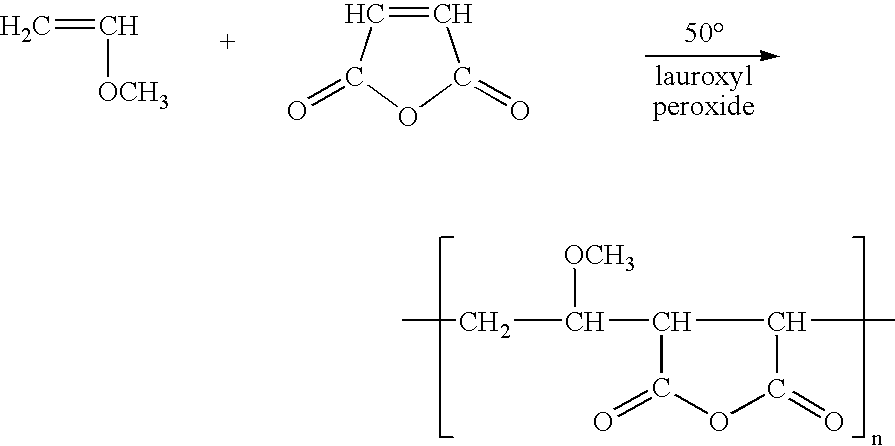
Patents
Literature
6752 results about "Polyvinylidene difluoride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
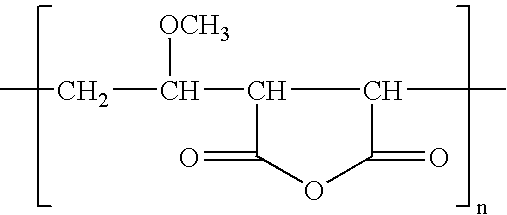
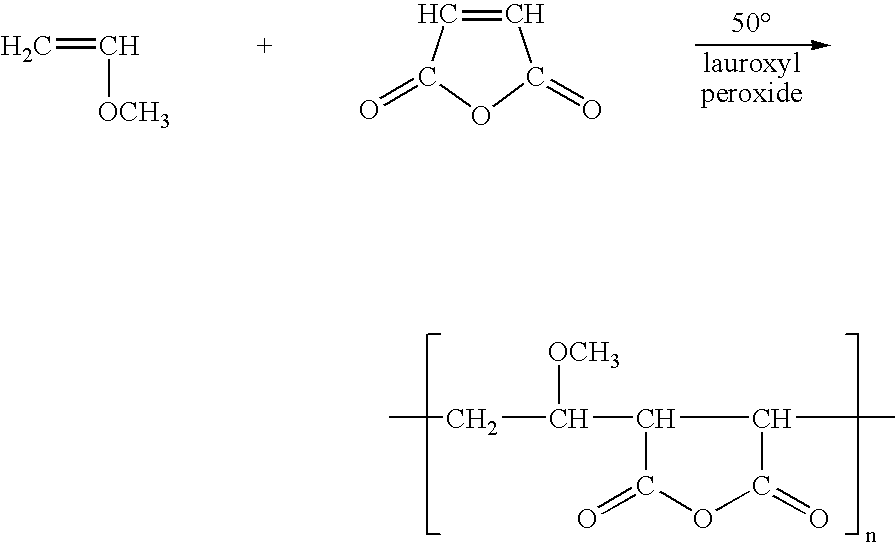
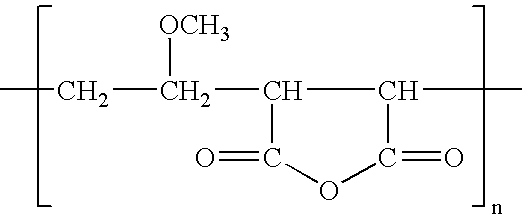
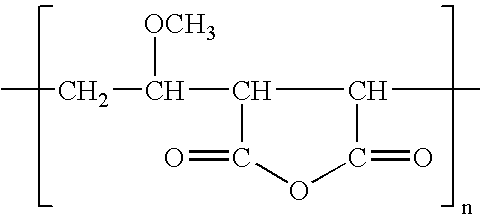
Polyvinylidene fluoride or polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) is a highly non-reactive thermoplastic fluoropolymer produced by the polymerization of vinylidene difluoride.
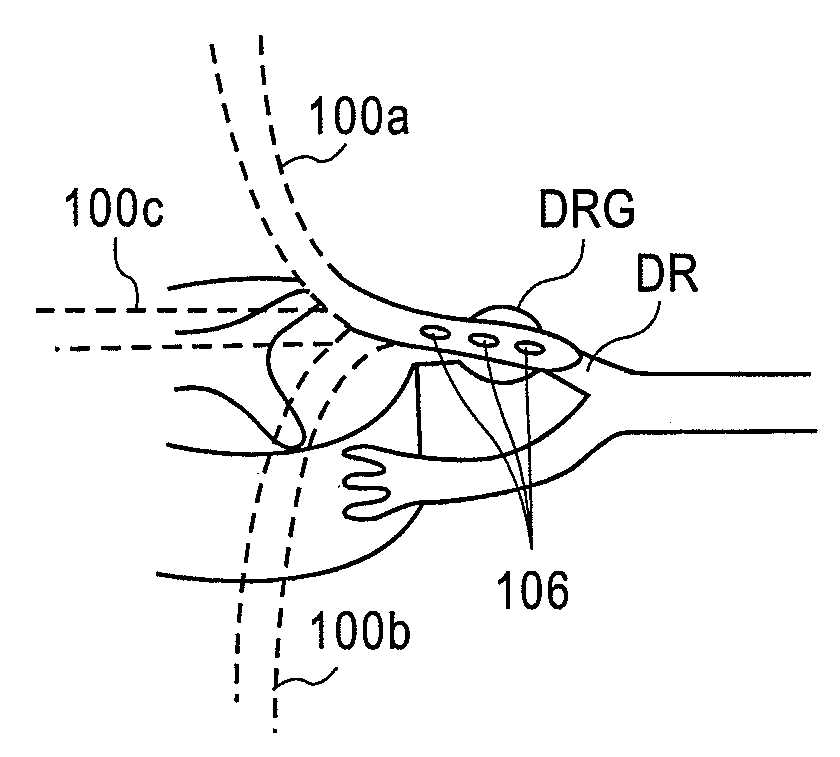
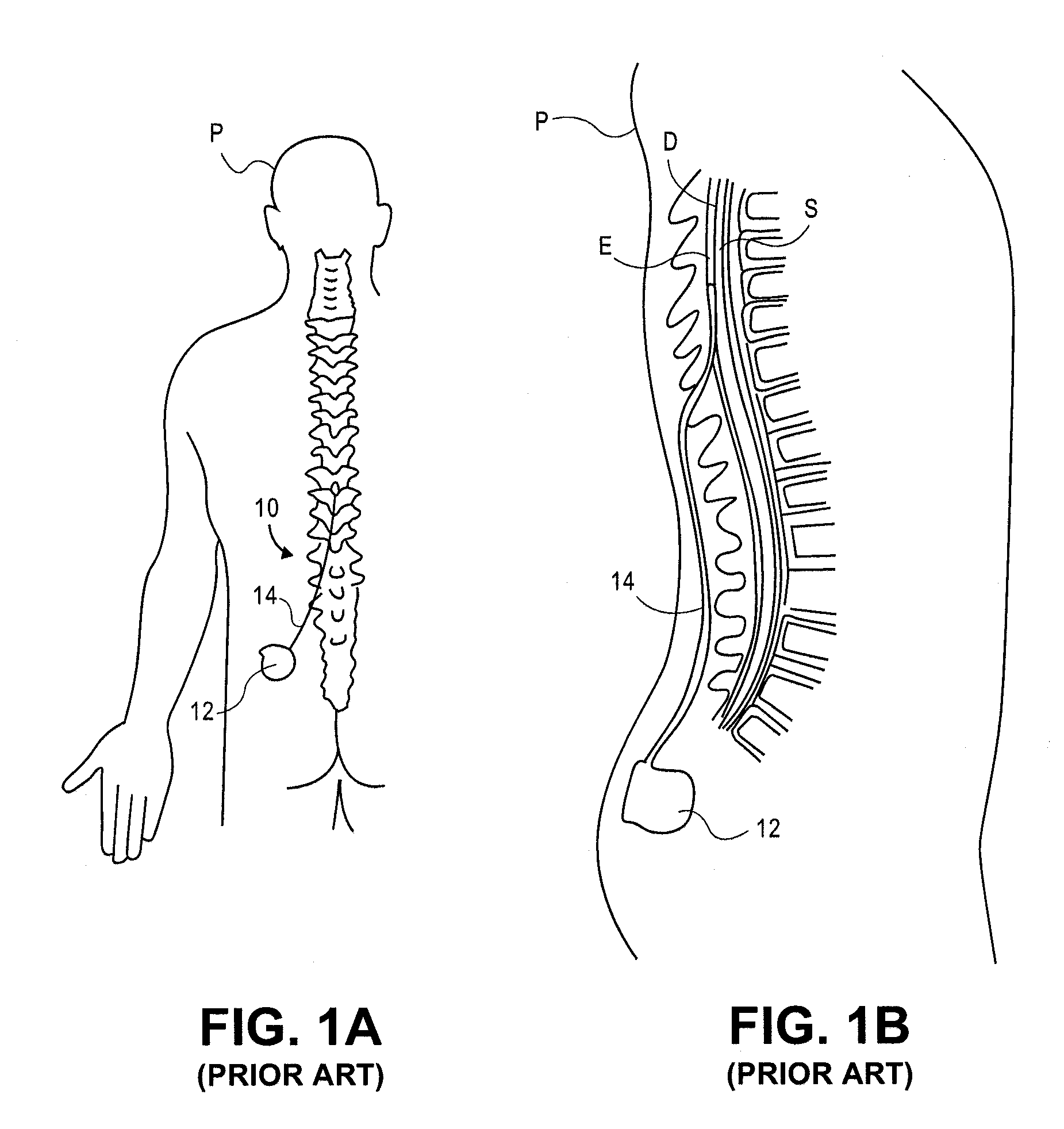
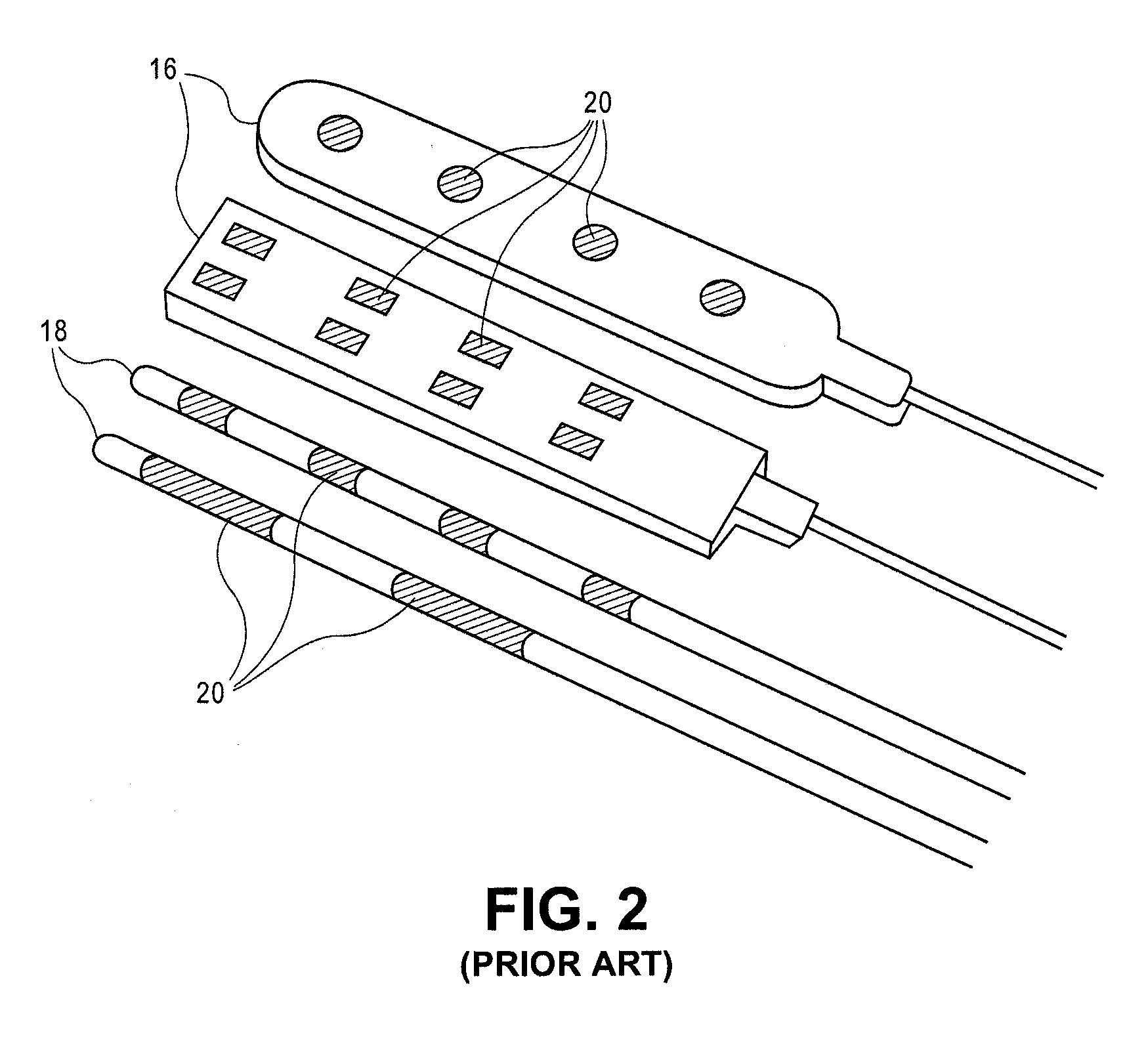
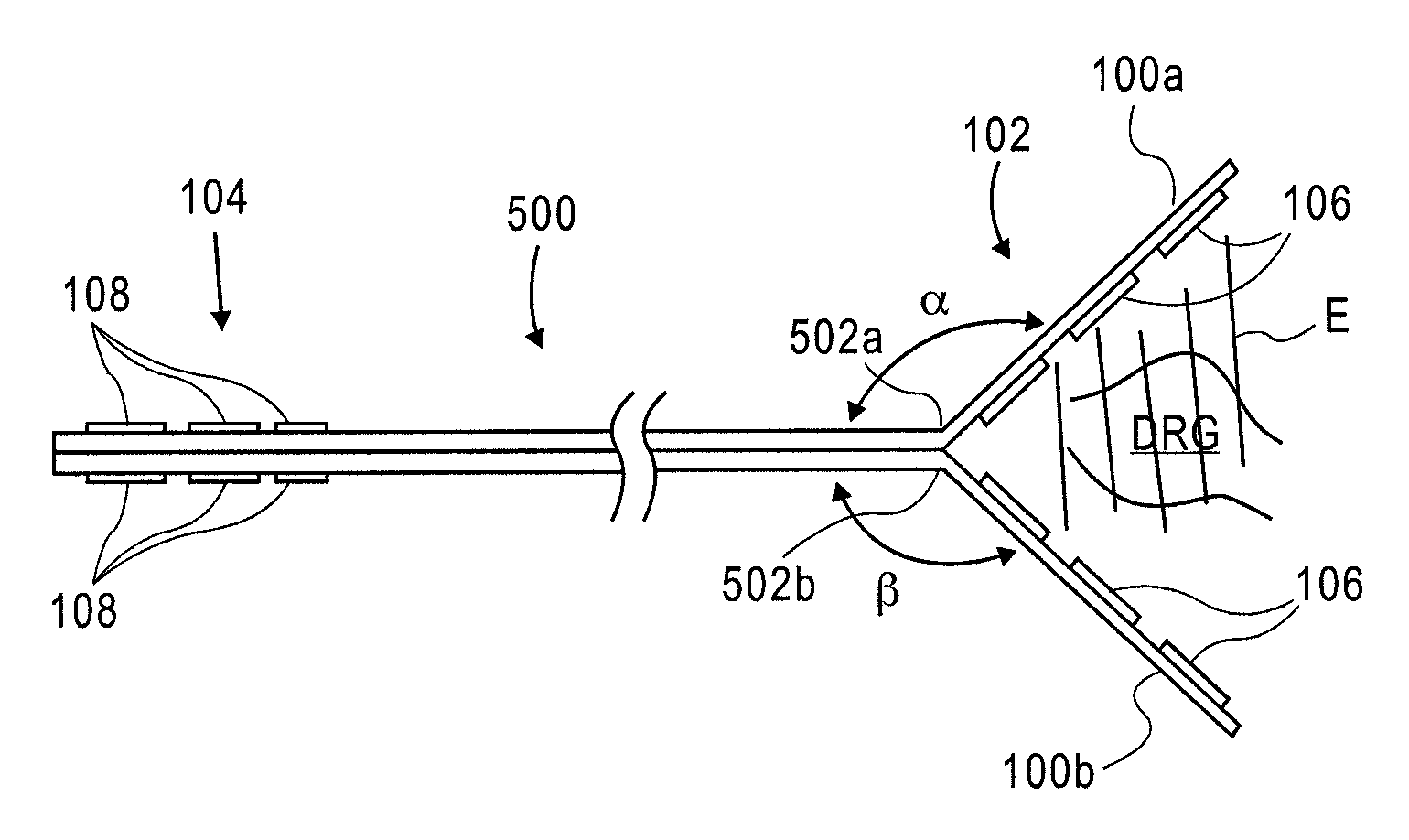
Implantable flexible circuit leads and methods of use
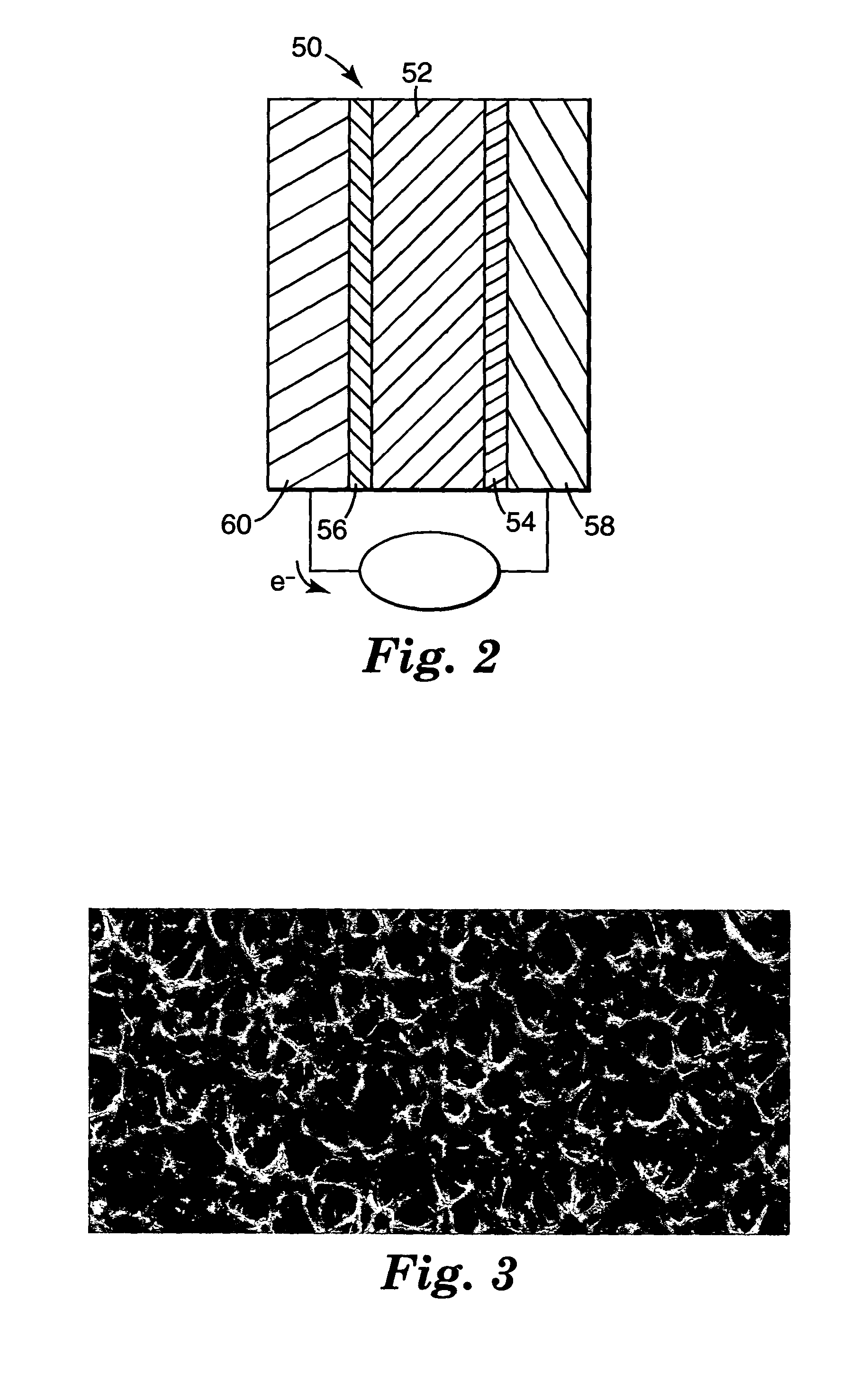
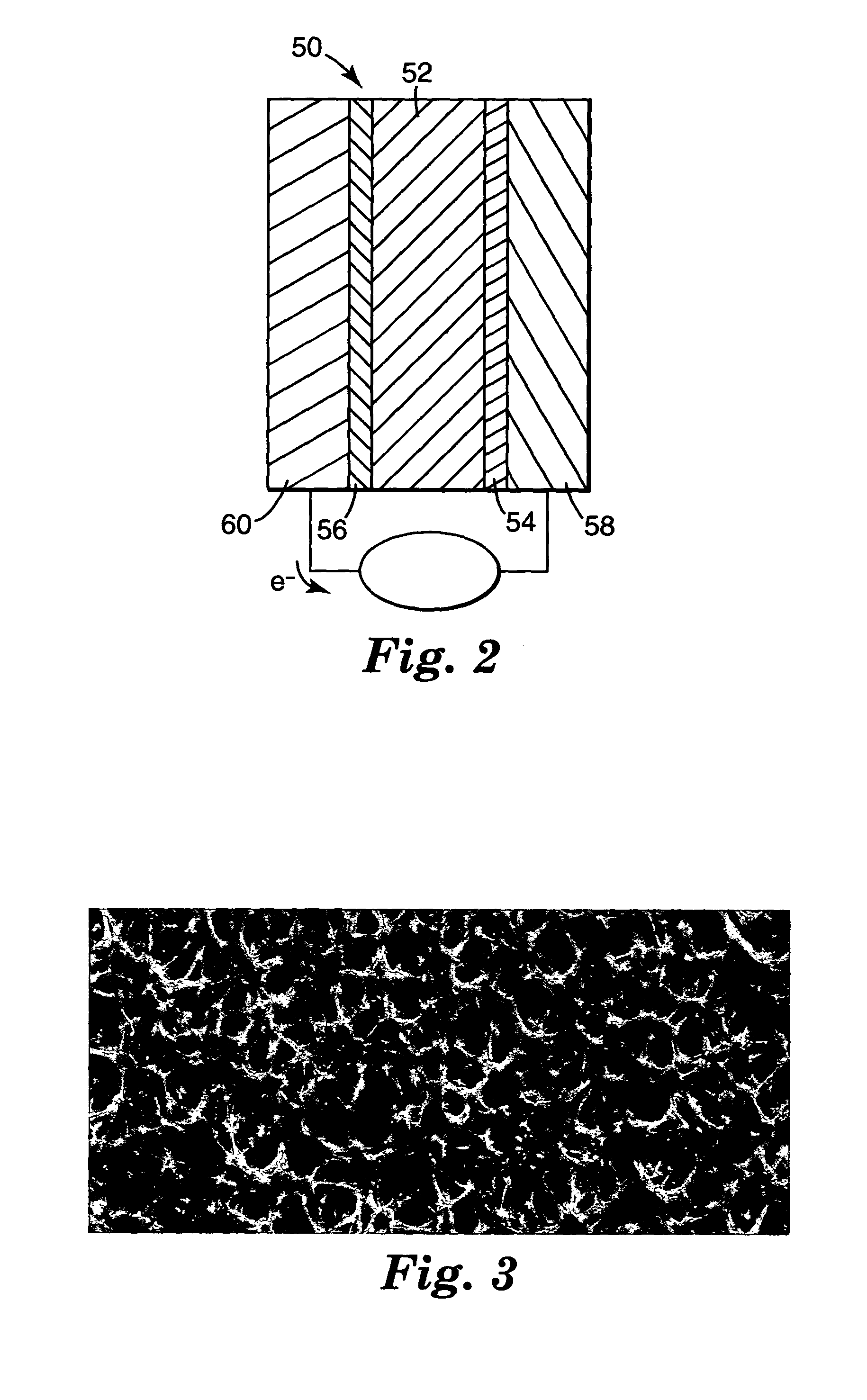
InactiveUS20080140152A1Easy to manufactureStrong specificitySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesDielectricFlexible circuits
Devices, systems and methods are provided for stimulation of tissues and structures within a body of a patient. In particular, implantable leads are provided which are comprised of a flexible circuit. Typically, the flexible circuit includes an array of conductors bonded to a thin dielectric film. Example dielectric films include polyimide, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) or other biocompatible materials to name a few. Such leads are particularly suitable for stimulation of the spinal anatomy, more particularly suitable for stimulation of specific nerve anatomies, such as the dorsal root (optionally including the dorsal root ganglion).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
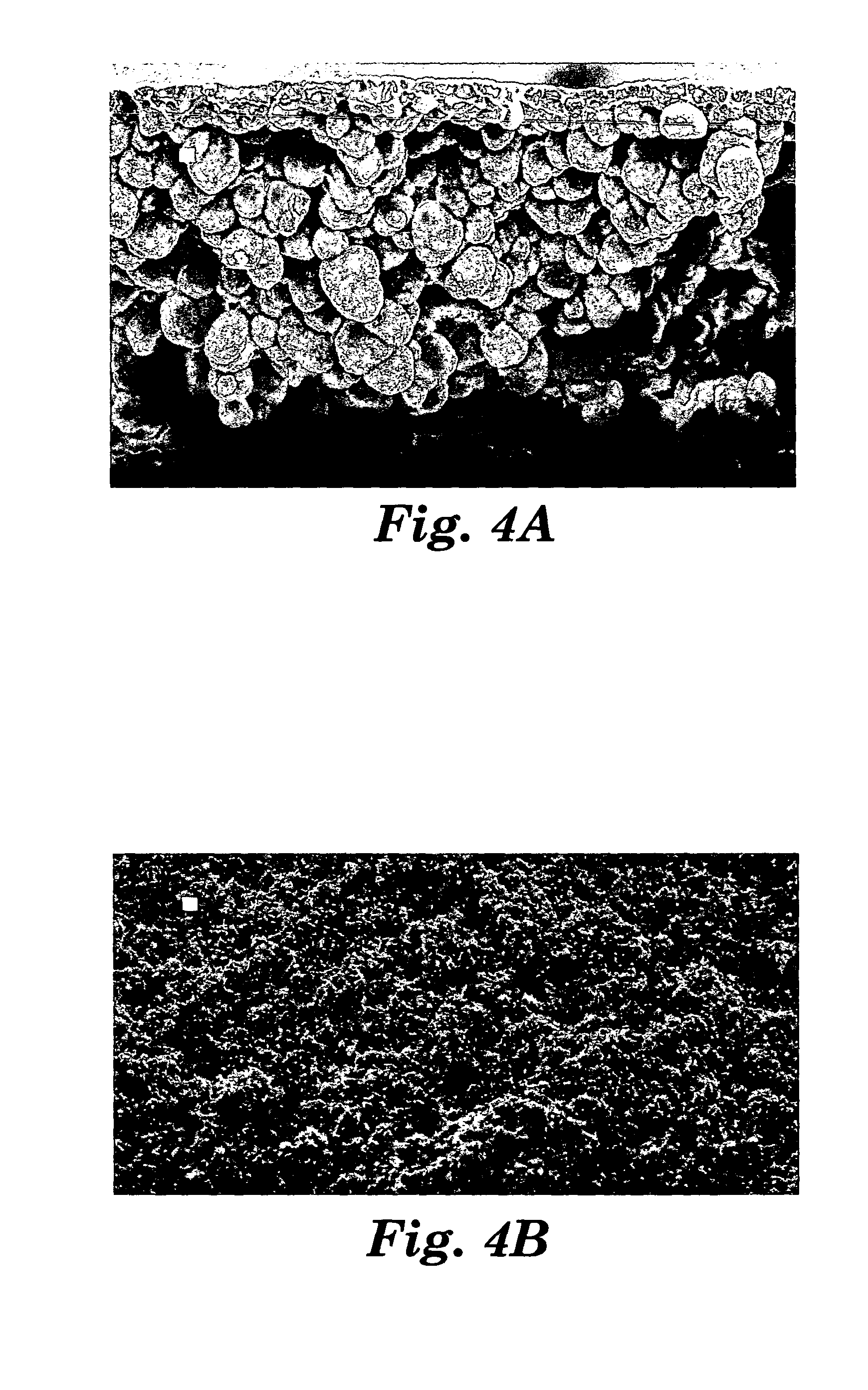
Microporous PVDF films
Shaped microporous articles are produced from polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and nucleating agents using thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) processes. The shaped microporous article is oriented in at least one direction at a stretch ratio of at least approximately 1.1 to 1.0. The shaped article may also comprise a diluent, glyceryl triacetate. The shaped microporous article may also have the micropores filled with a sufficient quantity of ion conducting electrolyte to allow the membrane to function as an ion conductive membrane. The method of making a microporous article comprises the steps of melt blending polyvinylidene fluoride, nucleating agent and glyceryl triacetate; forming a shaped article of the mixture; cooling the shaped article to cause crystallization of the polyvinylidene fluoride and phase separation of the polyvinylidene fluoride and glyceryl triacetate; and stretching the shaped article in at least one direction at a stretch ratio of at least approximately 1.1 to 1.0.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Microporous PVDF films and method of manufacturing
Shaped microporous articles are produced from polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and nucleating agents using thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) processes. The shaped microporous article is oriented in at least one direction at a stretch ratio of at least approximately 1.1 to 1.0. The shaped article may also comprise a diluent, glyceryl triacetate. The shaped microporous article may also have the micropores filled with a sufficient quantity of ion conducting electrolyte to allow the membrane to function as an ion conductive membrane. The method of making a microporous article comprises the steps of melt blending polyvinylidene fluoride, nucleating agent and glyceryl triacetate; forming a shaped article of the mixture; cooling the shaped article to cause crystallization of the polyvinylidene fluoride and phase separation of the polyvinylidene fluoride and glyceryl triacetate; and stretching the shaped article in at least one direction at a stretch ratio of at least approximately 1.1 to 1.0.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Aqueous polyvinylidene fluoride composition
ActiveUS20100304270A1Dry fastUseful electrodeLiquid electrolytic capacitorsConductive materialInterconnectivityPolyvinylidene difluoride
