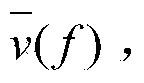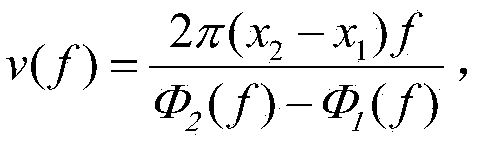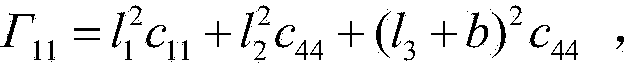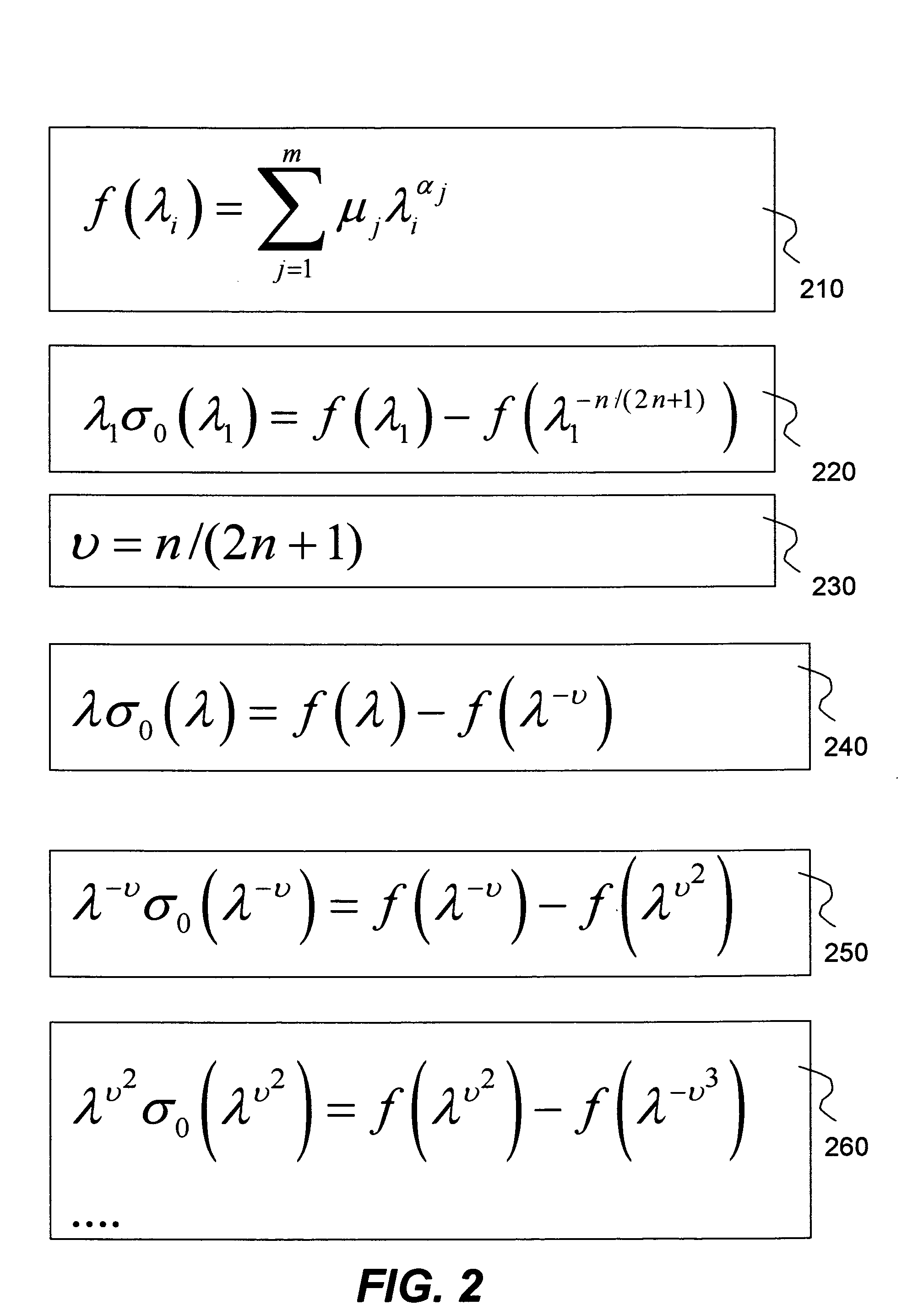Patents
Literature
108 results about "Bi-isotropic material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
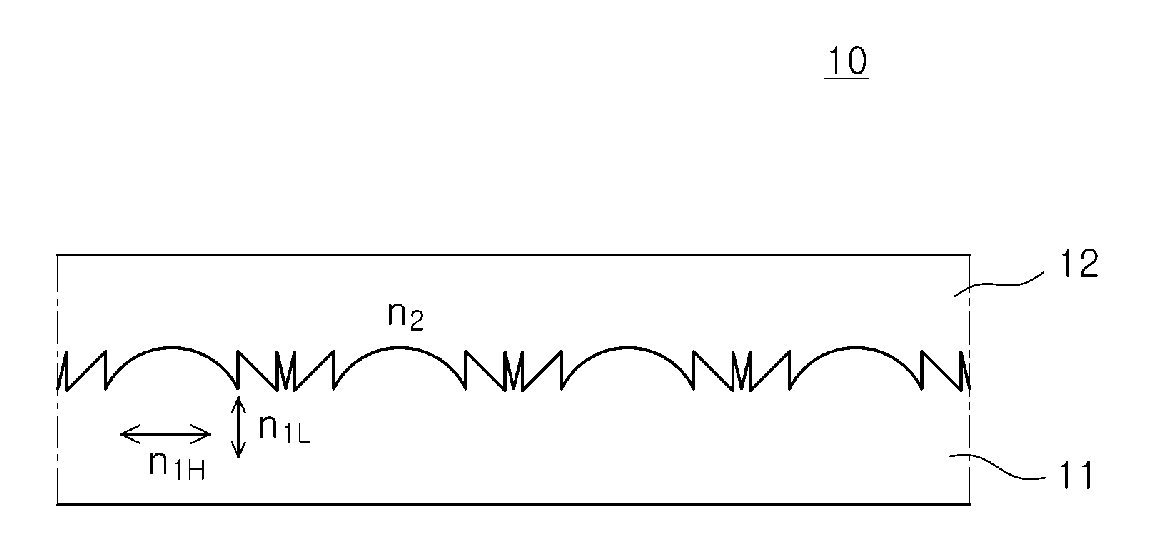
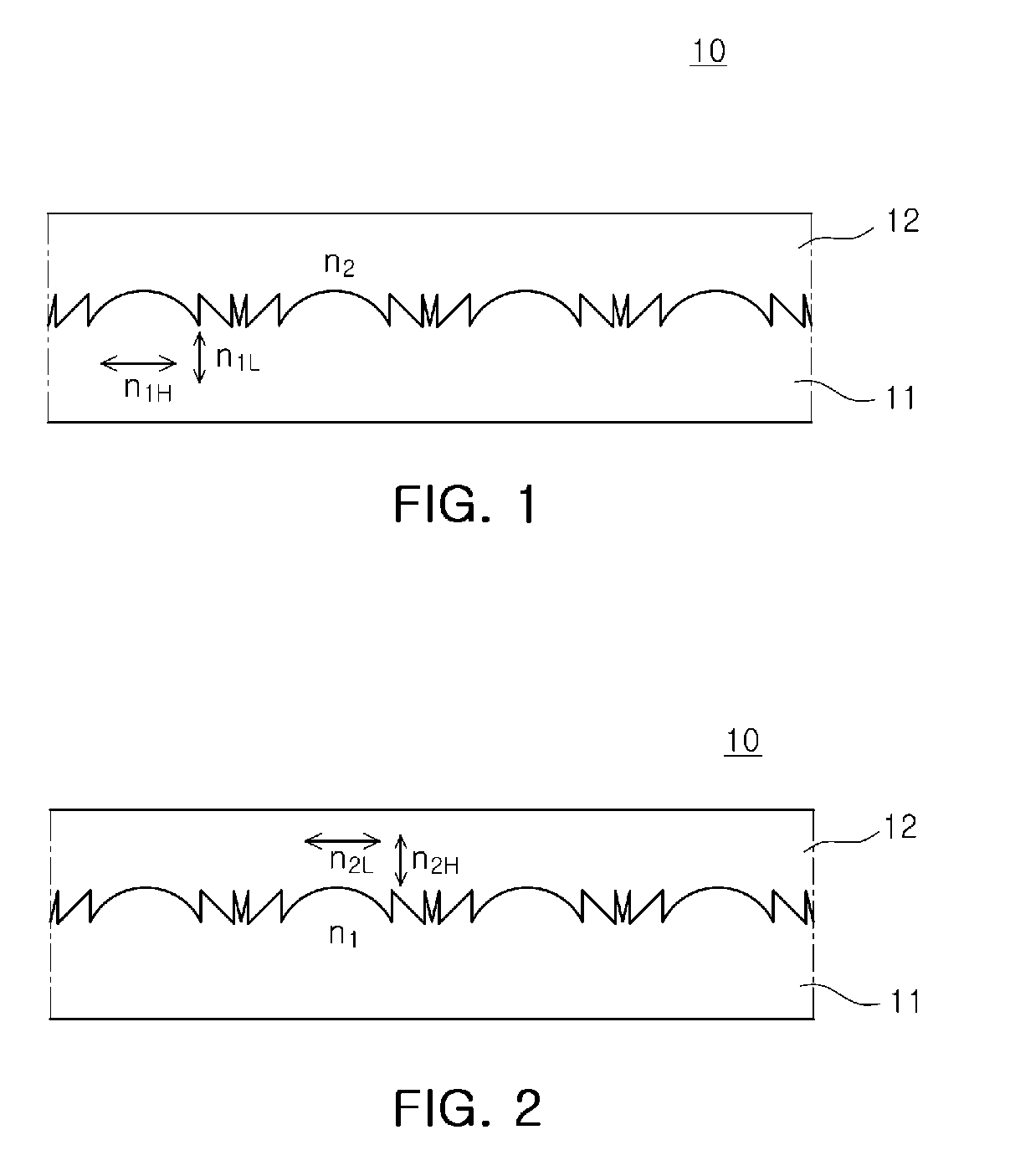
In physics, engineering and materials science, bi-isotropic materials have the special optical property that they can rotate the polarization of light in either refraction or transmission. This does not mean all materials with twist effect fall in the bi-isotropic class. The twist effect of the class of bi-isotropic materials is caused by the chirality and non-reciprocity of the structure of the media, in which the electric and magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave (or simply, light) interact in an unusual way.
Birefringent reflectors using isotropic materials and form birefringence
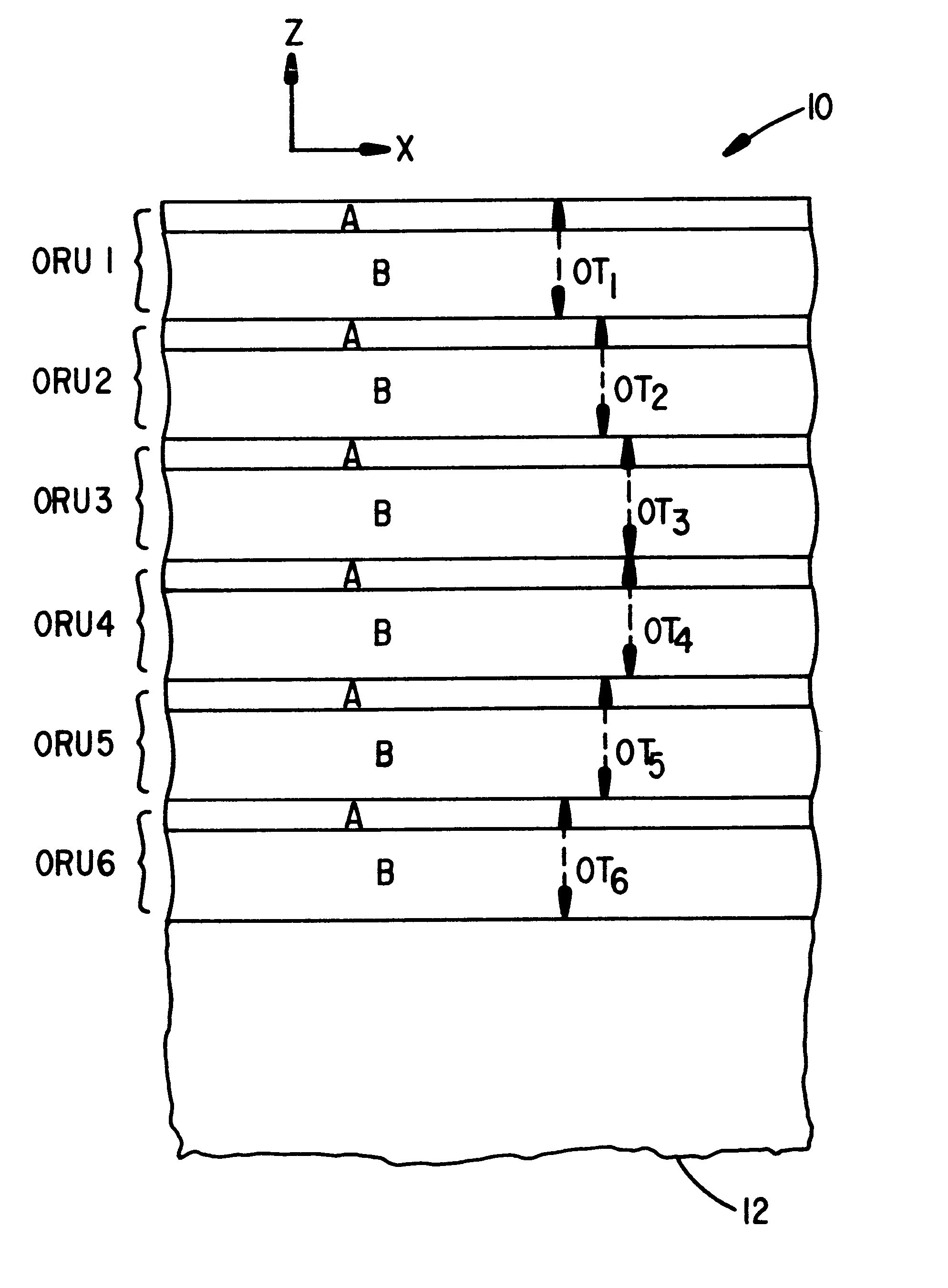
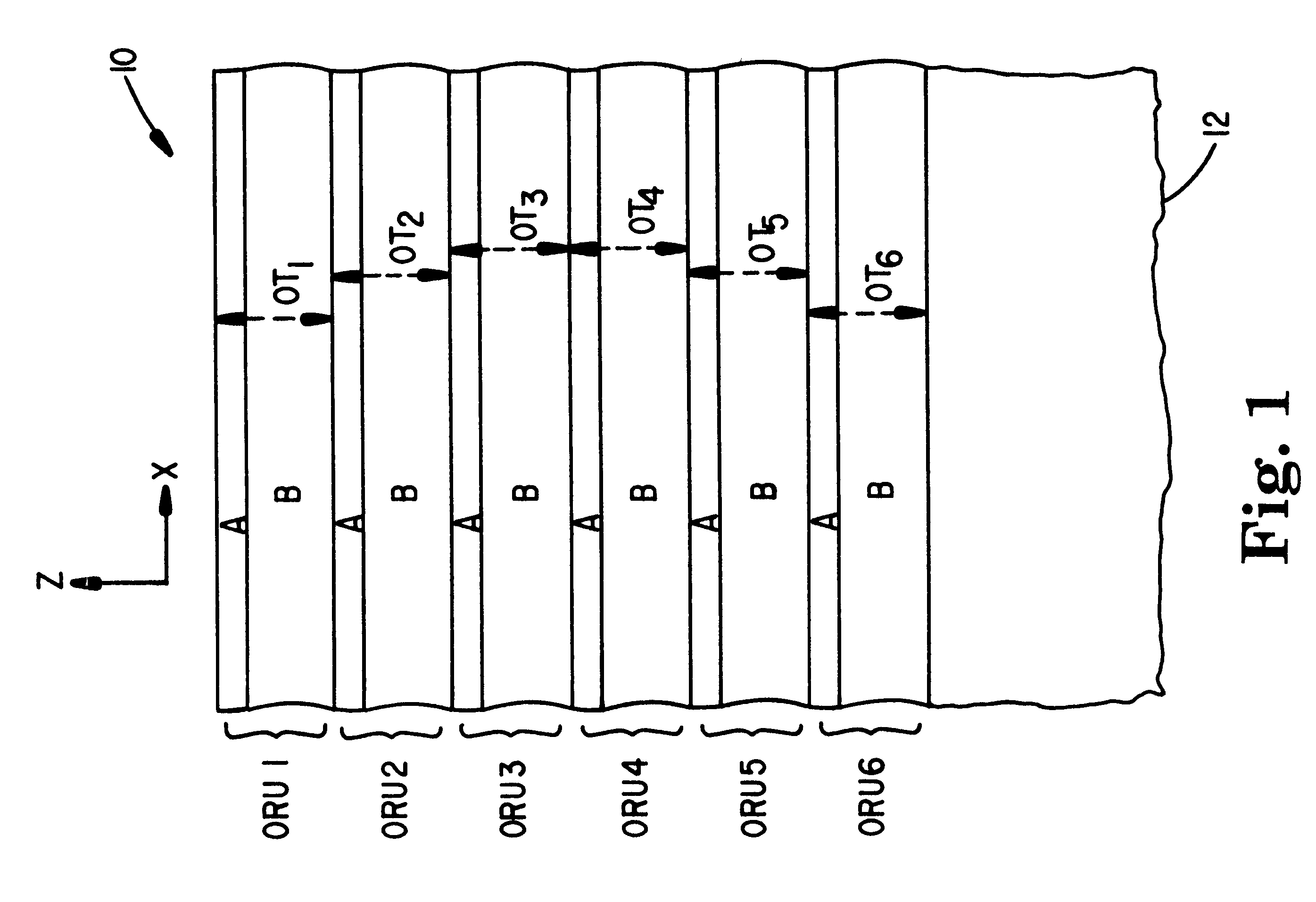
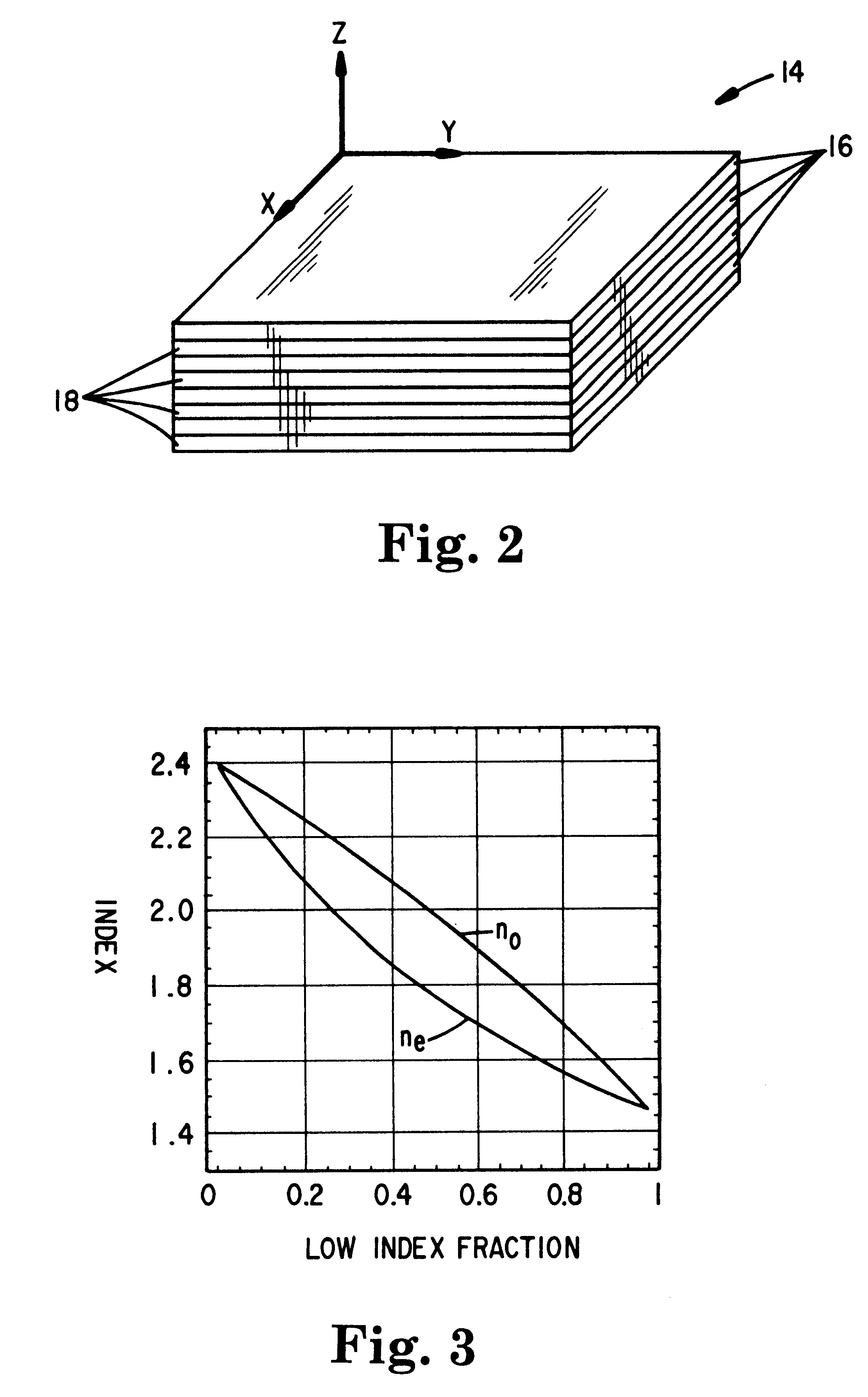
Multilayer thin film reflectors, such as mirrors and reflective polarizers, are described in which form birefringent optical layers are incorporated into a plurality of optical repeat units in the film. The form birefringent layers exhibit birefringence as a result of microscopic structures that have a dimension that is small compared to the wavelength of light but large compared to molecular distances. The optical layers within the optical repeat units have out-of-plane indices of refraction that are tailored to produce desired effects as a function of incidence angle for p-polarized light. The multilayer reflectors can be made by conventional vacuum deposition techniques using known inorganic optical materials, but can also be made entirely with polymeric materials by co-extrusion or other processes.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
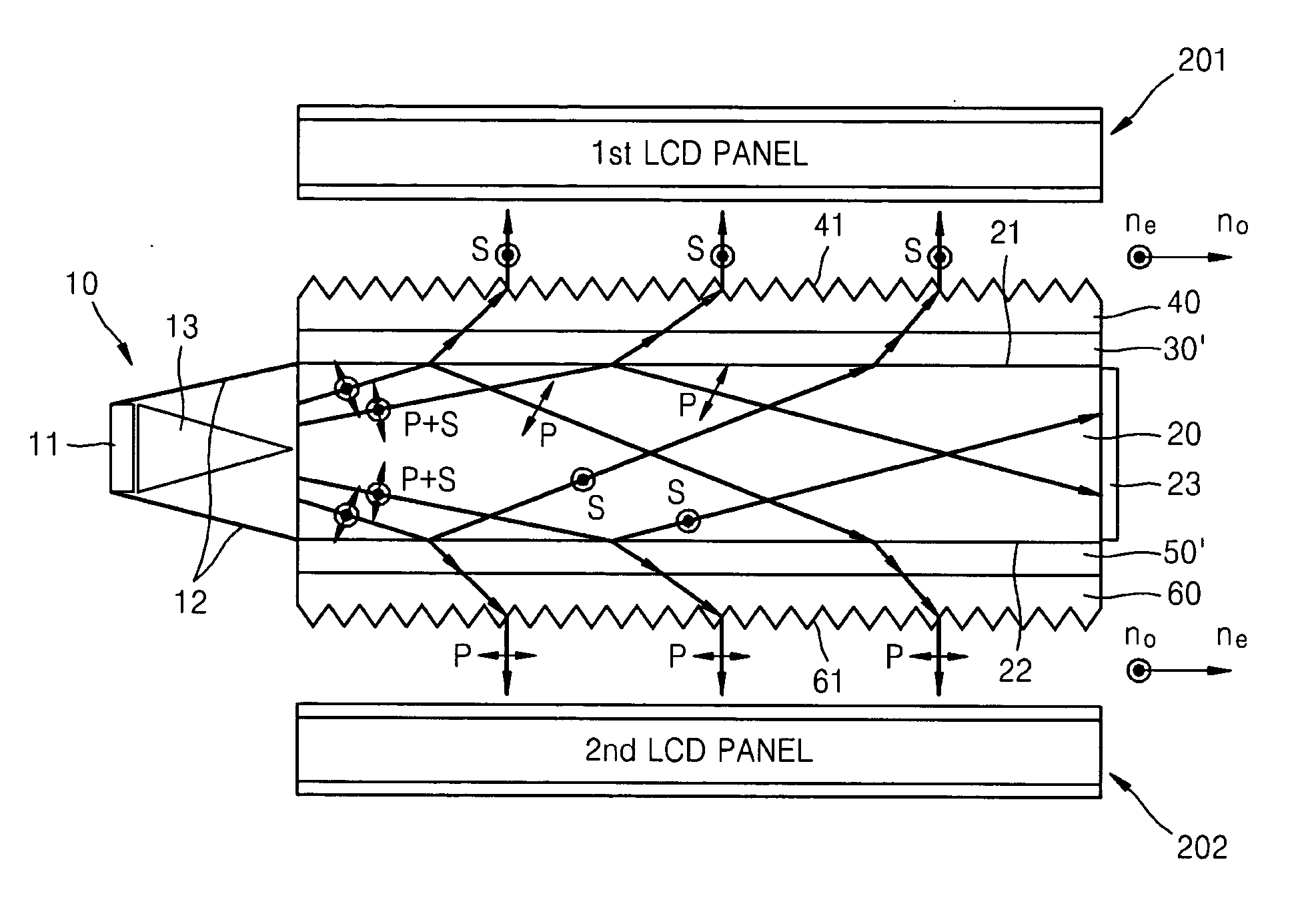
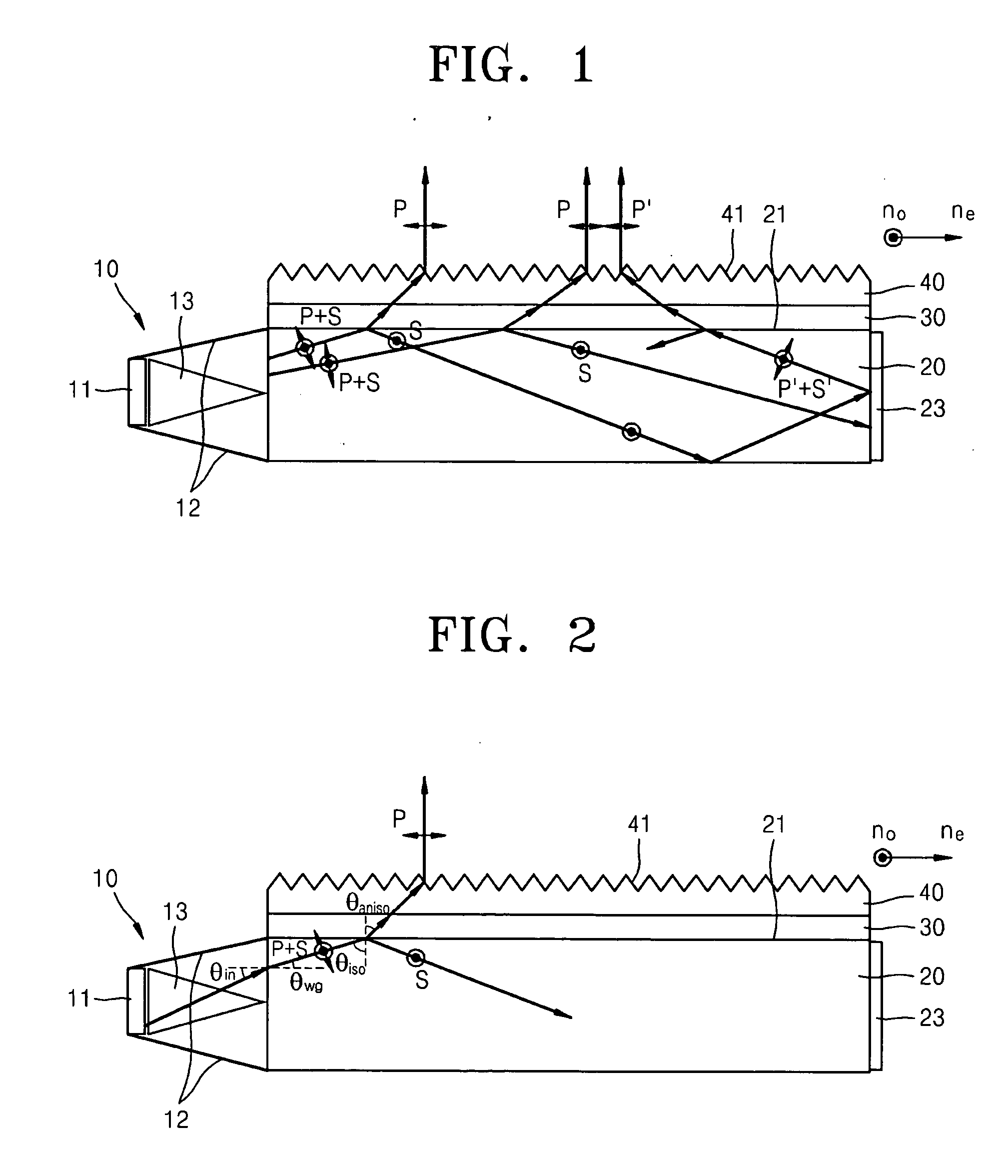
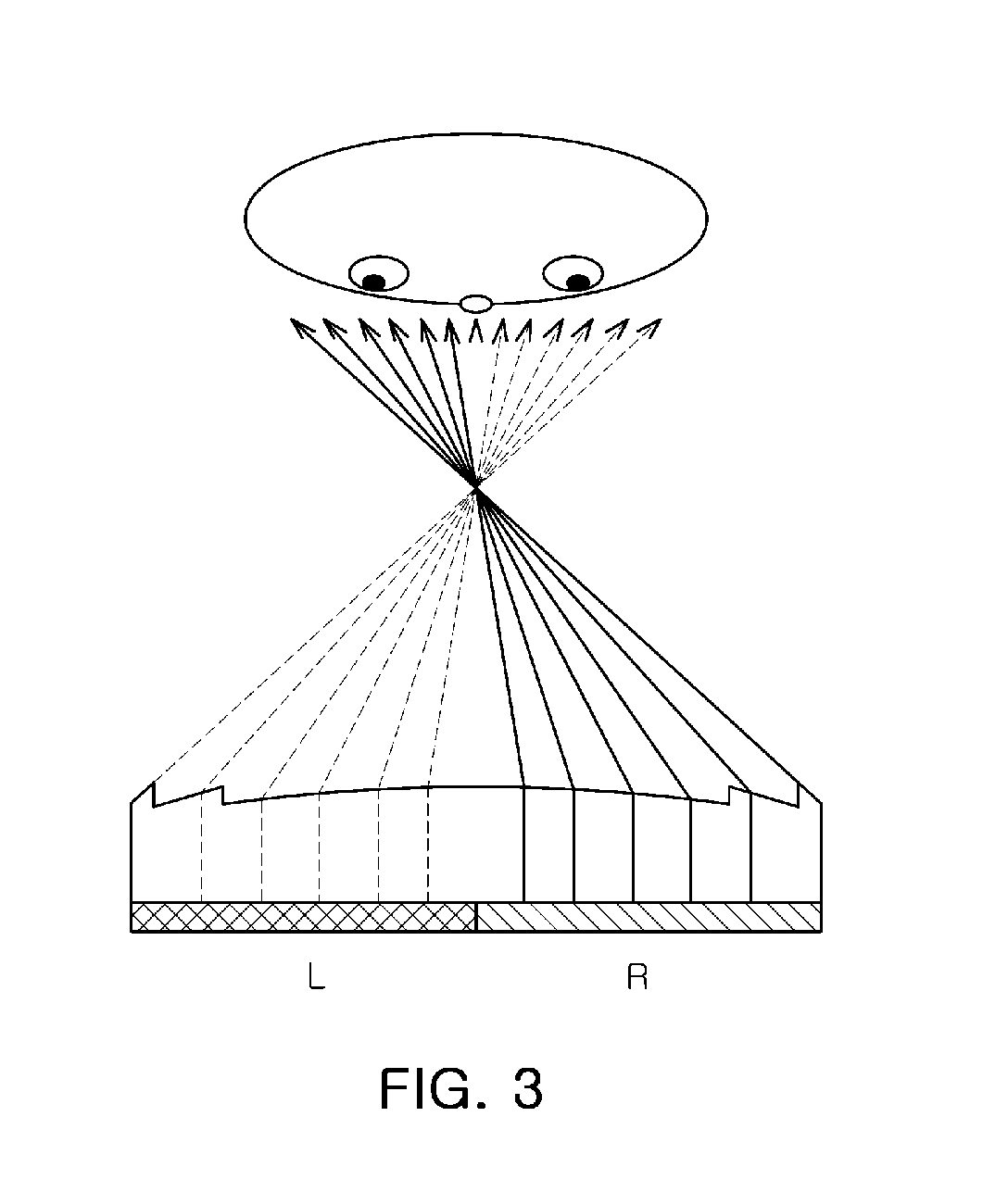
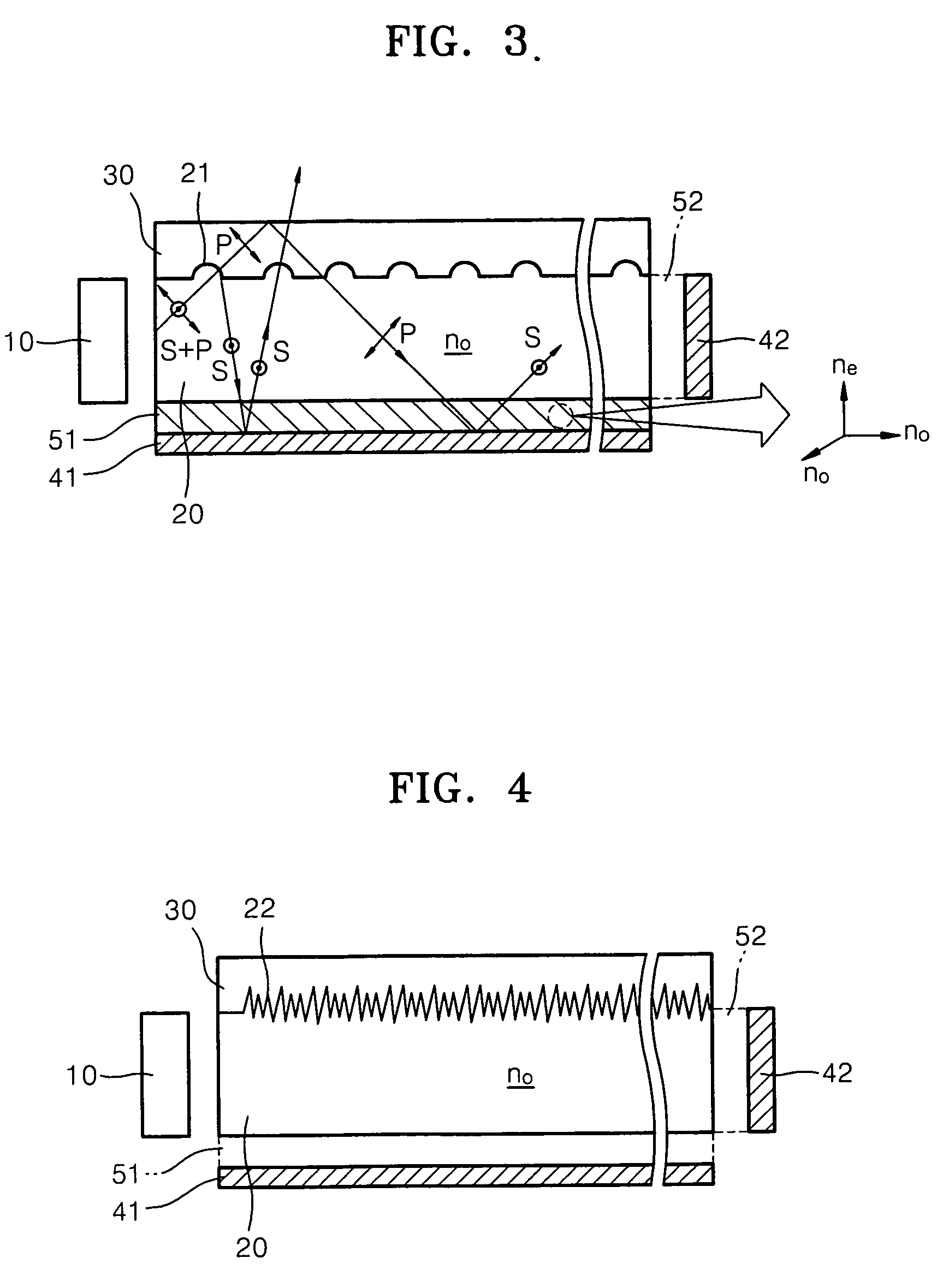
Directional display apparatus
ActiveCN1823292AImprove electrical switching performanceSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayBi-isotropic material
