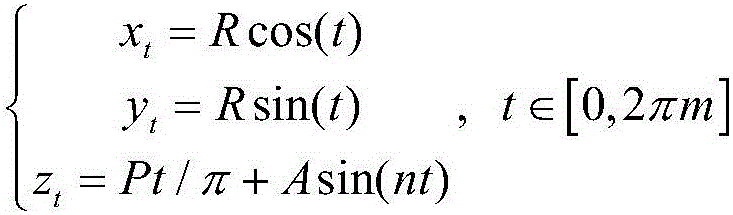Patents
Literature
75 results about "Electropolishing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electropolishing, also known as electrochemical polishing, anodic polishing, or electrolytic polishing (especially in the metallography field), is an electrochemical process that removes material from a metallic workpiece, reducing the surface roughness by levelling micro-peaks and valleys, improving the surface finish. It is used to polish, passivate, and deburr metal parts. It is often described as the reverse of electroplating. It may be used in lieu of abrasive fine polishing in microstructural preparation.
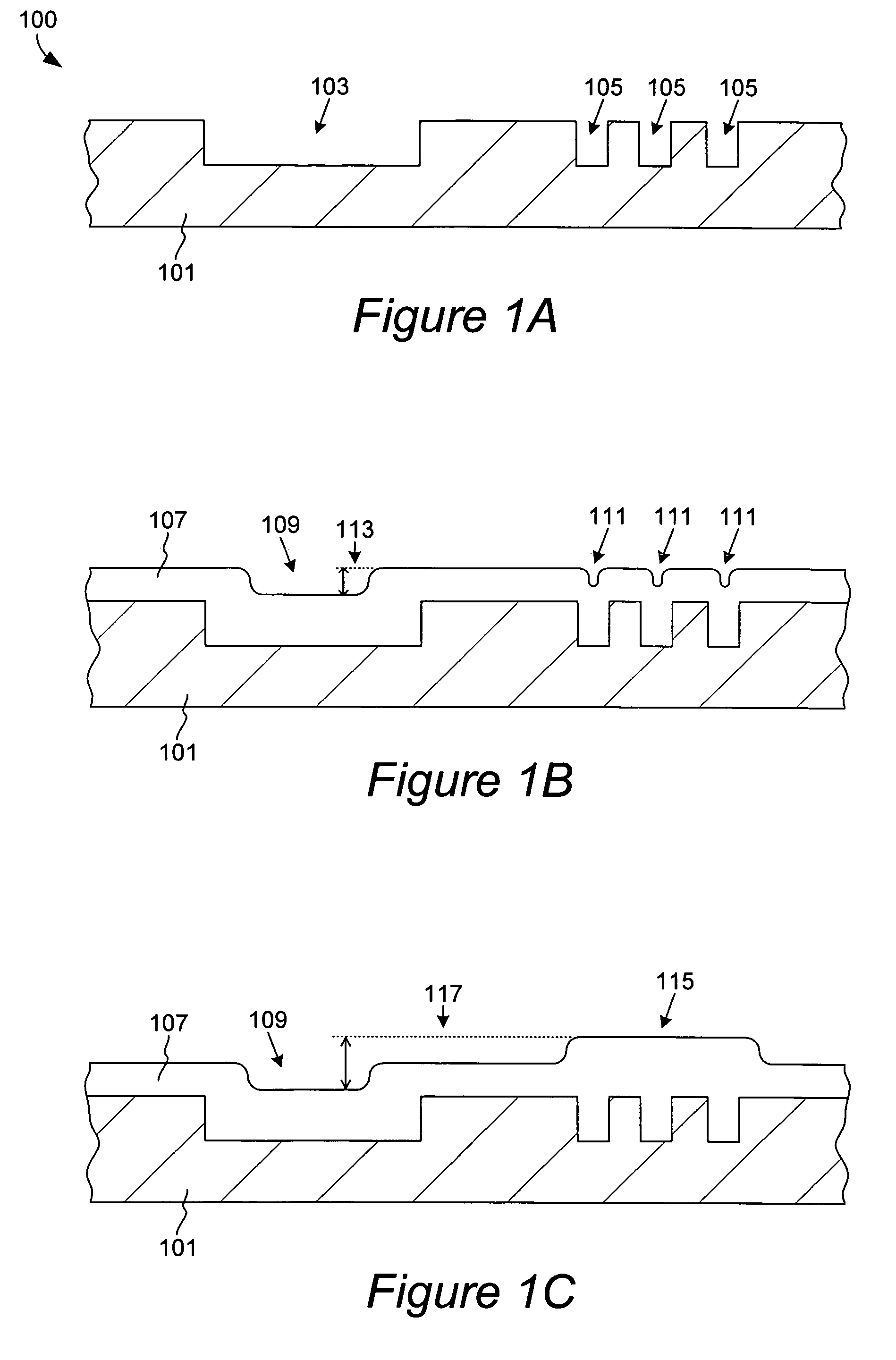
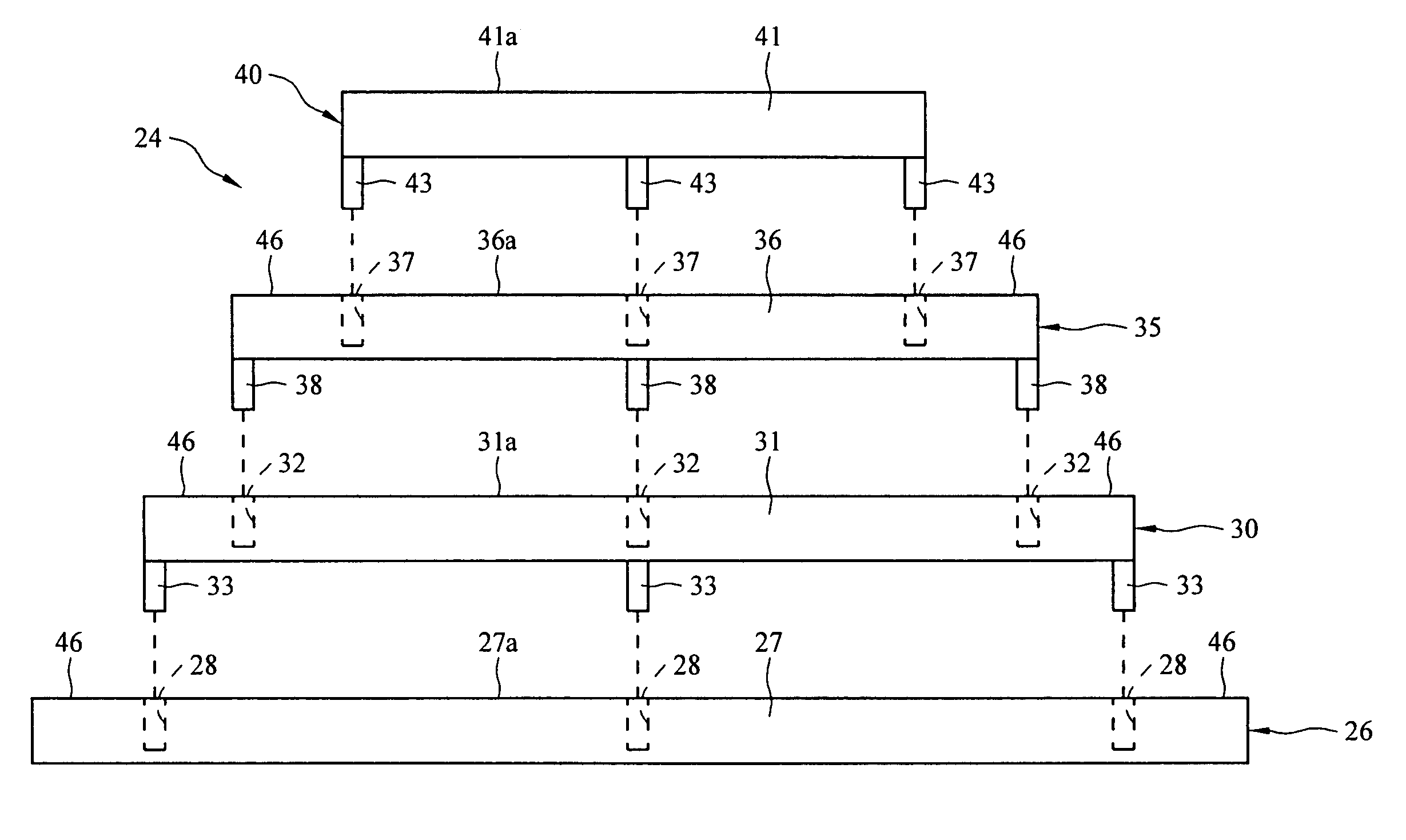
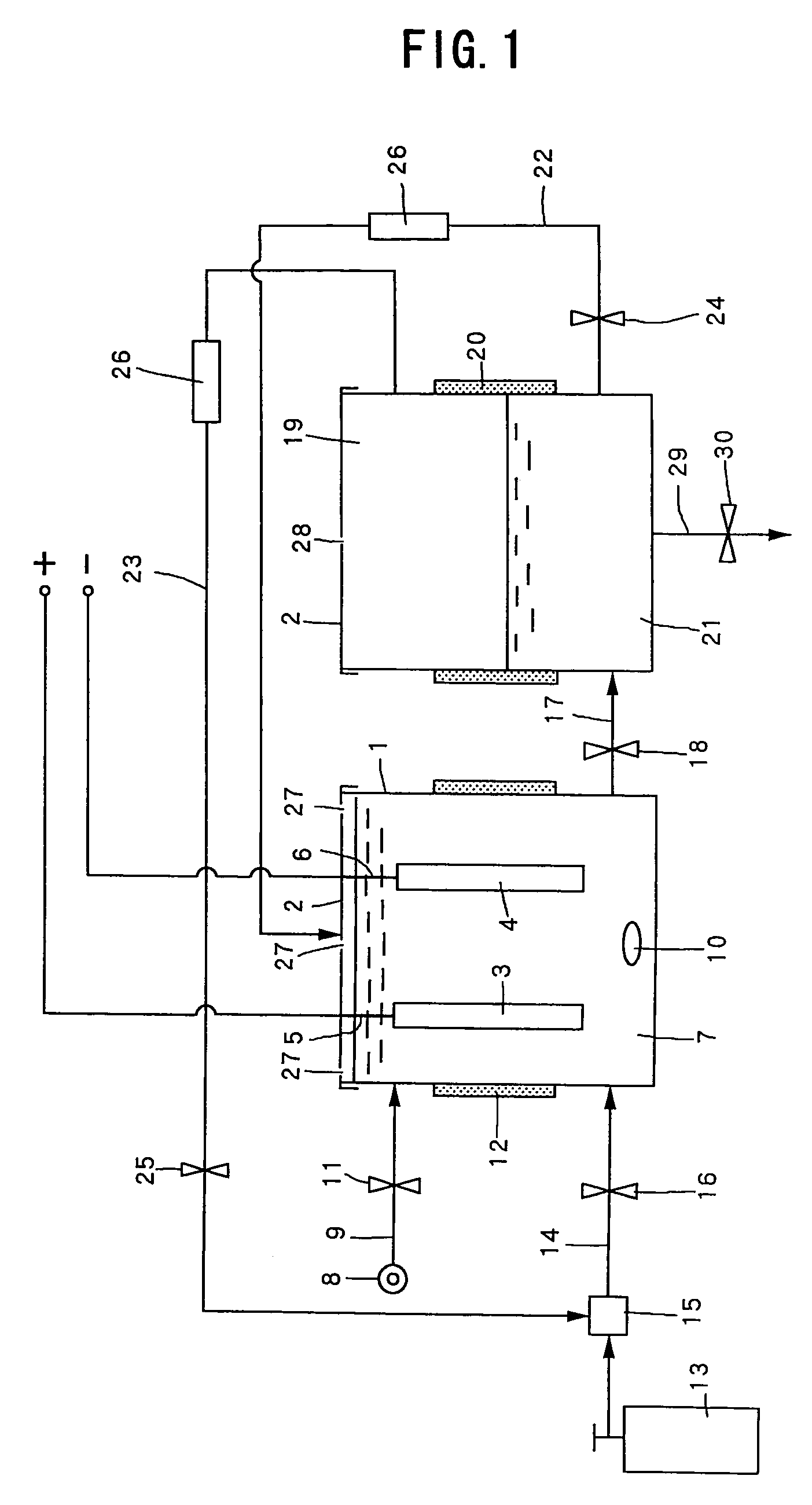
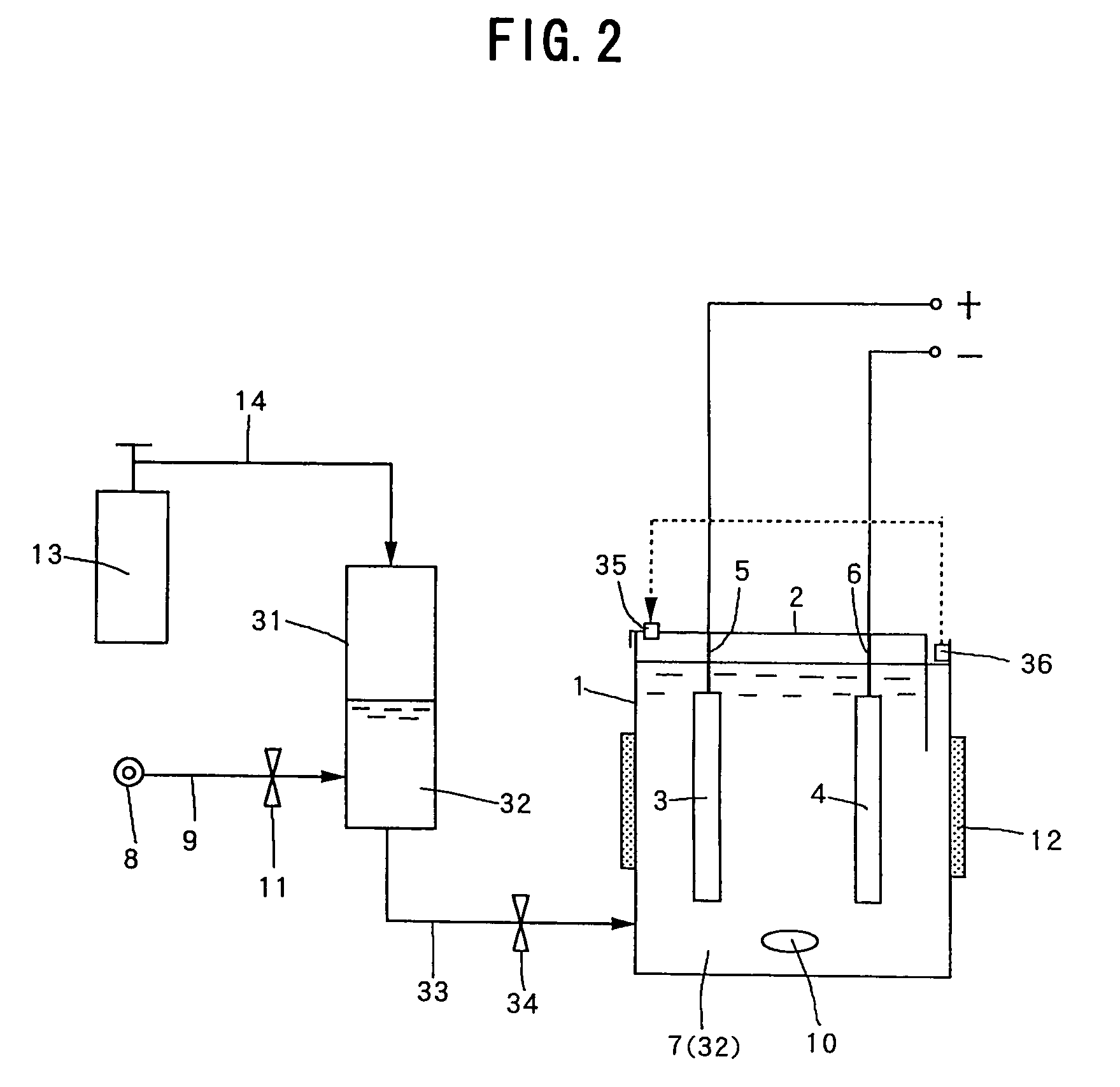
Method for manufacturing dielectric capacitor, dielectric memory device
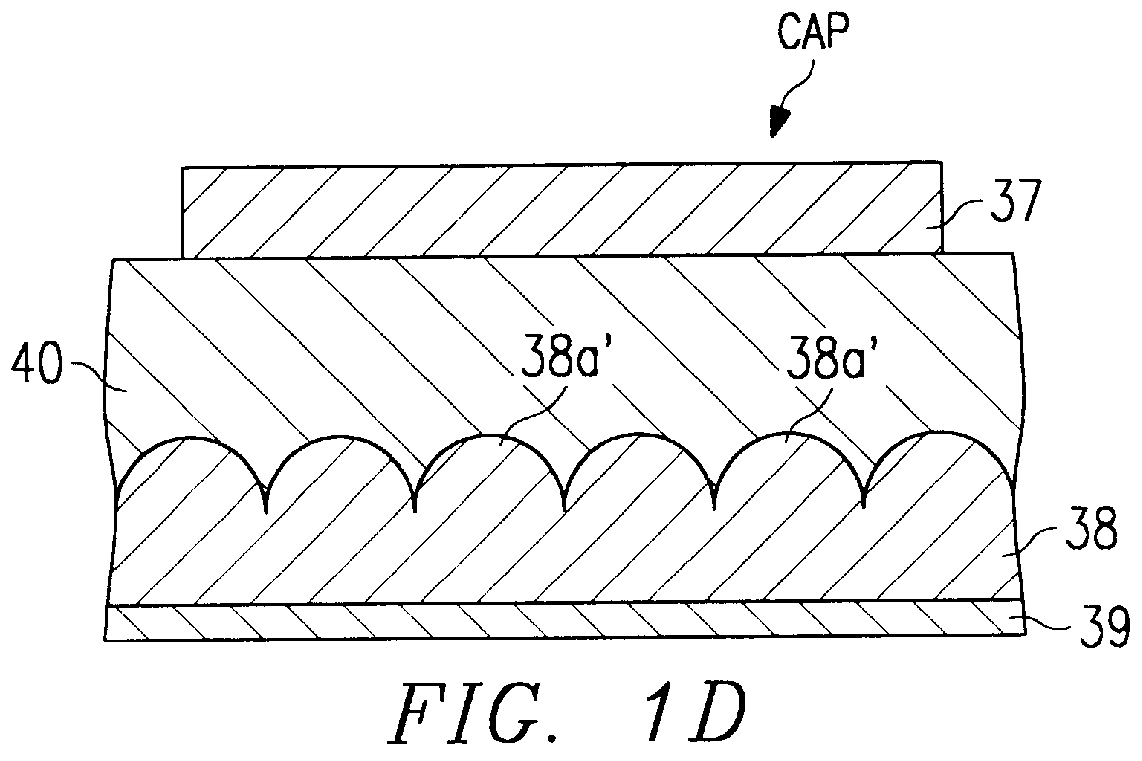
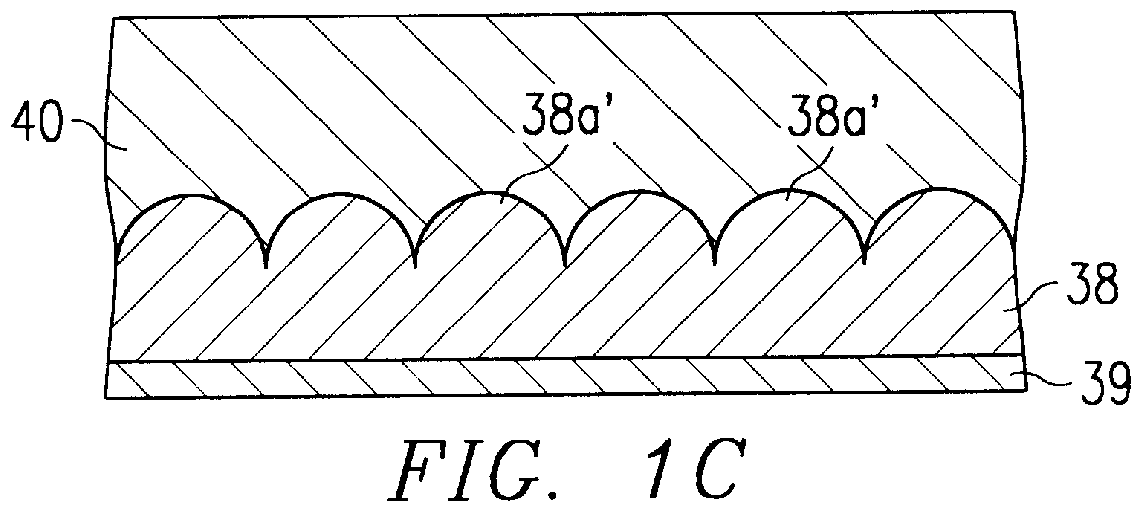
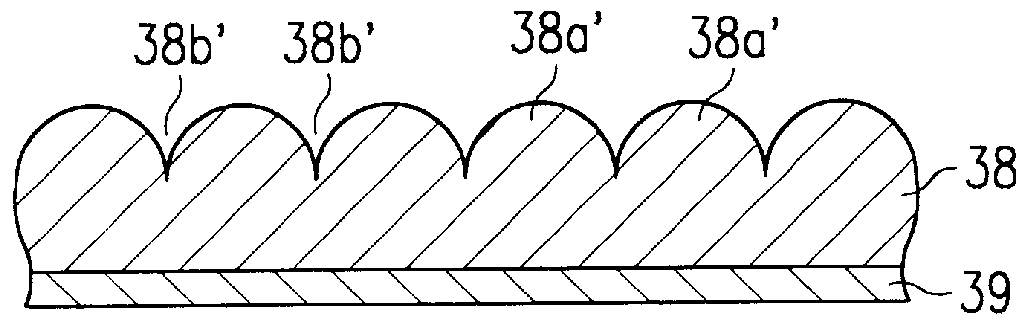
InactiveUS6033953AReduce leakage currentImprove flatnessTransistorThin/thick film capacitorElectrolysisCapacitor
A dielectric capacitor is provided which has a reduced leakage current. The surface of a first electrode (38) of the capacitor is electropolished and a dielectric film (40) and a second electrode (37) are successively laminated on it. The convex parts pointed end (38a) existing on the surface of the first electrode is very finely polished uniformly by dissolving according to electropolishing, a spherical curved surface in which the radius of curvature has been enlarged is formed, and the surface of the first electrode is flattened. Therefore, concentration of electrolysis can be prevented during the operation at the interface of the first electrode and the dielectric film, and the leakage current can be reduced considerably.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
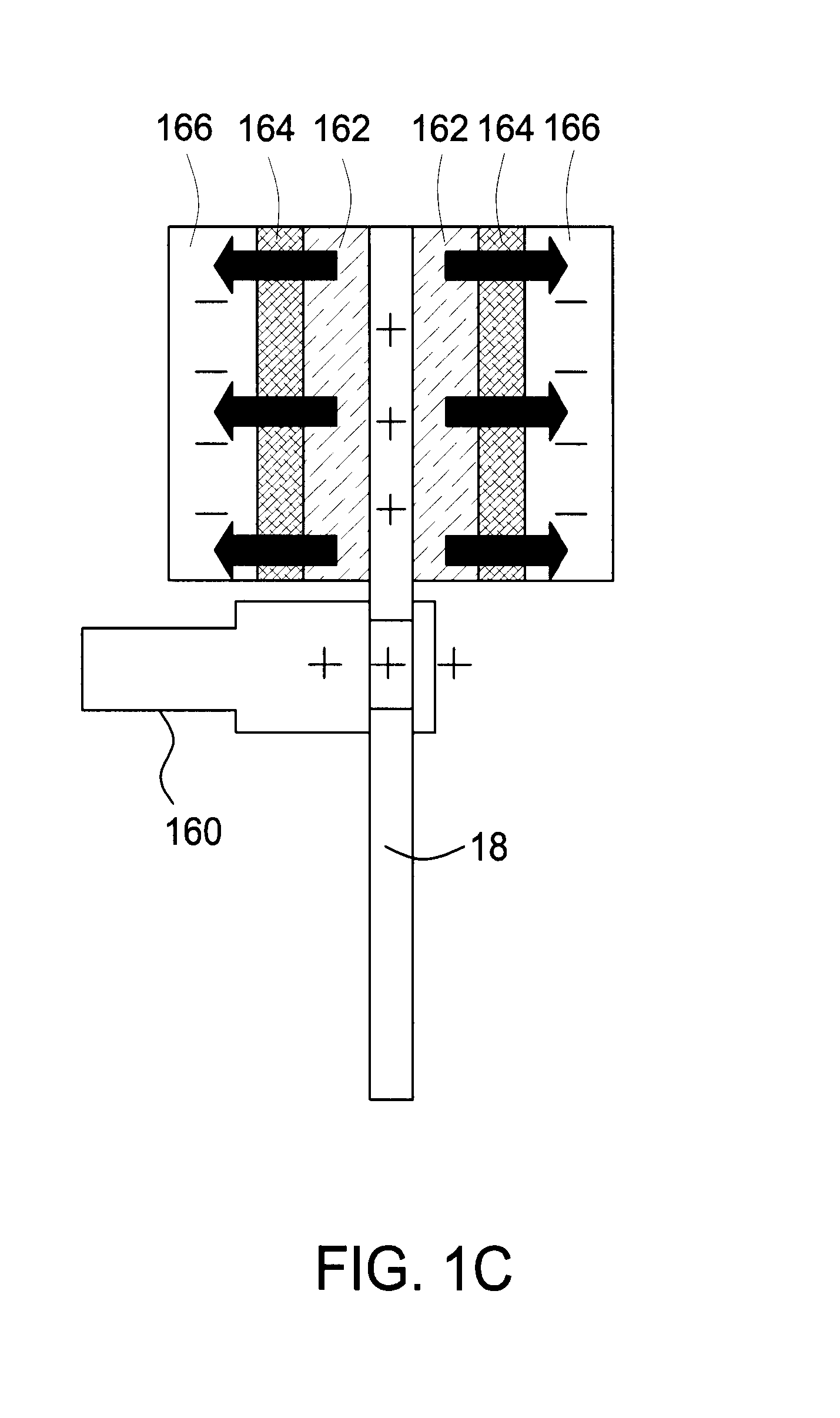
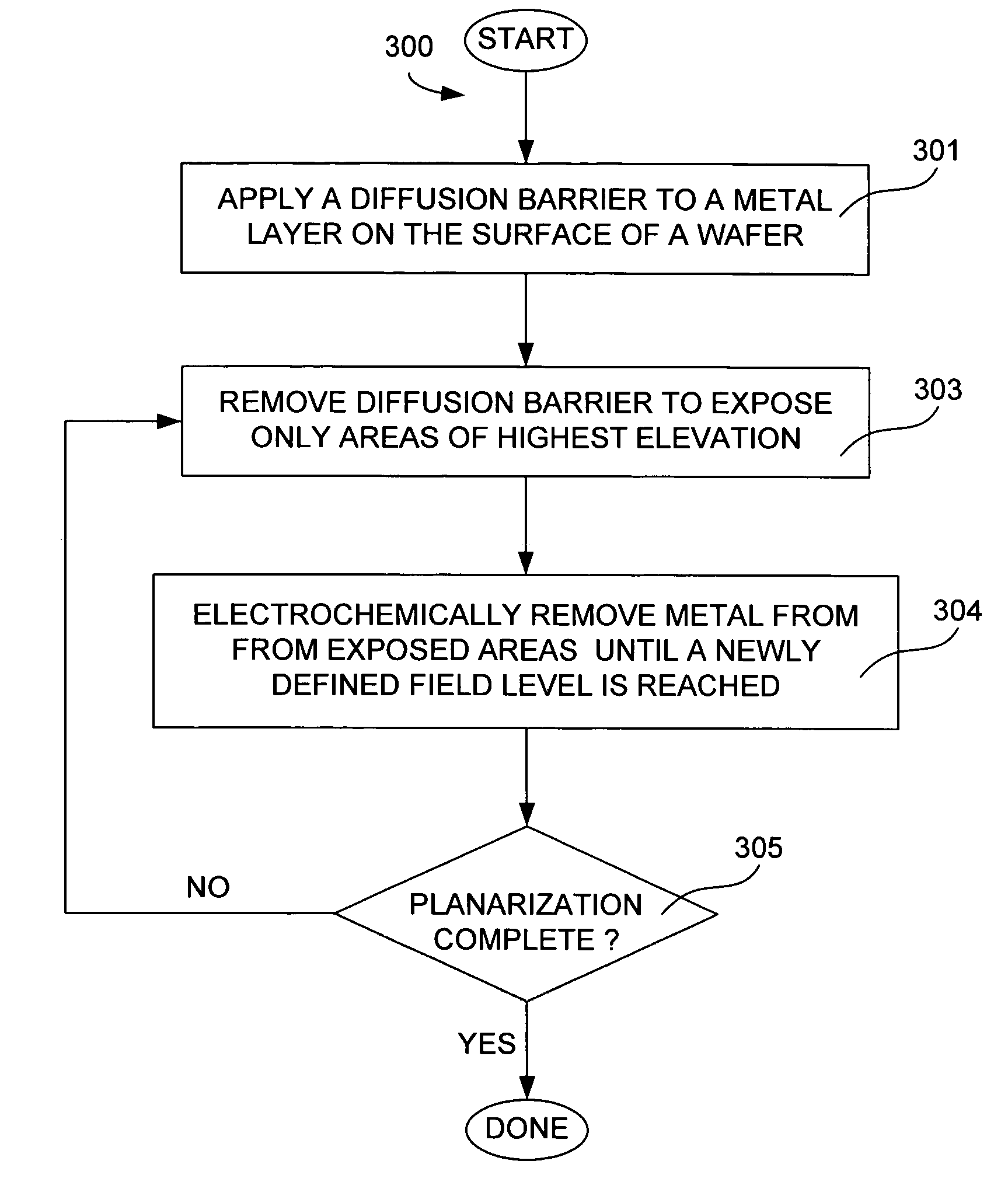
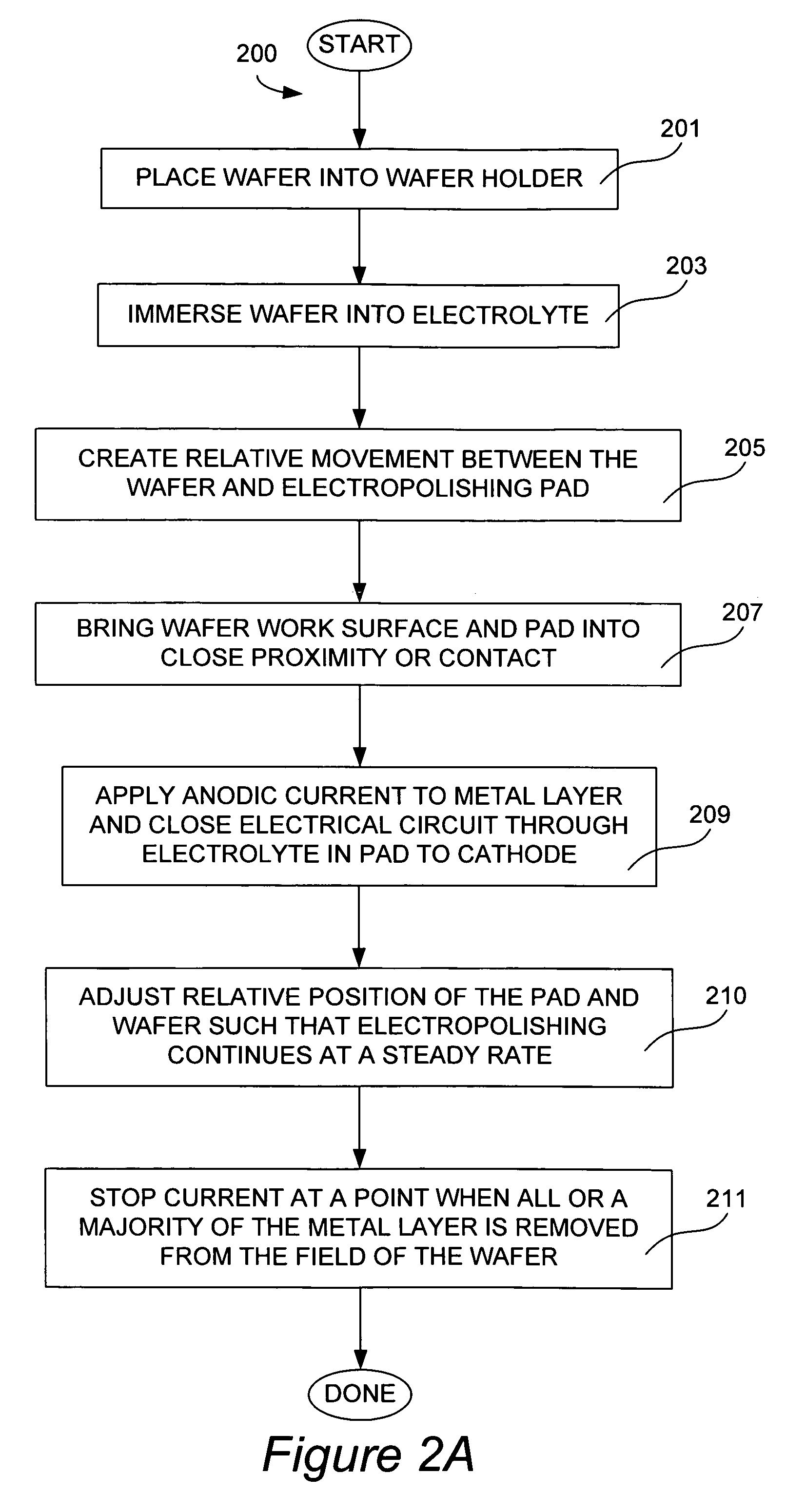
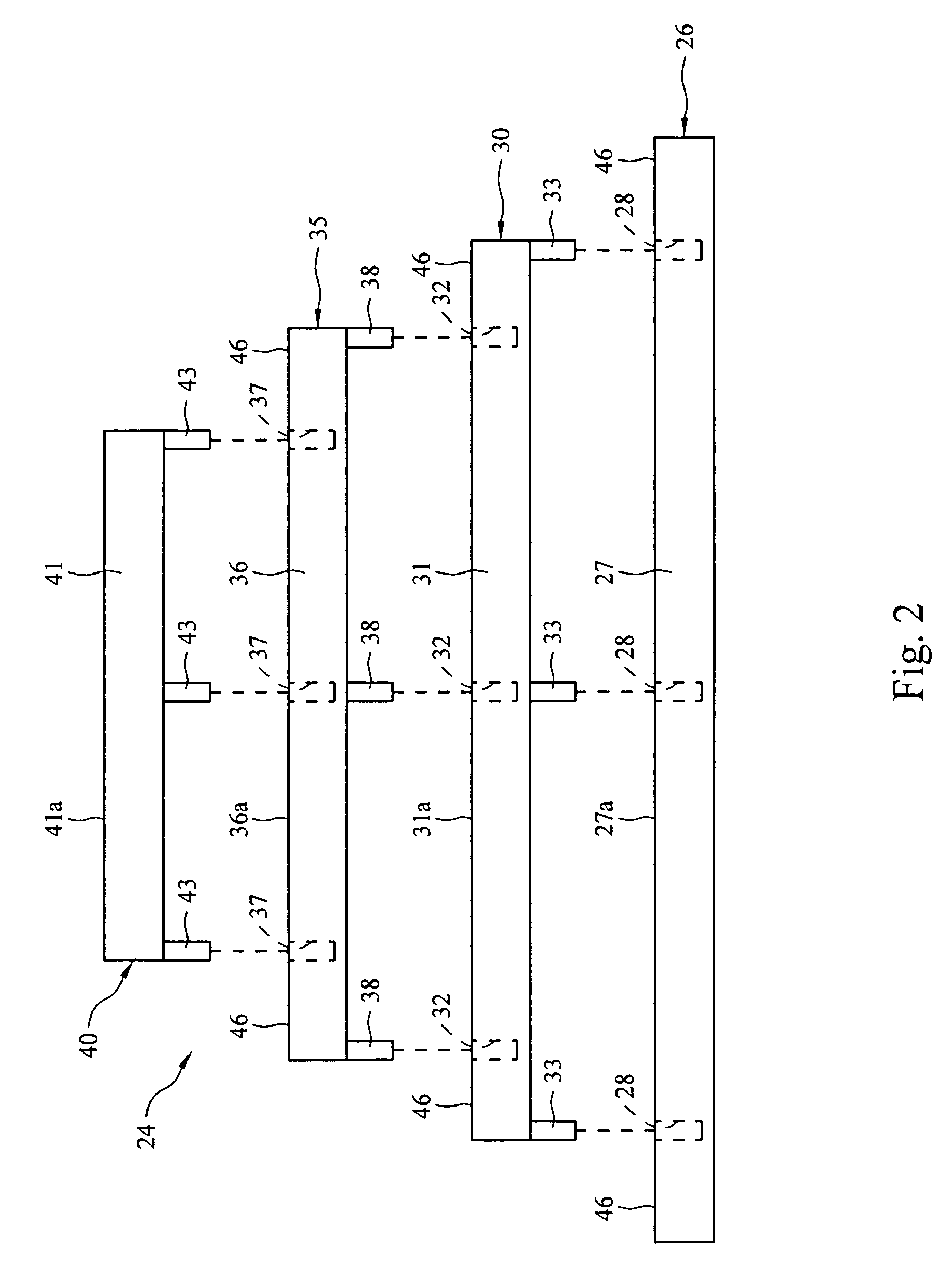
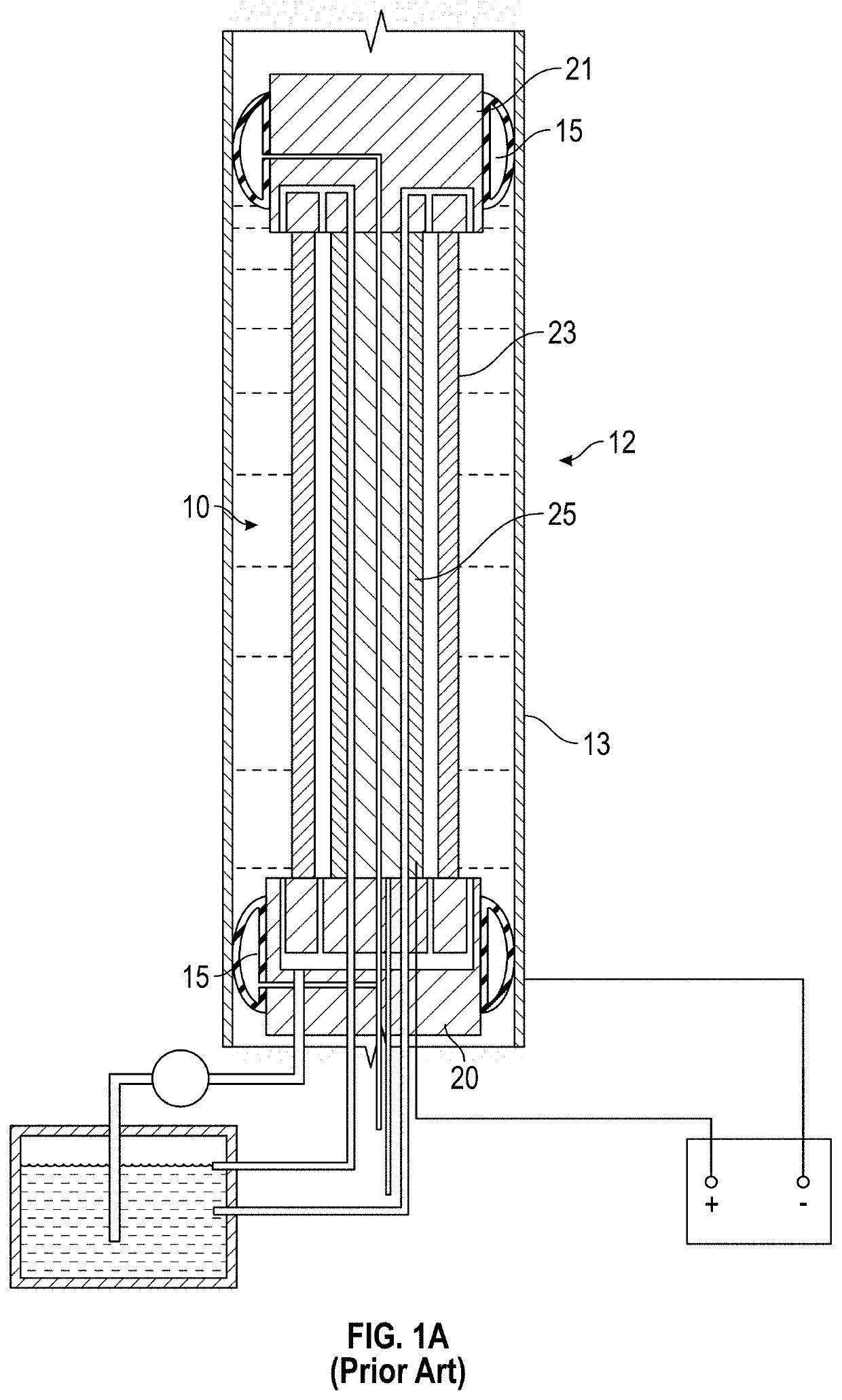
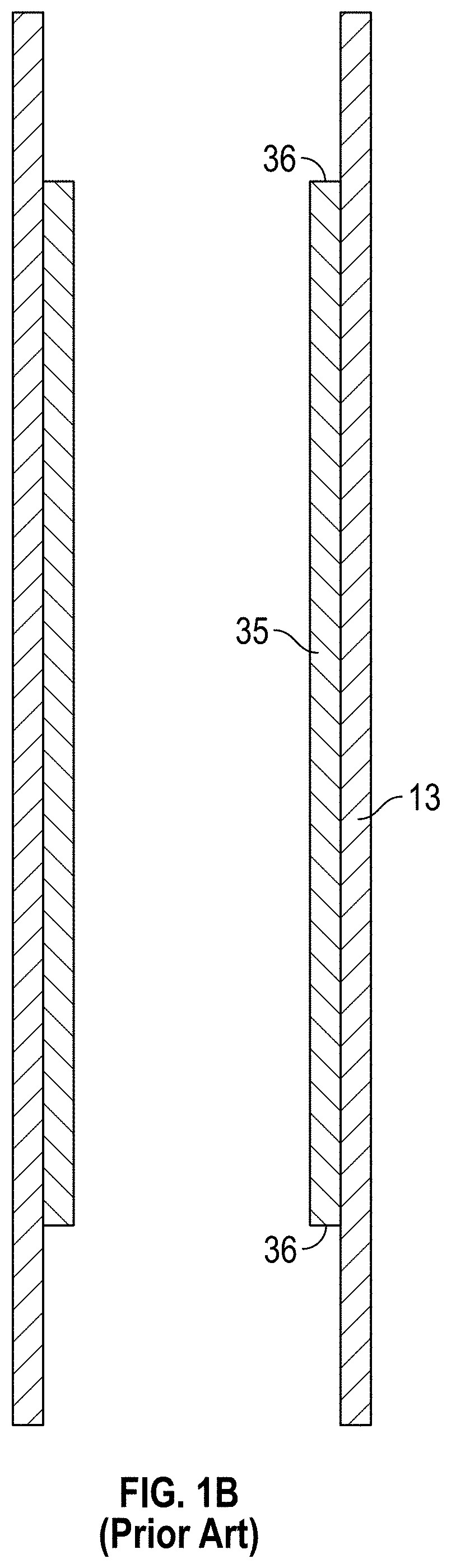
Method and apparatus for uniform electropolishing of damascene ic structures by selective agitation
InactiveUS20020074238A1Small apertureSufficiently porousElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityElectrolysis
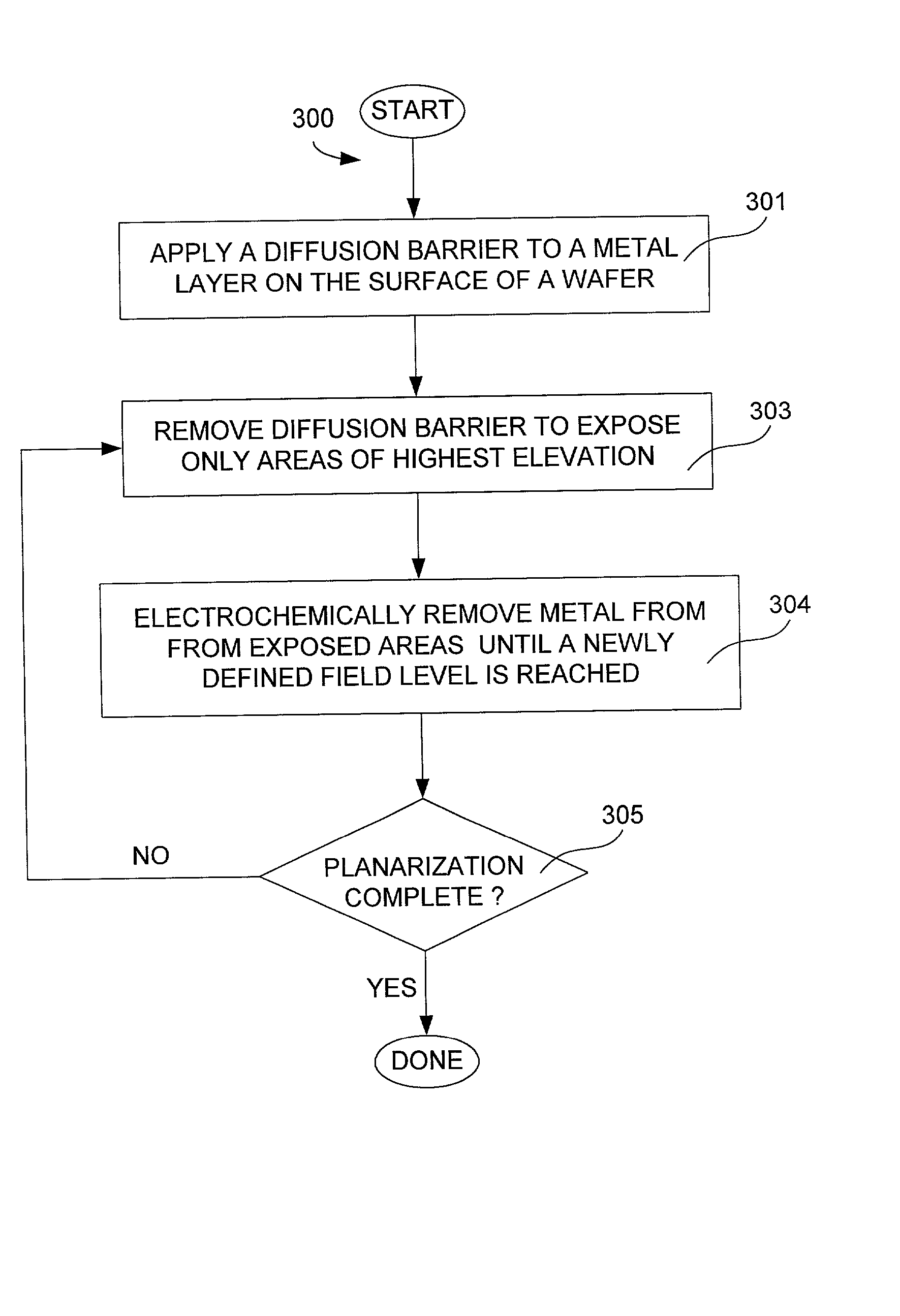
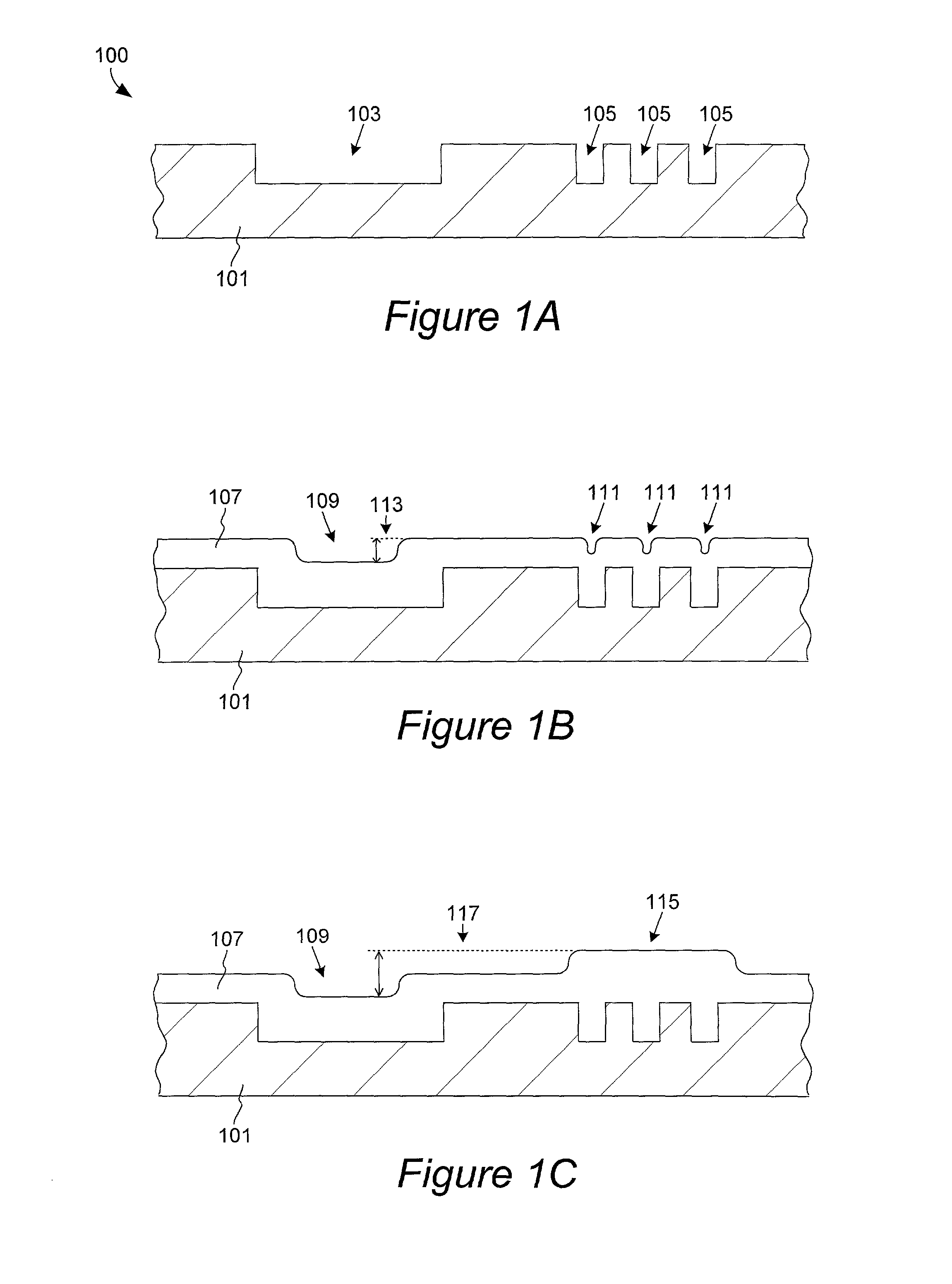
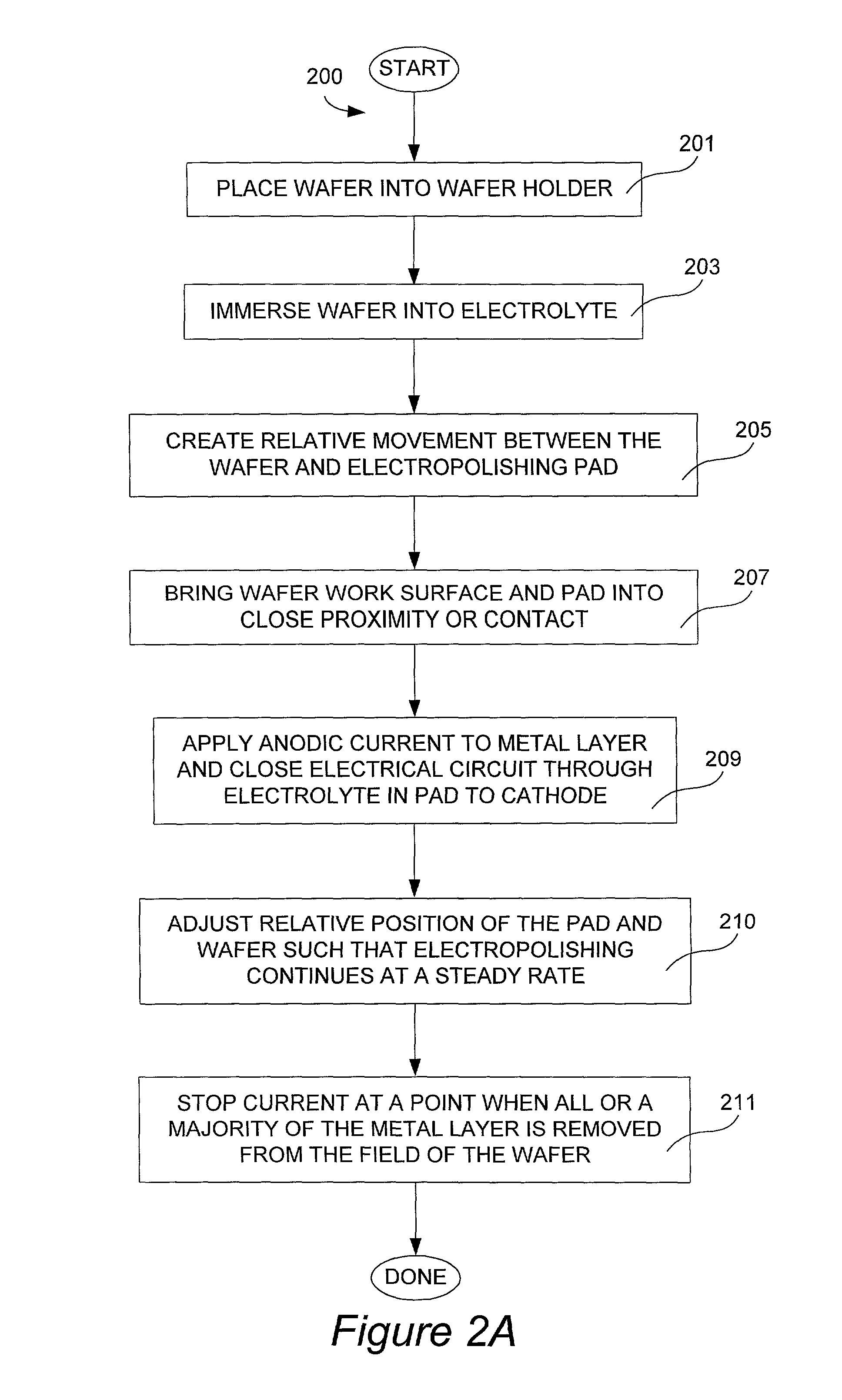
The present invention pertains to apparatus and methods for planarization of metal surfaces having both recessed and raised features, over a large range of feature sizes. The invention accomplishes this by increasing the fluid agitation in raised regions with respect to recessed regions. That is, the agitation of the electropolishing bath fluid is agitated or exchanged as a function of elevation on the metal film profile. The higher the elevation, the greater the movement or exchange rate of bath fluid. In preferred methods of the invention, this agitation is achieved through the use of a microporous electropolishing pad that moves over (either near or in contact with) the surface of the wafer during the electropolishing process. Thus, methods of the invention are electropolishing methods, which in some cases include mechanical polishing elements.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
