Patents
Literature
1088results about "Tanks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
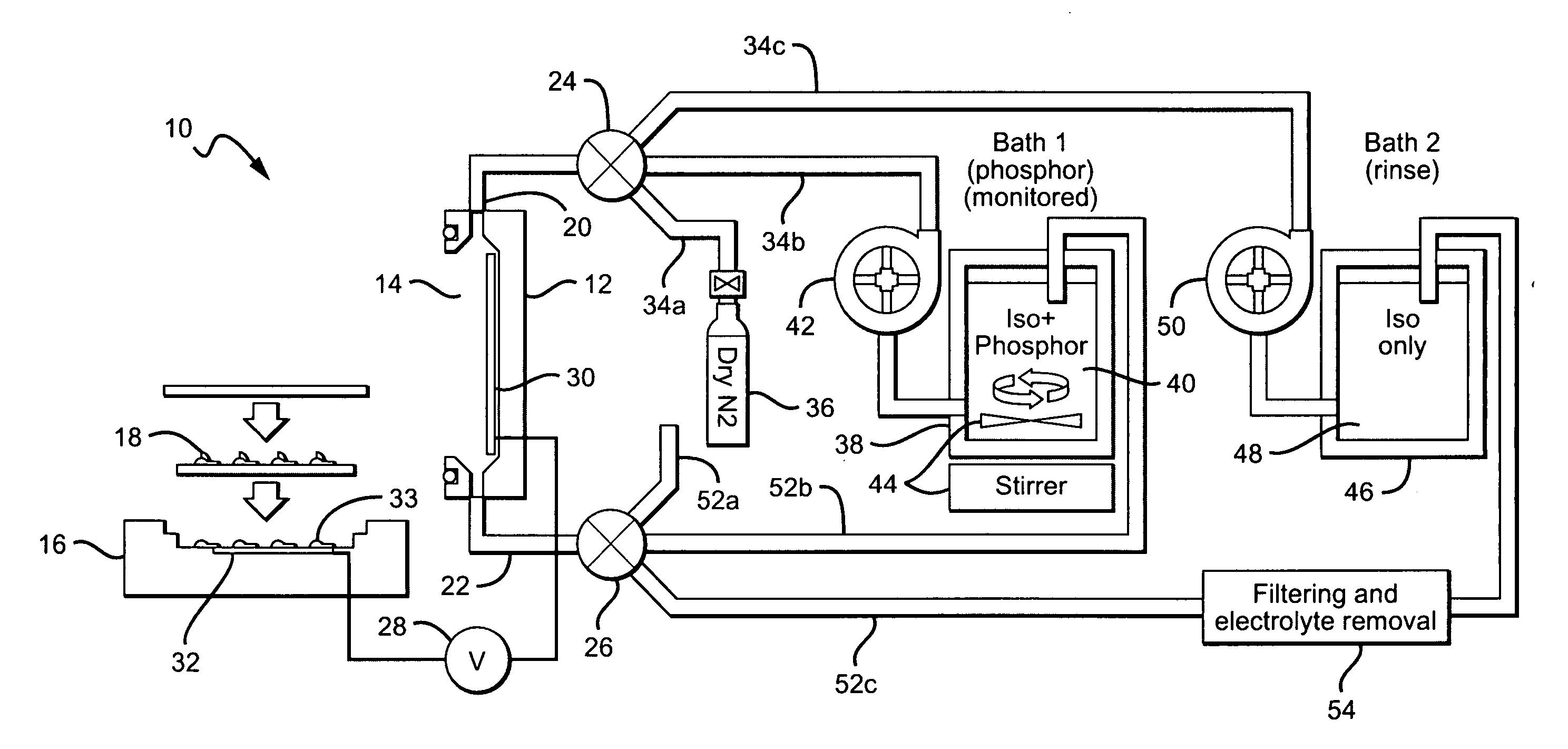
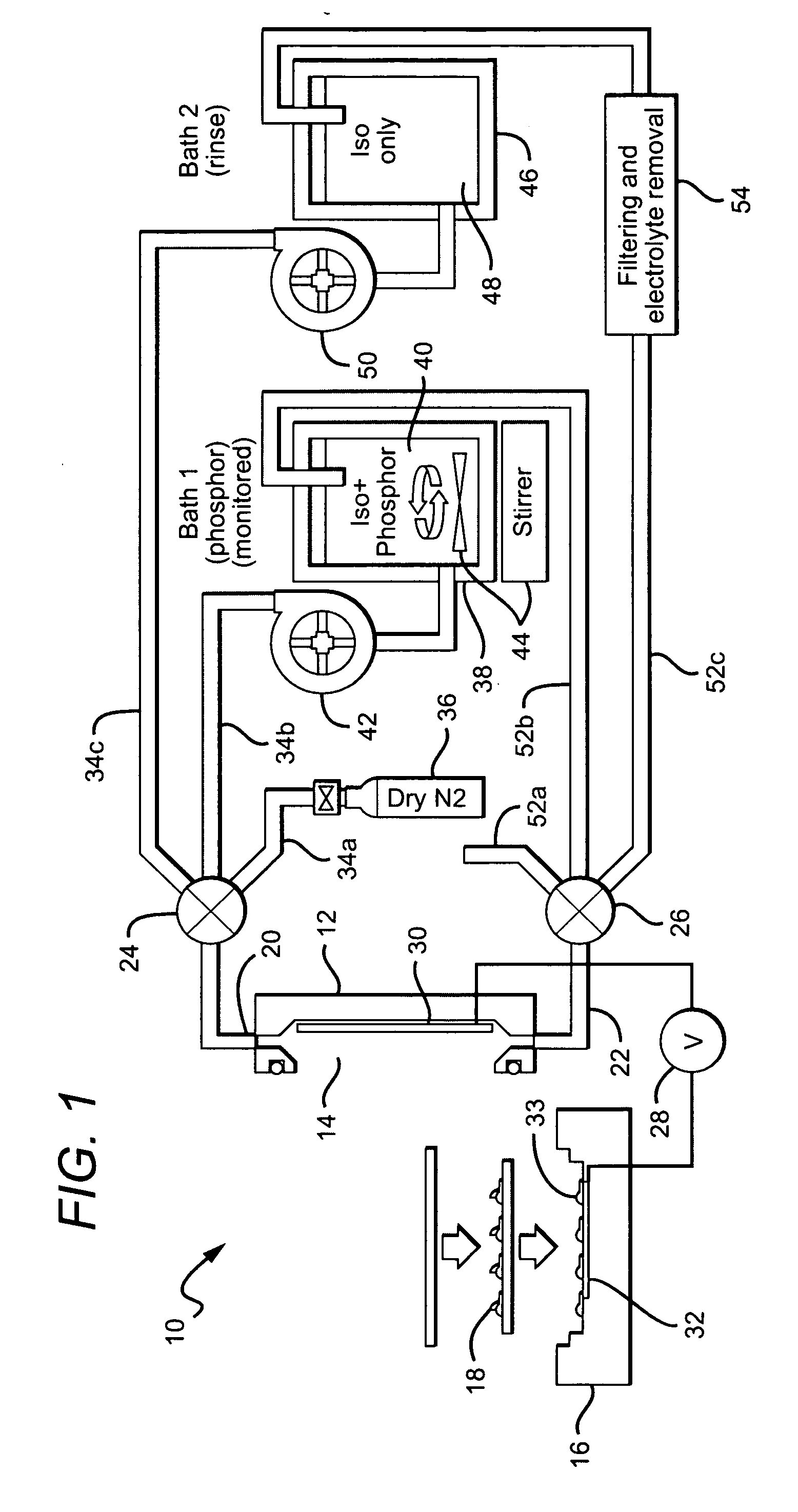
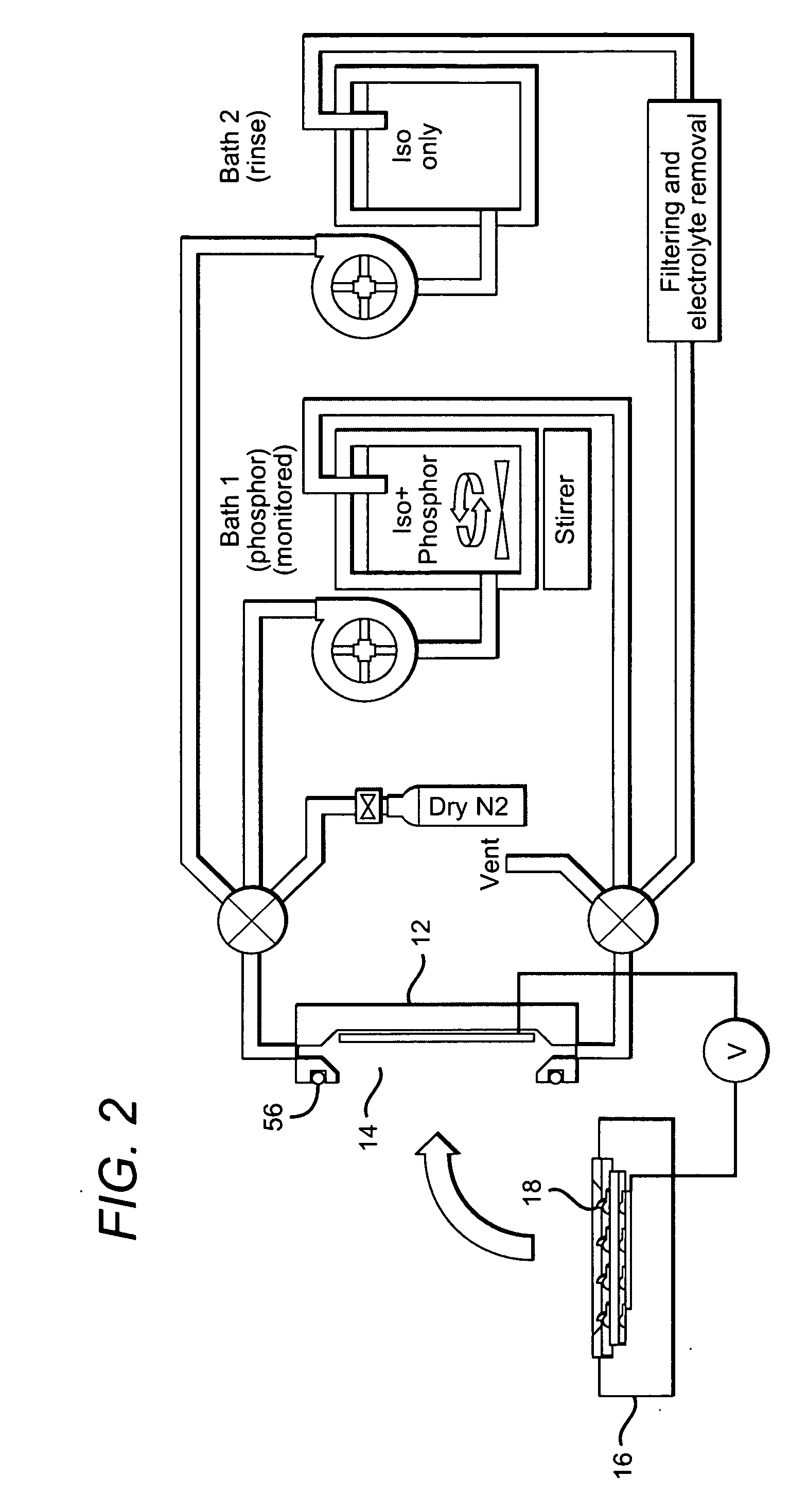
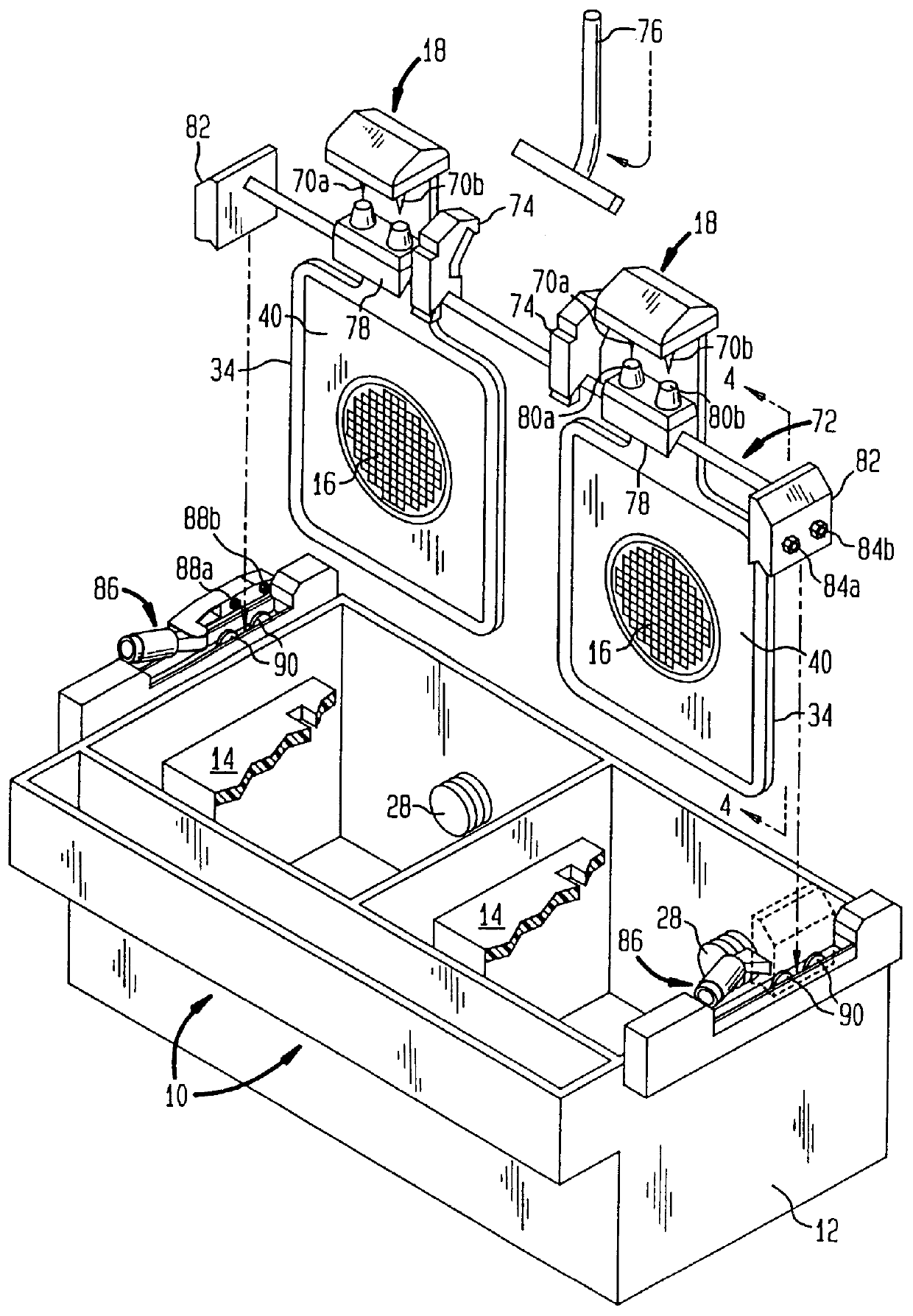
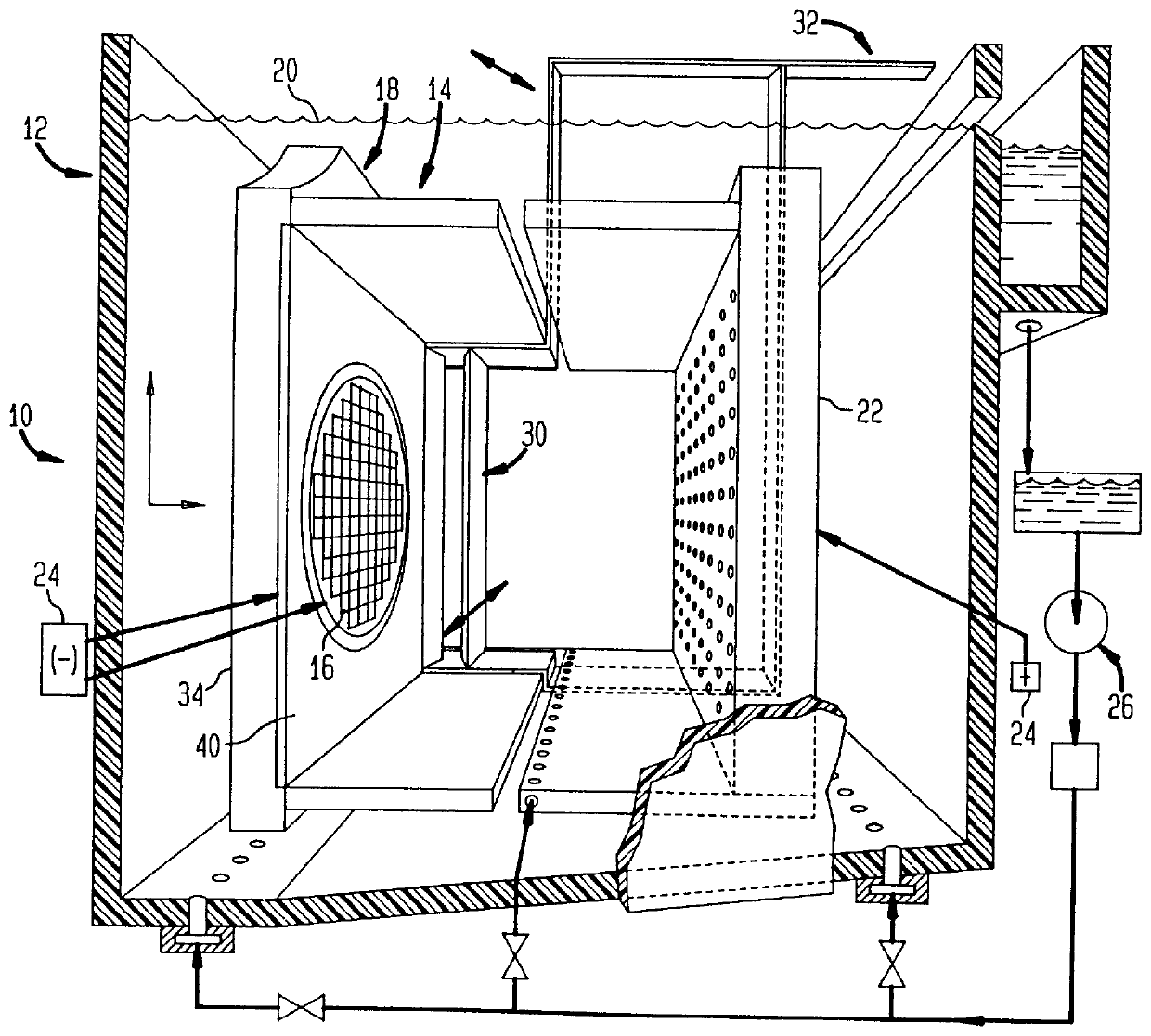
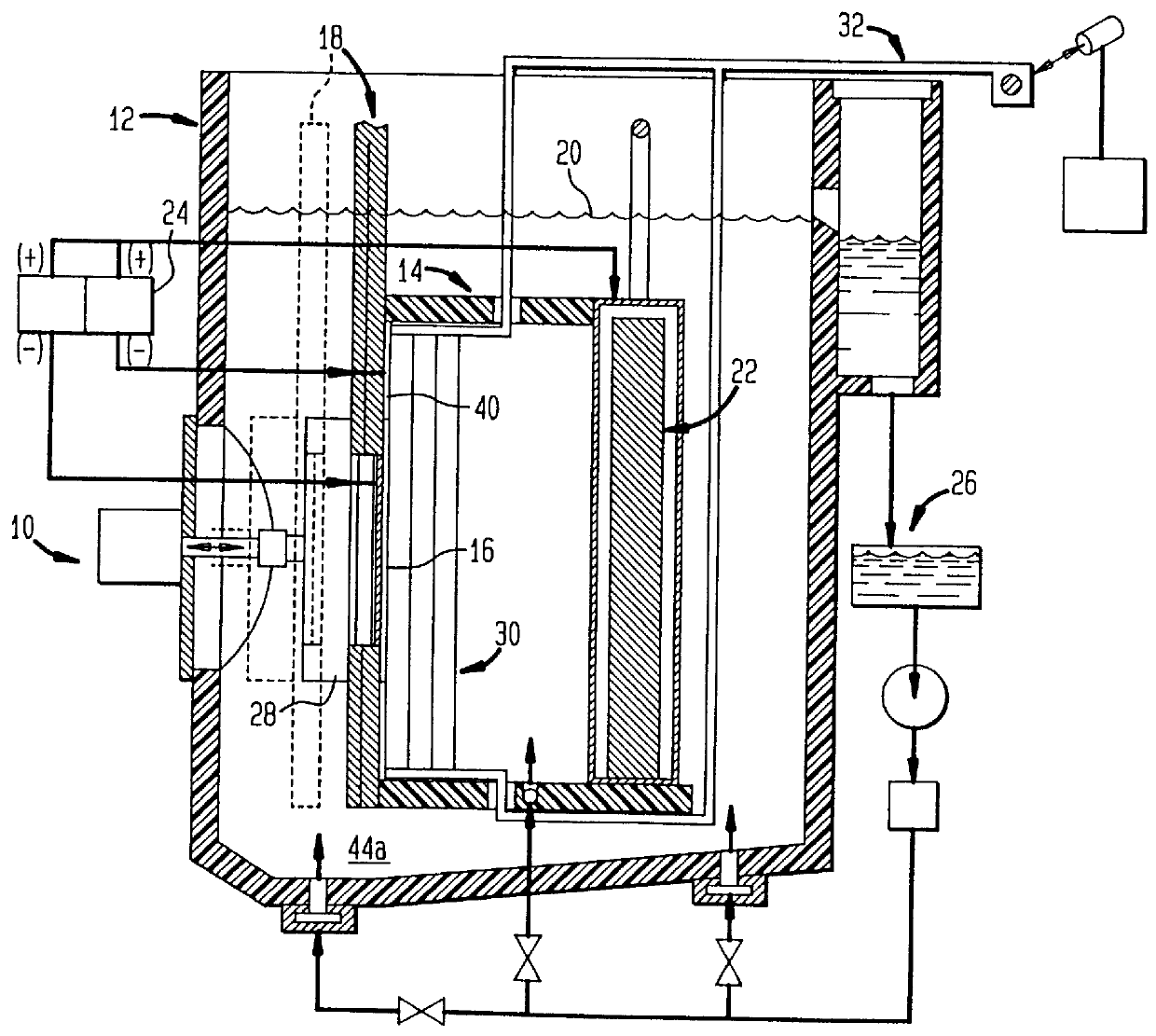
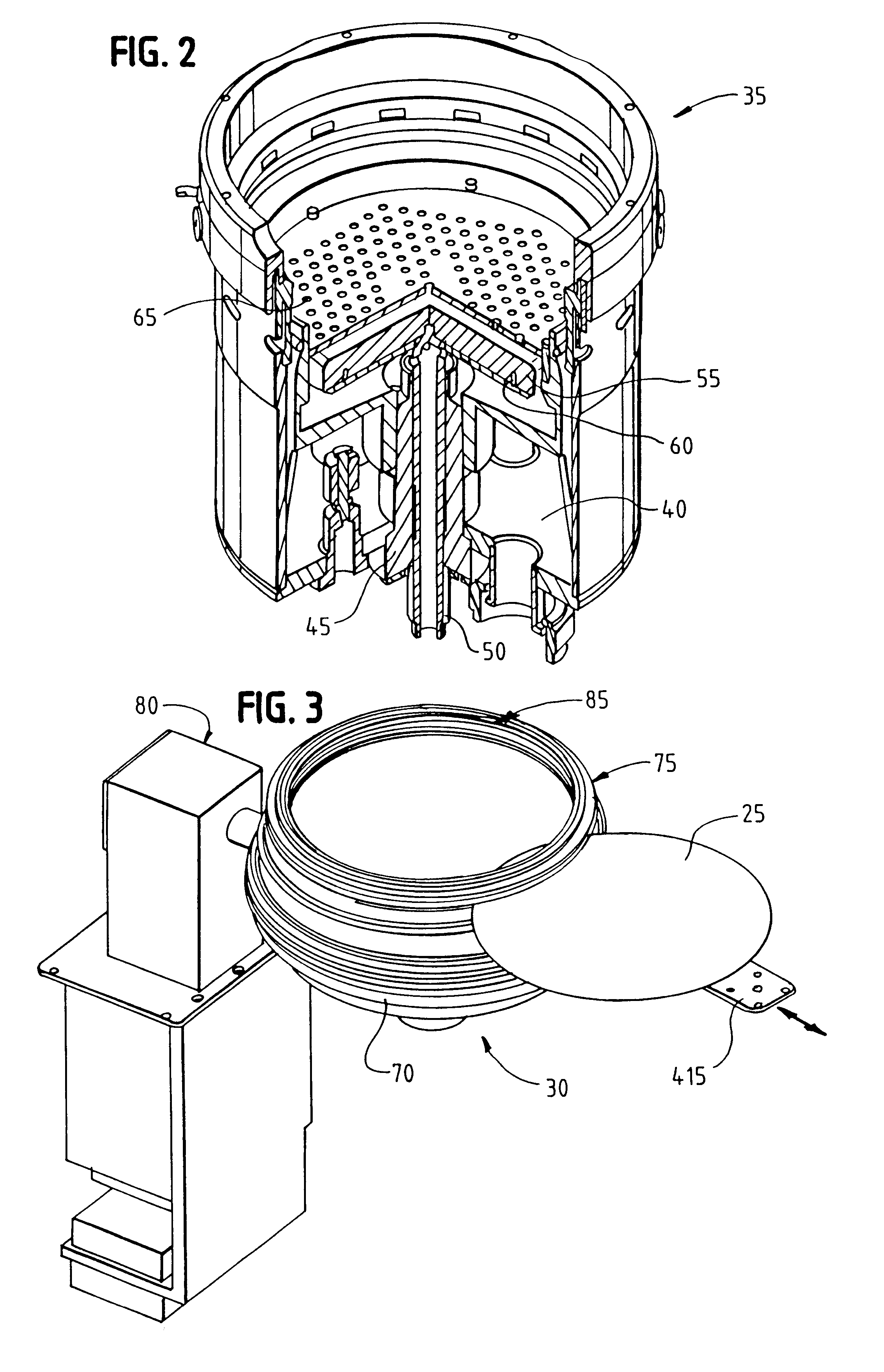
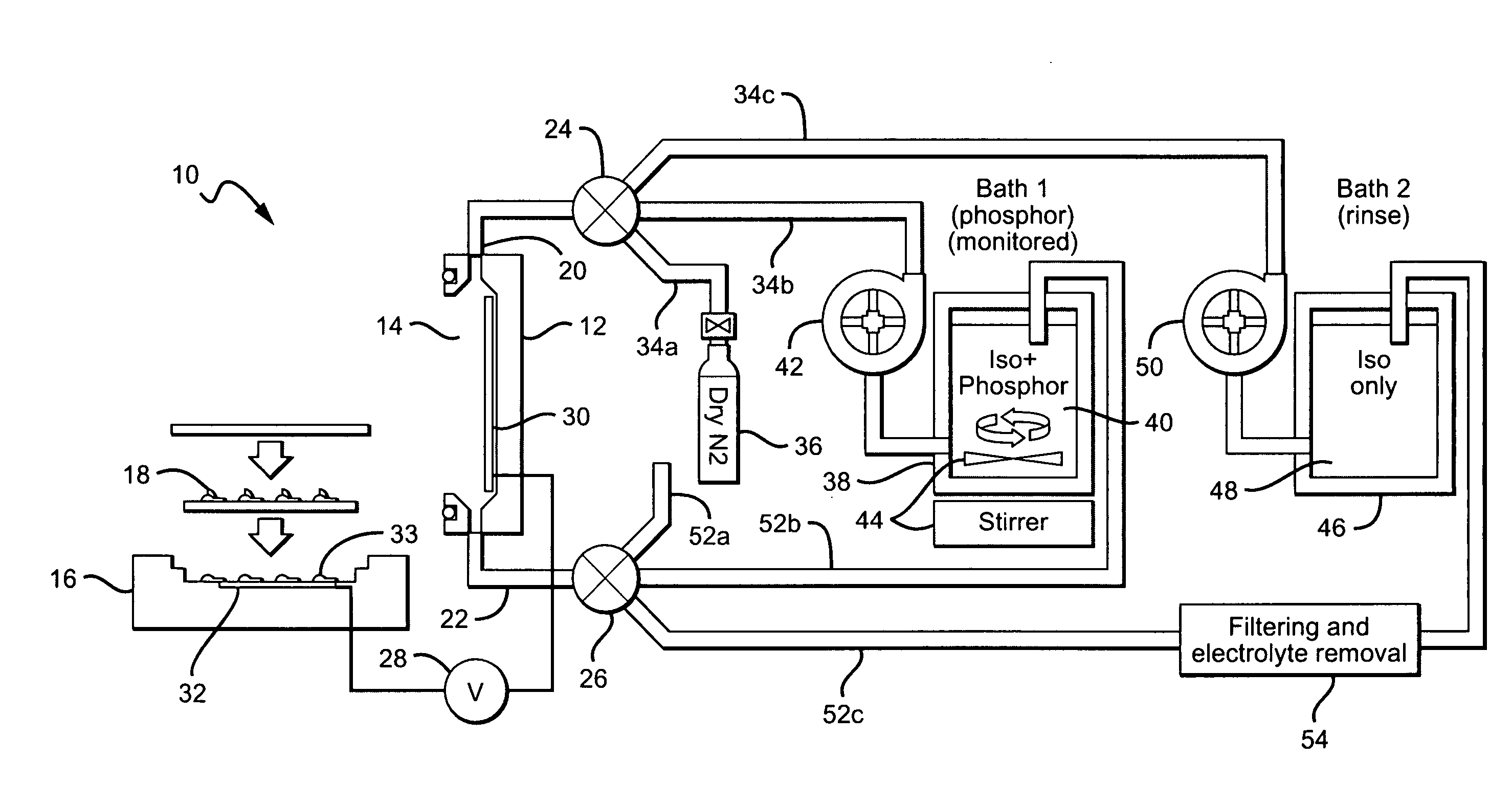
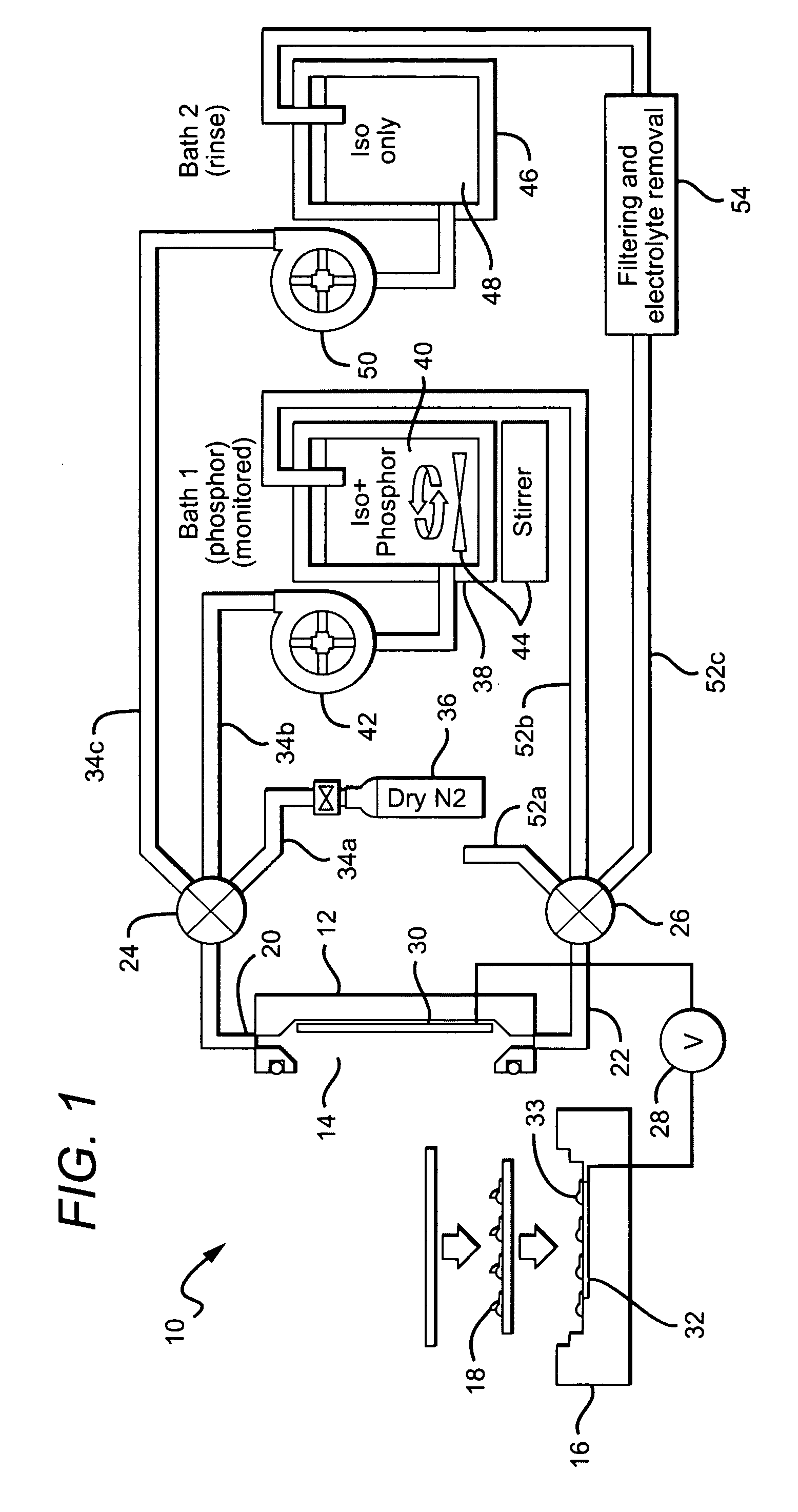
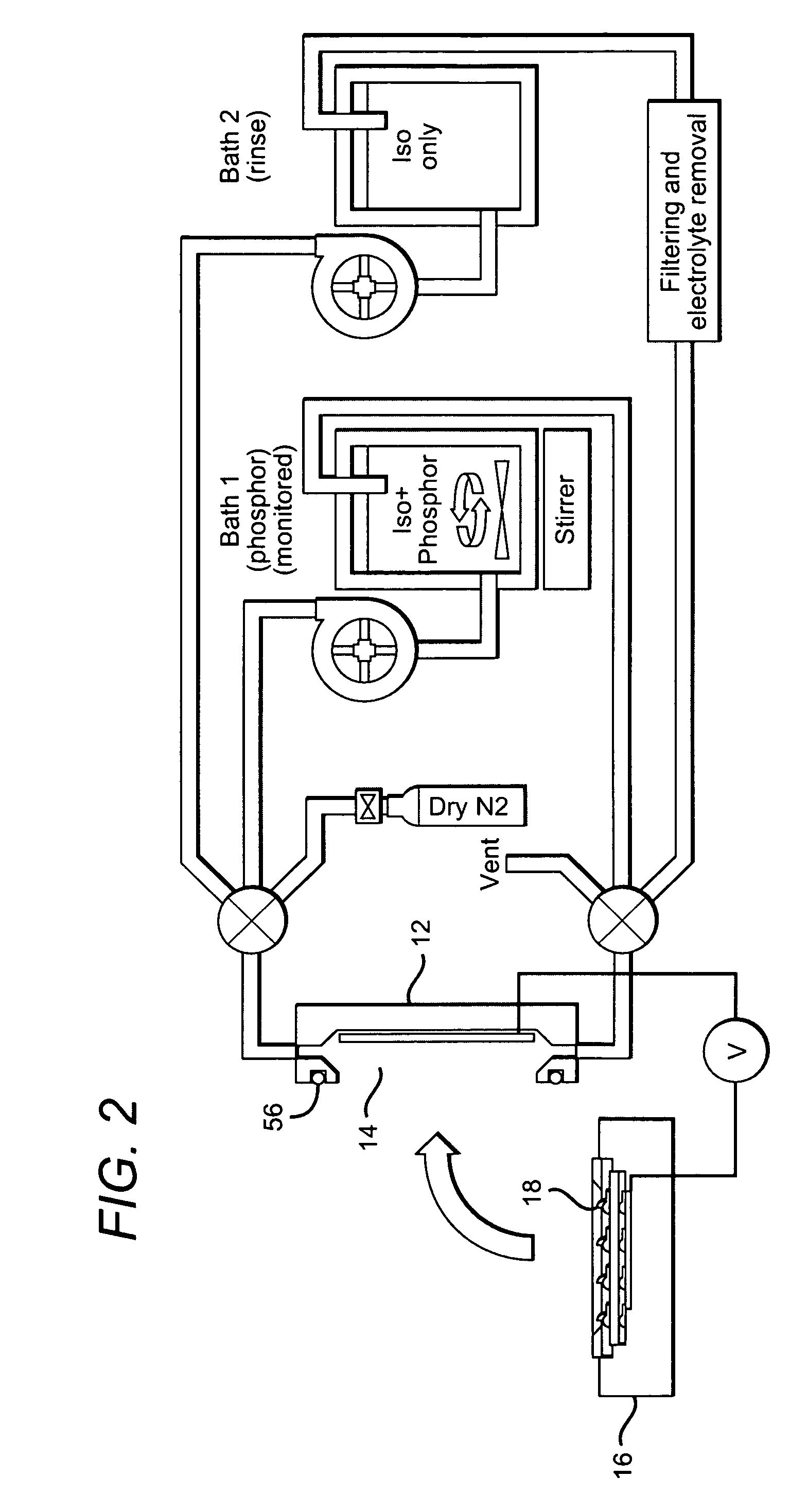
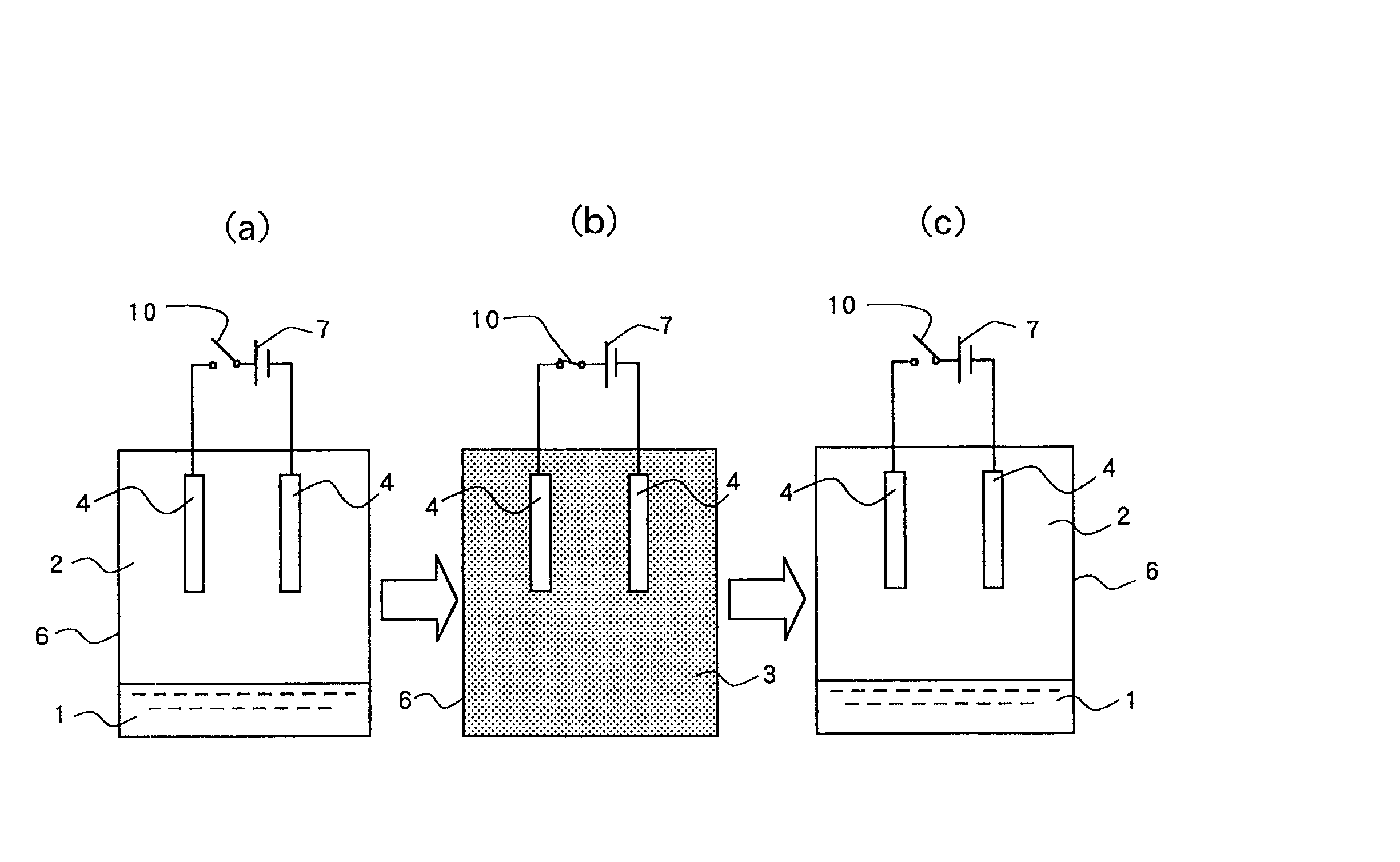
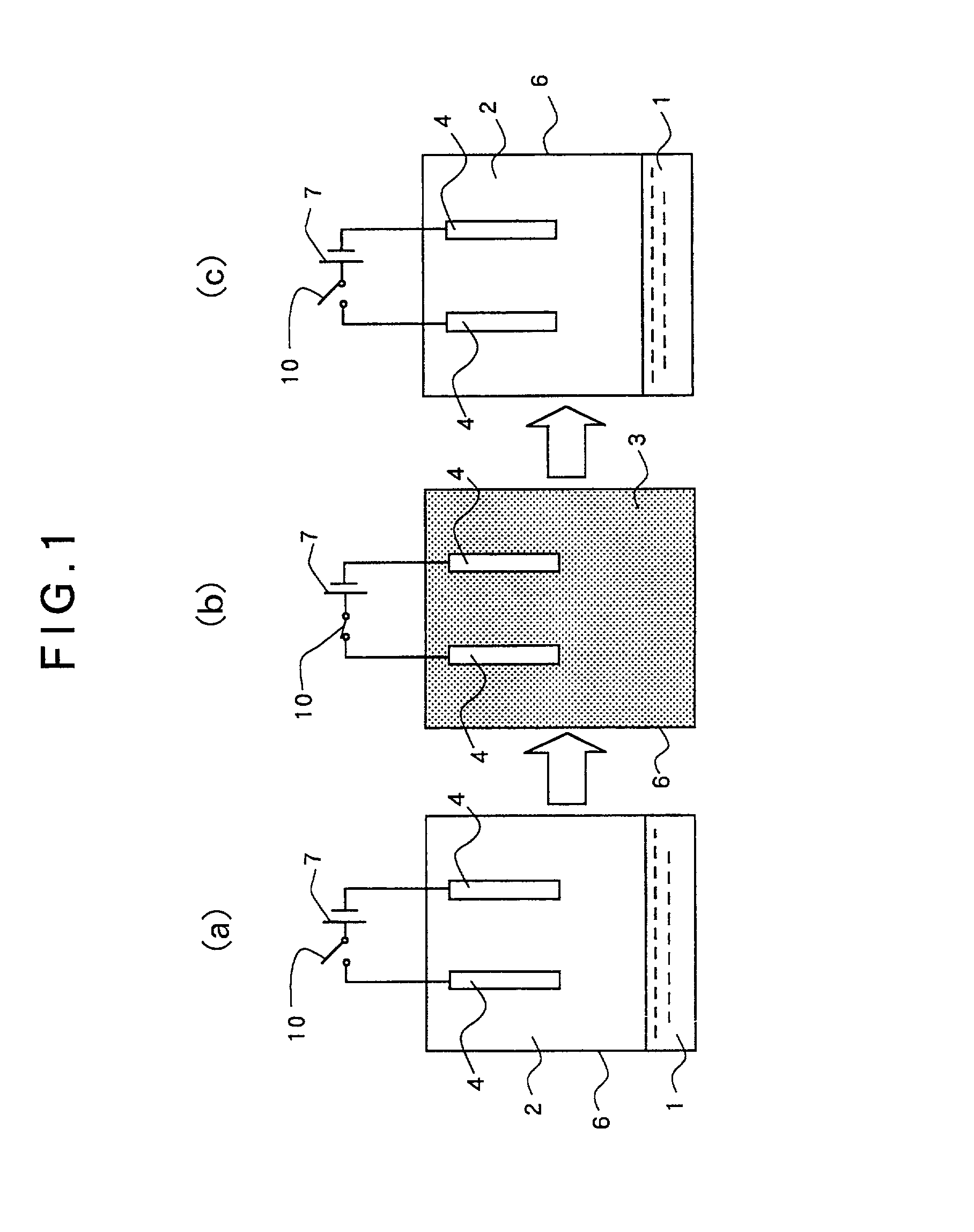
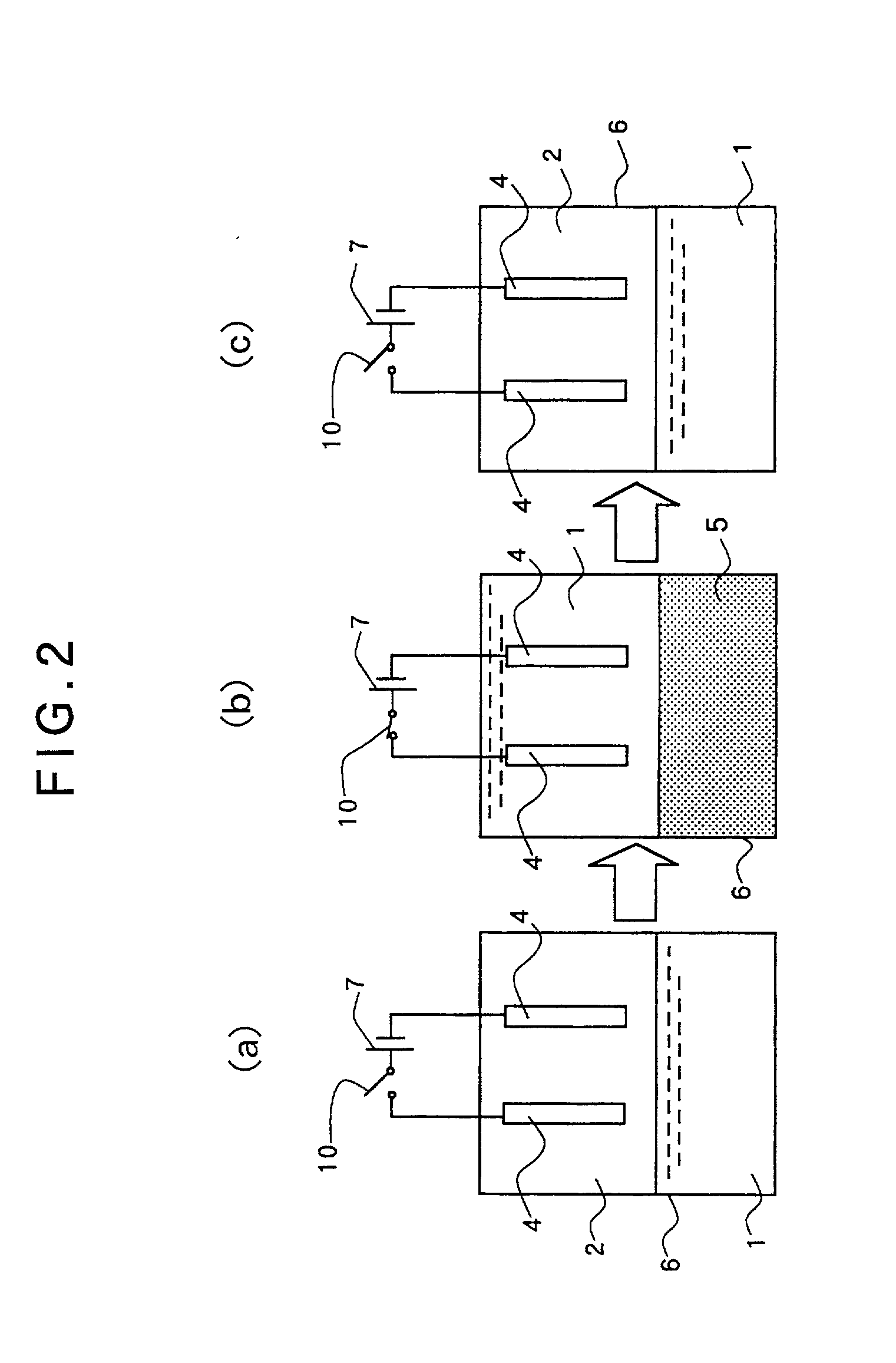
Close loop electrophoretic deposition of semiconductor devices
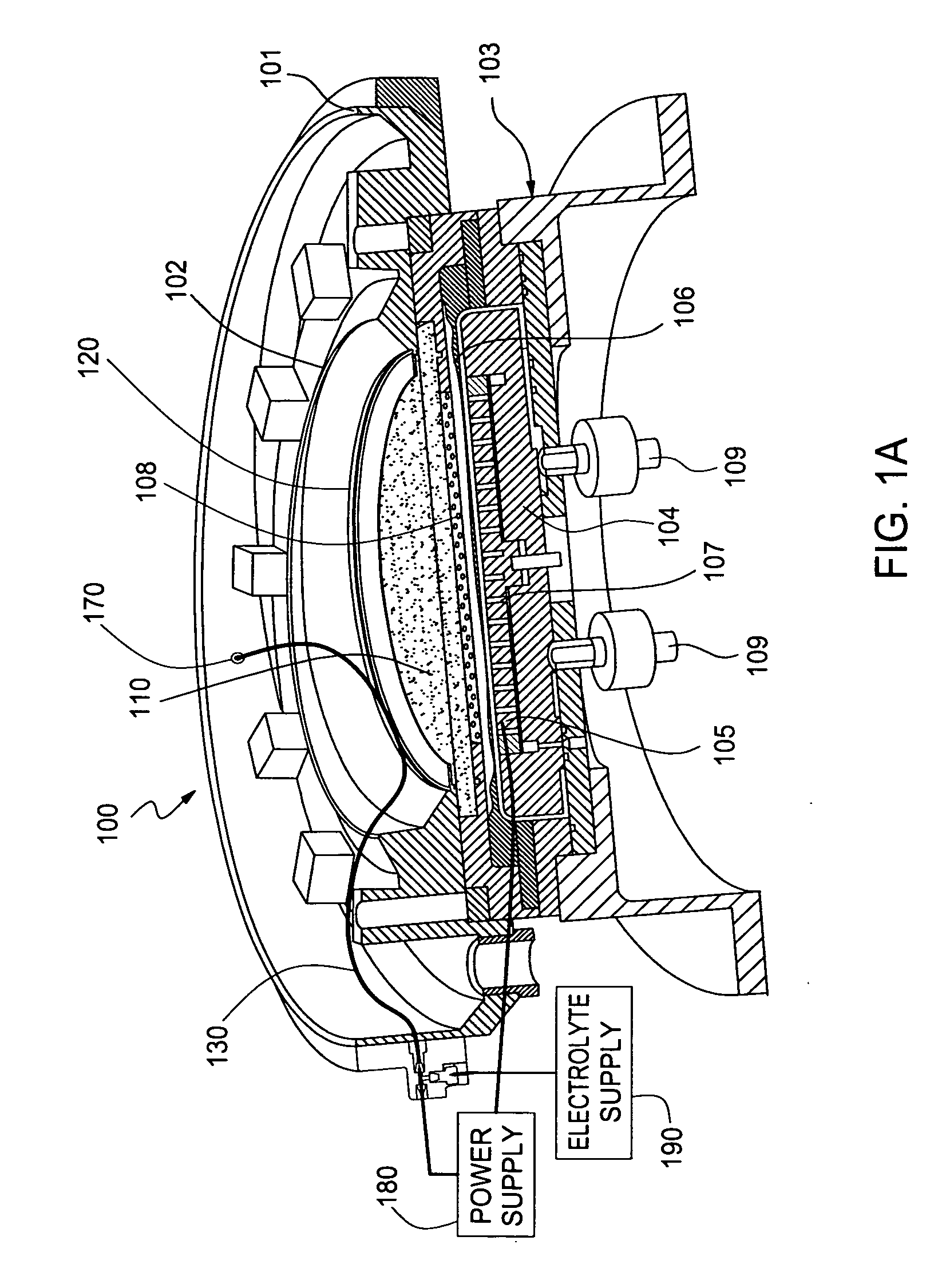
One close loop system and method for electrophoretic deposition (EPD) of phosphor material on light emitting diodes (LEDs). The system comprises a deposition chamber sealed from ambient air. A mixture of phosphor material and solution is provided to the chamber with the mixture also being sealed from ambient air. A carrier holds a batch of LEDs in the chamber with the mixture contacting the areas of the LEDs for phosphor deposition. A voltage supply applies a voltage to the LEDs and the mixture to cause the phosphor material to deposit on the LEDs at the mixture contacting areas.
Owner:CREELED INC
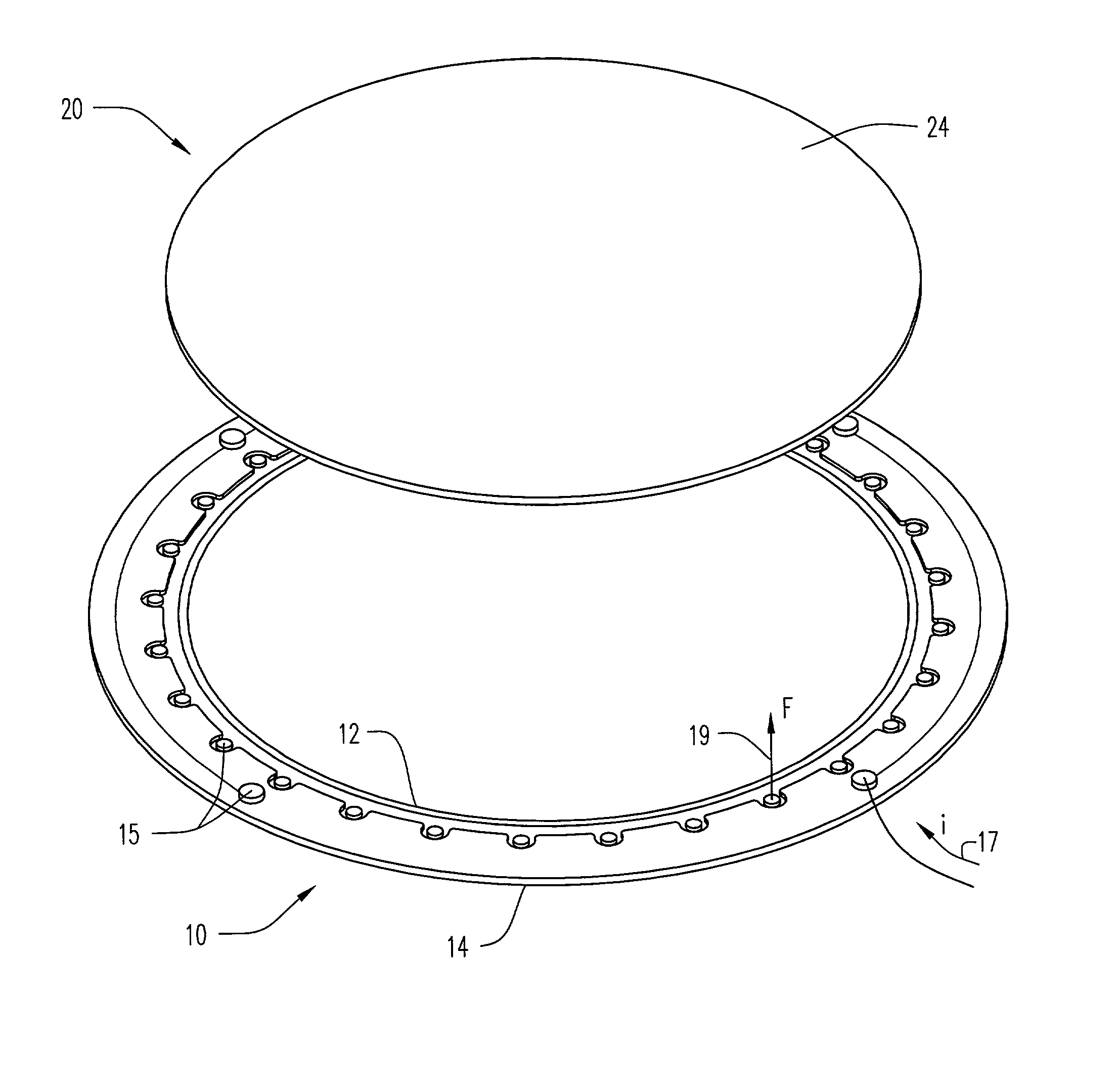
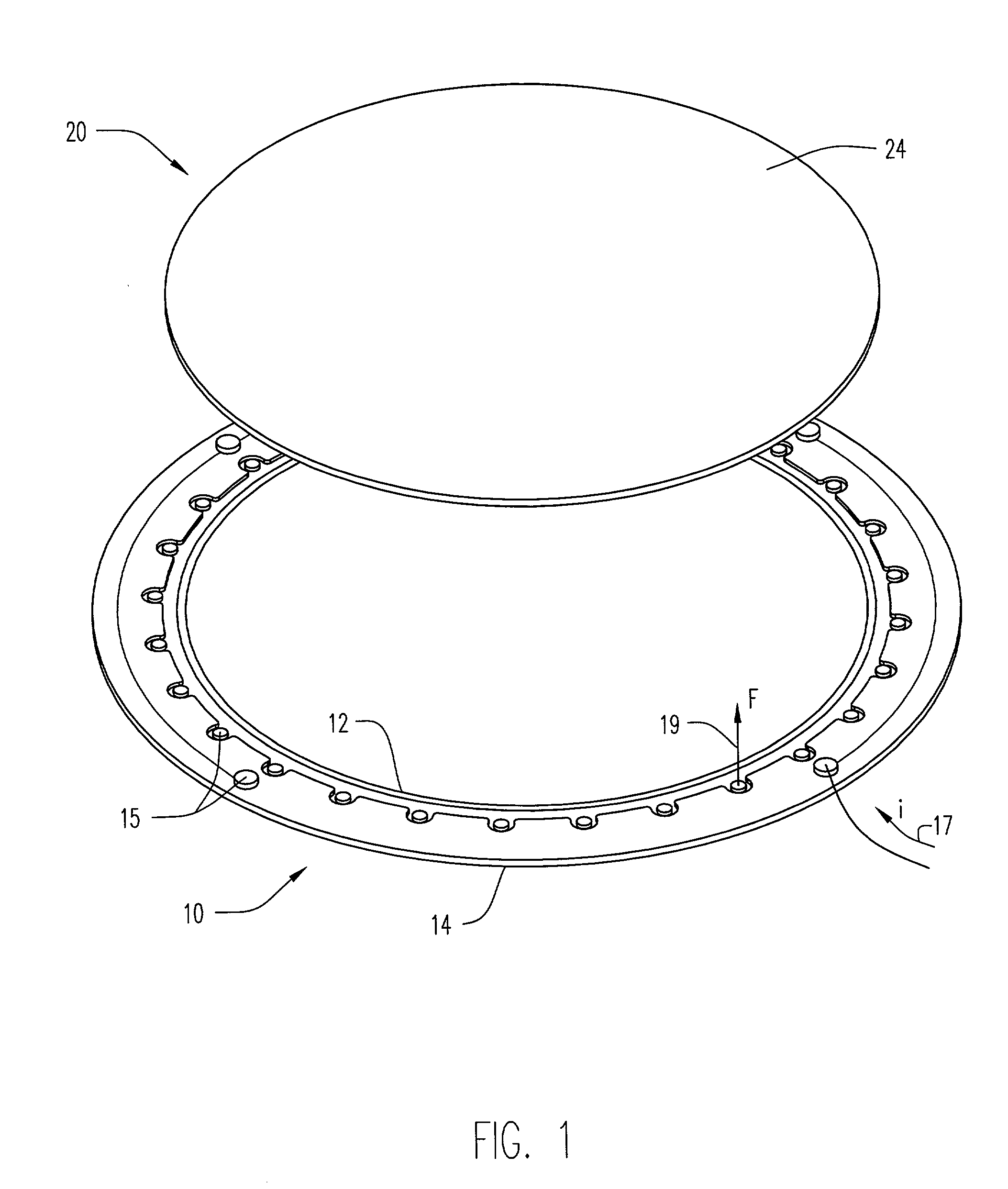
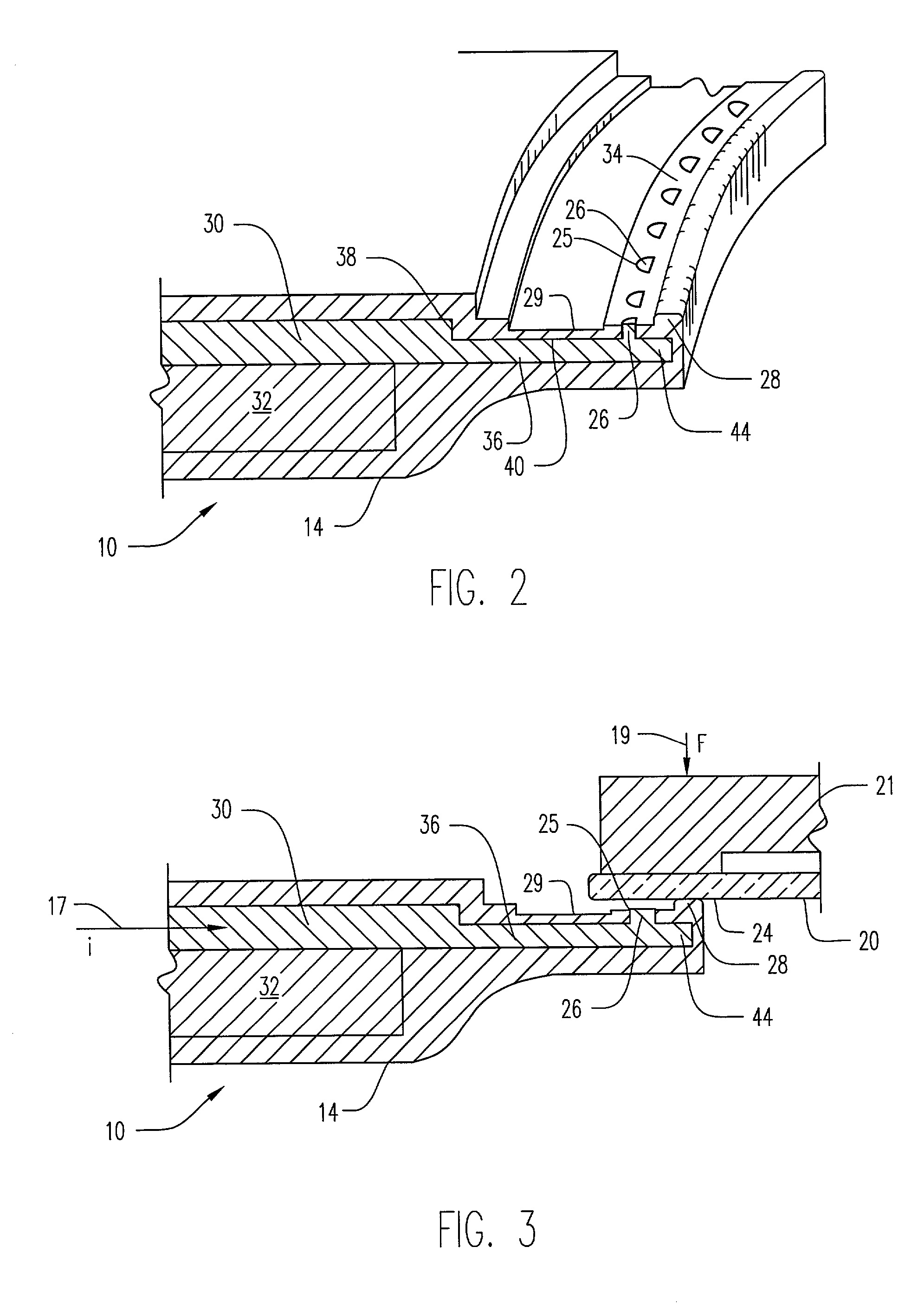
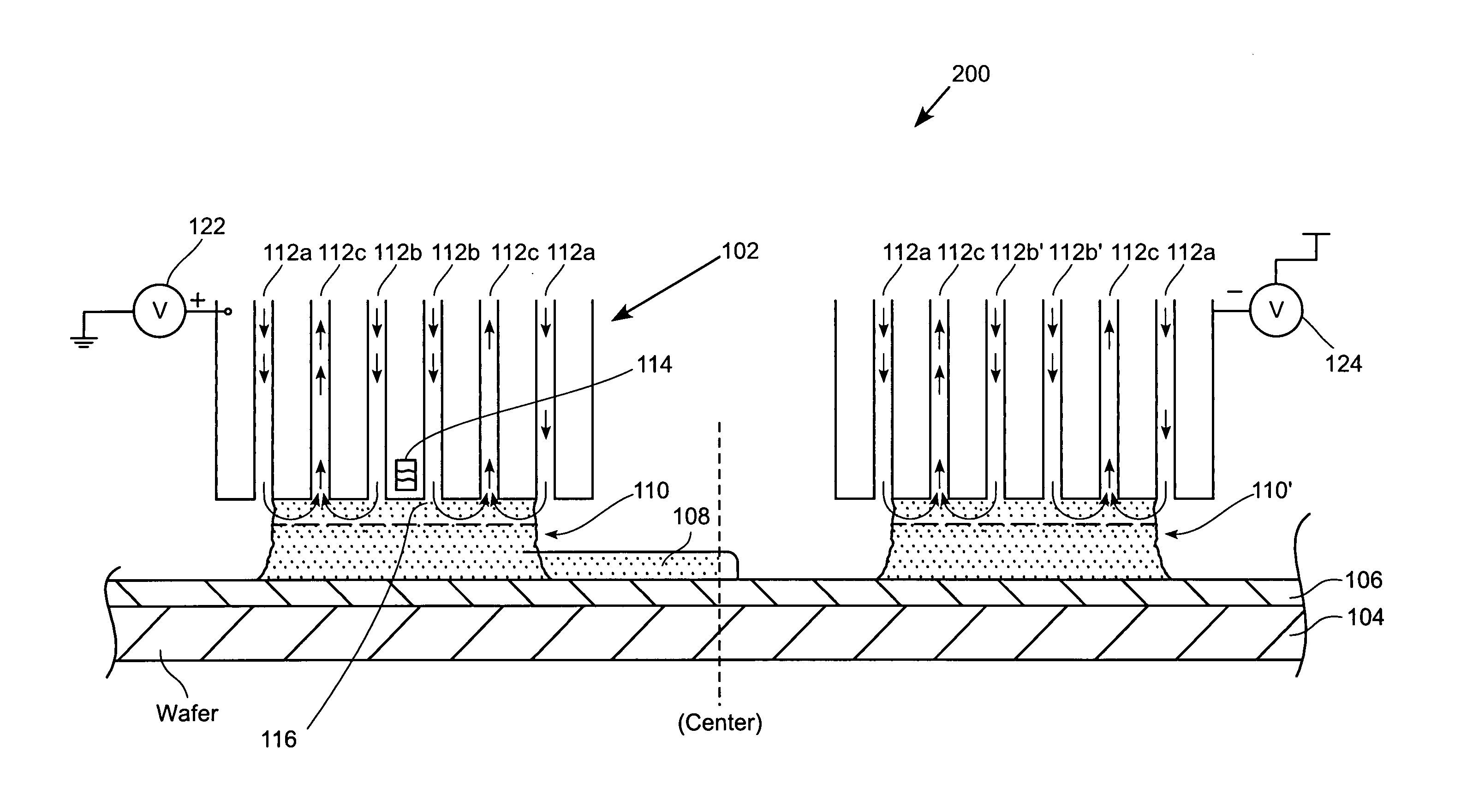
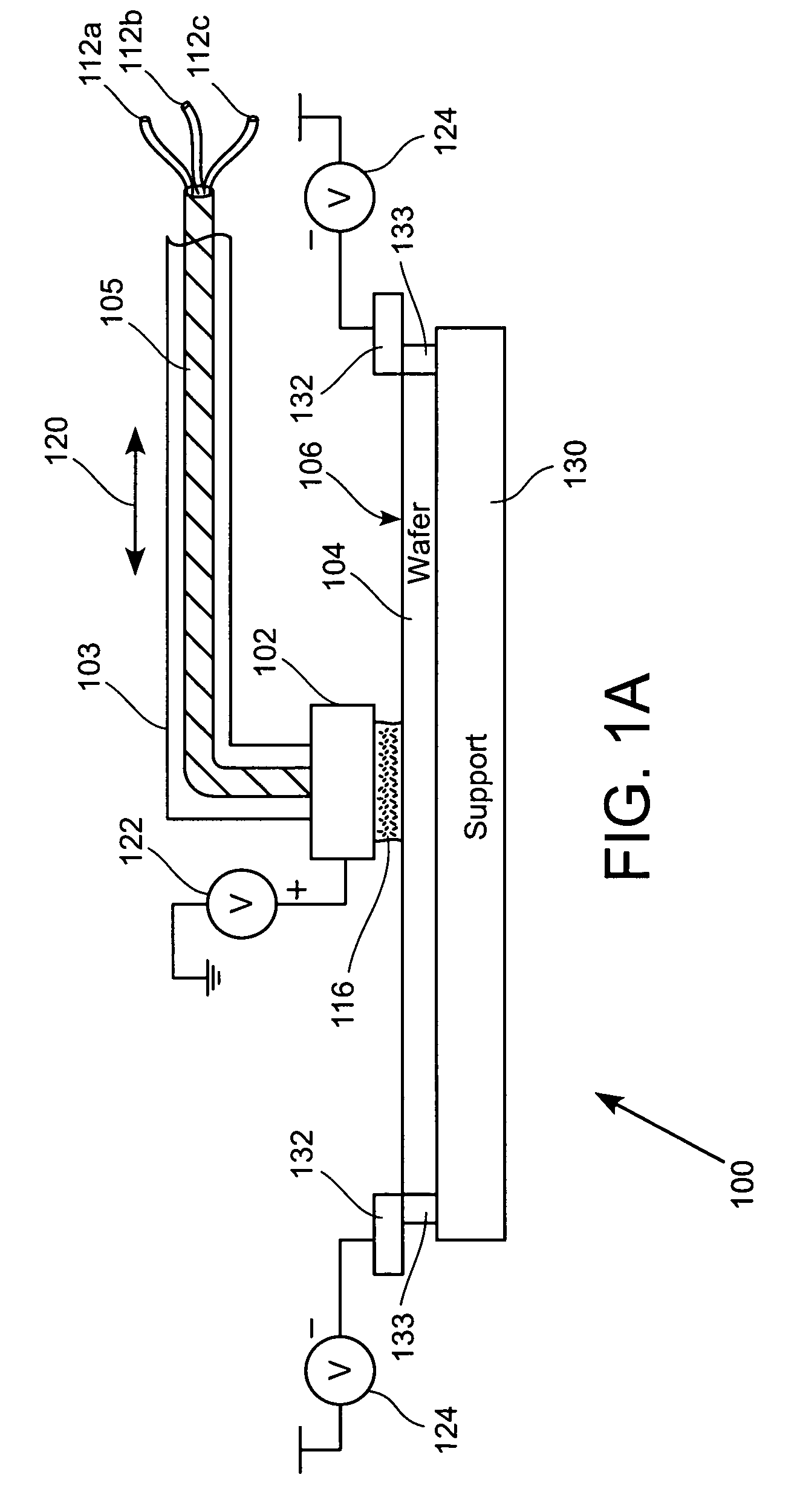
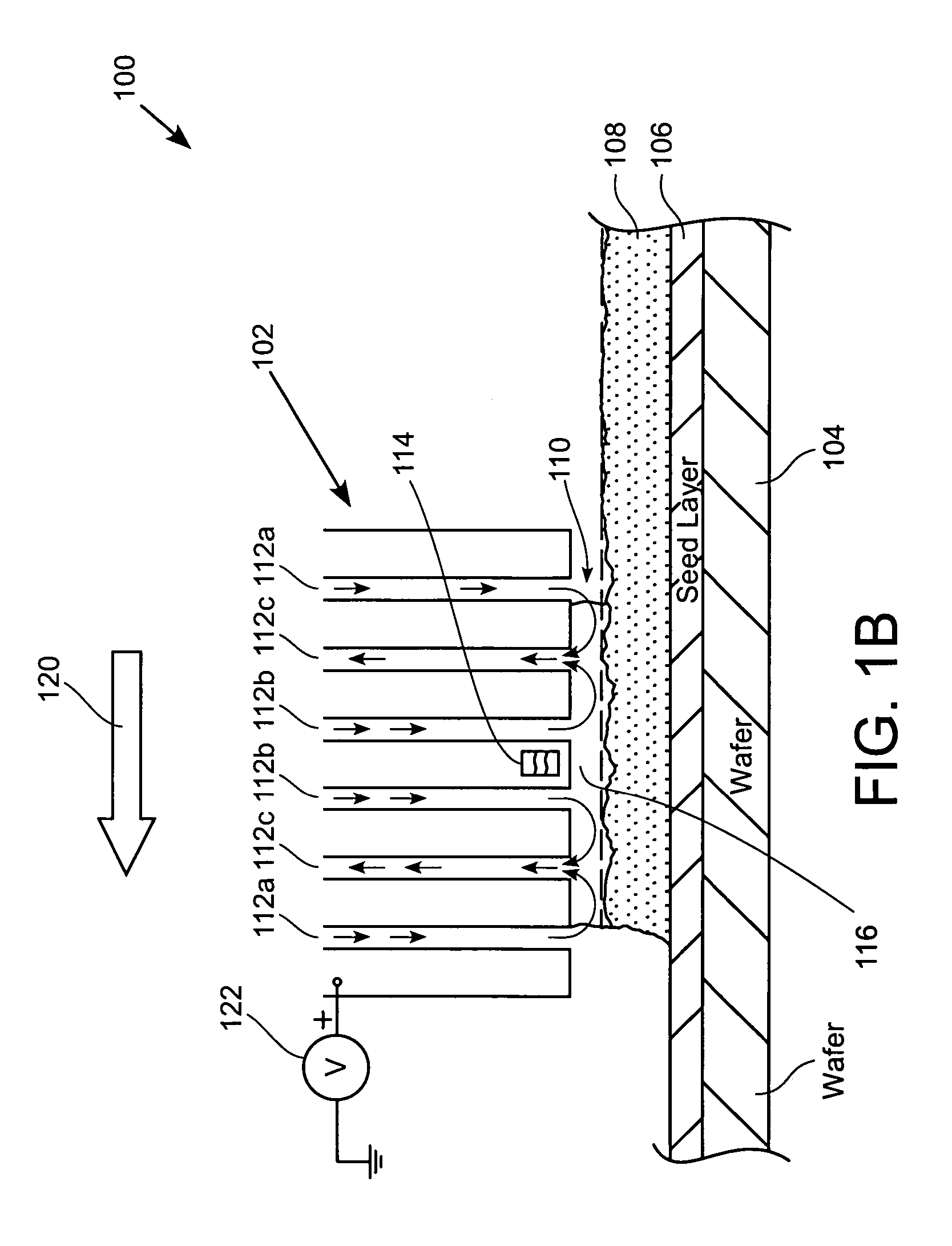
Electroplating workpiece fixture having liquid gap spacer
A fixture for supporting a workpiece during electroplating of a metal upon the workpiece in a conductive electroplating bath includes a non-conductive frame member for receiving the workpiece therein. The fixture further includes a current distribution means having a plurality of contacts. The plurality of contacts is disposed inwardly for providing an equally distributed electrical contact with an outer perimeter region of the workpiece. The workpiece is supported between the frame member and the current distribution