A bireffingent lens structure comprises a birefringent lens array capable of directing light of a given polarisation into a directional distribution, the bireffingent lens comprising a solid bireffingent material and an isotropic material having an interface having a refractive structure. A switchable liquid crystal layer capable of rotating the polarisation of light passing therethrough is arranged adjacent the first bireffingent material. The interface between the bireffingent material and the liquid crystal layer has an alignment microstructure providing alignment of the bireffingent material and the liquid crystal layer. A pair of electrodes for applying an electric field to switch the liquid crystal are arranged with both the lens array and the switchable liquid crystal layer therebetween and a conductive material is incorporated in the lens array to reduce the voltage drop across the lens array. To reduce reflection, the interface between the bireffingent material and the isotropic material has an interface having alignment microstructure providing alignment of the bireffingent material, and the refractive index of the isotropic material is substantially equal to the extraordinary refractive index of the birefringent material.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
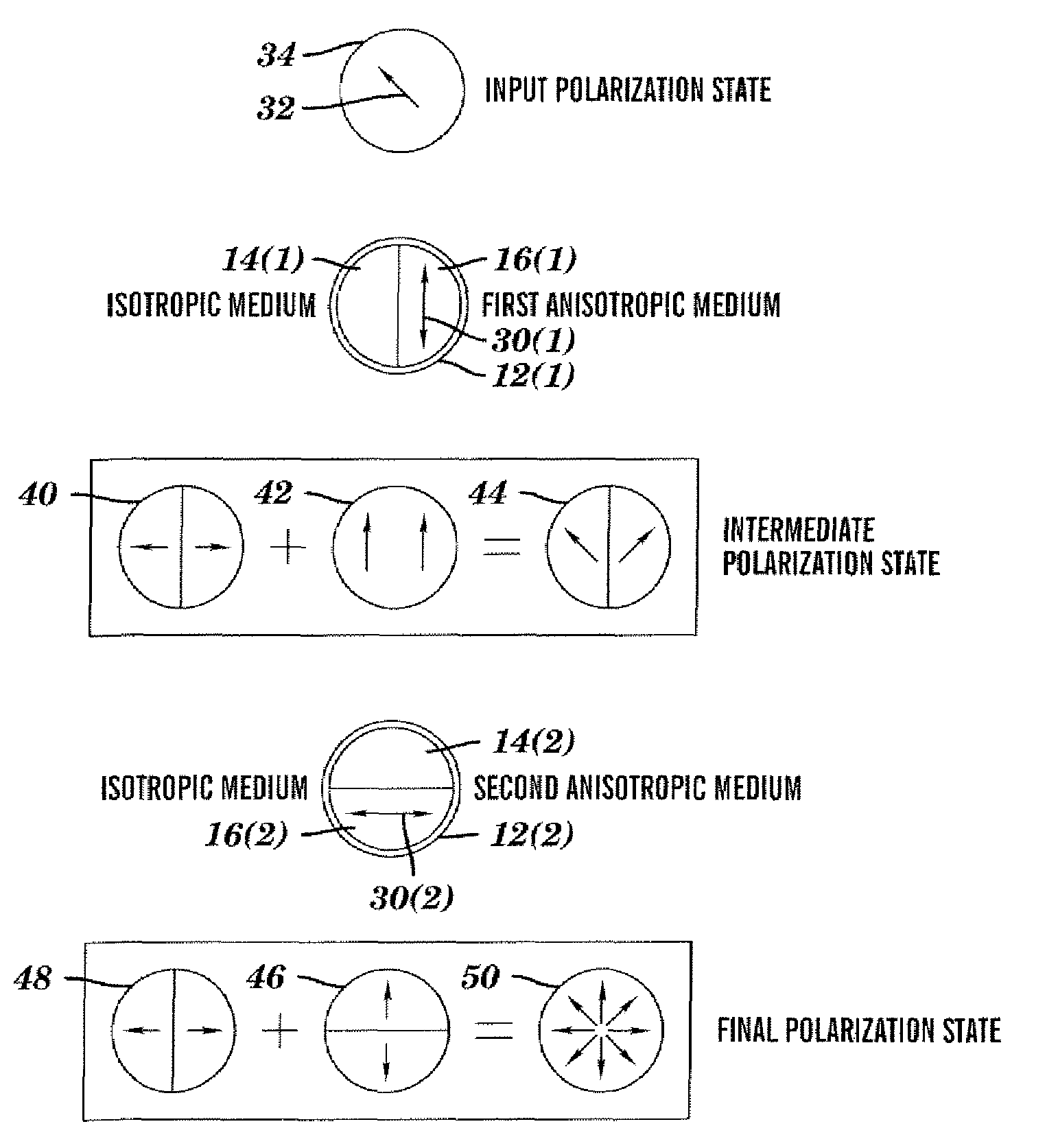
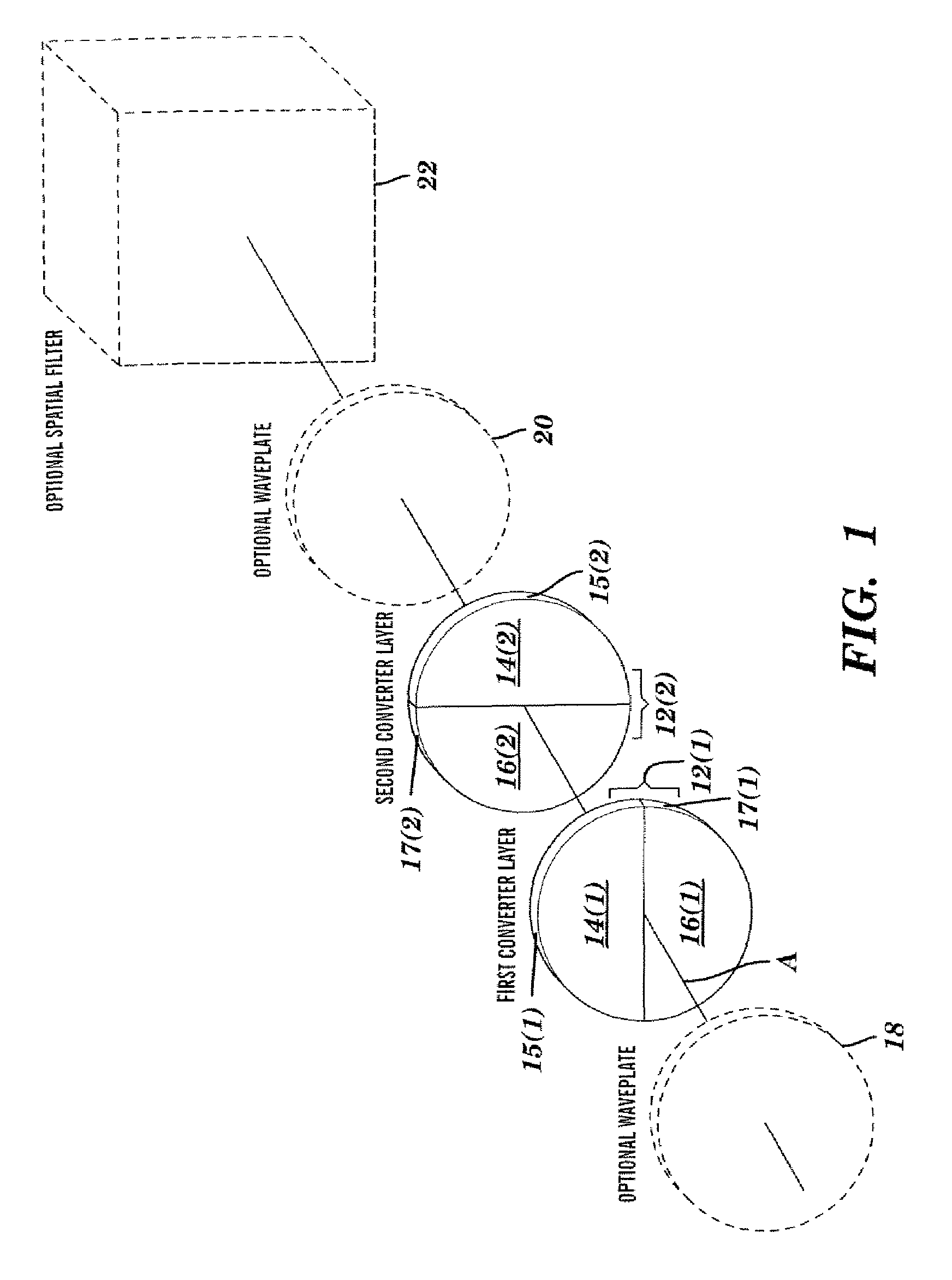
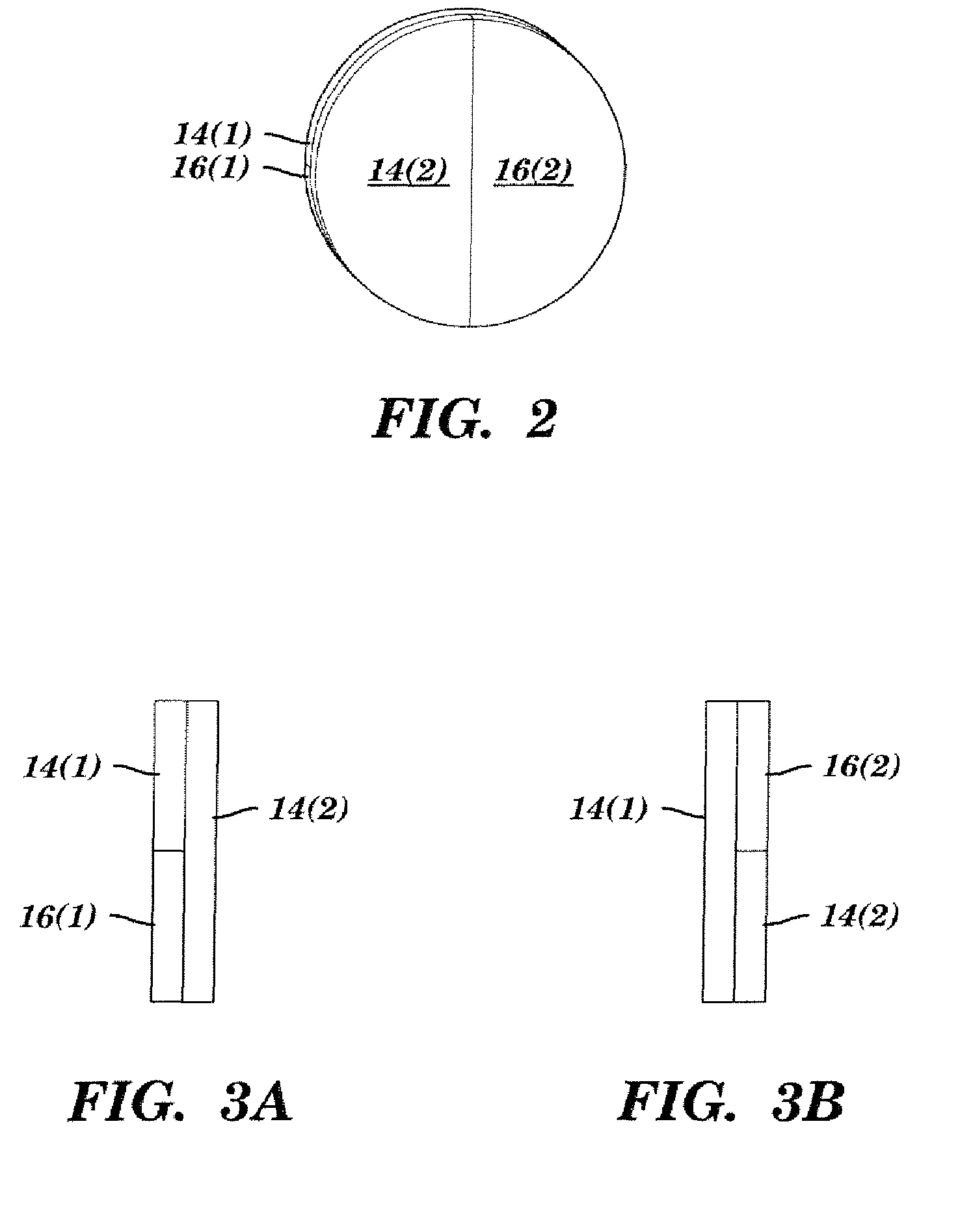
System and method converting the polarization state of an optical beam into an inhomogeneously polarized state
InactiveUS20050195480A1Inexpensive and robustPolarising elementsMicroscopesBi-isotropic materialLight beam
A system for converting the polarization state of an optical beam which propagates along a path from an initial polarization state into an inhomogeneous polarization state in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes a first anisotropic material positioned adjacent to the first isotropic material in a substantially transverse manner relative to the path of the optical beam, wherein the first anisotropic material has a first alignment axis that produces one of a radially, azimuthally, and counter-rotationally polarized optical beam when substantially aligned with respect to a polarization axis of the optical beam. The system may further include a second isotropic material and a second