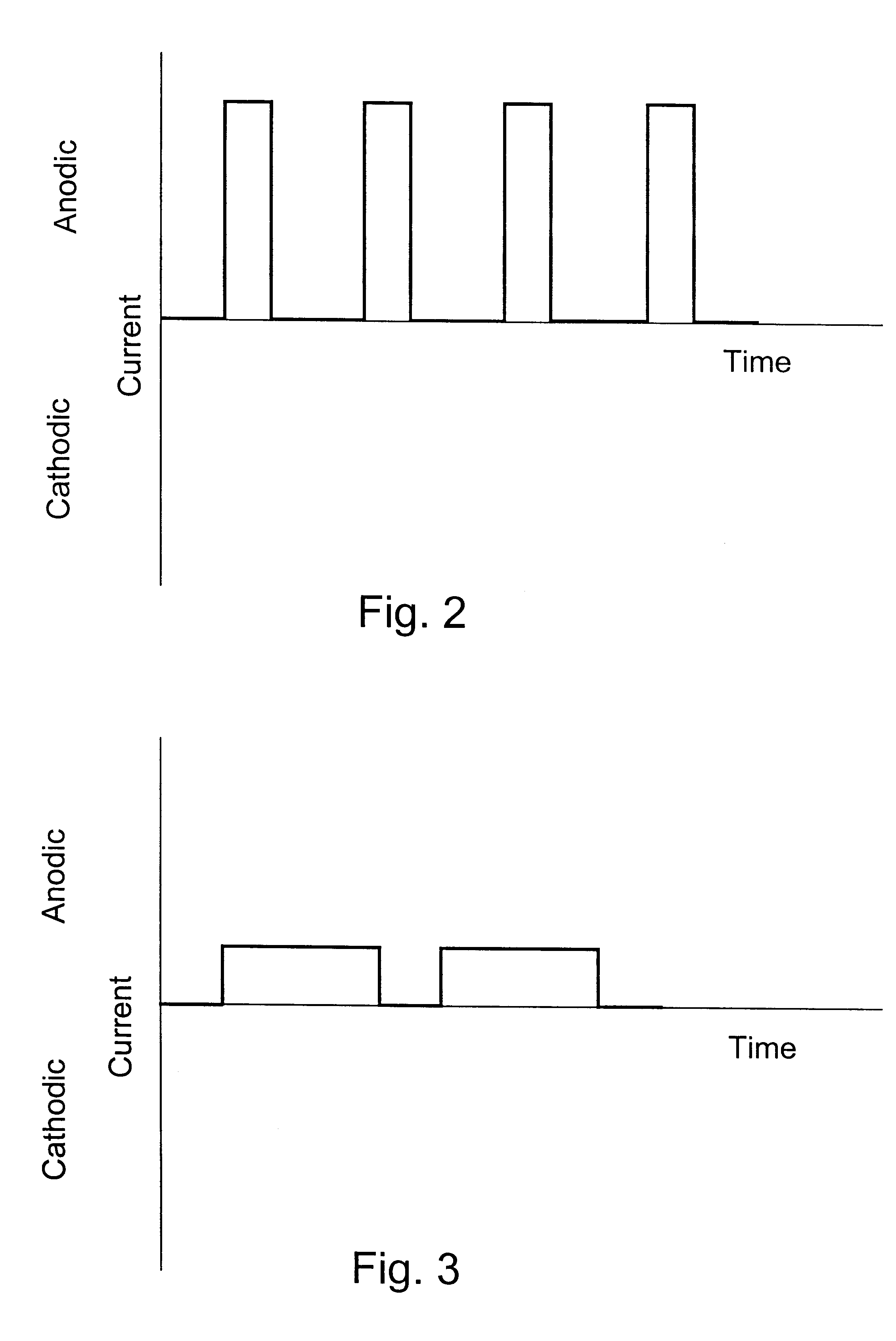
Sequential electromachining and electropolishing of metals and the like using modulated electric fields
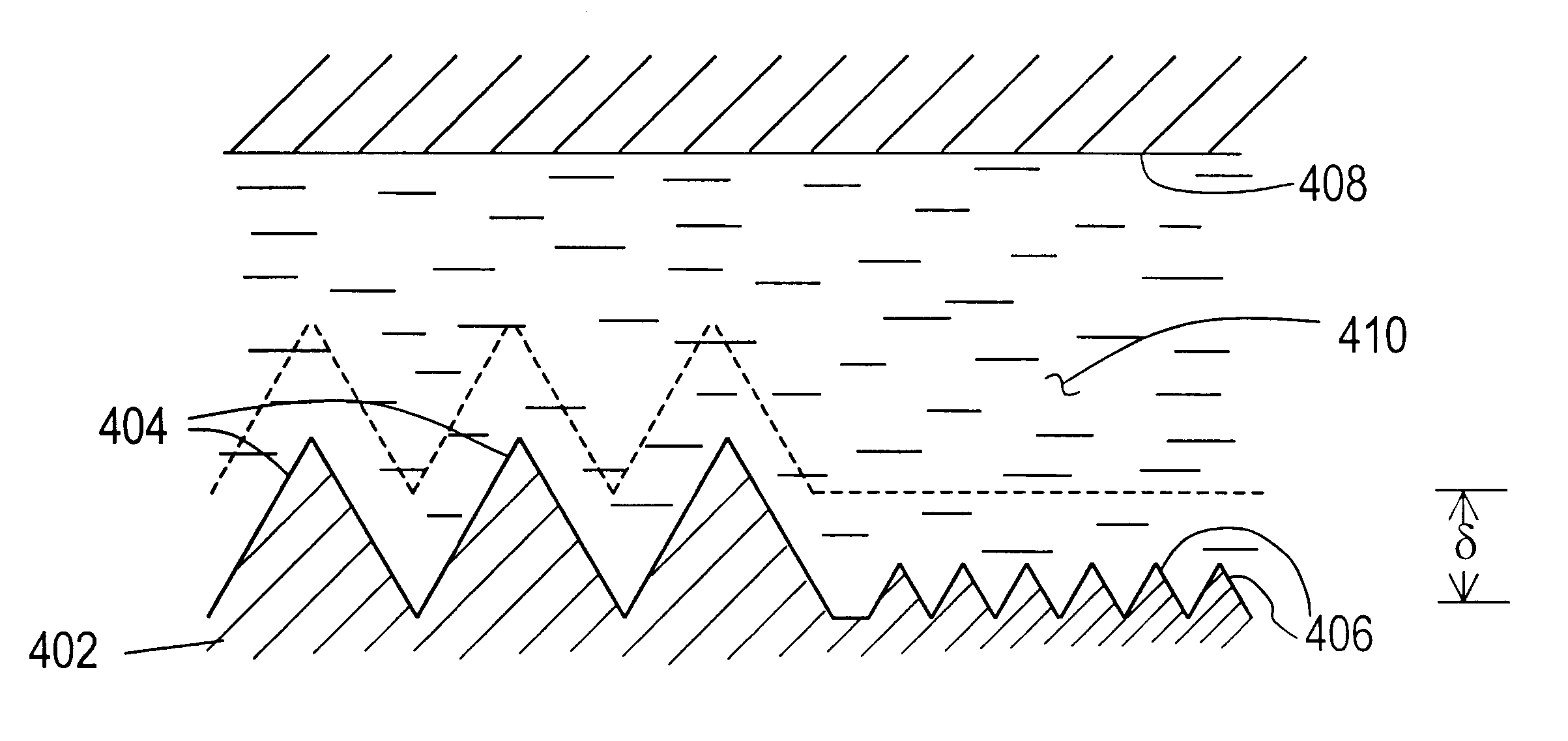
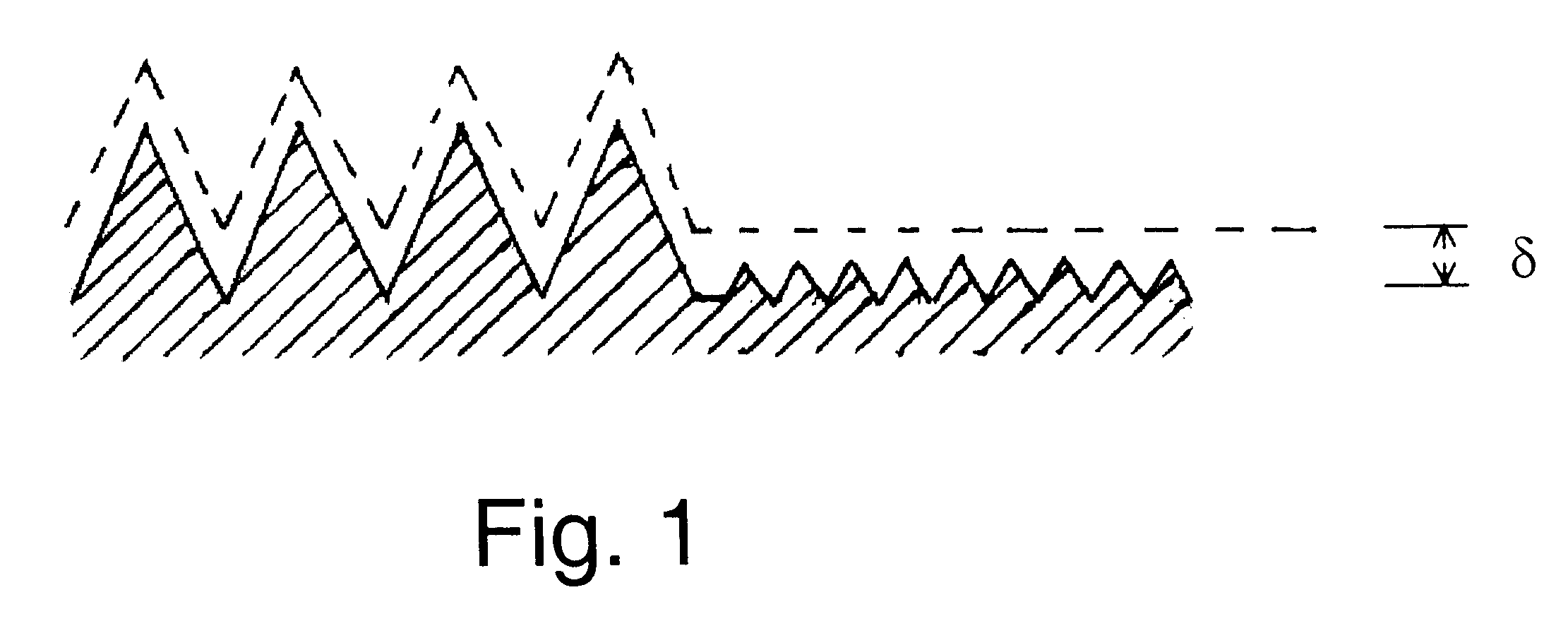
A surface of an electrolytically dissolvable material, e.g., an electrolytically dissolvable metal, is smoothed by a two-step electrochemical process wherein a the surface to be smoothed and a counterelectrode are contacted with an electrolyte and an electric current is passed between the substrate and counterelectrode, with the substrate as the anode. In a first step relatively large asperities on the substrate are reduced in height by maintaining a macroprofile regime by using a pulsed electric current with short pulses. In a second step, small asperities and the remainder of the large asperities are reduced or removed by maintaining a microprofile regime by using a pulsed current having longer pulses or a direct current.
Owner:FARADAY TECH INC
High selectivity and high planarity dielectric polishing
InactiveUS6866793B2Efficiently planarizedImprove planarization efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSlurryDielectric structure
A slurry includes a plurality of particles and at least one selective adsorption additive. The particles are preferably composite particles including a core surrounded by a shell provided by the selective adsorption additive. The slurry can be used to polish a structure including silicon dioxide or a low K dielectric film and a silicon nitride containing film, such as to form a shallow trench isolation (STI) structure or a metal-dielectric structure. The silicon nitride containing film surface substantially adsorbs the selective adsorption additive, whereas the silicon dioxide or low K dielectric film shows non-substantial adsorption characteristics to the adsorption additive. In another embodiment of the invention, silicon dioxide or low K dielectric film shows non-substantial adsorption of the selective adsorption additive at a pressure above a predetermined first pressure, and substantial adsorption of the selective adsorption additive for pressures below a predetermined second pressure, where the first pressure is greater than the second pressure.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA
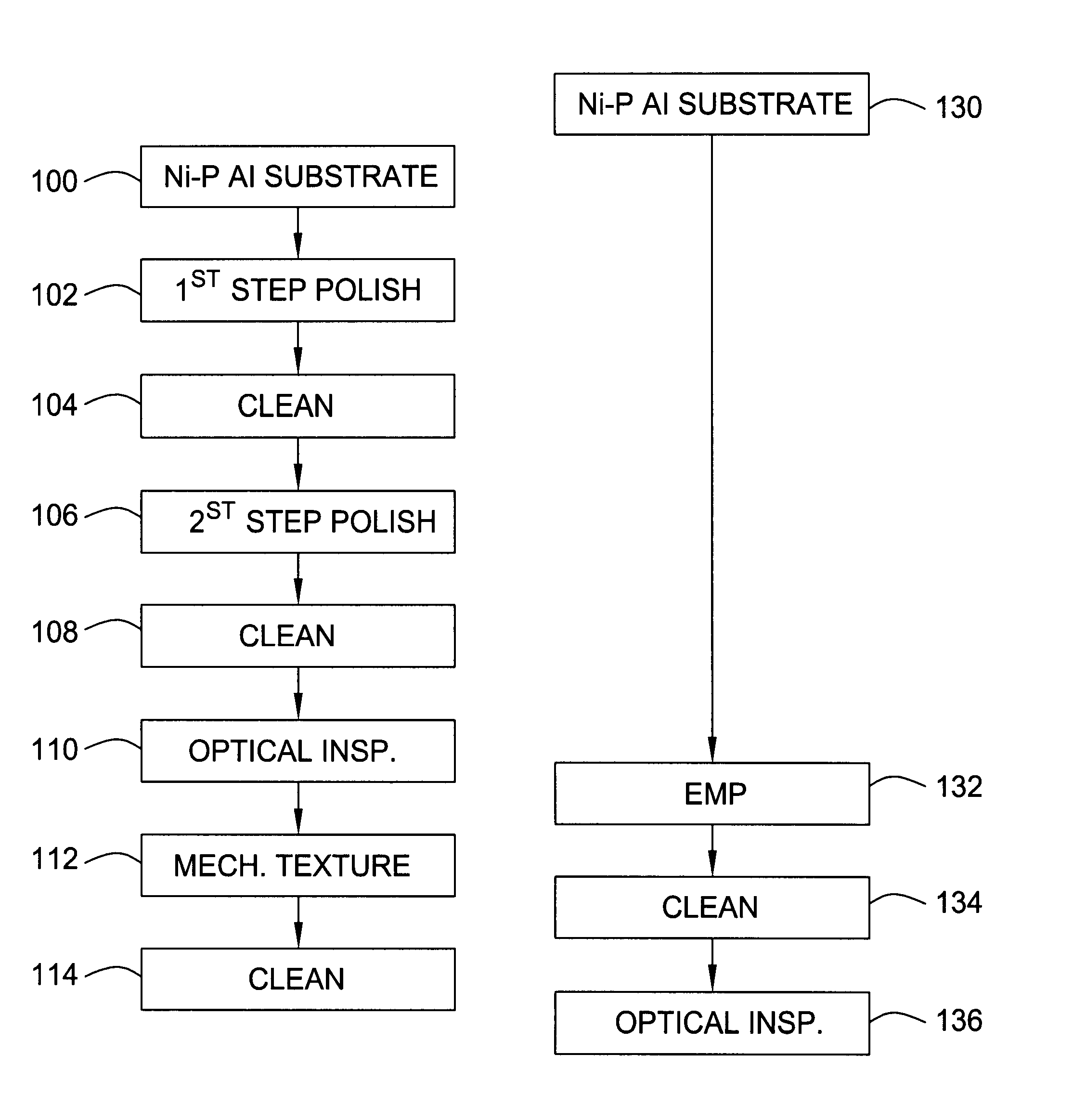
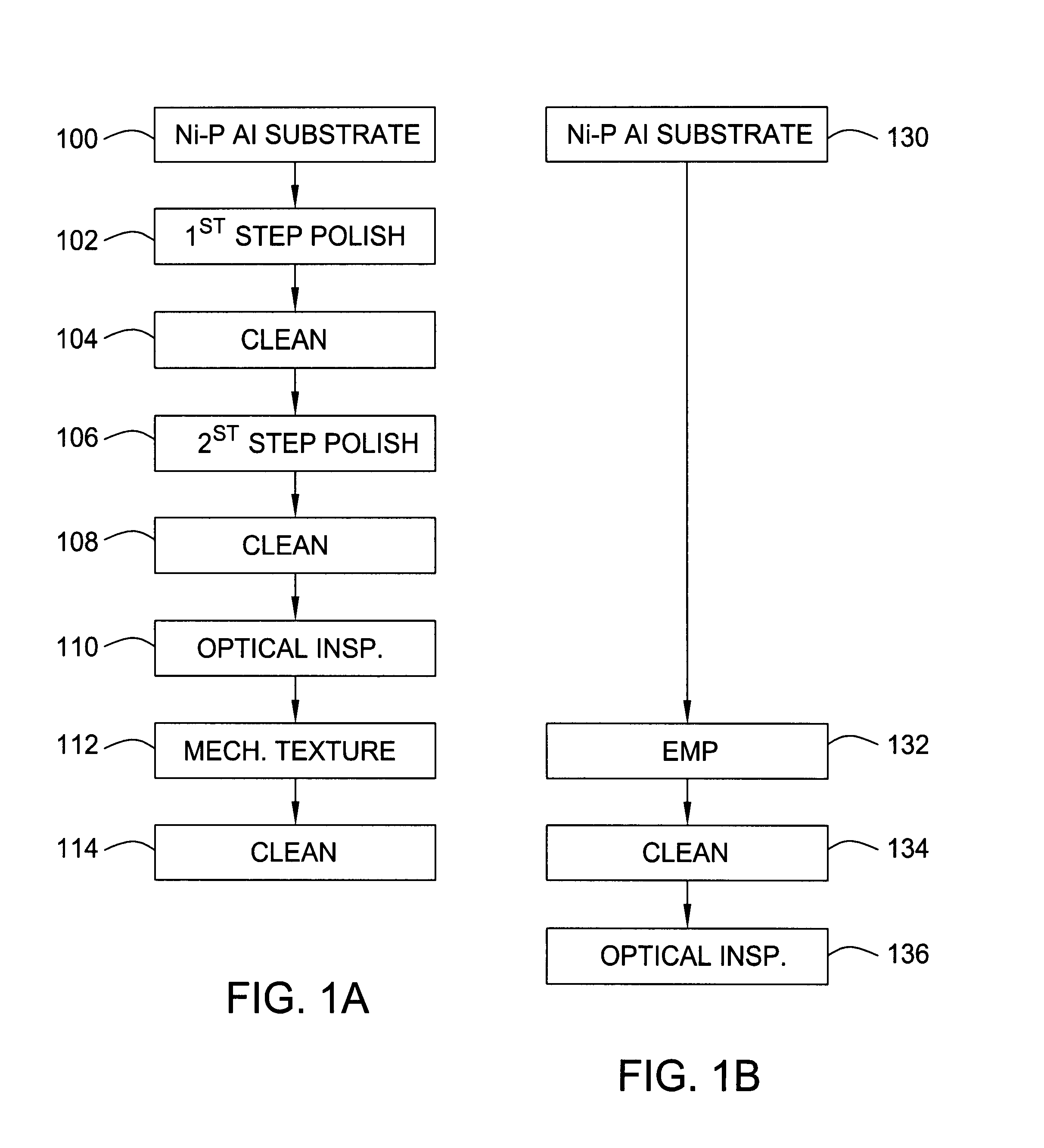
Single-step electromechanical mechanical polishing on Ni-P plated discs
InactiveUS6957511B1Reduce in quantityReduce processing timeBelt grinding machinesLapping machinesElectrical conductorSlurry
