Patents
Literature
317results about "Sealing devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
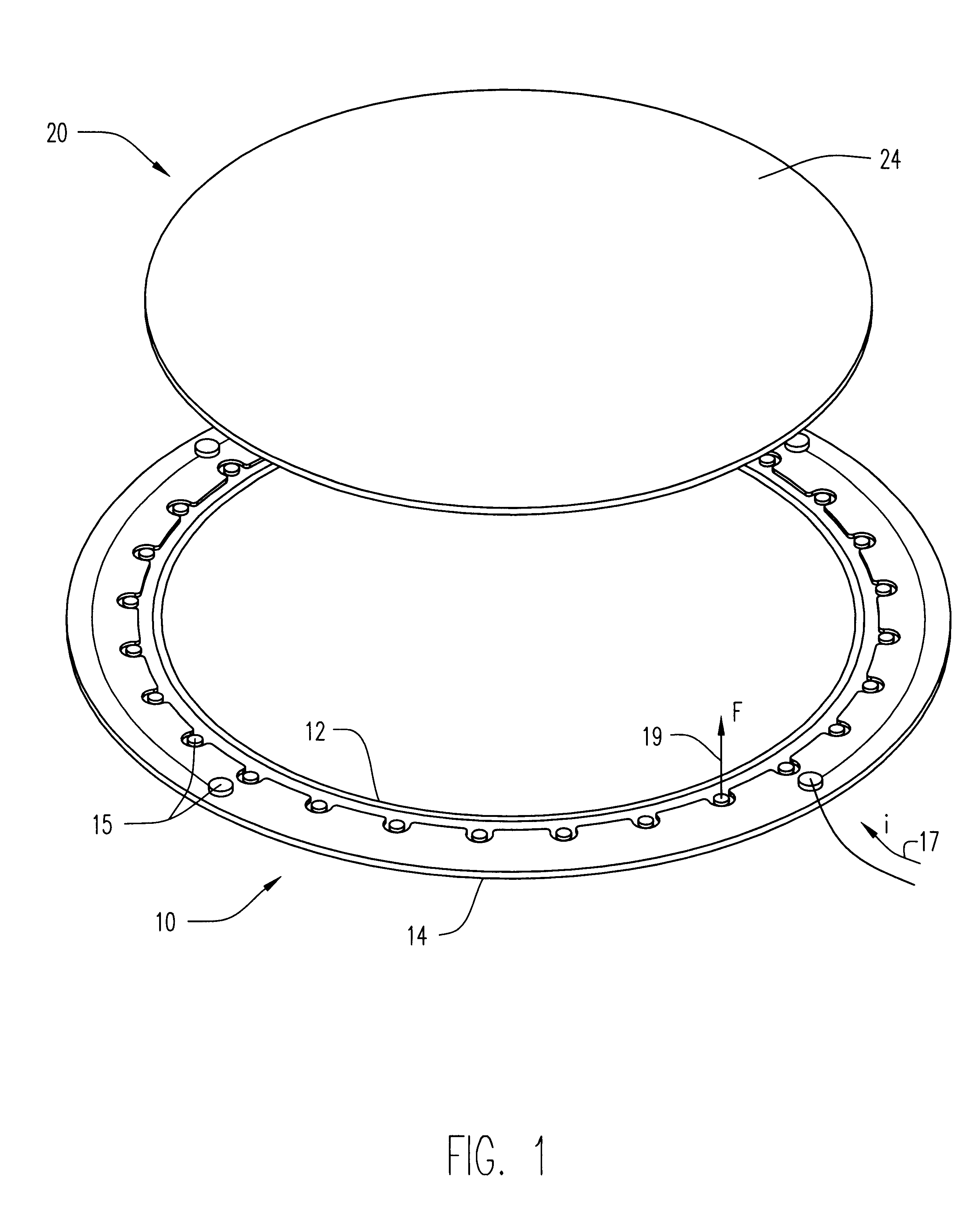
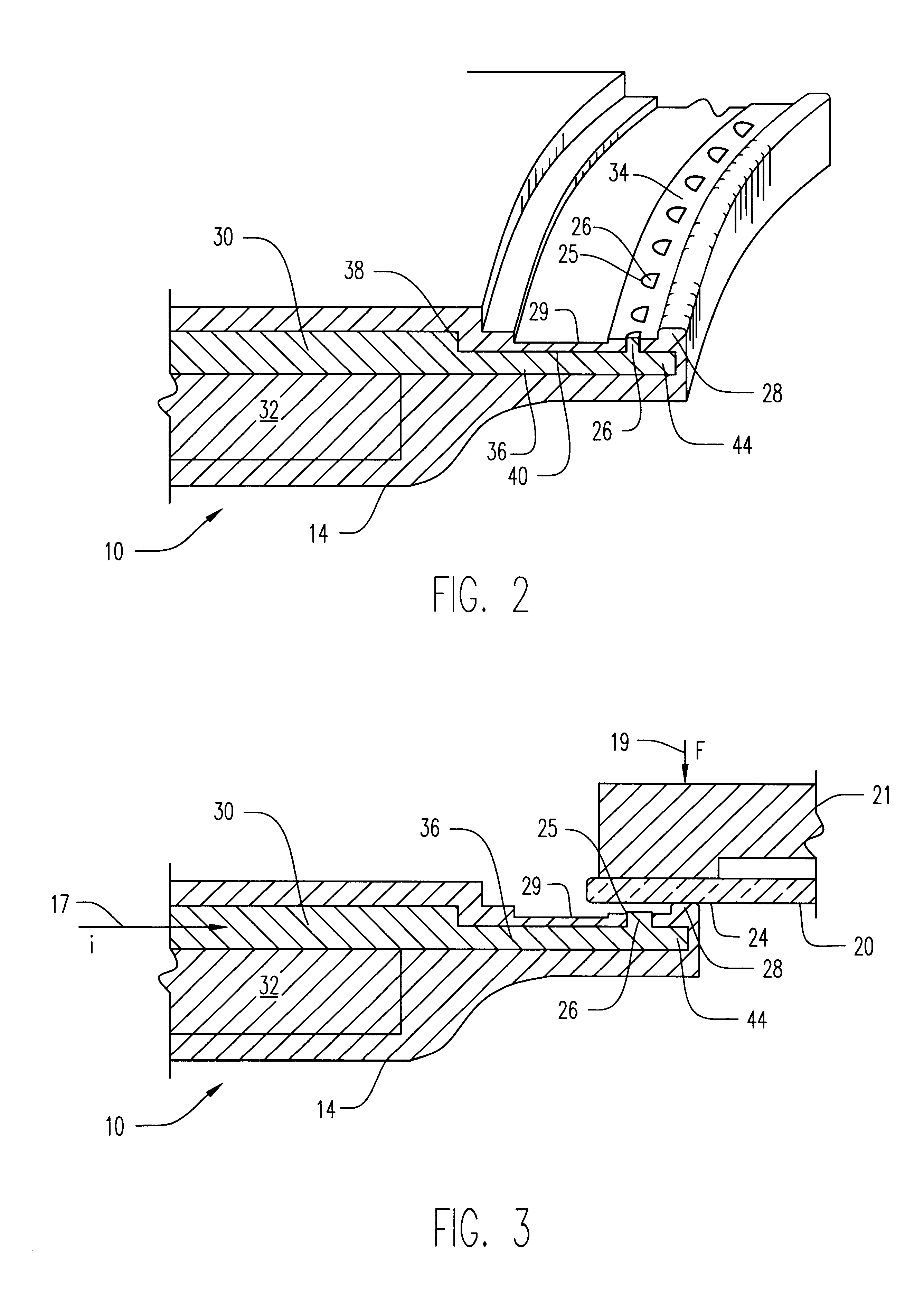
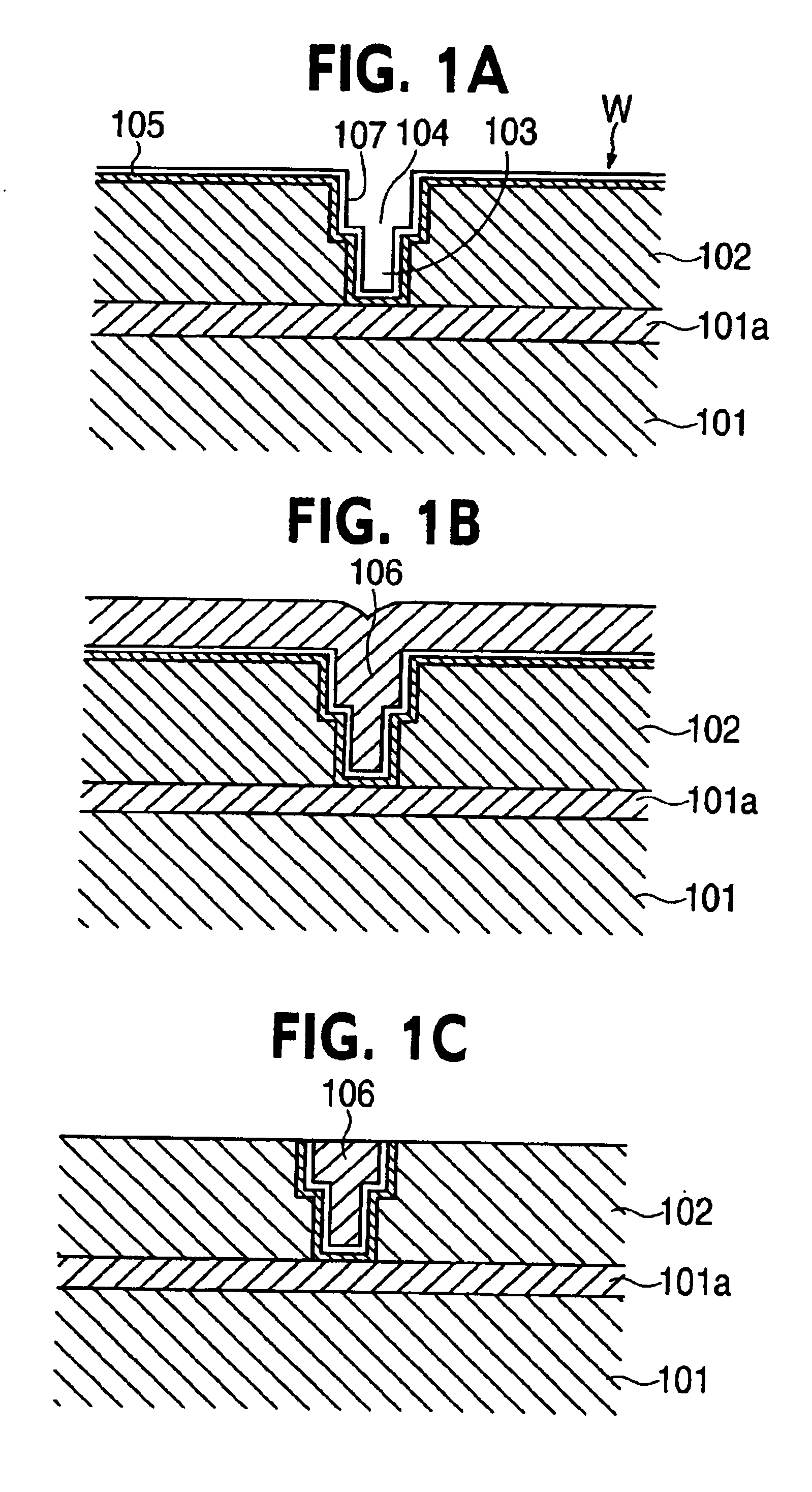
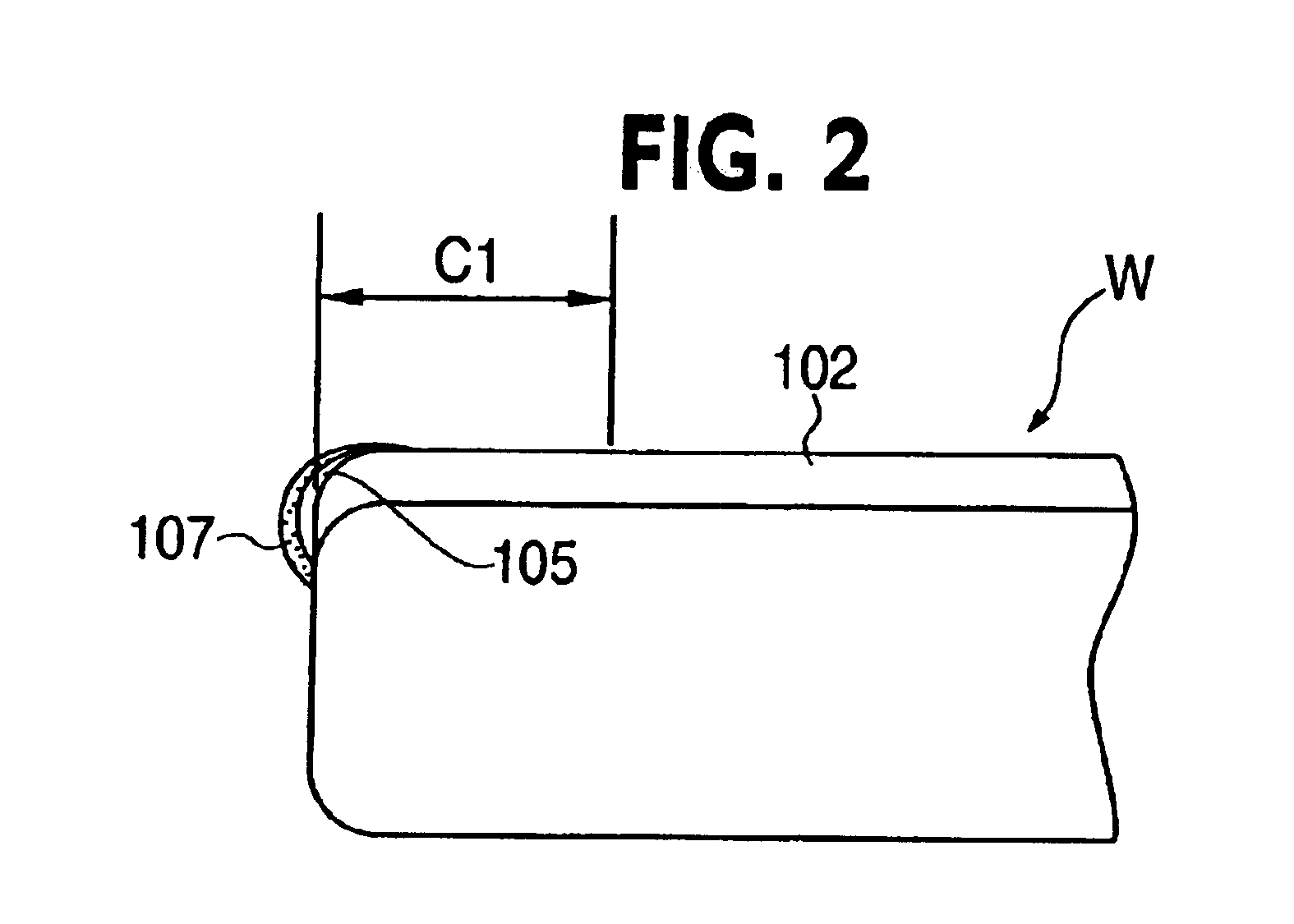
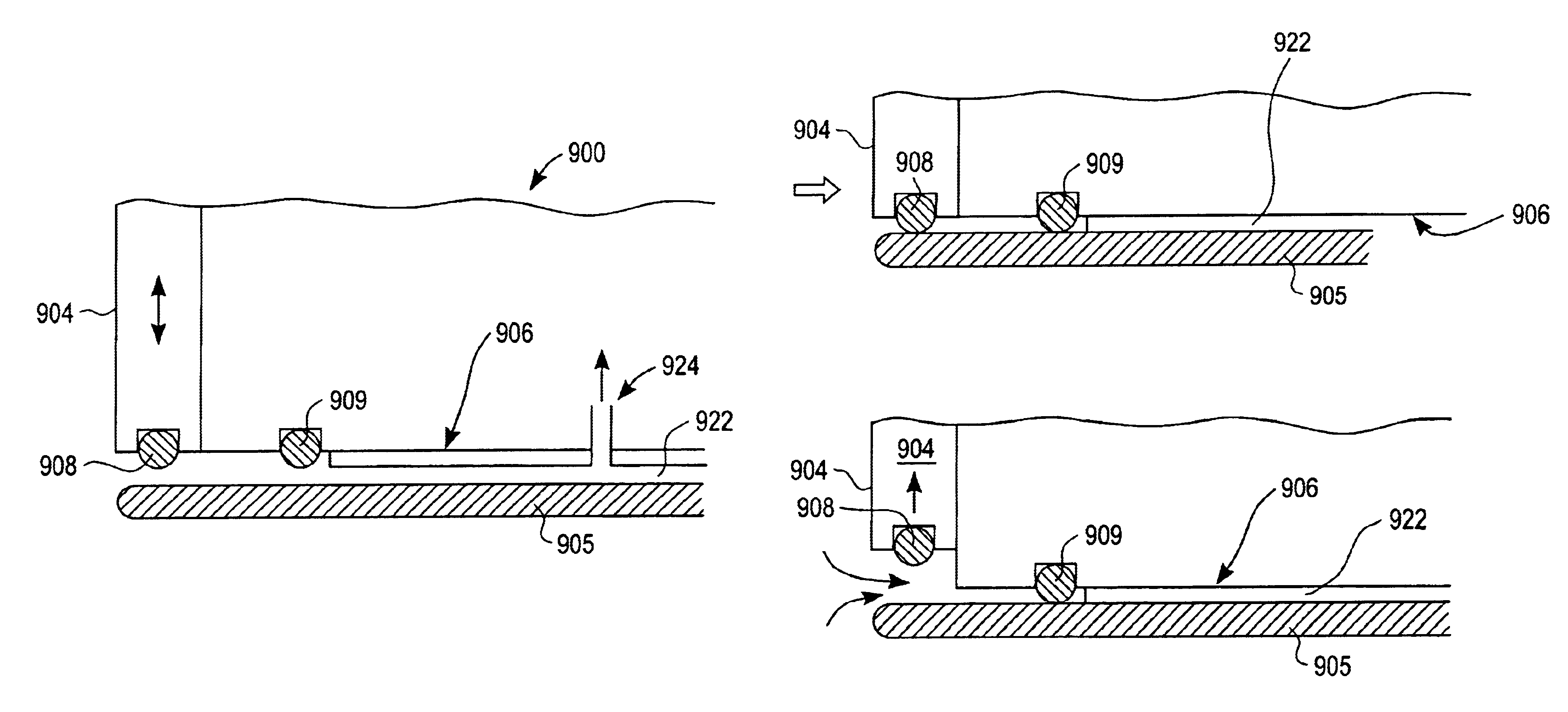
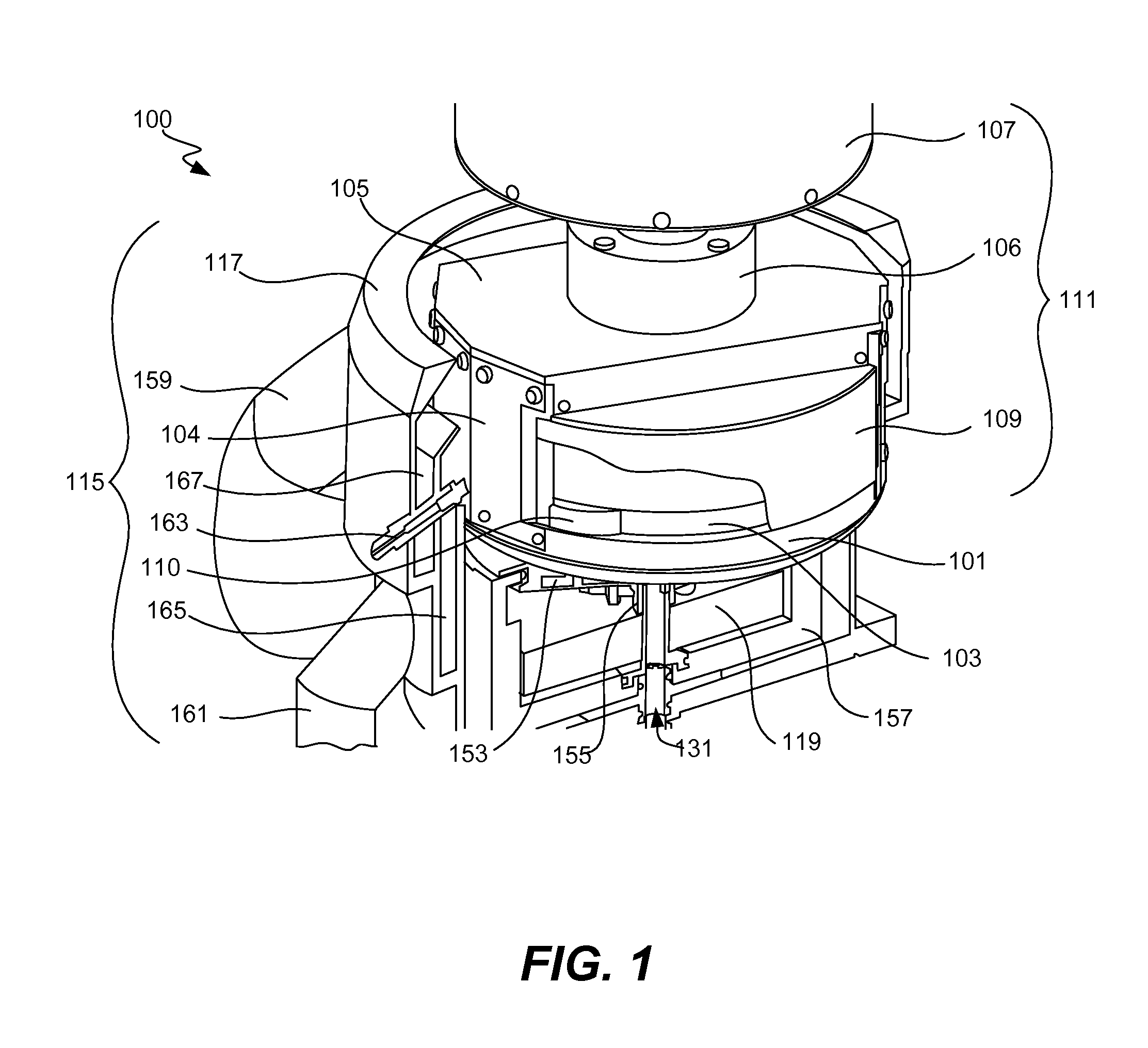
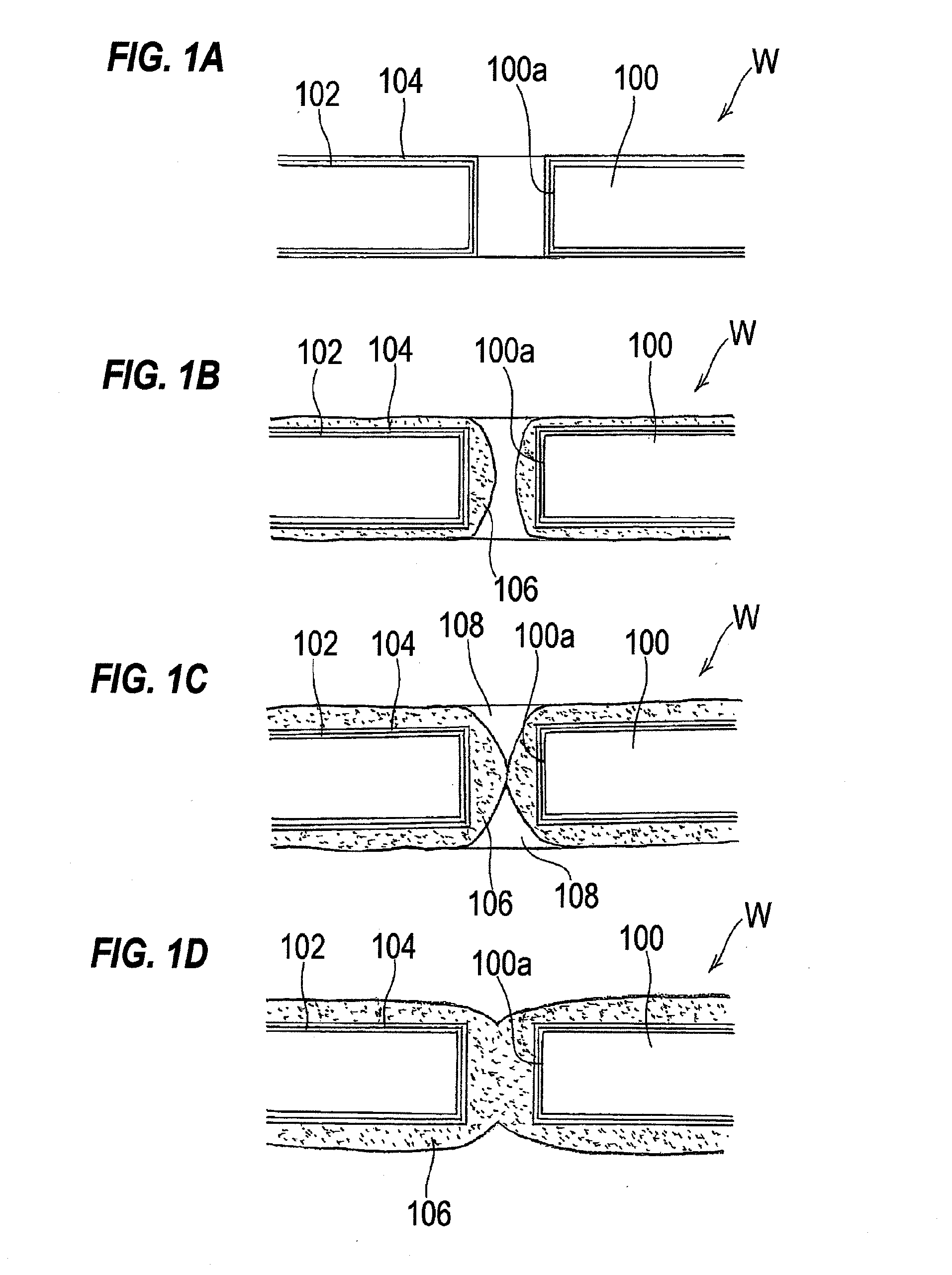
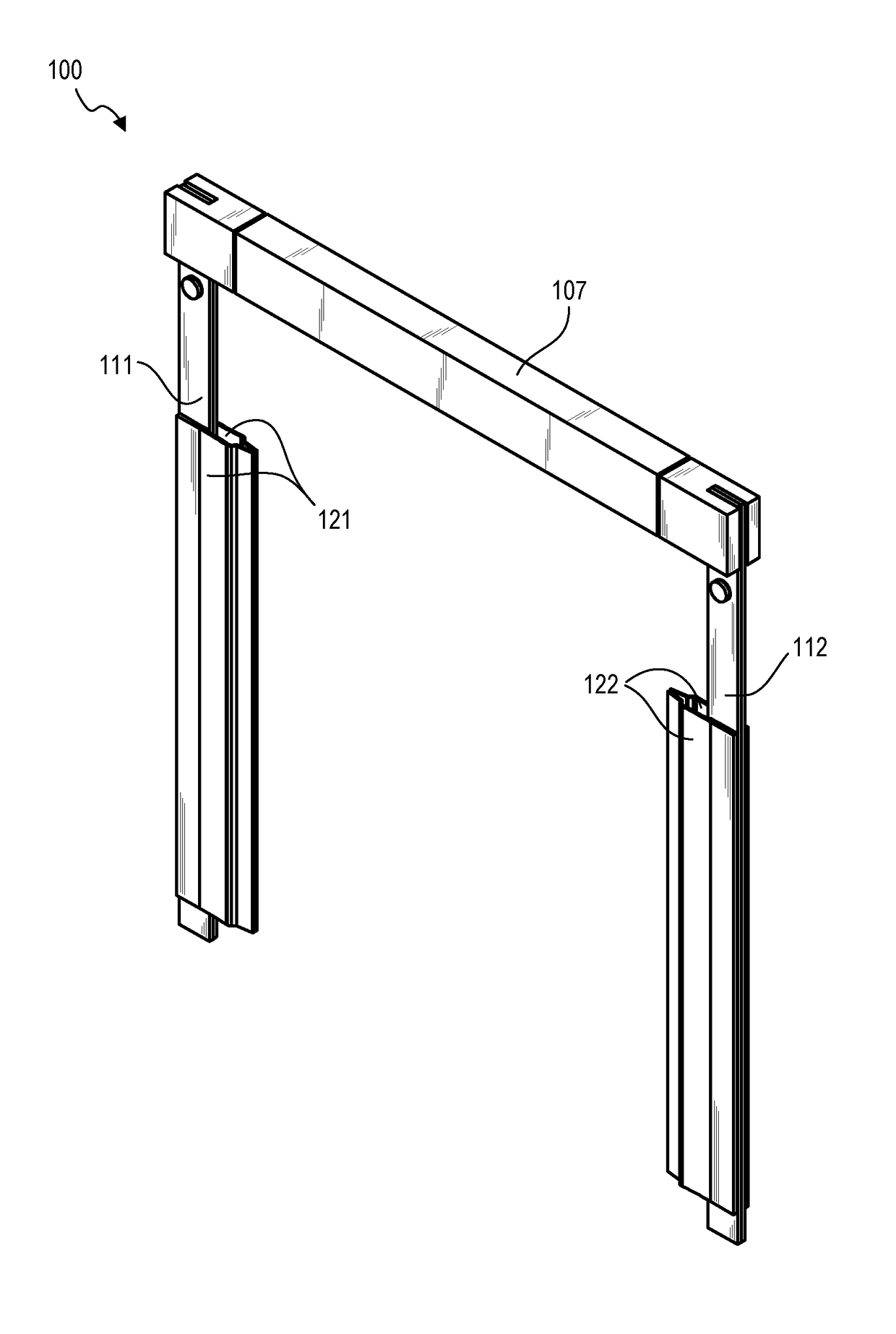
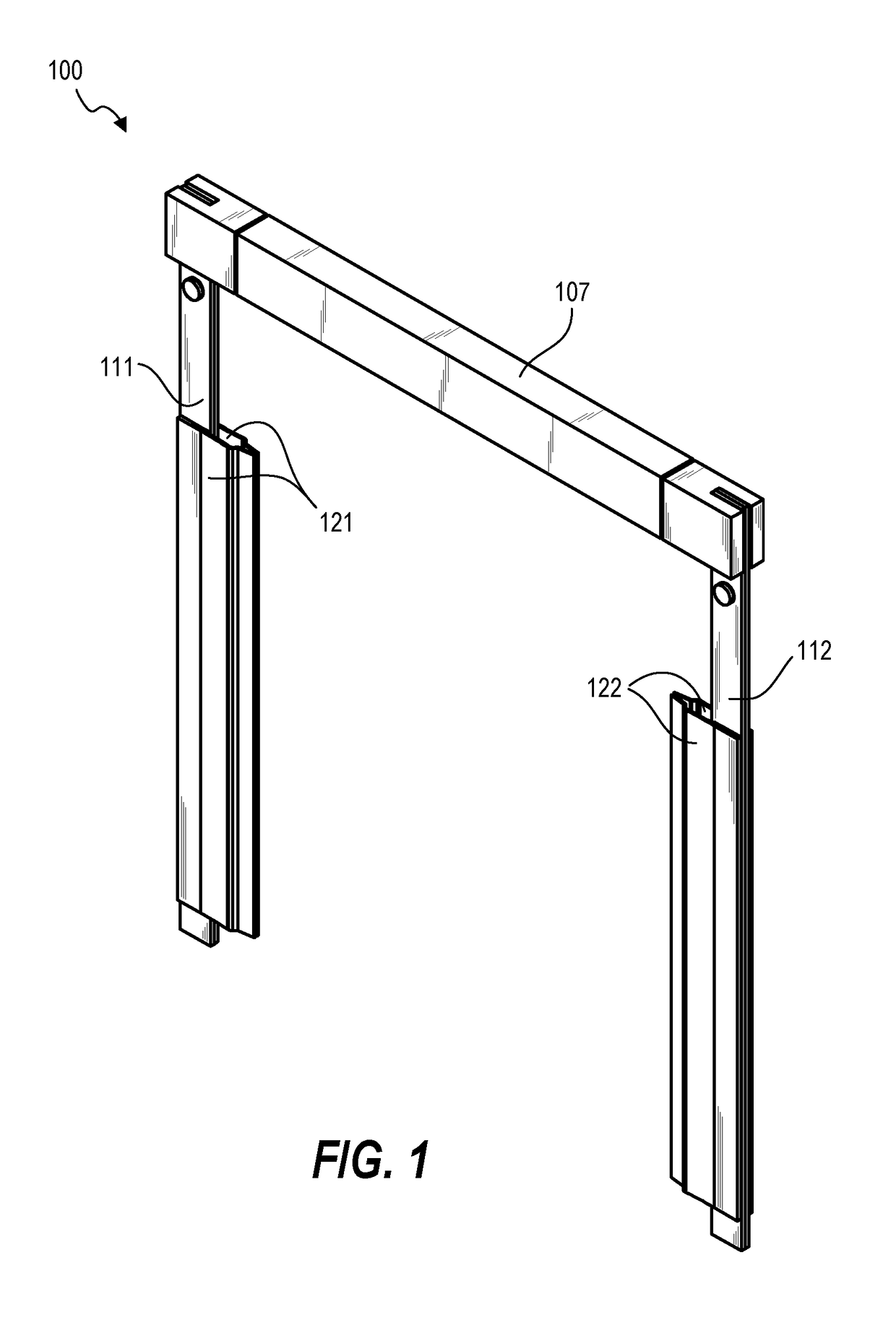
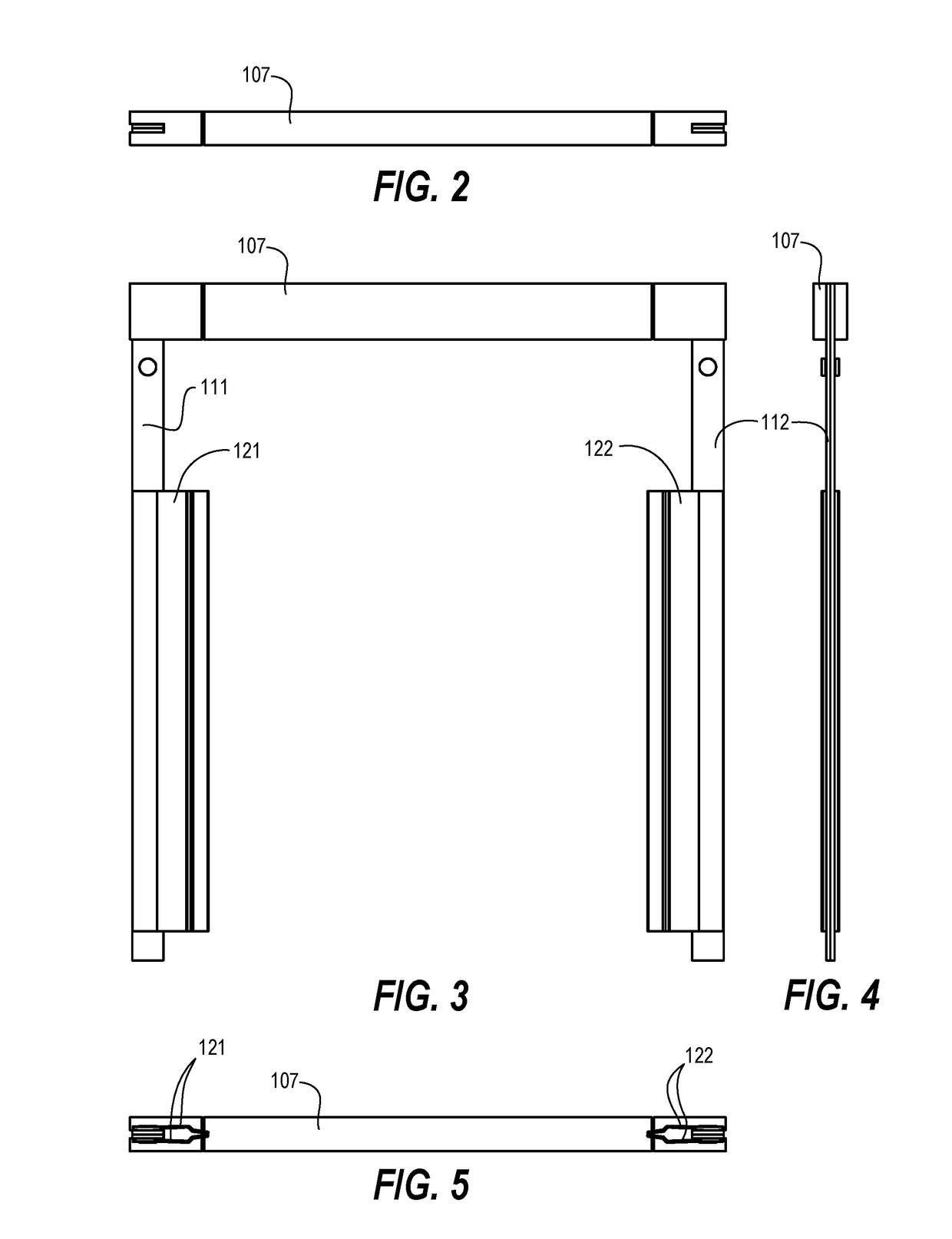
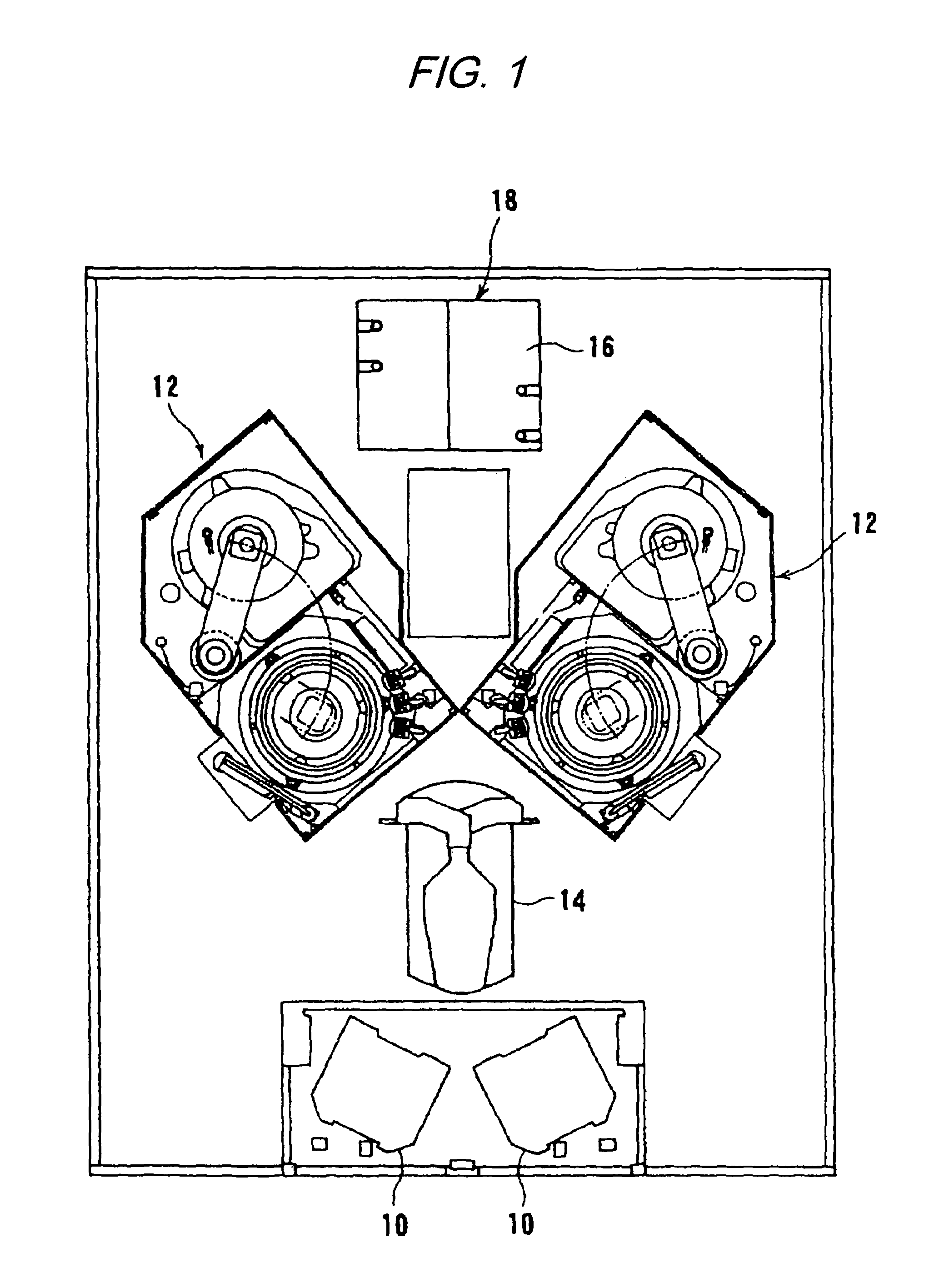
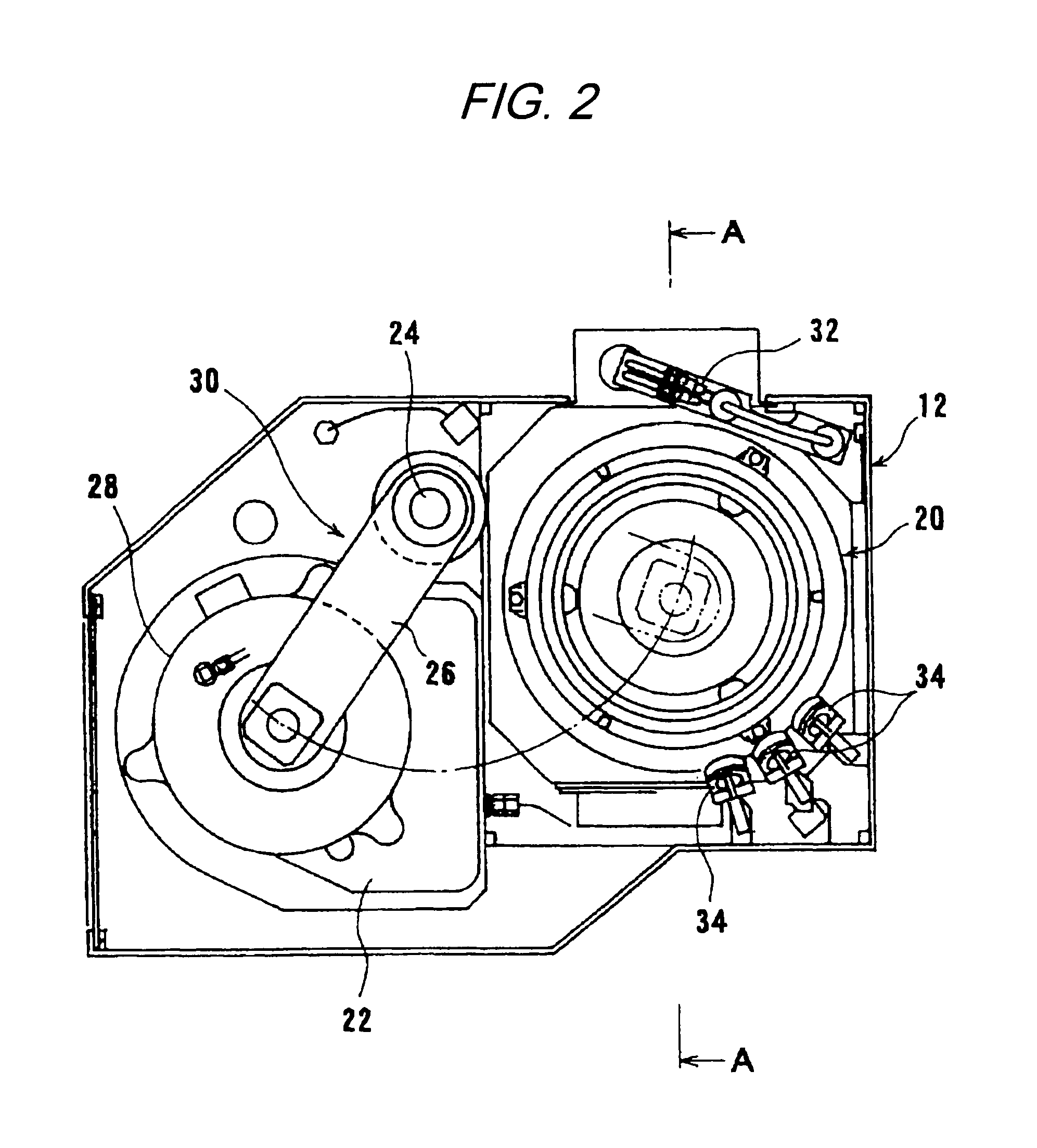
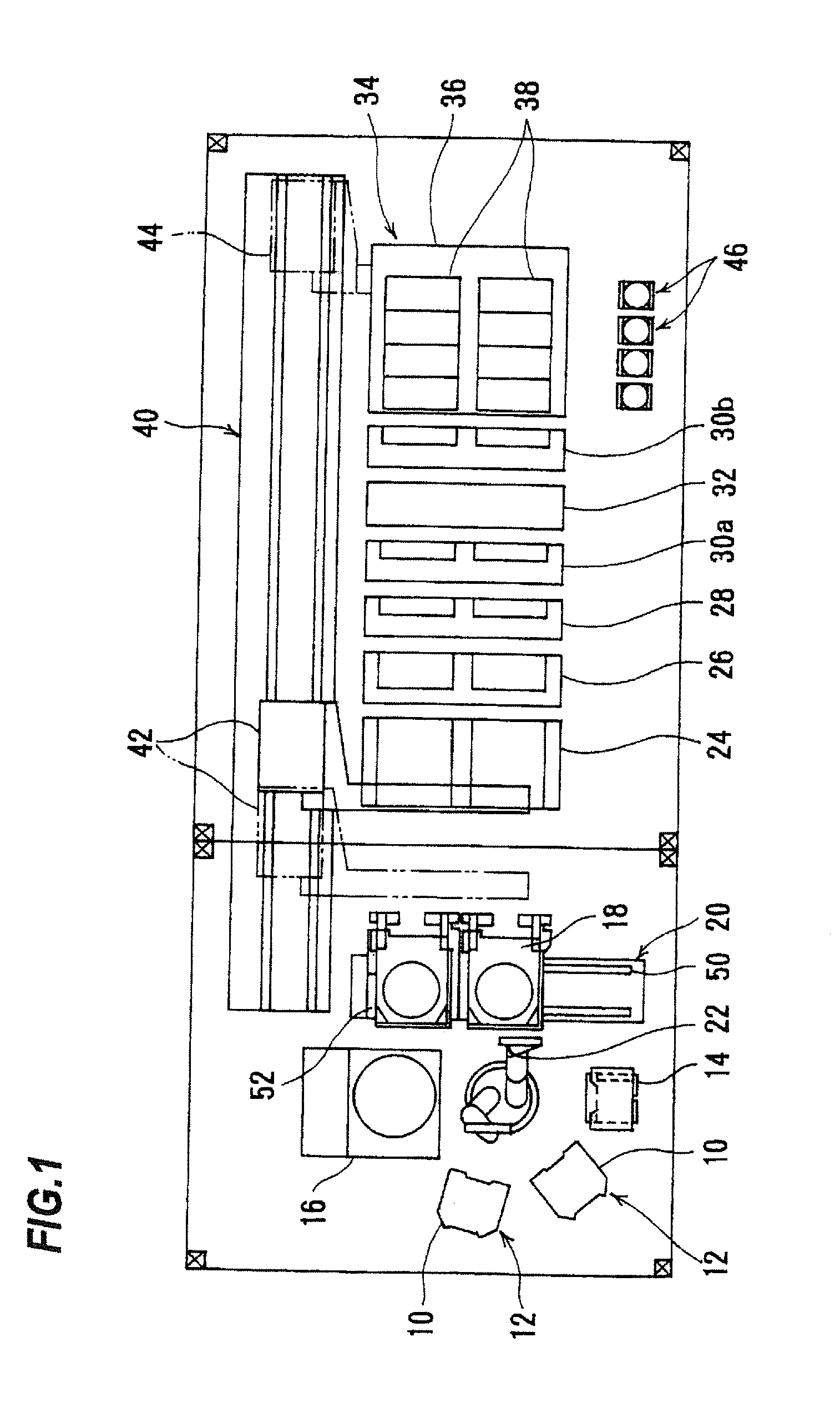
Method and apparatus of sealing wafer backside for full-face electrochemical plating
InactiveUS20030008602A1Efficient configurationMinimize irregularityEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesMechanical engineeringElectroplating
The present invention provides a wafer carrier that includes a plurality of concentric sealing members that provide a seal, with the outer seal independently movable to allow cleaning of a peripheral backside of the wafer to occur while the wafer is still attached to the wafer carrier, and a plurality of vacuum openings that a re disposed only adjacent to an inner side of the inner seal at a location corresponding to the backside periphery of the wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
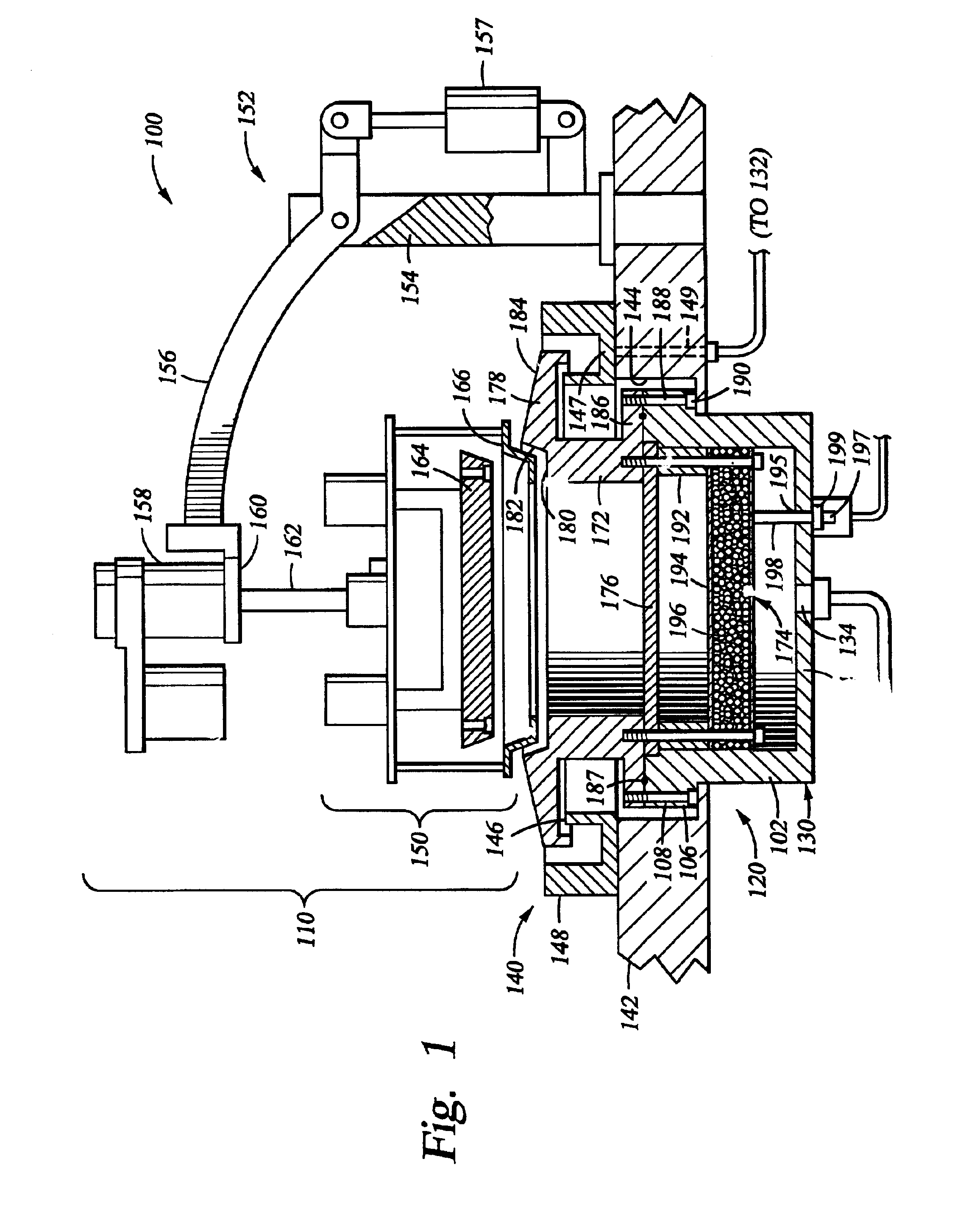
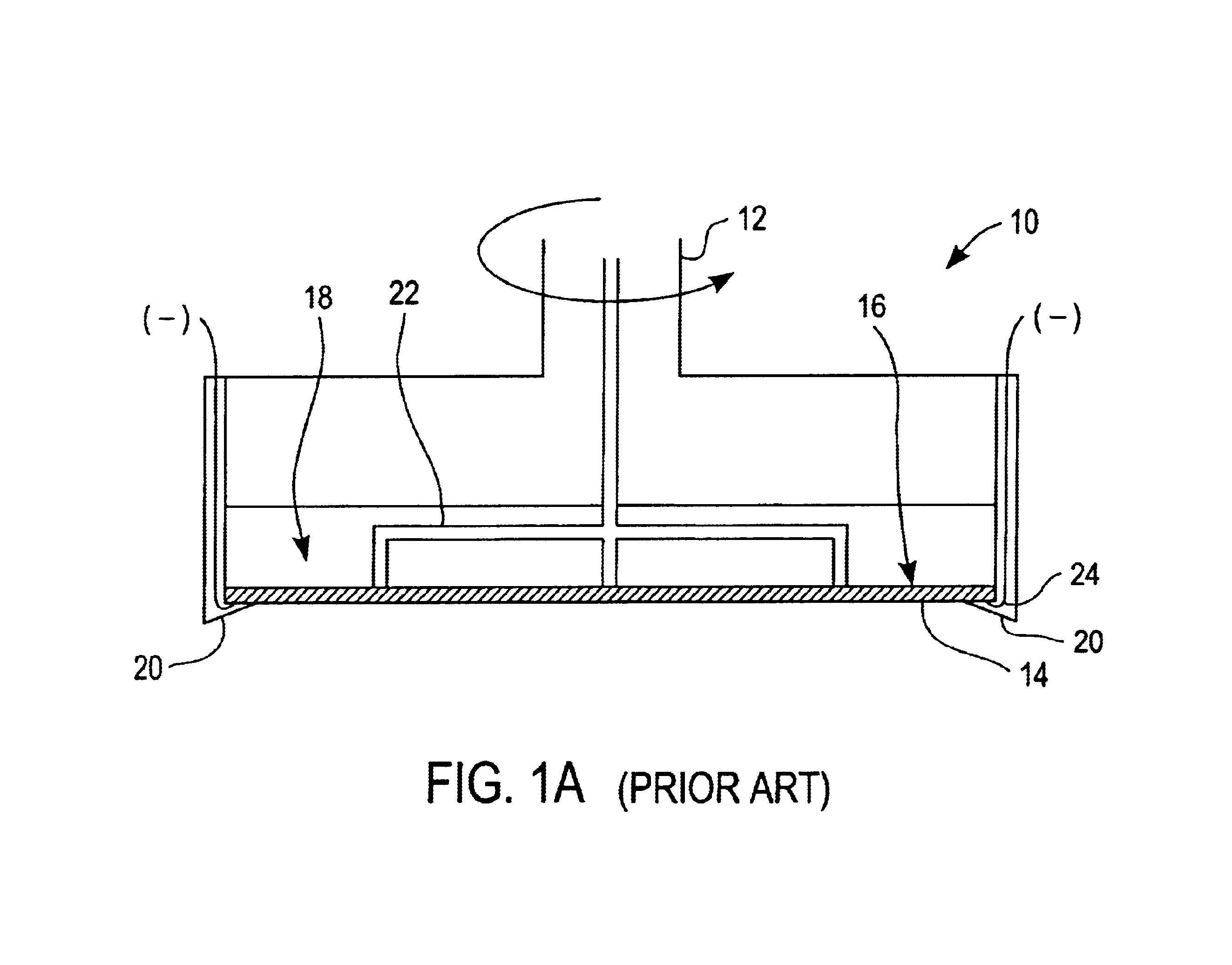
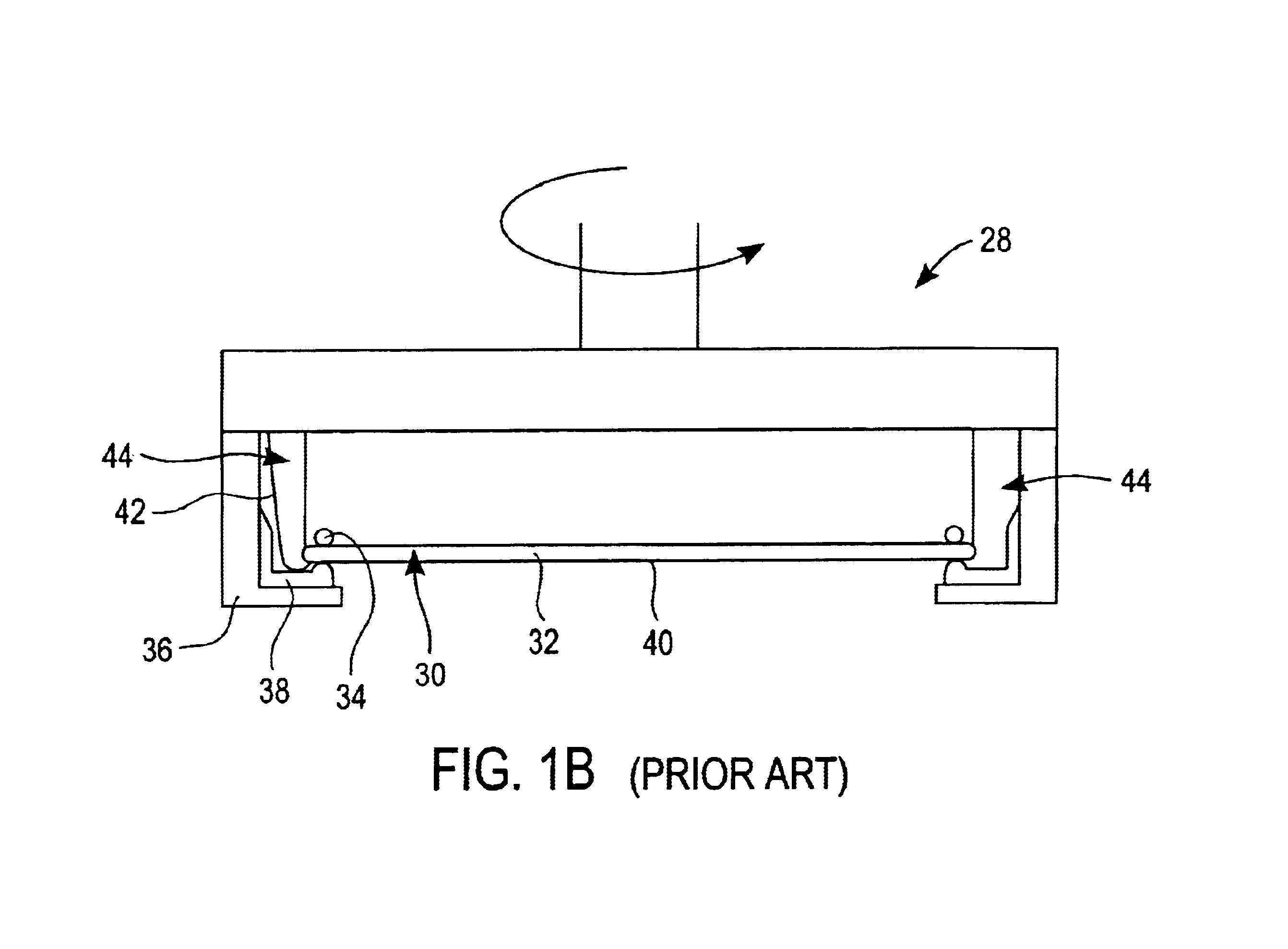
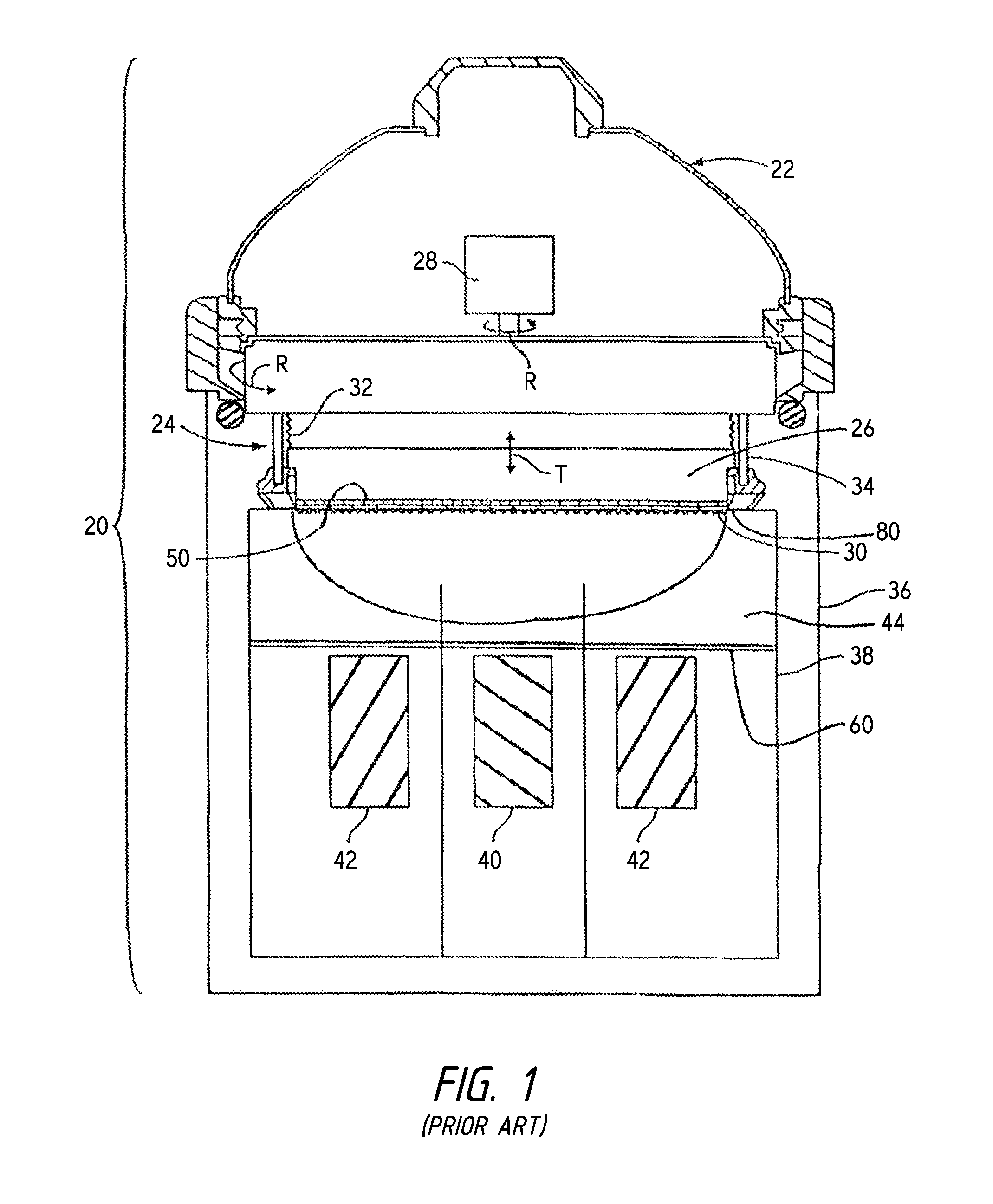
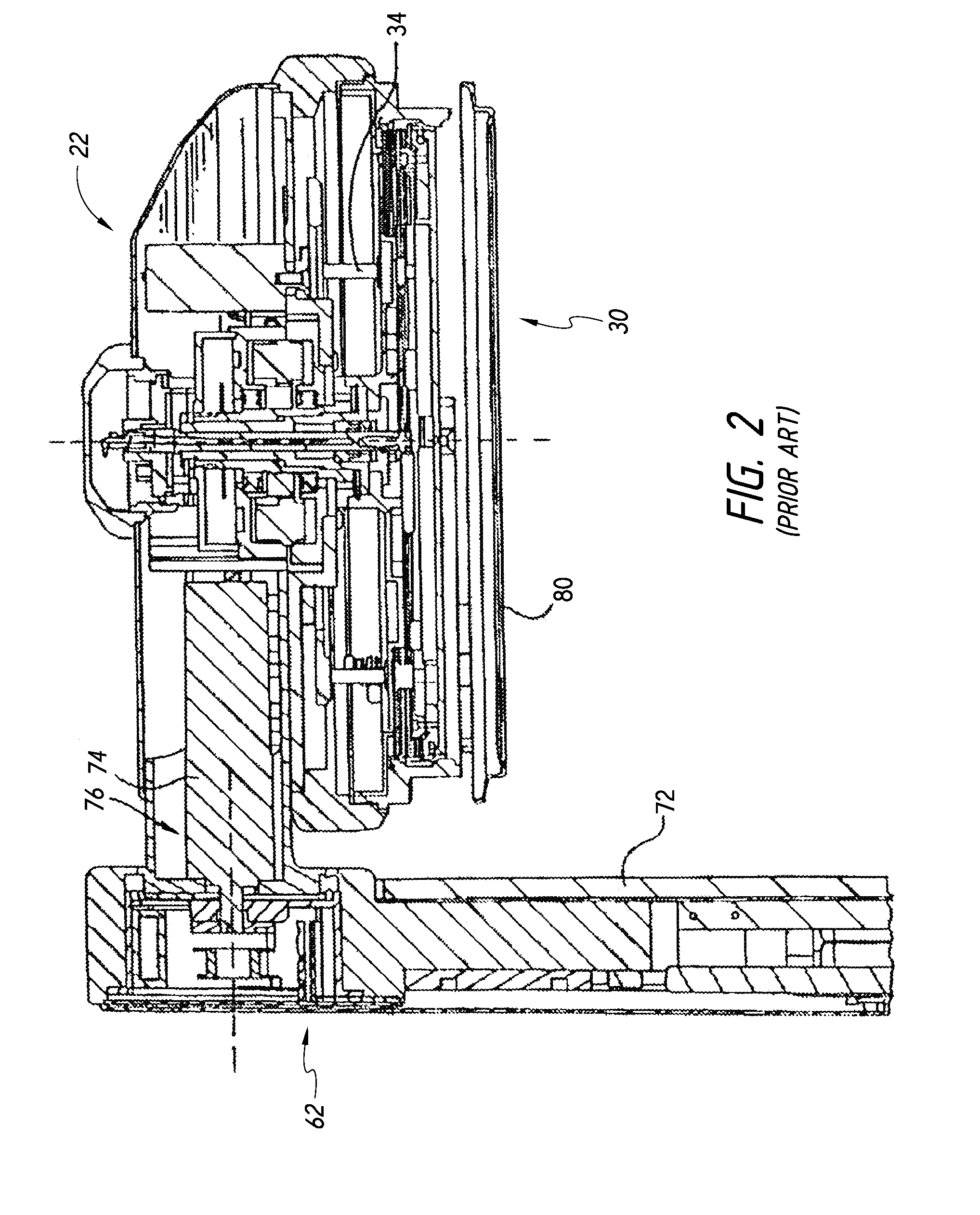
Method of and apparatus for fluid sealing, while electrically contacting, wet-processed workpieces
A method and apparatus for fluid sealing the underside of a workpiece, such as a semiconductor wafer and the like, during wet-processing such as electrodeposition and the like, employing an elastomeric encased ring of flexible fingers against which the periphery of the workpiece underside is forced to deflect the fingers downwardly and engage a peripheral sealing bead against the underside periphery of the workpiece; and where electrical contact with the workpiece is desired, resiliently engaging electrical contact tips protruding through peripheral openings in the elastomeric covering within the sealing ring, with the underside periphery of the workpiece.
