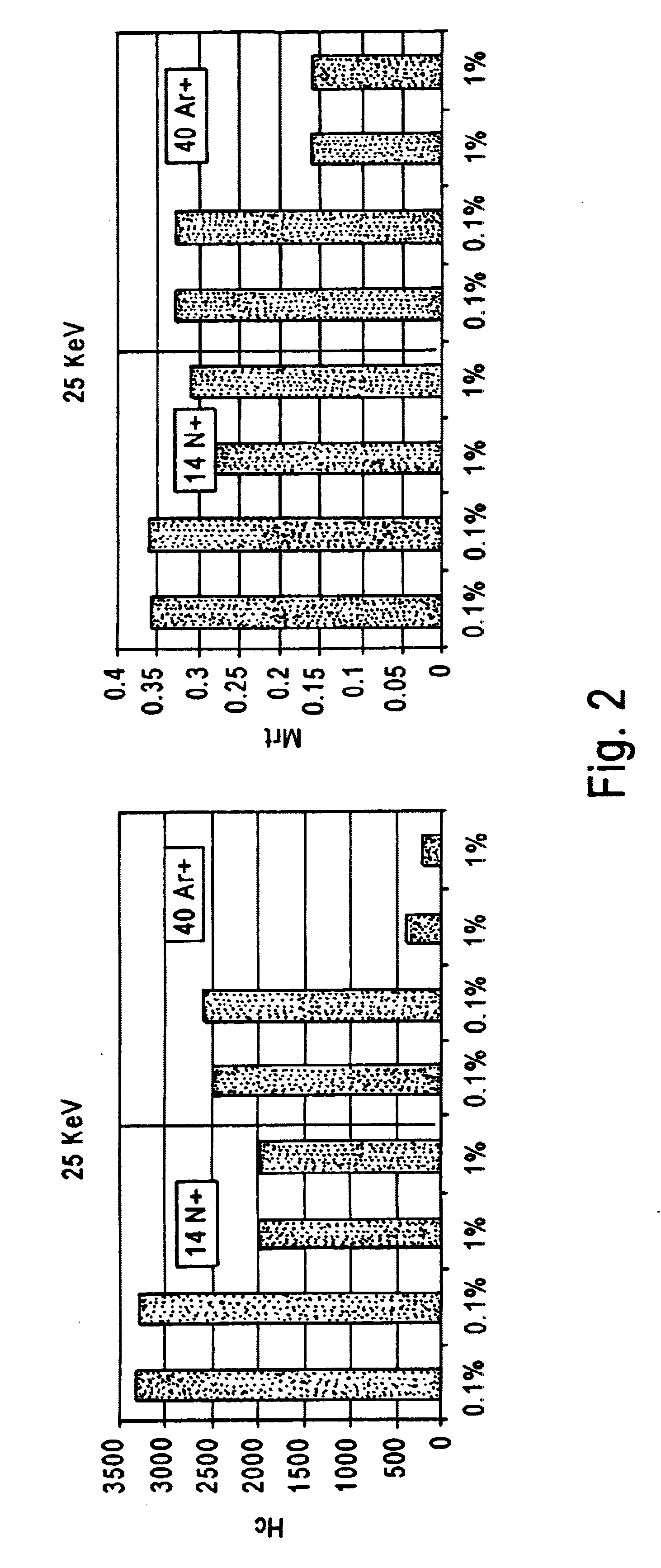
A magnetic recording medium is formed with a distribution of low coercivity regions functioning as a transition pattern for servo information capable of being sensed by a read / write head by exposing a masked magnetic layer to ions to change the coercivity of the exposed magnetic layer without substantially affecting the topography of the magnetic layer.Embodiments of the present invention include forming a series of substantially radially extending low coercivity regions used to divide the magnetic layer into a plurality of sectors comprising substantially concentric circumferentially extending data tracks by exposing a masked magnetic layer having a high coercivity, i.e. from about 2000 Oe to about 10000 Oe, to one or more heavy atom ion bombardments of gaseous ions, e.g. argon ions, at a dose of about 1×1013 atoms / cm2 to about 9×1015 atoms / cm2 having an implantation energy of about 10 KeV to about 50 KeV.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Magnetic recording medium and method of forming the same and magnetic disk drive
