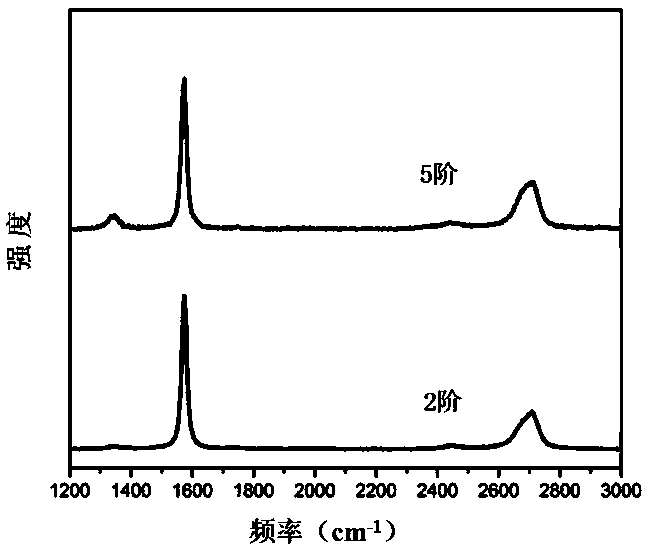
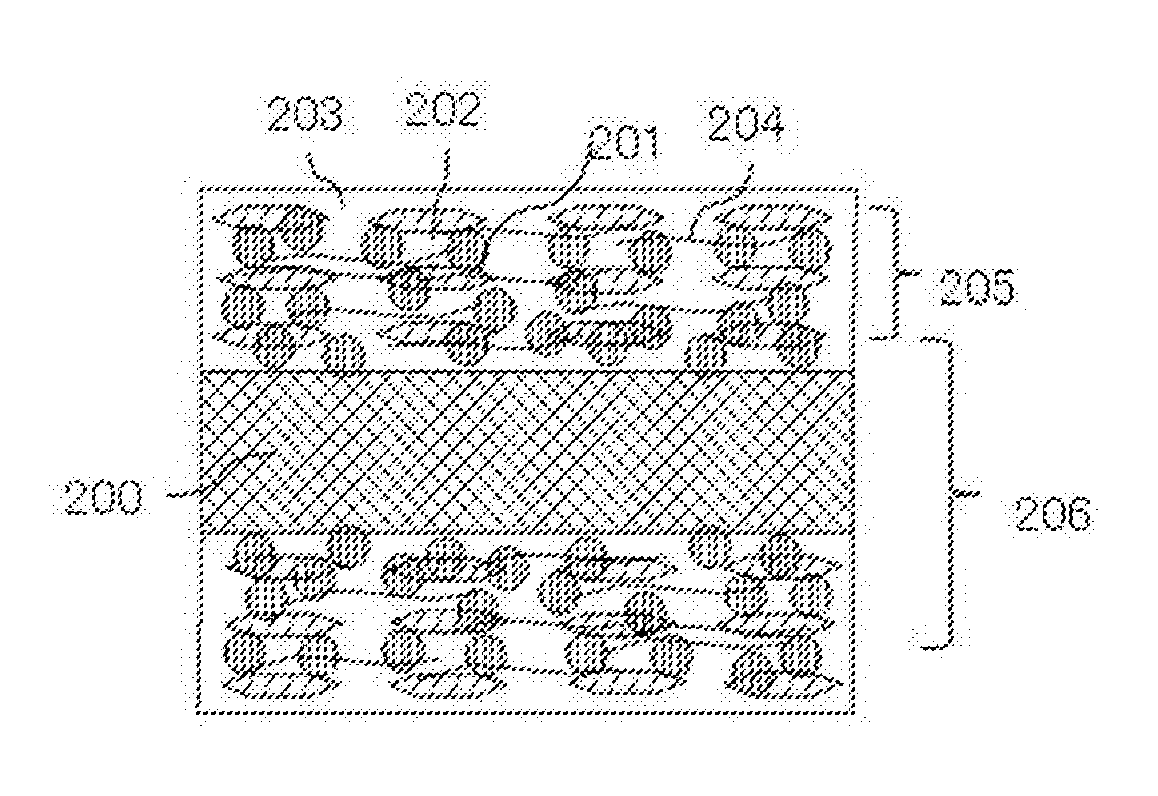
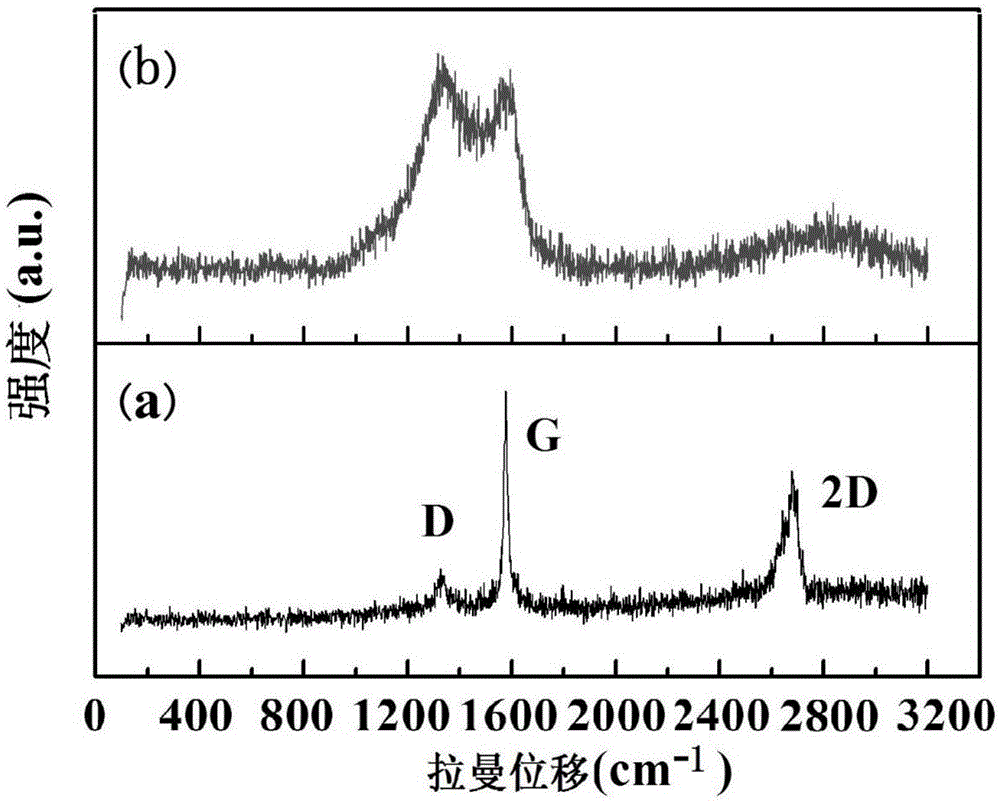
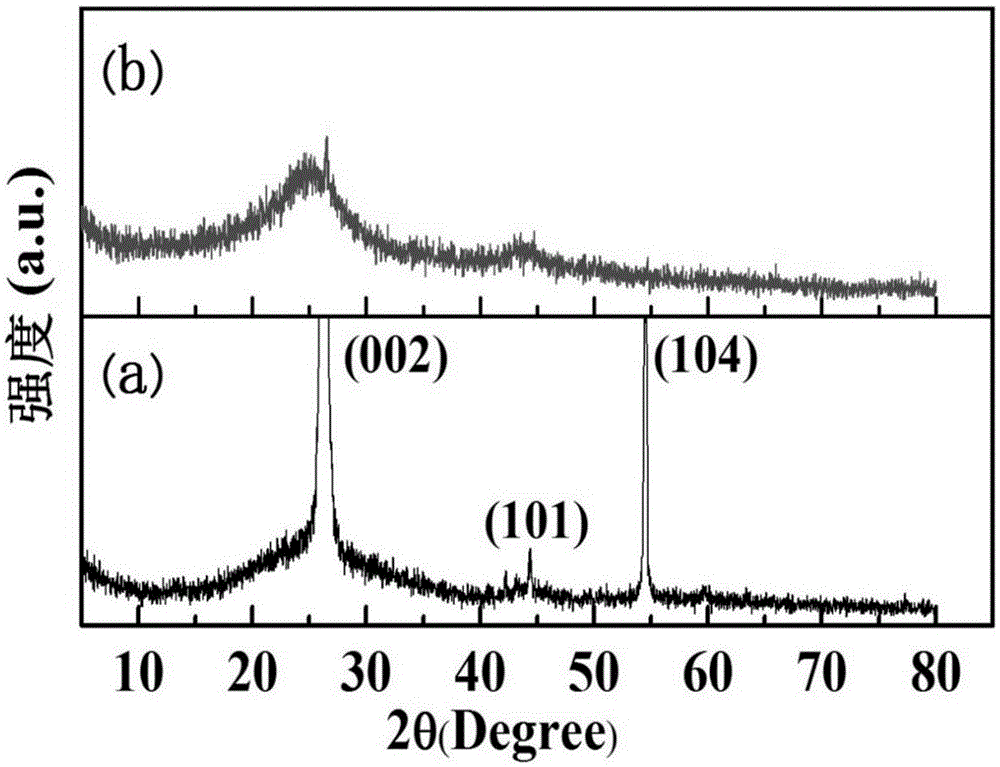
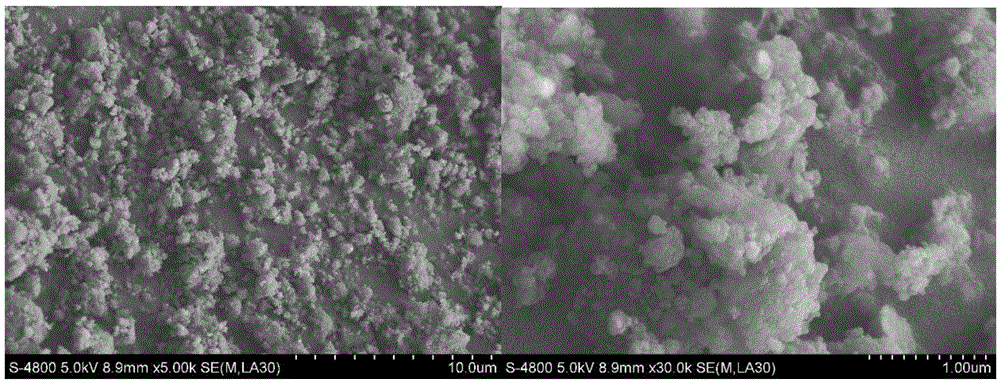
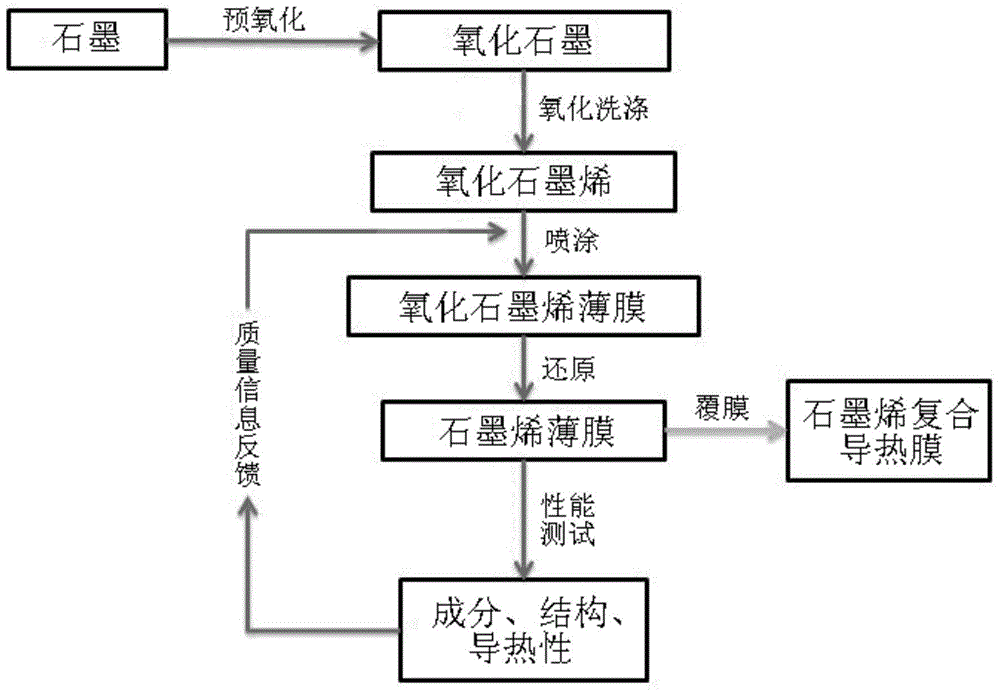
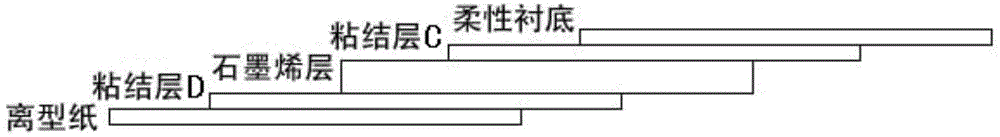
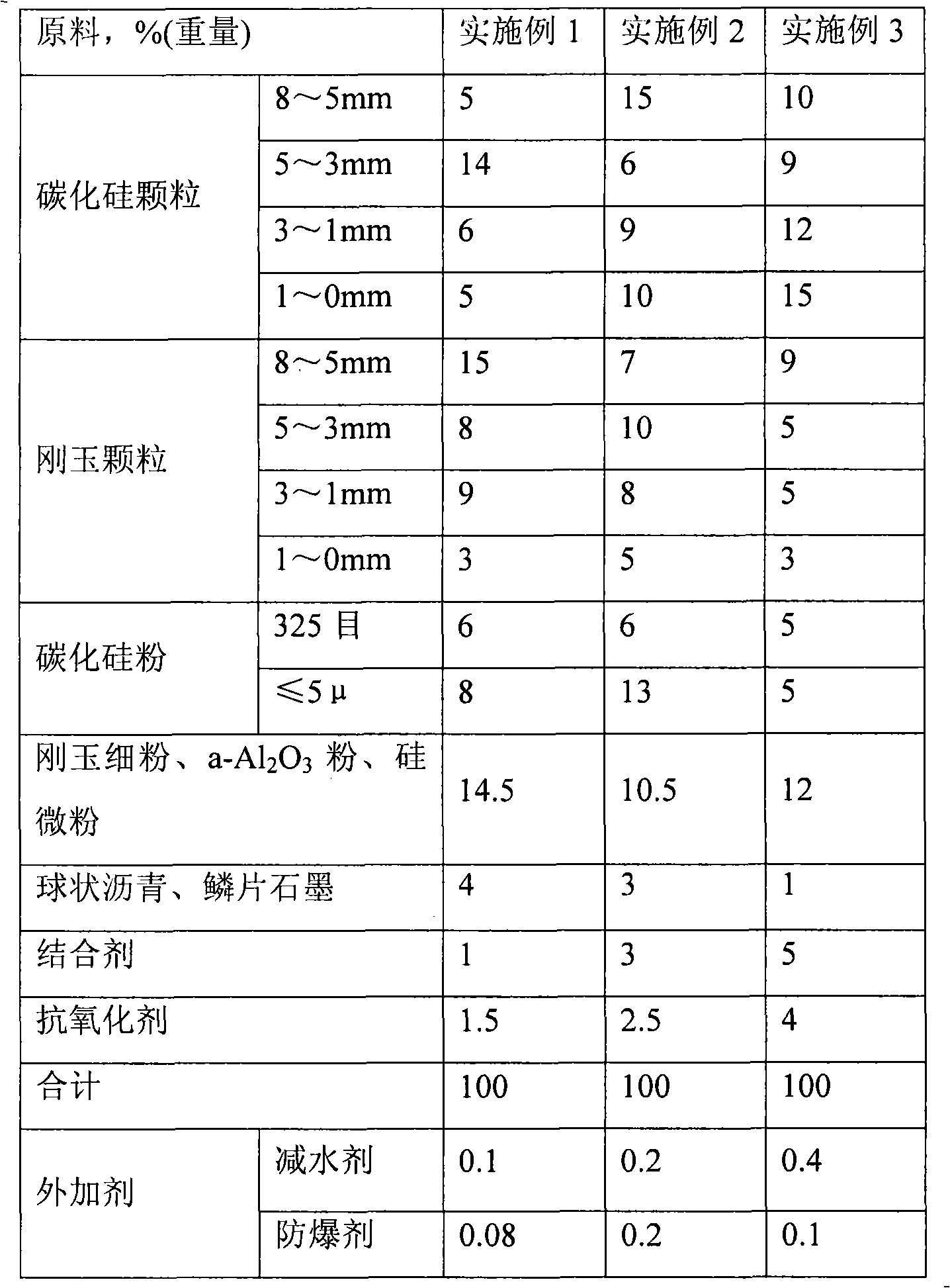
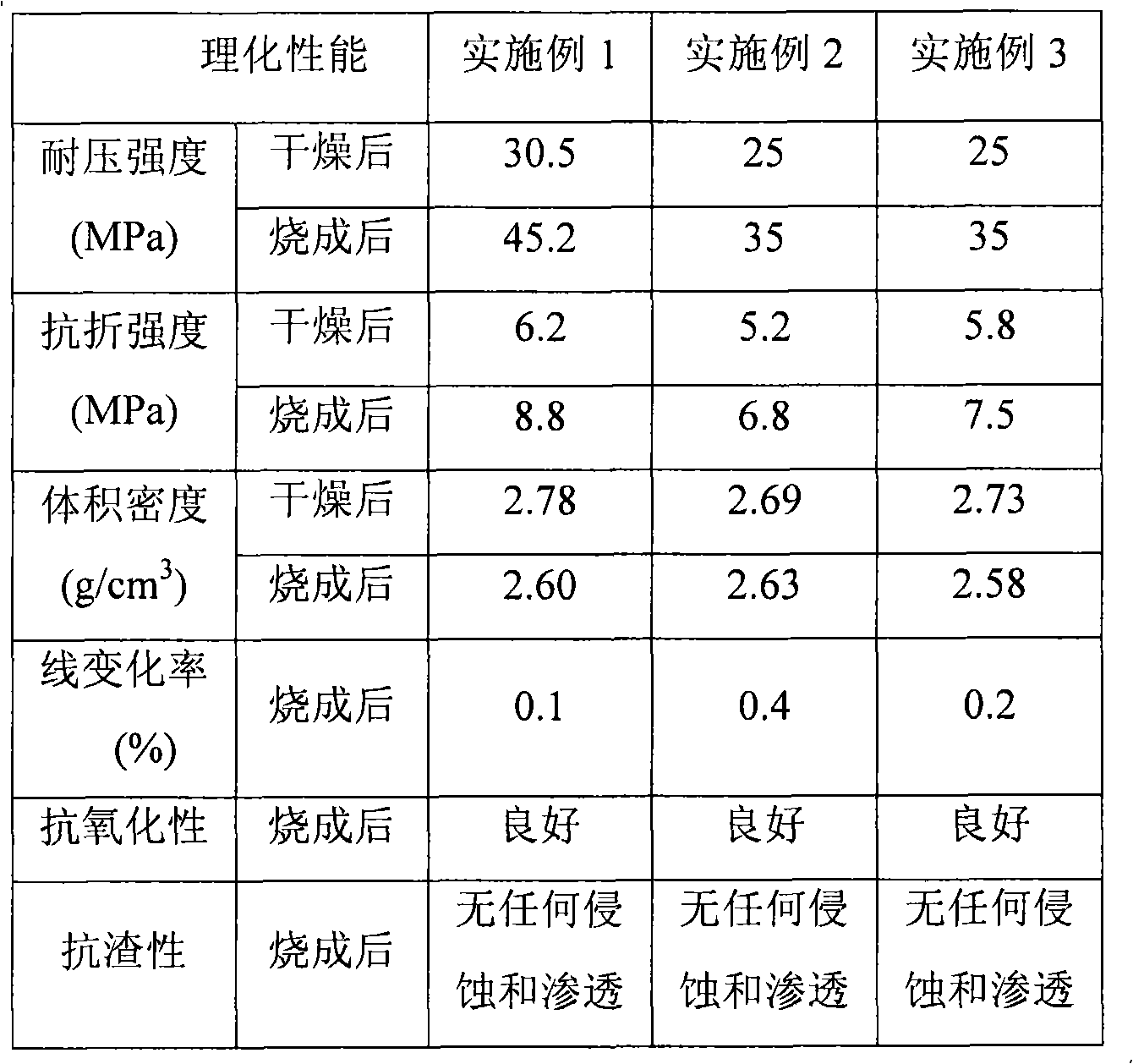
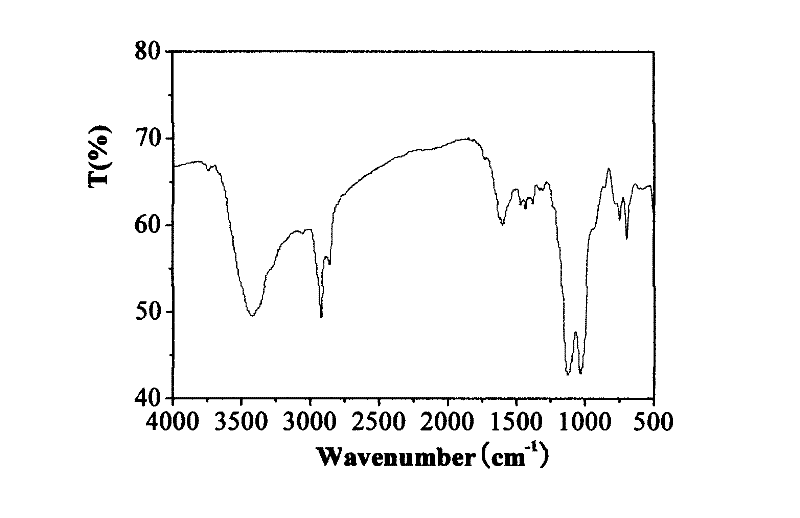
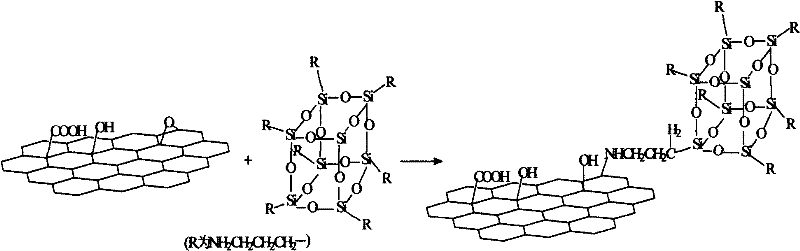
Patents
Literature
2391 results about "Flake graphite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flake Graphite. Flake graphite is a natural of graphite that is found as flakes ranging in size from 50-800 micrometers in diameter and 1-150 micrometers thick. This form of graphite has a high degree of crystallinity.
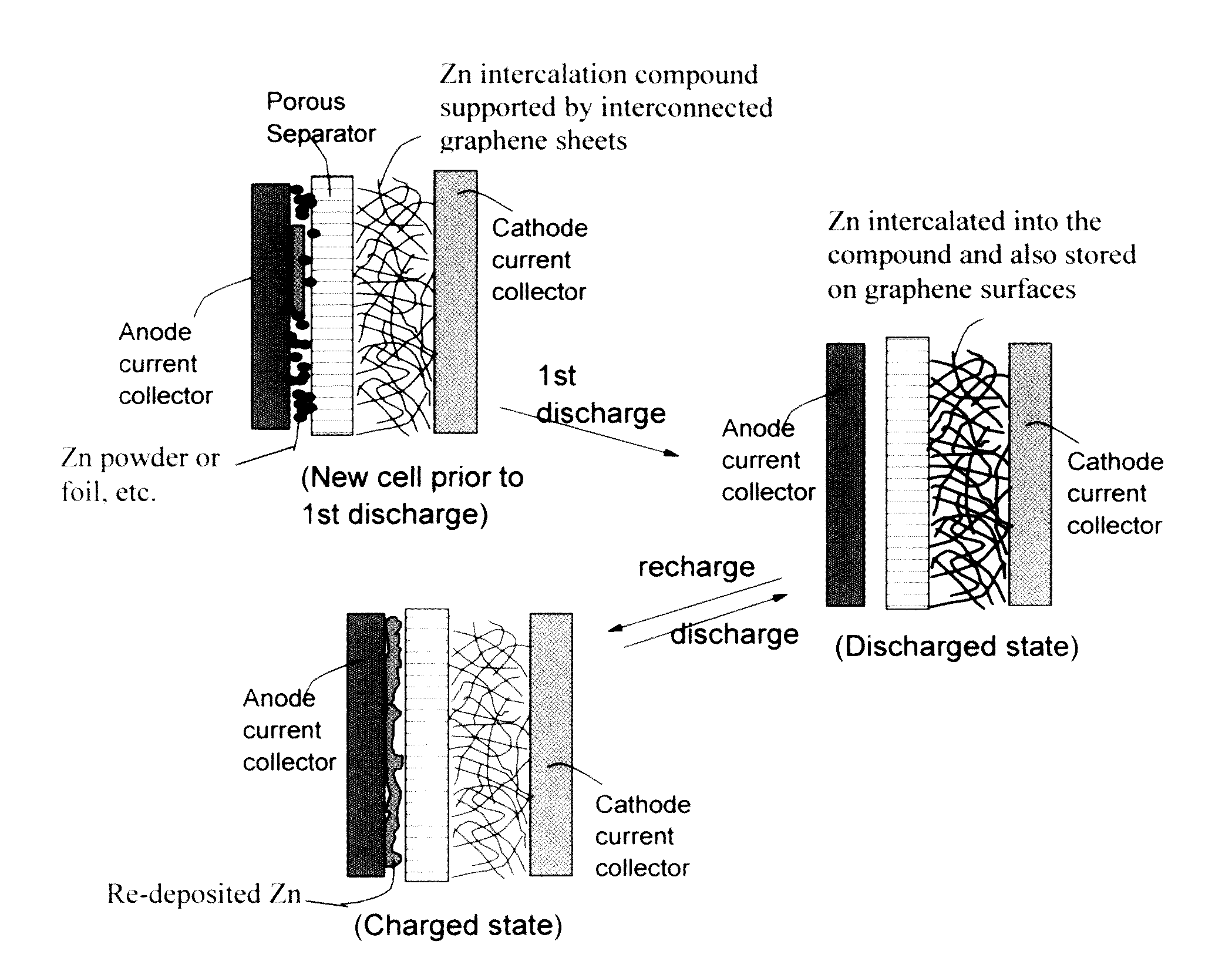
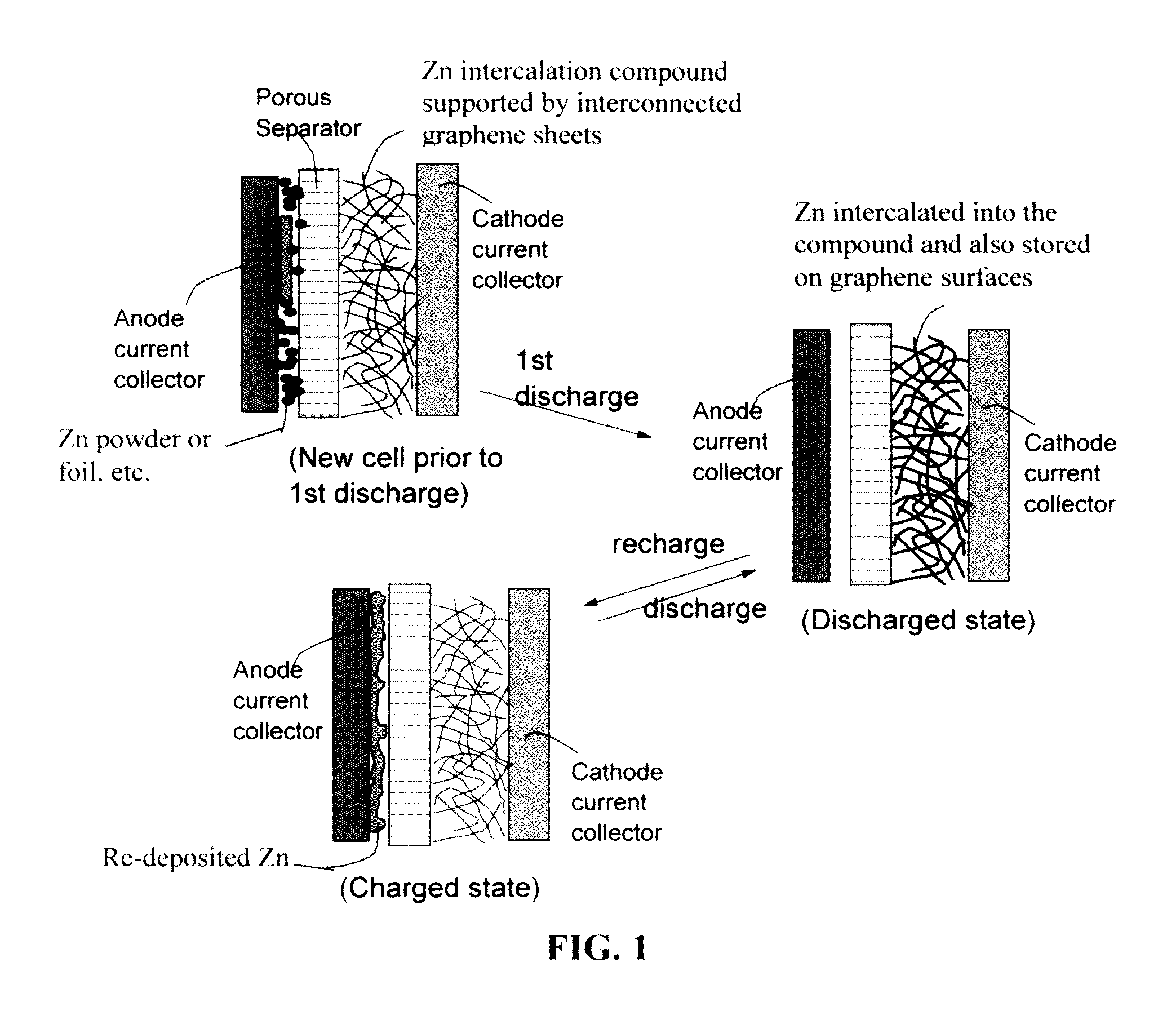
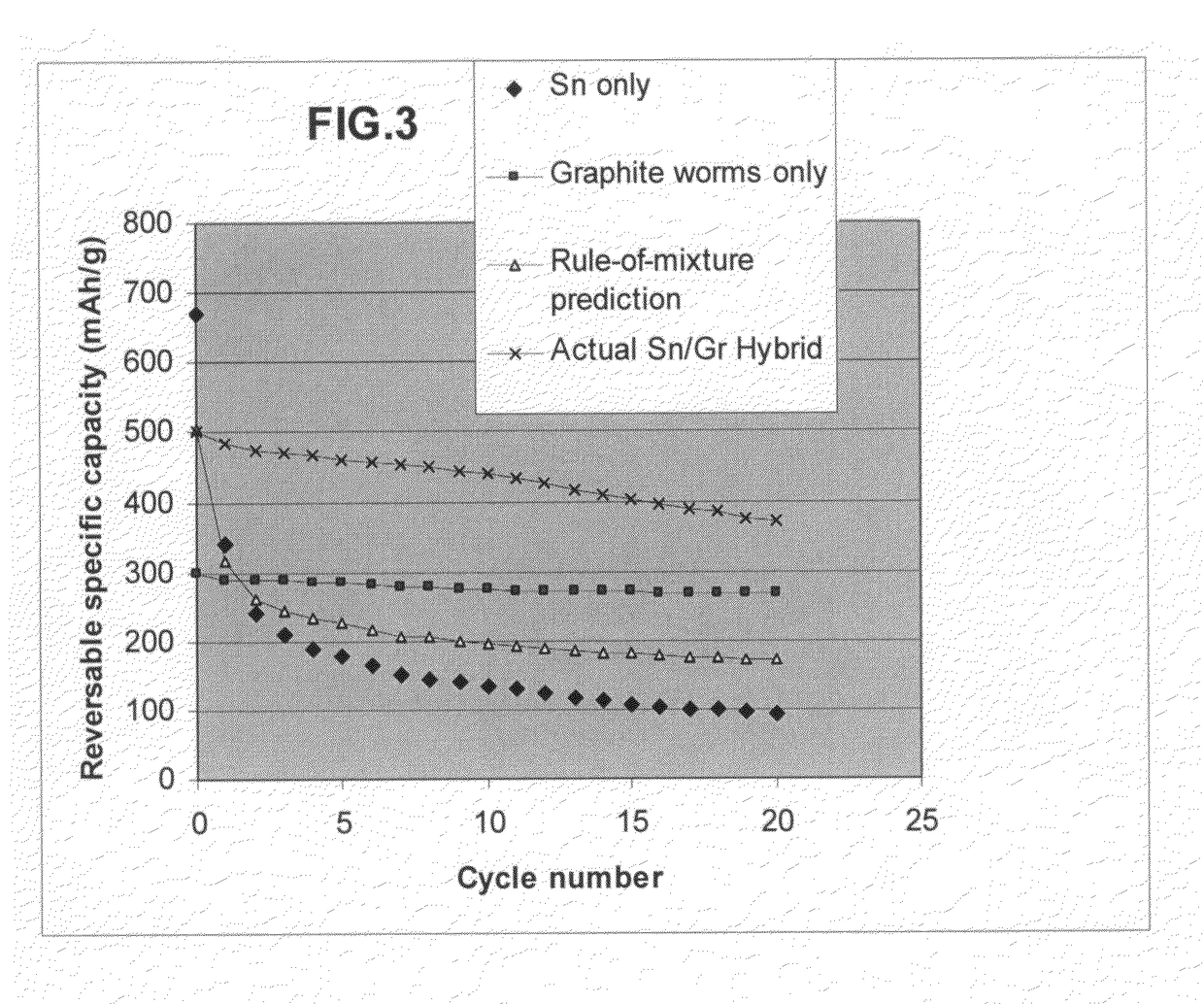
Zinc Ion-Exchanging Energy Storage Device
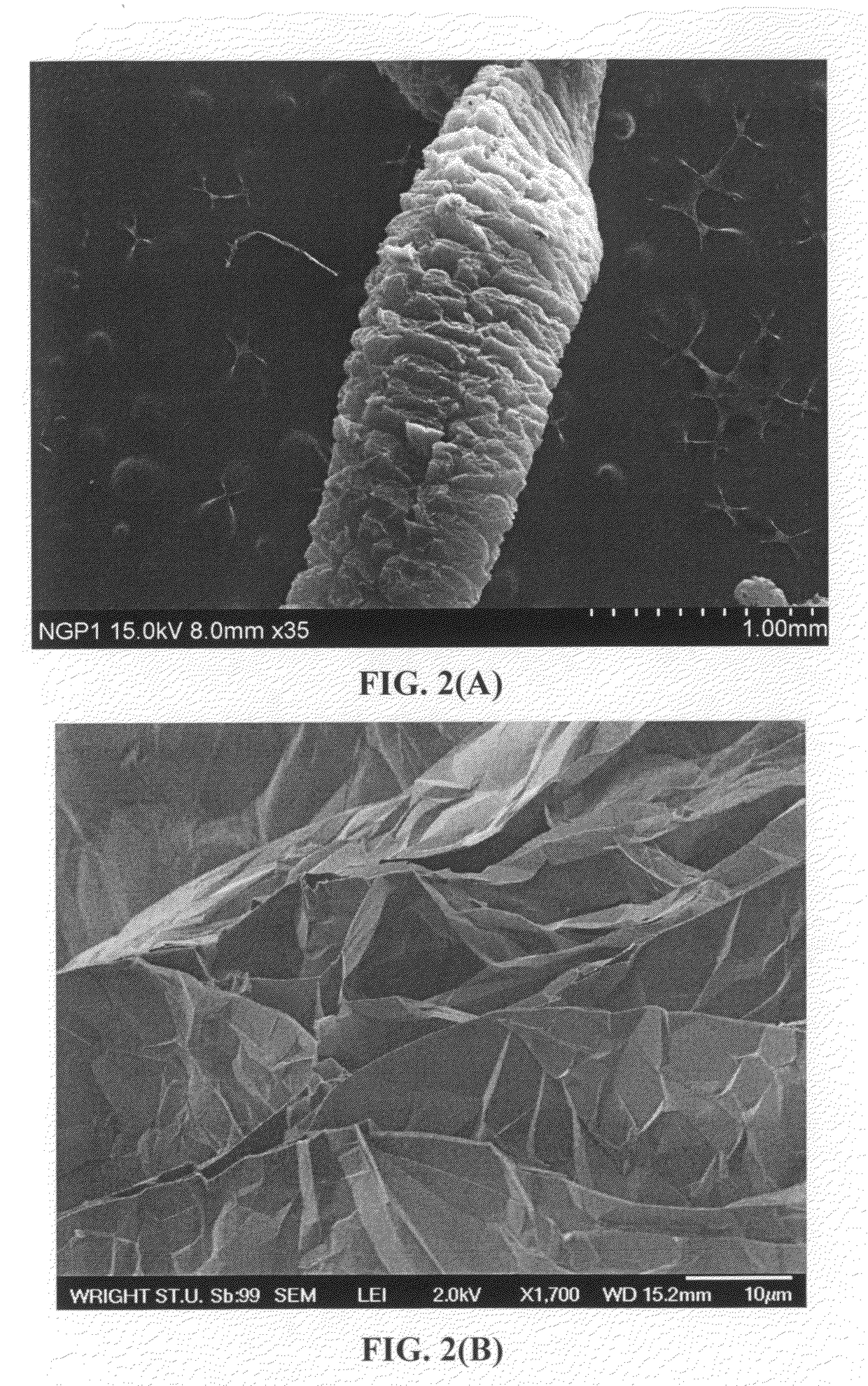
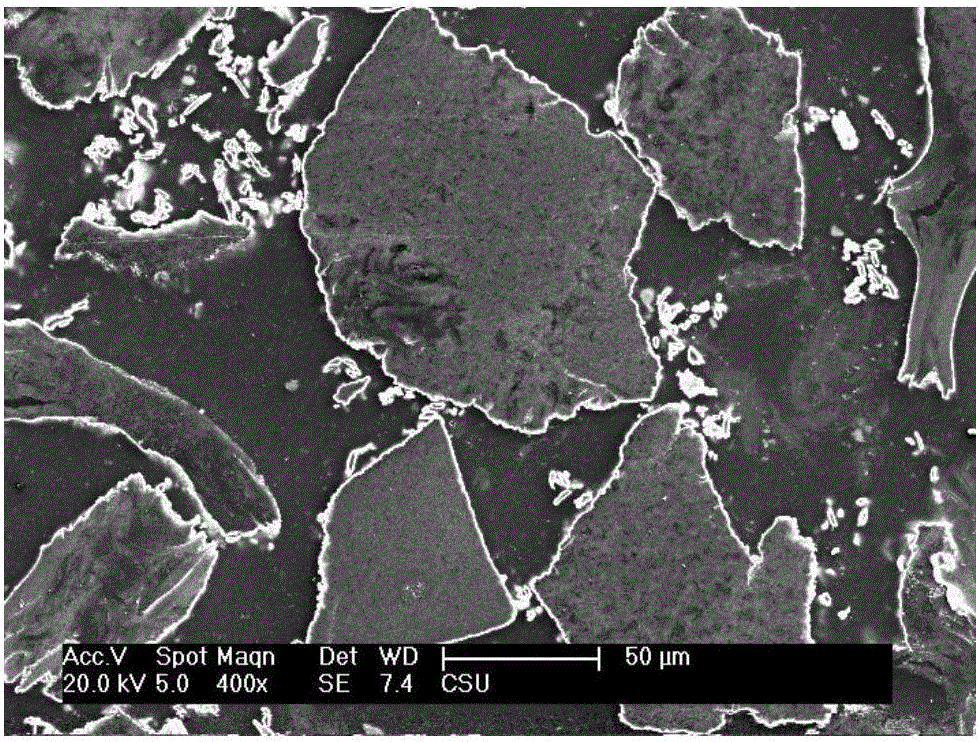
ActiveUS20160301096A1Quick releaseRapid depositionHybrid capacitor electrolytesAlkaline accumulatorsChemical treatmentZinc metal
A zinc ion-exchanging battery device comprising: (A) a cathode comprising two cathode active materials (a zinc ion intercalation compound and a surface-mediating material); (B) an anode containing zinc metal or zinc alloy; (C) a porous separator disposed between the cathode and the anode; and (D) an electrolyte containing zinc ions that are exchanged between the cathode and the anode during battery charge / discharge. The zinc ion intercalation compound is selected from chemically treated carbon or graphite material having an expanded inter-graphene spacing d002 of at least 0.5 nm, or an oxide, carbide, dichalcogenide, trichalcogenide, sulfide, selenide, or telluride of niobium, zirconium, molybdenum, hafnium, tantalum, tungsten, titanium, vanadium, chromium, cobalt, manganese, iron, nickel, or a combination thereof. The surface-mediating material contains exfoliated graphite or multiple single-layer sheets or multi-layer platelets of a graphene material.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
