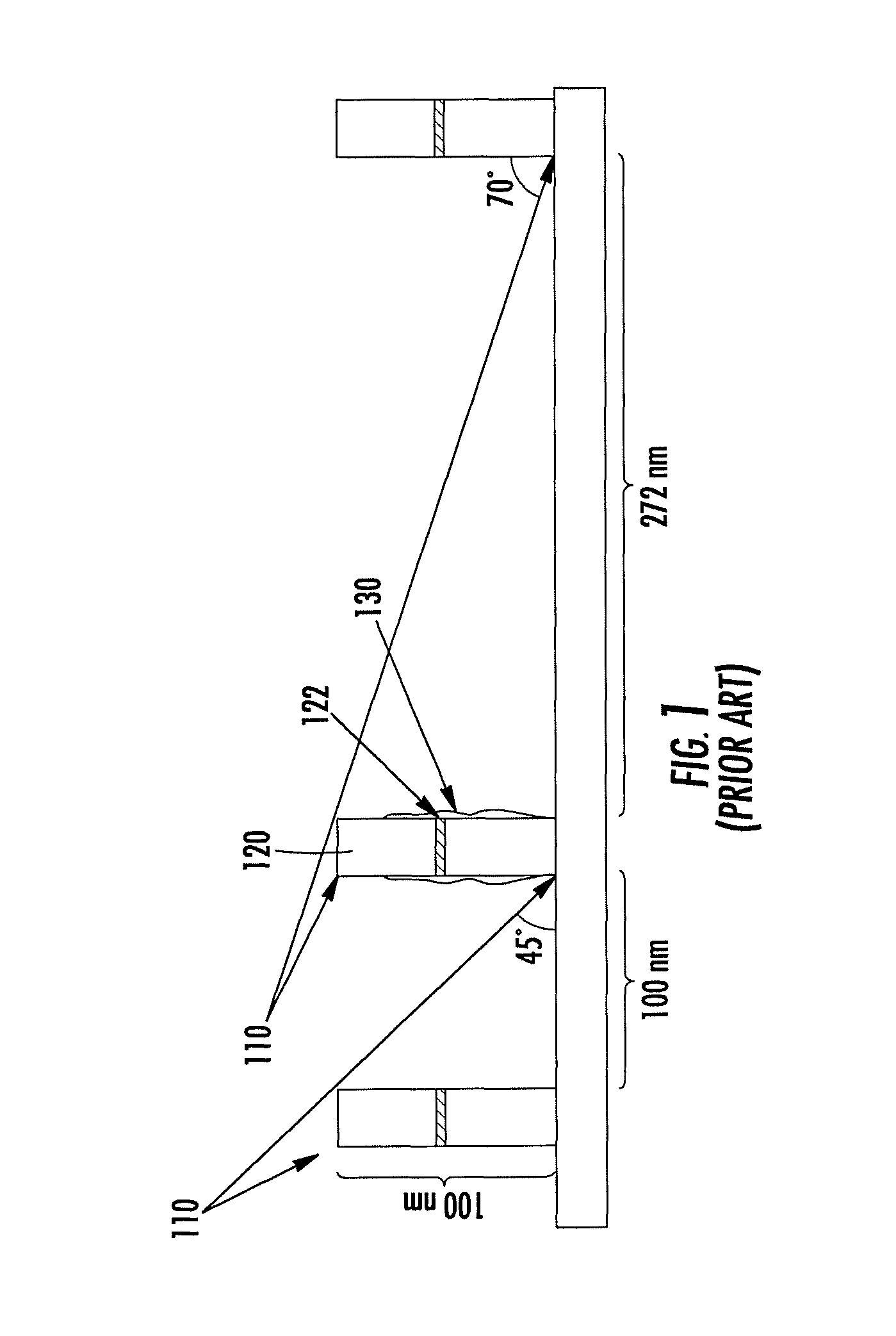
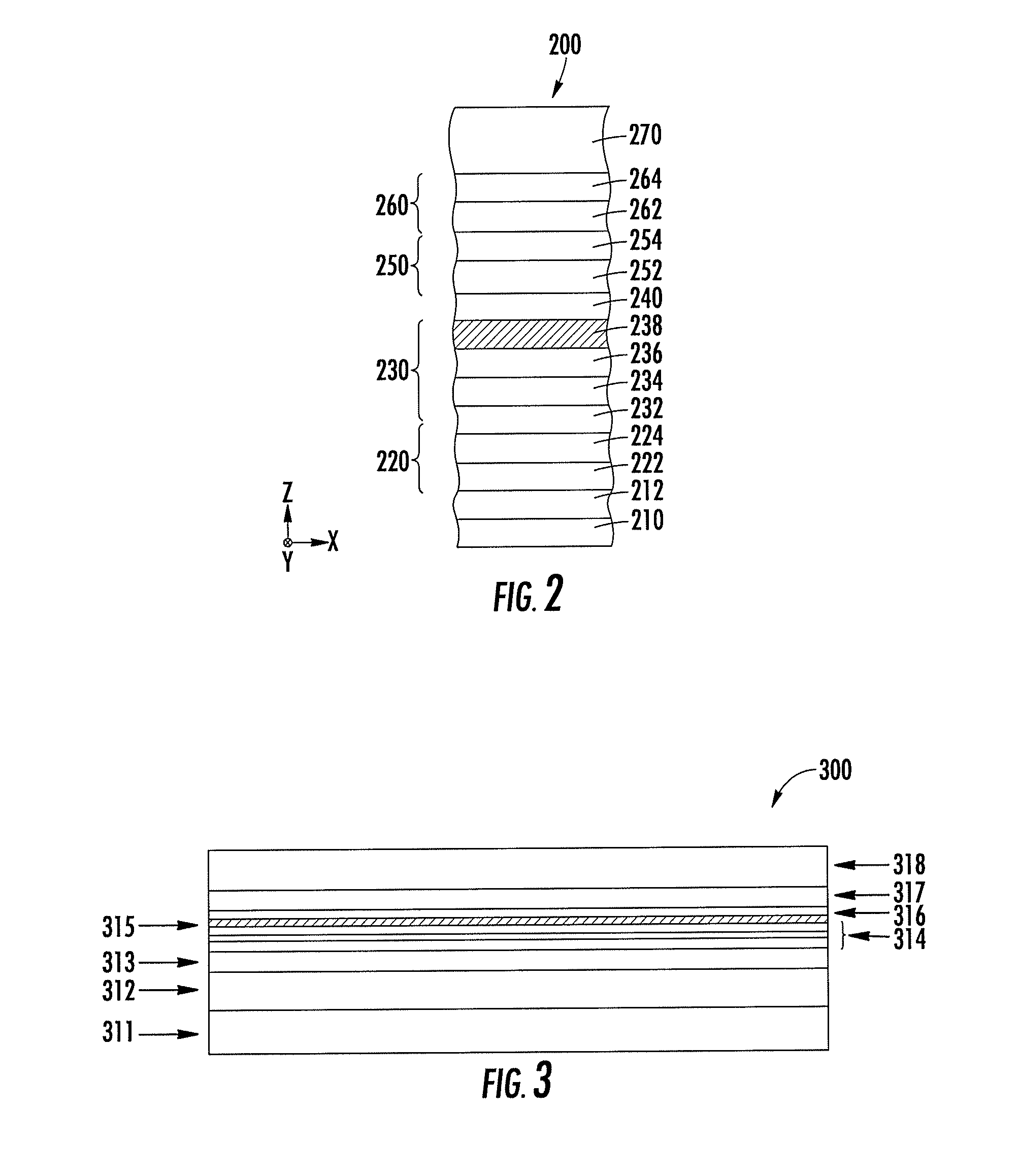
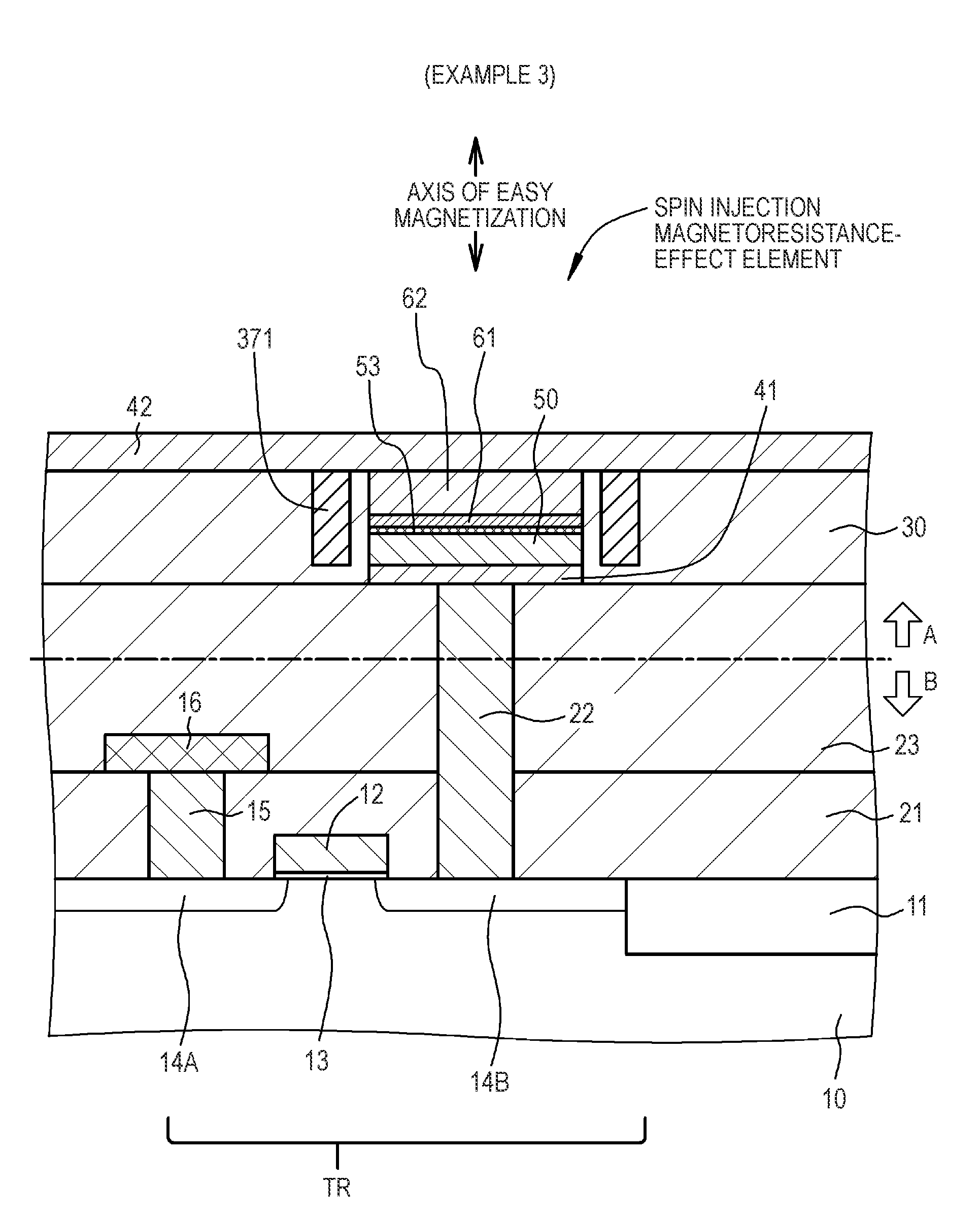
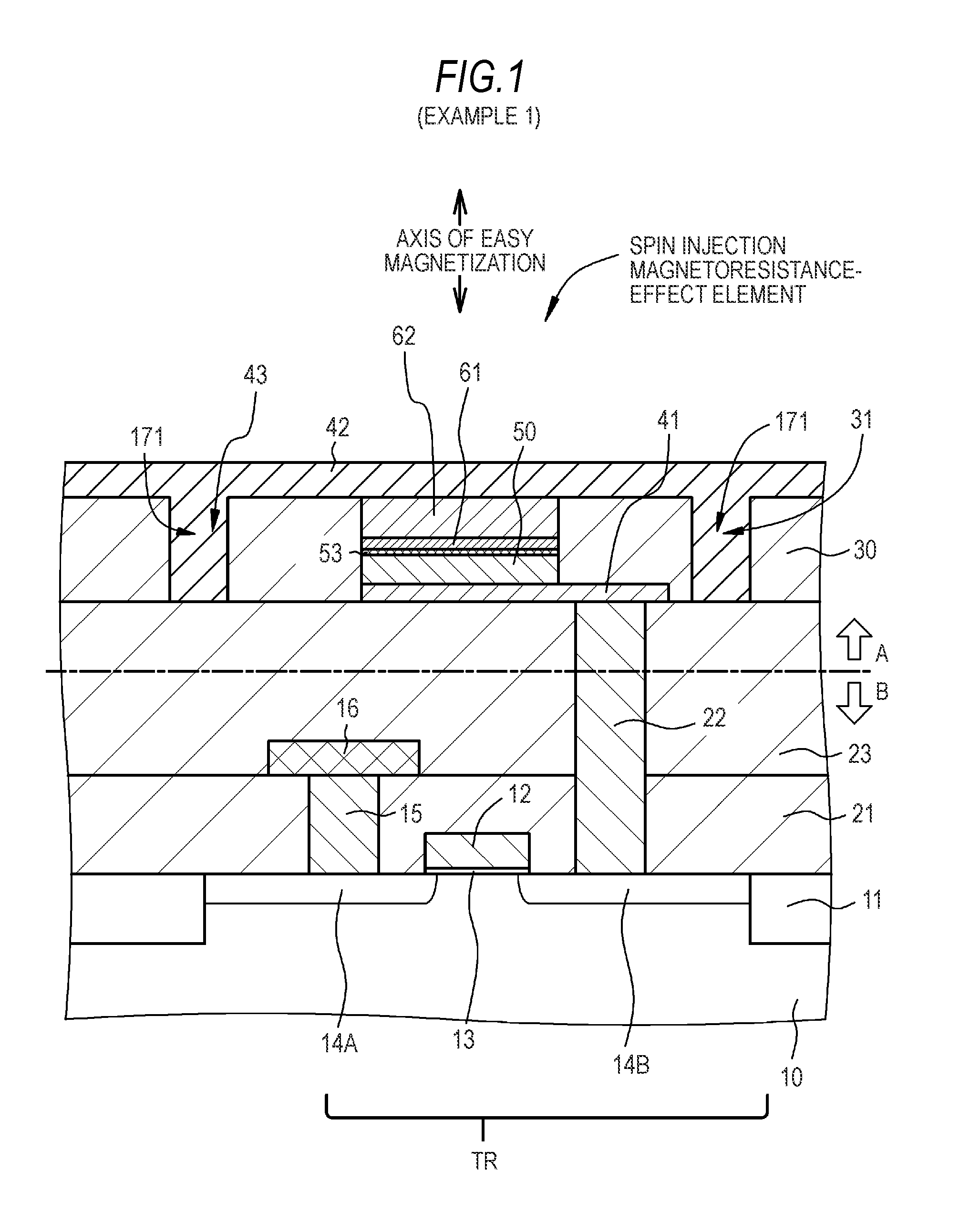
Patents
Literature
2067results about "Galvano-magnetic device details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
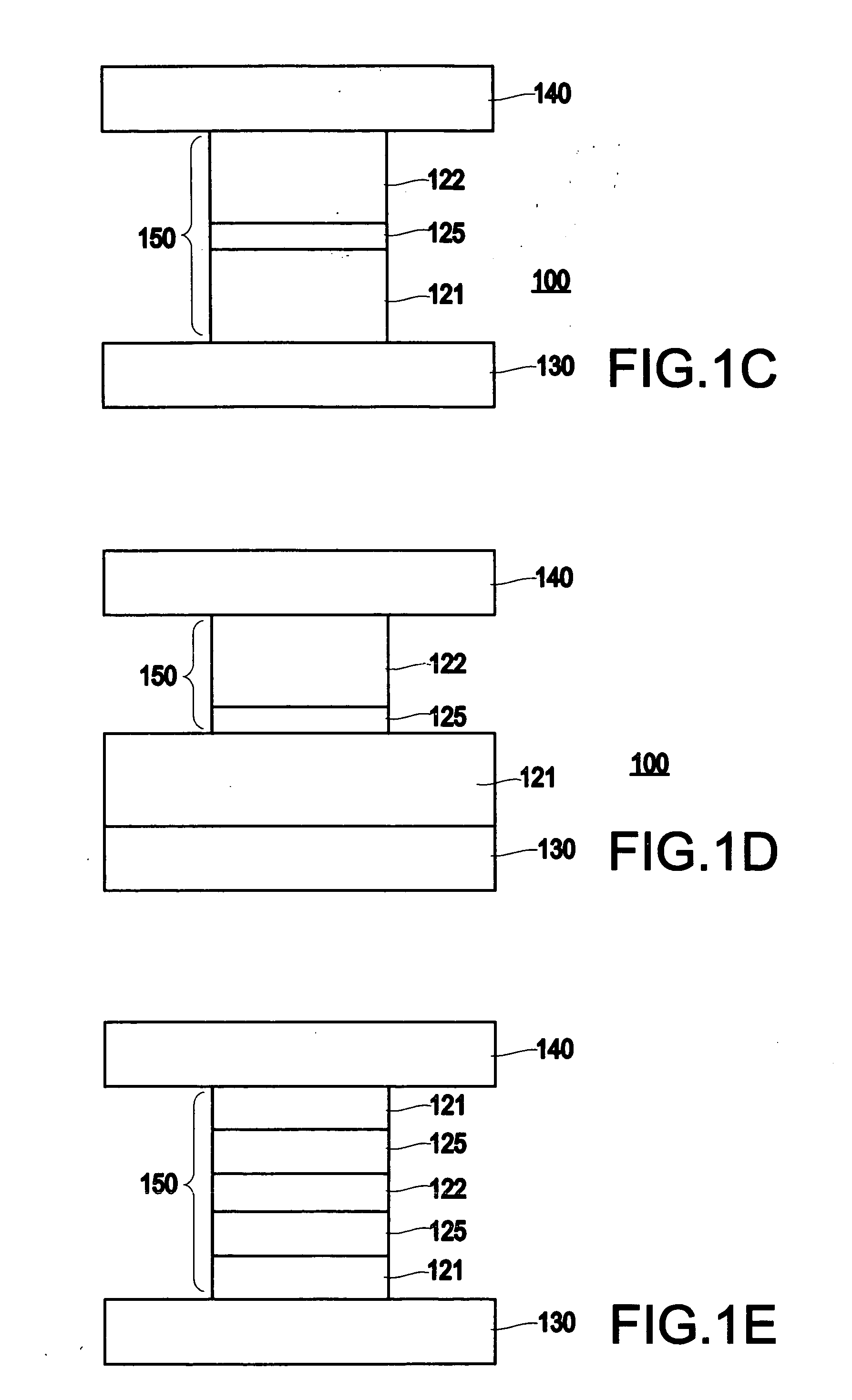
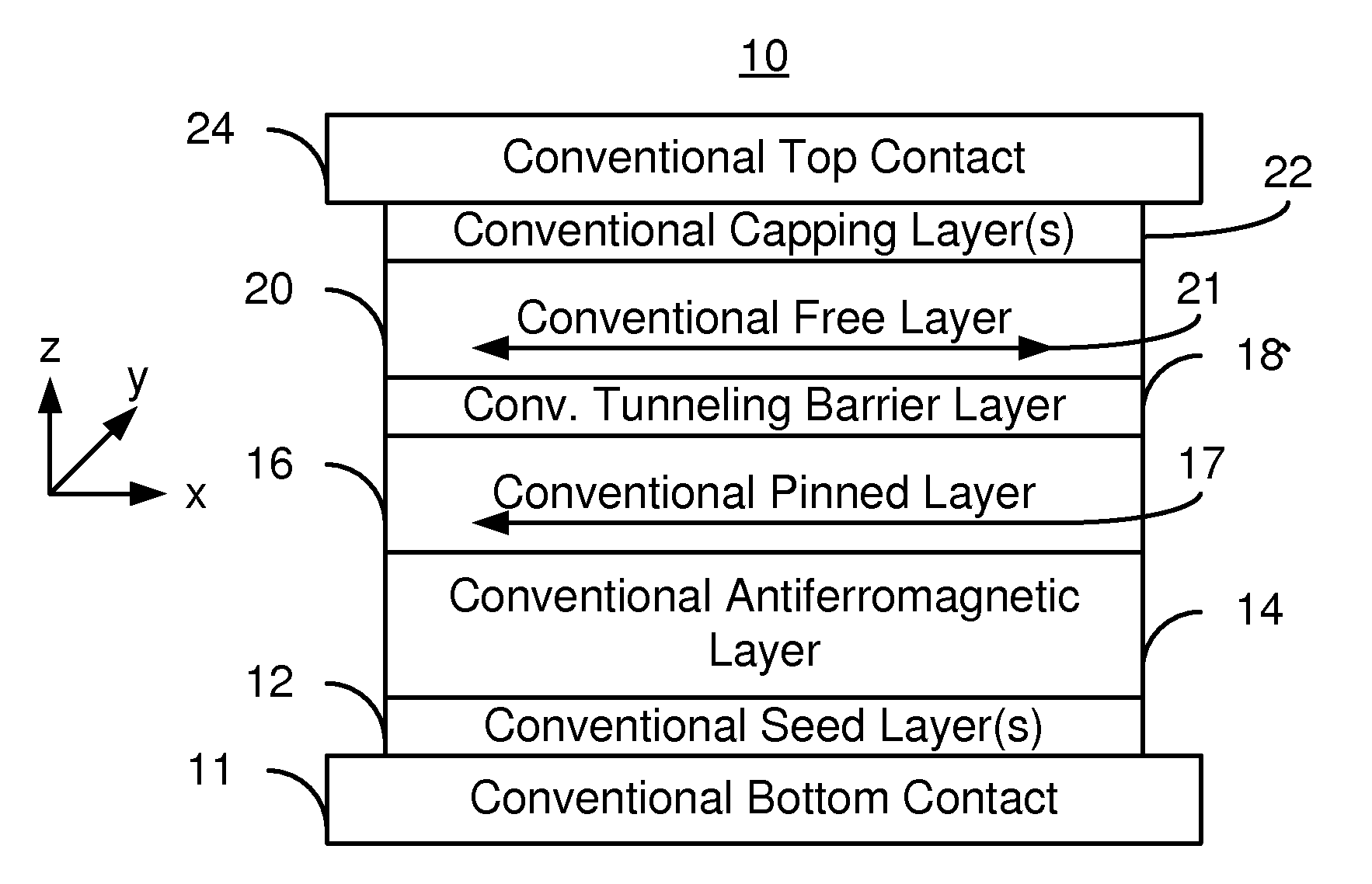
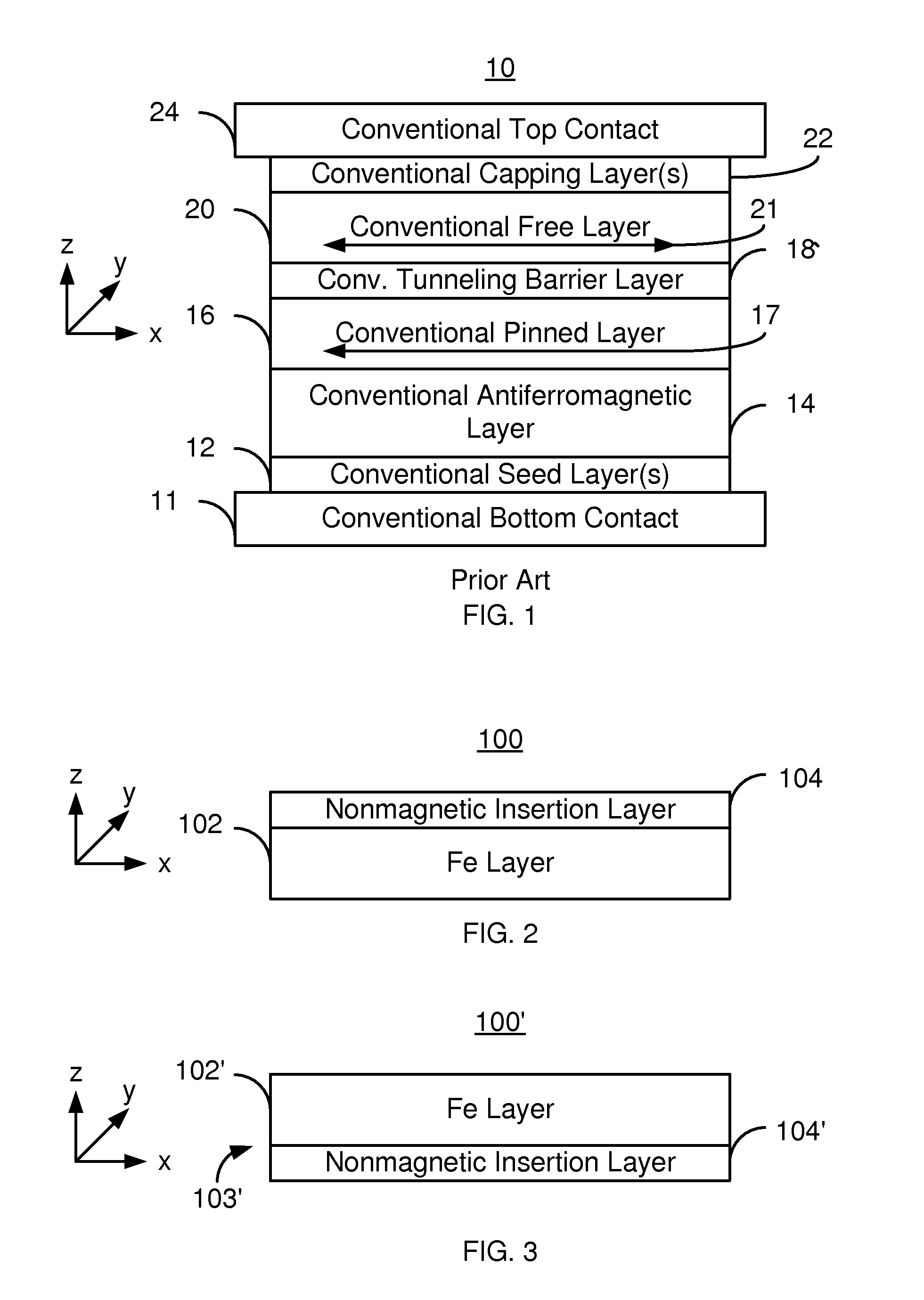
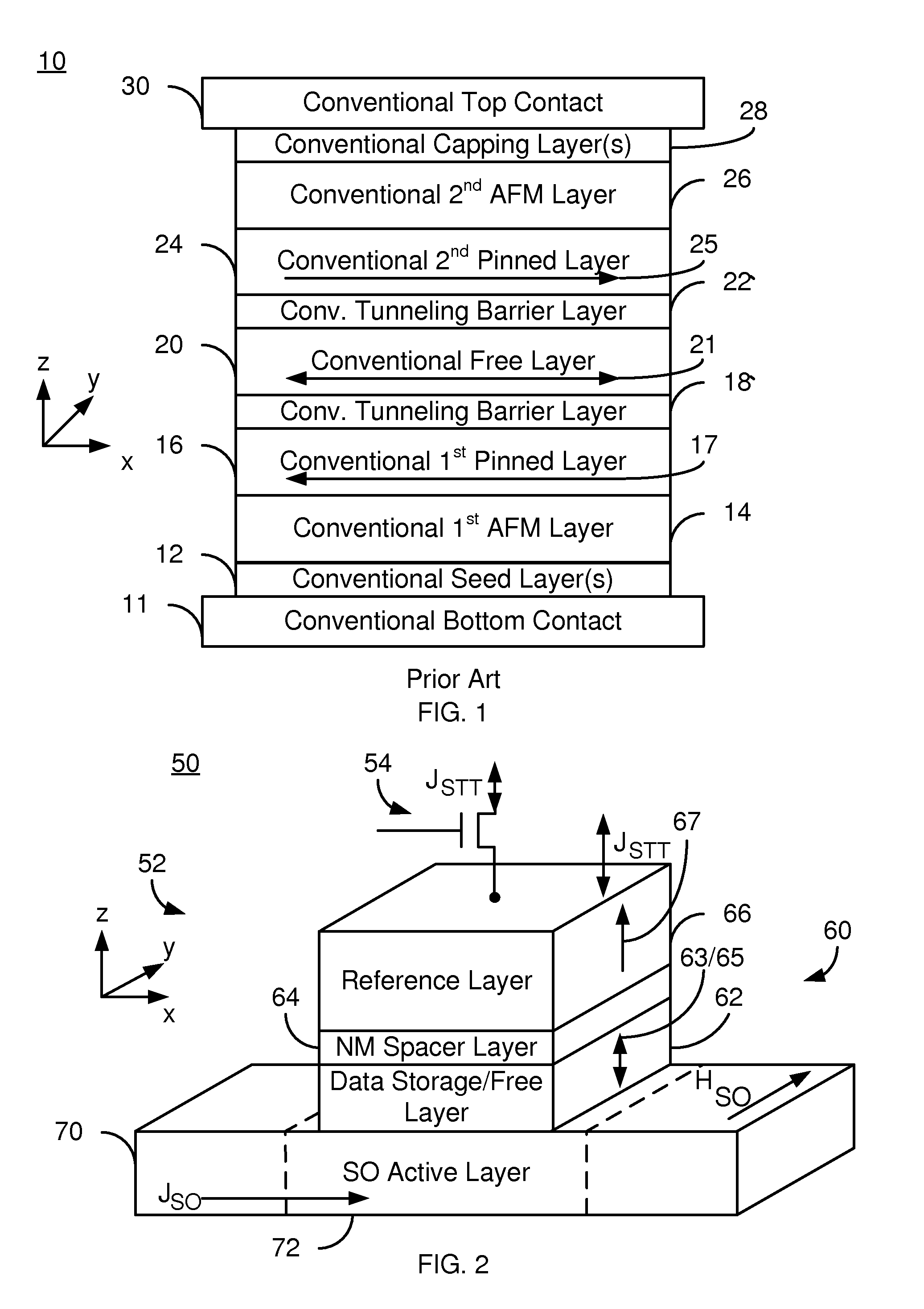
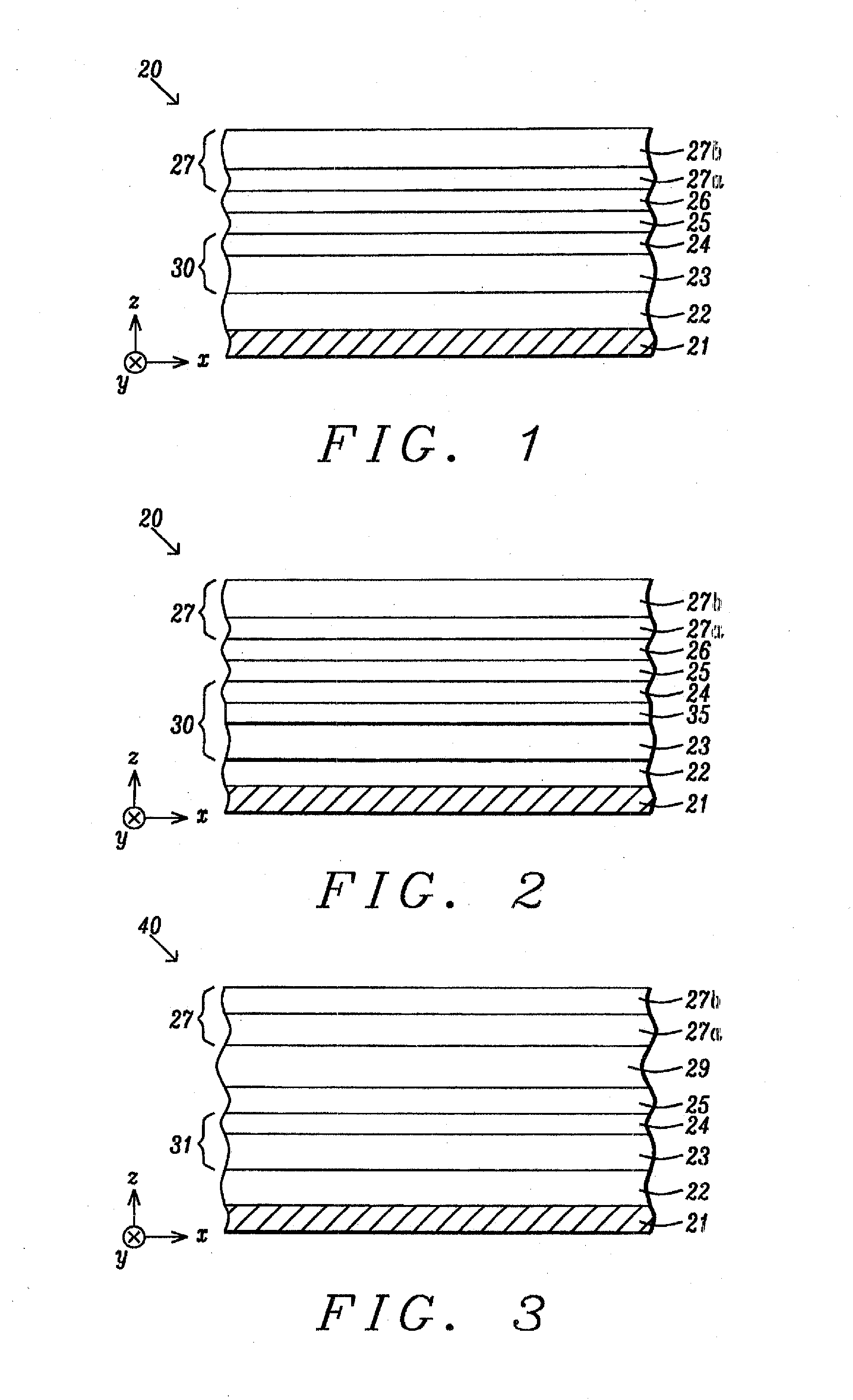
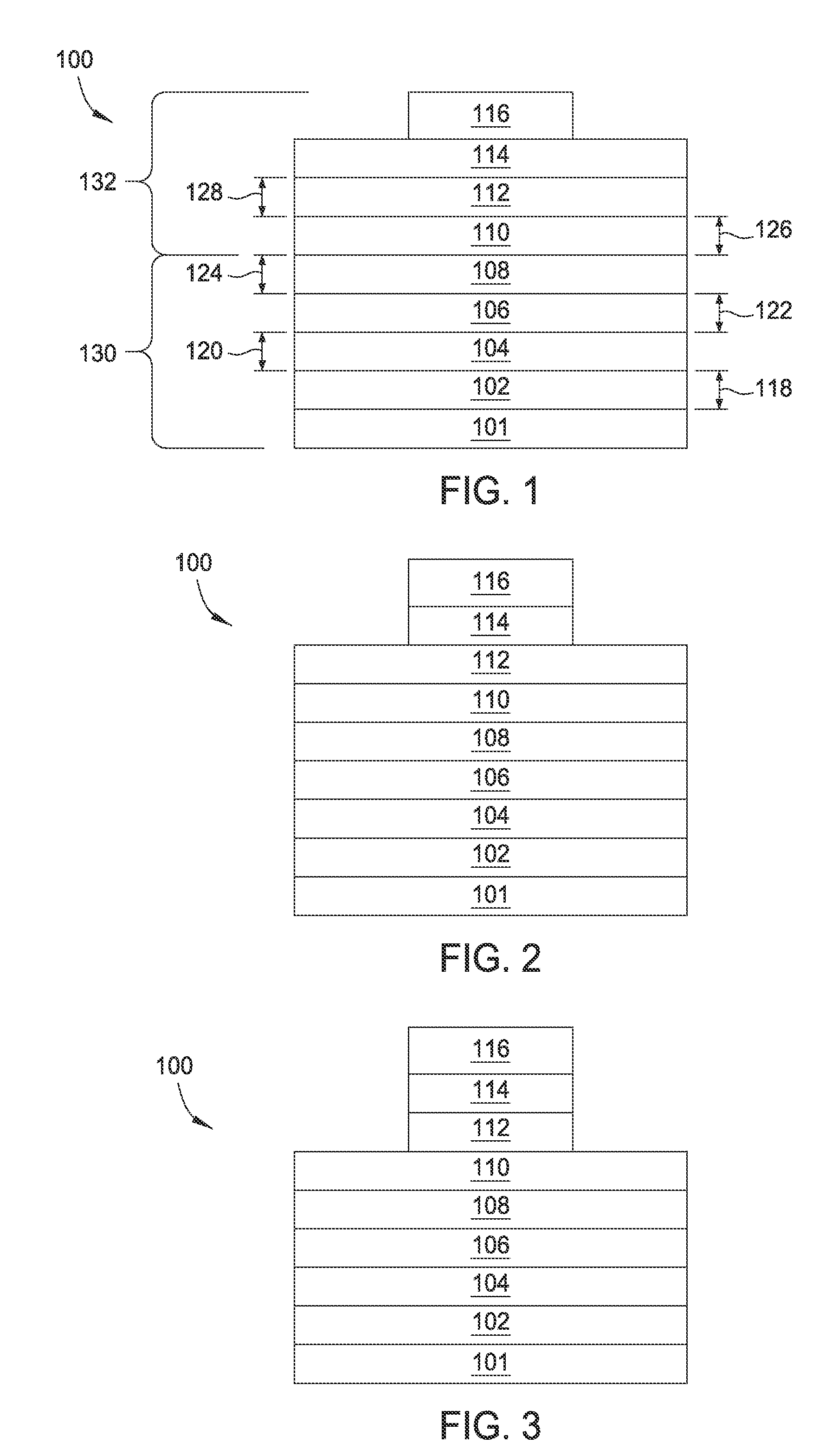
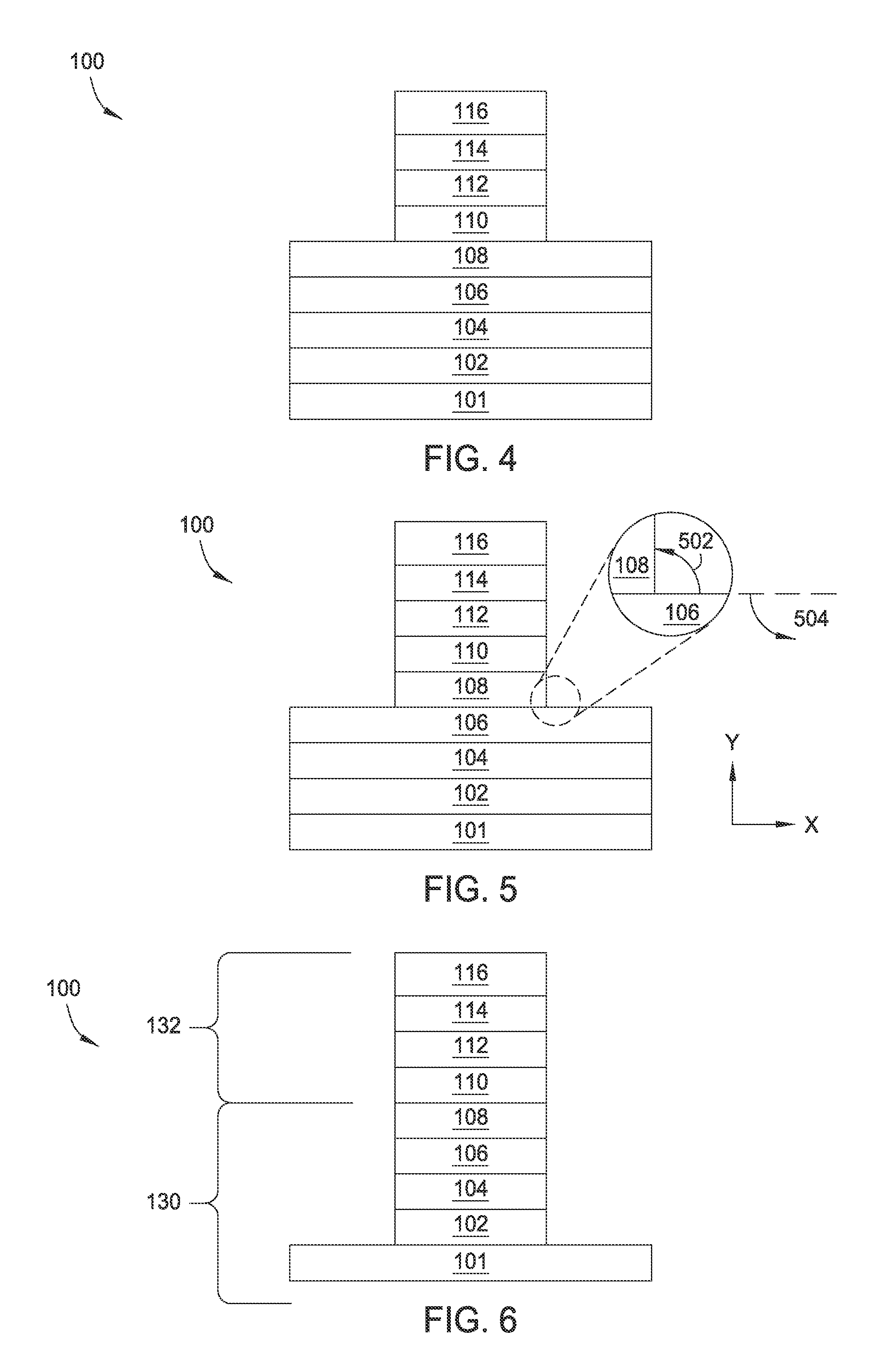
Multilayers having reduced perpendicular demagnetizing field using moment dilution for spintronic applications
ActiveUS20120280336A1Improve thermal stabilityHigh MR ratioMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular anisotropyAlloy
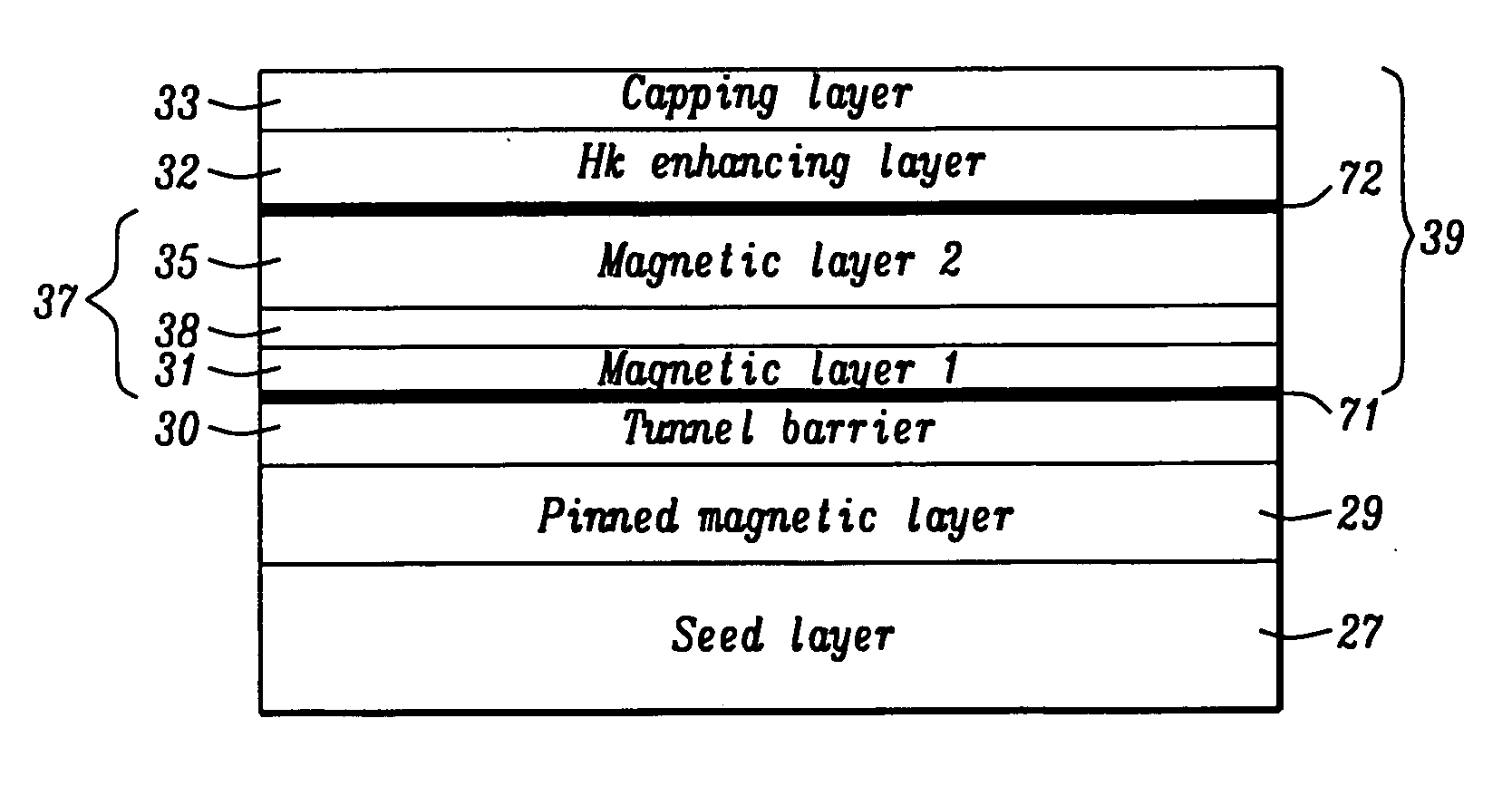
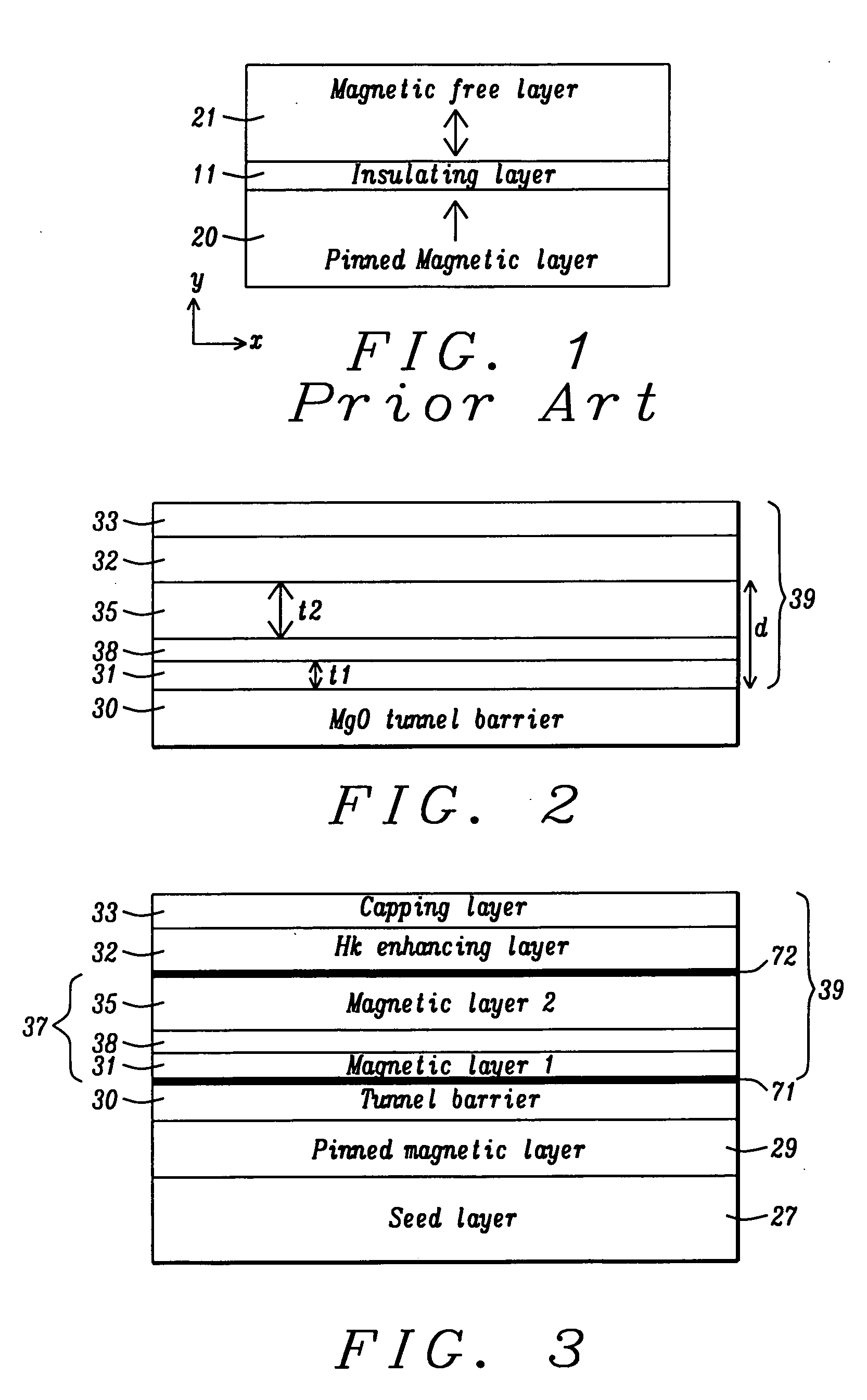
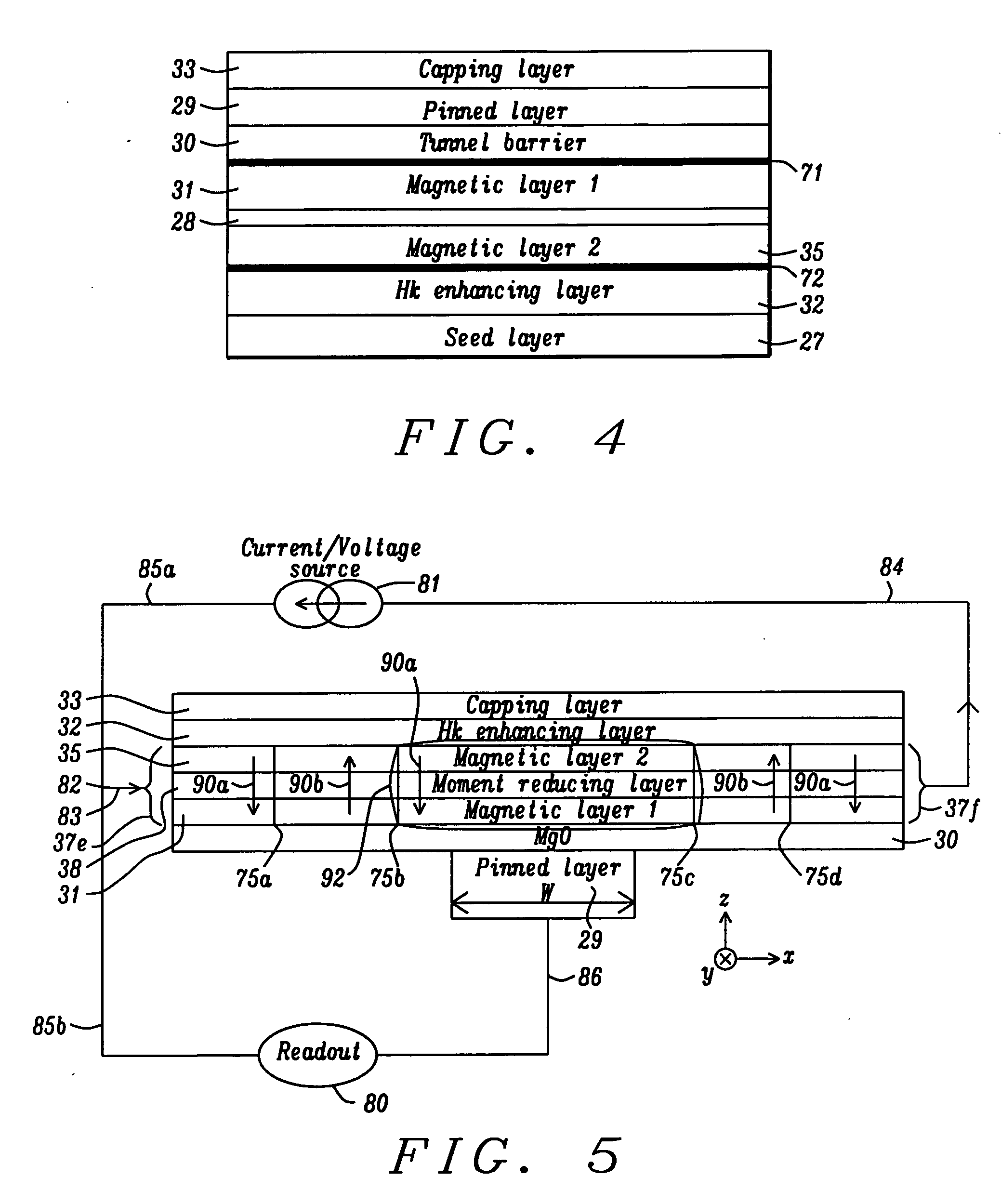
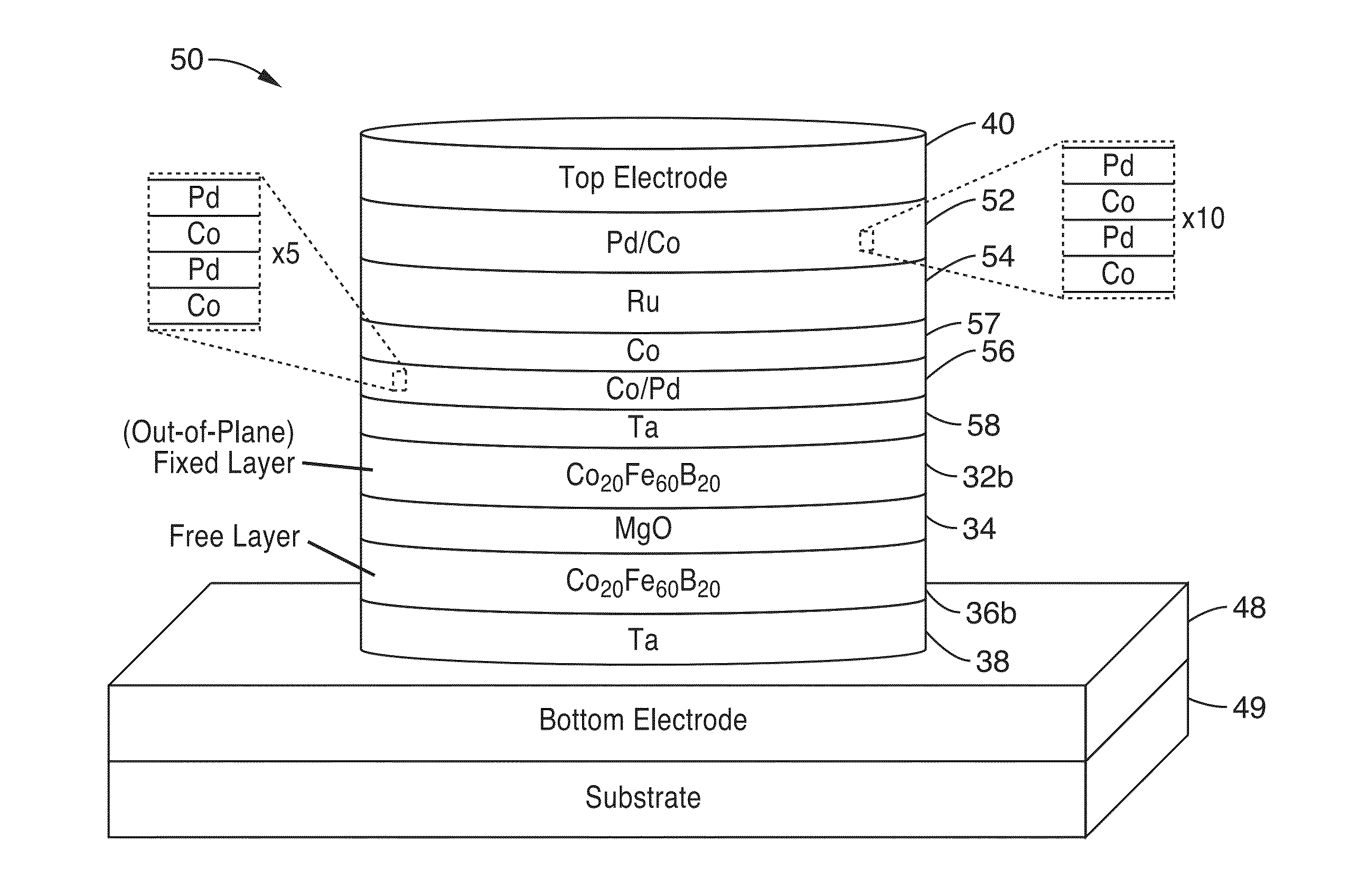
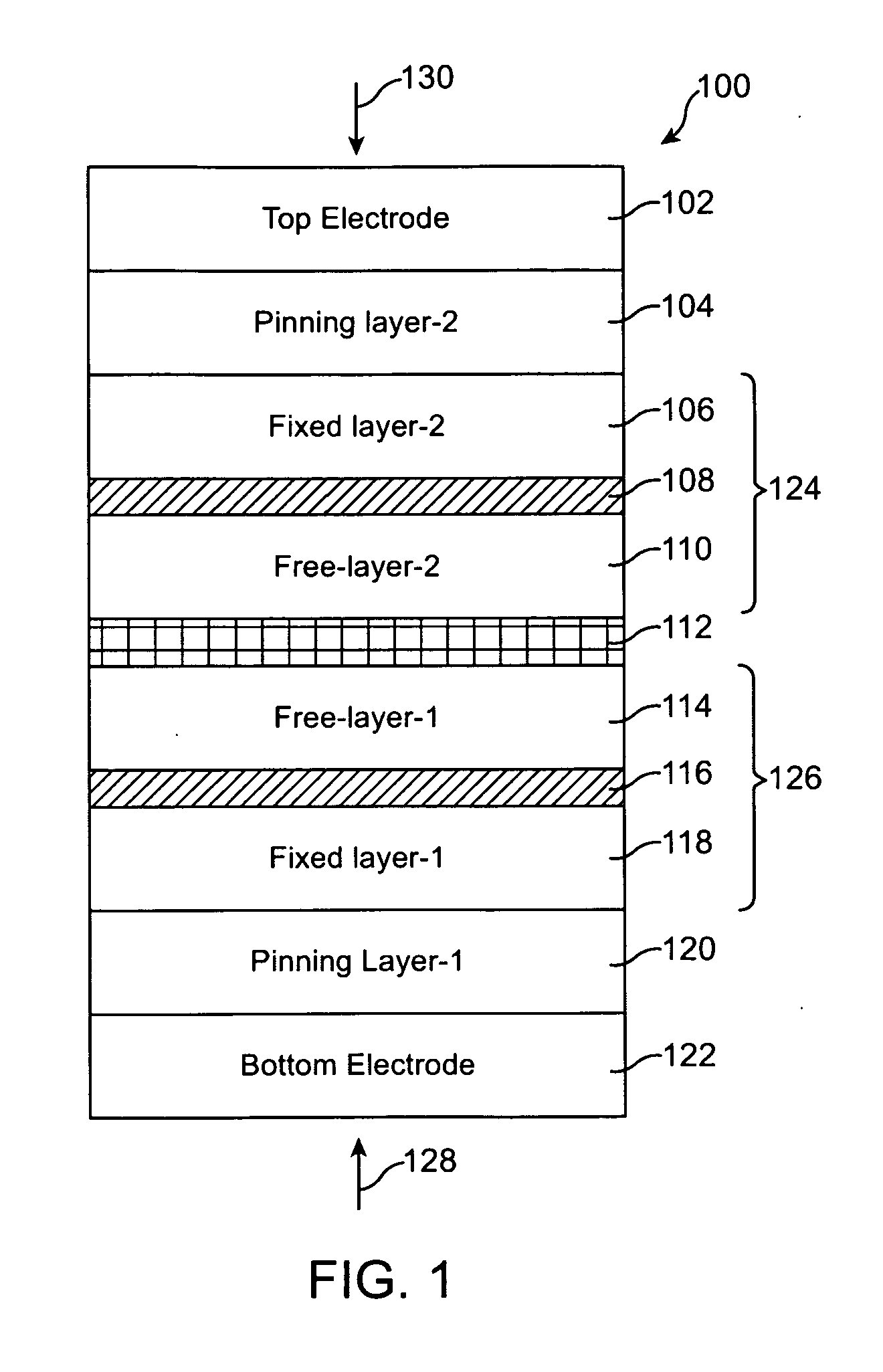
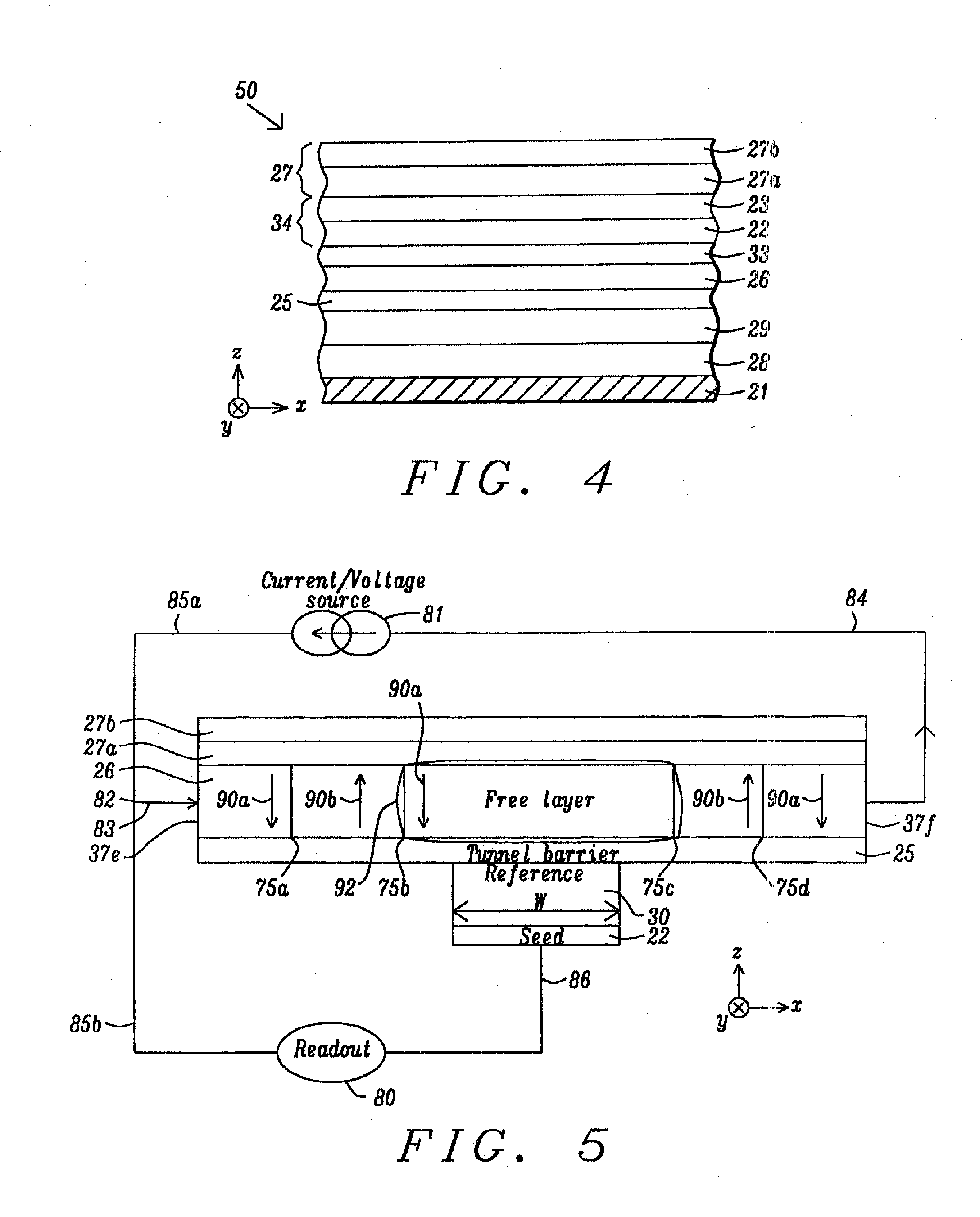
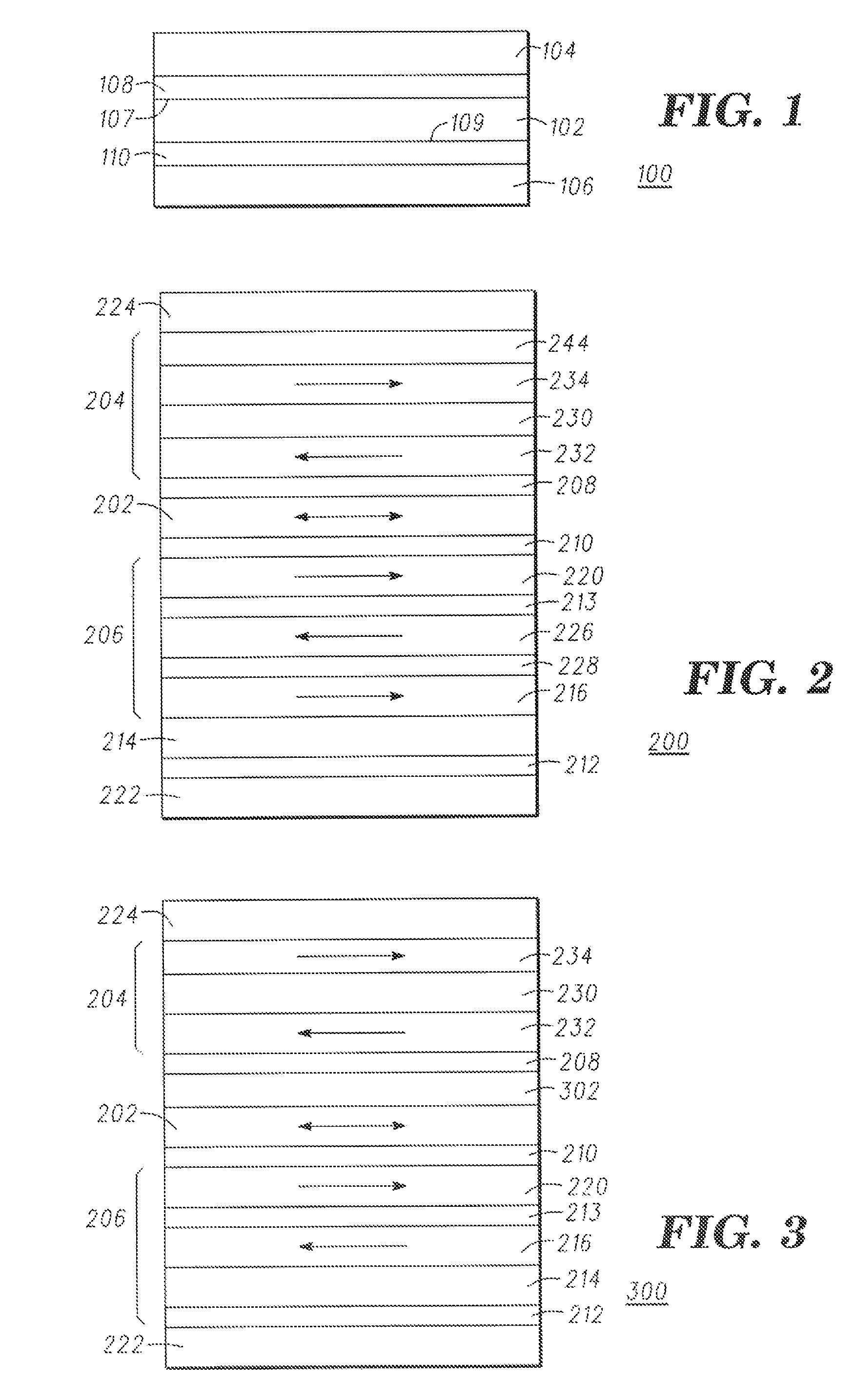
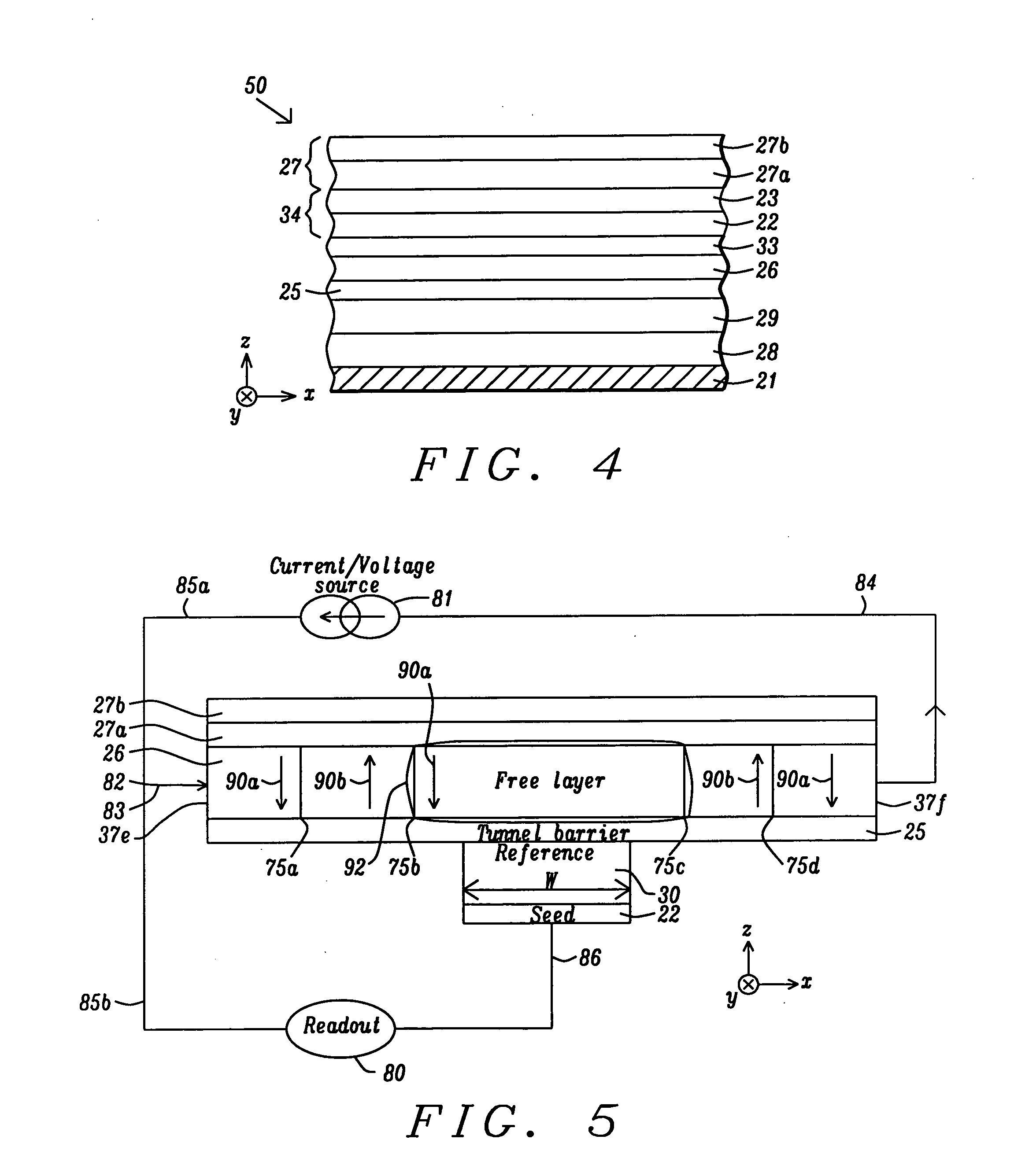
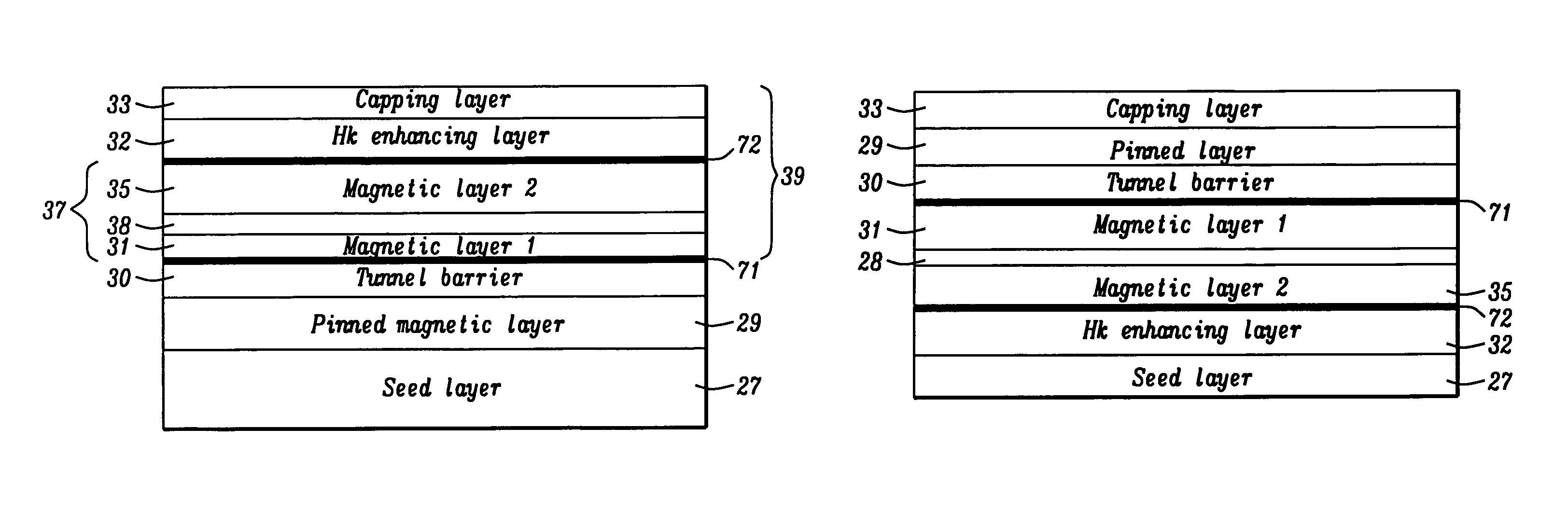
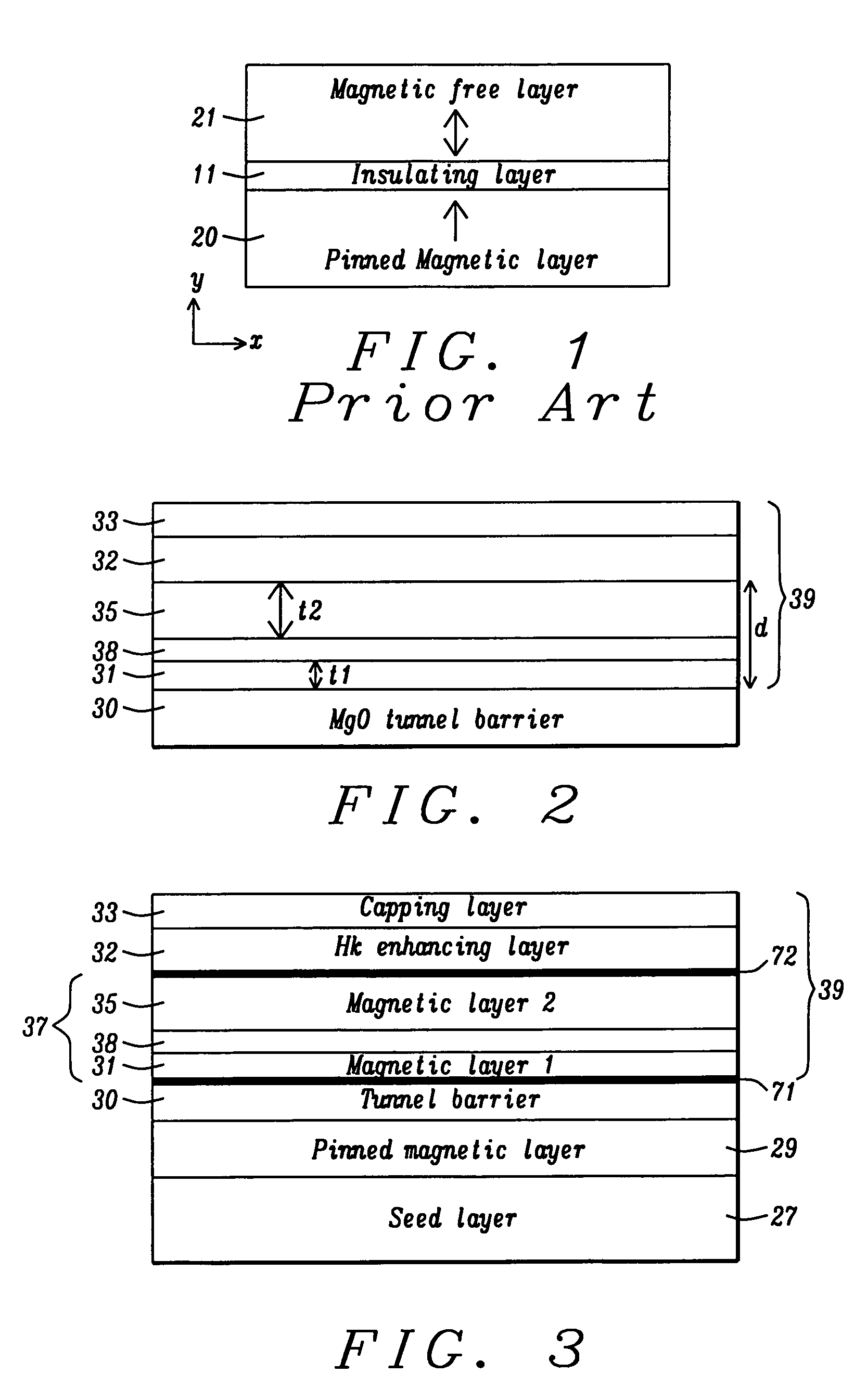
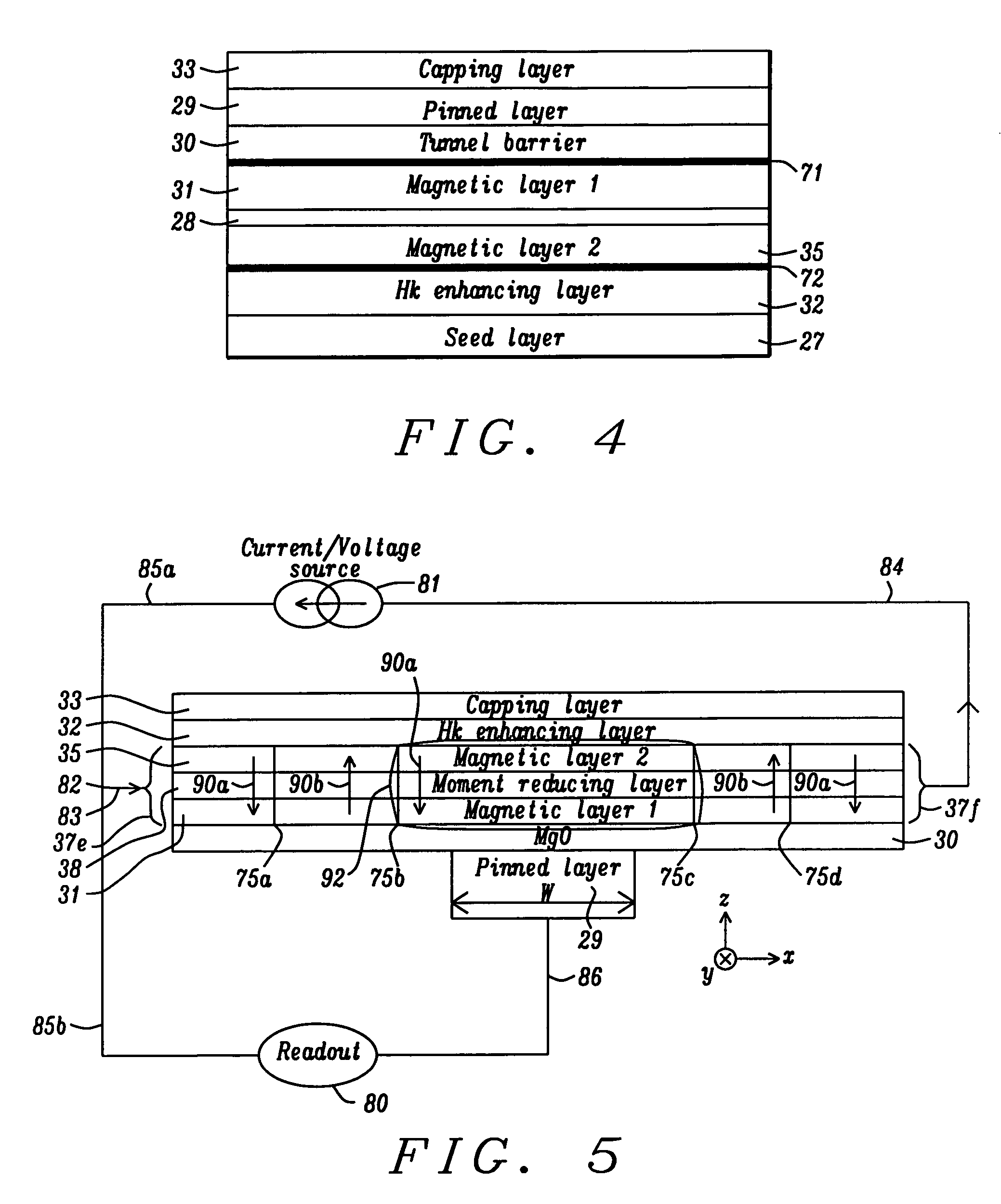
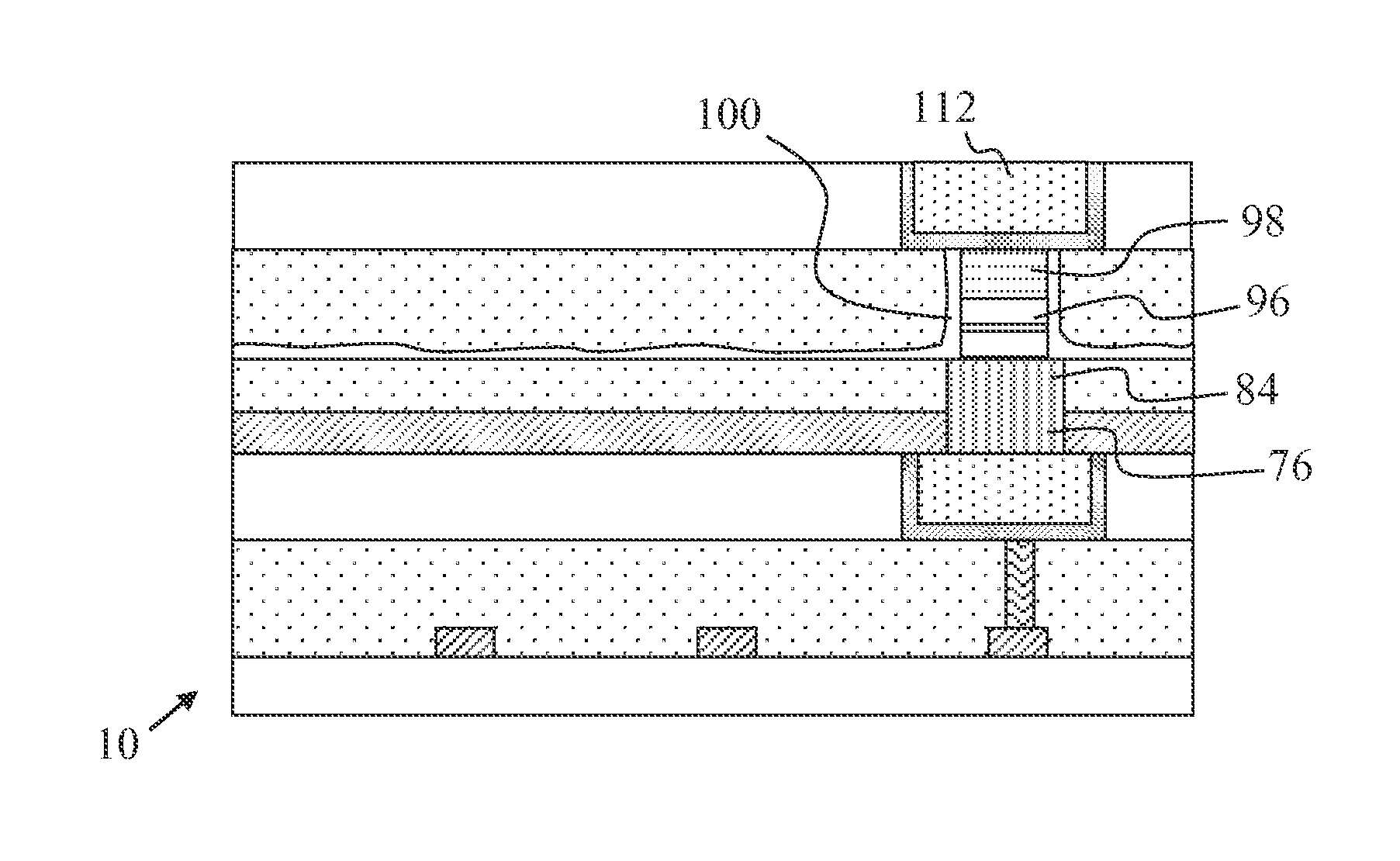
A magnetic element is disclosed that has a composite free layer with a FM1 / moment diluting / FM2 configuration wherein FM1 and FM2 are magnetic layers made of one or more of Co, Fe, Ni, and B and the moment diluting layer is used to reduce the perpendicular demagnetizing field. As a result, lower resistance x area product and higher thermal stability are realized when perpendicular surface anisotropy dominates shape anisotropy to give a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the FM1, FM2 layers. The moment diluting layer may be a non-magnetic metal like Ta or a CoFe alloy with a doped non-magnetic metal. A perpendicular Hk enhancing layer interfaces with the FM2 layer and may be an oxide to increase the perpendicular anisotropy field in the FM2 layer. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
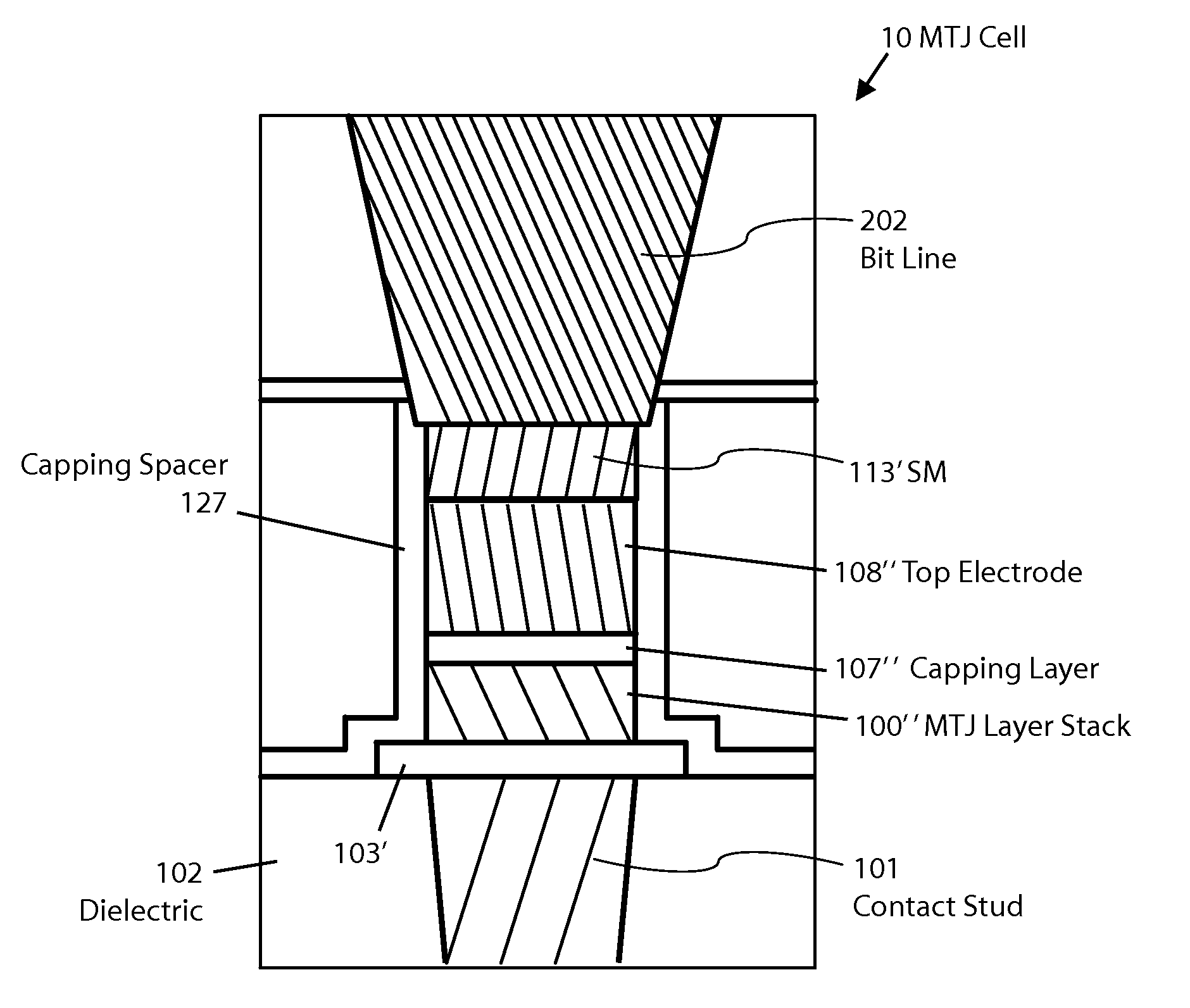
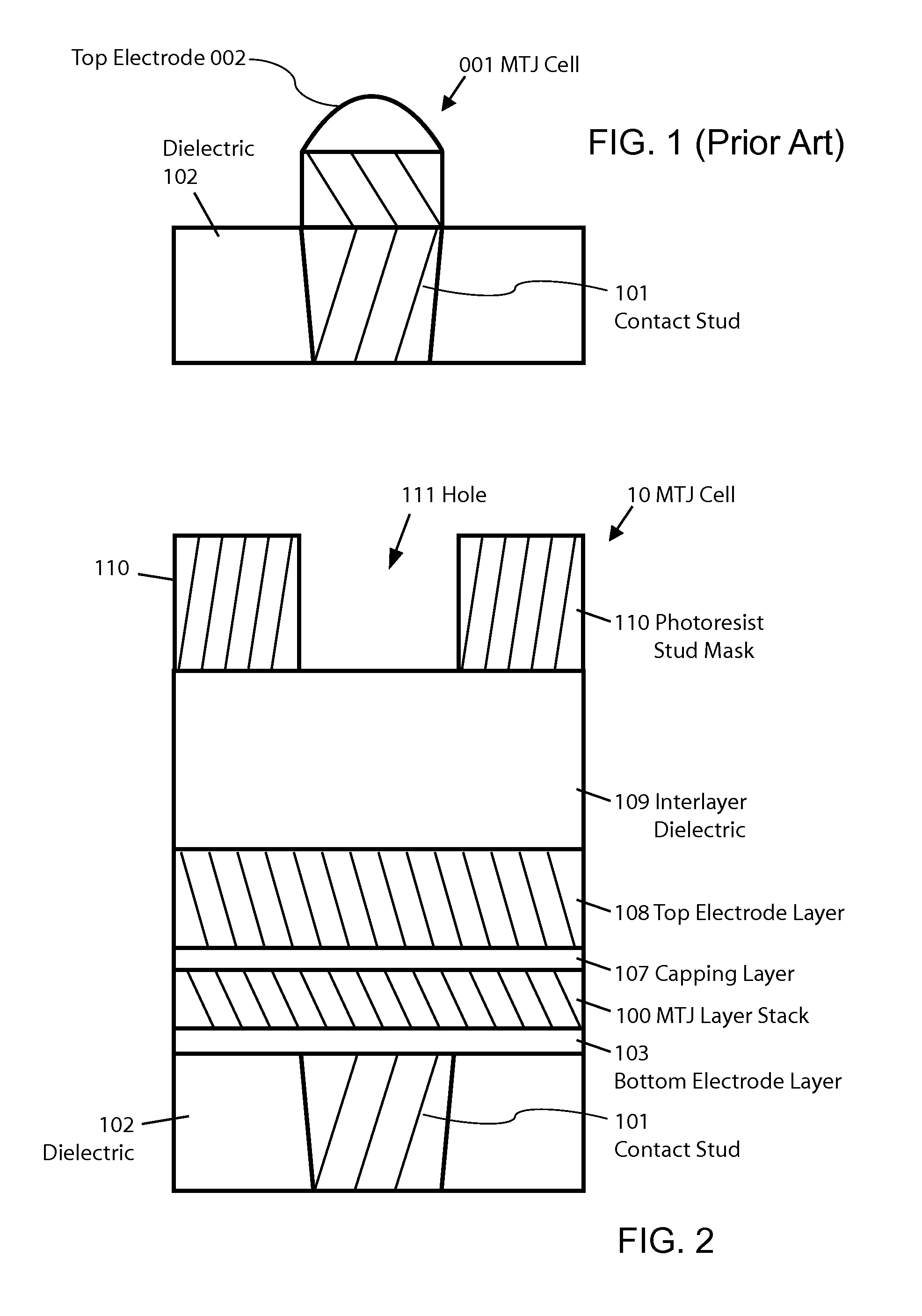
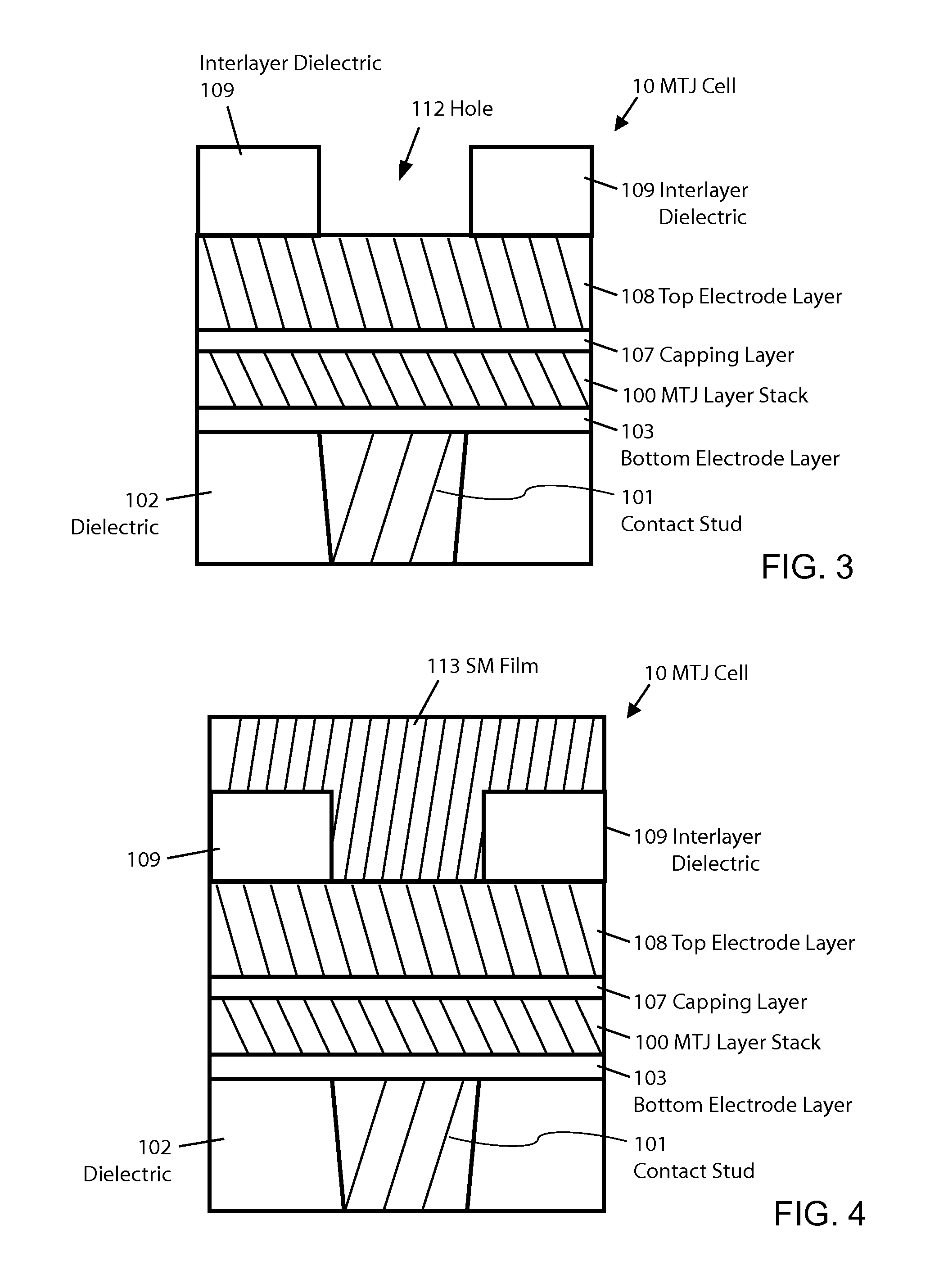
MTJ MRAM with stud patterning
ActiveUS8772888B2Reduce widthImprove errorMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesEtchingConductive materials