The invention relates to an aqueous fluoropolymer, and preferably polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), composition for manufacturing electrodes for use in non-aqueous-type electrochemical devices, such as batteries and electric double layer capacitors. The composition contains aqueous PVDF binder, and one or more powdery electrode-forming materials. In one embodiment, the composition is free of fluorinated surfactant In another embodiment, one or more fugitive adhesion promoters are added. The electrode formed from the composition of the invention exhibits interconnectivity and irreversibility that is achieved from the use of aqueous PVDF binder.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Method of fabricating a lithium ion secondary battery
To provide a process for producing a lithium ion secondary battery which can have any arbitrary shape, such as thin shape, and yet exhibits high performance. In a method of fabricating a battery comprising a positive electrode 1, a negative electrode 4, and a separator 7, a binder resin solution mainly comprising polyvinylidene fluoride is applied to the separator 7, and the positive electrode 1 and the negative electrode 4 are laid thereon, followed by drying to form a battery laminate, which is then impregnated with an electrolytic solution.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
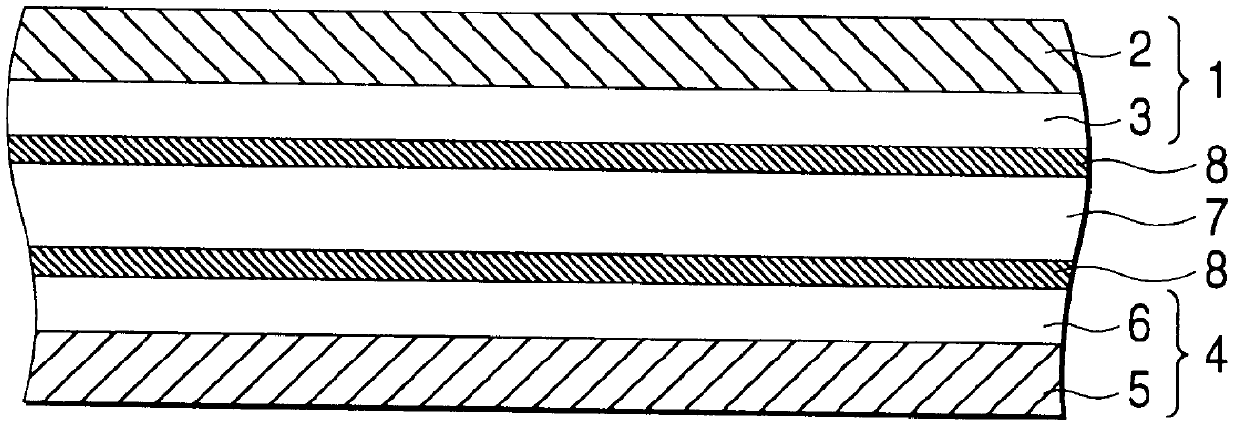
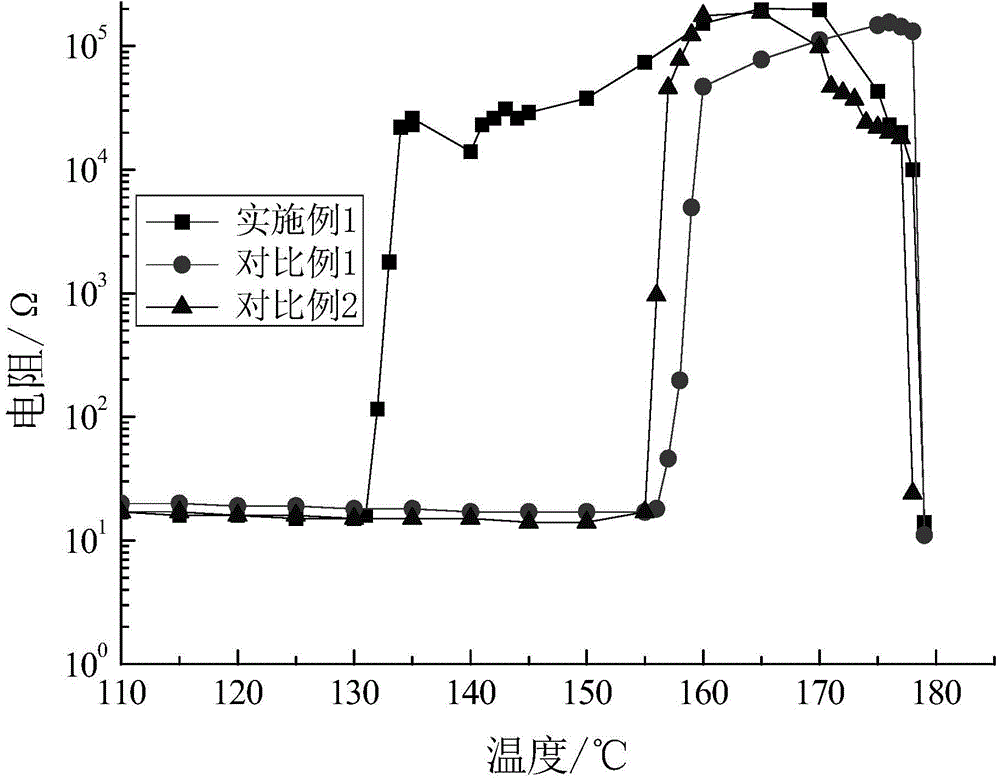
Ceramic-gel polymer multilayer composite lithium battery diaphragm and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104157819AImprove thermal safetyImprove wettabilitySecondary cellsCell component detailsCompound aSlurry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a ceramic-gel polymer multilayer composite lithium battery diaphragm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing aqueous PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) slurry and aqueous ceramic slurry; 2, thermally compounding a polypropylene diaphragm and a polyethylene diaphragm at 50-100 DEG C to obtain PP / PE (polypropylene / polyethylene) composite diaphragm; 3, with the PP / PE composite diaphragm obtained in the step 2 as a coating substrate, coating the aqueous slurry prepared in the step 1 onto the PE surface of the substrate: coating the aqueous ceramic slurry to form a ceramic layer first and then coating the aqueous PVDF slurry to form a gel polymer layer, with the coating speed of 5-100m / min, and drying in a drying box with the temperature of 30-100 DEG C to obtain a final four-layer composite diaphragm. The invention further discloses a ceramic-gel polymer multilayer composite lithium battery diaphragm prepared by the preparation method. The prepared ceramic-gel polymer multilayer composite lithium battery diaphragm has the advantages of high thermal safety and high capability of keeping electrolyte.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENIOR TECH MATERIAL
Large-capacity high power polymer ferric lithium phosphate power cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101409369AImprove securityIncrease capacityElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureSlurryElectric vehicle
The invention discloses a large-capacity high-power polymer lithium iron phosphate power battery. The weight ratio of anode slurry is as follows: 81 to 85 percent of lithium iron phosphate, 1 to 5.5 percent of superconduction carbon, 0 to 2.5 percent of conductive carbon soot, 0 to 4 percent of conductive black lead, 0 to 2.5 percent of crystalline flake graphite, 0 to 2 percent of carbon nanometer tube as well as 6 to 7.5 percent of polyvinylidene fluoride; the weight ratio of cathode slurry is as follows: 89 to 91 percent of cathode material, 1 to 3.5 percent of superconduction carbon, 0 to 2 percent of conductive carbon soot, 0 to 4 percent of conductive black lead, 2.5 to 3.5 percent of styrene-butadiene rubber as well as 1.5 to 2 percent of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose; the steps for preparing the battery are as follows: preparing slurry, coating the anode and the cathode, rolling and pressing a polar plate, transversely and separately cutting the polar plate, baking the polar plate, welding the polar ears of the anode and the cathode, preparing a battery cell, putting the electric core into a shell and sealing, baking the electric core, injecting liquid into the battery as well as forming the battery and dividing the volume of the battery. The invention relates to a lithium-ion secondary battery which can provide drive energies for electric tools, electric bicycles, motor cars and electric vehicles.
