Patents
Literature
2158 results about "Magnetic memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
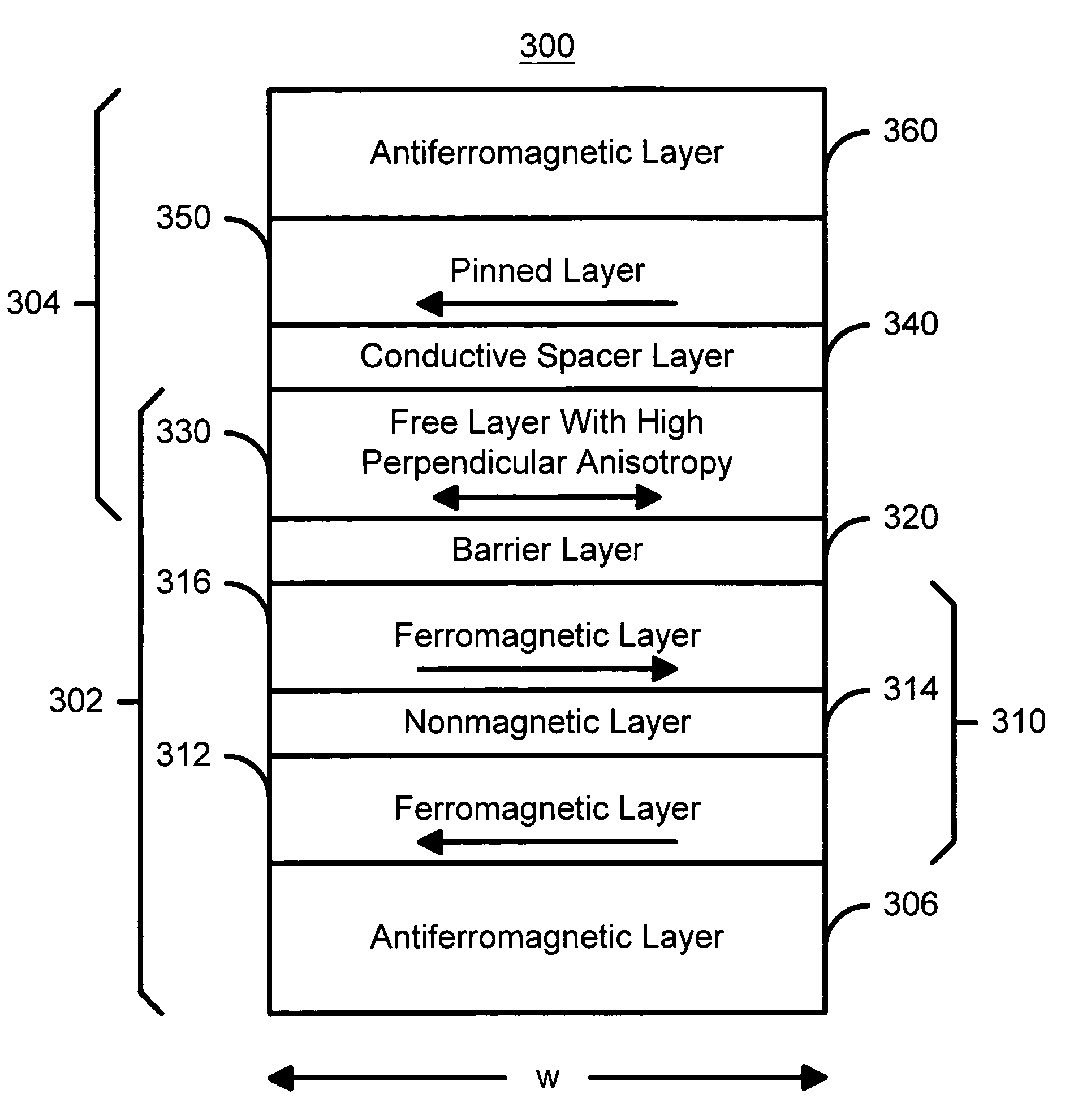
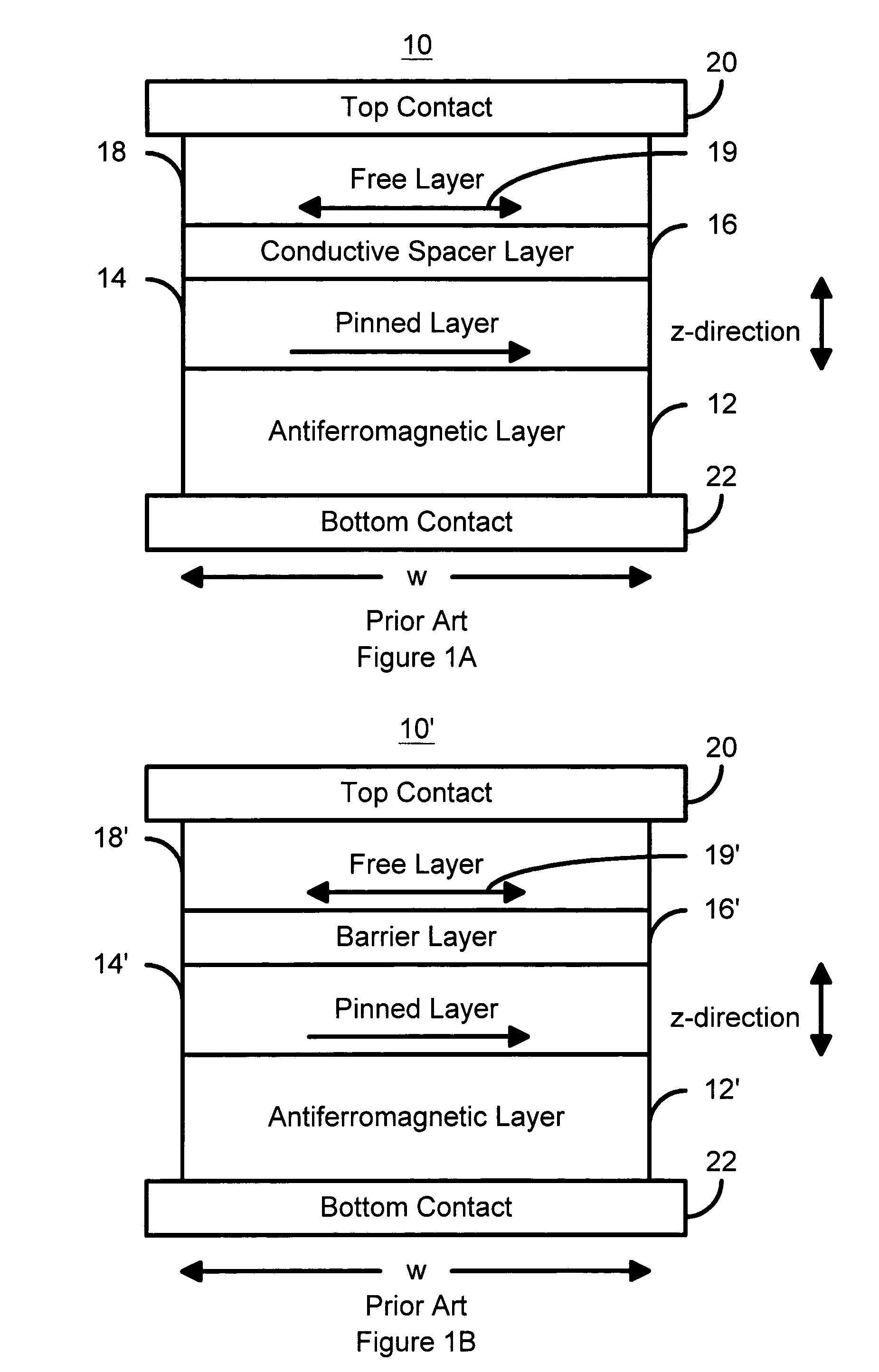
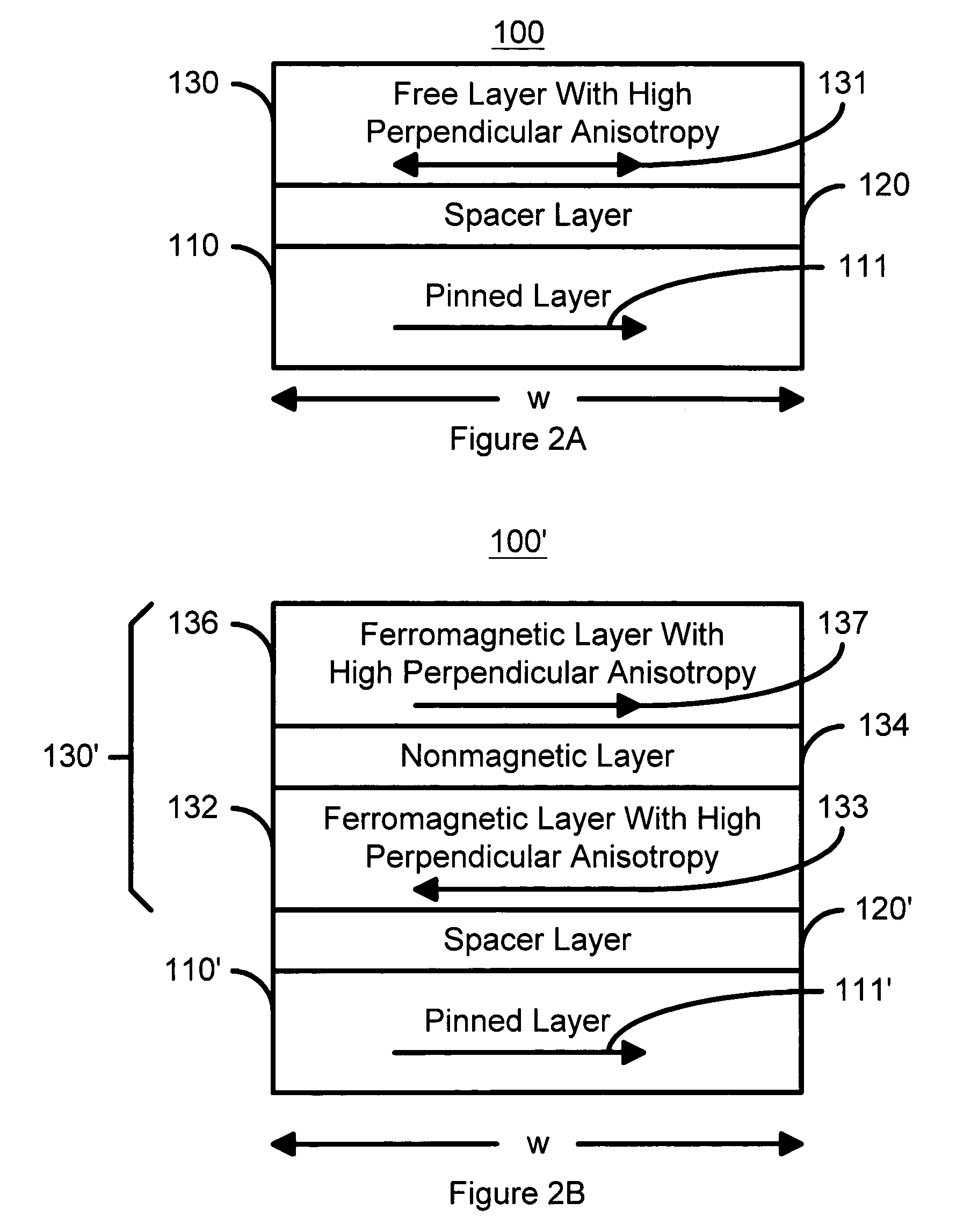
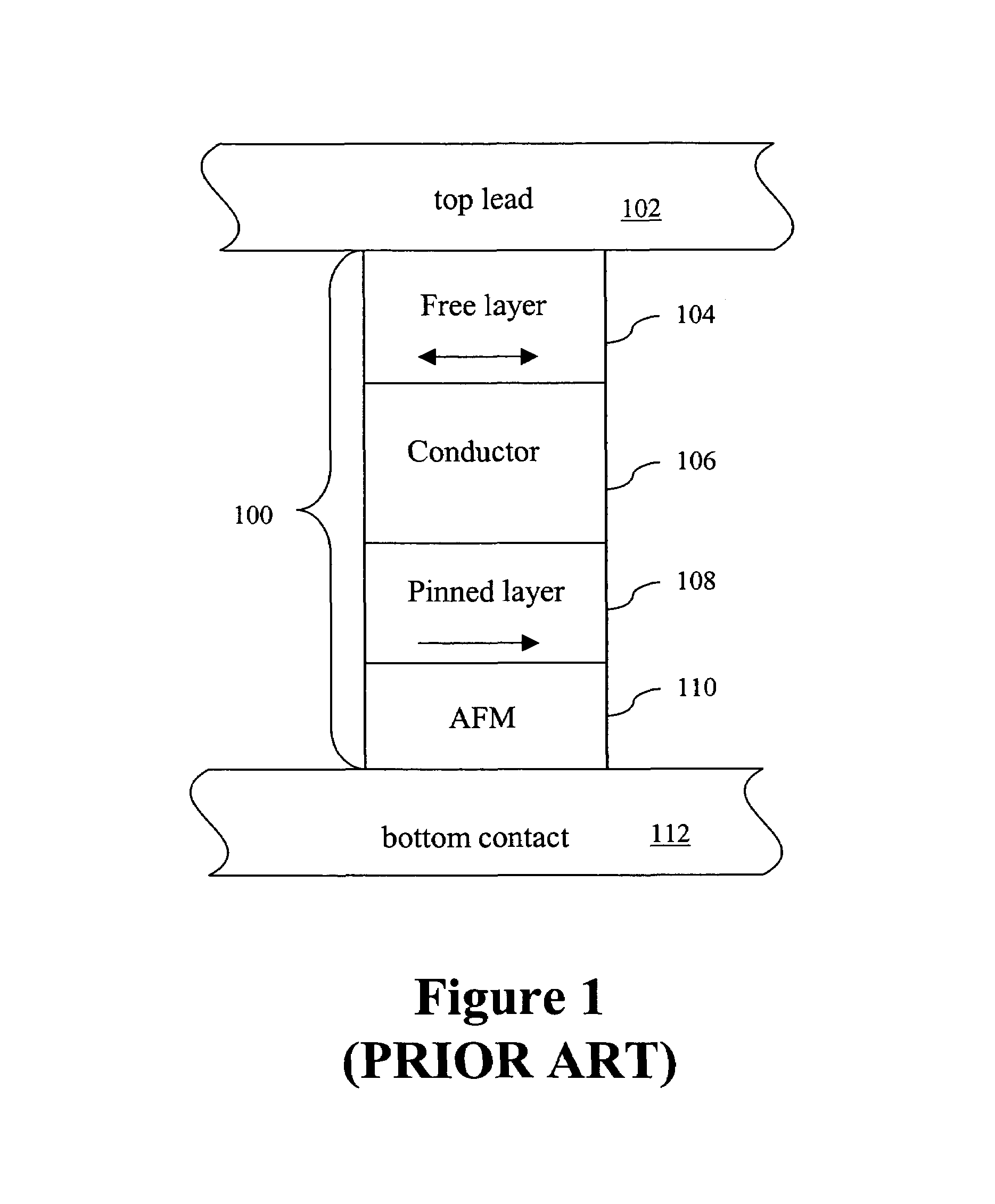
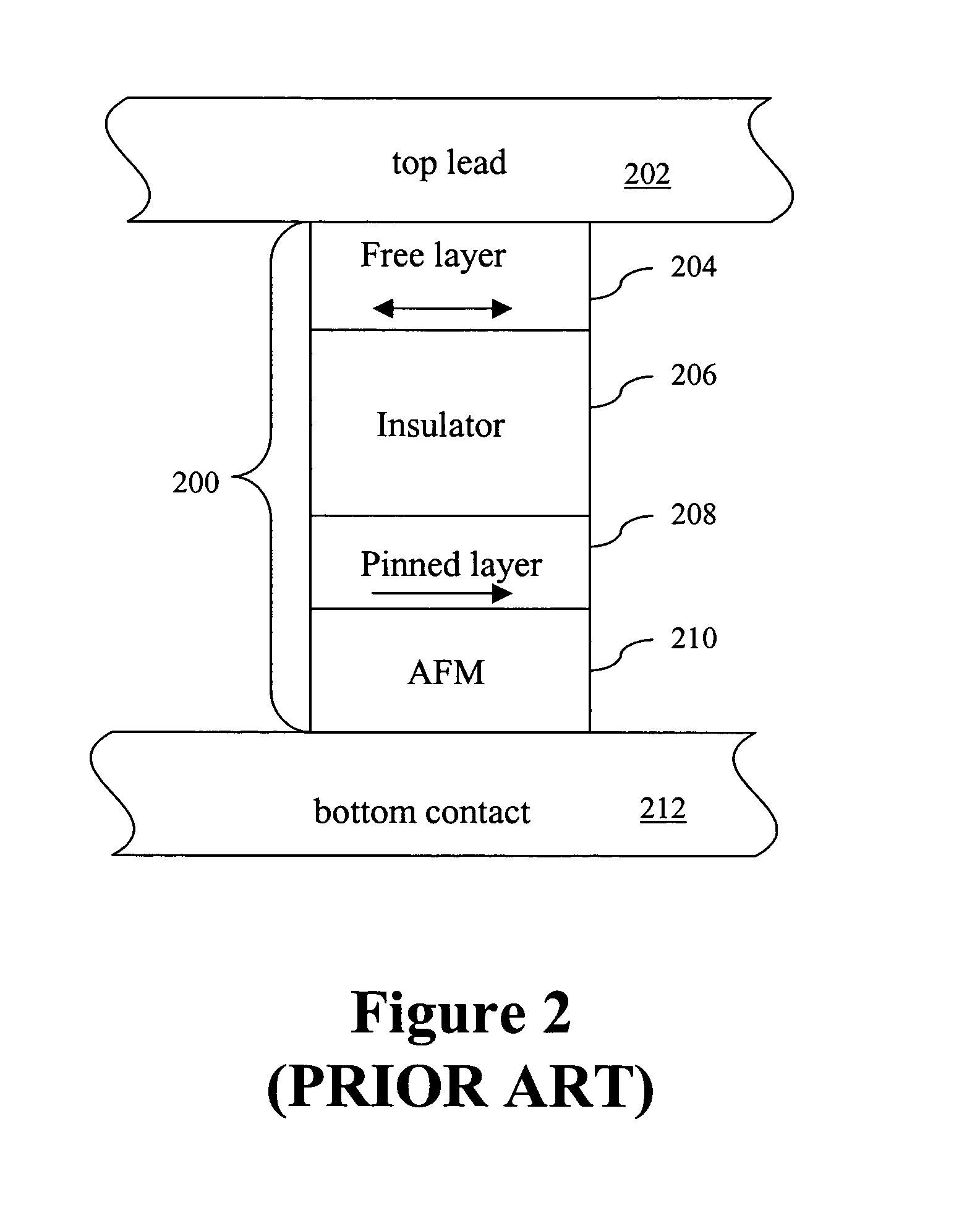
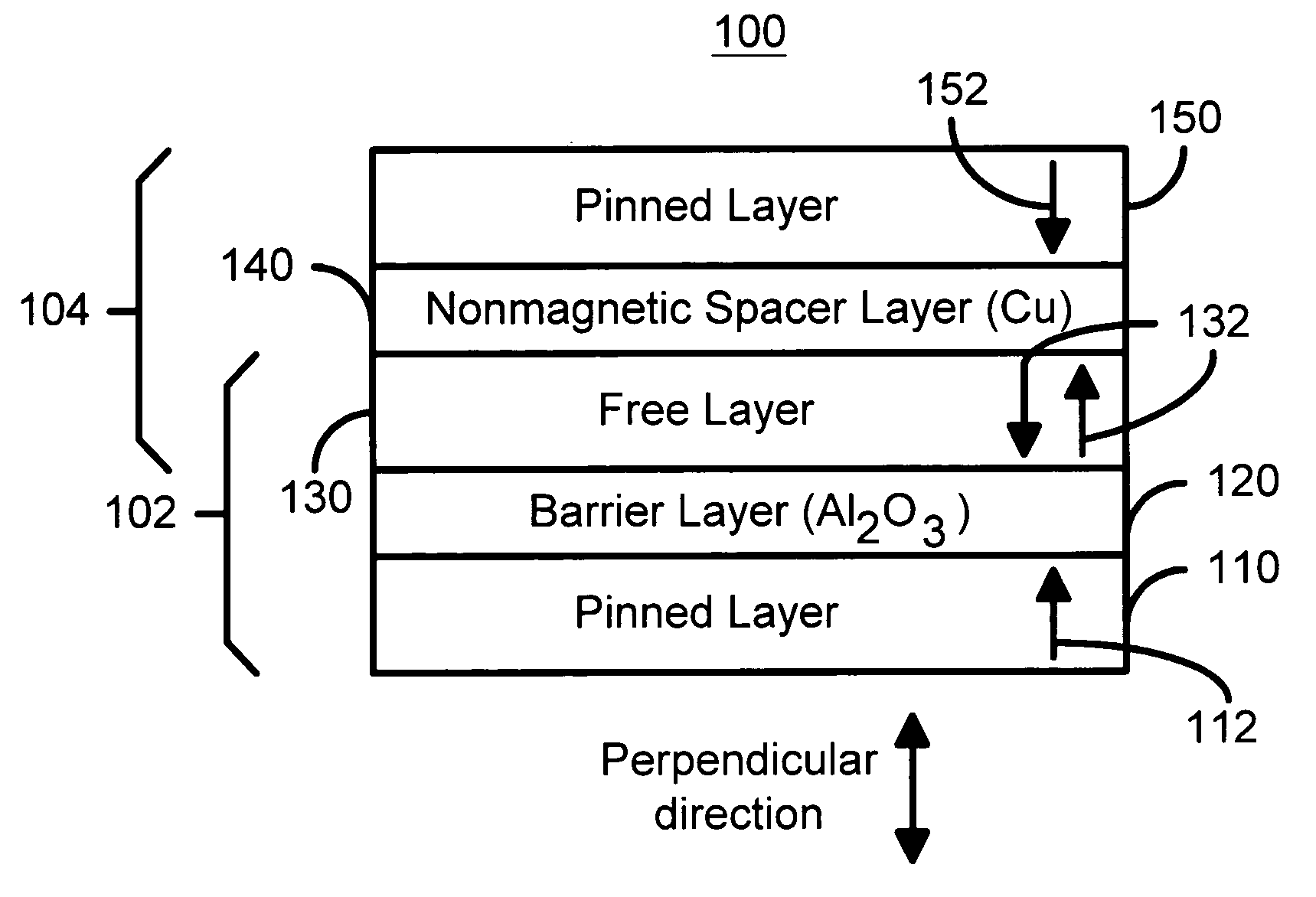
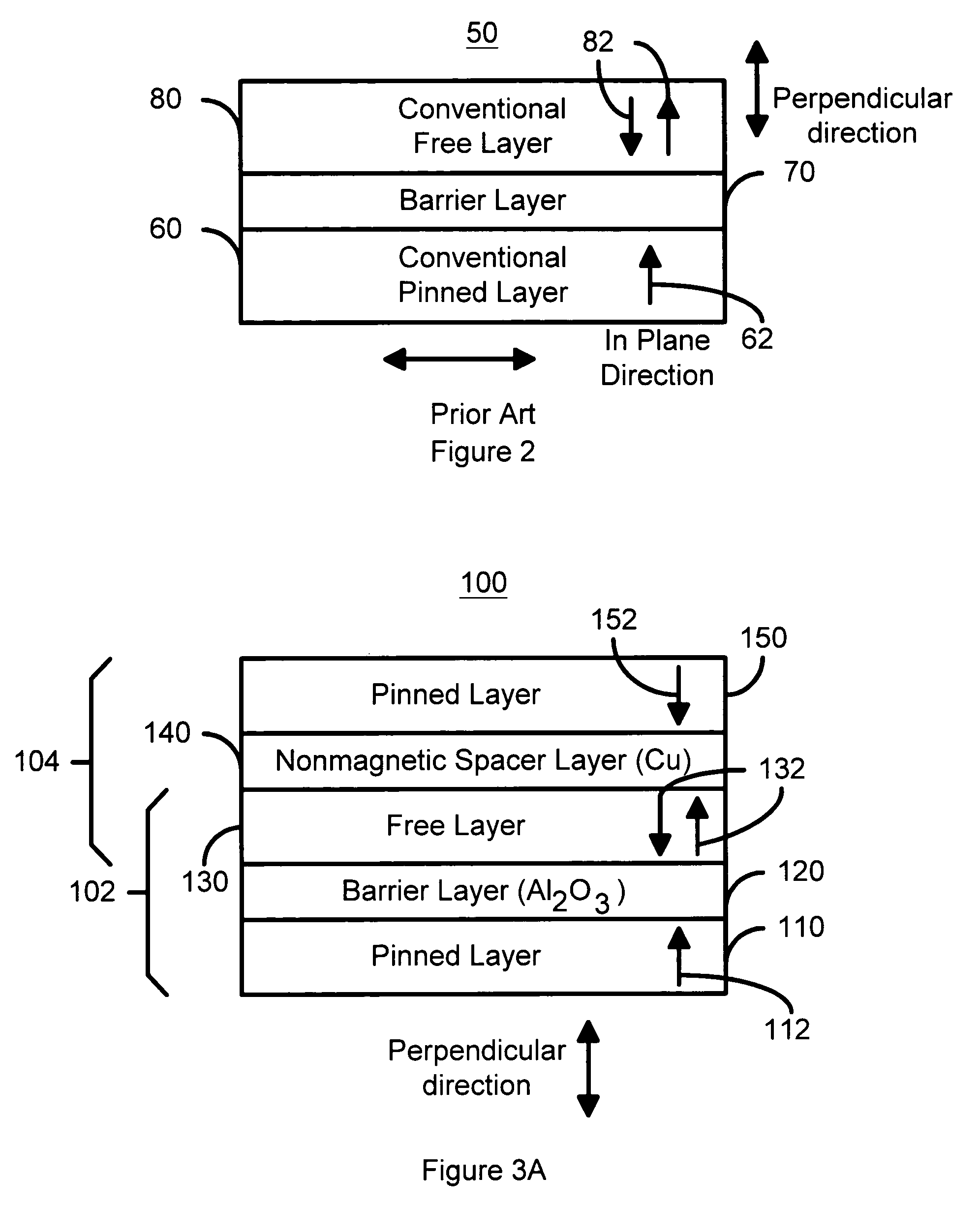
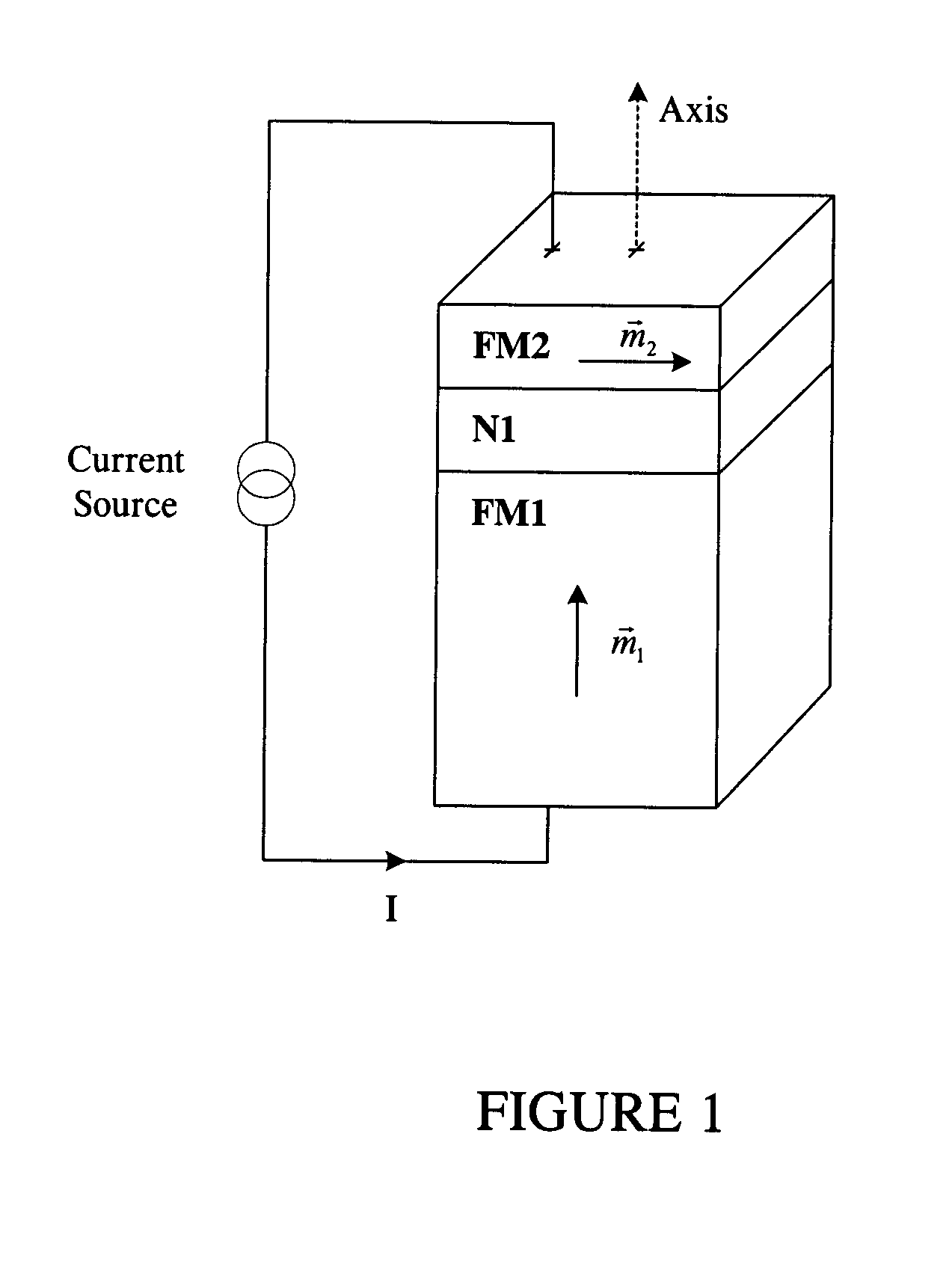
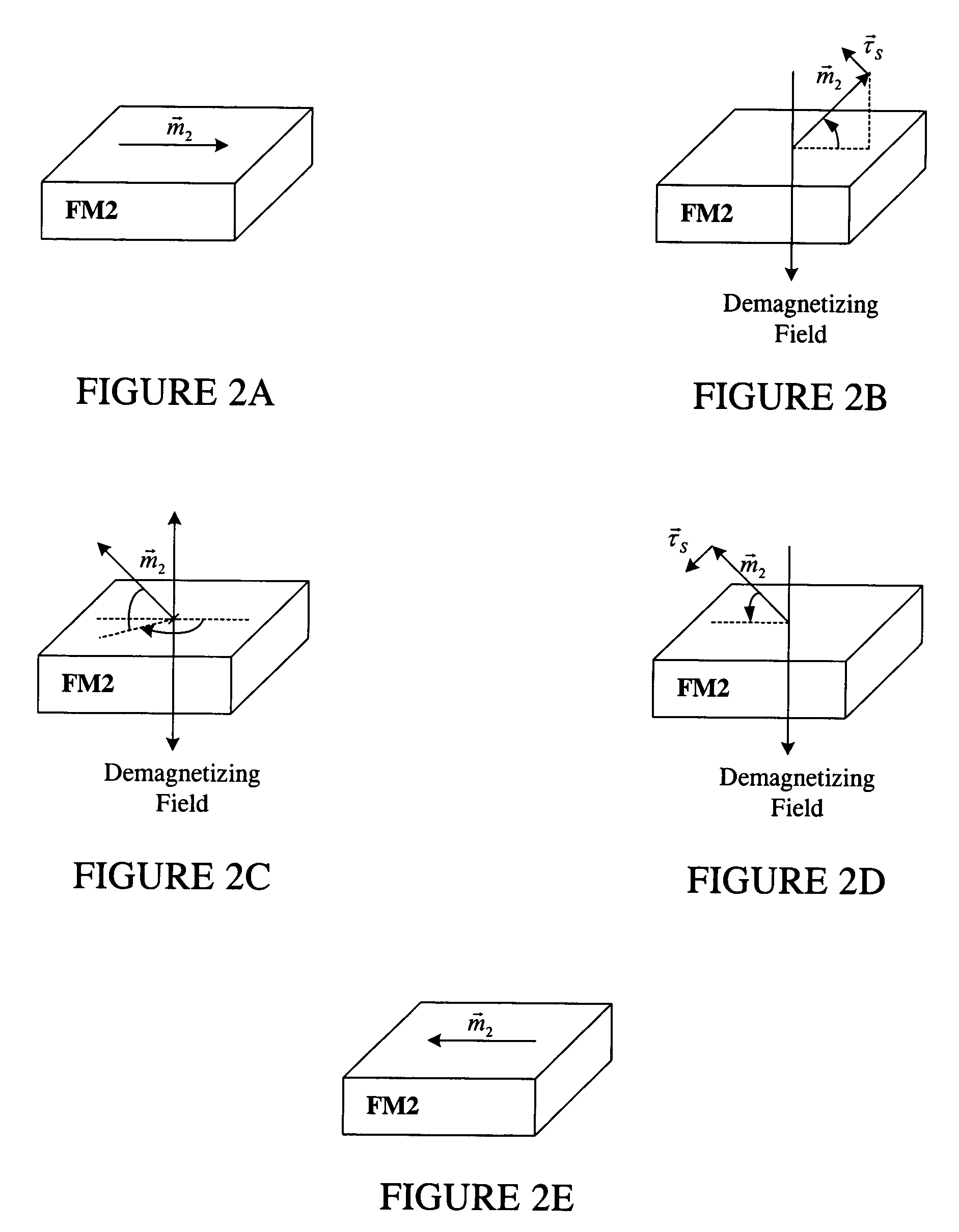
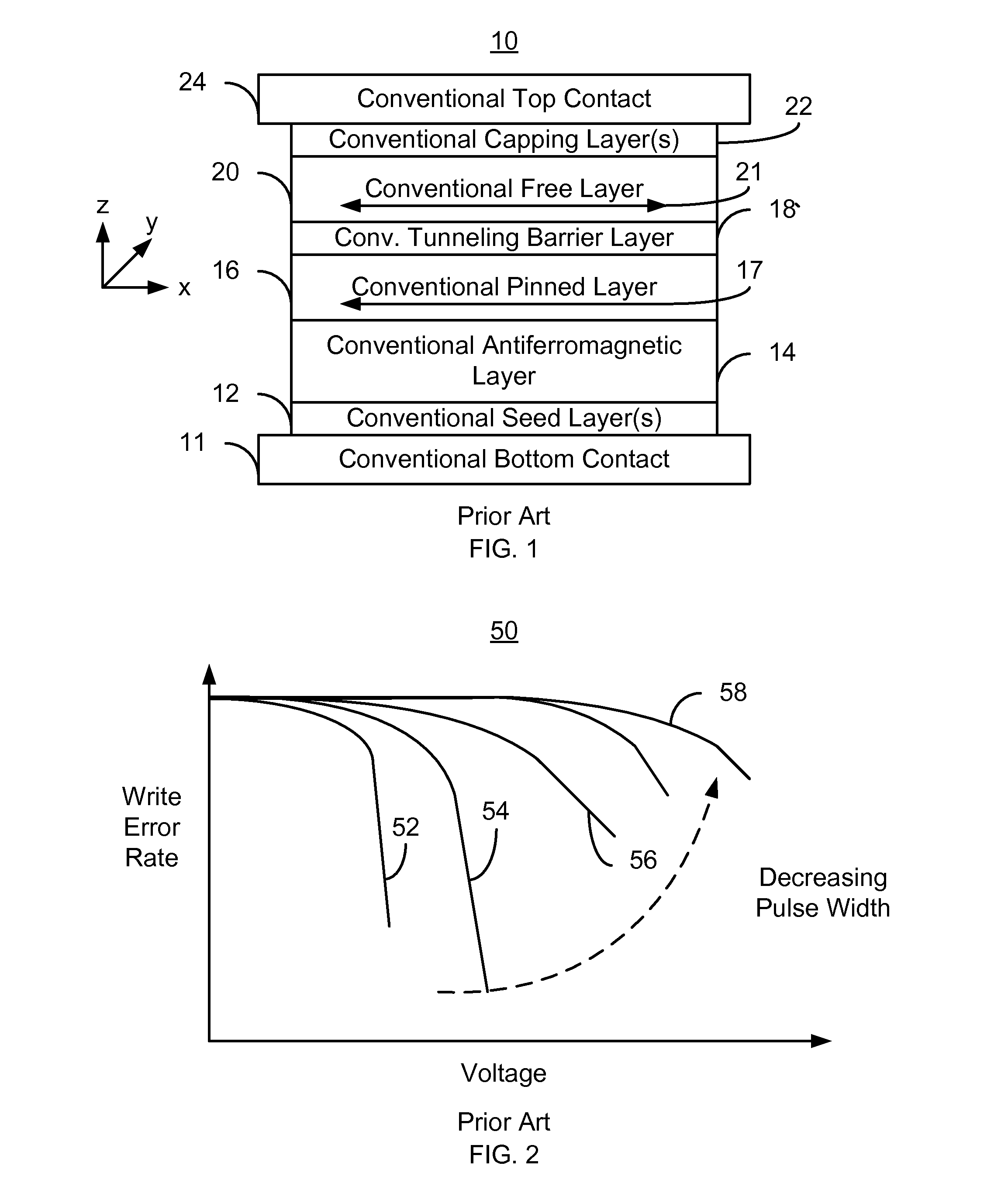
Spin transfer magnetic element with free layers having high perpendicular anisotropy and in-plane equilibrium magnetization
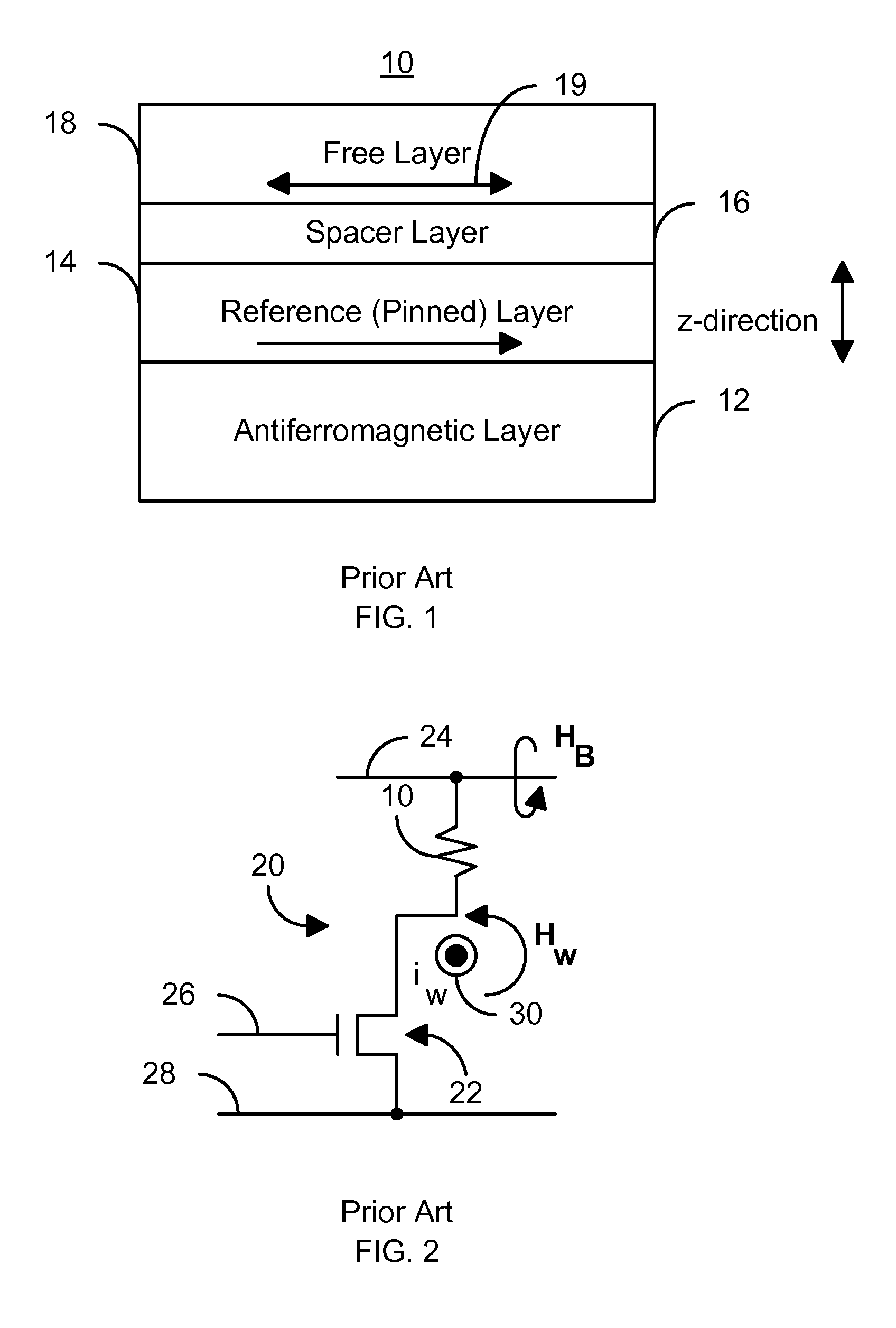
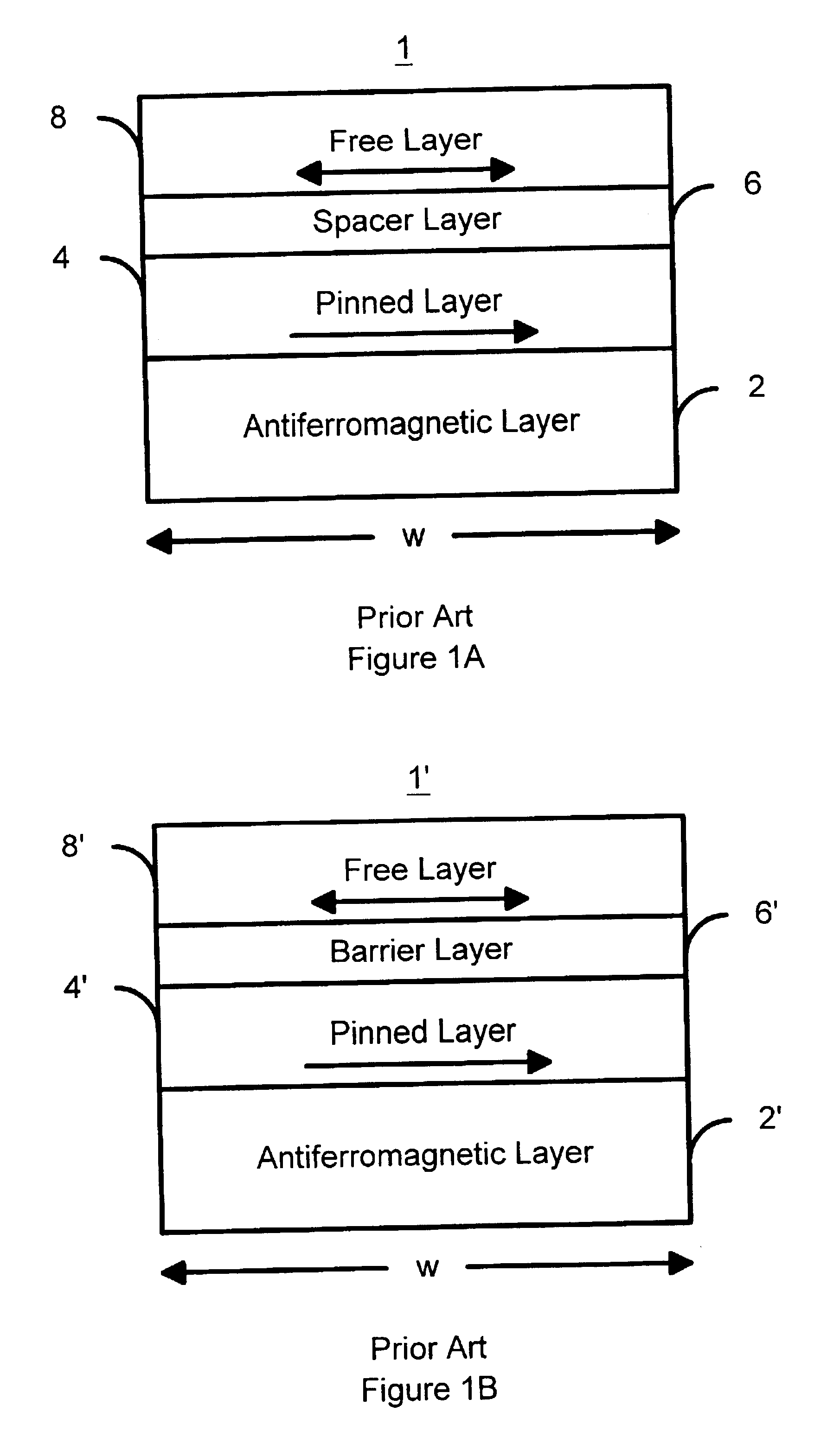
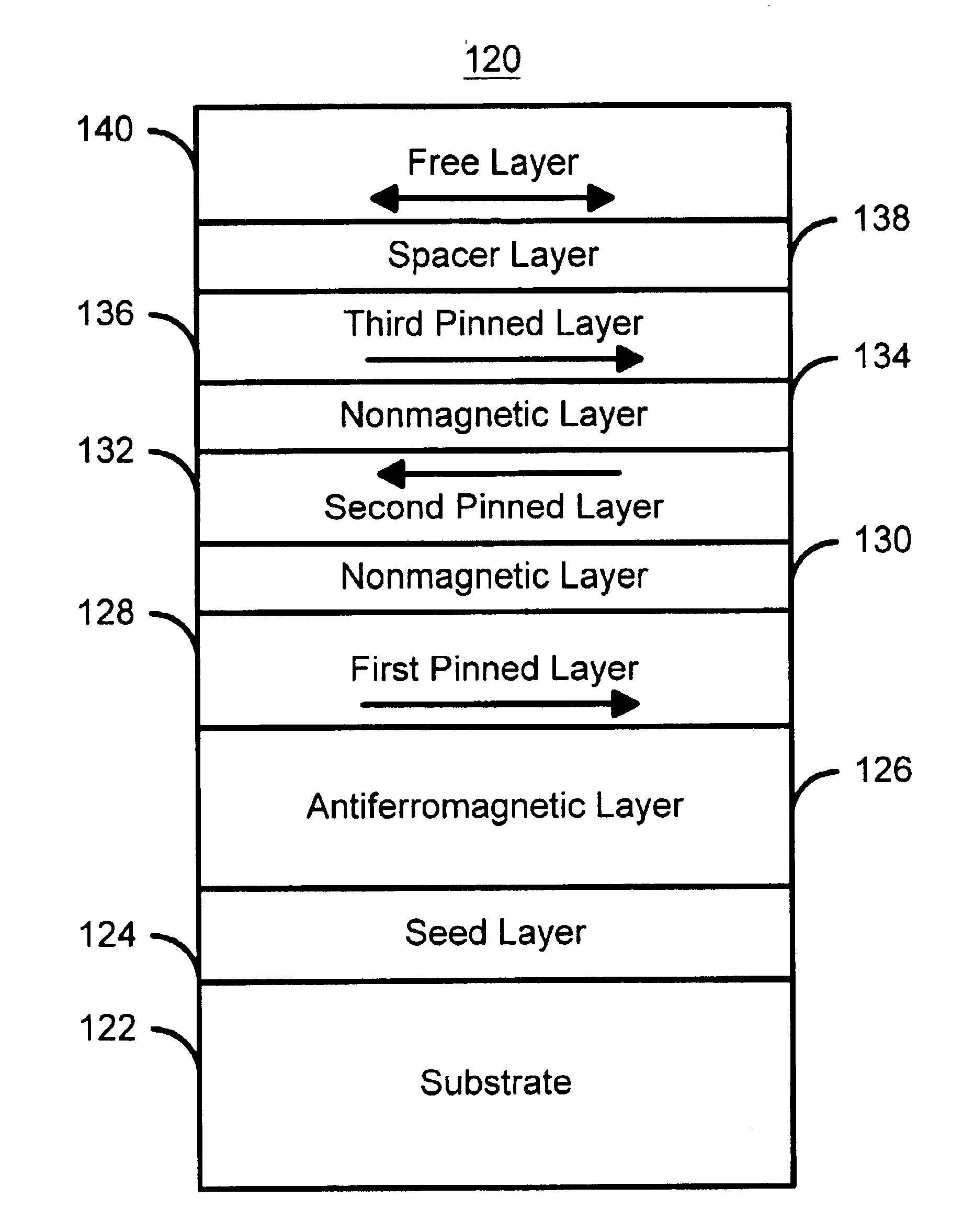
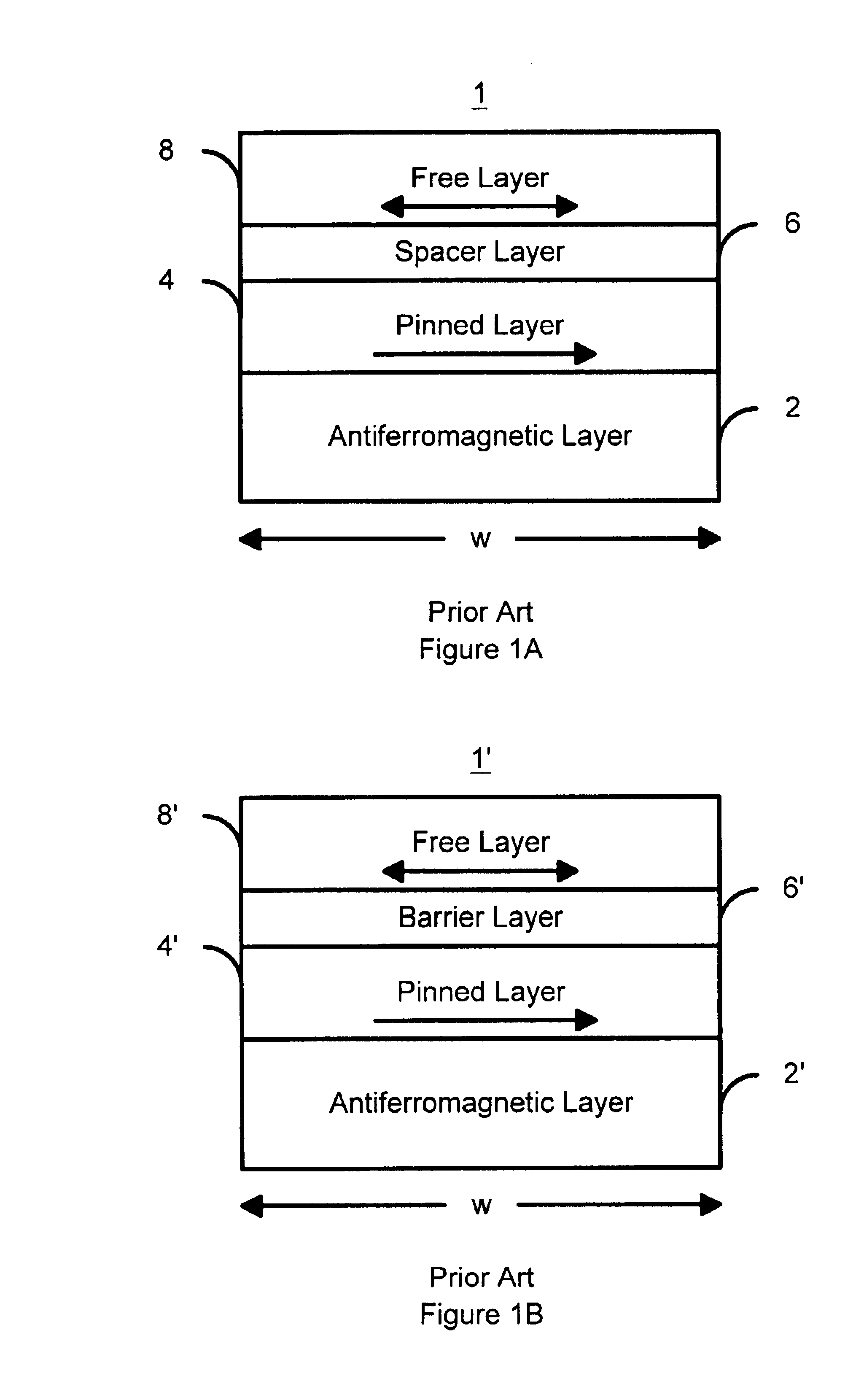
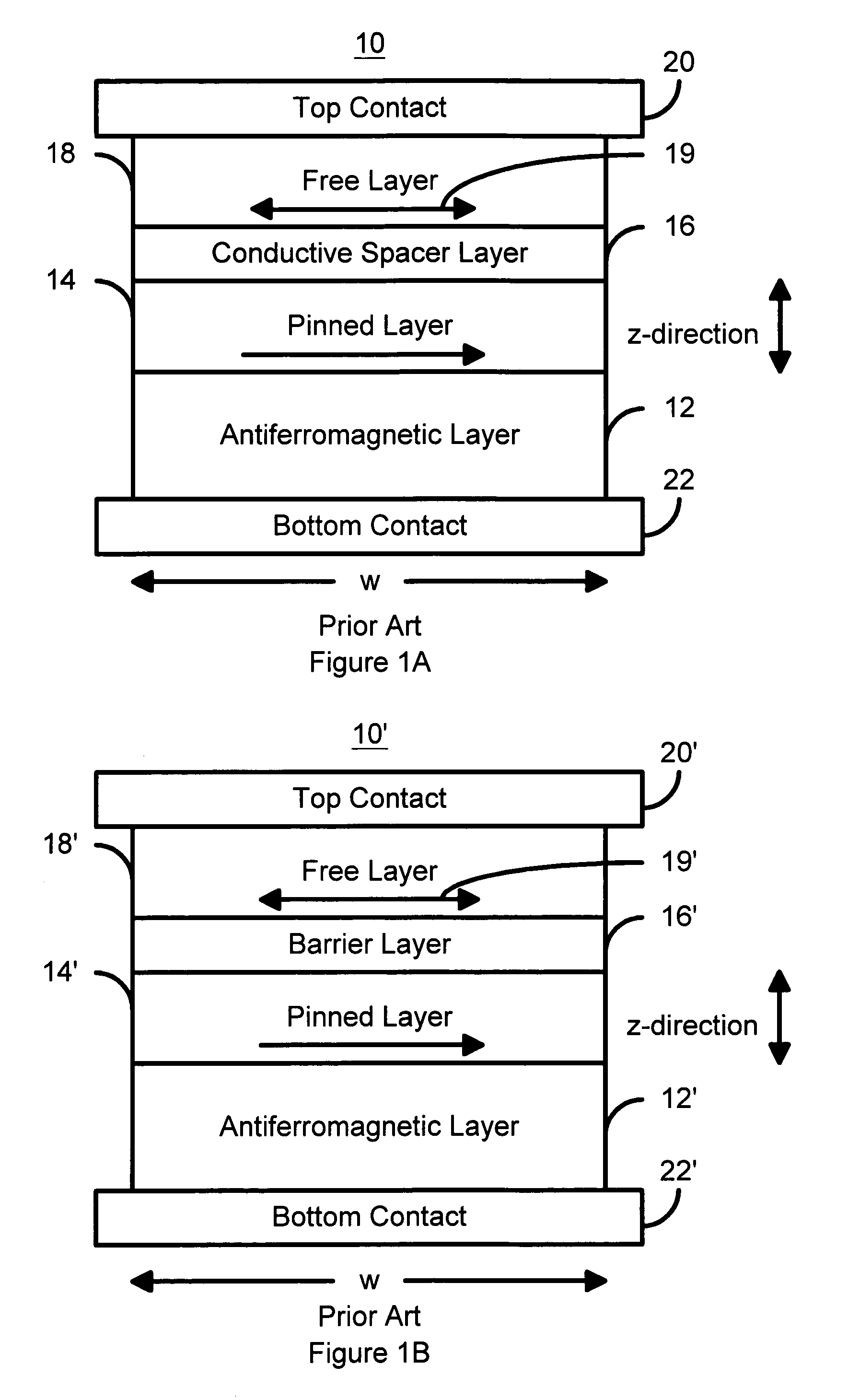
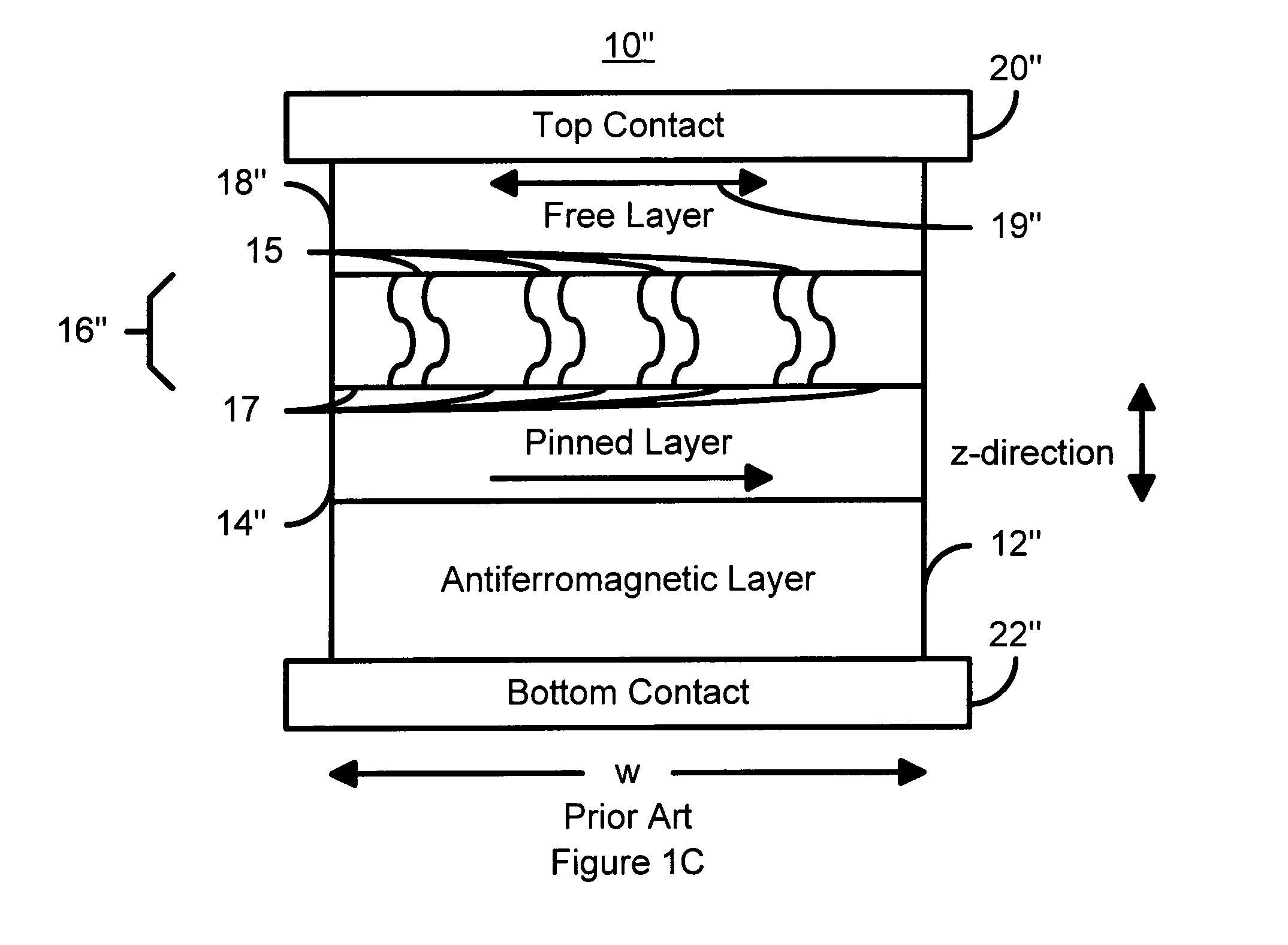
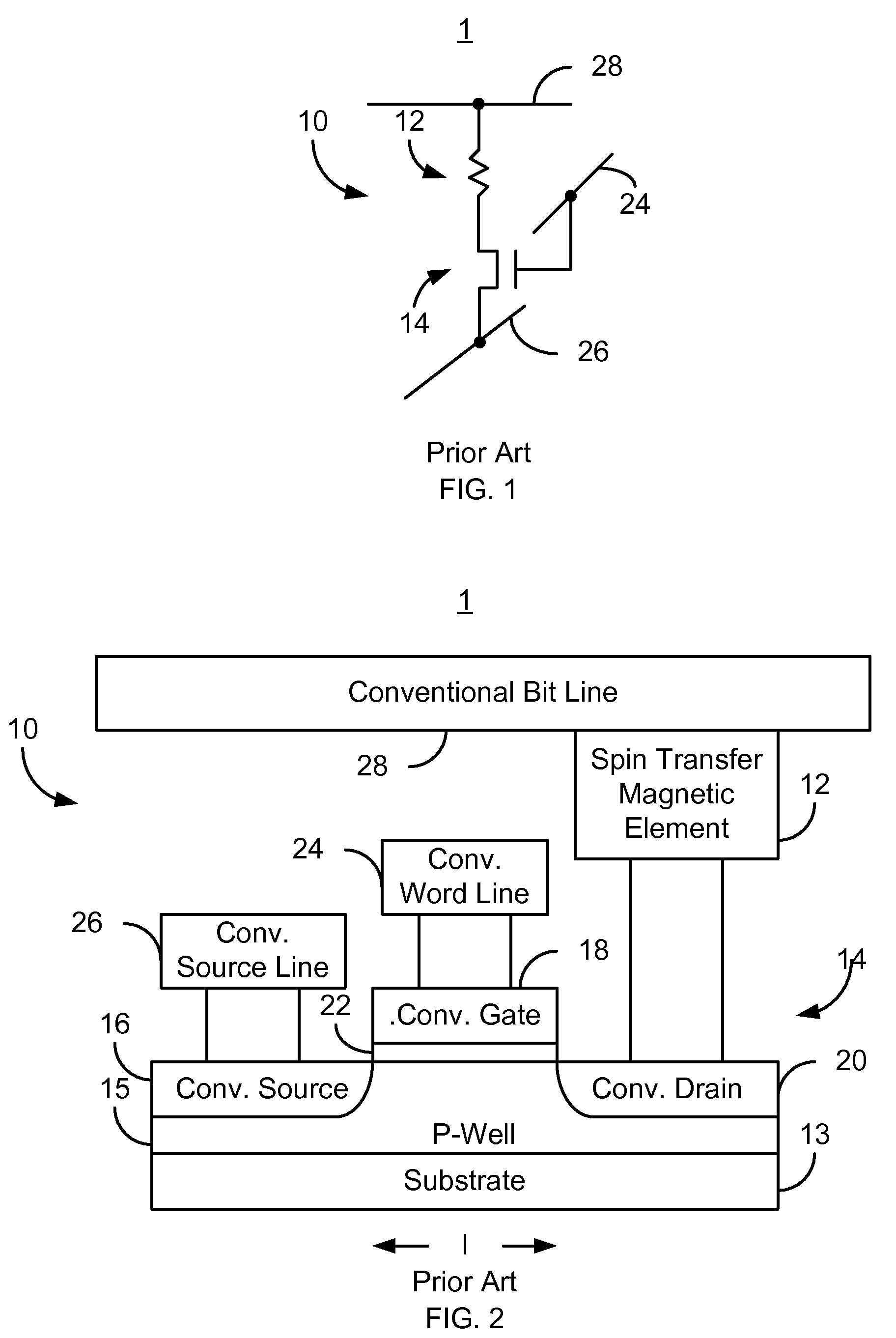
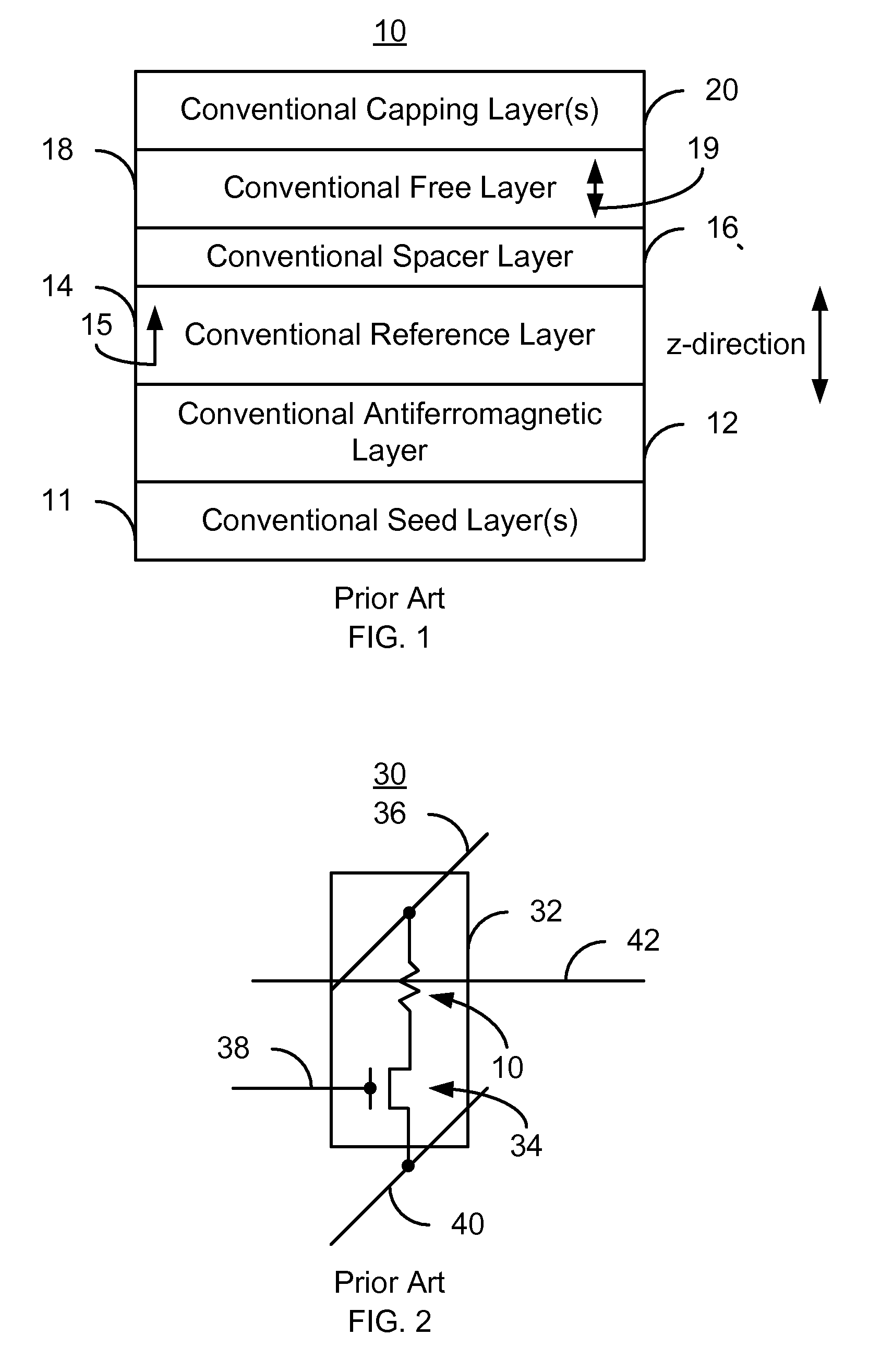
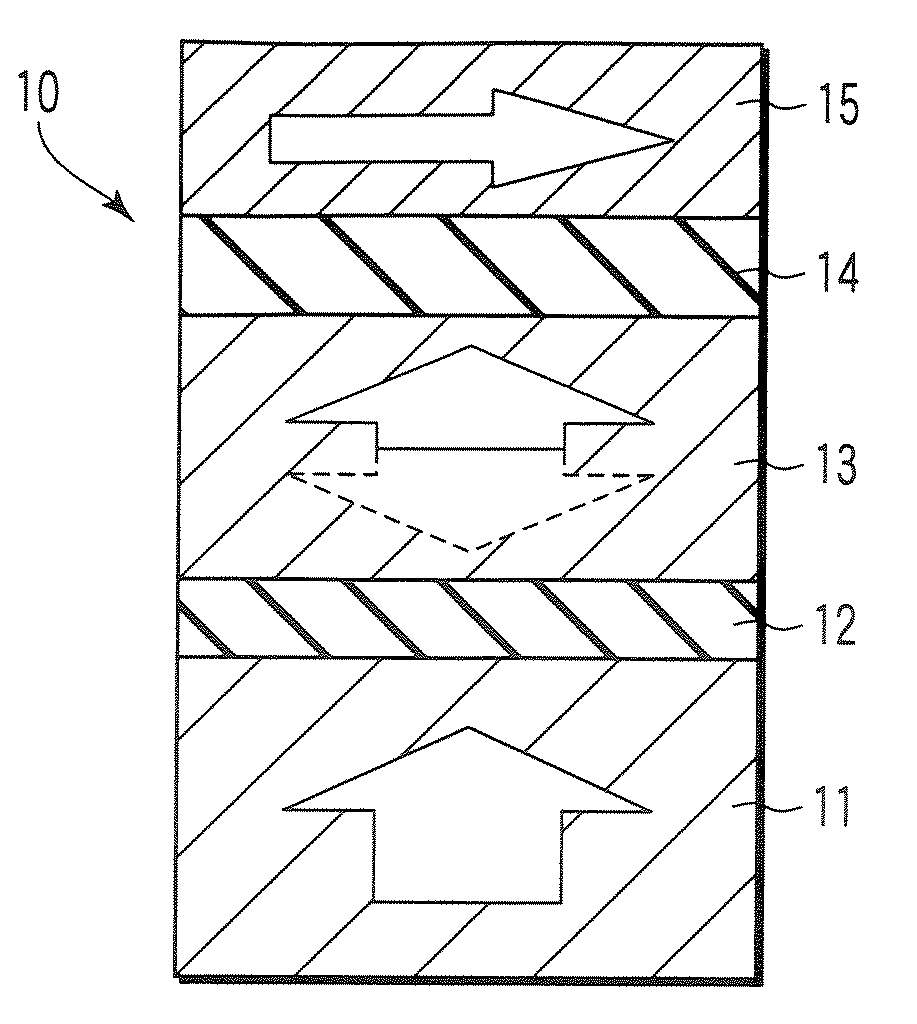
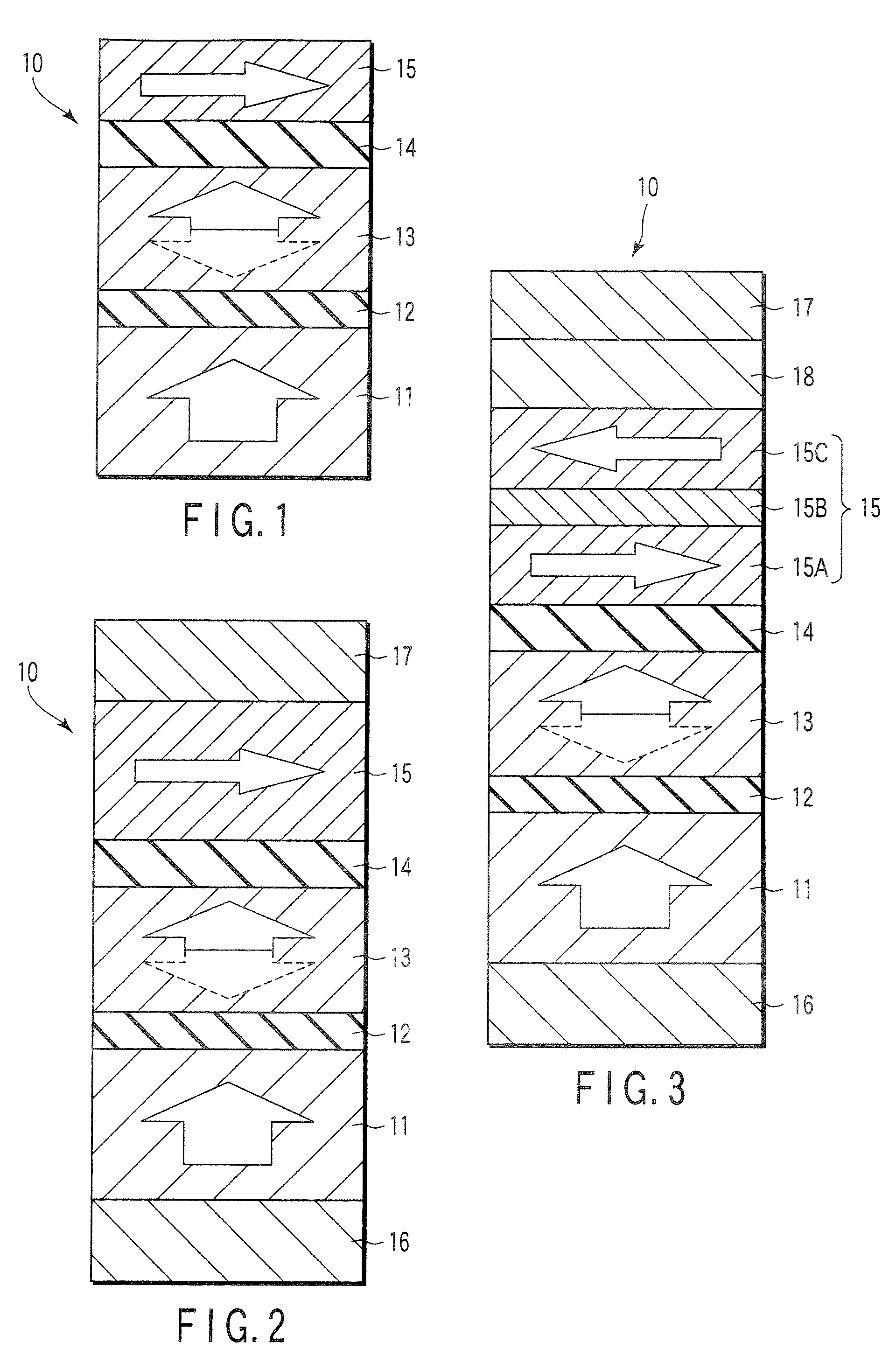
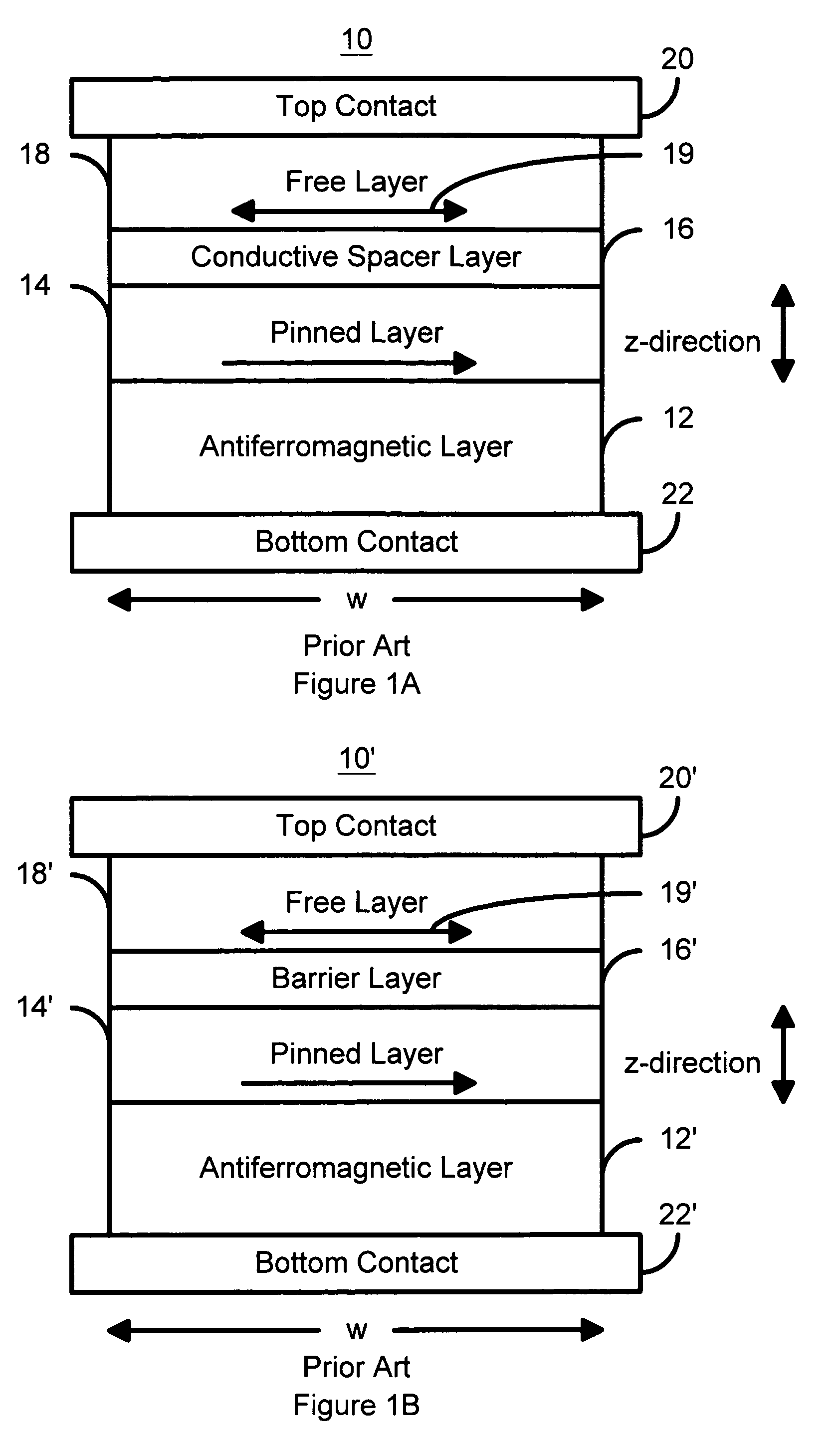
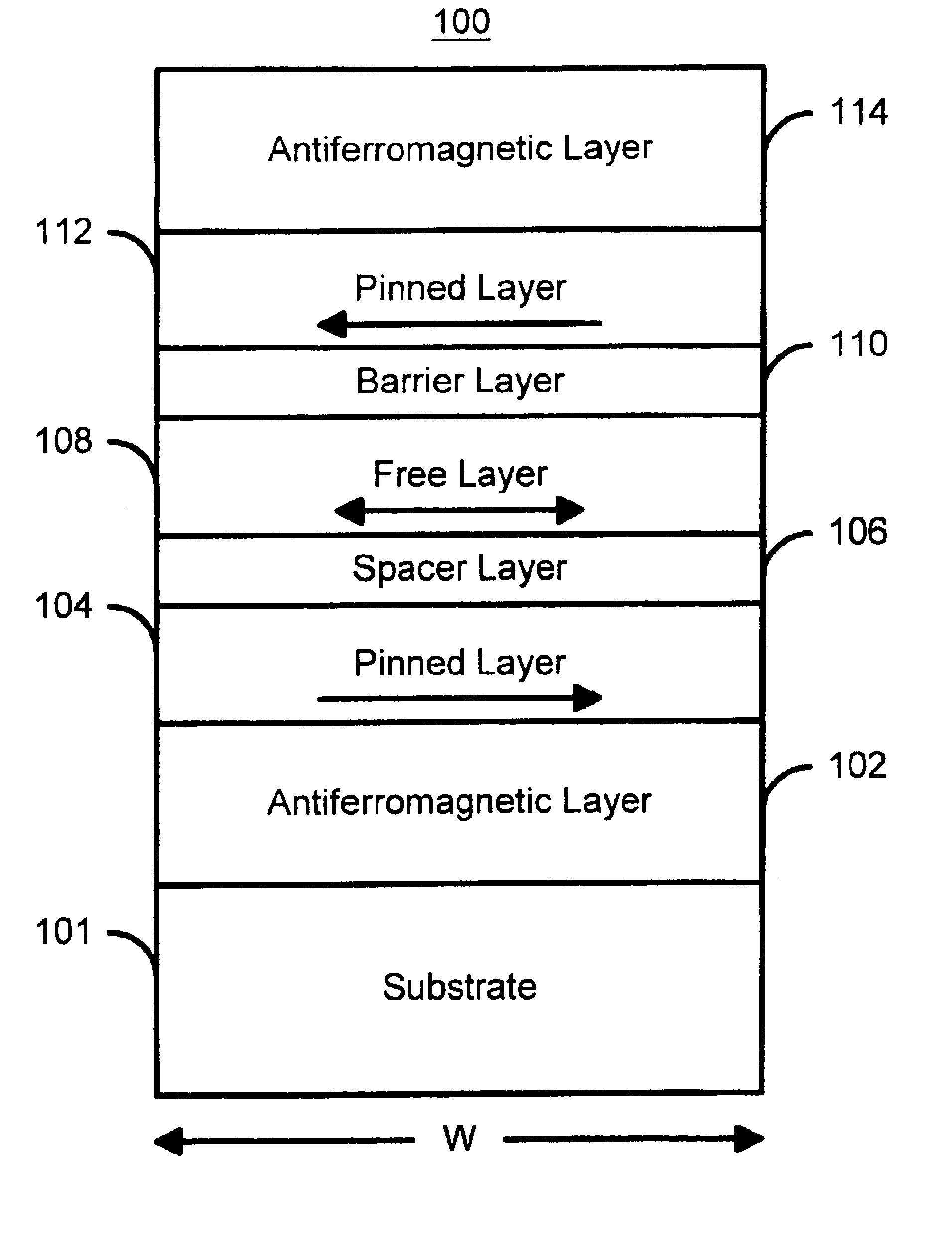
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The spacer layer resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The magnetic element may also include a barrier layer, a second pinned layer. Alternatively, second pinned and second spacer layers and a second free layer magnetostatically coupled to the free layer are included. At least one free layer has a high perpendicular anisotropy. The high perpendicular anisotropy has a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is at least twenty and less than one hundred percent of the out-of-plane demagnetization energy.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
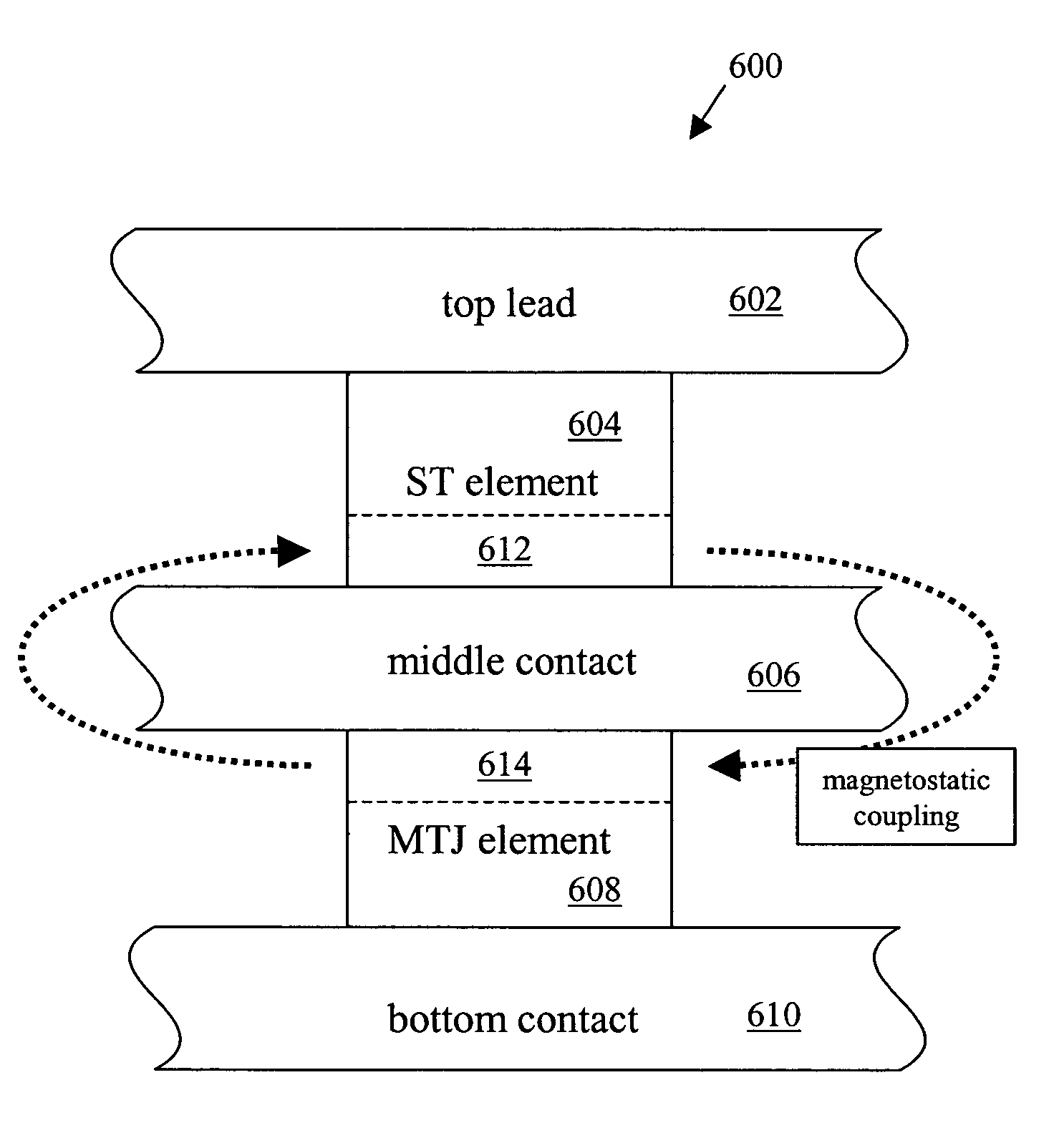
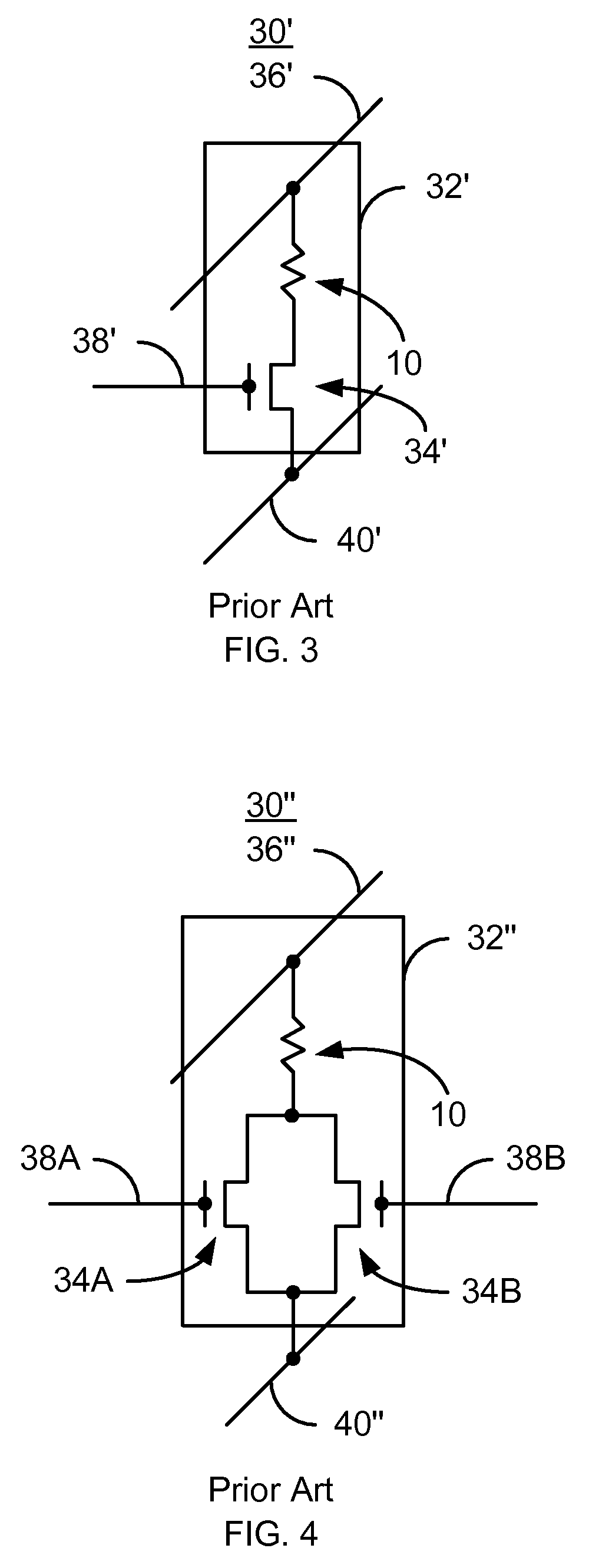
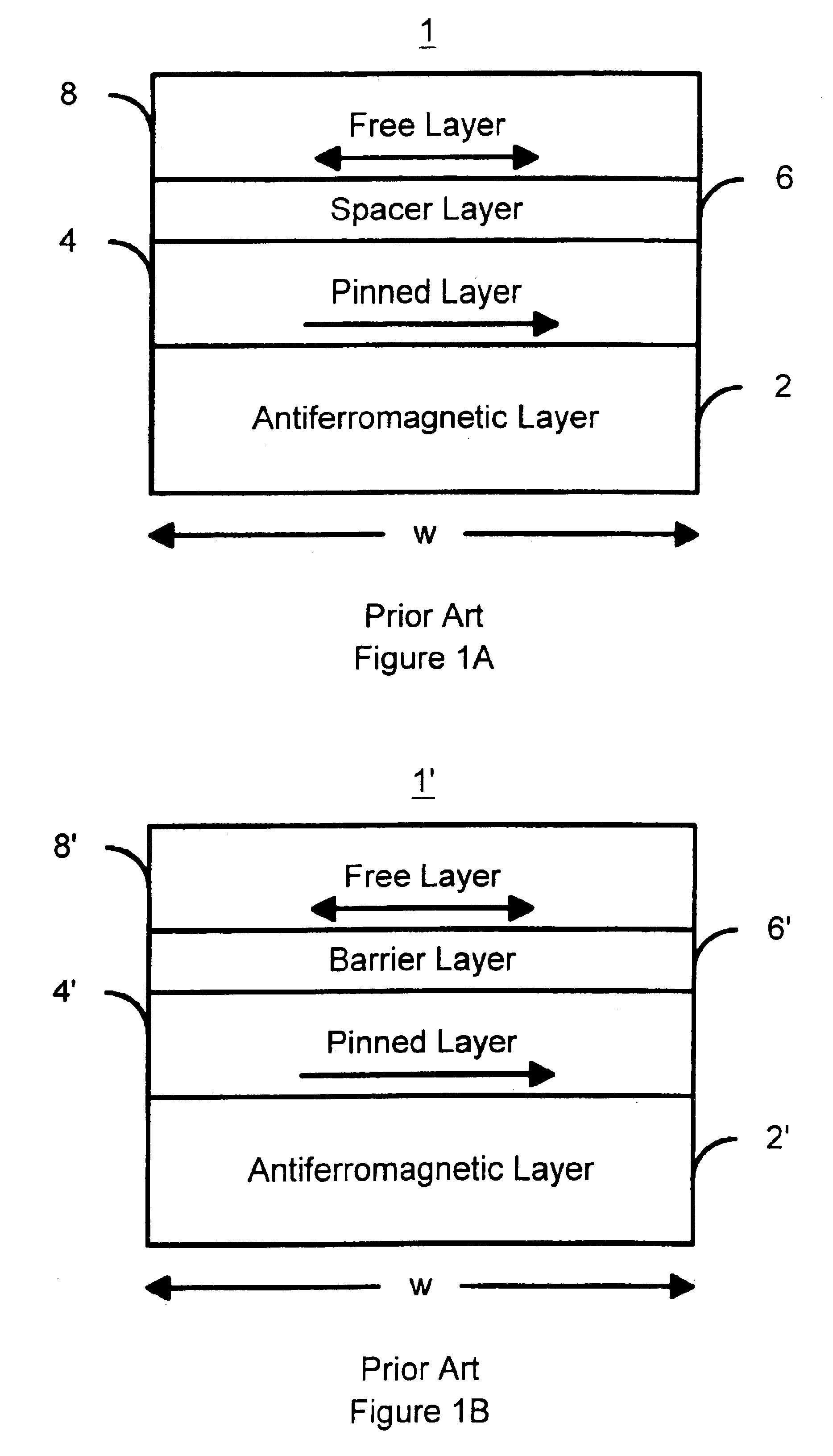
Three-terminal magnetostatically coupled spin transfer-based MRAM cell
