Patents
Literature
460results about "Current conducting devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
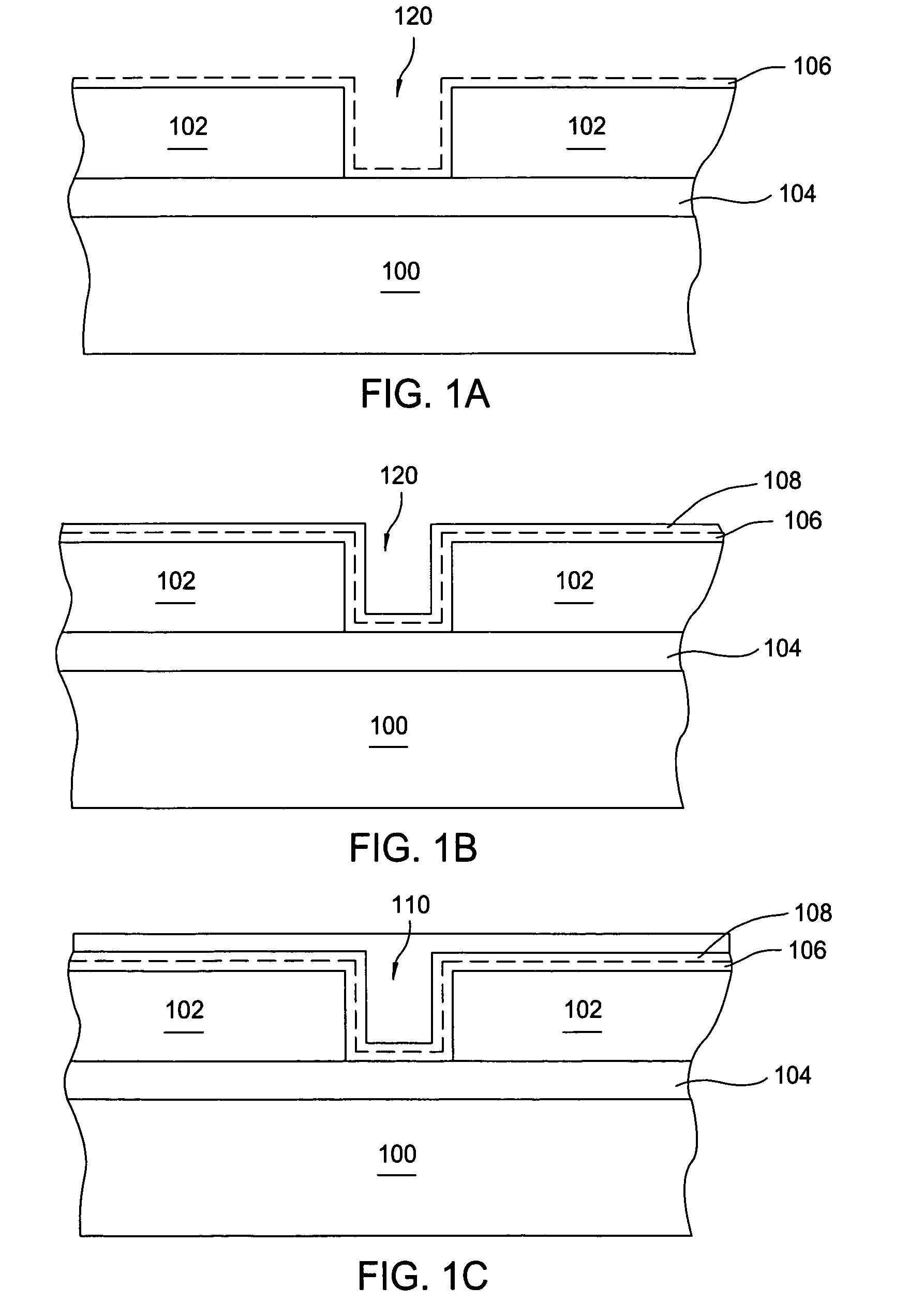
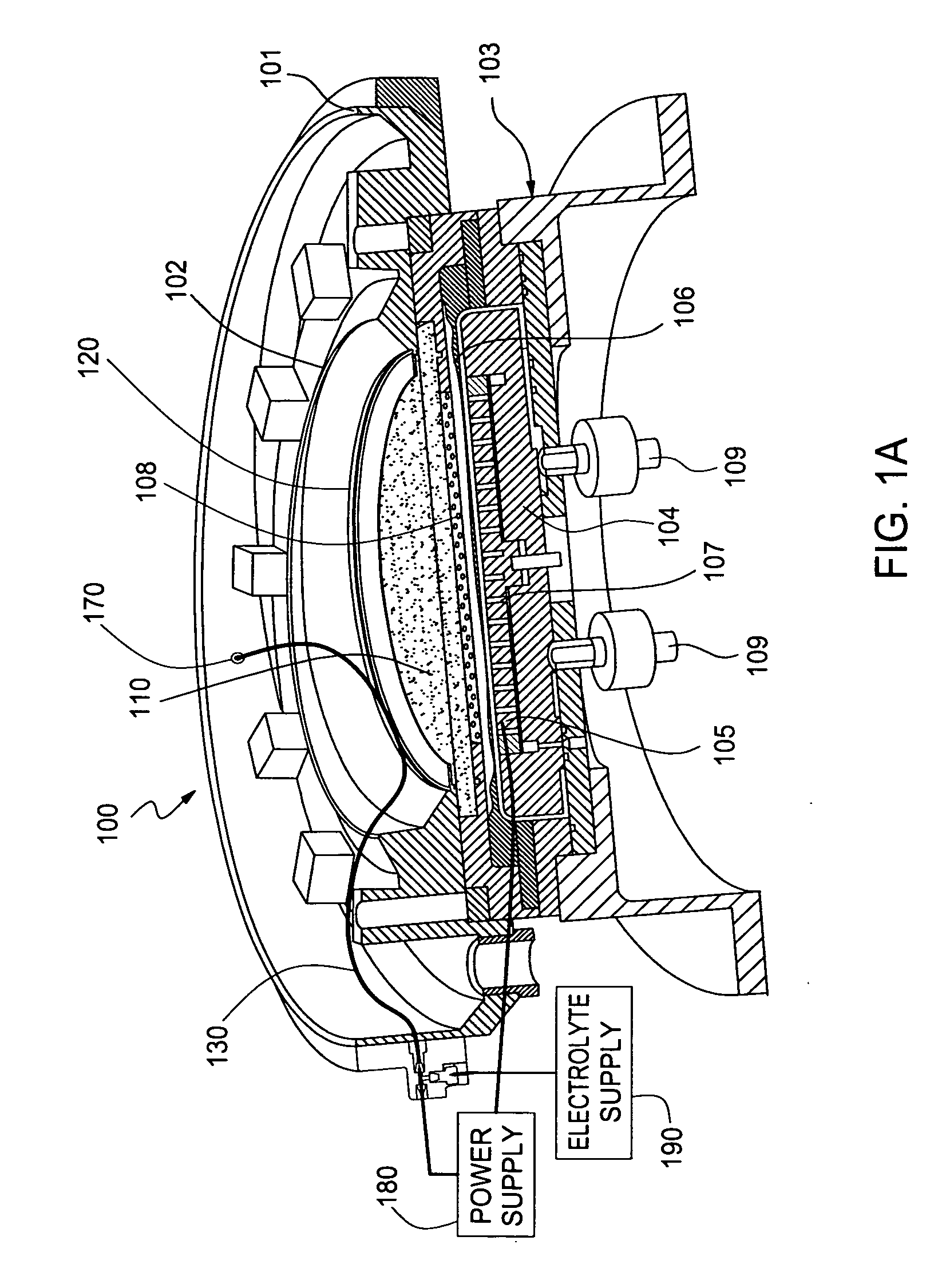
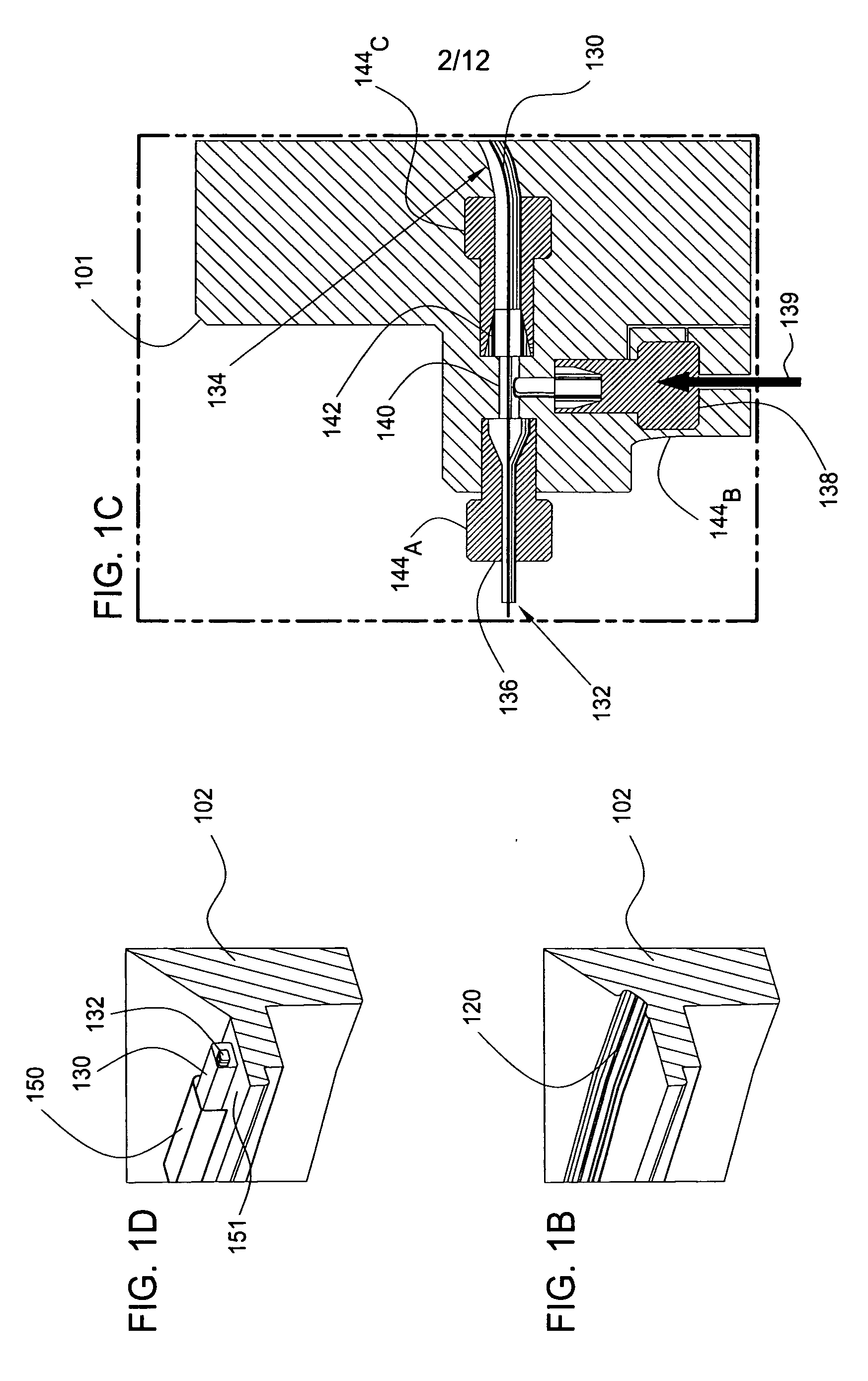
Method and apparatus for electroplating
ActiveUS20100032310A1Improve uniformityImprovement becomes significantly less pronounced or non-existentCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
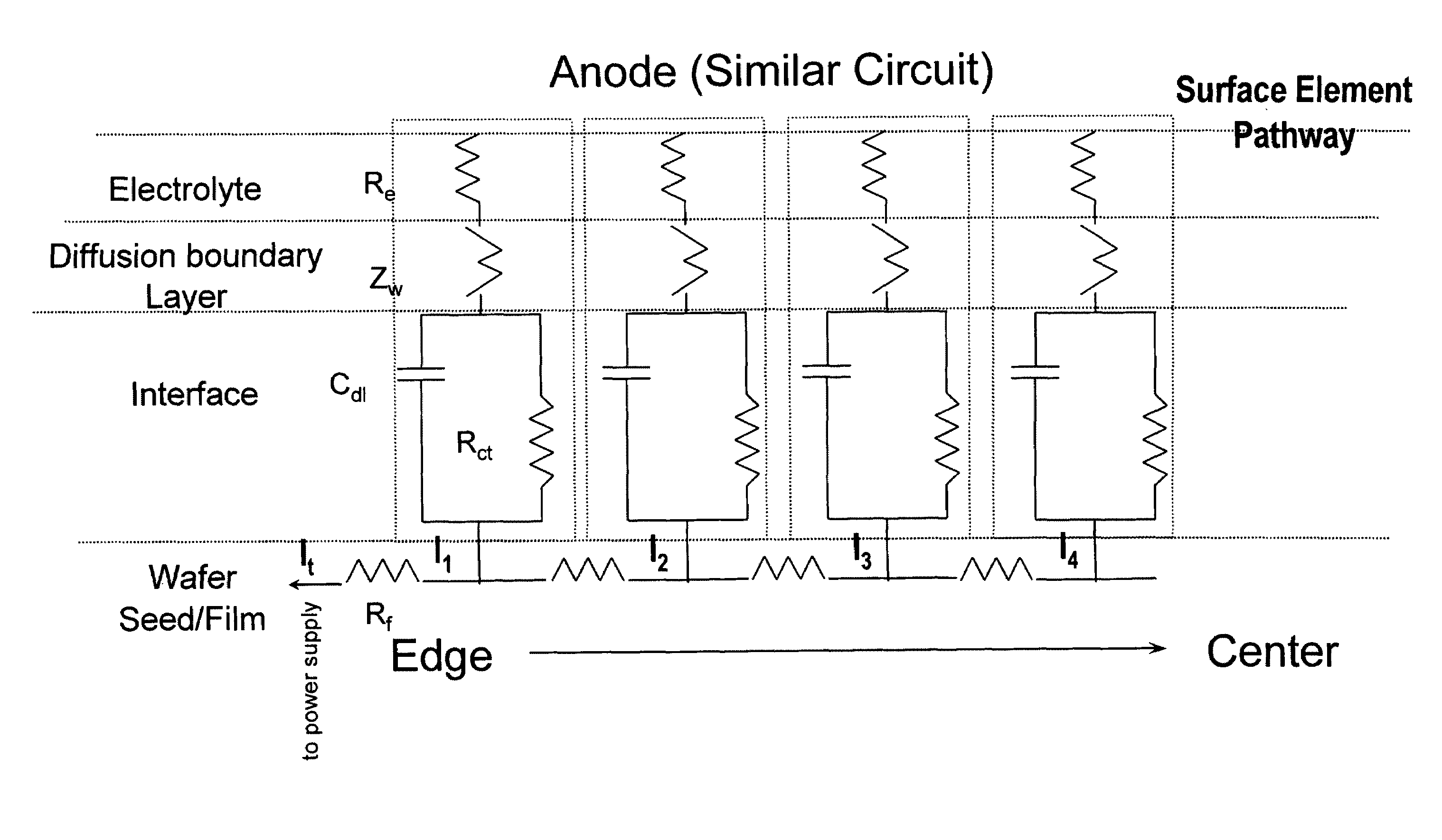
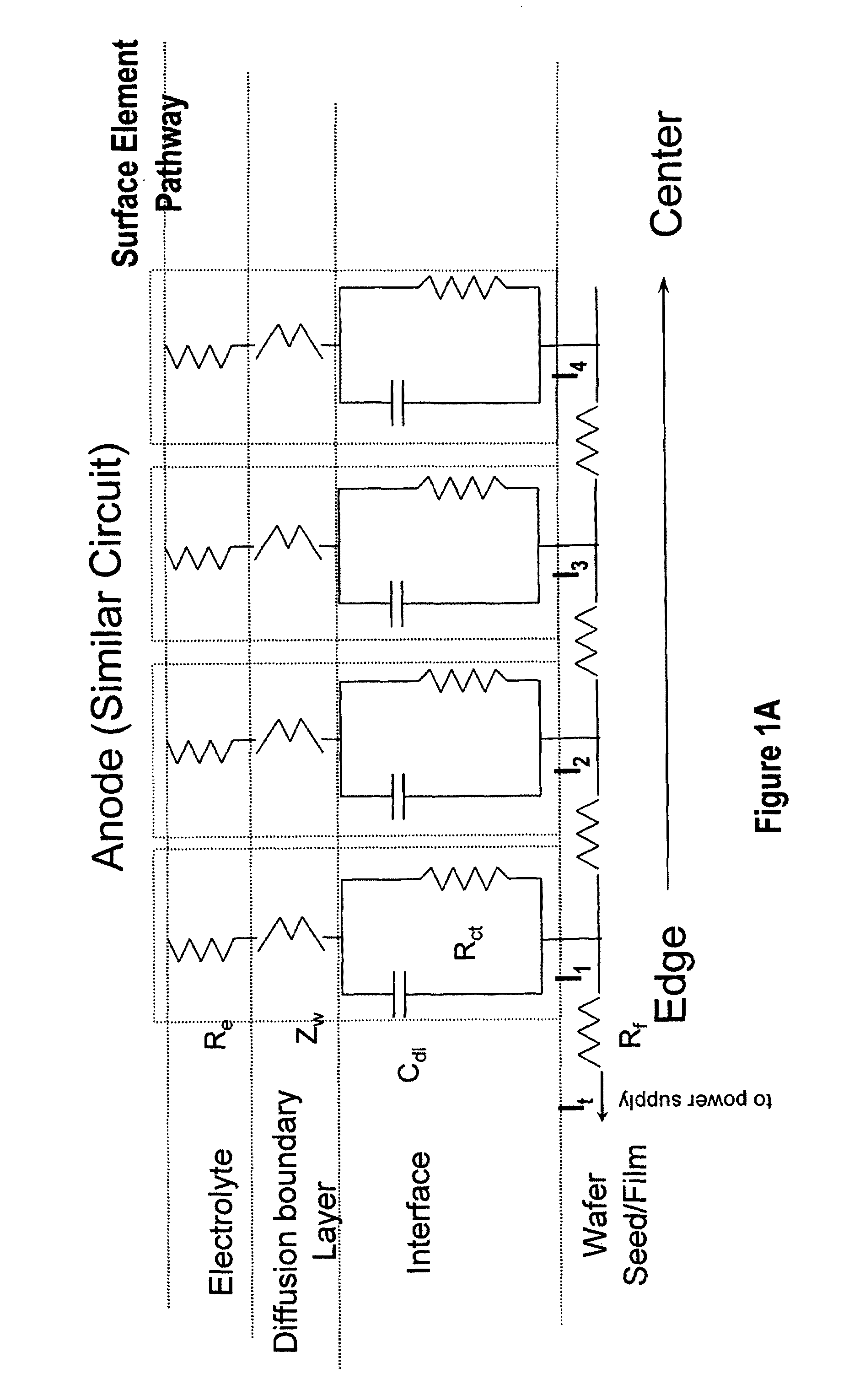
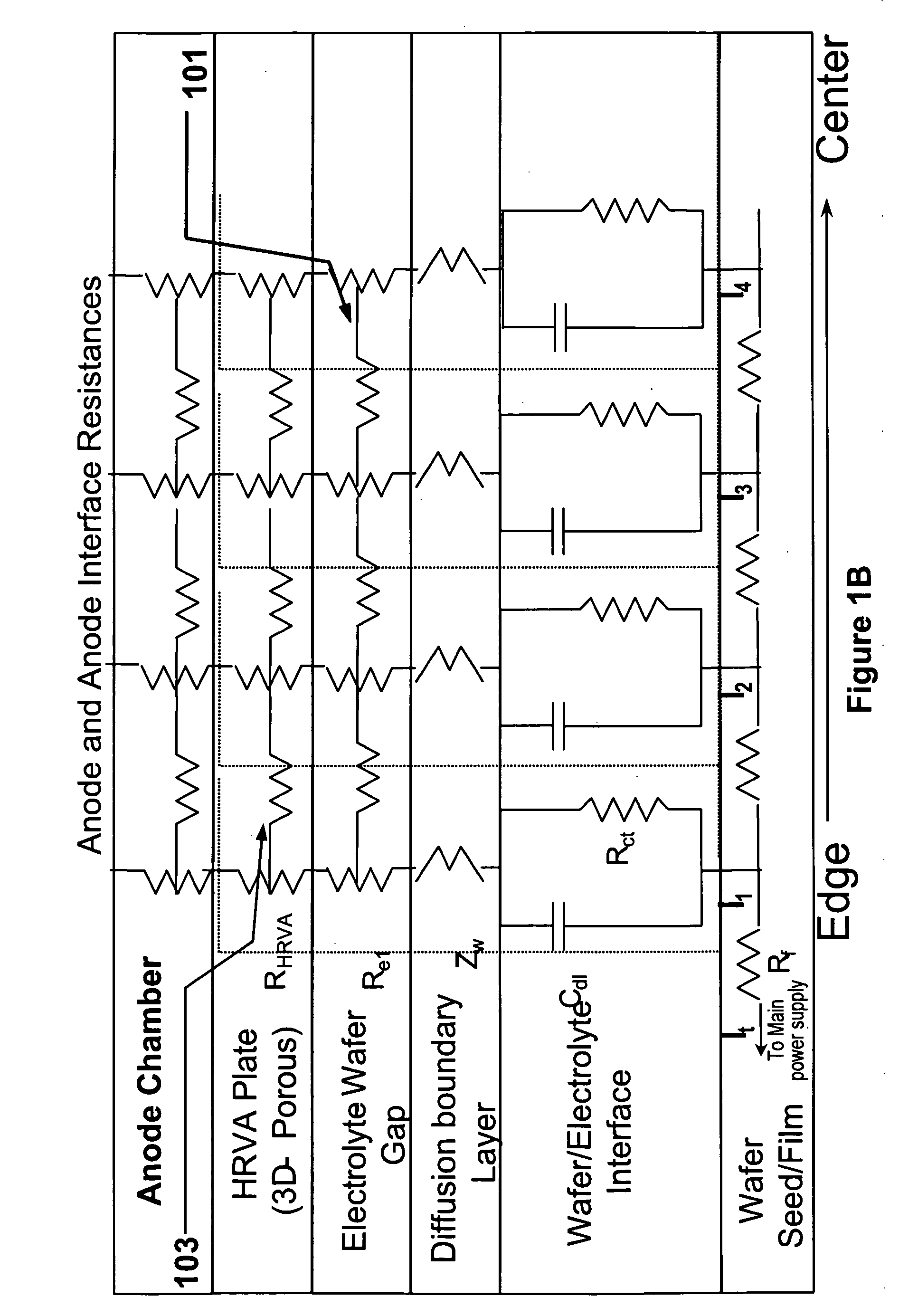
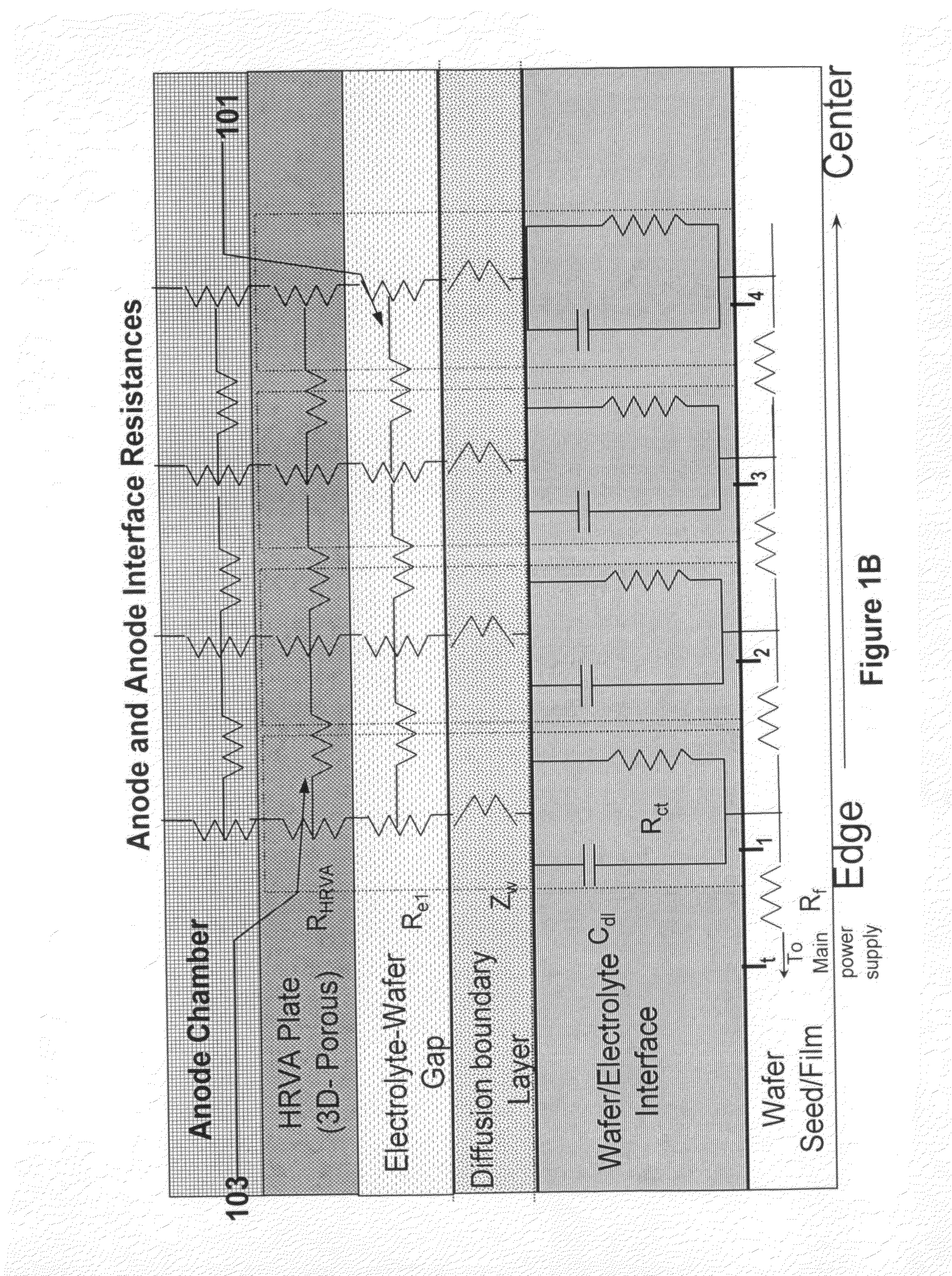
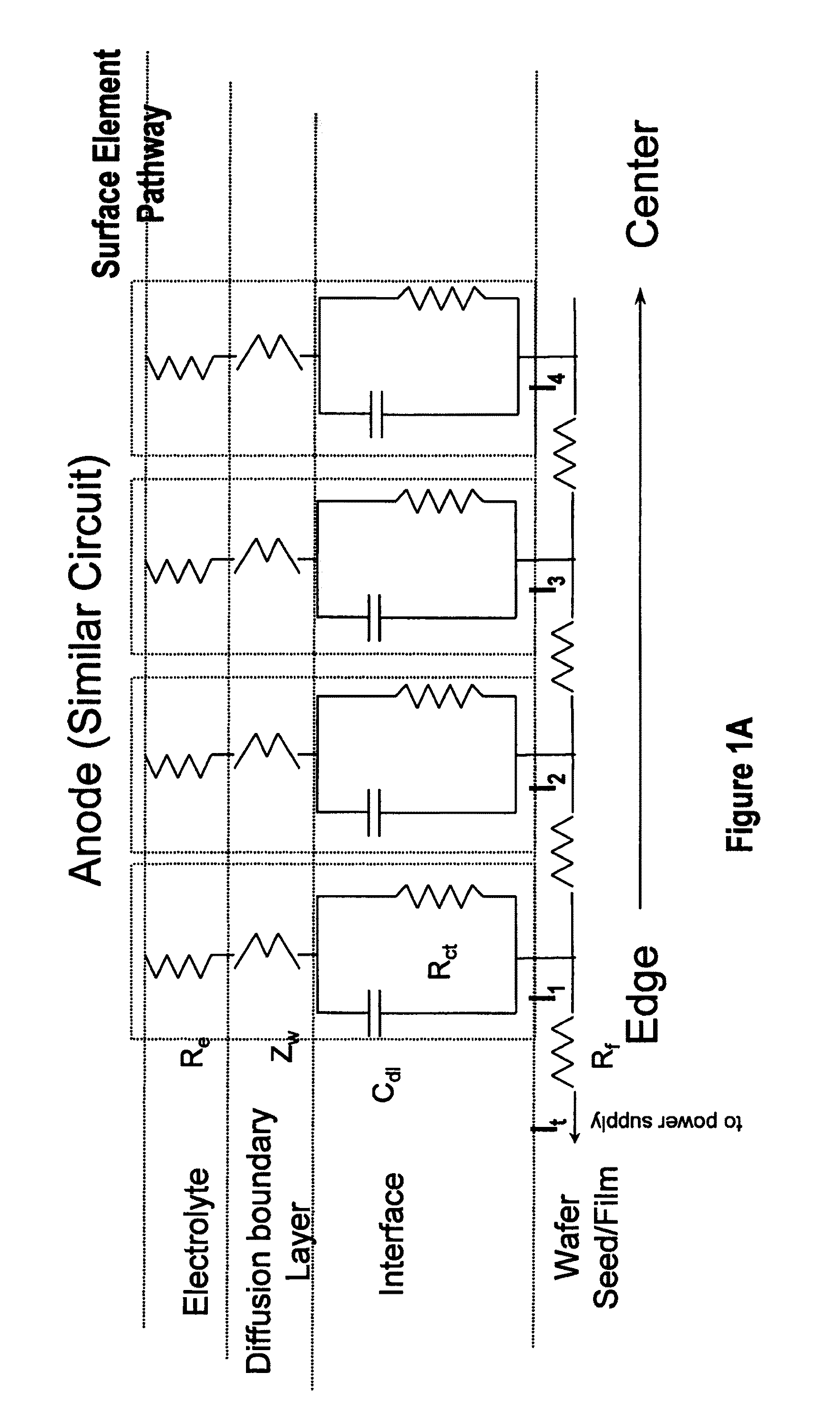
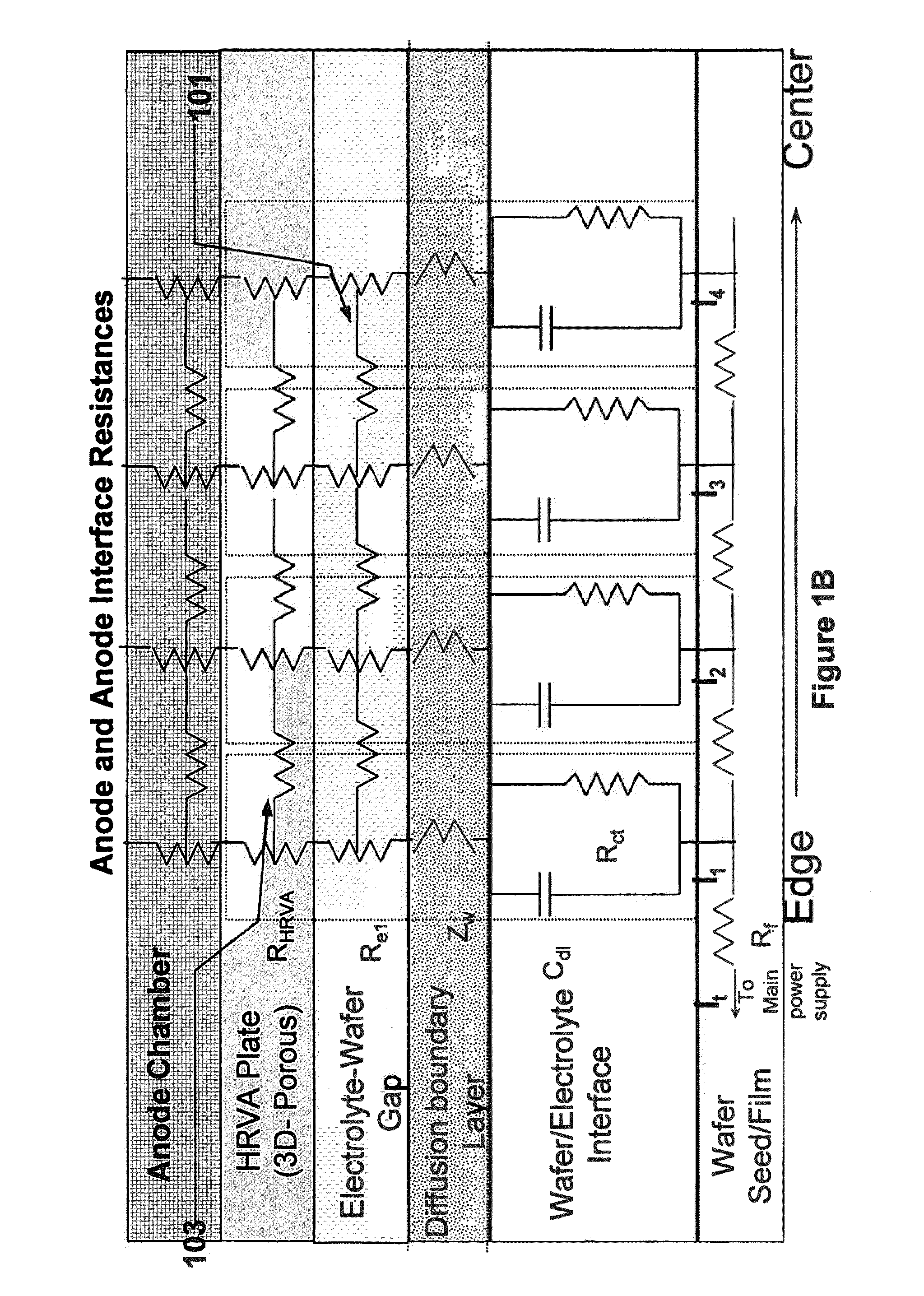
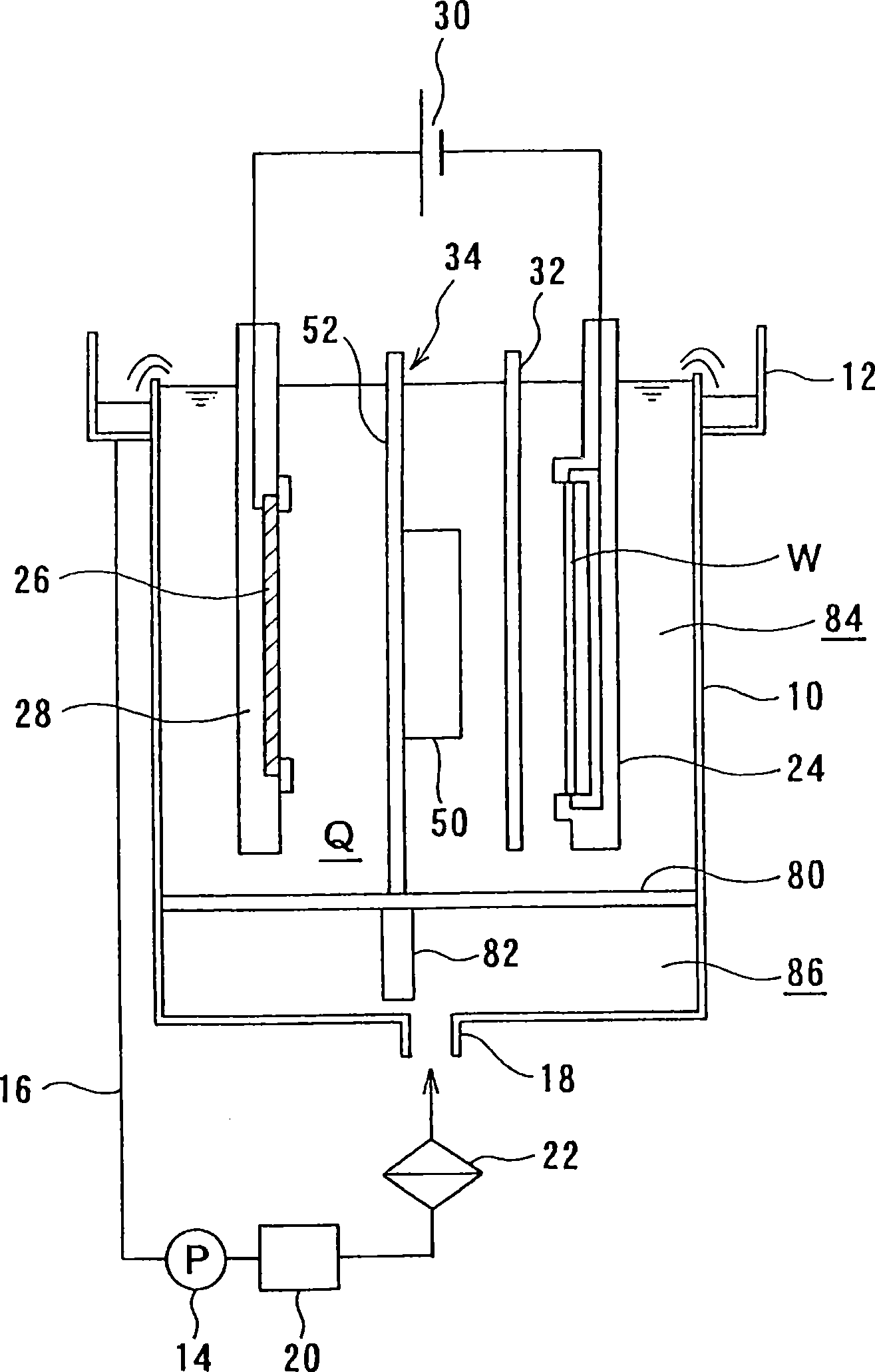
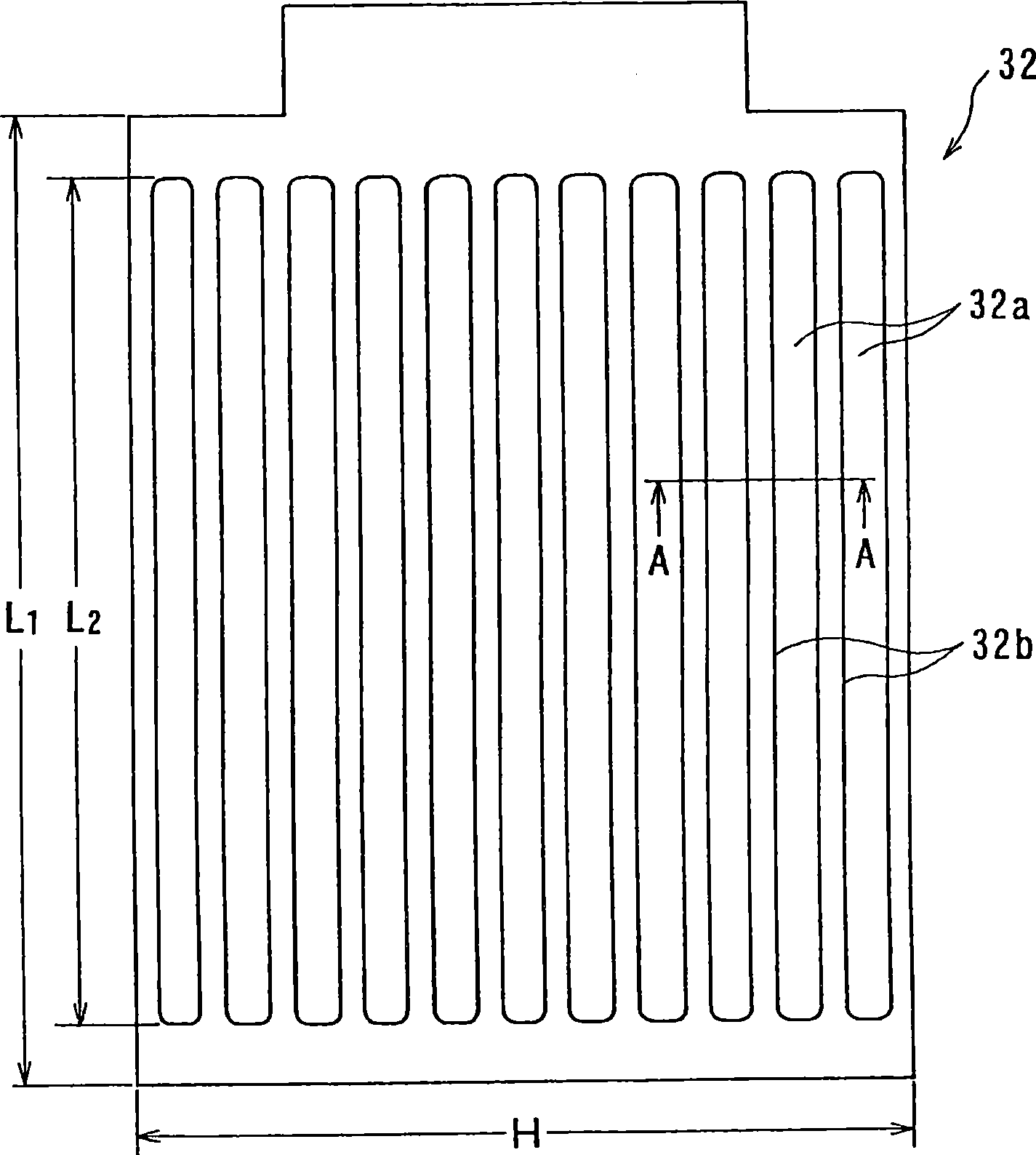
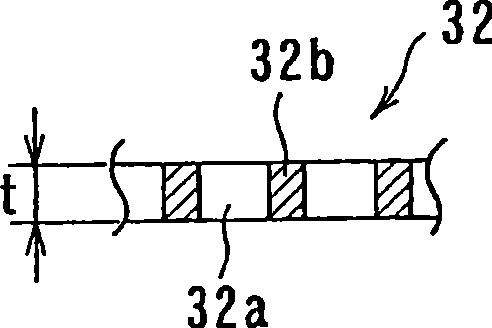
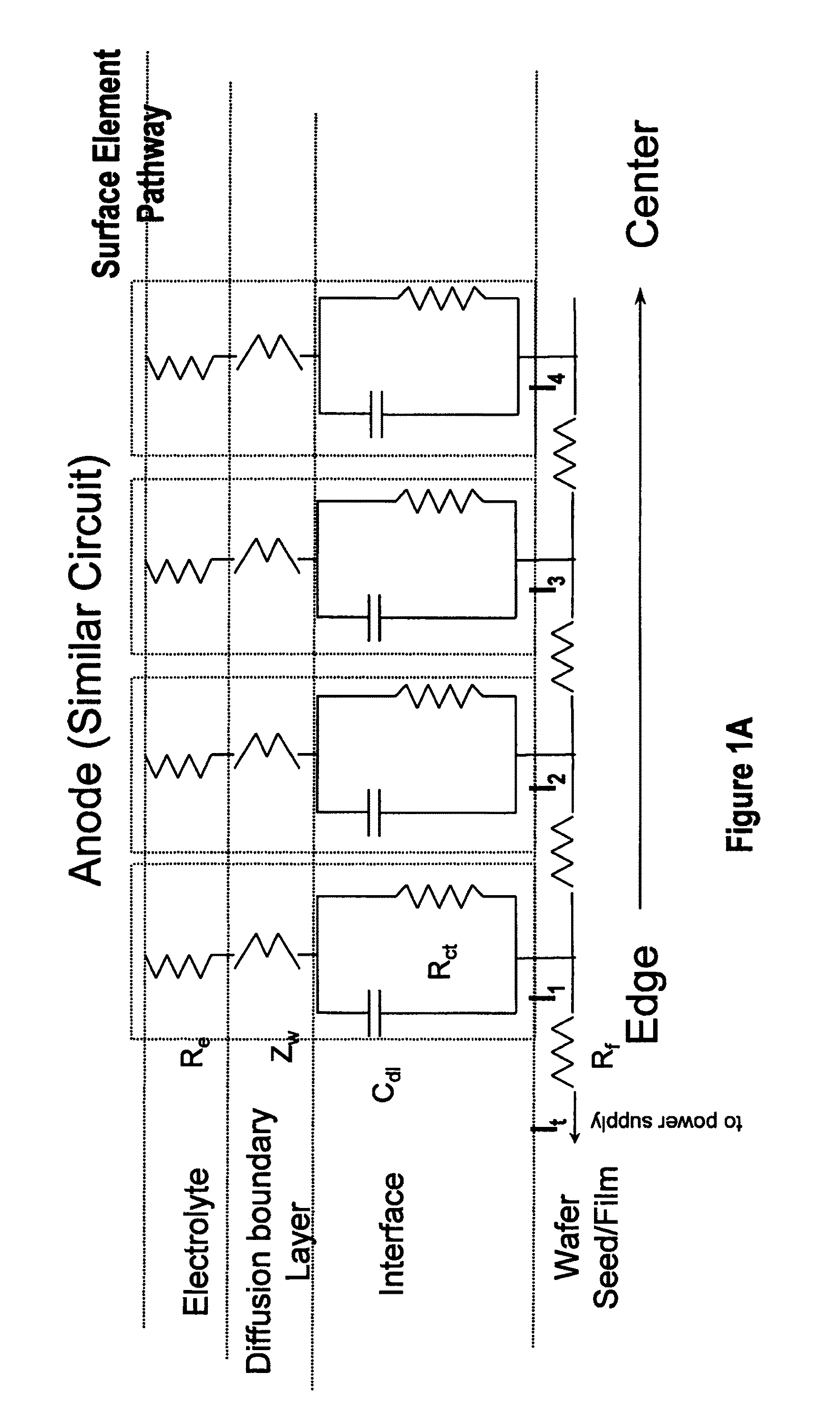
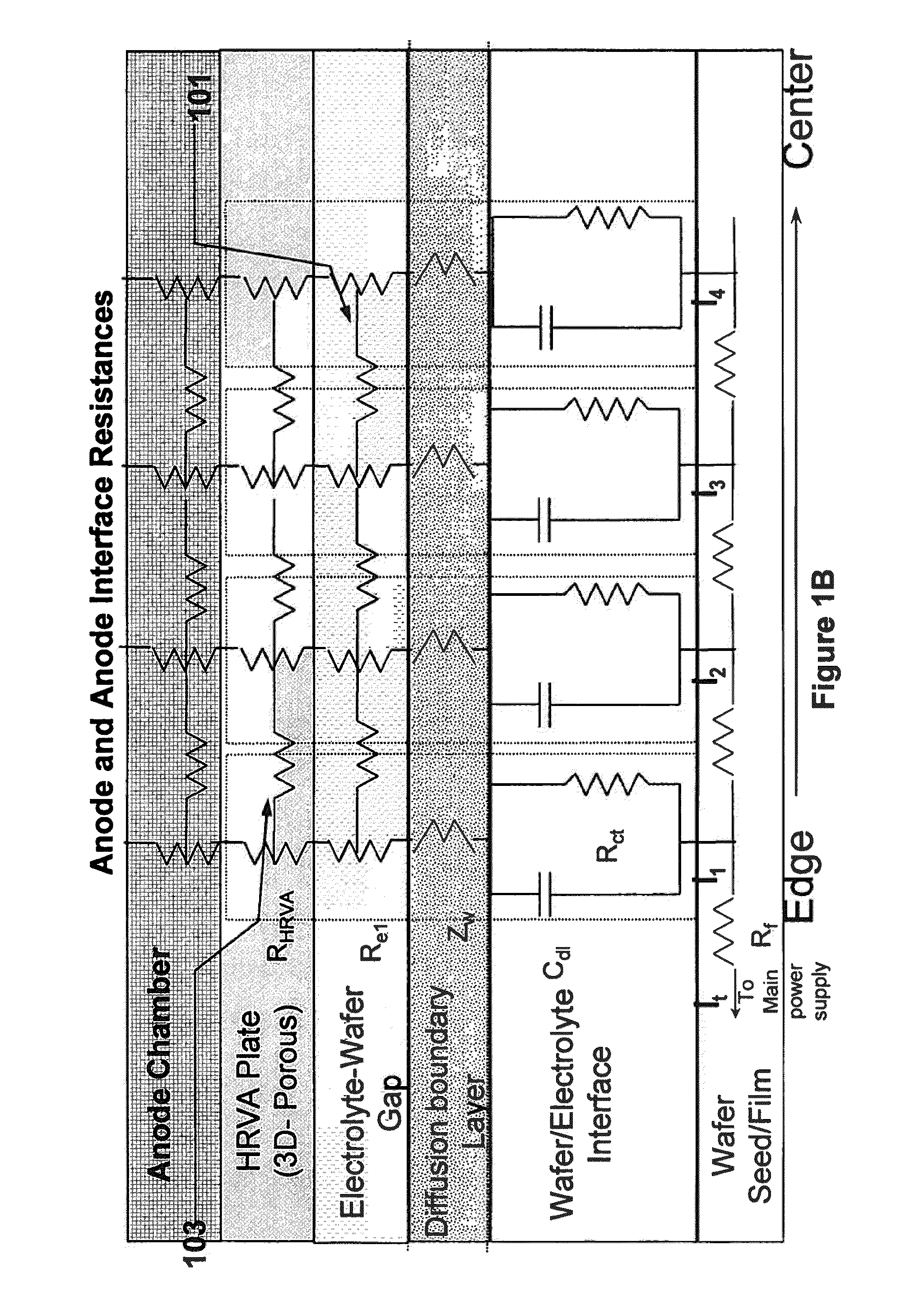
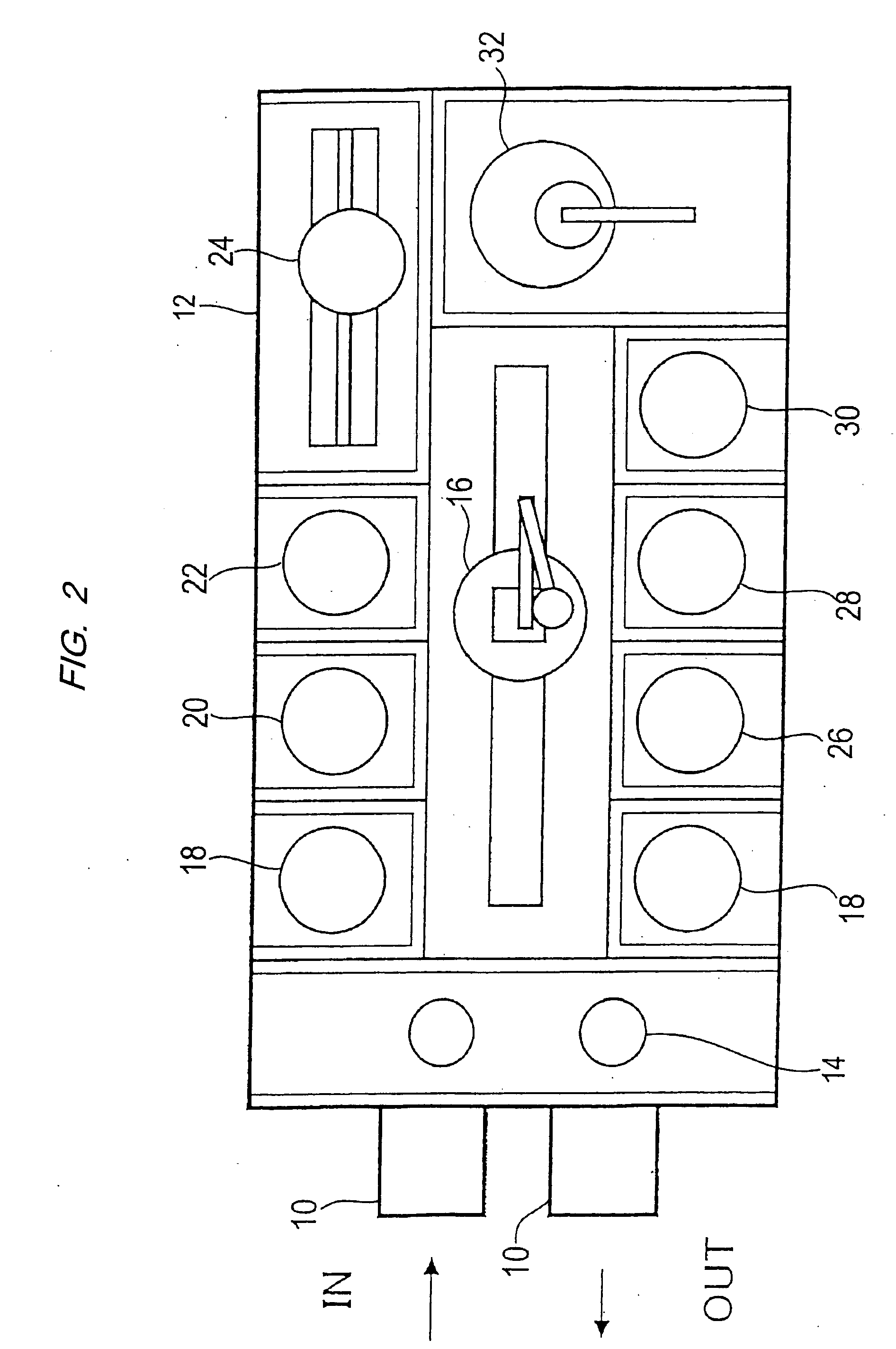
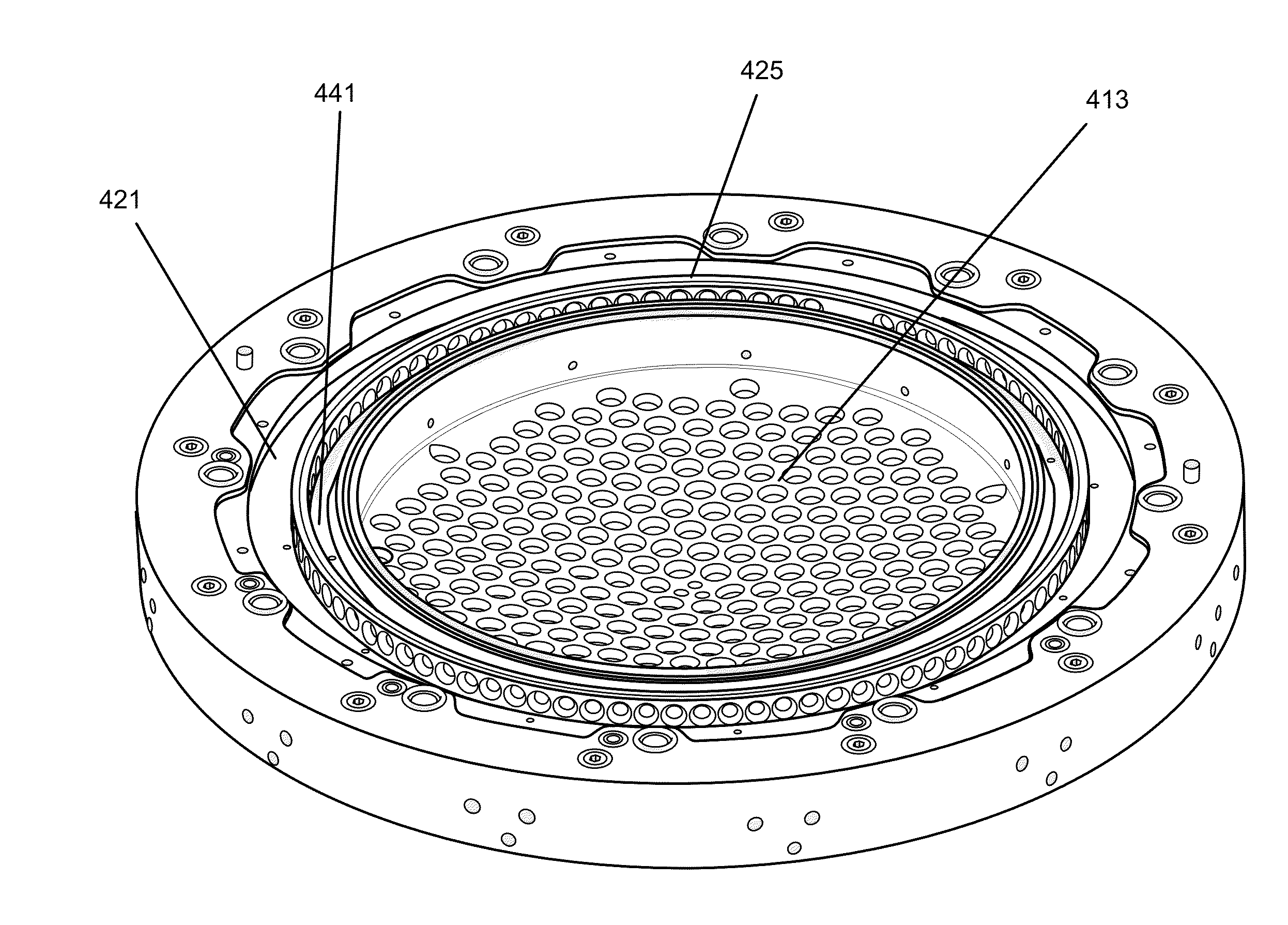
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal on the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer (preferably within 5 mm of the wafer surface) which serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface, and a second cathode configured to divert a portion of current from the wafer surface. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element in a preferred embodiment is a disk made of a resistive material having a plurality of perforations formed therein, such that perforations do not form communicating channels within the body of the disk. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Plating of a thin metal seed layer
InactiveUS20050145499A1CellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin metalAuxiliary electrode
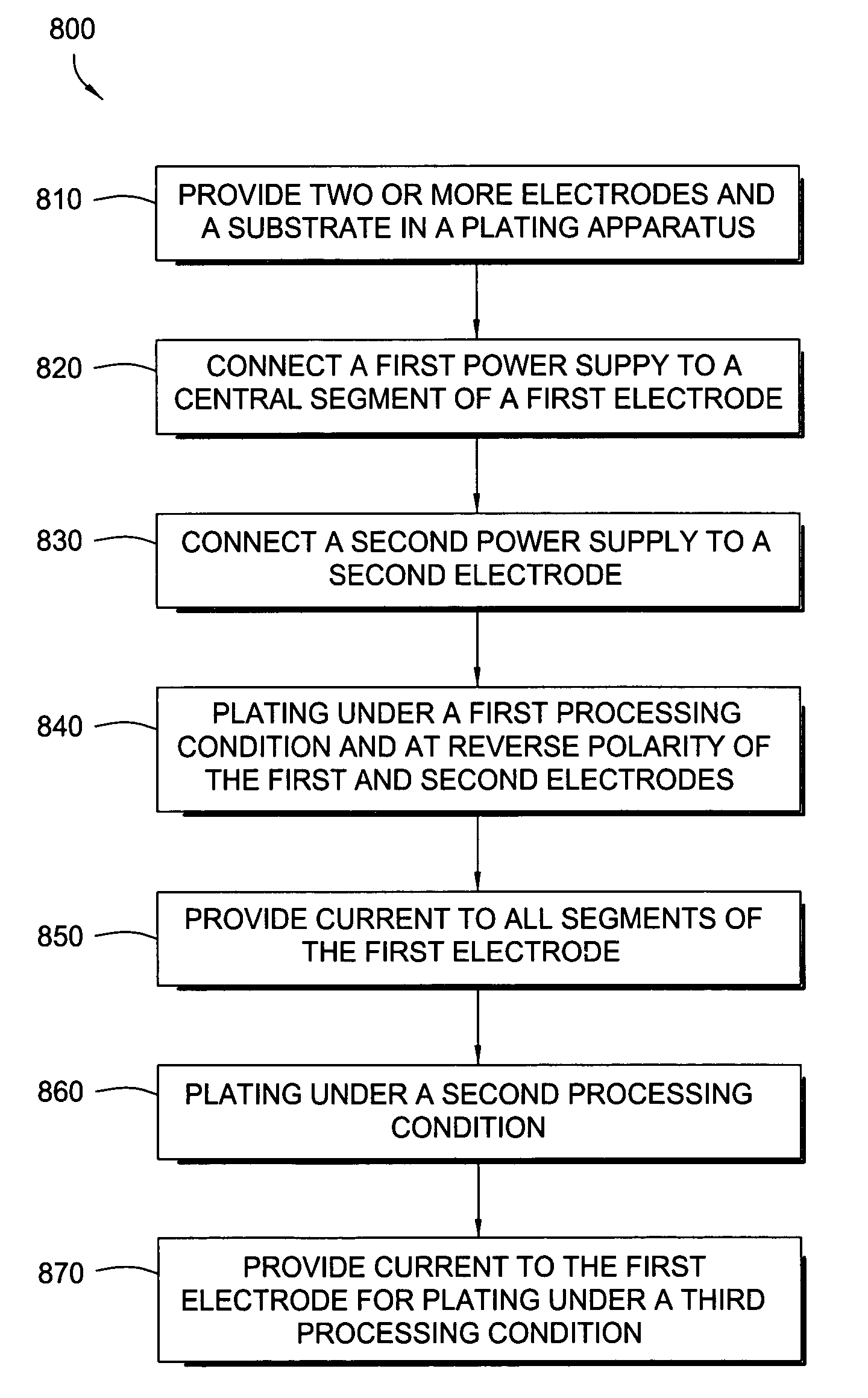
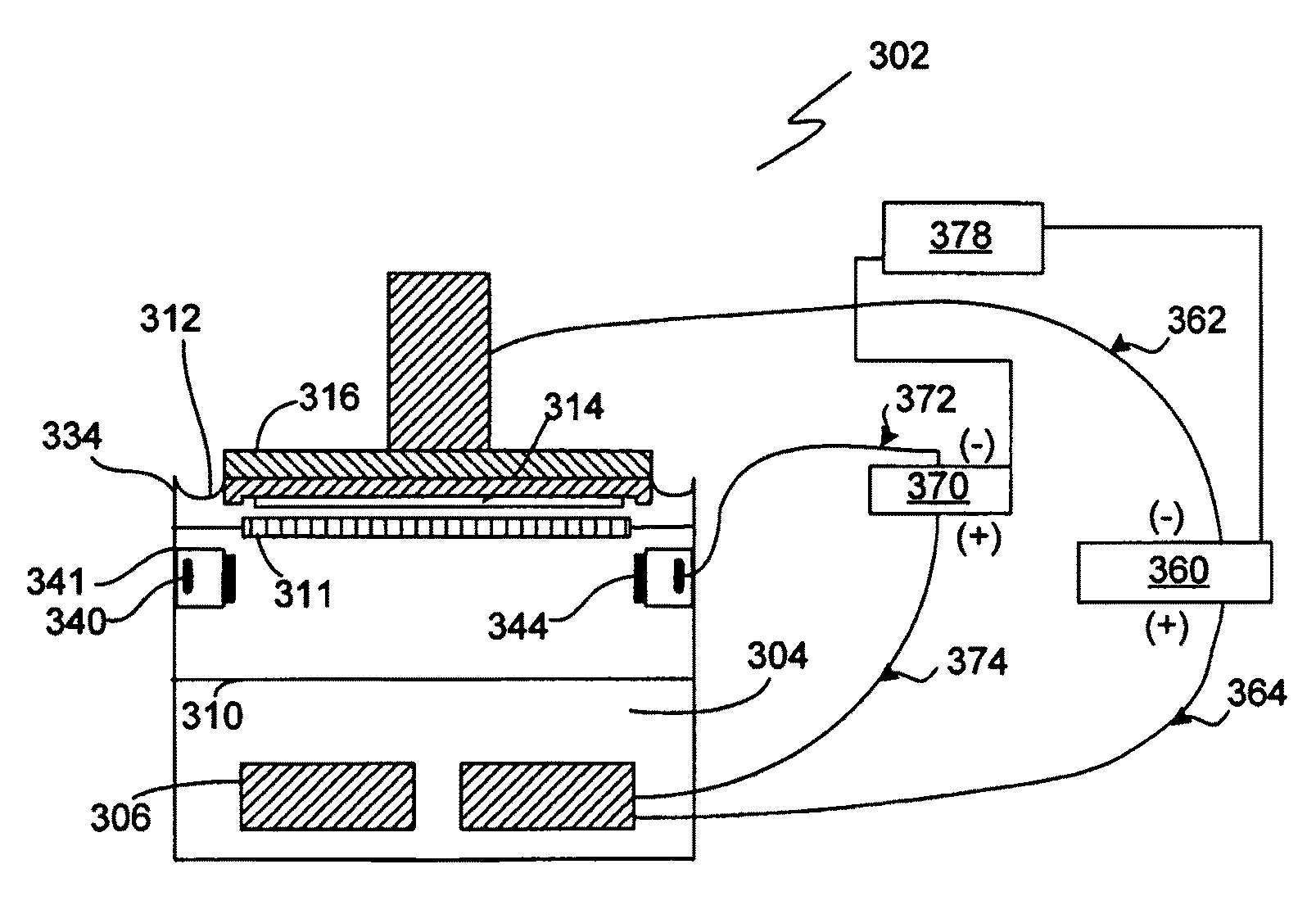
A method and apparatus for plating a metal layer onto a substrate is provided. The plating apparatus includes two or more segments of an anode and an auxiliary electrode. The plating method includes a first stage of plating a thin metal seed uniformly in the center of the substrate and near the edges of the substrate before metal gap filling and bulk metal plating are performed. The thin metal seed is plated on the substrate surface by applying a current pulse provided by a first power supply and a second power supply which are in electrical communication in reverse polarity with one segment of the anode and the auxiliary electrode. Thereafter, gap filling of features is performed by applying a second current pulse where current is provided to all segments of the anode.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for electroplating
ActiveUS8308931B2Improve uniformityImprovement becomes significantly less pronounced or non-existentCellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal on the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer (preferably within 5 mm of the wafer surface) which serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface, and a second cathode configured to divert a portion of current from the wafer surface. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element in a preferred embodiment is a disk made of a resistive material having a plurality of perforations formed therein, such that perforations do not form communicating channels within the body of the disk. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Method and apparatus for electroplating
