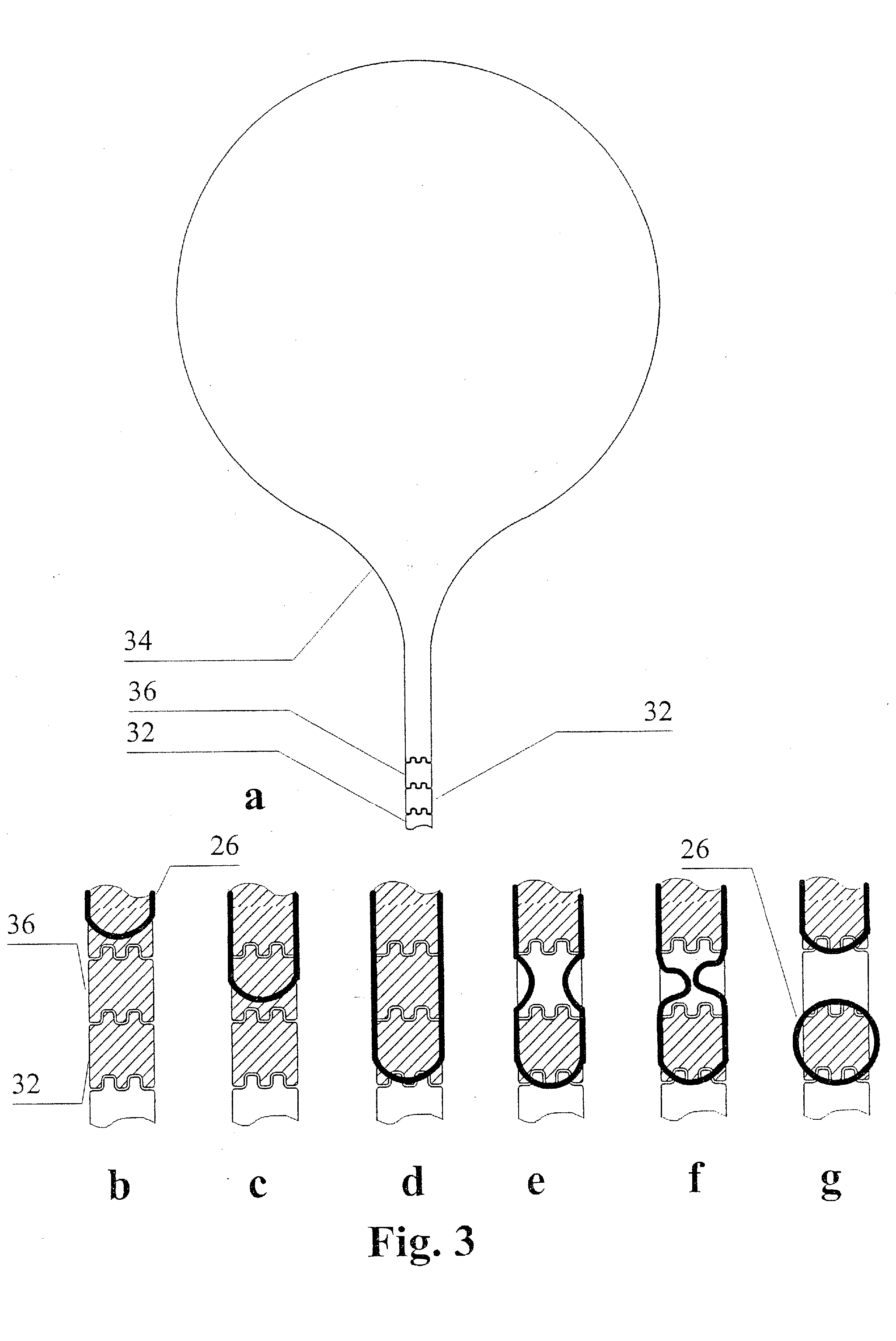
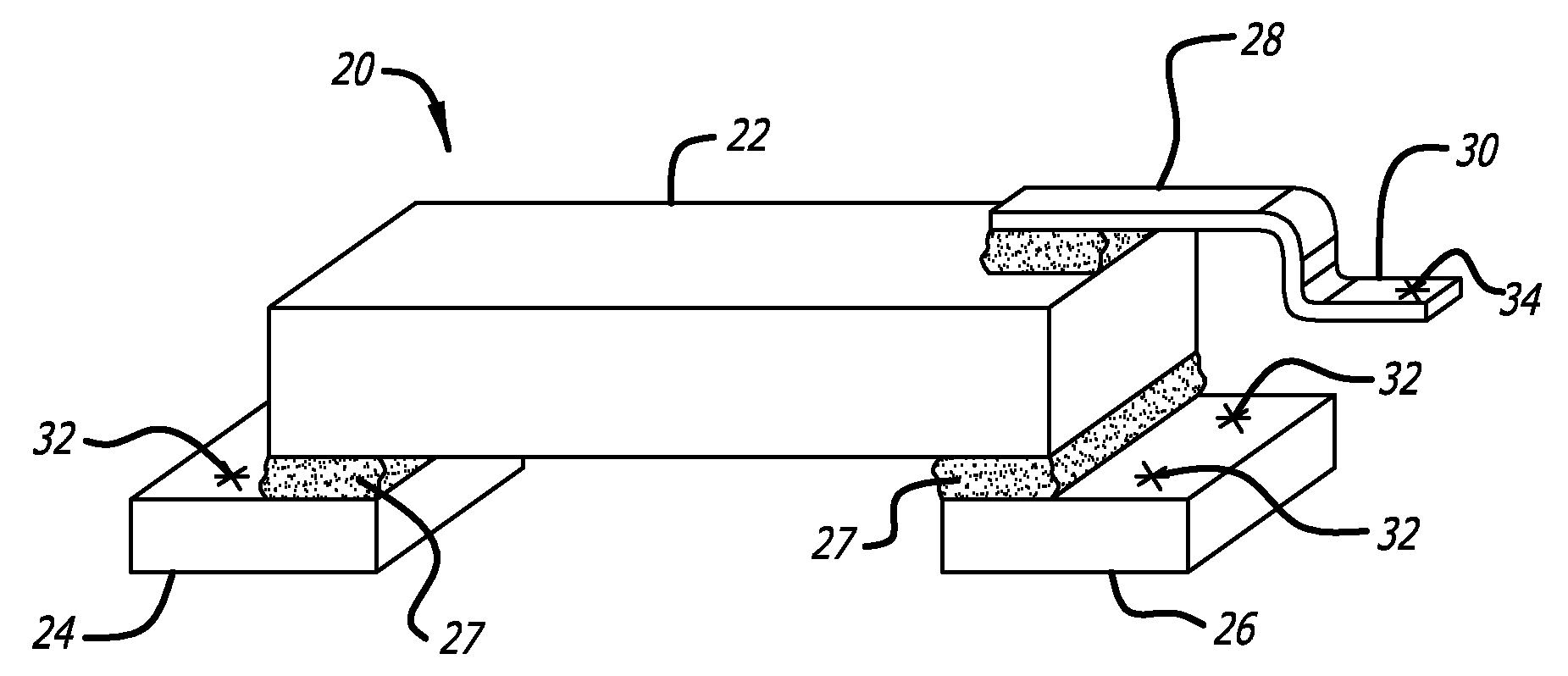
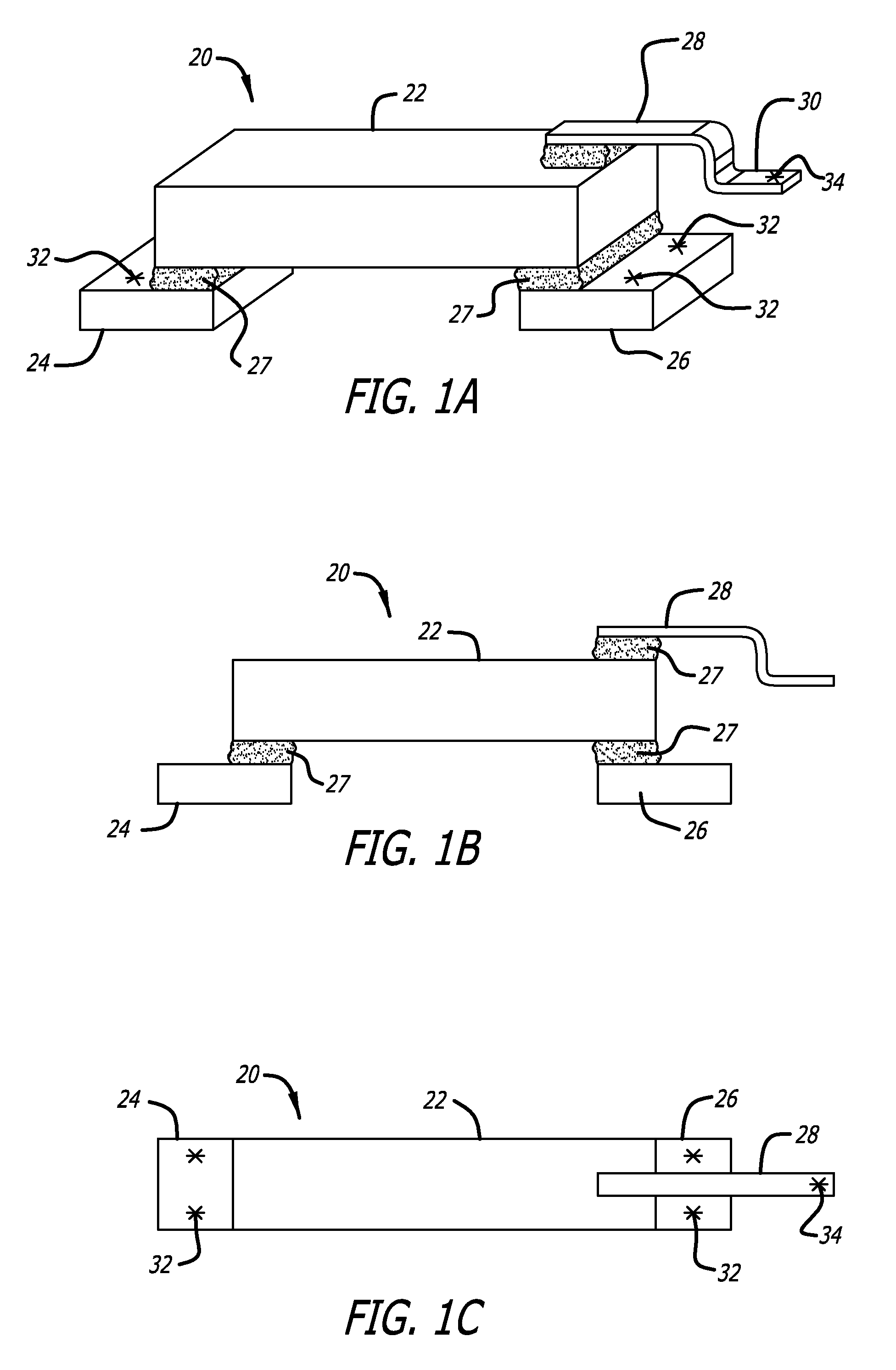
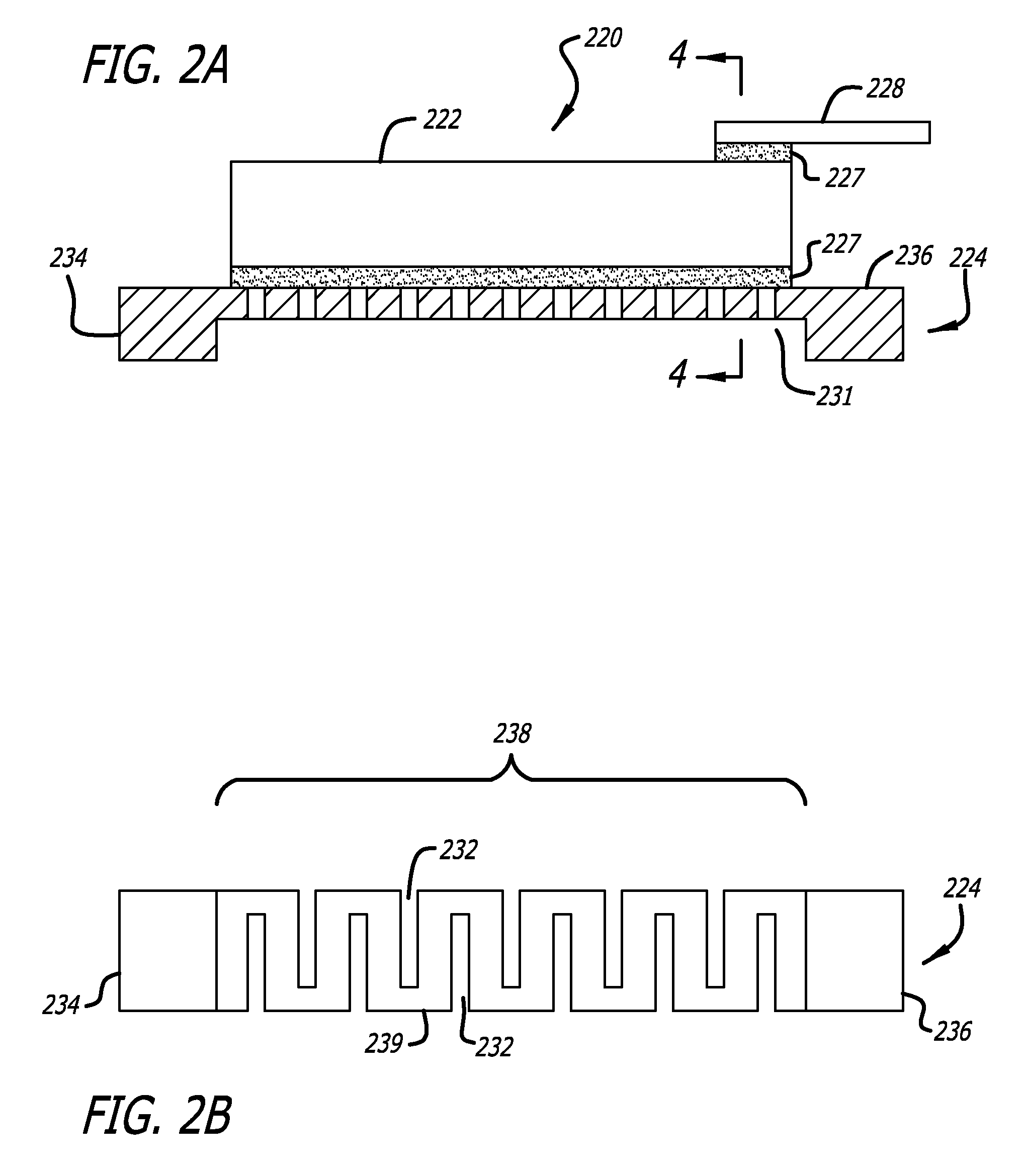