A magnetic memory device for reading and writing a data state comprises at least three terminals including first, second, and third terminals. The magnetic memory device also includes a spin transfer (ST) driven element, disposed between the first terminal and the second terminal, and a readout element, disposed between the second terminal and the third terminal. The ST driven element includes a first free layer, and a readout element includes a second free layer. A magnetization direction of the second free layer in the readout element indicates a data state. A magnetization reversal of the first free layer within the ST driven element magnetostatically causes a magnetization reversal of the second free layer in the readout element, thereby recording the data state.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
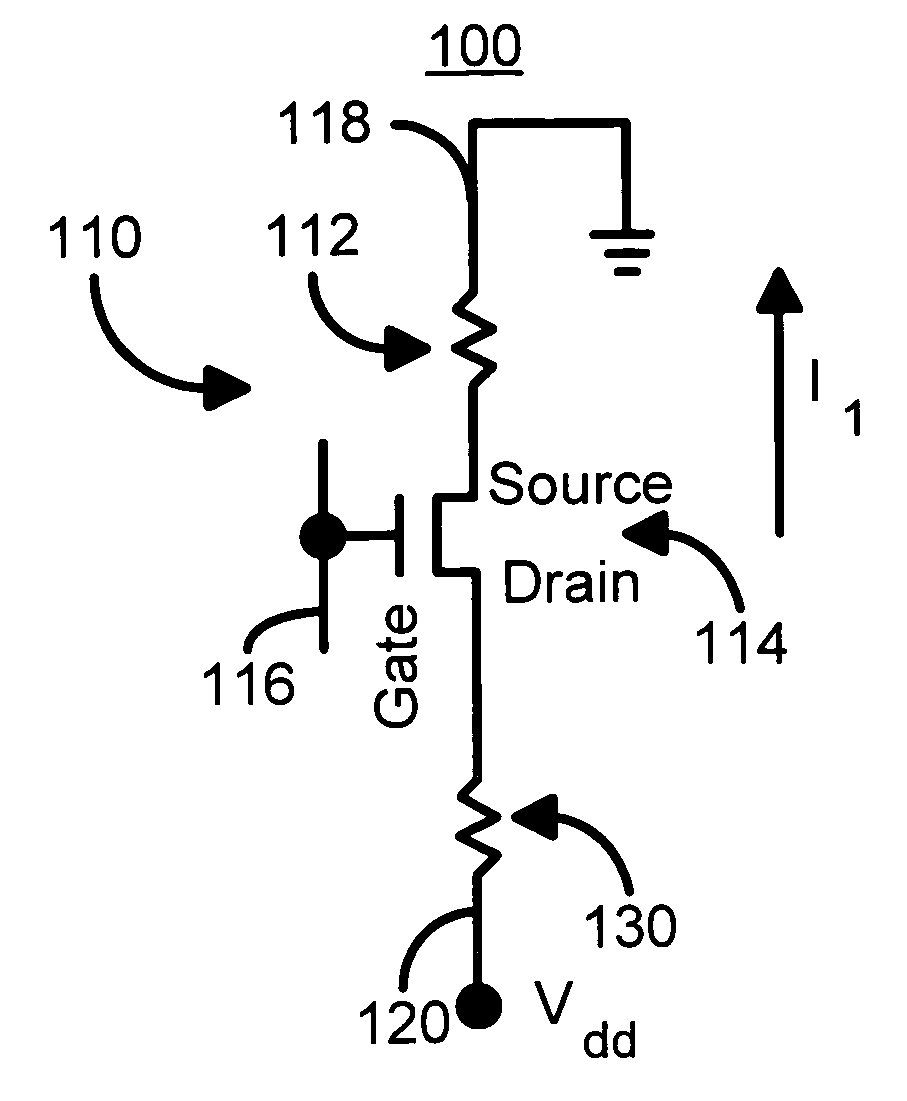
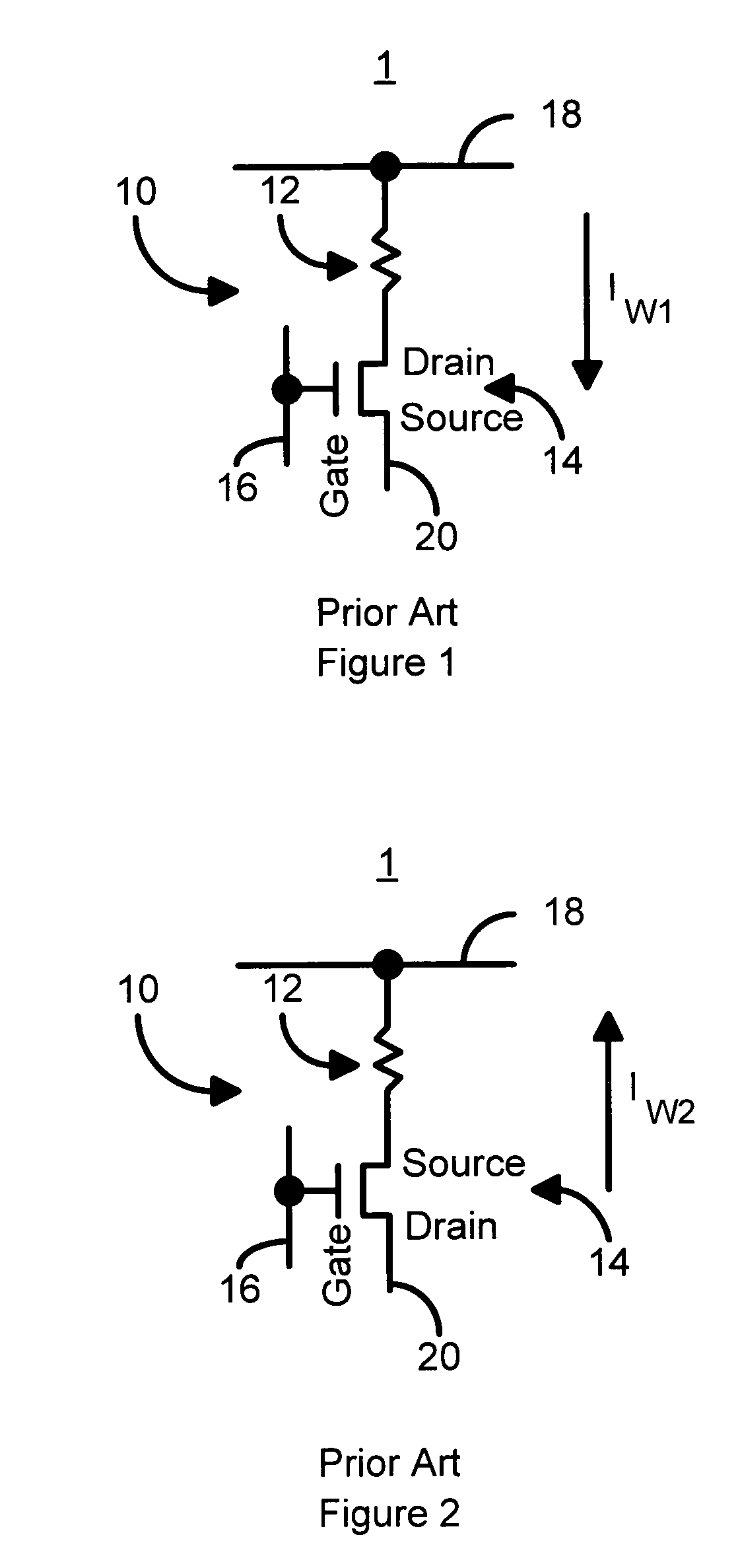
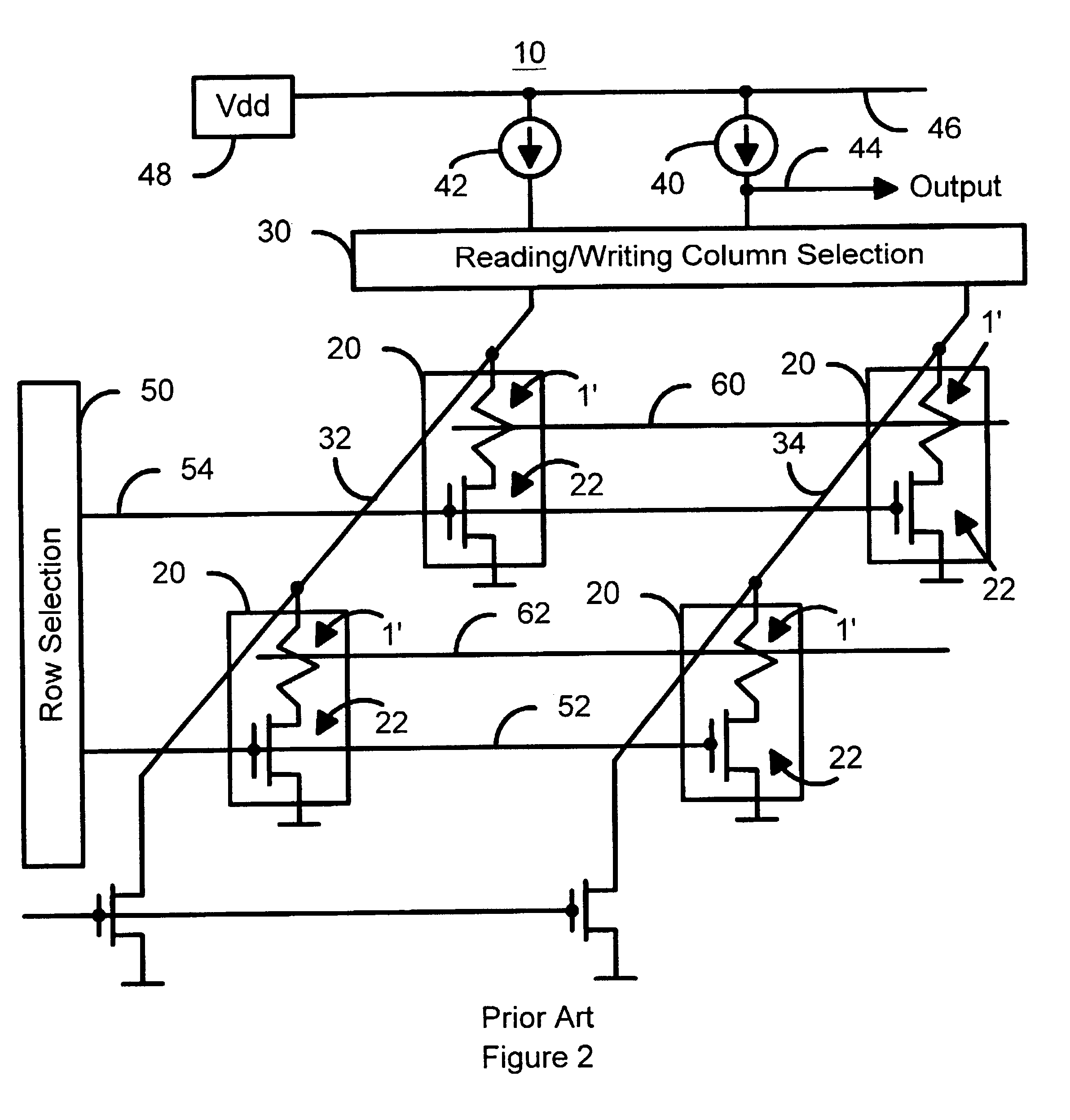
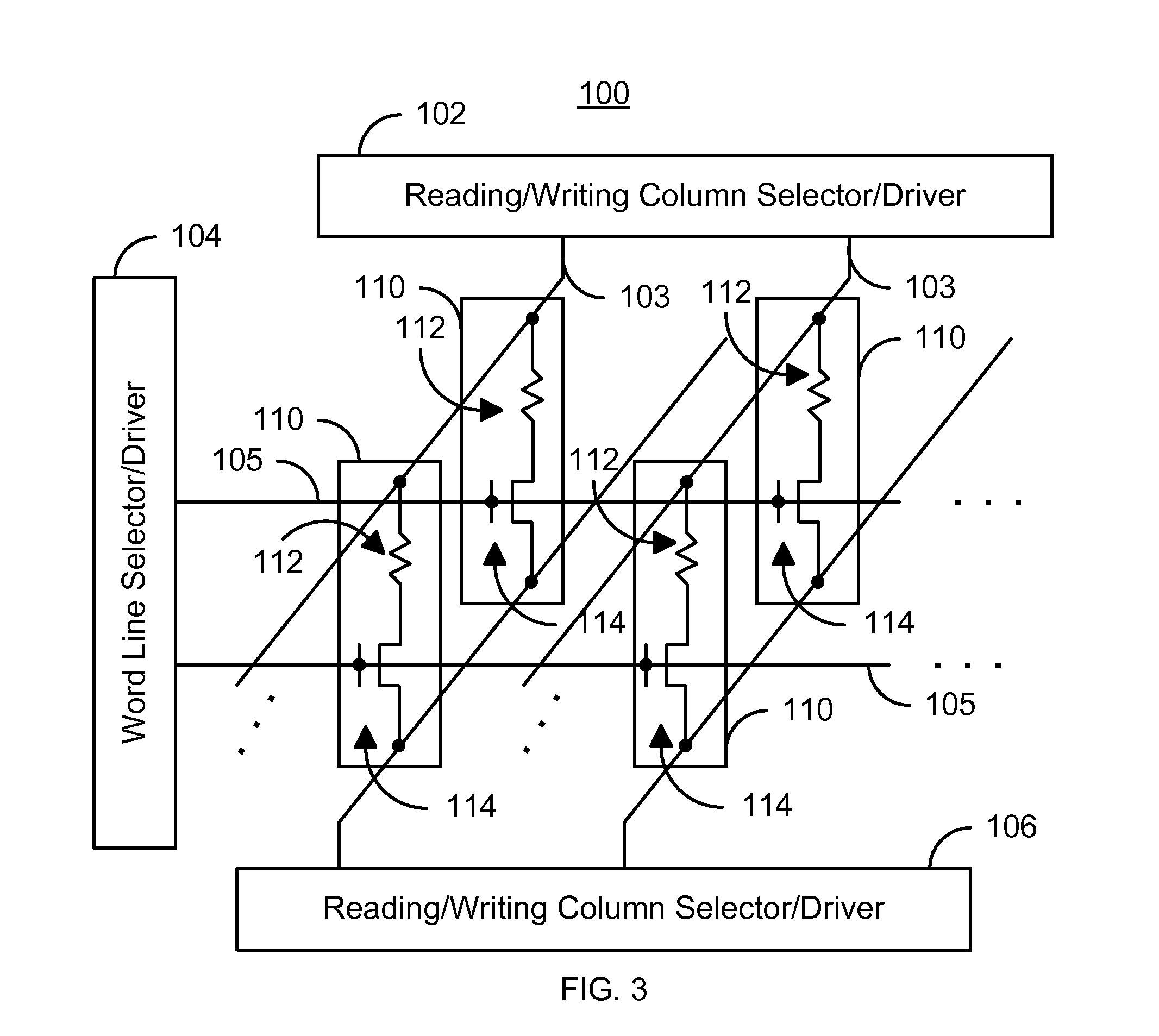
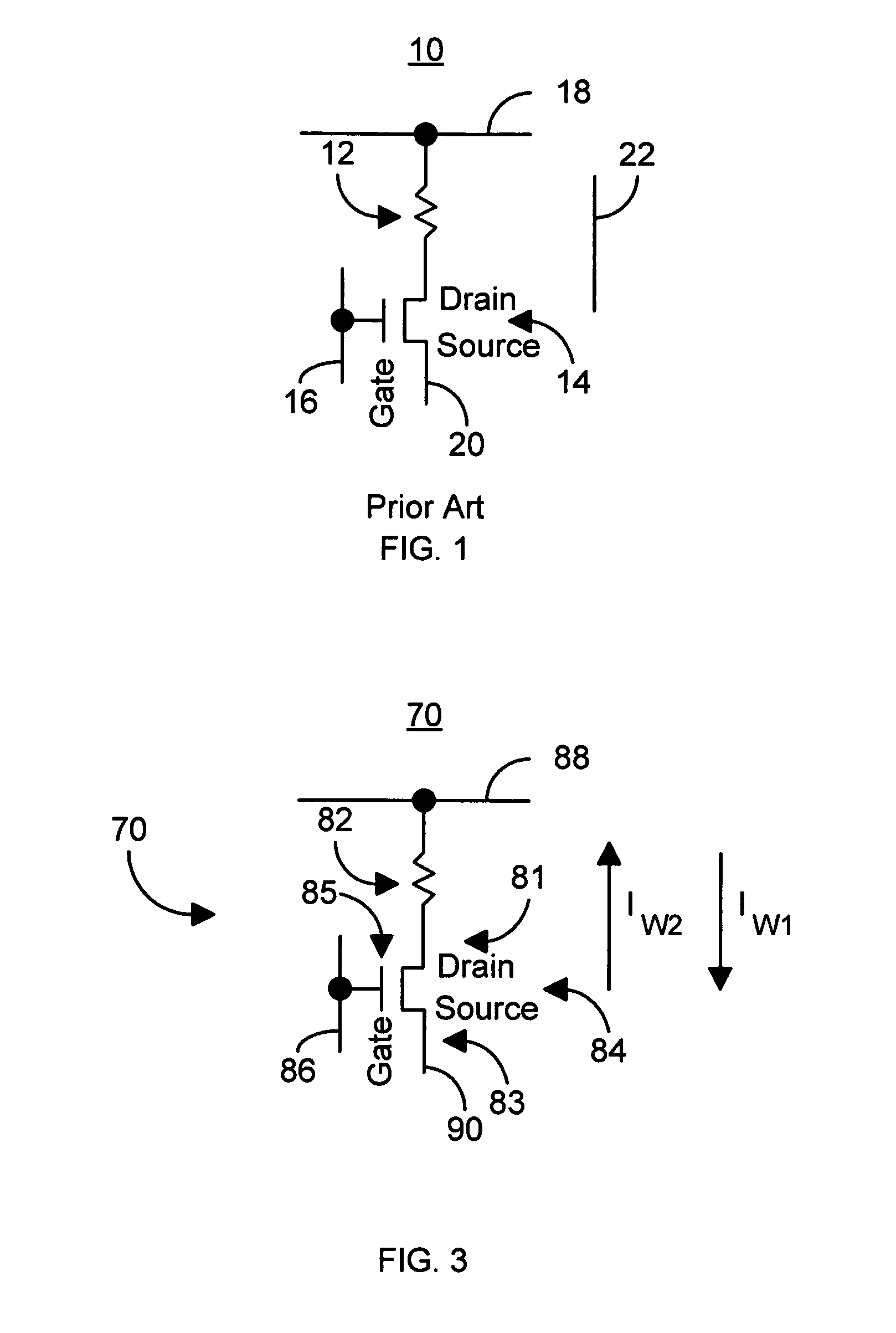
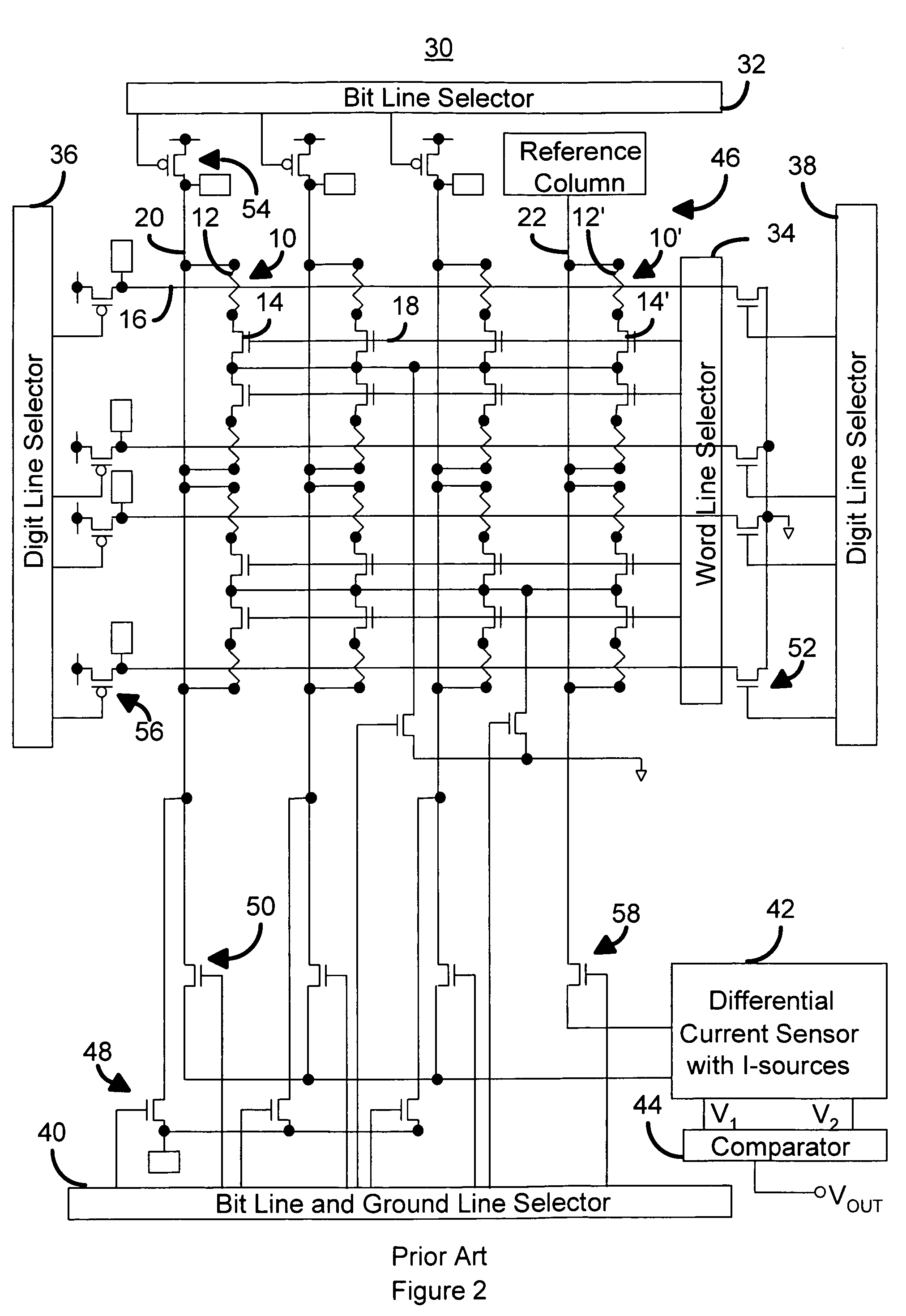
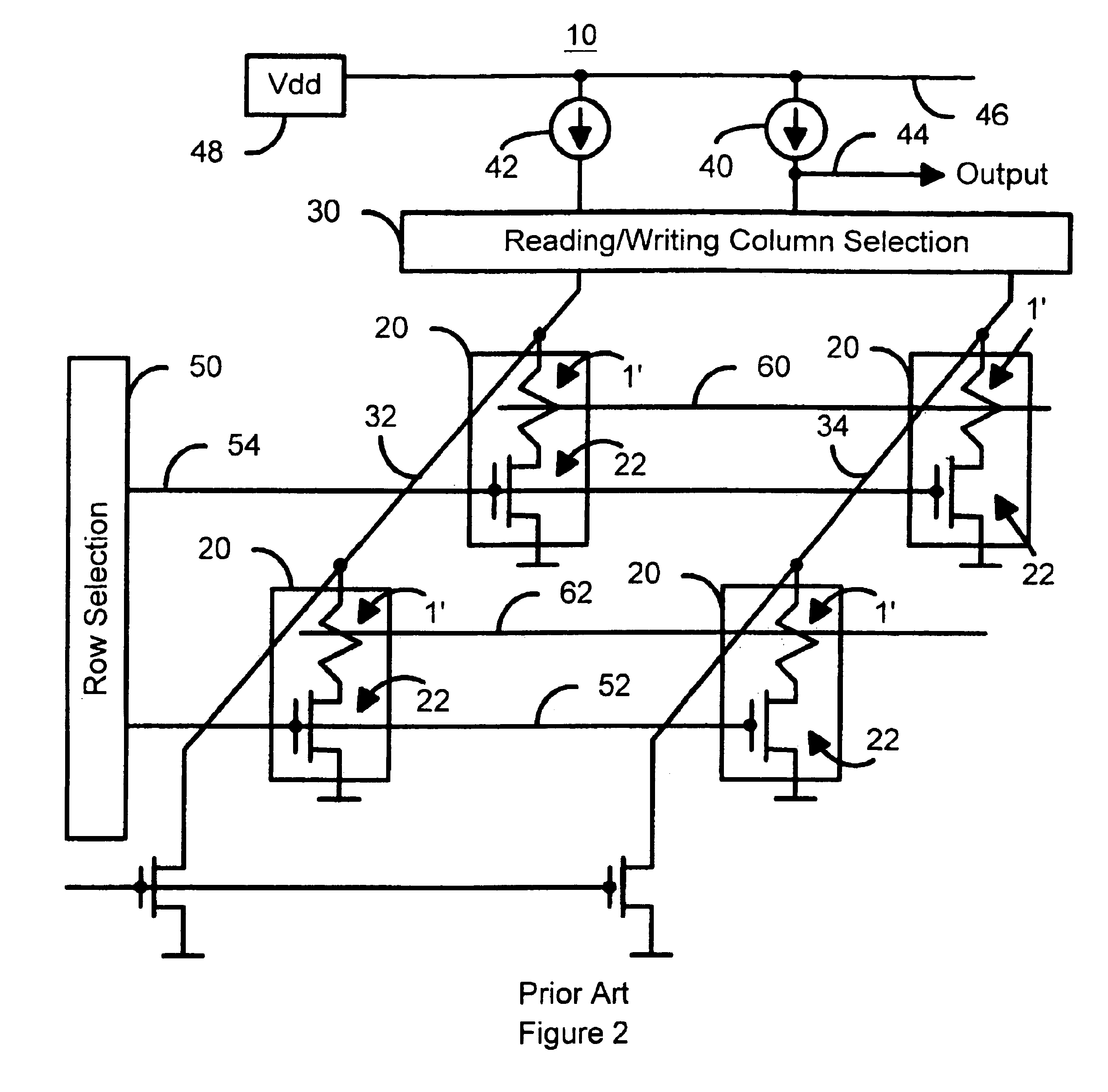
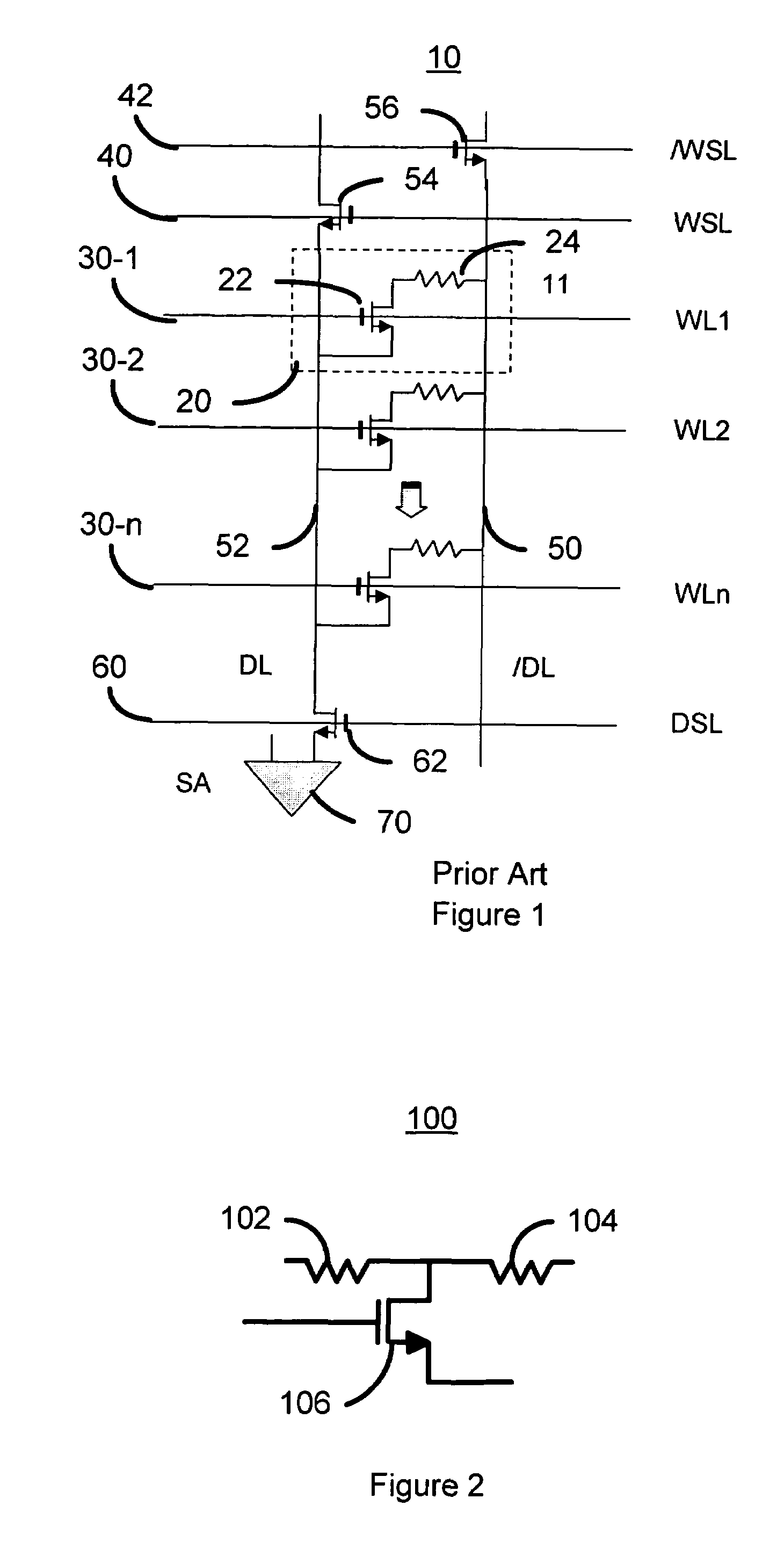
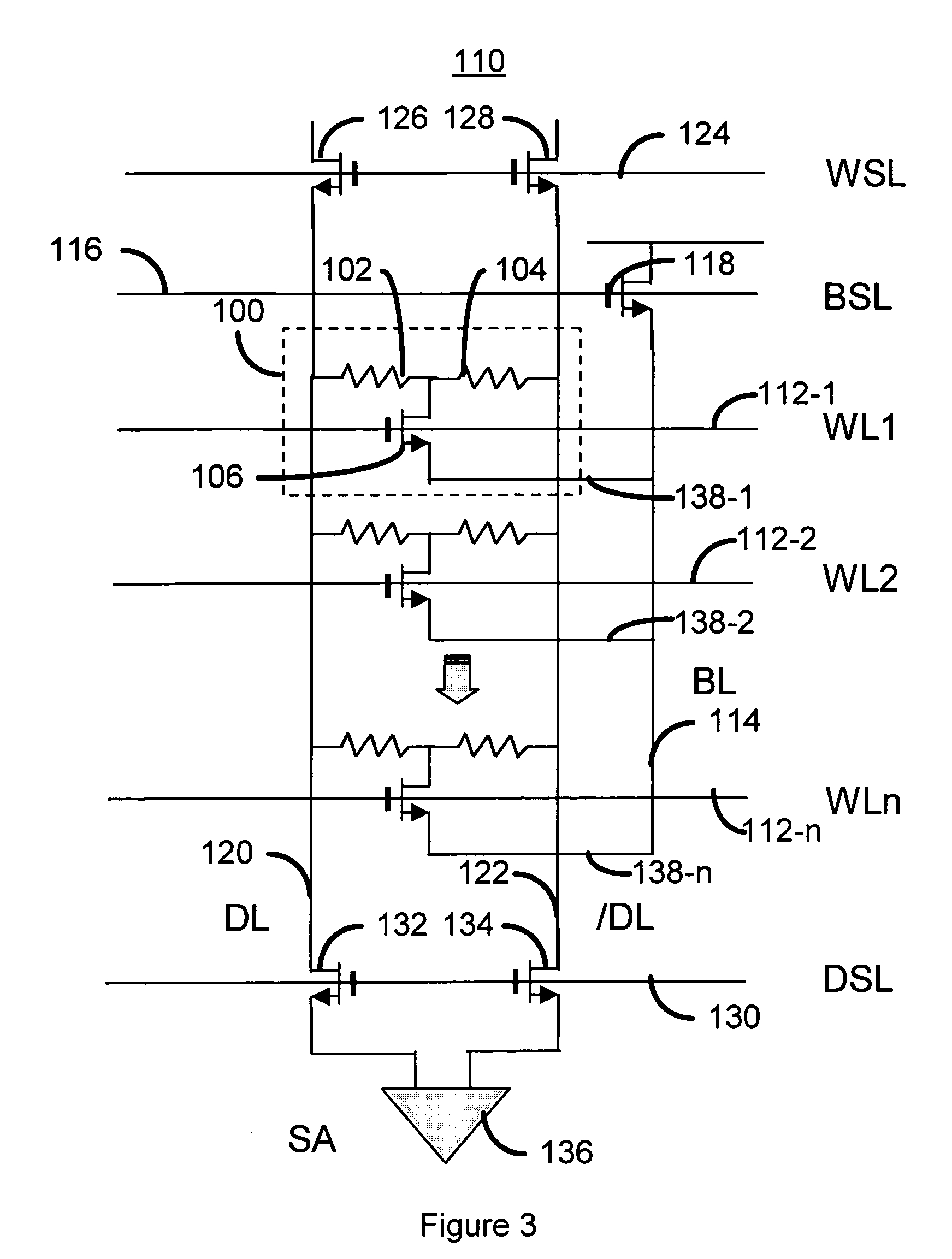
Method and system for providing current balanced writing for memory cells and magnetic devices
ActiveUS7187577B1Balanced write currentLower overall pressure dropDigital storageMagnetic memoryElectrical current
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is included. The method and system include providing at least one magnetic storage cell and at least one dummy resistor coupled with the at least one magnetic storage cell at least for a write operation of the at least one magnetic storage cell. Each of the at least one magnetic storage cell includes a magnetic element and a selection device coupled with the magnetic element. The magnetic element being programmed by a first write current driven through the magnetic element in a first direction and a second write current driven through the magnetic element in a second direction. The selection device is configured to be coupled between the magnetic element and the at least one dummy resistor.