Patents
Literature
897 results about "Out of plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Out of plane bending moments are those which are caused by out of plane forces such a building slab. The forces (dear, live) on the building slab are out of plane and thus they produce out of plane bending moments or in order words they make the slab concave down.
Medical staple and magazine
ActiveUS9610079B2Easy to useSmooth feedingSuture equipmentsStapling toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
There are provided a medical staple realizing smooth feeding when loaded in a magazine and a magazine which can realize stable feeding by using the medical staple. Where the medical staple includes a body portion; and a pair of legs formed at both ends of the body portion, wherein the legs are tilted at an angle in which the legs become closer to each other and either one leg is twisted with respect to a plane including the body portion and the other leg in the out-of-plane direction. The magazine includes a body guiding portion which has a size substantially equal to or slightly smaller than the length of the body portions of the staples and carries and guides the body portions thereon; wherein the plurality of staples are loaded in a state where the legs are tilted to the downstream side in the discharge direction and the body portions to the upstream side in the discharge direction.
Owner:MATSUTANI SEISAKUSHO CO LTD
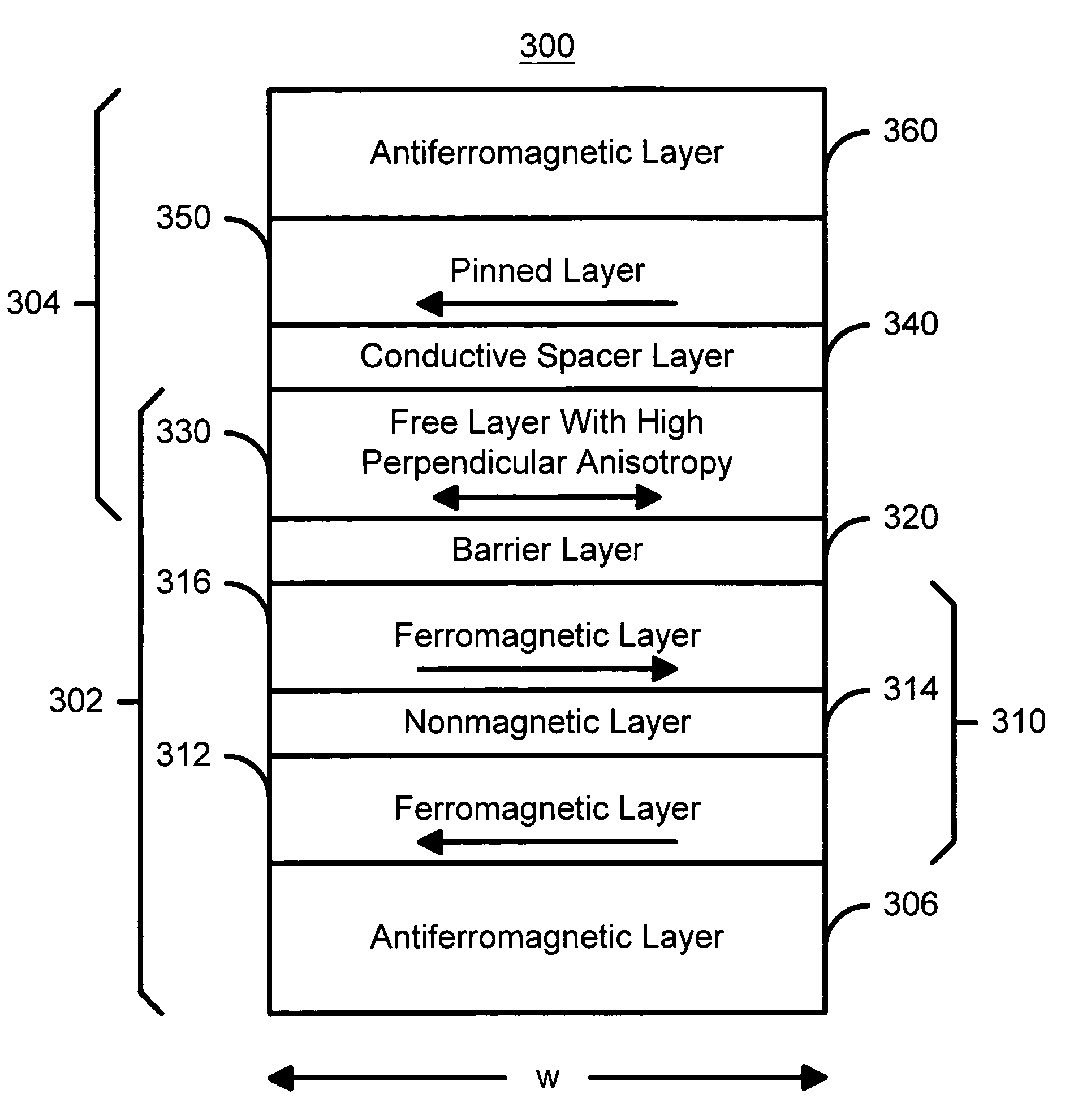
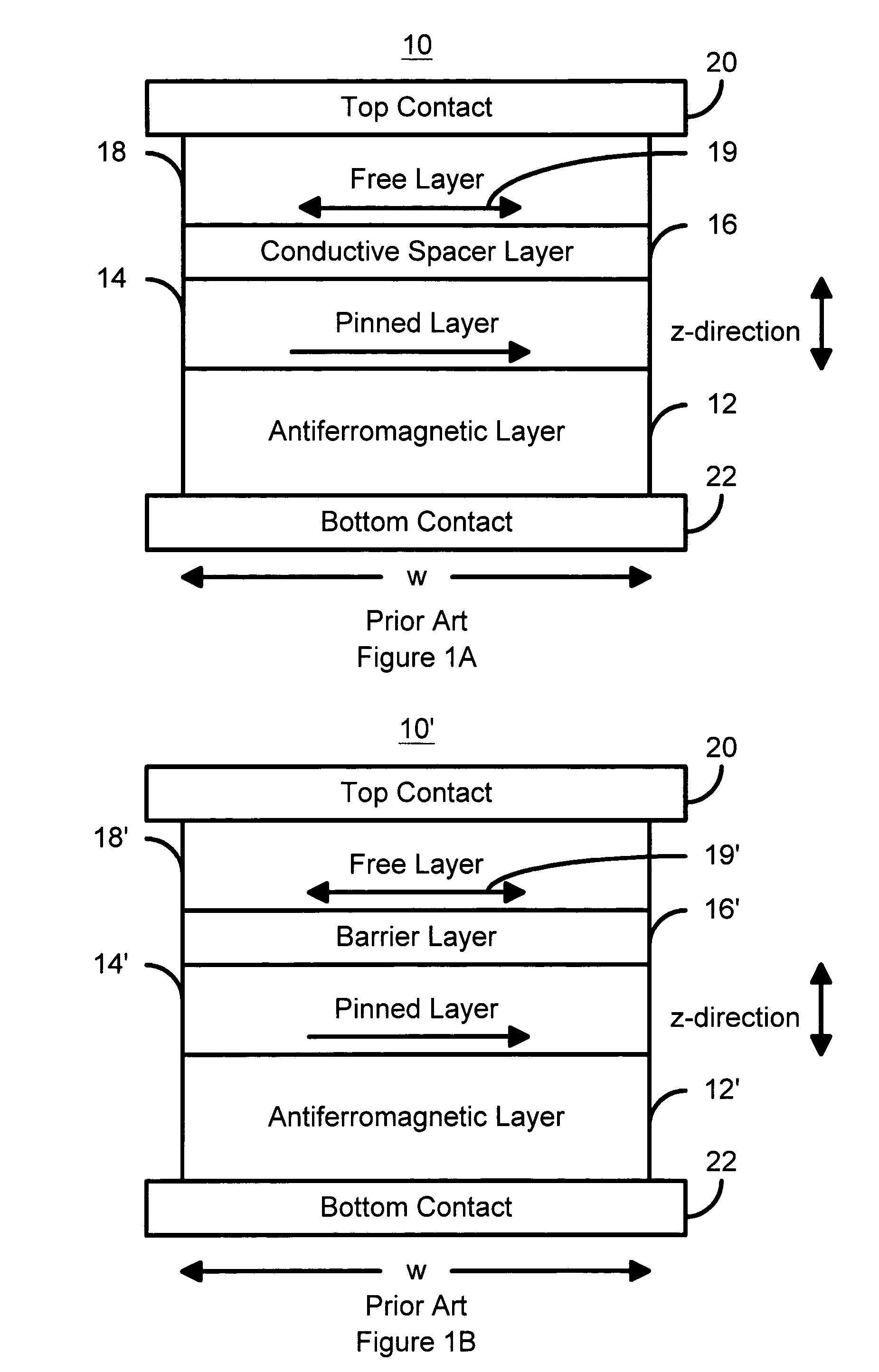
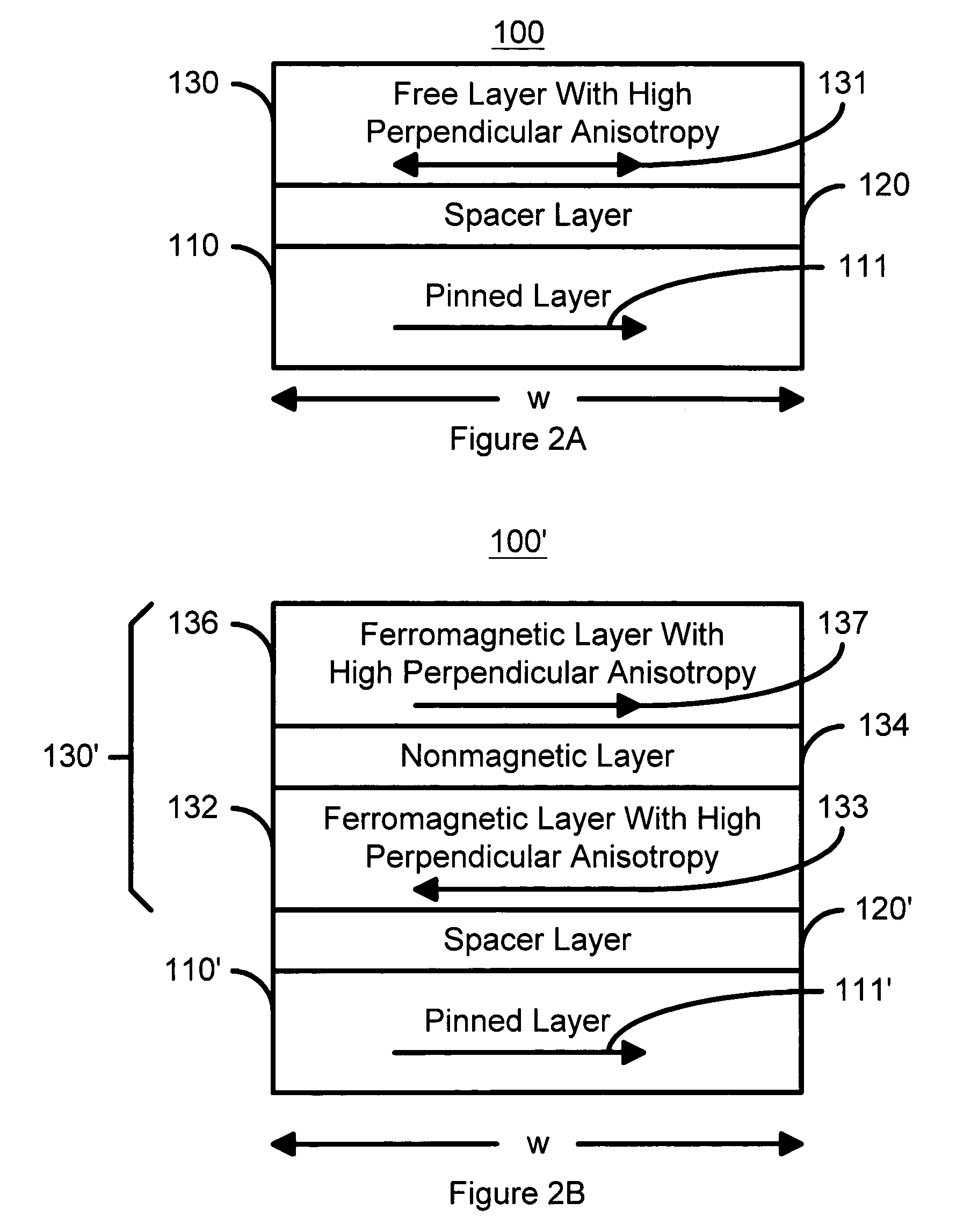
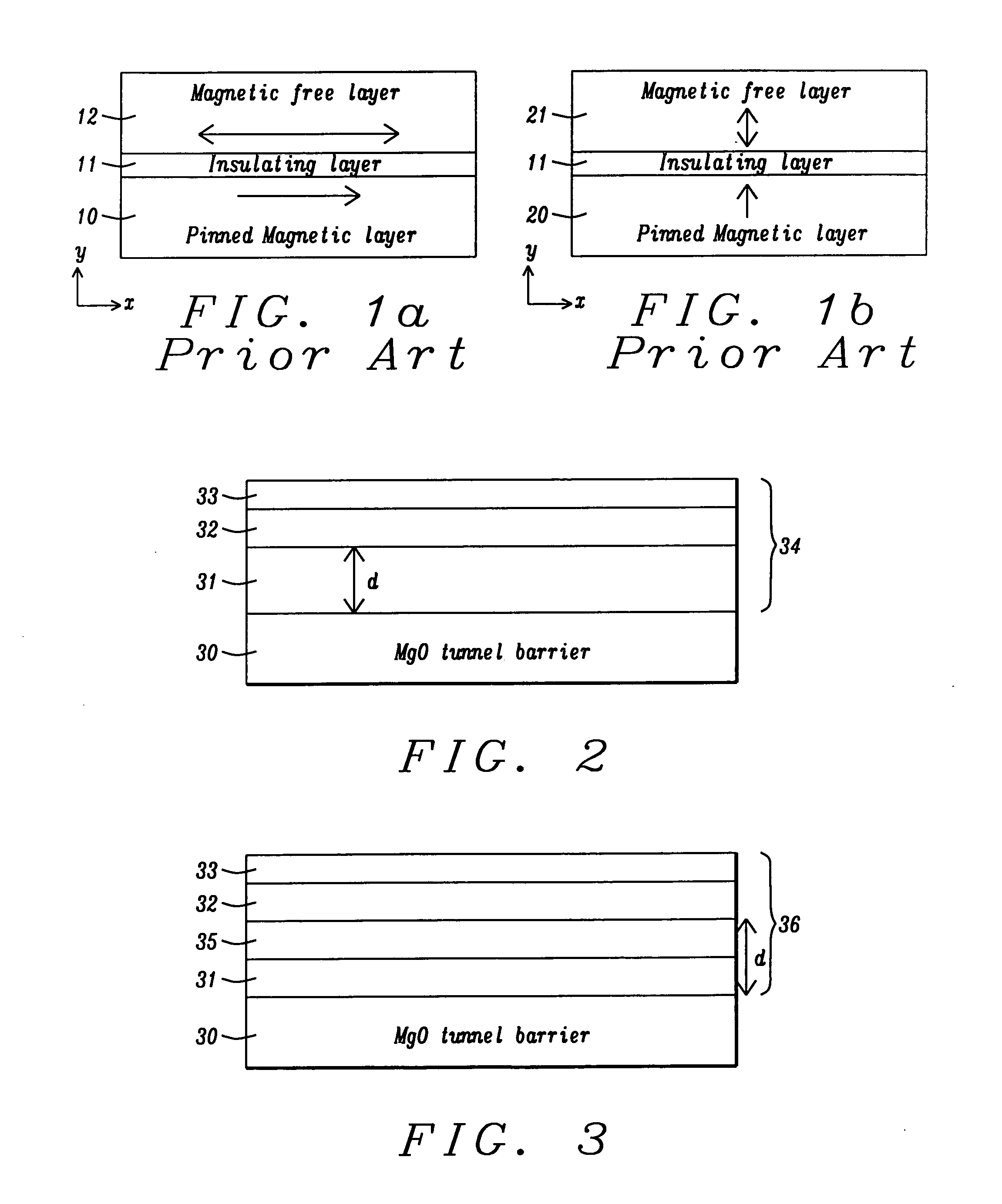
Spin transfer magnetic element with free layers having high perpendicular anisotropy and in-plane equilibrium magnetization
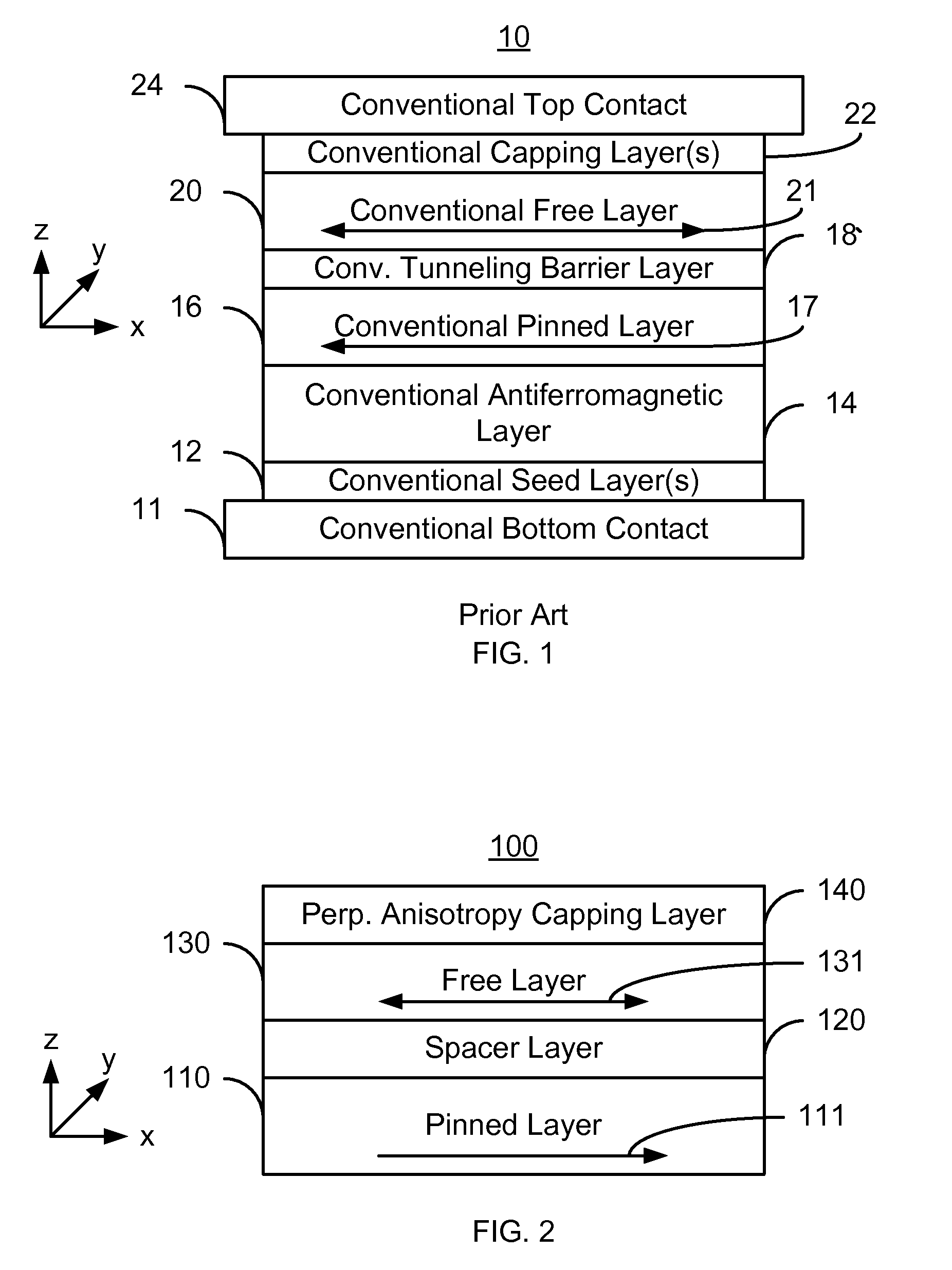
A method and system for providing a magnetic element that can be used in a magnetic memory is disclosed. The magnetic element includes pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The spacer layer resides between the pinned and free layers. The free layer can be switched using spin transfer when a write current is passed through the magnetic element. The magnetic element may also include a barrier layer, a second pinned layer. Alternatively, second pinned and second spacer layers and a second free layer magnetostatically coupled to the free layer are included. At least one free layer has a high perpendicular anisotropy. The high perpendicular anisotropy has a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is at least twenty and less than one hundred percent of the out-of-plane demagnetization energy.
