Patents
Literature
881results about How to "Low coercivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
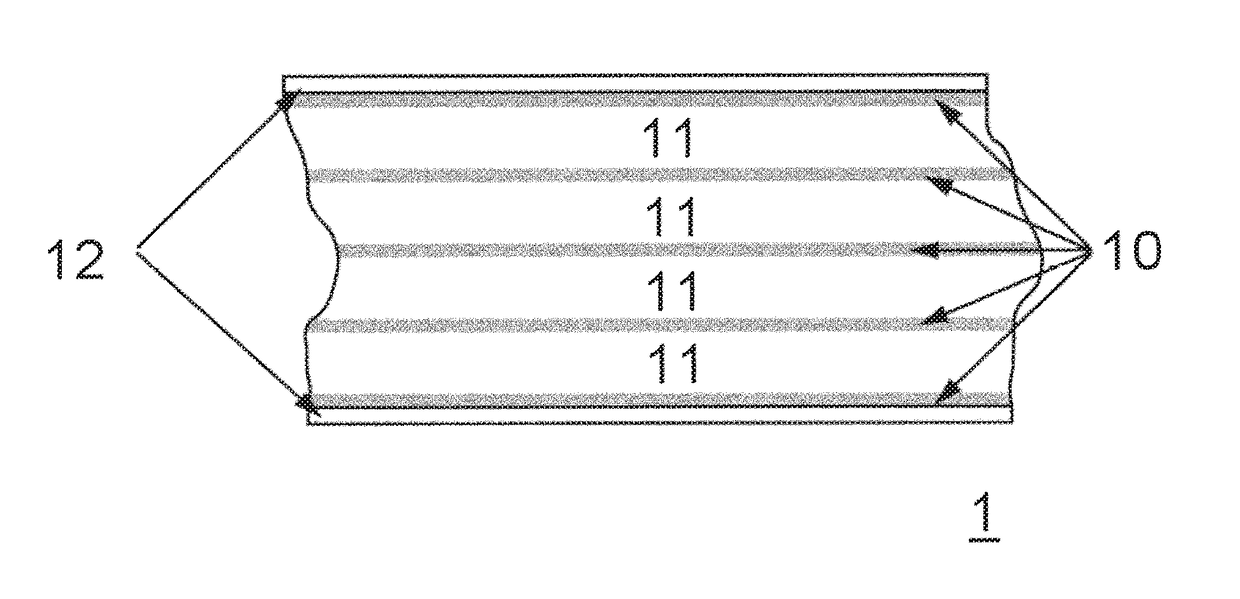
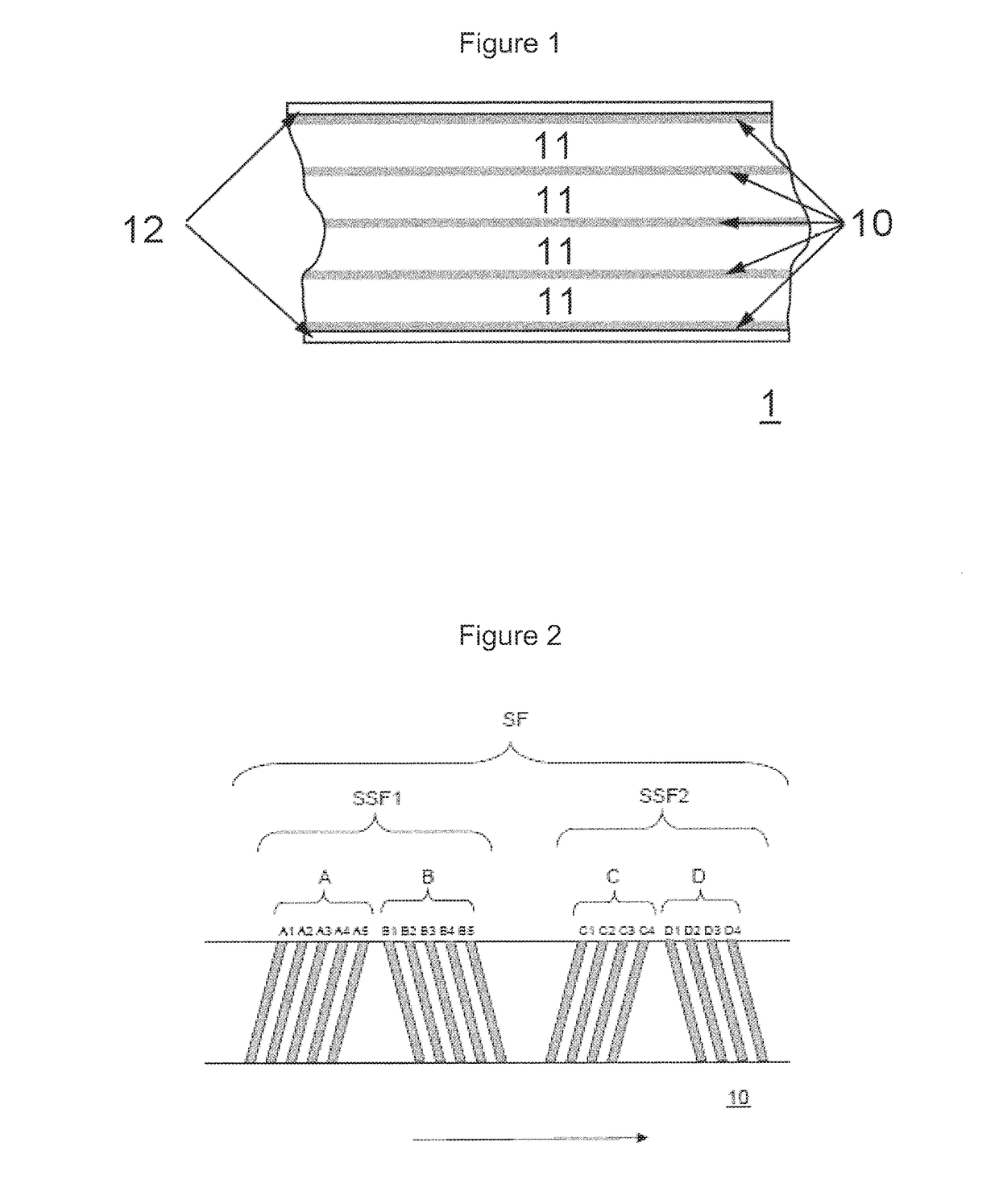
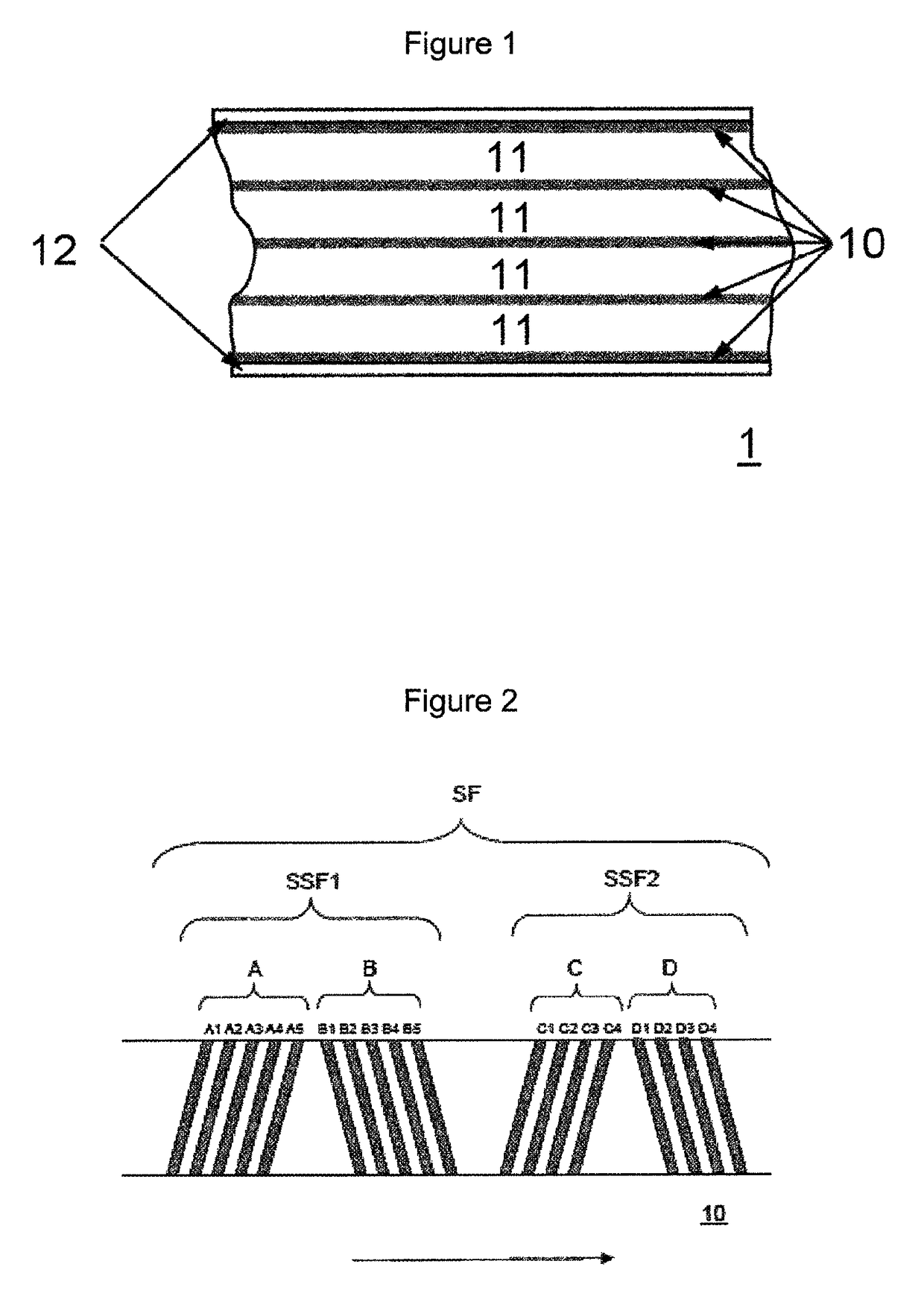
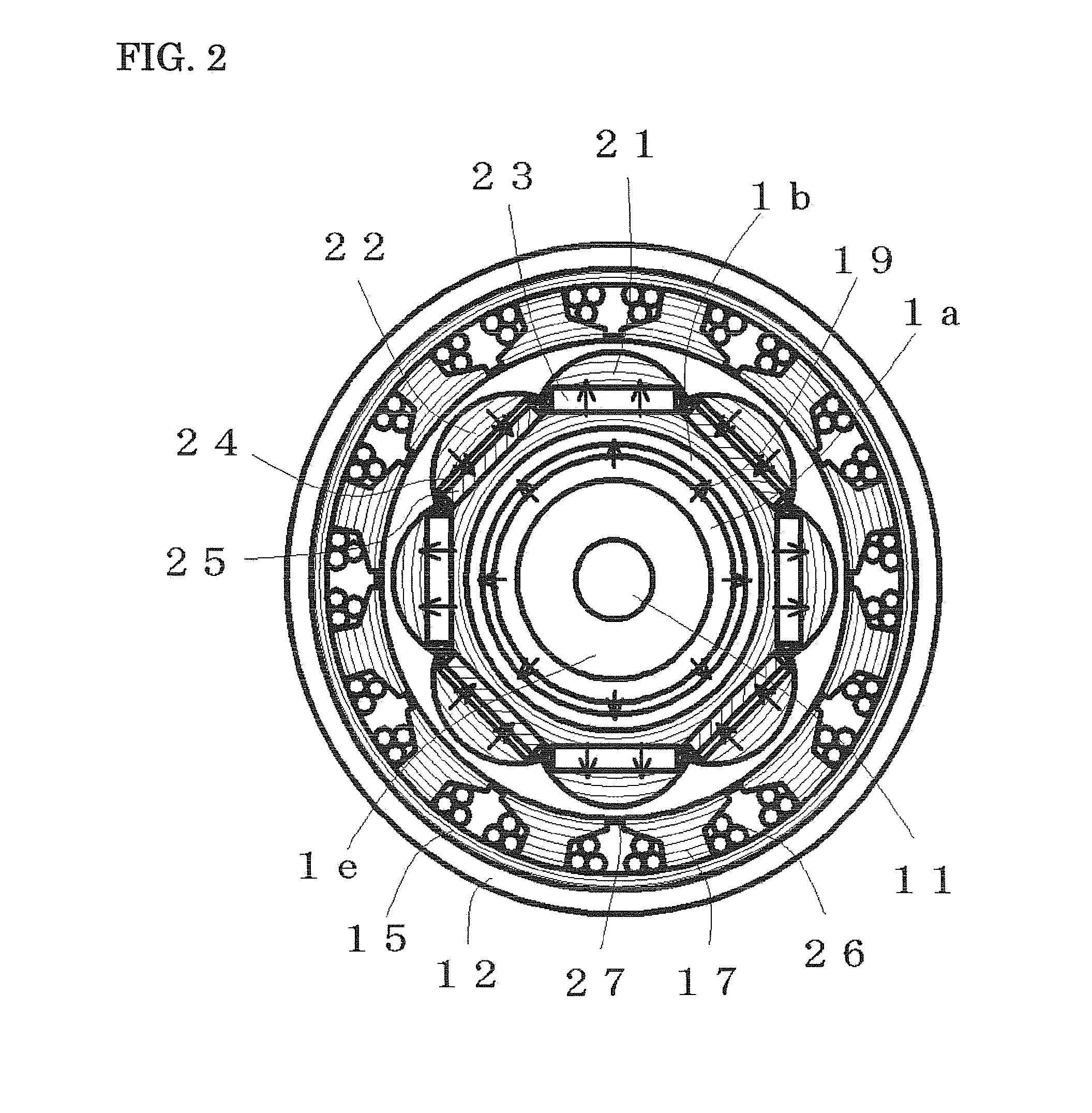
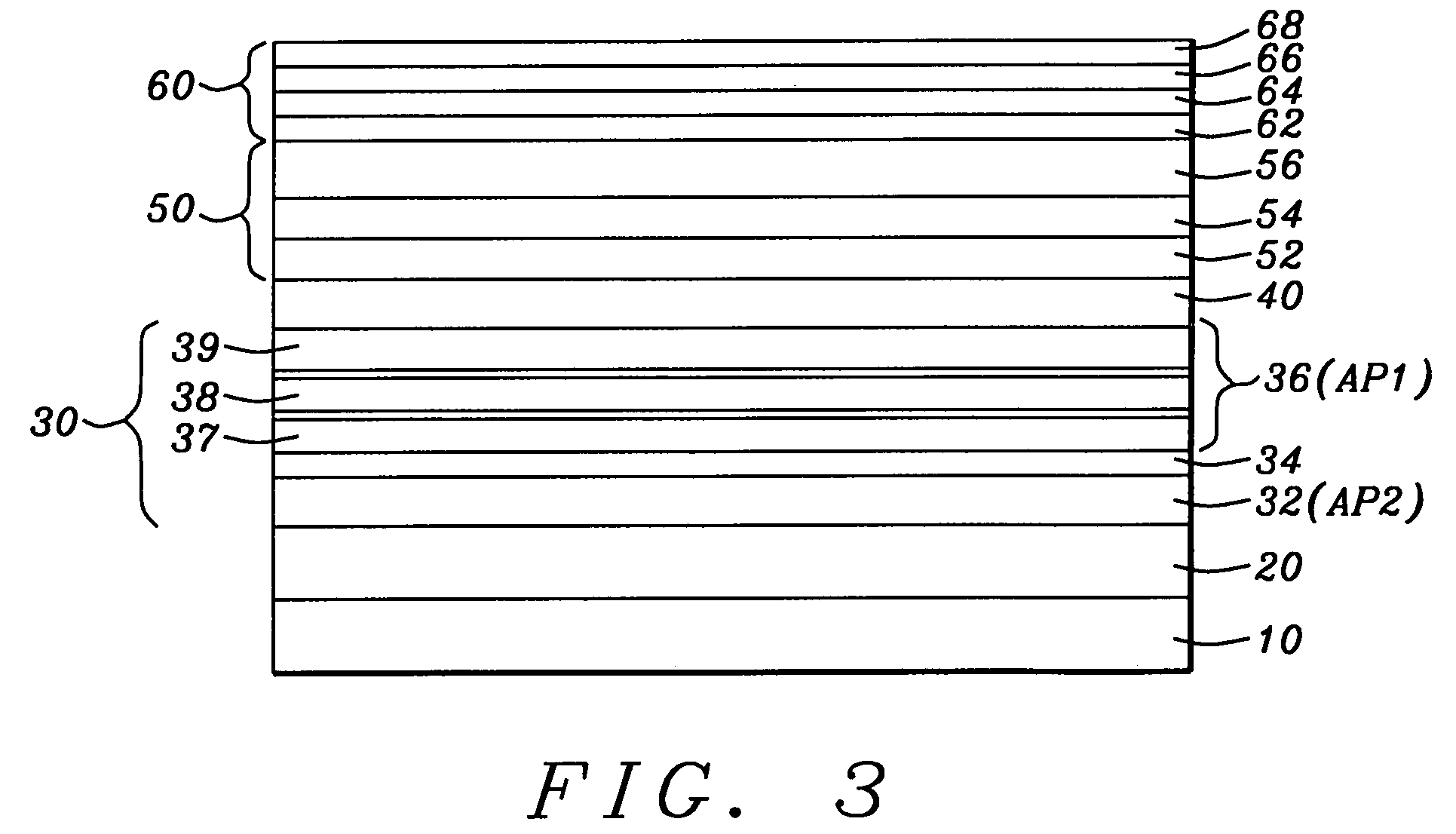
Magnetic tape and magnetic tape device
ActiveUS20170186460A1Increase capacityEnhance head positioningAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tension forceMagnetic force microscope
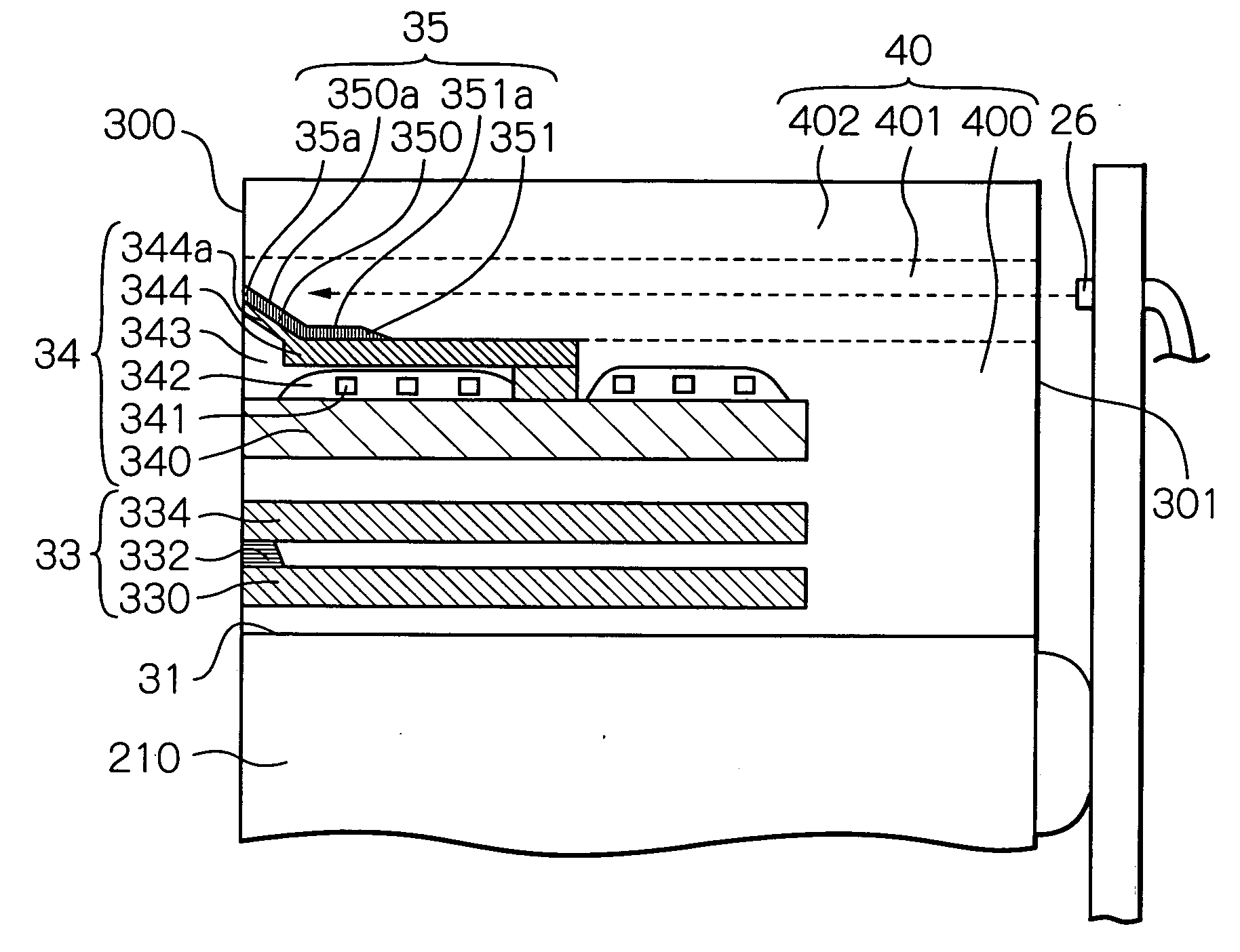
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the coercive force measured in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 167 kA / m, a timing-based servo pattern is present on the magnetic layer, and the edge shape specified by observing the timing-based servo pattern with a magnetic force microscope is a shape in which the difference between the value of the 99.9% cumulative distribution function of the width of misalignment from the ideal shape in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and the value L0.1 of the 0.1% cumulative distribution function, L99.9-L0.1, is less than or equal to 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
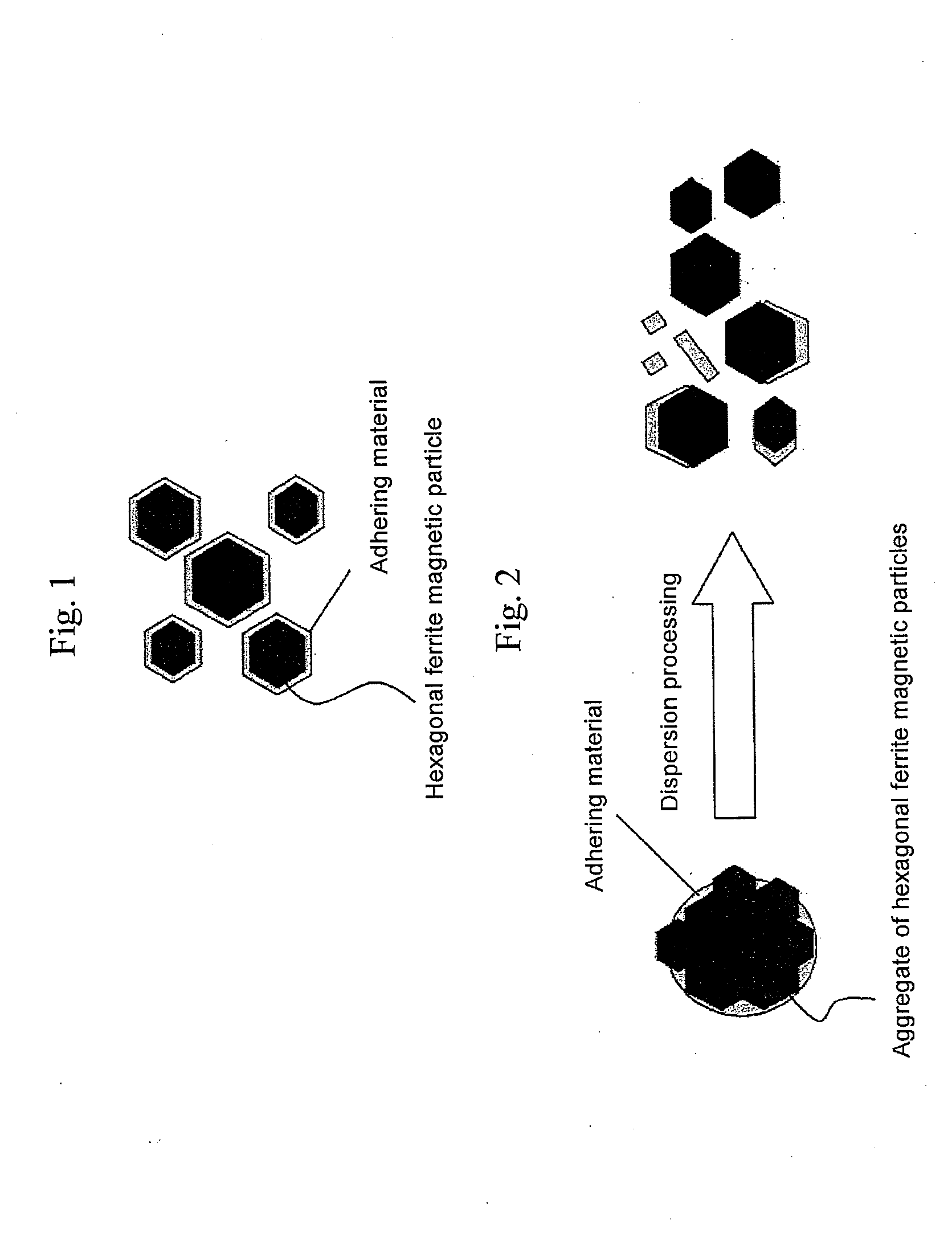
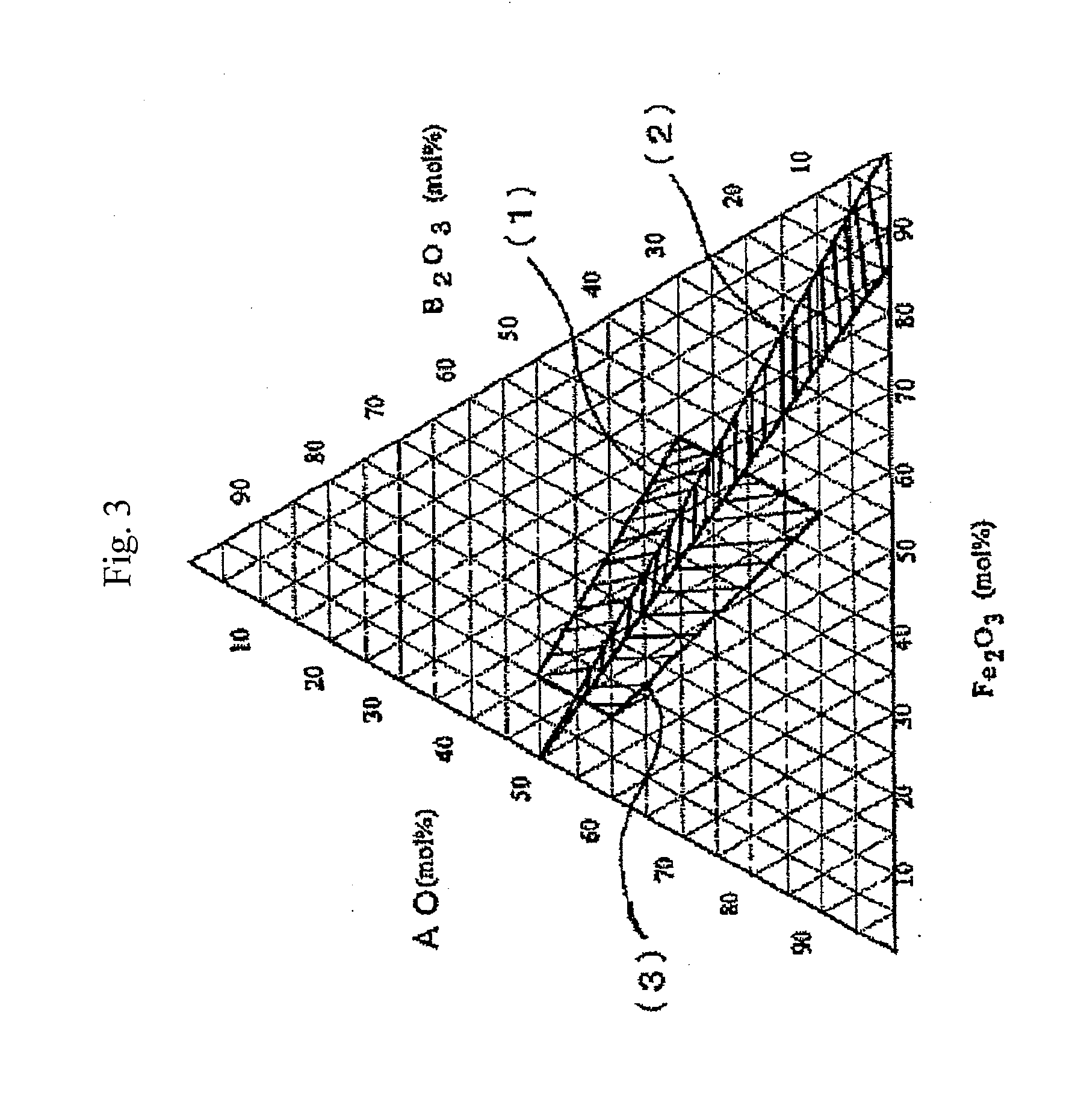
Hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle and method of manufacturing the same, and magnetic recording medium
ActiveUS20110244272A1Improve coercive forceReduce particlesMaterial nanotechnologyMagnetic materials for record carriersHeat treatedMaterials science
An aspect of the present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle comprising melting an Al-containing starting material mixture to prepare a melt and quenching the melt to obtain an amorphous material; subjecting the amorphous material to heat treatment to cause a hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle to precipitate in a product obtained by the heat treatment; collecting a hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle by subjecting the product to treatment with an acid and washing, wherein the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle collected has a particle size ranging from 15 to 30 nm, comprises 0.6 to 8.0 weight percent of Al, based on Al2O3 conversion, relative to a total weight of the particle, and Al adheres to a surface of the hexagonal ferrite magnetic particle.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic tape with specific servo pattern edge shape and magnetic tape device using same
