Patents
Literature
139results about How to "Eliminate relative rotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
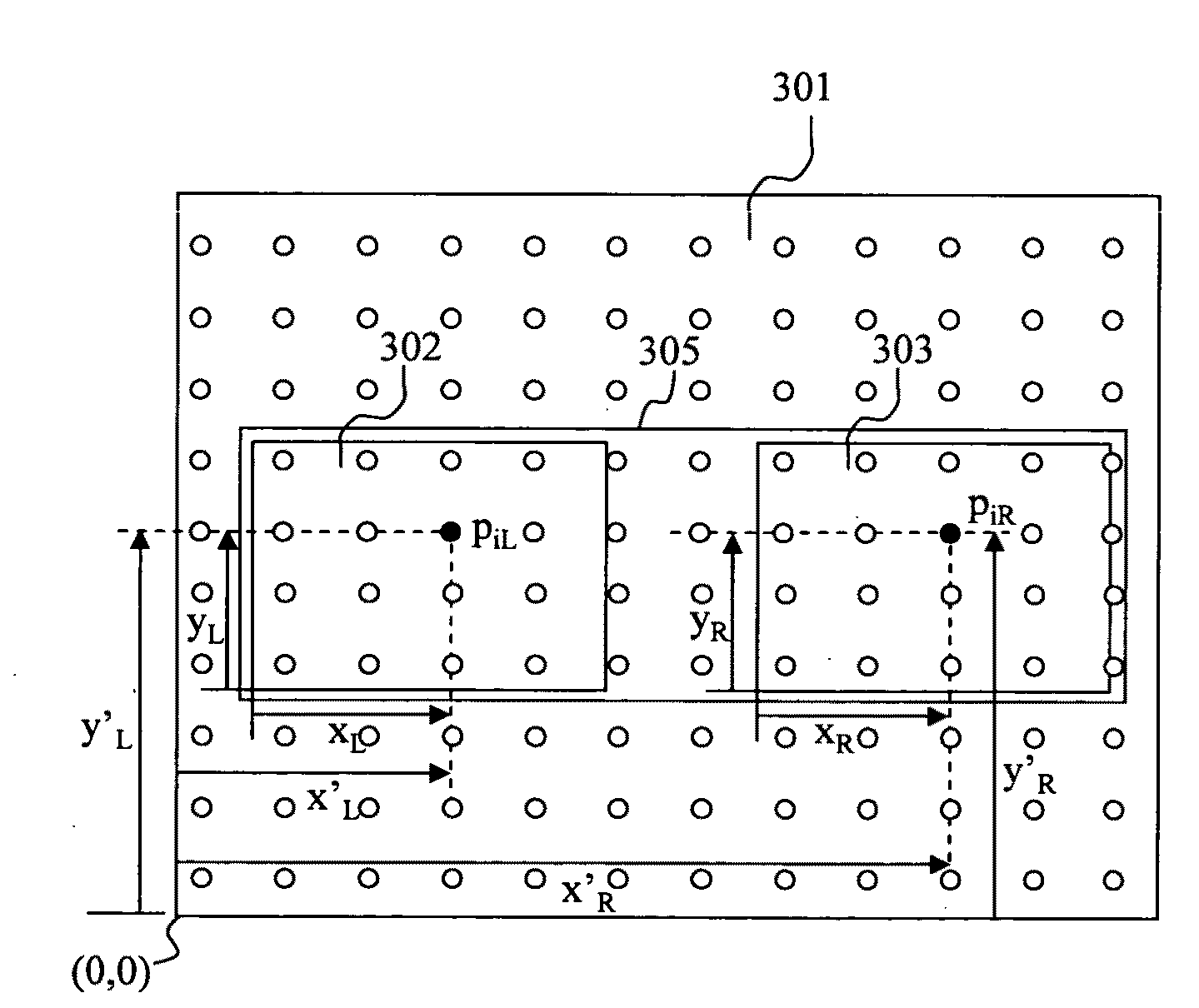
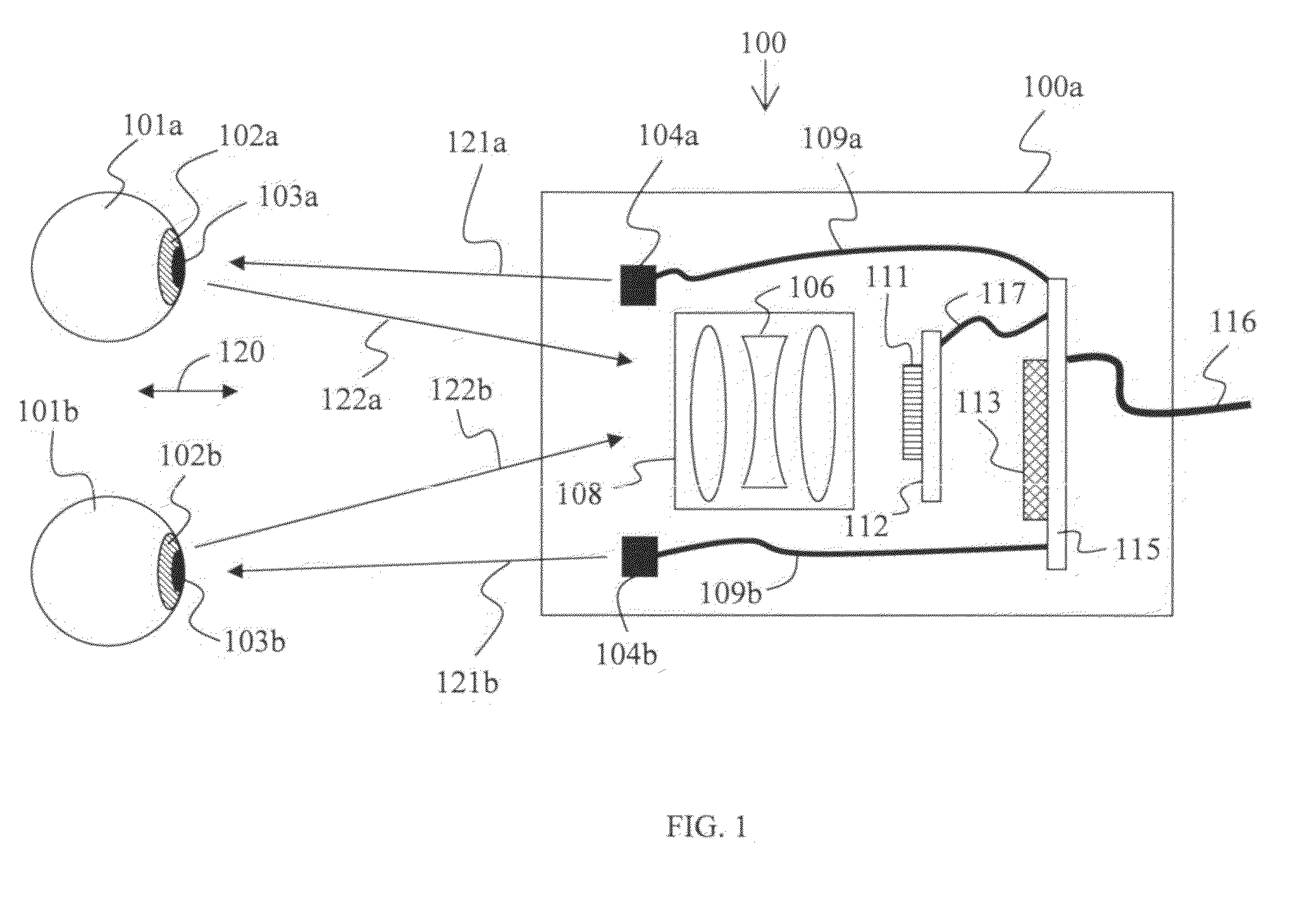
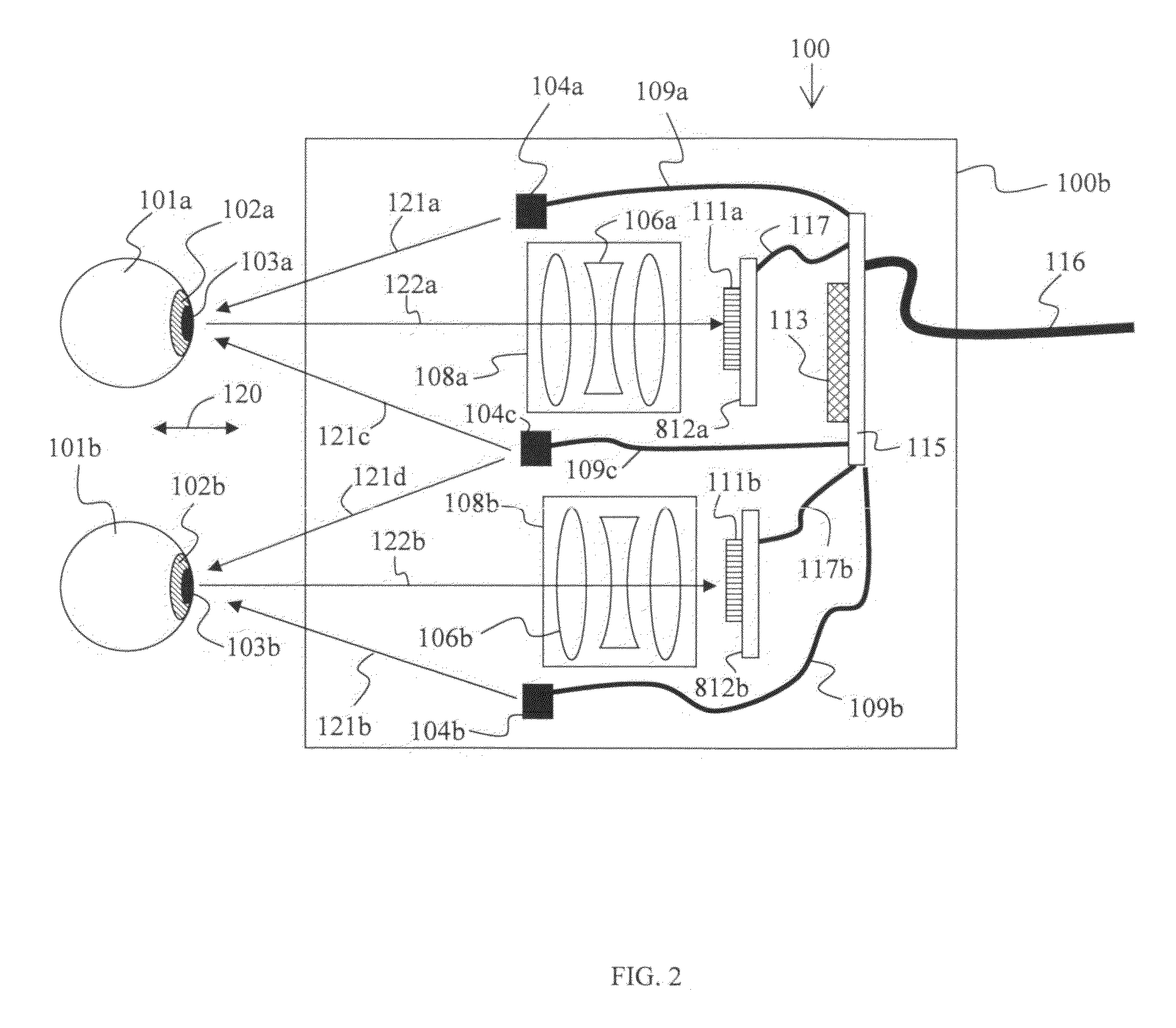
Apparatus and method for two eye imaging for iris identification
ActiveUS20100110374A1Improving iris recognitionEliminate relative rotationAcquiring/recognising eyesOthalmoscopesHorizontal axisSingle image
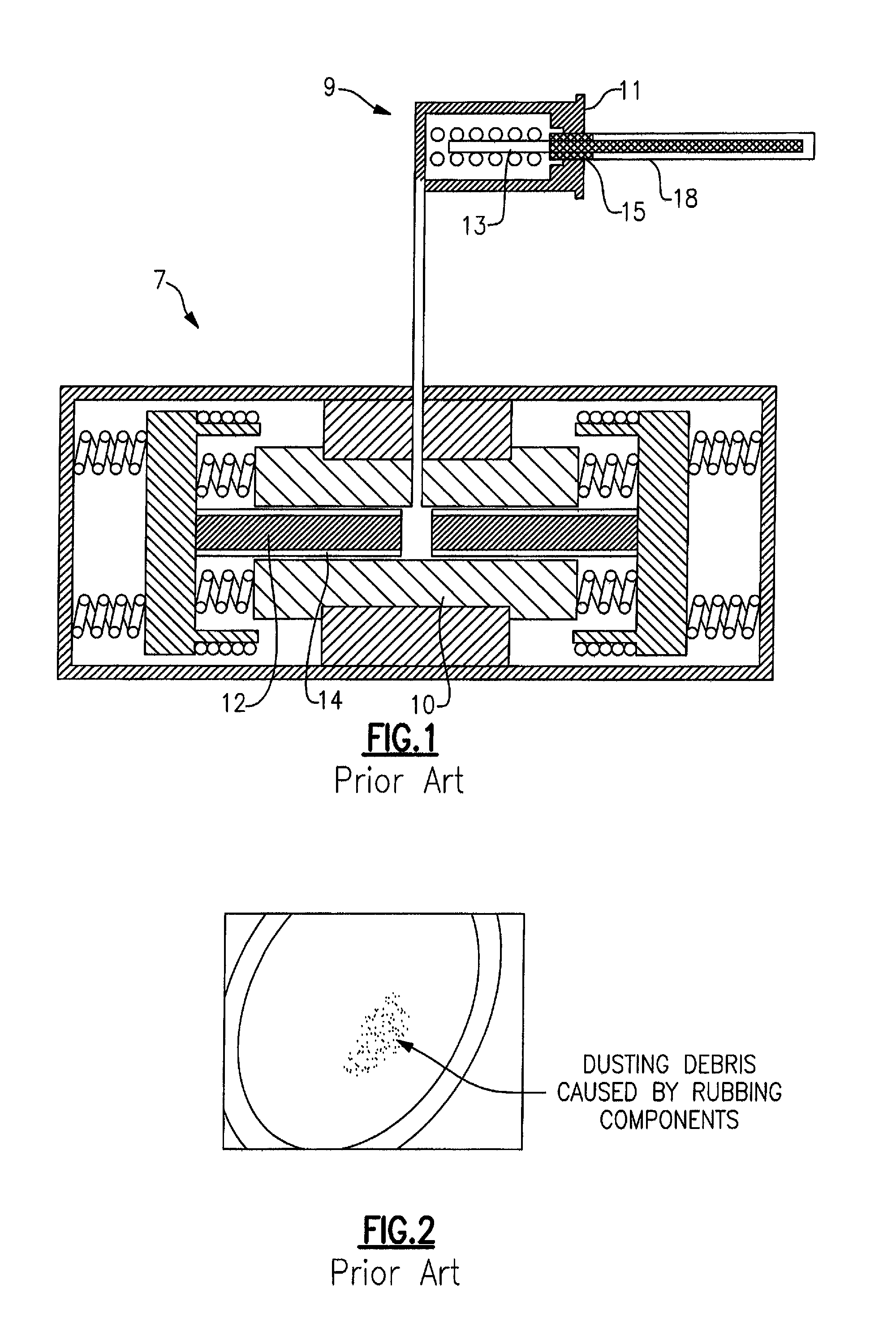
The apparatus represents a device having one or two sensors for capturing a single image or two images having the subject's eyes, in which a dimension, such as the horizontal axis, with respect to pixels in the single image or two first images characterizing zero head tilt, and processors in one or more of a housing with the one or two sensors or in a computer system which receives the single image or two images. Such processors determine a head tilt angle between a virtual line extending between the two eyes of the subject in accordance with predefined features, such as pupil or iris center, in the single image or two images and the dimension characterizing zero head tilt, segment left and right iris images from the single image or two images, and rotate the segmented left and right iris image in accordance with the angle to substantially remove head tilt when present. A database of identification data may be provided storing at least templates representative of right and left irises of a plurality of subjects without substantial head tilt, and the processors generate template(s) representative of the left and right irises of the subject, which are either added or compared to the identification data. The processor may also determine interpupillary distance (IPD) or IPD-to-iris ratio using the single image or two images, and as such may be used for comparative searching of the identification data having IPD or IPD-to-iris ratio of the plurality of subjects.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
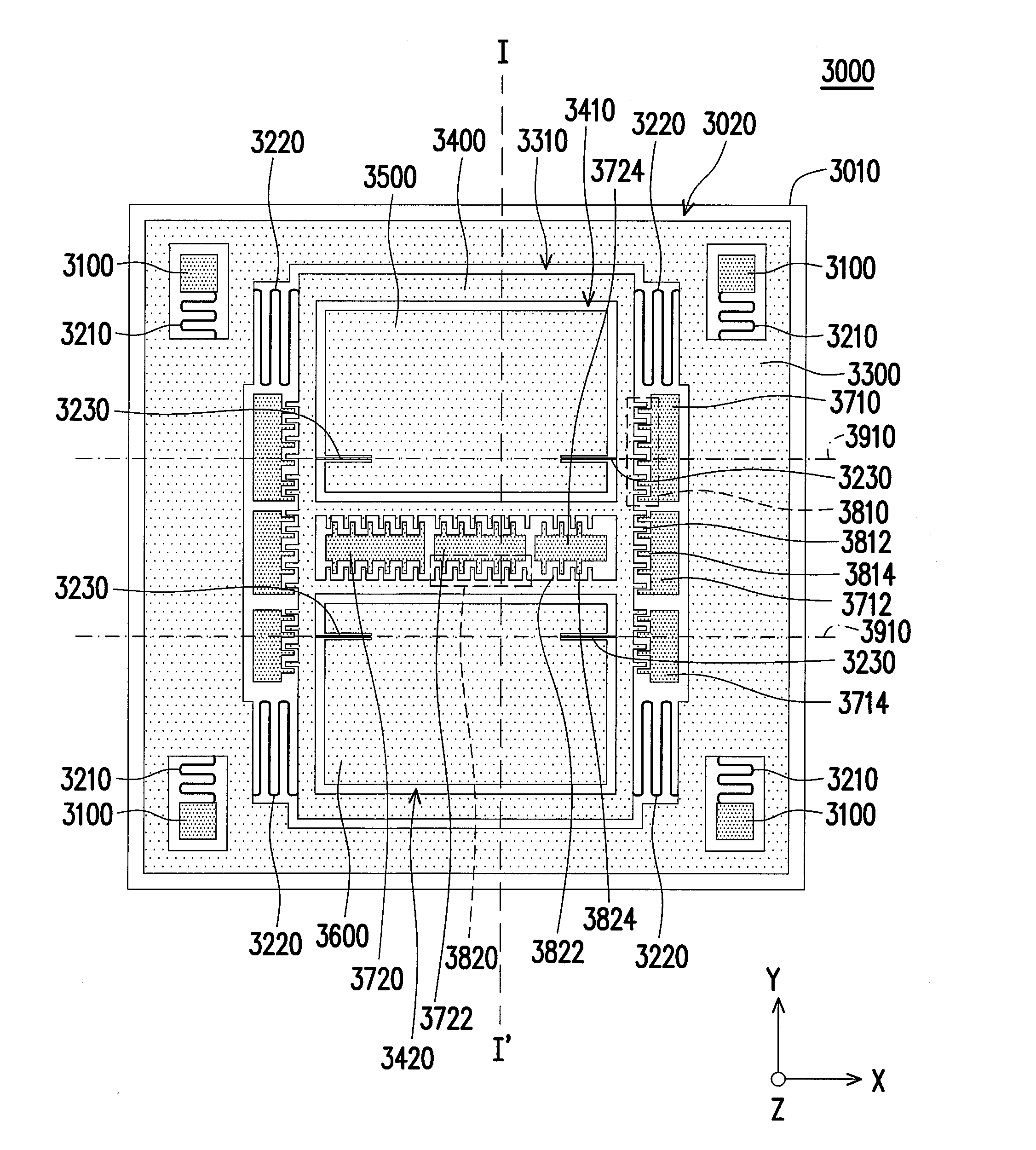
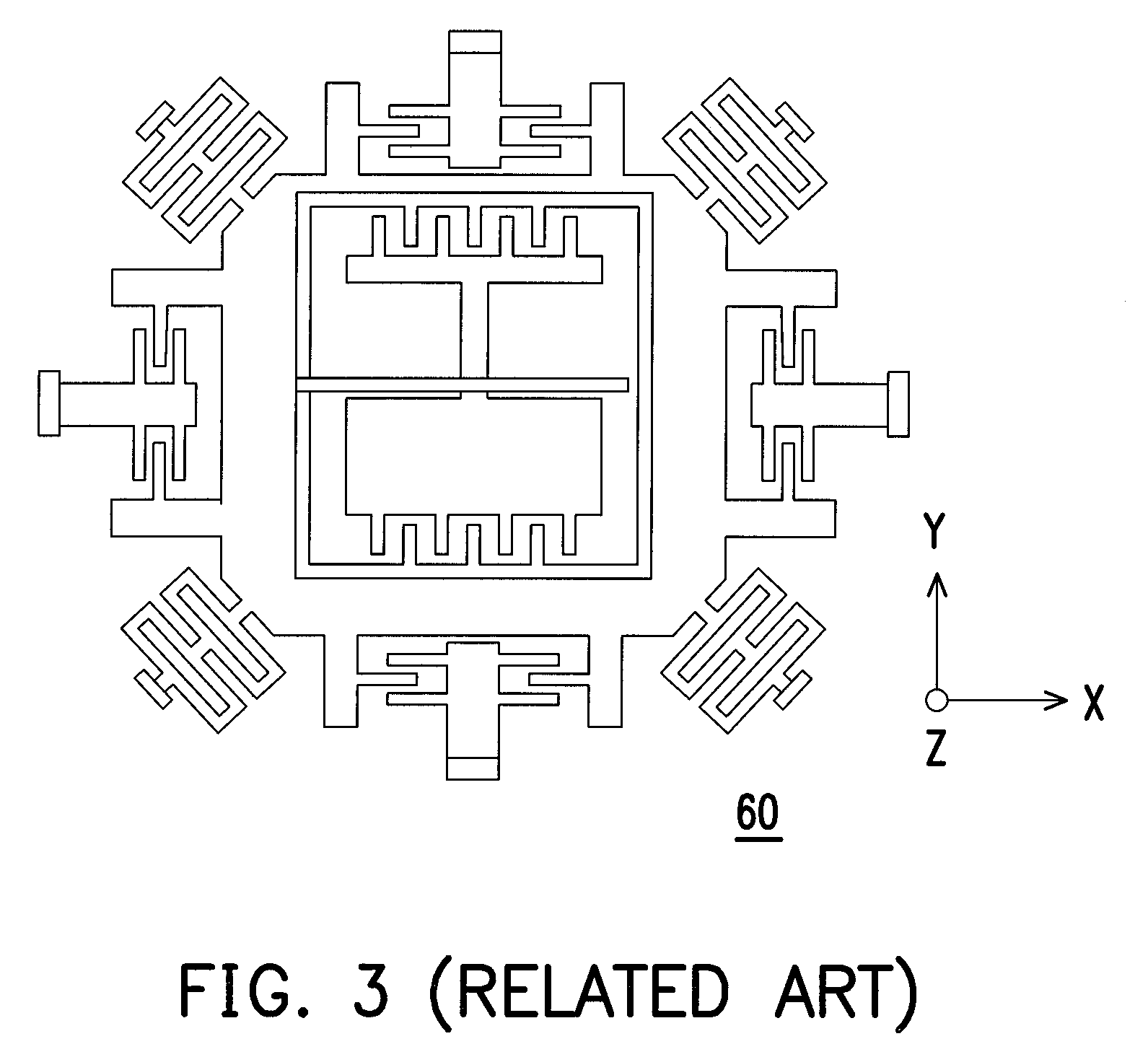
Multi-axis capacitive accelerometer
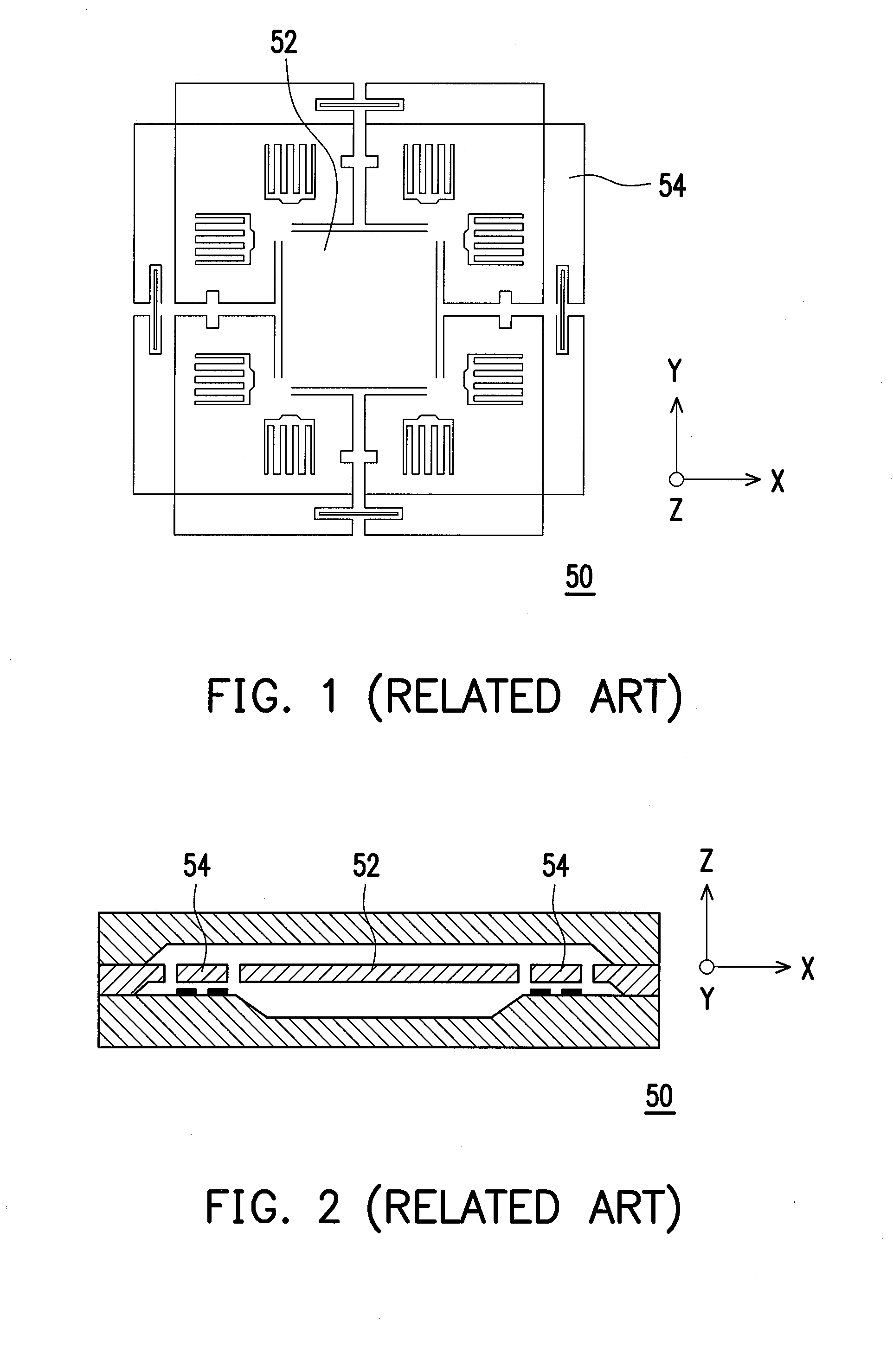
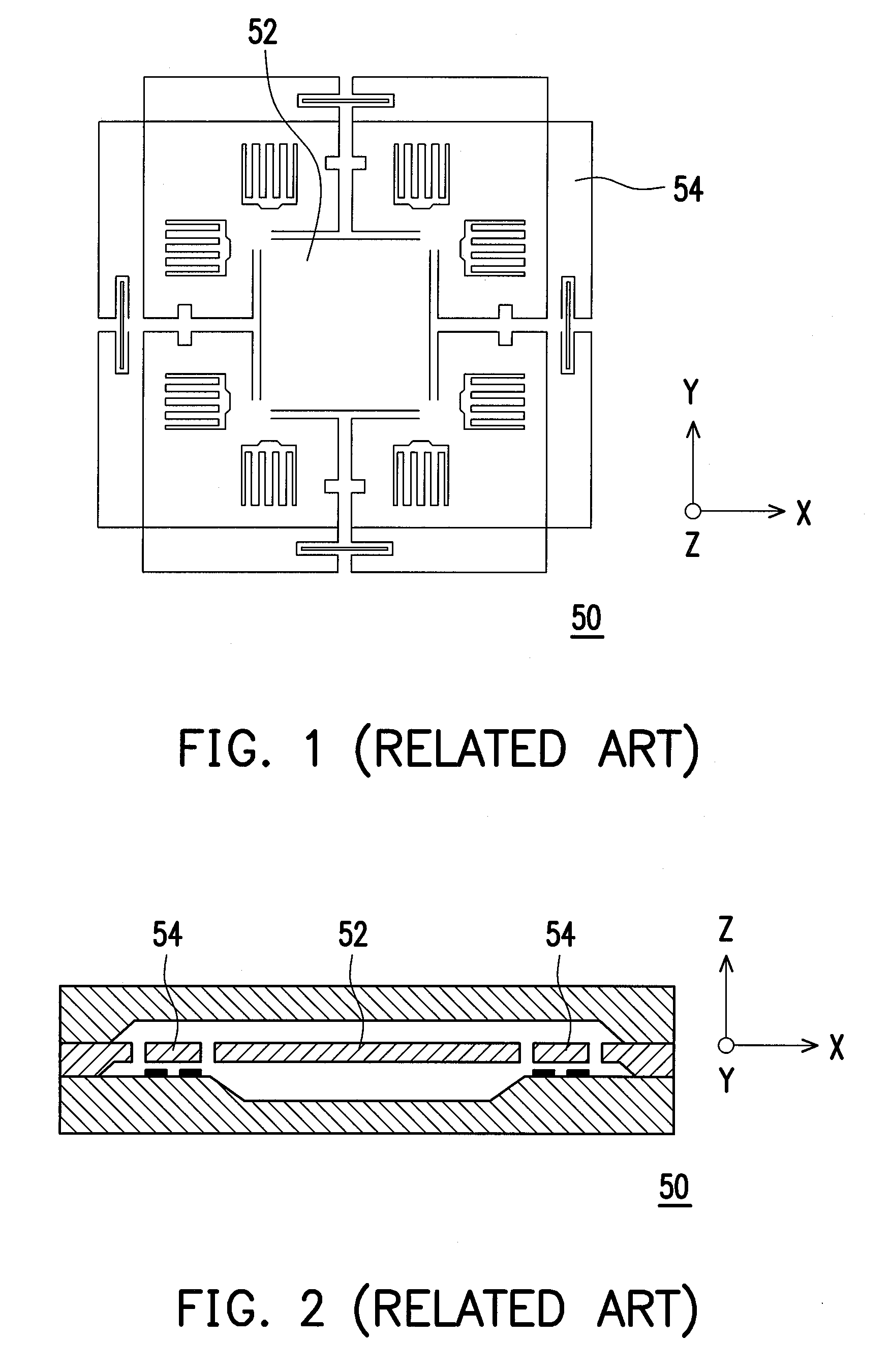
ActiveUS20100122579A1Improve linearityEliminate relative rotationAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsIn planeClassical mechanics
A multi-axis accelerometer is consisted of a substrate with sensing electrodes and a structure layer. The structure layer includes anchor bases fixed on the substrate. A first proof mass is disposed over the substrate and has a first opening and a second opening symmetric to each other. The first proof mass is suspended to the anchor bases. Fixed sensing blocks are disposed on the substrate, and capacitors are formed between each fixed sensing block and the first proof mass for sensing acceleration along two in-plane directions. A second proof mass and a third proof mass are disposed in the first opening and the second opening and are asymmetrically suspended. Separate electrodes are disposed on the substrate and form two differential capacitors with the second proof mass and the third proof mass for sensing the out-of-plane acceleration.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Multi-axis capacitive accelerometer
