Patents
Literature
91 results about "Immobilized Antibodies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
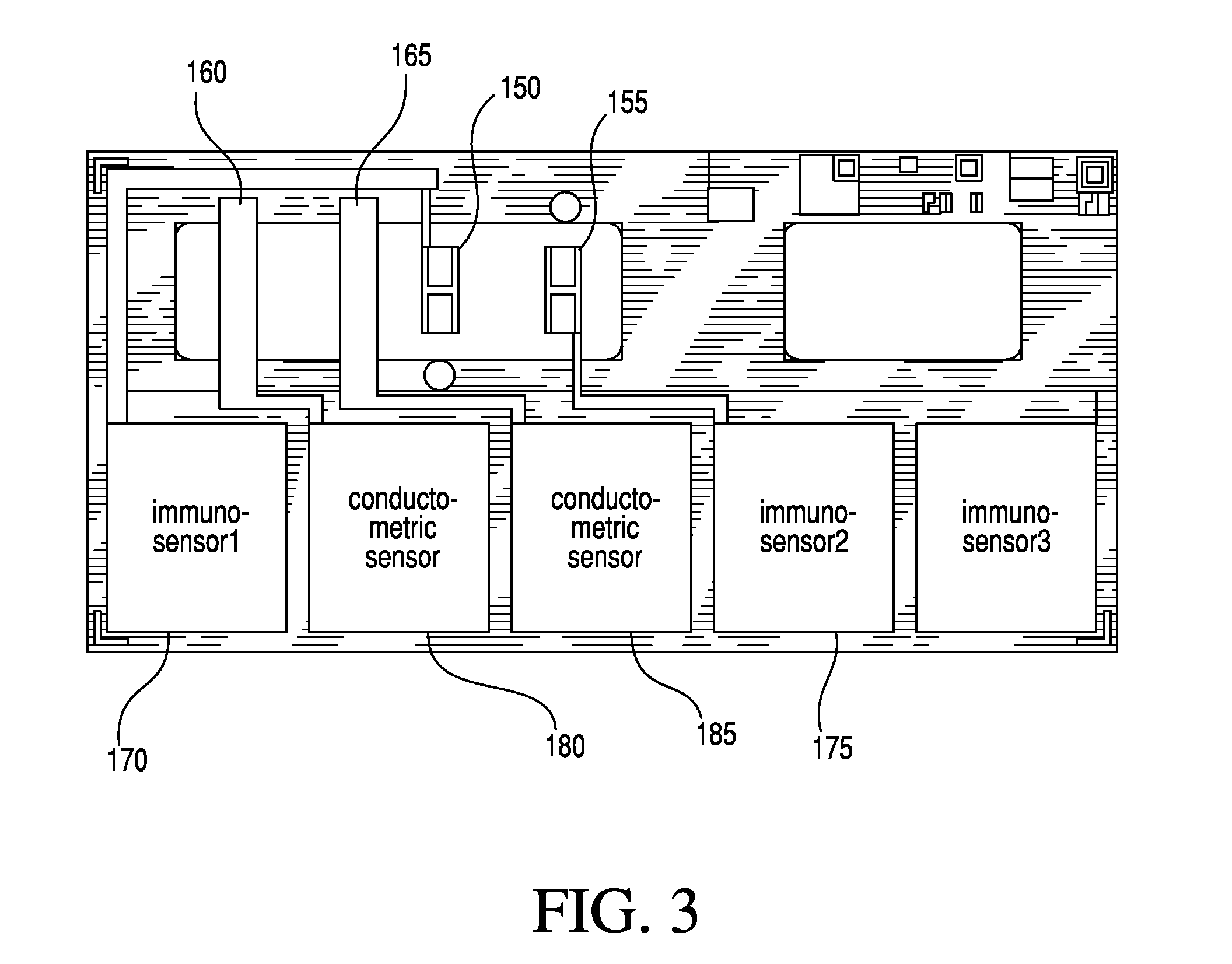
Immunoassay device with immuno-reference electrode
InactiveUS20060160164A1Reduce distractionsIncrease ionic strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmune profilingImmobilized Antibodies
An electrochemical immunosensor system with reduced interference, comprising: a first immunosensor that generates an electrochemical signal based on the formation of a sandwich between an immobilized antibody, a target analyte and a labeled antibody, wherein a portion of the signal arises from non-specific binding of the labeled antibody in the region of the first immunosensor, and a second immunosensor that acts as an immuno-reference sensor and generates a signal that is the same as or predictably related to the degree of non-specific binding which occurs in the region of the first immunosensor, and has an immunocomplex between an immobilized antibody and an endogenous or exogenous protein that is in the sample and that is not the target analyte.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Immunoassay device with immuno-reference electrode
InactiveUS7723099B2Increase ionic strengthReduce distractionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein insertionNon specific
An electrochemical immunosensor system with reduced interference, comprising: a first immunosensor that generates an electrochemical signal based on the formation of a sandwich between an immobilized antibody, a target analyte and a labeled antibody, wherein a portion of the signal arises from non-specific binding of the labeled antibody in the region of the first immunosensor, anda second immunosensor that acts as an immuno-reference sensor and generates a signal that is the same as or predictably related to the degree of non-specific binding which occurs in the region of the first immunosensor, and has an immunocomplex between an immobilized antibody and an endogenous or exogenous protein that is in the sample and that is not the target analyte.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
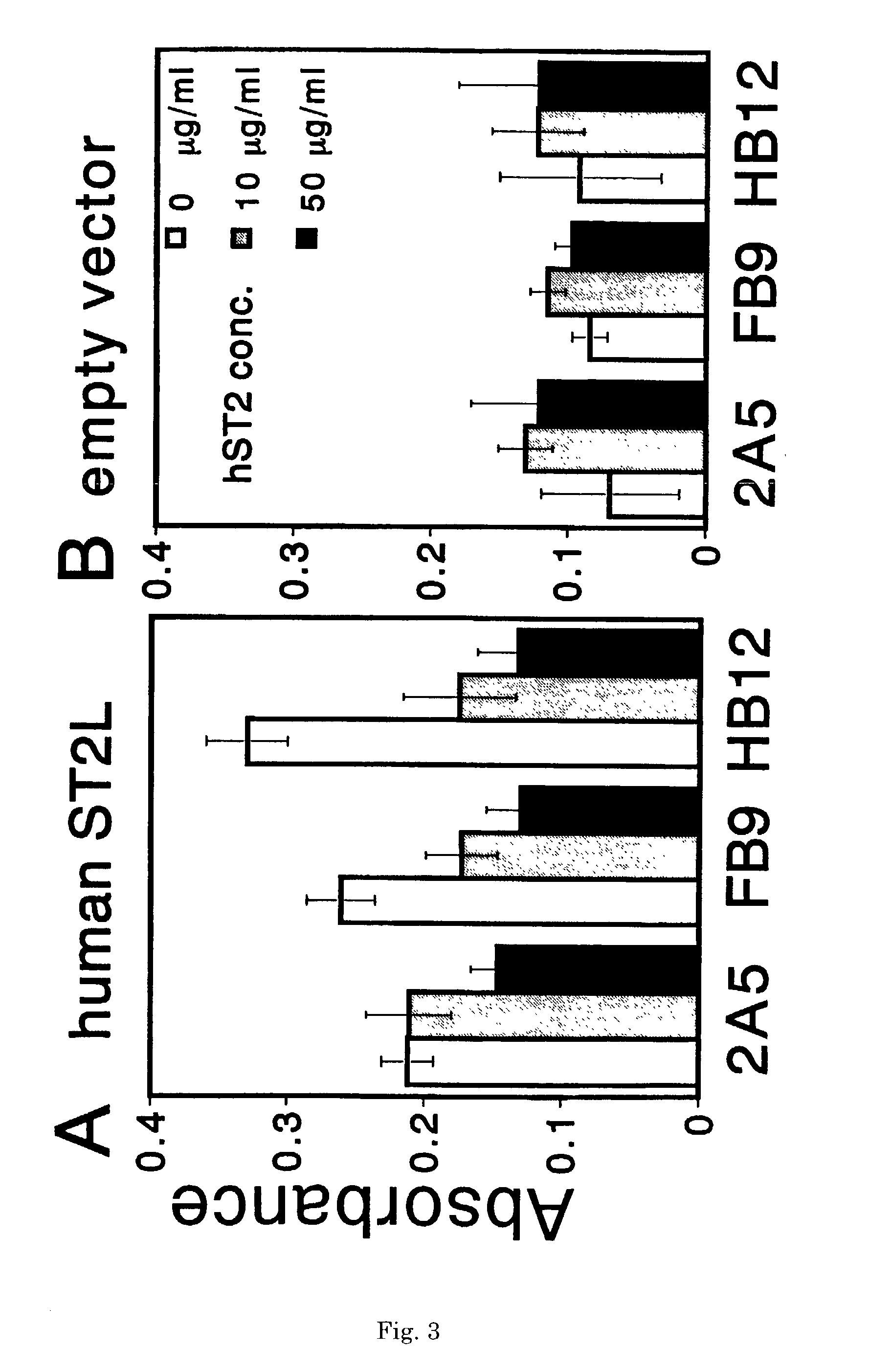
Monoclonal antibody and method and kit for immunoassay of soluble human ST2
InactiveUS7087396B2The process is convenient and fastAnimal cellsEnzymologyImmobilized AntibodiesMonoclonal antibody
A method for determining a soluble human ST2 in a sample conveniently at a high sensitivity and an assay kit are provided. By an immunological method comprising a step for bringing a sample into contact with an immobilized antibody formed by binding to an insoluble support a first anti-human ST2 antibody which binds specifically to a non-denatured human ST2, a step for labelling a first reaction product generated in the previous step by reacting said first reaction product with a second anti-human ST2 antibody which binds specifically to a non-denatured human ST2 by recognizing a site different from the site on ST2 where said first anti-human ST2 antibody binds and which is labelled with a label, and a step for determining the amount of the label on said first reaction product which has been labelled, a soluble human ST2 in a sample is determined. In addition, a recombinant ST2 is employed as a standard to prepare a calibration curve, based on which the ST2 in a sample is quantified.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
