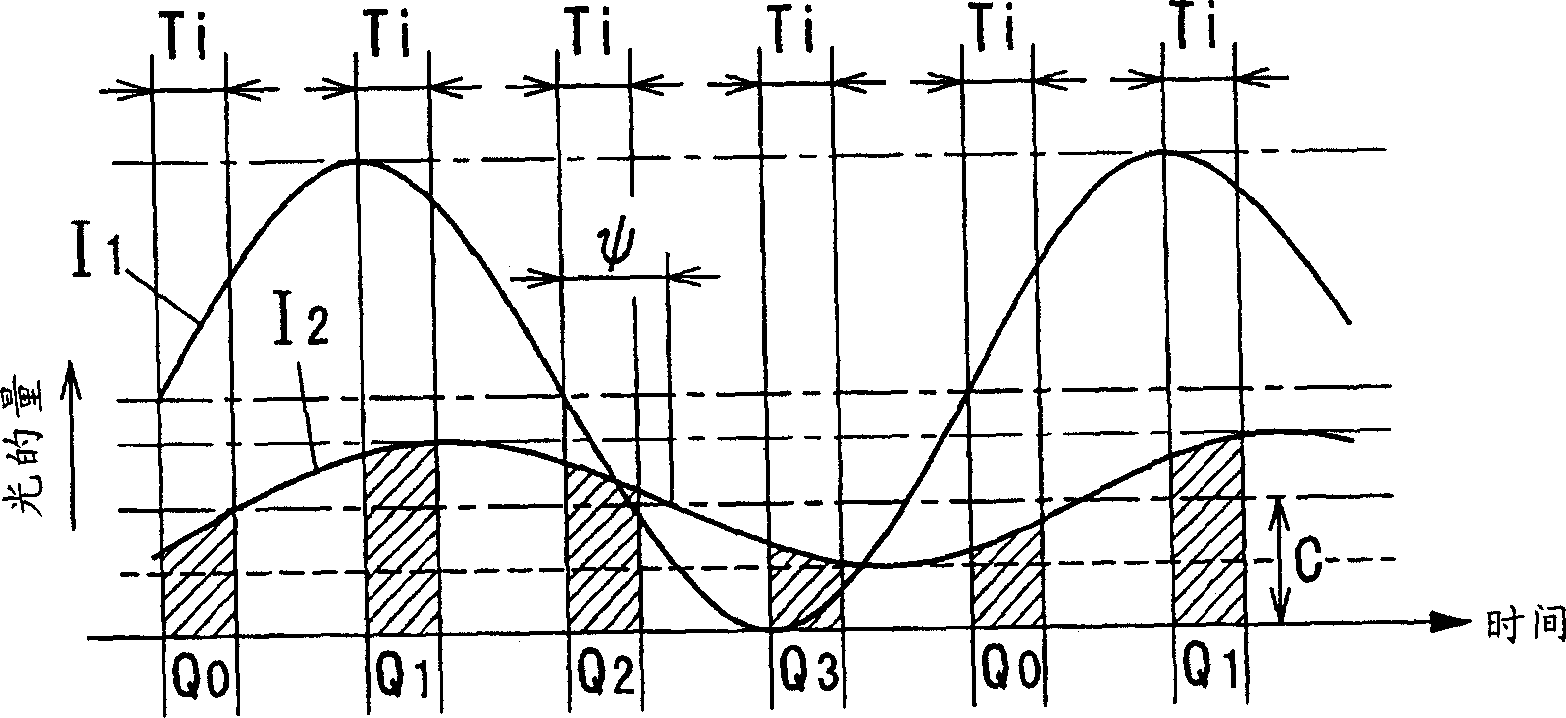
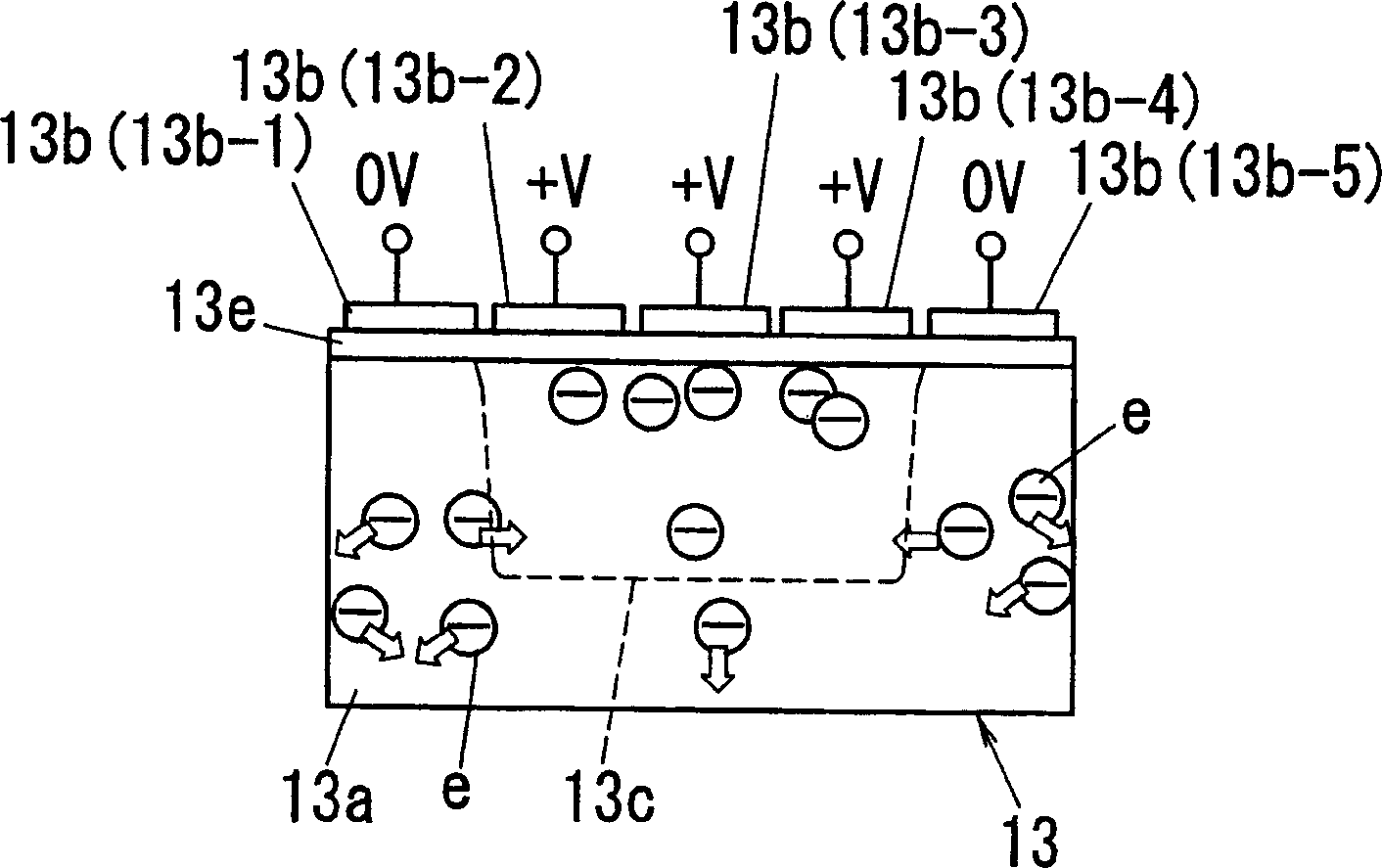
Patents
Literature
118results about How to "Improve S/N ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
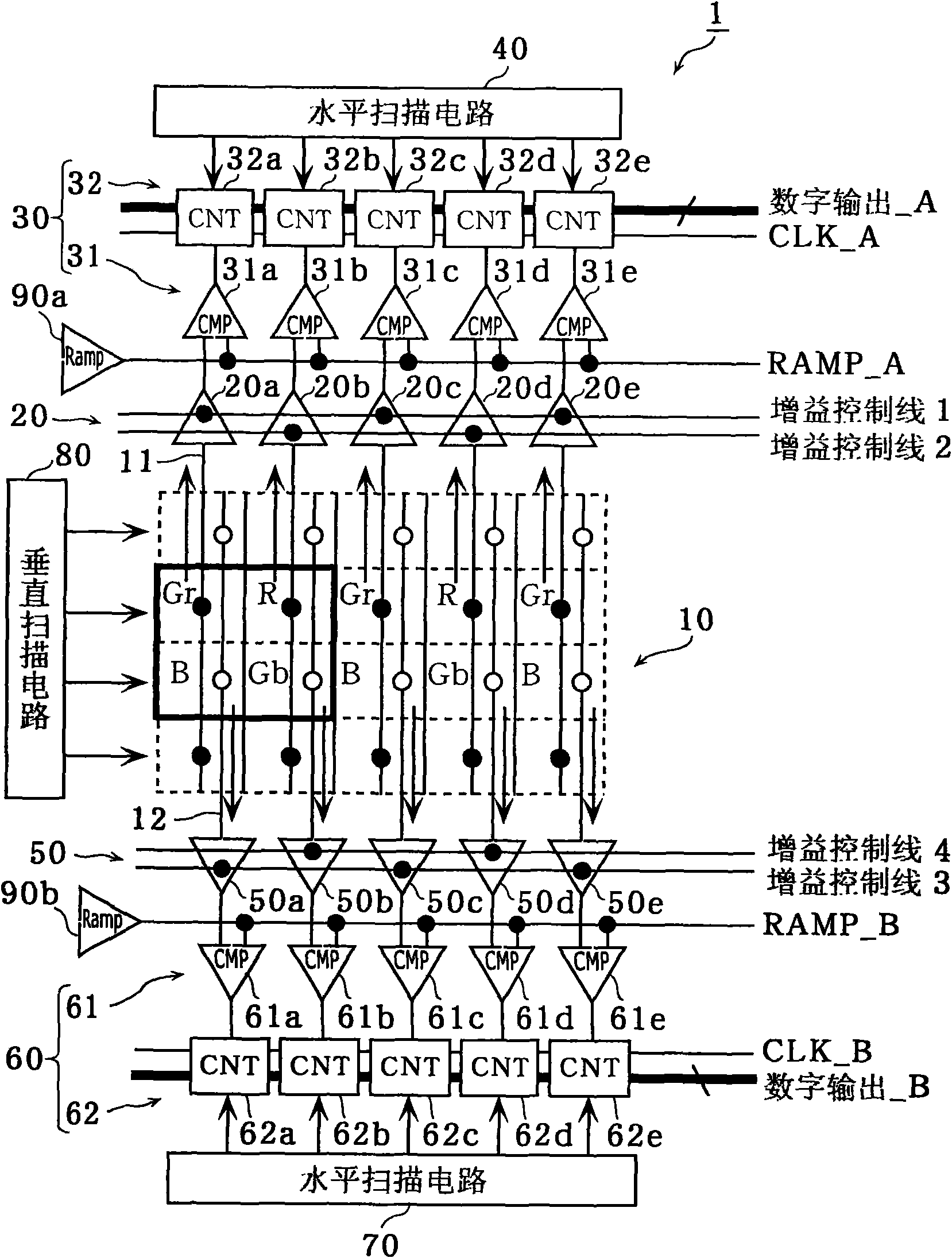
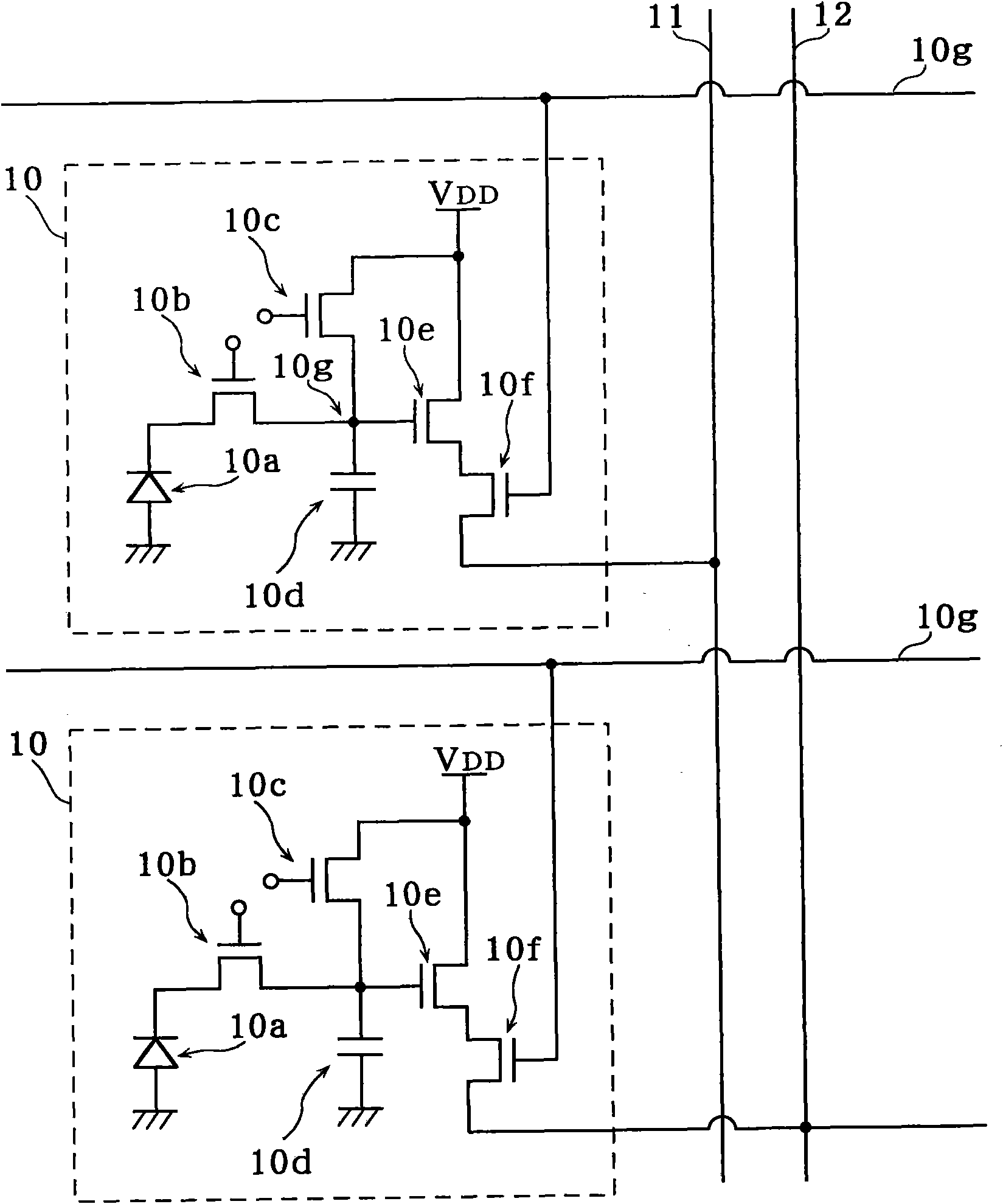
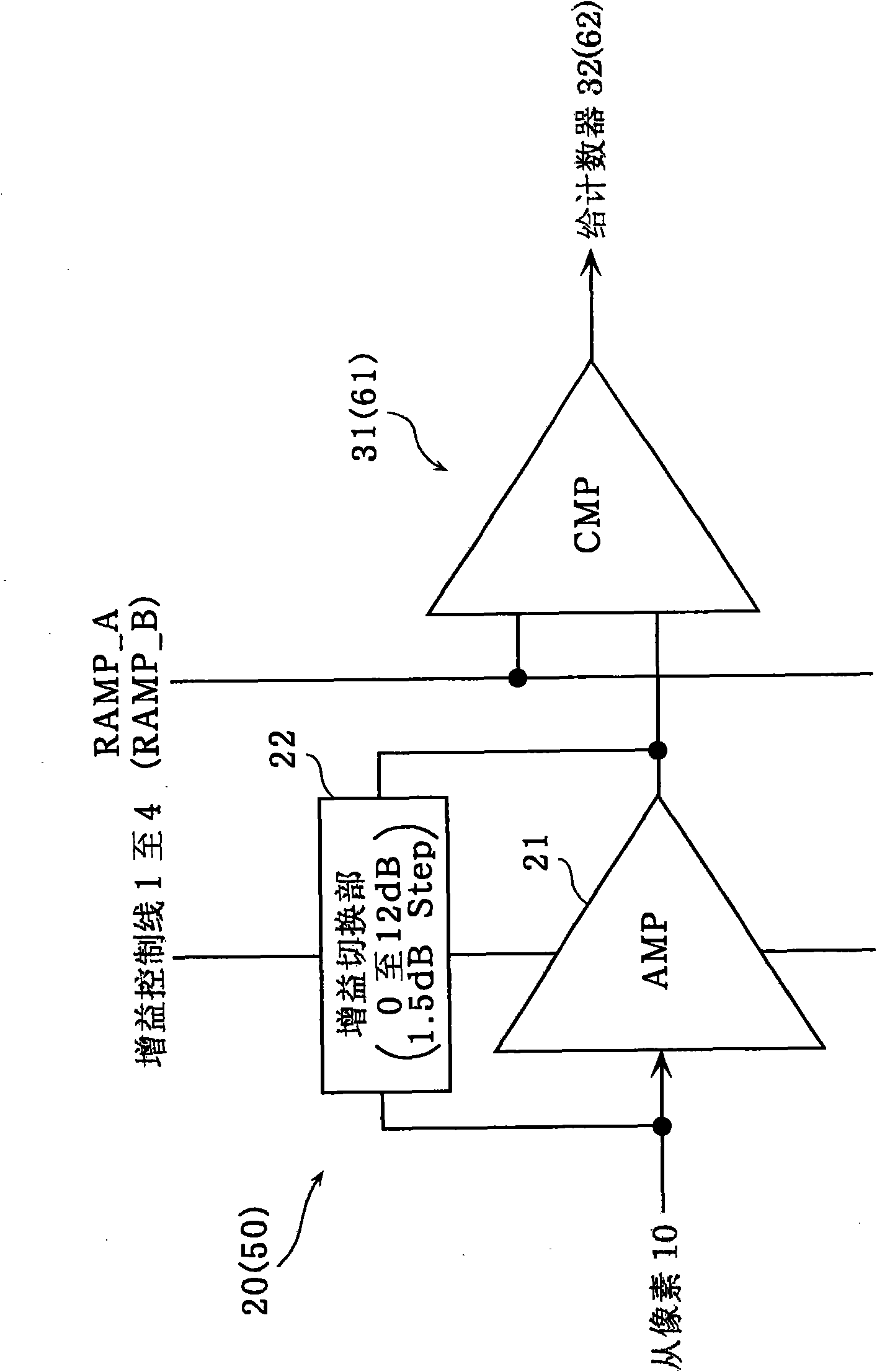
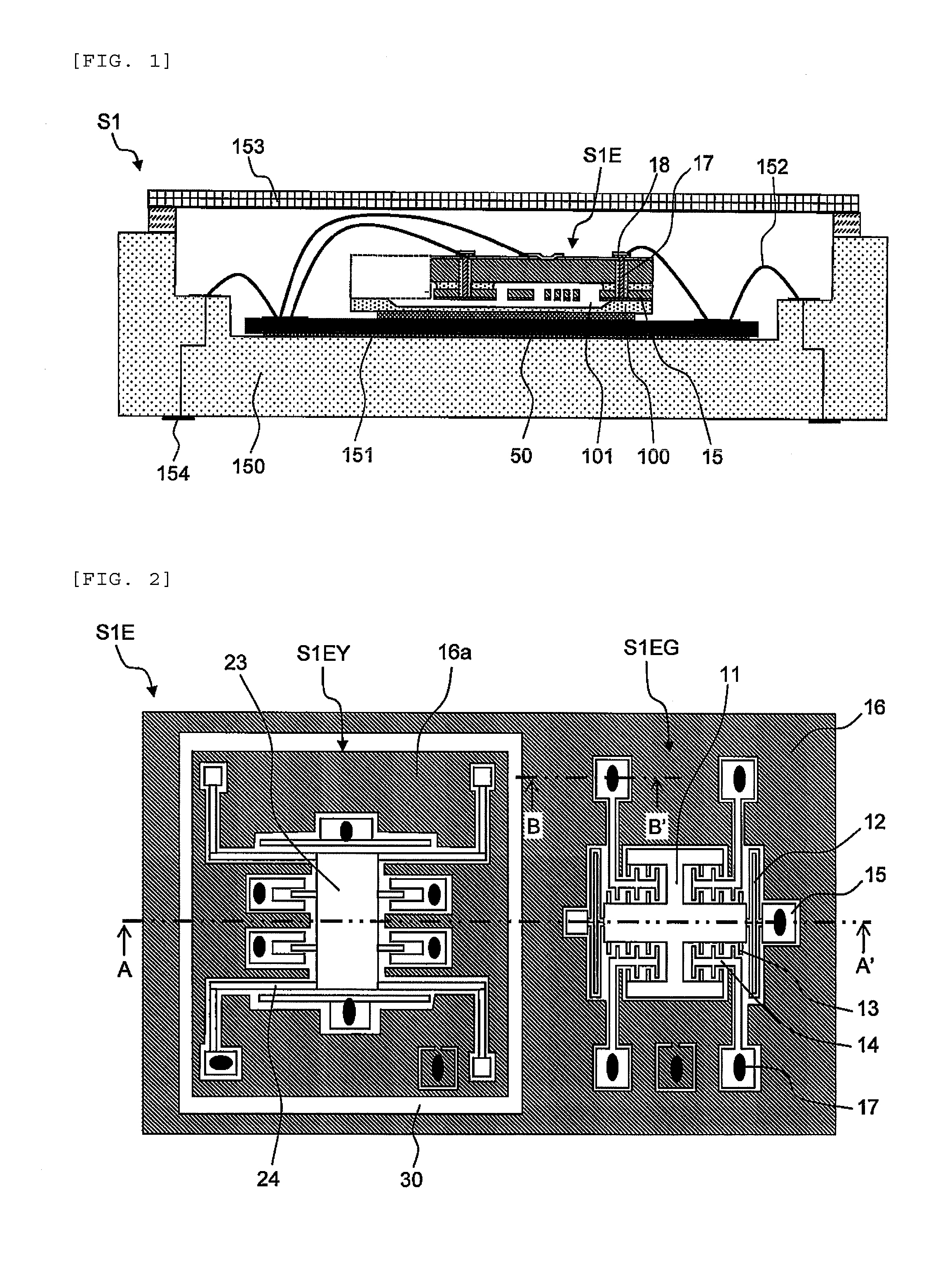
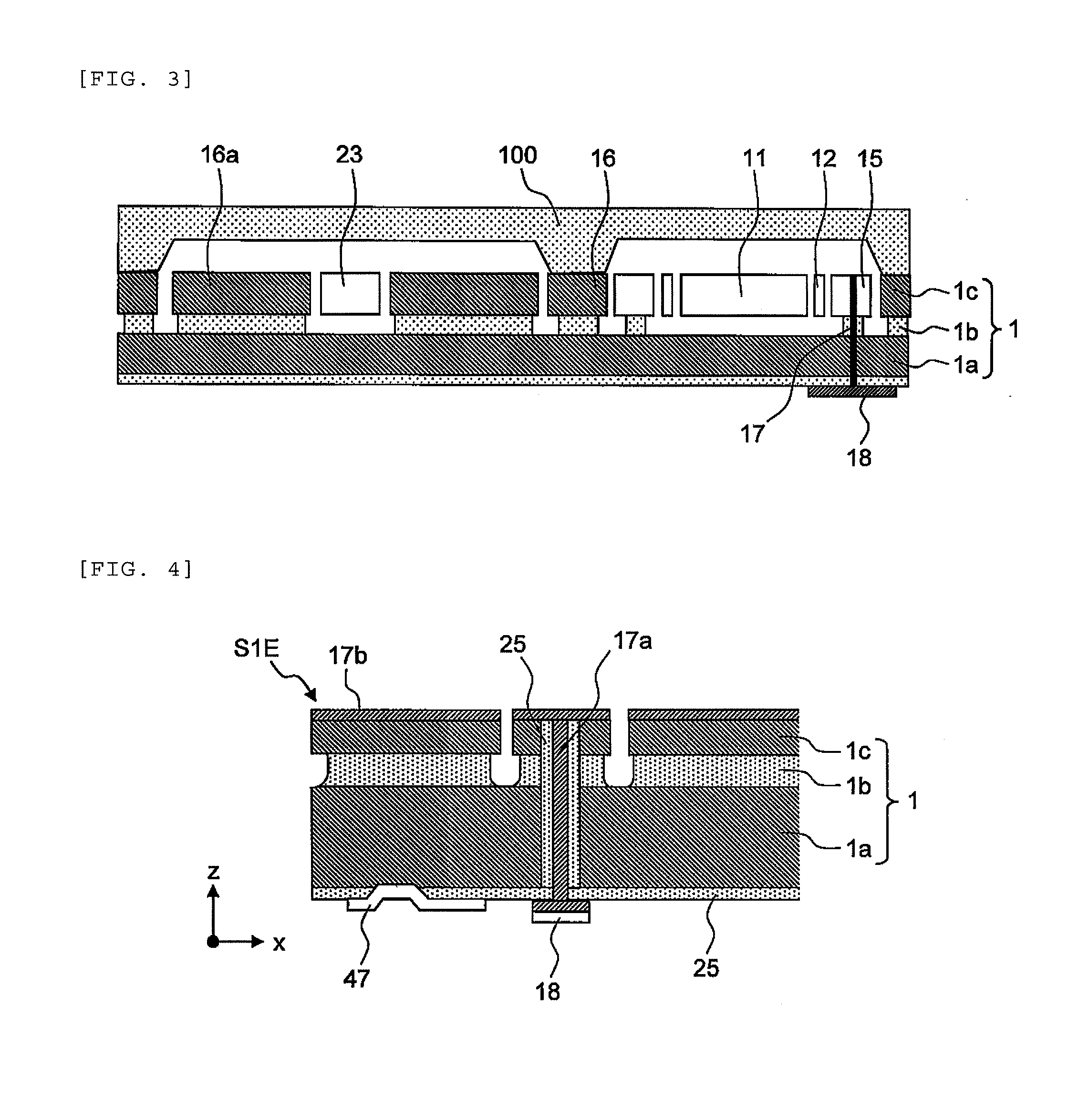
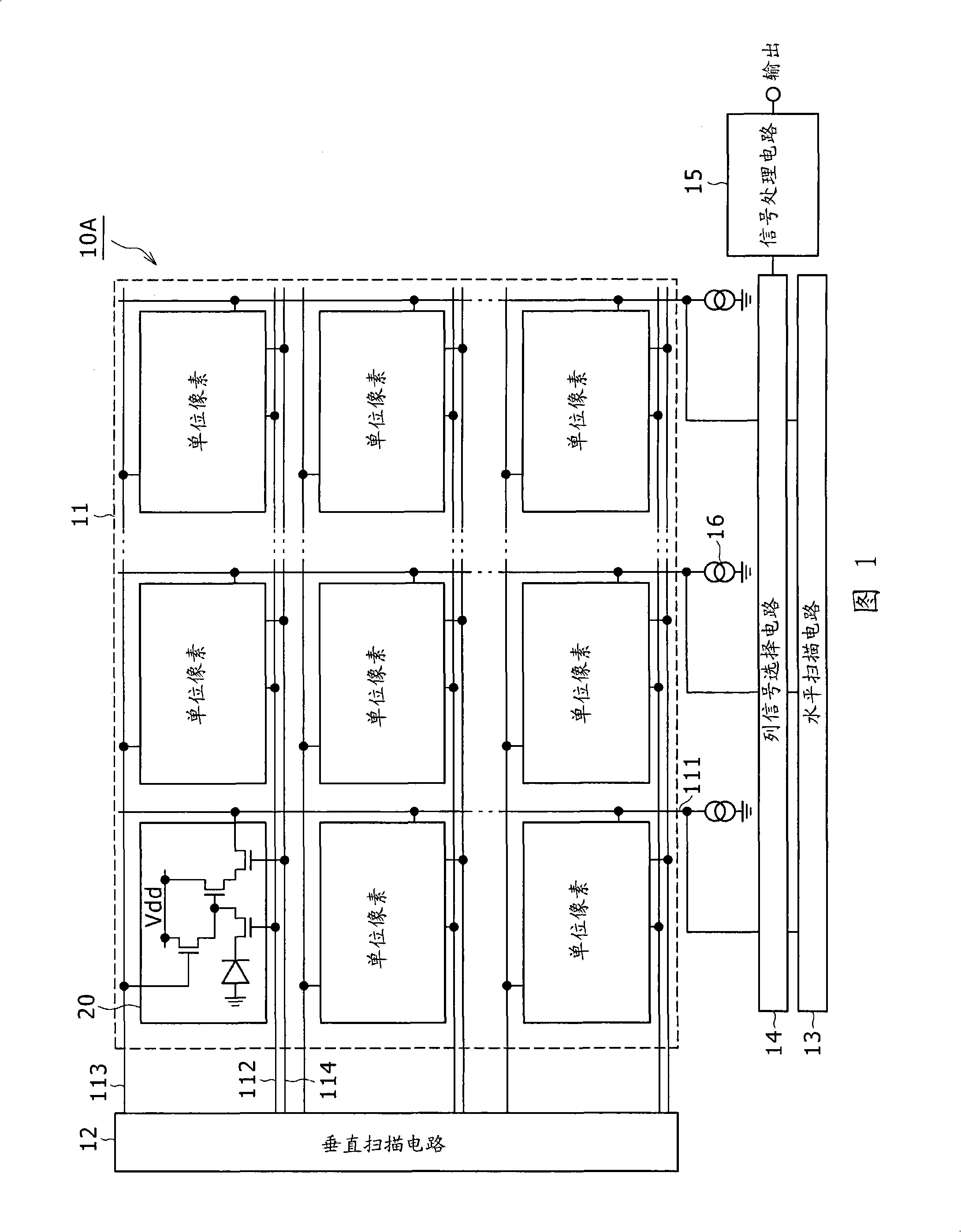
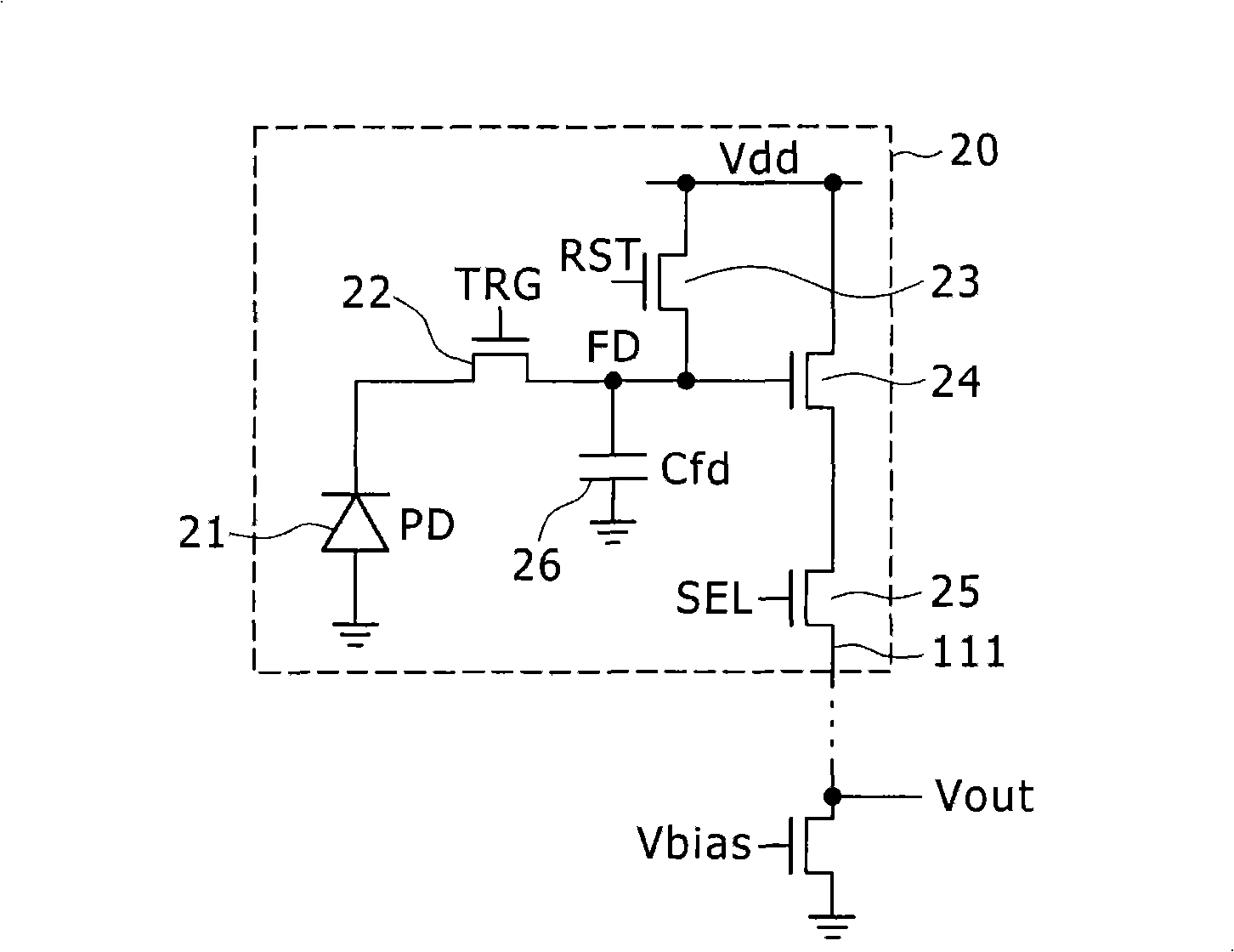
Radiation image pickup apparatus and its control method
InactiveUS20050264665A1Decrease distanceImprove S/N ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRadiationShift register
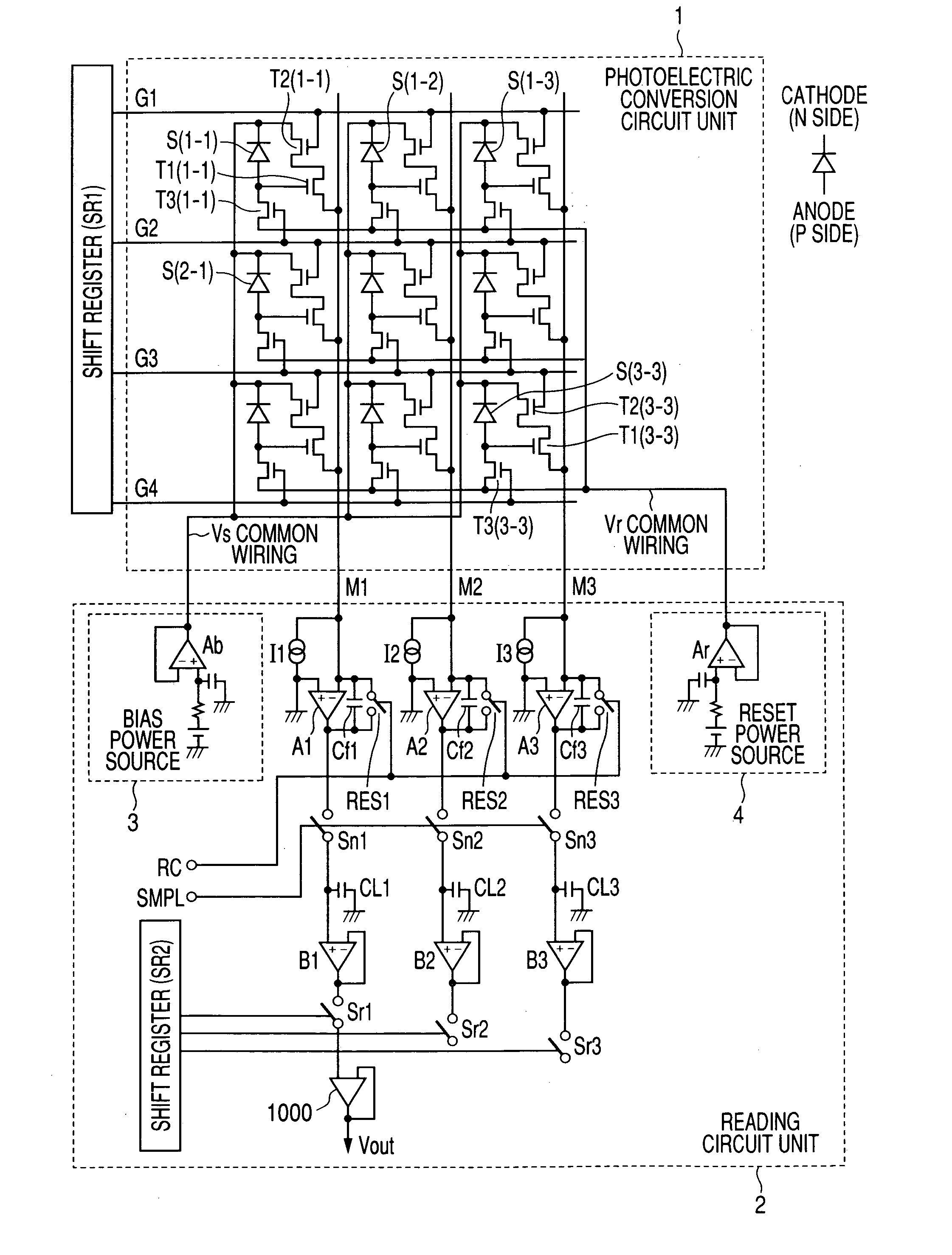
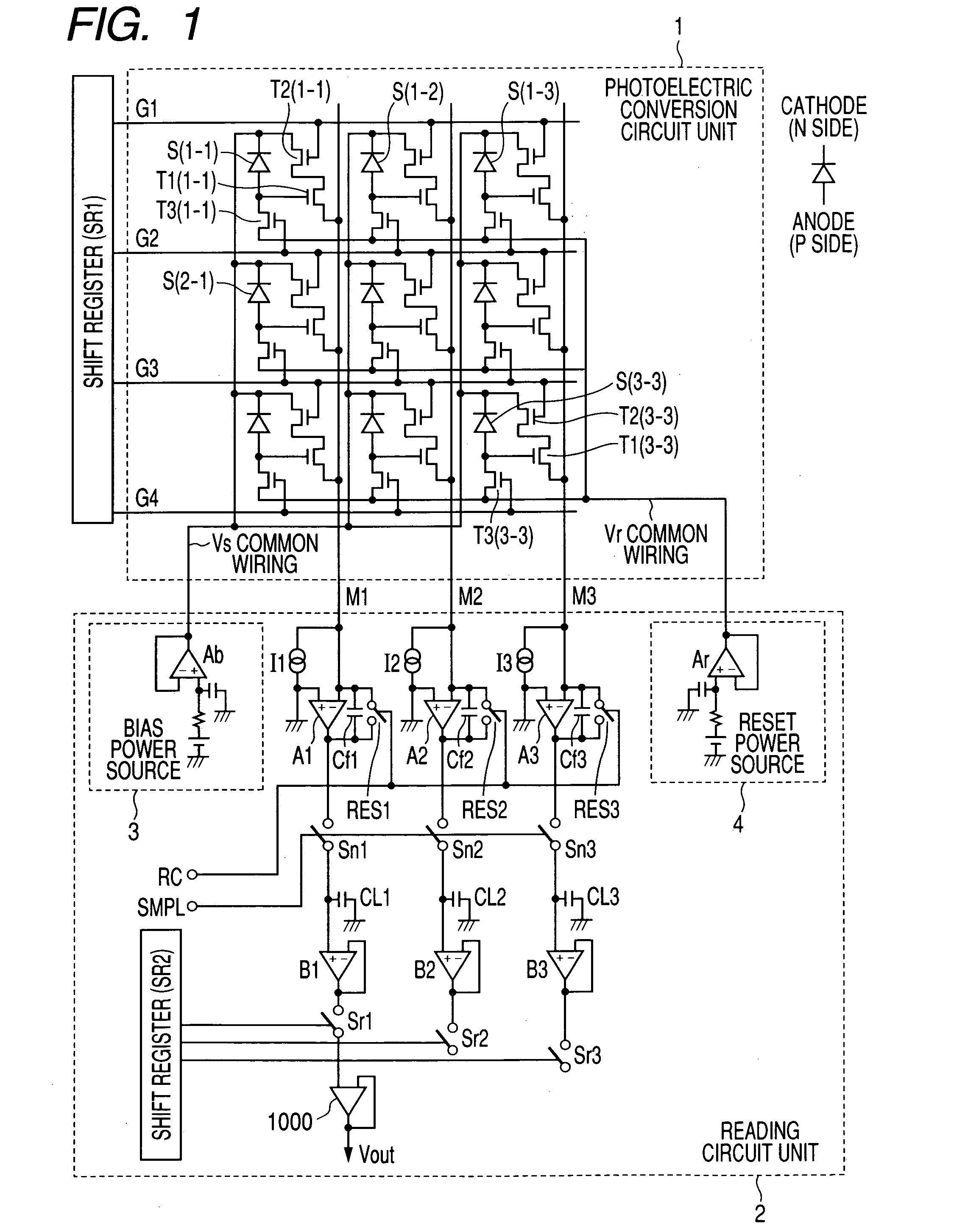
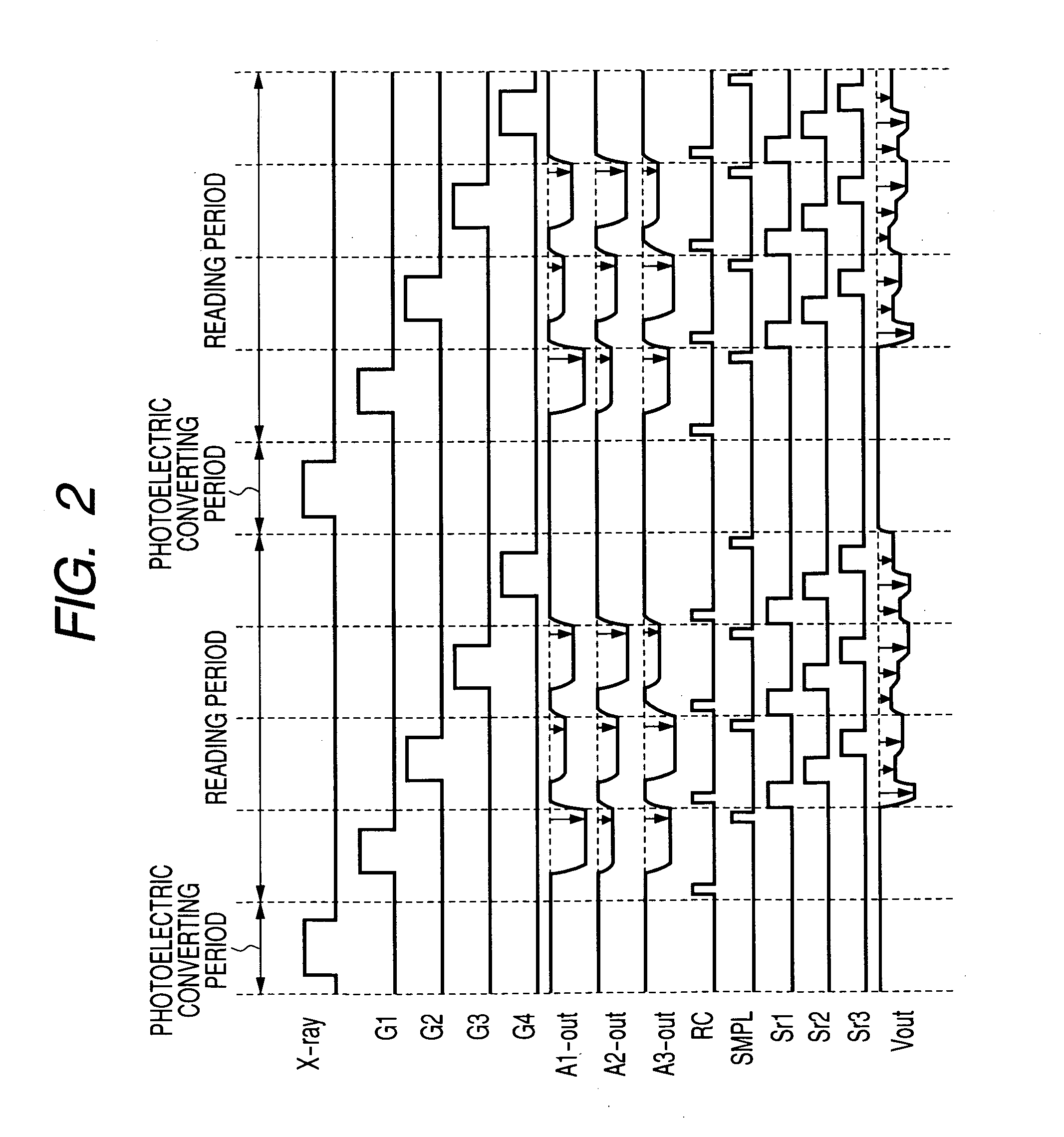
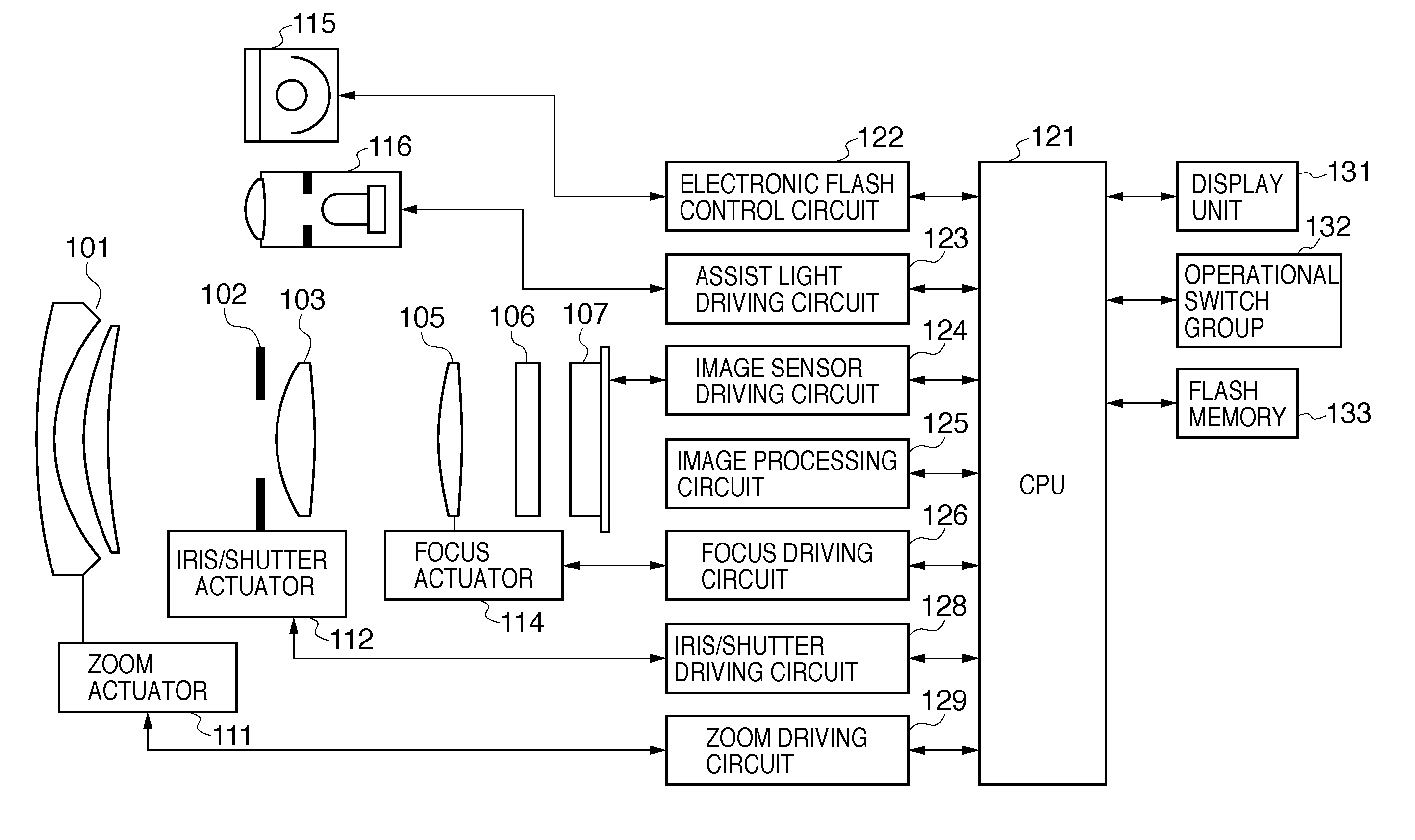
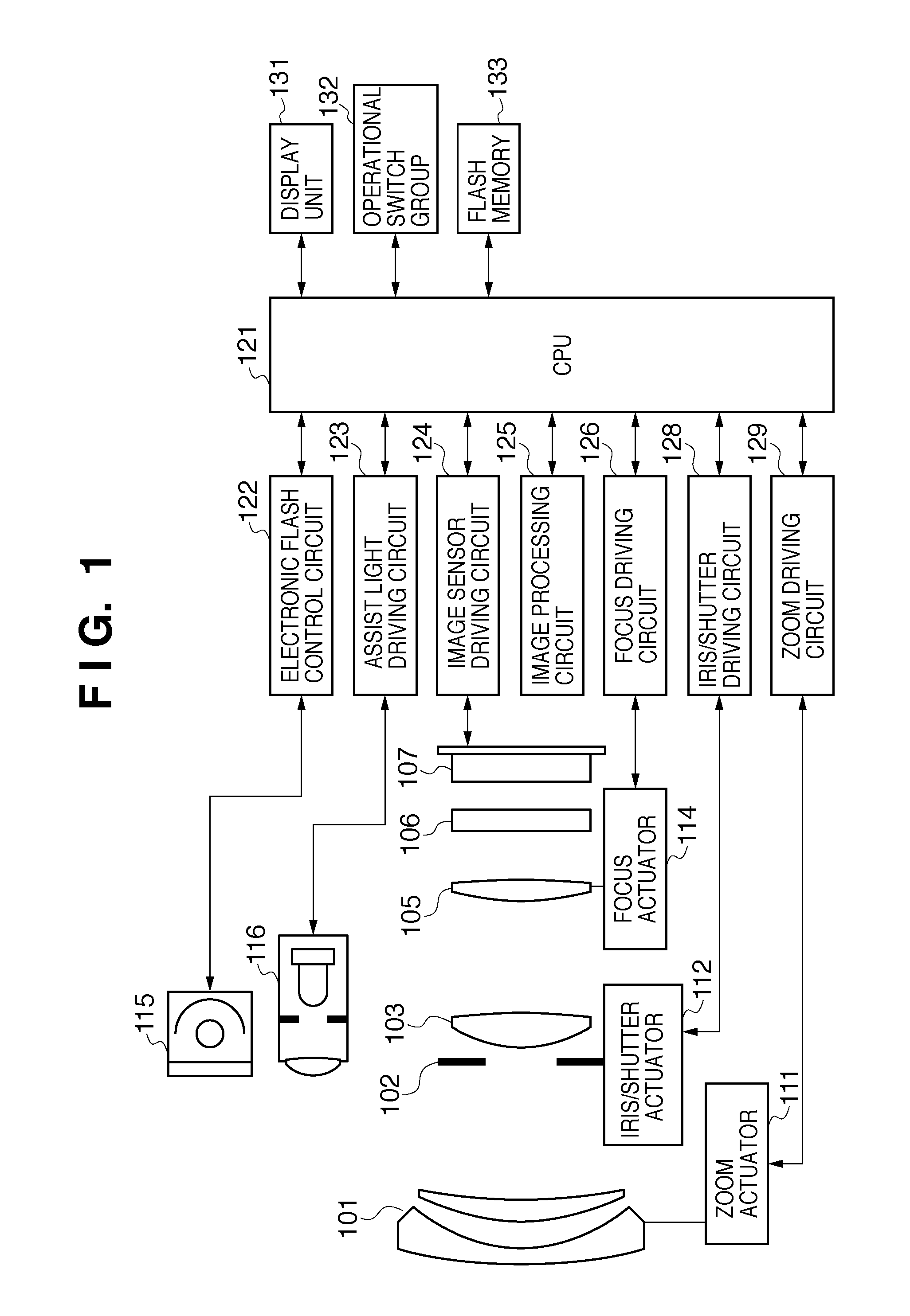
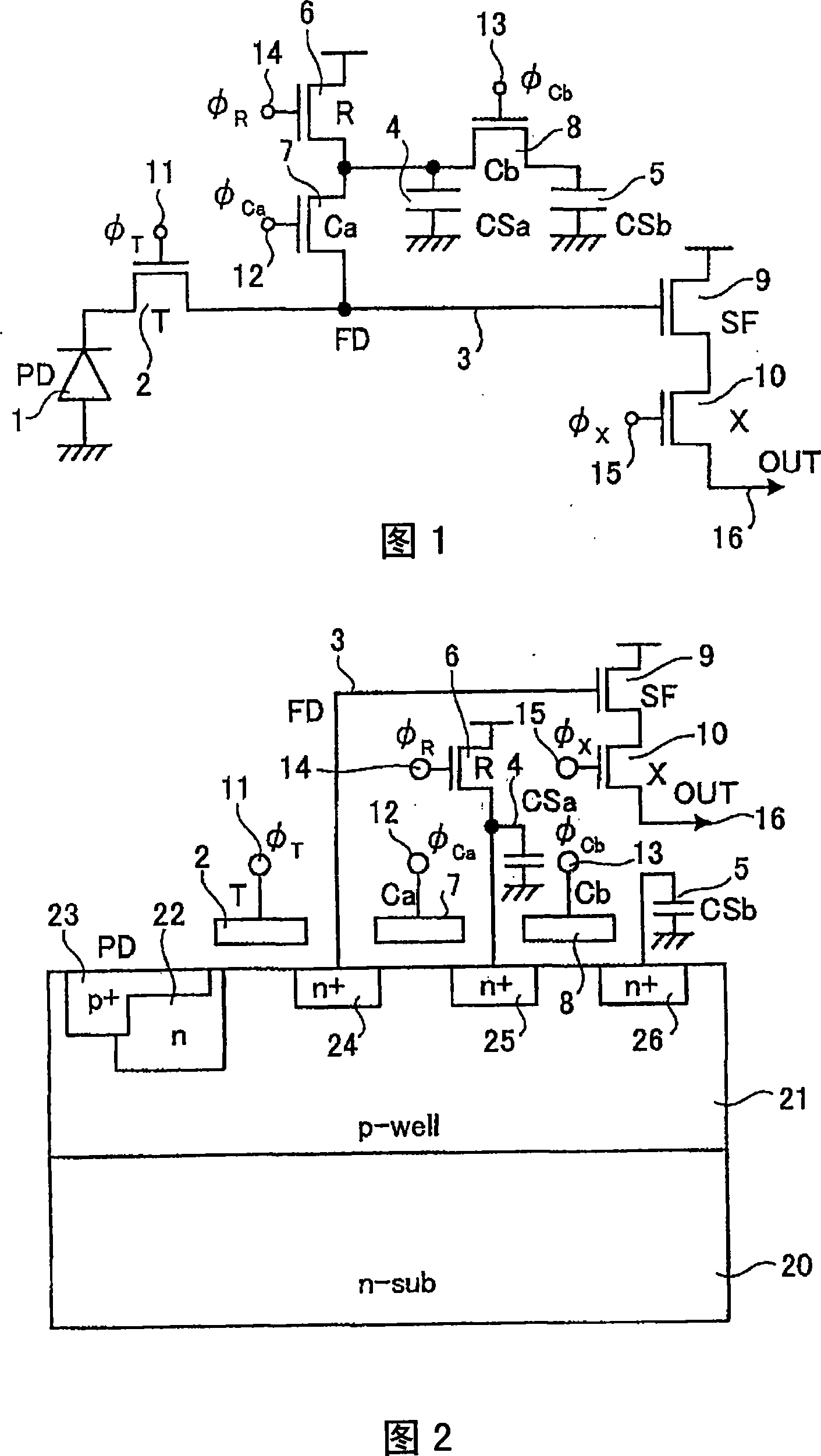
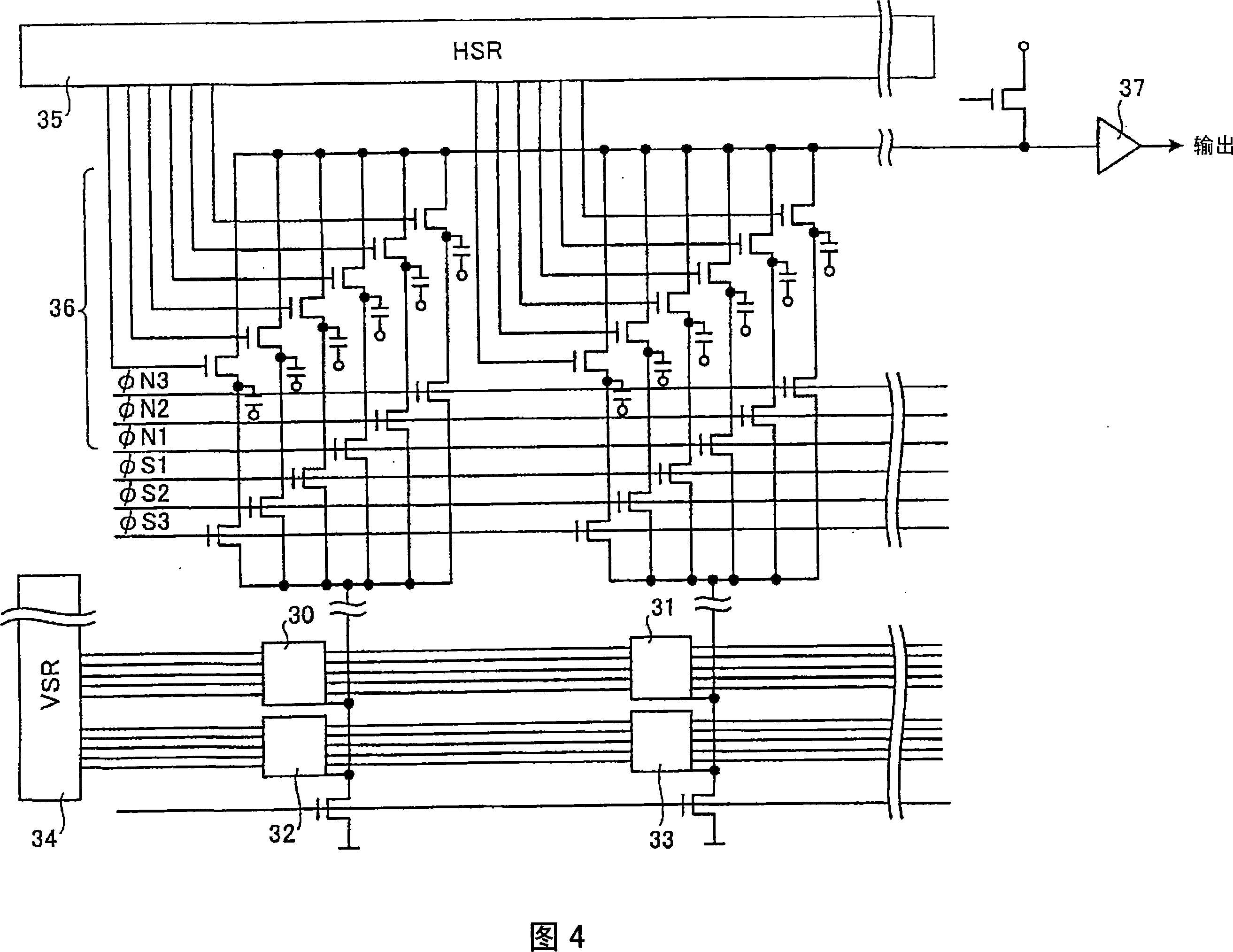
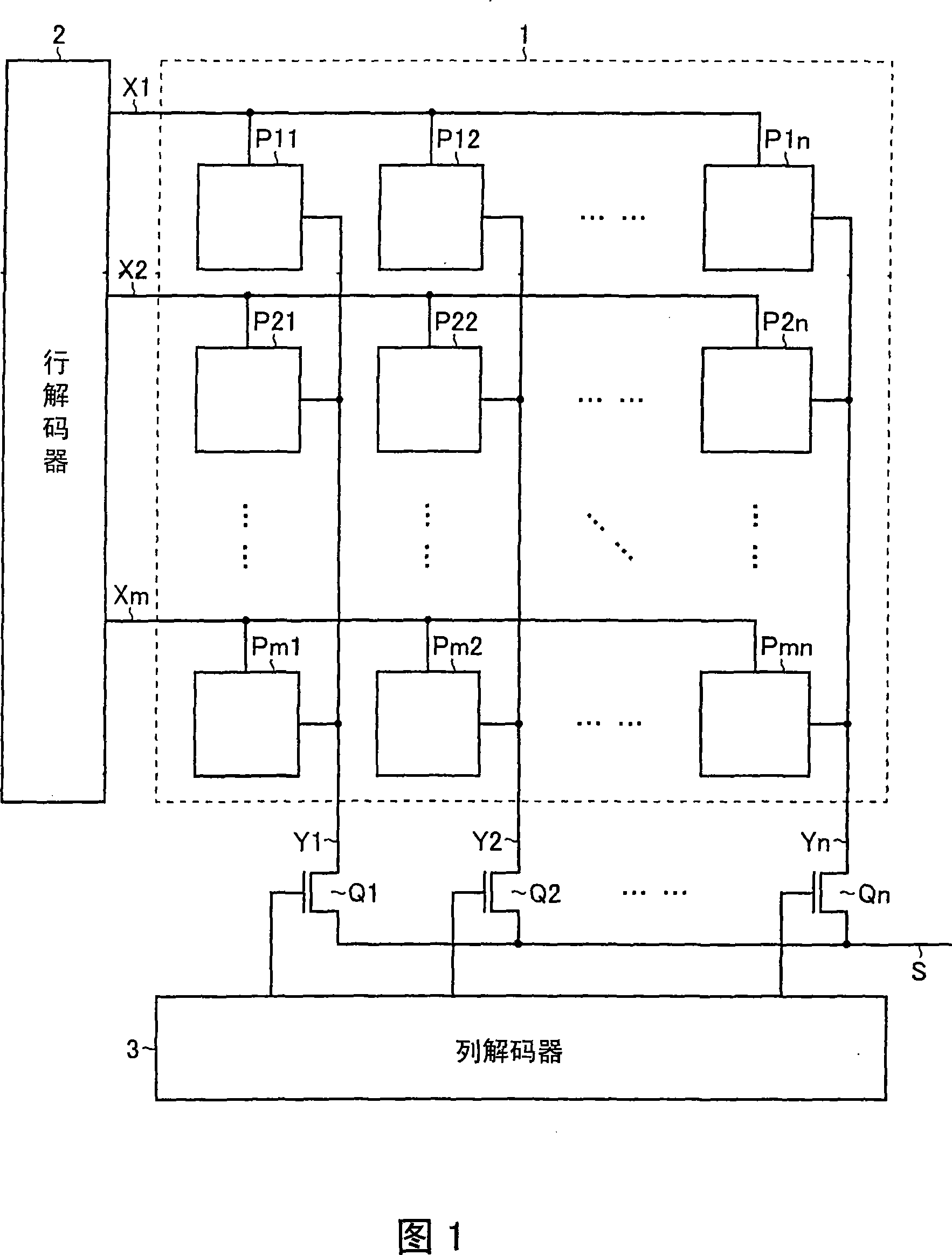
Each pixel is provided with a photoelectric converting device S1(1-1) or the like, a source-follower-type first transistor T1(1-1) or the like, a second transistor Te(1-1) to be turned on when reading an electrical signal from a pixel selected by a shift register SR1 for each line and outputting the signal to a readout circuit unit and a third transistor T3(1-1) to be turned on when resetting a photoelectric converting device set to a pixel selected by a shift register SR1 for each line. Moreover, a bias power source for supplying a photoelectric conversion bias to a photoelectric converting device and a reset power source for supplying a reset bias to a photoelectric converting device are set in the readout circuit unit. By using the radiation image pickup apparatus and its control method, it is possible to improve the S / N ratio while restraining noises and preferably, it is possible to perform stable and high-speed dynamic-image photographing and restrain dark current.