ActiveUS9773519B2Accurate informationImprove positionAlignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageMagnetic tension forceMagnetic force microscope
The magnetic tape has a magnetic layer containing ferromagnetic powder and binder on a nonmagnetic support, wherein the coercive force measured in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape is less than or equal to 167 kA / m, a timing-based servo pattern is present on the magnetic layer, and the edge shape specified by observing the timing-based servo pattern with a magnetic force microscope is a shape in which the difference between the value L99.9 of the 99.9% cumulative distribution function of the width of misalignment from the ideal shape in the longitudinal direction of the magnetic tape and the value L0.1 of the 0.1% cumulative distribution function, L99.9−L0.1, is less than or equal to 180 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Magnetic media with improved exchange coupling
InactiveUS6899959B2Easy and fast switchingImprove thermal stabilityDifferent record carrier formsRecord information storageInter layerMagnetic media
A magnetic recording medium includes a substrate, an underlayer, a lower magnetic layer formed on the underlayer, an intermediate layer, and an upper magnetic layer formed on the intermediate layer. The intermediate layer is typically Ru, and promotes antiferromagnetic coupling between the upper and lower magnetic layers. The upper and lower magnetic layers are typically Co alloys. The lower magnetic layer has a high saturation magnetization Ms to promote high exchange coupling between the upper and lower magnetic layers. The dynamic coercivity of the lower magnetic layer is lower than the exchange field to ensure rapid switching of the lower magnetic layer.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Thin-film magnetic head with near-field-light-generating layer
ActiveUS20070139818A1Improve reliabilityLow coercivityCombination recordingArm with optical waveguideMagnetic mediaBiomedical engineering
A thin-film magnetic head that has a configuration in which the element-formed surface and the opposed-to-medium surface are perpendicular to each other, and a light source is sufficiently distanced from the medium surface is provided. The head comprises at least one near-field-light-generating layer for heating a part of a magnetic medium during write operation by generating a near-field light, having a shape tapered toward a head end surface on the opposed-to-medium surface side, and comprising a