means. Lastly, a thief electrode is perimetrically disposed about the workpiece and spaced a prescribed distance from the workpiece by a gap region. During plating of a metal upon the workpiece, the gap region between the thief and the workpiece is filled with the conductive electroplating bath. An electroplating apparatus having a fixture for supporting a workpiece during an electroplating process and a method of supporting the workpiece to be electroplated are also disclosed.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Wet Processing Systems and Methods with Replenishment
InactiveUS20140273497A1Liquid surface applicatorsSequential/parallel process reactionsComputer scienceTreatment system
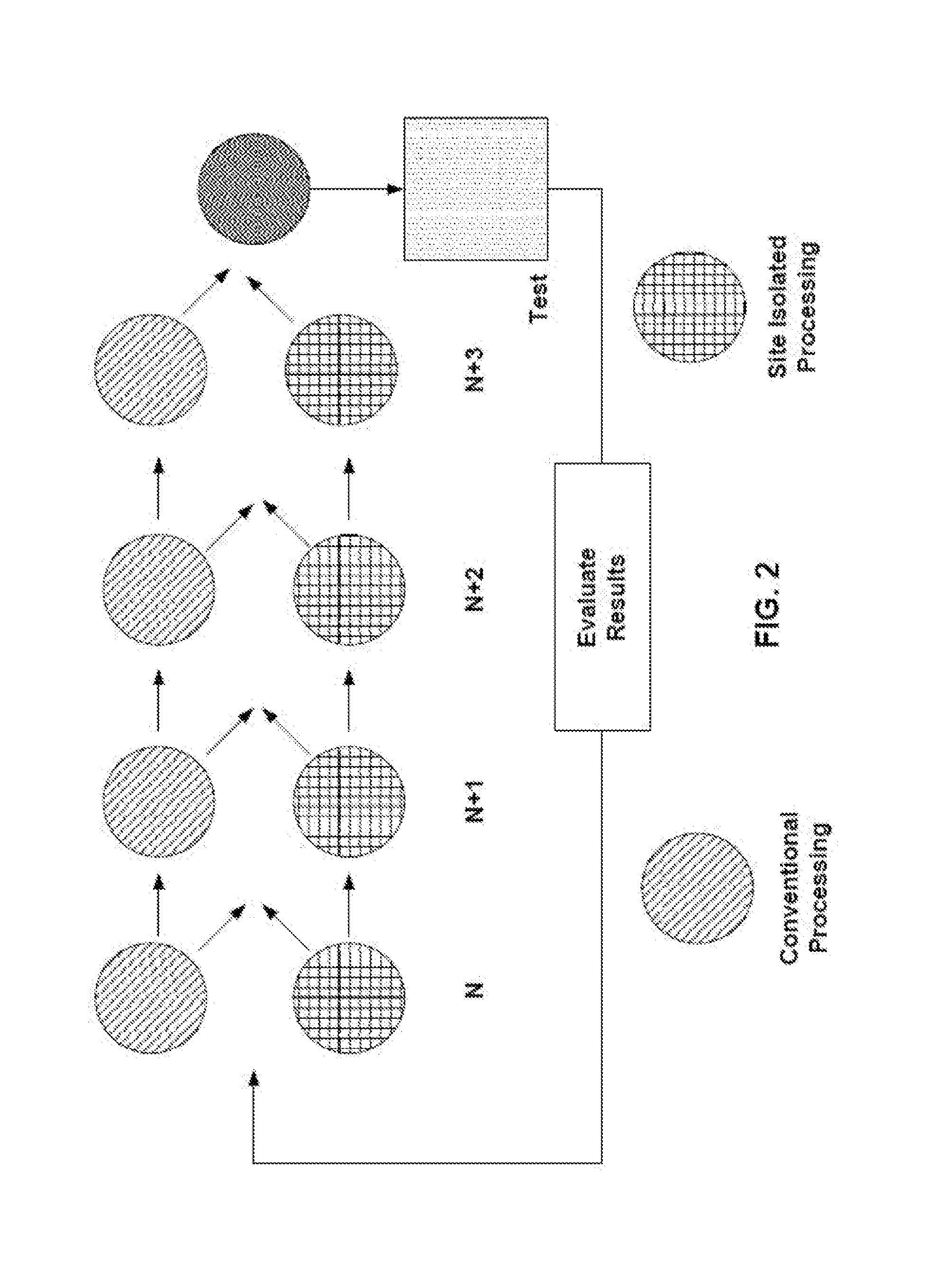
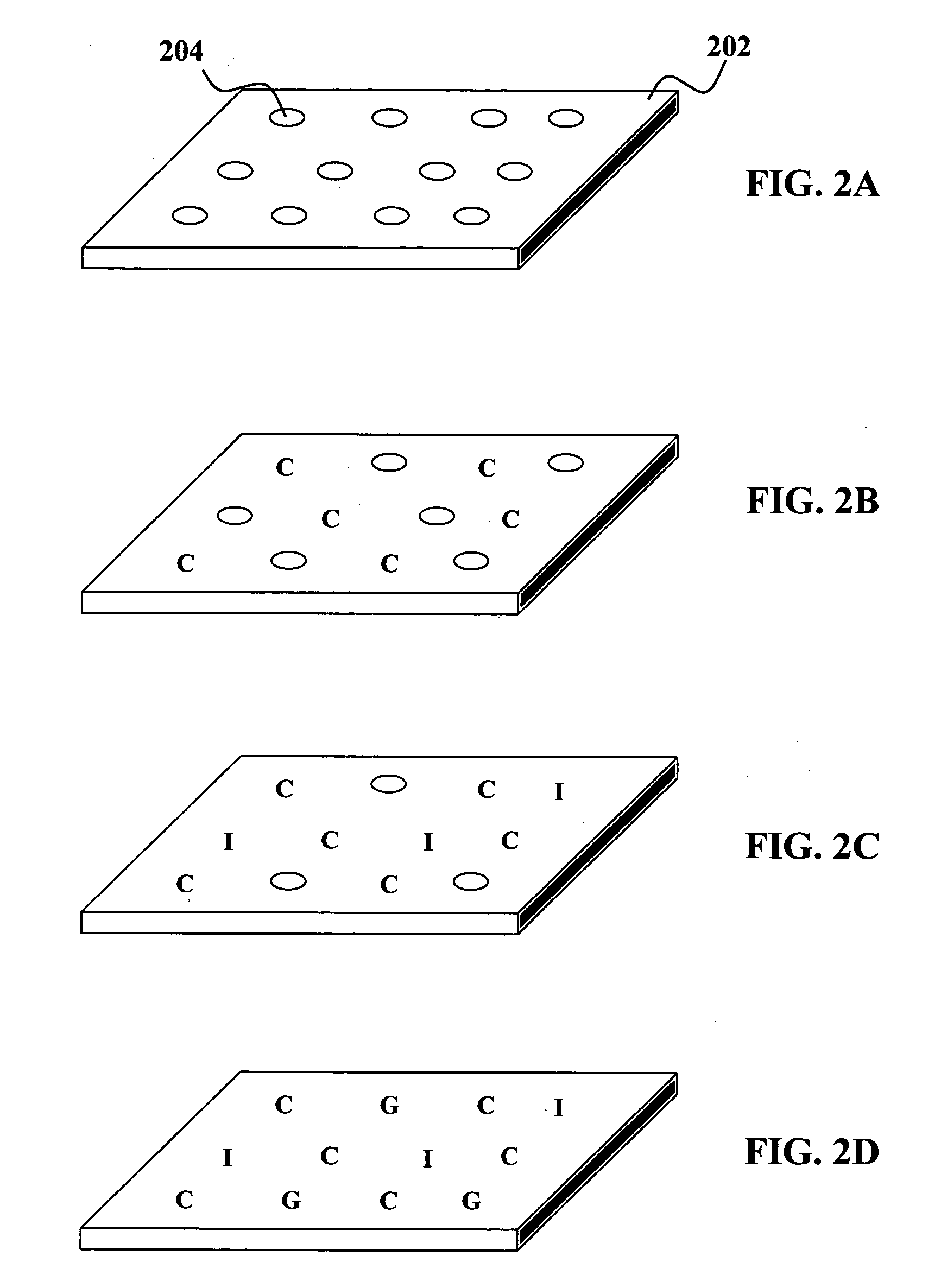
Embodiments provided herein describe systems and methods for processing substrates. A substrate having a plurality of site-isolated regions defined thereon is provided. A plurality of wet processes is simultaneously performed. Each of the plurality of wet processes is performed on one of the plurality of site-isolated regions defined on the substrate. The simultaneously performing includes exposing each of the plurality of site-isolated regions to one of a plurality of wet processing formulations. Each of the plurality of wet processing formulations includes a component. The respective component is added to at least some of the plurality of wet processing formulations during the exposing. A processing condition is varied between at least two of the plurality of wet processes in a combinatorial manner.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Formation of CIGS absorber layer materials using atomic layer deposition and high throughput surface treatment
An absorber layer may be formed on on a substrate using atomic layer deposition reactions. An absorber layer containing elements of groups IB, IIIA and VIB may be formed by placing a substrate in a treatment chamber and performing atomic layer deposition of a group IB element and / or one or more group IIIA elements from separate sources onto a substrate to form a film. A group VIA element is then incorporated