Patents
Literature
642 results about "Absorption band" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
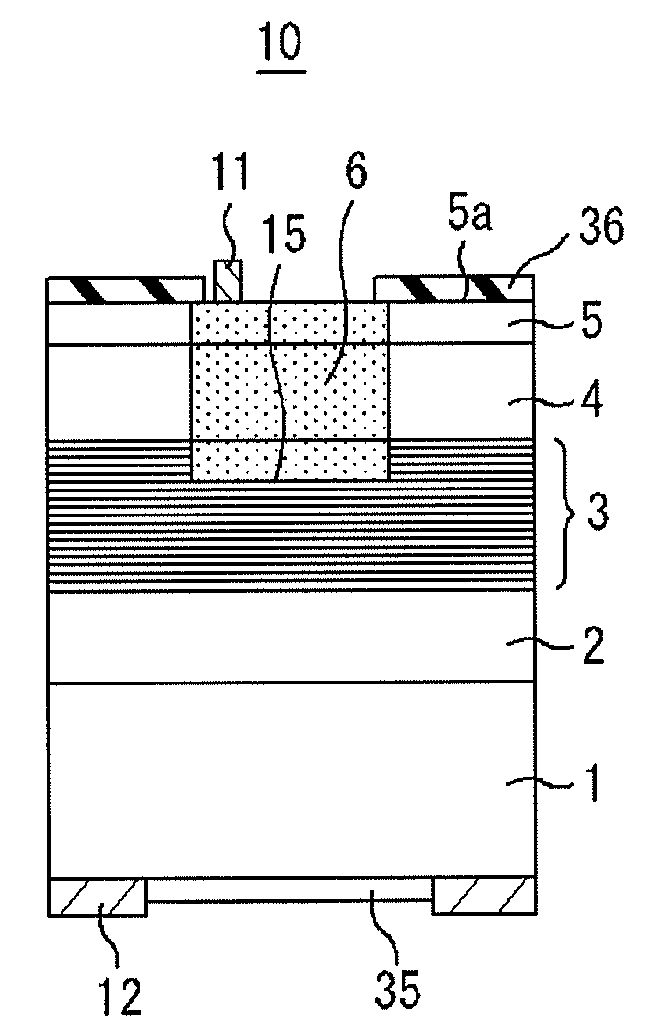
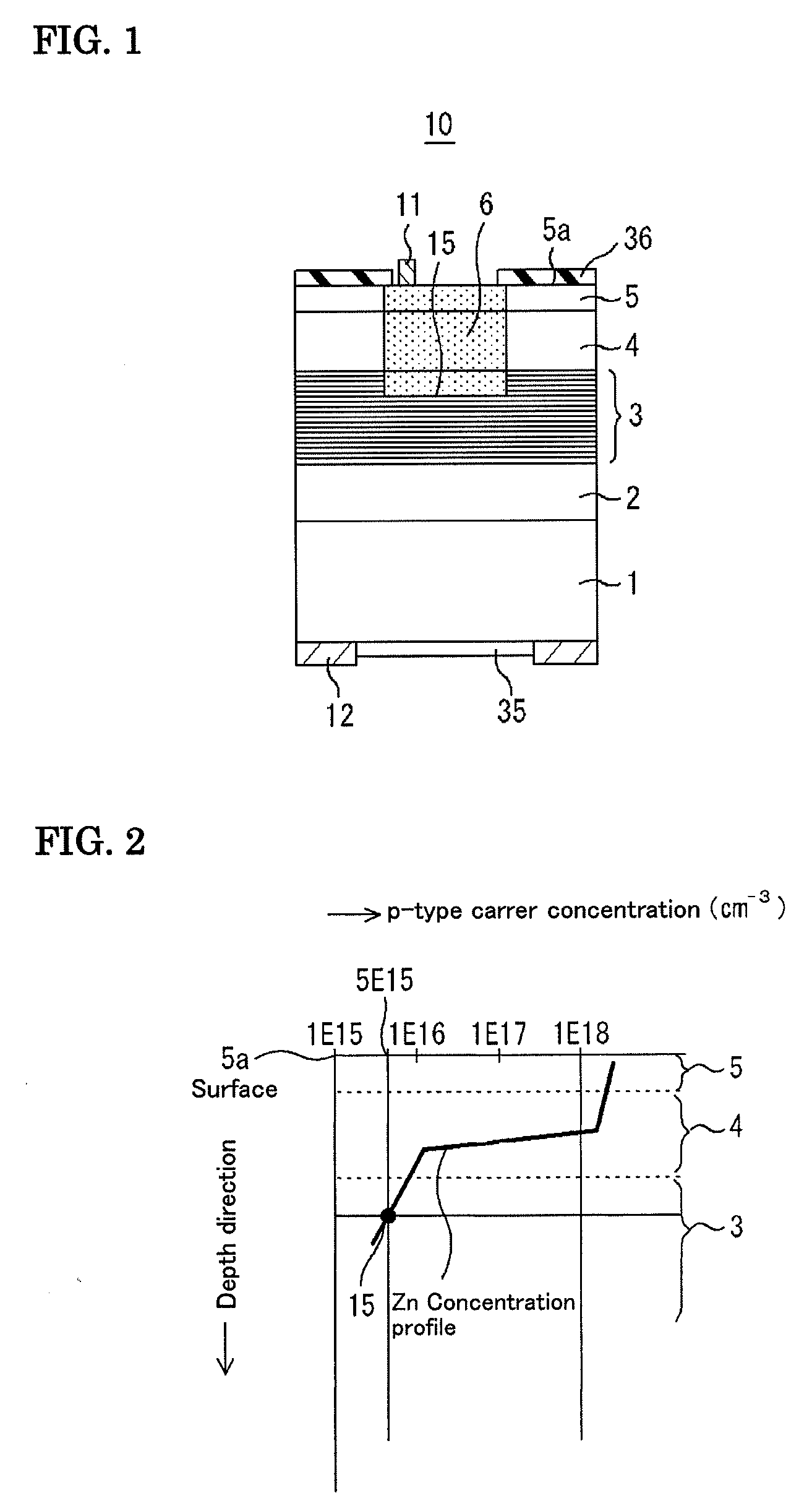
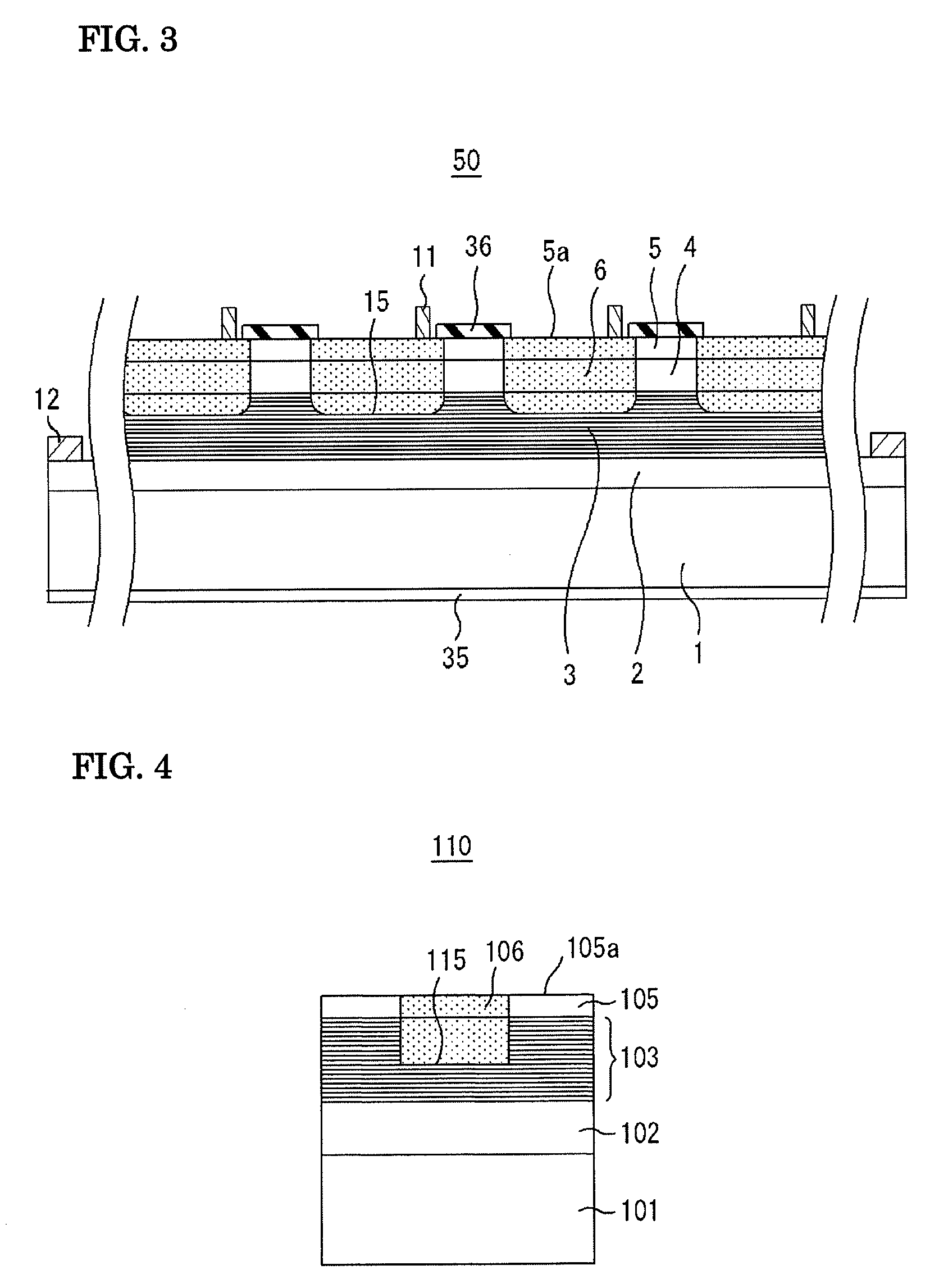
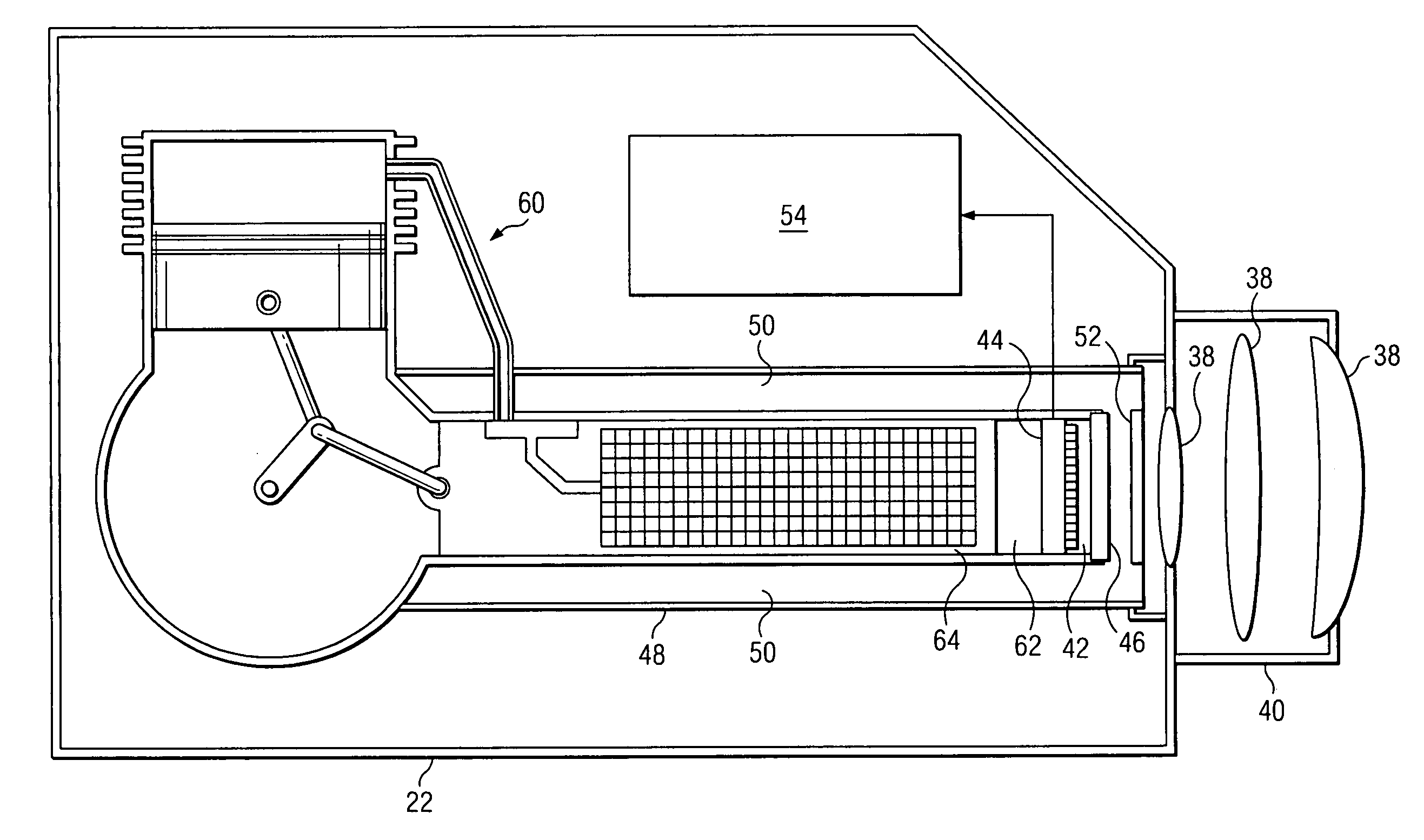
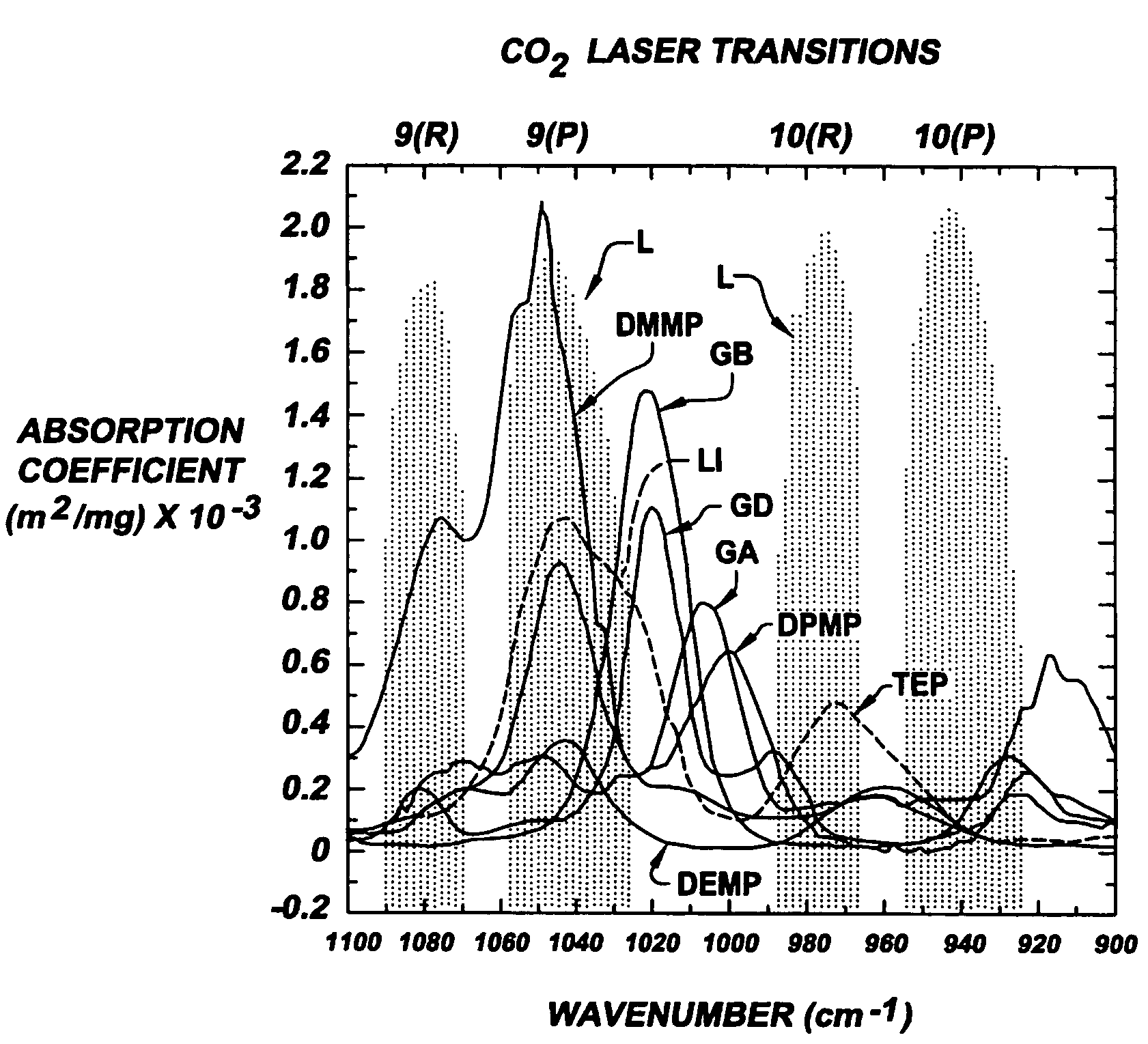
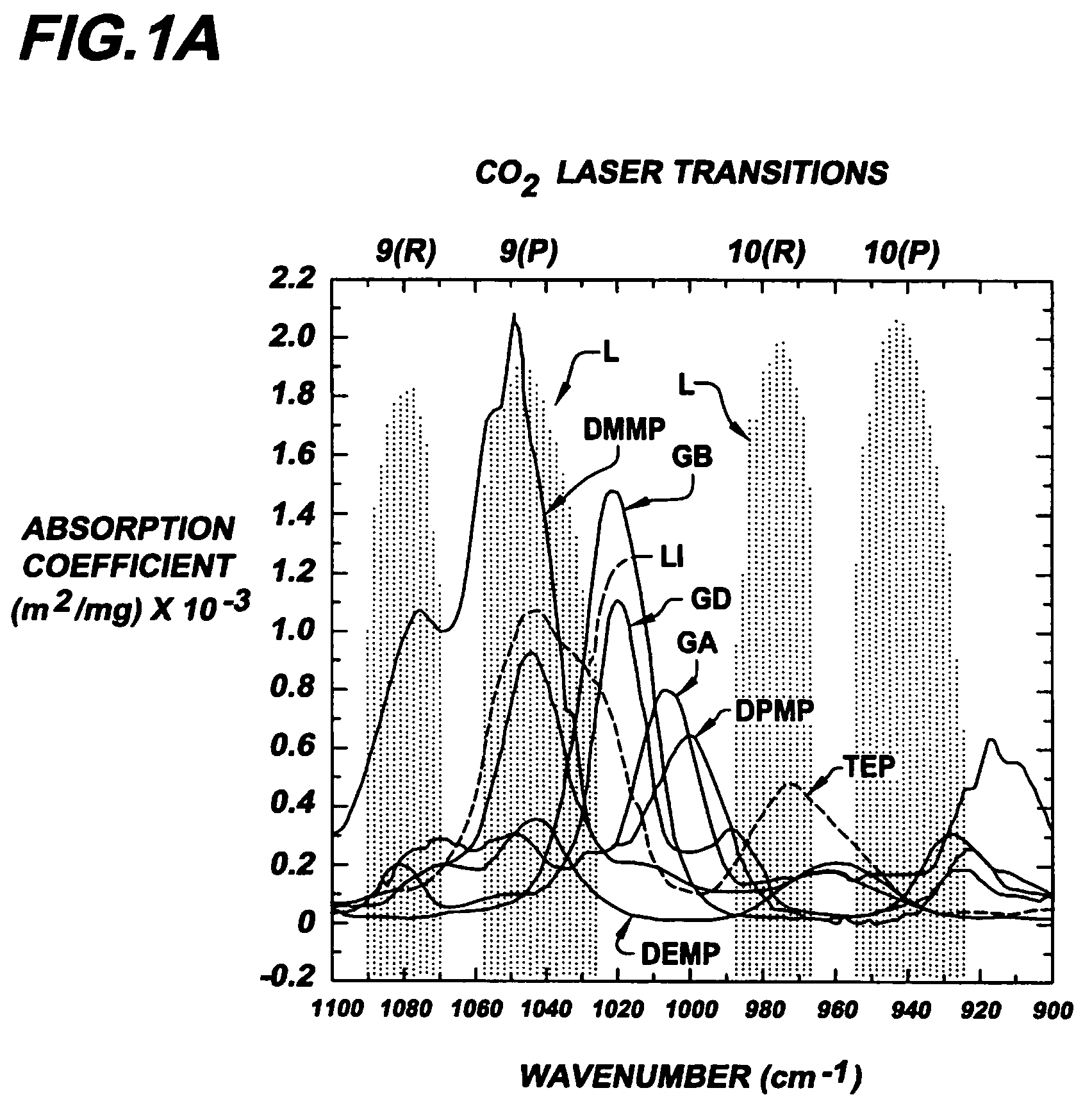
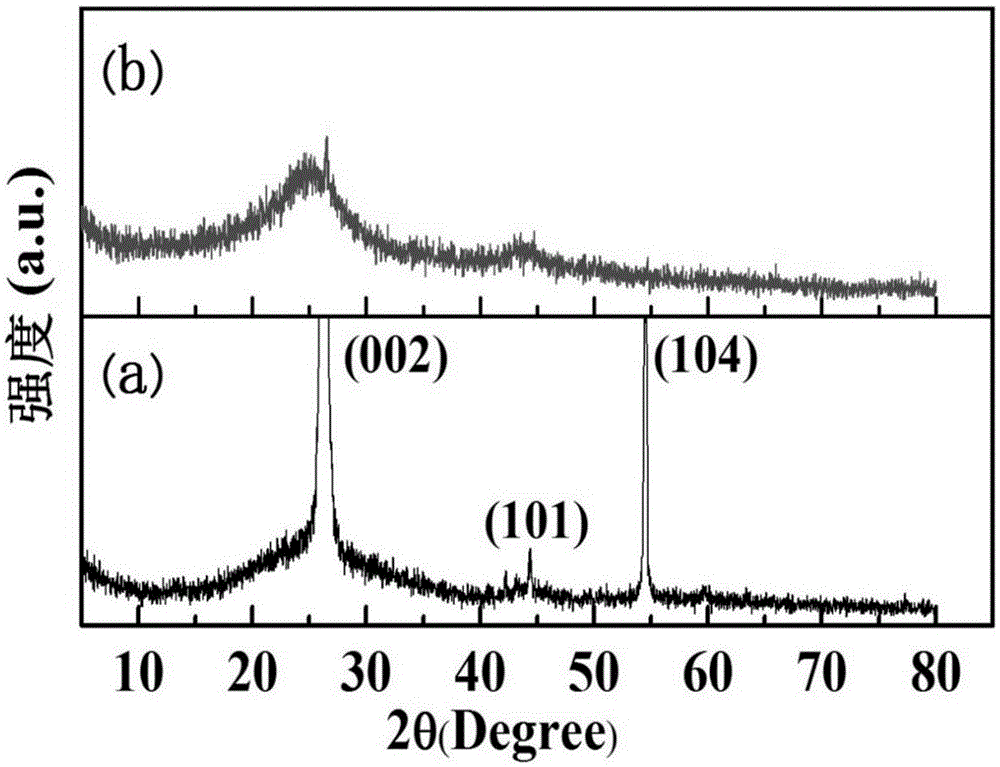
According to quantum mechanics, atoms and molecules can only hold certain defined quantities of energy, or exist in specific states. When such quanta of electromagnetic radiation are emitted or absorbed by an atom or molecule, the energy of the radiation changes the state of the atom or molecule from an initial state to a final state. An absorption band is a range of wavelengths, frequencies or energies in the electromagnetic spectrum which are characteristic of a particular transition from initial to final state in a substance.
