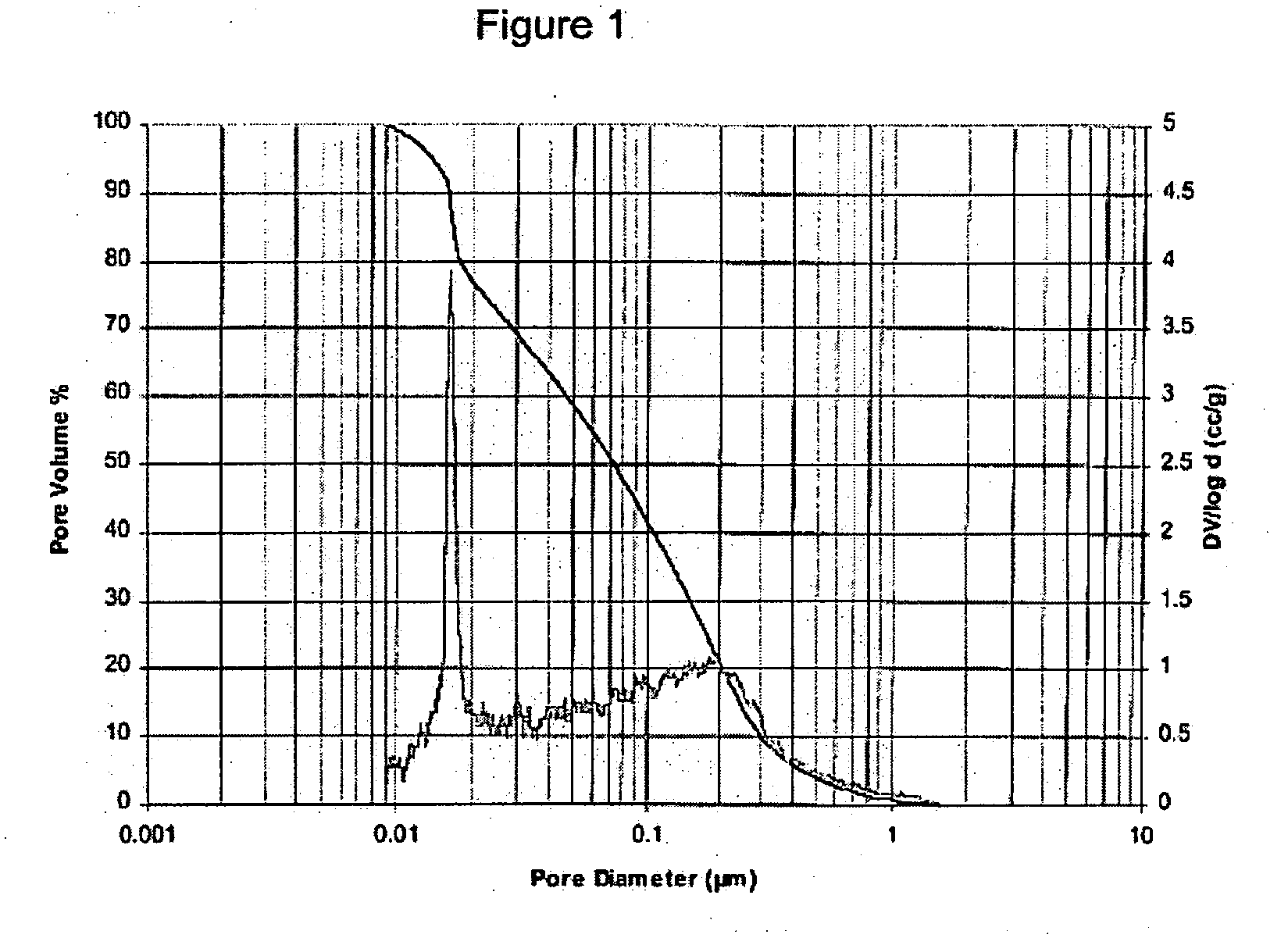
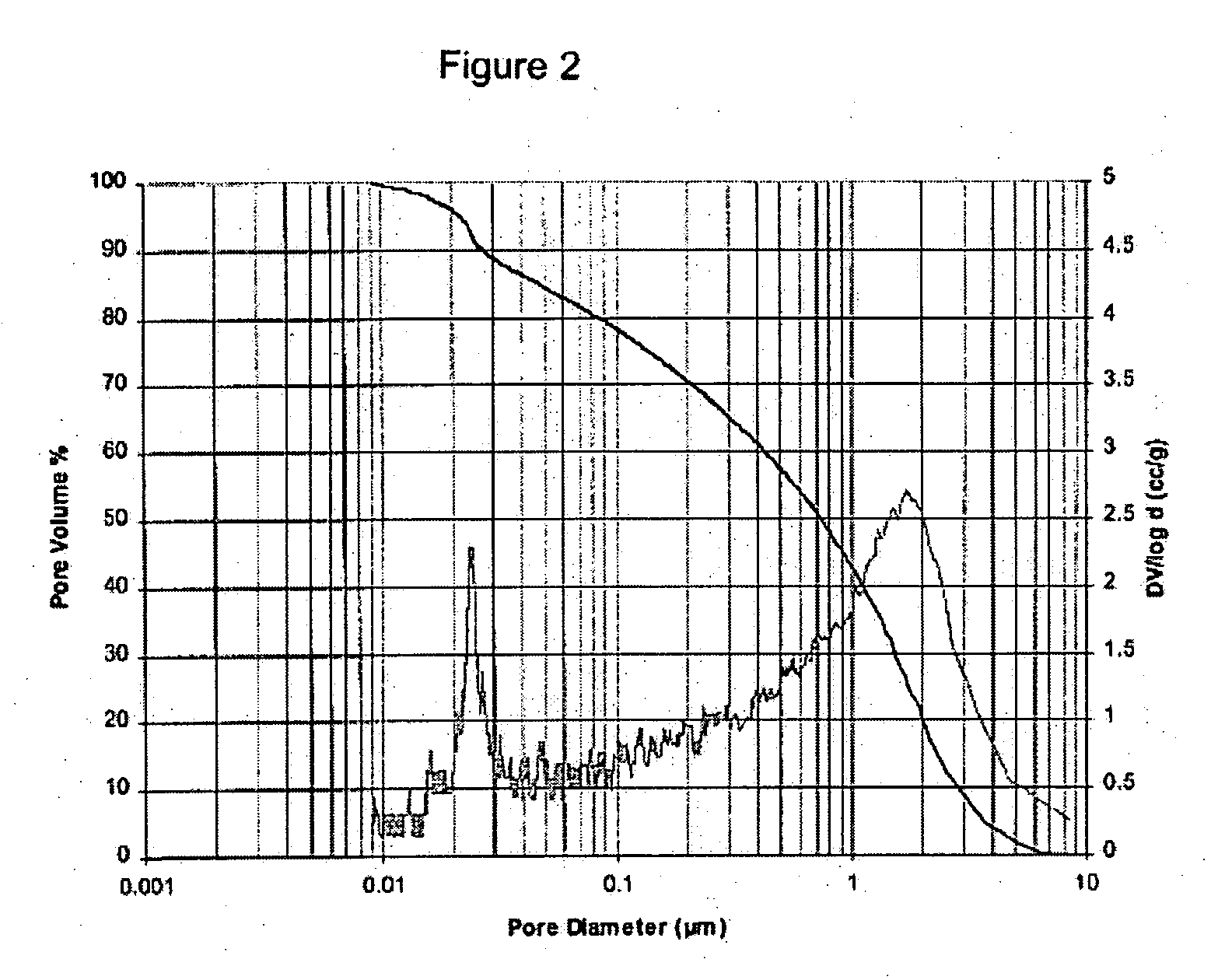
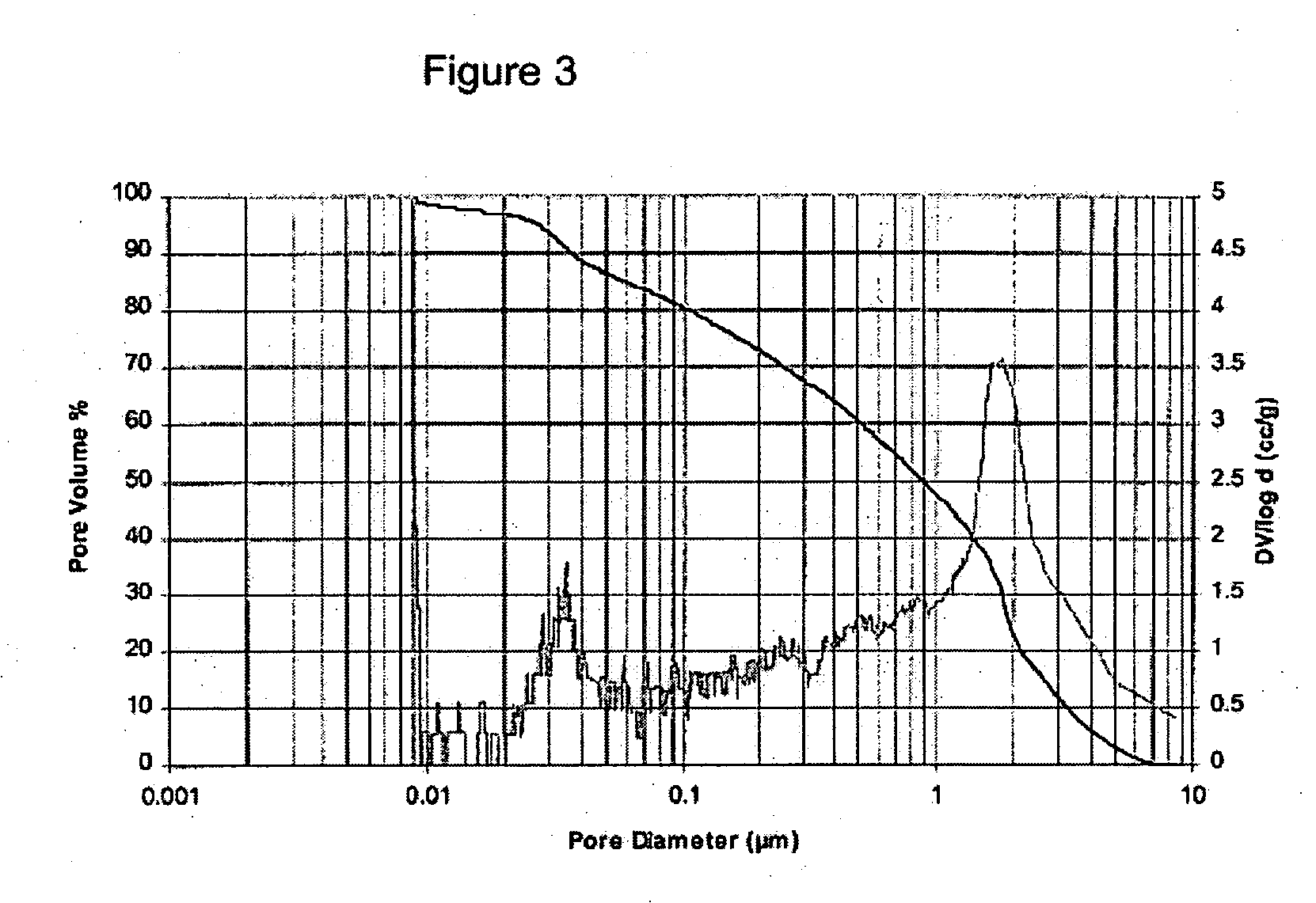
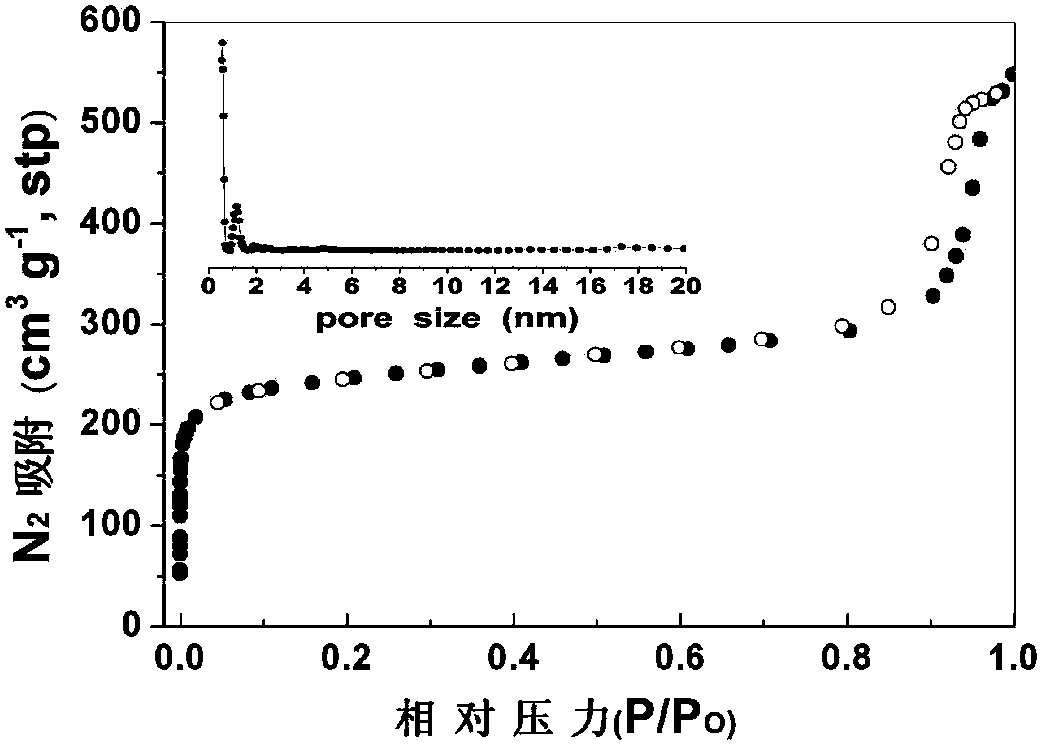
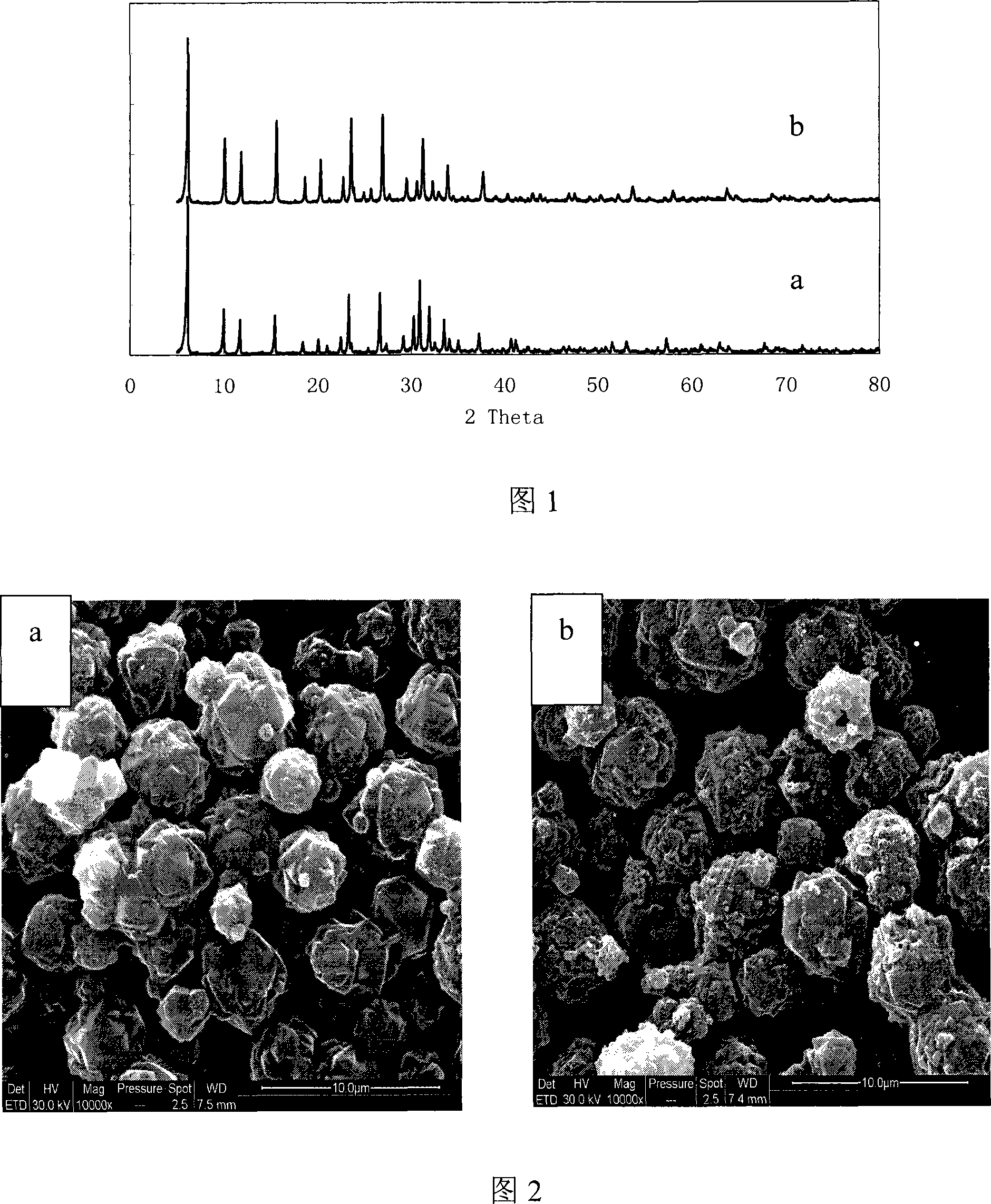
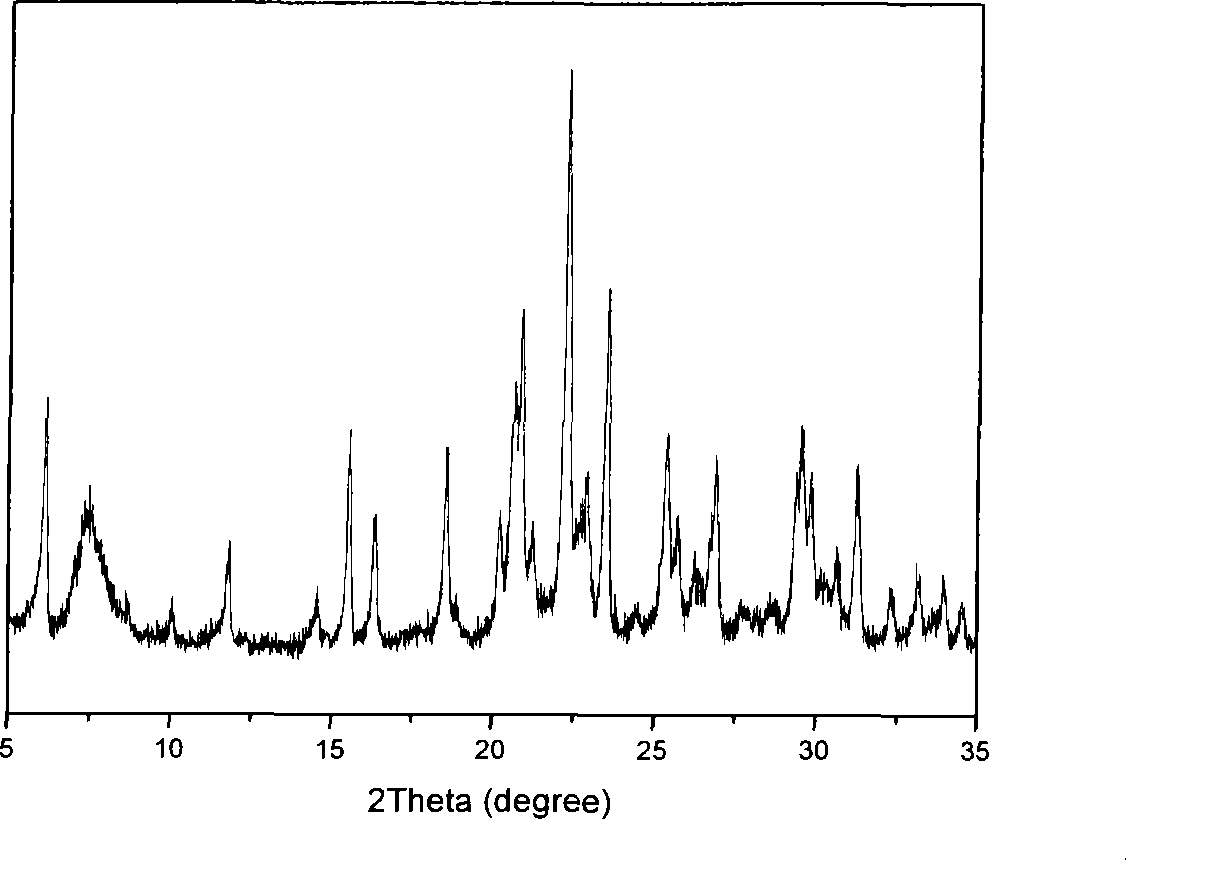
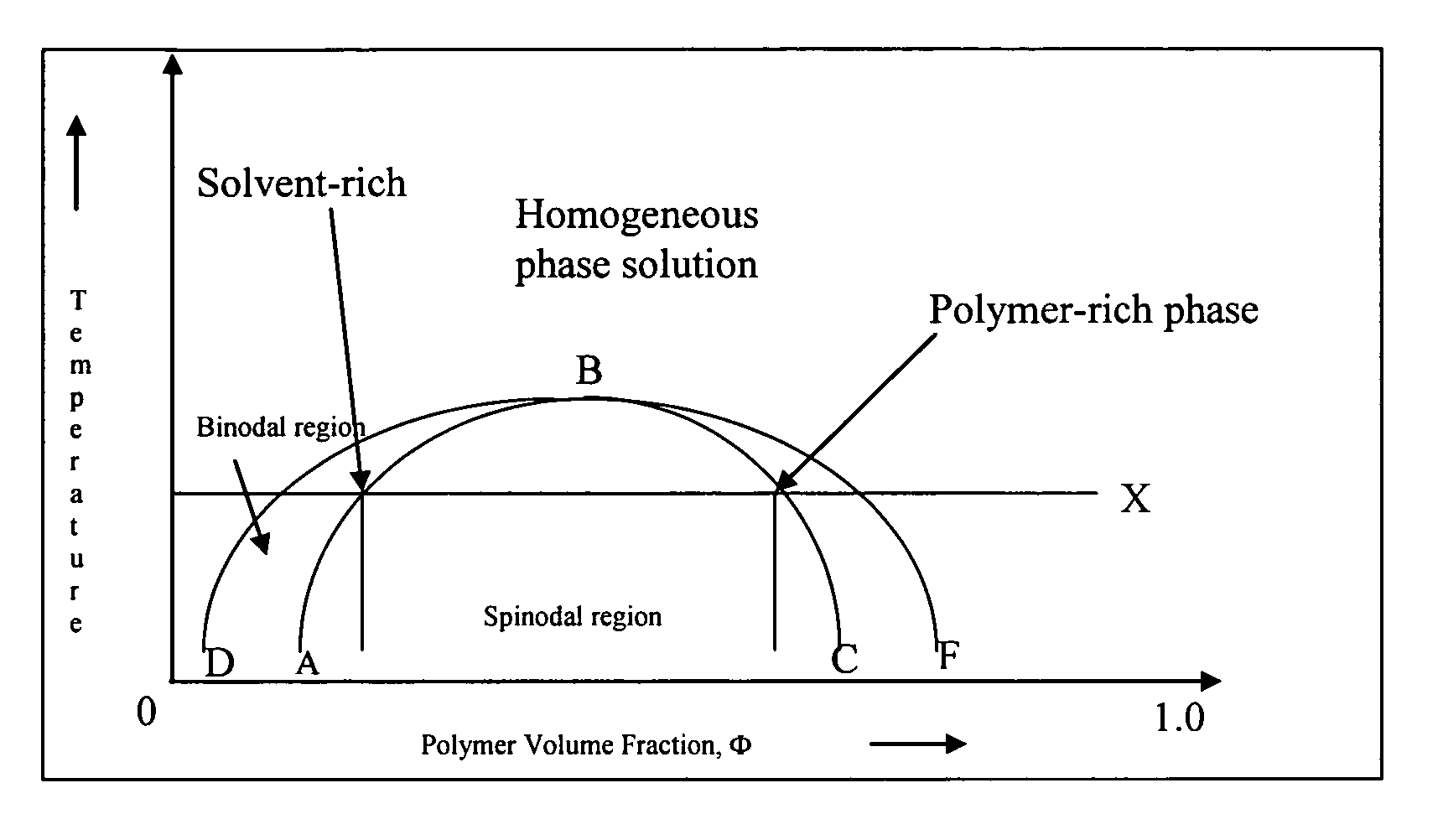
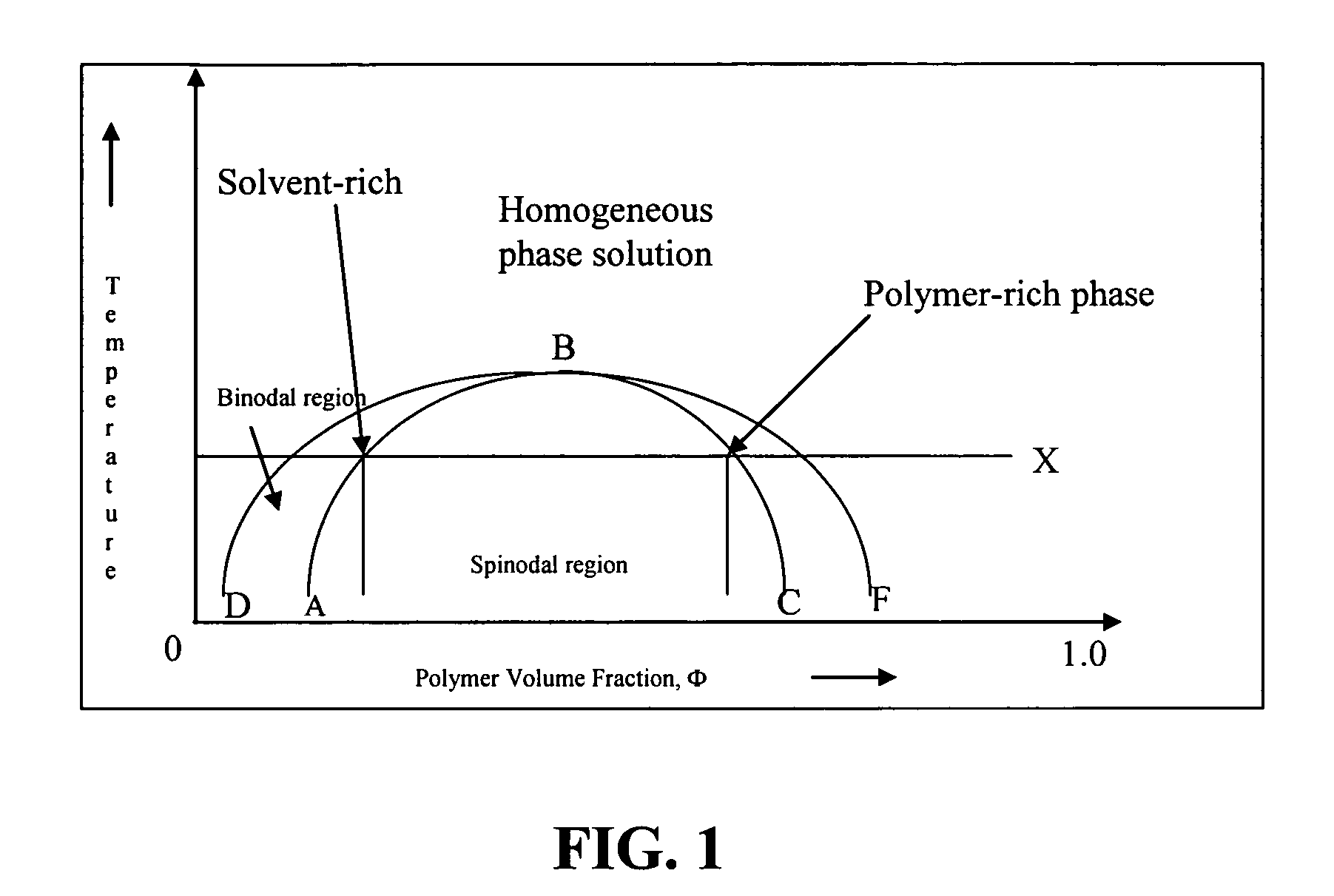
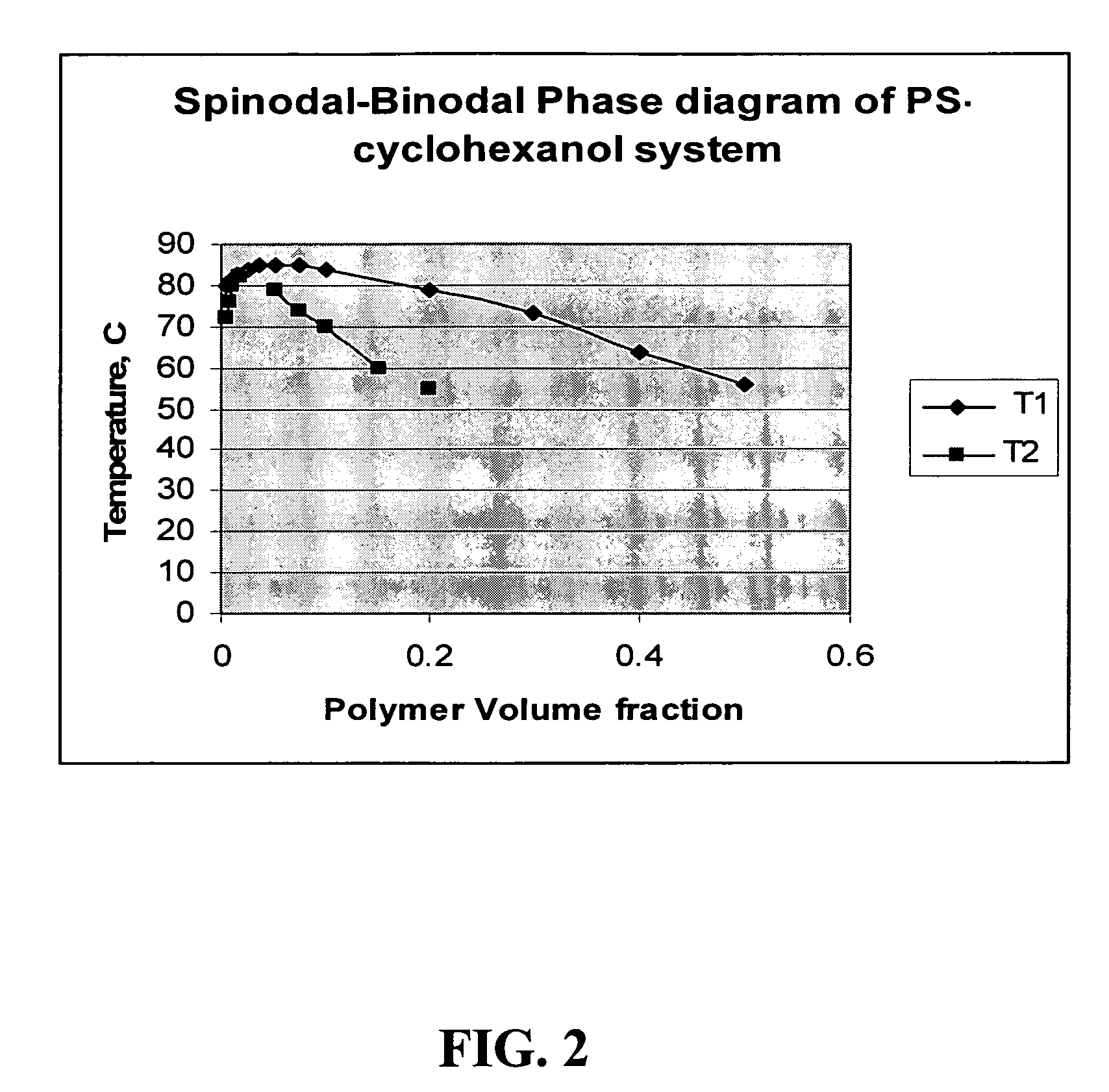
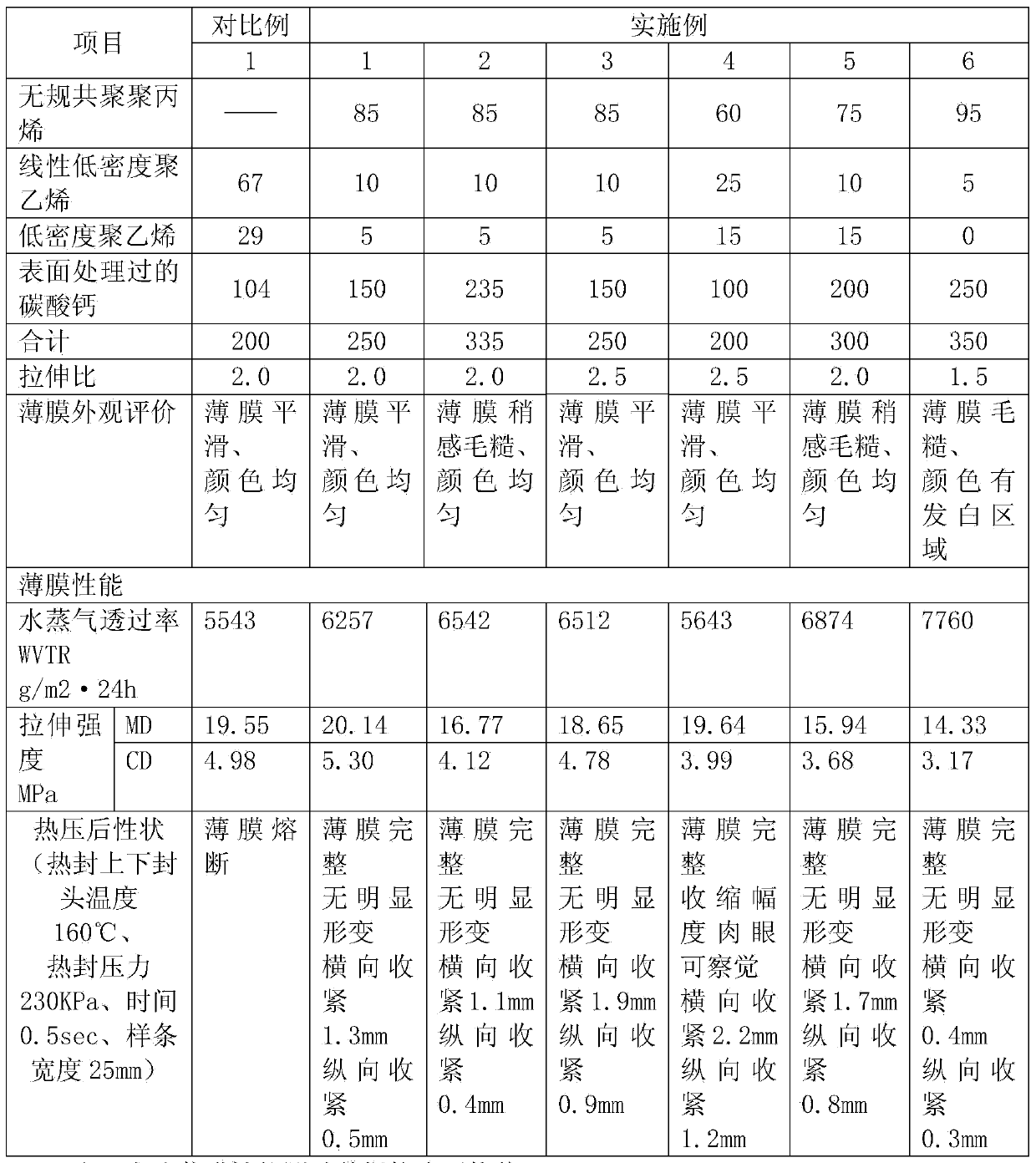