Owner:CANON KK
Capacitance detecting circuit and detecting method, and fingerprint sensor employing the same
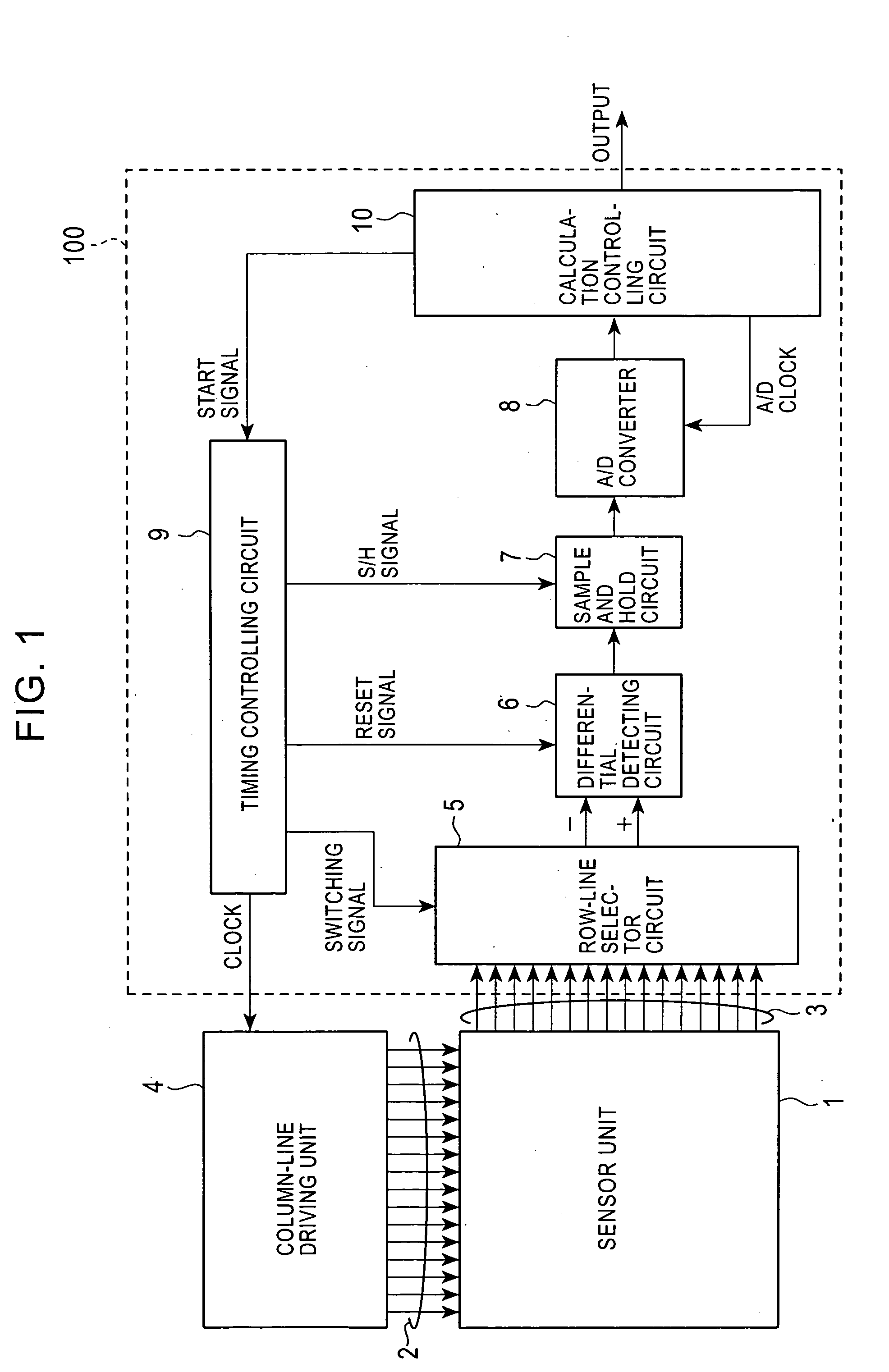
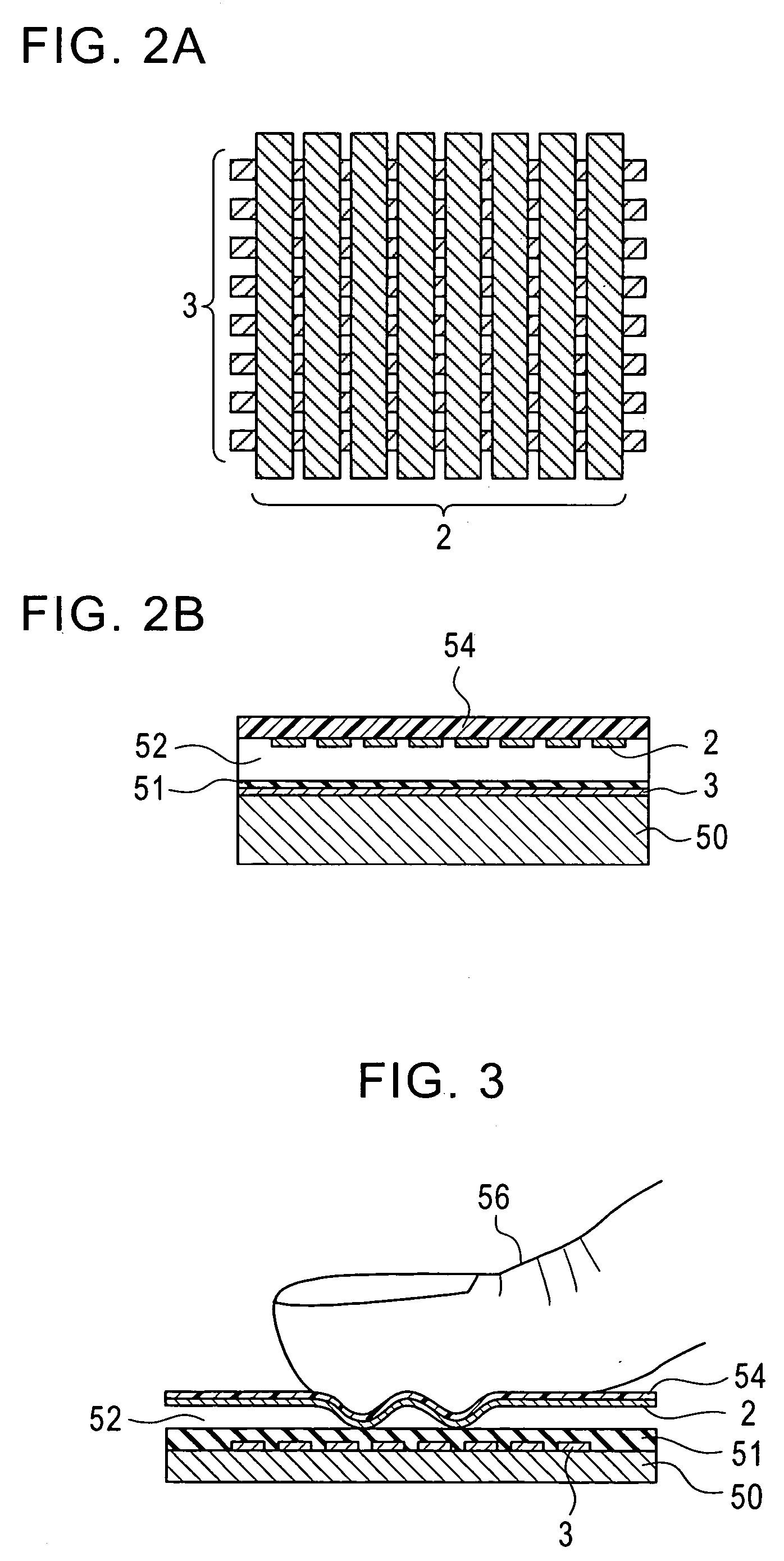
ActiveUS20050122785A1Improve S/N ratioDampening effectResistance/reactance/impedenceElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsFingerprintCapacitance
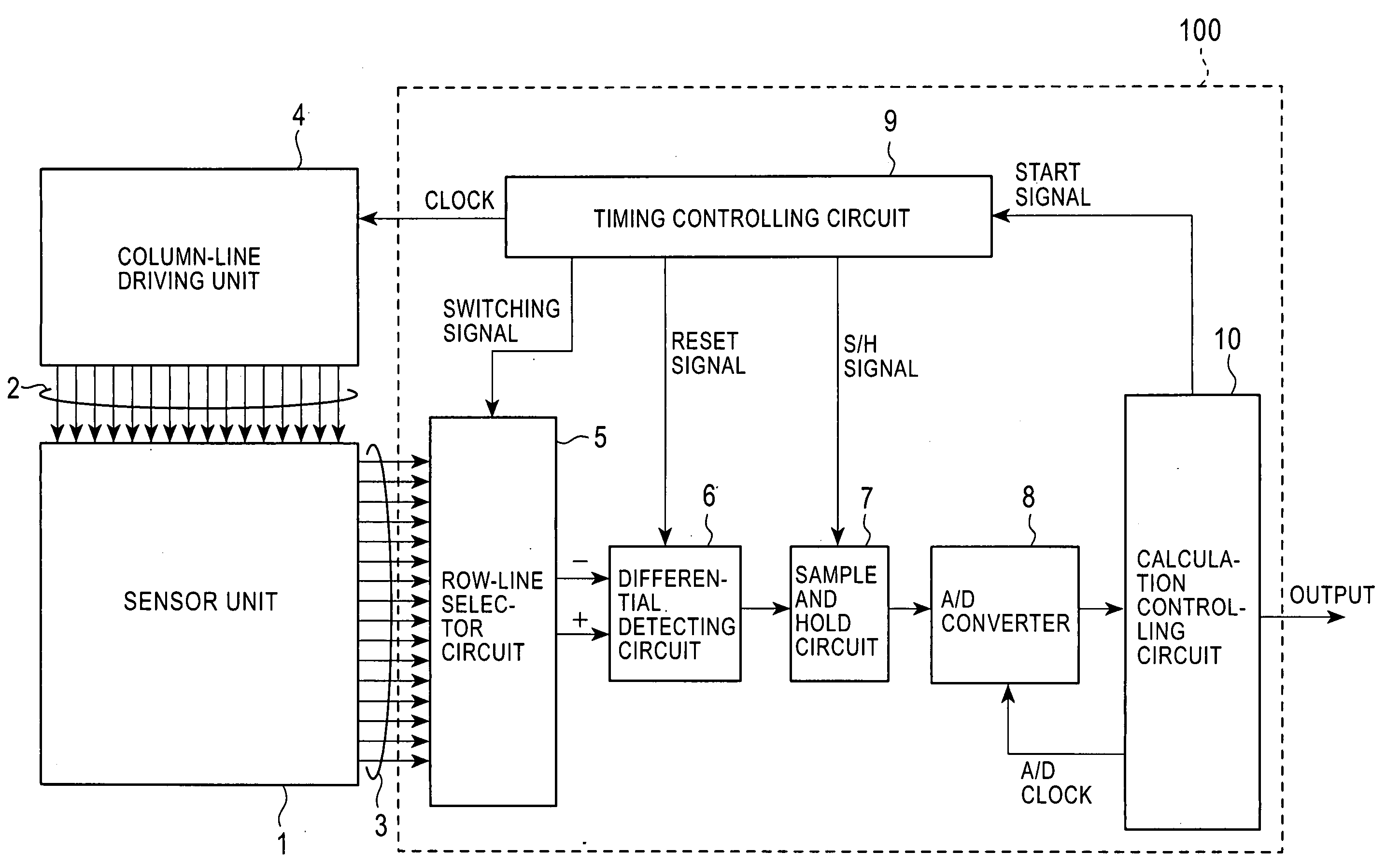
A capacitance detecting circuit detects, in terms of voltage, change in capacitance at intersections of a plurality of column lines and a plurality of row lines crossing each other. The capacitance detecting circuit includes a column-line driving unit for driving a column line; a row-line selector for selecting a specific row line from the plurality of row lines; and a capacitance calculator for calculating a capacitance at an intersection of the specific row line and the driven column line based on a reference current that flows in relation to a reference capacitance and a current that flows in relation to the capacitance at the intersection.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Organism information measuring device and organism information measuring method
InactiveUS20050253047A1Improve S/N ratioIncrease measurement accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCounting objects on conveyorsPhysicsMeasurement device
To improve an S / N ratio and increase a measurement accuracy of an organism information. There is provided an organism information measuring device possessing a main body disposed under a state that its lower face has contacted with an organism surface, a light irradiating part which is disposed in the lower face of the main body and irradiates a light toward an organism, a 1st light receiving part which is disposed in the lower face of the main body and near the light irradiating part, receives a backward scattered light from the organism and generates an organism information signal complying with a received light quantity, a 2nd light receiving part which is disposed in the lower face of the main body and in a position spaced from the light irradiating part more than a distance between the 1st light receiving part and the light irradiating part, receives a backward scattered light from the organism and generates an organism information signal complying with a received light quantity, and an organism information operating part which calculates an organism information on the basis of the organism information signals having been generated by the 1st light receiving part and the 2nd light receiving part.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Image capturing apparatus
ActiveUS20120038810A1Improve S/N ratioImprove signal-to-noise ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsThinningImage sensor
An image capturing apparatus includes: an image sensor including image sensing pixels that generate a signal for image generation, and focus detection pixels dividing the pupil region of an imaging lens into pupil regions and generating a signal for phase difference detection by photoelectrically converting object images from the pupil regions obtained by the division; a switching unit that switches between an all-pixel readout mode in which signals from all of the multiple pixels are read out and a thinning readout mode in which the signals of the multiple pixels are thinned and read out; and a control unit that, in the case where the mode has been switched by the switching unit to the thinning readout mode, controls the accumulation of charges in imaging rows used for image generation and focus detection rows including the focus detection pixels independent from each other.
Owner:CANON KK
Solid-state imaging device, driving method thereof, and camera
InactiveCN101610419AHigh gainReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierEngineering
A solid-state imaging device which optimizes gains for each color without a need for complicated control of changing the resistance values of variable resistances and switching switches depending on pixels from which signals are to be read, while preventing an S / N deterioration in AD conversion. The solid-state imaging device comprises: a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix; column amplifiers, each amplifying signals generated by pixels of a corresponding one of columns of the matrix; and column AD converters, each performing AD conversion on a signal generated by a corresponding one of the column amplifiers, wherein each of the plurality of pixels corresponds to a color among colors, and each of the column amplifiers amplifies output signals generated by all pixels of a corresponding one of the colors, among pixels of the corresponding column of the matrix.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Display apparatus
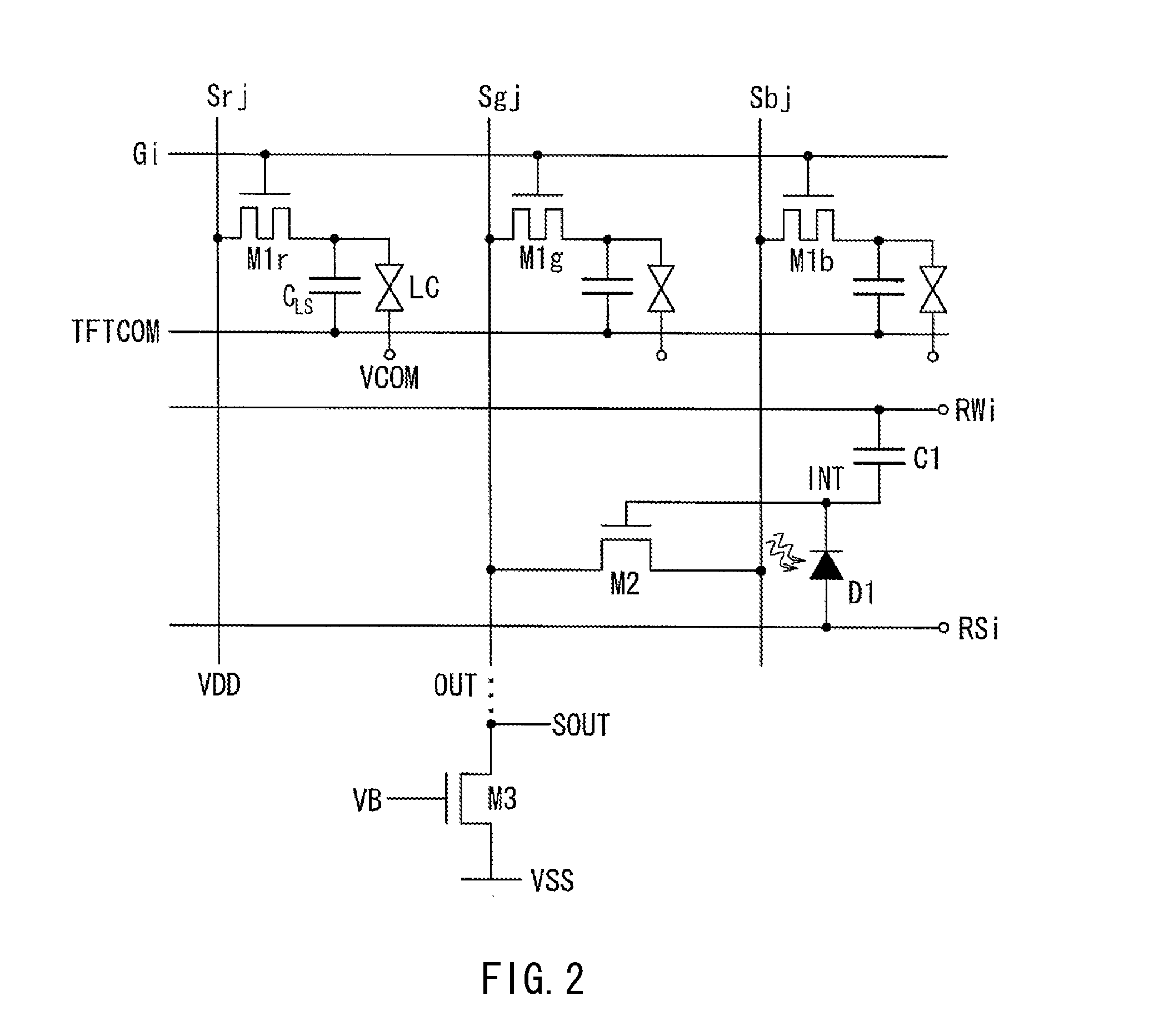
InactiveCN101452137AImprove utilizationImprove S/N ratioStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsOptoelectronics
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Solid-state imaging device, optical sensor, and solid-state imaging device operation method
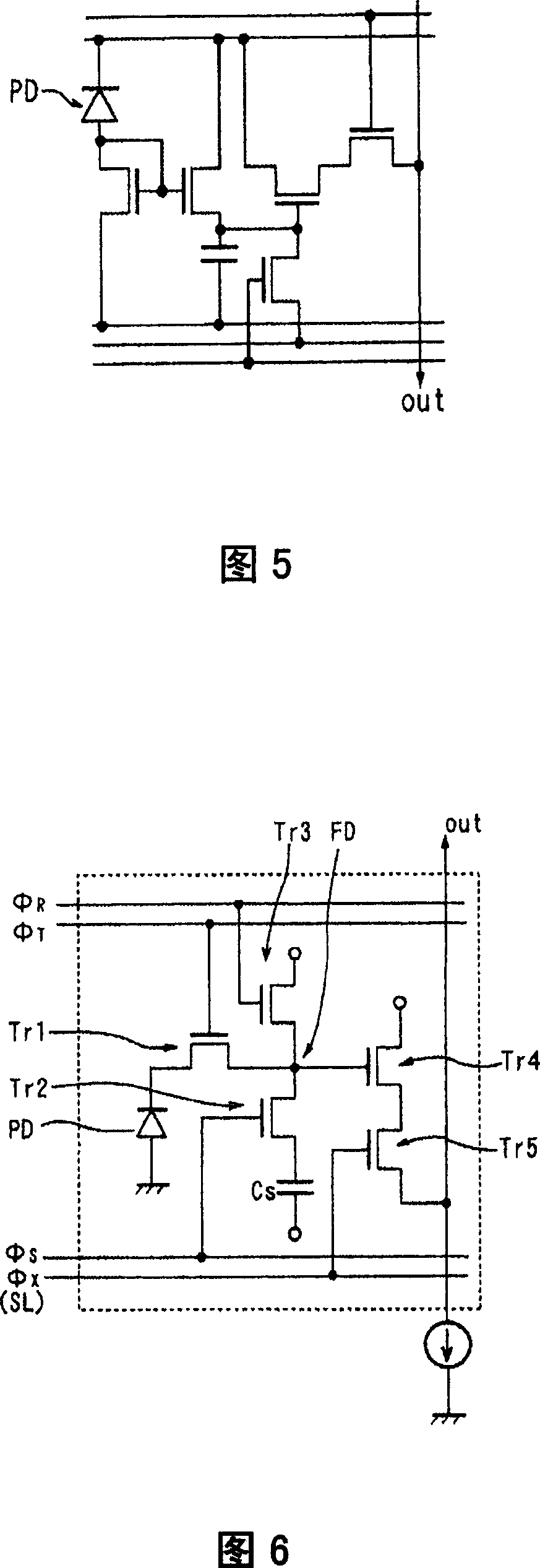
ActiveCN1965572AHigh sensitivityImprove S/N ratioTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCapacitanceEngineering
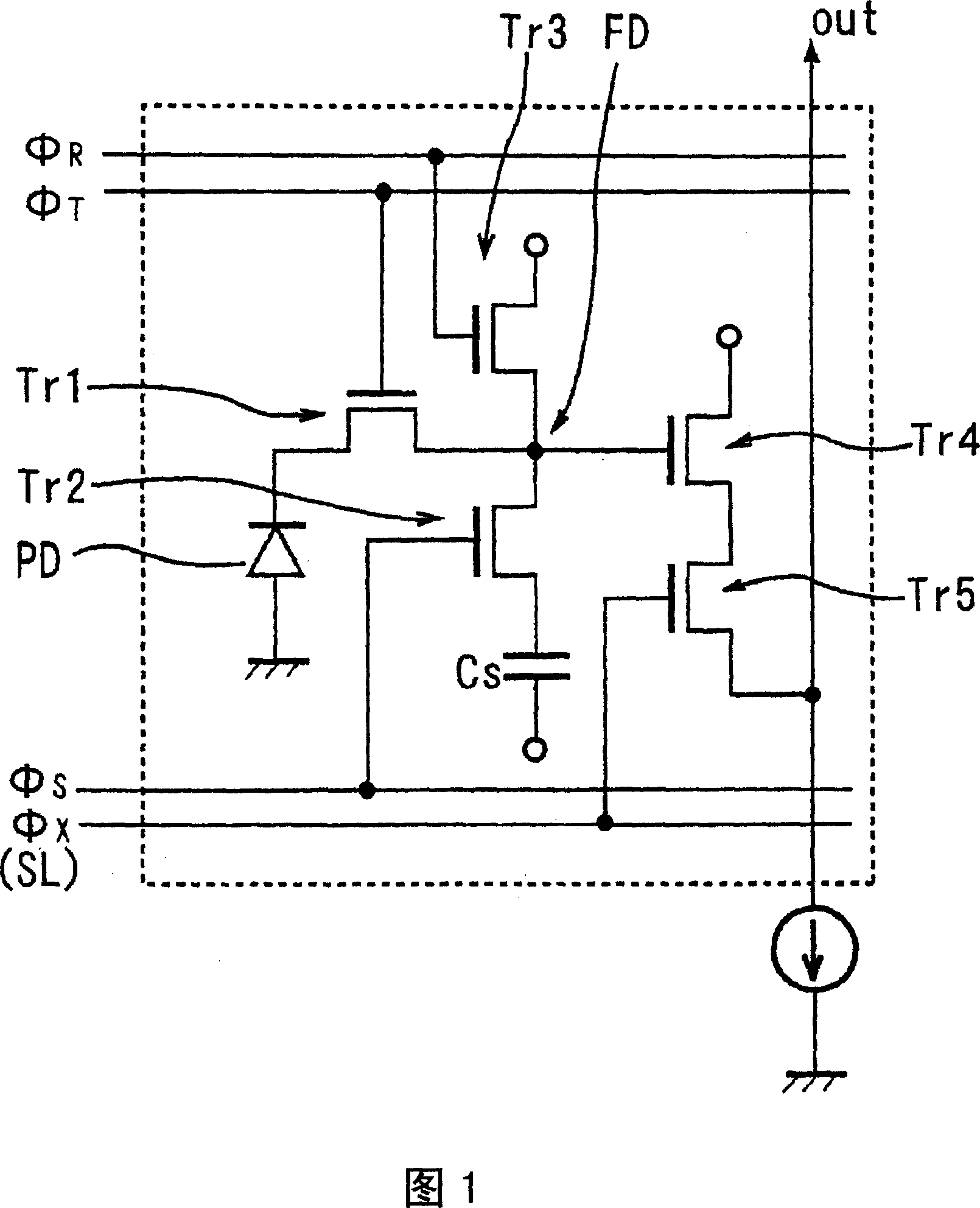
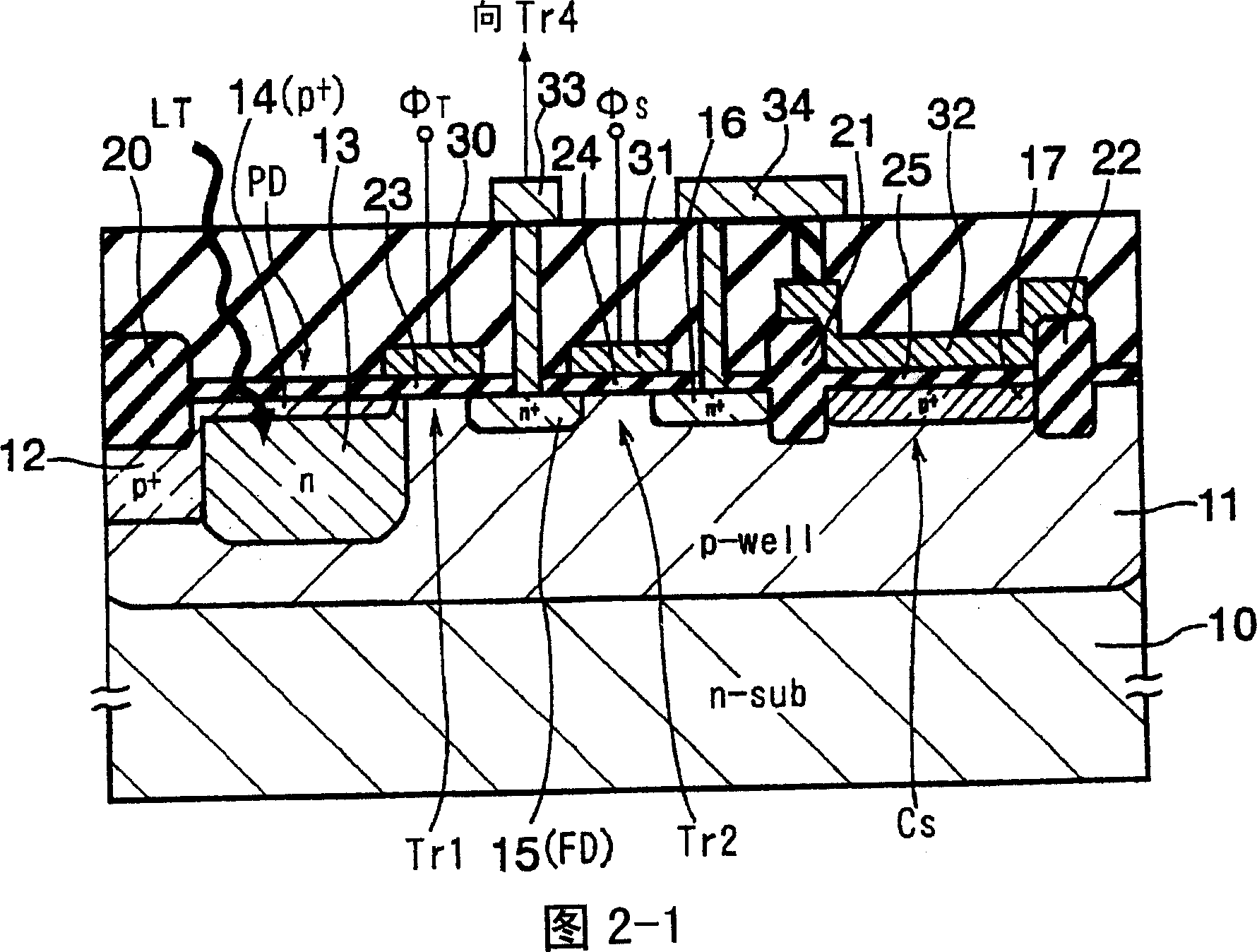
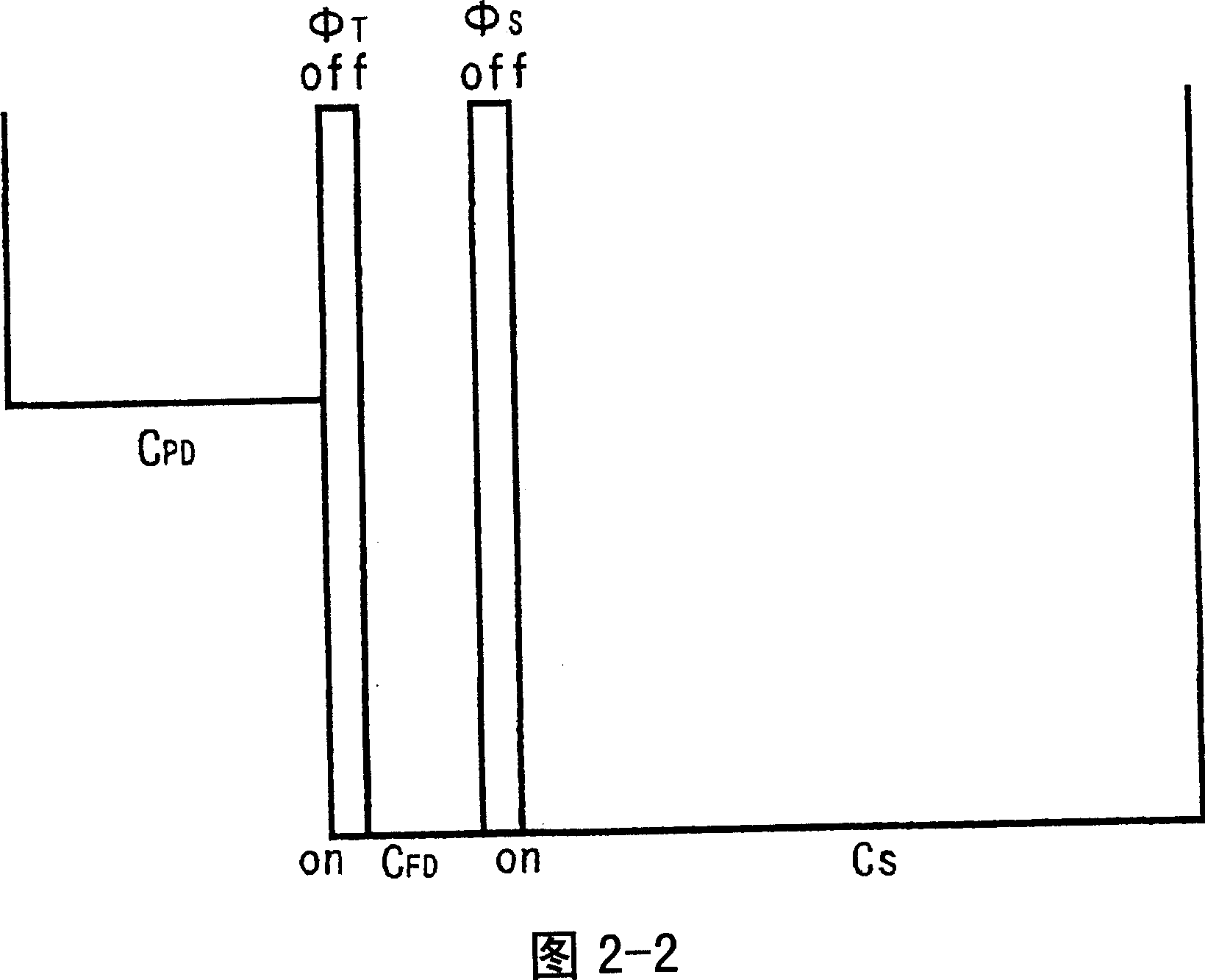