ActiveUS8205498B2Improve linearityEliminate relative rotationAcceleration measurement in multiple dimensionsIn planeClassical mechanics
A multi-axis accelerometer is consisted of a substrate with sensing electrodes and a structure layer. The structure layer includes anchor bases fixed on the substrate. A first proof mass is disposed over the substrate and has a first opening and a second opening symmetric to each other. The first proof mass is suspended to the anchor bases. Fixed sensing blocks are disposed on the substrate, and capacitors are formed between each fixed sensing block and the first proof mass for sensing acceleration along two in-plane directions. A second proof mass and a third proof mass are disposed in the first opening and the second opening and are asymmetrically suspended. Separate electrodes are disposed on the substrate and form two differential capacitors with the second proof mass and the third proof mass for sensing the out-of-plane acceleration.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
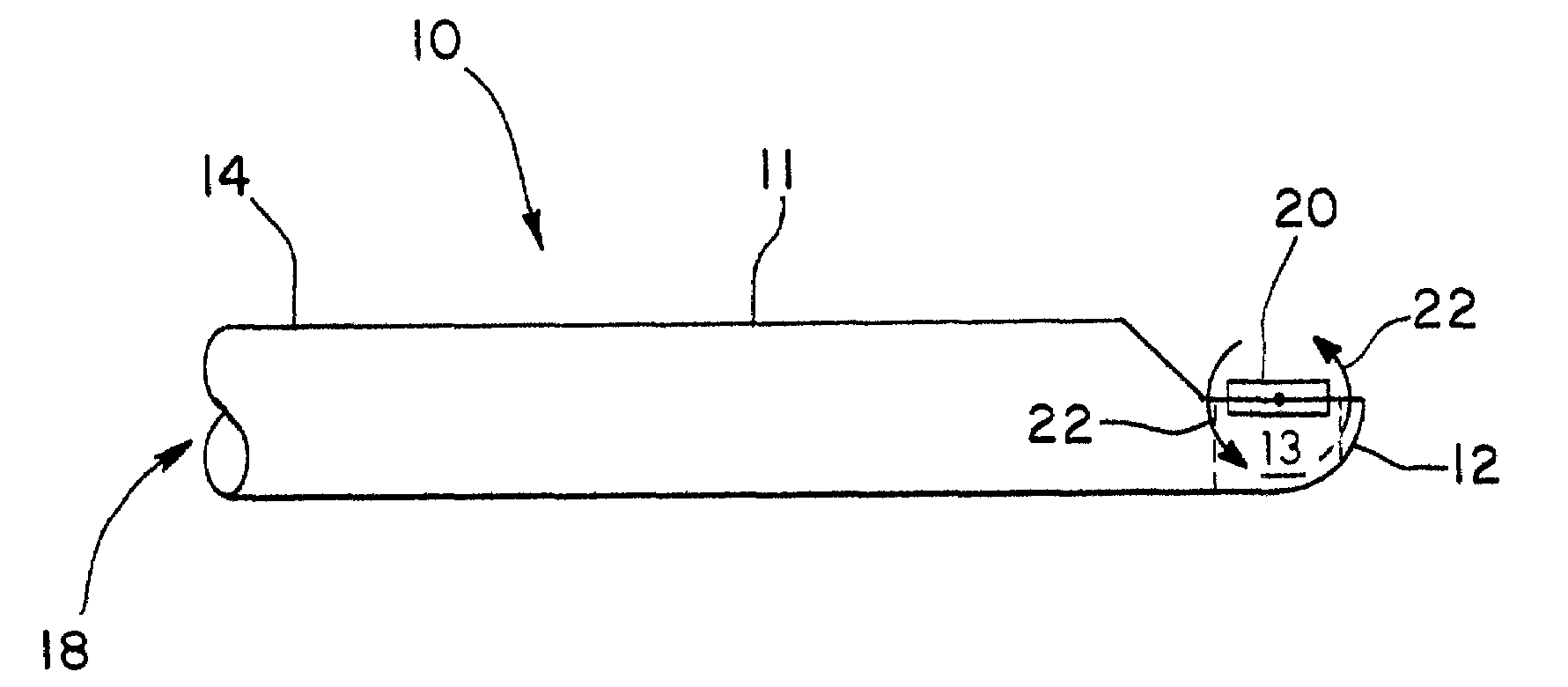
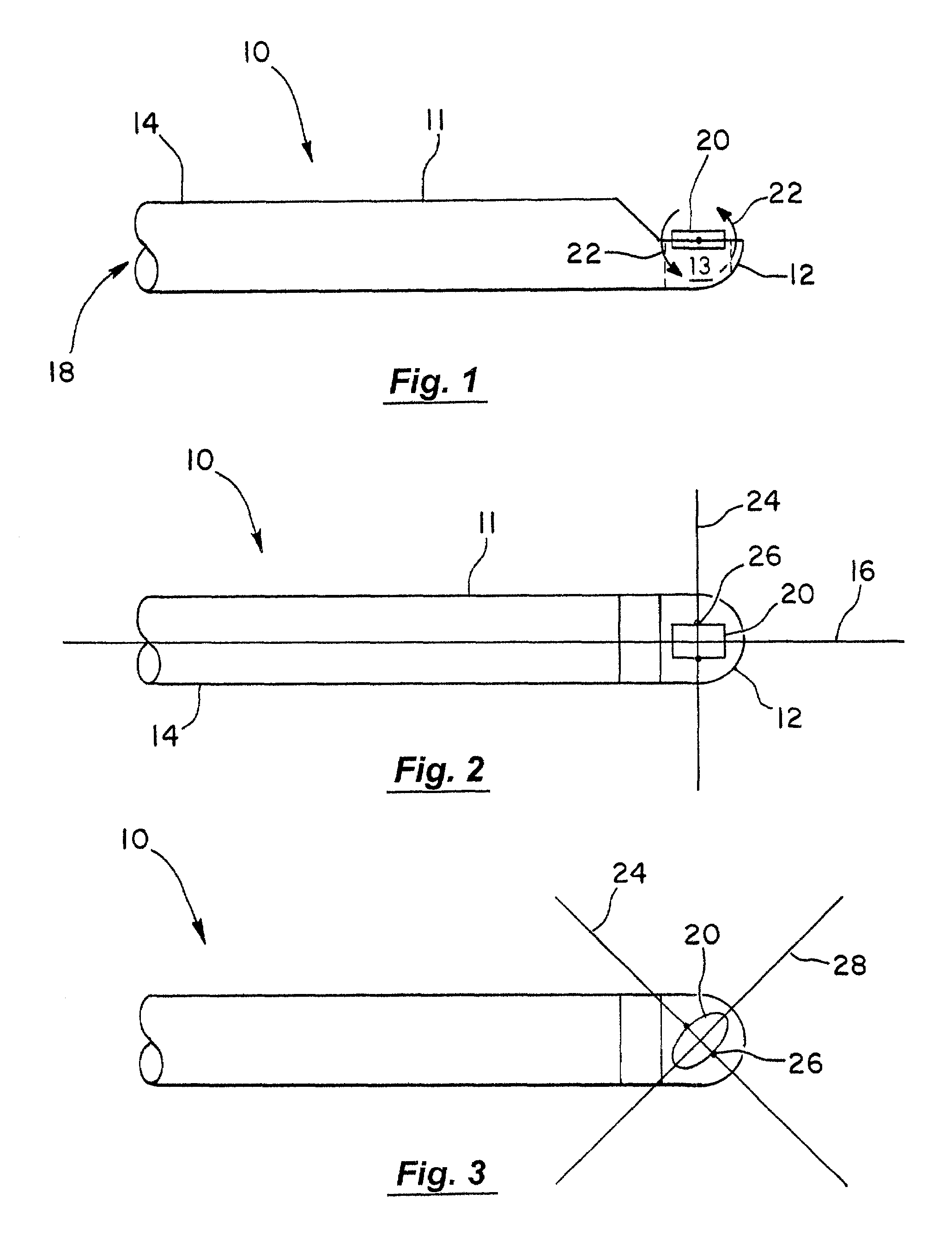
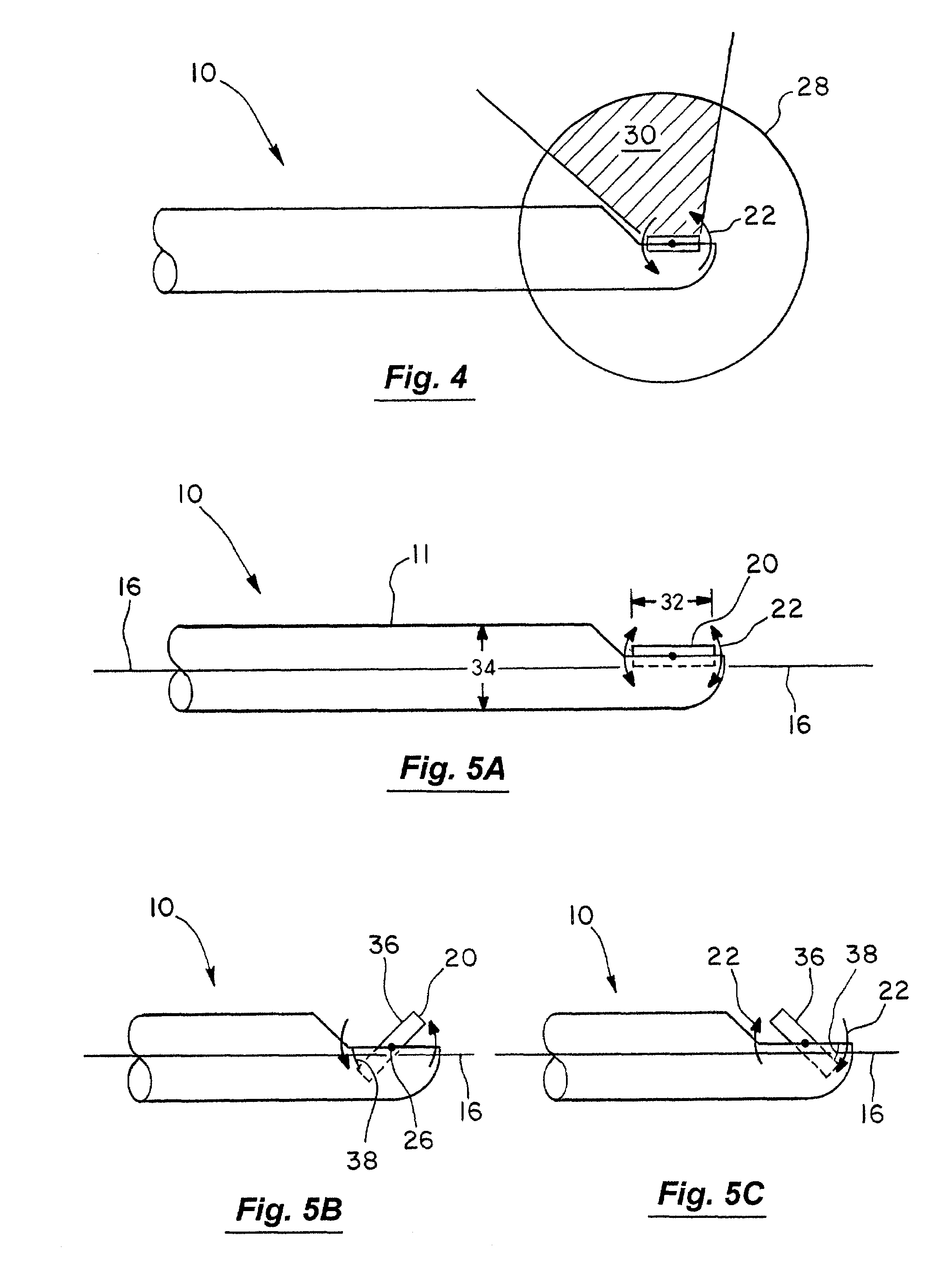
Imaging catheter and methods of use for ultrasound-guided ablation
InactiveUS7488289B2Simple and inexpensiveSimple and inexpensive apparatusUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterUltrasound imagingTransducer
The present invention provides ultrasound imaging catheters, systems and methods for their use which will be particularly useful to monitor the positioning of ablation catheters. In one embodiment, an imaging catheter (10) includes a catheter body (11) having a distal end (12), a proximal end (14) and a longitudinal axis (16). A transducer (20) is rotatably coupled to the distal end. The transducer has an axis of rotation (24) that is at a non-zero angle relative to the catheter body longitudinal axis. Such a configuration provides an exemplary side-looking imaging catheter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
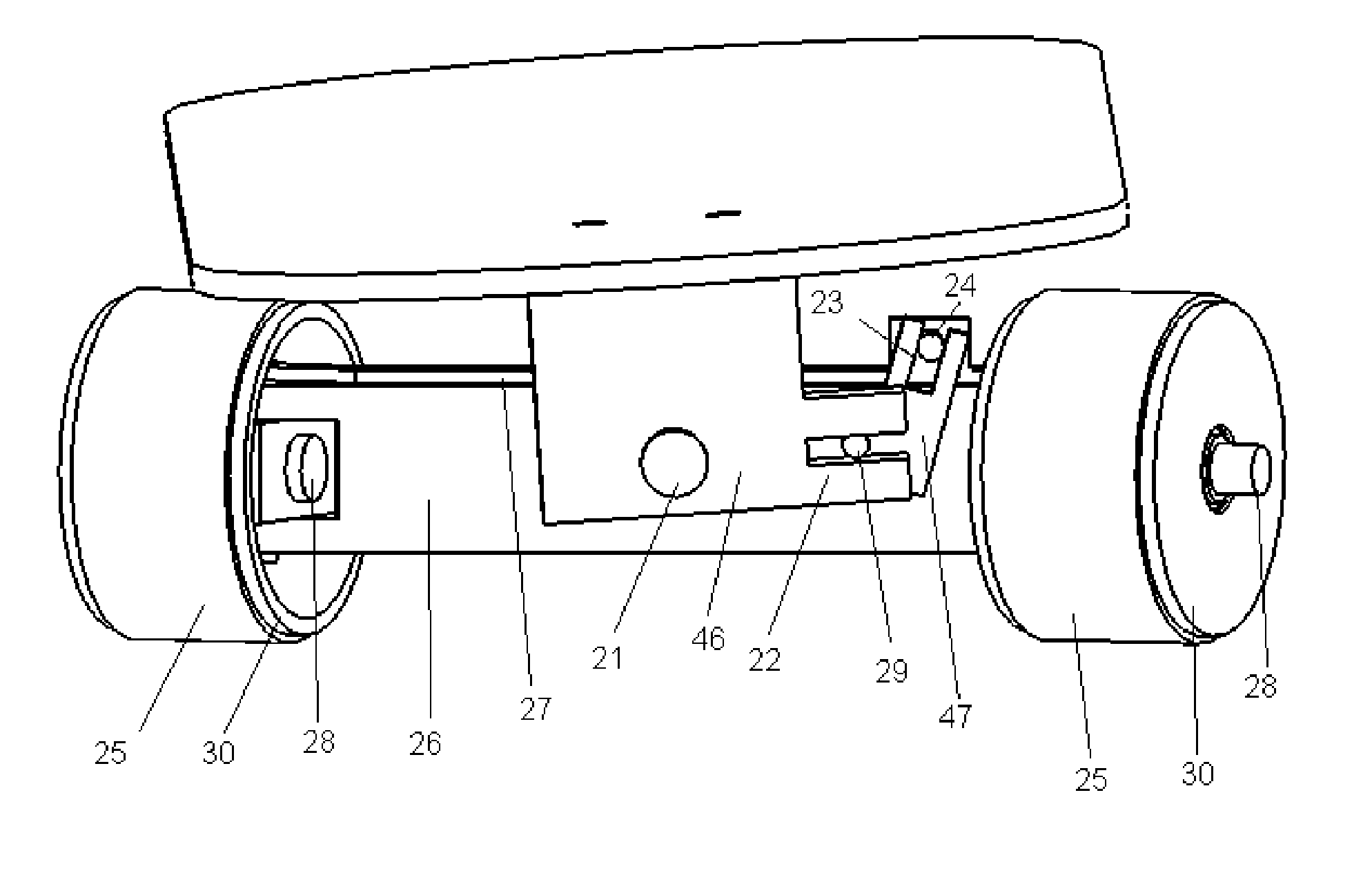
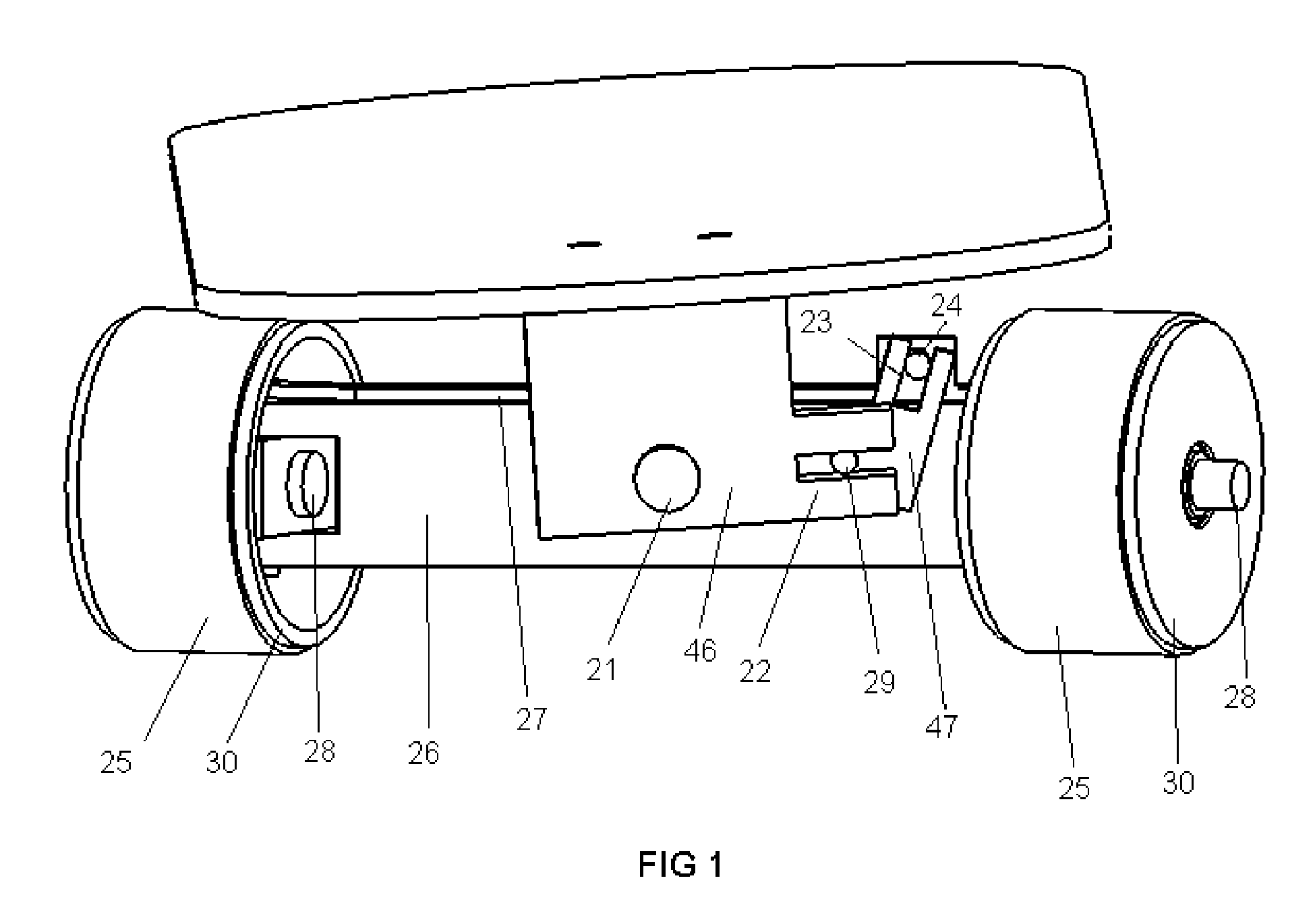
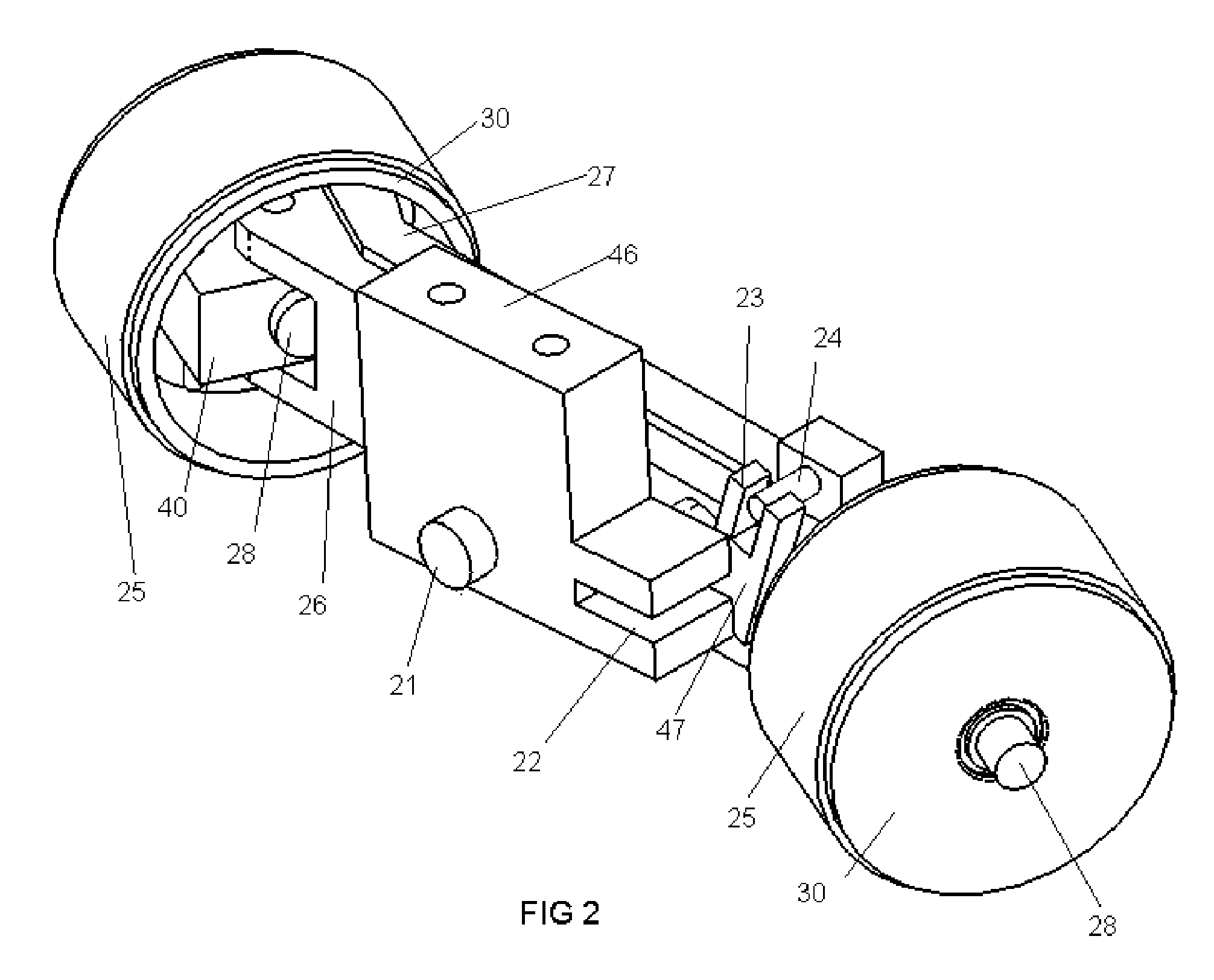
Skateboard Steering Assembly
An improved skateboard truck assembly provides very tight, small turning radius capability without the need to lift the forward truck assembly or the entire skateboard from the surface on which it is riding. Turning and riding under all conditions is stable and without wobble. Steering output is adjustable and configurable. The steering assembly uses automotive type mechanisms allowing for caster, camber, pivot and Ackerman steering adjustments.
Owner:NELSON STEVEN DAVID +1