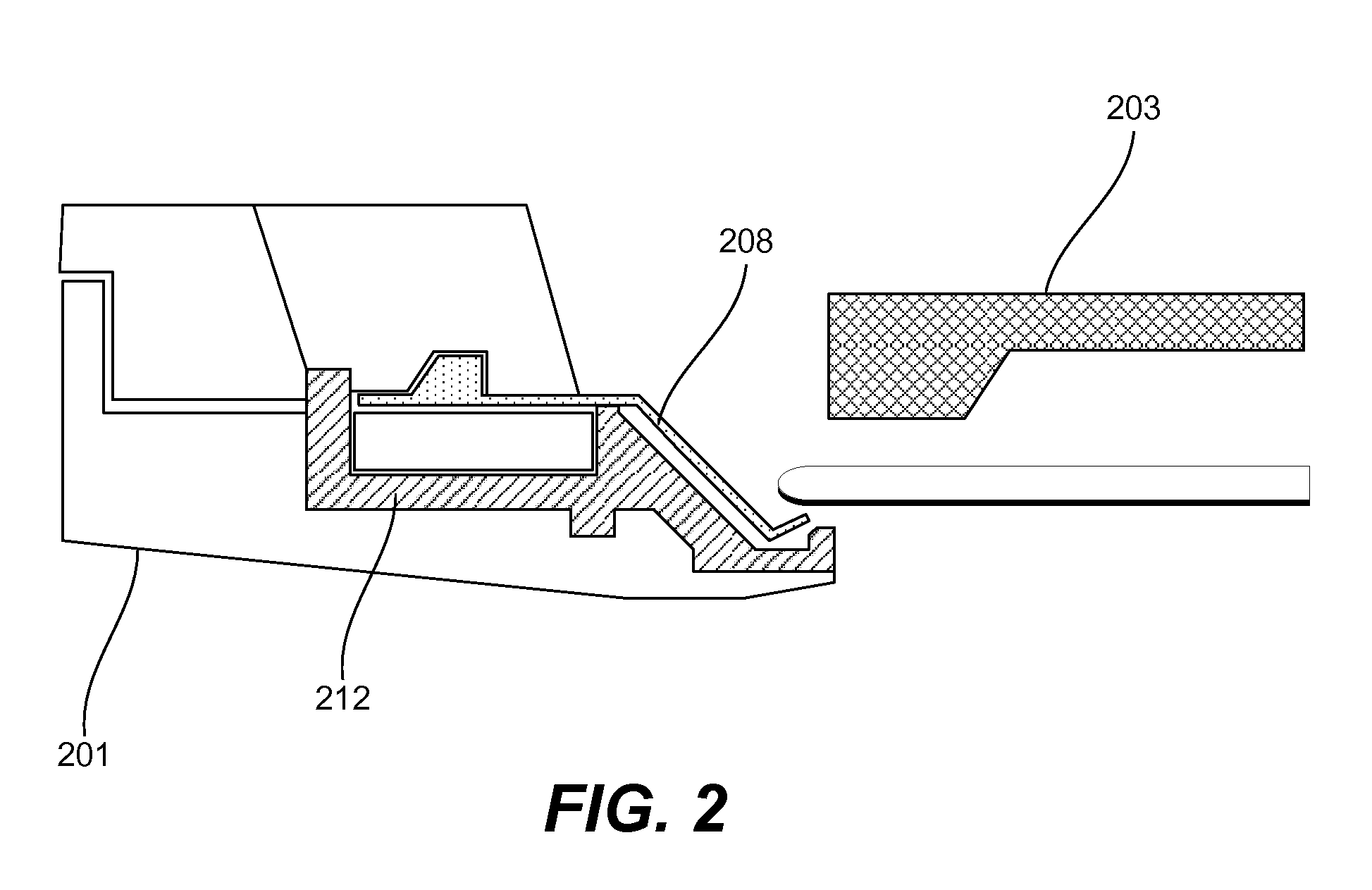
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer and an auxiliary cathode located between the anode and the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface. The auxiliary cathode is configured to shape the current distribution from the anode. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Electroplating apparatus for tailored uniformity profile
ActiveUS20120258408A1Maximizing randomization of flow patternSimple processCellsMachining electric circuitsRadial positionEngineering
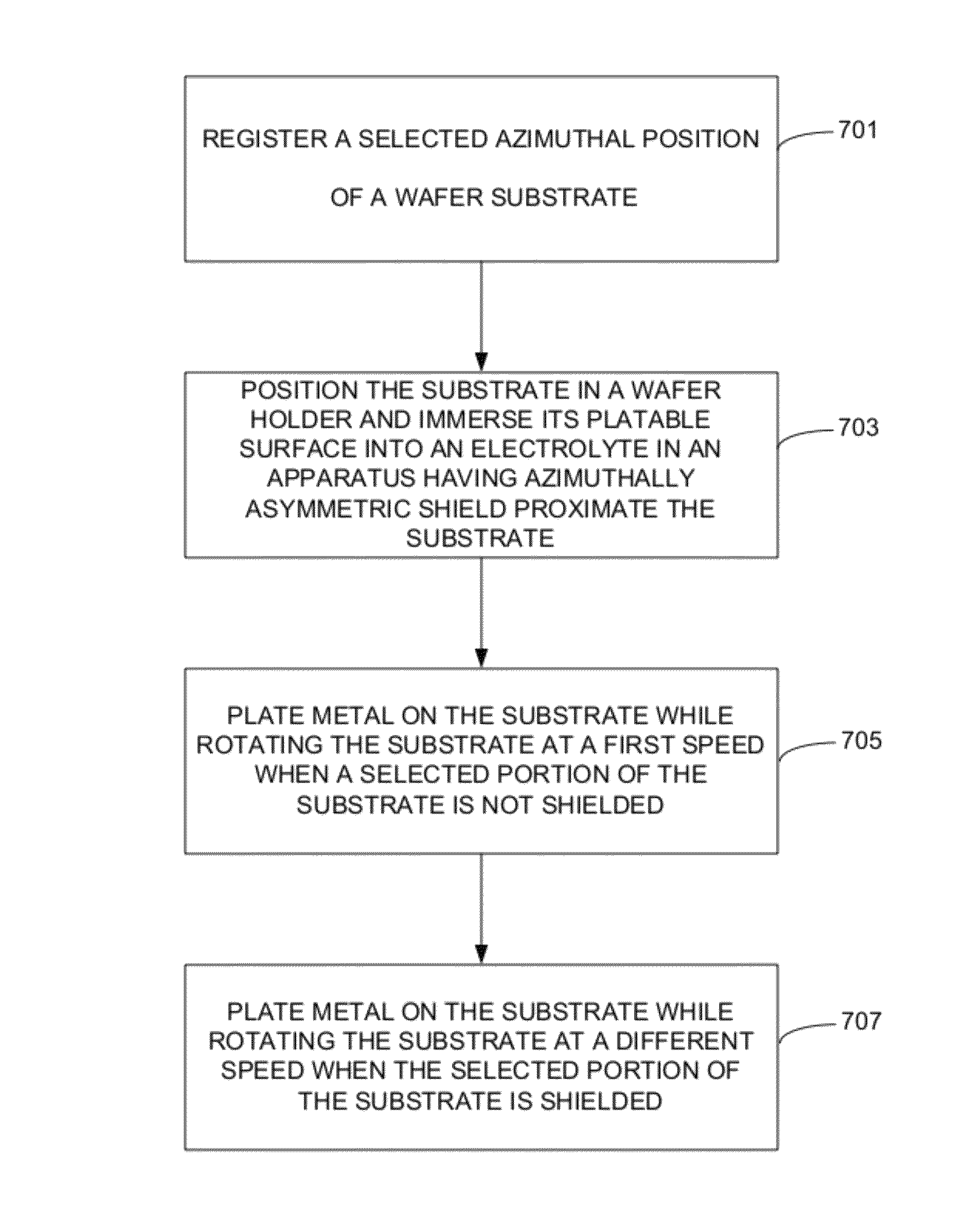
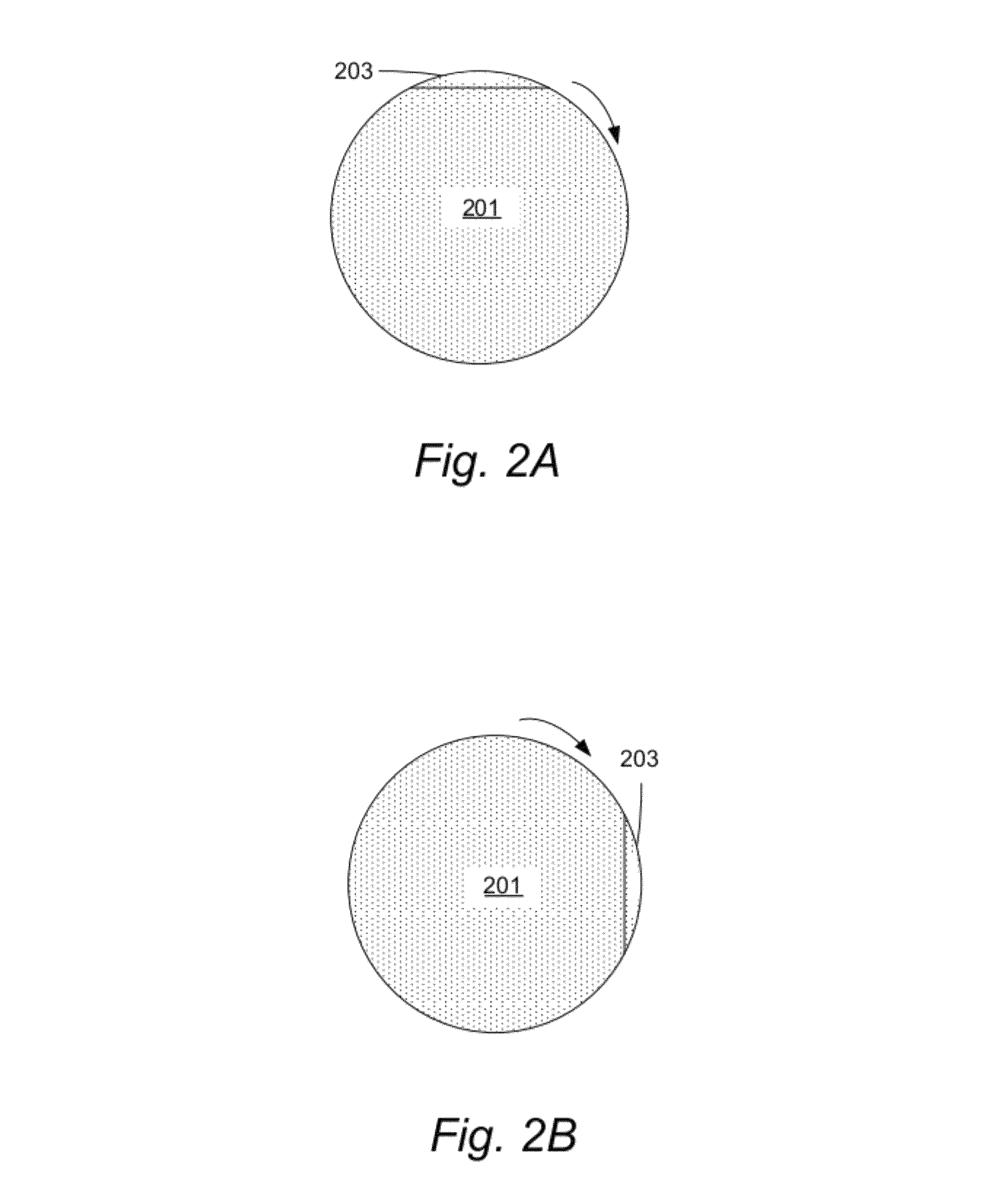
Methods of electroplating metal on a substrate while controlling azimuthal uniformity, include, in one aspect, providing the substrate to the electroplating apparatus configured for rotating the substrate during electroplating, and electroplating the metal on the substrate while rotating the substrate relative to a shield such that a selected portion of the substrate at a selected azimuthal position dwells in a shielded area for a different amount of time than a second portion of the substrate having the same average arc length and the same average radial position and residing at a different angular (azimuthal) position. For example, a semiconductor wafer substrate can be rotated during electroplating slower or faster, when the selected portion of the substrate passes through the shielded area.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
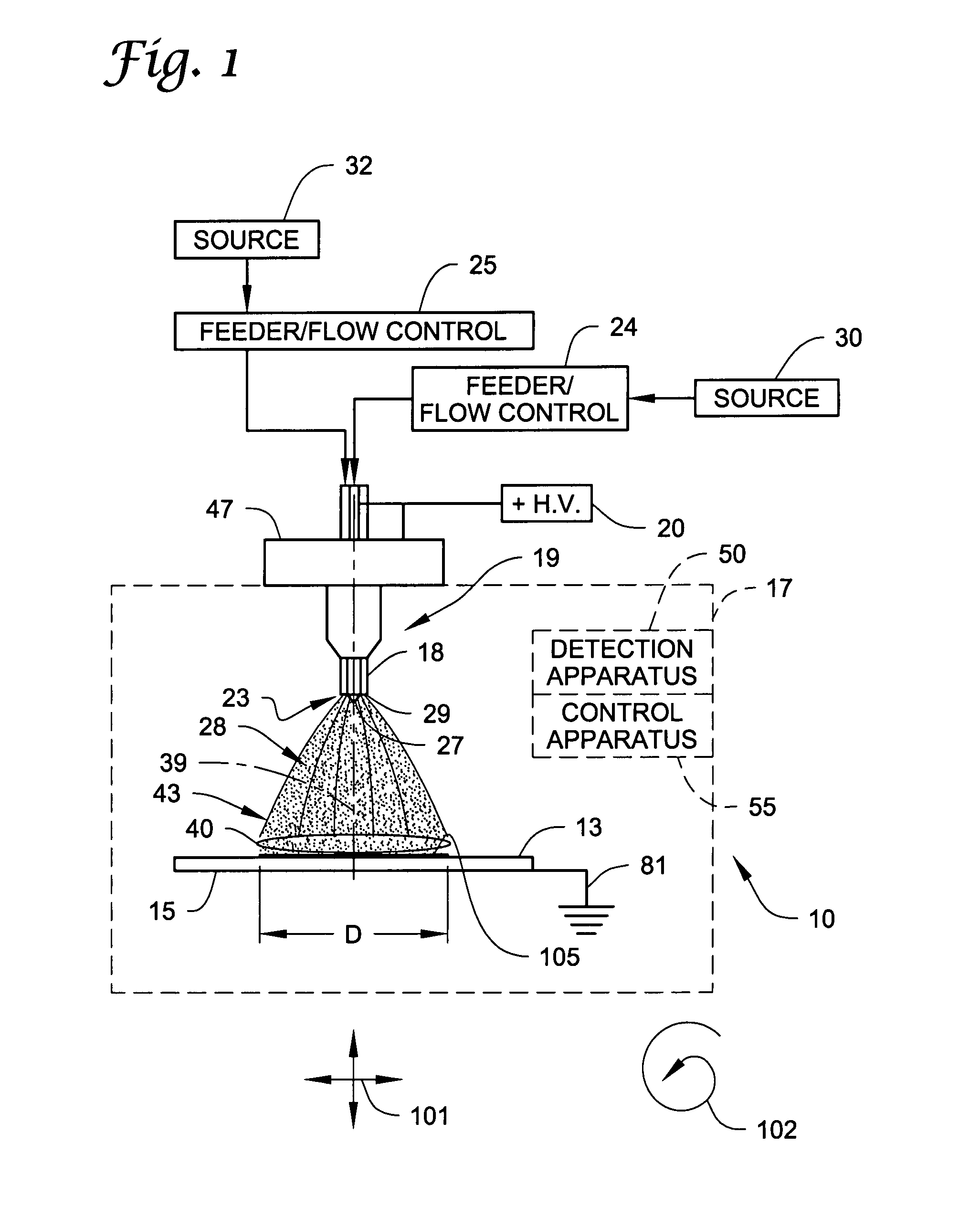
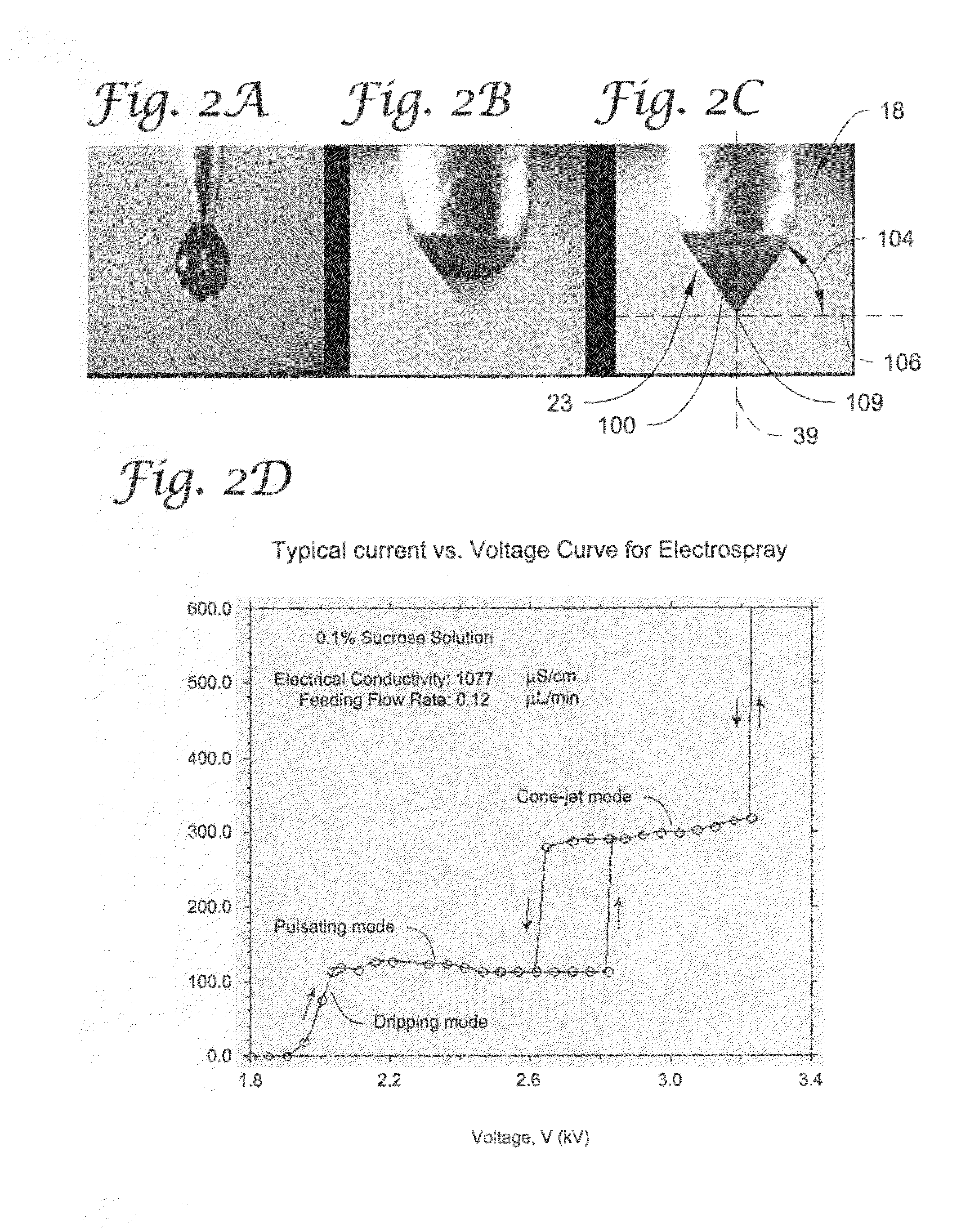
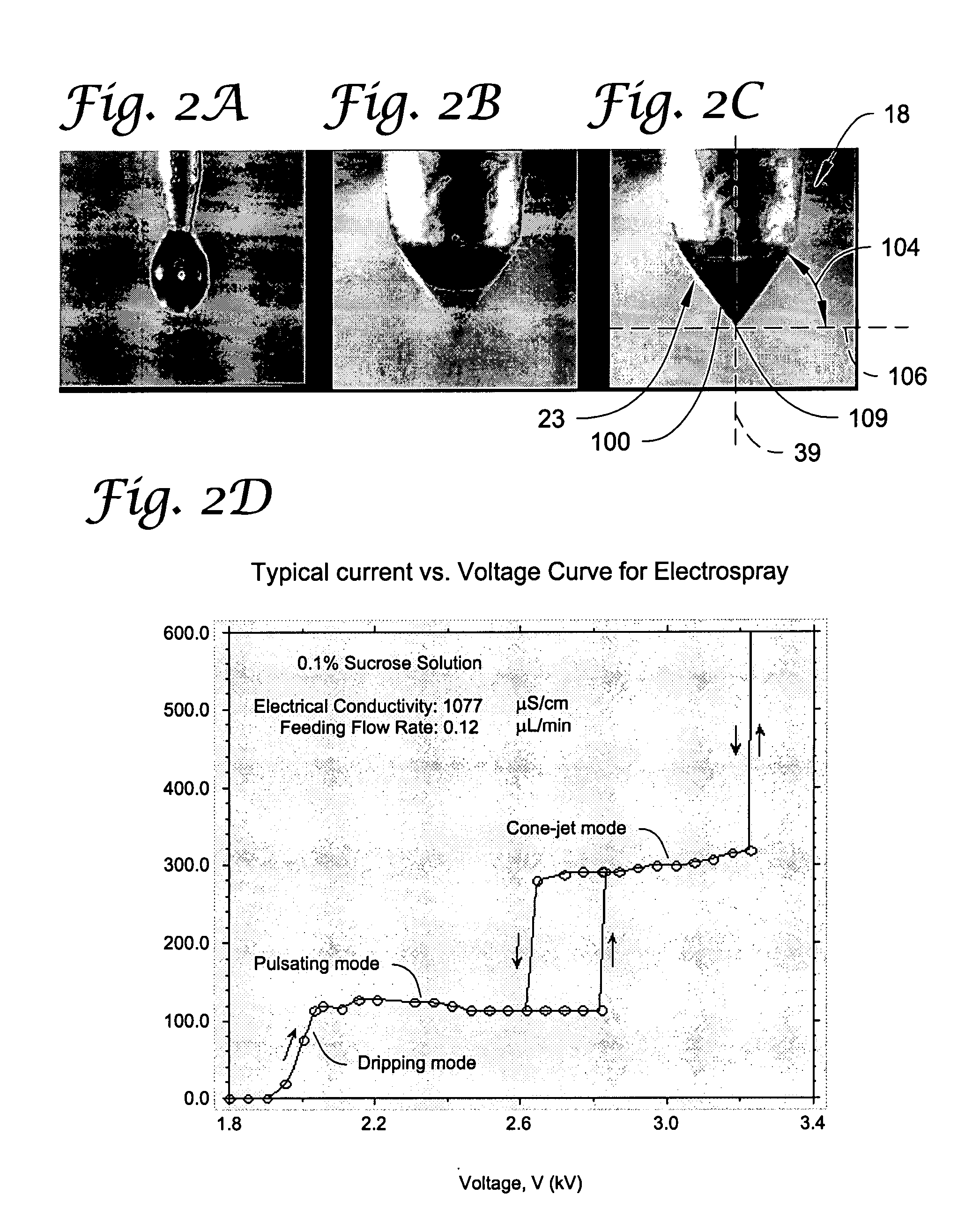
Electrospray coating of objects
Electrospray methods and systems for coating of objects (e.g., medical devices such as a stent structure) with an open matrix coating. The open matrix coating is formed by electrospray using one or more nozzle structures each having at least an inner and outer opening. A first flow of a liquid spray composition is provided to the inner opening and a second flow of a liquid diluent composition is provided to the outer opening (e.g., the liquid diluent composition including at least one solvent, such as a composition having a dielectric constant equal to or greater than 10).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
Electrospray coating of objects
InactiveUS20070199824A1Stable cone-jetPretreated surfacesSurface layering apparatusMedical deviceFilm-coated tablet
Electrospray methods and systems for coating of objects (e.g., medical devices such as a stent structure) with selected types of coatings (e.g., open matrix coating and closed film coating)
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
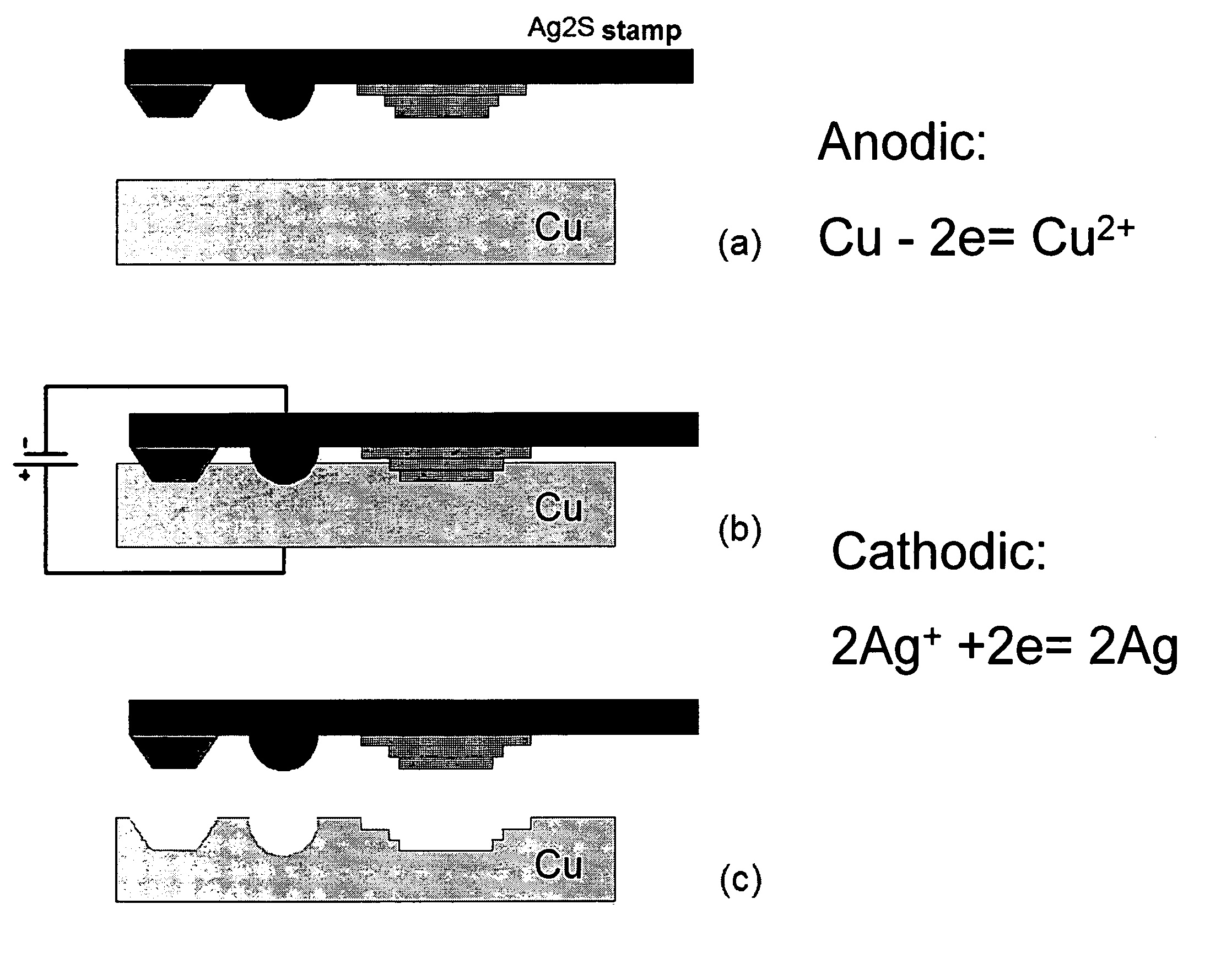
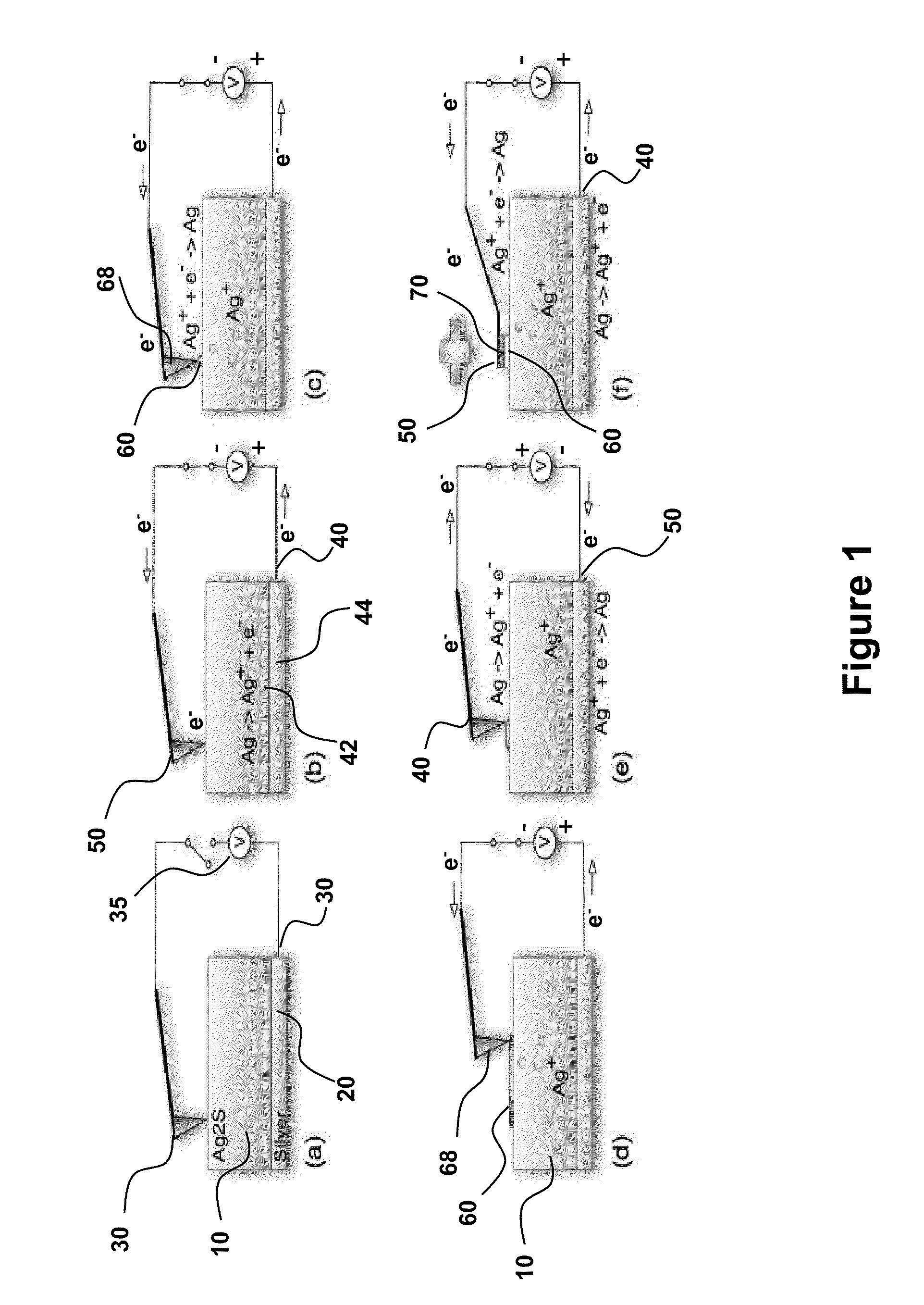