There are provided a solid-sate imaging device and an optical sensor which can have a wide dynamic range while maintaining a high sensitivity and a high S / N ratio, and a solid-state device operation method for having a wide dynamic range while maintaining the high sensitivity and the high S / N ratio. Each of the pixels has a photodiode PD for receiving light and generating and accumulating photoelectric charge and an accumulation capacity element Cs for accumulating photoelectric charge flowing out from the photodiode which are connected via a transfer transistor Tr1. The pixels are accumulated in an array shape. Here, the accumulation capacity element Cs has a configuration for accumulating photoelectric charge flowing out from the photodiode PD in the accumulation capacity element accumulation period Tcs set with a predetermined period ratio from the accumulation period of the photodiode PD.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Disc-shaped recording medium disc driving device and method and apparatus for producing disc
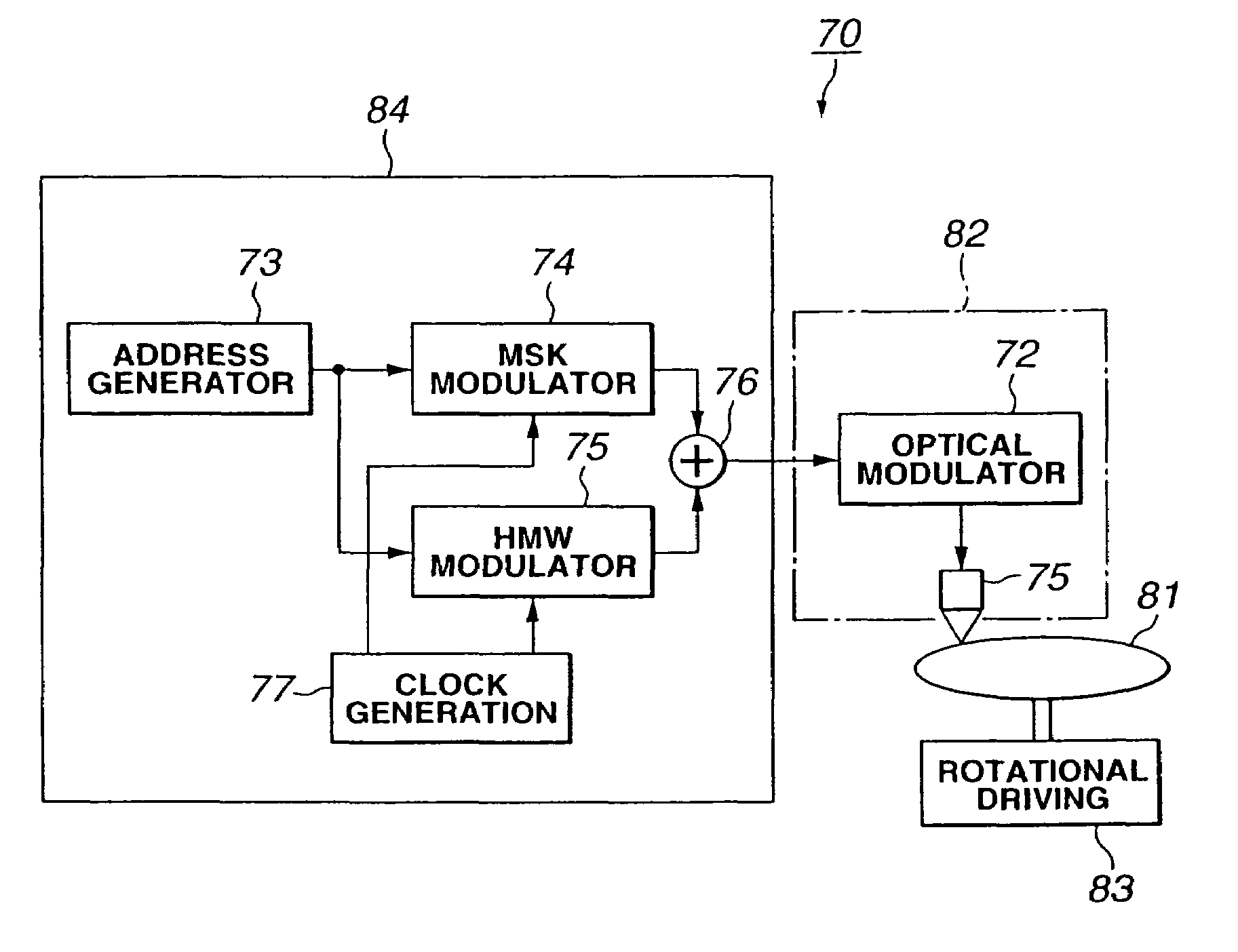
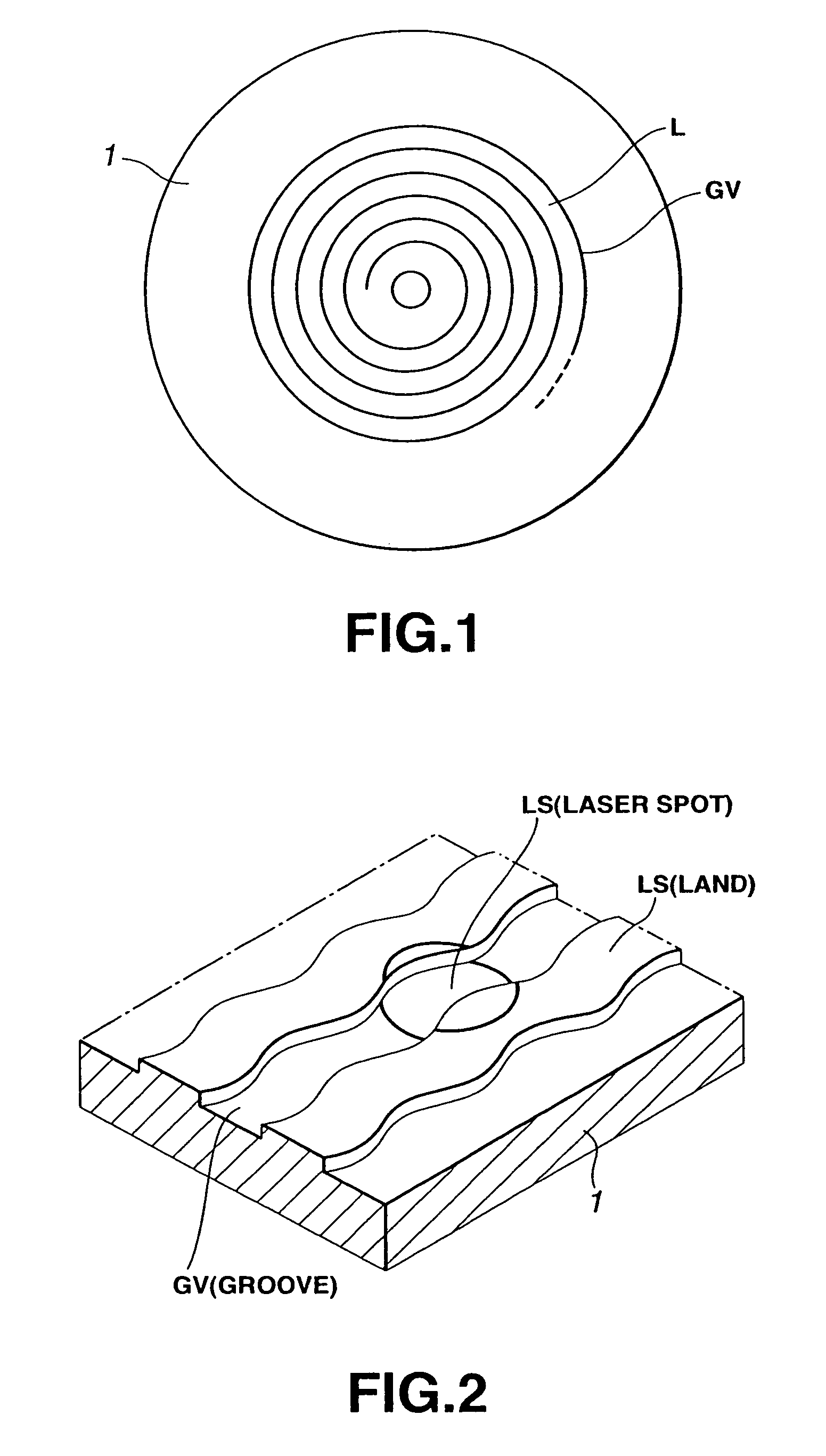
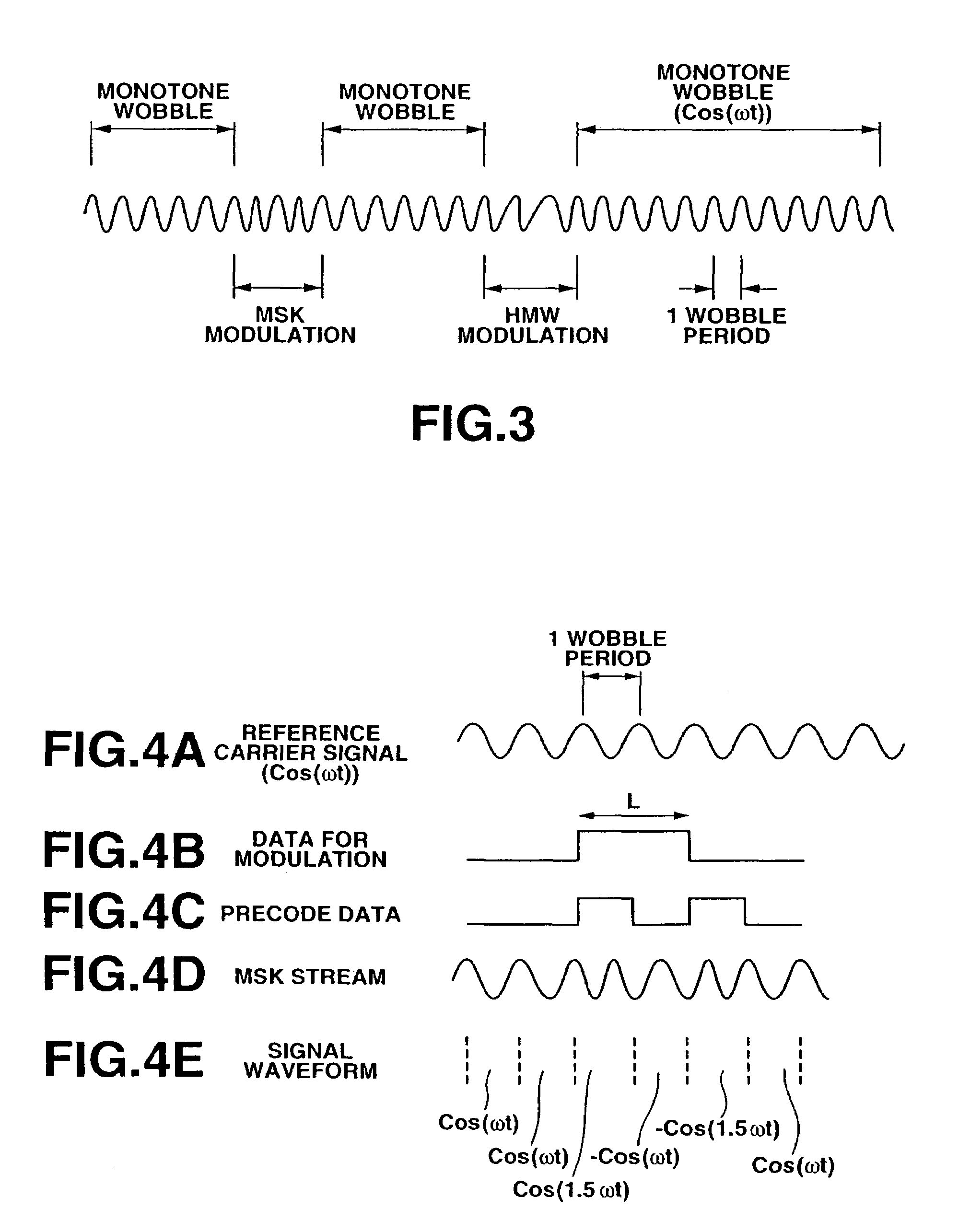
ActiveUS7123557B2S/N ratioImprove S/N ratioTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersCarrier signalEngineering
The information such as address is to be efficiently formed into wobble components and further the S / N ratio in reproducing the information formed into the wobble components is to be improved. In an optical disc of the present invention, there are recorded in a wobble the address information modulated in accordance with the MSK (minimum shift keying) system and the address information modulated in accordance with a modulation system in which even harmonics signals are added to a sinusoidal carrier signal and in which the polarity of the harmonics signal is changed depending on the sign of the data for modulation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP +2
Sensor unit of thermal analysis equipment and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080080591A1Uniform quantityExclude influenceWave amplification devicesMaterial heat developmentTemperature controlReference sample
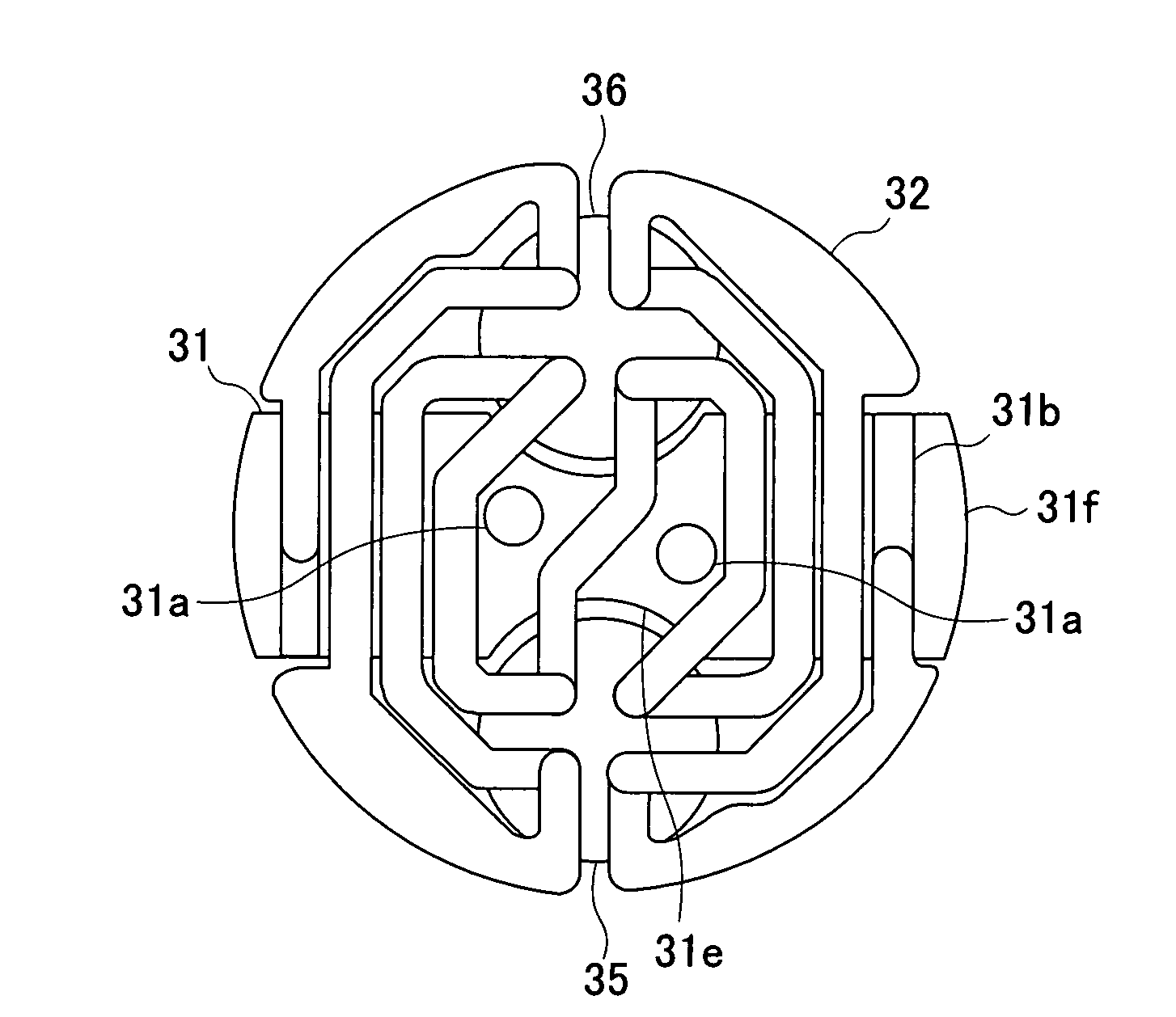
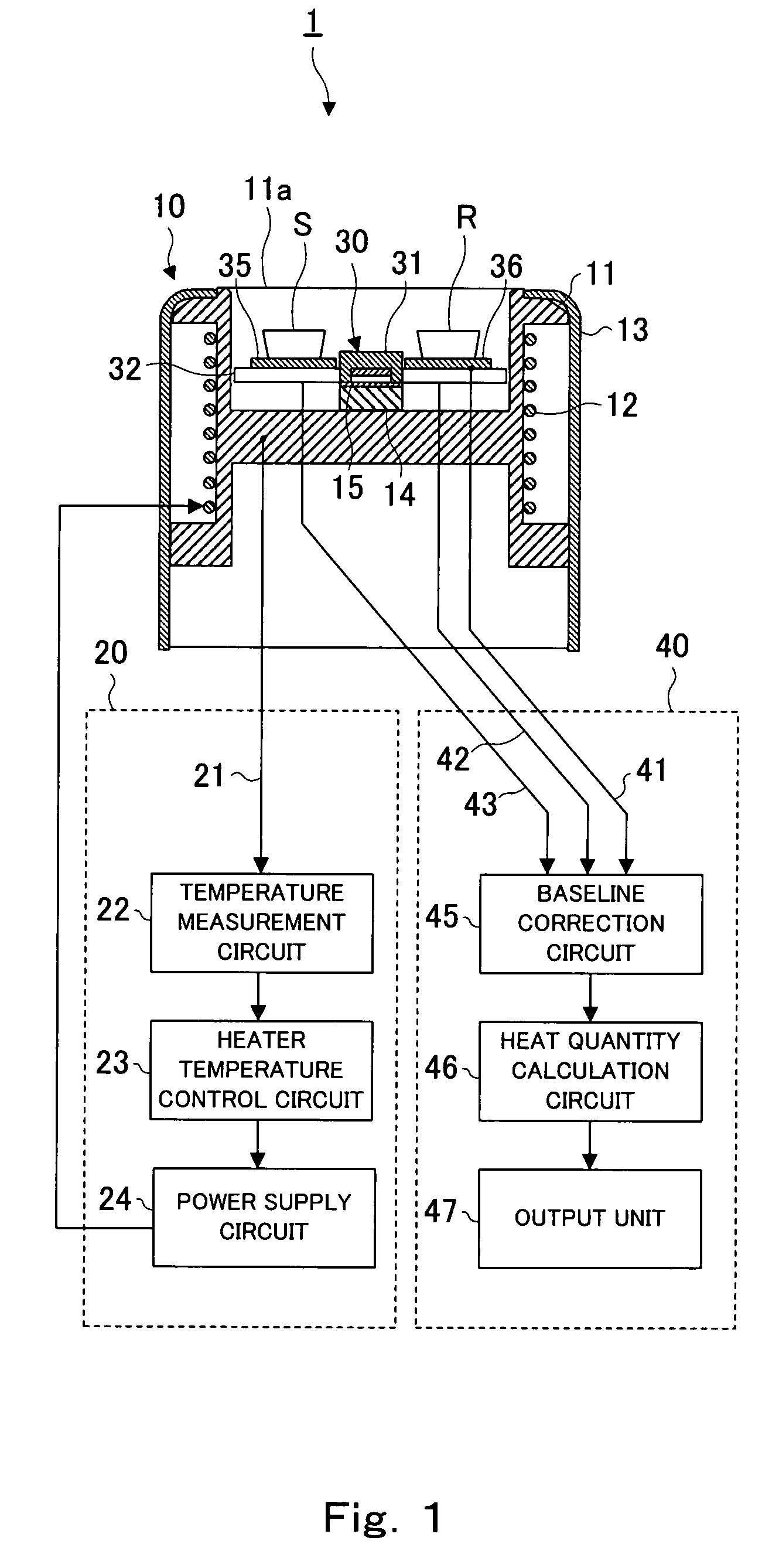
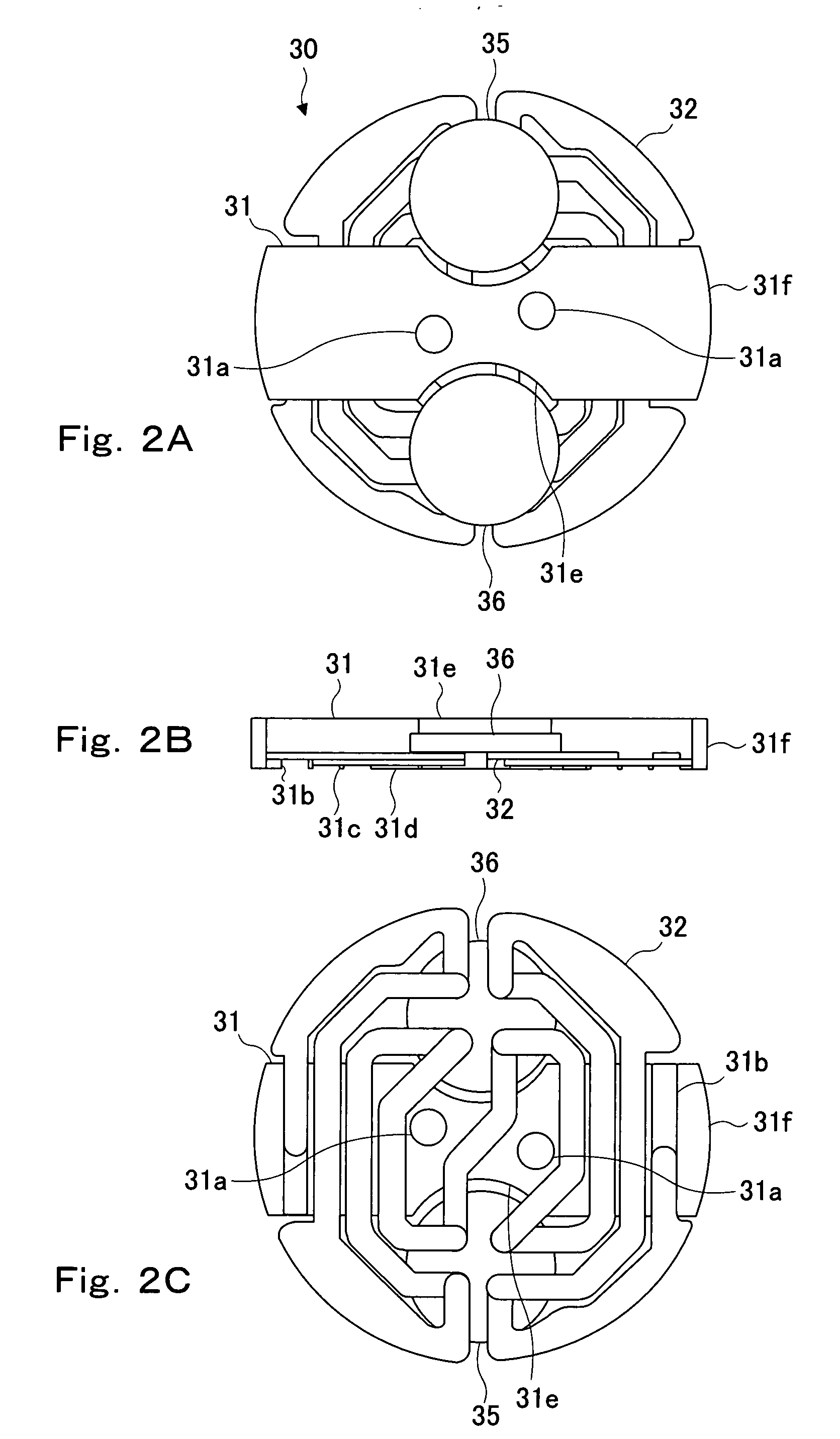
There are provided a sensor unit of thermal analysis equipment capable of keeping heat conduction between a furnace body and samples to detect a temperature difference between the samples with high sensitivity, while suppressing the heat conduction between a measurement sample and a reference sample, and a method of manufacturing the same. According to the present invention, a sensor unit 30 of a thermal analysis equipment 1 that detects a temperature difference between a measurement sample S and a reference sample R in each sample container, includes: a base part 31 formed of an insulator and provided in the vicinity of a temperature-controlled furnace unit; a multiple thermocouple 32 formed by joining two kinds of thermocouple elements alternately, a particular part of the thermocouple element being joined to the base part; and a pair of heat sensitive parts 35, 36 formed of an insulator, having a mounting surface on which each sample container is mounted, and joining to element junctions of the multiple thermocouple, wherein the pair of heat sensitive parts 35, 36 are provided spaced apart from the base part 31.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Optical sensor, solid-state imaging device, and operation method of solid-state imaging device
ActiveCN101164334AHigh sensitivityImprove S/N ratioTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceEngineering
In optical devices such as a light sensor provided with a photodiode which generates optical charges by receiving light and a transfer transistor (or an overflow gate) which transfers optical charges, and a solid-state image pickup device, optical charges overflowed from the photodiode are stored in a plurality of storage capacitor elements during storing operation, through the transfer transistor or the overflow gate. Thus, the optical devices which maintain a high sensitivity and a high S / N ratio and have a wide dynamic range can be obtained.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Optical sensor and display device
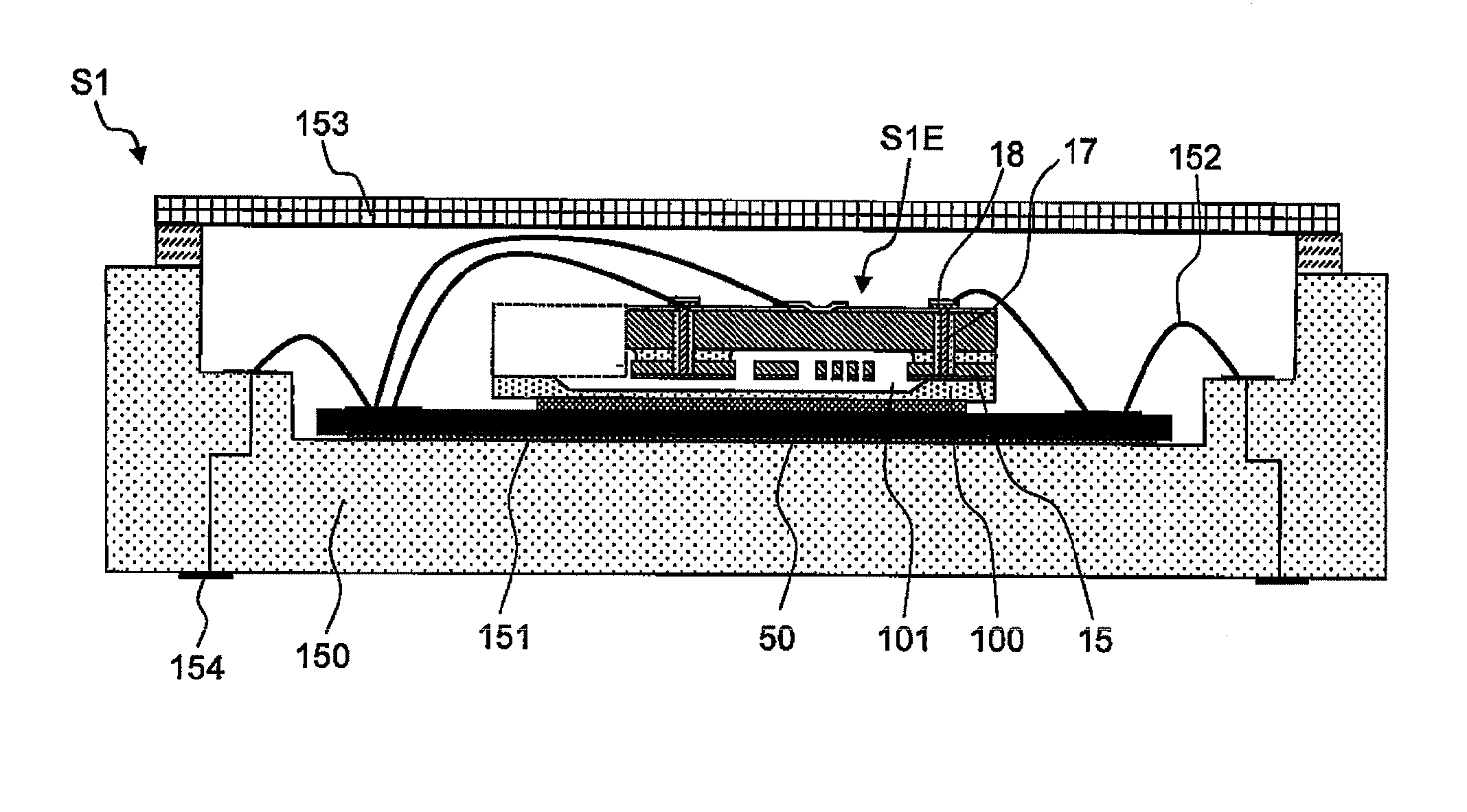
InactiveUS20120169962A1Reduce noise light incidentImprove S/N ratioPhotometry electrical circuitsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLiquid crystal
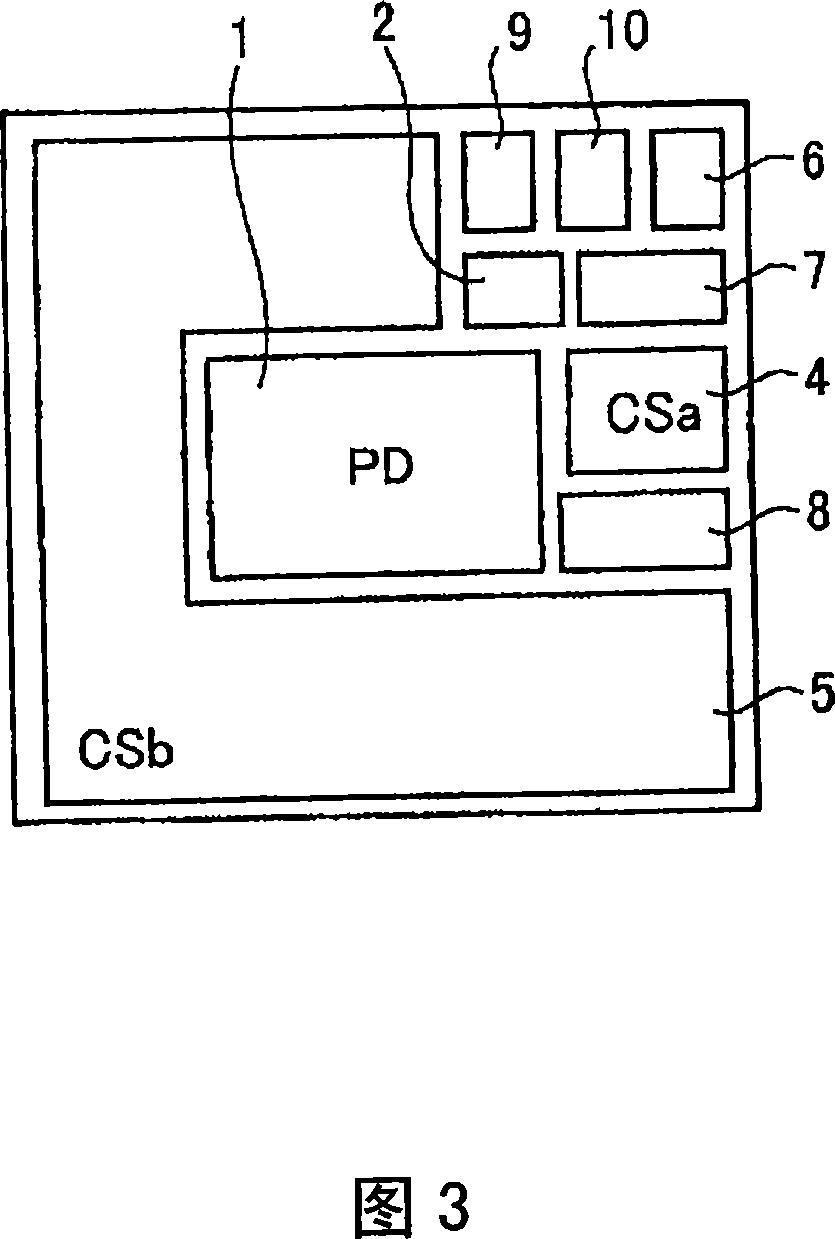
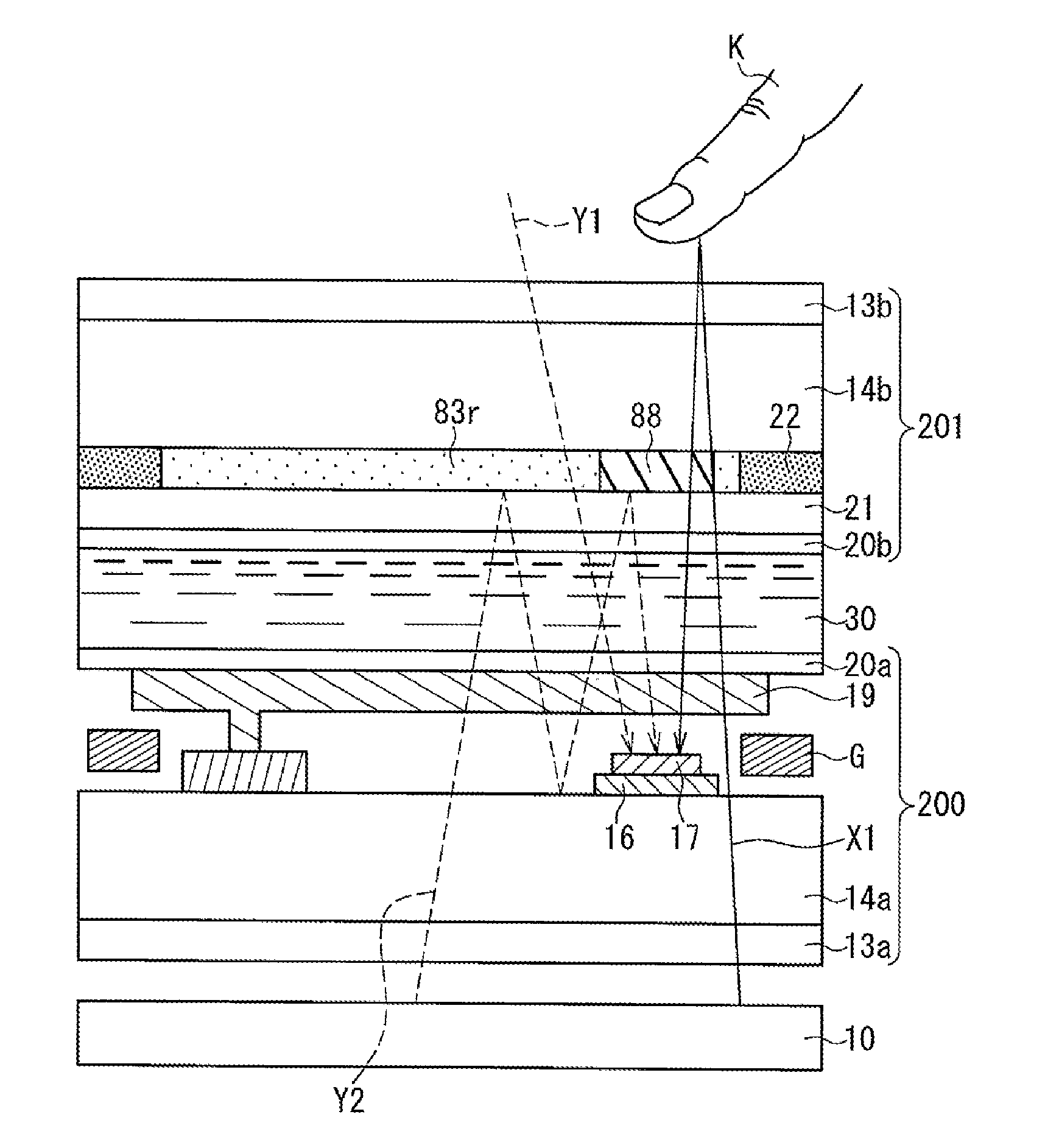
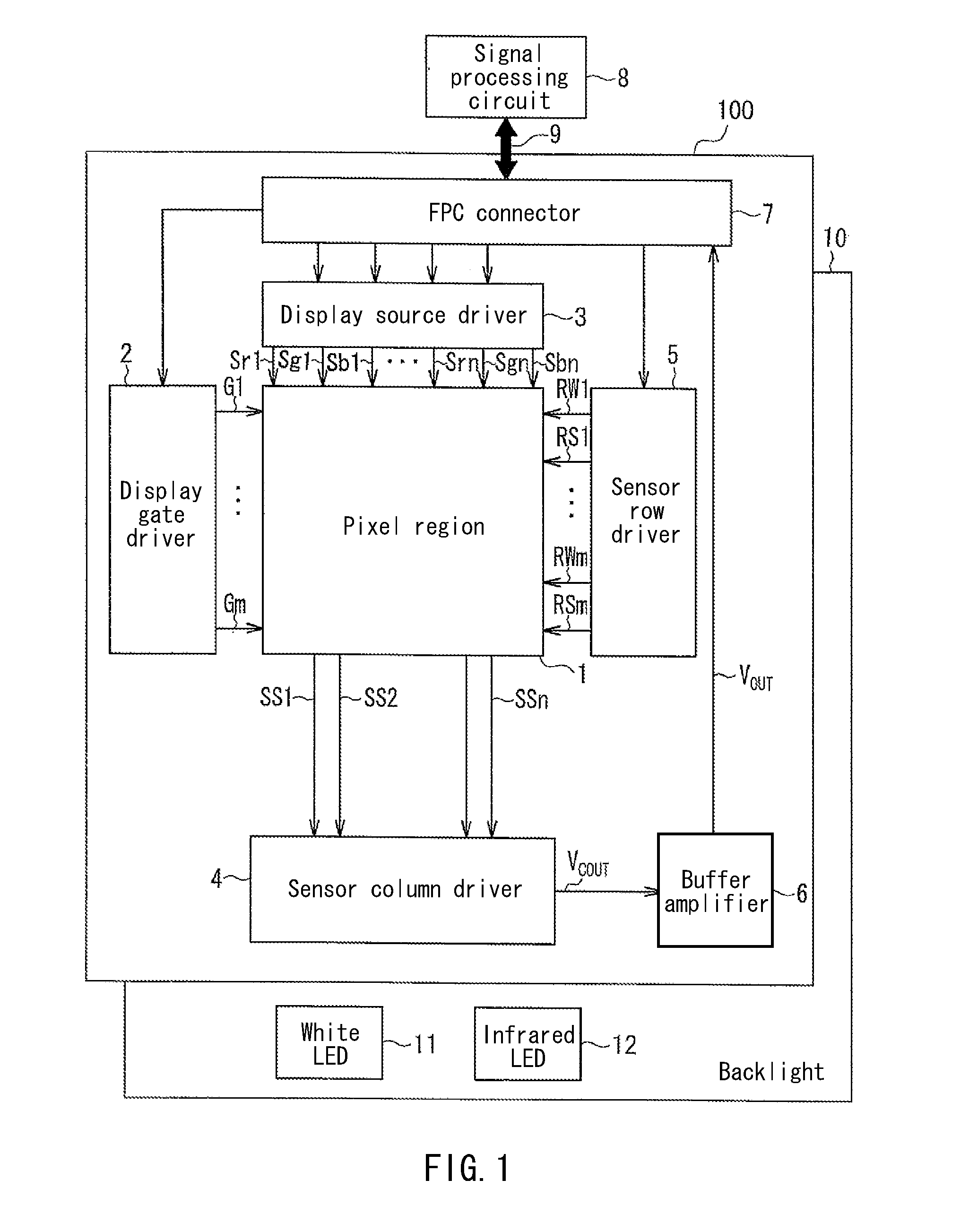
In a liquid crystal display device, noise light to a photodetecting element is reduced, whereby an improved S / N ratio is achieved. The liquid crystal display device includes: a first substrate (100) on which a pixel circuit is provided; a second substrate (101) arranged so as to face the first substrate (100) with a liquid crystal layer (30) being interposed therebetween; a photodetecting element (17) provided on the first substrate (100); and a detection light filter (18) that is provided between the photodetecting element (17) and the liquid crystal layer (30) and that cuts off light in a band outside a signal light band that is a band of light to be detected by the photodetecting element (17).