into the film and annealed to form the absorber layer. The absorber layer may be greater than about 25 nm thick. The substrate may be coiled into one or more coils in such a way that adjacent turns of the coils do not touch one another. The coiled substrate may be placed in a treatment chamber where substantially an entire surface of the one or more coiled substrates may be treated by an atomic layer deposition process. One or more group IB elements and / or one or more group IIIA elements may be deposited onto the substrate in a stoichiometrically controlled ratio by atomic layer deposition using one or more self limiting reactions.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Methods and apparatus for holding and positioning semiconductor workpieces during electropolishing and/or electroplating of the workpieces
A wafer chuck assembly for holding a wafer during electroplating and / or electropolishing of the wafer includes a wafer chuck for receiving the wafer. The wafer chuck assembly also includes an actuator assembly for moving the wafer chuck between a first and a second position. When in the first position, the wafer chuck is opened. When in the second position, the wafer chuck is closed.
Owner:ACM RES
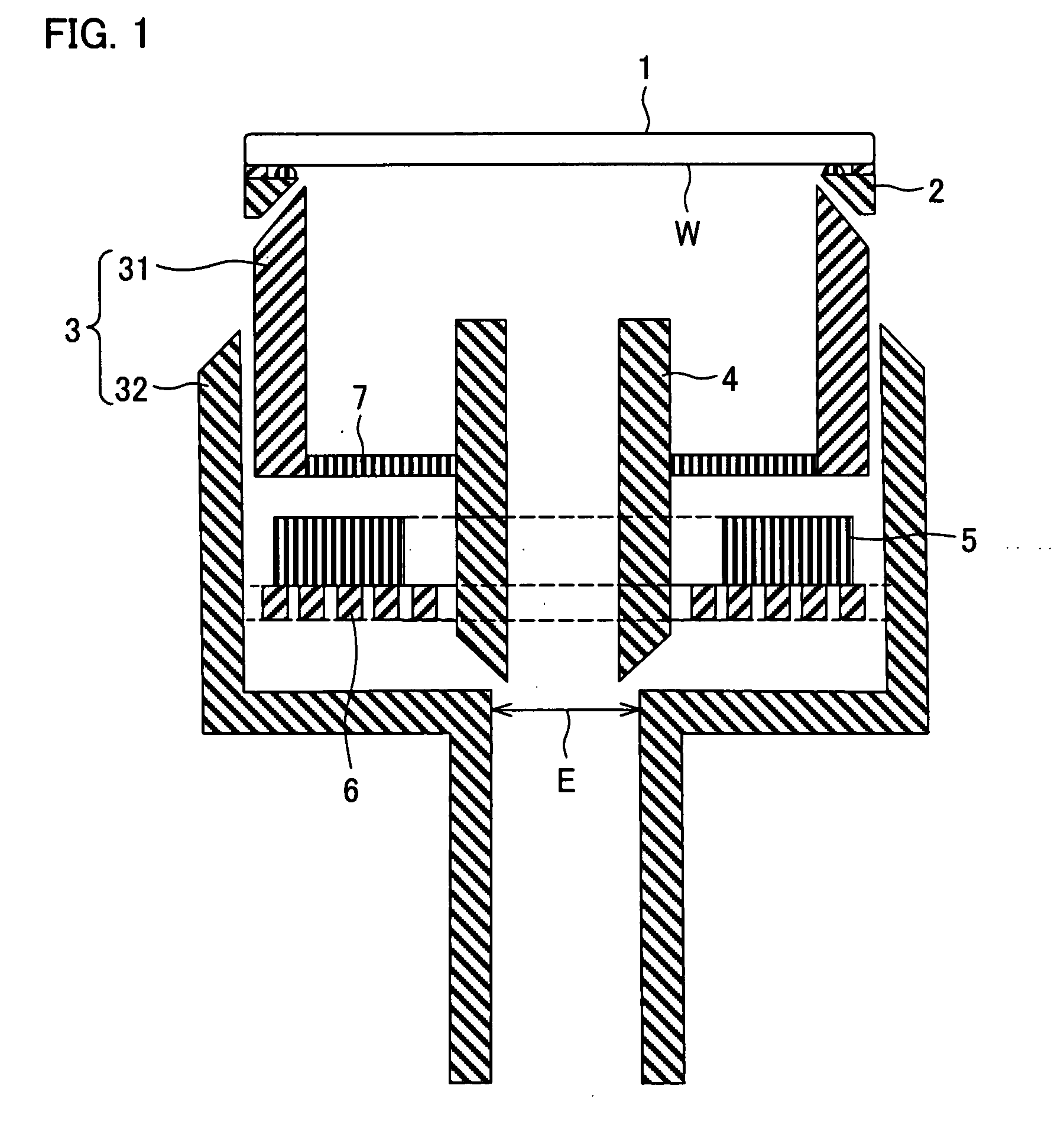
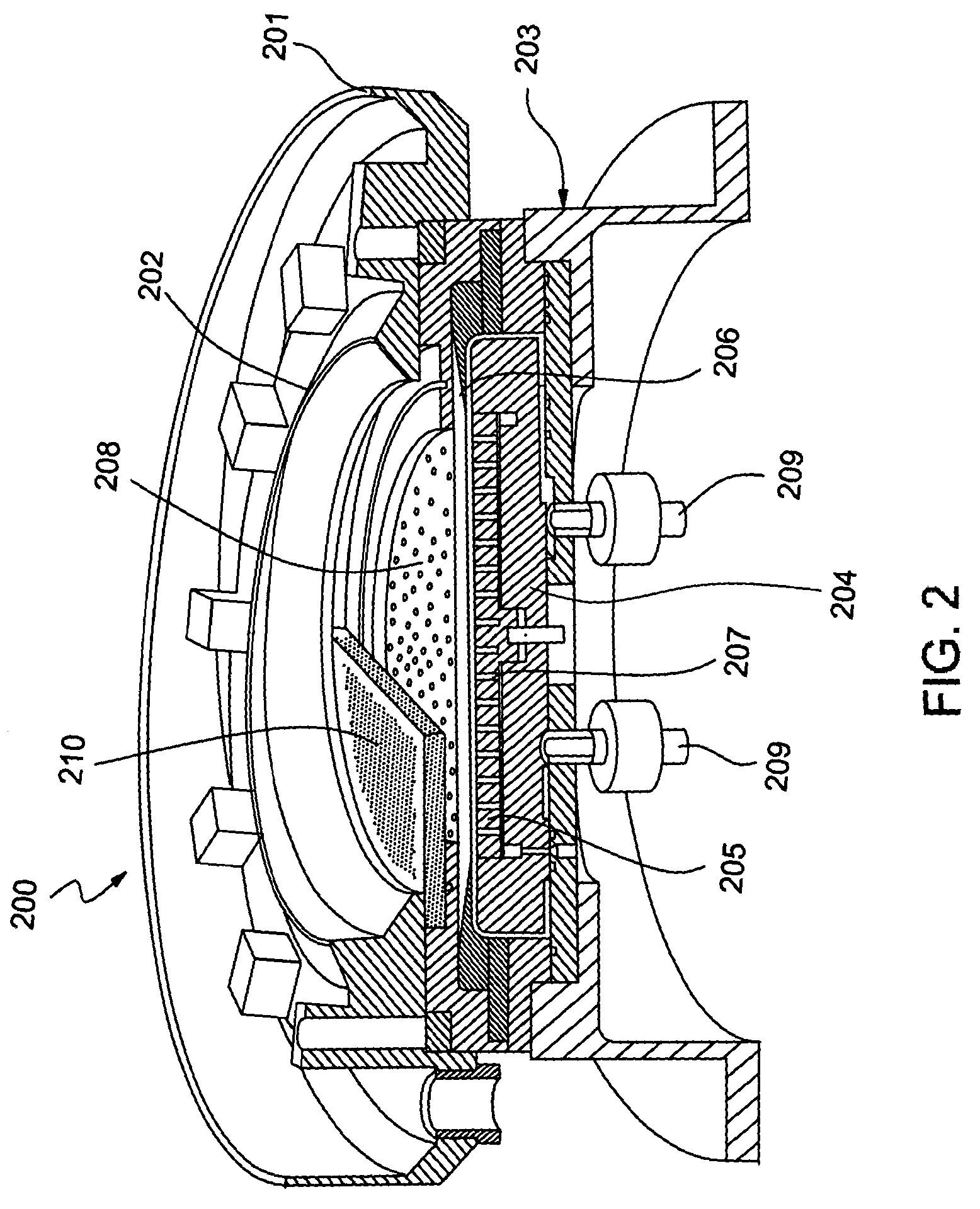
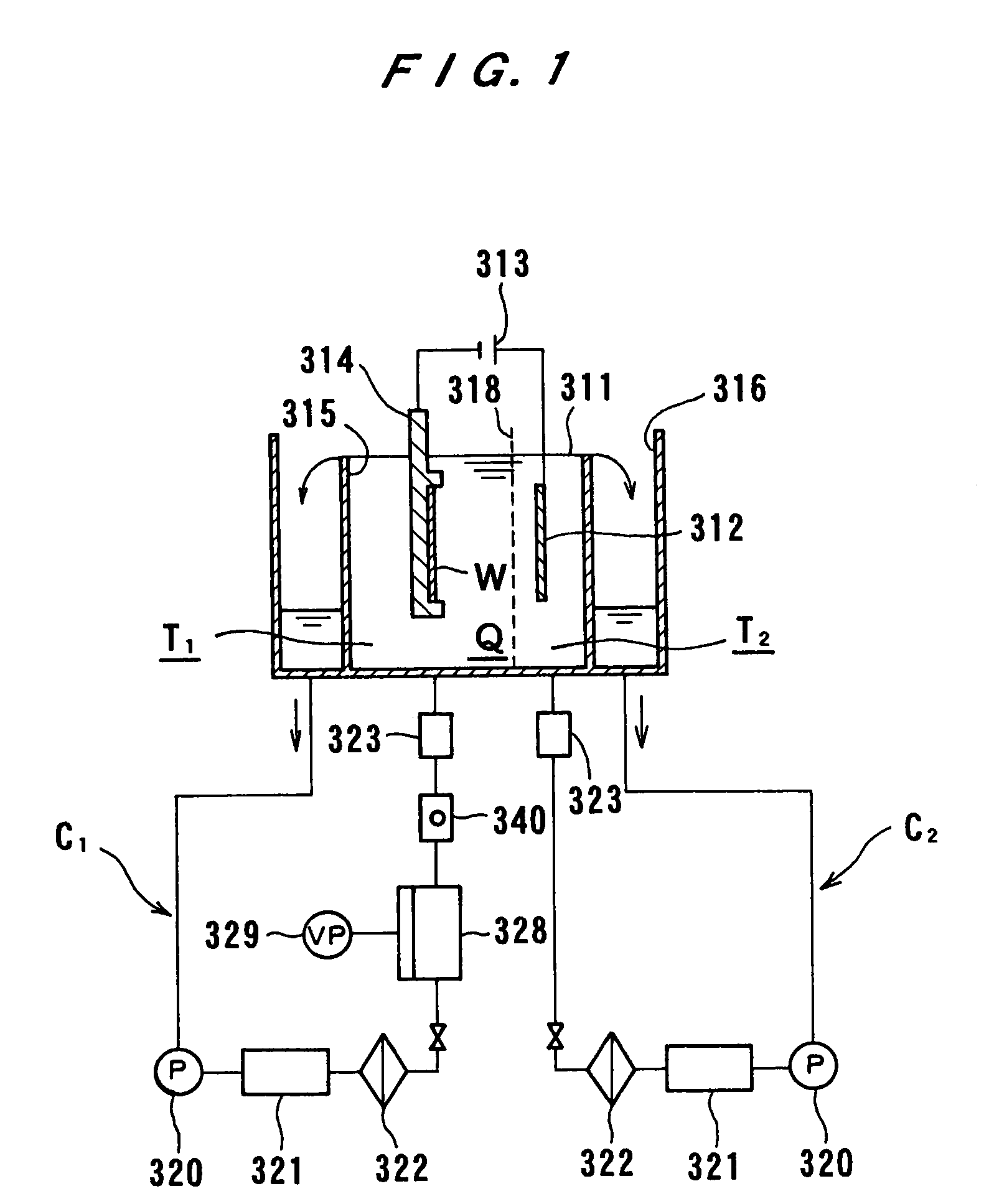
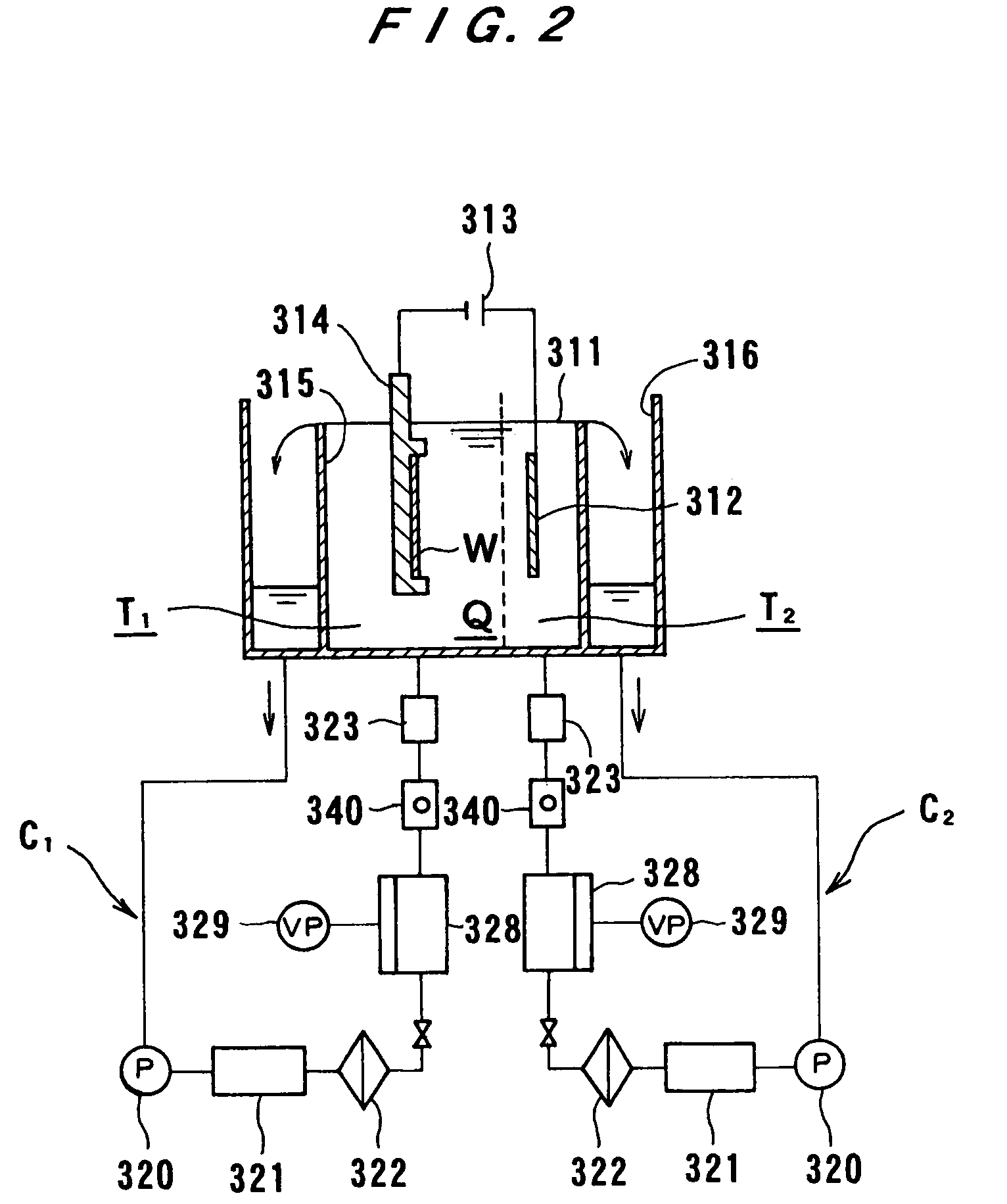
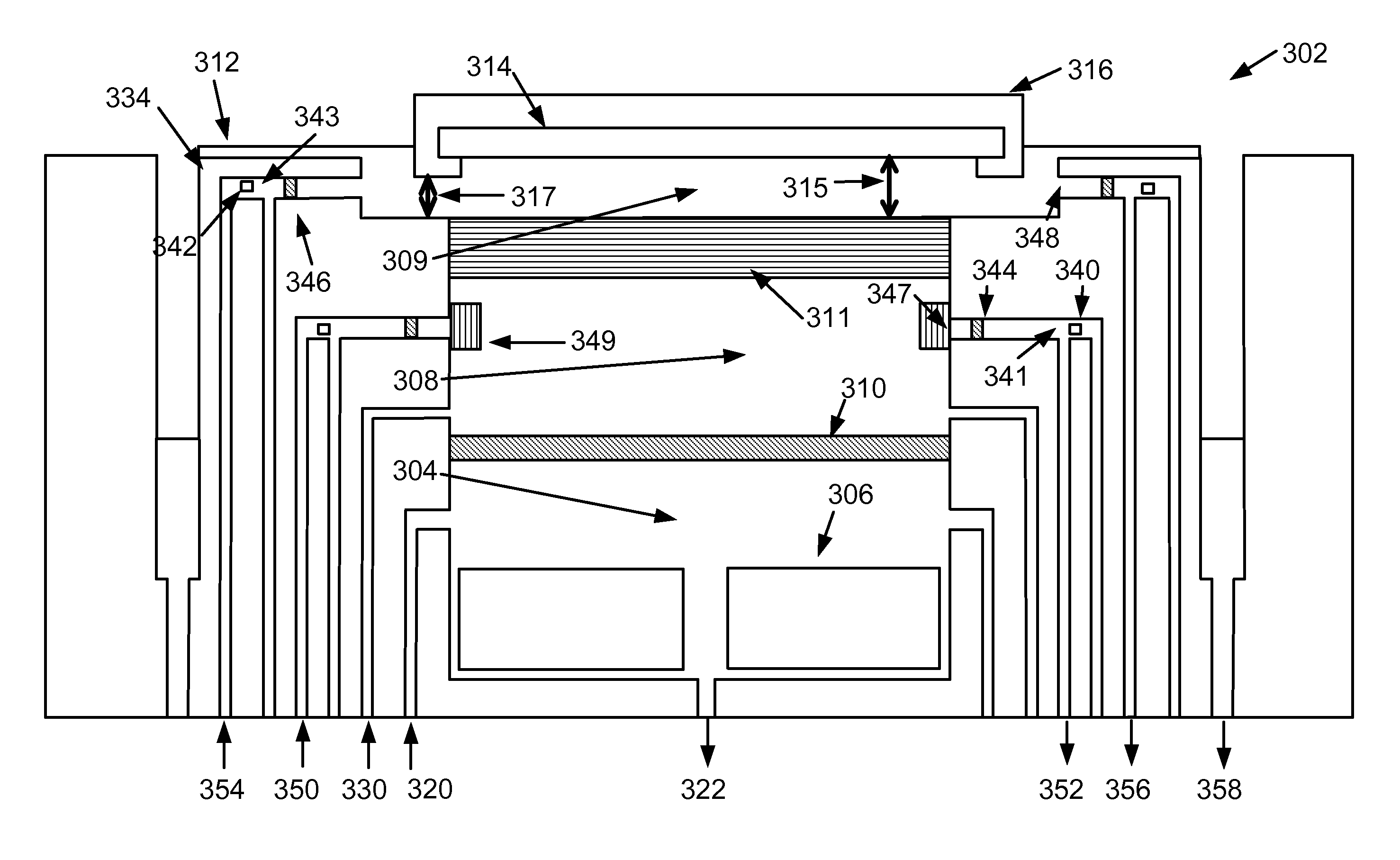
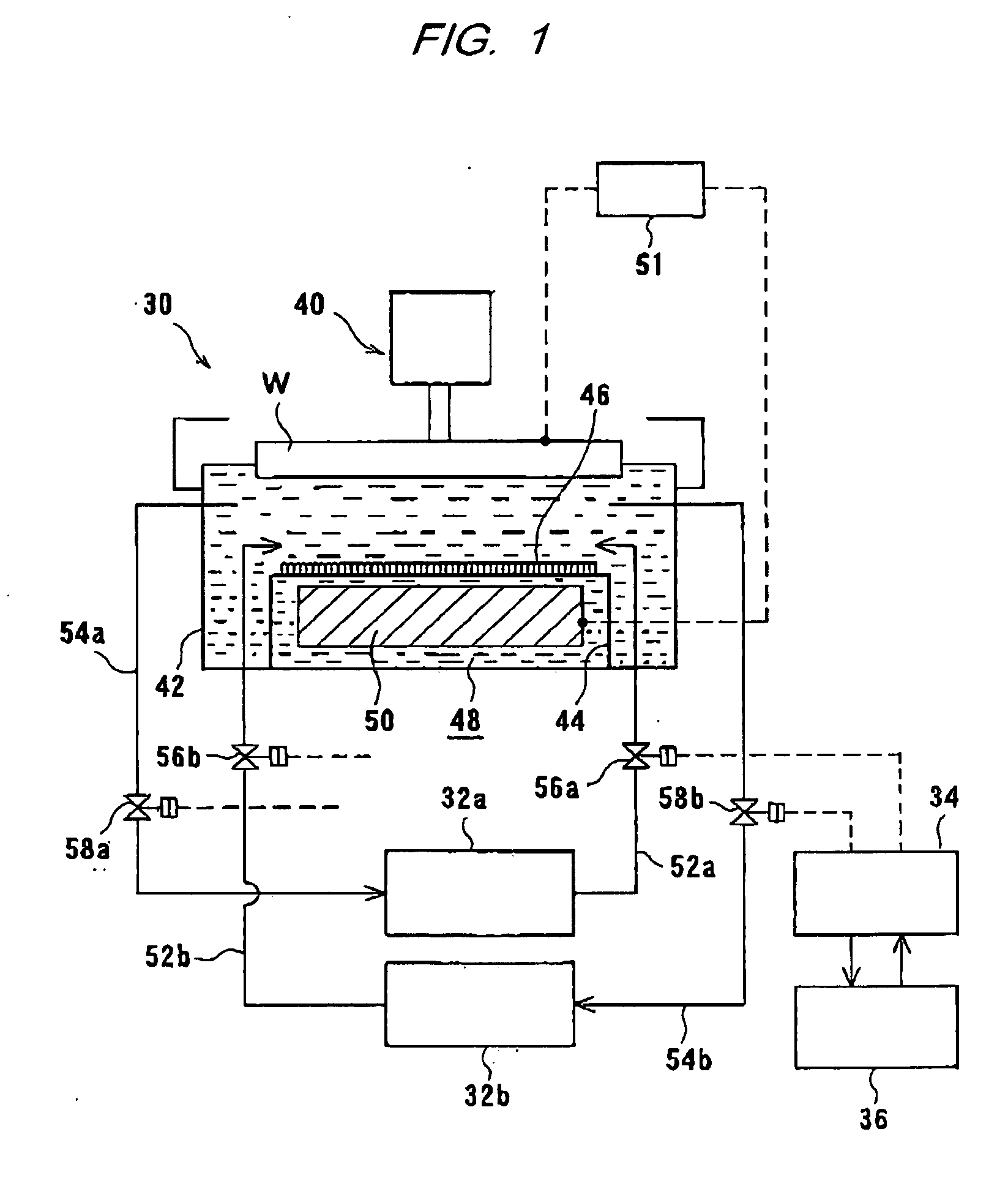
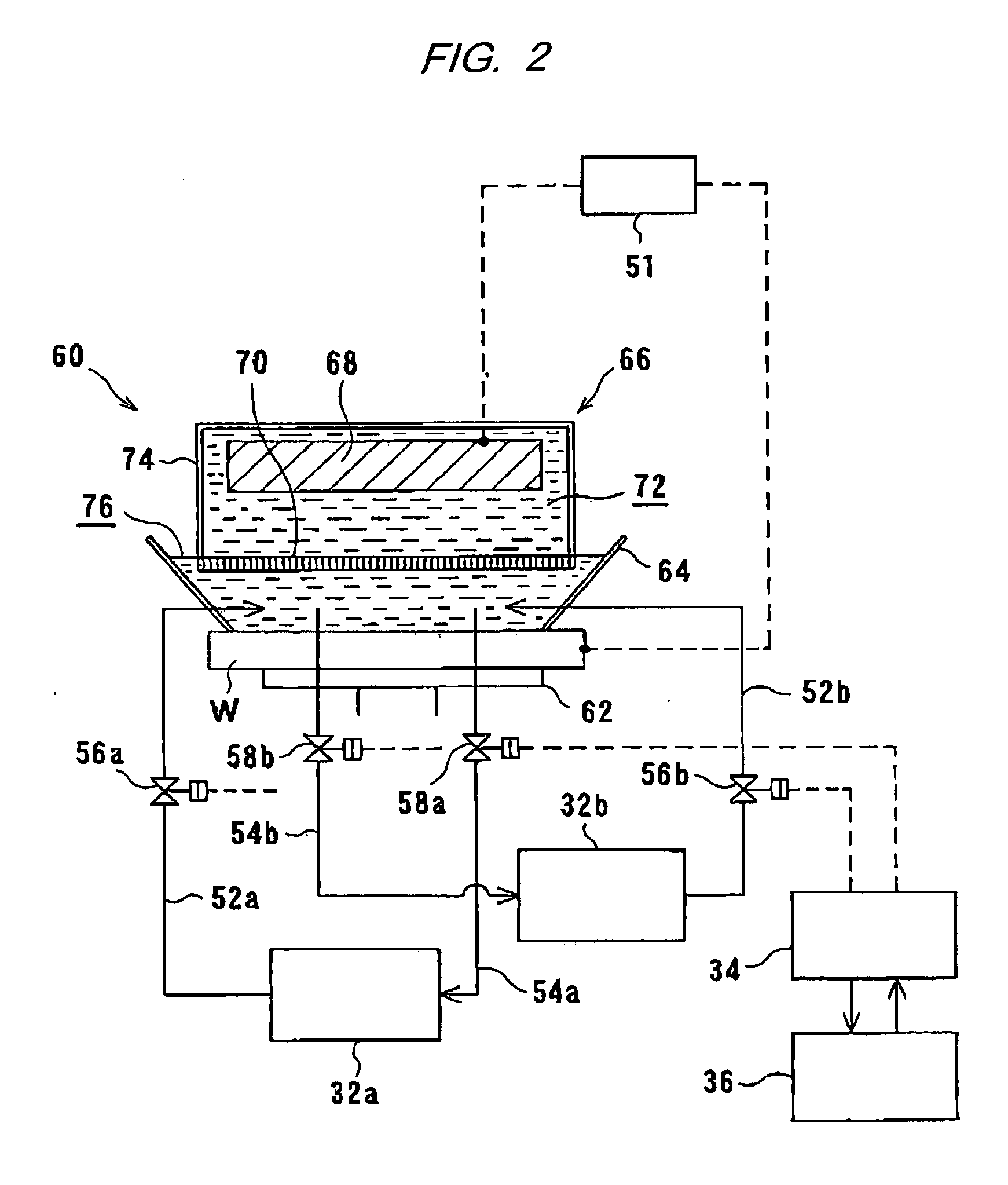
Plating Device, Plating Method, Semiconductor Device, And Method For Manufacturing Semiconductor Device
An object of the present invention is to provide a face-down type jet plating device in which deterioration in plating quality due to minute solid foreign matters derived from a black film etc. is prevented without impairing operativity. The plating device is designed such that a partition (7) is provided between a semiconductor wafer (1) and an anode (5) so that the anode (5) and the semiconductor wafer (7) are separated from each other and a plating tank (100) is divided into a substrate-to-be-plated chamber and an anode chamber.
