Solid-state imaging device, optical sensor, and solid-state imaging device operation method
A solid-state imaging device and pixel technology, which can be used in radiation control devices, image communication, color TV components, etc., can solve problems such as low sensitivity, high sensitivity and wide dynamic range, and inability to match two images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
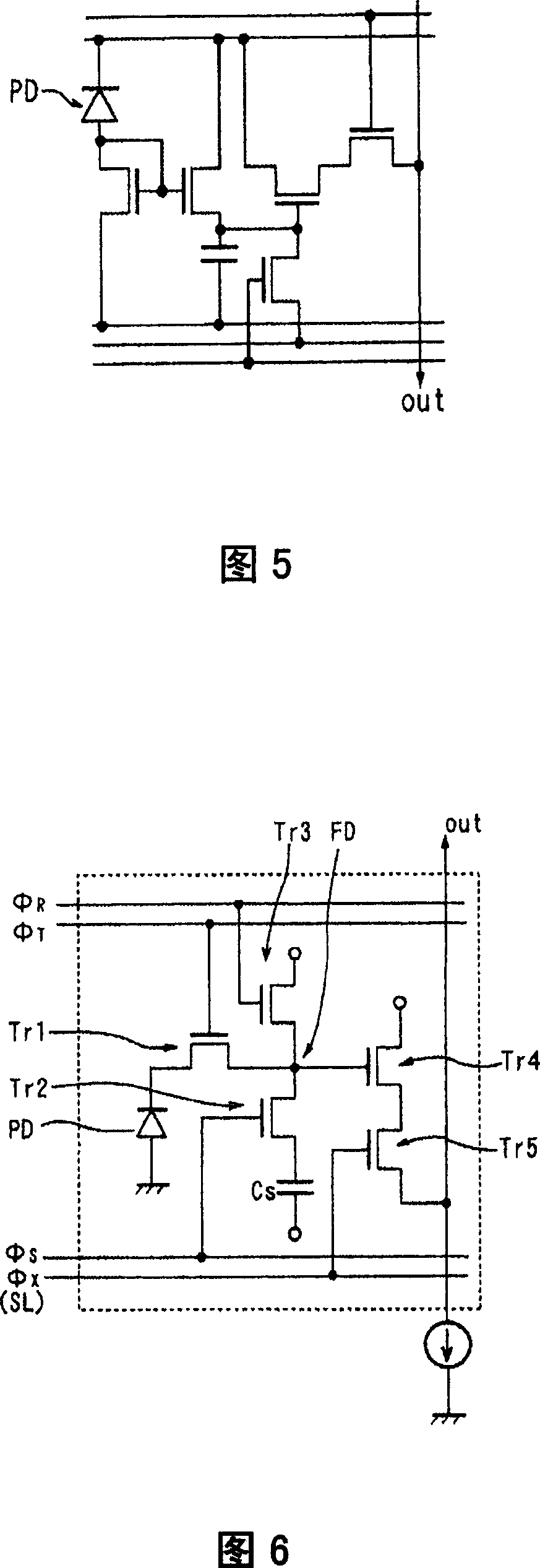
[0105] The solid-state imaging device of this embodiment is a CMOS image sensor, and FIG. 6 is an equivalent circuit diagram of one pixel.
[0106] Each pixel consists of a photodiode PD that receives light and generates and accumulates photocharges, a transfer transistor Tr1 that transfers photocharges from the photodiode PD, and a floating diffusion FD that transfers photocharges through the transfer transistor. Said photodiode overflows the photocharge accumulation capacitor element C S , The floating diffusion FD and the storage capacitor element C S The storage transistor Tr2 that is combined or divided by the potential of the floating diffusion FD is connected to the reset transistor Tr3 that is formed on the floating diffusion FD and used to discharge the photocharge in the floating diffusion FD, and amplifies and converts the photocharge in the floating diffusion FD into a voltage signal. The amplifying transistor Tr4 and the selection transistor Tr5 connected to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0192] The CMOS image sensor of this embodiment is the same as the CMOS image sensor of Embodiment 1, but the driving method is different.
[0193] Figure 16 shows the drive line (Φ T 、Φ S 、Φ R ) Timing diagram of the voltage applied across . Like Embodiment 1, it can be about Φ T Add the 3 levels of the energy level represented by (+α).
[0194] First, at time T when a new picture starts 0 , at Φ T is off, Φ S In the state of on, Φ R When it is on, the photocharge generated in the previous screen is completely discharged and reset.
[0195] for C PD The savings period T PD from time T 0 Previous Φ T start at the moment of off, in C PD The accumulation of photoelectric charge starts.
[0196] Then, at time T 0 The moment after the reset of T 1 , Φ R is off. At this time, become C FD and C S combined state, put the C FD +C S signal of the reset level as noise N 2 Read and store in the frame memory. At supersaturation, the noise N 2 is very small, so ins...
Embodiment 3
[0232] The CMOS image sensor of embodiment 1 and 2, or in embodiment 1 from moment T 0 Storage capacitor storage period T CS To start the mode of CMOS image sensor, put C FD +C S signal of the reset level as noise N 2 Read out and store in the frame memory FM, thereby canceling the sum of the charge signal before saturation and the oversaturated charge signal (S 1 +S 2 ) noise during sampling, but in the CMOS image sensor of this embodiment, no frame memory is used, which can reduce chip cost.
[0233] C FD +C S signal of the reset level (N2 ) The sampling timing ratio of the modulated pre-saturation charge signal and the sum of the oversaturation charge signal (S 1 ’+S 2 ’+N 2 ) sampling timing occurs earlier by 1 frame, so a frame memory is necessary.
[0234] Here, C FD +C S signal of the reset level (N 2 ) by C FD signal of the reset level (N 1 ) or N of the next frame 2 (expressed as N 2 ”) substitution, which cancels out the threshold bias of the in-pixe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com