Direct Nanoscale Patterning of Metals Using Polymer Electrolytes
InactiveUS20090050487A1Improve throughputRobust and commercially attractive manufacturing pathwayMachining electrodesMaterial nanotechnologySpatial OrientationsElectrical conductor
Disclosed herein are electrochemical fabrication platforms for making structures, arrays of structures and functional devices having selected nanosized and / or microsized physical dimensions, shapes and spatial orientations. Methods, systems and system components use an electrochemical stamping tool such as solid state polymeric electrolytes for generating patterns of relief and / or recessed features exhibiting excellent reproducibility, pattern fidelity and resolution on surfaces of solid state ionic conductors and in metal. Electrochemical stamping tools are capable high throughput patterning of large substrate areas, are compatible with commercially attractive manufacturing pathways to access a range of functional systems and devices including nano- and micro-electromechanical systems, sensors, energy storage devices, metal masks for printing, interconnects, and integrated electronic circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
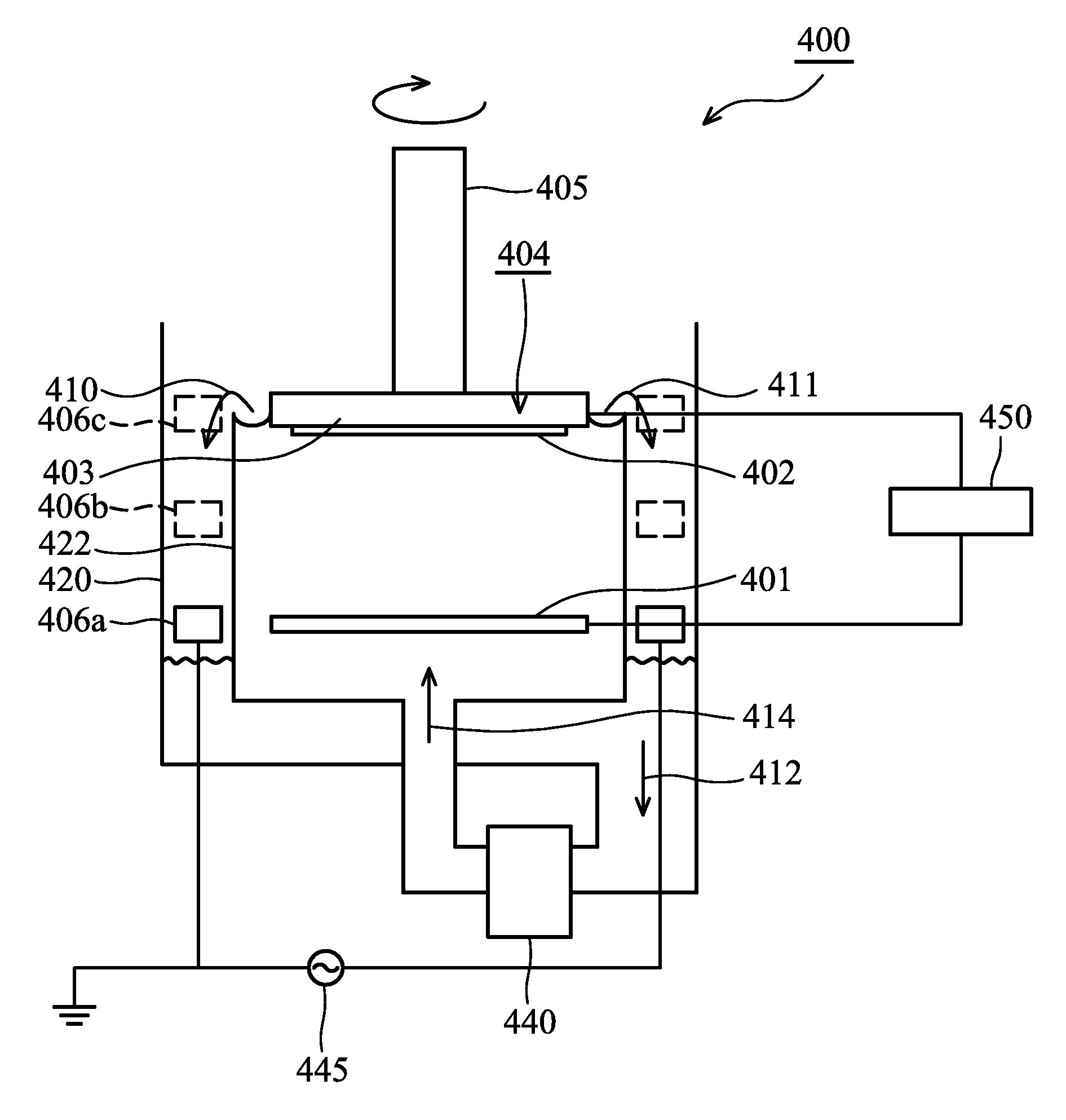
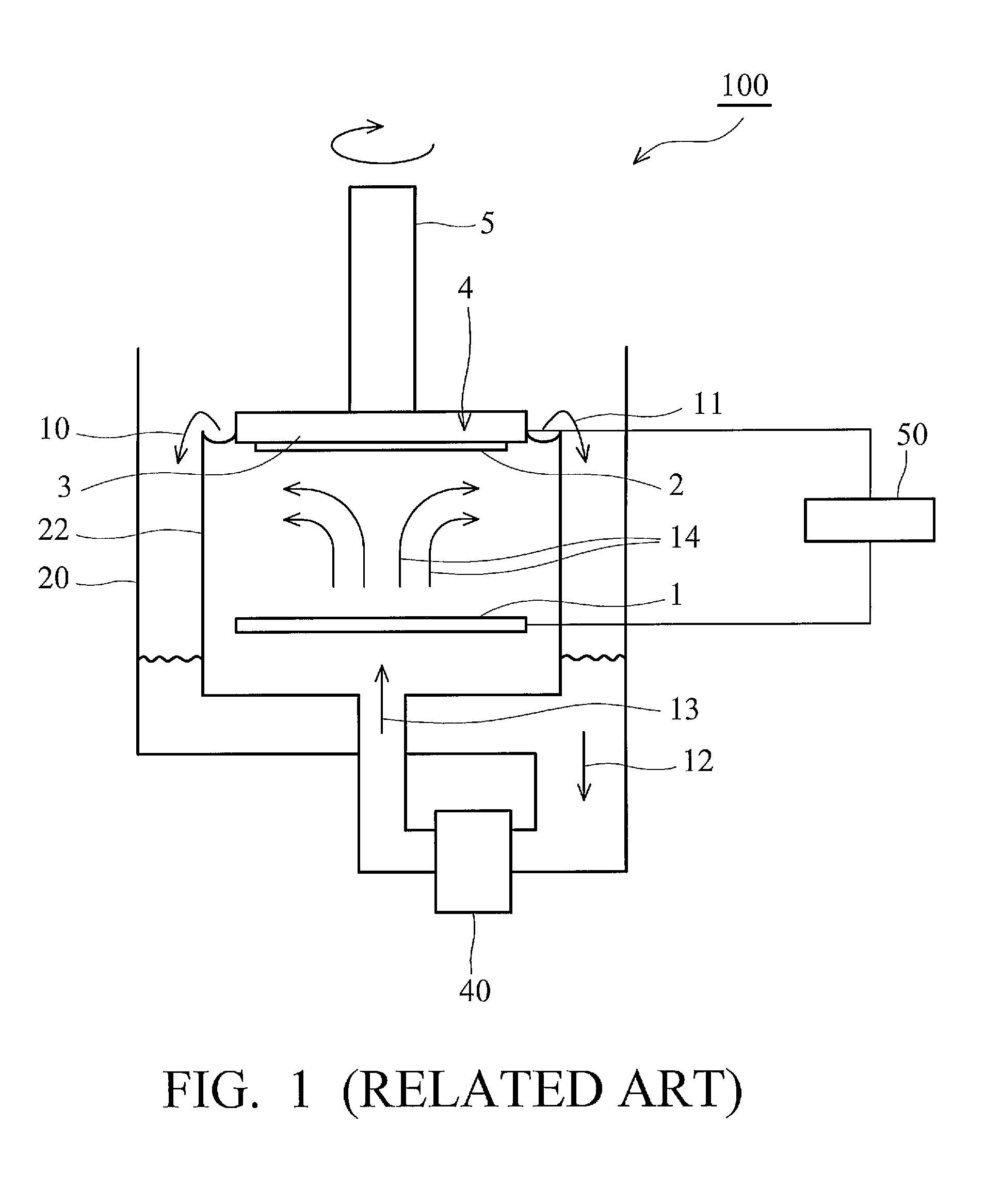
Plating apparatus and plating method
ActiveUS20090139871A1Easy alignmentImprove in-plane uniformityCellsAnodisationHigh current densityIn plane
A plating apparatus can form a bump having a flat top or can form a metal film having a good in-plane uniformity even when the plating of a plating object (substrate) is carried out under high-current density conditions. The plating apparatus includes a plating tank for holding a plating solution; an anode to be immersed in the plating solution in the plating tank; a holder for holding a plating object and disposing the plating object at a position opposite the anode; a paddle, disposed between the anode and the plating object held by the holder, which reciprocates parallel to the plating object to stir the plating solution; and a control section for controlling a paddle drive section which drives the paddle. The control section controls the paddle drive section so that the paddle moves at a velocity whose average absolute value is 70 cm / sec to 100 cm / sec.
Owner:EBARA CORP
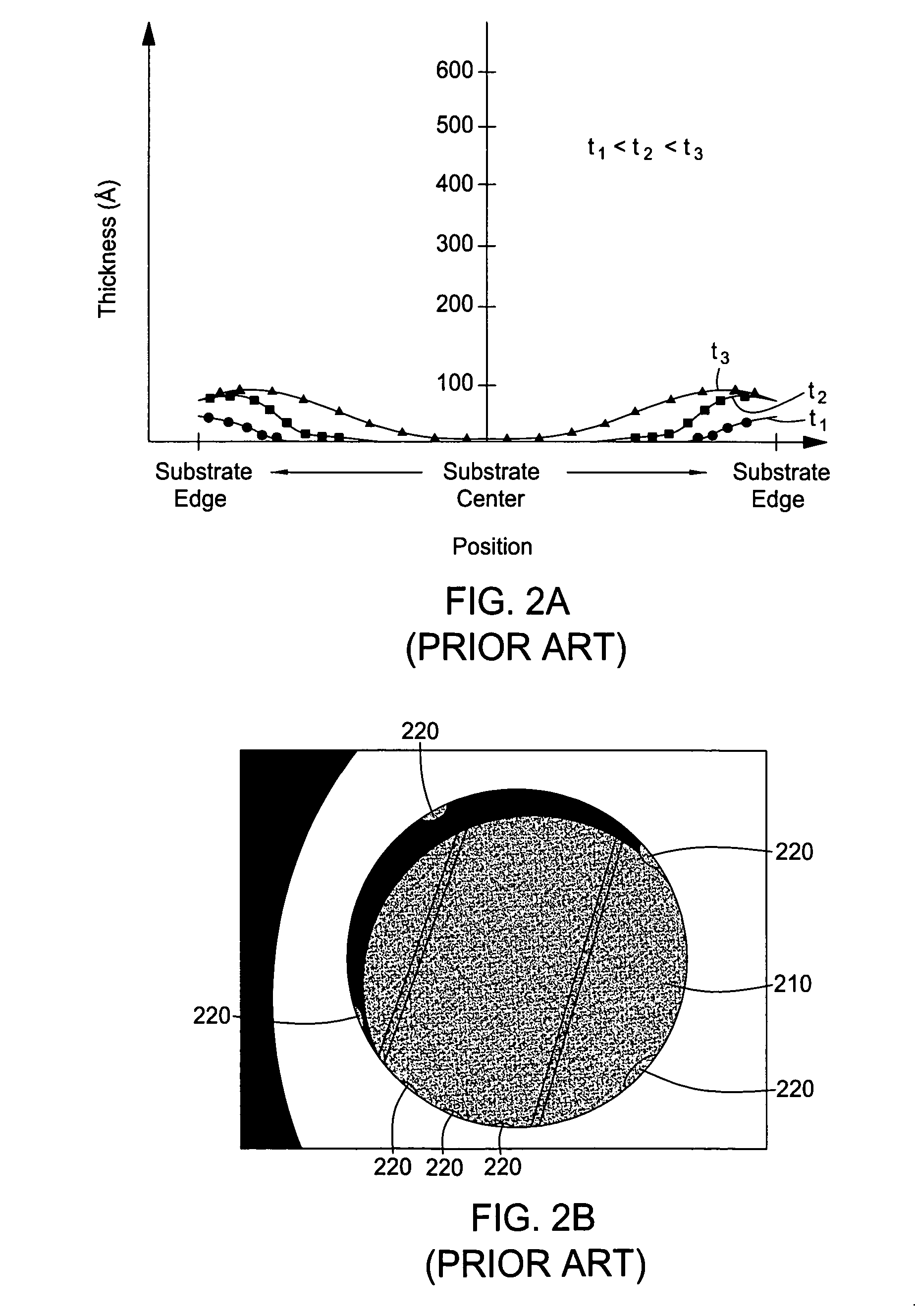
Apparatus and method for improving uniformity in electroplating
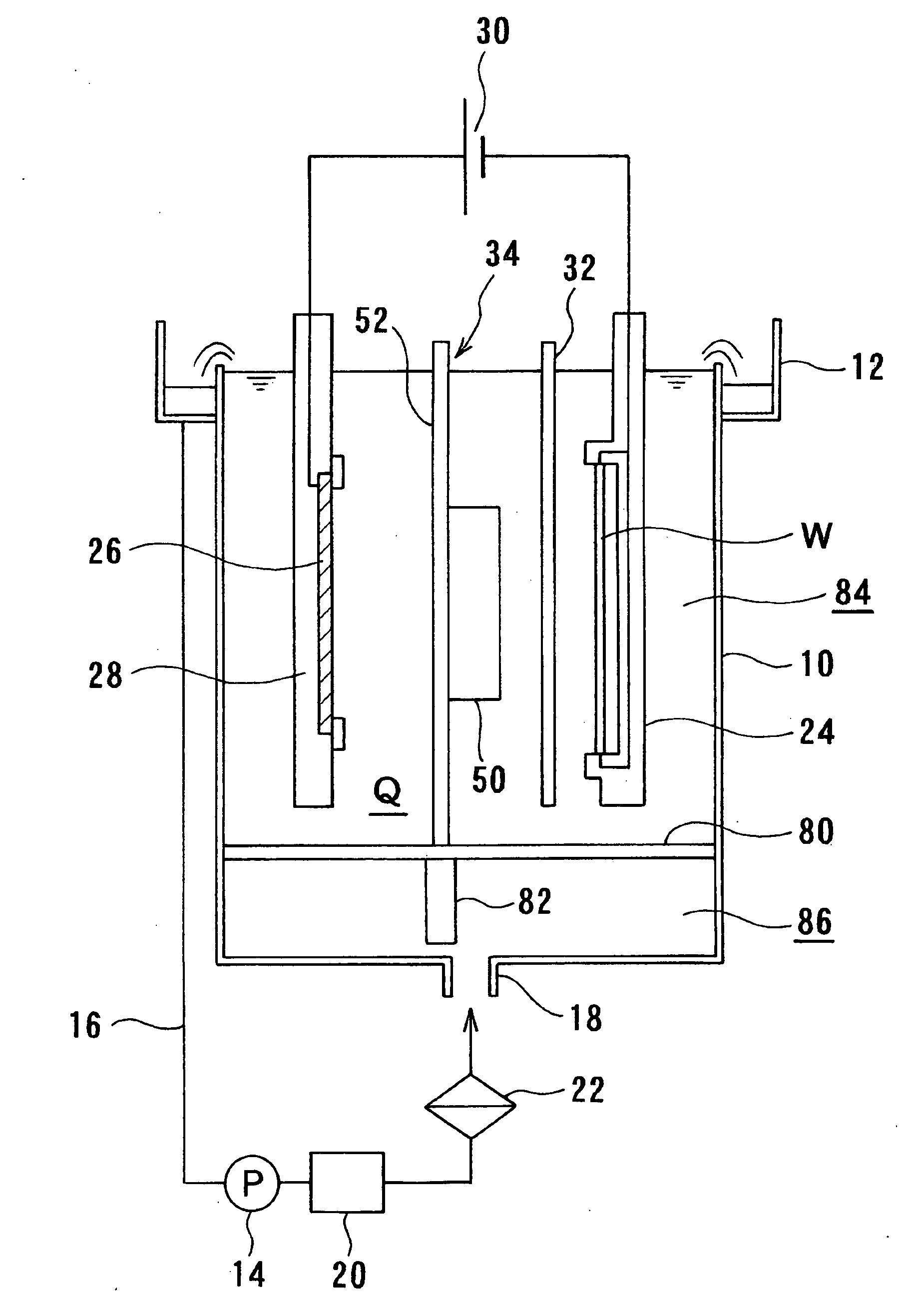
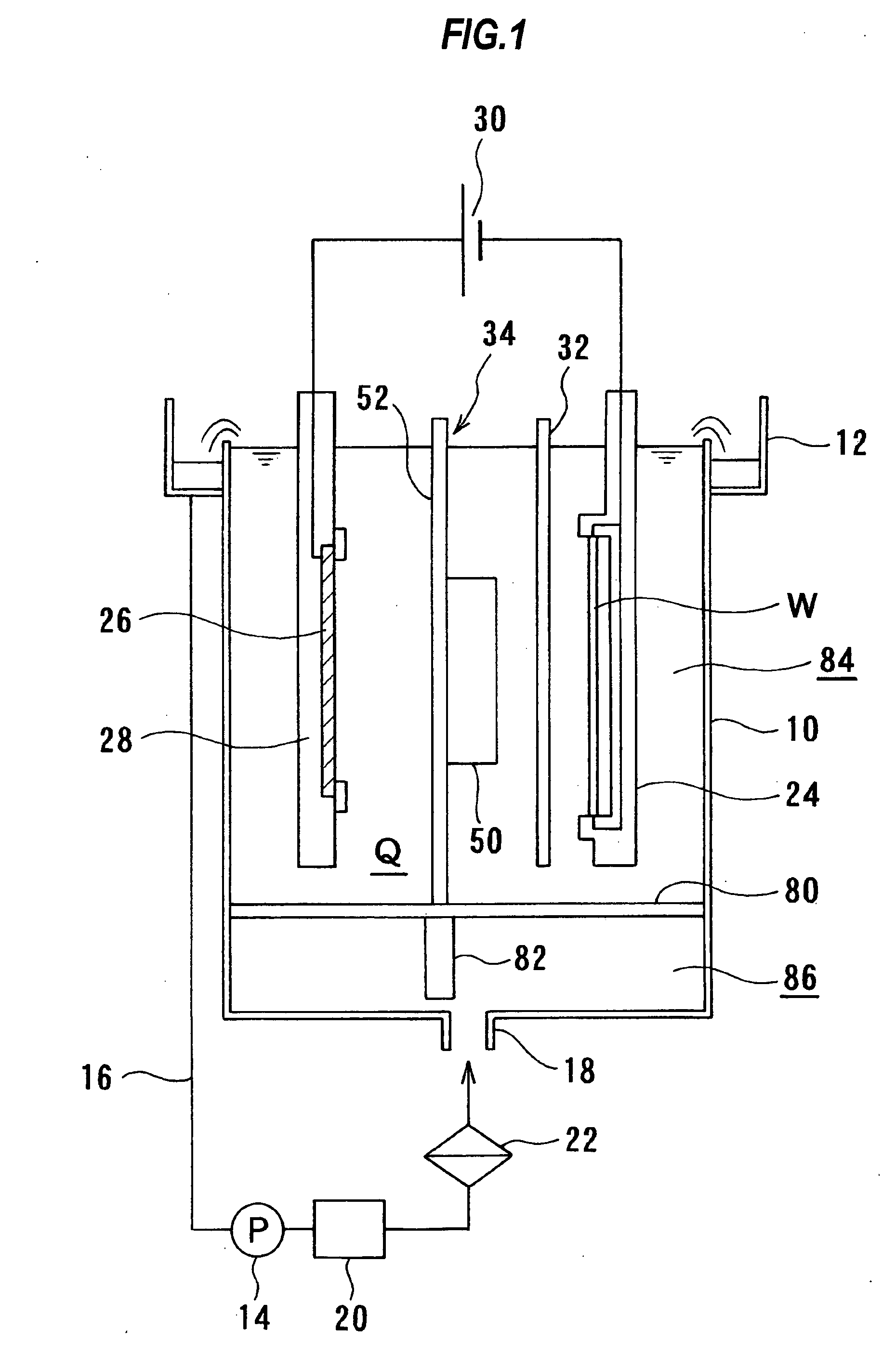
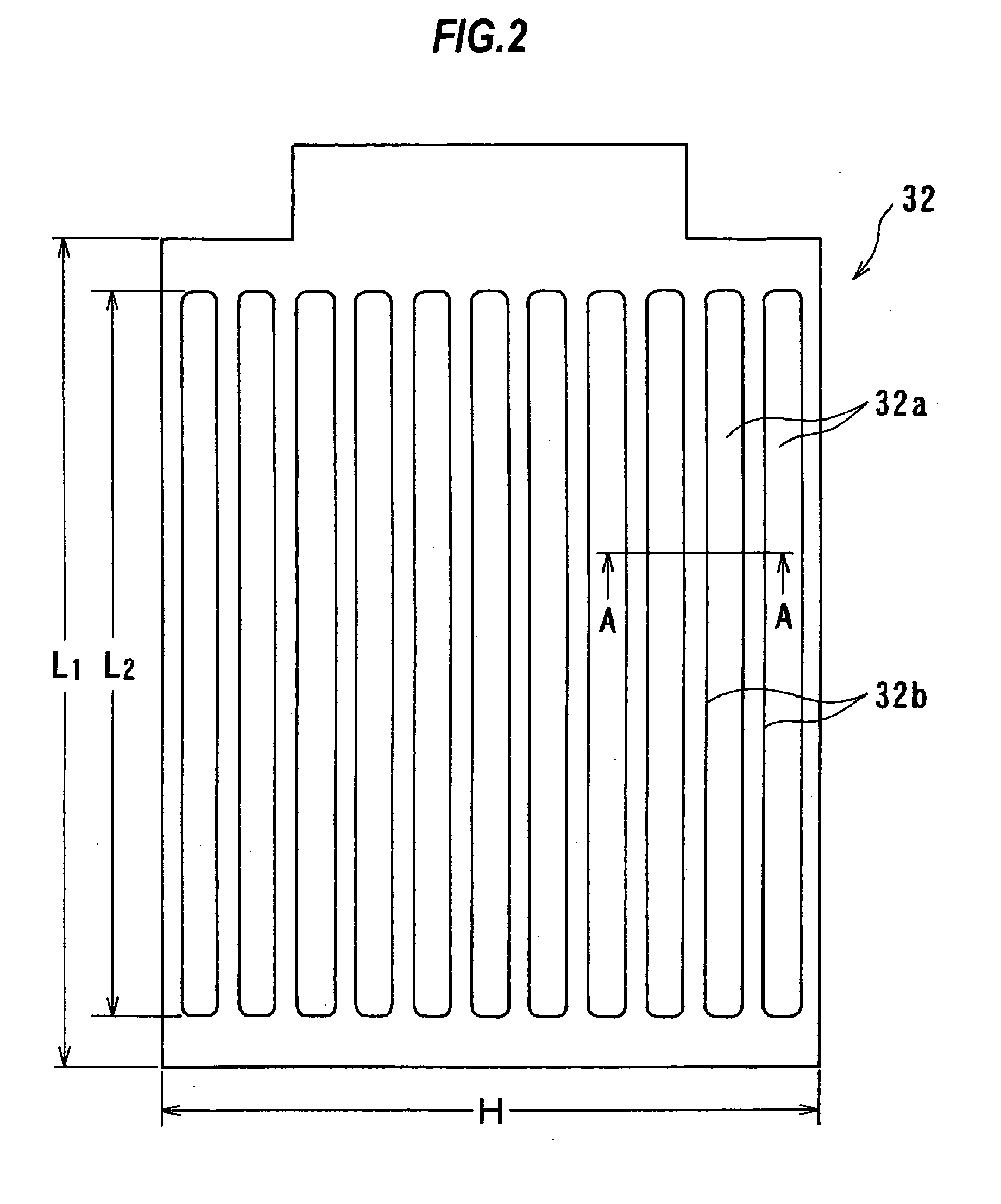
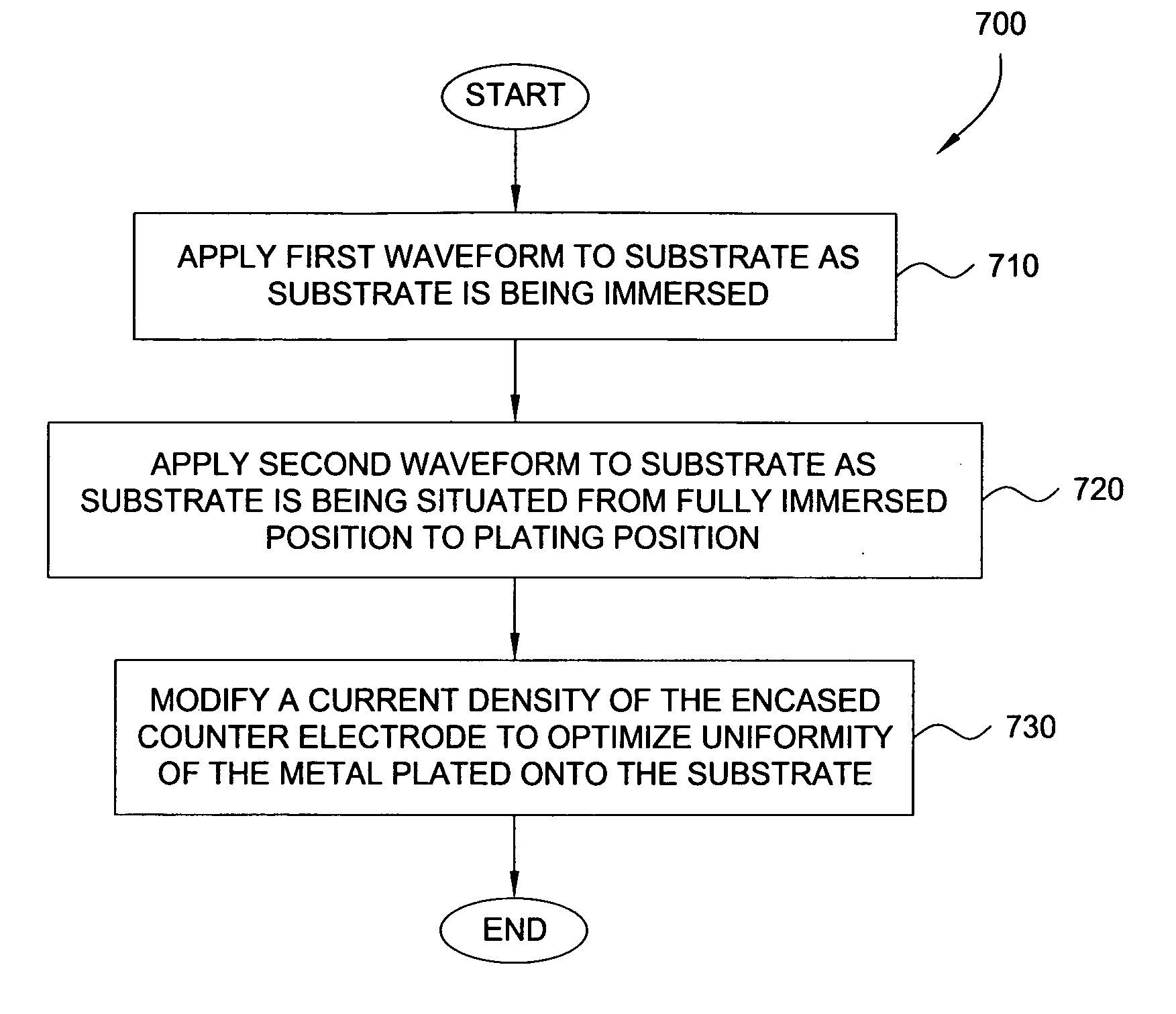
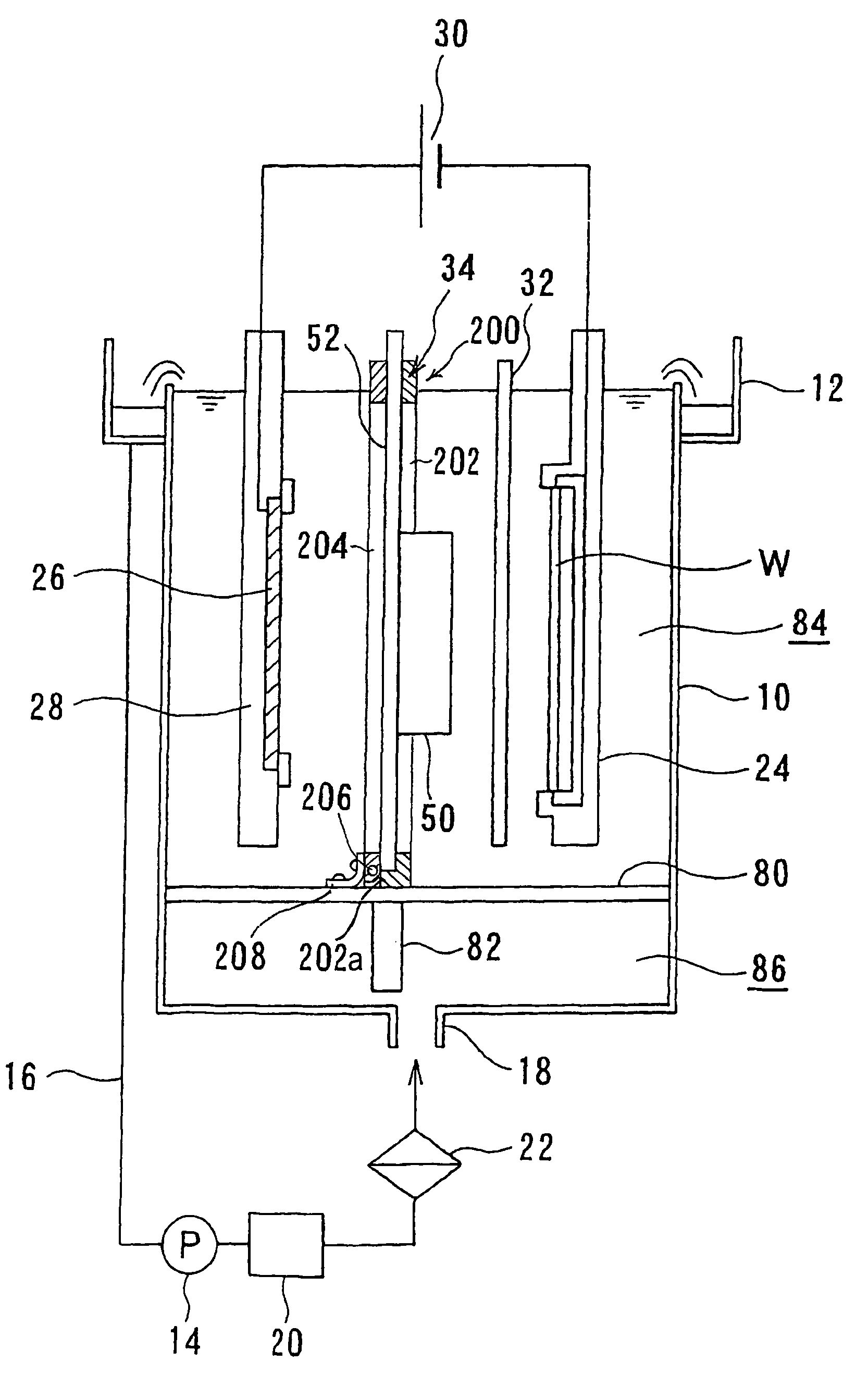
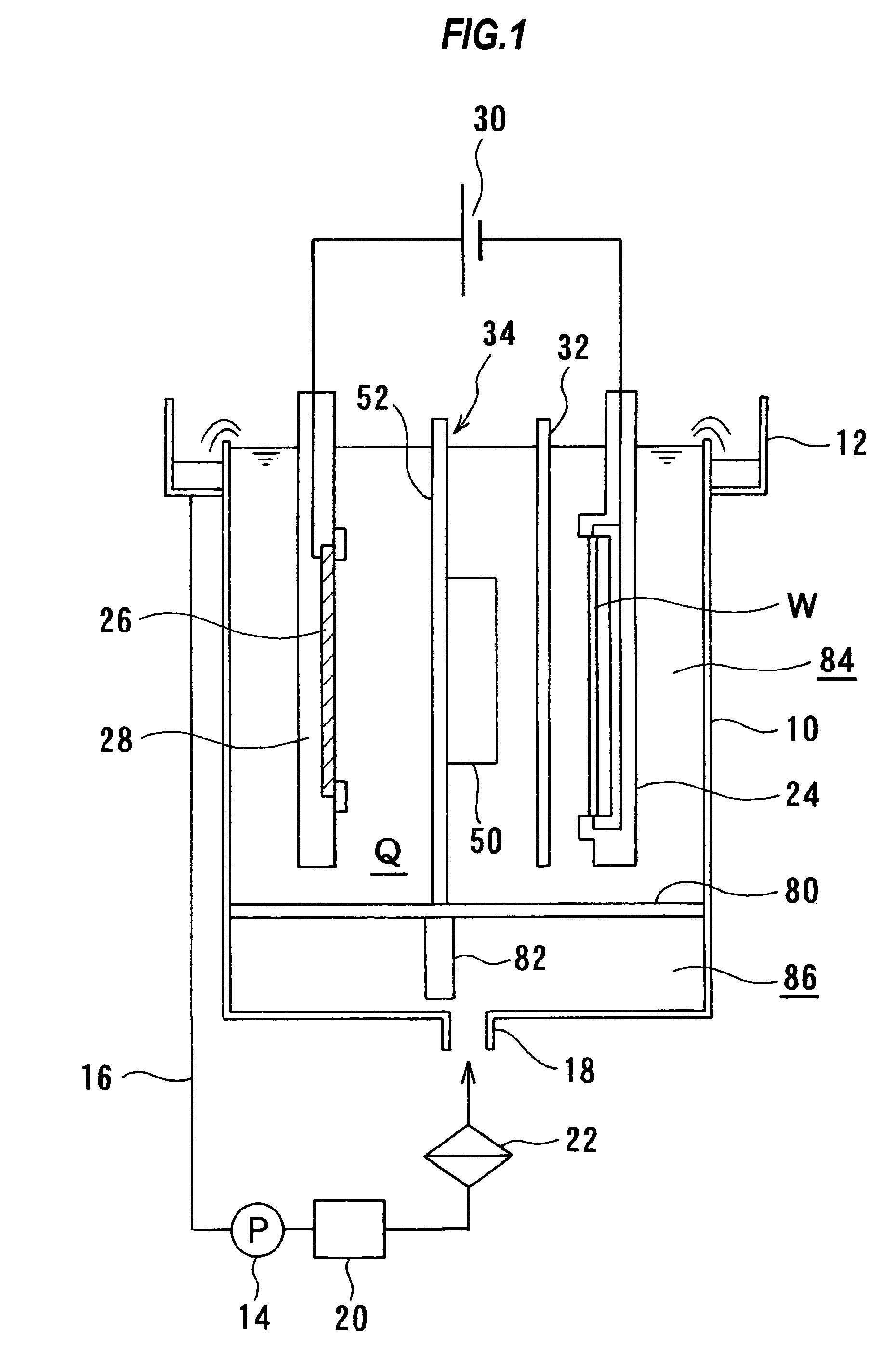
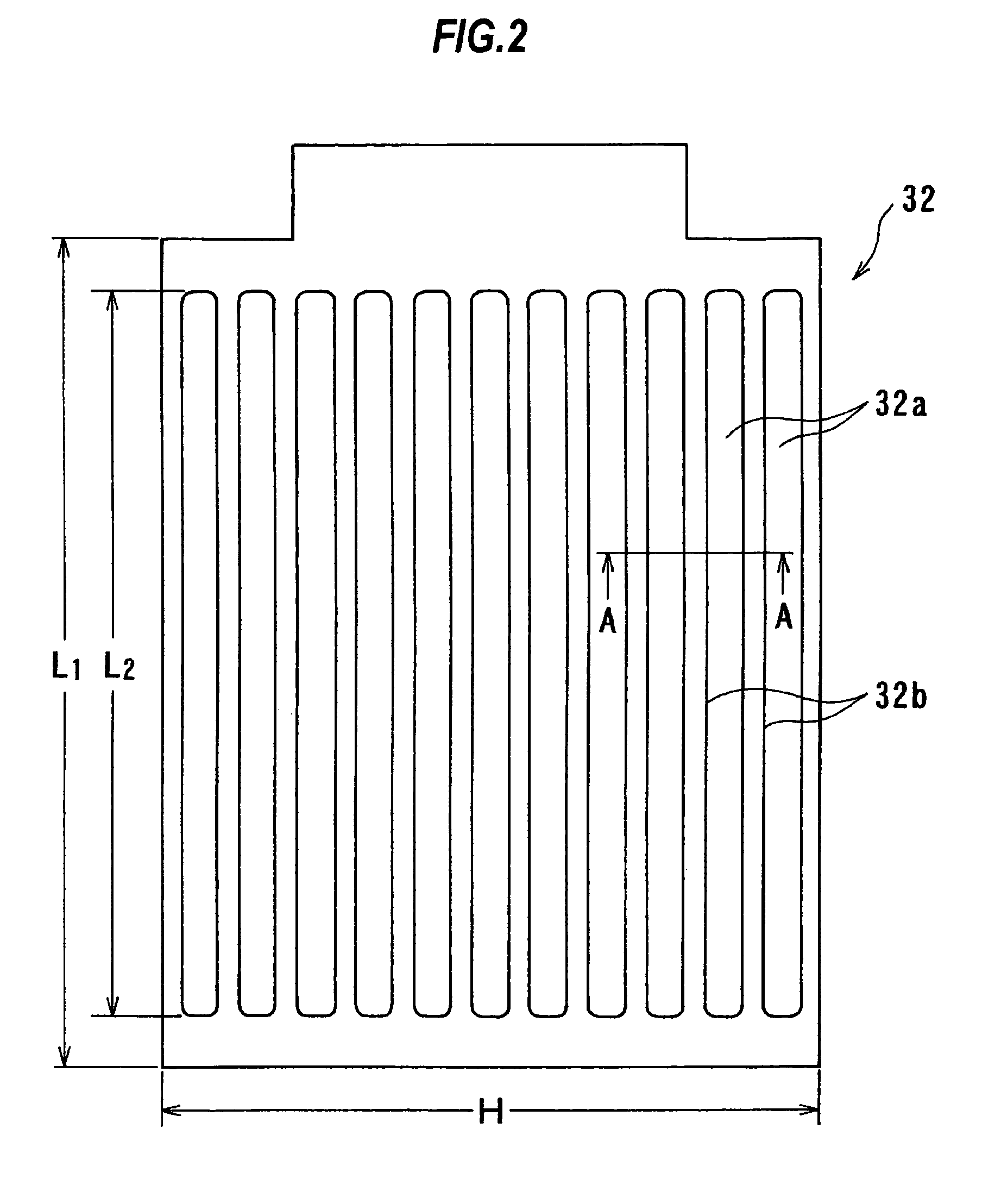
A method and apparatus for plating a metal onto a substrate. One embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus for electroplating a substrate. The apparatus comprises a fluid basin, an anode disposed near a bottom of the fluid basin, a restrictor disposed above the anode, and a substrate support member configured to move the substrate within the fluid basin among different elevations relative to the restrictor. Plating profiles on the substrate may be adjusted by changing the elevation of the substrate during plating.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatuses for electrochemical deposition, conductive layer, and fabrication methods thereof