near-field-light-generating portion having a light-received surface and a tip reaching the head end surface on the opposed-to-medium surface side, and the light-received surface being sloped in respect to the element-formed surface and being provided in a position where an incident light propagating from a head end surface opposite to the opposed-to-medium surface can reach at least a part of the light-received surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Method of adjusting CoFe free layer magnetostriction
InactiveUS6998150B2Low constantLow coercivityNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismCopperOXYGEN EXPOSURE
It has been found that the insertion of a copper laminate within CoFe, or a CoFe / NiFe composite, leads to higher values of CPP GMR and DRA. However, this type of structure exhibits very negative magnetostriction, in the range of high −10−6 to −10−5. This problem has been overcome by giving the copper laminates an oxygen exposure treatment When this is done, the free layer is found to have a very low positive magnetostriction constant. Additionally, the value of the magnetostriction constant can be adjusted by varying the thickness of the free layer and / or the position and number of the oxygen treated copper laminates.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Systems and methods for implementing magnetoelectric junctions having improved read-write characteristics
ActiveUS20140124882A1Low coercivityGalvano-magnetic material selectionGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic anisotropyPotential difference
Embodiments of the invention implement MEJs having improved read-write characteristics. In one embodiment, an MEJ includes: ferromagnetic fixed and free layers, a dielectric layer interposed between the ferromagnetic layers, and an additional dielectric layer proximate the free layer, where the fixed layer is magnetically polarized in a first direction, where the free layer has a first easy axis that is aligned with the first direction, and where the MEJ is configured such that when subject to a potential difference, the magnetic anisotropy of the free layer is altered such that the relative strength of the magnetic anisotropy along a second easy axis that is orthogonal to the first easy axis, compared to the strength of the magnetic anisotropy along the first easy axis, is magnified during the application of the potential difference, where the extent of the magnification is enhanced by the presence of the additional layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
