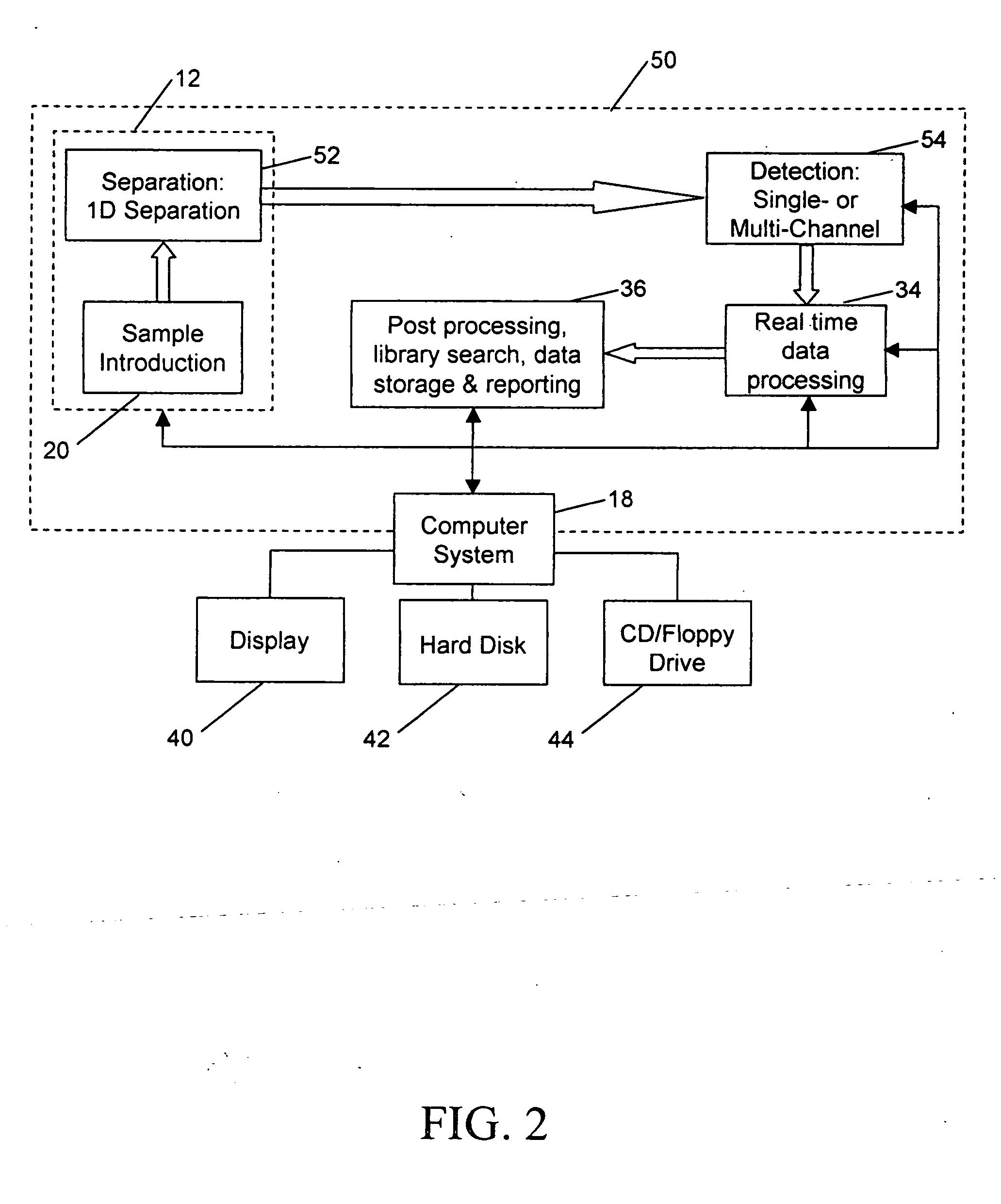
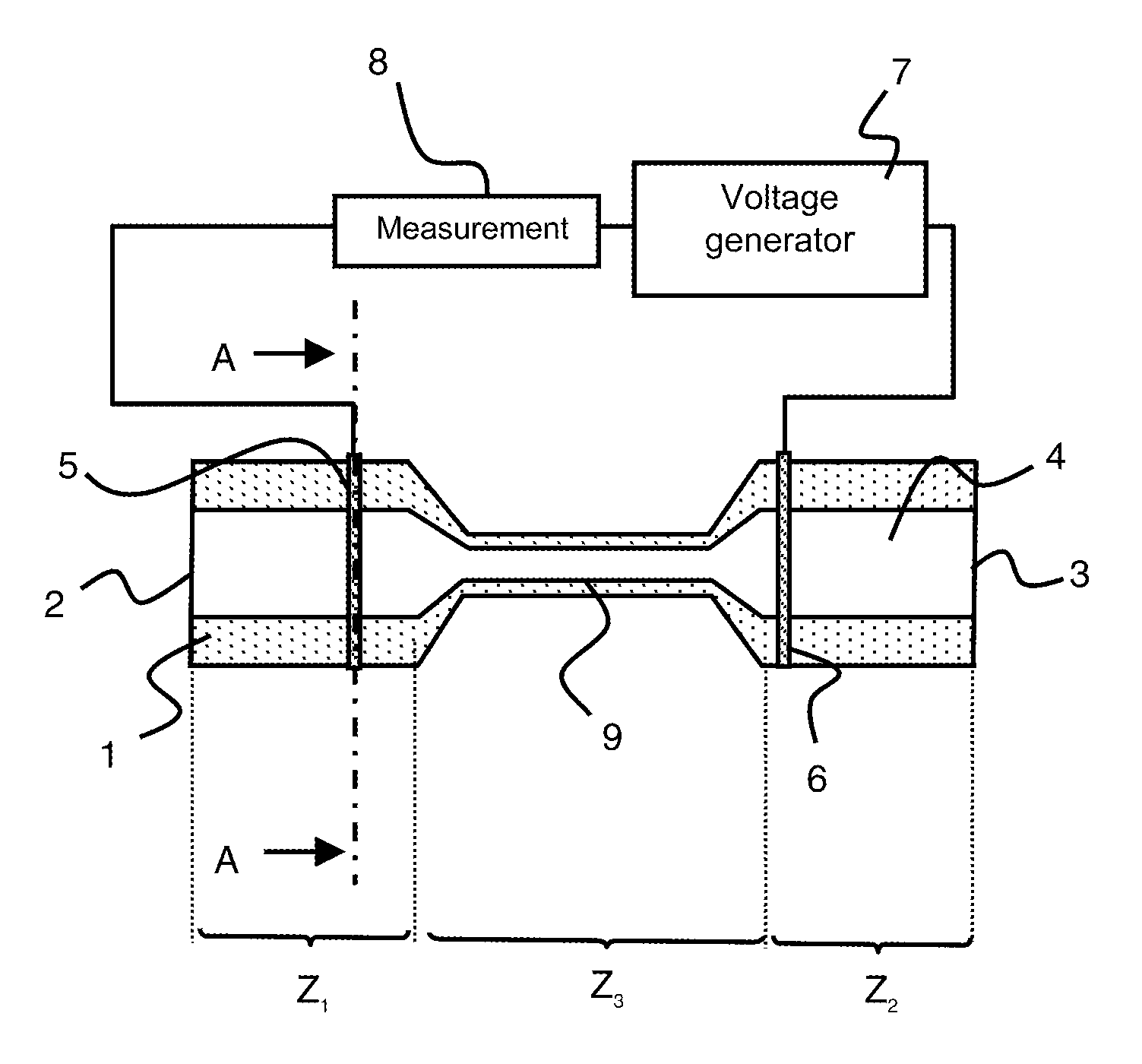
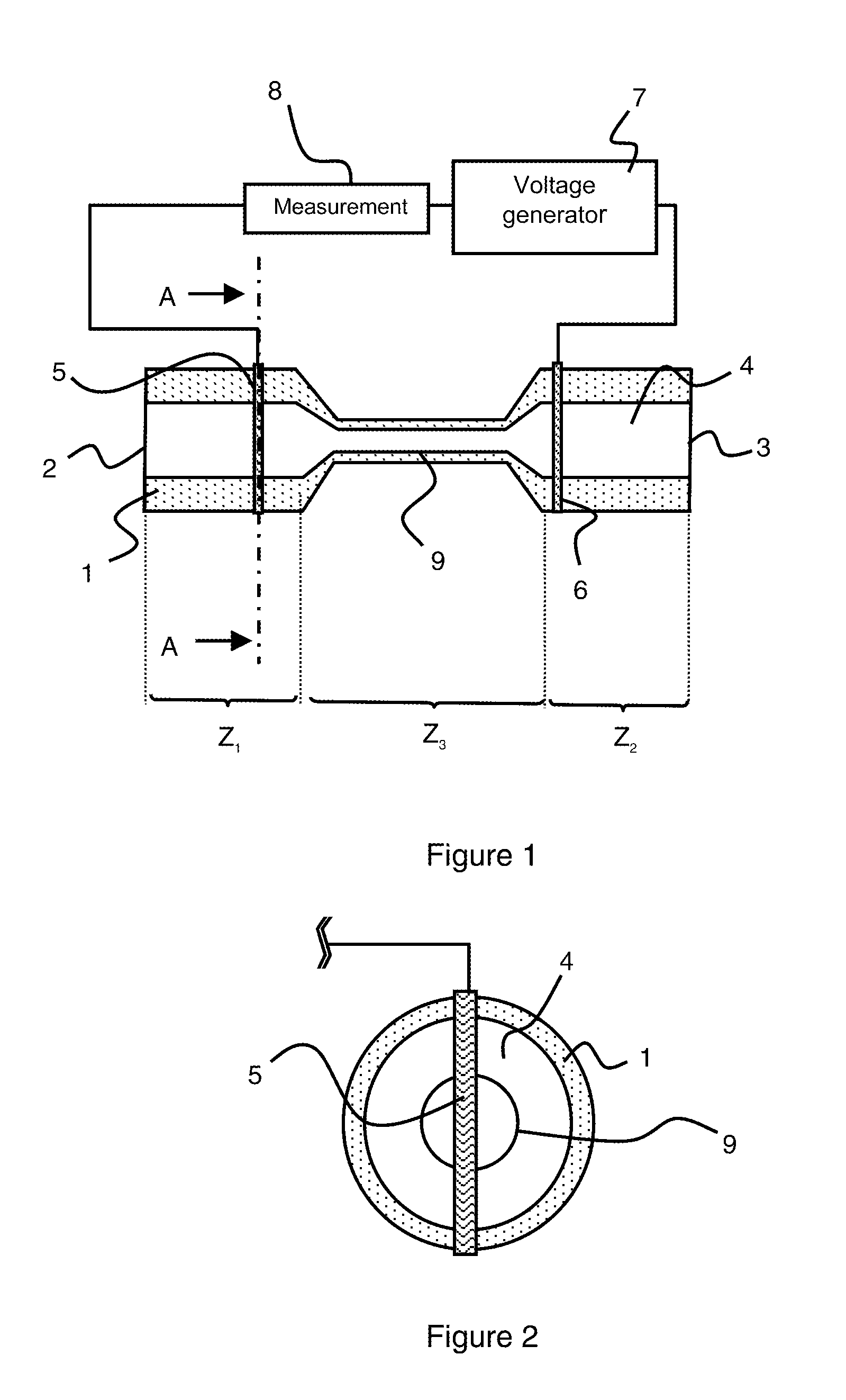
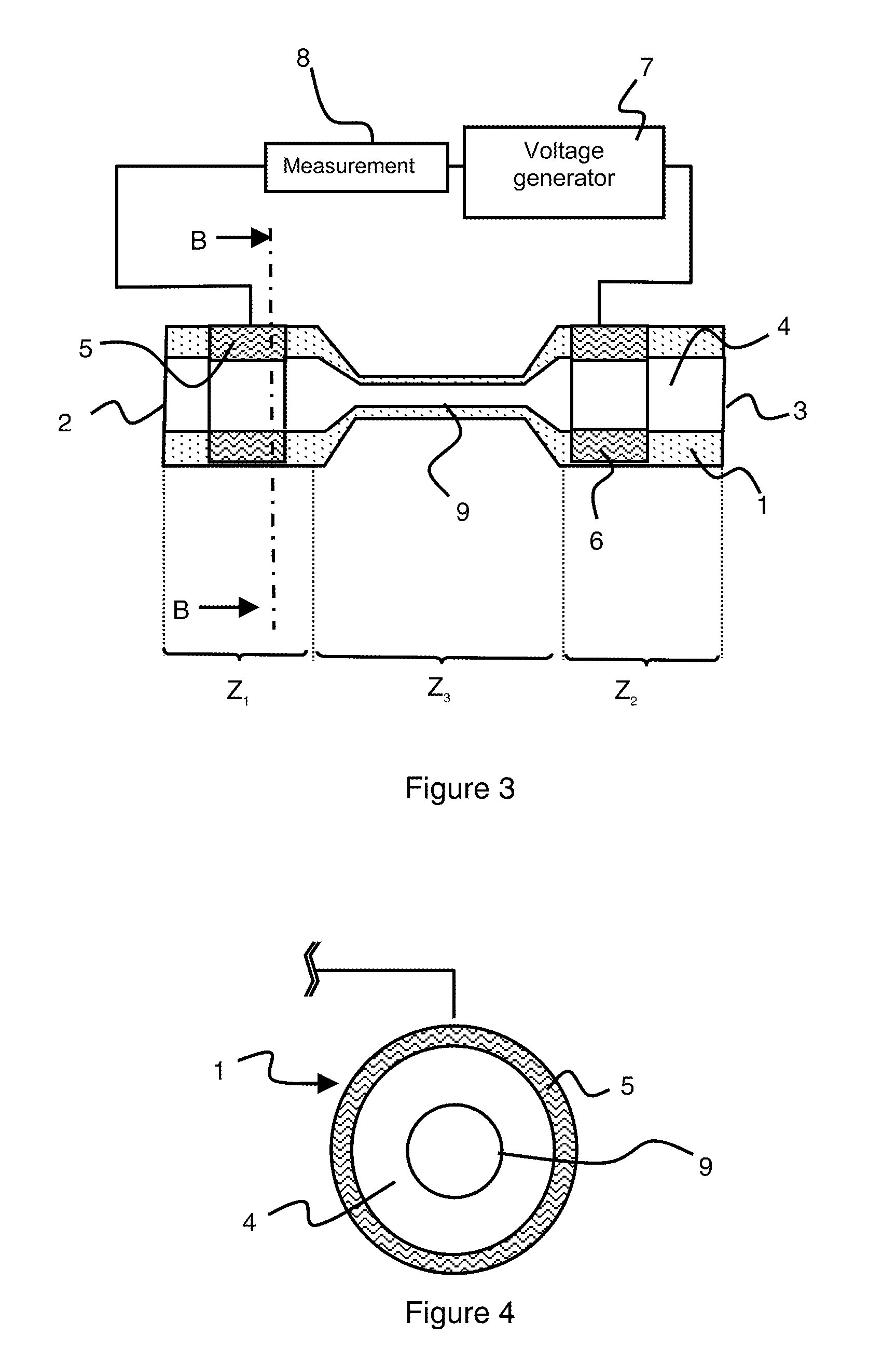
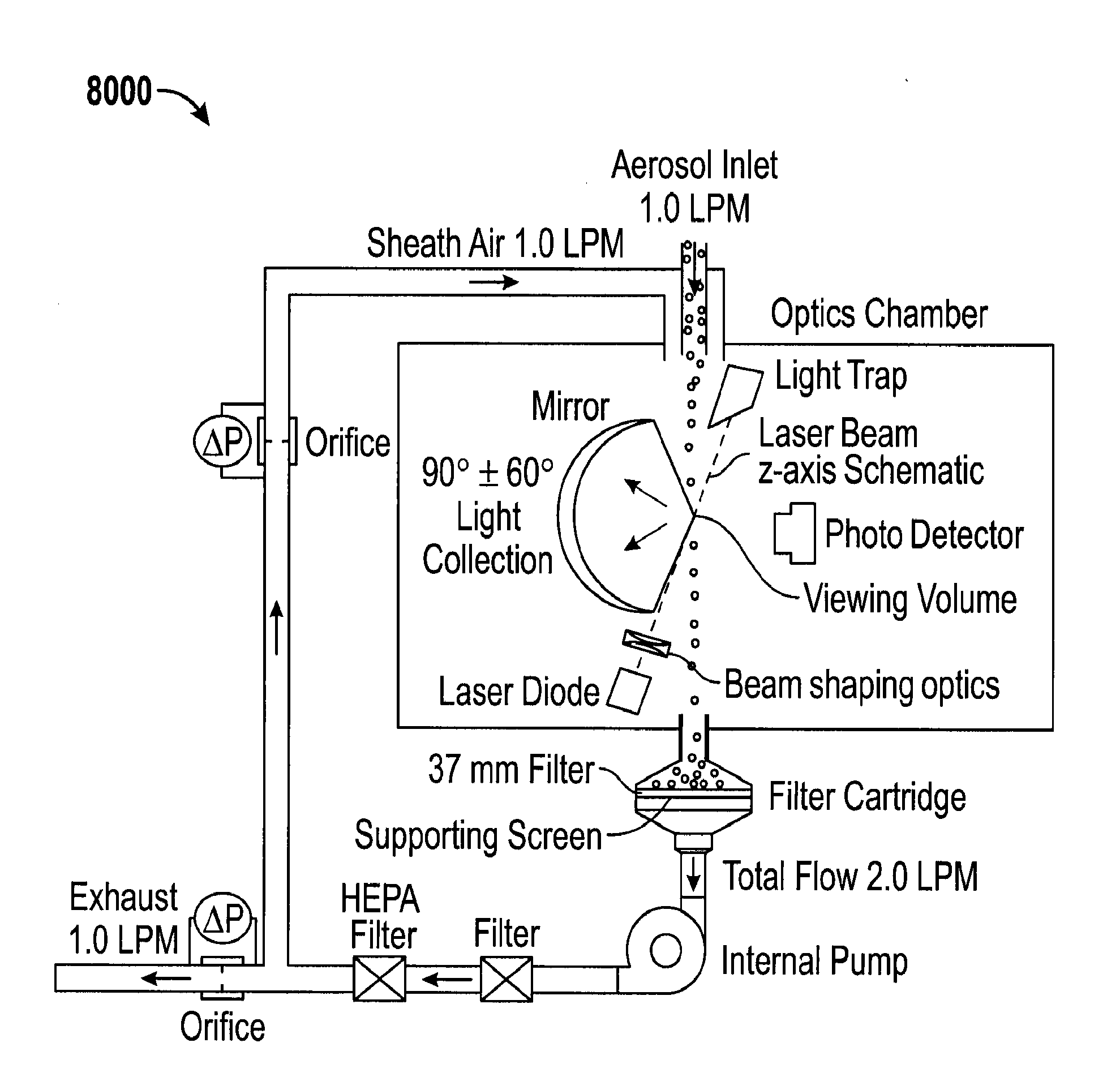
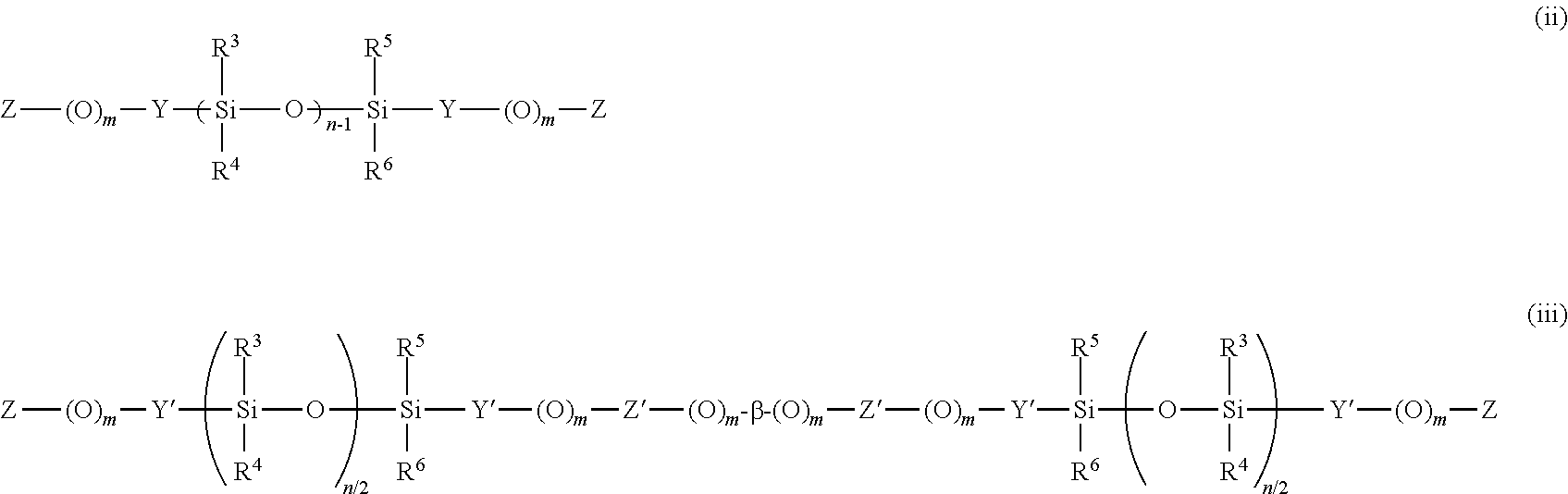Patents
Literature
1530 results about "Calibration curve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In analytical chemistry, a calibration curve, also known as a standard curve, is a general method for determining the concentration of a substance in an unknown sample by comparing the unknown to a set of standard samples of known concentration. A calibration curve is one approach to the problem of instrument calibration; other standard approaches may mix the standard into the unknown, giving an internal standard.