Owner:HERCULES TECH GROWTH CAPITAL
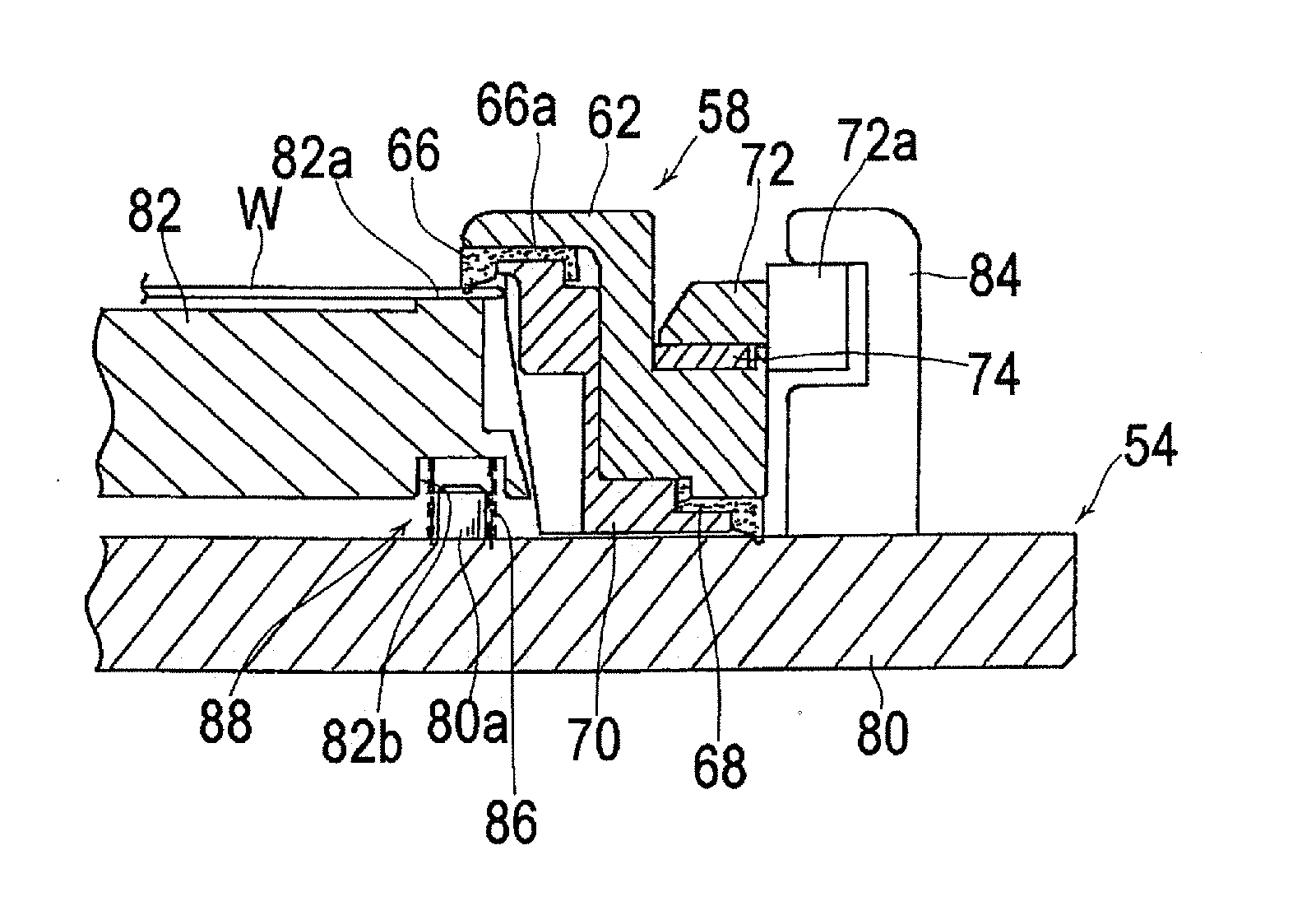
Substrate holder and plating apparatus
ActiveUS20050014368A1Sealing effectTake a substrate out of it easily and securelyCellsContacting devicesMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:EBARA CORP
Method and apparatus for encapsulation of an edge of a substrate during an electro-chemical deposition process
InactiveUS6908540B2Easy to understandCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingContact padEngineering
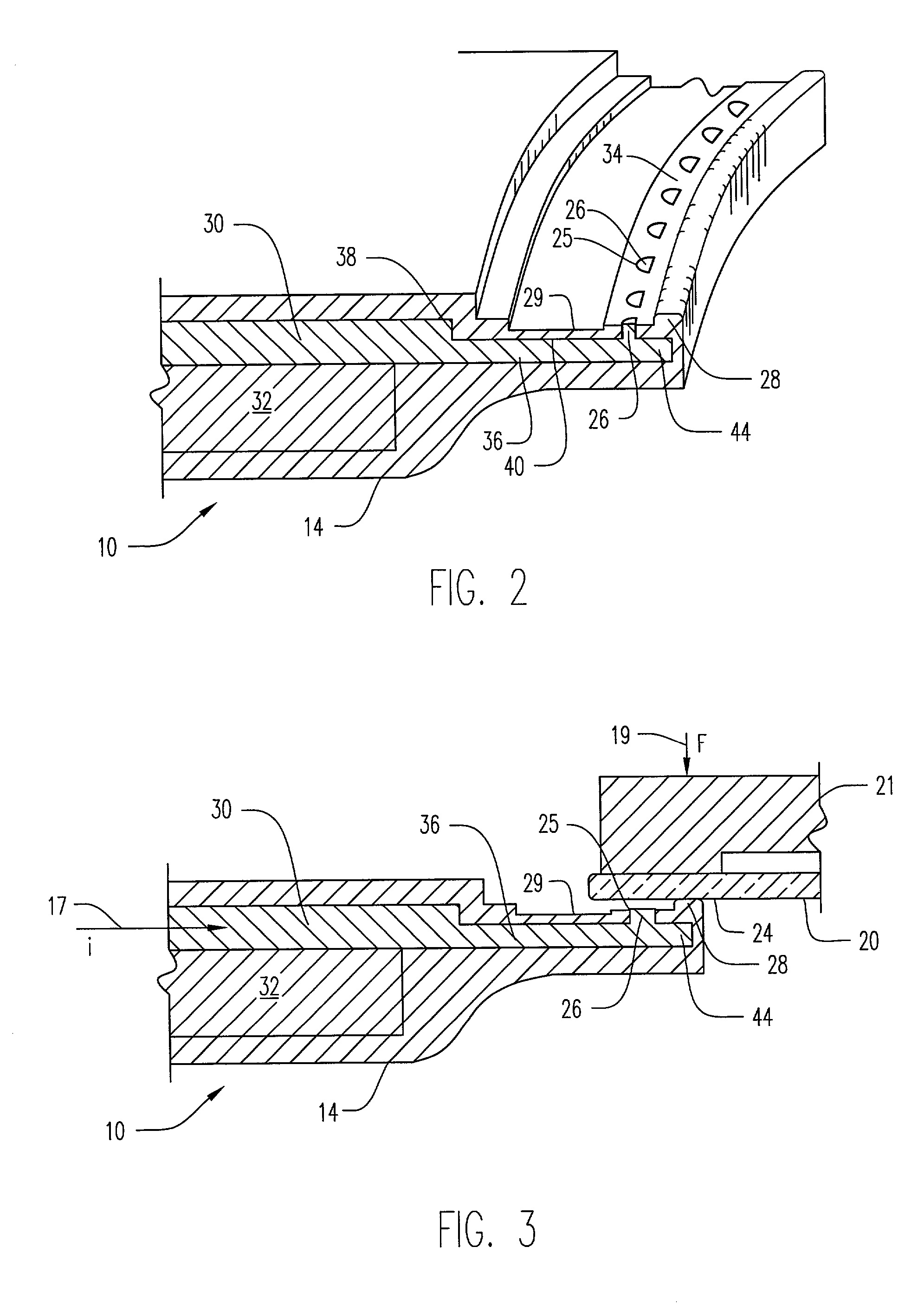
An electro-chemical deposition method and apparatus that encapsulates a substrate's edge to prevent deposition thereon is generally provided. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a contact ring, one or more electrical contact pads disposed on the contact ring and a thrust plate axially movable relative to the contact ring. A first seal is disposed inward of the contact pad and seals with the contact ring. A second seal is coupled to the thrust plate. The first and second seals are adapted to sandwich the substrate therebetween when the contact ring and the thrust plate are moved towards each other. In another embodiment, a third seal provides a seal between the thrust plate and contact ring, and, with the first and second seals, defines an exclusion zone encapsulating the substrate's edge. One or more electrical contact pads are protected from the electrolyte by being disposed within the exclusion zone.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Base plate, contact ring, lipseal, electroplating device and electroplating method
Methods, apparatuses, and various apparatus components, such as base plates, lipseals, and contact ring assemblies are provided for reducing contamination of the contact area in the apparatuses. Contamination may happen during removal of semiconductor wafers from apparatuses after the electroplating process. In certain embodiments, a base plate with a hydrophobic coating, such as polyamide-imide (PAI) and sometimes polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), are used. Further, contact tips of the contact ring assembly may be positioned further away from the sealing lip of the lipseal. In certain embodiments, a portion of the contact ring assembly and / or the lipseal also include hydrophobic coatings.