Highly cost-effective analytical device for performing immunoassays with ultra high sensitivity
InactiveUS20020110803A1Highly cost-effectiveEasy to manufactureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWater insolubleAdhesive
A simple easy to manufacture analytical device capable of performing membrane based immunoassays on batch of samples within 3 to 10 minutes wherein the method permits focused application of samples, costly labeled immunoassay and signal amplification reagents, said device includes an antibody-immobilized micro porous membrane, breadth corner layer of which is directly attached to a semi-rigid liquid-impervious body with water insoluble adhesive; absorbent body is provided separately and is not attached to analytical device during manufacture, absorbent body is wetted and is placed proximal to the lower surface of the membrane thereby forming networks of capillary channels with the absorbent body; flow of samples or reagents is always kept downwards and focused without application of any force to the absorbent body and the use of disposable adsorbent body permits stepwise addition of signal amplification reagents for ultra sensitive detection of diagnostically important molecules by visual examination of the membrane surface.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
Concentration measuring method, concentration measuring kit, and sensor chip for use in the method
InactiveUS20060194345A1Easy to measureImprove accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmobilized AntibodiesWaveguide
The method for measuring the concentration of the measuring object uses a sensor chip comprising an optical waveguide layer and an antibody immobilized layer formed on the surface of the optical waveguide layer, which comprises immobilizing the measuring object and an enzyme-labeled antibody labeled with a labeling enzyme on the antibody immobilized layer of the sensor chip having an immobilized antibody, producing a color-developing and precipitating enzyme reaction product by allowing to react a coloring reagent with the labeling enzyme on the antibody immobilized layer to precipitate the enzyme reaction product on the antibody immobilized layer, allowing to totally reflect a light impinged on the sensor chip from the outside at an interface between the optical waveguide layer and the antibody immobilized layer, and observing to a physical value of the totally reflected light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Ultra-sensitive superparamagnetic nano immunization microsphere and GP73 antigen detection method
ActiveCN105699653AThe detection process is fastStrong specificityBiological testingMicrosphereEnzyme immunoassays