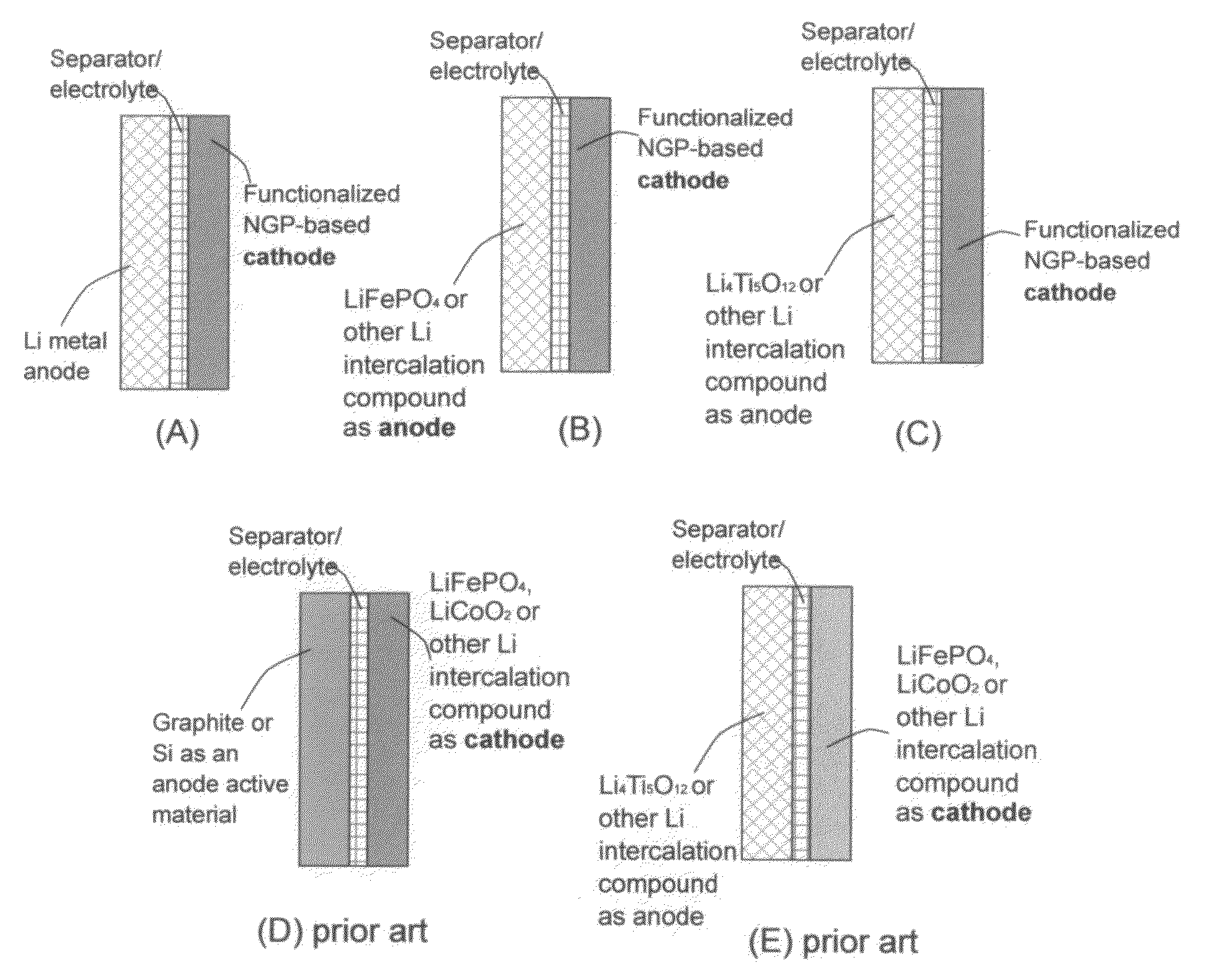
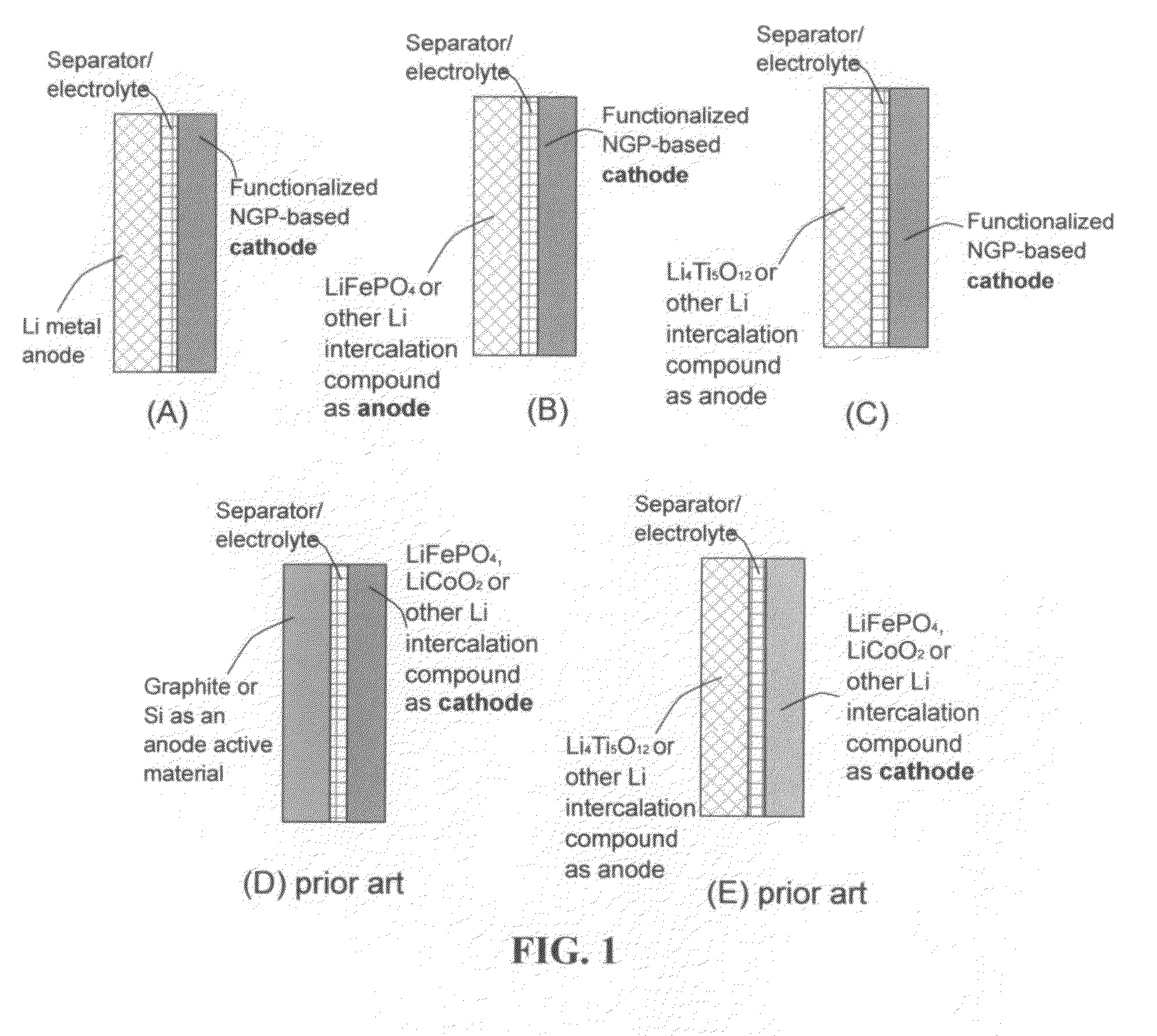
Lithium super-battery with a functionalized nano graphene cathode
An electrochemical energy storage device, lithium super-battery, comprising a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a porous separator disposed between the two electrodes, and a lithium-containing electrolyte in physical contact with the two electrodes, wherein the positive electrode comprises a plurality of chemically functionalized nano graphene platelets (f-NGP) or exfoliated graphite having a functional group that reversibly reacts with a lithium atom or ion. In a preferred embodiment, a lithium super-battery having a f-NGP positive electrode and Li4Ti5O12 negative electrode exhibits a gravimetric energy ˜5 times higher than conventional supercapacitors and a power density ˜10 times higher than conventional lithium-ion batteries. This device has the best properties of both the lithium ion battery and the supercapacitor.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC +1
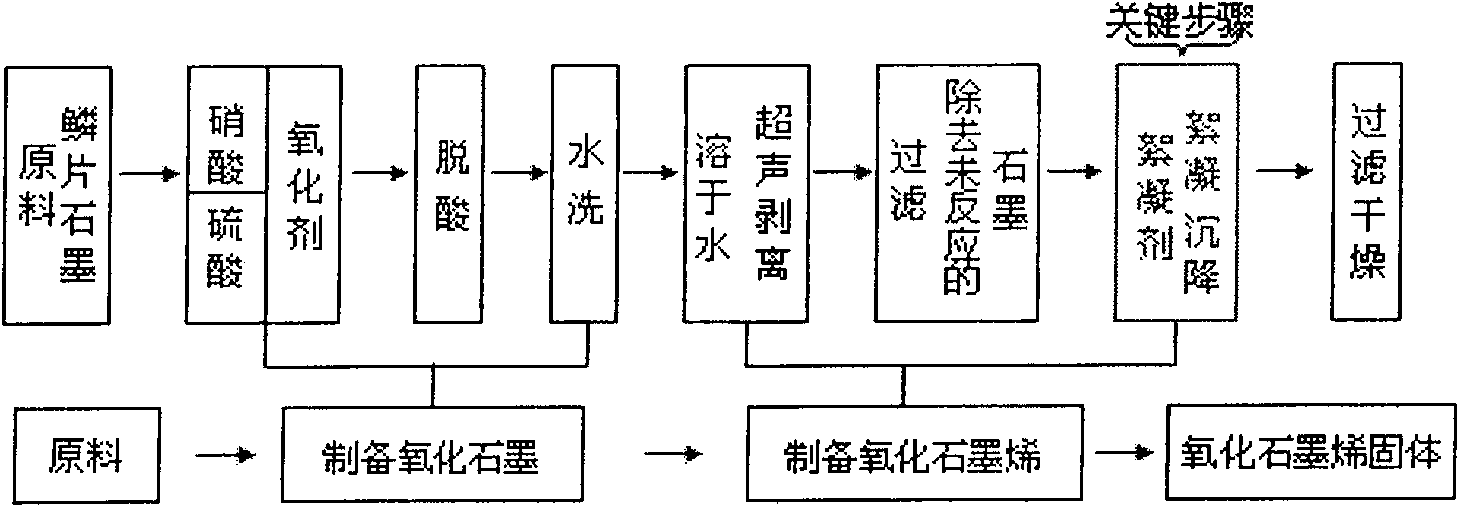
Method for realizing large-scale preparation of monolayer oxidized graphene
The invention relates to a method used for realizing large-scale preparation of monolayer oxidized graphene. The method comprises the following steps: oxidizing natural crystalline flake graphite by an oxidant to obtain oxidized graphite; after ultrasonic stripping, carrying out filtration to remove unreacted graphite and obtain the aqueous solution of oxidized graphene; and adding a flocculating agent to obtain oxidized graphene solid after settlement, filtration and drying. The method can easily separate the oxidized graphene solid from aqueous