Patents
Literature
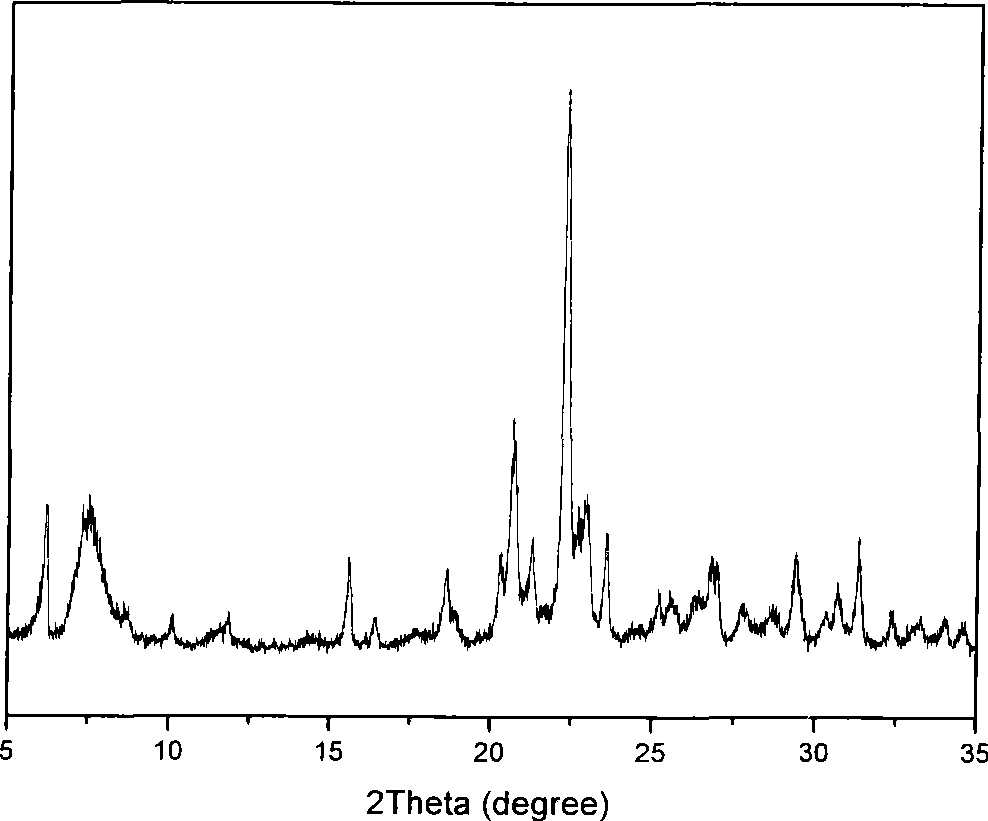
795 results about "Microporous material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microporous material is a material containing pores with diameters less than 2 nm. Examples of microporous materials include zeolites and metal-organic frameworks. Porous materials are classified into several kinds by their size.