Owner:SHARP KK
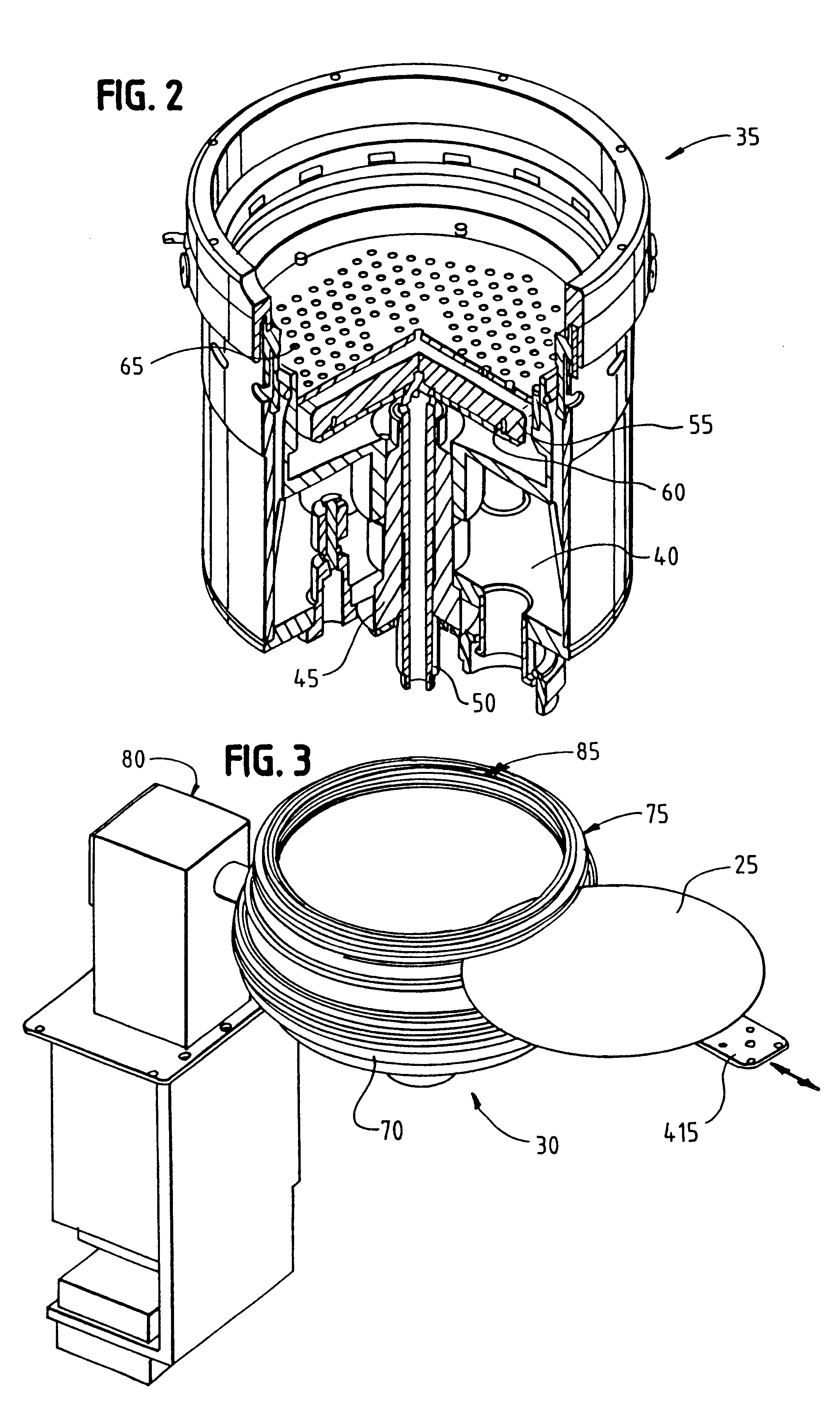
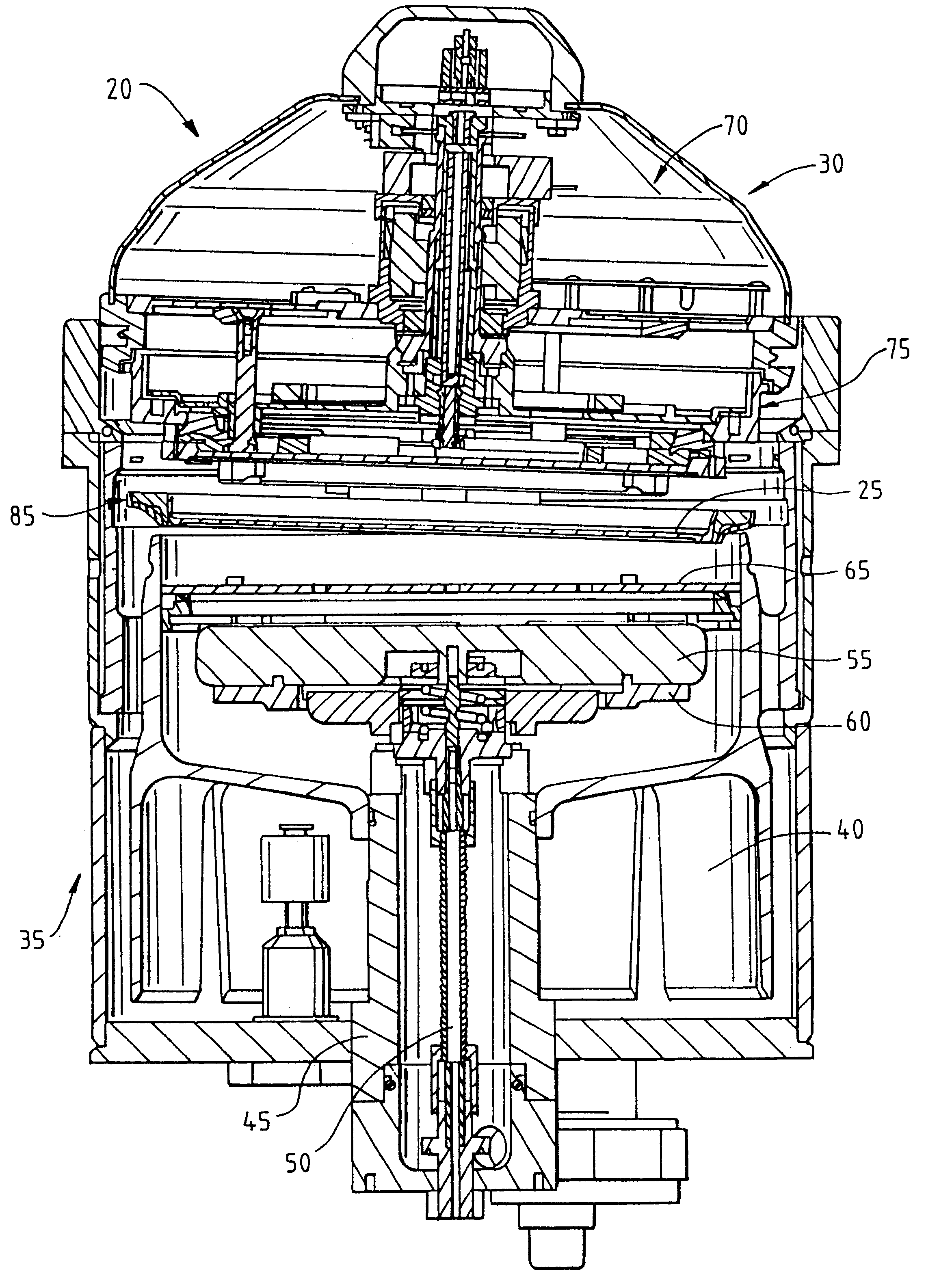
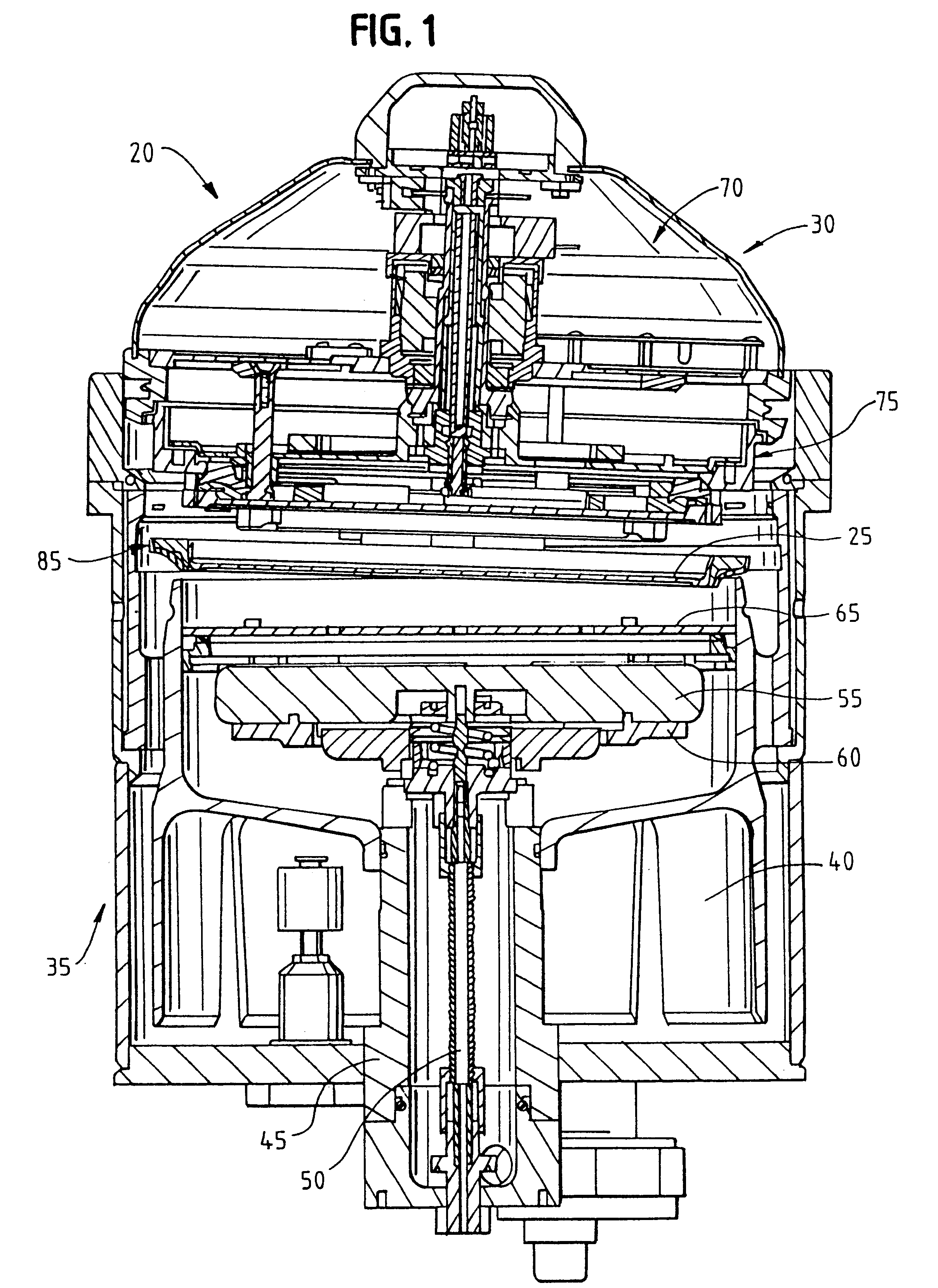
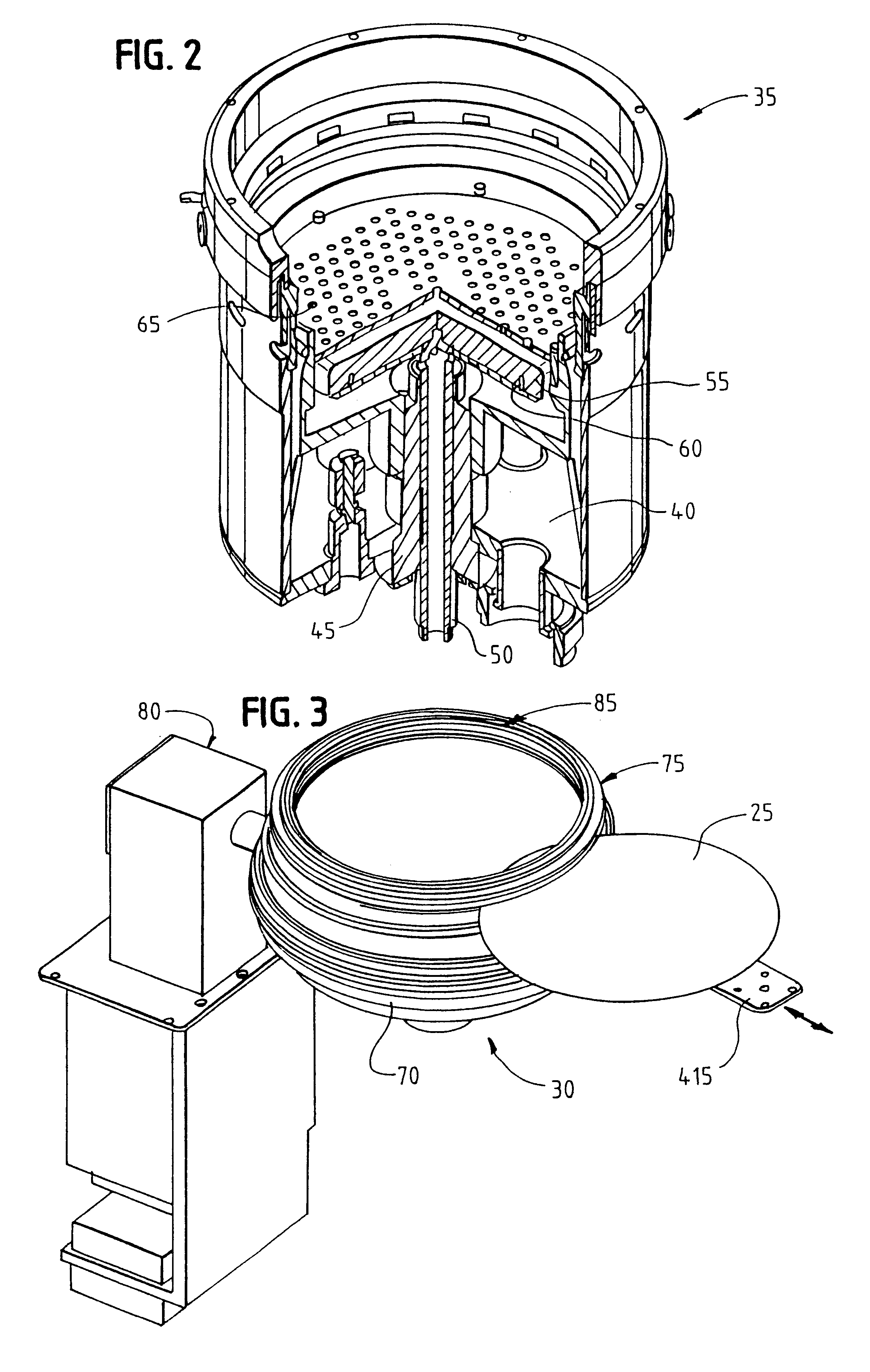
Methods and apparatus for processing the surface of a microelectronic workpiece
InactiveUS6309524B1Reduce the risk of contaminationReduce downtimeCellsTanksEngineeringMechanical engineering
A reactor for plating a metal onto a surface of a workpiece is set forth. The reactor comprises a reactor bowl including an electroplating solution disposed therein and an anode disposed in the reactor bowl in contact with the electroplating solution. A contact assembly is spaced from the anode within the reactor bowl. The contact assembly includes a plurality of contacts disposed to contact a peripheral edge of the surface of the workpiece to provide electroplating power to the surface of the workpiece. The contacts execute a wiping action against the surface of the workpiece as the workpiece is brought into engagement therewith. The contact assembly also including a barrier disposed interior of the plurality of contacts. The barrier includes a member disposed to engage the surface of the workpiece to assist in isolating the plurality of contacts from the electroplating solution. In one embodiment, the plurality of contacts are in the form of discrete flexures while in another embodiment the plurality of contacts are in the form of a Belleville ring contact. A flow path may be provided in the contact assembly for providing a purging gas to the plurality of contacts and the peripheral edge of the workpiece. The purging gas may be used to assist in the formation of the barrier of the contact assembly. A combined electroplating / electroless plating tool and method are also set forth.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus for high deposition rate solder electroplating on a microelectronic workpiece
The present invention is directed to an improved electroplating method, chemistry, and apparatus for selectively depositing tin / lead solder bumps and other structures at a high deposition rate pursuant to manufacturing a microelectronic device from a workpiece, such as a semiconductor wafer. An apparatus for plating solder on a microelectronic workpiece in accordance with one aspect of the present invention comprises a reactor chamber containing an electroplating solution having free ions of tin and lead for plating onto the workpiece. A chemical delivery system is used to deliver the electroplating solution to the reactor chamber at a high flow rate. A workpiece support is used that includes a contact assembly for providing electroplating power to a surface at a side of the workpiece that is to be plated. The contact contacts the workpiece at a large plurality of discrete contact points that isolated from exposure to the electroplating solution. An anode, preferably a consumable anode, is spaced from the workpiece support within the reaction chamber and is in contact with the electroplating solution. In accordance with one embodiment the electroplating solution comprises a concentration of a lead compound, a concentration of a tin compound, water and methane sulfonic acid.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
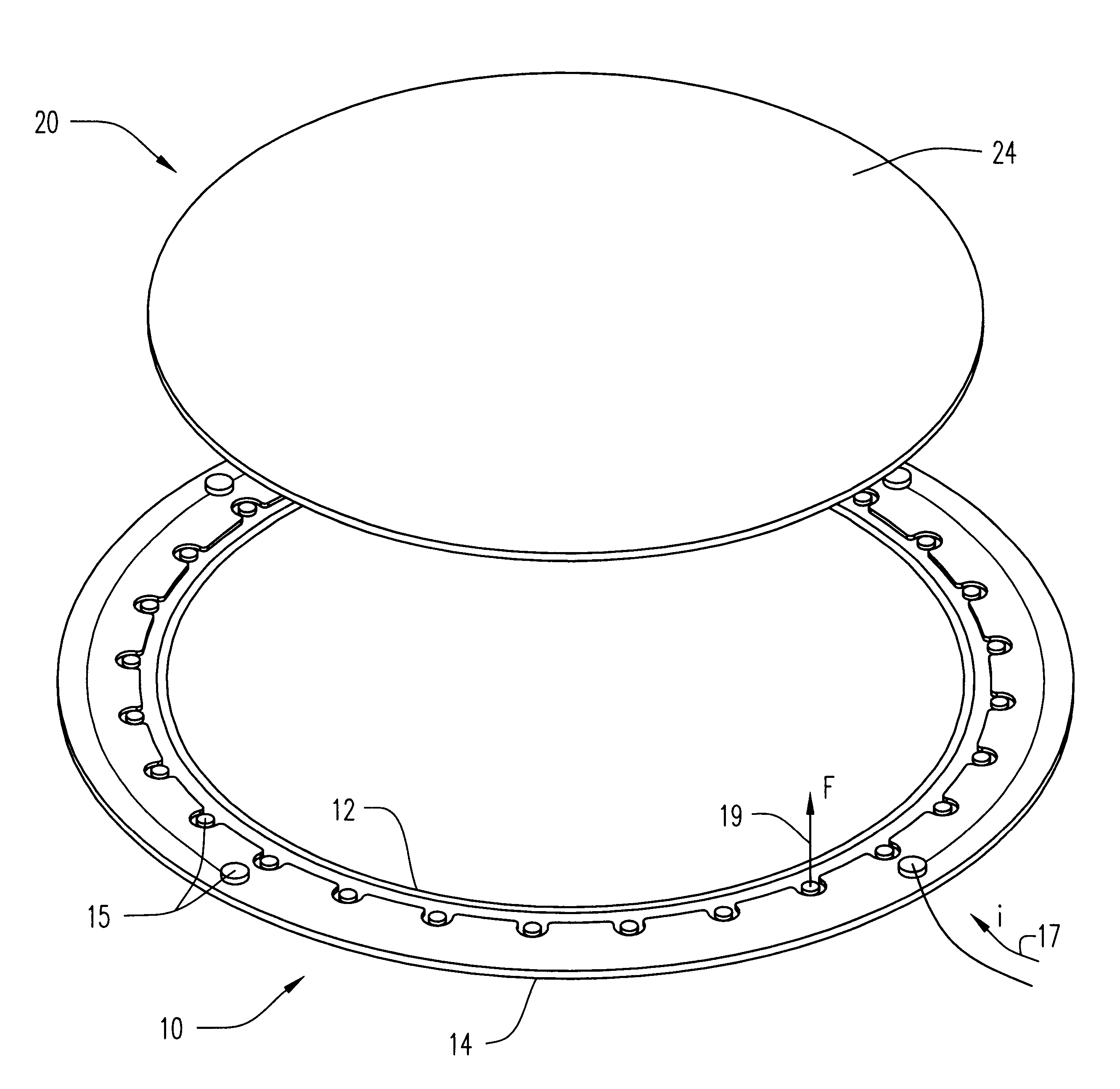
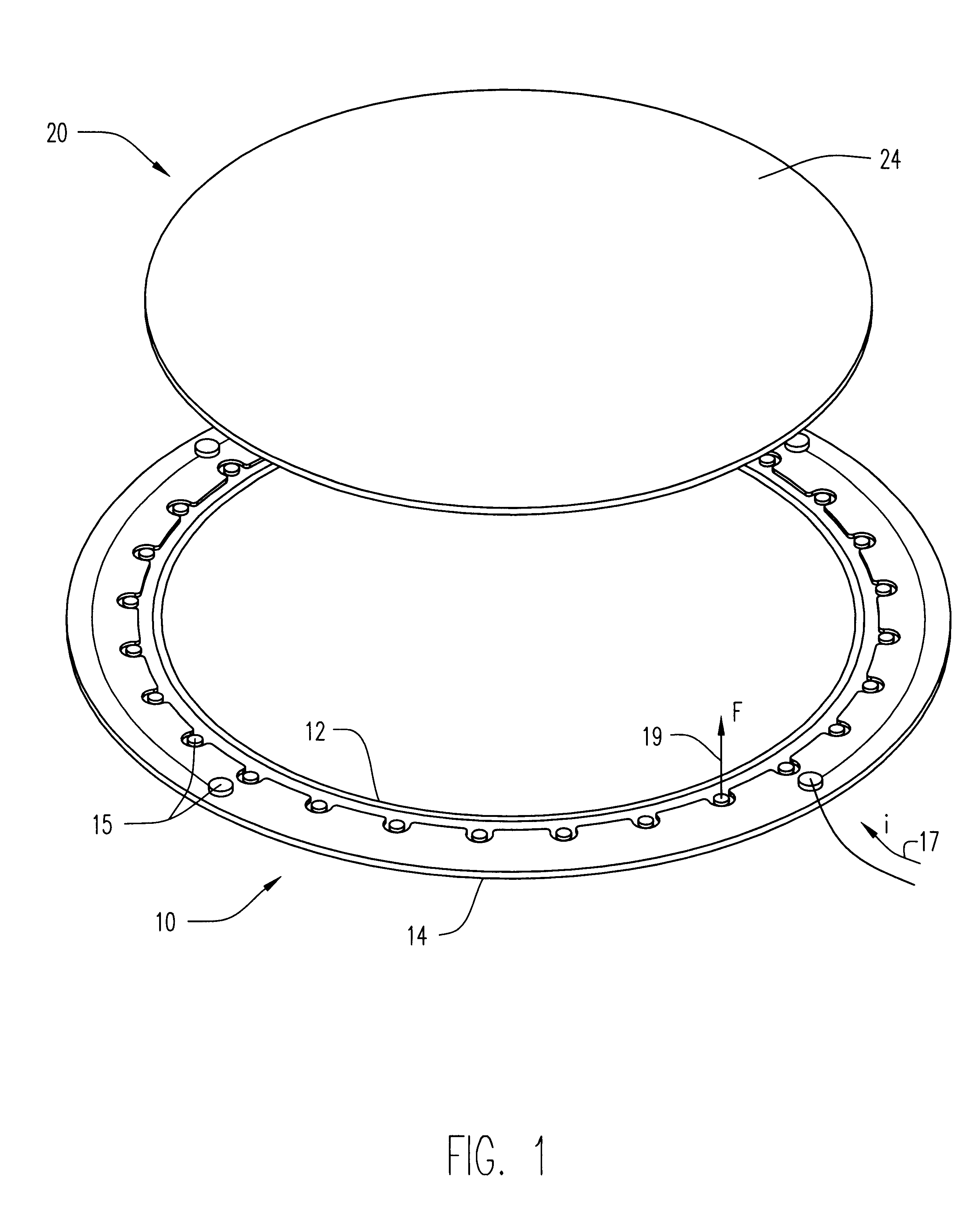
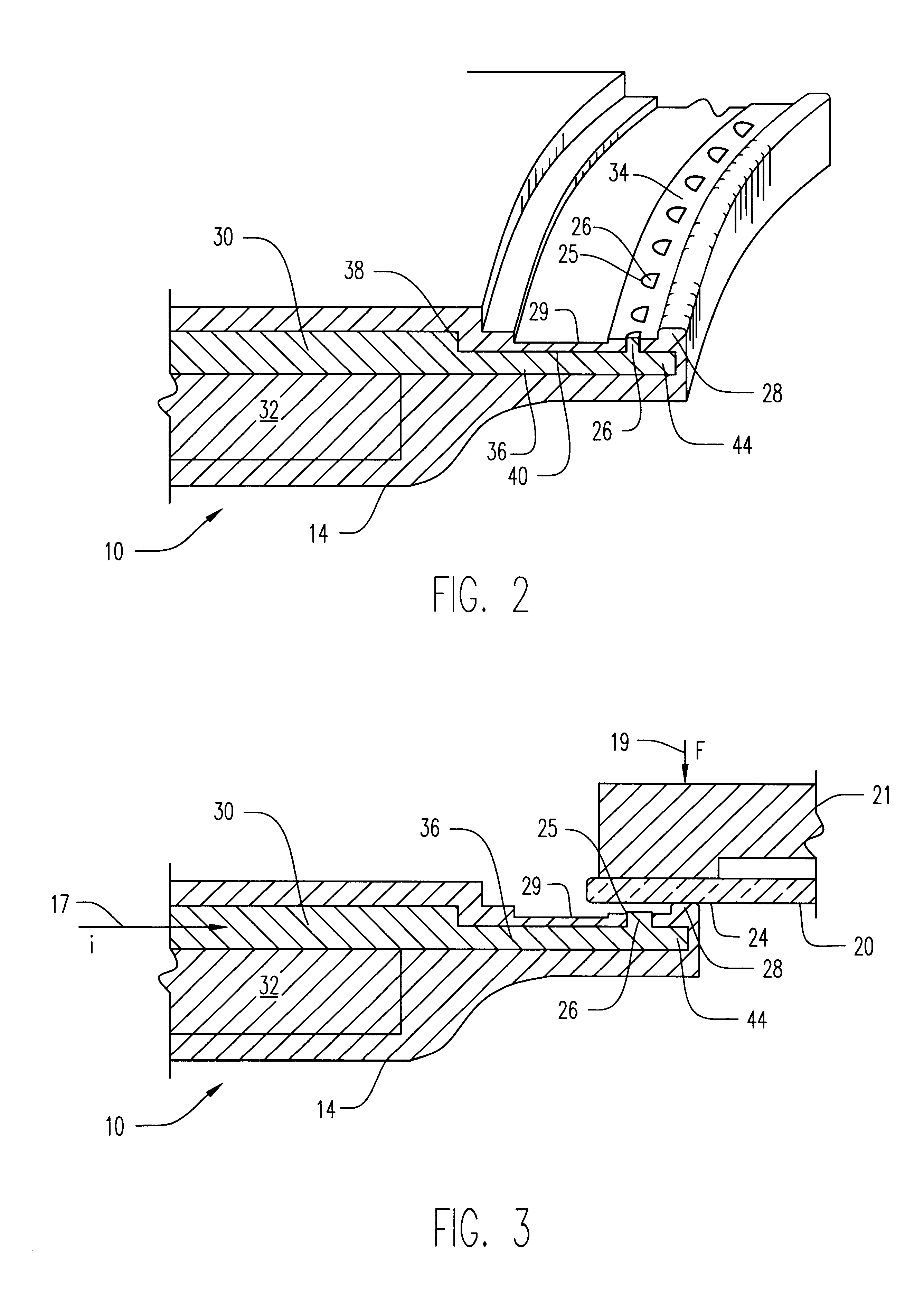
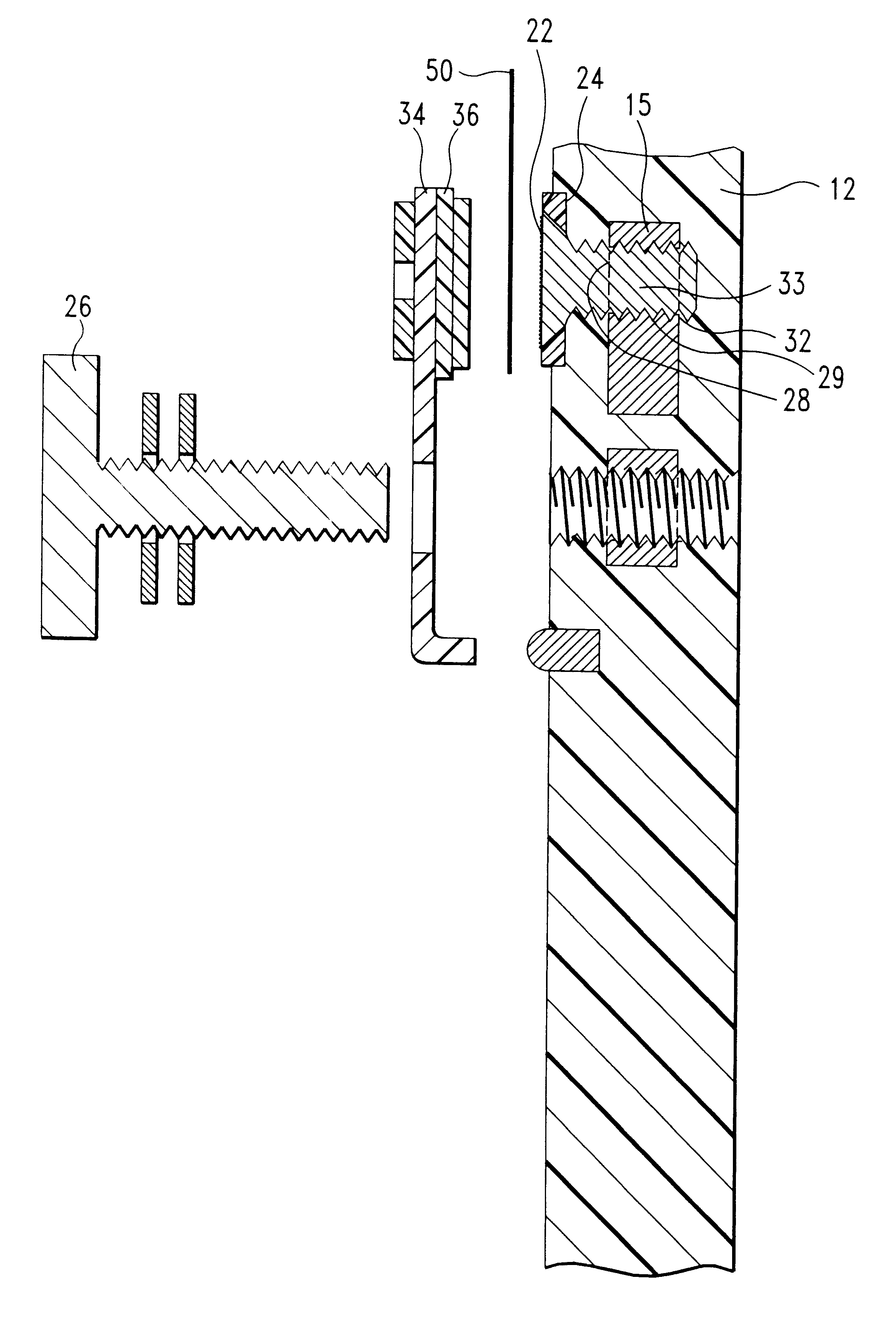
Method of and apparatus for fluid sealing, while electrically contacting, wet-processed workpieces
A method and apparatus for fluid sealing the underside of a workpiece, such as a semiconductor wafer and the like, during wet-processing such as electrodeposition and the like, employing an elastomeric encased ring of flexible fingers against which the periphery of the workpiece underside is forced to deflect the fingers downwardly and engage a peripheral sealing bead against the underside periphery of the workpiece; and where electrical contact with the workpiece is desired, resiliently engaging electrical contact tips protruding through peripheral openings in the elastomeric covering within the sealing ring, with the underside periphery of the workpiece.