dispersion solution through flocculating settlement, thereby realizing large-scale preparation of graphene; moreover, the method has cheap and accessible raw materials, easy operation, simple process and good reproducibility, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production. The monatomic oxidized graphene prepared by the method can be used as flake reinforced phase of composite materials to prepare materials with high mechanical property and barrier property; moreover, the oxidized graphene can also be used for preparing fingerprint collecting materials, and the like. Graphene, namely the reduction product of the oxidized graphene can be used for constructing two-dimensional photoelectron components such as nano computer chips, solar battery electrodes and field effect transistors and the like.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Dispersible and conductive Nano Graphene Platelets
ActiveUS20100055458A1Impart dispersibilityImpart solubilityMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsDisplay deviceSolar cell
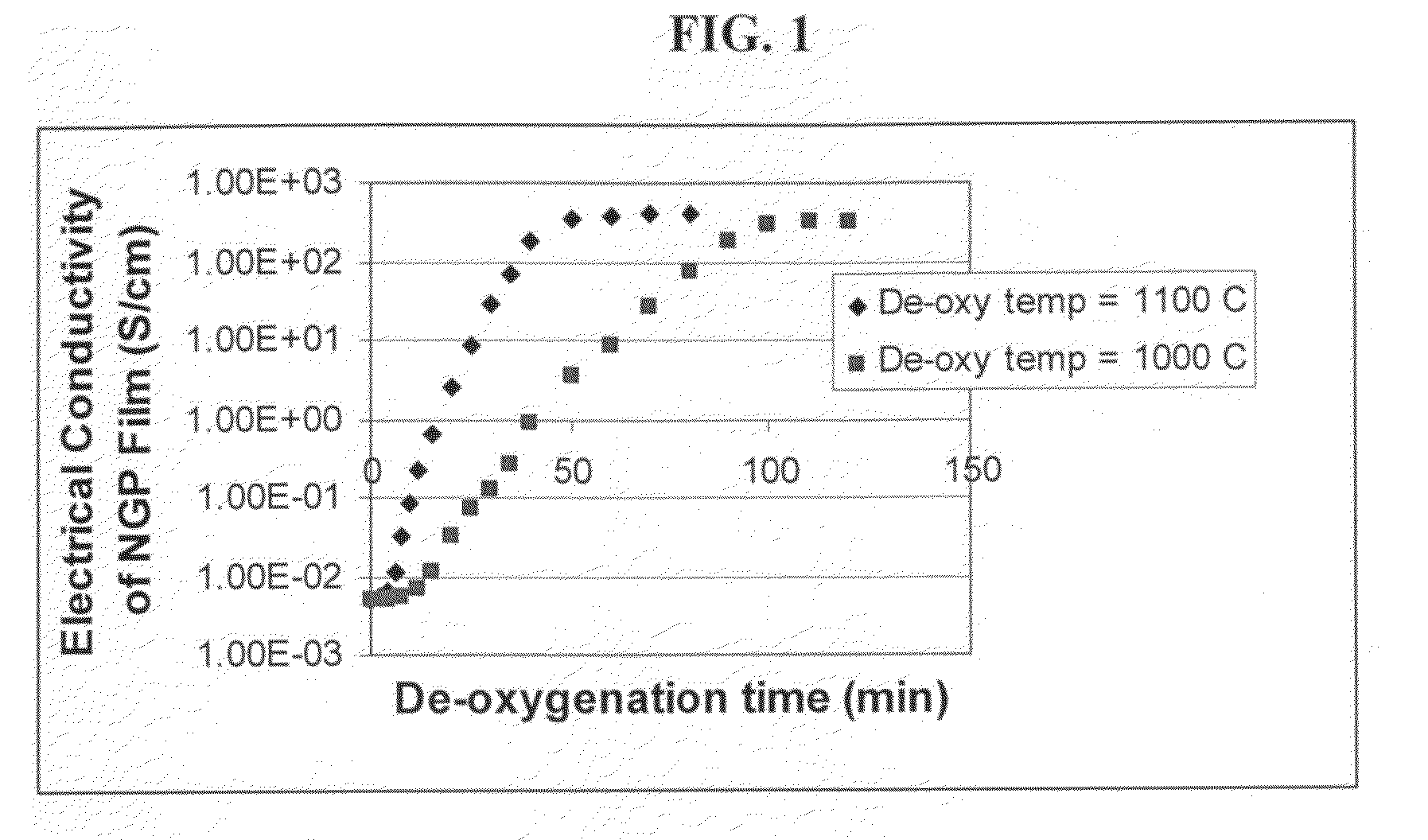
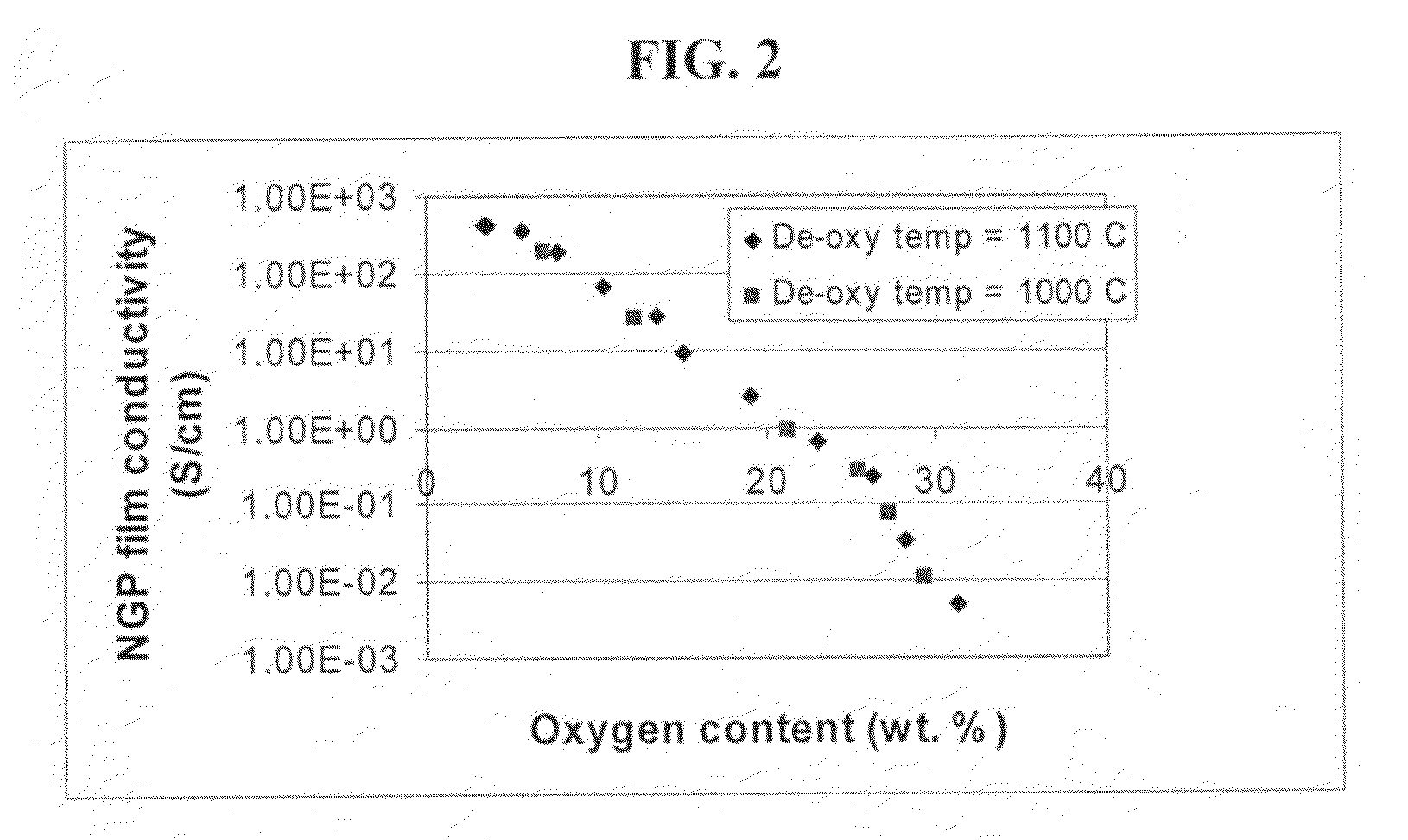
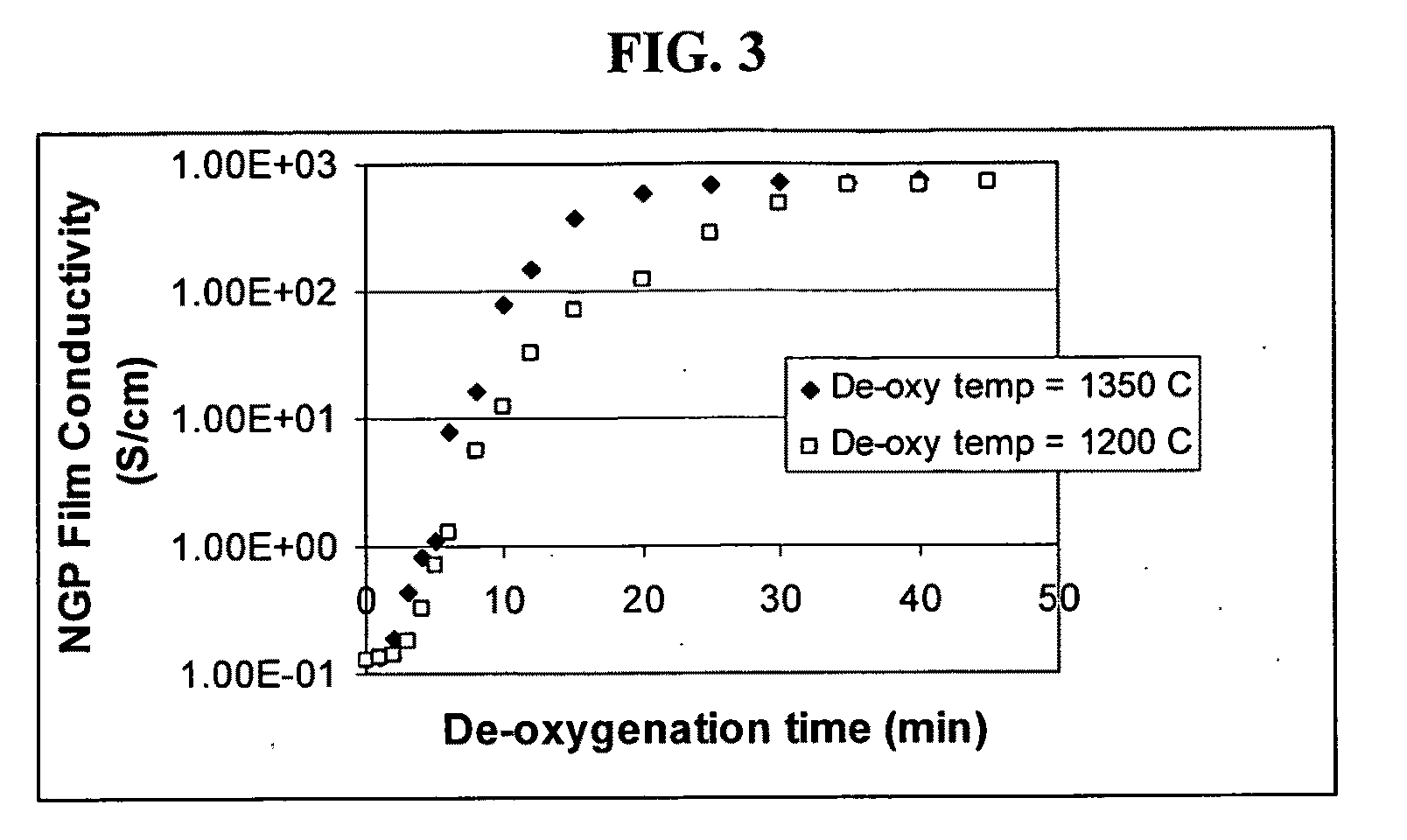
The present invention provides a dispersible and electrically conductive nano graphene platelet (NGP) material comprising at least a single-layer or multiple-layer graphene sheet, wherein the NGP material has an oxygen content no greater than 25% by weight and no less than 5% by weight. This NGP material can be produced by: (a) preparing a pristine NGP material from a graphitic material; and (b) subjecting the pristine NGP material to an oxidation treatment. Alternatively, the production process may comprise: (A) preparing a graphite oxide (GO) from a laminar graphite material; (b) exposing the GO to a first temperature for a first period of time to obtain exfoliated graphite; and (c) exposing the exfoliated graphite to a second temperature in a protective