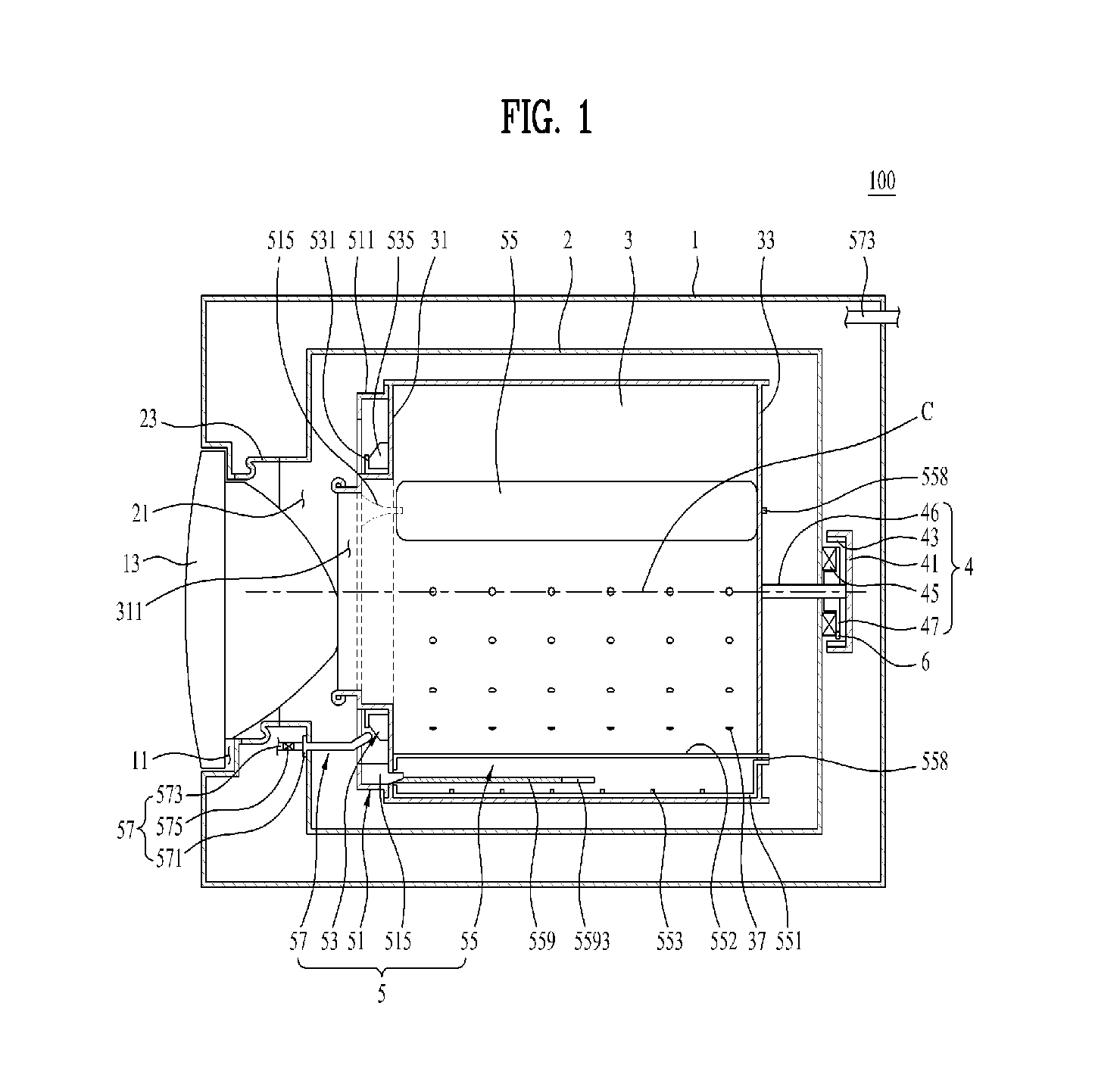
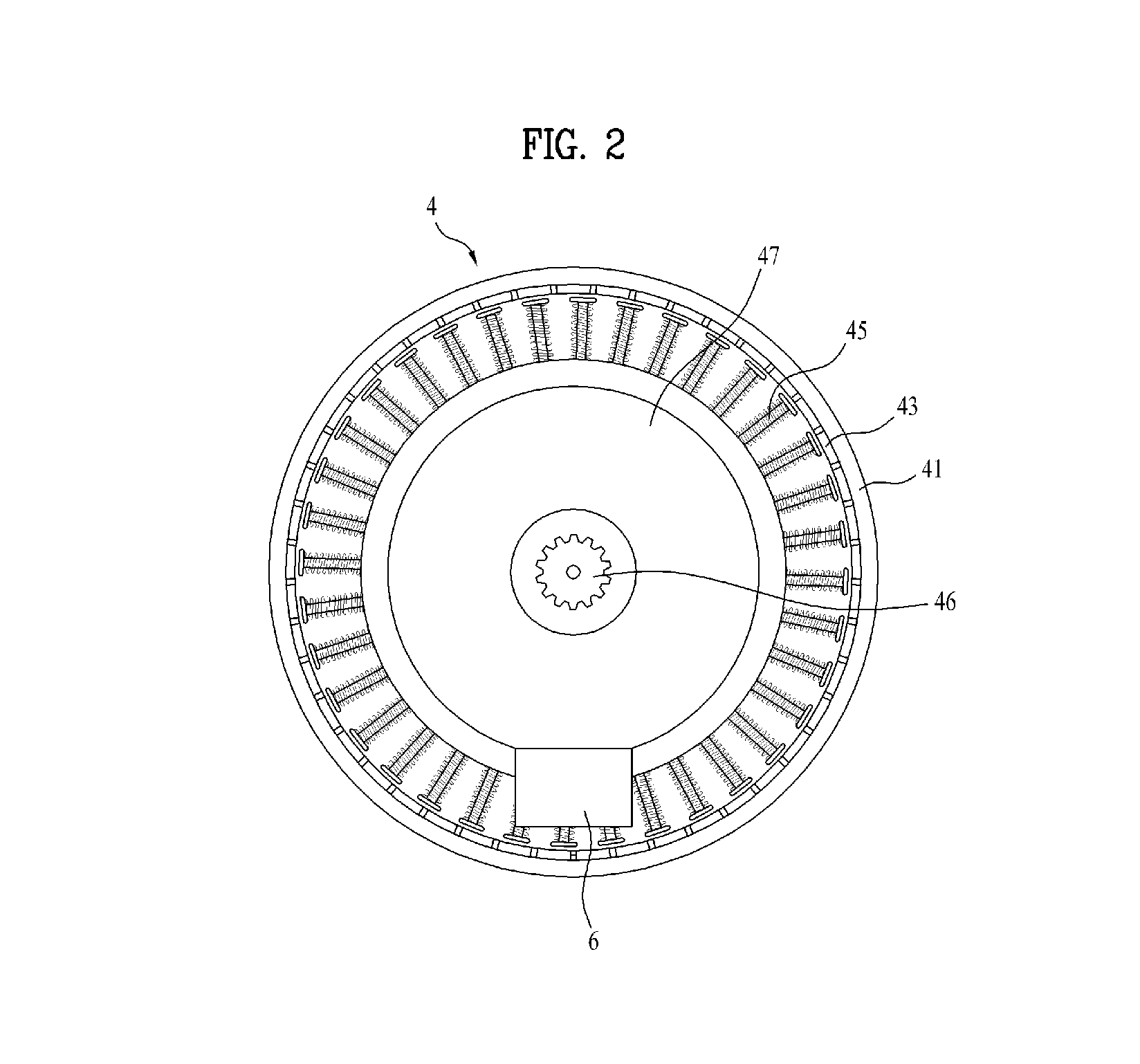
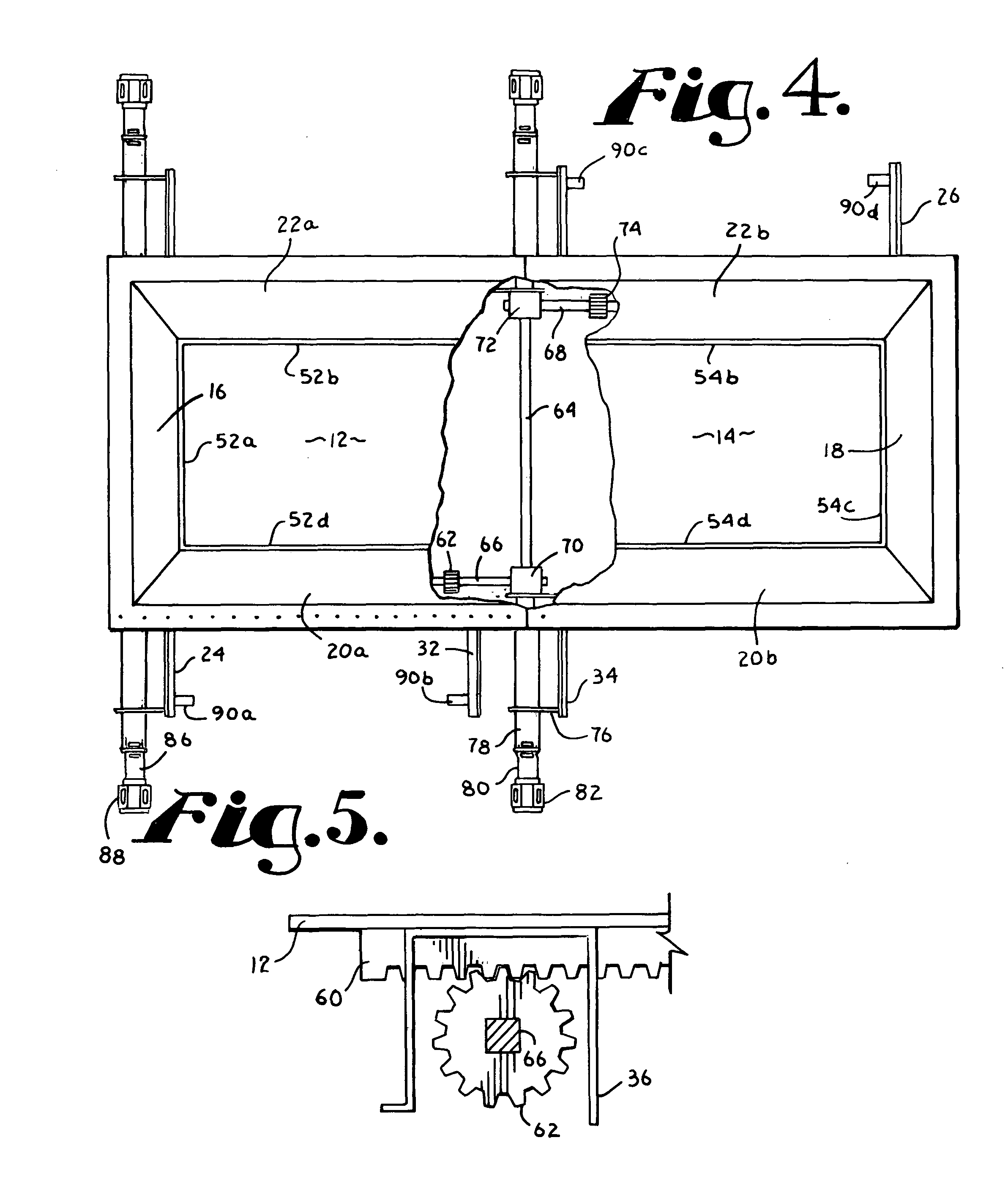
Laundry treatment apparatus
ActiveUS20140223969A1Prevent movementEliminate relative rotationRotating bodies balancingOther washing machinesEngineeringLaundry
A laundry treatment apparatus including a rotatable drum in which laundry is stored, at least three balancers mounted to the drum so as to be spaced apart from one another by the same angle around a rotation center of the drum. Liquid is introduced into and discharged from the balancers via a feeder supplying the liquid and a flow path structure mounted to the drum to guide liquid supplied from the feeder to the balancer located in a direction for removal of unbalance of the drum.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
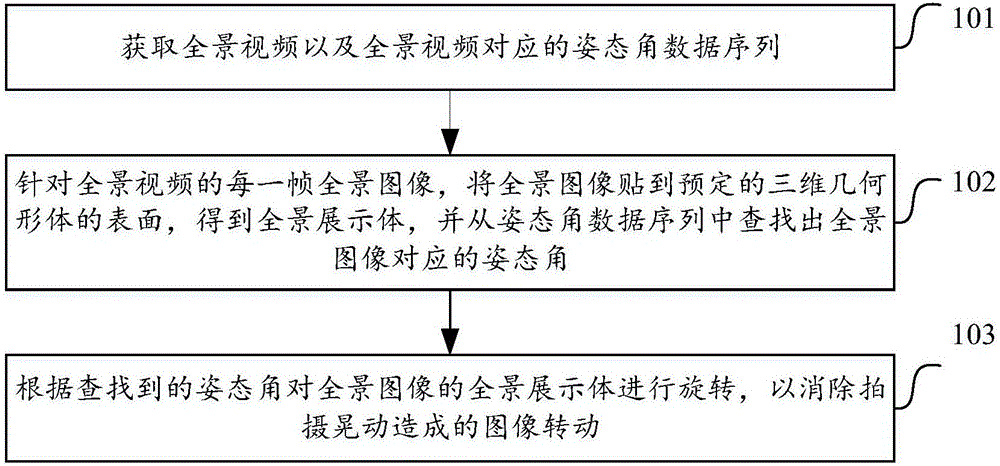
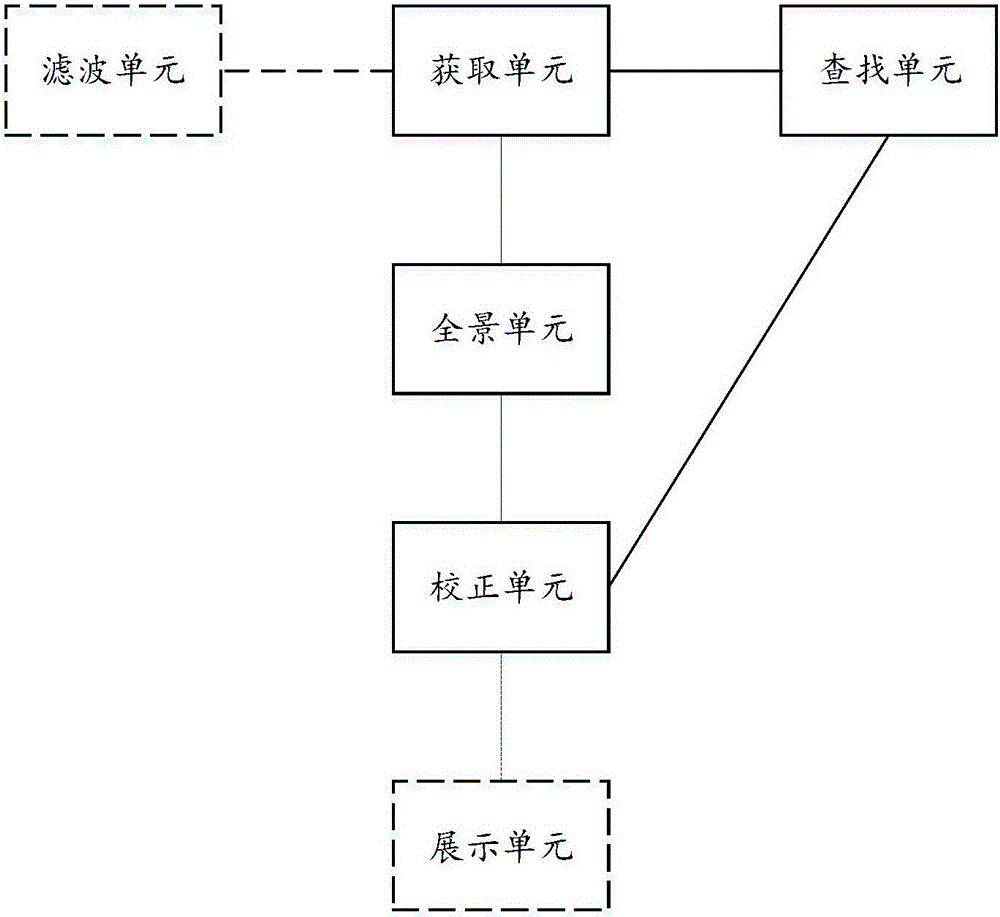
Method and device for correction of panorama video display visual angle
ActiveCN106507094AEliminate relative rotationImprove viewing experienceSteroscopic systemsComputer graphics (images)Data sequences
The present invention discloses a method and device for correction of a panorama video display visual angle. The method comprises: obtaining a panorama video and an attitude angle data sequence corresponding to the panorama video; aiming at the frame panorama images of the panorama video, patching the panorama video to a presetting three-dimensional geometrical feature surface, obtaining a panorama display body, and finding out the attitude angles corresponding to the panorama images from the attitude angle data sequence; and performing rotation of the panorama display body of the panorama images according to the found attitude angles to eliminate the image rotation caused by the shooting shaking. The method and device for correction of the panorama video display visual angle can eliminate the generated frame shaking, jittering or rotation when the panorama video is shot to allow the playing video frame to always keep stable so as to increase viewers' watching experience.
Owner:BEIJING MADV TECH CO LTD
Joint of mechanical arm
The invention provides a joint of a mechanical arm, and belongs to the technical field of machinery. The joint solves the problem that the joint of an existing mechanical arm is large in size. The joint of the mechanical arm comprises a shell, a motor and a harmonic reducer, wherein the motor and the harmonic reducer are integrated in the shell; the inner end of a rotating shaft of the motor is connected with the input end of the harmonic reducer; the output end of the harmonic reducer is connected with an output shaft; the rotating shaft of the motor is hollow; the inner end of the output shaft is fixed with the output end of the harmonic reducer, and the outer end of the output shaft penetrates through the outer end of the rotating shaft of the motor; a motor raster is fixed at the outer end of the rotating shaft