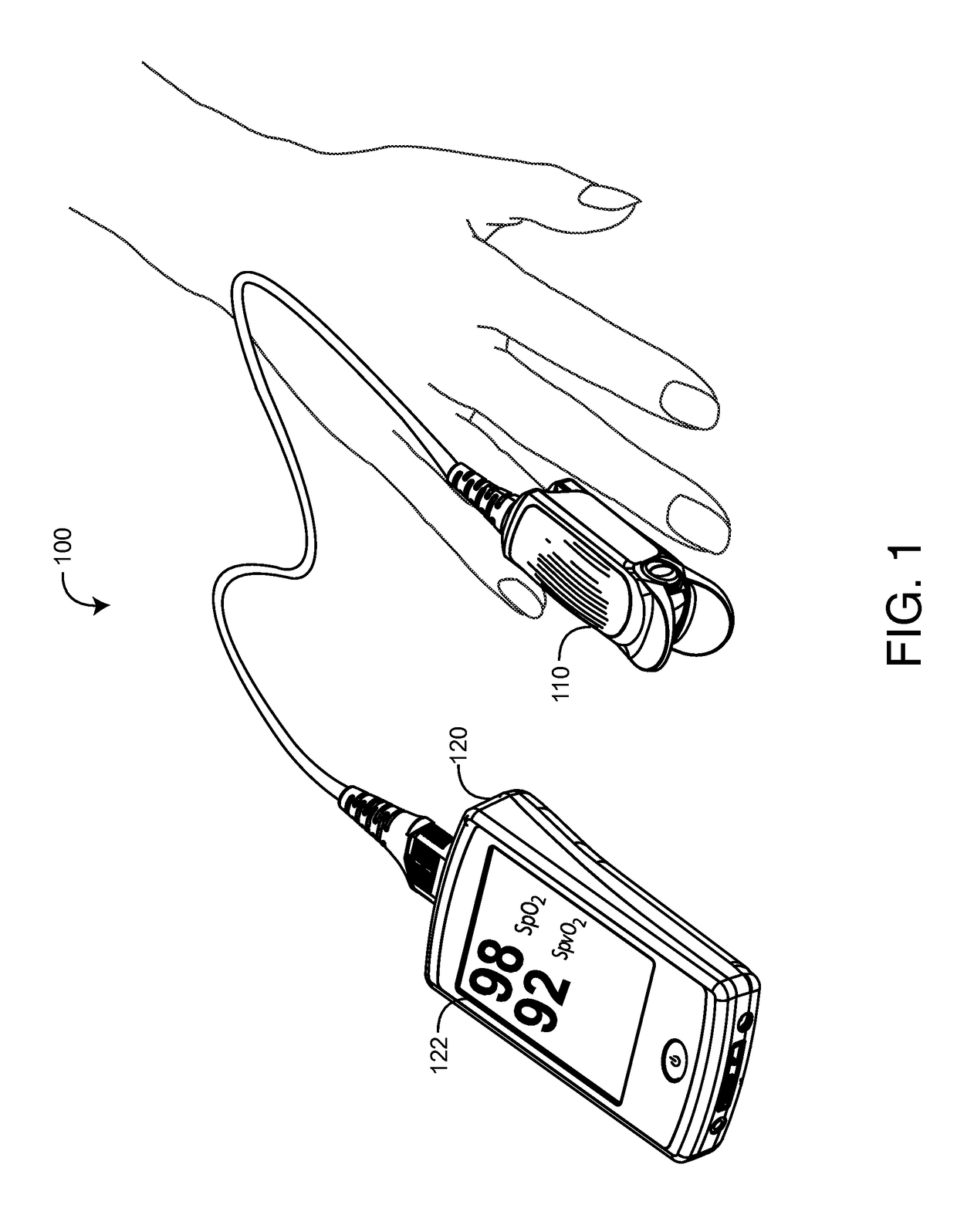
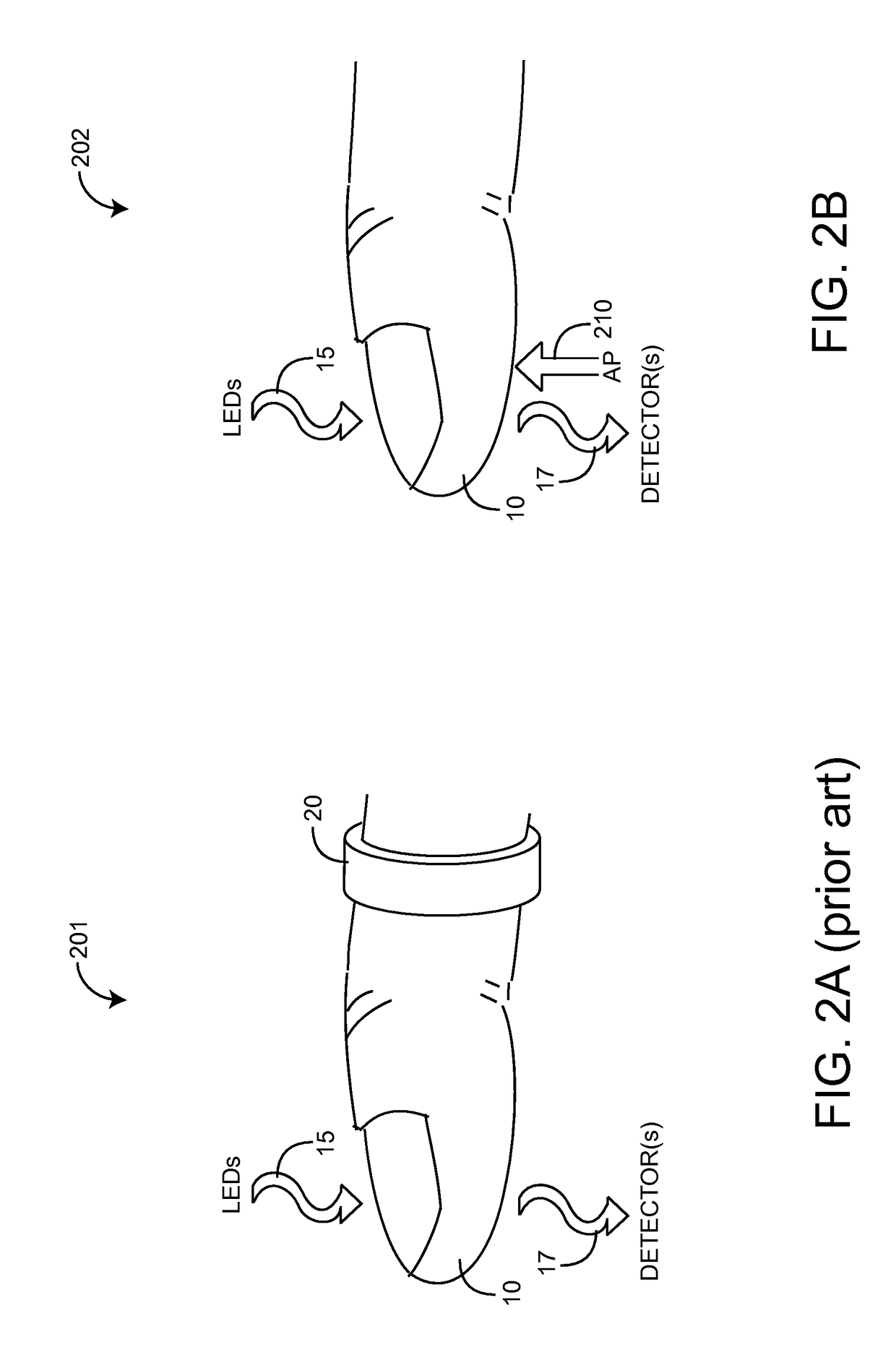
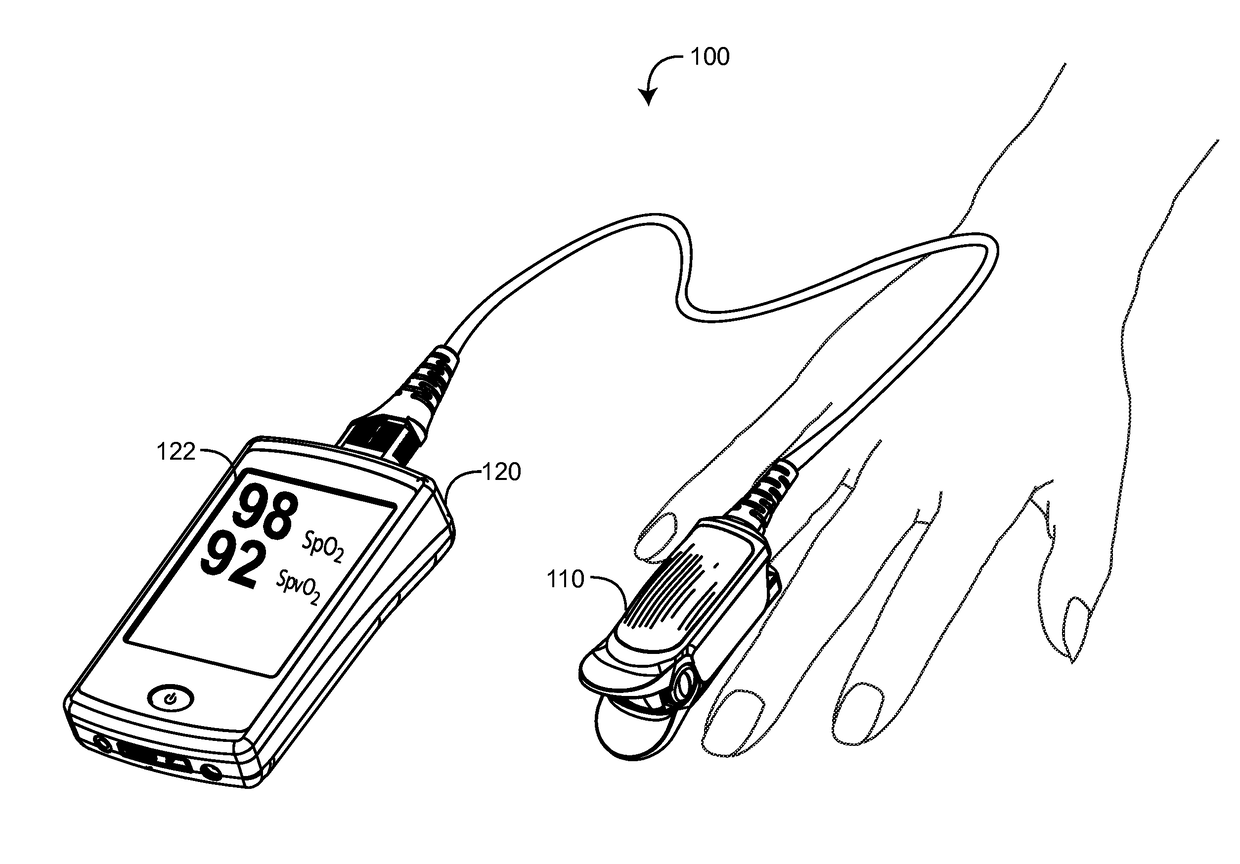
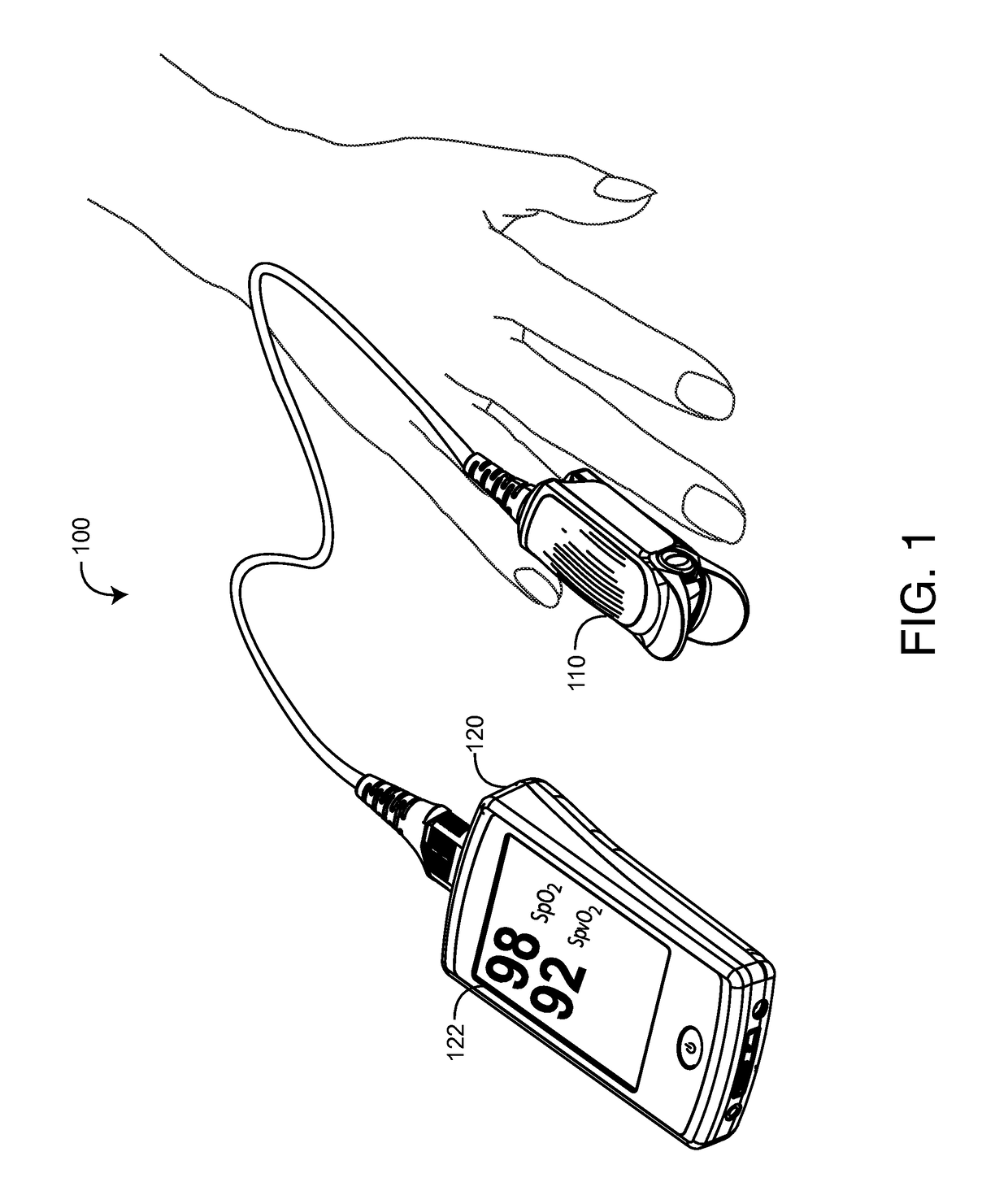
Non-invasive sensor calibration device
ActiveUS8418524B2Reliable timeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOptically investigating flaws/contaminationNon invasiveAcoustics
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Active-pulse blood analysis system
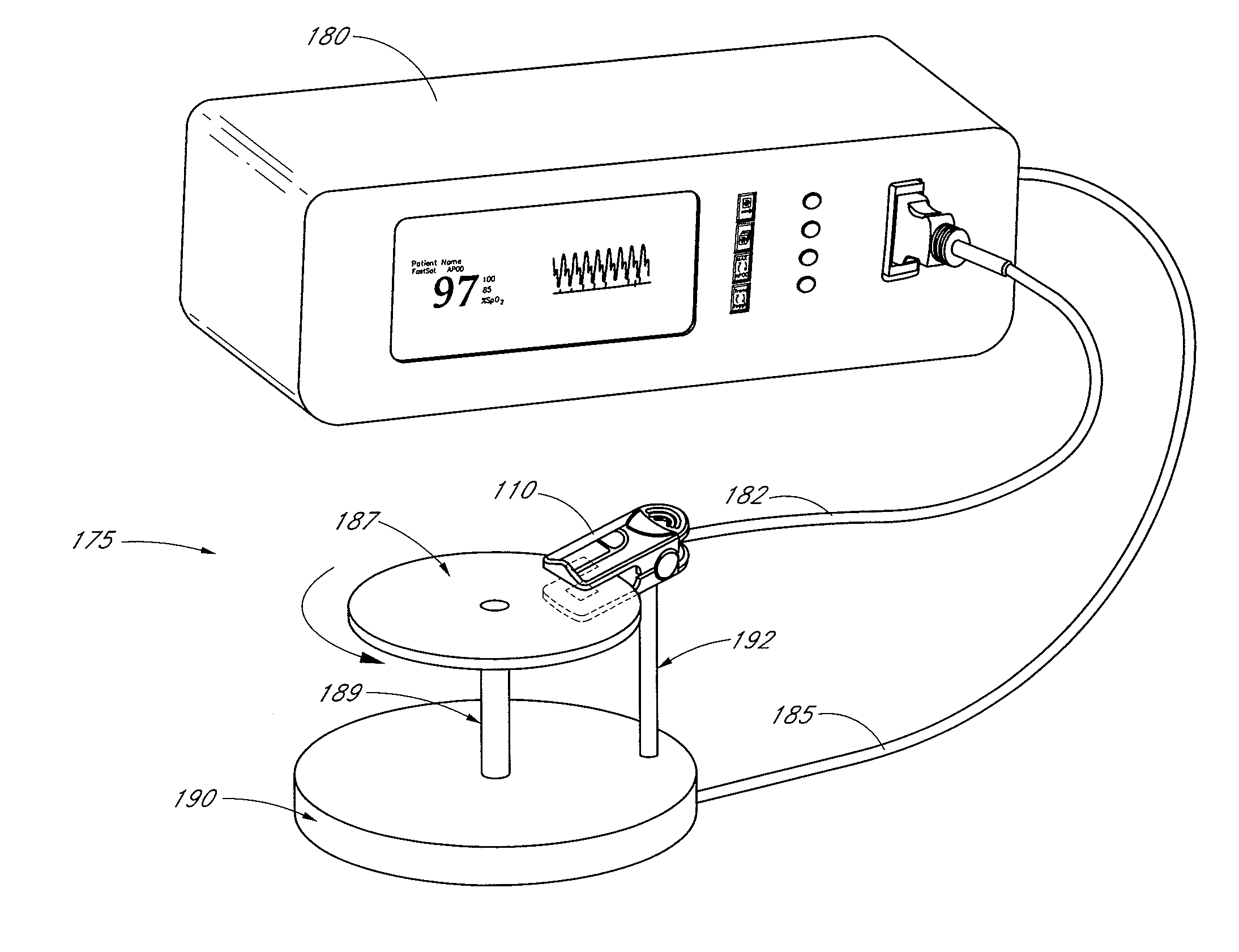
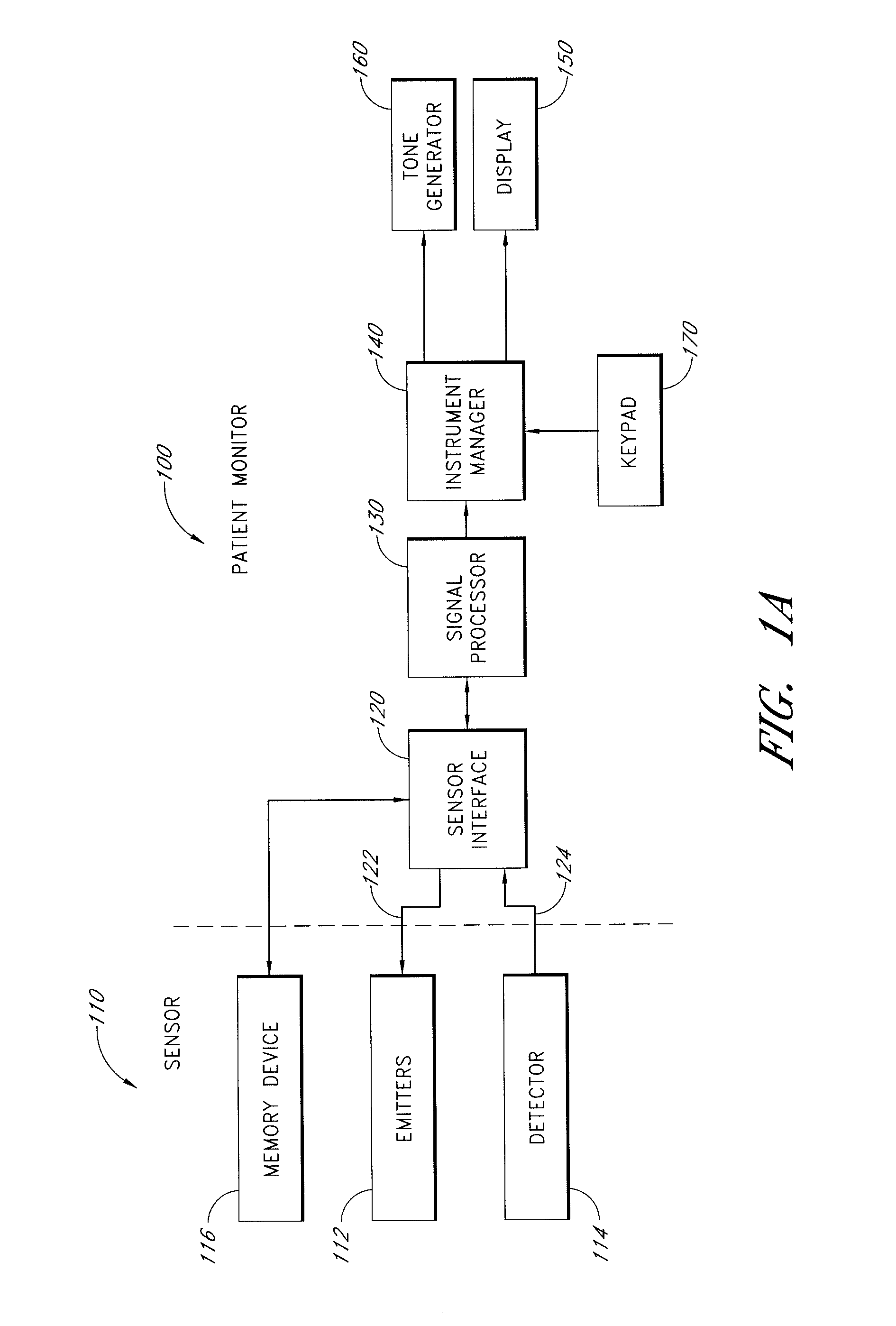
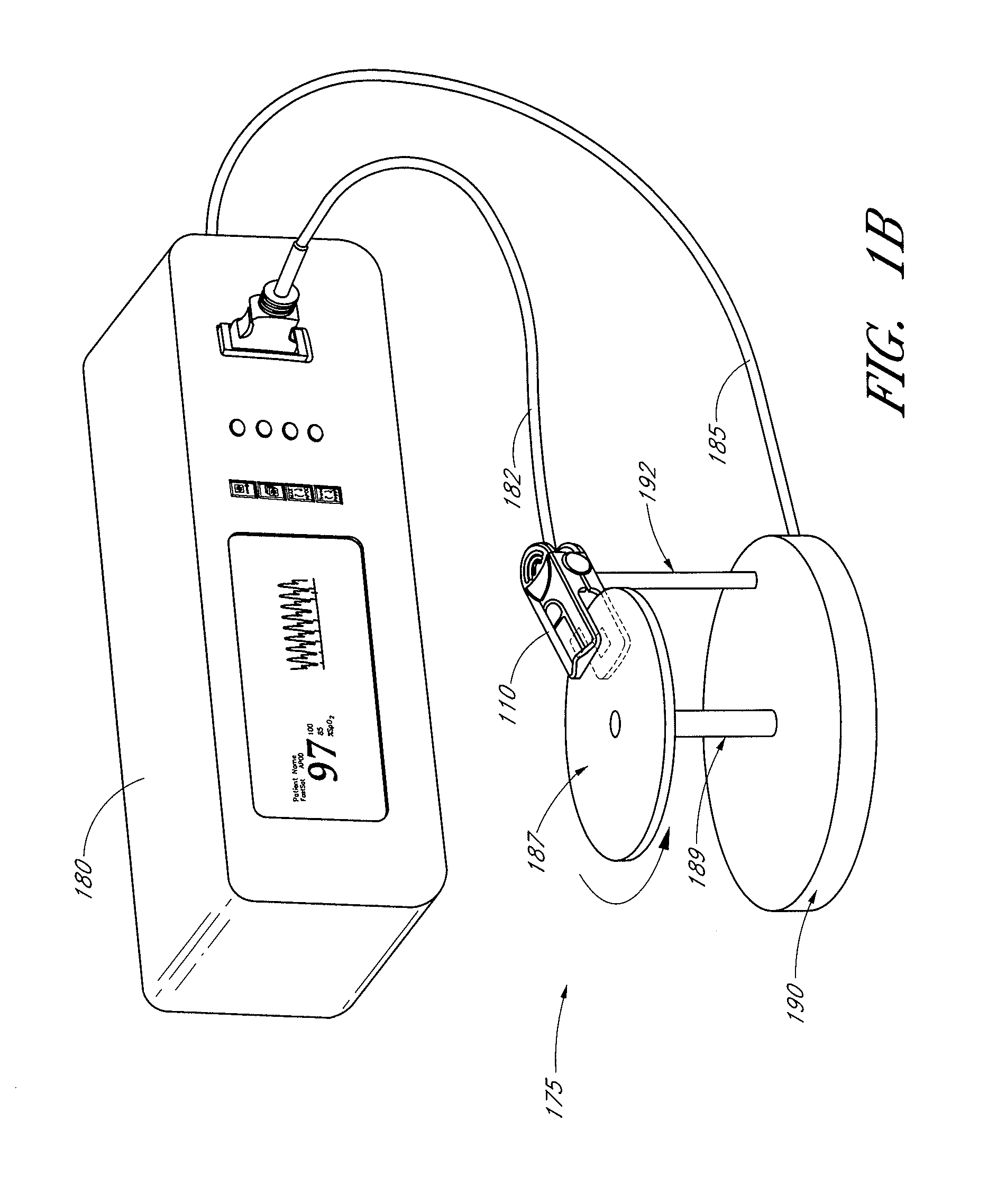
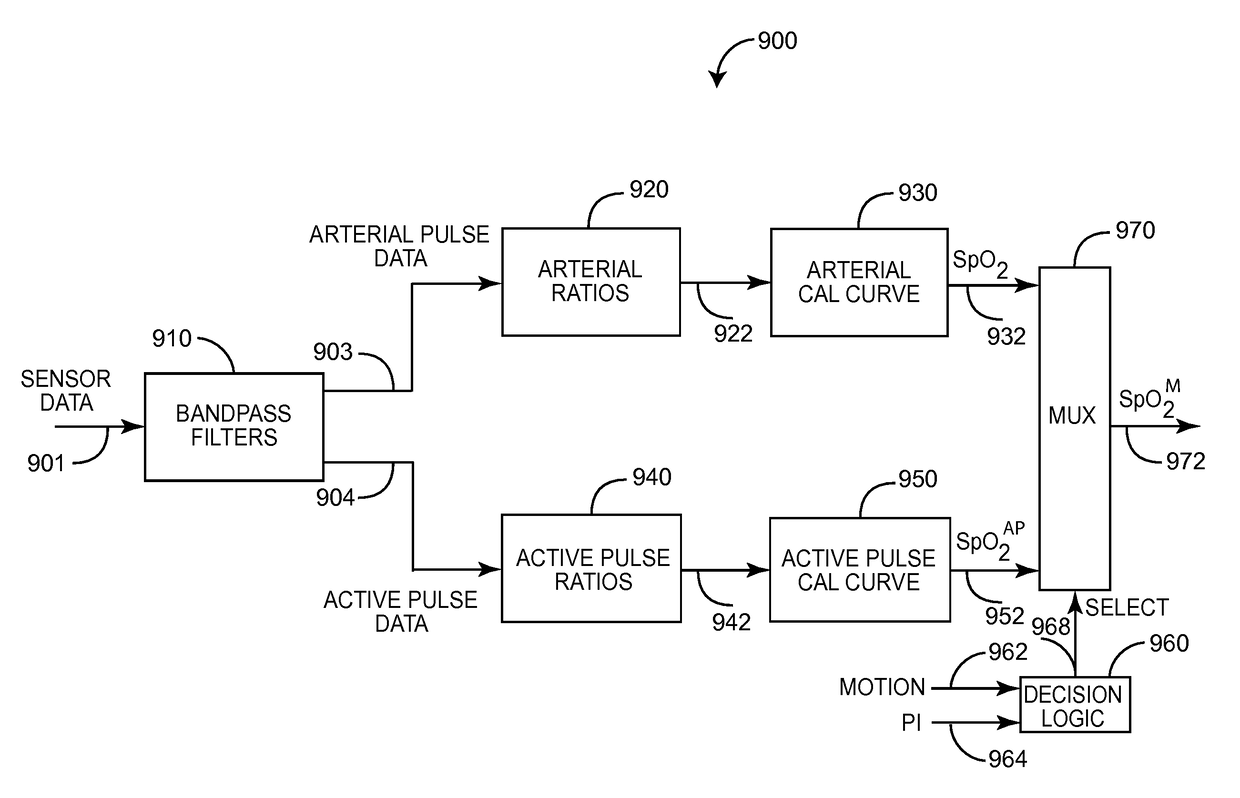
An active-pulse blood analysis system has an optical sensor that illuminates a tissue site with multiple wavelengths of optical radiation and outputs sensor signals responsive to the optical radiation after attenuation by pulsatile blood flow within the tissue site. A monitor communicates with the sensor signals and is responsive to arterial pulses within a first bandwidth and active pulses within a second bandwidth so as to generate arterial pulse ratios and active pulse ratios according to the wavelengths. An arterial calibration curve relates the arterial pulse ratios to a first arterial oxygen saturation value and an active pulse calibration curve relates the active pulse ratios to a second arterial oxygen saturation value. Decision logic outputs one of the first and second arterial oxygen saturation values based upon perfusion and signal quality.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Active-pulse blood analysis system
An active-pulse blood analysis system has an optical sensor that illuminates a tissue site with multiple wavelengths of optical radiation and outputs sensor signals responsive to the optical radiation after attenuation by pulsatile blood flow within the tissue site. A monitor communicates with the sensor signals and is responsive to arterial pulses within a first bandwidth and active pulses within a second bandwidth so as to generate arterial pulse ratios and active pulse ratios according to the wavelengths. An arterial calibration curve relates the arterial pulse ratios to a first arterial oxygen saturation value and an active pulse calibration curve relates the active pulse ratios to a second arterial oxygen saturation value. Decision logic outputs one of the first and second arterial oxygen saturation values based upon perfusion and signal quality.