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Magnetic memory element utilizing spin transfer switching and storing multiple bits
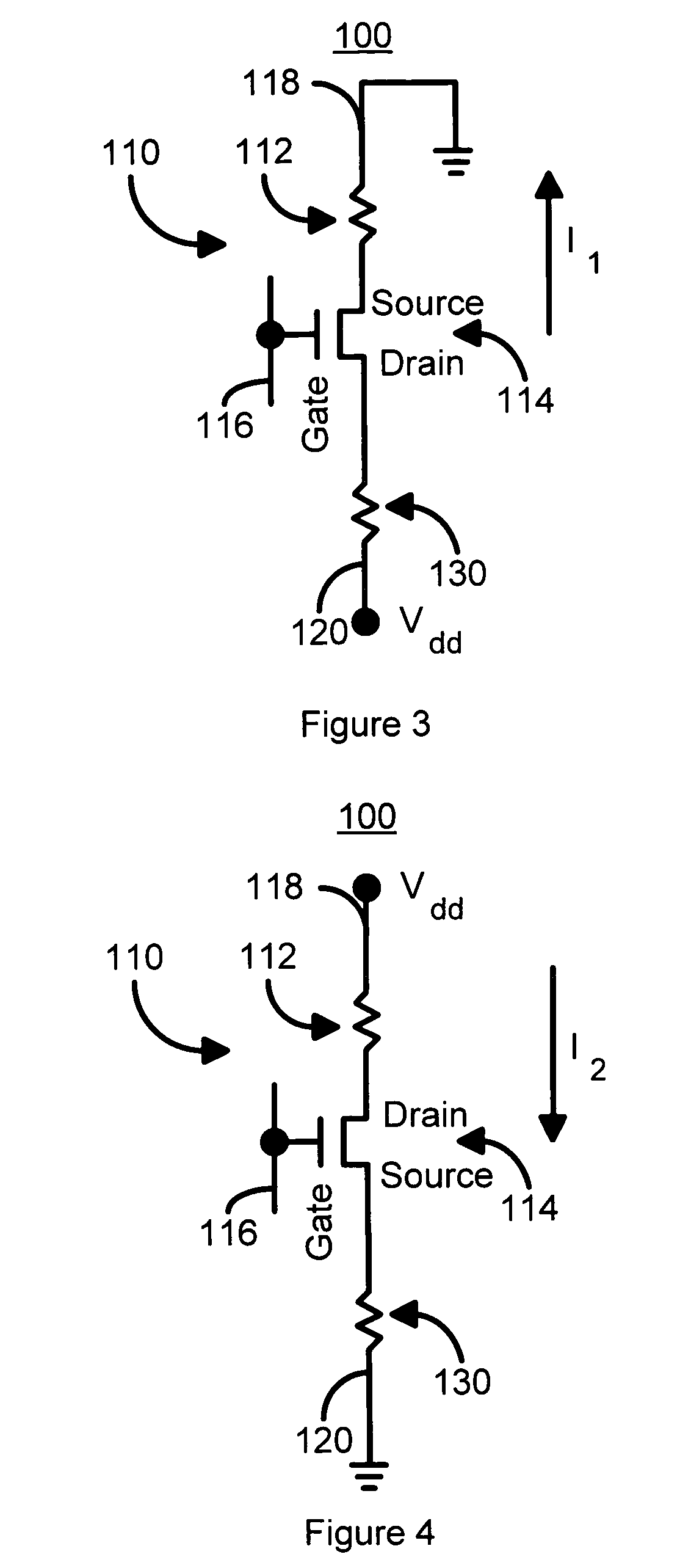
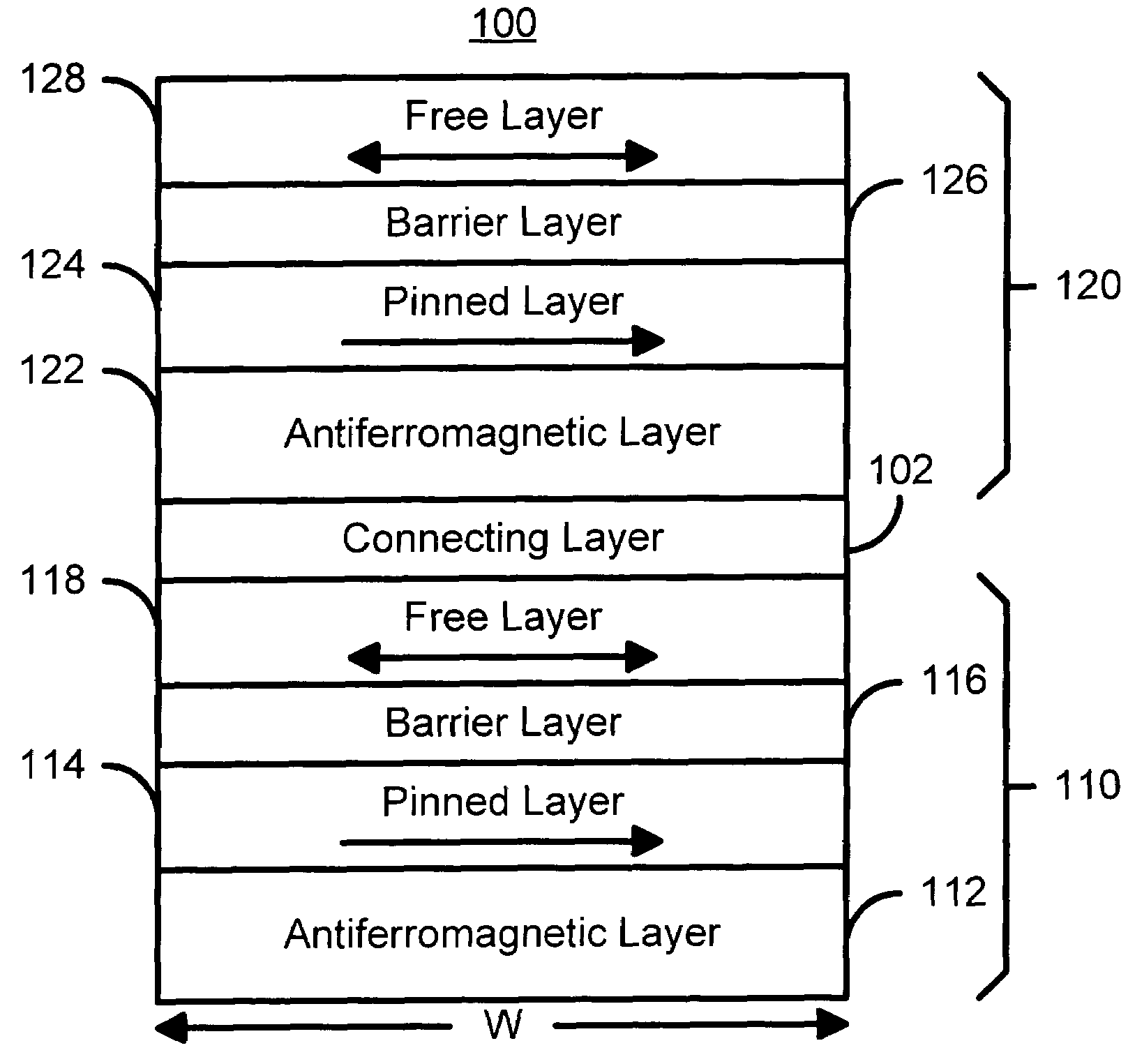
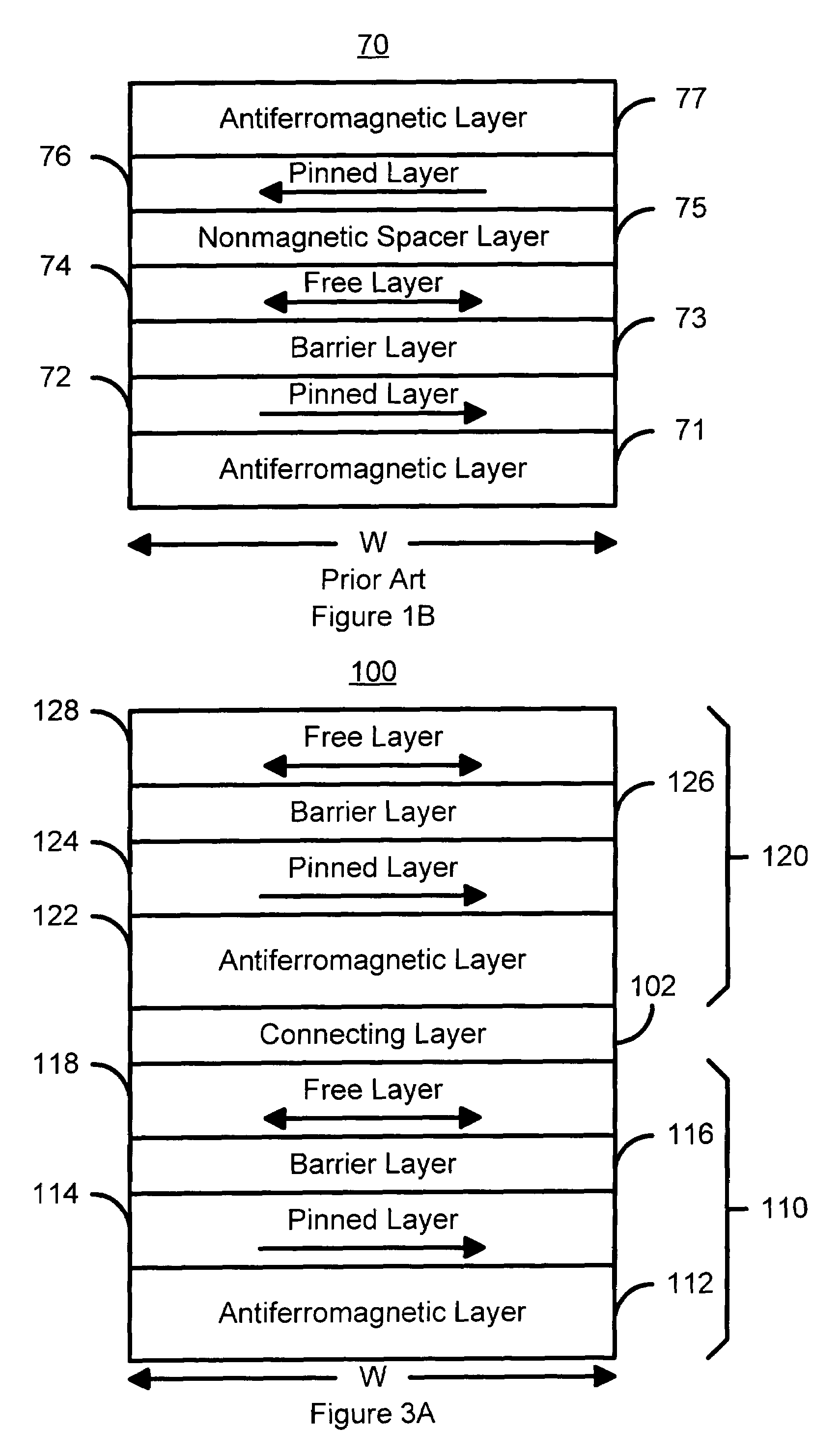
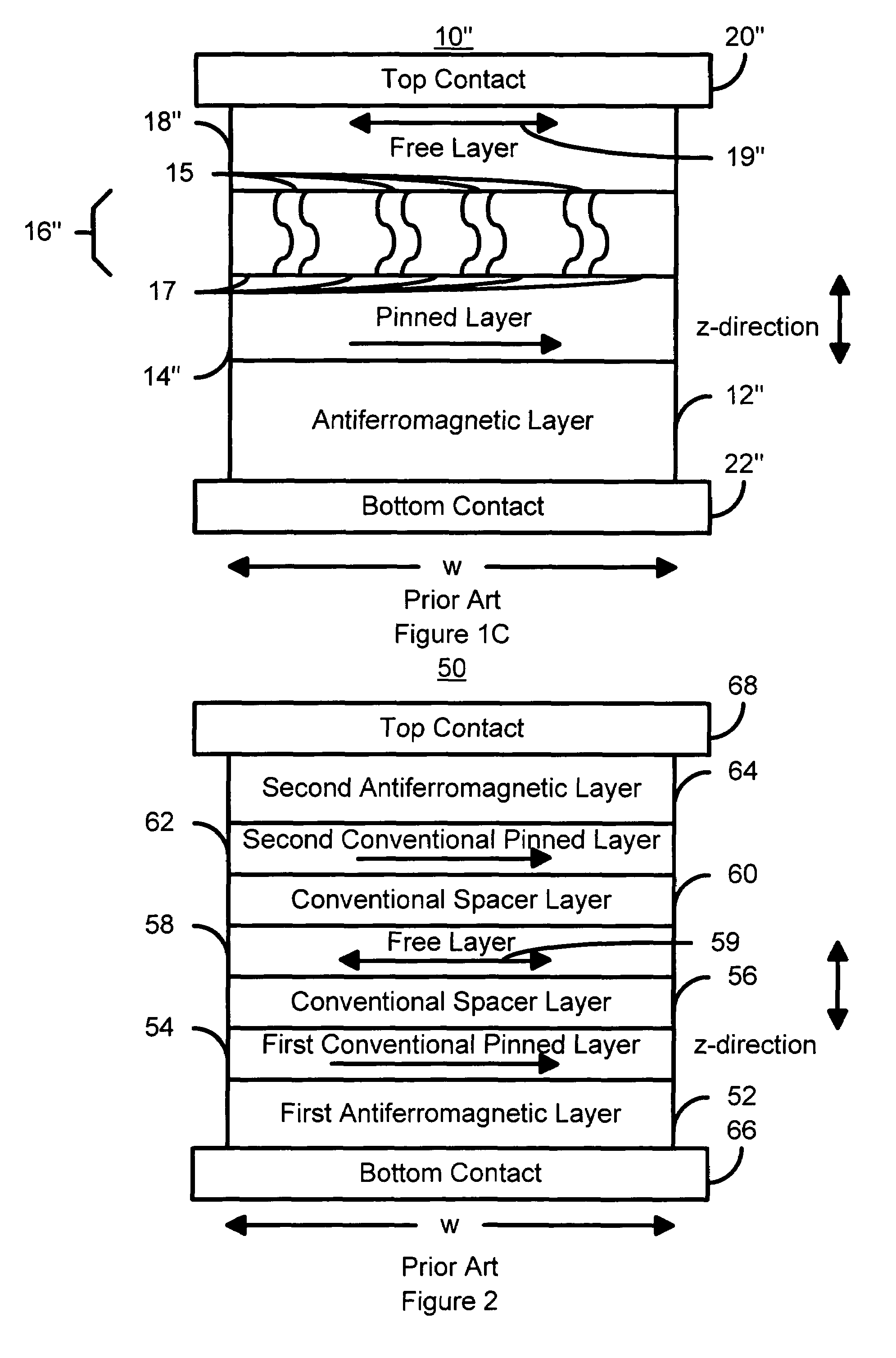
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of storing multiple bits is disclosed. The method and system include providing first pinned layer, a first nonmagnetic layer, a first free layer, a connecting layer, a second pinned layer, a second nonmagetic layer and a second free layer. The first pinned layer is ferromagnetic and has a first pinned layer magnetization pinned in a first direction. The first nonmagnetic layer resides between the first pinned layer and the first free layer. The first free layer being ferromagnetic and has a first free layer magnetization. The second pinned layer is ferromagnetic and has a second pinned layer magnetization pinned in a second direction. The connecting layer resides between the second pinned layer and the first free layer. The second nonmagnetic layer resides between the second pinned layer and the second free layer. The second free layer being ferromagnetic and having a second free layer magnetization. The magnetic element is configured to allow the first free layer magnetization and the second free layer magnetization to change direction due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Perpendicular magnetization magnetic element utilizing spin transfer