of the motor; an output shaft raster is fixed at the outer end of the output shaft; an encoder is fixed in the shell; the output shaft raster and the motor raster are respectively positioned on the upper side and the lower side of the encoder; optoelectronic switches matched with output shaft raster and the motor raster are respectively arranged on the upper side and the lower side of the encoder. The joint has the advantages of small size, high space utilization rate, long service life and the like.
Owner:QIXING INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Machined spring with integral retainer for closed cycle cryogenic coolers
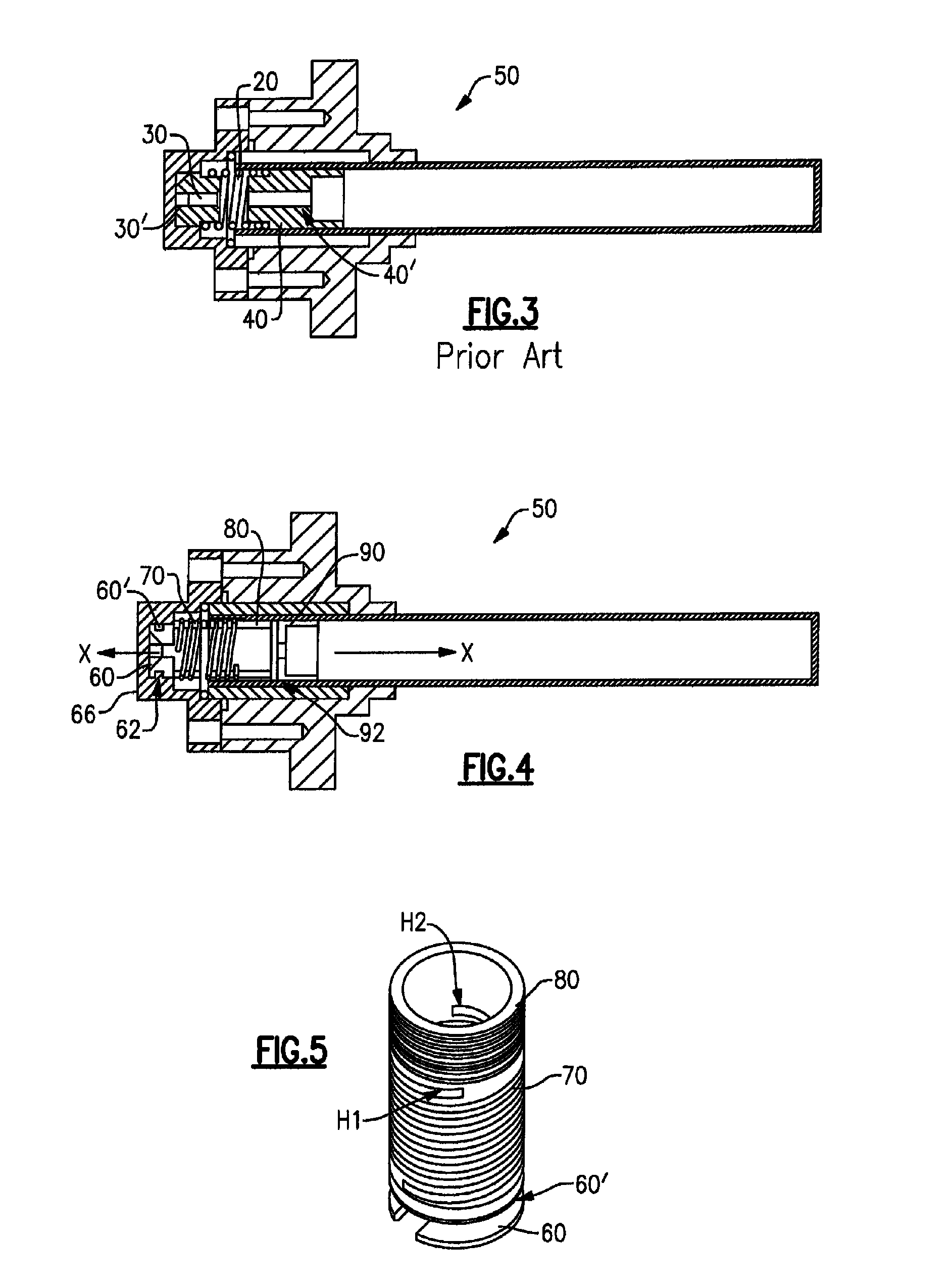
ActiveUS8127560B2Increased axial stabilityReduce debris generationSpringsCompression machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A retainer and spring with threaded end are machined from a single piece of material for threading to a piston in a closed cycle cryogenic cooler. Since the machined retainer and spring are a unitary part, they cannot rub against each other during operation of the piston which reduces debris generation. The spring is preferably formed as a double start helix which further increases axial stability and reduces side loading. The spring extends into an integrally formed, threaded end at the end thereof opposite the retainer.
Owner:COBHAM MISSION SYST DAVENPORT LSS INC
Video signal image processing method and device
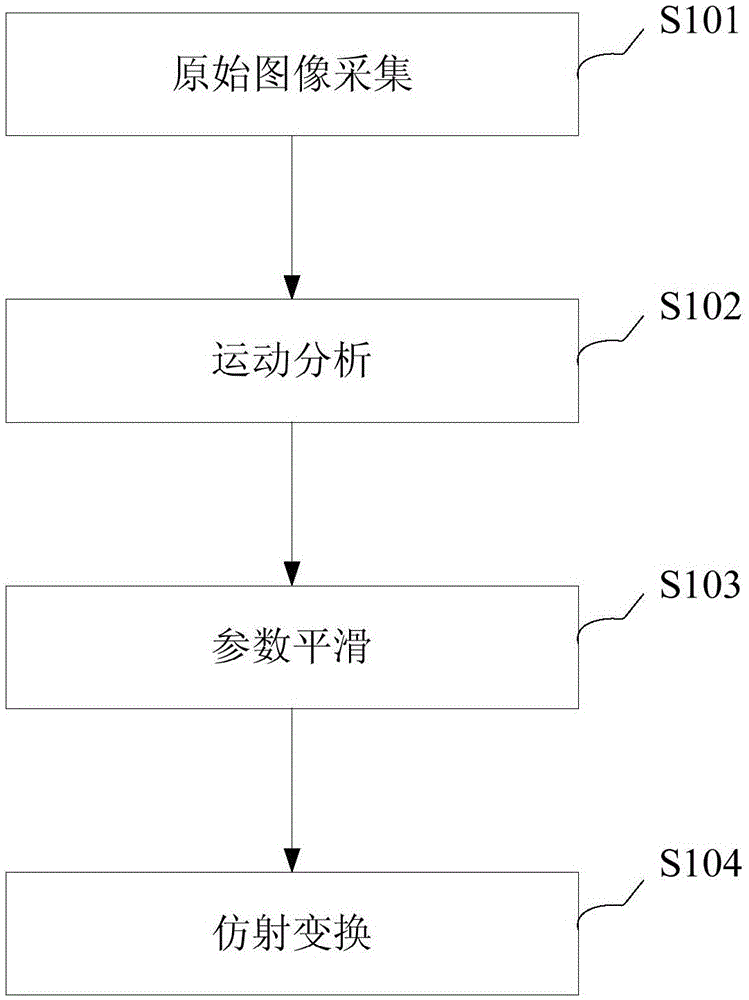
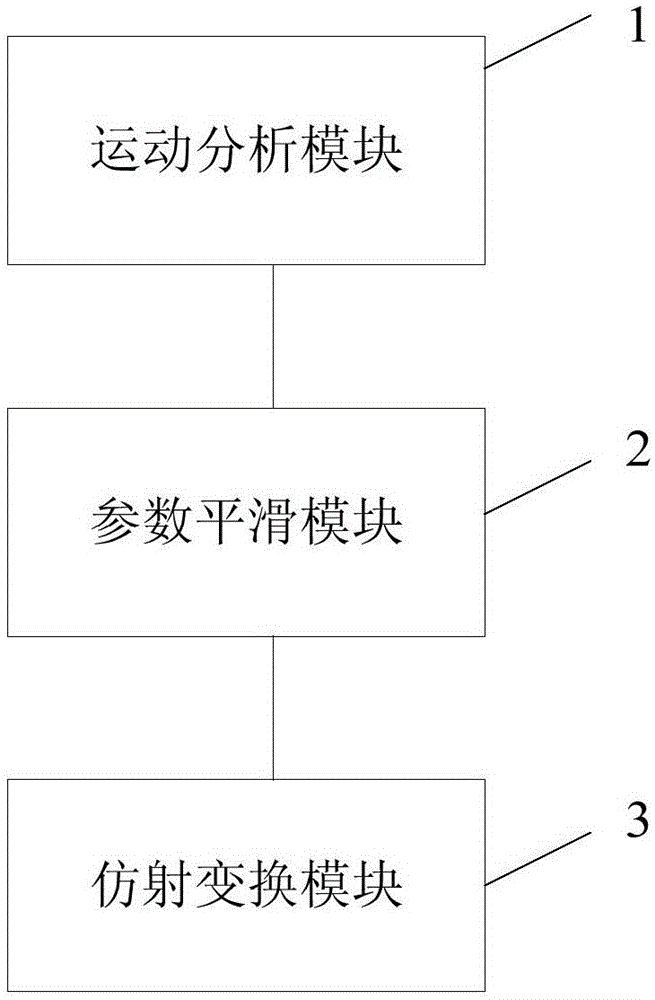
ActiveCN105141807AImprove qualityEliminate relative rotationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFeature extractionImaging processing
The invention provides a video signal image processing method and a device. The method comprises following steps of movement analysis including extracting characteristics of original image and calculating overall situation movement affine matrix among successive frames, wherein the overall situation movement affine matrix comprises movement parameters among the successive frames and the successive frames of the original image form the movement track of the original image; parameter smoothing including filtering the movement parameters among multiple successive frames, obtaining a movement parameter between the current frame and the previous frame after smoothing, and forming the movement track after the smoothing according to the movement parameter of the successive frames after the smoothing; and affine transformation including forming a new overall situation movement affine matrix and calculating the corresponding image of the current frame after the smoothing according to the movement parameter between the current frame and the previous frame after smoothing and the difference between the movement track of the original image and the movement track after smoothing. In this way, translation, rotation or shaking of overall movement of video images can be reduced or removed.