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Revolution member supporting apparatus and semiconductor substrate processing apparatus
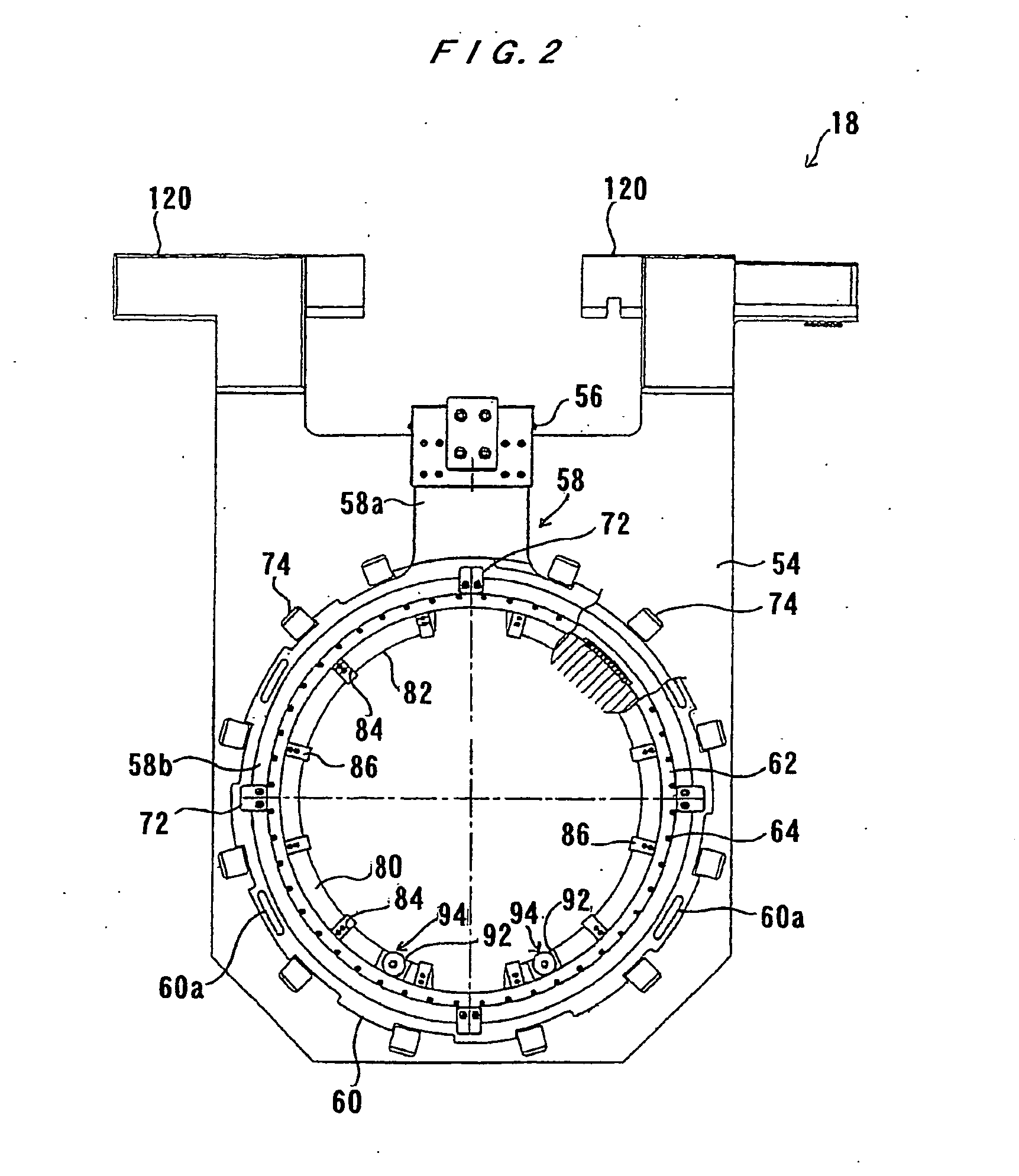
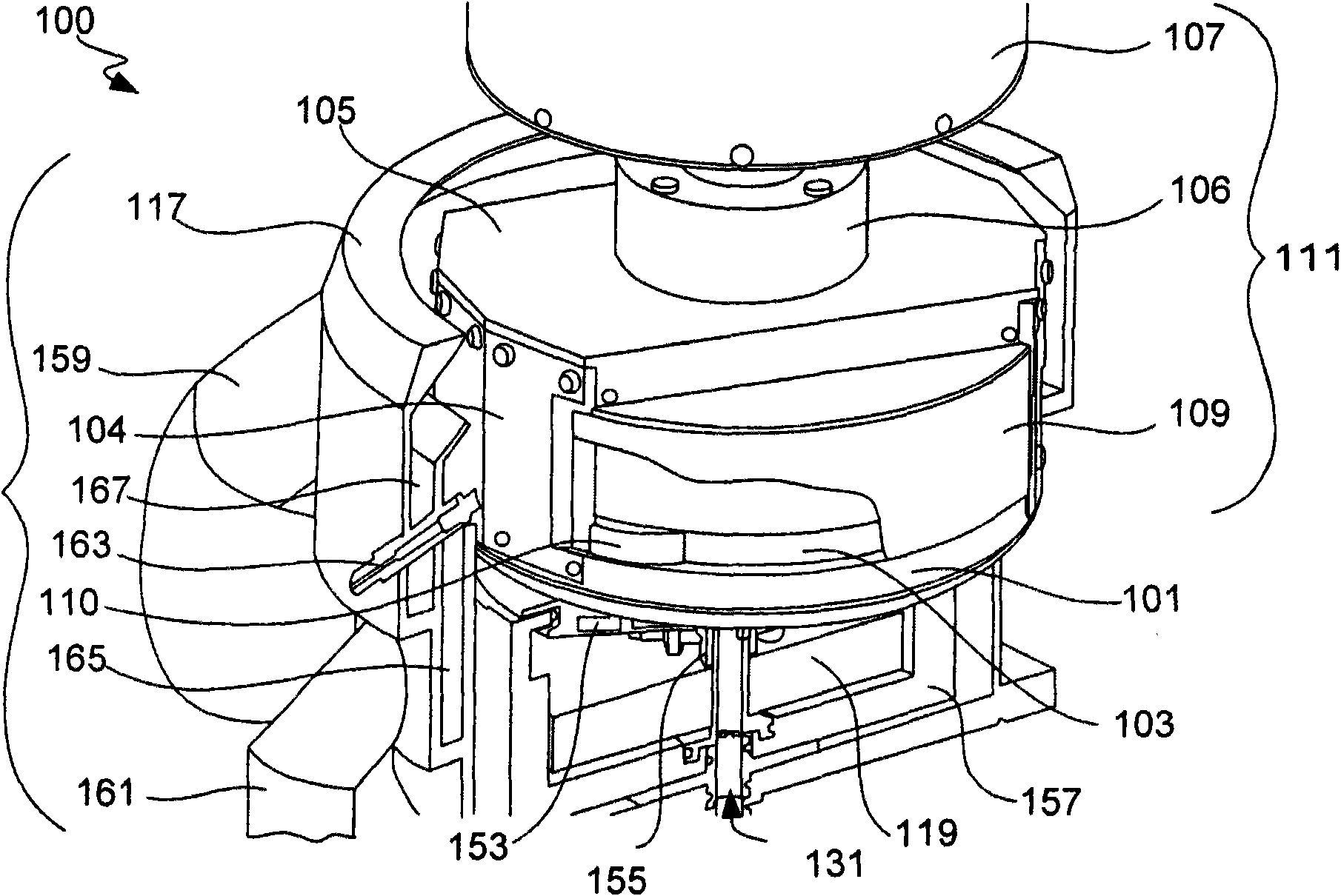
InactiveUS6921466B2Avoid it happening againLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSealing devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A revolution member supporting apparatus holds and rotates a disc-shaped object (object to be rotated) such as a semiconductor wafer. The revolution member supporting apparatus includes a rotatable member which rotates about an axis of roation, and a plurality of holding members which are disposed along a circle having a center corresponding to the axis of rotation of the rotatable member, and which revolve around the axis of rotation when the rotatable member rotates, wherein the holding members are allowed to swing about their own central axes.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Method of and apparatus for fluid sealing, while electrically contacting, wet-processed workpieces, as in the electrodeposition of semi-conductor wafers and the like and for other wet processing techniques and workpieces
A method and apparatus for fluid sealing the underside of a workpiece, such as a semiconductor wafer and the like, during wet-processing such as electrodeposition and the like, employing an elastomeric encased ring of flexible fingers against which the periphery of the workpiece underside is forced to deflect the fingers downwardly and engage a peripheral sealing bead against the underside periphery of the workpiece; and where electrical contact with the workpiece is desired, resiliently engaging electrical contact tips protruding through peripheral openings in the elastomeric covering within the sealing ring, with the underside periphery of the workpiece.