Beginning with a smooth ground aluminum blank with a relatively thin layer of leveled Ni—P, circumferential electropolishing / texturing is carried out to achieve a smooth oriented surface. A conductive slurry is provided between the disc and a porous texturing tape which is in contact with a conducting plate or equivalent conductor. The disc serves as the anode, and the conducting plate as the cathode, while the slurry, being conductive, functions as an electrolyte. In the presence of current, a reverse electroplating occurs so that the Ni—P dissolves to form Ni2+, or nickel ions which are carried away by the conductive slurry. The conductive slurry further supports or carries therein abrasive material so that by moving the porous texturing tape past the disc surface, the texturing tape picks up the abrasive material in the slurry and simultaneously with the reverse electroplating, provides the desired mechanical abrasion to achieve texturing of the disc surface. The abrasive material comprises diamond particles. The circumferential electropolishing / texturing polish is achieved by spinning the disc while applying the mechanical-chemical action through the slurry system to the disc surface with electric current passing through the electrically conducting interface during processing.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for uniform electropolishing of damascene IC structures by selective agitation
InactiveUS7531079B1Small apertureSufficiently porousElectrolysis componentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiomedical engineeringLarge range
The present invention pertains to apparatus and methods for planarization of metal surfaces having both recessed and raised features, over a large range of feature sizes. The invention accomplishes this by increasing the fluid agitation in raised regions with respect to recessed regions. That is, the agitation of the electropolishing bath fluid is agitated or exchanged as a function of elevation on the metal film profile. The higher the elevation, the greater the movement or exchange rate of bath fluid. In preferred methods of the invention, this agitation is achieved through the use of a microporous electropolishing pad that moves over (either near or in contact with) the surface of the wafer during the electropolishing process. Thus, methods of the invention are electropolishing methods, which in some cases include mechanical polishing elements.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
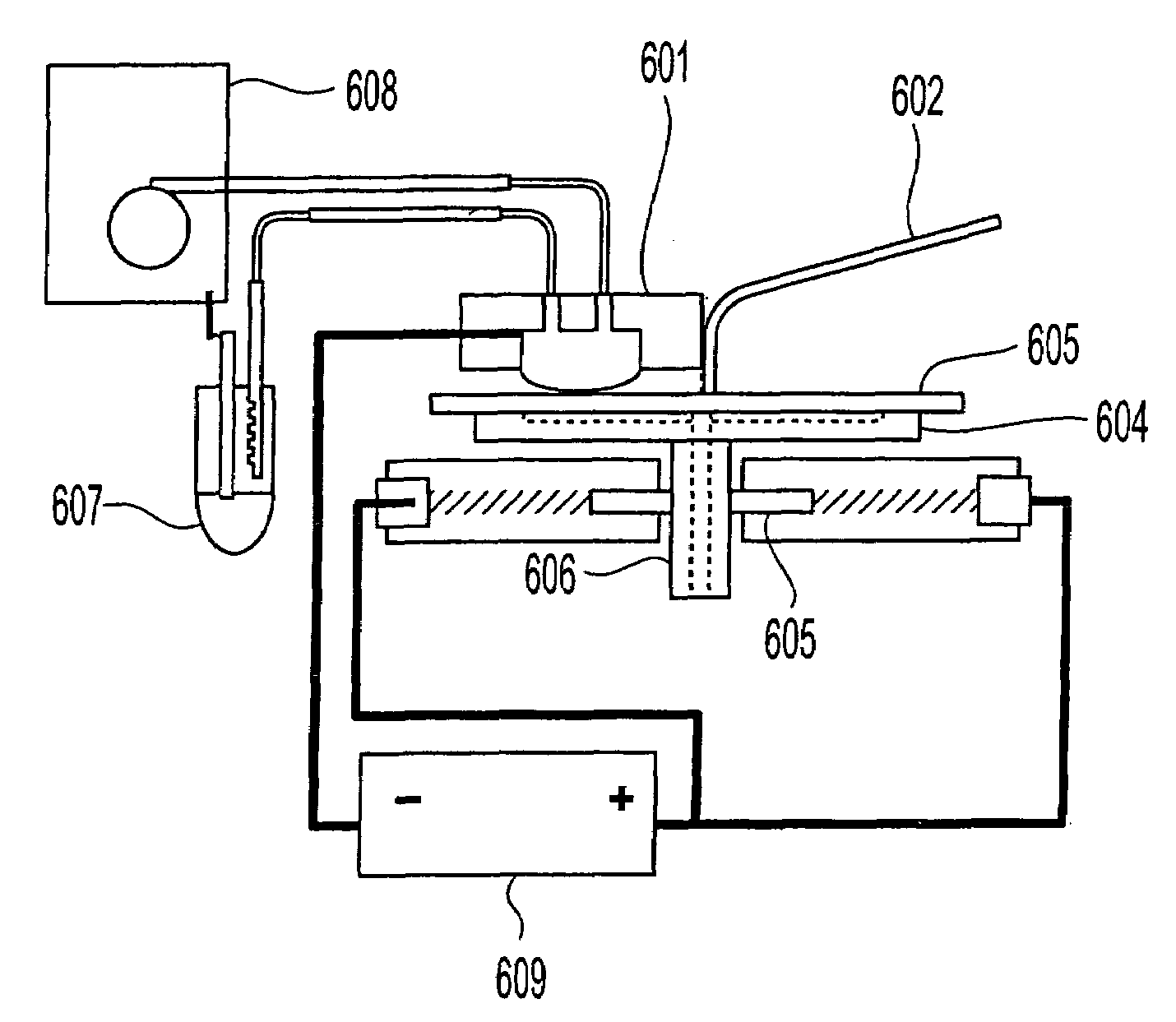
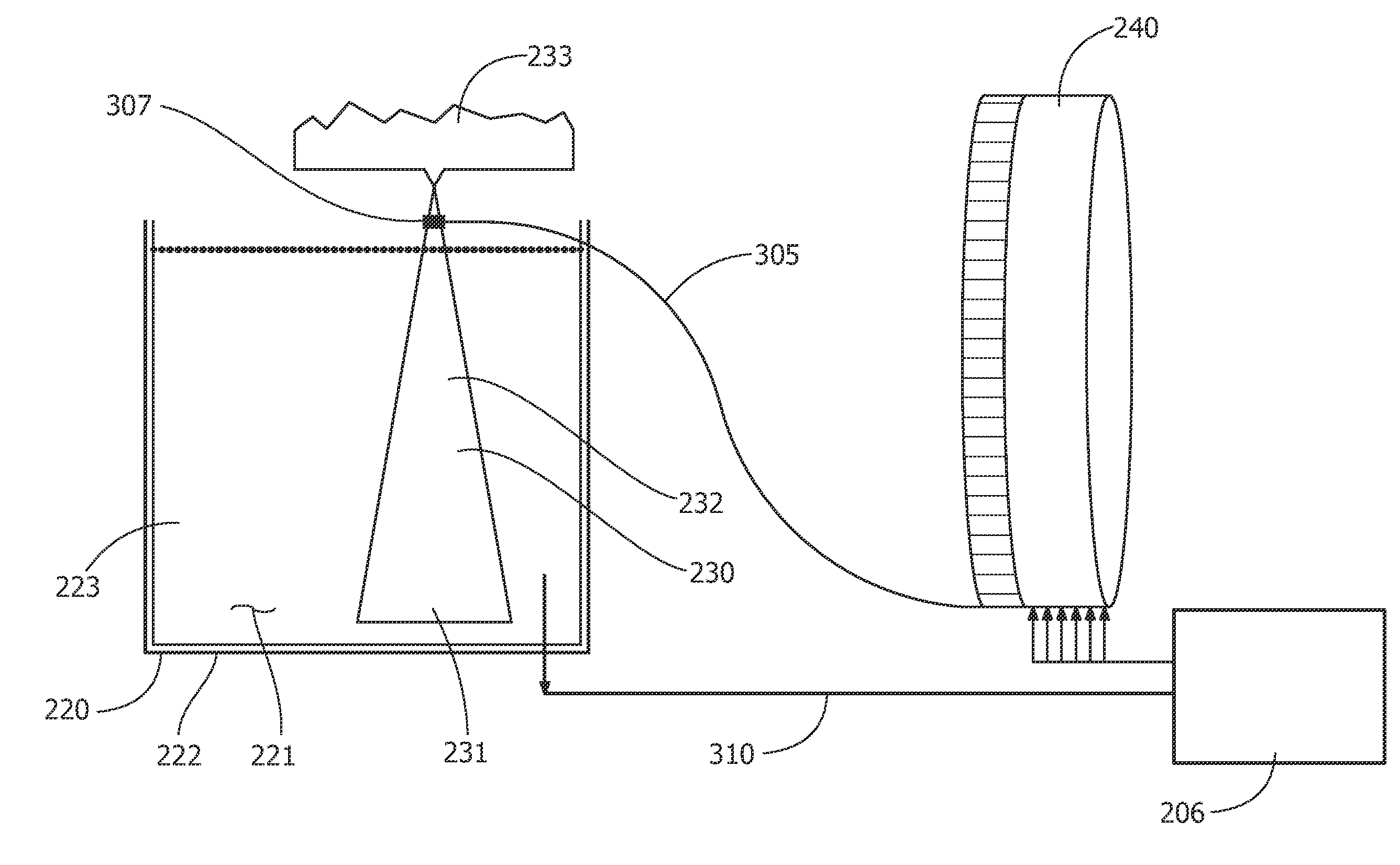
Apparatus adapted for membrane-mediated electropolishing
InactiveUS7566385B2Generates virtually no waste productEfficient processingCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrolysisElectrical battery
This invention provides a membrane-mediated electropolishing apparatus for polishing and / or planarizing metal work-pieces. The work-piece is wetted with a low-conductivity fluid. The wetted work-piece is contacted with a first side of a charge-selective ion-conducting membrane, wherein the second side contacts a conductive electrolyte solution in electrical contact with a electrode. Current flow between the electrode and the work-piece electropolishes metal from the work-piece. This invention also provides a half-cell adapted for use in membrane-mediated