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Spin-current switched magnetic memory element suitable for circuit integration and method of fabricating the memory element
A magnetic memory element switchable by current injection includes a plurality of magnetic layers, at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy component and including a current-switchable magnetic moment, and at least one barrier layer formed adjacent to the plurality of magnetic layers (e.g., between two of the magnetic layers). The memory element has the switching threshold current and device impedance suitable for integration with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuits.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Magnetic stack having assist layer
A magnetic memory cell having a ferromagnetic free layer and a ferromagnetic pinned reference layer, each having an out-of-plane magnetic anisotropy and an out-of-plane magnetization orientation and switchable by spin torque. The cell includes a ferromagnetic assist layer proximate the free layer, the assist layer having a low magnetic anisotropy less than about 500 Oe. The assist layer may have in-plane or out-of-plane anisotropy.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Voltage-controlled magnetic memory element with canted magnetization
ActiveUS20140169085A1High tunneling magnetoresistance (TMRImprove adjustabilitySolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionStable stateMagnetic memory
A memory cell including information that is stored in the state of a magnetic bit (i.e. in a free layer, FL), where the FL magnetization has two stable states that may be canted (form an angle) with respect to the horizontal and vertical directions of the device is presented. The FL magnetization may be switched between the two canted states by the application of a voltage (i.e. electric field), which modifies the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy of the free layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
MRAM having spin hall effect writing and method of making the same
InactiveUS20140252439A1Easy to switchEasy to reverseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic reluctanceRecording layer
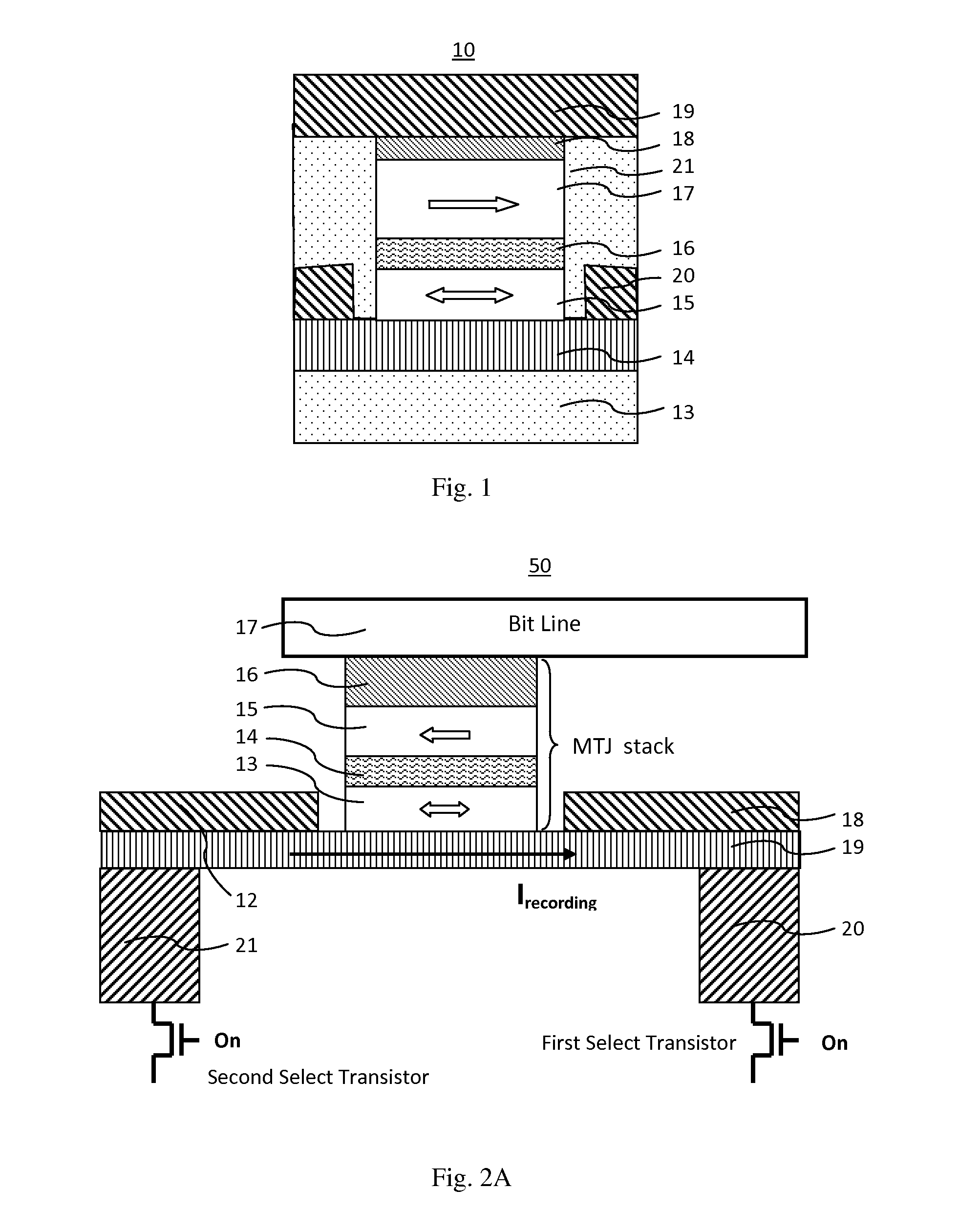
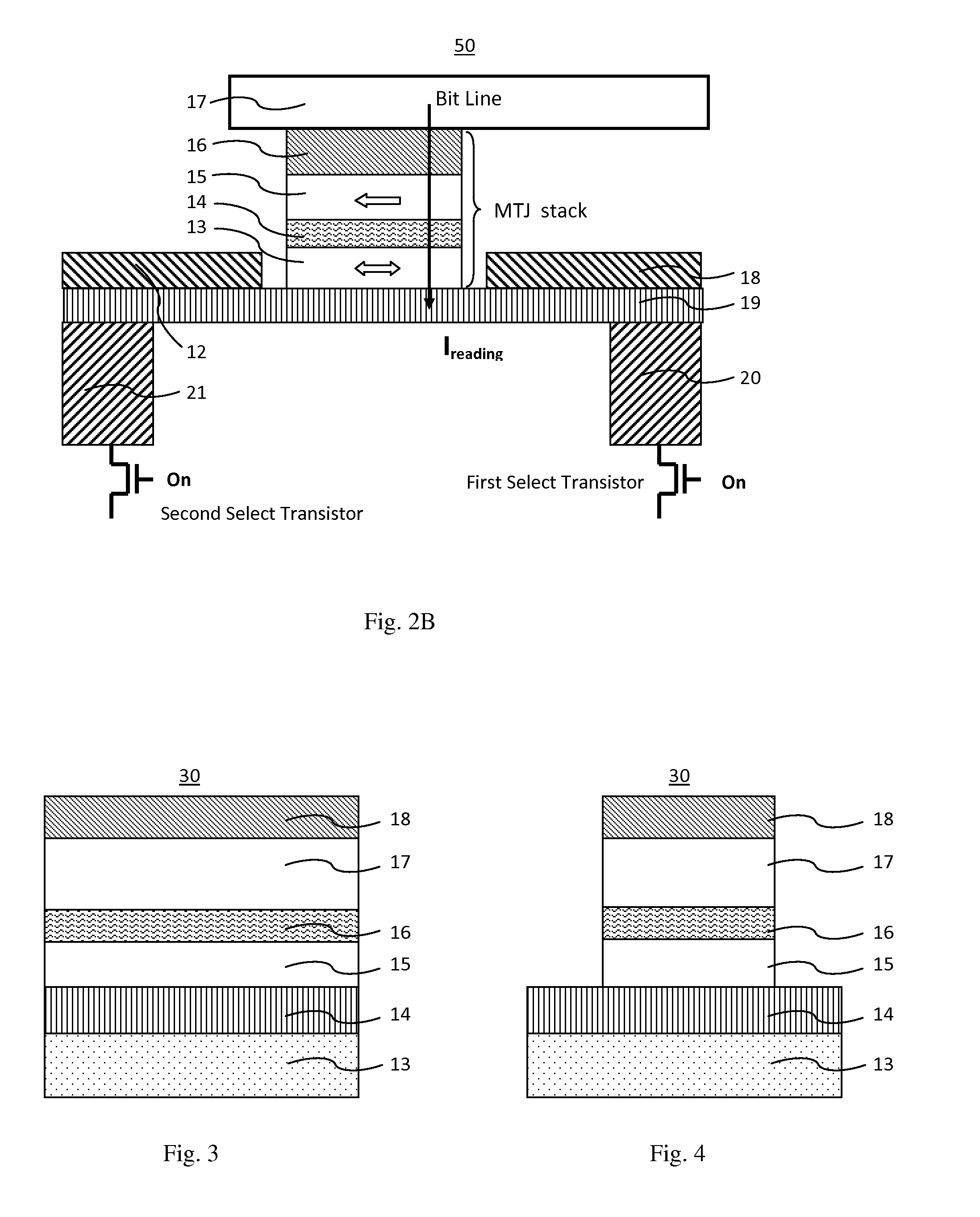