anisotropic material positioned adjacent to the second isotropic material in a substantially transverse manner relative to the path of the optical beam, wherein the second isotropic material and second anisotropic material are positioned downstream of the first isotropic material and first anisotropic material along the path of the optical beam, and wherein the second anisotropic material has a second alignment axis that produces one of a radially, azimuthally, and counter-rotationally polarized optical beam when substantially aligned with respect to the polarization axis of the optical beam. In addition, the present invention relates to an optical beam having an inhomogeneous polarization state in which the polarization rotates in a continuous and counterclockwise manner while traversing a circular path around the beam axis in a clockwise direction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Fabric with equal modulus in multiple directions
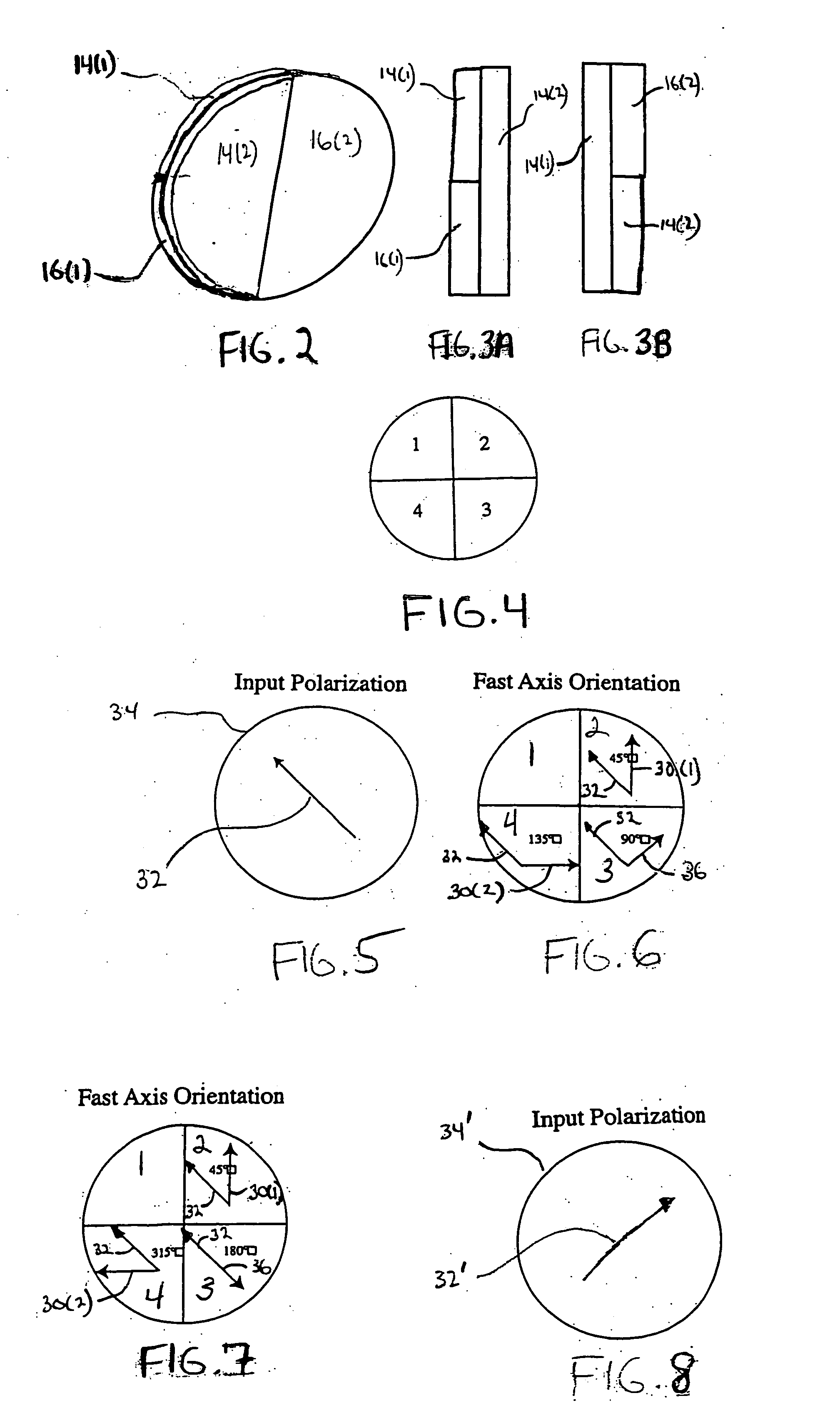
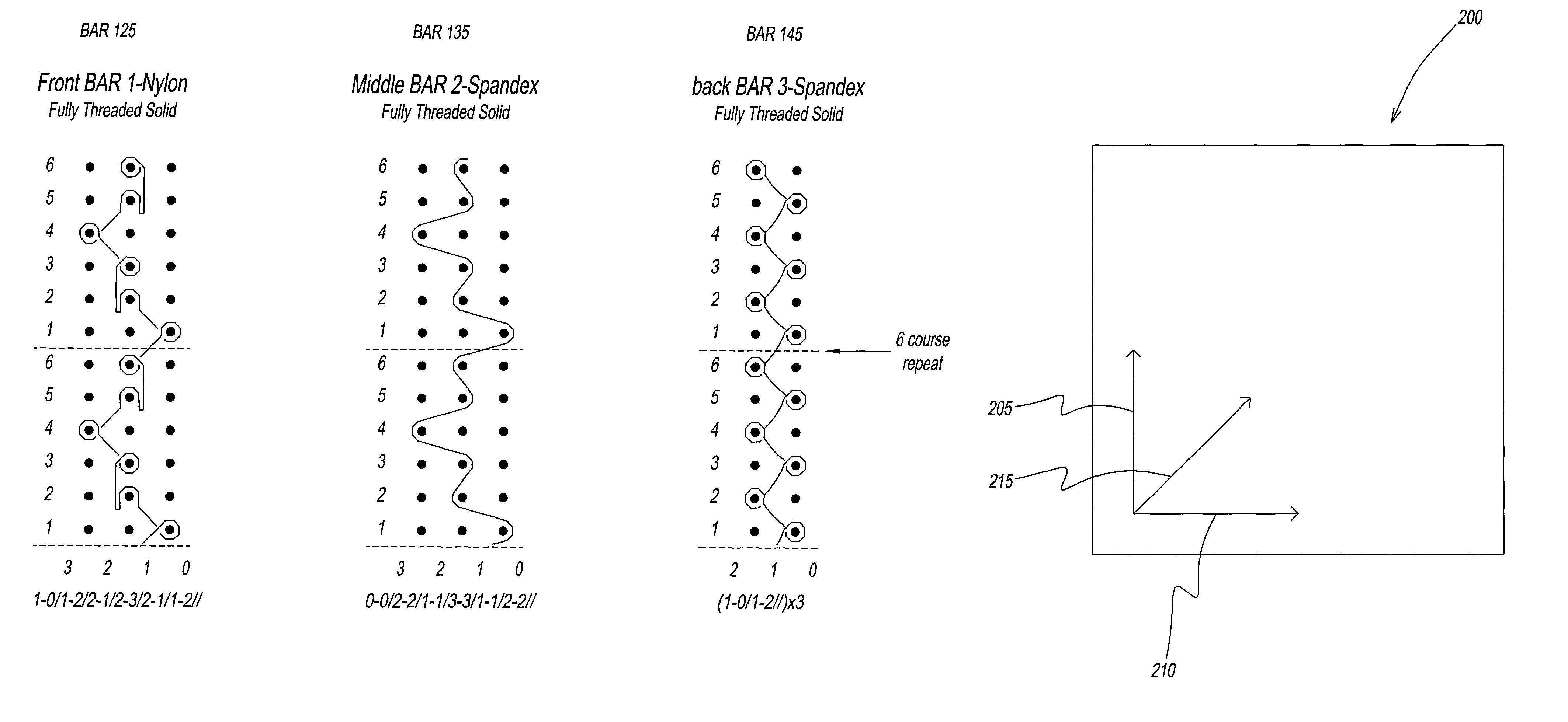
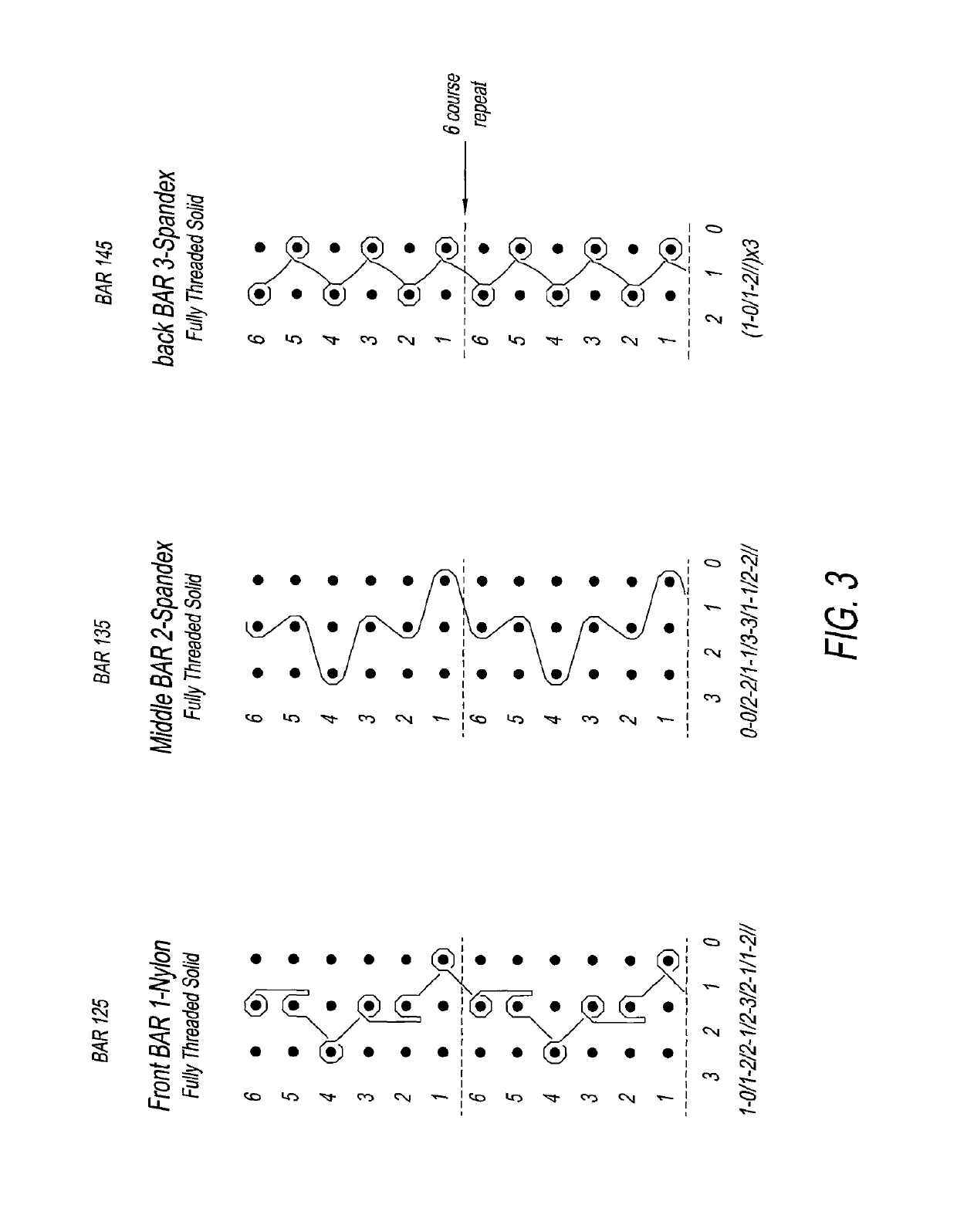
ActiveUS8726700B2Balance balanceControl balanceStraight-bar knitting machinesWoven fabricsBi-isotropic materialEngineering
Owner:GLOBAL TRADEMARKS
Power transformers and power inductors for low-frequency applications using isotropic material with high power-to-weight ratio
InactiveUS6879237B1Increase power to weightTransformers/inductances coolingTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsBi-isotropic materialTransformer
A transformer for low frequency applications of from 50 Hz to 1000 Hz is described. The transformer comprises a core having a cylindrical symmetry around a main revolution axis. The core is formed of a soft isotropic magnetic composite material composed of iron and resin. Windings are enclosed in the magnetic core and disposed about a central column of the magnetic core and magnetically coupled with the inductor for low frequency applications, DC to 1000 Hz of similar construction is also described, the inductor comprises a core having a cylindrical symmetry around a main revolution axis. The core is formed of a soft isotropic magnetic composite material composed of iron and resin. Winding is enclosed in the magnetic core and disposed about a central column of the magnetic core and magnetically coupled with the magnetic core. The core is formed by core sections.