electropolishing having a fully or partially enclosed volume, a conductive electrolyte which partially or essentially fills the enclosed volume, an electrode which is in contact with the electrolyte, and a charge-selective ion-conducting membrane which seals one surface of the enclosed volume, cavity or vessel in such a way that the internal surface of said membrane contacts the electrolyte solution or gel and the external surface is accessible to contact the work-piece.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Electropolishing process for titanium
InactiveUS20080217186A1Electrolysis componentsElectrochemical machining apparatusMedronic acidTitanium
The present invention relates to a method of electrochemical polishing of surfaces of titanium or titanium-containing alloys, such as Nitinol. An electrolyte is used that comprises methanesulfonic acid and one or more alkanediphosphonic acids. These alkanediphosphonic acids can optionally be substituted with hydroxy and / or amino groups. A further aspect of the present invention relates to the use of said electrolyte for the electropolishing of titanium or titanium-containing alloys.
Owner:POLIGRAT GMBH
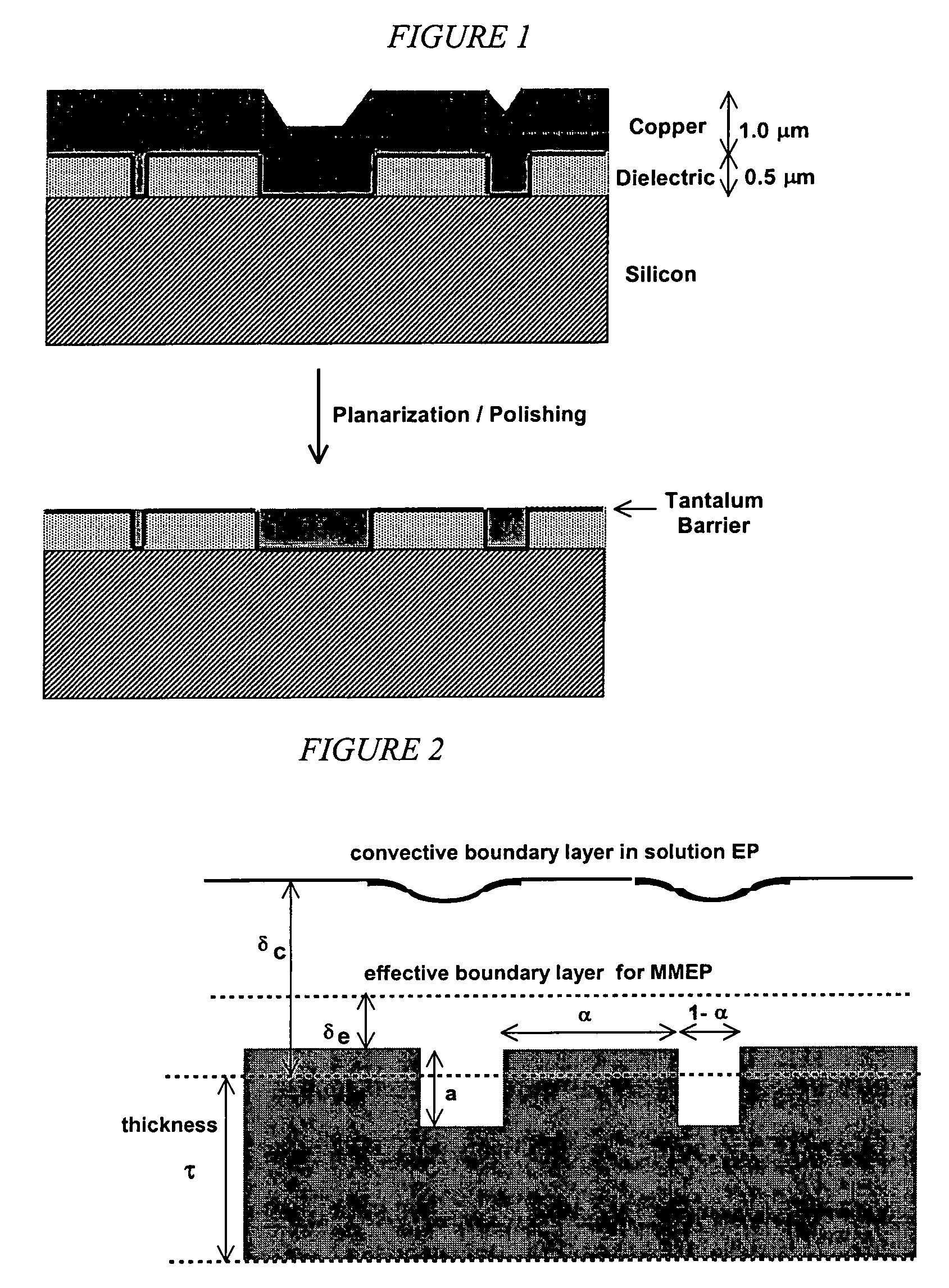
Membrane-mediated electropolishing with topographically patterned membranes
This invention provides membrane-mediated electropolishing (MMEP) processes for polishing and / or planarizing metal work pieces using topographically patterned membranes. The processes can be used for both pure metals and alloys, and provide advantages over conventional electropolishing processes and known MMEP processes using smooth membranes. This invention also provides a cathode half-cell and an apparatus useful in membrane-mediated electropolishing processes. The invention also provides processes for electroengraving and electromachining topographic patterns, holes and / or grooves into the surface of a metal work piece.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
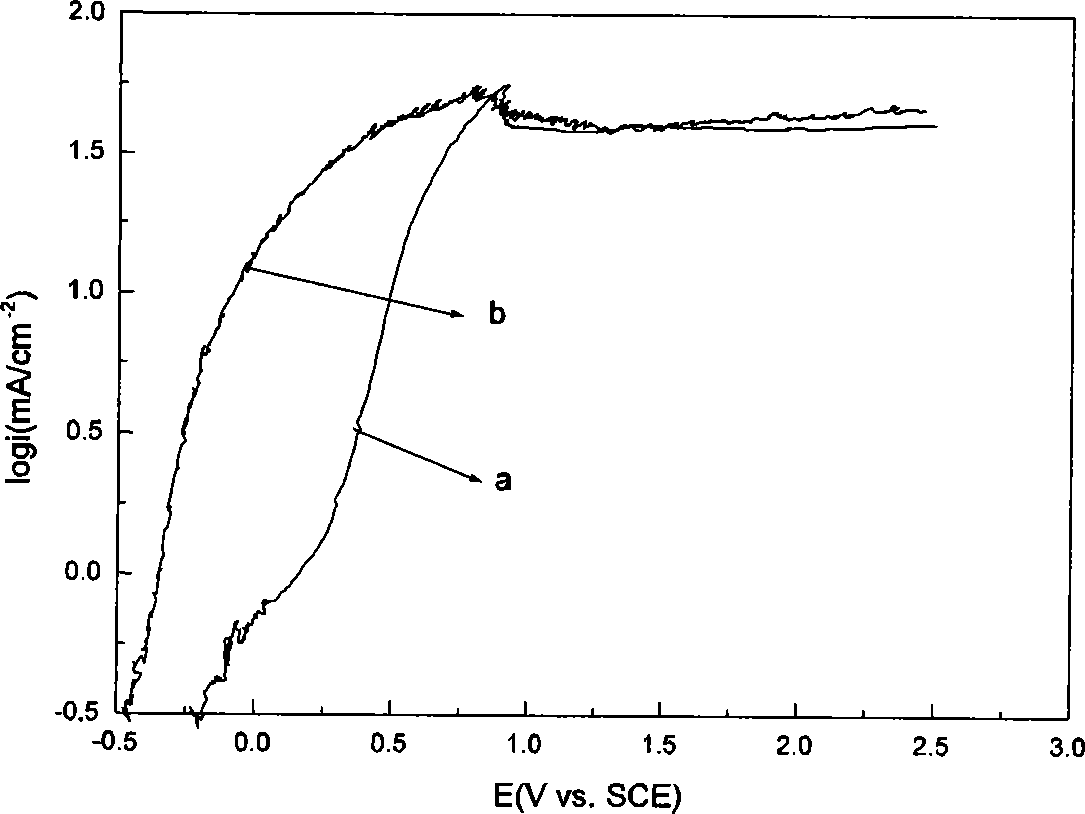
Electropolishing method for austenitic stainless steel orifice
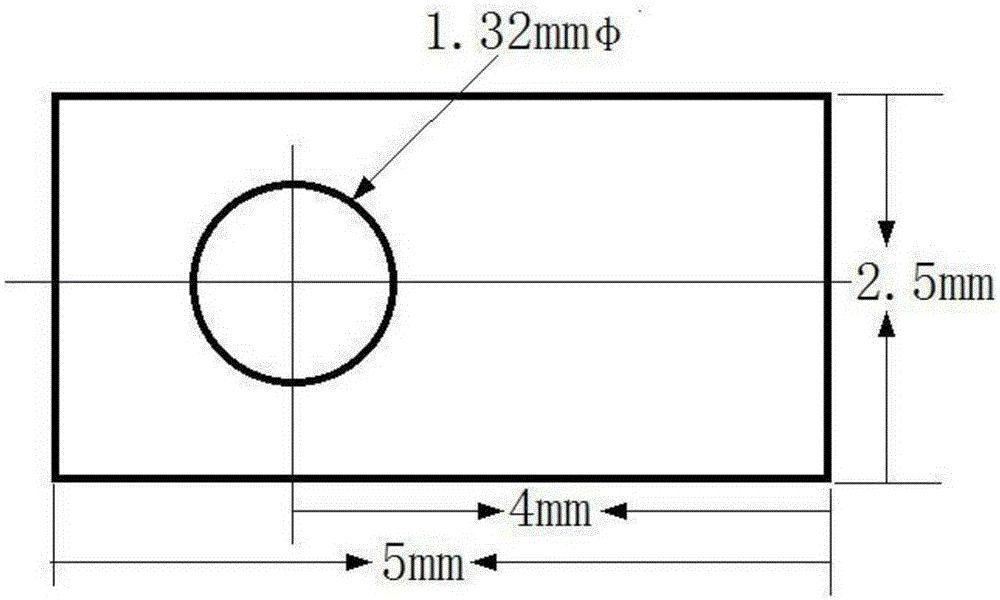
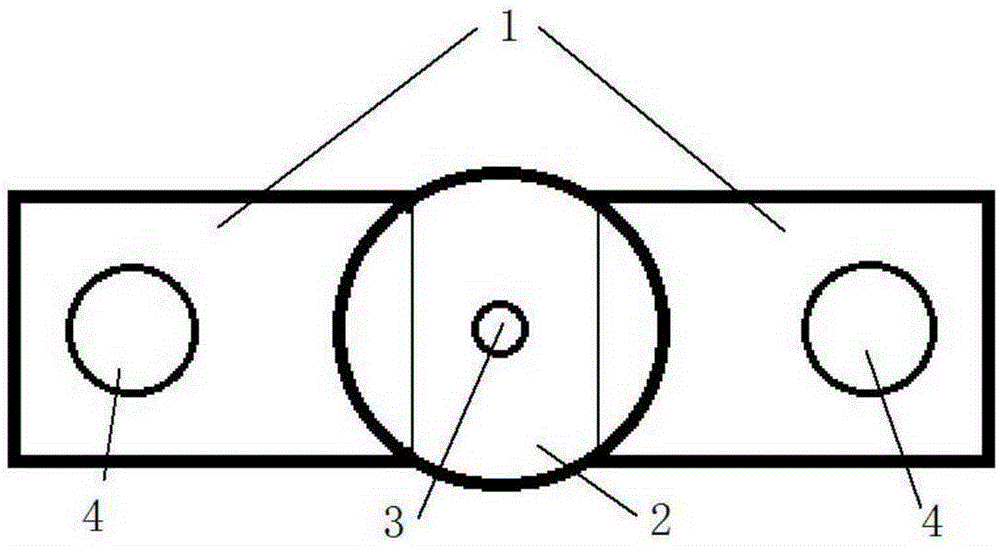
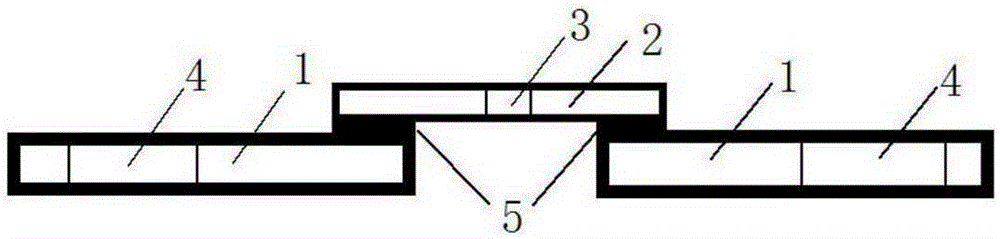
The invention discloses a polishing solution for electropolishing an austenitic stainless steel orifice. Each litre of electropolishing polishing solution contains 1000 to 1250g phosphoric acid, 200 to 260g sulfuric acid and 180 to 240g absolute ethyl alcohol. The electropolishing of the austenitic stainless steel orifice is well realized by reasonably designing the electropolishing solution and electropolishing technological parameters. The electropolishing of stainless steel orifices, deep blind holes and cross holes with relatively small aperture of more than or equal to 1mm and relatively large ratio of depth to diameter of more than or equal to 10mm is realized, The polishing effect of the invention is obviously better than that of the traditional mechanical or physical method and can be as high as the polishing effect of a mirror surface according to the surface condition of the unpolished orifice.