Patents
Literature
334 results about "Microactuator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microactuator is a microscopic servomechanism that supplies and transmits a measured amount of energy for the operation of another mechanism or system.
Droplet-based particle sorting
InactiveUS20080053205A1Large facilityEasy to testSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementChemical physicsParticle sorting
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
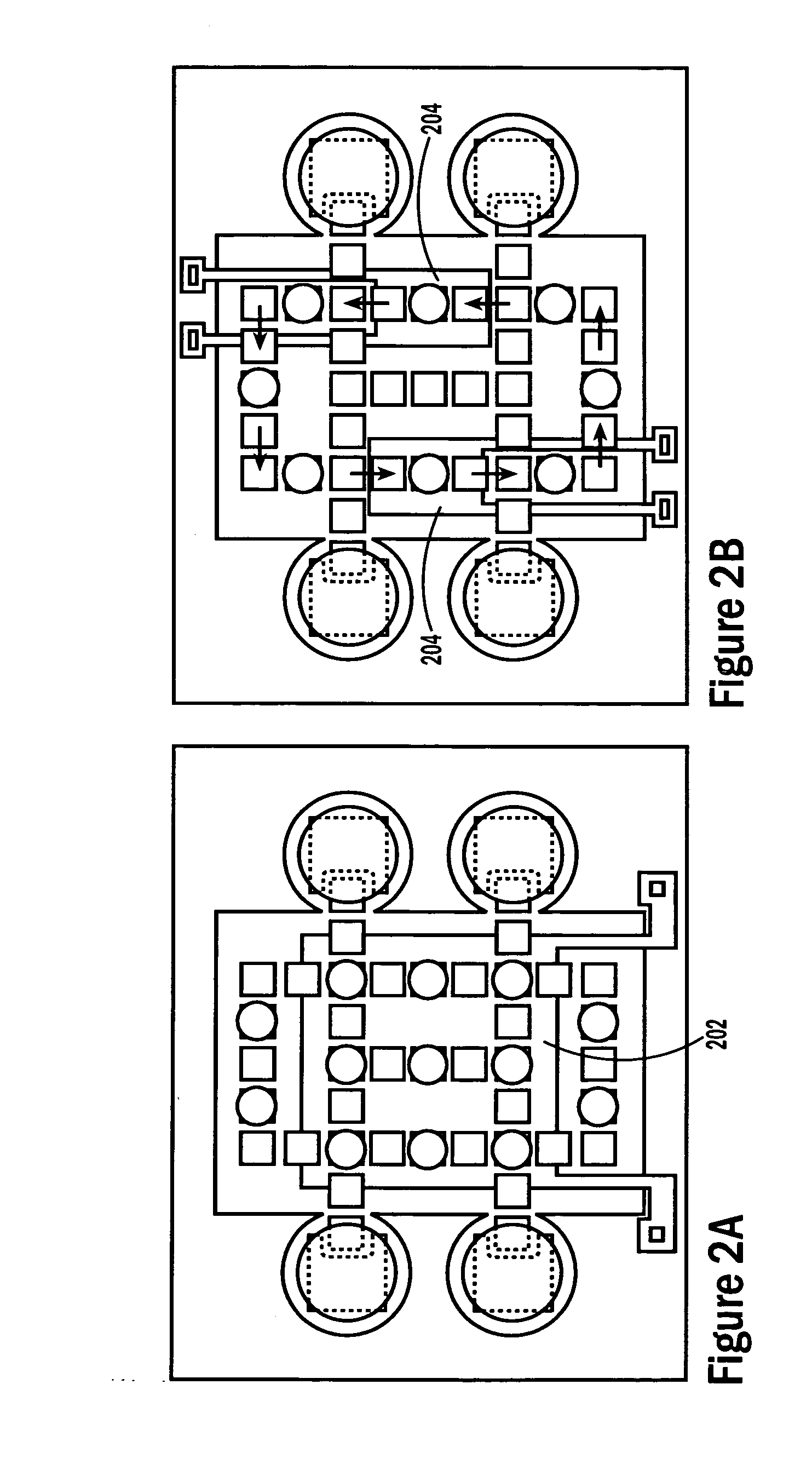
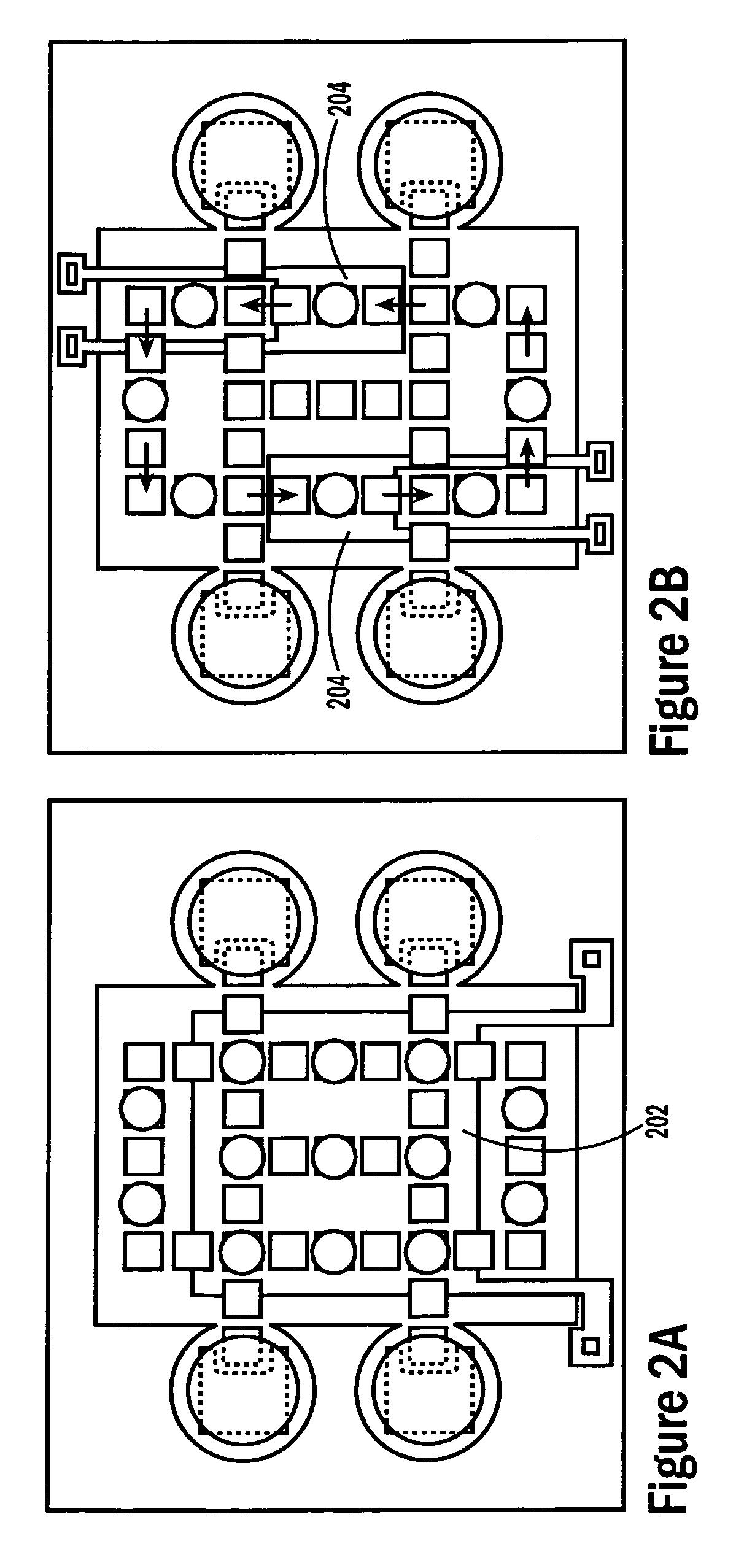
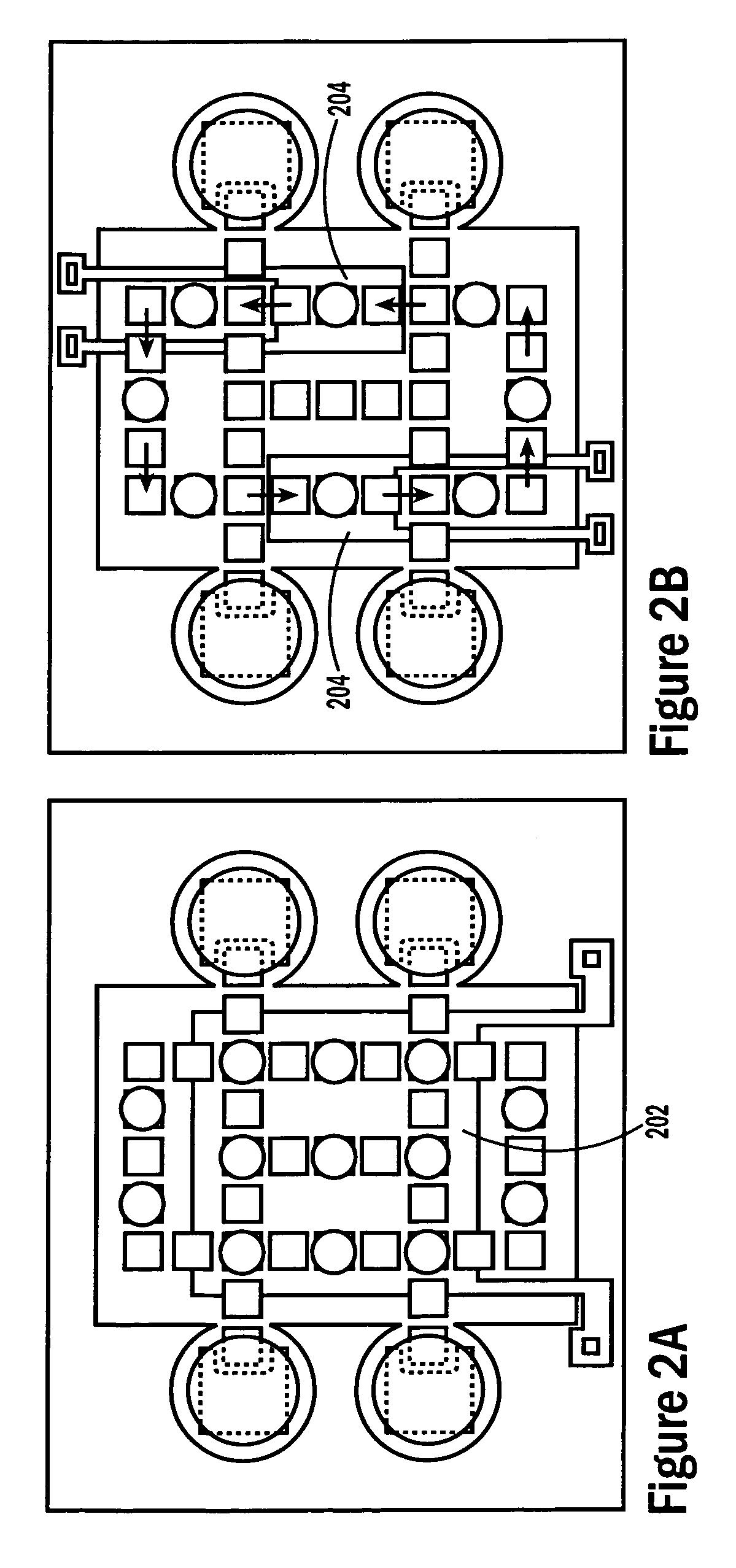