A spin-transfer-torque magnetoresistive memory comprises apparatus and method of manufacturing a three terminal magnetoresistive memory element having highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid on top of a SHE-metal layer in the regions outside of an MTJ stack. The memory cell comprises a bit line positioned adjacent to selected ones of the plurality of magnetoresistive memory elements to supply a reading current across the magnetoresistive element stack and two highly conductive bottom electrodes overlaid and electrically contacting on top of a SHE-metal layer in the outside of an MTJ region and to supply a bi-directional spin Hall effect recording current, and accordingly to switch the magnetization of the recording layer. Thus magnetization of a recording layer can be readily switched or reversed to the direction in accordance with a direction of a current along the SHE-metal layer by applying a low write current.
Owner:T3MEMORY
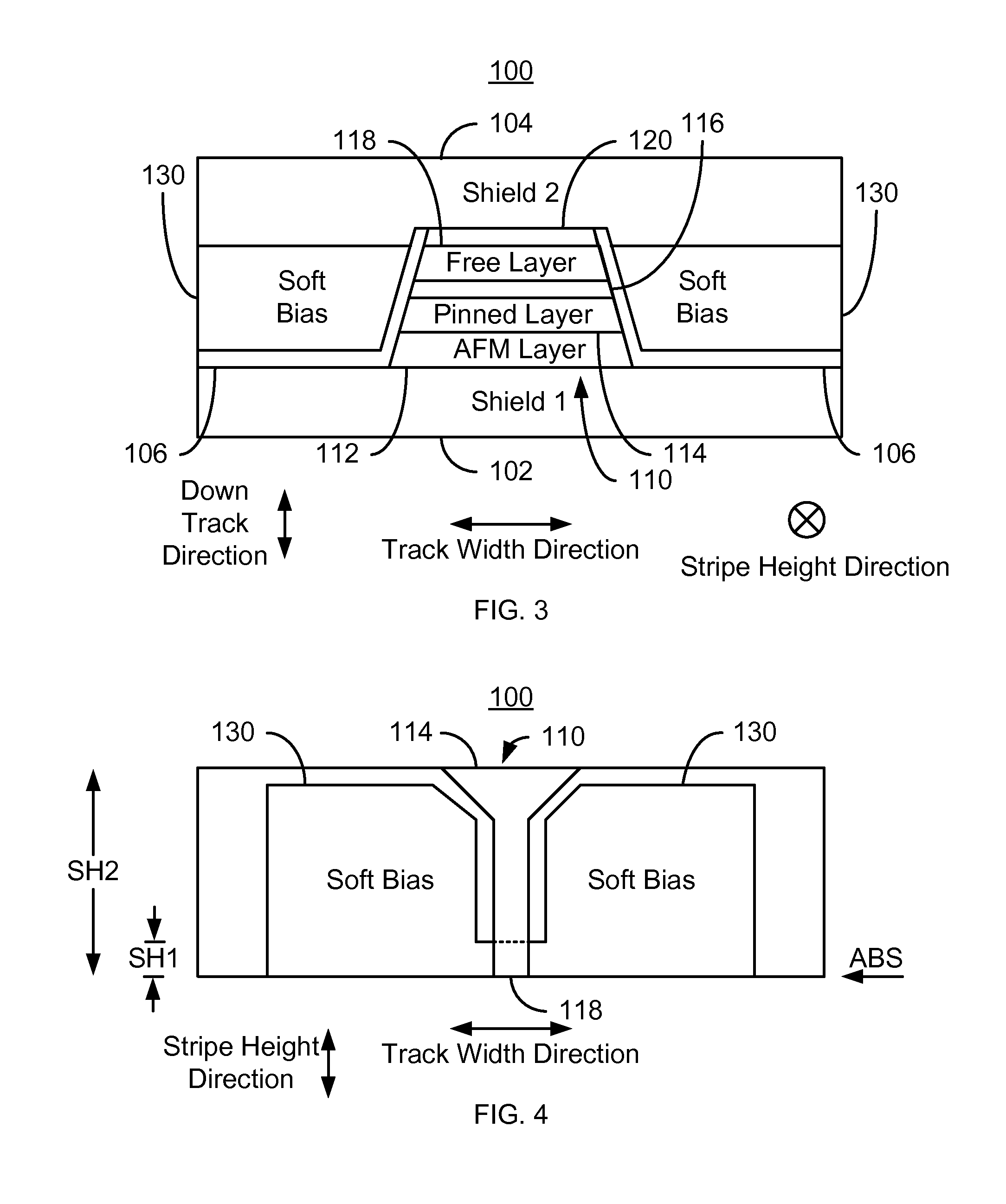
Method and system for providing a read transducer having an extended pinned layer and soft magnetic bias structures with improved stability
ActiveUS8760822B1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsRecord information storageMagnetic transducersAir bearing surface
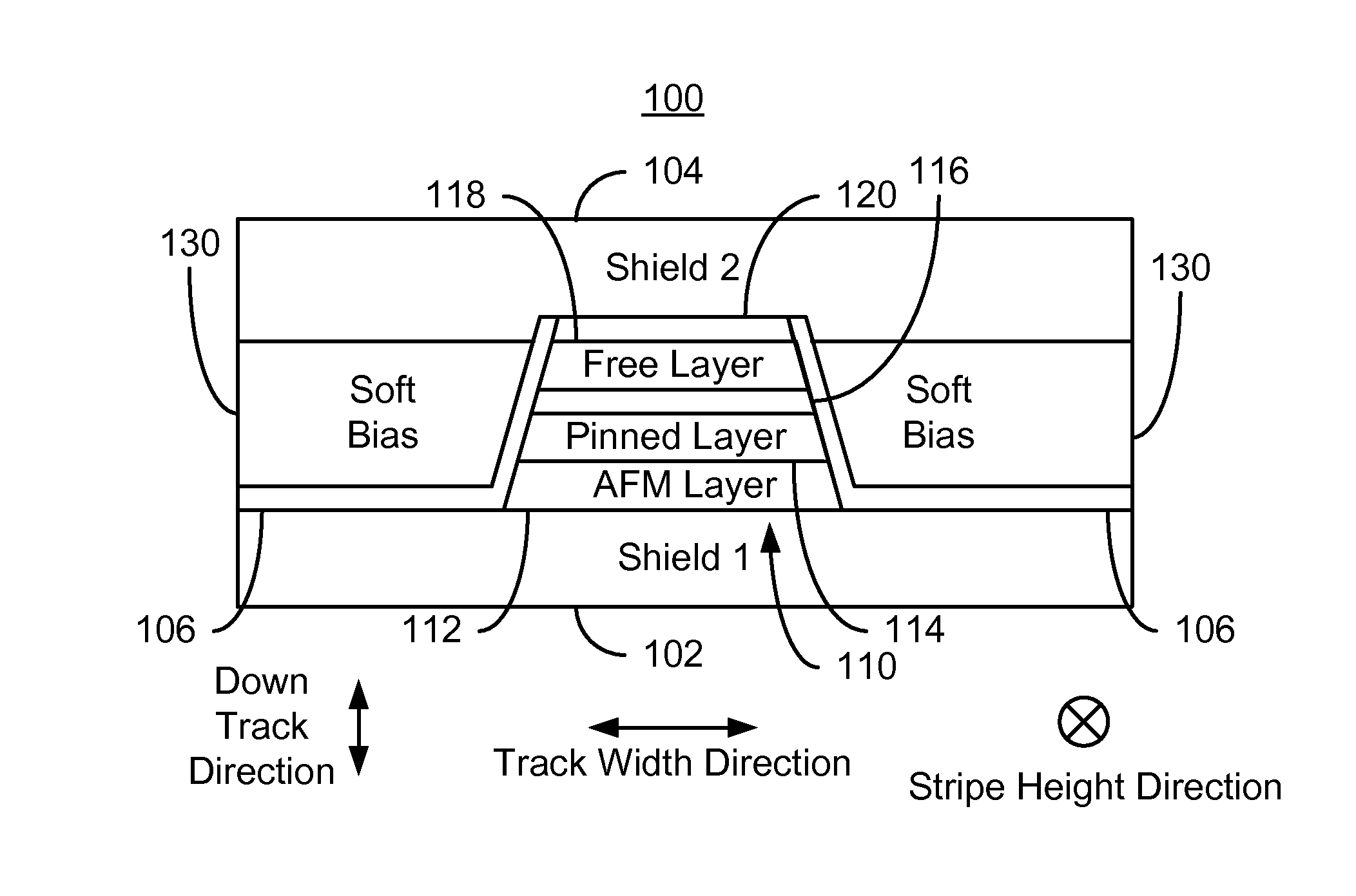
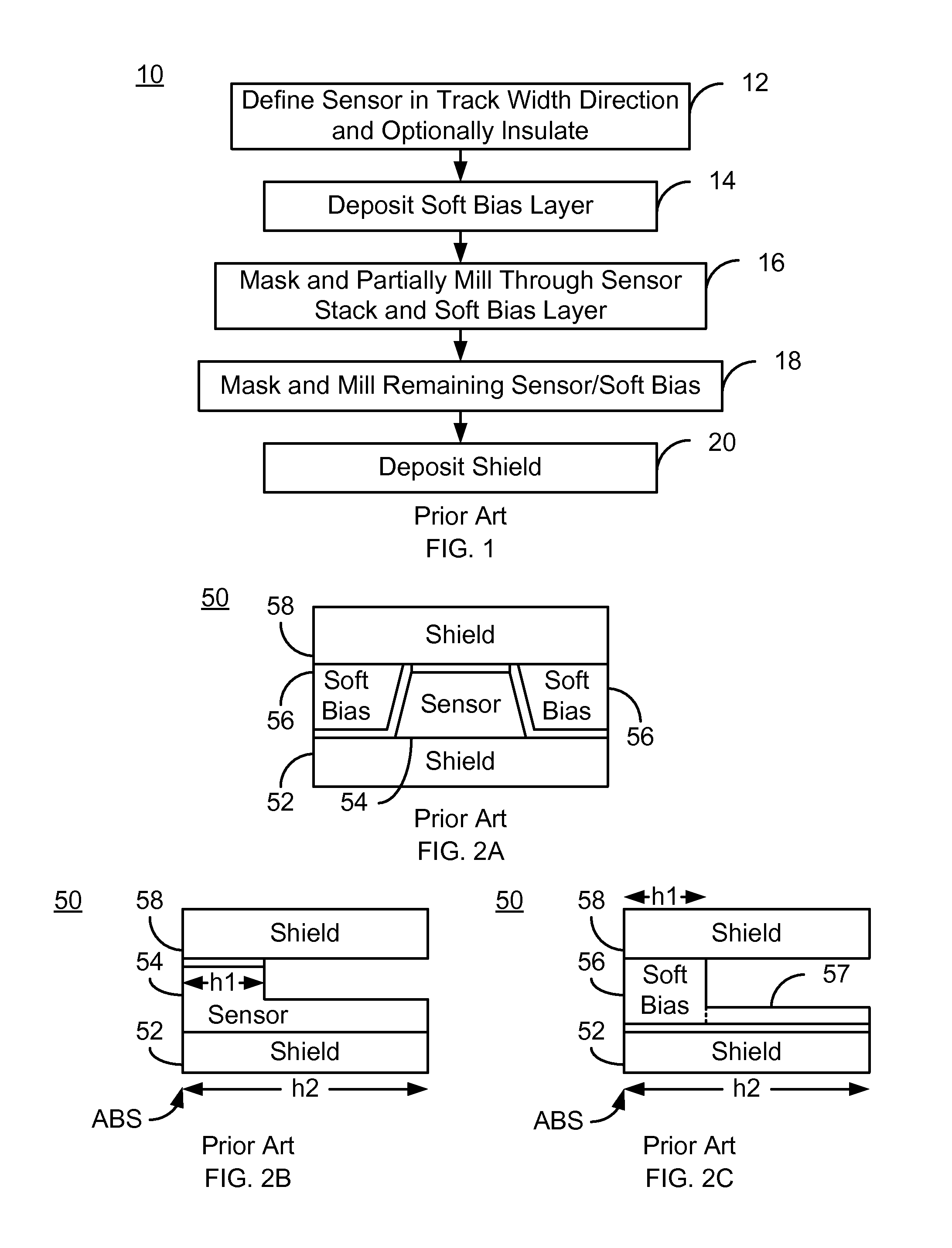
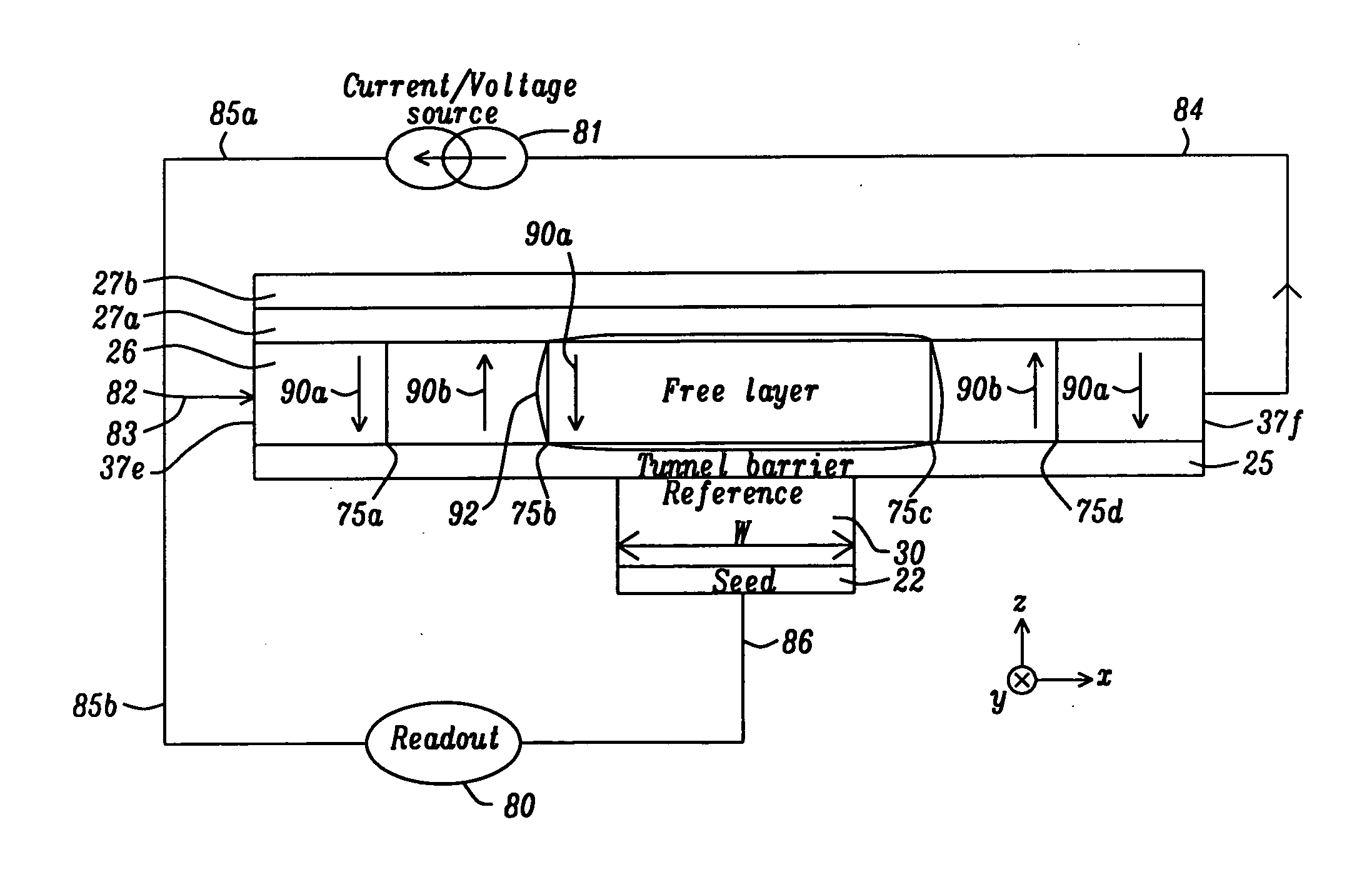
A method and system provide a magnetic transducer having an air-bearing surface (ABS). The magnetic transducer includes a first shield, a read sensor, at least one soft magnetic bias structure and a second shield. The read sensor includes a sensor layer, a pinned layer and edge(s). The sensor layer has a first stripe height in a stripe height direction perpendicular to the ABS. The pinned layer has a second stripe height in the stripe height direction. The second stripe height is greater than the first stripe height. The soft magnetic bias structure(s) are adjacent to the edge(s) of the sensor. A portion of the soft magnetic bias structure(s) is further from the ABS than the first stripe height. The read sensor is between the first shield and the second shield. The soft magnetic bias structure(s) extend to the second shield.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
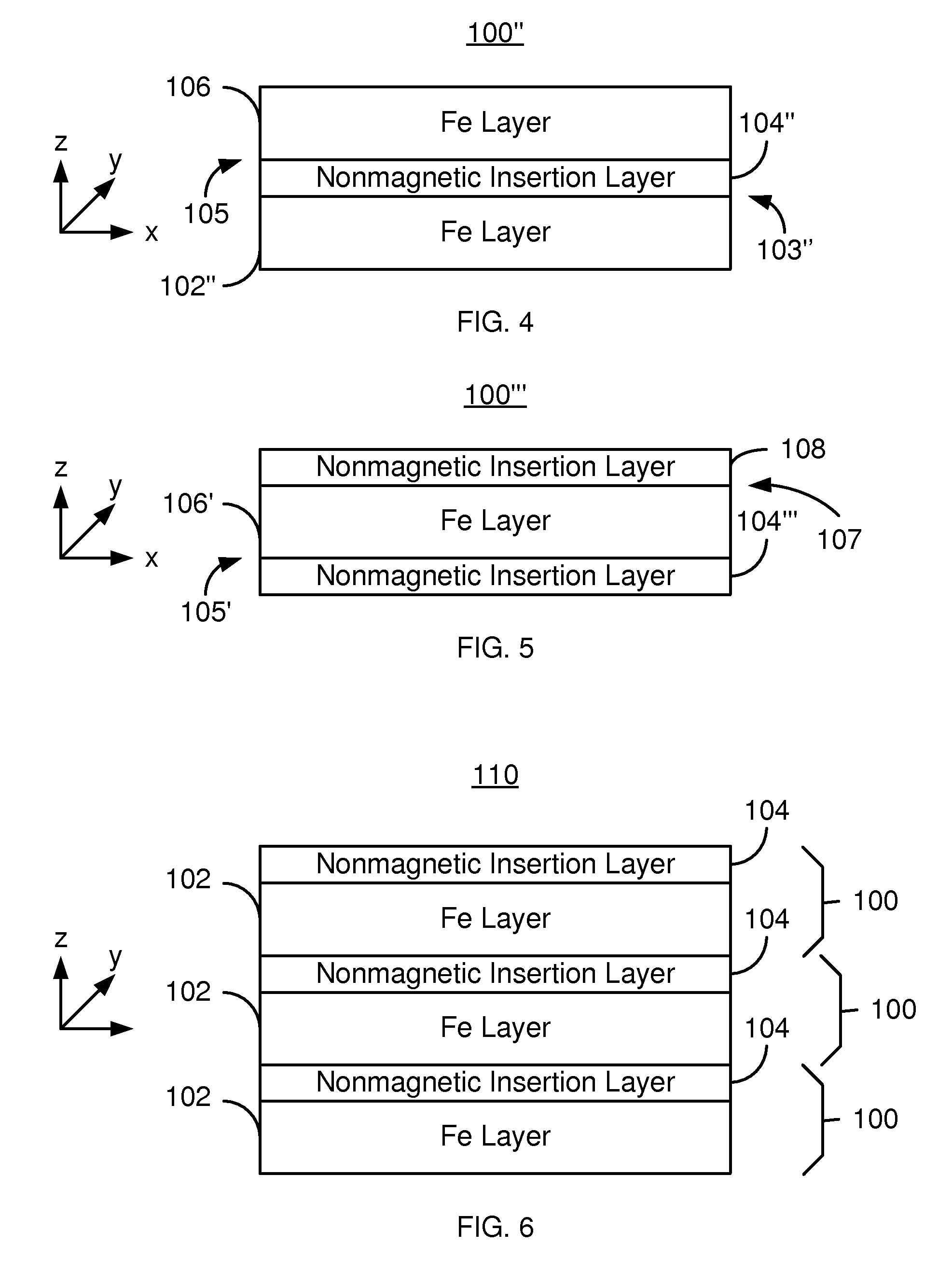
Magnetic junctions having insertion layers and magnetic memories using the magnetic junctions
ActiveUS20140264671A1Galvano-magnetic material selectionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMagnetic memoryNon magnetic