ActiveUS6967863B2Reduce currentNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular magnetizationMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The method and system include providing a first pinned layer, a barrier layer, a free layer, a conductive nonmagnetic spacer layer, and a second pinned layer. Each pinned layer has a pinned layer easy axis. At least a portion of the pinned layer easy axis is in a perpendicular direction. The barrier layer resides between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The spacer layer is between the free layer and the second pinned layer. The free layer has a free layer easy axis, at least a portion of which is in the perpendicular direction. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the free layer to be switched due to spin transfer effect when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. Because of the perpendicular magnetization(s), the writing current for spin transfer may be significantly reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
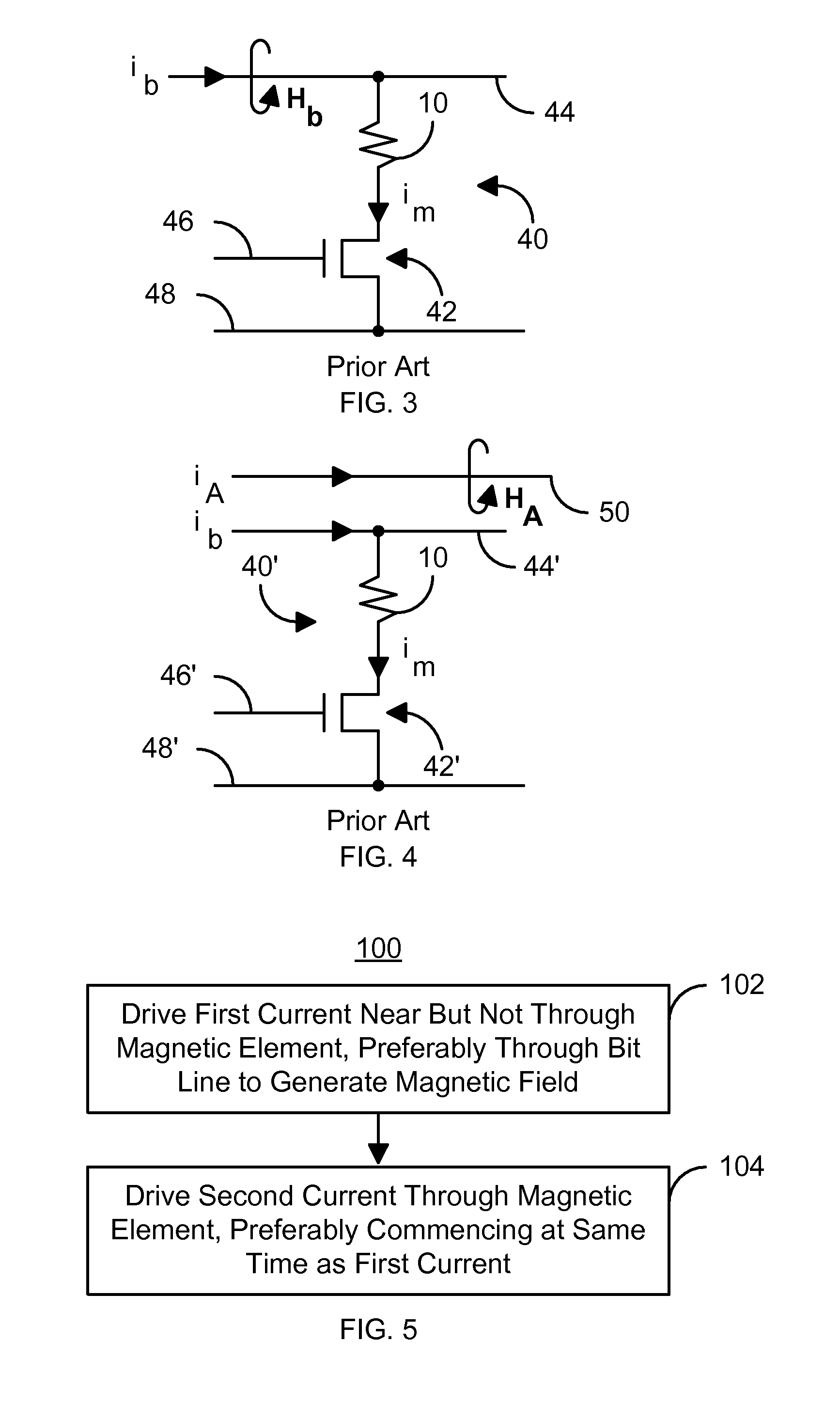
Method and system for using a pulsed field to assist spin transfer induced switching of magnetic memory elements
A method and system for providing and utilizing a magnetic memory are described. The magnetic memory includes a plurality of magnetic storage cells. Each magnetic storage cell includes magnetic element(s) programmable due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element(s) and selection device(s). The method and system include driving a first current in proximity to but not through the magnetic element(s) of a portion of the magnetic storage cells. The first current generates a magnetic field. The method and system also include driving a second current through the magnetic element(s) of the portion of the magnetic storage cells. The first and second currents are preferably both driven through bit line(s) coupled with the magnetic element(s). The first and second currents are turned on at a start time. The second current and the magnetic field are sufficient to program the magnetic element(s).