Owner:QUEBEC METAL POWDERS
Machinable composite mold
Machinable composite molds for use in making a composite structure. The mold includes a mold body having a tool surface that is shaped to provide the molded surface of the composite structure. The mold body is made up of at least one mold layer composed of a quasi-isotropic material composed of a plurality of randomly oriented fiber bundles or chips impregnated with a resin. The use of randomly oriented fiber chips allows post-cure machining of the mold body.
Owner:HEXCEL
Display Backlight System
InactiveUS20140340865A1Improve polarization efficiencyEfficient polarizationMechanical apparatusNanoopticsBi-isotropic materialDisplay device
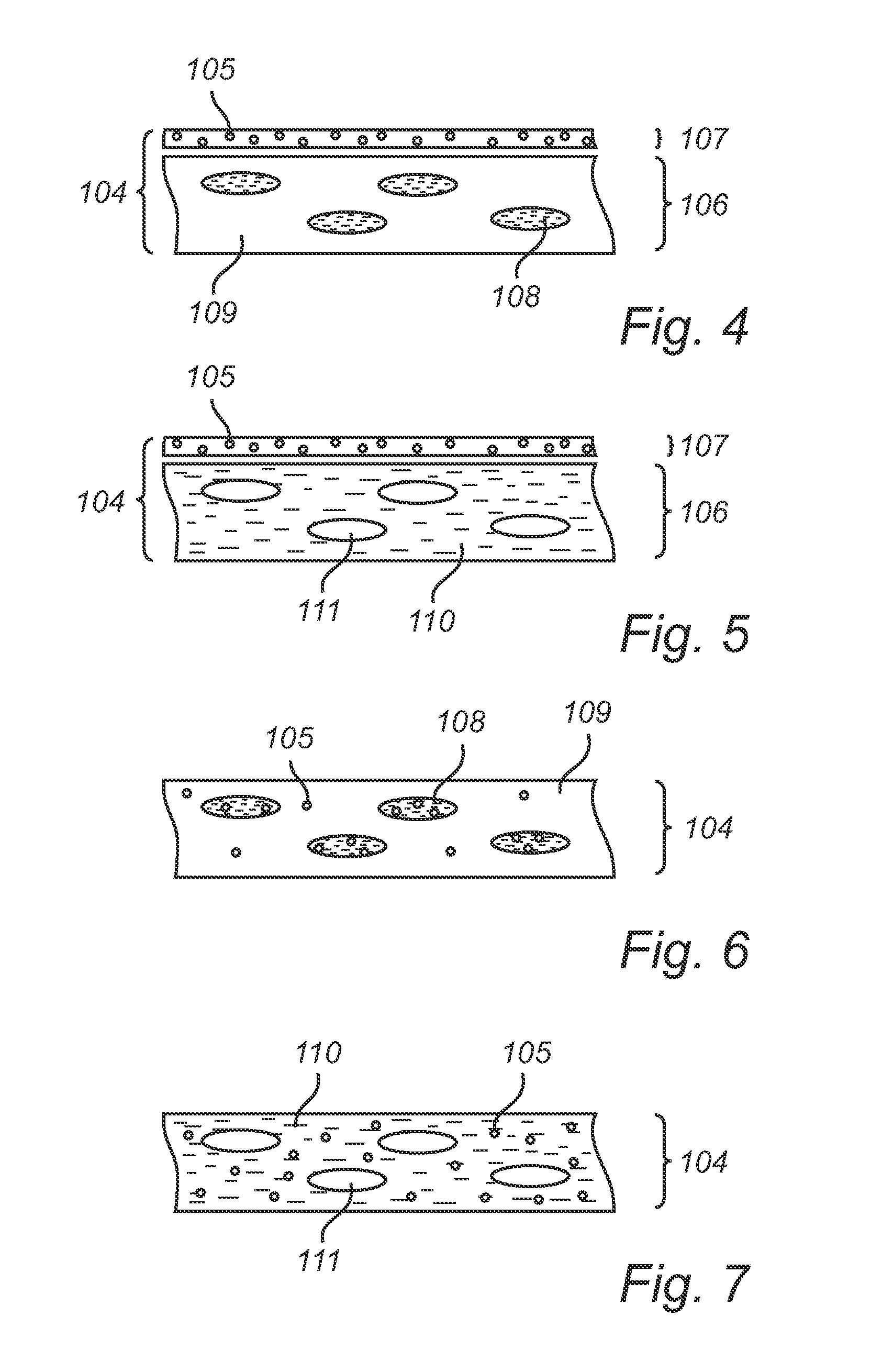
A lighting device is provided, comprising:a light-emitting arrangement comprising a solid state light source capable of emitting light of a first wavelength range, and having a light outcoupling surface; anda polarizing color converting layer (104) arranged to receive light that is outcoupled from said light outcoupling surface, and comprising i) a color converting elements (105) capable of converting light of said first wavelength range into light of a second wavelength range, and ii) at least one region of an optically anisotropic material (108), and at least one region of an optically isotropic material (109), wherein said polarizing color converting layer is capable of preferentially scattering one linear polarization direction of light received from the light-emitting arrangement. The lighting device of the invention provides improved polarization efficiency. The lighting device may be used as a backlight in a display device, e.g. LCD device.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Machinable composite mold
Machinable composite molds for use in making a composite structure. The mold includes a mold body having a tool surface that is shaped to provide the molded surface of the composite structure. The mold body is made up of at least one mold layer composed of a quasi-isotropic material composed of a plurality of randomly oriented fiber bundles or chips impregnated with a resin. The use of randomly oriented fiber chips allows post-cure machining of the mold body.