Owner:HERCULES TECH GROWTH CAPITAL
Plating apparatus and plating method
InactiveUS20060086616A1Low costIncreased cost of platingCellsMachining electric circuitsPower flowCathode electrode
A plating apparatus can securely carry out a flattening plating of a substrate to form a plated film having a flat surface without using a costly mechanism, and without applying an extra plating to the substrate. The plating apparatus includes a substrate holder; a cathode section having a seal member for watertightly sealing a peripheral portion of the substrate, and a cathode electrode for supplying an electric current to the substrate; an anode disposed in a position facing the surface of the substrate; a porous member disposed between the anode and the surface of the substrate; a constant-voltage control section for controlling a voltage applied between the cathode electrode and the anode at a constant value; and a current monitor section for monitoring an electric current flowing between the cathode electrode and the anode, and feeding back a detection signal to the constant-voltage control section.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
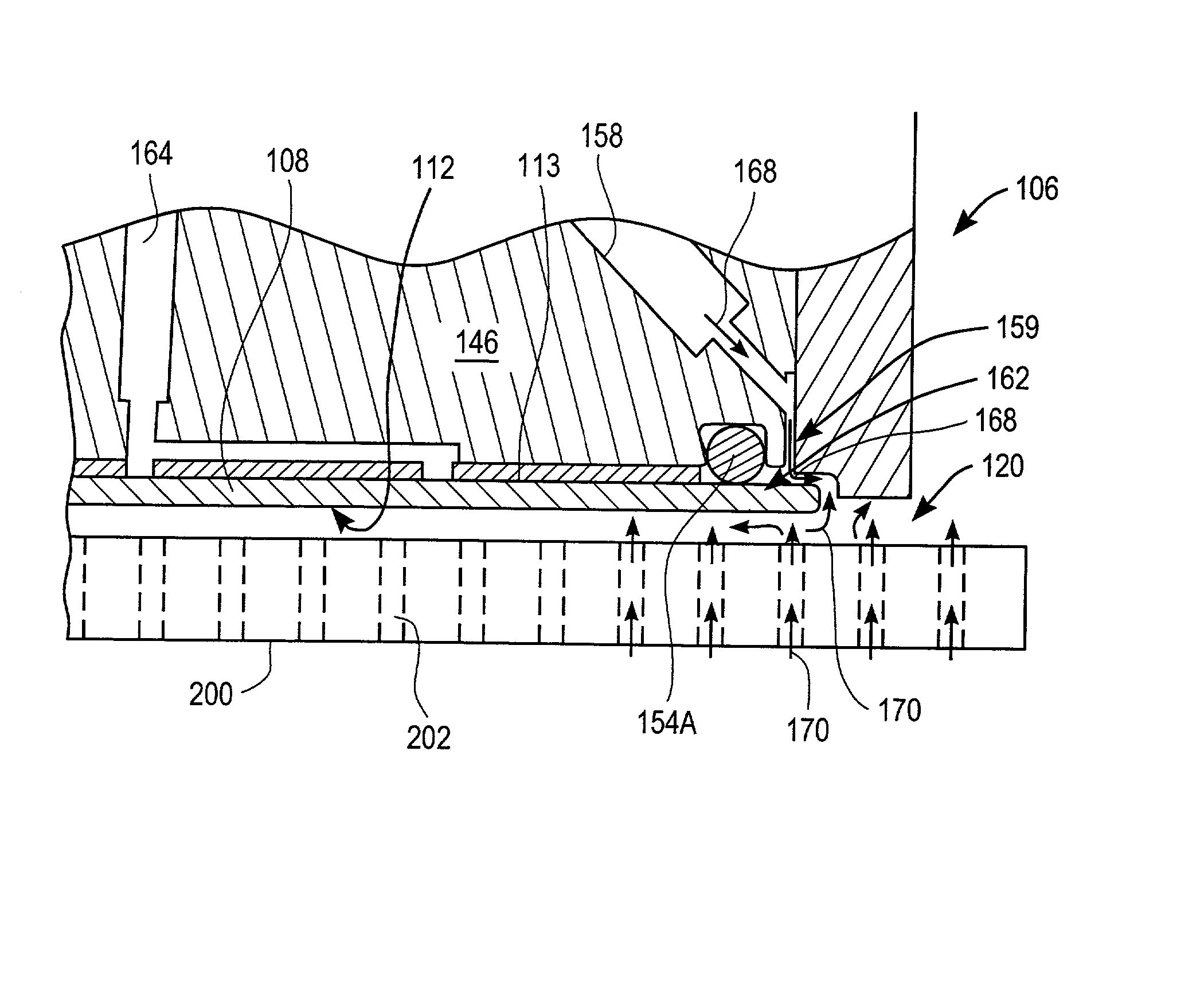
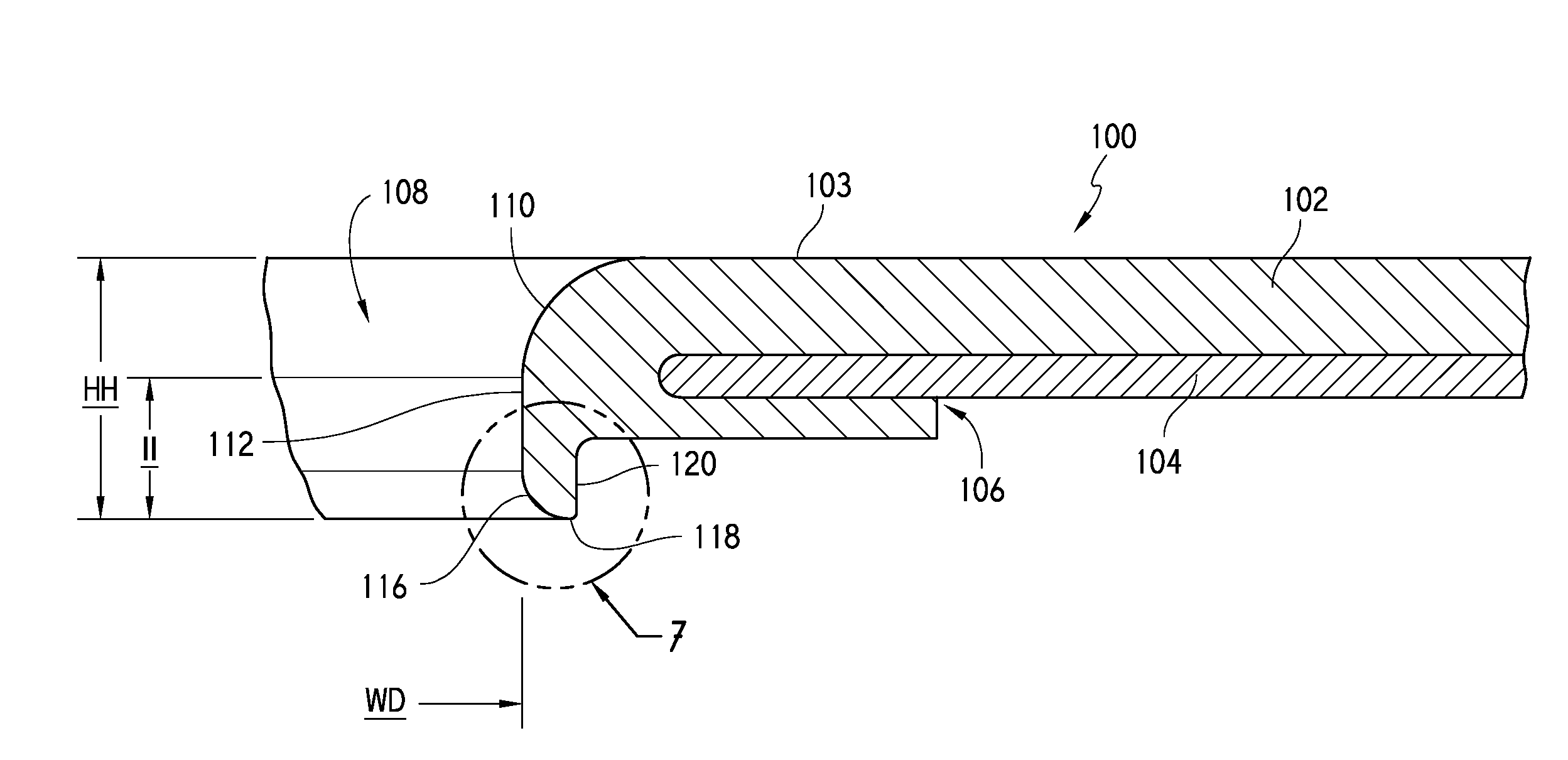
Method and apparatus of sealing wafer backside for full-face electrochemical plating
InactiveUS6939206B2Prevented from reachingEfficient configurationEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesMechanical engineeringElectroplating
The present invention provides a wafer carrier that includes a plurality of concentric sealing members that provide a seal, with the outer seal independently movable to allow cleaning of a peripheral backside of the wafer to occur while the wafer is still attached to the wafer carrier, and a plurality of vacuum openings that a re disposed only adjacent to an inner side of the inner seal at a location corresponding to the backside periphery of the wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Plating apparatus and method
Owner:EBARA CORP
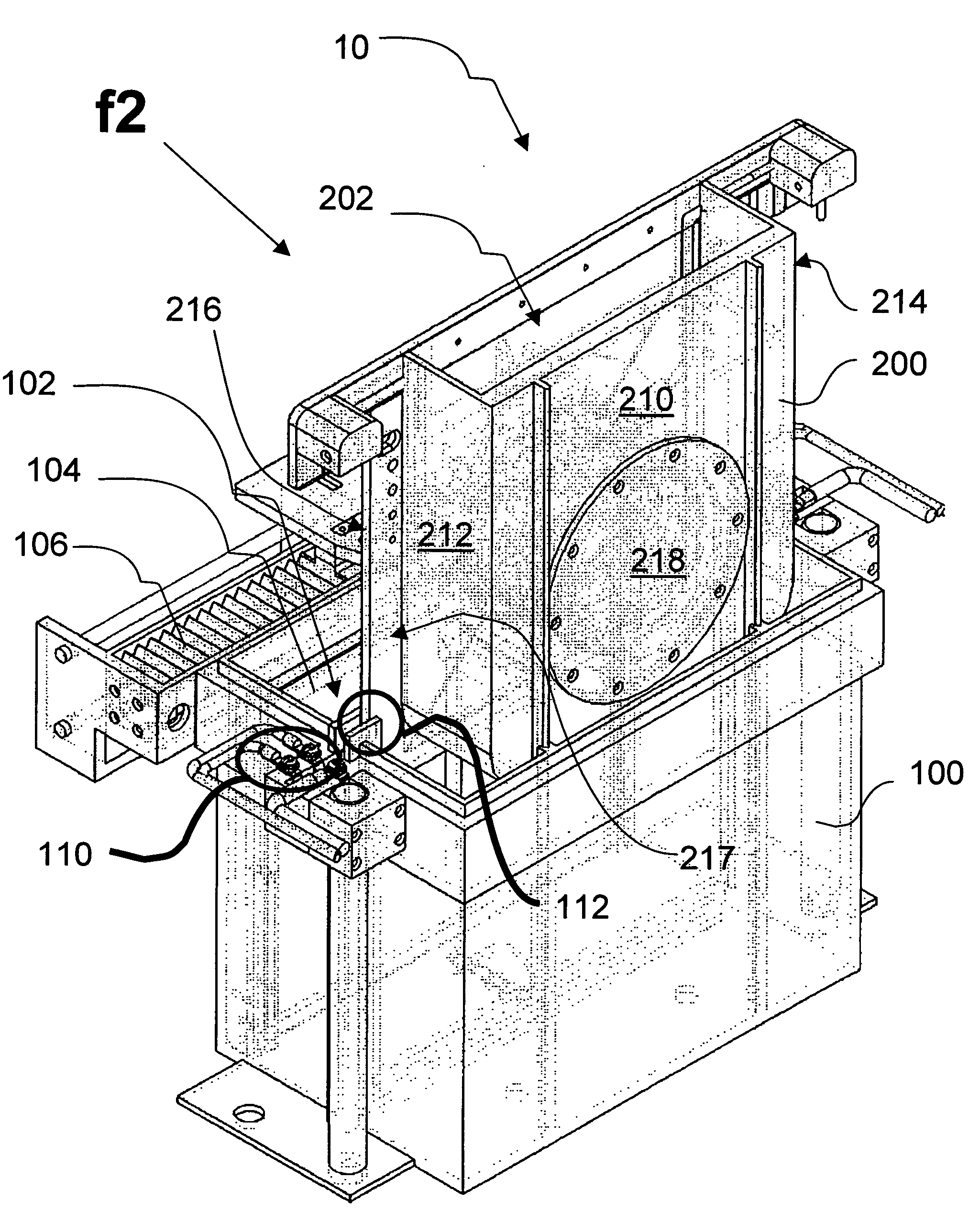
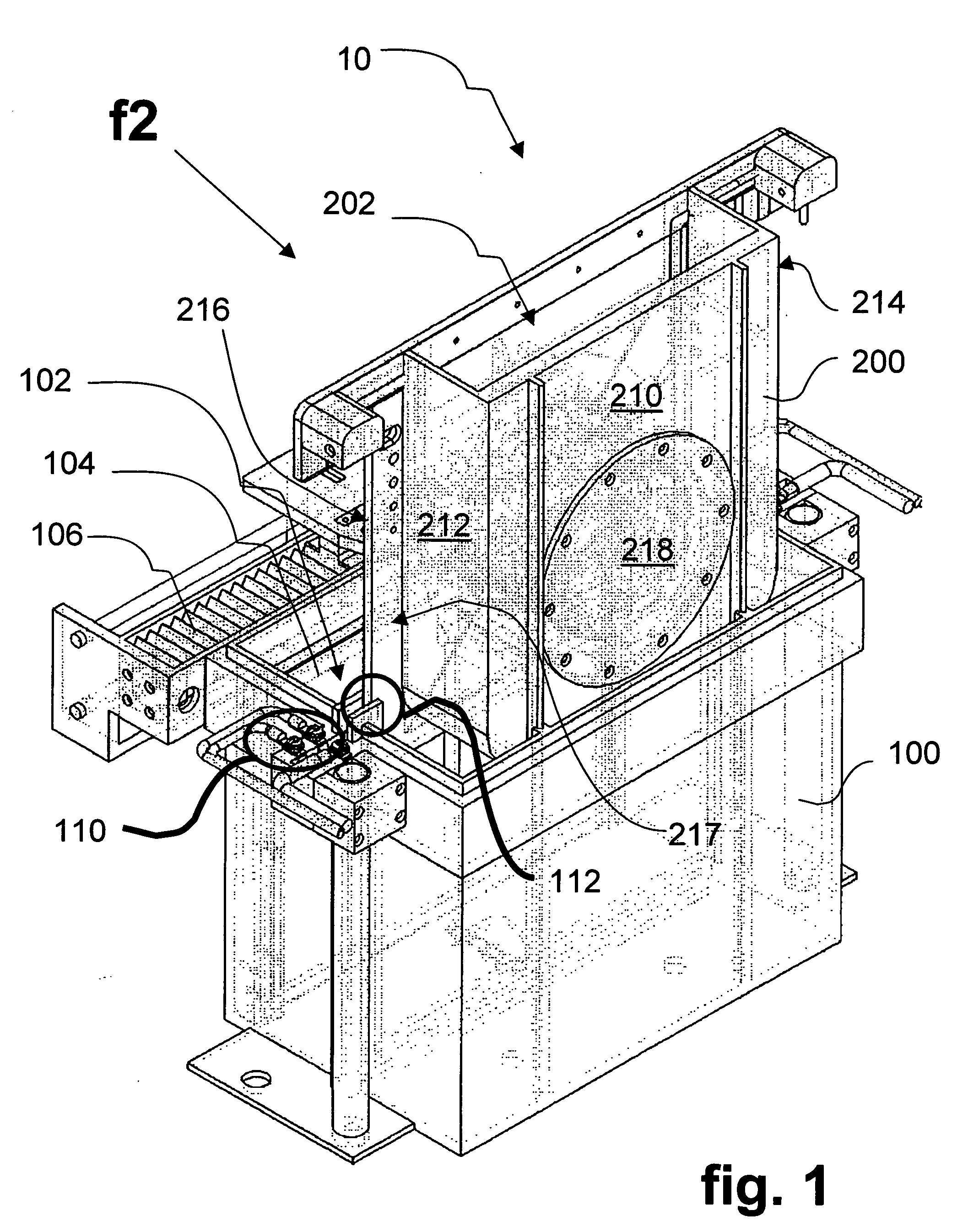
Plating cup with contoured cup bottom