Owner:SAMSUNG SEMICON
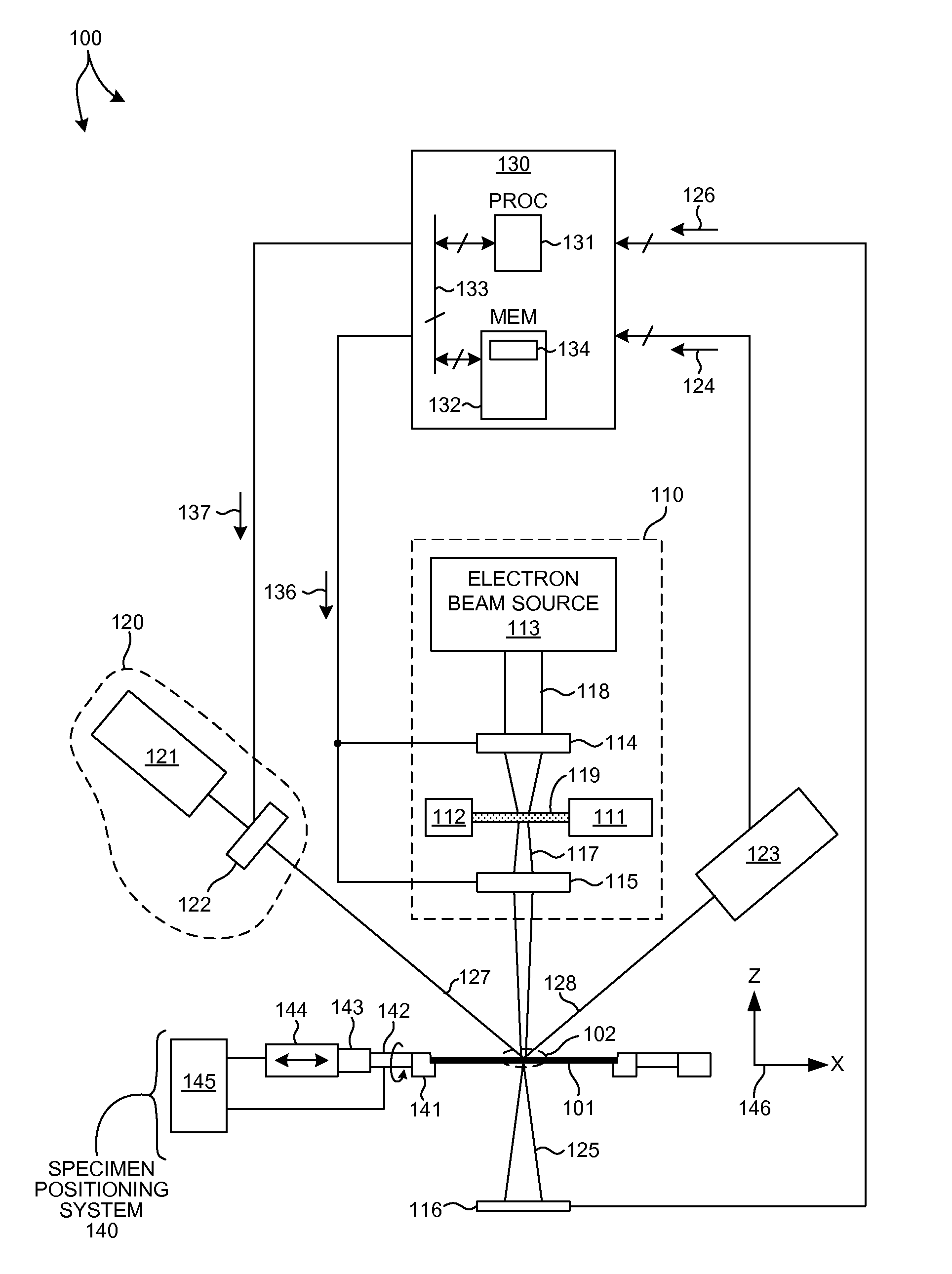
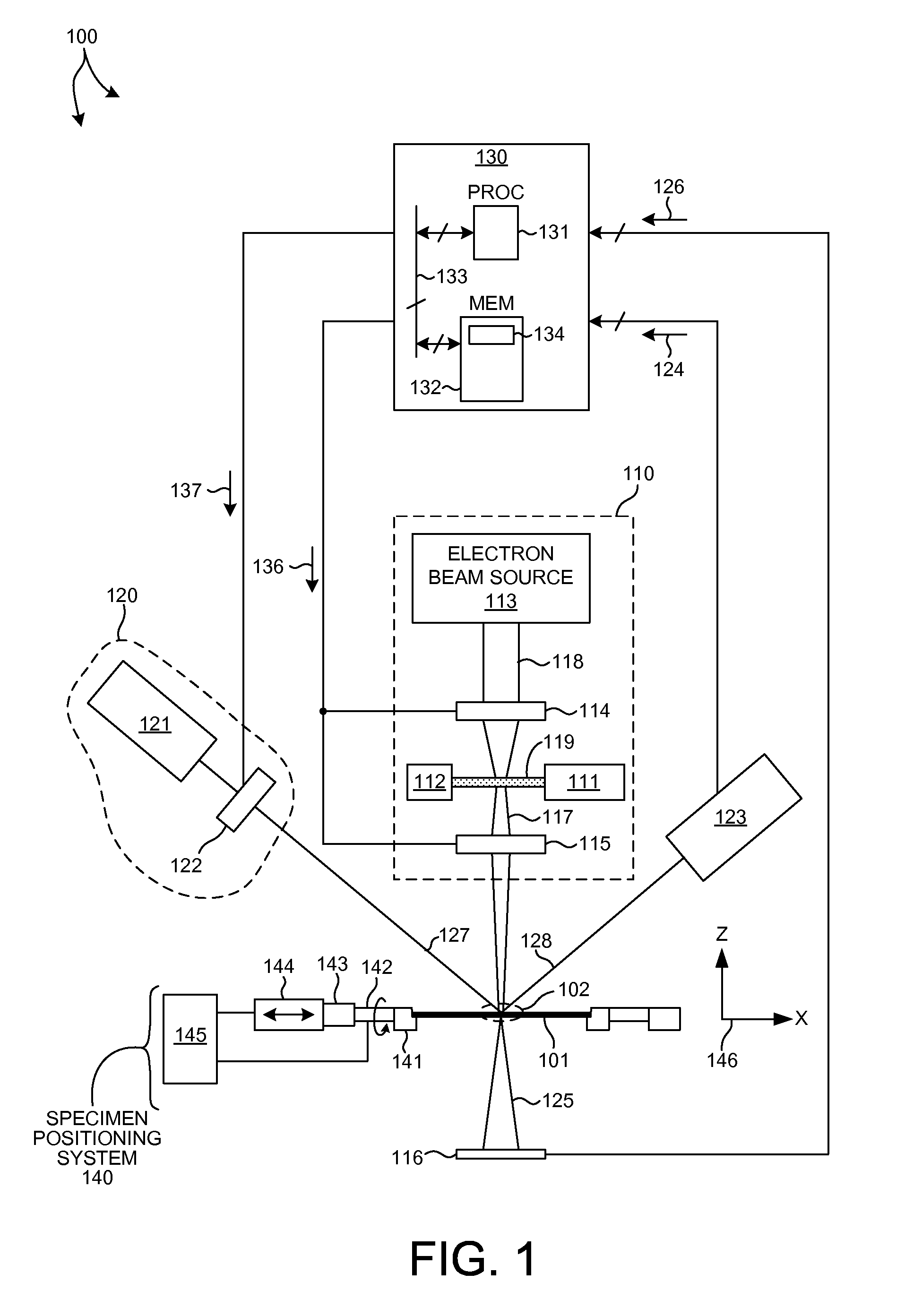
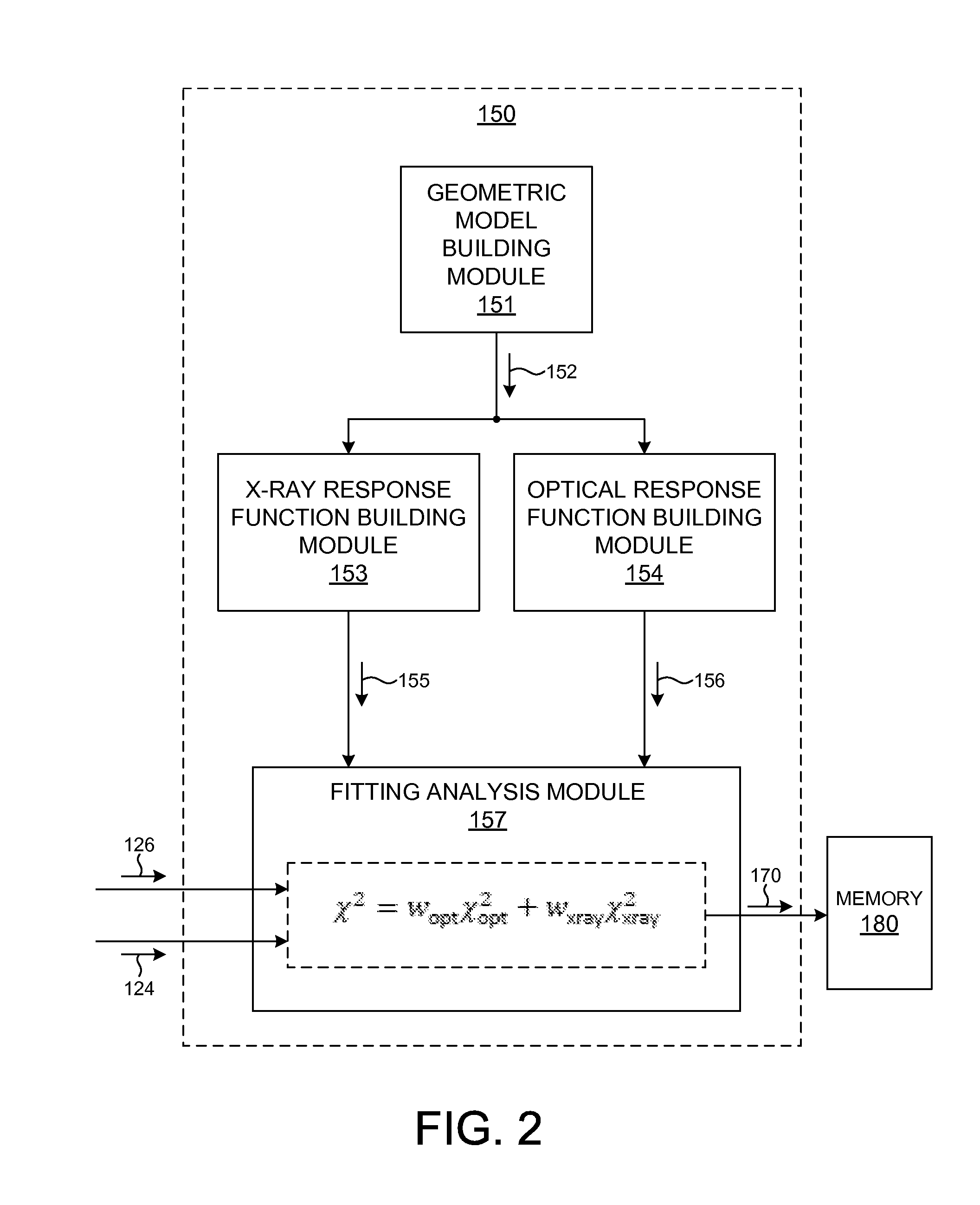
Metrology Tool With Combined X-Ray And Optical Scatterometers
ActiveUS20130304424A1Reduce correlationImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceData setMetrology
Methods and systems for performing simultaneous optical scattering and small angle x-ray scattering (SAXS) measurements over a desired inspection area of a specimen are presented. SAXS measurements combined with optical scatterometry measurements enables a high throughput metrology tool with increased measurement capabilities. The high energy nature of x-ray radiation penetrates optically opaque thin films, buried structures, high aspect ratio structures, and devices including many thin film layers. SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements of a particular location of a planar specimen are performed at a number of different out of plane orientations. This increases measurement sensitivity, reduces correlations among parameters, and improves measurement accuracy. In addition, specimen parameter values are resolved with greater accuracy by fitting data sets derived from both SAXS and optical scatterometry measurements based on models that share at least one geometric parameter. The fitting can be performed sequentially or in parallel.
Owner:KLA CORP
Optical off-chip interconnects in multichannel planar waveguide devices
The multichannel waveguide device includes an array of waveguides located in a plane. Each waveguide channel has a redirecting element for redirecting a guided wave out of said plane, or vice versa. The redirecting elements are staggered in the direction of the waveguides so as to transform a one-dimensional array of in-plane waves into a two-dimensional array of out-of-plane waves, or vice versa.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Image guided radiosurgery method and apparatus using registration of 2D radiographic images with digitally reconstructed radiographs of 3D scan data
ActiveUS20050049478A1Rapid and accurate methodThe process is fast and accurateImage enhancementImage analysisIn plane3d image
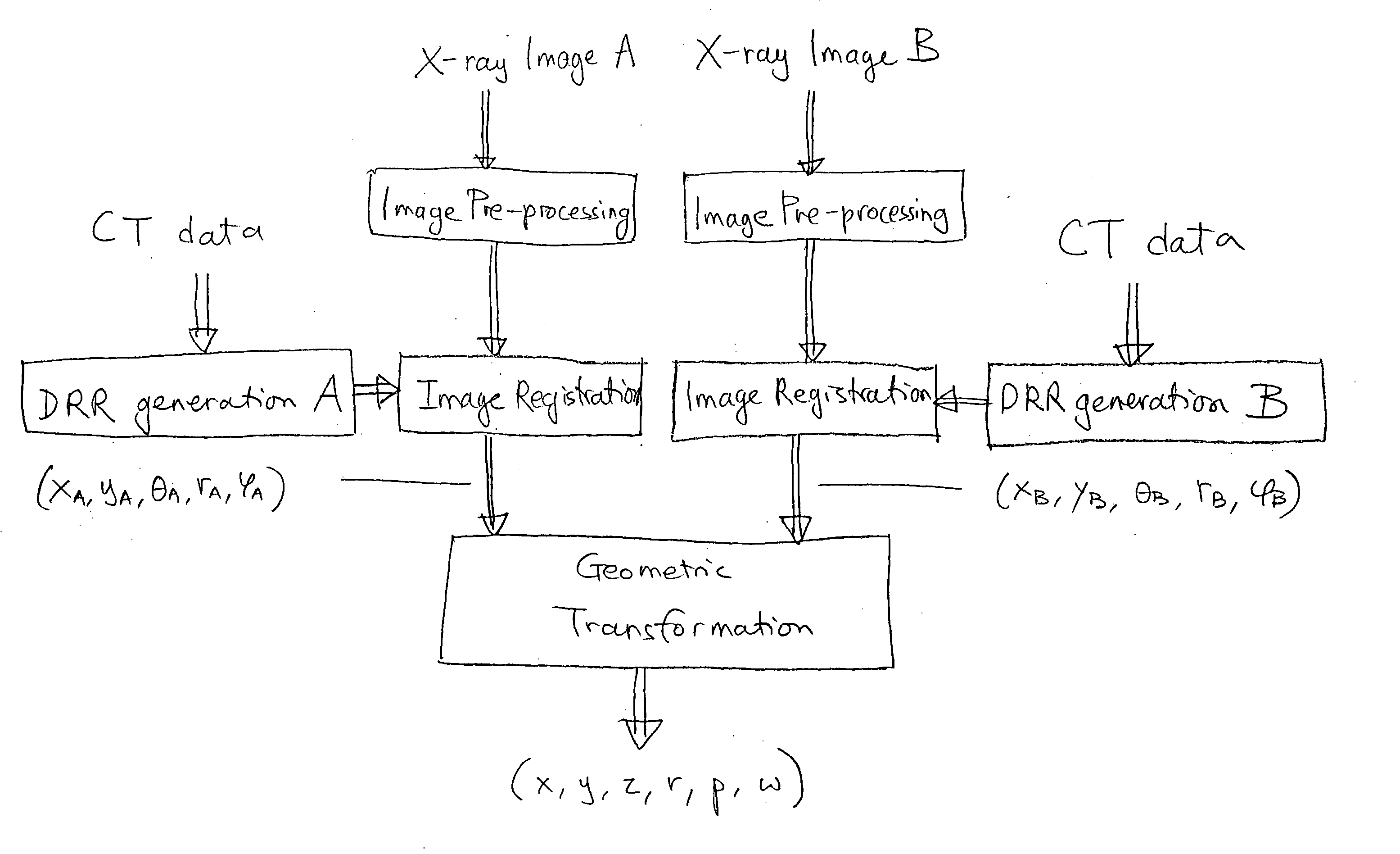
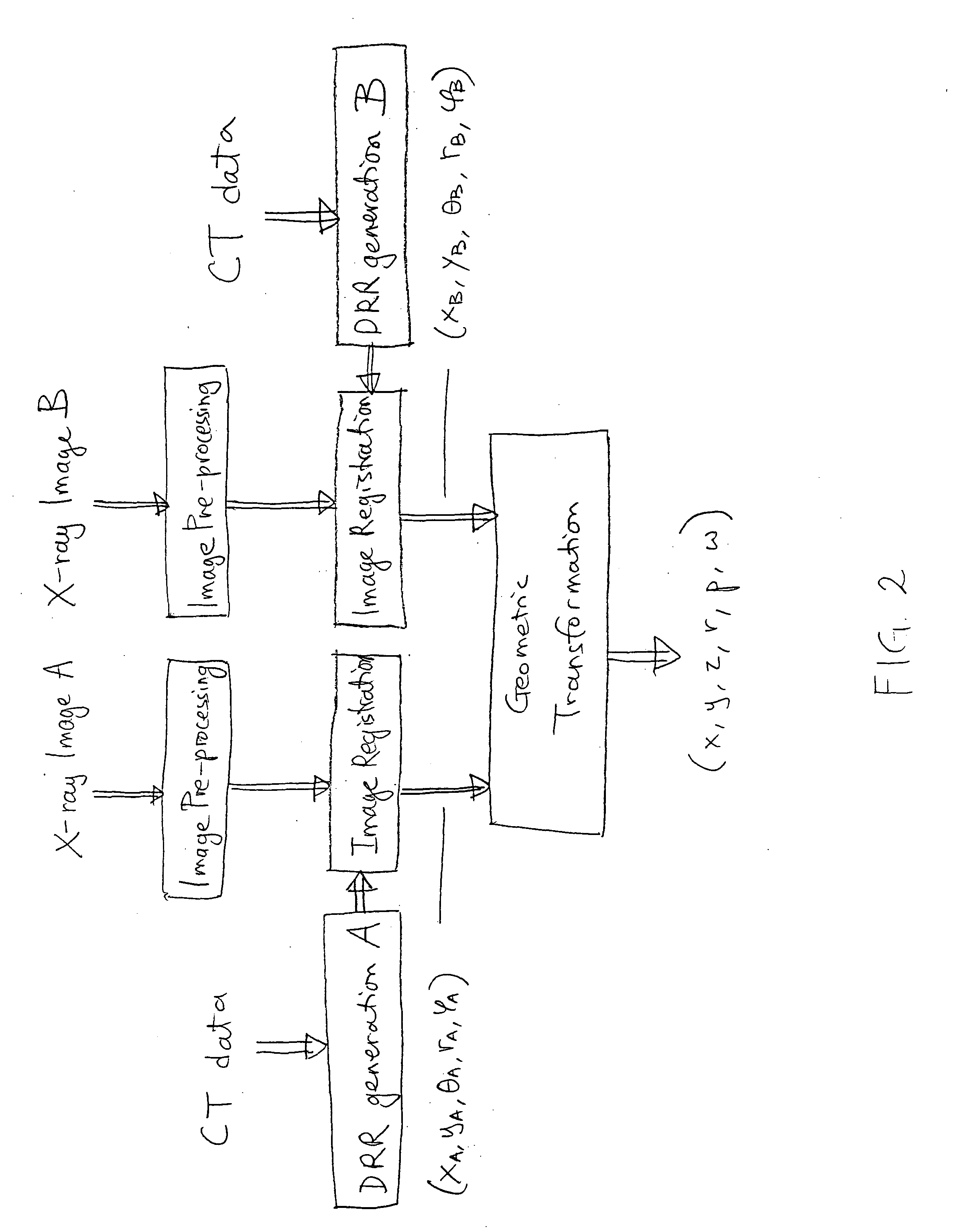
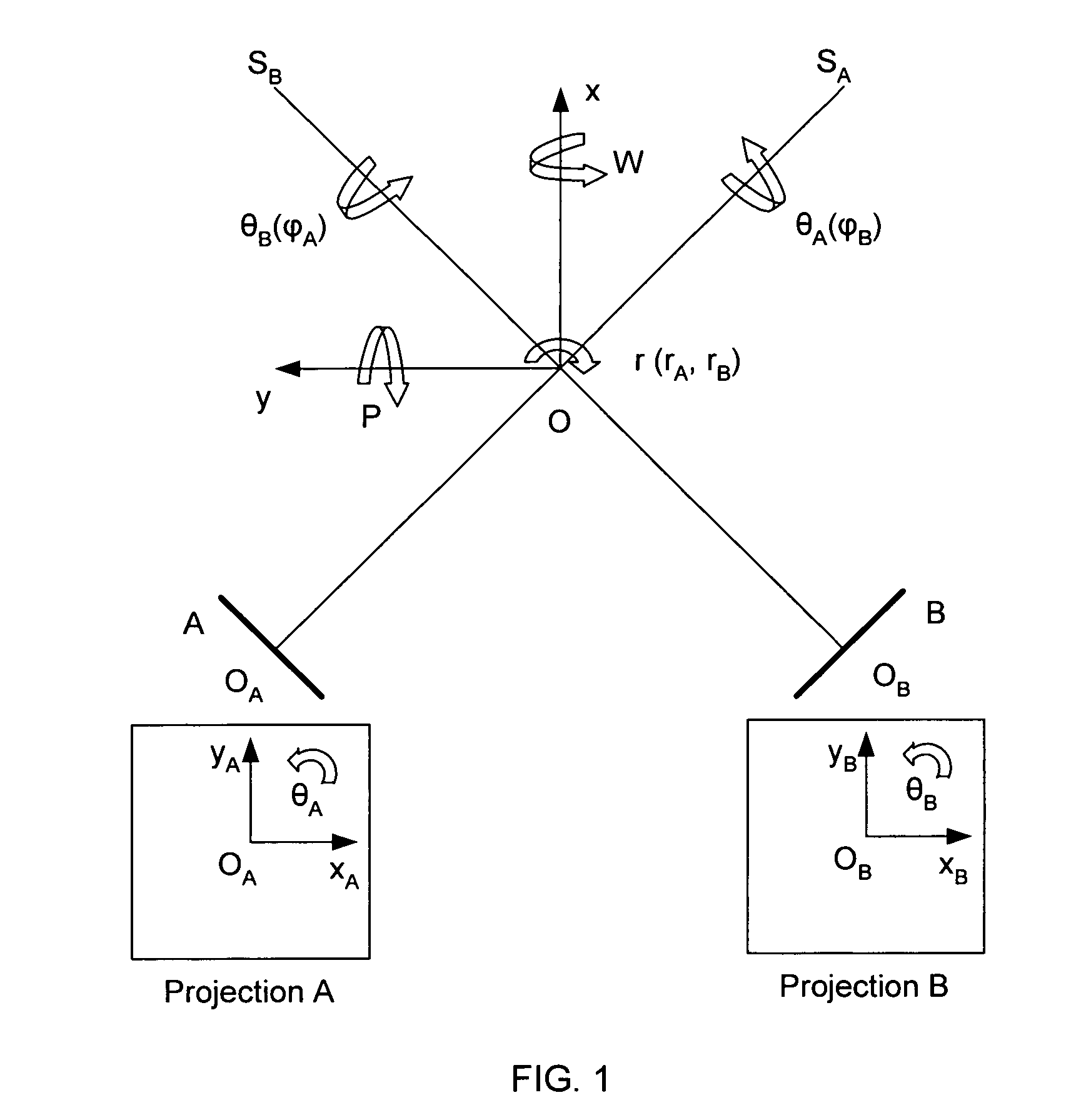
An image-guided radiosurgery method and system are presented that use 2D / 3D image registration to keep the radiosurgical beams properly focused onto a treatment target. A pre-treatment 3D scan of the target is generated at or near treatment planning time. A set of 2D DRRs are generated, based on the pre-treatment 3D scan. At least one 2D x-ray image of the target is generated in near real time during treatment. The DRRs are registered with the x-ray images, by computing a set of 3D transformation parameters that represent the change in target position between the 3D scan and the x-ray images. The relative position of the radiosurgical beams and the target is continuously adjusted in near real time in accordance with the 3D transformation parameters. A hierarchical and iterative 2D / 3D registration algorithm is used, in which the transformation parameters that are in-plane with respect to the image plane of the x-ray images are computed separately from the out-of-plane transformation parameters.
Owner:ACCURAY
Apparatus and method for registering 2D radiographic images with images reconstructed from 3D scan data
InactiveUS7204640B2Precise and rapidImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisIn planeTransformation parameter
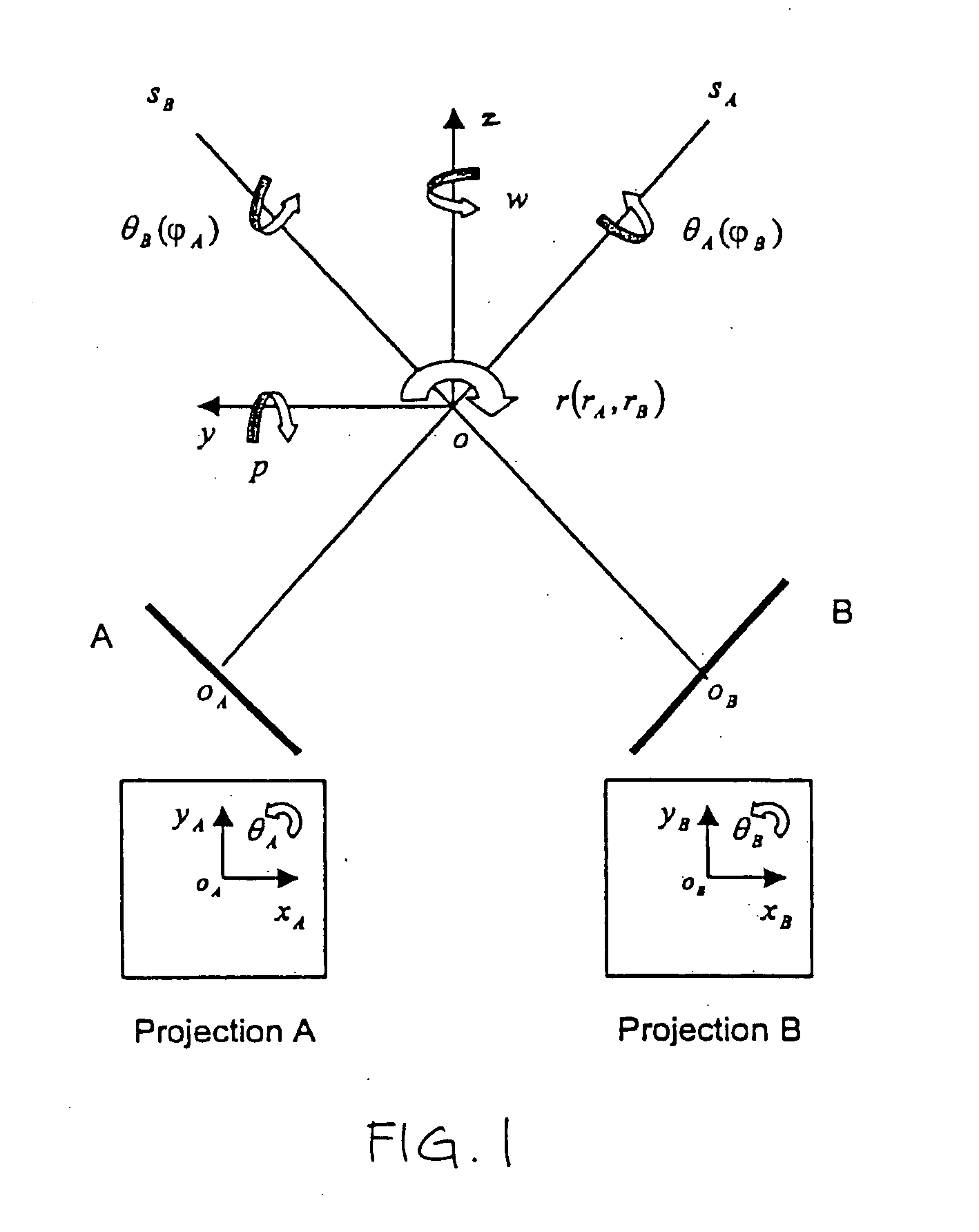
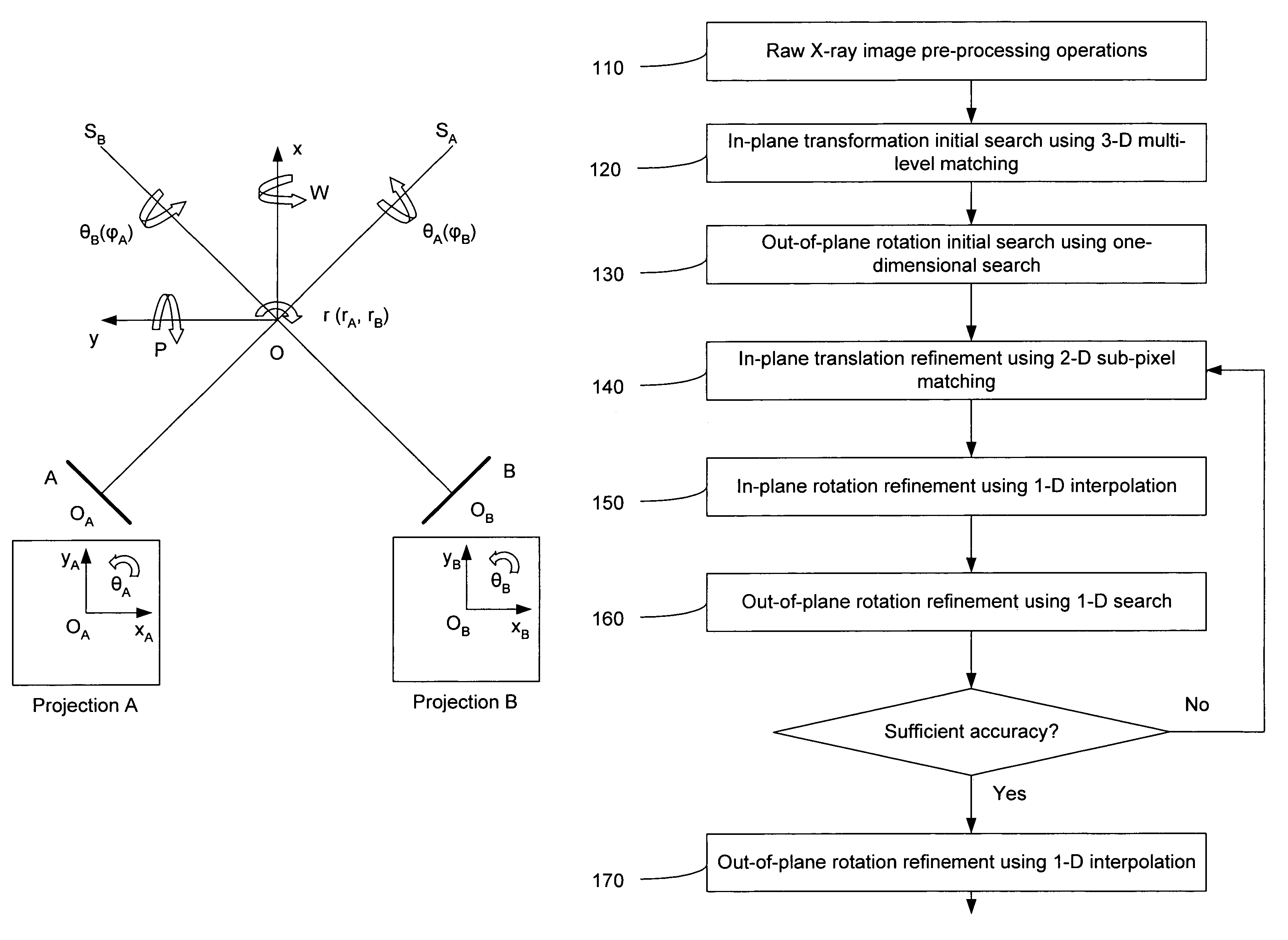
A method and system is provided for registering a 2D radiographic image of a target with previously generated 3D scan data of the target. A reconstructed 2D image is generated from the 3D scan data. The radiographic 2D image is registered with the reconstructed 2D images to determine the values of in-plane transformation parameters (x, y, θ) and out-of-plane rotational parameters (r, Φ), where the parameters represent the difference in the position of the target in the radiographic image, as compared to the 2D reconstructed image. An initial estimate for the in-plane transformation parameters is made by a 3D multi-level matching process, using the sum-of-square differences similarity measure. Based on these estimated parameters, an initial 1-D search is performed for the out-of-plane rotation parameters (r, Φ), using a pattern intensity similarity measure. The in-plane parameters (x, y, θ) and out-of-plane parameters (r, Φ) are iteratively refined, until a desired accuracy is reached.