A method and system for providing a magnetic junction usable in a magnetic device are described. The magnetic junction includes a reference layer, a nonmagnetic spacer layer and a free layer. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the reference layer and the free layer. The magnetic junction is configured such that the free layer is switchable between a plurality of stable magnetic states when a write current is passed through the magnetic junction. A portion of the magnetic junction includes at least one magnetic substructure. The magnetic substructure includes at least one Fe layer and at least one nonmagnetic insertion layer. The at least one Fe layer shares at least one interface with the at least one nonmagnetic insertion layer. Each of the at least one nonmagnetic insertion layer consists of at least one of W, I, Hf, Bi, Zn, Mo, Ag, Cd, Os and In.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Memory system having thermally stable perpendicular magneto tunnel junction (MTJ) and a method of manufacturing same
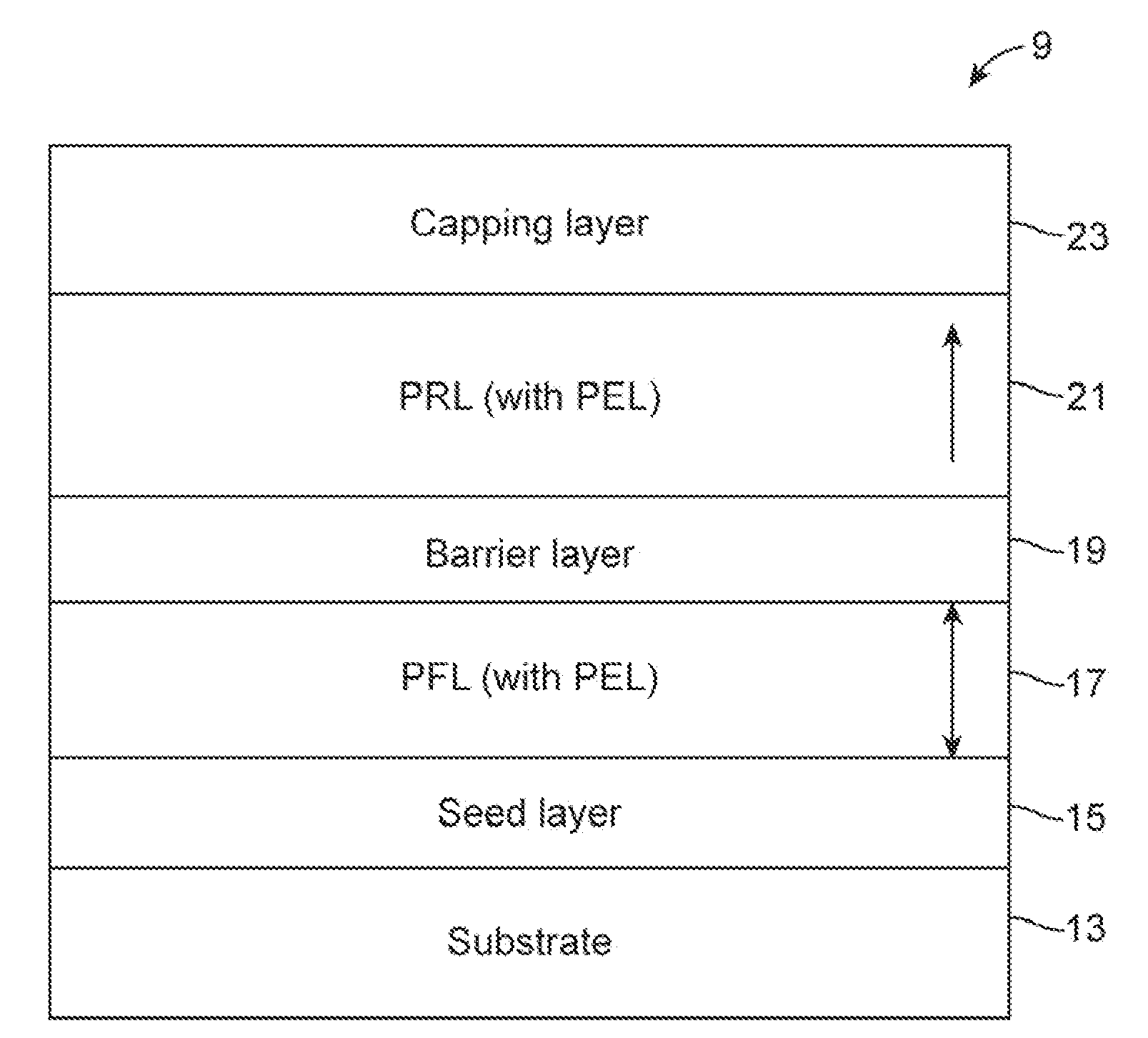
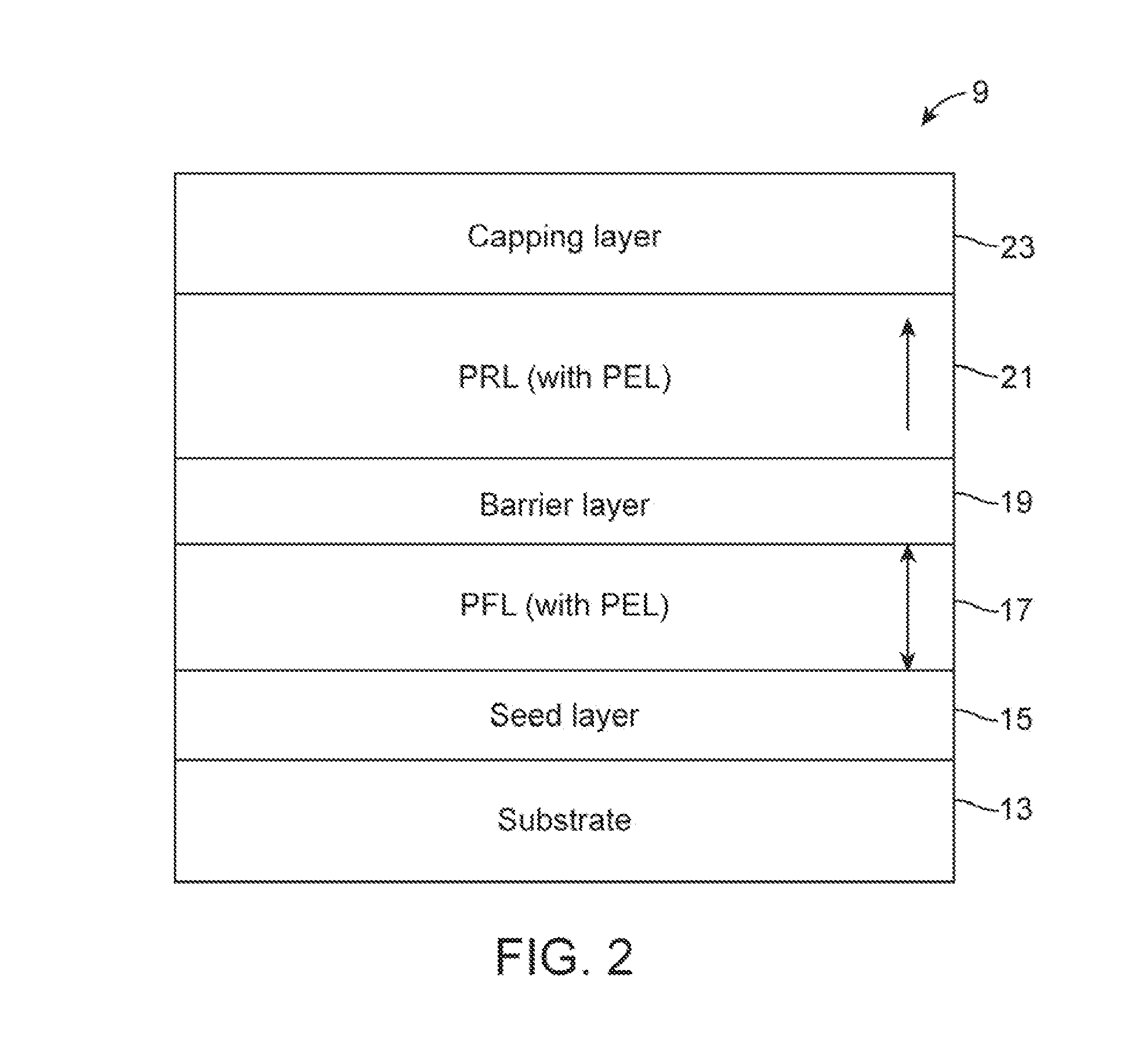
InactiveUS20120146167A1Increase stiffnessReduced dampingMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device detailsRandom access memoryMagneto
A spin-torque transfer magnetic random access memory (STTMRAM) element employed to store a state based on the magnetic orientation of a free layer, the STTMRAM element is made of a first perpendicular free layer (PFL) including a first perpendicular enhancement layer (PEL). The first PFL is formed on top of a seed layer. The STTMRAM element further includes a barrier layer formed on top of the first PFL and a second perpendicular reference layer (PRL) that has a second PEL, the second PRL is formed on top of the barrier layer. The STTMRAM element further includes a capping layer that is formed on top of the second PRL.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
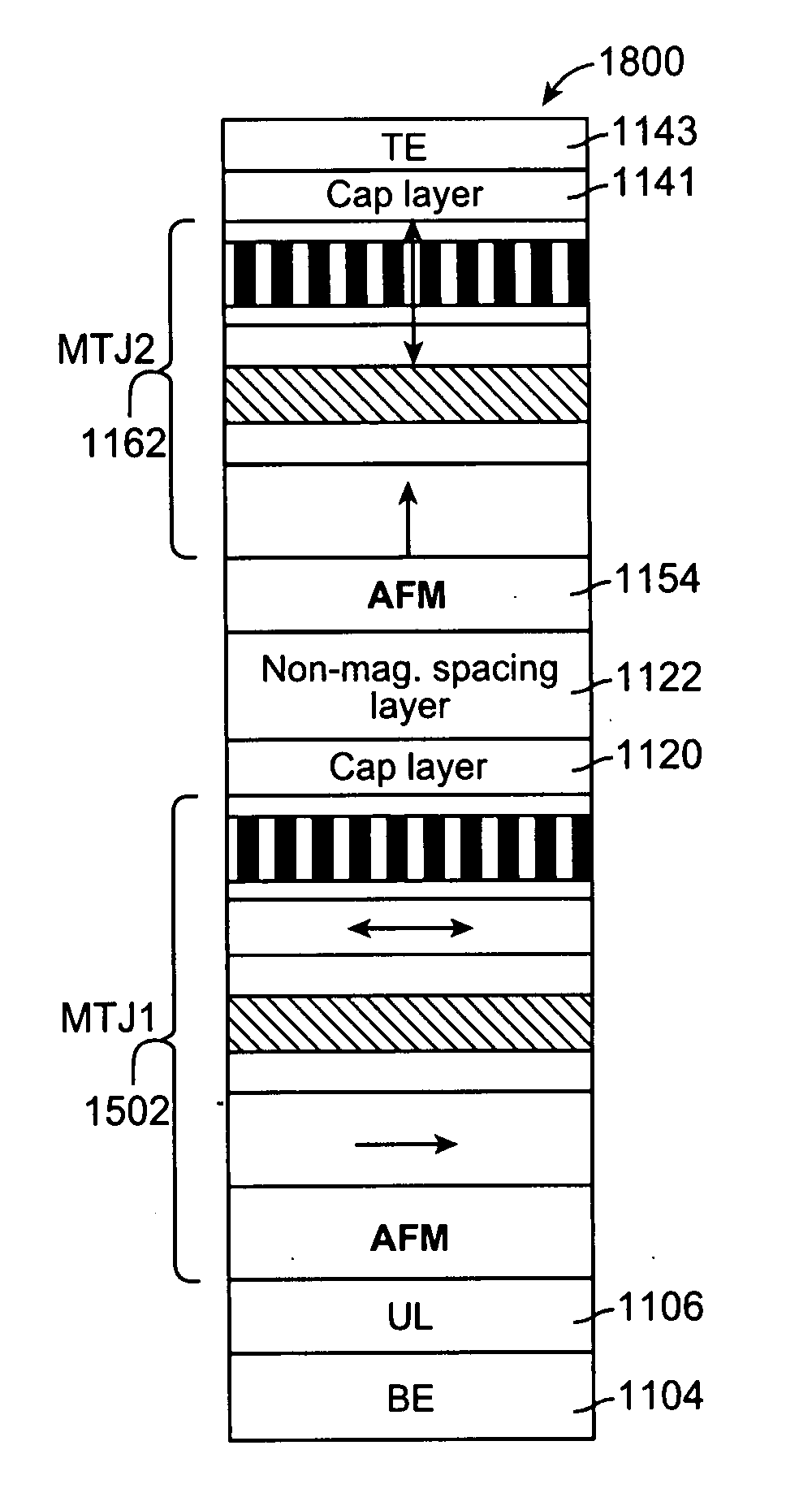
Multi-state spin-torque transfer magnetic random access memory
InactiveUS20090218645A1Reduced switching currentImprove thermal stabilityNanotechMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsMagnetic anisotropyRandom access memory