Microporous PVDF films
Shaped microporous articles are produced from polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and nucleating agents using thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) processes. The shaped microporous article is oriented in at least one direction at a stretch ratio of at least approximately 1.1 to 1.0. The shaped article may also comprise a diluent, glyceryl triacetate. The shaped microporous article may also have the micropores filled with a sufficient quantity of ion conducting electrolyte to allow the membrane to function as an ion conductive membrane. The method of making a microporous article comprises the steps of melt blending polyvinylidene fluoride, nucleating agent and glyceryl triacetate; forming a shaped article of the mixture; cooling the shaped article to cause crystallization of the polyvinylidene fluoride and phase separation of the polyvinylidene fluoride and glyceryl triacetate; and stretching the shaped article in at least one direction at a stretch ratio of at least approximately 1.1 to 1.0.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
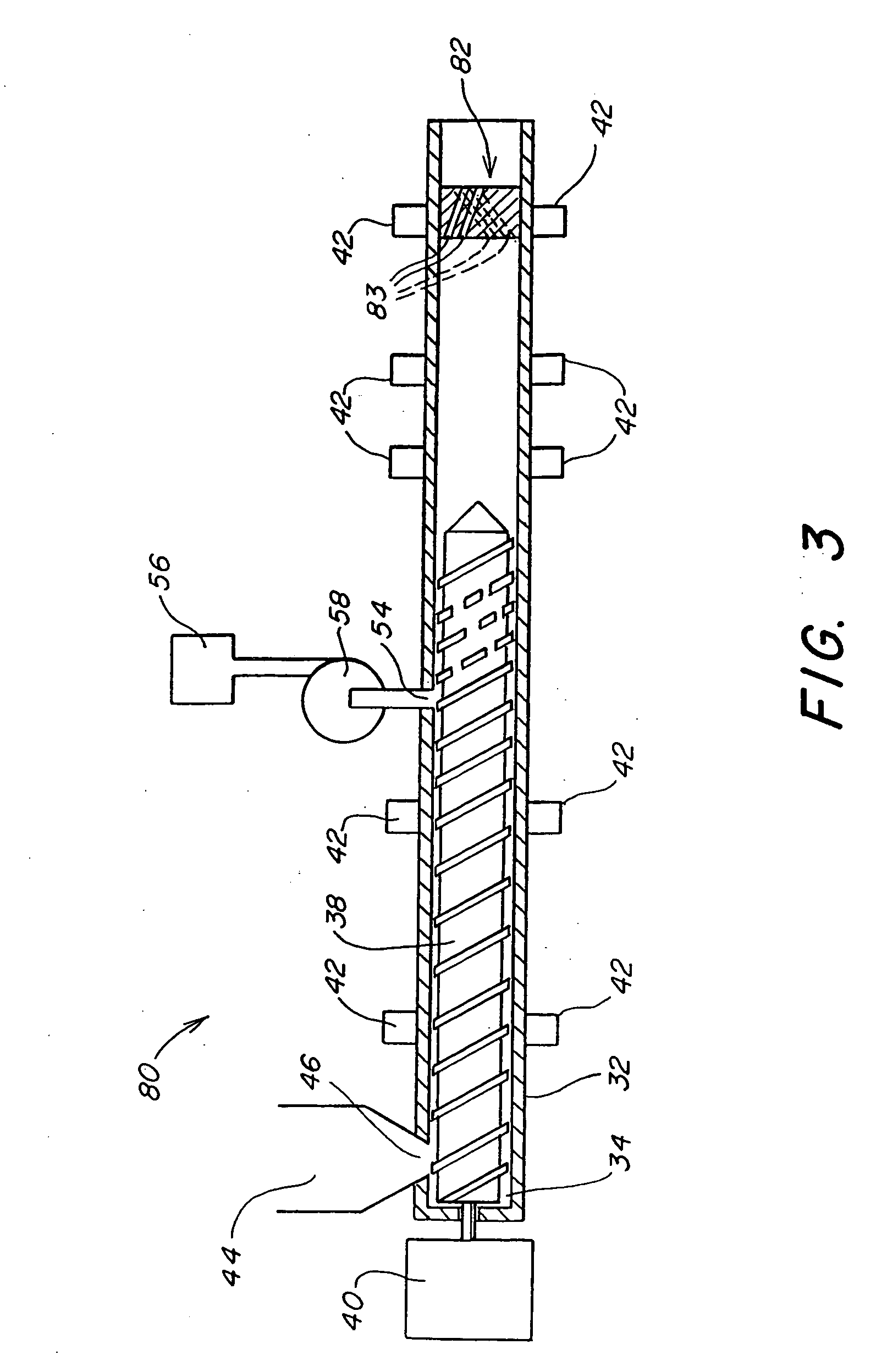
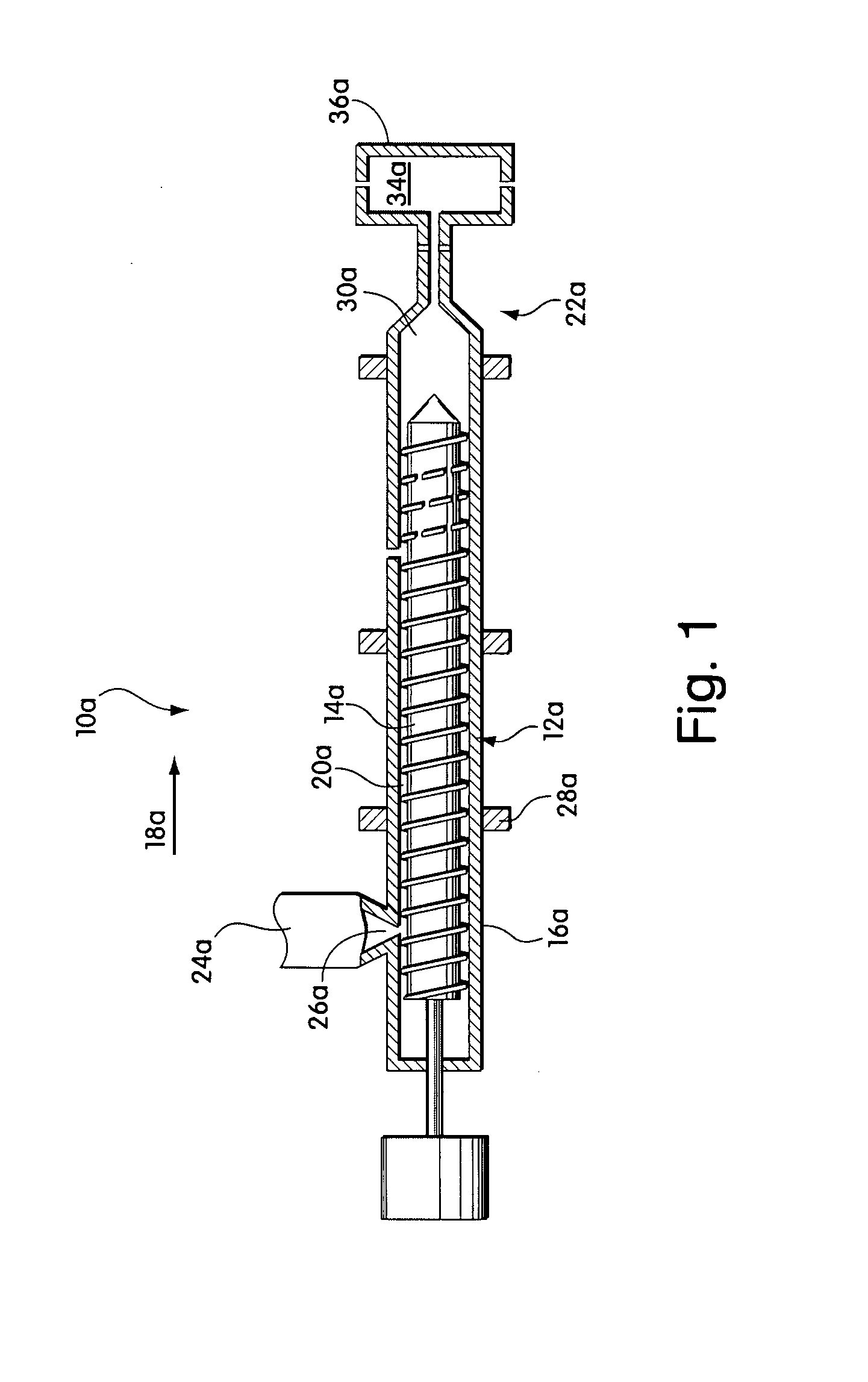
Method and apparatus for microcellular polymer extrusion
Continuous polymeric extrusion nucleation systems and methods useful for making polymeric microcellular foamed materials, including crystalline and semi-crystalline polymeric microcellular materials, are provided. Pressure drop rate is an important feature in some embodiments, and the invention provides systems for controlling these and other parameters. One aspect involves a multiple-pathway nucleator that is separated from a shaping die by a residence chamber. Another aspect involves a die for making advantageously thick articles, including a multiple-pathway nucleation section. Microcellular material can be continuously extruded onto wire, resulting in a very thin, essentially closed-cell microcellular insulating coating secured to a wire. Other very thin microcellular products can be fabricated as well.
Owner:TREXEL
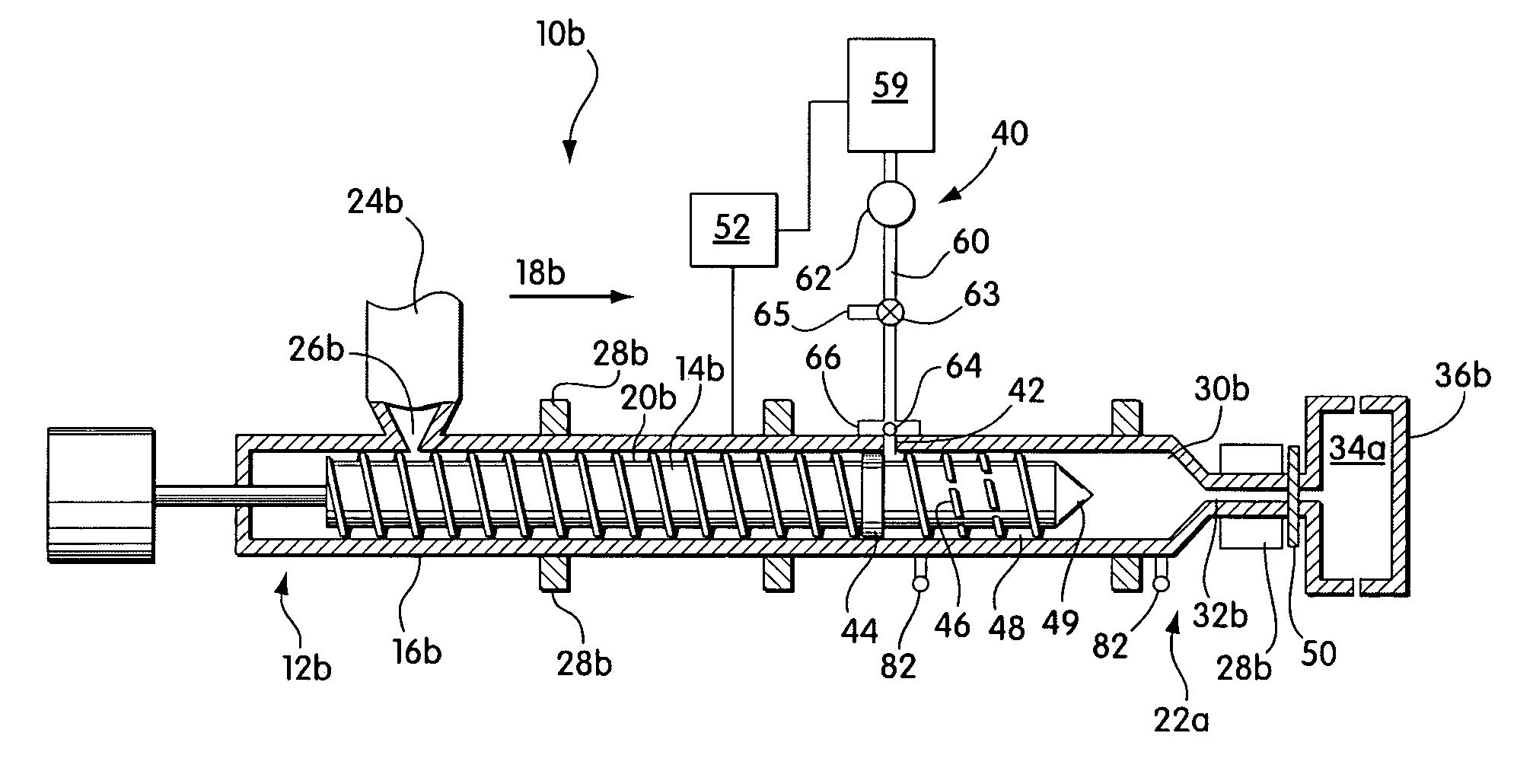
Injection molding of polymeric material
Injection molding systems and methods useful for making microcellular foamed materials are provided as well as microcellular articles. Pressure drop rate and shear rate are important features in some embodiments, and the invention provides systems for controlling these parameters in an injection molding system. Another aspect involves an injection molding system including a nucleator that is upstream of a pressurized mold. Another aspect involves an extrusion system with the reciprocating screw for forming a single phase solution of non-nucleated blowing agent and polymeric material. Another aspect involves very thin walled microcellular material and very thin walled polymeric material. Another aspect provides a method for producing high weight reductions in very thin-walled parts with surfaces that have no noticeable differences from non-foamed parts.