Owner:HERCULES TECH GROWTH CAPITAL
Method and apparatus for electroplating
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer and an auxiliary cathode located between the anode and the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface. The auxiliary cathode is configured to shape the current distribution from the anode. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Aparatus for processing the surface of a microelectronic workpiece
InactiveUS6303010B1Reduce the risk of contaminationReduce downtimeCellsTanksEngineeringMechanical engineering
A reactor for plating a metal onto a surface of a workpiece is set forth. The reactor comprises a reactor bowl including an electroplating solution disposed therein and an anode disposed in the reactor bowl in contact with the electroplating solution. A contact assembly is spaced from the anode within the reactor bowl. The contact assembly includes a plurality of contacts disposed to contact a peripheral edge of the surface of the workpiece to provide electroplating power to the surface of the workpiece. The contacts execute a wiping action against the surface of the workpiece as the workpiece is brought into engagement therewith The contact assembly also including a barrier disposed interior of the plurality of contacts. The barrier includes a member disposed to engage the surface of the workpiece to assist in isolating the plurality of contacts from the electroplating solution. In one embodiment, the plurality of contacts are in the form of discrete flexures while in another embodiment the plurality of contacts are in the form of a Belleville ring contact. A flow path may be provided in the contact assembly for providing a purging gas to the plurality of contacts and the peripheral edge of the workpiece. The purging gas may be used to assist in the formation of the barrier of the contact assembly. A combined electroplating / electroless plating tool and method are also set forth.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
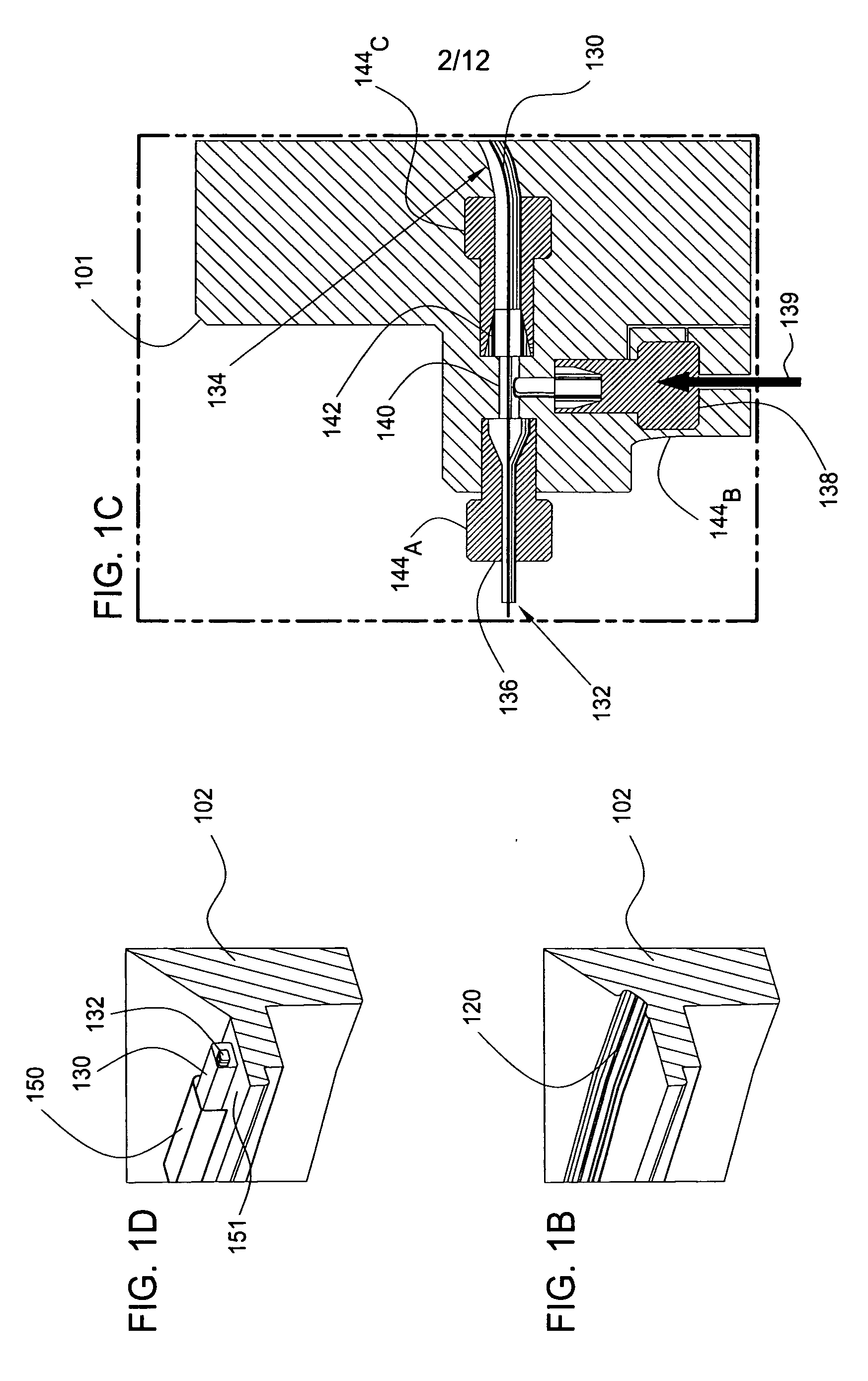
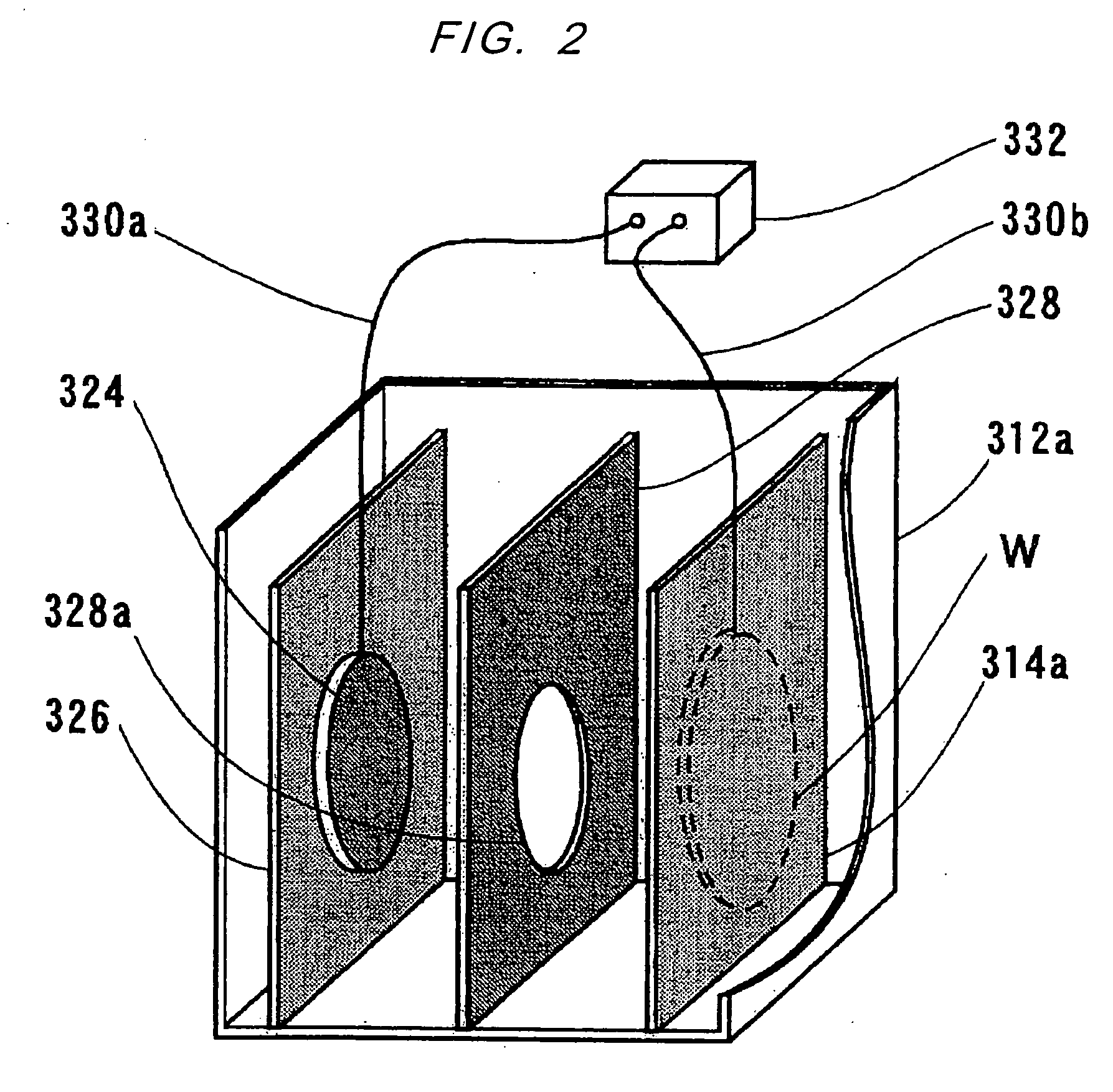
System for and method for closed loop electrophoretic deposition of phosphor materials on semiconductor devices
One close loop system and method for electrophoretic deposition (EPD) of phosphor material on light emitting diodes (LEDs). The system comprises a deposition chamber sealed from ambient air. A mixture of phosphor material and solution is provided to the chamber with the mixture also being sealed from ambient air. A carrier holds a batch of LEDs in the chamber with the mixture contacting the areas of the LEDs for phosphor deposition. A voltage supply applies a voltage to the LEDs and the mixture to cause the phosphor material to deposit on the LEDs at the mixture contacting areas.
Owner:CREELED INC
Methods of and apparatus for making high aspect ratio microelectromechanical structures
Various embodiments of the invention present techniques for forming structures (e.g. HARMS-type structures) via an electrochemical extrusion (ELEX(TM)) process. Preferred embodiments perform the extrusion processes via depositions through anodeless conformable contact masks that are initially pressed against substrates that are then progressively pulled away or separated as the depositions thicken. A pattern of deposition may vary over the course of deposition by including more complex relative motion between the mask and the substrate elements. Such complex motion may include rotational components or translational motions having components that are not parallel to an axis of separation. More complex structures may be formed by combining the ELEX(TM) process with the selective deposition, blanket deposition, planarization, etching, and multi-layer operations of EFAB(TM).
Owner:MEMGEN
Apparatus and method for improving uniformity in electroplating
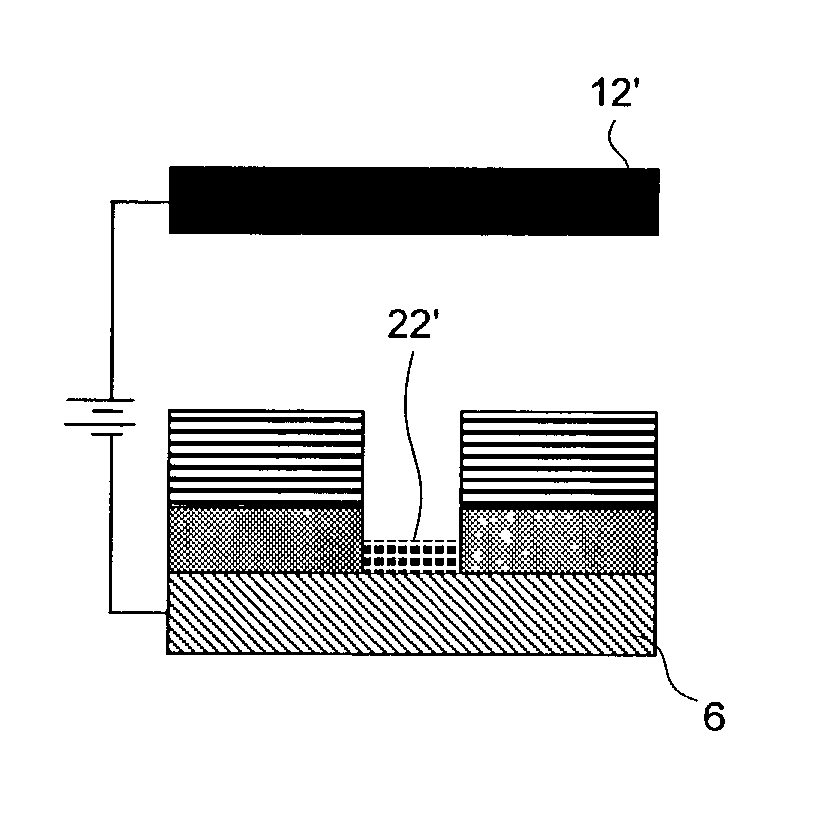
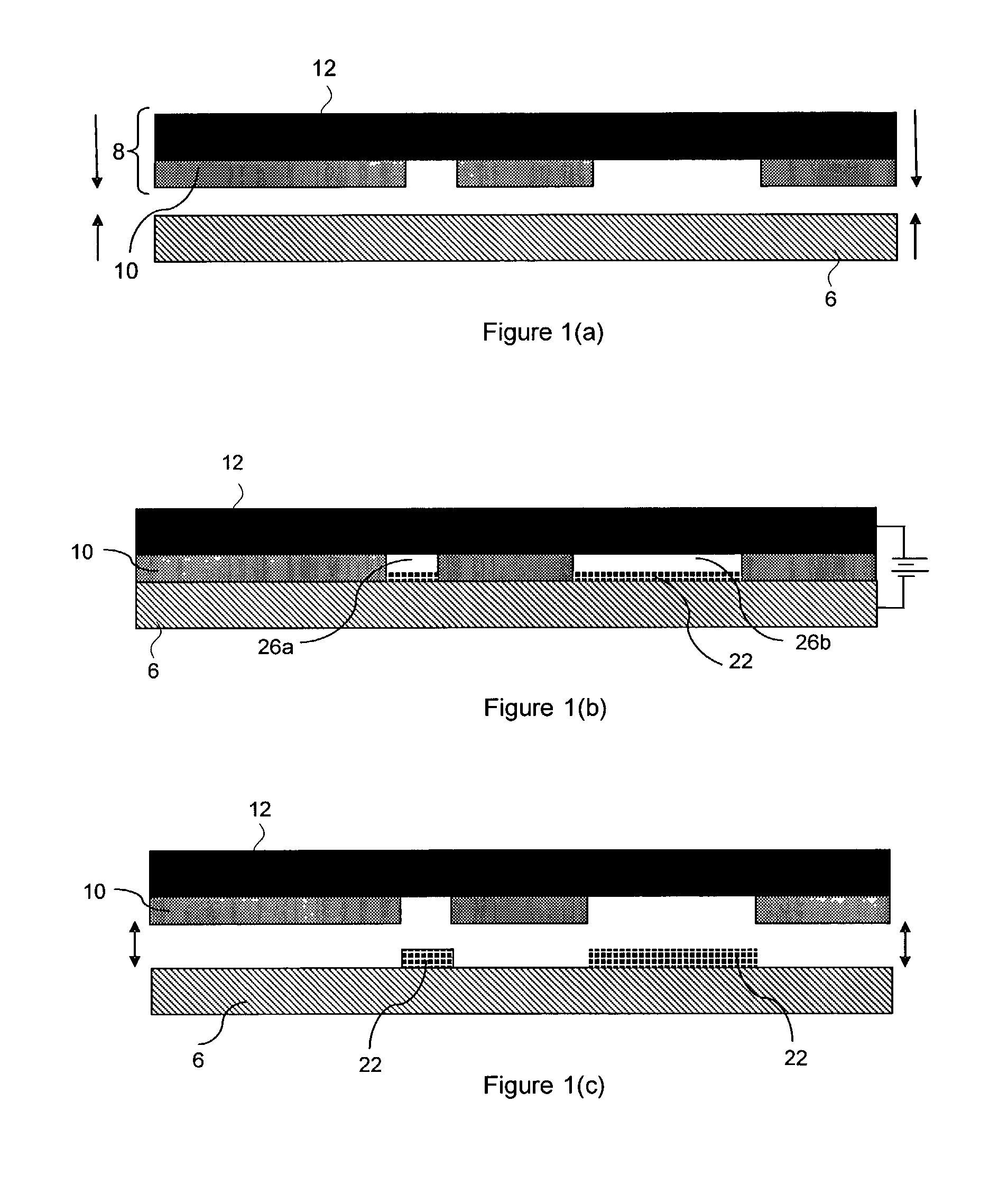
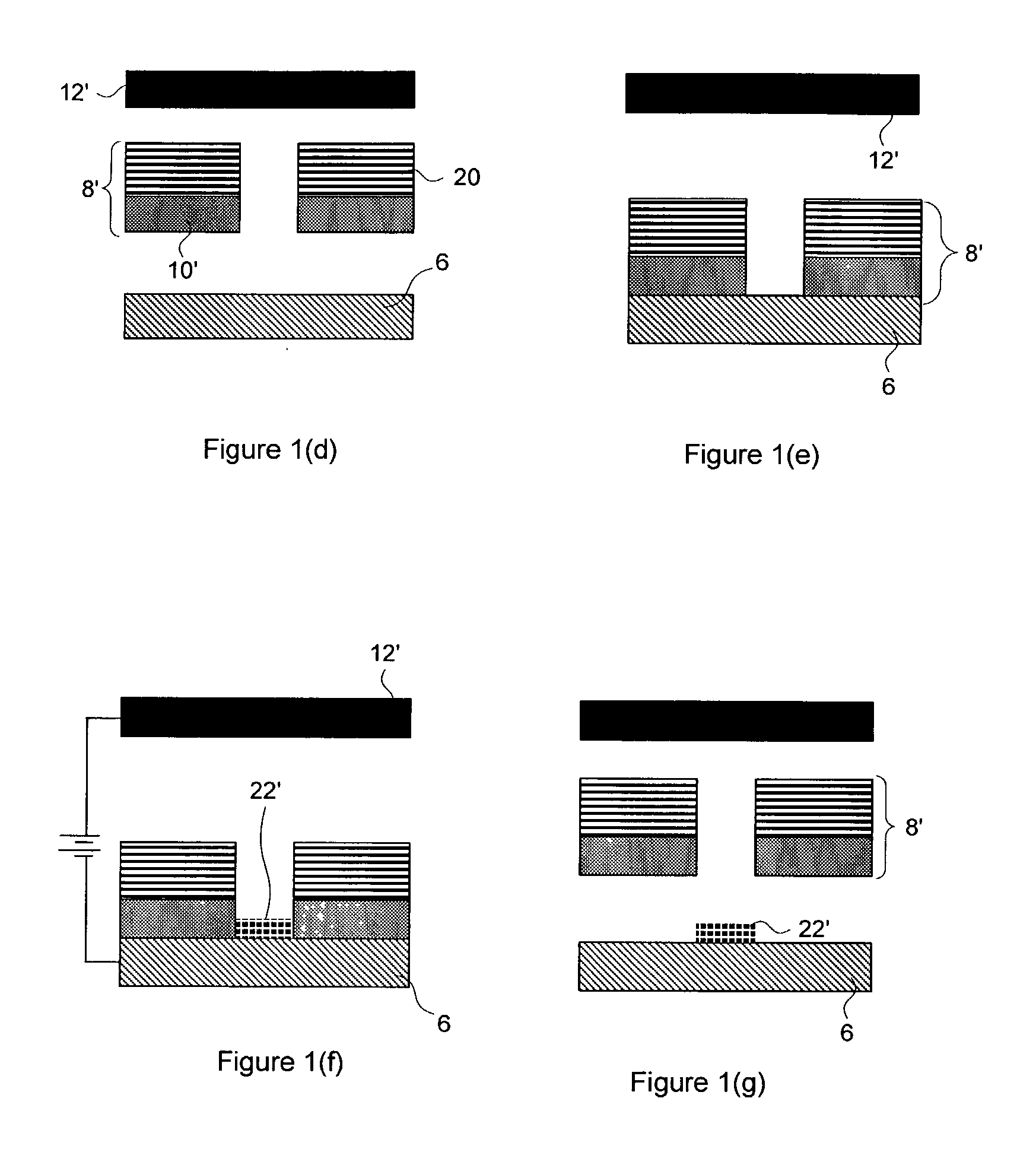
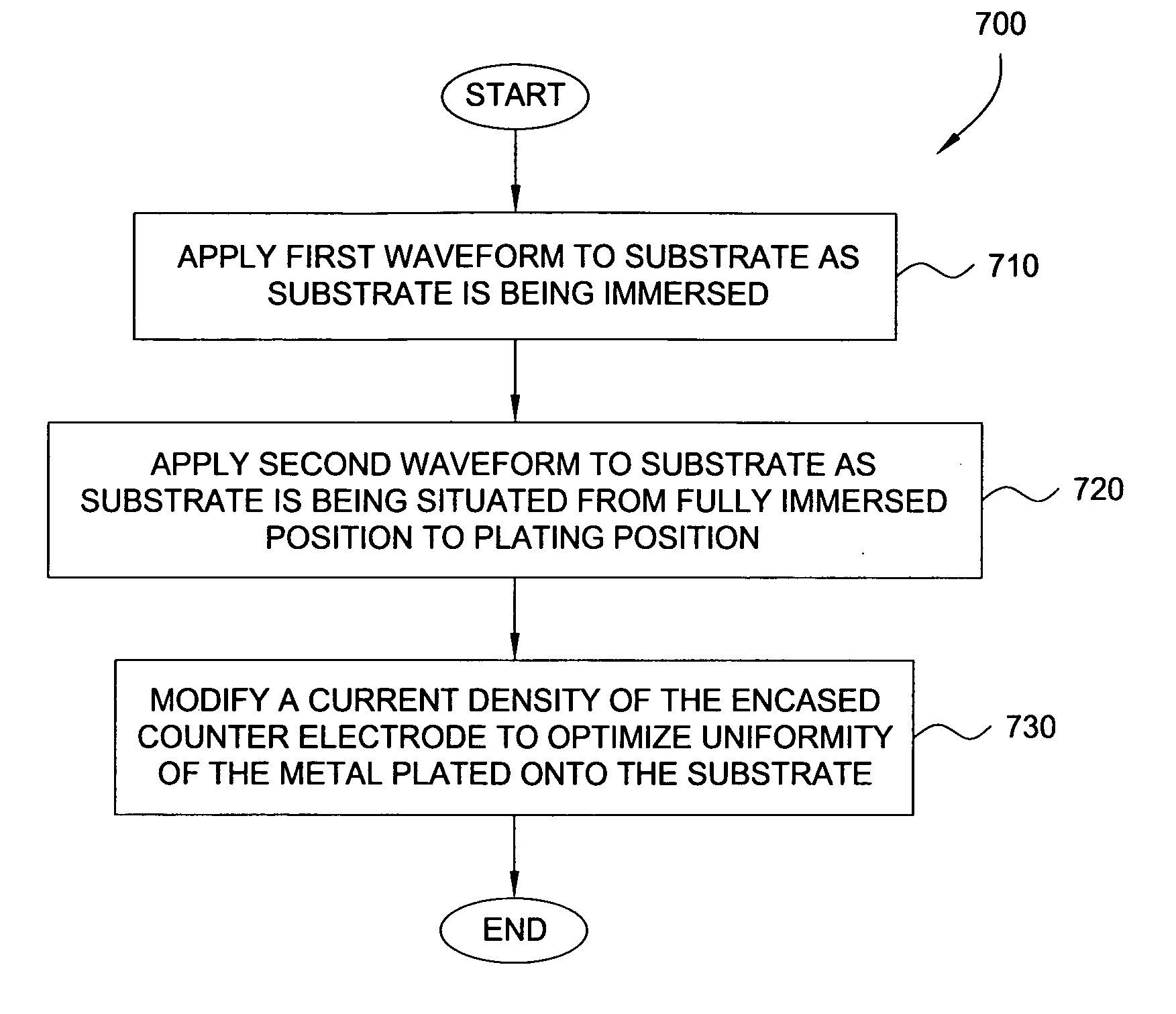
A method and apparatus for plating a metal onto a substrate. One embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus for electroplating a substrate. The apparatus comprises a fluid basin, an anode disposed near a bottom of the fluid basin, a restrictor disposed above the anode, and a substrate support member configured to move the substrate within the fluid basin among different elevations relative to the restrictor. Plating profiles on the substrate may be adjusted by changing the elevation of the substrate during plating.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plating apparatus and plating method
Owner:EBARA CORP
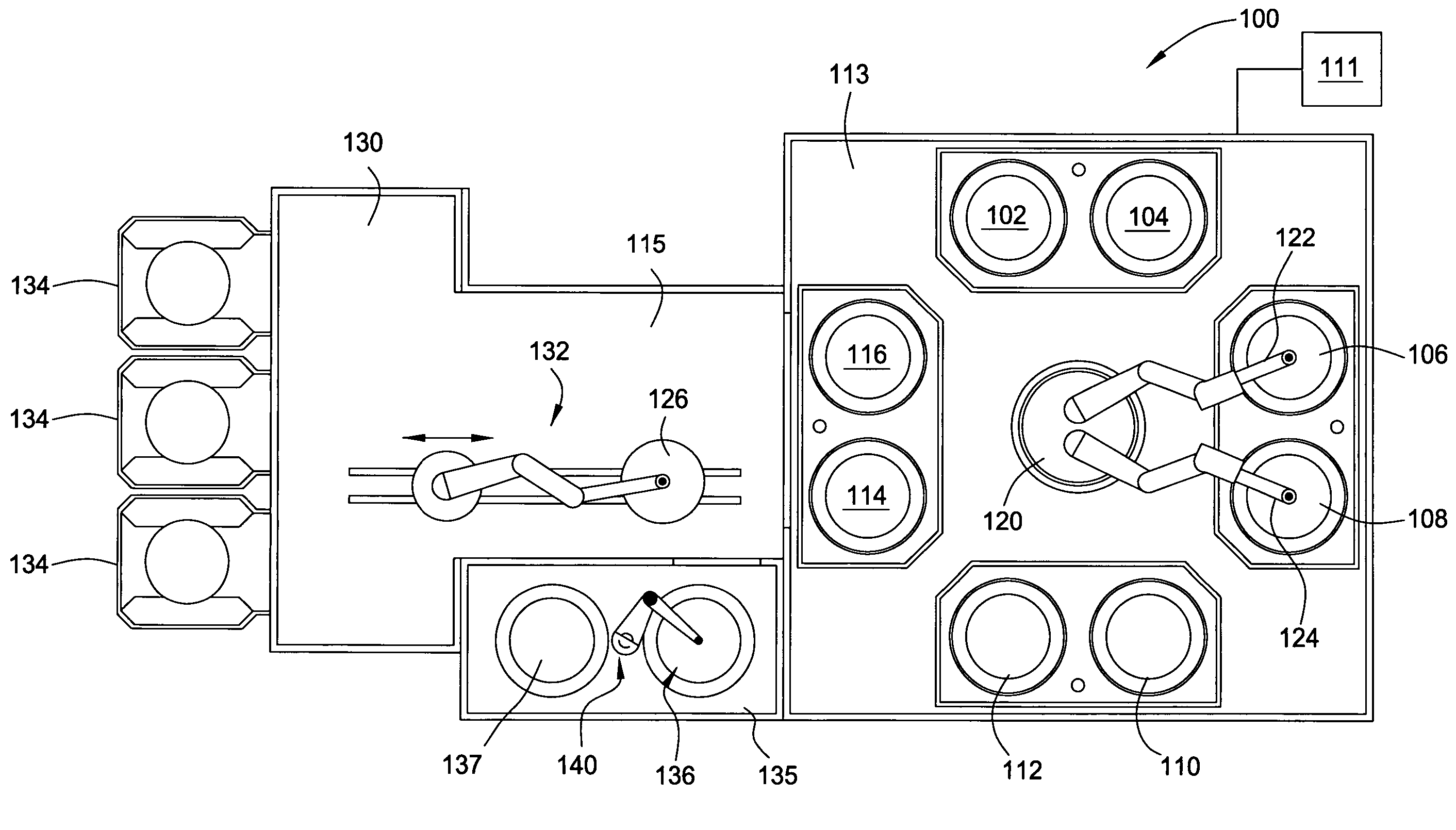
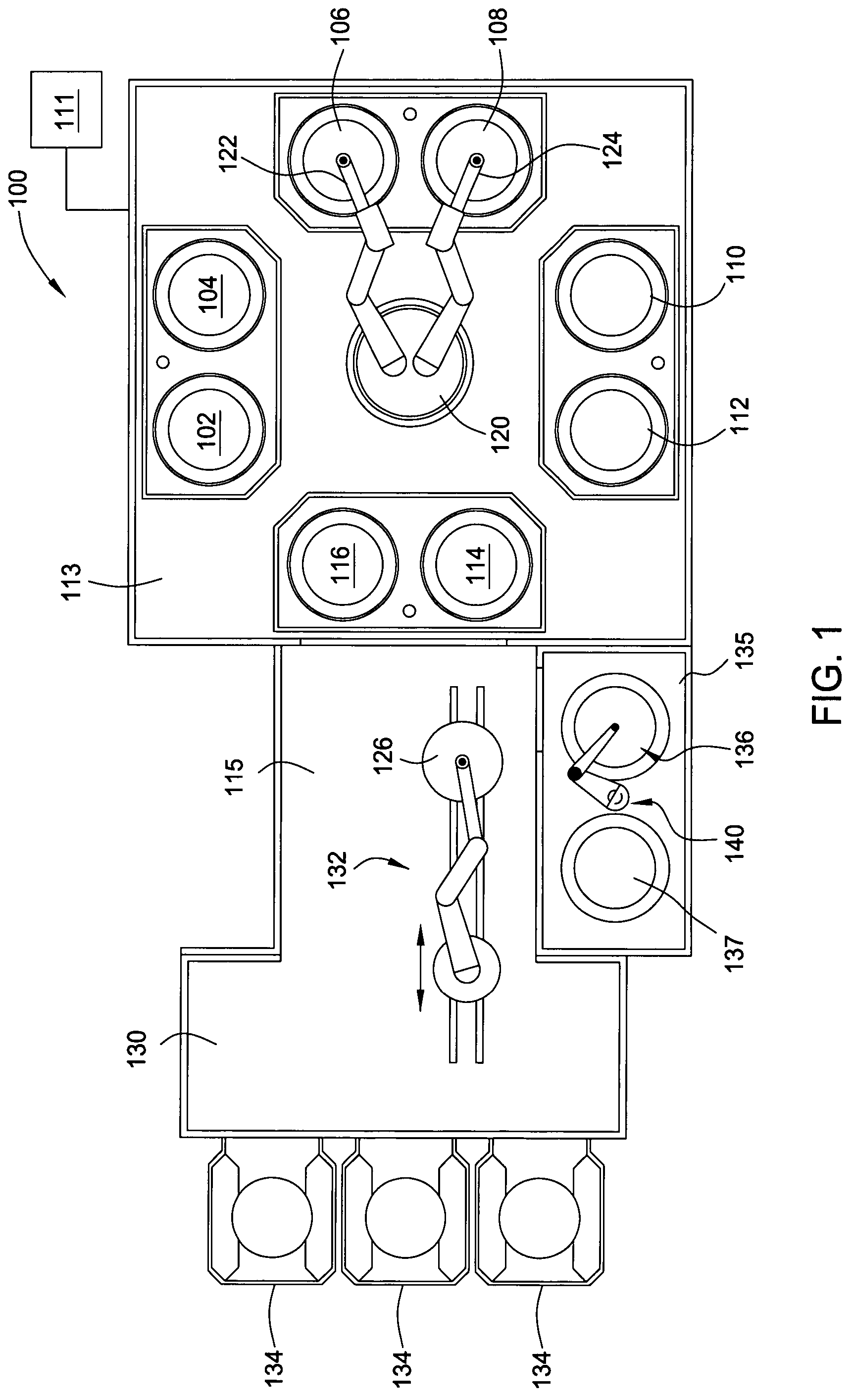
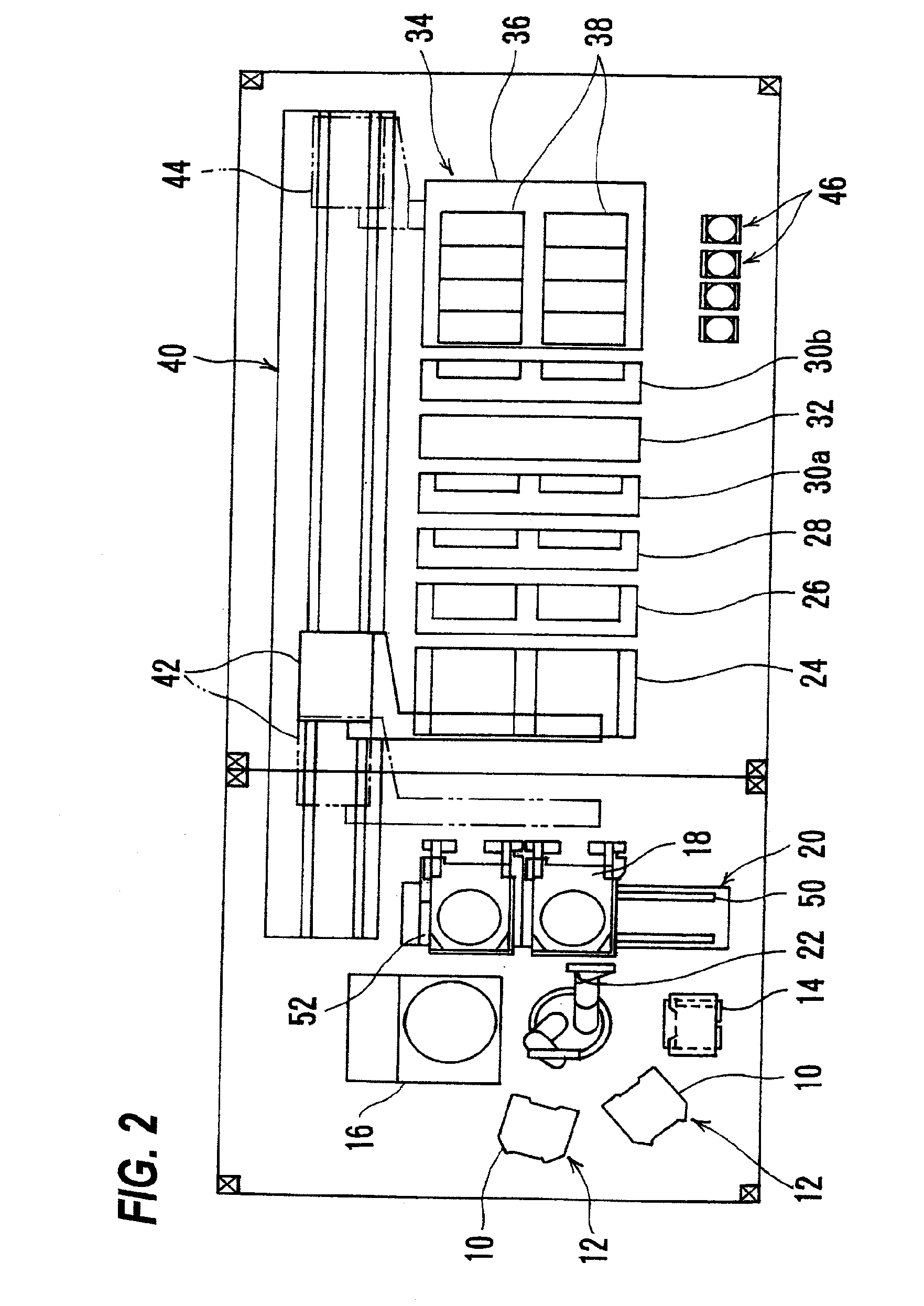
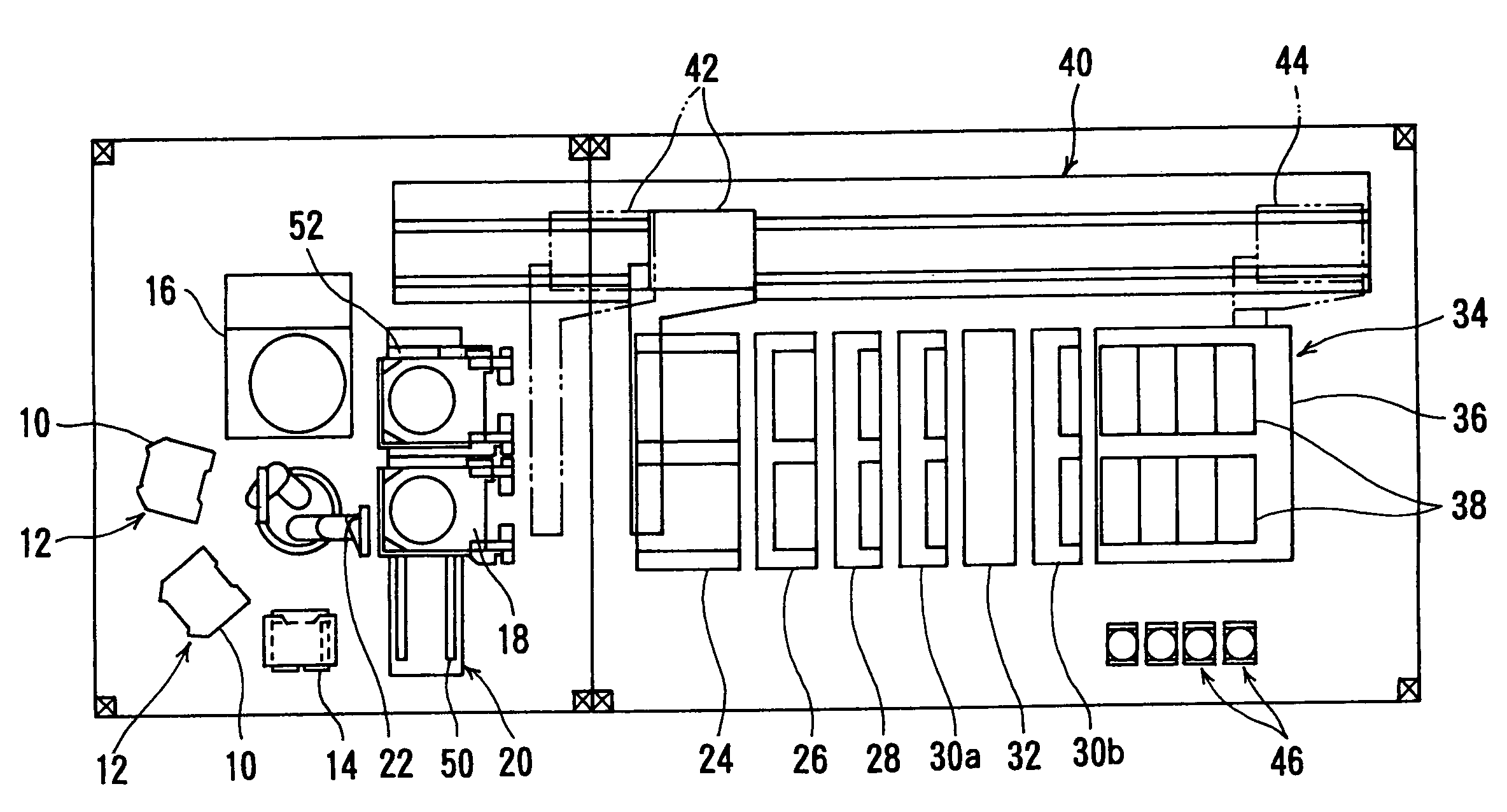
Multi-chemistry plating system
Embodiments of the invention generally provide an electrochemical plating system. The plating system includes a substrate loading station positioned in communication with a mainframe processing platform, at least one substrate plating cell positioned on the mainframe, at least one substrate bevel cleaning cell positioned on the mainframe, and a stacked substrate annealing station positioned in communication with at least one of the mainframe and the loading station, each chamber in the stacked substrate annealing station having a heating plate, a cooling plate, and a substrate transfer robot therein.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method of and apparatus for fluid sealing, while electrically contacting, wet-processed workpieces, as in the electrodeposition of semi-conductor wafers and the like and for other wet processing techniques and workpieces
A method and apparatus for fluid sealing the underside of a workpiece, such as a semiconductor wafer and the like, during wet-processing such as electrodeposition and the like, employing an elastomeric encased ring of flexible fingers against which the periphery of the workpiece underside is forced to deflect the fingers downwardly and engage a peripheral sealing bead against the underside periphery of the workpiece; and where electrical contact with the workpiece is desired, resiliently engaging electrical contact tips protruding through peripheral openings in the elastomeric covering within the sealing ring, with the underside periphery of the workpiece.