Owner:BEIJING AIRLANGO TECH CO LTD
Reciprocating saw with fastening device for a saw blade
InactiveUS7748125B2Quick changeSecure attachmentMetal sawing devicesSleeve/socket jointsKnife bladesEngineering
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Noninvasive birefringence compensated sensing polarimeter
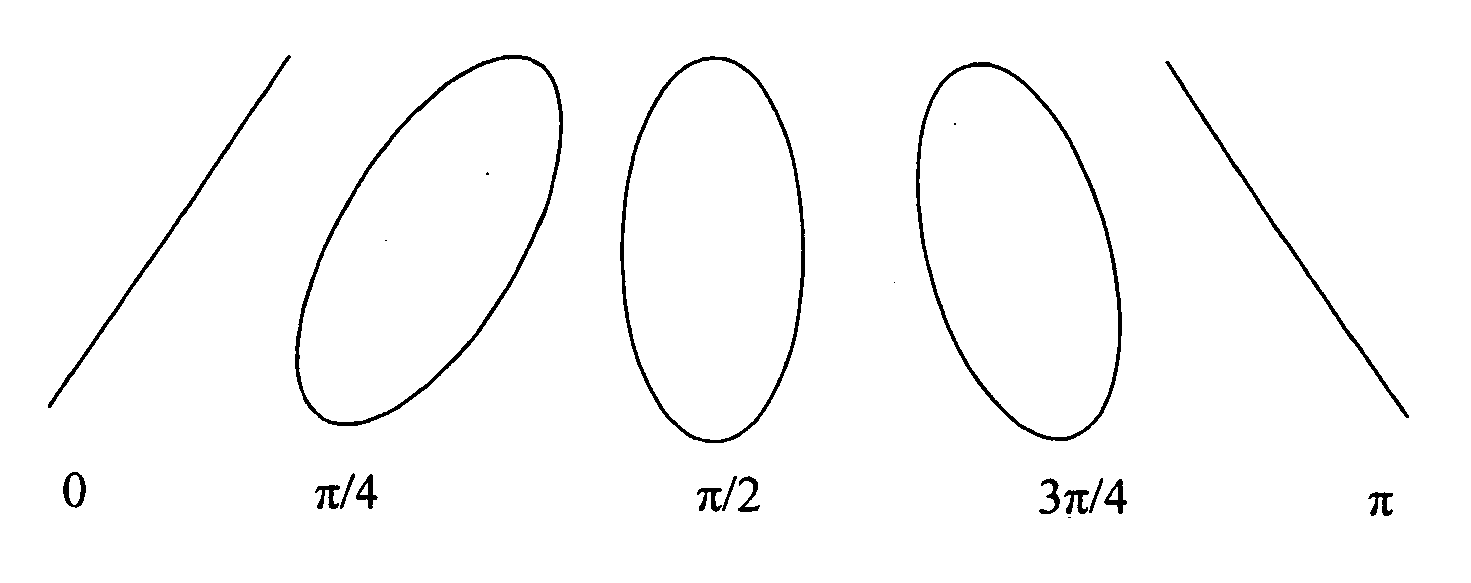
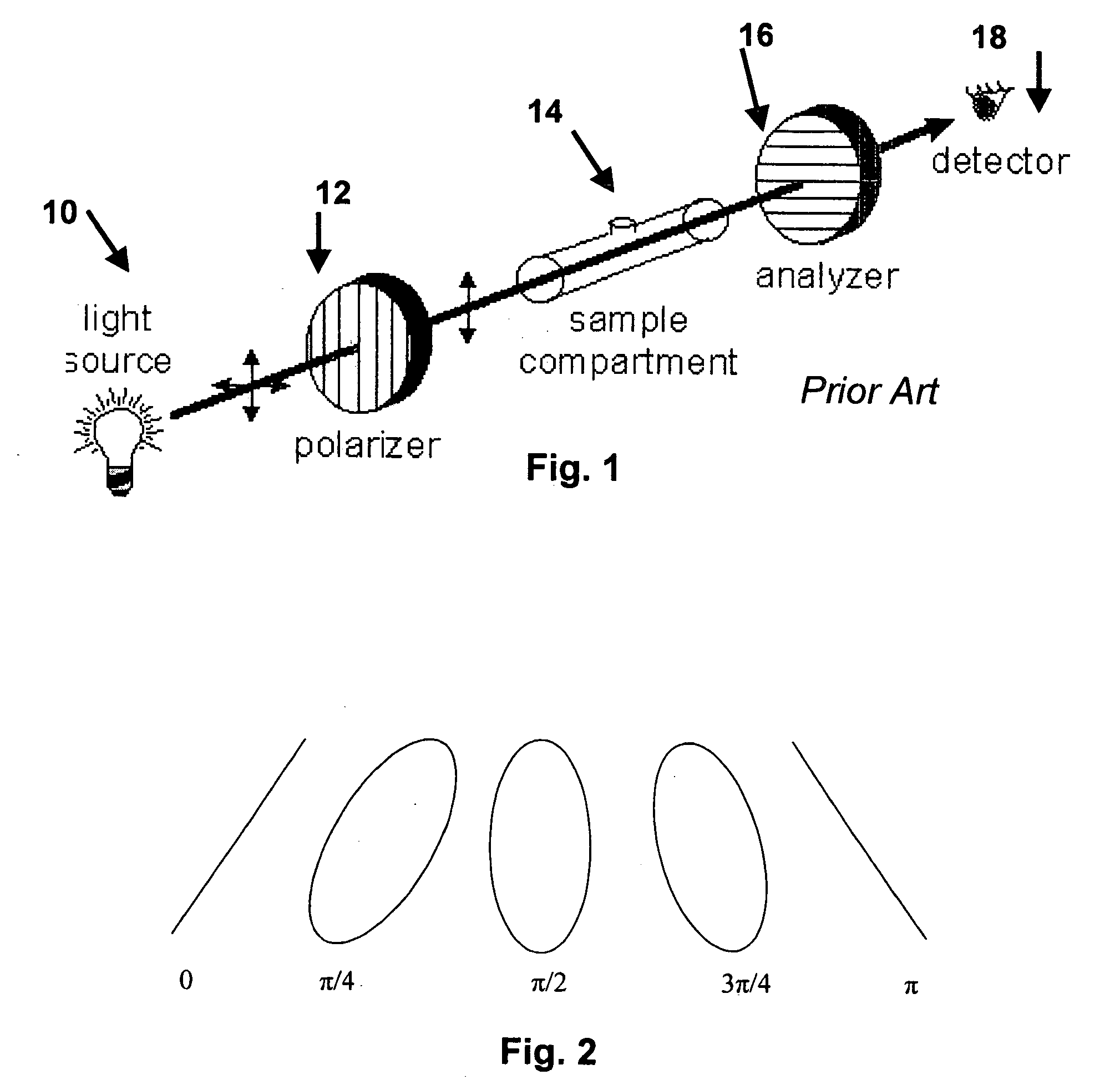
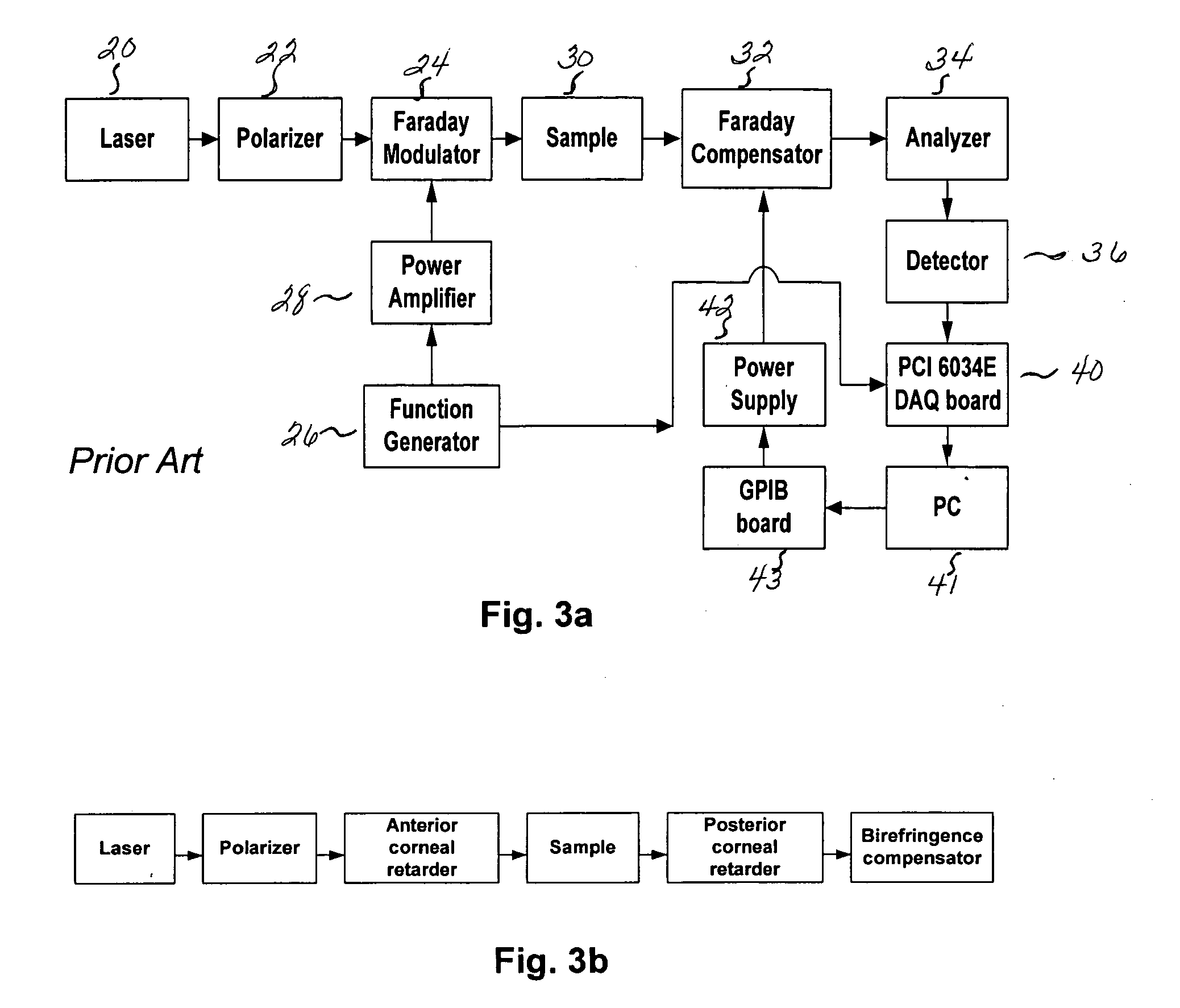
InactiveUS20050154269A1Minimize effectReducing main error componentDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringAnalyser
The present invention relates to a system and method for compensating for the effects of birefringence in a given sample and employs an optical birefringence analyzer to sense the real-time birefringence contributions and then provides a feedback signal to a compound electro-optical system that negates the birefringence contributions found in the given sample. The birefringence contribution vanishes, thus significantly reducing the main error component for polarimetric measurements.
Owner:TOLEDO UNIV OF
Mutual capacitance large panel phase shift mitigation
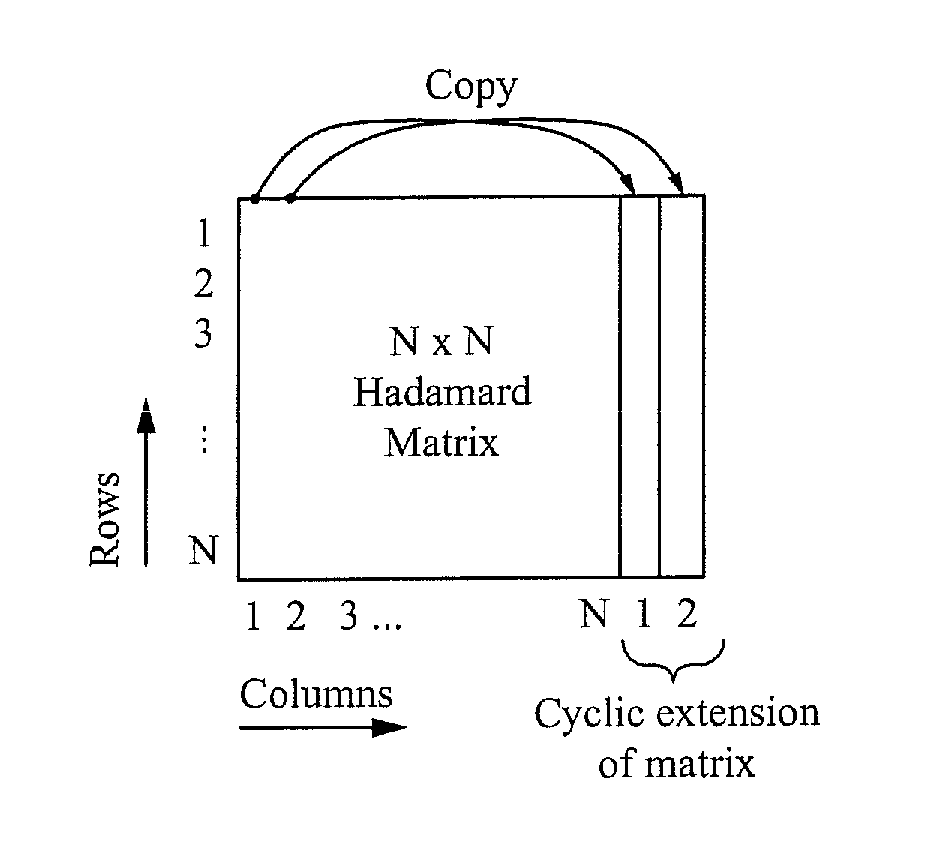
ActiveUS9235280B1Reduce areaReduce consumptionInput/output processes for data processingElectrical conductorPhase shifted
A method of mitigating a phase shift in a mutual capacitance touch screen panel having a plurality of row conductors intersecting with a plurality of column conductors to form a matrix of pixels, the method comprising: driving the row conductors with row drive signals formed from an excitation matrix, wherein each row in the excitation matrix is orthogonal to every other row in the excitation matrix, and the excitation matrix has a dimension larger than the matrix of pixels; sensing signals from the column conductors; and determining the mutual capacitance of the pixels using the sensed signals and an inverse of the excitation matrix. The excitation matrix can be a Hadamard matrix or a modified Hadamard matrix and can comprise a cyclic extension at the end of each row. A different region-specific phase shift can be applied to different clusters of signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Hopper car gate with a laterally opening door
Owner:AERO TRANSPORTATION PRODS
Feeding distributor with anti-eddy flow baffle plate
InactiveCN1843567AEliminate relative rotationEliminate entrainmentDispersed particle separationDistillation separationEngineeringTower
The invention provides a feeding distributor with anti-cyclone baffle plate, which comprises an inner muffle, a cover plate, a guide plate and an anti-cyclone baffle plate. Wherein, the guide plate is arranged between the tower wall and the inner muffle; the surface of guide plate that back to the inlet has a strengthen bar; the anti-cyclone baffle plate is arranged at the inner side of inner muffle whose side surface has a tie-bar; another end of tie-bar is fixed on the inner muffle; the cover plate is annular at the top of inner muffle whose one end is fixed on the tower wall and another end is fixed on the inner muffle; the baffle plate is used to resist the revolution of ascending airflow to reduce the entrainment on the liquid and distribute the ascending airflow. The invention has the advantages that: it can eliminate the airflow revolution caused by cyclone material feeding and eliminate the entrainment on the liquid drops, to avoid the non-uniformity of gas caused by the break of flow area and speed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
IBD Expandable Ti
InactiveUS20160074174A1Minimize the trauma of ALIFRelieve pressureBone implantSpinal implantsRange of motionEngineering
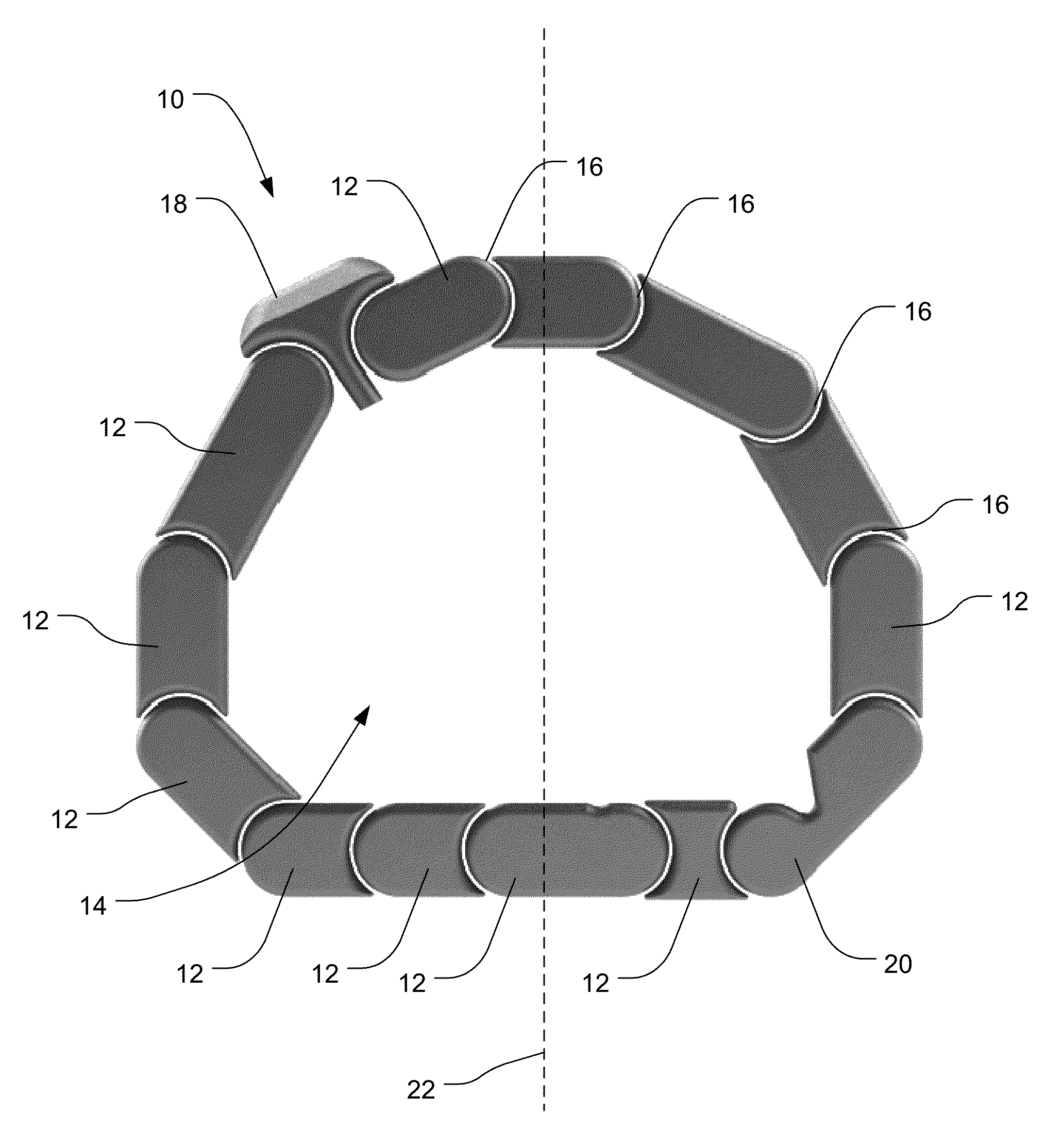
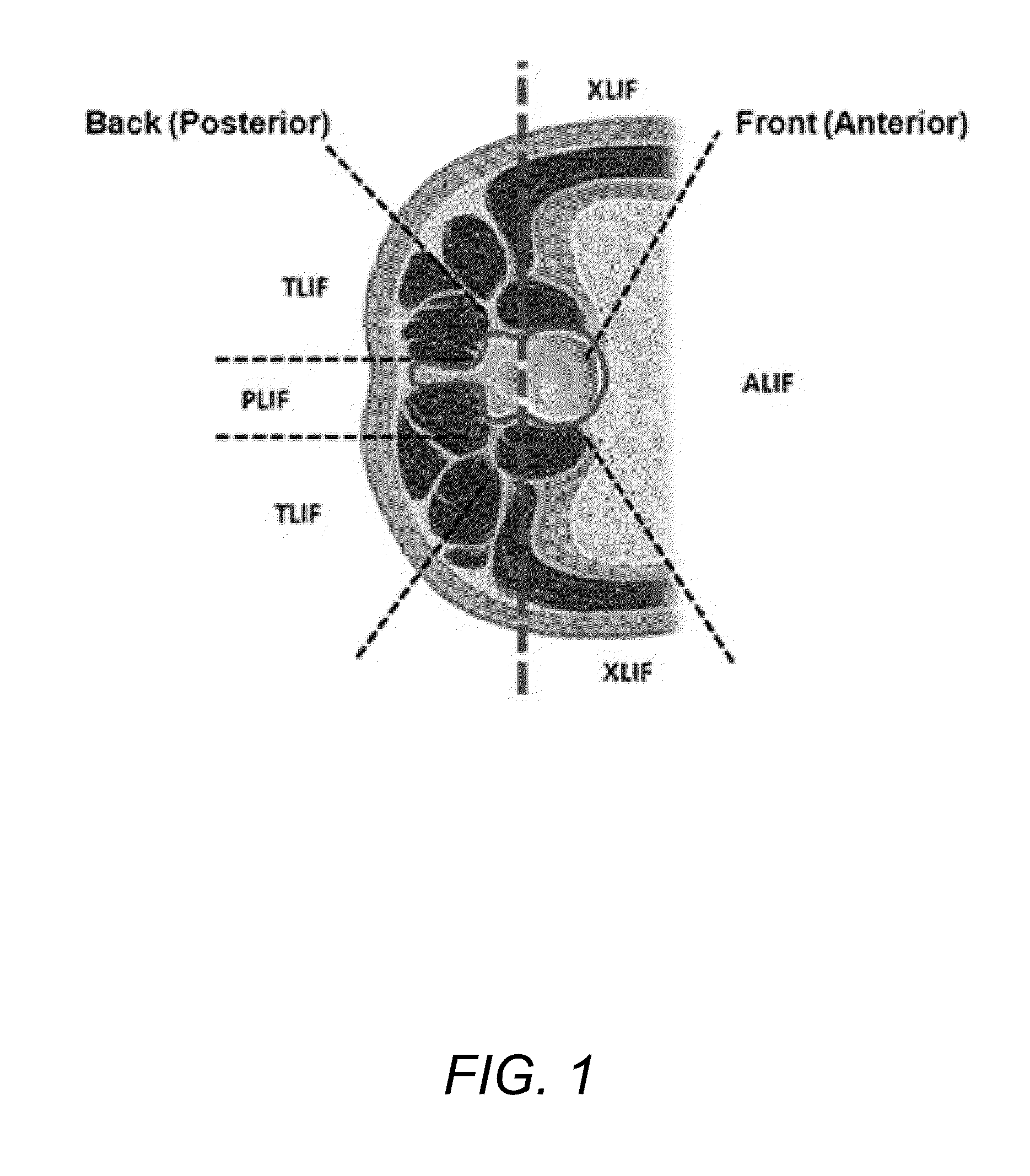
An expandable interbody spacer for use in spinal fusion procedures includes a plurality of rigid segments connected by flexible connections to form a ring encompassing and defining a hollow central area of variable dimensions. The flexible connections between the plurality of rigid segments may include flexible regions formed between the rigid segments or a continuous flexible member extending along a multisegmented region. The flexible regions formed between the rigid segments may be integrally formed with the rigid segments. One or more of the flexible regions formed between the rigid segments may include a plurality of flexure divisions extending between adjacent rigid segments. One or more of the flexible regions formed between the rigid segments may include a flexure extending between adjacent rigid segments. The rigid segments may include surfaces to limit the range of motion between adjoining rigid segments.