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
Off-axis pinned layer magnetic element utilizing spin transfer and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6888742B1Enhanced output signalWriting time becomes shortDigital storageMagnetic memorySpin transfer
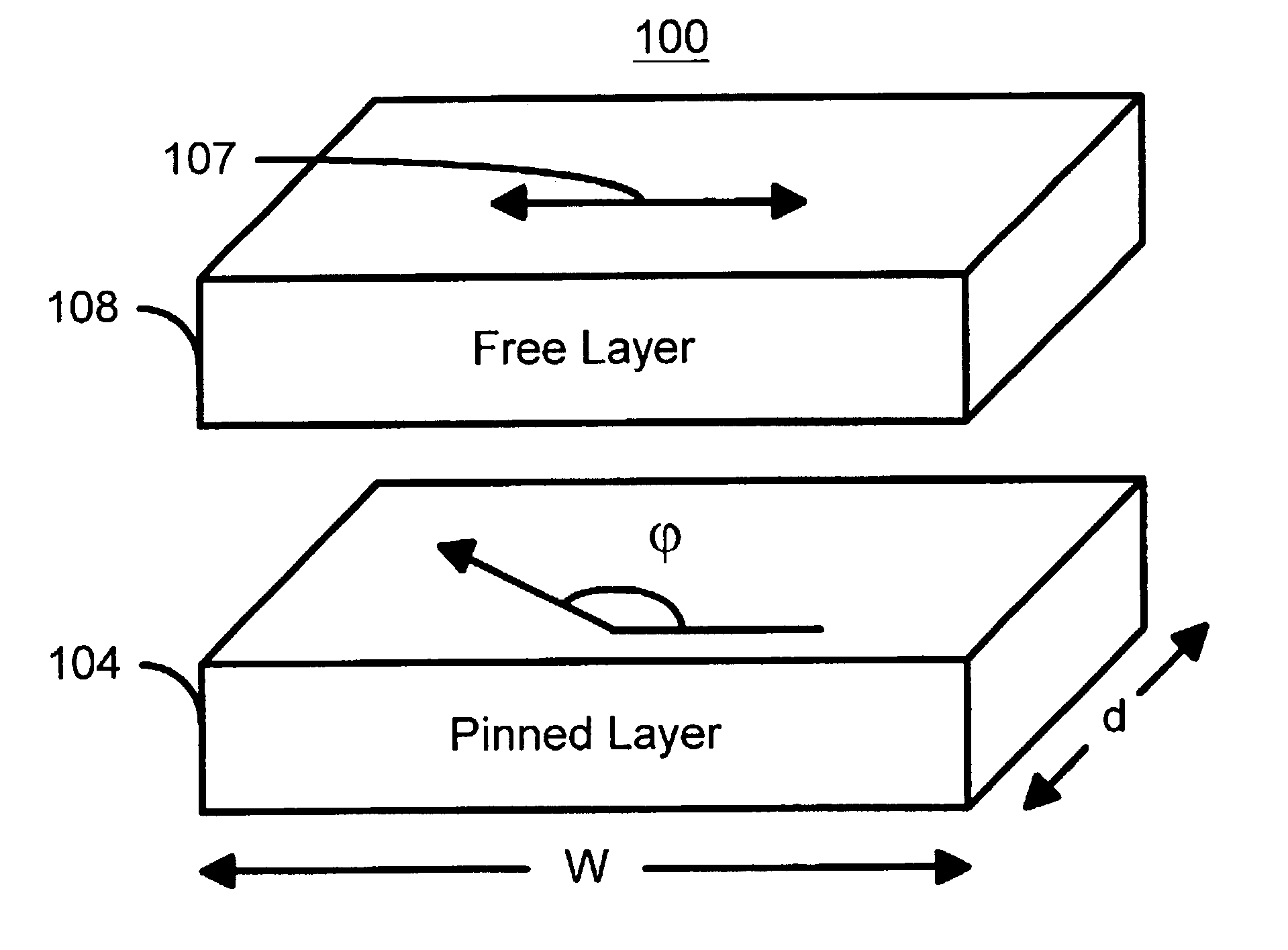
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of being written in a reduced time using the spin-transfer effect while generating a high output signal and a magnetic memory using the magnetic element are disclosed. The magnetic element includes a ferromagnetic pinned layer, a nonmagnetic intermediate layer, and a ferromagnetic free layer. The pinned layer has a magnetization pinned in a first direction. The nonmagnetic intermediate layer resides between the pinned layer and the free layer. The free layer has a magnetization with an easy axis in a second direction. The first direction is in the same plane as the second direction and is oriented at an angle with respect to the second direction. This angle is different from zero and π radians. The magnetic element is also configured to allow the magnetization of the free layer to change direction due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
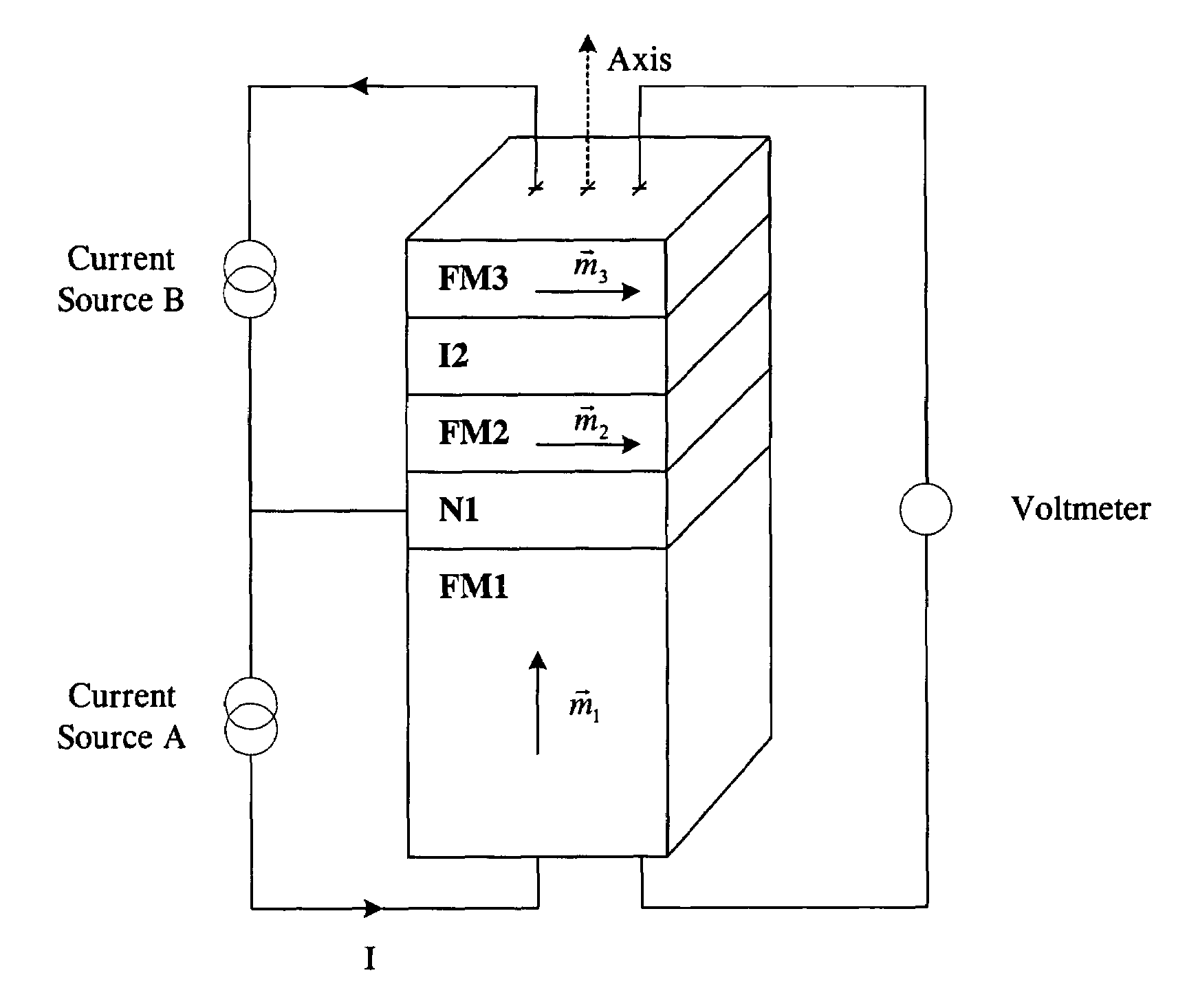
Thermally stable magnetic elements utilizing spin transfer and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6838740B2Improve performanceImprove thermal stabilityTransistorNanomagnetismAntiferromagnetic couplingMagnetic memory
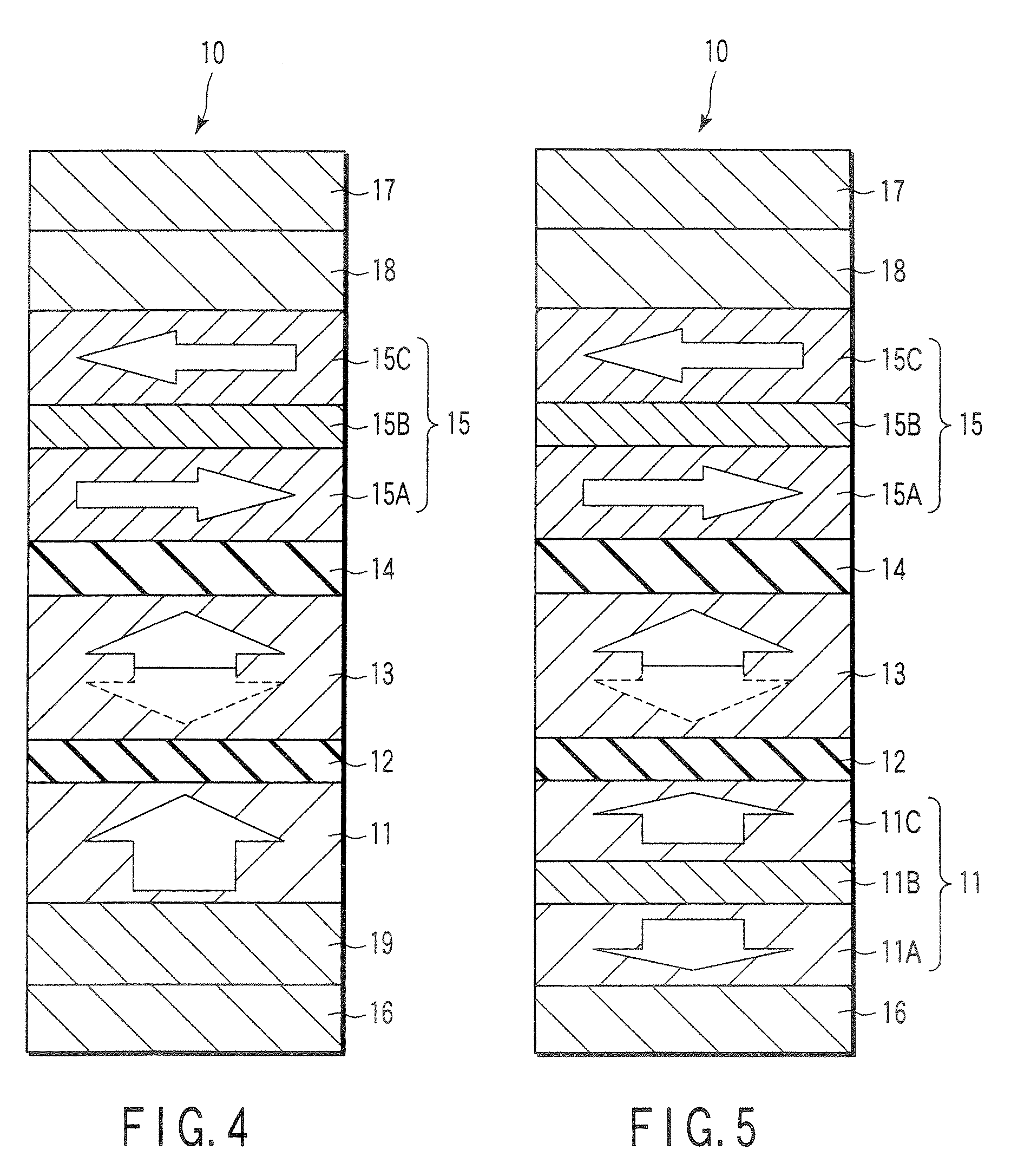
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of being written using spin-transfer effect while being thermally stable and a magnetic memory using the magnetic element are disclosed. The magnetic element includes a first, second and third pinned layers, first and second nonmagnetic layers, a free layer and a nonmagnetic spacer layers. The first, second and third pinned layers are ferromagnetic and have first, second and third magnetizations pinned in first, second and third directions. The first and second nonmagnetic layers include first and second diffusion barriers, respectively. The first and second nonmagnetic layers are between the first and second pinned layers and the second and third pinned layers, respectively. The first and second pinned layers and the second and third pinned layers are antiferromagnetically coupled. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is conductive and resides between the free layer and the third pinned layer. In addition, performance can be further improved by doping Co containing ferromagnetic layers with Cr and / or Pt.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
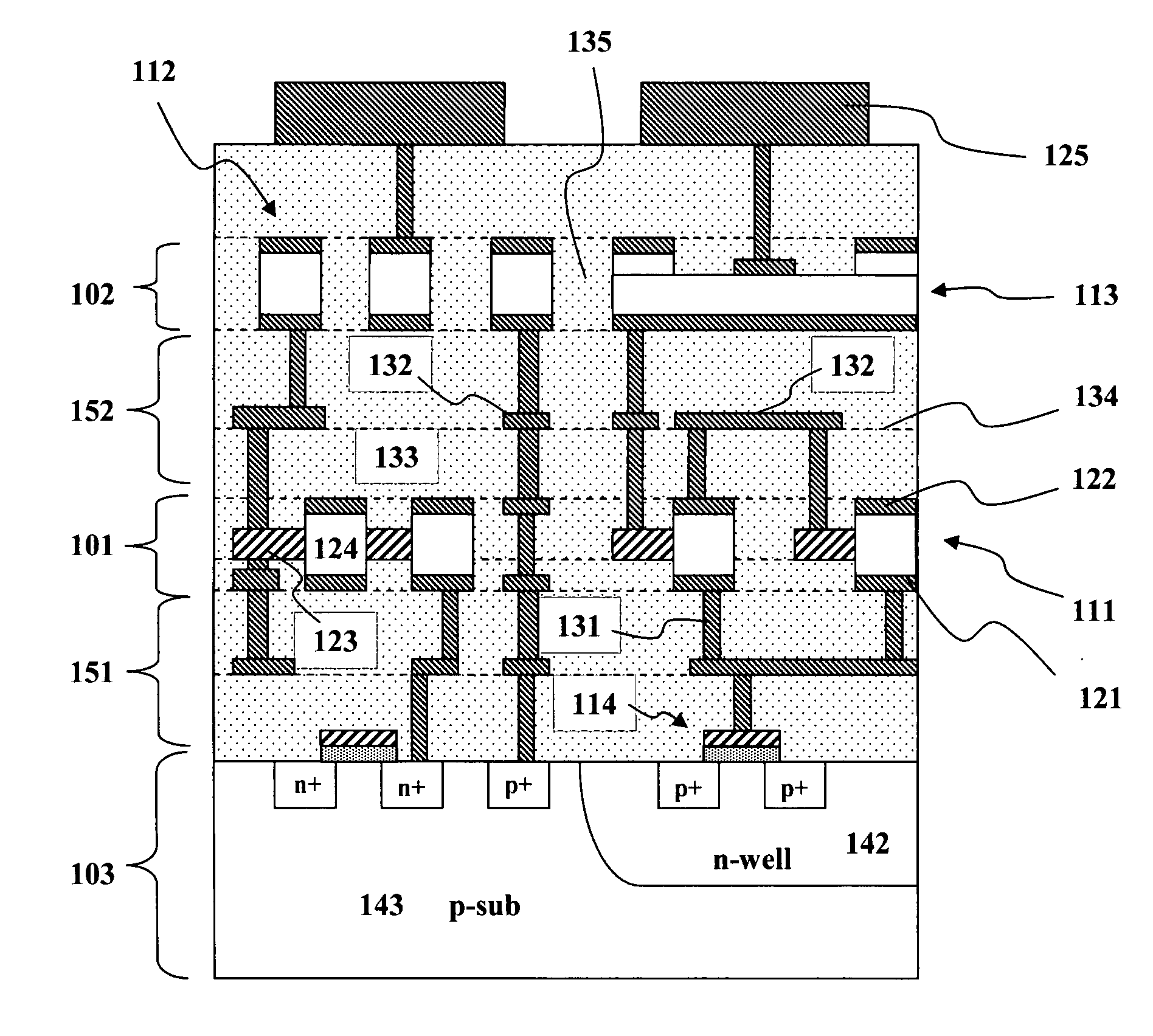
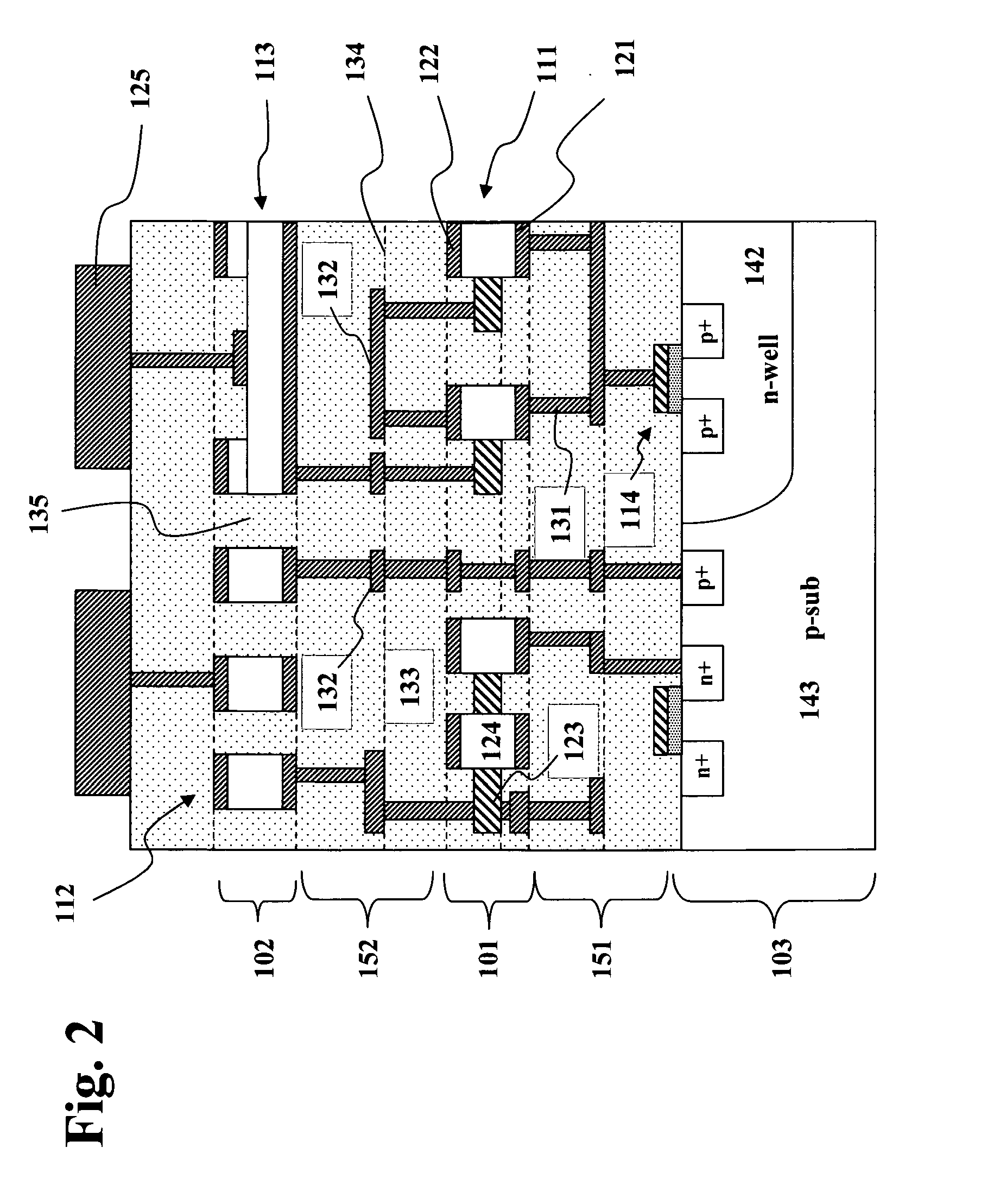
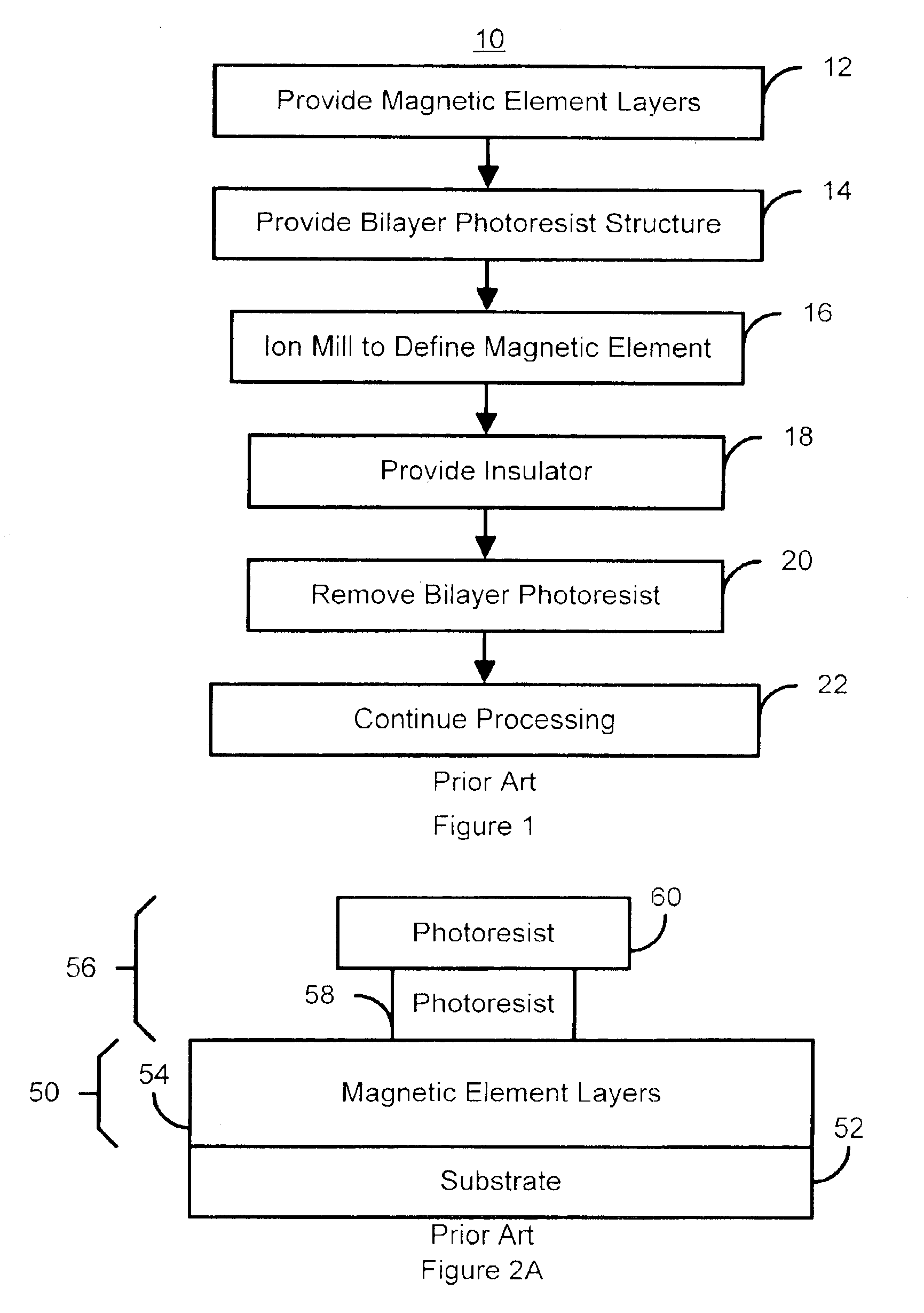
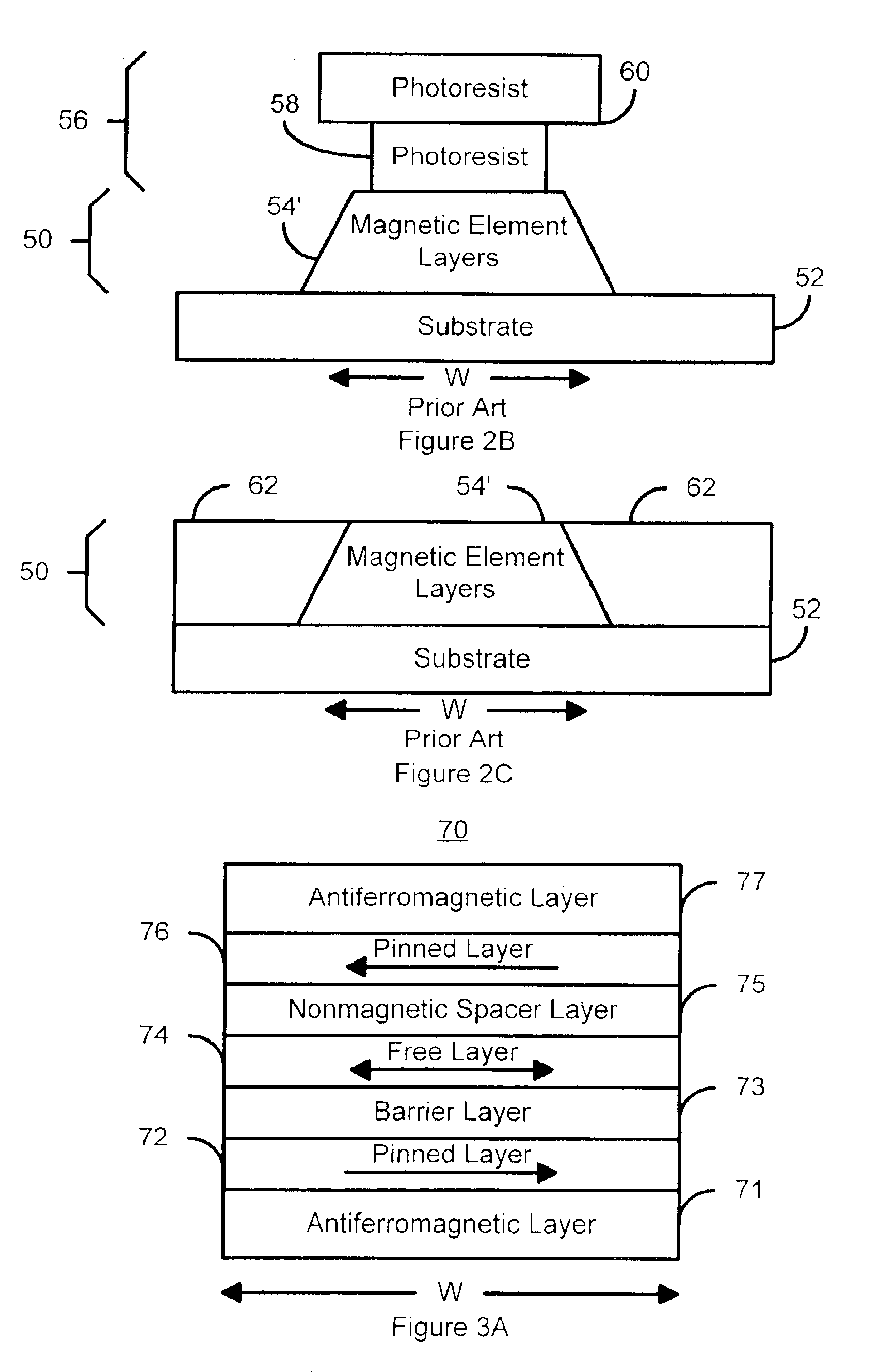
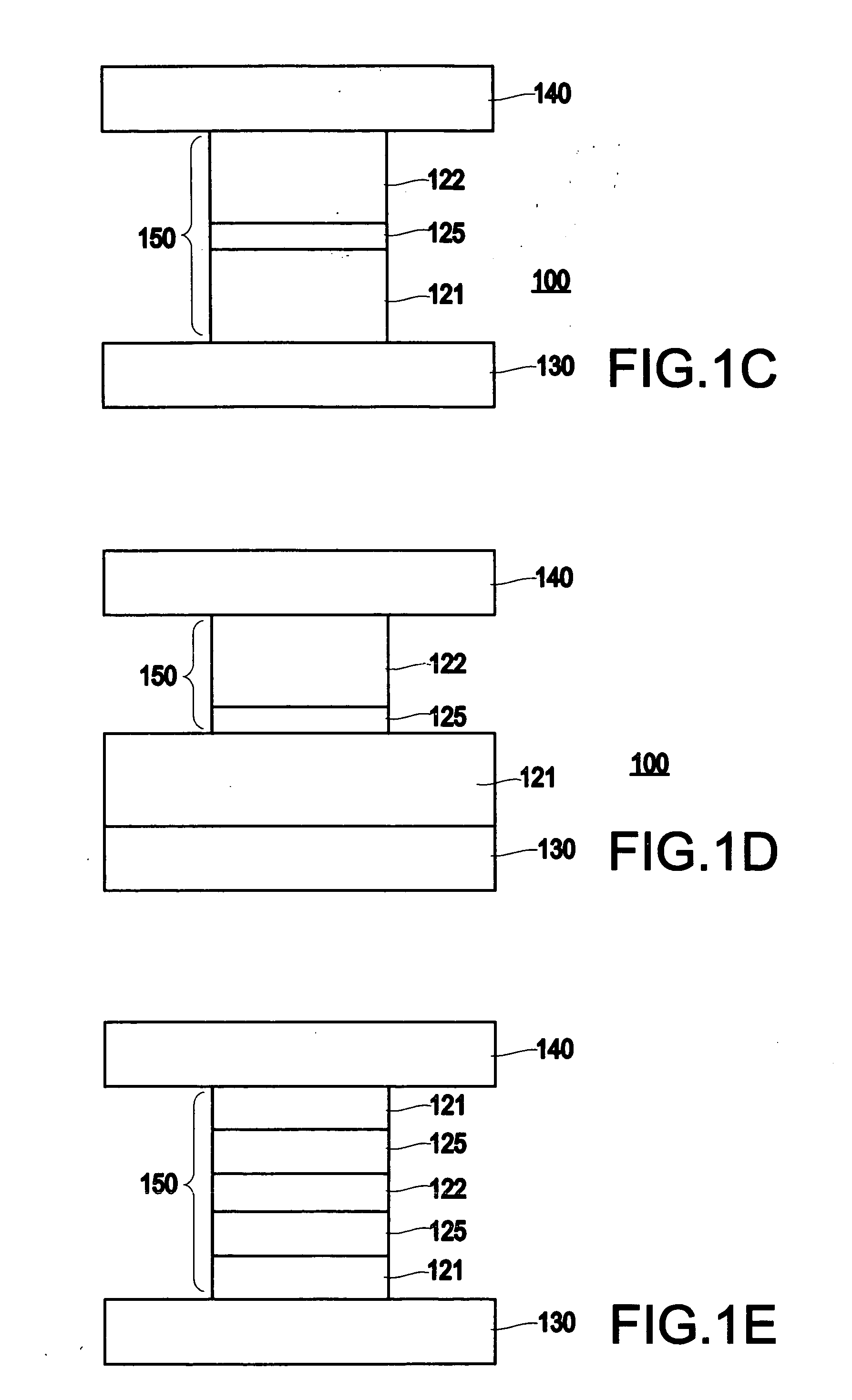
Methods for providing a sub .15 micron magnetic memory structure
ActiveUS6933155B2Small sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGalvano-magnetic device manufacture/treatmentMagnetic memoryEngineering
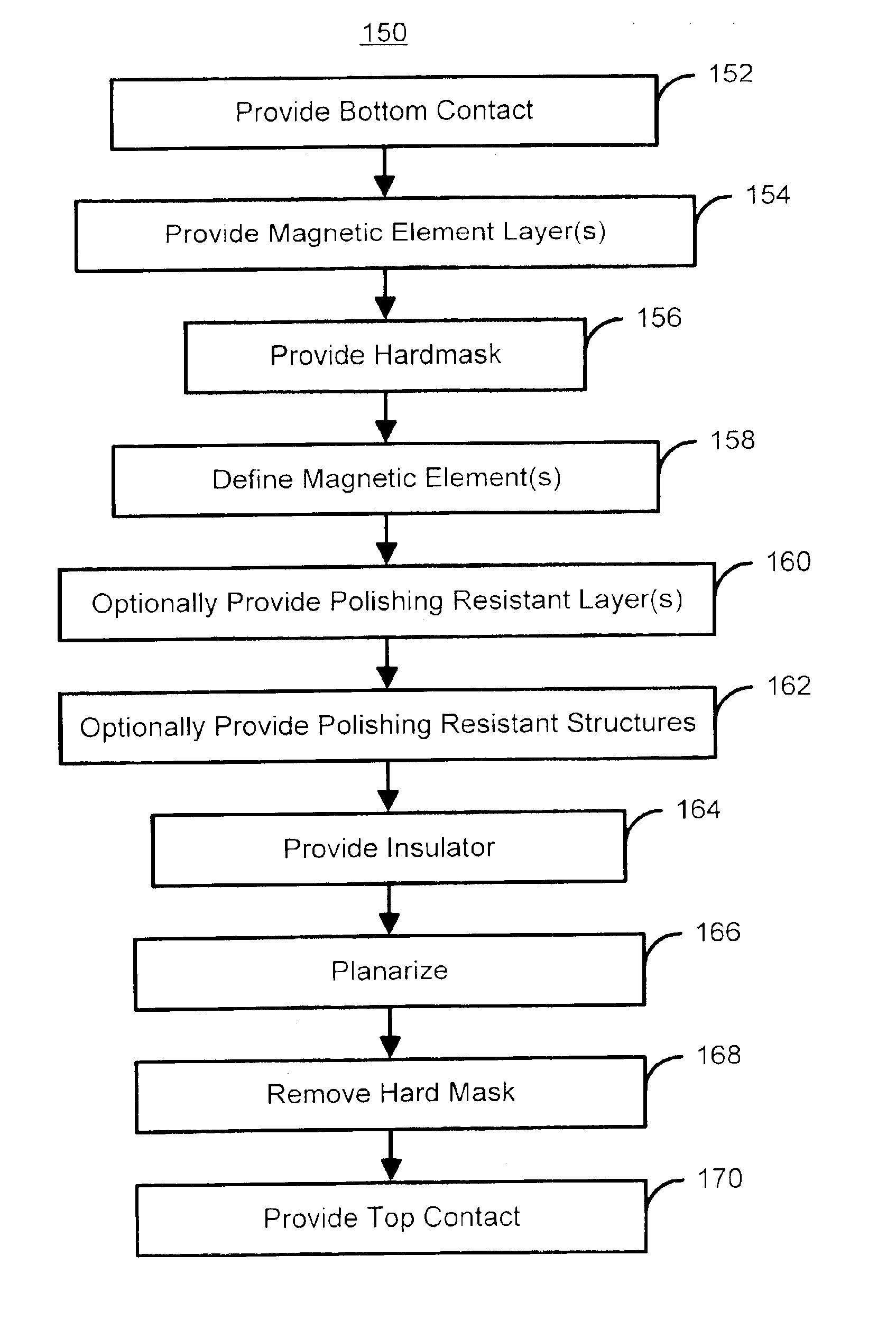