Owner:TREXEL
Plasma treatment of porous materials
InactiveUS6878419B2Improve wettabilityEfficient processingSemi-permeable membranesLayered productsCapacitanceMicrometer
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Microporous material and a method of making same
ActiveUS20060121269A1Improved dimensional stability and physical propertyElectrolyte holding meansSemi-permeable membranesPlasticizerStretch ratio
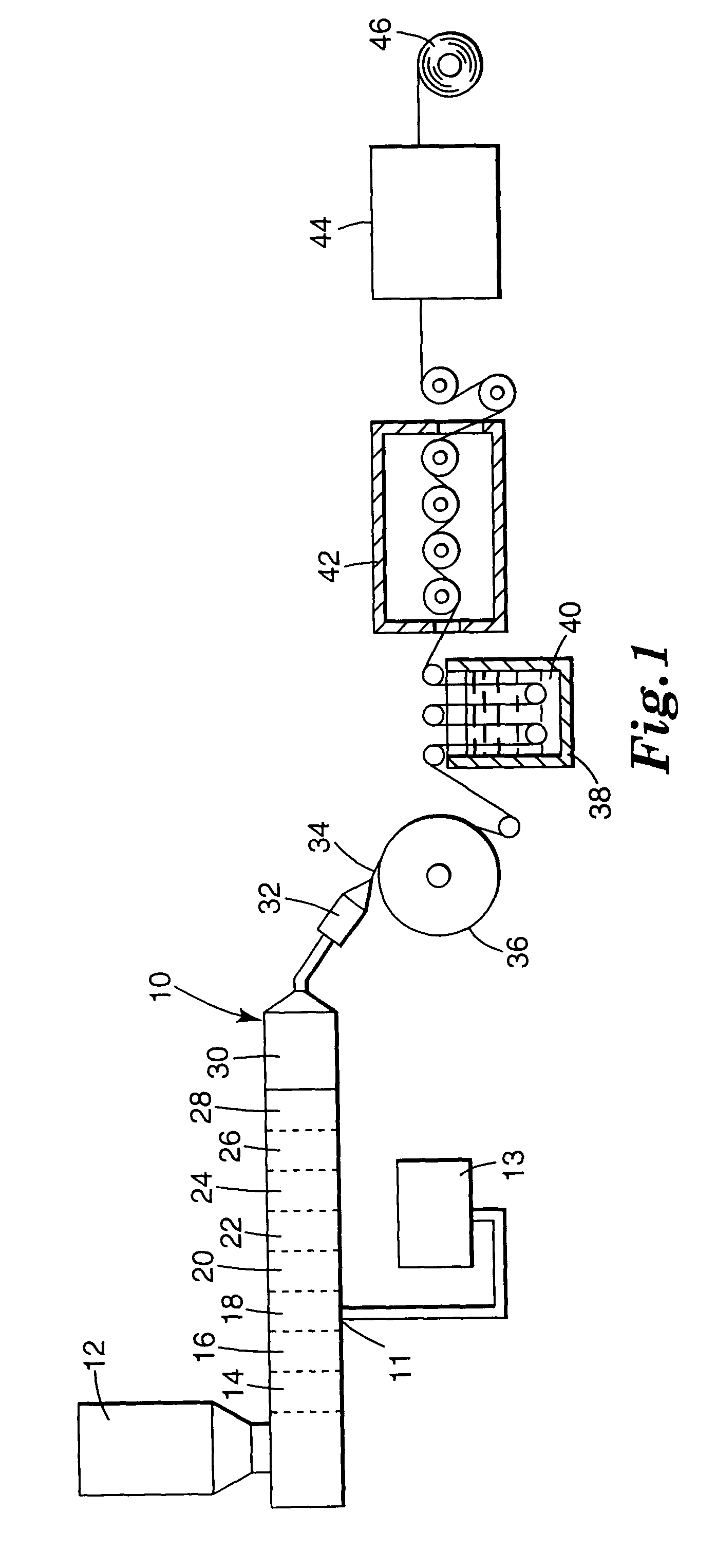
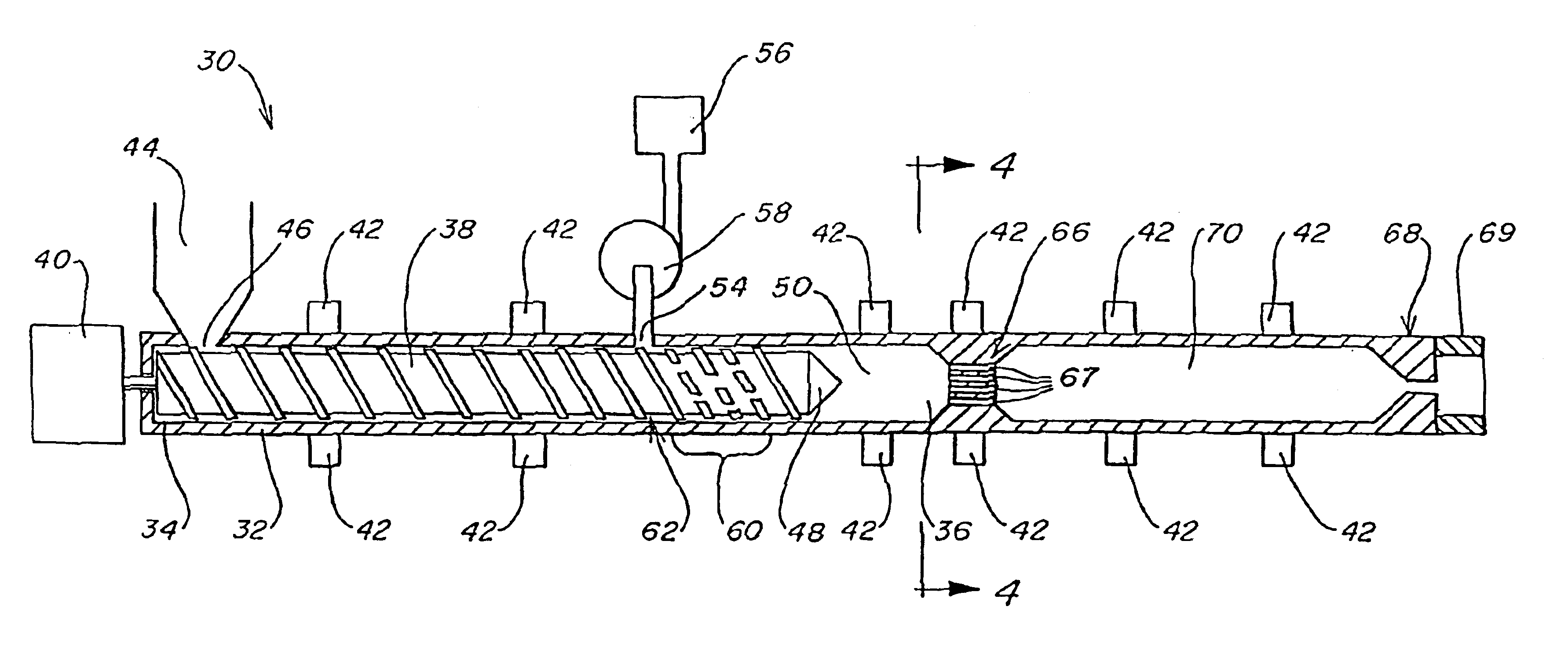
A method for producing a microporous material comprising the steps of: providing an ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE); providing a filler; providing a processing plasticizer; adding the filler to the UHMWPE in a mixture being in the range of from about 1:9 to about 15:1 filler to UHMWPE by weight; adding the processing plasticizer to the mixture; extruding the mixture to form a sheet from the mixture; calendering the sheet; extracting the processing plasticizer from the sheet to produce a matrix comprising UHMWPE and the filler distributed throughout the matrix; stretching the microporous material in at least one direction to a stretch ratio of at least about 1.5 to produce a stretched microporous matrix; and subsequently calendering the stretched microporous matrix to produce a microporous material which exhibits improved physical and dimensional stability properties over the stretched microporous matrix.
Owner:DARAMIC LLC
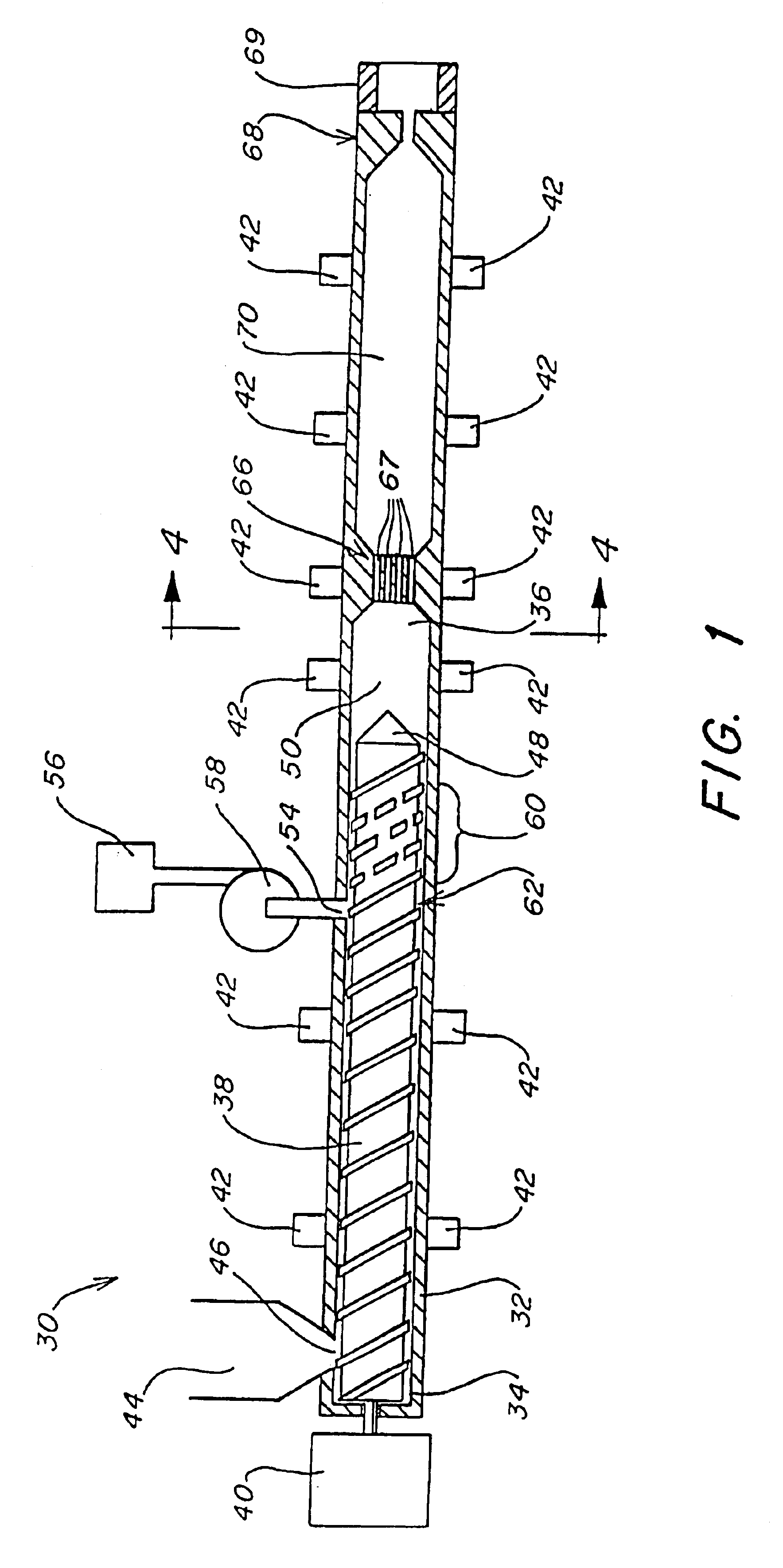
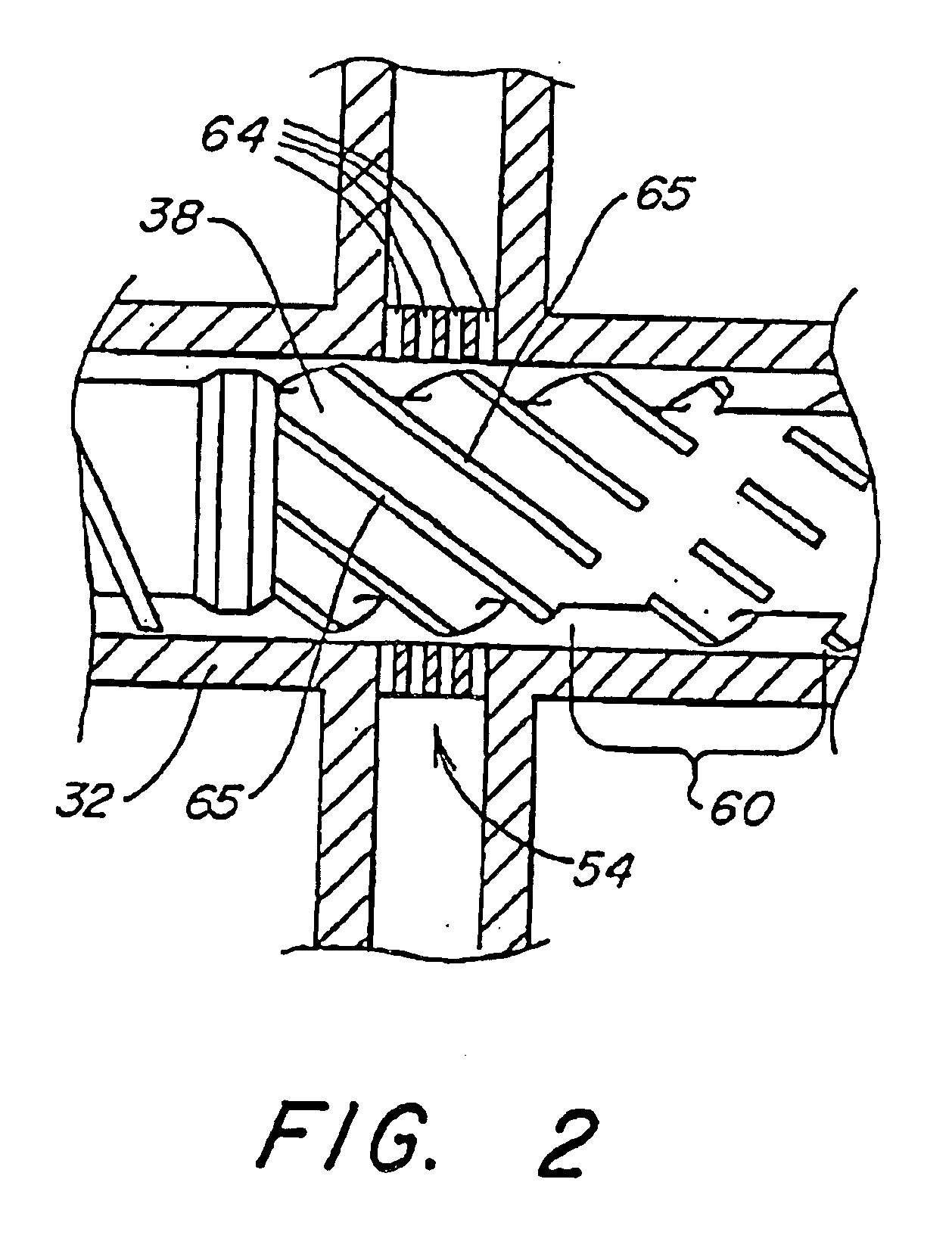
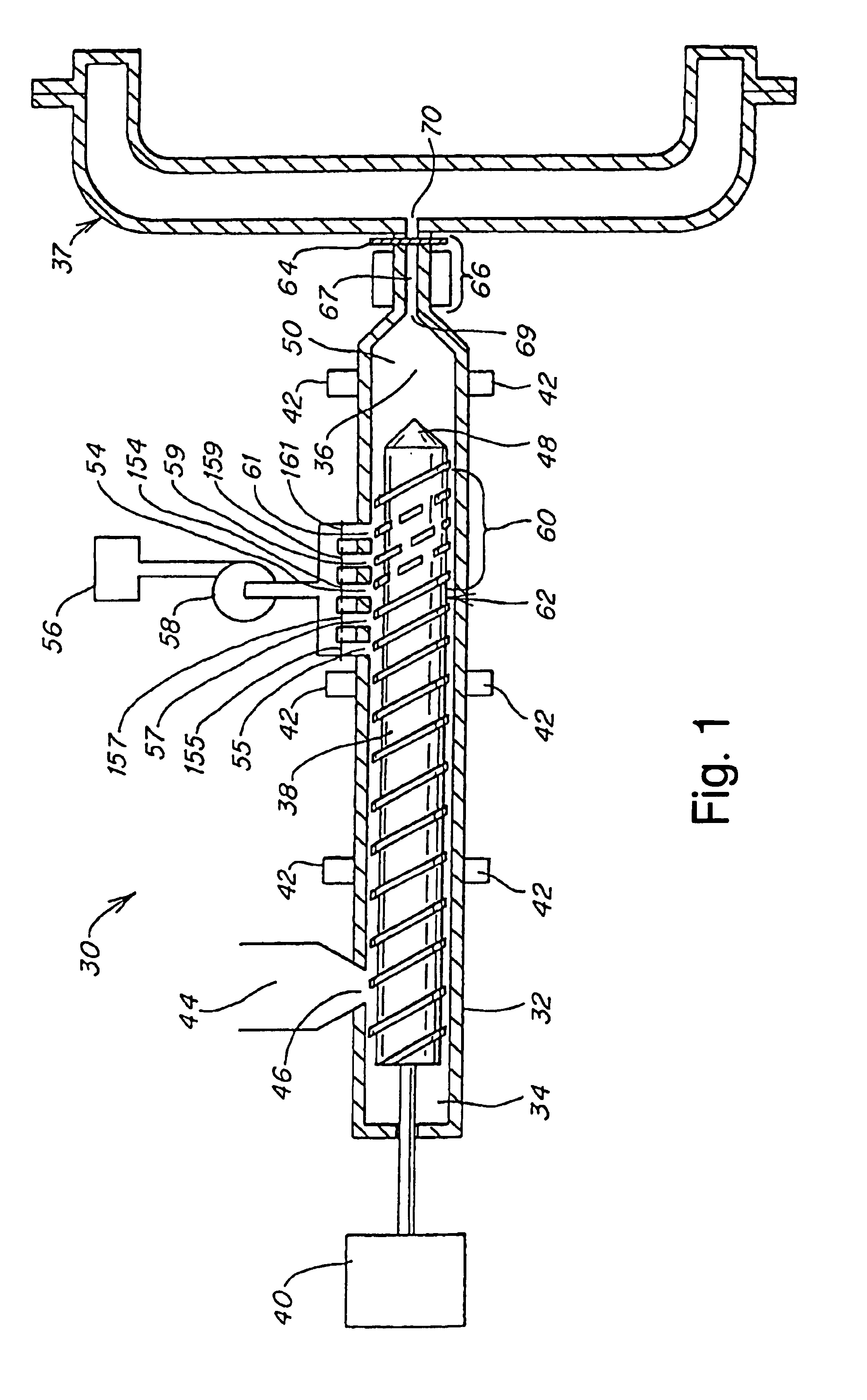
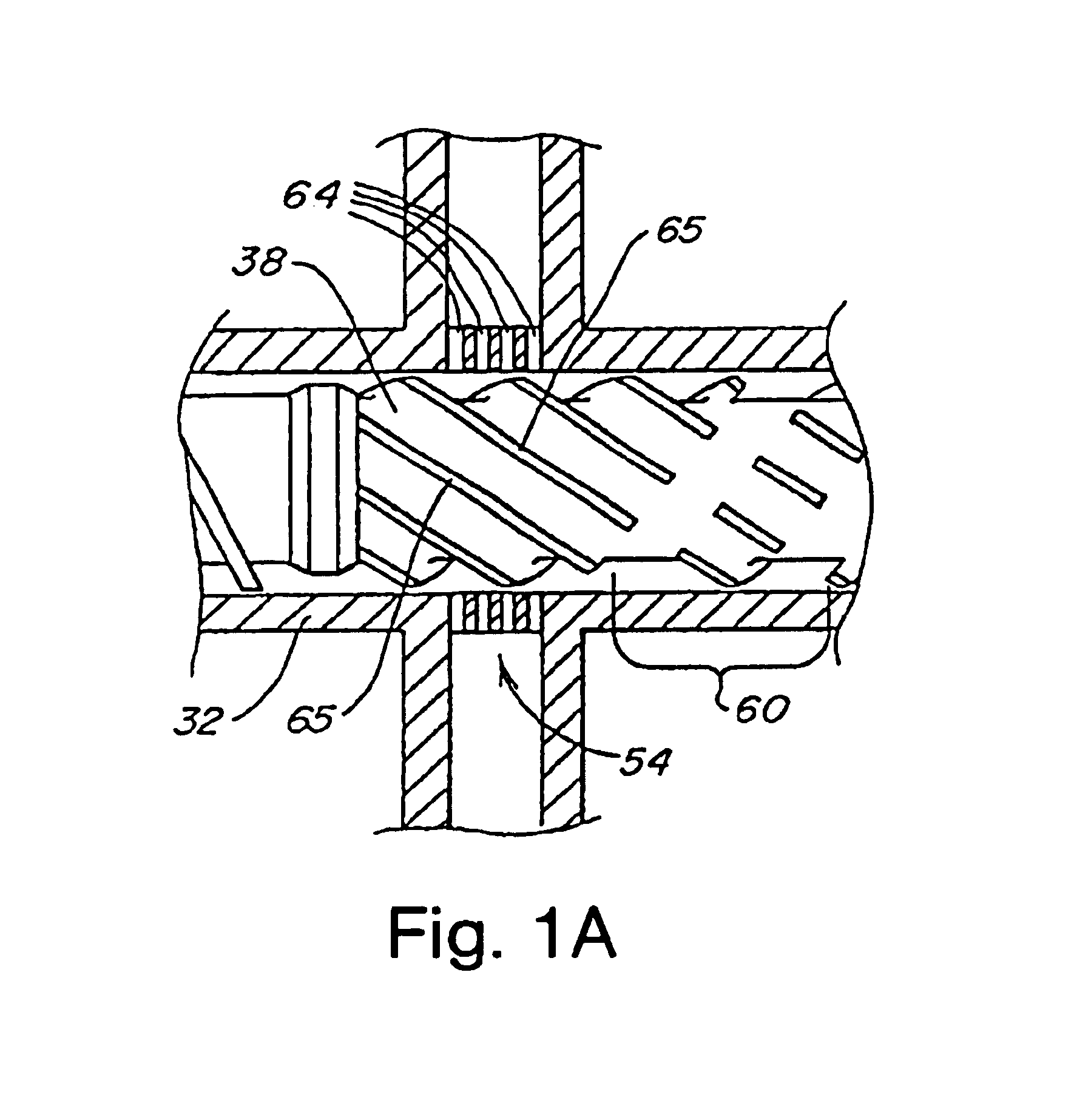
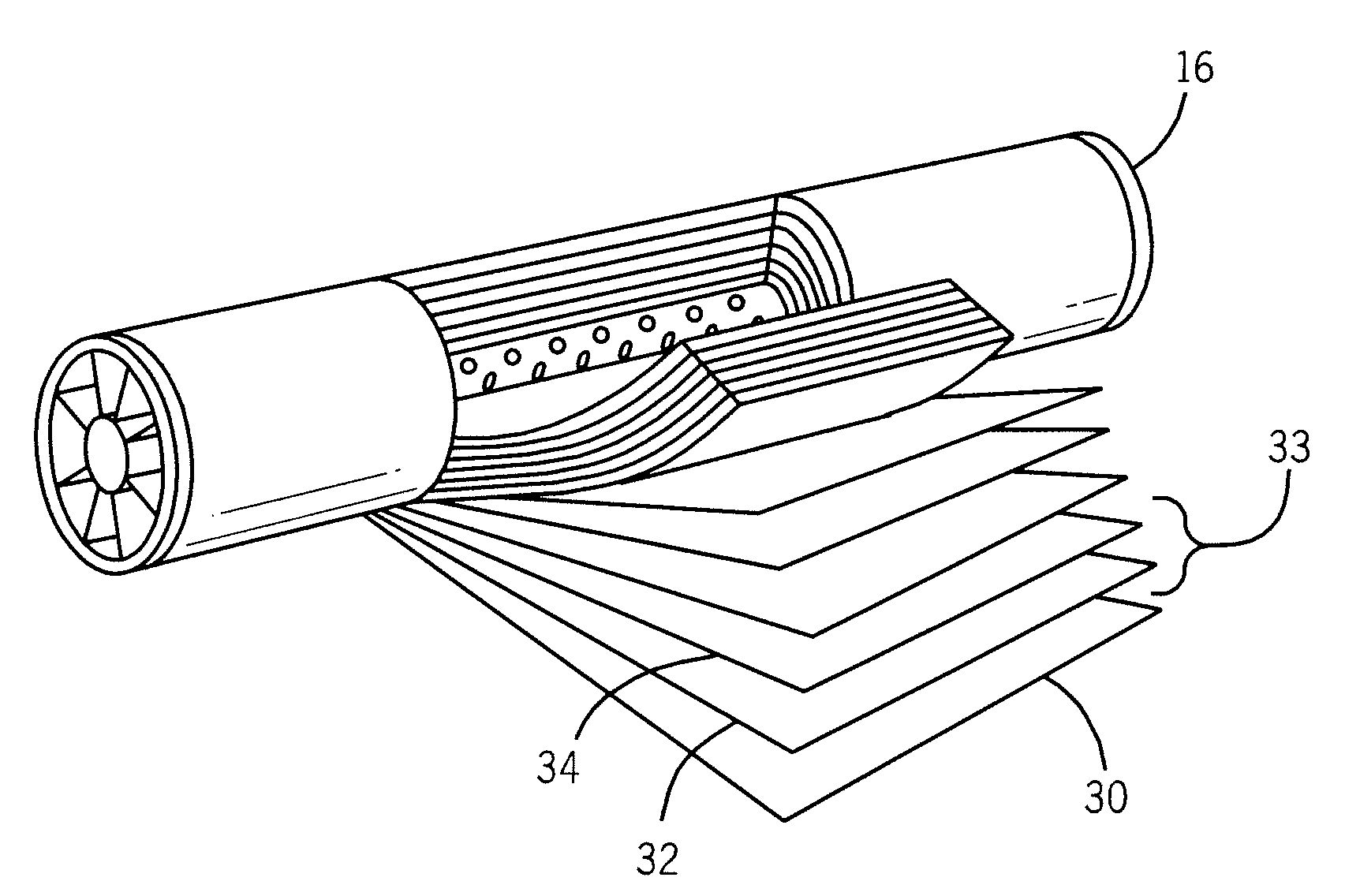
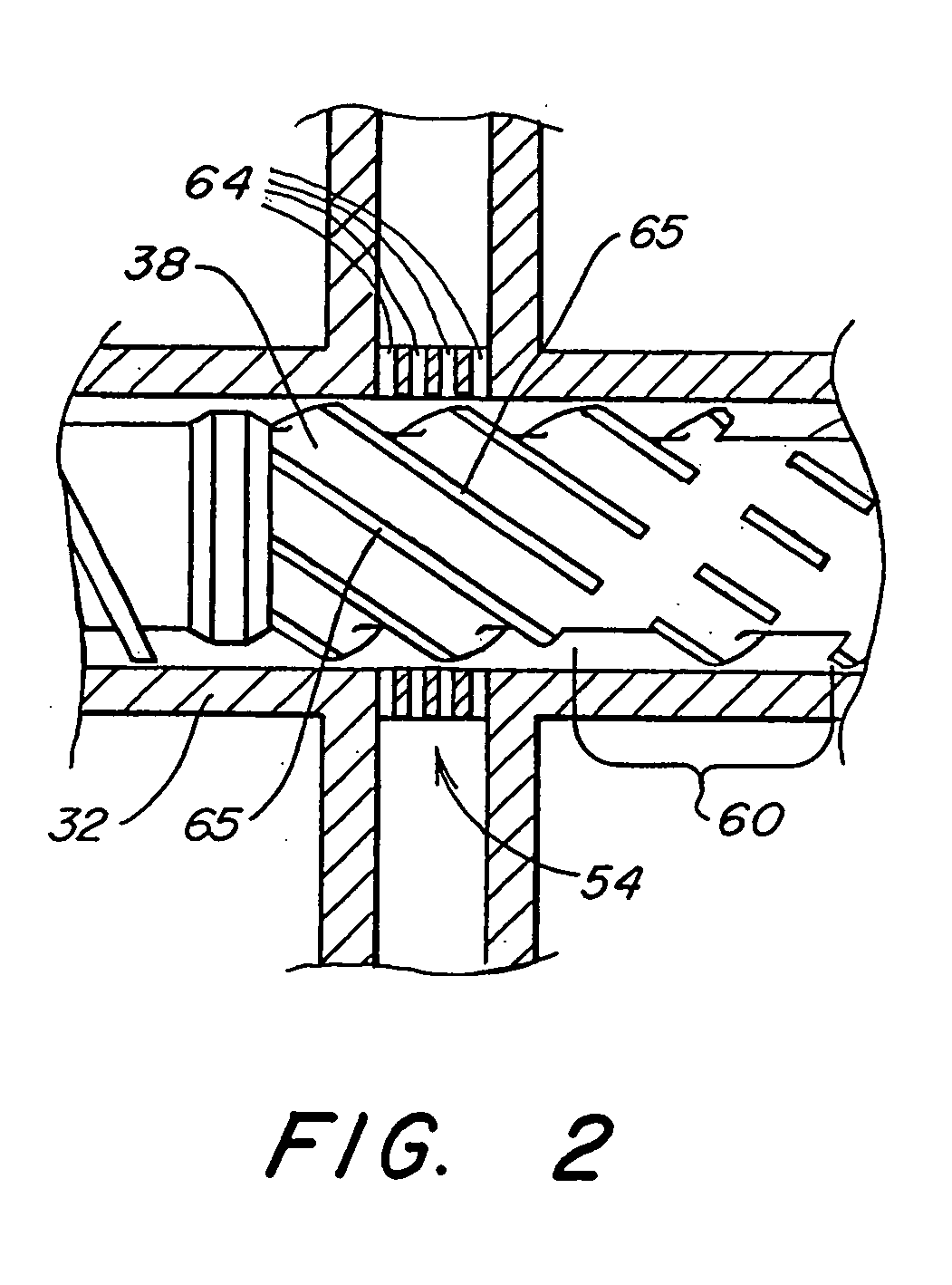
Heating device, atomizing unit, atomizer and electronic cigarette having same
The present disclosure relates to a heating device for heating tobacco liquid. The heating device includes a heating element, and a liquid conducting body configured for guiding the tobacco liquid to the heating element. The liquid conducting body includes a main body and at least one liquid conducting arm extending from the main body. The heating element is inserted in the main body, and is integrally formed with the main body. The at least one liquid conducting arm and the main body are made of micro-porous material.
Owner:SHENZHEN FIRST UNION TECH CO LTD
Multi-functional coatings on microporous substrates
InactiveUS20070272606A1Maintain porosityOvercome limitationsMembranesSemi-permeable membranesPorosityMicroporous material
A composition is described wherein a coating is provided on a microporous substrate, such as a low surface energy microporous substrate, which coating provides multiple functionalities to the underlying microporous material, while still maintaining porosity within at least a portion of the microporous substrate.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Microporous articles and methods of preparation
Provided are methods of preparing an article in which a microporous layer is coated on a temporary carrier substrate and a substrate is then laminated to the microporous layer, prior to removing the temporary carrier substrate from the microporous layer. The microporous layer comprises one or more microporous xerogel layers. Optionally, the microporous layer assembly may comprise one or more non-microporous coating layers which are in contact with at least one of the microporous xerogel layers, and one of the non-microporous coating layers may be coated on the temporary carrier substrate prior to coating the microporous layer. Also provided are articles, such as electrochemical cells, capacitors, fuel cells, ink jet ink printing media, and filtration media, prepared by such methods.
Owner:SION POWER CORP +1
Microwave method for synthesizing nanometer silicate basic hole material
InactiveCN1730391AFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMordenite aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveMicrowave method
The invention relates to a microwave synthesizing process for nano-size silicate based poromeric material, which consists of dissolving aluminium source into water, charging silicon source while agitating, continuously agitating, carrying out microwave processing directly for 3-180 minutes to the reaction solution, microwave heating 3-30 minutes, crystallizing 1-8 days at 60-100 deg C, centrifugally separating, filtering, scouring, dry scouring to neutral, thus obtaining nano-size molecular sieve with adjustable particle size.
Owner:朱广山
Membrane, water treatment system, and associated method
A membrane assembly is provided that includes a support comprising a micro-porous material; and an insoluble layer secured to a surface of the support. The insoluble layer is a reaction product of a reactant solution comprising a chain-capping reagent. A system and associated method are provided also.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for microcellular polymer extrusion
Continuous polymeric extrusion nucleation systems and methods useful for making polymeric microcellular foamed materials, including crystalline and semi-crystalline polymeric microcellular materials, are provided. Pressure drop rate is an important feature in some embodiments, and the invention provides systems for controlling these and other parameters. One aspect involves a multiple-pathway nucleator that is separated from a shaping die by a residence chamber. Another aspect involves a die for making advantageously thick articles, including a multiple-pathway nucleation section. Microcellular material can be continuously extruded onto wire, resulting in a very thin, essentially closed-cell microcellular insulating coating secured to a wire. Other very thin microcellular products can be fabricated as well.