Owner:HERCULES TECH GROWTH CAPITAL
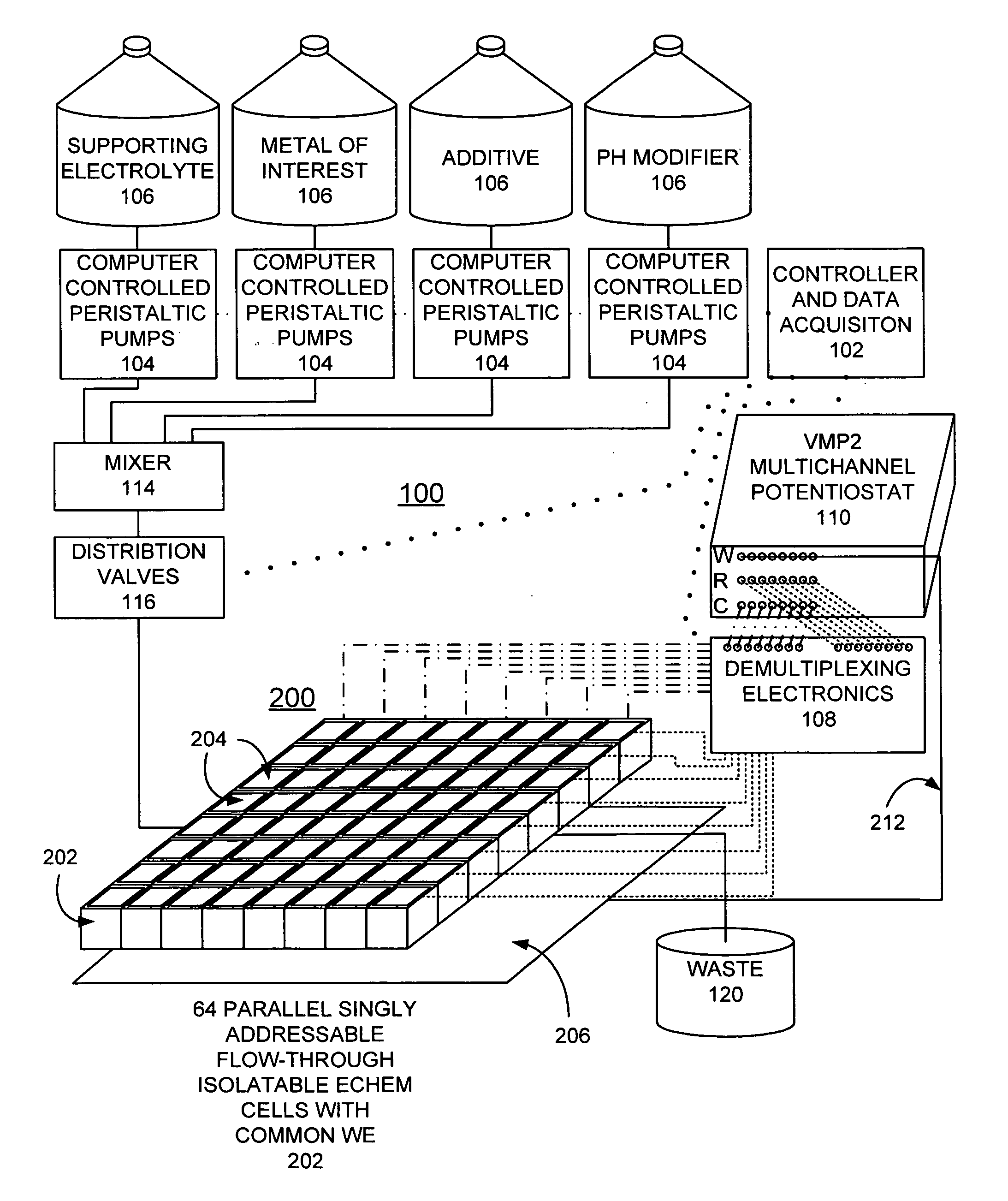
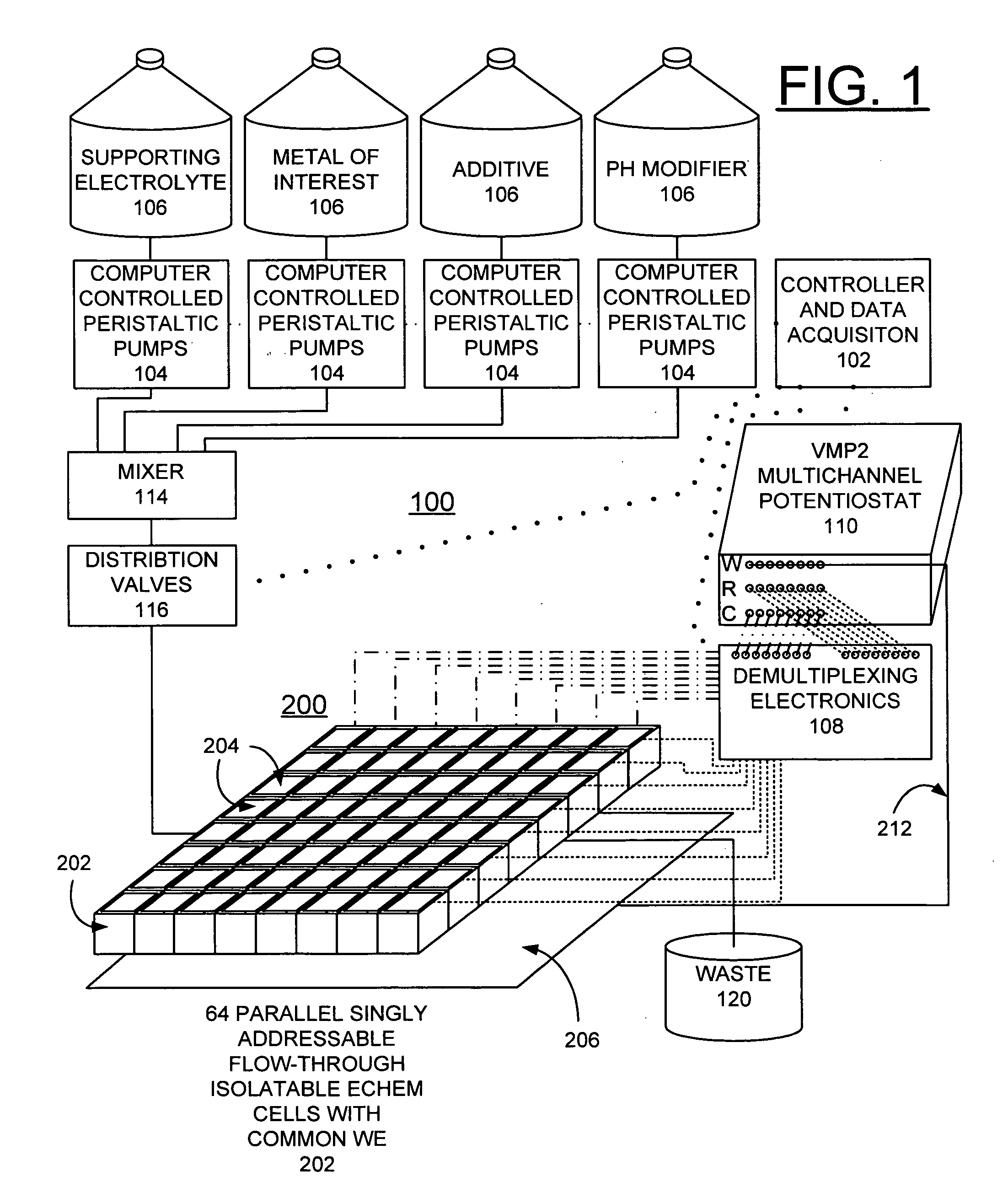
Combinatorial electrochemical deposition system
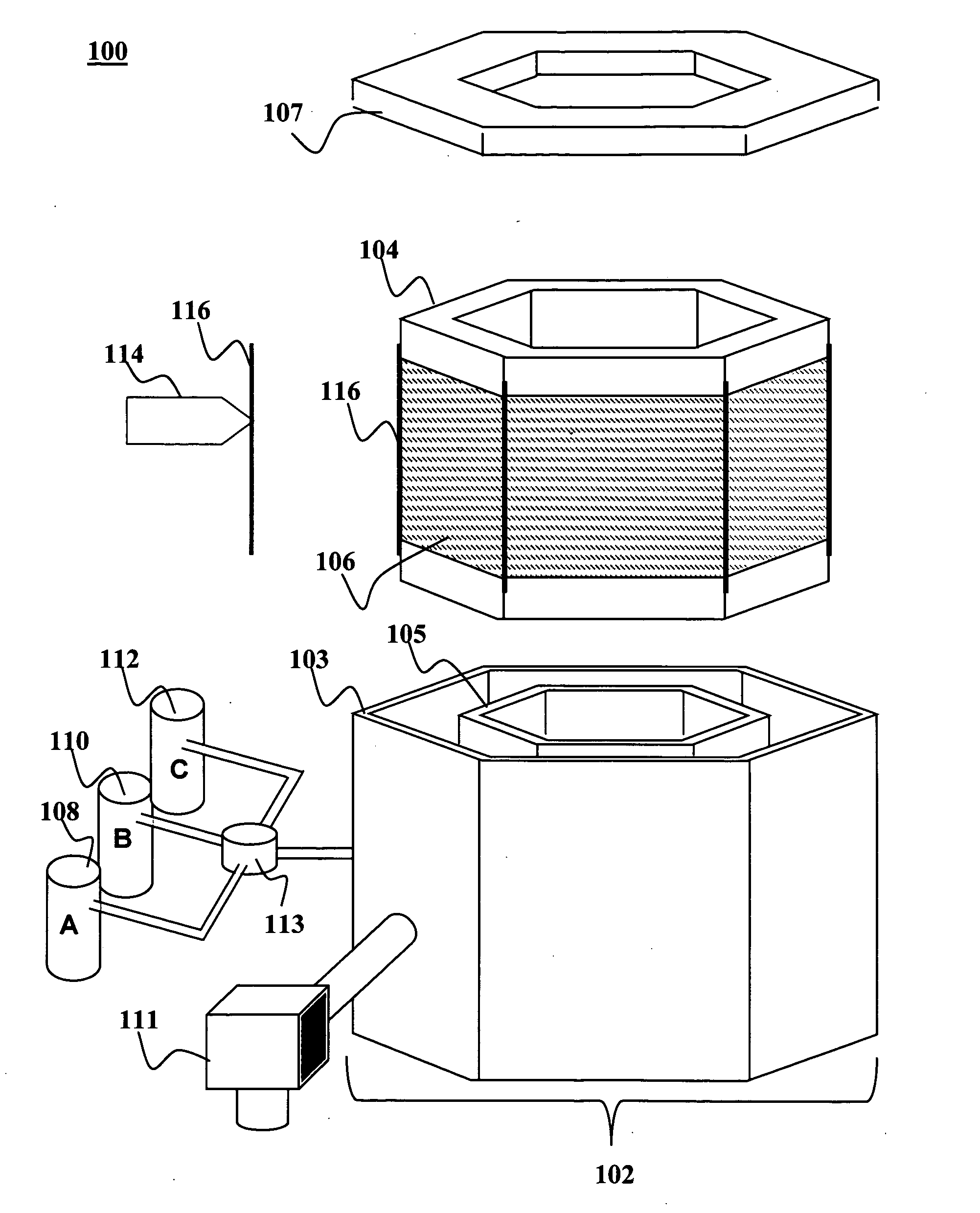
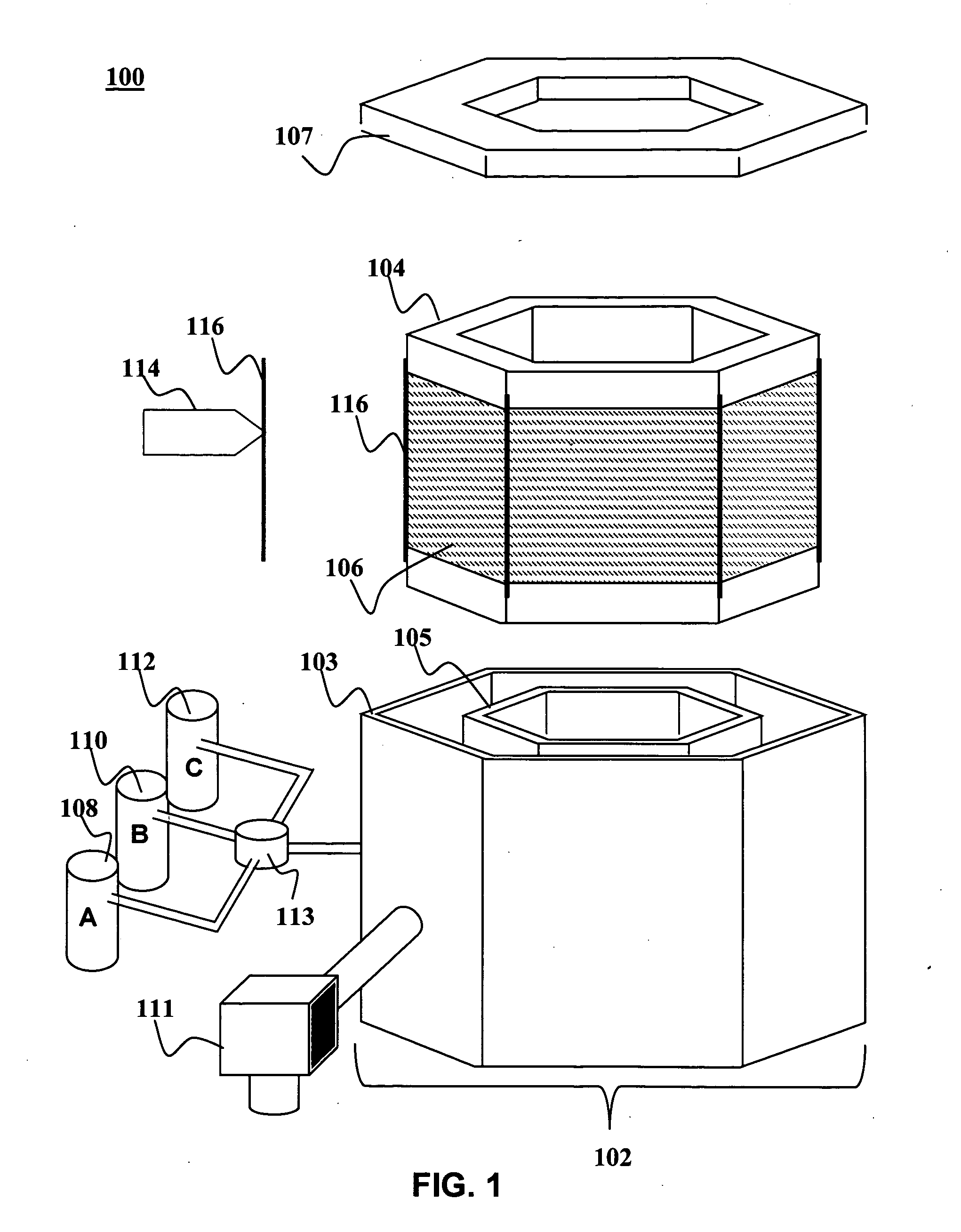
A combinatorial electrochemical deposition system enables computer control over multiple parameters and allows for systematic exploration of the parameter space. The combinatorial electrochemical deposition system includes a computer providing system control and data acquisition functions. The computer controls a plurality of pumps; each pump is connected to a respective material supply source. The plurality of pumps is coupled via a mixer and a plurality of distribution valves of a cell and fluidics distribution network to deposit a particular composition of materials or solution concentration to individual electrochemical cells of an electrochemical cell array. The computer controls the mixer and the plurality of distribution valves. The electrochemical cell array includes a plurality of singly addressable flow-through isolatable electrochemical cells with a common working electrode.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC +1
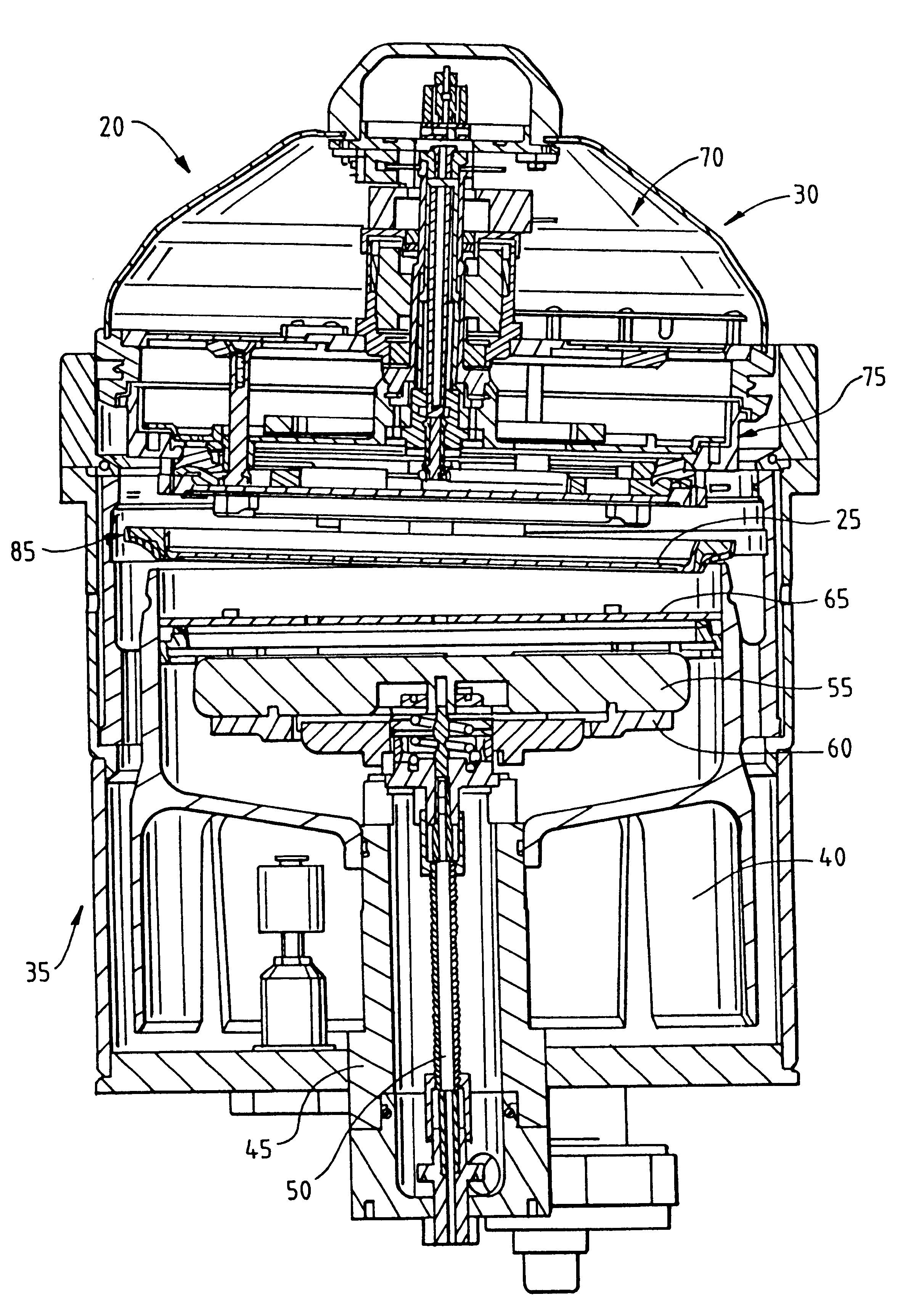
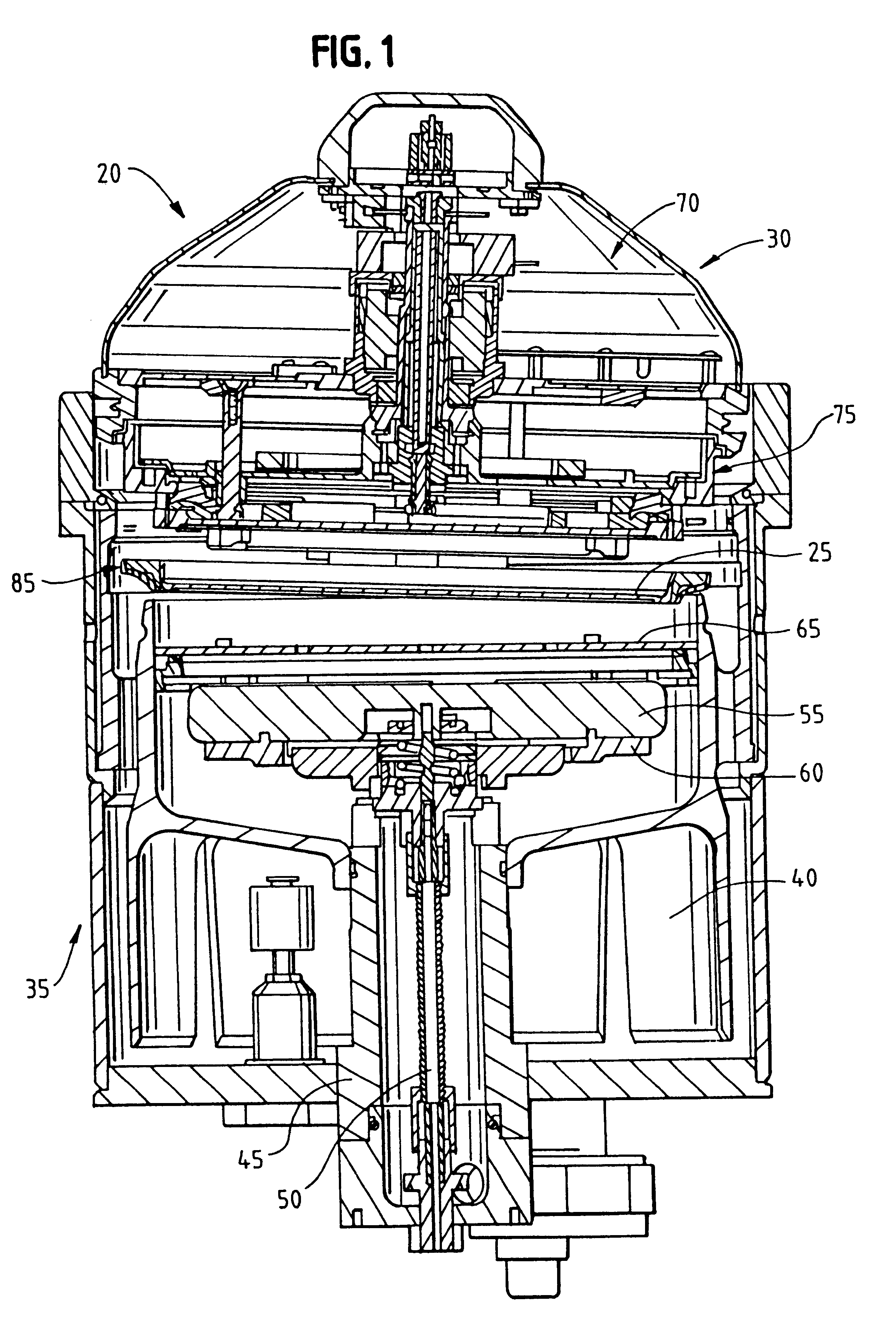
Substrate holder and plating apparatus
A substrate holder enables easy maintenance, especially easy replacement of seal members. The substrate holder includes a fixed holding member and a movable holding member for detachably holding a substrate by gripping a peripheral portion of the substrate therebetween, and an inner seal member and an outer seal member which are fixed to the movable holding member and which, when the substrate is held by the movable holding member and the fixed holding member, seal the connection between the movable holding member and a peripheral portion of the substrate and the connection between the movable holding member and the fixed holding member, respectively. The movable holding member includes a seal holder, and the inner seal member and the outer seal member are fixed between the seal holder and a fixing ring secured to the seal holder.