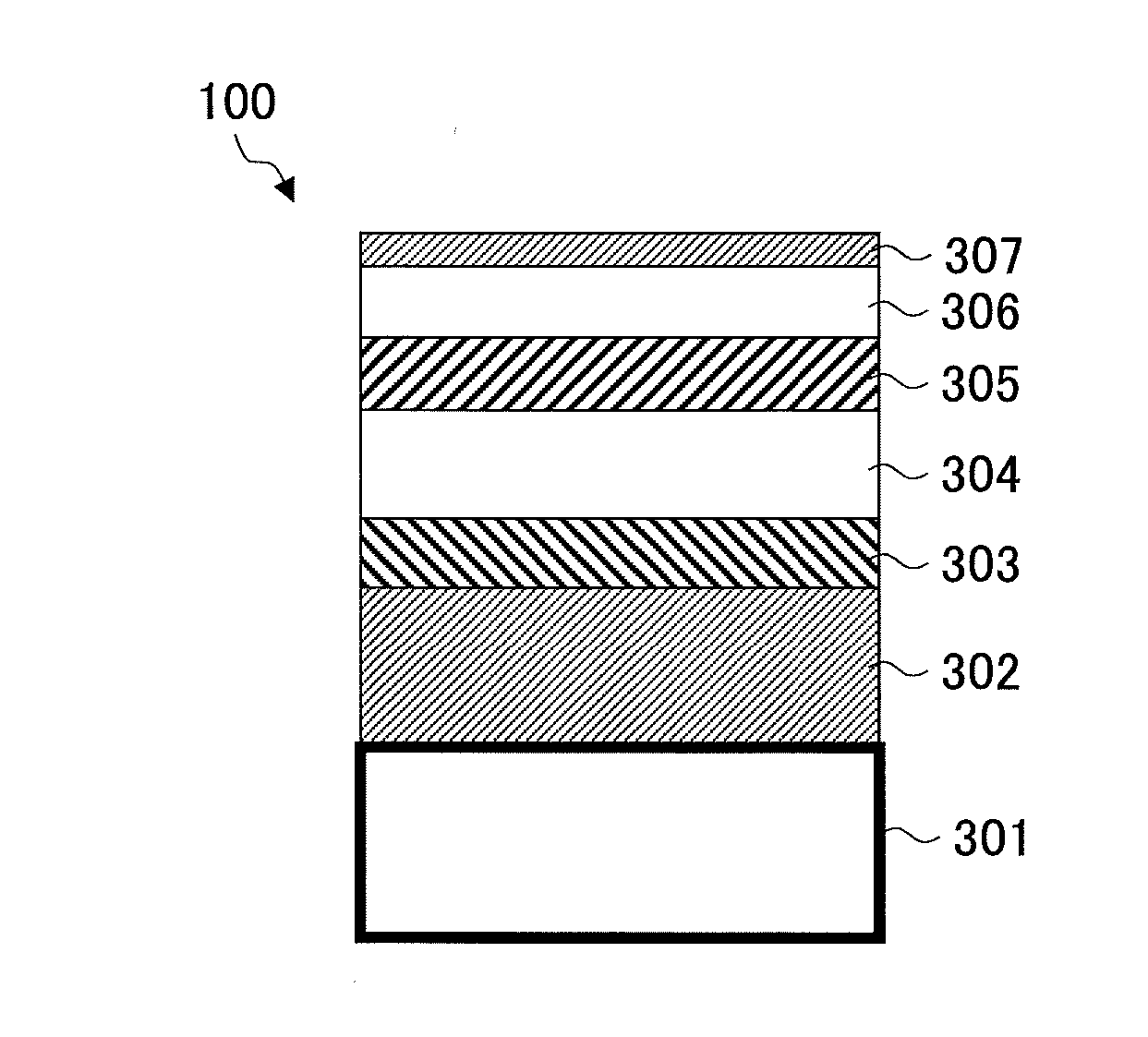
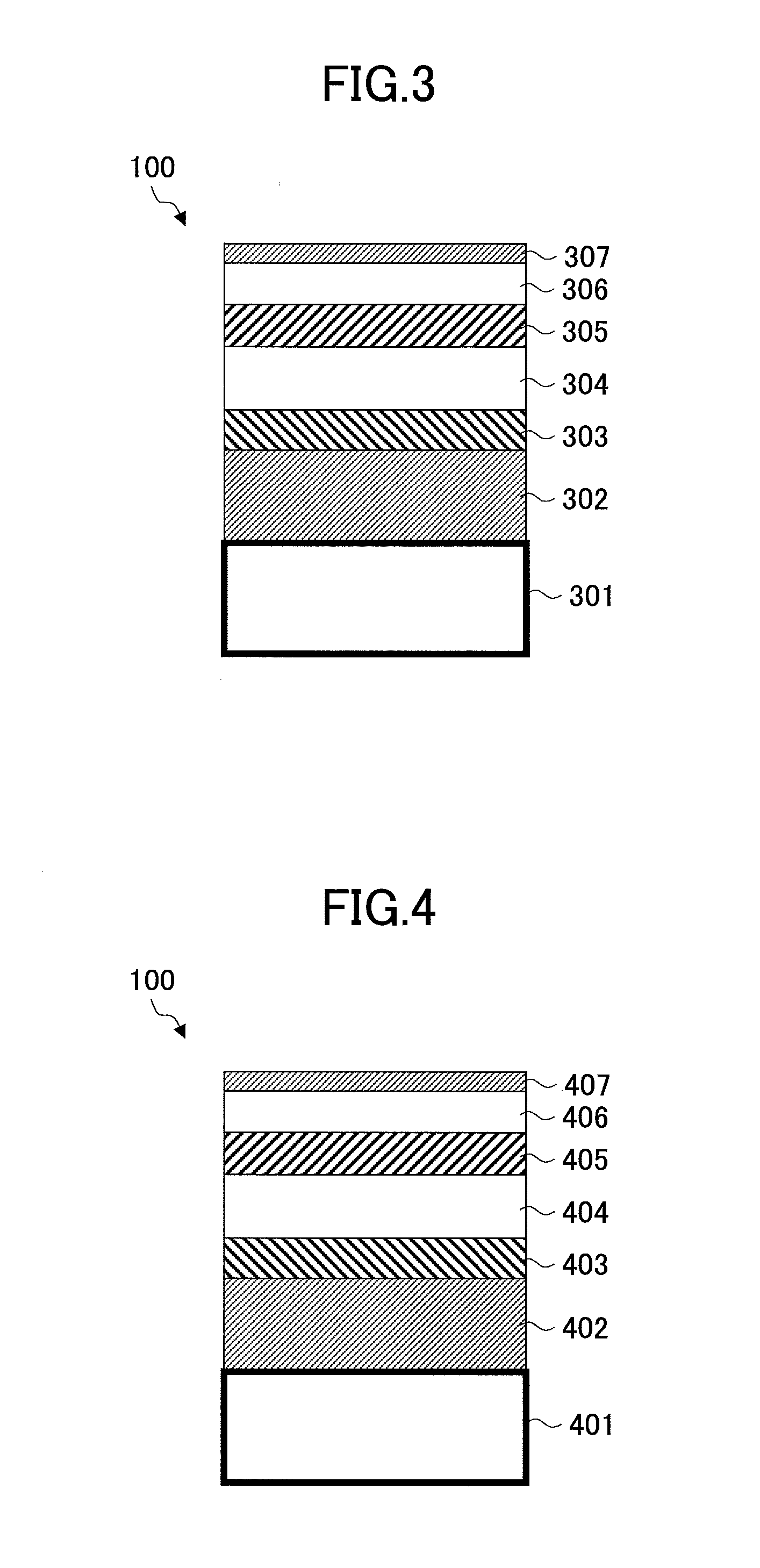
Thermally assisted magnetic recording disk with ion-implant facilitated non-magnetic regions, manufacturing method thereof, and magnetic recording method
ActiveUS8634155B2Low coercivityPatterned record carriersNanoinformaticsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingThermal expansion
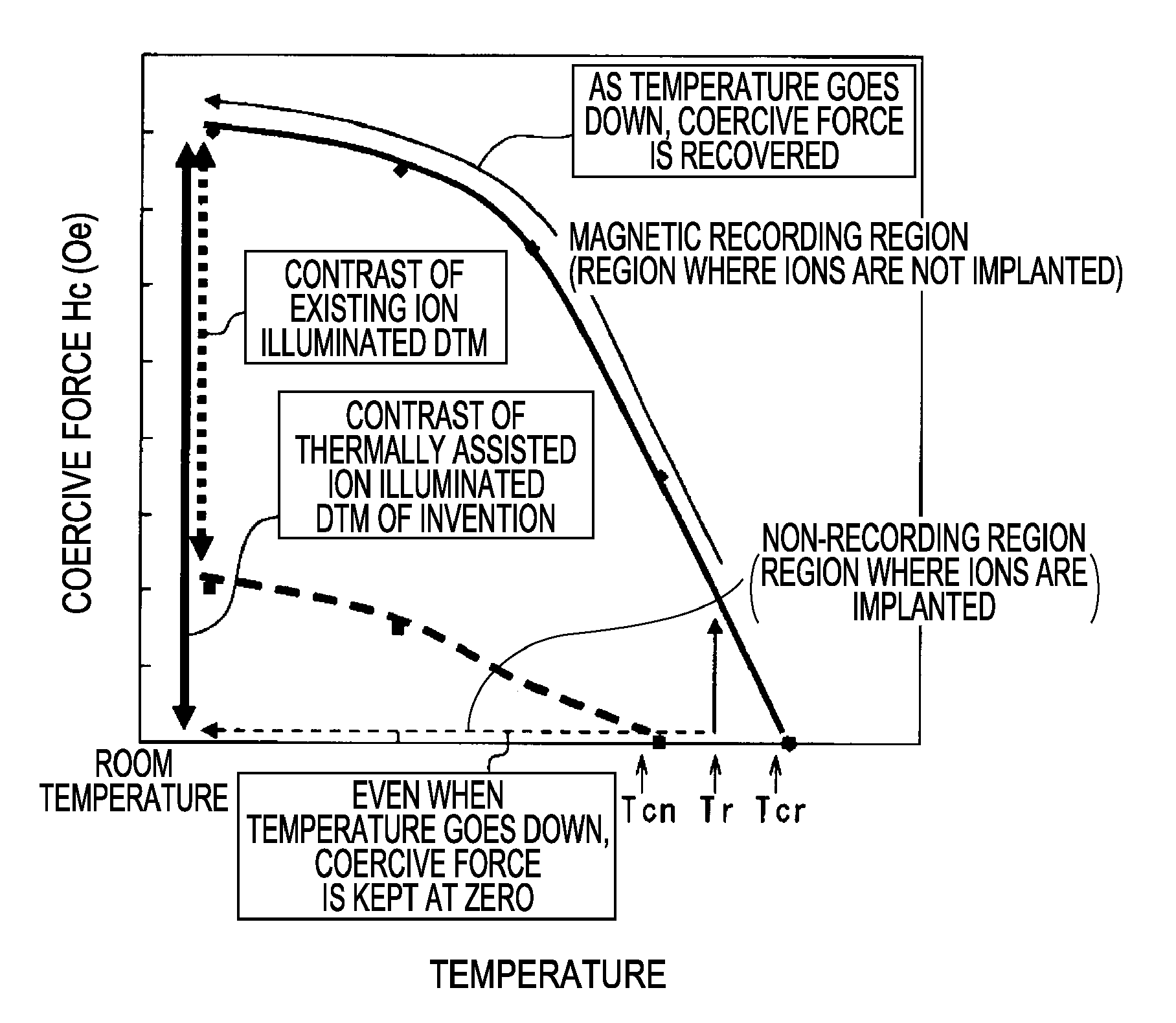
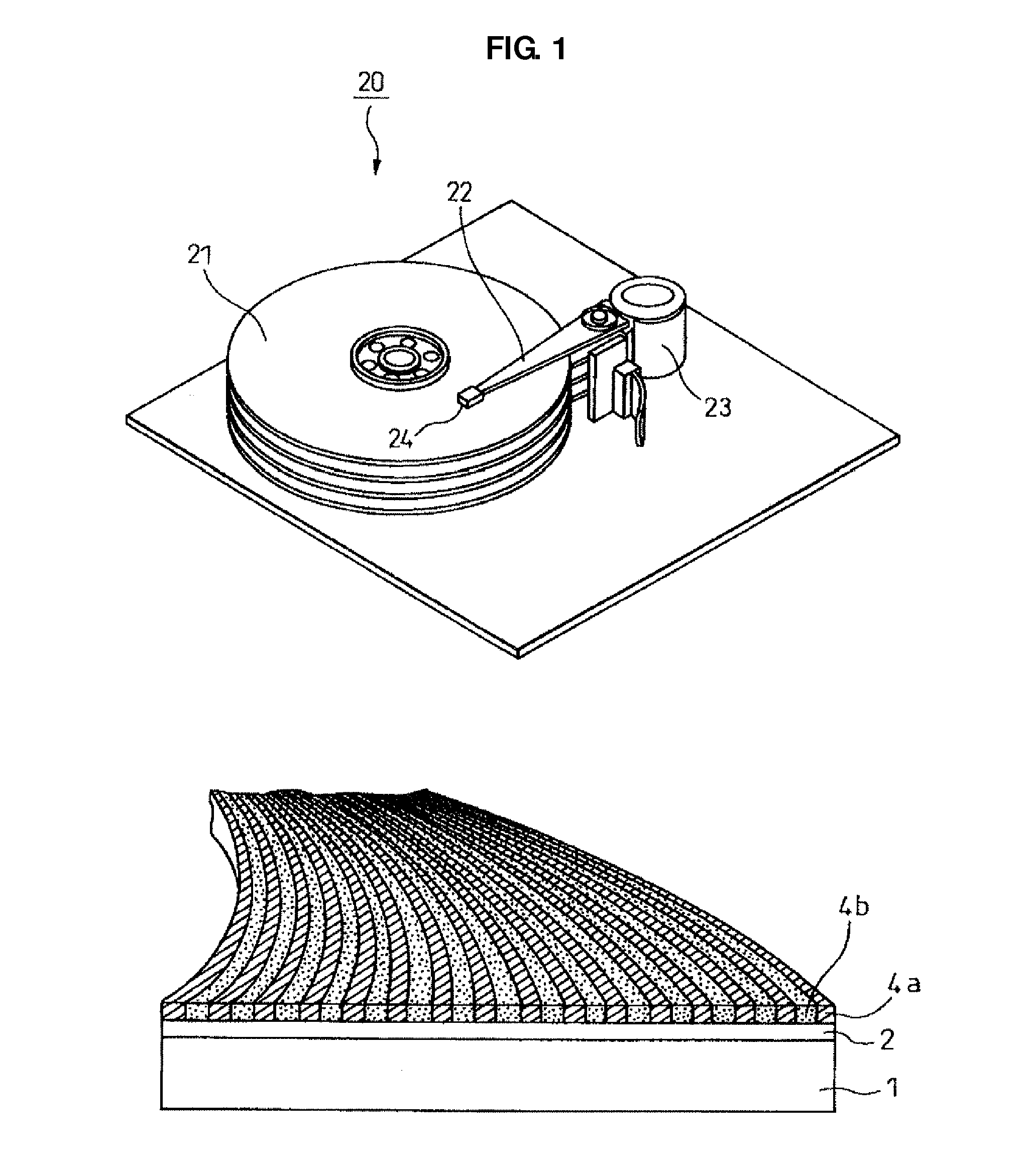
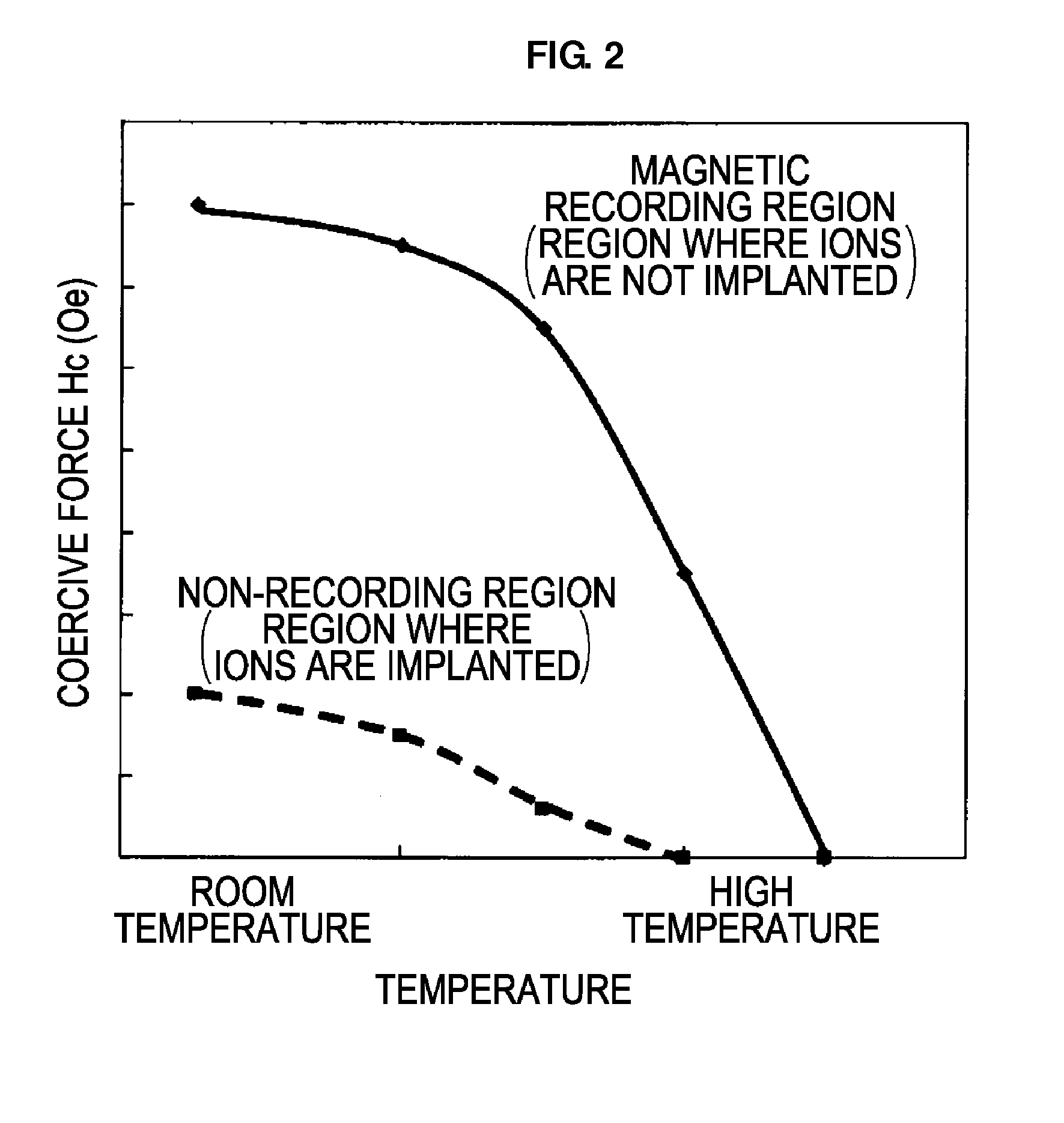
The invention provides a magnetic disk that solves (1) a problem of cross-talk that cannot be solved even by an existing thermally assisted recording method or a discrete method (DTM or the like), (2) a problem of surface flatness, which an existing embedding type DTM or the like has, and (3) a problem of a difference in thermal expansion coefficient between materials when a thermally assisted method is applied to the DTM, and that (4) does not necessitate a special medium structure, and is excellent in a surface flatness and economically and functionally high in realizability. A DTM manufactured by ion implantation is excellent in the surface flatness, and can solve the cross-talk problem by conducting the thermally assisted recording at a temperature between a Curie temperature (Tcn) of a portion where ions are implanted (non-recording region) and a Curie temperature (Tcr) of a portion where ions are not implanted (recording region).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
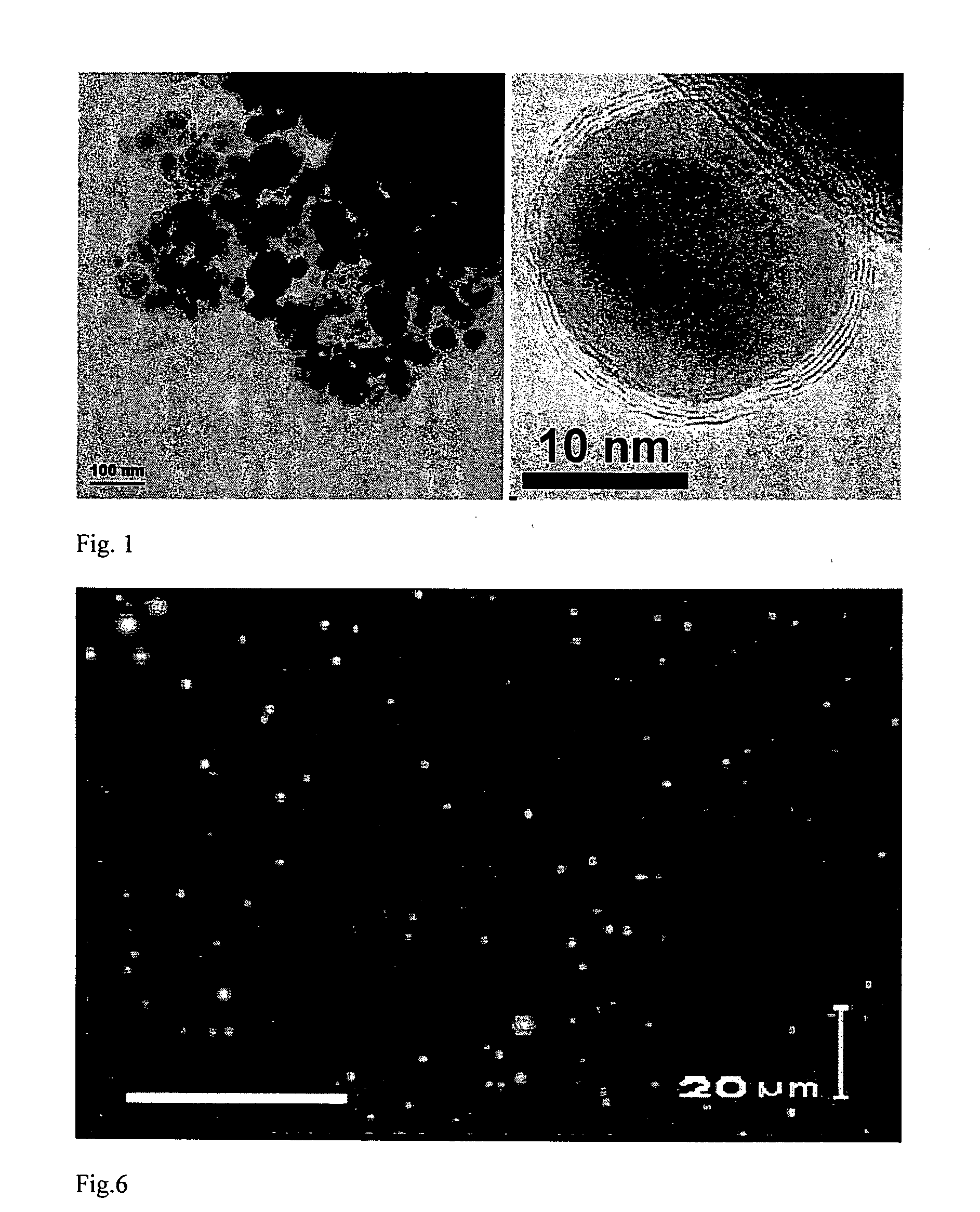
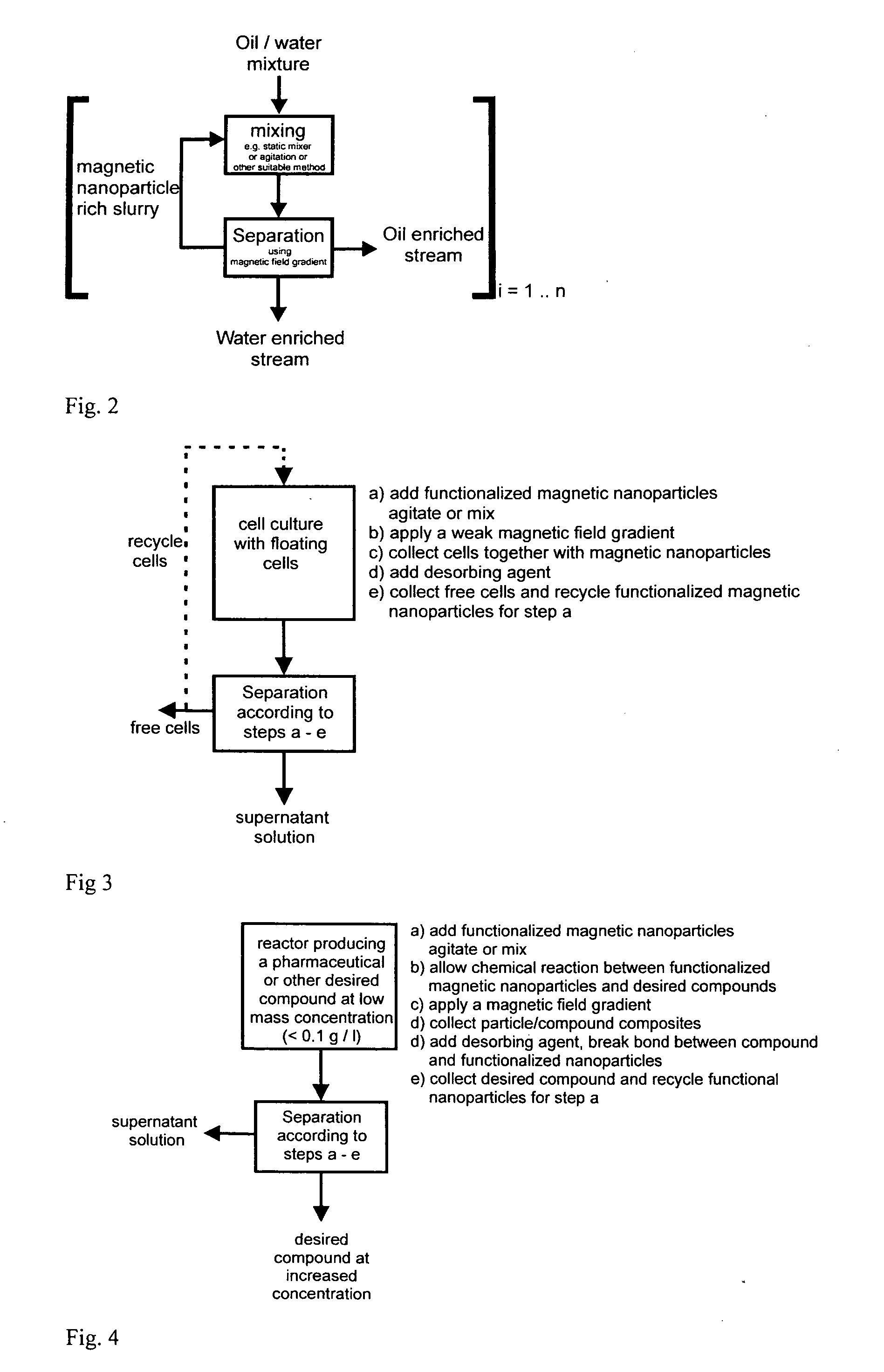
Carbon Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles and Their Use in Separation Processes
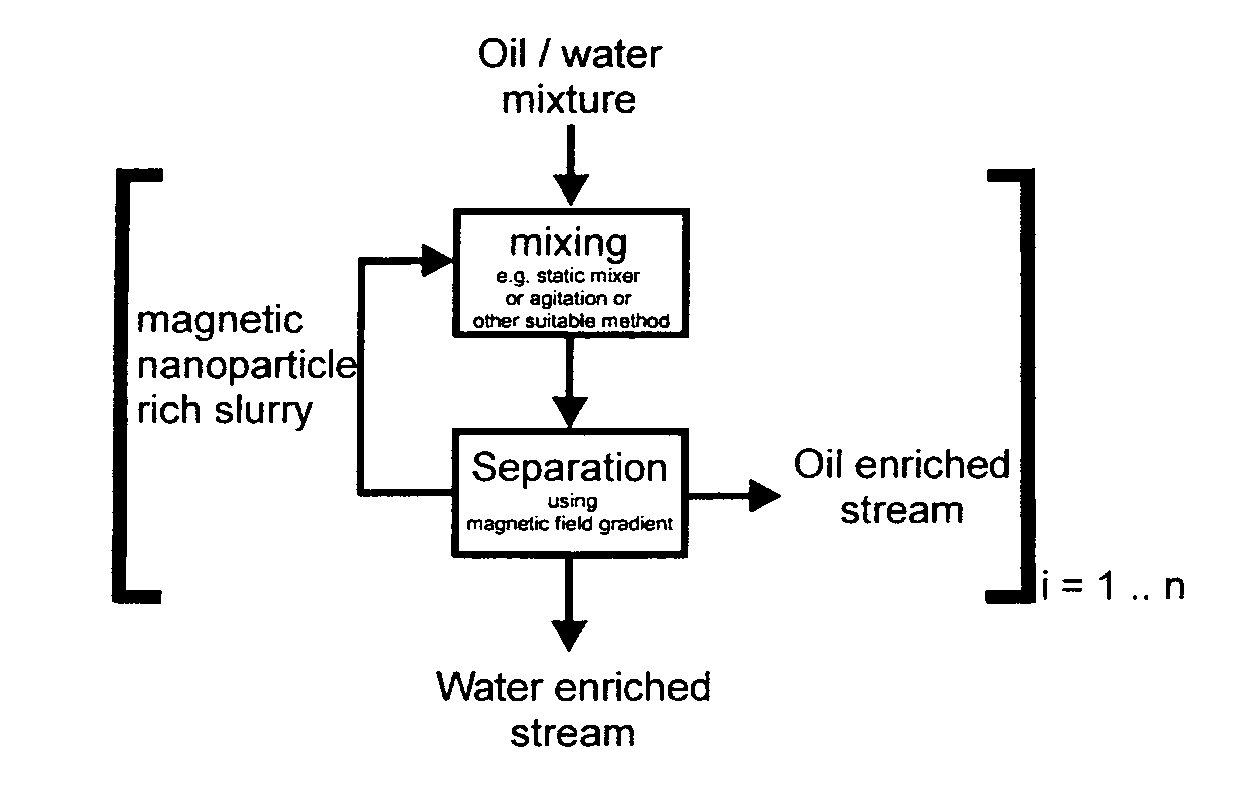
ActiveUS20100059449A1Improve mobilityRapidity and efficiencyNanomagnetismLiquid separation by electricityMagnetic field gradientMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention relates to a process for separating a dispersed phase from a continuous phase comprising the steps of i) contacting said phases with an effective amount of nanoparticles; ii) applying a magnetic field gradient to the obtained system; iii) separating the obtained phases wherein said nanoparticles are of the core shell type, said core consists of a metal or alloy having soft magnetic properties and said shell contains a graphene layers which are optionally functionalized; to new nanoparticles and method of manufacturing such nanoparticles.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Magnet for a dynamoelectric machine, dynamoelectric machine and method