Owner:MCNAIR TECH
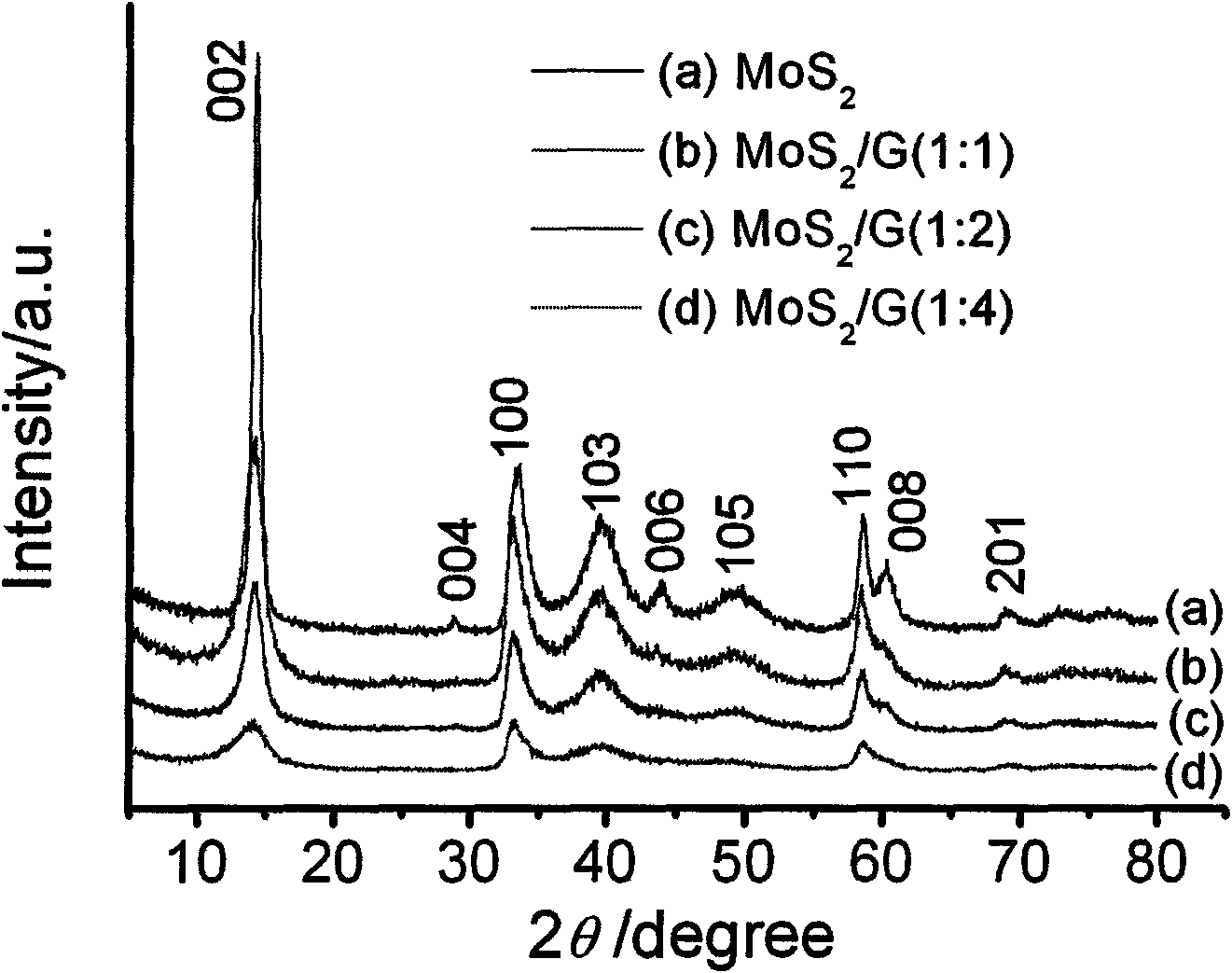
Graphene/MoS2 compound nano material lithium ion battery electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102142537ALarge specific surface areaImprove mechanical propertiesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLithium-ion batteryMaterials science
The invention discloses a graphene / molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) compound nano material lithium ion battery electrode and a preparation method thereof. The electrode comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 75 to 85 percent of compound nano material serving as an active substance, of a graphene nano slice and MoS2, and 5 to 10 percent of acetylene black and 10 percent of polyvinylidene fluoride; and the mass ratio of the graphene nano slice to the MoS2 nano material in the compound nano material active substance is (1 to 1)-(4 to 1). The preparation method of the electrode comprises the following steps of: preparing an oxidized graphite nano slice by using graphite as a raw material by a chemical oxidization method; synthesizing by a one-step hydrothermal in-situ reduction method in the presence of the oxidized graphite nano slice to obtain a graphene nano slice / MoS2 compound nano material; and finally, preparing the electrode by using the graphene nano slice / MoS2 compound nano material as the active substance. The electrode has high electrochemical lithium storage reversible capacity and cyclic stabilization performance, and can be widely applied to new generation lithium ion batteries.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
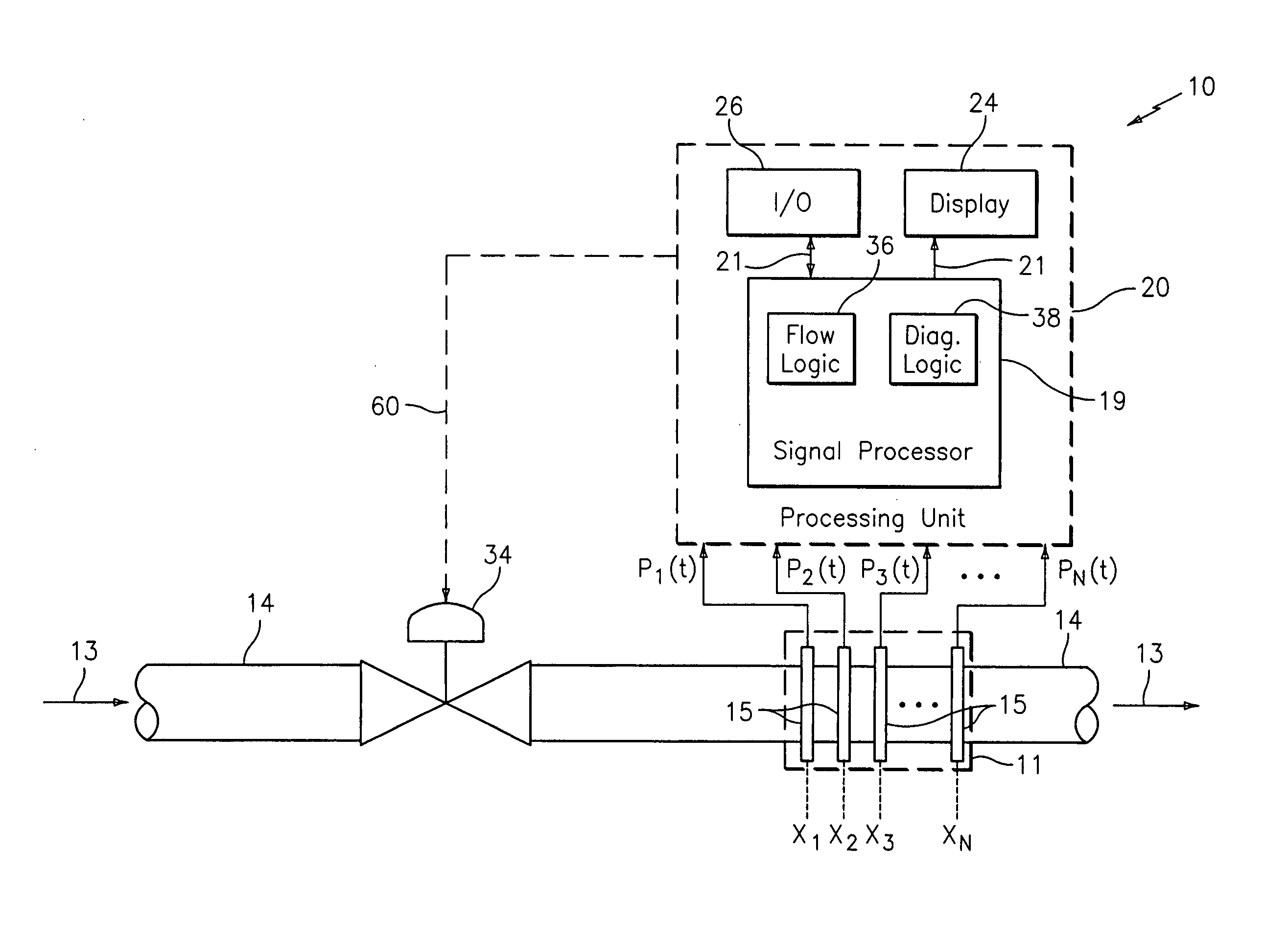
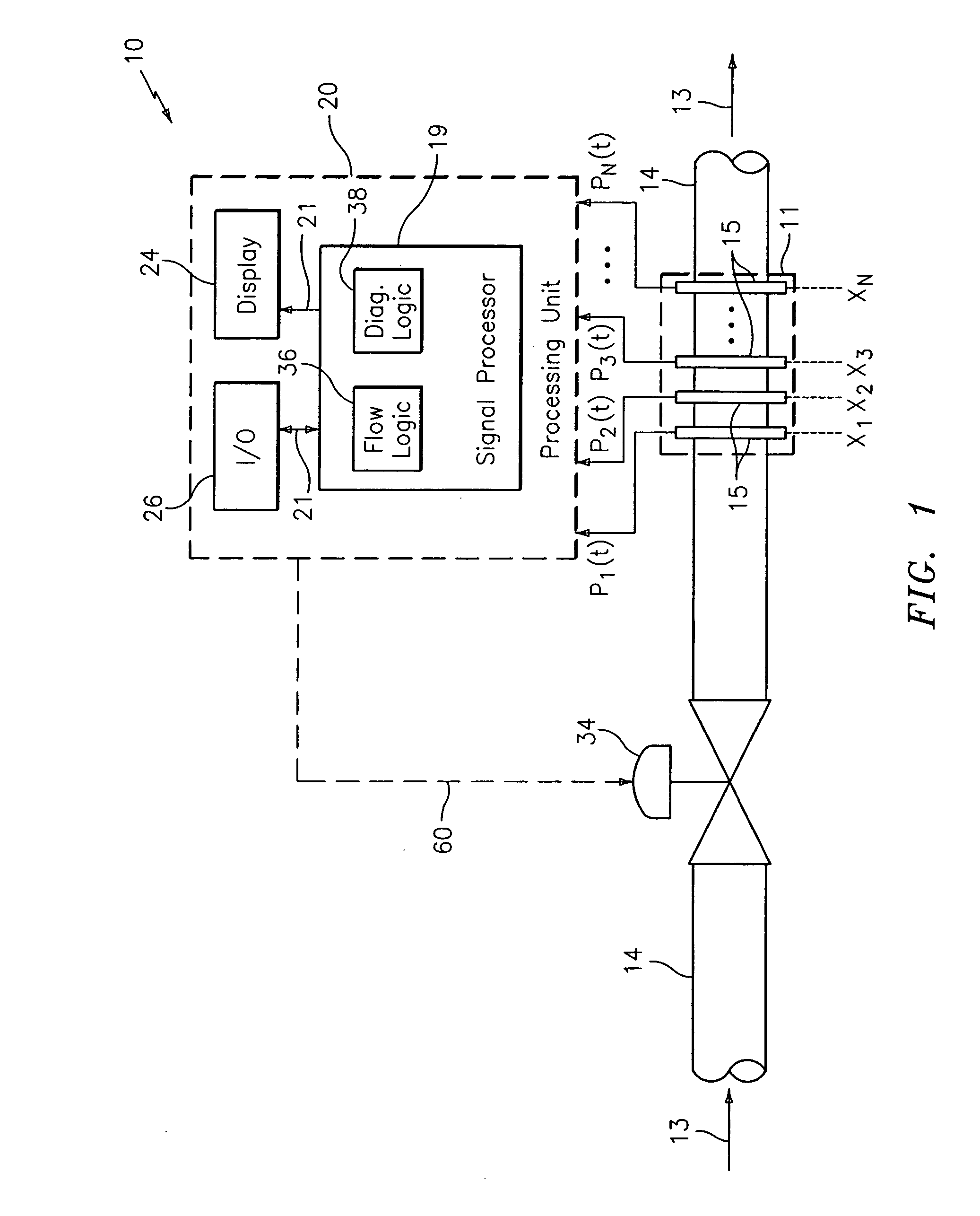
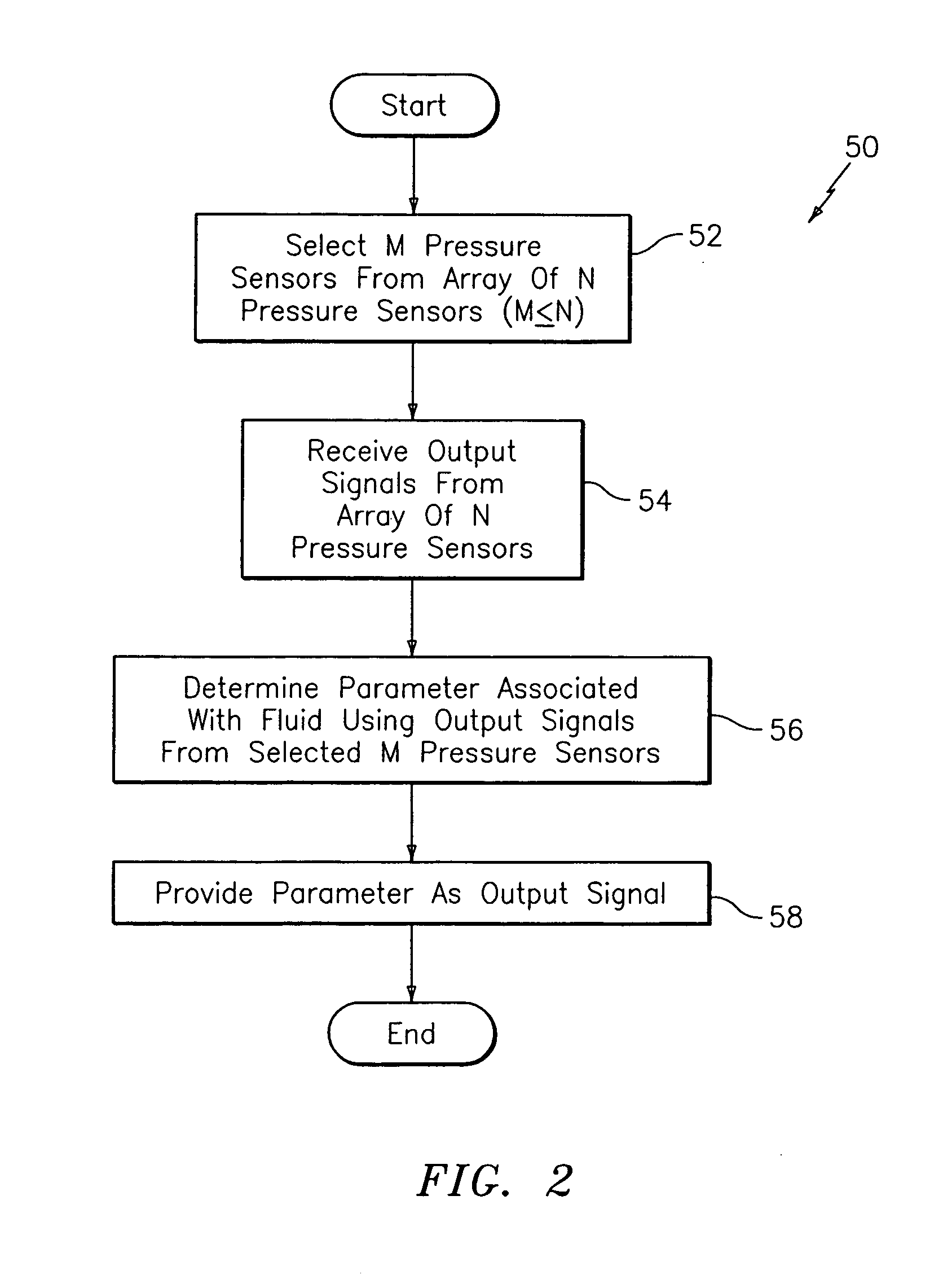
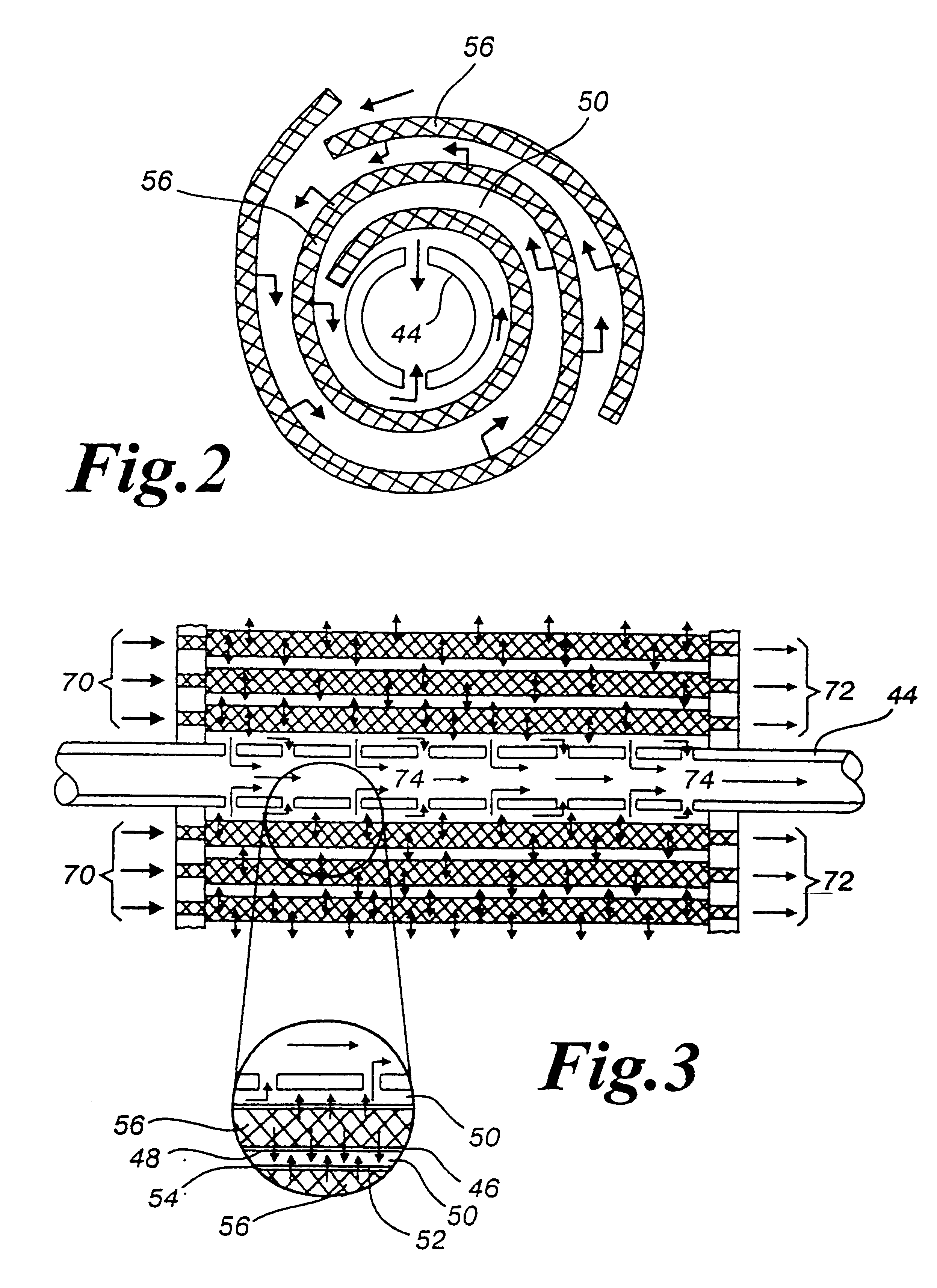
Method and apparatus for measuring parameters of a fluid flowing within a pipe using a configurable array of sensors
ActiveUS20050039520A1Detection of fluid at leakage pointMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSensor arrayEngineering
An apparatus for measuring at least one parameter associated with a fluid flowing within a pipe includes a spatial array of pressure sensors disposed at different axial locations x1. . . xN along the pipe. Each of the pressure sensors provides a pressure signal P(t) indicative of unsteady pressure within the pipe at a corresponding axial location of the pipe. A signal processor