The present invention relates to the technical field of diagnostic reagents, and particularly relates to a magnetic immunization in-vitro diagnostic reagent. In order to solve the technical problems of smaller capacity of an immobilized antibody, long reaction time, relatively low sensitivity and low stability of the immobilized antibody of a conventional enzyme immunoassay, the present invention provides a GP73 monoclonal antibody and a superparamagnetic nano immunization microsphere with the GP73 monoclonal antibody coupled with the surface, and a human serum or plasma GP73 antigen detection method using the superparamagnetic nano immunization microsphere by double-antibody sandwich enzyme immunoassay or chemiluminescence method. An antigen for producing the GP73 monoclonal antibody has the following amino acid sequence AAAERGAVELKK. The superparamagnetic nano immunization microsphere has the characteristics of being capable of coupling more antibodies, fast in immunoreaction speed, high in specificity, good in repeatability, low in cost, and simple in experimental condition requirements and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF HEPATOLOGY +1
Test strip for chromatography and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20040161857A1Reduce in quantitySufficient quantityBiological material analysisImmobilized AntibodiesBiochemistry
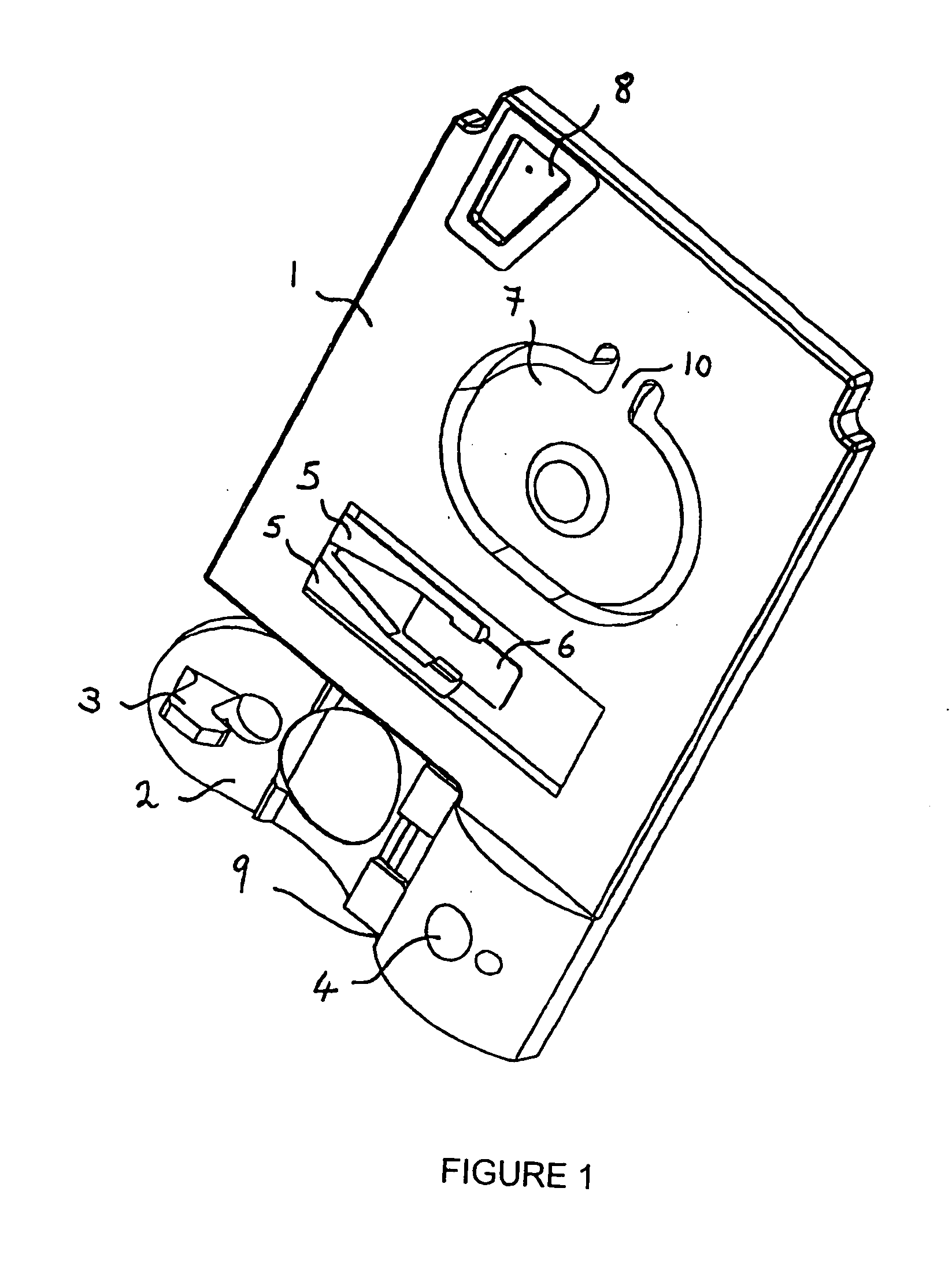
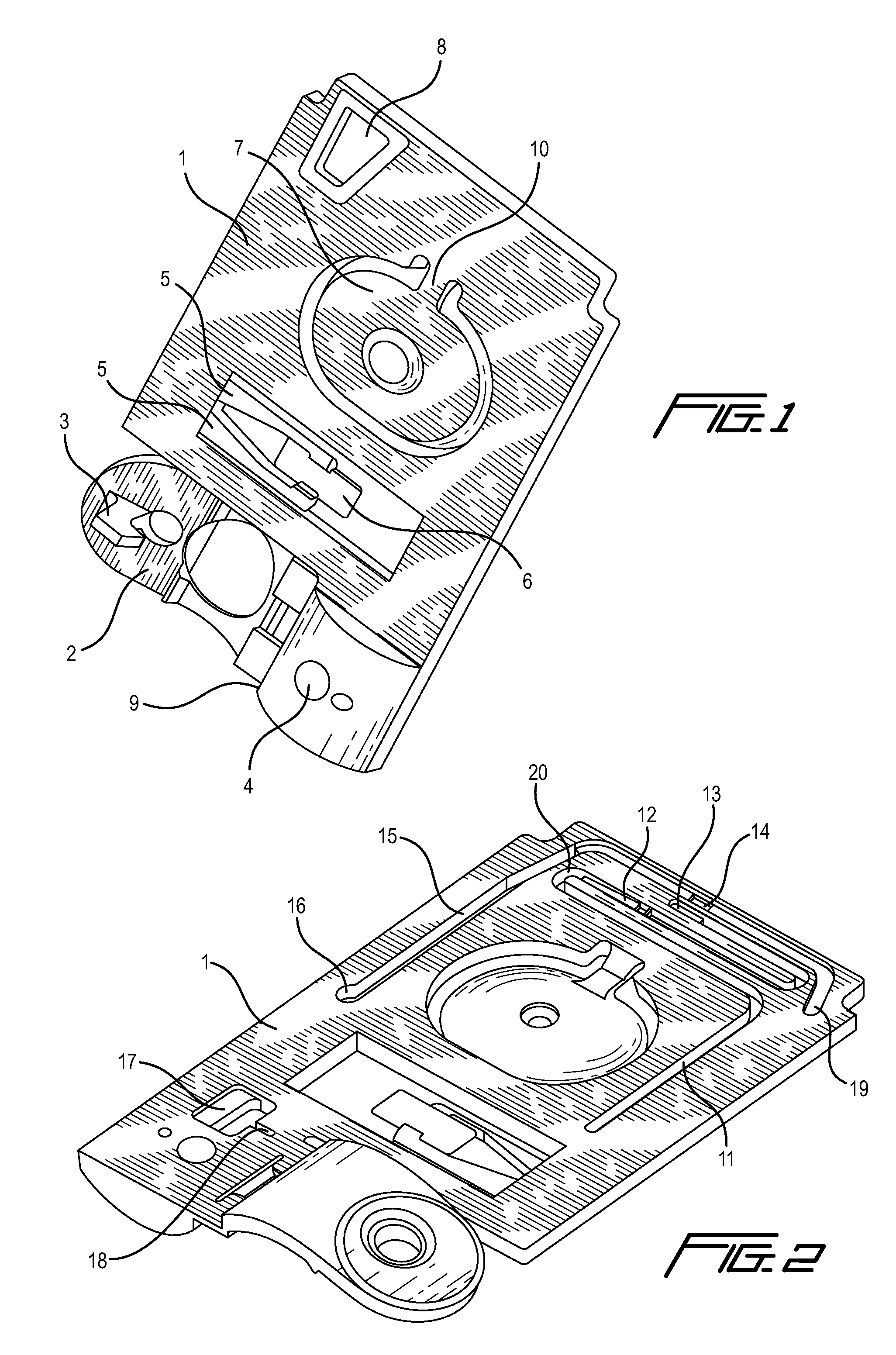
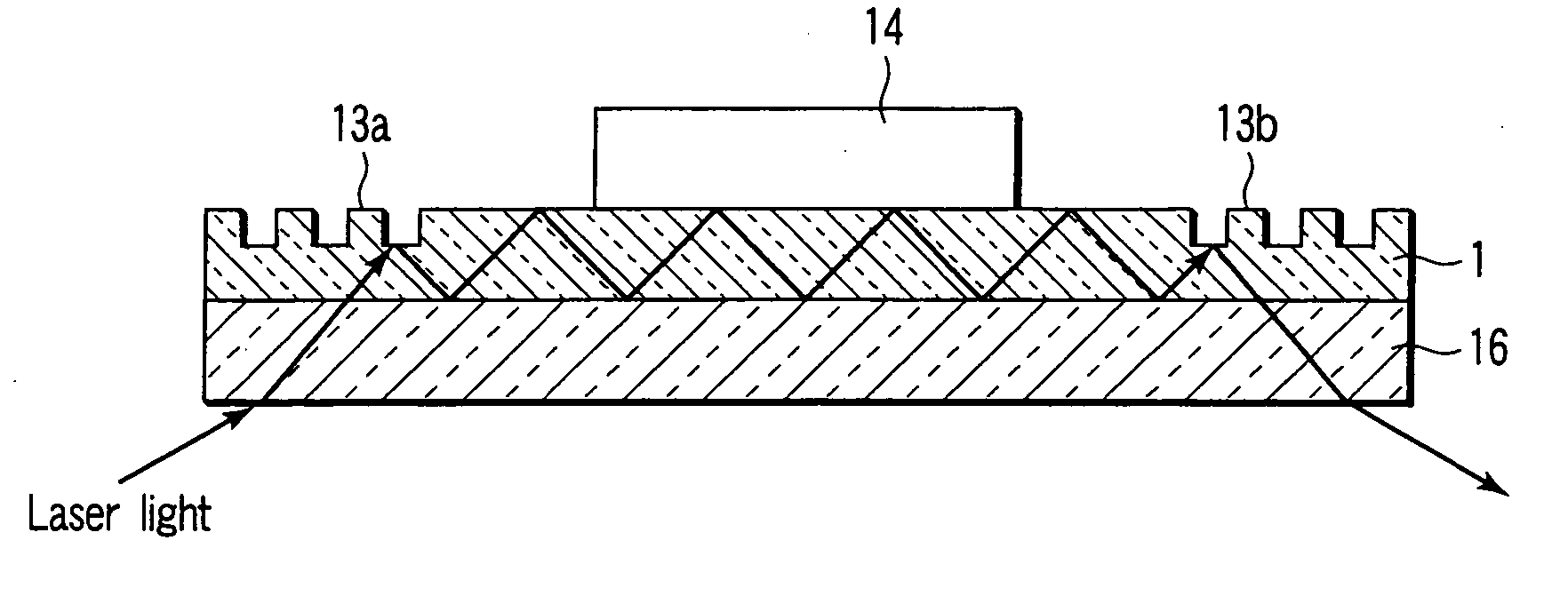
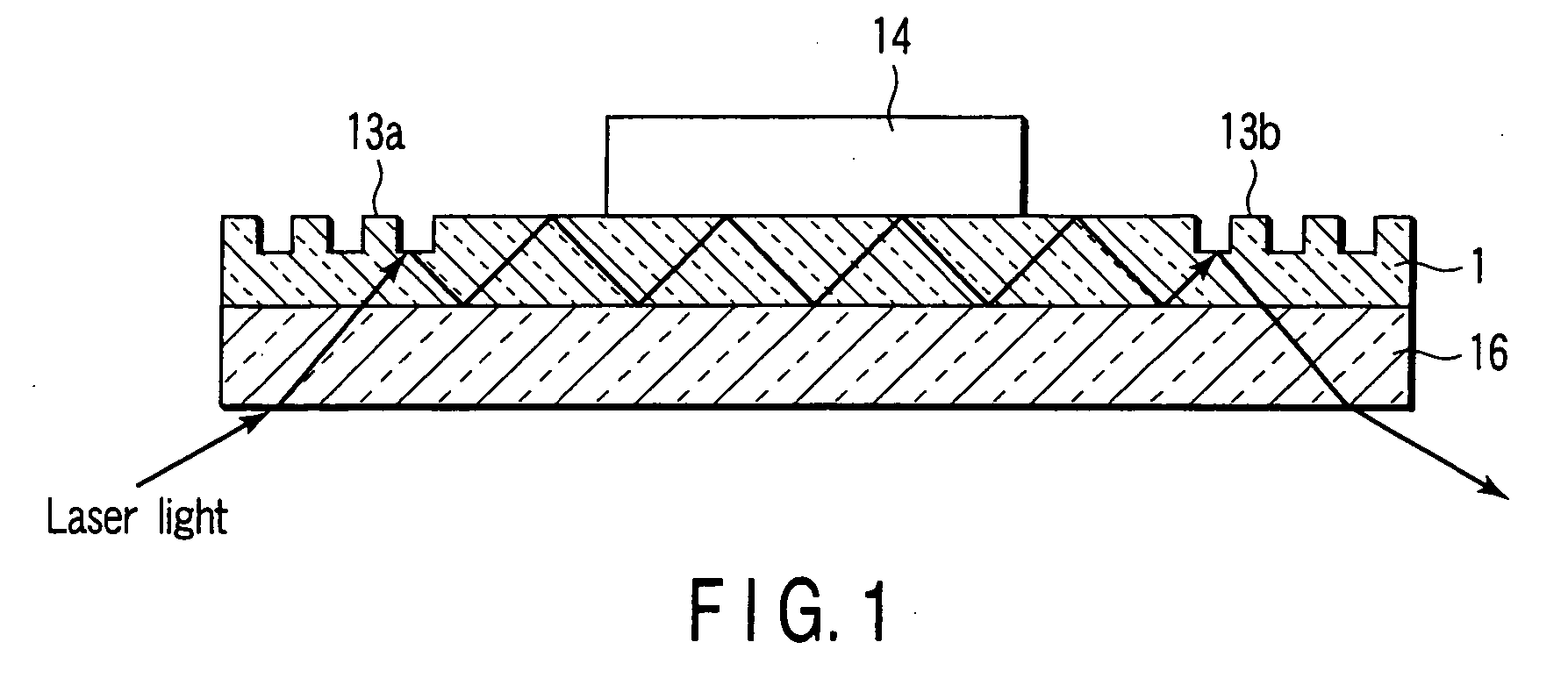
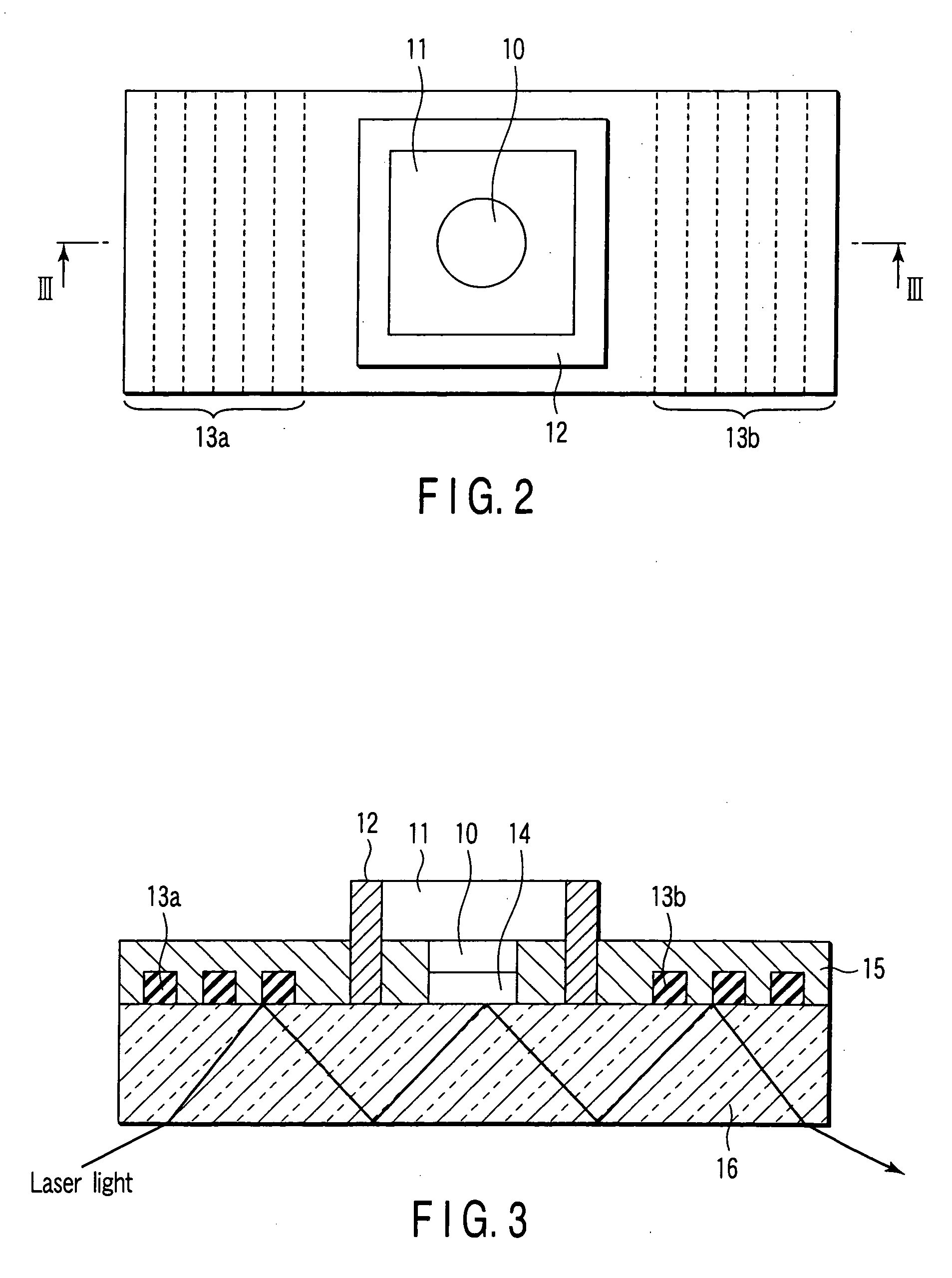
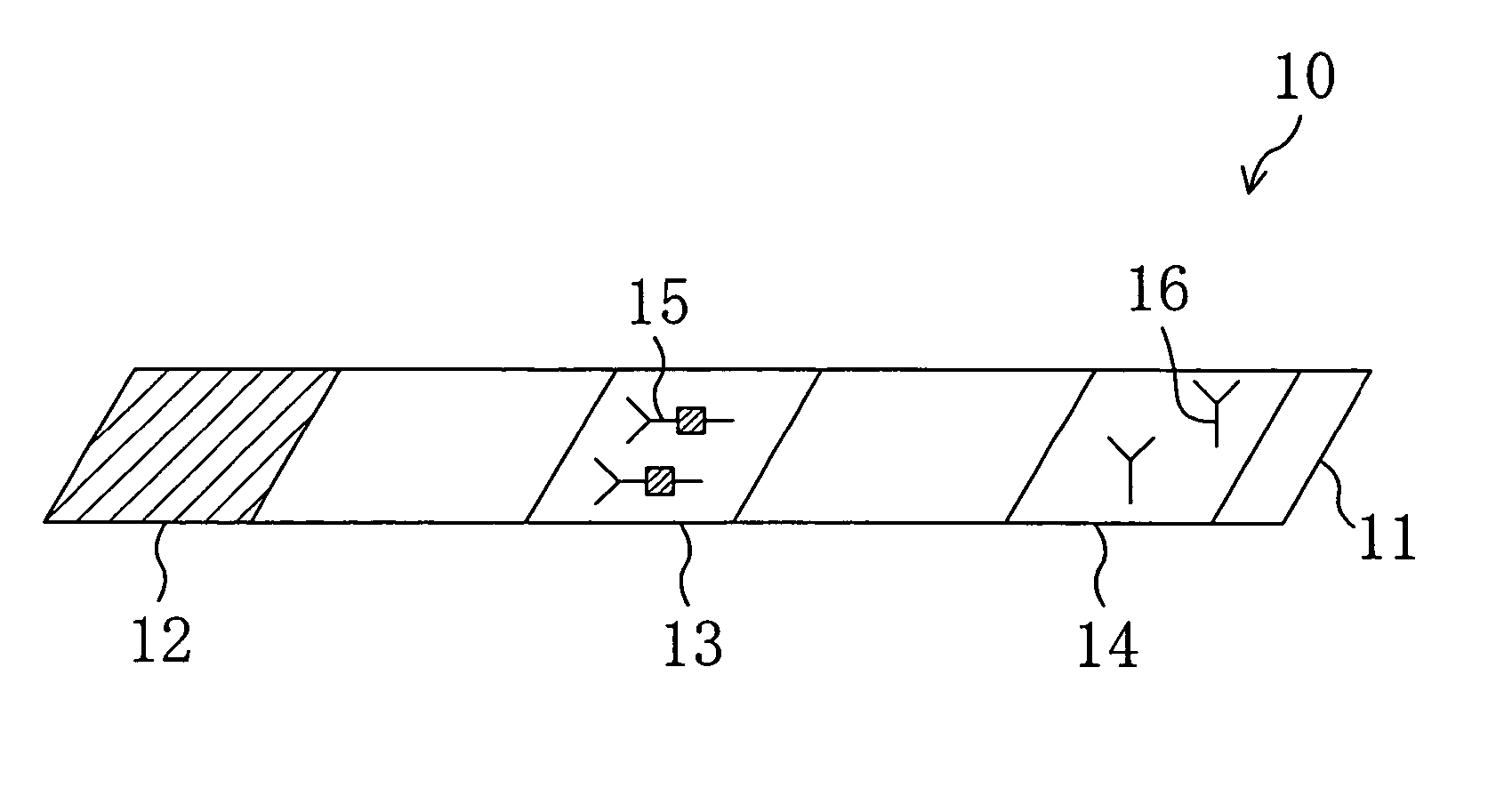
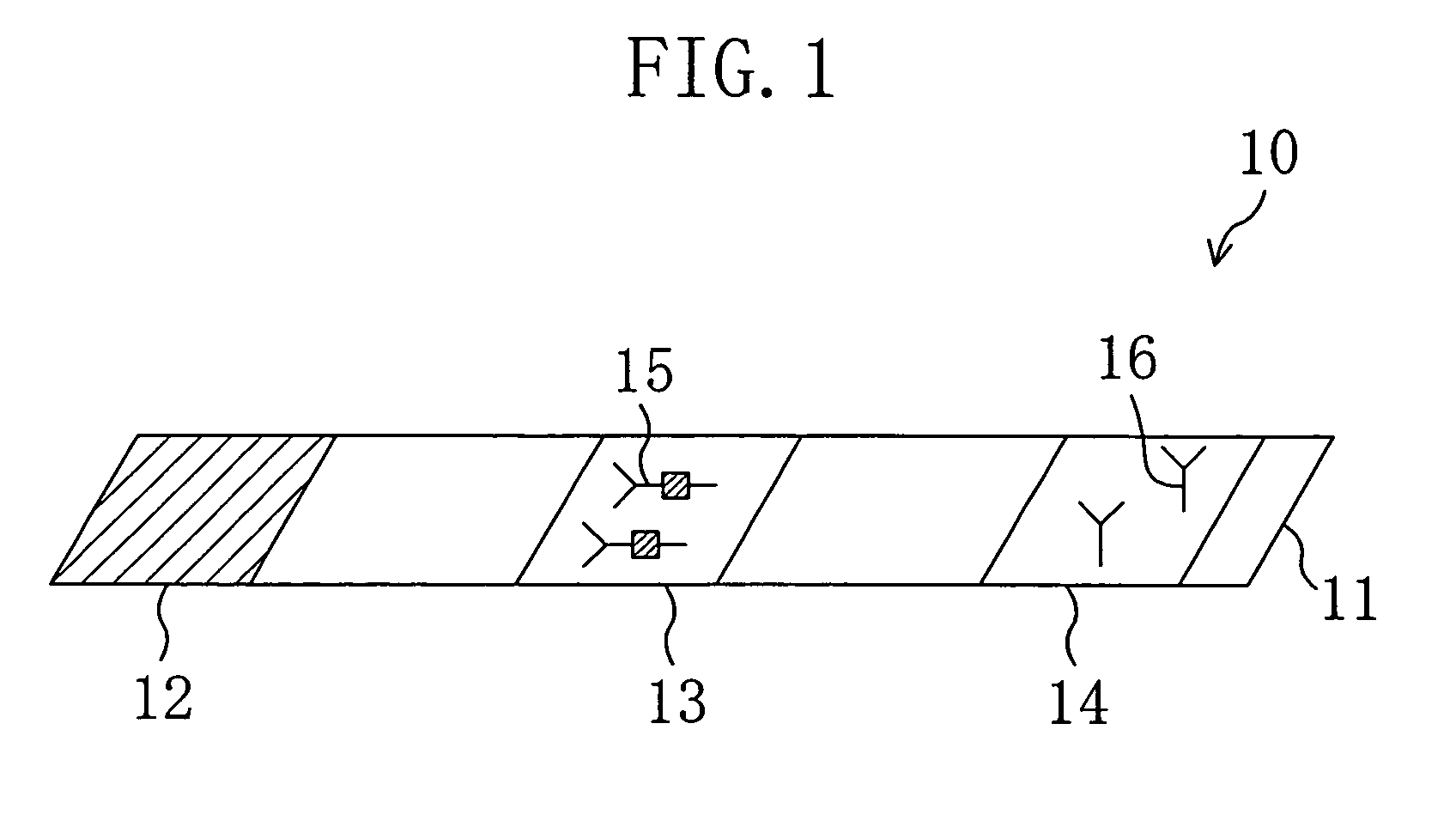
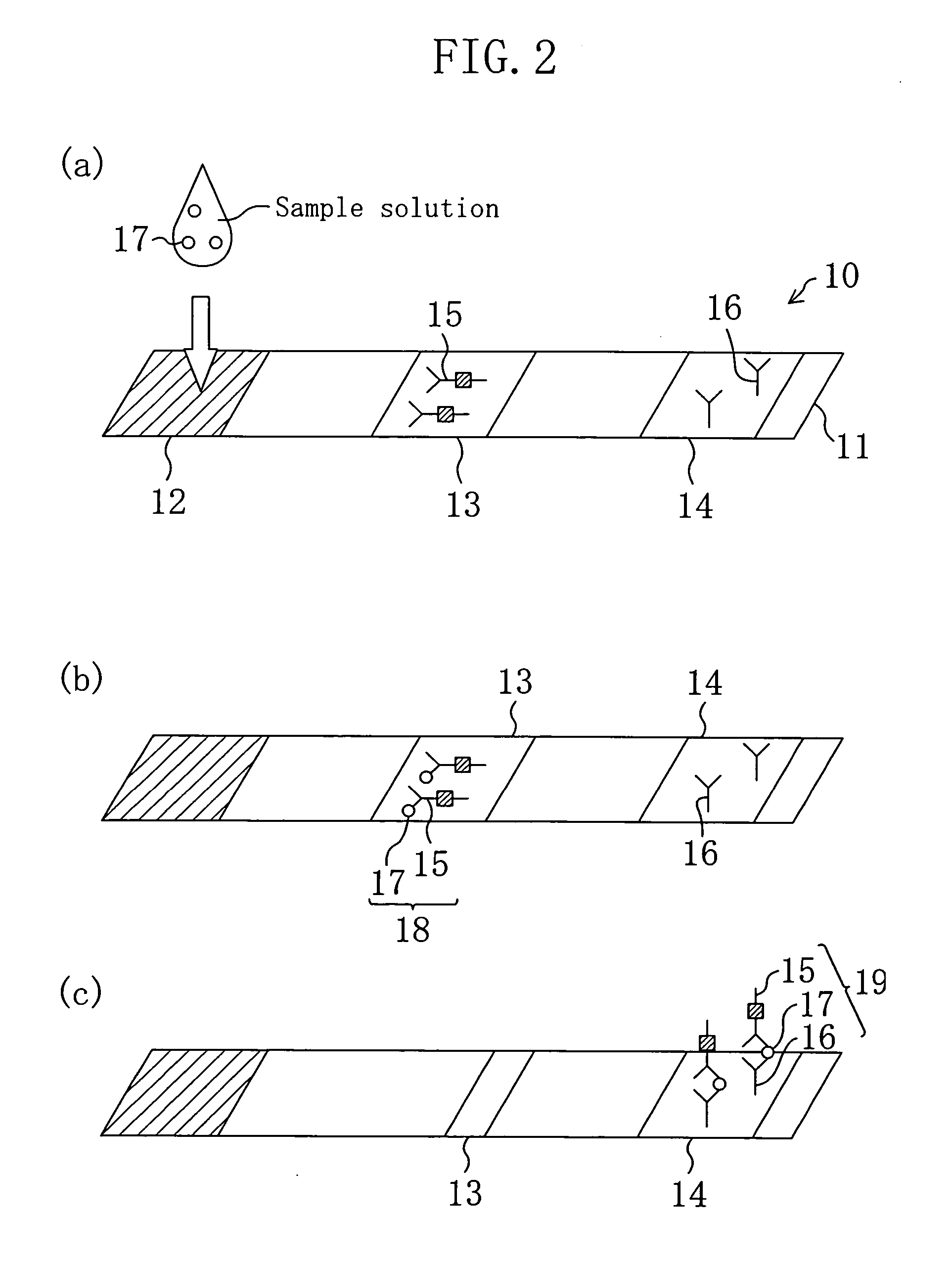
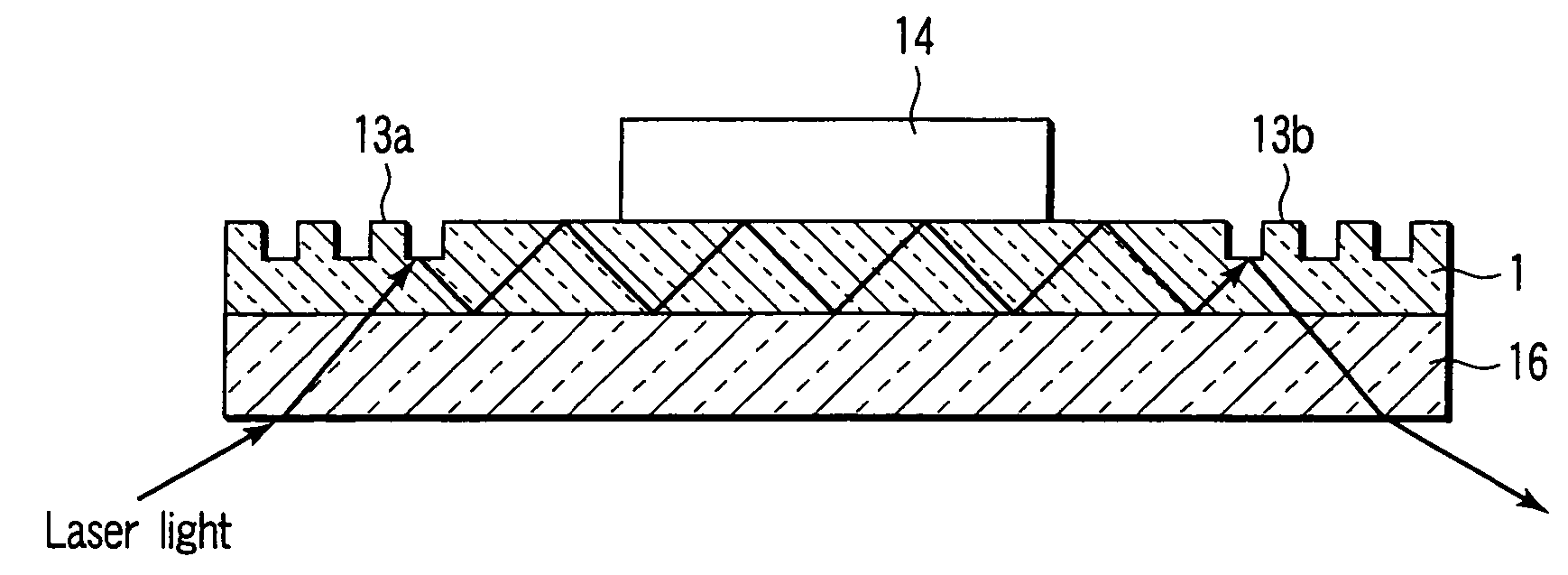
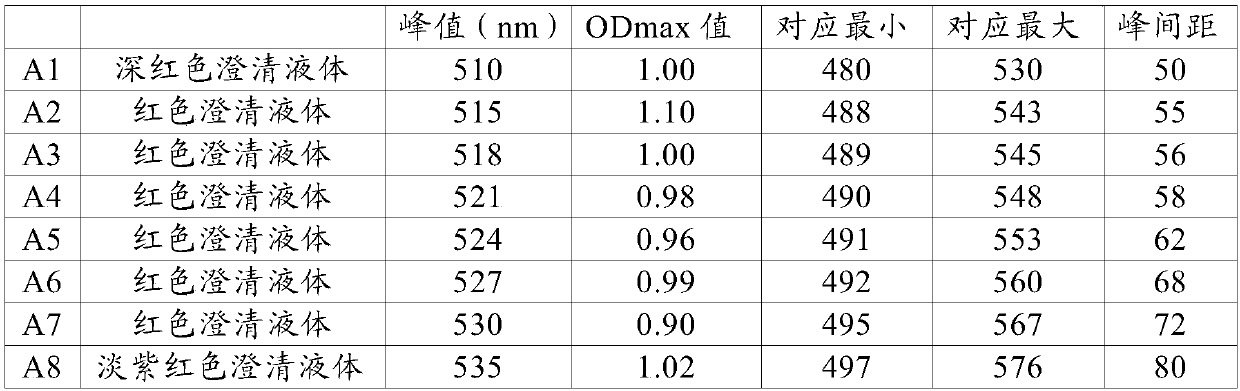
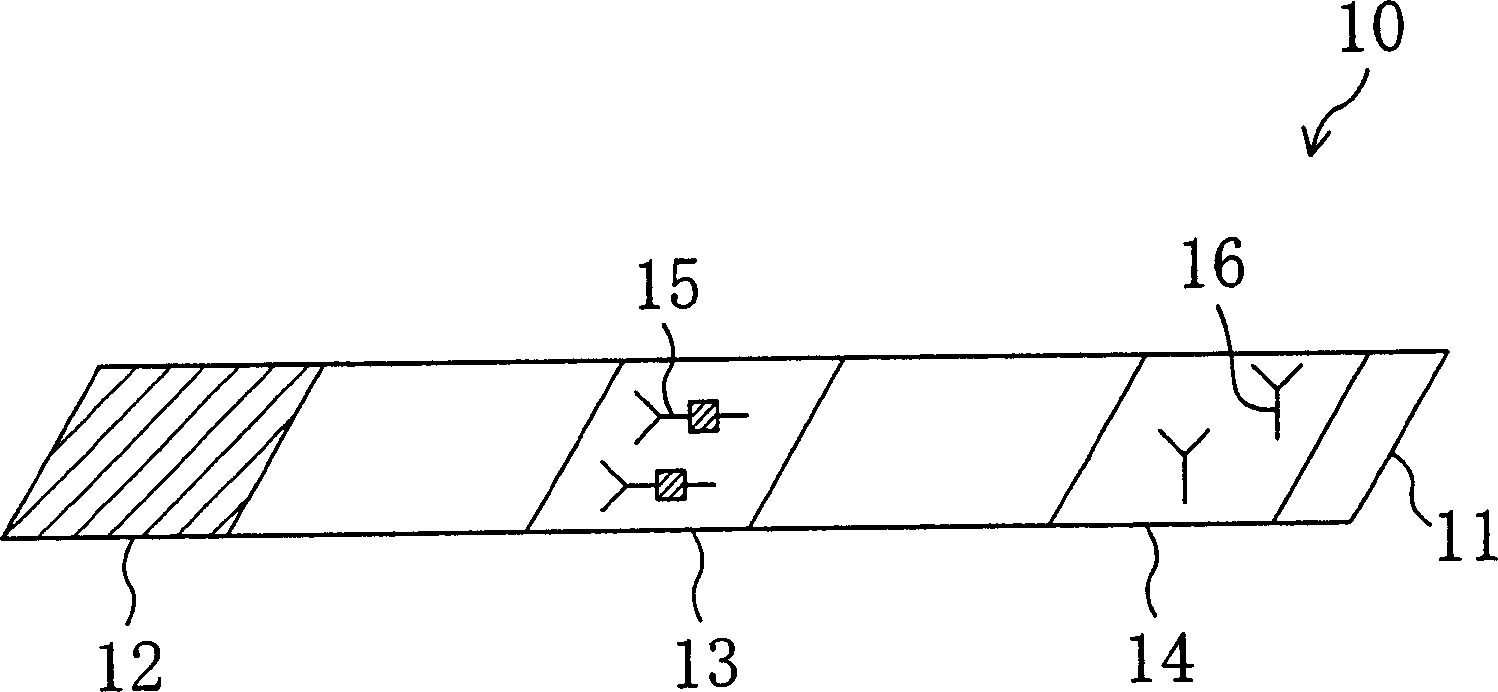
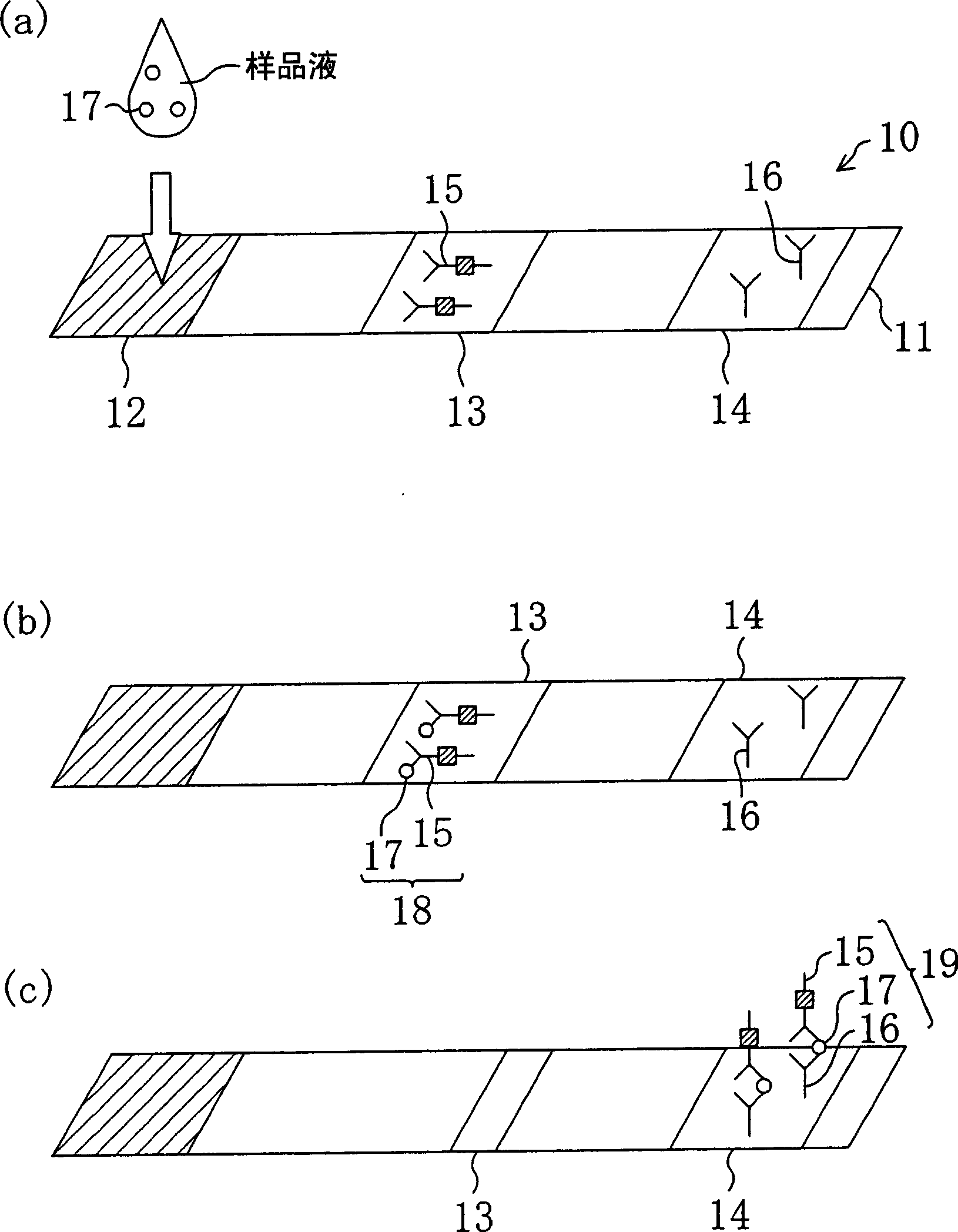
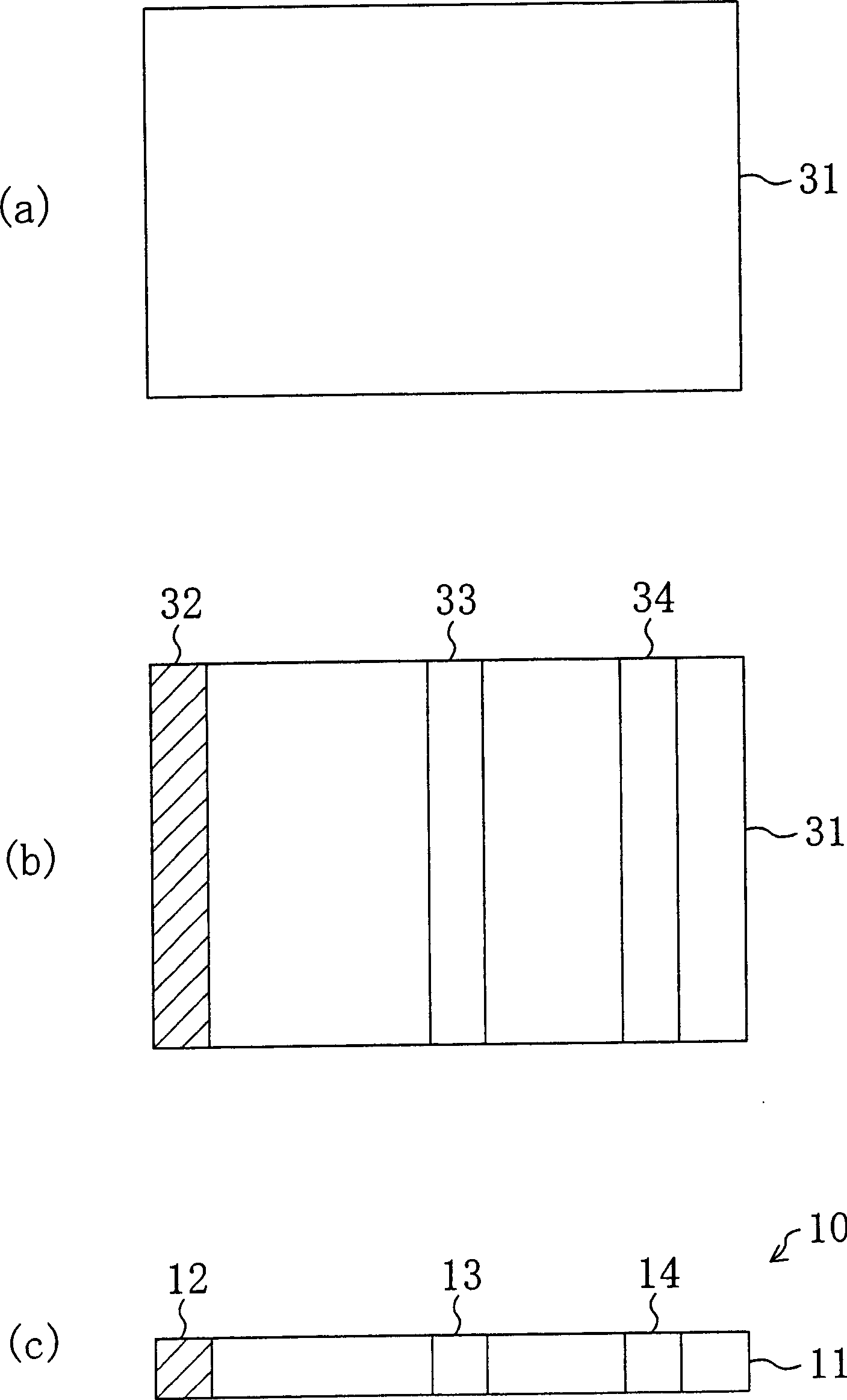
As shown in FIG. 1, an immunochromatography test strip 10 of the present embodiment is made of a base material 11 which includes a sample introduction section 12, a labeling section 13 and an immobilization section 14. The base material 11 is made of a material that is capable of being impregnated with a solvent of a sample solution containing a detection target substance. The material allows migration of a solvent of a sample solution by capillary action. The sample introduction section 12 is a region where a sample solution containing a detection target substance is introduced (e.g., dripped). The sample introduction section 12 contains a metal salt supported thereon. The labeling section 13 contains a labeled antibody 15, which is labeled with a labeling substance, in a state such that the labeled antibody 15 can be eluted into the sample solution. The labeled antibody 15 used herein specifically binds to a detection target substance. The immobilization section 14 contains an immobilized antibody 16. The immobilized antibody 16 used herein specifically binds to the detection target substance.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Simple immunochemical semi-quantitative assay method and apparatus
InactiveUS6582970B1Easy to adjustHigh sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalyteQuantitative determination
The present invention relates to a simple immunochemical semi-quantitative assay method according to chromatography, which comprises trapping a certain amount of an analyte in a sample with a predetermined amount of a fixed antibody for the analyte before qualitative analysis of the analyte, the certain amount corresponding to the amount of the fixed antibody, and thereby decreasing a concentration of the analyte to be subjected to subsequent immunochemical qualitative determination, and an apparatus therefor.