Owner:TREXEL
Polymer processing systems including screws
Owner:TREXEL
Method of making microporous material
ActiveUS7445735B2Improved dimensional stability and physical propertyElectrolyte holding meansSemi-permeable membranesPlasticizerStretch ratio
Owner:DARAMIC LLC
Preparation method for multiple micropore negative ion far-infrared electric field biological affinity packing
ActiveCN103203179AExtended duty cycleImprove adsorption conditionsDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatment by sorptionFiberSynthetic Polymeric Macromolecules
The invention provides a preparation method for multiple micropore negative ion far-infrared electric field biological affinity packing. The preparation method is characterized by taking synthetic polymer particles as base materials, adding multiple micropore biological affinity materials or other modified materials, and simultaneously adding natural materials continuously and automatically generating the negative ion and the far-infrared ray to the base materials, then adding all the materials into a mixer, adding dispersing agent to have all the materials fully and evenly mixed, transferring the mixture to a mixing hopper of a injection molding machine to have various types of random-packed packing directly injected in mould; or having the various types of the random-packed packing made into synthetic macromolecule multiple micropore negative ion far-infrared electric field biological affinity function master batch, adding proper fresh macromolecule materials to be shifted to a drawing mill, pulling out elastic packing strips prior to being processed into elastic packing; and / or shifting the fresh macromolecule materials to spinning equipment to make the same into fiber strips, utilizing a needle machine to have the fiber strips woven into curtain-type packing strips. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation method is fully used for absorbing and bearing a great deal of multiple types of microorganisms to play a role of synergistic degradation; and absorption of the micropore materials and degradation of the microorganism play a synergistic function together during the course of pollutant removal.
Owner:重庆干城环保科技有限公司
Preparation and application of hierarchical pore metal-organic framework loaded heteropolyacid catalyst
InactiveCN107694611AGuarantee structureImprove stabilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsMetal-organic frameworkCatalytic oxidation
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a hierarchical pore metal-organic framework loaded heteropolyacid catalyst. The catalyst adopts hydrothermal-extraction method for preparation. The method includes: dissolving an organic ligand, a template agent, a metal salt and Keggin type heteropolyacid in a solvent, conducting hydrothermal synthesis of a crystal product, and thenperforming Soxhlet extraction to obtain a catalyst. The obtained catalyst has a meso-micro hierarchical porous structure, realizes high dispersion of the active component heteropolyacid and ultra-highloading capacity, and at the same time solves the problems of large mass transfer resistance, long diffusion path and small reaction place in microporous materials. The catalyst provided by the invention shows excellent catalytic performance in both photocatalytic degradation of dye wastewater and catalysis of oxidation-extraction desulfurization reaction, the catalysis reaction uses visible light and hydrogen peroxide respectively, the process is clean, environment-friendly and green, and after repeated use, the catalyst still maintains high activity, and has high industrial application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
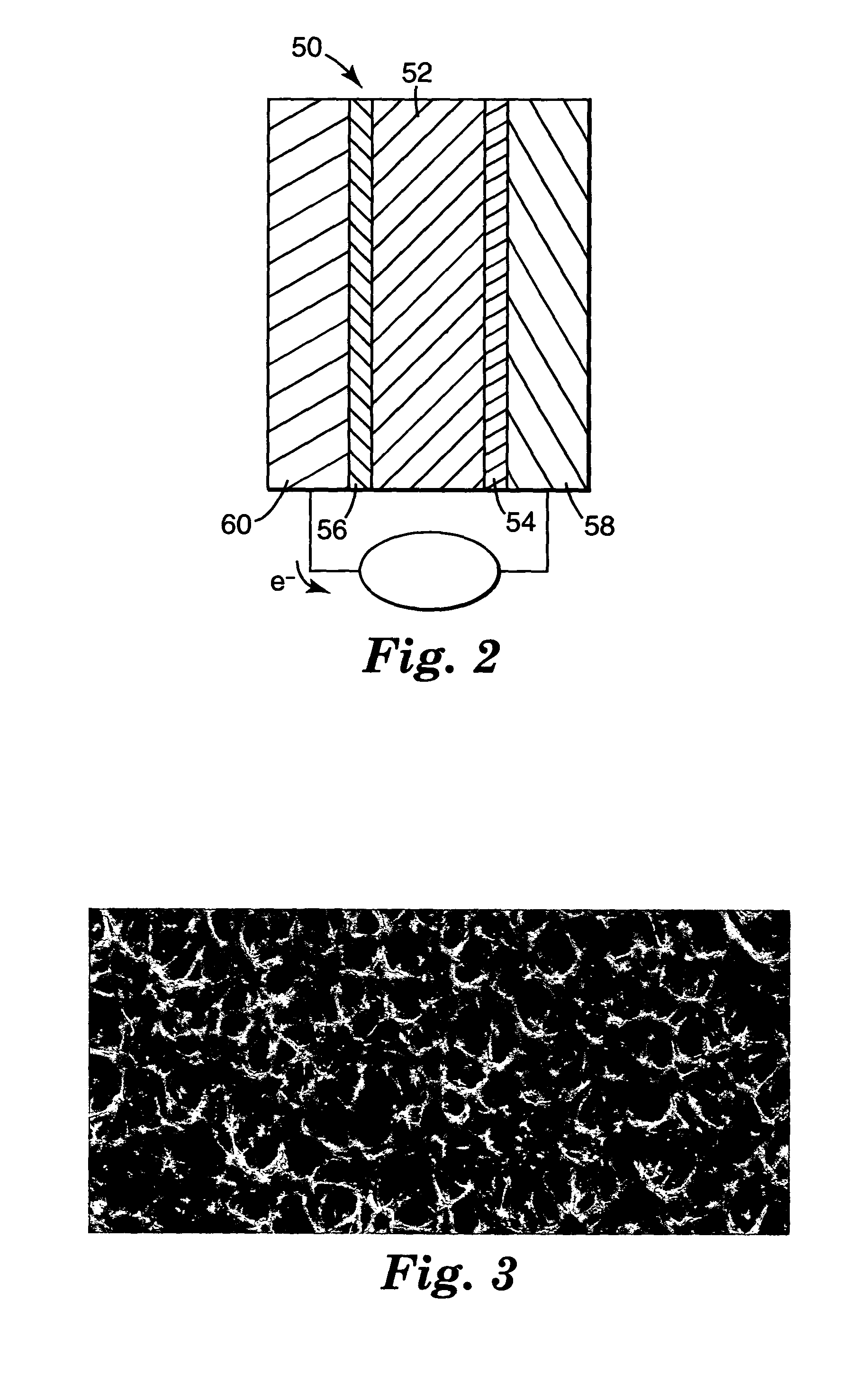
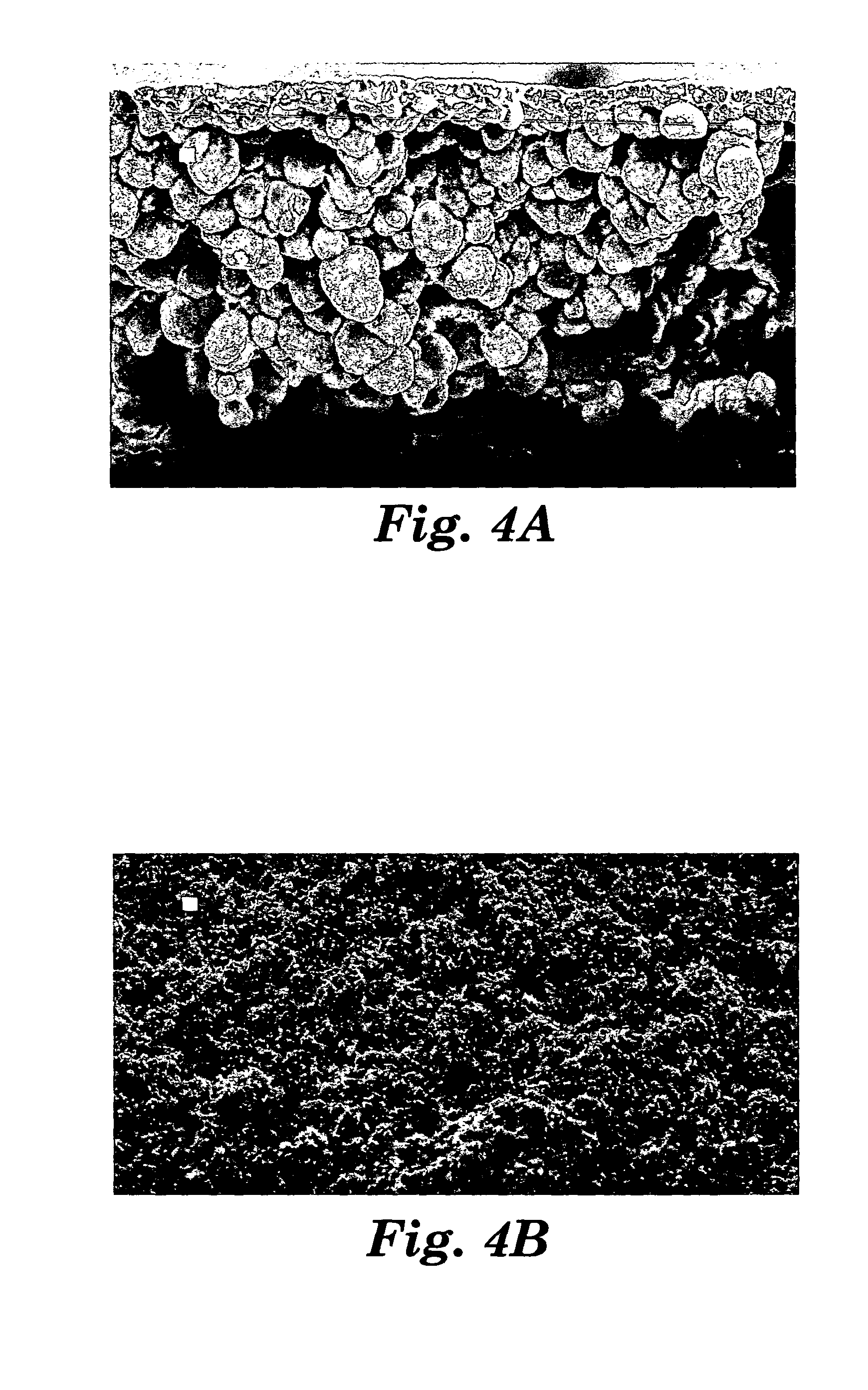
Microporous material
ActiveUS20110256364A1Synthetic resin layered productsTobacco devicesPolyolefinVolumetric Mass Density
Microporous materials that include thermoplastic organic polyolefin polymer (e.g., ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin, such as polyethylene), particulate filler (e.g., precipitated silica), and a network of interconnecting pores, are described. The microporous materials of the present invention possess controlled volatile material transfer properties. The microporous materials can have a density of at least 0.8 g / cm3; and a volatile material transfer rate, from the volatile material contact surface to the vapor release surface of the microporous material, of from 0.04 to 0.6 mg / (hour*cm2). In addition, when volatile material is transferred from the volatile material contact surface to the vapor release surface, the vapor release surface is substantially free of volatile material in liquid form.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Microporous material