atmosphere for a second period of time. Conductive NGPs can find applications in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays, additives for battery and supercapacitor electrodes, conductive nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Large-capacity high power polymer ferric lithium phosphate power cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101409369AImprove securityIncrease capacityElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureSlurryElectric vehicle
The invention discloses a large-capacity high-power polymer lithium iron phosphate power battery. The weight ratio of anode slurry is as follows: 81 to 85 percent of lithium iron phosphate, 1 to 5.5 percent of superconduction carbon, 0 to 2.5 percent of conductive carbon soot, 0 to 4 percent of conductive black lead, 0 to 2.5 percent of crystalline flake graphite, 0 to 2 percent of carbon nanometer tube as well as 6 to 7.5 percent of polyvinylidene fluoride; the weight ratio of cathode slurry is as follows: 89 to 91 percent of cathode material, 1 to 3.5 percent of superconduction carbon, 0 to 2 percent of conductive carbon soot, 0 to 4 percent of conductive black lead, 2.5 to 3.5 percent of styrene-butadiene rubber as well as 1.5 to 2 percent of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose; the steps for preparing the battery are as follows: preparing slurry, coating the anode and the cathode, rolling and pressing a polar plate, transversely and separately cutting the polar plate, baking the polar plate, welding the polar ears of the anode and the cathode, preparing a battery cell, putting the electric core into a shell and sealing, baking the electric core, injecting liquid into the battery as well as forming the battery and dividing the volume of the battery. The invention relates to a lithium-ion secondary battery which can provide drive energies for electric tools, electric bicycles, motor cars and electric vehicles.