Owner:TEIKOKU HORMONE MFG
Concentration measuring method, concentration measuring kit, and sensor chip for use in the method
InactiveUS7498145B2Improve accuracyEasy to measureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmobilized AntibodiesWaveguide
The method for measuring the concentration of the measuring object uses a sensor chip comprising an optical waveguide layer and an antibody immobilized layer formed on the surface of the optical waveguide layer, which comprises immobilizing the measuring object and an enzyme-labeled antibody labeled with a labeling enzyme on the antibody immobilized layer of the sensor chip having an immobilized antibody, producing a color-developing and precipitating enzyme reaction product by allowing to react a coloring reagent with the labeling enzyme on the antibody immobilized layer to precipitate the enzyme reaction product on the antibody immobilized layer, allowing to totally reflect a light impinged on the sensor chip from the outside at an interface between the optical waveguide layer and the antibody immobilized layer, and observing to a physical value of the totally reflected light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
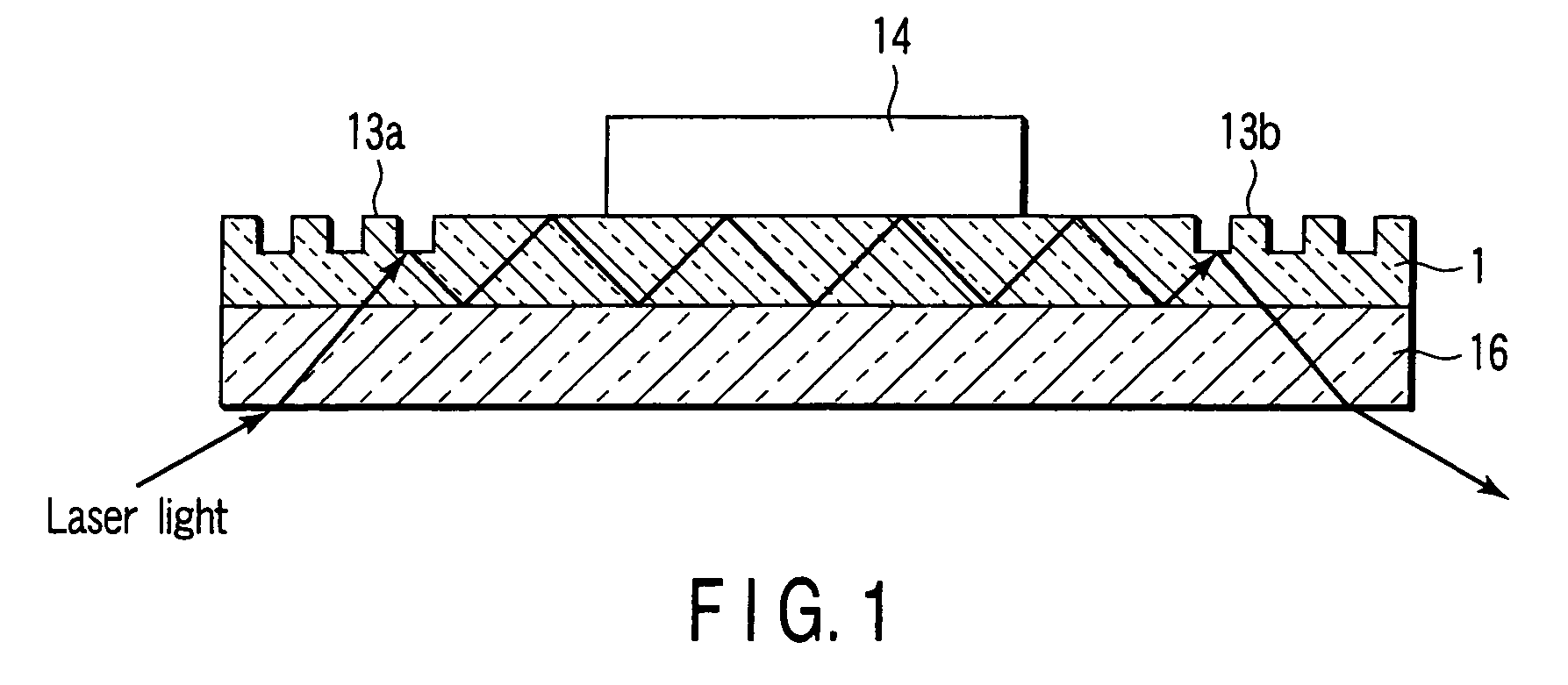
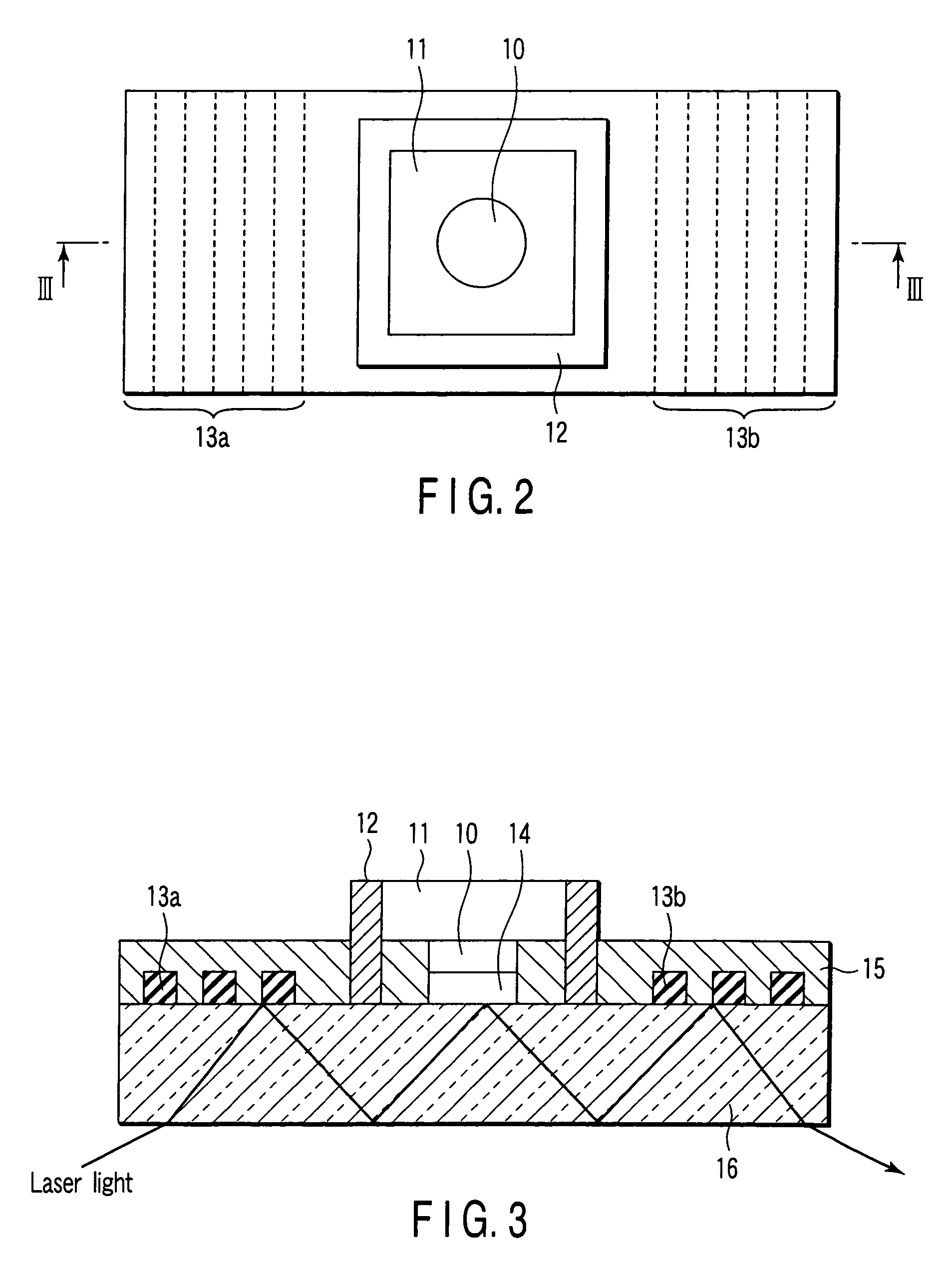
Apparatus and method for identifying a hook effect and expanding the dynamic range in point of care immunoassays
The present invention relates to systems and methods for the rapid in situ determination of the existence of a hook effect and expansion of the dynamic range of a point of care immunoassay. For example, a system for identifying a hook effect and expanding the dynamic range of an immunoassay is provided that may include a primary sensor having first immobilized antibodies that may be configured to generate a first signal based on a presence or absence of a target analyte in a sample. The system may further include an attenuated sensor having second immobilized antibodies at a reduced concentration relative to a concentration of the first immobilized antibodies on the primary sensor and that may be configured to generate a second signal based on the presence or absence of the target analyte in the sample. The system may further include a processor configured to determine a presence of a hook effect in the immunoassay based on relative values of the first and second signals and optionally determine the target analyte concentration of the sample.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Ultrasensitive immunoassays
InactiveUS20050233351A1Reduce the numberMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyImmobilized AntibodiesOligonucleotide
The present invention relates to an immunological test kit and immunoassay using a first immobilized antibody having affinity for a specific antigen. The invention is characterized by a second and third antibody being specific for different determinants of the antigen and modified with cross-linkable oligonucleotides. For detection, the oligonucleotides are amplified, whereby only such oligonucleotides will be amplified which have been cross-linked to each other. In this way unspecific background is avoided and detection is possible down to single molecules.
Owner:LANDEGREN ULF
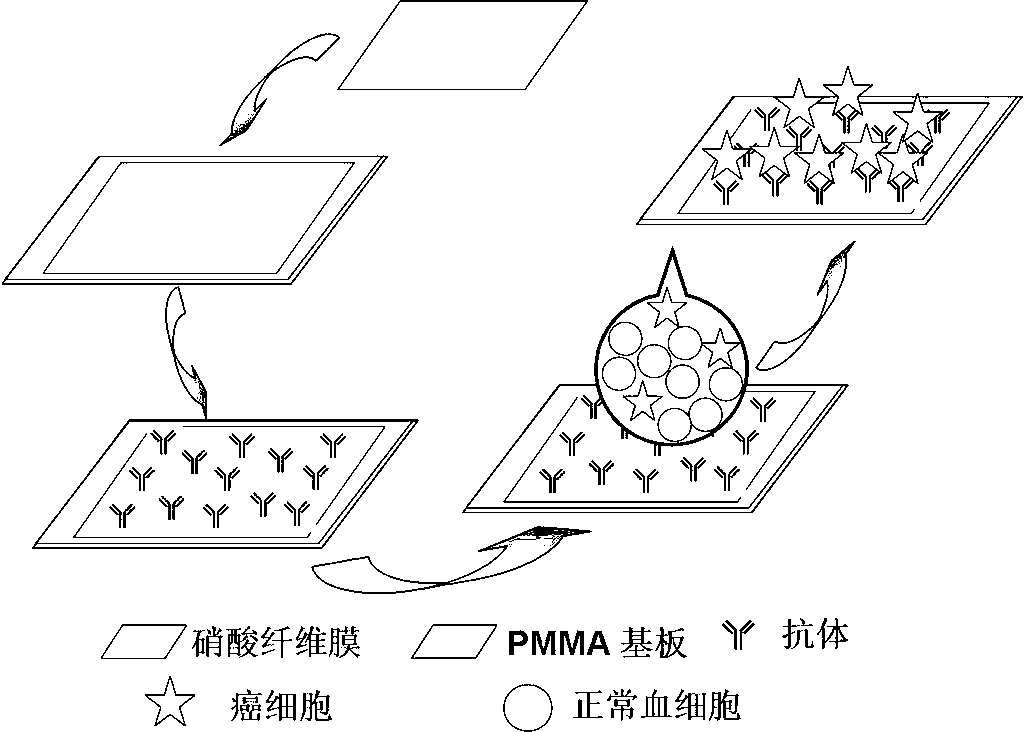
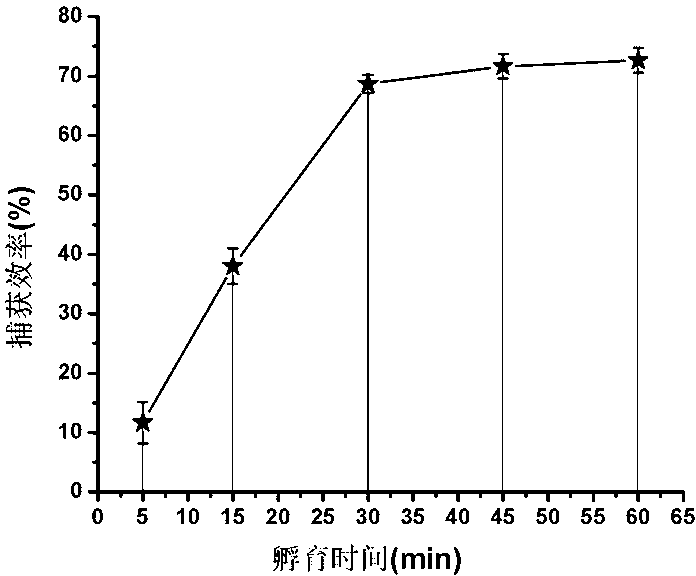
Nitrocellulose-membrane-based chip for conveniently capturing cancer cells
InactiveCN103235124AGood biocompatibilityImprove efficiencyMaterial analysisNon small lung cancerAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioanalysis and detection, and in particular relates to a circulating tumor cell (CTC) capturing chip as well as a manufacturing method and an application thereof. A nitrocellulose membrane is used as a main body of a CTC chip, an antibody is fixed by using the ultrastrong adsorption capacity of the nitrocellulose membrane for proteins, and further cancer cells in blood are specifically captured. Experiment results show that the CTC chip has very high capturing efficiency for non-small lung cancer cells NCI-H1650 and successfully separates and detects micro cancer cells in human whole blood. The CTC capturing chip is novel and convenient, practical and high-efficient and great in clinical popularization and application potentials.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
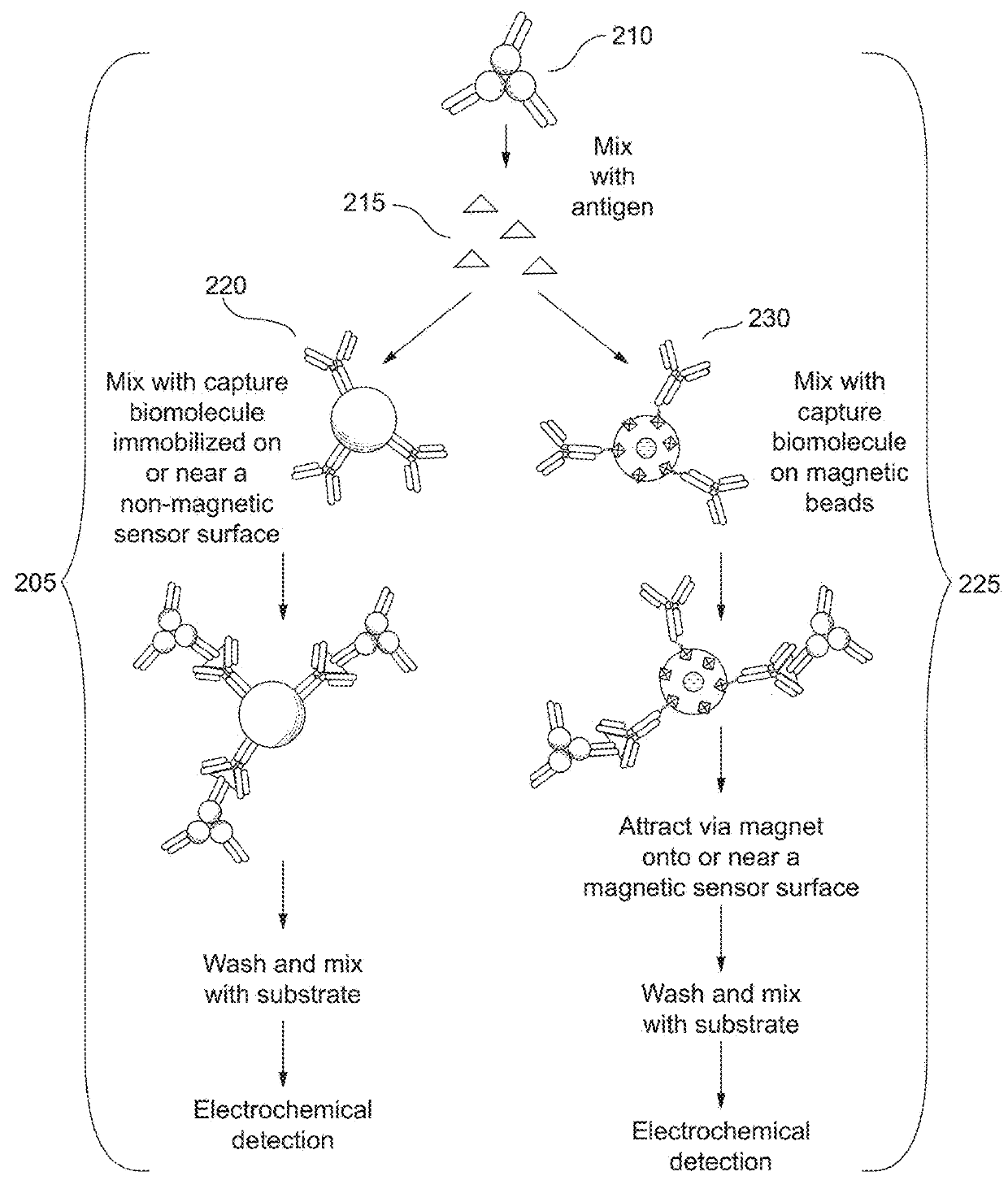
Combined immunoassay and magnetic immunoassay systems and devices for extended range of sensitivity
ActiveUS20180164303A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresImmobilized AntibodiesAnalyte
The present invention relates to systems that utilize a combination of immunoassay and magnetic immunoassay techniques to detect an analyte within an extended range of specified concentrations. In particular, a device is provided for detecting an analyte in a biological sample. The device includes a first electrochemical sensor positioned on a substrate. The first electrochemical sensor includes an immobilized layer of antibody configured to bind to the analyte. The device further includes a second electrochemical sensor positioned adjacent to the first electrochemical sensor on the substrate, and a magnetic material that generates a magnetic field aligned with respect to the second electrochemical sensor. The magnetic field captures magnetic beads that have an immobilized layer of antibody configured to bind to the analyte, and concentrates the magnetic beads on or near a surface of the second electrochemical sensor.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
Highly cost-effective analytical device for performing immunoassays with ultra high sensitivity
InactiveUS7087389B2Highly cost-effectiveEasy to manufactureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAdhesiveWater insoluble
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
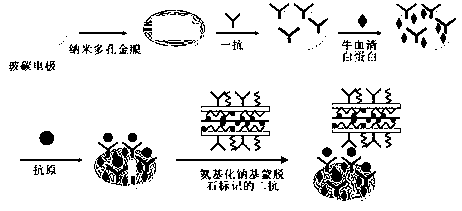
Preparation based on tumor marker sensor of sodamide group smectite and application
InactiveCN102998449AHigh sensitivityGood biocompatibilityMaterial electrochemical variablesImmobilized AntibodiesEngineering
The invention discloses a sandwich type electrochemistry immunosensor which is prepared based on a sodamide group smectite and a nanometer multi-hole gold membrane, and belongs to the technical field of function materials and biological sense. The sandwich type electrochemistry immunosensor provided by the invention can carry out amido functionalization on the sodium group smectite, an antibody and enzyme are conveniently fixed, and meanwhile, the favorable biological activities of the antibody and the enzyme are kept; a favorable three-dimensional serial perforated structure and biocompatibility of the nanometer multi-hole gold membrane are utilized, and the favorable catalytical property of the antibody is directly fixed, and the sensitivity of the sensor is notably improved; and the sodium group smectite which is cheap and is easily available is utilized, and the cost of the sensor is greatly reduced. The sandwich type electrochemistry immunosensor provided by the invention can realize high sensitiveness and specificity and rapid exact detection of multiple tumor markers.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Canine parvovirus colloidal gold immunochromatography test strip and preparation method
InactiveCN103604924AQuick checkMeet the needs of on-site testingBiological material analysisPolyesterNitrocellulose
The invention discloses a canine parvovirus colloidal gold immunochromatography test strip and a preparation method. The test strip comprises a sample absorbing area, a gold label probe area, an immobilized antibody area, a water absorbing area and a bottom plate, wherein the sample absorbing area, the gold label probe area, the immobilized antibody area and the water absorbing area are sequentially paved on the bottom plate and partially overlapped each other; the gold label probe area is coated with a colloidal gold labeled anti-canine parvovirus monoclonal antibody F1; the immobilized antibody area is sequentially provided with a test line and a control line, the test line is coated with an anti-canine parvovirus monoclonal antibody B6, and the control line is coated goat anti-mouse IgG (immunoglobulin G). According to the preparation method, a glass fiber membrane, a polyester membrane coated with the anti-canine parvovirus monoclonal antibody F1, a nitrocellulose membrane coated with the test line and the control line, and water absorbing filter paper are assembled onto a polyethylene plate to obtain the canine parvovirus colloidal gold immunochromatography test strip. The test strip is fast to test, high in accuracy rate, high in specificity, and simple and convenient to carry and operate.