Owner:SHARP KK
Solid-state imaging device and manufacturing method therefor
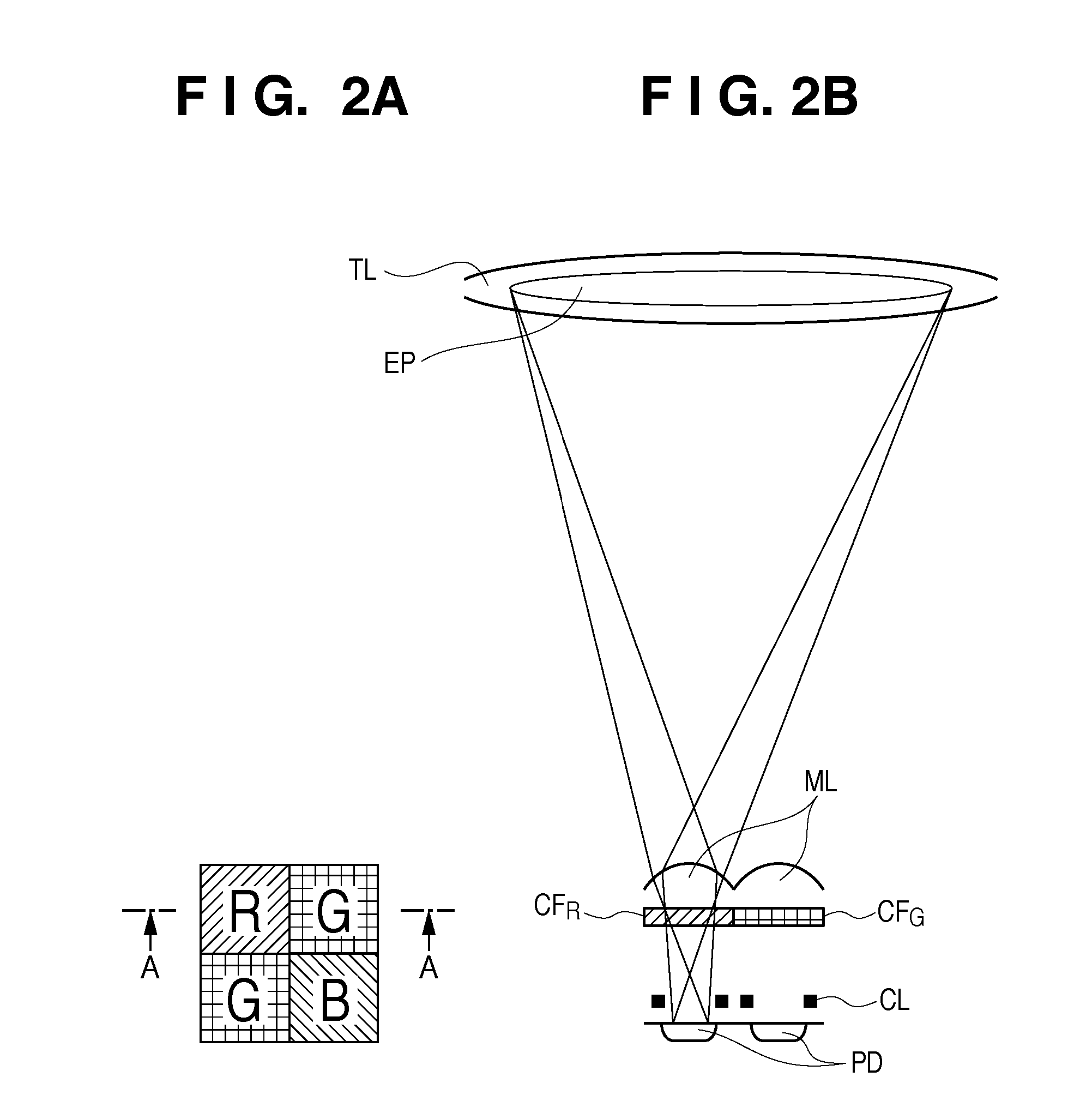
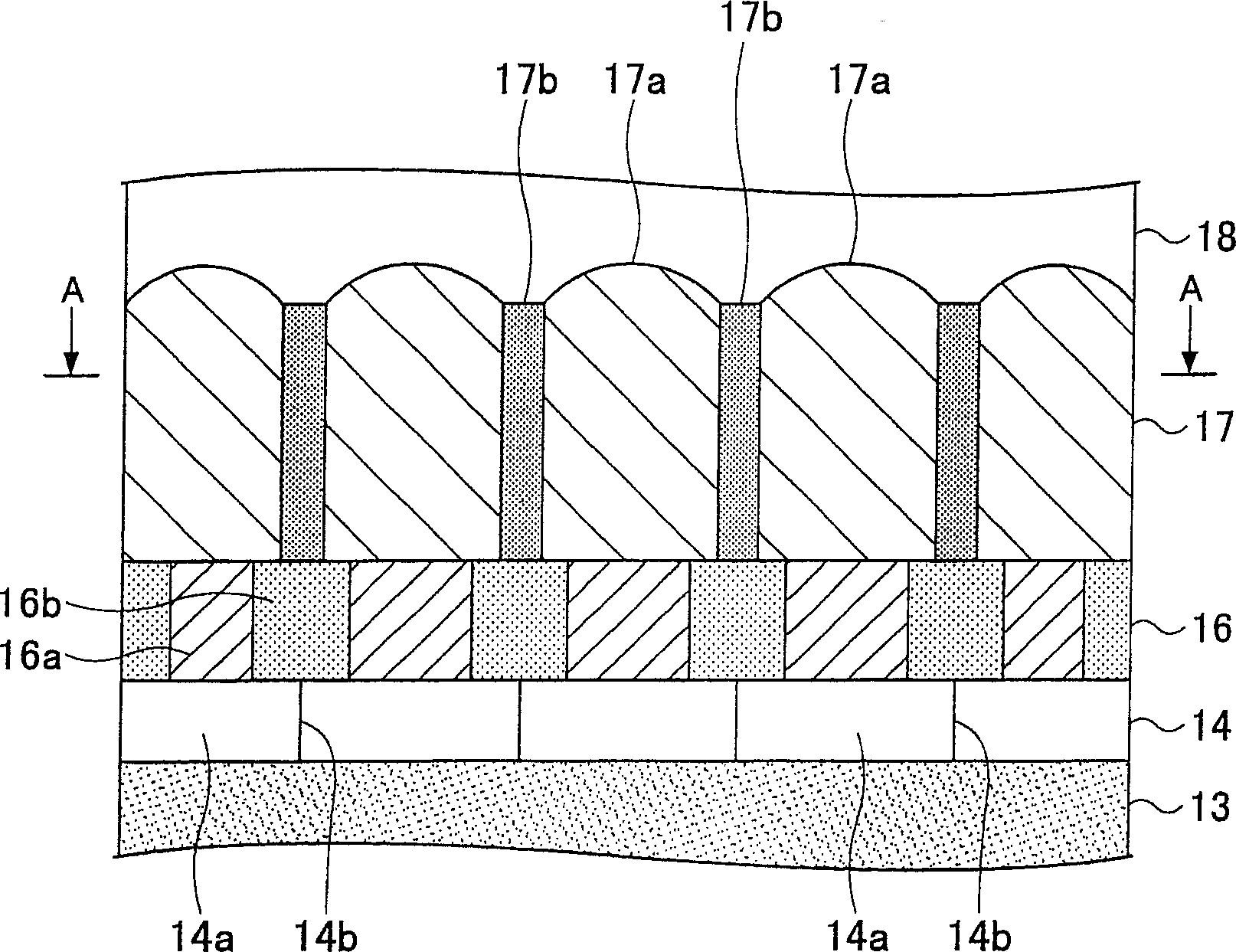
A solid-state imaging device includes a plurality of two-dimensionally arranged photo diodes and a plurality of microlenses having substantially hemispherical shapes which cover the respective photo diodes. The microlens has a multilayer structure including at least a transparent resin upper layer which forms at least a portion of the substantially hemispherical shape, and a colored lower layer provided on a portion of the transparent resin upper layer which is located above the photo diode, with an interface between the colored lower layer and the transparent resin upper layer having a shape conforming to a surface of the photo diode.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Optical information detecting method, optical head, and optical disc apparatus
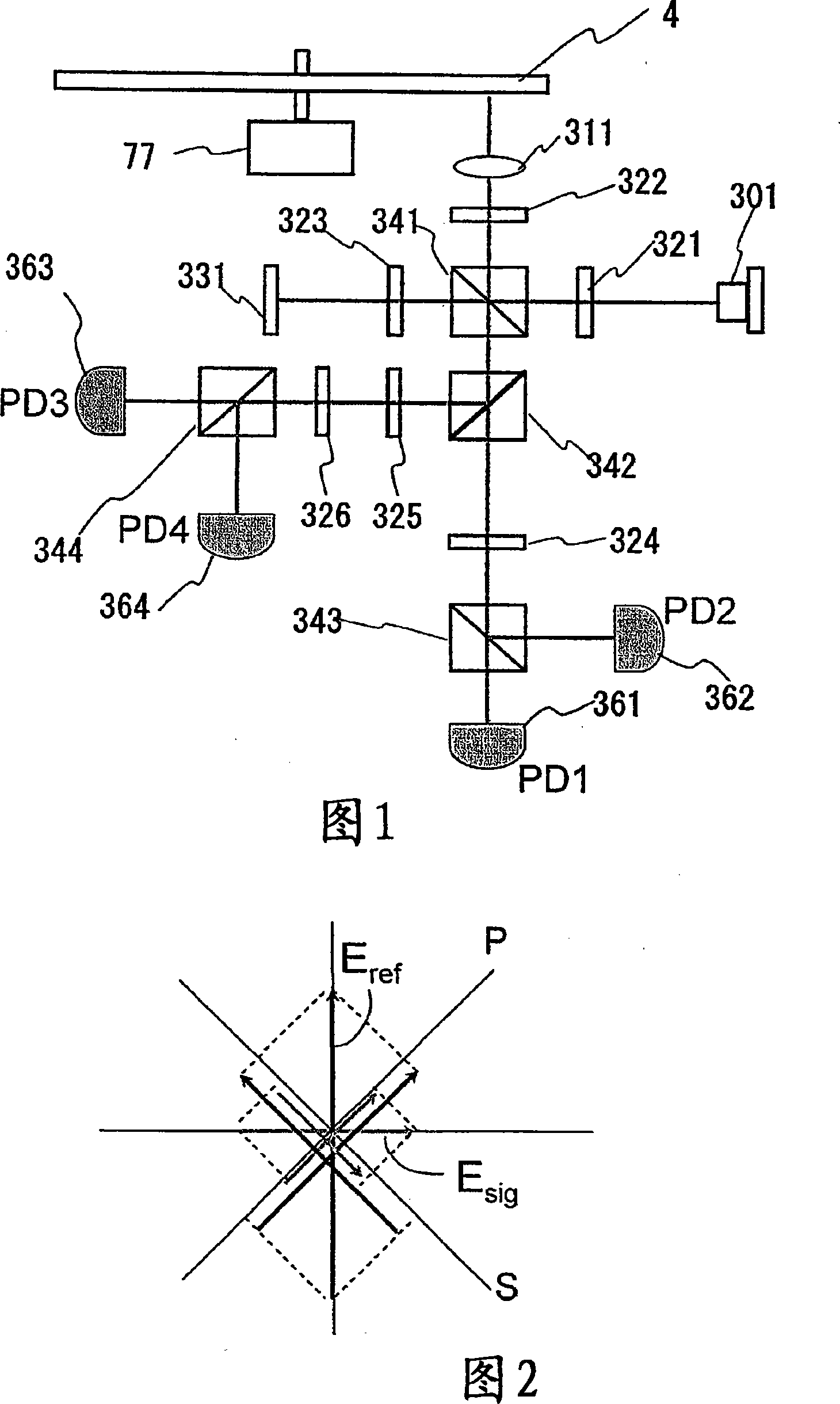
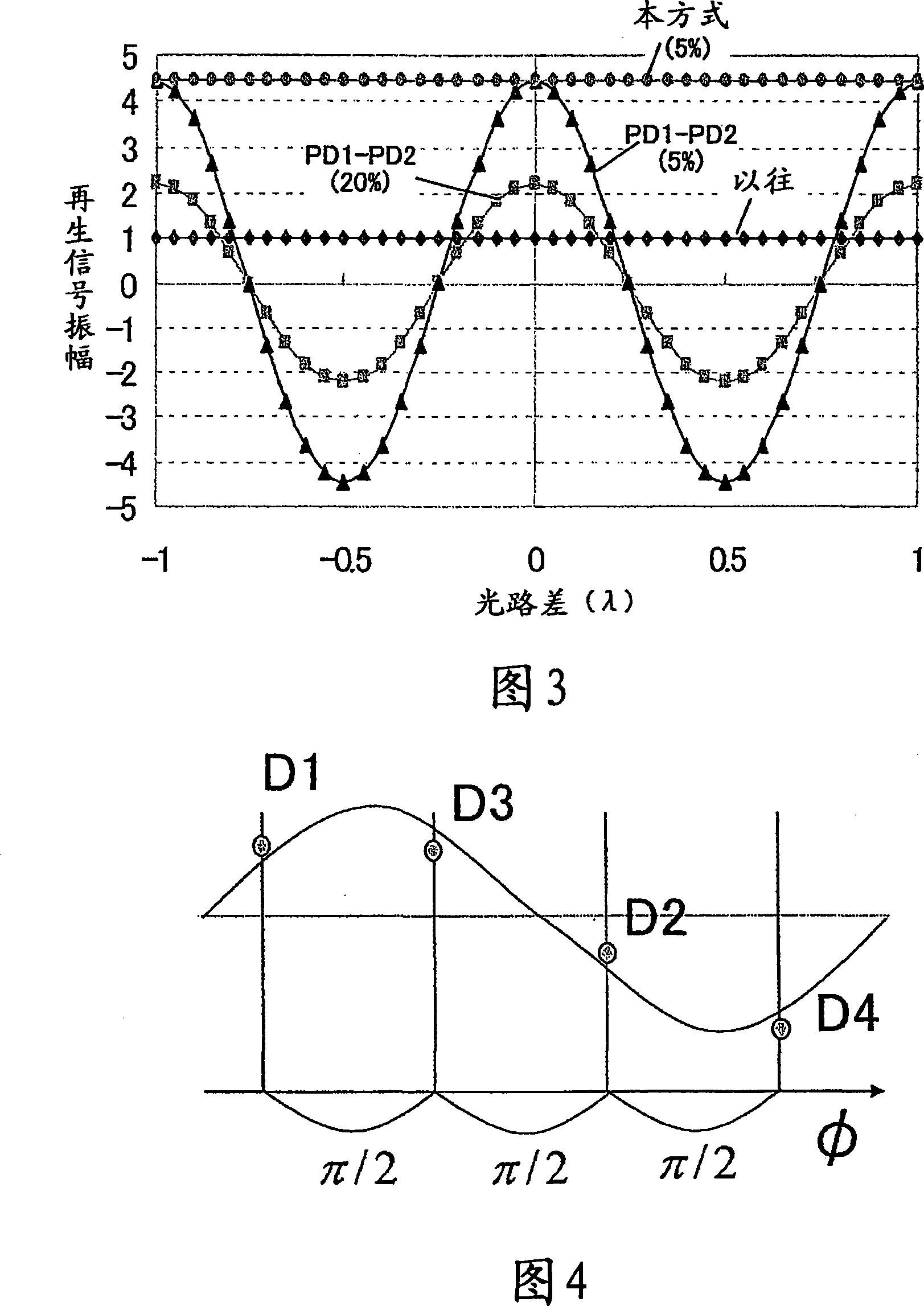
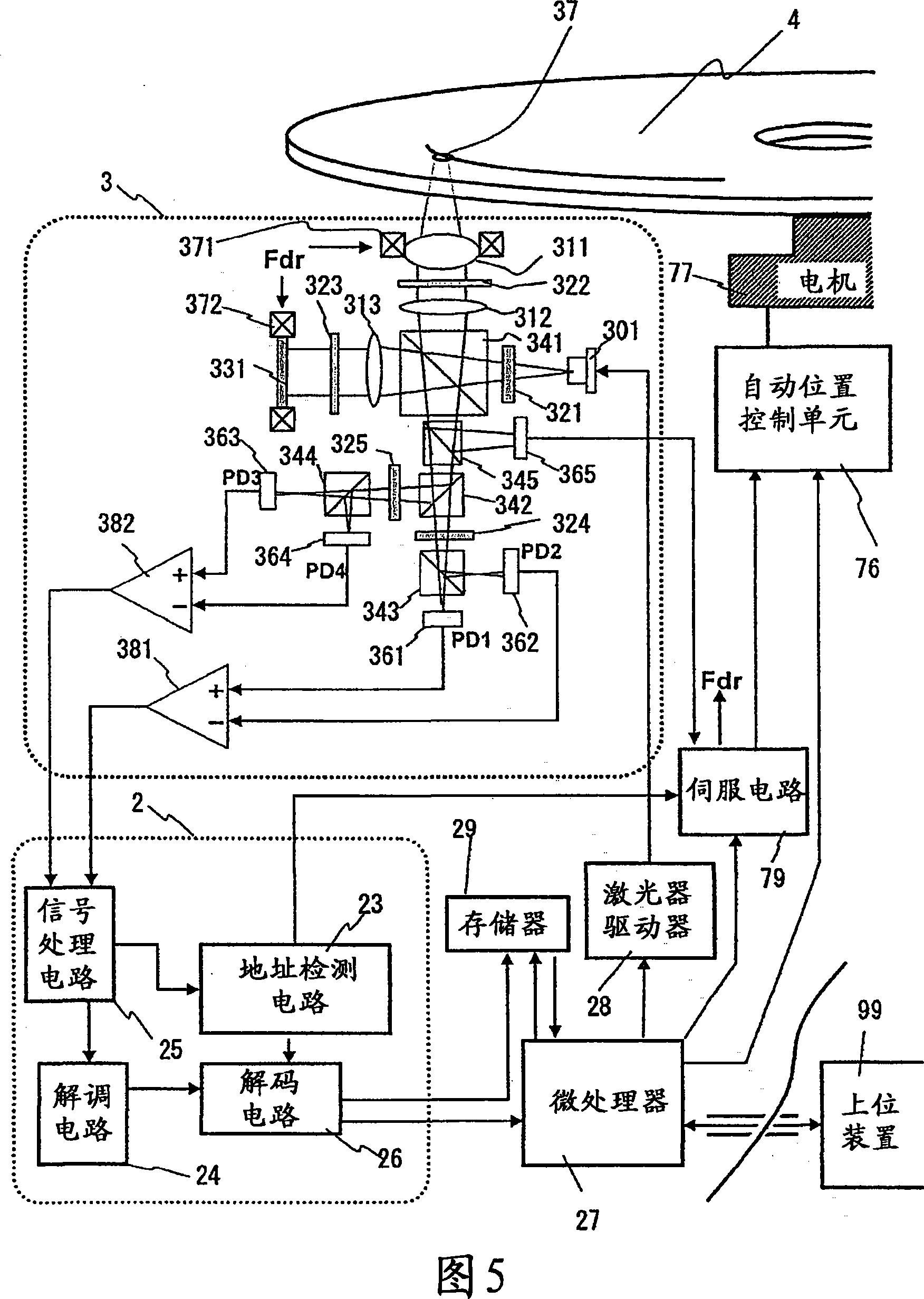
InactiveCN101145358AImprove S/N ratioEnhanced signal amplificationRecord information storageOptical recording/reproducingSignal qualitySignal light
In multilayer optical discs and high-speed optical discs, the amount of reproduction light per unit time greatly decreases and the reproduction signal quality (S / N) significantly drops due to the low effective reflectivity and the short read time of the medium. These problems are solved by causing reflected signal light from the optical disc and reference light, which is separated from the same light source and introduced into a detector without being shone onto the optical disc, to interference with each other on the detector. Detector outputs having four different interference states are simultaneously obtained, the interference states being displaced at intervals of 90 DEG in terms of the phase relationship between the reference light and the signal. Based on a operation of the four detector outputs, a reproduction signal can be obtained that is stable at all times and amplified with high quality, even when there is an optical path length variation due to disc undulations.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP
Combined Sensor
ActiveUS20130312517A1Improve S/N ratioHigh sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsPotential differenceEngineering
An object of the invention is to provide a combined sensor capable of suppressing the influence of electrostatic force generated by a potential difference and preventing a reduction in the S / N ratio or a variation in the sensitivity of a sensor.A combined sensor according to the invention includes first and second movable portions and first and second dummy portions provided around the first and second movable portions, which are formed in a layer of a laminated substrate. The first dummy portion and the second dummy portion are electrically separated from each other. A first potential is applied to the first movable portion and the first dummy portion and a second potential is applied to the second movable portion and the second dummy portion (see FIG. 2).