Microporous materials that include thermoplastic organic polyolefin polymer (e.g., ultrahigh molecular weight polyolefin, such as polyethylene), particulate filler (e.g., precipitated silica), and a network of interconnecting pores, are described. The microporous materials of the present invention possess controlled volatile material transfer properties. The microporous materials can have a density of at least 0.8 g / cm3; and a volatile material transfer rate, from the volatile material contact surface to the vapor release surface of the microporous material, of from 0.04 to 0.6 mg / (hour*cm2). In addition, when volatile material is transferred from the volatile material contact surface to the vapor release surface, the vapor release surface is substantially free of volatile material in liquid form.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
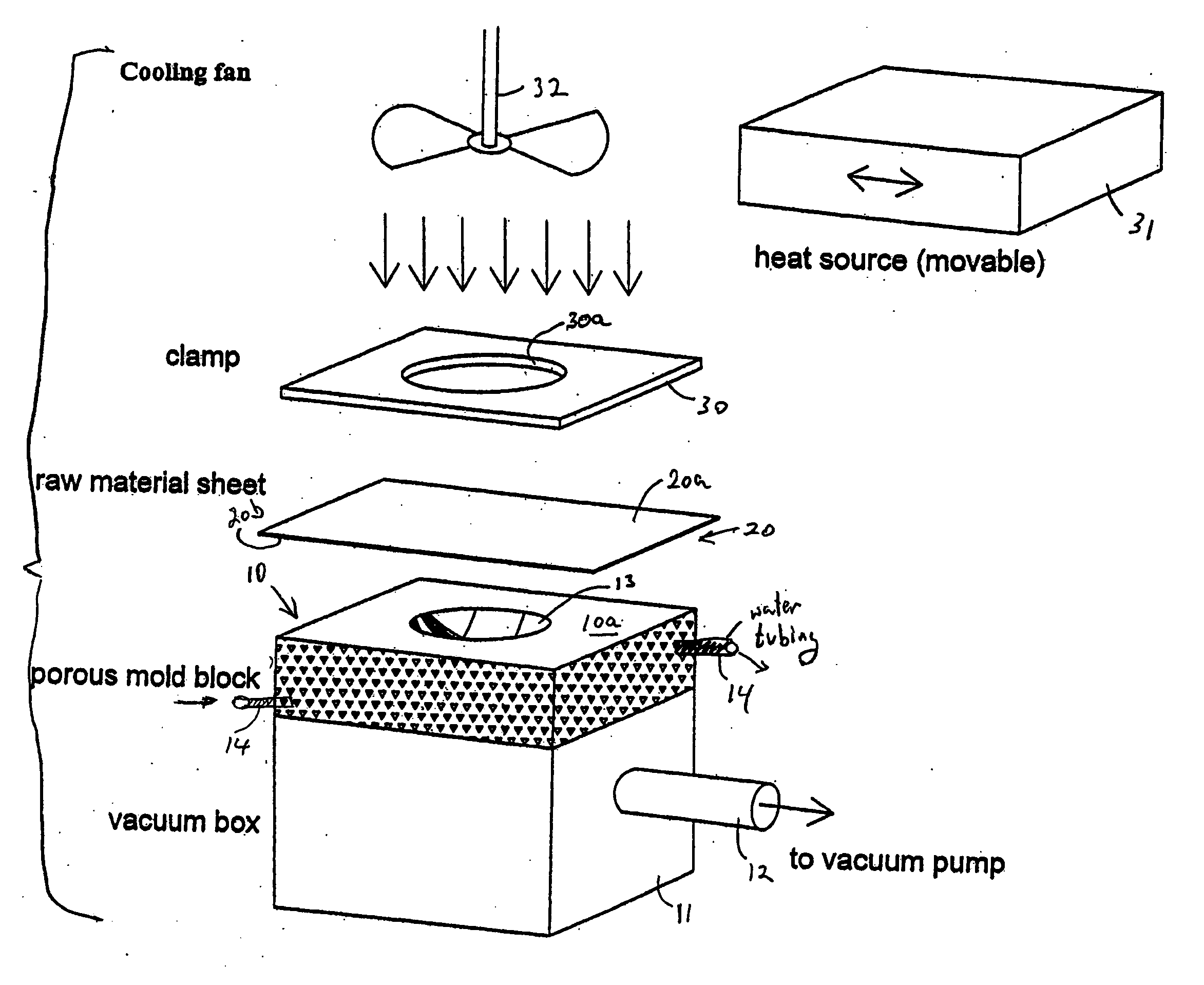
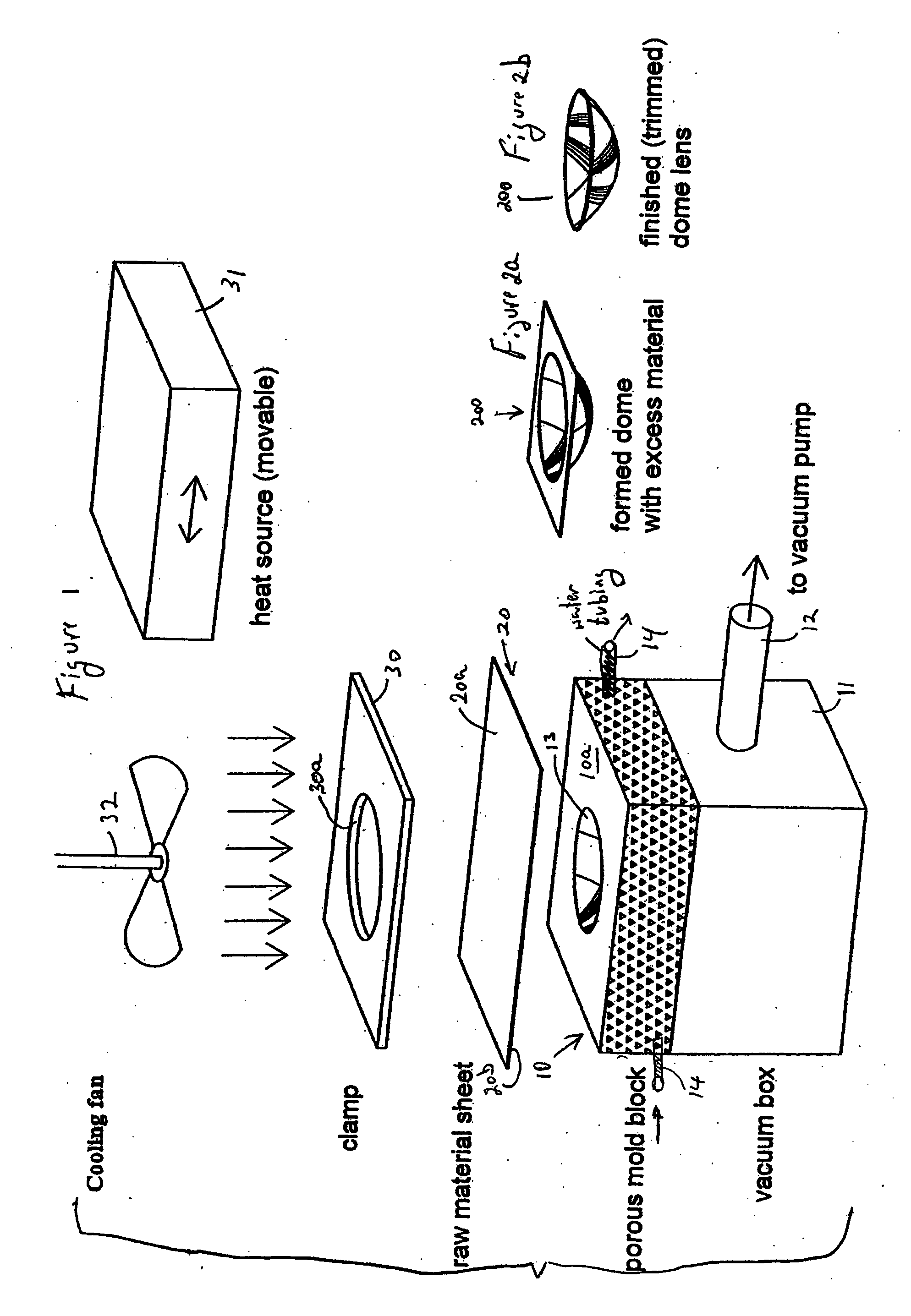
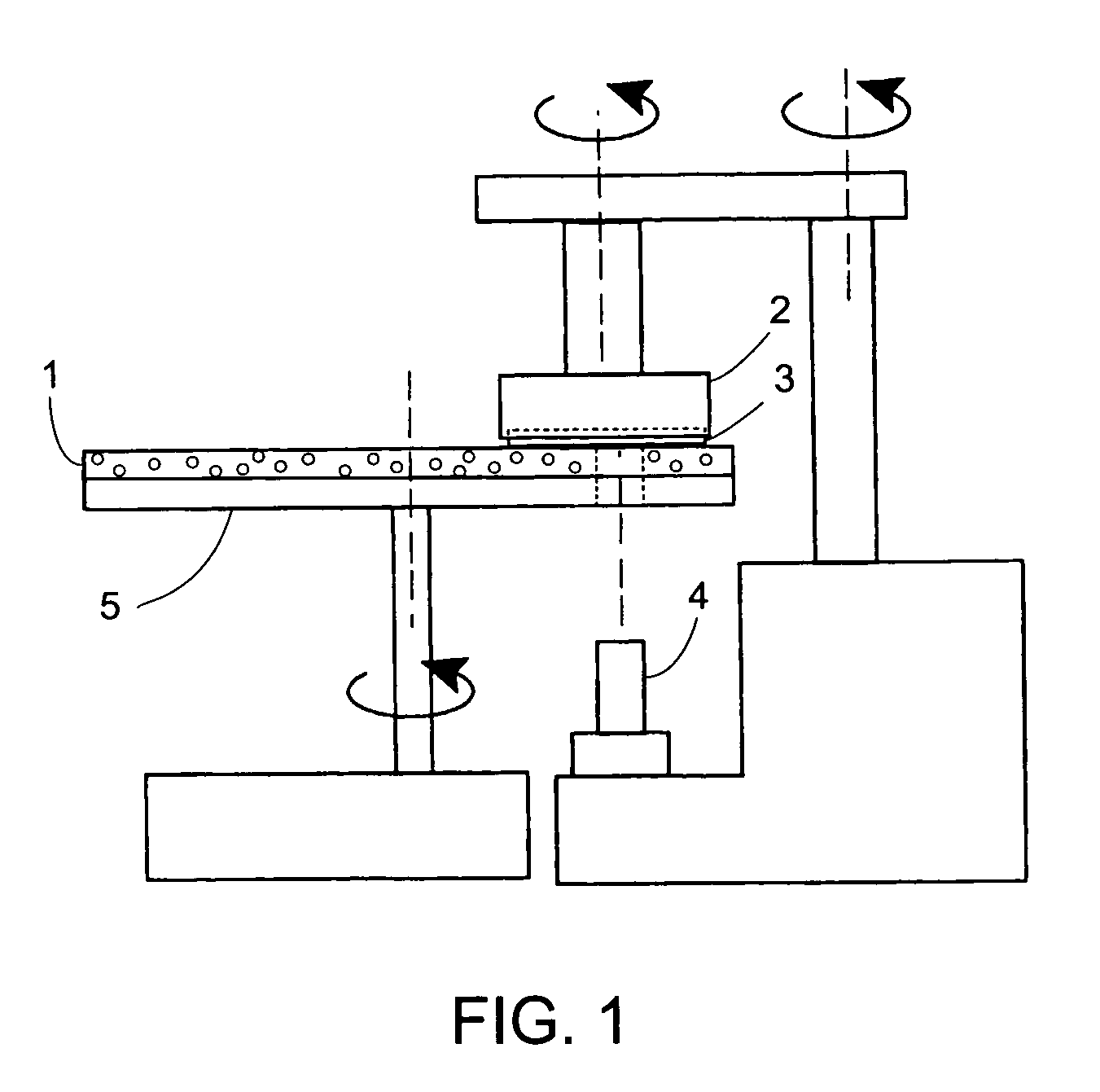
Process for thermo-molding convex mirrors
A low cost process of particular utility in manufacturing optical grade objects such as mirrors from a plastic sheet, comprising the steps of selecting a predefined three dimensional shape to be formed and machining a block of a microporous material, to provide the selected three dimensional shape on one surface thereof. A sheet of plastic is placed over the machined three dimensional shape and distanced therefrom. The sheet of plastic is heated a vacuum is applied through the microporous material to draw the heated plastic sheet to conform to the shape in the block. A surface of the conformed shape plastic is metallized to a form an optical mirror surface.
Owner:REPLEX MIRROR
Preparation method of boron/nitrogen-doped microporous carbon material
InactiveCN103508434AGood hydrogen storage performanceStrong selective adsorption performanceOther chemical processesCarbon preparation/purificationArgon atmosphereNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a preparation method and gas adsorption properties of a boron / nitrogen-doped microporous carbon material, particularly a boron / nitrogen-doped microporous carbon material prepared by using metal organic framework ZIF-8 (zeolitic imidazolate framework-8) and boron nitrogen compounds as precursors by a high-temperature sintering method and gas adsorption properties of the boron / nitrogen-doped microporous carbon material for hydrogen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing the porous metal organic framework ZIF-8; 2) limiting the boron nitrogen compounds (such as ammonia borane) to the inside of the pores of the metal organic framework ZIF-8 by a solution impregnating method; and 3) carrying out high-temperature sintering on the composite material in an argon atmosphere to obtain the boron / nitrogen-doped microporous carbon material. The preparation technique is simple; and the prepared carbon material implements simultaneous doping of boron and nitrogen and centralized distribution of micropore sizes, and has favorable adsorption property for hydrogen and selective adsorption property for carbon dioxide.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ion exchange method for preparing lithium type low silicon aluminum X-shape zeolite molecular sieve
InactiveCN101125664AAvoid wastingOvercome shortcomings such as uneven exchangeFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteLithiumMolecular sieve
An ion exchange method for preparing lithium low-silicon low-aluminum X-type zeolite molecule sieve pertains to microporous material technique field. The invention is characterized in that: firstly, a sodium low-silicon low-aluminum X-type zeolite molecule sieve (Na-LSX) is endowed with a certain Li-ion exchange degree through the exchange of Li-ion water solution, then the lithium low-silicon low-aluminum X-type zeolite (Li-LSX) is obtained through a solid phase exchange method, and the Li-ion exchange degree of the final product is larger than 96 percent. Compared with the traditional ion exchange method, the method has the advantages of low cost, simple technique and thorough exchange, etc., and the prepared Li-LSX type zeolite molecule sieve has wide universal application potentials in the field of the fine chemical and absorption exchange, etc.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Composite double microporous material and preparation thereof
ActiveCN101376506AImprove catalytic performanceHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a Y / Beta composite dual-microporous material. A composite molecular-sieve material has the structure that a Y molecular-sieve is taken as a kernel, a Beta molecular-sieve is taken as a shell, the two molecular-sieves are closely combined into a composite molecular-sieve particle, the Beta molecular-sieve wraps the Y molecular-sieve, and the content of the Y molecular-sieve is 30 to 70 percent in a composite molecular-sieve. The synthesis method of the composite molecular-sieve adopts a one-step crystallization method and utilizes a liquid concentration principle to lead a template agent and amorphous Si and Al in the Y molecular-sieve to form a secondary structure unit of the Beta molecular-sieve and even a Beta molecular-sieve seed crystal; then the Beta molecular-sieve grows through the guiding effect of the seed crystal. The Y / Beta composite dual-microporous material which is synthesized by adopting the method has the high composite advantage; the Beta molecular-sieve wraps the surface of the Y molecular-sieve, and the Beta molecular-sieve in the composite dual-microporous material is in the nano-scale, so the catalytic performance of the whole composite dual-microporous material is enhanced markedly; and the medium oil selectivity of the hydrocracking reaction can be increased, and the reaction temperature is reduced.