InactiveUS7837841B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilityLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical batteryEngineering
Electrochemical plating (ECP) apparatuses with auxiliary cathodes to create uniform electric flux density. An ECP apparatus for electrochemical deposition includes an electrochemical cell with an electrolyte bath for electrochemically depositing a metal on a substrate. A main cathode and an anode are disposed in the electrolyte bath to provide a main electrical field. A substrate holder assembly holds a semiconductor wafer connecting the cathode. An auxiliary cathode is disposed outside the electrochemical cell to provide an auxiliary electrical field such that a flux line density at the center region of the substrate holder assembly substantially equals that at the circumference of the substrate holder assembly.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Pattern transfer by solid state electrochemical stamping
InactiveUS20070215480A1Good reproducibilityExcellent pattern fidelityMaterial nanotechnologyMachining electrodesSpatial OrientationsElectrical conductor
The present invention provides an electrochemical fabrication platform for making structures, arrays of structures and functional devices having selected nanosized and / or microsized physical dimensions, shapes and spatial orientations. Methods, systems and system components of the present invention use an electrochemical stamping tool for generating patterns of relief and / or recessed features exhibiting excellent reproducibility, pattern fidelity and resolution on surfaces of solid state ionic conductors and in metal. Electrochemical stamping tools of the present invention are capable high throughput patterning of large substrate areas and, thus, enable a robust and commercially attractive manufacturing pathway to a range of functional systems and devices including nano- and micro-electromechanical systems, sensors, energy storage devices and integrated electronic circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Plating apparatus and plating method
ActiveCN101451264AExcellent in-plane uniformityImprove in-plane uniformityCellsSolid-state devicesHigh current densityIn plane
A plating apparatus can form a bump having a flat top or can form a metal film having a good in-plane uniformity even when the plating of a plating object (substrate) is carried out under high-current density conditions. The plating apparatus includes a plating tank for holding a plating solution; an anode to be immersed in the plating solution in the plating tank; a holder for holding a plating object and disposing the plating object at a position opposite the anode; a paddle, disposed between the anode and the plating object held by the holder, which reciprocates parallel to the plating object to stir the plating solution; and a control section for controlling a paddle drive section which drives the paddle. The control section controls the paddle drive section so that the paddle moves at a velocity whose average absolute value is 70 cm / sec to 100 cm / sec.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Method and apparatus for electroplating