InactiveUS20070284960A1Improve electrical performanceImprove the level ofMagnetic circuit stationary partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnet
Disclosed herein is an apparatus relating to a magnet member for a dynamoelectric machine comprising, a first portion of the magnet member made of a first magnetic material and a second portion of the magnet member made of a second magnetic material. Further disclosed is a method that relates to increasing performance of an electric machine comprising, determining locations of high demagnetization fields at the dynamoelectric machine, and positioning a magnetic member having a first portion having a higher level of coercivity and a second portion having a lower level of coercivity in the machine such that the portion having a higher level of coercivity is more proximate the location of high demagnetization fields than the portion having the lower level of coercivity.
Owner:REMY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Soft magnetic composite powder and magnetic powder core preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106229104AHigh bulk densityCost-effectiveTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusPowder metallurgyMagnetic powder
The invention relates to soft magnetic composite powder and a magnetic powder core preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of powder metallurgy and magnetic materials. According to different magnetic performance characteristics of metal soft magnetic powder, amorphous and nano-crystalline powder and ferrite powder, magnetic performances are linearly calculated and optimally designed, so that the requirements of different magnetic properties are met. Besides, powder sizes are calculated and coordinately designed, the powder is shaped, screened, annealed, coated in an insulated manner and mixed, and the powder with different components is respectively passivated and insulated, weighed according to weight ratio and uniformly mixed to form the composite powder. The prepared soft magnetic composite powder is regular in morphology and good in dispersity and has good apparent density and flowability. In addition, the magnetic performance of a magnetic powder core prepared from the soft magnetic composite powder can be calculated and designed as required, the magnetic powder core has high cost performance and good comprehensive magnetic performance, and the blank of the performance and application of an existing magnetic powder core is effectively filled in.