Owner:NEXUS SPINE L L C
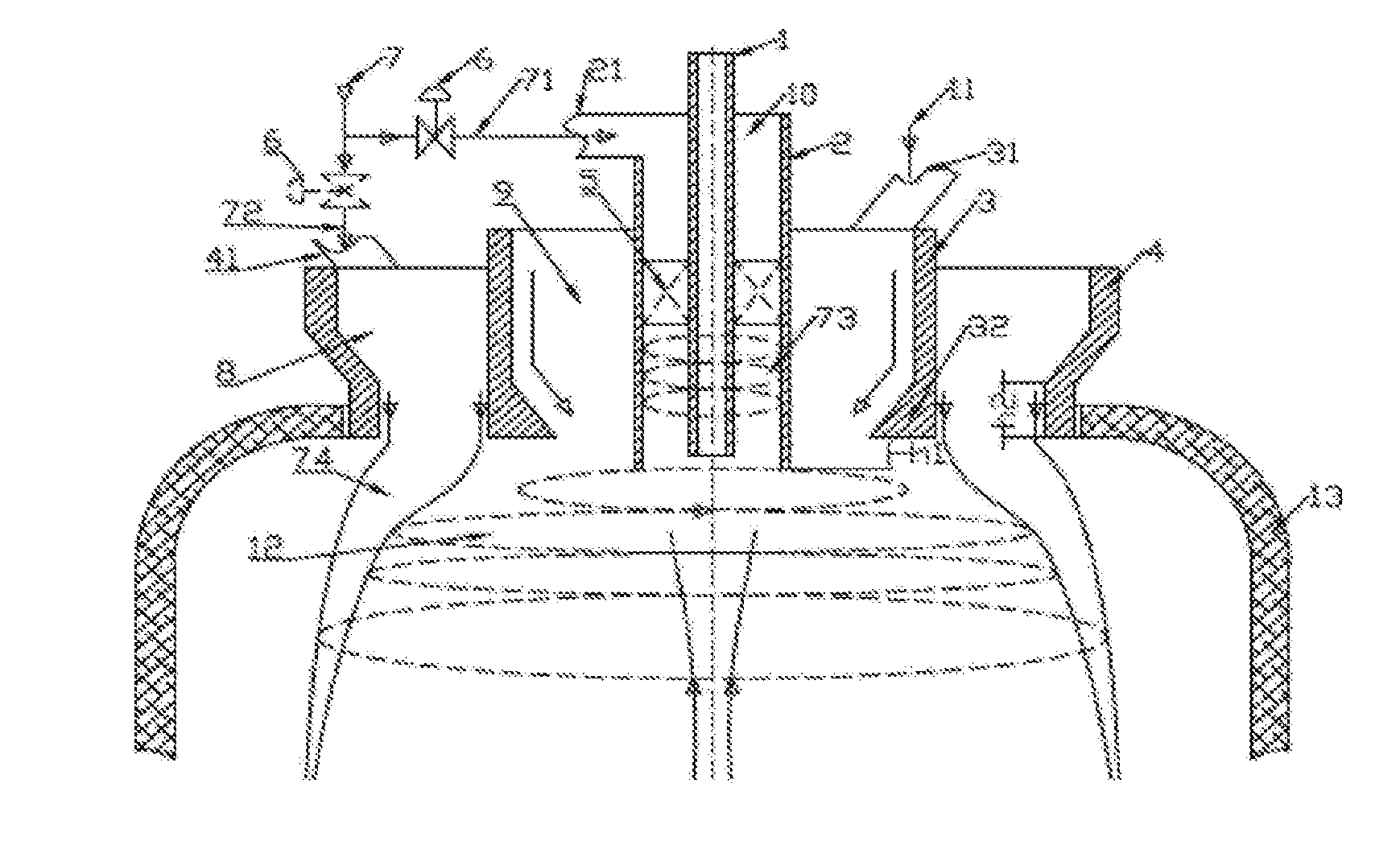
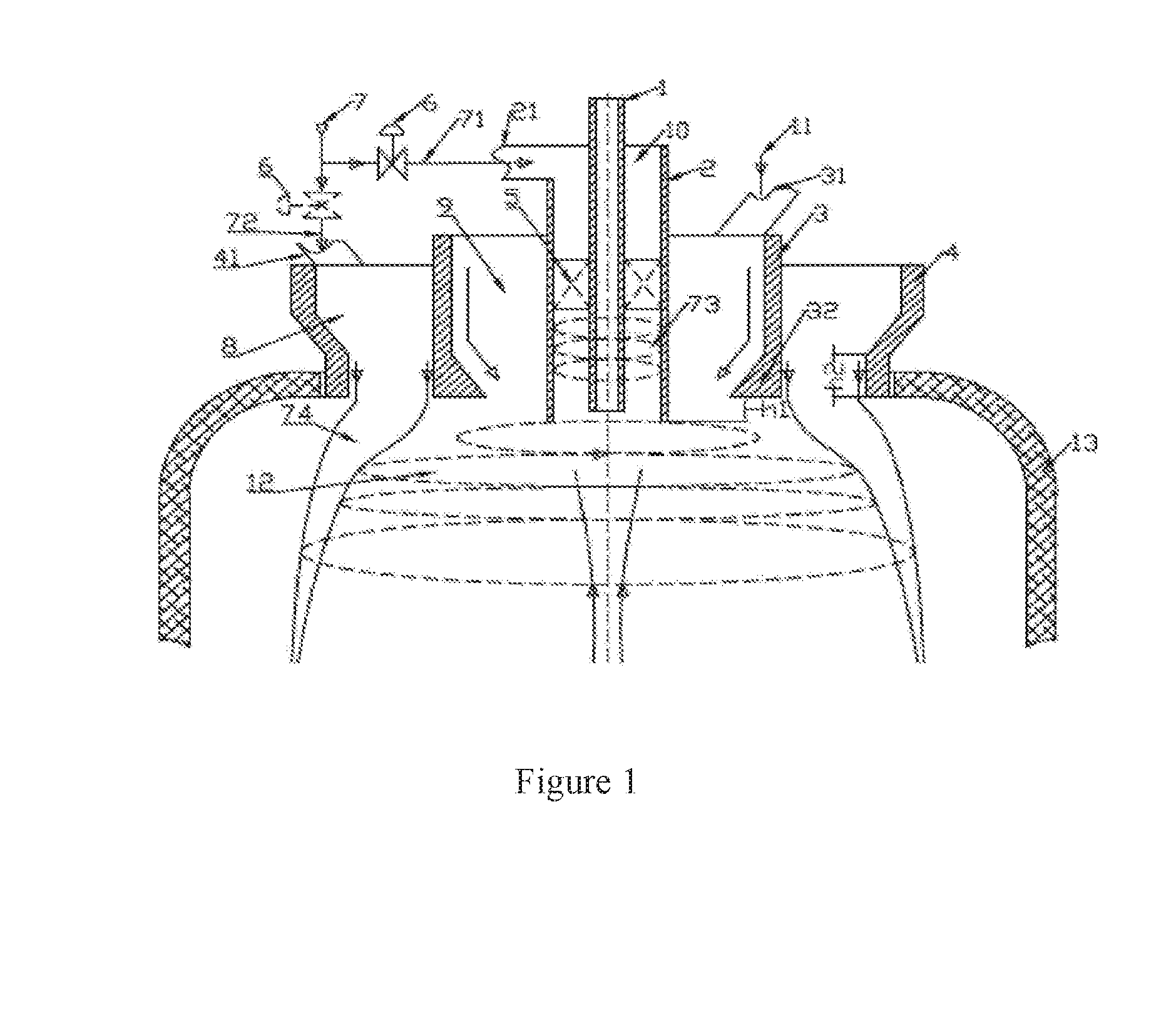
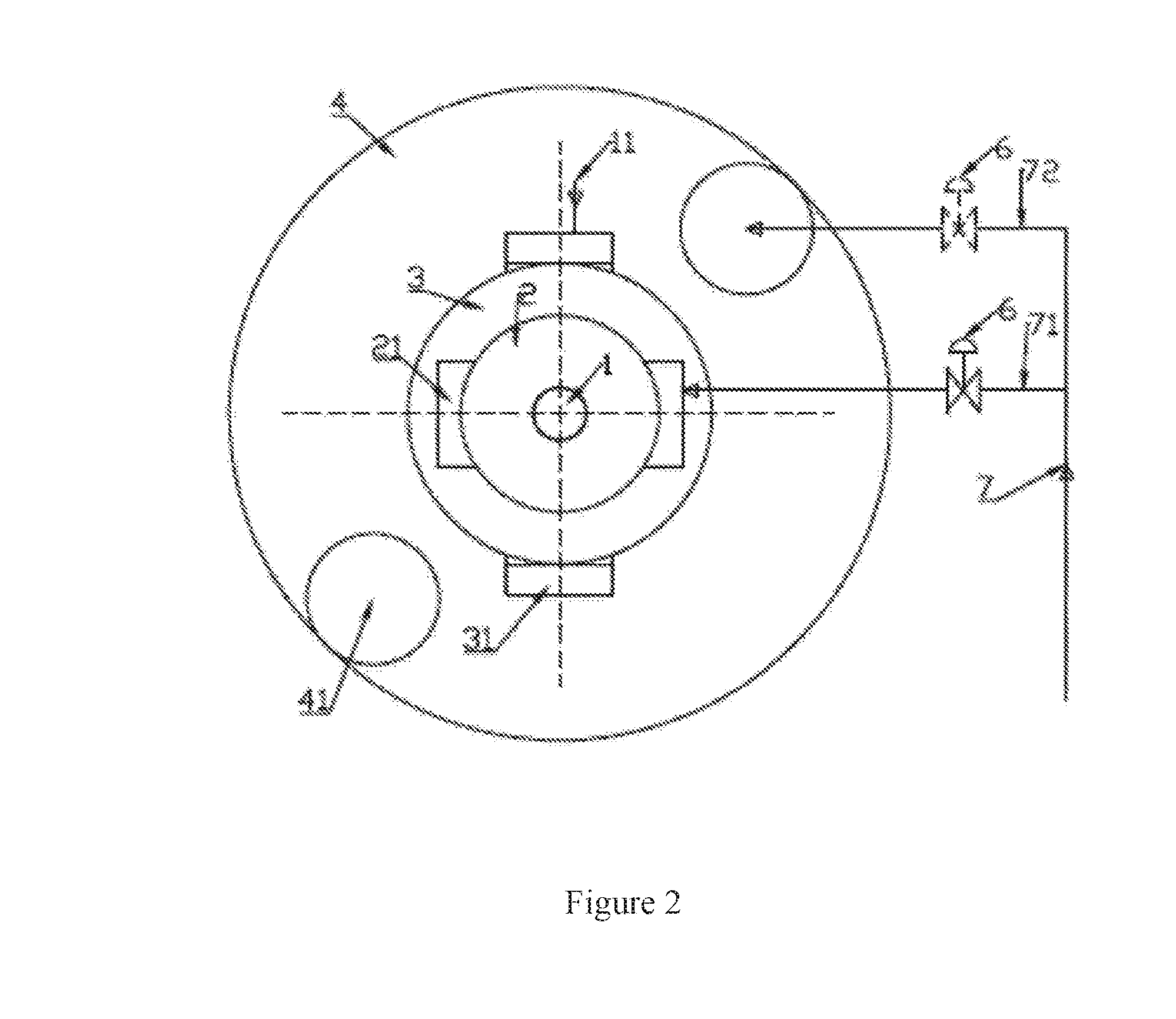
Turbofan or turbojet arrangement for vehicles, craft, aircraft and the like
InactiveUS20060054739A1Eliminate relative rotationReduce probabilityEngine manufactureJet type power plantsFlight vehicleTurbine
Owner:PEREZ FRANCISCO ANGEL +1
Micro mechanical acceleration sensitive structure for inhibiting crosstalk in high-precision single-shaft optical micro-accelerometer, and manufacturing method thereof
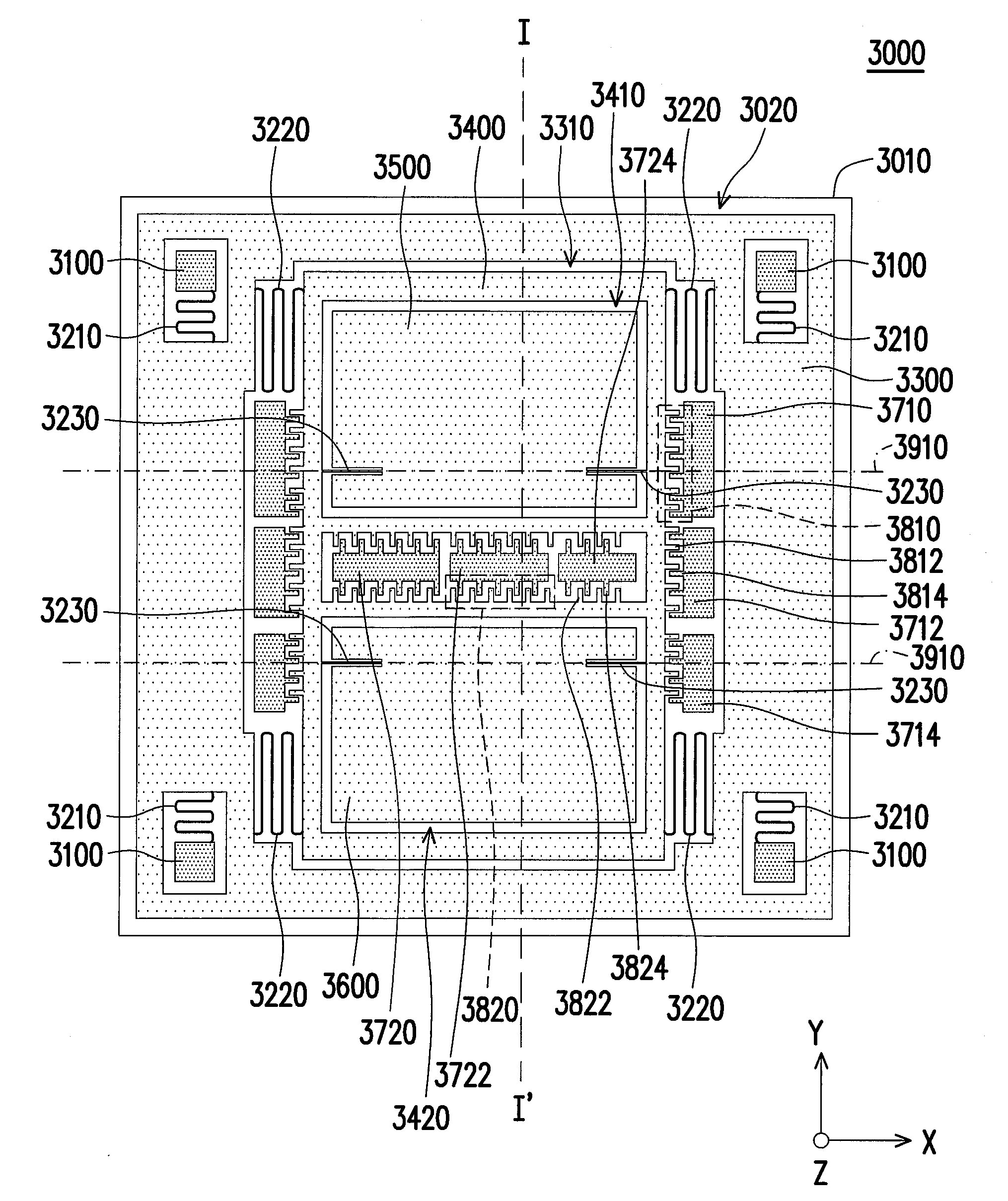
ActiveCN105372449ASuppresses Off-Axis CrosstalkLarge acceleration-displacement sensitivityAcceleration measurementSurface micromachiningCantilevered beam
The invention discloses a micro mechanical acceleration sensitive structure for inhibiting crosstalk in a high-precision single-shaft optical micro-accelerometer, and a manufacturing method thereof. The micro mechanical acceleration sensitive structure comprises a bulk silicon sensitive mass block, four symmetrically distributed crab-leg-shaped cantilever beams, a silicon substrate connected with the cantilever beams, and a reflective film plated on the surface of the sensitive mass block. It can be ensured that the gravity center of the sensitive mass block is disposed at a center plane of the cantilever beams through a specially designed microprocessing process, the direction of the sensitive shaft of the single-shaft optical micro-accelerometer is vertical to the center plane, and thus off-axis crosstalk is fundamentally inhibited through adjustment of the position of the gravity center; and the micro mechanical acceleration sensitive structure cooperates with the diffraction grating based optical micro-accelerometer so that the off-axis crosstalk can be effectively inhibited under the condition that the sensitivity of high-acceleration measurement is ensured, the applied surface microprocessing technology can be compatible with an IC technology, and batch manufacture is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Reciprocating saw with fastening device for a saw blade
InactiveUS20070151112A1Prevent movementEliminate time-consuming rotationMetal sawing devicesSleeve/socket jointsMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Hopper Car Gate with a Laterally Opening Door
ActiveUS20100107924A1Cargo carry capacity of be greatly increasedFacilitate dischargeHopper carsWagons/vansCar doorEngineering
Owner:AERO TRANSPORTATION PRODS
Three-degree-of-freedom integrated stick-slip linear positioning device
InactiveCN102506785ACompact structureReduce volumeNanostructure manufactureMeasurement devicesThree degrees of freedomEngineering
A three-degree-of-freedom integrated stick-slip linear positioning device relates to a positioning device and solves the problems that existing positioning devices are large in size, high in assembling error and low in positioning precision. The Three-degree-of-freedom integrated stick-slip linear positioning device comprises a bearing plate and a cap matched with a driving unit. The cap is fixedly connected to a surface of the bearing plate. The driving unit comprises a first press block, a second press block, an elastic driving base, a piezoelectric ceramic driver, a guide pillar, a contact, a shifting plate, a pretightened press plate and multiple balls, the upper end face of the piezoelectric ceramic driver is connected with the lower end face of the upper elastic plate of the elastic driving base, the lower end face of the piezoelectric ceramic driver is connected with the upper end face of the contact, the lower end face of the contact is connected with the upper end face of the shifting plate, the lower end face of the pretightened press plate is connected with the upper end face of a lower elastic plate of the elastic driving base, and two longitudinal ends of the shifting plate are disposed outside a square cavity of the elastic driving base and detachably connected with a base respectively. The three-degree-of-freedom integrated stick-slip linear positioning device is used for positioning articles.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Wet type multi-plate clutch
InactiveUS20060169567A1Relative rotationReduce part wearFluid actuated clutchesAutomatic clutchesClutchPiston
The present invention provides a wet type multi-plate clutch comprising a first friction engaging element coaxially arranged within a clutch housing, a second friction engaging element alternately disposed with the first friction engaging element and a piston for applying an axial load to engage the first and second friction engaging elements with each other and wherein a projection protruding toward the piston is provided on the clutch housing and a recessed portion is provided in the piston so that a relative rotation between the clutch housing and the piston is prevented by engaging the projection with the recessed portion.