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an ionically resistive ionically permeable element located in close proximity of the wafer and an auxiliary cathode located between the anode and the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. The ionically resistive ionically permeable element serves to modulate ionic current at the wafer surface. The auxiliary cathode is configured to shape the current distribution from the anode. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Plating apparatus and plating method
InactiveUS20050241946A1CellsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringElectric current
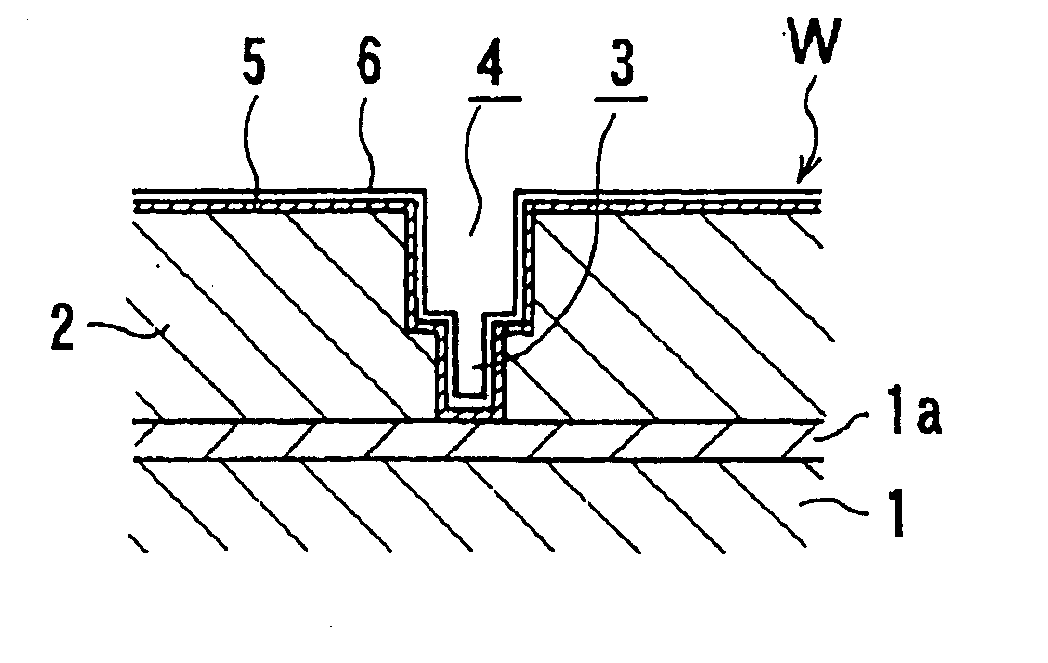
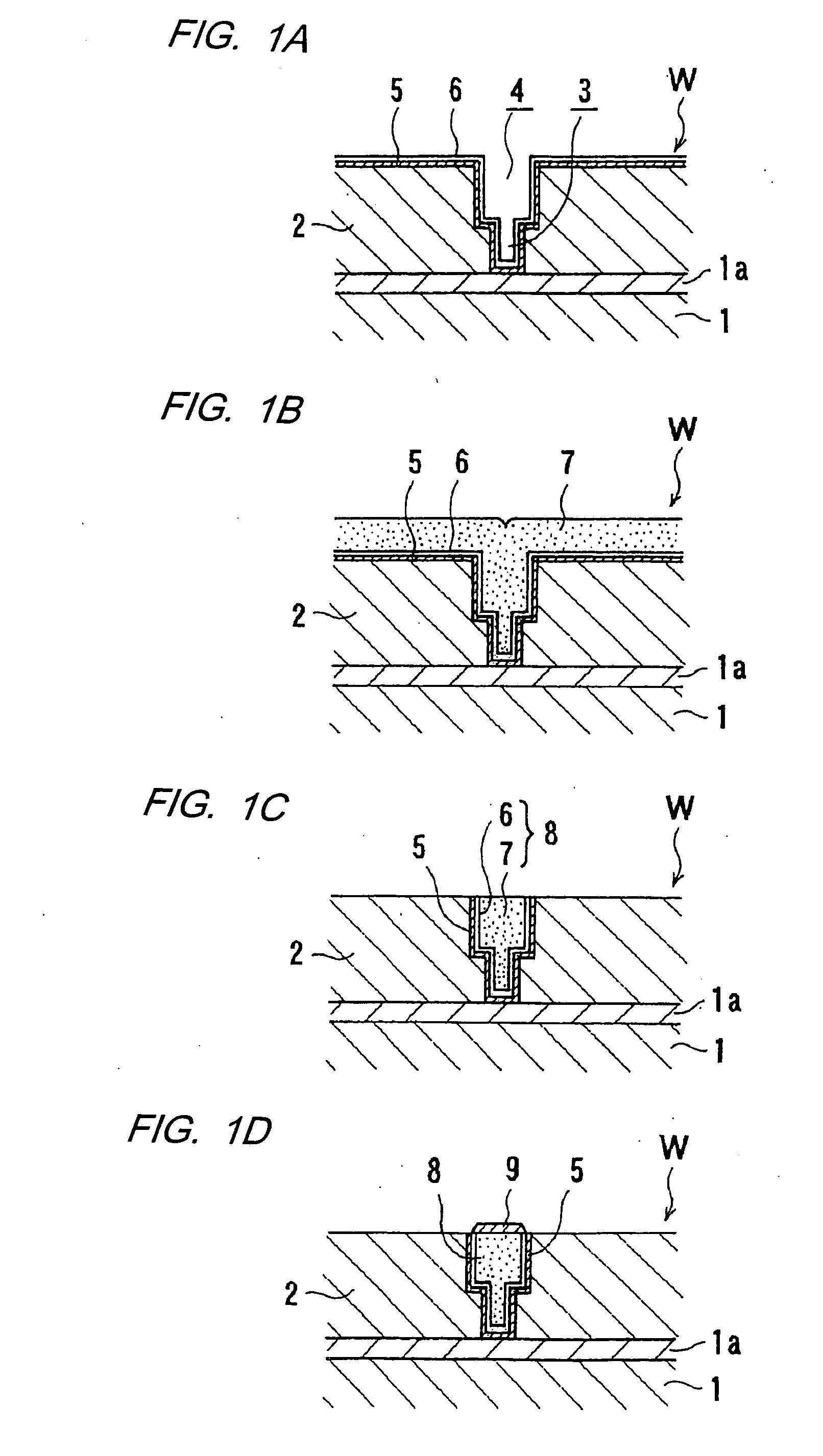
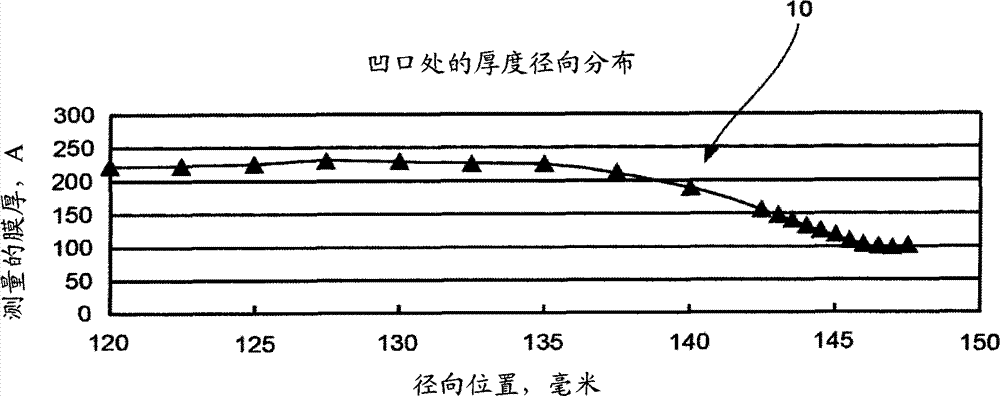
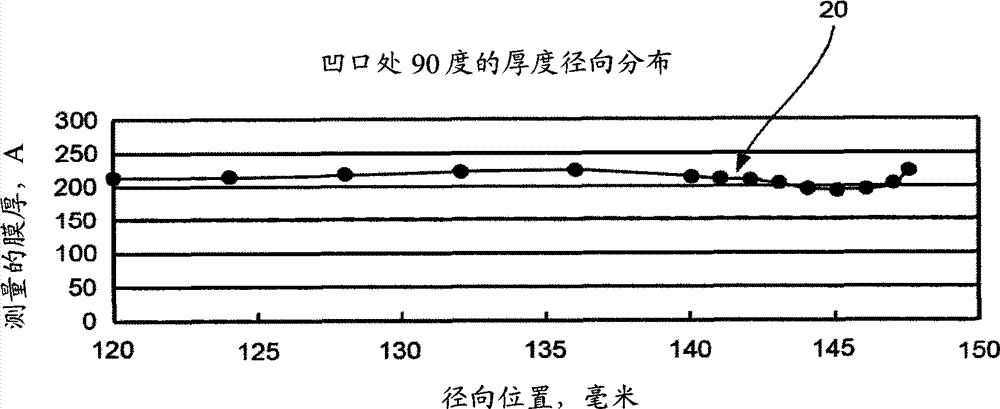
A plating method is capable of mechanically and electrochemically preferentially depositing a plated film in fine interconnect recesses such as trenches and via holes, and depositing the plated film to a flatter surface. The plating method including: disposing a substrate having fine interconnect recesses such that a conductive layer faces an anode; disposing a porous member between the substrate and the anode; filling a plating solution between the substrate and the anode; and repeating a process of holding the conductive layer and the porous member in contact with each other and moving the conductive layer and the porous member relatively to each other, a process of passing an electric current between the conductive layer and the anode while keeping the conductive layer still with respect to the porous member, and a process of stopping the supply of the electric current between the conductive layer and the anode.
Owner:EBARA CORP +1
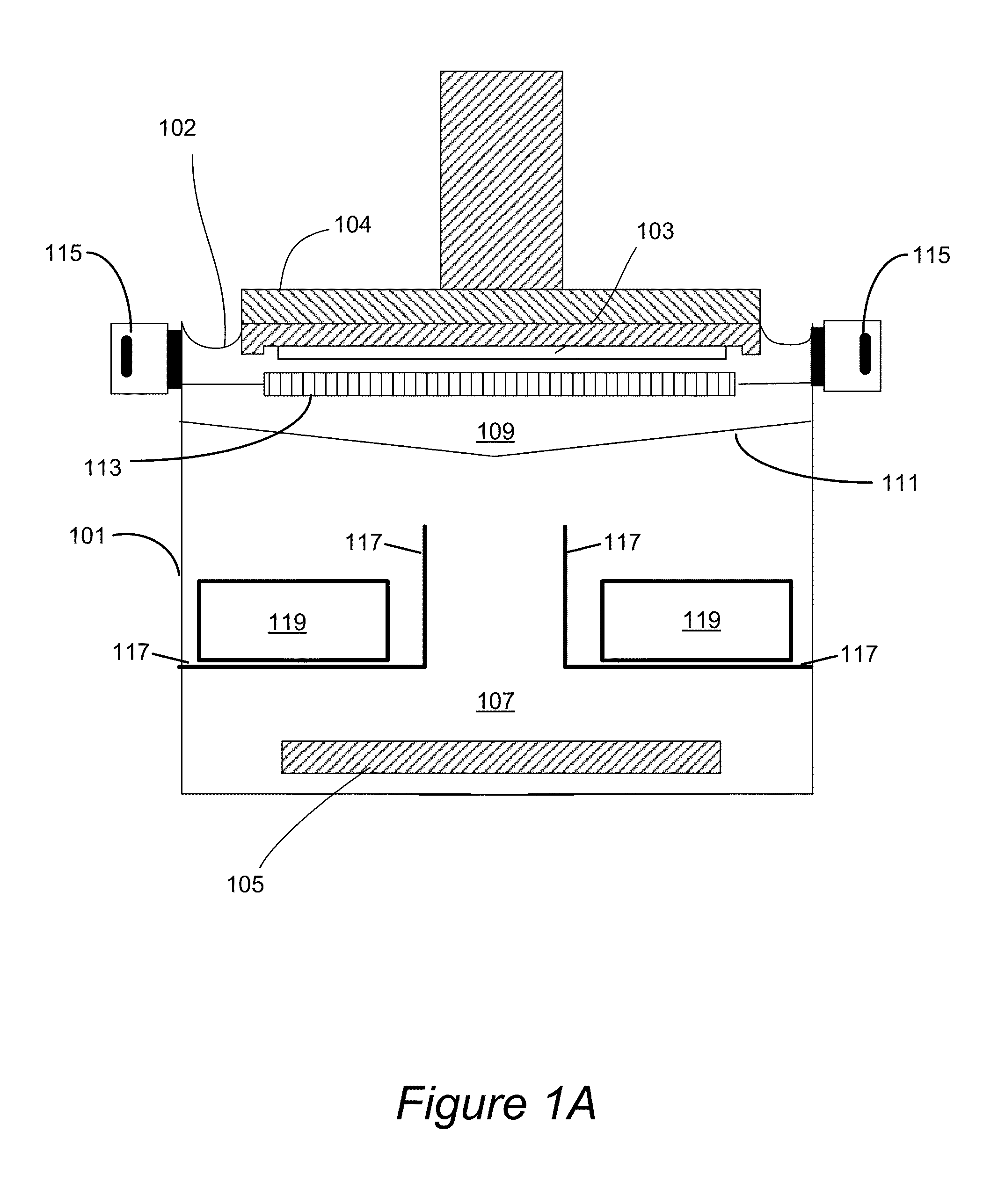
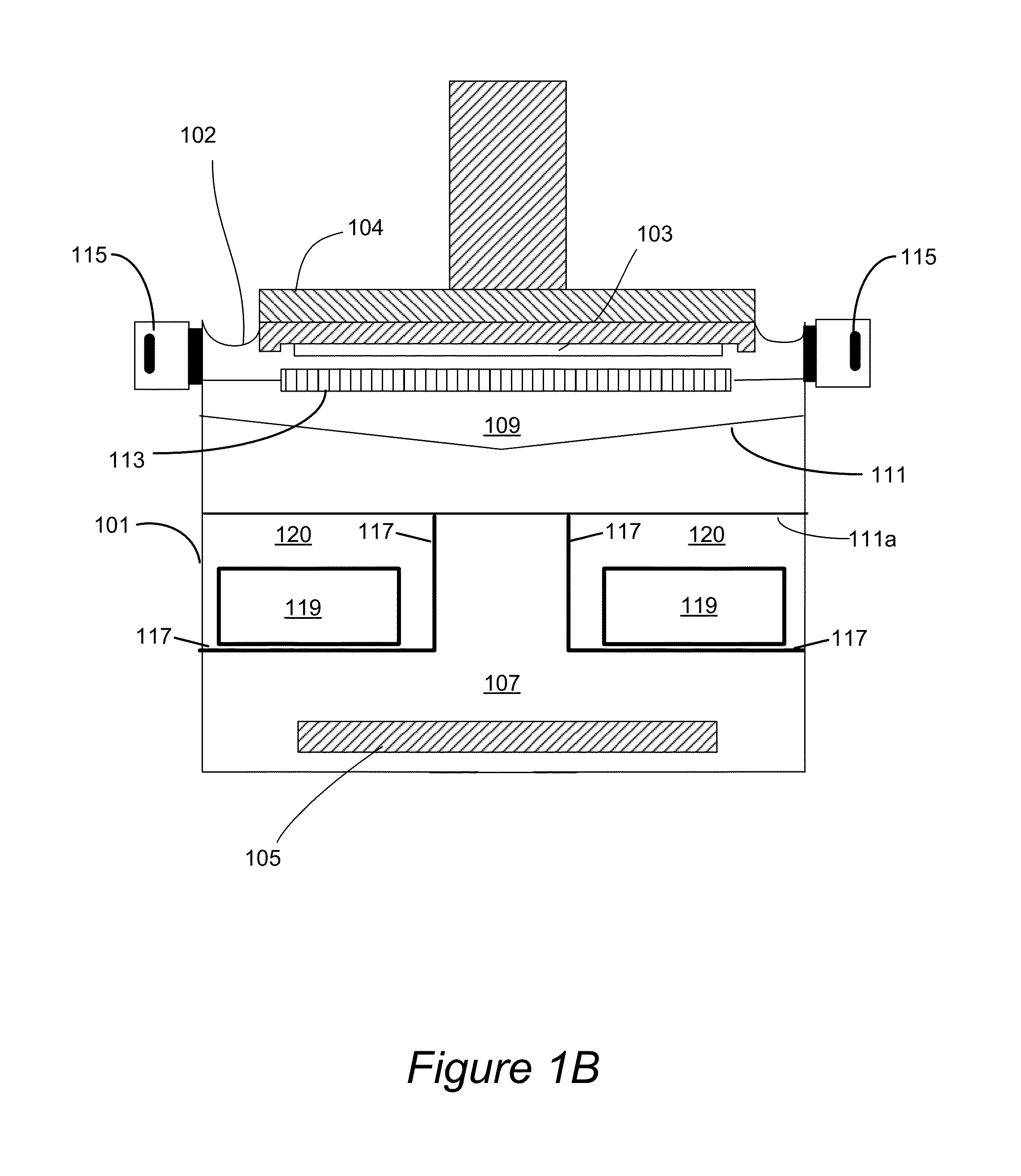
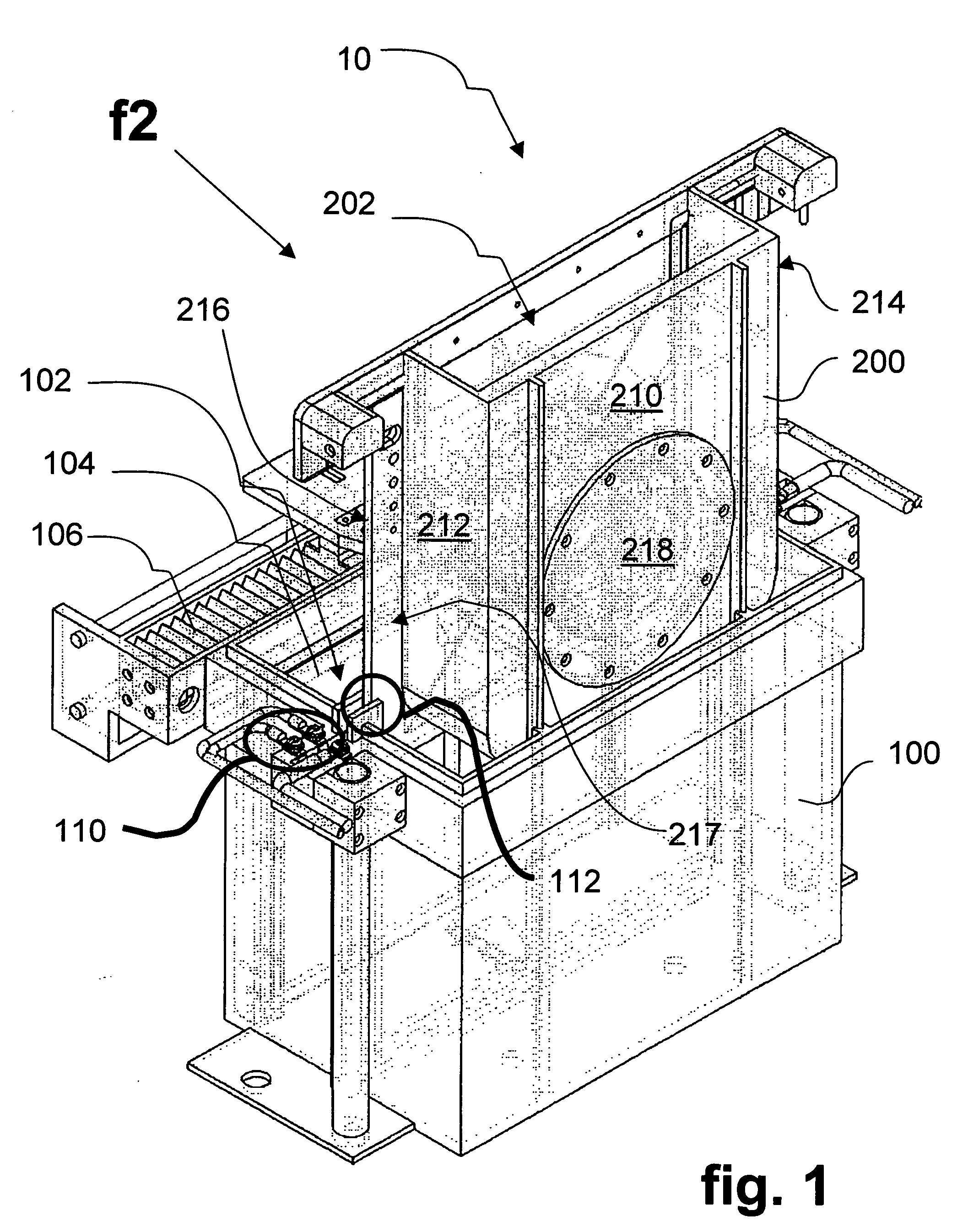
Plating cup with contoured cup bottom
Disclosed herein are cups for engaging wafers during electroplating in clamshell assemblies and supplying electrical current to the wafers during electroplating. The cup can comprise an elastomeric seal disposed on the cup and configured to engage the wafer during electroplating, where upon engagement the elastomeric seal substantially excludes plating solution from a peripheral region of the wafer, and where the elastomeric seal and the cup are annular in shape, and comprise one or more contact elements for supplying electrical current to the wafer during electroplating, the one or more contact elements attached to and extending inwardly towards a center of the cup from a metal strip disposed over the elastomeric seal. A notch area of the cup can have a protrusion or an insulated portion on a portion of a bottom surface of the cup where the notch area is aligned with a notch in the wafer.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Apparatus and method for dynamic control of plated uniformity with the use of remote electric current