receives the pressure signals from each of the pressure sensors and determines the parameter of the fluid using pressure signals from selected ones of the pressure sensors. By selecting different pressure sensors, the signal processor can configure the array to meet different criteria. In one embodiment, the array of pressure sensors may be formed on a single sheet of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) that is wrapped around at least a portion of an outer surface of the pipe. This arrangement allows a large number of pressure sensors to be quickly and economically installed.
Owner:EXPRO METERS
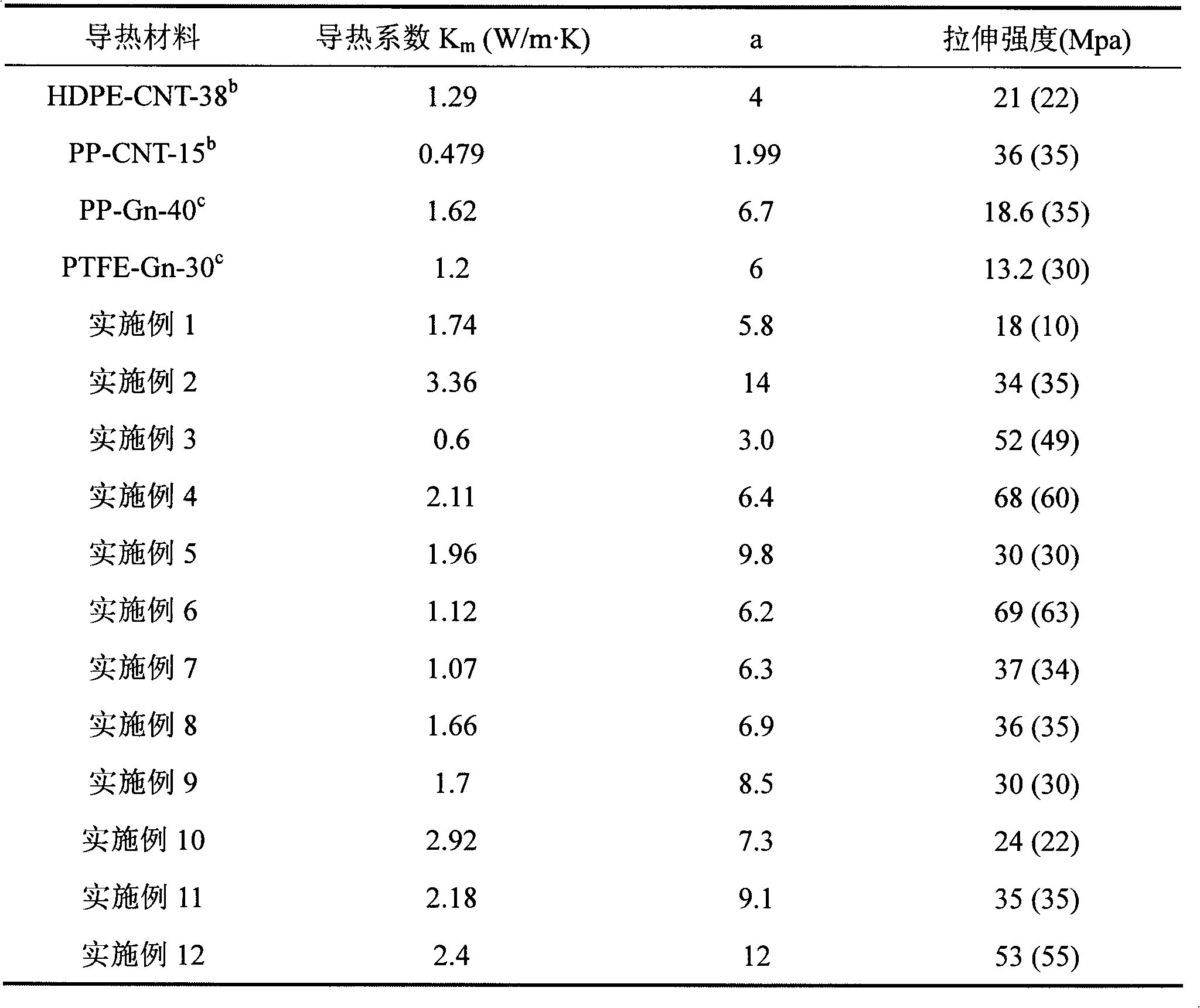
High-heat-conductivity composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102040761AImprove thermal conductivitySmall amount of thermally conductive fillerFiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a high-heat-conductivity composite material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: evenly mixing fibrous heat-conduction filler and high-heat-conductivity filler graphene in a mass ratio of 1:1-1:200 with thermoplastic polymer, dispersing for 0.5-24 hours, granulating to obtain high-heat-conductivity composite grains, and putting the grains in a die to carry out hot molding at 170-280 DEG C under the pressure of 10-18 MPa. The thermoplastic polymer is any one of polyethylene, polypropylene, polyvinylidene fluoride, polytetrafluoroethylene, polyperfluoroalkoxy ester, nylon, polymethyl methacrylate, polycarbonate and polyvinyl chloride. The fibrous heat-conduction filler is carbon fiber or carbon nanotube, and the high-heat-conductivity filler accounts for 5-35 wt% of the high-heat-conductivity composite material. The high-heat-conductivity composite material has the advantages of excellent heat-conduction property, low consumption of heat-conduction filler, favorable mechanical properties, simple preparation technique and low cost.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Modified membranes
InactiveUS20050029186A1Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesVinyl etherReverse osmosis
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Implantable flexible circuit leads and methods of use
InactiveUS9314618B2Easy to manufactureStrong specificitySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringDielectricAnatomical structures
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