Owner:BEIJING COMPO ADVANCED TECH
Magnetic tunneling junction film structure with process determined in-plane magnetic anisotropy
ActiveUS7105372B2Data efficientSmall sizeNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeMagnetic anisotropy
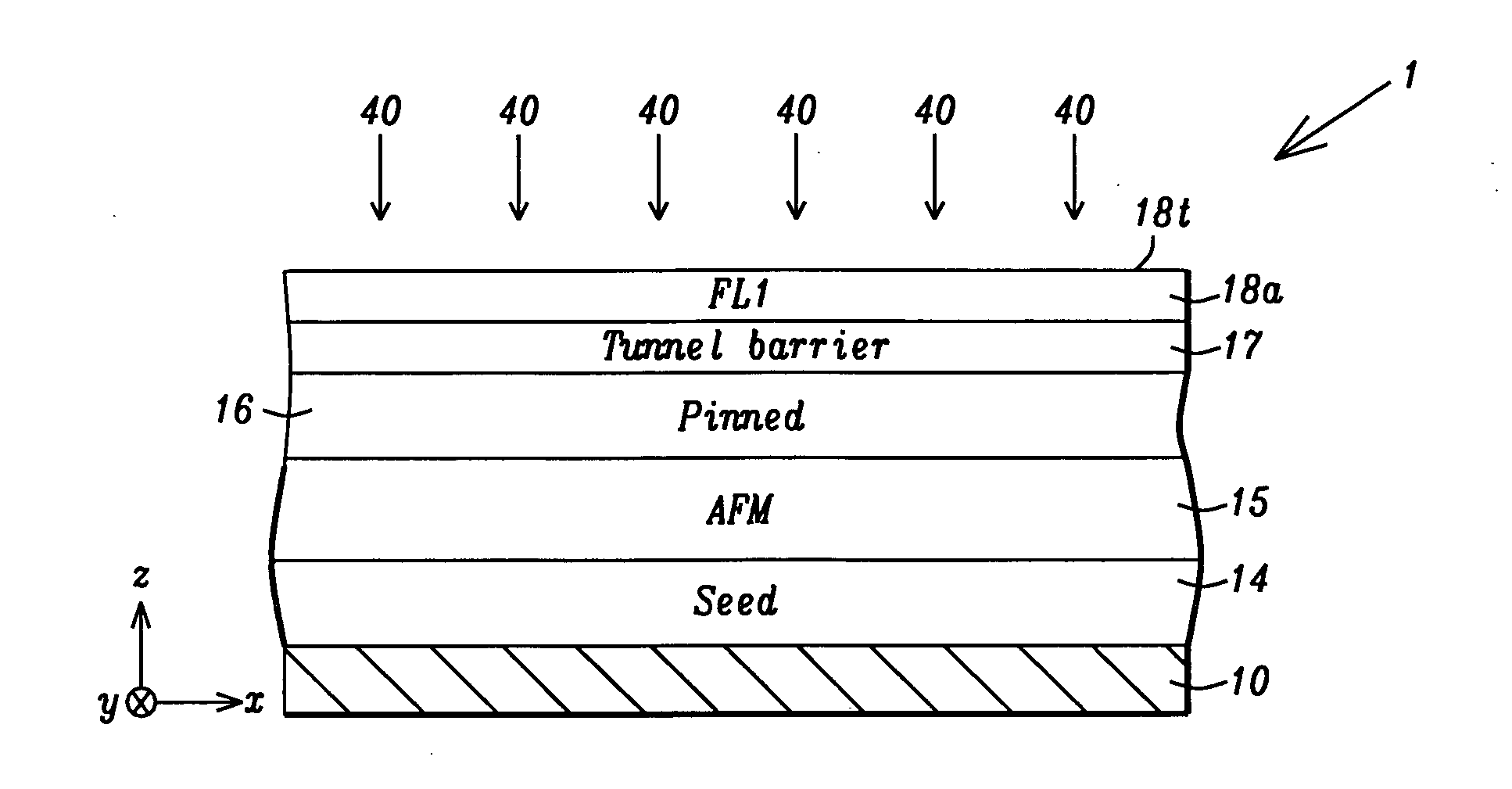
A method of forming an MTJ memory cell and / or an array of such cells is provided wherein each such cell has a small circular horizontal cross-section of 1.0 microns or less in diameter and wherein the ferromagnetic free layer of each such cell has a magnetic anisotropy produced by a magnetic coupling with a thin antiferromagnetic layer that is formed on the free layer. The MTJ memory cell so provided is far less sensitive to shape irregularities and edge defects than cells of the prior art.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
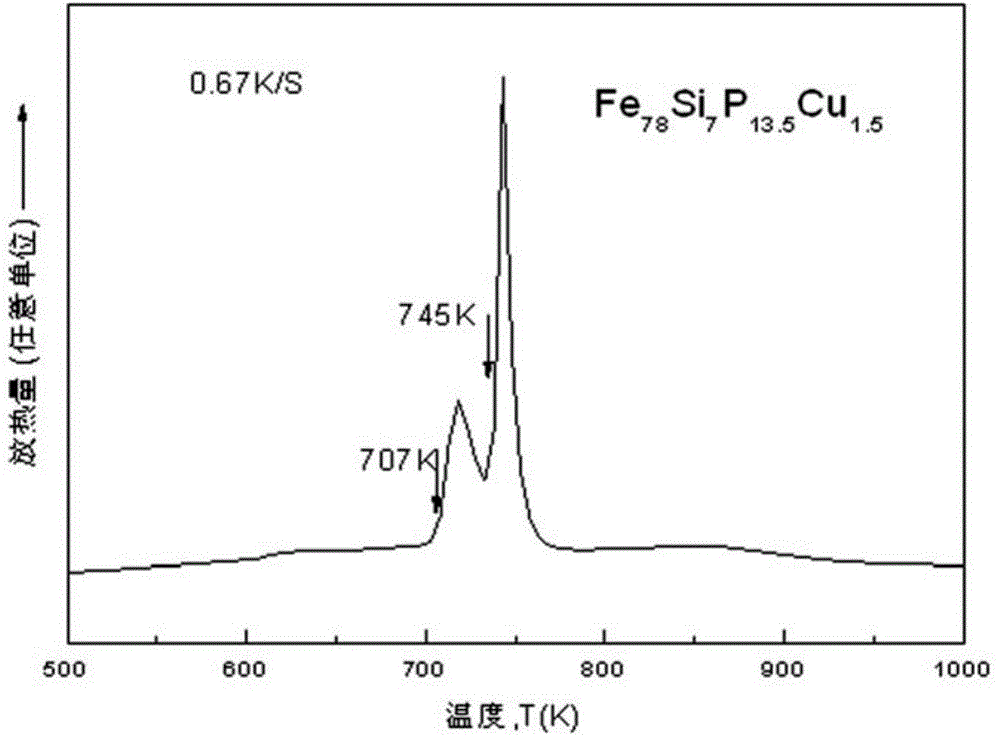
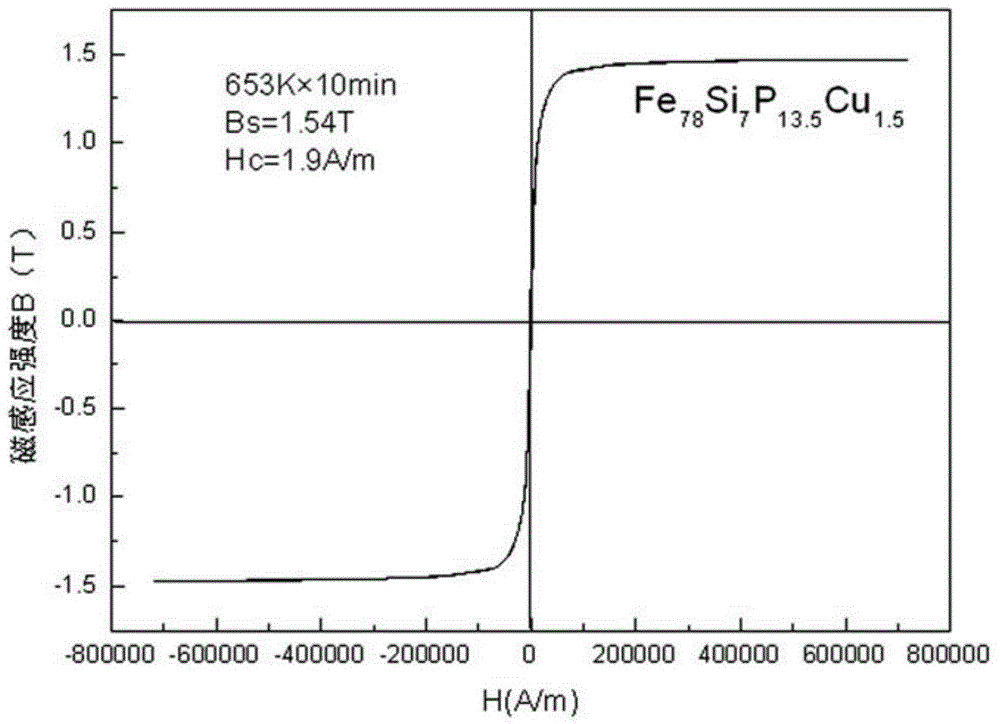
Iron-based amorphous magnetically soft alloy with uniform element distribution and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104073749AImprove thermal stabilityHigh saturation magnetic inductionMagnetic materialsTransformerMaterials science
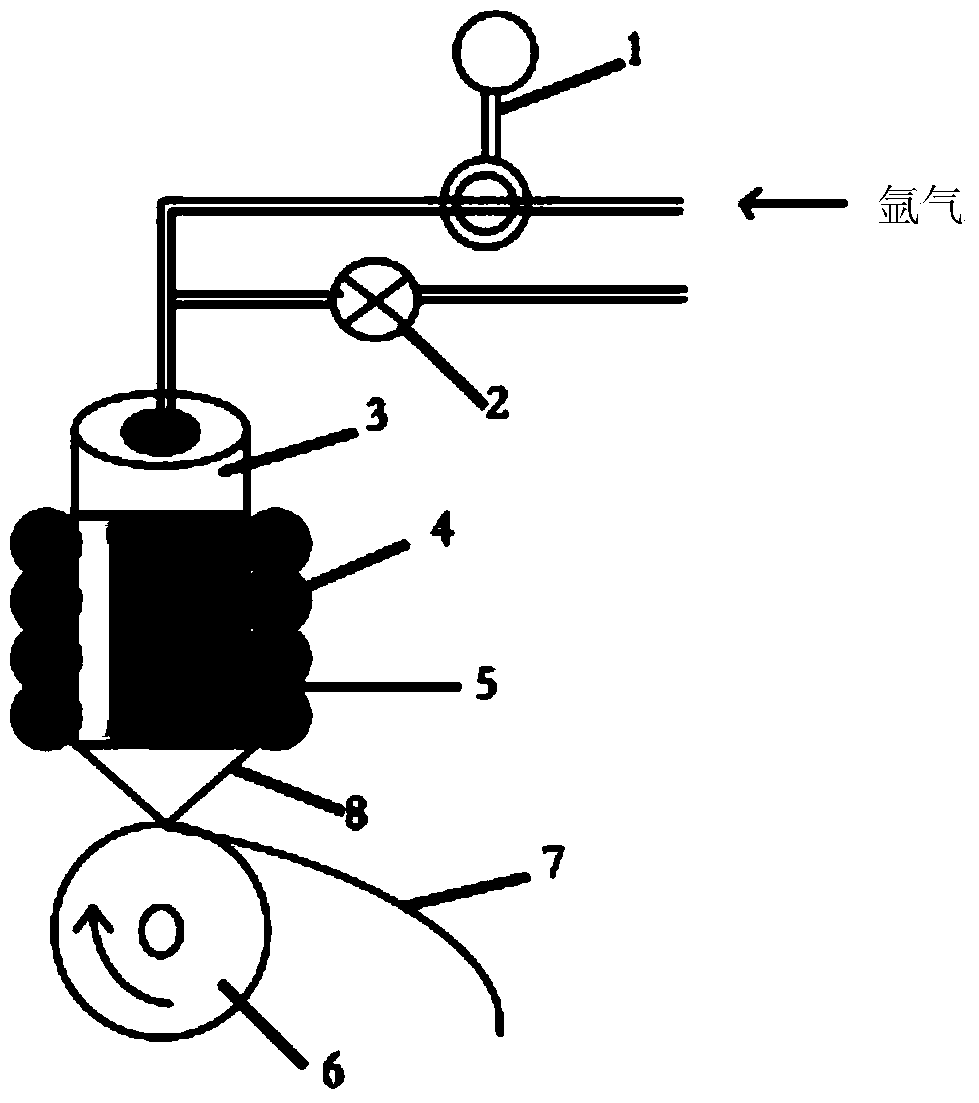
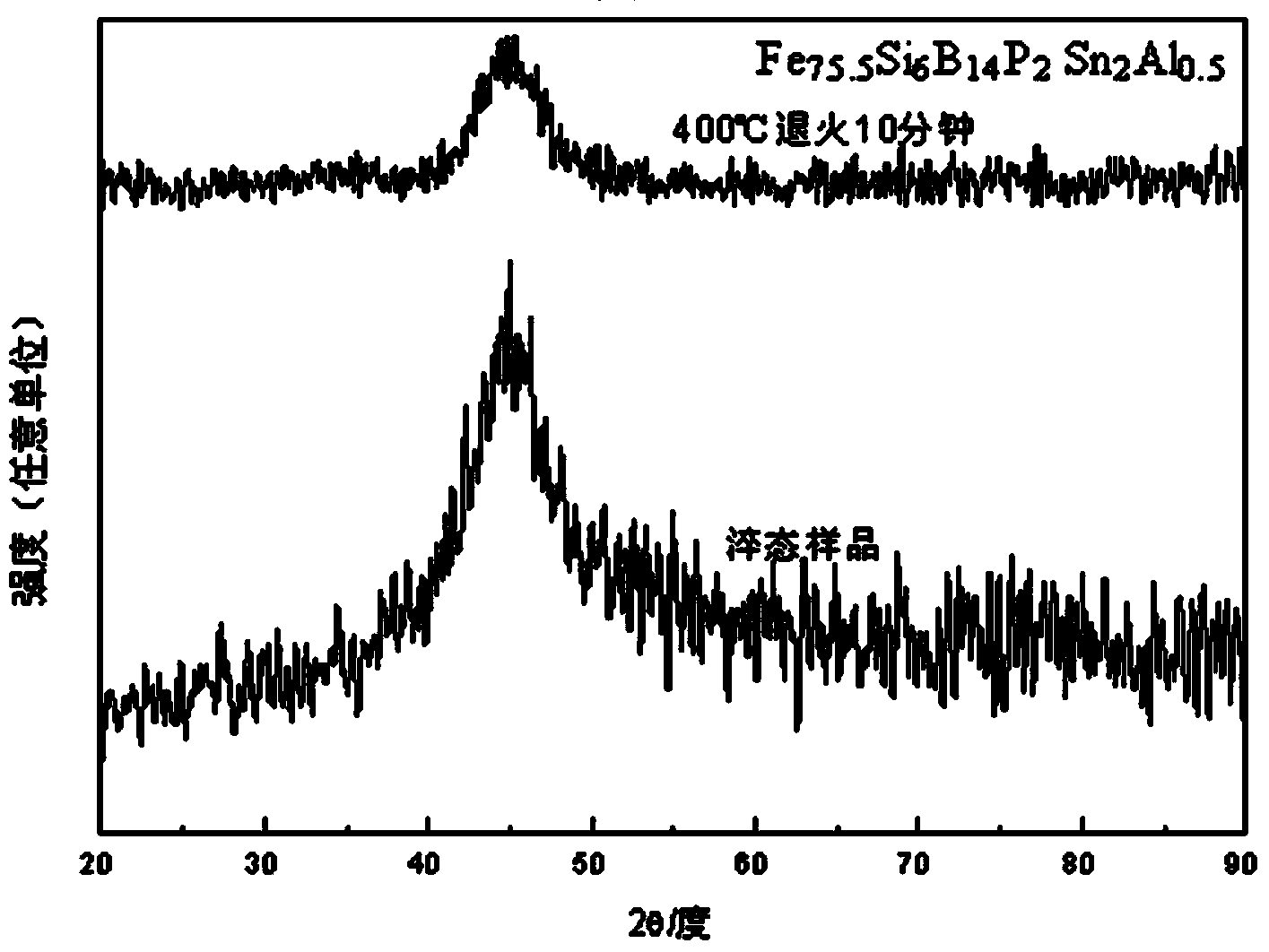
The invention discloses an iron-based amorphous magnetically soft alloy with uniform element distribution and a preparation method thereof. The expression of the alloy is FeaSibBcPdMe, a, b, c, d and e in the expression represent the atomic percent contents of corresponding components respectively, and meet the following conditions: a is not less than 70 and not greater than 84, b is not less than 2 and not greater than 10, c is not less than 5 and not greater than 18, d is not less than 0.001 and not greater than 8, e is not less than 0.0001 and not greater than 2.5, a+b+c+d+e=100%, and M is one or more of C, N, Sn, Ge, Ga, Al, S, Te, Be, Pb, Mg and Cu. The amorphous strip prepared from the alloy under a high vacuum and argon shield has the characteristic of uniform element distribution, particularly solves the problem of non-uniform distribution of element P in the amorphous alloy, has excellent magnetically soft performance, and is suitable for transformers, engines, power generators, magnetic sensors and the like.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
TMR device with novel free layer structure
ActiveUS20110188157A1Improve crystal orientationLow magnetostrictionMagnetic measurementsDecorative surface effectsAlloyNon magnetic
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Thin-film magnetic head with near-field-light-generating layer
ActiveUS7911882B2Improve reliabilityLow coercivityRecording by magnetic meansArm with optical waveguideMagnetic mediaEngineering
A thin-film magnetic head that has a configuration in which the element-formed surface and the opposed-to-medium surface are perpendicular to each other, and a light source is sufficiently distanced from the medium surface is provided. The head comprises at least one near-field-light-generating layer for heating a part of a magnetic medium during write operation by generating a near-field light, having a shape tapered toward a head end surface on the opposed-to-medium surface side, and comprising a near-field-light-generating portion having a light-received surface and a tip reaching the head end surface on the opposed-to-medium surface side, and the light-received surface being sloped in respect to the element-formed surface and being provided in a position where an incident light propagating from a head end surface opposite to the opposed-to-medium surface can reach at least a part of the light-received surface.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
High resistance magnet and motor using the same
InactiveUS20080054738A1Improve magnetic propertiesImprove propertiesLayered productsNanoinformaticsRare-earth elementHigh resistance