Owner:MCNAIR TECH
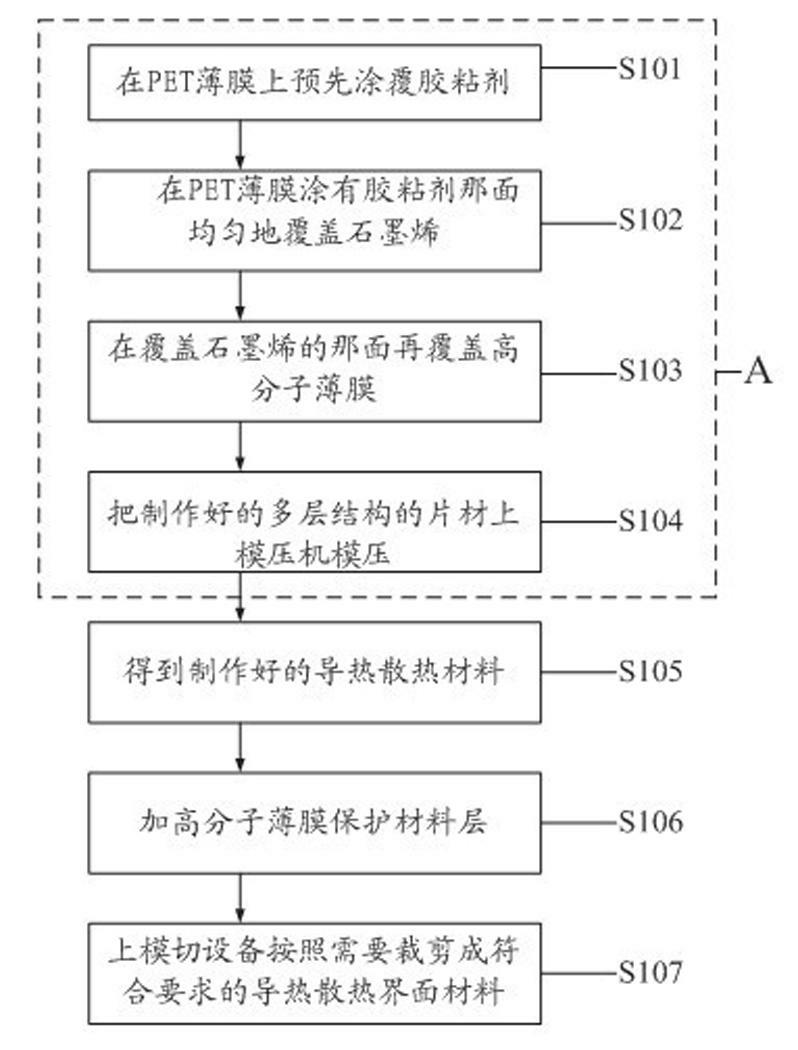
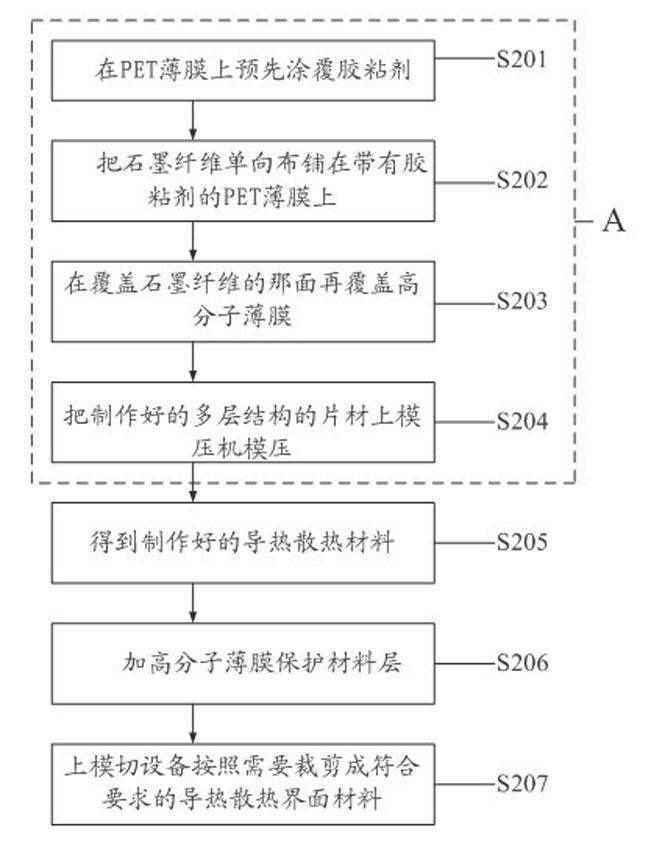
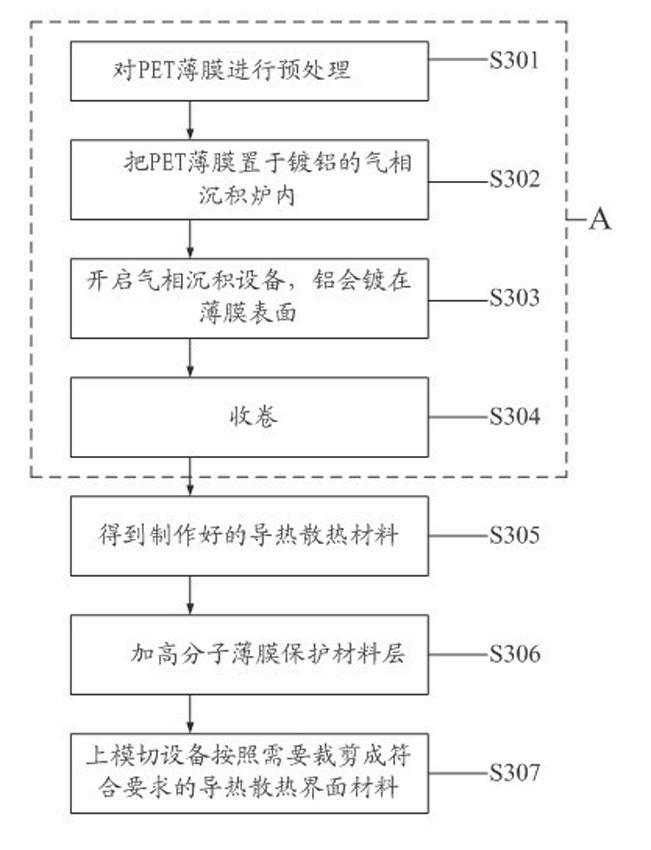
Heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102651961AReduce volumeThe overall thickness is thinLayered productsCooling/ventilation/heating modificationsMetal fiberCalcium silicate
The invention provides a heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material and a manufacturing method thereof, wherein the heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material is applied to the field of heat dissipation of electronic products. The heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material comprises a heat-conduction heat-dissipation layer and a surface protective material layer, wherein the heat-conduction heat-dissipation layer consists of one or more of graphite, nano graphite, crystalline flake graphite, graphene, pyrolytic carbon, pyrolytic graphite, graphite powder, carbon nano tubes, carbon fibers, graphite fibers, resin, ceramic fibers, quartz fibers, metal fibers, zirconia, boron nitride, silicon nitride, boron carbide, silicon carbide, magnesia powder, metasillicio acid fibers, calcium silicate aluminum fibers, aluminium oxide fibres, copper power, aluminium power, silver power, tungsten power and molybdenum power; and the surface protective material layer is a polymeric membrane. The heat-conduction heat-dissipation interface material manufactured according to the materials and the method provided by the invention has the advantages of effectively improved heat-dissipation performance, small volume, light weight and small thickness, can be used for prolonging the service life of an electronic component, and simultaneously is easy to produce and process.
Owner:SHANGHAI QI JIE CARBON MATERIALS
Preparation method of high purity and high concentration graphene suspension
InactiveCN101830458AFacilitate the reduction reactionInhibition of agglomerationHigh concentrationUltrasonic radiation
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high purity and high concentration graphene suspension, which comprises the following steps of: reacting natural crystalline flake graphite with a strong oxidizer to obtain graphite oxide; spreading the graphite oxide into a dispersing agent, and obtaining a graphene oxide suspension by ultrasonic dispersion; mixing the graphene oxide suspension with hydrazine hydrate under the protection of nitrogen and reacting at constant temperature under ultrasonic radiation to prepare stable graphene suspension. Compared with the traditional method for preparing the graphene suspension, the method introduces ultrasonic in the reduction process of the graphite oxide. The invention has the following advantages that the prepared graphene suspension has high concentration (higher than 1 mg.mL<-1>), high purity (without influence of surface active agents and other impurities), high dispersionstability (time for stable dispersion is more than 60 days) and the like; the graphene prepared by the method has high electrical conductivity (high than 700 S.m<-1>), less number of layers, is simple and easy to implement, and is very suitable for large scale production in industy.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Hybrid anode compositions for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS8119288B2Improve conductivityLower internal resistanceAlkaline accumulatorsConductive materialPhysical chemistryHybrid material
The present invention provides an exfoliated graphite-based hybrid material composition for use as an electrode, particularly as an anode of a lithium ion battery. The composition comprises: (a) micron- or nanometer-scaled particles or coating which are capable of absorbing and desorbing alkali or alkaline metal ions (particularly, lithium ions); and (b) exfoliated graphite flakes that are substantially interconnected to form a porous, conductive graphite network comprising pores, wherein at least one of the particles or coating resides in a pore of the network or attached to a flake of the network and the exfoliated graphite amount is in the range of 5% to 90% by weight and the amount of particles or coating is in the range of 95% to 10% by weight. Also provided is a lithium secondary battery comprising such a negative electrode (anode). The battery exhibits an exceptional specific capacity, excellent reversible capacity, and long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
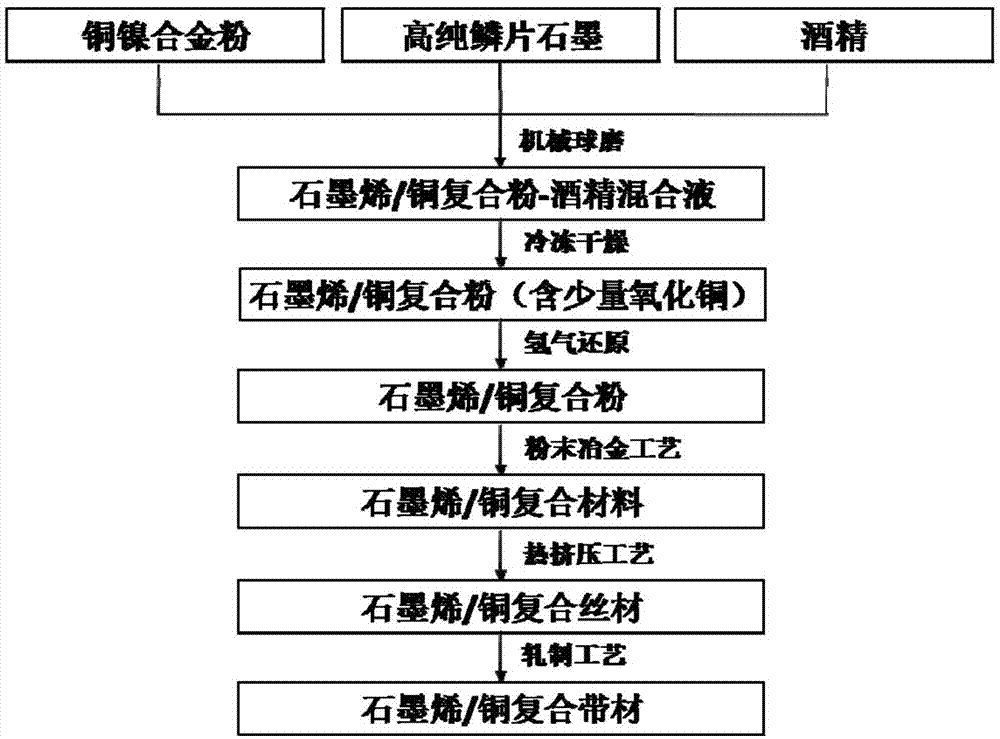
Graphene/copper composite and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a graphene / copper composite and a preparation method of the graphene / copper composite. Copper-nickel alloy powder and crystalline flake graphite are ball-milled mechanically jointly, alcohol is added as a wet milling medium during mechanical ball milling, and copper powder oxidation can be avoided. Graphene is stripped from the graphite by virtue of a mechanical force; at the same time, due to the presence of copper-nickel micro powder, a stripping process of the graphite is promoted; the spherical copper-nickel alloy powder is changed into sheeted powder by the action of the ball milling to obtain graphene / copper composite powder preliminarily; and a graphene / copper composite block, a composite wire and a composite tape are obtained by powder metallurgy, hot extrusion and rolling technologies. According to the composite, the graphene is dispersed uniformly; interface bonding between a matrix and a reinforcement; and the graphene / copper composite has excellent physical properties. According to the composite and the method, a technology is simple, a process is easy to control, and a scale production application is easy to achieve.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIWAVE COMPOSITE MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for preparing large-size high-quality graphene with controllable number of layers
The invention discloses a method for preparing large-size high-quality graphene with controllable number of layers, wherein graphite powder or flake graphite is mainly adopted as a raw material. The method specifically comprises the steps of intercalating the graphite raw material by virtue of an intercalating agent to initially weaken the intercalation interaction force and obtain different orders of graphite intercalation compounds (GICs); soaking the GICs in an appropriate expander, and then under the case that an auxiliary agent is added or not, enabling the intercalation materials to be quickly reacted with the expander to release a gases to obtain highly expanded wormlike graphene aggregate and further to cause the distances among graphene lamellar layers to be increased; and after certain processing, peeling, and then repeatedly centrifuging and dispersing to obtain a graphene dispersion with different numbers of layers. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the intercalation-expansion-peeling process is involved, raw materials are cheap, the reaction process is simple and easily controlled, and the number of layers of graphene is precisely controlled; the obtained graphene lamellar layers have the advantages of few defects, large size, high conductivity, high yield and the like, the large-scale industrial production is easily implemented, and the problems of high cost, low productivity, poor quality, small size, uncontrollable number of layers and the like in an existing graphene preparation technology are solved.