Owner:ACCURAY
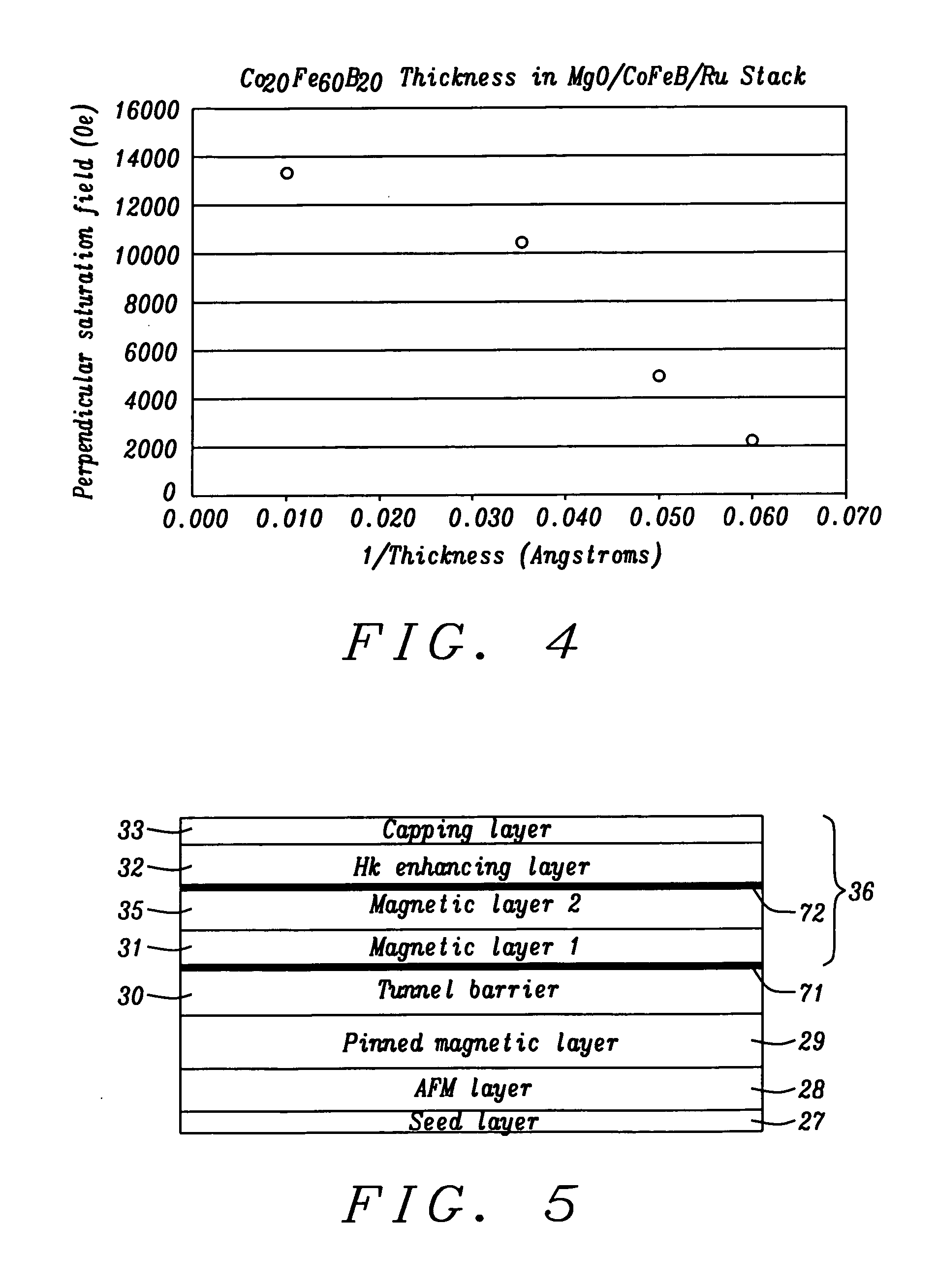
Magnetic element with improved out-of-plane anisotropy for spintronic applications
ActiveUS20120205758A1Without degrading thermal stability and MR ratioEnhanced interfacial perpendicular anisotropyMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsGalvano-magnetic material selectionPerpendicular anisotropyAlloy
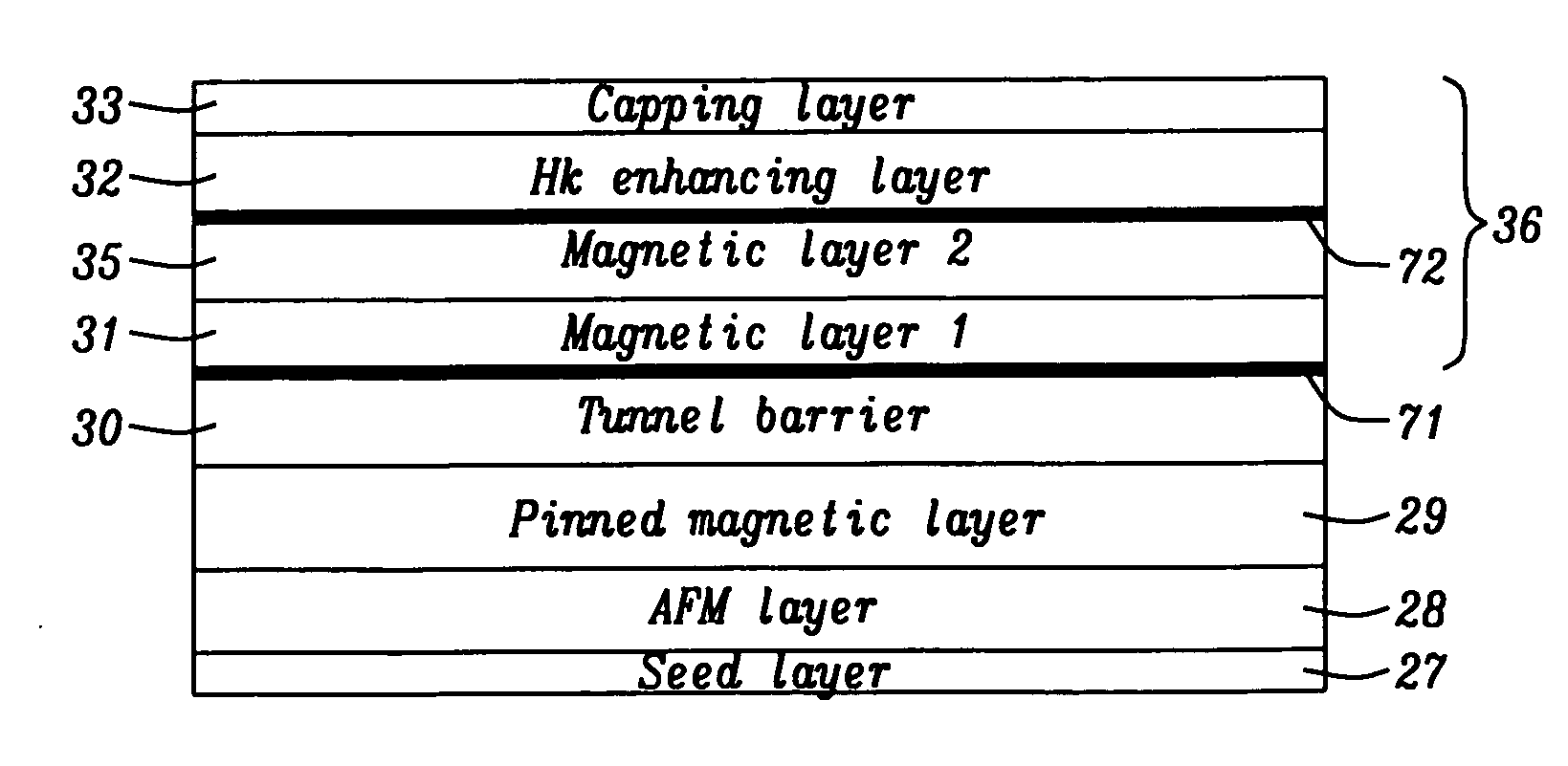
A magnetic element is disclosed wherein first and second interfaces of a free layer with a Hk enhancing layer and tunnel barrier, respectively, produce enhanced surface perpendicular anisotropy to lower switching current or increase thermal stability in a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). In a MTJ with a bottom spin valve configuration where the Hk enhancing layer is an oxide, the capping layer contacting the Hk enhancing layer is selected to have a free energy of oxide formation substantially greater than that of the oxide. The free layer may be a single layer or composite comprised of an Fe rich alloy such as Co20Fe60B20. With a thin free layer, the interfacial perpendicular anisotropy may dominate the shape anisotropy to generate a magnetization perpendicular to the planes of the layers. The magnetic element may be part of a spintronic device or serve as a propagation medium in a domain wall motion device.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
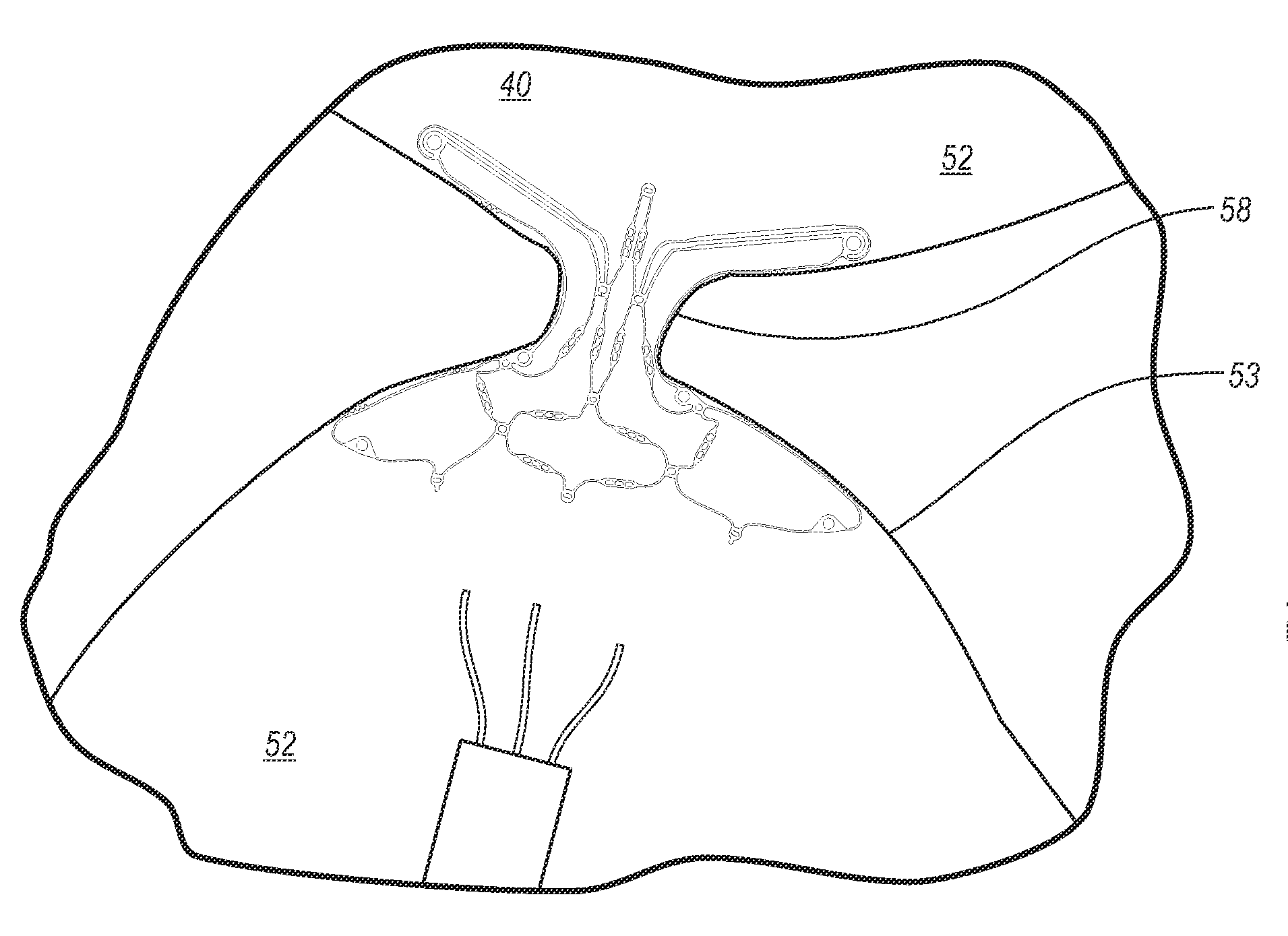
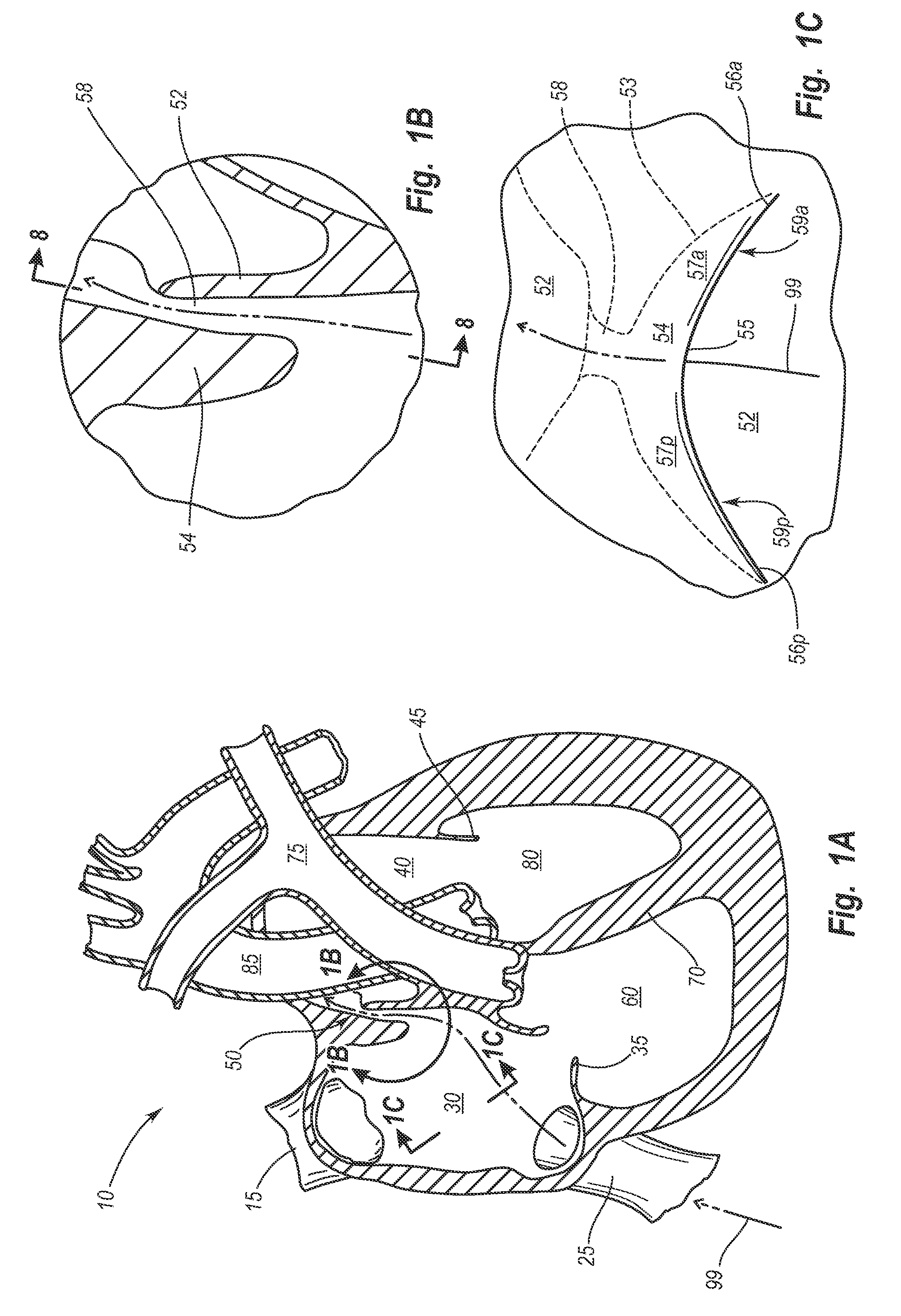
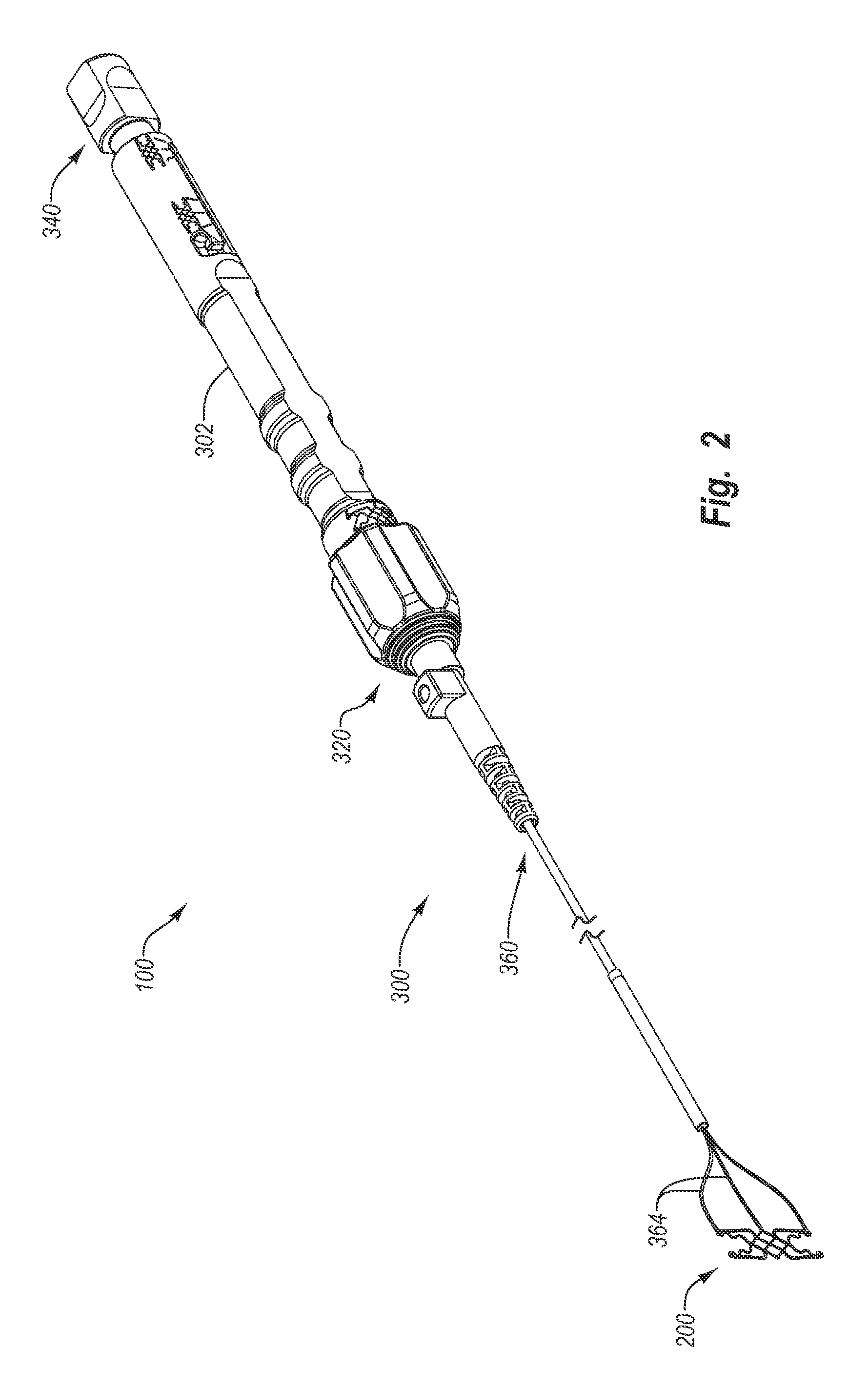
Devices for reducing the size of an internal tissue opening
A medical system for treating an internal tissue opening can include a closure device and associated delivery device. The closure device can include a body portion operatively associated with a first anchor and a second anchor. The body portion can include a plurality of segments defining a multi-cellular structure. The closure device can be configured to apply lateral force to tissue of the internal tissue opening to bring tissue together. The closure device can have a substantially flat aspect, and have a depth thickness that is substantially greater than the thickness or width of a majority of the members forming the closure device to reduce out of plane bending. The closure device can also include a member adapted to induce tissue growth.
Owner:COHEREX MEDICAL
Magnetic stack having assist layer
A magnetic memory cell having a ferromagnetic free layer and a ferromagnetic pinned reference layer, each having an out-of-plane magnetic anisotropy and an out-of-plane magnetization orientation and switchable by spin torque. The cell includes a ferromagnetic assist layer proximate the free layer, the assist layer having a low magnetic anisotropy less than about 500 Oe. The assist layer may have in-plane or out-of-plane anisotropy.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Pavement joint
InactiveUS7806624B2Reduce wastePotential tripping hazards to pedestrians are reducedPaving detailsBuilding insulationsRoad surfaceEngineering
A pavement joint 101, 102 disposed between two contiguous pavement slabs 103, 104 and 105 incorporating a shear key (12, 13, 22 and 23) and at least one hinge (37, 38, 39 and 40). The shear key and the at least one hinge are operative when at least one of the slabs is subjected to out-of-plane action P with the shear key transferring shear between the slabs, and the at least one hinge accommodating angular displacement of the slabs relative to the joint axis in at least one direction. In one form, a joint member 10, 20, 40, 50 and 60 is disposed between the slabs to provide the shear key and hinge. A joint member and pavement slab for use in the joint is also described.