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
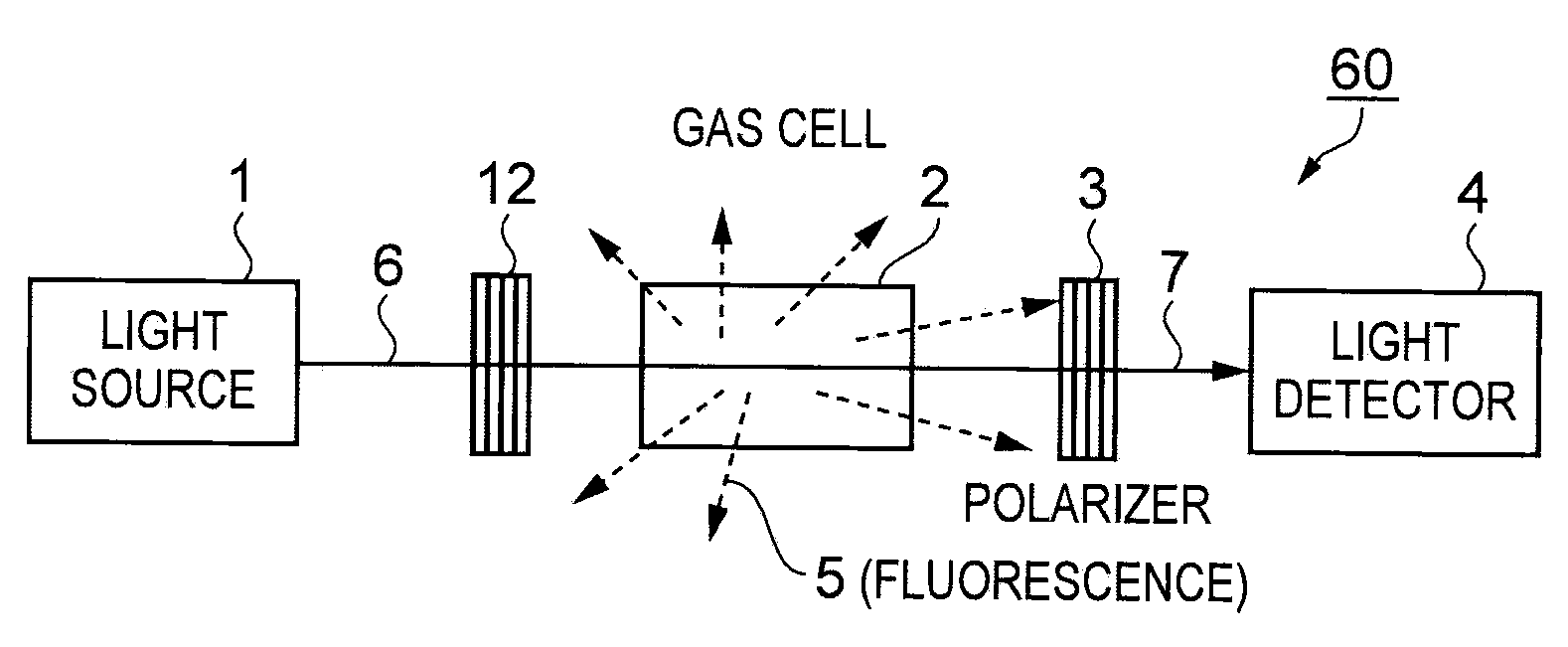
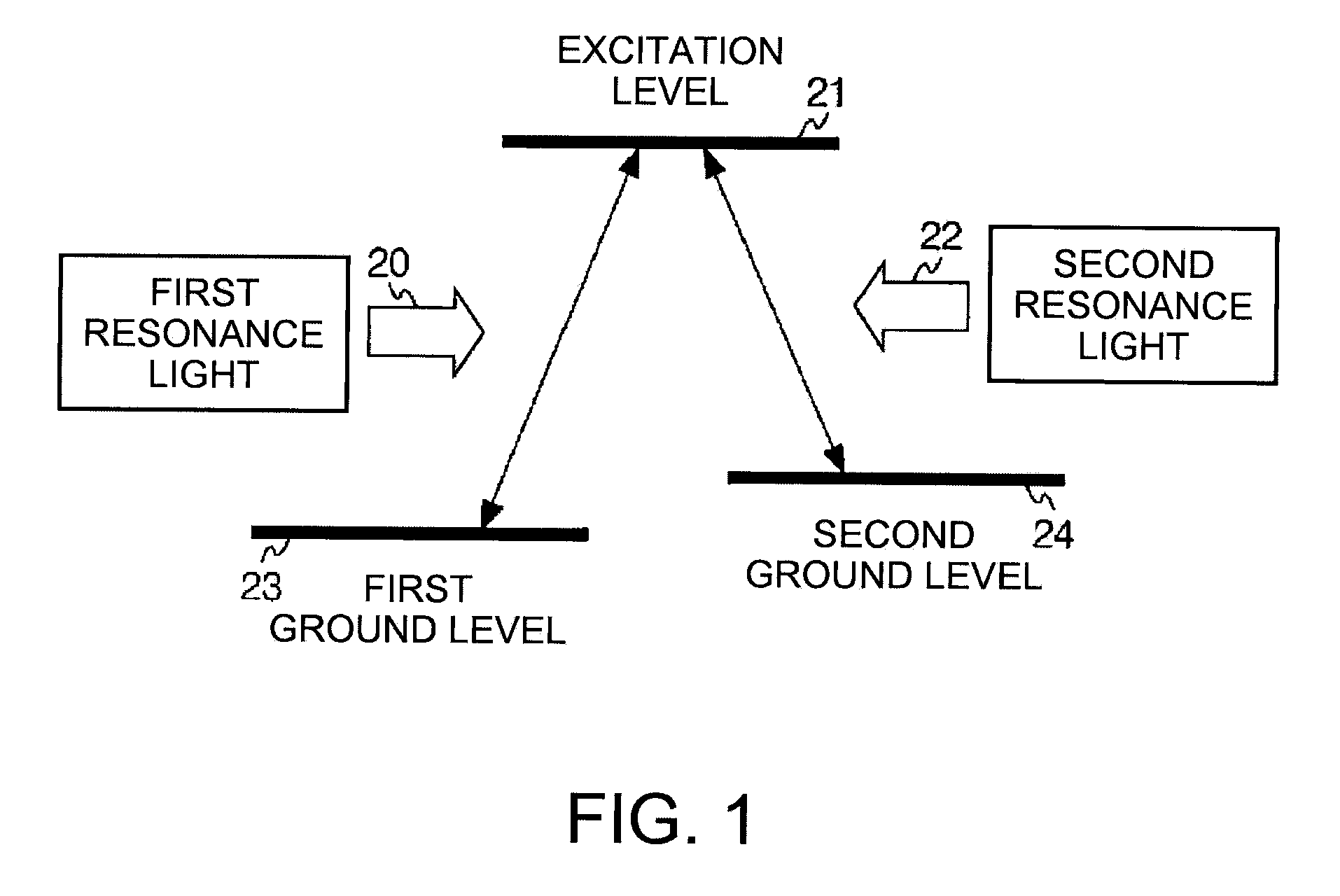
Optical system of atomic oscillator and atomic oscillator
InactiveUS20100002231A1Improve S/N ratioImprove levelPulse automatic controlGaseous masersFluorescencePopulation
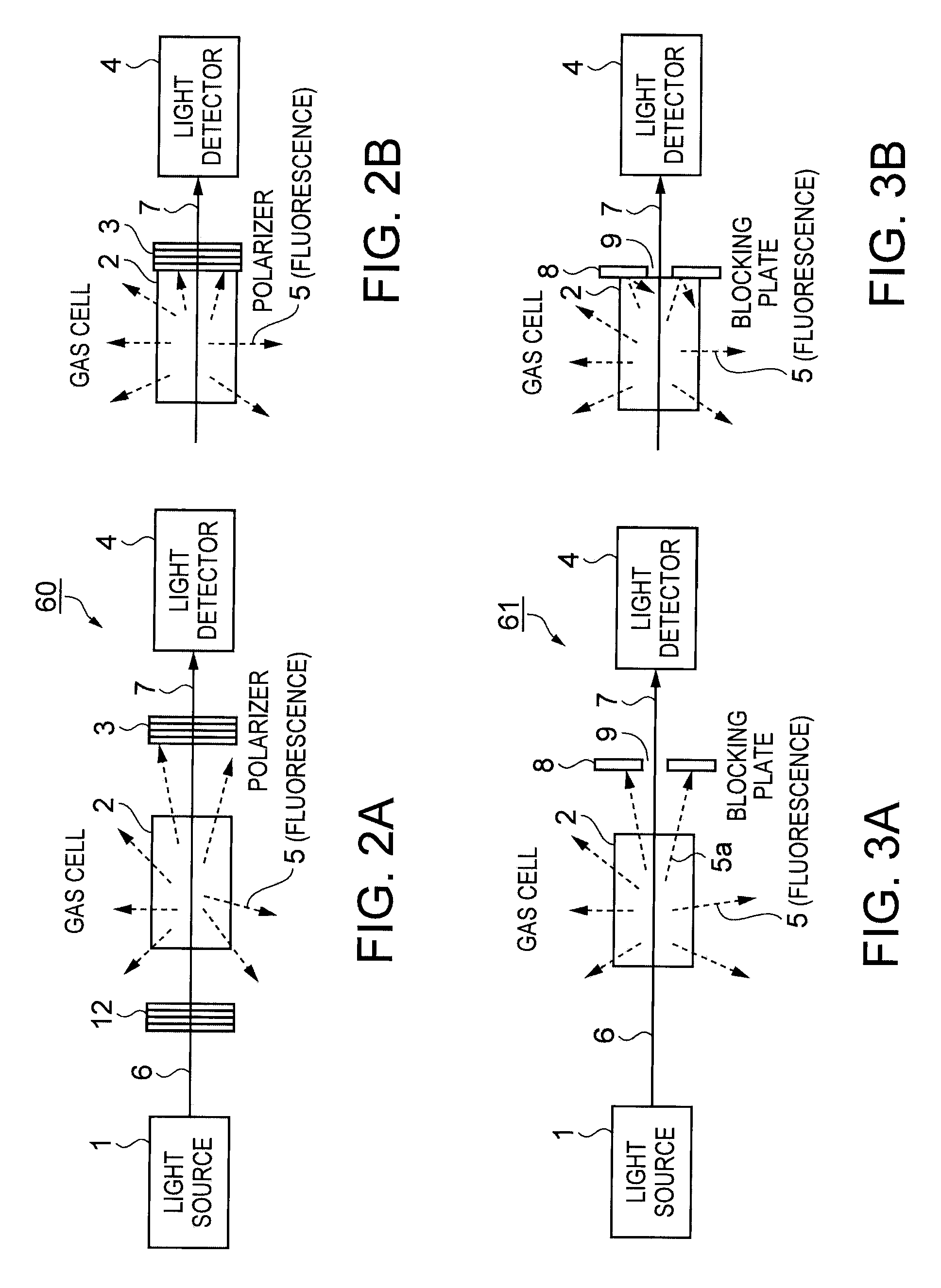
An optical system of an atomic oscillator that regulates an oscillation frequency by using an optical absorption property by one of a double resonance method utilizing light and micro waves and a coherent population trapping (CPT) method utilizing a quantum interference effect produced by two kinds of resonance light, includes: a light source emitting the resonance light; a gas cell disposed at an emitting side of the light source, sealing a gaseous metal atom therein and transmitting the resonance light through a metal atom gas; a light detecting unit detecting the transmitted light that is transmitted through the metal atom gas; and a fluorescence blocking unit blocking at least a part of fluorescence, which is emitted from the metal atom gas to the light detecting unit, and disposed between the metal atom gas and the light detecting unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Solid-state imagine device, line sensor, optical sensor, and method for operating solid-state imaging device
ActiveCN1926688AHigh sensitivityImprove S/N ratioTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCapacitanceLine sensor
A solid-state imaging device having a widened dynamic range while maintaining a high sensitivity and a high S / N ratio, a line sensor, an optical sensor, and a method for operating a solid-state imaging device adopted so as to widen the dynamic range of the solid-state imaging device while maintaining a high sensitivity and a high S / N ratio are disclosed. The solid-state imaging device is composed of an array of integrated pixels each of which comprises a photodiode (PD) for generating optical charges on receiving light, a transfer transistor (Tr1) for transferring the optical charges, and a storage capacitive element (Cs) connected to the photodiode (PD) at least through the transfer transistor (Tr1) and serving to store the optical charges overflowing from the photodiode (PD) at least through the transfer transistor (Tr1) during storage operation.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
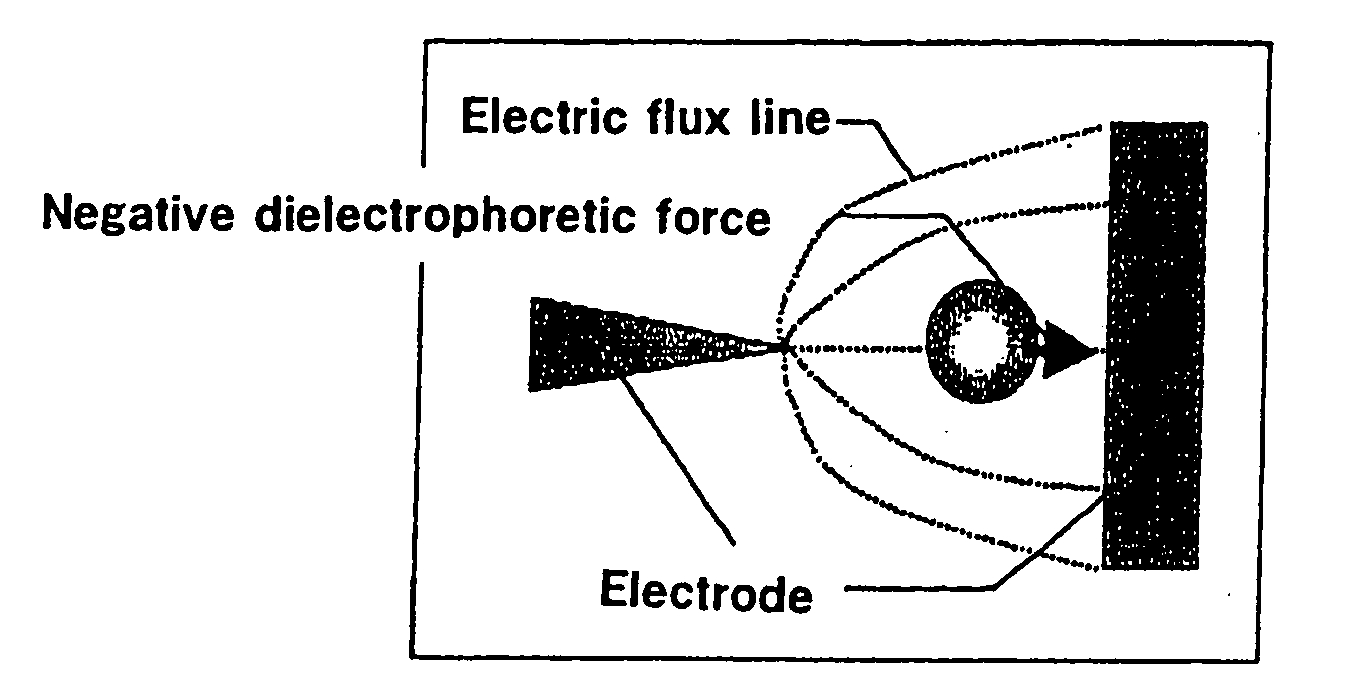
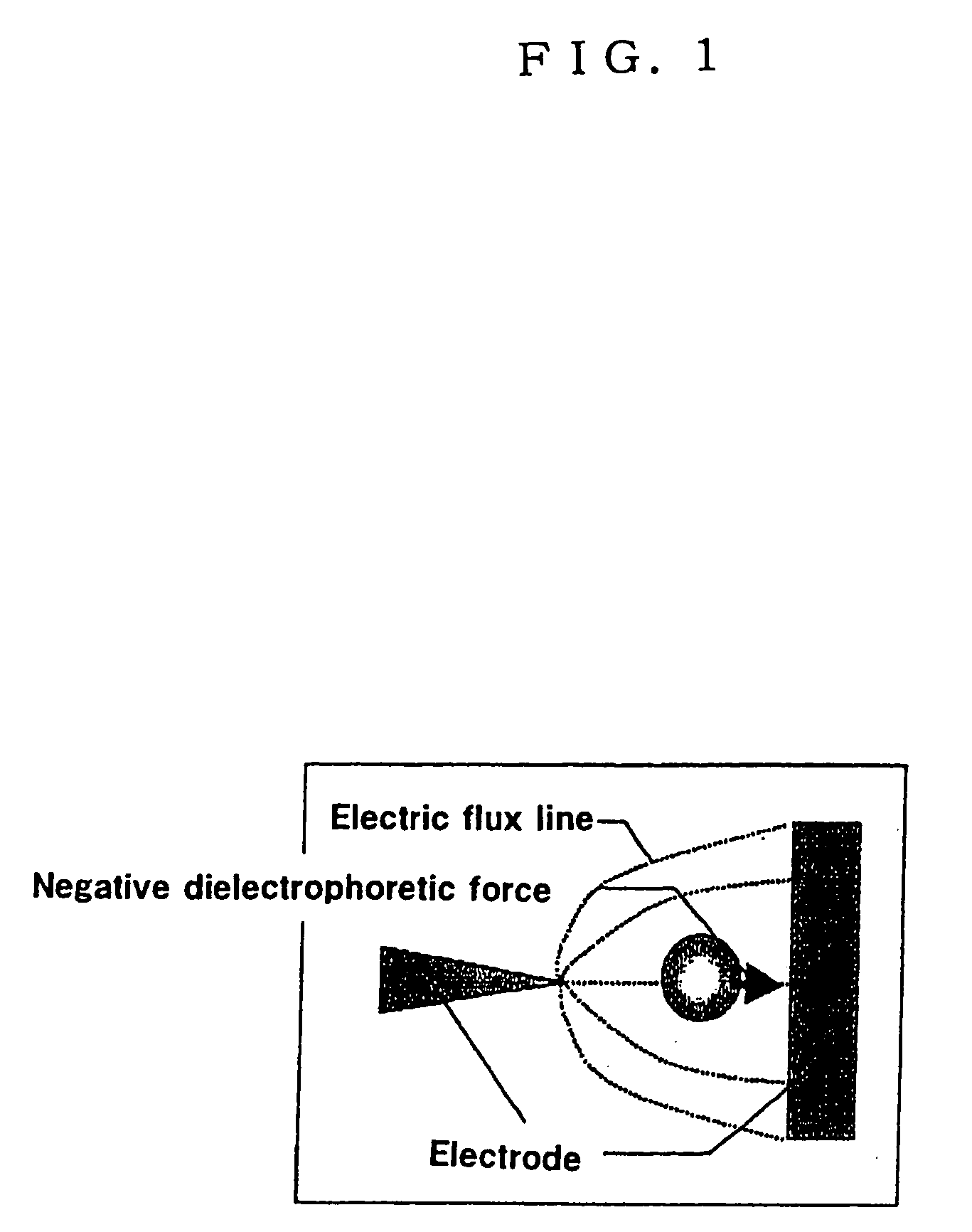
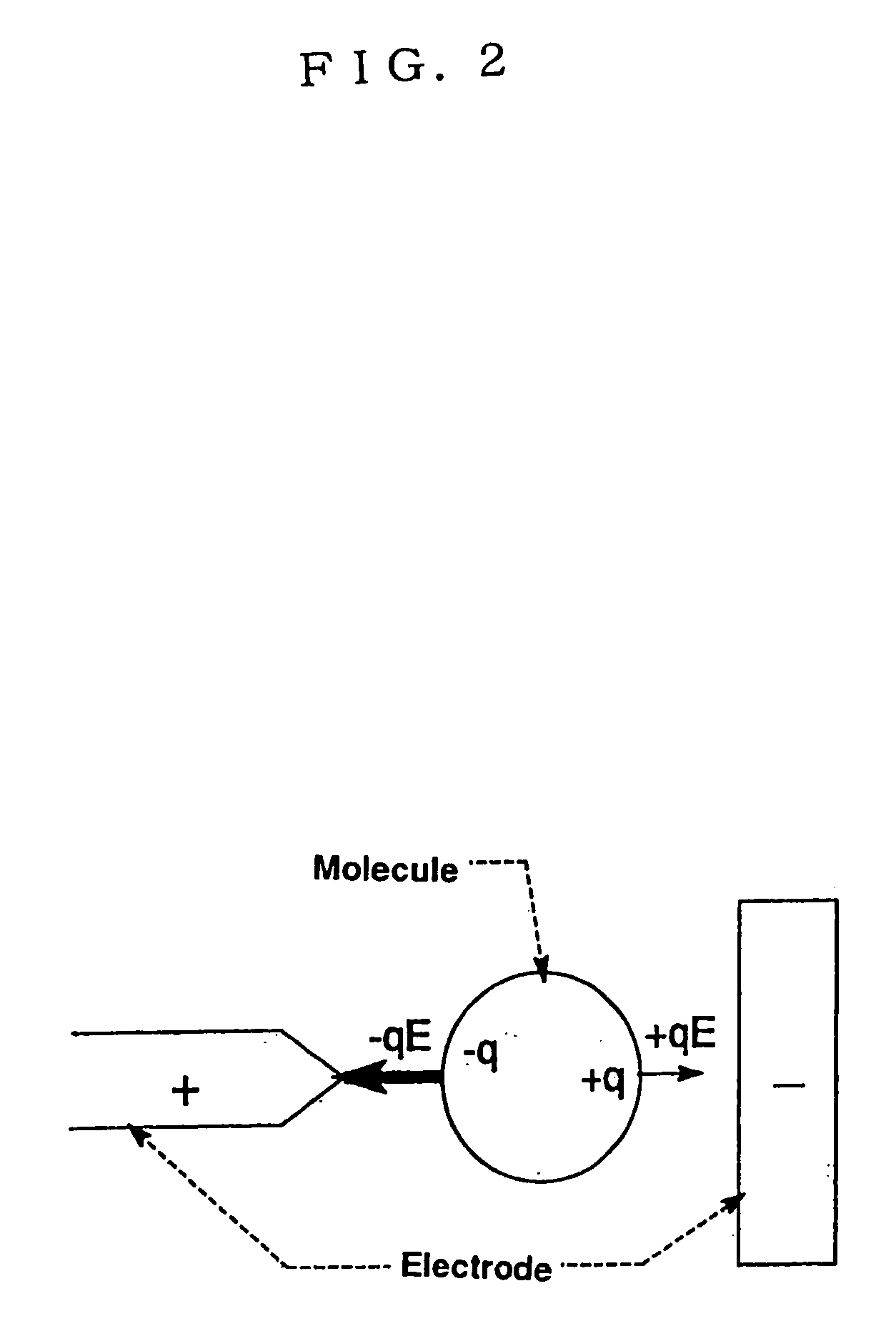
Electrode for dielectrophoretic apparatus, dielectrophoretic apparatus, method for manufacturing the same, and method for separating substances using the electrode or dielectrophoretic apparatus
InactiveUS20050139473A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioLow backgroundSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsSubstance useElectrophoresis
To provide an electrode for a dielectrophoretic apparatus in which a background detected by reflecting an excited light on an electrode present under the substance (molecule) is reduced and an S / N ratio is enhanced. Also, there is provided an dielectrophoretic apparatus, in an apparatus in which a liquid containing substances to be separated is present in a non-uniform electric field formed by a dielectrophoretic electrode, and separation is carried out by a dielectrophoretic force exerting on the substances, wherein the collecting ability of substances is enhanced. The present invention is characterized in that a vacant space is provided in an electrode whereby substances subjected to influence by a negative dielectrophoretic force can be concentrated in said vacant space of an electrode, or above or below portion of the space.
Owner:WAKO PURE CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
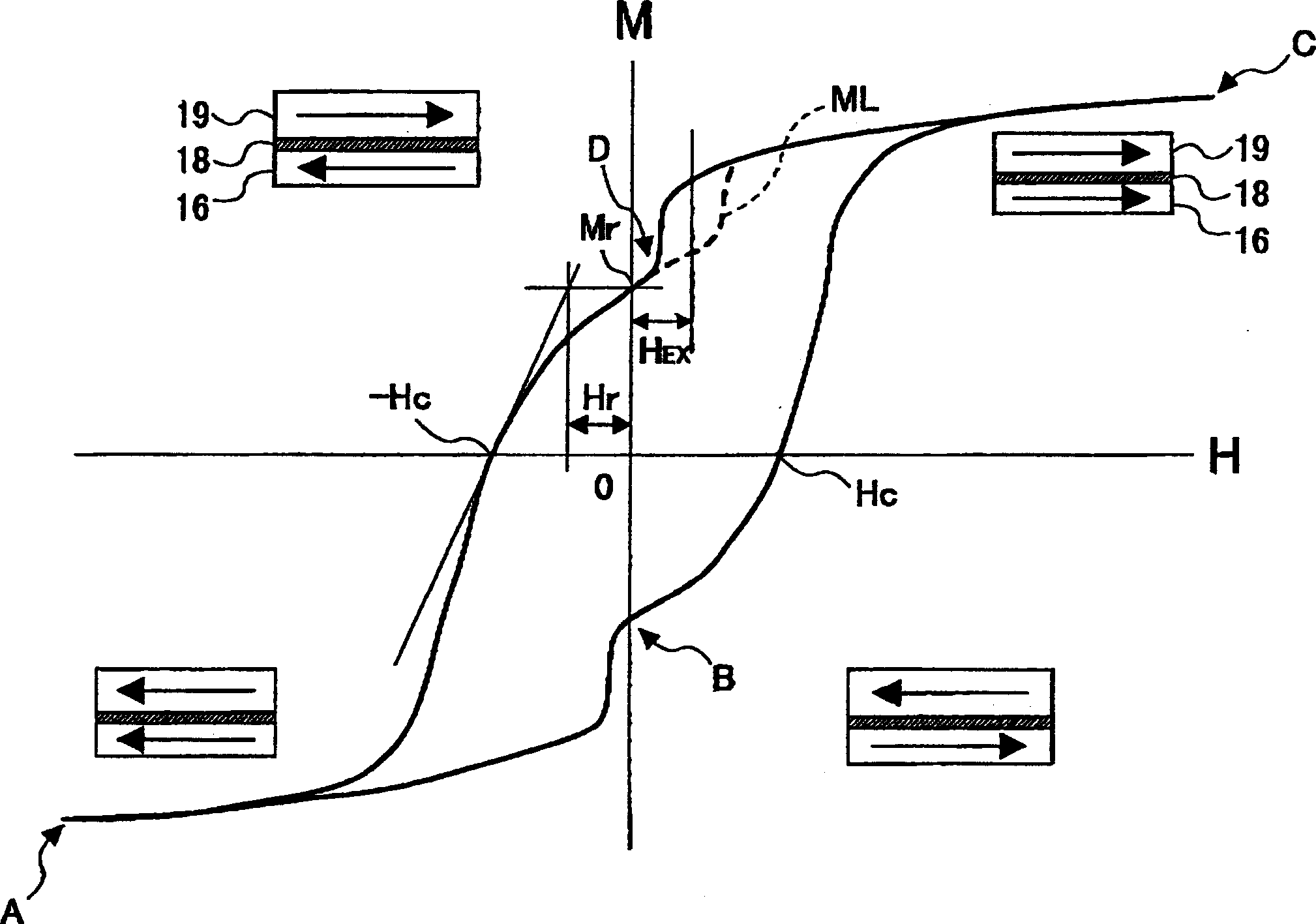
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium, manufacturing method thereof, and magnetic storage device
ActiveCN1841512AAdequate isolationAvoid combiningRecord information storageMagnetic recordingHigh densityMagnetic storage
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium for enabling high density recording is disclosed. The perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a substrate on which a soft magnetic underlayer, a seed layer made of a non-crystalline material, an underlayer made of Ru or an Ru alloy including Ru as a main component, and a recording layer including a first magnetic layer and a second magnetic layer. The first and second magnetic layers include a plurality of magnetic grains having easy magnetization axes in a substantially perpendicular direction with respect to the substrate surface, and first and second nonmagnetic non-soluble phases segregating the magnetic grains of the first and second magnetic layers, respectively. The first magnetic layer includes the first non-soluble phase at a first atomic concentration that is higher than a second atomic concentration of the second non-soluble phase in the second magnetic layer.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Detector, physical quantity measuring device, and electronic apparatus
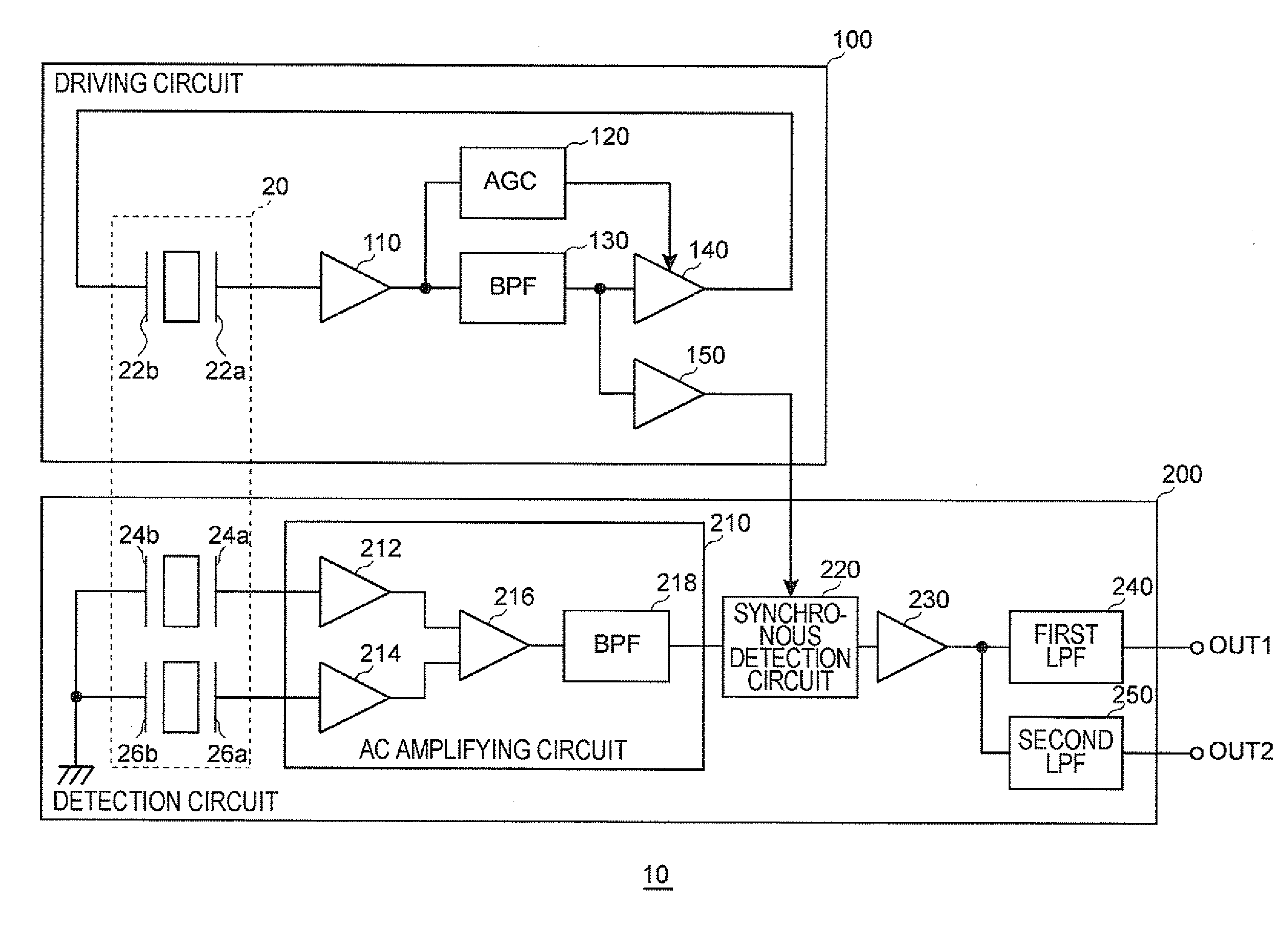
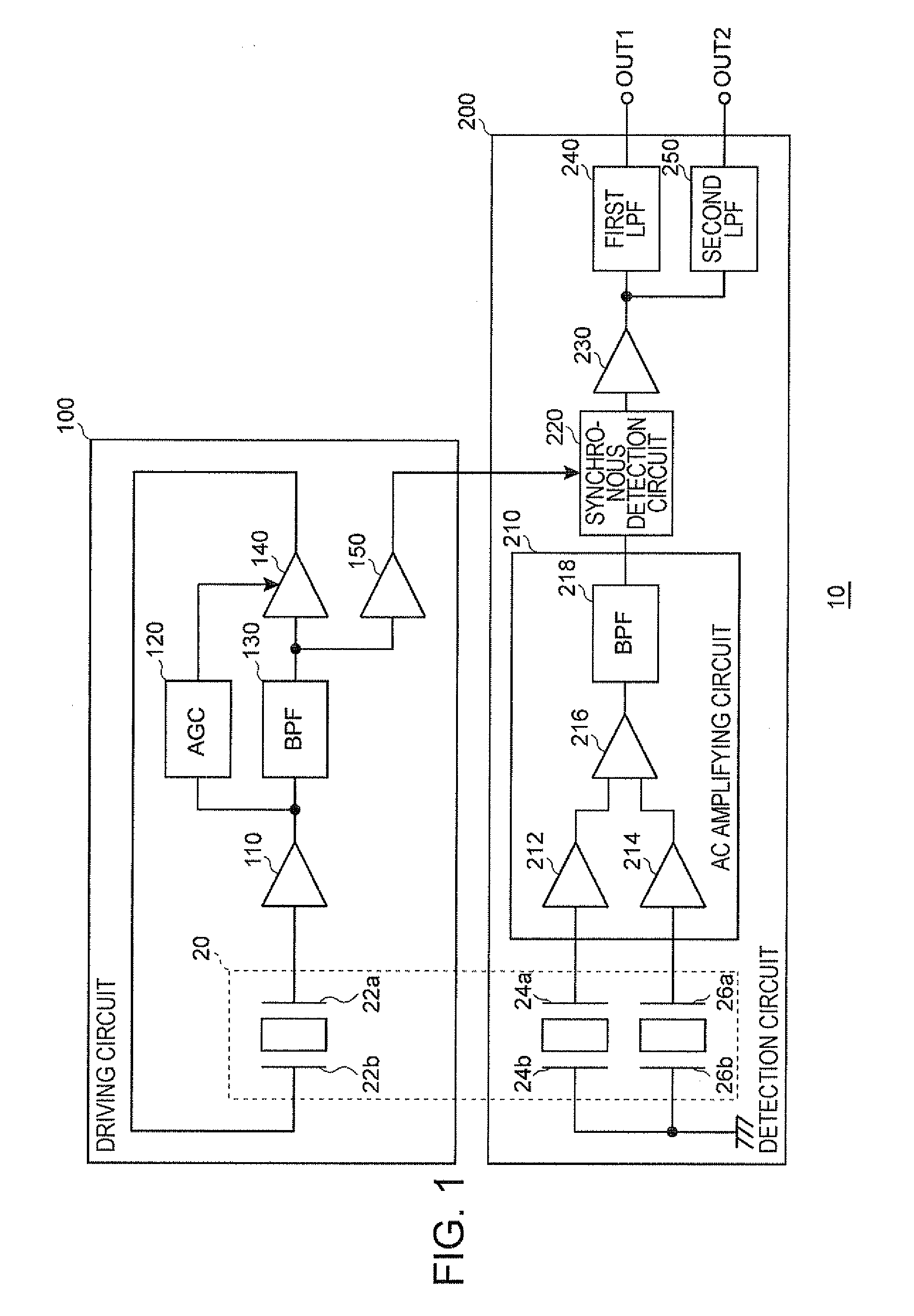
ActiveUS20110061461A1Small offset voltage differenceImprove S/N ratioAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSwitched capacitor networksPhysicsSynchronous detection
A detector that detects a detection signal corresponding to a driving vibration, which excites a vibrator in an oscillation loop, and a physical quantity to be measured, includes: an amplifying circuit that amplifies a signal corresponding to the driving vibration and the physical quantity; a synchronous detection circuit that detects the amplified signal of the amplifying circuit in synchronization with an oscillation signal in the oscillation loop; an impedance conversion circuit that converts an output impedance of the synchronous detection circuit; a first low pass filter to which an output signal of the impedance conversion circuit is supplied and which outputs a first detection signal; and a second low pass filter to which the output signal of the impedance conversion circuit is supplied and which outputs a second detection signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Light guide and mfg. method thereof
InactiveCN1410786AGood sealingImprove S/N ratioCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideUV curingLight guide
The present invention provides an optical wave guide that may be produced by reproduction method in easy and simple manner, and has a structure that prevents light signal in its inside from leaking out from core, and a method for producing the same optical wave guide. A concave slot 3 for forming a core is formed on the upper surface of a cladding substrate 2. And on both sides of the concave slot 3, cavities 6 are formed via flat portions 5. An ultraviolet ray hardening type transparent resin 8 is applied onto the surface of the cladding substrate 2, thereafter the transparent resin 8 is pressed by a stamper 13. At this moment, a core 4 is formed in the concave slot 3 and excessive transparent resin 8 pressed between the stamper 13 and the flat portions 5 flows into cavities 6, as a result, it is possible to make the transparent resin 8 thin in a short time. Thereby, it is possible to make the transparent resin 8 left on the flat portions 5 into thickness and width enough to prevent light in the core 4 from leaking out.