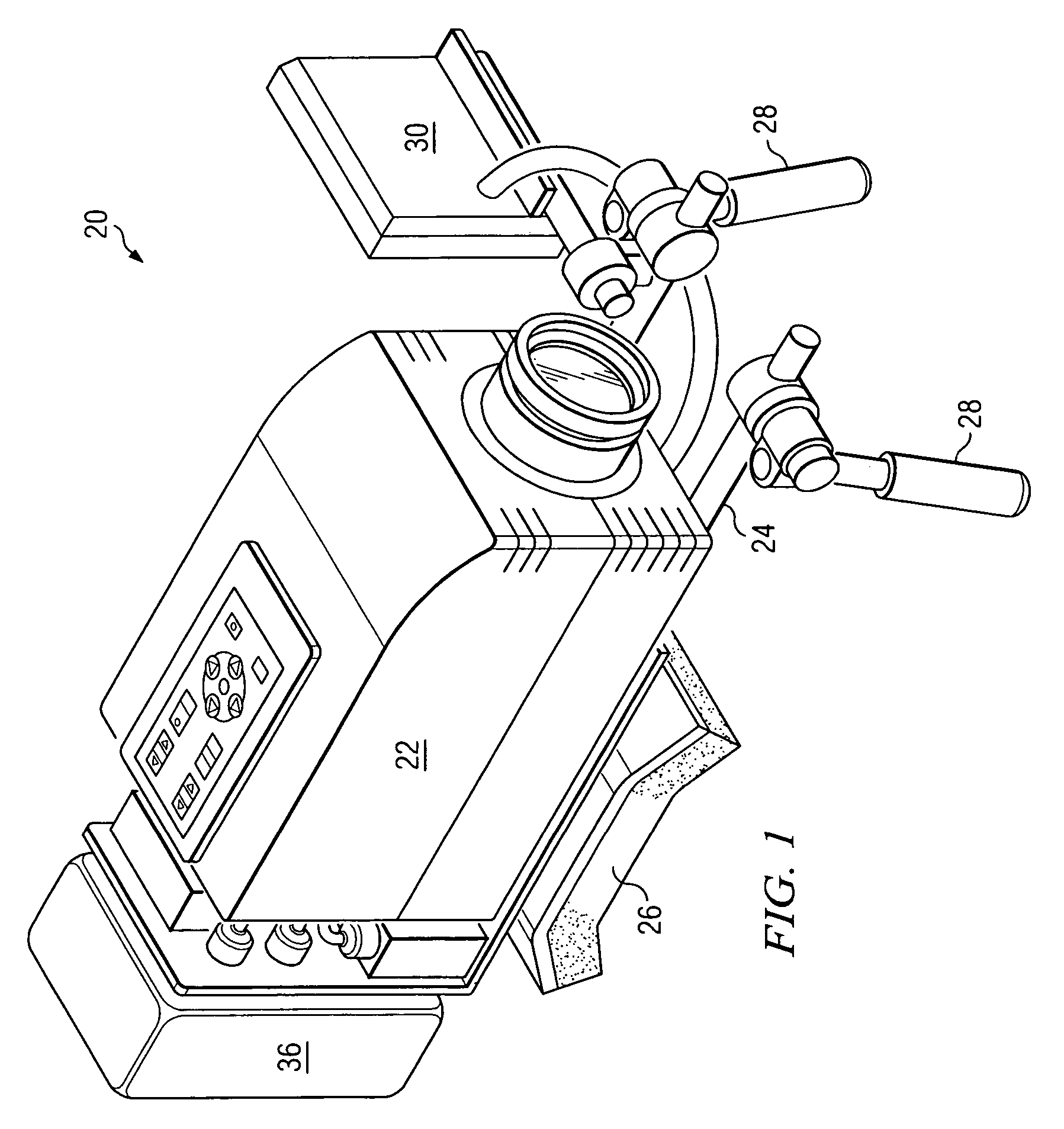
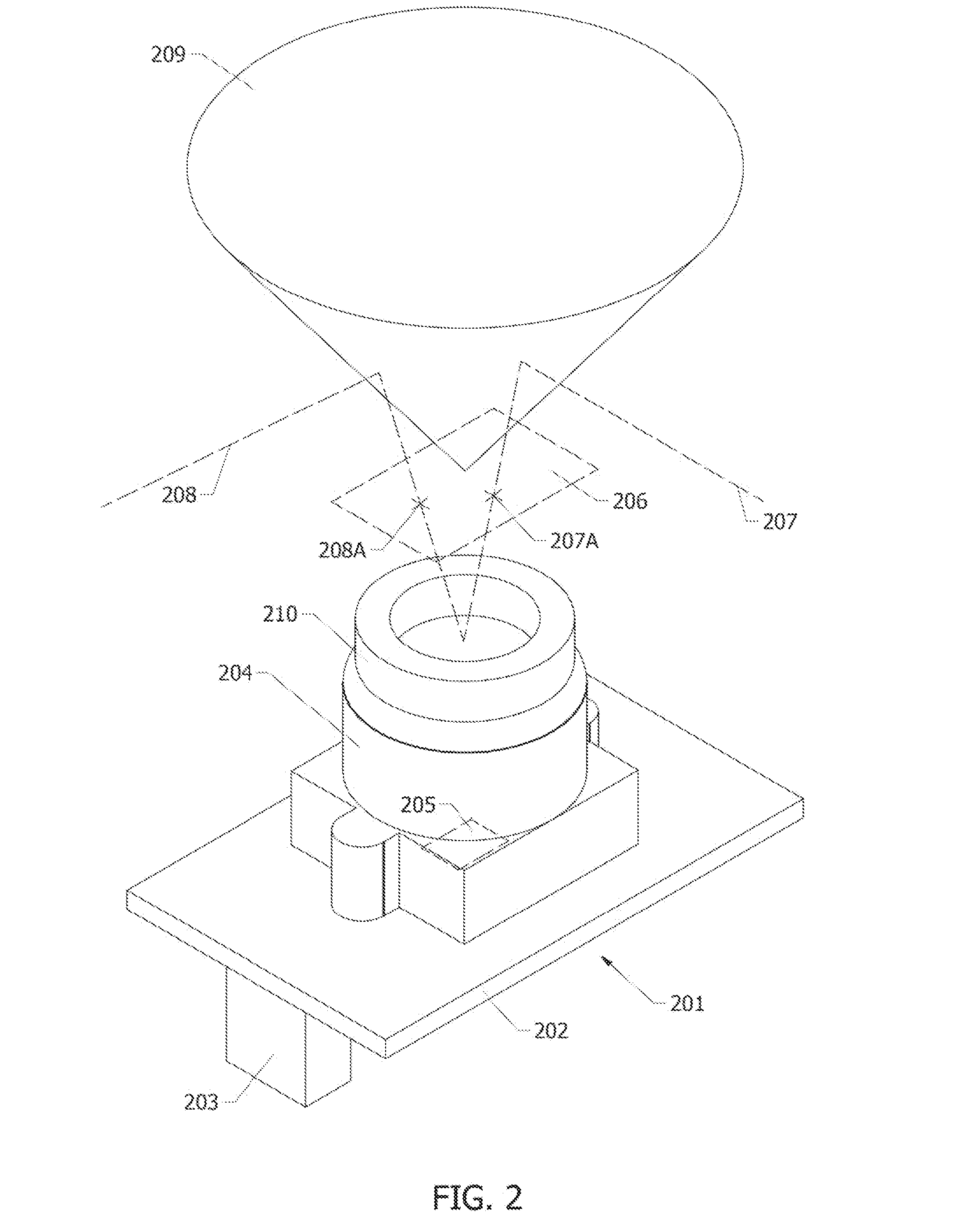
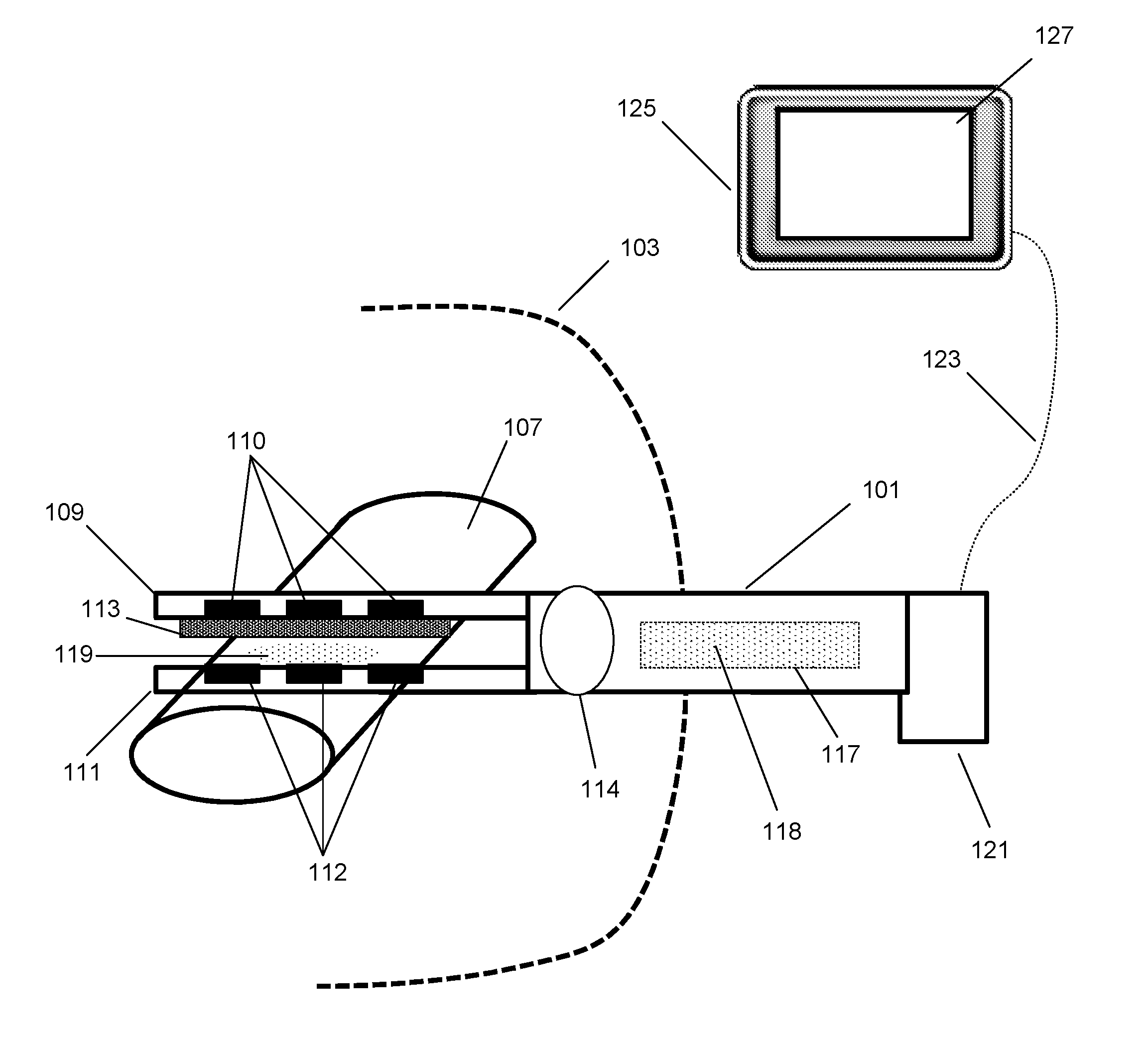
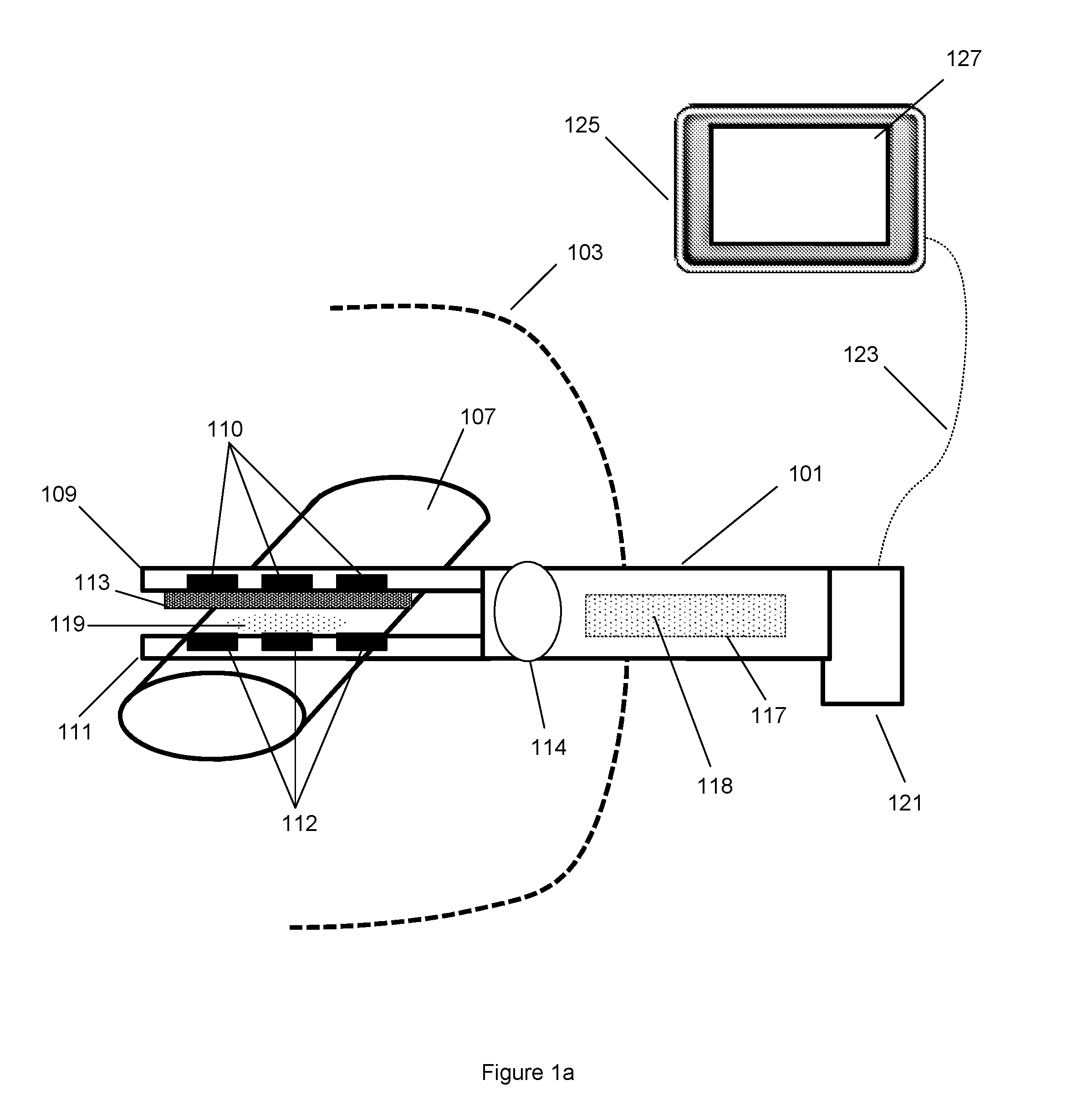
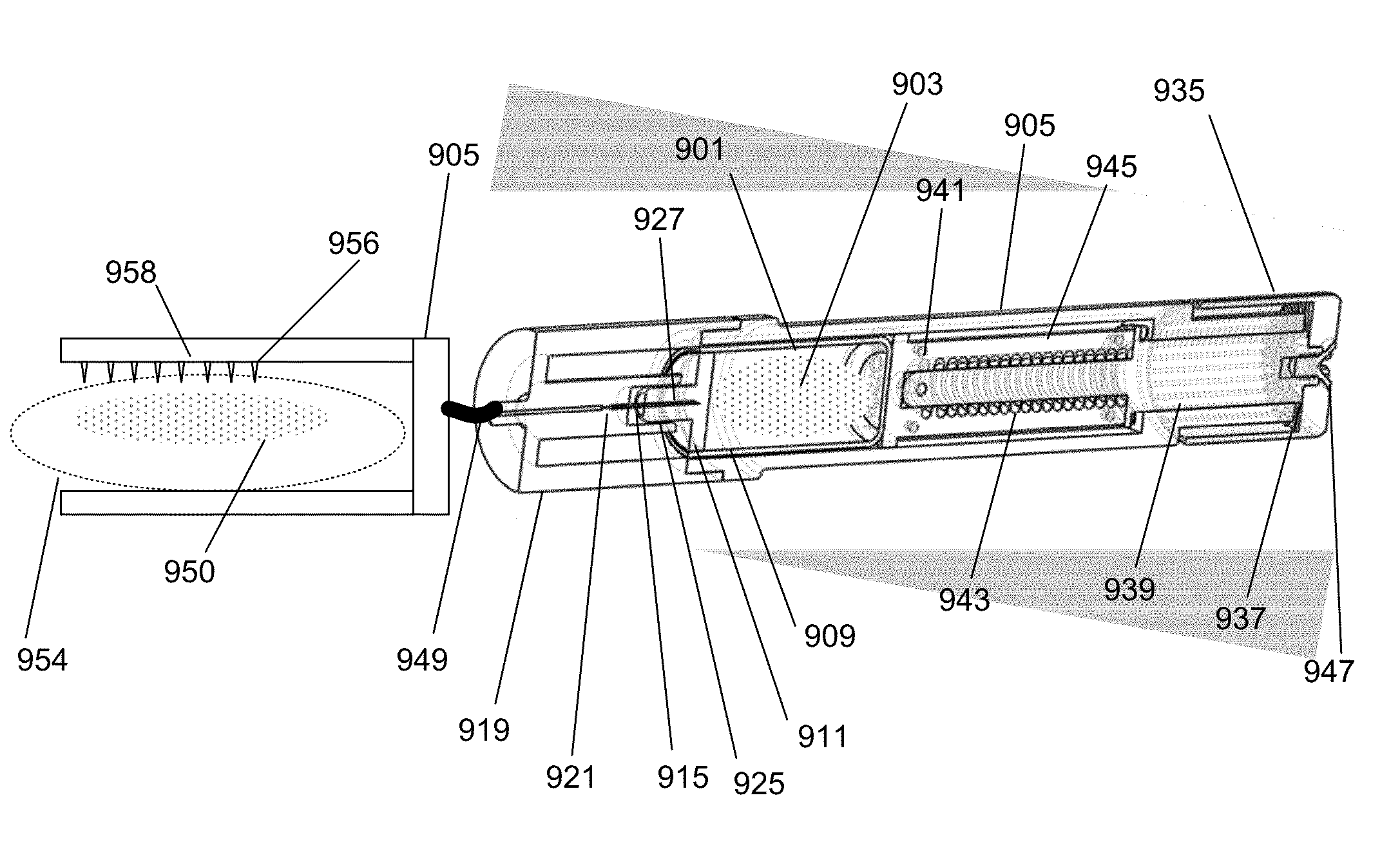
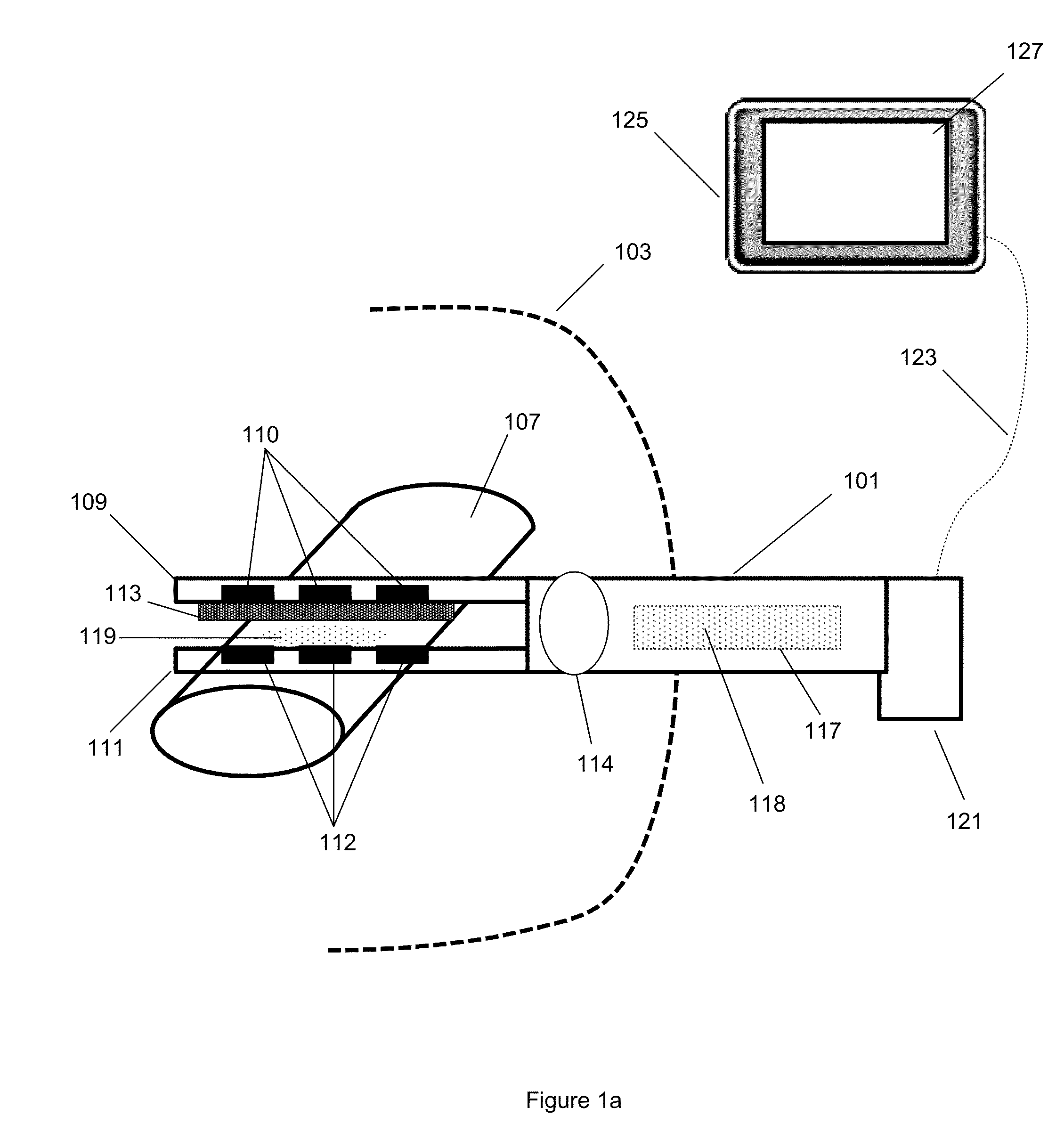
Apparatus, systems and methods for determining tissue oxygenation
A surgical instrument may be configured to sense a light re-emitting probe to resolve tissue oxygenation, the surgical instrument including: an optical emitter configured to excite the light re-emitting probe within an absorption band of the light re-emitting probe; an optical detector configured to receive the re-emitted light from the probe; and a signal processor configured to resolve the tissue oxygenation based on the received light. The surgical instrument can be a surgical stapler anvil or a flexible substrate having a tissue interfacing surface. Further, a monitoring device may be configured to map oxygenation of a tissue containing a light re-emitting probe, the monitoring device including: an optical emitter configured to excite the light re-emitting probe; at least one optical detector configured to receive the re-emitted light from the probe; and a signal processor that is configured to resolve the tissue oxygenation at multiple points to generate an oxygen map.
Owner:SURGISENSE CORP
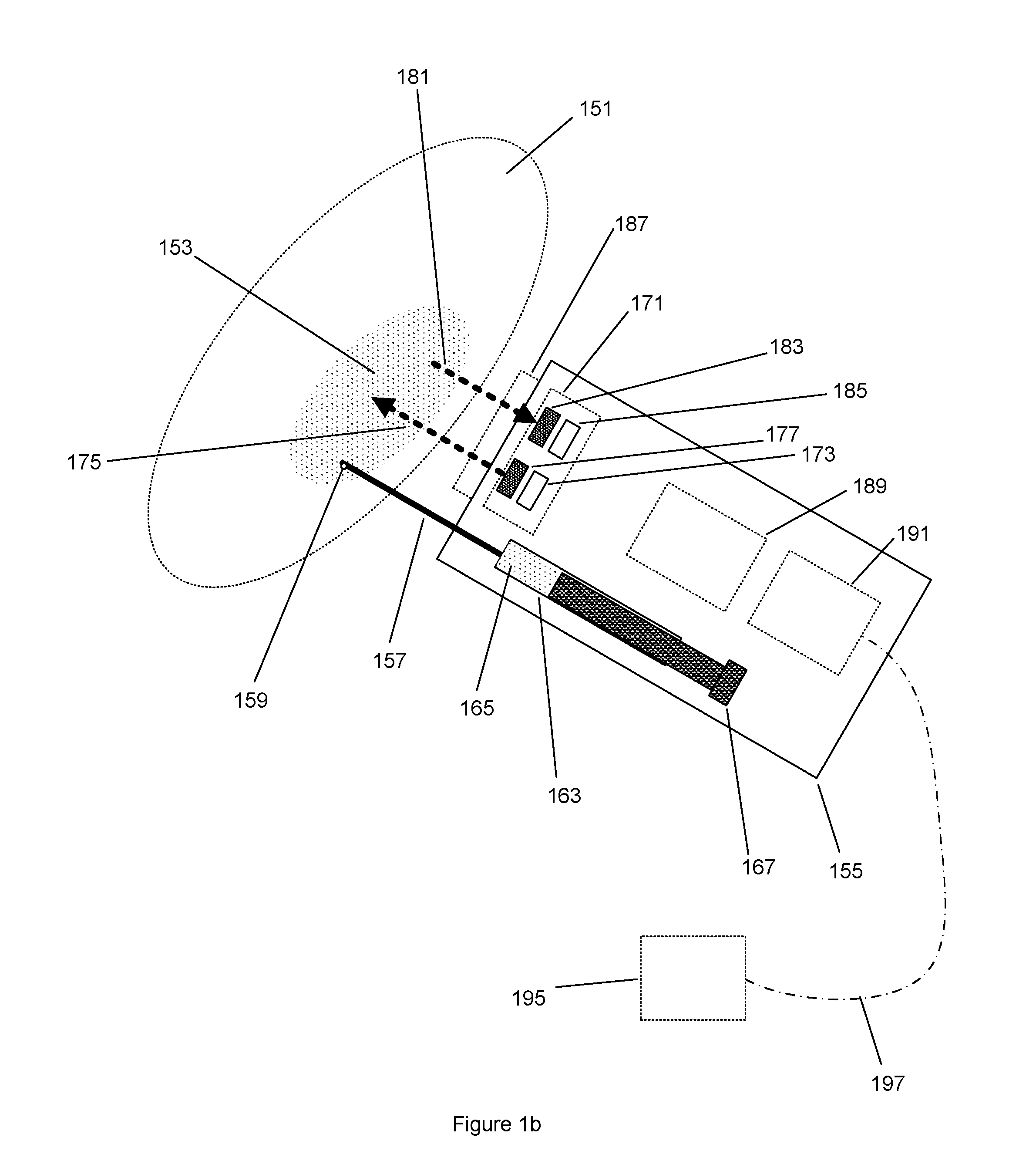
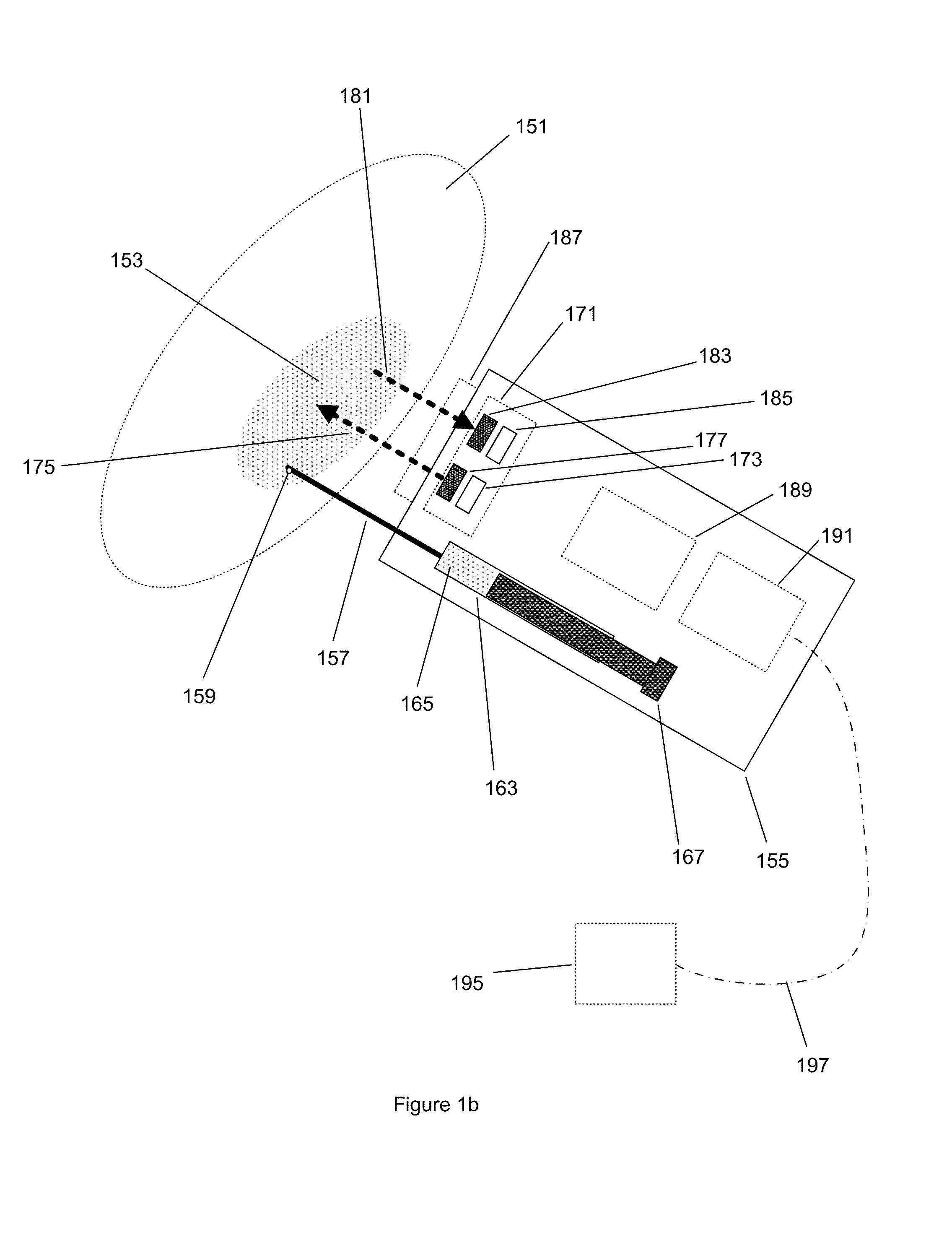
System and method for detecting and identifying an analyte
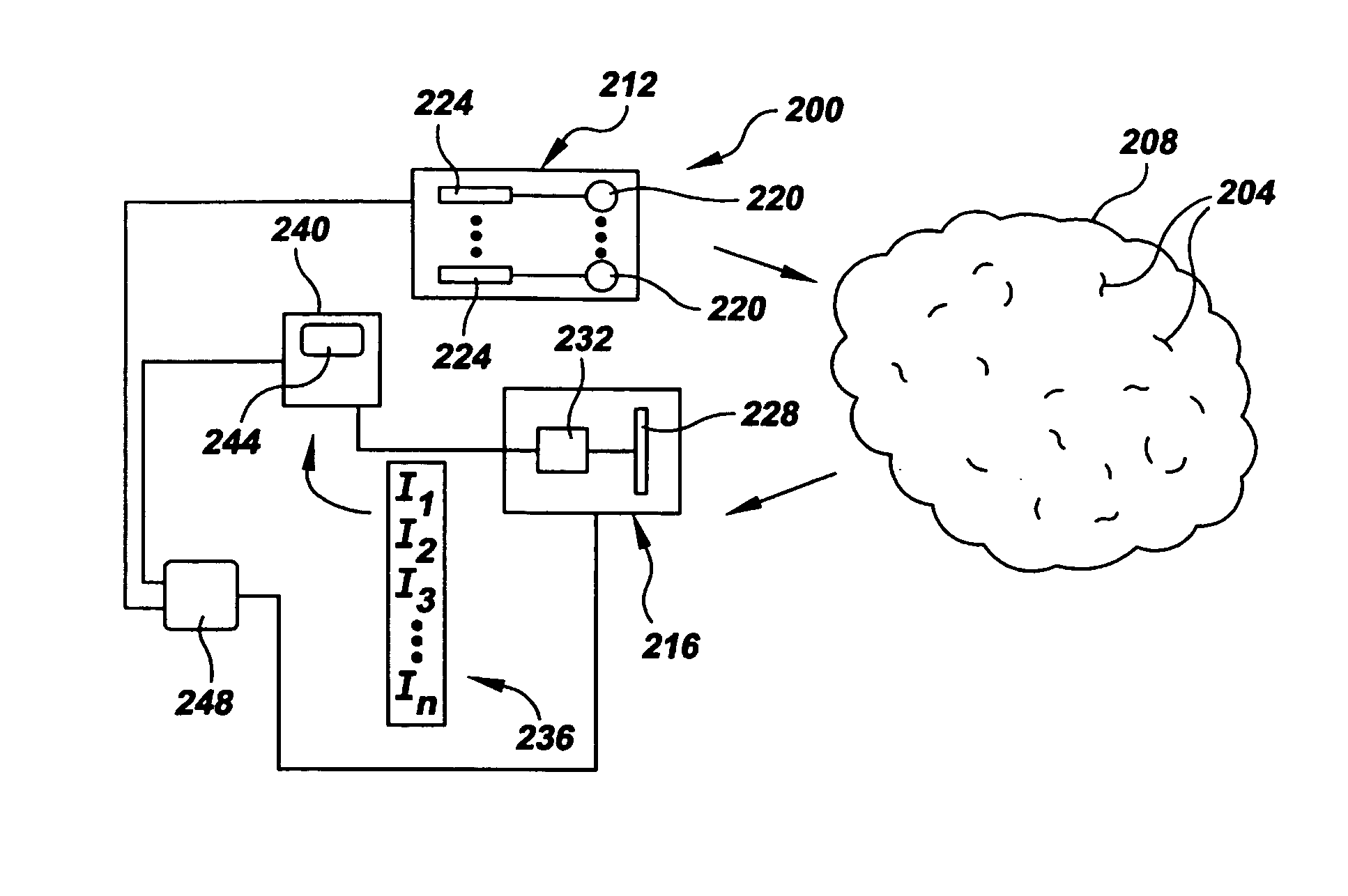
A sensor (200, 900) comprising an illuminator (212, 500, 804, 832, 858, 904), a receiver (216, 400, 420, 460, 480, 808, 836, 862, 924) and an analyzer (240) for detecting and identifying an analyte having a characteristic absorption band that is present in a sample region (208, 812, 824, 874, 922). The illuminator includes an illumination source (220) for illuminating the sample region with spectral energy across at least a portion of the characteristic absorption band. The receiver includes a detector (228, 404, 424, 460, 484, 866, 928) for sensing predetermined portions of the spectral energy band and for creating a sample spectral data vector (236). The analyzer uses the spectral data vector and known characteristic data to detect and identify the analyte.