Owner:TRIPSTOP TECH
Absorbent core for disposable absorbent article
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Method and system for providing magnetic tunneling junction elements having improved performance through capping layer induced perpendicular anisotropy and memories using such magnetic elements
InactiveUS20110031569A1Improve thermal stabilityNanomagnetismMagnetic measurementsPerpendicular anisotropyMagnetic memory
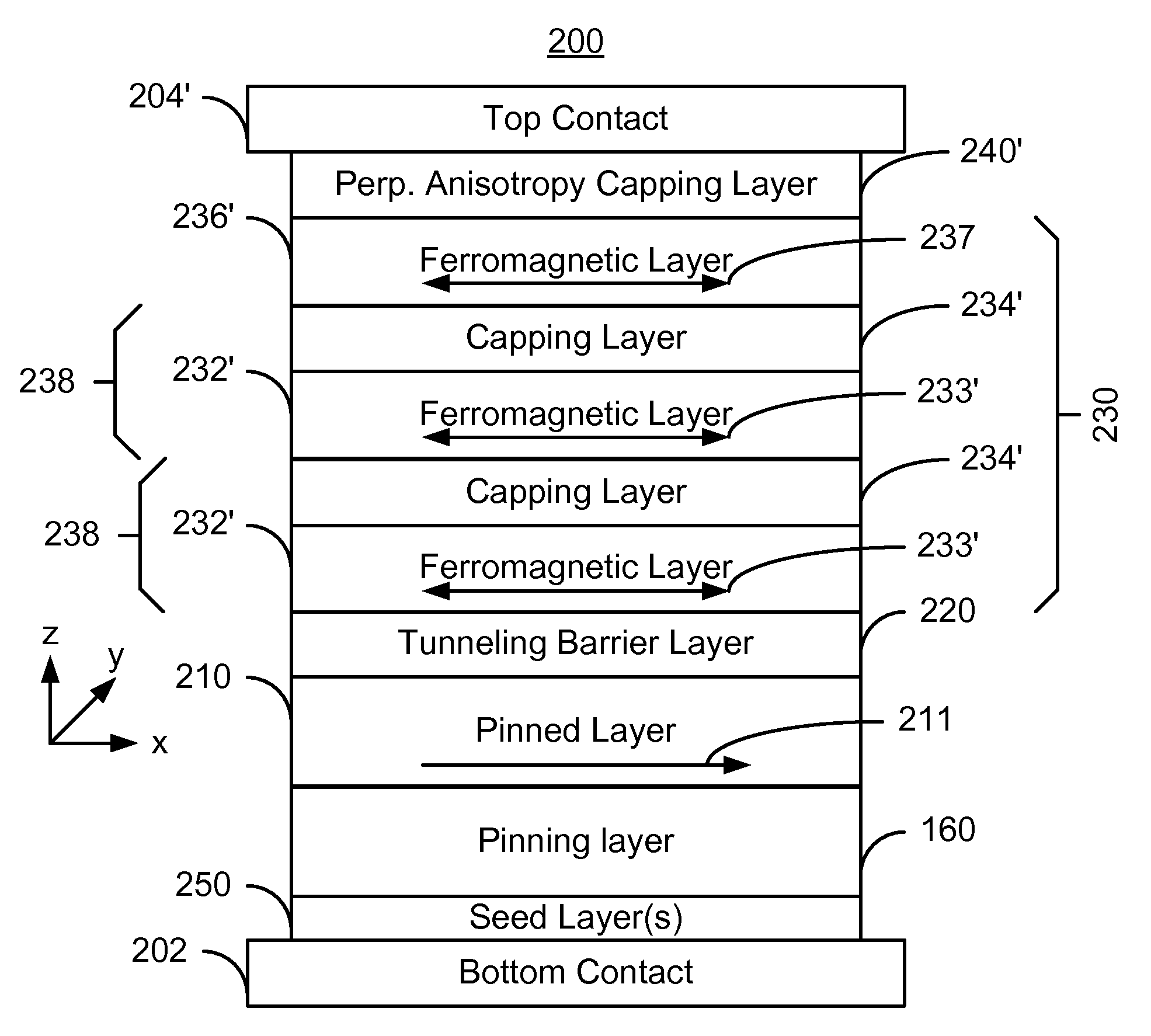
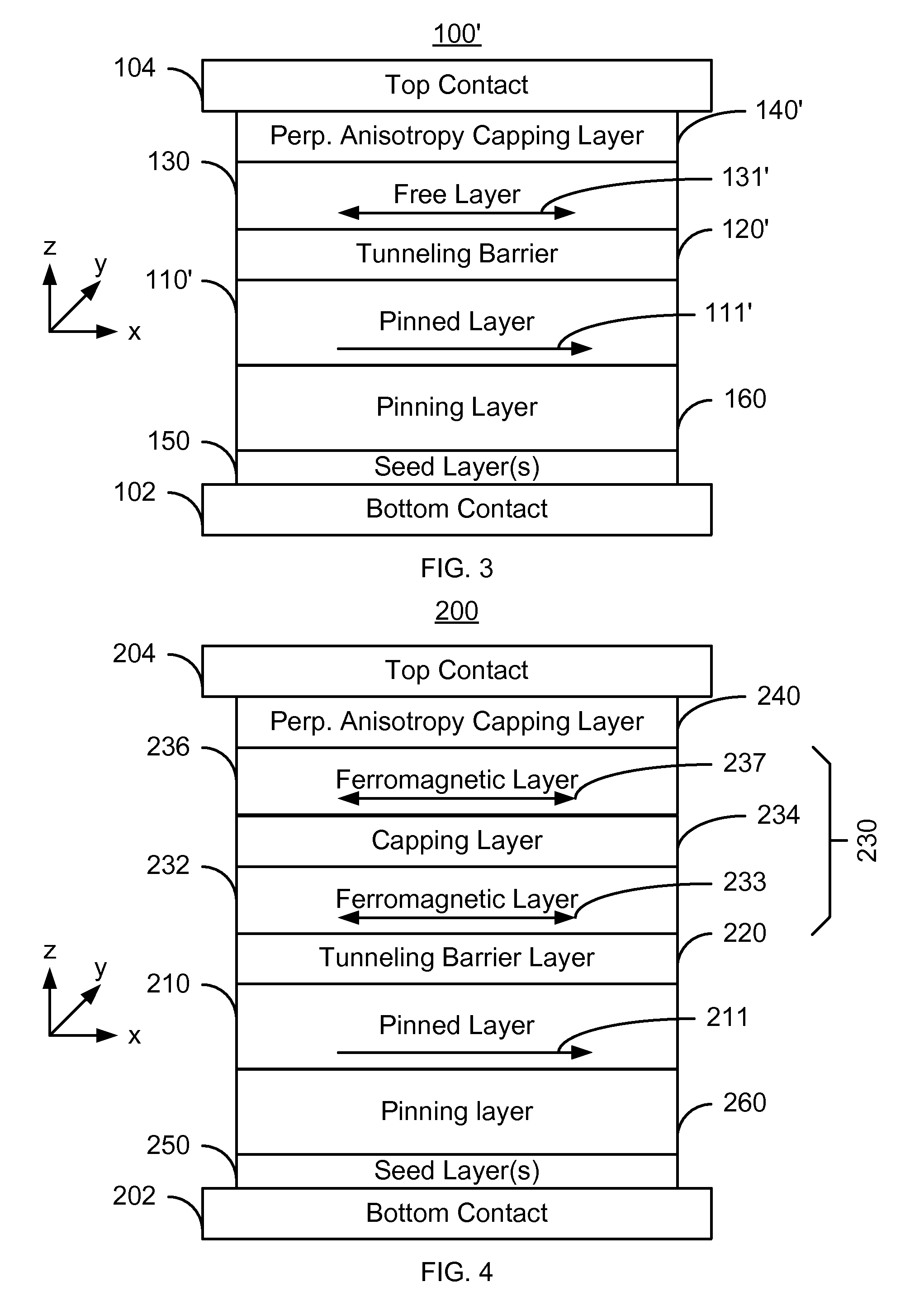
A method and system for providing a magnetic element and a magnetic memory utilizing the magnetic element are described. The magnetic element is used in a magnetic device that includes a contact electrically coupled to the magnetic element. The method and system include providing pinned, nonmagnetic spacer, and free layers. The free layer has an out-of-plane demagnetization energy and a perpendicular magnetic anisotropy corresponding to a perpendicular anisotropy energy that is less than the out-of-plane demagnetization energy. The nonmagnetic spacer layer is between the pinned and free layers. The method and system also include providing a perpendicular capping layer adjoining the free layer and the contact. The perpendicular capping layer induces at least part of the perpendicular magnetic anisotropy in the free layer. The magnetic element is configured to allow the free layer to be switched between magnetic states when a write current is passed through the magnetic element.
Owner:GRANDIS
Grating trim retarders
InactiveUS20070070276A1Improve image contrastEasily integrated into oneColor television detailsNon-linear opticsIn planeZeroth order
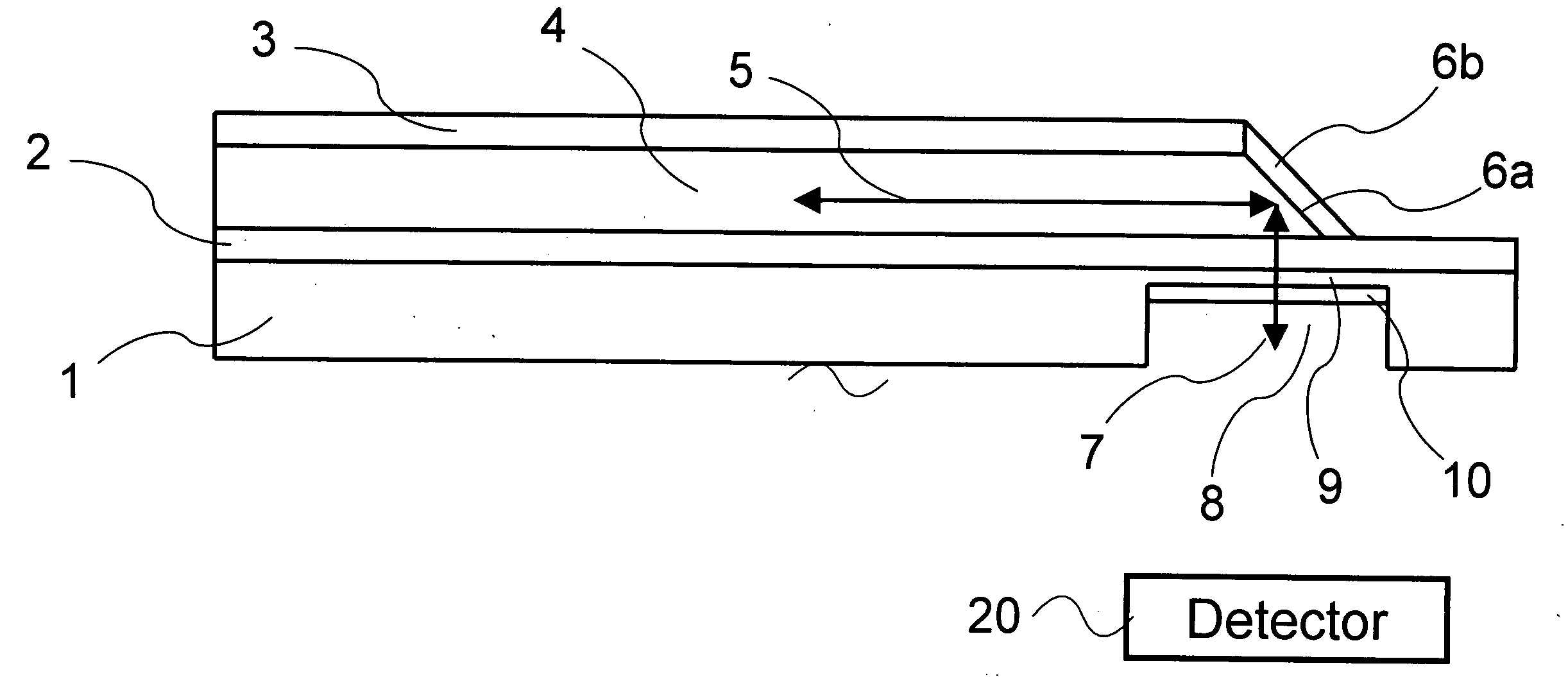
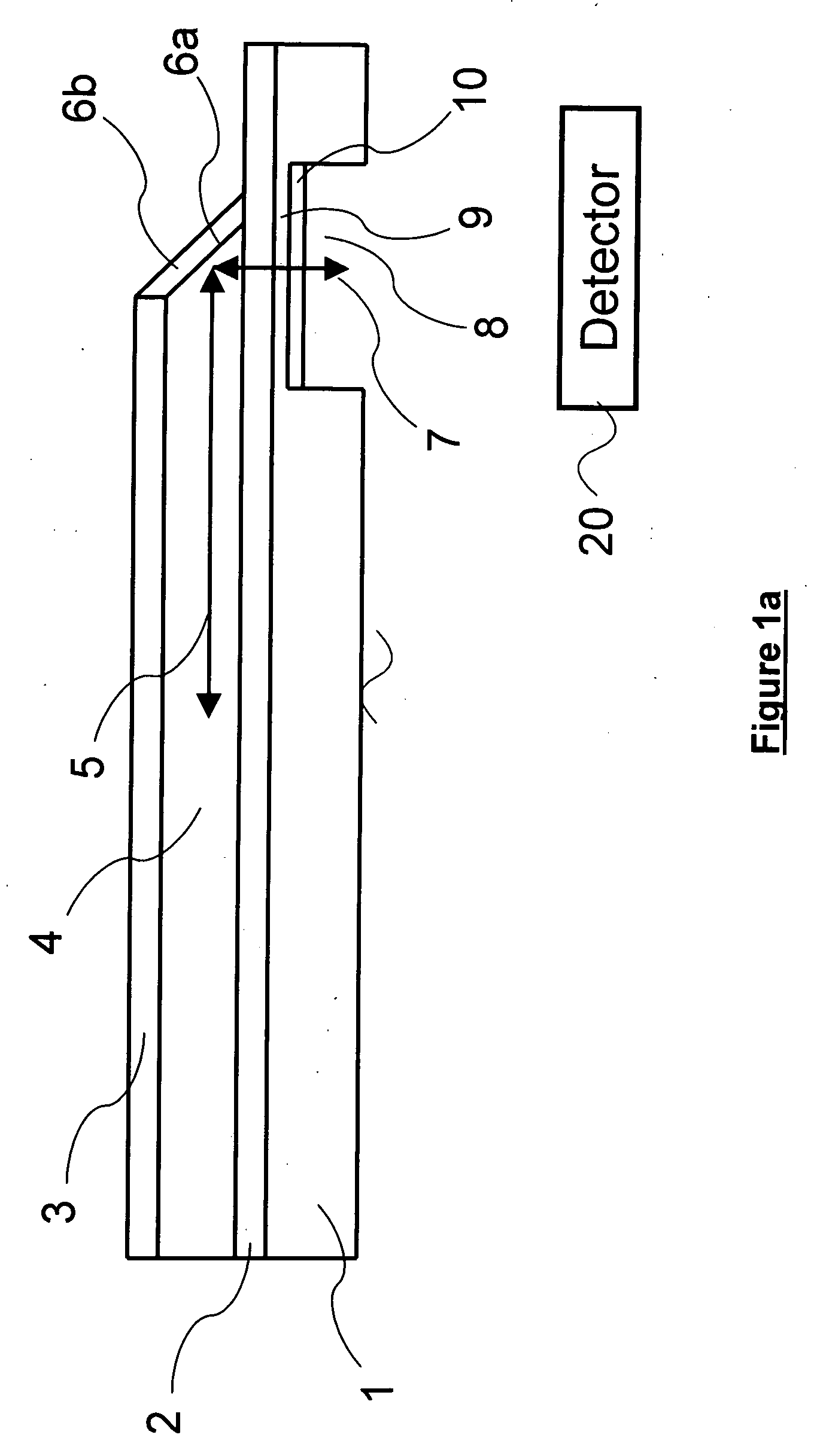
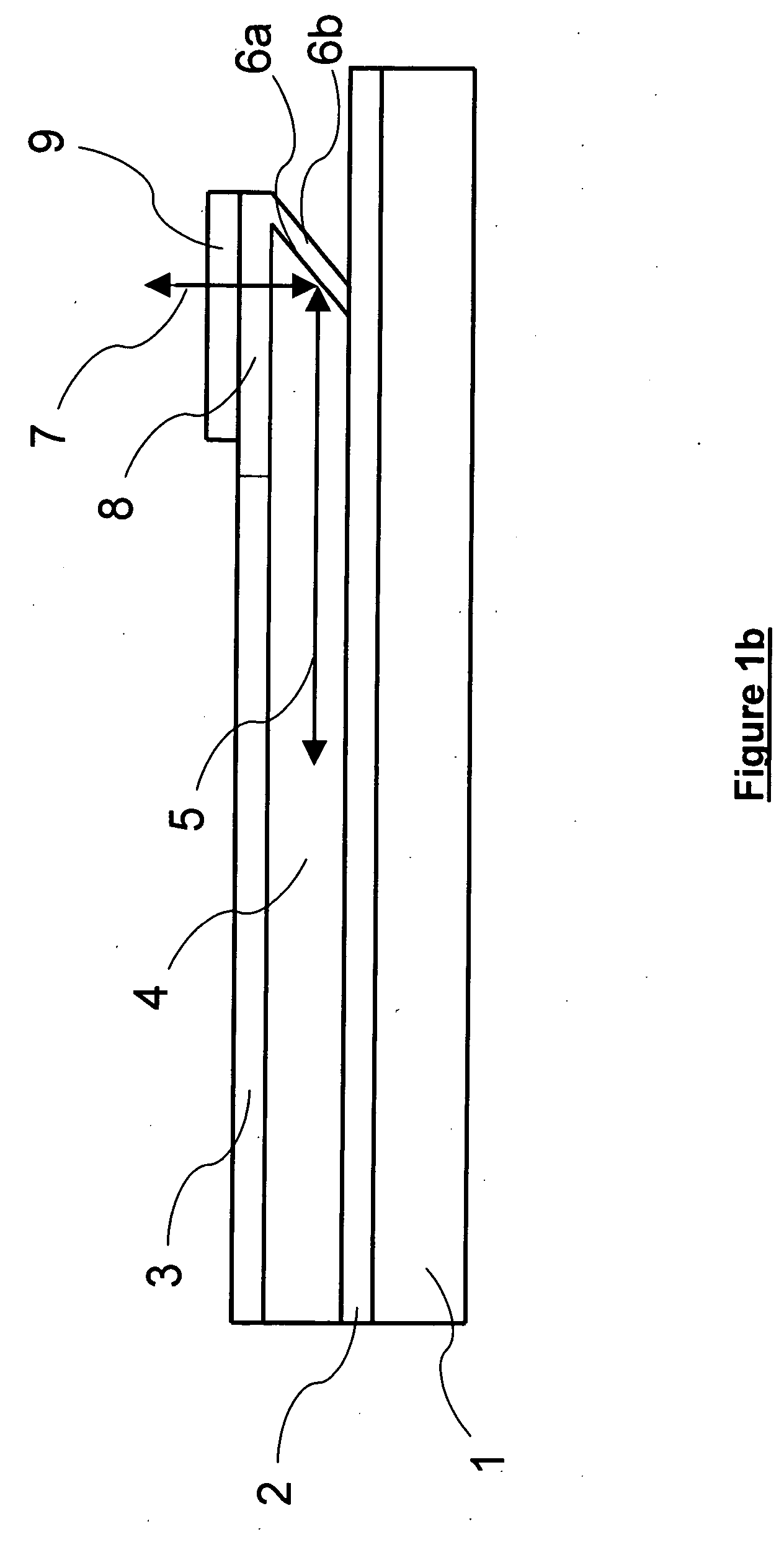
A grating trim retarder fabricated from a form-birefringent multi-layer dielectric stack including at least one anti-reflection coating and supported on a transparent substrate is provided. The form-birefringent dielectric stack includes an axially-inhomogeneous element in the form of a −C-plate grating and a transversely-inhomogeneous element in the form of an A-plate grating. Each of the −C-plate and the A-plate gratings are fabricated with dimensions to form a zeroth order sub-wavelength grating structure. Fabricating the grating trim retarder with anti-reflection coatings and / or a segment where the −C-plate and A-plate grating overlap enables the in-plane and out-of-plane retardances to be tailored independently according to the desired application.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Birefringent reflectors using isotropic materials and form birefringence
Multilayer thin film reflectors, such as mirrors and reflective polarizers, are described in which form birefringent optical layers are incorporated into a plurality of optical repeat units in the film. The form birefringent layers exhibit birefringence as a result of microscopic structures that have a dimension that is small compared to the wavelength of light but large compared to molecular distances. The optical layers within the optical repeat units have out-of-plane indices of refraction that are tailored to produce desired effects as a function of incidence angle for p-polarized light. The multilayer reflectors can be made by conventional vacuum deposition techniques using known inorganic optical materials, but can also be made entirely with polymeric materials by co-extrusion or other processes.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