Owner:MASIMO CORP
Method for determining stimulation parameters
InactiveUS7174215B2Efficiently determinedElectrotherapyArtificial respirationMedicineCalibration curve
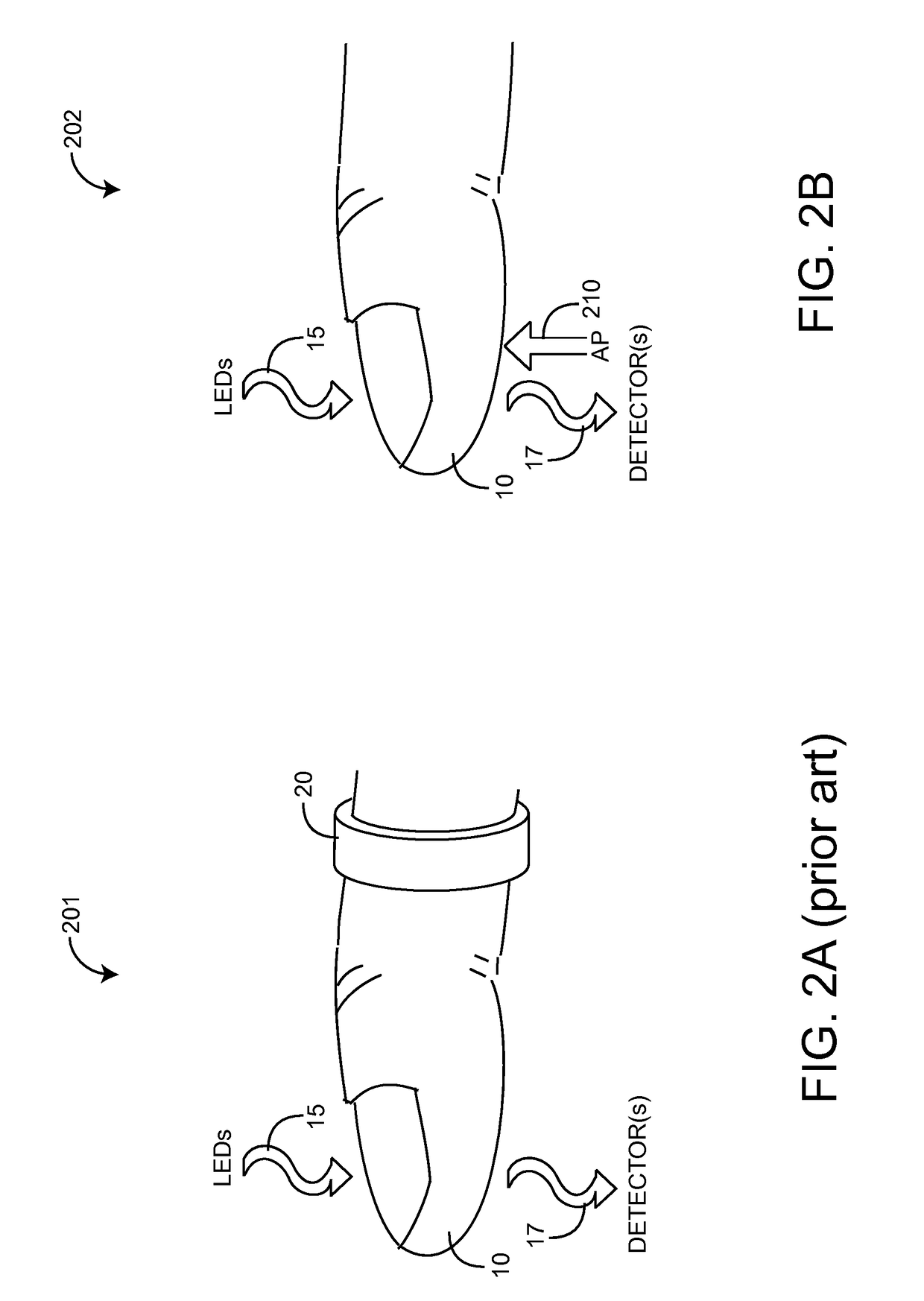
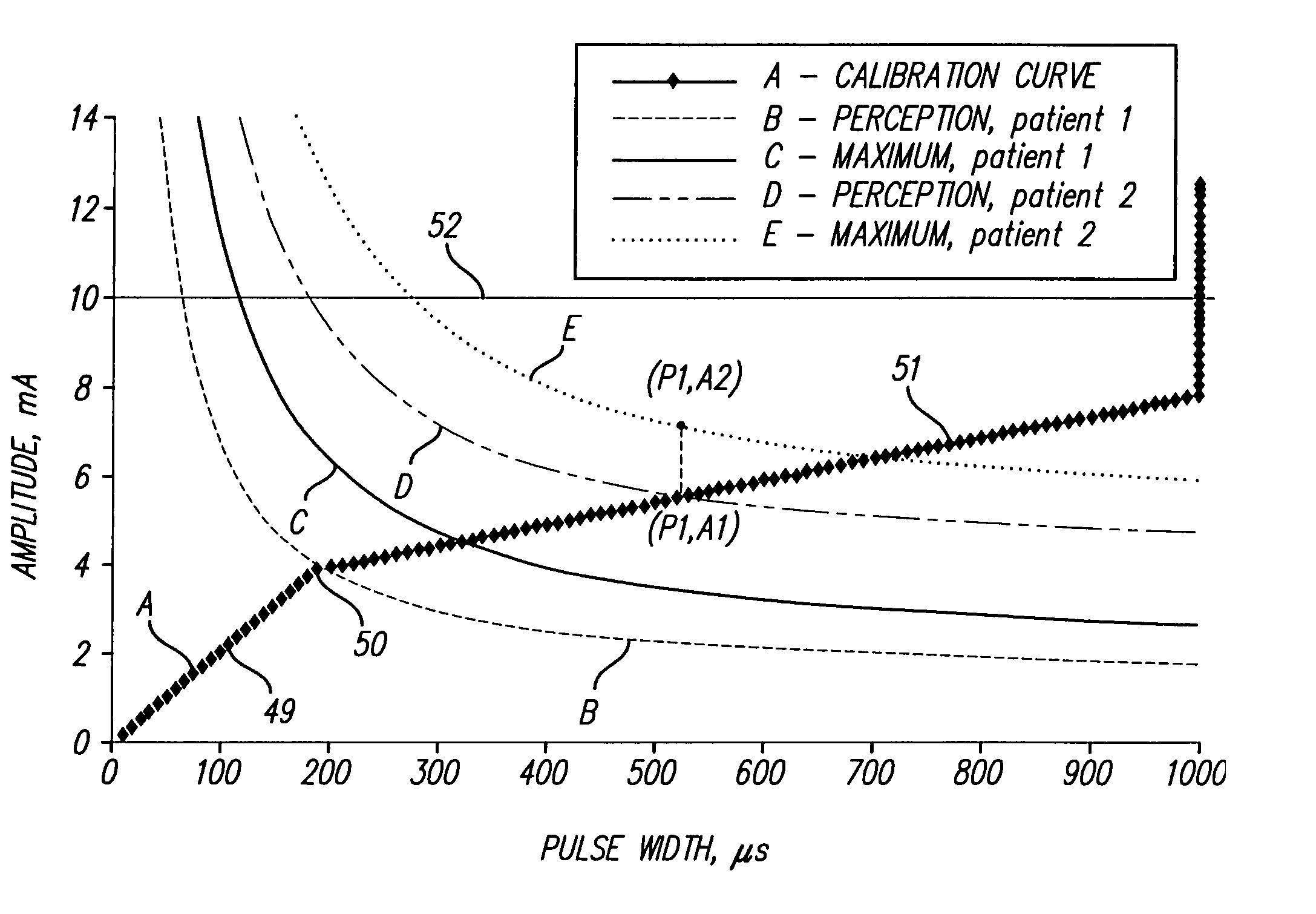
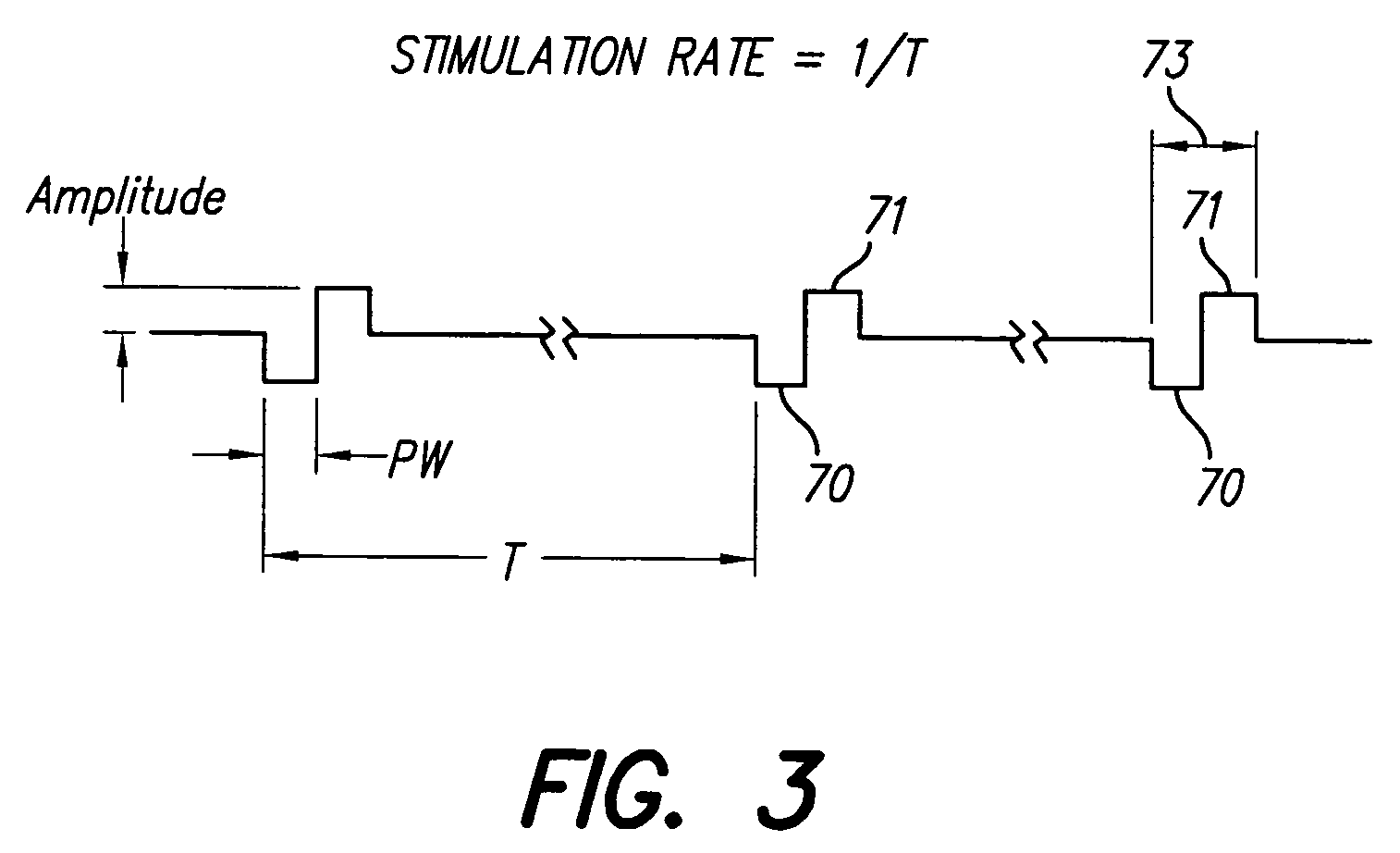
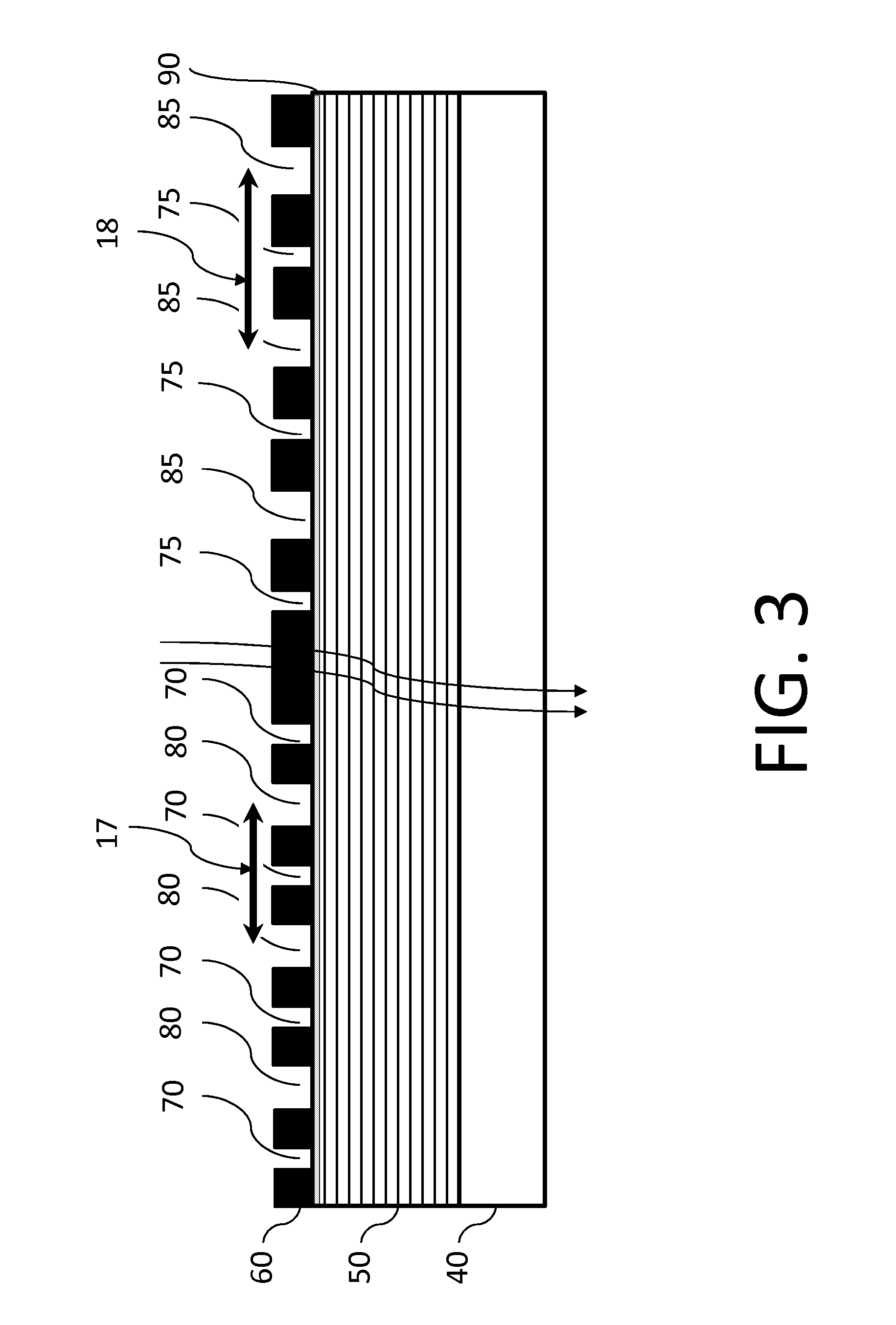
A method is provided for determining optimal stimulus pulsewidth and stimulus amplitude for stimulating nerves with at least one electrode (17). The method comprises: providing a predetermined calibration curve comprising a set of pulsewidth and amplitude values; and delivering sets of pulsewidths and amplitude values which are part of the calibration curve to the at least one electrode (17) to determine at least the optimal pulsewidth. A pulsewidth (70) and an amplitude can be efficiently selected that is efficacious and provides an ample clinical usage range (UR).
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method for quantitative analysis of a nucleic acid amplification reaction
InactiveUS6911327B2Reduce decreaseReduce in quantityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusTest sampleNucleic acid sequencing
A method for determining an unknown starting quantity of a target nucleic acid sequence in a test sample comprises amplifying the unknown starting quantity of the target nucleic acid sequence in the test sample and known starting quantities of a calibration nucleic acid sequence in respective calibration samples; and determining a respective threshold value for each of the nucleic acid sequences using a derivative of a growth curve derived for the sequence. The starting quantity of the target nucleic acid sequence in the test sample is determined using the threshold value determined for the target sequence and a calibration curve derived from the threshold values determined for the known starting quantities of the calibration nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:CEPHEID INC
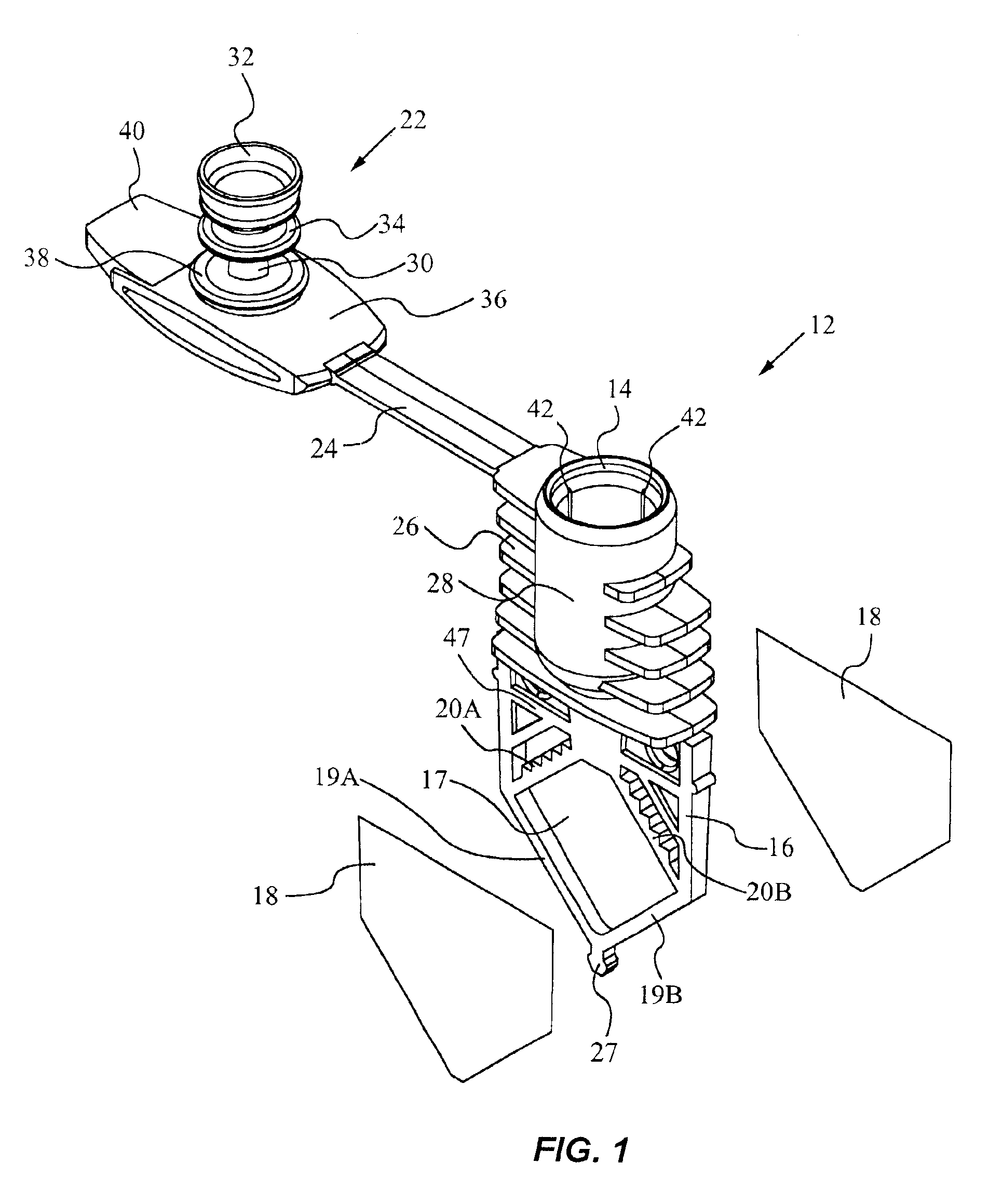
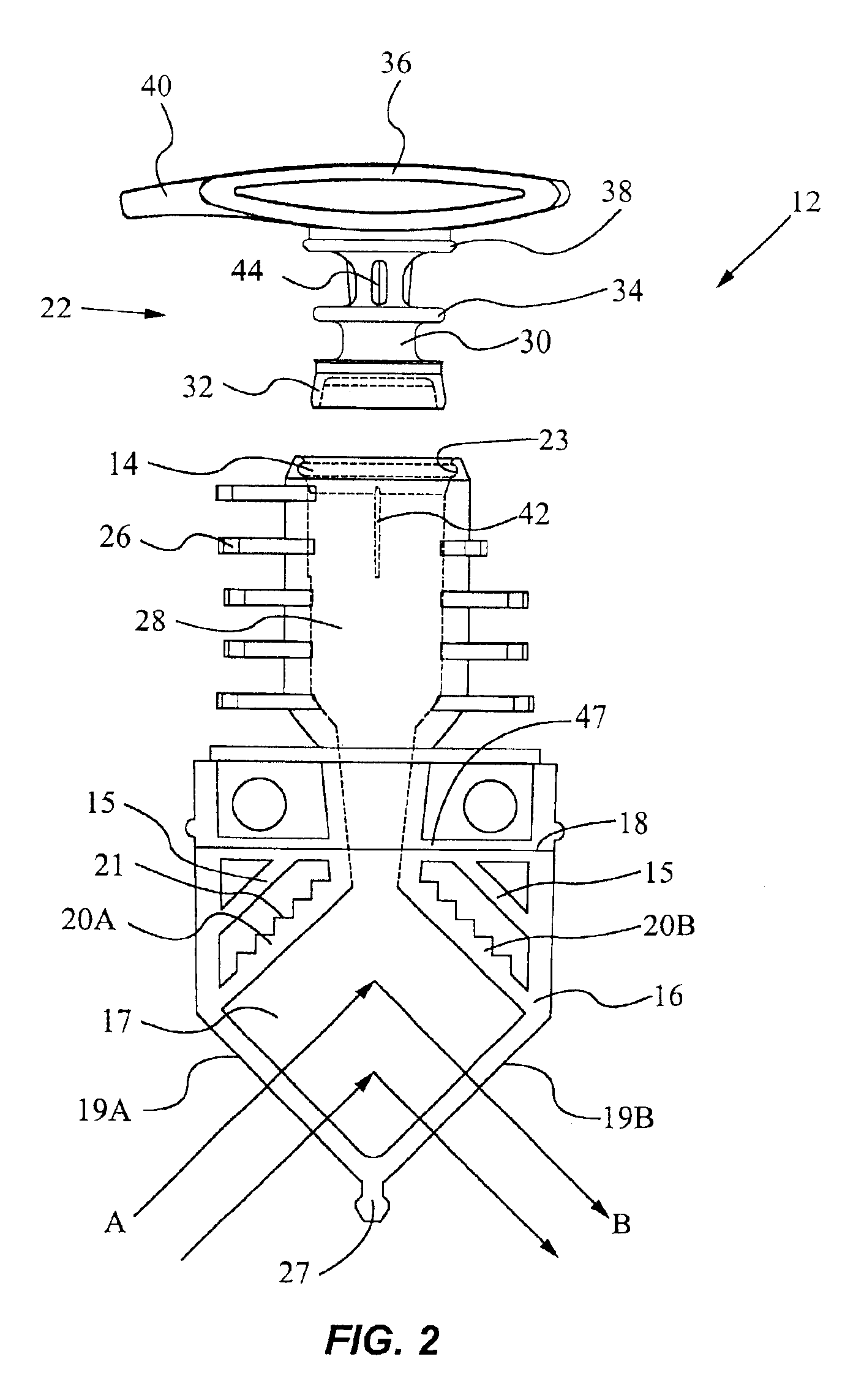
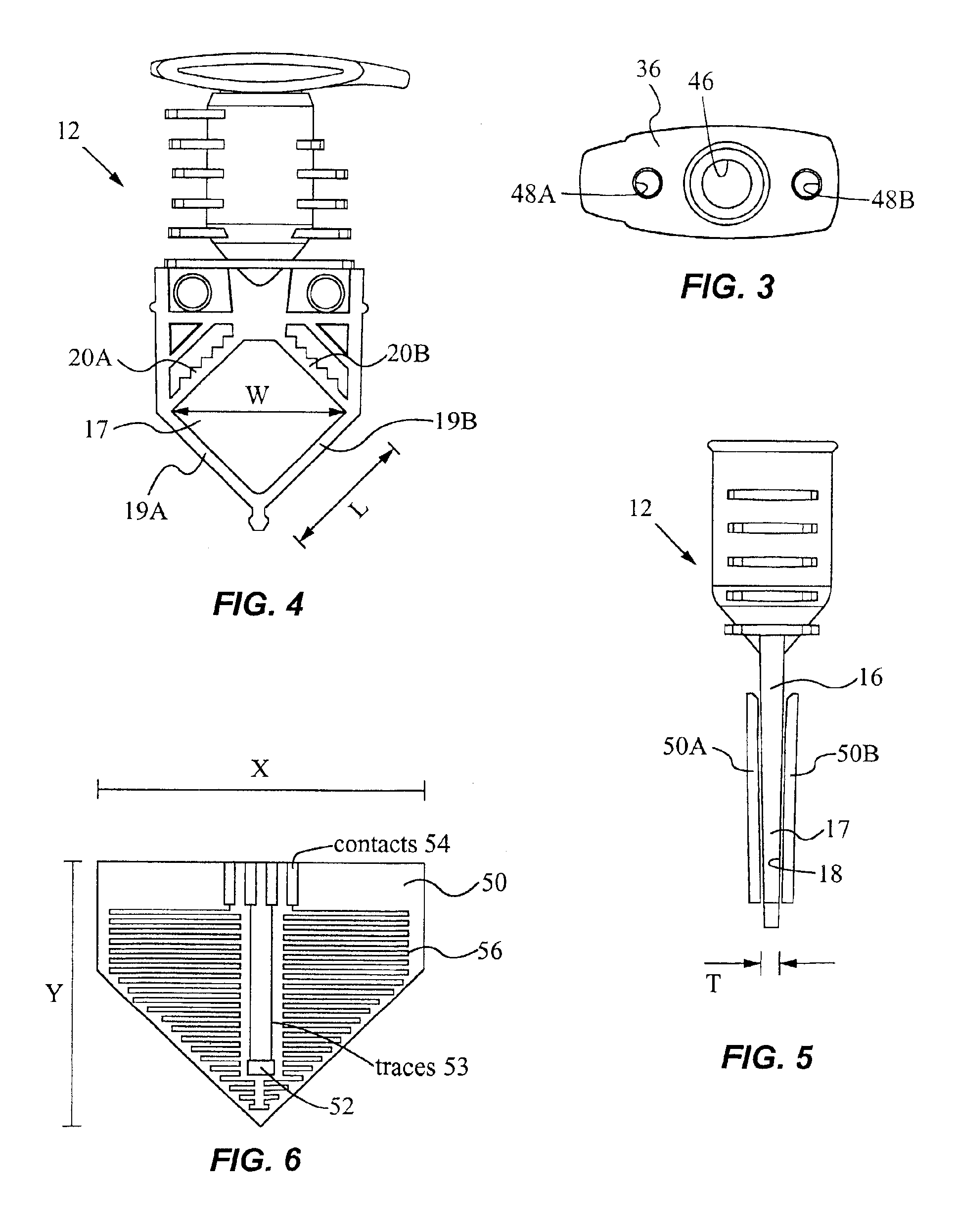
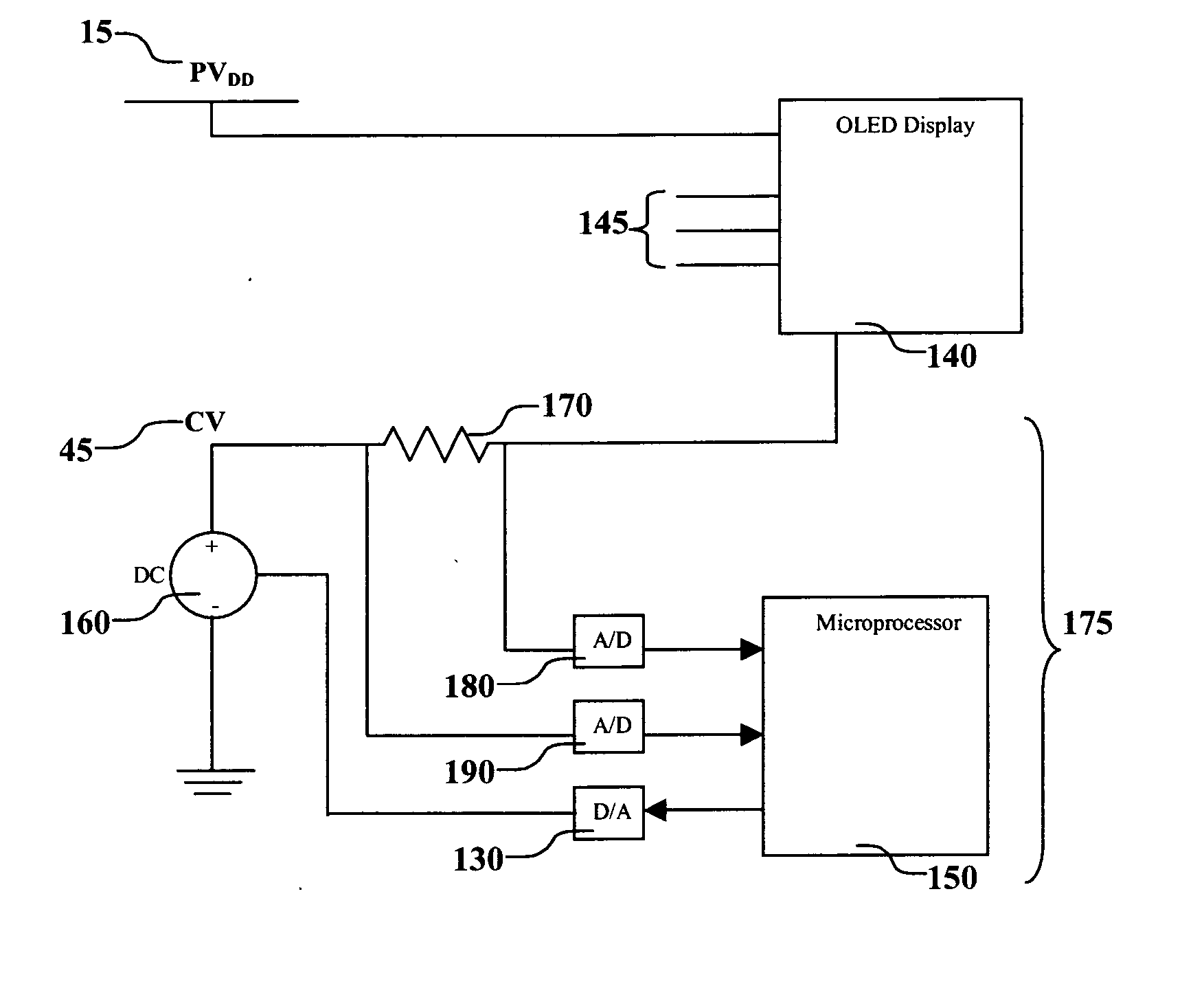
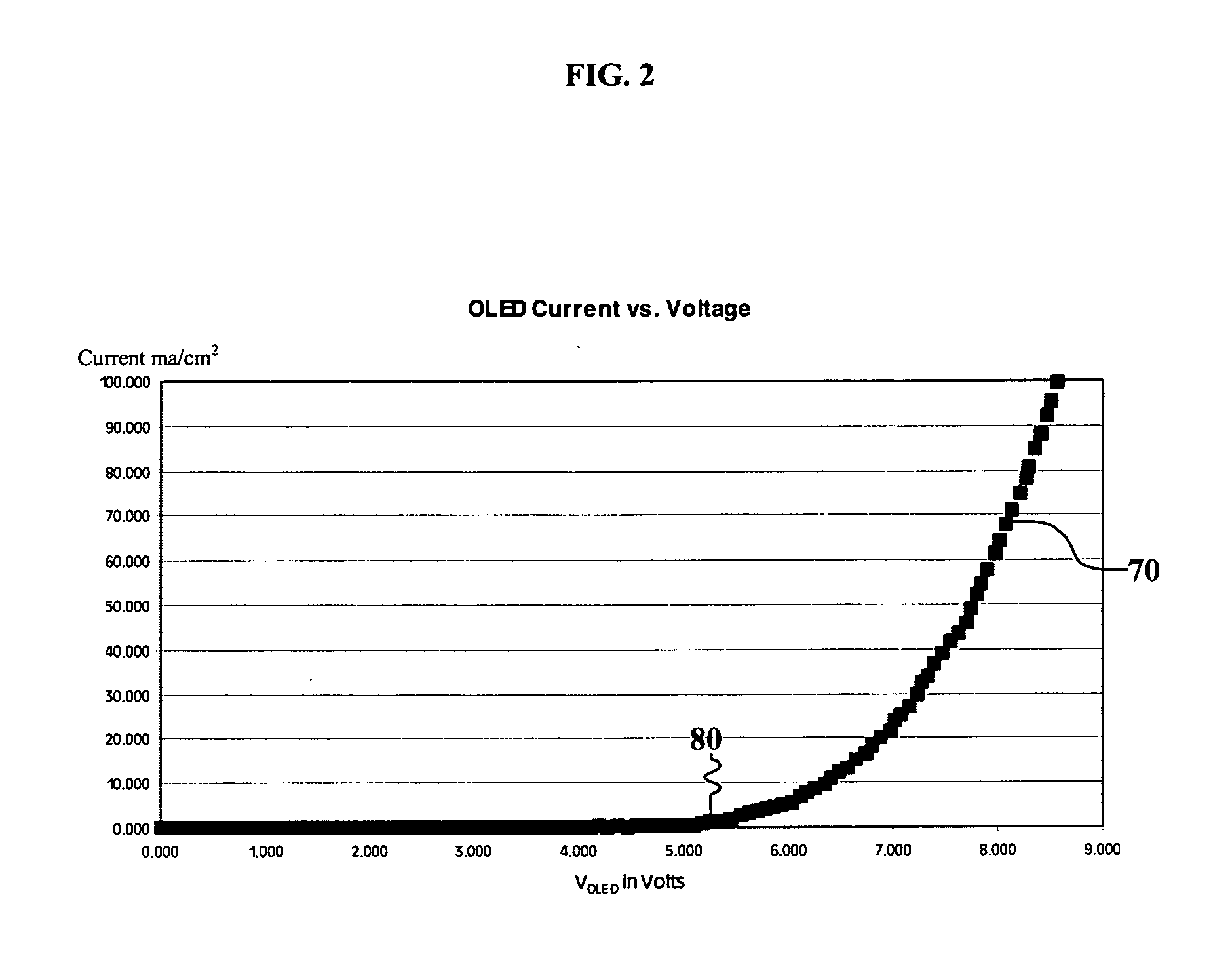
Selecting adjustment for OLED drive voltage
InactiveUS20060044227A1Reduce power consumptionExtended service lifeStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
A method for selecting an adjustment for at least one drive voltage used to drive an OLED display to reduce power consumption including operating the display to produce a calibration curve which depicts the drive voltage versus current or luminance, and selecting the adjustment for the drive voltage based upon the calibration curve so as to reduce the power consumed by the OLED display while maintaining desired luminance throughout the lifetime of the OLED display.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Systems and methods for acquiring calibration data usable in a pulse oximeter
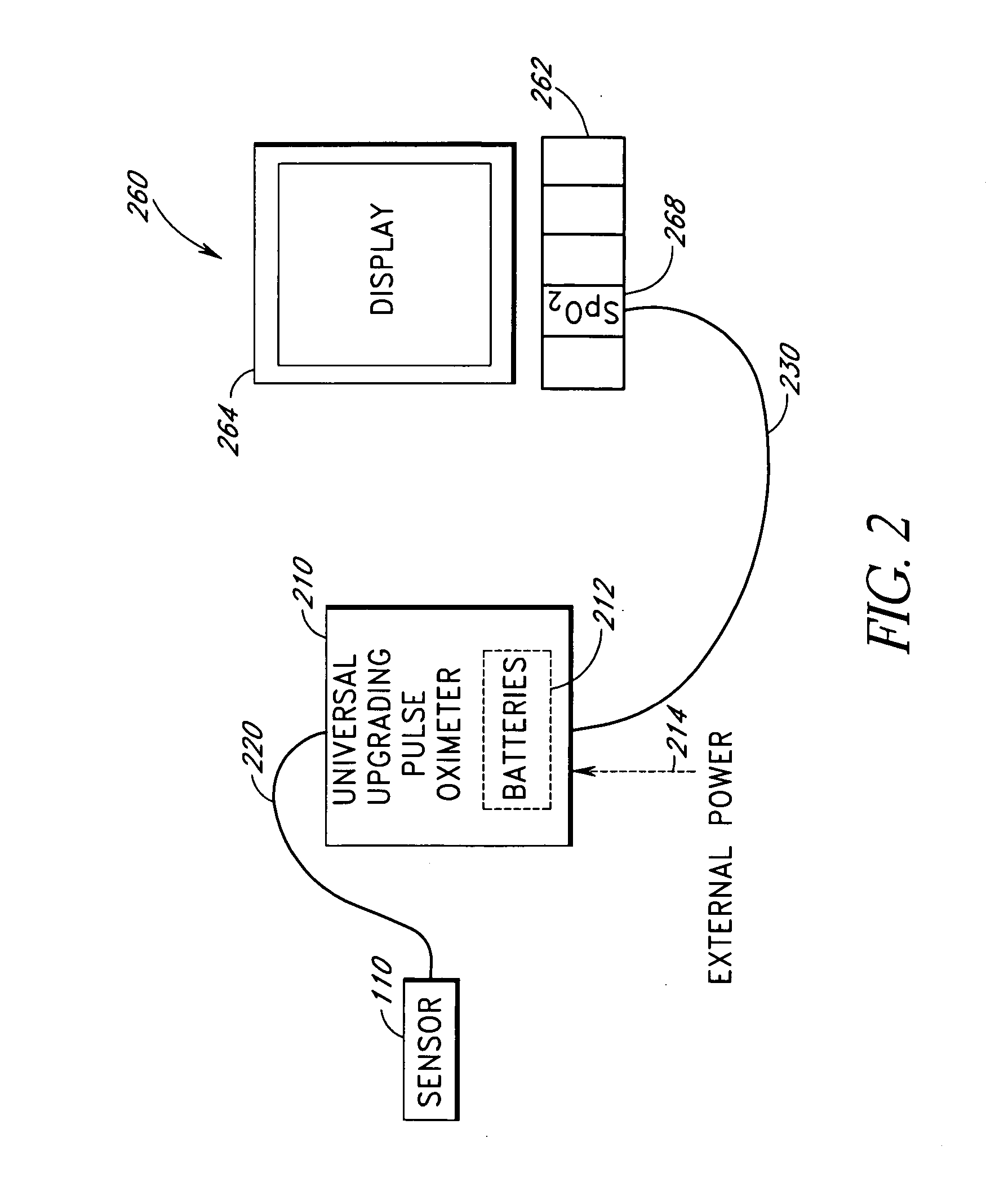
The present disclosure includes a pulse oximeter attachment having an accessible memory. In one embodiment, the pulse oximeter attachment stores calibration data, such as, for example, calibration data associated with a type of a sensor, a calibration curve, or the like. The calibration data is used to calculate physiological parameters of pulsing blood.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Concentration measuring method
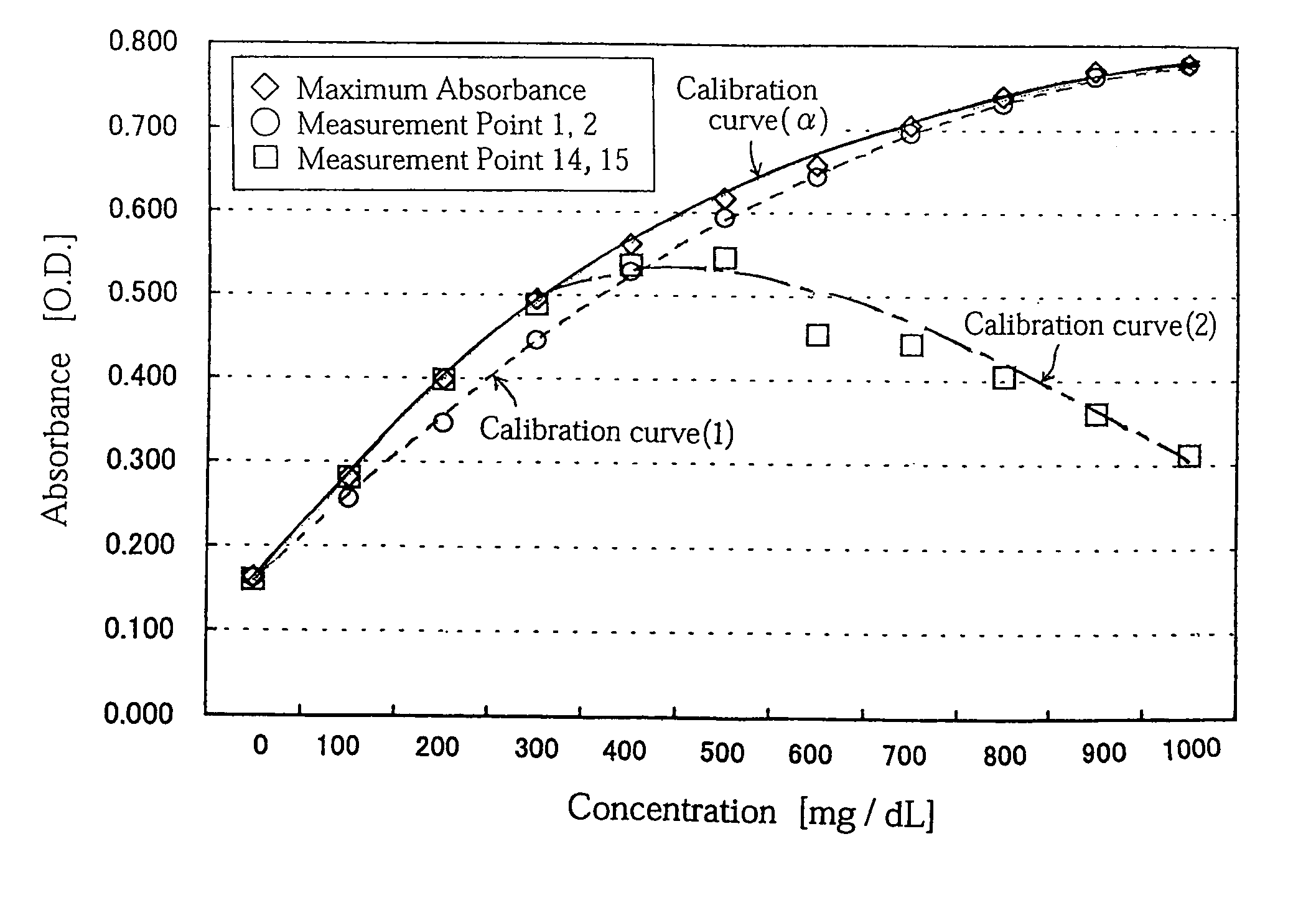
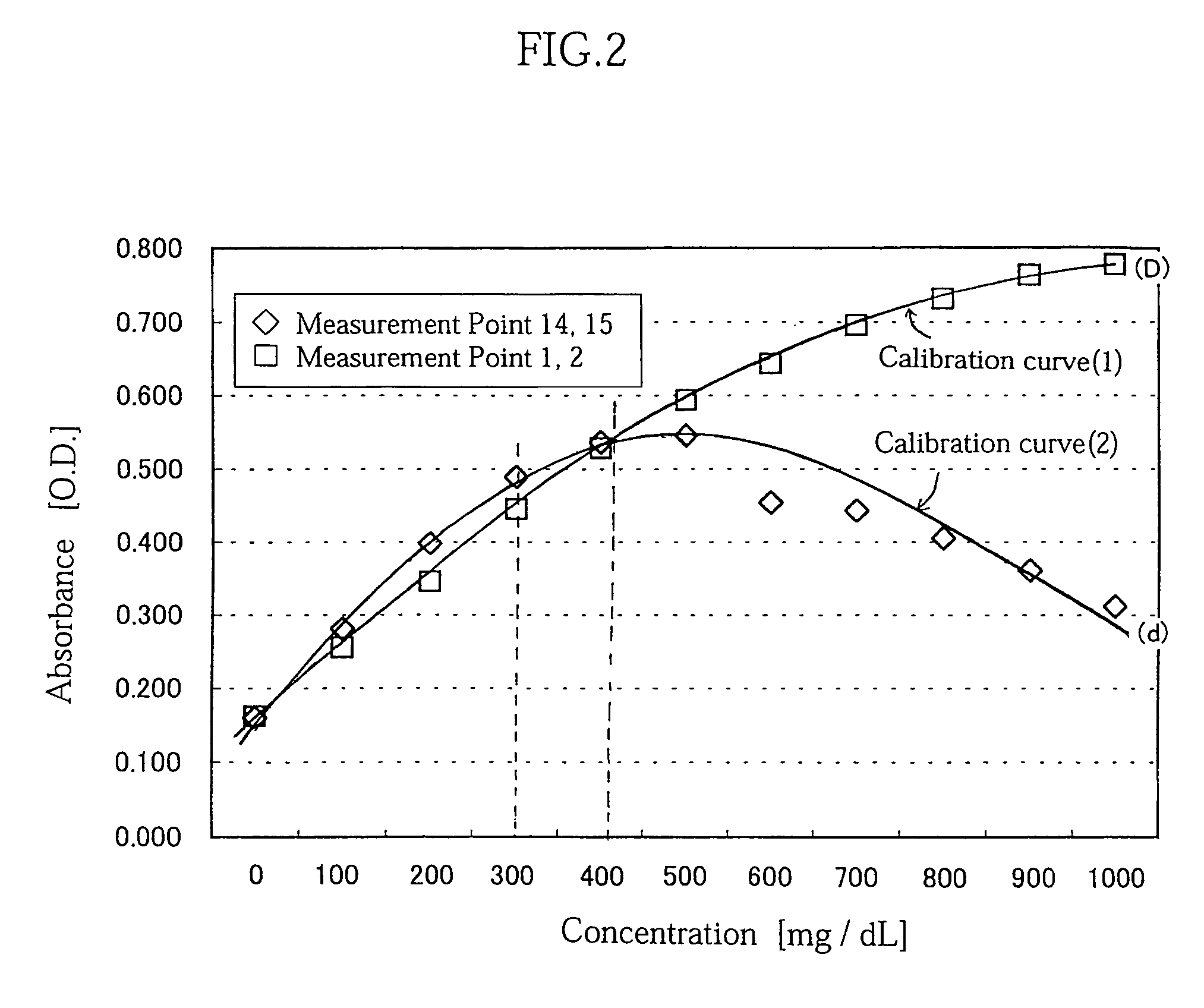
InactiveUS7054759B2Easily and inexpensively prevent deteriorationReduce resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCalibration curveReaction system
A concentration measuring method includes selecting a calibration curve optimum for computing the concentration of a measurement target substance from a plurality of calibration curves based on an output from a reaction system containing the target substance and a reactant capable of reacting with the target substance, and computing the concentration of the target substance based on the optimum calibration curve and the output. Each of the calibration curves is prepared based on a plurality of outputs generated upon lapse of a same reaction time from a plurality of standard reaction systems each containing a standard reagent of a known different concentration and the reactant. The plurality of calibration curves differ from each other in reaction time based on which the calibration curves are prepared.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Hot pepper and determining method for 96 pesticide residues in product of hot pepper
ActiveCN103512993ARealize quantitative analysisPromote healthy developmentComponent separationEthylenediamineMatrix solution
The invention discloses hot pepper and a determining method for 96 pesticide residues in a product of the hot pepper. The determining method comprises the following steps: homogenously extracting residual pesticide in a sample with 1% acetic acid-acetonitrile solution, purifying the extracting solution with a Florisil solid phase extraction column, dispersing and purifying the extracting solution with ethylenediamine-N-propyl silane (PSA) and octadecyl silane bonded phase (C18) substrate, detecting 69 pesticide residuals in the purified concentrated liquid of the Florisil column by GC-MS (gaschromatographic mass spectrometry), detecting 27 pesticide residuals in the substrate dispersed purified liquid by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS / MS), using the black substrate solution dilution standard to construct the updated calibration curves, adopting an internal standard method to quantify when using GC / MS to detect the residuals, and adopting an external standard method to quantify when using LC-MS / MS to detect the residuals. The average recovery rate of the method is 70.7-118.6%; the average relative standard deviation (RSD) is 3.2-11.4%; the detection limit is 0.13-28.2 ug / kg. The determining method has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, high speed, accuracy, high sensitivity and good repeatability.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Monoclonal antibody and method and kit for immunoassay of soluble human ST2
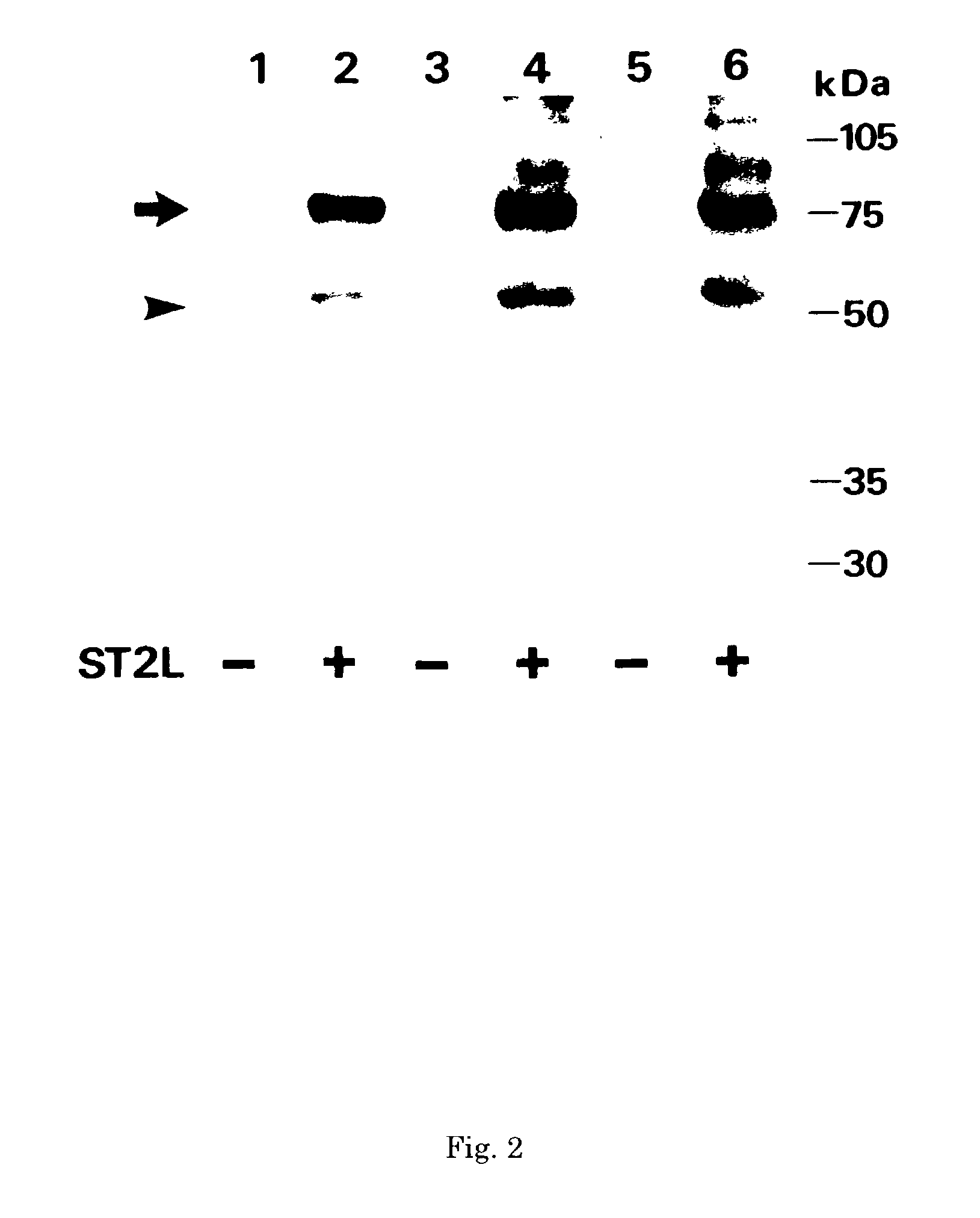
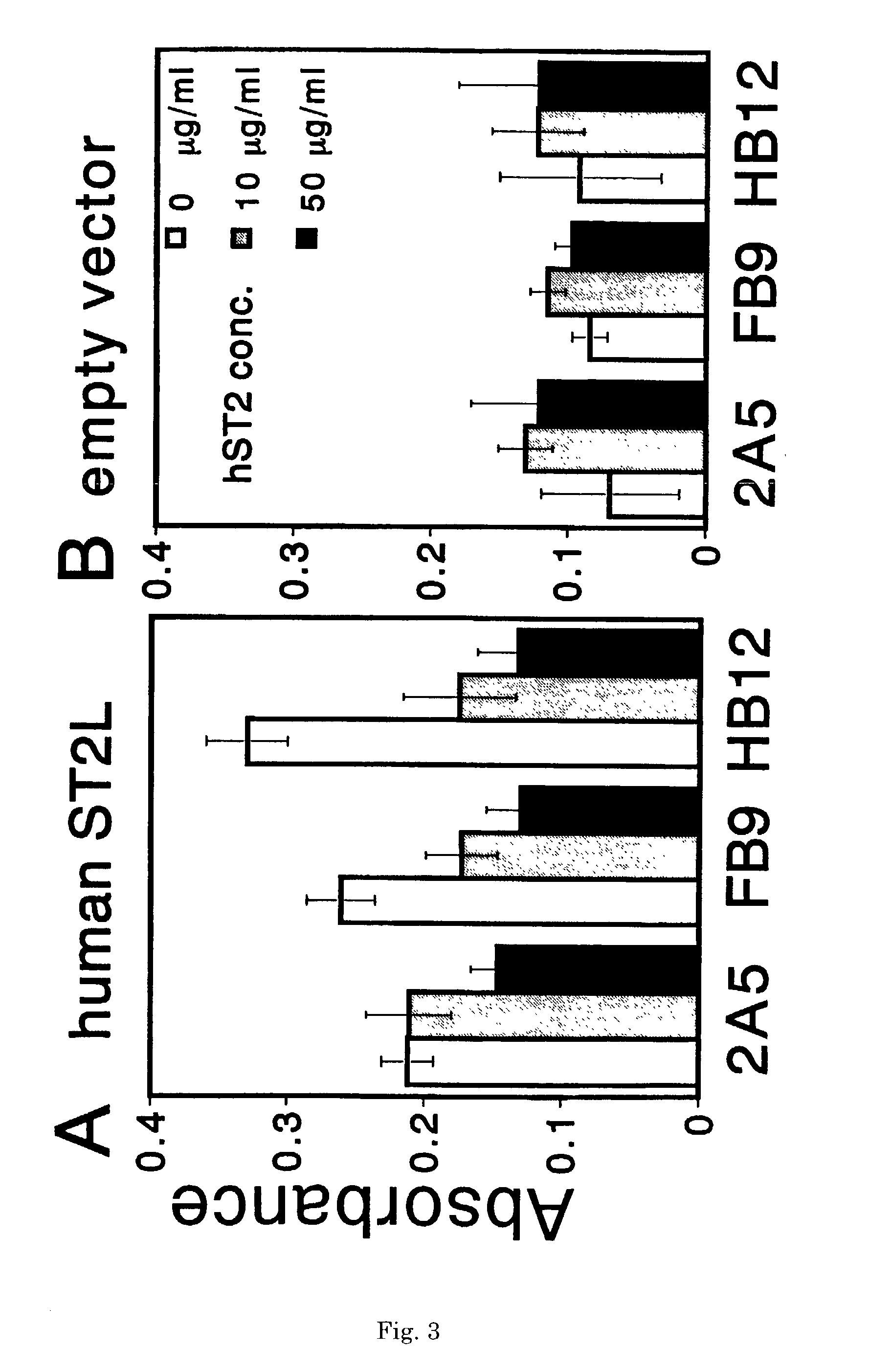
InactiveUS7087396B2The process is convenient and fastAnimal cellsEnzymologyImmobilized AntibodiesMonoclonal antibody