Owner:QUANTASPEC
Methods for performing inspections and detecting chemical leaks using an infrared camera system
InactiveUS20060091310A1Detection of fluid at leakage pointTelevision system detailsBandpass filteringCamera lens
A method of visually detecting a leak of a chemical emanating from a component. The method includes: aiming a passive infrared camera system towards the component; filtering an infrared image with an optical bandpass filter, the infrared image being that of the leak; after the infrared image passes through the lens and optical bandpass filter, receiving the filtered infrared image with an infrared sensor device; electronically processing the filtered infrared image received by the infrared sensor device to provide a visible image representing the filtered infrared image; and visually identifying the leak based on the visible image. The passive infrared camera system includes: a lens; a refrigerated portion including therein the infrared sensor device and the optical bandpass filter (located along an optical path between the lens and the infrared sensor device). At least part of a pass band for the optical bandpass filter is within an absorption band for the chemical.
Owner:LEAK SURVEYS
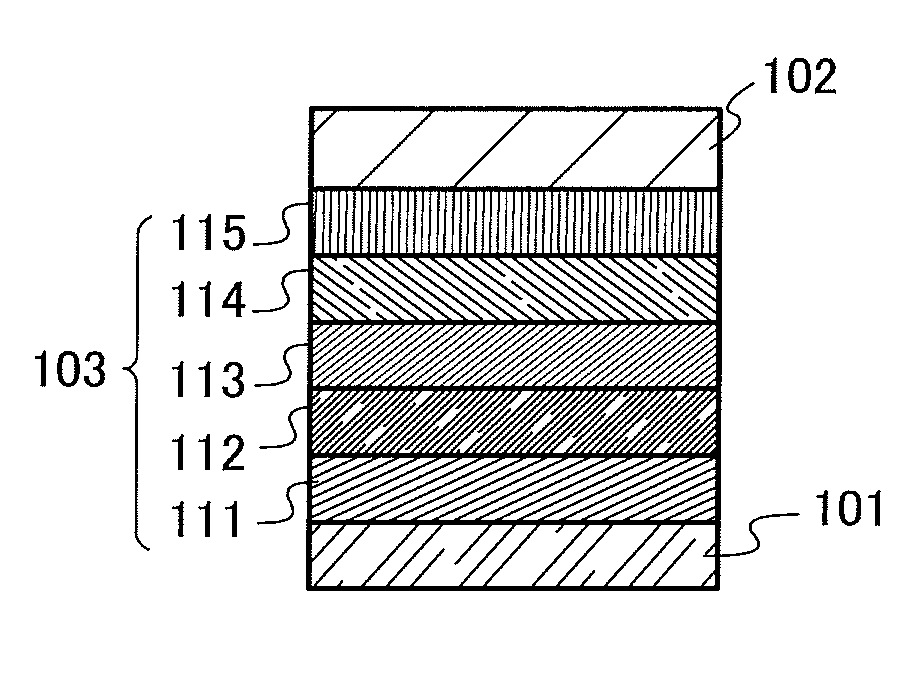
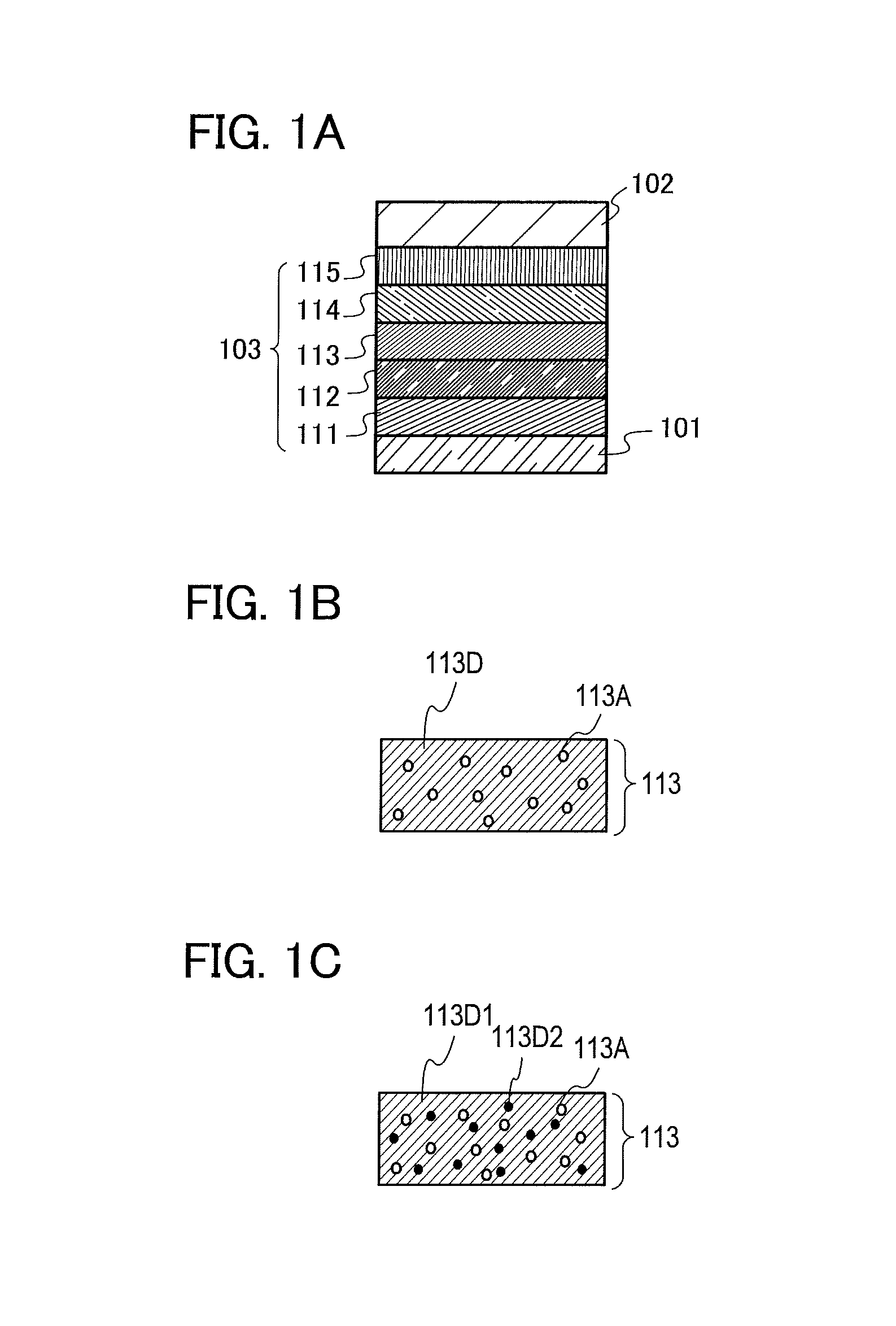
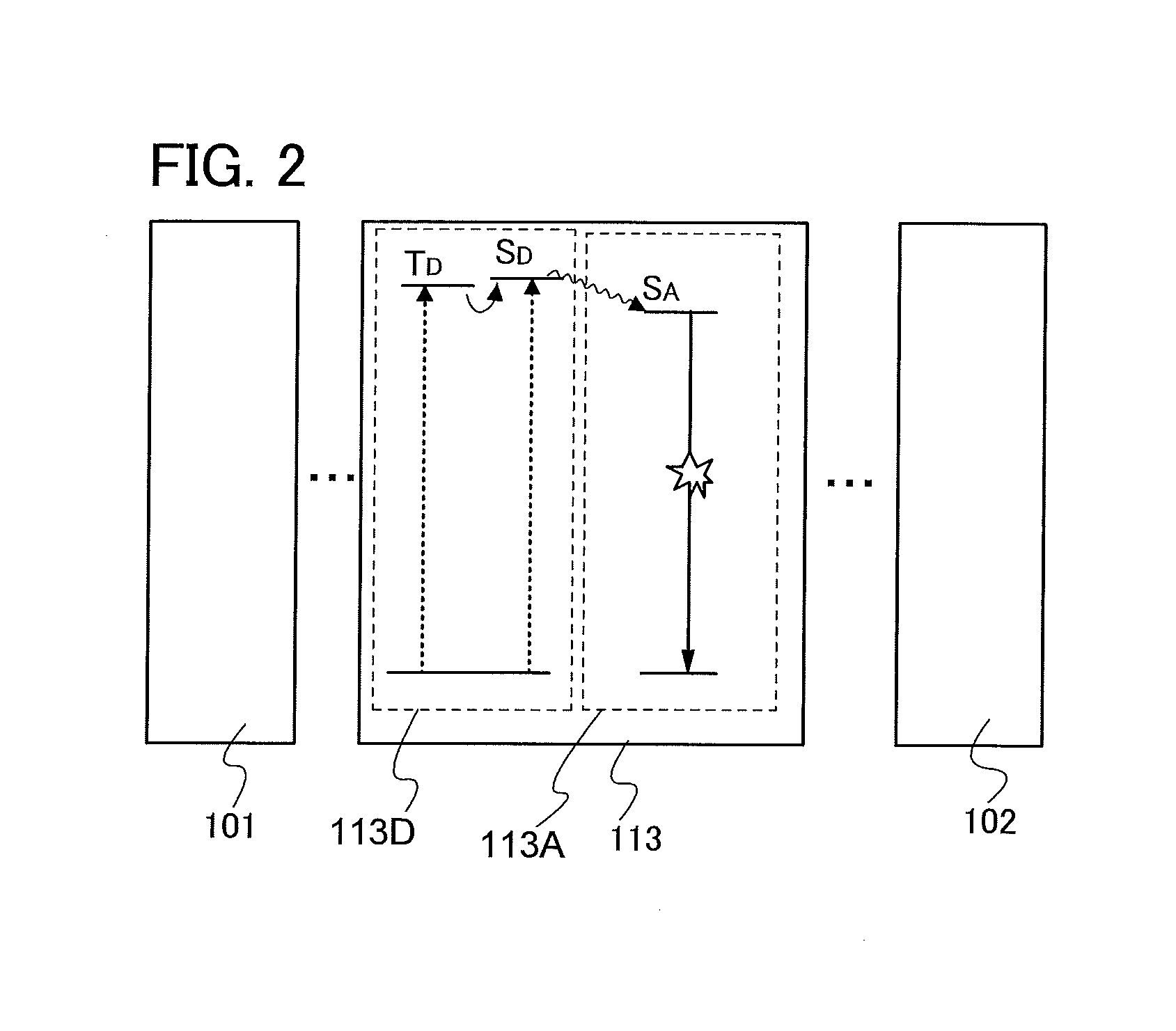
Light-emitting element, light-emitting device, display device, electronic device, and lighting device
ActiveUS20130306945A1Improve emission efficiencyReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescenceDisplay device
An object is to provide a light-emitting element which includes an exciplex being used as an energy donor capable of efficiently transferring energy to a substance exhibiting thermally activated delayed fluorescence. The exciplex comprises two kinds of substances and its singlet and triplet excited states are close to each other. Thus, by making light emission of the exciplex overlap with an absorption band on the longest wavelength side which corresponds to absorption by the substance exhibiting thermally activated delayed fluorescence, i.e., an energy acceptor, in a singlet excited state, it becomes possible to achieve efficient energy transfer from a singlet excited state of the exciplex to a singlet excited state of the substance exhibiting thermally activated delayed fluorescence, and it also becomes possible to achieve efficient energy transfer from a triplet excited state of the exciplex to a triplet excited state of the substance exhibiting thermally activated delayed fluorescence.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Visibly transparent dyes for through-transmission laser welding
InactiveUS6911262B2Add little or no light scatteringEffective radiationMechanical working/deformationLamination ancillary operationsSelection criterionThrough transmission
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Method for producing UV polarizers
The invention relates to a method for producing UV polarizers, according to which spheroid particles situated near the surface of the glass are incorporated into the support material (primarily standard float glass) in a novel arrangement. According to the method for producing UV polarizers, after the introduction of metal ions (e.g., silver ions) into the glass surface, a large size distribution of particles is achieved by multiple alternation of a heat treatment for separating out spherical metal particles, followed by the renewed introduction of metal ions and a subsequent heat treatment. A deformation of the glass produces spheroid particles of various sizes and different semi-axis relationships. The particles are characterized by their large size distribution and are deformed differently in relation to their spheroid shape. In this way UV polarizers are produced which have a wide absorption range since the absorption bands having different maximum positions overlap.
Owner:F O B GES ZUR FERTIGUNG FARBIGER OPTOELEKTRONISCHER BAUELEMENTE
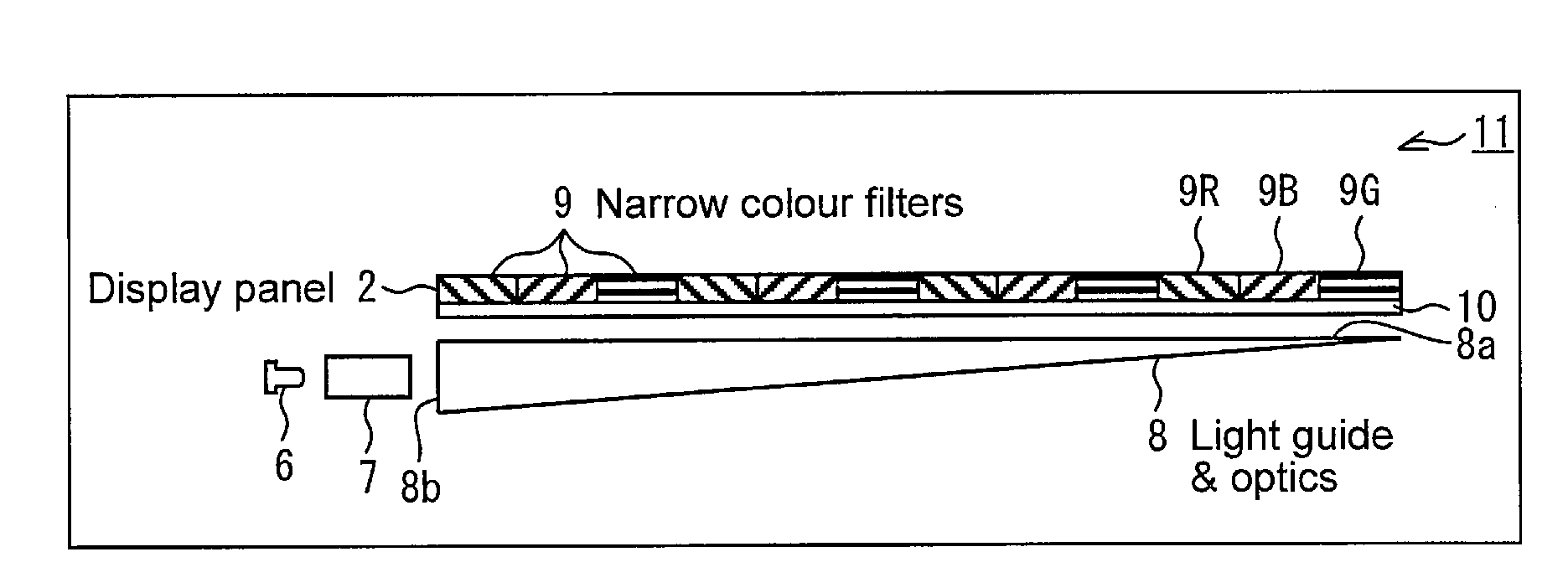
Display
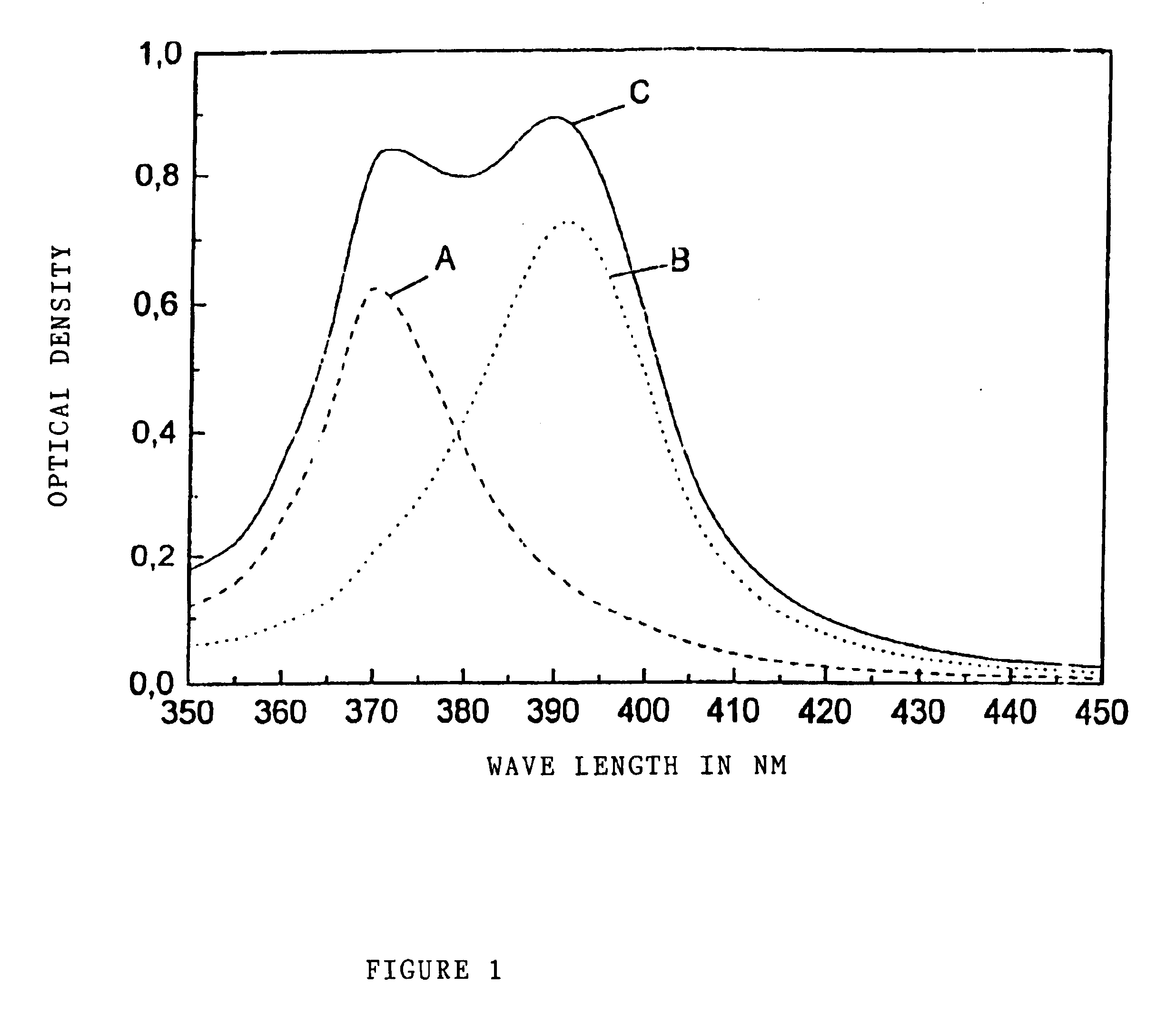
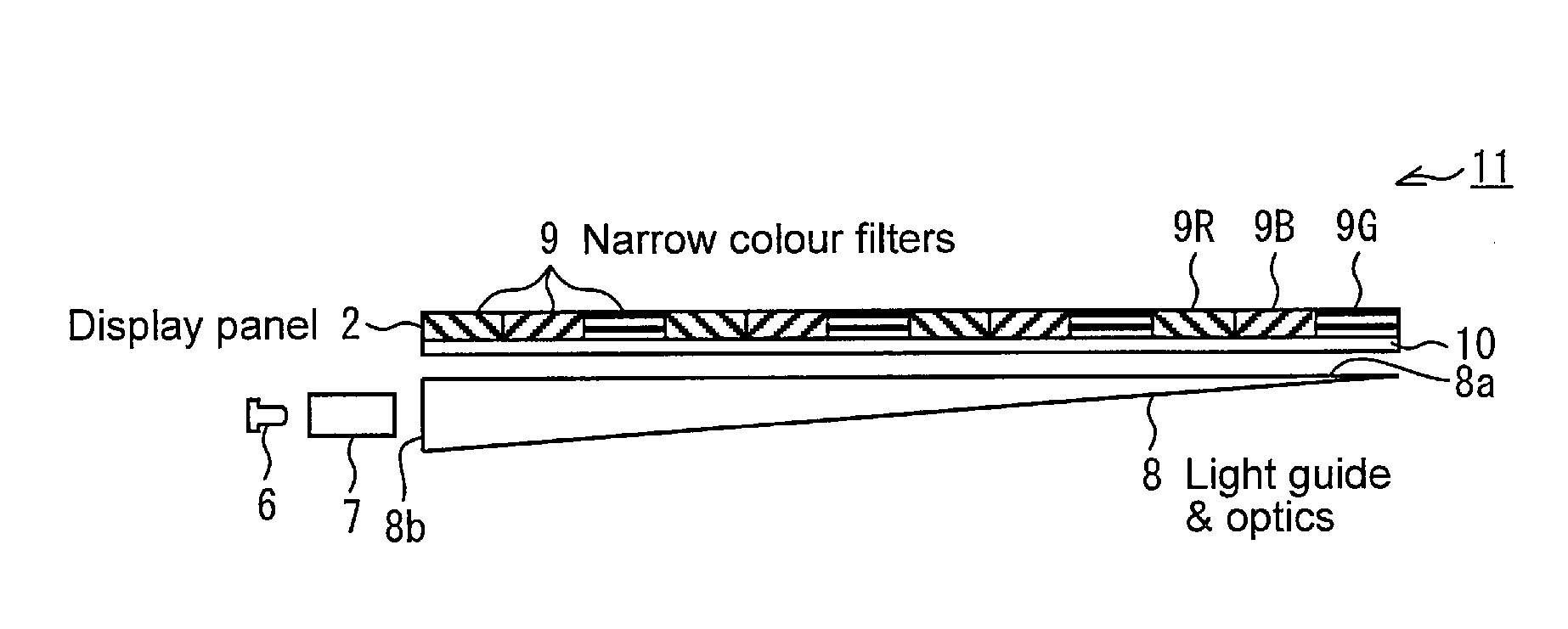
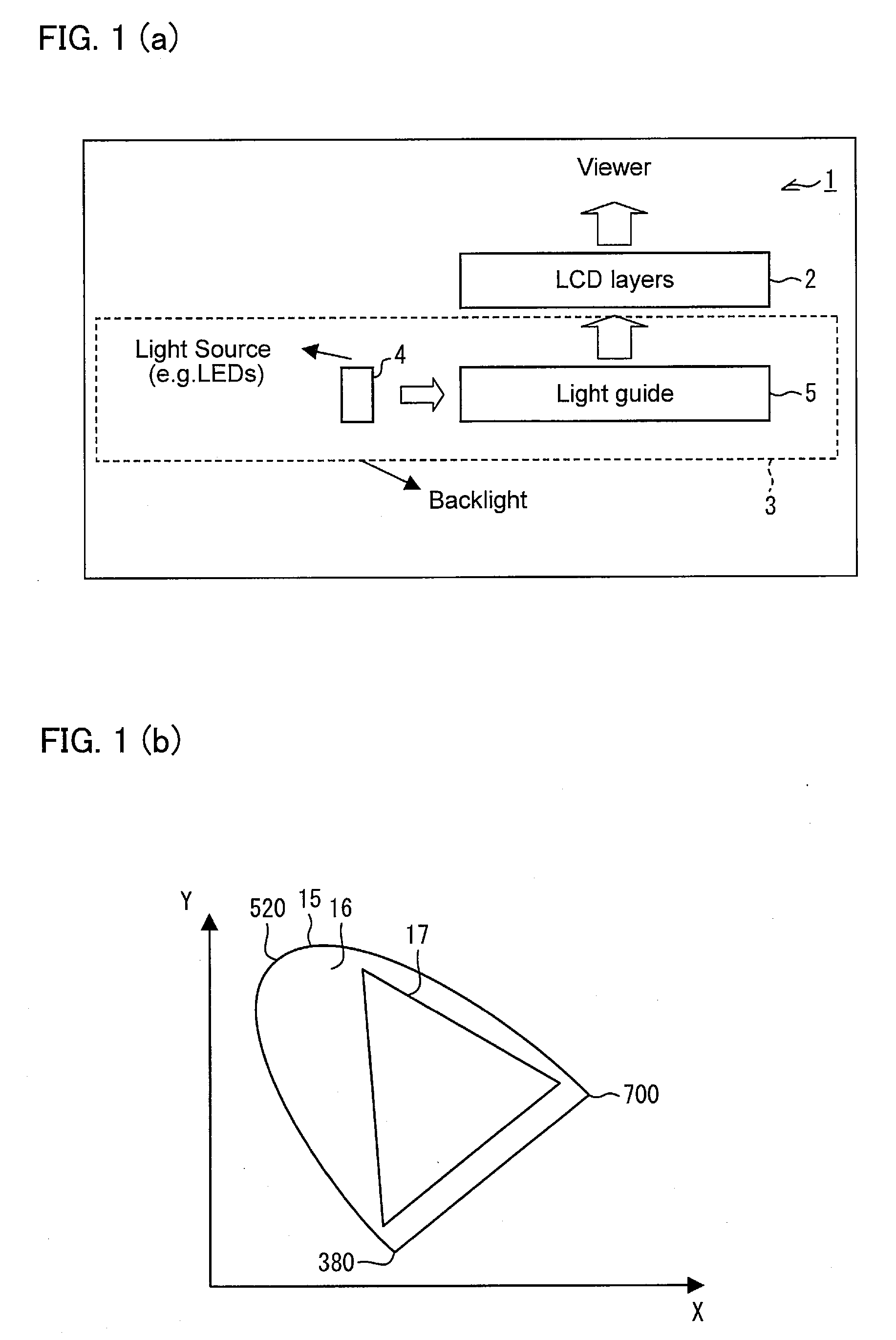
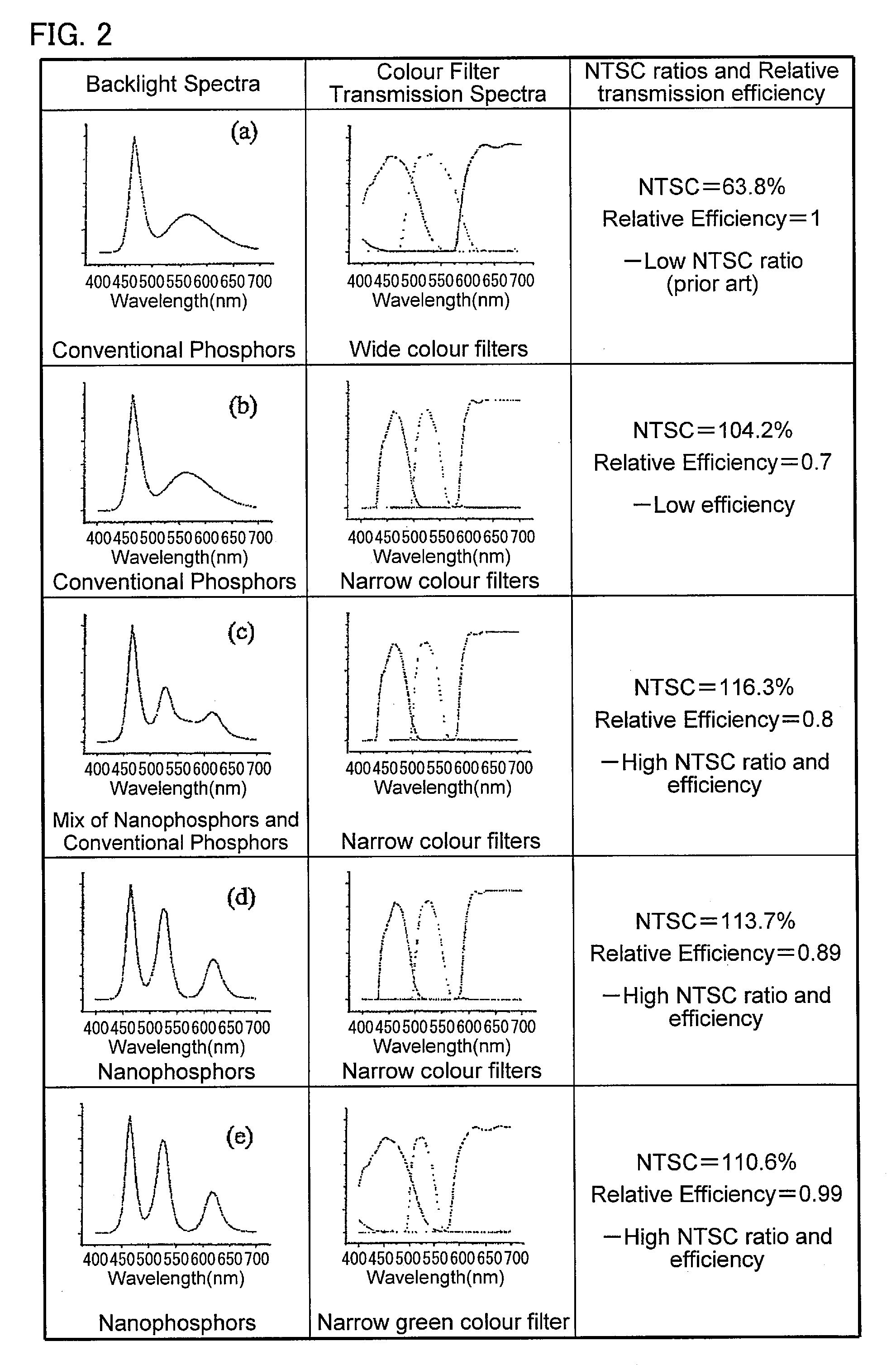
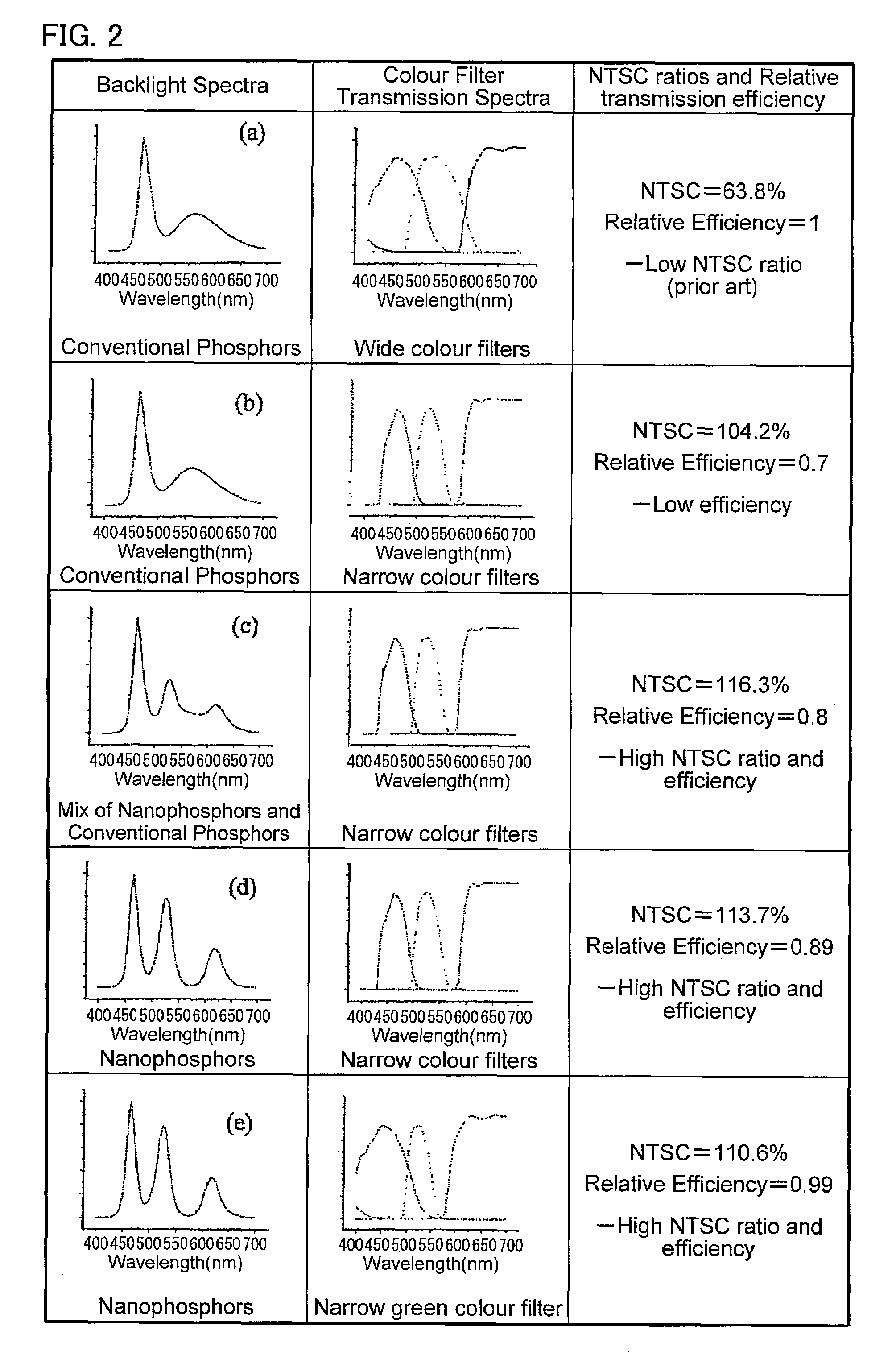
InactiveUS20080084706A1High NTSC ratioIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceWavelength range
A display comprises a light source and an image display panel disposed in an optical path from the light source. The light source comprises a primary light source for illuminating a re-emission material which comprises at least a first nanophosphor material for, when illuminated by light from the primary light source, re-emitting light in a first wavelength range different from the emission wavelength range of the primary light source. The image display panel comprises a first filter having a first narrow passband or a first narrow absorption band, the first narrow passband or first narrow absorption band being aligned or substantially aligned with the first wavelength range. The combination of a narrow wavelength range emitted by the first nanophosphor material and the narrow passband or narrow absorption band of the filter allows a display with high efficiency and a high NTSC ratio to be obtained.