ST-RAM Cells with Perpendicular Anisotropy
ActiveUS20100109110A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsDigital storagePerpendicular anisotropySpins
Magnetic spin-torque memory cells, often referred to as magnetic tunnel junction cells, which have magnetic anisotropies (i.e., magnetization orientation at zero field and zero current) of the associated ferromagnetic layers aligned perpendicular to the wafer plane, or “out-of-plane”. A memory cell may have a ferromagnetic free layer, a first pinned reference layer and a second pinned reference layer, each having a magnetic anisotropy perpendicular to the substrate. The free layer has a magnetization orientation perpendicular to the substrate that is switchable by spin torque from a first orientation to an opposite second orientation.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Micromirror systems with concealed multi-piece hinge structures
InactiveUS6906848B2Sufficient flexibilityPromotes relative motionNon-linear opticsOptical elementsOut of planeHinge angle
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
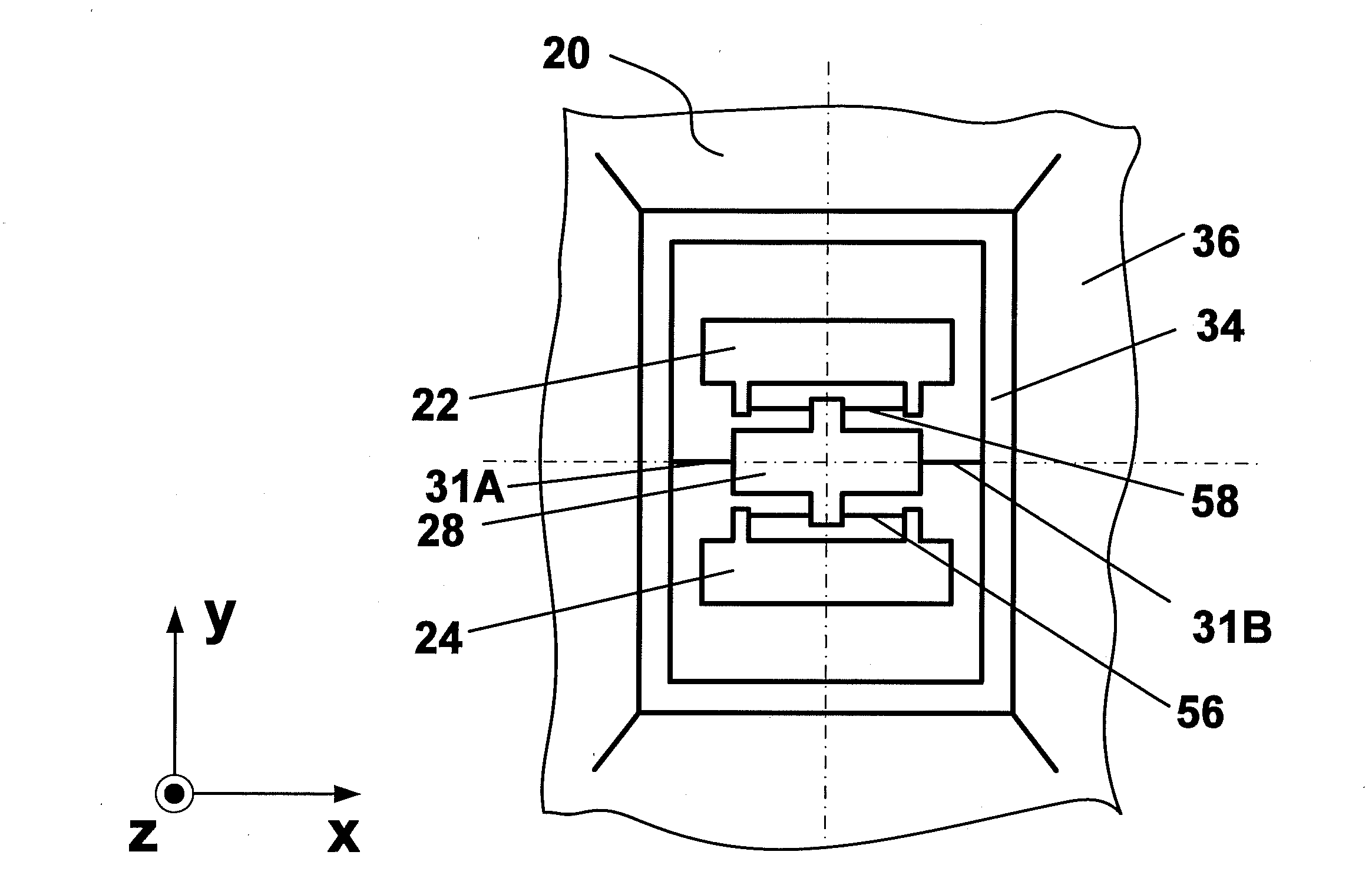
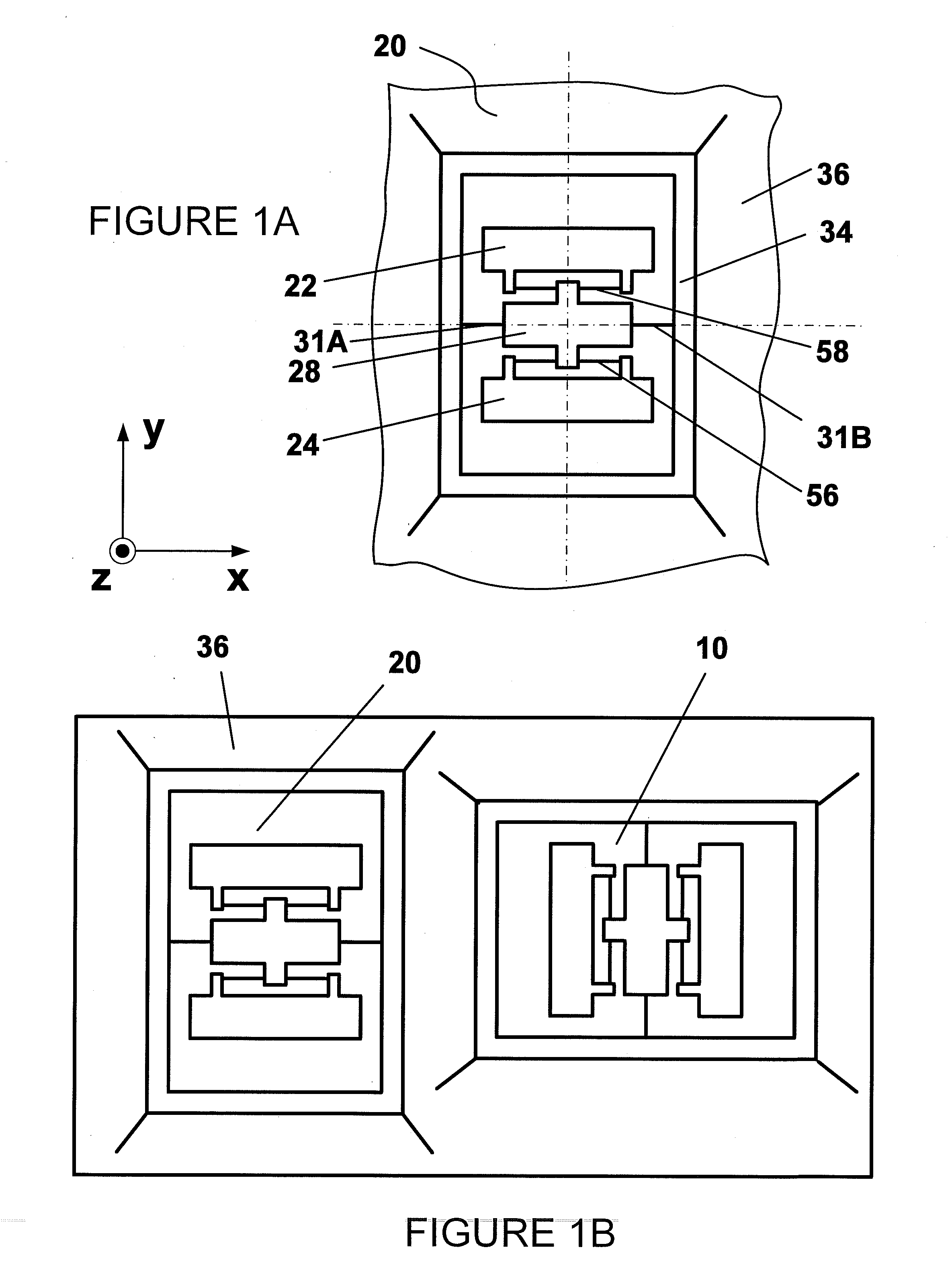
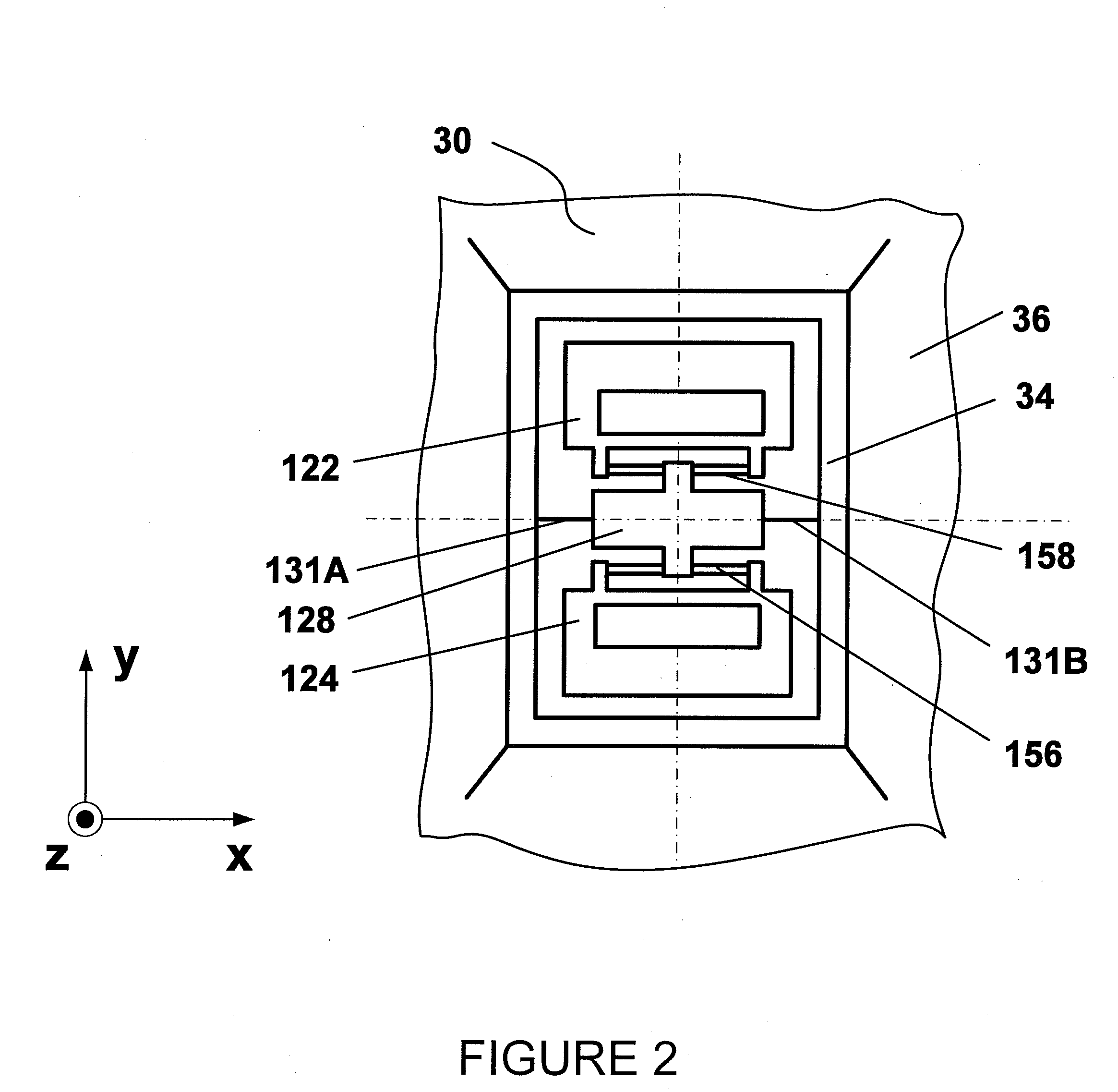
Integrated multiaxis motion sensor
InactiveUS20100071467A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsIn planeAngular velocity
A system and method describes an inertial sensor assembly, the assembly comprises a substrate parallel to the plane, at least one in-plane angular velocity sensor comprising a pair proof masses that are oscillated in anti-phase fashion along an axis normal to the plane. The first in-plane angular velocity sensor further includes a sensing frame responsive to the angular velocity of the substrate around the first axis parallel to the plane and perpendicular to the axis normal to the plane. The assembly also includes at least one out-of-plane angular velocity sensor comprising a pair of proof masses that are oscillated in anti-phase fashion in the plane parallel to the plane. The out-of-plane angular velocity sensor further comprises a sensing frame responsive to the angular velocity of the substrate around the axis normal to the plane.
Owner:INVENSENSE
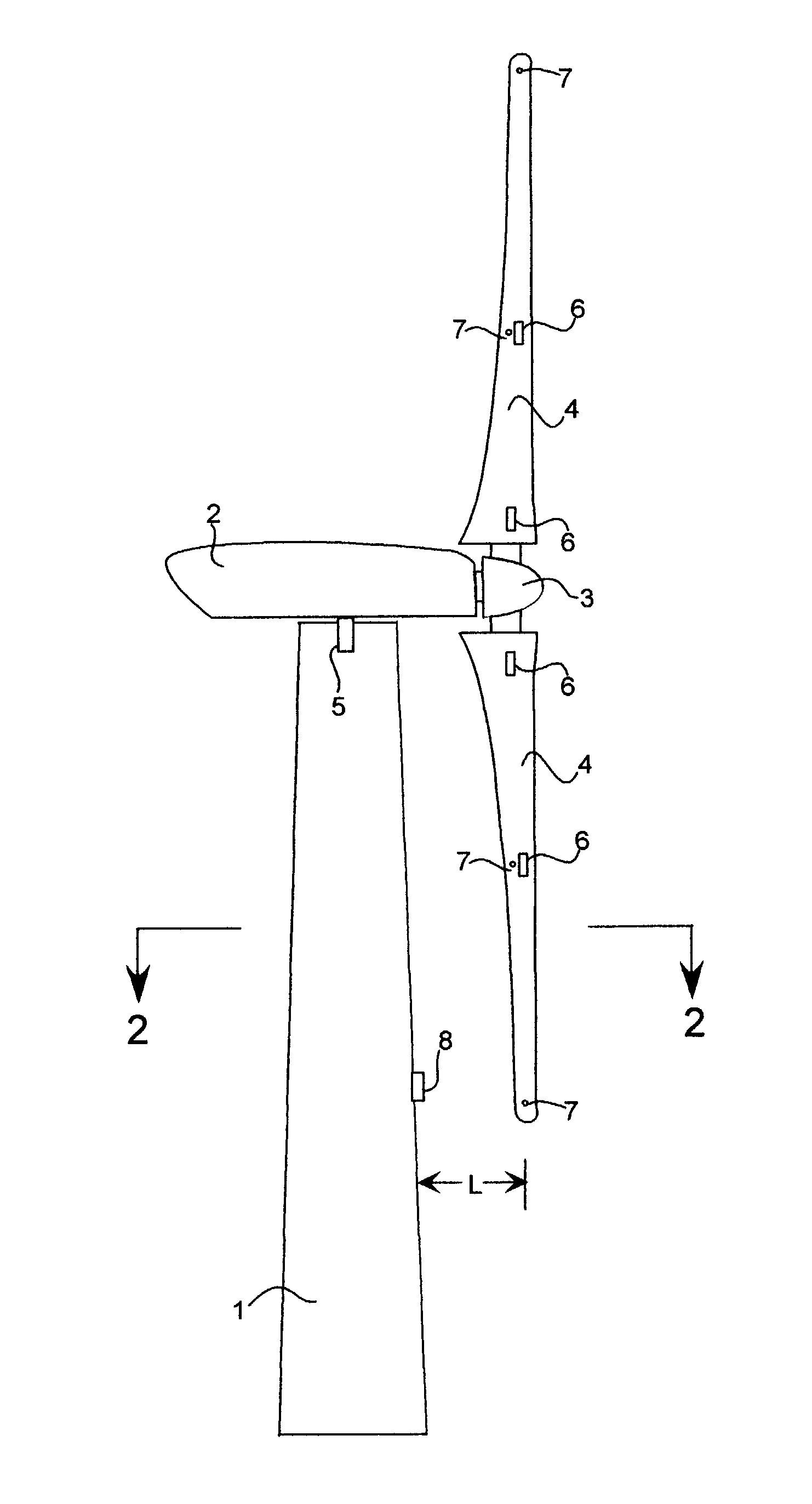
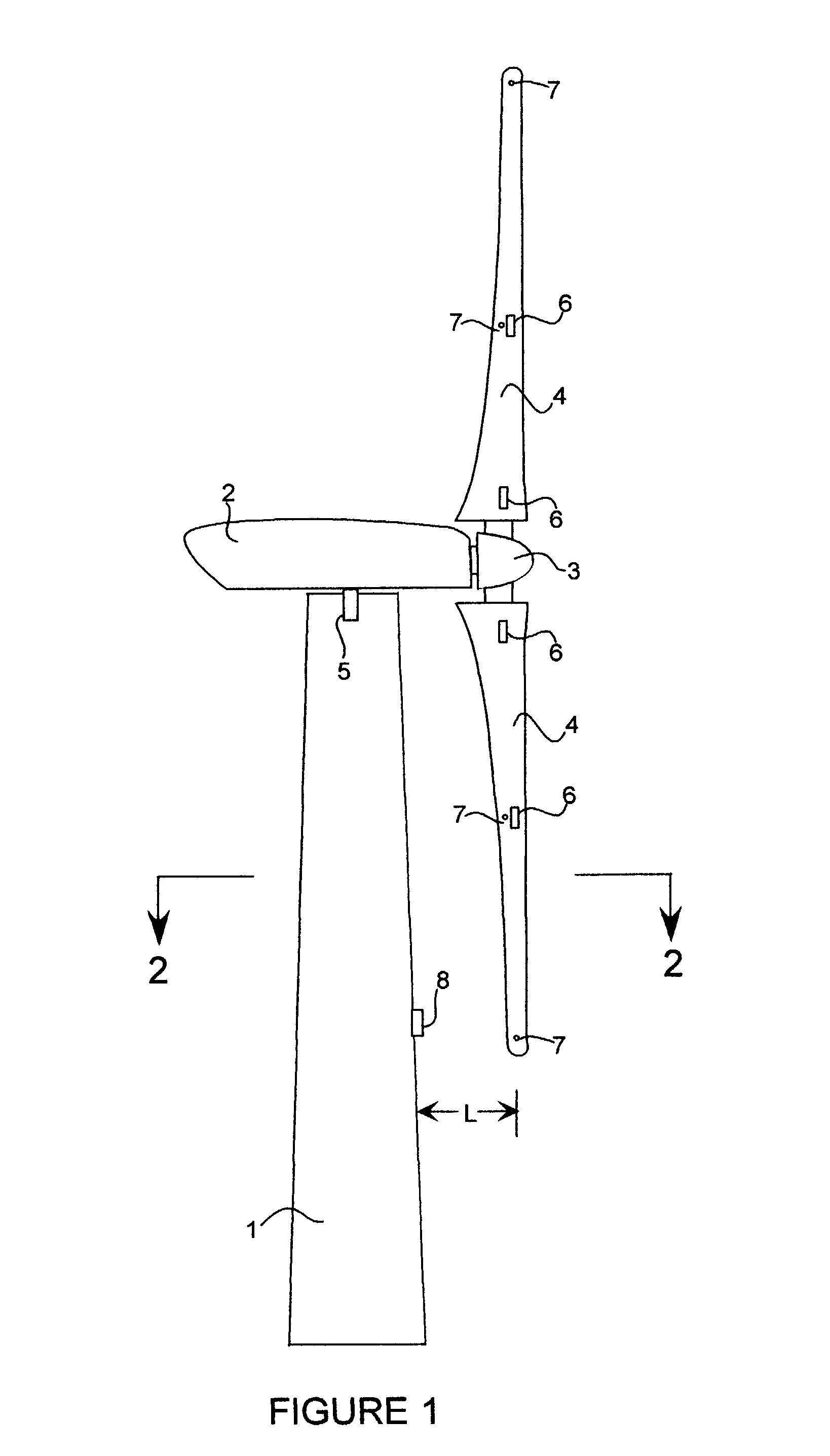
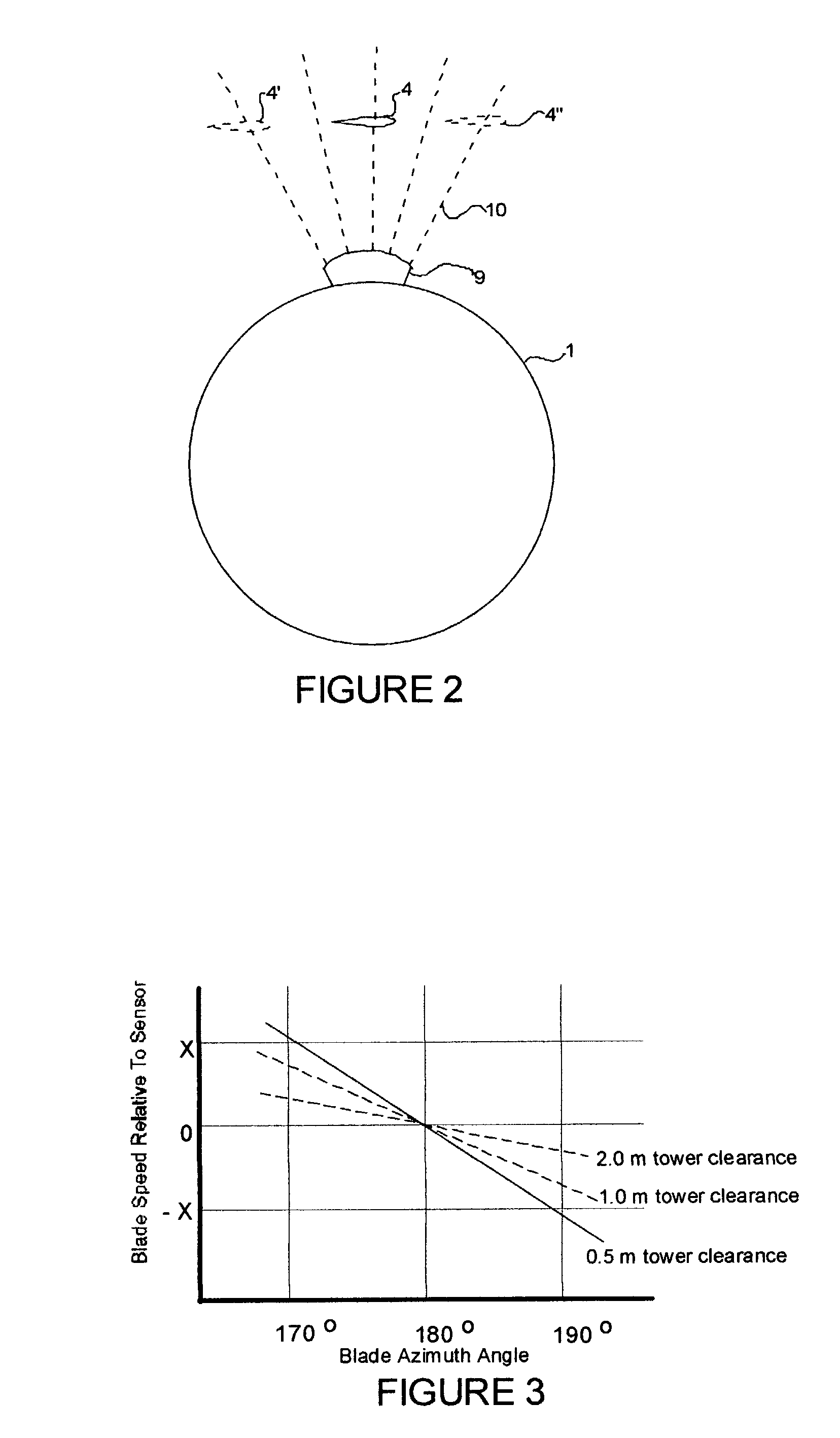
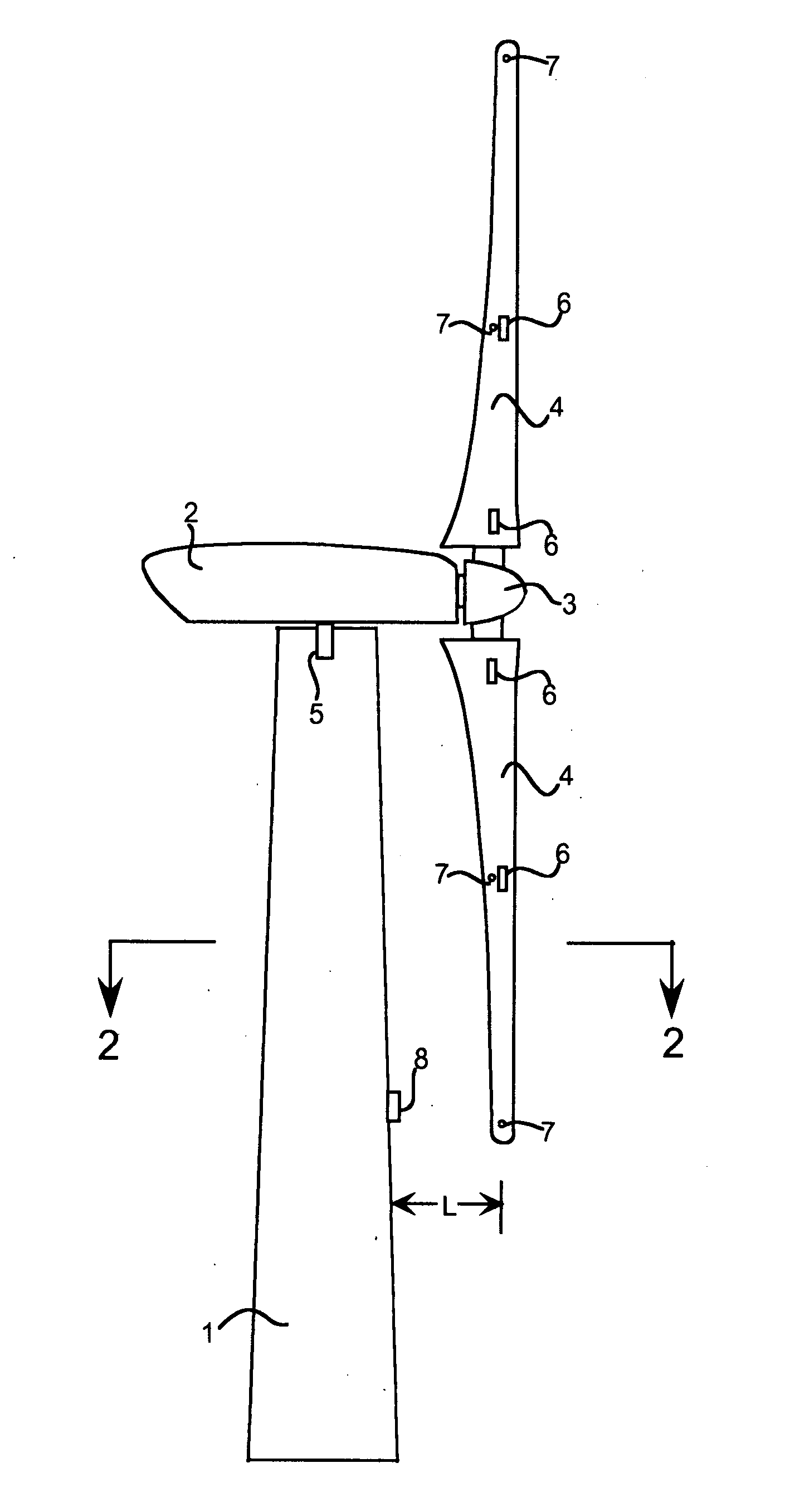
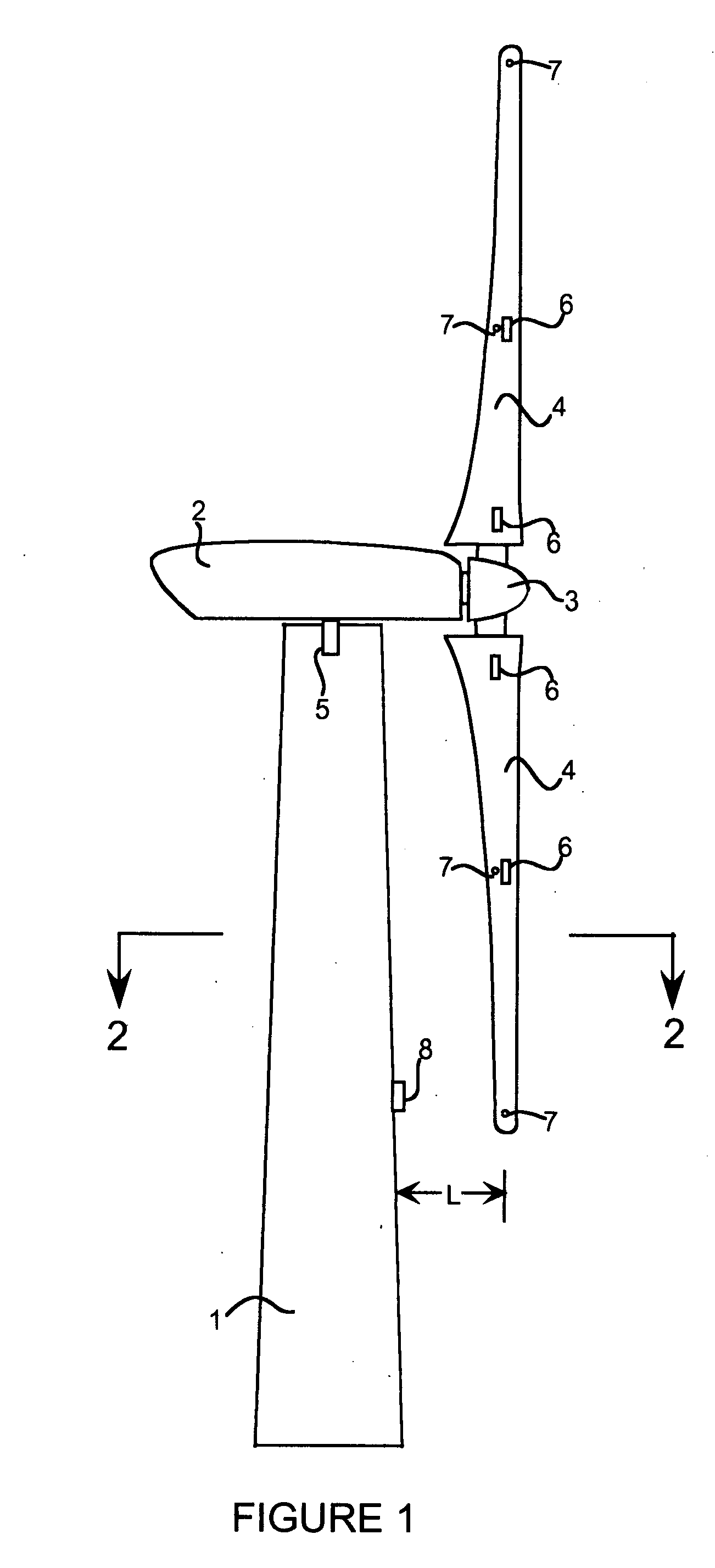
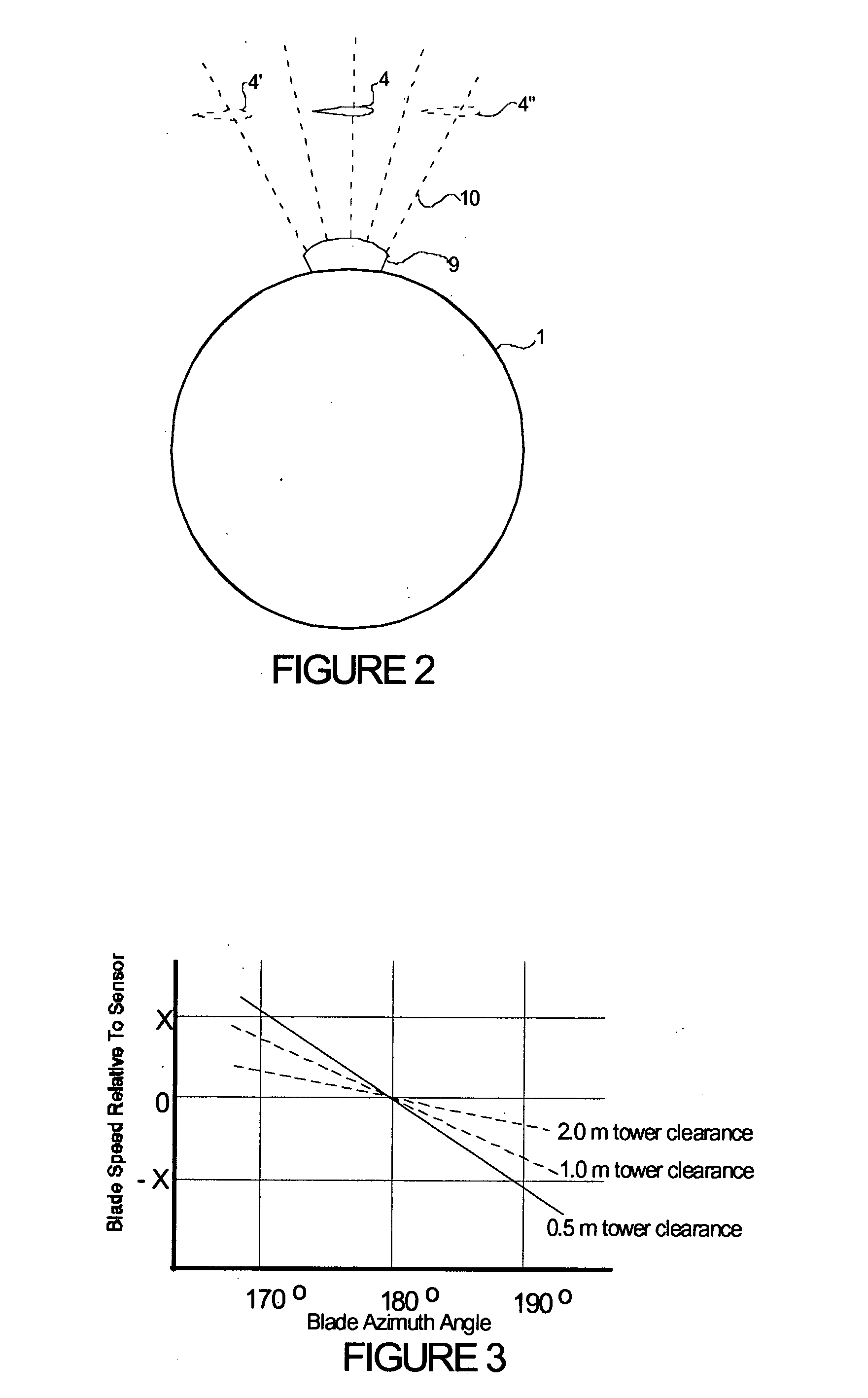
Wind turbine blade deflection control system
A wind turbine with a sensor that measures the out-of-plane deflection of the blades and a controller that uses the signal from the sensor to determine the risk of a tower strike. The controller takes any necessary action to prevent a tower strike when it determines that the risk of a strike is high. The sensor can include strain gages or accelerometers mounted on the blades or it can include a fixed sensor mounted on the side of the tower to measure tower clearance as the blade passes by. The control action taken can include pitching blades, yawing the nacelle, or stopping the turbine. The controller is preferably a fuzzy logic controller.