A method for determining a soluble human ST2 in a sample conveniently at a high sensitivity and an assay kit are provided. By an immunological method comprising a step for bringing a sample into contact with an immobilized antibody formed by binding to an insoluble support a first anti-human ST2 antibody which binds specifically to a non-denatured human ST2, a step for labelling a first reaction product generated in the previous step by reacting said first reaction product with a second anti-human ST2 antibody which binds specifically to a non-denatured human ST2 by recognizing a site different from the site on ST2 where said first anti-human ST2 antibody binds and which is labelled with a label, and a step for determining the amount of the label on said first reaction product which has been labelled, a soluble human ST2 in a sample is determined. In addition, a recombinant ST2 is employed as a standard to prepare a calibration curve, based on which the ST2 in a sample is quantified.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
Chromatographic and mass spectral date analysis
InactiveUS20060255258A1Improve accuracyEasy to quantifyParticle separator tubesComponent separationAnalyteRegression analysis
Apparatus, methods, and computer readable media having computer code for calibrating chromatograms to achieve chromatographic peak shape correction, noise filtering, peak detection, retention time determination, baseline correction, and peak area integration. A method for processing a chromatogram, comprises obtaining at least one actual chromatographic peak shape function from one of an internal standard, an external standard, or an analyte represented in the chromatogram; performing chromatographic peak detection using known peak shape functions with regression analysis; reporting regression coefficients from the regression analysis as one of peak area and peak location; and constructing a calibration curve to relate peak area to known concentrations in the chromatogram. A method for constructing an extracted ion chromatogram, comprises calibrating a low resolution mass spectrometer for both mass and peak shape in profile mode; performing mass spectral peak analysis and reporting both mass locations and integrated peak areas; specifying a mass defect window of interest; summing up all detected peaks with mass defects falling within the specified mass defect window to derive summed intensities; and plotting the summed intensities against time to generate a mass defect filtered chromatogram.
Owner:CERNO BIOSCI
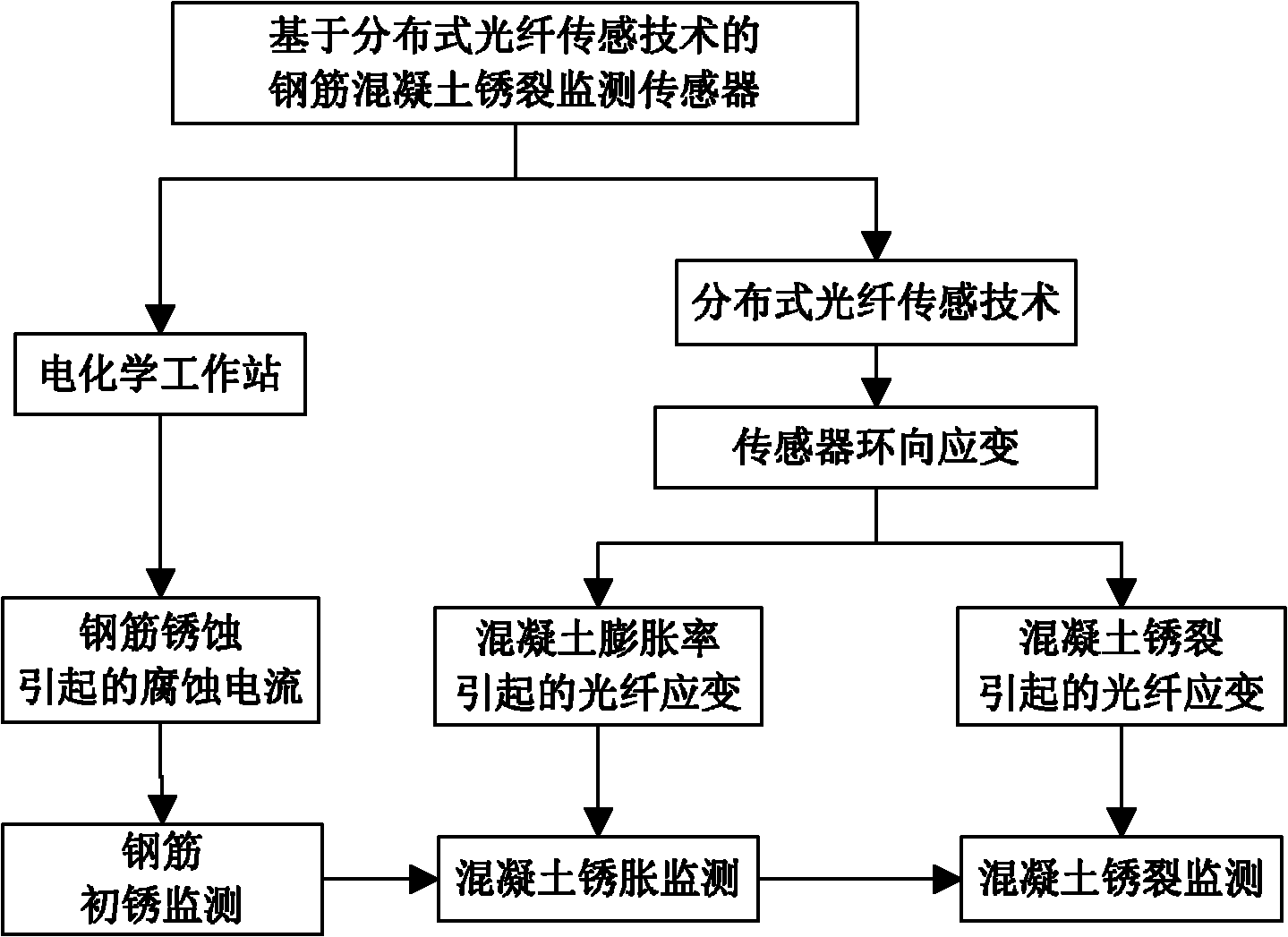
Method for monitoring corrosion cracks of reinforced concrete and sensor
InactiveCN102095677AEfficient managementDistributed withWeather/light/corrosion resistanceUsing optical meansPower flowReinforced concrete
The invention discloses a discloses a method for monitoring the corrosion cracks of reinforced concrete based on distributed optical fiber sensing technique. The method comprises the following steps: periodically detecting the polarization current of a steel bar and a stainless steel segment embedded in a sensor by an electrochemical work station to determine the initial corrosion time of the steel bar; monitoring the optical fiber strain by the distributed optical fiber sensing technique in real time through using sensing optical fibers surrounding the steel bar and laid in the sensor to deduce the corrosion expansion or corrosion crack stage of the reinforced concrete; and determining the corrosion expansion or corrosion crack degree by a calibration curve. The invention also discloses a sensor for executing the above method. The sensor can be used for monitoring the total corrosion cracking process of reinforced concrete at any position without damaging the structure of the concrete by monitoring the polarization current and the sensing optical fiber strain of the corroded steel bar, and can determine the corrosion crack stage and the degree of the reinforced concrete. The sensor is used for monitoring and evaluating the durability of reinforced concrete structure in the field of civil engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
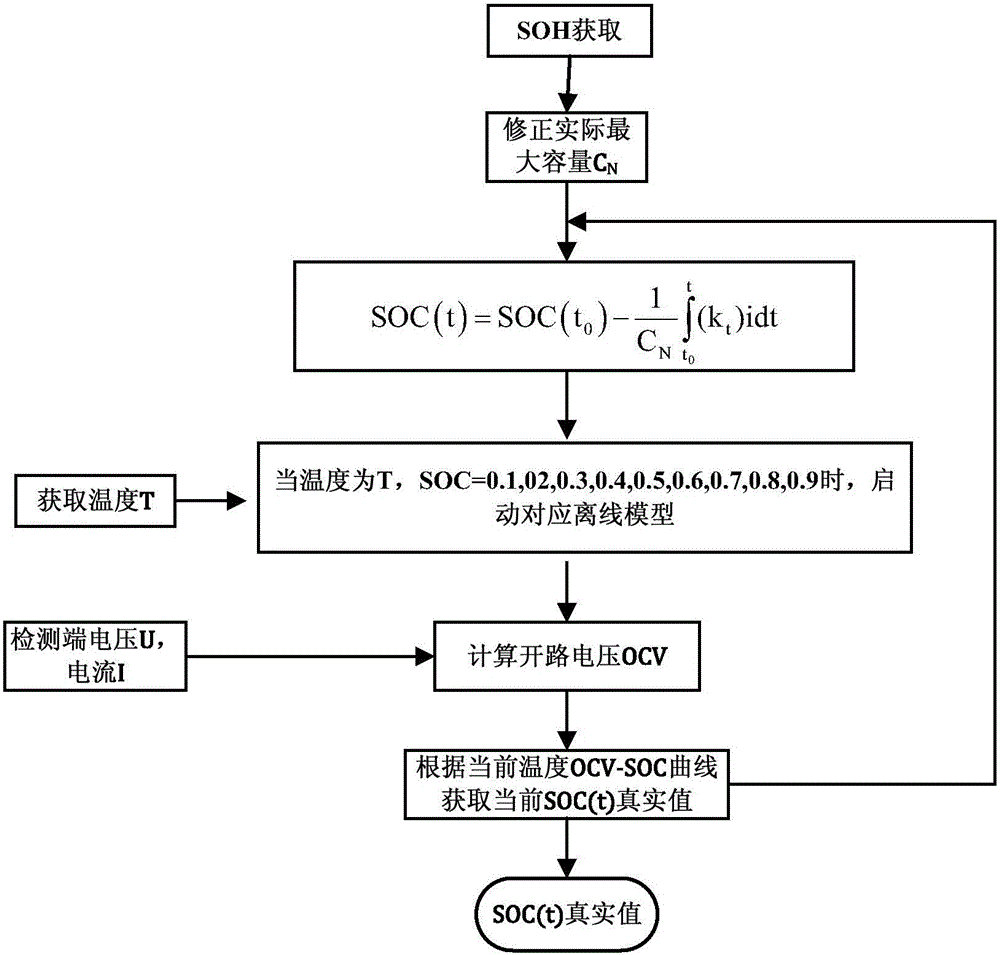
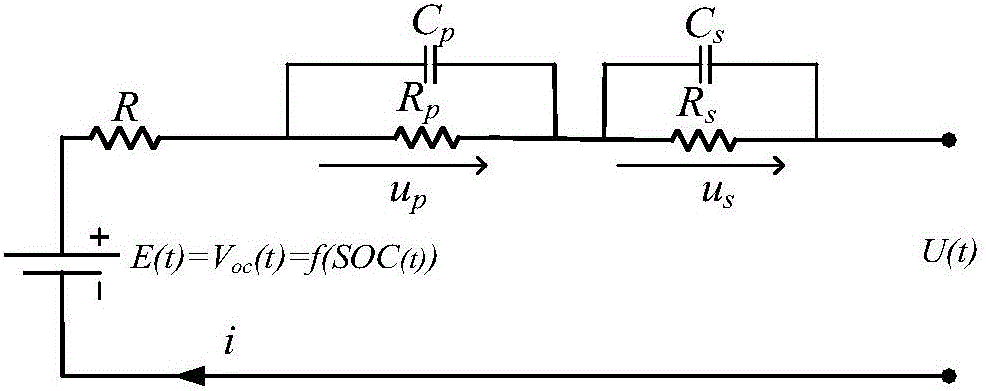
Method for estimating SOC of lithium battery
InactiveCN106646265AImprove estimation accuracyEliminate cumulative errorsElectrical testingPower flowTerminal voltage
The invention discloses a method for estimating an SOC of a lithium battery. The method comprises the following steps of (S1) obtaining an SOH value of the battery, and determining the current maximum available capacity CN of the battery; (S2) calculating a current SOC value of the battery online by using an ampere-hour integral method; (S3) starting a corresponding offline model parameter according to a sampling temperature T and an estimated value of the current SOC of the battery, and calculating current open-circuit voltage OCV by combining the current sampling current I and terminal voltage U; (S4) obtaining a real value SOC (t)* of the current SOC of the battery according to the estimated value of the current SOC of the battery in the step (S2), the current open-circuit voltage OCV in the step (S3) and an OCV-SOC calibration curve; (S5) correcting the current estimated SOC value of the ampere-hour integral method by using the real value SOC (t)* of the current SOC of the battery, and further carrying out calculation by using the ampere-hour integral method; and (S6) repeating the steps (S3), (S4) and (S5). According to the method, piecewise correction is carried out on a traditional algorithm for estimating the SOC by the ampere-hour integral method, an accumulative error of the ampere-hour integral method is effectively eliminated, and the estimation accuracy of the SOC is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
High throughput multi-antigen microfluidic fluorescence immunoassays
InactiveUS20060263818A1Reduce total integrated backgroundIncreased signal noiseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenPoint of care
The development of a high-throughput multi-antigen microfluidic fluorescence immunoassay system is illustrated in a 100-chamber PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) chip which performs up to 5 tests for each of 10 samples. Specificity of detection is demonstrated and calibration curves produced for C-Reactive Protein (CRP), Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA), ferritin, and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). The measurements show sensitivity at and below levels that are significant in current clinical laboratory practice (with SIN>8 at as low as 10 pM antigen concentration). The chip uses 100 nL per sample for all four tests and provides an improved instrument for use in scientific research and “point-of-care” testing in medicine.