Owner:FUSHUN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS SINOPEC CORP
Gas Diffusion Electrode and Solid Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell
ActiveUS20080299430A1Suppress power consumptionSave fuel consumptionCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFiberCarbon fibers
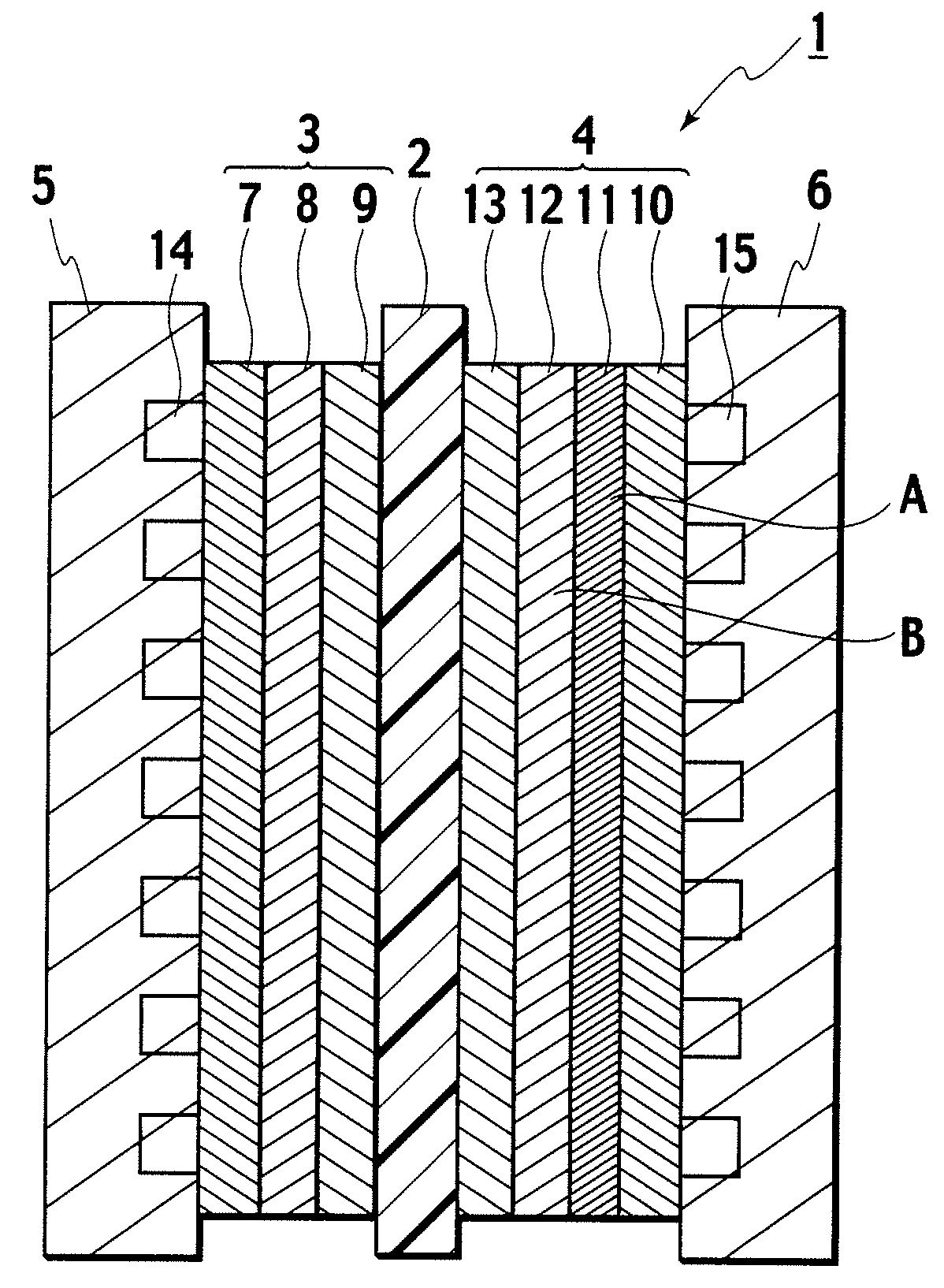
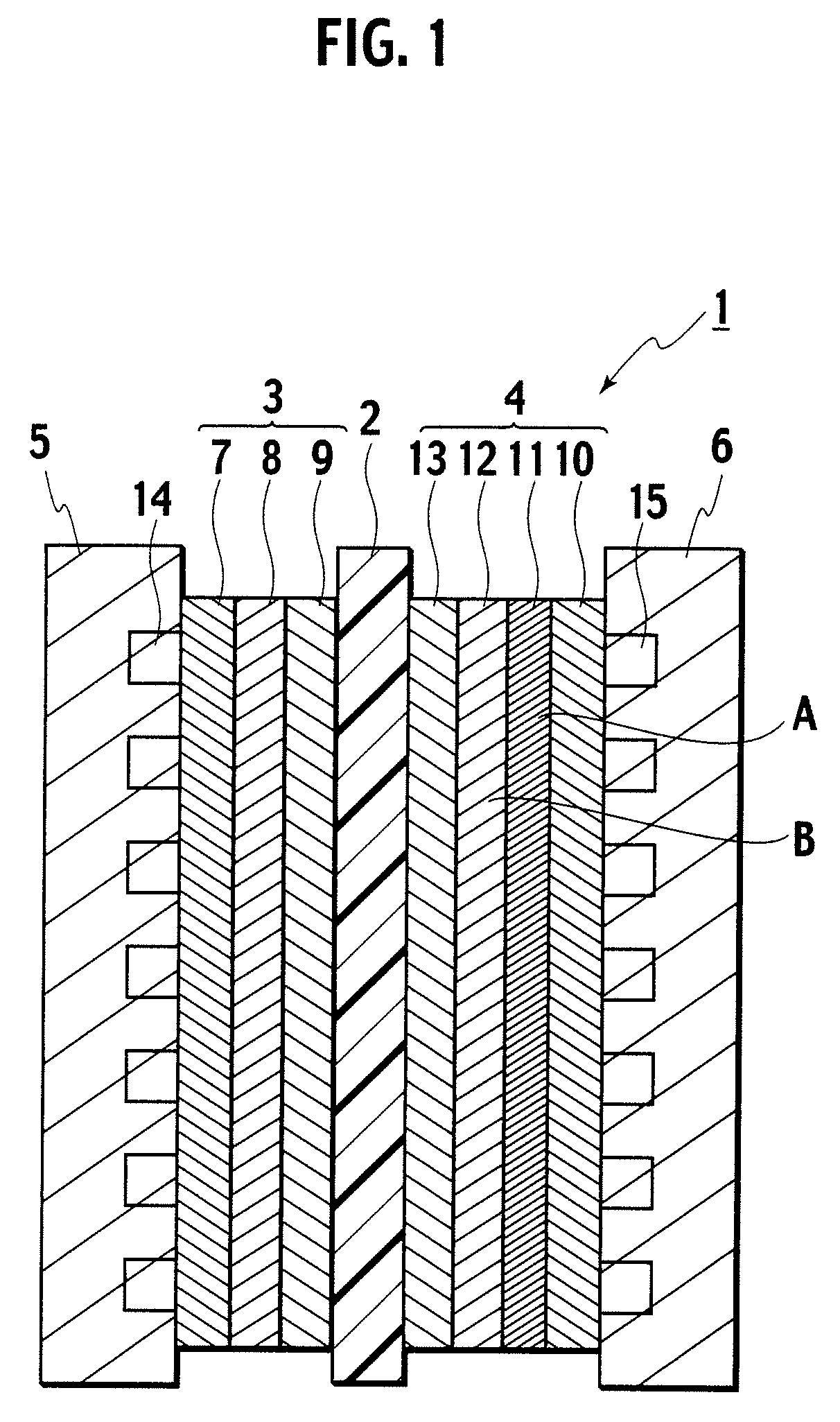
A gas diffusion electrode includes: an electrode catalyst layer 13; microporous layers 11 and 12 arranged on the electrode catalyst layer 13 and including at least two layers which are second and first microporous layers 12 and 11 formed of materials having different water repellencies, wherein the second microporous layer 12 disposed on the electrode catalyst layer 13 side is composed to have higher water repellency than the first microporous layer 11; and an oxidant gas diffusion substrate 10 disposed on the microporous layers 11 and 12 and formed of carbon fiber. According to the gas diffusion electrode of the present invention, drainability of generated water from the electrode catalyst layer to the gas diffusion layer and moisture retention and gas diffusibility of the electrode catalyst layer can be enhanced. Moreover, according to a solid polymer electrolyte fuel cell of the present invention, stable power generation characteristics can be obtained even under an operating condition with wide humidity range and current density range.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Transparent microporous materials for CMP
InactiveUS7435165B2Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesOptical transmittanceWavelength
The invention is directed to a chemical-mechanical polishing pad substrate comprising a porous material having an average pore size of about 0.01 microns to about 1 micron. The polishing pad substrate has a light transmittance of about 10% or more at at least one wavelength of about 200 nm to about 35,000 nm. The invention is further directed to a polishing pad comprising the polishing pad substrate, a method of polishing comprising the use of the polishing pad substrate, and a chemical-mechanical apparatus comprising the polishing pad substrate.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
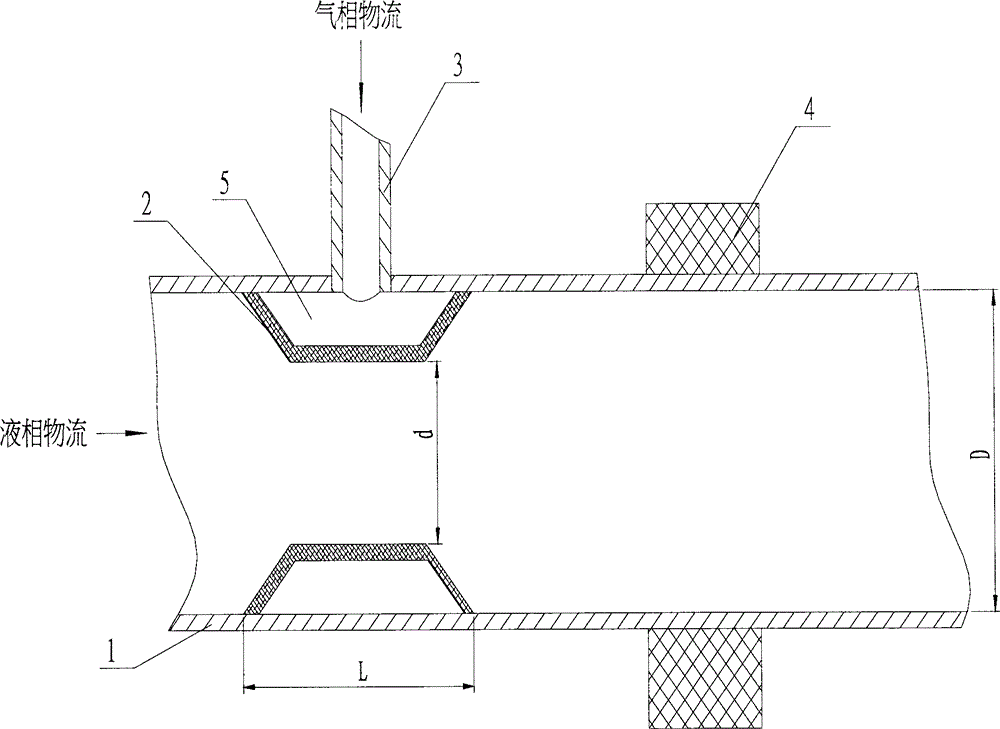
Microbubble generator for reinforced hydrogenation technology
The invention discloses a microbubble generator for a reinforced hydrogenation technology. The microbubble generator mainly comprises a main pipe, a Venturi tube, an air inlet pipe and an ultrasonic generator. The Venturi tube and the main pipe are coaxially arranged and are welded to the inner wall of the main pipe. A detached annular air-inlet space is formed between the outer wall of the Venturi tube and the inner wall of the main pipe. The air inlet pipe is welded to the outer wall of the main pipe and is communicated with the annular air-inlet space. The Venturi tube is prepared from a microporous material. The air inlet pipe, the annular air-inlet space and micropores of the Venturi tube form gas channels. The inner wall of the Venturi tube and the inner wall of the main pipe form a gas-liquid channel. The ultrasonic generator is installed on the outer wall of the main pipe and is located in the downstream of the Venturi tube. The microbubble generator can improve hydrogenation efficiency and realize deep and high efficiency hydrotreatment or hydrocracking of an oil product.