A multi-state spin-torque transfer magnetic random access memory (STTMRAM) is formed on a film and includes a first magnetic tunneling junctions (MTJ) having a first fixed layer, a first sub-magnetic tunnel junction (sub-MTJ) layer and a first free layer. The first fixed layer and first free layer each have a first magnetic anisotropy. The STTMRAM further includes a non-magnetic spacing layer formed on top of the first MTJ layer and a second MTJ formed on top of the non-magnetic spacing layer. The second MTJ has a second fixed layer, a second sub-MTJ layer and a second free layer. The second fixed and second free layers each have a second magnetic anisotropy, wherein at least one of the first or second magnetic anisotropy is perpendicular to the plane of the film.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Joystick and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090212766A1Manual control with multiple controlled membersControlling membersJoystickEngineering
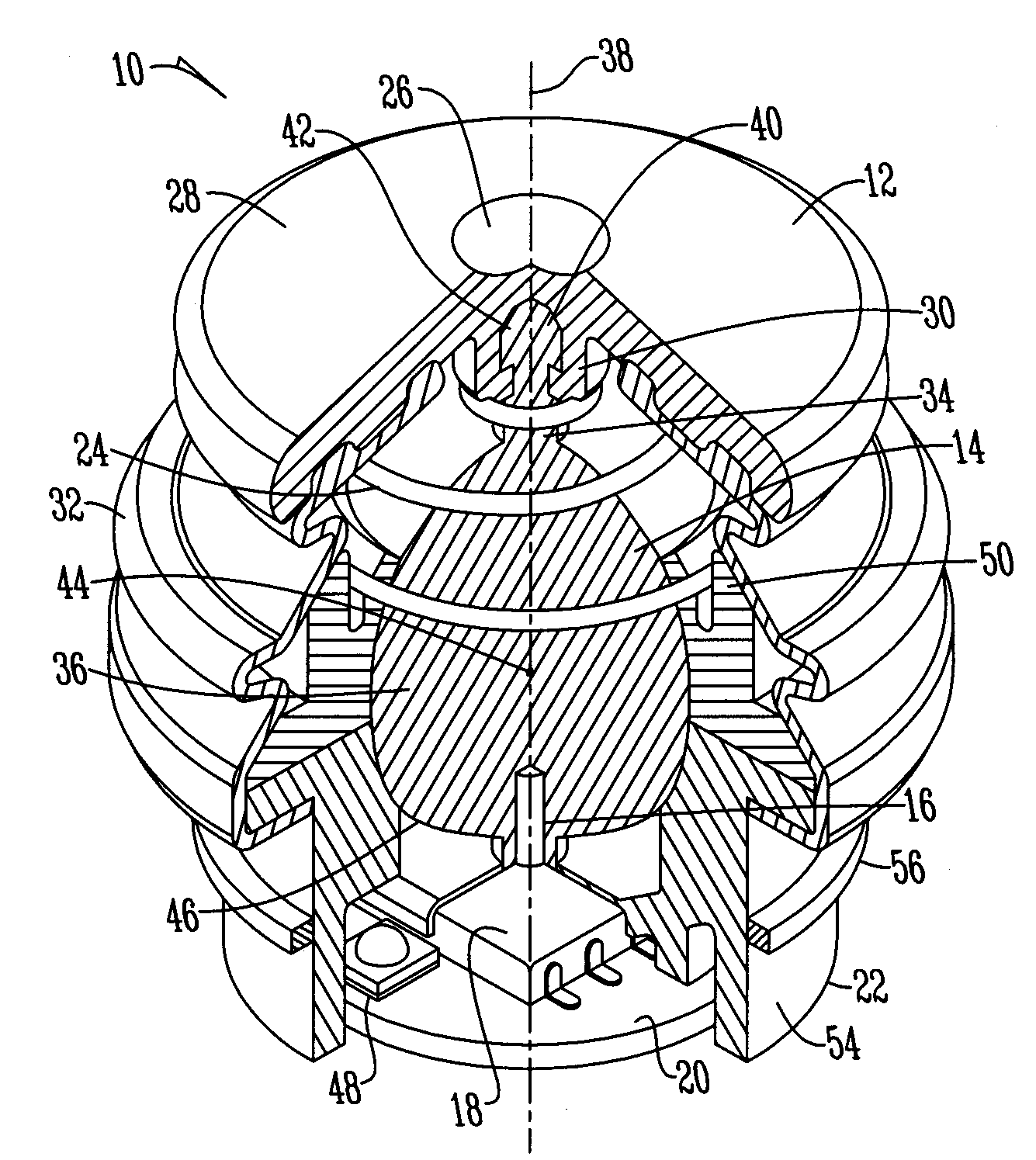
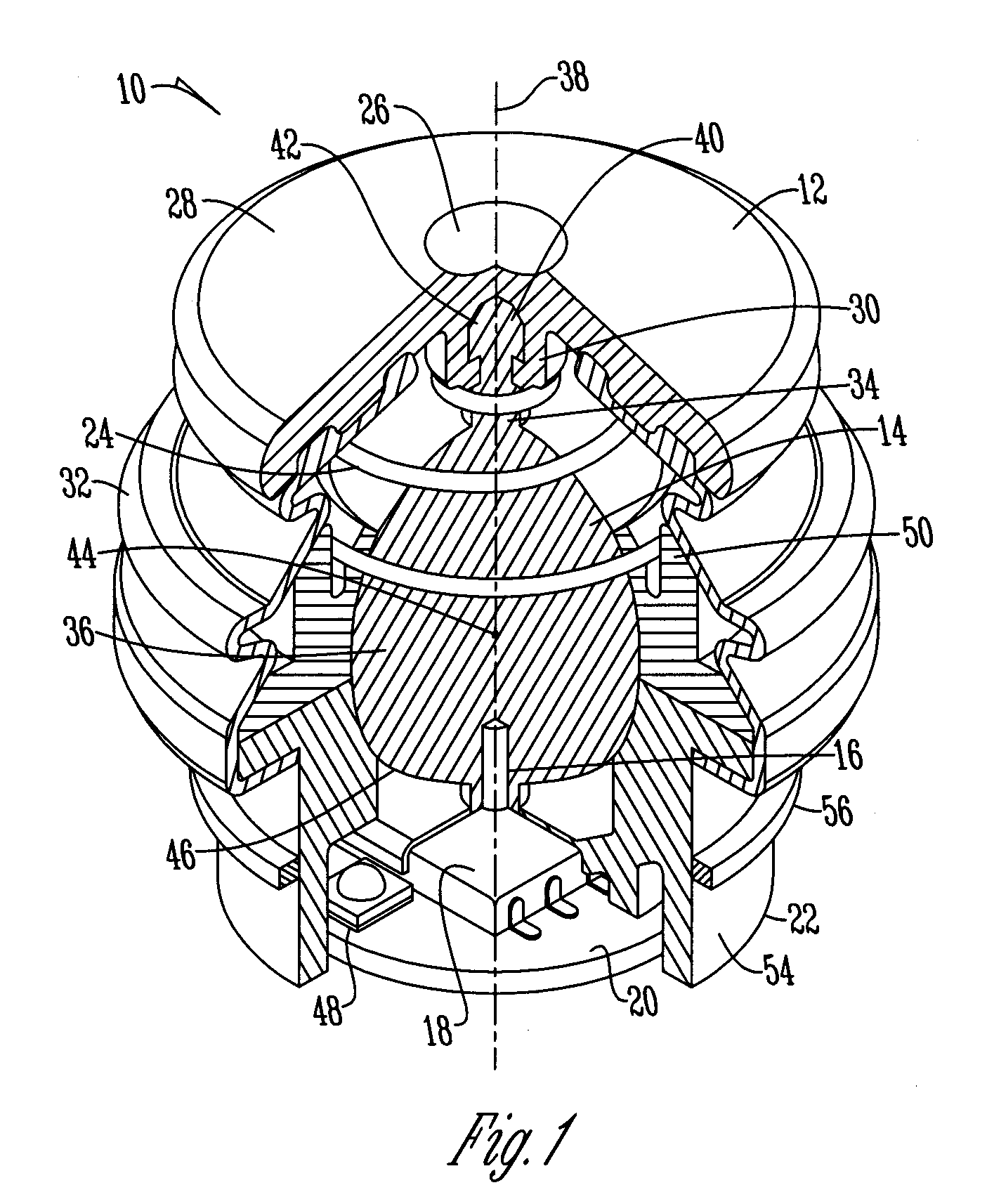
A joystick having a movable member that includes a shaft portion and a spherical portion wherein the shaft portion has a diameter less than the spherical portion. An actuating member is secured to the shaft portion of the movable member to provide actuation of the movable member. A magnet is disposed within the spherical portion of the movable member and positioned adjacent a three axis sensor such that the magnet moves in a hemispherical pattern along the three axis sensor to operate a device.
Owner:DANFOSS POWER SOLUTIONS INC
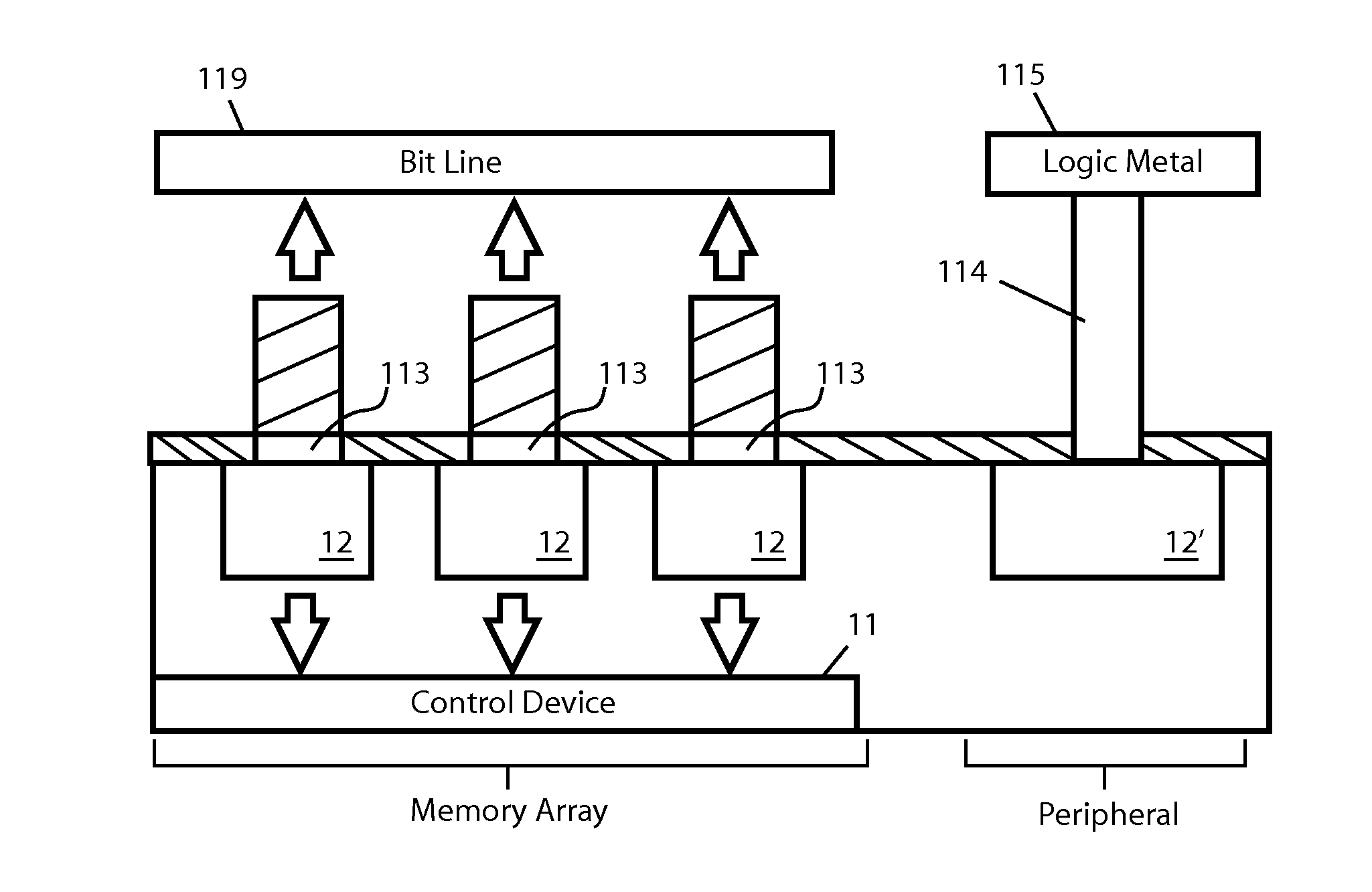
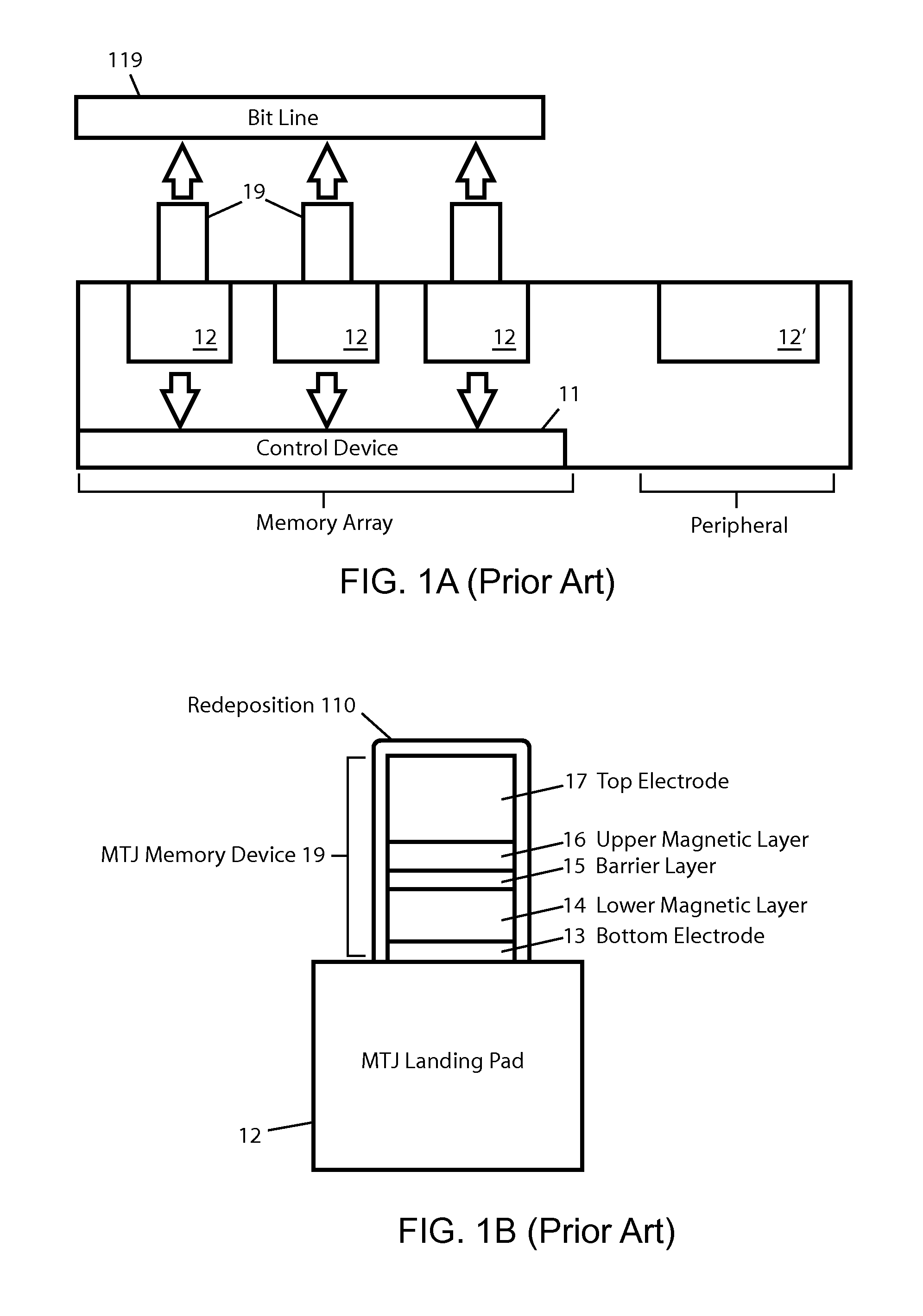
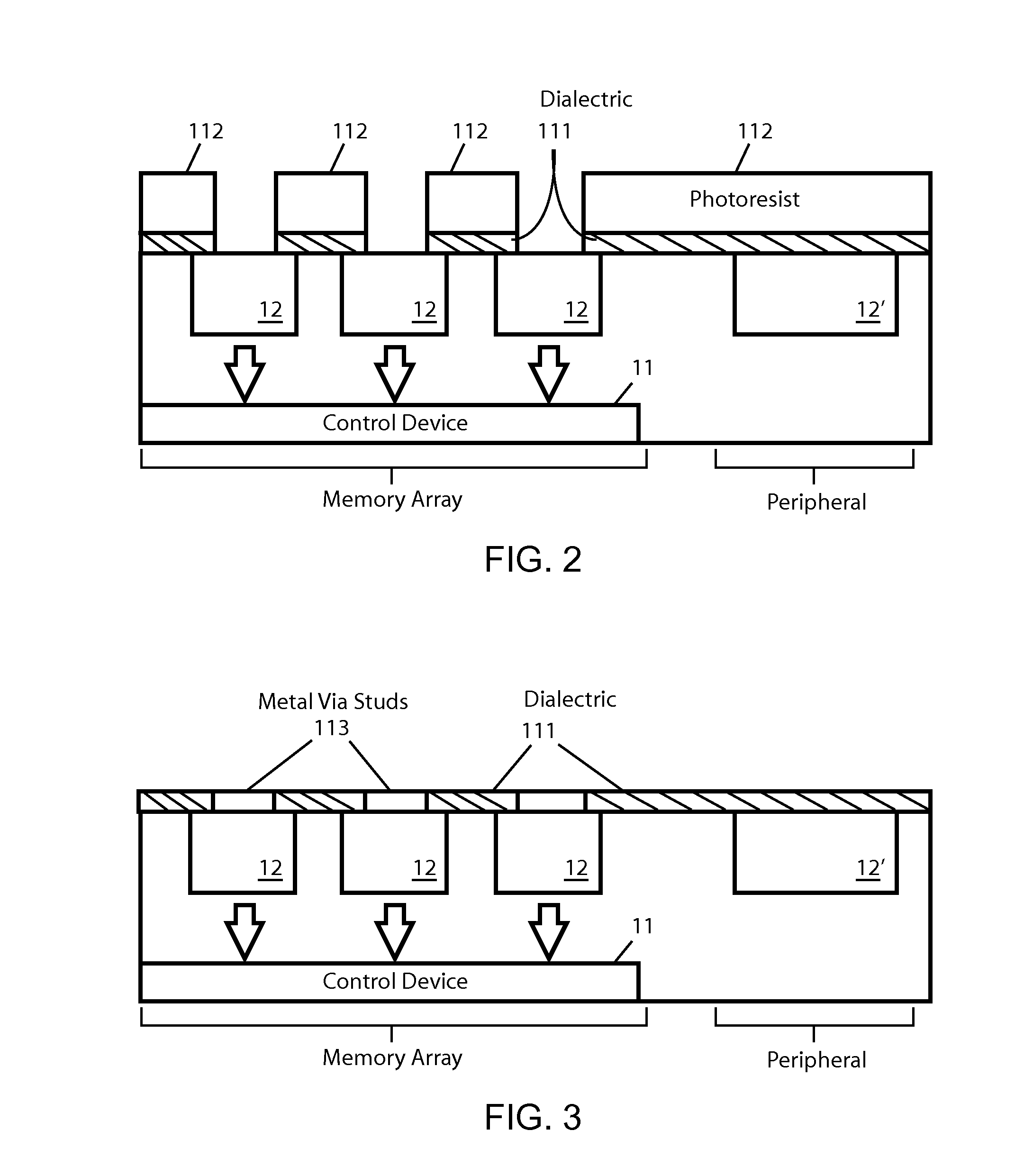
Redeposition Control in MRAM Fabrication Process
ActiveUS20130341801A1Reduce and eliminate redeposition materialReduce materialSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEtchingEngineering
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Magnetic tunnel junction for MRAM device
InactiveUS20150279904A1Improve performanceSwitching currentMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesTantalum nitrideSoftware engineering
A magnetoresistive random-access memory device with a magnetic tunnel junction stack having a significantly improved performance of the free layer in the magnetic tunnel junction structure. The memory device includes an antiferromagnetic structure and a magnetic tunnel junction structure disposed on the antiferromagnetic structure. The magnetic tunnel junction structure includes a reference layer and a free layer with a barrier layer sandwiched therebetween. Furthermore, a capping layer including a tantalum nitride film is disposed on the free layer of the magnetic tunnel junction structure.