Owner:SCHERER AXEL +3
Method for determining the temperature of semiconductor substrates from bandgap spectra
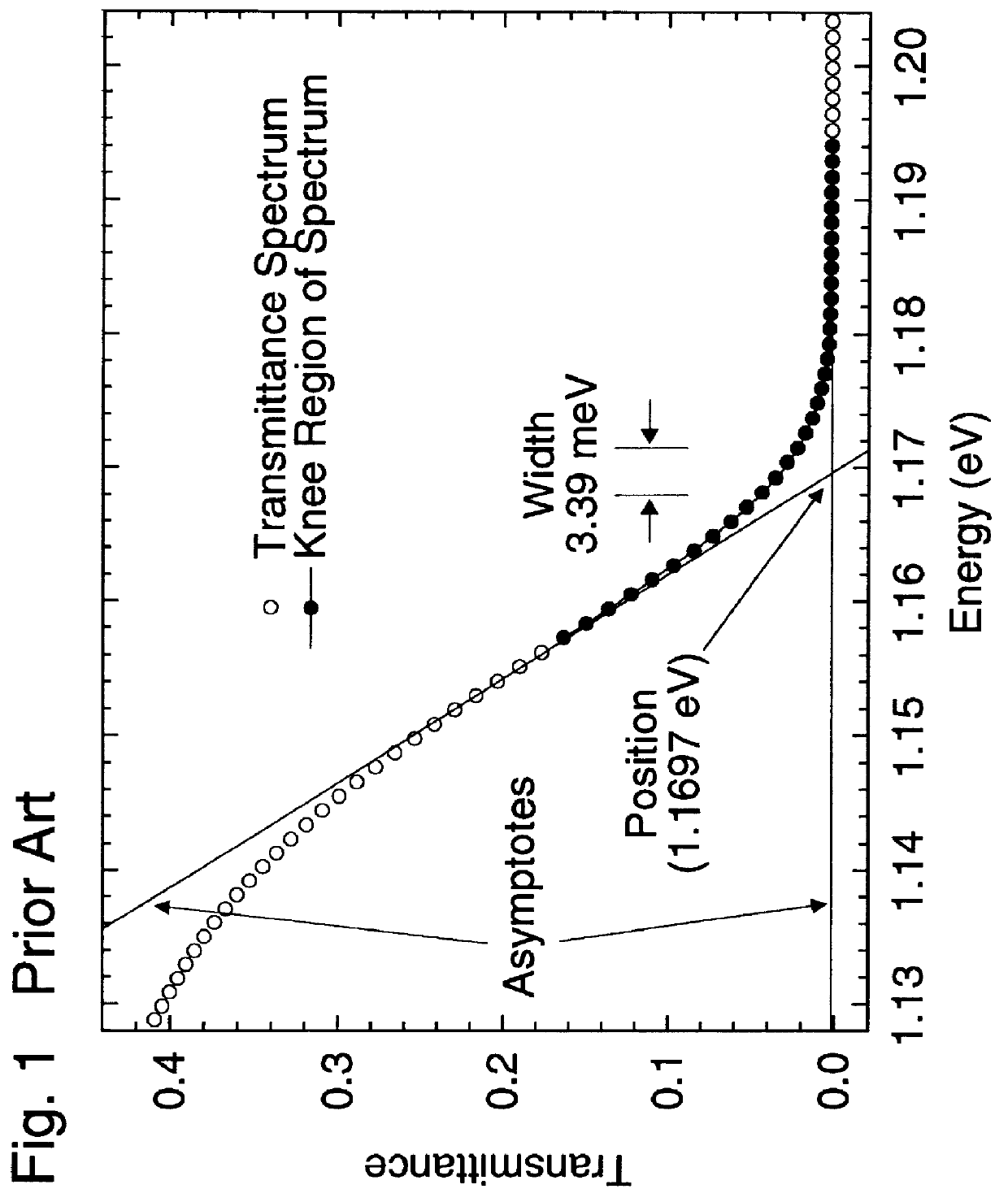
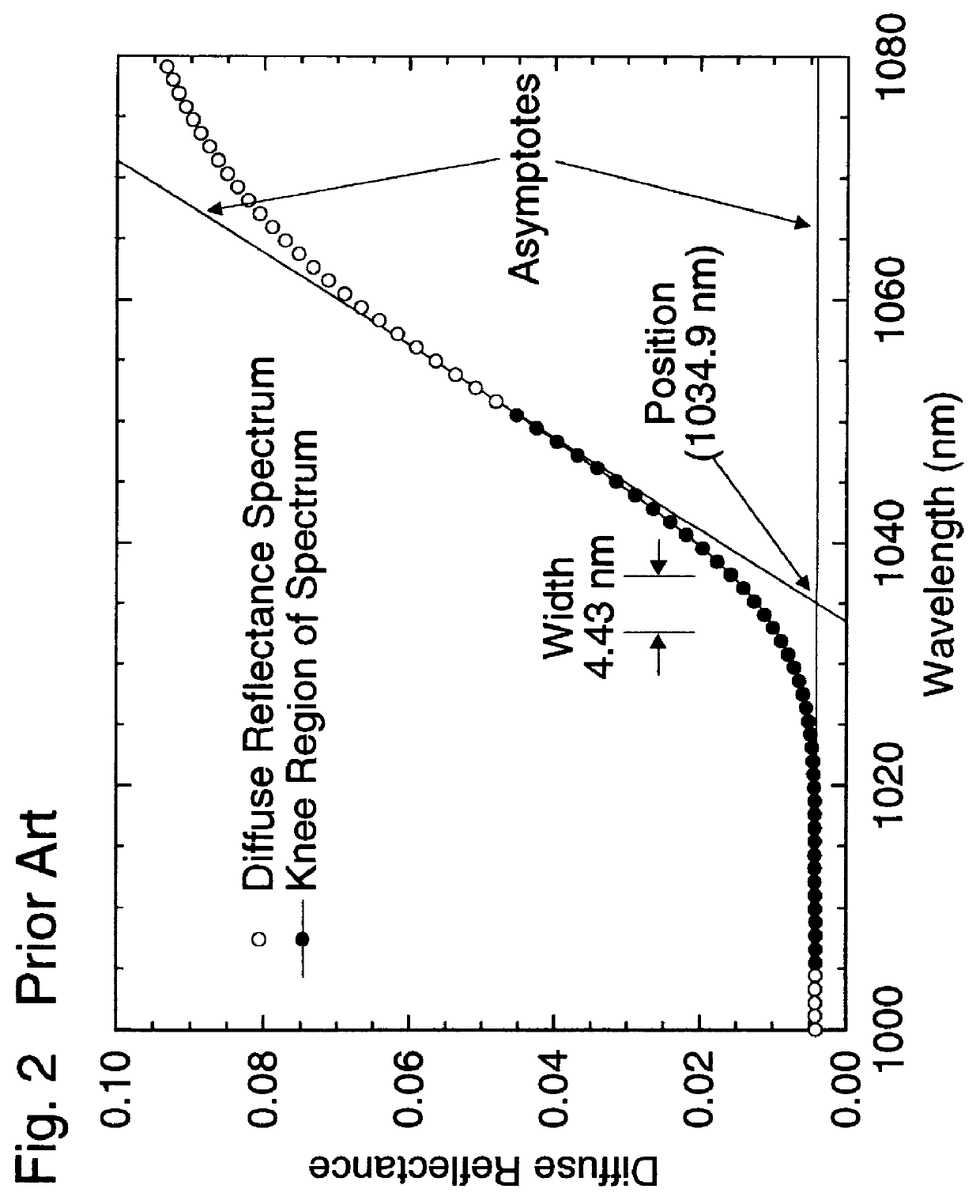
InactiveUS6116779AThermometer detailsThermometers using physical/chemical changesAbsorptanceLength wave
An optical method for measuring the temperature of a substrate material with a temperature dependent band edge. In this method both the position and the width of the knee of the band edge spectrum of the substrate are used to determine temperature. The width of the knee is used to correct for the spurious shifts in the position of the knee caused by: (i) thin film interference in a deposited layer on the substrate; (ii) anisotropic scattering at the back of the substrate; (iii) the spectral variation in the absorptance of deposited layers that absorb in the vicinity of the band edge of the substrate; and (iv) the spectral dependence in the optical response of the wavelength selective detection system used to obtain the band edge spectrum of the substrate. The adjusted position of the knee is used to calculate the substrate temperature from a predetermined calibration curve. This algorithm is suitable for real-time applications as the information needed to correct the knee position is obtained from the spectrum itself. Using a model for the temperature dependent shape of the absorption edge in GaAs and InP, the effect of substrate thickness and the optical geometry of the method used to determine the band edge spectrum, are incorporated into the calibration curve.
Owner:JOHNSON SHANE R +1
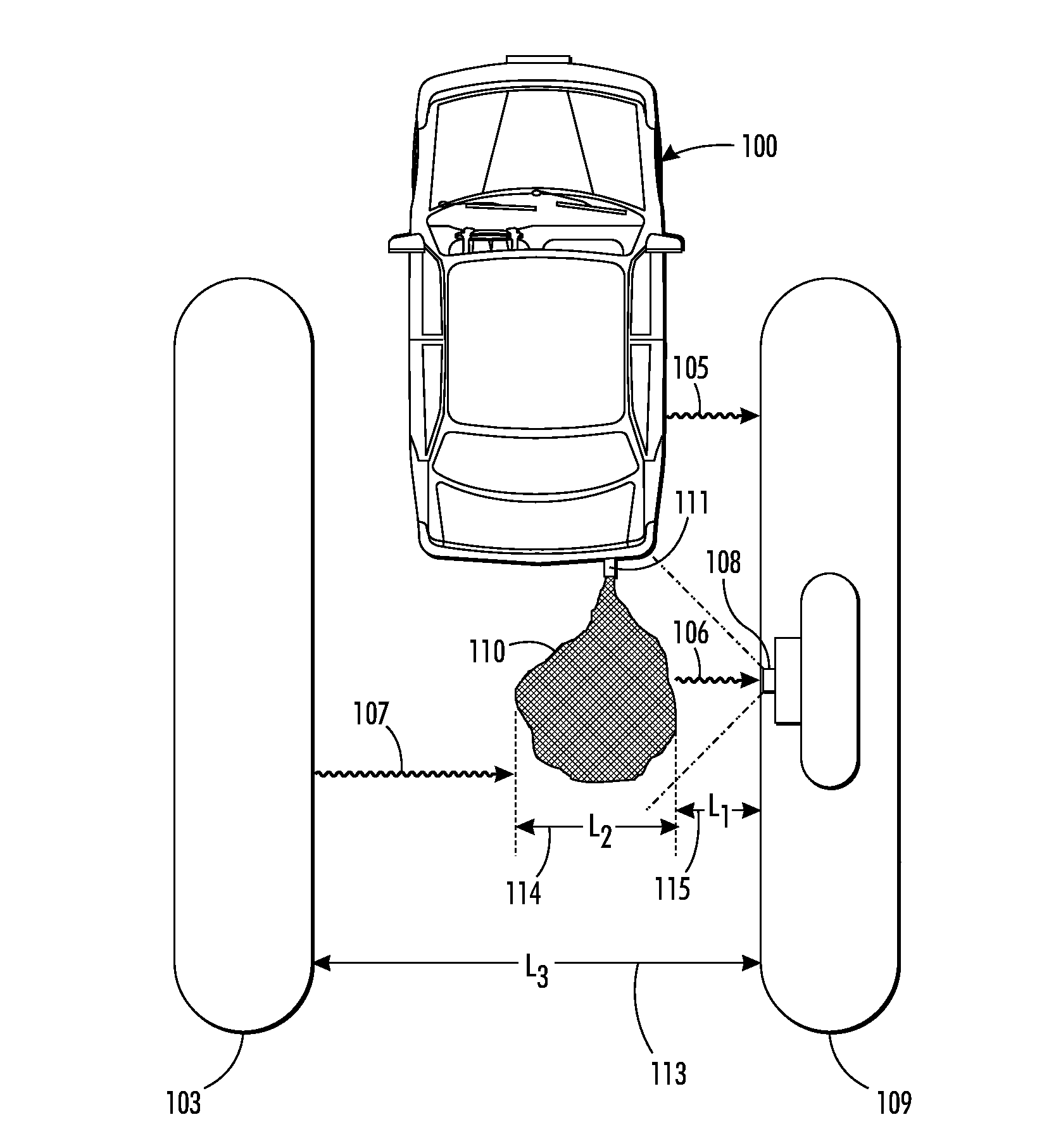
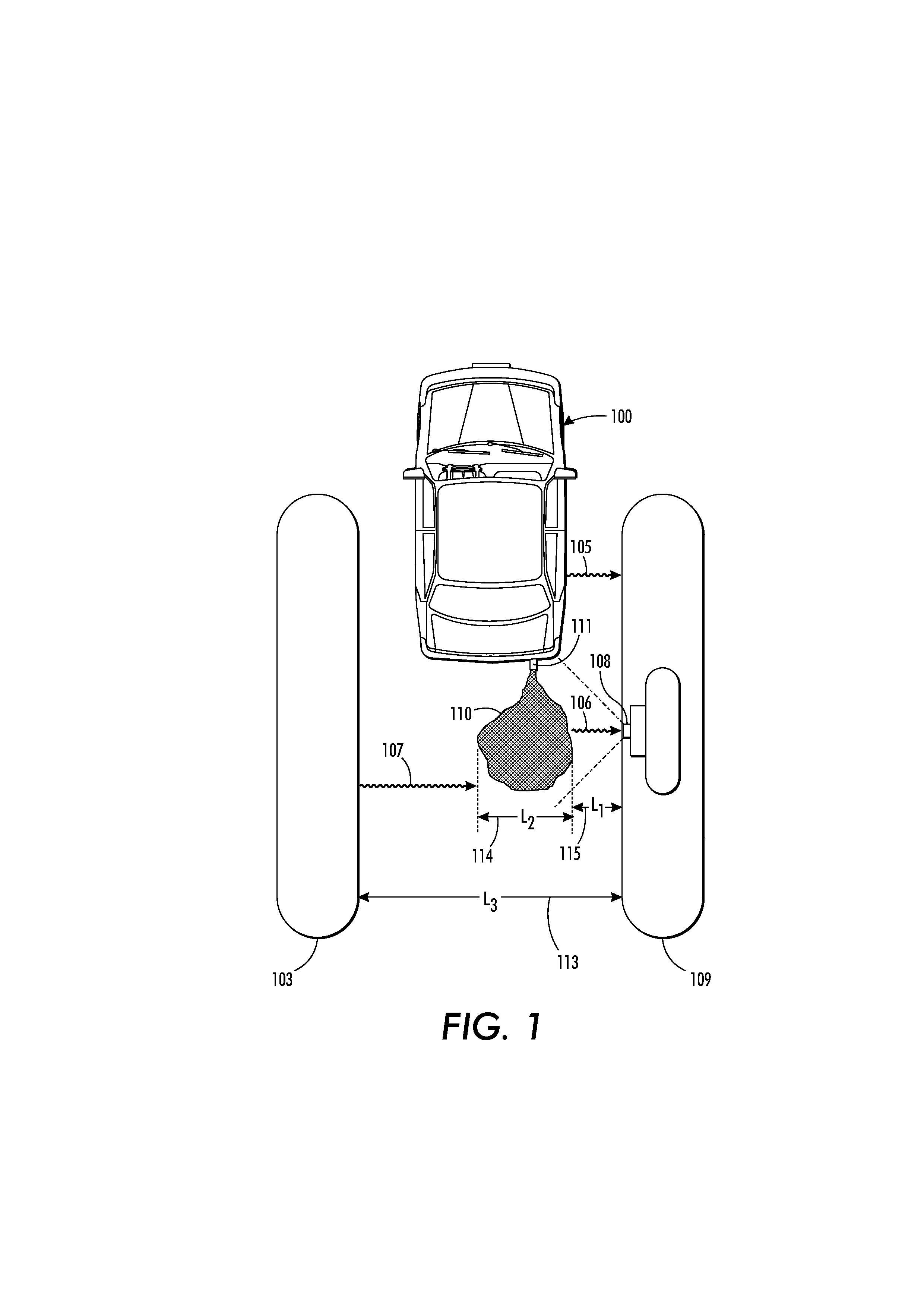
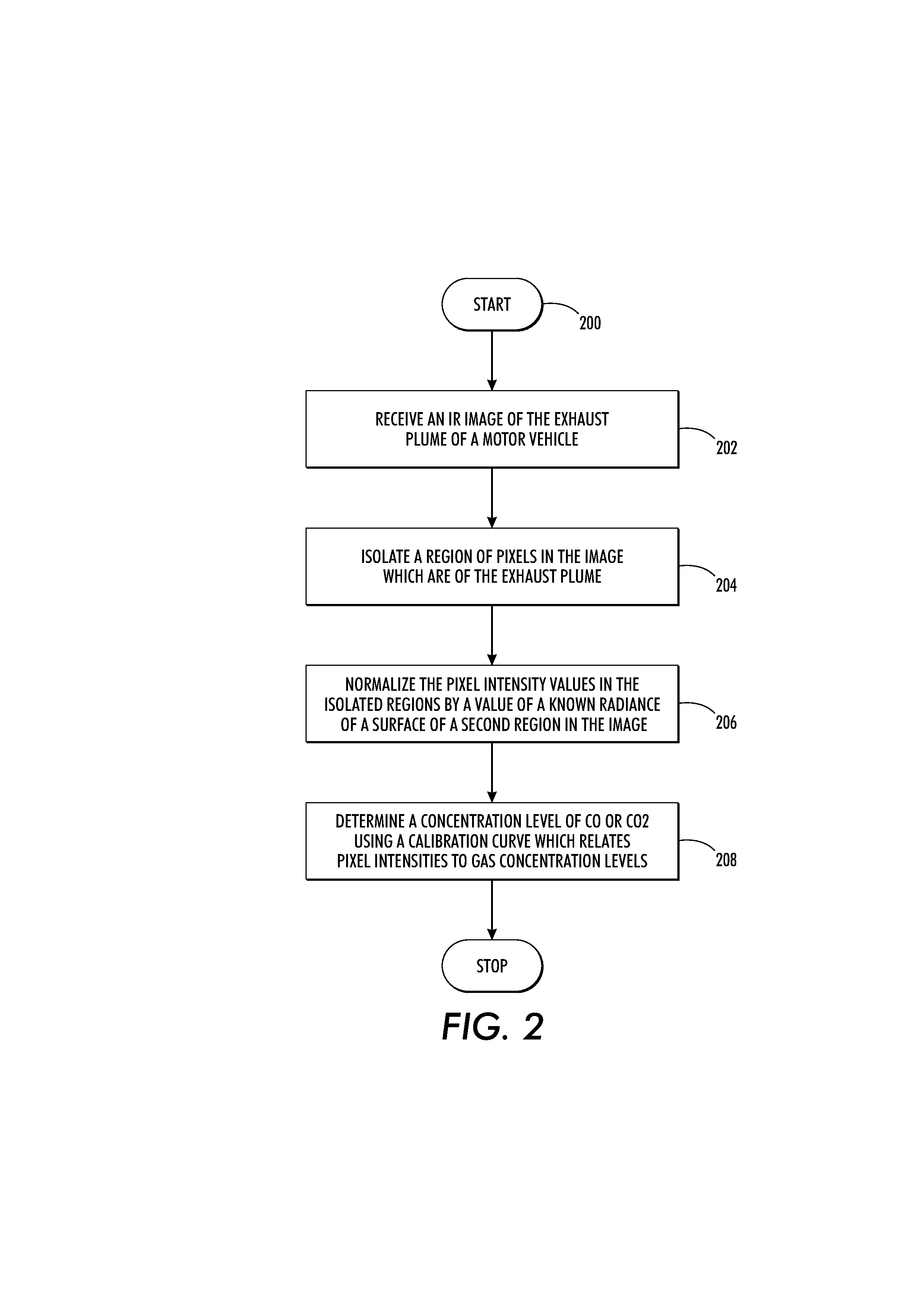
Image-based determination of co and co2 concentrations in vehicle exhaust gas emissions
ActiveUS20130181836A1Readily apparentEngine testingCharacter and pattern recognitionPresent methodEmission standard
What is disclosed is a system and method for image-based determination of concentration of CO and CO2 in a vehicle's exhaust gas in an emissions testing environment. In one embodiment, the present method involves receiving an IR image of the exhaust plume of a motor vehicle intended to be tested for CO and CO2 concentrations. The IR image has been captured using a mid-wave infrared camera with at least one optical filter tuned to the infrared absorption band of CO and CO2. The images are pre-processed to isolate pixels which contain the exhaust plume. The intensity values of pixels in those isolated regions are normalized and concentrations of CO and CO2 are determined via a calibration curve which relates pixel intensities to concentrations. The concentrations are compared to an emissions standard set for the vehicle to determine whether the vehicle is a gross polluter.
Owner:CONDUENT BUSINESS SERVICES LLC
Small container fluid dynamics to produce optimized inspection conditions
ActiveUS7430047B2Improved detection and measurementSmall sizeOptically investigating flaws/contaminationIndividual particle analysisAlgorithmMicrosphere
New methodology, realizable with both manual and new semi-automatic imaging technology, has transformed both the inspection and the batch release Attribute Sampling Inspection for contaminating visible particles in injectable solutions into statistically replicable procedures. In this new non-destructive inspection procedure, a calibration curve relates NIST traceable measurement of maximum particle size to the rejection probability of the particle. Data for this calibration curve is determined with a graduated set of single durable stainless steel and glass microspheres that are sized with NIST traceability. Use of the calibration curve transforms the probabilistic variability of visible particle inspection data described by Knapp into the ‘simply replicable form’ required by the Attribute Sampling Tables. The present invention uses cutting edge imaging technology to achieve 1% sizing accuracy within 10 μm from 50 to 1,000 μm. An improved alternative sizing technique used in this invention uses the particle information to achieve an integral particle sizing function.