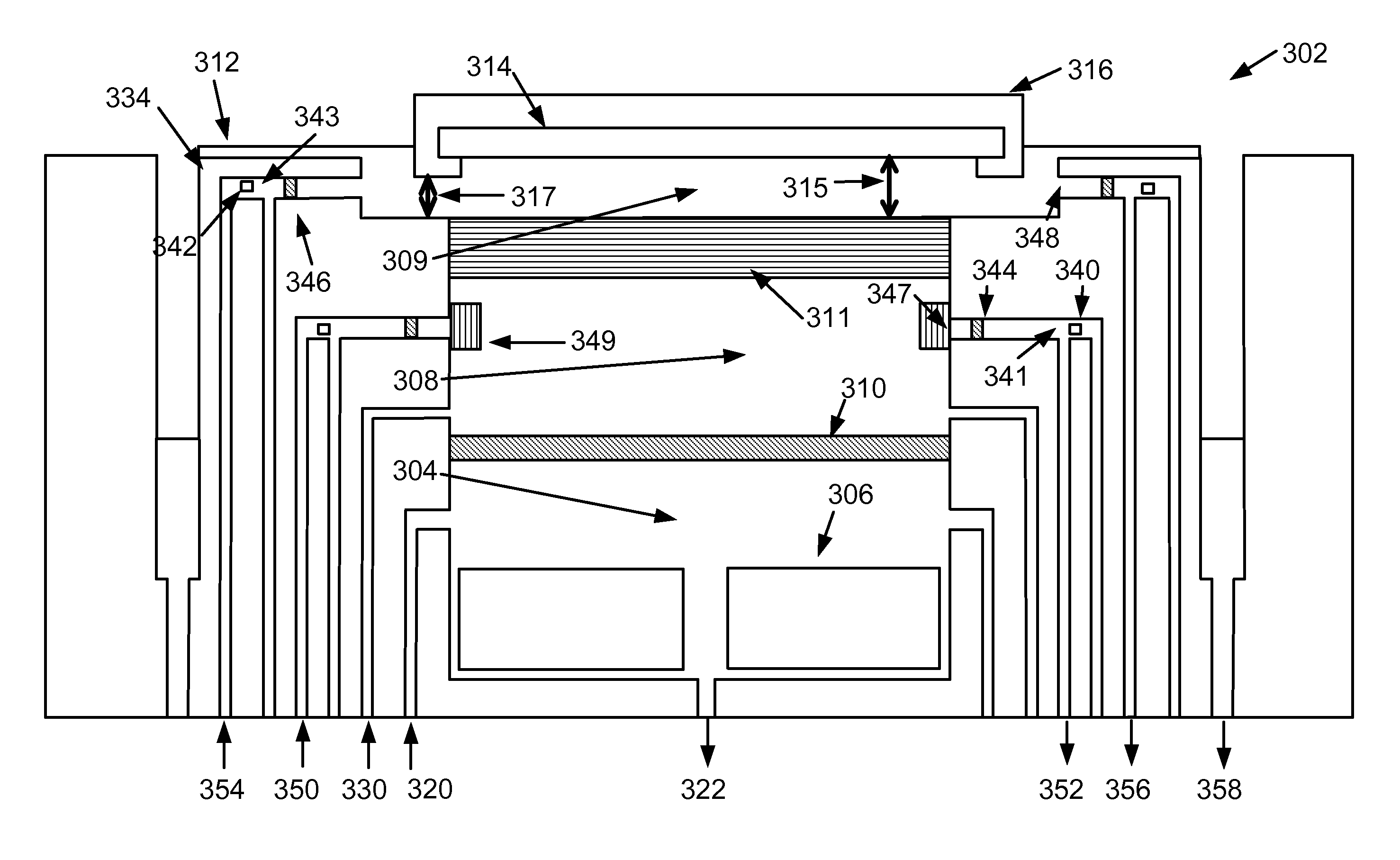
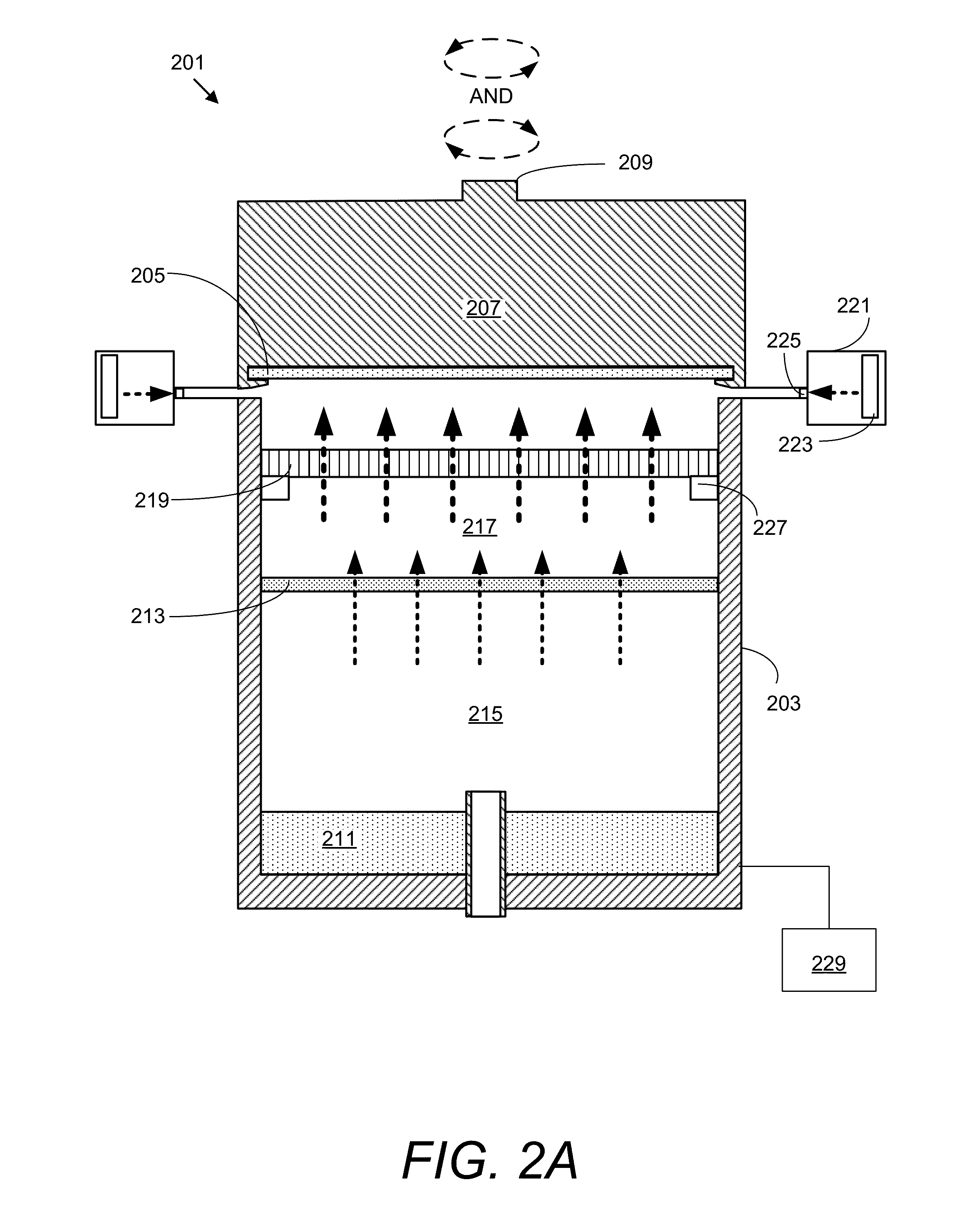
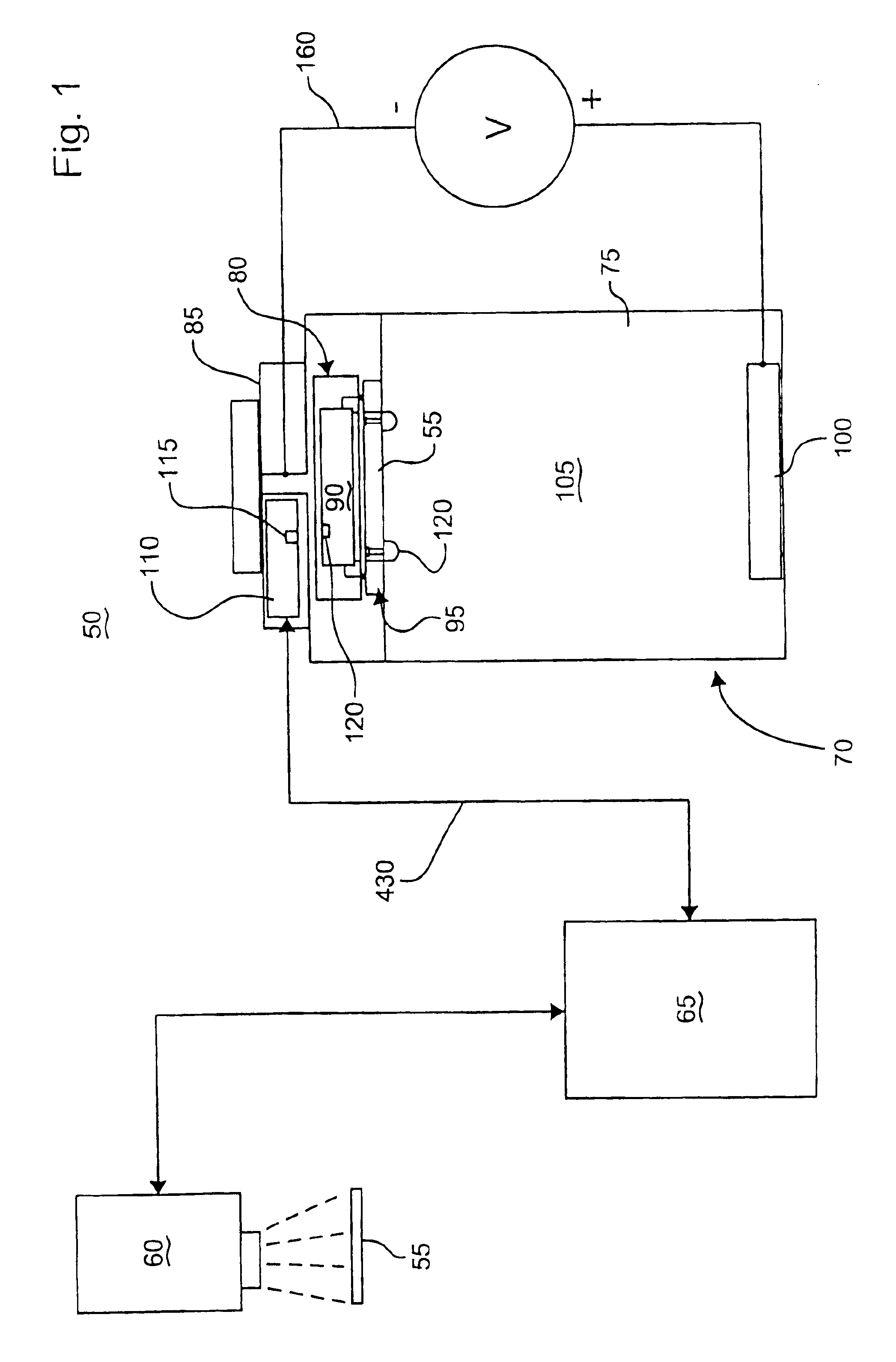
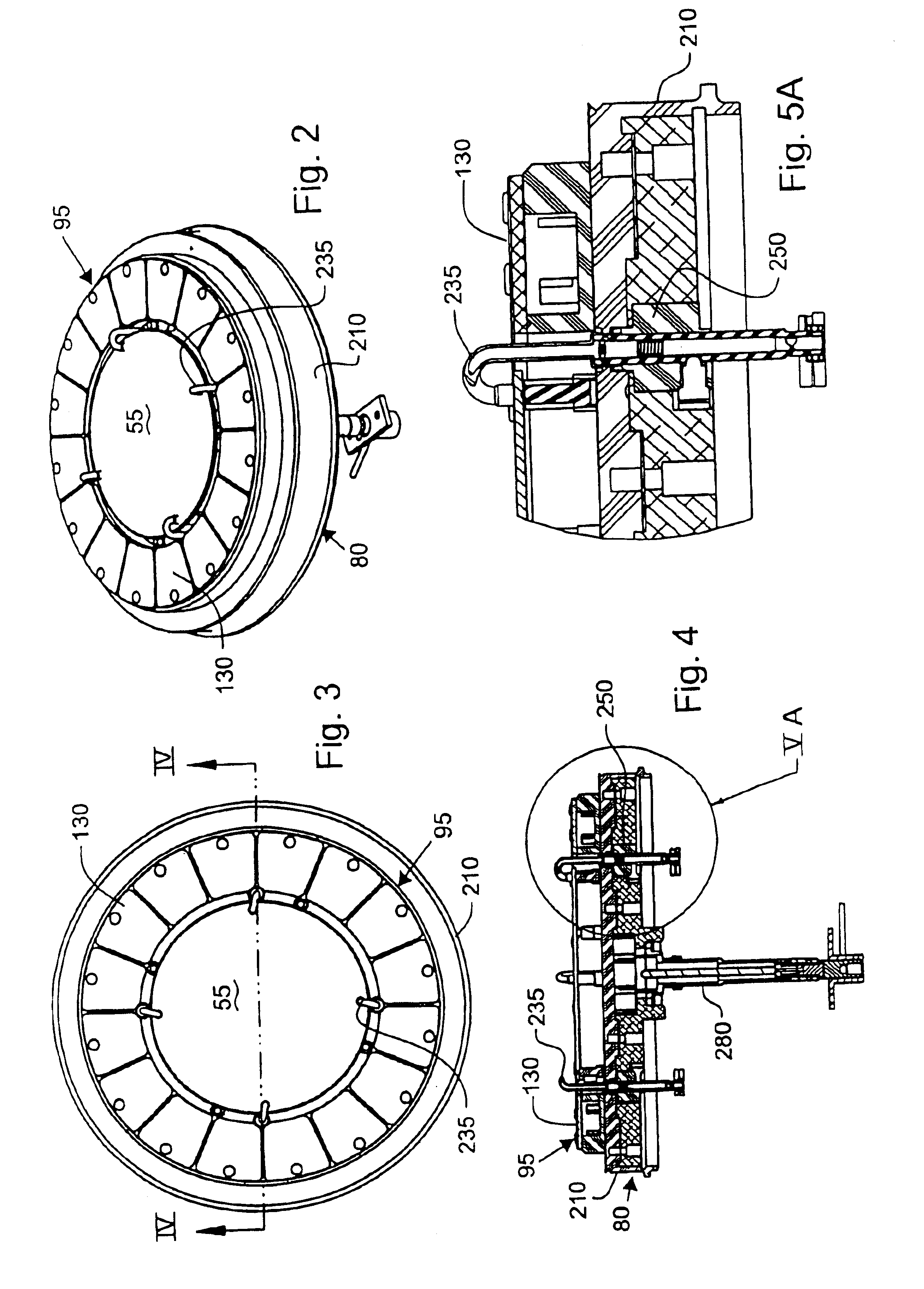
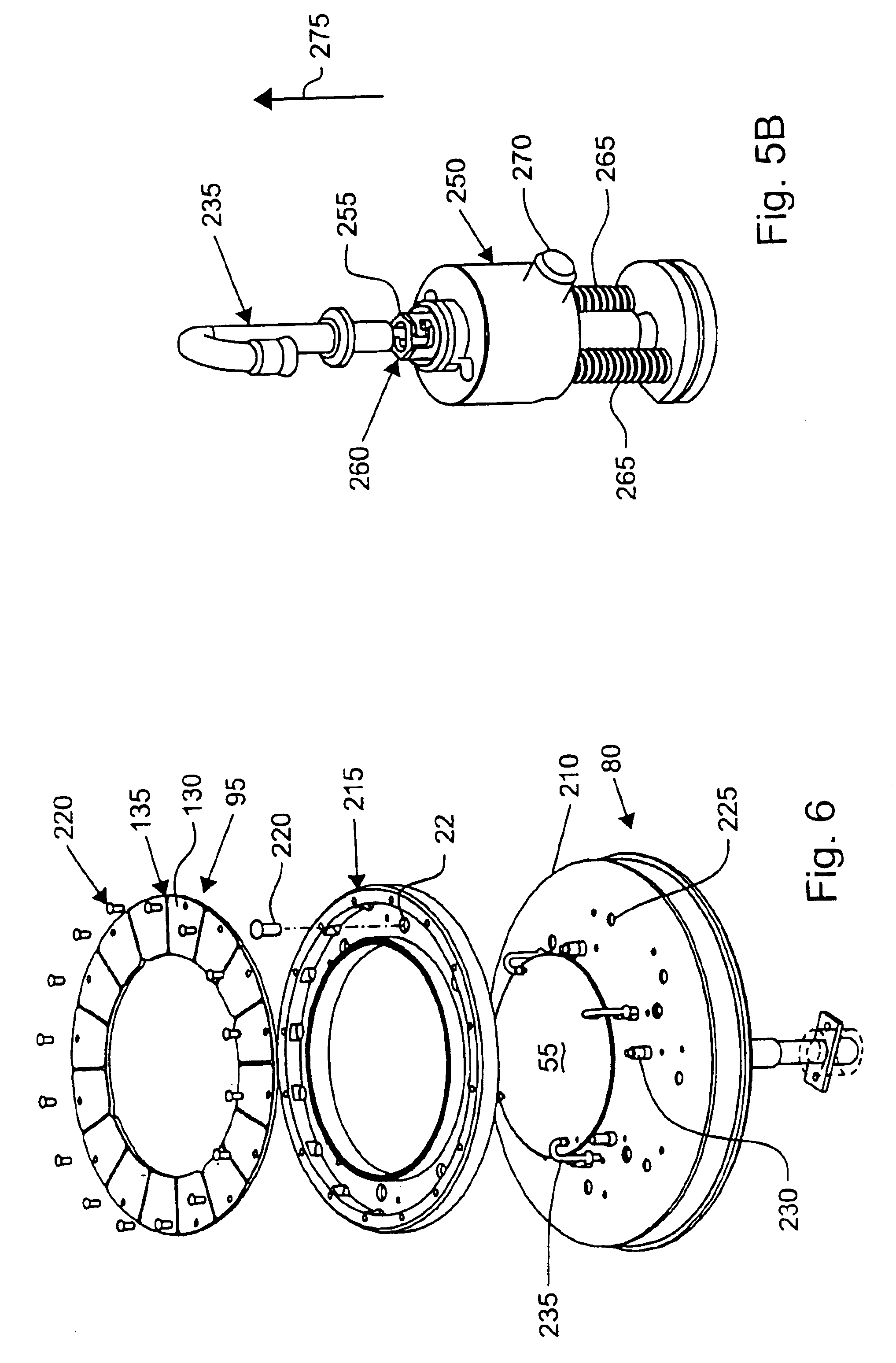
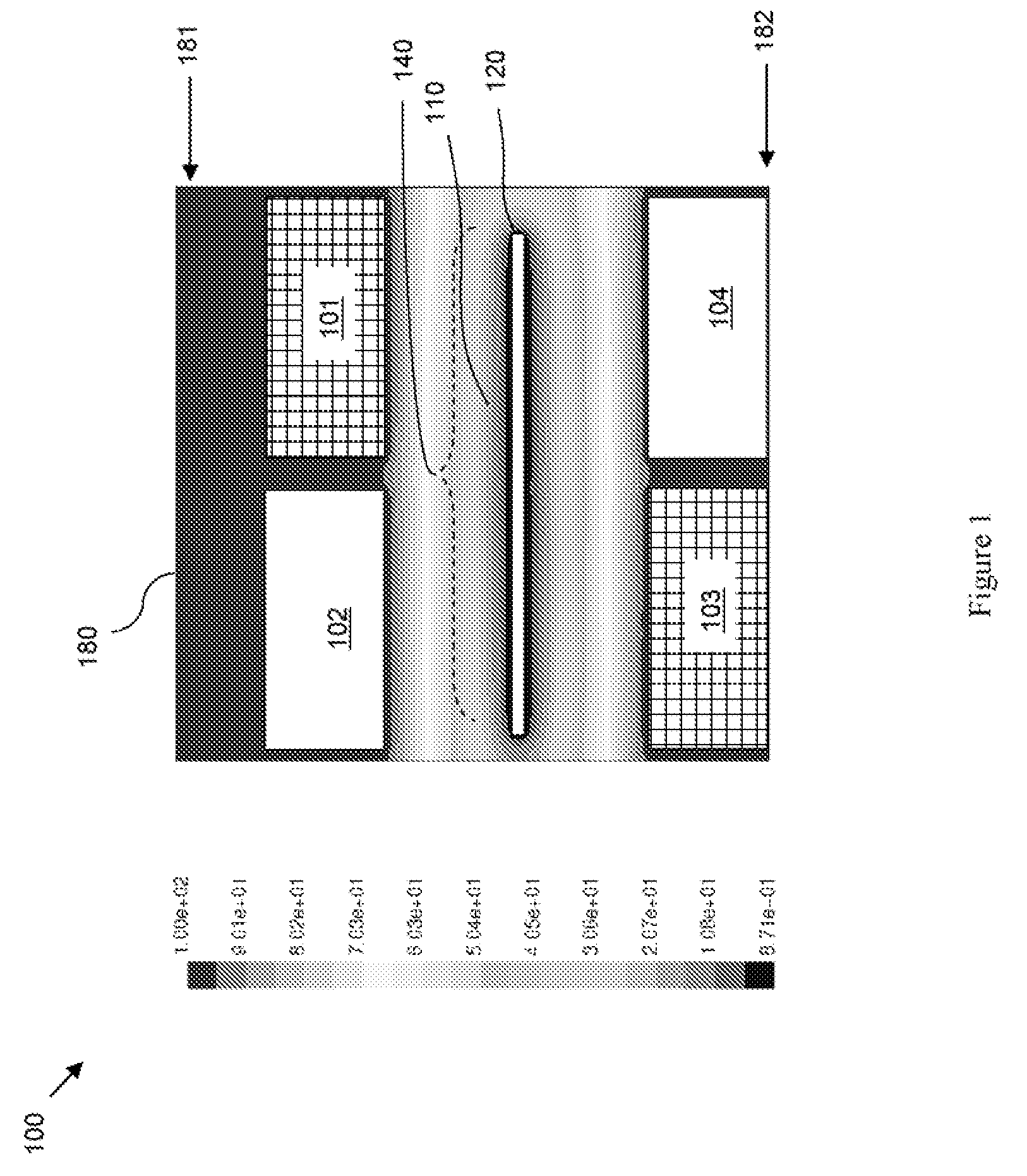
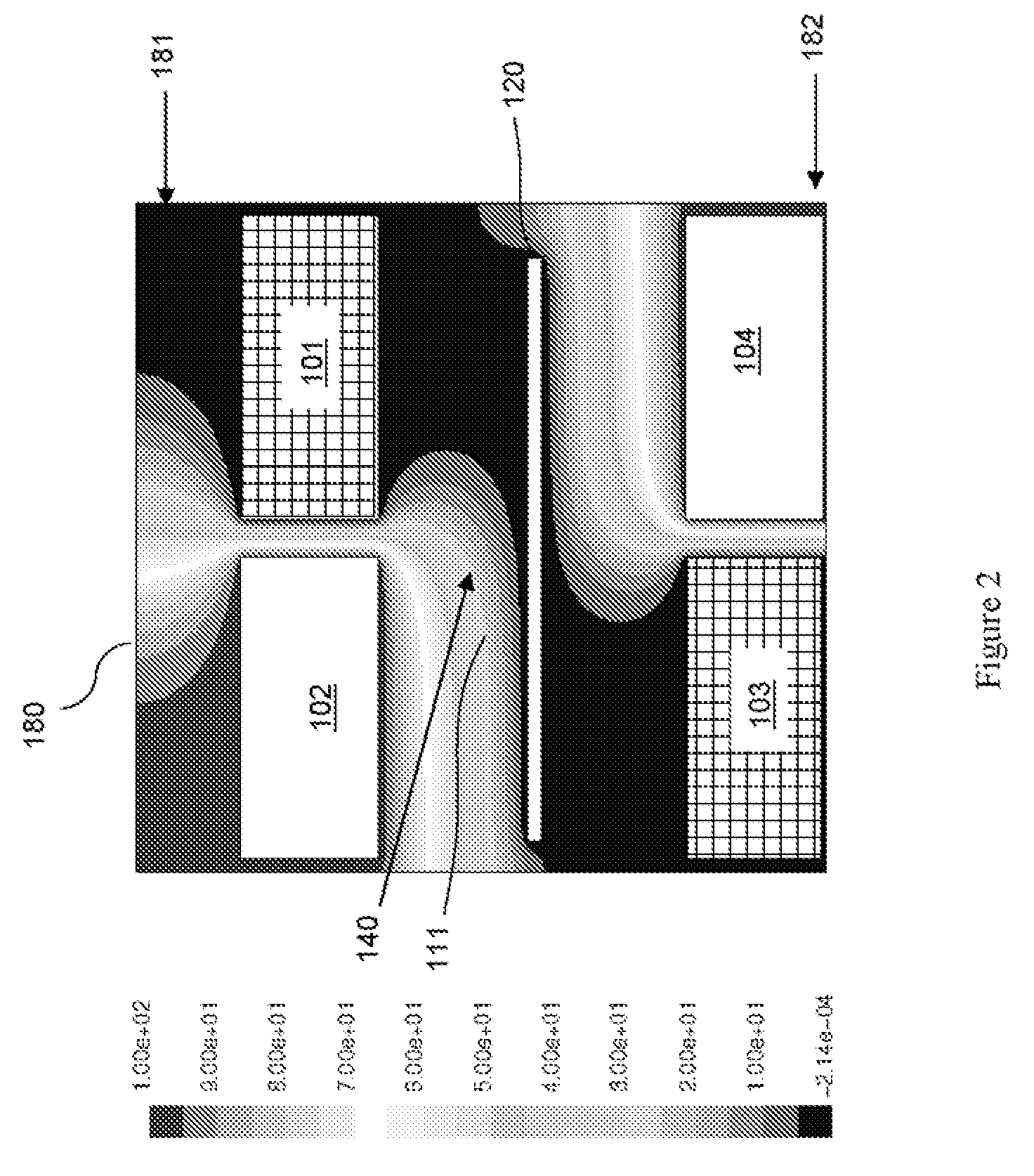
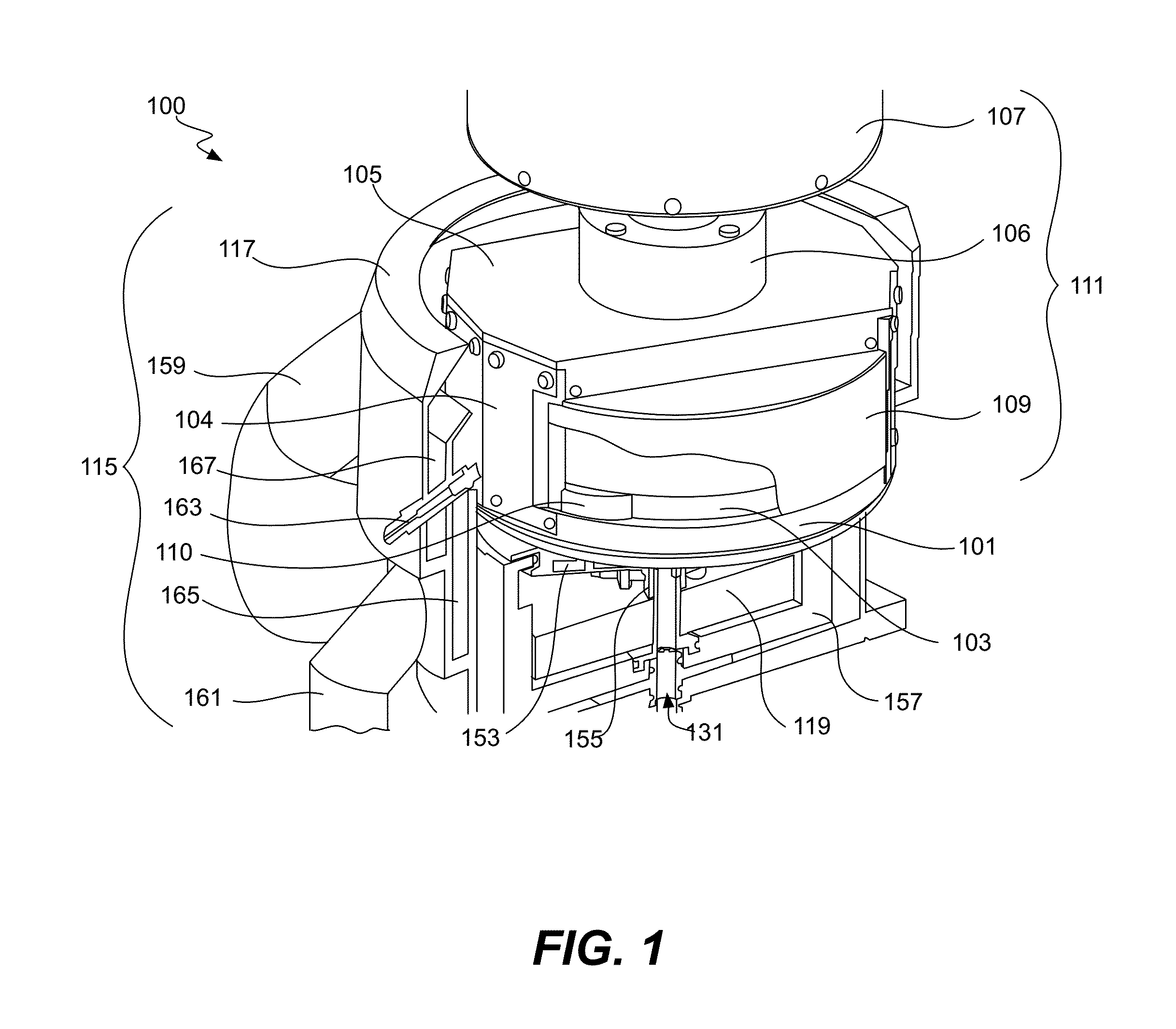
ActiveUS20160215408A1Reduce processReduce downtimeCellsCurrent conducting devicesEngineeringAuxiliary electrode
An apparatus for electroplating metal on a substrate while controlling plating uniformity includes in one aspect: a plating chamber having anolyte and catholyte compartments separated by a membrane; a primary anode positioned in the anolyte compartment; an ionically resistive ionically permeable element positioned between the membrane and a substrate in the catholyte compartment; and a secondary electrode configured to donate and / or divert plating current to and / or from the substrate, wherein the secondary electrode is positioned such that the donated and / or diverted plating current does not cross the membrane separating the anolyte and catholyte compartments, but passes through the ionically resistive ionically permeable element. In some embodiments the secondary electrode is an azimuthally symmetrical anode (e.g., a ring positioned in a separate compartment around the periphery of the plating chamber) that can be dynamically controlled during electroplating.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
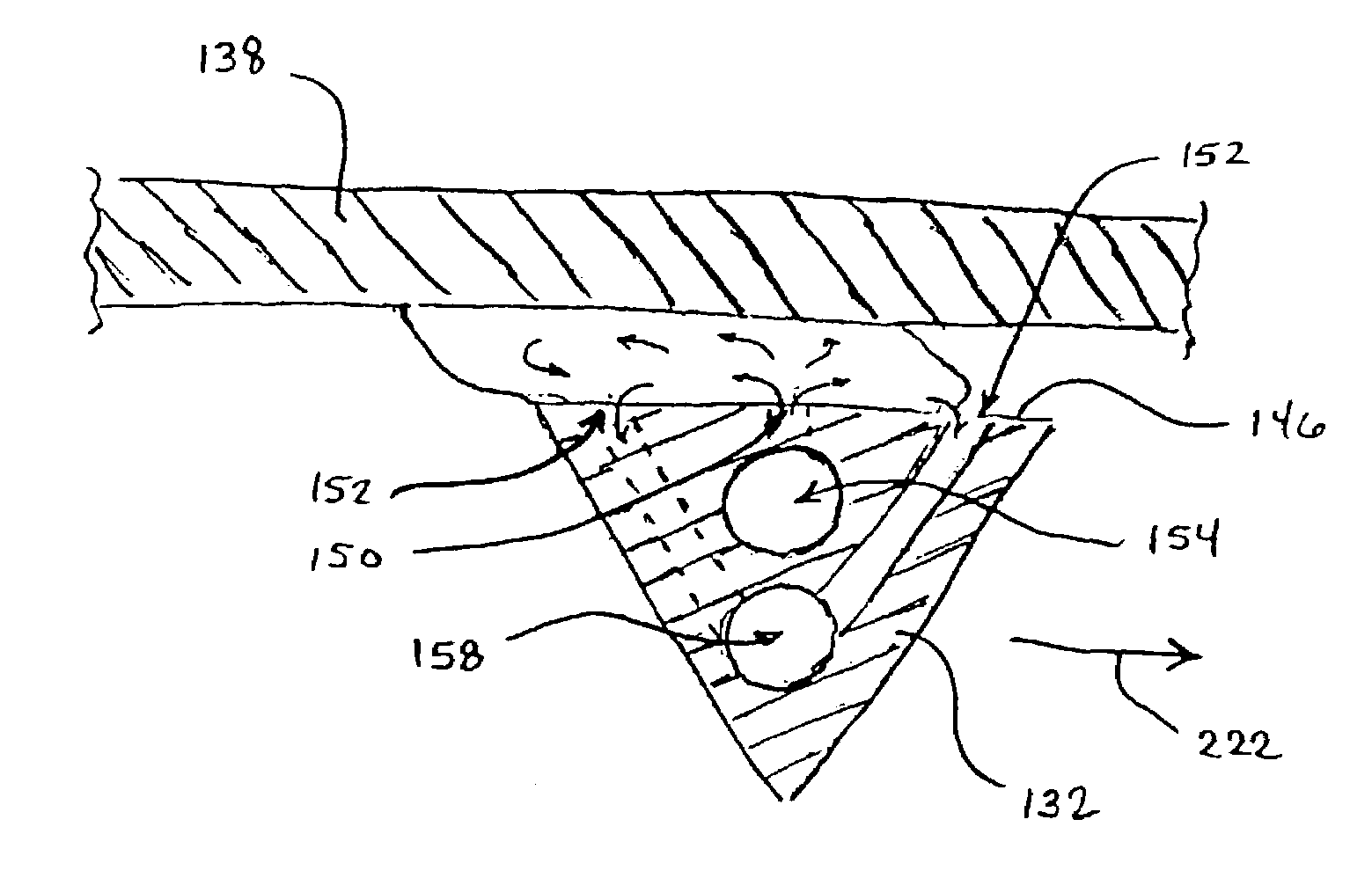
Method and apparatus for dynamic current distribution control during electroplating
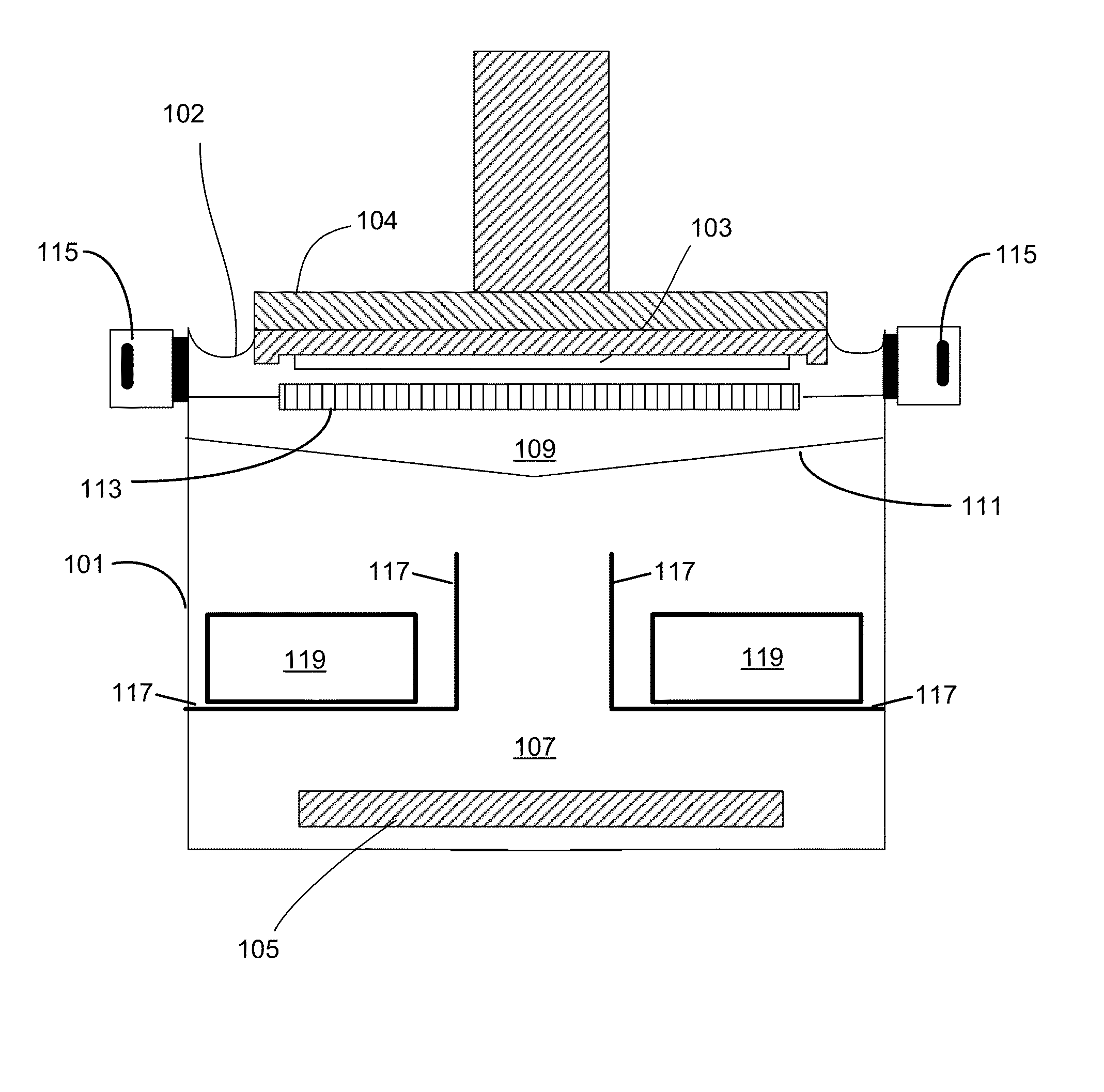
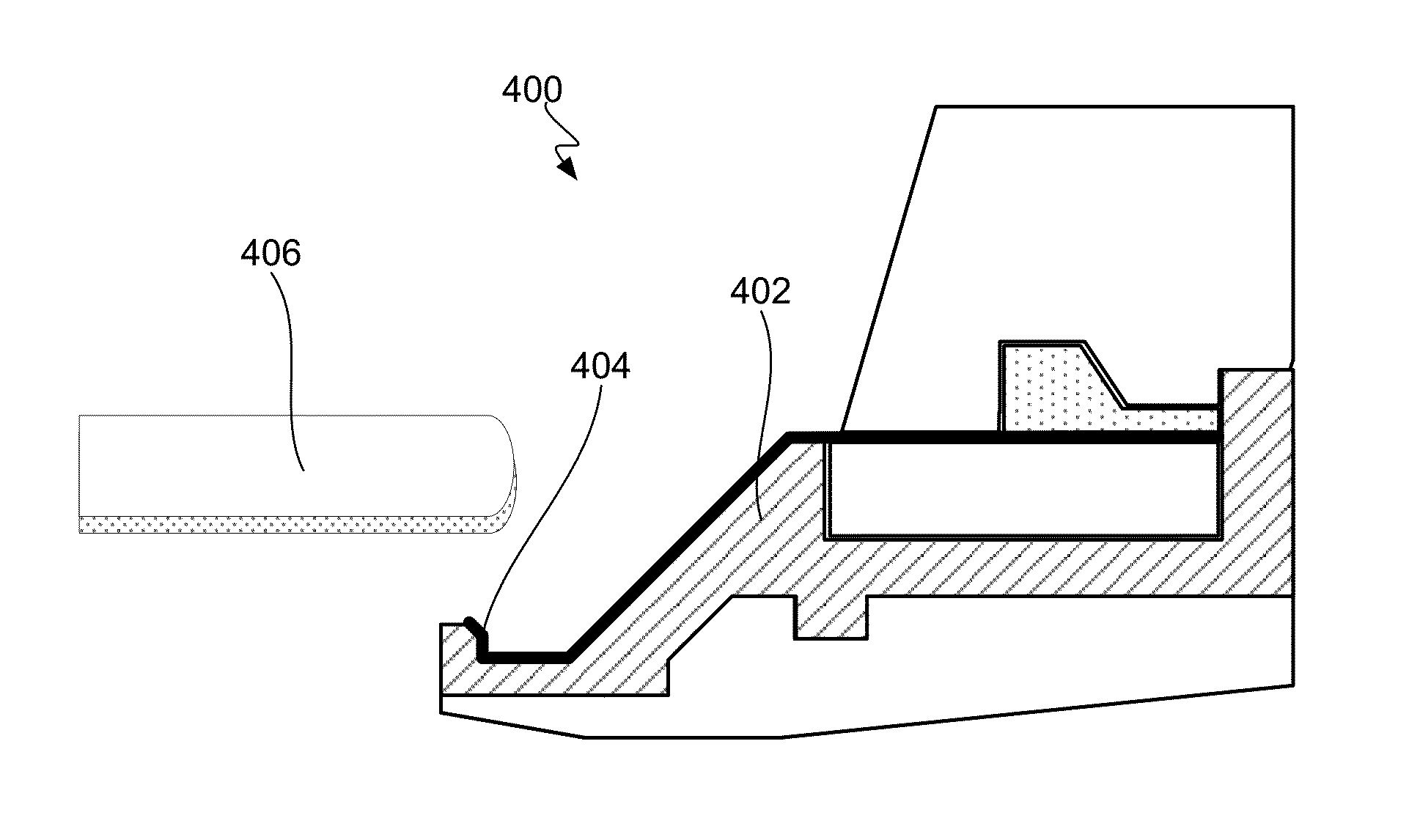
ActiveUS20140144781A1Reducing terminal effectCellsMachining electric circuitsPower flowCurrent distribution
An apparatus for electroplating a layer of metal onto the surface of a wafer includes an auxiliary electrode that is configured to function both as an auxiliary cathode and an auxiliary anode during the course of electroplating. The apparatus further includes an ionic current collimator (e.g., a focus ring) configured to direct ionic current from the main anode to central portions of the wafer. The provided configuration effectively redistributes ionic current in the plating system allowing plating of uniform metal layers and mitigating the terminal effect. In one example, the auxiliary electrode functions as an auxiliary cathode in the beginning of electroplating when the terminal effect is pronounced, and subsequently is anodically biased.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
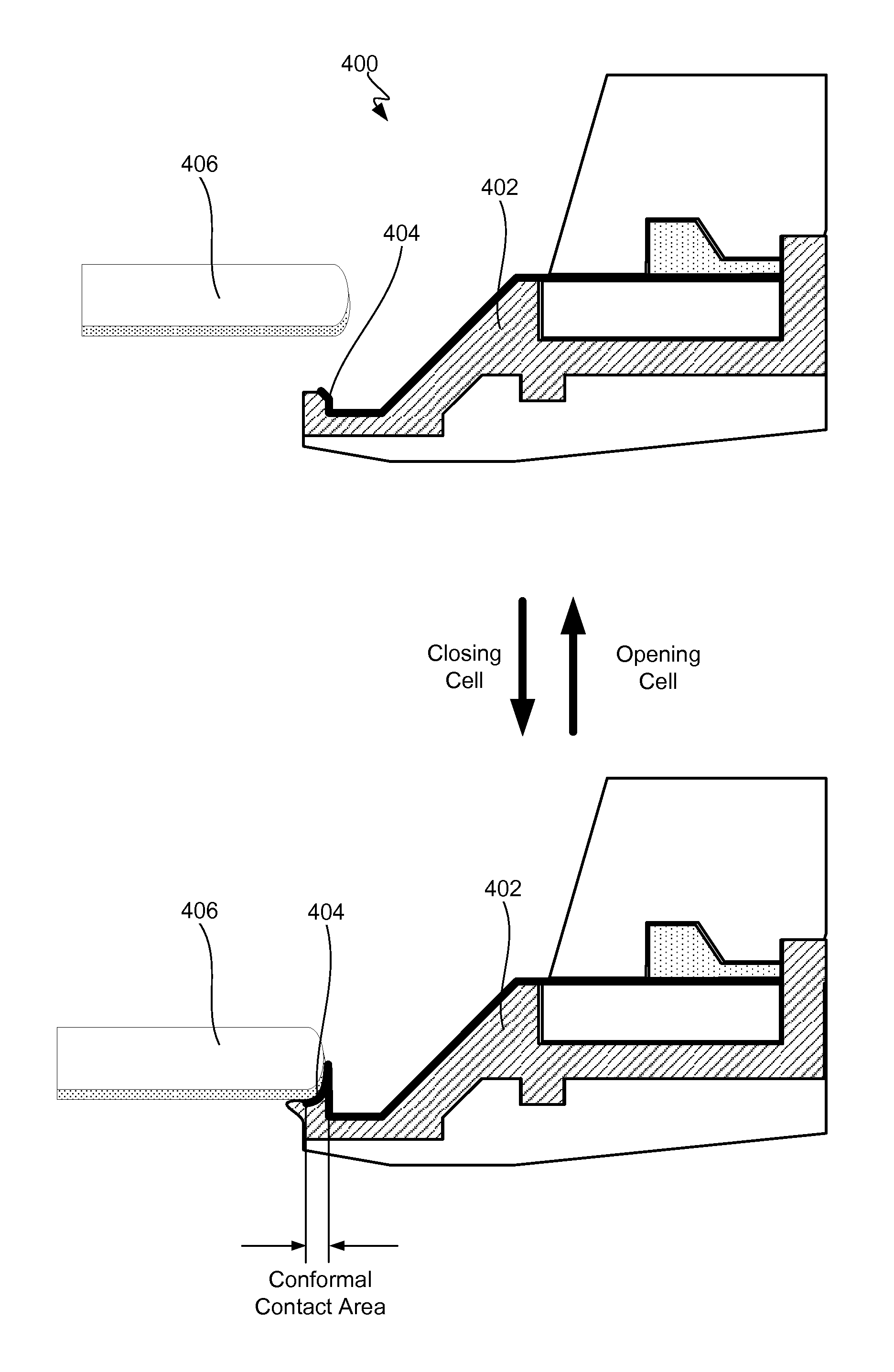
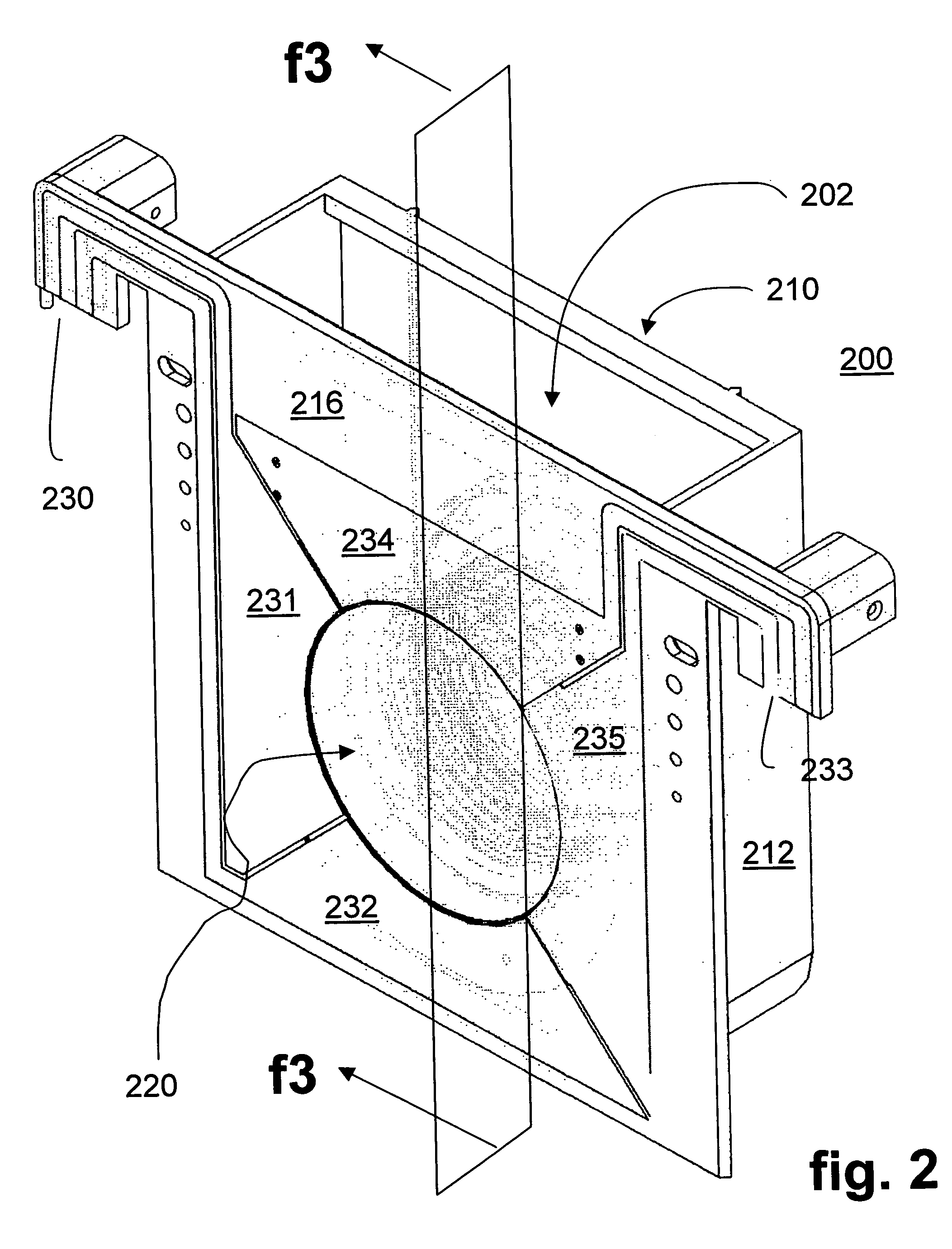
Lipseals and contact elements for semiconductor electroplating apparatuses