A magnetic recording medium having magnetic patterns into which servo information are written and a magnetic recording layer into which data are written comprises a nonmagnetic substrate, a magnetic recording layer formed on the substrate, and a hard magnetic layer contacted the magnetic recording layer within servo signal recording regions on the substrate and constituting servo patterns of film thicknesses of which are varied in the track length direction. Thereby, more precise reading of the servo signals by the magnetic head is assured and a surface of the magnetic recording medium can be flatted.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Method of patterning magnetic products using chemical reactions
InactiveUS6841224B2Improve productivityFlat surfaceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesHalogenChemical reaction
A method of patterning magnetic material includes forming a ferromagnetic material layer containing one element selected from the group consisting of Fe, Co and Ni on a substrate, selectively masking a surface of the ferromagnetic material layer, and making nonferromagnetic. The making nonferromagnetic step includes exposing an exposed portion in halogen-containing reaction gas, changing magnetism of the exposed portion and a lower layer thereof by chemical reaction, and making the exposed portion a nonferromagnetic material region. A magnetic recording medium is fabricated by using the magnetic material patterning method and includes a plurality of recording regions made of ferromagnetic materials, each containing at least one element selected from the group consisting of Fe, Co and Ni, and a nonferromagnetic material region for separating the recording regions from each other. The nonferromagnetic material region is a compound region of the ferromagnetic material and halogen.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
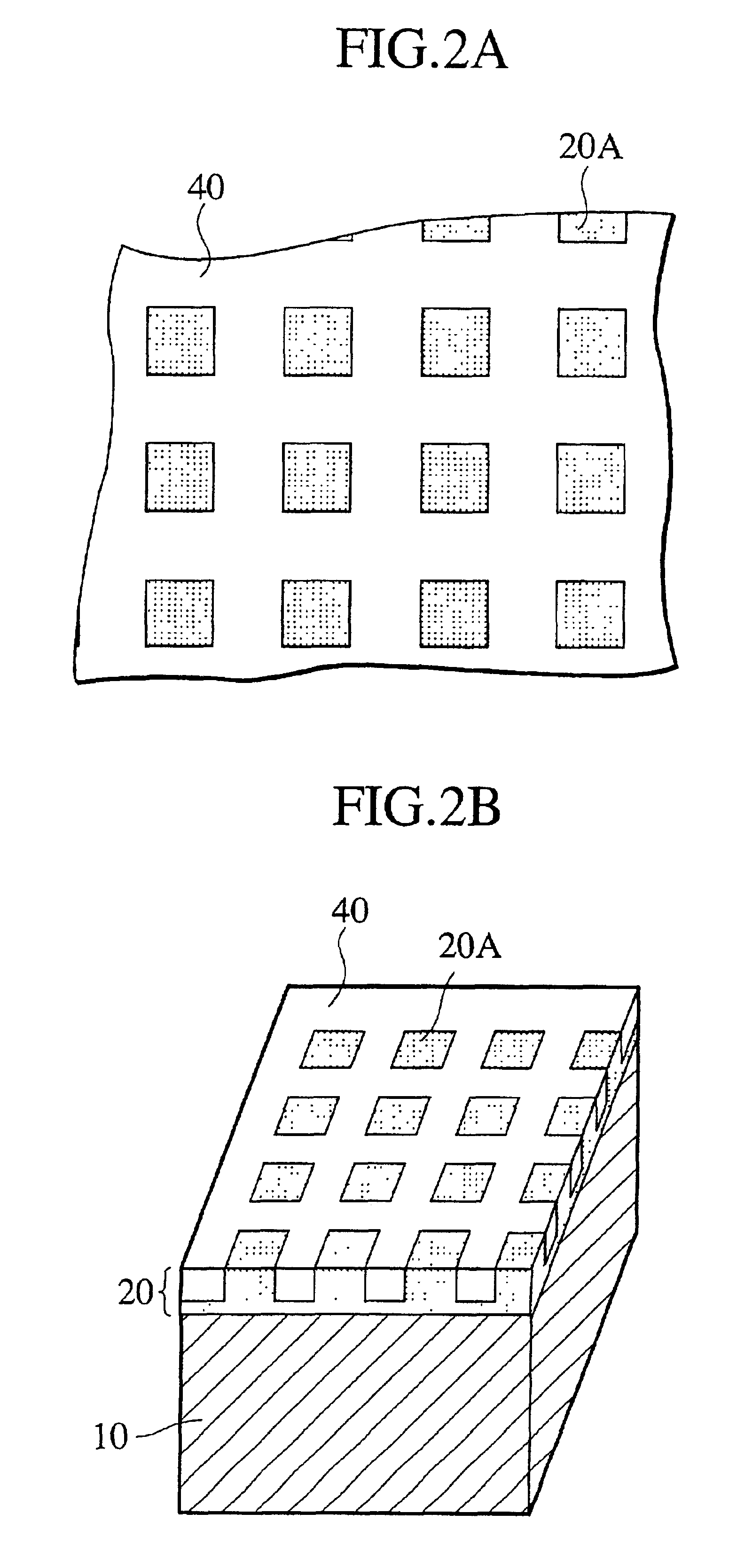
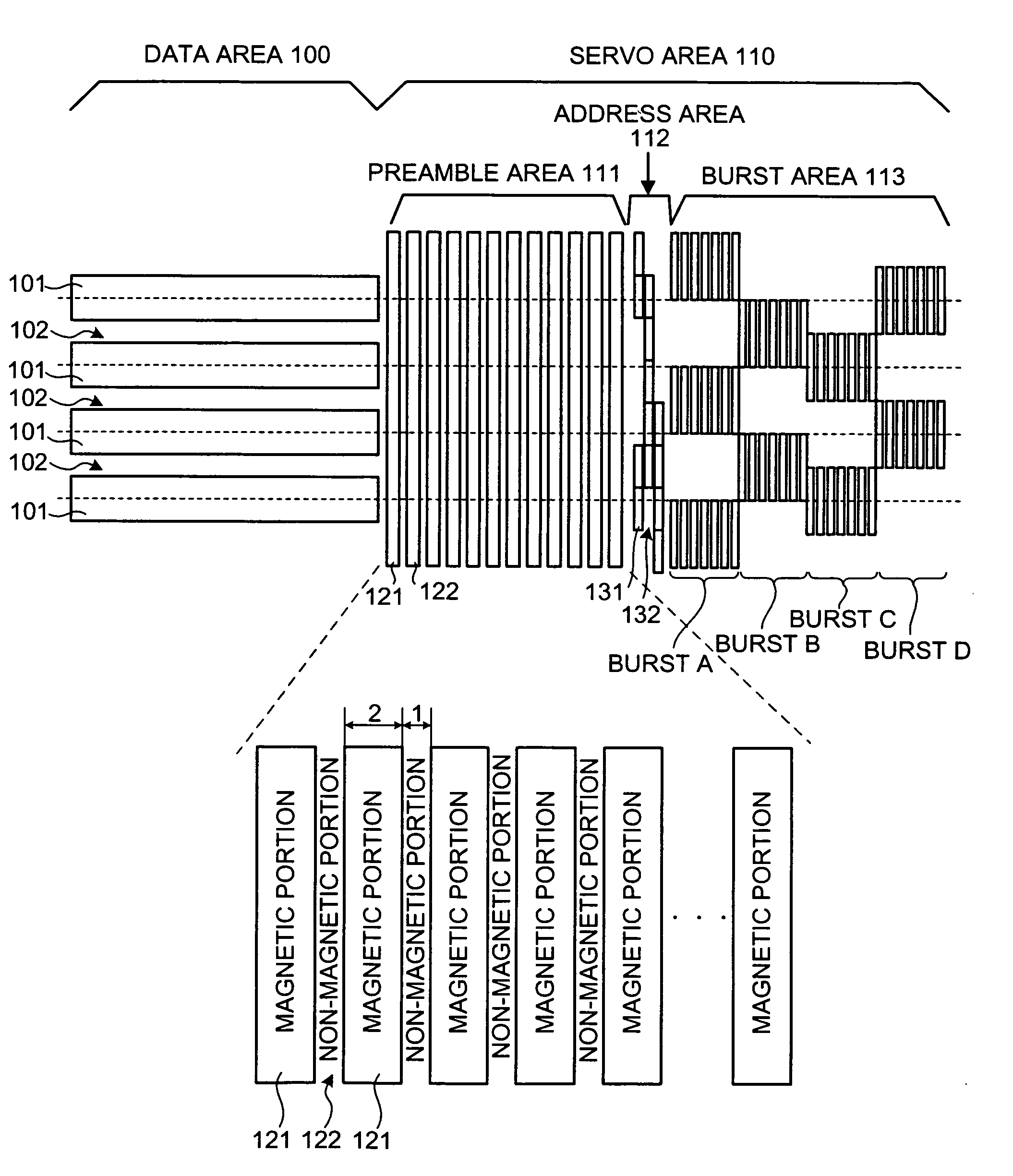
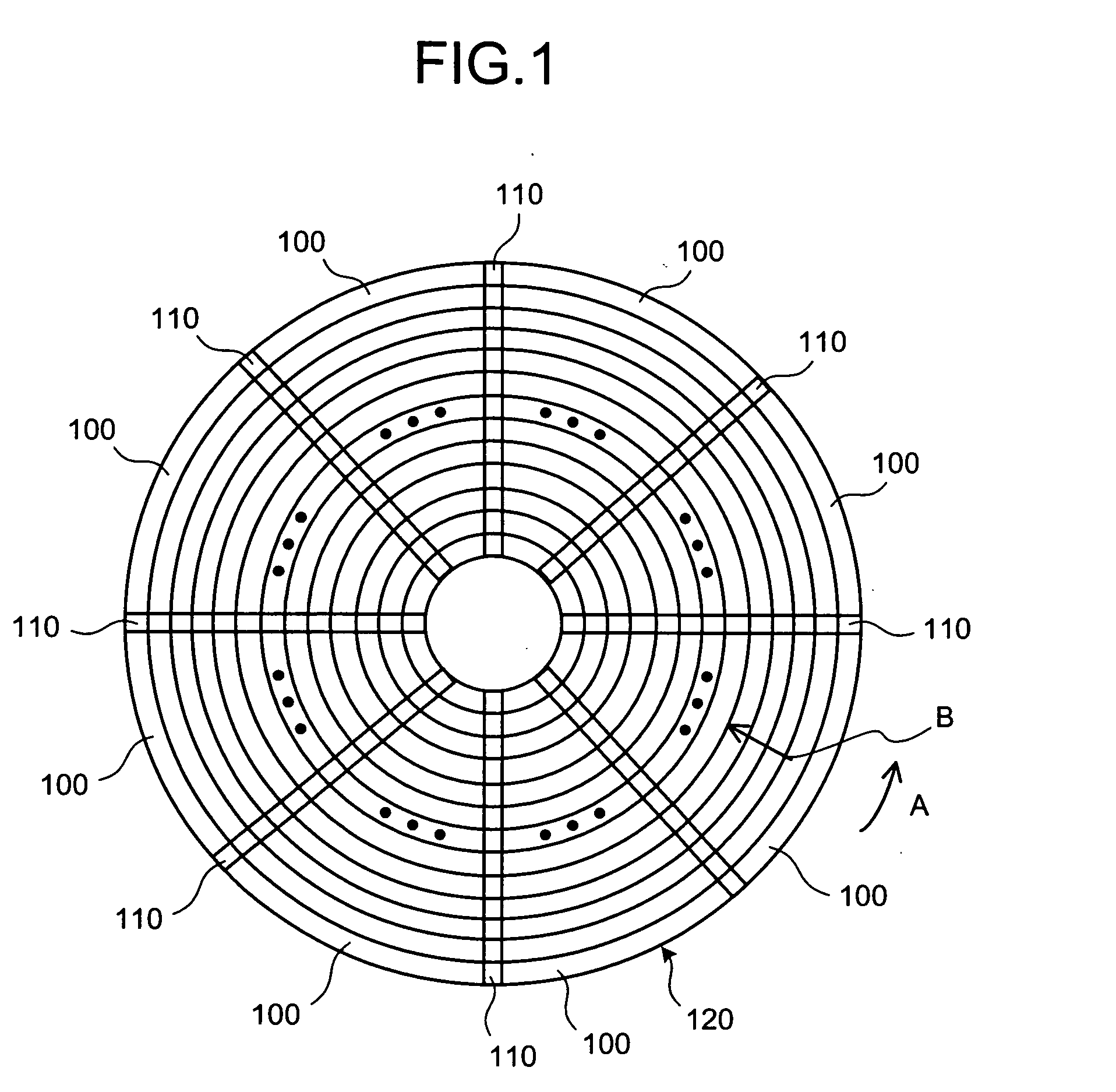
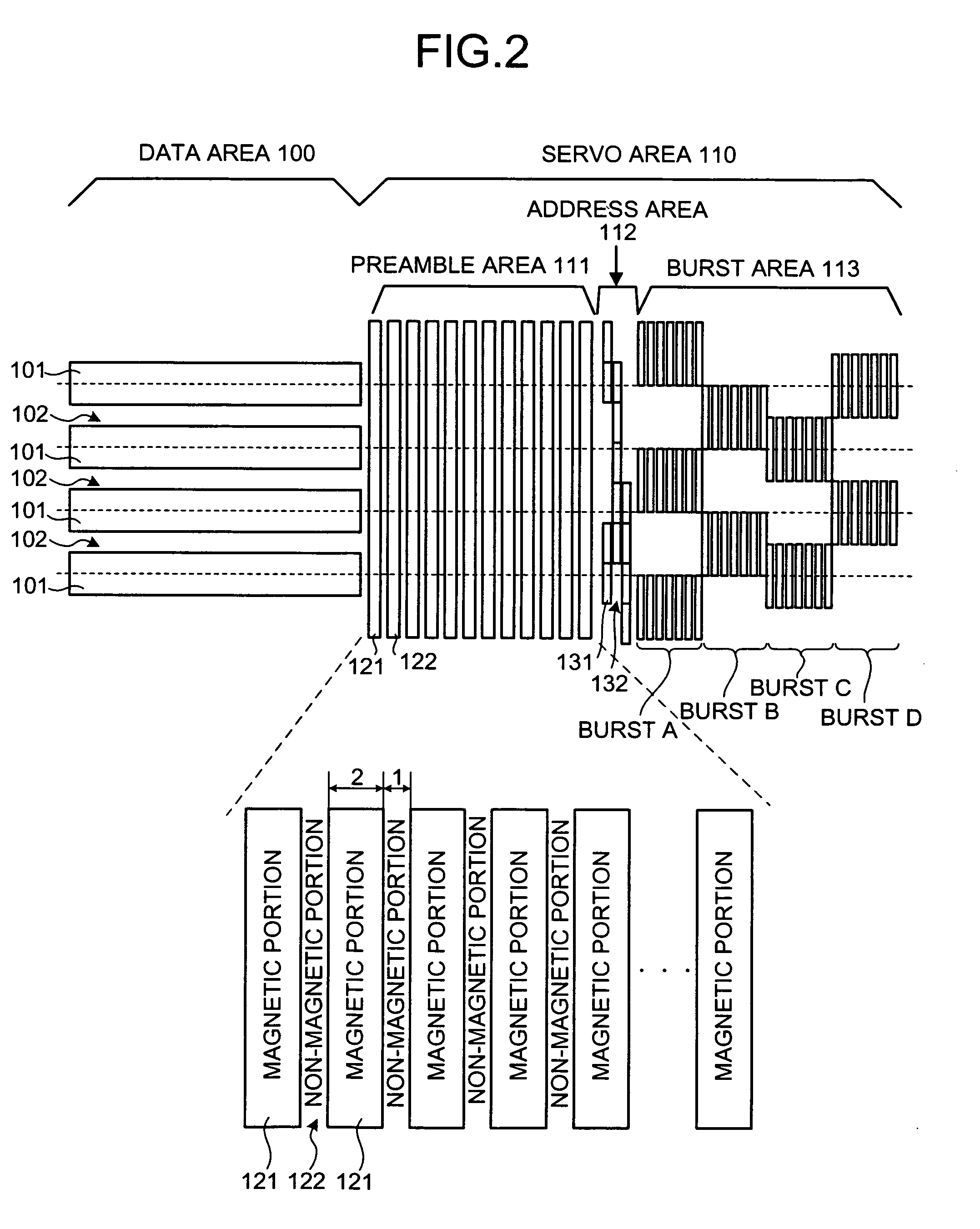
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic recording/reproducing apparatus, and stamper for manufacturing magnetic recording medium
A magnetic recording medium includes a servo area that has a preamble area where a magnetic portion and a non-magnetic portion for clock synchronization are formed; and a data area where user data is written into. The magnetic portion is different in an occupancy to the preamble area from the non-magnetic portion.