Owner:BEIJING SEVENSTAR ELECTRONICS CO LTD
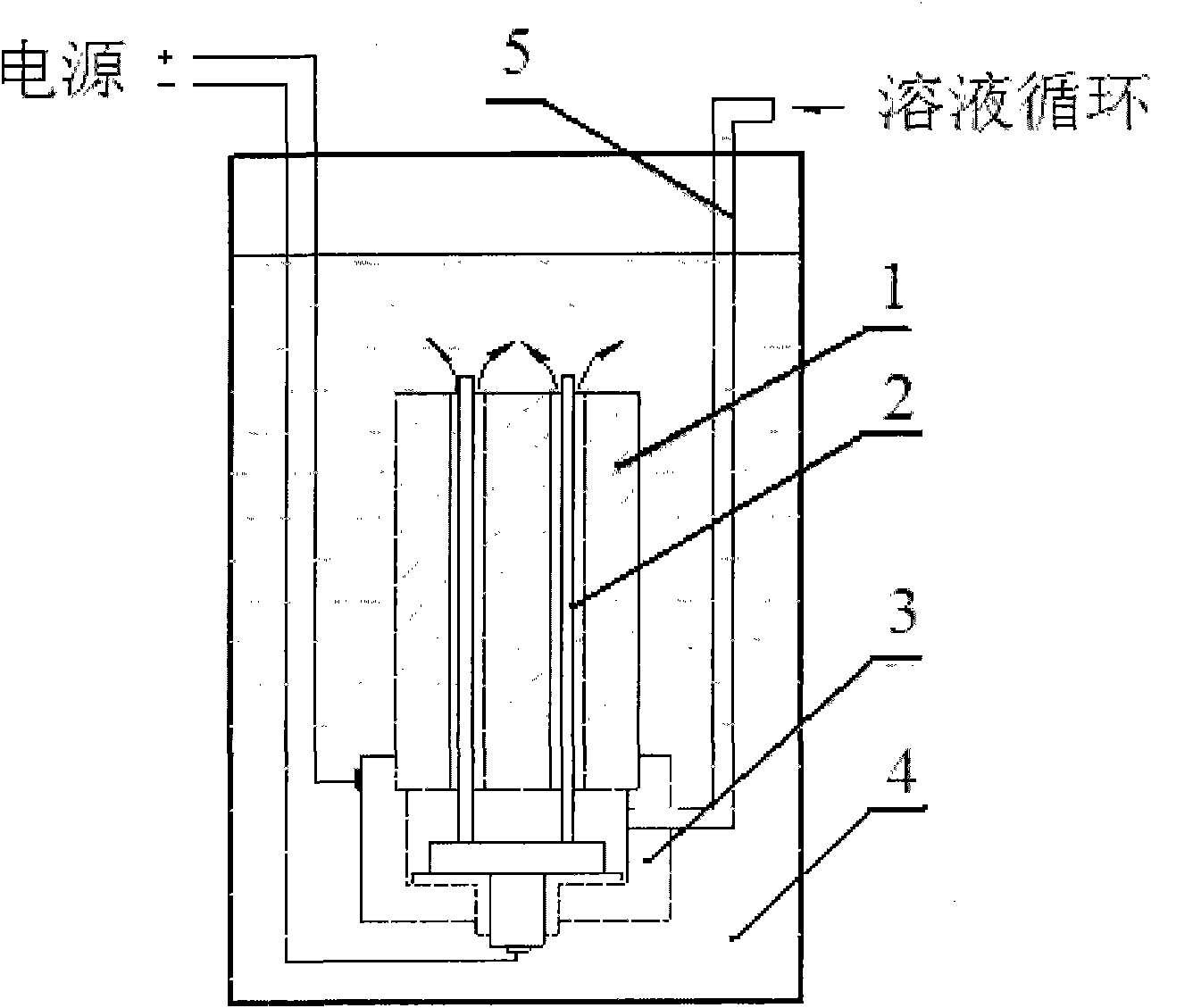
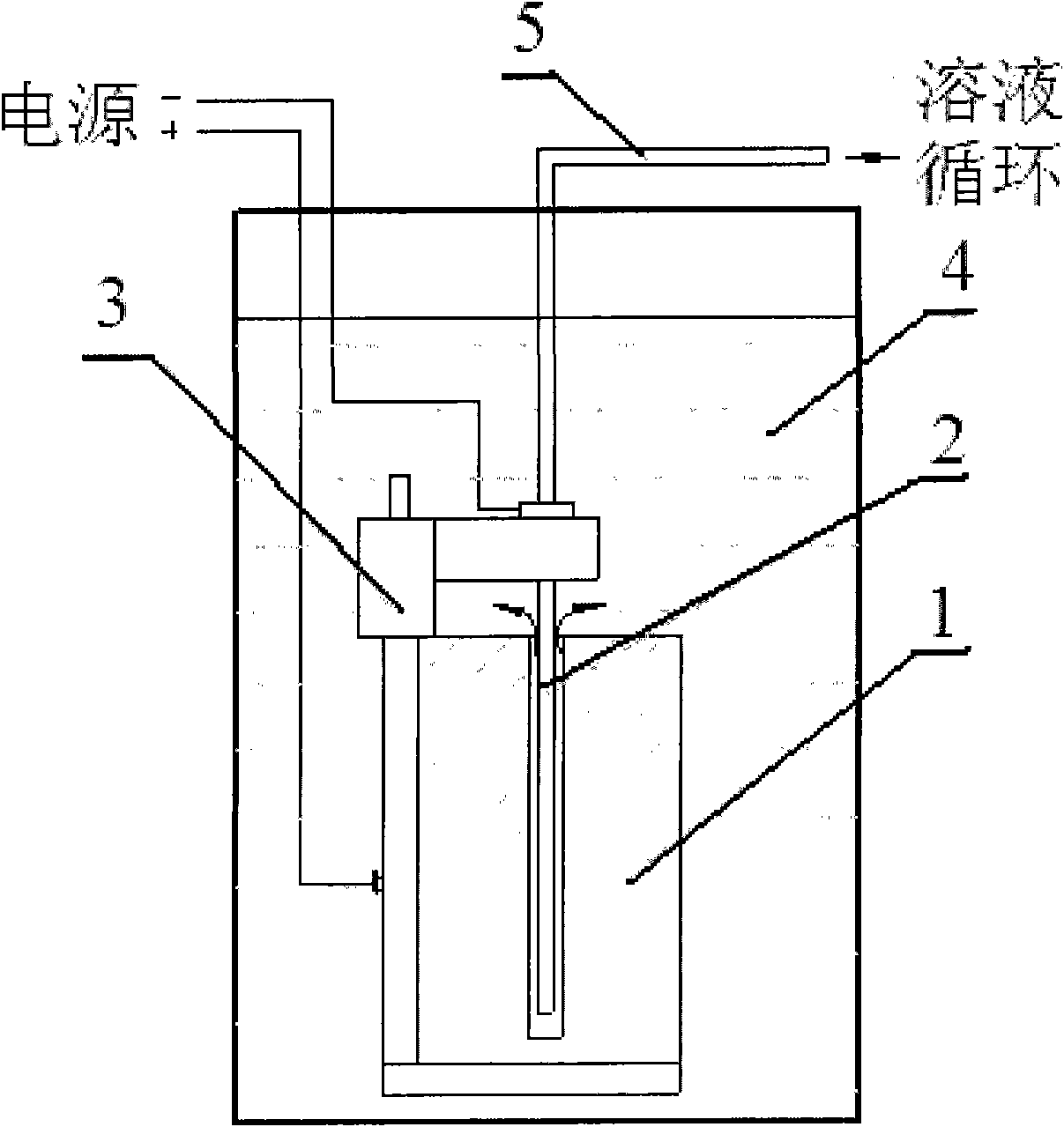
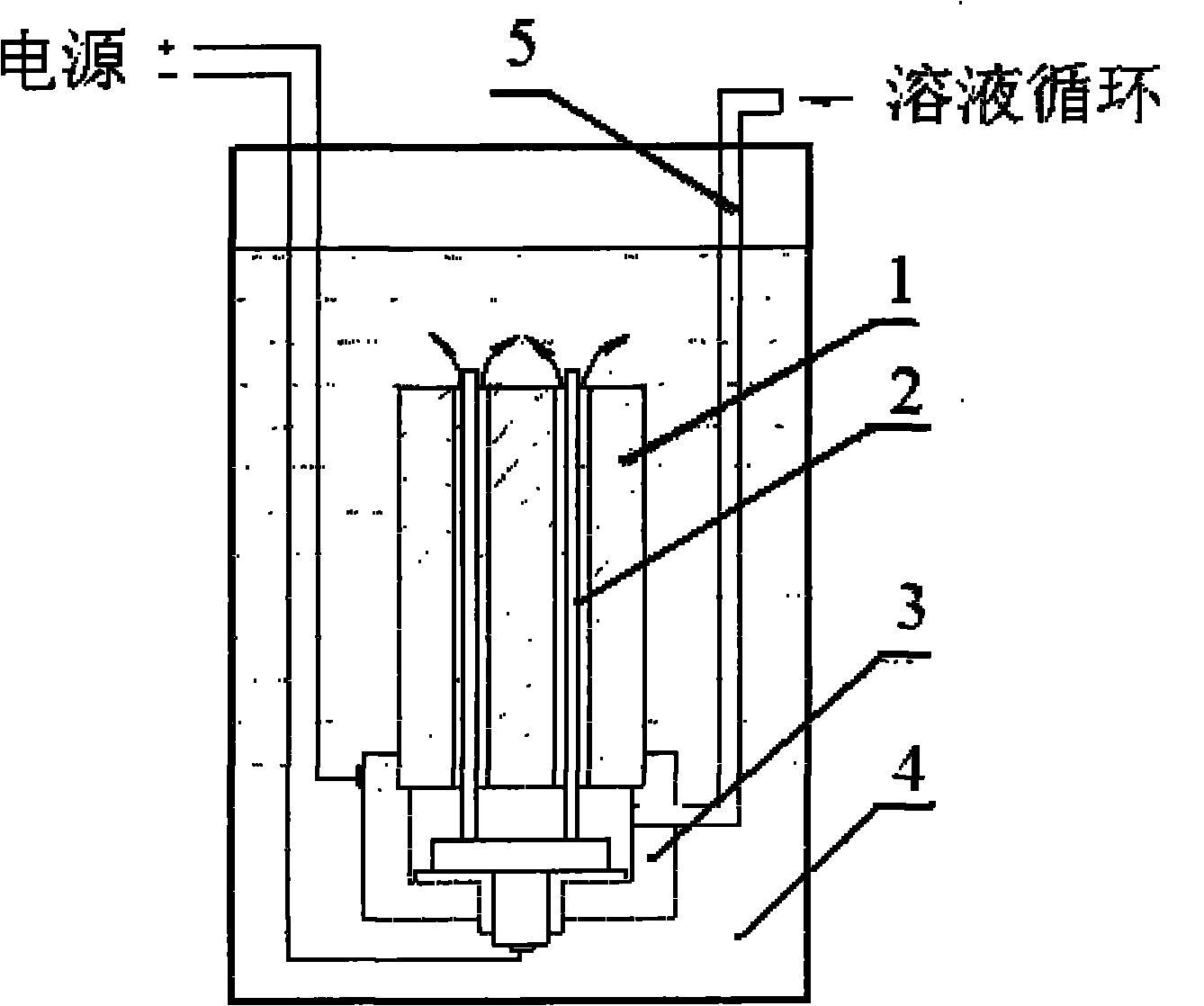
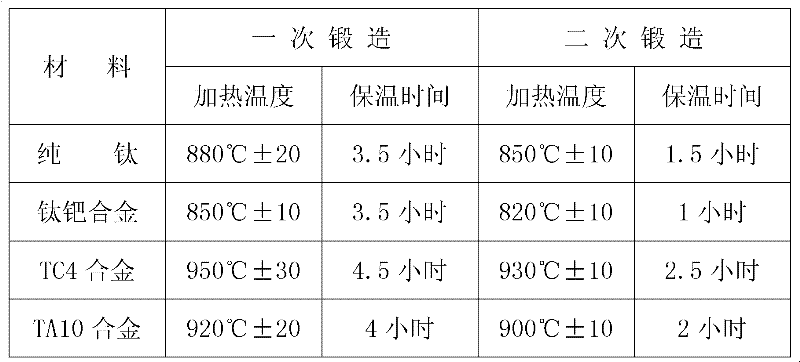
Process for fabricating high precision titanium and titanium alloy plates
InactiveCN102225504AGuaranteed permutation rulesGuaranteed physical propertiesTitaniumTitanium alloy
The invention provides a process for fabricating high precision titanium and titanium alloy plates, employs the processes of material selection, smelting, forging, plate milling, mechanical grinding, composite electropolishing and the like, and solves the difficult problems of titanium and titanium alloy plates of which the surface can not be a mirror surface in precision and roughness, so that the average roughness of the titanium and titanium alloy plates can reach about 0.03 mu m, an oxide film can be formed on the surface during the polishing process, and the corrosion resistance of the plates can be improved effectively.
Owner:BAOJI XINZE TITANIUM NICKEL
Machining technology for small deep step hole of high-precision medical apparatus and instrument
The invention relates to a machining technology for a small deep step hole of a high-precision medical apparatus and instrument, and belongs to the technical field of product machining of the medical apparatus and instrument. The technology mainly comprises center through hole drilling, outer circle turning, boring through a grinding head assembly, honing, step milling, electropolishing and the like. The defects that when a traditional boring cutter carries out boring, the boring cutter is likely to be broken, the boring roughness is large, the machining efficiency is low, and the machining cost is high are mainly overcome.
Owner:杭州锐健医疗股份有限公司
Electrochemical surface treatment method and electrochemical surface treatment device for porous metal material
ActiveCN103710735AUniform treatment effectEasy to handleElectrolytic inorganic material coatingElectrolytic agentMetallic materials
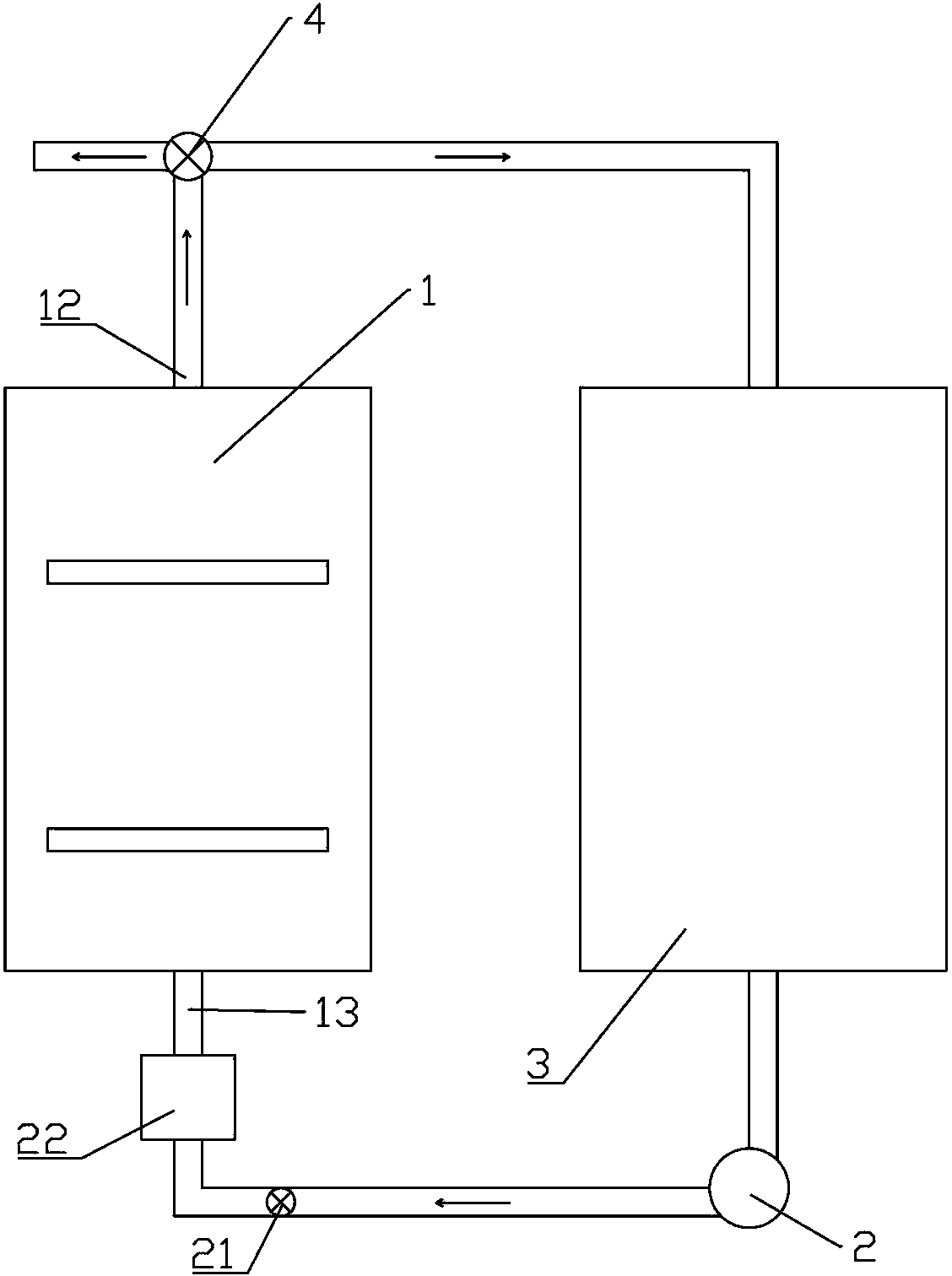
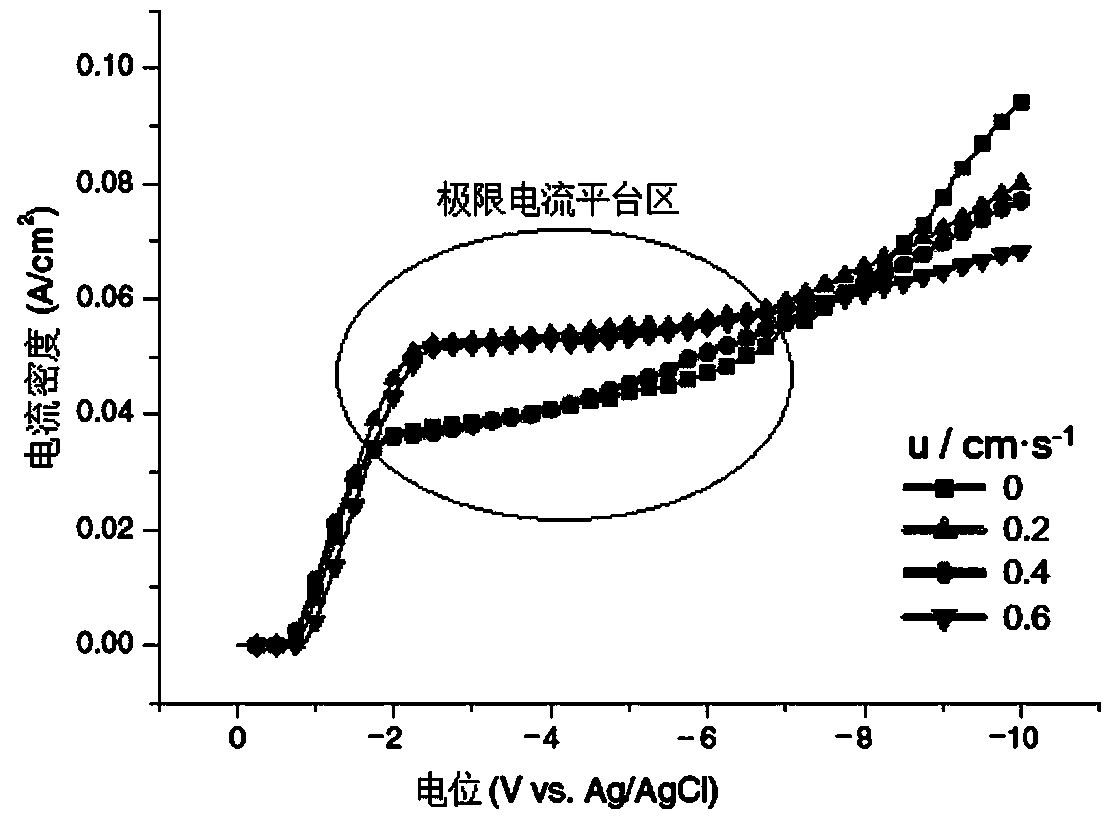
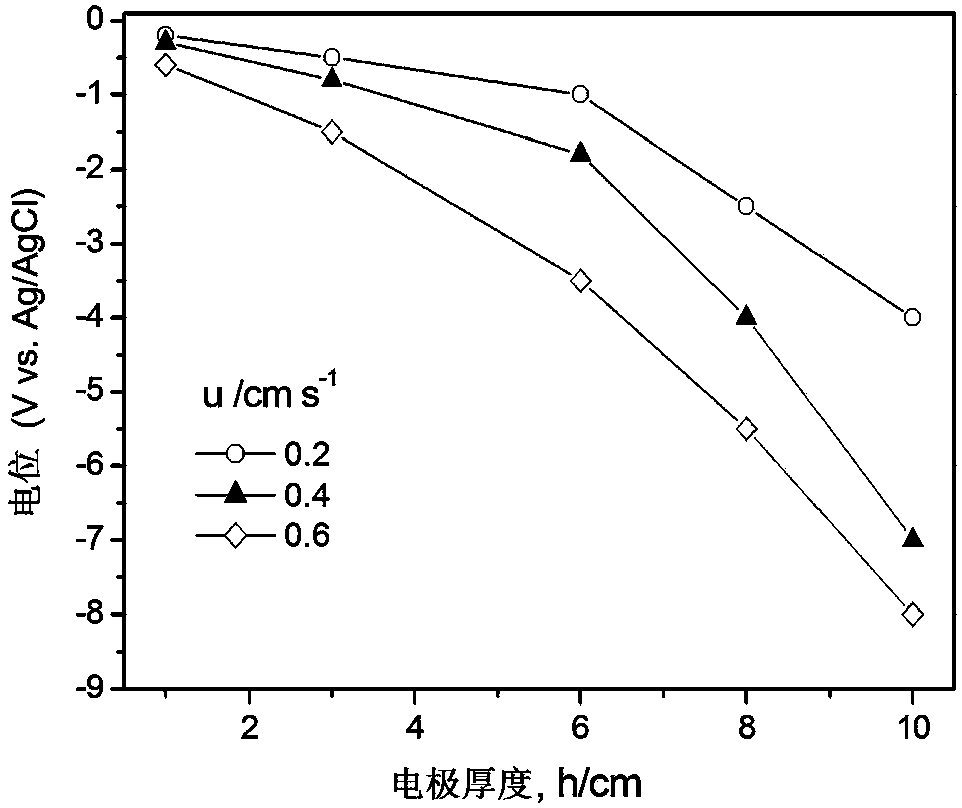
The invention discloses an electrochemical surface treatment method and an electrochemical surface treatment device for a porous metal material. The method comprises the following steps: on the basis of applying a compact metal material which is the same as a to-be-treated porous metal material as a working electrode, utilizing an electrochemical working station to measure a steady-state cathode polarization curve of the compact metal material in the working electrolyte, determining a platform zone of a current-potential curve, and obtaining limitation diffusion-controlled electrochemical treatment condition of electro-deposition reaction; on the basis of applying to-be-treated porous metal material as a working electrode, enabling the working electrolyte to perform single-direction or circulating flow in an electrolytic cell; applying the determined limitation diffusion-controlled electrochemical treatment condition to carry out electrochemical surface treatment on the porous metal material until a set value is reached. The electrochemical surface treatment method disclosed by the invention can be used for treating the inner surface of the porous metal material more effectively, so that the outer-layer surface and inner-layer surface of the porous structure of the metal material are more uniform in treatment effect, and therefore, a better electro-deposition treatment effect or electro-polishing effect is obtained.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
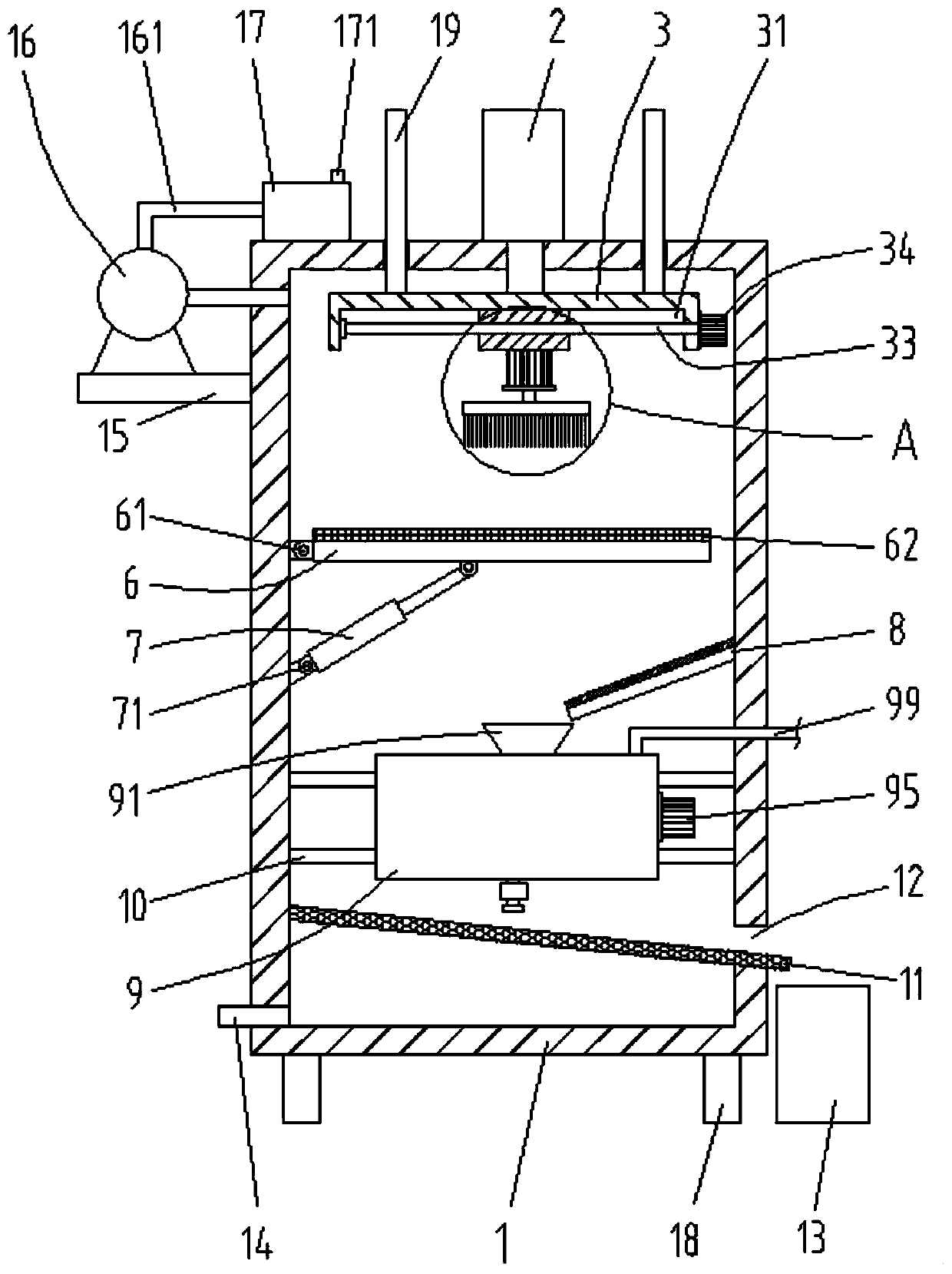
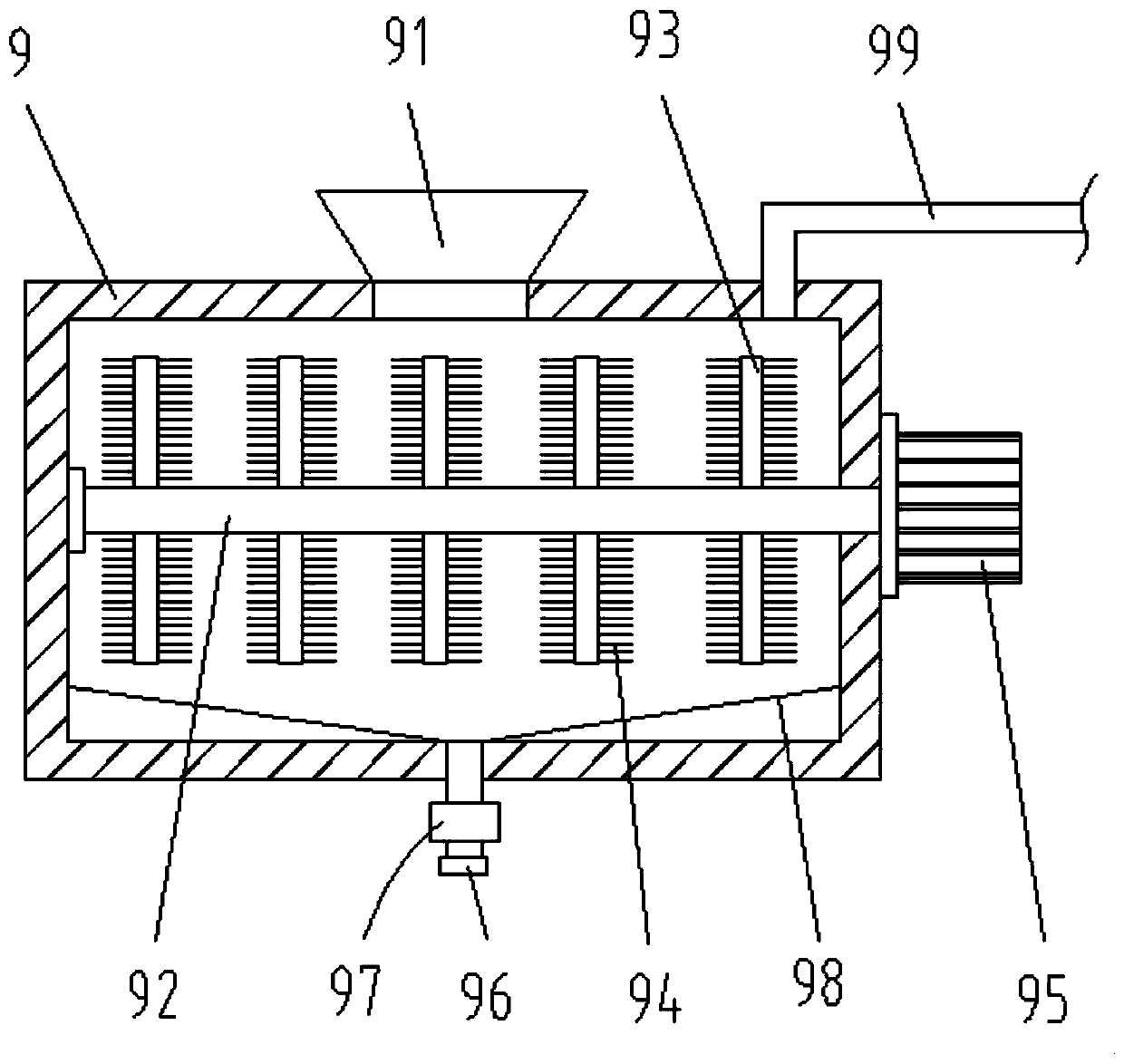
High-precision workpiece polishing device
The invention provides a high-precision workpiece polishing device. The high-precision workpiece polishing device comprises a box body; the center of the upper side of the box body is provided with afirst electric telescopic rod; and the telescopic end of the first electric telescopic rod vertically downwards penetrates through the box body. According to the high-precision workpiece polishing device provided by the invention, an electromagnet is powered on to fixedly suck a component; the first electric telescopic rod is used for downwards pushing a horizontal plate to drive a grinding brushpositioned at the lower side of the horizontal plate to reach the optimal polishing height; a first motor is used for rotating the grinding brush to polish the component positioned on the electromagnet; a dust collector can be used for sucking out the dust generated in a polishing process, and the dust is discharged via air vents after being filtered by a filter box; a second electric telescopic rod is used for downwards pulling a working plate to rotate so that the electromagnet positioned at the upper side of the working plate is inclined towards the lower right direction; the electromagnetis powered off; the polished component obliquely slides on a sliding plate by virtue of the electromagnet and slides into a washing tank through the sliding plate; and a third motor is used for rotating a rotating shaft to drive washing bristles positioned at the outer side of a stirring rod to brush the component.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for passivating metallic implantable medical devices including radiopaque markers
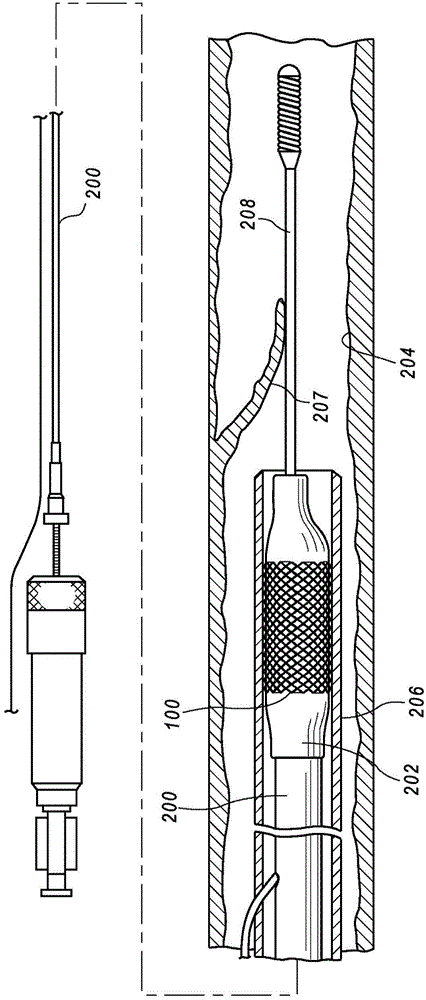
The present disclosure is directed to methods of manufacturing and passivating stents and other implantable medical devices including one or more attached radiopaque markers. In one embodiment, the method includes providing a metallic implantable medical device body without any radiopaque marker(s) attached thereto, primary electropolishing the device body without any markers attached thereto, attaching one or more radiopaque markers to the device body, and lightly electropolishing the device including device body and attached radiopaque markers. Light electropolishing removes no more than about 5 percent by weight of the device (i.e., the device body and attached marker(s)). Light electropolishing passivates the exposed surfaces of the device body and markers, while also providing electropolishing to the region of any welds where the radiopaque marker(s) attach to the device body.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Full-automatic electropolishing equipment