Disclosed herein are lipseal assemblies for use in electroplating clamshells which may include an elastomeric lipseal for excluding plating solution from a peripheral region of a semiconductor substrate and one or more electrical contact elements. The contact elements may be structurally integrated with the elastomeric lipseal. The lipseal assemblies may include one or more flexible contact elements at least a portion of which may be conformally positioned on an upper surface of the elastomeric lipseal, and may be configured to flex and form a conformal contact surface that interfaces with the substrate. Some elastomeric lipseals disclosed herein may support, align, and seal a substrate in a clamshell, and may include a flexible elastomeric upper portion located above a flexible elastomeric support edge, the upper portion having a top surface and an inner side surface, the later configured to move inward and align the substrate upon compression of the top surface.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Electroplating apparatus for tailored uniformity profile
ActiveUS8858774B2Maximizing randomization of flow patternSimple processAnodisationCellsRadial positionEngineering
Methods of electroplating metal on a substrate while controlling azimuthal uniformity, include, in one aspect, providing the substrate to the electroplating apparatus configured for rotating the substrate during electroplating, and electroplating the metal on the substrate while rotating the substrate relative to a shield such that a selected portion of the substrate at a selected azimuthal position dwells in a shielded area for a different amount of time than a second portion of the substrate having the same average arc length and the same average radial position and residing at a different angular (azimuthal) position. For example, a semiconductor wafer substrate can be rotated during electroplating slower or faster, when the selected portion of the substrate passes through the shielded area.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
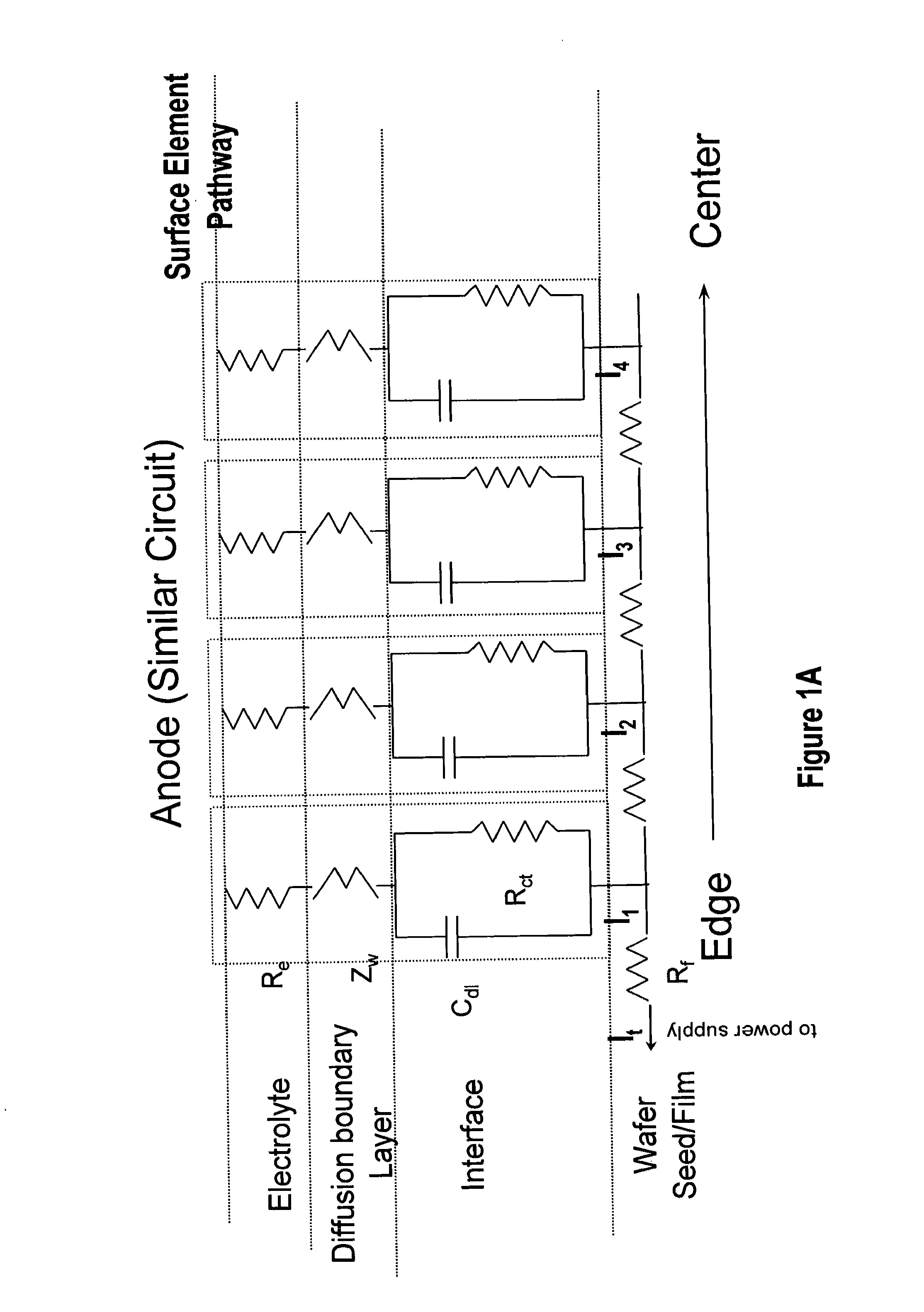
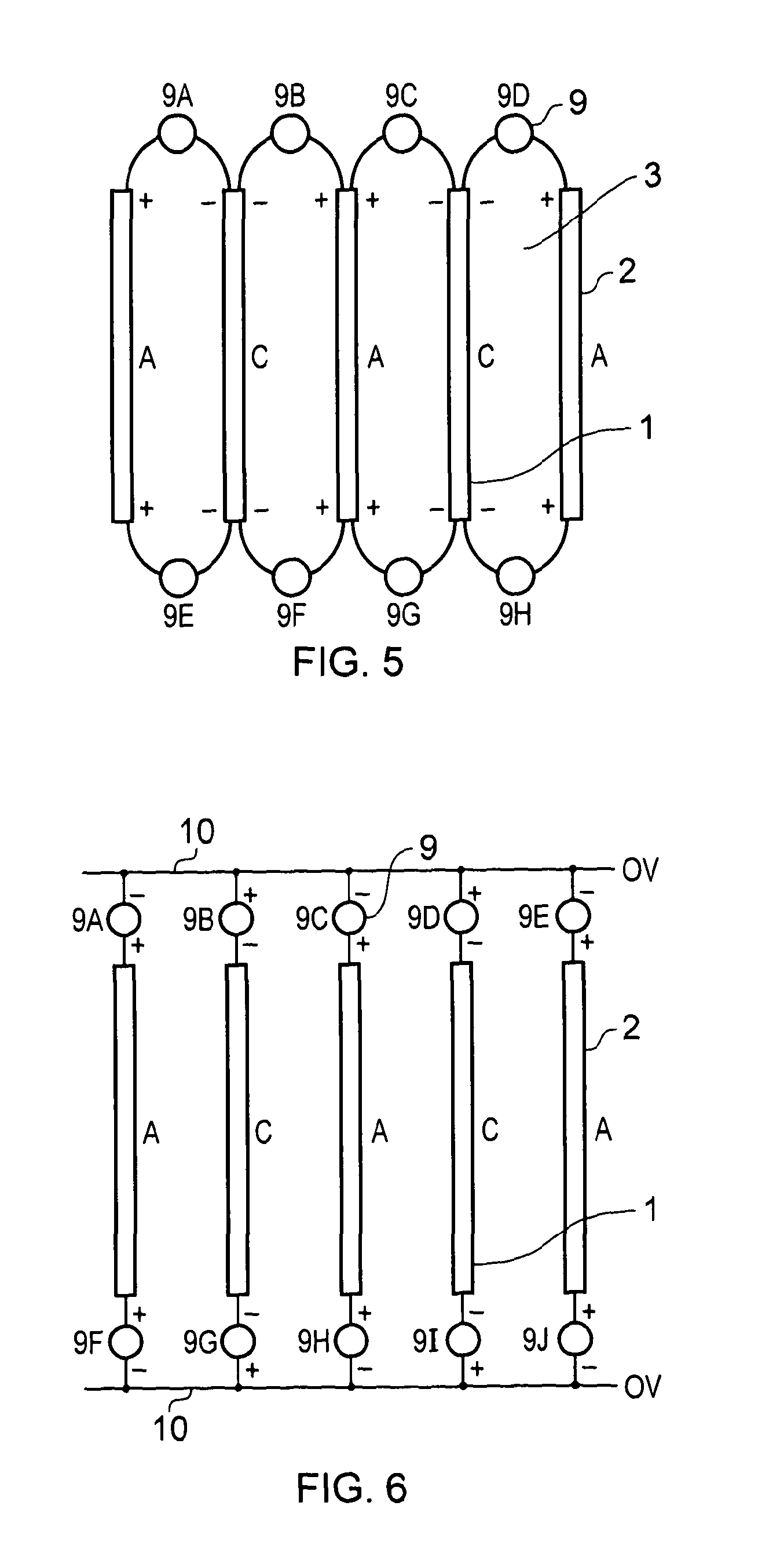
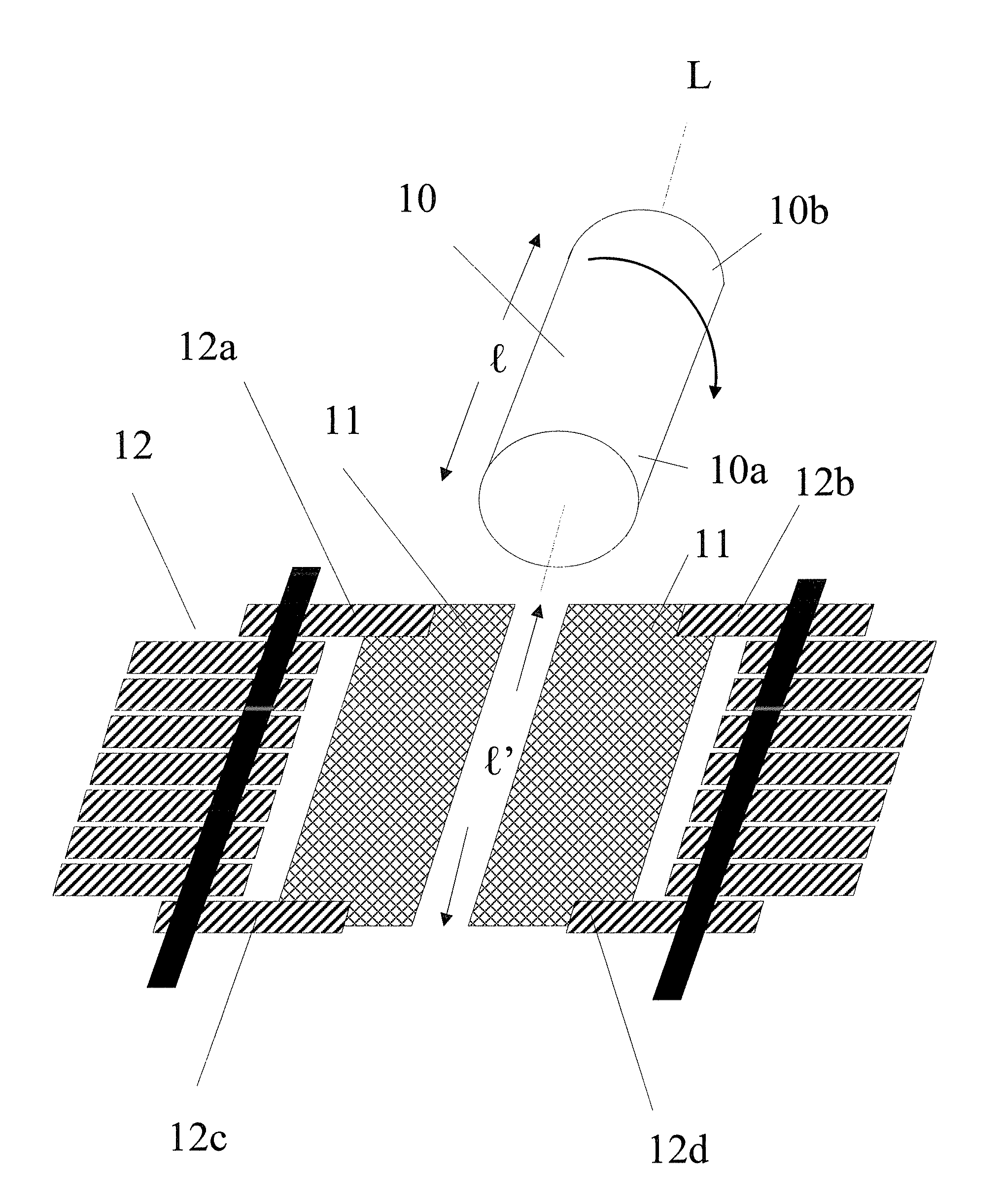
Cathode current control system for a wafer electroplating apparatus
InactiveUS6843894B2CellsMachining electric circuitsElectrical resistance and conductanceAutomatic control
A cathode current control system employing a current thief for use in electroplating a wafer is set forth. The current thief comprises a plurality of conductive segments disposed to substantially surround a peripheral region of the wafer. A first plurality of resistance devices are used, each associated with a respective one of the plurality of conductive segments. The resistance devices are used to regulate current through the respective conductive finger during electroplating of the wafer. Various constructions are used for the current thief and further conductive elements, such as fingers, may also be employed in the system. As with the conductive segments, current through the fingers may also be individually controlled. In accordance with one embodiment of the overall system, selection of the resistance of each respective resistance devices is automatically controlled in accordance with predetermined programming.