Owner:BUDD GERALD WALTER +1
Apparatus and method for determining service life of electrochemical energy sources using combined ultrasonic and electromagnetic testing
InactiveUS20080028860A1Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMeasurement testSonification
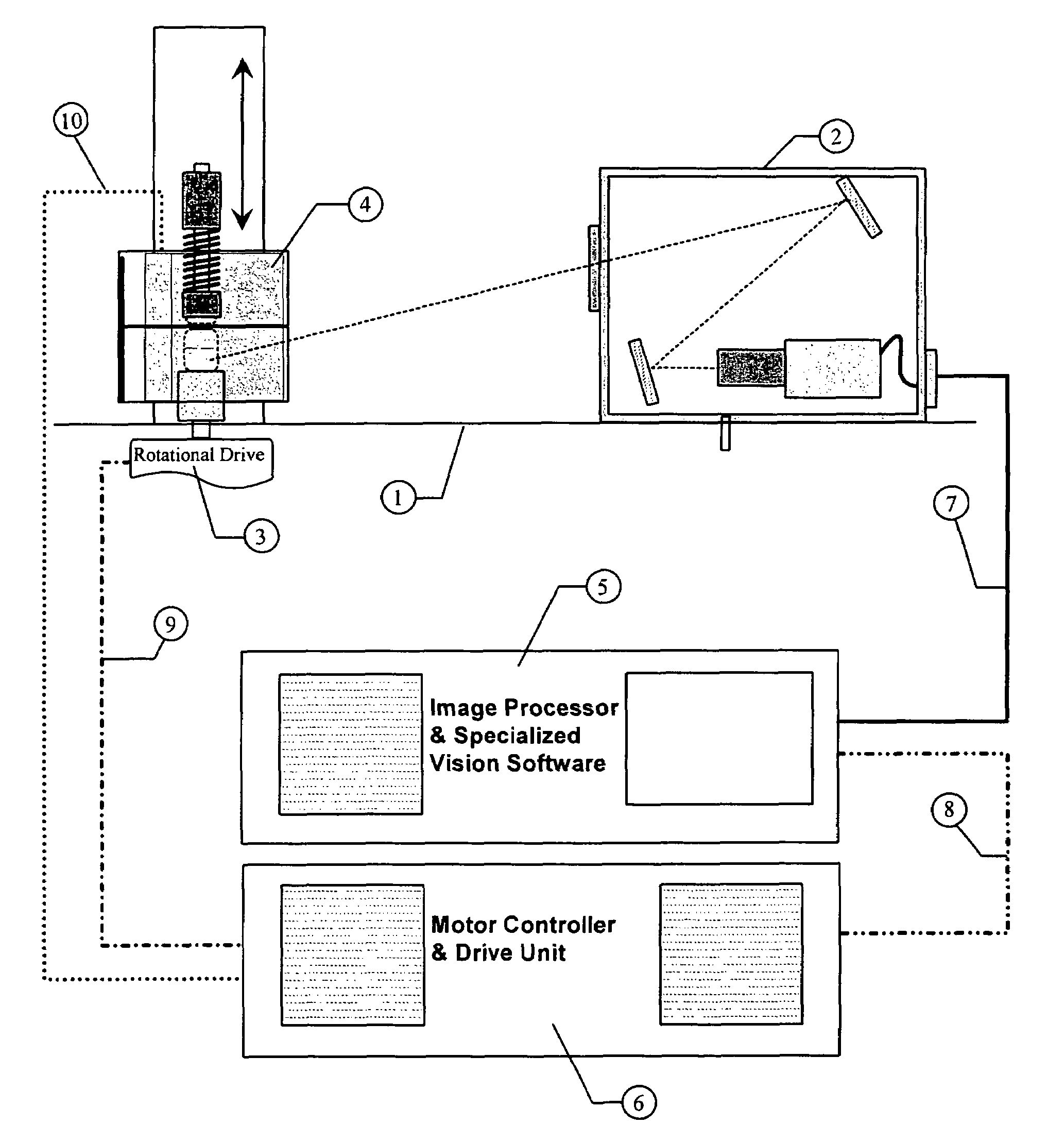
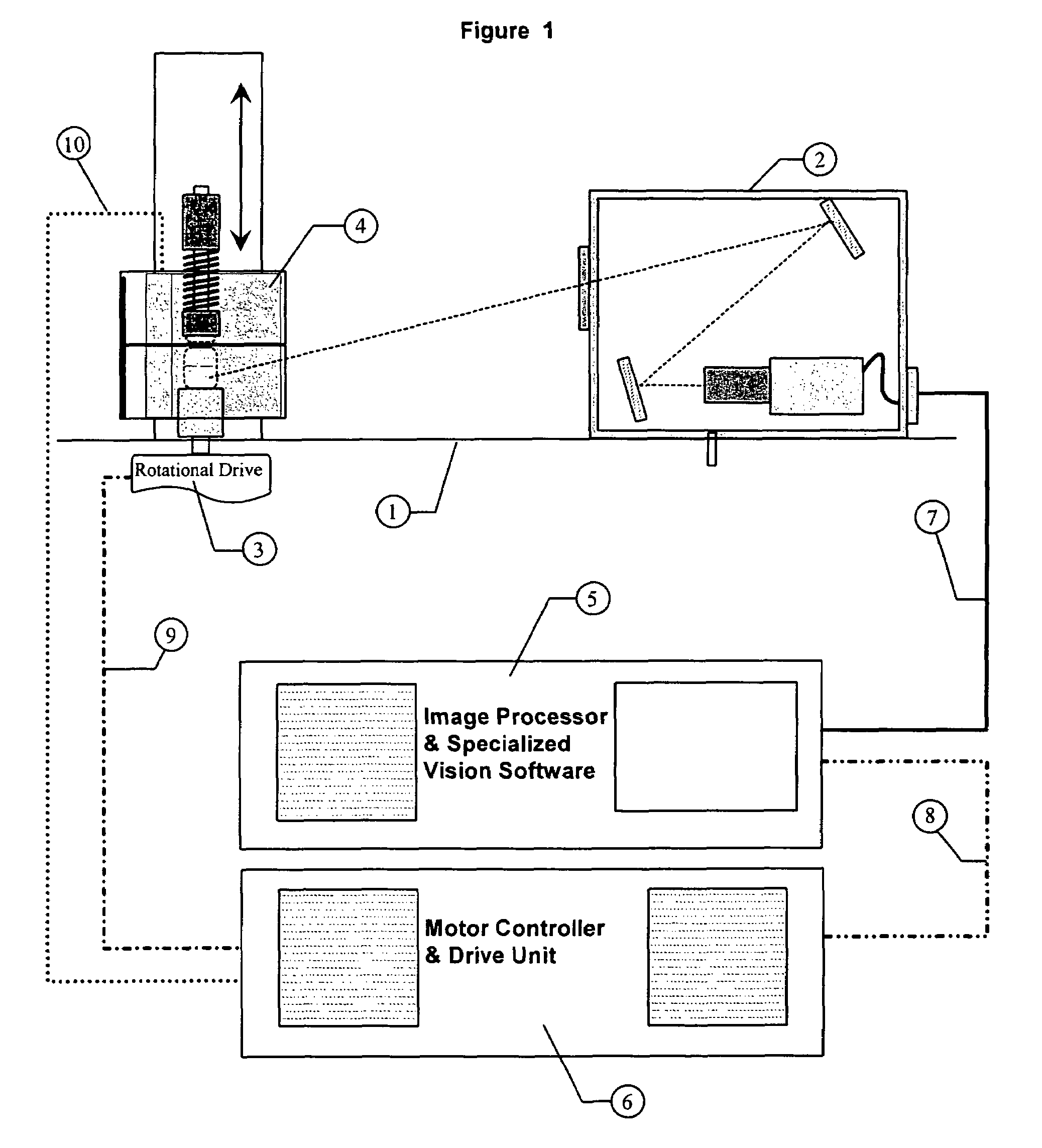
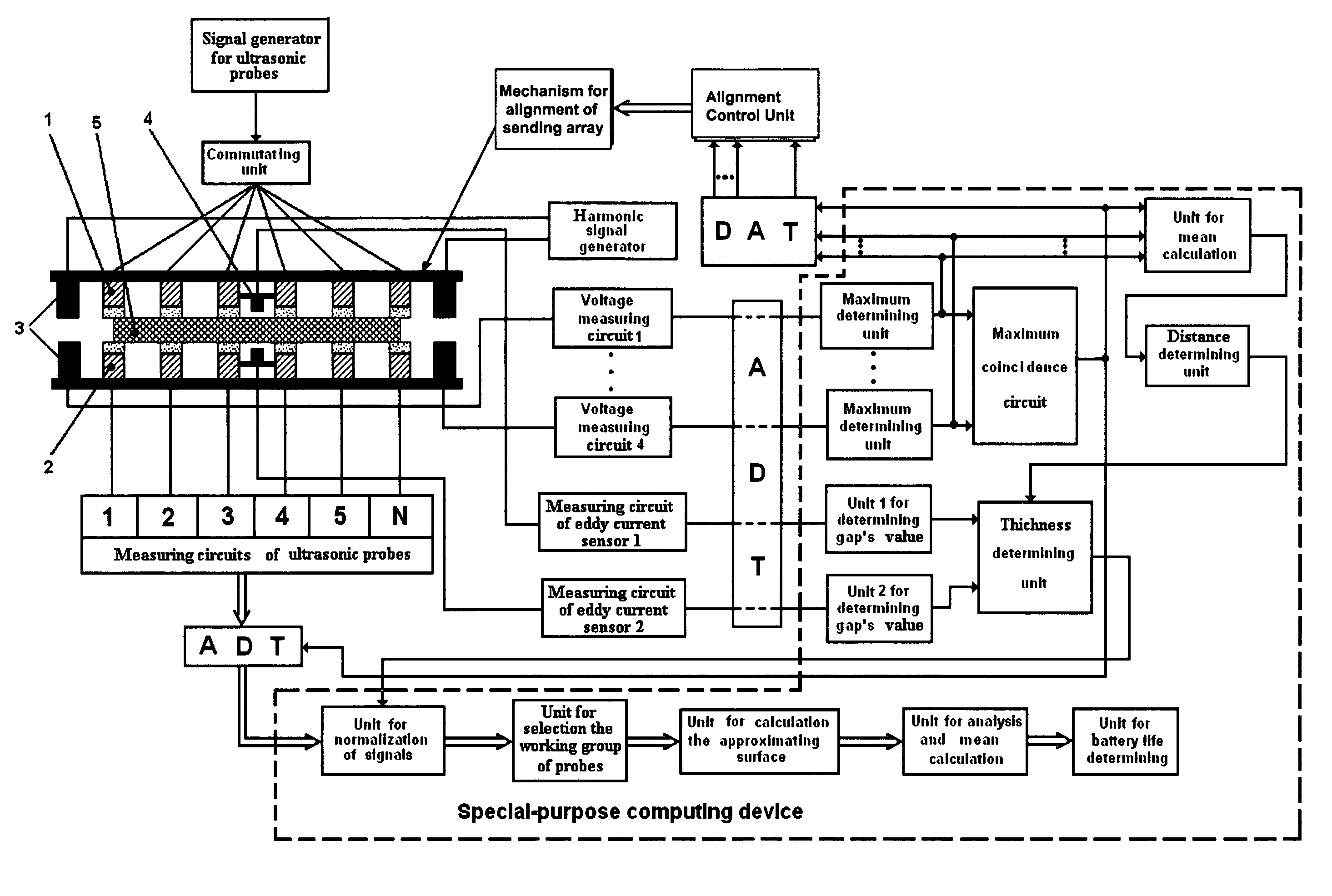
The present invention is an apparatus and method for determining the remaining service life of electrochemical energy generation and storage device including batteries, supercapacitors, DSSC solar cells and fuel cell. Measurements are performed by passing ultrasonic oscillations through the test object. The apparatus of the present invention comprises two arrays of transmitting and receiving ultrasonic probes between which the object being tested is affixed. Polyurethane tips are used for matching the acoustic resistance of the probes with the test object body. The apparatus includes means for positioning the transmitting and the receiving probe arrays relative to each other. The apparatus includes an electromagnetic means for measuring the test object thickness. The calibration characteristic for determining the remaining service life of a the test object are established from the signal values from the ultrasonic probes related to the number of charge-discharge cycles obtained at various charge values. A three-dimensional approximating dependence surface is constructed using the normalized signals from the receiving probes. The average value of this surface is determined. The remaining service life of the test object is determined using a calibration curve based on the average level of the surface
Owner:ENERIZE CORP
Method and device for measuring dielectric constant
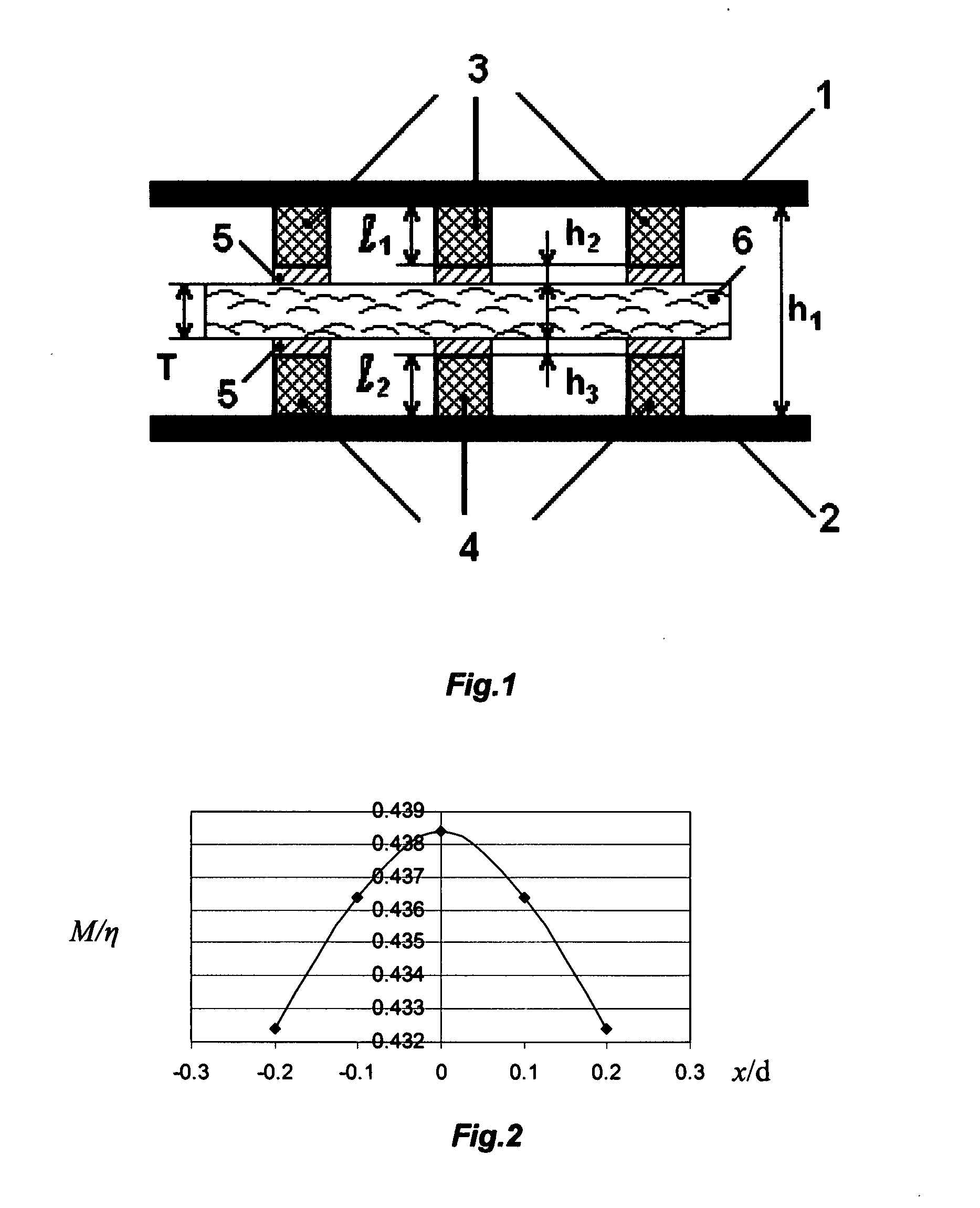
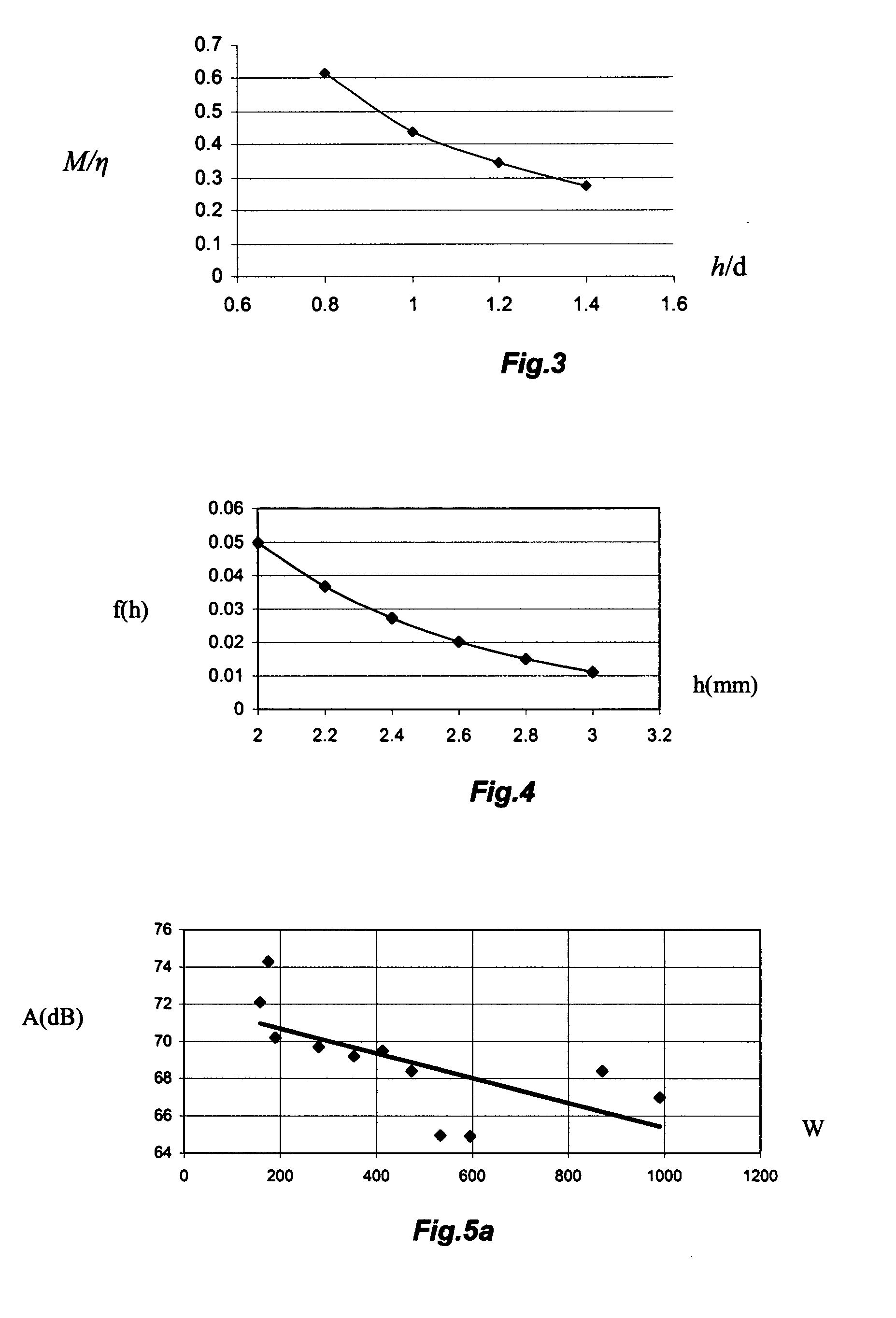
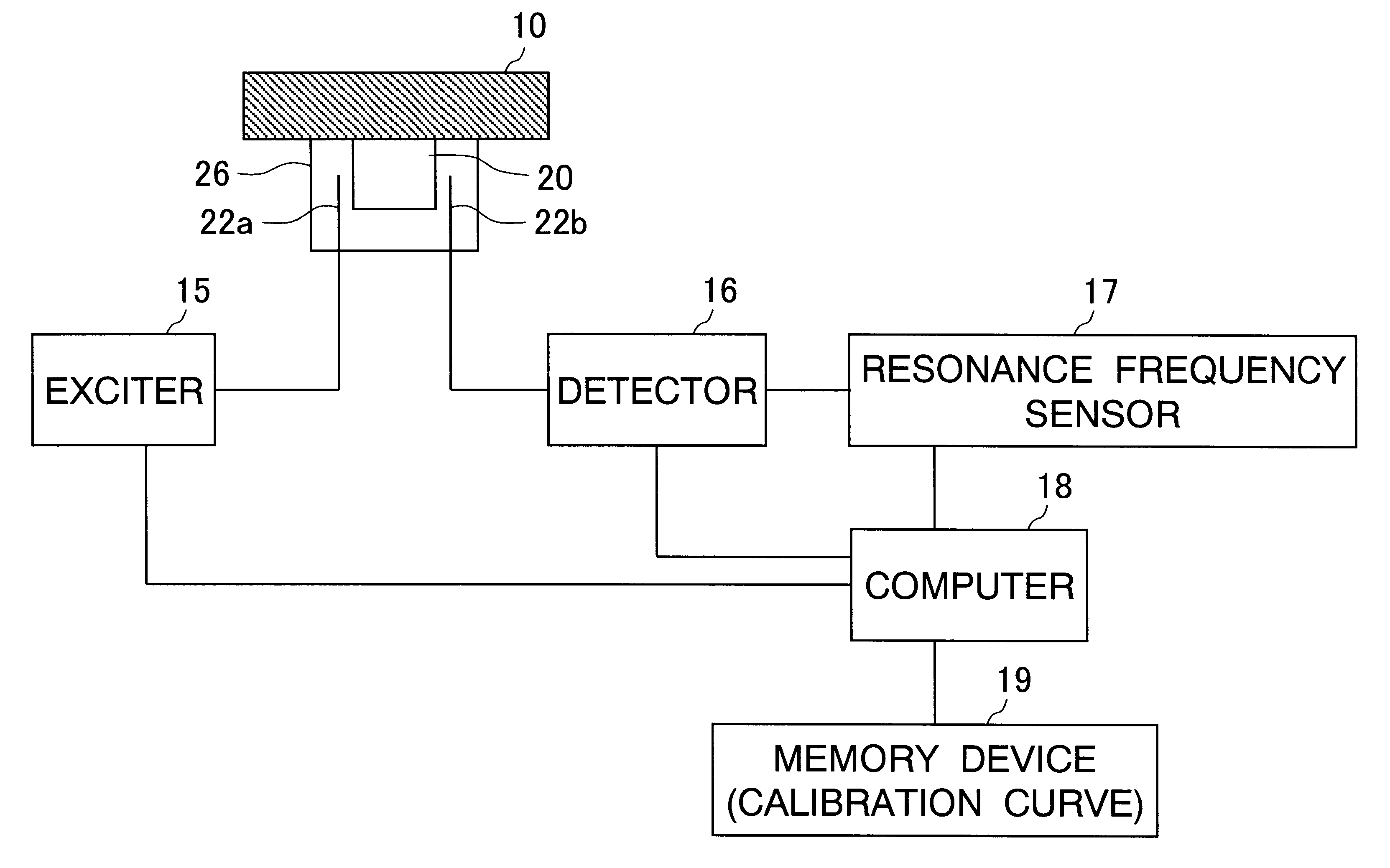
InactiveUS6496018B1Dielectric property measurementsMaterial analysis using microwave meansSample MeasureResonance
The sample measuring face of a dielectric resonator (20) is placed near a standard sample having a known dielectric constant at a fixed interval D. While appropriately varying the dielectric constant and thickness of the standard sample under the above condition, the variation of the resonance frequency of the dielectric resonator (20) is measured for each varied dielectric constant and thickness to draw a calibration curve of the varied resonance frequency depending on the dielectric constant and thickness. Under the same condition where calibration curve is drawn, the variation of the resonance frequency of the dielectric resonator (20) for a sample having a known thickness is measured. The dielectric constant of the sample is found from the measurement value and the calibration curve. The dielectric constant of not only a sheetlike sample but also a three-dimensional molded article or a liquid sample can be measured easily.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
Scanning Electron Microscope System, Pattern Measurement Method Using Same, and Scanning Electron Microscope
ActiveUS20160379798A1High aspect ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectron microscopeCalibration curve
In order to allow detecting backscattered electrons (BSEs) generated from the bottom of a hole for determining whether a hole with a super high aspect ratio is opened or for inspecting and measuring the ratio of the top diameter to the bottom diameter of a hole, which are typified in 3D-NAND processes of opening a hole, a primary electron beam accelerated at a high accelerating voltage is applied to a sample. Backscattered electrons (BSEs) at a low angle (e.g. a zenith angle of five degrees or more) are detected. Thus, the bottom of a hole is observed using “penetrating BSEs” having been emitted from the bottom of the hole and penetrated the side wall. Using the characteristics in which a penetrating distance is relatively prolonged through a deep hole and the amount of penetrating BSEs is decreased to cause a dark image, a calibration curve expressing the relationship between a hole depth and the brightness is given to measure the hole depth.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
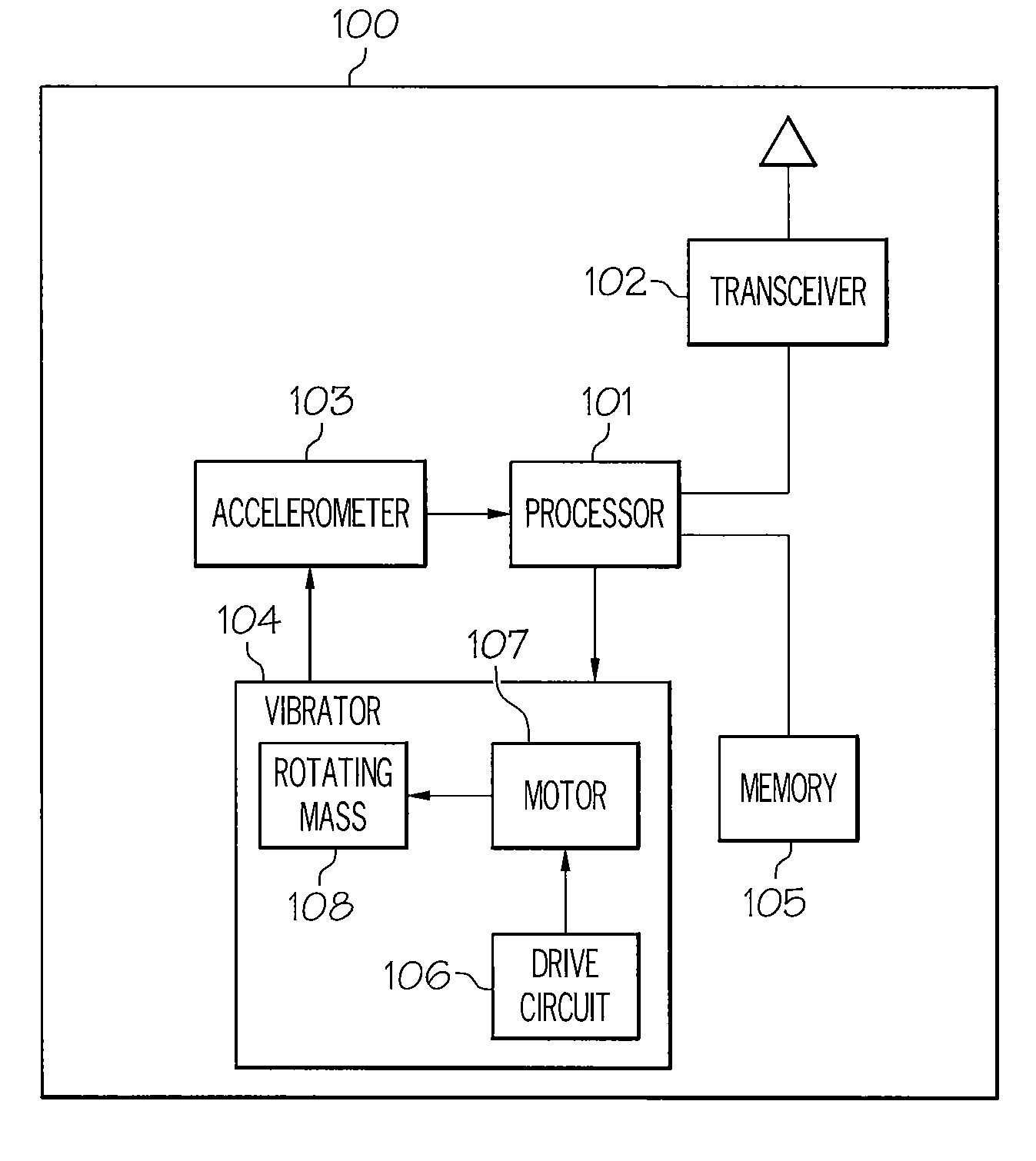
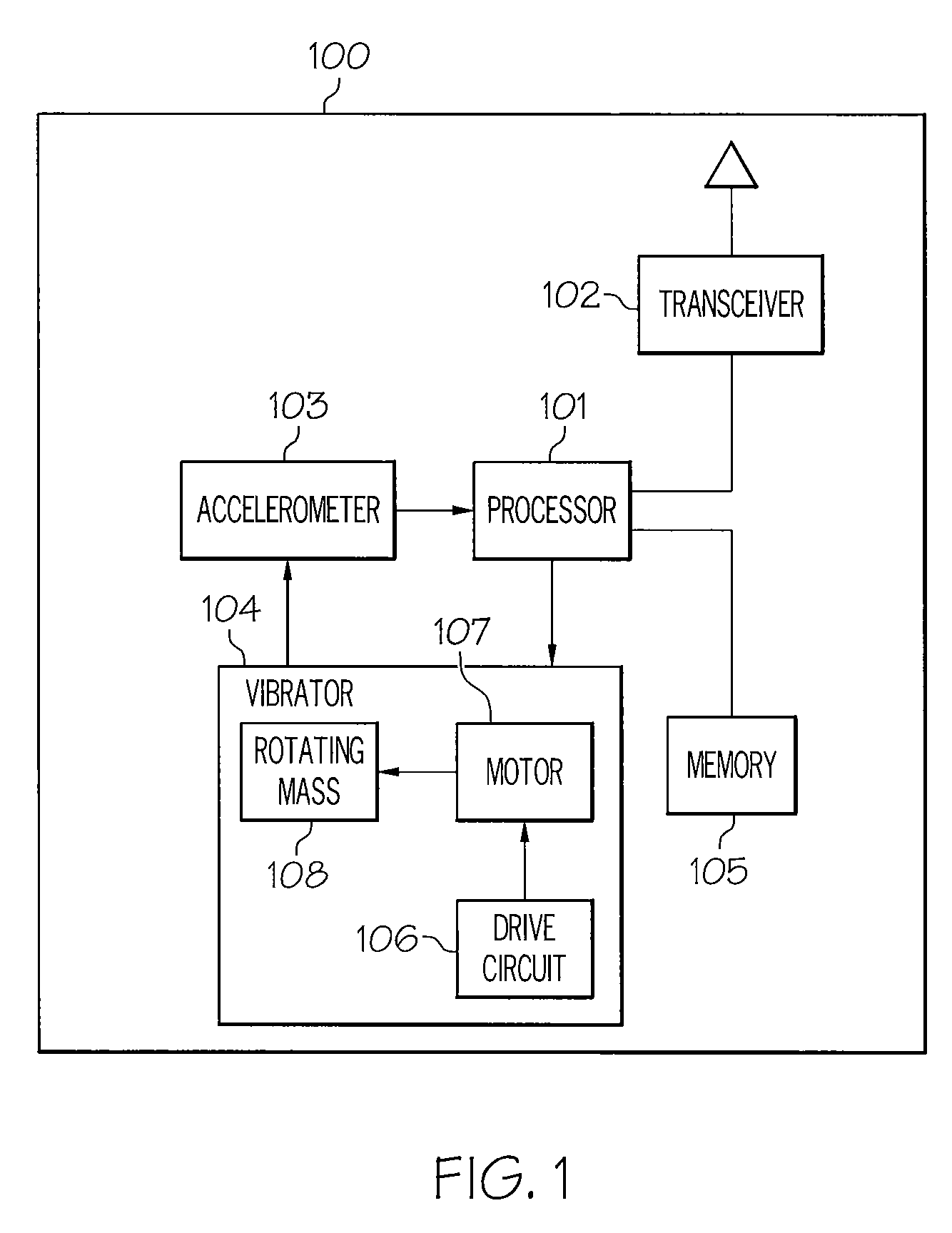
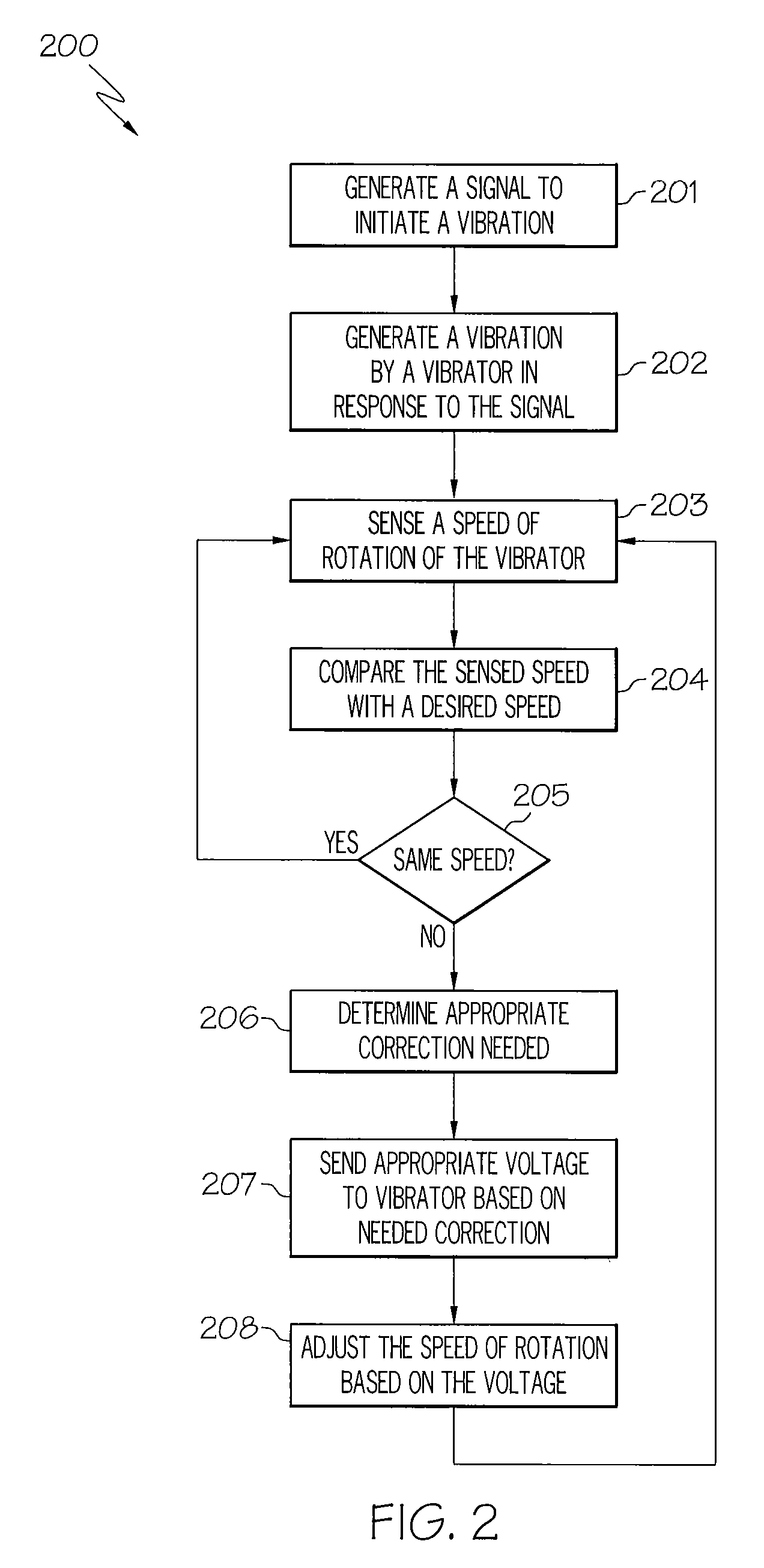
Use of an accelerometer to control vibrator performance
InactiveUS8084968B2Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlVibration amplitudeAccelerometer
A mobile device includes a vibrator, an accelerometer that senses a parameter of rotation, and a processor. The vibrator includes a drive motor and a drive circuit. The accelerometer senses a speed of rotation of the vibrator. The processor analyzes the sensed speed of rotation and generates a drive voltage that is received by the drive circuit to adjust the drive motor to produce a pre-determined, desired rotational speed. In another embodiment, the accelerometer senses an amplitude of a vibration produced by the vibrator. The processor analyzes the sensed amplitude of a vibration and generates a drive voltage that is received by the drive circuit to adjust the drive motor to produce a pre-determined, desired vibration amplitude. The processor may also compare the sensed parameter with a pre-determined desired parameter of rotation and generate a signal responsive to a result of the comparison and based on stored vibrator calibration curves.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