Owner:SPIN MEMORY INC
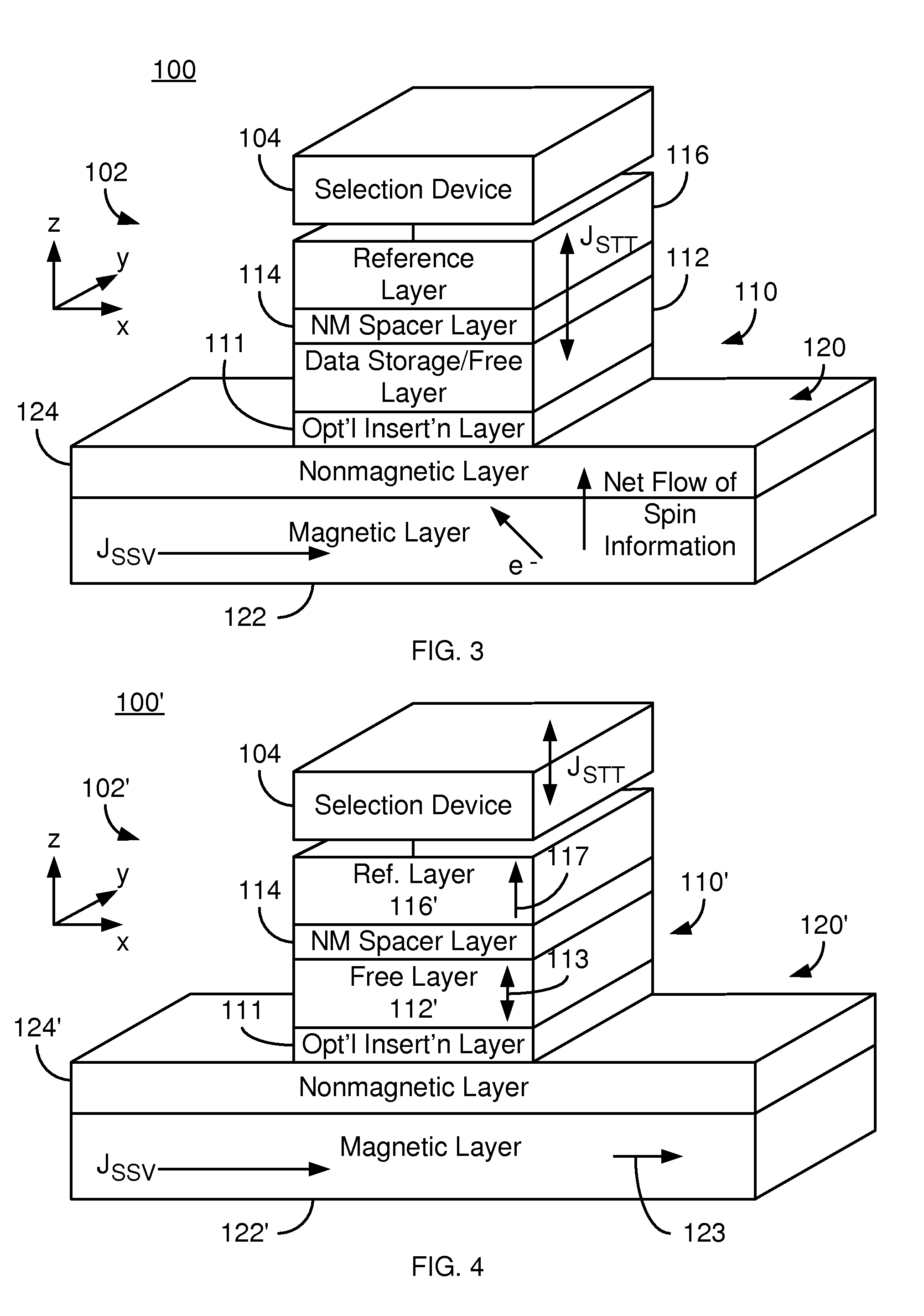
Method and system for providing magnetic memories switchable using spin accumulation and selectable using magnetoelectric devices
A magnetic memory is described. In one aspect, the magnetic memory includes magnetic junctions and at least one semi-spin valve (SSV) line adjacent to the magnetic junctions. Each magnetic junction includes a magnetic free layer. The SSV line(s) include a ferromagnetic layer and a nonmagnetic layer between the ferromagnetic layer and the magnetic junctions. The SSV line(s) are configured to exert a spin accumulation induced torque on at least a portion of the magnetic junctions due to an accumulation of spin polarized current carriers from a current that is substantially in-plane. The free layer is configured to be written using at least the spin accumulation induced torque. In another aspect, the magnetic memory includes magnetic memory cells and at least one spin torque (ST) line that is analogous to the SSV line. Each magnetic memory cell includes magnetic junction(s) analogous to those above and magnetoelectric selection device(s).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
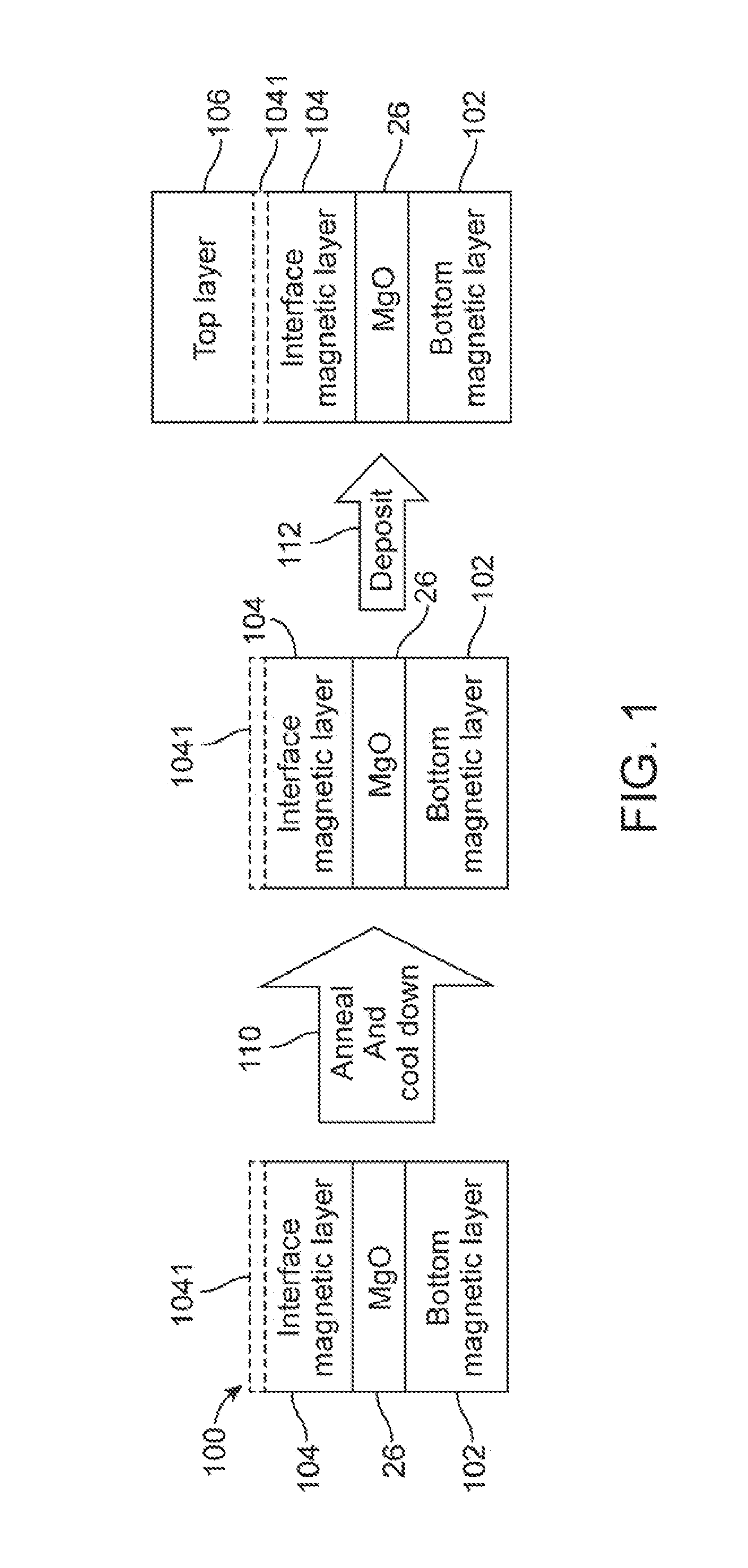
Co/Ni Multilayers with Improved Out-of-Plane Anisotropy for Magnetic Device Applications
ActiveUS20120299134A1Raise the ratioStrong textureMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionAlloyElectron
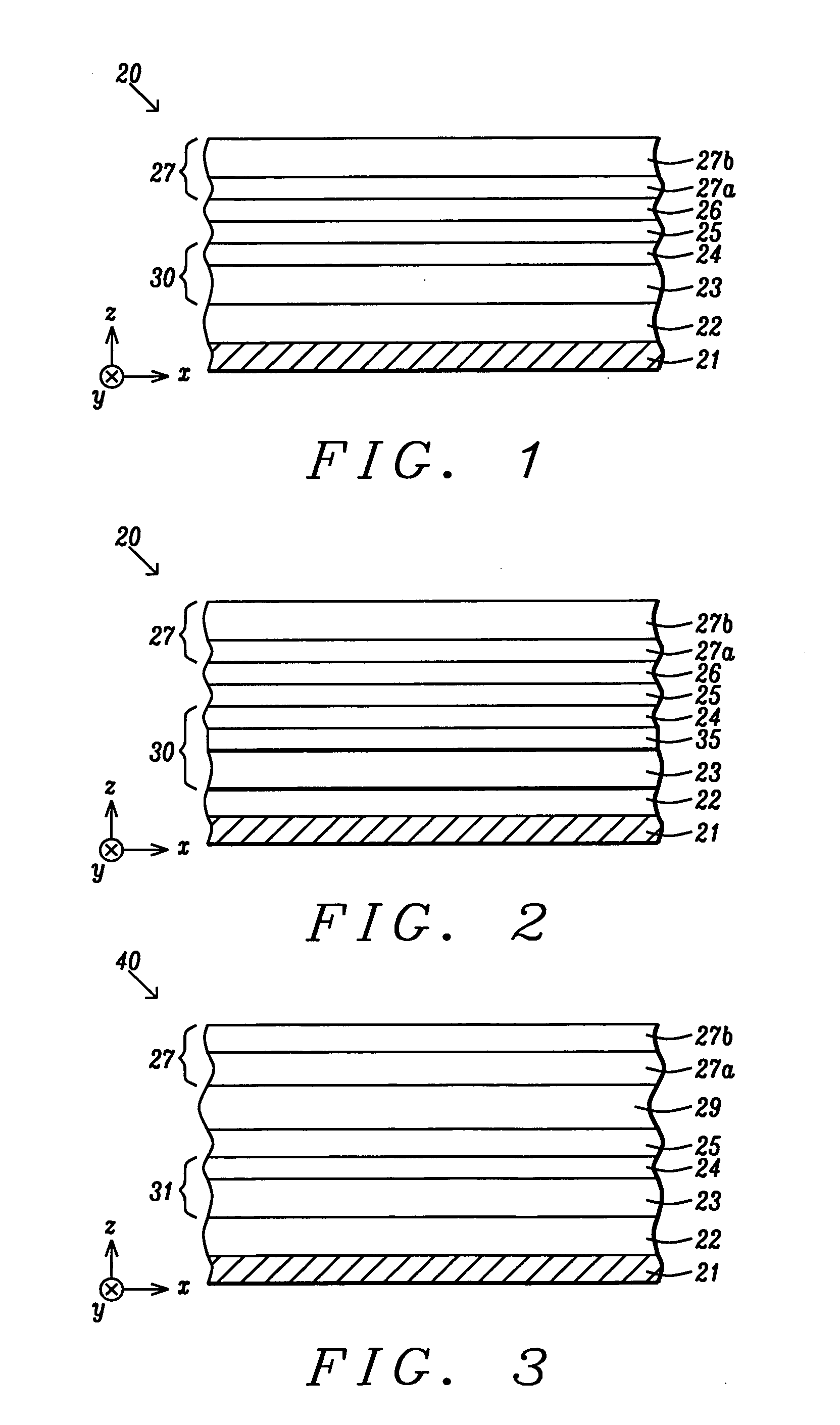
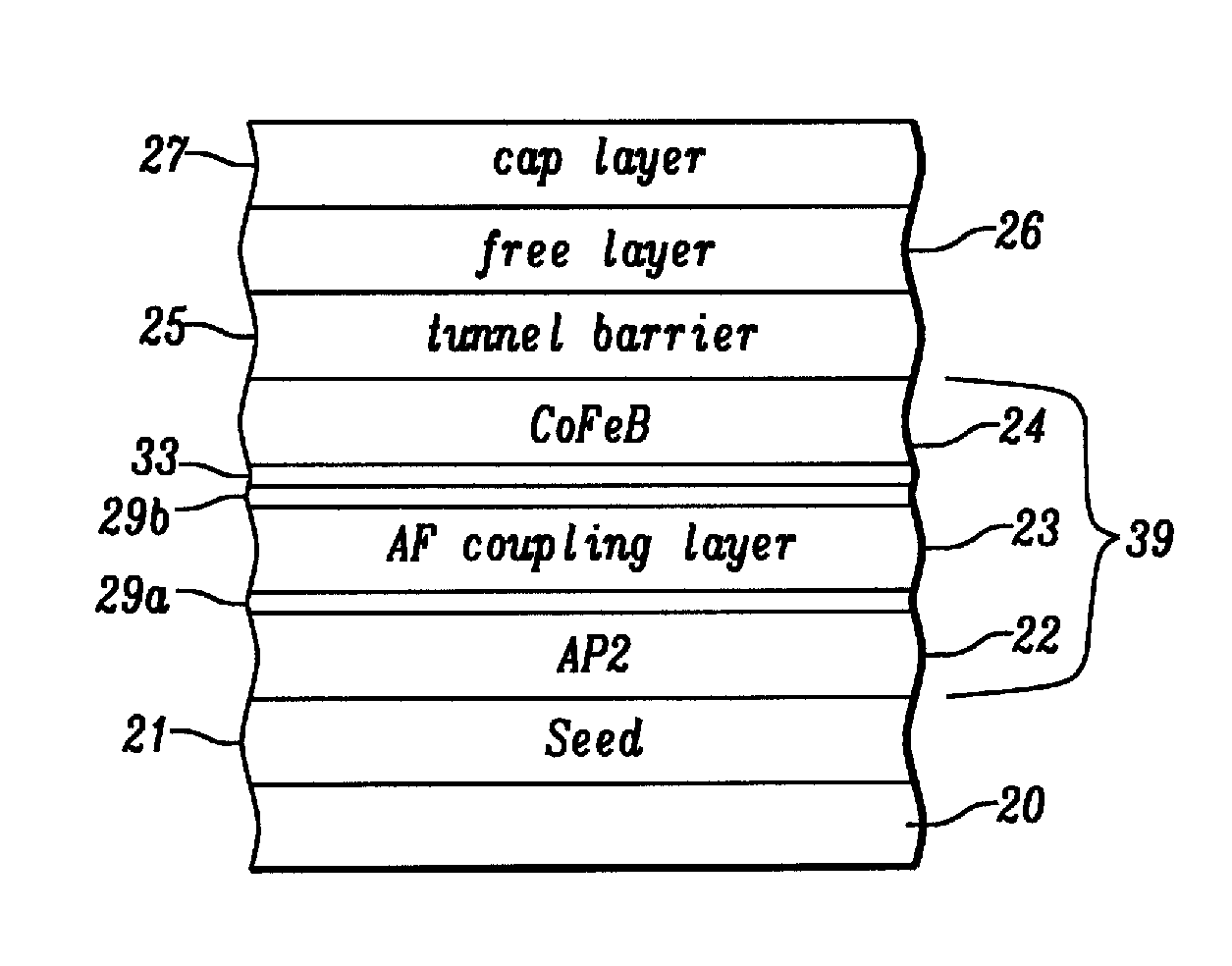
A MTJ for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a thin seed layer that enhances perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying laminated layer with a (Co / X)n or (CoX)n composition where n is from 2 to 30, X is one of V, Rh, Ir, Os, Ru, Au, Cr, Mo, Cu, Ti, Re, Mg, or Si, and CoX is a disordered alloy. A CoFeB layer may be formed between the laminated layer and a tunnel barrier layer to serve as a transitional layer between a (111) laminate and (100) MgO tunnel barrier. The laminated layer may be used as a reference layer, dipole layer, or free layer in a MTJ. Annealing between 300° C. and 400° C. may be used to further enhance PMA in the laminated layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetic tunnel junction structure for MRAM device
ActiveUS20160087193A1Increase TMR valueOptimized free layer magnetic propertiesNanomagnetismSolid-state devicesTantalum nitridePolarizer
A magnetic tunnel junction stack is provided that includes nonmagnetic spacer layers between the free layer and the polarizer layer formed from magnesium oxide and tantalum nitride materials that balance the spin torques acting on the free layer. The design provided enables a deterministic final state for the storage layer and significantly improves the tunneling magnetoresistance value and switching characteristics of the magnetic tunnel junction for MRAM applications.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION CAYMAN INC
Magnetic stack having assist layer
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
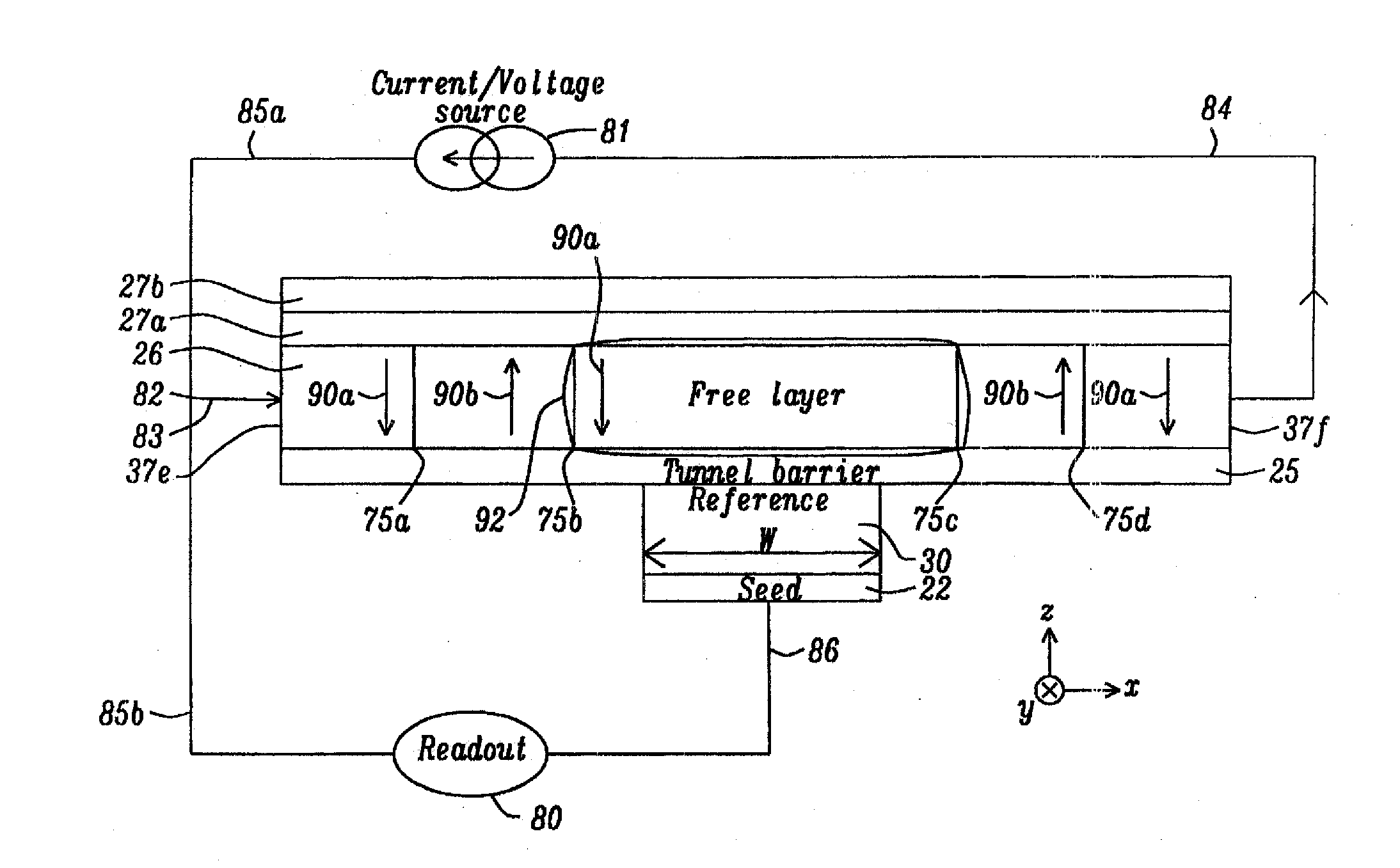
Spin-torque magnetoresistive memory element and method of fabricating same
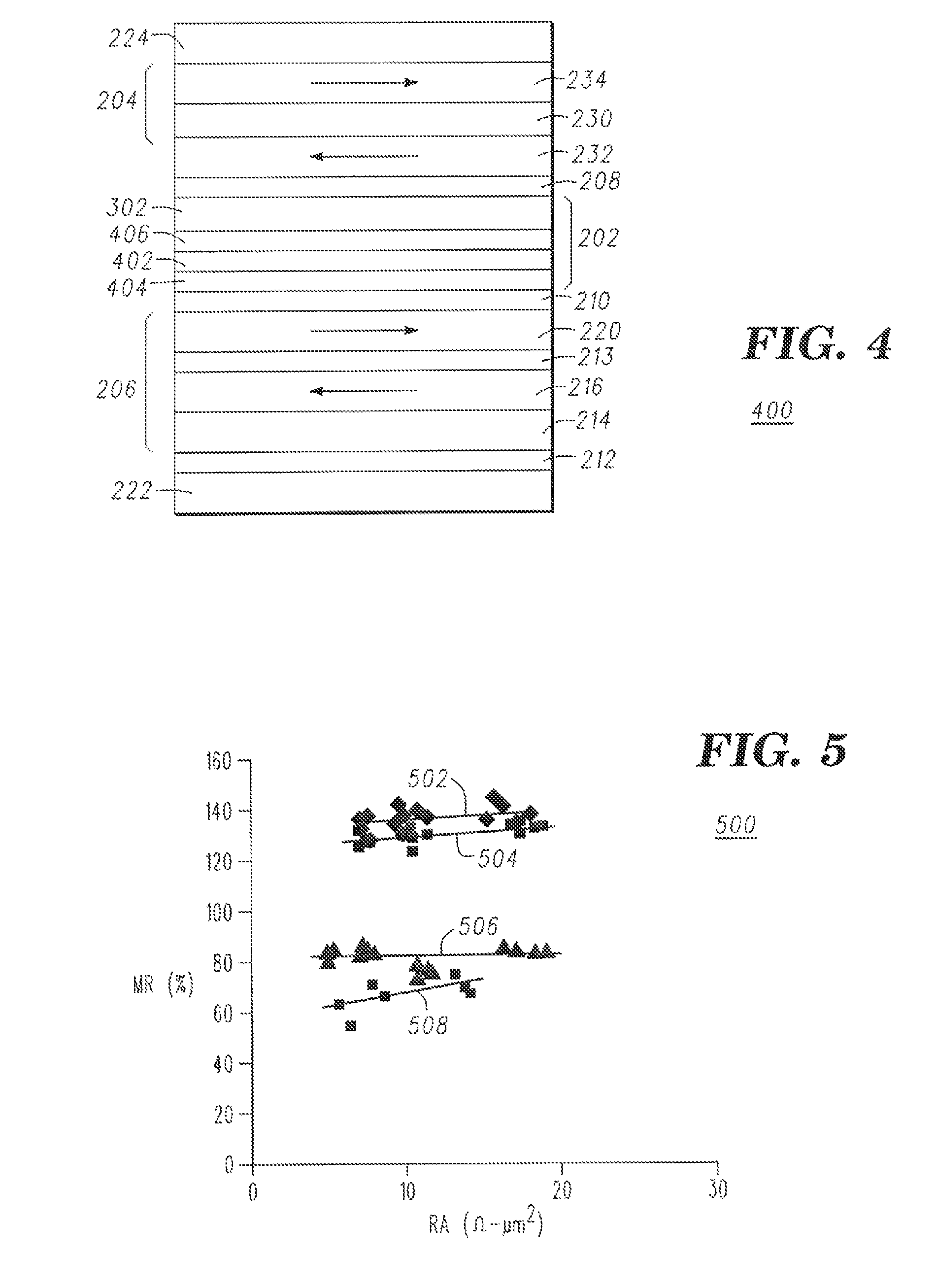
A spin-torque magnetoresistive memory element has a high magnetoresistance and low current density. A free magnetic layer is positioned between first and second spin polarizers. A first tunnel barrier is positioned between the first spin polarizer and the free magnetic layer and a second tunnel barrier is positioned between the second spin polarizer and the free magnetic layer. The magnetoresistance ratio of the second tunnel barrier has a value greater than double the magnetoresistance ratio of the first tunnel barrier.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
Co/Ni multilayers with improved out-of-plane anisotropy for magnetic device applications
ActiveUS20120286382A1Raise the ratioStrong textureMagnetic measurementsMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsOptoelectronicsMagnetic layer
A MTJ for a spintronic device is disclosed and includes a thin seed layer that enhances perpendicular magnetic anisotropy (PMA) in an overlying laminated layer with a (Co / Ni)n composition or the like where n is from 2 to 30. The seed layer is preferably NiCr, NiFeCr, Hf, or a composite thereof with a thickness from 10 to 100 Angstroms. Furthermore, a magnetic layer such as CoFeB may be formed between the laminated layer and a tunnel barrier layer to serve as a transitional layer between a (111) laminate and (100) MgO tunnel barrier. There may be a Ta insertion layer between the CoFeB layer and laminated layer to promote (100) crystallization in the CoFeB layer. The laminated layer may be used as a reference layer, dipole layer, or free layer in a MTJ. Annealing between 300° C. and 400° C. may be used to further enhance PMA in the laminated layer.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Minimal thickness synthetic antiferromagnetic (SAF) structure with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy for STT-MRAM