Owner:WUHAN CHOPPER BIOLOGY
Porcine circovirus 2 (PCV2) antibody colloidal gold immunity chromatography detection test paper and making method thereof
InactiveCN103364561AQuick checkMeet the needs of on-site testingMaterial analysisImmobilized AntibodiesMonoclonal antibody
The invention discloses a PCV2 antibody colloidal gold immunity chromatography detection test paper and a making method thereof. The test paper comprises a sample absorption zone, a colloidal-gold probe zone, an immobilized antibody zone, a water absorption zone and a support plate, and the sample absorption zone, the colloidal-gold probe zone, the immobilized antibody zone and the water absorption zone are laid on the support plate and sequentially partially overlap with each other; the sample absorption zone is coated with PCV2-Cap proteins; the colloidal-gold probe zone is coated with a colloidal-gold probe 1 and a colloidal-gold probe 2 which are colloidal-gold labeled PCV2 monoclonal antibody and rabbit IgG respectively; and the immobilized antibody zone is sequentially coated with a contrast line C1 coated goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody, a test line T coated goat anti-pig IgG antibody, a contrast line C2 coated goat anti-rabbit IgG antibody and a contrast line C3 coated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody. The test paper has the advantages of rapid detection, high accuracy, strong specificity, and convenient carrying and operation, and is used for determining the level of the PCV2 antibody according to the deepness of the color of the contrast line.
Owner:WUHAN CHOPPER BIOLOGY
Detection, isolation and analysis of rare cells in biological fluids
InactiveCN104364389AMeeting urgent needsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisImmobilized AntibodiesRare cell
Owner:KELLBENX
Method for quantitative detection of biological toxins
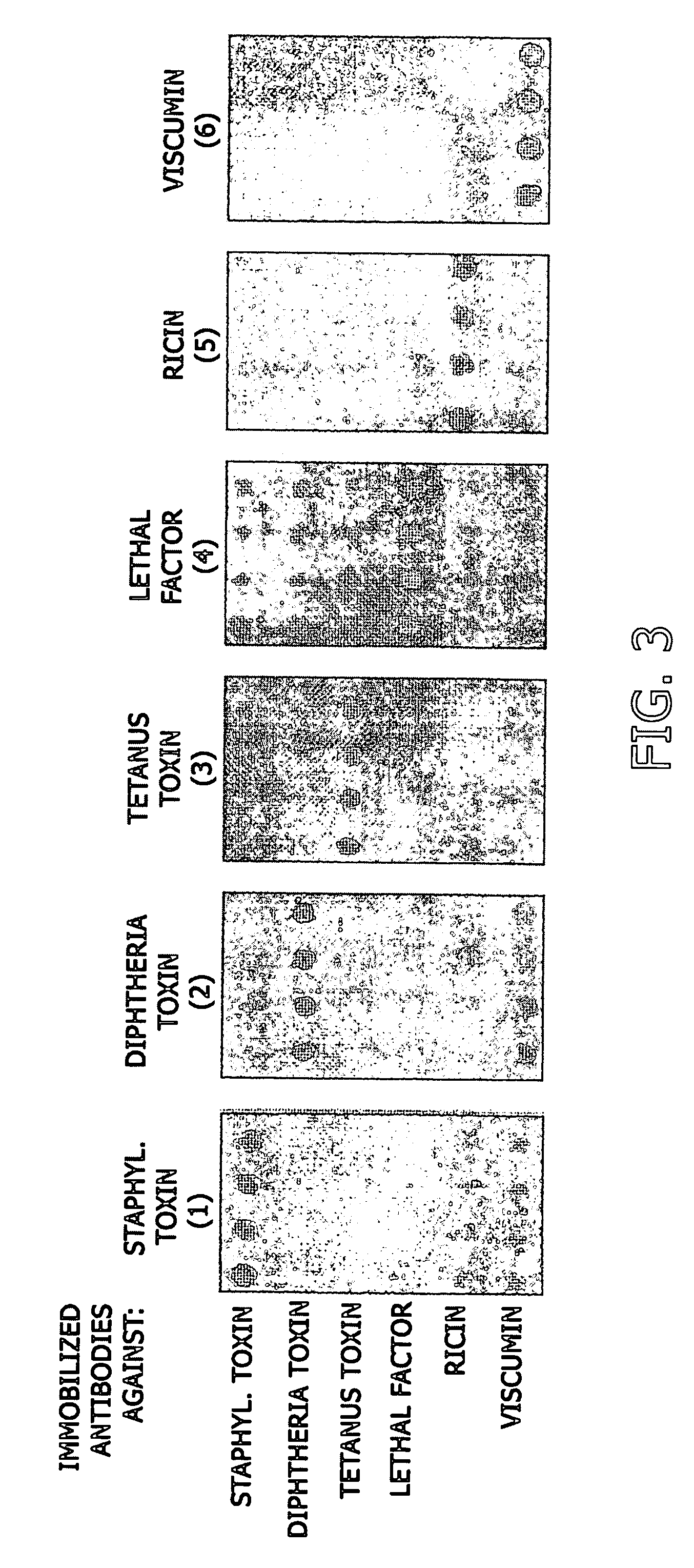
InactiveUS20070172904A1Overcome disadvantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyFood industryImmobilized Antibodies
The invention relates to analytical chemistry and to quantitative immunochemical analysis, in particular, to a method for immunochemical quantitative detection of various biological toxins by using biological microchips. A biological microchip comprises an ordered array of three-dimensional hydrogel cells on a solid support, which are produced by a method of photo- or chemically induced polymerization and contain immobilized antibodies to various bacterial, plant and animal biotoxins, or biotoxins. The use of microchips makes it possible to analyze a sample simultaneously for the presence of several biotoxins. The proposed method for detecting biotoxins can be used in medicine, in food industry, and in environmental protection.
Owner:INST MOLEKULJARNOJ BIOLOGII IM V A EHNGELGARDTA RAN +1
Microorganism sample rapid detection method and detection device thereof
ActiveCN102879565AHigh sensitivityIncrease fixed amountMaterial analysisImmune complex depositionBiology
The invention discloses a microorganism sample rapid detection method and a detection device thereof, which is realized by a mesoporous biochip. The detection method comprises the following steps: firstly fixing antibodies on micropore tunnel surfaces of a mesoporous biochip, allowing a test sample to flow through the chip micropore tunnels with the antibodies fixed so as to realize separation and enrichment of pathogenic microorganisms or other biological substances by the chip, then injecting a solution containing a fluorescence-labeled or an enzyme-labeled antibody into the chip micropore tunnel to form a sandwich-type antibody-antigen-labeled antibody immune complex, and detecting the pathogenic microorganisms or other biological substances by detecting the fluorescence intensity of the fluorescence-labeled antibody or the light absorption or chemiluminiscence intensity of the product of the enzymic catalytic reaction so as to realize the detection of the microorganisms to be detected. The mesoporous biochip has a great number of micropore tunnels, which greatly increases the reaction area, and thus when used for microorganism sample detection, the detection method and the detection device of the invention have the characteristics of high detection sensitivity and high detection speed.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method and application of sandwich type photoelectrochemical sensor for detecting prostate specific antigen
ActiveCN110927238AImprove conductivityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesPsa antigenDoped graphene
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a sandwich type photoelectrochemical sensor for detecting a prostate specific antigen (PSA). Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQDs) and cadmium sulfide (CdS) quantum dots double-sensitized sea urchin-shaped titanium dioxide (TiO2) are used as photoactive materials to be immobilized on the surface of the conductive glass. The compound of electron holes (e<-> / h<+>) is effectively inhibited, a remarkable photocurrent signal is generated, and rich functional groups are provided for immobilizing PSA antibodies. A gold-carbon nanotube (Au / MWCNTs) nano-composite is adopted as a label of a second antibody, and exciton-plasma resonance (EPI) is generated according to different mechanisms. In the system, Au NPs are enabled to generate surface plasma resonance (SPR) in an optical excitation state. Along with the energy resonance transfer (ET) process, the photocurrent intensity is reduced to a certain extent, and the sensitivity of the sensor is improved. In addition, Au / MWCNTs have a large surface area and biocompatibility. The loading capacity of the second antibody is increased, due to the fact that the steric hindrance effect hinders electron transfer, the photocurrent is reduced, the sensitivity of the sensor is further improved, specific detection of the prostate specific antigen is achieved, a novel and feasible detection method is provided for early detection of PSA, and the prostate specific antigen sensor has potential application prospects in clinic.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Microfluidic chip for detection of tumor marker group
ActiveCN106706916AEnable self-service testingPainlessMaterial analysisImmobilized AntibodiesQuality control
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip for detection of a tumor marker group; the microfluidic chip comprises a base plate and a cover plate positioned above the base plate; the cover plate is provided with a blood collecting microneedle array, and the interior of each blood collecting microneedle is provided with a microtube; the cover plate and the base plate are glued or are subjected to thermocompression bonding to form an overflow chamber, a sample introduction chamber, a reaction chamber, a capillary flow passage and a waste liquid chamber; the sample introduction chamber communicates with the reaction chamber in a vertical space; the sample introduction chamber is internally provided with water absorbent paper and filter paper; the reaction chamber is located below the filter paper, the reaction chamber is internally provided with a microcolumn array, the bottom surface of the reaction chamber and the surface of the microcolumn array are coated with labelled antibodies coupled with chromophoric groups; the bottom of a tail end region of the capillary flow channel is provided with a plurality of test strips and quality control strips printed with immobilized antibody reagents. The self-service detection is achieved, assistance of professional devices is not needed, and an examinee operates the device by self. The blood collecting volume is extremely low, and only a drop of fingertip blood is needed and can be used for detecting various tumor marker indexes at the same time.
Owner:孙翠敏
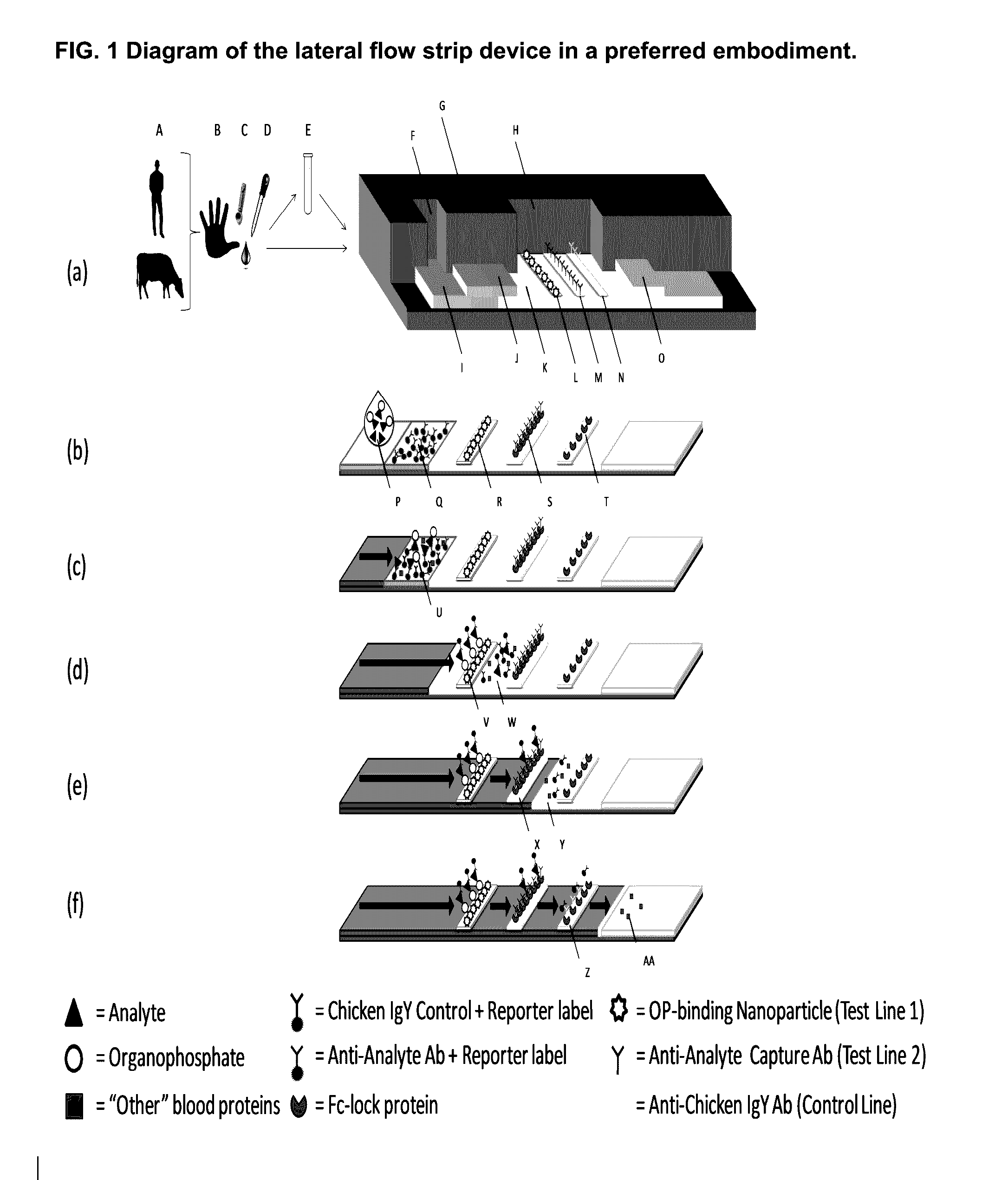
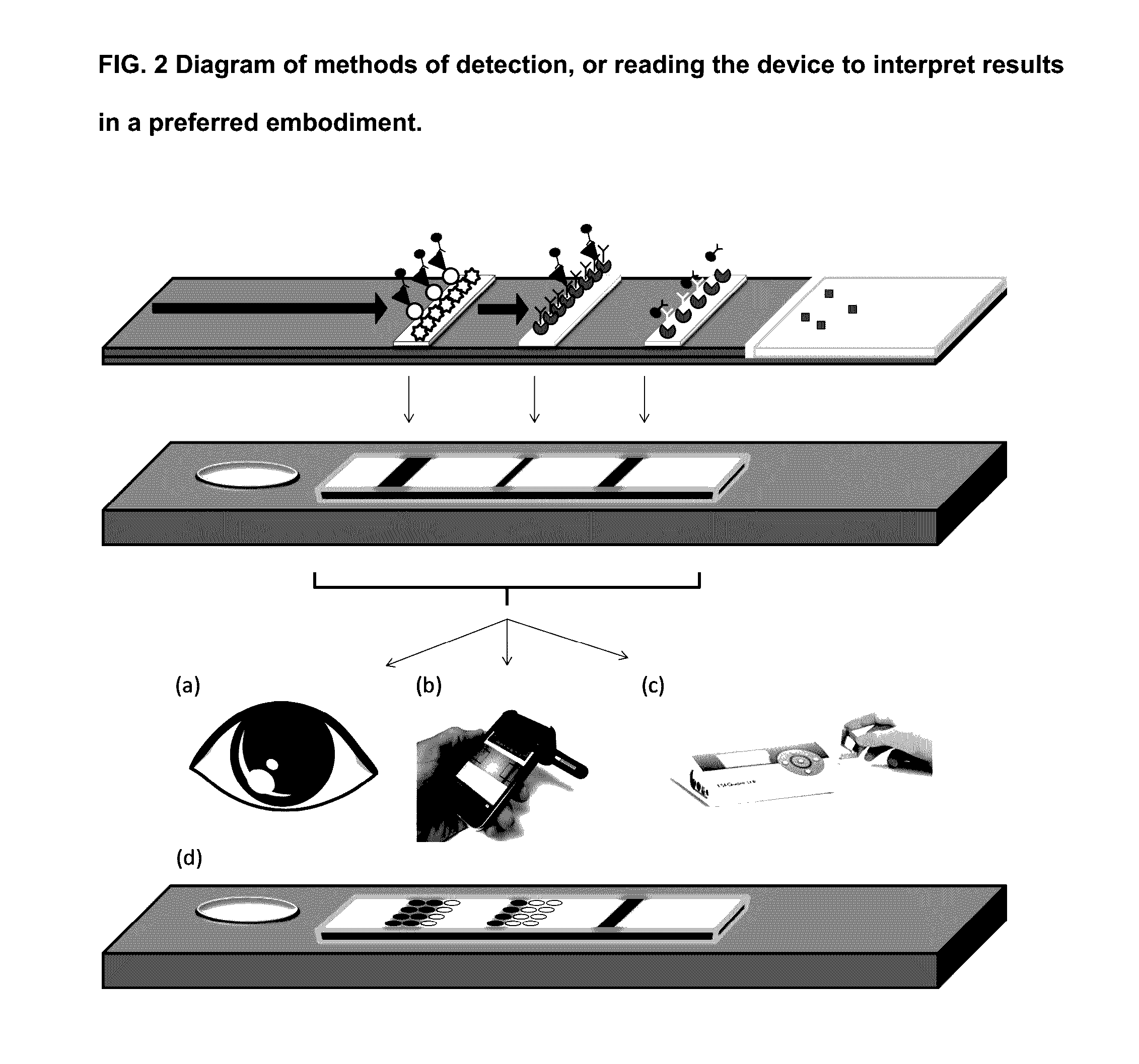
Detection of the degree of exposure to chemical warfare nerve agents and organophosphate pesticides with lateral flow assays
A sample analysis device used to detect a level of exposure of organophosphorus within a sample comprising a sample collection pad, at least one conjugate zone comprising an anti-analyte antibody that is conjugated with a reporter label, and a control antibody that is conjugated with a reporter label, a blocking and / or test zone comprising an immobilized nanoparticle or other molecule that captures the Organophosphate-bound analyte, a second blocking and / or test zone comprising an immobilized antibody that binds to the unbound analyte and an optional third blocking and / or control zone comprising an immobilized antibody that binds to the control molecule wherein, when the analyte is bound by the Organophosphate in the sample it will bind to the first test line, and if the analyte is “free’ from the Organophosphate it will bind to the second test line, and the control antibody will bind to the control line.