InactiveCN106400100AGood effectSolve the problem of high currentElectrolysis componentsResource utilizationEngineering
The invention provides full-automatic electropolishing equipment which comprises an anode plate platform, polishing cups placed on the anode plate platform and cathode bars arranged at a certain distance from the anode plate platform. In the electropolishing process, the polishing cups containing electrolyte are fixed to the anode plate platform, the cathode bars stretch into the corresponding polishing cups by a certain distance through moving devices along the axes of the polishing cups without making contact with the inner walls of cup bodies of the polishing cups, and then the anode plate platform and the cathode bars are electrified to electropolish the polishing cups. Since only the inner walls of the polishing cups are electropolished, the utilization rate of production resources is improved; and since it is ensured that the cathode bars can not make contact with the polishing cups, it is ensured that the cathode and the anode can not short-circuit, and the phenomenon that in the prior art, short-circuit occurs due to the fact that cathode bars are prone to making contact with products to be polished is avoided.
Owner:湖北帕尔森机电设备有限公司
In-situ tensile sample for transmission electron microscope and preparation method of in-situ tensile sample
ActiveCN105223055APreparing sample for investigationConventional transmission electron microscopeElectron transmission
The invention discloses an in-situ tensile sample for a transmission electron microscope. The in-situ tensile sample comprises two standard substrates and a standard electron transmission sample body, wherein each standard substrate is a rectangular pop can sheet; a circular hole is formed in each pop can sheet; the standard electron transmission sample body is circular; a hole is formed in the center of the standard electron transmission sample body after the standard electron transmission sample body is subjected to twin-jet electropolishing; the standard electron transmission sample body is fixed on the two standard substrates symmetrically in a bridging manner.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
Method for removing electroplated metal facets and reusing a barrier layer without chemical mechanical polishing
ActiveUS20150072516A1Low costLower the thresholdSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesRedistribution layerAlloy
A method for avoiding using CMP for eliminating electroplated copper facets and reusing barrier layer in the back end of line (“BEOL”) manufacturing processes. Electropolishing is employed to remove the deposited surface metal, stopping at the barrier layer to form a smooth surface that may be utilized in subsequent steps. The method is suitable for the electropolishing of metal surfaces after formation of filled vias for through-silicon via processes employing metals such as copper, tungsten, aluminum, or alloys thereof. The remaining barrier layer may be reused to fabricate the redistribution layer.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR ADVANCED PACKAGING
A production process for a step stencil
A step stencil and a hybrid production process thereof. The step stencil is a metal mask having up steps on a PCB surface, and the base material of the mask is one of stainless steel, pure nickel and a nickel-iron alloy. The hybrid production process flow is as follows: (1) the fabrication of the up step area on the stencil PCB surface; (2) the fabrication of a half-etched blind hole of the stencil; (3) the fabrication of stencil openings; and (4) subsequent processing of the stencil openings. The hybrid production process includes three processes of etching, laser cutting and electropolishing, by using which the metal stencil having the PCB surface with up step can be produced. Through the fabrication of the half-etched blind holes, alignment holes for precise alignment can be produced; the metal screen has an opening pattern both in the flat area and the up step area; and the opening has good quality, smooth hole walls, and no blurs; by using the etching process, the stencil surface can be made to be flat and no-tilting phenomenon; and the flat area of the metal stencil has good thickness uniformity.
Owner:KUN SHAN POWER STENCIL
Method for producing metal substrates for hts coating arrangements
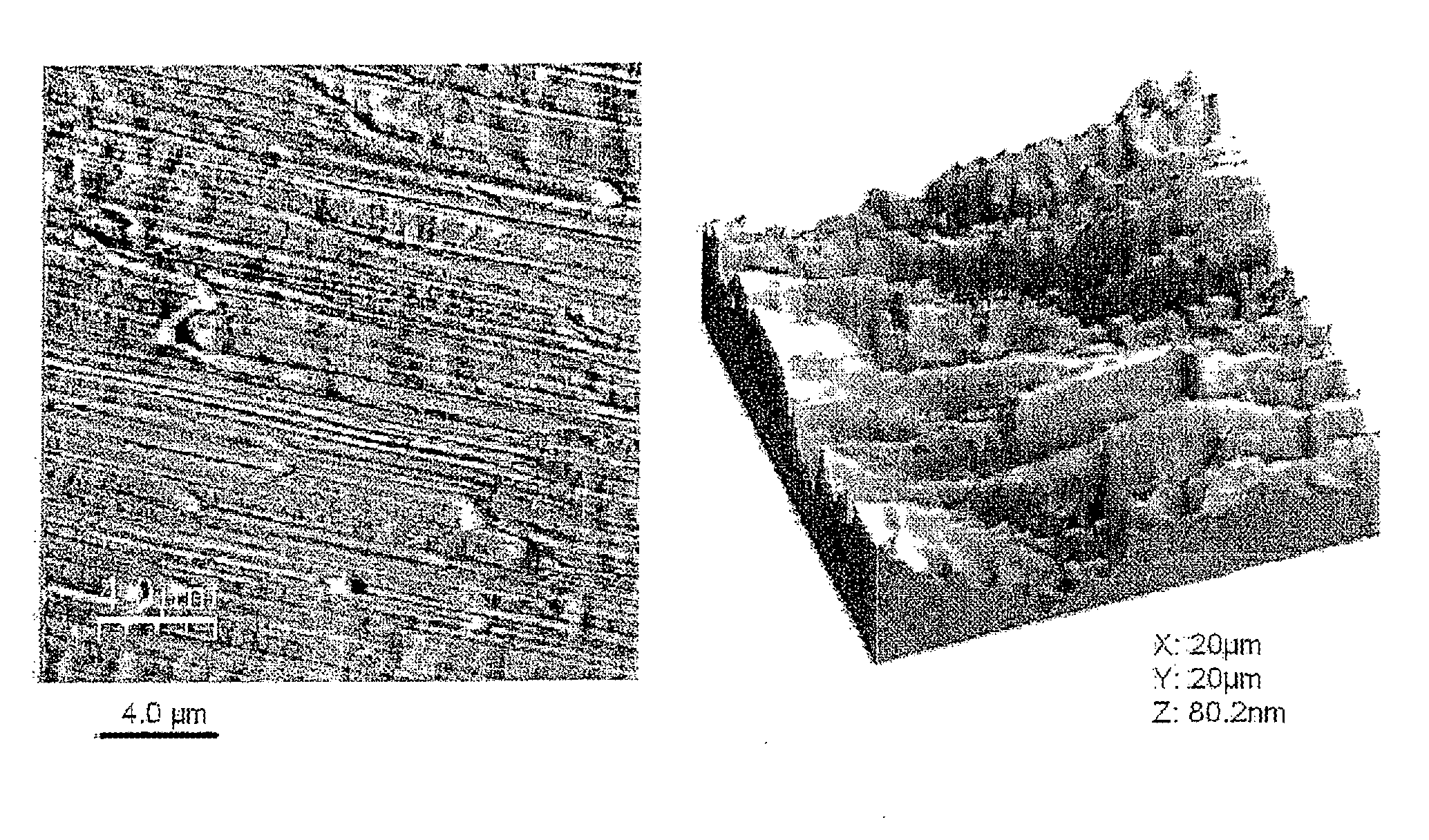
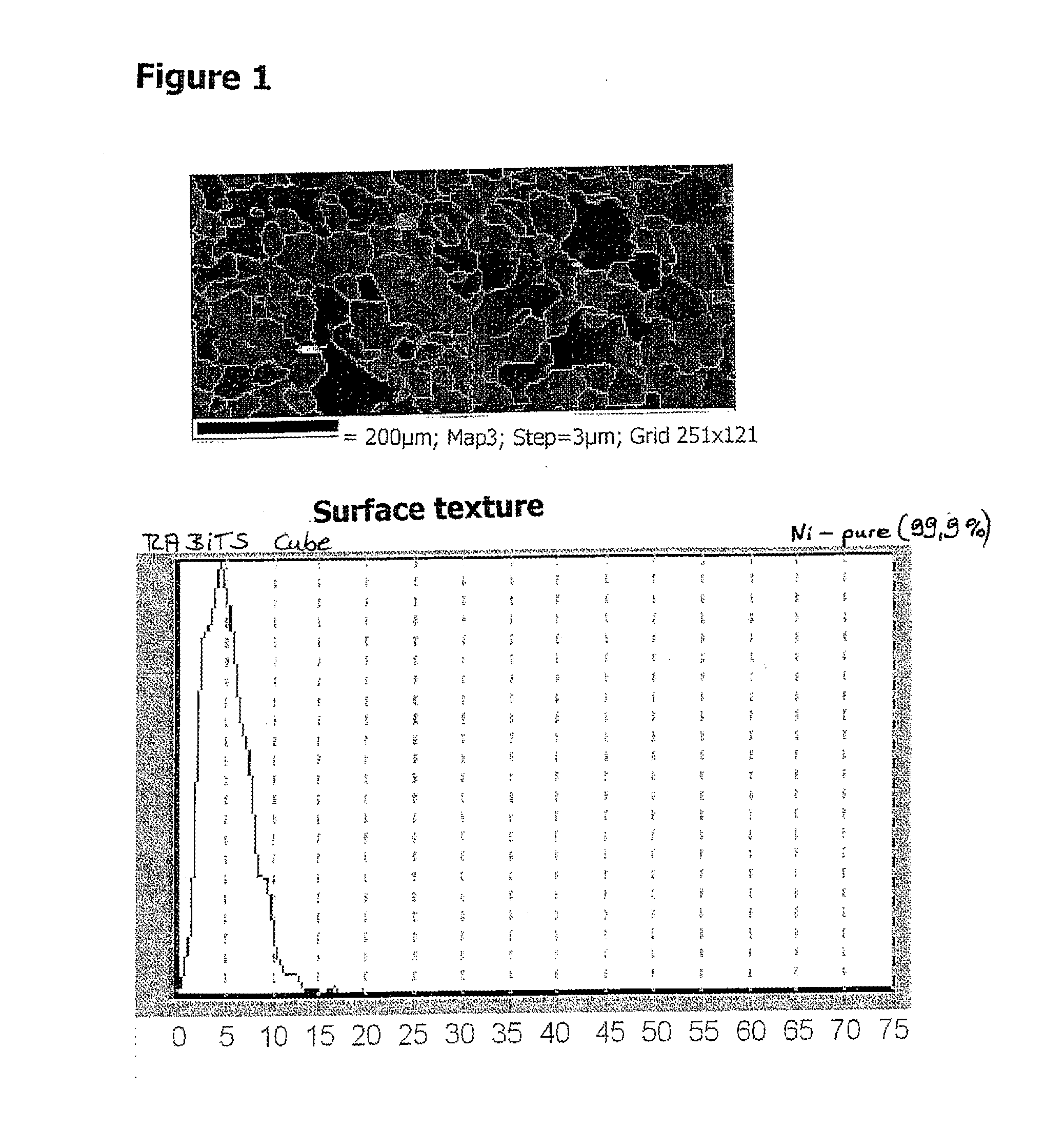
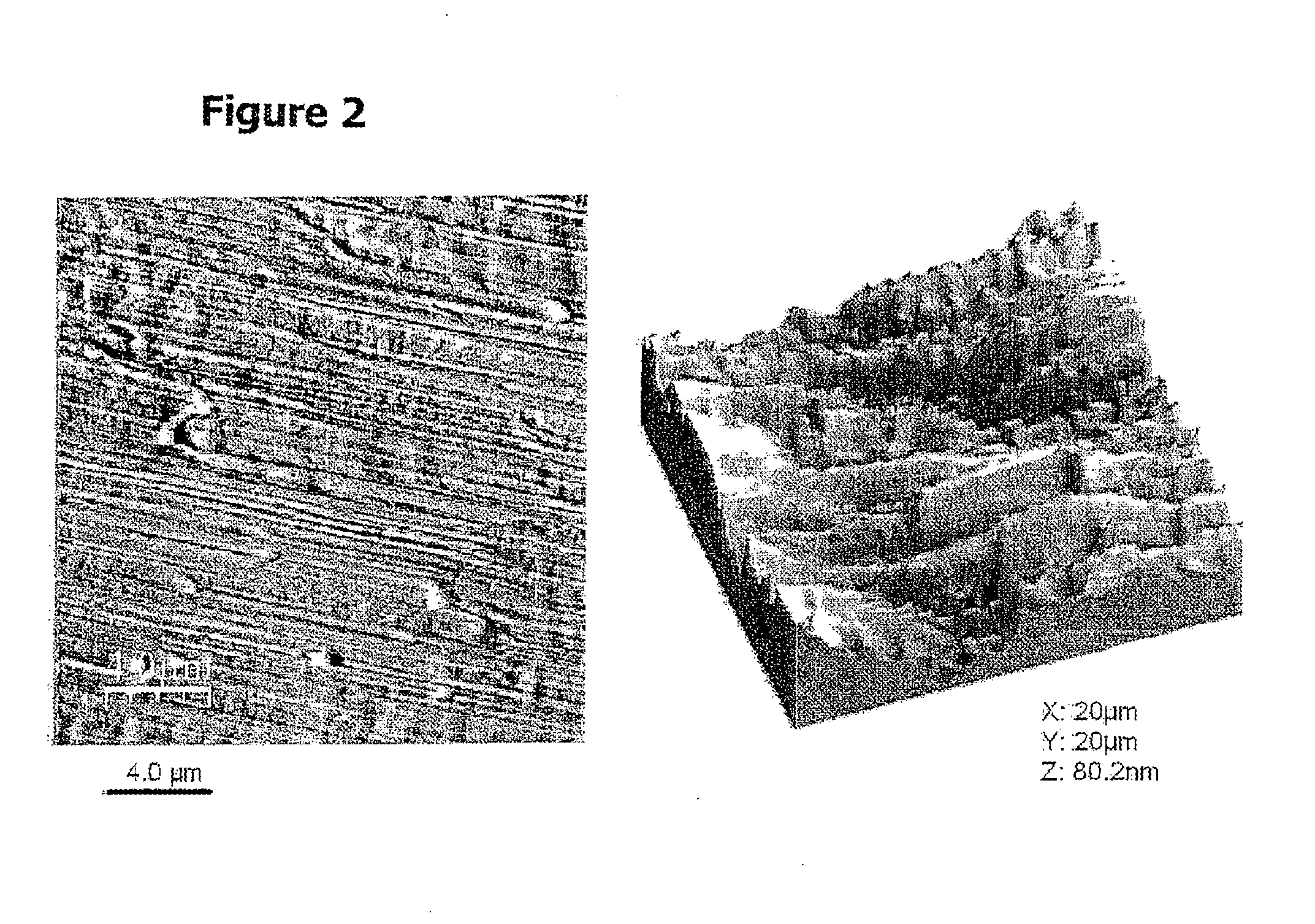
ActiveUS20110237441A1High texture transferSpeed up the transfer processPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
A method is proposed for producing a biaxially textured metal substrate having a metal surface, wherein the substrate is modified in order to produce a high-temperature superconductor coating arrangement and wherein the metal surface is modified in order to deposit a buffer layer or another intermediate layer epitaxially thereon and / or to deposit an oriented high-temperature superconductor (HTS) layer thereon. The method includes producing a biaxially textured metal substrate, subjecting the metal substrate surface to a polishing treatment, in particular an electropolishing treatment, and subjecting the metal substrate to a post-annealing after the surface polishing treatment and before a subsequent coating is performed involving epitaxial deposition of a layer of the HTS coating arrangement. This method results in smooth metal substrates with high textural overcoats and thereby improved HTS layers.
Owner:BASF AG
Electropolishing process
InactiveUS20080121530A1Improve conductivityCostly coolingElectrolysis componentsElectrochemical machining apparatusAlcoholMetal alloy
The present invention relates to a method for the electropolishing of surfaces of metals and metal alloys. Said method is characterized in particular in that it can be applied to a wide range of metals. Thus, it is suitable for the electropolishing of metal surfaces comprising iron, tungsten, magnesium, aluminum or an alloy of these metals. The electrolyte used in the method comprises methanesulfonic acid and at least one alcoholic compound selected from aliphatic diols of general formula CnH2n(OH)2 with n=2-6 and alicyclic alcohols of general formula CmH2m-1OH with m=5-8.