Owner:安徽百特新材料科技有限公司
Inorganic hydrated salt expanded graphite composite phase-changing heat storage material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an inorganic hydrated salt expanded graphite composite phase-changing heat storage material. In the preparation method thereof, 85-89 mass parts of inorganic hydrated salt sodium acetate trihydrate as a heat storage matrix, 5.5-6.5 mass parts of disodium hydrogenphosphate as a nucleating agent, 2.5-3.5 mass parts of carboxymethyl cellulose as a thickening agent, and 3-4.5 mass parts of expanded graphite is blended in an inorganic hydrated salt mixture as a material with a high thermal conductivity. Due to the use of the expanded graphite, the material not only maintains excellent properties of natural flake graphite such as good thermal conductivity, no toxicity and the like, but also has adsorbability which the natural flake graphite does not have. The invention solves the problems of sub-cooling degree, phase stratification and low thermal conductivity during the heat storage process. The composite phase-changing material has a low sub-cooling degree after the phase changing performance is improved, the solution thereof is uniform without sedimentation and stratification during the solid-liquid phase change, the performance is stable, the repeatability of good, and the phase-changing heat storage can be enhanced through improving the thermal conductivity of the material.
Owner:ENG COLLEGE OF ENG CORPS PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Negative electrode material for power storage device, electrode structure, power storage device, and production method for each
ActiveUS20170200943A1Inhibition formationHigh initial lithium insertion/extraction efficiencyHybrid capacitor electrolytesElectrode thermal treatmentLithiumSurface layer
Provided is an anode active material for energy storage devices capable of electrochemically inserting and extracting lithium ions and production method thereof, an electrode structure including the active material and flake graphite, and an energy storage device using the electrode structure as an anode. The anode active material includes secondary particles that are aggregates of 10-300 nm primary particles containing silicon as a main component. The primary particles each include, as a surface layer, a composite metal oxide layer containing at least one or more metal elements selected from at least Al, Zr, Mg, Ca, and La and Li.
Owner:KAWAKAMI SOICHIRO
Wave-absorbing material based on grapheme and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105647468AImprove absorbing abilityImprove absorbing performanceOther chemical processesDielectricElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a wave-absorbing material based on grapheme and a preparation method thereof. The wave-absorbing material is formed by mixing graphite powder (or taking graphite powder as a main material) with one of three magnetic dielectric materials: ferrite, carbonyl iron powder and ultrafine metal powder, wherein the graphite powder is prepared by flake graphite through a mechanical stripping method and has a mass percentage content of 60-99 percent. The wave-absorbing material provided by the invention has the characteristics of being high in absorption strength, wide in absorption band, low in density and the like and has the excellent characteristics of the grapheme and the magnetic dielectric materials in electromagnetic performance; the preparation method is easy for large scale, low in cost, environment-friendly and suitable for industrialized production. The wave-absorbing material has wide application potential and market prospect in the fields of wave-absorbing materials, anti-electrostatic materials and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:兰州天烁新能源有限公司
Preparation method of composite heat conduction graphene film and composite heat conduction graphene film
ActiveCN104085143AIncrease layer spacingThoroughly oxidizedMetal layered productsPotassium persulfateFiltration
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite heat conduction graphene membrane and the composite heat conduction graphene film. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, putting crystalline flake graphite or graphite powder into a mixed solution of concentrated sulfuric acid, potassium persulfate and phosphorus pentoxide, soaking for a day and a night, then carrying out suction filtration, drying, and carrying out pre-oxidizing; S2, oxidizing pre-oxidized graphite further by adopting a Hummers method, that is, oxidizing fully in concentrated sulfuric acid and potassium permanganate, then adding deionized water for diluting, and carrying out repeated washing and suction filtration, so as to obtain an oxidized graphene aqueous solution; S3, spraying the oxidized graphene aqueous solution on a substrate by adopting a thermal spray method, and depositing, so as to obtain an oxidized graphene film; S4, reducing the oxidized graphene film, so as to obtain the graphene film; and S5, laminating the graphene film, so as to obtain the composite heat conduction graphene film. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method is simple, the cost is low, and the prepared composite heat conduction graphene film has a favorable heat conduction performance.
Owner:成都科愿慧希科技有限公司
Metallic composite low carbon magnesium carbon brick for ladle slag wire and manufacture method thereof
The invention discloses a metal complex low-carbon magnesia carbon brick used for ladle slag lines, the weight percentage of the added materials is as following, 50 to 70 percent of magnesia particles, 25 to 35 percent of magnesia powder, and 3 to 6 percent of organic binder, furthermore, the following components are added which are produced by mixing, striating materials, forming and heat-treatment, 0 to 4 percent of flake graphite, 3 to 15 percent of metal powder, and 0.5 to 3 percent of antioxidant containing boron. The antioxidant properties, slag-resistance performance, high temperature strength and the thermal shock resistance of the ladle slag line used metal complex low-carbon magnesia carbon brick are greatly improved, the service life is prolonged, the consumption cost of each ton of refractories is lowered. The preparation method of ladle slag line used metal complex low-carbon magnesia carbon bricks is also disclosed, and the carbon content in the ladle slag line used metal complex low-carbon magnesia carbon bricks produced by the method is less than or equal to 6 percent, little carbon is added so as to reduce the pollution towards liquid steel, and residual strength ratio of the thermal shock resistance is kept at 70 to 80 percent.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV +1
Raw paper of high-performance environment-friendly paper based friction material and manufacturing method of friction plate
ActiveCN101805589AGood physical and mechanical propertiesIncrease coefficient of frictionOther chemical processesNon-macromolecular organic additionAdhesiveStatic friction
The invention discloses raw paper of a high-performance environment-friendly paper based friction material and a manufacturing method of a friction plate. The high-performance environment-friendly paper based friction material is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by weight: a substrate comprises 7-15% of carbon fiber, 5-10% of chopped aramid fiber, 5-10% of aramidpulp and 9-30% of bamboo fiber pulp; a friction agent comprises 10-20% of kieselguhr and 8-12% of cashew nut shell powder; a frictional property regulator adopts 2-4% of rubber particles, 5-10% of calcium carbonate and 10-15% of flake graphite; and a forming adhesive comprises 1-2% of fluororubber, 3-15% of silicone resin and 3-15% of phenolic resin. The invention fully forms the materials of thefriction material into a whole by changing the traditional impregnation process, effectively improves the physical and mechanical properties of the friction plate, improves the friction factors, regulates the dynamic and static friction ratio factors, and reduces the abrasion ratio of the friction plate.
Owner:陕西帕若德新材料科技有限公司
Preparation method of Al2O3-SiC-C castable material for slag line of main trough of blast furnace
The invention relates to an Al2O3-SiC-C castable material for a slag line of a main trough of a large blast furnace and a preparation method thereof. The castable material comprises an aggregate, a matrix, a bonding agent, an antioxidant and an admixture; wherein, the aggregate comprises corundum grains and carborundum grains; the matrix comprises ball pitch, flake graphite, corundum fine powder, a-Al2O3 ultrafine powder, silicon powder and carborundum ultrafine powder; the bonding agent is aluminate cement; the antioxidant is a compound of aluminium powder and silicon powder; the admixture comprises a water reducing agent and a detonation suppressor. The castable material is prepared by the steps of mixing various raw materials evenly, adding water, stirring, casting molding, maintaining and drying. The castable material has strong anti-slag corrosion and anti-scour capabilities, good high temperature resistance, abrasion resistance and thermal shock resistance, slight reheating change and long service life.
Owner:BEIJING TONGDA REFRACTORY TECH CO LTD
Preparation method of graphene oxide grafted POSS (polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) modified epoxy resin
The invention discloses a preparation method of graphene oxide grafted POSS (polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) modified epoxy resin. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking crystalline flake graphite as a raw material, preparing graphite oxide through adopting a Hummers oxidation method, further adding the graphite oxide into distilled water, forming a uniformly-dispersed graphene oxide mixed solution under an ultrasonic environment, further adding POSS and a strong catalyst, performing full reaction, then filtering, washing and drying to get black powder; and further uniformly dispersing graphene oxide / POSS in an epoxy resin matrix, cross-linking and bonding under the action of a curing agent to get a composite material, molding by casting, cooling and demolding. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the POSS is successfully grafted on a graphene oxide sheet layer, and advantages of the graphene oxide structure and the POSS structure are complemented, so that the preparation method has the advantages of low cost and easy obtaining of the raw material, easy operation, simple process, good reproducibility and obvious toughening modification effect against the epoxy resin.
Owner:福州乐道知识产权运营有限公司
Method for modifying epoxy resin through amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer-grafted graphene oxide
The invention discloses a method for modifying epoxy resin through amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer-grafted graphene oxide. The method comprises the following steps: preparing graphite oxide from flake graphite utilized as a raw material by adopting a Hummers oxidation method, adding the graphite oxide into a beaker, adding distilled water and forming a graphene oxide mixed solution by virtue of ultrasonic waves; stirring for dissolving triethylene tetramine in N,N-dimethylformamide, raising the temperature to 55-65 DEG C, dropwise adding a mixed solution of methyl methacrylate and methanol, continuously raising the temperature to 80-120 DEG C and reacting for 6-10 hours to get an amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer; further adding the graphene oxide mixed solution and NaOH, regulating the PH value to be 5-10, performing ultrasonic dispersion for 2-8 hours at the temperature of 80-120 DEG C, evaporating the methanol, cooling to room temperature, adding water to precipitate a product, drying to get the amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer-grafted graphene oxide capable of toughening and modifying the epoxy resin. The method disclosed by the invention is wide in raw material source, simple in preparation process, pollution-free, lower in cost and beneficial to industrial large-scale production.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of graphene with nano ferroferric oxide precipitated on surface
InactiveCN102674334AGive full play to the nano effectImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsResin matrixCvd graphene
The invention belongs to the technical field of materials, and particularly relates to a preparation method of graphene with nano ferroferric oxide precipitated on surface, which concretely comprises the steps of: firstly, oxidizing natural flake graphite and obtaining graphite oxide; further carrying out ultrasonic stripping on the graphite oxide and forming graphene oxide suspension; then, carrying out reduction reaction on the graphene oxide suspension under the action of strong reducing agent, and obtaining black flocculent flake graphene; and finally, taking hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant, and depositing Fe3O4 on the surface of the graphene in an alkaline solution. The invention realizes the modification of nanoscale Fe3O4 for the surface of the graphene. The obtained modified graphene is not doped with other elements except the Fe element, and can be well dispersed in a high-performance resin matrix, so that the mechanical property, the thermal performance, the electromagnetic performance and the friction property of the resin matrix can be improved, and phenolic resin, bismaleimide, cyanate ester and other products can be updated, or a new application field can be developed..