Owner:BOSCHE JOHN VANDEN
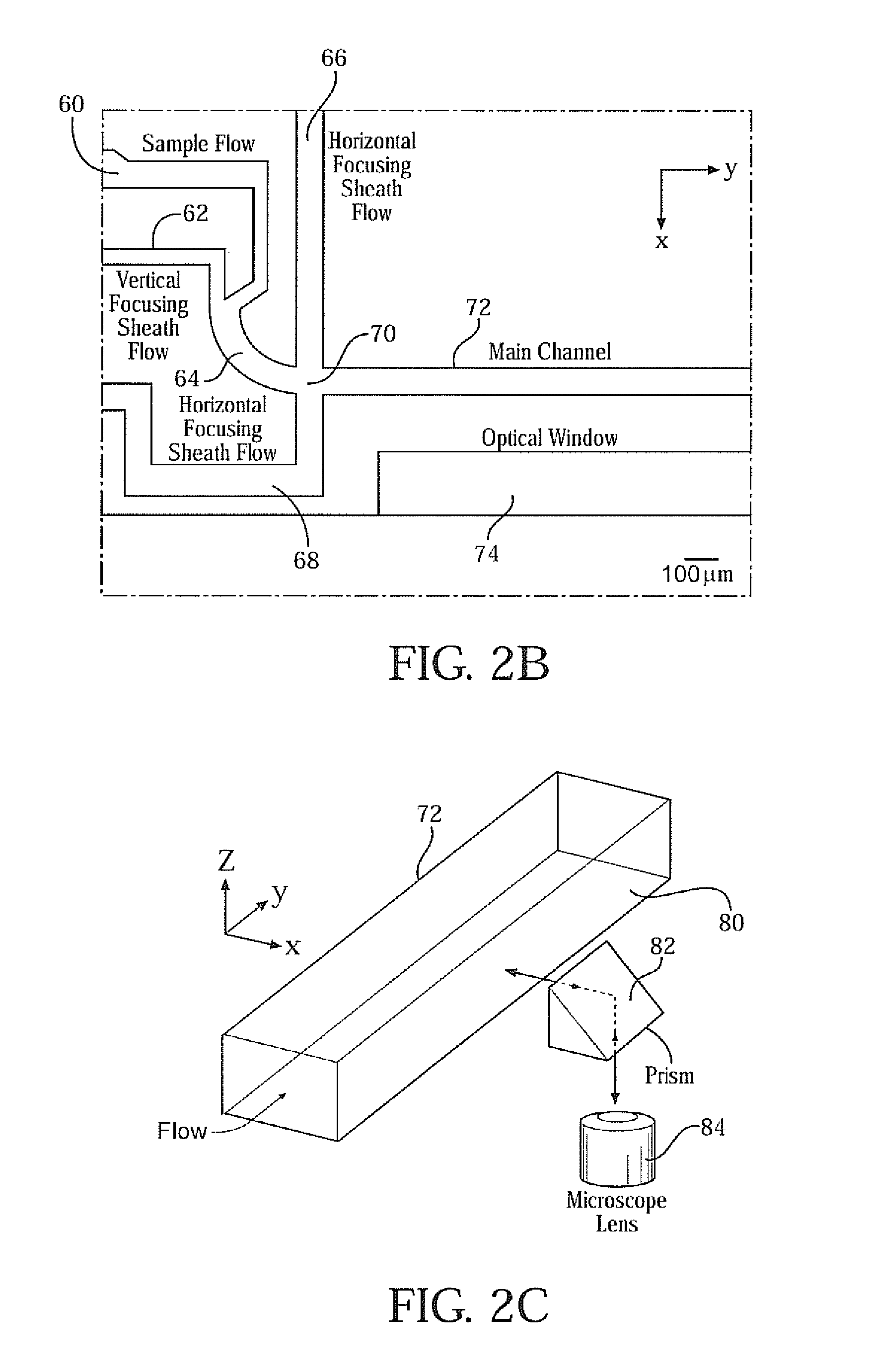
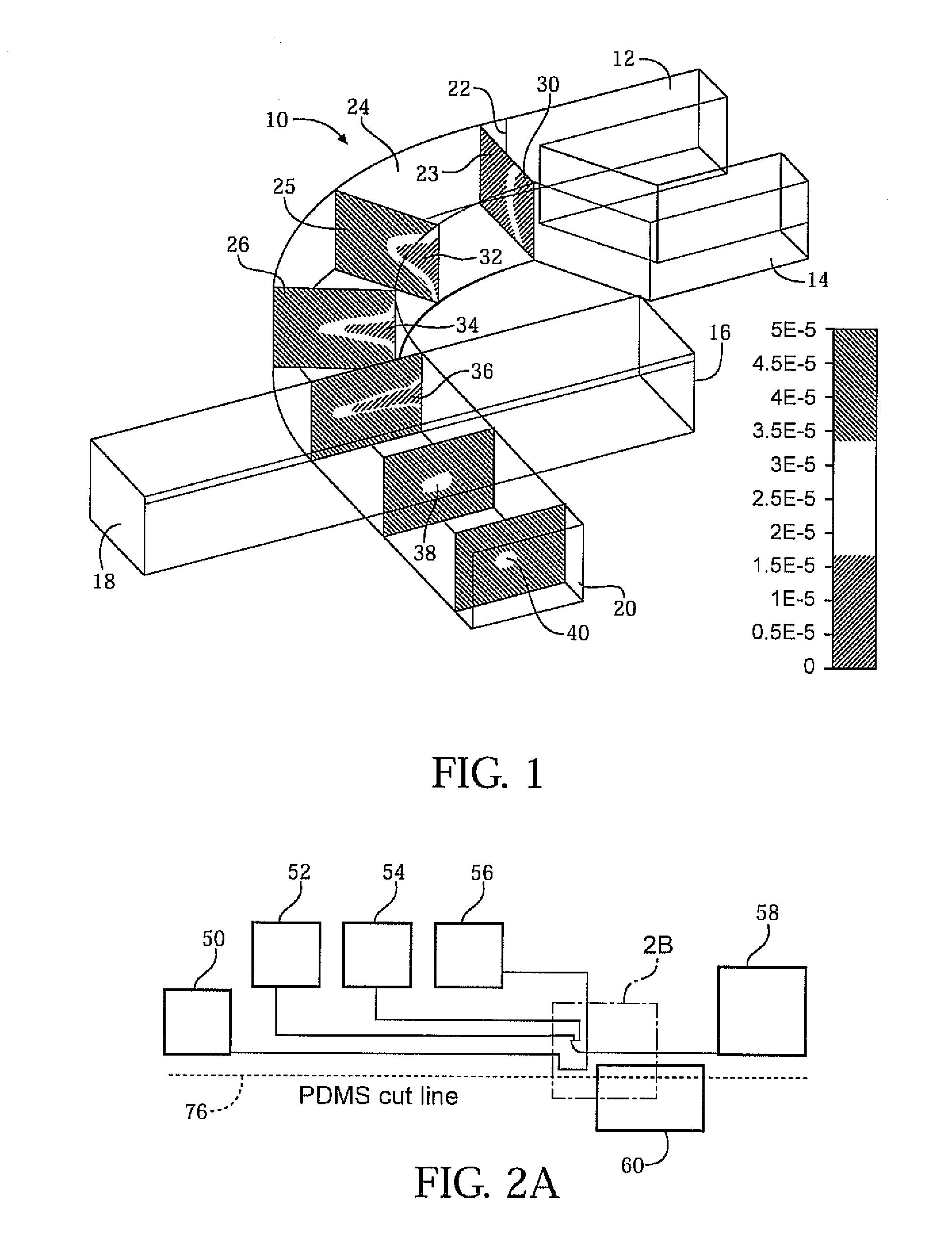
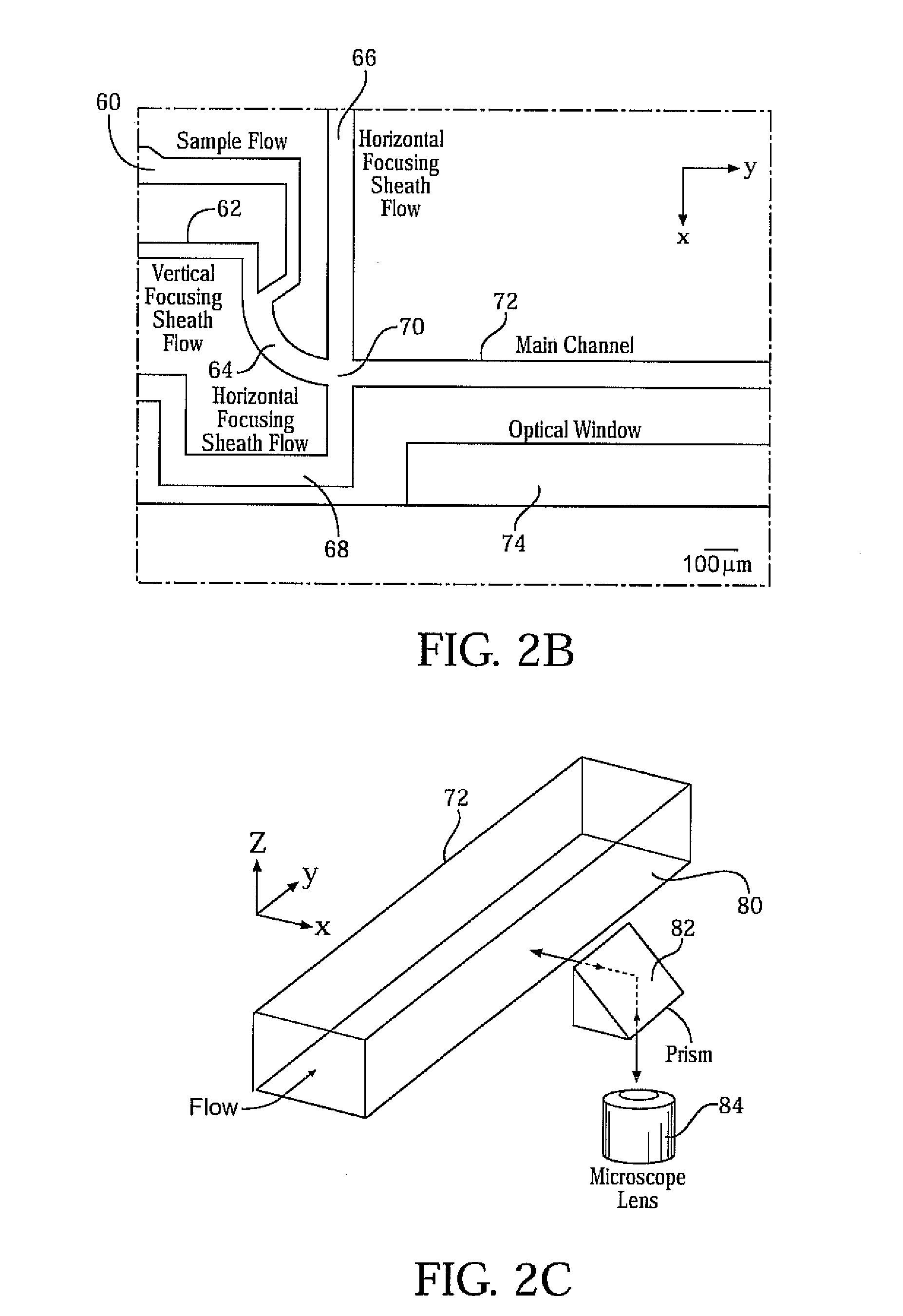
Three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing using a microfluidic device
InactiveUS20120196314A1Reliable single molecule sensitivityFocusBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOut of planePhysics
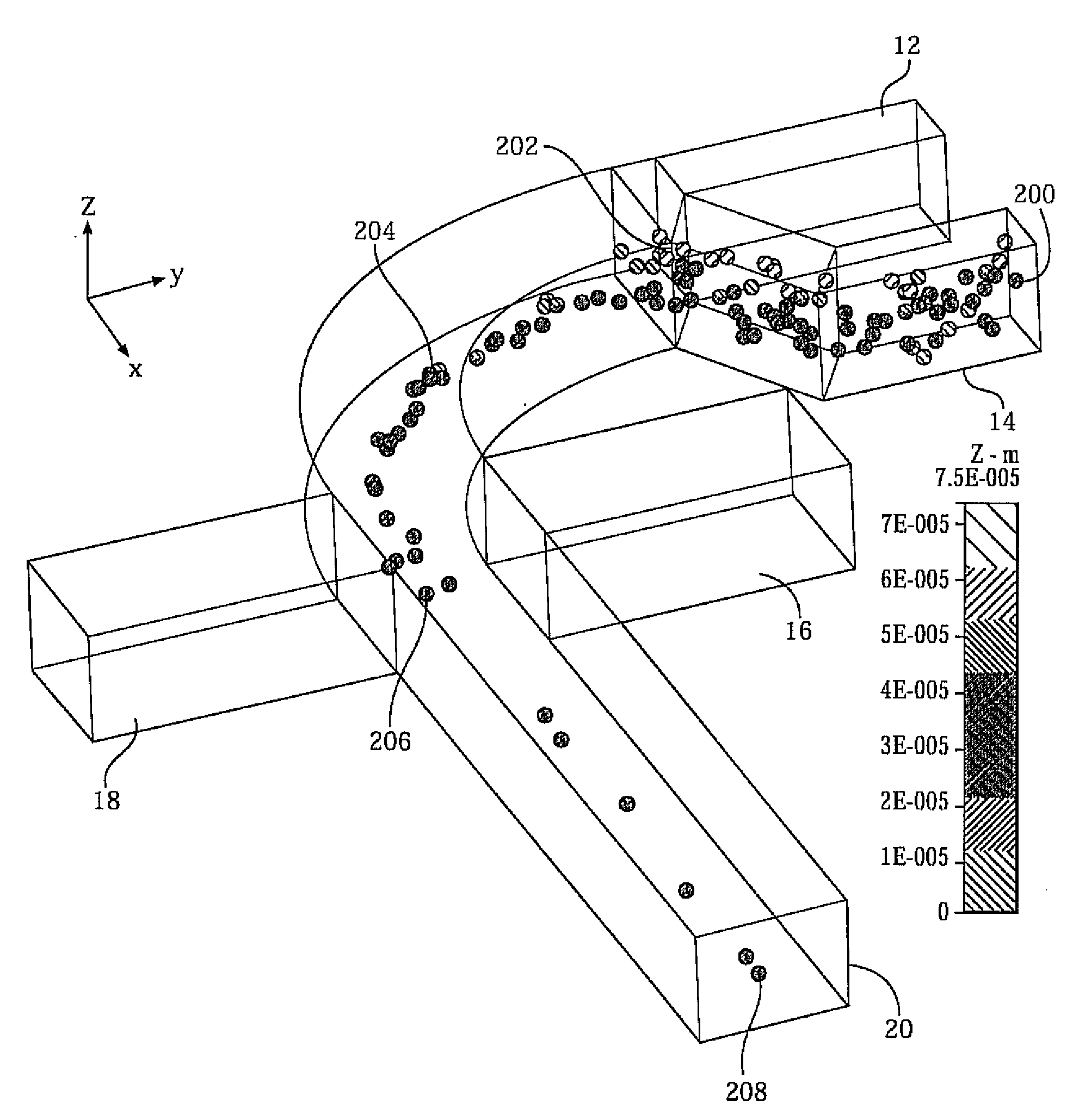
A microfluidic device comprises inlets for a sample flow and an out-of-plane focusing sheath flow, and a curved channel section configured to receive the sample flow and out-of-plane focusing sheath and to provide hydrodynamic focusing of the sample flow in an out-of-plane direction, the out-of-plane direction being normal to a plane including the curved channel. Examples of the invention also include improved flow cytometers.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
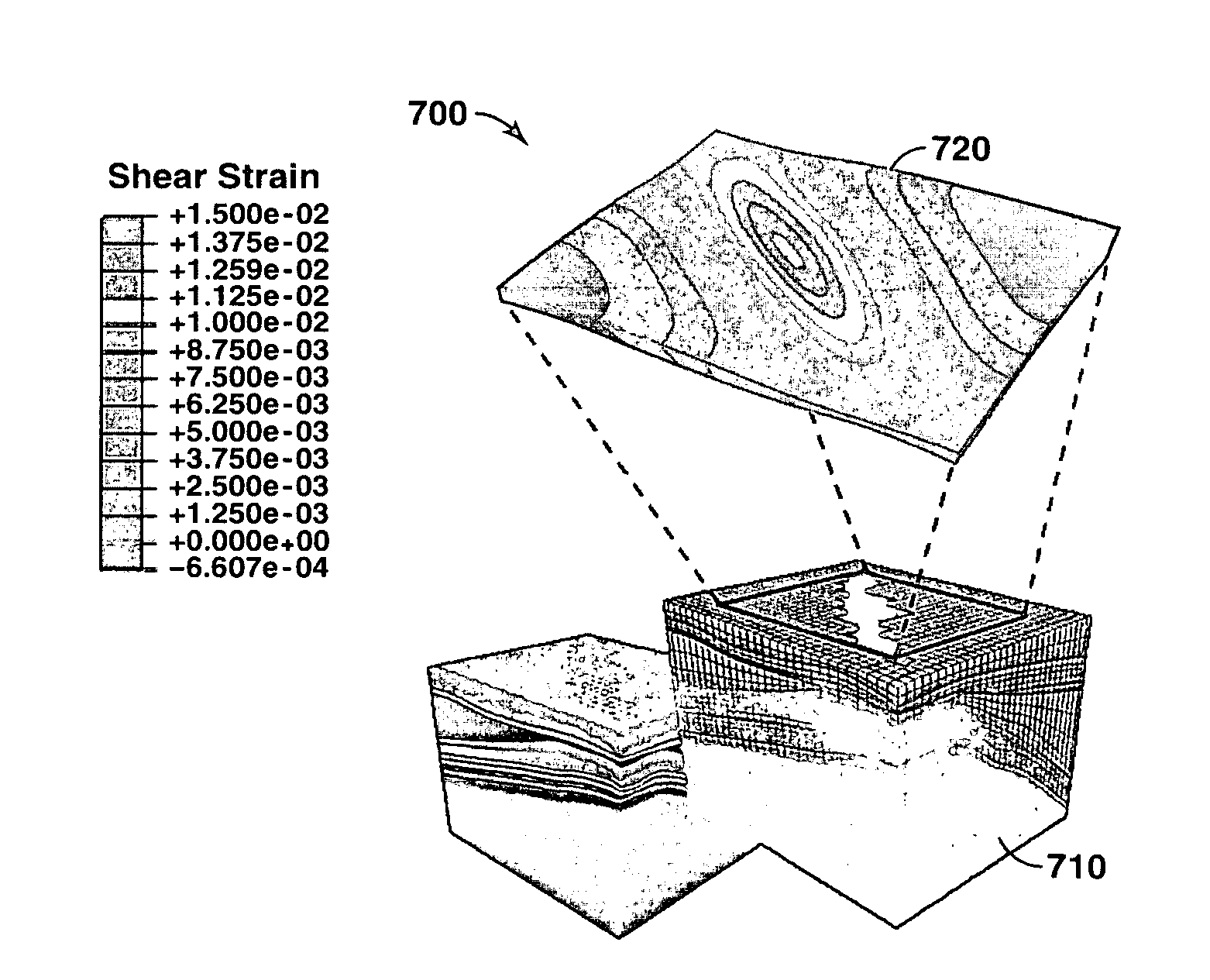
Method For Predicting Well Reliability By Computer Simulation
Methods of predicting earth stresses in response to pore pressure changes in a hydrocarbon-bearing reservoir within a geomechanical system, include establishing physical boundaries for the geomechanical system and acquiring reservoir characteristics. Geomechanical simulations simulate the effects of changes in reservoir characteristics on stress in rock formations within the physical boundaries to determine the rock formation strength at selected nodes in the reservoir. The strength of the rock formations at the nodes is represented by an effective strain (εeff), which includes a compaction strain (εc) and out-of-plane shear strains (γ1-3, Y2-3) at a nodal point. The methods further include determining an effective strain criteria (εeffcr) from a history of well failures in the physical boundaries. The effective strain (εeffcr) at a selected nodal point is compared with the effective strain criteria (εeffcr) to determine if the effective strain (εeff) exceeds the effective strain criteria (εeffcr).