Disclosed herein are cups for engaging wafers during electroplating in clamshell assemblies and supplying electrical current to the wafers during electroplating. The cup can comprise an elastomeric seal disposed on the cup and configured to engage the wafer during electroplating, where upon engagement the elastomeric seal substantially excludes plating solution from a peripheral region of the wafer, and where the elastomeric seal and the cup are annular in shape, and comprise one or more contact elements for supplying electrical current to the wafer during electroplating, the one or more contact elements attached to and extending inwardly towards a center of the cup from a metal strip disposed over the elastomeric seal. A notch area of the cup can have a protrusion or an insulated portion on a portion of a bottom surface of the cup where the notch area is aligned with a notch in the wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
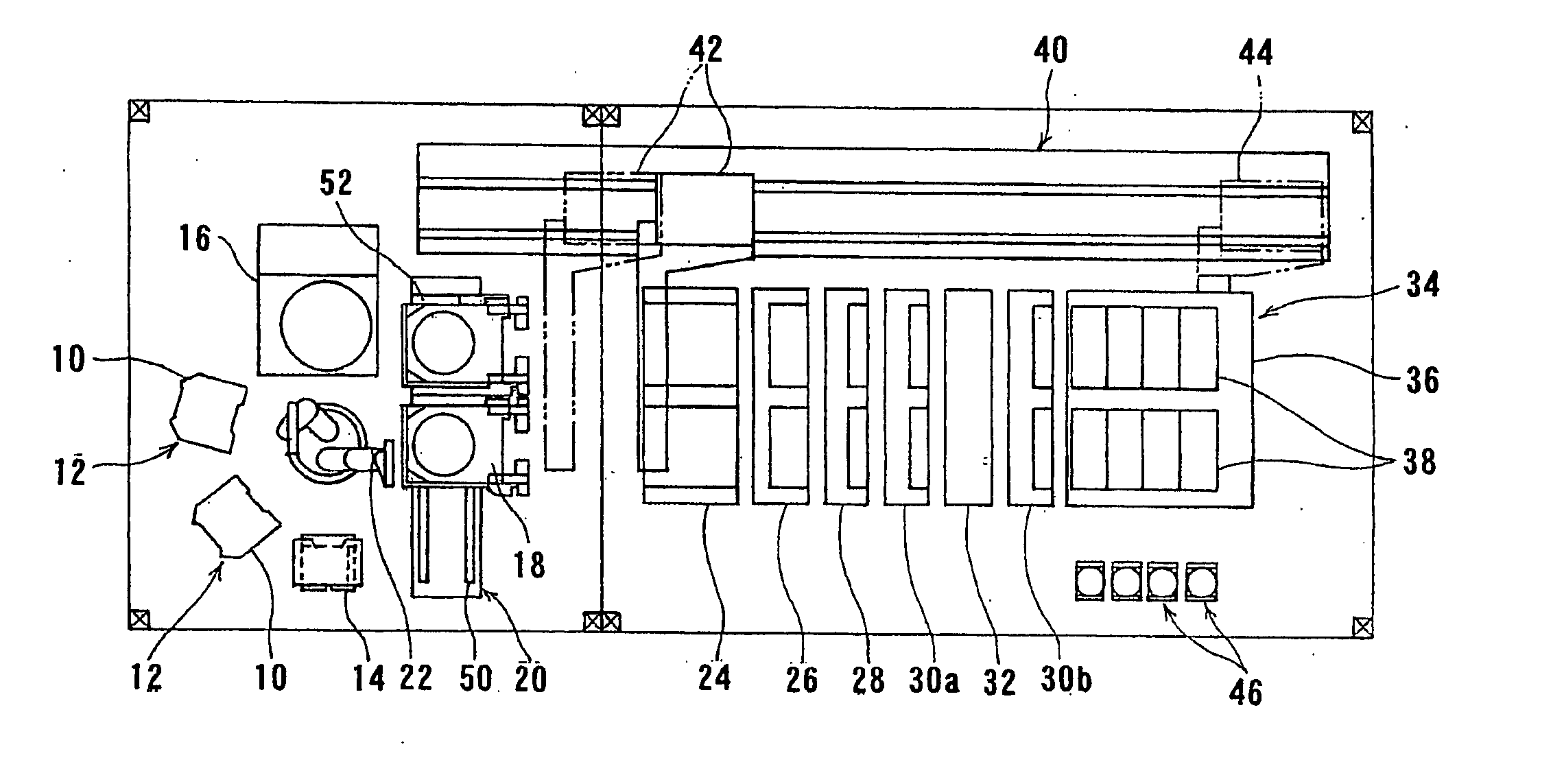
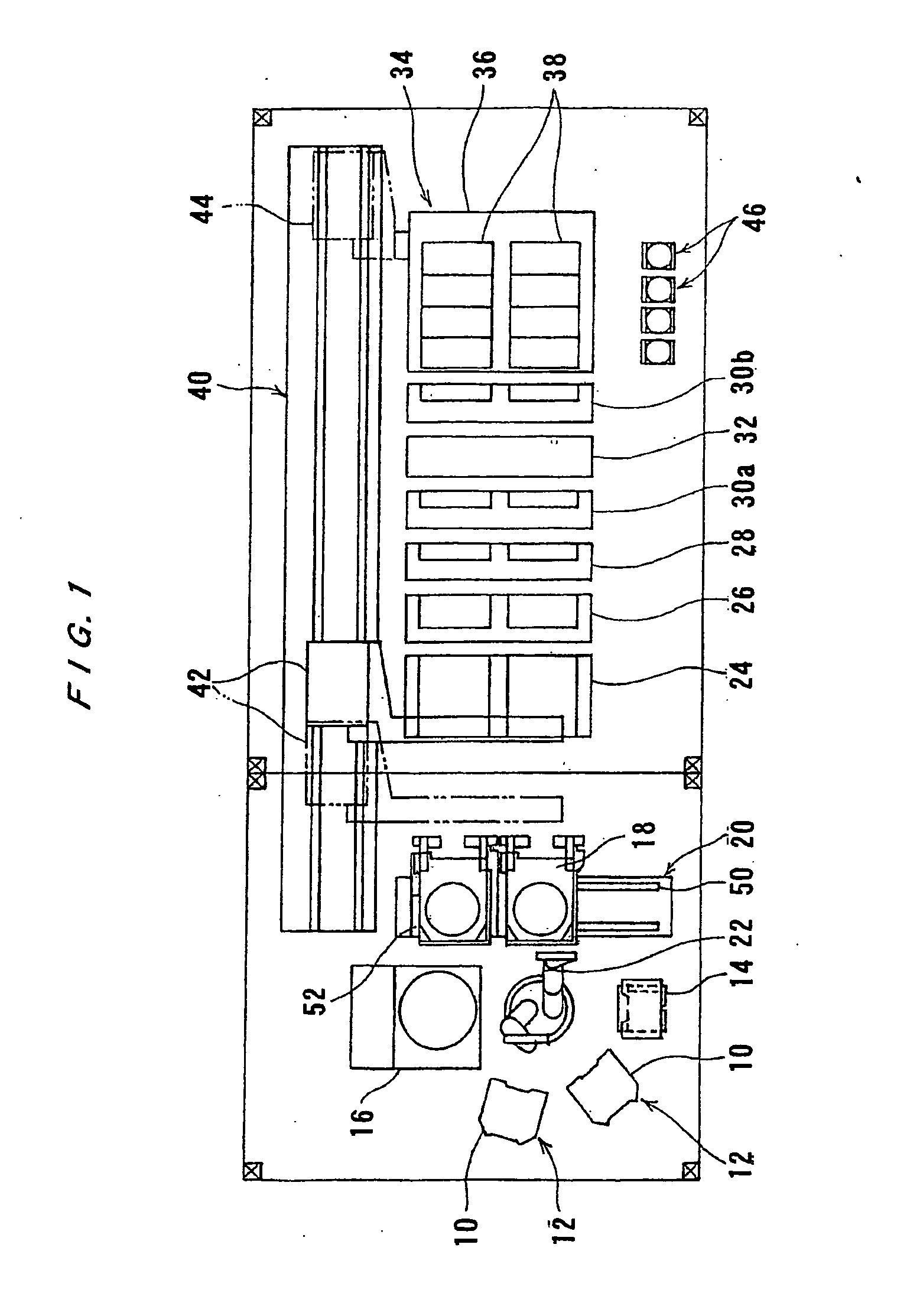
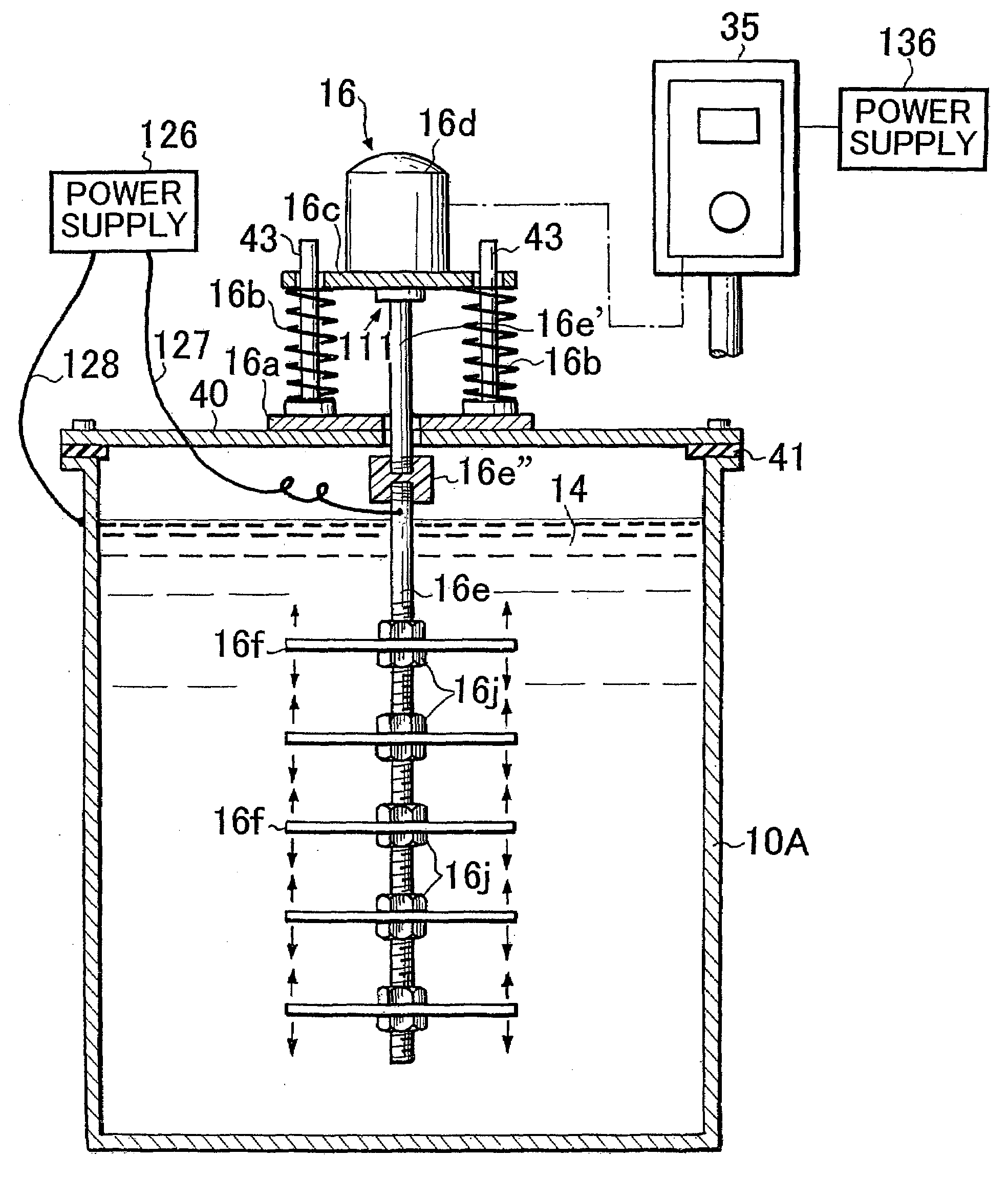
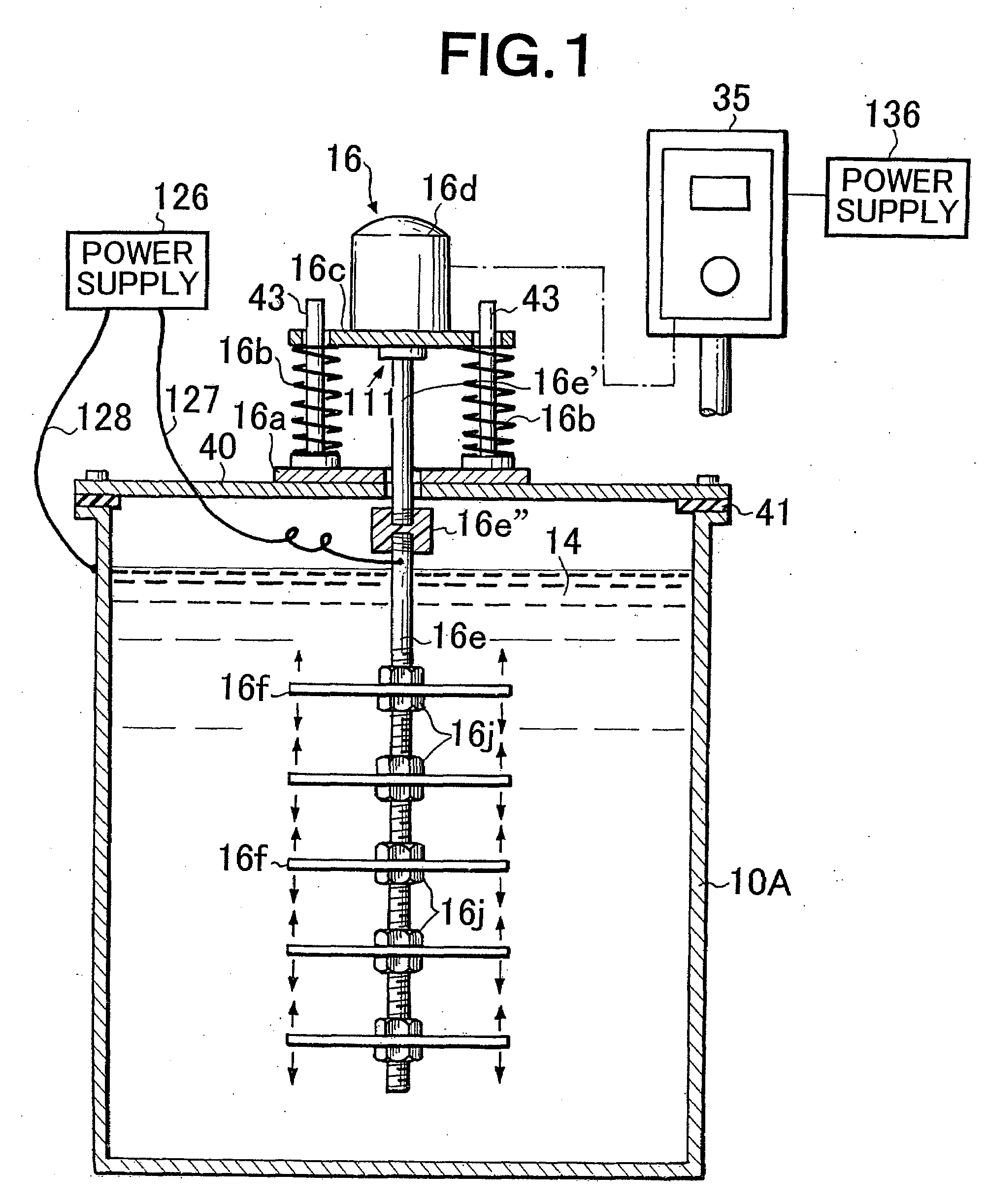
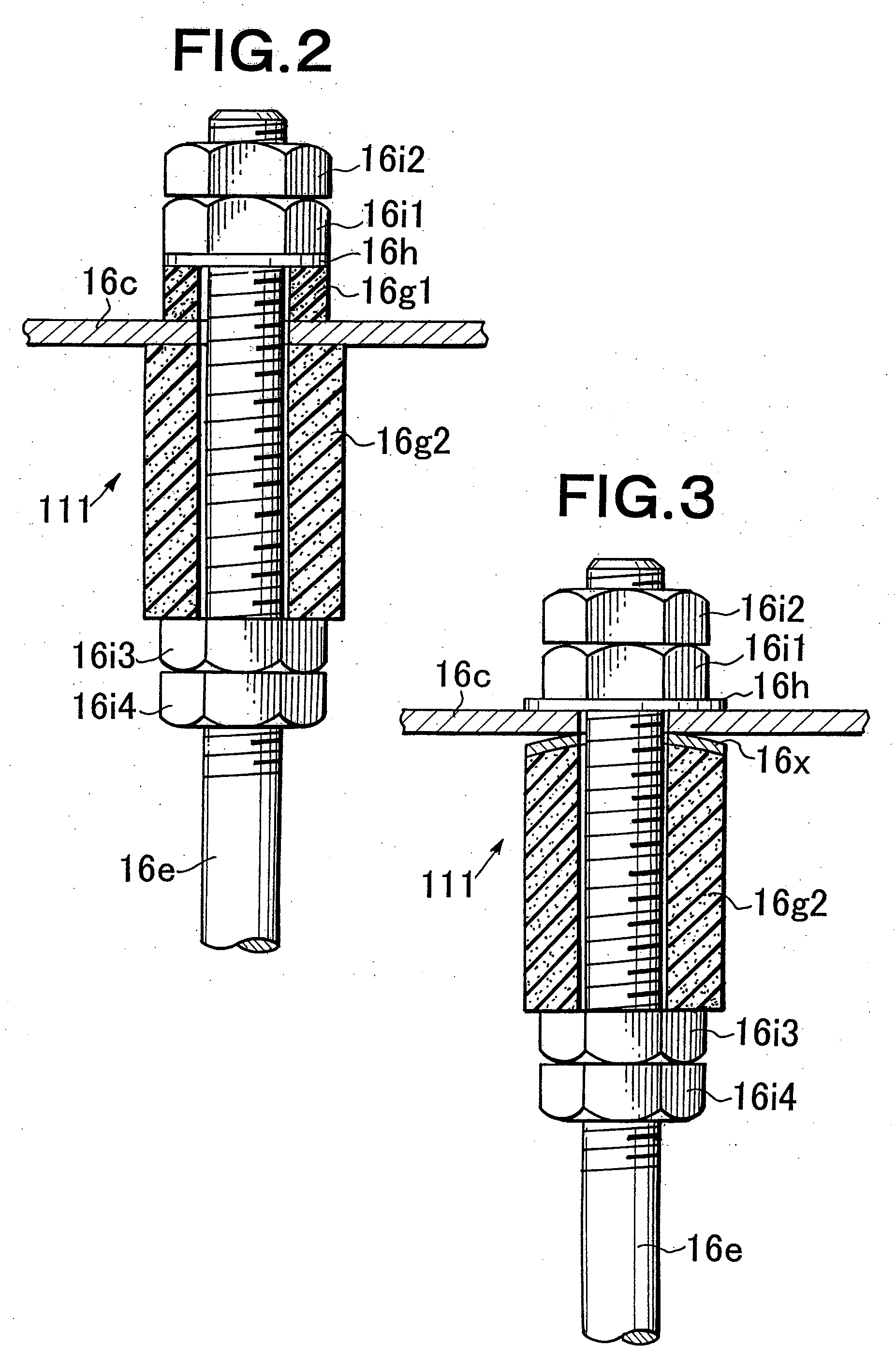
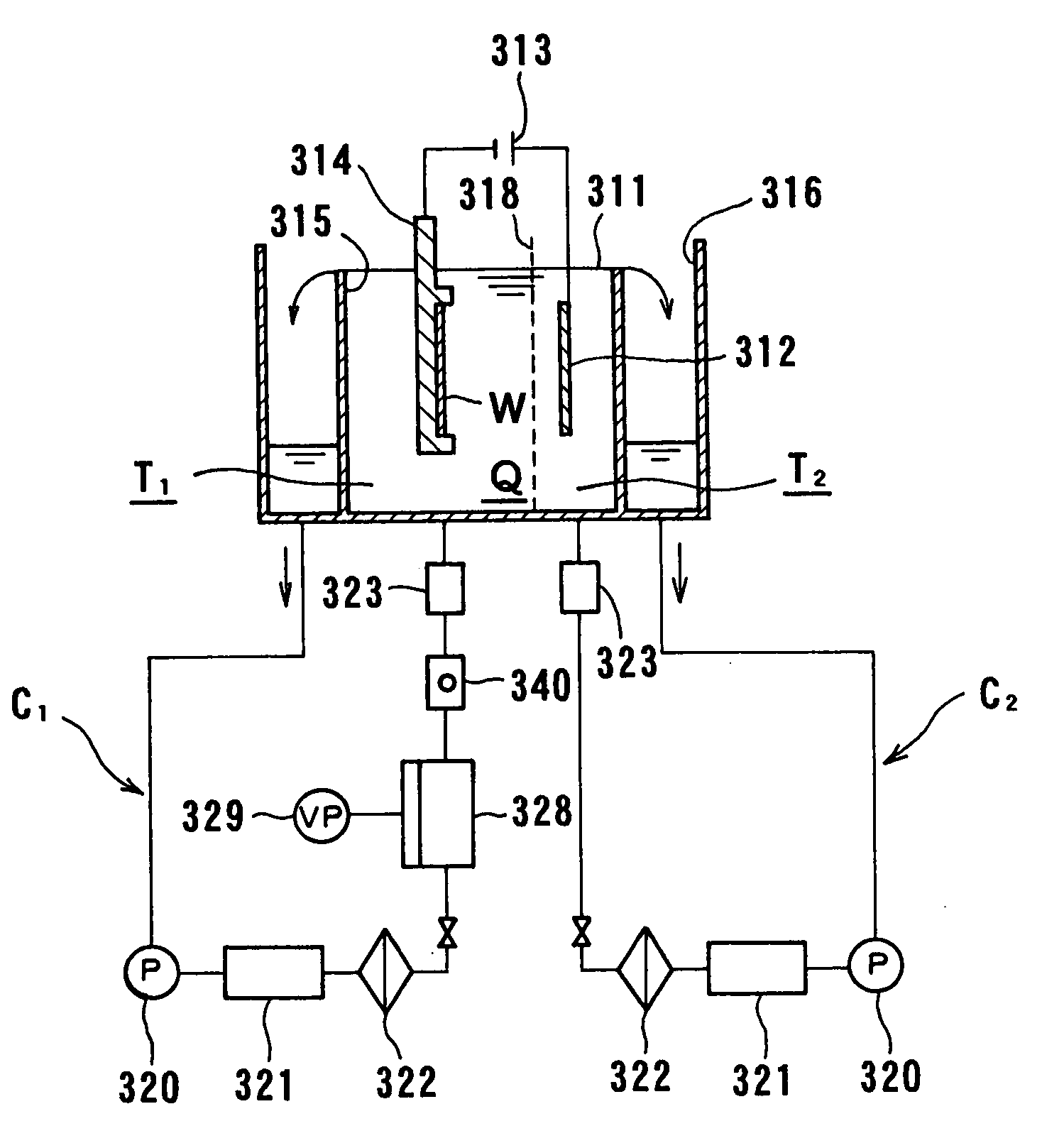
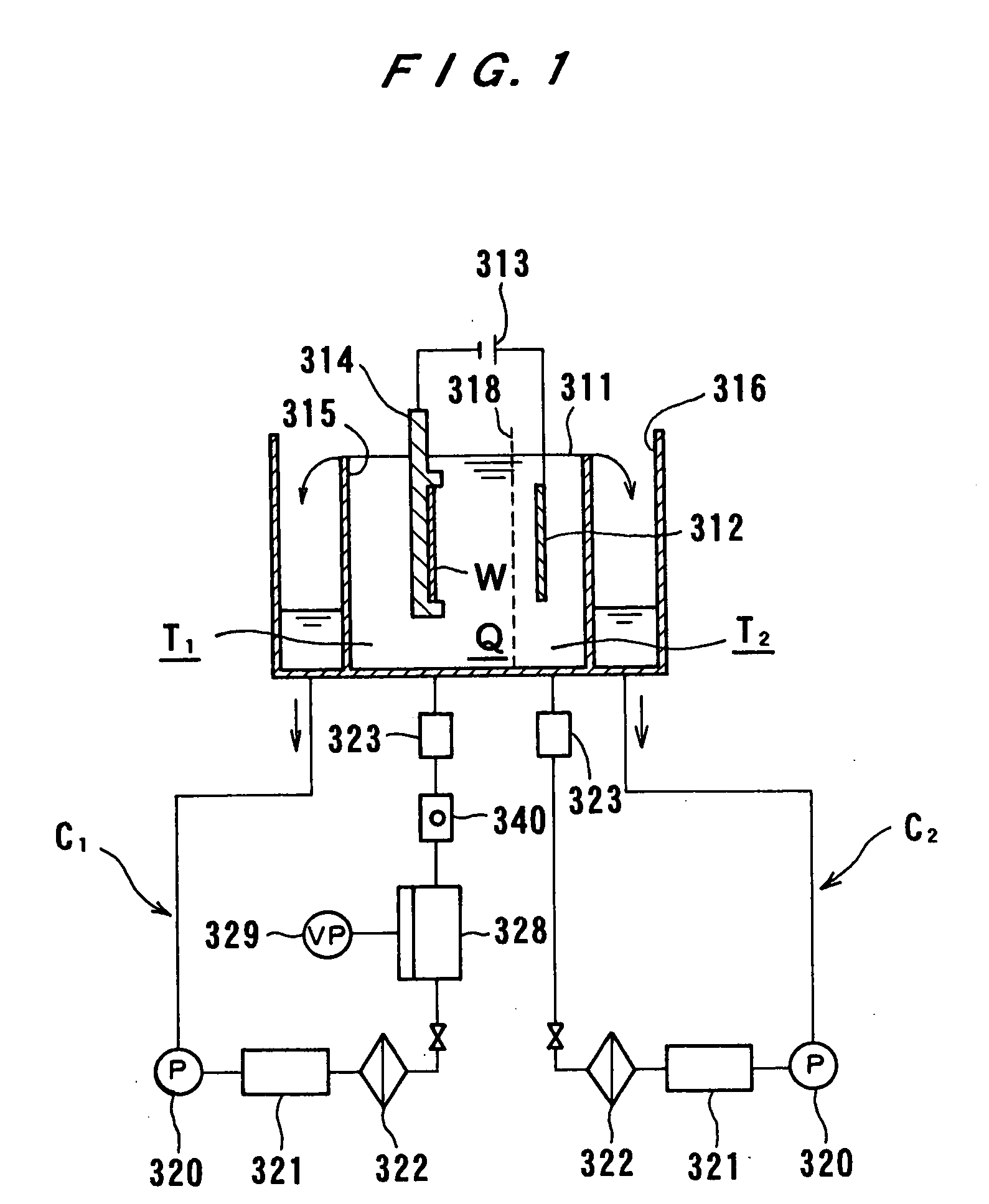
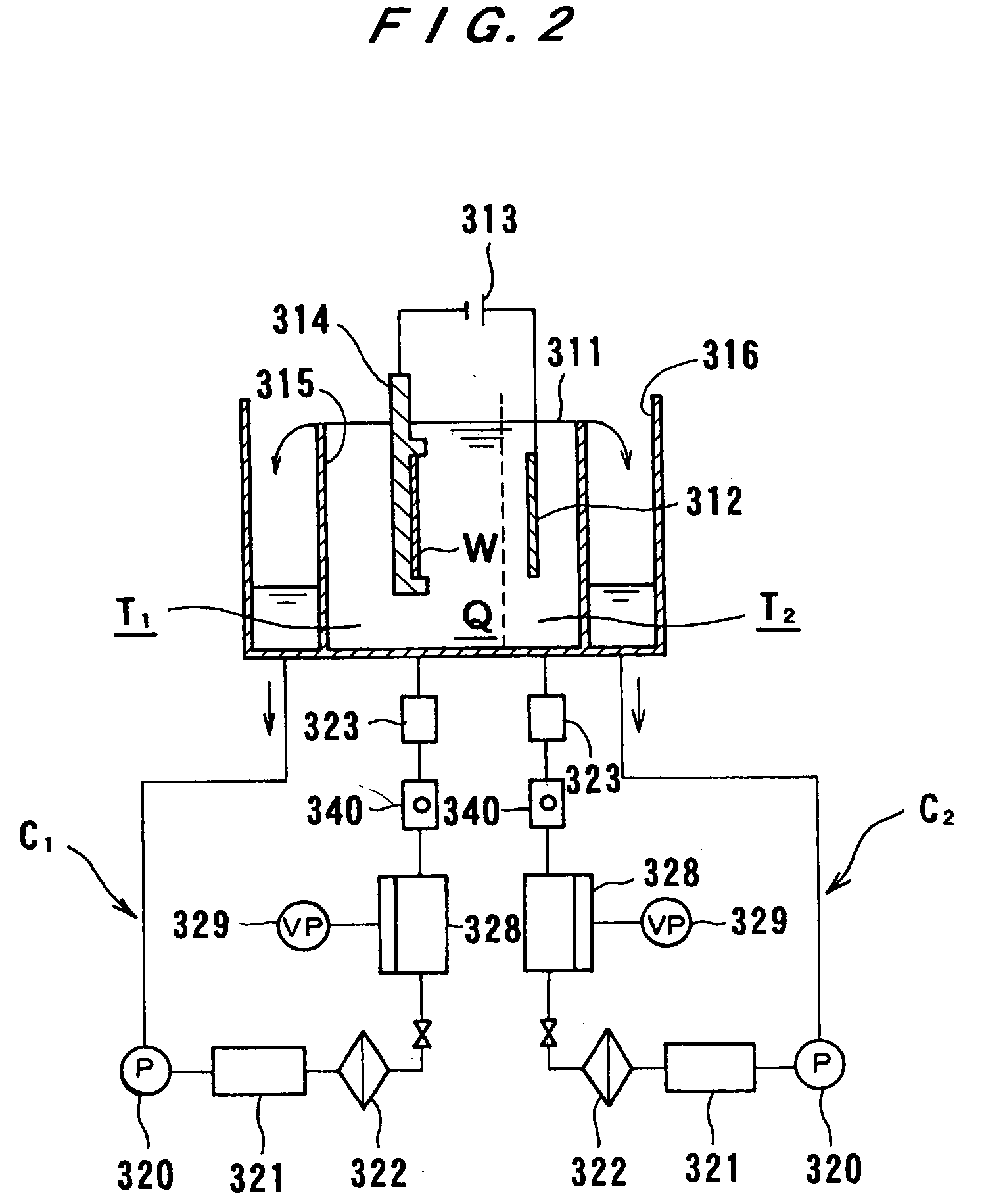
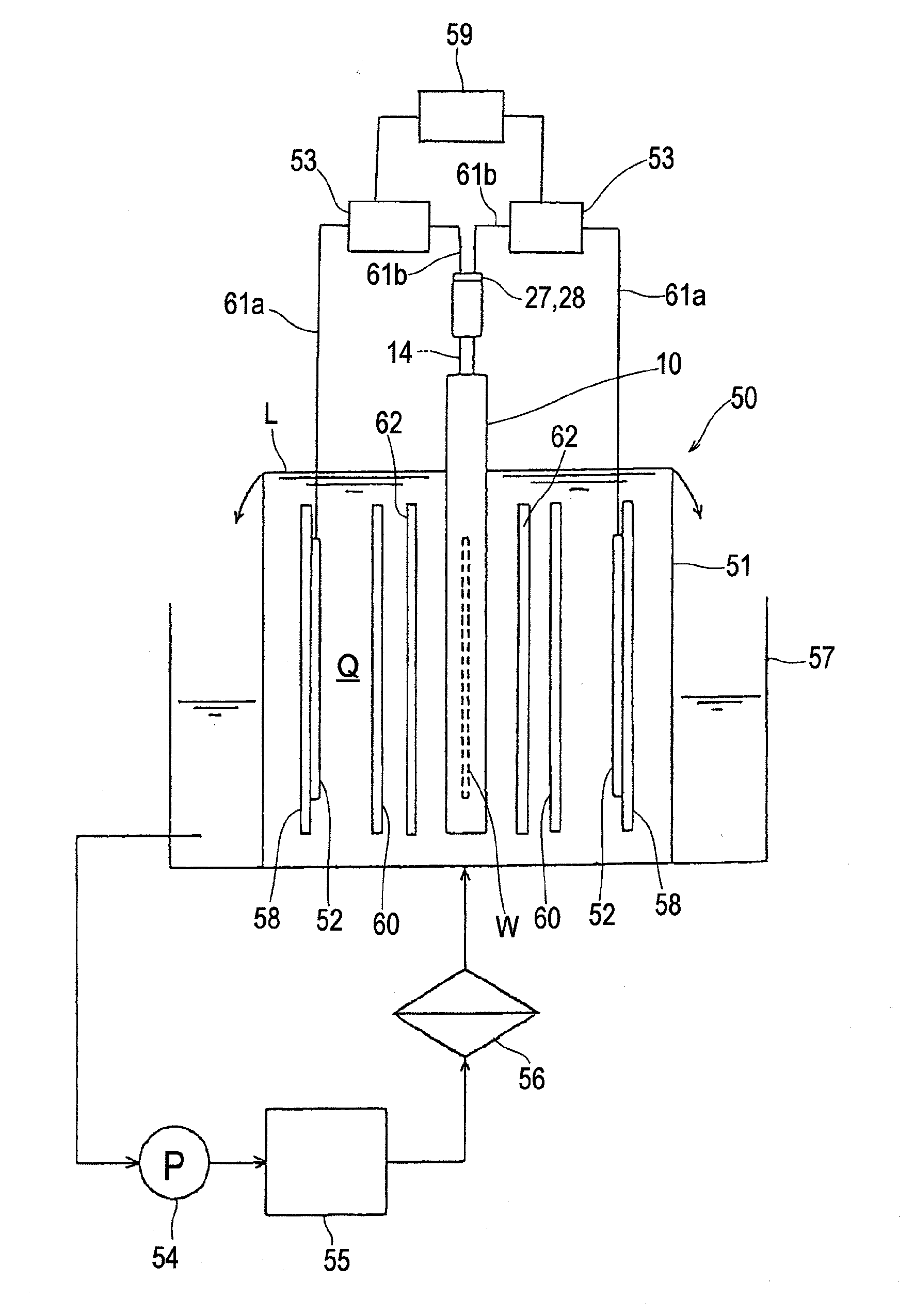
Vibratingly Stirring Apparatus, and Device and Method for Processing Using the Stirring Apparatus
InactiveUS20080117711A1Improve performanceCellsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersEngineeringElectric power
An insulated vibration-stirring apparatus comprising: a vibration generating means containing a vibration motor and a vibrating member attached to that motor, and a vibrating rod attached by an installation piece to allow vibration lined with the vibration generating means, and vibrating vanes installed on this vibrating rod. An electrical insulation area made from hard rubber is installed on a section nearer to the installation section to the installation piece than the section where the vibrating vanes are mounted on the vibrating rod. An electrical line is connected to the lower section of the vibrating rod on the electrical insulation area side where the vibrating vanes are installed. This electrical line conducts power to the vibrating vanes by way of the lower section of the vibrating rod. A power supply applies a voltage across the lower section of the vibrating rod and vibrating vanes and treatment tank by way of the electrical lines, and while applying power to the processing liquid within the treatment tank, the insulation vibration stirring apparatus vibrates and stirs the processing liquid.