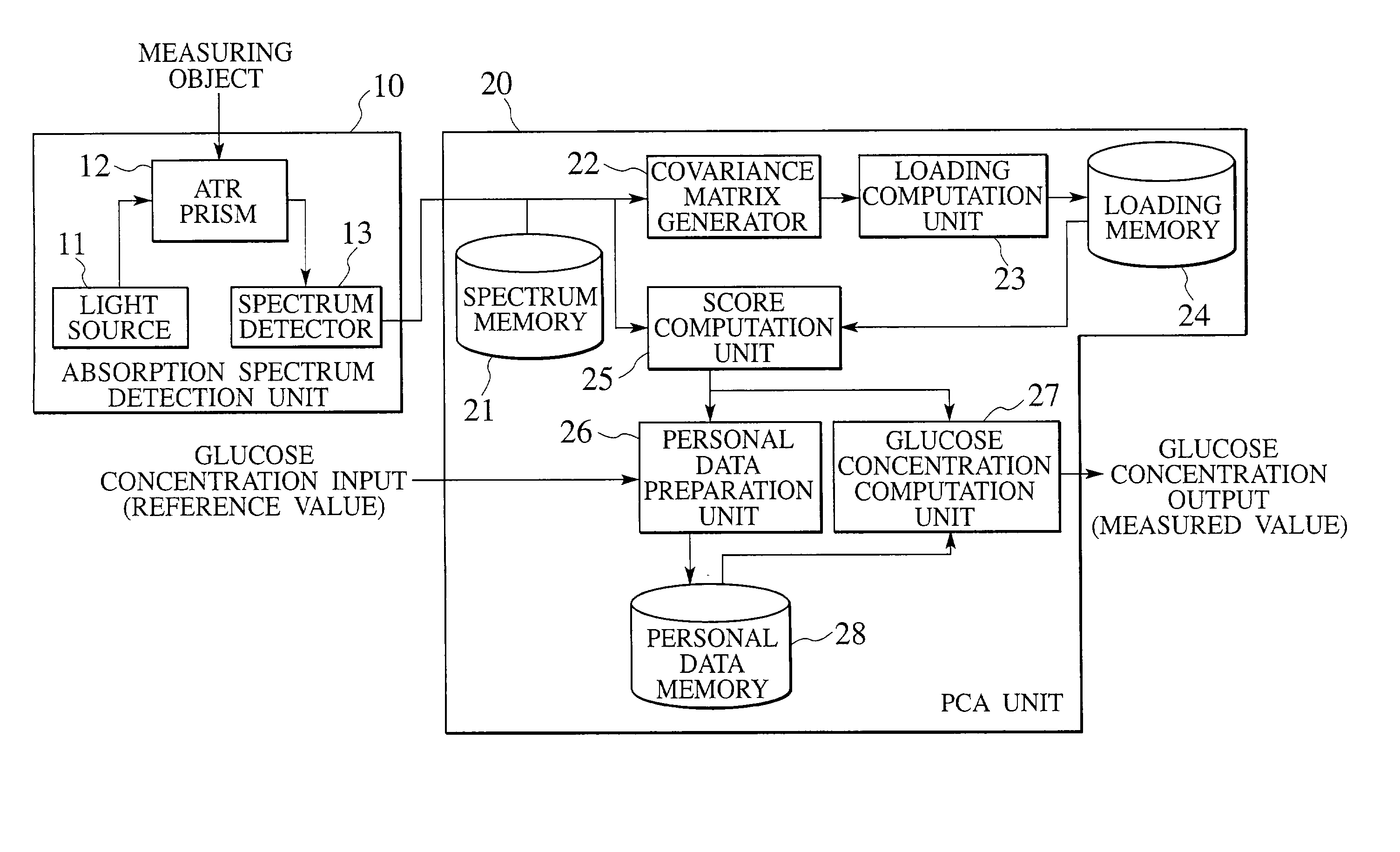
Apparatus for measuring glucose concentration
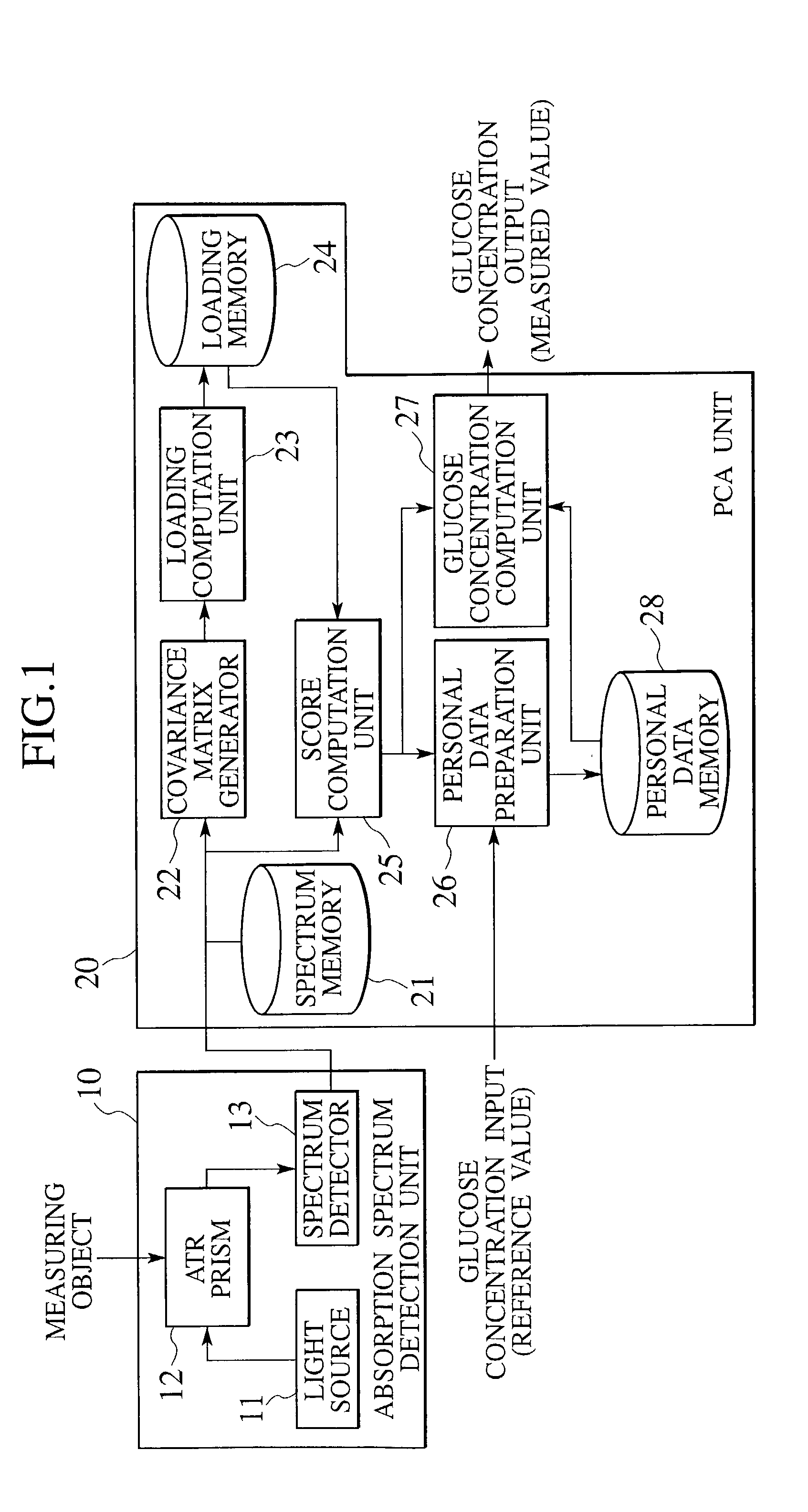
InactiveUS20030031597A1Spectrum investigationLaboratory glasswaresConcentrations glucosePrincipal component analysis
An apparatus for measuring a glucose concentration is noninvasive, accurate, and compact. The apparatus includes a detection unit (10) and a principal component analysis (PCA) unit (20). The detection unit includes a light source (11) to emit mid-infrared light, an ATR prism (12) to receive the mid-infrared light with a measuring object placed on the ATR prism, and a spectrum detector (13) to detect an absorption spectrum from the mid-infrared light from the ATR prism. The PCA unit includes a loading memory (24) to store a glucose corresponding loading and a personal data memory (28) to store personal data in the form of a calibration curve. According to the detected absorption spectrum, stored loading, and stored personal data, the PCA unit computes a glucose concentration of the measuring object.
Owner:PHOTOSCI INC
Apparatus and method for high temperature viscosity and temperature measurements
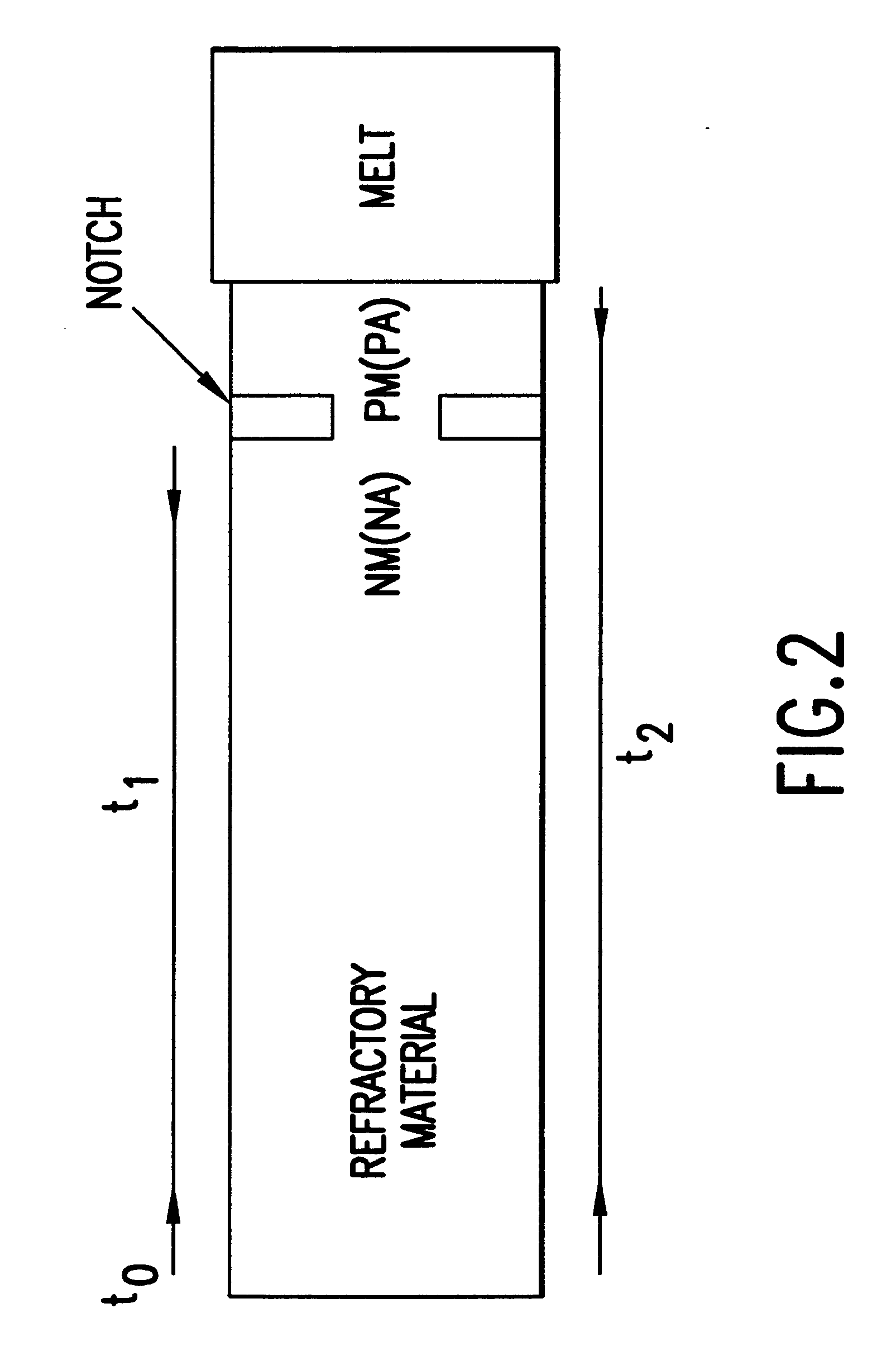
InactiveUS6296385B1Thermometer detailsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesRefractoryTransducer
A probe for measuring the viscosity and / or temperature of high temperature liquids, such as molten metals, glass and similar materials comprises a rod which is an acoustical waveguide through which a transducer emits an ultrasonic signal through one end of the probe, and which is reflected from (a) a notch or slit or an interface between two materials of the probe and (b) from the other end of the probe which is in contact with the hot liquid or hot melt, and is detected by the same transducer at the signal emission end. To avoid the harmful effects of introducing a thermally conductive heat sink into the melt, the probe is made of relatively thermally insulative (non-heat-conductive) refractory material. The time between signal emission and reflection, and the amplitude of reflections, are compared against calibration curves to obtain temperature and viscosity values.
Owner:MISSISSIPPI STATE UNIVERSITY
Measuring instrument and concentration measuring device
ActiveUS7491303B2Prevents incorrect concentration measurementProduction cost advantageImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectricityMeasuring instrument
The measurement instrument includes an attribute information output section to output attribute information about the attributes of the measurement instrument as an electric physical value. The attribute information is based on at least one of the conditions including a resistance of the attribute information output section, a location of the attribute information output section, and the size of a region on which the attribute information output section is formed. The attribute information may be used to select the calibration curve suitable for the measurement instrument. The attribute information may be one that relates to a specific measurement standard applied to the measurement instrument.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Method and cell for measuring the global ion concentration of a body fluid
ActiveUS20110079521A1Simple and precise quantitative measurementEasy to integrateImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBody fluidElectrochemistry
Method for measuring the global ion concentration of a body fluid that comprises application of a stable DC voltage between first and second electrodes of a cell for measuring the global ion concentration of a body fluid so as to cause electrochemical hydrolysis reactions of the body fluid water to occur at the level of said first and second electrodes, measurement of a hydrolysis current generated by said electrochemical hydrolysis reactions of the water and determination of the global ion concentration of the body fluid by comparison with a previously defined calibration curve. The measuring cell comprises a fluid channel having an internal cross-section smaller than or equal to 1.5 mm.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
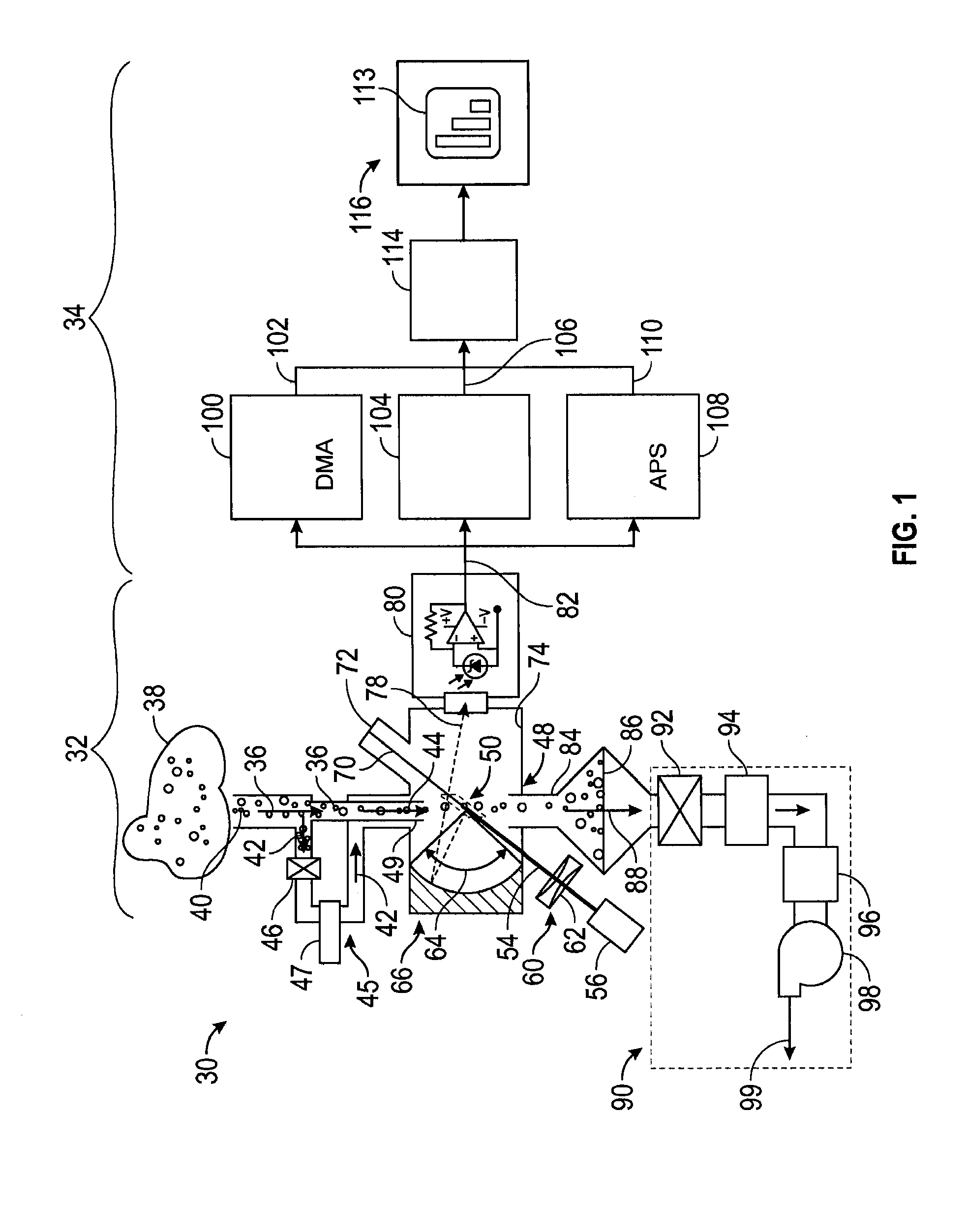
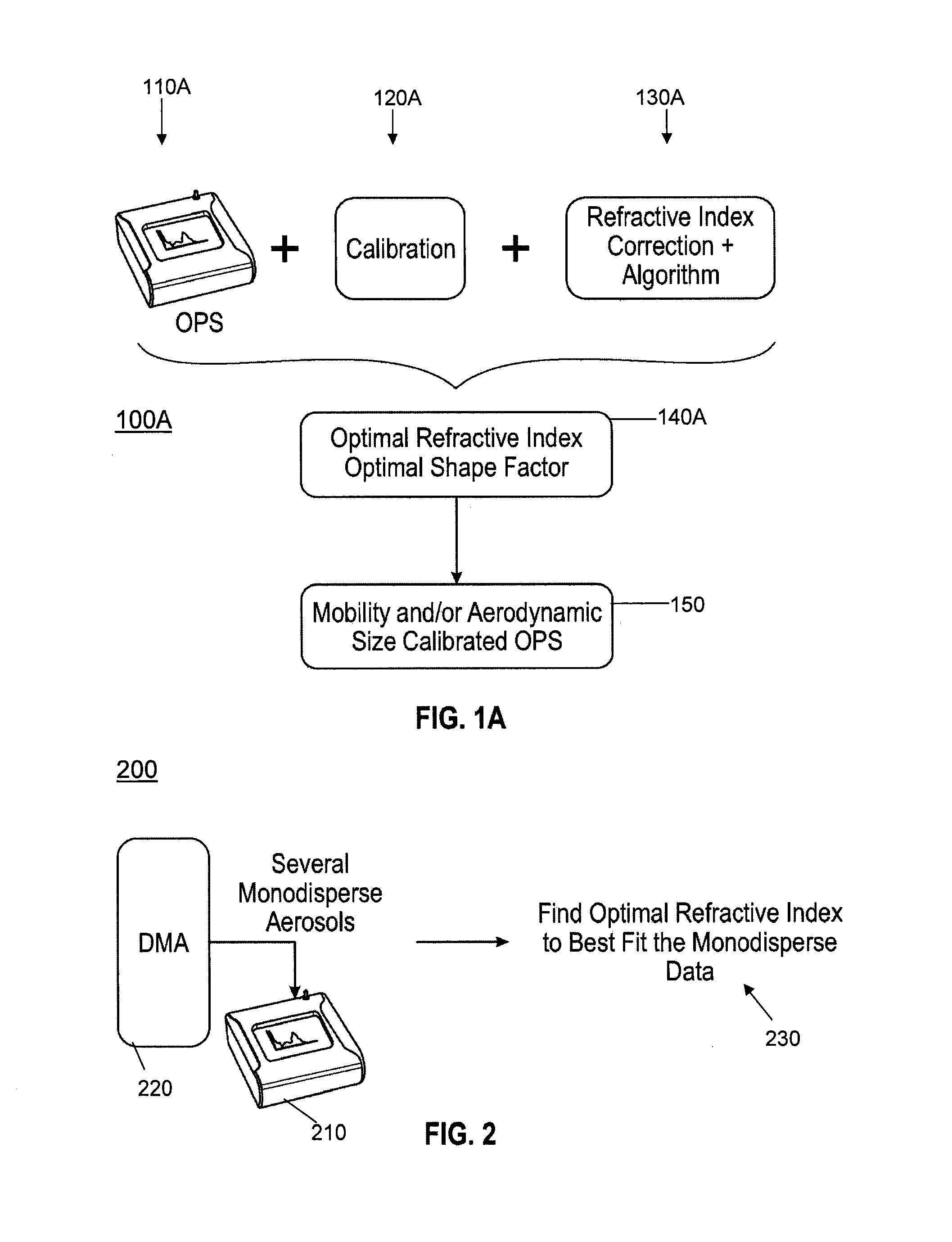
System and method for converting optical diameters of aerosol particles to mobility and aerodynamic diameters
ActiveUS20140247450A1Low costProvide quicklyMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle size analysisOptical propertyRefractive index
A system and a method of measuring a particle's size in a select aerosol using the optical diameter of the particle to perform a mobility and / or aerodynamic diameter conversion without any knowledge about the particle's shape and its optical properties in the aerosol being characterized. In one example embodiment of the invention, the method includes generating a set of calibration data and finding the optimal refractive index and shape that best fits the calibration data. In addition, the method includes creating a new calibration curve that provides a mobility-equivalent or aerodynamic-equivalent diameter.