A method for providing a magnetic element is disclosed. The method includes providing at least one magnetic element layer and providing a hard mask structure for masking a portion of the at least one magnetic element layer. The hard mask structure is made from hard mask material(s) that are etchable for defining the hard mask structure. The hard mask structure also acts as a mask during definition of a width of the magnetic element. The method also includes defining the width of the magnetic element by removing a portion of the at least one magnetic element layer using the hard mask structure as a mask. The hard mask structure preferably acts as a polishing stop for a planarization step, such as a chemical mechanical polish, polishing resistant structures might be provided to improve planarization of a magnetic memory incorporating the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
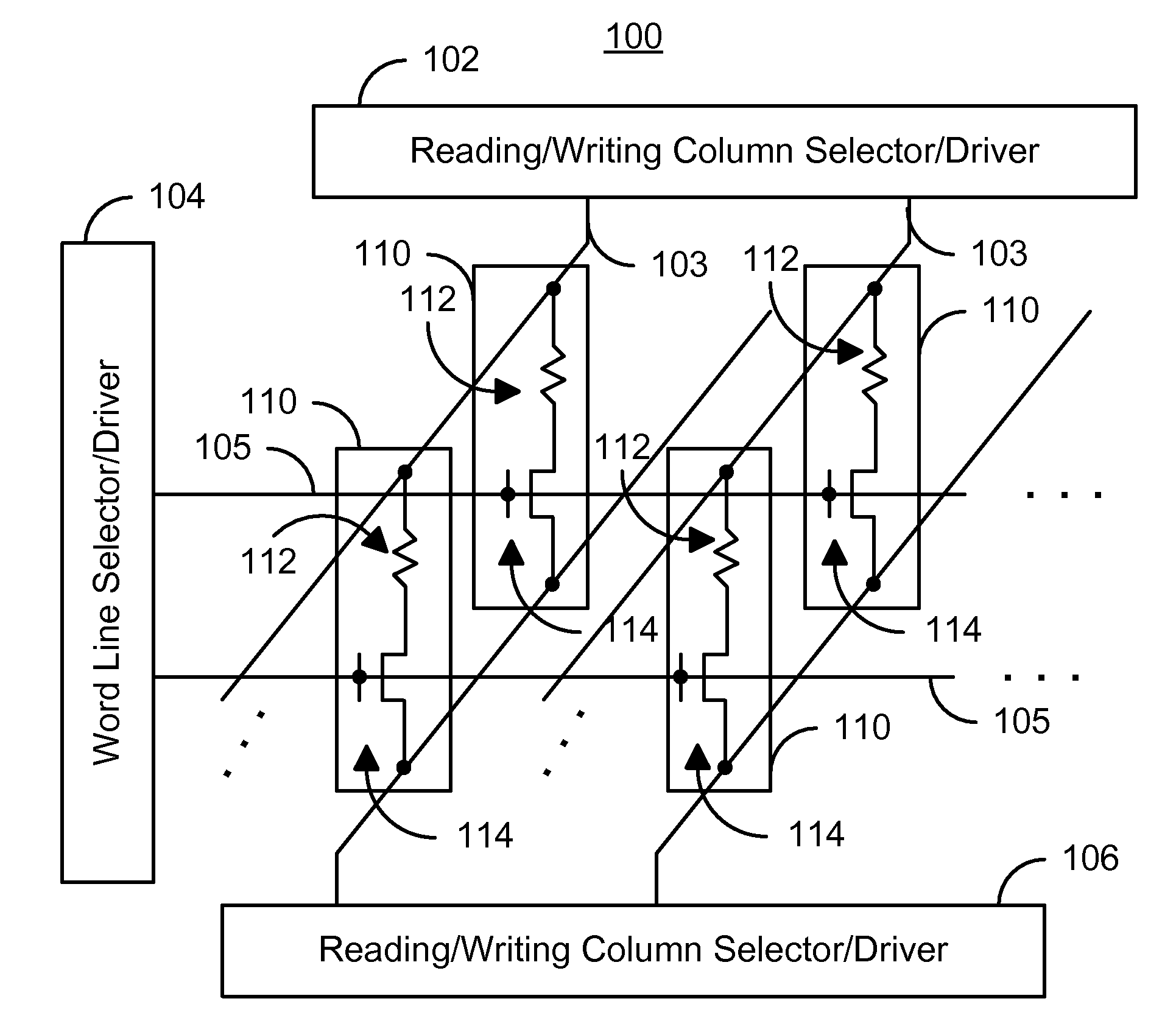
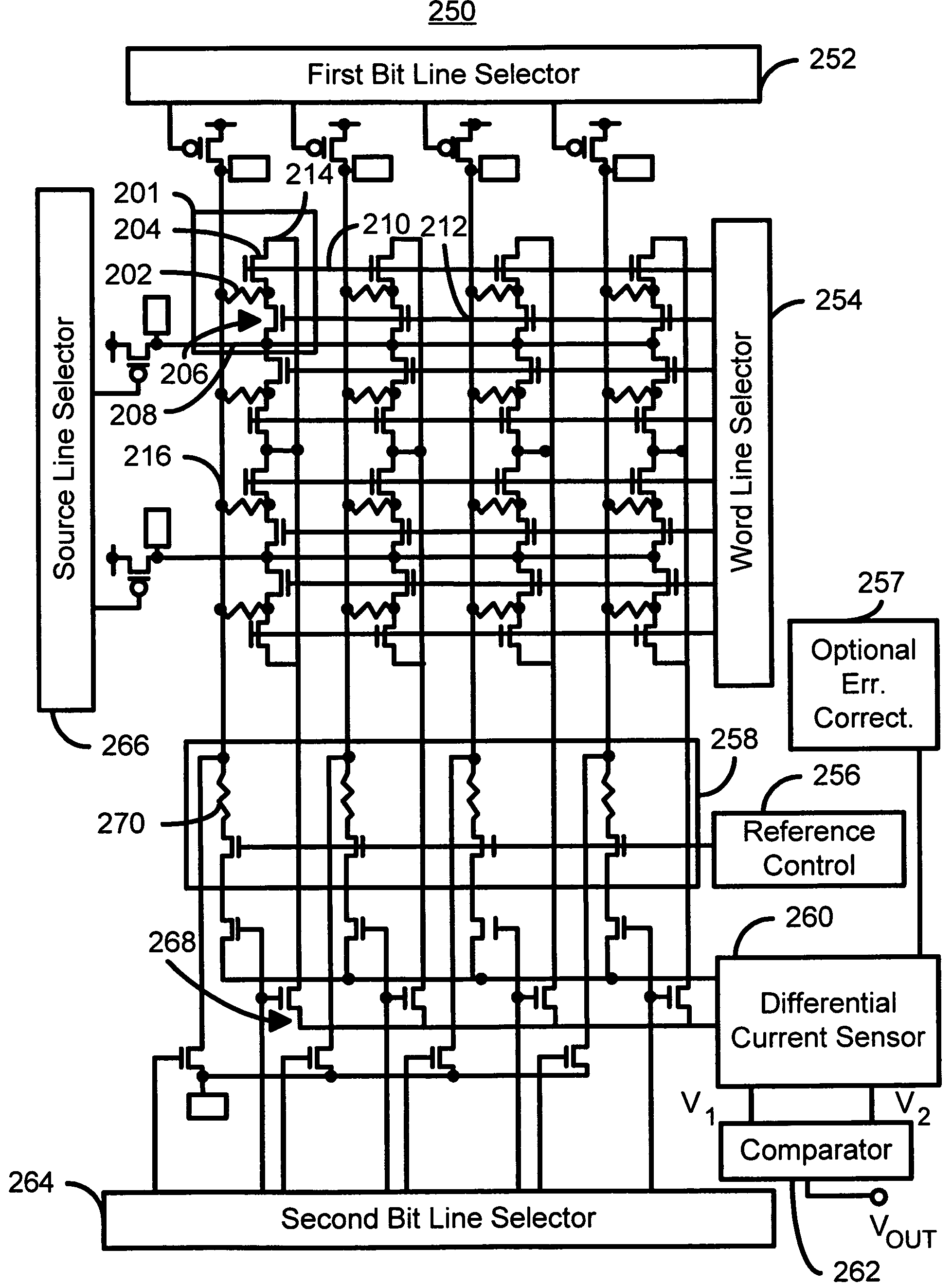
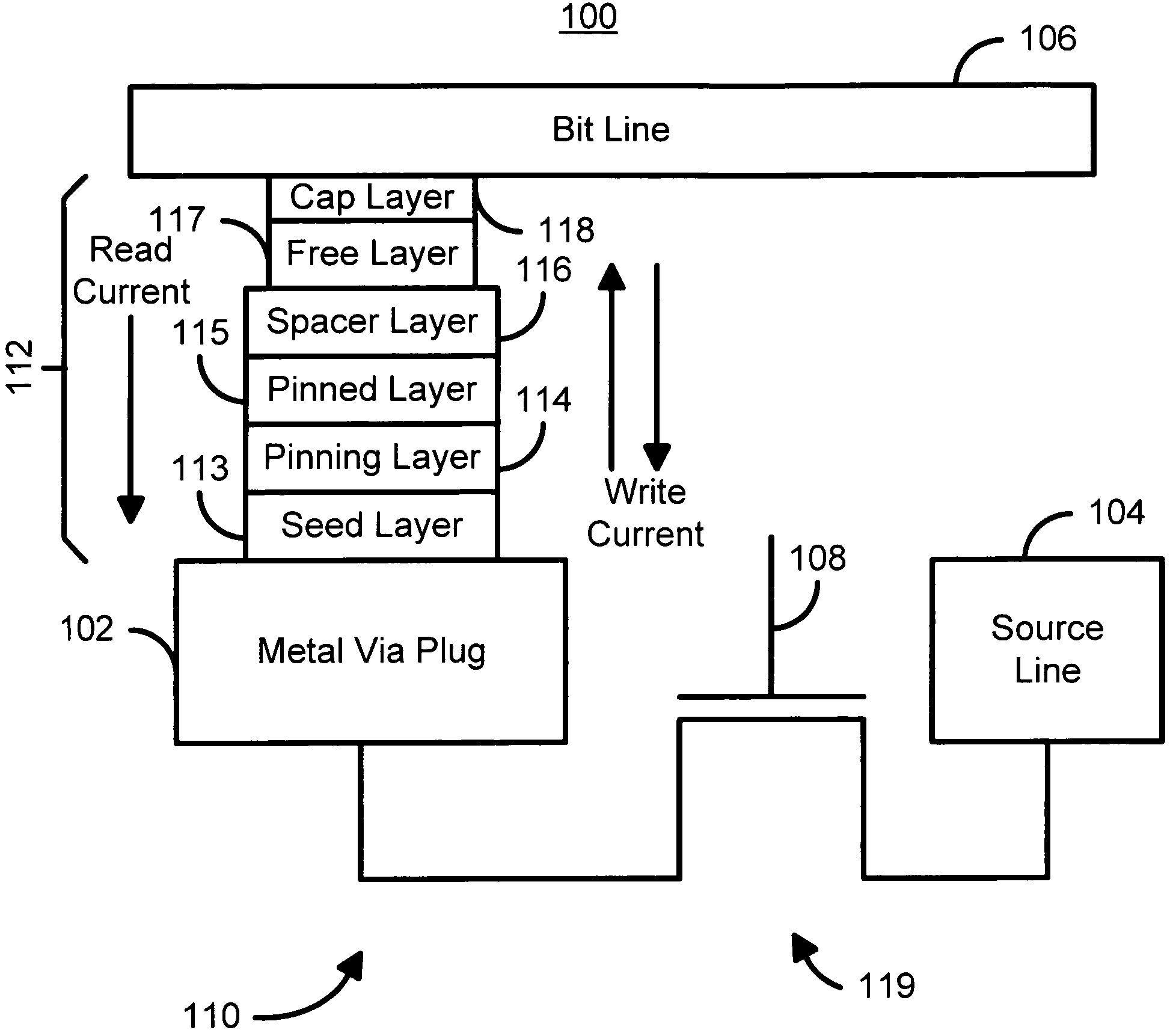
Method and system for providing spin transfer tunneling magnetic memories utilizing non-planar transistors
A magnetic memory cell and a magnetic memory incorporating the cell are described. The magnetic memory cell includes at least one magnetic element and at least one non-planar selection device. The magnetic element(s) are programmable using write current(s) driven through the magnetic element. The magnetic memory may include a plurality of magnetic storage cells, a plurality of bit lines corresponding to the plurality of magnetic storage cells, and a plurality of source lines corresponding to the plurality of magnetic storage cells.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
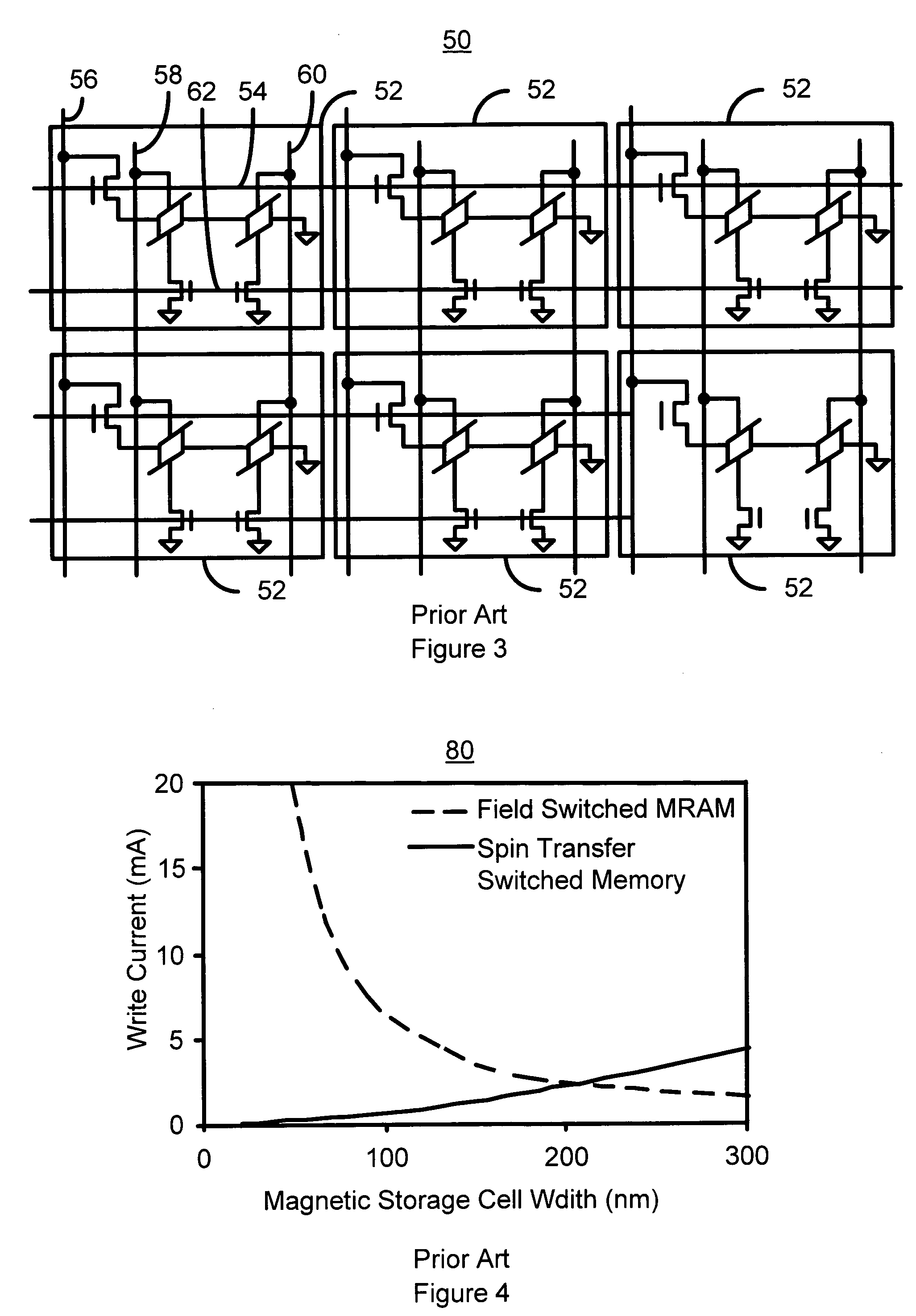
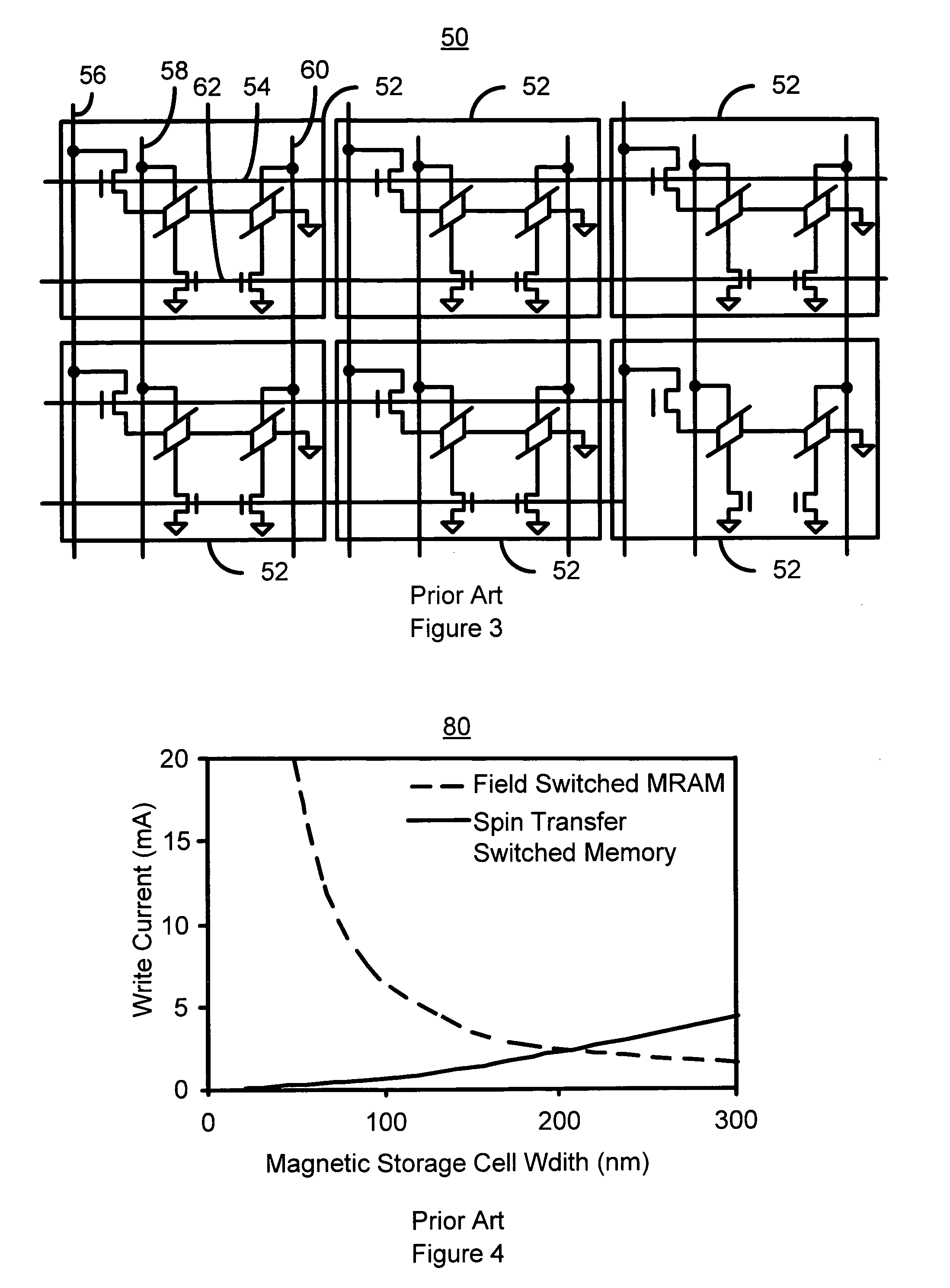
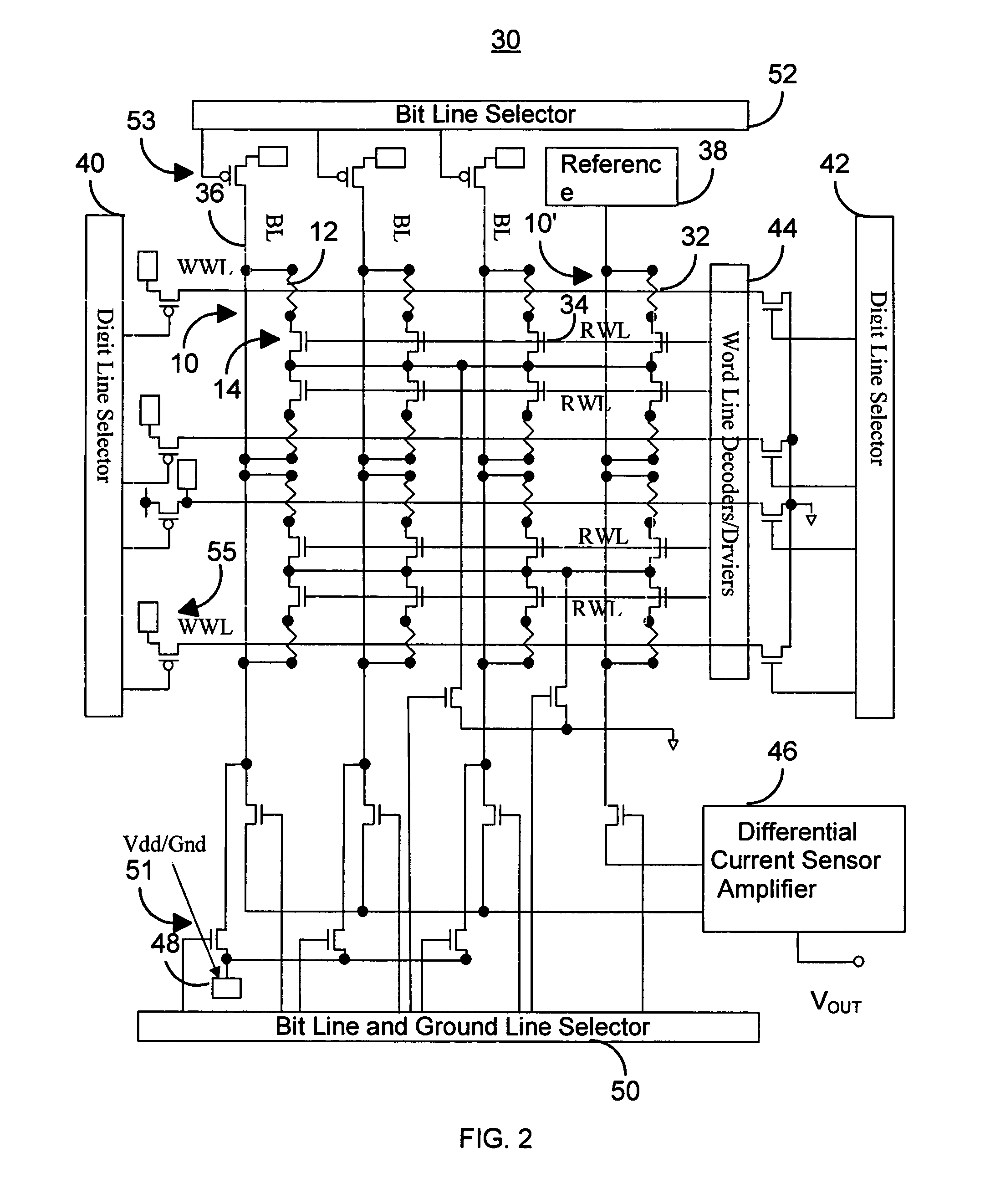
Current driven switching of magnetic storage cells utilizing spin transfer and magnetic memories using such cells
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is described. The method and system include providing a plurality of magnetic storage cells. Each of the plurality of magnetic storage cells includes a magnetic element and a selection transistor. The magnetic element may be programmed using spin transfer induced switching by a write current driven through the magnetic element. The selection transistor includes a source and a drain. The plurality of magnetic storage cells are grouped in pairs. The source of the selection transistor for one magnetic storage cell of a pair shares the source with the selection transistor for another magnetic storage cell of the pair.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
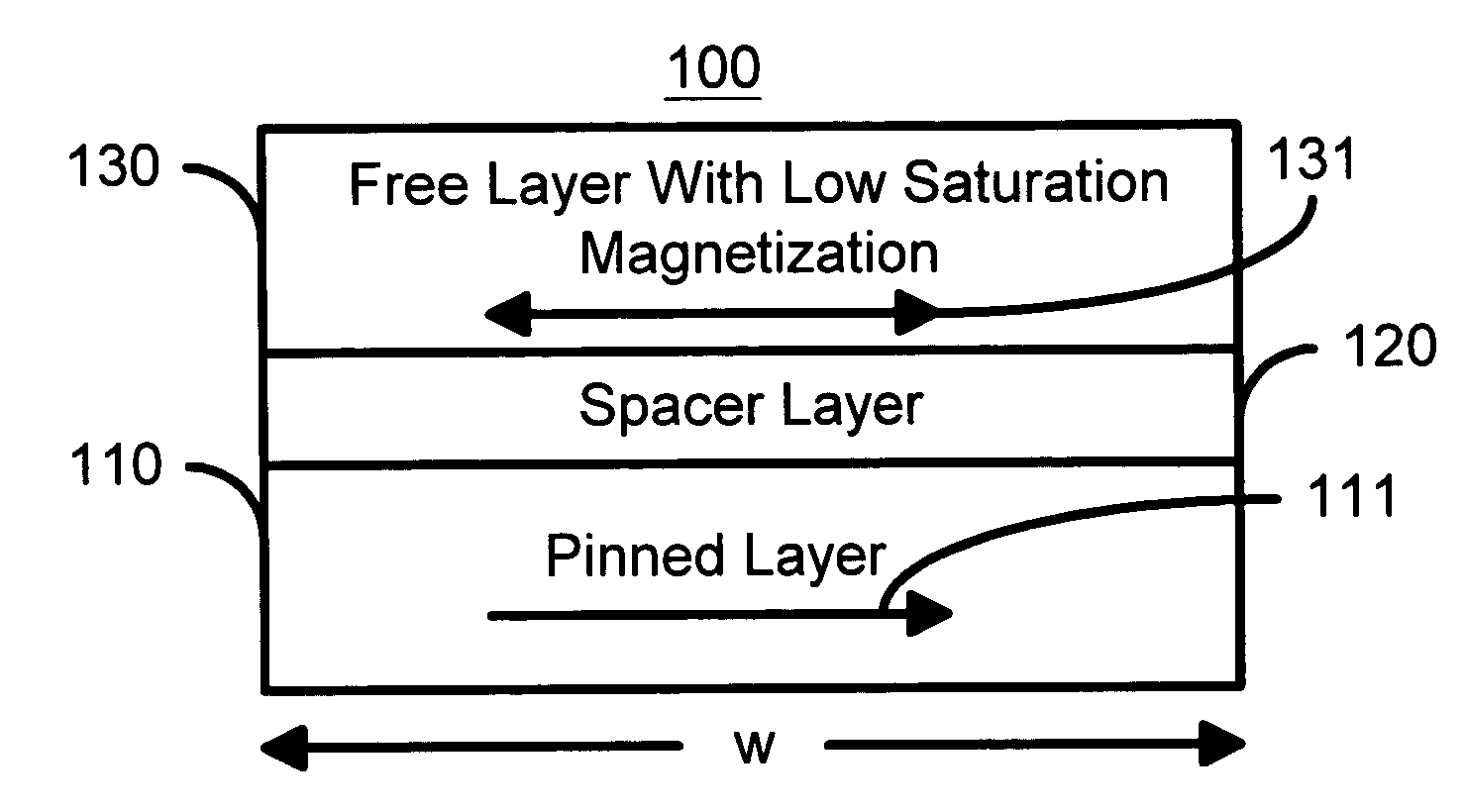
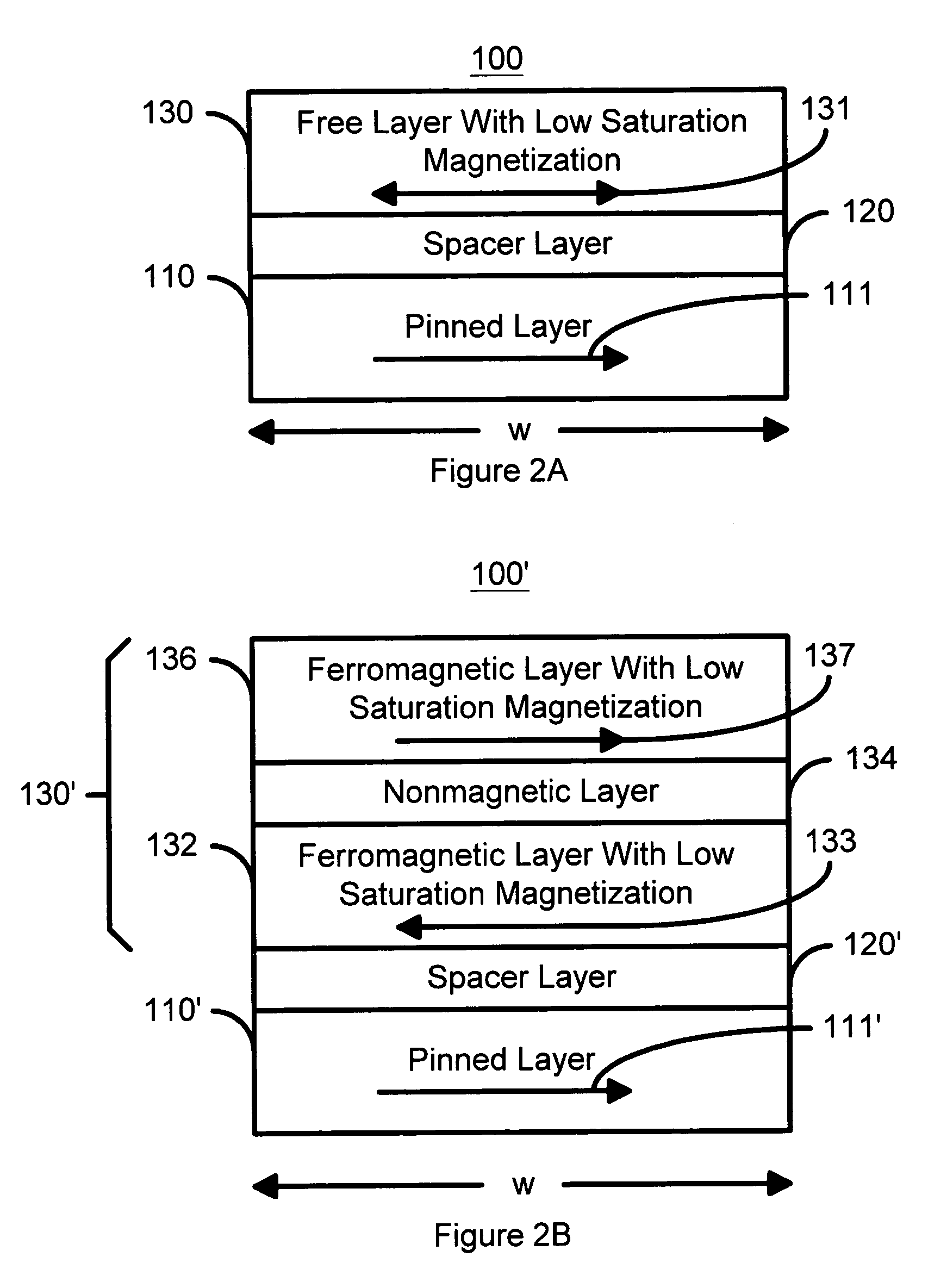
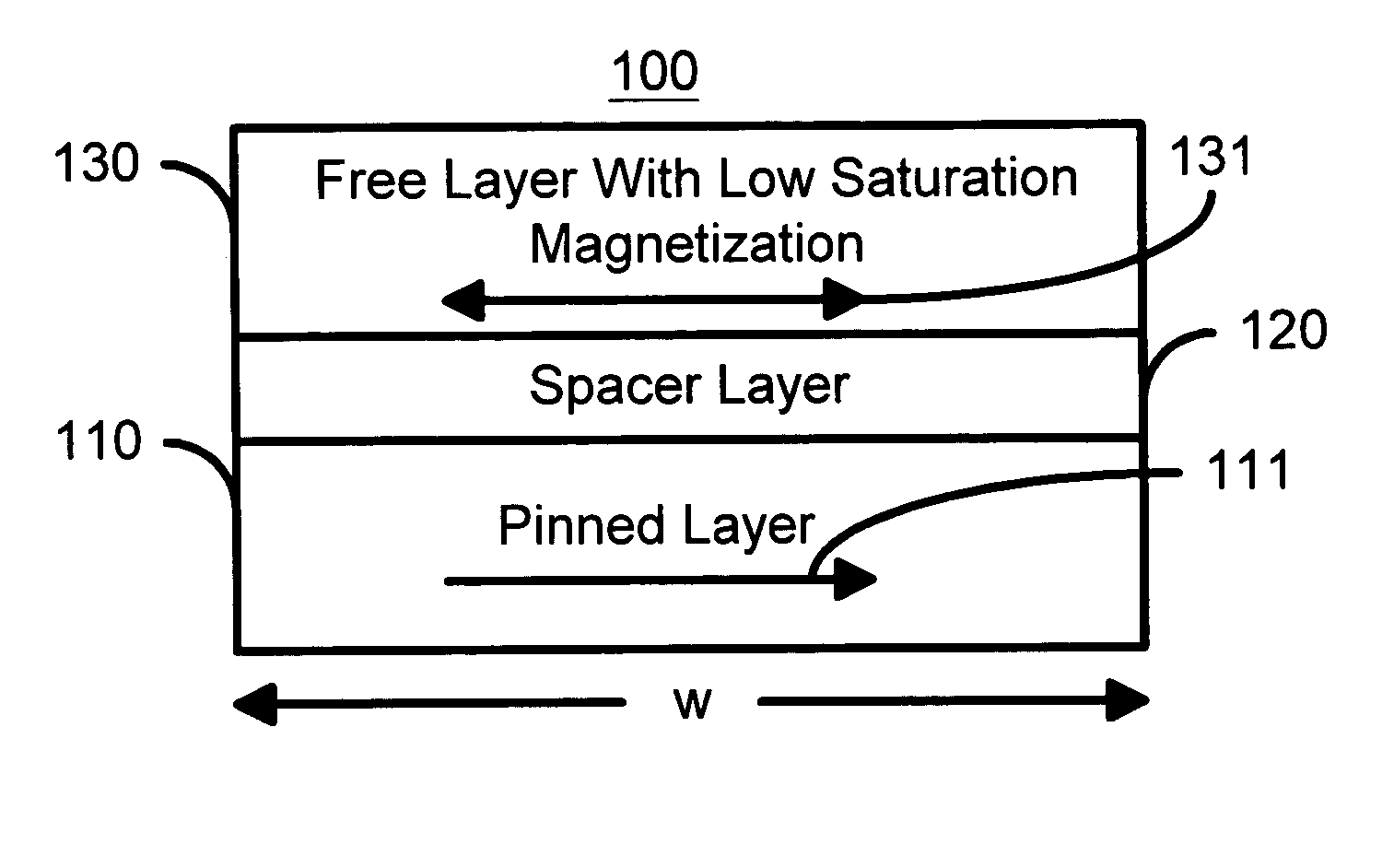
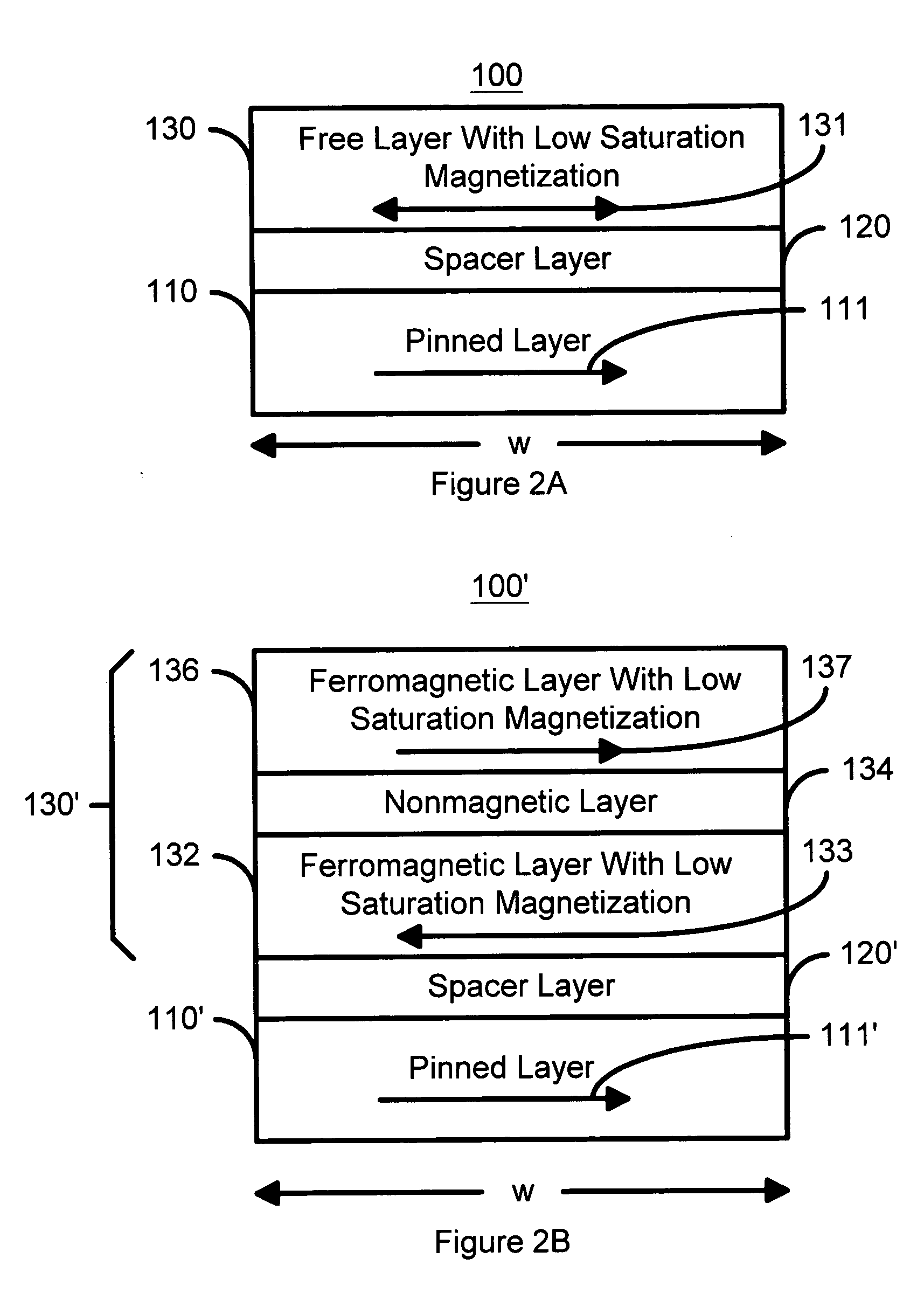
Spin transfer magnetic element having low saturation magnetization free layers
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The spacer layer resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The magnetic element may also include a barrier layer, a second pinned layer. Alternatively, second pinned and second spacer layers and a second free layer magnetostatically coupled to the free layer are included. In one aspect, the free layer(s) include ferromagnetic material(s) diluted with nonmagnetic material(s) and / or ferrimagnetically doped to provide low saturation magnetization(s).