Owner:LUOYANG PETROCHEMICAL ENG CORP SINOPEC +1
Transparent microporous materials for CMP
InactiveUS7267607B2Polishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesMicroporous materialPolymer
The invention is directed to a chemical-mechanical polishing pad substrate comprising a microporous closed-cell foam characterized by a narrow pore size distribution in the range of about 0.01 microns to about 10 microns. The polishing pad is produced by foaming a solid polymer sheet with a supercritical gas under an elevated temperature and pressure until the sheet is saturated with gas. The invention is further directed to a polishing pad comprising the polishing pad substrate, a method of polishing comprising the use of the polishing pad substrate, and a chemical-mechanical apparatus comprising the polishing pad substrate.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
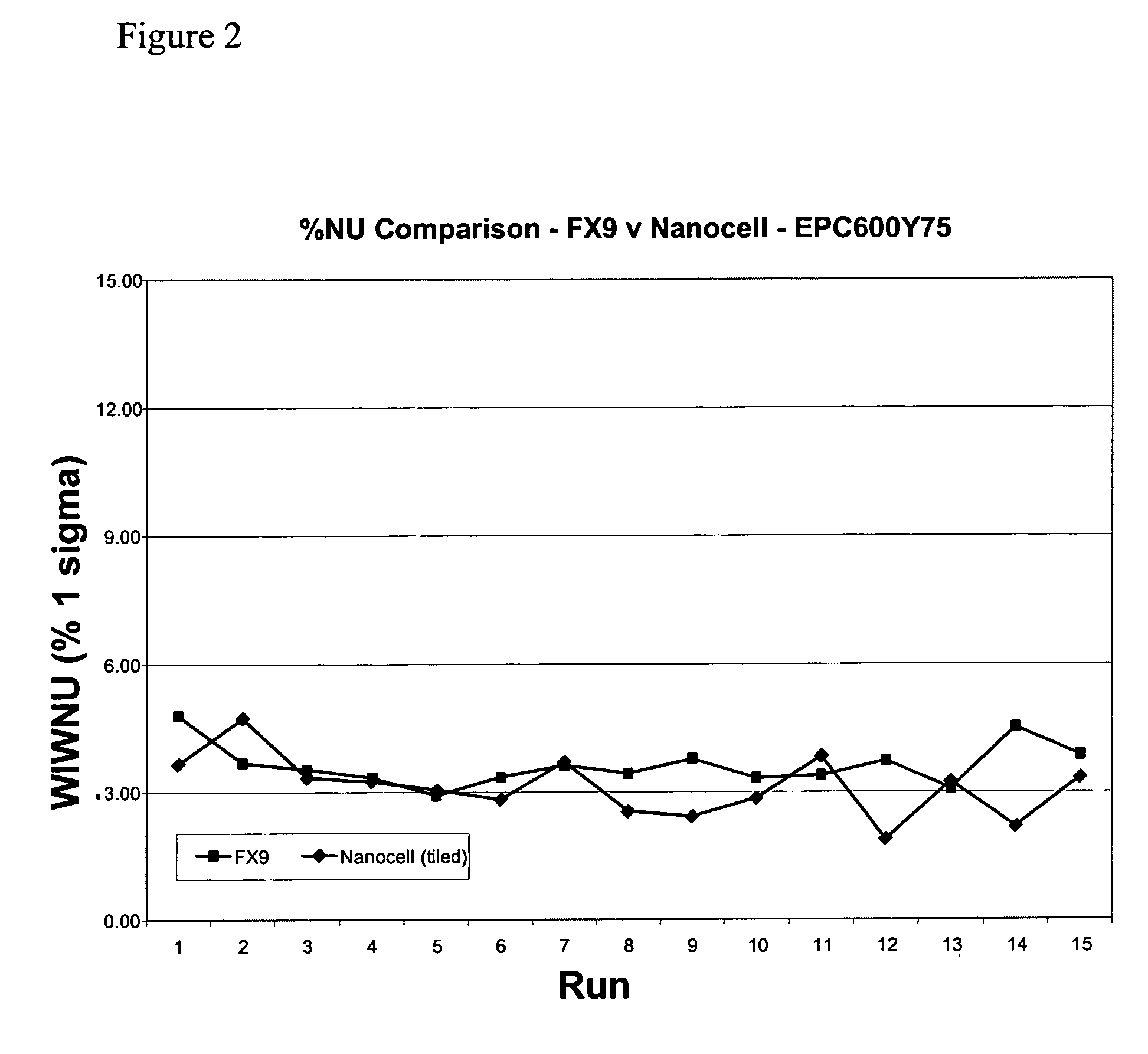
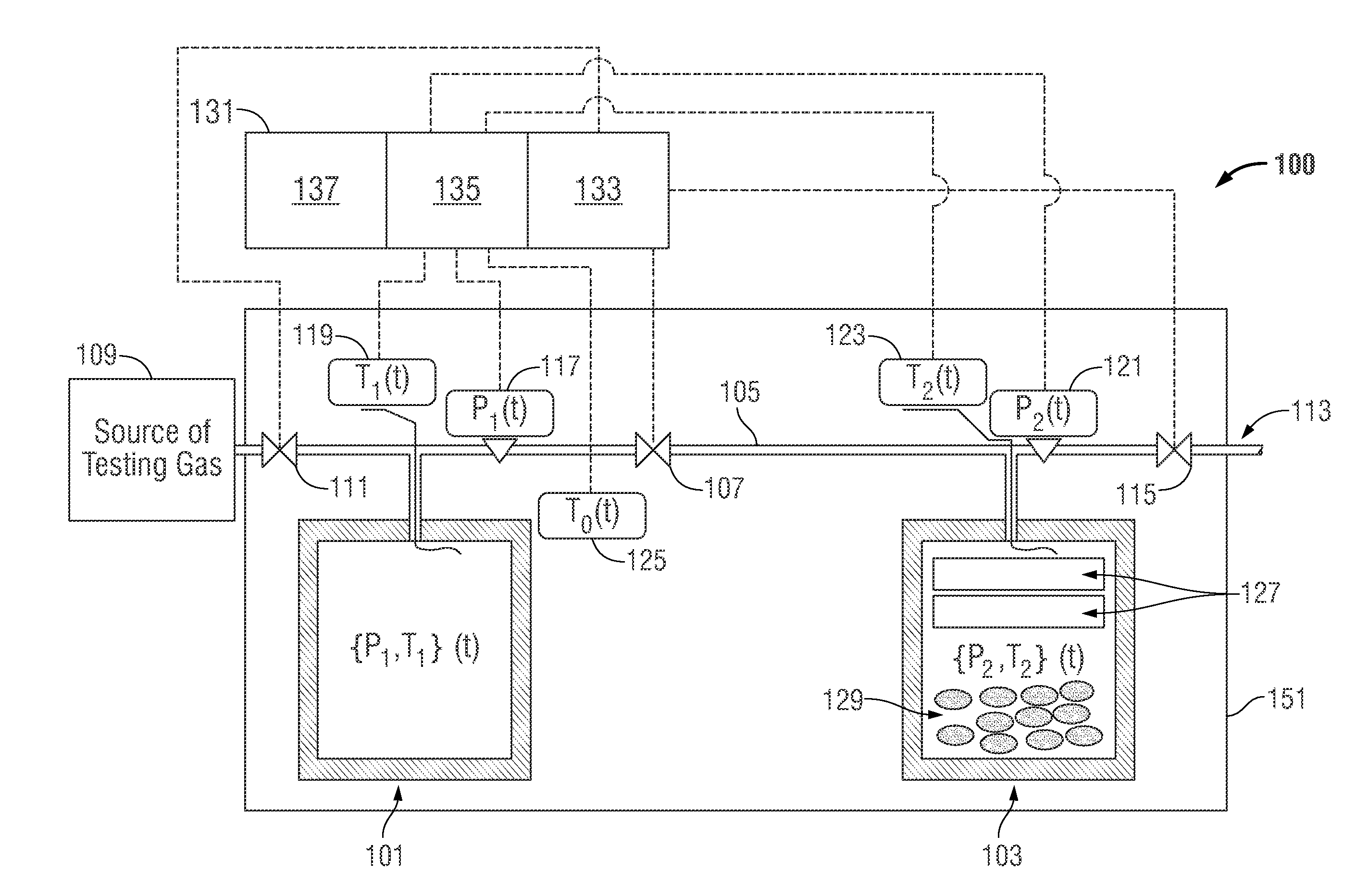
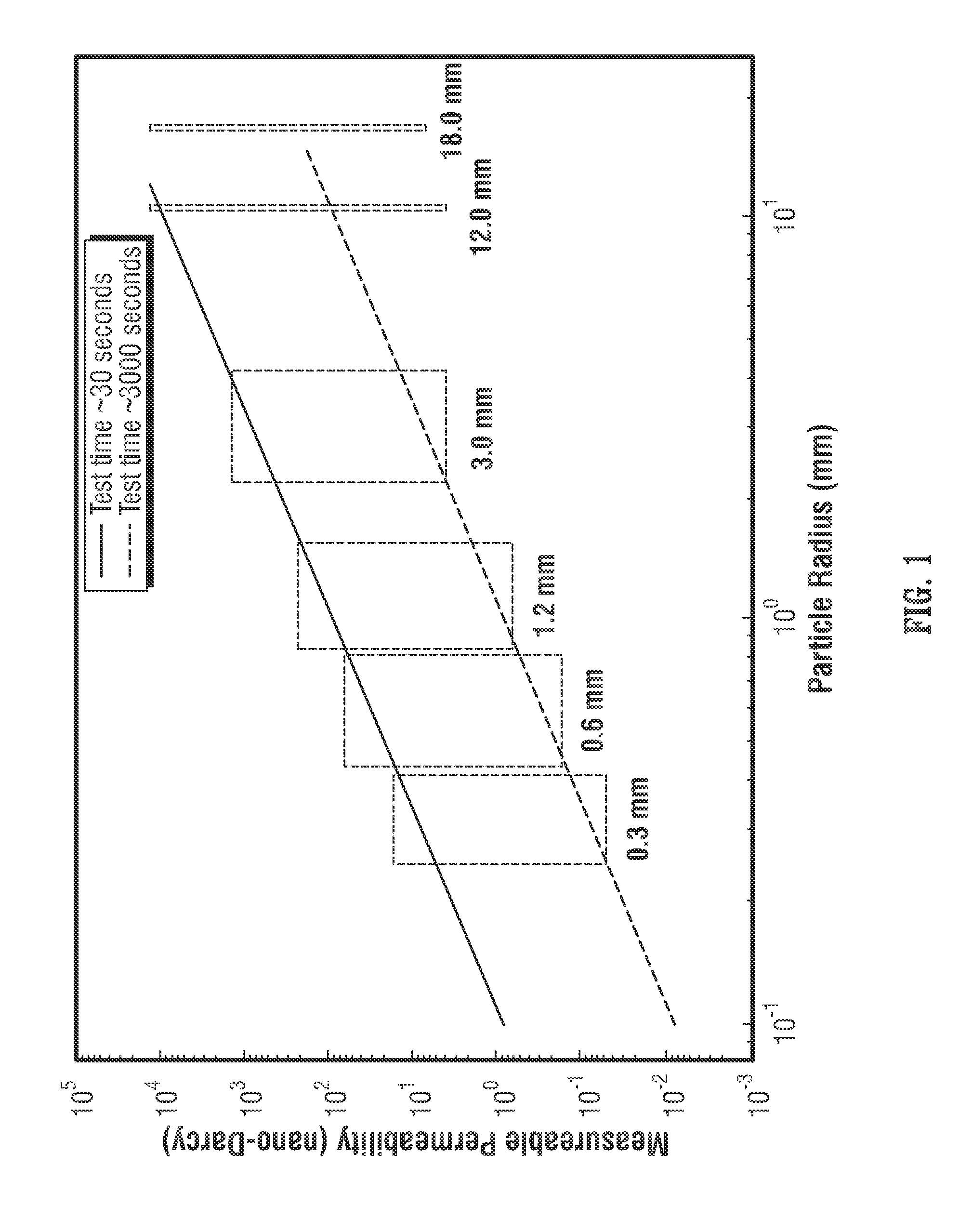
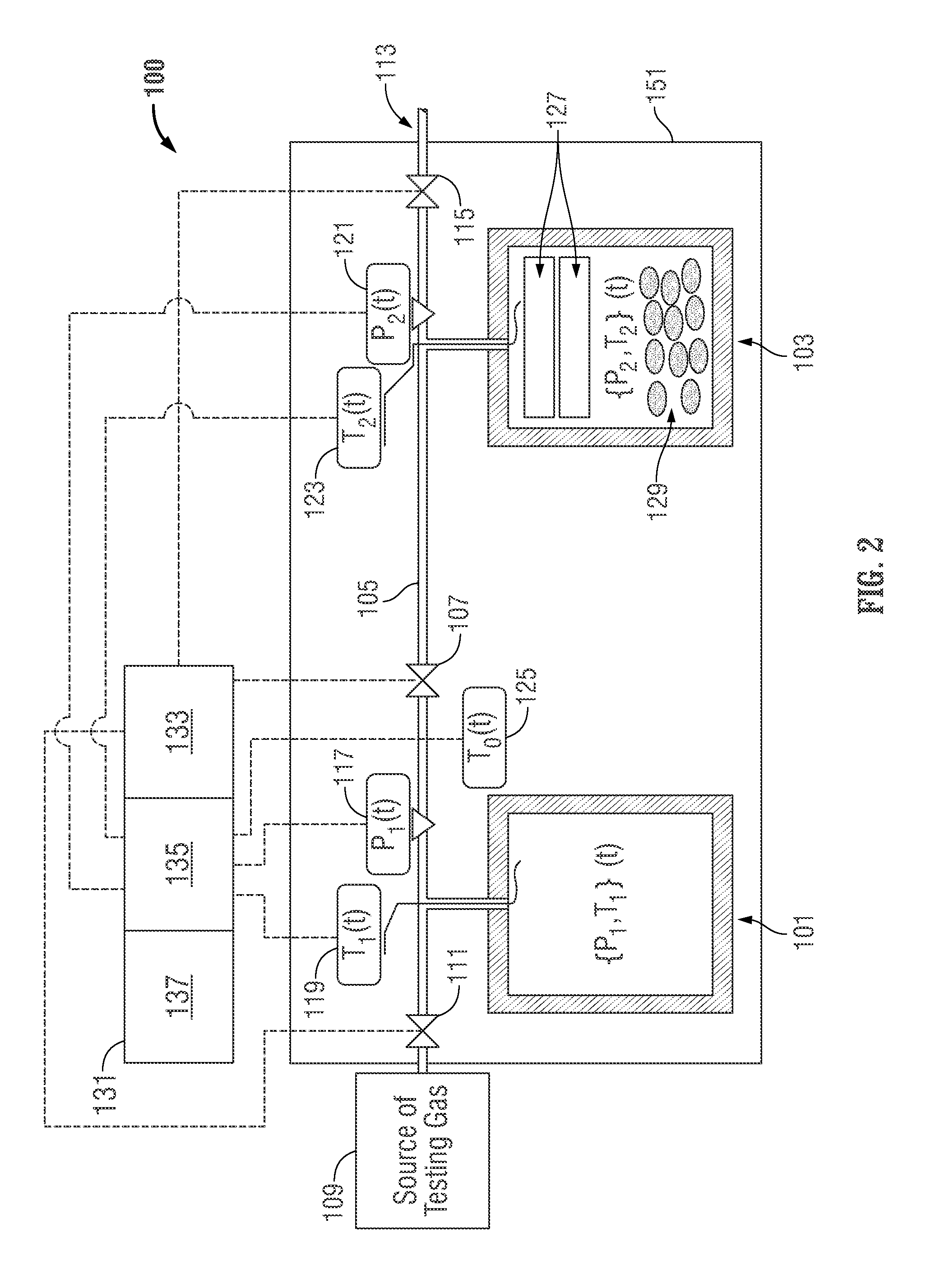
Apparatus and methodology for measuring properties of microporous material at multiple scales
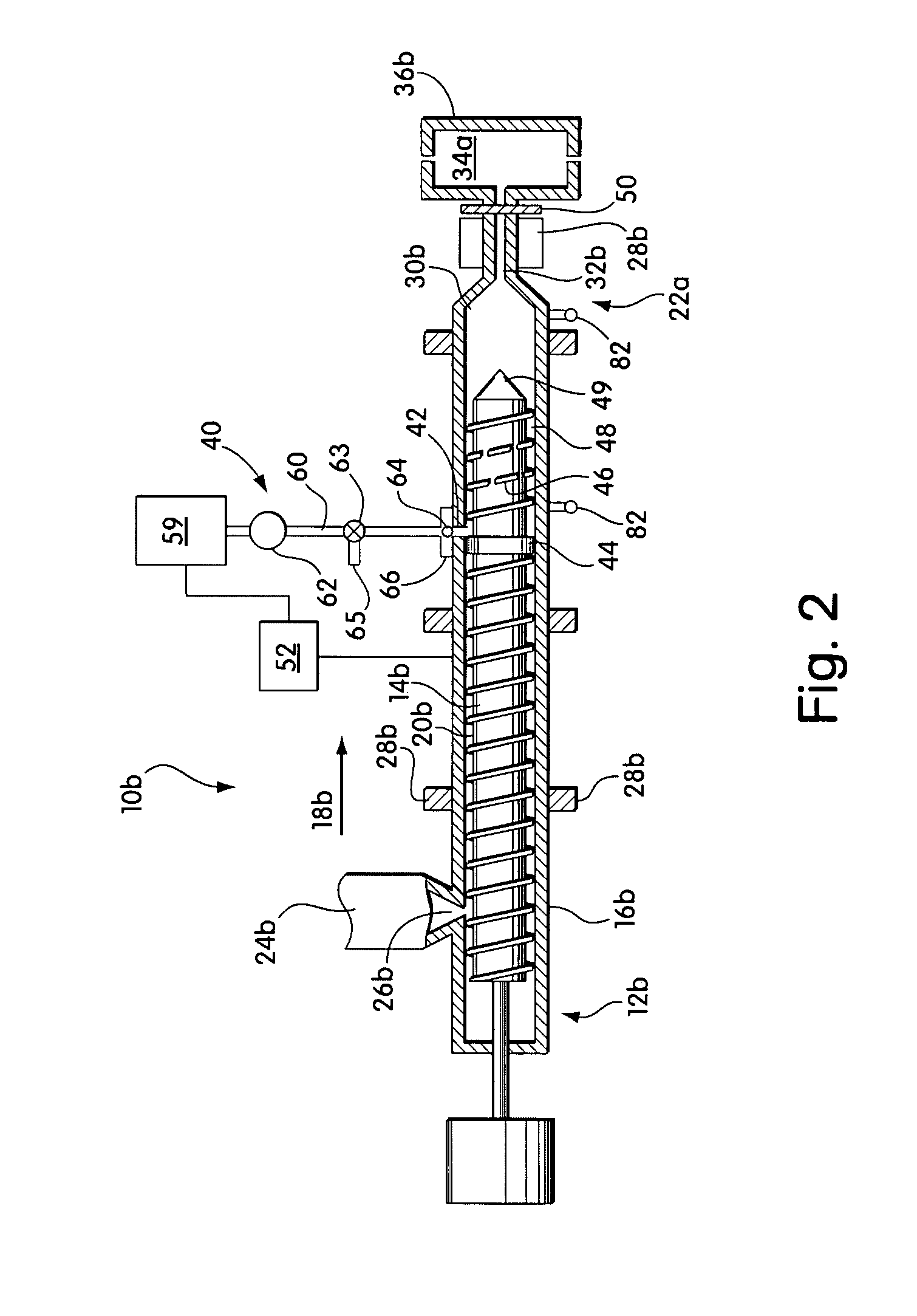
ActiveUS20150362419A1Rapid temperature measurementLarge heat capacityEarth material testingPermeability/surface area analysisIsolation valveExhaust valve
A test apparatus (and method of operation) for characterizing properties of a sample under test (such as porous material, for example, samples of reservoir rock) that operates in conjunction with a source of test fluid. The test apparatus includes an intake valve fluidly coupled to the source of test fluid, a reference cell fluidly coupled to the source of test fluid via the intake valve, a sample cell that holds the sample under test, an isolation valve fluidly coupled between the reference cell and the sample cell, an exhaust port, an exhaust valve fluidly coupled between the sample cell and the exhaust port, a first pressure sensor associated with the reference cell for measuring pressure within the reference cell, and a second pressure sensor associated with the sample cell for measuring pressure within the sample cell. The method of operation includes calibration procedures to compensate for systematic measurement errors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Composite natural micro porous material sewage treating agent
InactiveCN1587082AImprove adsorption capacityReduce operating costsWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSorbentWater quality
The composite natural microporous sewage treating agent is for treatment of sewage containing heavy metal ion, phenol, amine and other organic pollutant. The present invention features that the composite natural microporous sewage treating agent consists of diatomite of 0.1-10 micron granularity in 50-70 wt%, zeolite of 1-4 nm granularity in 20-40 wt%, and bentonite of 10-50 nm granularity in 0-15 wt%. The present invention selects cheap natural microporous material with excellent adsorbing performance and different pores as adsorbent carrier, and modifies the microporous material to prepare sewage treating agent suitable for various sewage quality. The present invention has excellent sewage treating effect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for manufacturing microporous CMP materials having controlled pore size
A method of manufacturing a chemical-mechanical polishing (CMP) pad comprises the steps of (a) forming a layer of a polymer resin liquid solution (i.e., a polymer resin dissolved in a solvent); (b) inducing a phase separation in the layer of polymer solution to produce an interpenetrating polymeric network comprising a continuous polymer-rich phase interspersed with a continuous polymer-depleted phase in which the polymer-depleted phase constitutes about 20 to about 90 percent of the combined volume of the phases; (c) solidifying the continuous polymer-rich phase to form a porous polymer sheet; (d) removing at least a portion of the polymer-depleted phase from the porous polymer sheet; and (e) forming a CMP pad therefrom. The method provides for microporous CMP pads having a porosity and pore size that can be readily controlled by selecting the concentration polymer resin in the polymer solution, selecting the solvent based on the solubility parameters of the polymer in the solvent polarity of solvent, selecting the conditions for phase separation, and the like.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Laser markable microporous material
ActiveUS20110198837A1Improve laser marking effectOther printing matterFilm/foil adhesivesPolyolefinWater insoluble
Provided is a microporous material including a polyolefin matrix material; finely divided, substantially water-insoluble filler distributed throughout the matrix material, where the filler includes a positive amount of titanium dioxide; a network of interconnecting pores communicating throughout the microporous material; and optionally, a contrasting enhancing amount of a contrast enhancing material. The sum of the weight percent of the titanium dioxide and the weight percent of the optional contrast enhancing material is at least 3 weight percent based on total weight of the microporous material. Multilayer articles having a layer of the microporous material also are provided.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Polyolefin microporous air-permeable membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103739962AImprove process rangeDoes not affect processing performancePolymer sciencePolyolefin
The invention discloses a polyolefin microporous air-permeable membrane and a preparation method thereof. The microporous air-permeable membrane is prepared from a polyolefin substrate filled with a calcium carbonate filler with processed surface by means of casting extruding, stretching, and heat setting and film-forming. During the preparation, the polyolefin and the calcium carbonate filler with the processed surface are blended, extruded and pelletized, so as to prepare air-permeable particles; the air-permeable particles are extruded and molten by a casting extruder; the melt temperature is kept at 240-255 DEG C; the melt is continuously extruded to form a film through a die lip clearance of a T-shaped die head of a casting machine; the film is subjected to one-step or two-step stretching in a uniaxial manner; the draw ratio is controlled to be 1.5-2.5; the film obtained in the stretching manner is subjected to heat setting treatment at the heat setting temperature of 70-85 DEG C. The polyolefin microporous air-permeable membrane disclosed by the invention can ensure high air permeability and mechanical property of the microporous air-permeable membrane, meanwhile, the processing performance of the product is not affected, and the resistance to high temperature and high pressure of the film is also improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZIHUA FILM TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com