Owner:JAPAN TECH CO LTD (JP)
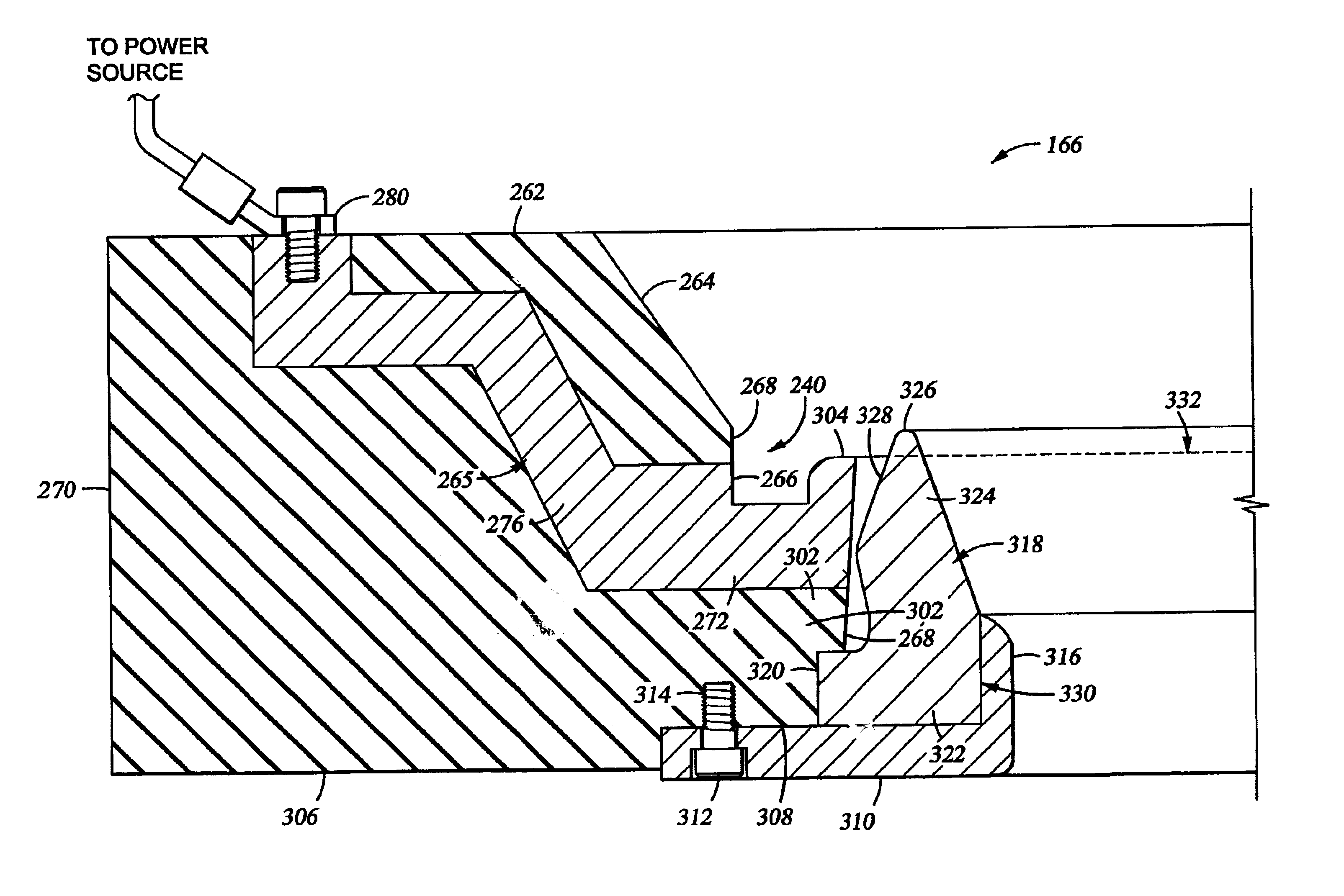
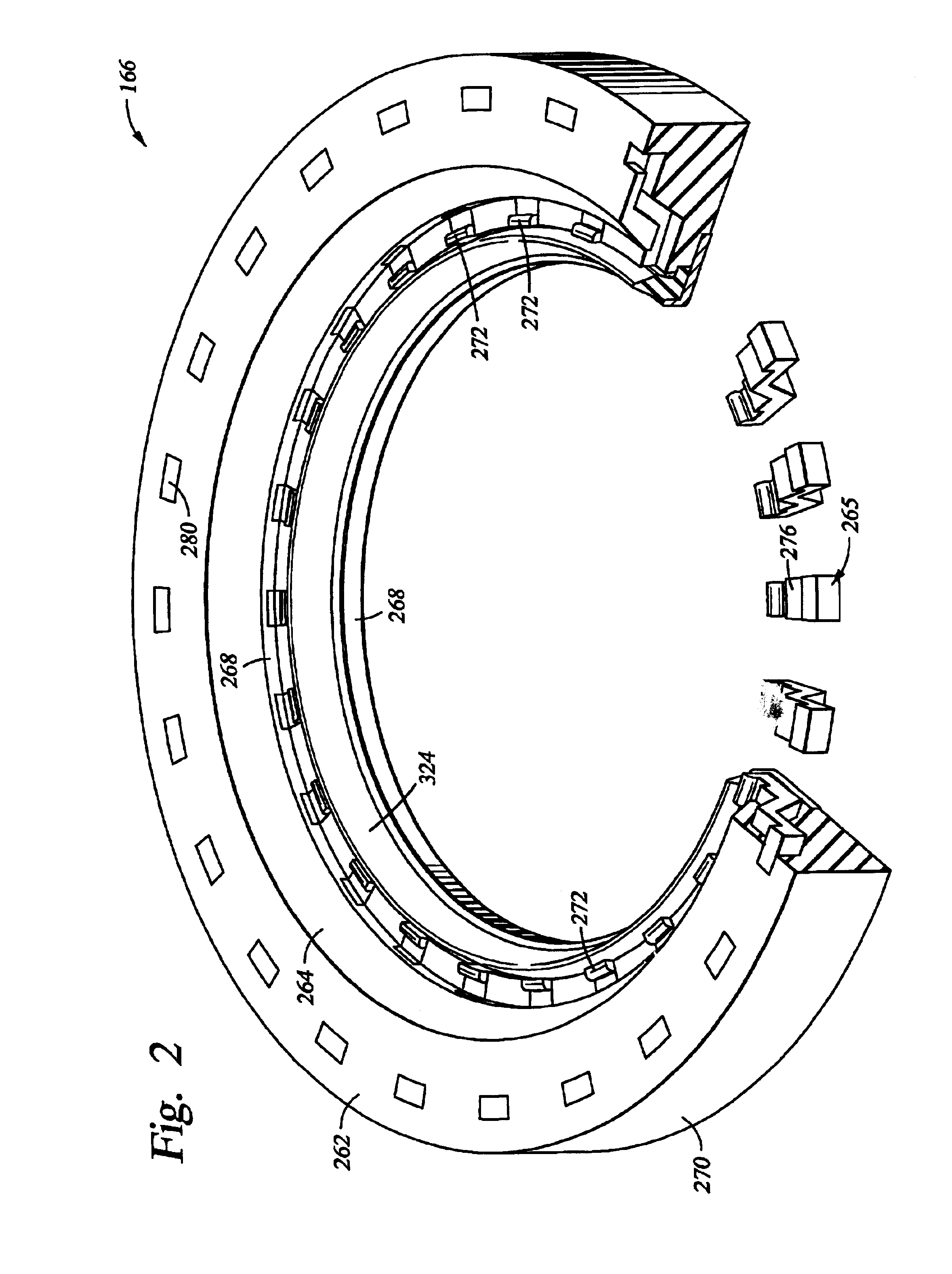
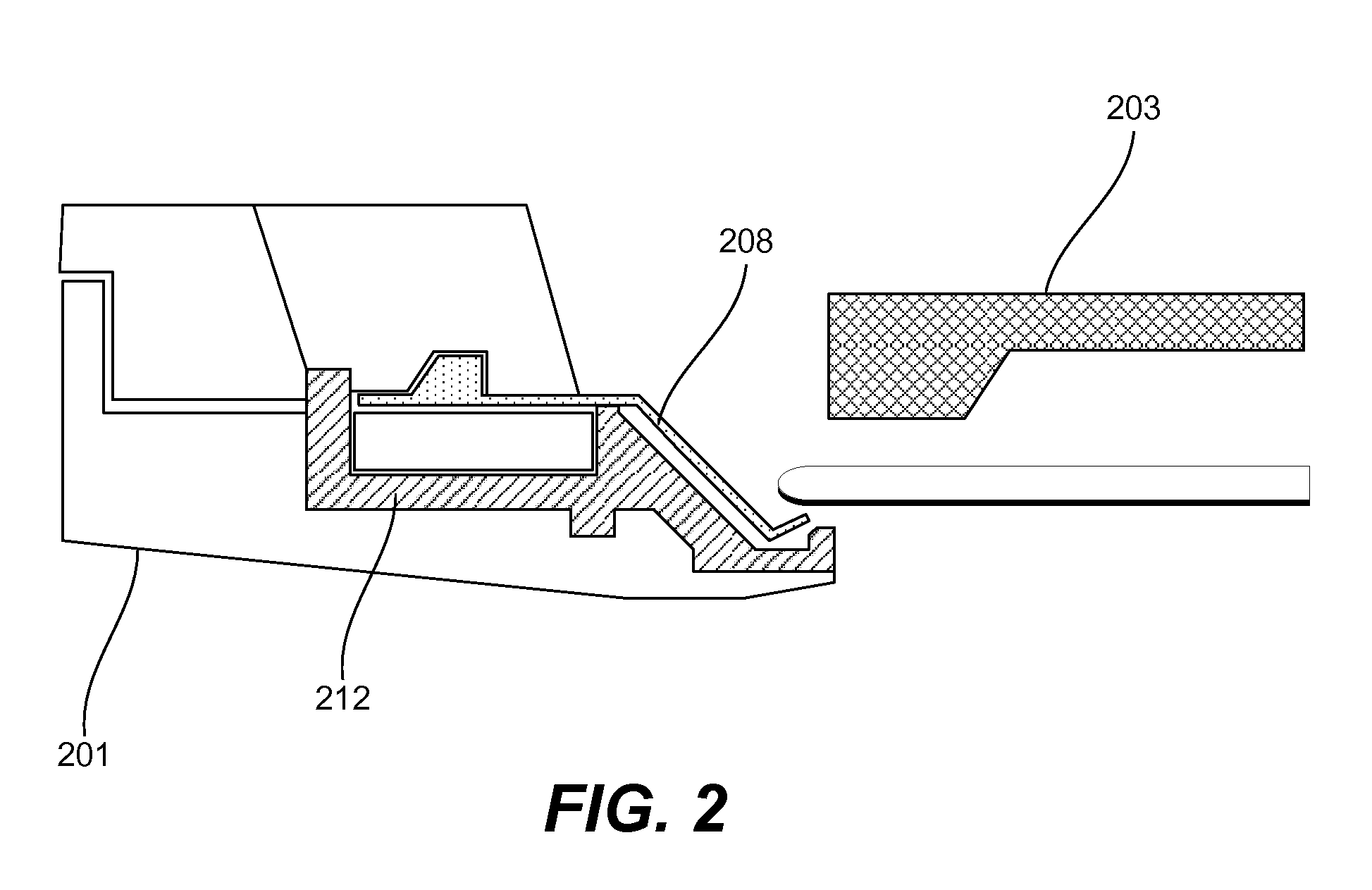
Lipseals and contact elements for semiconductor electroplating apparatuses
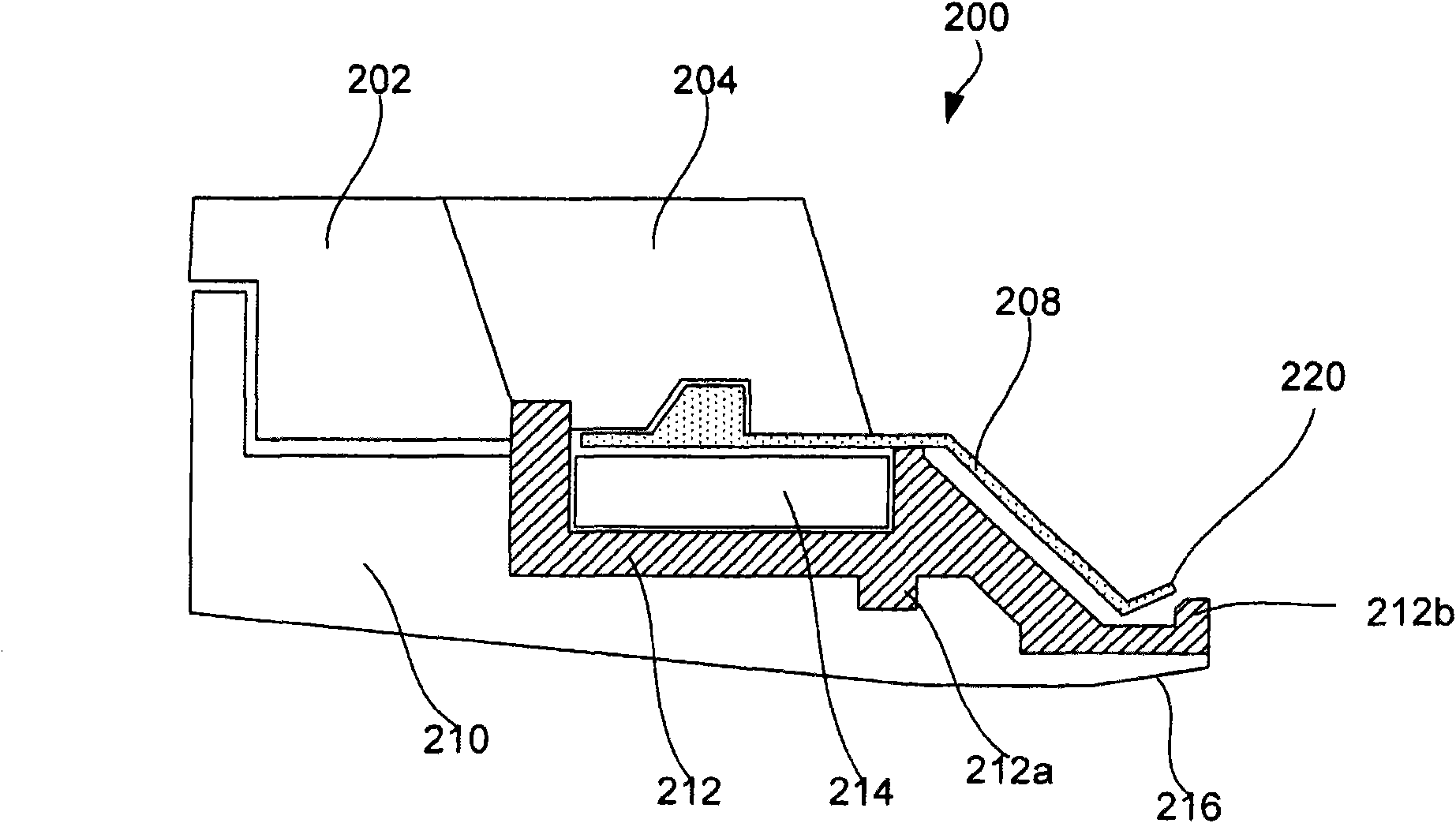
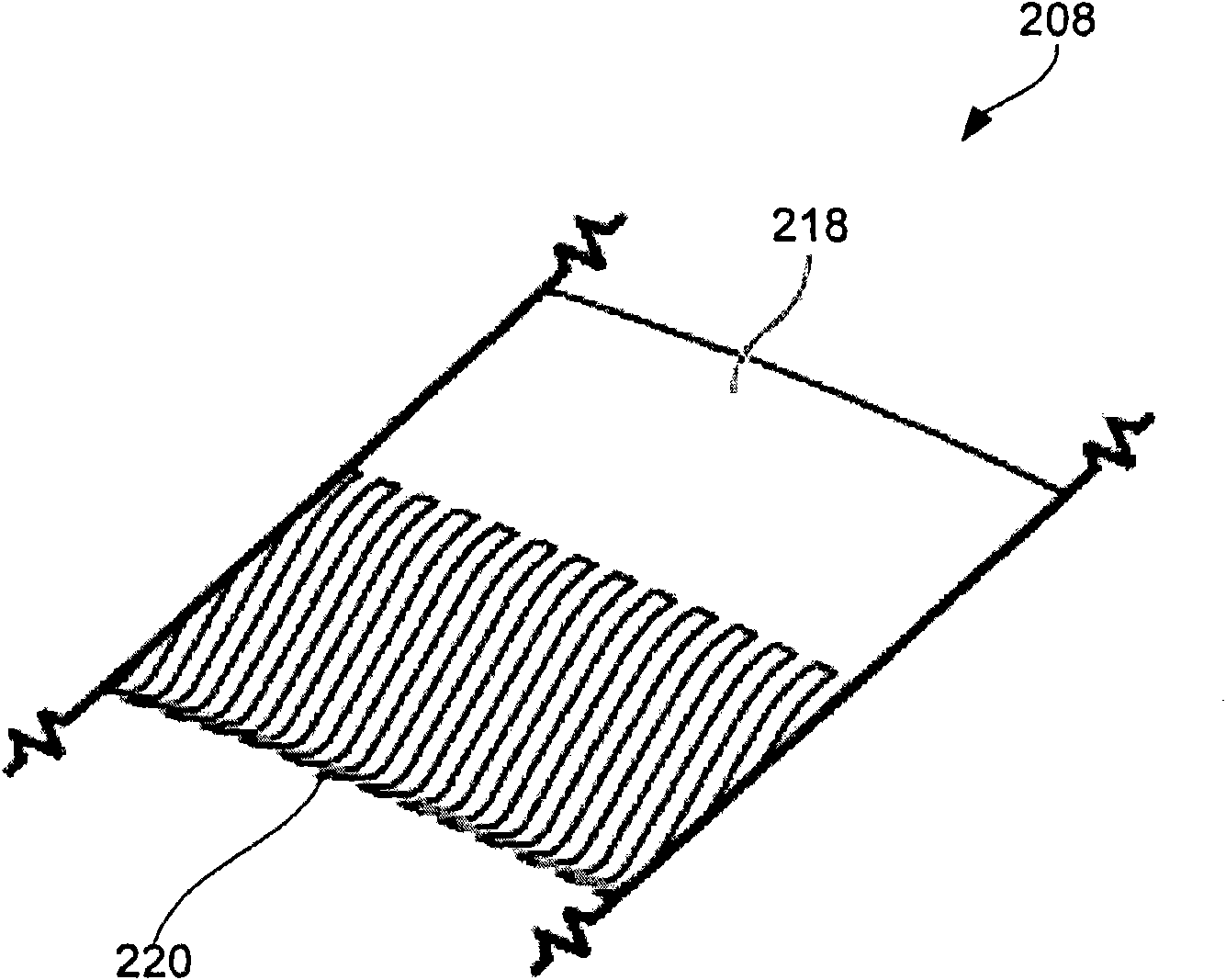
Disclosed are cup assemblies for holding, sealing, and providing electrical power to a semiconductor substrate during electroplating which may include a cup bottom element having a main body portion and a moment arm, an elastomeric sealing element disposed on the moment arm, and an electrical contact element disposed on the elastomeric sealing element. The main body portion may be such that it does not substantially flex when a substrate is pressed against the moment arm, and it may be rigidly affixed to another feature of the cup structure. The ratio of the average vertical thickness of the main body portion to that of the moment arm may be greater than about 5. The electrical contact element may have a substantially flat but flexible contact portion disposed upon a substantially horizontal portion of the sealing element. The elastomeric sealing element may be integrated with the cup bottom element during manufacturing.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Lipseals and contact elements for semiconductor electroplating apparatuses
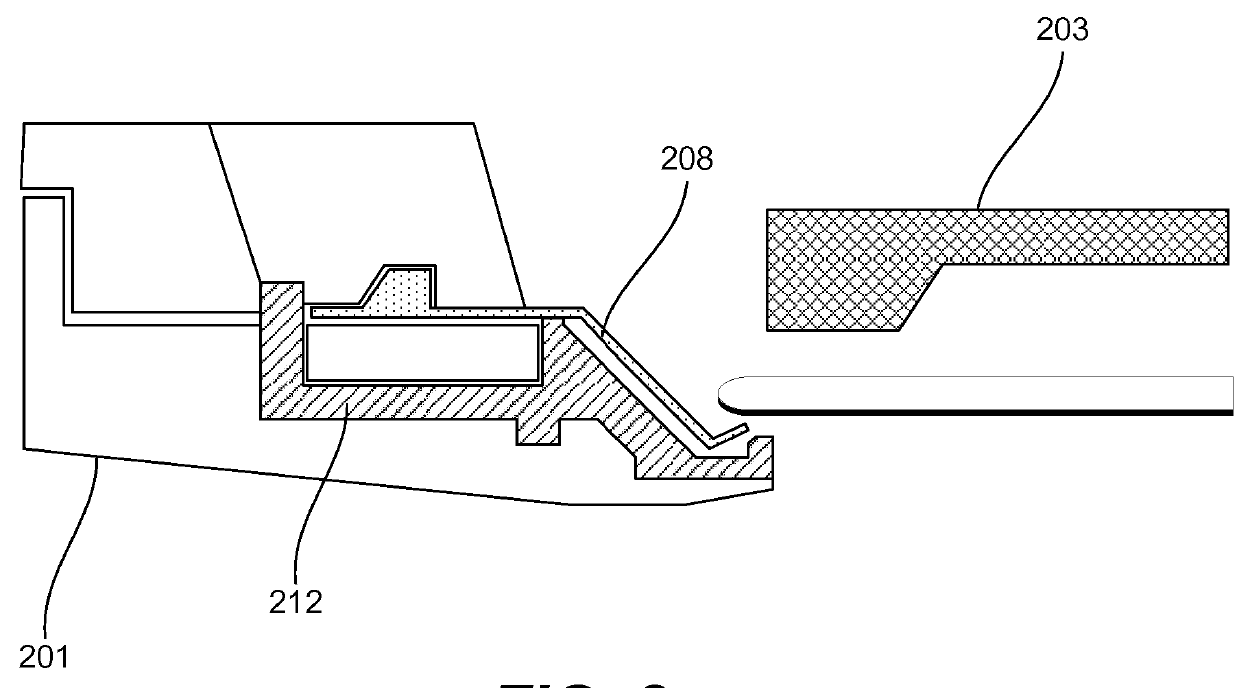
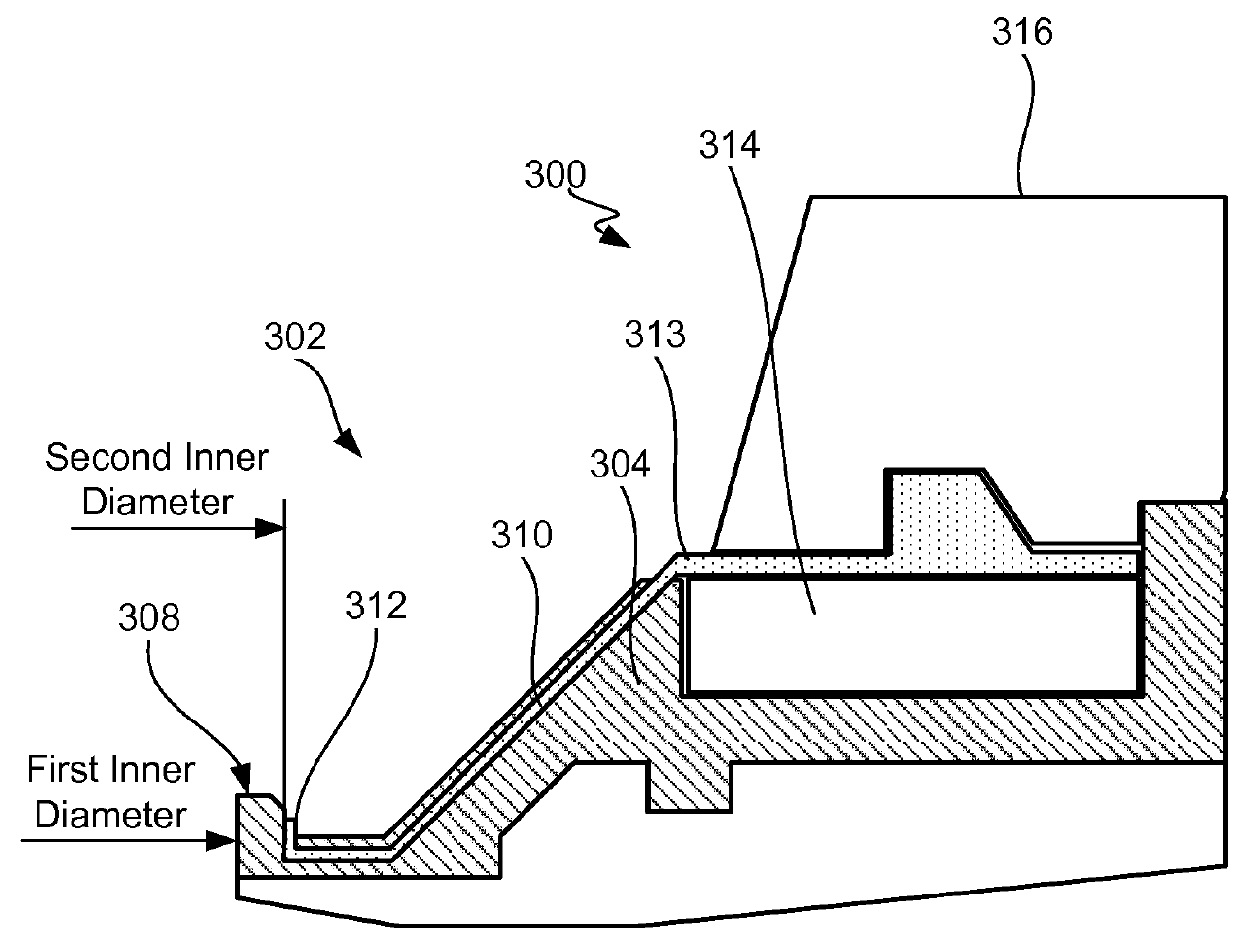
Disclosed herein are lipseal assemblies for use in electroplating clamshells which may include an elastomeric lipseal for excluding plating solution from a peripheral region of a semiconductor substrate and one or more electrical contact elements. The contact elements may be structurally integrated with the elastomeric lipseal. The lipseal assemblies may include one or more flexible contact elements at least a portion of which may be conformally positioned on an upper surface of the elastomeric lipseal, and may be configured to flex and form a conformal contact surface that interfaces with the substrate. Some elastomeric lipseals disclosed herein may support, align, and seal a substrate in a clamshell, and may include a flexible elastomeric upper portion located above a flexible elastomeric support edge, the upper portion having a top surface and an inner side surface, the later configured to move inward and align the substrate upon compression of the top surface.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
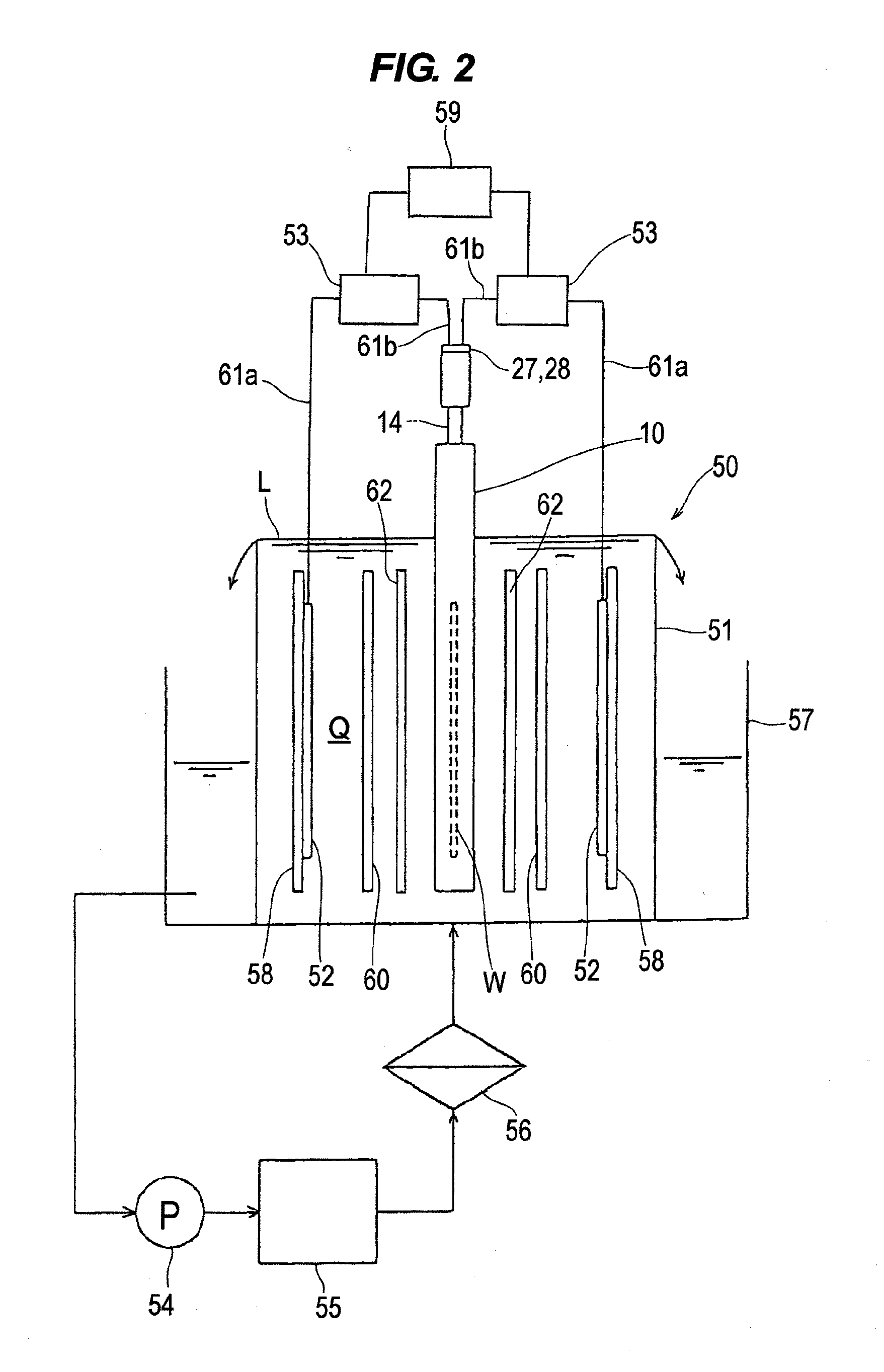
Fixtureless vertical paddle electroplating cell
InactiveUS20060070883A1Increase productionEliminate needSealing devicesCurrent conducting devicesMechanical engineeringElectrode
A submersible assembly for exposing respective front surfaces of different work-pieces to an electroplating bath as a partial respective electrodes thereof, while protecting opposing, rear surfaces of the work-pieces from the bath. The assembly includes a wall, having a front surface also partially forming a first electrode of the bath, and having an opening smaller in size than the perimeter of a work-piece while substantially corresponding in size to the portion of the front surface of the work-piece to be exposed to the bath. The assembly also includes a chuck mechanism for applying pressure against the rear surface of the work-piece to thereby hold the work-piece against a rear surface of the wall and create a fluid-tight seal between the rear surface of the wall and the perimeter of the front surface of the work-piece, thereby exposing the front surface of the work-piece to the bath while protecting the rear surface of the work-piece from exposure to the bath.
Owner:CHEM SAFETY TECH
Plating method and plating apparatus
ActiveUS20130255360A1Shorten the timeShort timeCellsDetection of fluid at leakage pointVacuum pressureEngineering
A plating method includes holding a substrate with a substrate holder while bringing a sealing member into pressure contact with a peripheral portion of the substrate to form an enclosed internal space in the substrate holder; performing a first-stage leakage test of the substrate holder by producing a vacuum in the internal space and checking whether pressure in the internal space reaches a predetermined vacuum pressure within a certain period of time; and if the substrate holder has passed the first-stage leakage test, performing a second-stage leakage test of the substrate holder by closing off the internal space after producing the vacuum therein and checking whether a change in the pressure in the internal space reaches a predetermined value within a certain period of time.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Plating apparatus and method
An apparatus forms a plated film in fine trenches and plugs for interconnects and in the openings of a resist formed in the surface of a substrate such as a semiconductor wafer, and forms bumps (protruding electrodes) on the surface of a semiconductor wafer. The apparatus includes a substrate holder capable of opening and closing for holding a substrate such that the front surface of the substrate is exposed while the backside and the edge thereof are hermetically sealed. A plating tank accommodates a plating liquid in which an anode is immersed. A diaphragm is provided in the plating tank and disposed between the anode and the substrate held by the substrate holder. Plating liquid circulating systems circulate the plating liquid to respective regions of the plating tank, separated by the diaphragm. A deaerating unit is disposed in at least one of the plating liquid circulating systems.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Electroplating method
InactiveUS20120160696A1Shorten the time periodEfficient fillingAnodisationContacting devicesEngineeringSupply current
A substrate with a through-hole is immersed in a plating solution in a plating tank. A pair of anodes are disposed in the plating solution in the plating tank in facing relation to face and reverse sides, respectively, of the substrate in the plating solution. A plurality of plating processes are performed on the face and reverse sides by supplying pulsed currents respectively between the face side of the substrate and one of the anodes which faces the face side of the substrate, and between the reverse side of the substrate and the other anode which faces the reverse side of the substrate. A reverse electrolyzing process is performed on the face and reverse sides between adjacent plating processes by supplying currents in an opposite direction to the pulsed currents respectively between the face side of the substrate and one of the anodes, and between the reverse side of the substrate and the other anode.