Modified membranes
InactiveUS6884350B2Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesMembranesSemi-permeable membranesVinyl etherPolyamide
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
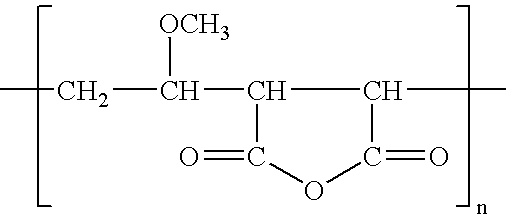
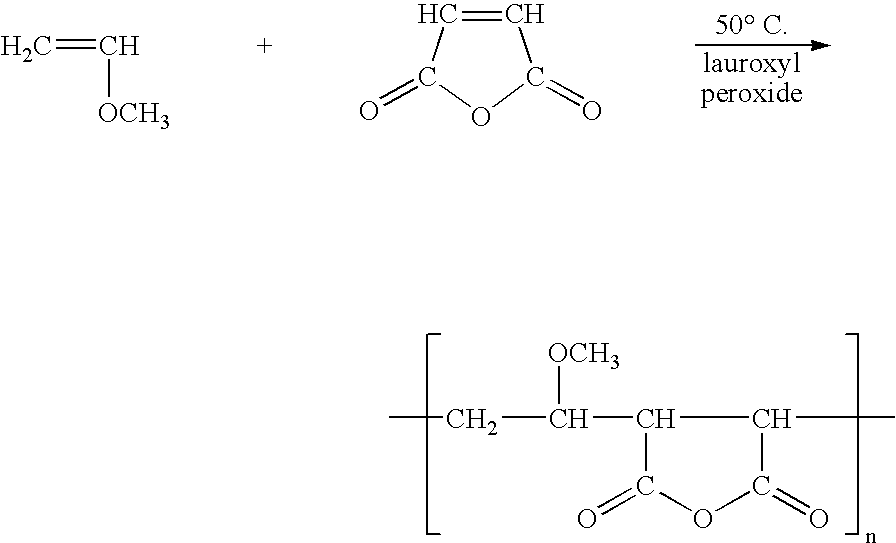
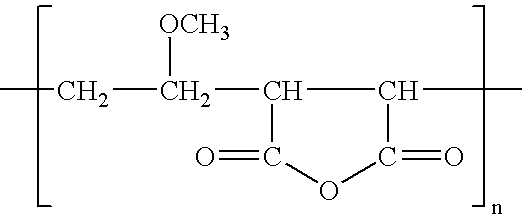
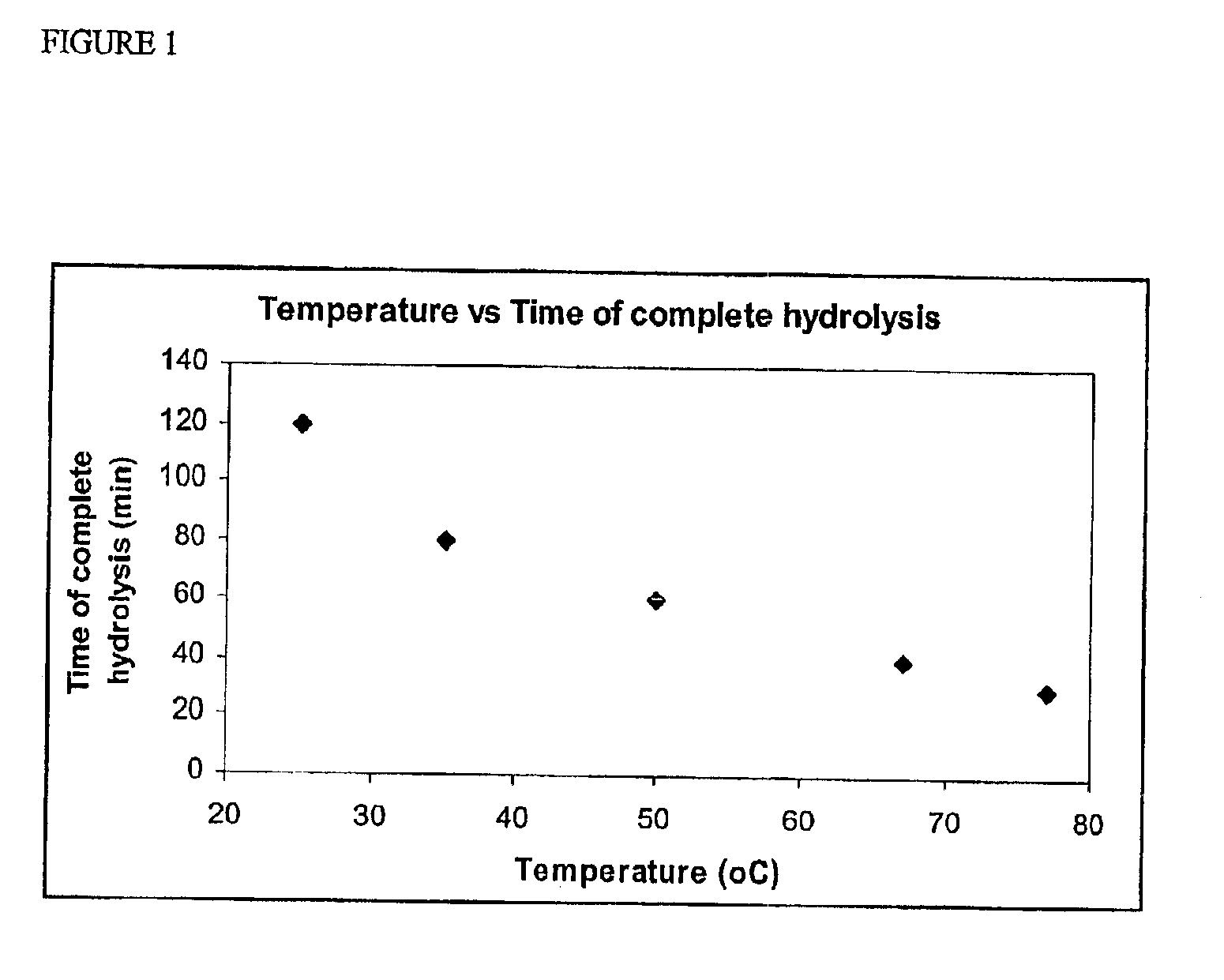
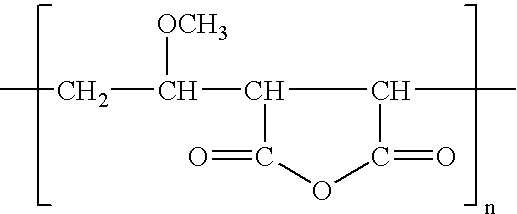
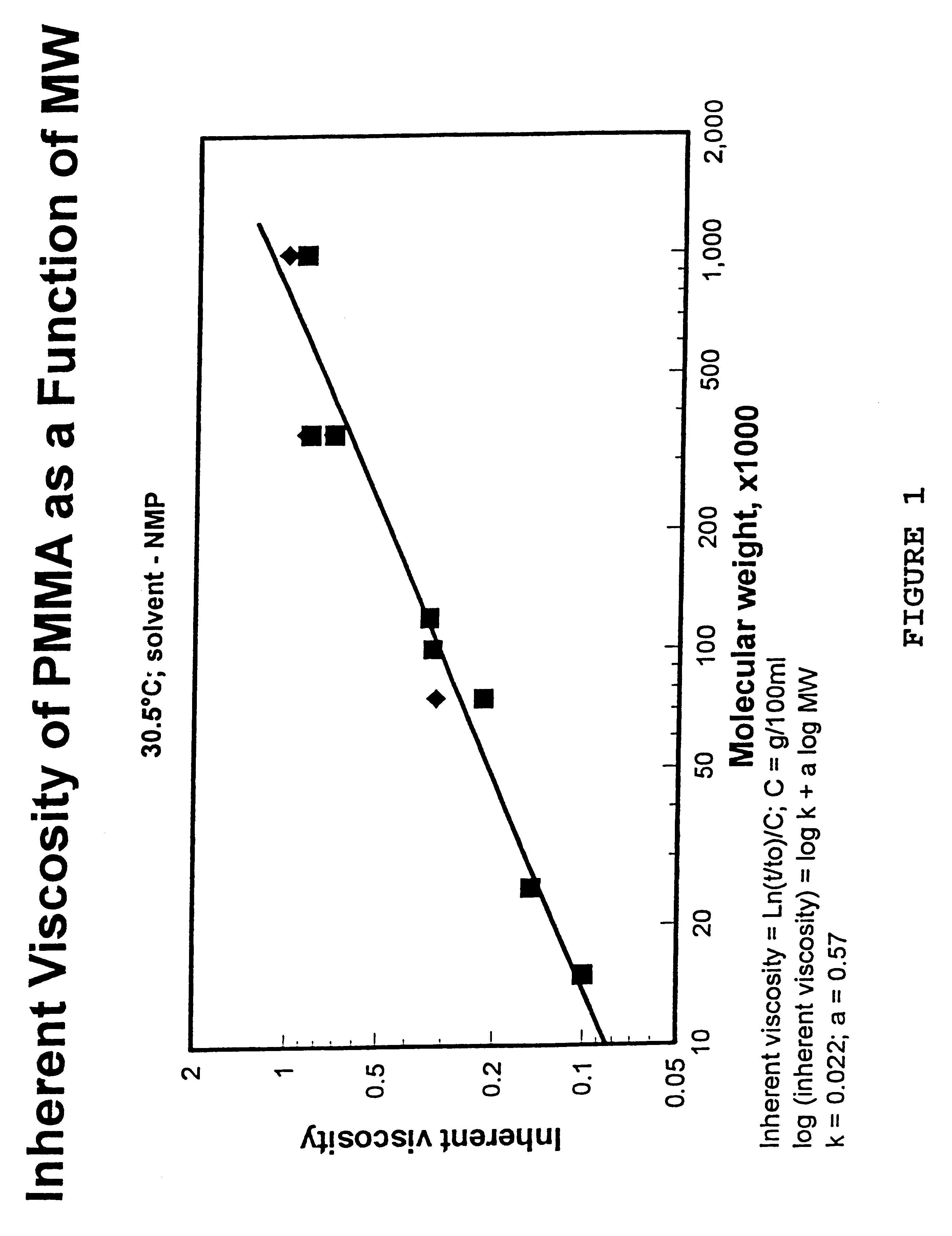
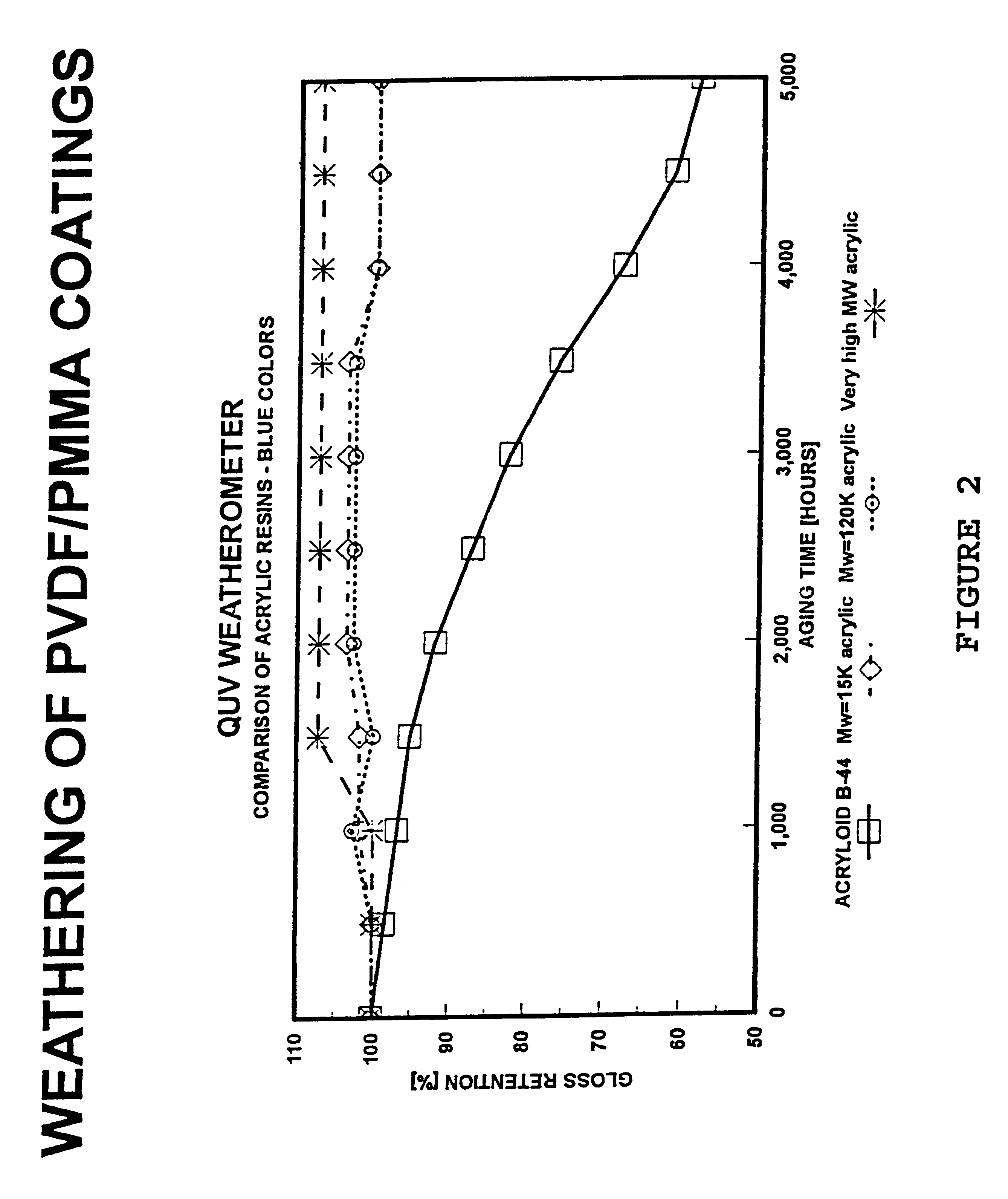
Polyvinylidene fluoride weather resistant coating compositions including polymethyl methacrylate
InactiveUS6362271B1Improve adhesionReduce the shrinkage of the polyvinylidene fluorideMixing methodsCoatingsMethacrylatePolymethyl methacrylate
A weather resistant coating composition comprising a miscible polymer blend of highly crystalline polyvinylidene fluoride polymer and polyalkyl methacrylate, such as PVDF and PMMA. The miscible blend comprises from about 50 weight percent to about 90 weight percent polymer comprising polyvinylidene fluoride and from about 10 weight percent to about 50 weight percent polyalkyl methacrylate. The polyalkyl methacrylate having a molecular weight within the range of about 25,000 grams per mole to about 200,000 grams per mole. The crystallinity of the polyvinylidene fluoride polymer is about 20% to about 70%. The weather resistant coating has excellent and unexpected physical characteristics, including solvent resistance and gloss retention.
Owner:SOLVAY SOLEXIS
Corneal optic formed of degradation resistant polymer
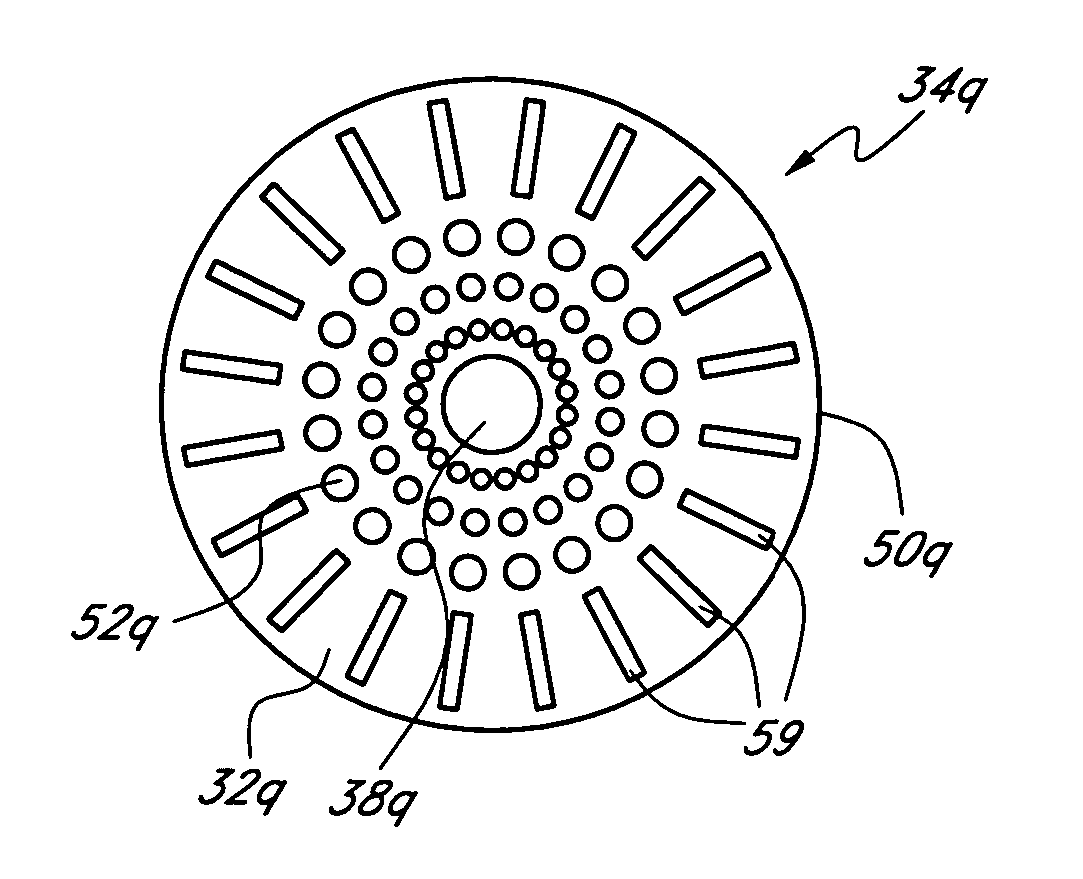
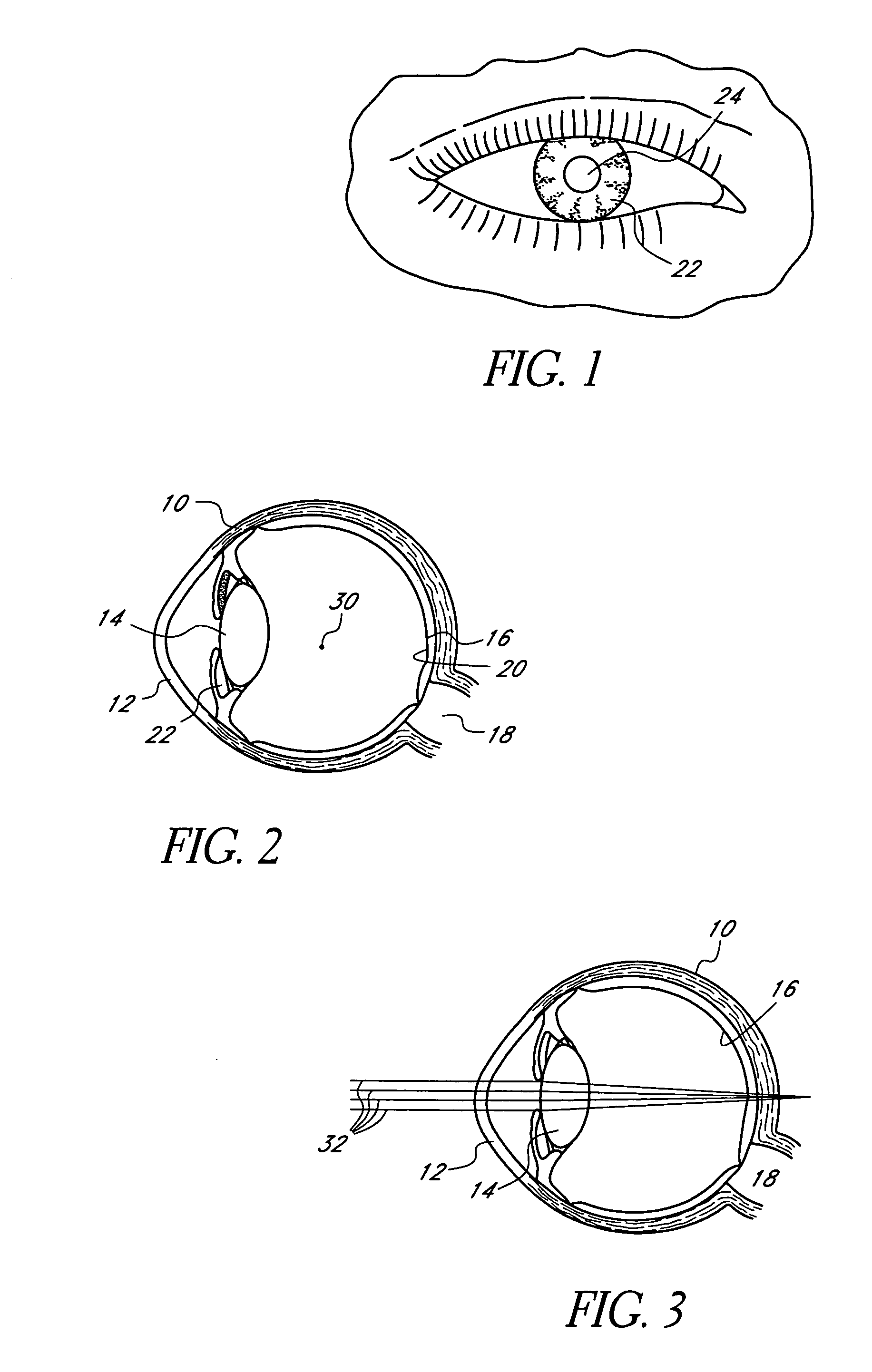
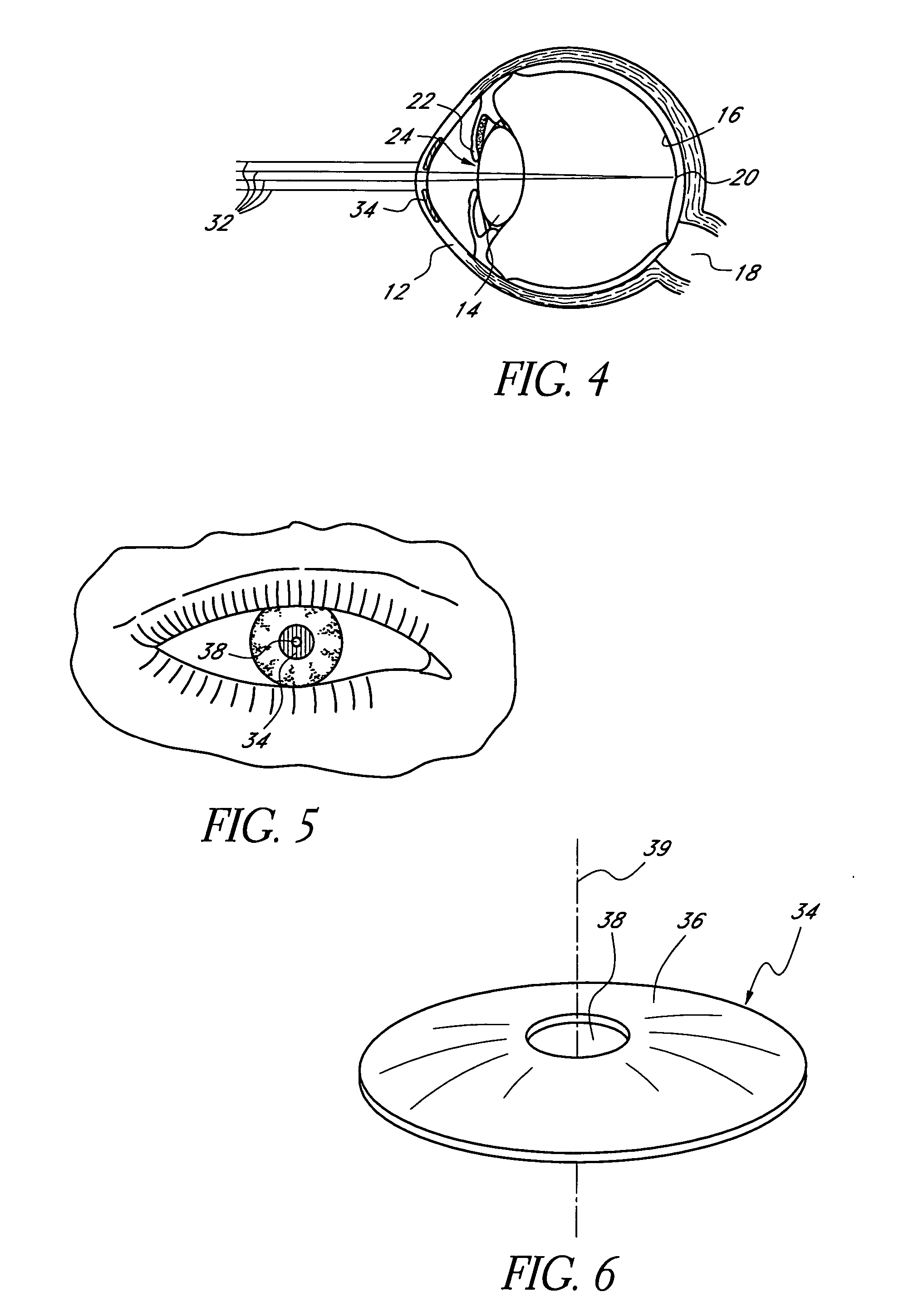
Disclosed are mask optics configured to be implanted in a cornea of a patient. In one embodiment, the body of the optic has a light transmitting portion, a light blocking portion disposed about the light transmitting portion, and an outer periphery surrounding the light blocking portion. The optic is adapted to reside between two intracorneal layers of a cornea. The mask optic may be formed from a material comprising a highly fluorinated polymeric material and an opacification agent. Preferred highly fluorinated polymeric materials include polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and preferred opacification agents include carbon. The highly fluorinated polymeric material is preferably resistant to degradation upon exposure to ultraviolet light.