Owner:COUNTERVAIL CORP
Method for constructing electrochemical luminescence sensor based on double amplification of perylenetetracarboxylic acid signals of cobalt-based metal organic framework
ActiveCN111208178AReliable resultsHigh luminous intensityMaterial electrochemical variablesLuminous intensityMetal-organic framework
The invention discloses a method for constructing an electrochemical luminescence sensor based on double amplification of perylenetetracarboxylic acid signals of a cobalt-based metal organic framework. According to the method, perylenetetracarboxylic acid PTCA is loaded on ZIF-67 as a luminous body to form PTCA(at)ZIF-67 as a signal probe, wherein the ZIF-67 is used as a reinforcing agent and cancatalyze S2O8 < 2-> to generate more SO4 <-> so that double amplification of signals is realized. Besides, heptapeptide HGC is introduced to fix the antibody so that the biological activity of the sensor is maintained, the incubation efficiency of the antibody is improved and the sensitivity of constructing the sensor is greatly improved. The beta-amyloid protein A beta with different concentrations can be combined with different amounts of secondary antibody markers Ab2-Au-PTCA (at) ZIF-67 so that the luminous intensity of the sensor is changed and the ultra-sensitive detection of the A betais realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
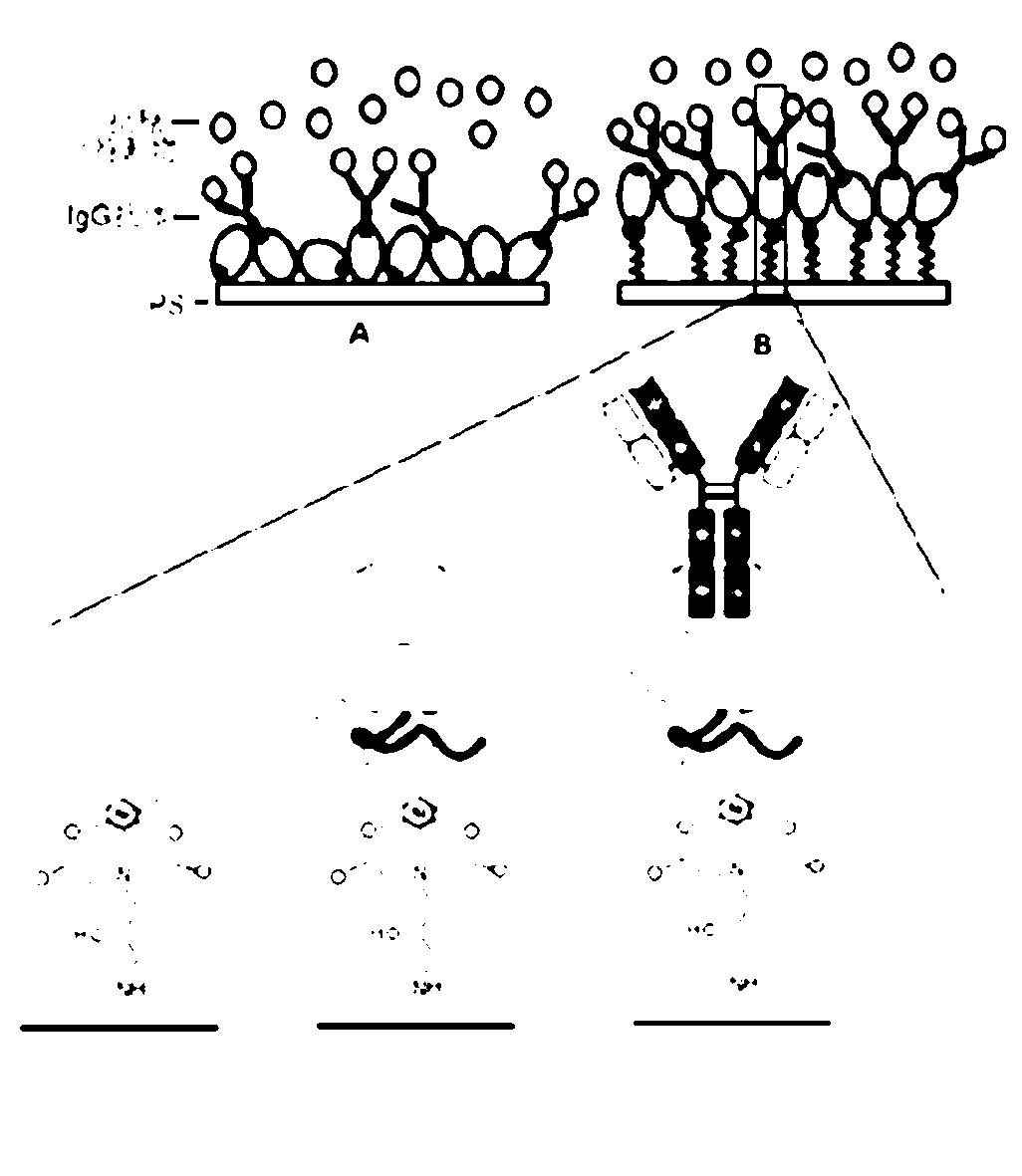
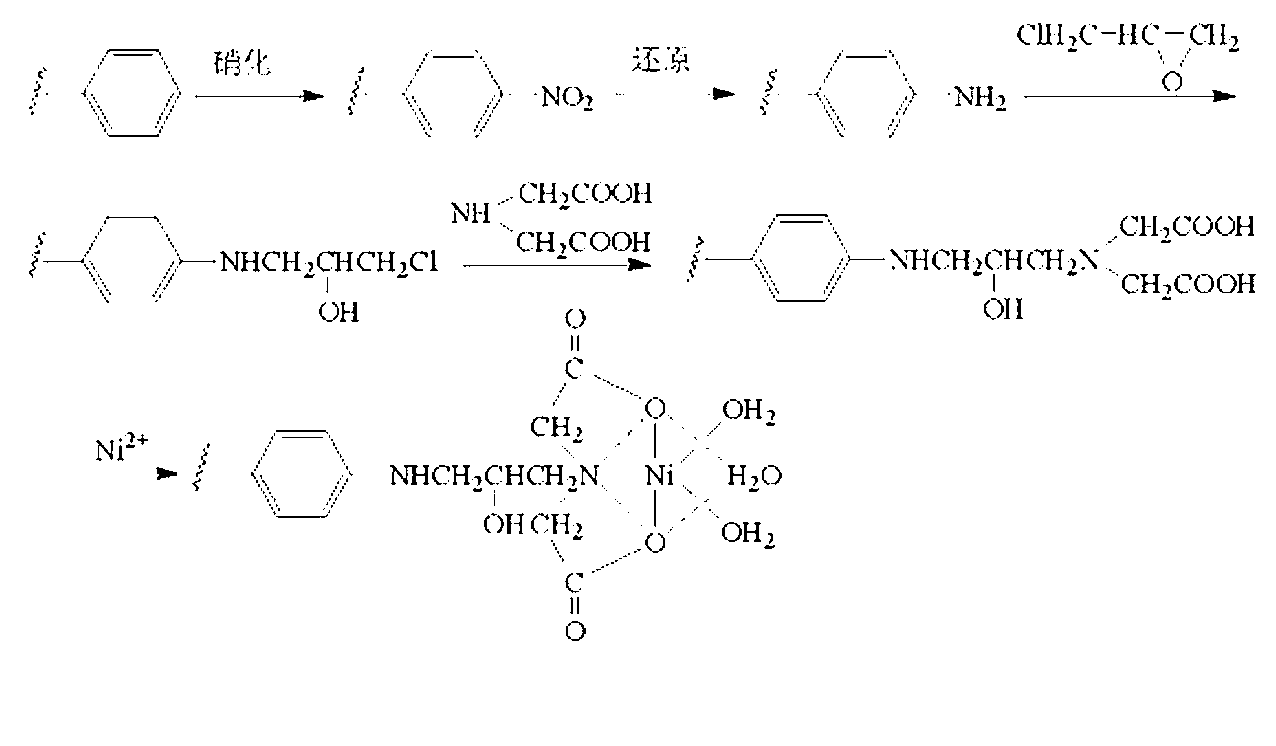
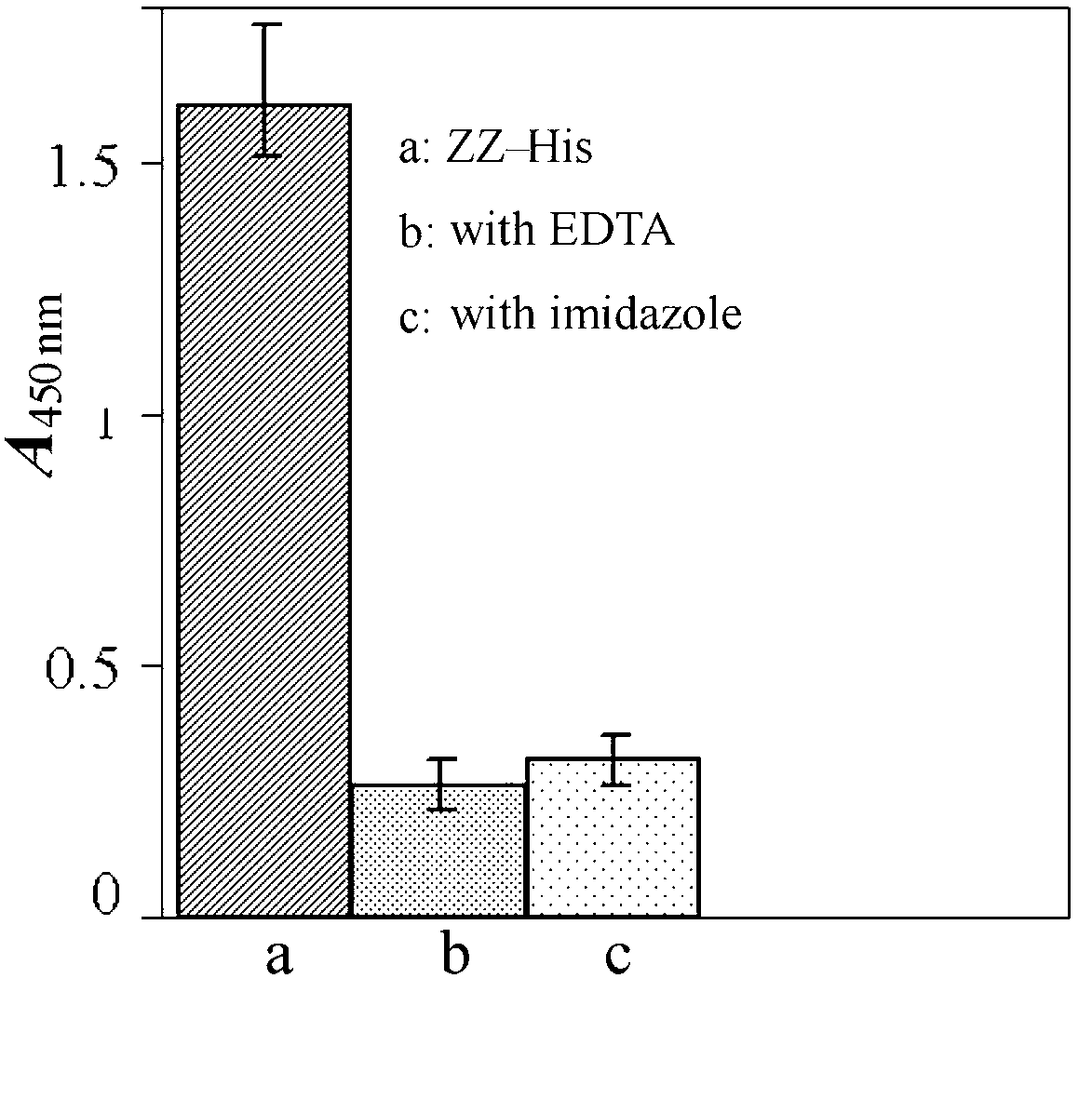
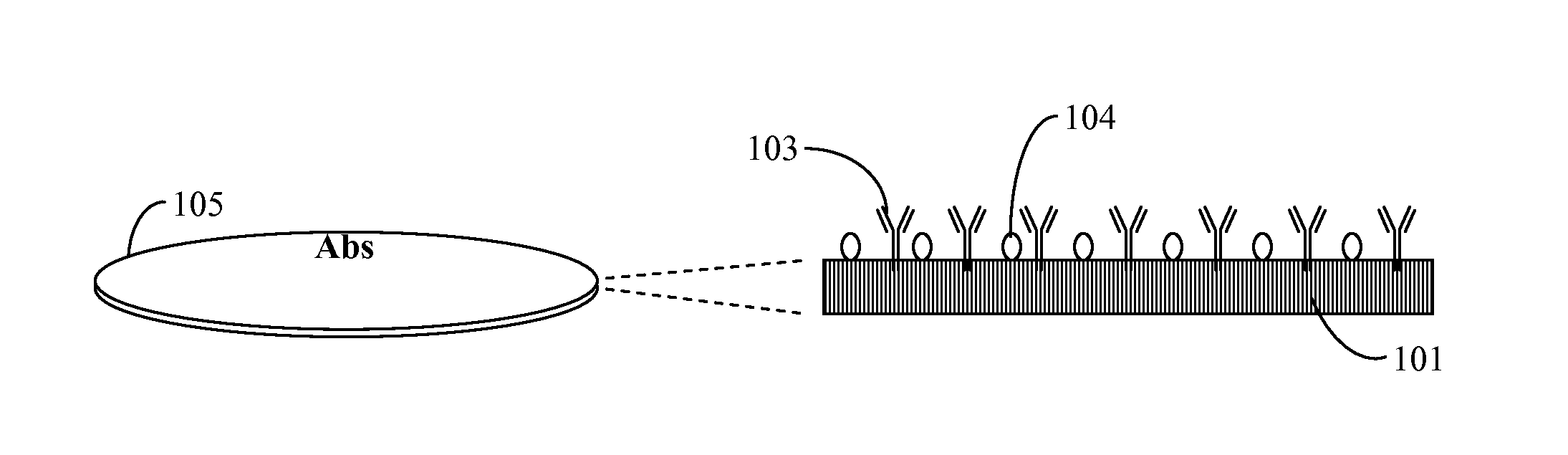
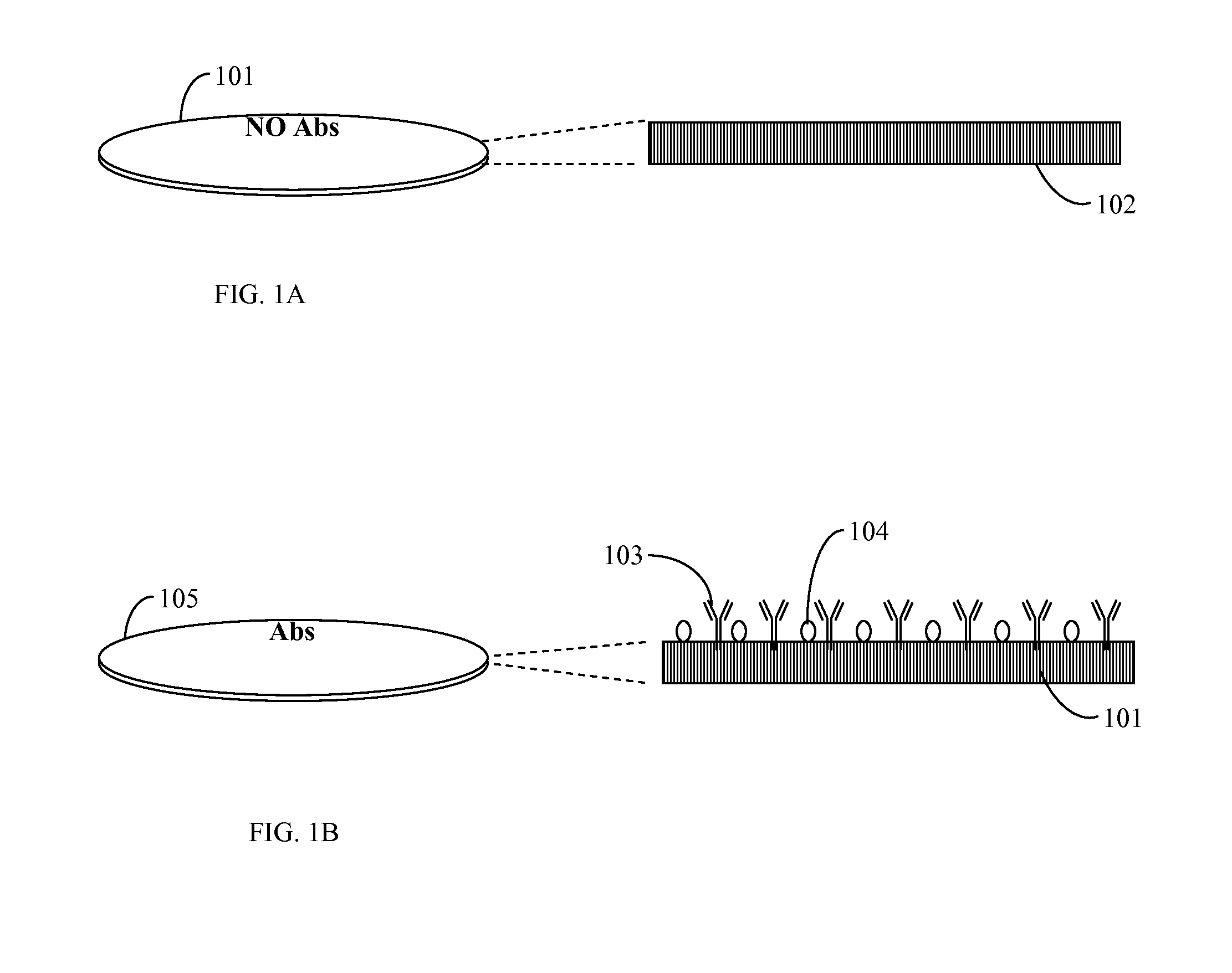
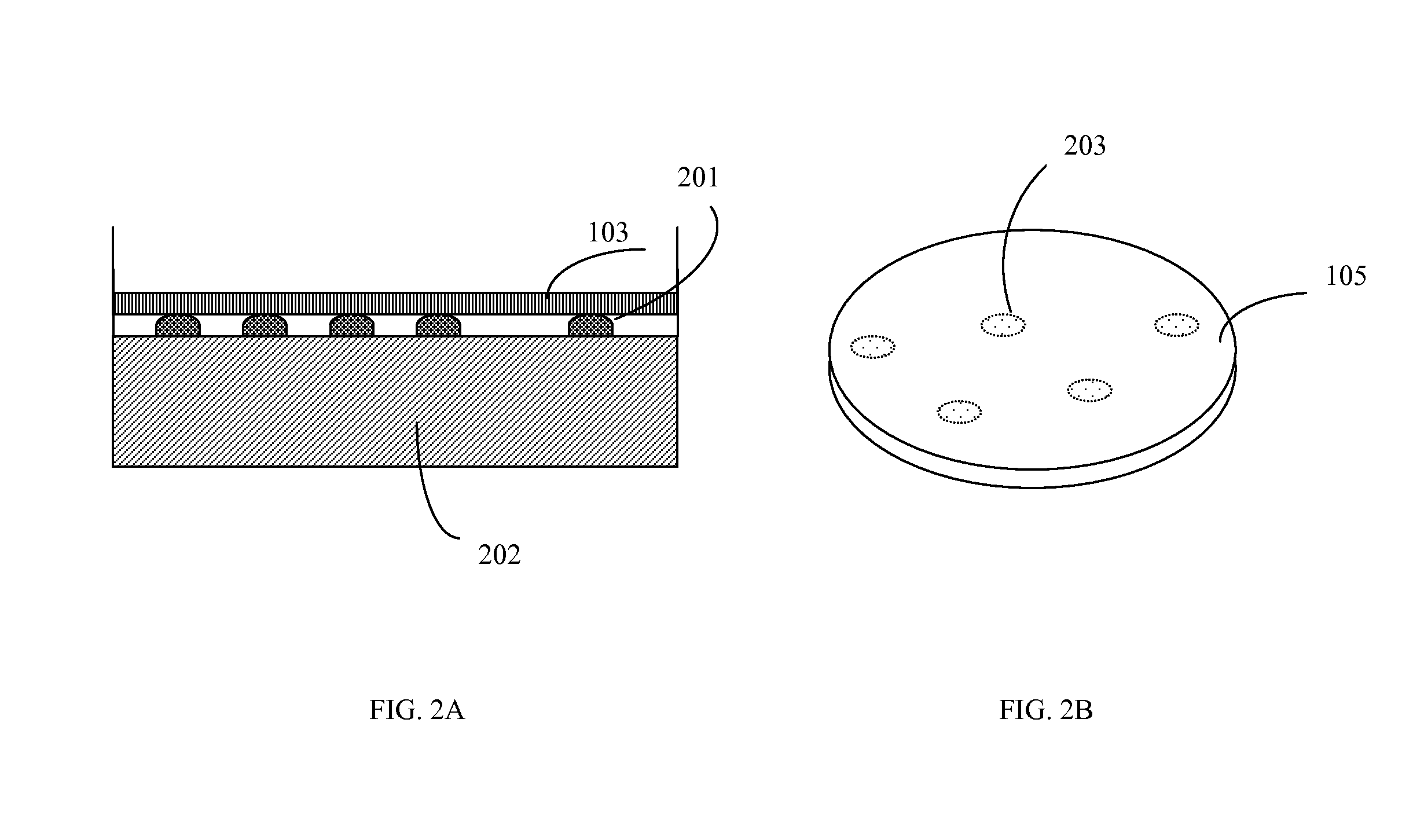
Stereotactic fixing method of IgG antibody on surface of polystyrene carrier
The invention discloses a stereotactic fixing technology of an IgG antibody, wherein the IgG antibody fixed on the surface of a polystyrene carrier is uniform, the Fab segment is exposed adequately and the high antigen binding activity of the IgG antibody is maintained, so that the sensitivity, specificity and stability of solid phase immunoassay are effectively improved. The stereotactic fixing method of IgG antibody provided by the invention specifically comprises the following steps: grafting a 'metal ion arm' on the surface of polystyrene by a chemical modification method; constructing a ZZ affinity peptide with Histag by a genetic engineering technology; mediating the ZZ affinity peptide based on Histag and metal ion affinity characteristics to be stereotactically fixed on the surface of polystyrene, so as to exert the immunological properties of the ZZ affinity peptide; specifically combining the Fc section of the IgG antibody to obtain a metal ion-(ZZ-His)-Fc assembled body in a biological affinity mode, so as to stereotactically fix the Fab segment of the IgG antibody.
Owner:WEIFANG MEDICAL UNIV
Method and Apparatus for Rapid Detection and Identification of Live Microorganisms Immobilized On Permeable Membrane by Antibodies
InactiveUS20100227338A1Quick checkQuick identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismImmobilized Antibodies