A magnet comprising grains of a ferromagnetic material whose main component is iron and a fluorine compound layer or an oxy-fluorine compound layer of fluoride compound particles of alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and rare earth elements, present on the surface of the ferromagnetic material grains, wherein an amount of iron atoms in the fluorine compound particles is 1 to 50 atomic %.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Low-loss magnetic powder core, and switching power supply, active filter, filter, and amplifying device using the same
InactiveUS6897718B2Reduced core lossLess distortionDc-dc conversionInorganic material magnetismMetallurgyAlloy
A magnetic powder core comprises a molded article of a mixture of a glassy alloy powder and an insulating material. The glassy alloy comprises Fe and at least one element selected from Al, P, C, Si, and B, and has a texture primarily composed of an amorphous phase. The glassy alloy exhibits a temperature difference ΔTx, which is represented by the equation ΔTx=Tx−Tg, of at least 20 K in a supercooled liquid, wherein Tx indicates the crystallization temperature and Tg indicates the glass transition temperature. The magnetic core precursor is produced mixing the glassy alloy powder with the insulating material, compacting the mixture to form a magnetic core precursor, and annealing the magnetic core precursor at a temperature in the range between (Tg−170) K and Tg K to relieve the internal stress of the magnetic core precursor. The glassy alloy exhibits low coercive force and low core loss.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Iron-based nanocrystalline soft-magnetic alloy with excellent high-frequency performance and preparation method thereof
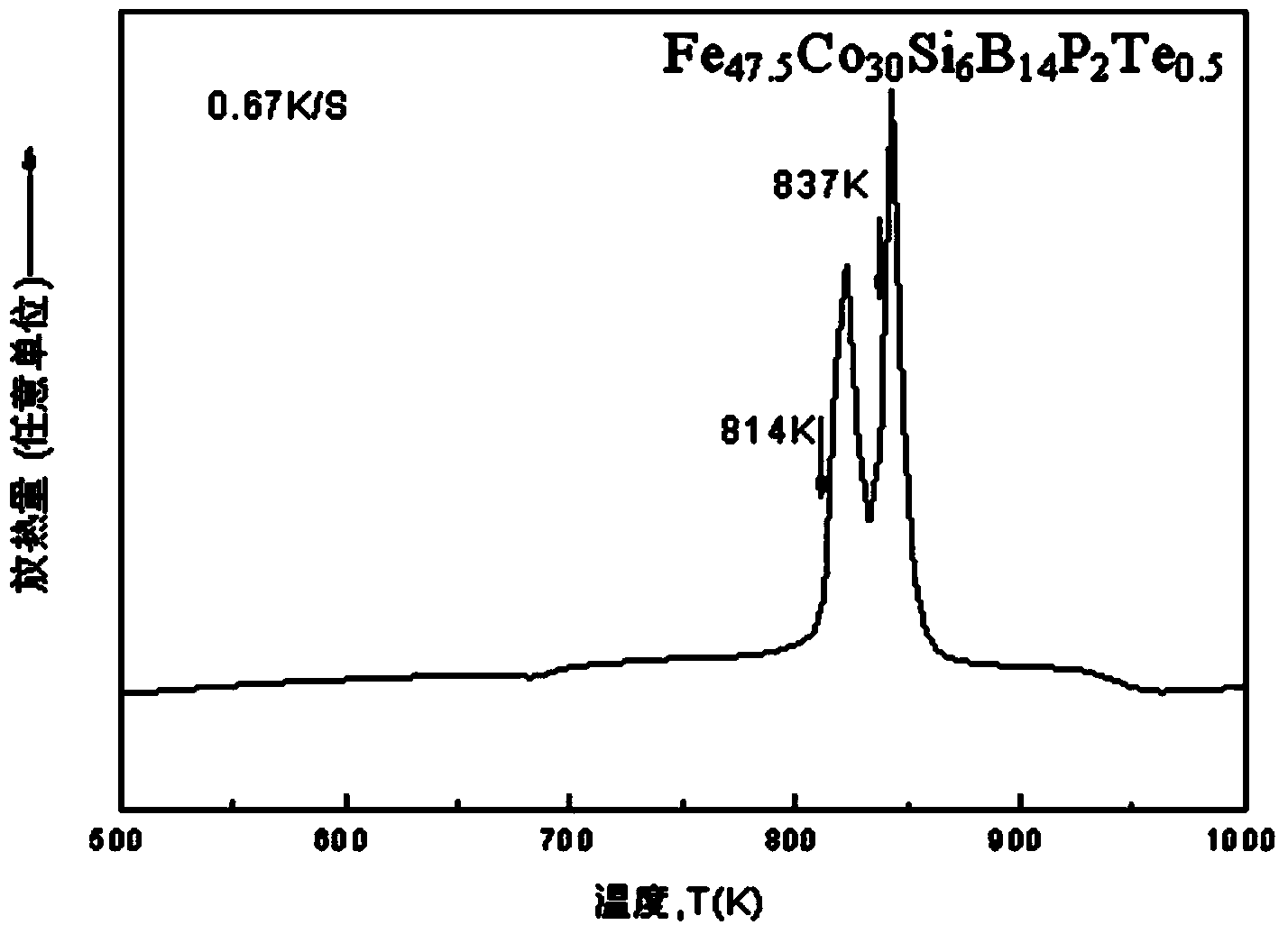
ActiveCN104087833AHigh saturation magnetic inductionImprove thermal stabilityMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementNanocrystalline silicon
The invention discloses iron-based nanocrystalline soft-magnetic alloy with excellent high-frequency performance and a preparation method thereof. The expression of the alloy is FeaSibPcCuxMy, wherein a, b, c, x and y respectively represent the atomic percent content of corresponding compositions and satisfy the following conditions: 70<=a<=85, 5<=b<=15, 5<=c<=18, 0.0001<=x<=3, 0<=y<=5, a+b+c+x+y=100%, and M is one or more of Zr, Ti, Ta, Hf, Nb, V, W, Mo, Mn, Cr, Re, Zn, In, As, Sb, Bi, Ca, platinum group elements, rare earth elements, N, Sn, Ge, Ga and Al. The alloy is a nanocrystalline soft-magnetic alloy band prepared by employing a single-roller quick-cooling method under the conditions of high vacuum and argon protection. The alloy does not contain B elements, is good in soft magnetic property, high in thermal stability, low in high-frequency loss and low in magnetostriction coefficient.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Magnetic flux controllable rotating electric machine system
InactiveUS20100213885A1Easily magnetizedIncreases amount of magnetic fluxSynchronous motors startersWindingsExcitation currentWave shape
In a magnet-exciting rotating electric machine system, a rotor surface has magnetic salient poles and island-shaped magnetic poles alternately in circumferential direction, and the island-shaped magnetic poles are constituted so that magnetic flux coming from an external source does not flow through. A magnetic excitation part magnetizes the island-shaped magnetic poles and the magnetic salient poles collectively in the same direction, and then control a flux amount flowing through an armature. The armature has armature coils that face the magnetic salient pole and the island-shaped magnetic pole simultaneously so that driving torque fluctuation or power generation voltage waveform distortion is controlled. The magnetic excitation part changes magnetization state of a field magnet irreversibly, or changes an excitation current to an excitation coil to control a flux crossing the armature.