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Surface deformation electroactive polymer transducers
InactiveUS20080289952A1Augments out-of-plane deflectionsIncrease awarenessPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEfficient propulsion technologiesPolymeric surfaceVisibility
The present invention provides electroactive polymer transducers that produce out-of-plane deflections. The transducers form a set of surface features based on deflection of an electroactive polymer. The set of surface features may include elevated polymer surface features and / or depressed electrode surface features. Actuation of an active area may produce the polymer deflection that creates one or more surface features. A passive layer may operably connect to a polymer. The passive layer may comprise a thicker and softer material to amplify polymer thickness changes and increase surface feature visibility.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
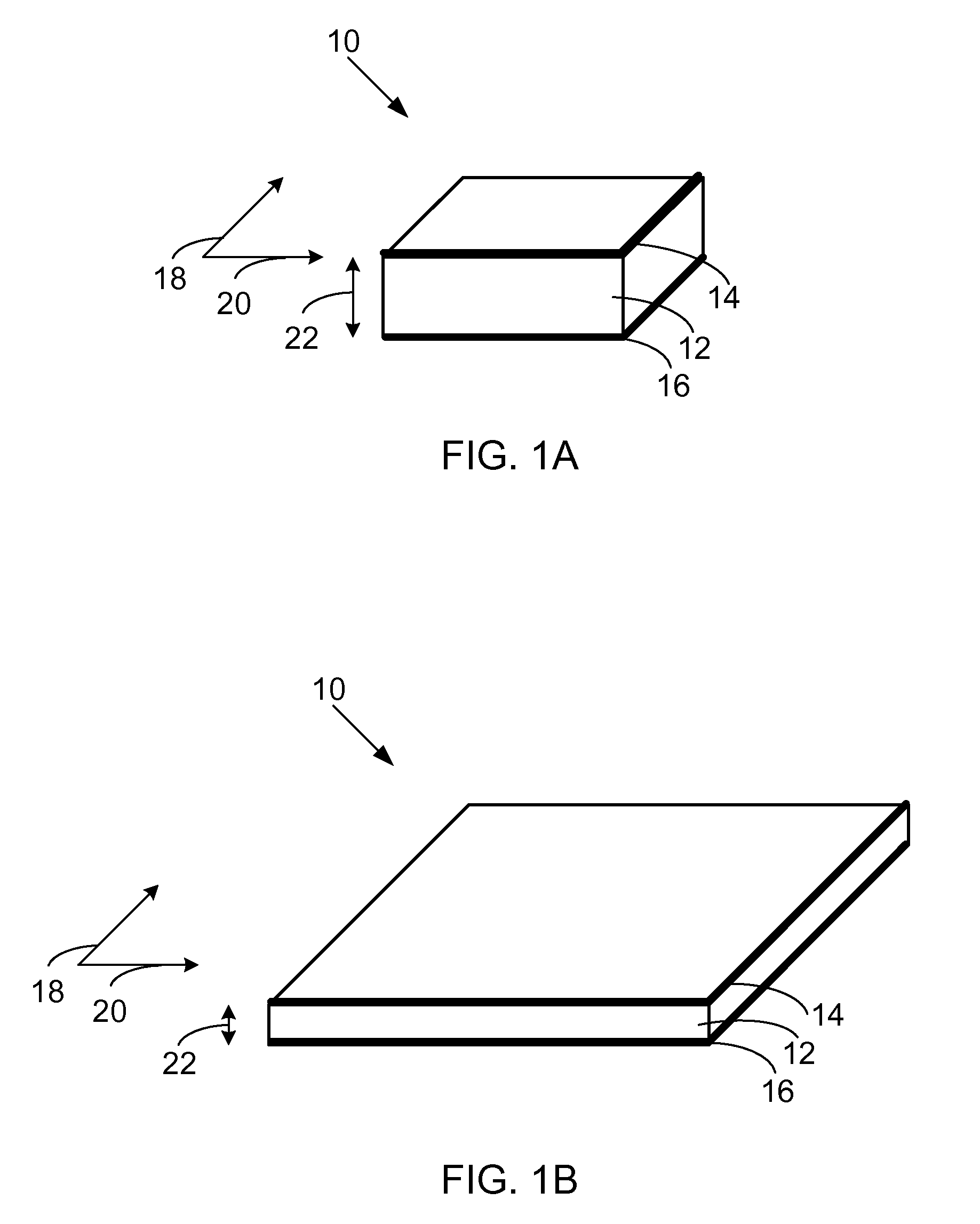
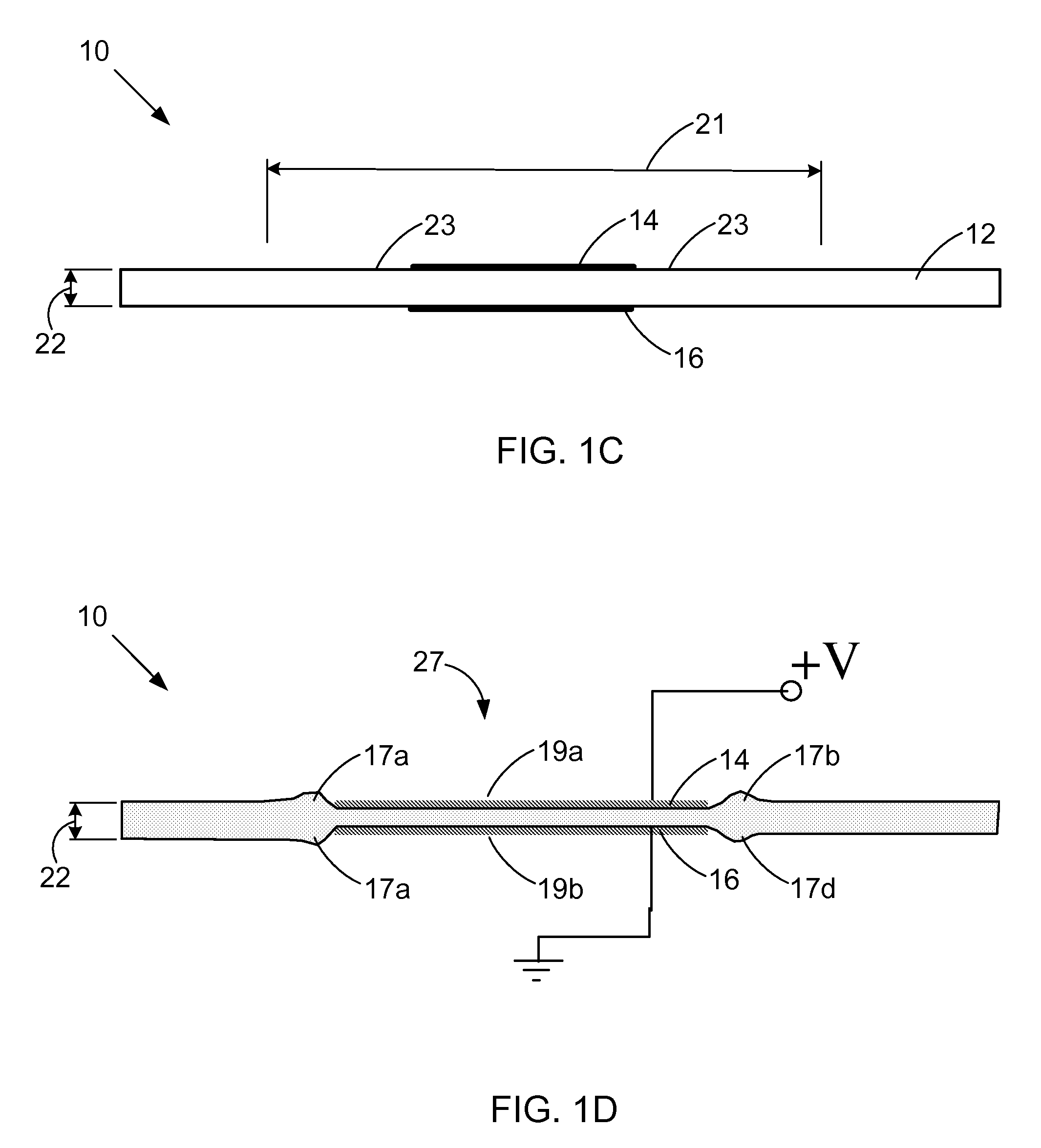
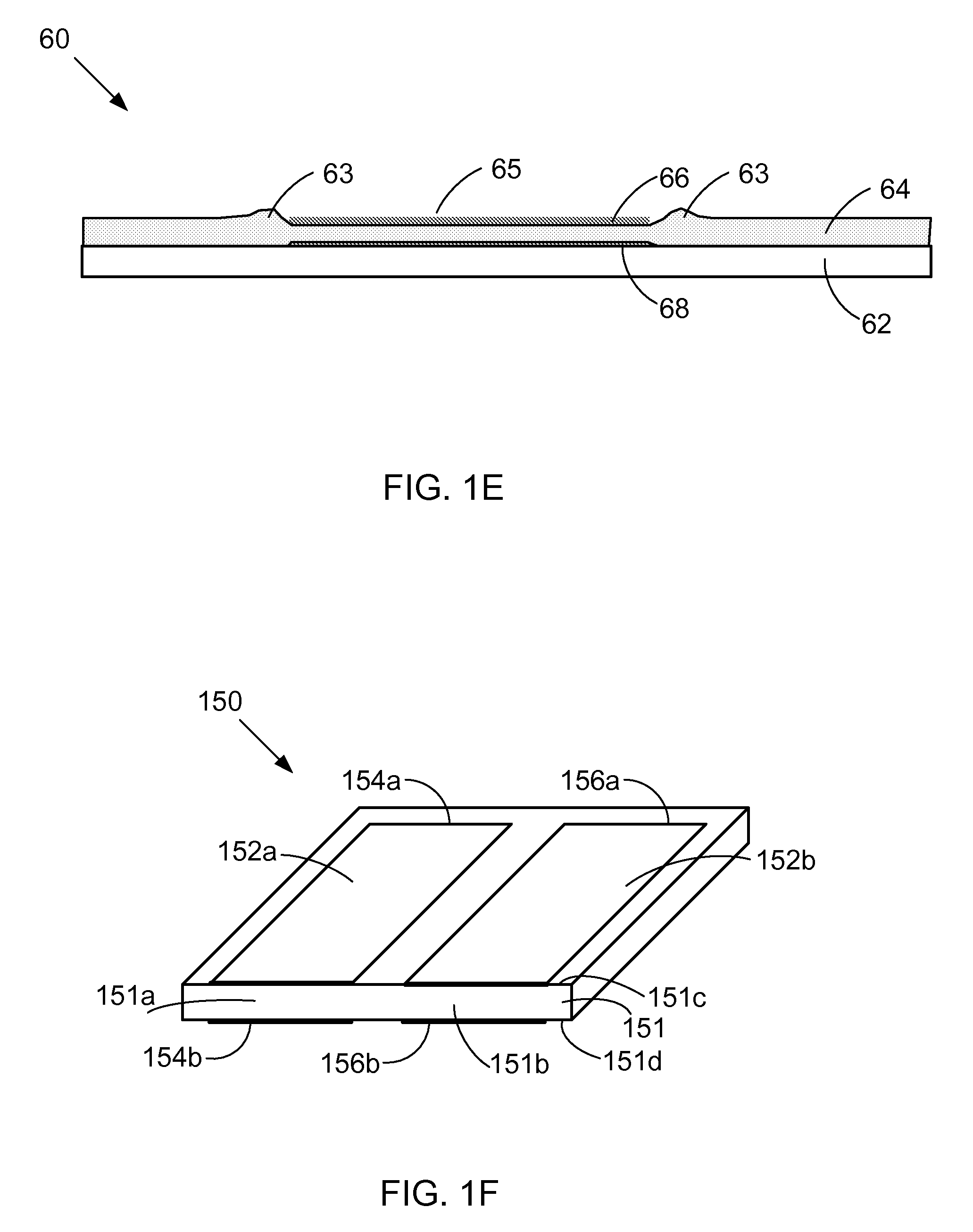
Magnetic planarization of pigment flakes
InactiveUS7258900B2Improve visual appearanceGood lookingPretreated surfacesPattern printingOut of planePigment
A magnetic field is applied to planarize magnetic pigment flakes relative to a surface. Pigment flakes, such as optically variable pigment flakes, are used in a variety of paints, inks, extrusions, powder coatings, and other forms for decorative and security applications. In many applications pigment flakes tend to align parallel to each other and to the surface to which they are applied. If the pigment flakes include a suitable magnetic structure, a magnetic field can be applied to subsequently align the flakes or enhance the alignment of the flakes in the plane of the substrate if the carrier that the flakes are dispersed in is still fluid. In some printing operations, pigment flakes that are applied parallel to the substrate are pulled out of plane when the print screen or printing die is lifted off the substrate. Application of a magnetic field can re-align pigment flakes to the plane of the substrate, enhancing the visual quality of the printed image, especially with optically variable pigments.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Multi-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS20100122579A1Improve linearityEliminate relative rotationAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsIn planeClassical mechanics
A multi-axis accelerometer is consisted of a substrate with sensing electrodes and a structure layer. The structure layer includes anchor bases fixed on the substrate. A first proof mass is disposed over the substrate and has a first opening and a second opening symmetric to each other. The first proof mass is suspended to the anchor bases. Fixed sensing blocks are disposed on the substrate, and capacitors are formed between each fixed sensing block and the first proof mass for sensing acceleration along two in-plane directions. A second proof mass and a third proof mass are disposed in the first opening and the second opening and are asymmetrically suspended. Separate electrodes are disposed on the substrate and form two differential capacitors with the second proof mass and the third proof mass for sensing the out-of-plane acceleration.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
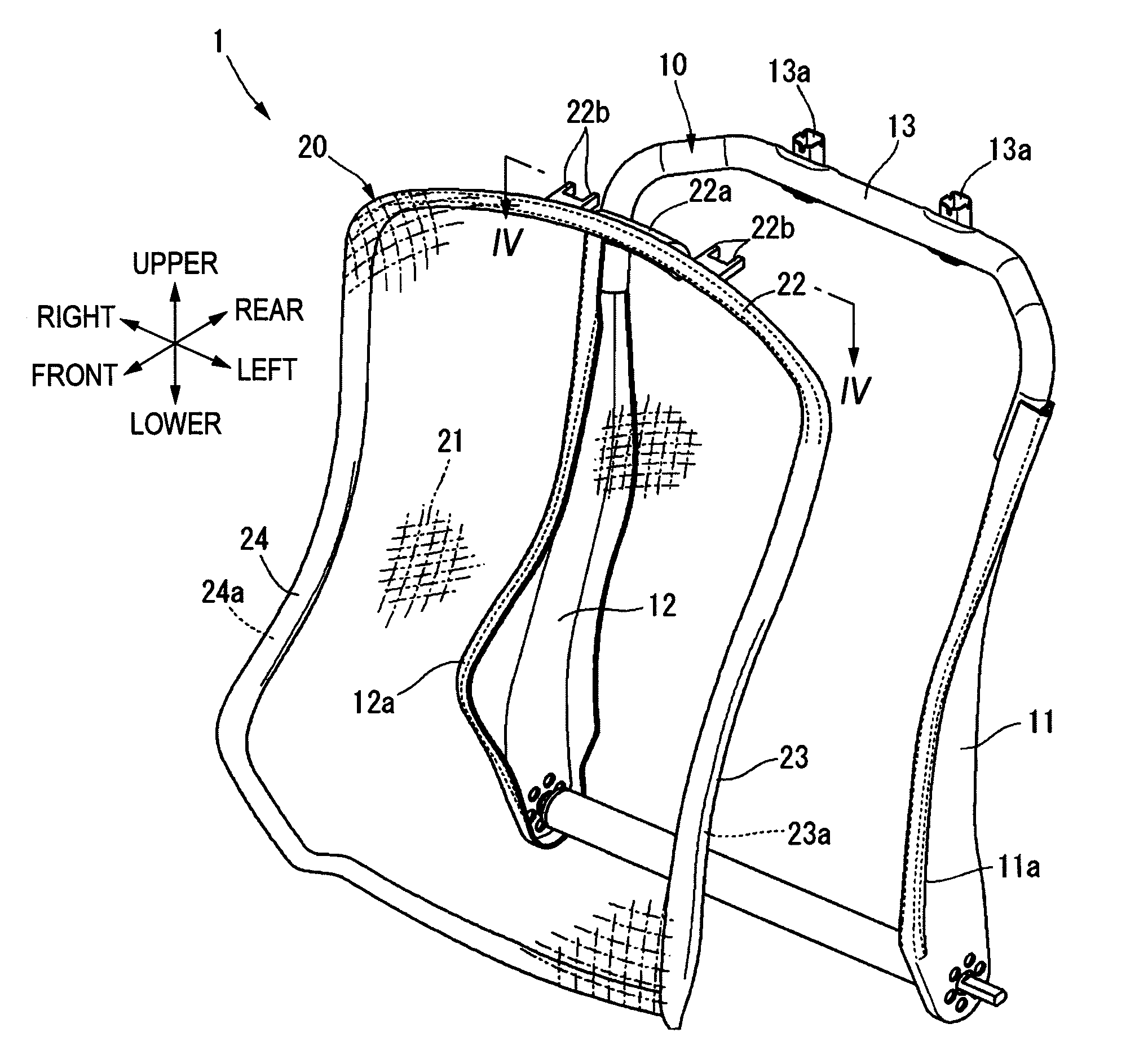
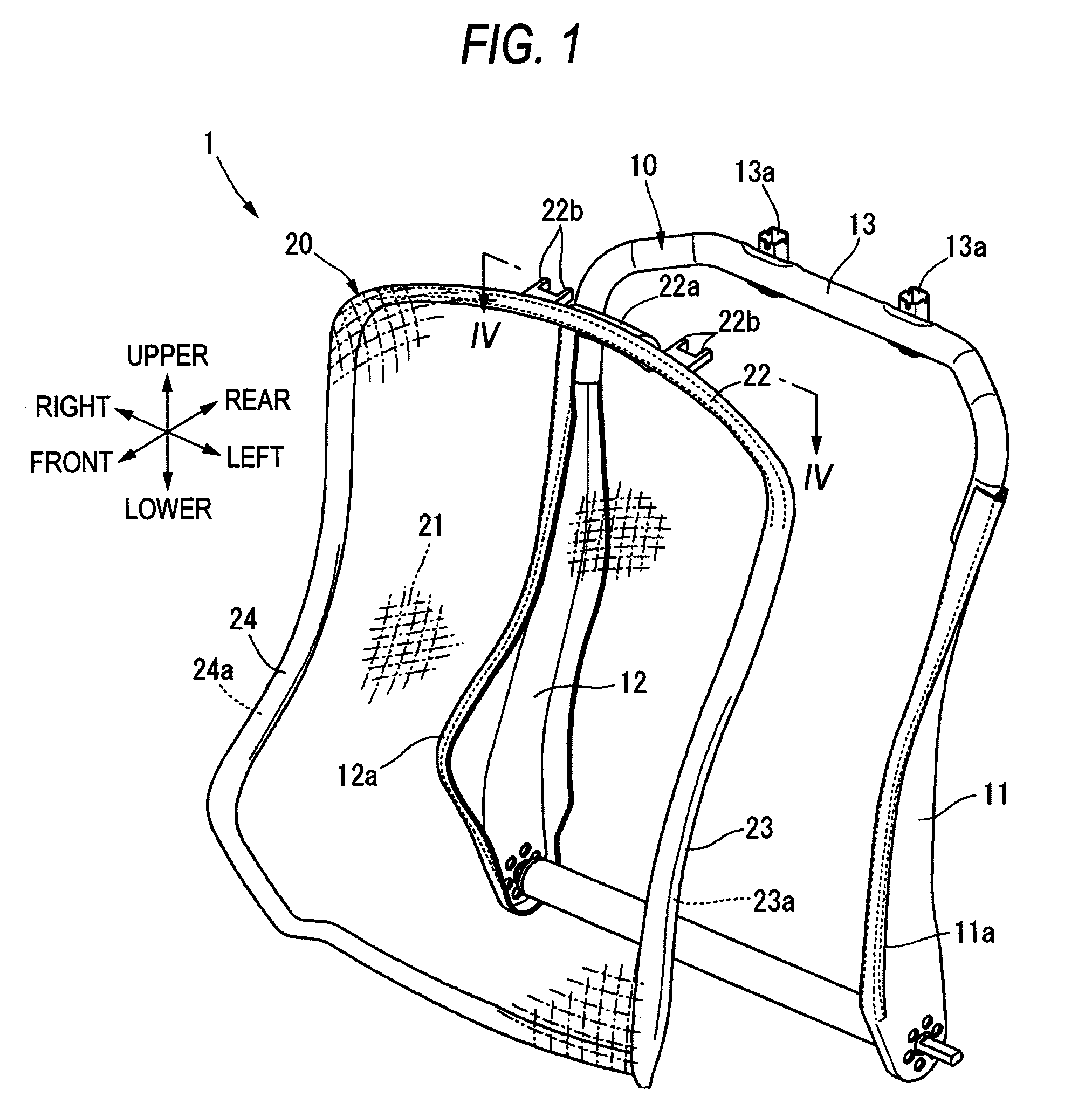
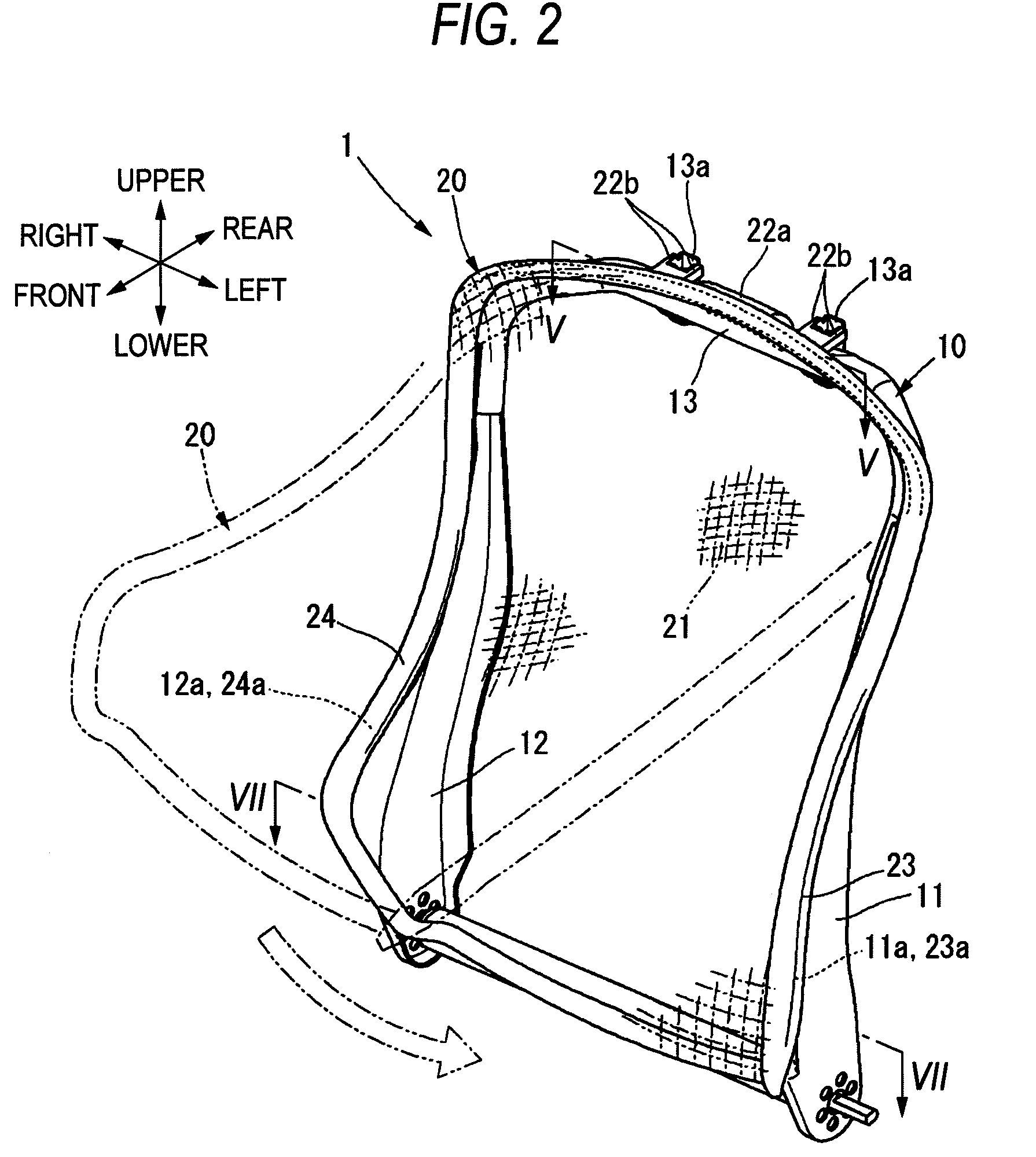
Assembling structure of planar elastic body of vehicle seat
An assembling structure for a vehicle seat includes: an assembly frame having a frame shape and configured to be detachably attached to a seat main body of the vehicle seat, the seat main body having a backbone frame having a frame shape; a planar elastic body configured to elastically support a body of an occupant and is stretched on the assembly frame; an elastic latching unit configured to be detachably attached to a part of the backbone frame, the elastic latching unit formed on a part of a periphery of the assembly frame, wherein the assembly frame further includes a hook portion, the backbone frame further includes a portion to be hooked, and the planar elastic body is prevented from moving in an out-of-plane direction of the planar elastic body when the hook portion of the assembly frame is hooked on the portion to be hooked of the backbone frame.