Owner:TSI INC
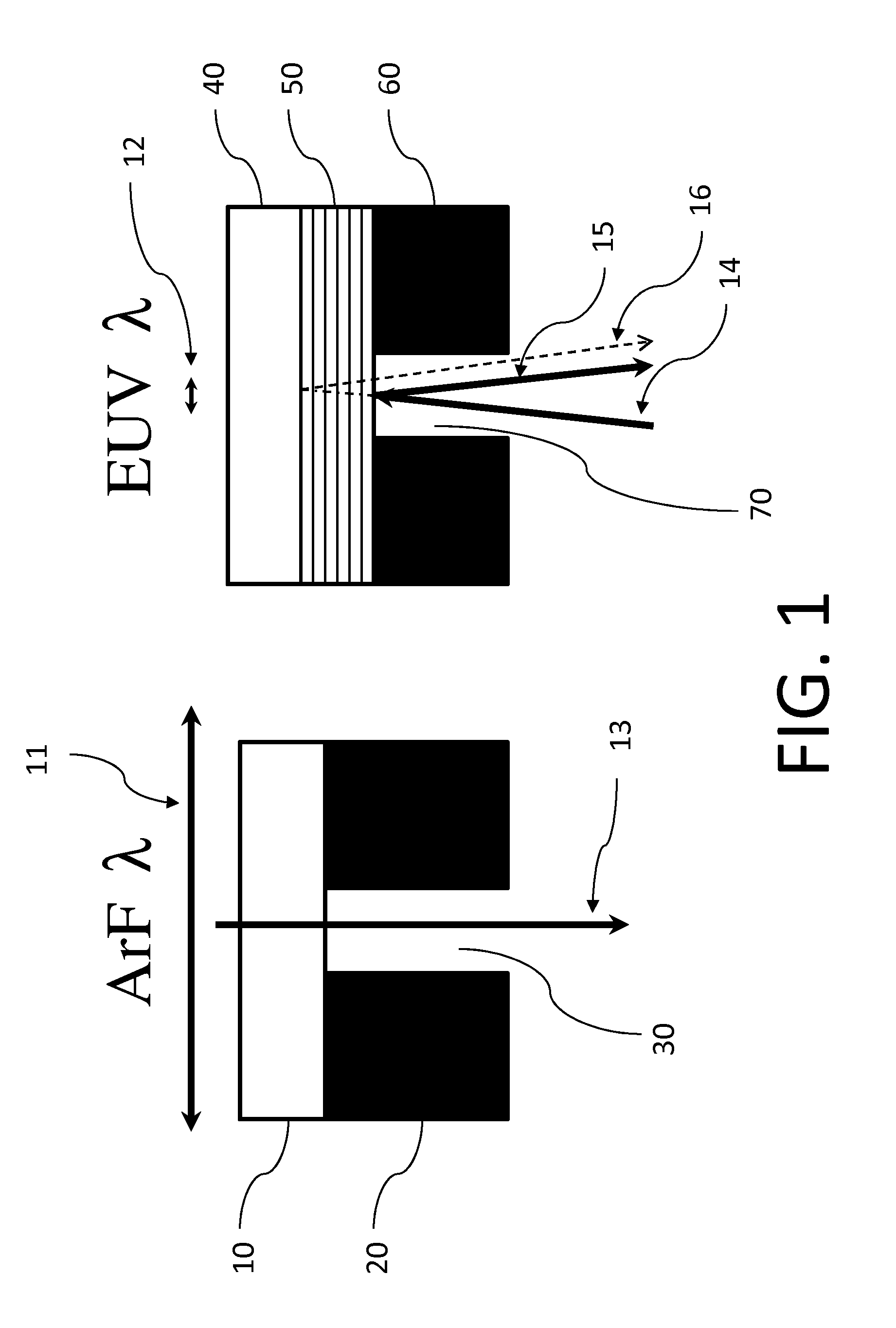
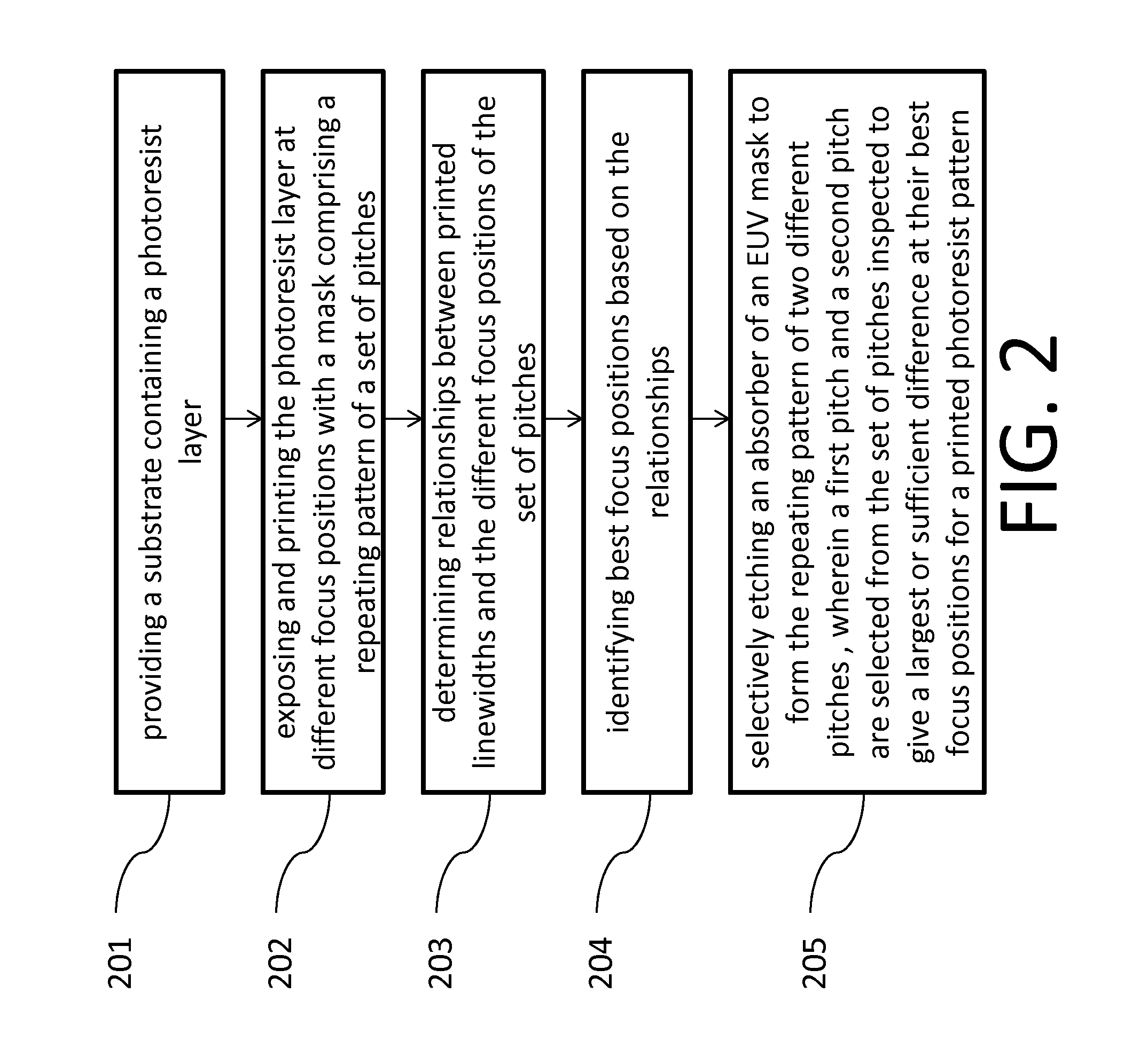
Method for monitoring focus in EUV lithography
ActiveUS20160238939A1High resolutionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusCalibration curveResist
This invention relates to a method of obtaining optimal focus for exposing a photoresist in an EUV lithography with an EUV mask containing a pattern with an assist feature. The invention also relates to an EUV mask with a special focus test target for monitoring focus in EUV lithography, and a method of fabricating this EUV mask by designing the special focus test target. The EUV mask contains a repeating pattern, wherein the repeating pattern has two different pitches, i.e. a first pitch and a second pitch, and contains an assist feature between main features. Because the two different pitches have different focus offsets, the difference between linewidths of said gratings provides a calibration curve which is a measure of focus. The method for monitoring focus is performing an EUV exposure using a focus position with a pre-determined focus position as calibrated using the linewidth difference between the two gratings. The EUV mask for monitoring focus of present invention is applicable to both test and product masks.
Owner:IBM CORP
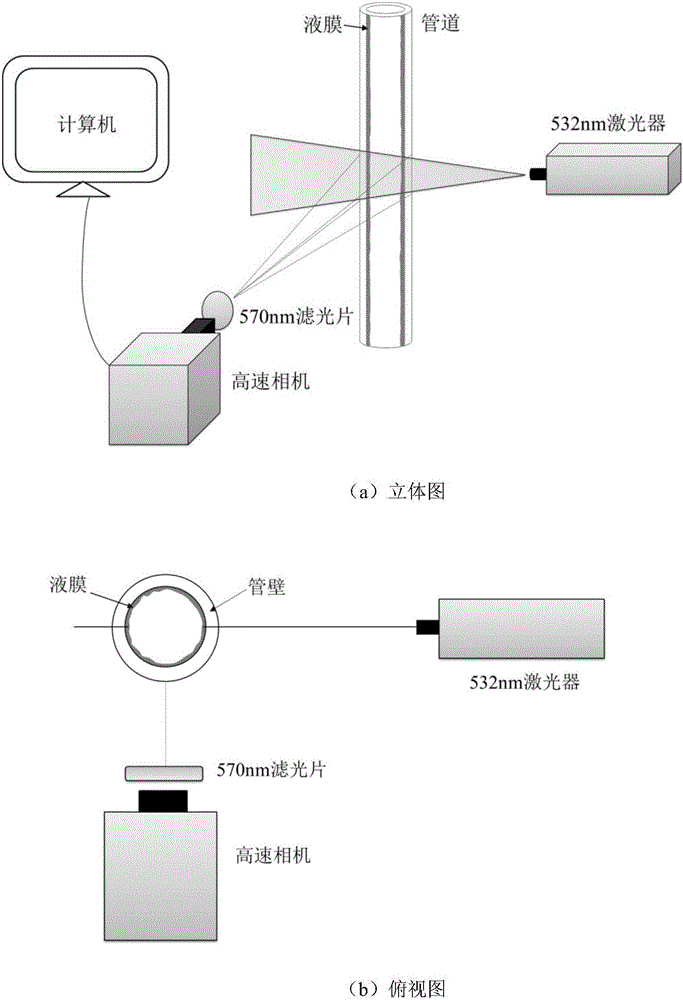
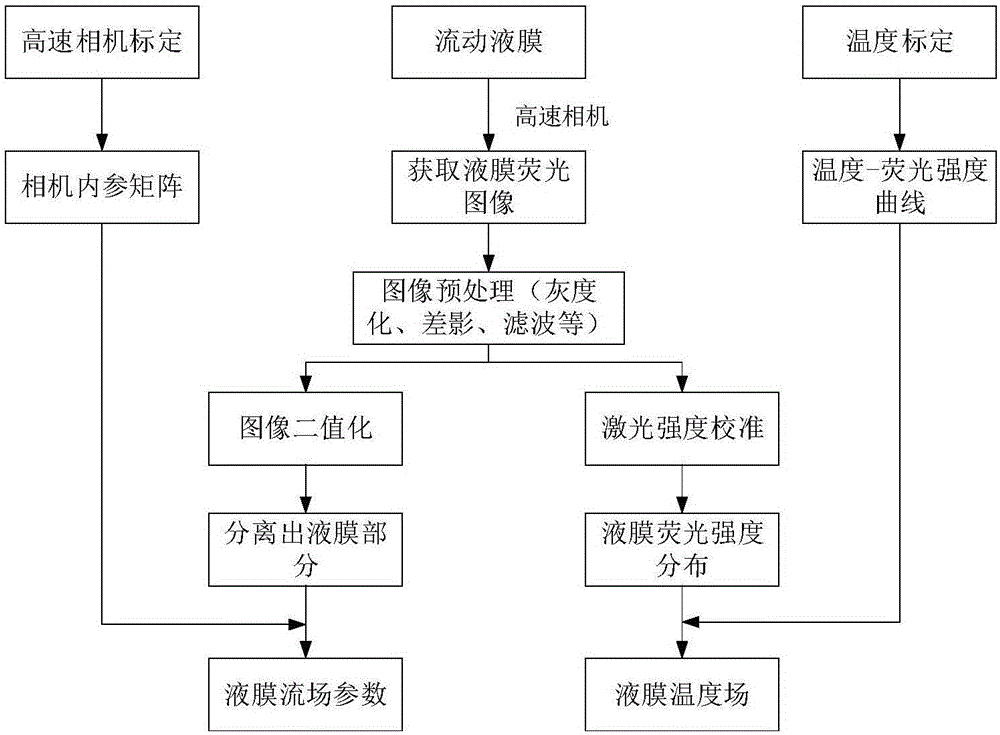
Liquid film temperature field and flow field simultaneous measurement method based on laser induced fluorescence
InactiveCN106525137ARealize simultaneous measurementGood spatio-temporal resolutionMeasurement devicesLaser intensityLaser-induced fluorescence
The invention relates to the field of two-phase / multi-phase flow measurement, aims to realize the non-intrusive and high precision synchronization acquisition of the flow parameters of a liquid film in (outside) a pipeline and temperature field distribution, and is used for the deep study of a liquid film flow characteristic, a heat transfer characteristic and the like. The employed technical scheme is that according to the liquid film temperature field and flow field simultaneous measurement method based on laser induced fluorescence, when a liquid film with dissolved fluorescent dye forms a dynamic liquid film in a pipeline inner / outer wall or a flat panel, a liquid film fluorescence image is taken through a high speed camera, for a same taken fluorescence image, based on a high speed calibration parameter, the geometric feature of the liquid film fluorescence image is accurately extracted, and flow field characteristics comprising a liquid film thickness and a velocity are obtained. At the same time, based on a calibrated temperature-fluorescence intensity calibration curve, laser intensity calibration and a fluorescence intensity extraction method, a liquid film fluorescence image brightness is accurately extracted, and the instantaneous and time averaged temperature field distribution of the liquid film are obtained. The method is mainly applied to a two-phase / multi-phase flow measurement occasion.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
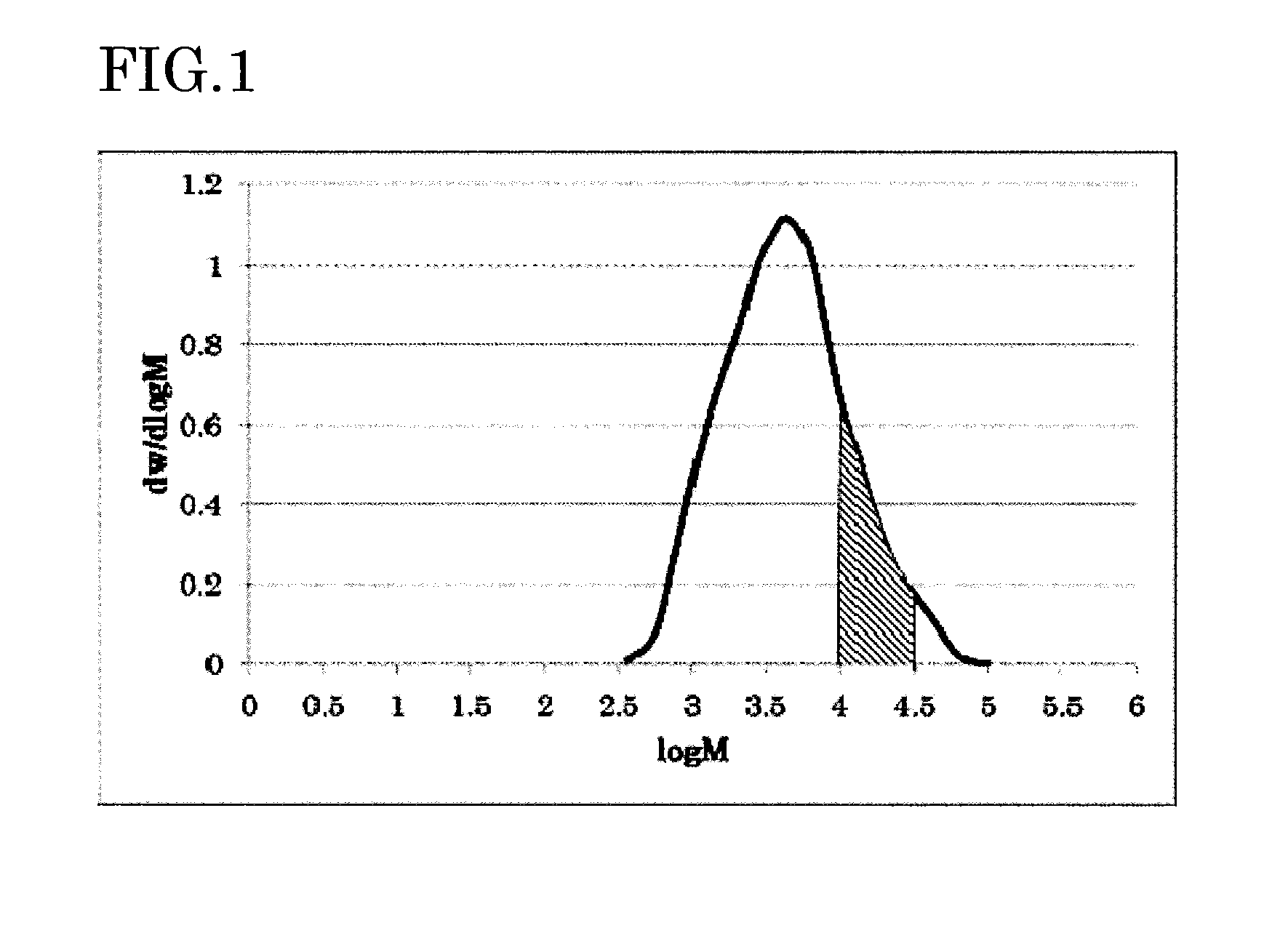
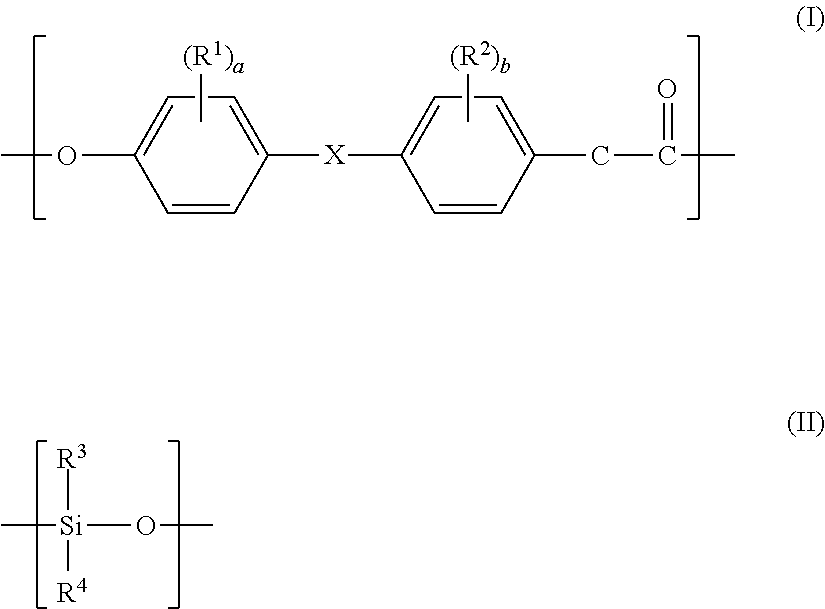
Polycarbonate-polyorganosiloxane copolymer and method for producing same
Provided is a polycarbonate-polyorganosiloxane copolymer, including a specific polycarbonate block unit (A) and a specific polyorganosiloxane block unit (B), in which in a differential molecular weight distribution curve obtained from measurement of the polyorganosiloxane block unit (B) by gel permeation chromatography using the polystyrene calibration curve, the curve having an axis of abscissa indicating a logarithmic value log(M) of a molecular weight M and an axis of ordinate indicating dw / d log(M) obtained by differentiating a concentration fraction w with respect to the logarithmic value log(M) of the molecular weight, (1) a dw / d log(M) value becomes maximum in a range of 3.4≦log(M)≦4.0, and (2) in the differential molecular weight distribution curve, a ratio of a value obtained by integrating the dw / d log(M) value over a range of 4.0≦Log(M)≦4.5 to a value obtained by integrating the dw / d log(M) value over the entire range of the log(M) is 6% or more and 40% or less.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Apparatus and method for assessing the liquid flow performances through a small dispensing orifice
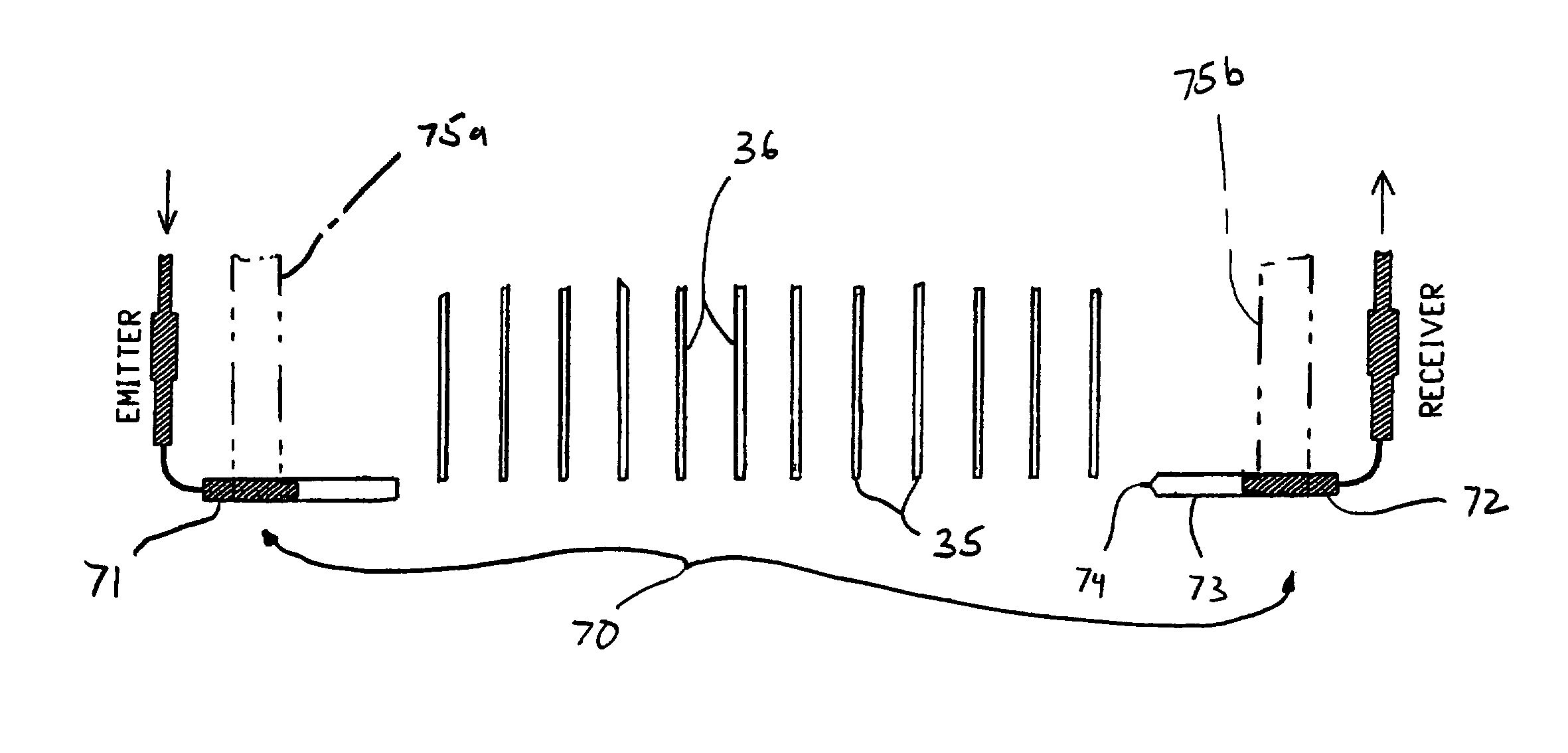
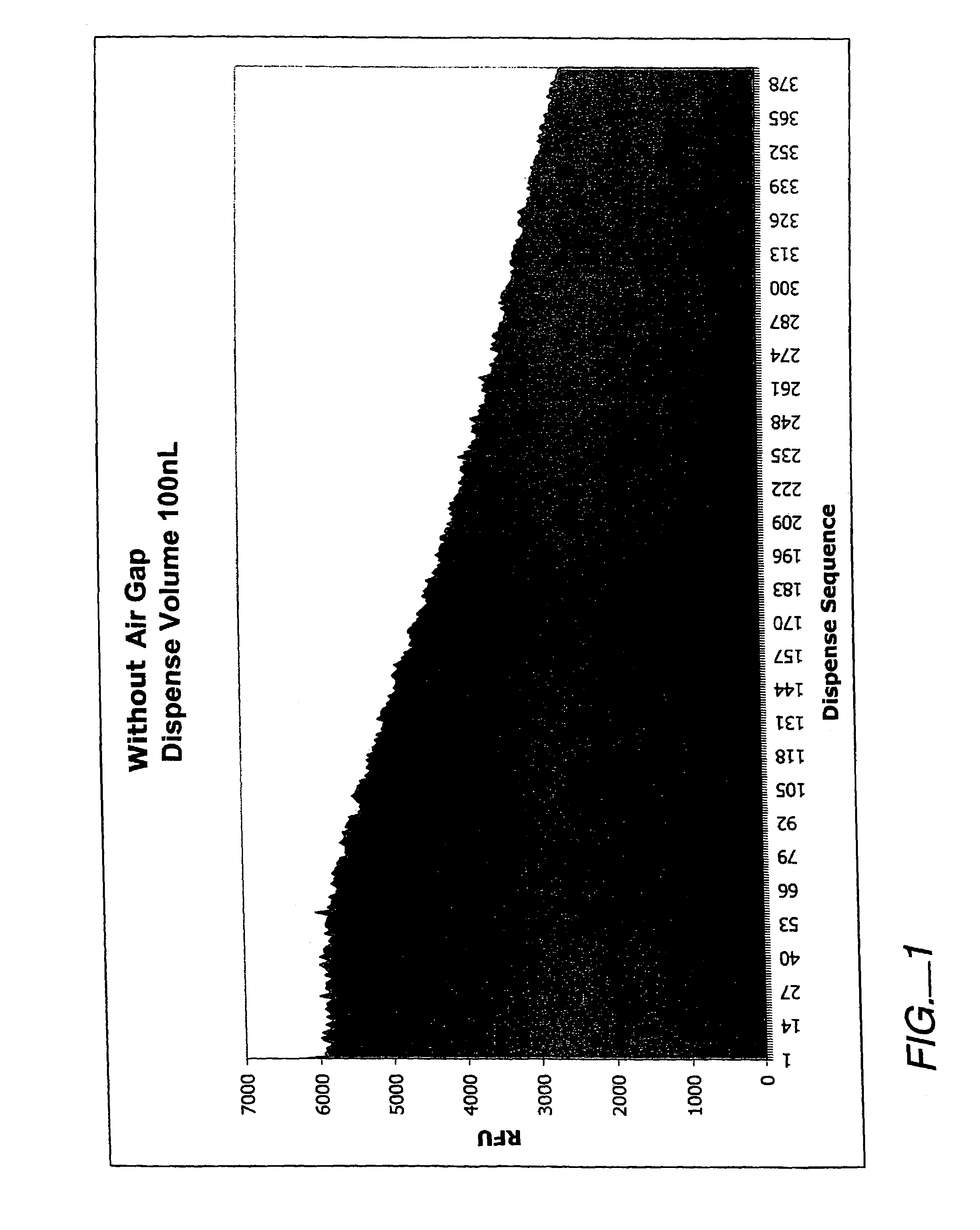
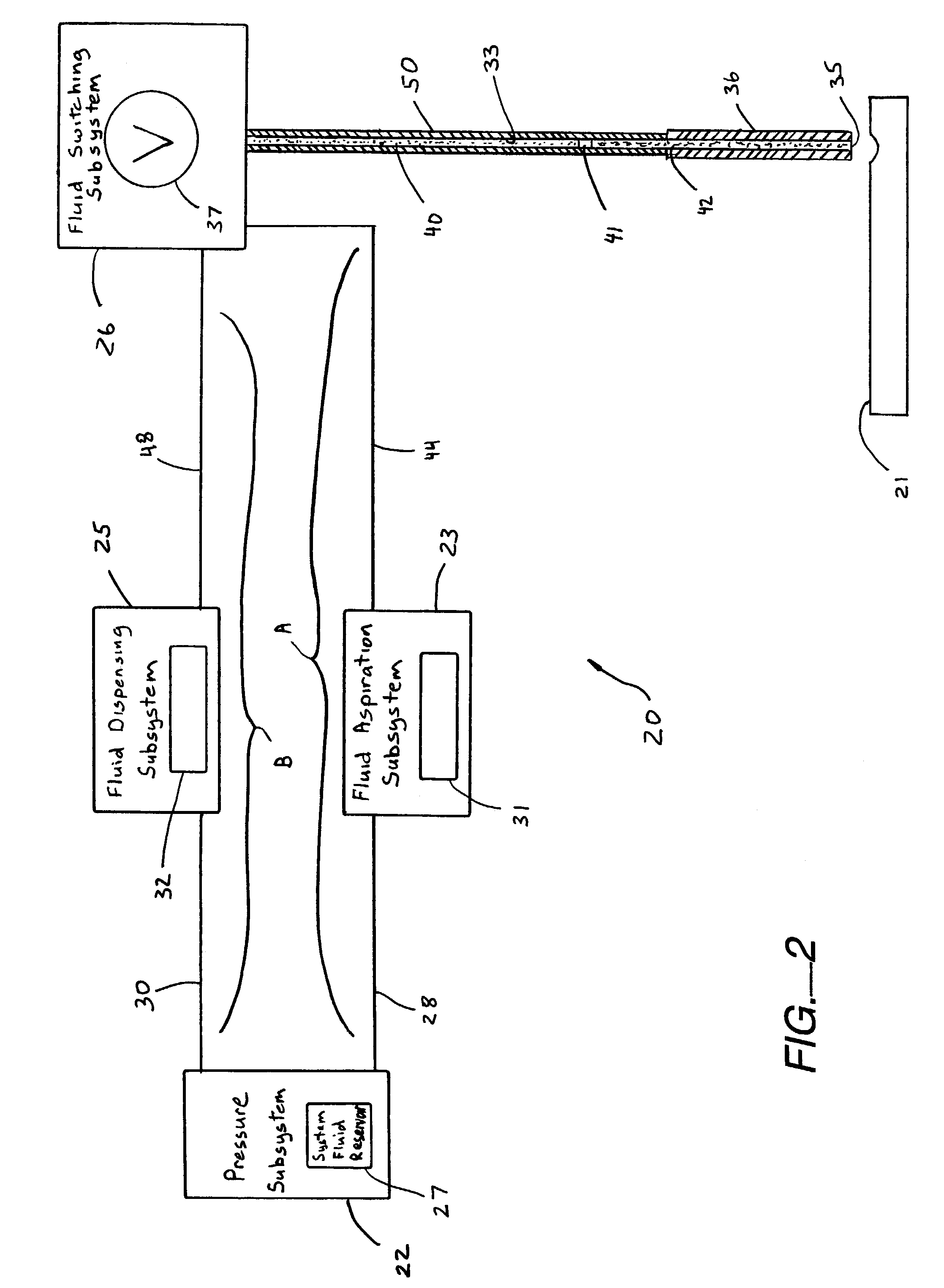
InactiveUS6983636B2Testing/calibration apparatusInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsEngineeringCalibration curve
A universal calibration apparatus and method to estimate the dispense output from a low volume, non-contact, liquid dispensing systems that may be applied for every hardware configuration (e.g., tube length, orifice diameter, tip design, etc), reagent solution property and environmental condition. This same calibration technique is applied to calibrate or tune these non-contact liquid dispensing systems to dispense desired volumes (in the range of about 0.050 μL to 50 μL), irrespective of the hardware configuration or the solution properties. That is, the calibration technique is not dependent on any variables, but the result (the actual dispense volume) is dependant on the variable mentioned. By actuating selected pulse widths, and measuring the resulting volume, a Calibration Profile can be generated correlating the liquid volume dispensed from the orifice to the respective pulse width of the dispensing valve thereof through calibration points. In particular, one is selected to deliver a first volume of liquid that is less than a lower base pulse width correlating to the lowest volume of the selected range of volumes of liquid, while a second pulse width is selected to deliver a second volume of liquid dispensed that is greater than an upper ceiling pulse width correlating to the highest volume of the selected range of volumes of liquid. Intermediary pulse widths are also applied, each selected to deliver a different, spaced-apart, respective intermediary low volumes of liquid dispensed from the dispensing orifice between the first volume and the second volume. Thus, applying the Calibration Profile, the pulse widths correlating to the one or more targeted discrete volumes for liquid dispensing can be extrapolated.
Owner:BIONEX SOLUTIONS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com