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Grout compositions having high thermal conductivities and methods of using the same
Grout slurries are provided that have high thermal conductivities of greater than about 1.4 Btu / hr-ft-° F. and low hydraulic conductivities ranging from about 5×10-9 cm / s to about 1×10-8 cm / s. Such grout slurries comprise water and a grout composition that is available as a one-sack product. The grout composition includes calcium bentonite present in an amount of from about 15% to about 45%, sodium bentonite present in an amount of from about 15% to about 45%, silica flour present in an amount of from about 10% to about 35%, and flaked graphite present in an amount of from about 10% to about 75%, all by weight of the grout composition. Further, methods of installing a conduit such as a heat transfer loop in a hole in the earth include placing the conduit in the hole, forming the foregoing grout slurry, and placing the grout slurry in the hole adjacent to the conduit.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
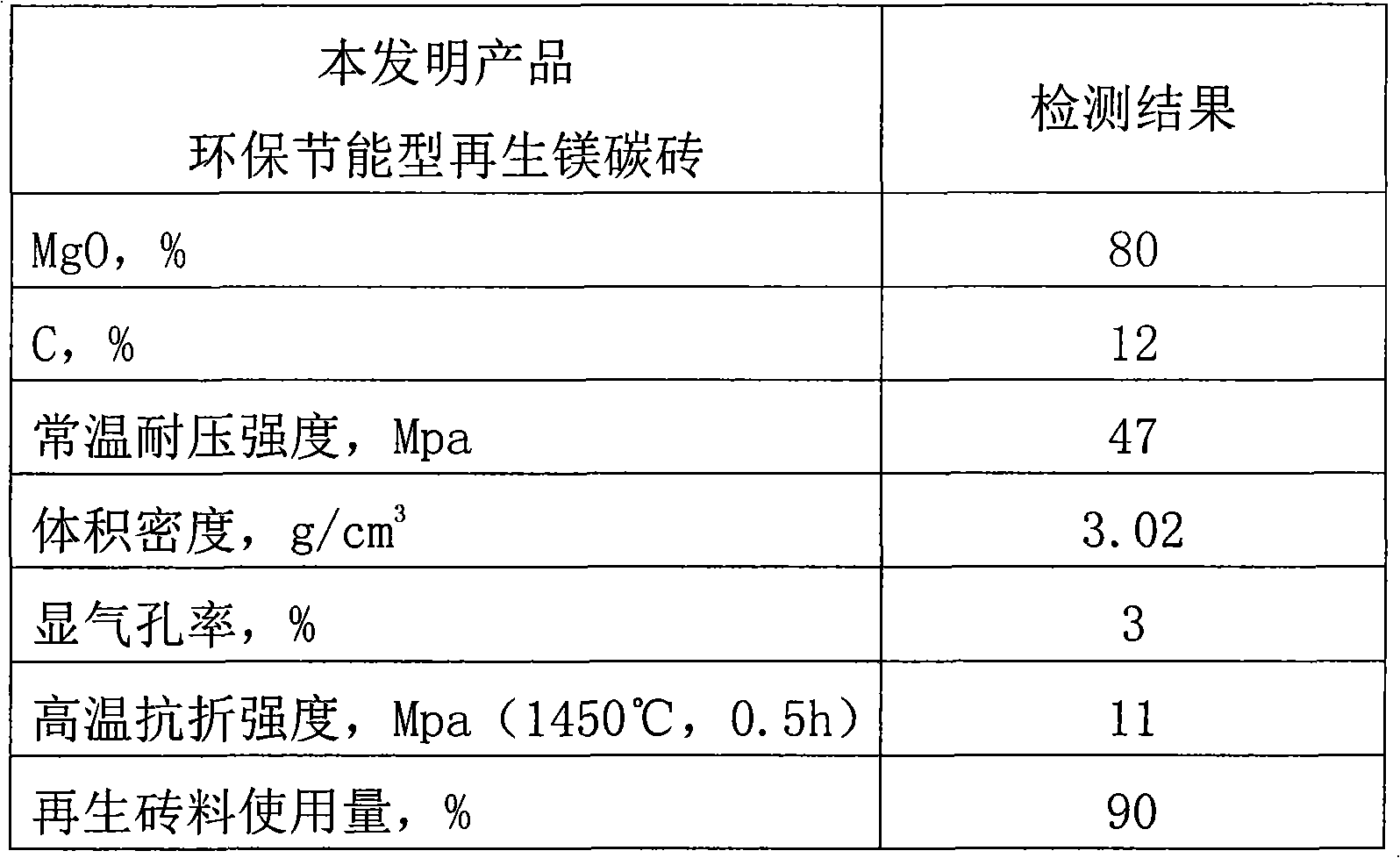
Production method of environment-friendly and energy-saving type regenerative magnesia-carbon brick
InactiveCN101851103AImprove recycling ratesSolve the problem of unstable performanceSolid waste managementBrickResonance
The invention discloses a production method of an environment-friendly and energy-saving type regenerative magnesia-carbon brick, comprising the following production steps: (1) sorting and crushing waste magnesia-carbon bricks; (2) powdering with weak acid aqueous solution; (3) carrying out high-temperature drying to dehydrate and electromagentic resonance to homogenize; (4) carrying out crushing, particle shaping, iron removing and screening; (5) mixing materials: mixing regenerative aggregates, fine powder and newly-added and electrically-fused magnesite aggregates, and fine powder; and (6)forming. The mixed material is added with a bonding agent, is treated by high-speed constant-temperature mixing, hydraulic forming and electric heating drying and obtains a regenerative magnesia-carbon brick product. The production method solves the problem that the product in the prior art has unstable performance, can retain usable components such as electrically-fused magnesite, crystalline flake graphite and the like in the raw material furthest, has high recovery and utilization rate and is energy-saving and environment-friendly.
Owner:吴钦合
Air brick for magnesia carbon ladle and method for producing the same
The invention discloses an air brick used for a magnesium and carbon ladle, and a producing method thereof, aiming at producing high-quality air bricks used for the ladles. The mass percentage of the chemical compositions of the air brick is: 55 to 99 percent of MgO, 0 to 20 percent of C, 0 to 20 percent of AI2O3, 0 to 5 percent of ZrO2, 0 to 5 percent of AI, 0 to 5 percent of AI-Mg alloy, 0 to 5 percent of CaB6, and 0 to 2 percent of B4; the physical property indexes are: volume density (g / cm<3>): 3.00 to 3.15, apparent porosity (%): 1.5 to 5.0, cold compressive strength (MPa): 40 to 65, and distortion resistance at high temperature (MPa): 14.0 to 25.0. Raw materials adopted by the invention comprise fused magnesite, magnesite clinker, crystalline flake graphite, corundum, zirconia and oxidation inhibitor. The raw materials are added into a pug mill and externally added with a bonding agent for mulling. Mulled pug is added into a mould, and molded by utilizing isopressing equipment or a friction brick press or a hydraulic press. The invention obviously reduces the apparent porosity of the air brick, not only can improve the basic slag corrosion resistant capability of the air brick, but also can reduce the cost of the raw materials by more than two thirds.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
Preparation method of graphene oxide modified polycarboxylic acid type water-reducer
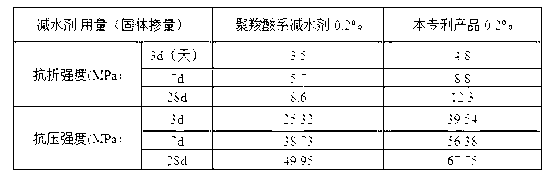
ActiveCN103241983AHigh flexural and compressive strengthRaw materials are easy to getCarbon compoundsCarboxylic acidWater reducer
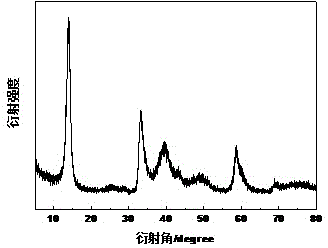
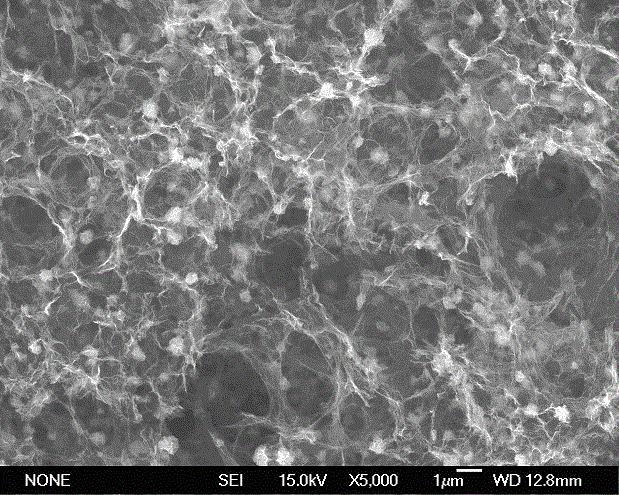
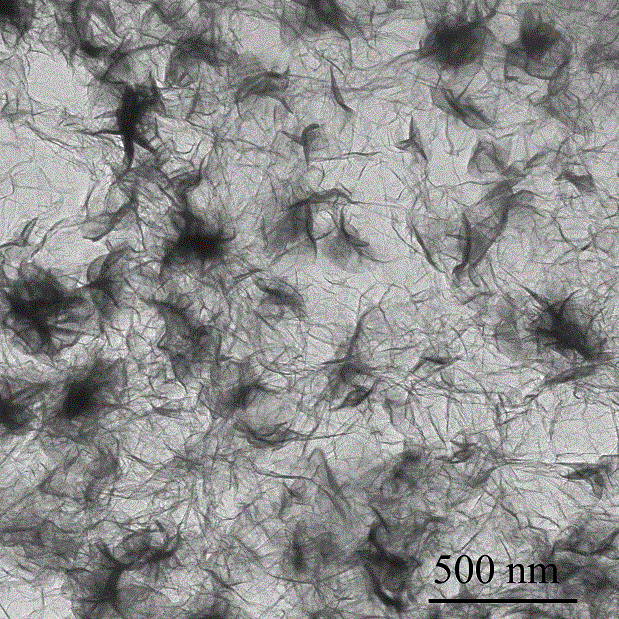
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene oxide modified polycarboxylic acid type water-reducer. A polycarboxylic acid type water-reducer is a novel efficient water-reducer following a naphthalene type water-reducer, a melamine water-reducer and an amino sulfonic acid based water-reducer, but the mechanical property of concrete cannot be obviously improved by adding the polycarboxylic acid type water-reducer. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing graphene oxide with natural flake graphite, sodium nitrate, concentrated sulfuric acid and potassium permanganate as raw materials; carrying out ultrasonic dispersion on the graphene oxide; and then adding the polycarboxylic acid type water-reducer with a certain proportion to form an intercalation compound of the graphene oxide and the polycarboxylic acid type water-reducer. With the adoption of the modified water-reducer, on the basisthat the existing water-reducing rate is kept, the flexural strength and the compressive strength of a cement-based composite are obviously strengthened, the relevant raw materials are easily obtained, a preparation technology is reasonable, pollution in a preparation process is little, the performance of products is excellent, and the graphene oxide modified polycarboxylic acid type water-reducer is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:广西科达新材料集团有限公司
Flake MoS2/graphene composite aerogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104600315AHigh electrical conductivityDeformation stableCell electrodesThioureaFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a flake MoS2 / graphene composite aerogel and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of anode materials of lithium ion batteries. The preparation method comprises the following steps: ultrasonically dispersing a certain quantity of graphene oxide solution into deionized water, adding a certain quantity of water-soluble molybdate and thiourea, then adding 0.1-3mL organic amine solution, taking out a cylindrical product after hydrothermal reaction at the temperature of 160-240 DEG C, freeze-drying, and then carrying out thermal treatment for 2h in the mixed atmosphere of argon and hydrogen at the temperature of 800 DEG C to obtain the flake MoS2 / graphene composite aerogel. According to the flake MoS2 / graphene composite aerogel and the preparation method thereof disclosed by the invention, thin layers of graphene are connected with one another in a staggering mode to form a three-dimensional ordered conductive network and form micron pore canals, MoS2 is uniformly dispersed on the ultra-large superficial area, and thus, the problems of volume expansion and crushing materials are effectively solved; meanwhile, the structure stability and the cycle performance of the flake MoS2 / graphene composite aerogel, serving as the anode material, are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Modified graphene and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses modified graphene and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: performing oxidation treatment on natural flake graphite to obtain graphene oxide, and enabling graphene oxide to react with sulfoxide chloride to obtain graphene containing acyl chloride groups on the surface; then performing nucleophilic substitution reaction with 1,3-propane diamine, cyanuric chloride and a dihydric alcohol compound in sequence to obtain water-soluble graphene with hydroxyl groups on the surface, wherein the hydroxyl group content is 0.005-0.02%. Obtained modified graphene has relatively good water solubility, and is beneficial to stable dispersion of graphene; by adopting the characteristics of modified graphene, modified graphene can be mixed and uniformly dispersed with other concrete preparation materials very conveniently to prepare a reinforcing and toughening concrete product. In addition, operating conditions for preparing modified graphene can be easily met; moreover, modified graphene disclosed by the invention is easily-available in raw material, can be used for effectively reducing the cost and improving the economic benefits, and has relatively good application prospects.
Owner:FUJIAN JIANGXIA UNIV
High-performance semi-metallic brake pad
ActiveCN101555915ASensitive brakesReduce brake noiseFriction liningGraphite particleAluminium silicate
A high-performance semi-metallic brake pad comprises the following components according to weight percentages: 4-6% of nitrile rubber powder, 2-4% of tyre powder, 3-5% of crystalline flake graphite, 6-9% of foam iron powder, 9-13% of boron containing phenolic resin, 8-12% of chopped steel fibre, 2-4% of alumina fibre, 8-11% of red copper fibre, 2-5% of cashew nut oil friction powder, 2-3% of graphite particle, 2-3% of calcined petroleum coke, 7-13% of barite, 3-4% of chromite, 2-3% of magnetite, 2-4% of diatomite, 7-10% of glued aluminium silicate fibre, 3-5% of flake aluminium powder, 2-4% of molybdenum disulfide, 0.2-0.5% of zinc stearate, 0.7-1% of antimony sulphide, 0.5-1% of copper sulphide, and 0.3-0.5% of tungsten carbide. After the brake pad is used, the car brake is sensitive, brake noise is low and comfort performance is good. The brake drum or brake disc has no damage in long-term use.
Owner:摩擦一号制动科技(仙桃)有限公司
Copper-carbon composite material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN106424713APromotes even distributionImprove performanceTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusFiberCarbon composites
The invention discloses a copper-carbon composite material and a preparing method thereof. Natural flake graphite, colloidal graphite, nano graphite, carbon fiber and the like can be selected as a carbon material in the copper-carbon composite material. The preparing method of the copper-carbon composite material includes the steps that firstly, a chemical nickel plating method is used for preparing a nickel plating carbon material; then a chemical copper plating method is used for plating copper on the nickel plating carbon material; and finally, vacuum semi-solid-state low-pressure sintering is conducted on the copper plating carbon material under the copper melting point temperature, and the copper-carbon composite material is prepared. The copper-carbon composite material and the preparing method thereof have the beneficial effects that a layer of even thin nickel plating layer is formed on the surface of carbon through the nickel plating method so as to reduce the wetting angle of the carbon material, the copper plating layer is formed on the surface of the nickel plating carbon material through the copper plating method so that a three-dimensional copper network can be formed by the material in the sintering process, and the bonding strength of a base body is improved through vacuum semi-solid-state low-pressure sintering. The two phases of the base body and the carbon of the copper-carbon composite material prepared through the method are distributed evenly and are well combined, and the good electricity and mechanical properties and the good frictional wear performance are achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Abrasion-resisting surfacing flux-cored wire for coal milling roller
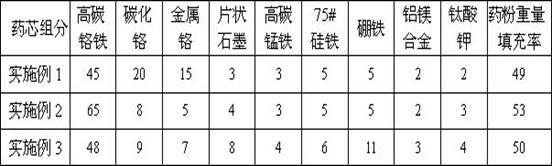
InactiveCN102554503AArc stabilizationLess slagWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHigh carbonFerrosilicon
The invention relates to an abrasion-resisting surfacing flux-cored wire for a coal milling roller, which is composed of high carbon ferro chrome 45-65%, chromium carbide 8-20%, chromium metal 5-15%, flake graphite 3-8%, high carbon ferromanganese 3-6%, 75# ferrosilicon 5-7%, ferroboron 5-15%, aluminum magnesium alloy 2-5% and an agglutinant 2-8%. The diameter of a welding wire is phi 3.2-phi 4.0mm, welding wire metal is a low carbon steel strip, and 49%-53% of cored powder by mass is filled in the formed low carbon steel strip. No protective gas is additionally arranged outside the flux-cored wire, and the manufacturability is good in the self protection open arc welding. During the welding, the arc is stable, the spatter lose rate is low, molten slag is little, the welding can be continuously performed, the welding joint is attractive in forming, the self-protection effect is good, and no air holes is on the surface of the flux-cored wire. The hardness of the abrasion-resisting surfacing flux-cored wire for the coal milling roller reaches above 62 HRC after multilayer surfacing by metal piling, the evenness of the whole hardness is + / -2HRC, and the performance resistant to abrasion of low-stress grinding materials is good.