Owner:TOYOTA BOSHOKU KK
MEMS tunable capacitor based on angular vertical comb drives
InactiveUS7085122B2Appreciates the drawbacks inherent in lateral drive MEMS capacitorsIncrease tuning rangeMultiple-port networksMechanically variable capacitor detailsCapacitanceComb finger
A MEMS tunable capacitor with angular vertical comb-drive (AVC) actuators is described where high capacitances and a wide continuous tuning range is achieved in a compact space. The comb fingers rotate through a small vertical angle which allows a wider tuning range than in conventional lateral comb drive devices. Fabrication of the device is straightforward, and involves a single deep reactive ion etching step followed by release and out-of-plane assembly of the angular combs.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
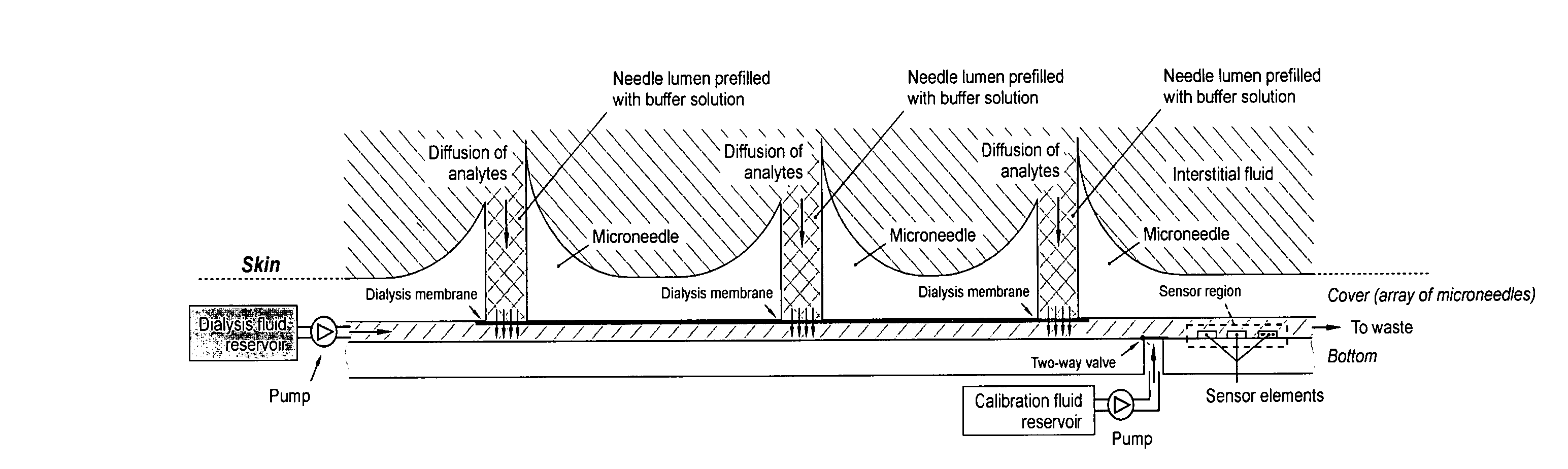
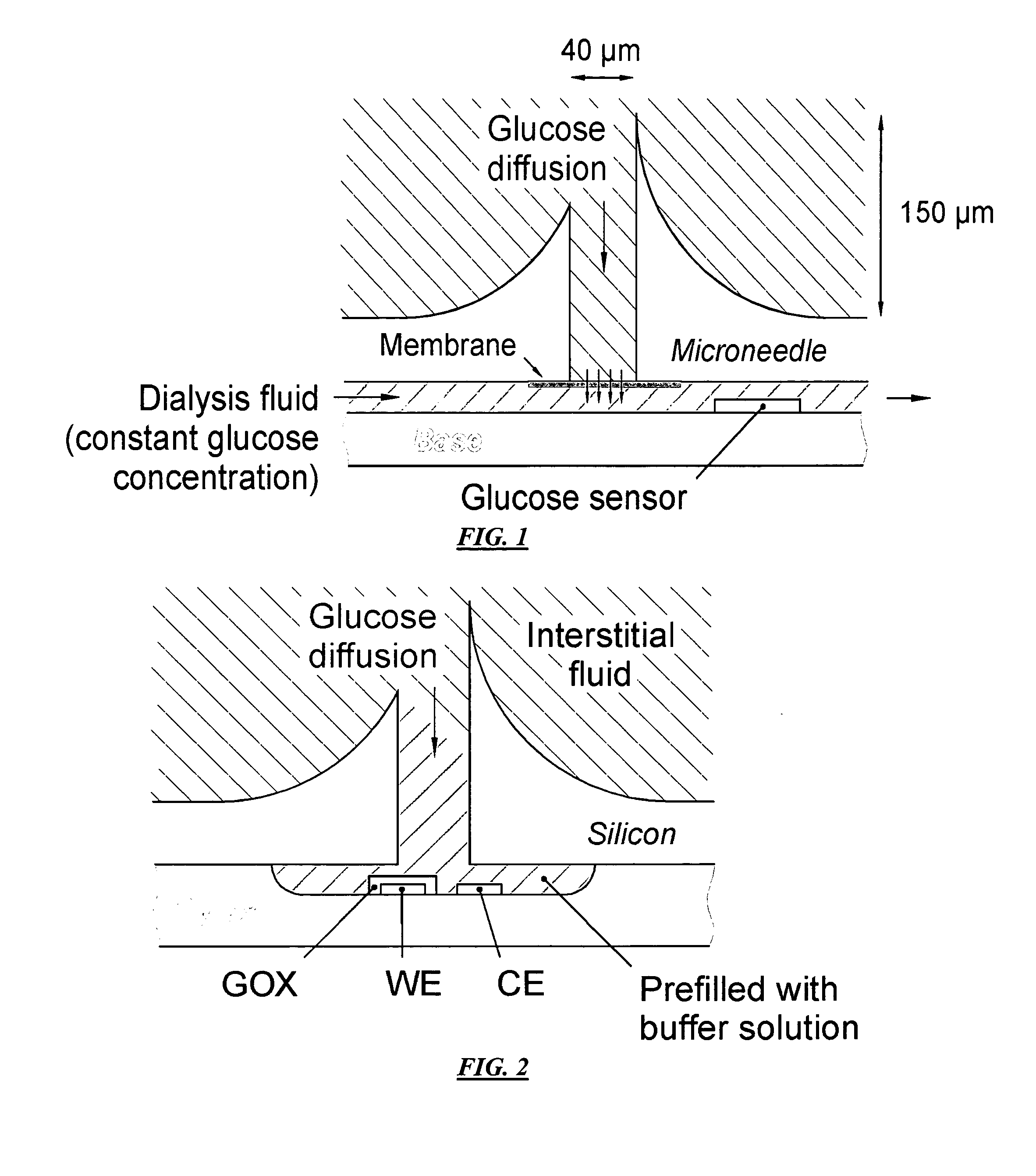
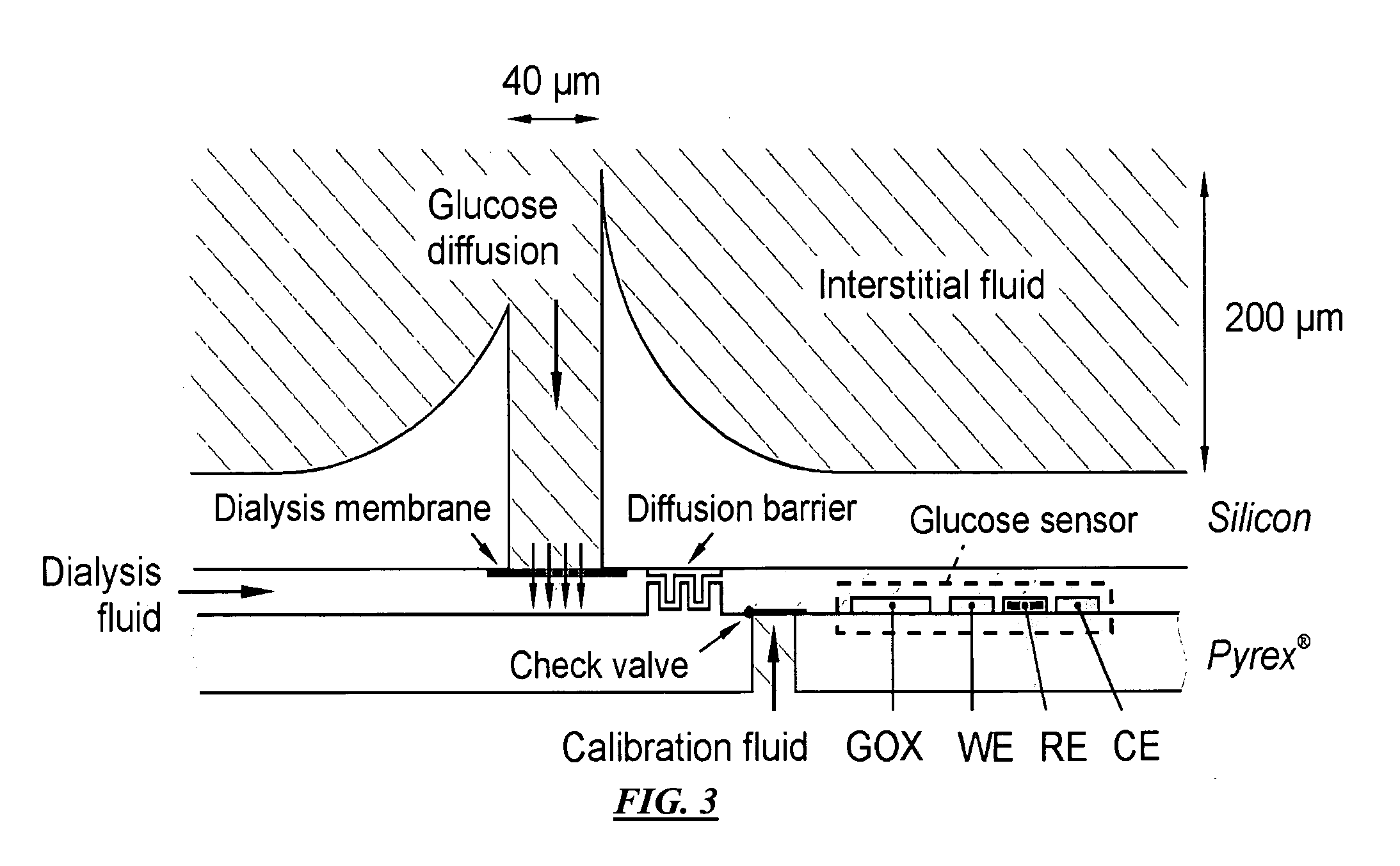
Monitoring method and/or apparatus
ActiveUS20060211933A1Easy recalibrationMinimally invasiveSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisDialysis membranesContinuous glucose monitoring
A method and apparatus for substance monitoring. One application is an easy to handle continuous glucose monitor using a group of hollow out-of-plane silicon microneedles to sample substances in interstitial fluid from the epidermal skin layer. The glucose of the interstitial fluid permeates a dialysis membrane and reaches a sensor. Using MEMS technology, for example, allows well-established batch fabrication at low cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Wind turbine blade deflection control system
A wind turbine with a sensor that measures the out-of-plane deflection of the blades and a controller that uses the signal from the sensor to determine the risk of a tower strike. The controller takes any necessary action to prevent a tower strike when it determines that the risk of a strike is high. The sensor can include strain gages or accelerometers mounted on the blades or it can include a fixed sensor mounted on the side of the tower to measure tower clearance as the blade passes by. The control action taken can include pitching blades, yawing the nacelle, or stopping the turbine. The controller is preferably a fuzzy logic controller.
Owner:BOSCHE JOHN VANDEN
Method and apparatus for micro electro-mechanical systems and their manufacture
InactiveUS20020127760A1Less driving voltageSemiconductor electrostatic transducersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOut of plane motionActuator
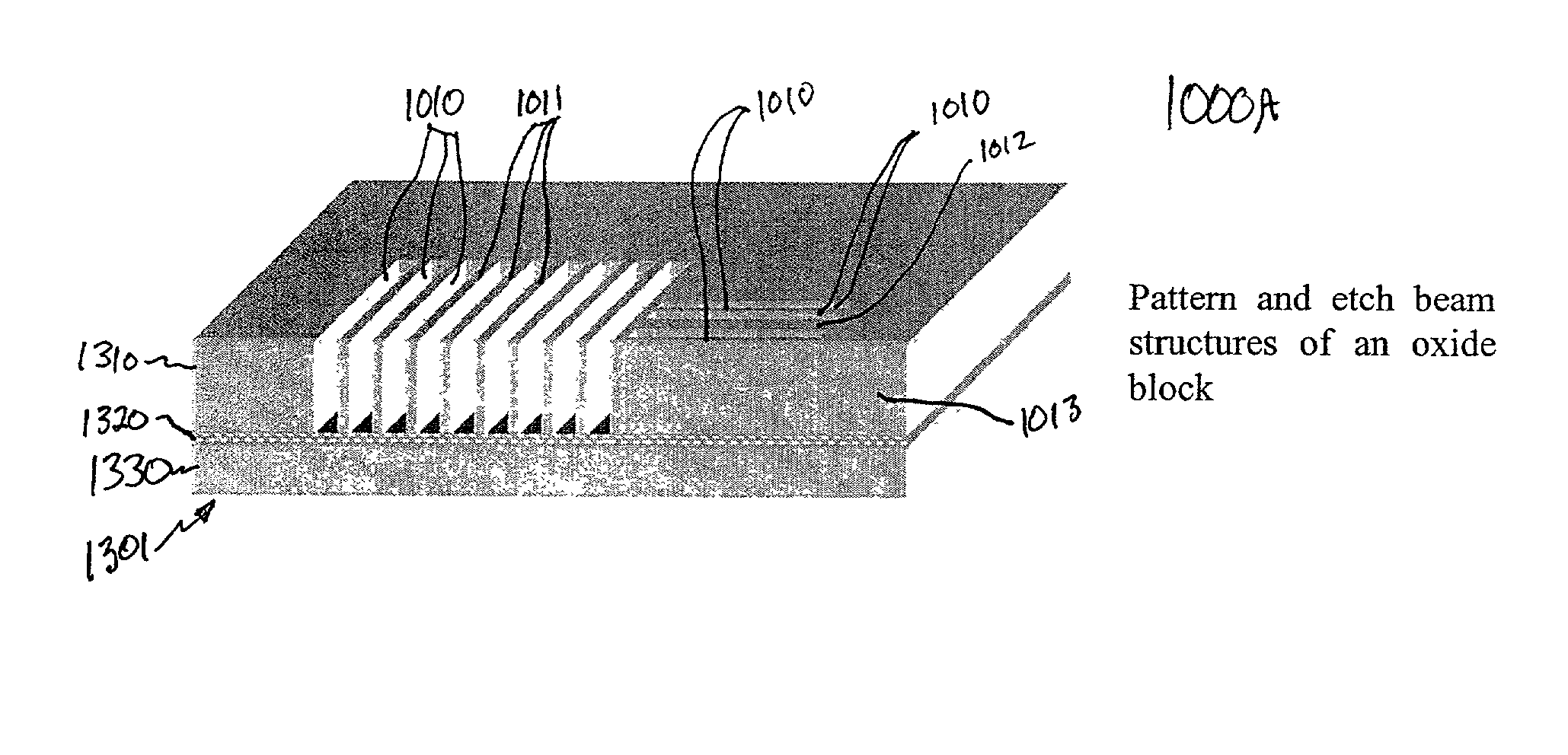
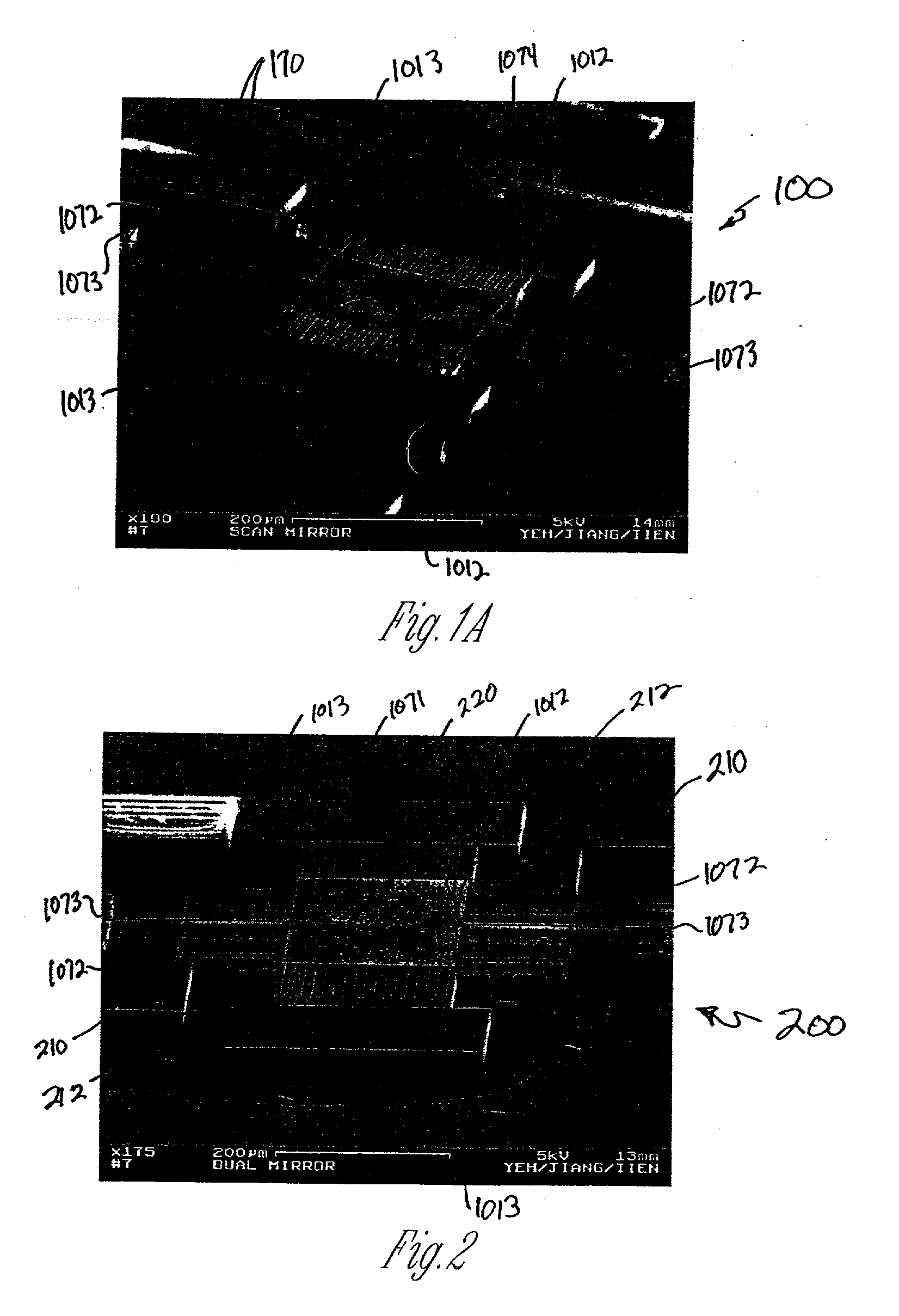
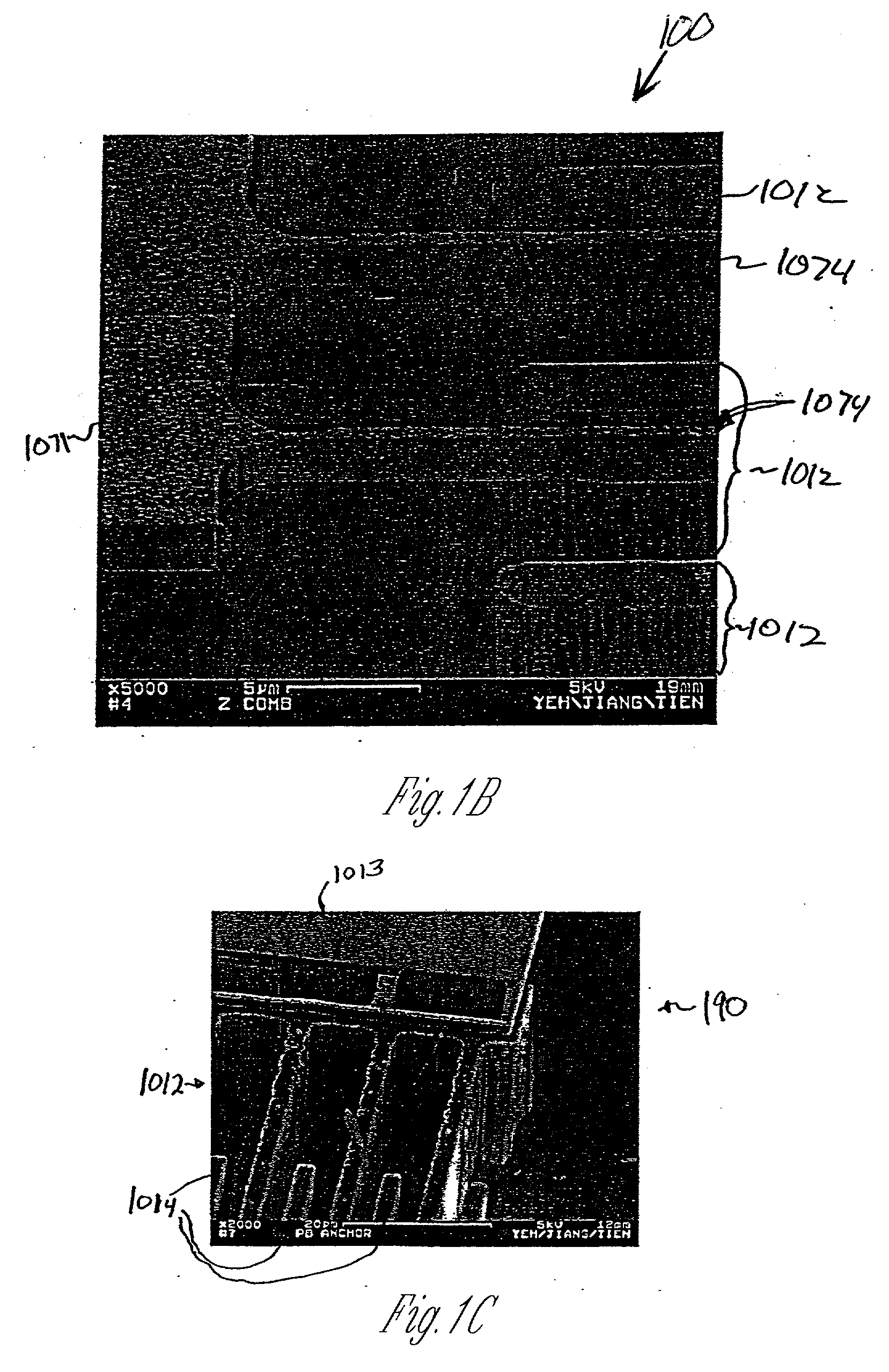
The present invention provides a fabrication process that integrates high-aspect-ratio silicon structures with polysilicon surface micromachined structures. In some embodiments the process includes forming an oxide block by etching a plurality of trenches to leave a plurality of vertical-walled silicon structures standing on the substrate, thermally and substantially completely oxidizing the vertical-walled silicon structures, and substantially filling spaces between the oxidized vertical-walled silicon structures with an oxide of silicon to form the oxide block. The process retains not only the high-aspect-ratio silicon structures possible with deep reactive ion etching (DRIE) but also the design flexibility of polysilicon surface micromachining. Using this process, polysilicon platforms have been fabricated, which are actuated by high-aspect-ratio combdrives for many applications such as x-y-z stages and scanning devices. The actuators include an asymmetric combdrive that actuates in torsional / out-of-plane motions, and a high-aspect-ratio combdrive that drives in translational motion.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Three-dimensional (3D) hydrodynamic focusing using a microfluidic device
InactiveUS20090066936A1Reliable single molecule sensitivityFocusOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOut of planePhysics
A microfluidic device comprises inlets for a sample flow and an out-of-plane focusing sheath flow, and a curved channel section configured to receive the sample flow and out-of-plane focusing sheath and to provide hydrodynamic focusing of the sample flow in an out-of-plane direction, the out-of-plane direction being normal to a plane including the curved channel.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Controllable nanomechanical memory element
A memory device includes a mechanical element that exhibits distinct bistable states under amplitude modulation. The states are dynamically bistable or multi-stable with the application of a drive signal of a given frequency. The natural resonance of the element in conjunction with a hysteretic effect produces distinct states over a specific frequency range. Devices with multiple elements that respond to different frequency ranges provided on a common contact are formed with improved density. The devices may be excited and read with magnetomotive, capacitive, piezoelectric and / or optical methods. The devices may be planar oriented or out of plane oriented to permit three dimensional memory structures. DC biases may be used to shift frequency responses to permit an alternate method for differentiating states of the element.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com