Owner:EBARA CORP
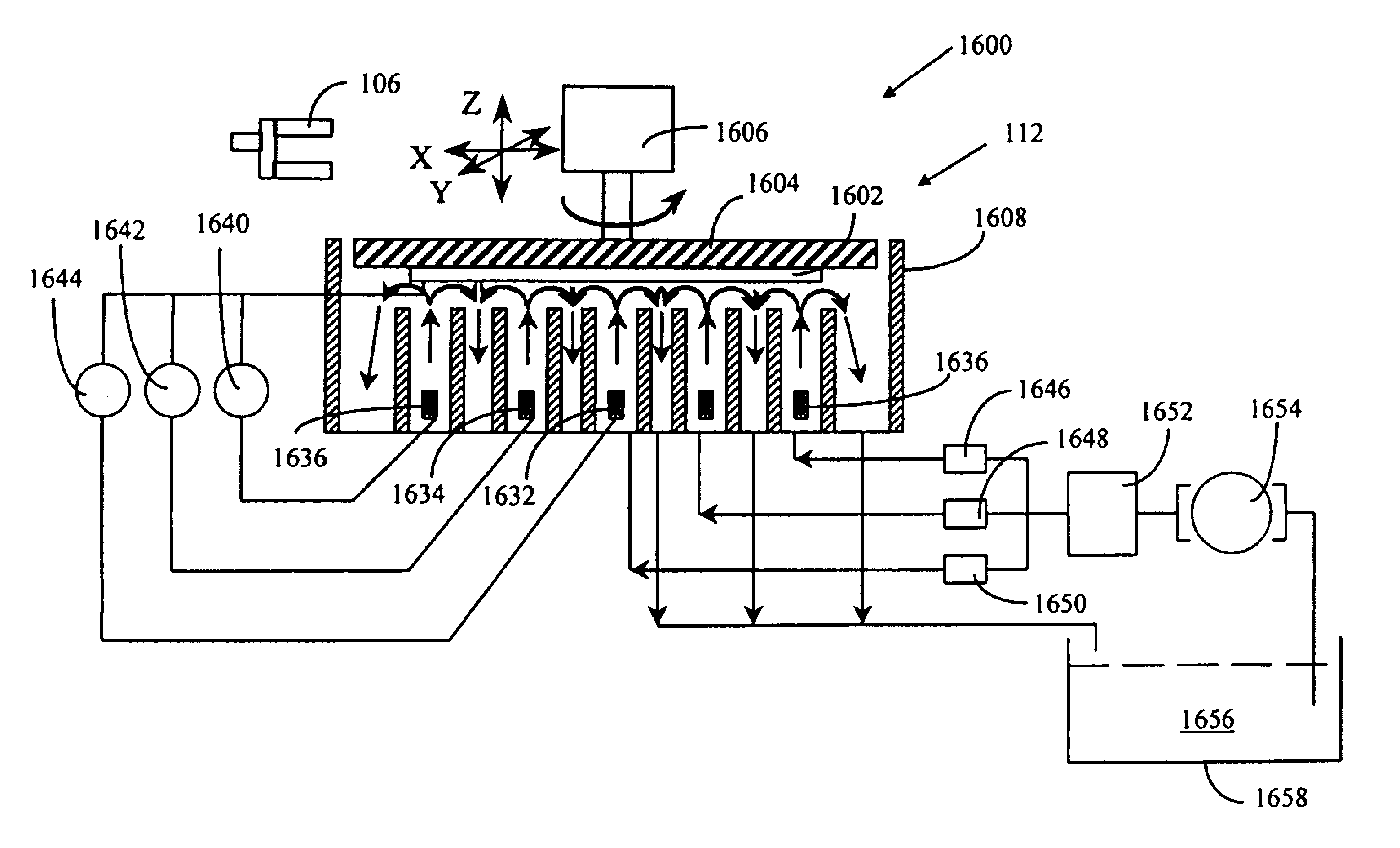
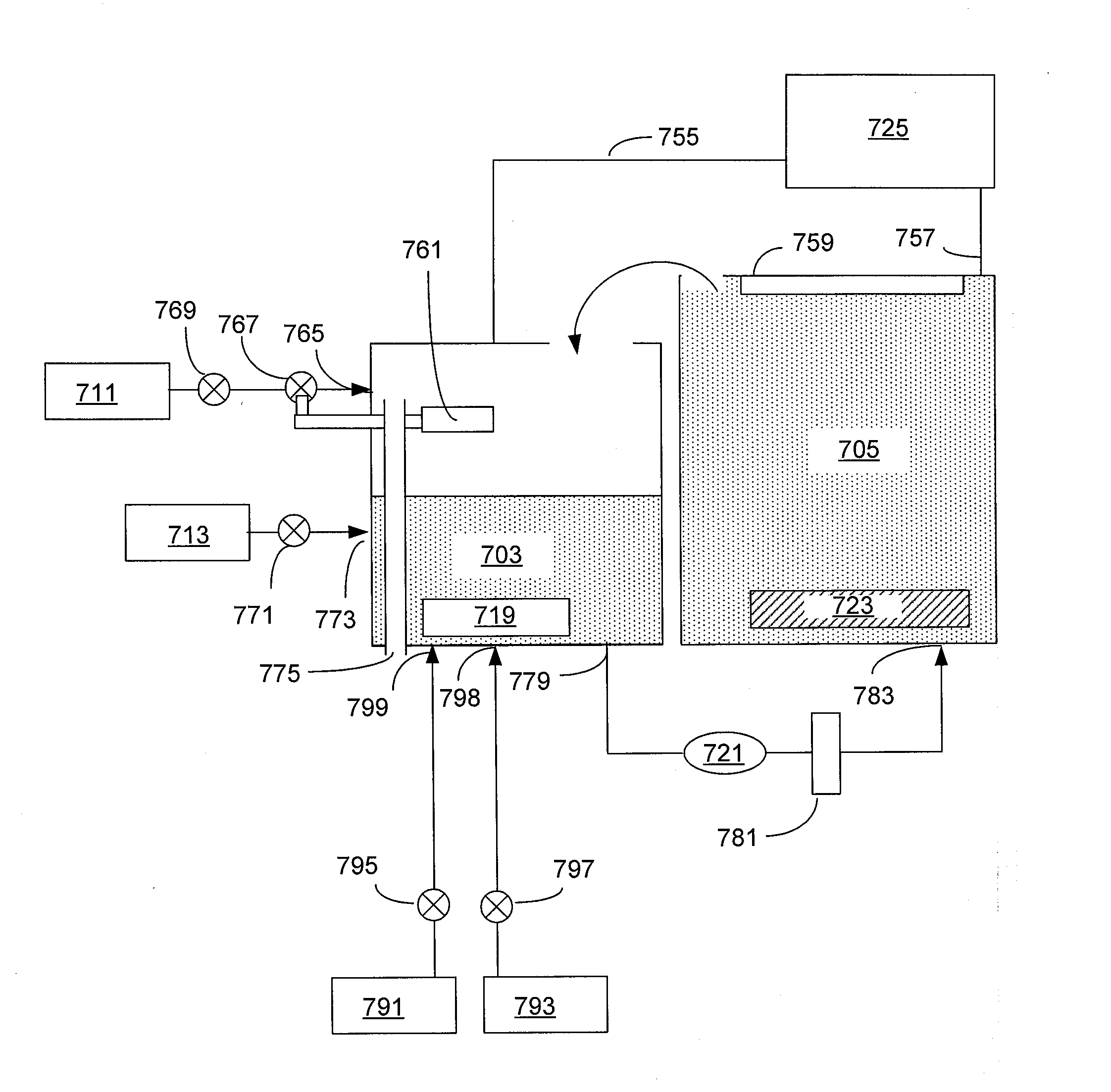
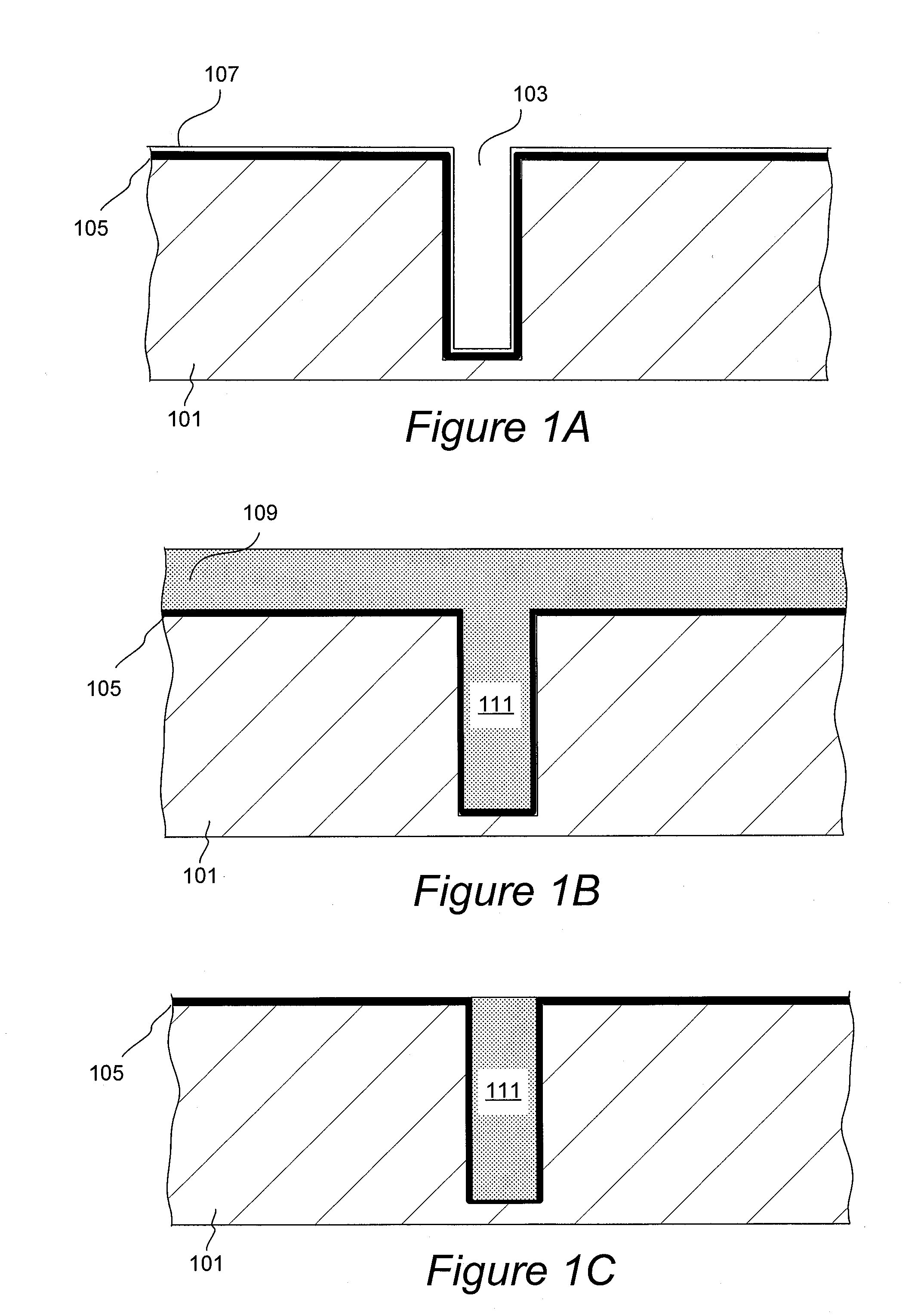
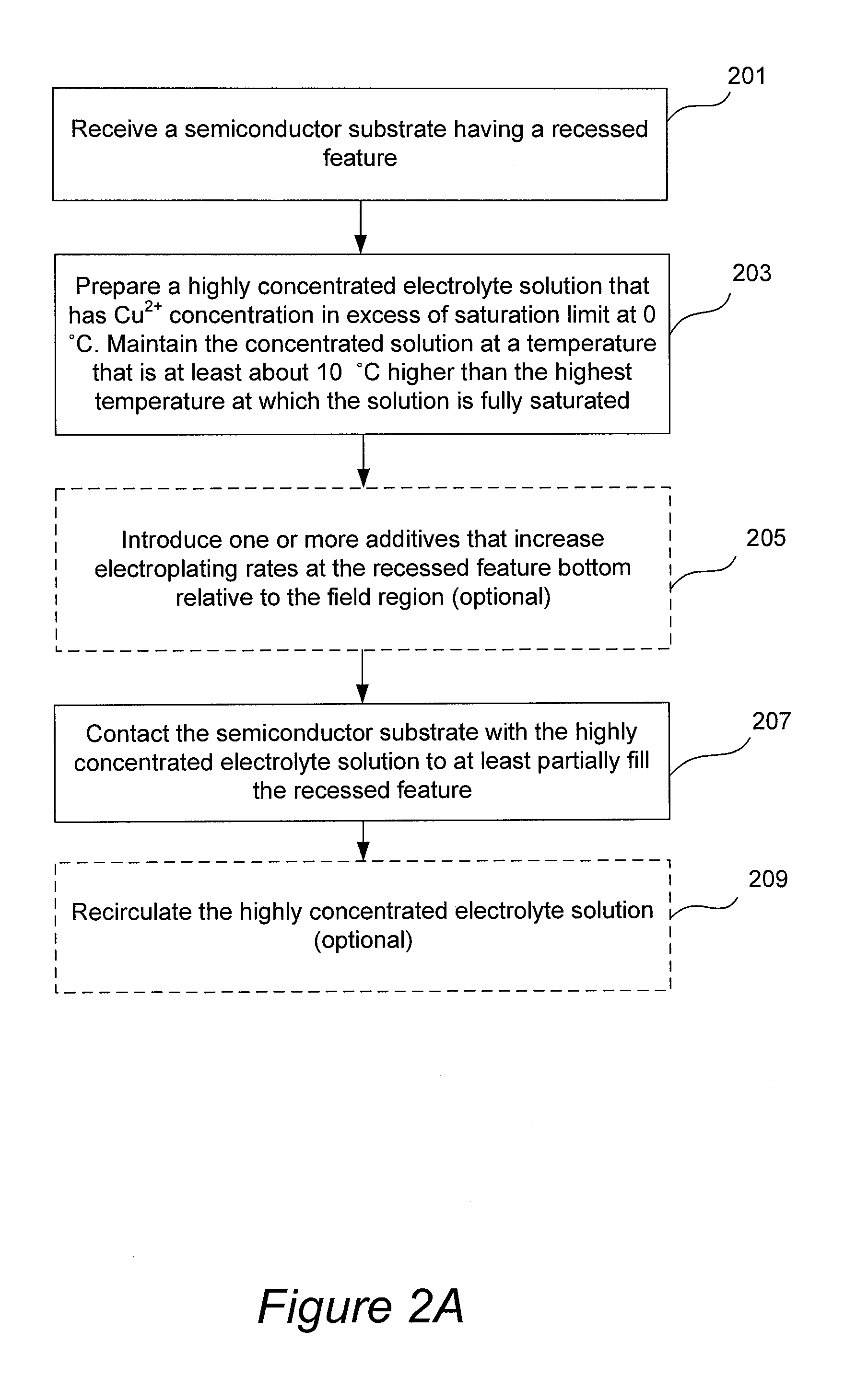
Electrolyte Concentration Control System for High Rate Electroplating
An electroplating apparatus for filling recessed features on a semiconductor substrate includes an electrolyte concentrator configured for concentrating an electrolyte having Cu2+ ions to form a concentrated electrolyte solution that would have been supersaturated at 20° C. The electrolyte is maintained at a temperature that is higher than 20° C., such as at least at about 40° C. The apparatus further includes a concentrated electrolyte reservoir and a plating cell, where the plating cell is configured for electroplating with concentrated electrolyte at a temperature of at least about 40° C. Electroplating with electrolytes having Cu2+ concentration of at least about 60 g / L at temperatures of at least about 40° C. results in very fast copper deposition rates, and is particularly well-suited for filling large, high aspect ratio features, such as through-silicon vias.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Apparatus and method for depositing and planarizing thin films of semiconductor wafers
An electroplating apparatus for depositing a metallic layer on a surface of a wafer is provided. In one example, a proximity head capable of being electrically charged as an anode is placed in close proximity to the surface of the wafer. A plating fluid is provided between the wafer and the proximity head to create localized metallic plating.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Plating apparatus and method
Owner:EBARA CORP
Insoluble anode with an auxiliary electrode
A method and apparatus for plating a metal onto a substrate. The apparatus includes a fluid basin configured to contain a plating solution, an anode fluid volume positioned in a lower portion of the fluid basin, a cathode fluid volume positioned in an upper portion of the fluid basin, an ionic membrane positioned to separate the anode fluid volume from the cathode fluid volume, a plating electrode centrally positioned in the anode fluid volume, and a deplating electrode positioned adjacent the plating electrode in the anode fluid volume.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Control of electrolyte hydrodynamics for efficient mass transfer during electroplating
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for electroplating
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer and an auxiliary cathode located between the anode and the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface. The auxiliary cathode is configured to shape the current distribution from the anode. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for electroplating
Electrolytic plating of a workpiece is enhanced by providing a resistor between the workpiece and electrically conductive support member.
Owner:IBM CORP
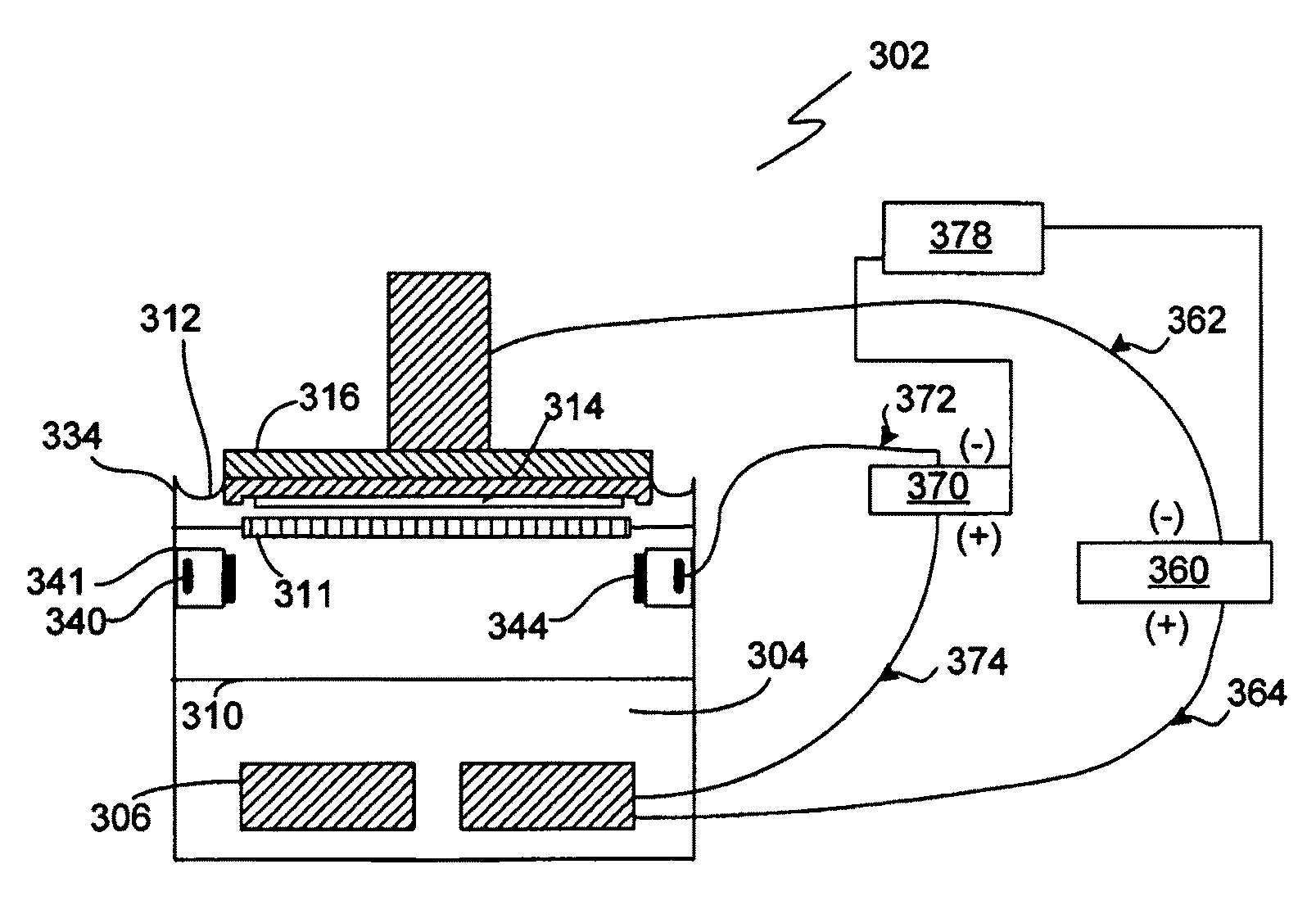
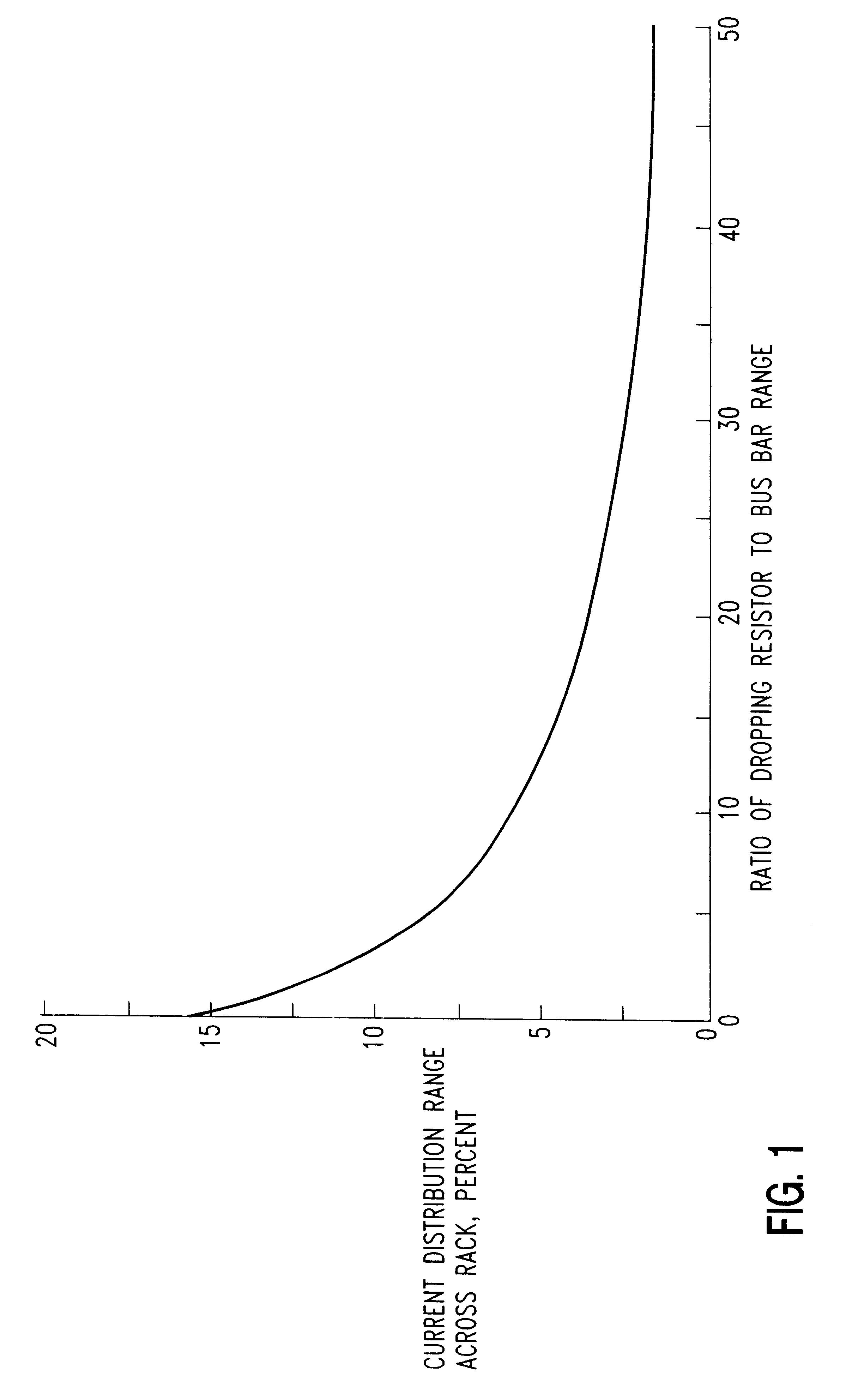
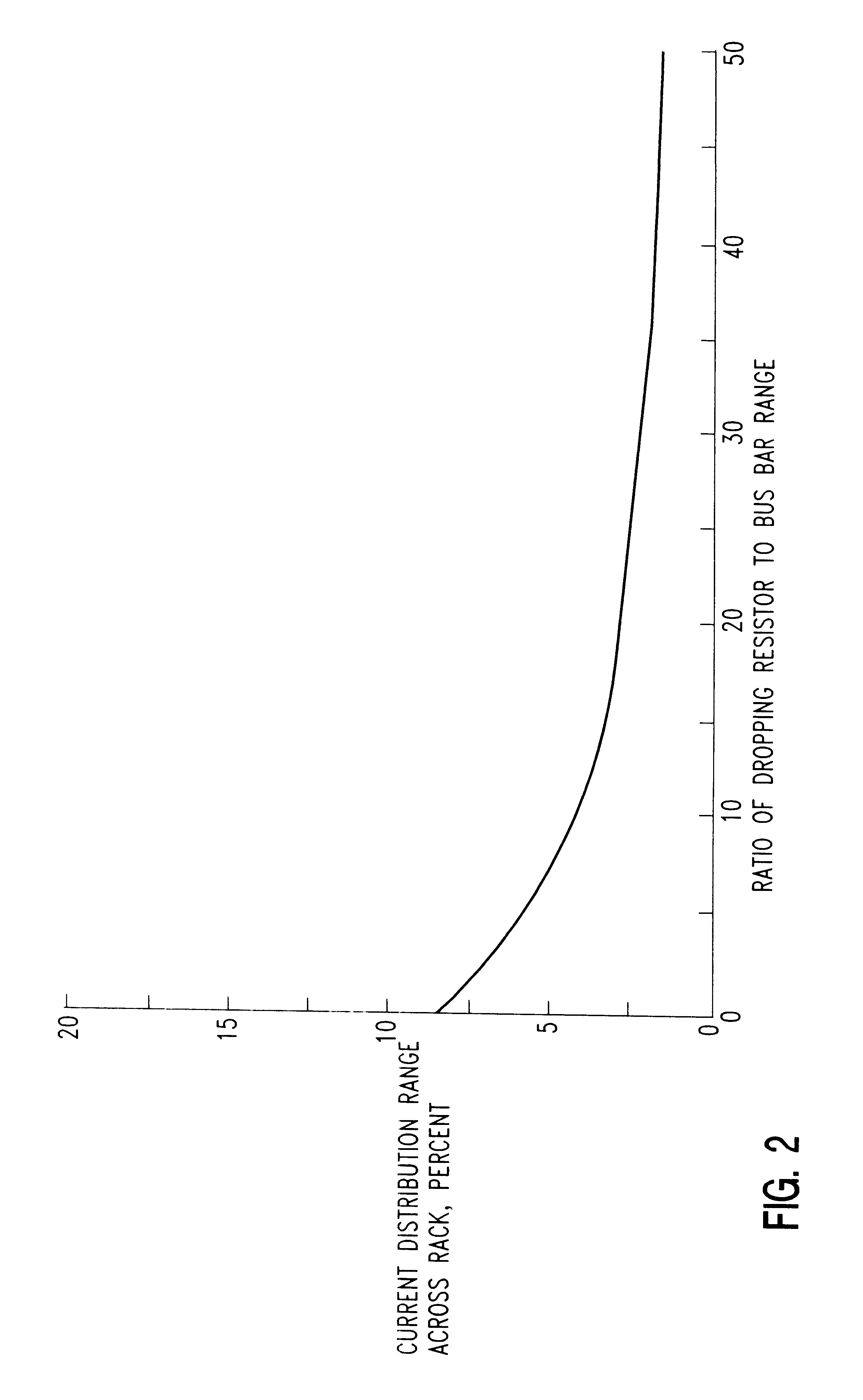
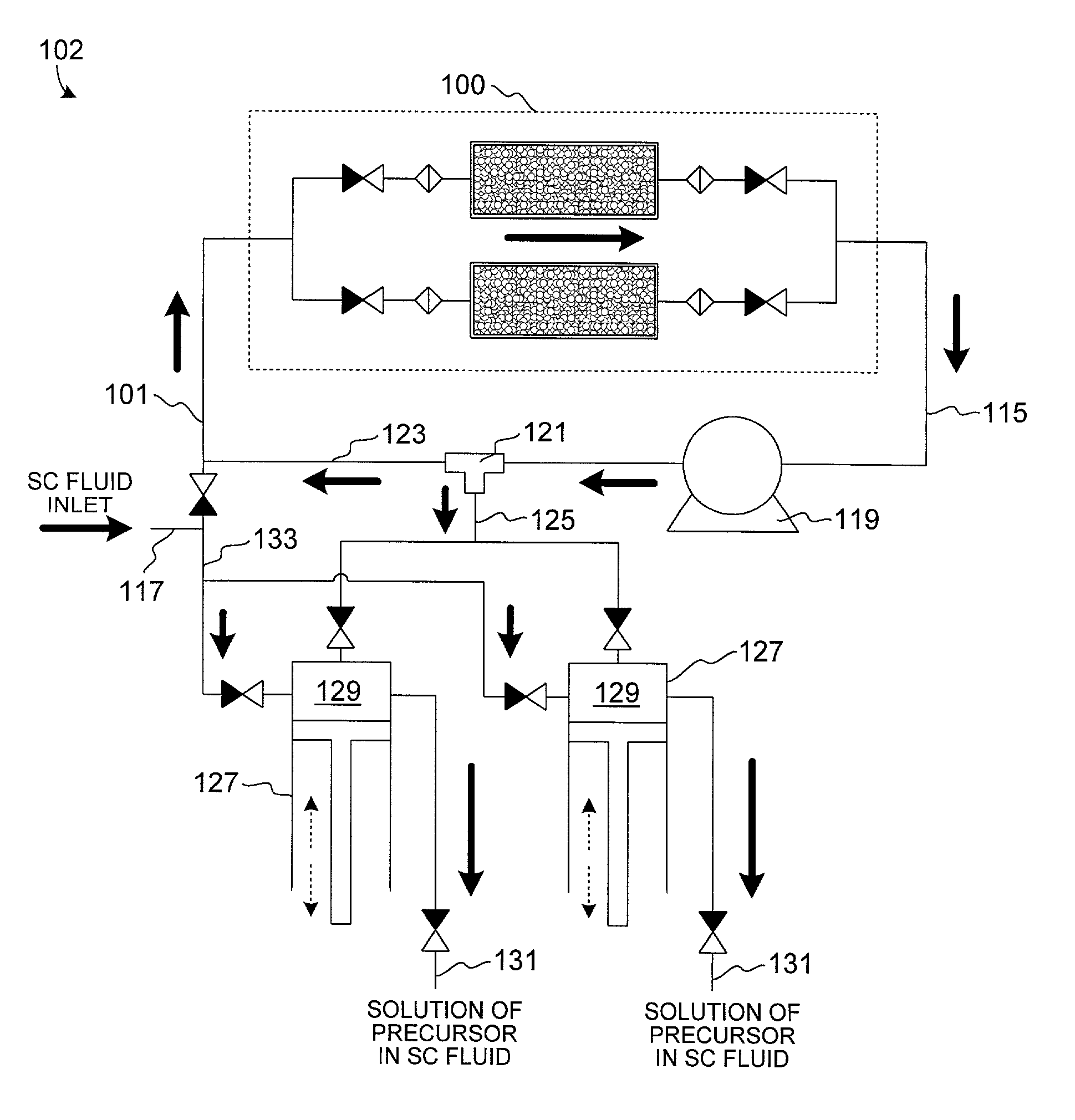
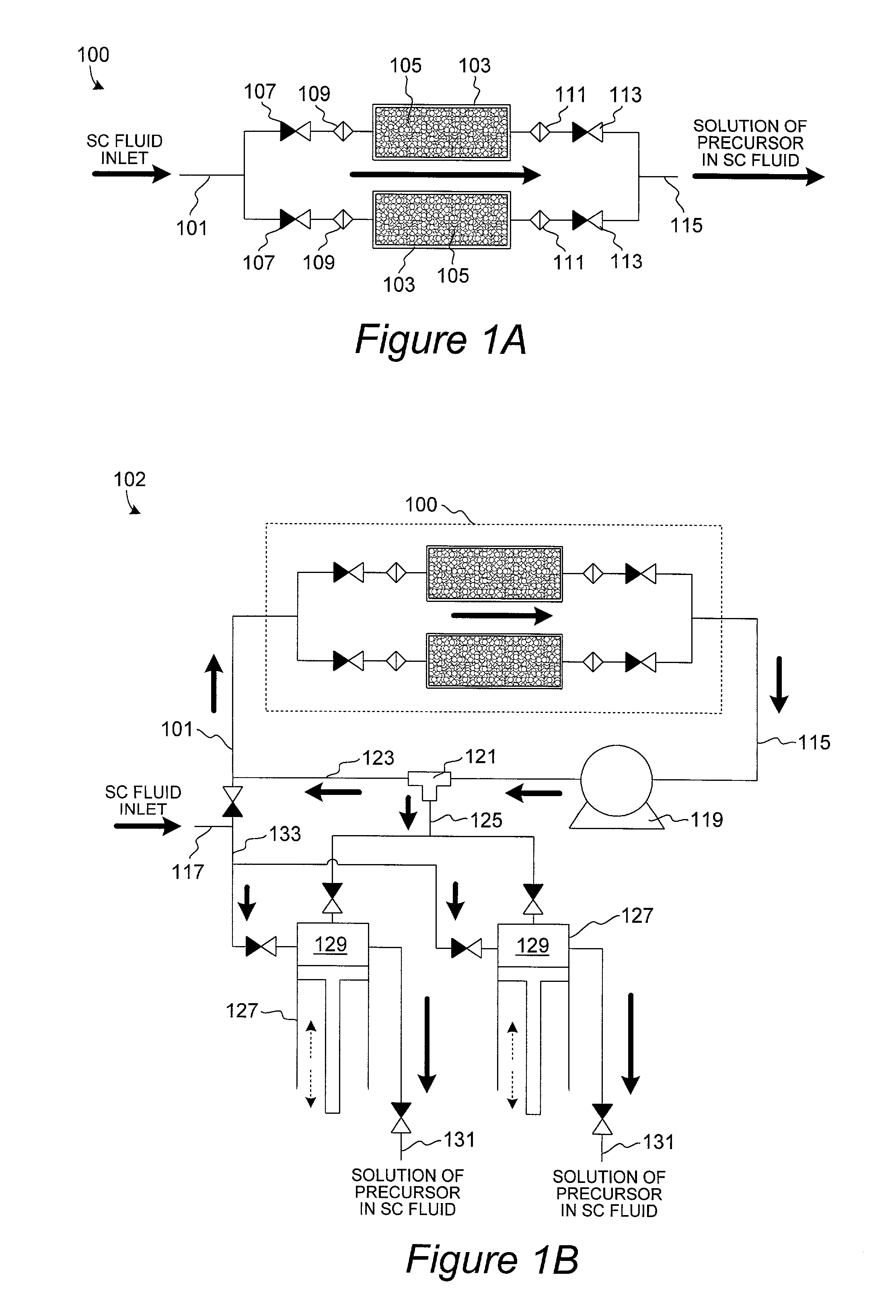
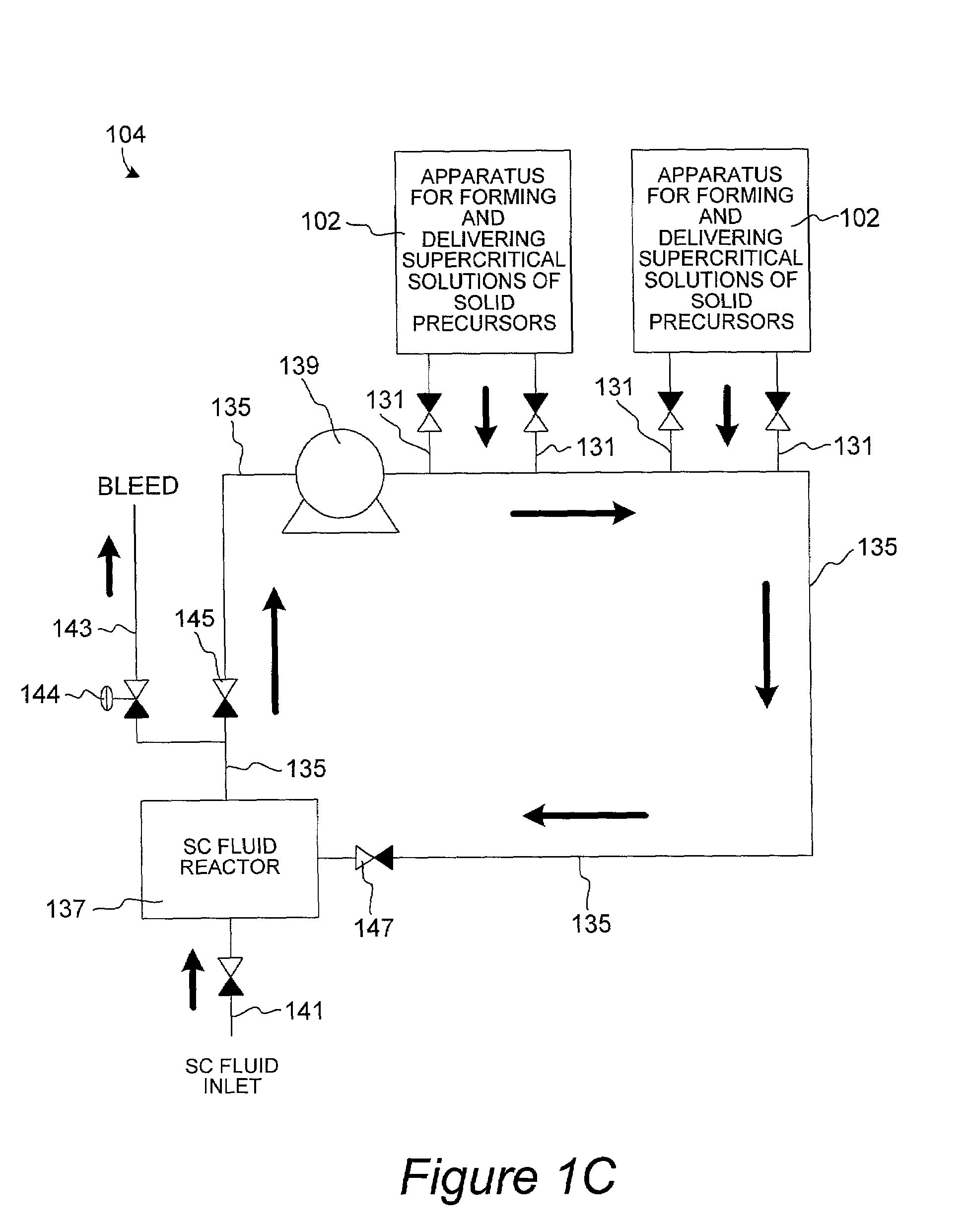
Method and apparatus for introduction of solid precursors and reactants into a supercritical fluid reactor
The present invention pertains to apparatus and methods for introduction of solid precursors and reactants into a supercritical fluid reactor. Solids are dissolved in supercritical fluid solvents in generator apparatus separate from the supercritical fluid reactor. Such apparatus preferably generate saturated solutions of solid precursors via recirculation of supercritical fluids through a vessel containing the solid precursors. Supercritical solutions of the solids are introduced into the reactor, which itself is charged with a supercritical fluid. Supercritical conditions are maintained during the delivery of the dissolved precursor to the reactor. Recirculation of supercritical precursor solutions through the reactor may or may not be implemented in methods of the invention. Methods of the invention are particularly well suited for integrated circuit fabrication, where films are deposited on wafers under supercritical conditions.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