Owner:HEXCEL
System and method converting the polarization state of an optical beam into an inhomogeneously polarized state
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Fabric with equal modulus in multiple directions
ActiveUSRE47397E1Balance balanceControl balanceWeft knittingWarp knittingBi-isotropic materialEngineering
Owner:GLOBAL TRADEMARKS
Illuminator for flat panel display device and illuminator for double-sided flat panel display device
InactiveUS20070052882A1Maximize light efficiencyReduce light lossOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLight guideBi-isotropic material
An illuminator for a flat panel display device is provided. The illuminator includes a light source generating light; a light guide plate that guides and distributes the light generated by the light source and is made of optically isotropic material; a collimator that is disposed between an end of the light guide plate and the light source and guides the light from the light source onto the light guide plate with a predetermined incident angle; a polarization separation layer that is made of optically anisotropic material having two refractive indices and formed on the light guide plate to transmit first polarized light from the light guide plate and reflect second polarized light from the light guide plate; and a beam out-coupling layer that is formed on the polarization separation layer and out-couples the light incident from the polarization separation layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Polarized light emitting light guide plate, method of manufacturing the same and illuminator for flat panel display device using polarized light emitting light guide plate
InactiveUS20070183038A1Easy to manufacturePolarising elementsOptical light guidesLight guideBi-isotropic material
A polarized light emitting light guide plate includes: a transparent substrate of optically isotropic material, in which the light incident through a lateral side thereof travels; an anisotropic liquid crystal polymer layer formed on an upper surface of the substrate and having first and second refractive indices with respect to first and second perpendicular polarization components; and a polarization separation microstructure formed at an interface between the transparent substrate and the liquid crystal polymer layer, which refracts or reflects the first polarization component and transmits the second polarization component. The refractive index of the polarization separation microstructure is substantially equal to the refractive index of the substrate; the first refractive index of the liquid crystal polymer layer is greater than the refractive index of the substrate, and the second refractive index of the liquid crystal polymer layer light is substantially equal to the refractive index of the substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method for detecting isotropic material surface Young modulus by using surface acoustic wave technology
InactiveCN103995053ALow technical requirementsSimplify the measurement stepsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalBi-isotropic materialYoung's modulus
A method for detecting isotropic material surface Young modulus by using surface acoustic wave technology. The method is as below: exciting broadband surface acoustic wave in an isotropic specimen surface to obtain a dispersion curve on a surface acoustic wave propagation direction; fitting the actual phase velocity data to obtain a closest truth-value phase velocity and a phase velocity fluctuation section; establishing a Cartesian coordinate geometry model to obtain a surface wave basic propagation equation containing unknown medium Young modulus, Poisson ratio, direction cosine of the propagation direction, amplitude attenuation coefficient given according to experience value, wave number and wave velocity; calculating assumption corresponding relation between wave velocity and wave number in the Cartesian coordinate geometry model and simultaneous theoretical relationship, to obtain mutual relationship of velocity, frequency and Young modulus under ideal conditions; and conducting reverse calculation to obtain the Young modulus in medium according to the mutual relationship of velocity, frequency and Young modulus under ideal conditions and the dispersion curve under actual conditions. The invention realizes effective measurement of isotropic material surface young modulus.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
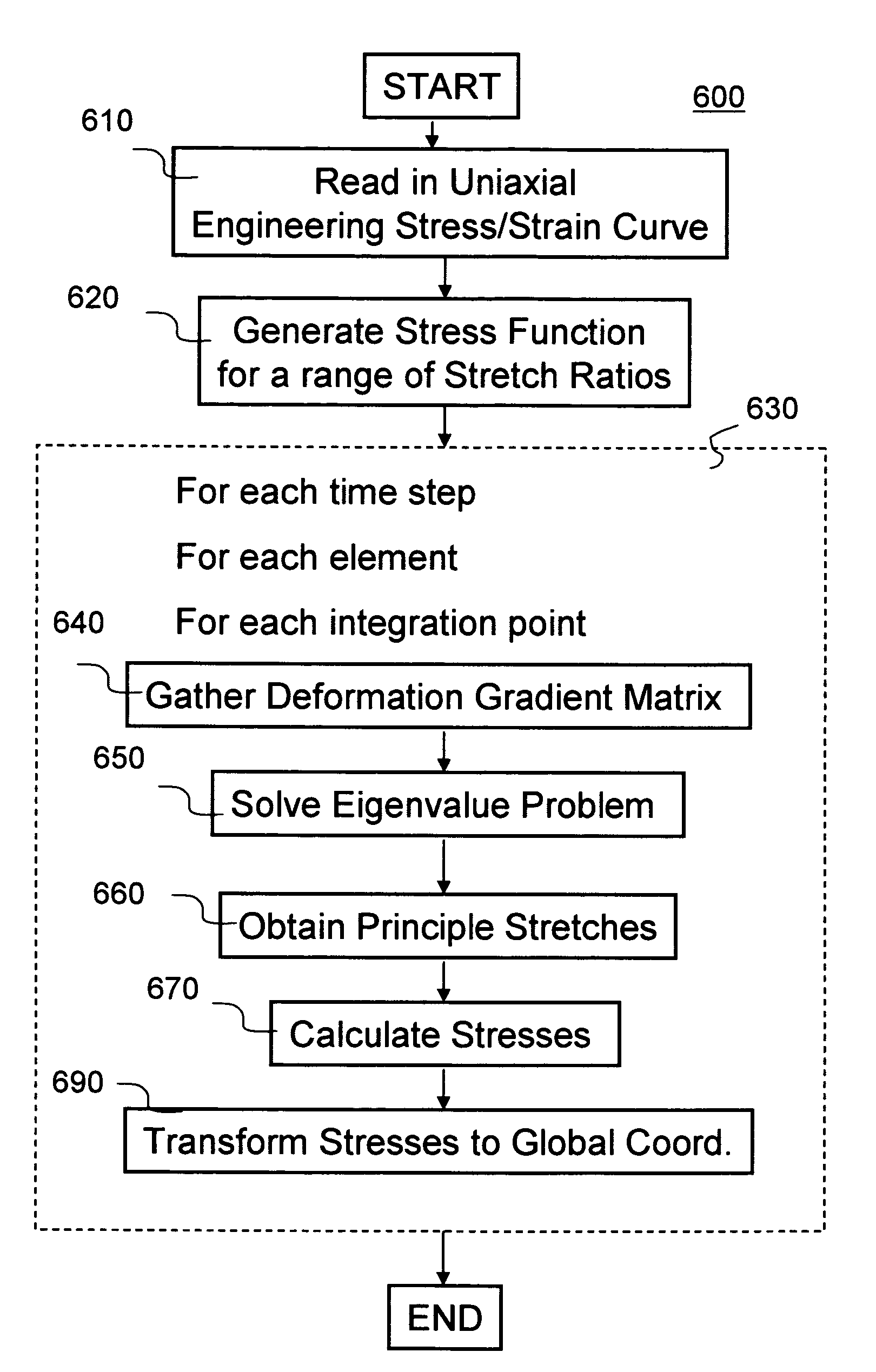
Method and system for numerically simulating foam-like material in finite element analysis
ActiveUS7308387B1High materialEliminate requirementsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsCompressible materialBi-isotropic material
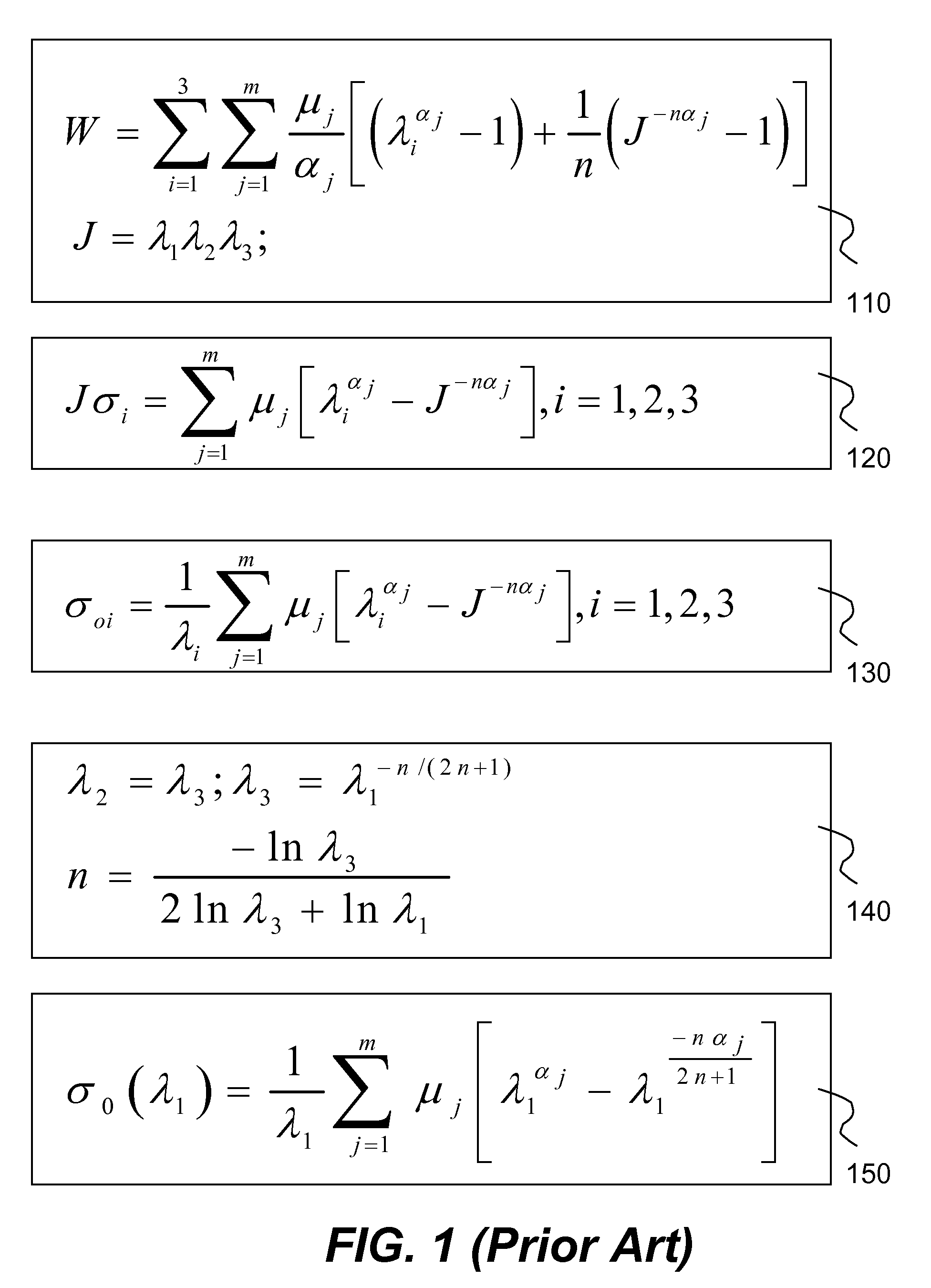
A method and system to numerically simulating structural responses of a highly compressible material such as foam in finite element analysis is disclosed. According to one aspect of the simulation, a new improved method for calculating structural responses is derived using the following assumptions: uniaxial loading and isotropic material. As a result of the new method, Ogden polynomial stress function f(λ) is replaced by a tabulated function depending upon only a set of stress-strain curves obtained via uniaxial tension and compression tests. The method is implemented in a finite element analysis software product.
Owner:ANSYS
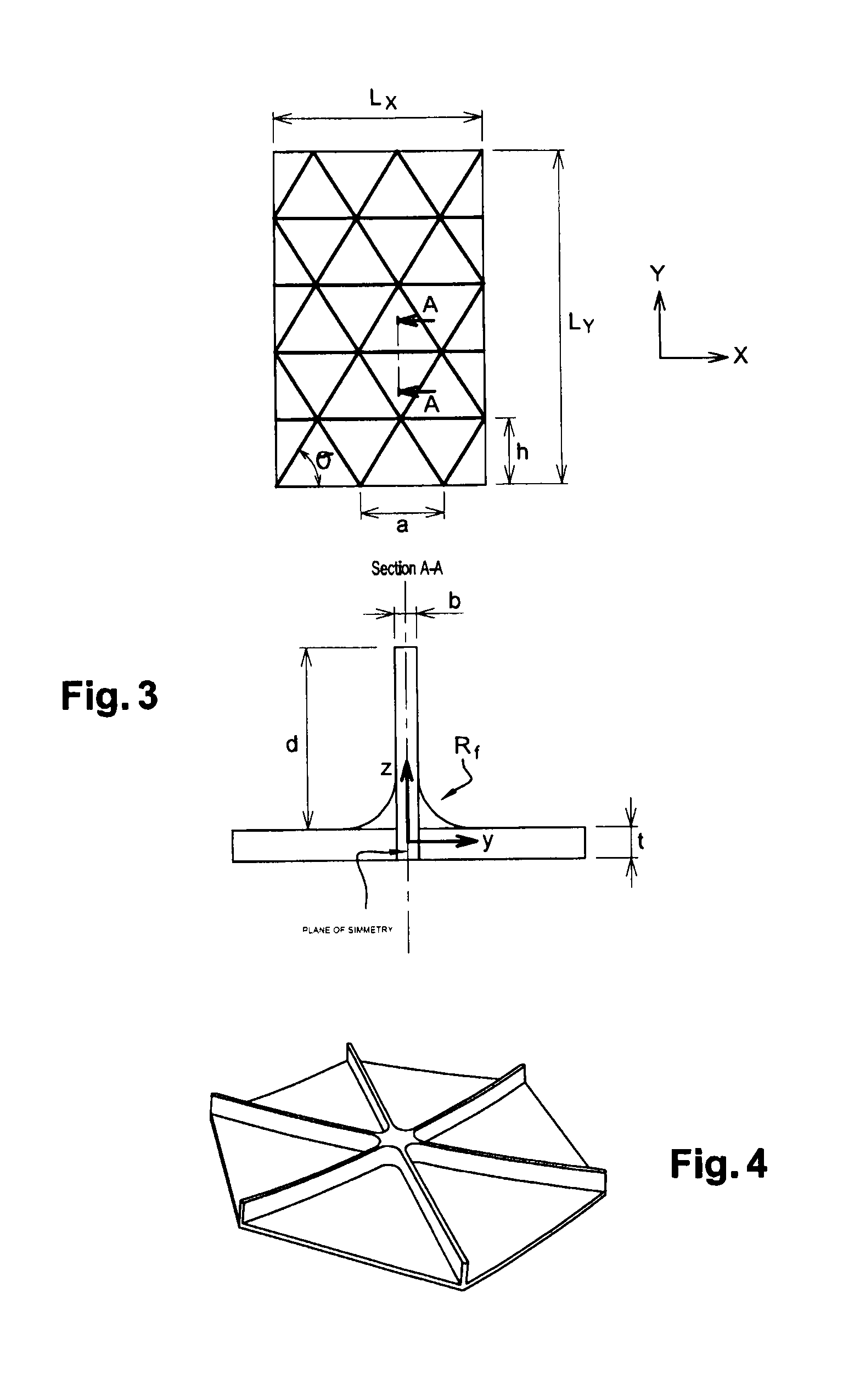
Method for the structural analysis of panels consisting of an isotropic material and stiffened by triangular pockets