Owner:ACUFOCUS
Composite thermotropic phase separation film-making method
The invention relates to a composite thermotropic phase isolated membrane preparation method which is characterized in that used composite diluent is the mixture of water-soluble good solvent and water-soluble additive of polymers. The membrane forming separation is a composite process which mainly takes the thermotropic membrane phase separation as the dominant role and non-solvent induced phaseseparation as the subsidiary role. The membrane prepared through the method has the advantages of high abruption strength, high abruption elongation and high water flux. The method is applicable to the preparation of membranes which are made of a plurality of polymers, including polyvinylidene fluoride, polysulfone, polyether sulfone, polyvinyl chloride and polyacrylonitrile. The performances of the membranes are improved greatly. Thus, the membranes can be widely applied to the fields of drinking water advanced treatment, pretreatment before reverse permeation, membrane bioreactor wastewatertreatment, reclaimed water reuse, etc.
Owner:湖南坎普尔环保技术有限公司
Novel solar battery backboard
ActiveCN101582458ANovel structureMaterials are readily availableSynthetic resin layered productsPhotovoltaic energy generationPolyurethane adhesiveAlloy
The invention relates to a novel solar battery backboard, which comprises the following components according to the adhesion in turn: a weathering layer, a first adhesive layer, a structure-enhancing layer, a second adhesive layer and an adhesive reflecting layer; wherein, the weathering layer is a polyvinylidene fluoride alloy layer modified by inorganic materials; the adhesive reflecting layer is a white polyethylene layer; preferably, the polyvinylidene fluoride alloy layer is a plastic alloy layer formed by the polyvinylidene fluoride and the inorganic materials with the thickness of 4-40 mum; the white polyethylene layer is a plastic alloy layer in which polyethylene is mixed with inorganic white pigment, anti-ultraviolet stabilizer and hot-oxygen ageing resistance stabilizer with the thickness of 10-300mum; the structure-enhancing layer is a polyethylene qlycol terephthalate layer; the first adhesive layer and the second adhesive layer can be one of the following three, namely, a polyurethane adhesive layer, an acrylic ester adhesive layer or an epoxy adhesive layer with the thickness of 1mum-30mum. The invention features novel structure, easily obtained materials, greatly reduced cost and good performance, conforms to the requirements of the backboard, and has important significance on solar energy industry.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIUV NEW MATERIALS
Modified membranes
InactiveUS20050032982A1Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesVinyl etherReverse osmosis
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:MULLER HEINZ JOACHIM
Multi-layer sheet having a weatherable surface layer
InactiveUS20060057392A1Synthetic resin layered productsElectrical equipmentPolymer scienceWeather resistance
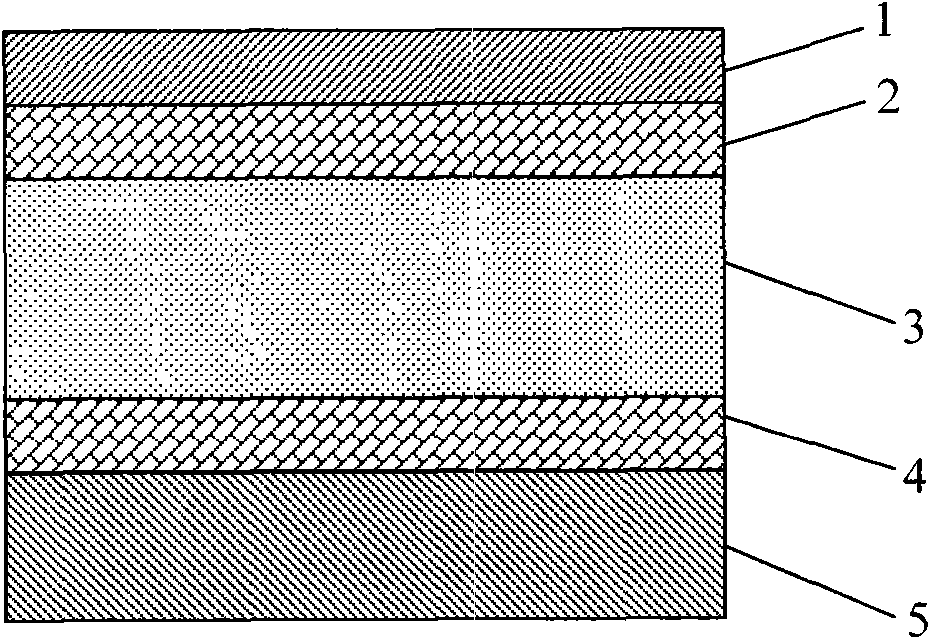
A multi-layer sheet and a process for producing the sheet are disclosed. The sheet can comprise a first polymer layer comprising a film of polyvinyl fluoride (PVF) or polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) having an adhesive coating on one side; second optionally pigmented polymer layer extruded onto the adhesive coating of the first polymer layer; and optionally a third polymer layer. Also a photovoltaic module comprising a prebonded backskin that comprises the multi-layer sheet.
Owner:PERFORMANCE MATERIALS NA INC
Modified membranes
InactiveUS20050029185A1Reduce dirtEssential mechanical properties of the membranesSemi-permeable membranesMembranesVinyl etherReverse osmosis
A porous polymeric membrane formed from a blend of a polymeric membrane forming material, such as polyvinylidene fluoride or polysulfone and a polymeric reactivity modifying agent adapted to modify the surface active properties of the porous polymeric membrane. The reactivity modifying agent is preferably a linear polymeric anhydride, such as poly(alkyl vinyl ether / maleic anhydride). The surface activity modifications include modification of the hydrophilicity / hydrophobicity balance of the membrane, or hydrolysis followed by reaction with a polyamine to form a crosslinked polyamide layer. Such modified membranes have use as reverse osmosis membranes.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
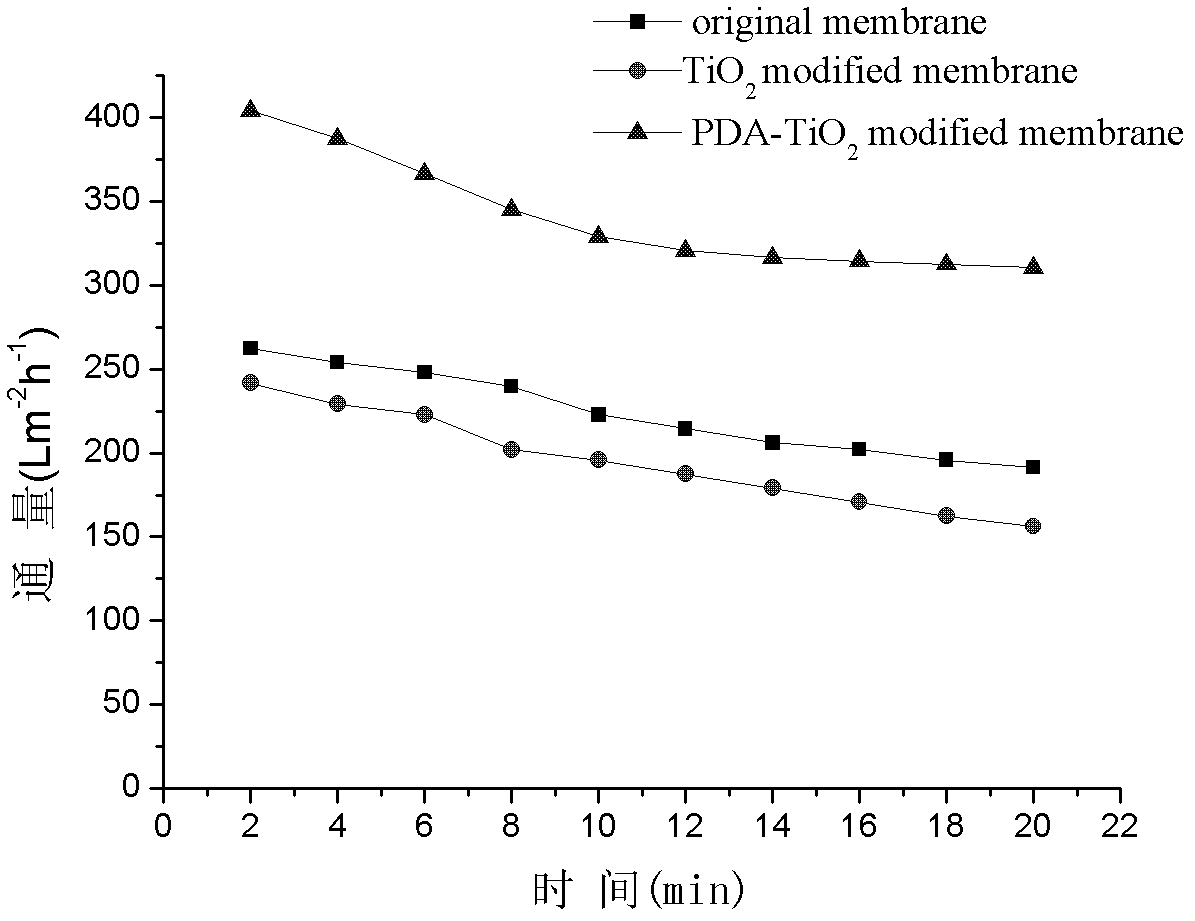
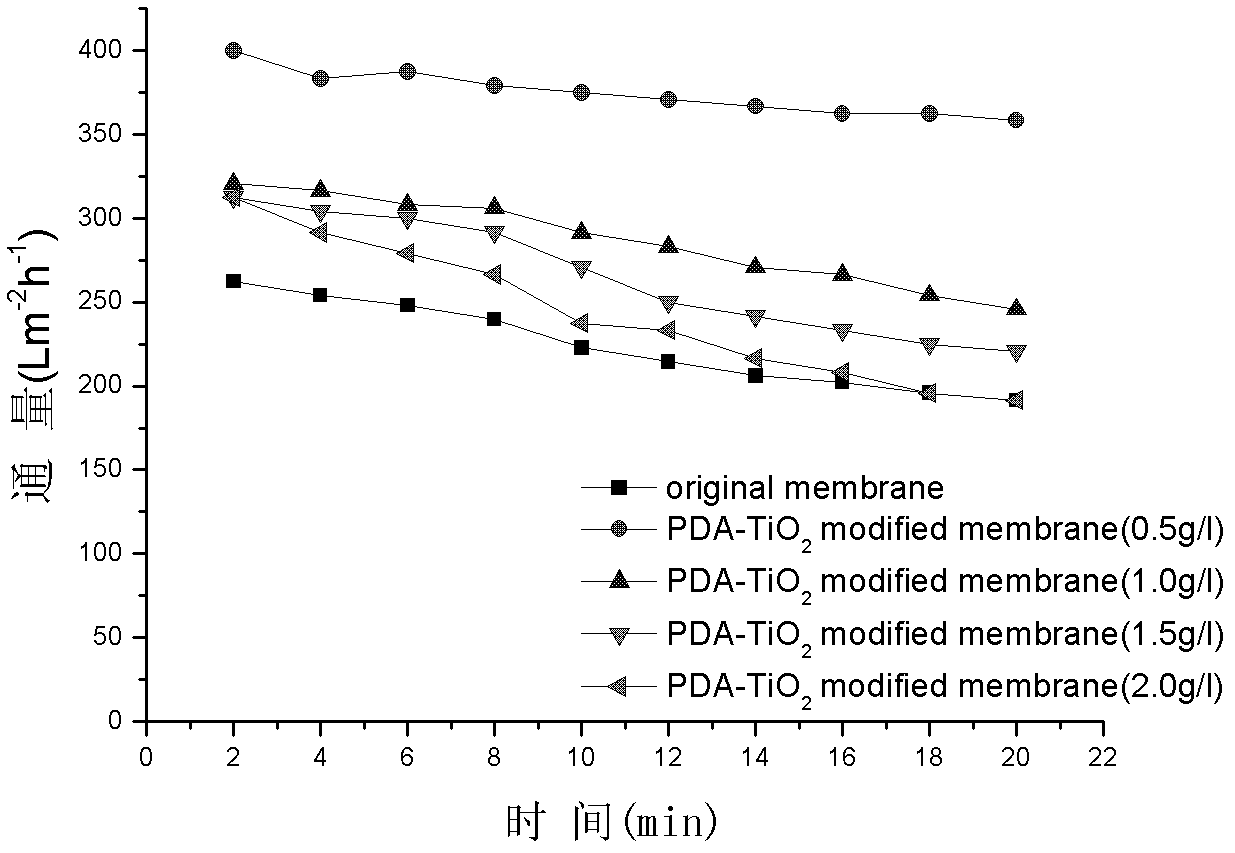
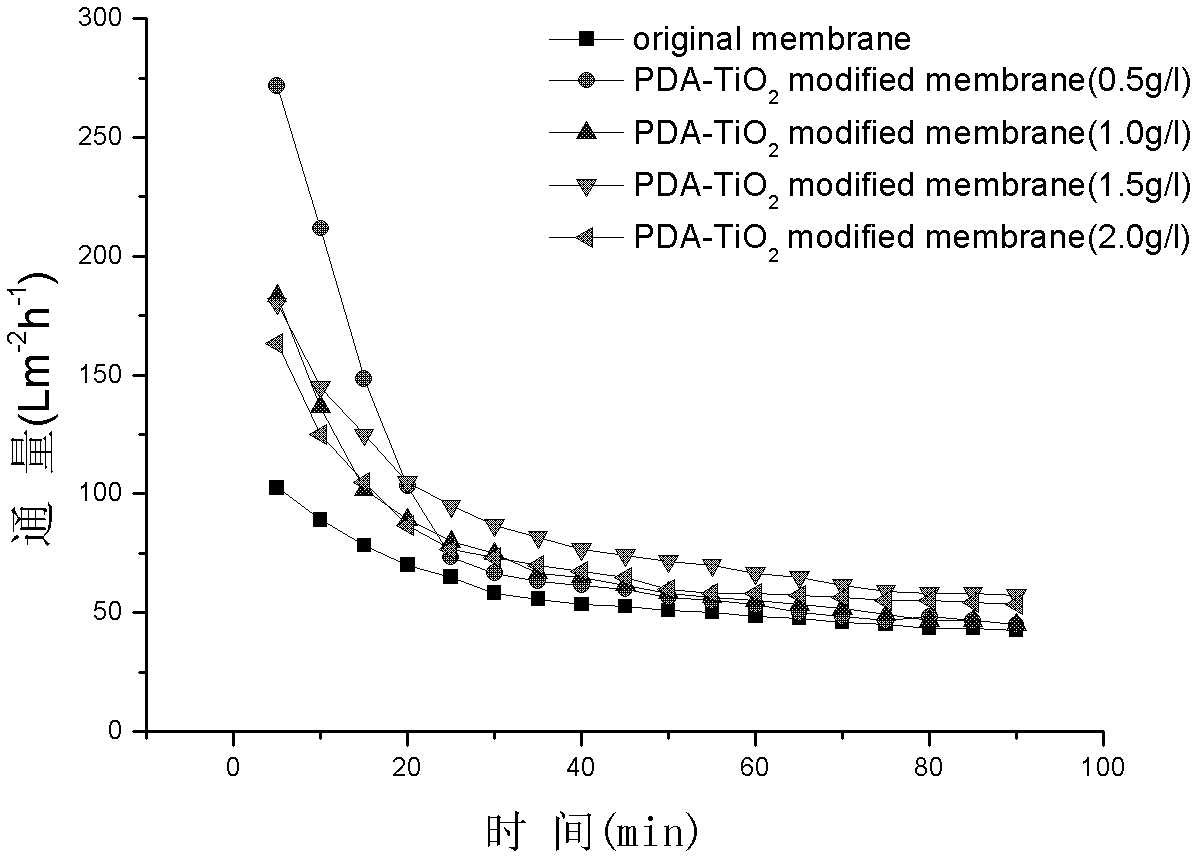
Method for preparing high-flux composite membrane from dopamine-modified nanometer material
InactiveCN102614783AImprove hydrophilicityImprove pollutionSemi-permeable membranesPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsOrganic solventHigh flux