Owner:LUOYANG SHUANGRUI SPECIAL ALLOY MATERIALS
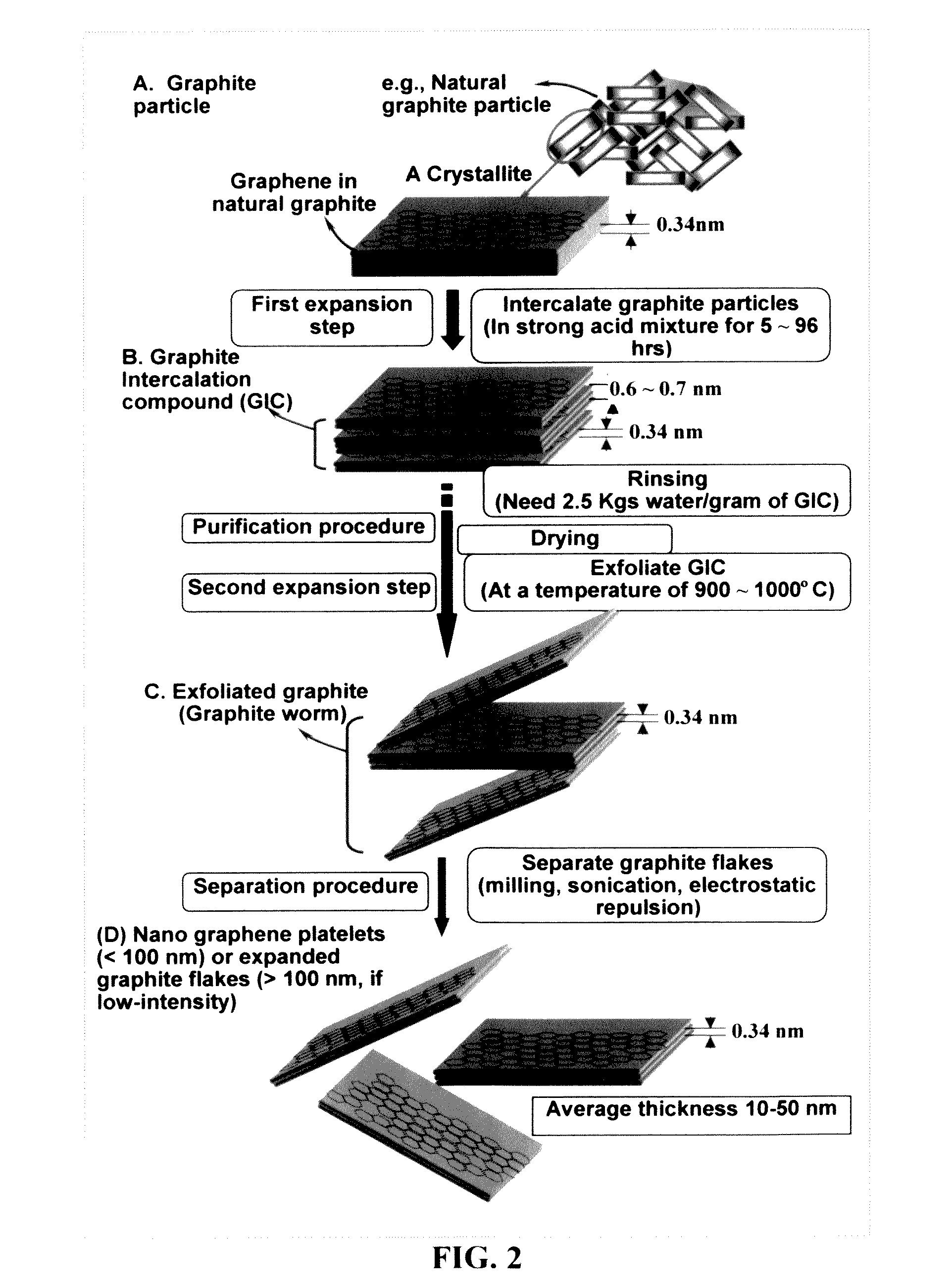
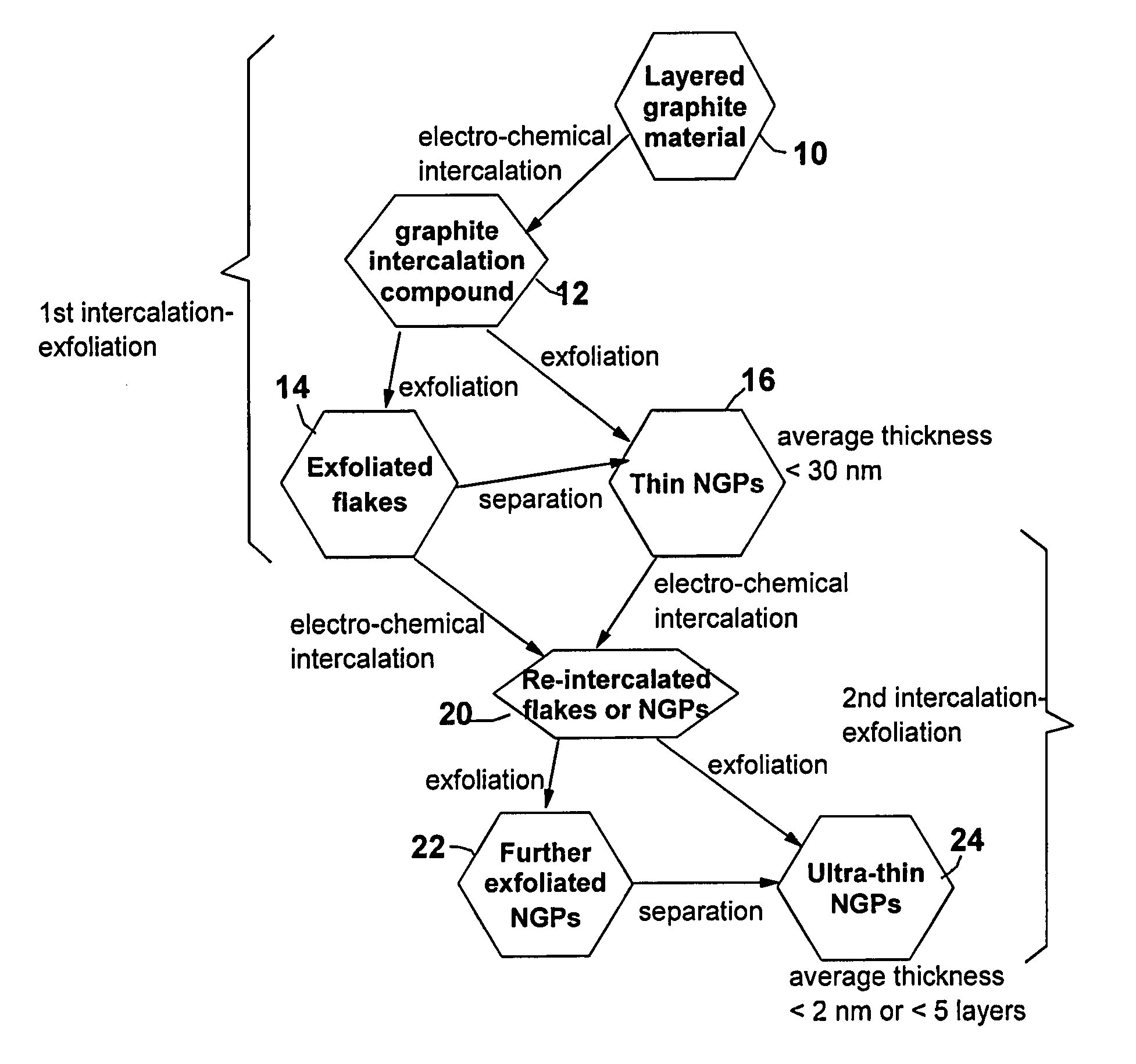
Electrochemical method of producing nano-scaled graphene platelets
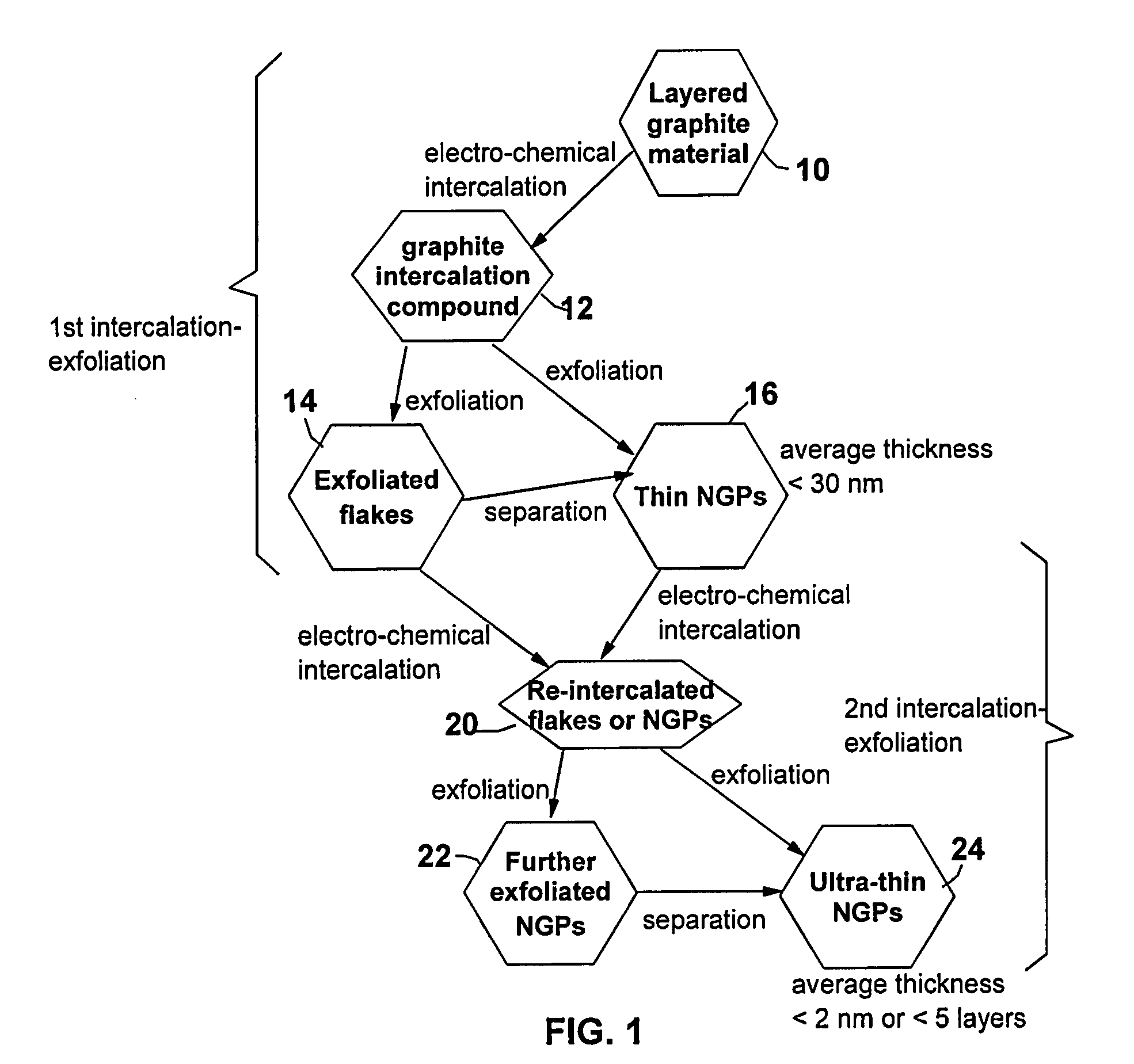
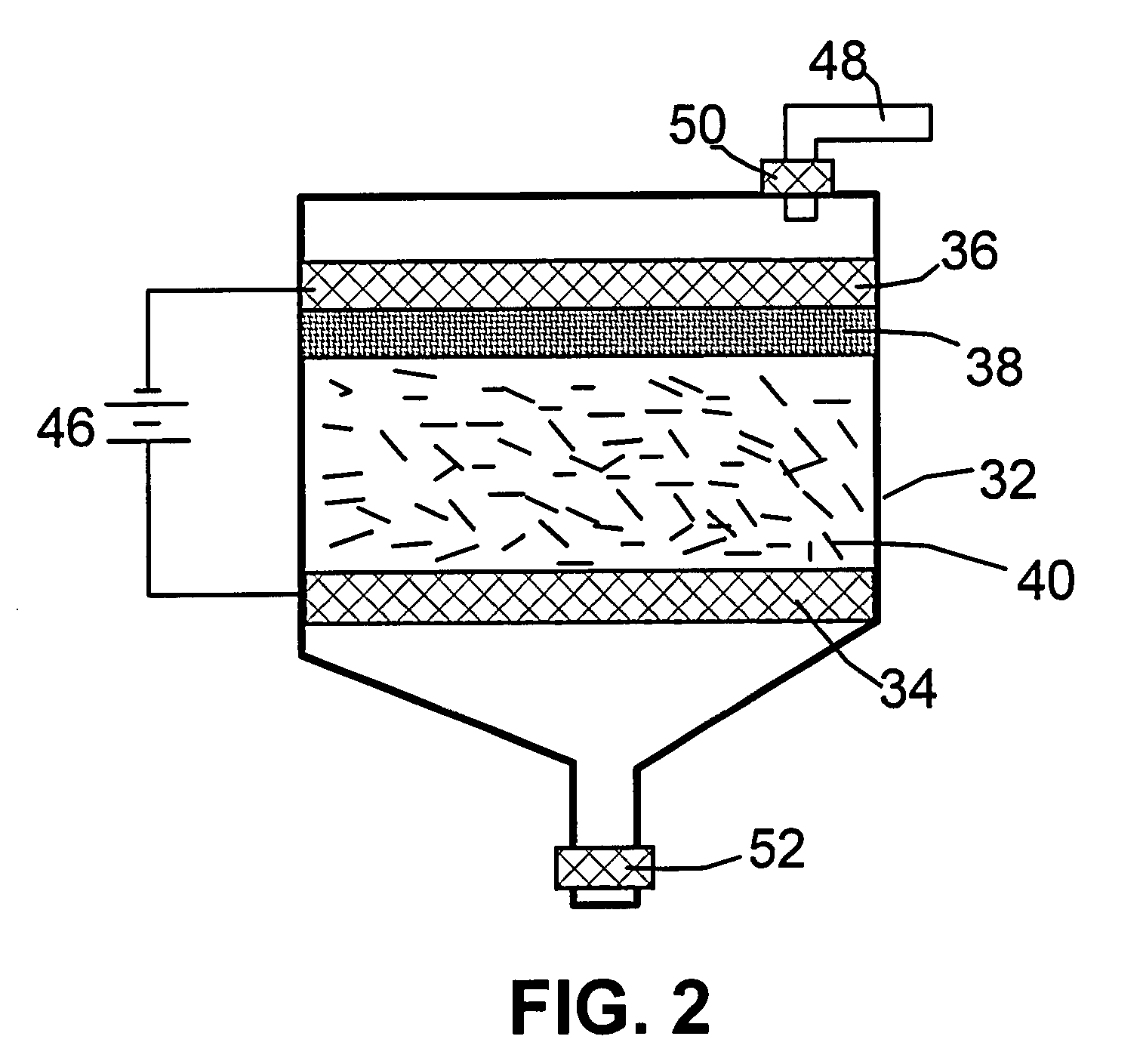
A method of producing nano-scaled graphene platelets with an average thickness smaller than 30 nm from a layered graphite material. The method comprises (a) forming a carboxylic acid-intercalated graphite compound by an electrochemical reaction; (b) exposing the intercalated graphite compound to a thermal shock to produce exfoliated graphite; and (c) subjecting the exfoliated graphite to a mechanical shearing treatment to produce the nano-scaled graphene platelets. Preferred carboxylic acids are formic acid and acetic acid. The exfoliation step in the instant invention does not involve the evolution of undesirable species, such as NOx and SOx, which are common by-products of exfoliating conventional sulfuric or nitric acid-intercalated graphite compounds. The nano-scaled platelets are candidate reinforcement fillers for polymer nanocomposites. Nano-scaled graphene platelets are much lower-cost alternatives to carbon nano-tubes or carbon nano-fibers.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com