An apparatus and method is provided for the rapid detection, identification and / or enumeration of one or more live target microorganisms growing on solid nutrient media or filtration membrane. Microcolonies or colonies attach to a porous transfer permeable membrane loaded with immobilized antibodies specific for target microorganisms. Non-specific cells are washed out of the permeable membrane and the membrane then is placed on a container containing a chromogenic and / or a fluorogenic substrate and incubated to allow coloration and subsequent identification and enumeration of color spots of targeted microorganisms and patterns of microcolonies or colonies.
Owner:NANOLOGIX INC
Immunochip test method of staphylococcus enterotoxins and fumonisin
InactiveCN102455356AImprove stabilityReduce experiment costFluorescence/phosphorescenceImmobilized AntibodiesStaphylococcus
The invention relates to an immunochip test method of staphylococcus enterotoxins (SEA and SEB) and fumonisin (AFB1), so as to realize the simultaneous test on the same chip. According to the invention, for the test of AFB1, the monoclonal antibody of AFB1 is immobilized on the surface of a piece of aldehyde glass and then added to the chip together with a complete antigen labeled by a certain amount of Cy3, and the technical research on the immunochip can be carried out by using a competition method. For the test of SEA and SEB, a double-antibody sandwich method is adopted and the optimization of experiment conditions is carried out; in the test, SEA and SEB are added to a reaction tank, SE which is not combined is washed off after reaction, and then a corresponding labeled antibody is added so as to form an immobilized antibody- objected to be determinand-labeled antibody sandwich structure, and the intensity of a fluorescence signal is increased with increase of the concentration of the objected to be determinand. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation, low in cost, sensitive and rapid, the result can be stably and reliably obtained, and the whole test process needs 1-2 hours. A new method for rapid test of various biotoxins is provided.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Double-anti-sandwich colloidal gold detection kit, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110320364AHigh sensitivityDoes not cause non-specific reactionsMaterial analysisAgainst vector-borne diseasesImmobilized AntibodiesColloid
Owner:LUOYANG PULIKE WANTAI BIOTECH +1
Test strip for chromatography and process for producing the same
InactiveCN1522368AAccurate measurementBiological material analysisImmobilized AntibodiesCapillary action
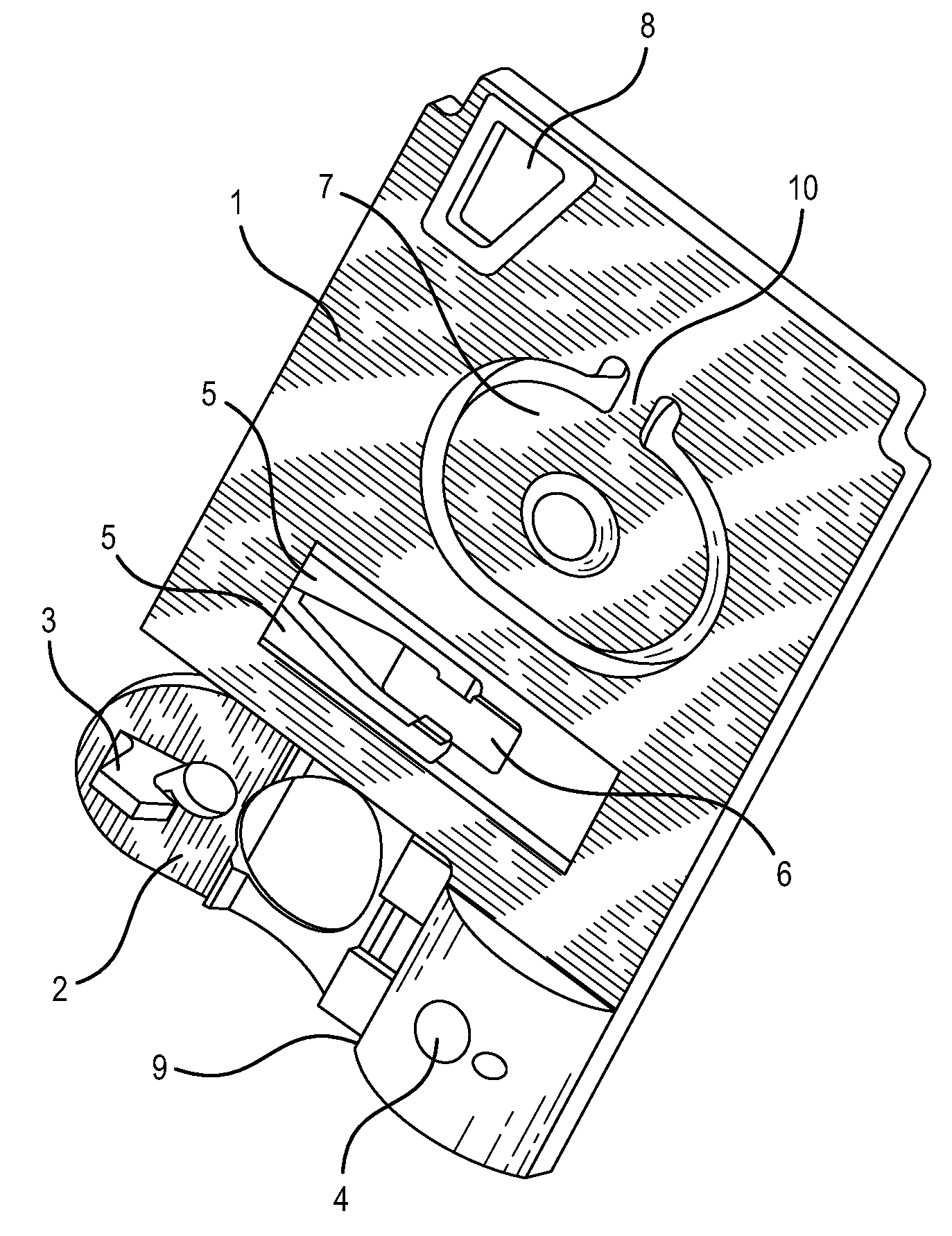