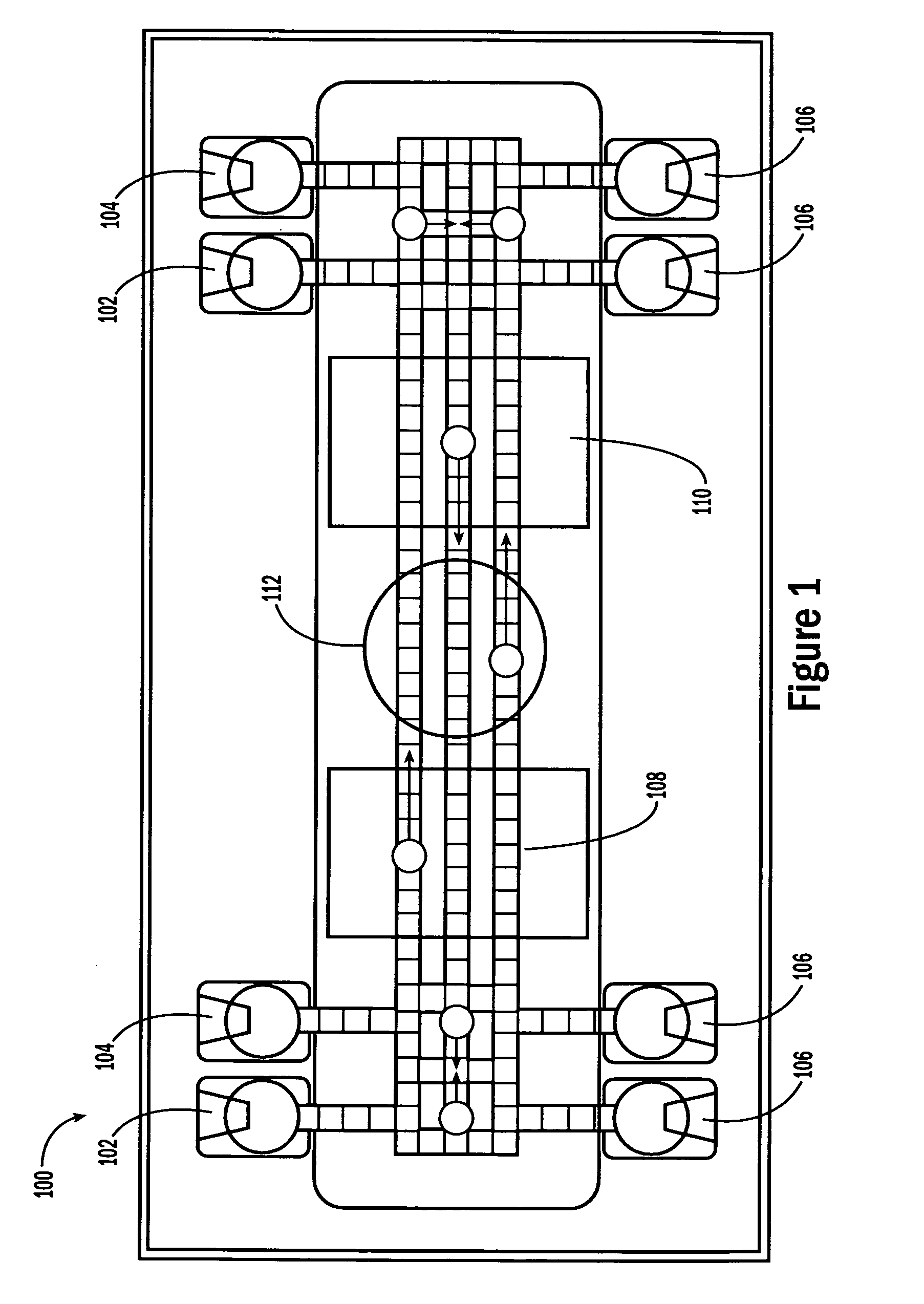
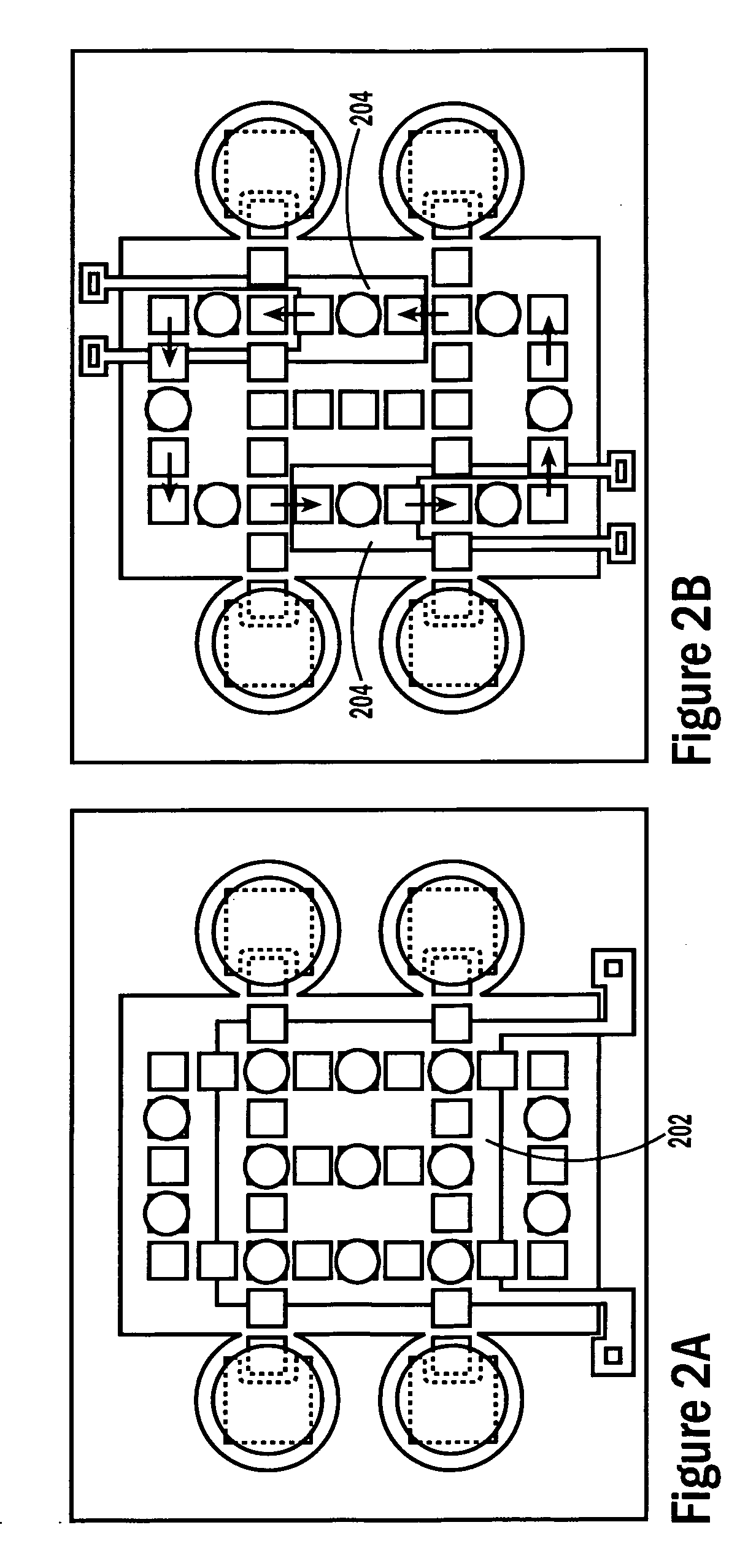
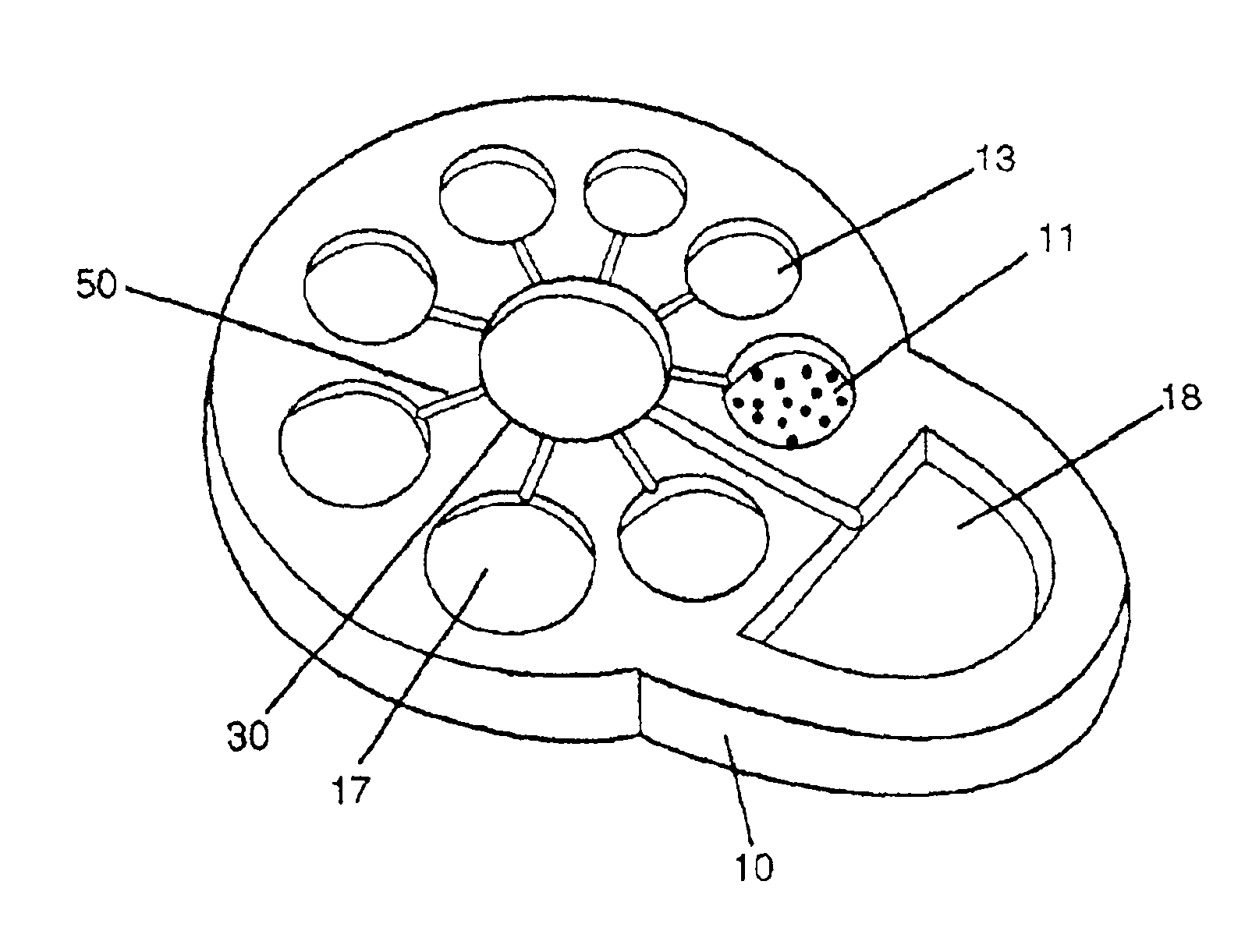