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
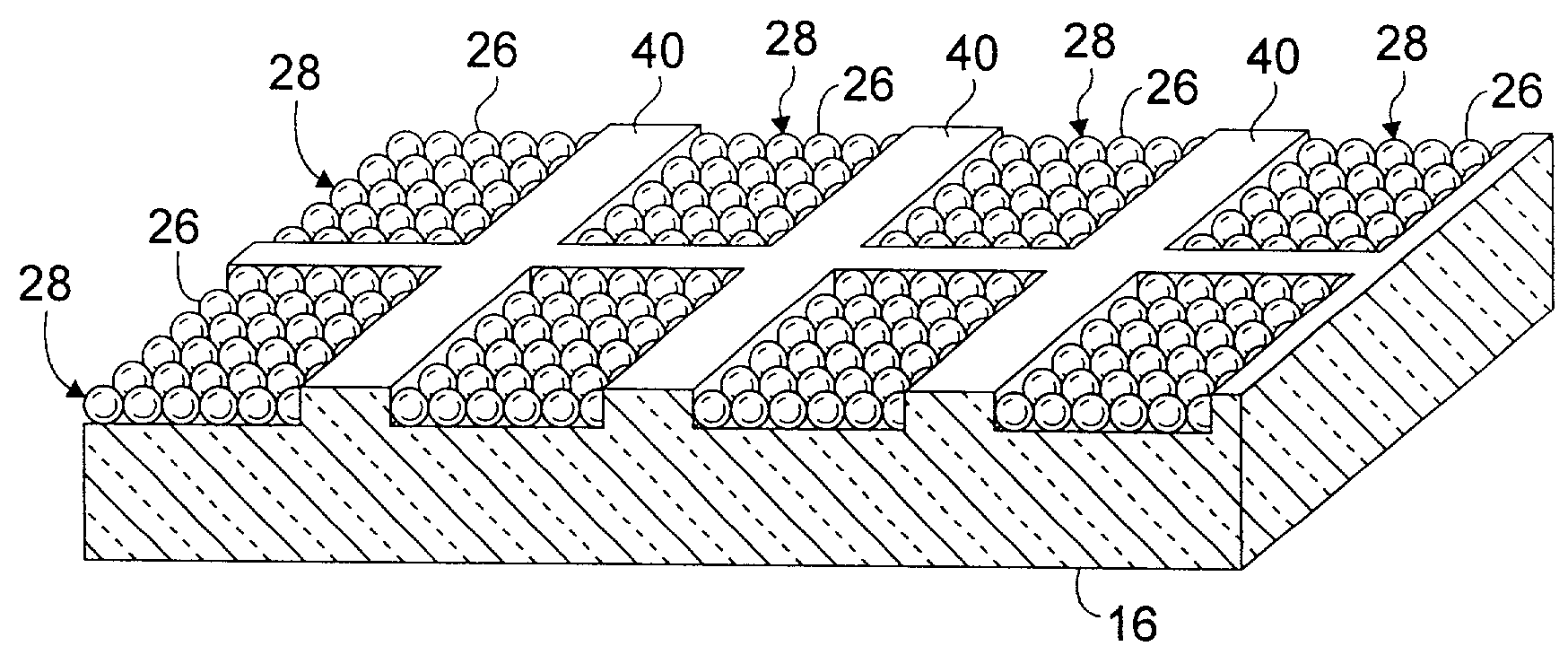
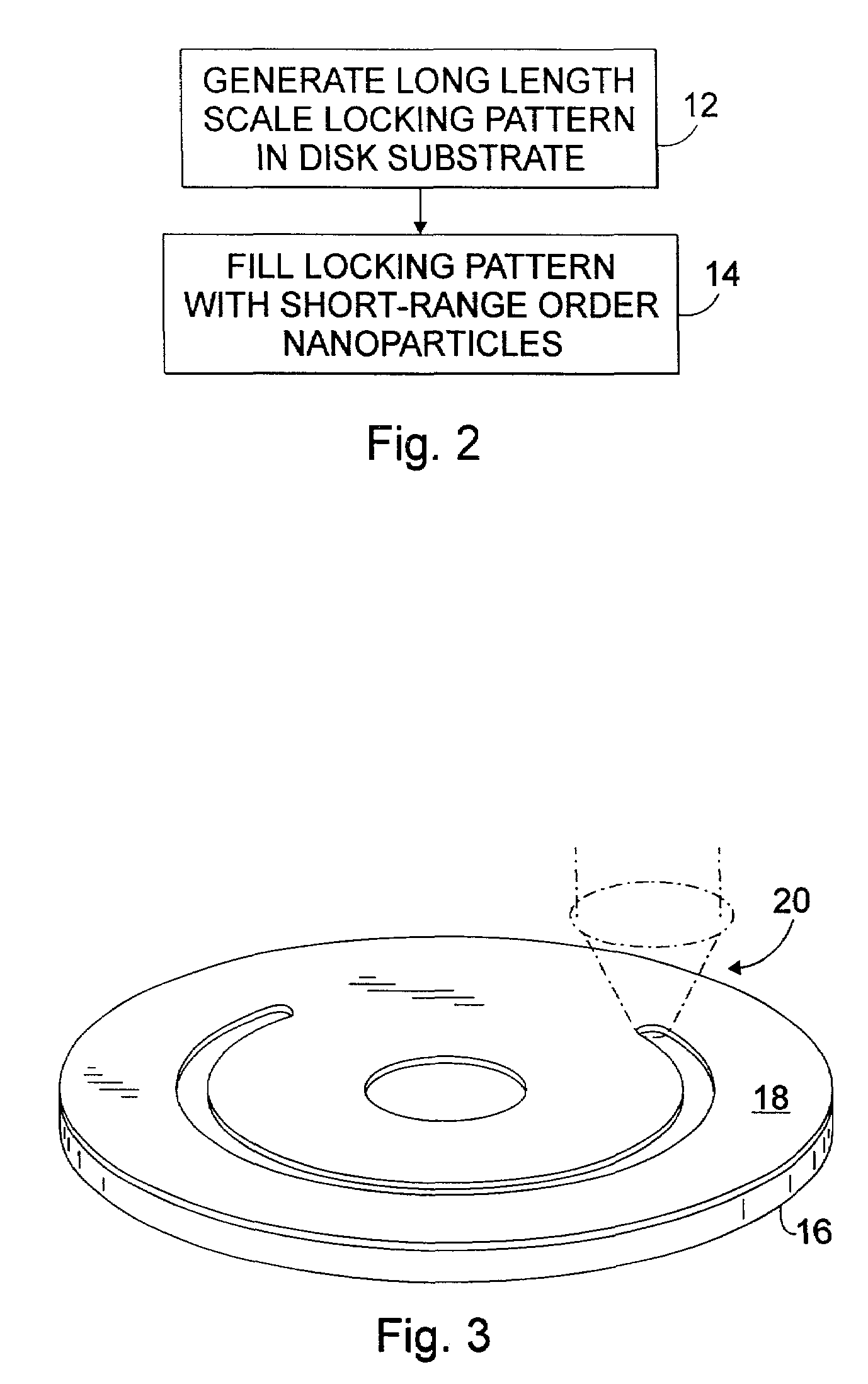
Magnetic recording media having self organized magnetic arrays
InactiveUS7041394B2Magnetic materials for record carriersPatterned record carriersChemical synthesisShort range order
A magnetic recording disc is provided according to the present invention for magnetic recording. The magnetic recording disc includes a disc substrate having a locking pattern etched therein. Chemically synthesized iron-platinum particles are provided in the locking pattern and completely fill the locking pattern. The chemically synthesized iron-platinum nanoparticles exhibit short-range order characteristics forming self organized magnetic arrays.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
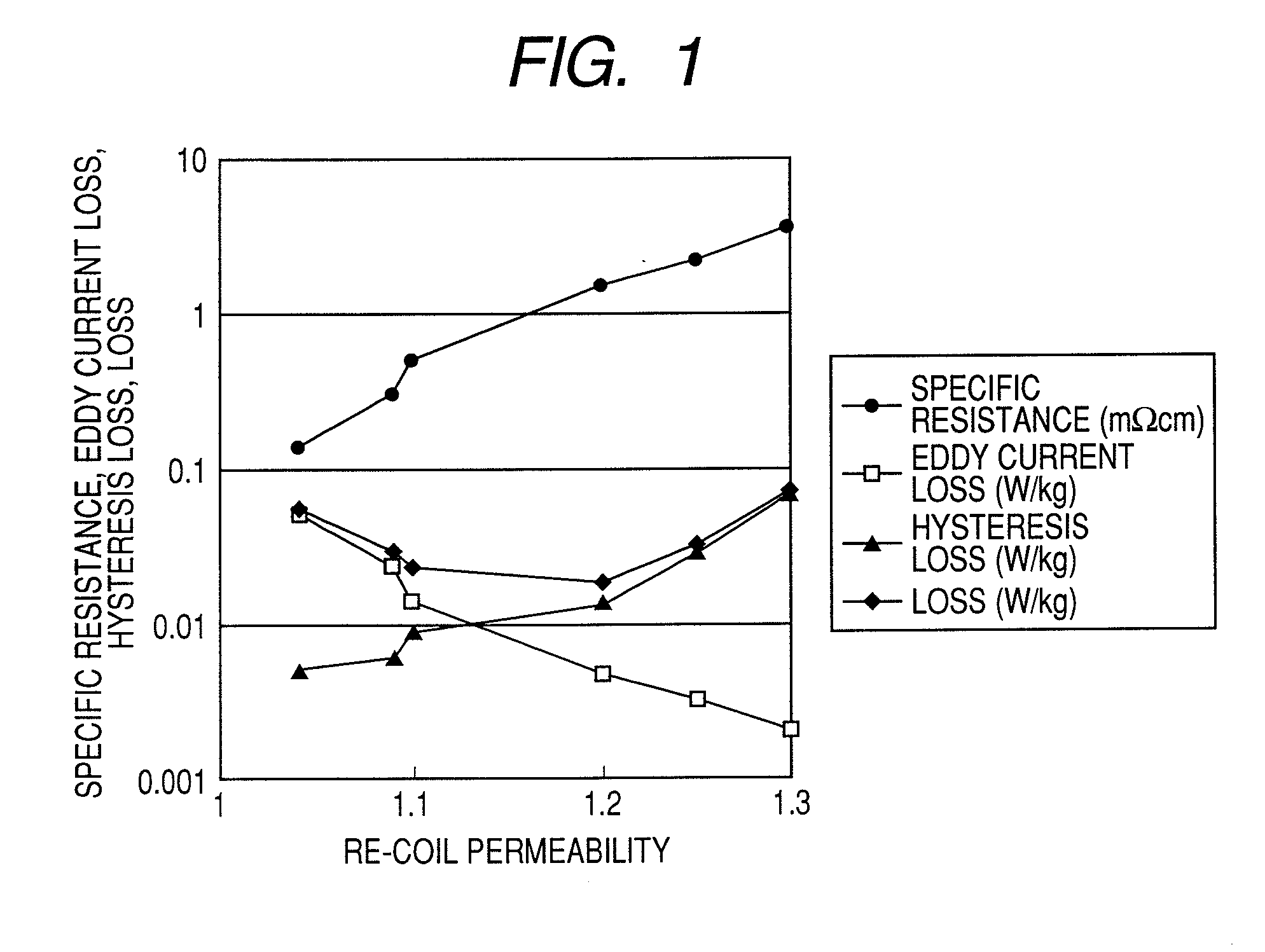
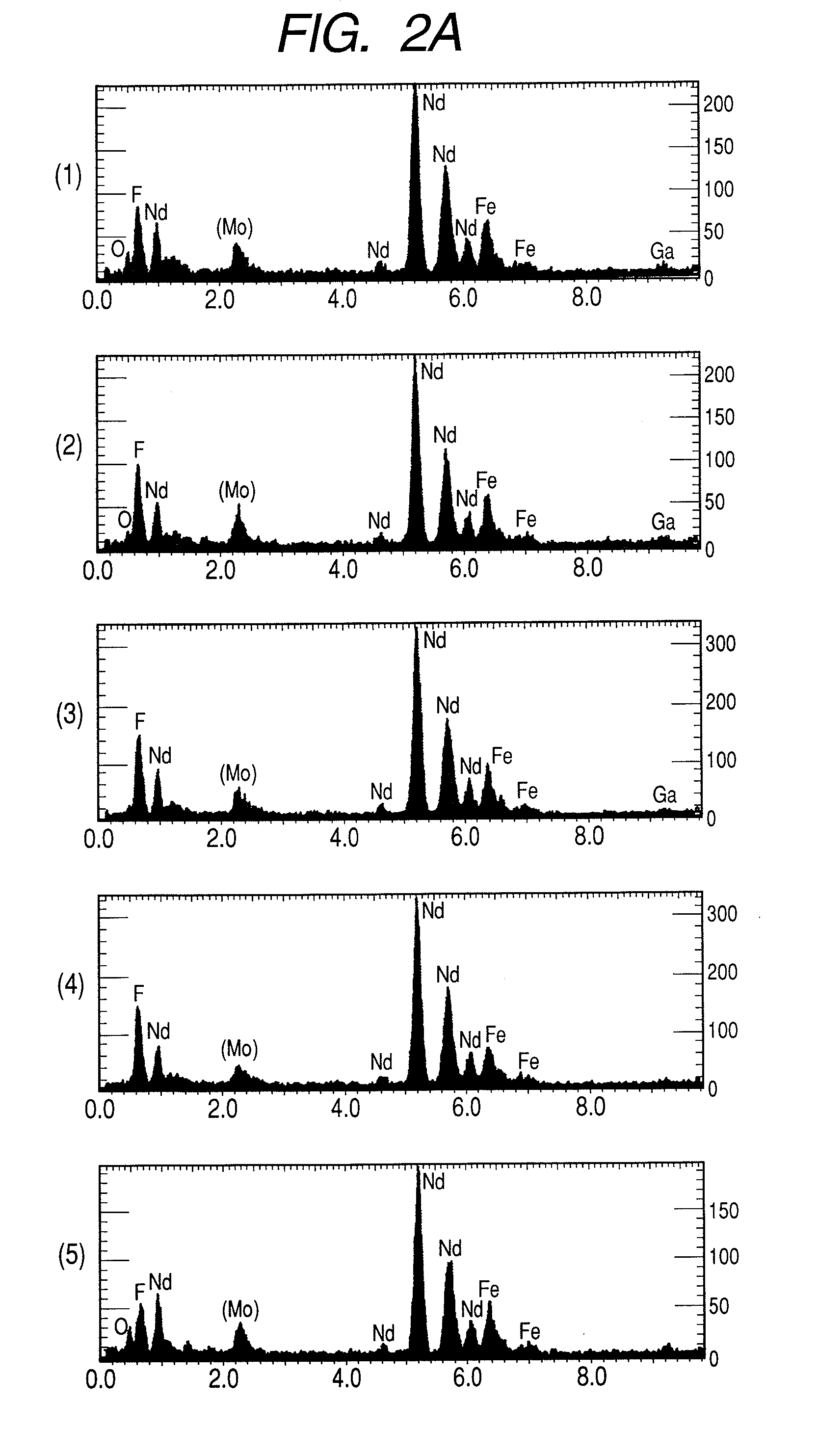
High resistance magnet and motor using the same
InactiveUS20080054738A1Improve magnetic propertiesImprove propertiesLayered productsNanoinformaticsRare-earth elementHigh resistance