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Current driven switching of magnetic storage cells utilizing spin transfer and magnetic memories using such cells having enhanced read and write margins
ActiveUS7379327B2Higher read and write marginDigital storageHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory. The magnetic memory includes magnetic storage cells in an array, bit lines, and source lines. Each magnetic storage cell includes at least one magnetic element. The magnetic element(s) are programmable by write currents driven through the magnetic element(s). Each magnetic element has free and pinned layer(s) and a dominant spacer. The magnetic memory is configured such that either the read current(s) flow from the free layer(s) to the dominant spacer if the maximum low resistance state read current divided by the minimum low resistance state write current is greater than the maximum high resistance state read current divided by the minimum high resistance state write current or the read current(s) flow from the dominant spacer to the free layer(s) if the maximum low resistance state read current divided by the minimum low resistance state write current is less than the maximum high resistance state read current divided by the minimum high resistance state write current.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON +1
Current driven switching of magnetic storage cells utilizing spin transfer and magnetic memories using such cells
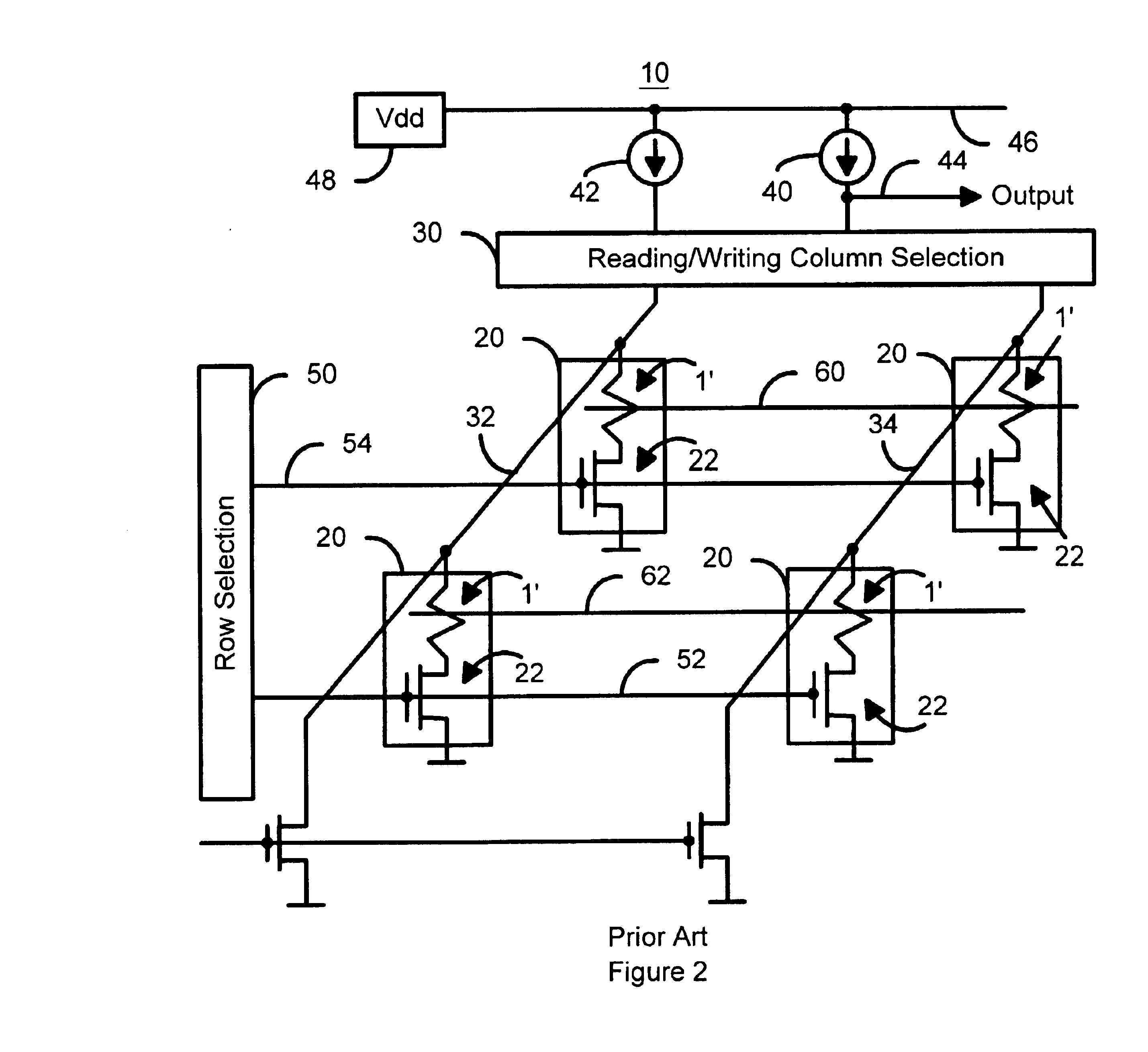
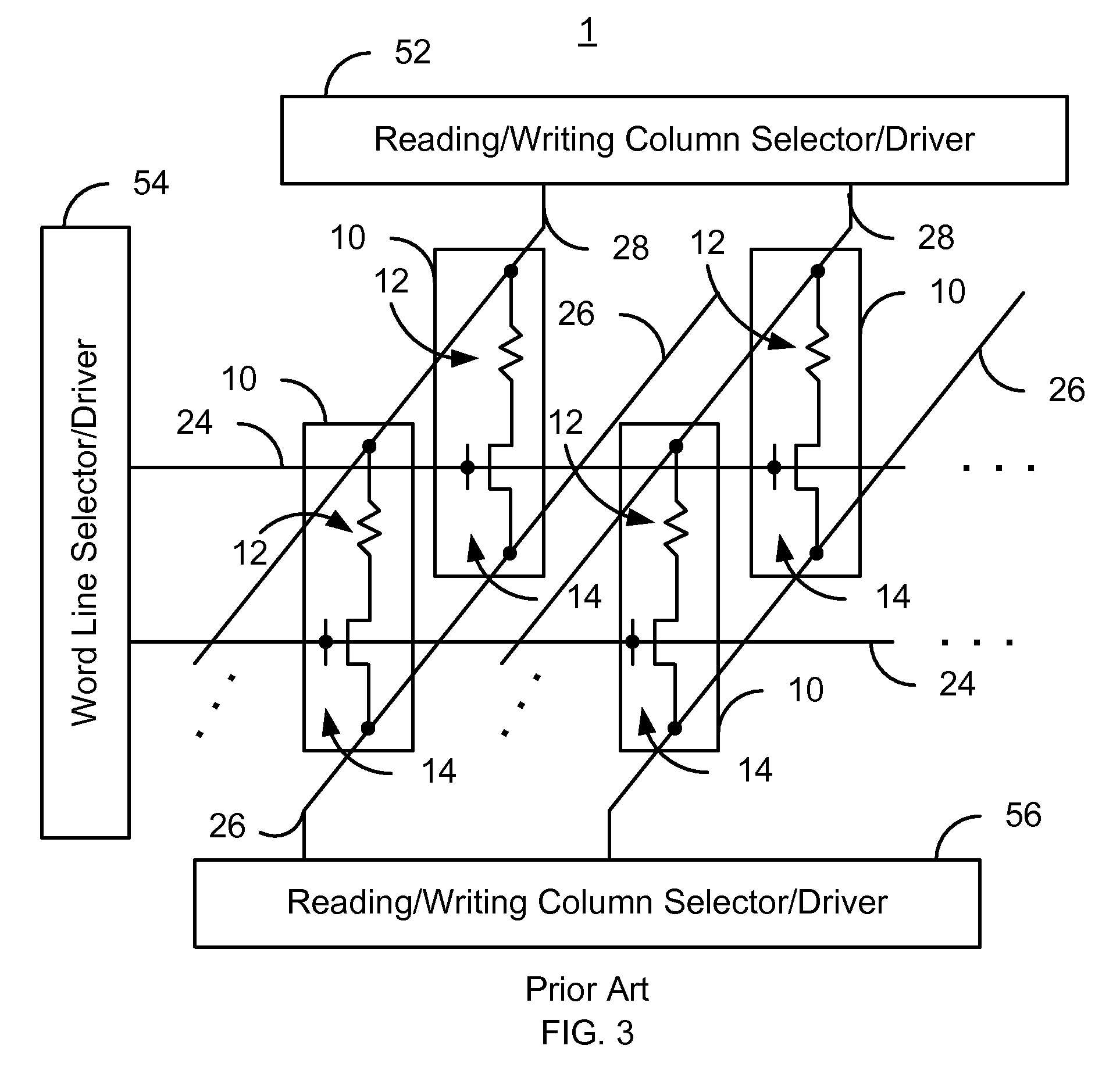
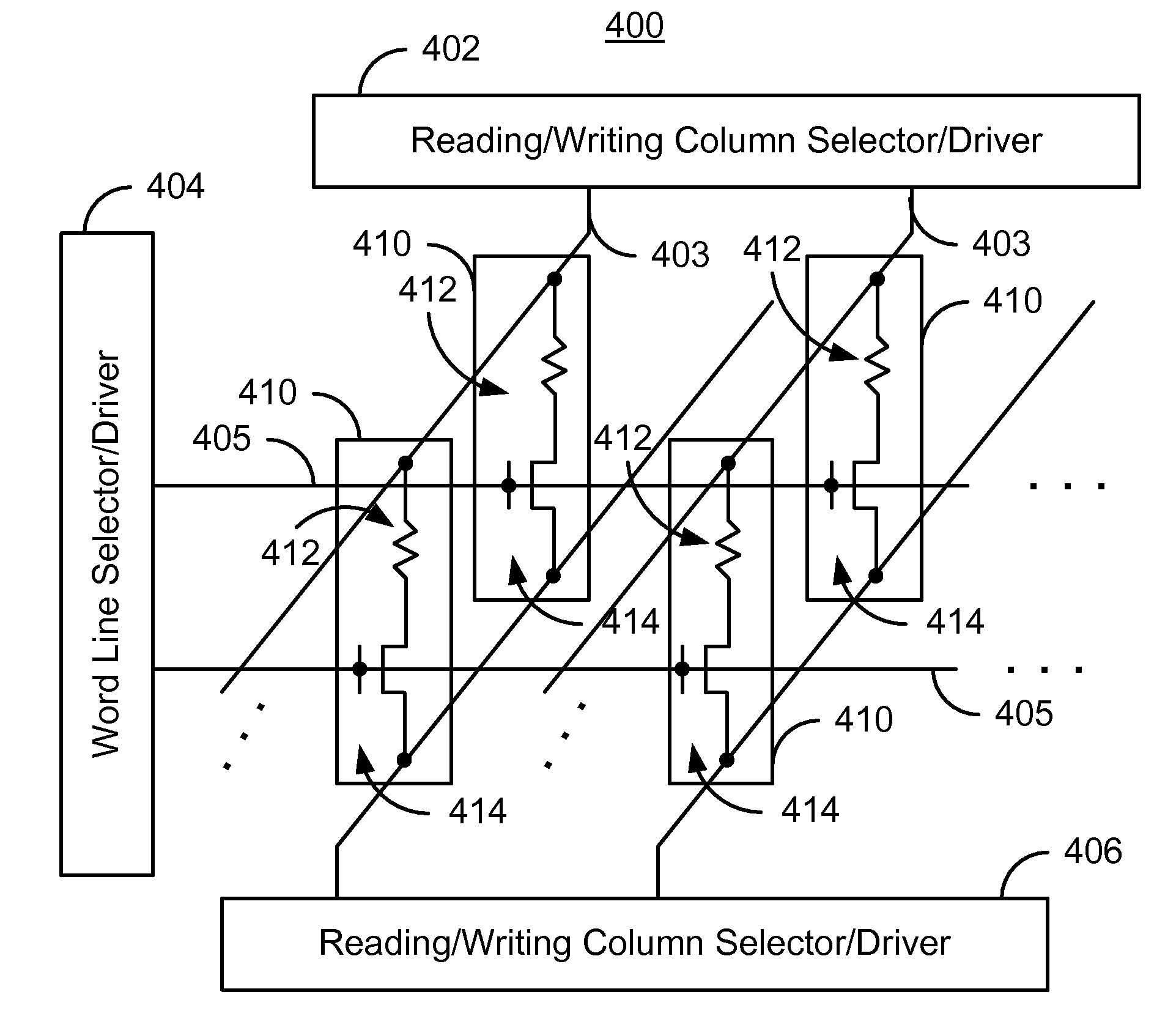
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is described. The method and system include providing a plurality of magnetic storage cells. Each of the plurality of magnetic storage cells includes at least one magnetic element and a plurality of selection transistors. The at least one magnetic element is capable of being programmed using spin transfer induced switching by a write current driven through the at least one magnetic element. The at least one selection transistor is configured to allow the magnetic element to be alternately selected for writing and reading. Architectures for reading and writing to the magnetic storage cells are also described.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Spin transfer magnetic element having low saturation magnetization free layers
ActiveUS20050184839A1Current densityNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismMagnetic memoryNon magnetic
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The spacer layer resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The magnetic element may also include a barrier layer, a second pinned layer. Alternatively, second pinned and second spacer layers and a second free layer magnetostatically coupled to the free layer are included. In one aspect, the free layer(s) include ferromagnetic material(s) diluted with nonmagnetic material(s) and / or ferrimagnetically doped to provide low saturation magnetization(s).
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
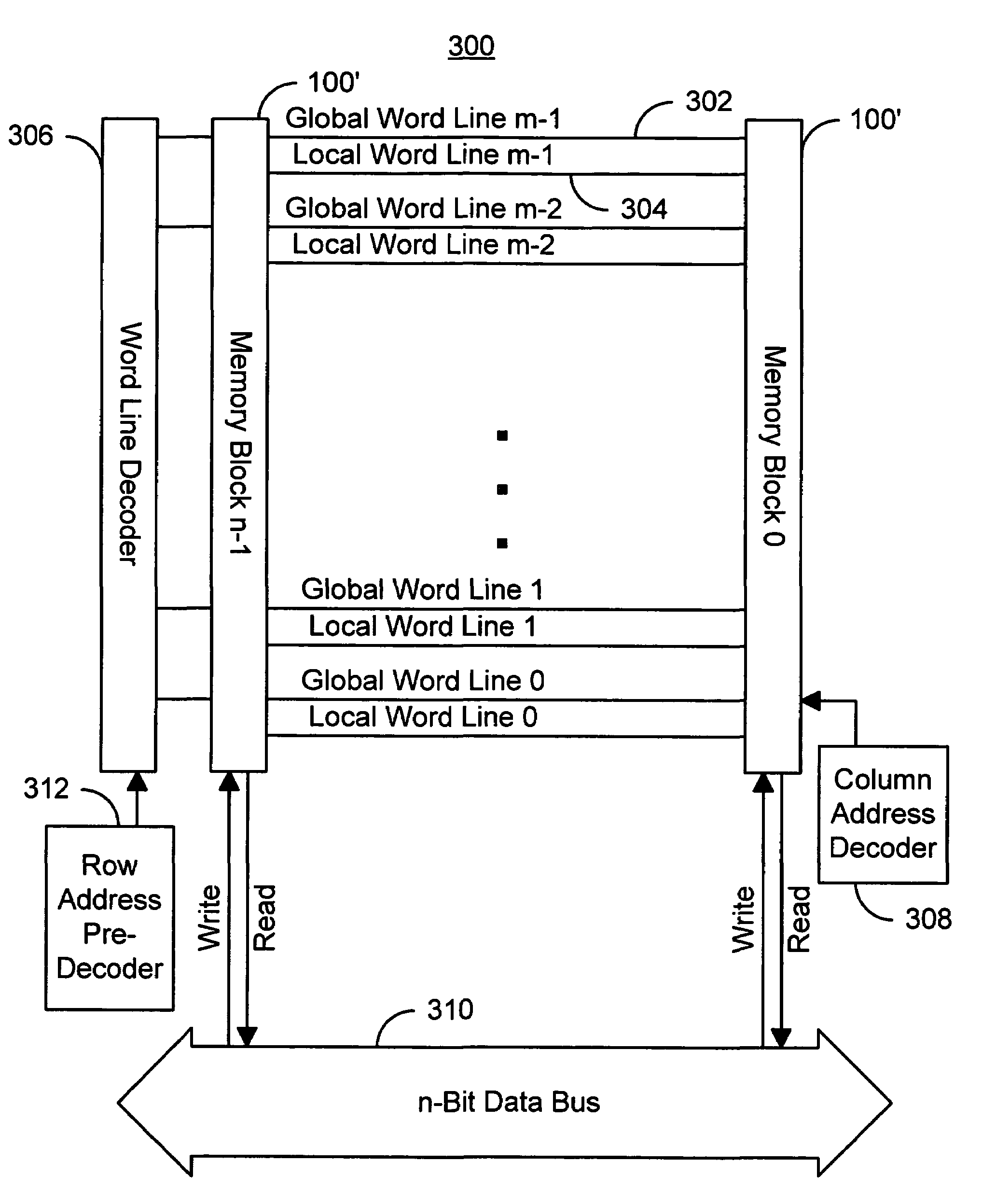
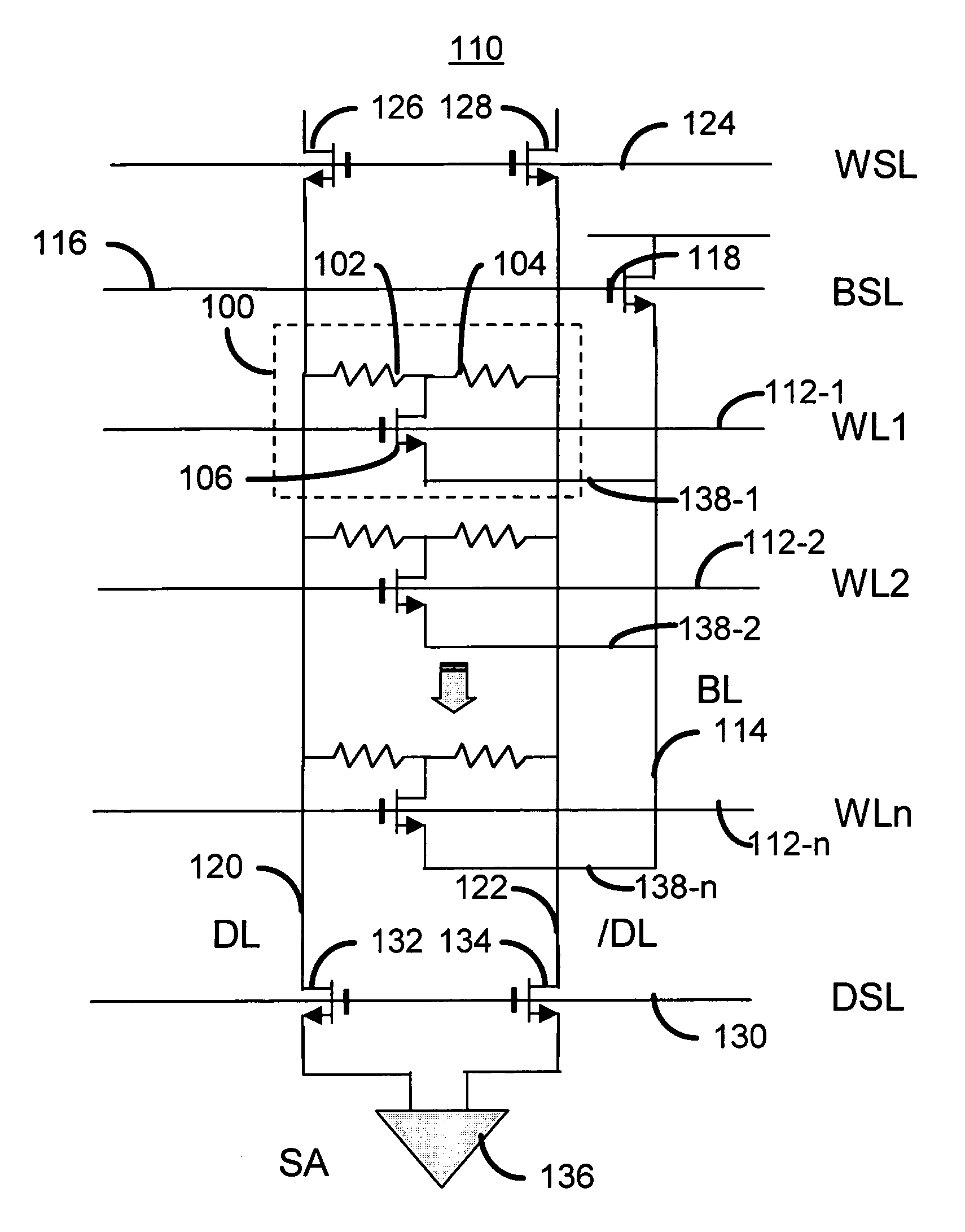
Method and system for providing a magnetic memory structure utilizing spin transfer
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is described. The method and system include providing magnetic memory cells, local and global word lines, bit lines, and source lines. Each magnetic memory cell includes a magnetic element and a selection device connected with the magnetic element. The magnetic element is programmed by first and second write currents driven through the magnetic element in first and second directions. The local word lines are connected with the selection device of and have a first resistivity. Each global word line corresponds to a portion of the local word lines and has a resistivity lower than the first resistivity. The bit lines are connected with the magnetic element. The source lines are connected with the selection device. Each source line corresponds to a more than one of the magnetic memory cells and carries the first and second write currents.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
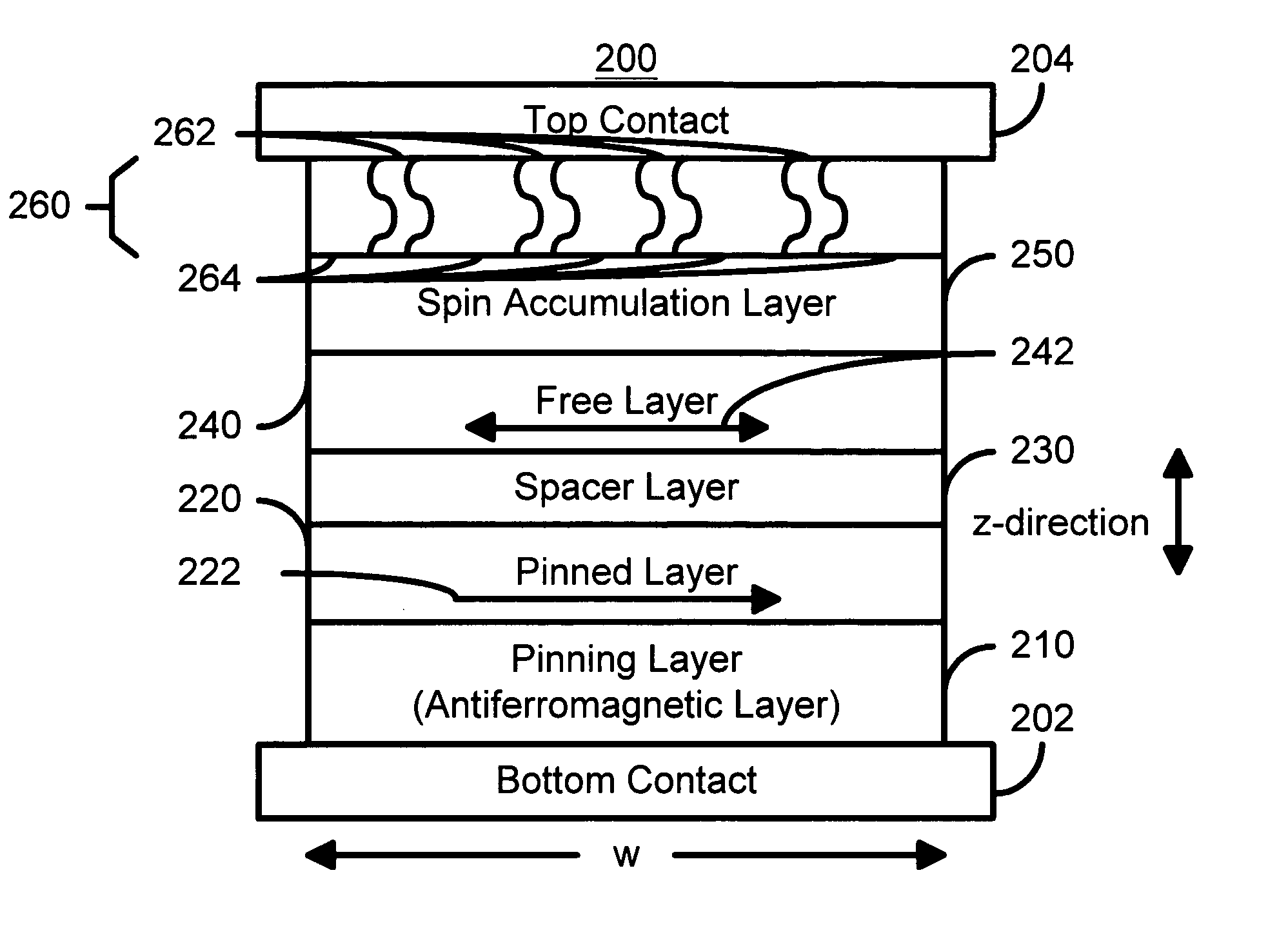
Spin barrier enhanced magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS7088609B2Reduce outer surfaceHigh areal resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDamping constantMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, spacer, free, and spin barrier layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The free layer resides between the spacer layer and the spin barrier layer. The spin barrier layer is configured to reduce an outer surface contribution to a damping constant of the free layer. In one aspect, the spin barrier layer has a high areal resistance and may substantially eliminate spin pumping induced damping. In another aspect, the magnetic element also includes a spin accumulation layer between the spin barrier and free layers. The spin accumulation layer has a high conductivity, preferably being metallic, and may have a long spin diffusion length.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Method for making a nano-stamp and for forming, with the stamp, nano-size elements on a substrate
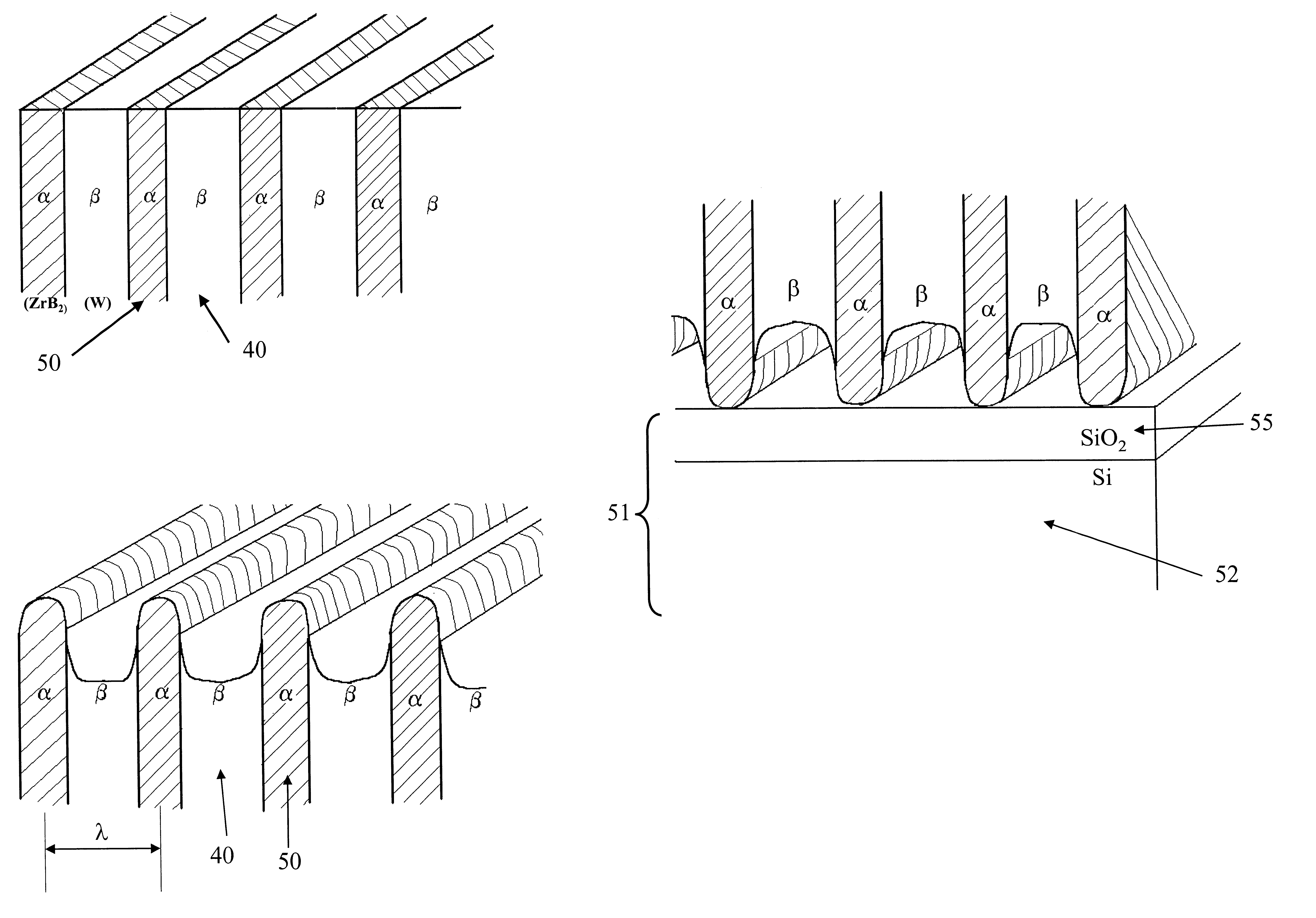
The stamping process and a method of fabrication of nano-stamps with characteristic dimensions below 1 nm and up to 100 nm intended for usage in making patterns of characteristic dimensions the same as those of the nano-stamp on surface of a substrate is provided. In the process a very hard stamp is fabricated by first depositing alternating layers of two materials, one of which has very high hardness, on some sacrificial substrate via PVD, CVD or any other deposition procedure that produces alternating layers of selected thickness, from sub 1 nm to above 100 nm. The layered film is then polished to an atomically smooth finish perpendicular to the plane of the layers and etched to produce dips in the softer layers. These steps produce a grid of parallel elevations and valleys on the etched surface, which now can be used as a stamp to stamp out patterns on a substrate of lower hardness than the hardness of the elevated layers. If the substrate is stamped twice with a turning of the stamp 90 degrees between first and second stampings, a square pattern of elevations or hills and valleys is formed, which can be used for magnetic memory storage by subsequently sputtering magnetic material on the tops of the elevations or hills.