Owner:SHARP KK
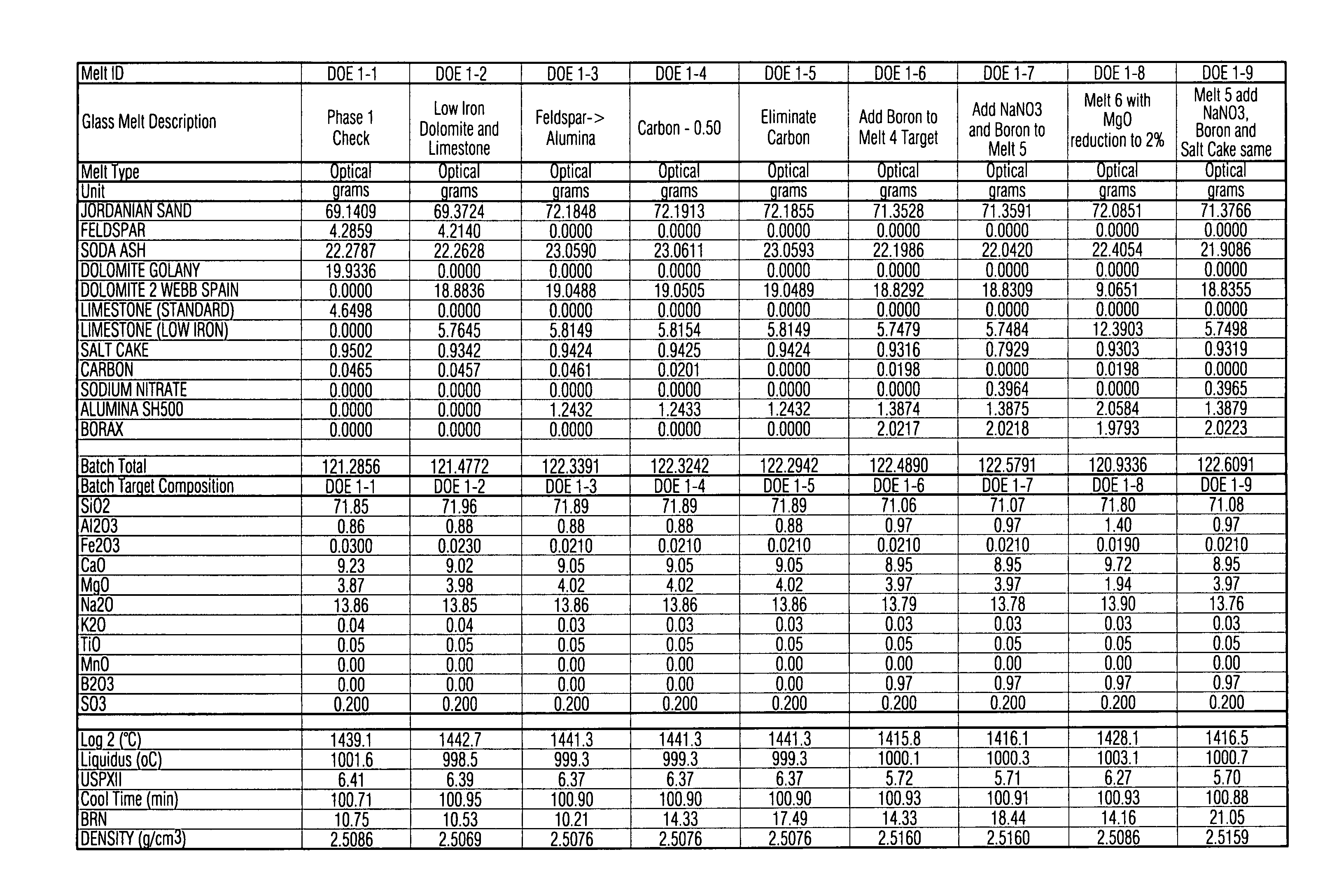
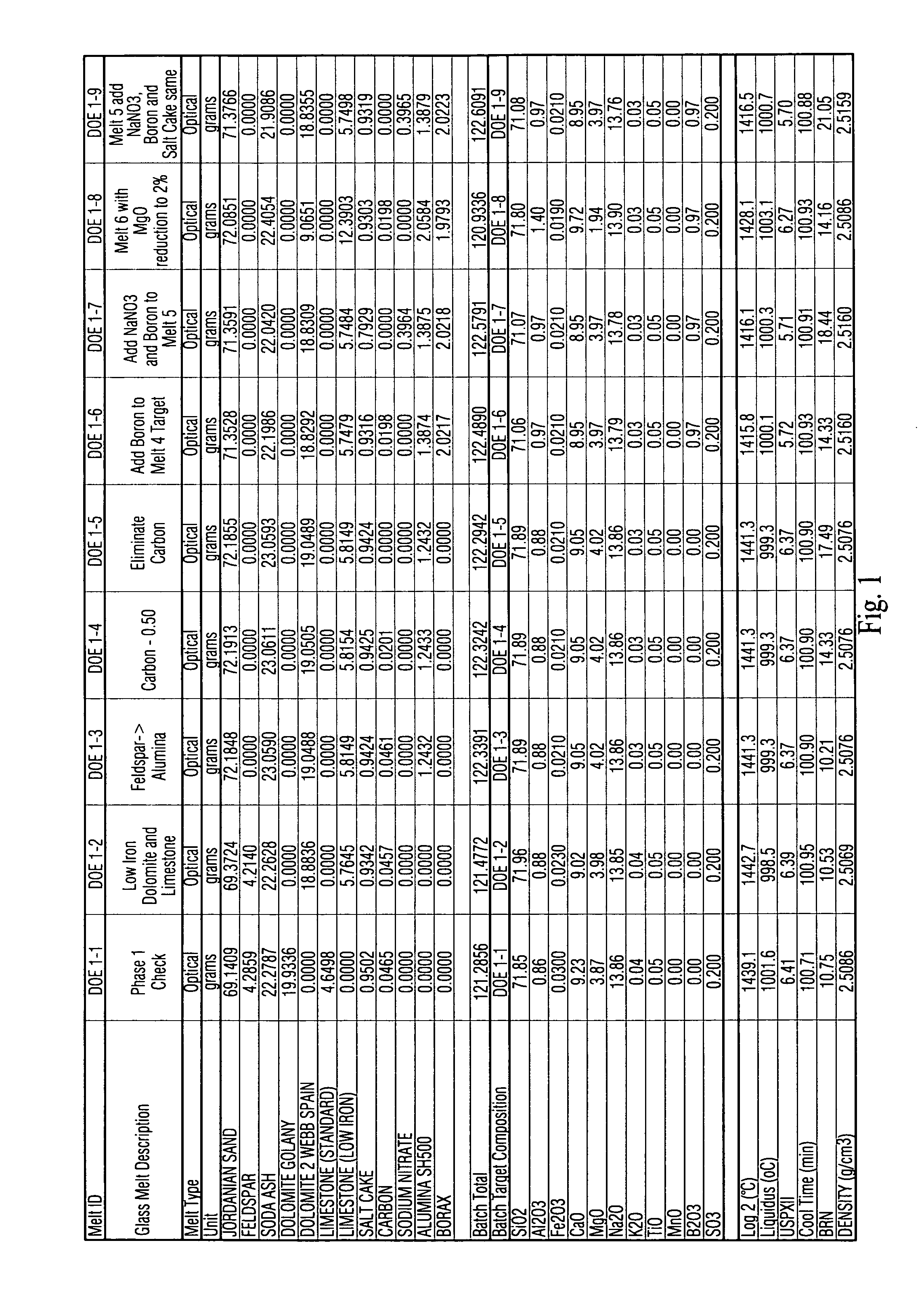
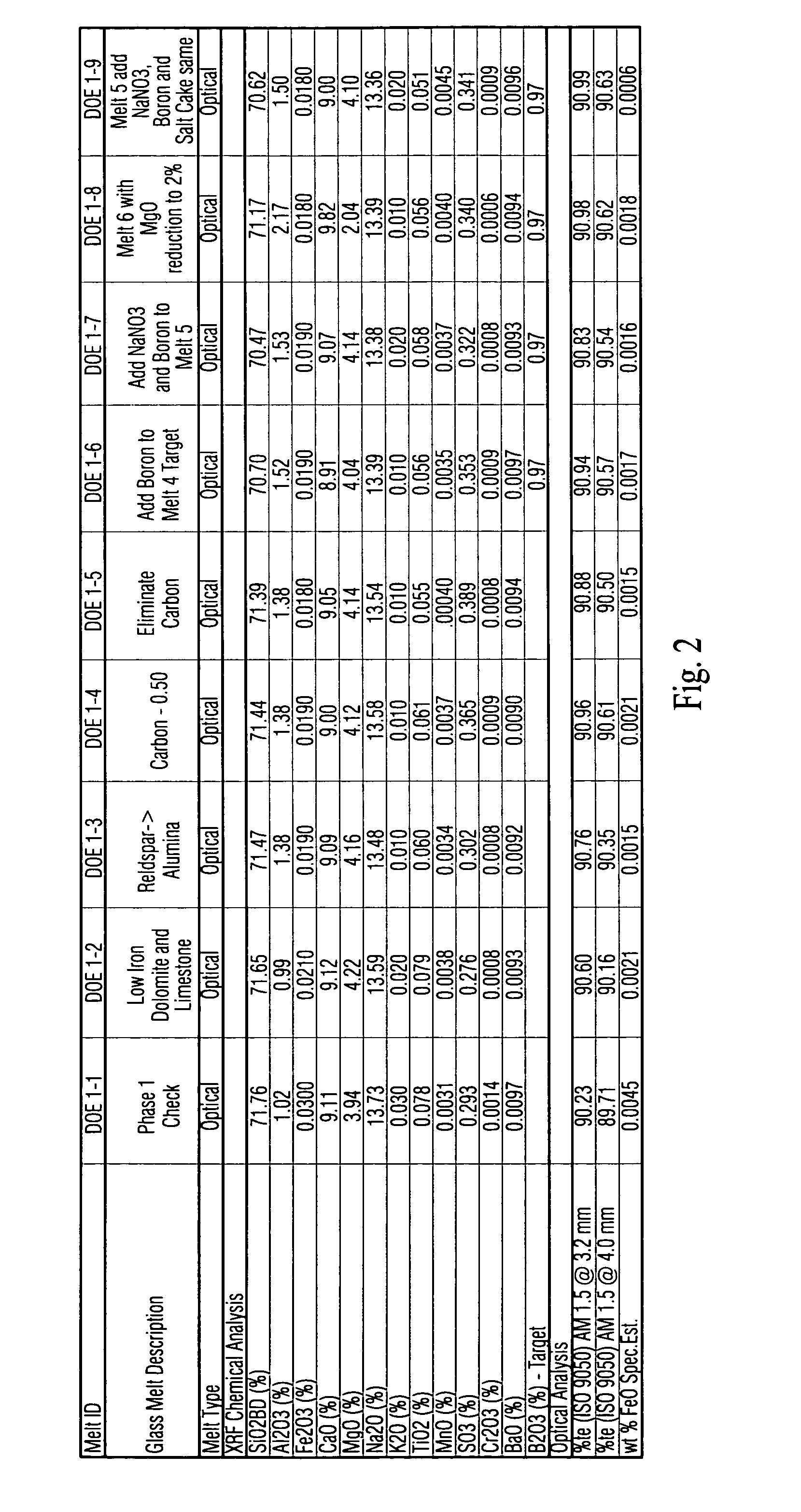
Low iron high transmission glass with boron oxide for improved optics, durability and refining, and corresponding method
This invention relates to a high transmission low iron glass that includes boron oxide. The boron oxide, added to this low iron glass, has the effect of improving glass refining, homogeneity and quality (lower seed count) through its flux action and improves glass optical parameters of green and clear glass through the change in refractive index and surface tension. Boron oxide lends to broader and weaker absorption band of such transition element(s) as iron which additionally improves the transmittance of low iron clear glass in certain example embodiments of this invention. In certain example embodiments, the addition of boron oxide in certain quantities in advantageous in that it improves the chemical durability of the glass by decreasing the USPX (or USPXIII) value of the glass via suppression of the silica, sodium ions in the glass structure.
Owner:PHOENICIA AMERICA ISRAEL FLAT GLASS +1
Apparatus, systems and methods for determining tissue oxygenation
A surgical instrument may be configured to sense a light re-emitting probe to resolve tissue oxygenation, the surgical instrument including: an optical emitter configured to excite the light re-emitting probe within an absorption band of the light re-emitting probe; an optical detector configured to receive the re-emitted light from the probe; and a signal processor configured to resolve the tissue oxygenation based on the received light. The surgical instrument can be a surgical stapler anvil or a flexible substrate having a tissue interfacing surface. Further, a monitoring device may be configured to map oxygenation of a tissue containing a light re-emitting probe, the monitoring device including: an optical emitter configured to excite the light re-emitting probe; at least one optical detector configured to receive the re-emitted light from the probe; and a signal processor that is configured to resolve the tissue oxygenation at multiple points to generate an oxygen map.
Owner:SURGISENSE CORP
Display
InactiveUS7686493B2Raise the ratioIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceWavelength range
A display comprises a light source and an image display panel disposed in an optical path from the light source. The light source comprises a primary light source for illuminating a re-emission material which comprises at least a first nanophosphor material for, when illuminated by light from the primary light source, re-emitting light in a first wavelength range different from the emission wavelength range of the primary light source. The image display panel comprises a first filter having a first narrow passband or a first narrow absorption band, the first narrow passband or first narrow absorption band being aligned or substantially aligned with the first wavelength range. The combination of a narrow wavelength range emitted by the first nanophosphor material and the narrow passband or narrow absorption band of the filter allows a display with high efficiency and a high NTSC ratio to be obtained.