Owner:COTTRELL +1
Image matching method based on corner point and single-line segment marshalling feature description operator
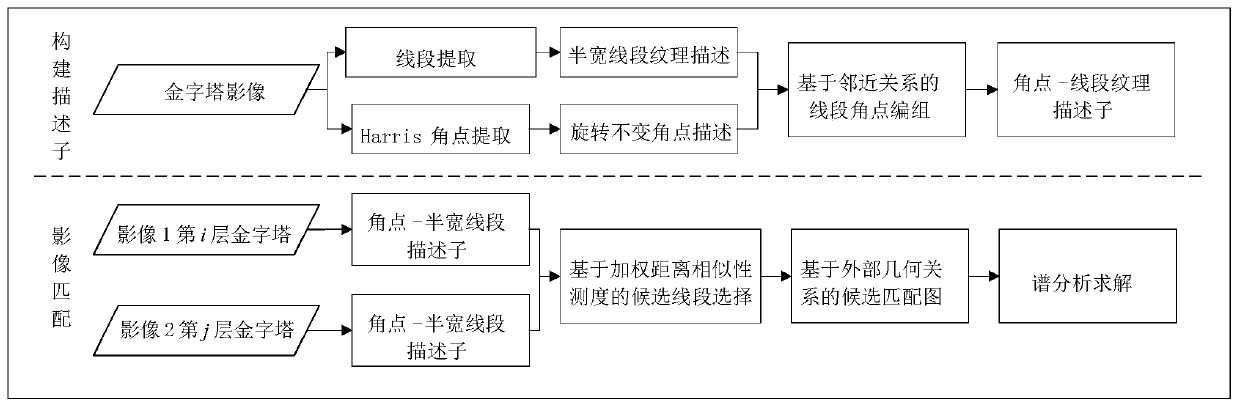
ActiveCN110490913AReduce time complexitySmooth rotationImage analysisShortest distanceRotational invariance
The invention discloses an image matching method based on a corner point and single-line segment marshalling feature description operator. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, extractingline segments and Harris corner points from an image; constructing a line segment, searching and grouping the line segment, constructing an angular point-single line segment texture descriptor with scale, rotation and illumination invariance by using a detected angular point and the line segment, the Harris angular point having the advantage of rotation invariance, and the line segment adopting ahalf-width descriptor can improve the reliability in a parallax change scene; performing spatial weighted shortest distance measurement to obtain a local matching result; finally, determining the candidate matching of each line segment, establishing a matching matrix and solving a global matching result through spectral analysis. The image matching description operator has the characteristics ofscale, rotation and illumination invariance. According to the invention, image pyramids are respectively established for three-dimensional images. The pyramids on different layers are matched one byone, so that the scale influence can be eliminated. The defects of large marshalling calculation amount and long consumed time in multi-line-segment matching can be overcome.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Snap-hook tether
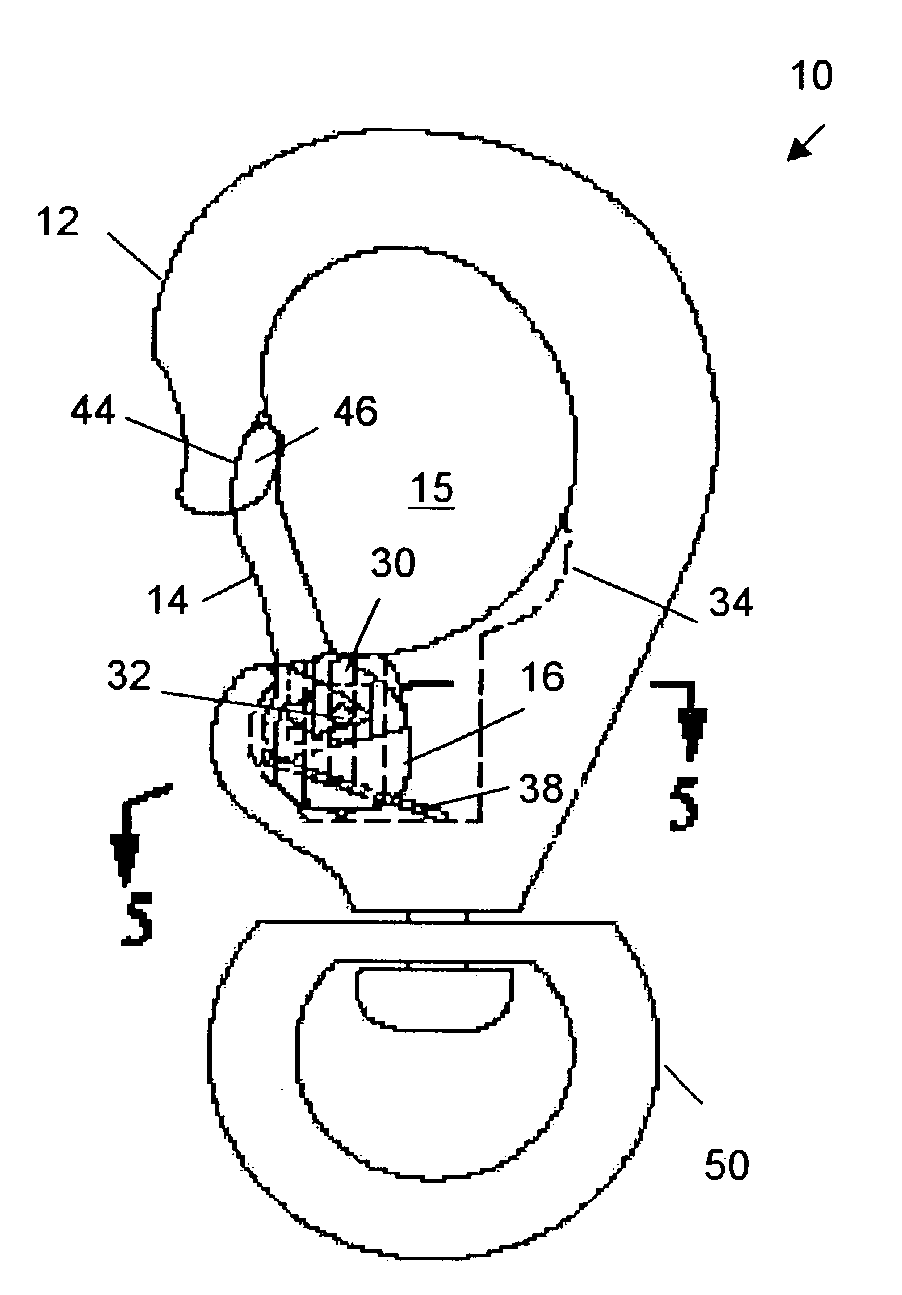
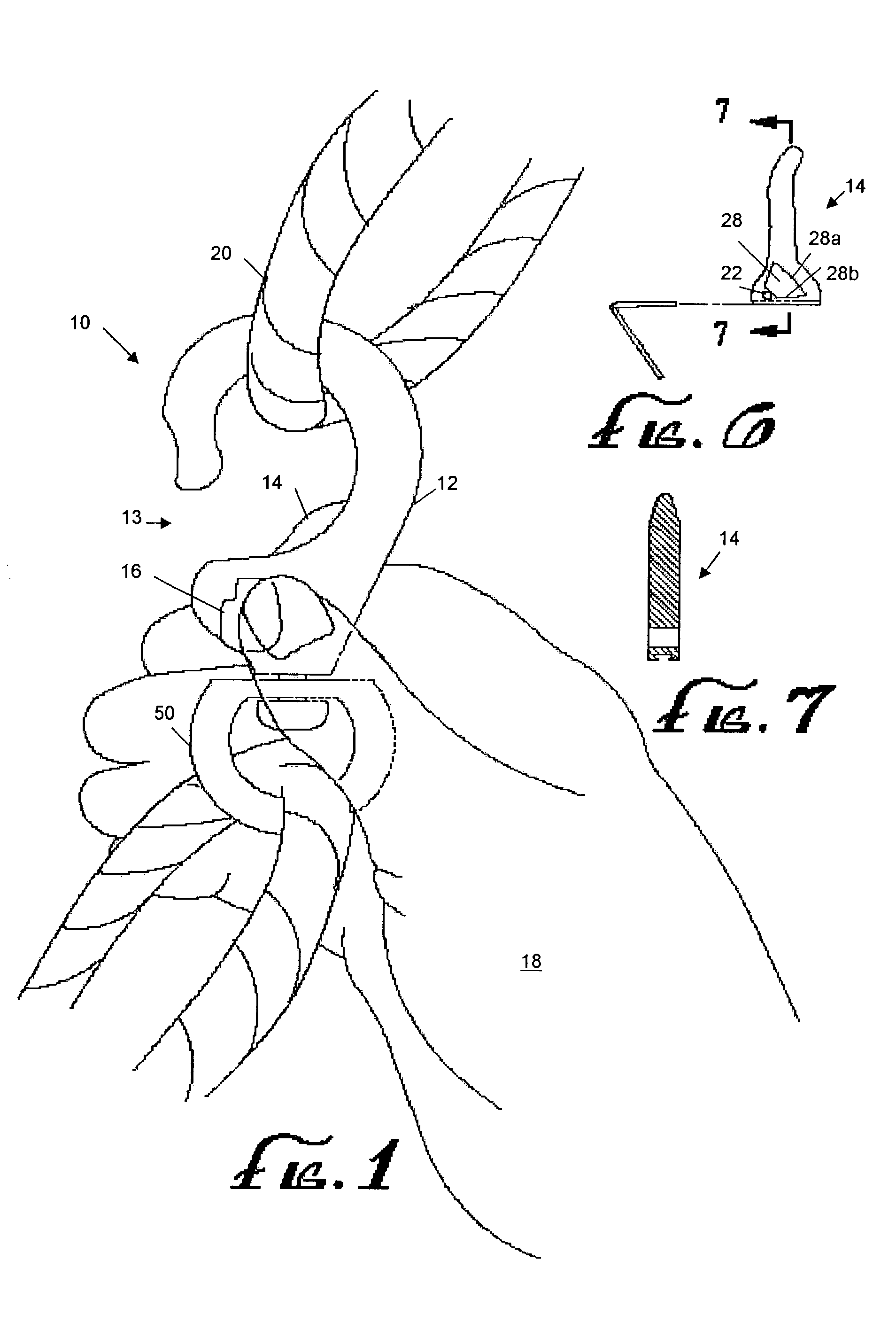
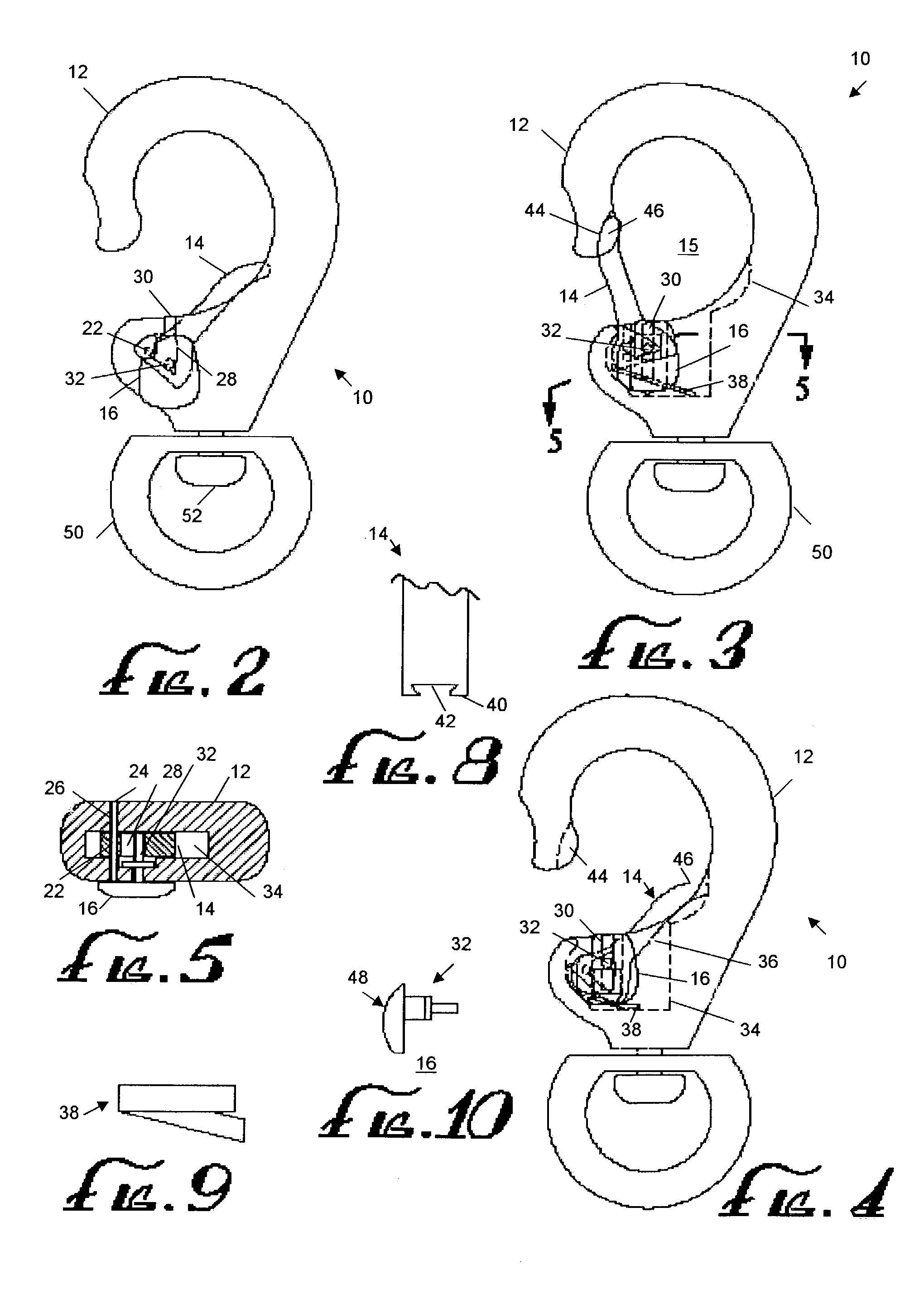
InactiveUS7093330B2Simple holdingEliminate relative rotationHook fastenersEye fastenersMechanical engineeringThumb
Owner:FERGUSON THOMAS
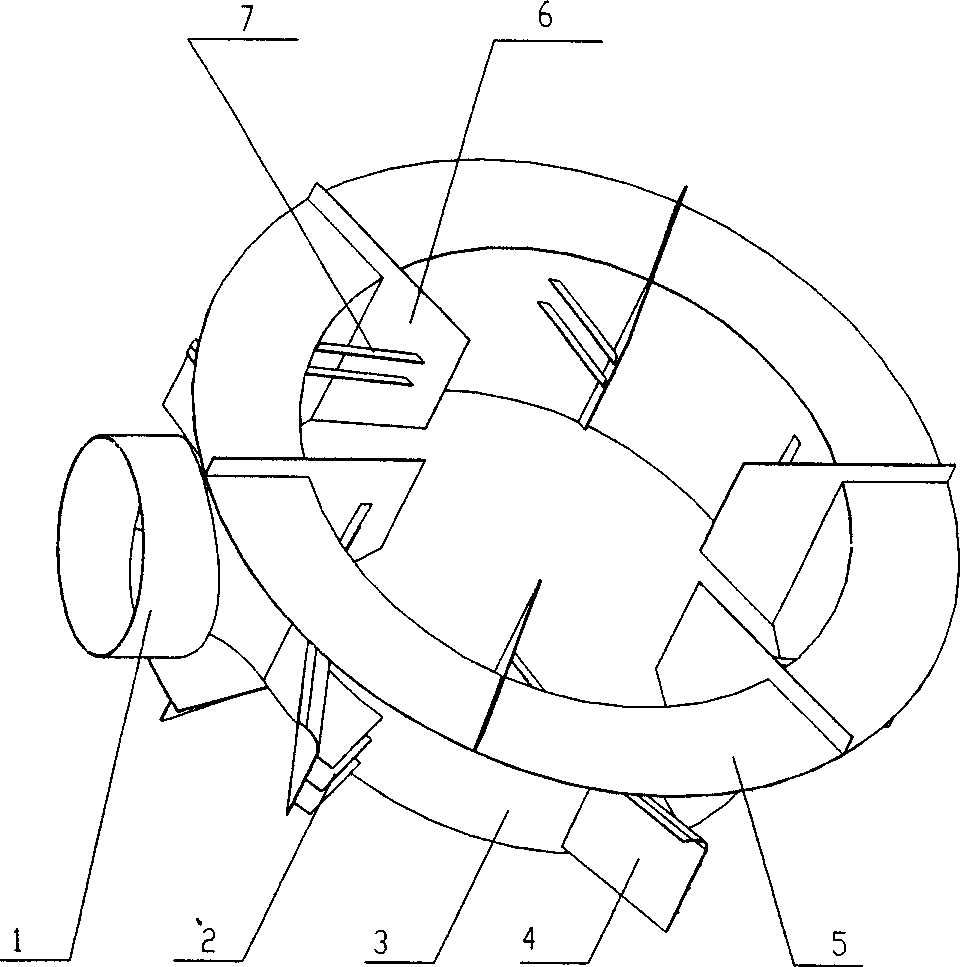
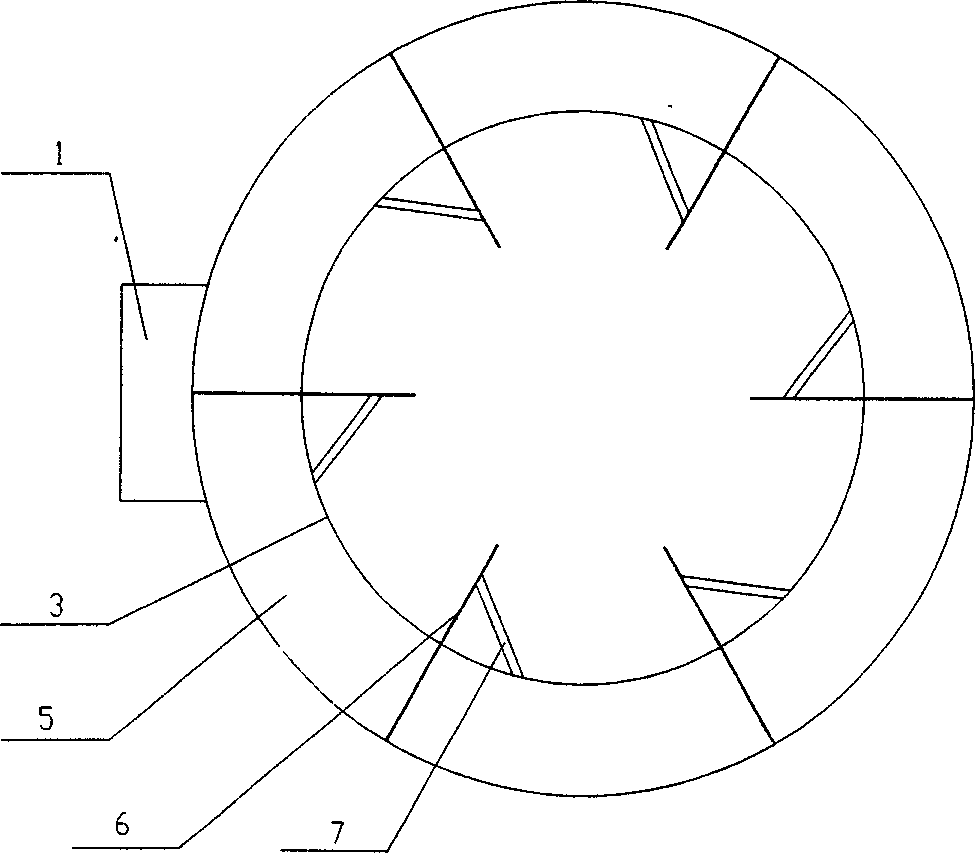
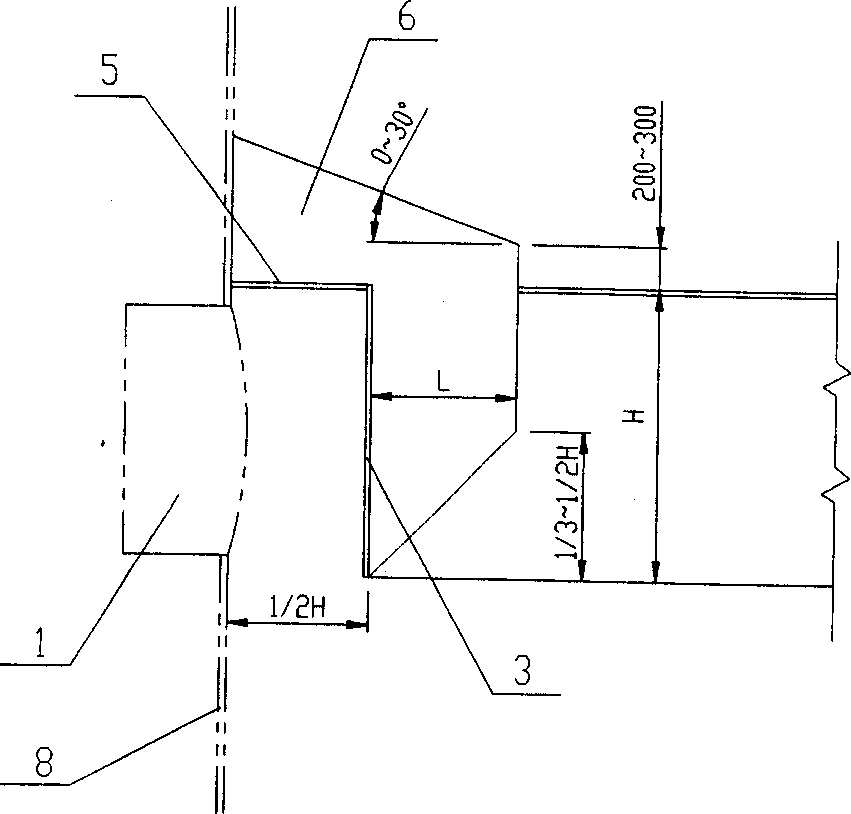
Centrifugal compressor for an exhaust gas turbocharger
ActiveCN103671265AIncrease air flow rateSmall gap widthPump componentsEngine fuctionsInlet channelTurbocharger
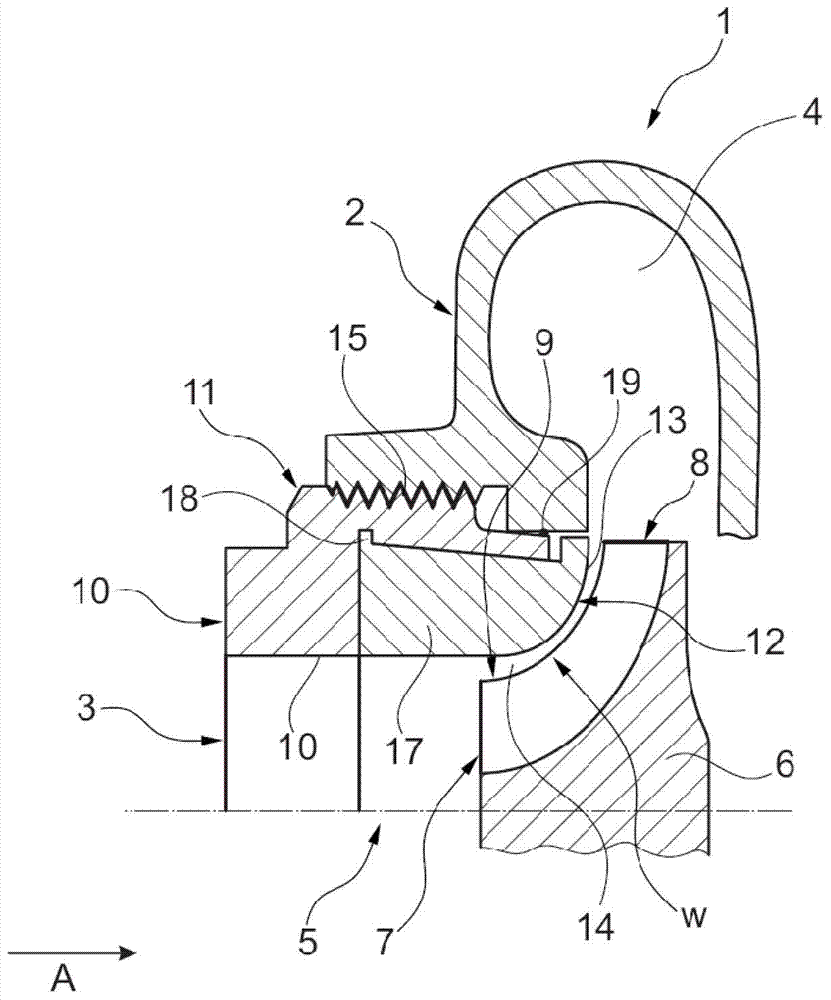
The invention relates to a centrifugal compressor (1) for an exhaust gas turbocharger, in particular an internal combustion engine. The centrifugal compressor has a compressor housing (2) comprising an axial inlet channel (3) and a centrifugal outlet channel (4); with a compressor impeller (6) for circulating and compressing a gas, wherein the compressor impeller (6) has an axial inlet side (7) facing towards an inlet passage (3), a centrifugal outlet side (8) facing an outlet channel (4), and an axial wheel surface contour (9) extending from the inlet side (7) extends up to the outlet side (8); a substantially sleeve-like adapter element (10) which may be axially inserted into an attachment portion (11) disposed at the compressor housing (2); wherein the adapter element (10) comprises, at least in sections, a surface contour (13) which is attached to the axial wheel surface contour (9), such that a gap width (W) between the adapter element (10) and the compressor impeller (6) can be adjusted along mutually facing surface contours (9, 13) through axial movement of the adapter member (10) in a fastening portion (11).