Owner:POLIGRAT GMBH
Current-leveling electroplating/electropolishing electrode
InactiveUS7803257B2Increase current densityImproving yield and reliabilityMachining electrodesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsElectrochemistry
A current-leveling electrode for improving electroplating and electrochemical polishing uniformity in the electrochemical plating or electropolishing of metals on a substrate is disclosed. The current-leveling electrode includes a base electrode and at least one sub-electrode carried by the base electrode. The at least one sub-electrode has a width which is less than a width of the base electrode to impart a generally tapered, stepped or convex configuration to the current-leveling electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for refurbishing turbine components
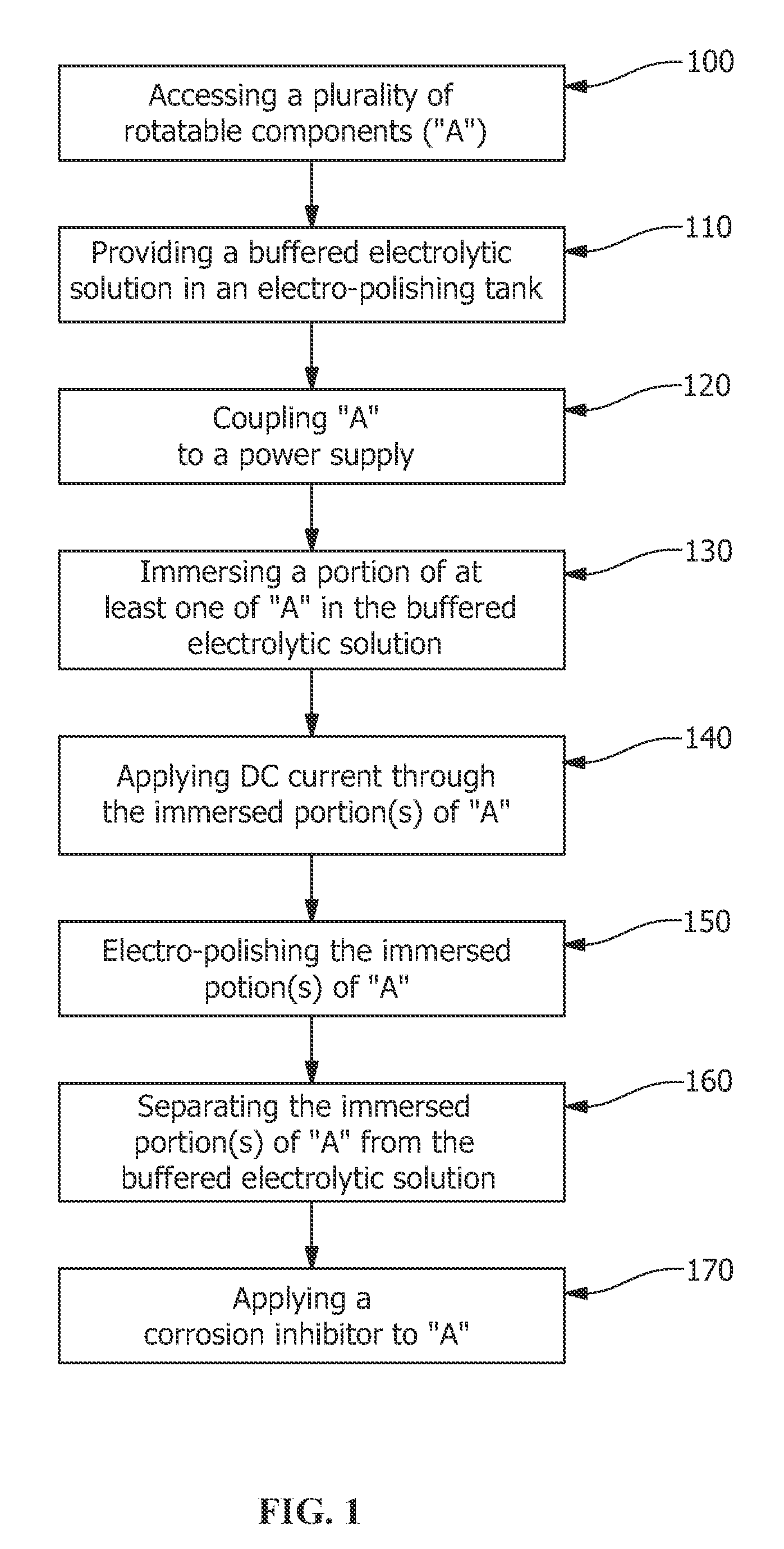
A refurbishing method, refurbishing apparatus and refurbished article are provided. The refurbishing method includes accessing a plurality of rotatable components attached to a turbine assembly, the turbine assembly being a portion of a turbomachine, providing a predetermined volume of a buffered electrolytic solution in an electro-polishing tank, coupling the plurality of rotatable components to a power supply, immersing an immersion portion of at least one of the plurality of rotatable components in the buffered electrolytic solution, passing an electrical energy through the immersion portion of at least one of the plurality of rotatable components while the immersion portion is immersed in the buffered electrolytic solution, wherein an electrical flux to the immersion portion electro-polishes the immersion portion, separating the immersion portion from the buffered electrolytic solution, and applying a corrosion inhibitor to the plurality of rotatable components.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrochemical polishing method for high purity aluminum under ultrasonic agitation
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
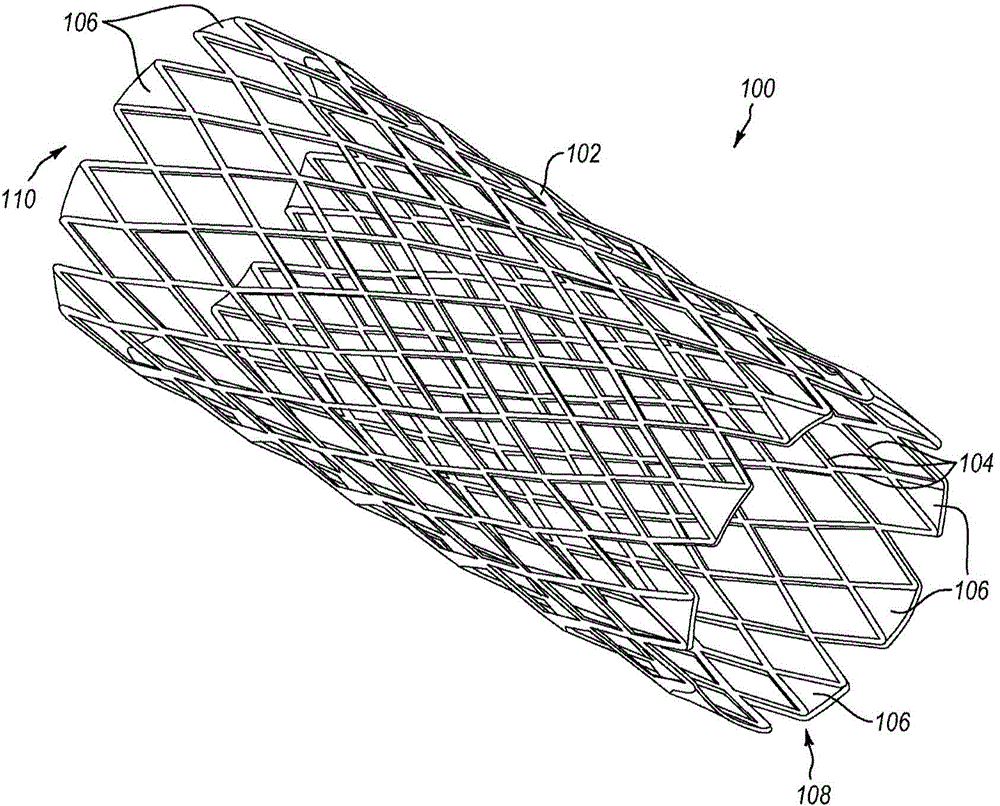
Aortic dissection vascular stent and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106726003AIncrease stickabilitySimple structureStentsBlood vesselsAortic dissectionInsertion stent
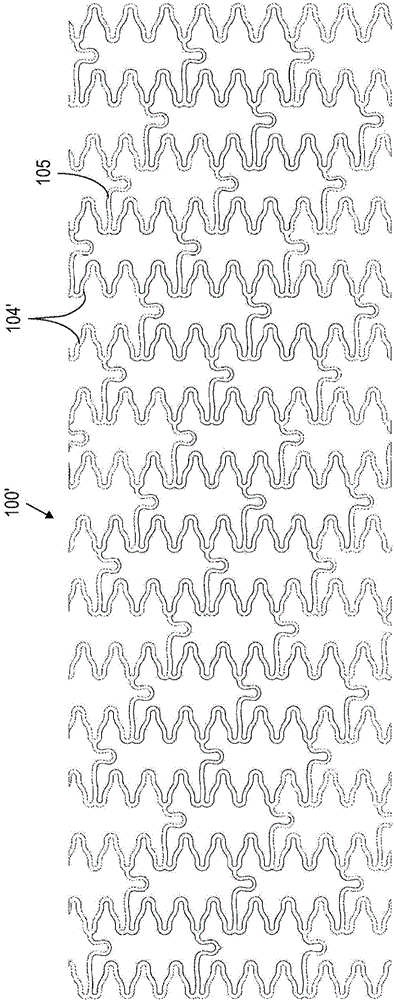
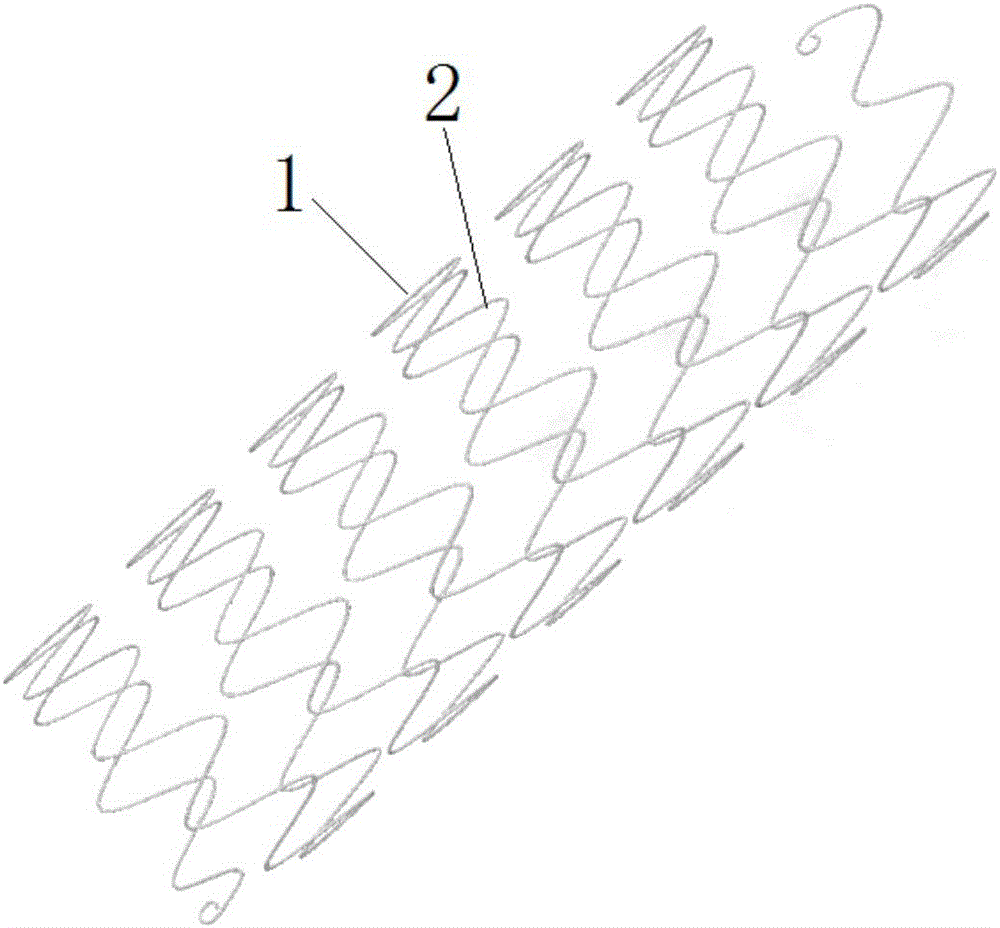
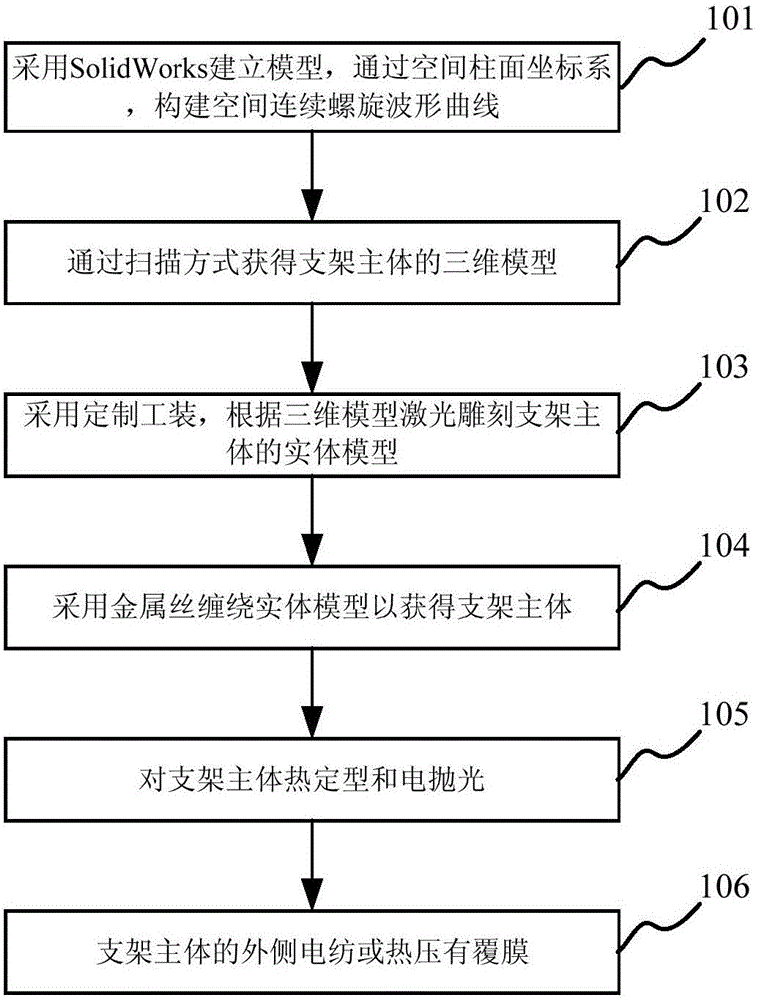
The invention discloses an aortic dissection vascular stent and a manufacturing method thereof. The aortic dissection vascular stent comprises a stent body and a membrane attached to the outer side of the stent body, the stent body is formed by multiple coils in a spiraling mode, and each coil is formed by multiple waves. The manufacturing method includes the steps that a spatial continuous spiral wave curve is constructed through a spatial cylindrical coordinate system; a three-dimensional model of the stent body is obtained in a scanning mode; an entity model of the stent body is made according to the three-dimensional model; a metal wire is wound around the entity model to obtain the stent body; heat shaping and electropolishing are carried out on the stent body; the membrane is arranged on the outer side of the stent body in an electrospinning or hot-pressing mode. Bending of the vascular stent in the bent lumen is uniformly distributed in the whole vascular stent, so that the fitness of the vascular stent is improved, and the situation that the vascular wall is bent or damaged is avoided. Besides, the vascular stent is specially designed for the aortic dissection and is simple in structure, convenient to operate, appropriate in supporting force and suitable for the pathological characteristics of the aortic dissection.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL +2
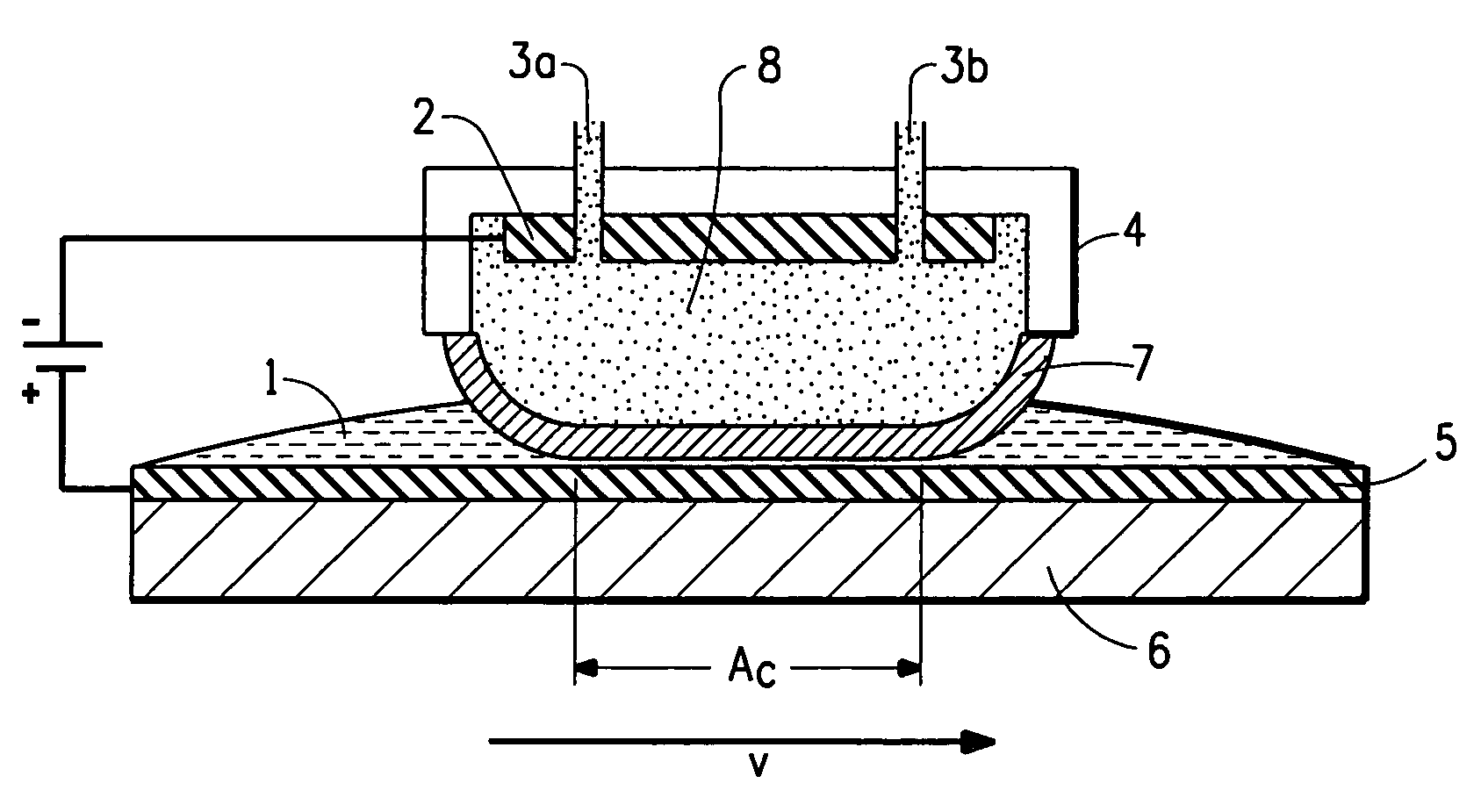
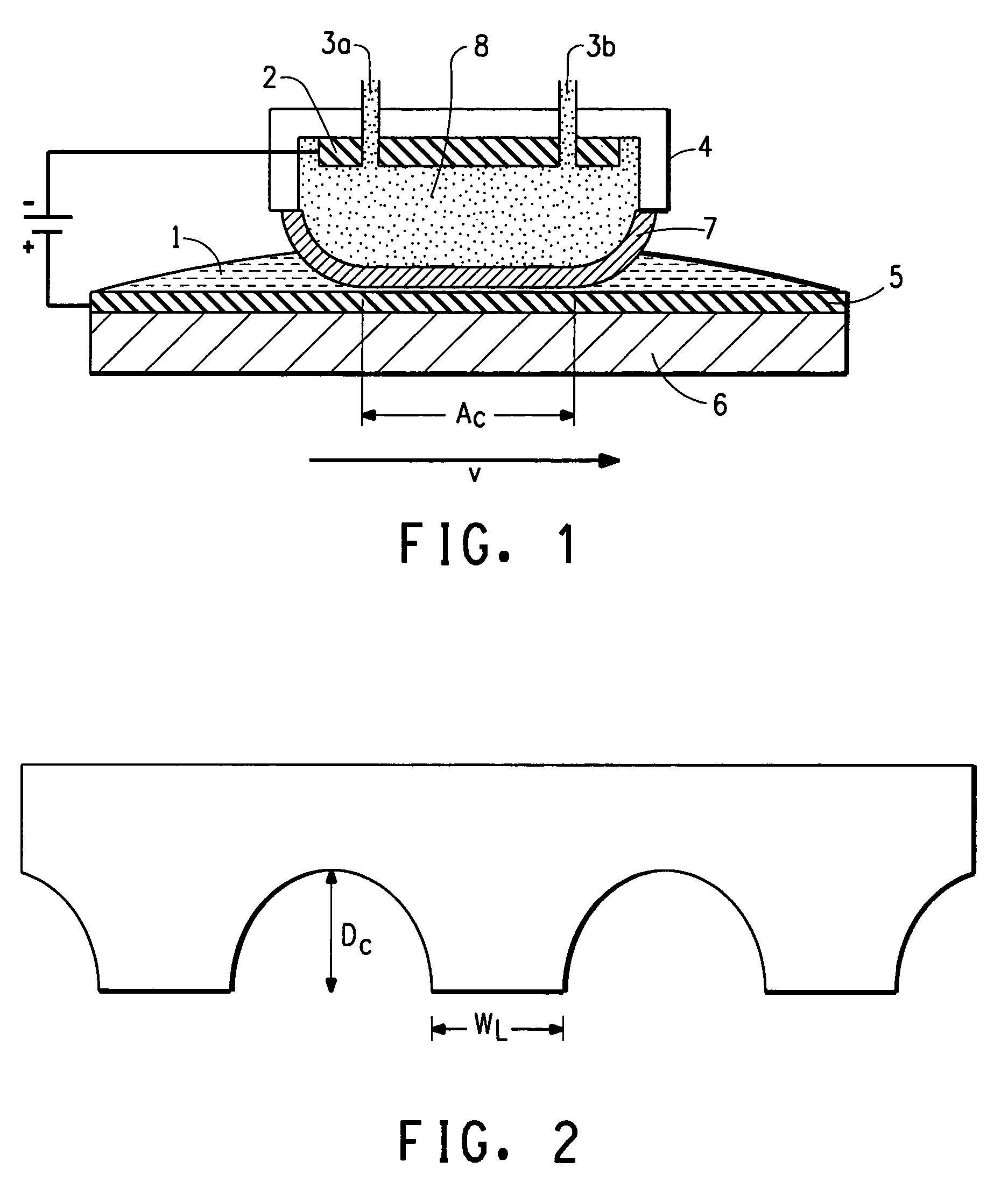
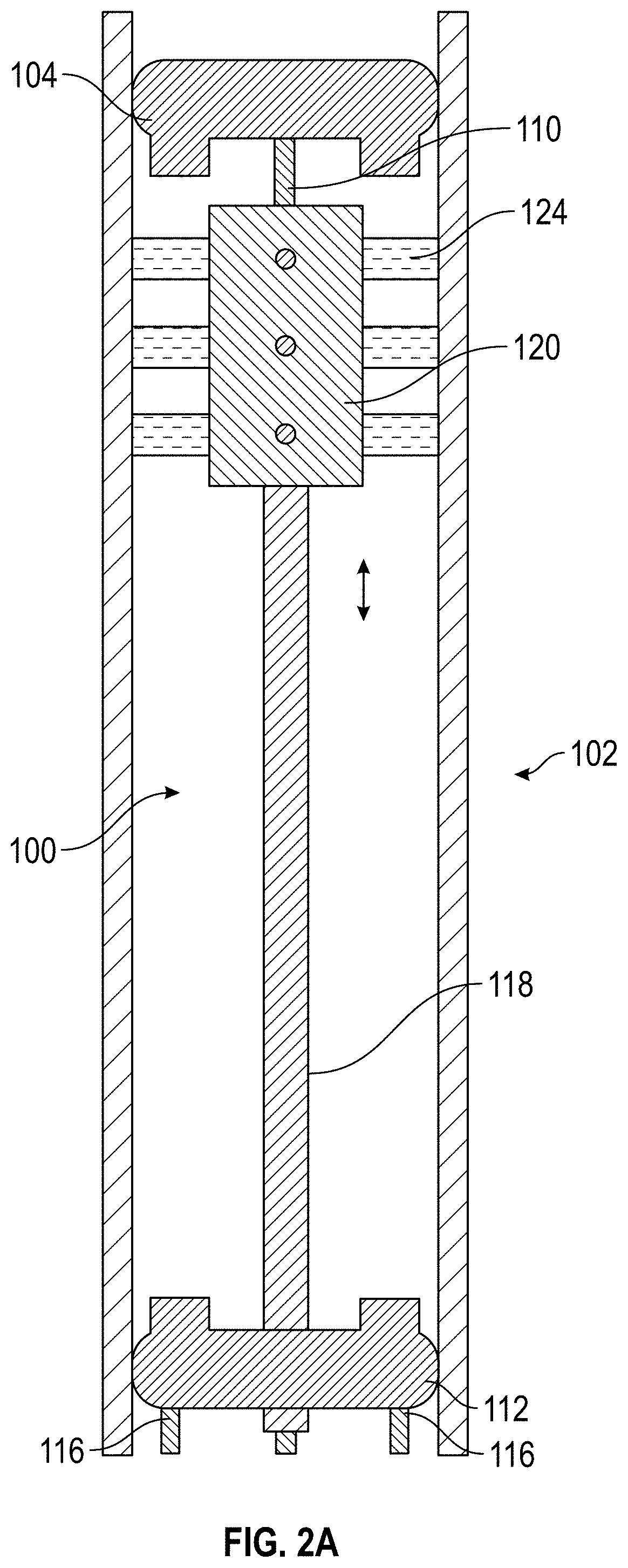
Apparatus and method for in-situ electrosleeving and in-situ electropolishing internal walls of metallic conduits
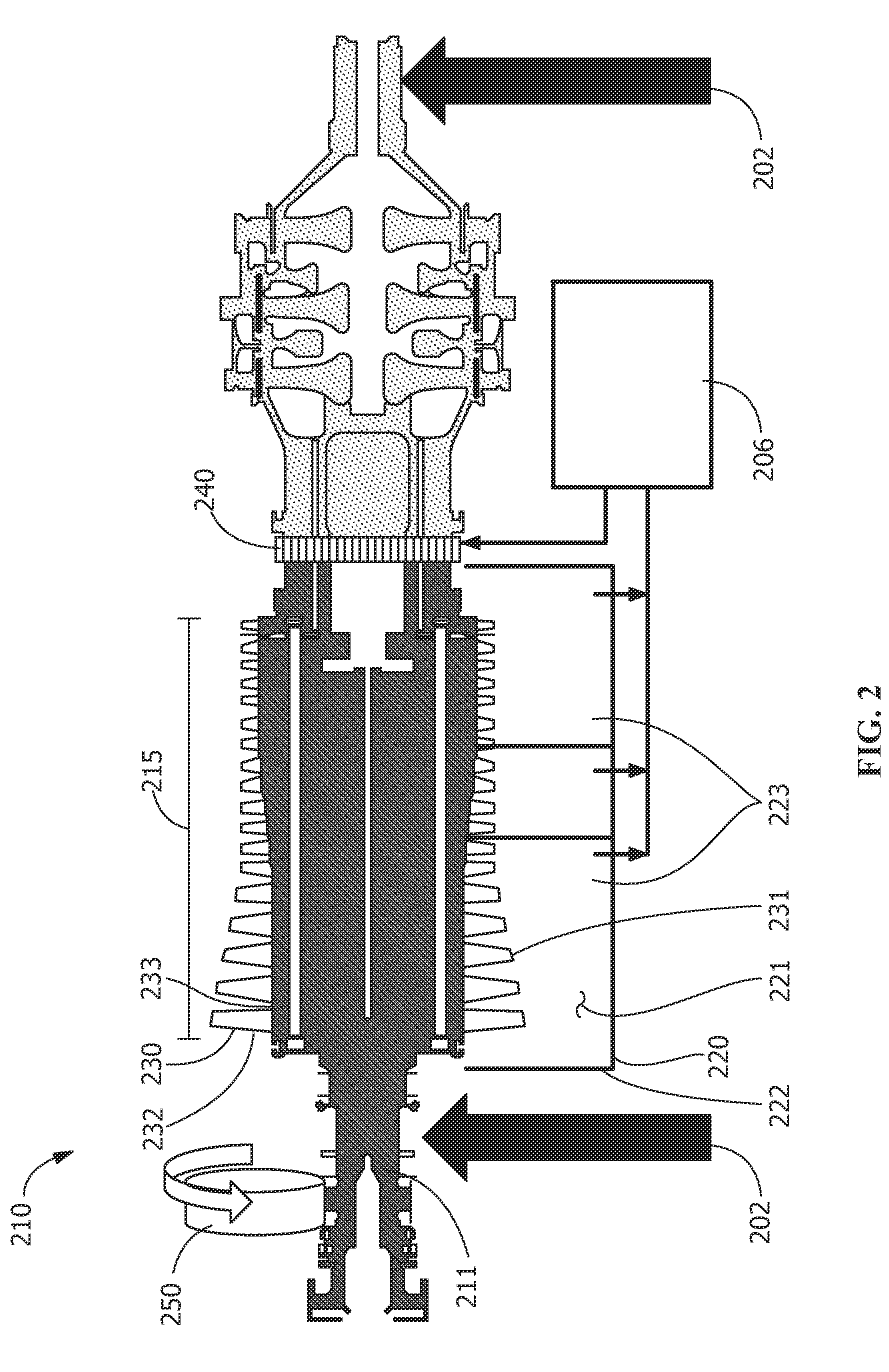
ActiveUS20210292930A1Avoid disintegrationReduce deposition thicknessSealing devicesCurrent conducting devicesStraight tubeMetallic materials
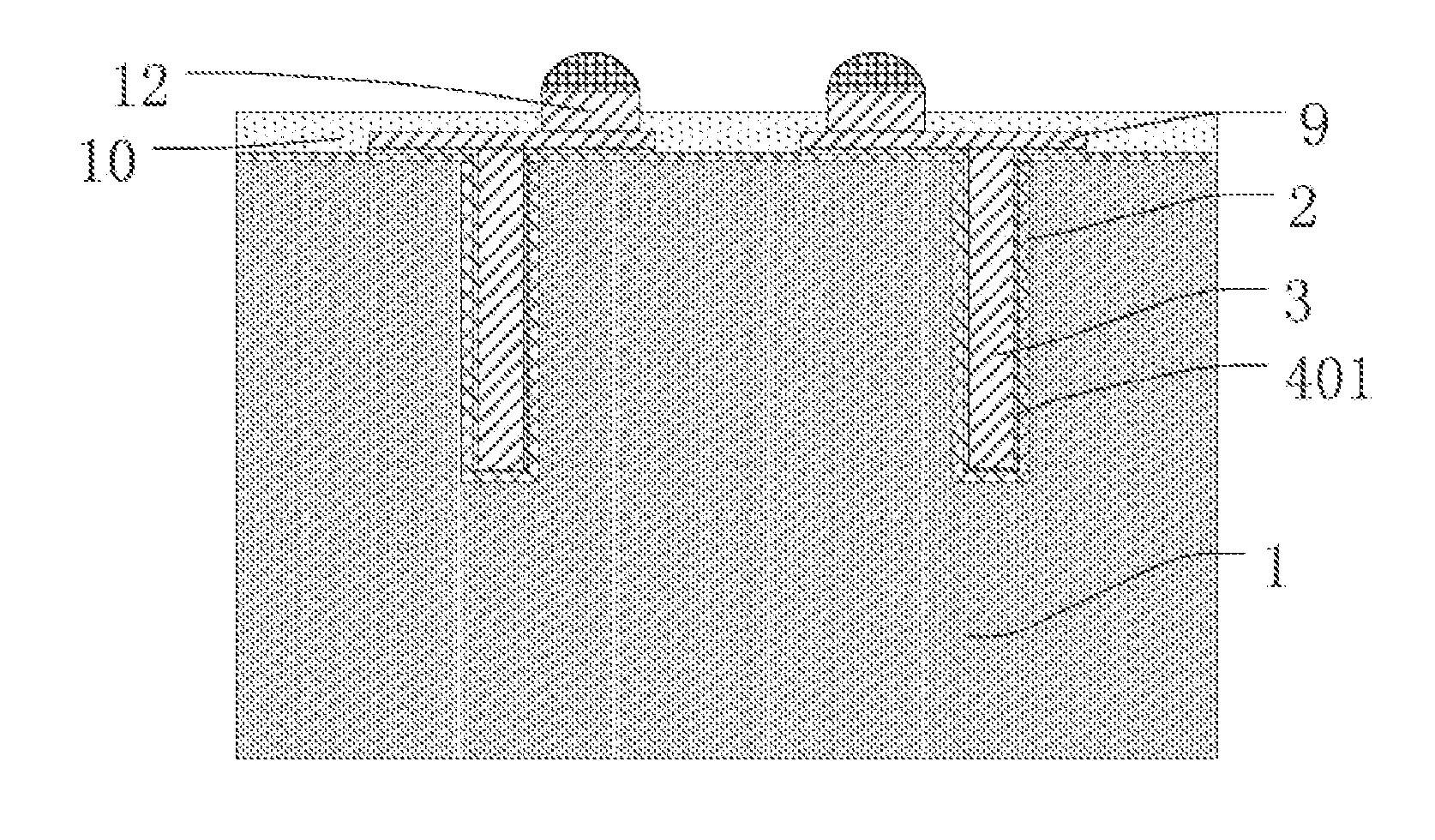
An apparatus and system for in-situ electropolishing and / or for in-situ electroforming a structural or functional reinforcement layer such as a sleeve of a selected metallic material on the internal surfaces of metallic tubular conduits are described. The apparatus and system can be employed on straight tubes, tube joints to different diameter tubes or face plates, tube elbows and other complex shapes encountered in piping systems. The apparatus includes components which can be independently manipulated and assembled on or near a degraded site and, after secured in place, form an electrolytic cell within the workpiece. The apparatus contains counter-electrodes which can be moved relative to the workpiece surface during the electroplating and / or electropolishing operation to provide flexibility in selecting and employing electropolishing process parameters and electroplating process parameters to design and optimize the surface roughness as well as the size, shape and properties of the electrodeposited reinforcing layer(s).