A magnet comprising grains of a ferromagnetic material whose main component is iron and a fluorine compound layer or an oxy-fluorine compound layer of fluoride compound particles of alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and rare earth elements, present on the surface of the ferromagnetic material grains, wherein an amount of iron atoms in the fluorine compound particles is 1 to 50 atomic %.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Magnetic recording medium, method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording/reproducing apparatus
A magnetic recording medium is obtained by easily patterning a magnetic recording layer without deteriorating its electromagnetic conversion characteristics, by forming a silicon-based protective film between the magnetic recording layer and a photoresist, and performing dry etching and oxygen plasma processing.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method for manufacturing magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20060124585A1Avoid disagreementProcessing is suppressedDecorative surface effectsPatterned record carriersFilling materialsEtching rate
A method for manufacturing a magnetic recording medium is provided, which can manufacture a magnetic recording medium that includes a recording layer having a concavo-convex pattern and has a sufficiently flat surface. The method includes the steps of: forming an object to be processed including a recording layer having a predetermined concavo-convex pattern formed over a substrate and a first mask layer (temporary underlying material) formed at least on recording elements (convex portions) of the recording layer; depositing a filling material on the object to be processed to fill concave portions; removing a part of the filling material by dry etching to expose at least side faces of the first mask layer; and removing the first mask layer by an etching method in which an etching rate of the first mask layer is higher than that of the filling material to flatten a surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Magnetic recording device
ActiveUS20090080109A1Magnetization is changedManufacture head surfacePatterned record carriersMagnetizationRecording layer