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high-flux composite membrane from a dopamine-modified nanometer material and belongs to the technical field of modification of membrane materials. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: forming an active poly-dopamine composite layer on the surfaces of titanium dioxide nanometer grains by utilizing automatic polymerization of dopamine, selecting different concentrations of dopamine-modified titanium dioxide grains, and adding the modified nanometer grains utilized as additives into a membrane casting solution, in which the mass fraction of PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) is 13% and the mass fraction of PVP (Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone) is 4%, so as to bend and modify according to different proportions, thus obtaining a composite membrane prepared from dopamine-modified nanometer titanium dioxide. The method for preparing the high-flux composite membrane from the dopamine-modified nanometer material, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages that dopamine-modified titanium dioxide can be greatly dispersed in an organic solvent to form a uniform dispersed phase; the additive can be used for effectively improving the hydrophilcity and anti-pollution capability of the high-flux composite membrane; and the dopamine modification method is simple, the condition is gentle, the flux of the prepared membrane is large and the anti-pollution capability is strong.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Membrane polymer compositions
InactiveUS7226541B2Good chemical stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHexafluoropropylenePolyvinylidene difluoride
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
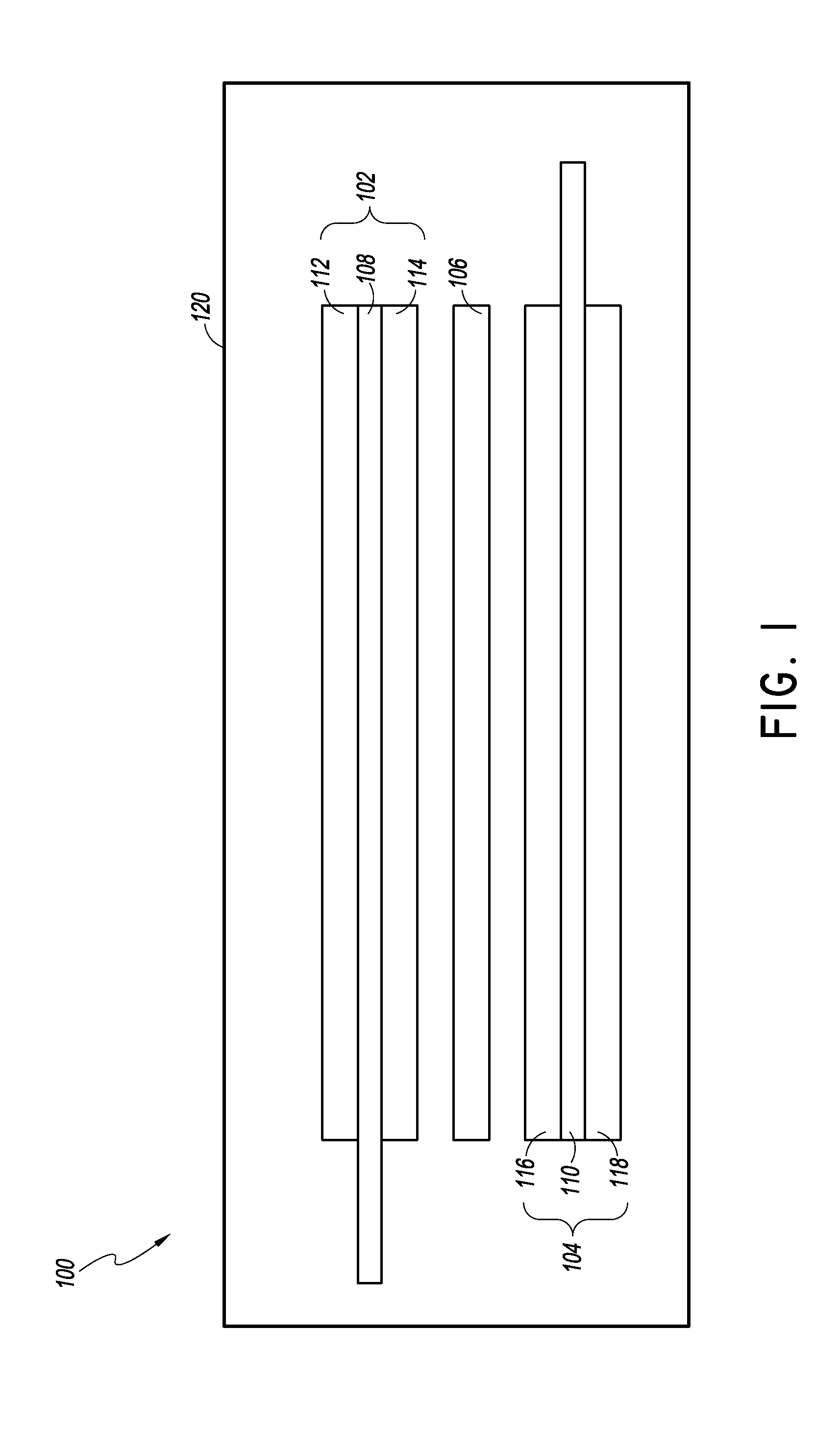
Dry energy storage device electrode and methods of making the same
ActiveUS20150303481A1Electrode rolling/calenderingSolid electrolytic capacitorsEthylene oxidePolyvinylidene difluoride
An energy storage device can include a cathode and an anode, where at least one of the cathode and the anode are made of a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) composite binder material including PTFE and at least one of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), a PVDF co-polymer, and poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO). The energy storage device can be a lithium ion battery, a lithium ion capacitor, and / or any other lithium based energy storage device. The PTFE composite binder material can have a ratio of about 1:1 of PTFE to a non-PTFE component, such a PVDF, PVDF co-polymer and / or PEO.
Owner:TESLA INC
Antimicrobial semi-permeable membranes
Cast semi-permeable membranes made from synthetic polymer used in reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration and microfiltration are treated with a non-leaching antimicrobial agent to prevent its bio-fouling and bacterial breakthrough. The semi-permeable membranes include a polymeric material and a non-leaching antimicrobial agent that is incorporated into and homogeneously distributed throughout the polymeric material. The polymeric material, in the case of one membrane, may be cellulose acetate. In the case of thin film composite polyamide membranes, the antimicrobial agent is incorporated in a microporous polysulfone layer that is sandwiched between a reinforcing fabric and an ultrathin polyamide material. The invention also includes a treatment of flat and hollow fiber semipermeable membranes made with polysulfones and polyvinylidene fluoride.
Owner:MICROBAN PROD CO INC
Method for preparing reticular fiber reinforced hollow fiber membrane of polyvinylidene fluoride
InactiveCN1864828AAperture size controllableStrong blast resistanceSemi-permeable membranesBursting strengthHollow fibre membrane
The invention discloses a method for preparing intensified netted hollow fiber membrane, belonging to technology for preparing hollow fiber membrane. The process comprises: taking polyvinylidene fluoride as membrane material, N,N-dimethyl formamide as disslovant, polyvinyl pyrrolidon as additive, preparing membrane liquid according to a certain proportion among them; textiling hollow fiber membrane under certain temperature, pressure and dragging speed; braiding net with synthetic fiber out of hollow fiber membrane, putting intensified hollow fiber membrane sequentially through membrane producing liquid and coagulating bath; coating and congealing under certain temperature, pressure and dragging speed, and getting final product. The invention is characterized in that there is no clogging, the flow resistance is small, stretching intensity amounts to 10-50 MPa, bursting strength is 0.5-1 MPa, and the process is continous and easy for industrialization.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
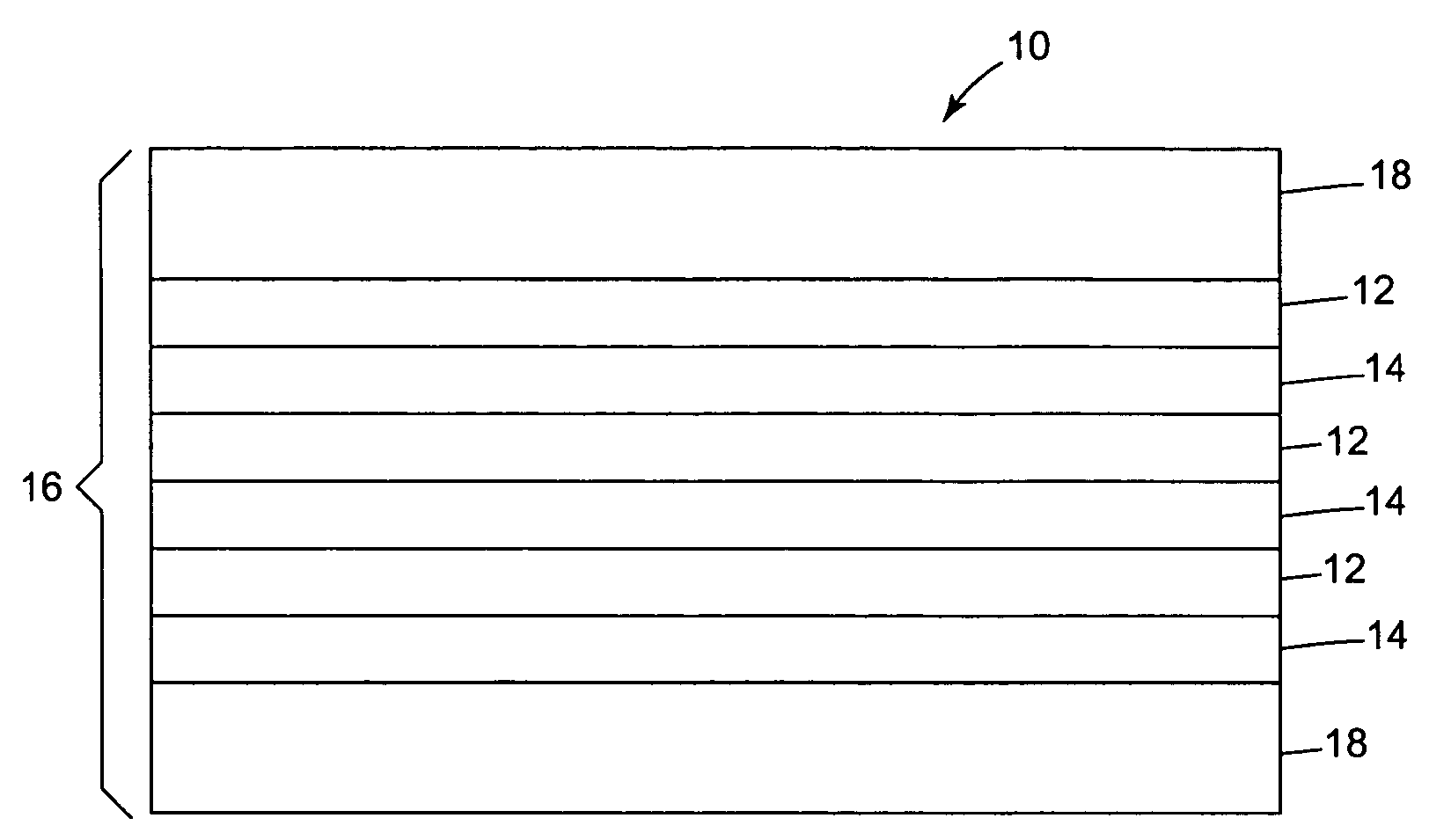
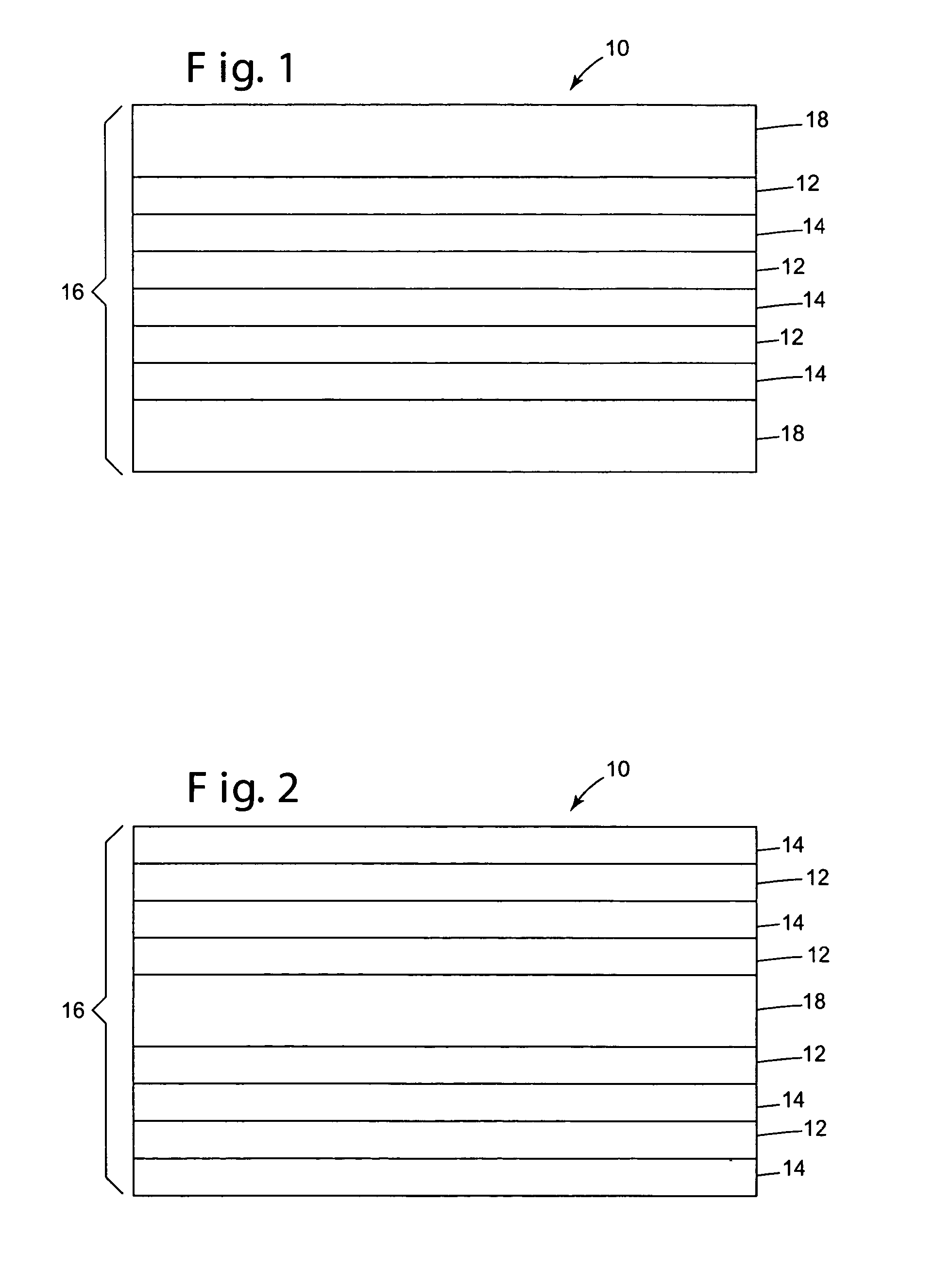
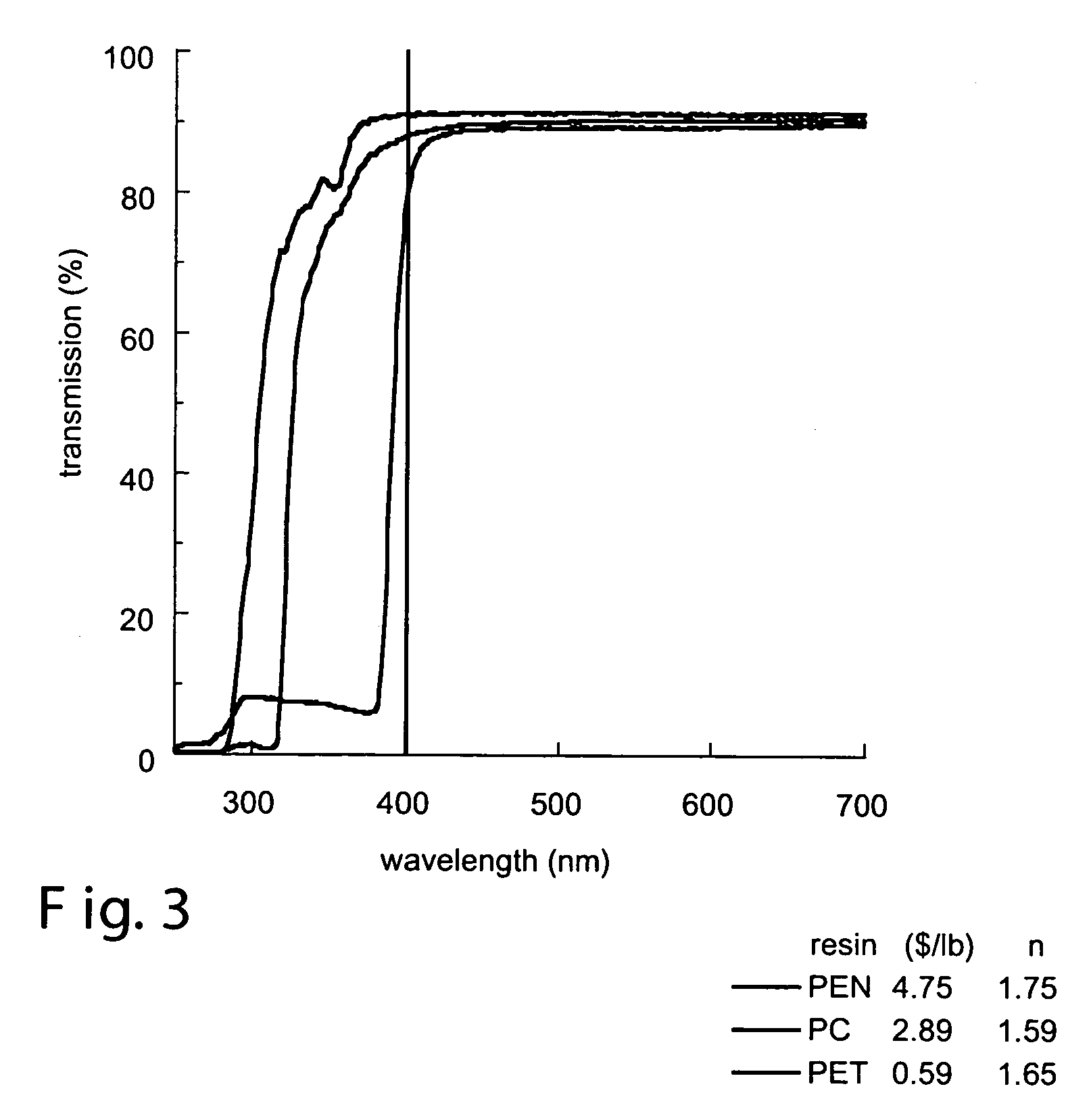
Multilayer optical bodies