Owner:SHARP KK
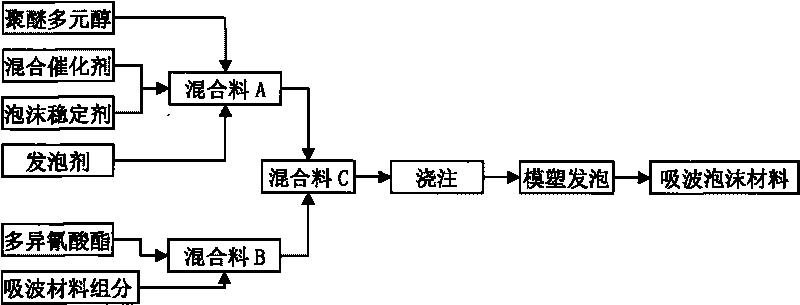
Lightweight and broadband wave absorbing material with foam sandwich structure and method for producing same
InactiveCN101700706ANo adhesionNon-existentSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationBroadbandVolumetric Mass Density
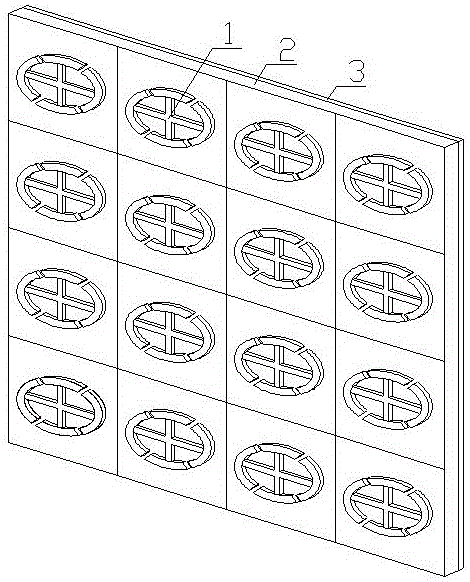
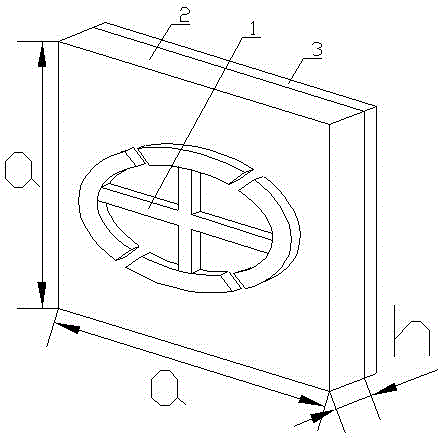
The invention relates to a lightweight and broadband wave absorbing material with foam sandwich structure, comprising a panel 1, a sandwich layer 2 and a bottom plate 3. The panel 1 is a wave-transparent material layer; the sandwich layer 2 is wave absorbing resin foam; and the bottom plate 3 is an electromagnetic wave absorbing and reflecting layer. The method for producing the lightweight and broadband wave absorbing material with foam sandwich structure comprises the steps of mixing raw materials, foaming the mixed raw material, curing the mixed raw material to obtain monolayer foam wave absorbing materials and adhering the monolayer foam materials to form multi-layer foam wave absorbing material. The lightweight and broadband wave absorbing material with foam sandwich structure has good low-frequency performance, broad absorption band, light surface density, superior environmental performance and the like. The method is mature and stable, can be used for the large-scale continuous production and is easy to realize the industrialization.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
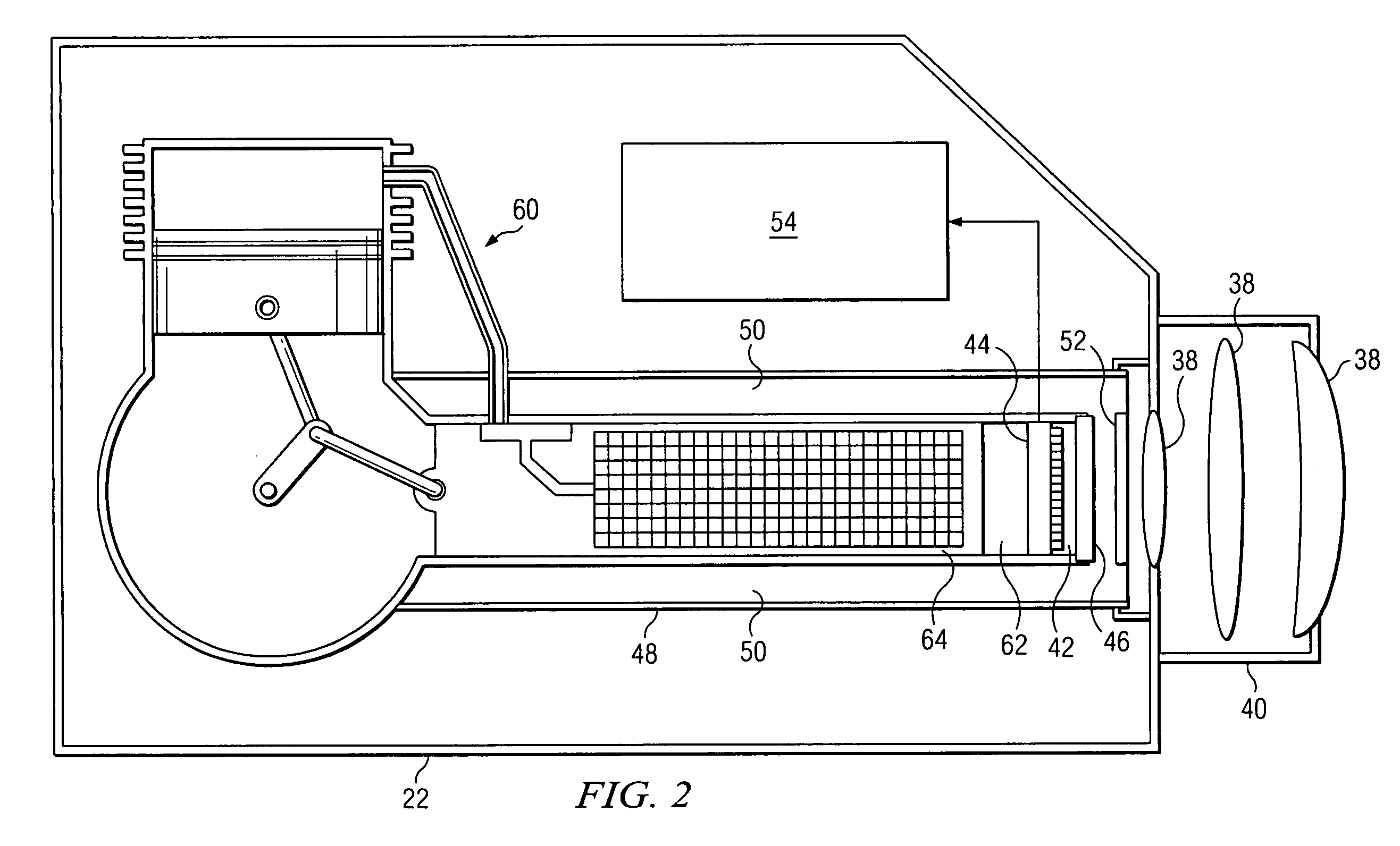
Backscatter absorption gas imaging systems and light sources therefore
ActiveUS7151787B2Low power operationLaser using scattering effectsColor/spectral properties measurementsAudio power amplifierLength wave
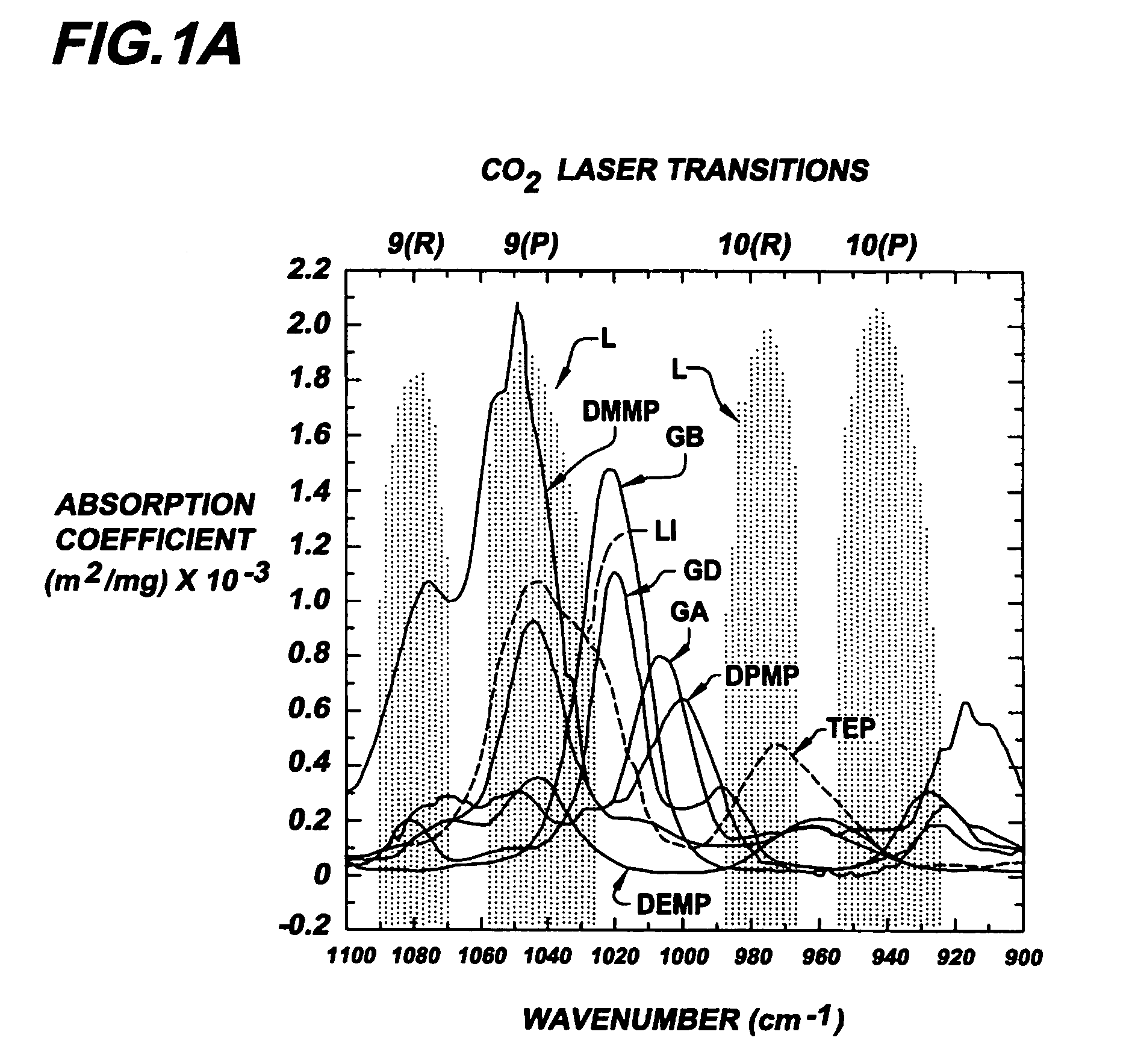
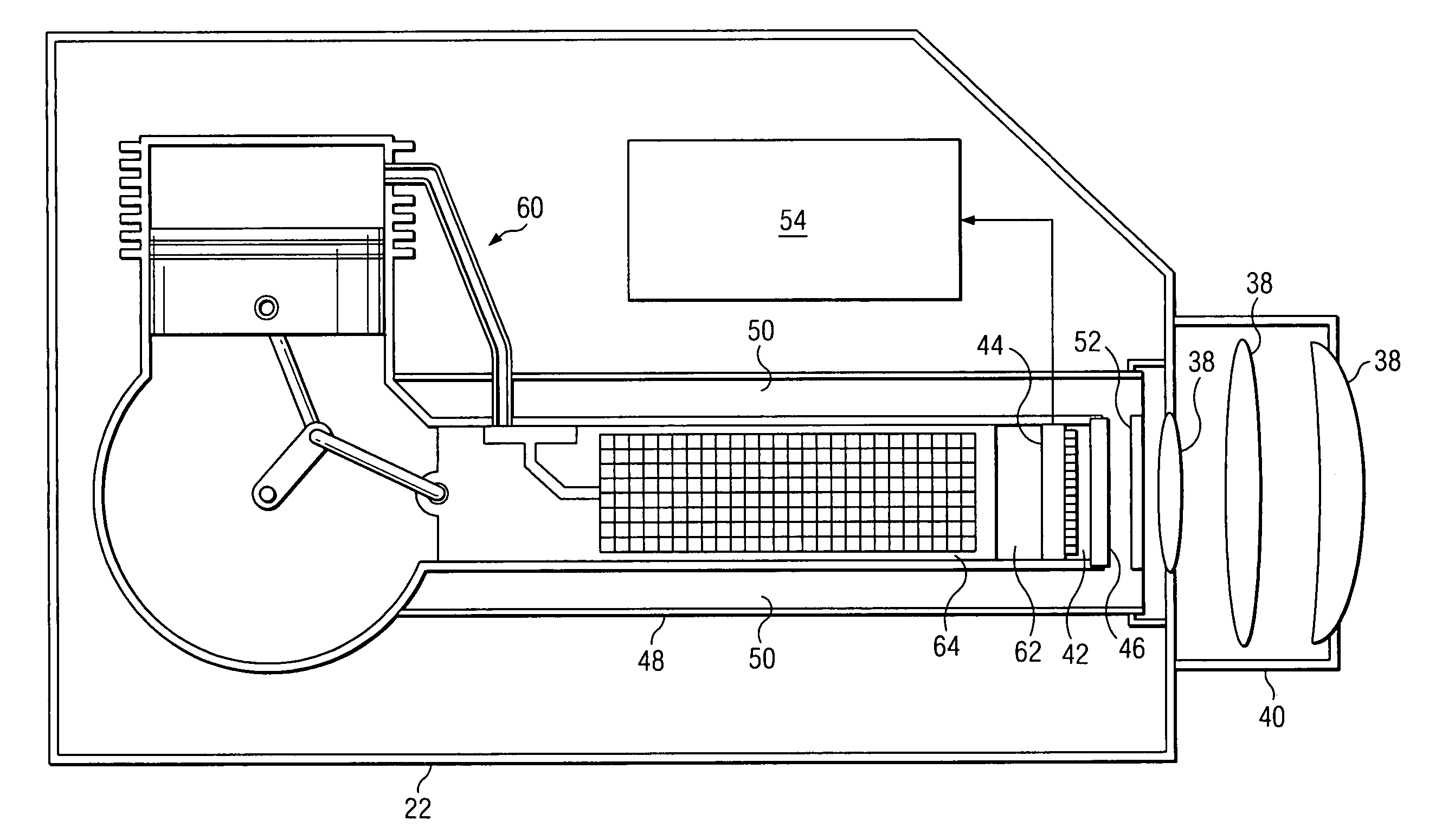
The location of gases that are not visible to the unaided human eye can be determined using tuned light sources that spectroscopically probe the gases and cameras that can provide images corresponding to the absorption of the gases. The present invention is a light source for a backscatter absorption gas imaging (BAGI) system, and a light source incorporating the light source, that can be used to remotely detect and produce images of “invisible” gases. The inventive light source has a light producing element, an optical amplifier, and an optical parametric oscillator to generate wavelength tunable light in the IR. By using a multi-mode light source and an amplifier that operates using 915 nm pump sources, the power consumption of the light source is reduced to a level that can be operated by batteries for long periods of time. In addition, the light source is tunable over the absorption bands of many hydrocarbons, making it useful for detecting hazardous gases.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Polyaniline/oxidized graphene/ferriferrous oxide absorbing material and preparation method
InactiveCN104163919AStrong dielectric loss performanceHigh surface energyMaterials preparationTernary complex
The invention belongs to the field of electromagnetic wave absorbing material preparation and relates to a polyaniline / oxidized graphene / ferriferrous oxide composite material and its preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing graphite oxide; (2) preparing ferriferrous oxide nanoparticles; (3) preparing a polyaniline / oxidized graphene / ferriferrous oxide ternary complex; and (4) weighing the polyaniline / oxidized graphene / ferriferrous oxide ternary complex and paraffin, and uniformly mixing to obtain the polyaniline / oxidized graphene / ferriferrous oxide absorbing material. The material provided by the invention has characteristics of low cost, simple preparation technology, strong electromagnetic wave absorbing capability, wide absorption band, low density and the like, has good electromagnetic property, and has important application value in the field of microwave absorption and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Infrared region selective reflection coat and infrared region selective reflection film
An infrared region selective reflection coat, having a layer exhibiting a structural color of which a central wavelength of a selective reflection band is in the range of 700 nm to 2,000 nm,wherein the infrared range selective reflection coat satisfies at least one of the following requirements A and B:A: the layer exhibiting a structural color contains a compound having a light-sensitive functional group; andB: the infrared range selective reflection coat further comprises a layer containing an infrared-absorbing dye or pigment having absorption maximum in the range of 700 nm to 2,000 nm and a half bandwidth of its absorption band in the range of 20 nm to 200 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Analyte detection with infrared light
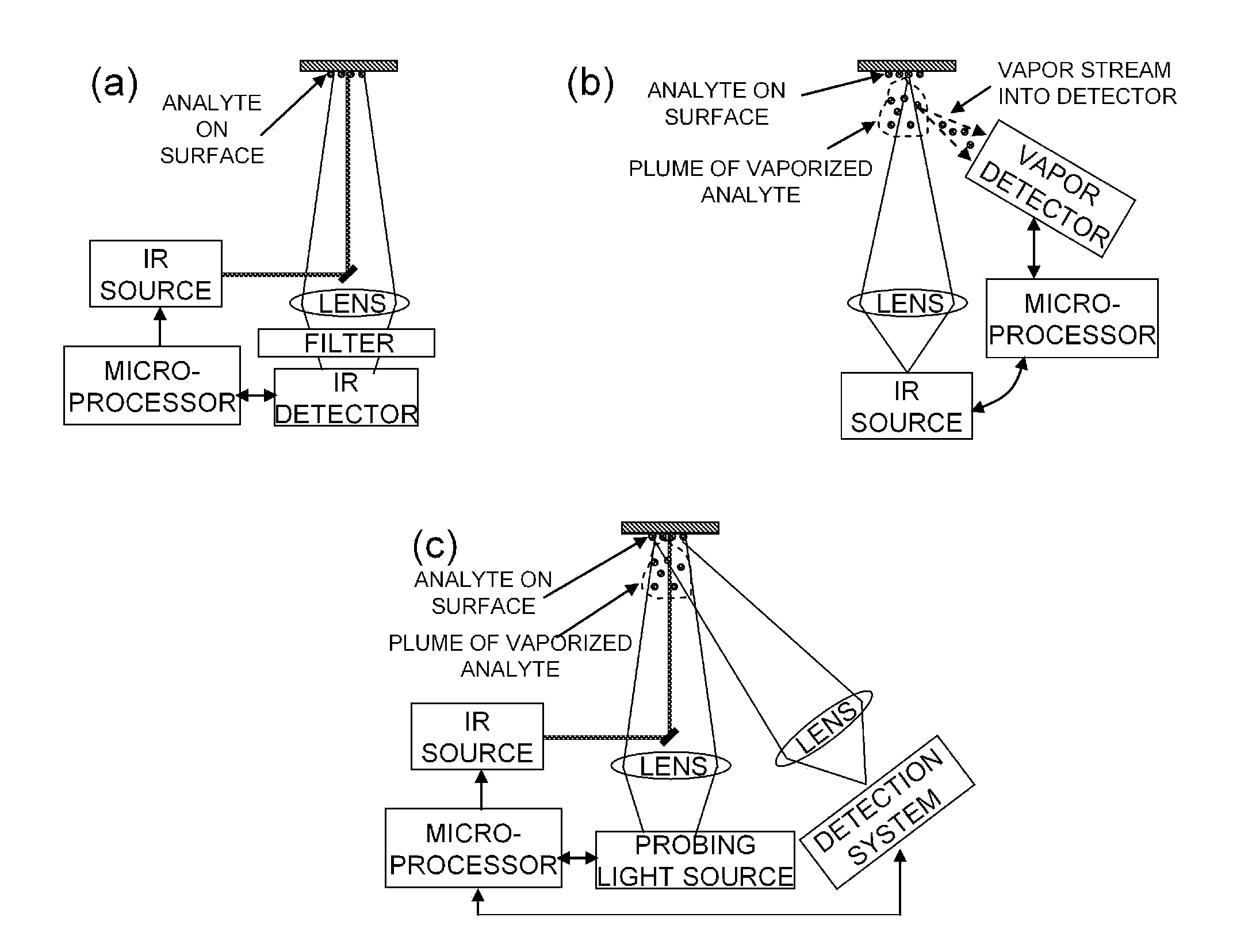
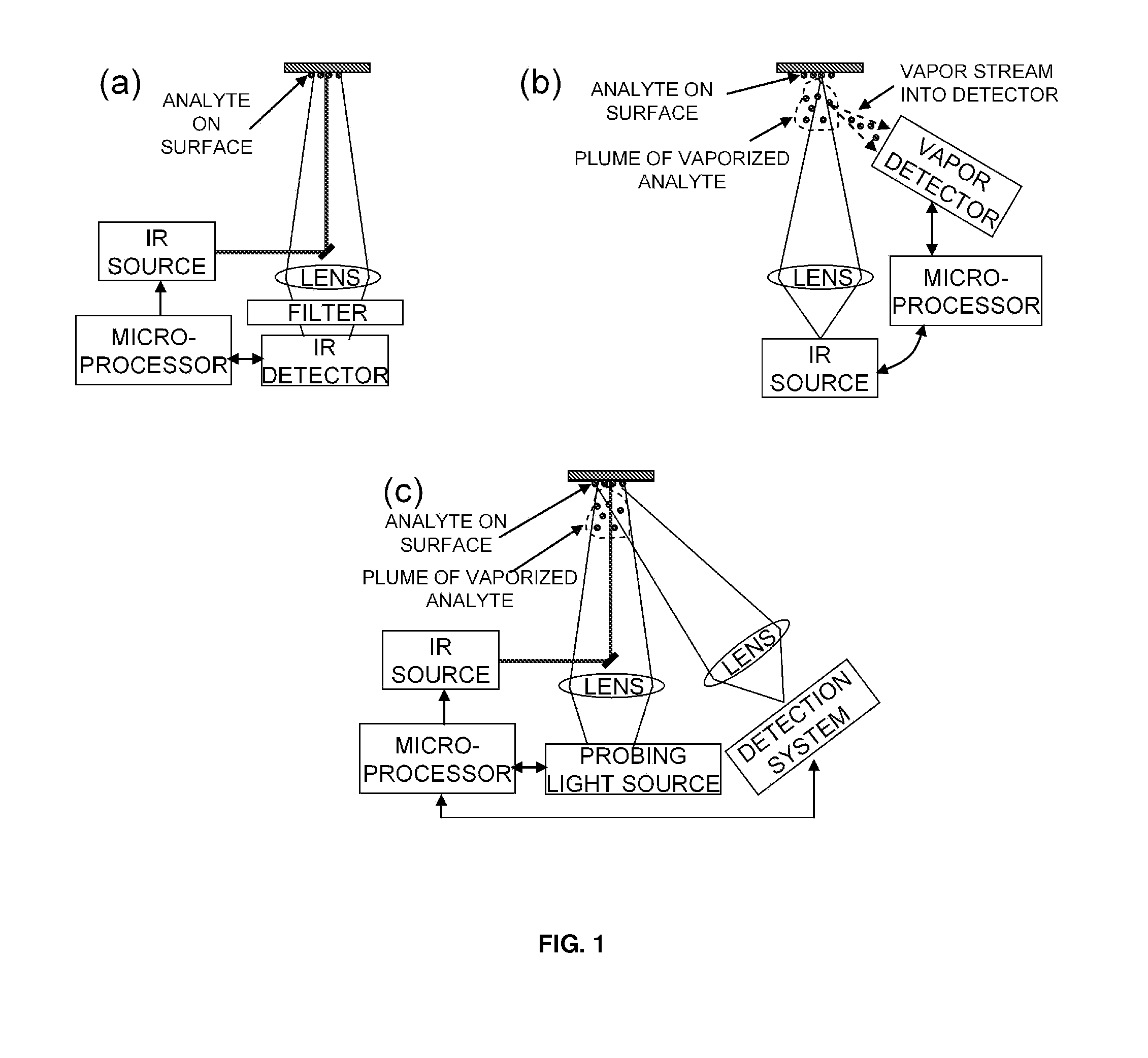
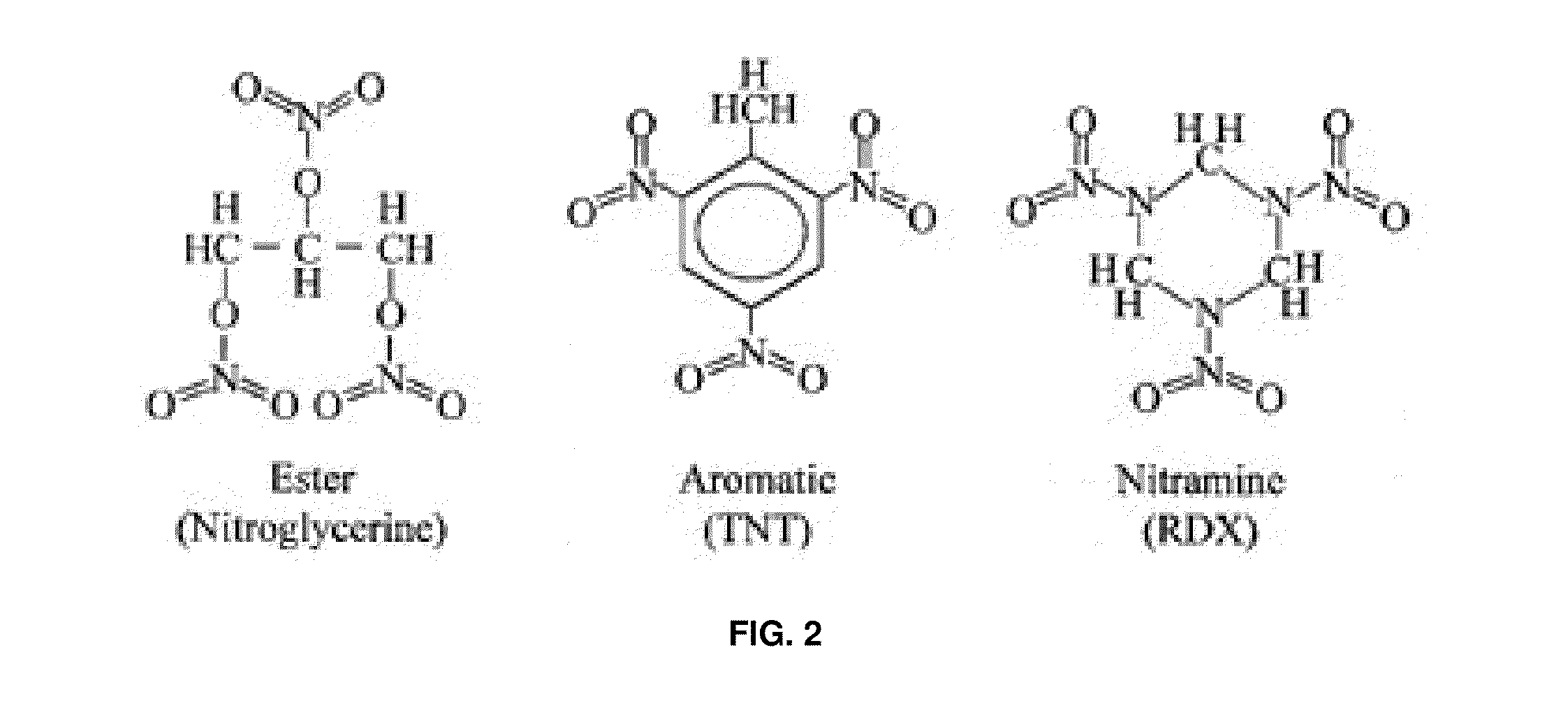
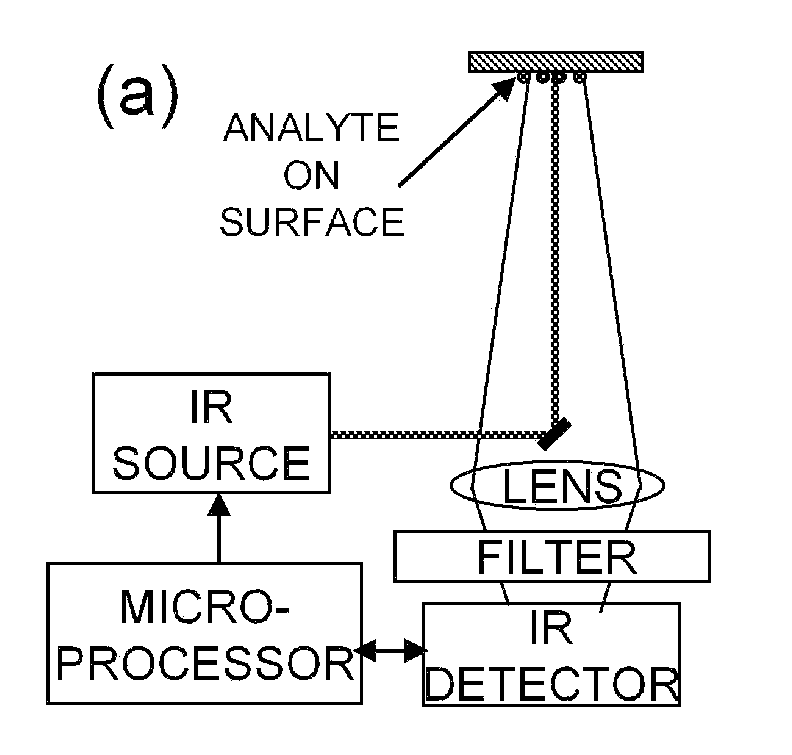
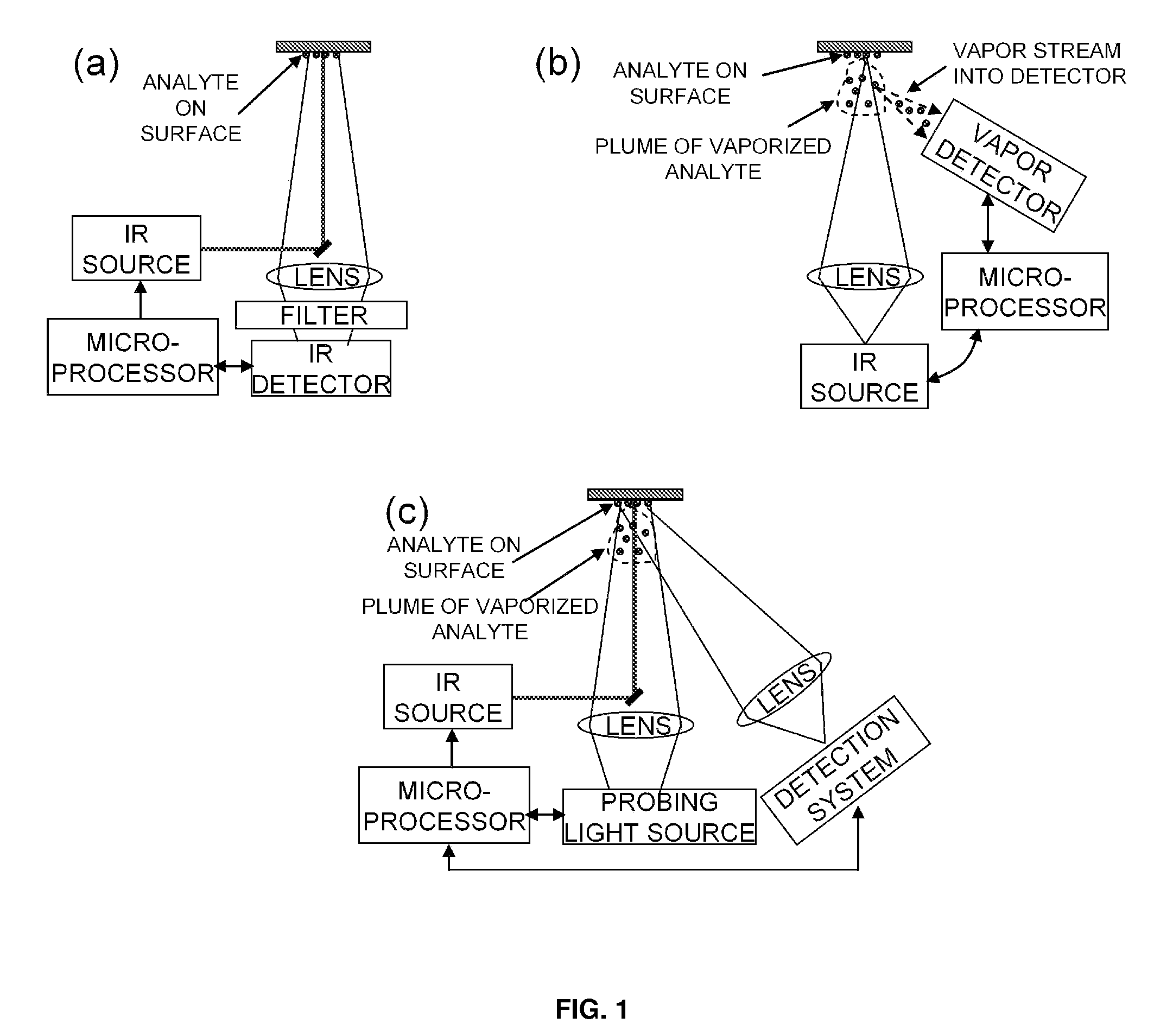
ActiveUS20110271738A1Efficiently vaporizeEfficiently probeComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationAnalyteChemical physics
The present invention is generally directed to a method for non-contact analyte detection by selectively exciting one or more analytes of interest using an IR source optionally operated to produce pulses of light and tuned to at least one specific absorption band without significantly decomposing organic analytes and determining if the analyte is present by comparing emitted photons with an IR detector signal collected one or more times before, during, after, or any combination thereof exciting the analyte. Another embodiment of the present invention provides a method for non-contact analyte detection by selectively exciting one or more analytes of interest using one or more IR sources that are optionally operated to produce pulses of light and tuned to at least one specific wavelength without significantly decomposing organic analytes, wherein the analyte is excited sufficiently to increase the amount of analyte in the gas phase, and wherein the content of the gas is examined to detect the presence of the analyte.