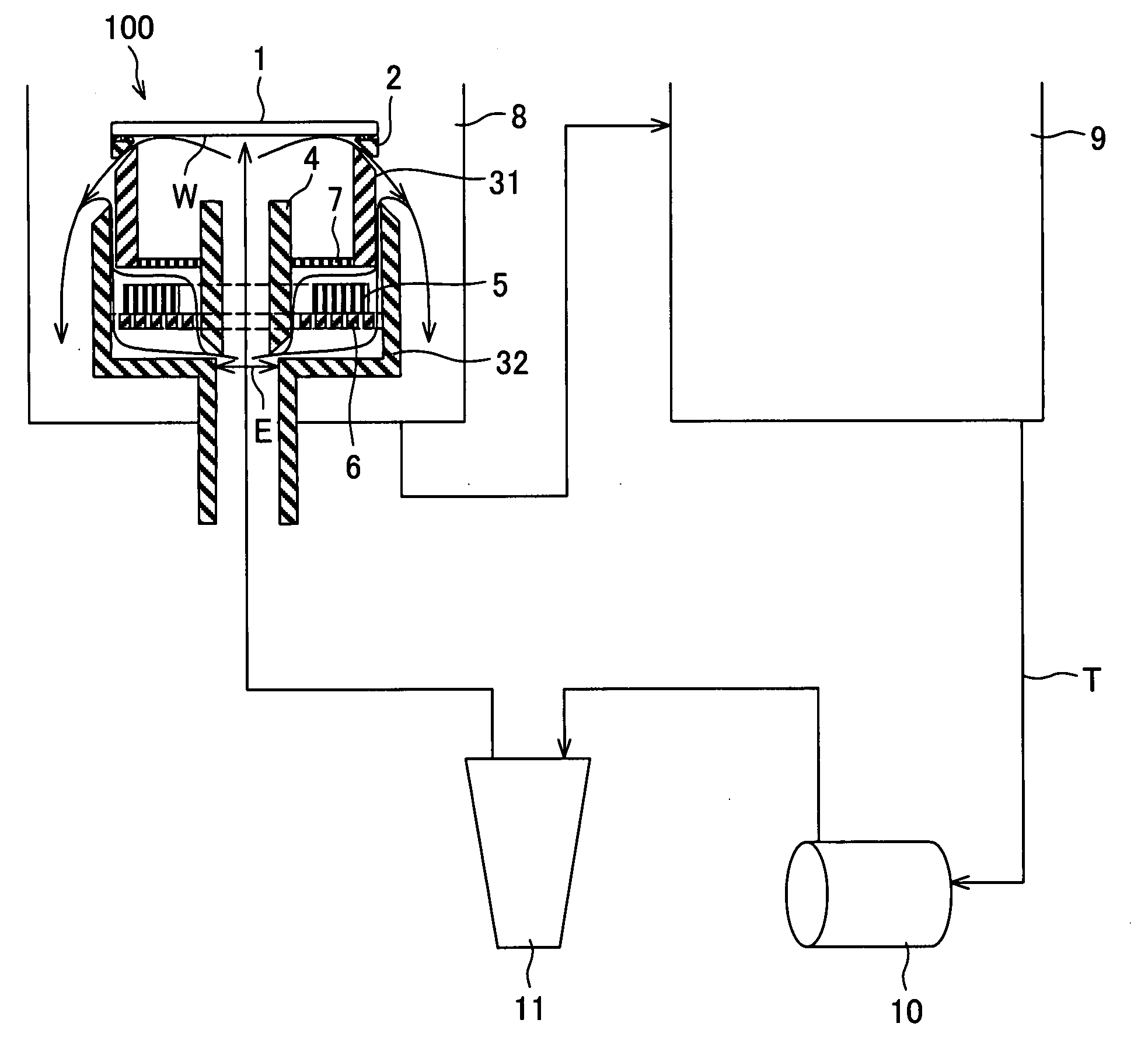
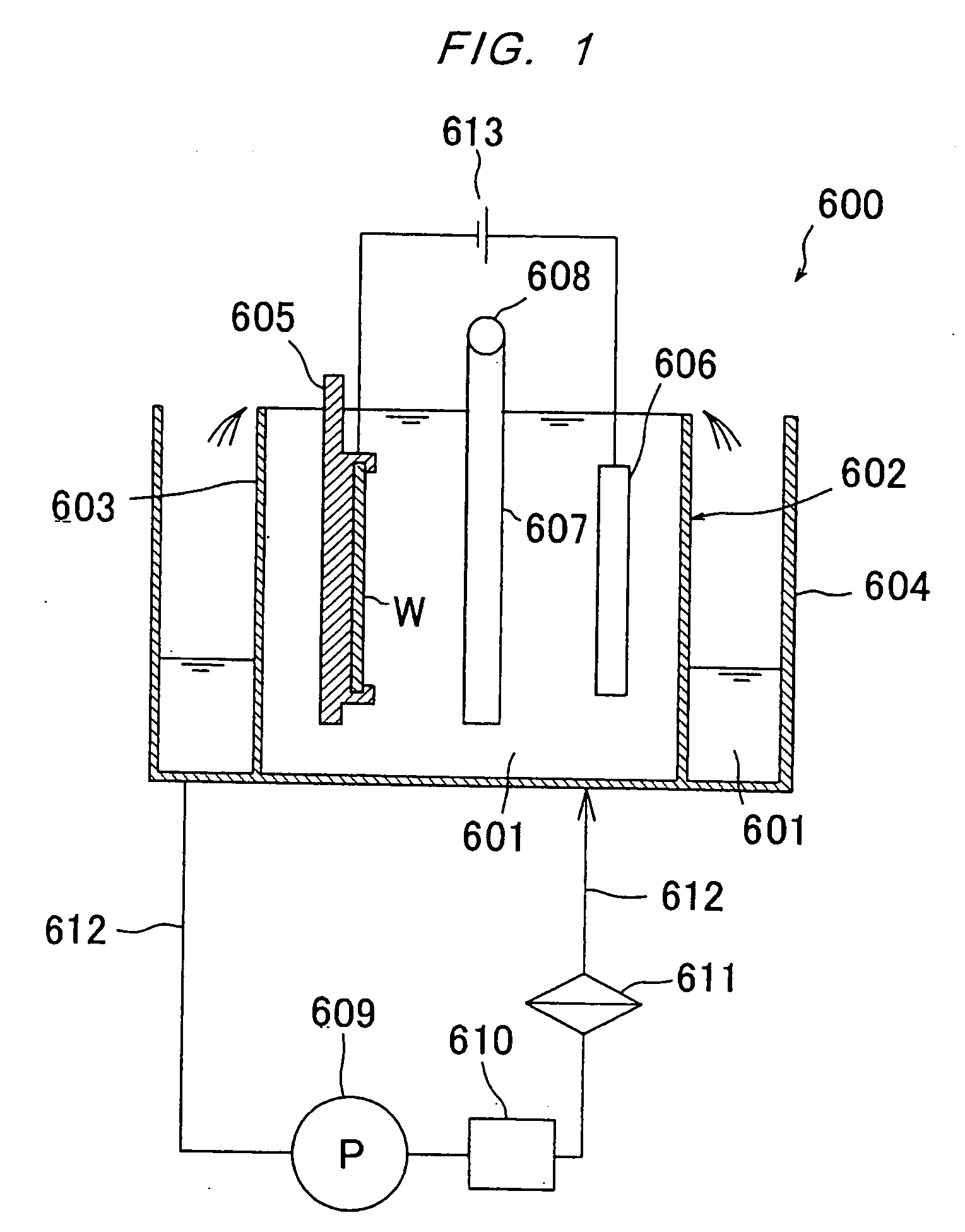
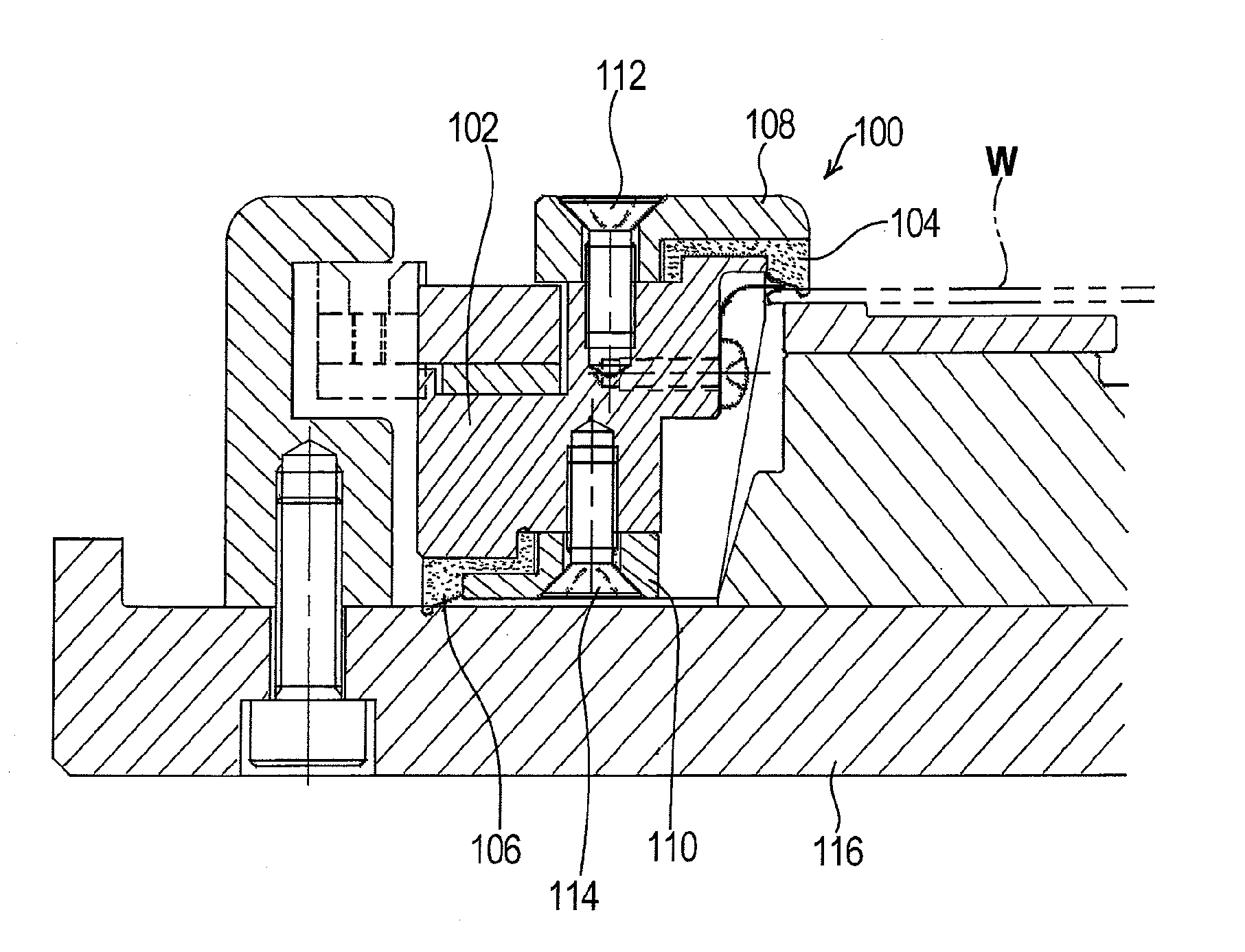
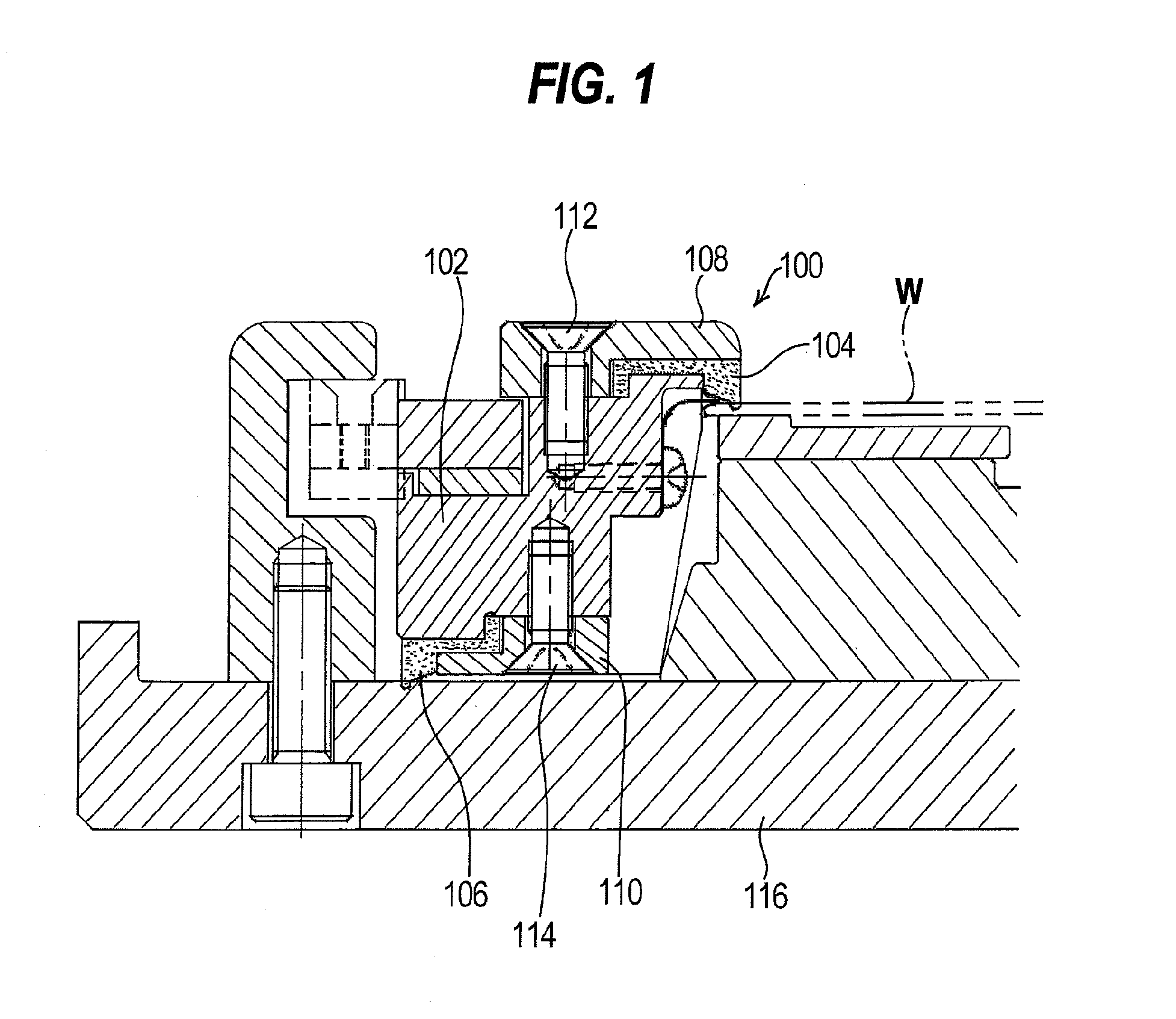
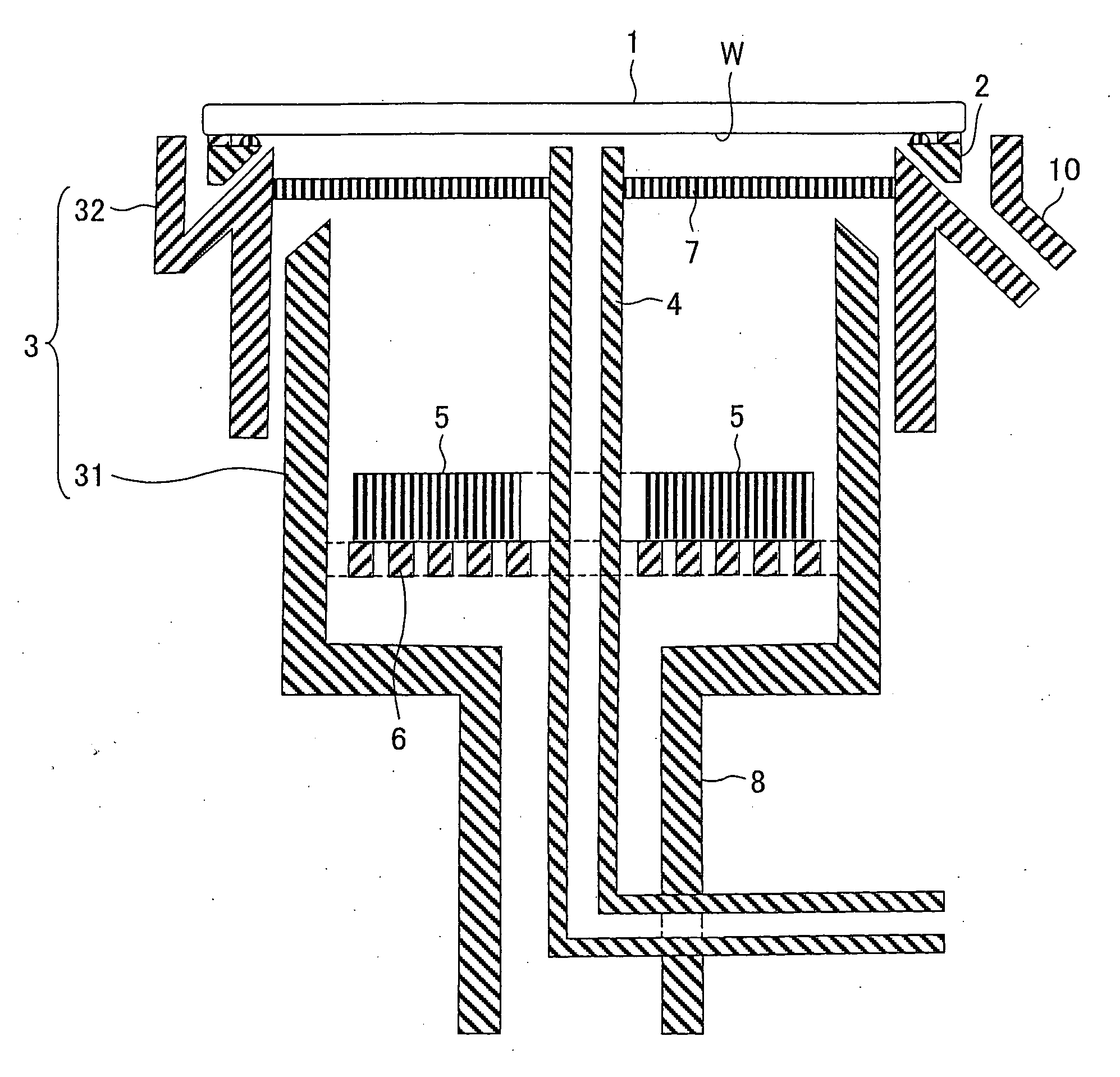
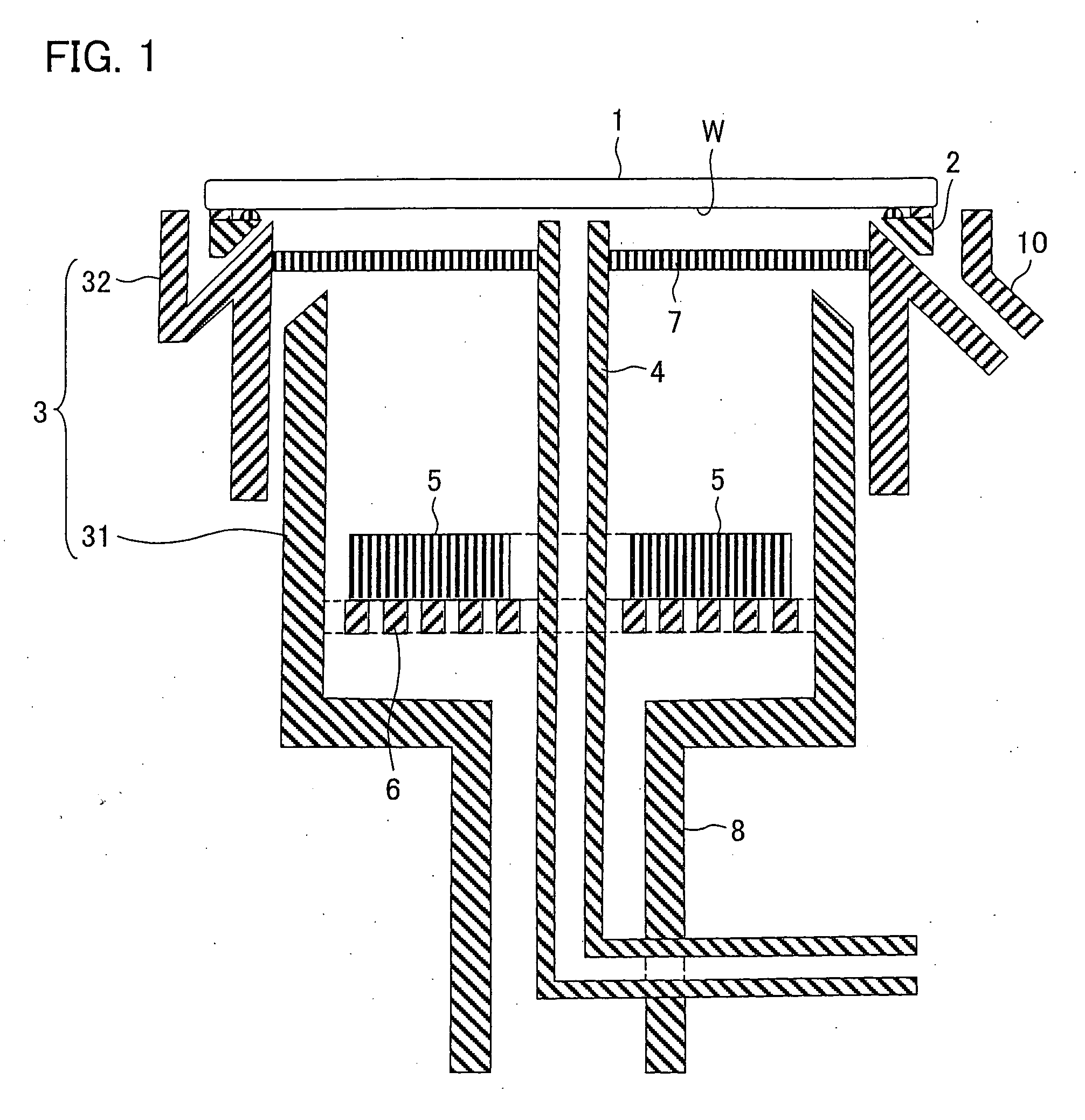
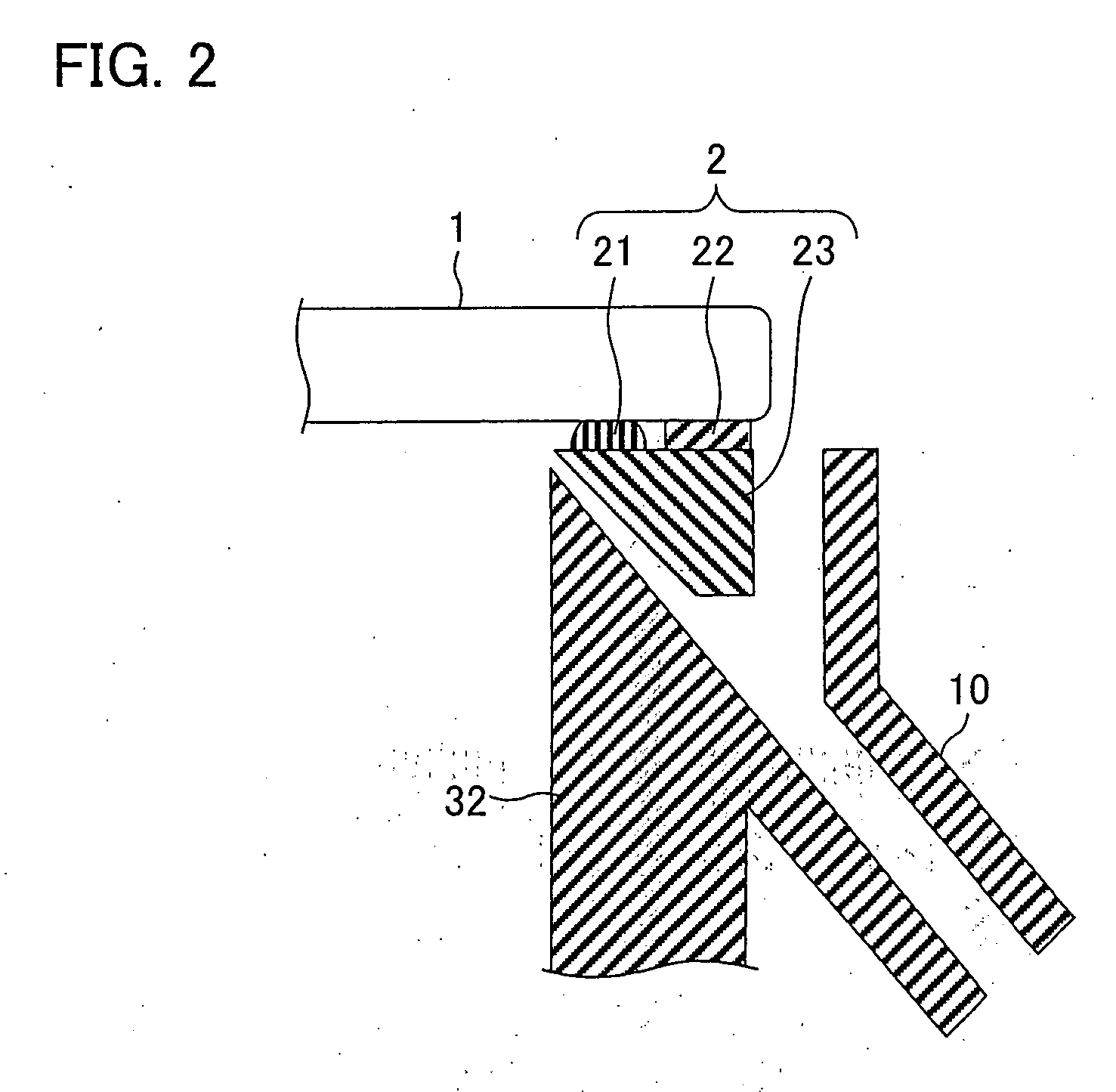
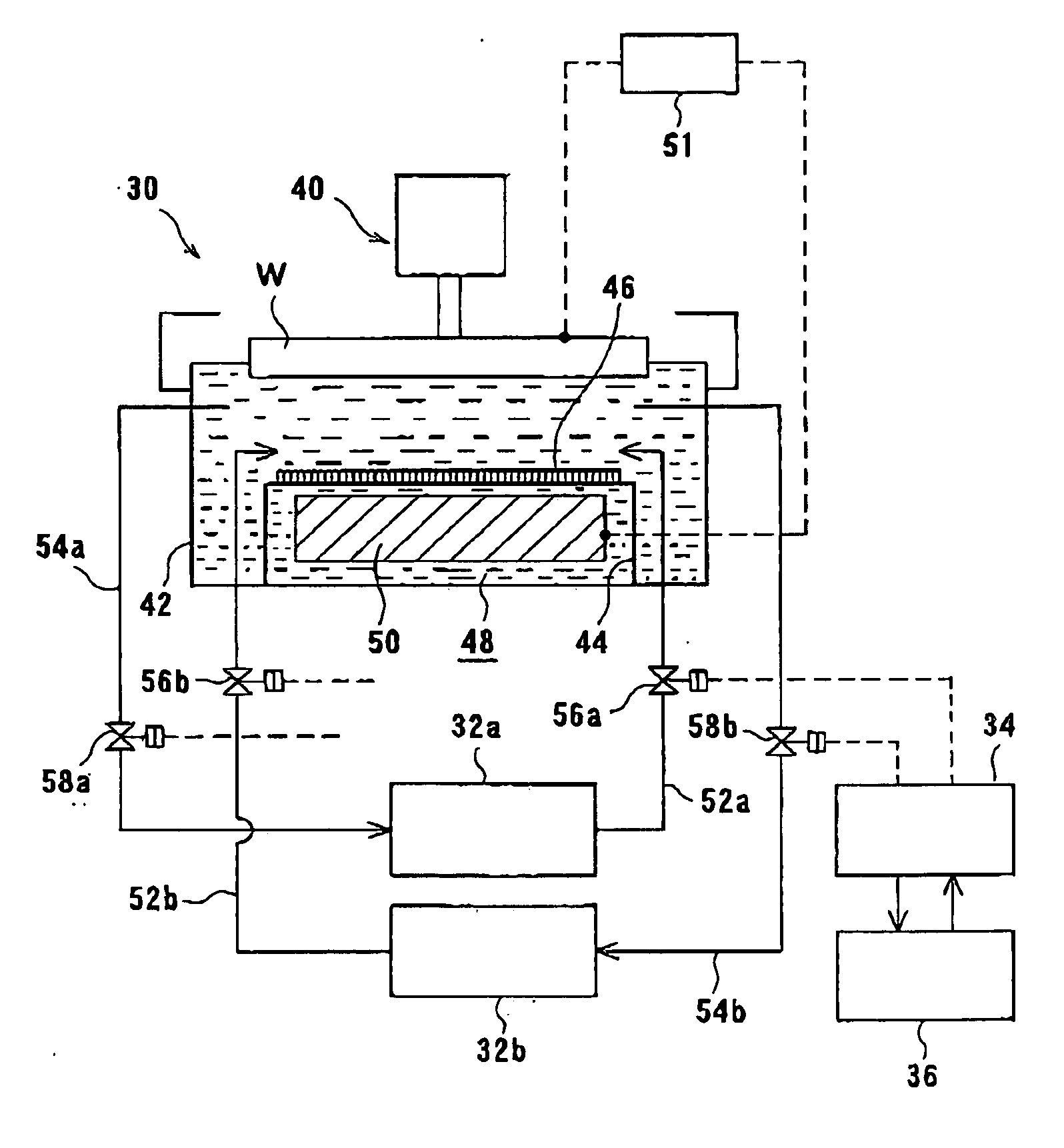
Plating apparatus, plating method, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
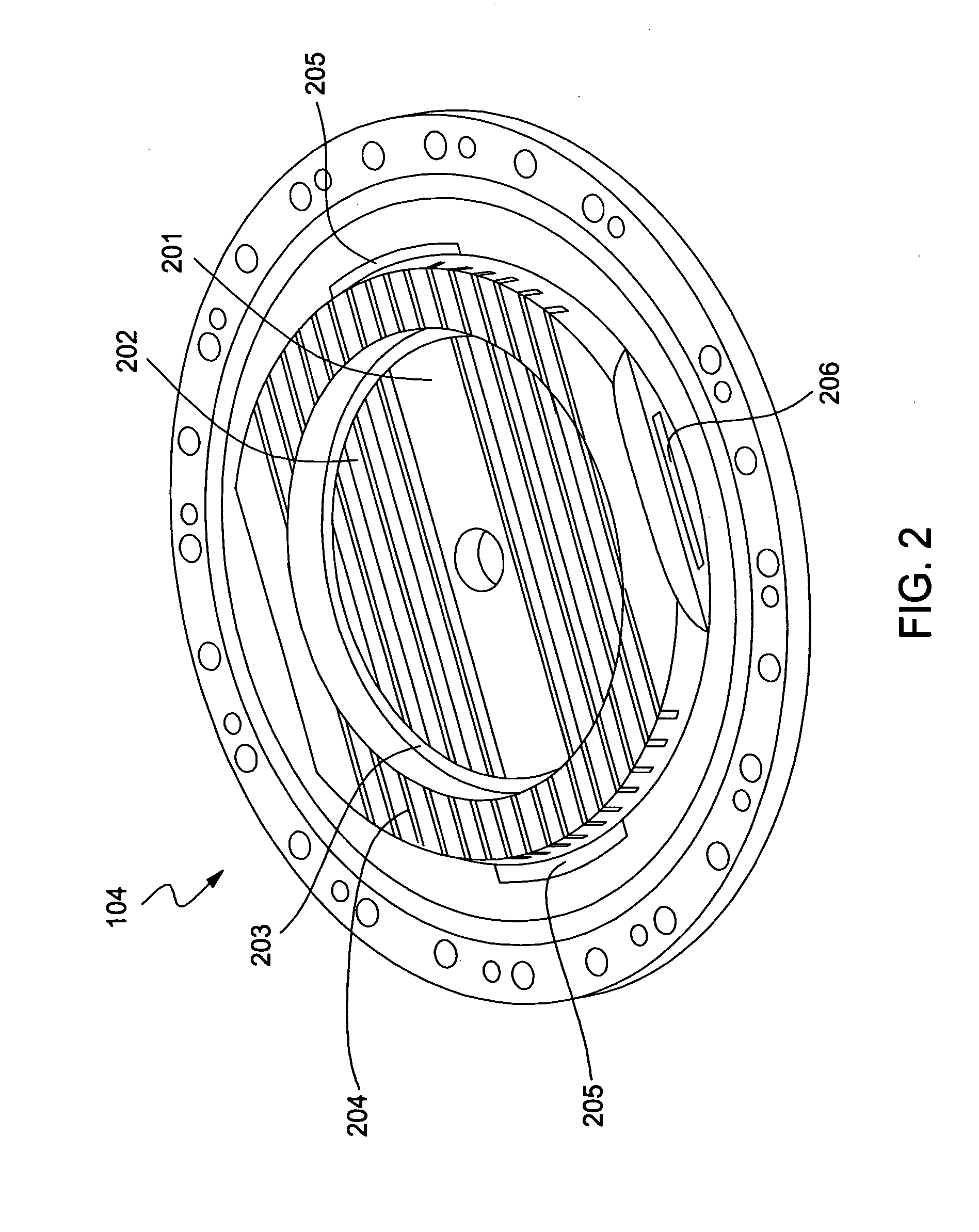
A plating apparatus according to the present invention is provided with a plating tank 100 in which an anode electrode 5 is provided, the plating apparatus performing the plating by (i) streaming a plating solution and an electrolytic liquid into the plating tank 100, (ii) emitting a jet of the plating solution to the plating-target face W of the semiconductor wafer 1 from the underneath of the semiconductor wafer 1, and (iii) streaming the electrolytic liquid to the anode electrode 5 while electrically conducting between the semiconductor wafer 1 and the anode electrode 5, the plating tank including a partition in between the semiconductor wafer 1 and the anode electrode 5, and the partition (i) separating the semiconductor wafer 1 and the anode electrode 5 and (ii) dividing the plating tank 100 into a plating-target substrate room and an anode electrode room. Thus, in a face-down type fountain plating apparatus, the plating quality would not be degraded by micro foreign solid particles originated from, for example, a black film while maintaining the operability of the apparatus.
Owner:SHARP KK
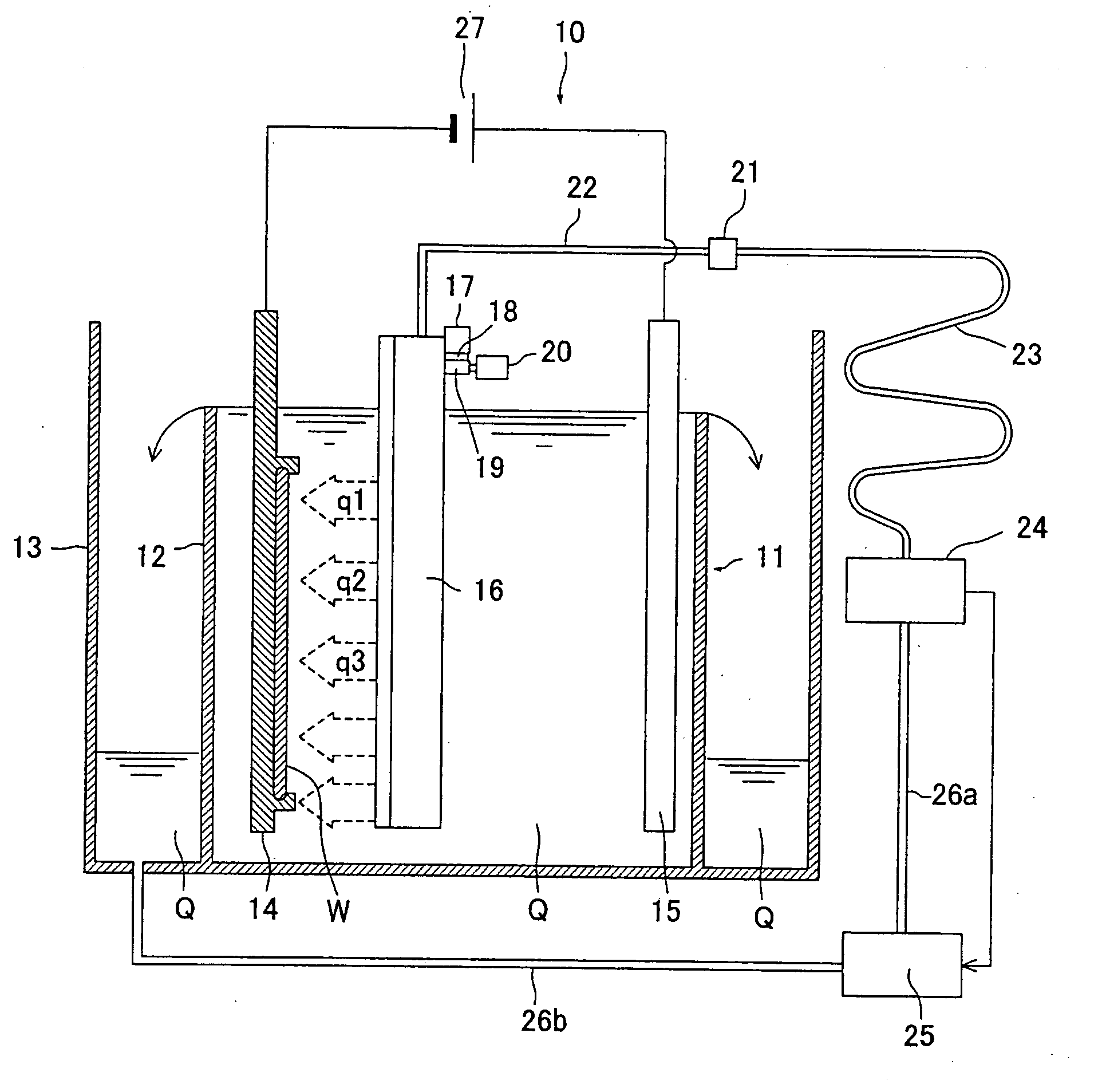
Electrochemical treating method such as electroplating and electrochemical reaction device therefor
InactiveUS20030019756A1Improve responseHigh constantAnodisationFrom normal temperature solutionsElectricityLiquid waste
A novel method of electrochemical treatment such as electroplating, etc. and an electrochemical reaction apparatus thereof which is high in reactability and able to be electrochemically reacted efficiently, which is small or zero in amount of generation of liquid waste such as electrolytic solution and cleaning liquid and therefore, amicable to the environment, and in which it is no more required to clean the electrode, etc. with cleaning liquid after reaction. Electrochemical reaction is executed in a reaction vessel (6) containing matter (5) which is in a supercritical or subcritical state and an electrolytic solution (1), and after reaction, the supercritical or subcritical matter (5) is shifted into a state of the matter (5) before being shifted into a critical state.
Owner:YOSHIDA +2
Electrolytic processing apparatus and method
There is provided an electrolytic processing apparatus and method which can produce products having various specifications with enhanced productivity, thus reducing the production cost, and which can respond flexibly to the movement toward finer interconnects in semiconductor devices. An electrolytic processing apparatus according to the present invention includes: an electrolytic processing unit including a substrate holder for holding a substrate, and a counter electrode plate disposed opposite the substrate held by the substrate holder, said electrolytic processing unit carrying out electrolytic processing by filling the space between the substrate held by the substrate holder and the counter electrode plate with an electrolysis solution while feeding electricity; and a plurality of electrolysis solution supply facilities for supplying different types of electrolysis solutions; wherein the electrolytic processing unit is selectively connectable to one of the plurality of electrolysis solution supply facilities.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Popular searches
Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing Electrophoretic coatings Semiconductor devices Electrical-based machining electrodes Electrode shape/forms Diaphragms Electrical-based auxillary apparatus Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurement Vacuum evaporation coating Sputtering coating
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com