Owner:EBARA CORP
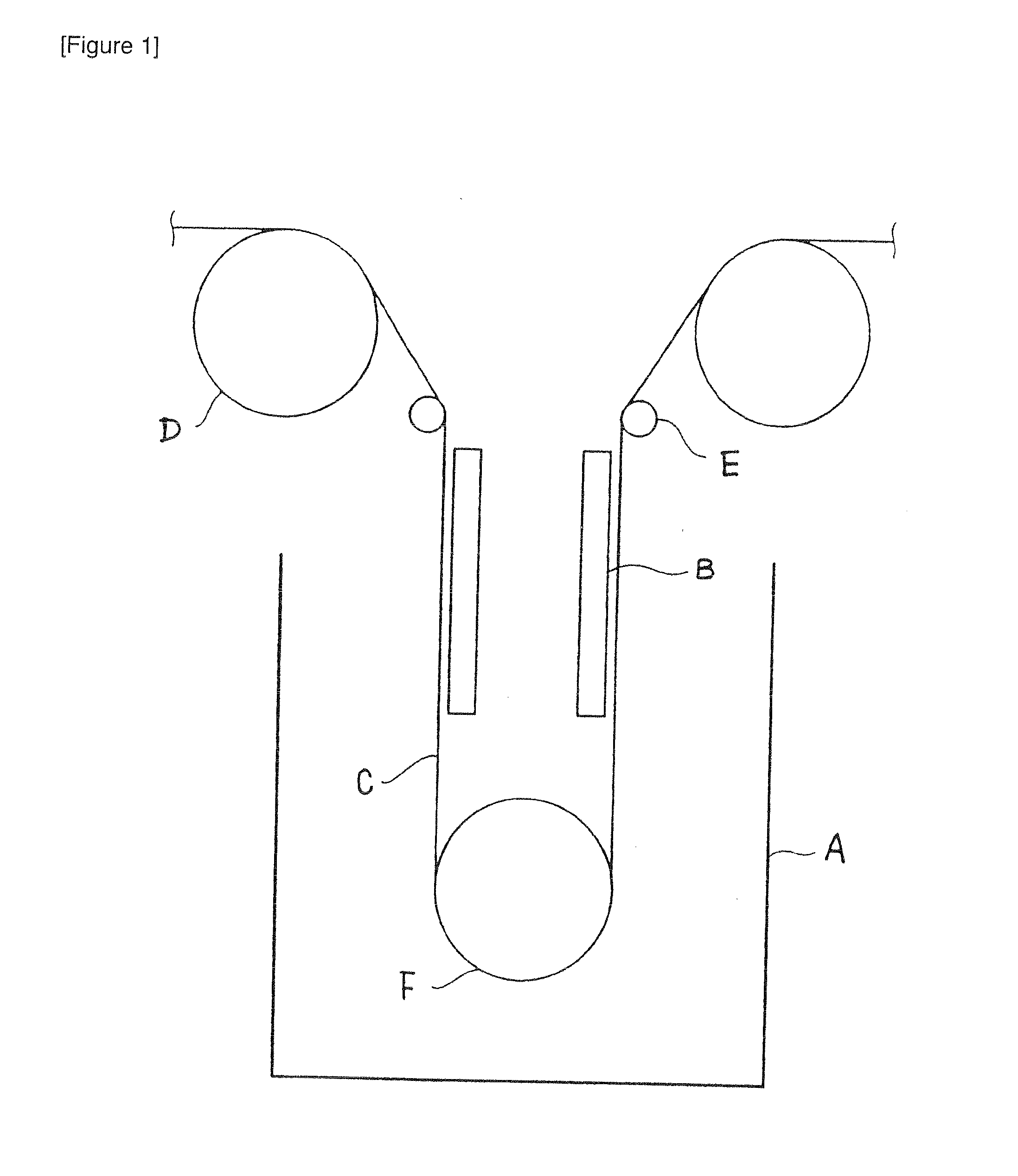
Roll Unit Dipped in Surface Treatment Liquid
Provided is a roll unit to be dipped in a surface treatment liquid of a copper foil, wherein a bearing box for housing a roil shaft is configured from two bearing boxes that are divisible, one of the bearing boxes is configured from a roll-side bearing box arranged on a roll main body-side and the other bearing box is configured from a shaft end-side bearing box arranged on the shaft end-side of the roll, a shaft sleeve covering an outer periphery of the roll shaft is provided in the roll-side bearing box and an oil seal is provided along an outer periphery of the shaft sleeve, and a bearing for rotatably supporting the shaft is disposed in the shaft end-side bearing box. Specifically, the present invention provides a roll unit to be used in electrochemical surface treatments such as roughening treatment, rust prevention treatment, and oxidized surface treatment (blackening treatment) to be continuously performed on a surface of a rolled copper foil or an electrolytic copper foil, and which is capable of inhibiting the abrasion and corrosion of the roll shaft of such roll unit by controlling the corrosion caused by the infiltration of the treatment liquid, and which enables the simple replacement of the bearing box, bearing, and other components.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Electrochemical device
InactiveUS20070000775A1Save spaceImprove reliabilityPrimary cell maintainance/servicingDouble layer capacitorsElectrochemistryMechanical engineering
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
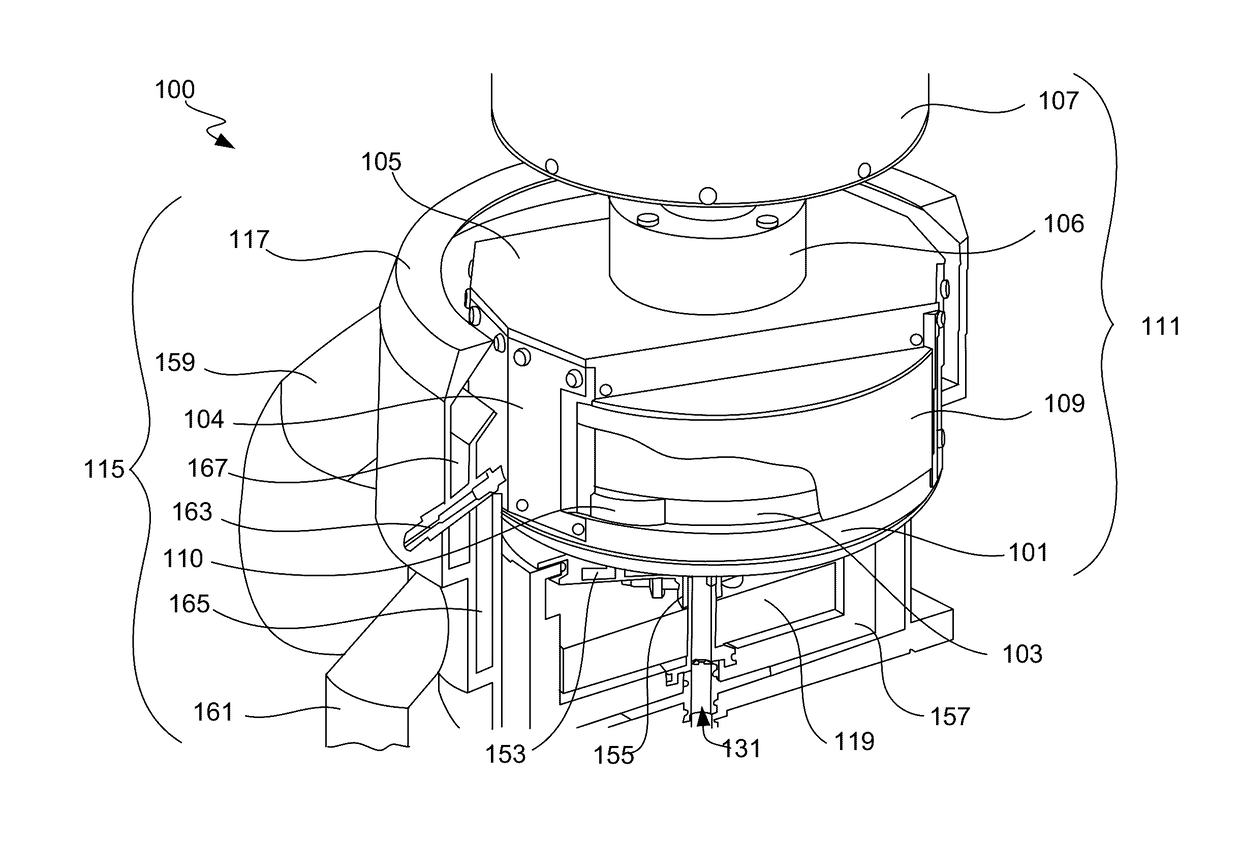
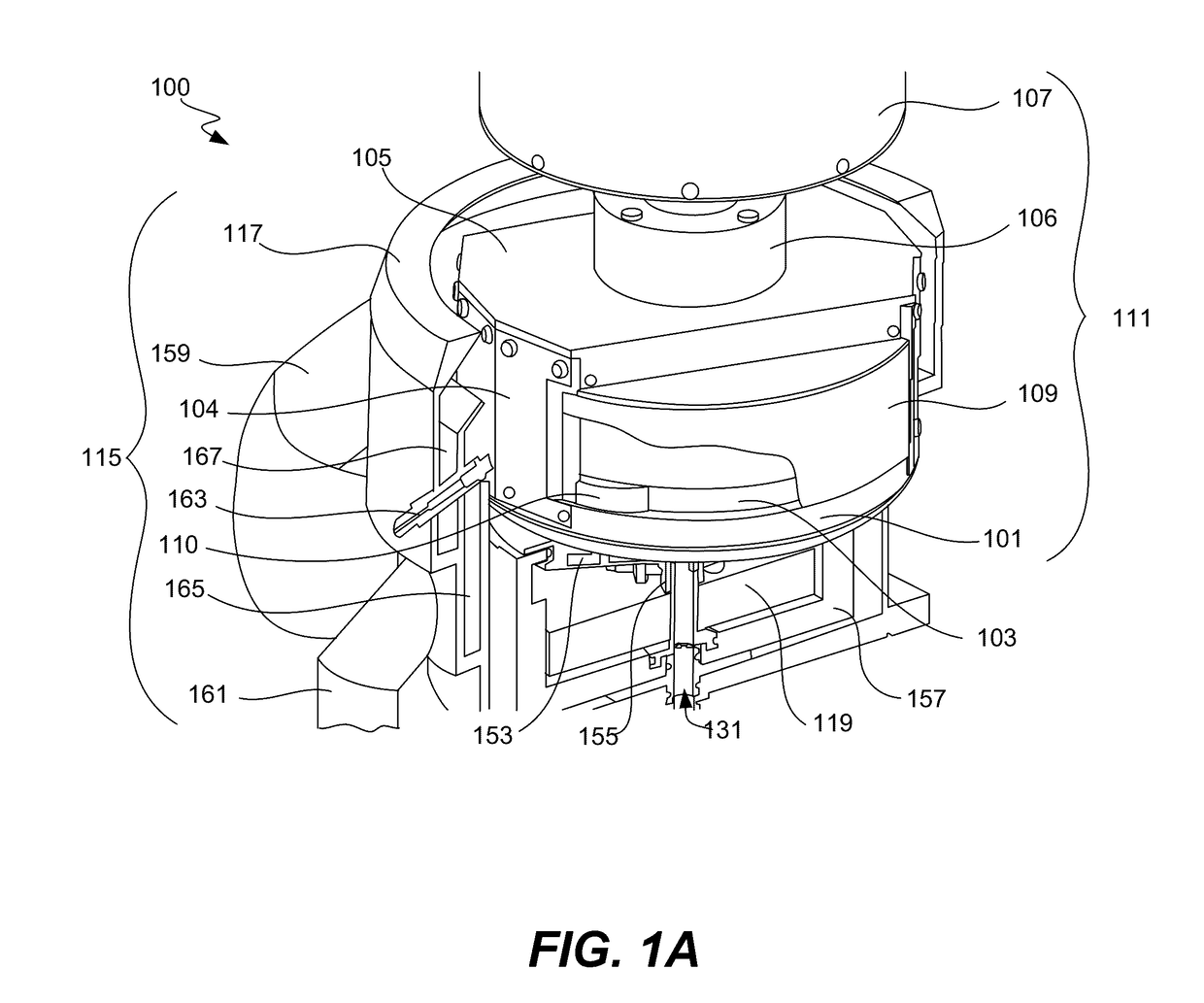
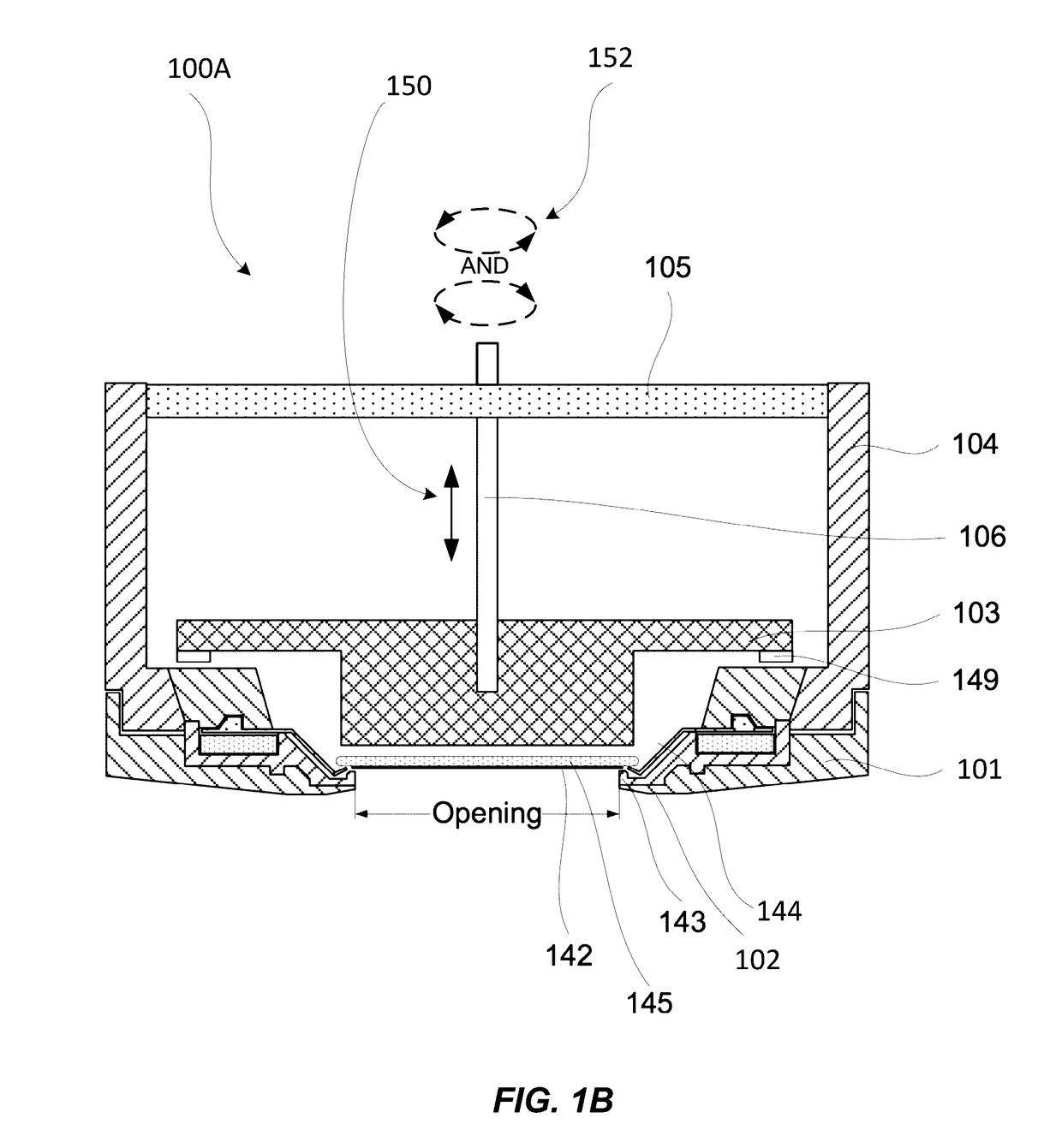
Workpiece holder for a wet processing system
ActiveUS20170372937A1Not specifySealing devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElastomerHandling system
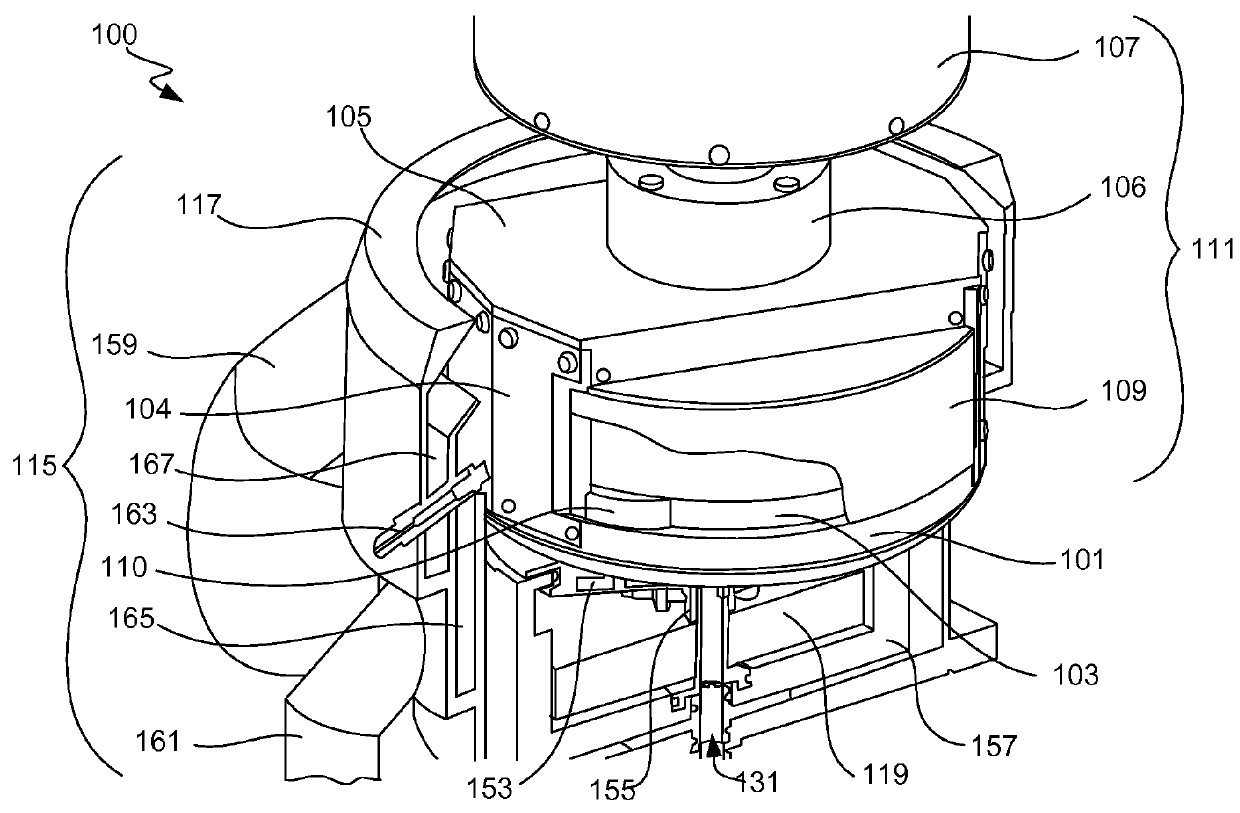
Techniques herein provide a workpiece holder that can hold relatively flexible and thin workpieces for transport and electrochemical deposition while avoiding electroplating fluid wetting contacts or contact regions of a given workpiece. A workpiece holder frame holds a workpiece by gripping the workpiece on opposing sides of the workpiece. A flexure structure is used for clamping a given workpiece and for providing an electrical path for supplying a current to the workpiece. An elastomer covering provides sealing and insulation of the electrical flexure structure. The workpiece holder also provides tension to the workpiece to help hold the workpiece flat during processing. Each flexure structure can provide an independent electrical path to the workpiece surface.
Owner:CAVIUM NETWORKS +1
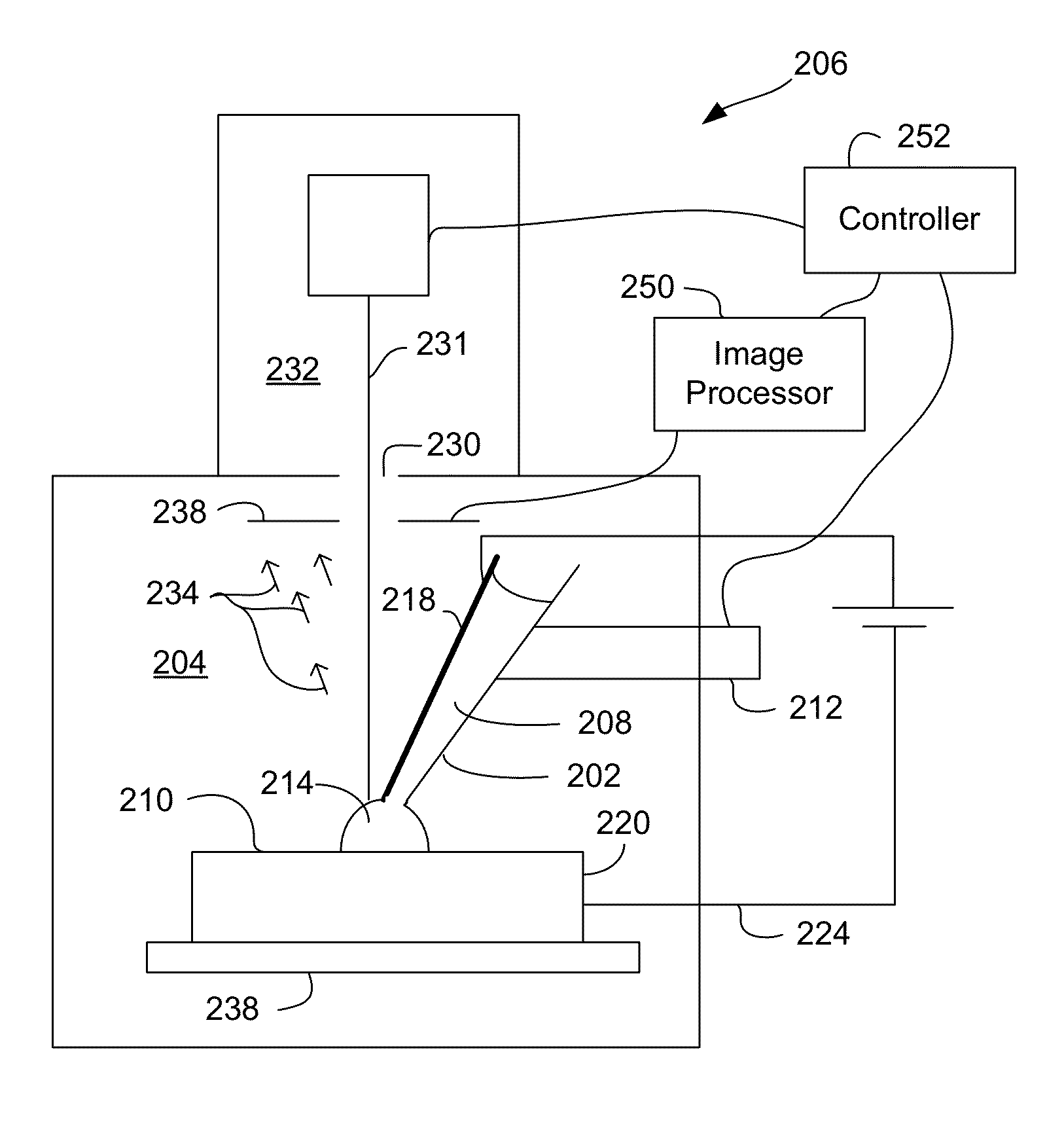
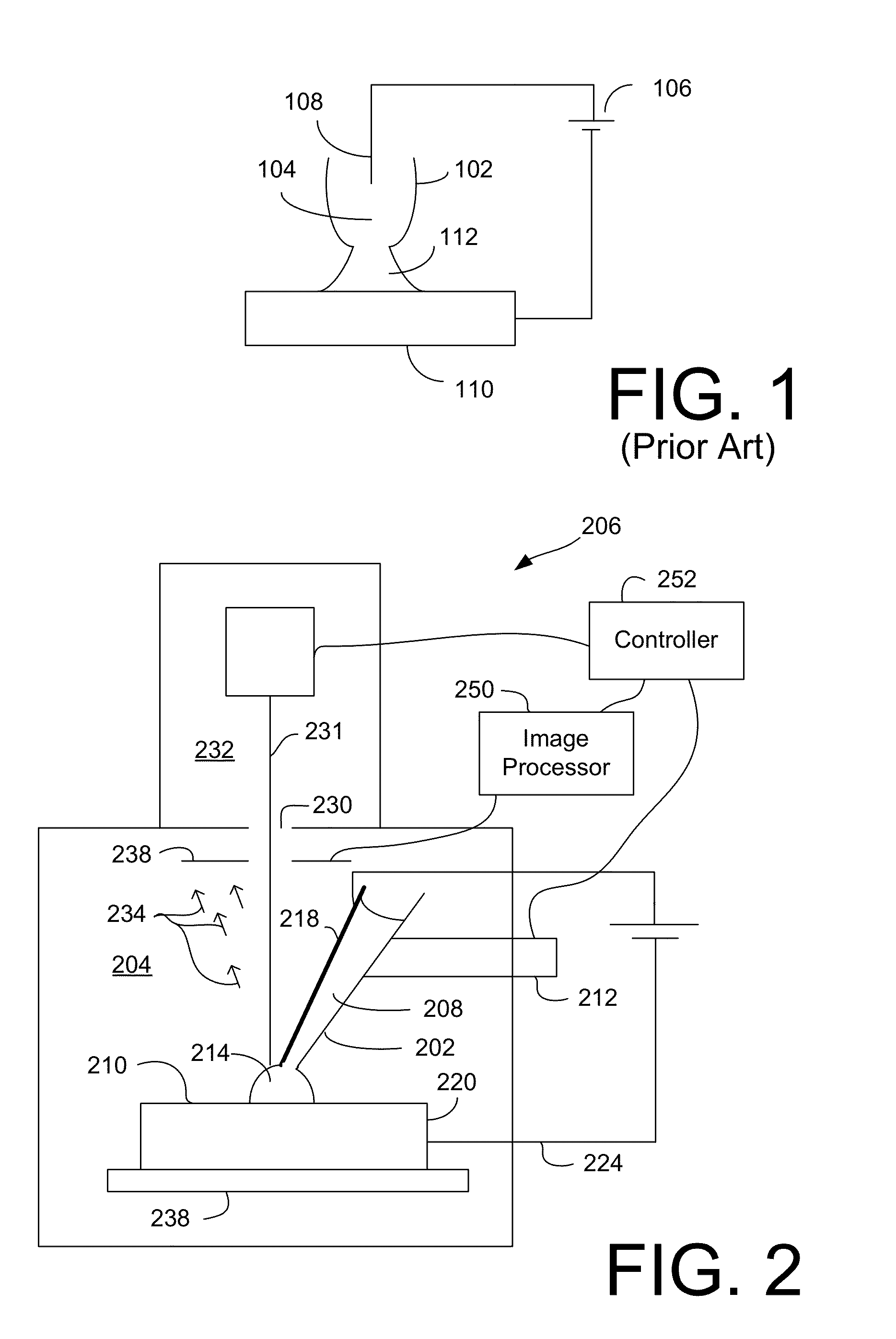
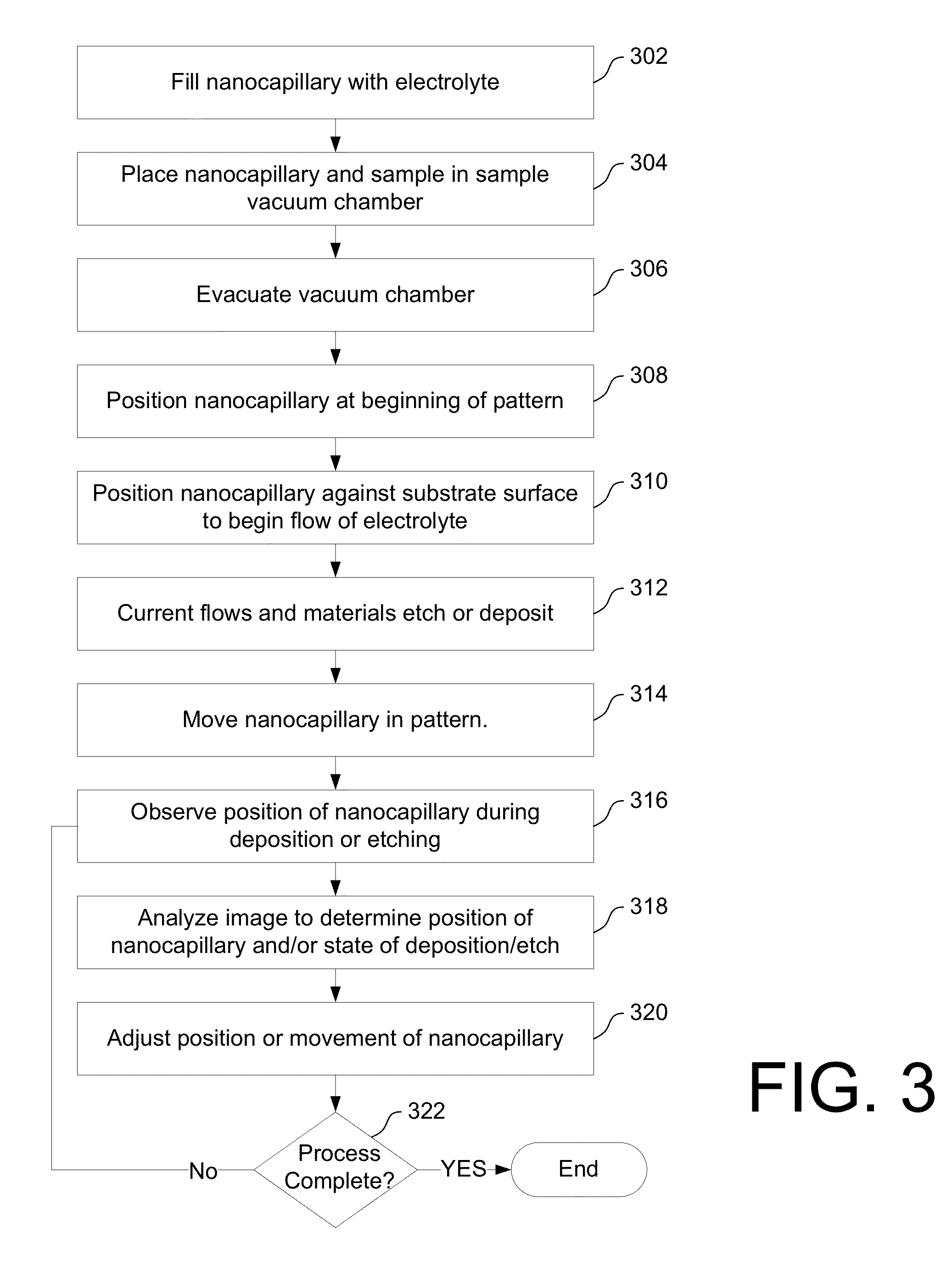
Localized, In-Vacuum Modification of Small Structures
ActiveUS20130068611A1Rapidly and precisely depositEasy to controlCellsElectric discharge tubesElectrical batteryEngineering
A charge transfer mechanism is used to locally deposit or remove material for a small structure. A local electrochemical cell is created without having to immerse the entire work piece in a bath. The charge transfer mechanism can be used together with a charged particle beam or laser system to modify small structures, such as integrated circuits or micro-electromechanical system. The charge transfer process can be performed in air or, in some embodiments, in a vacuum chamber.