A magnetic recording device includes: a magnetic recording medium containing a plurality of recording layers; a magnetic recording head for conducting magnetic writing of information in the magnetic recording medium; and a magnetic reproducing head for conducting magnetic reading out of the information from the magnetic recording medium; wherein the magnetic recording head includes a high frequency oscillator for magnetically assisting the magnetic writing of the information so as to change a magnetization of at least one of the plurality of recording layers of the magnetic recording medium, thereby recording a plurality of information different from one another in the magnetic recording medium commensurate with a total amount of magnetization of the plurality of recording layers.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
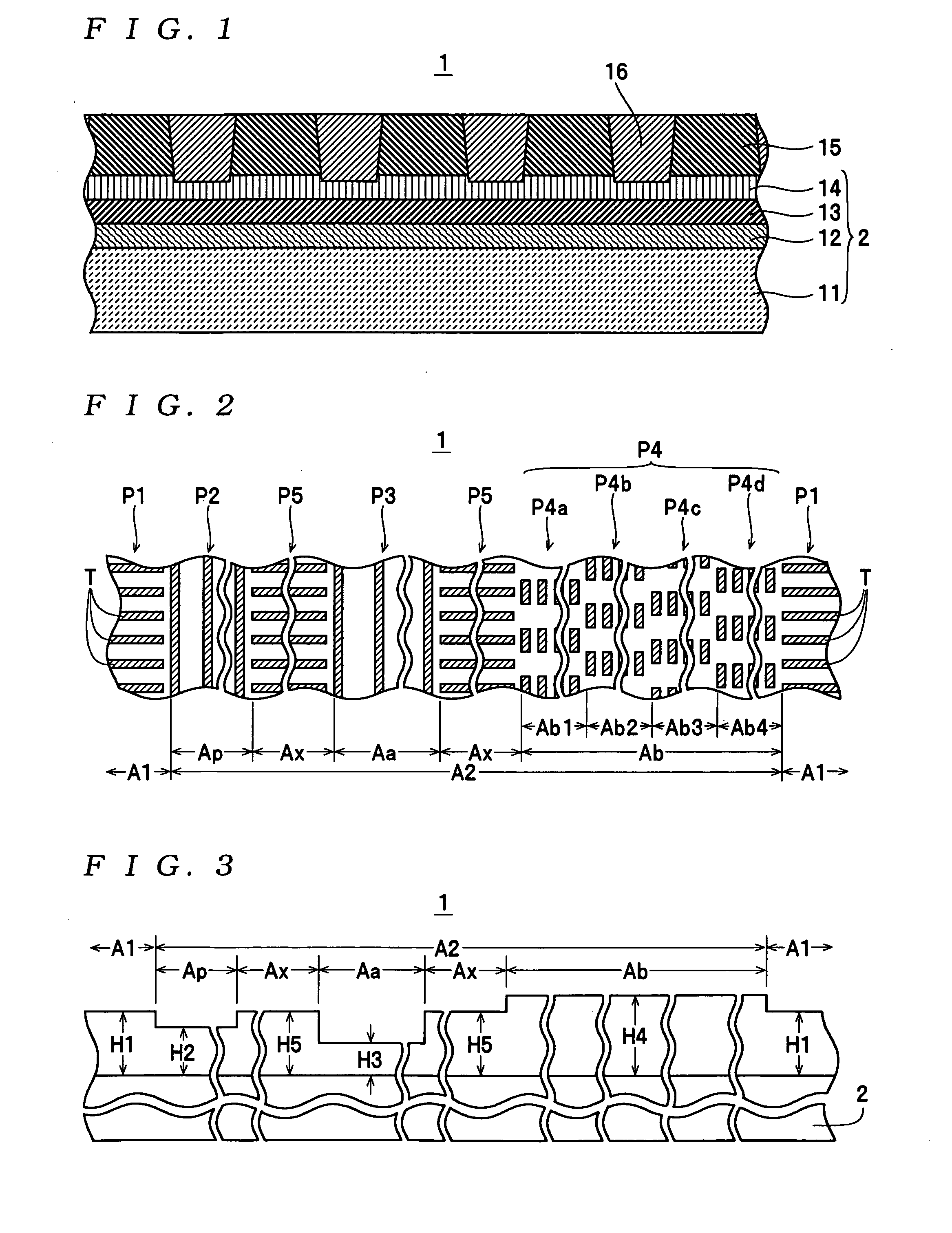
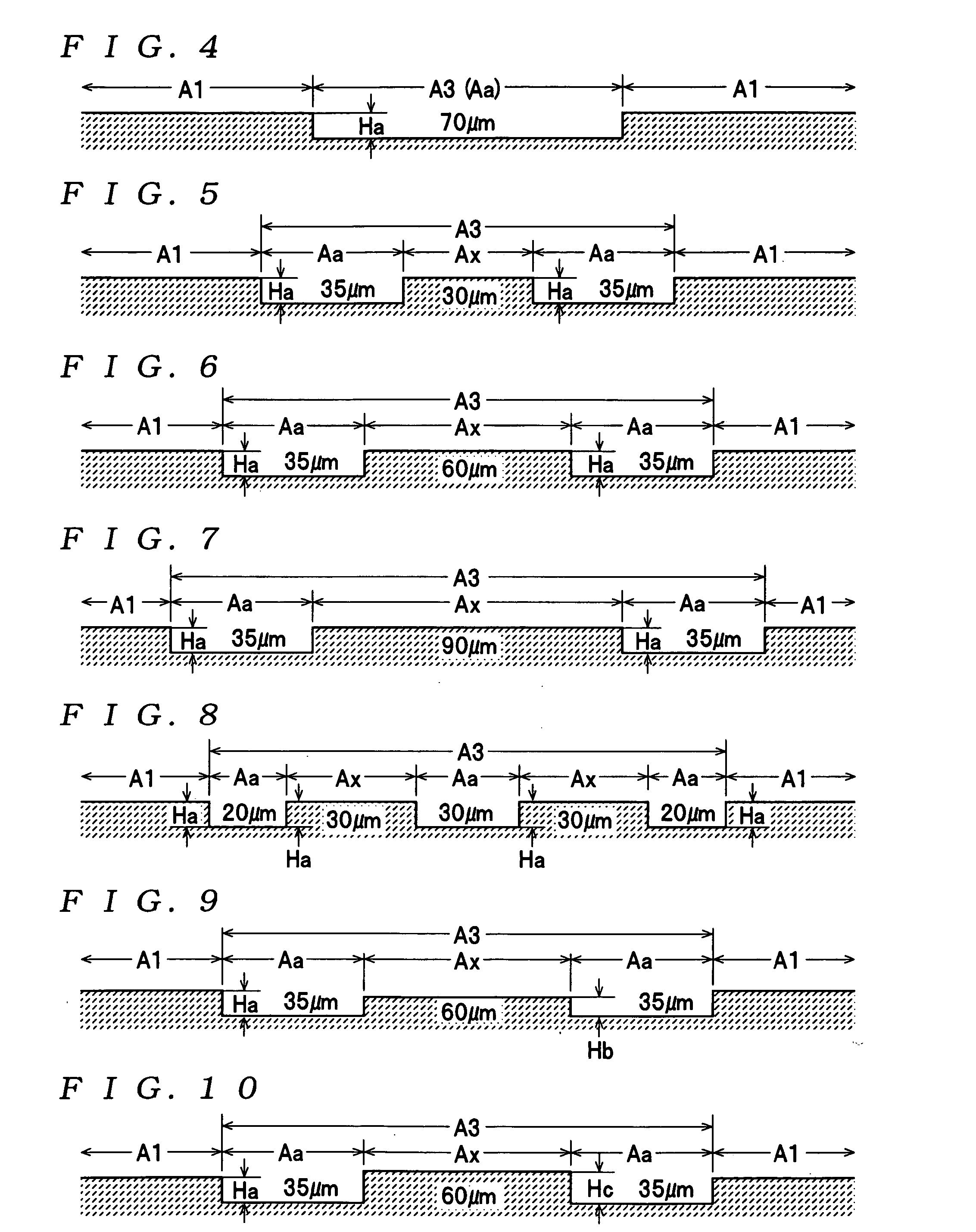
Magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS20050117253A1Reduce volatilitySuppress fluctuationsPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsControl signalEngineering
A data track area and a servo pattern area are formed on a magnetic recording medium by embedding a nonmagnetic material inside concaves in a plurality of types of convex / concave patterns formed of a magnetic material on a substrate. The servo pattern area includes a plurality of types of first functional areas, in which control signals for disk access are recorded during manufacturing using the convex / concave patterns, and a second functional area, in which a convex / concave pattern of a different type to the convex / concave patterns of the respective first functional areas is formed and in which the nonmagnetic material is embedded so that an average height within the second functional area is substantially equal to an average height in the data track area.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Popular searches
Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Bulk negative resistance effect devices Forming microstructural systems Microstructural device assembly Microelectromechanical systems Transistor Static storage Metal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalysts Record information storage Alignment for track following on disks
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com