Owner:U S A AS REPRENSENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY THE
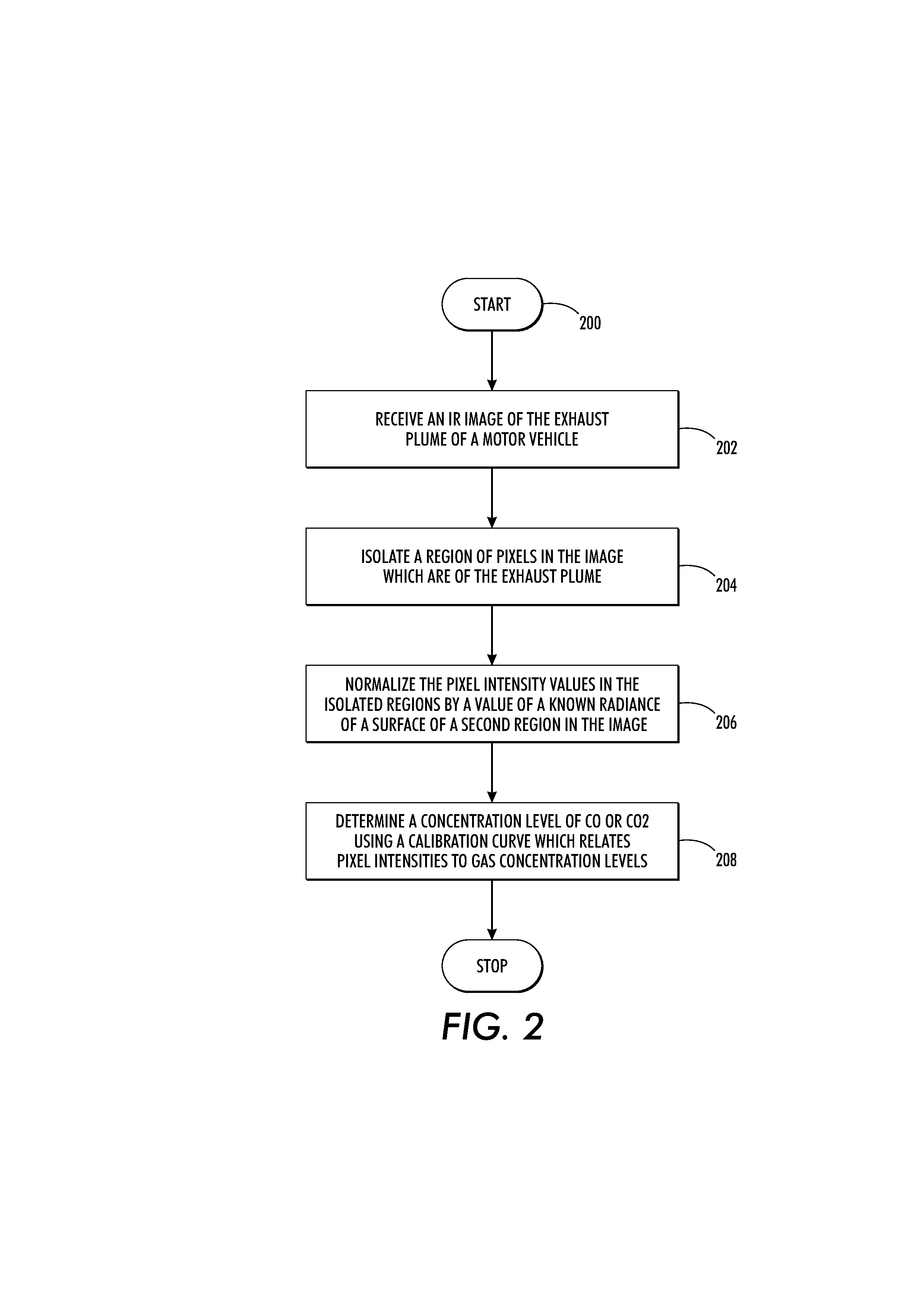
Image-based determination of co and co2 concentrations in vehicle exhaust gas emissions
ActiveUS20130181836A1Readily apparentEngine testingCharacter and pattern recognitionPresent methodEmission standard
What is disclosed is a system and method for image-based determination of concentration of CO and CO2 in a vehicle's exhaust gas in an emissions testing environment. In one embodiment, the present method involves receiving an IR image of the exhaust plume of a motor vehicle intended to be tested for CO and CO2 concentrations. The IR image has been captured using a mid-wave infrared camera with at least one optical filter tuned to the infrared absorption band of CO and CO2. The images are pre-processed to isolate pixels which contain the exhaust plume. The intensity values of pixels in those isolated regions are normalized and concentrations of CO and CO2 are determined via a calibration curve which relates pixel intensities to concentrations. The concentrations are compared to an emissions standard set for the vehicle to determine whether the vehicle is a gross polluter.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
Thermography camera tuned to detect absorption of infrared radiation in a selected spectral bandwidth
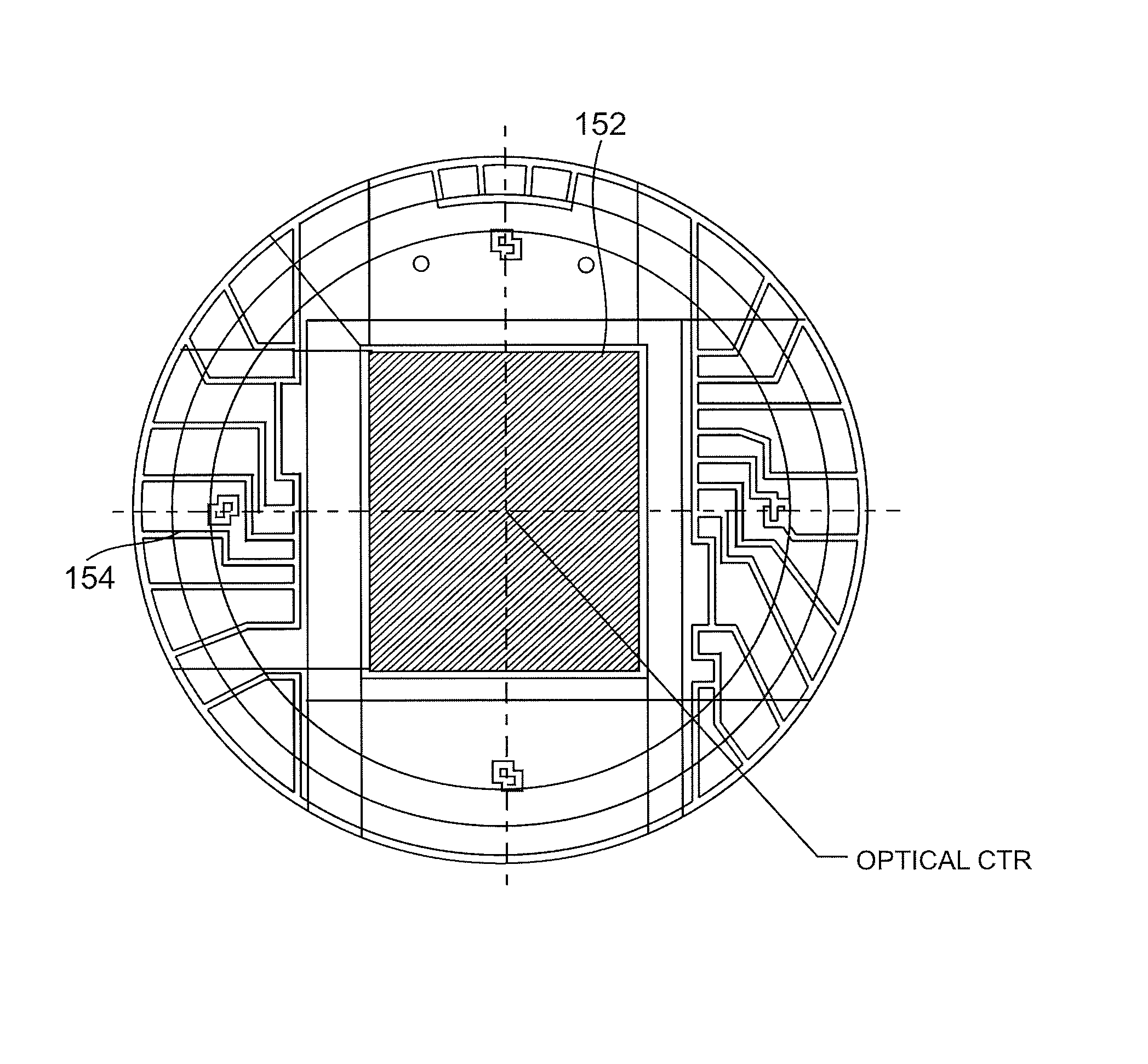
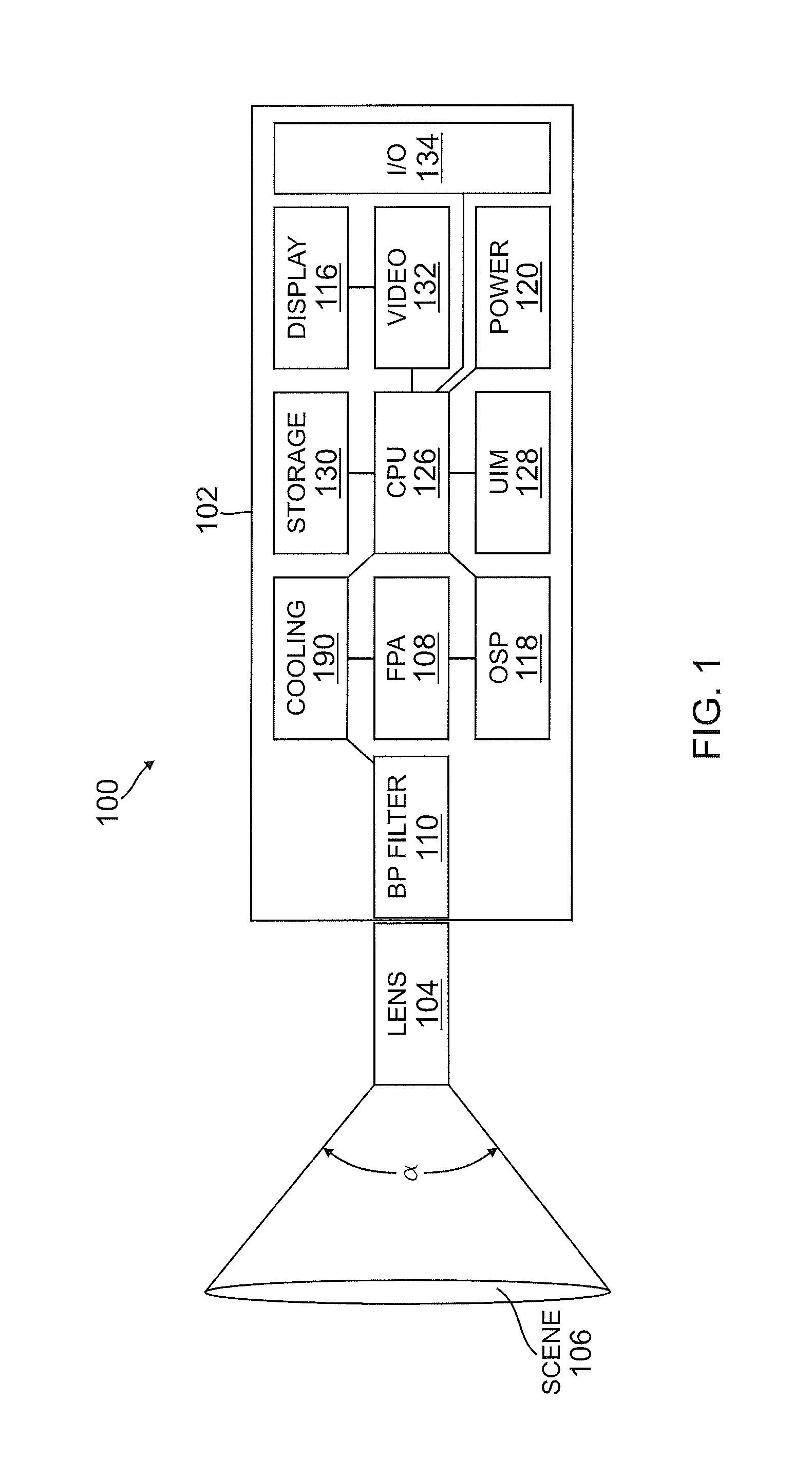
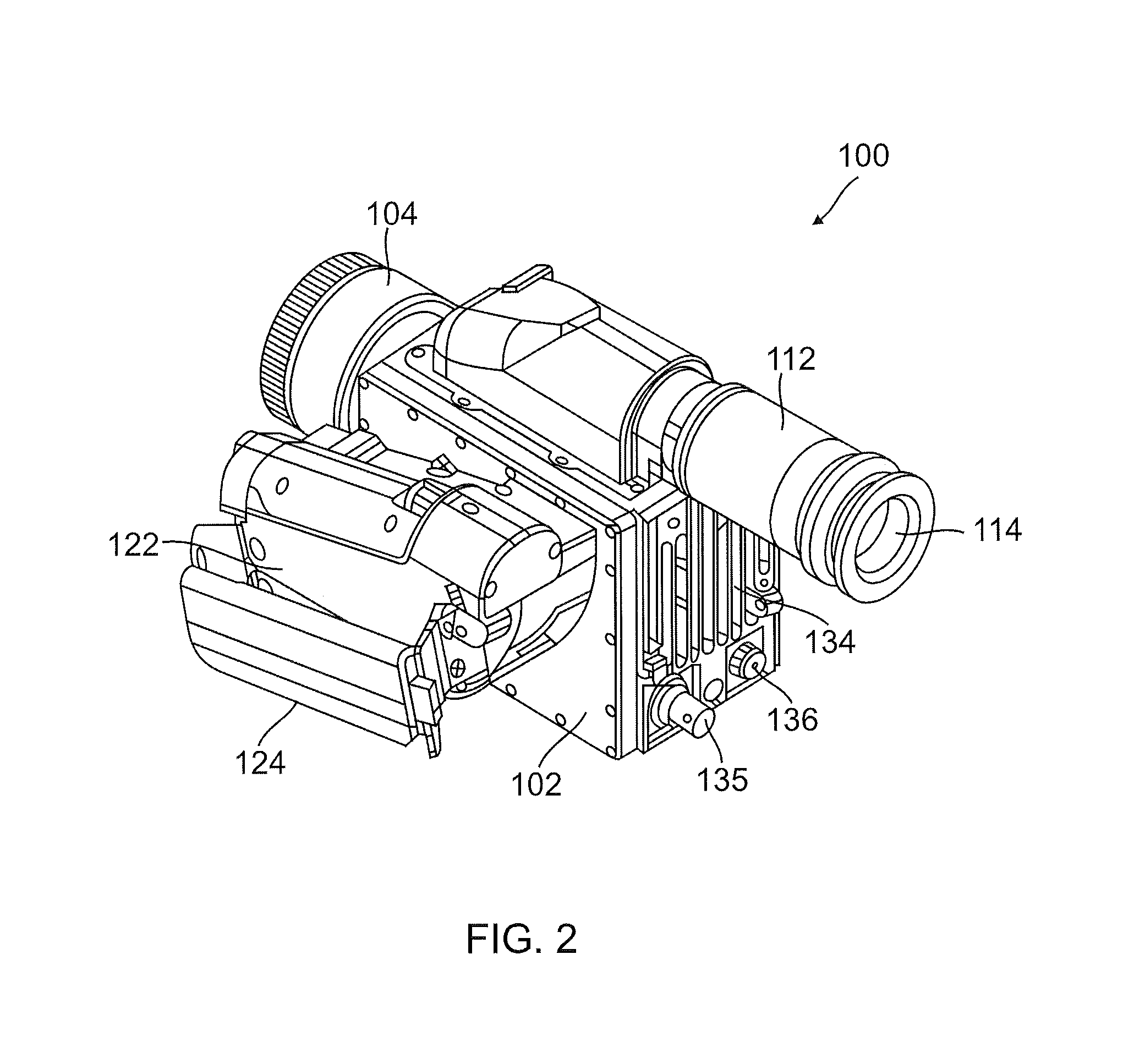
An infrared camera system is provided to detect absorption of infrared radiation in a selected spectral bandwidth. In one example, an infrared camera system includes a lens adapted to receive infrared radiation from a survey scene comprising one or more gasses. The infrared camera system also includes a focal plane array comprising a plurality of quantum well infrared photo detectors (QWIPs). The QWIPs are tuned to detect a limited spectral bandwidth of the infrared radiation corresponding to at least a portion of an infrared absorption band of the one or more gasses. The infrared camera system also includes an optical band pass filter positioned substantially between the lens and the focal plane array. The optical band pass filter is adapted to filter the infrared radiation to a wavelength range substantially corresponding to the limited spectral bandwidth of the QWIPs before the infrared radiation is received by the focal plane array.
Owner:TELEDYNE FLIR LLC
Detection of chemicals with infrared light
ActiveUS20100044570A1Safely pointedEfficiently vaporize and probeRadiation pyrometryAnalysis by thermal excitationAnalyteExplosive material
The present invention is generally directed to a method for non-contact or stand off chemical detection that may be eye-safe by selectively exciting one ore more analytes of interest using an IR source tuned to at least one specific absorption band without significantly decomposing the analyte and determining if the analyte is present by comparing emitted photons with an IR detector signal made before and during or shortly after exciting the analyte. Another embodiment of the present invention provides a method for non-contact or stand off chemical detection that may be eye-safe by selectively exciting one or more analytes of interest using an IR source tuned to at least one specific absorption band without significantly decomposing the analyte, wherein the analyte is excited sufficiently to generate a vapor plume, and wherein the plume is examined to detect the presence of the analyte. The analyte of interest may be an explosive, an additive to an explosive, a drug, a chemical warfare agent, a biochemical, or a biological warfare agent. Additionally, the present invention provides for a system for non-contact or stand off chemical detection that may be eye-safe.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Signature protected photosensitive optically variable ink compositions and process
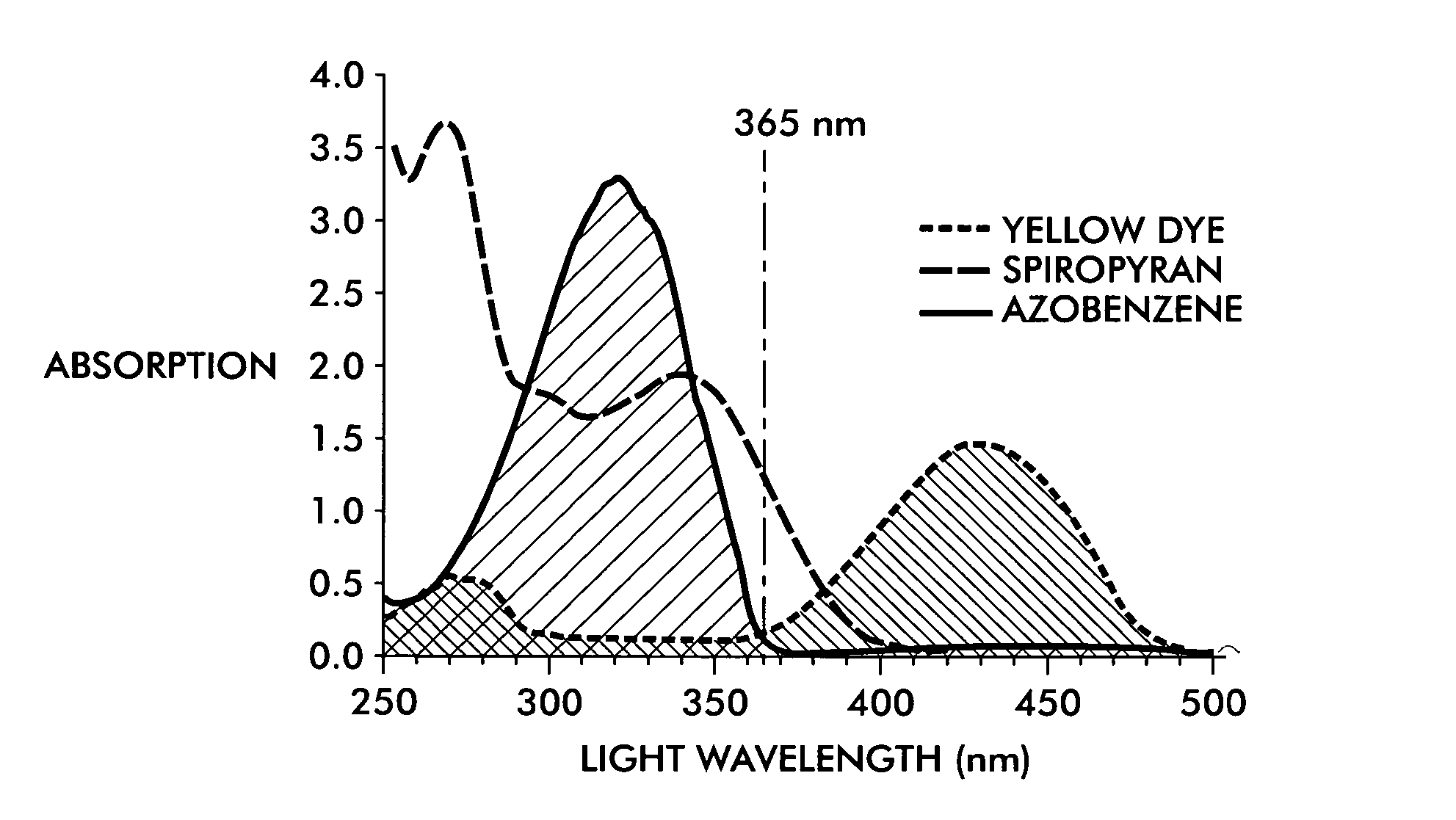
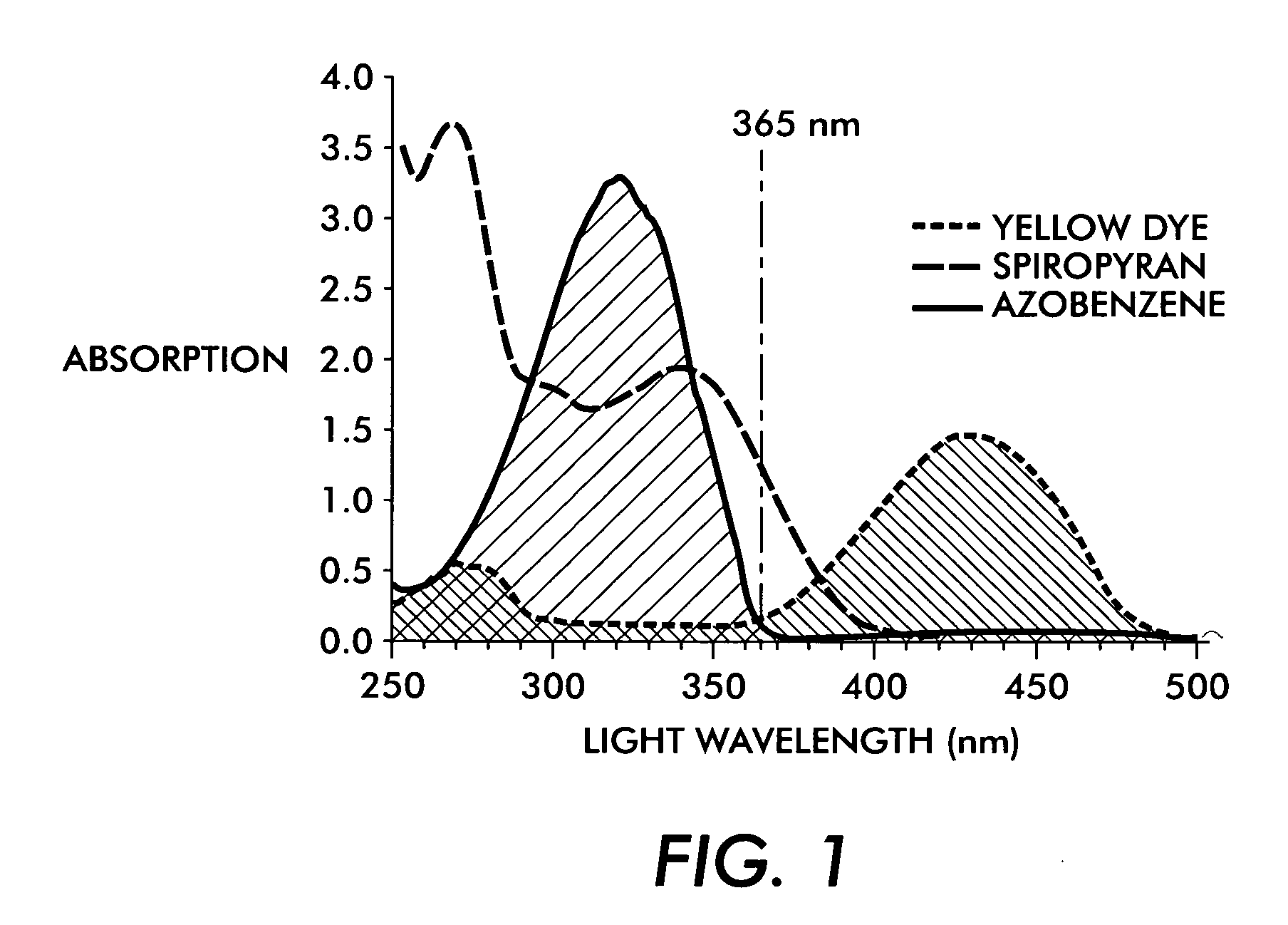
InactiveUS20050279248A1High saturation of luminescenceHigh quantum yieldInksLuminescent compositionsRare earthDark color
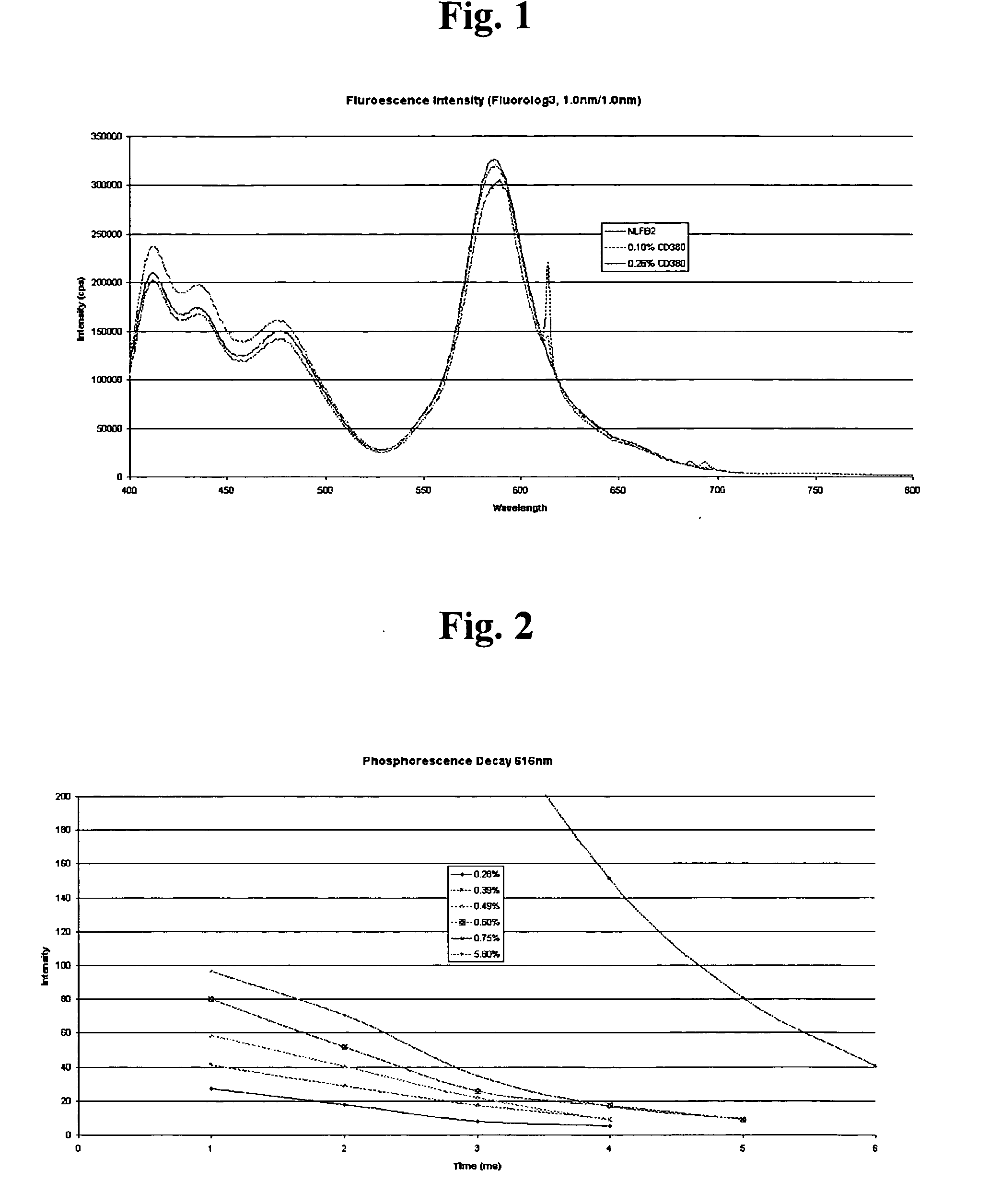
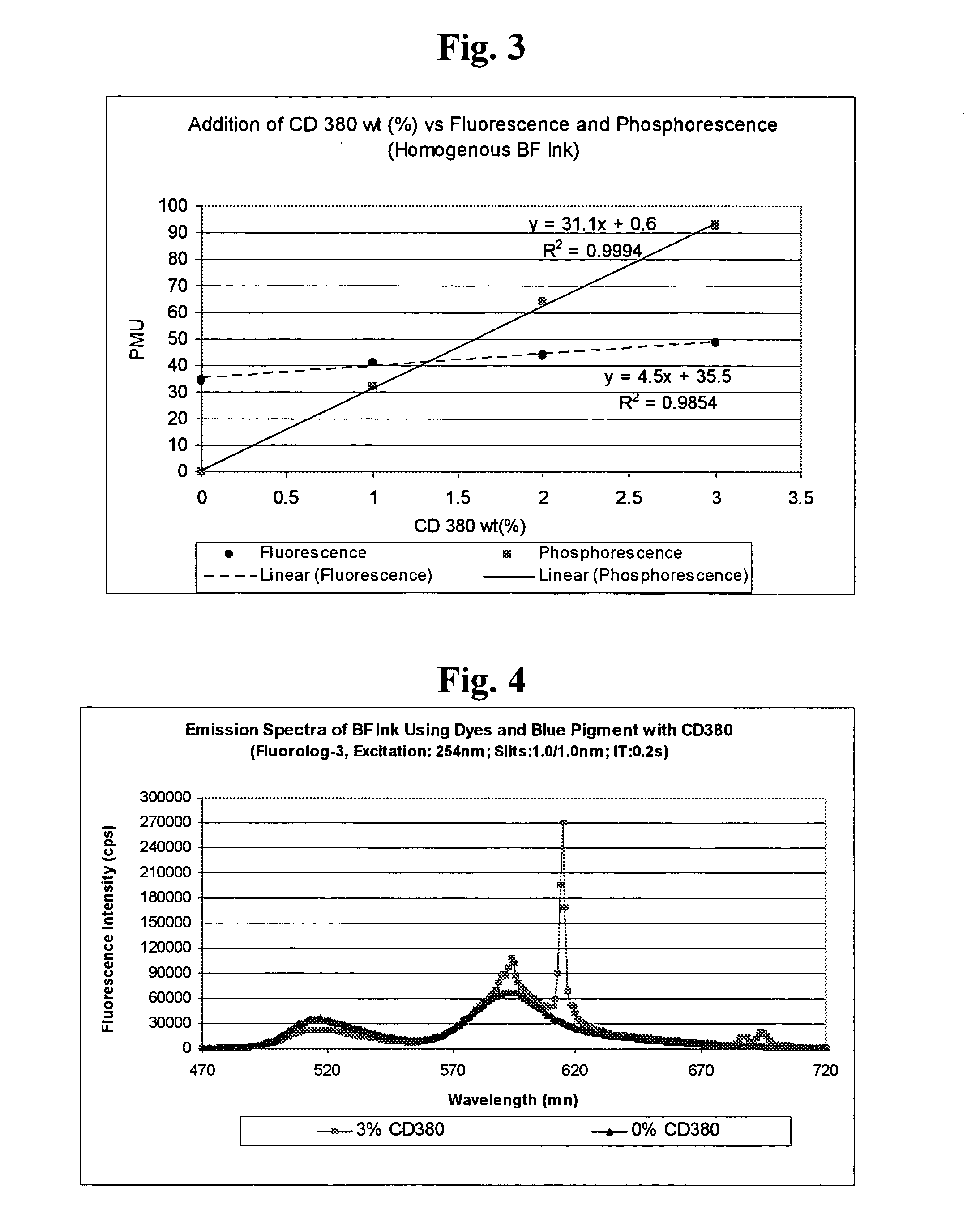
Signature protected photosensitive optically variable (POV) inks are provided, which are capable of providing a unique signature in addition to other security features of POV inks. The inks contain at least two types of colorants, and a third, signature component and other ingredients to enable printing. A first colorant comprises a fluorescent dye and / or pigment emitting light within a characteristic emission band when excited by fluorescent-exciting radiation. A second colorant comprises a dye and / or pigment having a light absorption band at overlapping or longer wavelengths than the characteristic emission band of the first colorant in such a way as to result in a dark color. The third component is a fluorescent / phosphorescent rare earth composition. The inks give dark visible ink images, which also produce detectable coincident fluorescent and phosphorescent images. The inks can be used with detectors of red phosphorescence to achieve a new level of security in high speed sorting operations.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
Light-emitting element
ActiveUS9276228B2High luminous efficiencyEfficient emissionsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLength waveMolecular physics