Owner:ORMON CORP
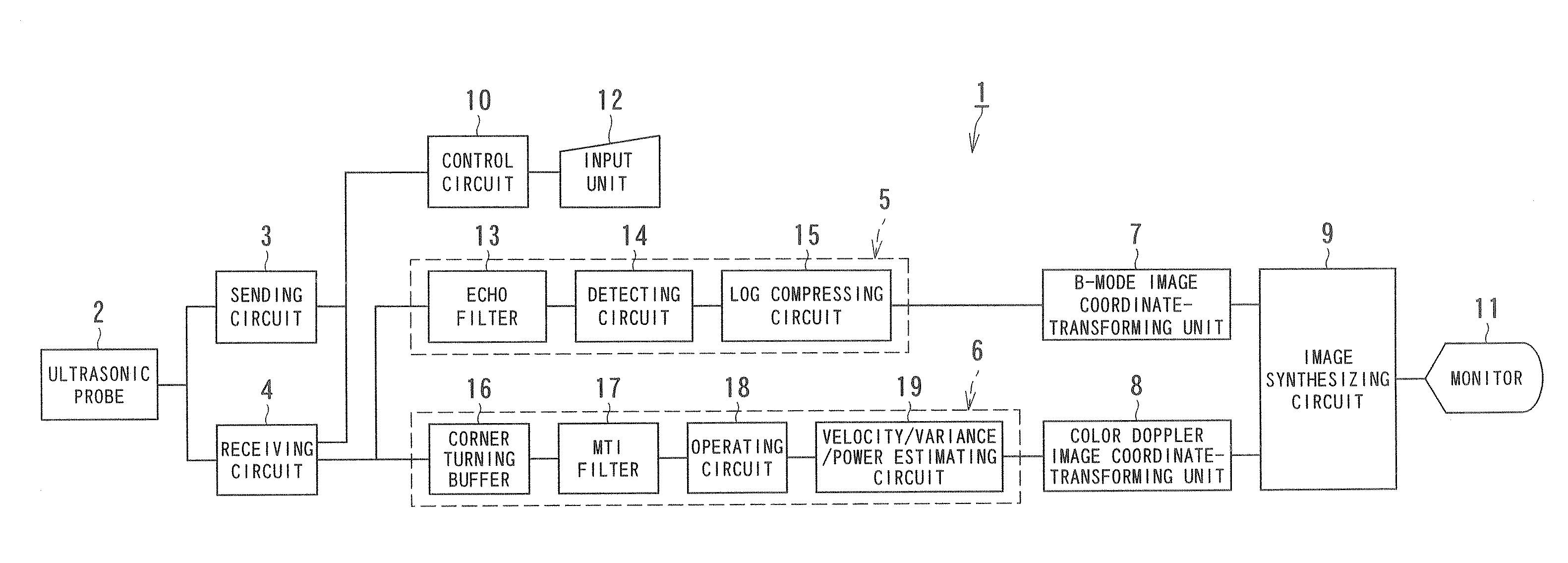
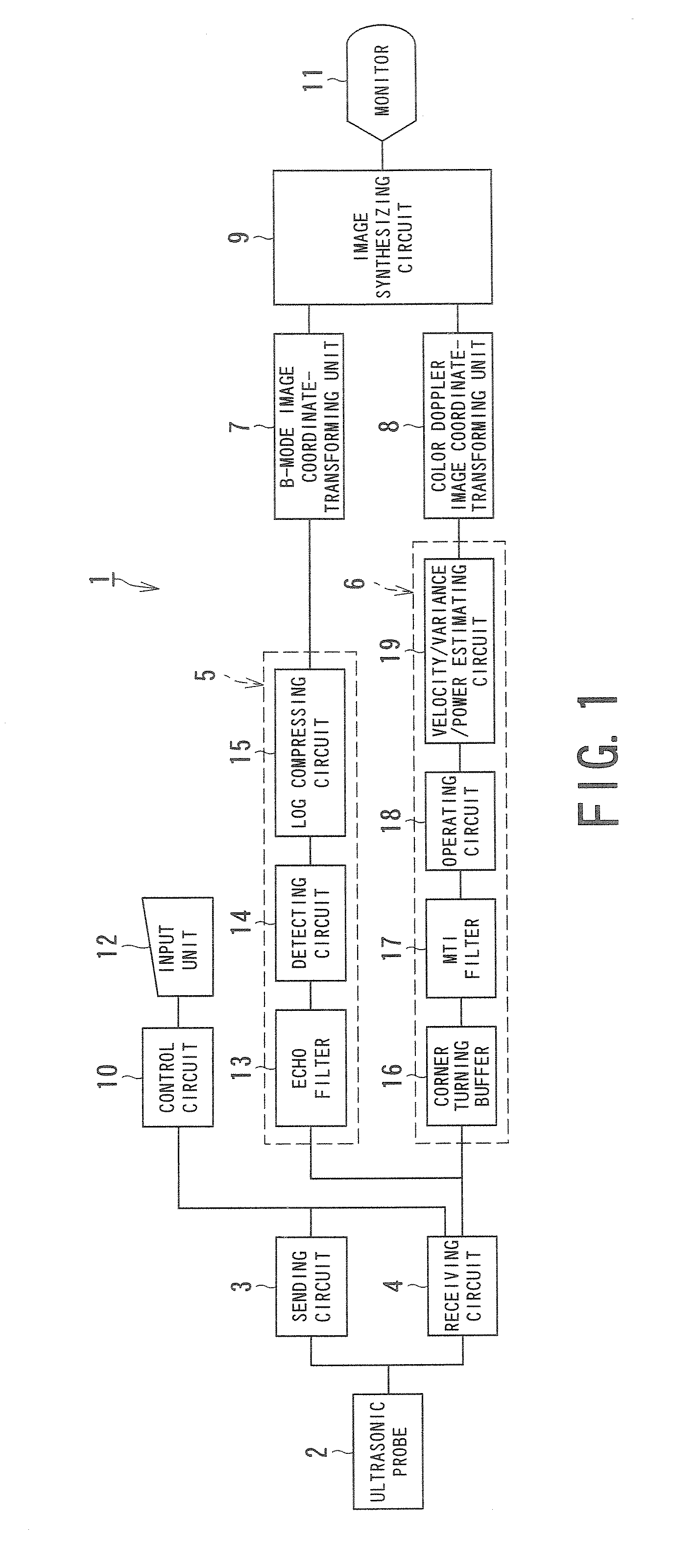
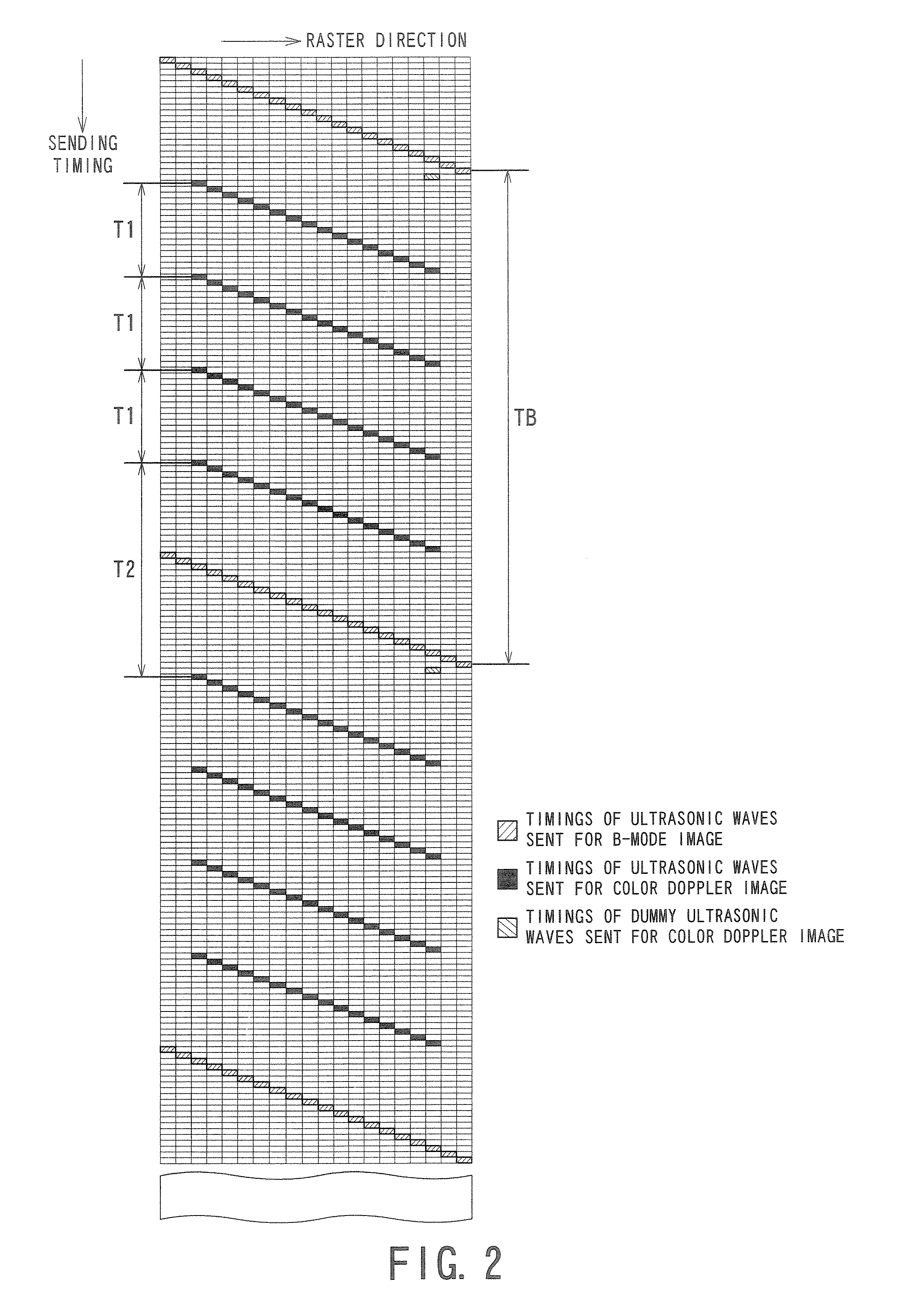
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus and ultrasonic diagnostic method
InactiveUS20070239015A1Improve S/N ratioUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound diagnosticsImage based
An ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus has a scanning executing unit, a Doppler signal obtaining unit, a storage unit, a removing unit, a blood flow information obtaining unit, and a B-mode image generating unit. The scanning executing unit executes a first scanning that is iteratively performed by a predetermined period so as to obtain a B-mode image of an object and executes a second scanning that is iteratively performed a predetermined number of times by a first period between the first scanning so as to obtain a two-dimensional distribution of a blood flow information and that is iteratively performed by a second period while inserting the first scanning. The Doppler signal obtaining unit sequentially obtains a Doppler signal from a reflection signal obtained by the second scanning. The storage unit stores, for each raster direction, a Doppler signal string at unequal time intervals collected for the first period and the second period by the Doppler signal obtaining unit. The removing unit obtains a blood flow signal by reading the Doppler signal string at the unequal time intervals from the storage unit and removes a signal component with a small motion. The blood flow information obtaining unit obtains the blood flow information based on the blood flow signal. The B-mode image generating unit generates the B-mode image based on the reflection signal obtained by the first scanning.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
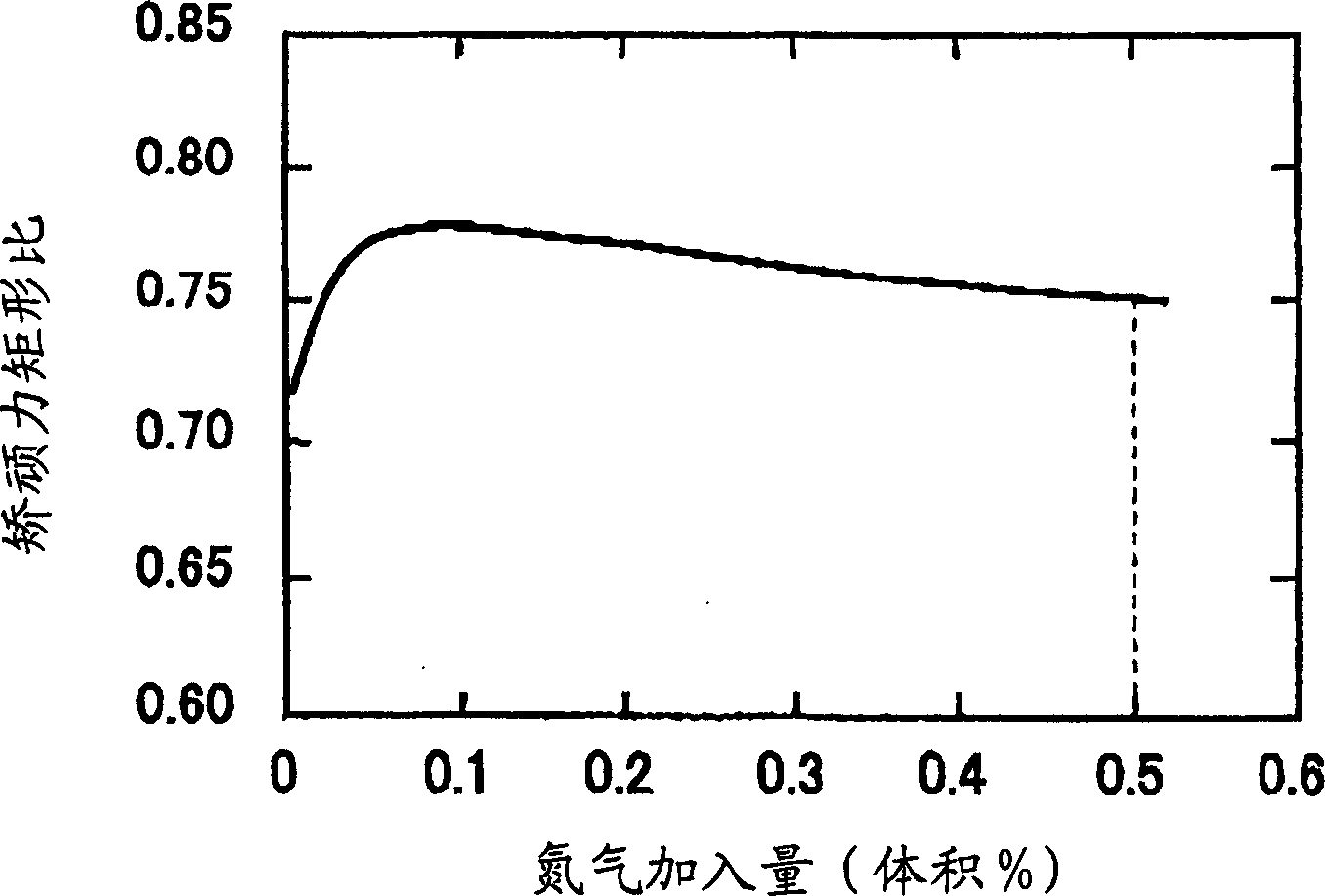
Magnetic recording medium , magnetic memory and method of producing magnetic recording medium
InactiveCN1652214AIncrease the coercive squareness ratioHigh-resolutionRecord information storageBase layer manufactureCouplingMagnetization
A method of producing a magnetic recording medium includes forming a underlayer on a base, and successively forming, on the underlayer, a first magnetic layer, a nonmagnetic coupling layer and a second magnetic layer. The first and second magnetic layers are exchange-coupled via the nonmagnetic coupling layer and have antiparallel magnetizations in a state where no external magnetic field is applied on the magnetic recording medium. The underlayer is made of Cr or a Cr alloy having a bcc crystal structure within an atmosphere including nitrogen gas.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
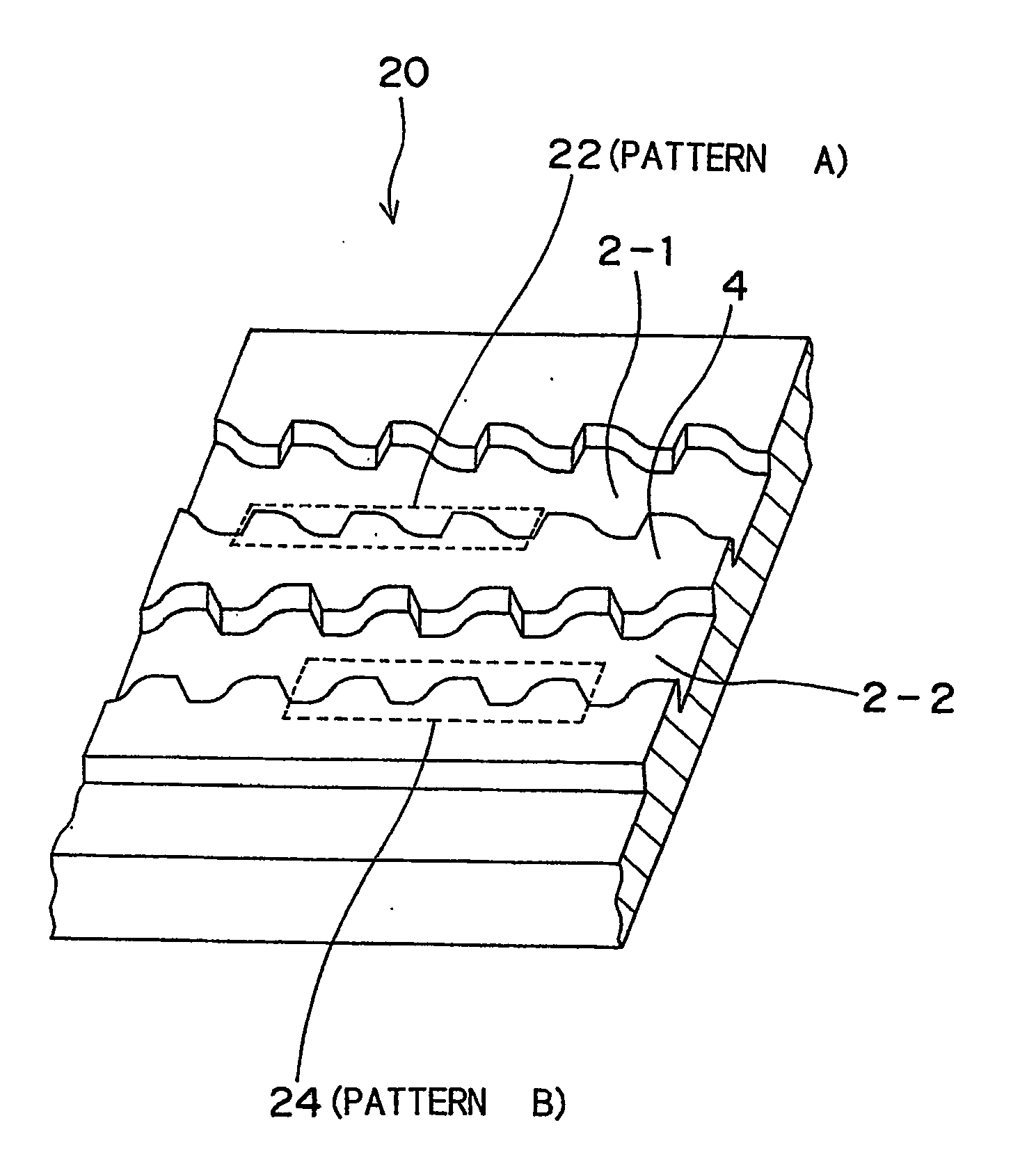
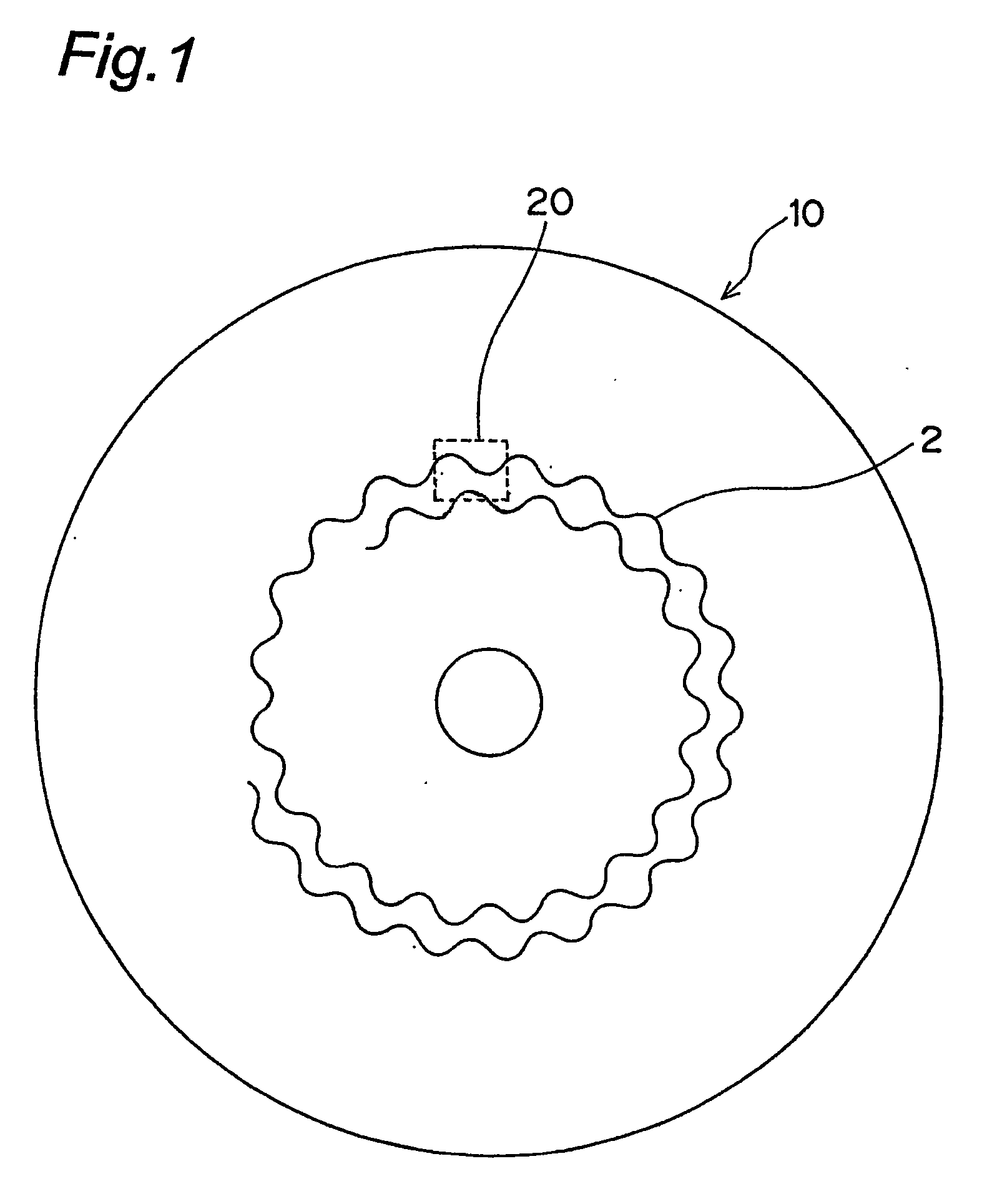
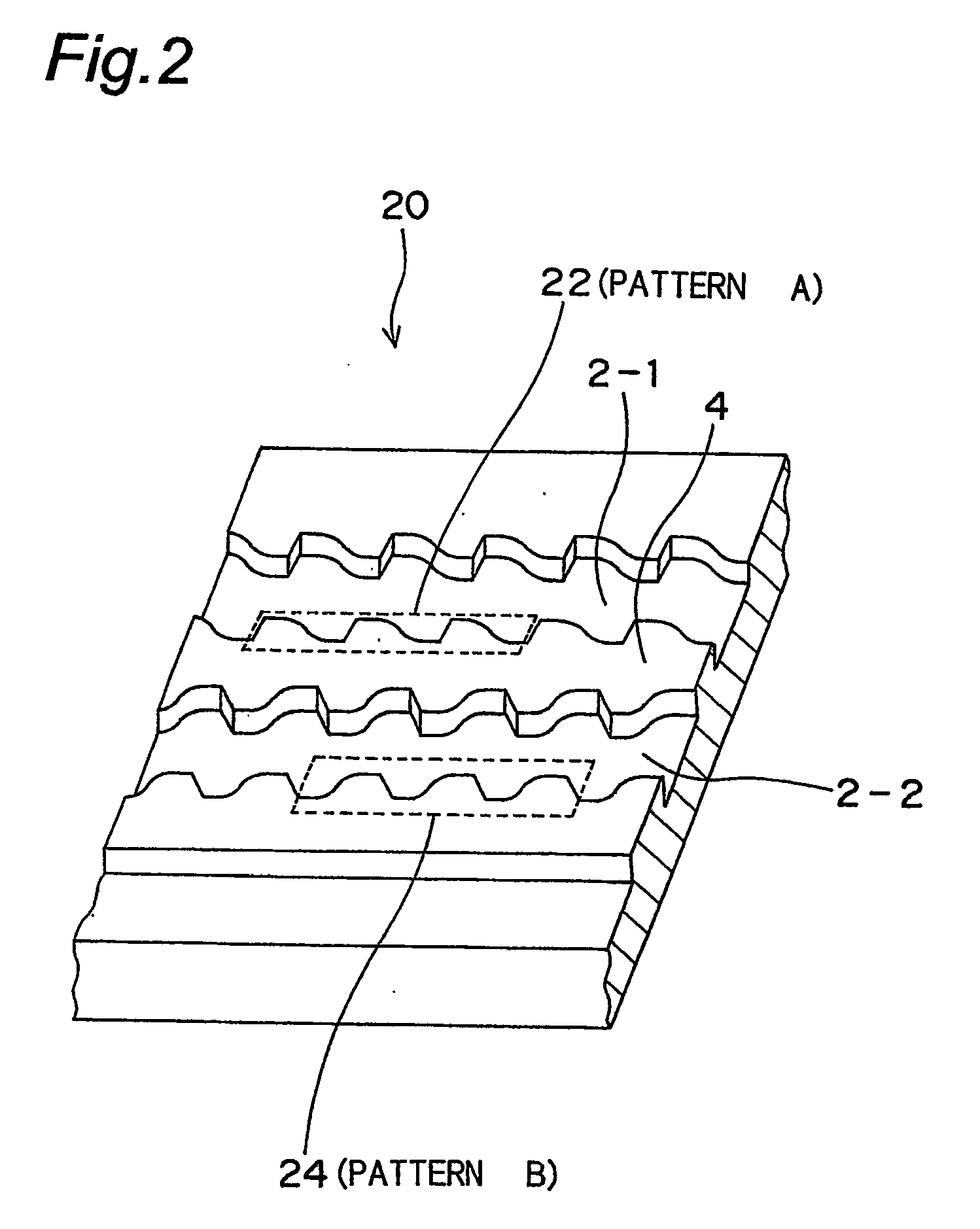
Optical disc with different wobble patterns in different grooves
ActiveUS20050058056A1Improve S/N ratioImprove signal-to-noise ratioInformation arrangementMagneto-optical discsFrequency bandEngineering
The S / N ratio is improved for recording data to grooves (2-1,2-2) of an optical disc so that as much information as possible can be recorded at the lowest possible frequency band. An optical disc using wobble patterns to record different information has a first groove (2-1) having a first wobble pattern (22) in which one wobble period has a sharp rising edge and a gradual falling edge; and a second groove (2-2) having a second wobble pattern (24) in which one wobble period has a gradual rising edge and a sharp falling edge. Each of the first and the second wobble pattern is represented by a first fundamental and a second harmonic of a Fourier series. The polarity of the second harmonic, which is an even harmonic, of the second wobble pattern is opposite that of the first wobble pattern. A method for manufacturing this optical disc is also provided.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV +1
Solid-state imaging device, signal processing method for the same, and imaging apparatus
InactiveCN101296305AAvoid accumulationImprove S/N ratioTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringSignal processing
Disclosed herein is a solid-state imaging device, including, a pixel array unit, driving means, signal processing means, level determining means and control means.
Owner:SONY CORP
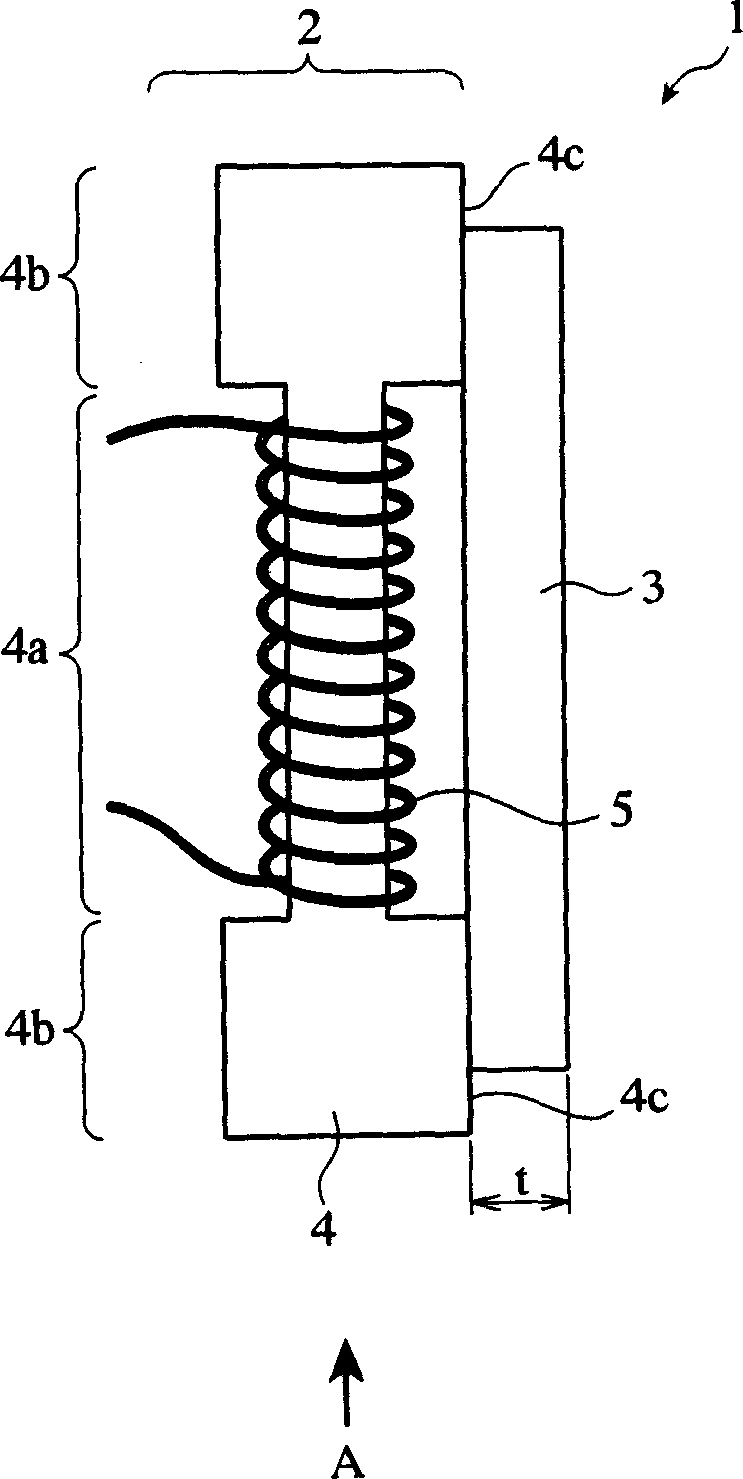
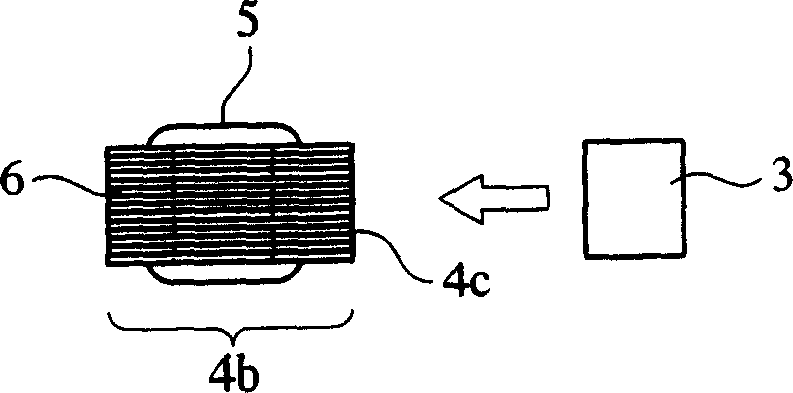
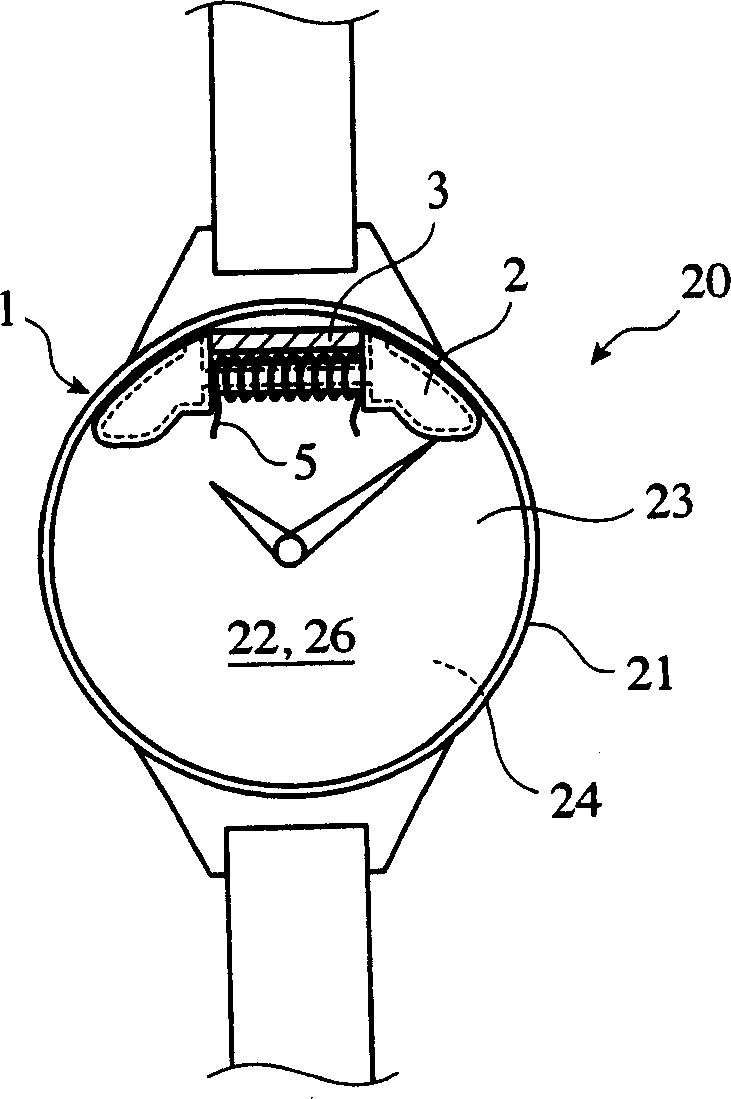
Antenna, and radio-controlled timepiece, keyless entry system and RFID system using same
InactiveCN1893181AHigh sensitivityImprove S/N ratioLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna supports/mountingsVoltageMagnetic core
An antenna of the invention comprises a magnetic main-path member comprising a coil wound around a magnetic core, and a magnetic sub-path member magnetically connected to the magnetic core for constituting a substantially closed magnetic path with the magnetic main-path member, the antenna meeting the relation of (S / N)1>(S / N)0, wherein (S / N)1 is a ratio of a signal voltage S obtained from the coil to a noise voltage N in this antenna, and (S / N)0 is a ratio of a signal voltage S to a noise voltage N in an antenna having the same structure except for having no magnetic sub-path member.