Owner:BMTS TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
Serpentine metal gasket
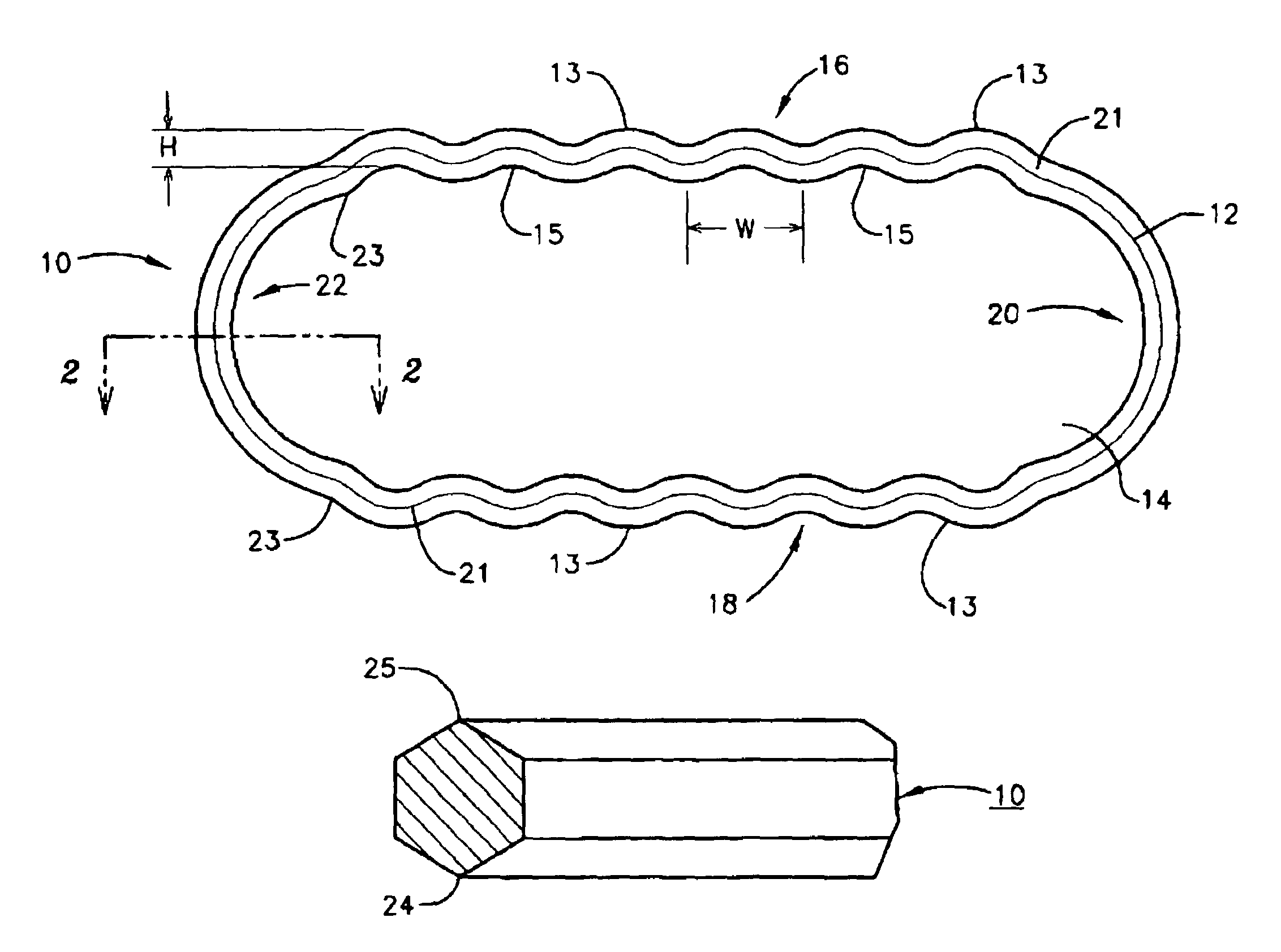
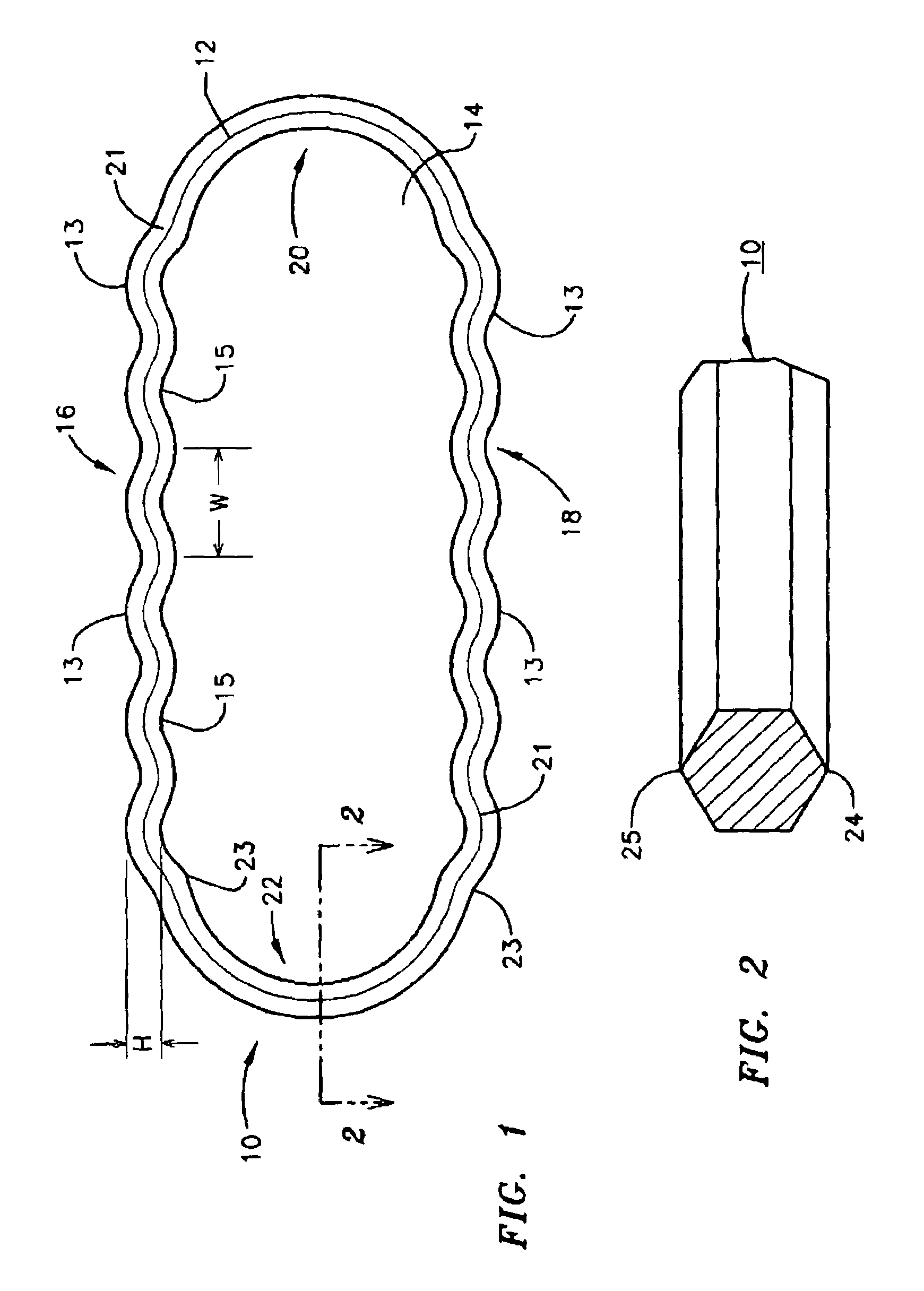
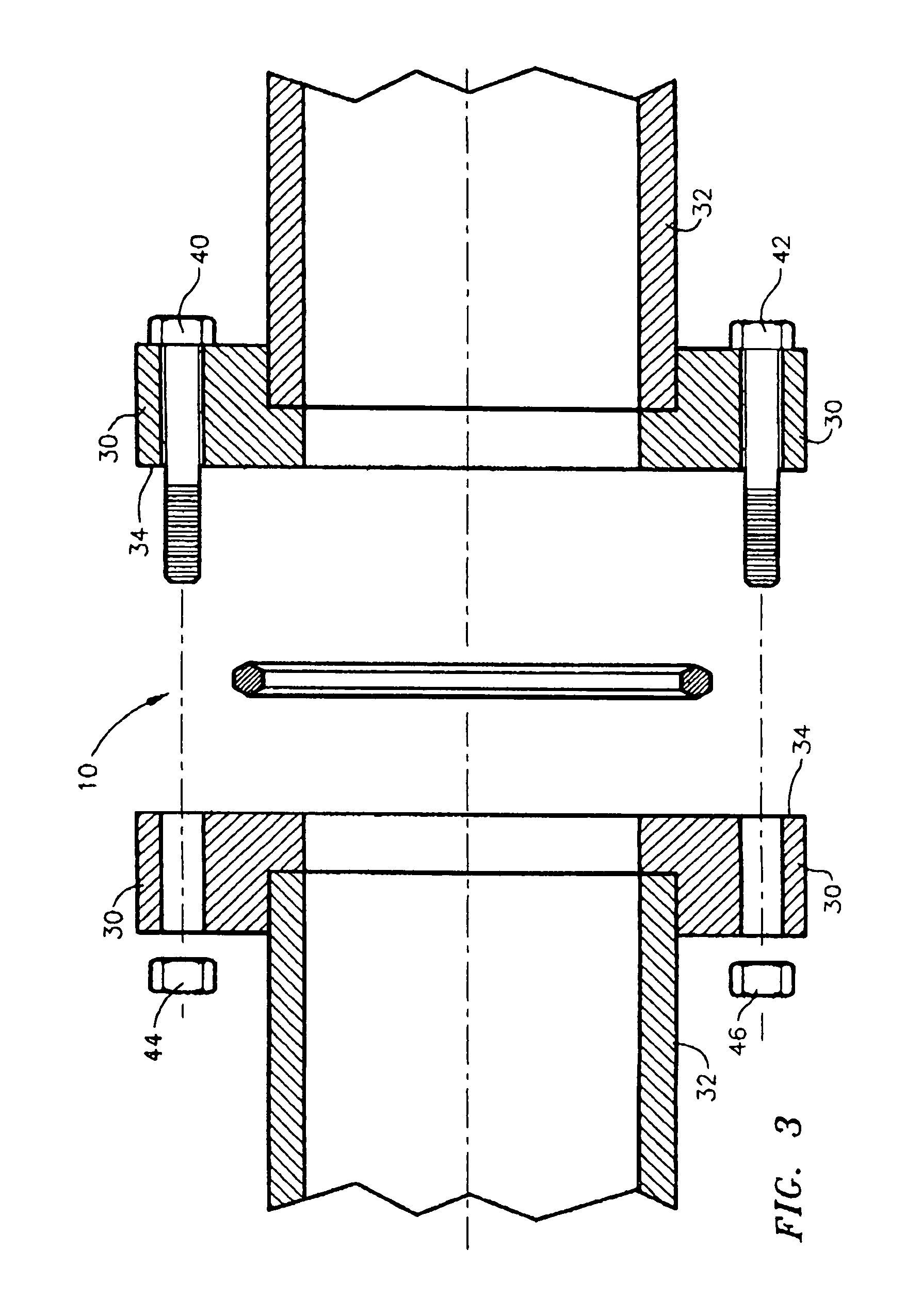
InactiveUS7540502B1Removal costEliminate relative rotationSleeve/socket jointsEngine sealsEngineeringGuide tube
A metallic seal or gasket for use in the joining of cryogenic fluid conduits, the seal or gasket having a generally planar and serpentine periphery defining a central aperture. According to a preferred embodiment, the periphery has at least two opposing elongated serpentine sides and two opposing arcuate ends joining the opposing elongated serpentine sides and is of a hexagonal cross-section.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
Apparatus and method for detecting imbalance in washing machines
InactiveCN1448577AReduce in quantityReduce the number of assembly stepsStatic/dynamic balance measurementOther washing machinesEngineeringWater tanks
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To obtain a device and a method for detecting an unbalance of a washing machine which reduce the number of components, simplify the structure and moreover enable stop of the rotation of a washing and dewatering tub corresponding to the amount of the unbalance, only when it is needed.SOLUTION: The washing and dewatering tub provided with a rotating blade at the bottom is disposed rotatably in a water tank 3 suspended and supported swingably in an outer box 1. In the washing machine having this constitution, the device for detecting the unbalance is disposed between the outer box 1 and the water tank 3 and fitted to a unit case 16 of a power supply unit disposed in the outer box 1.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
Tool Holding Apparatus
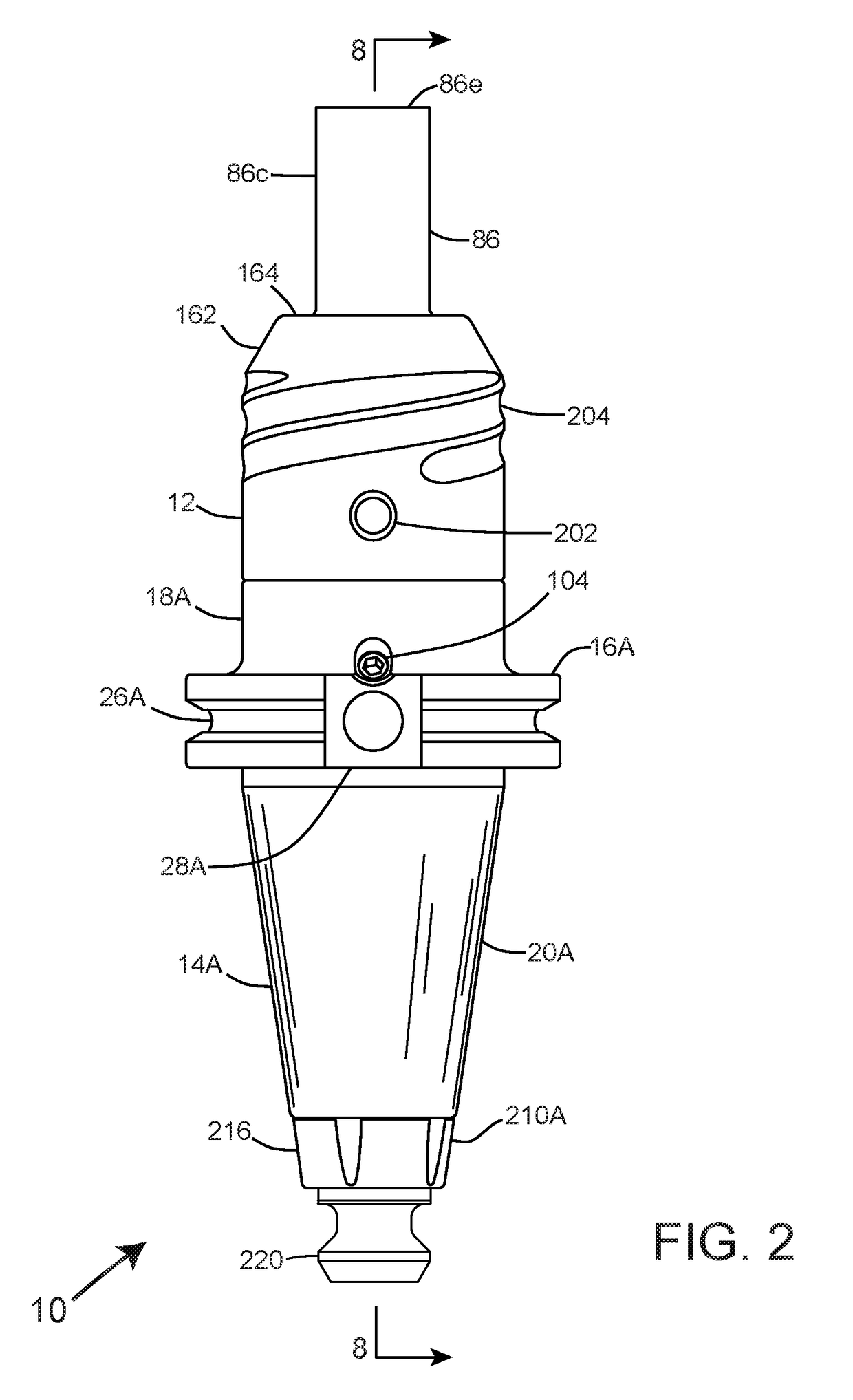
InactiveUS20180141132A1Improve accuracyReduce precisionSleeve/socket jointsMilling cuttersEngineeringScrew thread
A tool holding apparatus for interfacing a machine spindle receiver of a milling machine, which includes a holder nose connected to a holder body configured with a first divided section integrally connecting to a second divided section and a centralized axial bore for housing therewithin a tension bolt, a lock nut, and a thrust nut. The holder nose includes an axial bore incorporating a reverse-tapered configuration and three flat sectors to correspond with an equally configured shaft portion of a tool, whereupon the threaded attachment of the thrust nut to the holder nose furthers a locking arrangement of the tool within the axial bore to prevent inadvertent axial and rotational movement thereof during aggressive milling operations.
Owner:BERG CHARLES MICHAEL
Grinding machine spindle end mechanism
InactiveCN101269477AReduce splashImprove working environmentGrinding machine componentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a main shaft end apparatus of a grinding machine, which belongs to the technical field of a machining device. The apparatus comprises a taper body arranged at a main shaft end, a taper sleeve which is used for arranging a grinding wheel and provided with a taper hole in the middle and a screw tooth on the external circumference, and a compression nut. The main shaft end apparatus of the grinding machine is characterized in that the apparatus also comprises a holding disc and a screw; a screw hole is arranged in the middle of the holding disc; a pair of sleeve keys is arranged on the inner end face of the holding disc; a pair of shaft keys is arranged on the outer end face of the holding disc; correspondingly, sleeve key grooves used for the sleeve keys to be inserted are arranged on the outer end face at one side of the holding disc facing to the taper sleeve, and shaft key grooves used for the shaft keys to be inserted are arranged on the outer end face at one side of the holding disc facing to the taper body; after passing through the screw hole in the middle of the holding disc, and the screw is rotationally fixed with the screw hole arranged at the center of the taper hole. The main shaft end apparatus of the grinding machine has the advantages that the grinding wheel on the taper sleeve is ensured to be always in a compressed state, the splashing of abrasive particle is reduced through changing the rotation direction of the main shaft when complex workpieces are processed, thereby improving the working condition.
Owner:PACIFIC TEXTILE MACHINERY CHANGSHU CO LTD
Rotation-suspension smelting method, a burner and a metallurgical equipment
ActiveUS20160237522A1Avoid hard collisionPrevent outward expansionPulverulent fuel combustion burnersProcess efficiency improvementCombustorSulfidation
The invention provides a rotation-suspension smelting method, in which a powdered sulfide concentrate and an oxygen-containing gas are sprayed into a space within a high-temperature reaction tower through an equipment. The oxygen-containing gas is divided into two parts before entering the equipment: the second oxygen-containing gas is sprayed in the form of an annular direct flow into the reaction tower and forms a bell-shaped wind curtain; and the first oxygen-containing gas is transformed into a rotation-jet via the equipment and jetted into the center of the wind curtain. In the annular space between the two gas flows, the concentrate entering in a direction deviated towards the center is drawn in the rotation-jet, and a high-temperature off-gas from the bottom of the reaction tower is also sucked in, forming a gas-particle mixed two-phase rotation-jet. The sulfide concentrate is ignited by the high temperature, namely, starting a violent combustion reaction with oxygen and releasing SO2-rich off-gas, at the same time, a mixed melt containing matte (or metal) and slag is formed; and the matte (or metal) is finally separated from the slag at the bottom of the reaction tower, thereby completing the metallurgical process. To achieve the process object, the invention also provides a metallurgical equipment and a rotation-suspension smelting burner thereof.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com