To provide a light-emitting element which uses a fluorescent material as a light-emitting substance and has higher luminous efficiency. To provide a light-emitting element which includes a mixture of a thermally activated delayed fluorescent substance and a fluorescent material. By making the emission spectrum of the thermally activated delayed fluorescent substance overlap with an absorption band on the longest wavelength side in absorption by the fluorescent material in an S1 level of the fluorescent material, energy at an S1 level of the thermally activated delayed fluorescent substance can be transferred to the S1 of the fluorescent material. Alternatively, it is also possible that the S1 of the thermally activated delayed fluorescent substance is generated from part of the energy of a T1 level of the thermally activated delayed fluorescent substance, and is transferred to the S1 of the fluorescent material.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
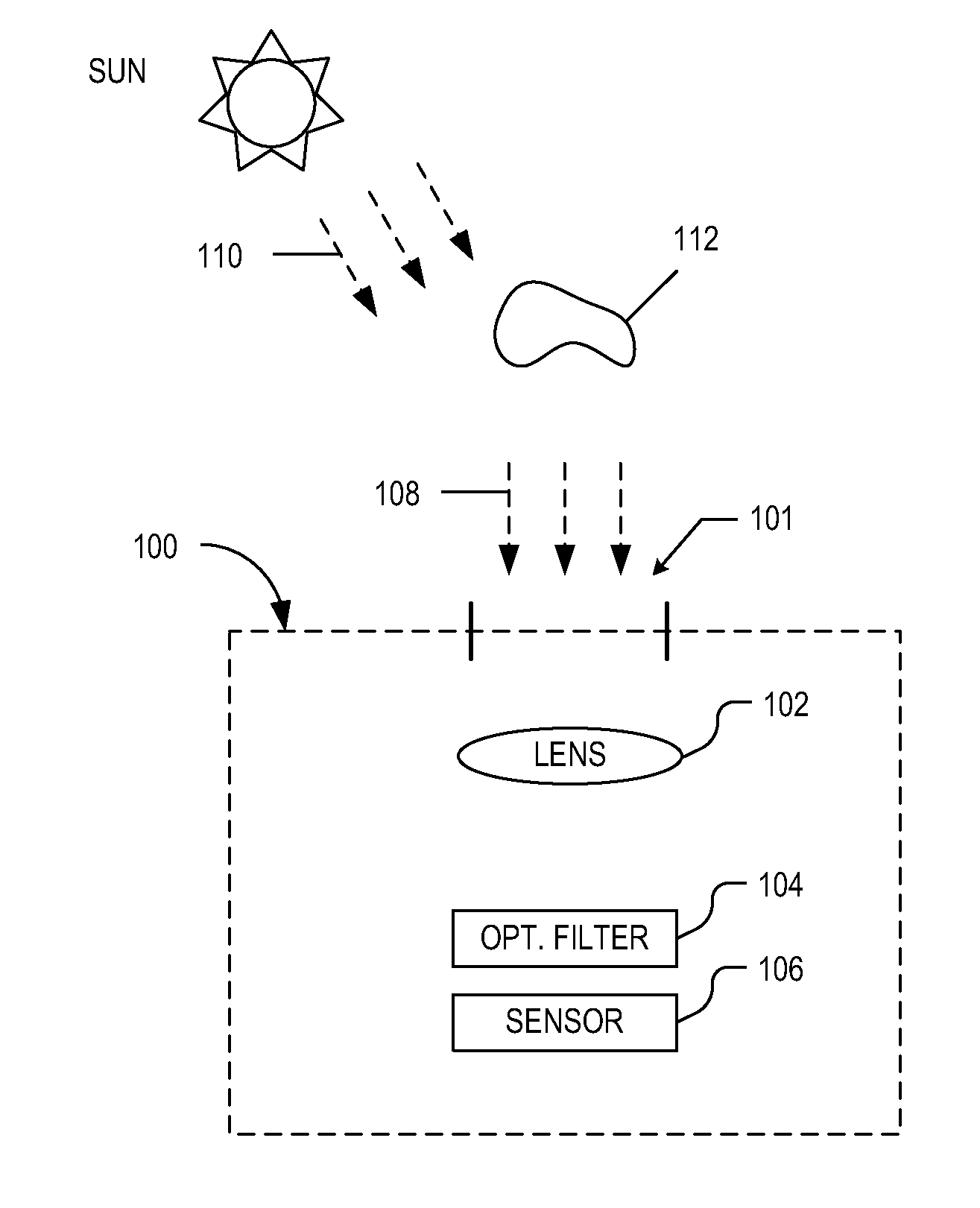
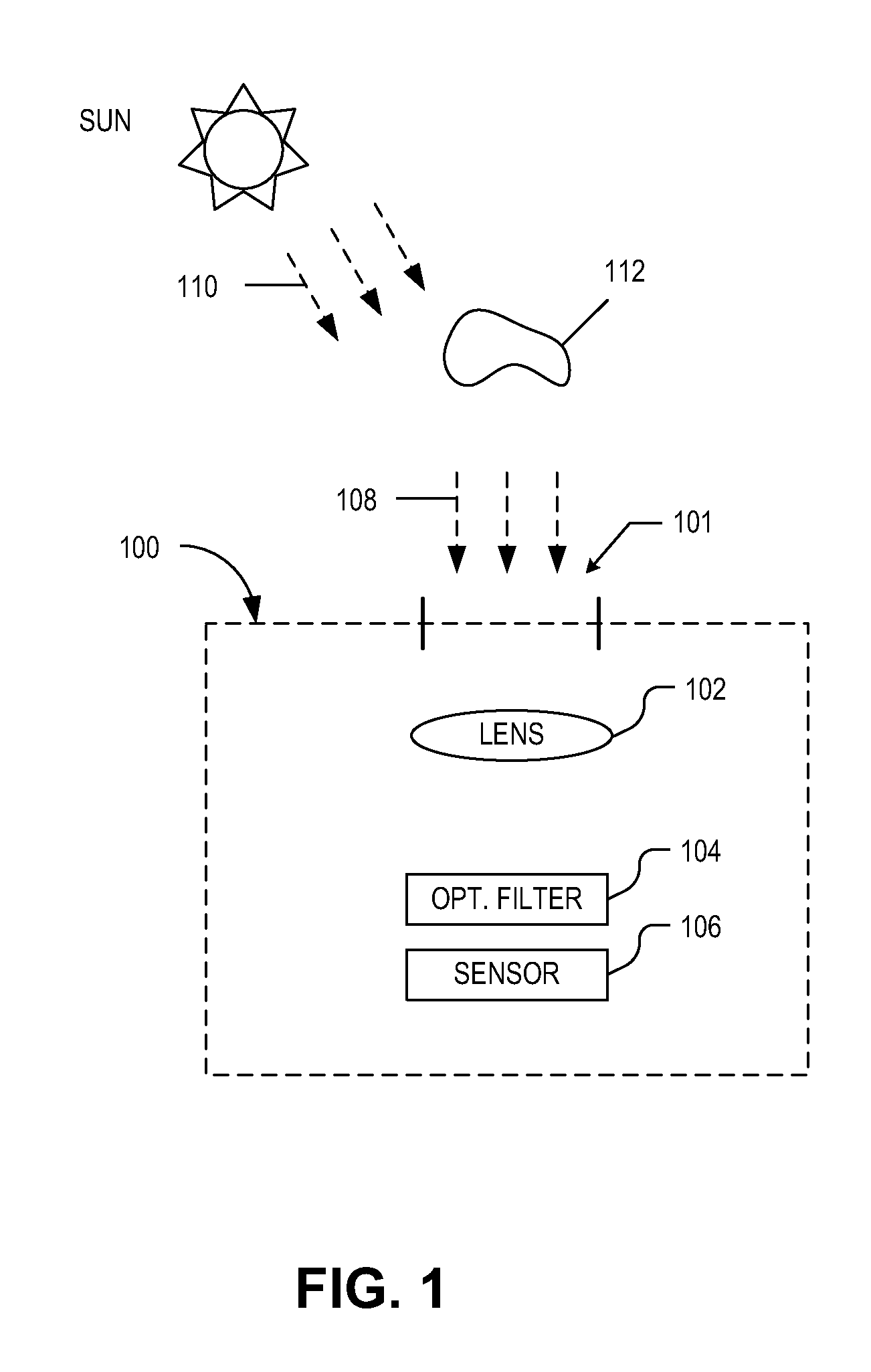
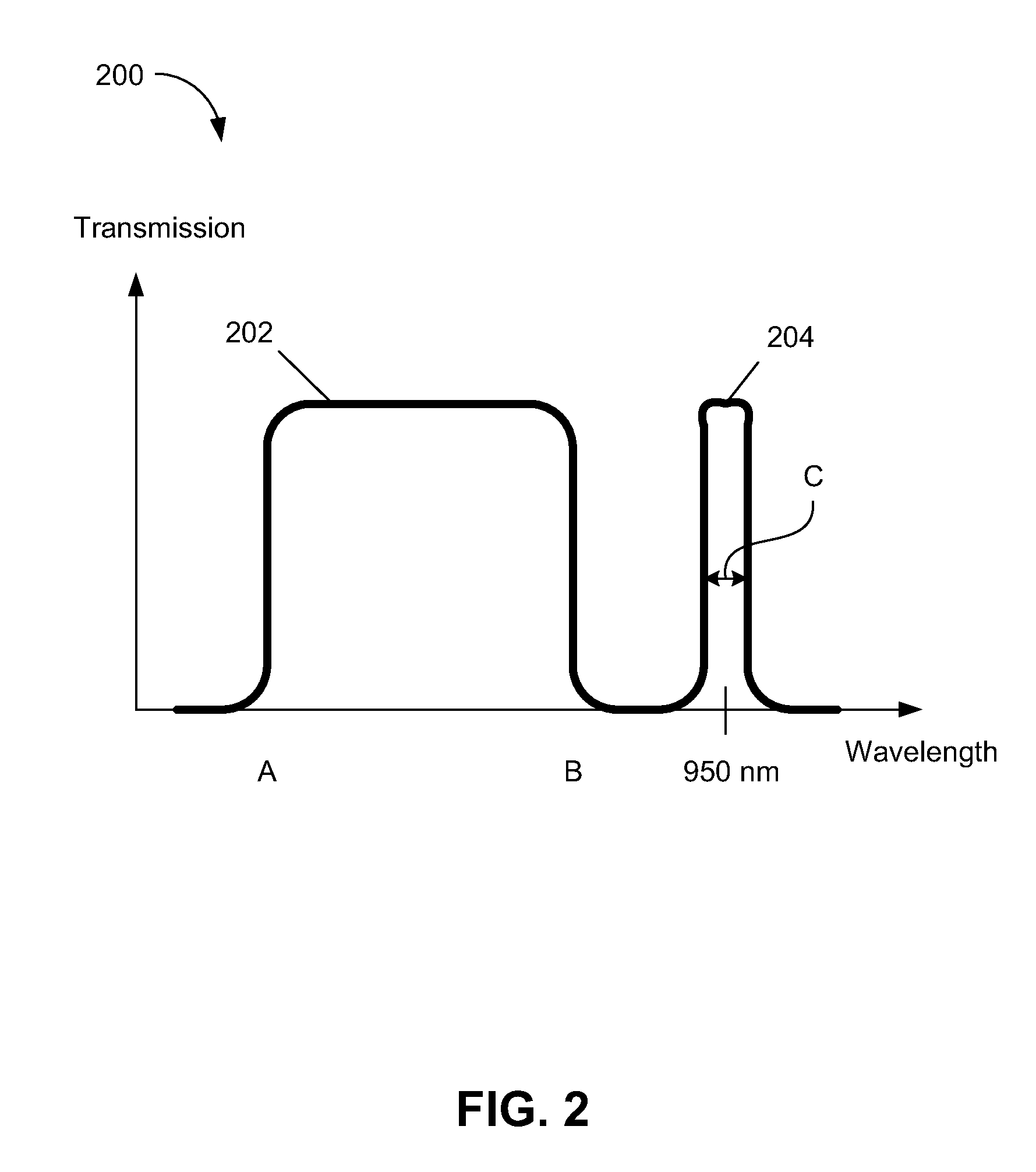
Visible and infrared dual mode imaging system
An imaging system includes an image sensor and an optical filter. The image sensor captures image data in response to incident light. The optical filter filters the light and includes a dual window transmission spectrum. The dual window transmission spectrum includes a first transmission window having a first pass band aligned to pass visible light and a second transmission window having a second pass band overlapping with an absorption band of infrared light in Earth's atmosphere.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
System and method for detecting and identifying an analyte
Owner:QUANTASPEC
Wave-absorbing material based on grapheme and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105647468AImprove absorbing abilityImprove absorbing performanceOther chemical processesDielectricElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a wave-absorbing material based on grapheme and a preparation method thereof. The wave-absorbing material is formed by mixing graphite powder (or taking graphite powder as a main material) with one of three magnetic dielectric materials: ferrite, carbonyl iron powder and ultrafine metal powder, wherein the graphite powder is prepared by flake graphite through a mechanical stripping method and has a mass percentage content of 60-99 percent. The wave-absorbing material provided by the invention has the characteristics of being high in absorption strength, wide in absorption band, low in density and the like and has the excellent characteristics of the grapheme and the magnetic dielectric materials in electromagnetic performance; the preparation method is easy for large scale, low in cost, environment-friendly and suitable for industrialized production. The wave-absorbing material has wide application potential and market prospect in the fields of wave-absorbing materials, anti-electrostatic materials and electromagnetic shielding.
Owner:兰州天烁新能源有限公司
Reimageable medium with light absorbing material
InactiveUS20050244742A1Photography auxillary processesRadiation applicationsLength wavePhotochromism
A reimageable medium for receiving an imaging light having a predetermined wavelength scope, the medium composed of: a substrate; a photochromic material capable of reversibly converting among a number of different forms, wherein one form has an absorption spectrum that overlaps with the predetermined wavelength scope; and a light absorbing material exhibiting a light absorption band with an absorption peak, wherein the light absorption band overlaps with the absorption spectrum of the one form.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Broadband THz metamaterial absorber based on multi-resonant absorption superposition
ActiveCN105896098AObvious absorption peak characteristicsImprove application efficiencyAntennasTerahertz metamaterialsLine width
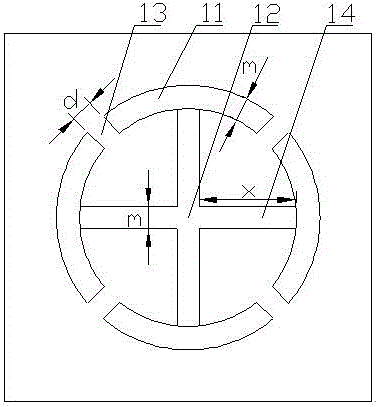
The invention discloses a broadband THz metamaterial absorber based on multi-resonant absorption superposition, belongs to a THz absorber in the field of metamaterials and electromagnetic functional technology, and aimed at that the broadband THz metamaterial absorber includes an upper patterned functional material layer, an intermediate medium layer and a lower metal reflective layer; the upper patterned functional material layer is formed by arranging metamaterial unit structures, each metamaterial unit structure includes a circular ring structure in which four parallel openings and a cross arm are disposed, and four connecting arms of each cross arm are connected with four ARC segments of each circular ring structure; the lattice period of a metamaterial unit structure array is a 10um to 100um, each metamaterial unit structure has a line width of 0.5um to 10um, the arm length x of each connecting arm is 3um to 50um, and the width d of each parallel opening is 0.5um to 50um. The invention does not require complicated procedures, a difficult process and high production cost to achieve the purpose of terahertz absorption band spread.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
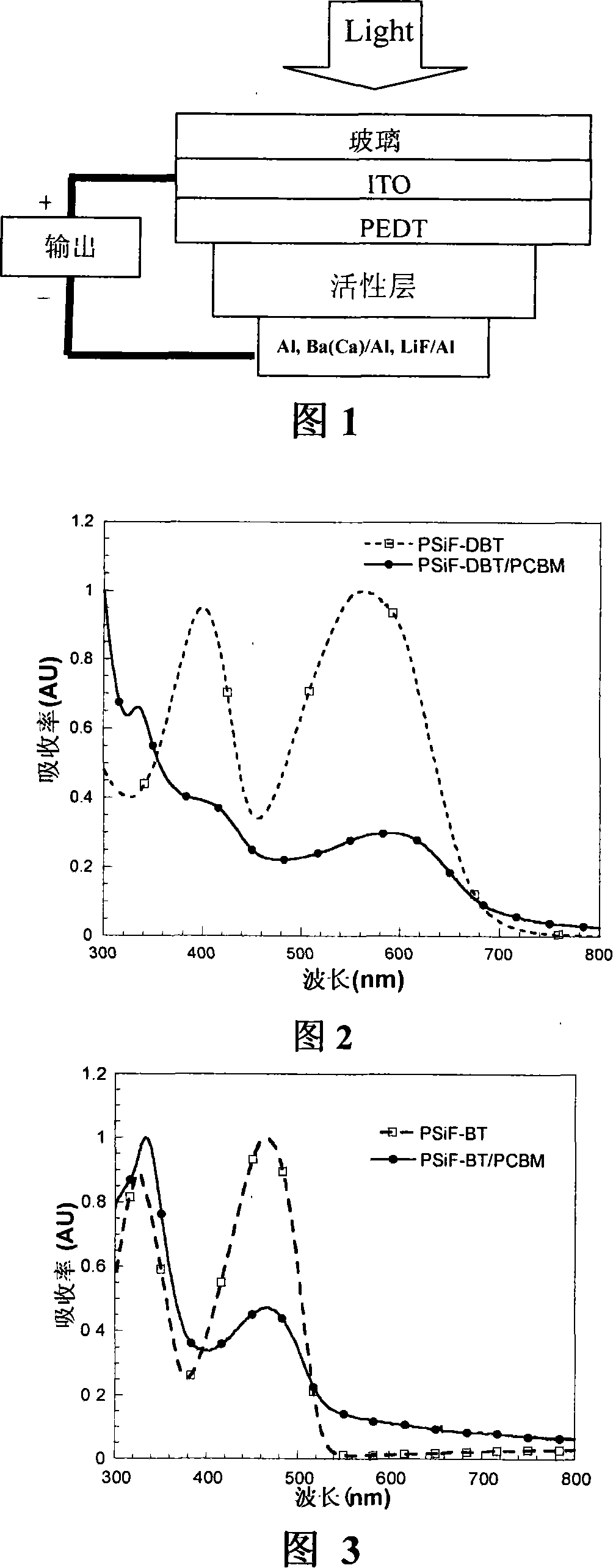
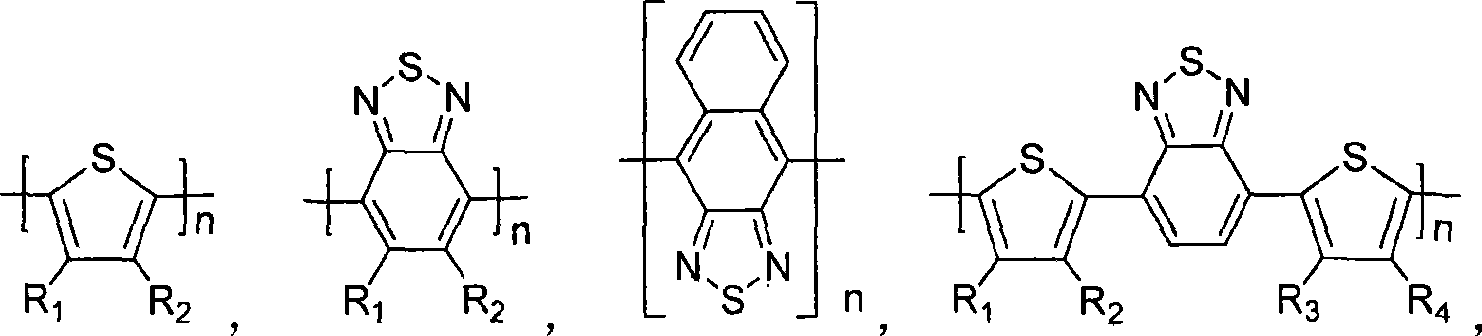
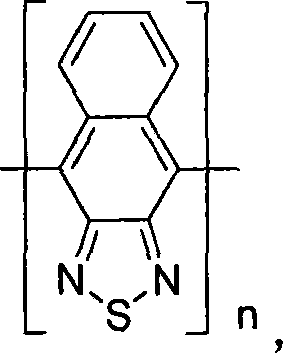
Silicon-containing fluorine conjugated polymer and its preparing process and application
ActiveCN101148495AHigh electron mobilityHigh photothermal oxidation stabilityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesHigh energyField-effect transistor
The present invention relates to silico fluorene copolymer and its application. The silico fluorene copolymer is copolymer of 2, 7-silico fluorine and narrow band gap monomer, and has absorption spectrum with absorption side band greater than 500 nm and absorption band side expanded to red light and near infrared region. It is prepared through copolymerizing 2, 7-silico fluorine and narrow band gap monomer containing hetero N and / or S atoms. It may be applied in making polymer solar cell, FET, etc. It has high mobility, high long-term stability and high energy converting efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