Owner:SEMITOOL INC
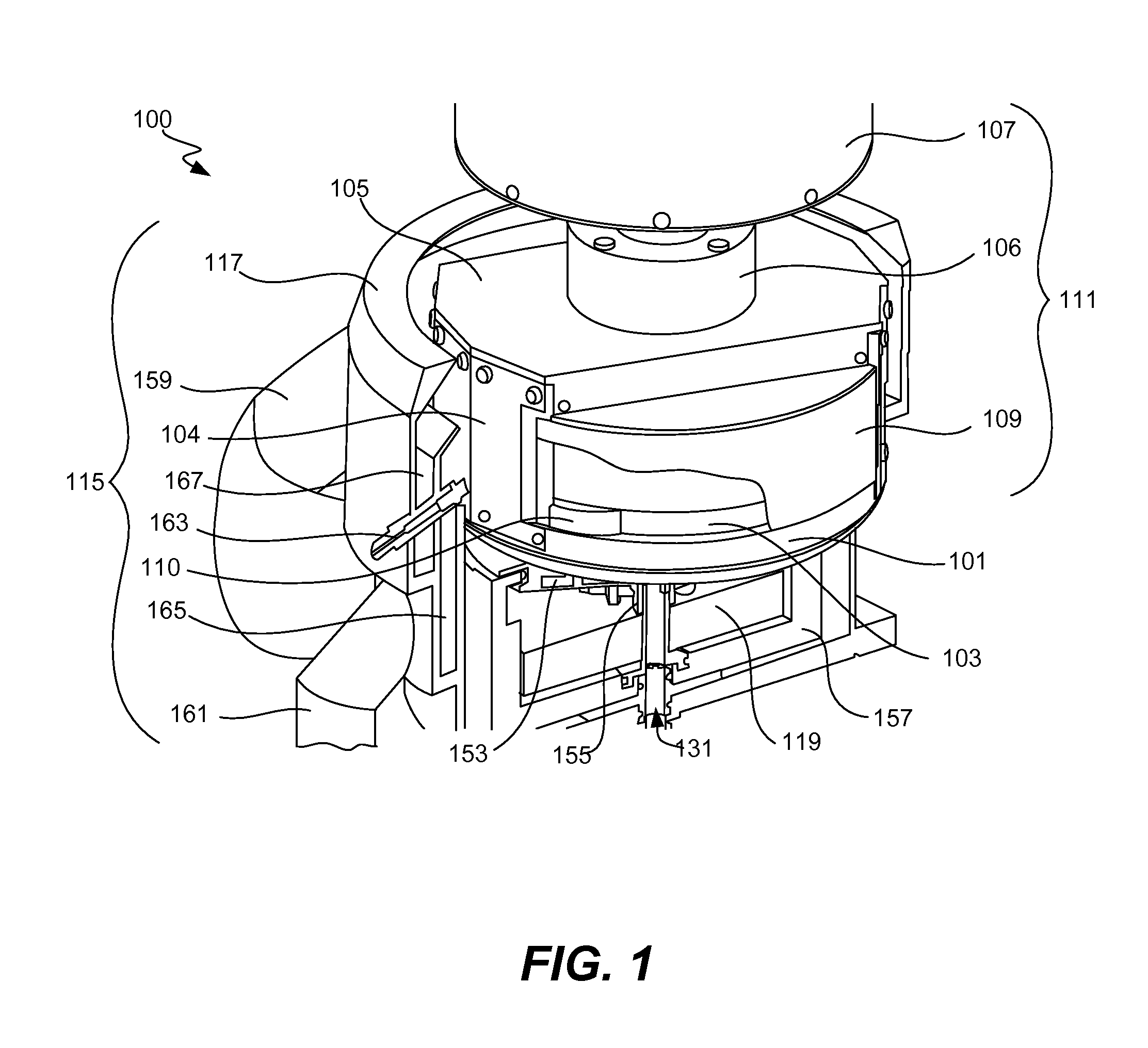
Fixtureless vertical paddle electroplating cell
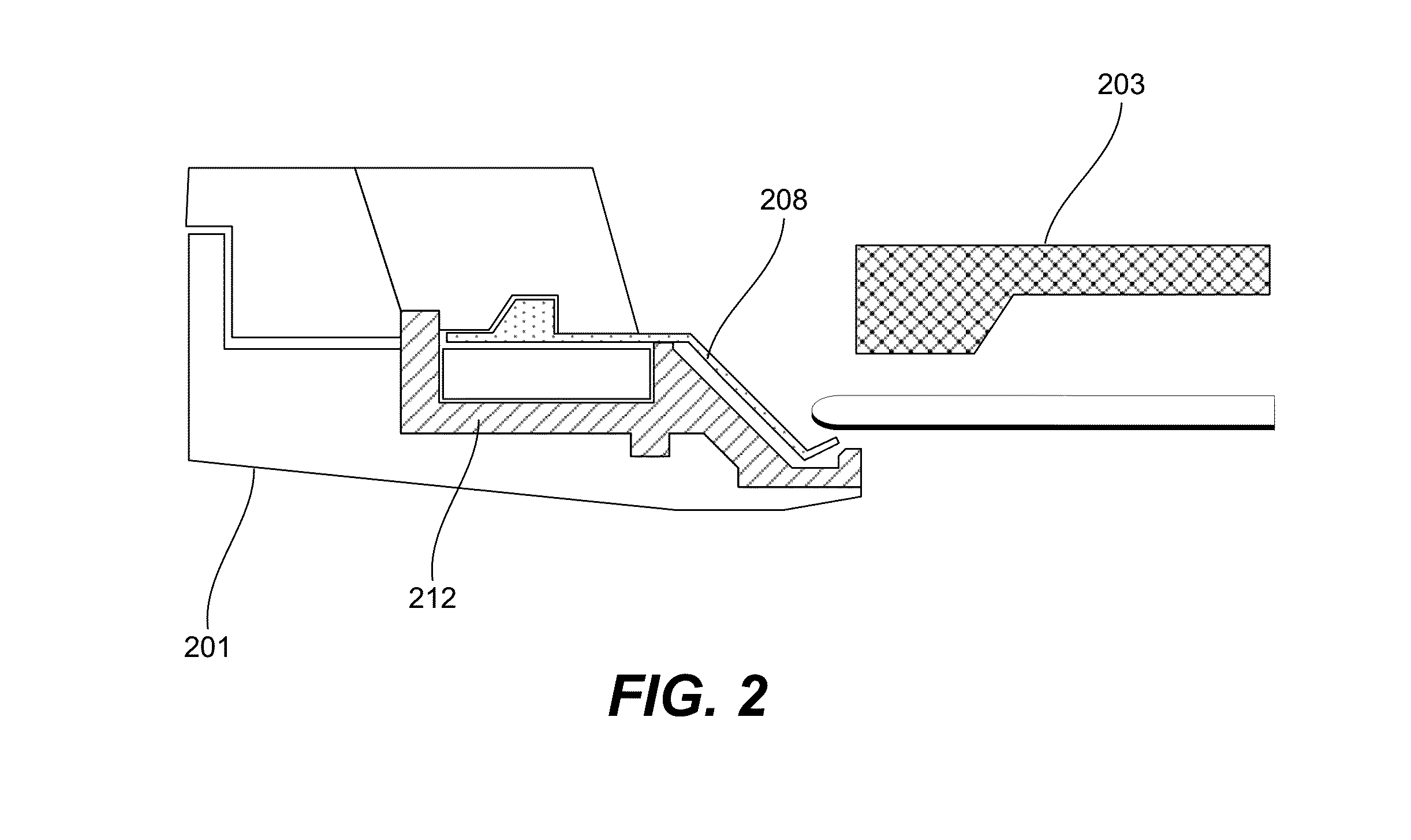
InactiveUS20060070883A1Increase productionEliminate needSealing devicesCurrent conducting devicesMechanical engineeringElectrode
A submersible assembly for exposing respective front surfaces of different work-pieces to an electroplating bath as a partial respective electrodes thereof, while protecting opposing, rear surfaces of the work-pieces from the bath. The assembly includes a wall, having a front surface also partially forming a first electrode of the bath, and having an opening smaller in size than the perimeter of a work-piece while substantially corresponding in size to the portion of the front surface of the work-piece to be exposed to the bath. The assembly also includes a chuck mechanism for applying pressure against the rear surface of the work-piece to thereby hold the work-piece against a rear surface of the wall and create a fluid-tight seal between the rear surface of the wall and the perimeter of the front surface of the work-piece, thereby exposing the front surface of the work-piece to the bath while protecting the rear surface of the work-piece from exposure to the bath.
Owner:CHEM SAFETY TECH
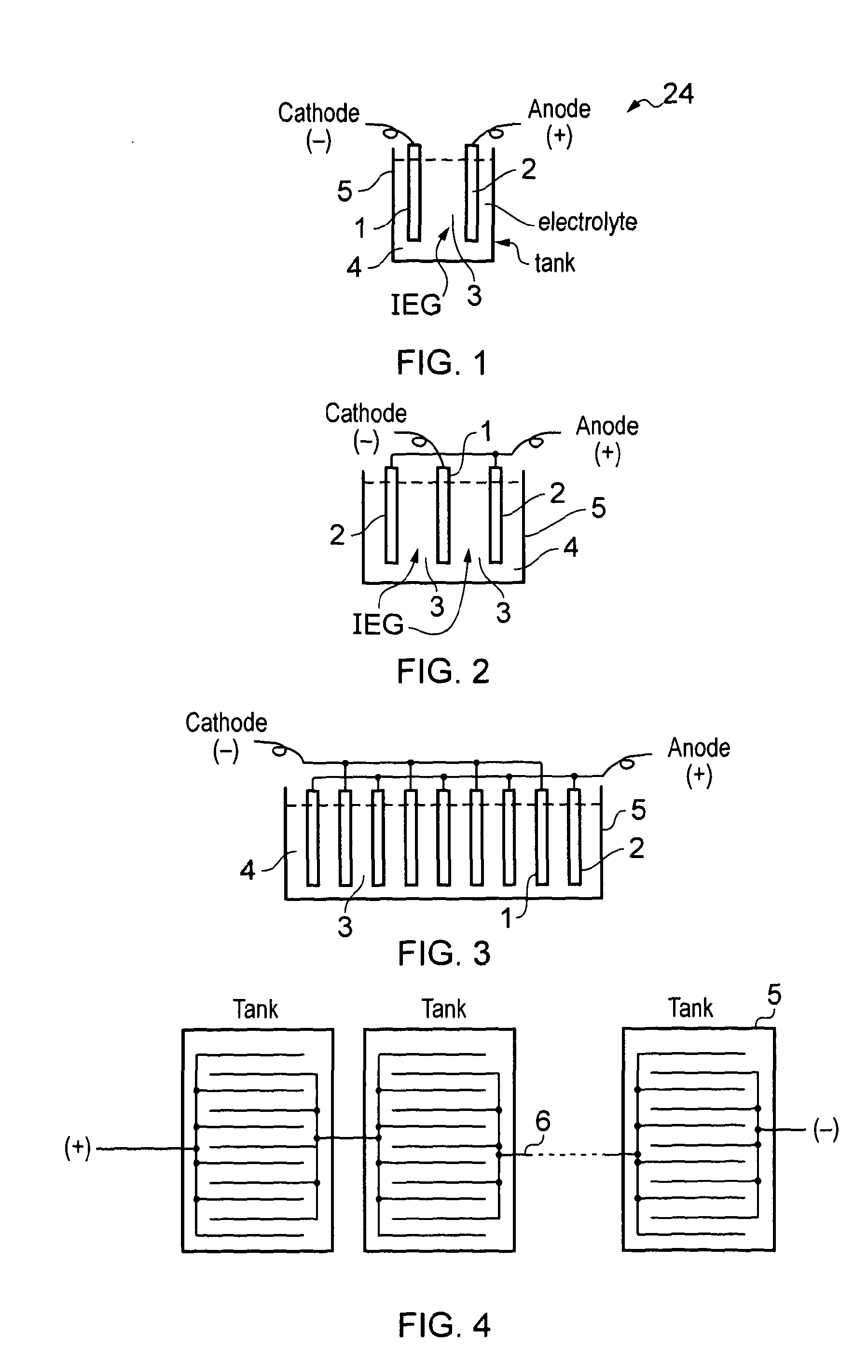
Apparatus for use in electrorefining and electrowinning
ActiveUS20130126337A1Poor controlPoor density controlCellsMachining electrodesElectrolysisElectrical battery
An apparatus for use in the electro-production of metals, comprising a plurality of anodes and a plurality of cathodes in an interleaved configuration, wherein each anode and cathode pair forms a cell; a plurality of power supplies, each cell associated with one or more respective power supplies; and the power supplies are arranged to control a direct current in the one or more cells to a predetermined value.
Owner:OUTOTEC FINDLAND OY
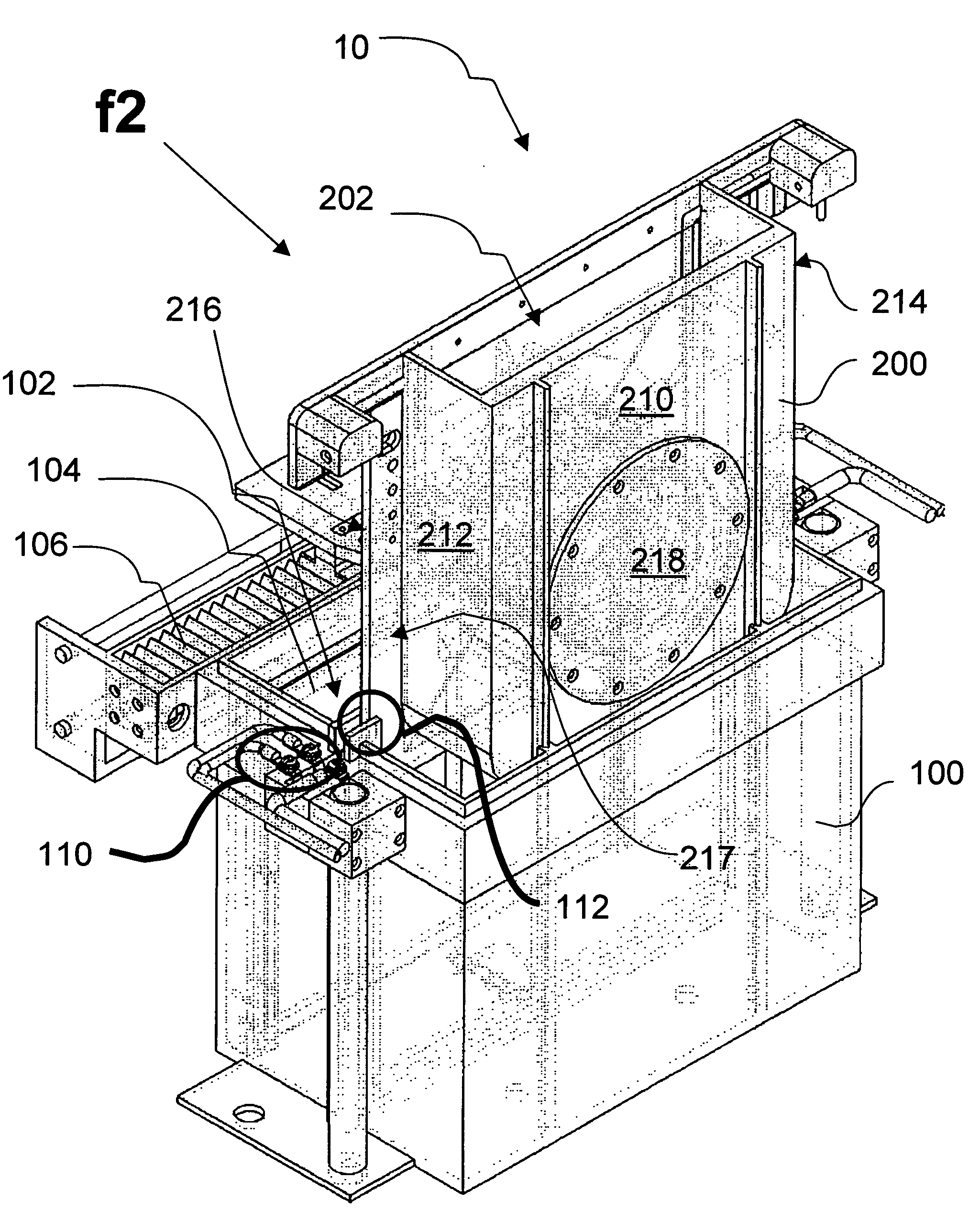
Microelectronic workpiece processing tool including a processing reactor having a paddle assembly for agitation of a processing fluid proximate to the workpiece
An integrated tool is provided including at least one workpiece processing station having a paddle assembly. In accordance with another independent aspect of the present invention, the workpiece processing station is adapted for adjusting the level of the processing fluid relative to a workpiece, wherein the portion of the workpiece to be processed and possibly the paddle is selectively immersed within the processing fluid. In accordance with a further independent aspect of the present invention, a paddle is provided for use proximate to a workpiece in a workpiece processing station. The paddle includes a one or more sets of delivery ports and one or more sets of fluid recovery ports. In at least one embodiment, the paddle provides for agitation of a processing fluid proximate to the surface of the workpiece. In at least another embodiment, the paddle provides for the delivery and / or recovery of one or more fluids to the portion of the workpiece to be processed. One aspect of the present invention enables the fluids supplied to the workpiece by the paddle to be limited to the space located between the workpiece and the paddle, thus avoiding mixing of these fluids with the processing fluid located within the bowl assembly not supplied by the paddle.
Owner:SEMITOOL INC
Direct nanoscale patterning of metals using polymer electrolytes
InactiveUS7998330B2Improve throughputRobust and commercially attractive manufacturing pathwayMaterial nanotechnologyMachining electrodesSpatial OrientationsElectrical conductor
Disclosed herein are electrochemical fabrication platforms for making structures, arrays of structures and functional devices having selected nanosized and / or microsized physical dimensions, shapes and spatial orientations. Methods, systems and system components use an electrochemical stamping tool such as solid state polymeric electrolytes for generating patterns of relief and / or recessed features exhibiting excellent reproducibility, pattern fidelity and resolution on surfaces of solid state ionic conductors and in metal. Electrochemical stamping tools are capable high throughput patterning of large substrate areas, are compatible with commercially attractive manufacturing pathways to access a range of functional systems and devices including nano- and micro-electromechanical systems, sensors, energy storage devices, metal masks for printing, interconnects, and integrated electronic circuits.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Multi-anode system for uniform plating of alloys
ActiveUS20080179192A1Uniform coating thicknessAvoid the needCellsCurrent conducting devicesElectricityPower flow
Disclosed are embodiments of an electroplating system and an associated electroplating method that allow for depositing of metal alloys with a uniform plate thickness and with the means to alter dynamically the alloy composition. Specifically, by using multiple anodes, each with different types of soluble metals, the system and method avoid the need for periodic plating bath replacement and also allow the ratio of metals within the deposited alloy to be selectively varied by applying different voltages to the different metals. The system and method further avoids the uneven current density and potential distribution and, thus, the non-uniform plating thicknesses exhibited by prior art methods by selectively varying the shape and placement of the anodes within the plating bath. Additionally, the system and method allows for fine tuning of the plating thickness by using electrically insulating selectively placed prescribed baffles.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
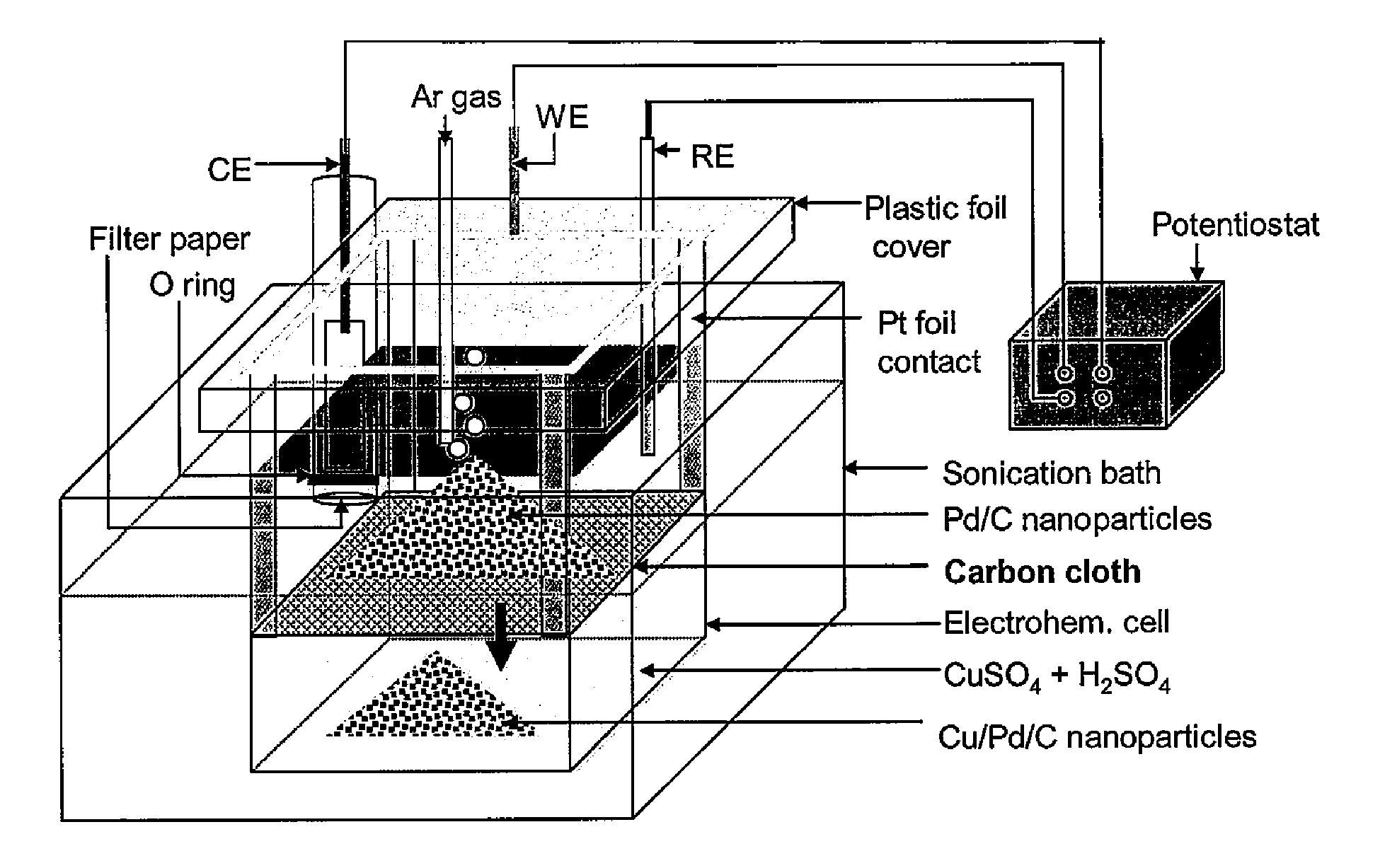
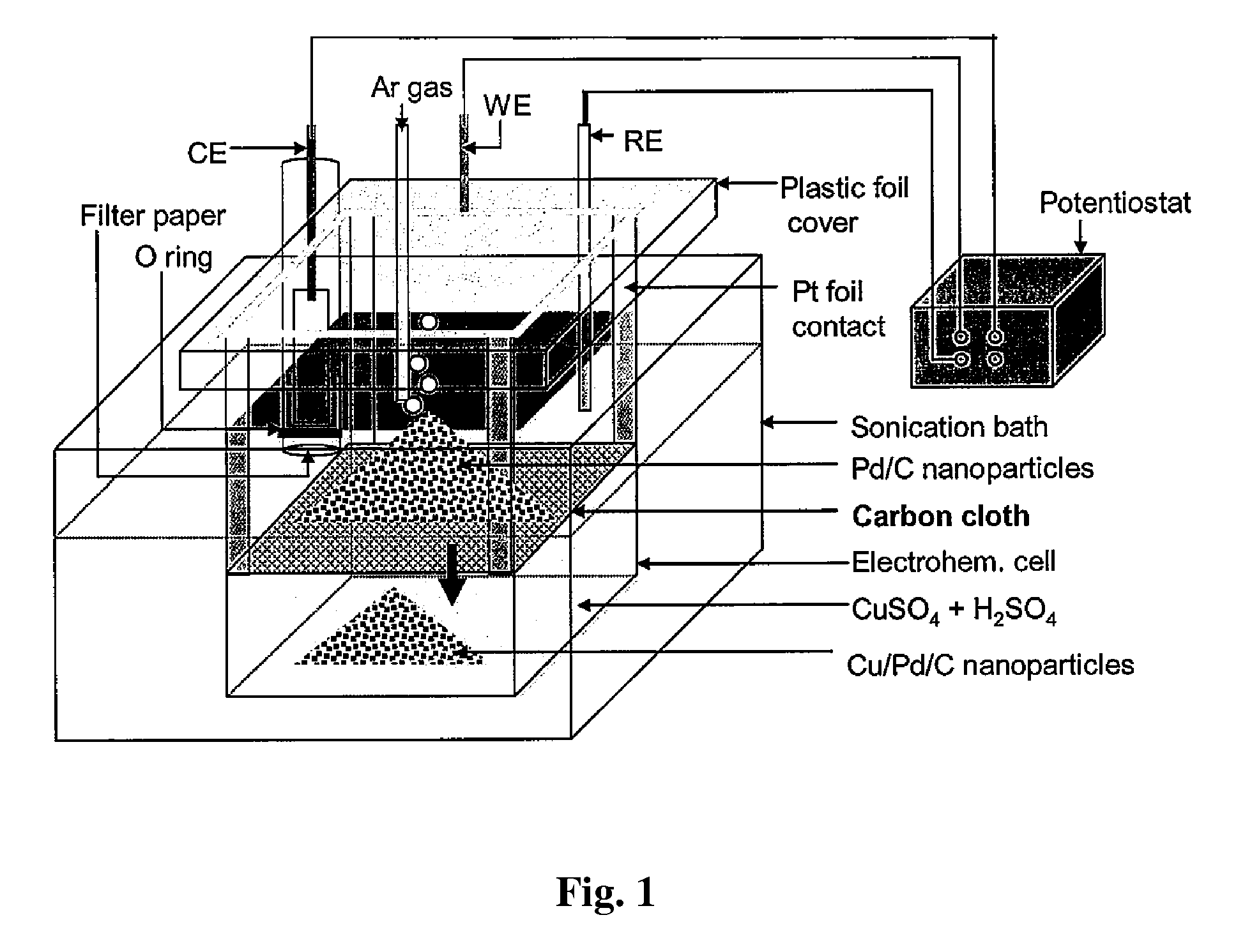
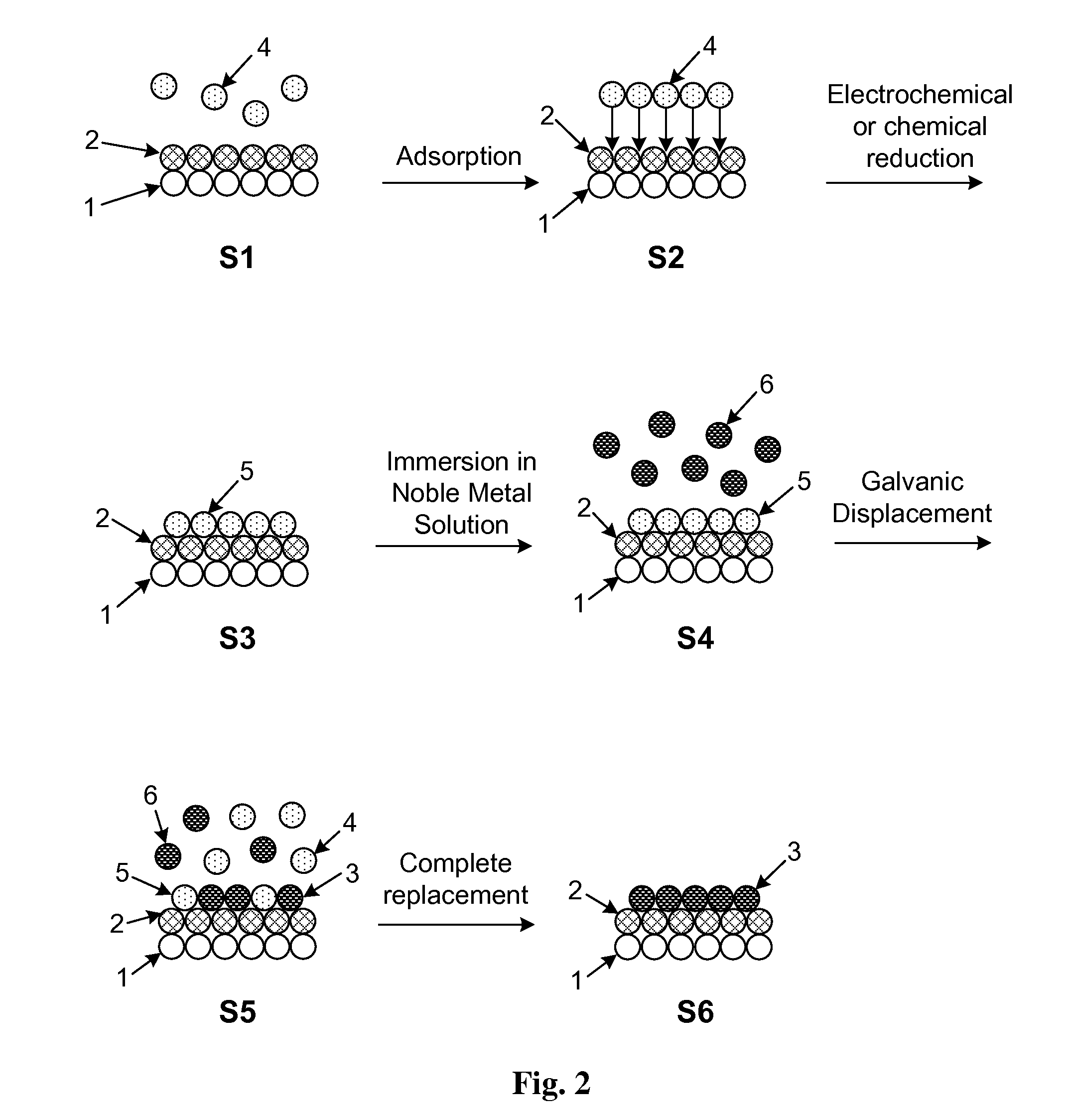
Method and Electrochemical Cell for Synthesis and Treatment of Metal Monolayer Electrocatalysts Metal, Carbon, and Oxide Nanoparticles Ion Batch, or in Continuous Fashion
InactiveUS20120245017A1Suitable for commercial applicationEasy to produceCellsMaterial nanotechnologyMaterials scienceMonolayer
An apparatus and method for synthesis and treatment of electrocatalyst particles in batch or continuous fashion is provided. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a sonication bath and a two-compartment chamber submerged in the sonication bath. The upper and lower compartments are separated by a microporous material surface. The upper compartment comprises a cover and a working electrode (WE) connected to a Pt foil contact, with the foil contact connected to the microporous material. The upper chamber further comprises reference counter electrodes. The lower compartment comprises an electrochemical cell containing a solution of metal ions. In one embodiment, the method for synthesis of electrocatalysts comprises introducing a plurality of particles into the apparatus and applying sonication and an electrical potential to the microporous material connected to the WE. After the non-noble metal ions are deposited onto the particles, the non-noble metal ions are displaced by noble-metal ions by galvanic displacement.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Plating apparatus and plating method
ActiveUS8177944B2Uniform supplyImprove in-plane uniformityAnodisationCellsHigh current densityIn plane
A plating apparatus can form a bump having a flat top or can form a metal film having a good in-plane uniformity even when the plating of a plating object (substrate) is carried out under high-current density conditions. The plating apparatus includes a plating tank for holding a plating solution; an anode to be immersed in the plating solution in the plating tank; a holder for holding a plating object and disposing the plating object at a position opposite the anode; a paddle, disposed between the anode and the plating object held by the holder, which reciprocates parallel to the plating object to stir the plating solution; and a control section for controlling a paddle drive section which drives the paddle. The control section controls the paddle drive section so that the paddle moves at a velocity whose average absolute value is 70 cm / sec to 100 cm / sec.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Multi-contact lipseals and associated electroplating methods
Disclosed herein are lipseal assemblies for use in an electroplating clamshell for engaging and supplying electrical current to a semiconductor substrate during electroplating, which include an elastomeric lipseal for engaging the semiconductor substrate during electroplating, and wherein upon engagement the elastomeric lipseal forms multiple radially-separated sealing contact surfaces with the substrate which substantially exclude plating solution from a peripheral region of the substrate. Said lipseal assemblies may also include one or more electrical contact elements for supplying electrical current to the semiconductor substrate during electroplating.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Thickness distribution control for electroplating
The invention is directed to an assembly for electroplating comprising an electroplating bath and non-conductive plates. The invention is also directed to an assembly for electroplating comprising an electroplating bath, elements with electrically adjustable resistance, and ampere-hour meters. The invention is further directed to methods for monitoring, controlling and adjusting the thickness distribution of an electroplated material on an object. The object can be of any shape as long as it can electrically charged.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com