Optical bodies, comprising: a plurality of first optical layers comprising a first polymer composition that comprises (i) a polyester portion having terephthalate comonomer units and ethylene glycol comonomer units; and(ii) a second portion corresponding to a polymer having a glass transition temperature of at least about 130° C.; and a plurality of second optical layers disposed in a repeating sequence with the plurality of first optical layers. Also disclosed are optical bodies comprising: (a) a plurality of first optical layers, each first optical layer being oriented; and (b) a plurality of second optical layers, disposed in a repeating sequence with the plurality of first optical layers, comprising a blend of polymethylmethacrylate and polyvinylidene fluoride. Methods of making the above-described optical bodies, and articles employing such optical bodies are also provided.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
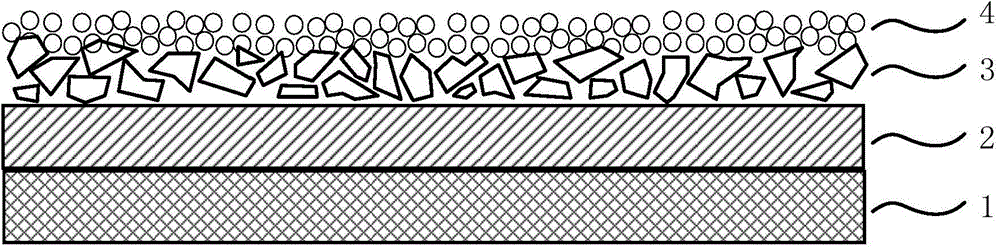
Composite diaphragm and method for preparing same
ActiveCN103515564AImprove thermal safetyImprove wettabilityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersPorosityAdhesive
The invention discloses a composite diaphragm which comprises a supporting layer and an organic / inorganic particle blended coating layer, laminated; the coating layer comprises a polymer particle and an inorganic particle, uniformly mixed in an adhesive; micropore structures are arranged on the surface and at the inner part of the coating layer; the porosity is 20%-80%; the aperture average is 0.01 to 10 micrometers; the polymer particle comprises one or more of polytetrafluoroethylene, polyvinylidene fluoride, polyvinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene copolymer, polyimide, polyacrylonitrile and aramid fiber resin; the particle size of the polymer particle is 0.01-10 micrometers; the inorganic particle comprises any one or more of SiO2, Al2O3, CaO, TiO2, MgO, ZnO, SnO2 and ZrO2; the particle size of the inorganic particle is 0.01-10 micrometers; the mass ratio of the polymer particle to the inorganic particle is (1:10) to (10:1). The invention further discloses a method for preparing the composite diaphragm. The composite diaphragm and the method have good thermal safety and strong in electrolyte absorption stiffness value, and meanwhile, and can achieve the advantages of low cost and low pollution.
Owner:SHENZHEN SENIOR TECH MATERIAL
Method for preparing polyvinylidene fluoride porous membrane
ActiveCN101362057AGuaranteed StrengthGuaranteed high water fluxSemi-permeable membranesMembranesHollow fibreFiber
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
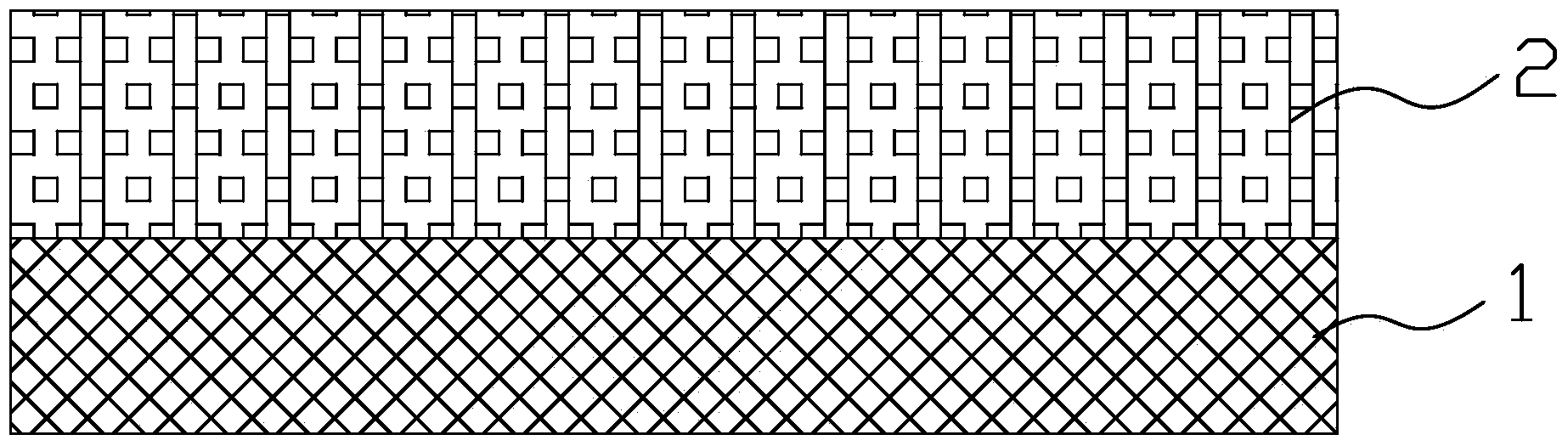
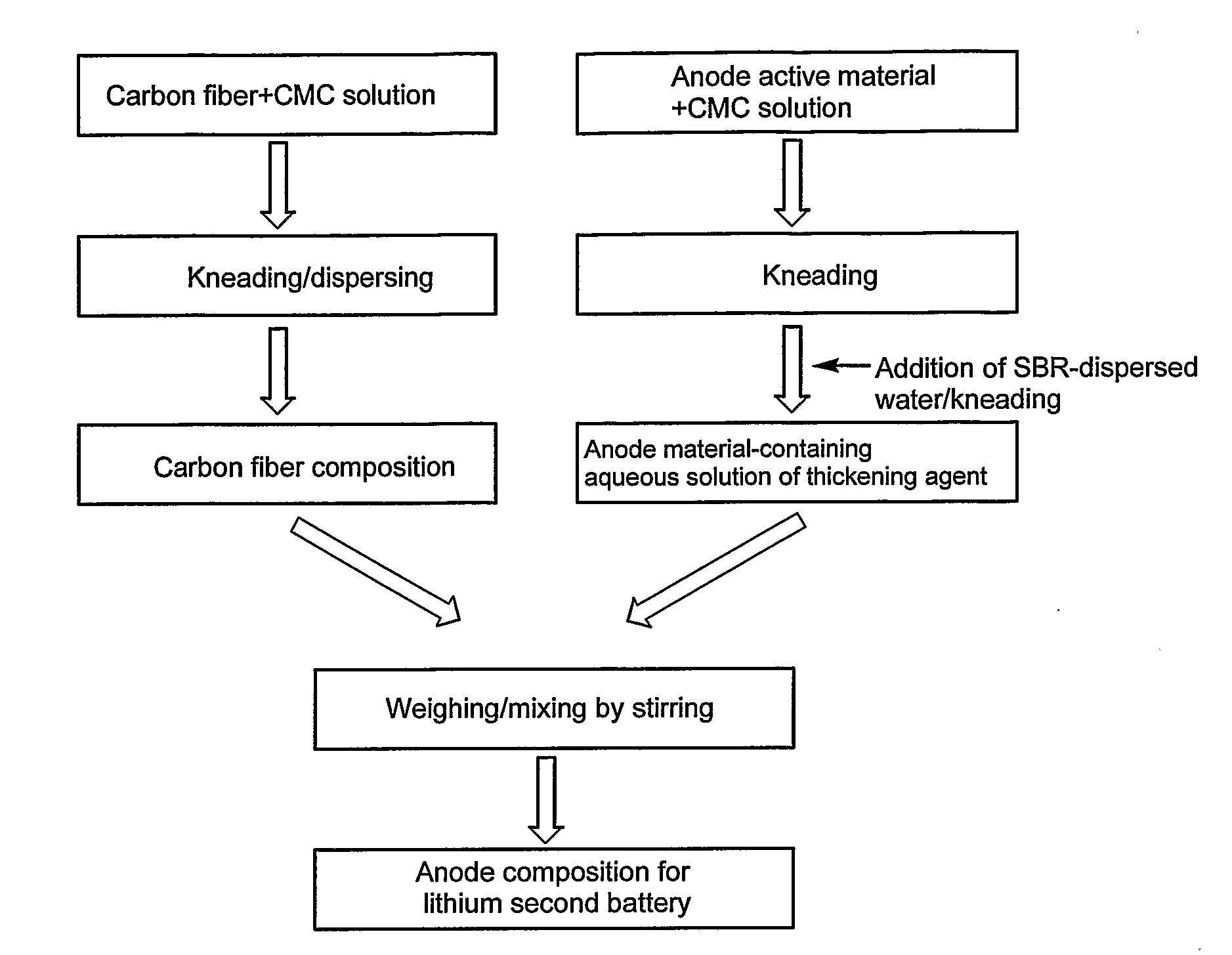
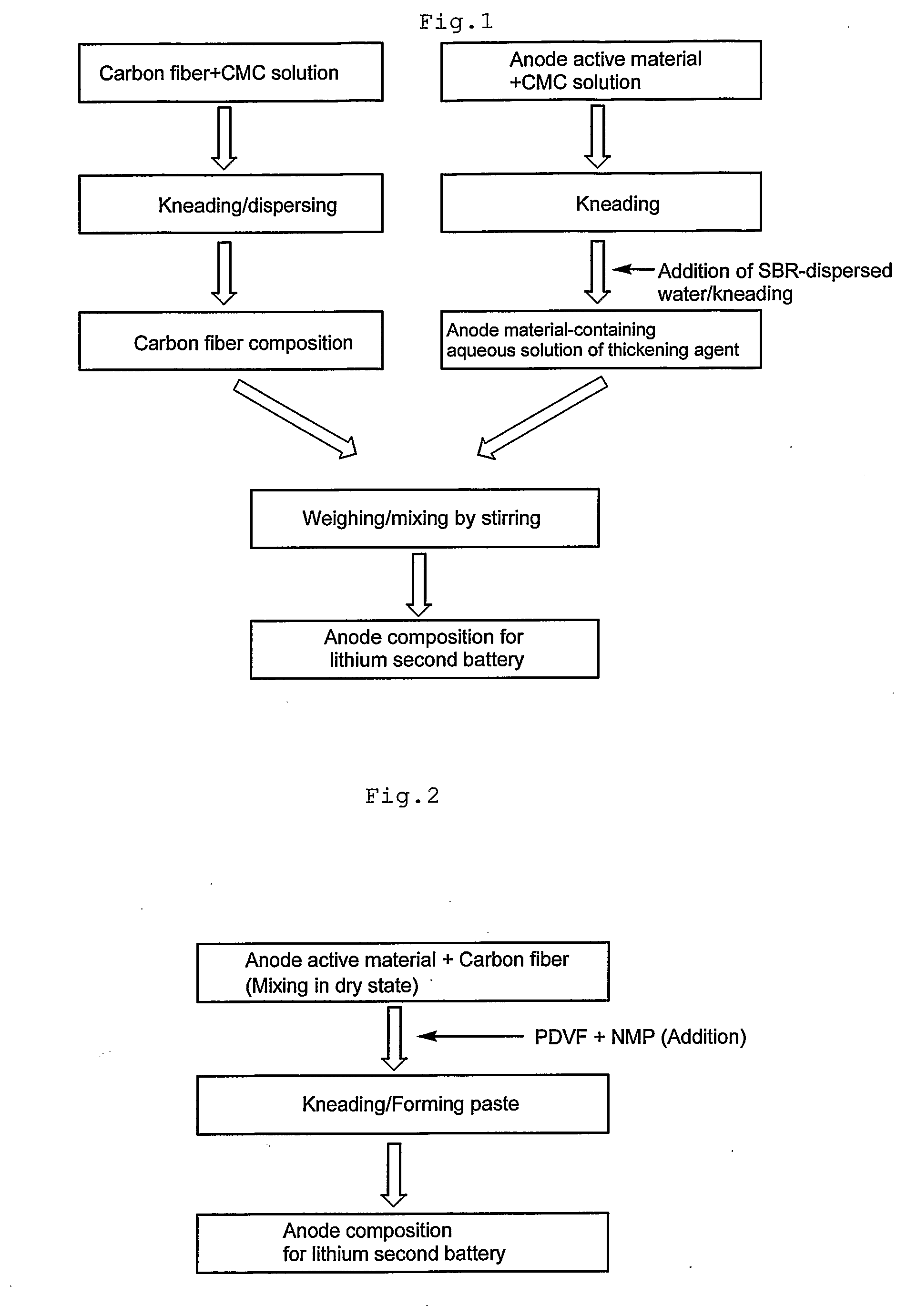
Method for producing anode for lithium secondary battery and anode composition, and lithium secondary battery
ActiveUS20090123850A1High capacity retentionImprove conductivityFinal product manufactureConductive materialFiberCarbon fibers
The invention relates to an anode for lithium secondary battery comprising vapor grown carbon fiber uniformly dispersed without forming an agglomerate of 10 μm or larger in an anode active material using natural graphite or artificial graphite, which anode is excellent in long cycle life and large current characteristics. Composition used for production for the anode can be produced, for example, by mixing a thickening agent solution containing an anode active material, a thickening agent aqueous solution and styrene butadiene rubber as binder with a composition containing carbon fiber dispersed in a thickening agent with a predetermined viscosity or by mixing an anode active material with vapor grown carbon fiber in dry state and then adding polyvinylidene difluoride thereto.
Owner:RESONAC CORP
Porous polyvinylidene blending porous membrane and process for producing same
InactiveCN101015773AAchieve hydrophilicImprove throughputSemi-permeable membranesSolventWater treatment
The invention discloses a plate-tubular porous membrane based on polyvinylidene fluoride mixture, and relative production. The membrane substantially comprises polyvinylidene fluoride, dual-block amphipathic epoxyethane, and inorganic particles. And the preparation comprises that mixing polyvinylidene fluoride, dual-block amphipathic epoxyethane, inorganic particles, aperture adjusting agent and polarity solvent to obtain the membrane preparing liquid, using said membrane preparing liquid into plate or tubular liquid membrane, immerging the liquid membrane into solidifying bath mainly comprising water to be solidified into plate or tubular membrane. And the apertures of plate membrane and tubular membrane are 0.01-5.0 and 0.01-0.2 micrometers. The hydrophilic chain section of amphipathic epoxyethane is abundant at the face or aperture walls of the membrane, while said two membranes are both better in hydrophilic property and permeable property, with significant resistance on organic adsorption, to be used as ultra-filter membrane and micro-filter membrane in membrane water treatment.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com