The invention relates to a method for dimensioning, by an analytical method, of an essentially plane panel consisting of a homogenous and isotropic material, said panel consisting of a skin reinforced by a set of three parallel bundles of stiffeners built into the panel. The pockets determined on the skin by said groups of stiffeners are triangular, the stiffeners are blade shaped and the stiffened panel must comply with specifications for mechanical resistance to predetermined external loads, the angles between bundles of stiffeners being such that the triangular pockets have any kind of isosceles form.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
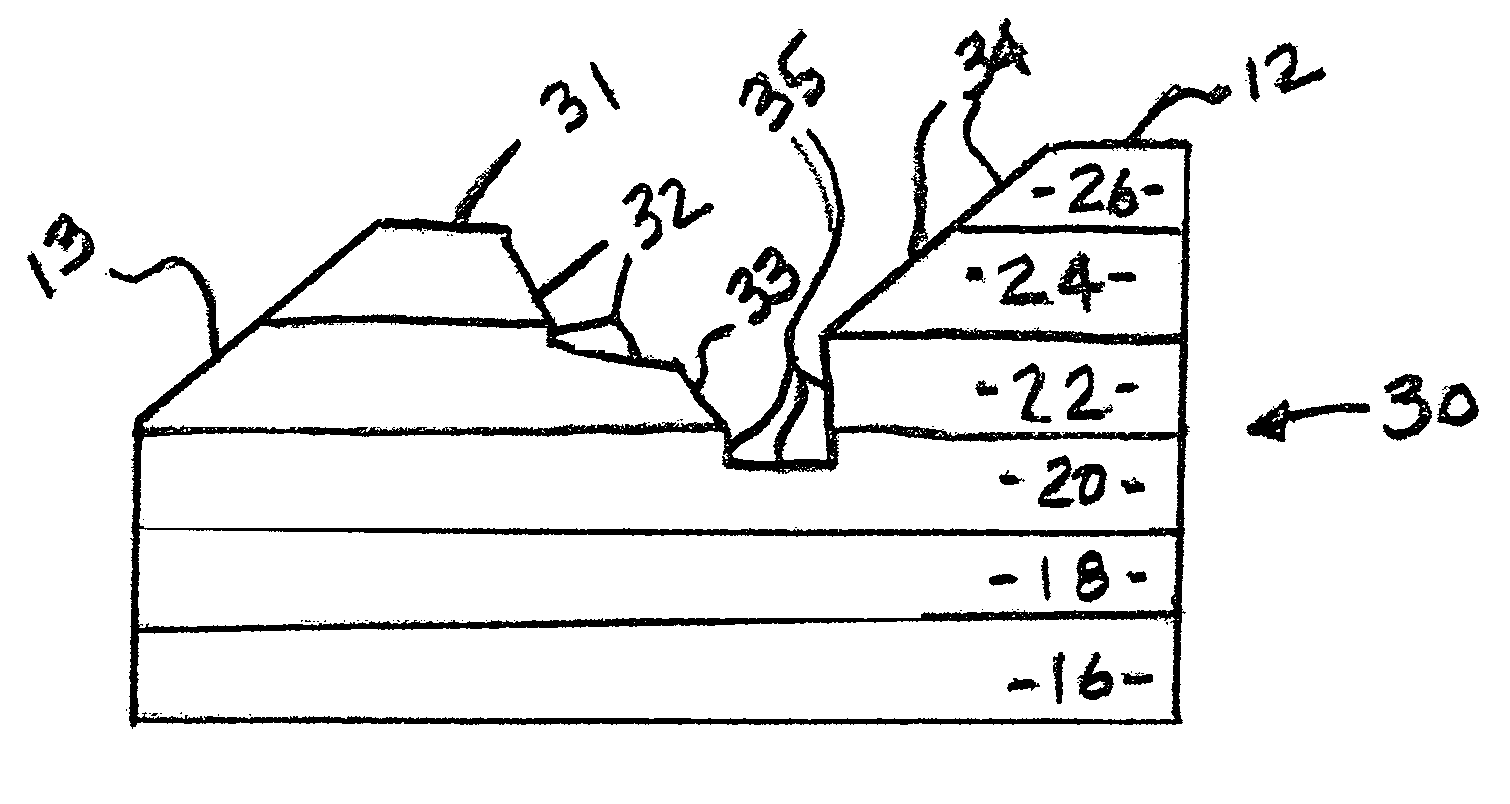
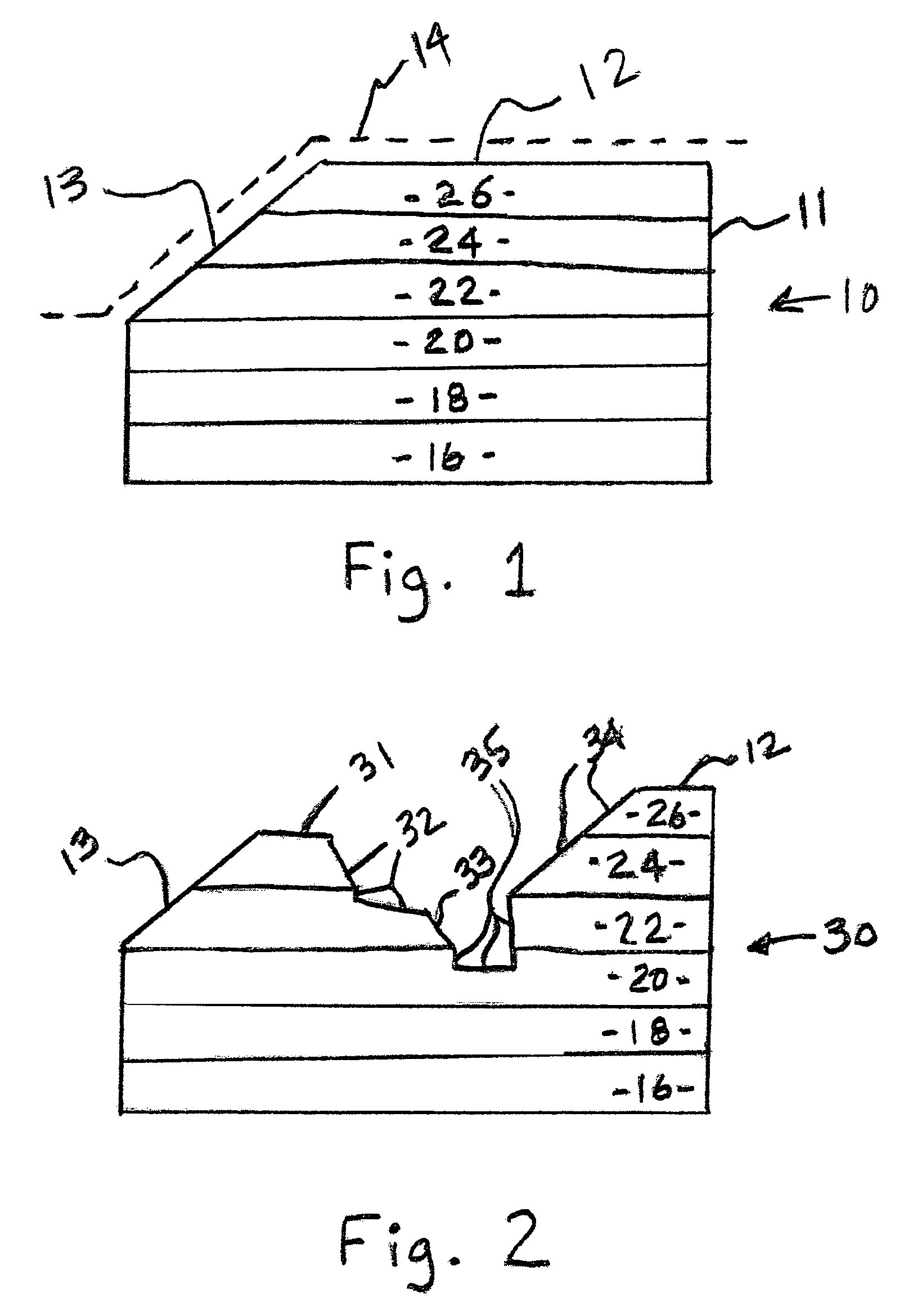
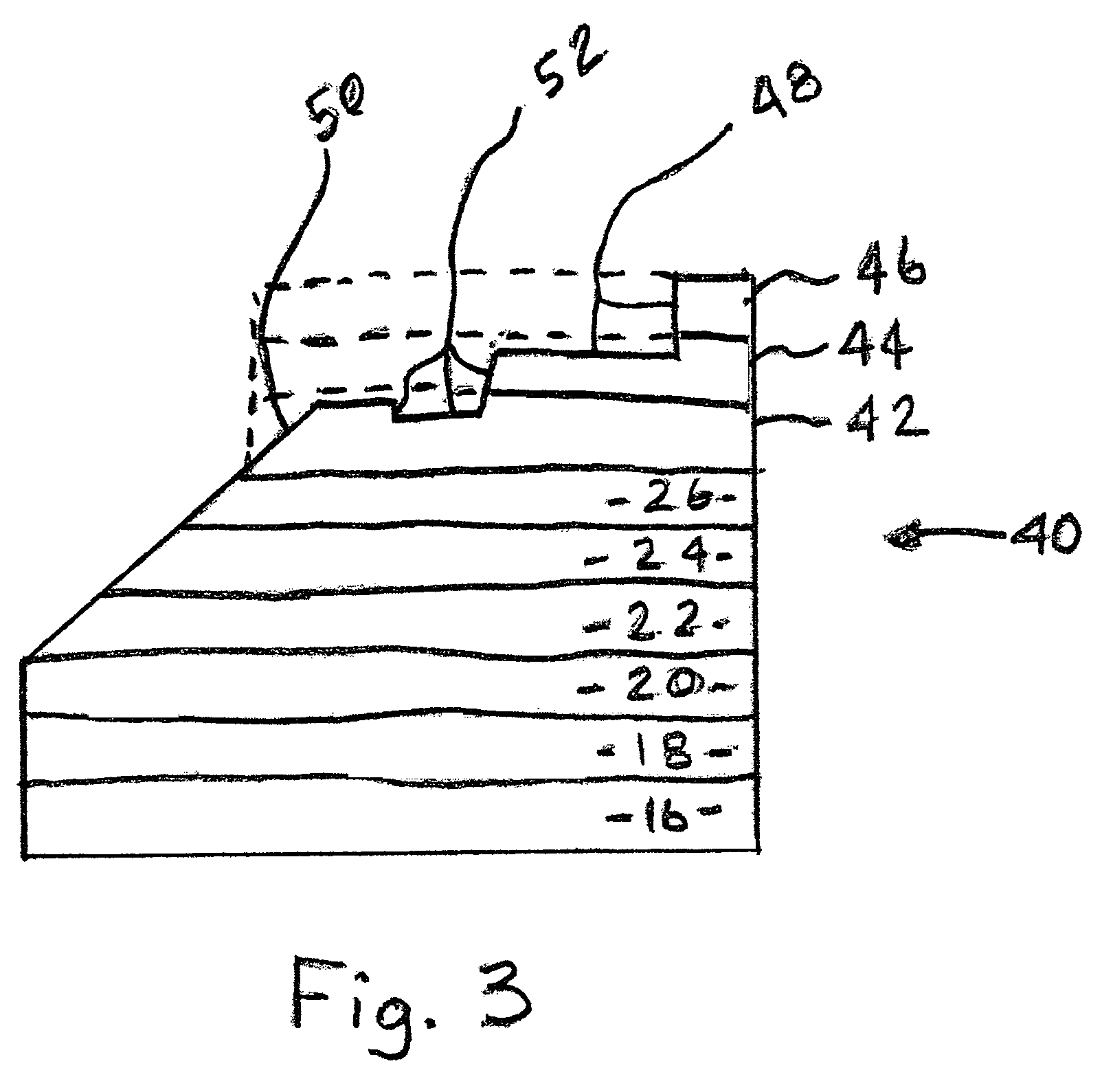
Semiconductor device with a high-k gate dielectric and a metal gate electrode
A semiconductor device is described. That semiconductor device comprises a high-k gate dielectric layer that is formed over a channel that is positioned within a substrate, and a metal gate electrode that is formed on the high-k gate dielectric layer. The high-k gate dielectric layer has off-state leakage characteristics that are superior to those of a silicon dioxide based gate dielectric, and on-state mobility characteristics that are superior to those of a high-k gate dielectric that comprises an isotropic material.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Fabric with equal modulus in multiple directions
ActiveUS20120192595A1Balance balanceControl balanceGarmentsStraight-bar knitting machinesBi-isotropic materialEngineering
Owner:GLOBAL TRADEMARKS
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20120069272A1Improve reuse efficiencyReduce power consumptionNon-linear opticsOptical elementsLiquid-crystal displayBi-isotropic material
The backlight has an anisotropic diffusion sheet disposed between the reflective polarizing plate and the optical path converter. The anisotropic diffusion sheet includes a refractive index anisotropic diffusion sheet stretched in an absorption axis direction in which a concave-convex portion is formed on a surface of the reflective polarized plate, and an isotropic material part laminated on a surface of the concave-convex part. The isotropic material part has an isotropic reflective index. The refractive index of the isotropic material part is the same as the refractive index in the transmission axis direction perpendicular to a stretching direction of the refractive index anisotropic sheet.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
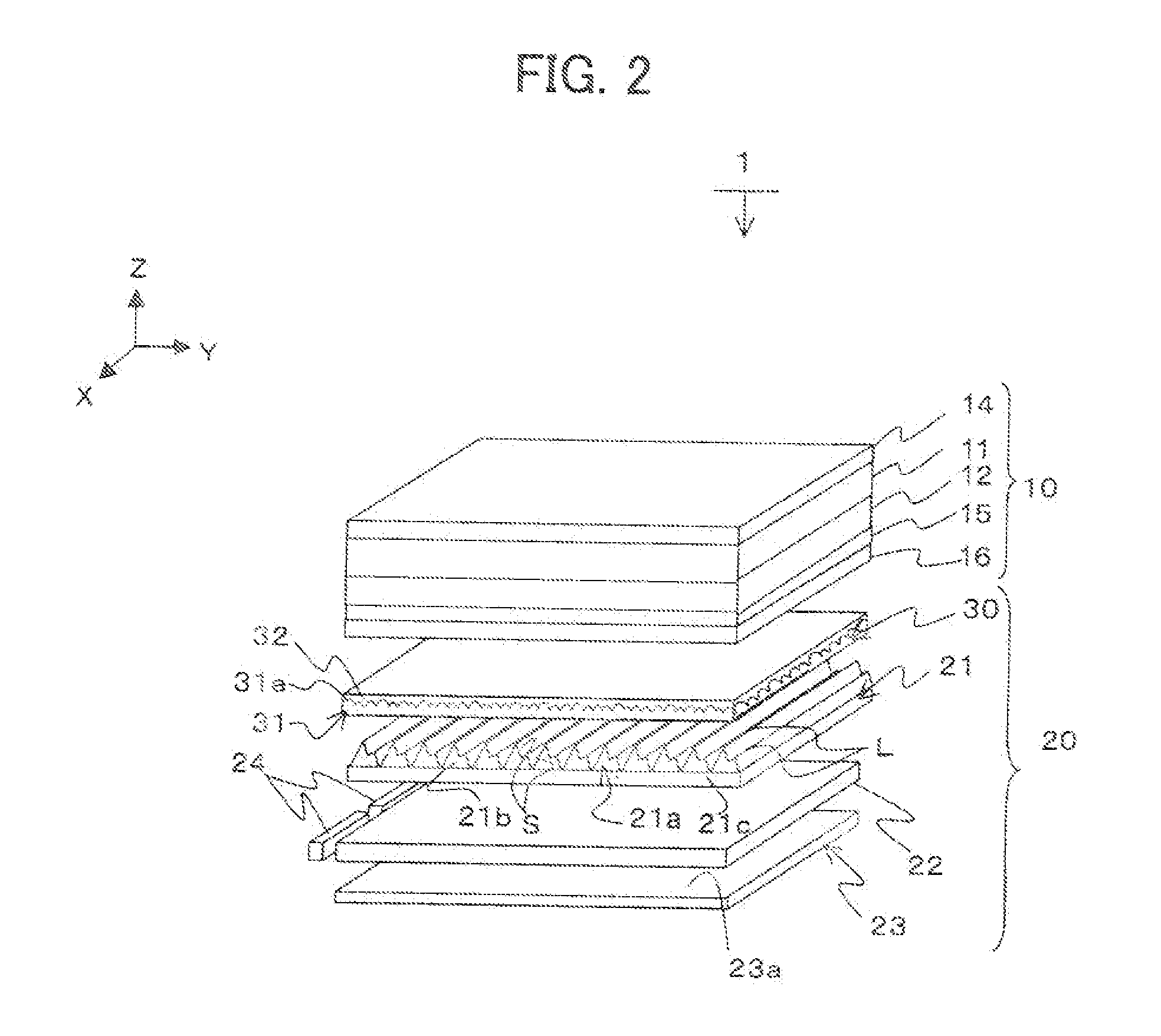
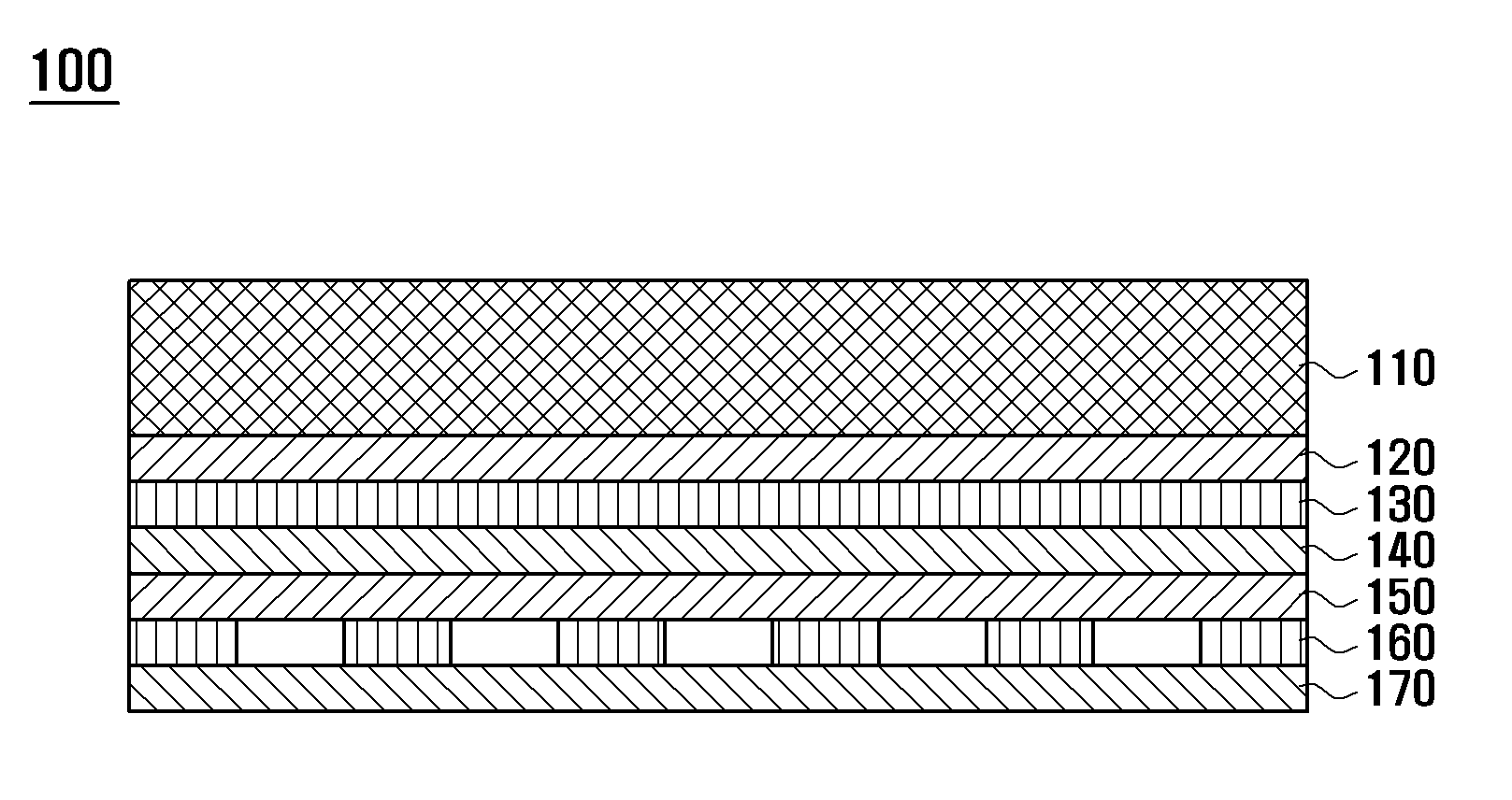
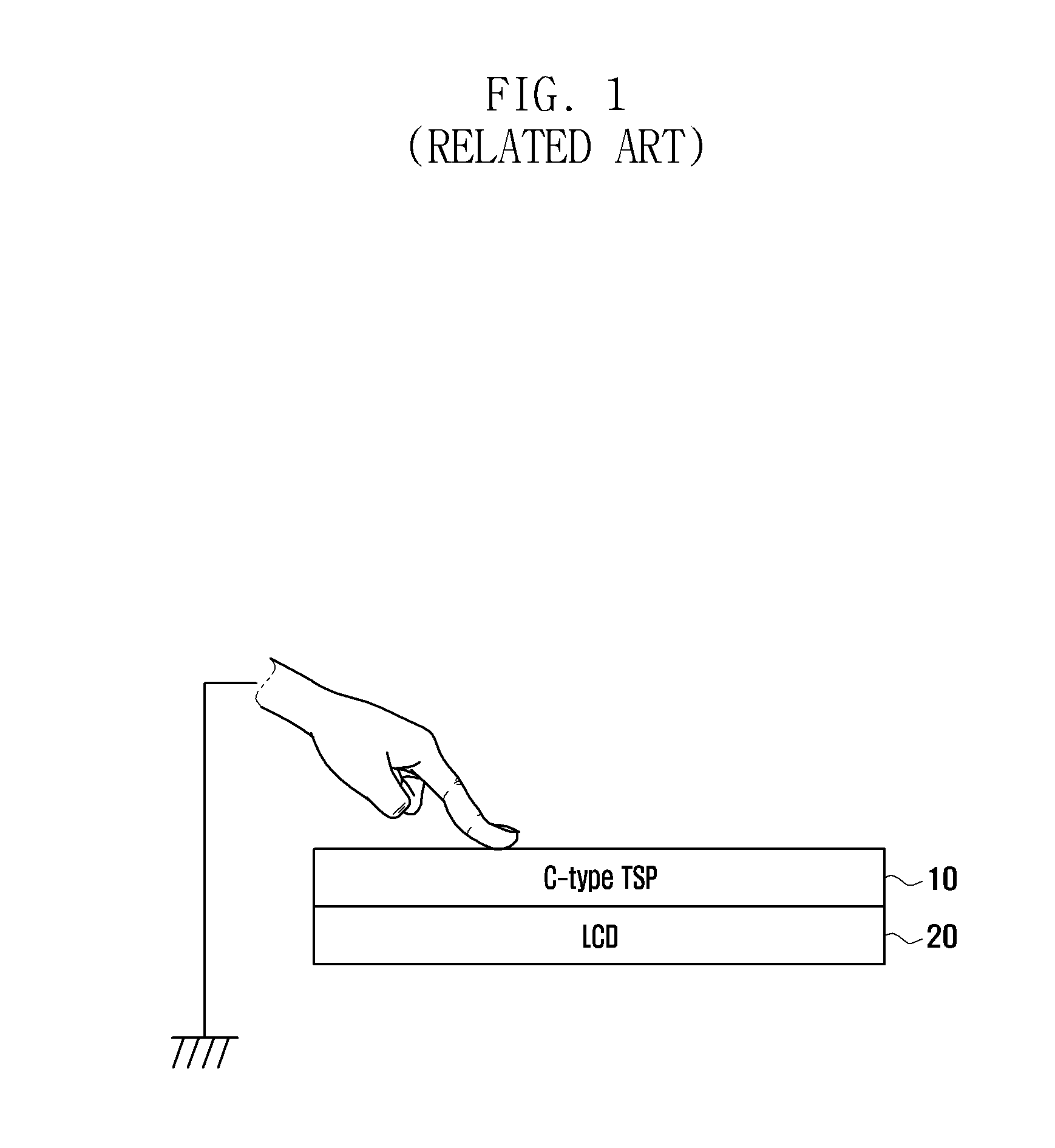
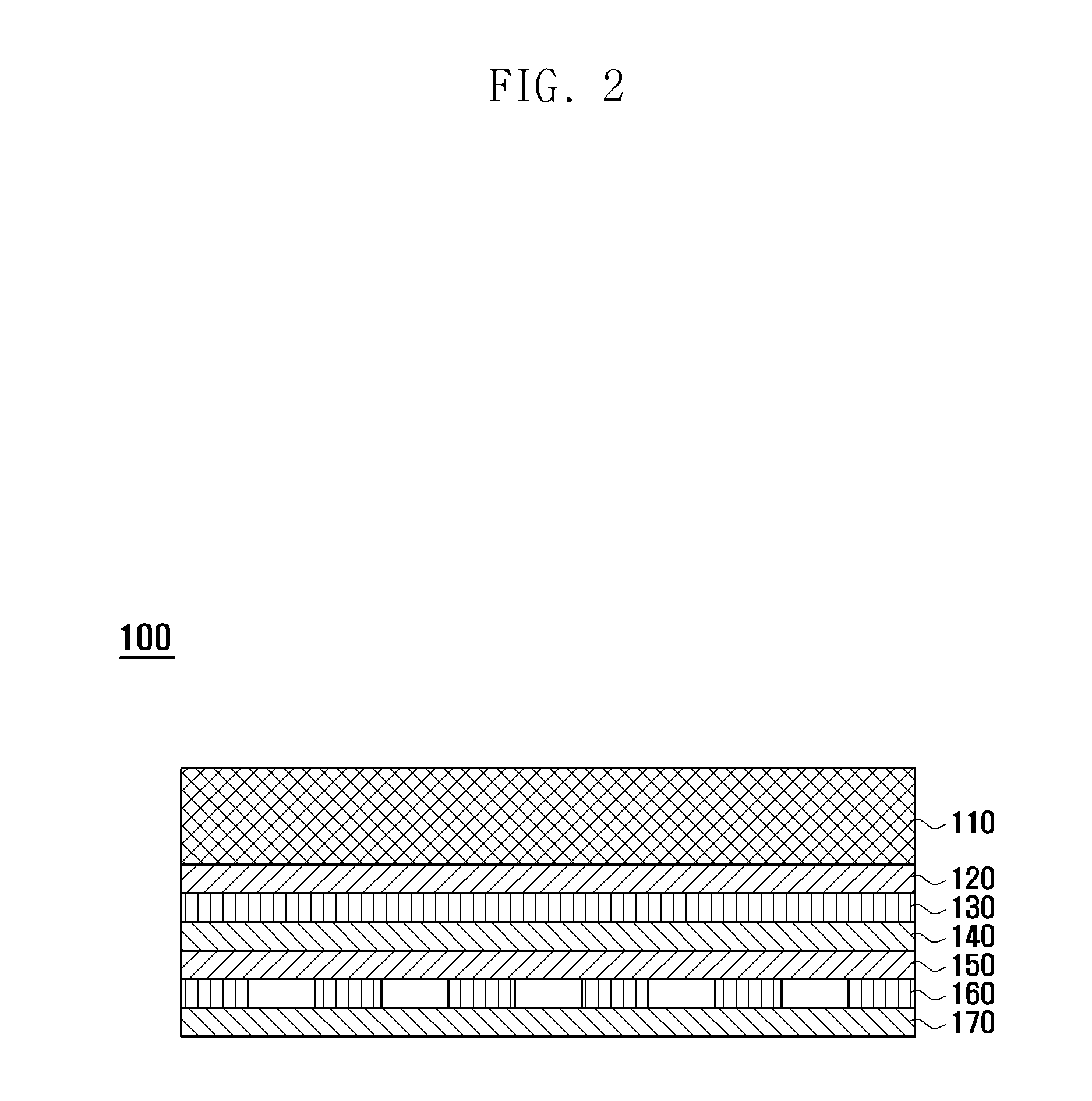
Capacitive type touch screen panel
InactiveUS20120223912A1Reduce image distortionInput/output processes for data processingBi-isotropic materialEngineering
A Capacitive type (C-type) Touch Screen Panel (TSP) is provided. The C-type TSP includes a window for protecting the TSP, an upper transparent adhesive layer bonded under the window, an upper transparent conductive layer bonded under the upper transparent adhesive layer and for detecting a touch point on the window, an upper transparent insulating substrate disposed under the upper transparent conductive layer and formed with polymer of an isotropic material, a lower transparent adhesive layer bonded under the upper transparent insulating substrate, a lower transparent conductive layer bonded under the lower transparent adhesive layer and for detecting a touch point on the window, and a lower transparent insulating substrate disposed under the lower transparent conductive layer and formed with polymer of an isotropic material.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Display backlight system
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
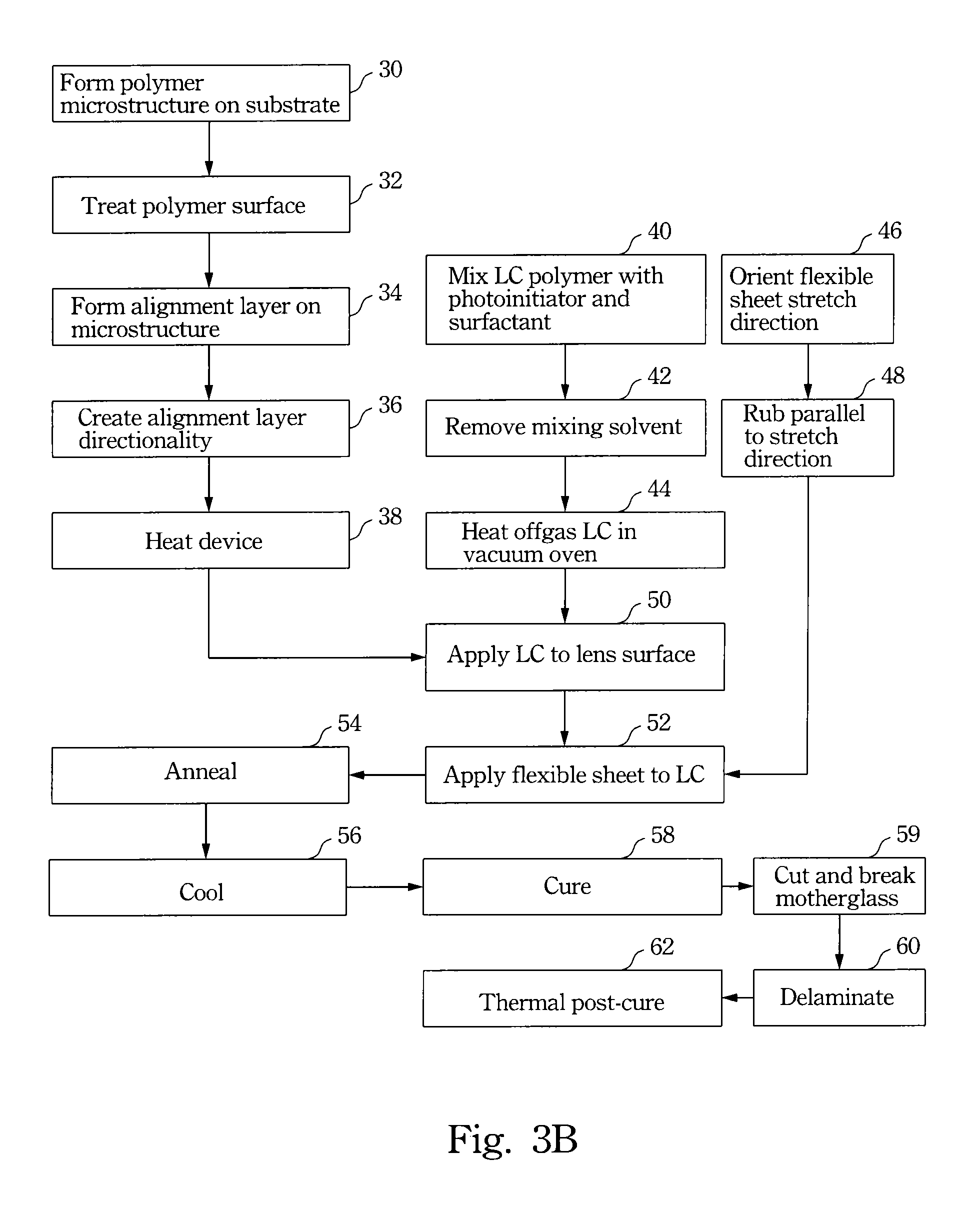
Manufacture of a Birefringent Liquid Crystal Component
ActiveUS20100007806A1Reduced reflection internal artifactLow surface visibilityNon-linear opticsOptical elementsBi-isotropic materialSurface relief
Manufacture of a birefringent liquid crystal cell is performed as follows. A layer of isotropic material having an outer surface which is shaped with a surface relief structure and is provided with a liquid crystal alignment property is formed. A flexible sheet having an outer surface provided with a liquid crystal alignment property is formed. A curable birefringent liquid crystal material is applied to one or both of the layer of isotropic material and the flexible sheet. The flexible sheet is applied over the layer of isotropic material with the outer surfaces of the layer of isotropic material and the flexible sheet facing one another with the liquid crystal material therebetween, thereby to form a liquid crystal cell. The liquid crystal material is cured and the flexible sheet is removed from the liquid crystal cell.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
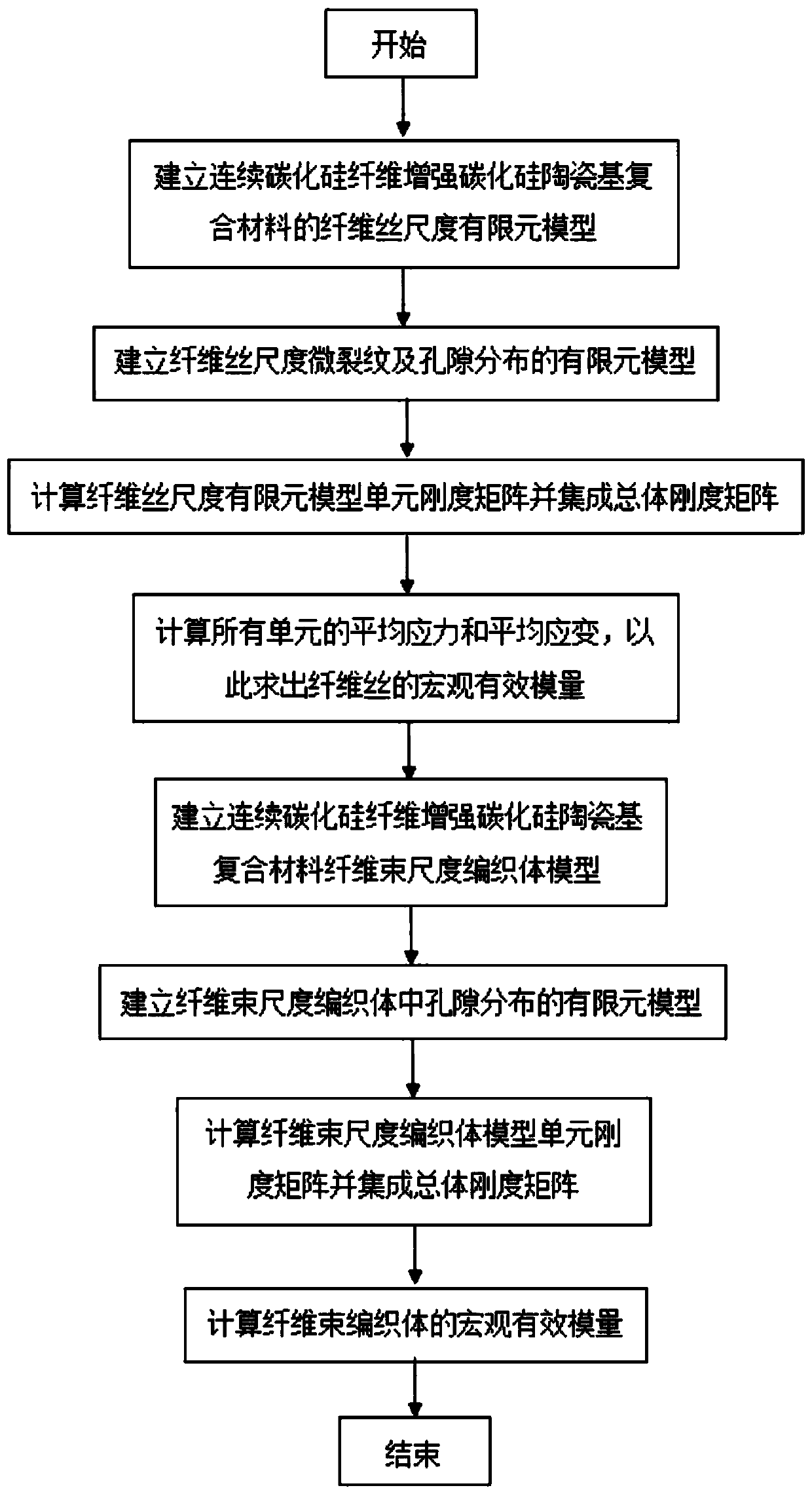
Fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composite microstructure accurate modeling and modulus calculation method
ActiveCN109583052AAccurate Macro Elastic Modulus ValuesDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelFiber bundle