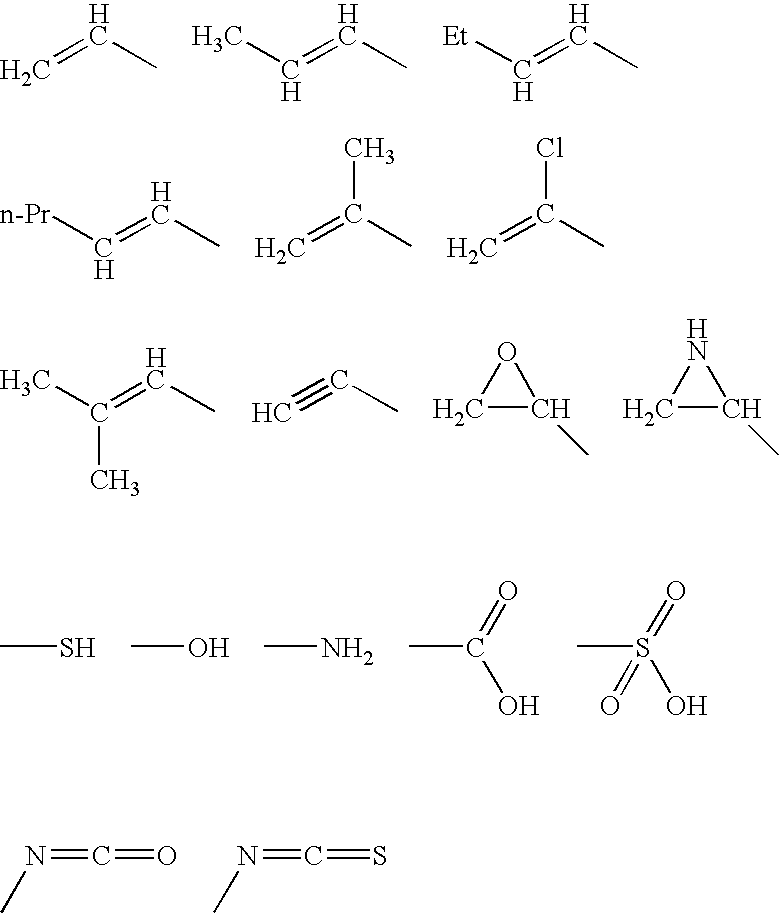
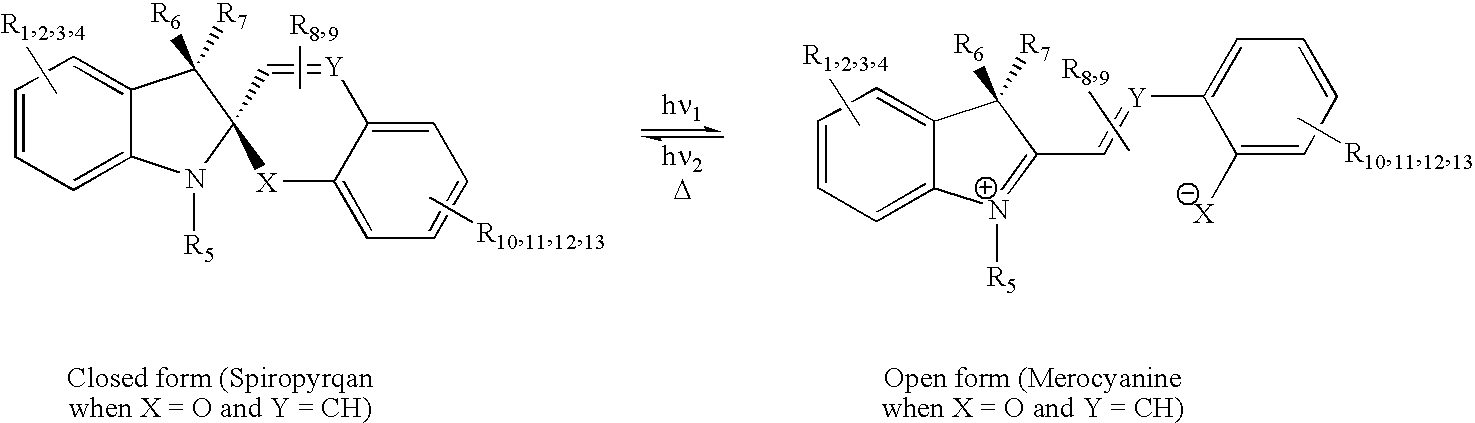
Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto
ActiveUS6984734B2Improve hydrophilicityImprove hydrophobicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsProtonationCoupling
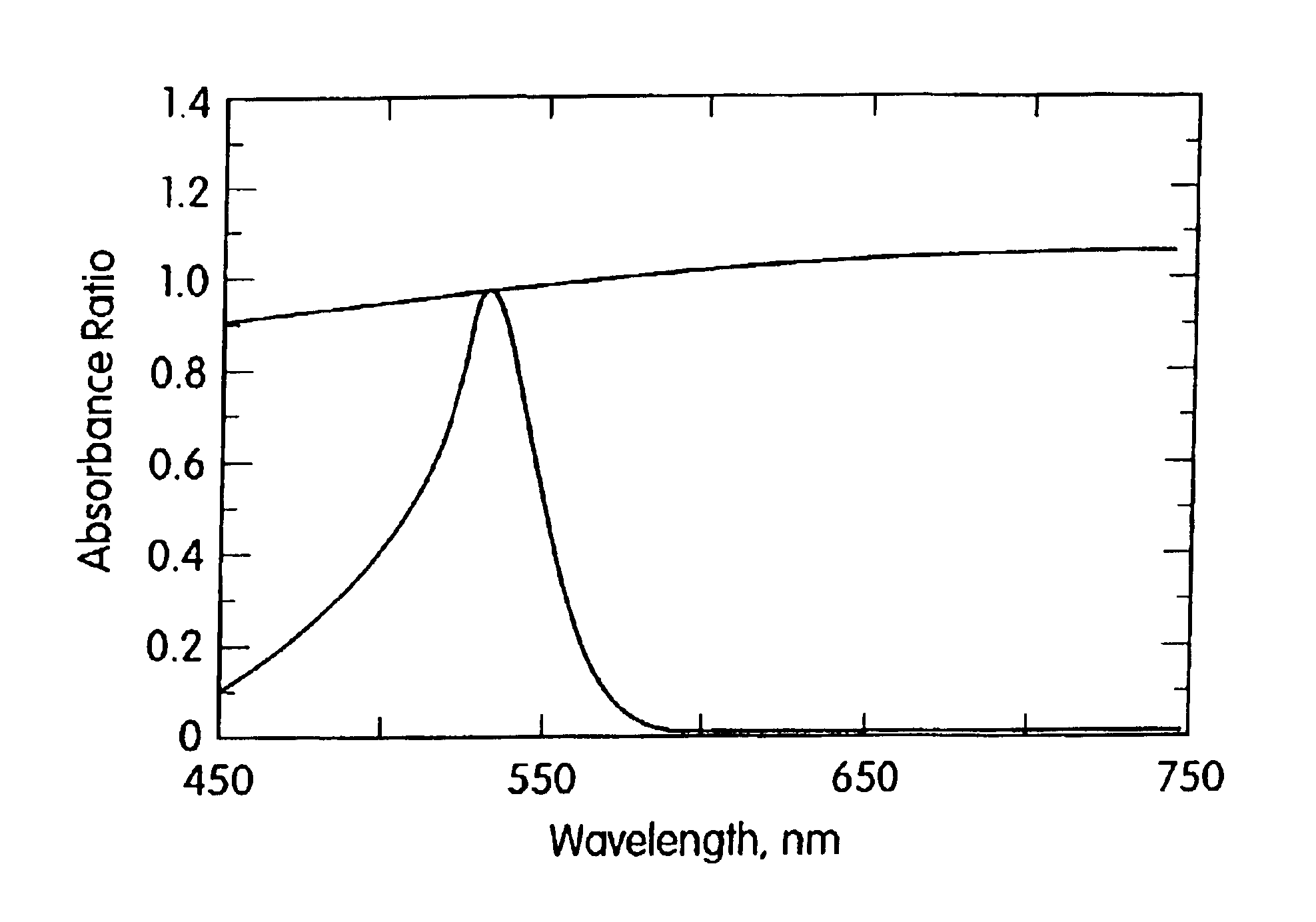
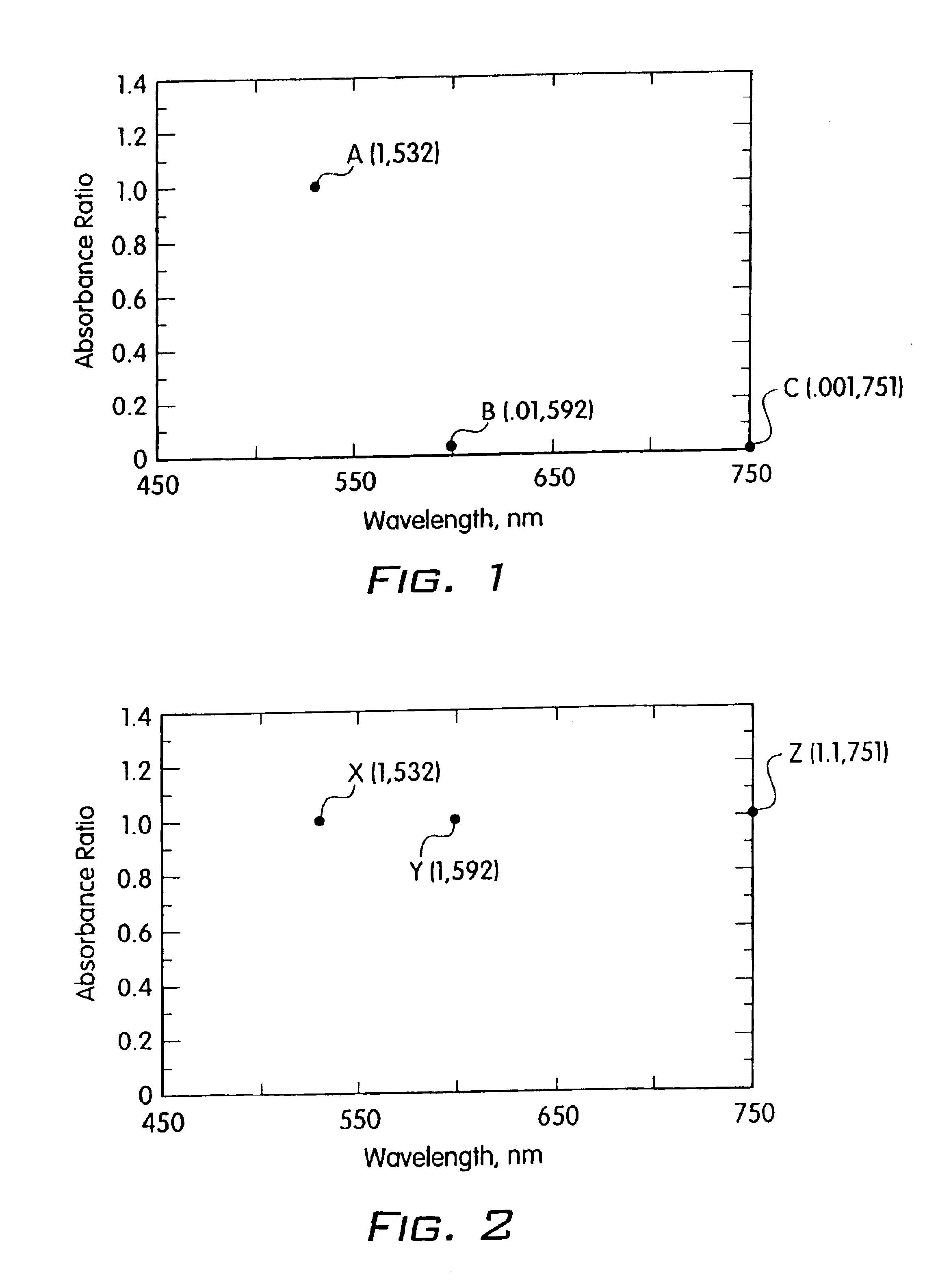
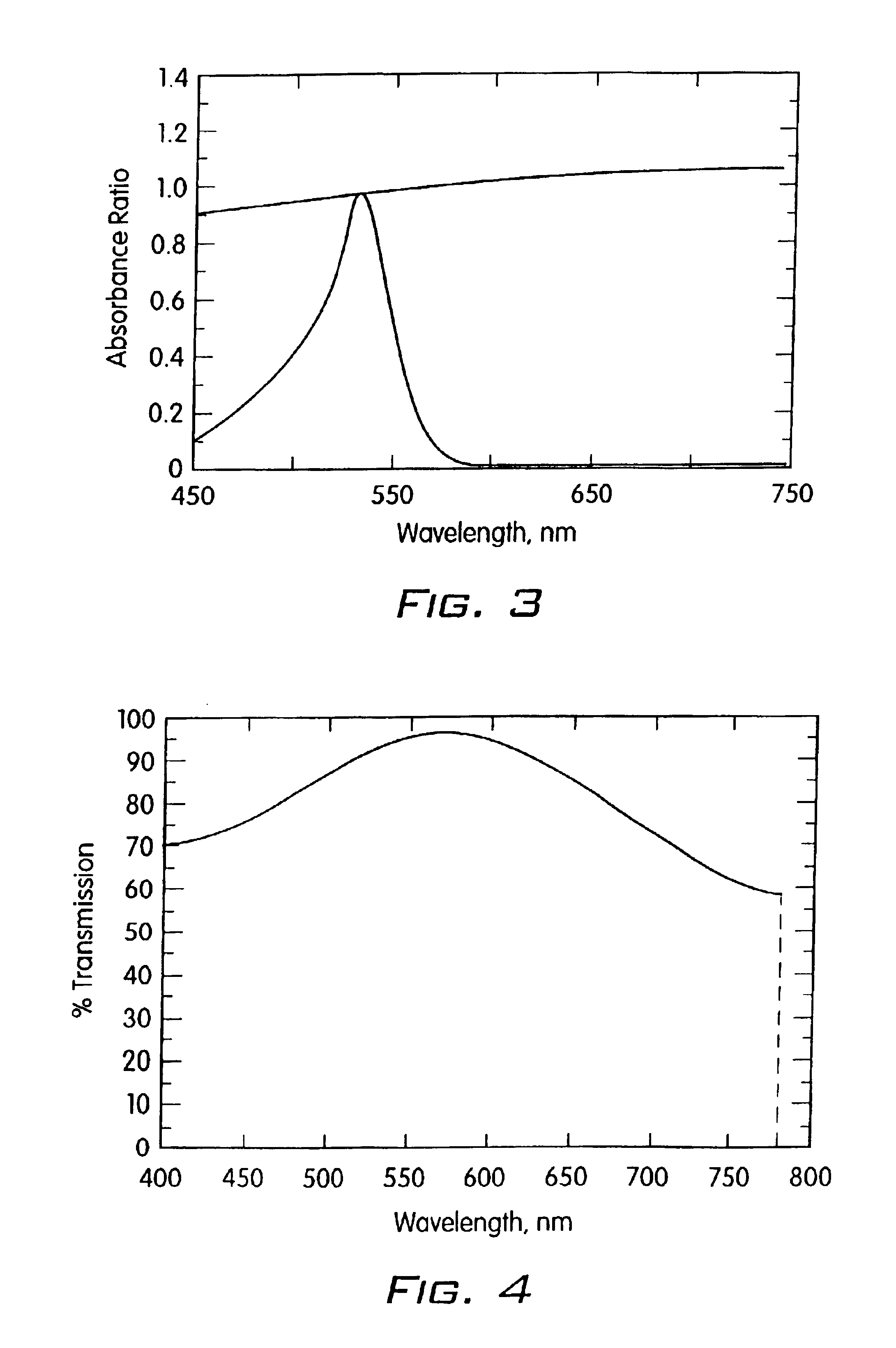
The present invention provides an oxidative coupling procedure that allows efficient synthesis of novel cyclo[n]pyrrole macrocycles. Therefore, the present invention provides cyclo[n]pyrroles where n is 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, or 12, and derivatives, multimers, isomers, and ion and neutral molecule complexes thereof as new compositions of matter. A protonated form of cyclo[n]pyrrole displays a gap of up to 700 nm between strong Soret and Q-like absorption bands in the electronic spectrum, demonstrating no significant ground state absorption in the visible portion of the electronic spectrum. Uses of cyclo[n]pyrroles as separation media, nonlinear optical materials, information storage media and infrared filters are provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Moisture detector, biological body moisture detector, natural product moisture detector, and product/material moisture detector
ActiveUS20100051905A1Easy to understandReduce the amount of noiseNanoinformaticsPhotometryBiological bodyNatural product
A moisture detector includes a light-receiving element including an absorption layer having a pn-junction, or an array of the light-receiving elements, wherein the absorption layer has a multiquantum well structure composed of a Group III-V semiconductor, the pn-junction is formed by selectively diffusing an impurity element into the absorption layer, and the concentration of the impurity in the absorption layer is 5×1016 / cm3 or less. The moisture detector receives light having at least one wavelength included in an absorption band of water lying in a wavelength range of 3 μm or less, thereby detecting moisture.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Methods for performing inspections and detecting chemical leaks using an infrared camera system
InactiveUS8193496B2Television system detailsDetection of fluid at leakage pointBandpass filteringCamera lens
A method of visually detecting a leak of a chemical emanating from a component. The method includes: aiming a passive infrared camera system towards the component; filtering an infrared image with an optical bandpass filter, the infrared image being that of the leak; after the infrared image passes through the lens and optical bandpass filter, receiving the filtered infrared image with an infrared sensor device; electronically processing the filtered infrared image received by the infrared sensor device to provide a visible image representing the filtered infrared image; and visually identifying the leak based on the visible image. The passive infrared camera system includes: a lens; a refrigerated portion including therein the infrared sensor device and the optical bandpass filter (located along an optical path between the lens and the infrared sensor device). At least part of a pass band for the optical bandpass filter is within an absorption band for the chemical.
Owner:LEAK SURVEYS
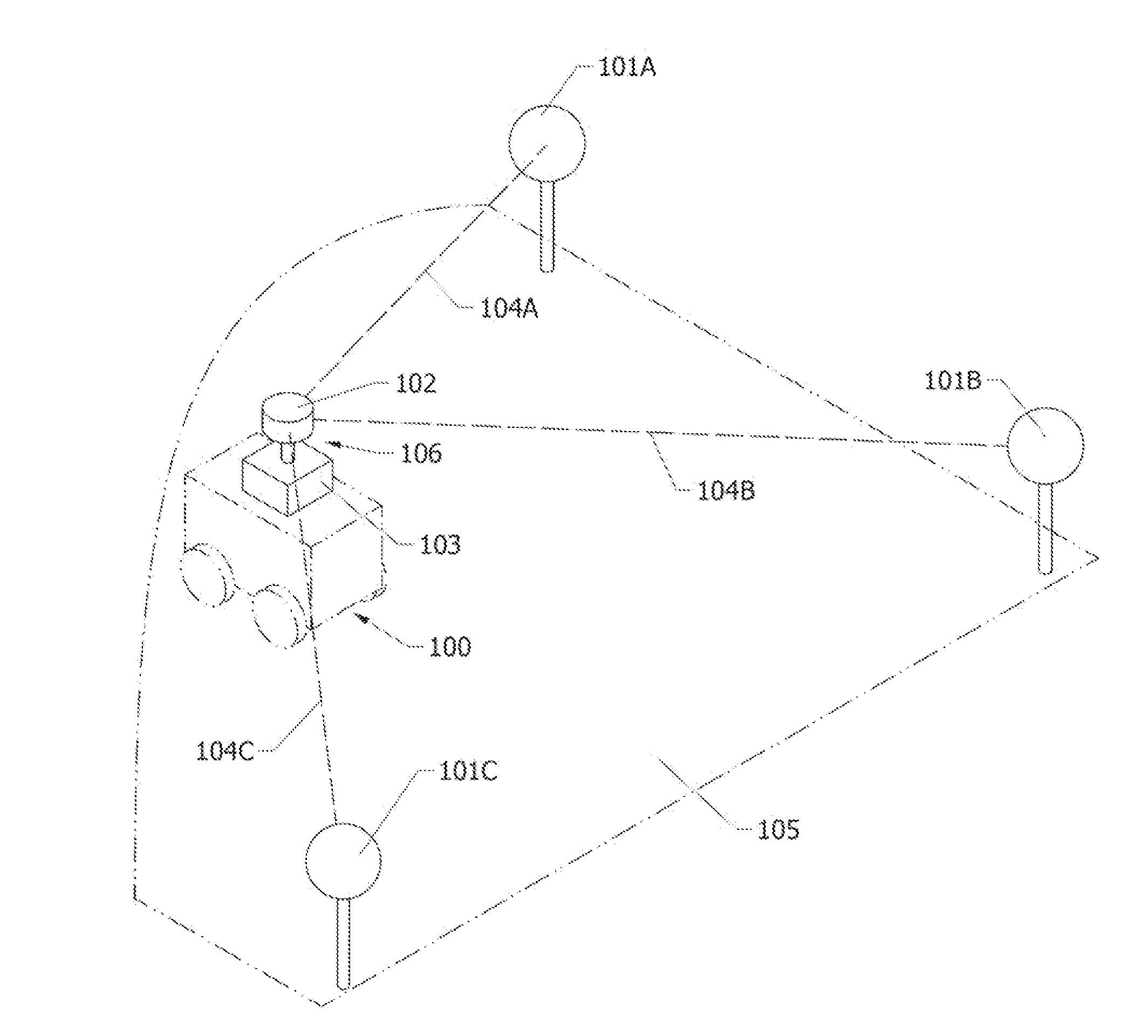
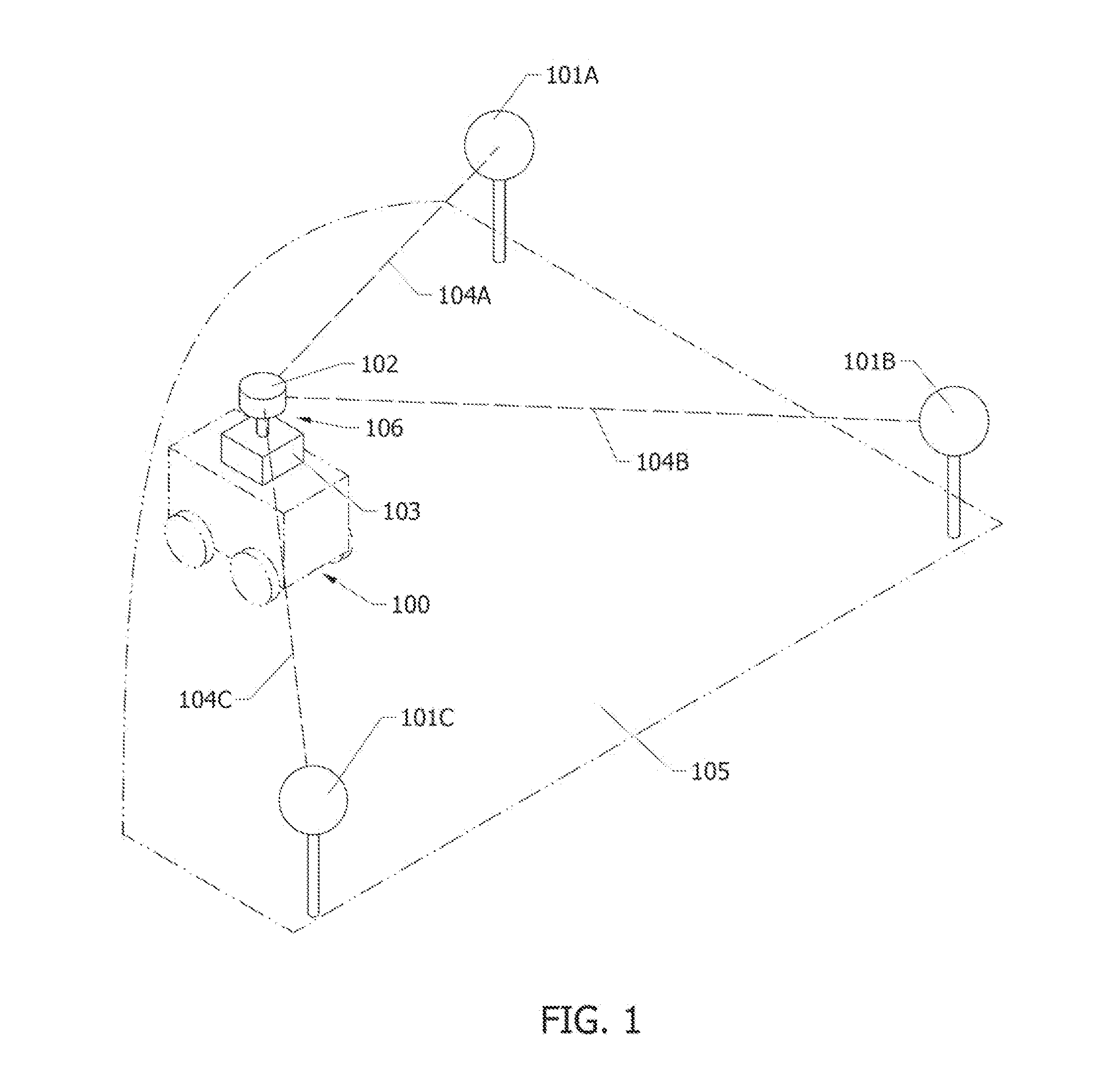
System and Method for Estimating the Position and Orientation of an Object using Optical Beacons
InactiveUS20140198206A1Quick identificationIdentification and processingOptical rangefindersPosition fixationPosition dependentComputer science
A system and method for determining the position and orientation of an object within an environment using optical beacons placed at known locations within the environment. The optical beacons are received by an imaging device mounted on the object to be positioned, The system derives the position and orientation of the object from data associated with the pixel locations of the beacons within images, the identity of the beacons within images, and the positions of the beacons within the environment. In one embodiment, the optical beacons emit signals that are patterned in such a way that they appear as a first signal when sampled a low sampling rate and appear as a second signal when sampled at a high sampling rate. The first signal is the same for each beacon, and is used to distinguish beacons from other sources of light in the environment. The second signal is different for each beacon, and is used to identify beacons. In another embodiment, the optical beacons are installed underground and rise on command. In another embodiment, the optical beacons may also emit light within an absorption band of the atmosphere m order to improve the signal to noise ratio of the beacons.
Owner:MURRAY KEVIN HUGH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


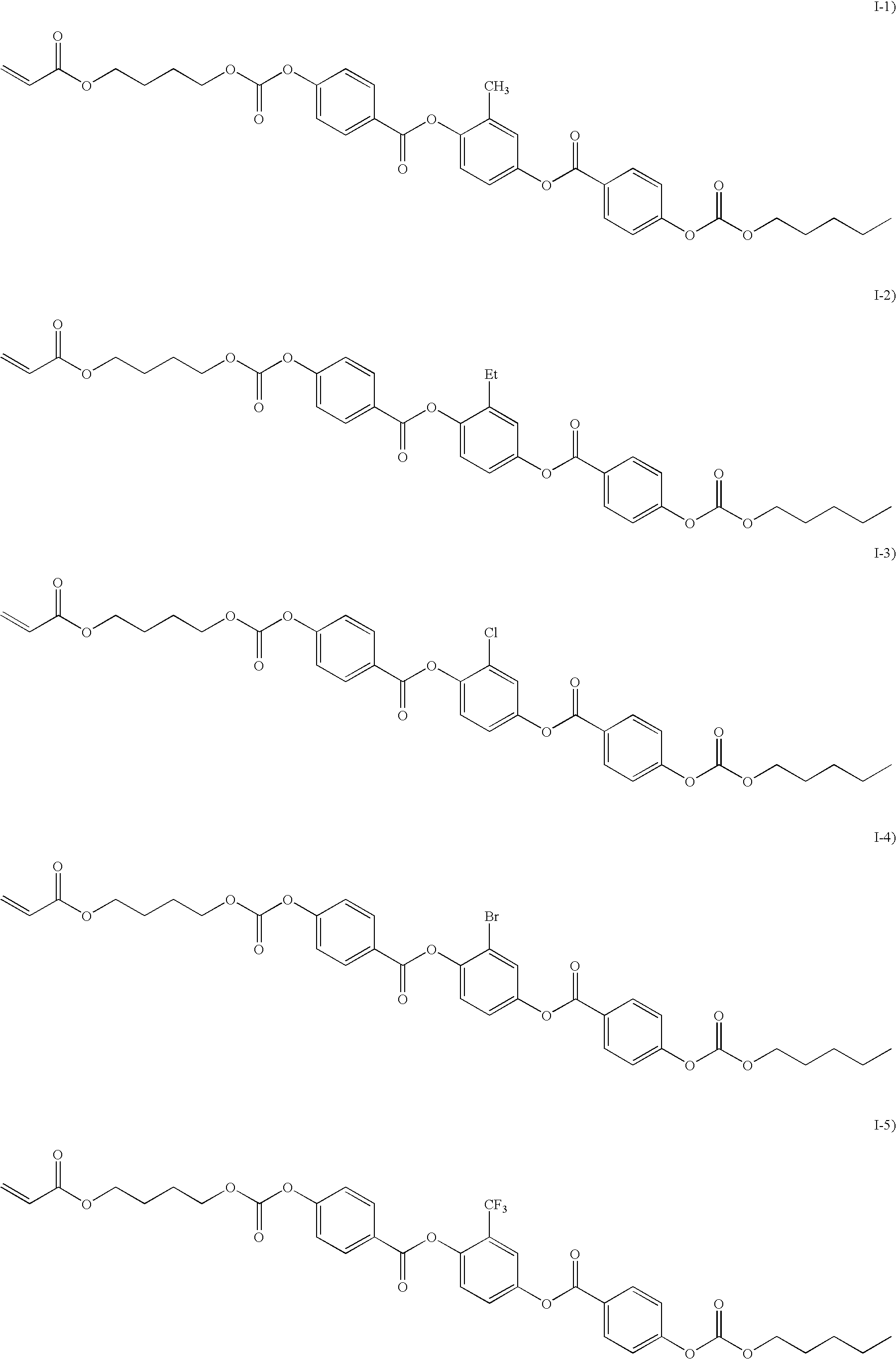
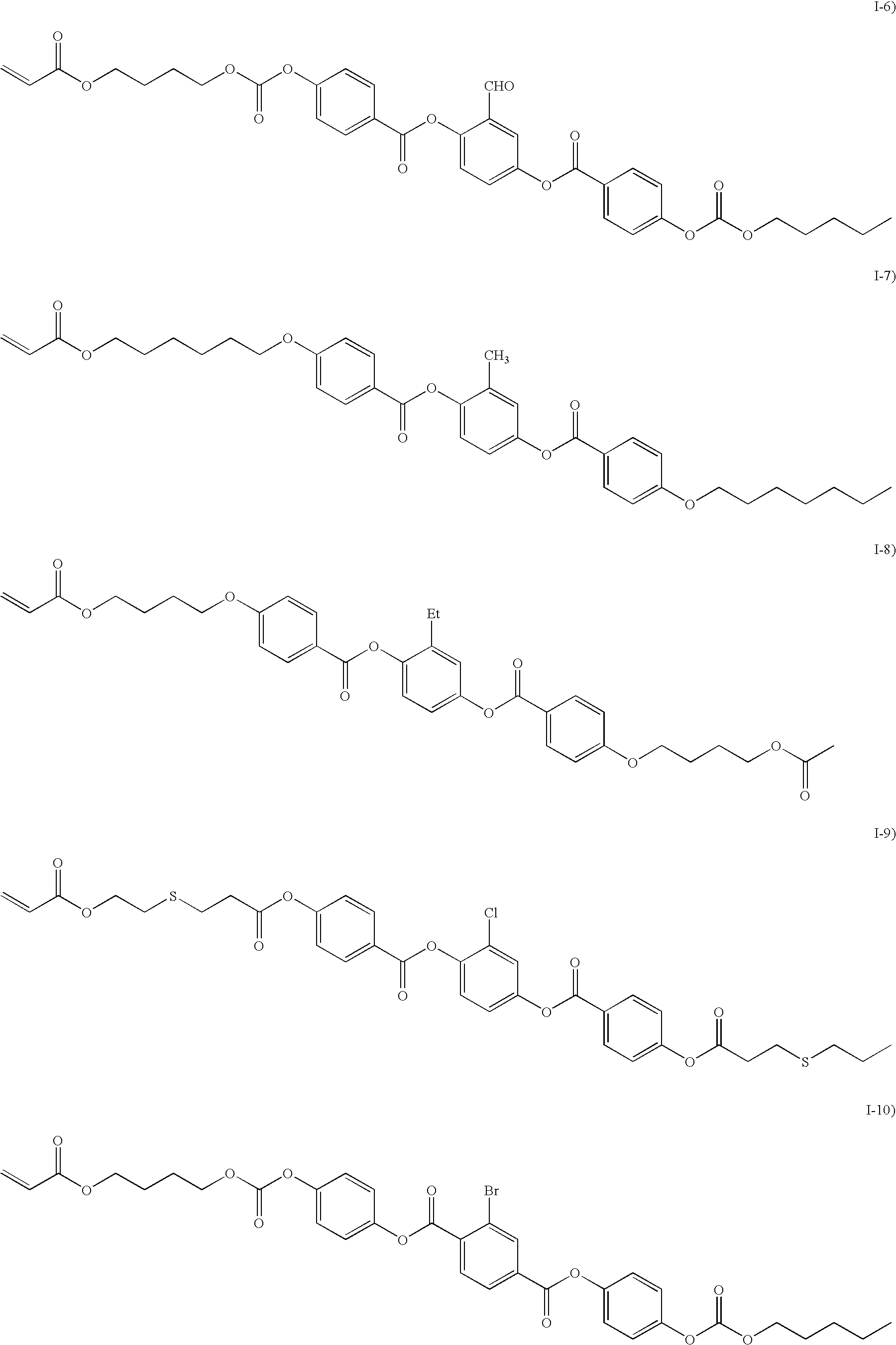
![Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/27c412f0-891d-44db-8e10-7058423dcbd3/US06984734-20060110-D00001.png)
![Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/27c412f0-891d-44db-8e10-7058423dcbd3/US06984734-20060110-D00002.png)
![Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto Cyclo[n]pyrroles and methods thereto](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/27c412f0-891d-44db-8e10-7058423dcbd3/US06984734-20060110-D00003.png)