Owner:FEI CO
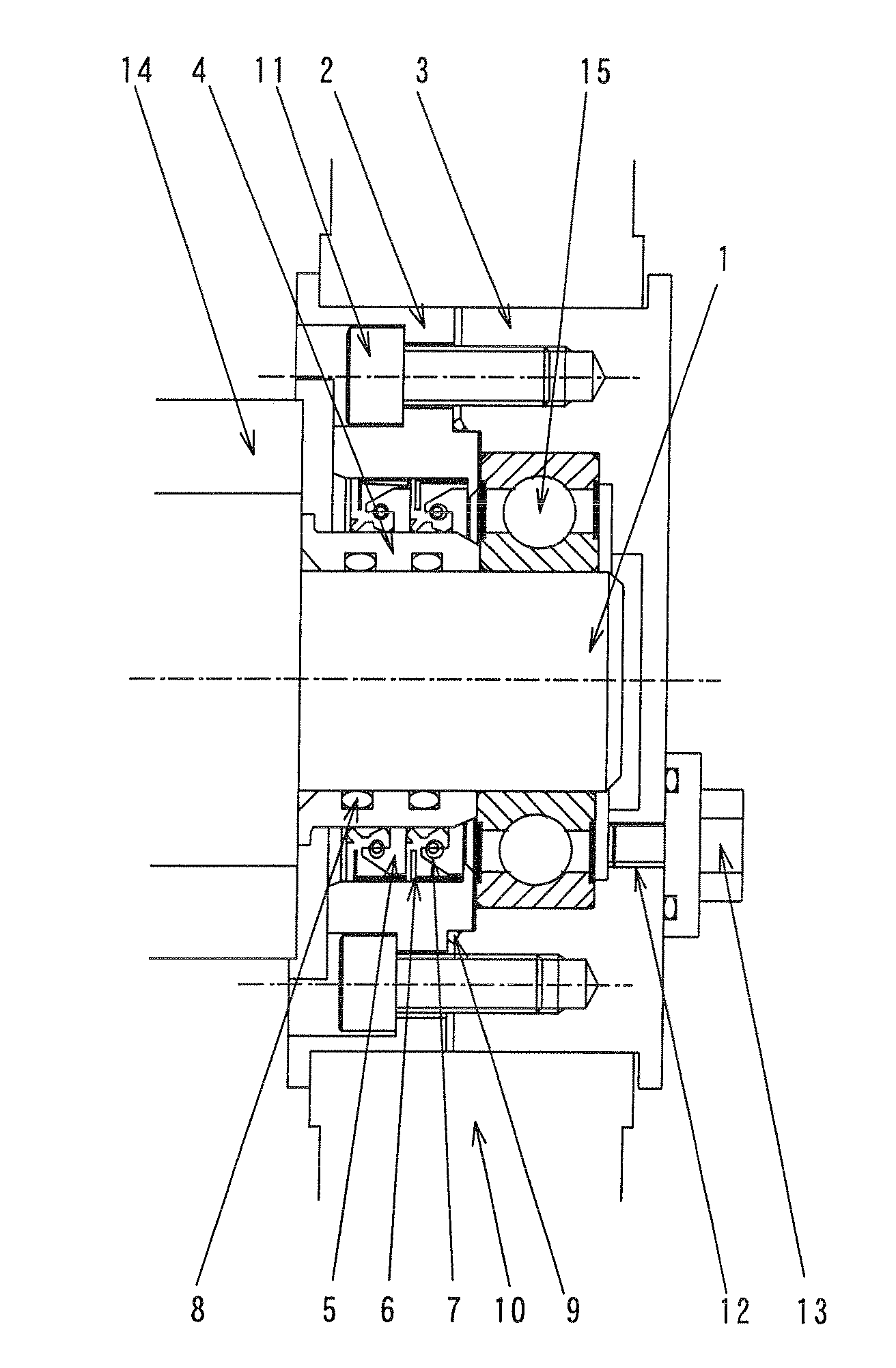
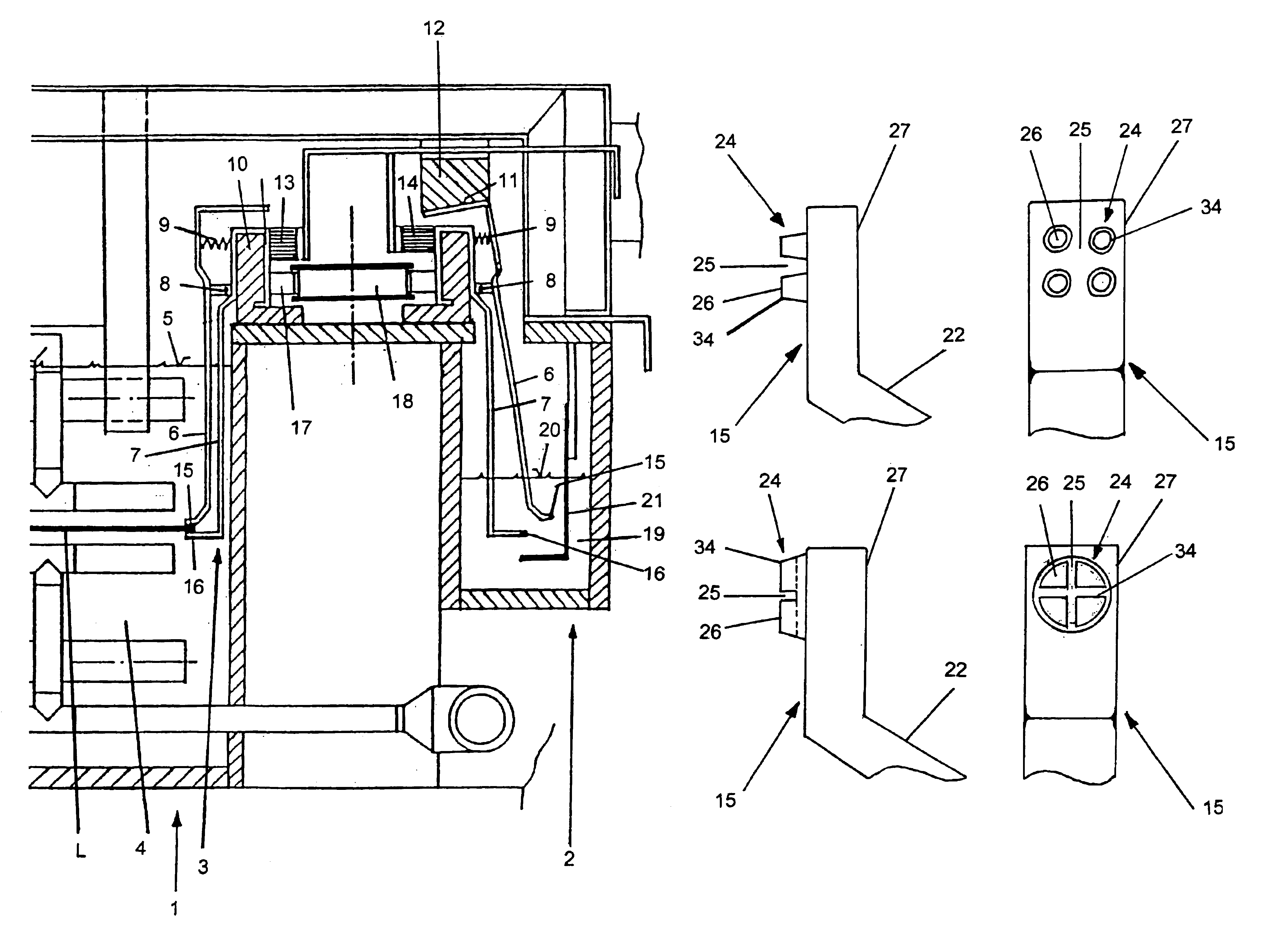
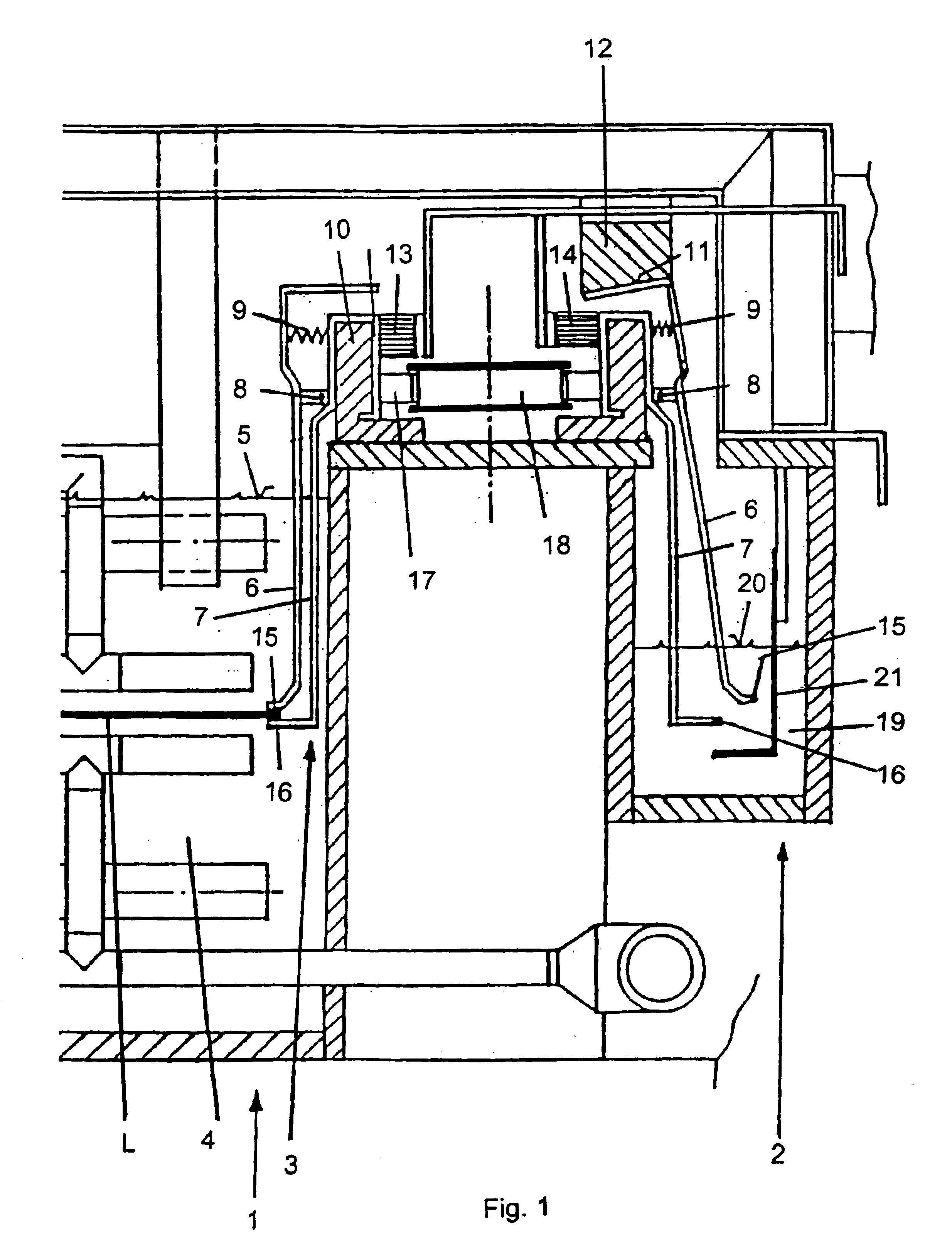
Contact element for use in electroplating
InactiveUS6887113B1Improve cooling effectEfficiently dissipatedCellsContact surface shape/structureEngineeringContact element
It is difficult to transmit large processing current on the surfaces of printed circuit boards (L) using clamp-type contact organs (6, 7). In order to solve said problem, contact elements (15, 16) having one or more contact surfaces (26) are disposed on the contact organs (6, 7). The shape of the contact surfaces (26) are configured in such a way that no damages occur in the areas of the conductive surfaces adjacent to the contact surfaces (26) when large currents are transmitted from the contact elements (15, 16) printed on the electrically conductive surface of printed board material (L) on the contact surfaces to the conductive surface.
Owner:ATOTECH DEUT GMBH
Multi-contact lipseals and associated electroplating methods
Disclosed herein are lipseal assemblies for use in an electroplating clamshell for engaging and supplying electrical current to a semiconductor substrate during electroplating, which include an elastomeric lipseal for engaging the semiconductor substrate during electroplating, and wherein upon engagement the elastomeric lipseal forms multiple radially-separated sealing contact surfaces with the substrate which substantially exclude plating solution from a peripheral region of the substrate. Said lipseal assemblies may also include one or more electrical contact elements for supplying electrical current to the semiconductor substrate during electroplating.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Seal rings in electrochemical processors
InactiveUS20130306465A1Precise sealing dimensionImprove performanceCellsEngine sealsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A seal ring for an electrochemical processor does not slip or deflect laterally when pressed against a wafer surface. The seal ring may be on a rotor of the processor, with the seal ring having an outer wall joined to a tip arc through an end. The outer wall may be a straight wall. A relatively rigid support ring may be attached to the seal ring, to provide a more precise sealing dimension. Knife edge seal rings that slip or deflect laterally on the wafer surface may also be used. In these designs, the slipping is substantially uniform and consistent, resulting in improved performance.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Electroplating apparatus and electroplating method
ActiveUS8029653B2Uniform thicknessImprove film qualityCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringCopper
An electroplating apparatus can form a plated film having a more uniform thickness and good film quality over an entire surface of a substrate having a conductive layer (seed layer) whose resistivity is equal to or higher than that of copper. The electroplating apparatus includes: a substrate holder for holding a substrate; a sealing member for contact with a peripheral portion of a surface of a substrate, held by the substrate holder, to seal the peripheral portion; a cathode contact for contact with a conductive layer formed in the surface of the substrate, held by the substrate holder, to feed electricity to the conductive layer; and a housing having therein an anode to be immersed in a plating solution, and a porous structure disposed at an open end facing the substrate held by the substrate holder, said porous structure defining a plating chamber in the housing; wherein the plating chamber is divided into rooms by a partition plate and the porous structure, and the anode is comprised of a plurality of divided anodes, each divided anode being disposed in each room of the plating chamber so that each divided anode can pass an independent plating current.
Owner:EBARA CORP
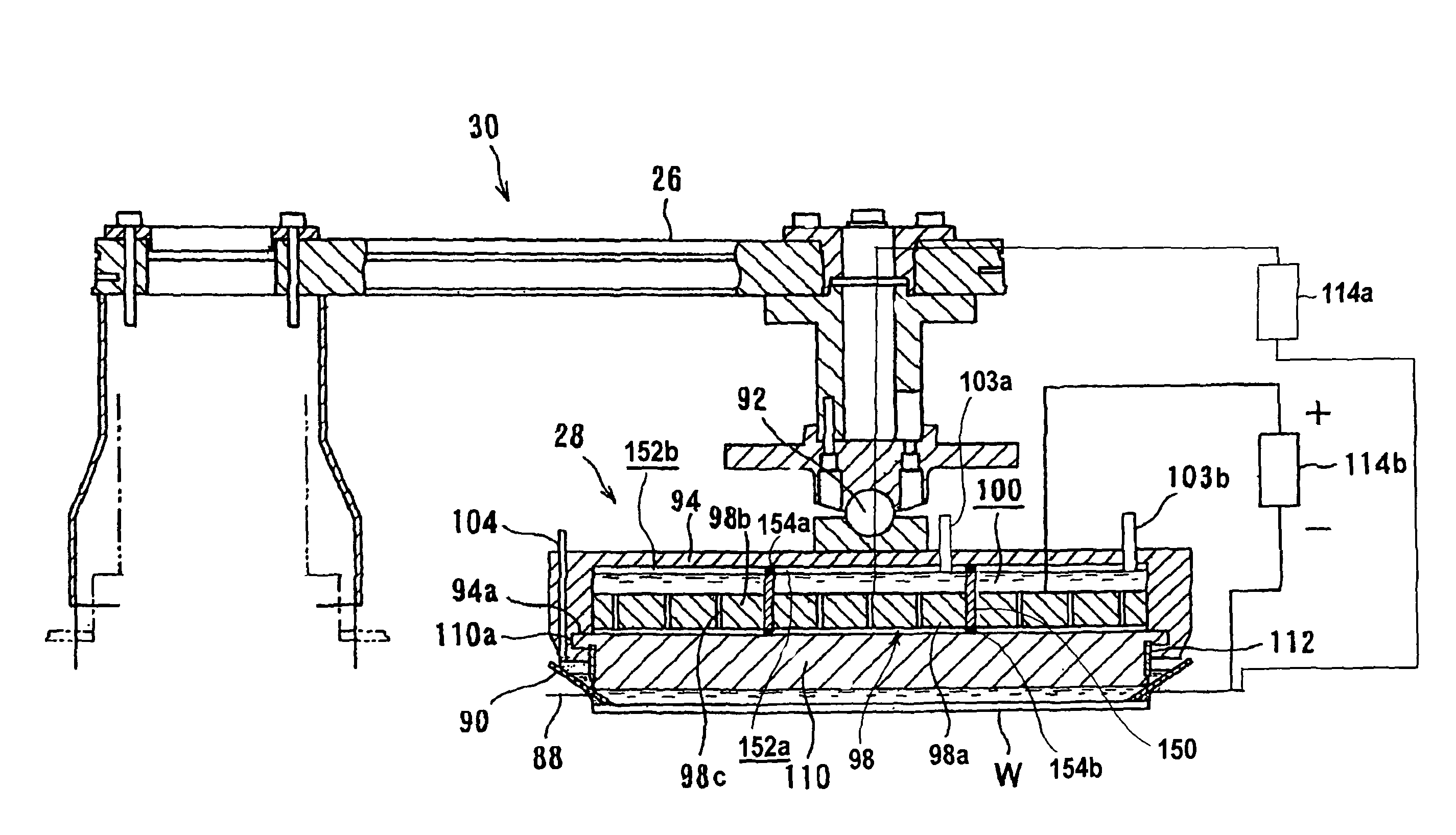
Substrate holder and plating apparatus
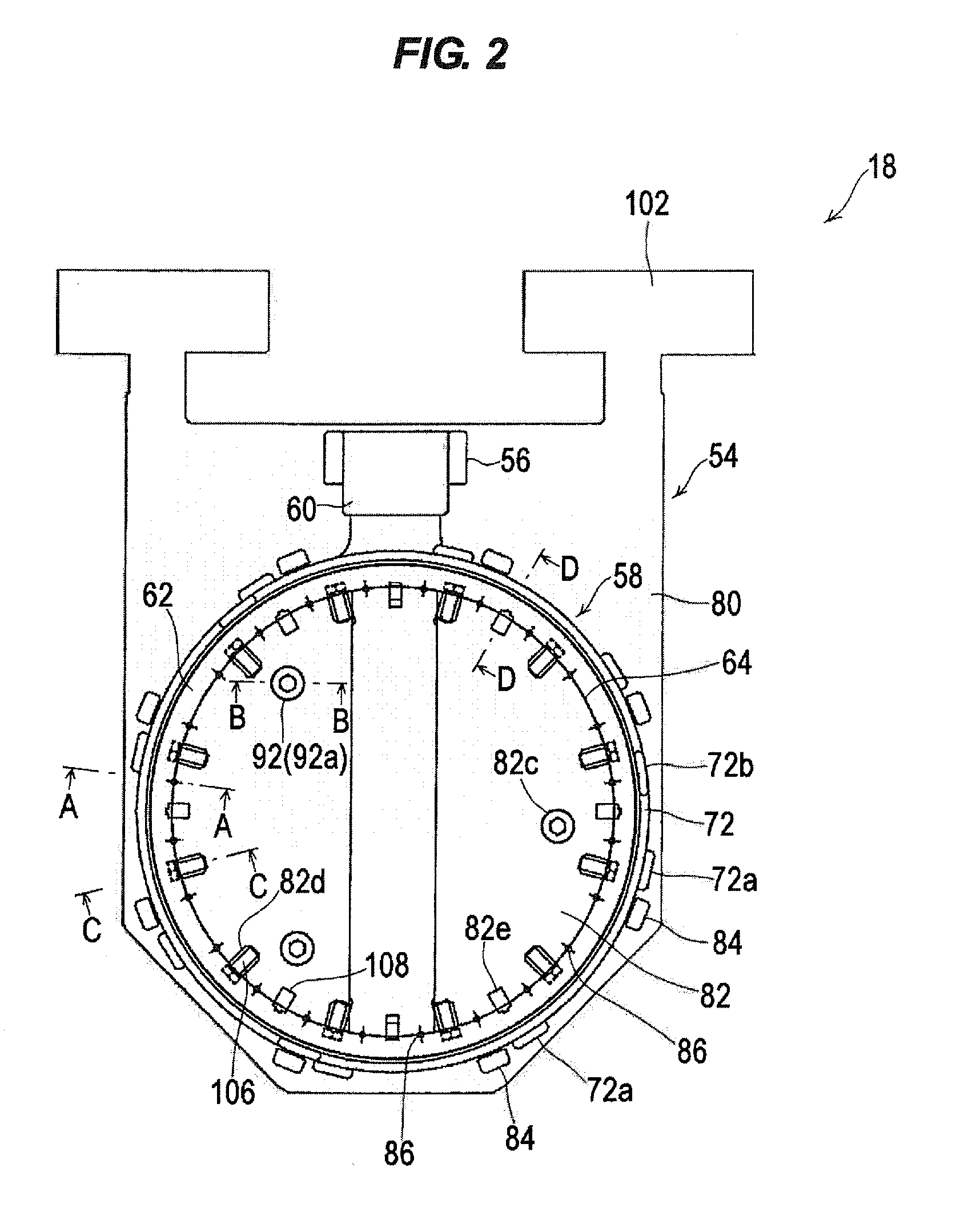
There is provided a substrate holder which can absorb a change in the thickness between substrates and can hold a substrate while preventing deflection of the substrate and keeping the amount of compression of a substrate sealing member within a certain narrow range. The substrate holder includes a first holding member and a second holding member, both for detachably holding a substrate by holding a peripheral portion of the substrate therebetween; and a substrate sealing member, mounted to the second holding member, for sealing the peripheral portion of the substrate along a substrate sealing line. The first holding member has a thickness absorbing mechanism which biases the substrate toward the second holding member at positions along the substrate sealing line.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Lipseals and contact elements for semiconductor electroplating apparatuses
Disclosed herein are lipseal assemblies for use in electroplating clamshells which may include an elastomeric lipseal for excluding plating solution from a peripheral region of a semiconductor substrate and one or more electrical contact elements. The contact elements may be structurally integrated with the elastomeric lipseal. The lipseal assemblies may include one or more flexible contact elements at least a portion of which may be conformally positioned on an upper surface of the elastomeric lipseal, and may be configured to flex and form a conformal contact surface that interfaces with the substrate. Some elastomeric lipseals disclosed herein may support, align, and seal a substrate in a clamshell, and may include a flexible elastomeric upper portion located above a flexible elastomeric support edge, the upper portion having a top surface and an inner side surface, the later configured to move inward and align the substrate upon compression of the top surface.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
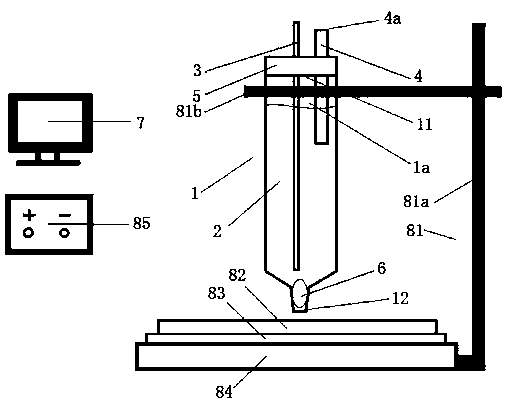
Electroplating pen device, intelligent electrochemical coating and 3D printing device and using methods thereof
ActiveCN109338427AAchieve temperature controlAvoid disconnectionCellsAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectricityMetal coating
The invention discloses an electroplating pen device, an intelligent electrochemical plating and 3D printing device and using methods of the electroplating pen device and intelligent electrochemical plating and 3D printing device. The electroplating pen device, the intelligent electrochemical plating and 3D printing device and the using methods of the electroplating pen device and intelligent electrochemical plating and 3D printing device mainly aim to solve the problem that a deposited workpiece needs to be limited in an electrolyte according to the current electrodeposition metal coating preparation technology. A new electrodeposition device is adopted to ensure that a to-be-plated workpiece does not need to be placed into the electrolyte to perform metal coating preparation in a specific area or even a point on the surface of the workpiece, and intelligent electrodeposition can be realized by controlling a to-be-plated workpiece platform through a computer. Meanwhile, when electrodepositing of the same material is carried out on the surface of the to-be-plated workpiece, electrochemical 3D printing (additive manufacturing) can be further realized through repeated deposition in the same area or the same pattern.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Durable low cure temperature hydrophobic coating in electroplating cup assembly
InactiveUS20170073832A1Easy constructionReduce the possibilityContacting devicesSealing devicesConductive materialsMelt temperature
Disclosed are electroplating cups for engaging wafers during electroplating, where the electroplating cup can include a ring-shaped cup bottom, an elastomeric seal, and an electrical contact element. The cup bottom may be repeatedly exposed to electroplating solution. The cup bottom can include a non-conductive material upon which a solid lubricant coating can be applied. The solid lubricant coating can be cured at a relatively low temperature, such as less than the melting temperature of the non-conductive material, and can be durable and hydrophobic.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com