The invention discloses a fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composite microstructure accurate modeling and modulus calculation method. The method comprises the following steps S1, establishing a fiber filament scale finite element model; S2, establishing a finite element model of cellosilk scale microcracks and pore distribution; S3, calculating a unit stiffness matrix of each unit; S4, calculatingaverage stress and average strain of all units of the fiber filament scale finite element model; S5, establishing a fiber bundle scale woven body model; S6, establishing a finite element model of poredistribution in the fiber bundle scale braided body; S7, calculating a unit stiffness matrix in each unit; And S8, calculating average stress and average strain of all units of the fiber bundle scalewoven body model. According to the method, the microstructure characteristics, the microcracks and the pores of the woven body with the fiber size and the fiber bundle size are comprehensively considered, the transverse isotropic material characteristics of the fiber bundles at different weaving positions are effectively set, and a more accurate macroscopic effective modulus value can be obtainedthrough calculation.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Fresnel lens structure and 2d/3d image switching display apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20120268816A1Thin thicknessOptical articlesPolarising elementsManufacturing cost reductionFresnel lens
There is provided a Fresnel lens structure including: a Fresnel lens layer; and a planarization layer disposed on the Fresnel lens layer, any one of the Fresnel lens layer and the planarization layer being formed of a birefringent material and the other being formed of an isotropic material having a refractive index equal to a highest refractive index or a lowest refractive index of the birefringent material. In the Fresnel lens structure, a 2 / 3D image switching structure is simplified and switching thereof is easy. 2 / 3D switching can be performed without using an apparatus with complicated structure, whereby a stereoscopic image display apparatus structure may be simplified and manufacturing costs may be reduced as compared with a lenticular lens by using a Fresnel shaped lens structure.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Versatile method and system for single mode VCSELs
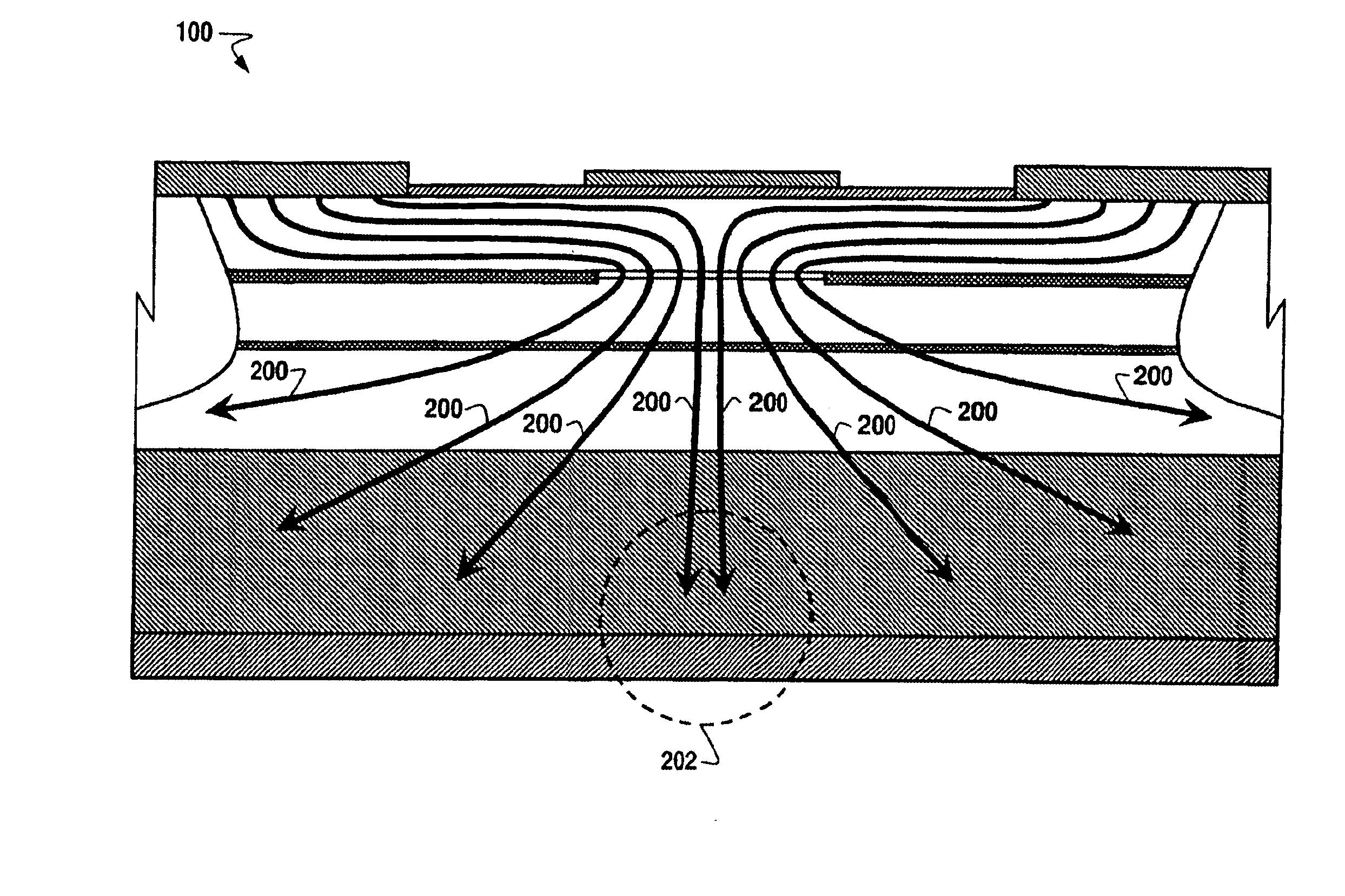
InactiveUS6905900B1Maximize lossOptical wave guidanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserBi-isotropic material
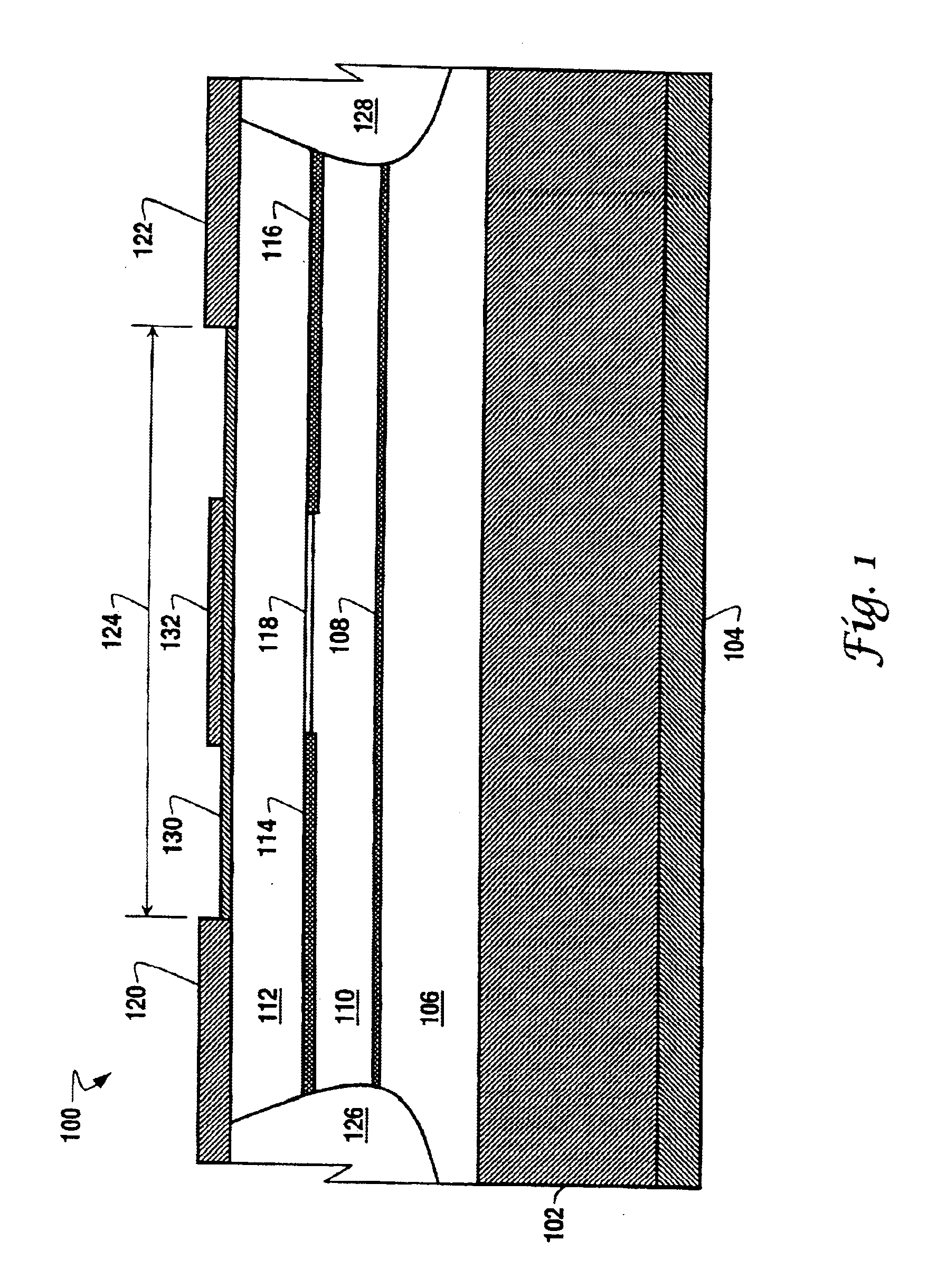
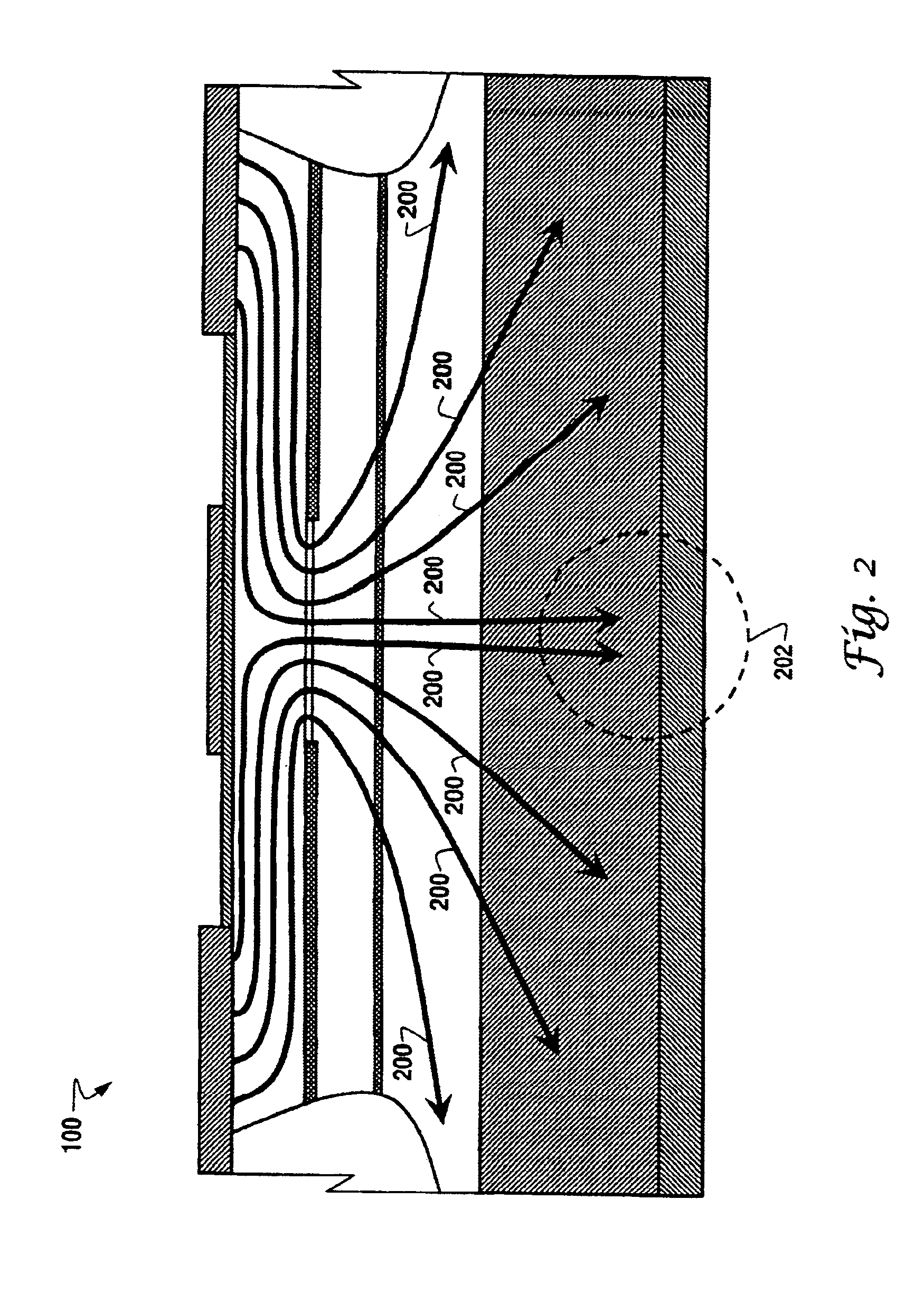
A system and method for providing a single mode VCSEL (vertical cavity surface emitting laser) component (100) is disclosed, comprising a semiconductor substrate (102) having a lower surface and an upper surface, a bottom electrical contact (104) disposed along the lower surface of the substrate, a lower mirror (106) formed of n-type material and disposed upon the upper surface of the substrate, an active region (108) having a plurality of quantum wells disposed upon the lower mirror portion, an upper mirror (110) formed from isotropic material and disposed upon the active region, an equipotential layer (112) disposed upon the upper mirror portion, a first upper electrical contact (120) disposed upon the equipotential layer, a second upper electrical contact (122) disposed upon the equipotential layer at a particular distance (124) from the first upper electrical contact, a first isolation region (126) disposed beneath the first upper contact and traversing the equipotential layer, the upper mirror, the active region, and the lower mirror, a second isolation region (128) disposed beneath the second upper contact and traversing the equipotential layer, the upper mirror, the active region, and the lower mirror, and an insulating layer (114, 116) interposed between the upper mirror and the equipotential layer and adapted to form therebetween an aperture (118) of smaller dimension than the particular distance between the first and second upper contacts.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Manufacture of a Birefringent Liquid Crystal Component
ActiveUS20110299000A1Low surface visibilityReduce reflectionVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureNon-linear opticsCrystallographyBi-isotropic material
Manufacture of a birefringent liquid crystal cell is performed as follows. A layer of isotropic material having an outer surface which is shaped with a surface relief structure and is provided with a liquid crystal alignment property is formed. A flexible sheet having an outer surface provided with a liquid crystal alignment property is formed. A curable birefringent liquid crystal material is applied to one or both of the layer of isotropic material and the flexible sheet. The flexible sheet is applied over the layer of isotropic material with the outer surfaces of the layer of isotropic material and the flexible sheet facing one another with the liquid crystal material therebetween, thereby to form a liquid crystal cell. The liquid crystal material is cured and the flexible sheet is removed from the liquid crystal cell.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
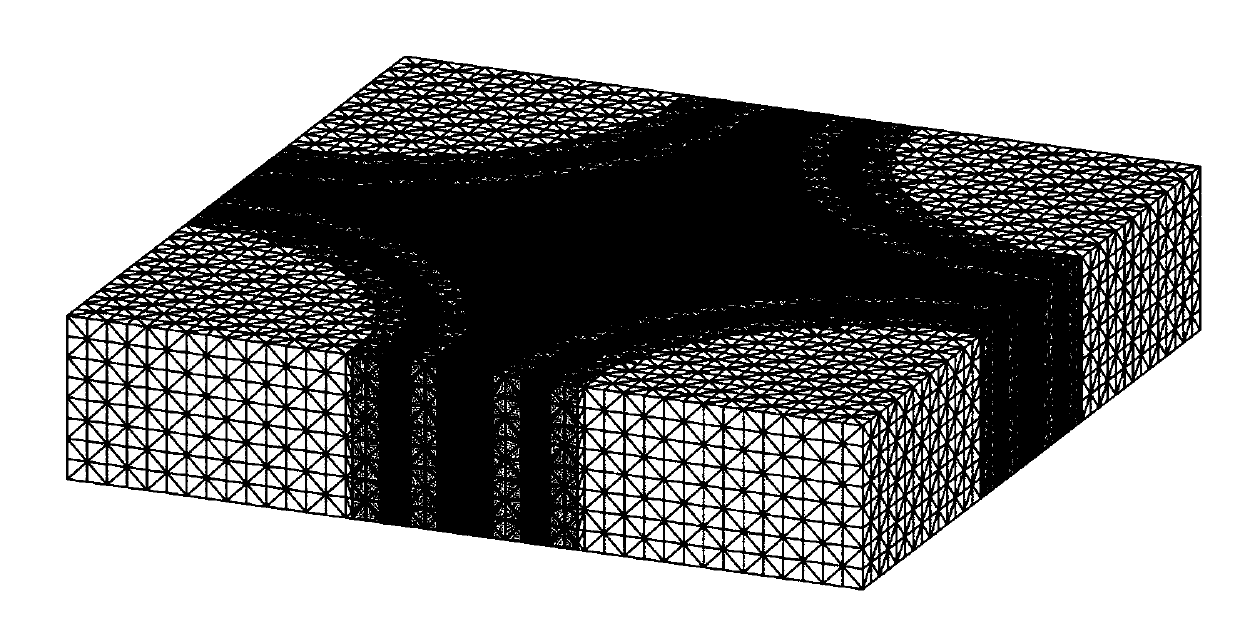
Automatic generating method of three-dimensional woven composite hexahedron finite element model
ActiveCN107330148AFast establishment of finite element model functionRemoving Barriers to Mesostructural CharacterizationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelFiber bundle
The invention discloses an automatic generating method of a three-dimensional woven composite hexahedron finite element model. The method includes the following steps that a space trajectory in the fiber bundle center weaving process is calculated, and position coordinates of the center of each fiber bundle are obtained; position coordinates of space trajectories of center points of the fiber bundles are read, in other words, the position coordinates of each tightened fiber bundle are read, and geometric creation, direction grouping and hexahedron meshing are carried out. By means of the method, the rapid finite element model establishment function of a complex geometric structure three-dimensional woven composite can be achieved only by inputting multiple simple macroparameters. In combination with the geometric structure and finite element modeling, grouping is carried out according to fiber bundle center direction vectors, material spindle direction setting of transverse isotropy materials of the fiber bundles is convenient, the change of internal zone, surface zone and corner zone fiber bundle sections is considered, and transverse isotropy finite element model establishment of the large-size three-dimensional woven composite can be achieved in reality from being manually feasible theoretically.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Acoustic emission source positioning method suitable for three-dimensional structure