ActiveUS8860156B2Raise the ratioTransformersGalvano-magnetic material selectionCouplingMagnetization
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Magnetic Field Sensors and Methods for Fabricating the Magnetic Field Sensors
ActiveUS20100141249A1Improve protectionPrevent over-boostingLamination ancillary operationsSynthetic resin layered productsLead frameCondensed matter physics
Magnetic field sensors and associated methods of manufacturing the magnetic field sensors include molded structures to encapsulate a magnetic field sensing element and an associated die attach pad of a lead frame and to also encapsulate or form a magnet or a flux concentrator.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Method for manufacturing MTJ memory device
ActiveUS9263667B1Reduce materialReduce harmMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionReactive-ion etchingPhotoresist
A method for manufacturing MTJ pillars for a MTJ memory device. The method includes depositing multiple MTJ layers on a substrate, depositing a hard mask on the substrate and coating a photoresist on the hard mask. Further, alternating steps of reactive ion etching and ion beam etching are performed to isolate MTJ pillars and expose side surfaces of the MTJ layers. An insulating layer is the applied to protect the side surfaces of the MTJ layers. A second insulating layer is deposited before the device is planarized using chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:INTEGRATED SILICON SOLUTION CAYMAN INC
Nonvolatile magnetic memory device
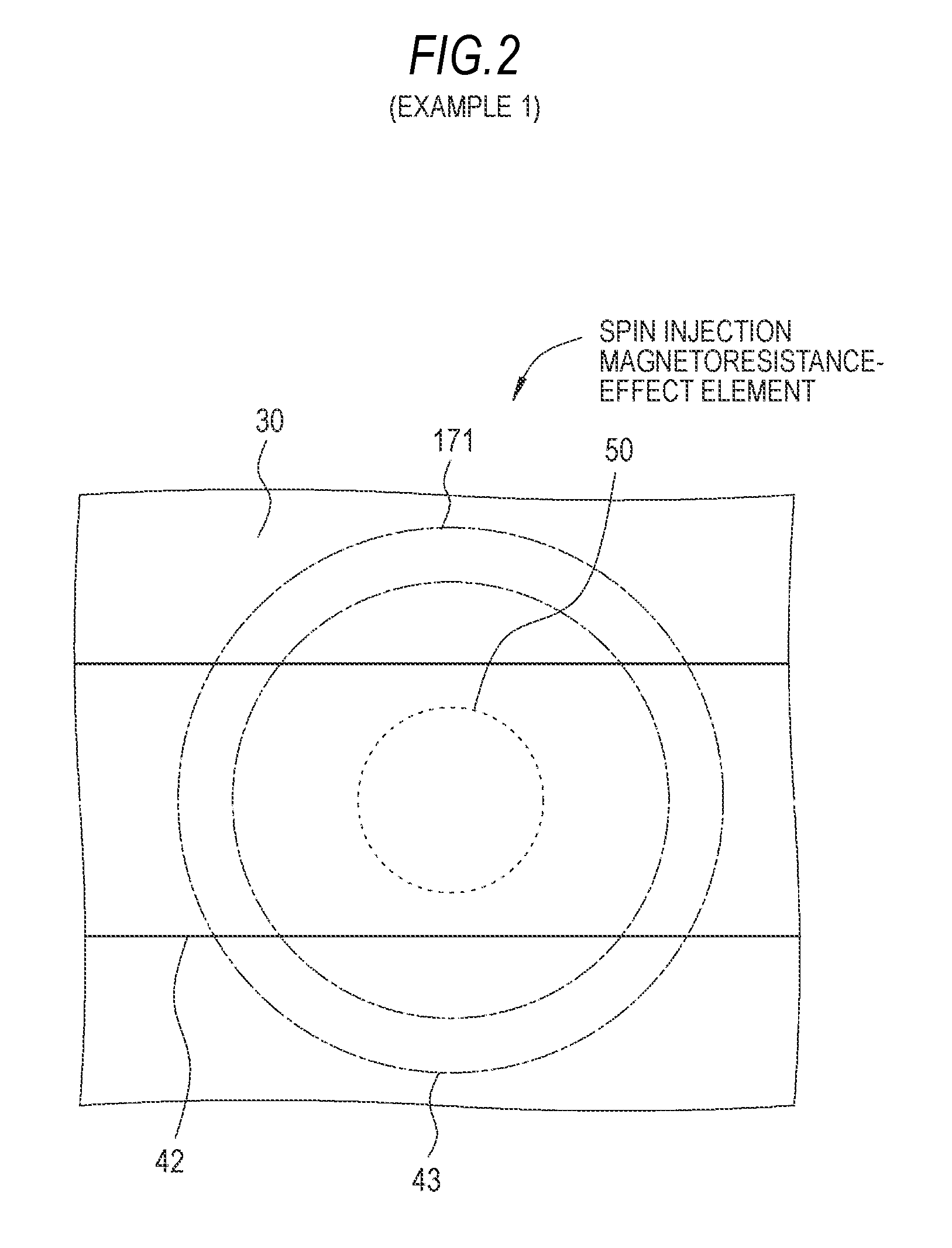
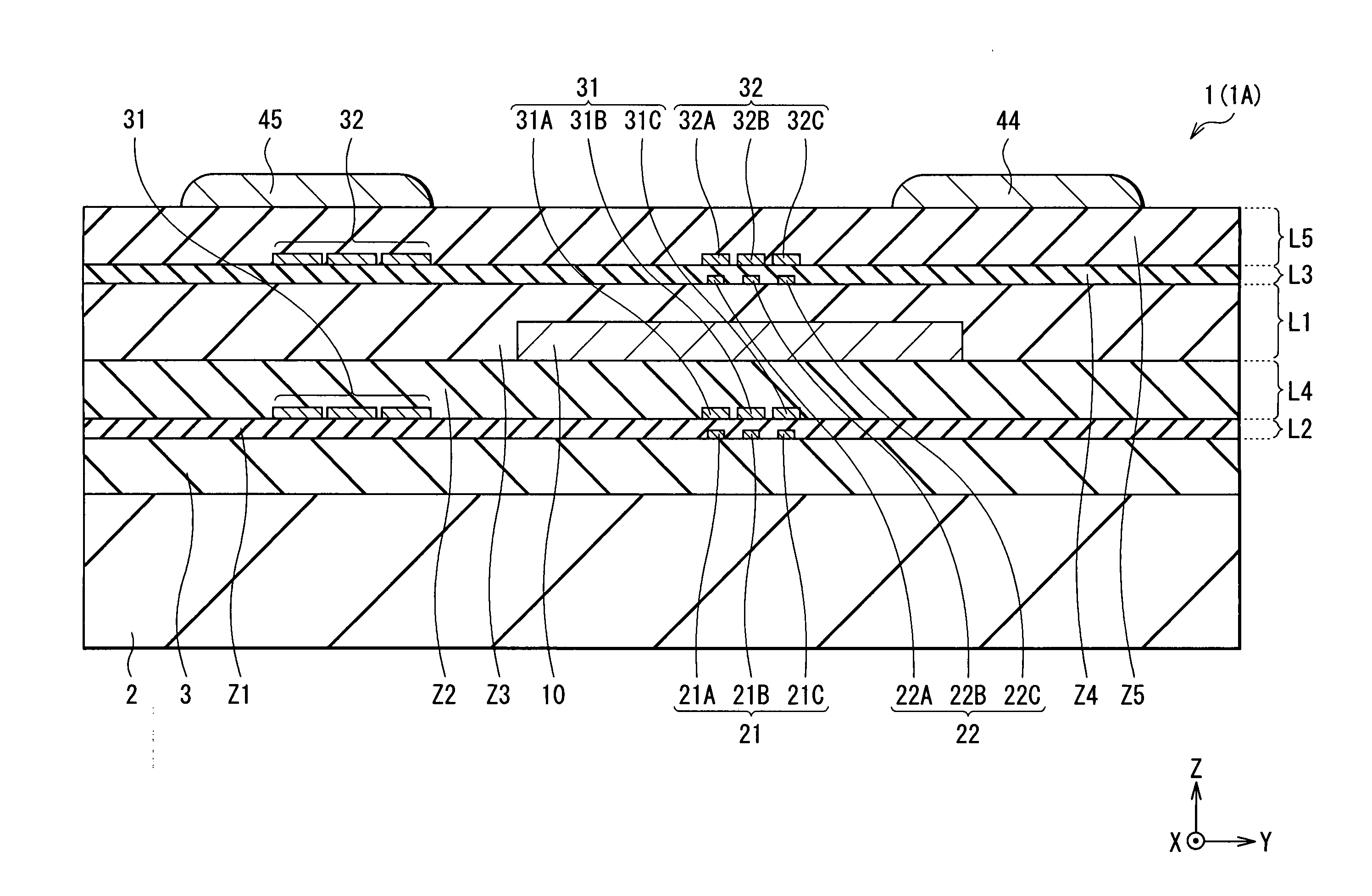
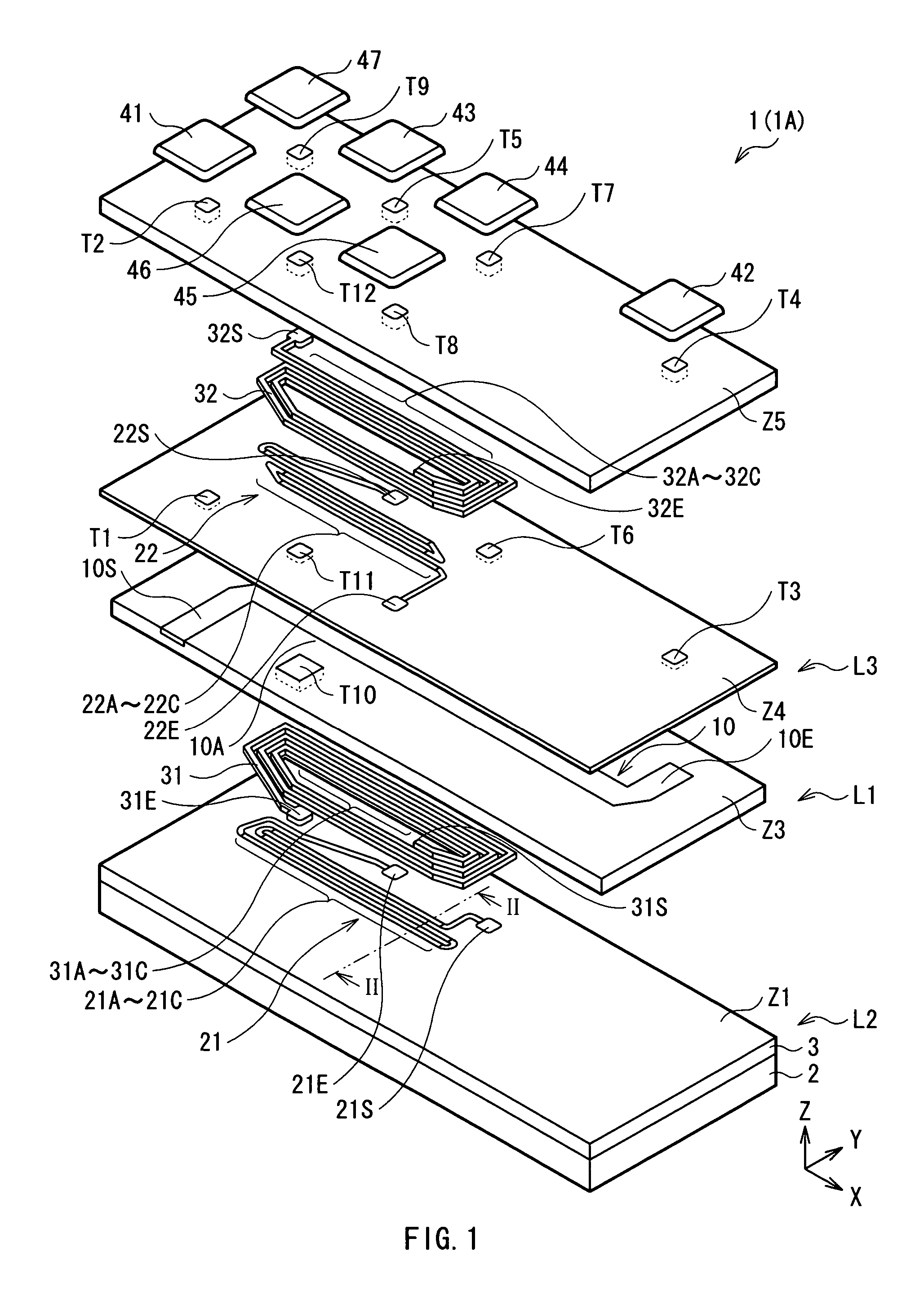
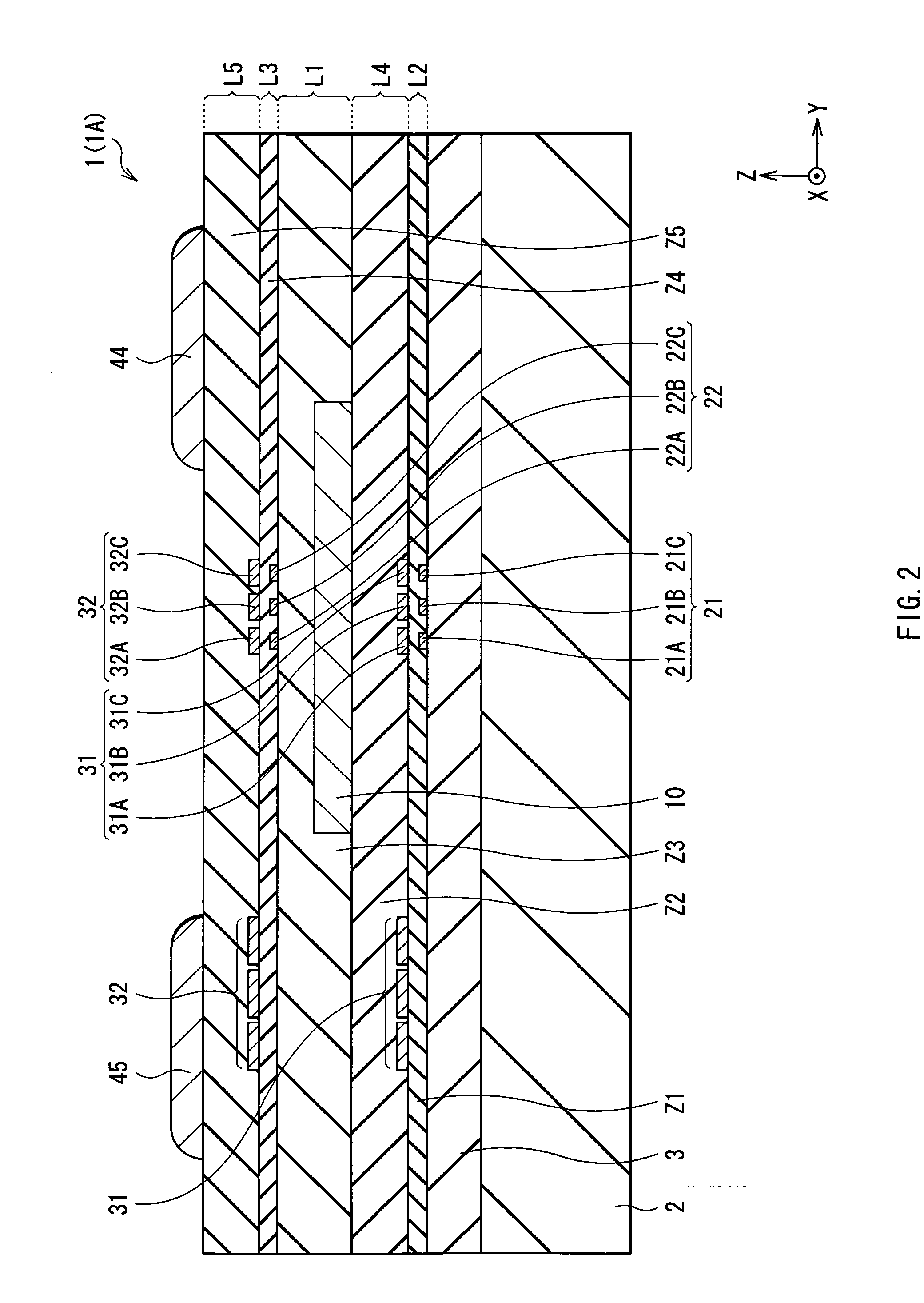
InactiveUS20100176472A1Reduce polarizabilitySmall MRNanomagnetismGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetizationMagnetic memory
A nonvolatile magnetic memory device having a magnetoresistance-effect element includes: (A) a laminated structure having a recording layer in which an axis of easy magnetization is oriented in a perpendicular direction; (B) a first wiring line electrically connected to a lower part of the laminated structure; and (C) a second wiring line electrically connected to an upper part of the laminated structure, wherein a high Young's modulus region having a Young's modulus of a higher value than that of a Young's modulus of a material forming the recording layer is provided close to a side surface of the laminated structure.
Owner:SONY CORP
Current sensor
ActiveUS20060091993A1High sensitivityImprove accuracyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceMagnetic reluctance
The present invention provides a current sensor capable of sensing a current to be detected with high precision. The current sensor includes a bus line which extends in an X direction at a first level and to which a current to be detected is supplied, a first magnetoresistive element extending in the X direction in a region corresponding to the bus line at a second level, and a second magnetoresistive element extending in the X direction in a region corresponding to the bus line at a third level. The resistance value of the first magnetoresistive element and that of the second magnetoresistive element change in directions opposite to the second level in accordance with a current magnetic field generated by the current to be detected. With the configuration, the first and second magnetoresistive elements and the bus line can be disposed close to each other. While realizing compactness, the current magnetic field can be detected with high sensitivity.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
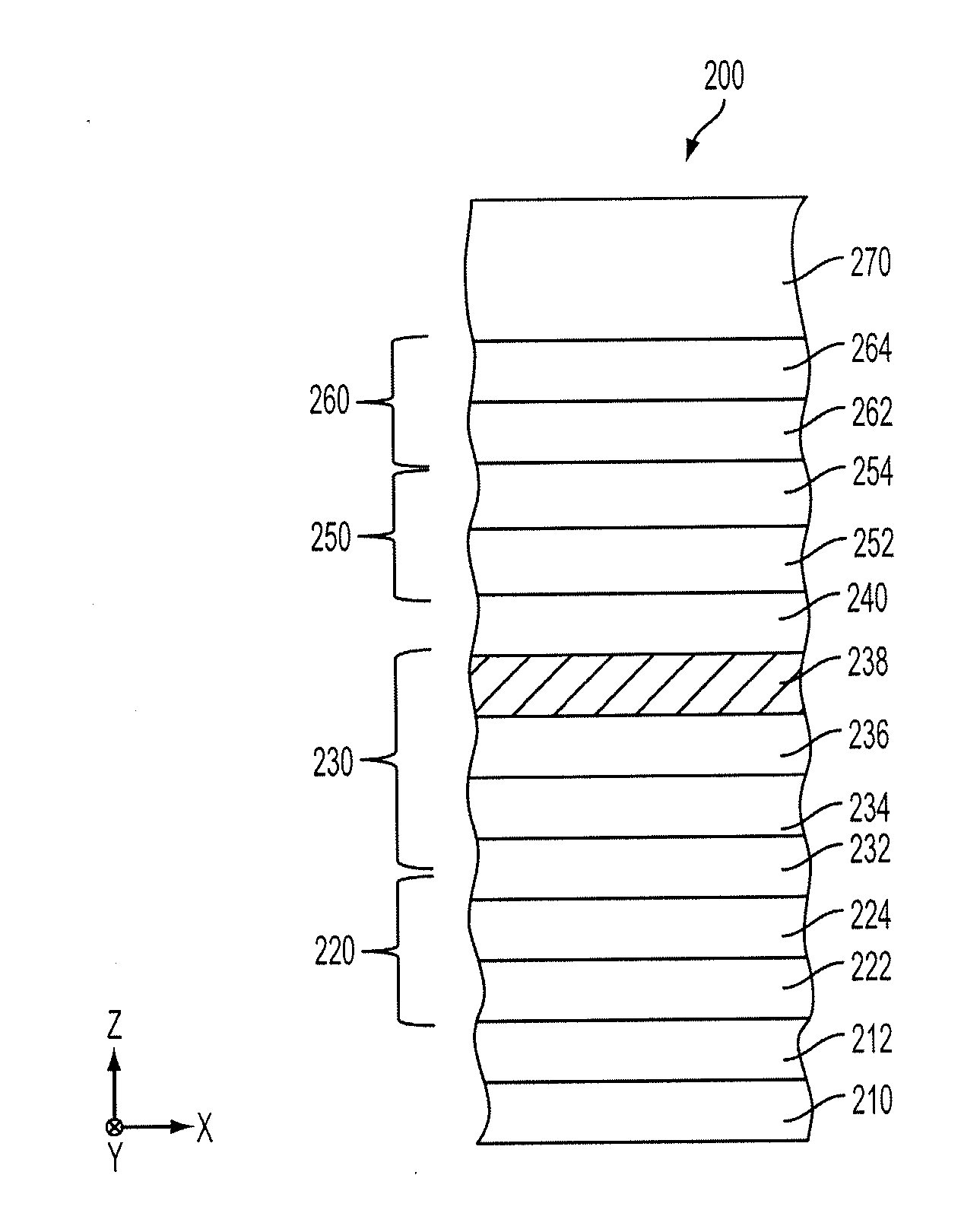
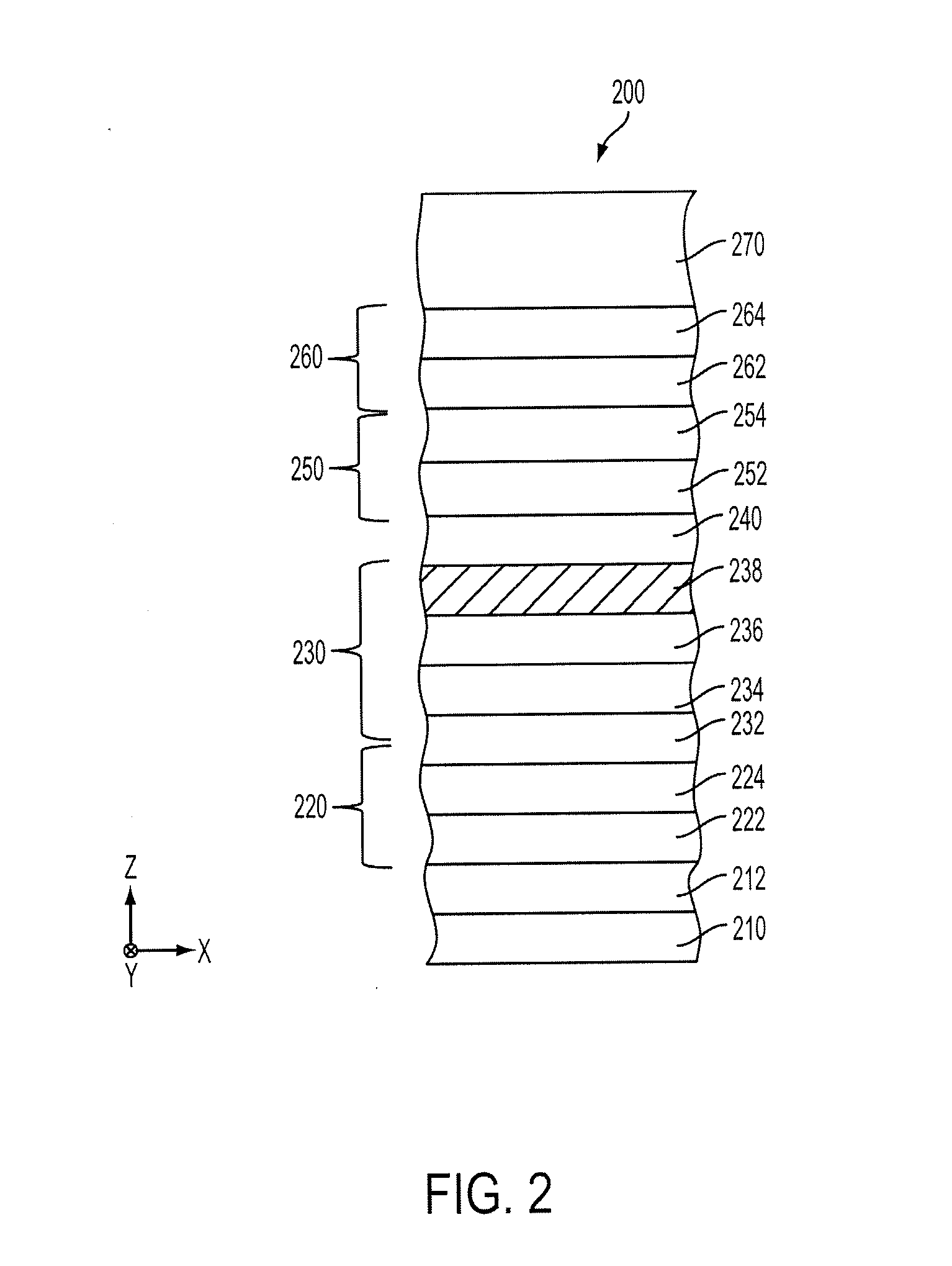
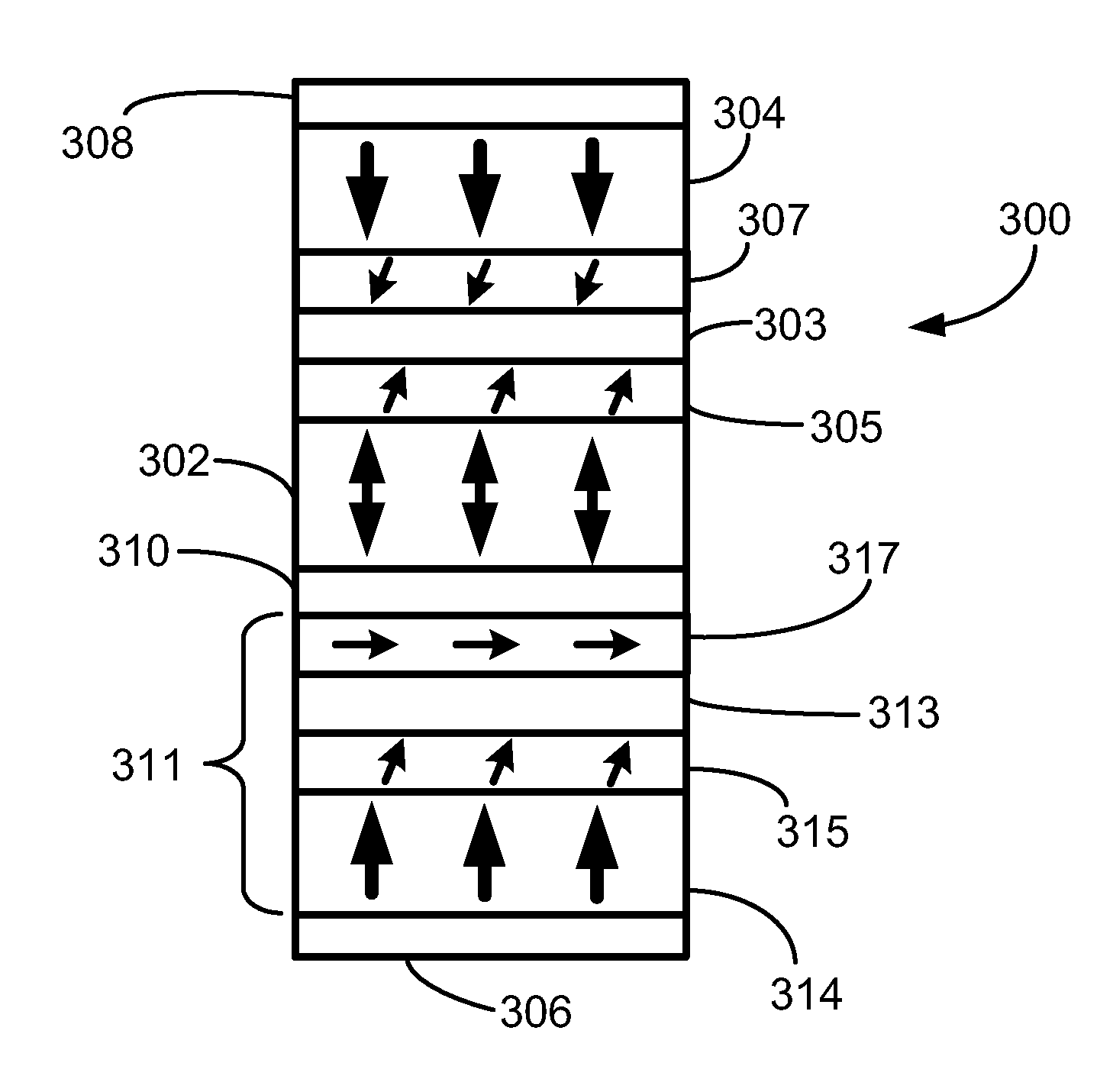
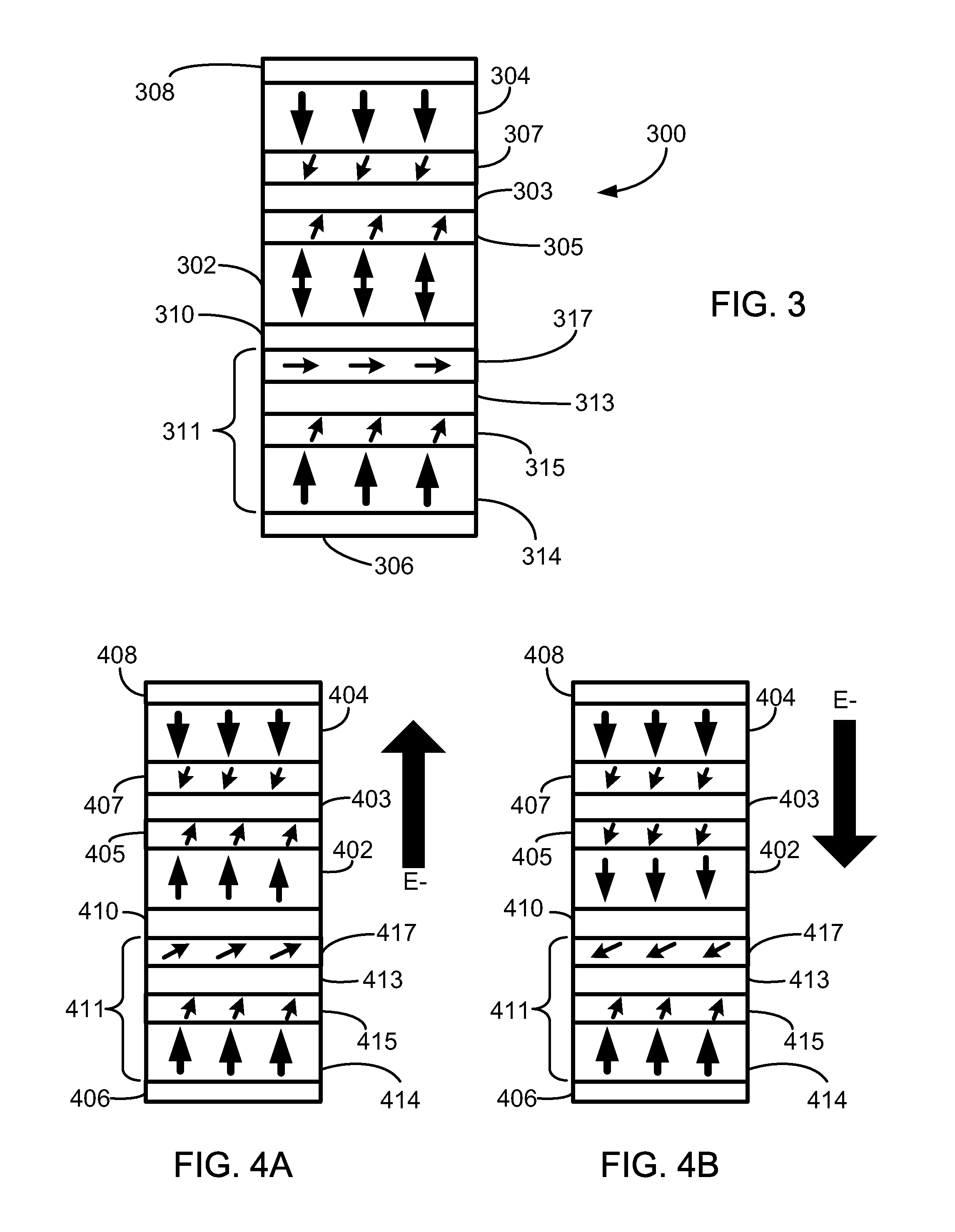
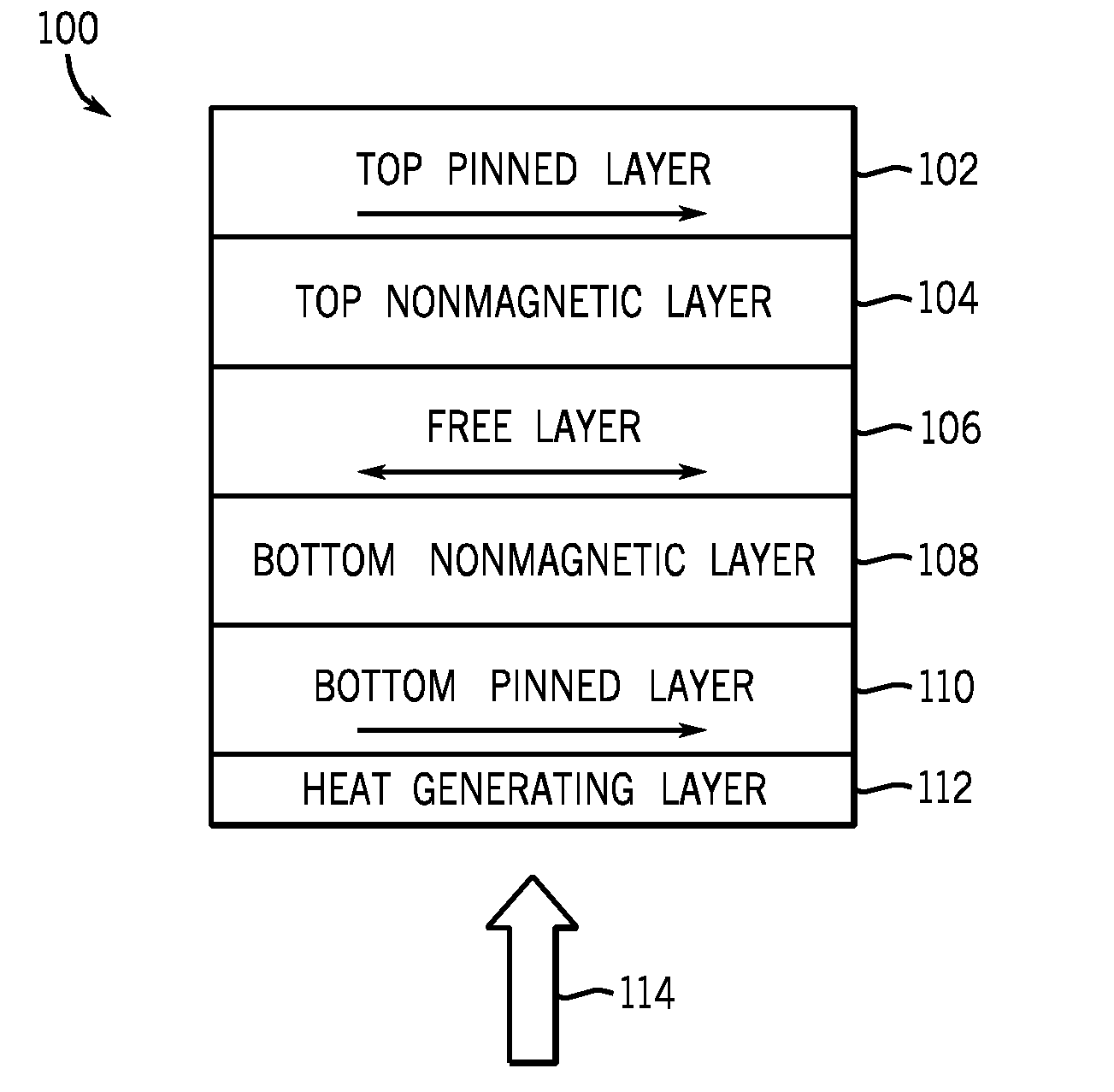
Multilayers having reduced perpendicular demagnetizing field using moment dilution for spintronic applications
ActiveUS8592927B2Improve thermal stabilityRaise the ratioMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionDemagnetizing fieldElectrical resistance and conductance
A magnetic element is disclosed that has a composite free layer with a FM1 / moment diluting / FM2 configuration wherein FM1 and FM2 are magnetic layers made of one or more of Co, Fe, Ni, and B and the moment diluting layer is used to reduce the perpendicular demagnetizing field. As a result, lower resistance x area product and higher thermal stability are realized when perpendicular surface anisotropy dominates shape anisotropy to give a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the FM1, FM2 layers. The moment diluting layer may be a non-magnetic metal like Ta or a CoFe alloy with a doped non-magnetic metal. A perpendicular Hk enhancing layer interfaces with the FM2 layer and may be an oxide to increase the perpendicular anisotropy field in the FM2 layer. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