Owner:INTEGRAN TECH
Anodic oxidation method and treatment apparatus thereof
InactiveUS7037420B2Low production costImprove the operating environmentAnodisationCellsElectrolysisWater discharge
The present invention relates to an anodic oxidation method and a treatment apparatus thereof which is suitable, for example, for generation of an oxide film and electropolishing of aluminum, capable of generating an oxide film at a low cost and rapidly by eliminating the use of electrolytic solution having a strong acid property and using a carbonated water as the electrolytic solution, capable of improving the oxide film generating operation and rationalizing the water discharging treatment, capable of preventing increase in temperature of the electrolytic solution without a need of a special equipment, capable of generating an oxide film in a stable manner and obtaining a good oxide film by eliminating the generation of oxide in the vicinity of an object to be treated, and capable of rationalization of the oxide film generating treatment and enhancing the productivity by using supercritical carbon dioxide. An object (3) to be treated is electrolyzed as an anode in an electrolytic solution. An oxide film is generated on the surface of the object (3). A pressurized carbon dioxide is dissolved in a predetermined quantity of water (7). An oxide film is generated by serving a carbonated water of a predetermined acid concentration as an electrolytic solution.
Owner:HIDEO YOSHIDA
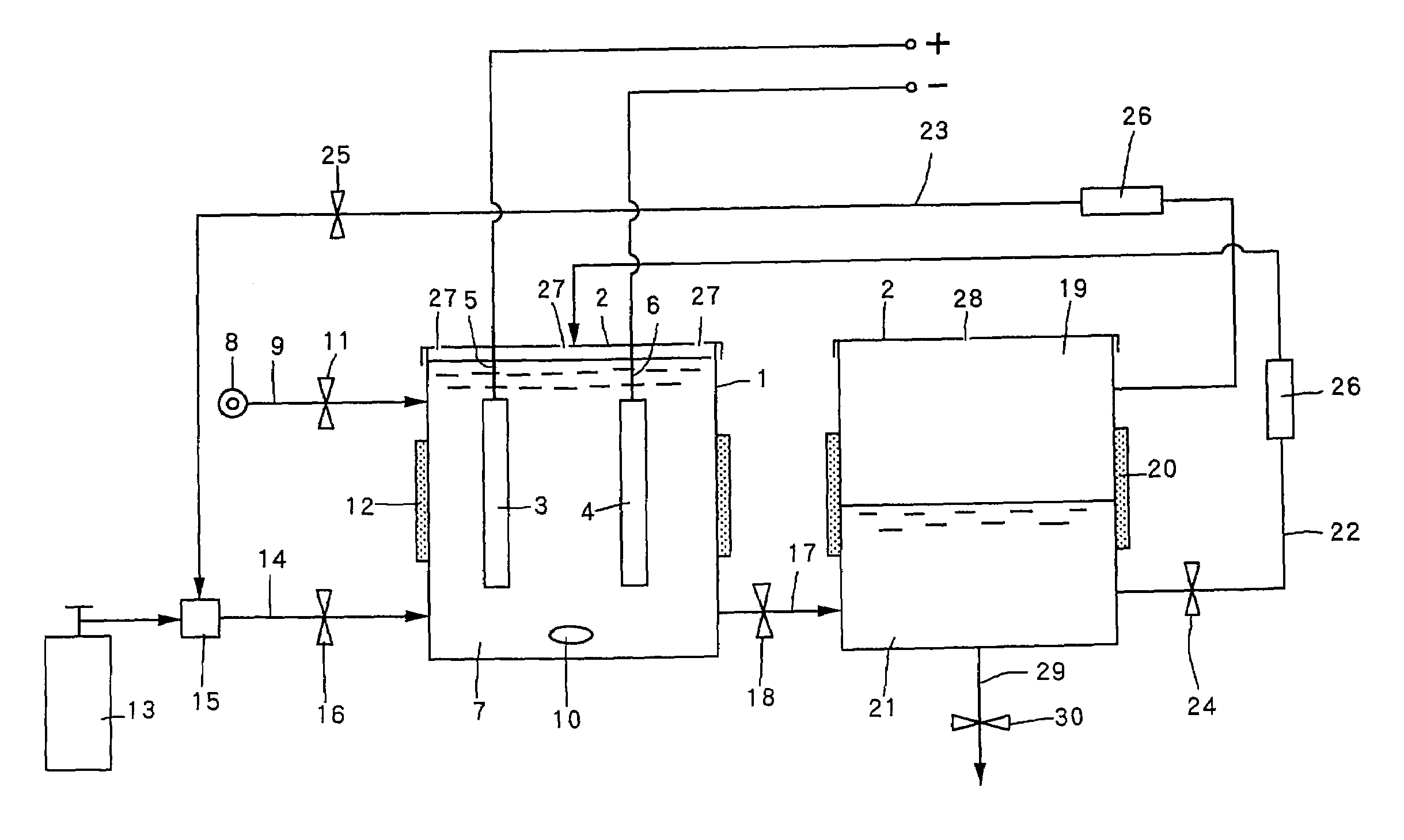
Electrolytic solution, electrolysis case, electropolishing system, and electropolishing method using these
InactiveUS20130319878A1CellsConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalElectrolytic agentPower flow
In an electropolishing method passing large current, an electrolytic solution is given a viscosity by reacting an organic acid (a phosphoric acid solution or a mixed solution of phosphoric acid and sulfuric acid) with a silicon dioxide as a gelling agent, the electrolytic solution is continuously introduced to an electrolysis case and concurrently the first introduced electrolytic solution is discharged to progress the electropolishing. The electrolysis case has a cathode at a specific height from a lower open end of a frame in a specific size and depth, an introduction port on the cathode for introducing the electrolytic solution with specific viscosity, and a discharge port for discharging the solution from the frame. It is possible to shorten the distance of the cathode in the electrolysis case from the open end corresponding to the work-piece surface, and control the resistant of the electrolytic solution, so that the large current can be passed and the operation time can be reduced.
Owner:MARUI MEKKI INDS
Edge bead removal process with ecmp technology
InactiveUS20090061617A1Electrolysis componentsMachining electric circuitsConductive materialsMechanical engineering
A method and apparatus for the removal of a deposited conductive layer along an edge of a substrate using a power ring configured to electro polish an edge of the substrate are provided. The electro polishing of the substrate edge may occur simultaneously with the electrochemical mechanical processing of a substrate face. In certain embodiments a method of electrochemically polishing a substrate having a conductive material disposed thereon is provided. A substrate is coupled with a carrier head comprising a power ring which surrounds an edge of the substrate, wherein the edge of the substrate includes the conductive material. A polishing pad is contacted with a face of the substrate. A first voltage is applied to the power ring to remove conductive material from the edge of the substrate. A second voltage different from the first voltage is applied to the polishing pad to remove a portion of the conductive material from the face of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
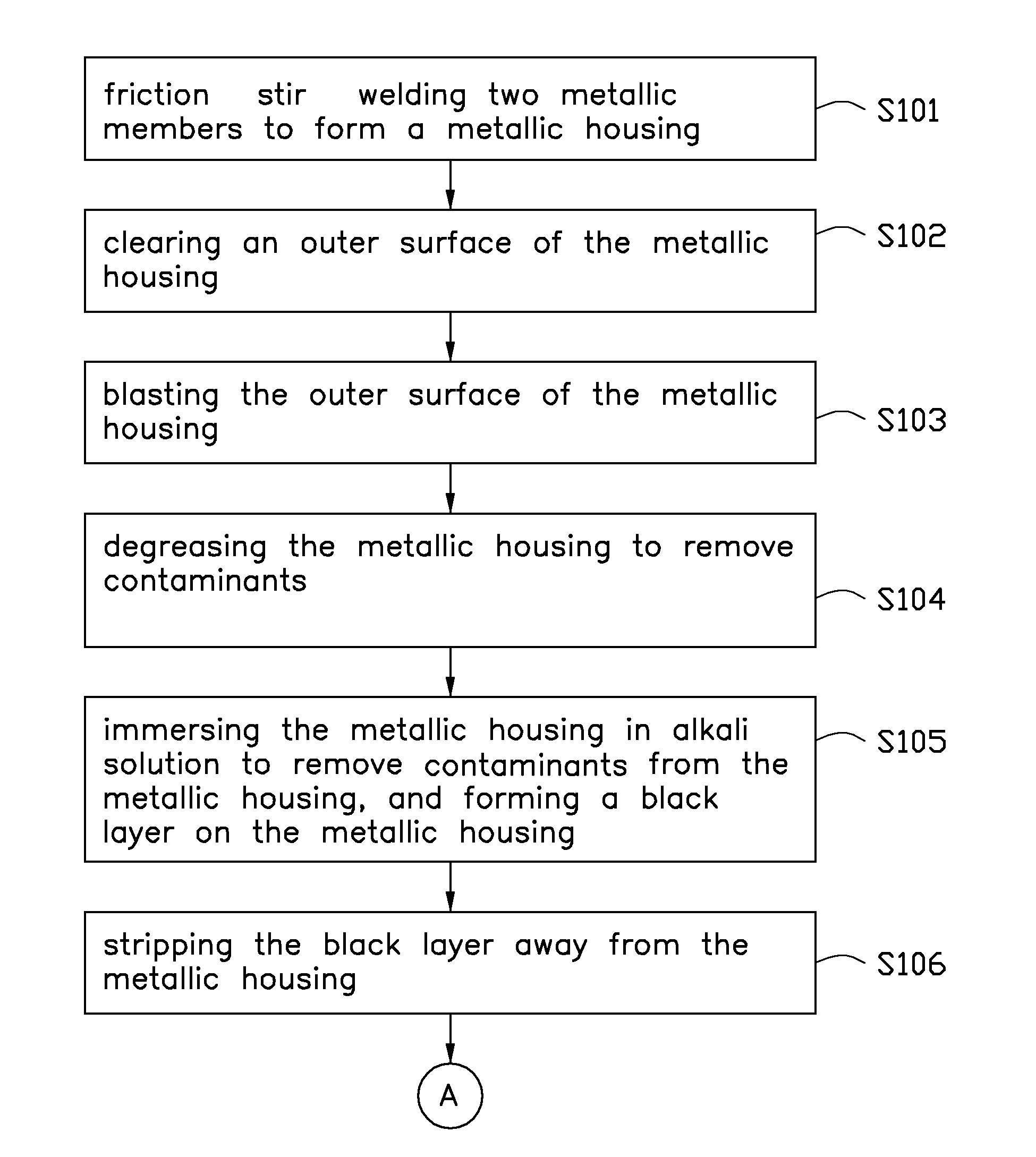
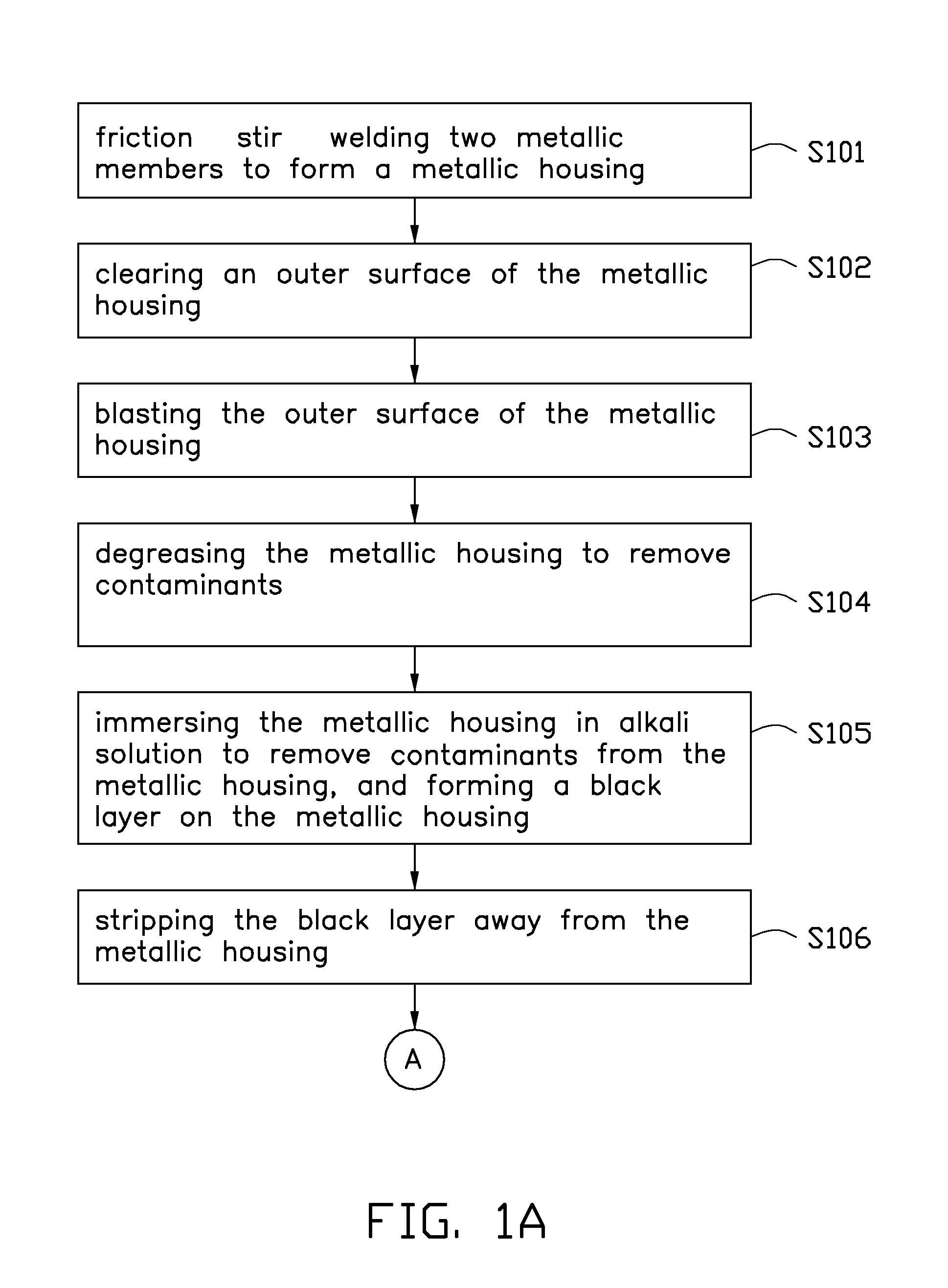
Metallic housing forming method
InactiveUS20130263428A1Low densityHigh conductivity coefficientAnodisationSurface-active detergent compositionsMetallic enclosureMetallurgy
A metallic housing forming method includes steps as follows: friction stir welding metallic members to form a metallic housing; immersing the metallic housing in an alkali solution to remove contaminants from the metallic housing, and forming a black salt layer on the metallic housing; stripping the black salt layer away from the metallic housing; electro-polishing the metallic housing to dissolve the outermost surface of the metallic housing; anode-oxiding the metallic housing; and sealing and drying the metallic housing.
Owner:FU TAI HUA IND SHENZHEN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com