Owner:KURA LAB
Fe-based nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy with strong amorphous forming ability and preparing method of Fe-based nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy
ActiveCN104934179AHigh saturation magnetic inductionLow coercivityMagnetic materialsCopper moldMagnetic alloy
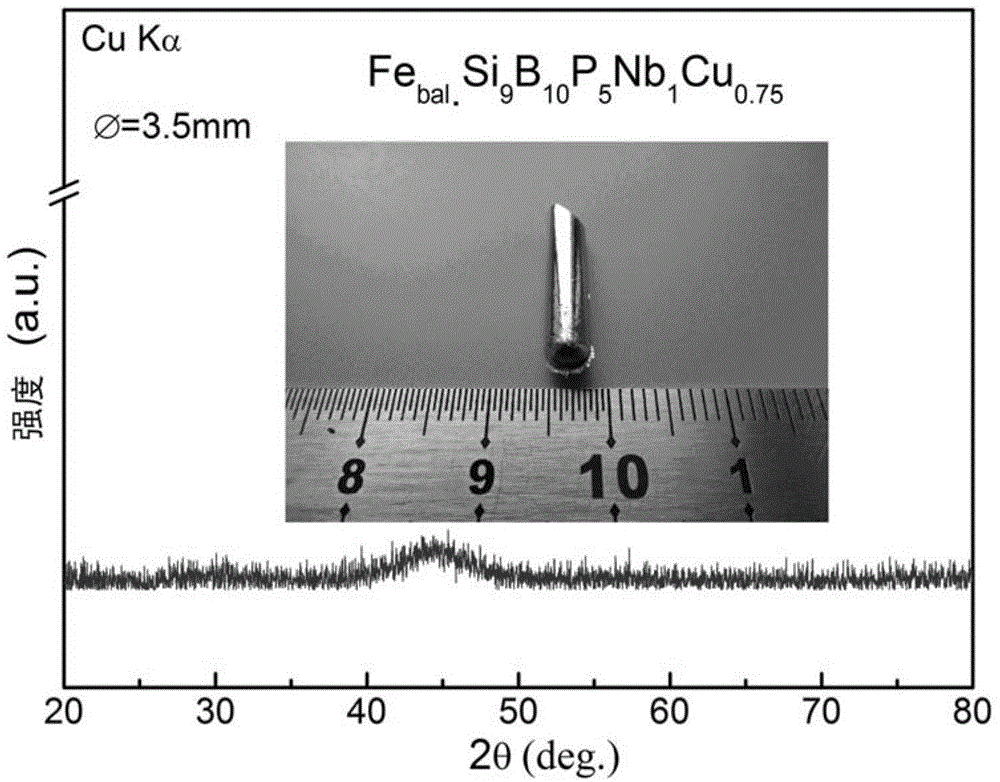
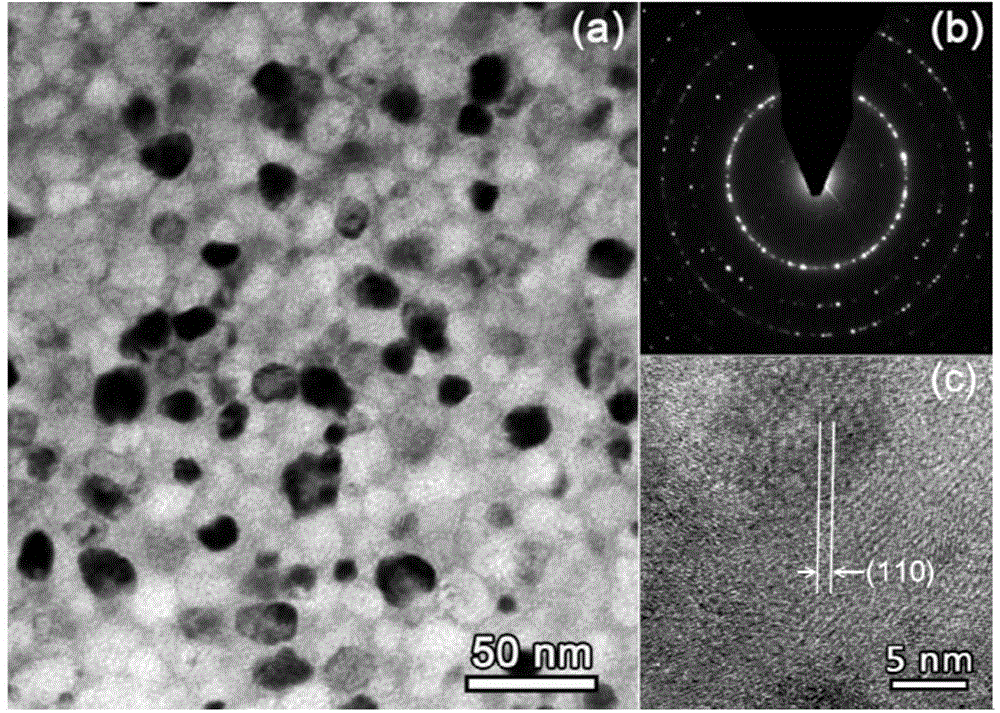
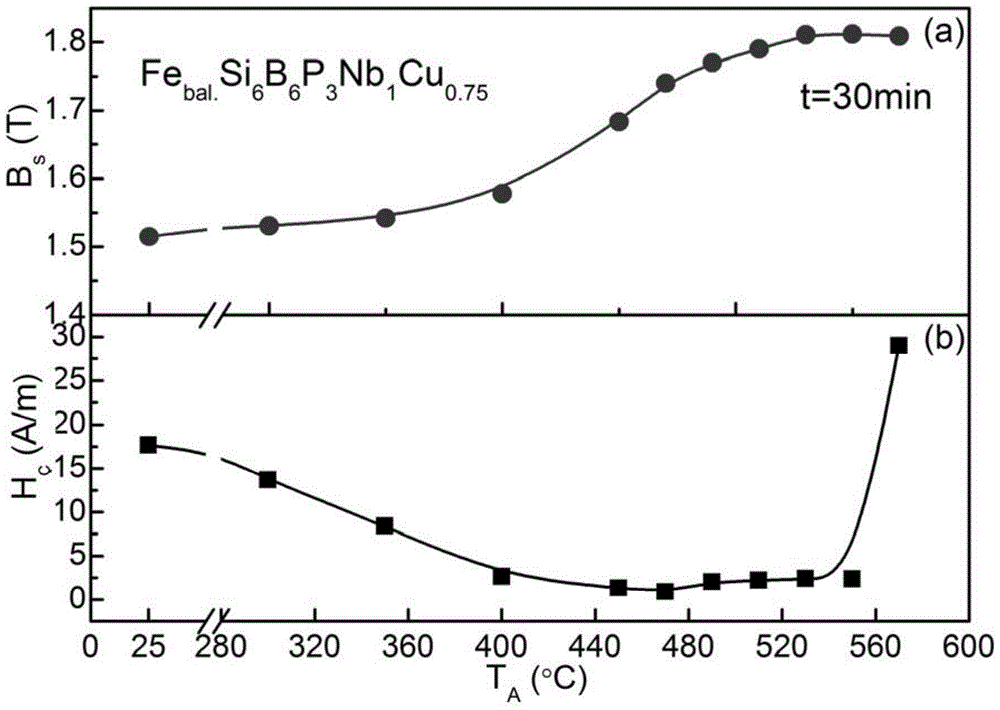
The invention discloses a Fe-based nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy with strong amorphous forming ability and a preparing method of the Fe-based nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy. The alloy has an expression of Fe<x>SiBP<c>Nb<d>Cu<e>, wherein in the expression, each of the x, the a, the b, the c, the d and the e shows the atomic percentage content of the corresponding ingredient, and meets the following conditions that the a is greater than or equal to 0.5 but smaller than or equal to 12; the b is greater than or equal to 0.5 but is smaller than or equal to 15; the c is greater than or equal to 0.5 but smaller than or equal to 12; the d is greater than or equal to 0.1 but smaller than or equal to 3; the e is greater than or equal to 0.1 but smaller than or equal to 3; the x is greater than or equal 70 but smaller than or equal to 85; and the sum of the x, the a, the b, the c, the d and the e is 100 percent. The soft magnetic alloy has the advantages that an ordinary copper mold casting method can be used for preparing a Fe-based amorphous alloy with the critical dimension being 3.5mm; after the annealing; the saturation flux density is greater than 1.5T; and the coercive force value is smaller than 1A / m.
Owner:ADVANCED TECHNOLOGY & MATERIALS CO LTD
Magnetoresistive effect element, magnetic memory element magnetic memory device and manufacturing methods thereof
InactiveUS7262064B2Low coercivityBarkhausen noise increaseNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismMagnetic memoryTunnel junction
In a magnetoresistive effect element using a ferromagnetic tunnel junction having a tunnel barrier layer sandwiched between at least a pair of ferromagnetic layers, a magnetization free layer comprising one of the ferromagnetic layers is composed of a single layer of a material having an amorphous or microcrystal structure or a material layer the main portion of which has an amorphous or microcrystal structure. The magnetoresistive effect element can produce excellent magnetic-resistance characteristics, and a magnetic memory element and a magnetic memory device using the magnetoresistive effect element as a memory element thereof can improve both of write and read characteristics at the same time.
Owner:SONY CORP
Magnetic tunneling junction film structure with process determined in-plane magnetic anisotropy
ActiveUS20050157544A1Data efficientSmall sizeNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeMagnetic anisotropy
A method of forming an MTJ memory cell and / or an array of such cells is provided wherein each such cell has a small circular horizontal cross-section of 1.0 microns or less in diameter and wherein the ferromagnetic free layer of each such cell has a magnetic anisotropy produced by a magnetic coupling with a thin antiferromagnetic layer that is formed on the free layer. The MTJ memory cell so provided is far less sensitive to shape irregularities and edge defects than cells of the prior art.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Oxide magnetic material, ferrite particles, bonded magnet, sintered magnet, process for producing the same, and magnetic recording medium
InactiveUS6402980B1Excellent magnetic propertiesIncrease valueMagnetic materials for record carriersInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementSintered magnets
The present invention provides an oxide magnetic material, which includes a primary phase of a hexagonal ferrite containing metallic elements Ca, R, Fe and M, where M represents at least one element selected from the group including Co, Ni and Zn, and R represents at least one element selected from the group including Bi and rare earth elements including Y, with La being essentially included in R; wherein the proportions of the metallic elements Ca, R, Fe and M with respect to the total amount of the metallic elements are from 1 to 13 atomic % for Ca, from 0.05 to 10 atomic % for R, from 80 to 95 atomic % for Fe, and from 1 to 7 atomic % for M. The present invention also provides ferrite particles, a bonded magnet, a sintered magnet, a process for producing them, and a magnetic recording medium, which contain the oxide magnetic material.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Thermally assisted magnetic head, head gimbal assembly, and hard disk drive
ActiveUS8077556B2Low coercivityHigh-density recordingRecord information storageMagnetic recordingHard disc drivePhoto irradiation
A thermally assisted magnetic head has a medium-facing surface facing a magnetic recording medium; a near-field light generator disposed on a light exit face in the medium-facing surface; a magnetic recording element located adjacent to the near-field light generator; and a light emitting element disposed so that emitted light thereof reaches the near-field light generator; the near-field light generator is comprised of a cusp portion and a base portion; when λin represents a wavelength of the emitted light from the light emitting element immediately before the emitted light reaches the near-field light generator, an intensity of near-field light generated when the material forming the cusp portion is irradiated with the light of the wavelength λin is stronger than an intensity of near-field light generated when the material forming the base portion is irradiated with the light of the wavelength λin.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Preparation method of flexible anisotropy bonding rare earth permanent magnet material
InactiveCN101800106AAbundant resourcesReduce manufacturing costInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetizationRare earth
The invention discloses a preparation method of flexible anisotropy bonding rare earth permanent magnet material, belonging to the field of magnetic materials. The material is prepared by combining the two-step approach accompanying temperature magnetic field orientation technology of which the calendaring process and the accompanying temperature magnetic field orientation process are separated. A certain quantity of anisotropy magnetic powder which is performed with surface treatment by the processing agent in advance, binder and processing agent are evenly mixed; the mixed material is calendered into flaky flexible bonding magnetic body by the calendaring technology; then, the flaky flexible bonding magnetic body is cut into parts which are heated at certain temperature under the condition of heat preservation for certain time, after that, the obtained product is put into an orientation magnetic field for accompanying temperature magnetic field orientation; and the direction of the orientation magnetic field is parallel to the plane normal direction of the flaky flexible bonding magnetic body. In the preparation technology, magnetic powder can overcome the constraint of a bonding system and rotates under the action of magnetic field force to ensure that the direction of easy magnetization of the magnetic powder generally points to the orientation direction, and the magnetic property of prepared flexible anisotropy bonding rare earth permanent magnet material can be greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Magnetoresistive spin valve sensor with tri-layer free layer
ActiveUS7333306B2High MR ratioLow coercivityNanomagnetismElectrical transducersMagnetic reluctanceThin layer
A TMR sensor, a CPP GMR sensor and a CCP CPP GMR sensor all include a tri-layered free layer that is of the form CoFe / CoFeB / NiFe, where the atom percentage of Fe can vary between 5% and 90% and the atom percentage of B can vary between 5% and 30%. The sensors also include SyAP pinned layers which, in the case of the GMR sensors include at least one layer of CoFe laminated onto a thin layer of Cu. In the CCP CPP sensor, a layer of oxidized aluminum containing segregated particles of copper is formed between the spacer layer and the free layer. All three configurations exhibit extremely good values of coercivity, areal resistance, GMR ratio and magnetostriction.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Magnetic recording medium and magnetic storage apparatus
ActiveUS20140308542A1Low coercivityMaintain relatively stableBase layers for recording layersRecord information storageMagnetic storageAlloy
A magnetic recording medium includes a substrate, multiple underlayers formed on the substrate, and a magnetic layer formed on the multiple underlayers. A main component of the magnetic layer is an alloy having a L10 structure. At least one of the multiple underlayers is a crystalline underlayer containing W. The W is a main component of the crystalline underlayer. The crystalline underlayer further contains 1 mol % or more to 20 mol % or less of one or more kinds of elements selected from B, Si, and C. A barrier layer including a material having a NaCl structure is formed between the crystalline underlayer and the magnetic layer.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Permanent magnetic RE material and preparation thereof
ActiveCN101364465ASmall temperature coefficientLow coercivityInorganic material magnetismCrystalline oxideSamarium–cobalt magnet
The invention relates to a rare earth permanent magnetic material and a preparation method thereof. The rare earth permanent magnetic material comprises a (Pr, Nd)-Fe-R-Co-Al-Cu-B-M system, and the rare earth as a main phase component has a phase volume ratio of 90%-98%; wherein R is at least two elements selected from Nb, Tb, Dy and Ho; M is at least two nanometer crystalline oxides with particle size of 10-100 nm selected from ZrO2, MgO and ZnO; and the weight of the nanometer crystalline oxides is 0.1%-3% of the total weight. The rare earth permanent magnetic material is a compound nanometer oxidizer enhanced and sintered praseodymium (Pr)-neodymium (Nd)-based permanent magnet with high coercitive force. The inventive product has magnetic features of low temperature coefficient, high coercitive force, low cost and 220 DEG C working temperature, and can overcome the shortcomings of lower coercitive force, high temperature coefficient and high cost of the prior sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet and the sintered samarium-cobalt magnet in application of large motor products. The preparation method provides a powerful guarantee for realizing the positive effects.
Owner:浙江西子富沃德电机有限公司
Method of adjusting CoFe free layer magnetostriction
InactiveUS20060061919A1Low constantLow coercivityNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismCopperOXYGEN EXPOSURE
It has been found that the insertion of a copper laminate within CoFe, or a CoFe / NiFe composite, leads to higher values of CPP GMR and DRA. However, this type of structure exhibits very negative magnetostriction, in the range of high −10−6 to −10−5. This problem has been overcome by giving the copper laminates an oxygen exposure treatment When this is done, the free layer is found to have a very low positive magnetostriction constant. Additionally, the value of the magnetostriction constant can be adjusted by varying the thickness of the free layer and / or the position and number of the oxygen treated copper laminates.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
Iron-based nanometer crystal magnetically soft alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102543347AReduce processing costsHigh saturation magnetic inductionMagnetic materialsAmorphous phaseAlloy
The invention discloses a novel iron-based nanometer crystal magnetically soft alloy and a preparation method thereof. The molecular formula of the iron-based nanometer crystal magnetically soft alloy is FexPyCzMaCub, wherein the M in the molecular formula is one or more than one of B, Si, Al, Cr, Mn, Mo and Ge; x,y,z,a and b respectively represent atom percentage composition of each corresponding component, wherein 70<=x<=90, 1<=y<=20, 1<=z<=20, 0<=a<=10, 0.1<=b<=2, and x+y+z+a+b=100; and a microstructure is coexistence of a body-centered stand alpha-Fe nanometer crystalline phase the size of which is 5-40 nm and a rich phosphatic and carbon amorphous phase. Compared with the existing nanometer crystal magnetically soft alloy, the alloy disclosed by the invention meanwhile has the advantages of high saturation induction density, low coercive force, low iron loss and high magnetic permeability; and in addition, precious metals such as Nb, Zr, Co, Ni, Y and the like are not contained, thus the processing cost is greatly reduced and the application prospect is good.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com