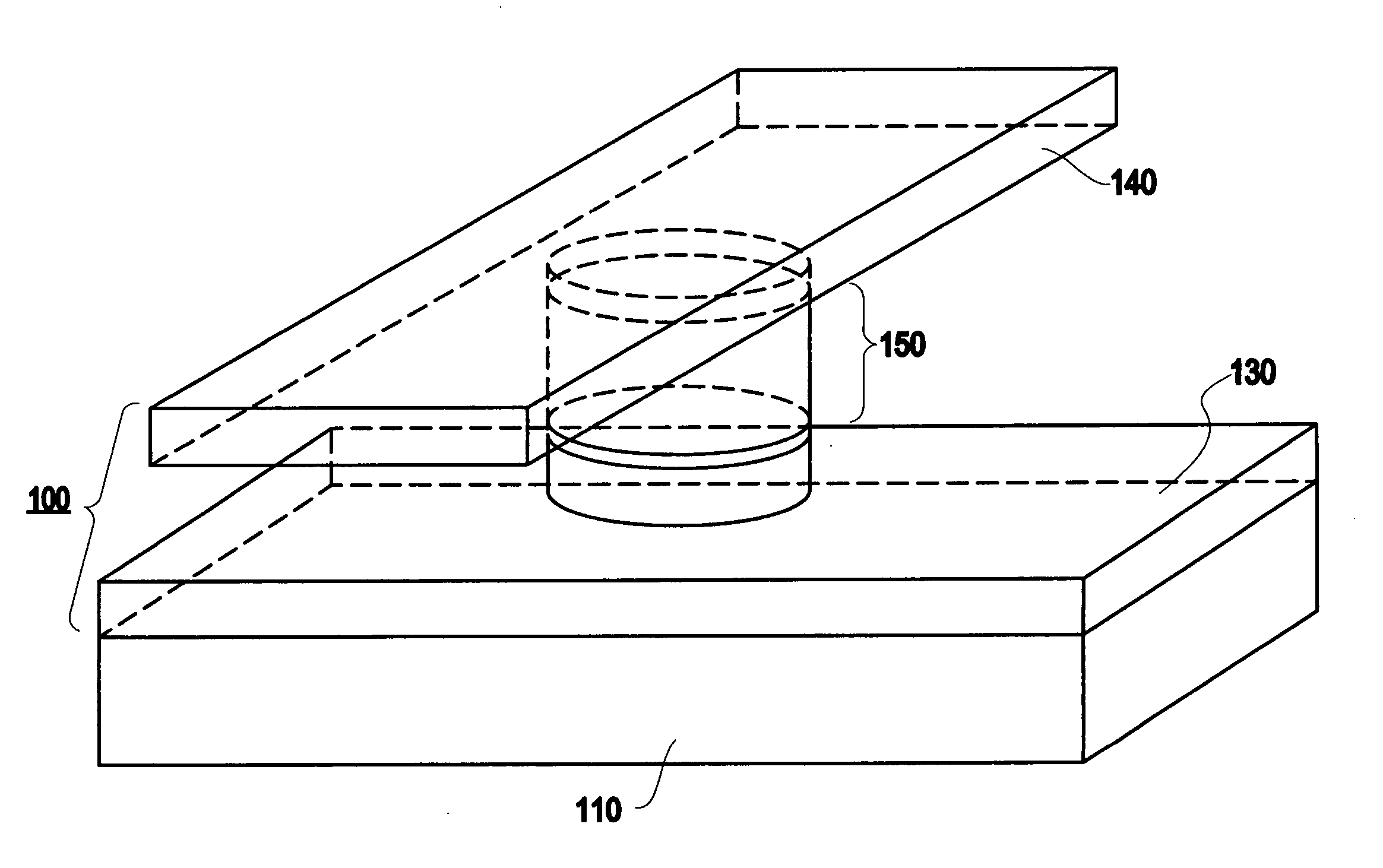
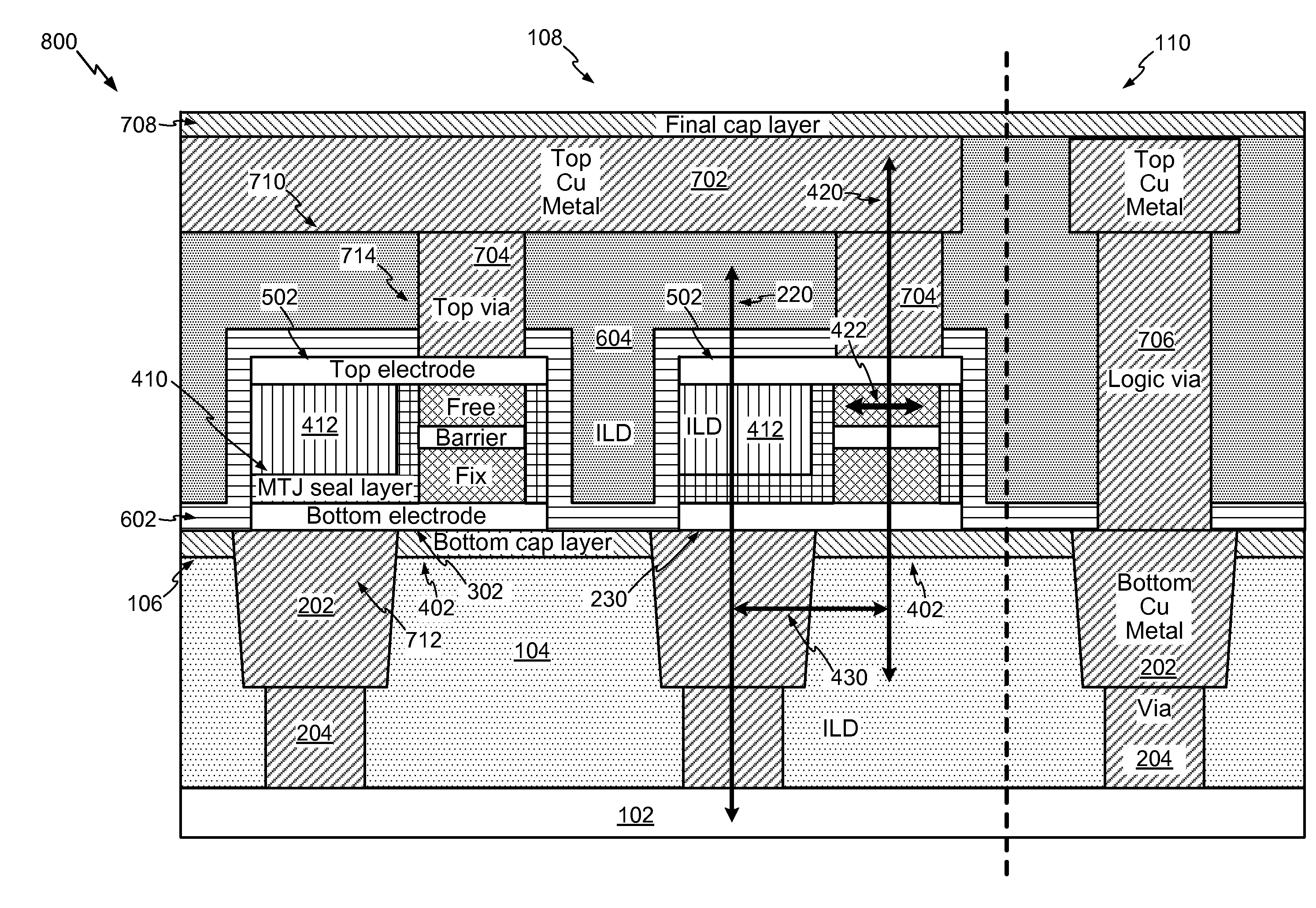
Integrated circuits having magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJ) and methods for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20150325622A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesDevice materialElectrical connection
Integrated circuits with magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) structures and methods for fabricating integrated circuits with MTJ structures are provided. An exemplary method for fabricating an integrated circuit includes forming a first conductive line in electrical connection with an underlying semiconductor device. The method exposes a surface of the first conductive line. Further, the method selectively deposits a conductive material on the surface of the first conductive line to form an electrode contact. The method includes forming a MTJ structure over the electrode contact.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Magnetic Tunnel Junction Device and Fabrication
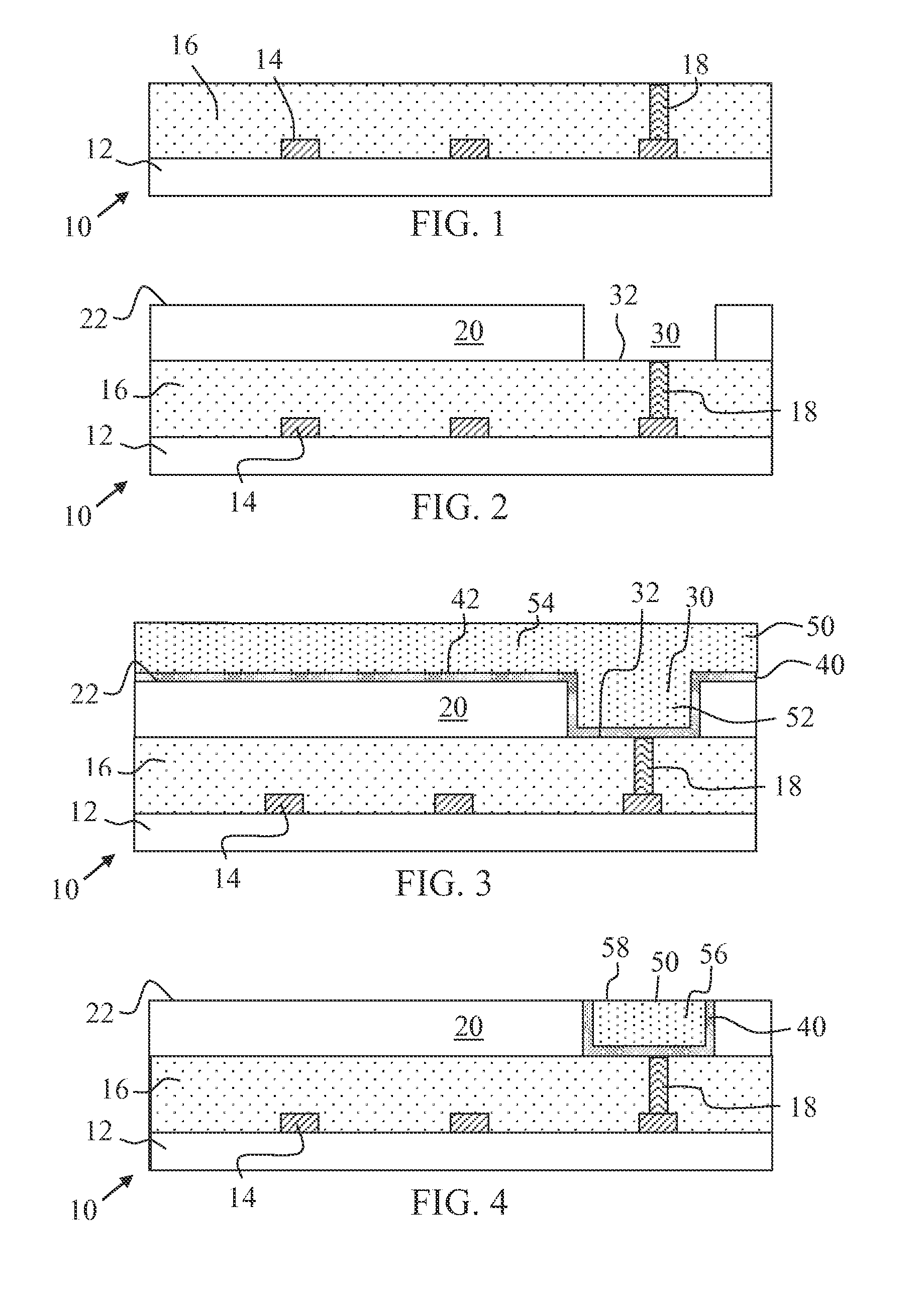
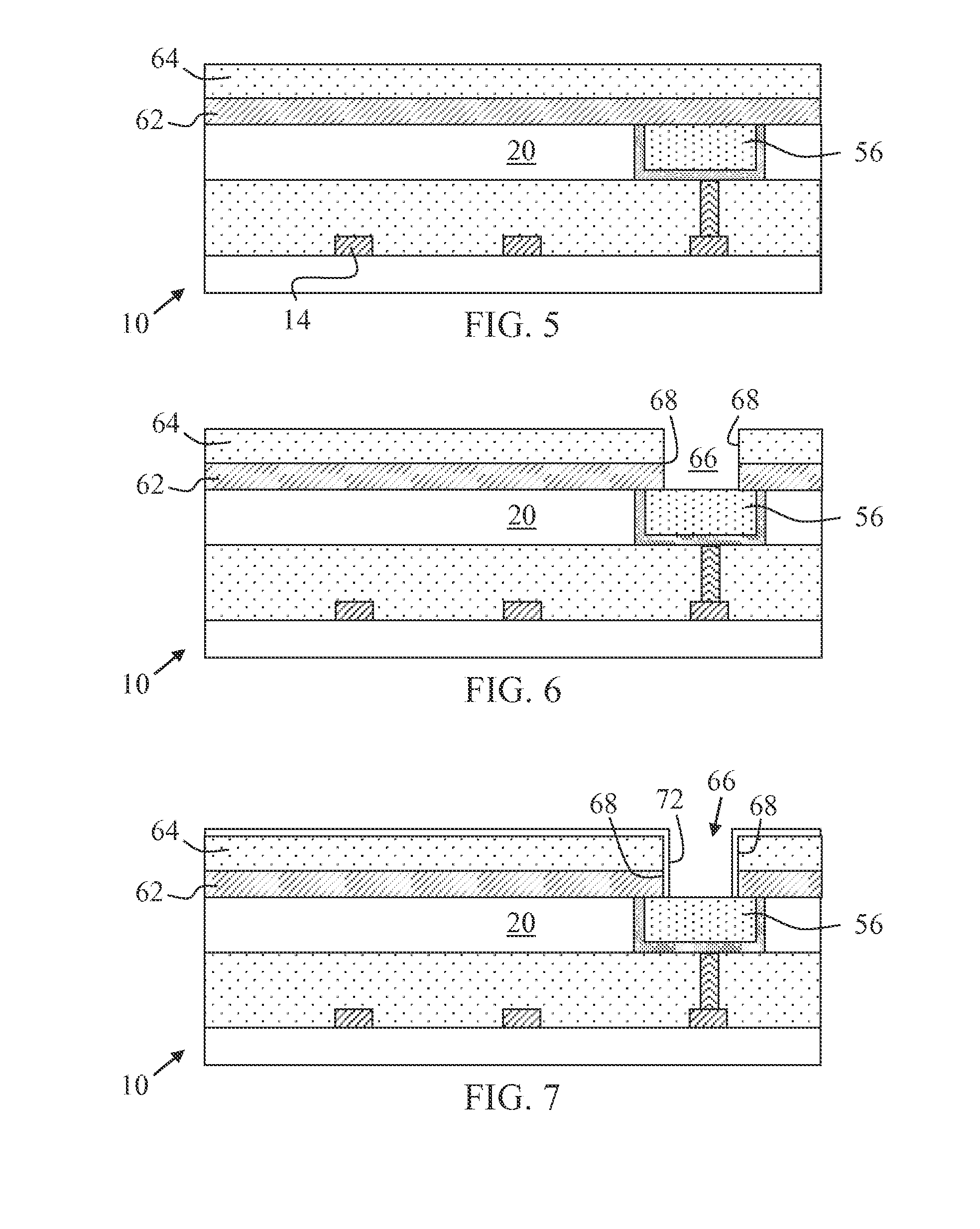
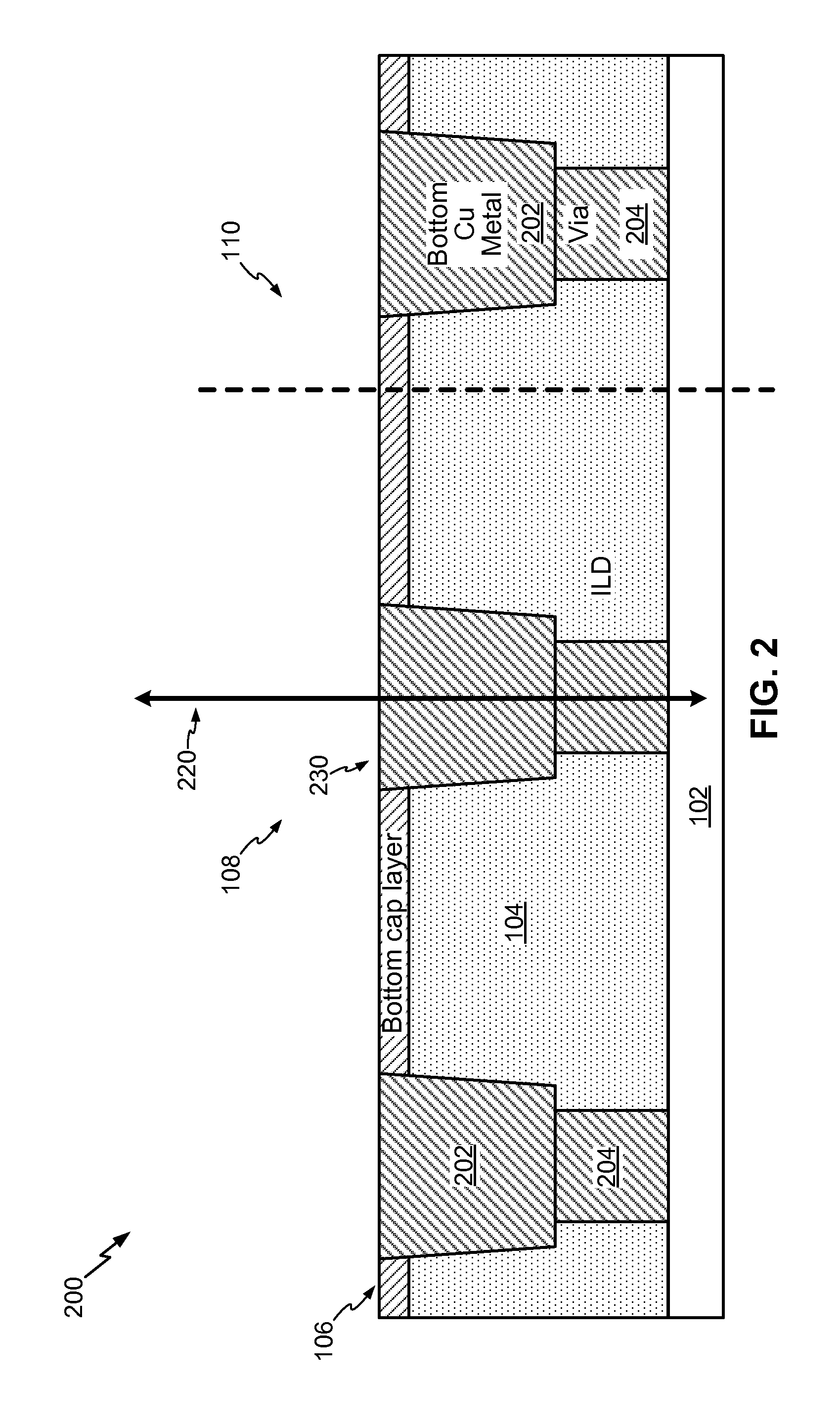
InactiveUS20100289098A1Eliminating surface roughness concernInhibition formationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTunnel junctionCondensed matter physics
A magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device and fabrication method is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, a method is disclosed that includes forming a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device on a structure that includes a bottom cap layer and a bottom metal-filled trench having a normal axis, the magnetic tunnel junction device including a bottom electrode, magnetic tunnel junction layers, a magnetic tunnel junction seal layer, a top electrode, and a logic cap layer, the magnetic tunnel junction device having an MTJ axis that is offset from the normal axis.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
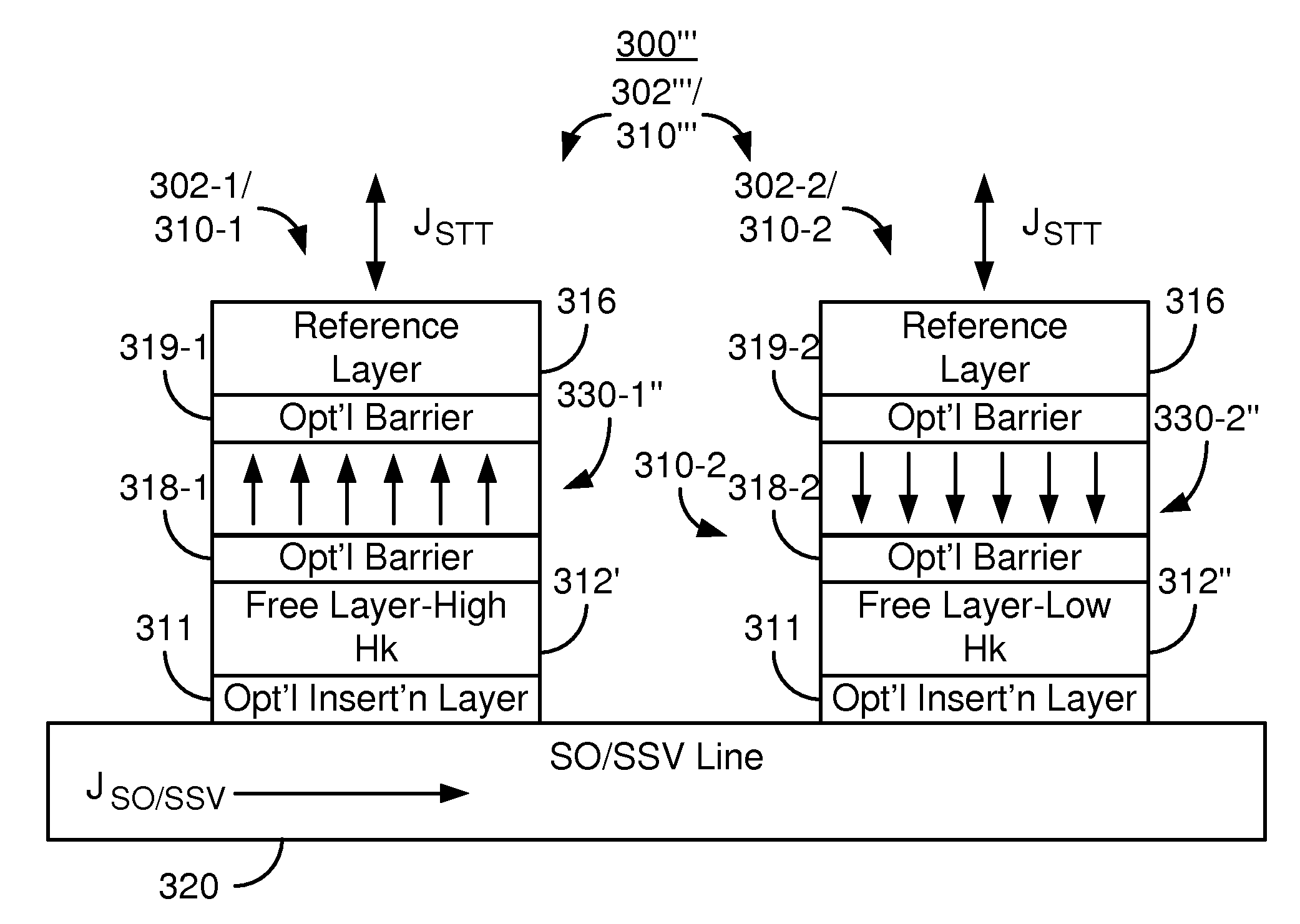
Method and system for providing dual magnetic tunneling junctions using spin-orbit interaction-based switching and memories utilizing the dual magnetic tunneling junctions
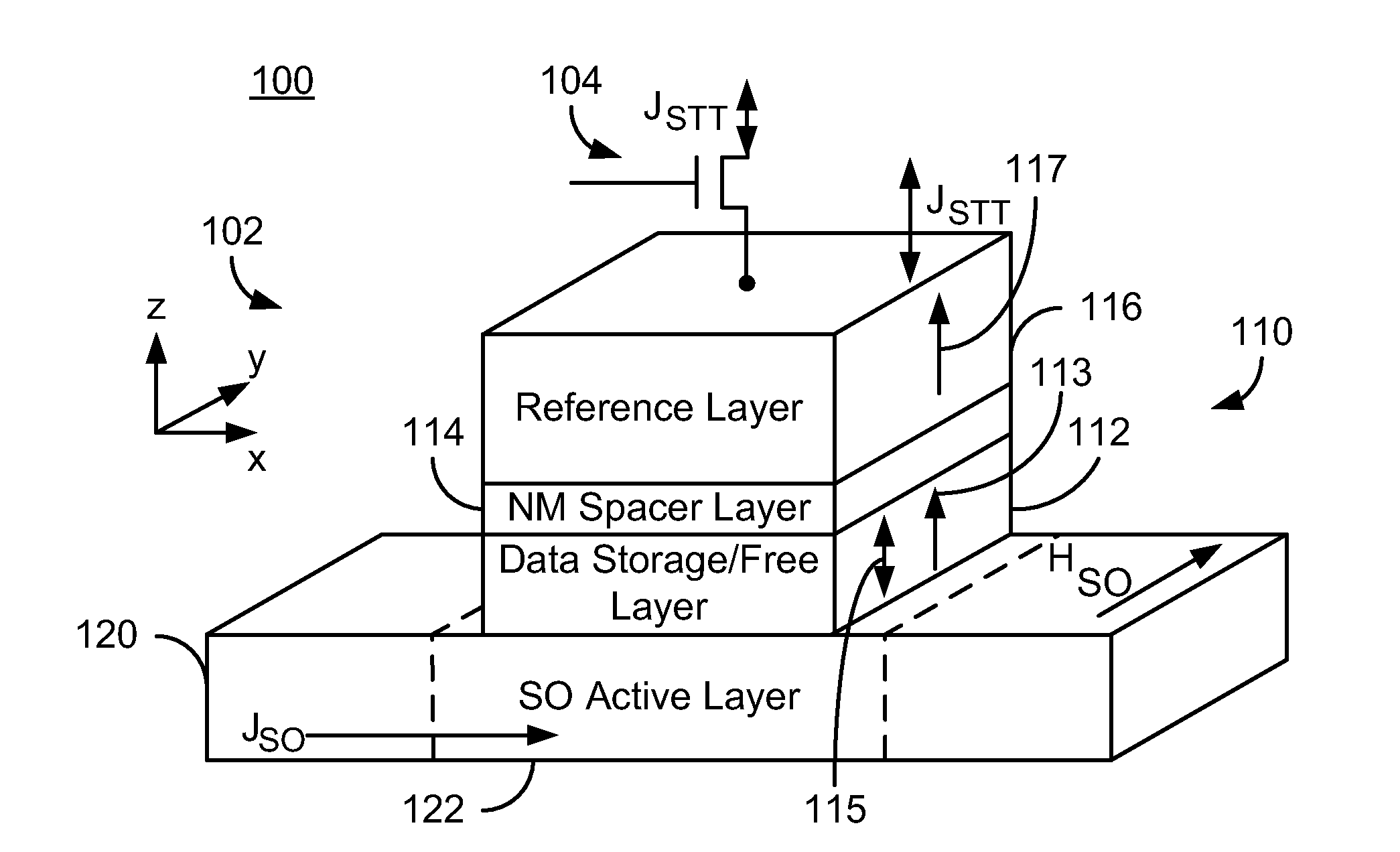
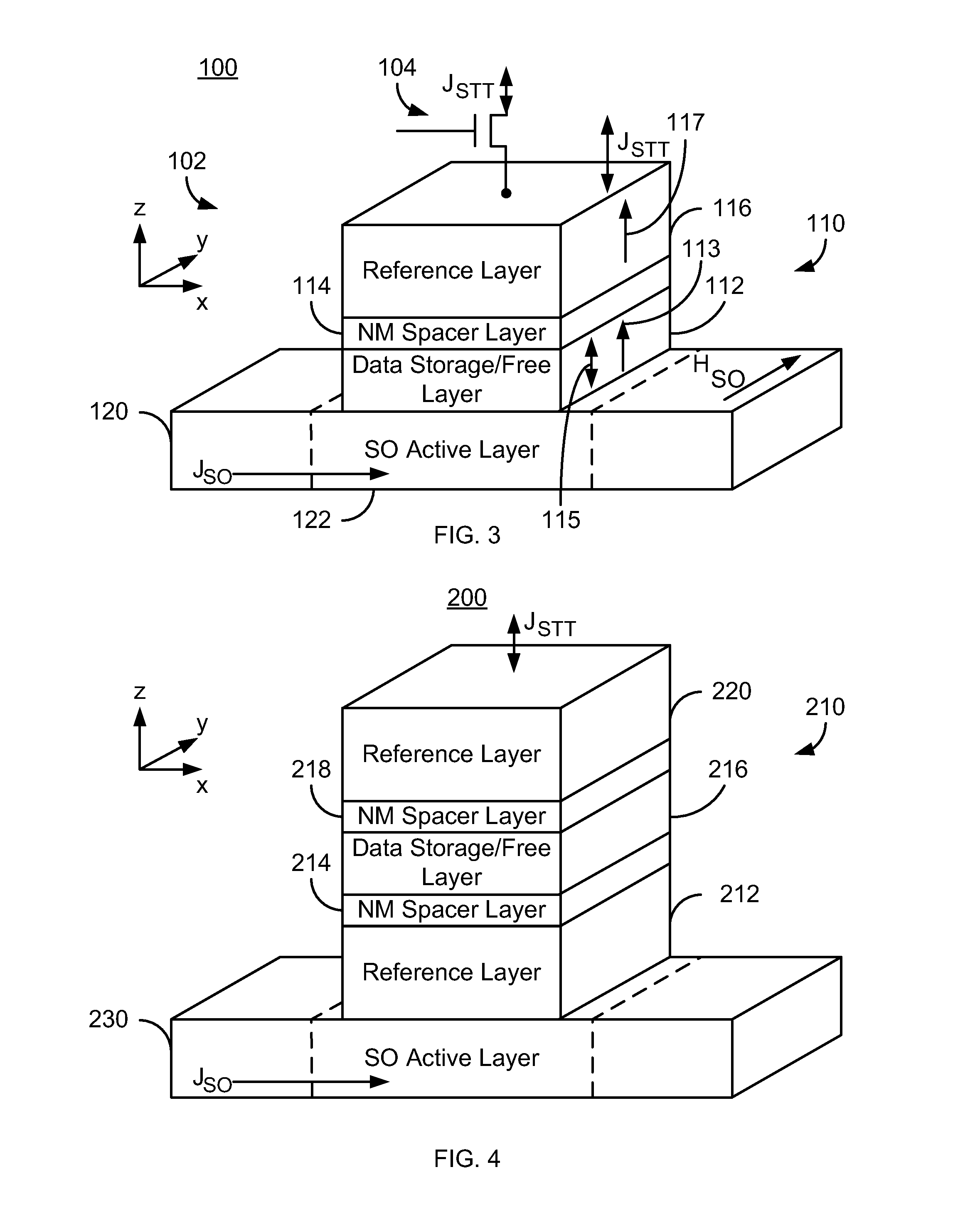
ActiveUS20140056061A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device detailsMagnetic memorySpin transfer
A magnetic memory is described. The magnetic memory includes dual magnetic junctions and spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer(s). Each dual magnetic junction includes first and second reference layers, first and second nonmagnetic spacer layers and a free layer. The free layer is magnetic and between the nonmagnetic spacer layers. The nonmagnetic spacer layers are between the corresponding reference layers and the free layer. The SO active layer(s) are adjacent to the first reference layer of each dual magnetic junction. The SO active layer(s) exert a SO torque on the first reference layer due to a current passing through the SO active layer(s) substantially perpendicular to a direction between the SO active layer(s) and the first reference layer. The first reference layer has a magnetic moment changeable by at least the SO torque. The free layer is switchable using a spin transfer write current driven through the dual magnetic junction.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Unidirectional spin torque transfer magnetic memory cell structure
ActiveUS20100080036A1Galvano-magnetic device detailsDigital storageRandom access memoryMagnetic memory
Spin torque transfer magnetic random access memory devices configured to be programmed unidirectionally and methods of programming such devices. The devices include memory cells having two pinned layers and a free layer therebetween. By utilizing two pinned layers, the spin torque effect on the free layer from each of the two pinned layers, respectively, allows the memory cells to be programmed with unidirectional currents.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
Hard mask for patterning magnetic tunnel junctions
InactiveUS20160351799A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic device detailsCarbon layerAnti-reflective coating
Device structures and methods for fabricating device structures are provided herein. Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) devices described herein may include a film stack comprising a magnetic tunneling junction layer, a dielectric capping layer, an etch stop layer, a conductive hard mask layer, a dielectric hard mask layer, a spin on carbon layer, and an anti-reflective coating layer. The film stack may be etched by one or more selected chemistries to achieve improved film stack sidewall verticality. Memory cells having increasingly uniform and reduced critical dimensions may be fabricated utilizing the methods and devices described herein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com