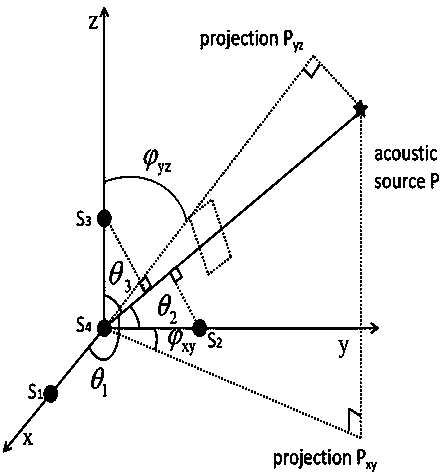
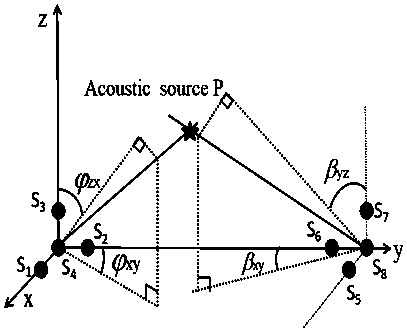
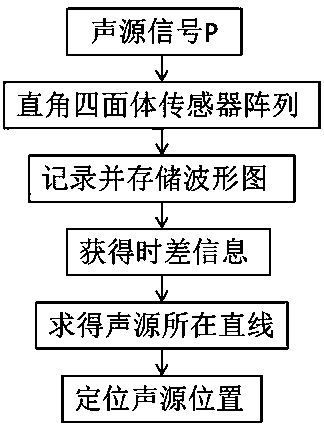
ActiveCN111239256AEnsure safetyLow costMaterial analysis using acoustic emission techniquesProcessing detected response signalSound source locationSensor array
The invention relates to an acoustic emission source positioning method suitable for a three-dimensional structure, belongs to the technical field of sound source positioning, and the position of theacoustic emission source is positioned through the time difference information and the space information of the right-angled tetrahedron type sensor array. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a three-dimensional sound emission source positioning sensor array, recording and storing sound wave signals from a sound source received by each sensor, analyzing a sound wave signal graphto obtain a required time difference, and determining the position of the sound source according to the time difference. The method is not only suitable for isotropic materials, but also can be wellsuitable for anisotropic materials; only eight ultrasonic sensors are needed, so that the cost of the continuous monitoring structure can be greatly reduced; any iterative algorithm is not needed, andthe positioning precision and speed are effectively improved. The invention provides a new method for sound source localization in acoustic emission detection, guarantees the safety of the structureby discovering damage and potential threats in time, and has a good application prospect in the fields of spaceflight and navigation, civil engineering, large and small machinery and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Light guide structure, backlight module and display device
InactiveCN104914624AReduce lossesIncrease profitPlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsBi-isotropic materialLight guide
The invention discloses a light guide structure, a backlight module and a display device which are used for solving the problem of the low light utilization rate caused by large loss in the light propagation process by means of a light guide structure in the prior art. The light guide structure comprises a light guide plate, a reflective brightening film, a lambda / 4 wave plate and a reflective film, wherein the light guide plate comprises a light emission face, a reflective face and a side face, wherein the light emission face and the reflective face are arranged oppositely, and the side face is connected with the light emission face and the reflective face, wherein the light guide plate is made of an isotropic material; the reflective brightening film is arranged on the side, where the light emission face is located, of the light guide plate, the lambda / 4 wave plate is arranged between the light emission face of the light guide plate and the brightening film, and an included angle between the slow axis of the lambda / 4 wave plate and a transmission axis of the brightening film is 45 degrees; the reflective film is arranged on the side, where the reflective face is located, of the light guide plate.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Illumination system for flat panel display device
InactiveUS7667788B2Effectively separated and emittedImprove energy efficiencyOptical waveguide light guideWaveguidesBi-isotropic materialLight guide
An illumination system for a flat panel display device includes: a light guide plate made of an optically isotropic material; a light source disposed at a side of the light guide plate; an upper layer disposed on a top surface of the light guide plate and made of an optically anisotropic material; and a polarization selection emitting structure which is disposed at an interface of the light guide plate and the upper layer. The upper layer has two different refractive indices and one of the two refractive indices is the same as a refractive index of the light guide plate. In the polarization selection emitting structure differently polarized light is differently refracted, reflected, diffracted, or scattered based on polarization direction.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Pad-assisted electropolishing
InactiveUS20090277802A1Avoid dishingAvoid erosionElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid layerElectrolysis
Pad-assisted electropolishing of the substrate is conducted by performing anodic dissolution of metal at a first portion of the substrate and simultaneously mechanically buffing a second portion of the substrate with a buffing pad. Anodic dissolution includes forming a thin liquid layer of electropolishing liquid between the anodic substrate and a cathodic electropolishing head. The location of electrical contacts between the substrate and power supply allow peripheral edge regions of the substrate to be mechanically buffed with the pad. Preferably, a substrate is further planararized using an isotropic material-removal technique. An apparatus includes an electropolishing head that is movable to a position proximate to a first portion of a substrate to form a thin gap, and a buffing pad that mechanically buffs a second portion of the substrate using minimal pressure.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com