As shown in FIG. 1, an immunochromatography test strip 10 of the present embodiment is made of a base material 11 which includes a sample introduction section 12, a labeling section 13 and an immobilization section 14. The base material 11 is made of a material that is capable of being impregnated with a solvent of a sample solution containing a detection target substance. The material allows migration of a solvent of a sample solution by capillary action. The sample introduction section 12 is a region where a sample solution containing a detection target substance is introduced (e.g., dripped). The sample introduction section 12 contains a metal salt supported thereon. The labeling section 13 contains a labeled antibody 15, which is labeled with a labeling substance, in a state such that the labeled antibody 15 can be eluted into the sample solution. The labeled antibody 15 used herein specifically binds to a detection target substance. The immobilization section 14 contains an immobilized antibody 16. The immobilized antibody 16 used herein specifically binds to the detection target substance.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
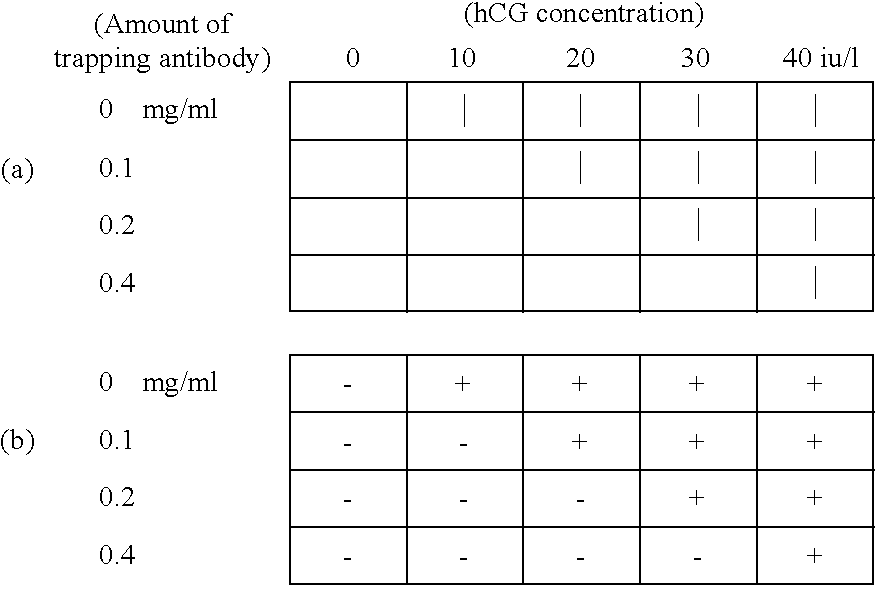
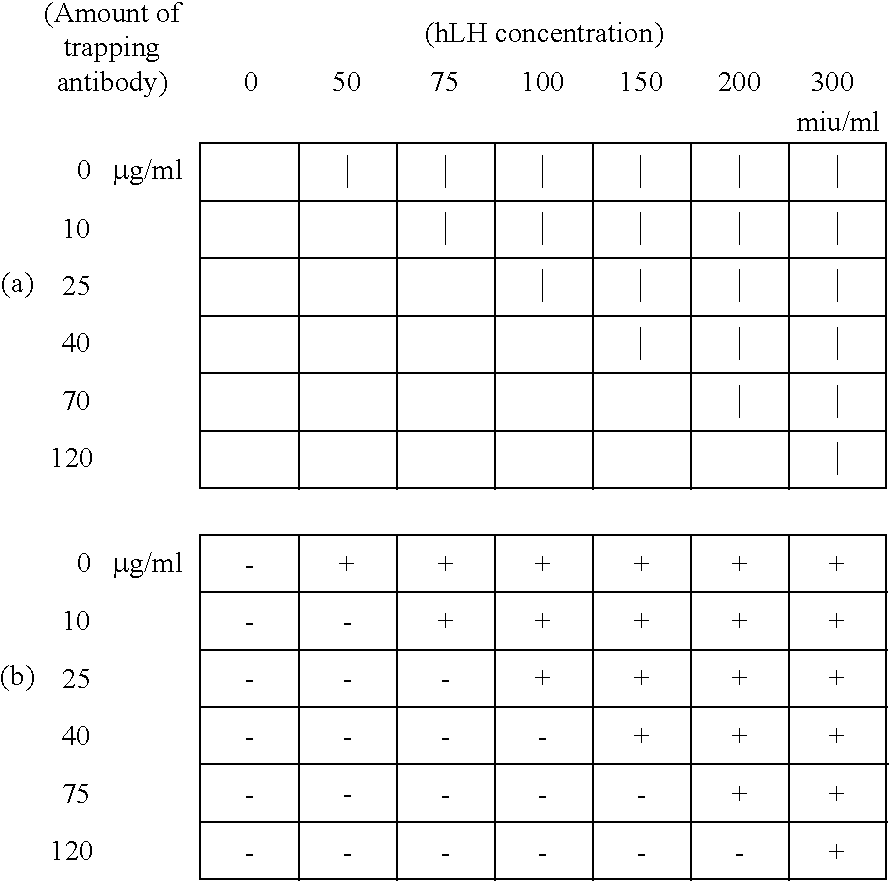
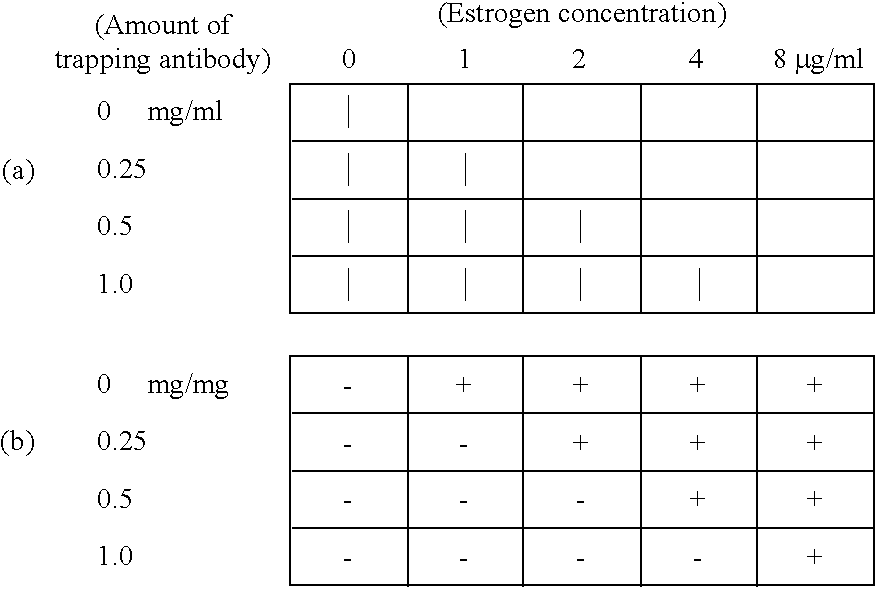
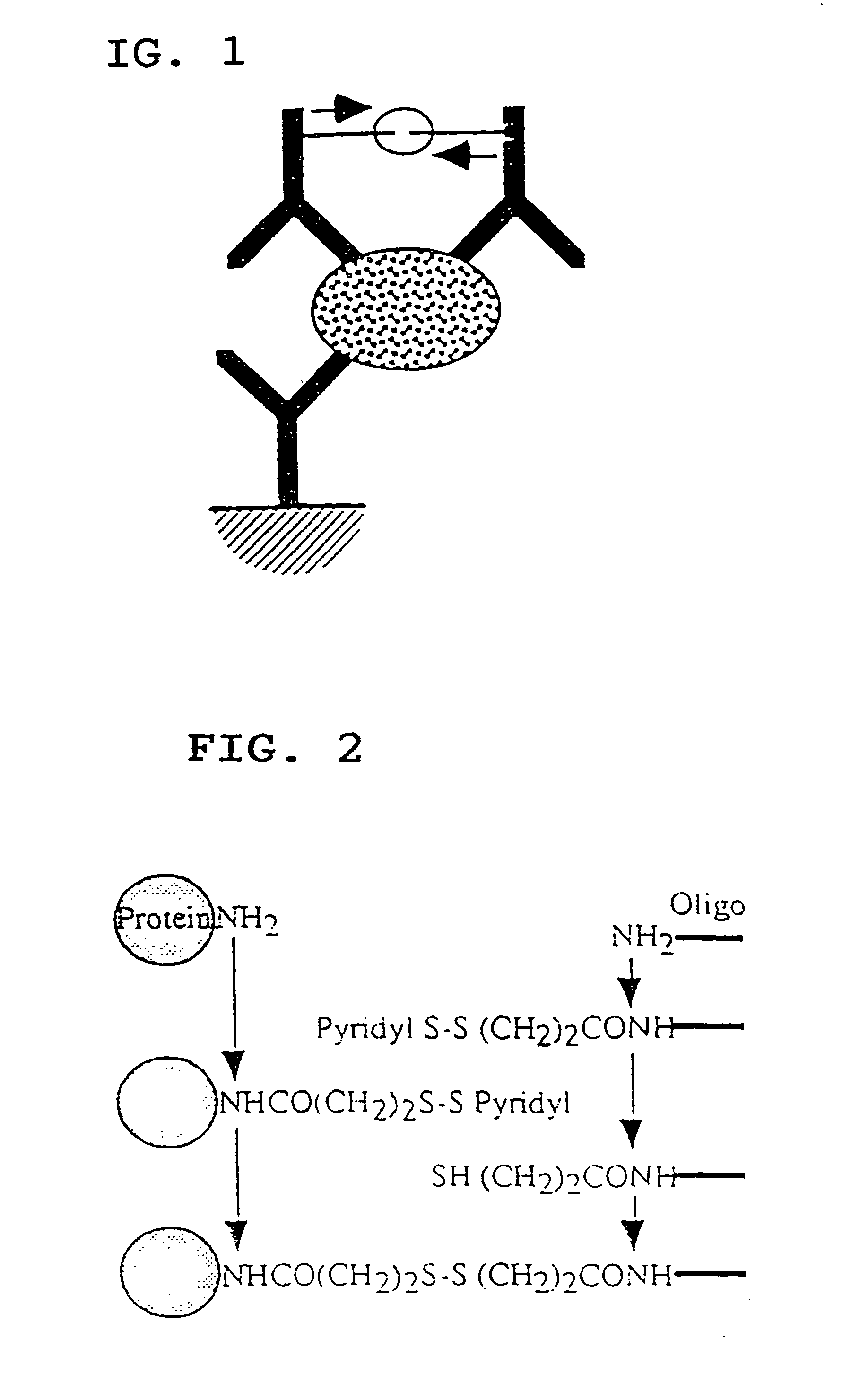
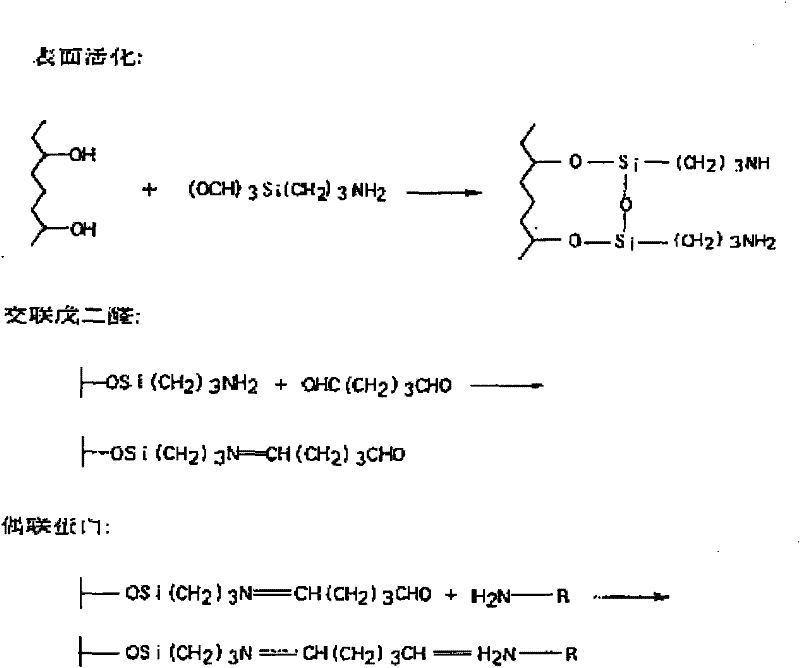
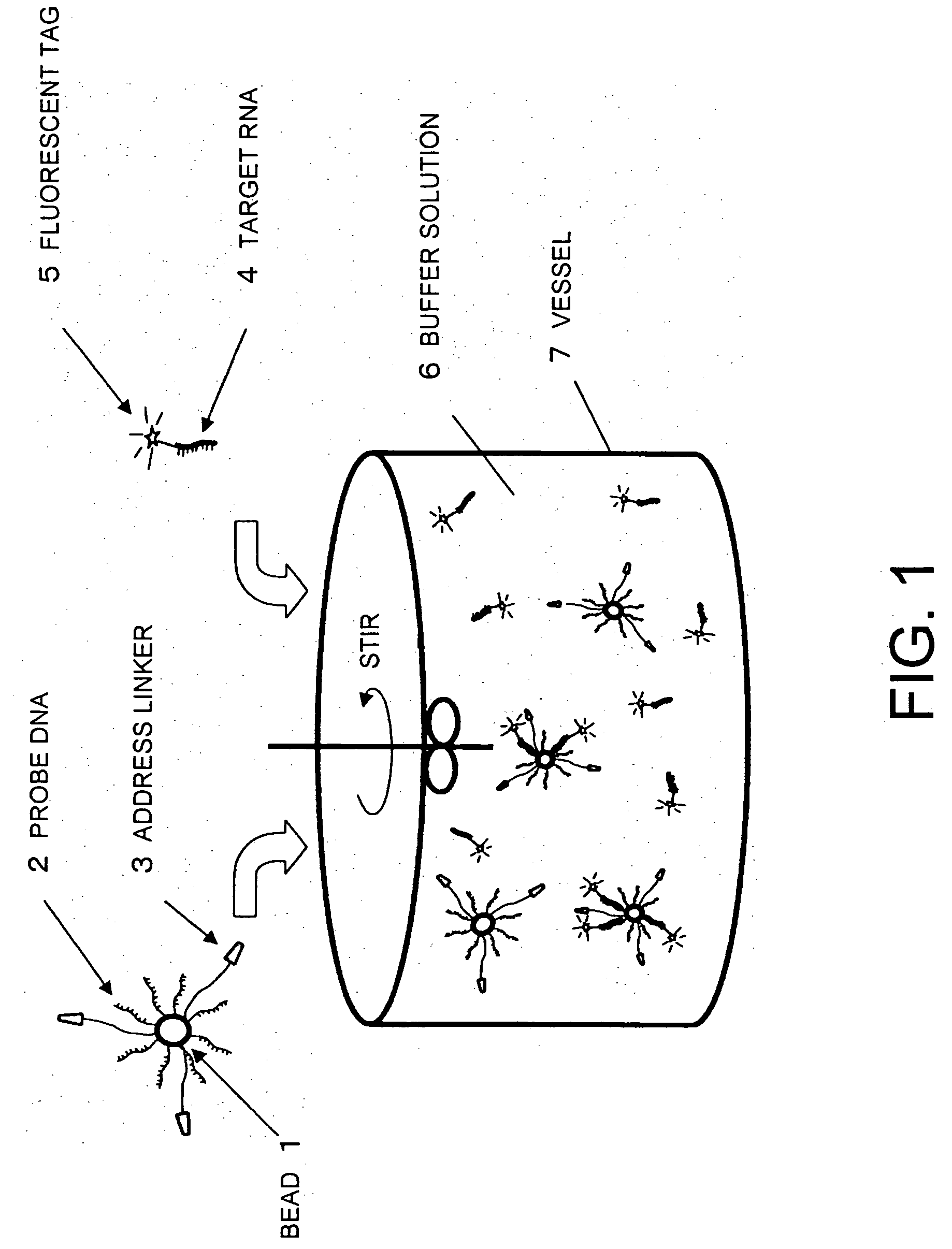
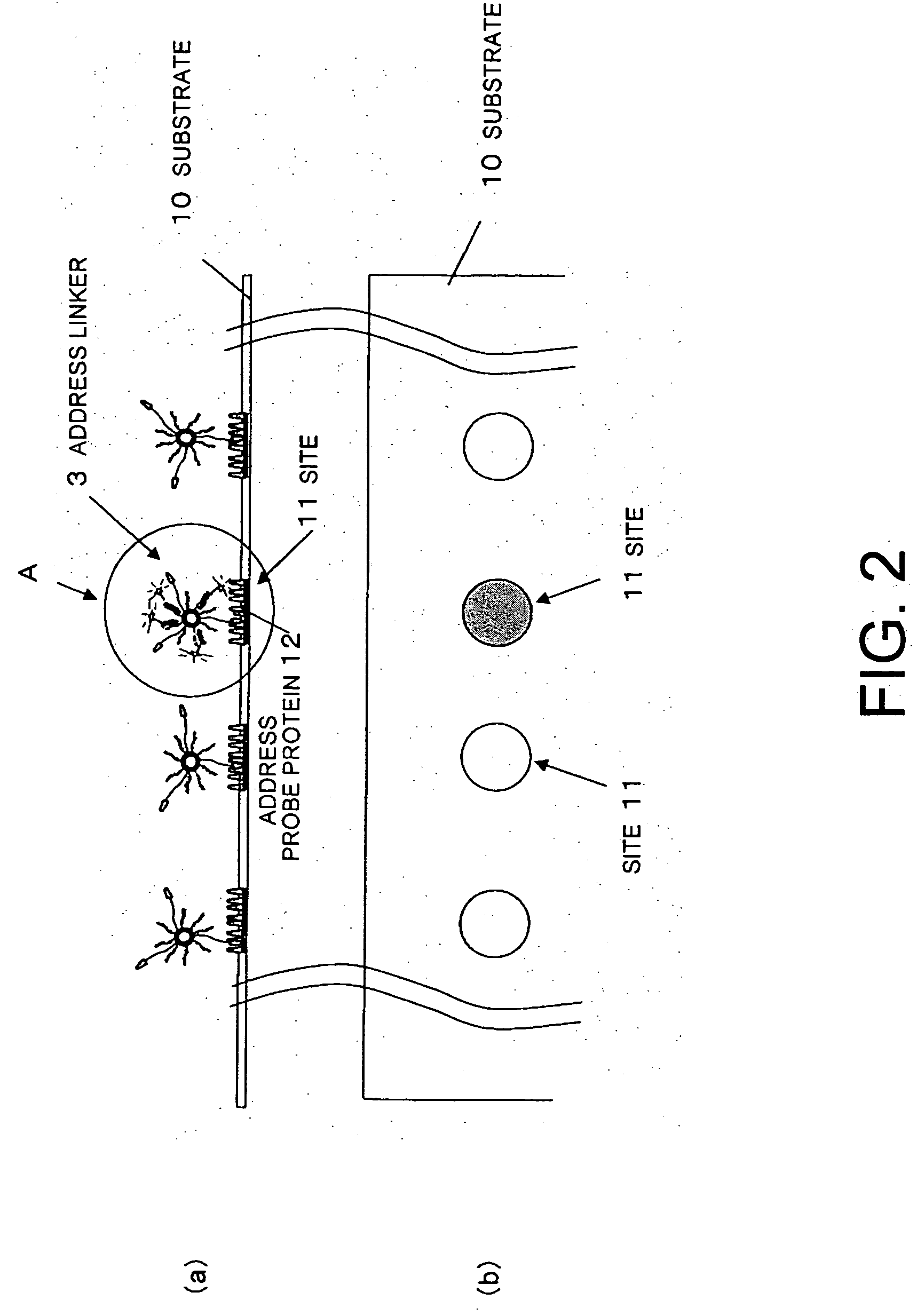
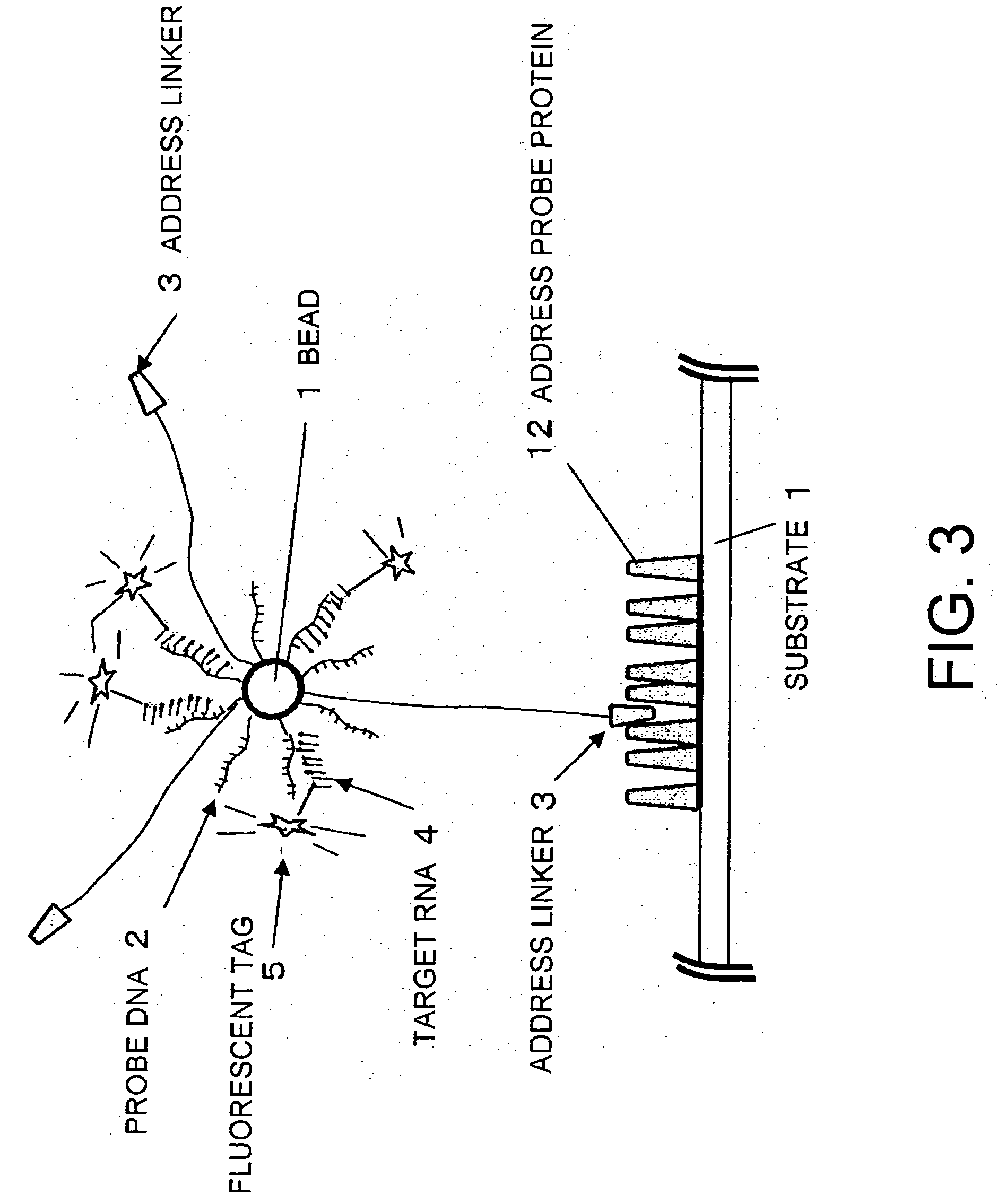
Methods for detecting biopolymers; biochips; methods for immobilizing antibodies; and substrates to which antibodies are immobilized
InactiveUS20050191644A1Improve S/N ratioHigh detection sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolyclonal antibodiesAntibody molecule
The present invention relates to biopolymer detection methods based on antigen-antibody interactions, wherein the methods show improved S / N ratios, improved detection sensitivities, and reduced detection times. The present invention also relates to application of these methods to biochips. The invention further relates to antibody fixation methods wherein antibody molecules are immobilized to amide group-containing gels, or amide group-containing gels on insoluble substances. Using such gels prevents the nonspecific adsorption of antibody-binding molecules. By embedding these antibody-binding molecules in such gels, their antibody-binding activity is prevented from deteriorating. The methods for detecting biopolymers by trapping target biopolymers to the substrate side, comprise the steps of: 1) placing target biopolymers, with probe biopolymers and beads that are identified by antibodies or address probe peptides or biopolymer address linkers attached to their surface, in a solution; 2) hybridizing the target biopolymers with the probe biopolymers; and 3) identifying the address linkers bound to a substrate by the address probe peptide or biopolymers or polyclonal antibody molecules through antigen-antibody interactions. The methods for immobilizing antibodies comprise the steps of: 1) applying an amide group-containing gel embedded with antibody-binding molecules on a substrate of an insoluble substance in two or three dimensions; and 2) attaching the base of the antibody molecules to antibody-binding molecules.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com