Owner:PROTERIAL LTD
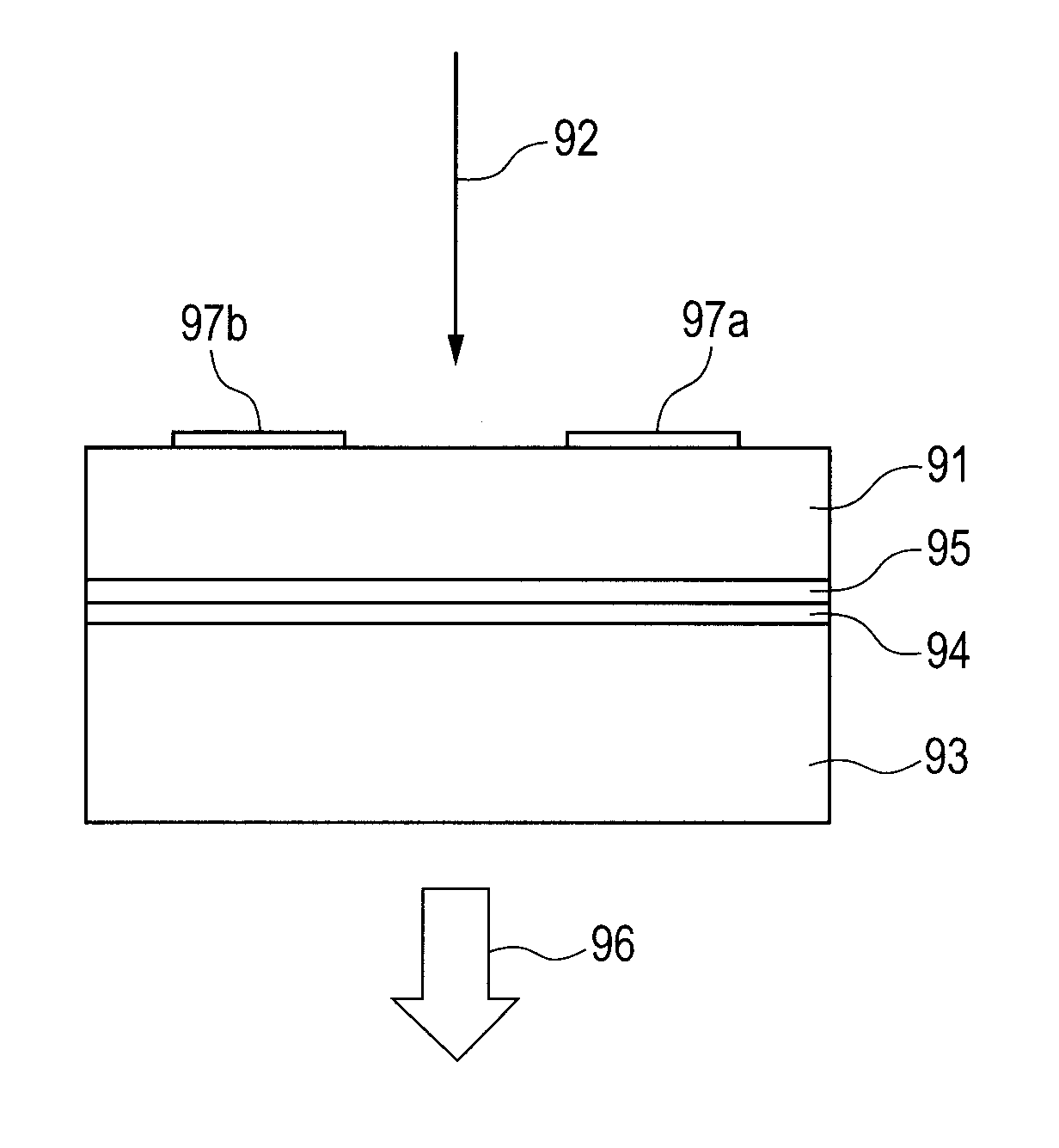
Photoconductive element
ActiveUS20120235040A1Improving terahertz wave generation efficiencyImprove S/N ratioPhotometrySolid masersSemiconductorDistortion
Provided is a photoconductive element which solves a problem inherent in an element for generating / detecting a terahertz wave by photoexcitation that terahertz wave generation efficiency is limited by distortions and defects of a low temperature grown semiconductor. The photoconductive element includes: a semiconductor substrate; a semiconductor low temperature growth layer; and a semiconductor layer, which is positioned between the semiconductor low temperature growth layer and the semiconductor substrate and is thinner than the semiconductor low temperature growth layer, in which the semiconductor low temperature growth layer includes a semiconductor which lattice-matches with the semiconductor layer and does not lattice-match with the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN101300685ALoud noiseImprove S/N ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotodiodeSemiconductor
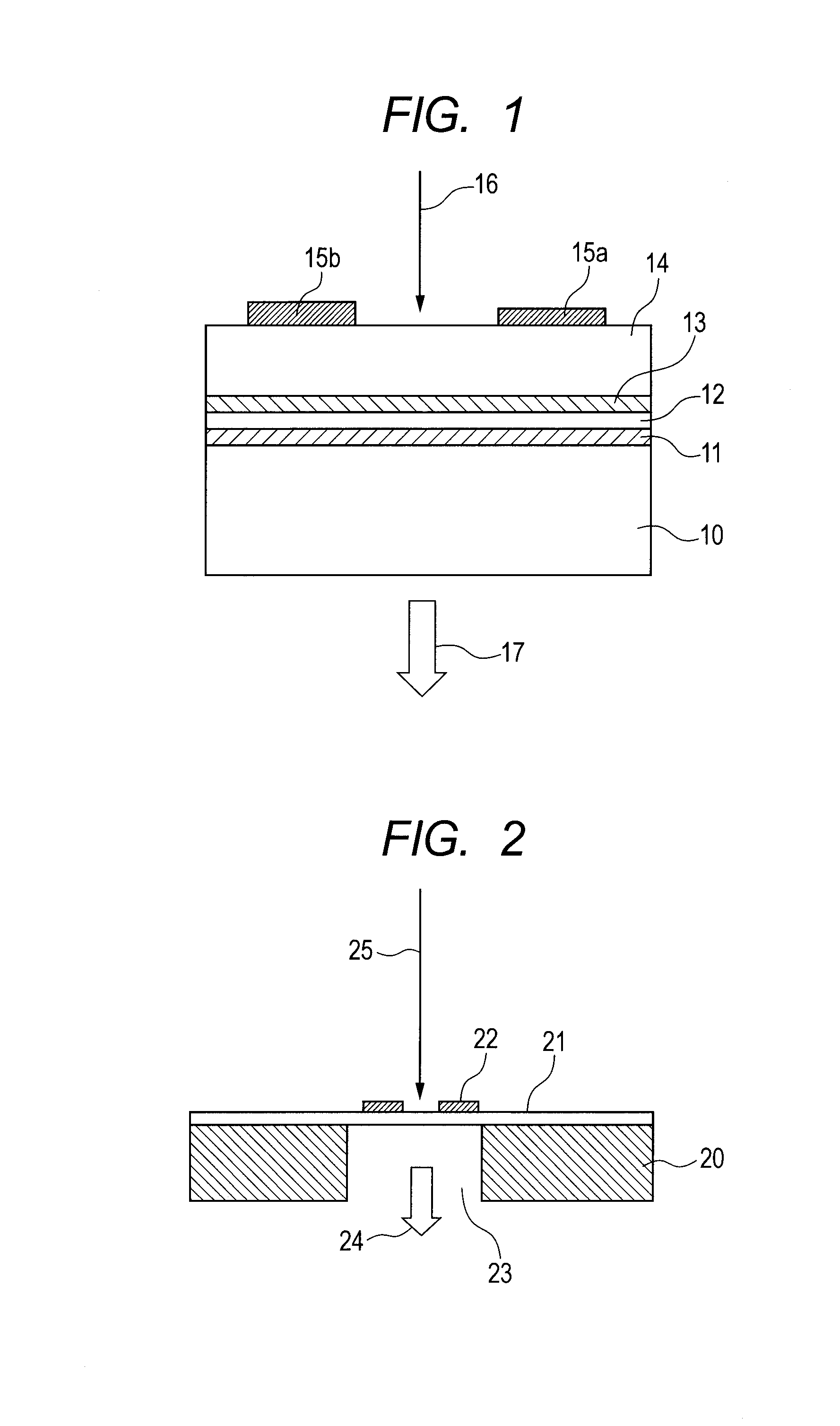
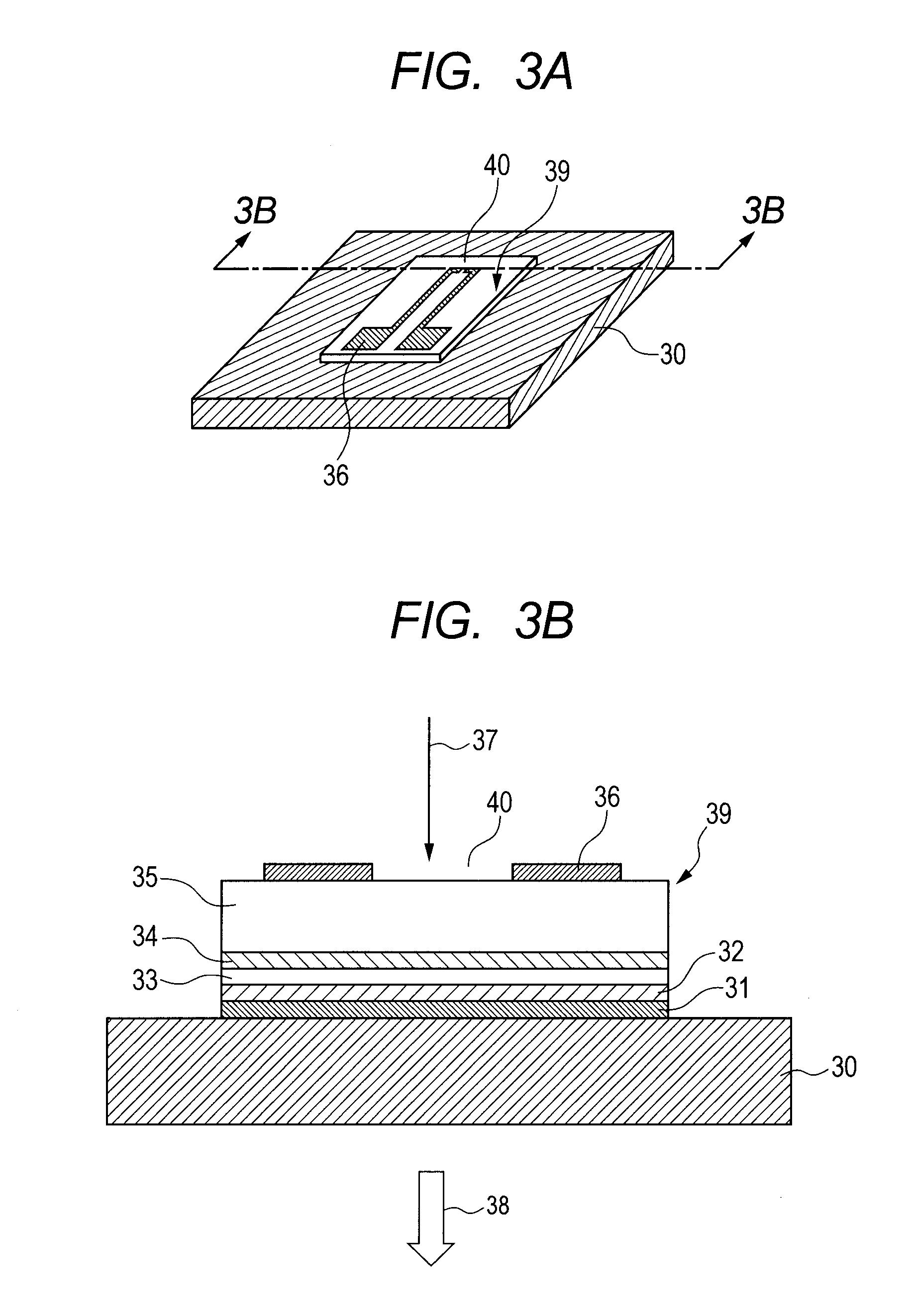
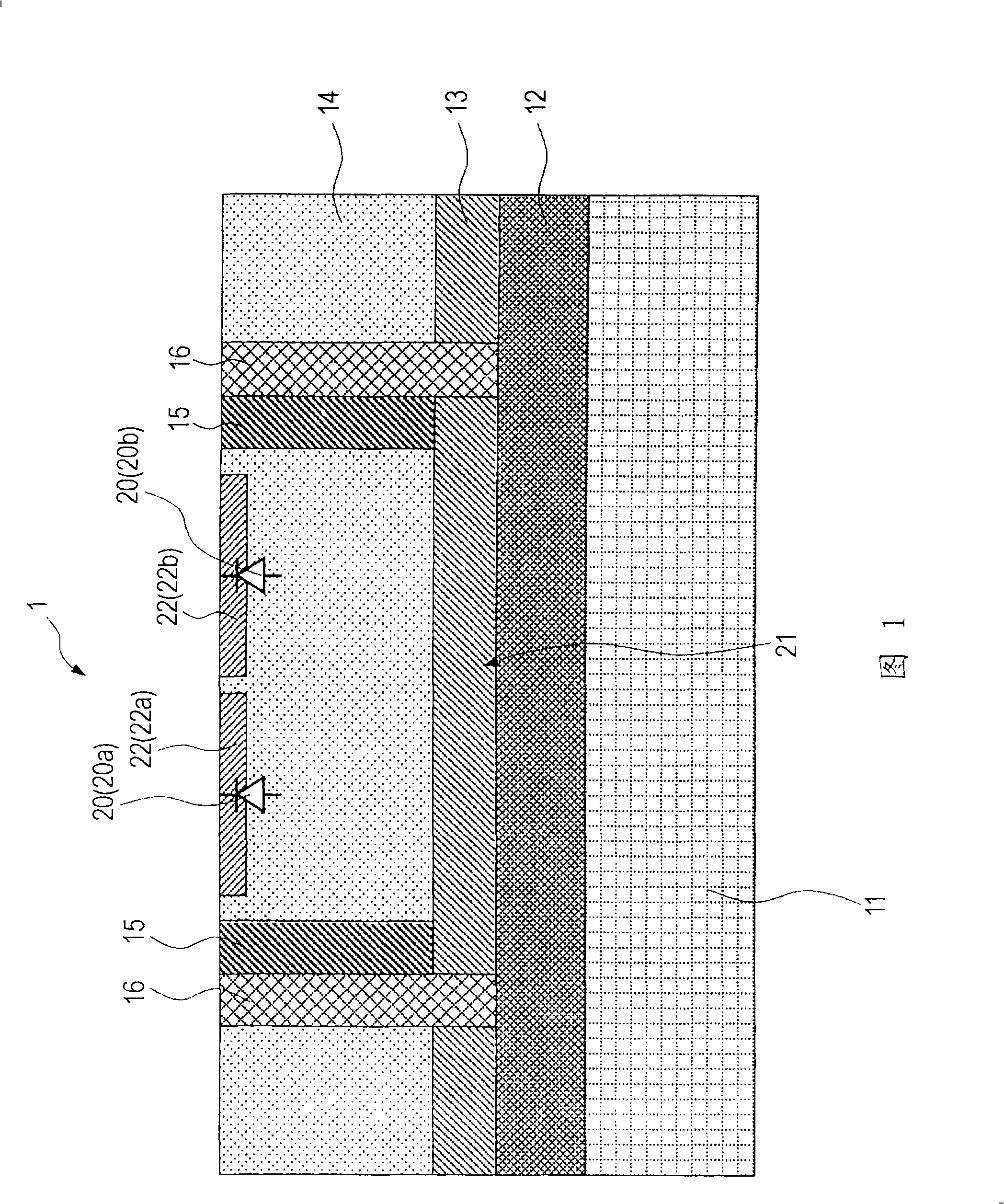
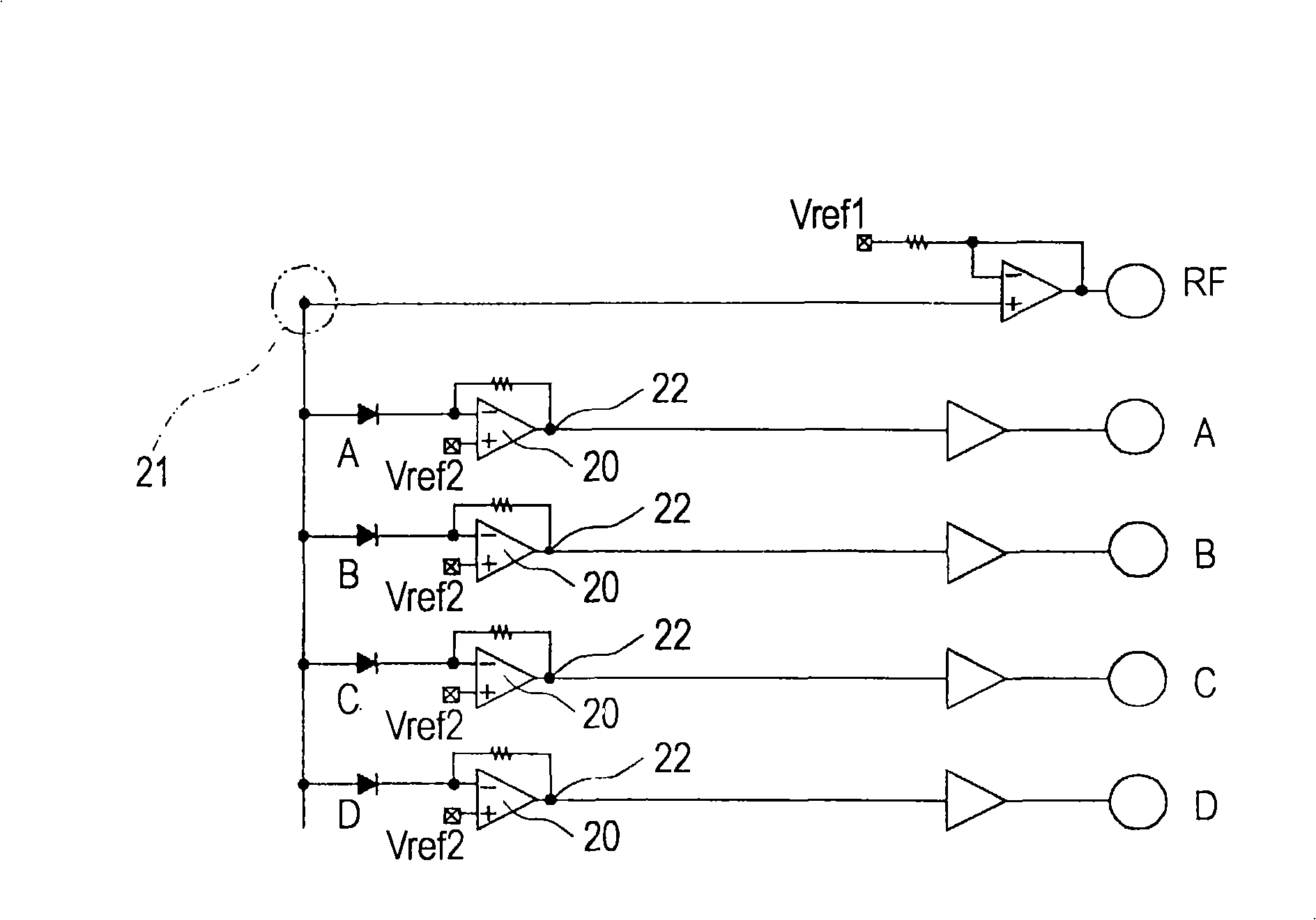
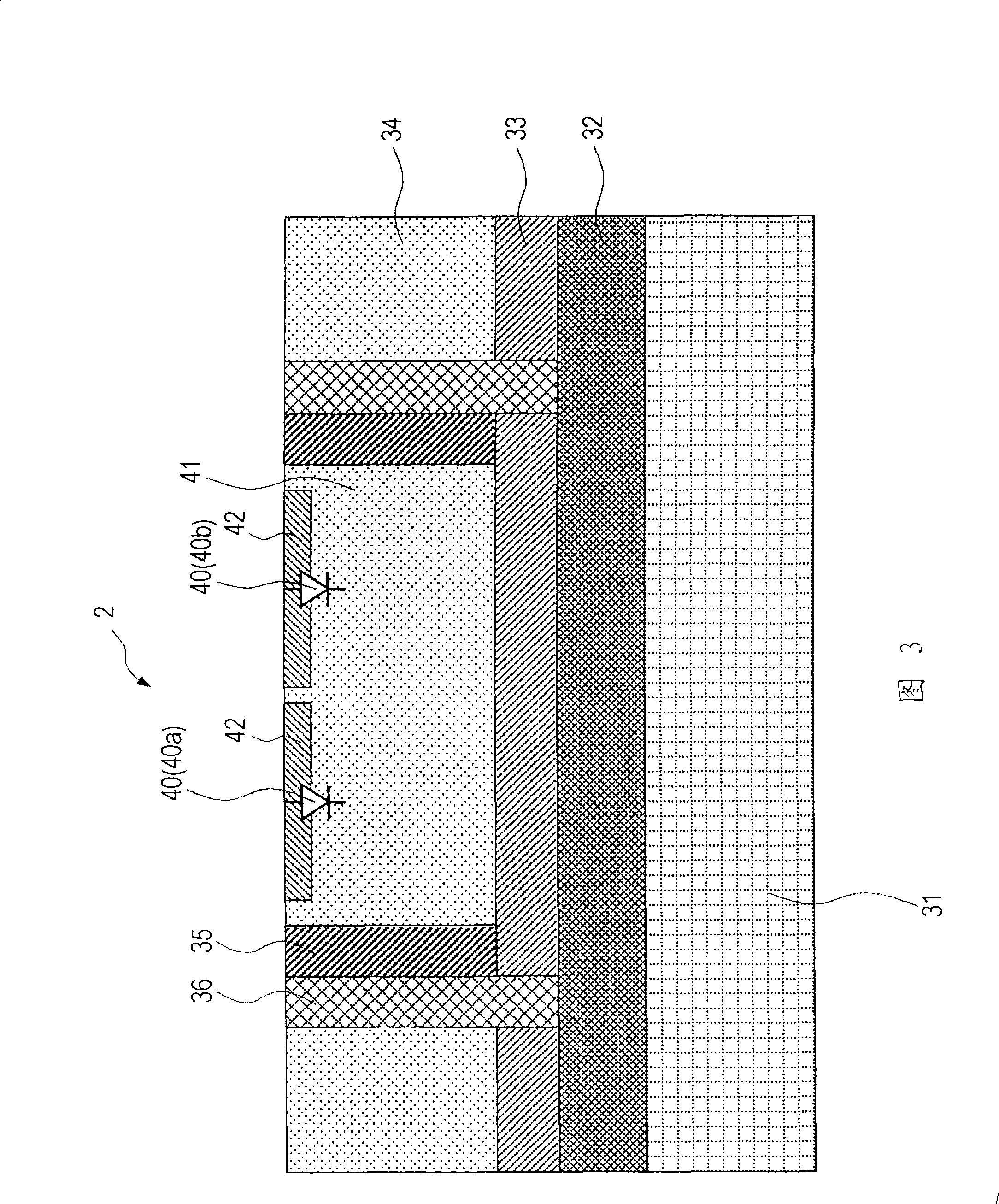
A semiconductor device (1) has a plurality of photodiodes (20) on a semiconductor substrate (11). The photodiodes (20(20a, 20b)) have cathodes (22) and a common anode (21), which are formed electrically independent of the semiconductor substrate (11). In the photodiodes having the common anode (21) and the separated cathodes (22), the output from the common anode (21) is treated as equivalent to the sum of the outputs of the separated photodiodes (20). Alternatively, a plurality of photodiodes have a common cathode and a plurality of separated anodes, and the output from the common cathode is treated as equivalent to the sum of the outputs of the separated photodiodes. The anode and cathode of a photodiode are completely isolated electrically from the substrate, whereby noise and crosstalk can be reduced.
Owner:SONY CORP
Photoelectric conversion circuit and solid-state image-sensing device using it
InactiveCN101102423AImprove S/N ratioImprove photosensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierTerminal voltage
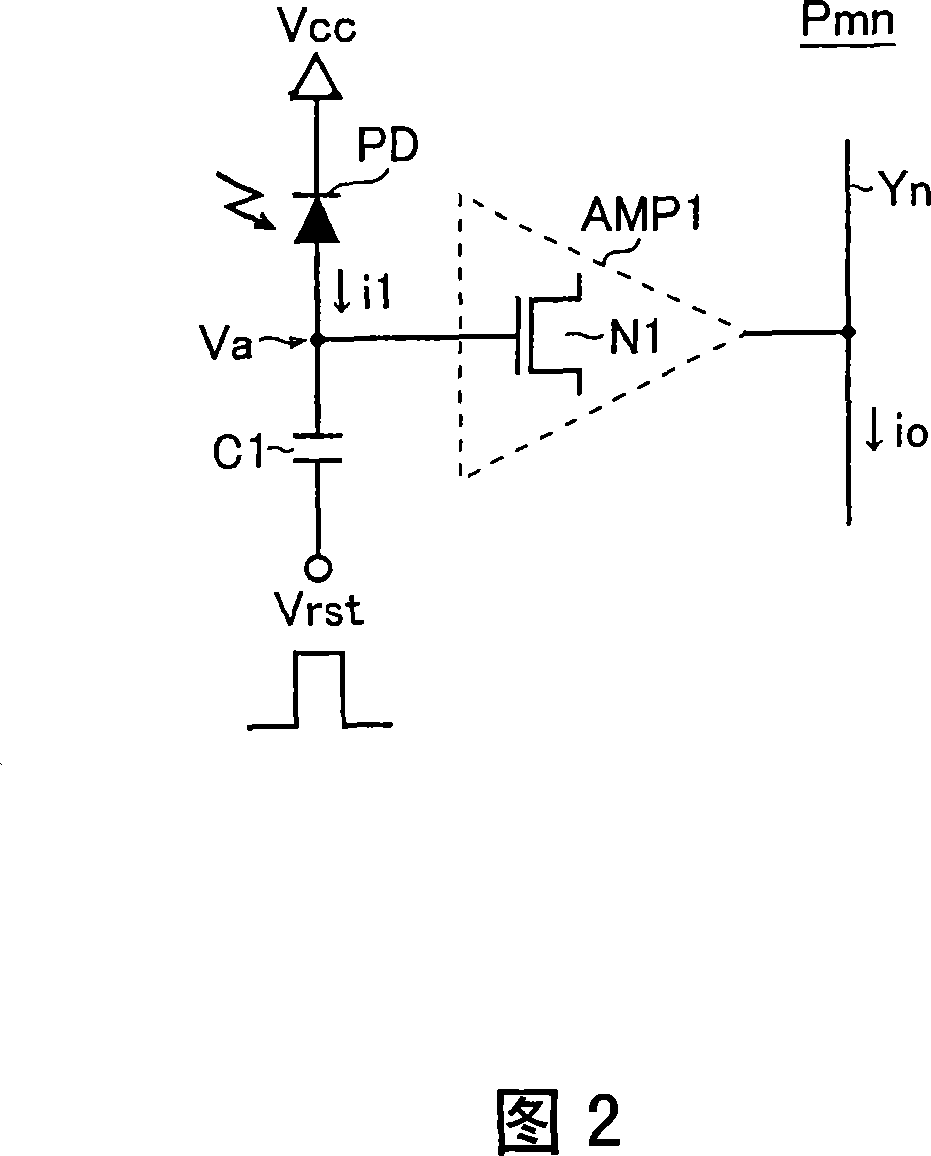
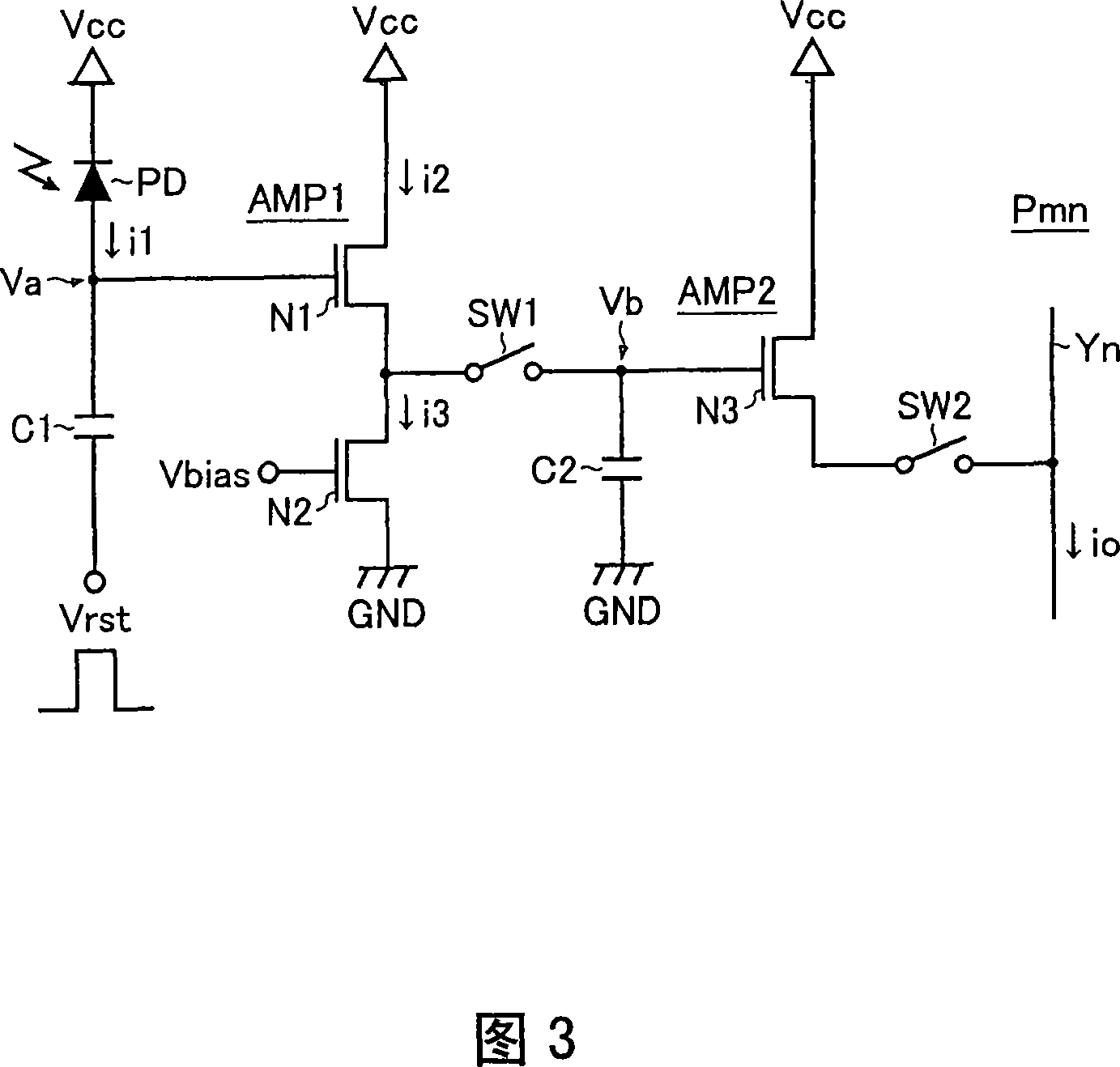
A photoelectric conversion circuit has: a photoelectric conversion element that produces a detection current commensurate with the amount of light received thereby; a capacitor having one end connected to one end of the photoelectric conversion element, the one end of the capacitor from which a terminal voltage commensurate with the integral of the detection current is drawn; and an amplifier that receives the terminal voltage of the capacitor and produces an amplified signal commensurate with the terminal voltage thus received. The photoelectric conversion circuit outputs a final optical signal (an output current) by using the amplified signal of the amplifier. As a current path that can serve as a charging / discharging path of the capacitor, the photoelectric conversion circuit includes only a current path along which the photoelectric conversion element is located. With this configuration, it is possible to enhance responsivity to light and improve the S / N ratio of a received optical signal by making the most of electric power obtained from a photoelectric conversion element.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Display device and electronic equipment
InactiveCN101634765AFully shieldedImprove S/N ratioPhotometry using reference valueStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
A range image sensor
InactiveCN1842723AHigh precisionAvoid saturationTelevision system detailsOptical rangefindersPhysicsImage sensor
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com