Owner:VIGIL THOMAS R +1
Current driven memory cells having enhanced current and enhanced current symmetry
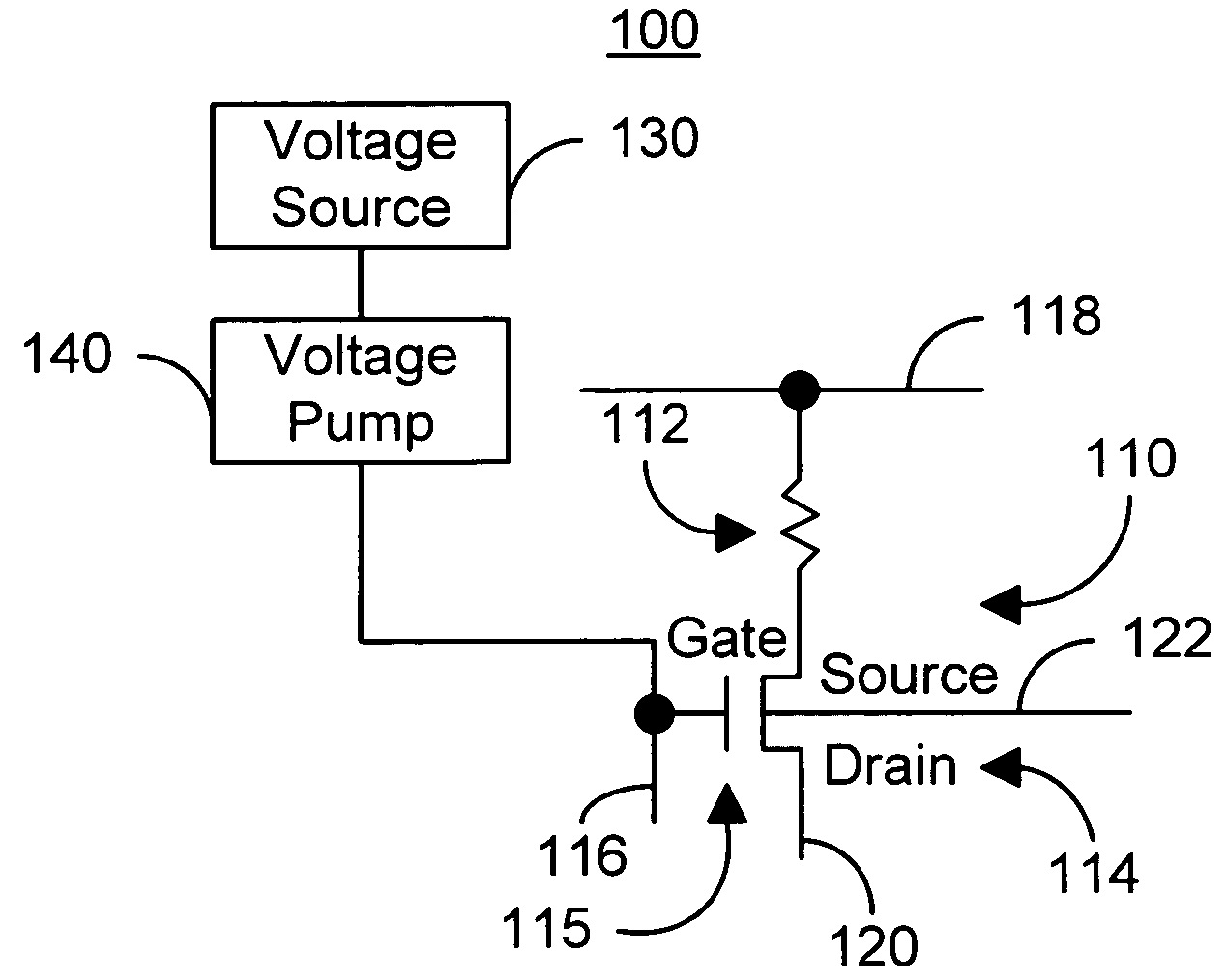
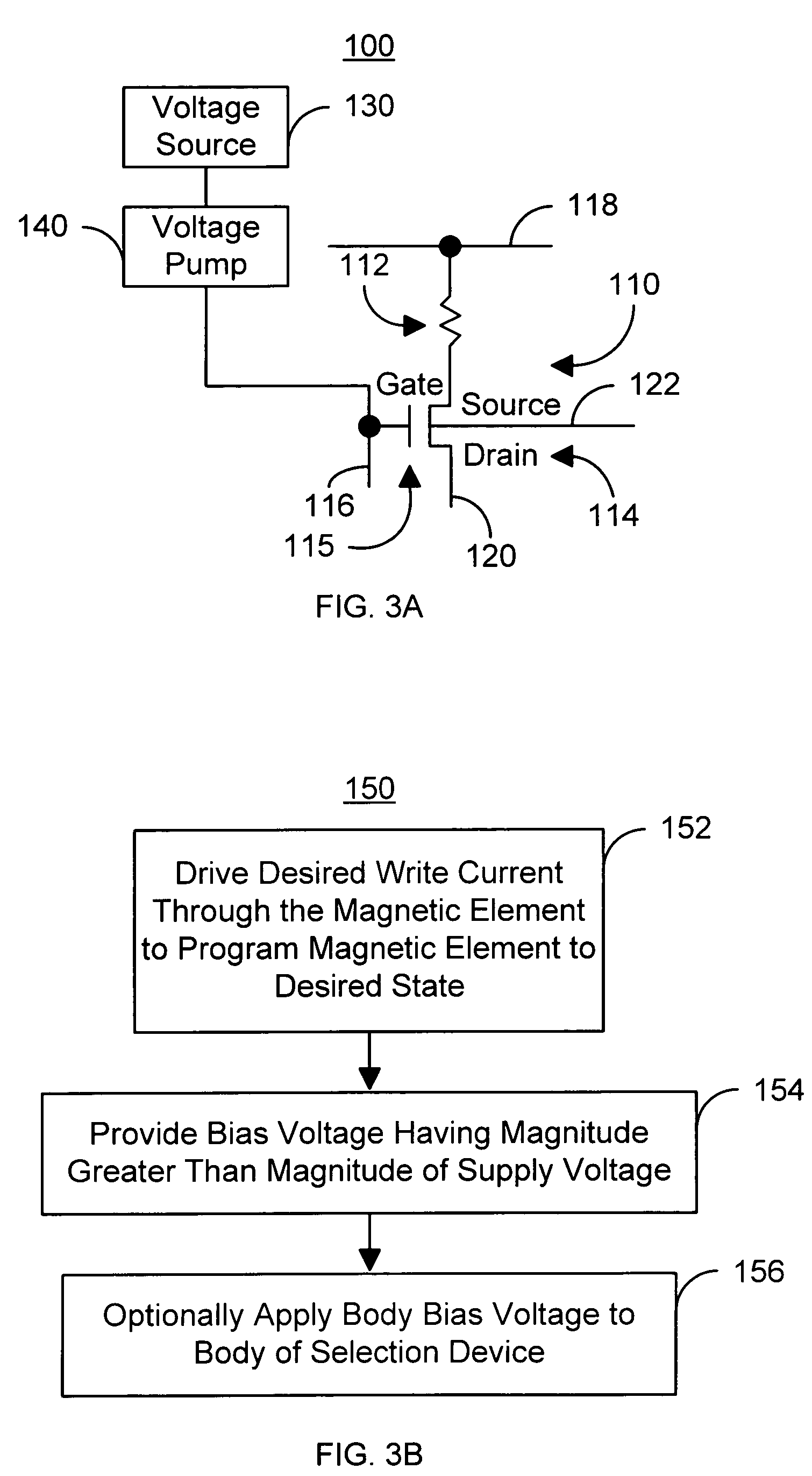
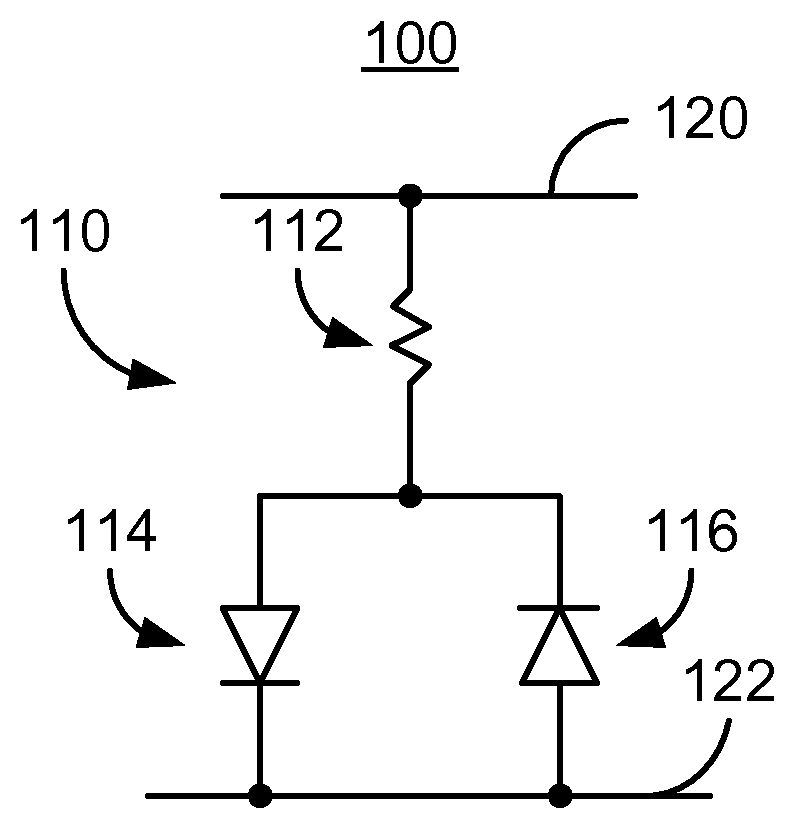
A method and system for providing and using a magnetic memory is described. The method and system include providing a plurality of magnetic storage cells. Each magnetic storage cell includes a magnetic element and a selection device coupled with the magnetic element. The magnetic element is programmed by write currents driven through the magnetic element in a first or second direction. In one aspect, the method and system include providing a voltage supply and a voltage pump coupled with the magnetic storage cells and the voltage supply. The voltage supply provides a supply voltage. The voltage pump provides to the selection device a bias voltage having a magnitude greater than the supply voltage. Another aspect includes providing a silicon on oxide transistor as the selection device. Another aspect includes providing to the body of the transistor a body bias voltage that is a first voltage when the transistor is off and a second voltage when the transistor is on.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Method and system for providing spin transfer tunneling magnetic memories utilizing unidirectional polarity selection devices
A magnetic memory cell and a magnetic memory incorporating the cell are described. The magnetic memory cell includes at least one magnetic element and a plurality of unidirectional polarity selection devices. The magnetic element(s) are programmable using write current(s) driven through the magnetic element. The unidirectional polarity selection devices are connected in parallel and such that they have opposing polarities. The magnetic memory may include a plurality of magnetic storage cells, a plurality of bit lines corresponding to the plurality of magnetic storage cells, and a plurality of source lines corresponding to the plurality of magnetic storage cells.
Owner:GRANDIS
Method and system for providing a magnetic element and magnetic memory being unidirectional writing enabled
A method and system for providing a magnetic element and memory utilizing the magnetic element are described. The magnetic element includes a reference layer, a nonferromagnetic spacer layer, and a free layer. The reference layer has a resettable magnetization that is set in a selected direction by a magnetic field generated externally to the reference layer. The reference layer is also magnetically thermally unstable at an operating temperature range and has KuV / kBT is less than fifty five. The spacer layer resides between the reference layer and the free layer. In addition, the magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched to each of a plurality of states when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP +1
High speed low power magnetic devices based on current induced spin-momentum transfer
InactiveUS6980469B2Operational advantageReduce the required powerNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic memoryMagnetization
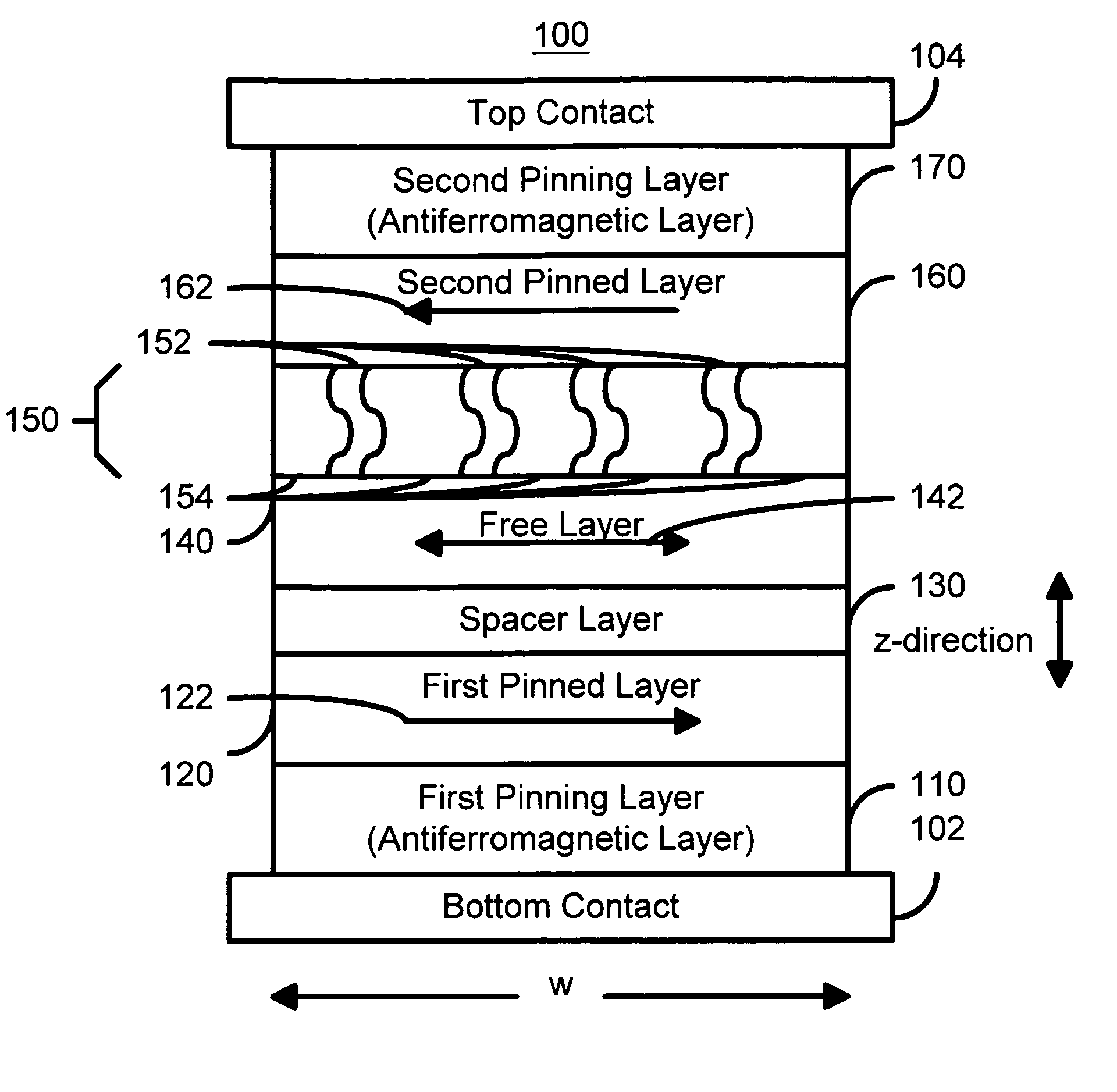
The present invention generally relates to the field of magnetic devices for memory cells that can serve as non-volatile memory. More specifically, the present invention describes a high speed and low power method by which a spin polarized electrical current can be used to control and switch the magnetization direction of a magnetic region in such a device. The magnetic device comprises a pinned magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction, a free magnetic layer with a free magnetization direction, and a read-out magnetic layer with a fixed magnetization direction. The pinned magnetic layer and the free magnetic layer are separated by a non-magnetic layer, and the free magnetic layer and the read-out magnetic layer are separated by another non-magnetic layer. The magnetization directions of the pinned and free layers generally do not point along the same axis. The non-magnetic layers minimize the magnetic interaction between the magnetic layers. A current is applied to the device to induce a torque that alters the magnetic state of the device so that it can act as a magnetic memory for writing information. The resistance, which depends on the magnetic state of the device, is measured to thereby read out the information stored in the device.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Magnetoresistive element and magnetic memory
InactiveUS20070297220A1Easily magnetizedNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsIn planeInter layer
A magnetoresistive includes a first magnetic reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a magnetic free layer having a magnetization direction which is changeable by being supplied with spin polarized electrons, a second magnetic reference layer having a fixed magnetization direction, a first intermediate layer provided between the first magnetic reference layer and the magnetic free layer, and a second intermediate layer provided between the magnetic free layer and the second magnetic reference layer. The magnetic free layer and the first magnetic reference layer have directions of easy magnetization perpendicular or parallel to an in-plane direction. The first magnetic reference layer and the second magnetic reference layer have directions of easy magnetization perpendicular to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Spin barrier enhanced dual magnetoresistance effect element and magnetic memory using the same
ActiveUS7057921B2Reduce outer surfaceHigh areal resistanceNanomagnetismMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDamping constantMagnetic memory
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes first pinned, spacer, free, spin barrier, and second pinned layers. The spacer layer is nonmagnetic and resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The free layer resides between the spacer and spin barrier layers. The spin barrier layer is between the free and second pinned layers. The spin barrier layer is configured to reduce an outer surface contribution to the free layer damping constant. In one aspect, the spin barrier layer has a high areal resistance and may substantially eliminate spin pumping induced damping. In another aspect, the magnetic element also includes a spin accumulation layer between the spin barrier and free layers. The spin accumulation layer has a high conductivity and may have a long spin diffusion length.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
Spin-current switched magnetic memory element suitable for circuit integration and method of fabricating the memory element
A magnetic memory element switchable by current injection includes a plurality of magnetic layers, at least one of the plurality of magnetic layers having a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy component and including a current-switchable magnetic moment, and at least one barrier layer formed adjacent to the plurality of magnetic layers (e.g., between two of the magnetic layers). The memory element has the switching threshold current and device impedance suitable for integration with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) integrated circuits.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Current driven switched magnetic storage cells having improved read and write margins and magnetic memories using such cells
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is described. The magnetic memory includes a plurality of magnetic storage cell and at least one bit line and a plurality of source lines corresponding to the plurality of magnetic storage cells. Each magnetic storage cell includes a magnetic element that is programmed to a high resistance state by a first write current driven through the magnetic element in a first direction and to a low resistance state by a second write current driven through the magnetic element in a second direction. The bit line(s) and the source lines are configured to drive the first write current through the magnetic element in the first direction, to drive the second write current through the magnetic element in the second direction, and to drive at least one read current through the magnetic element in a third direction that does not destabilize the low resistance state.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
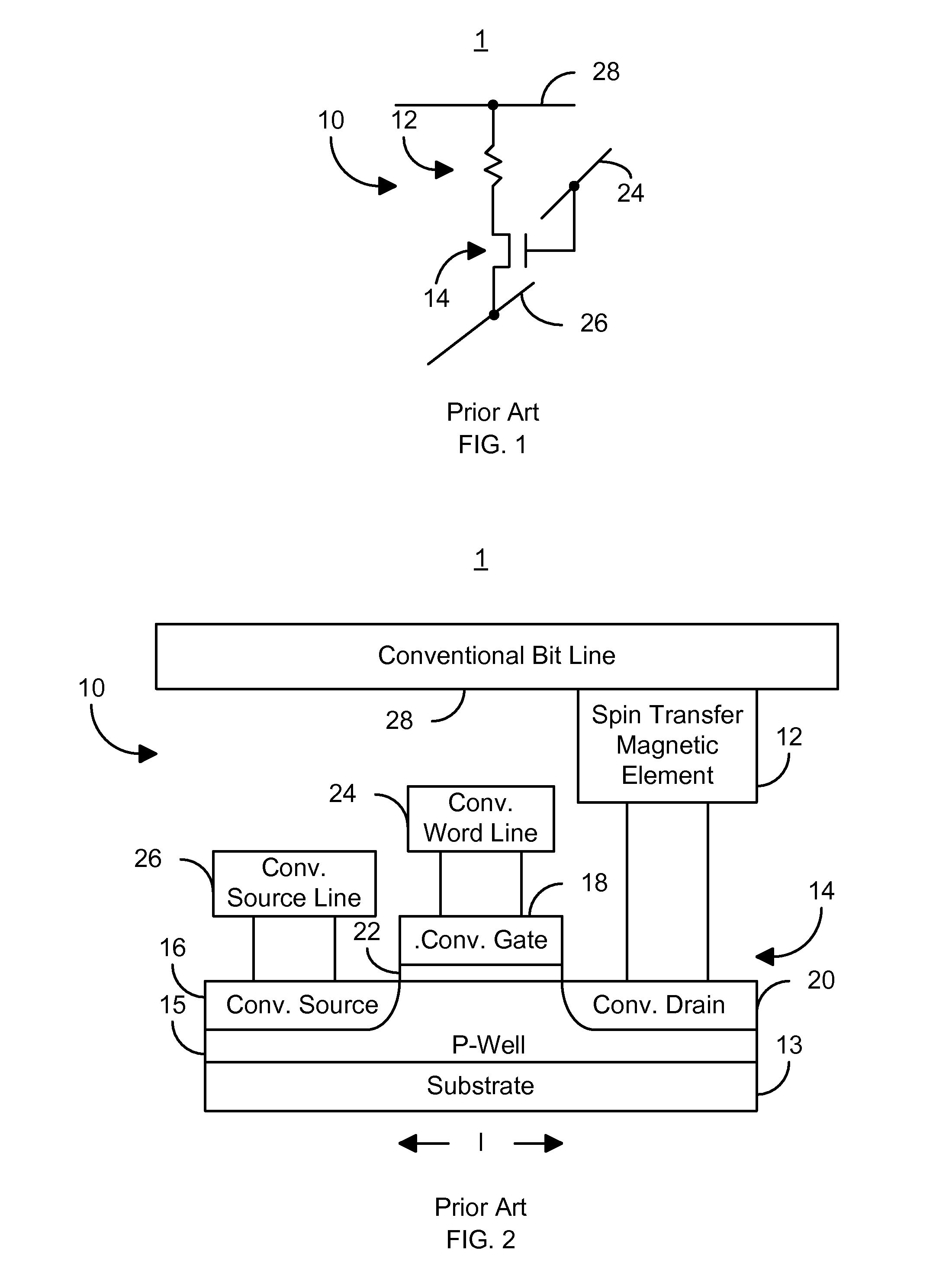
Magnetic element utilizing spin transfer and an MRAM device using the magnetic element
InactiveUS6920063B2Efficient and localized phenomenonEnhanced output signalNanostructure applicationNanomagnetismMagnetic memorySpin transfer
A method and system for providing a magnetic element capable of being written using spin-transfer effect while generating a high output signal and a magnetic memory using the magnetic element are disclosed. The magnetic element includes a first ferromagnetic pinned layer, a nonmagnetic spacer layer, a ferromagnetic free layer, an insulating barrier layer and a second ferromagnetic pinned layer. The pinned layer has a magnetization pinned in a first direction. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is conductive and is between the first pinned layer and the free layer. The barrier layer resides between the free layer and the second pinned layer and is an insulator having a thickness allowing electron tunneling through the barrier layer. The second pinned layer has a magnetization pinned in a second direction. The magnetic element is configured to allow the magnetization of the free layer to change direction due to spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
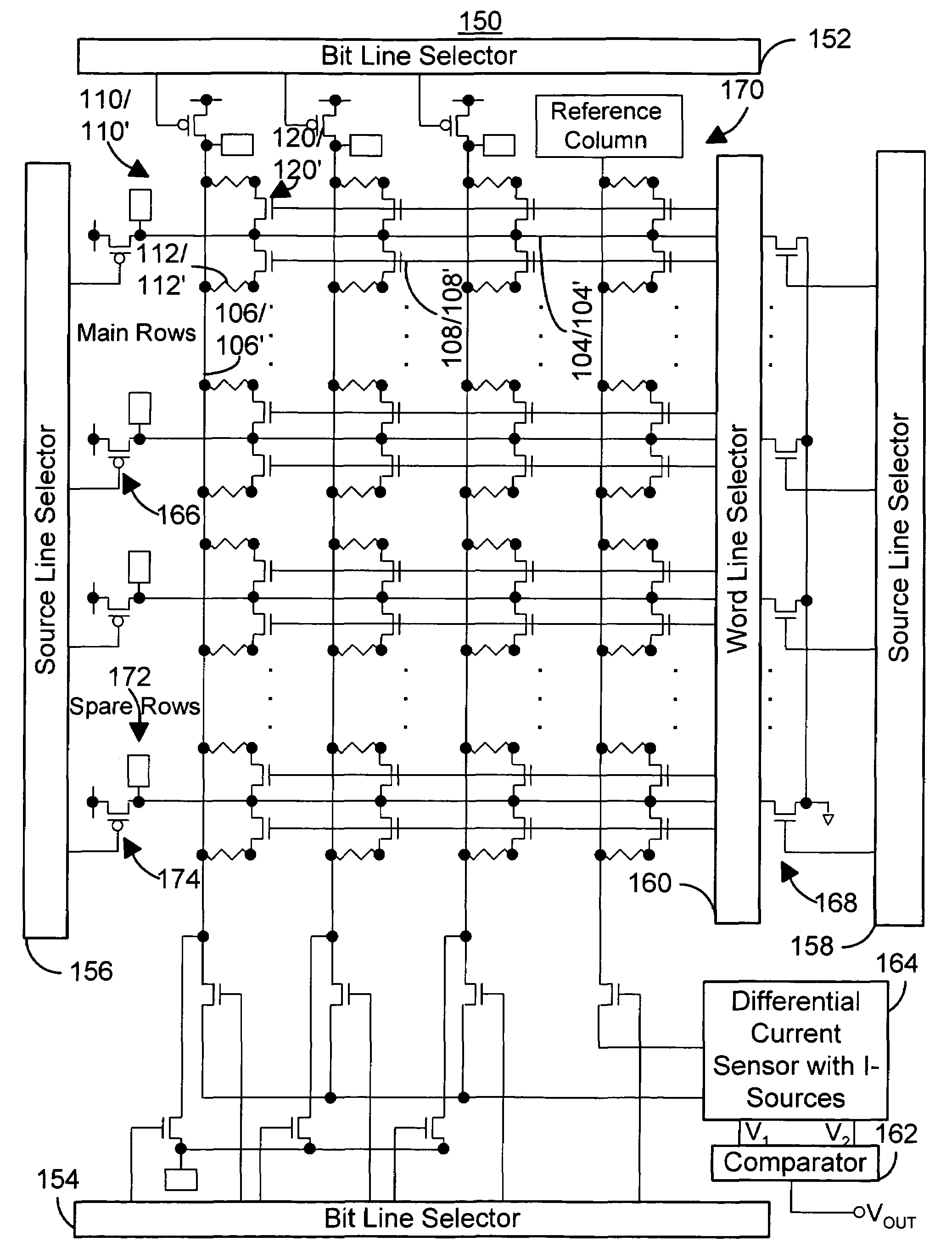
Fast magnetic memory devices utilizing spin transfer and magnetic elements used therein
A method and system for providing a magnetic memory is described. The method and system include providing a plurality of magnetic storage cells, a plurality of word lines, and a plurality of bit lines. Each of the plurality of magnetic storage cells includes a plurality of magnetic elements and at least one selection transistor. Each of the plurality of magnetic elements is capable of being programmed using spin transfer induced switching by a write current driven through the magnetic element. Each of the plurality of magnetic elements has a first end and a second end. The at least one selection transistor is coupled to the first end of each of the plurality of magnetic elements. The plurality of word lines is coupled with the plurality of selection transistors and selectively enables a portion of the plurality of selection transistors.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
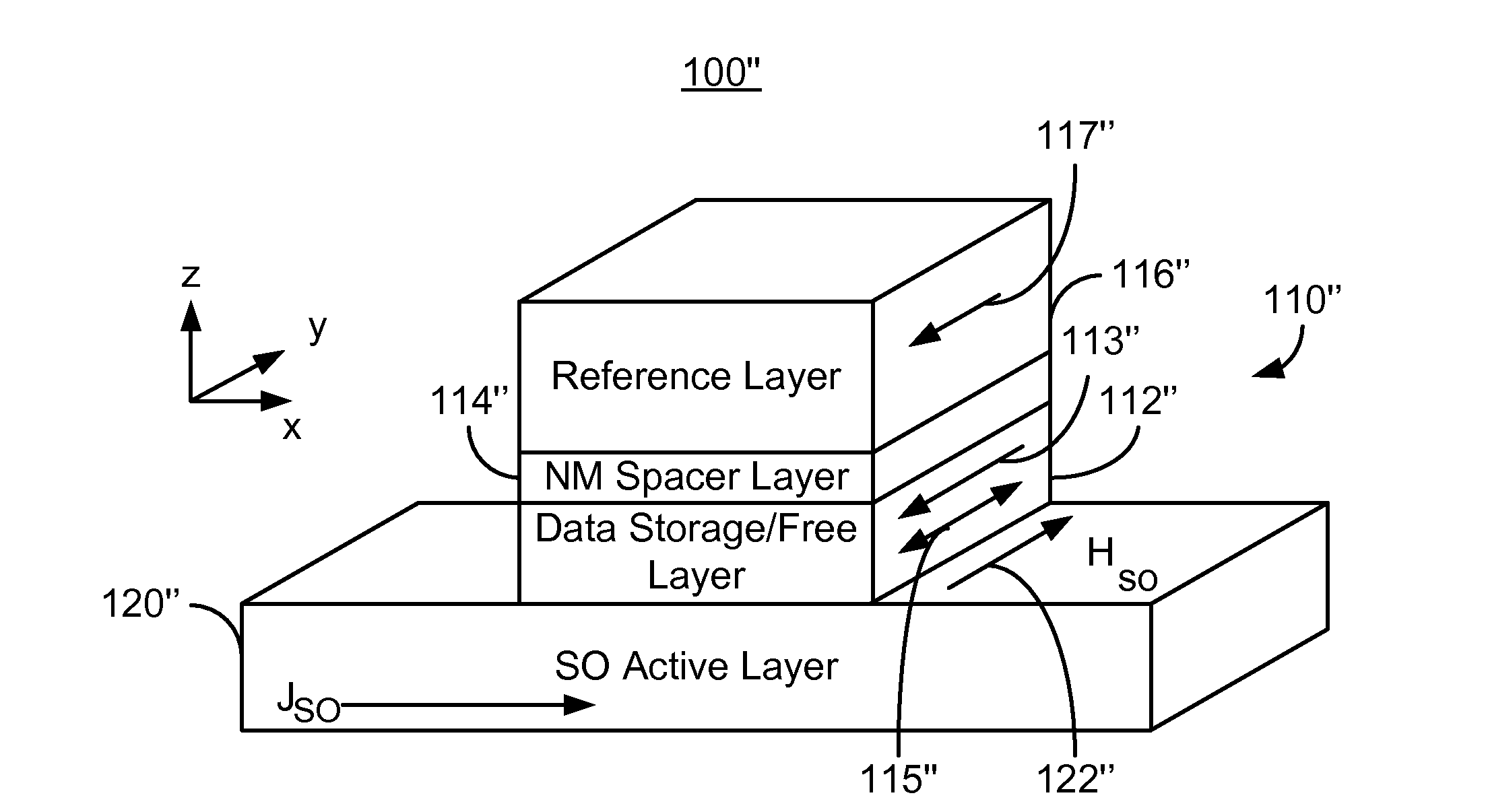
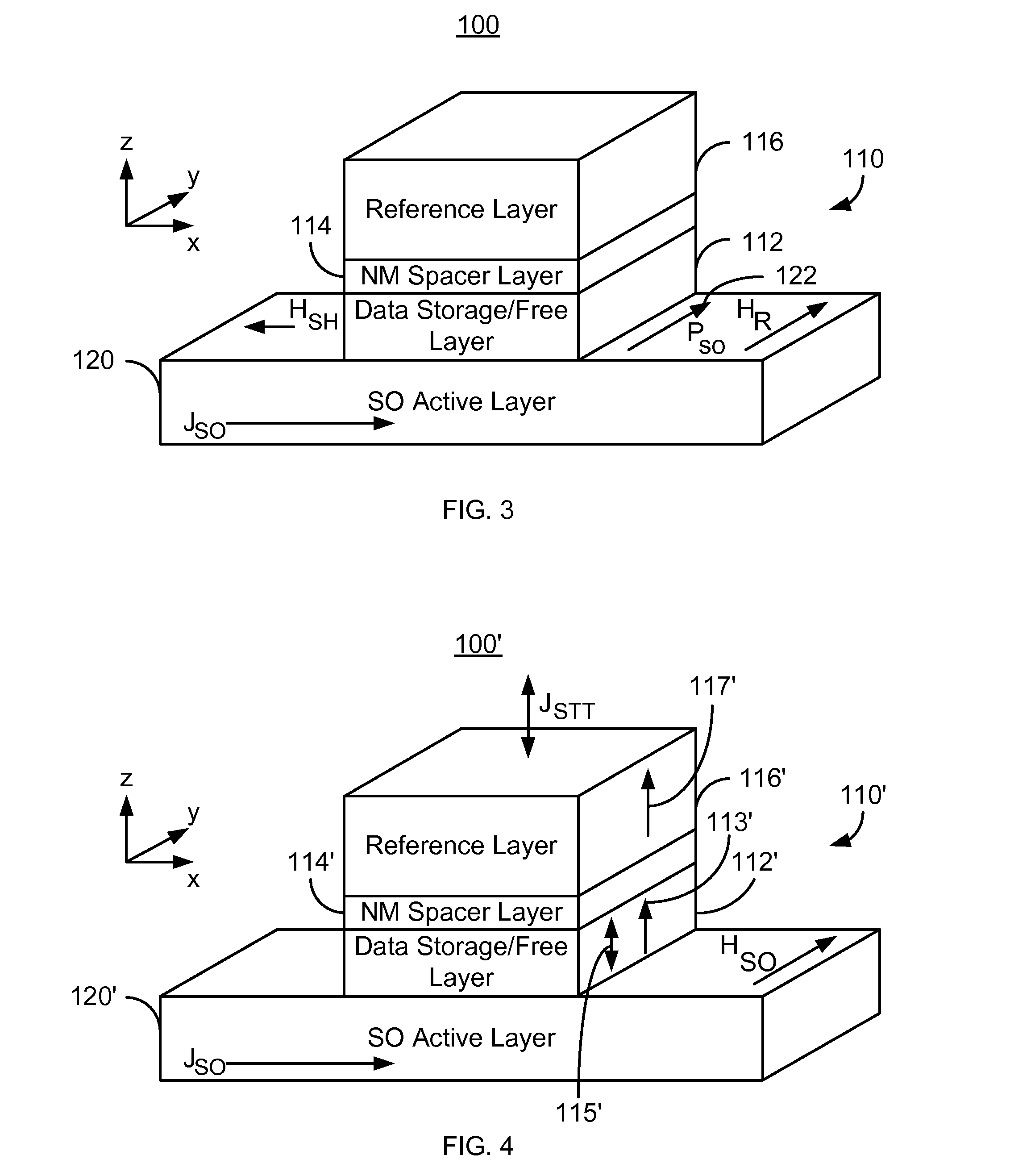
Method and system for providing a magnetic tunneling junction using spin-orbit interaction based switching and memories utilizing the magnetic tunneling junction
ActiveUS20140056060A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDigital storageMagnetic memoryActive layer
A magnetic memory is described. The magnetic memory includes magnetic junctions and at least one spin-orbit interaction (SO) active layer. Each of the magnetic junctions includes a data storage layer that is magnetic. The SO active layer(s) are adjacent to the data storage layer of the magnetic junction. The at SO active layer(s) are configured to exert a SO torque on the data storage layer due to a current passing through the at least one SO active layer in a direction substantially perpendicular to a direction between the at least one SO active layer and the data storage layer of a magnetic junction of the plurality of magnetic junctions closest to the at least one SO active layer. The data storage layer is configured to be switchable using at least the SO torque.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com