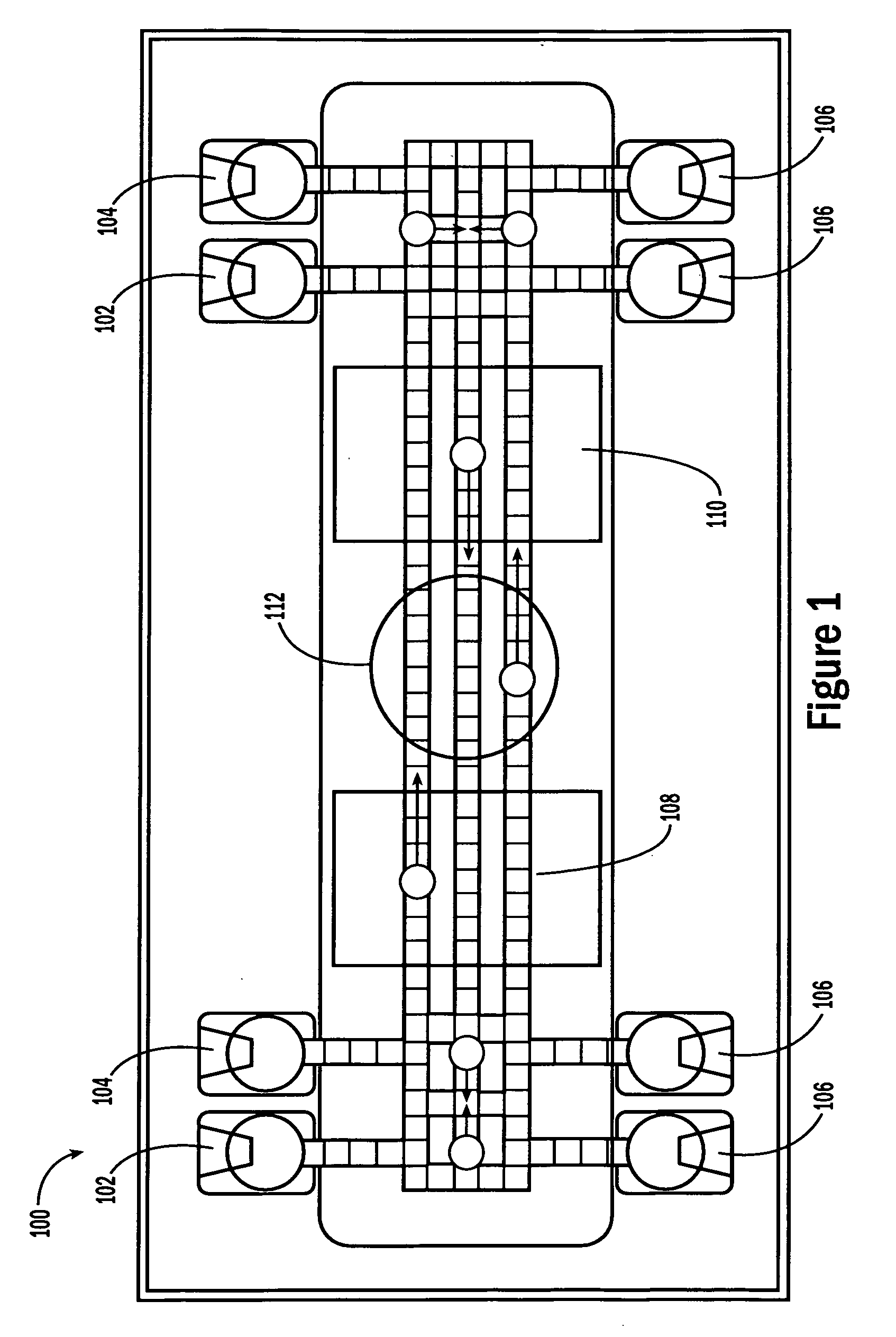
Self-contained microfluidic biochip and apparatus
InactiveUS20050221281A1Easy to implementEasy to storeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrofluidic channelMicroactuator
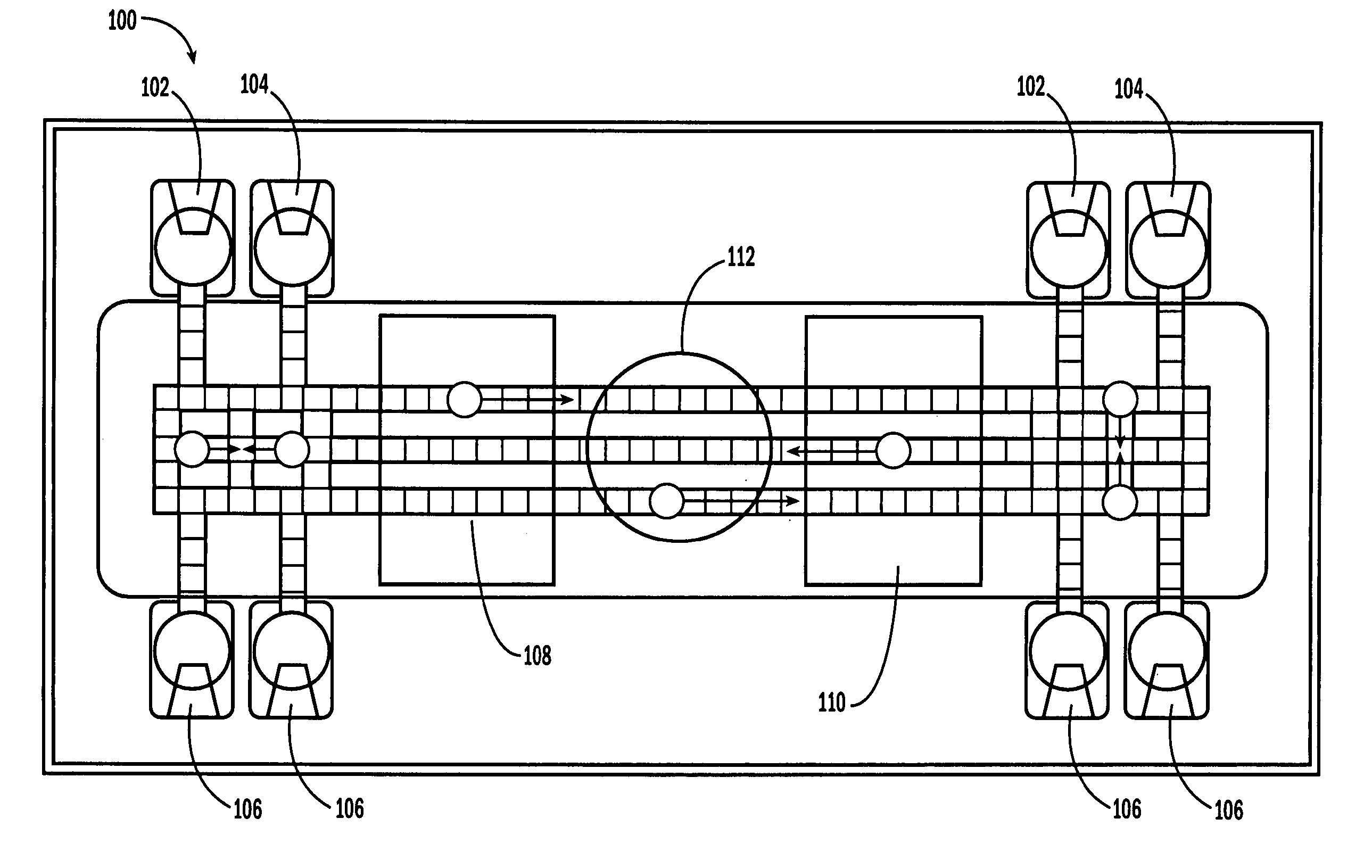
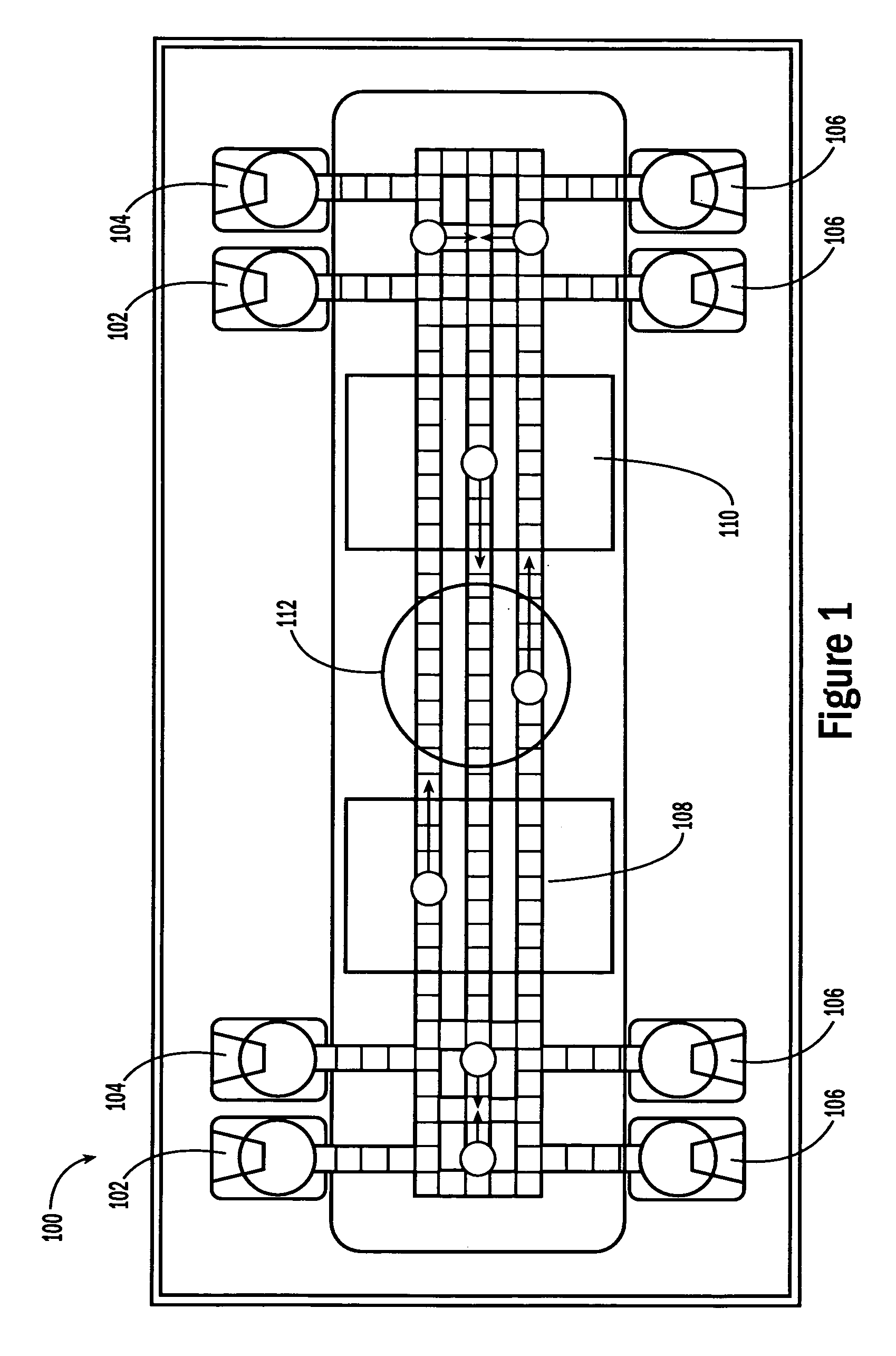
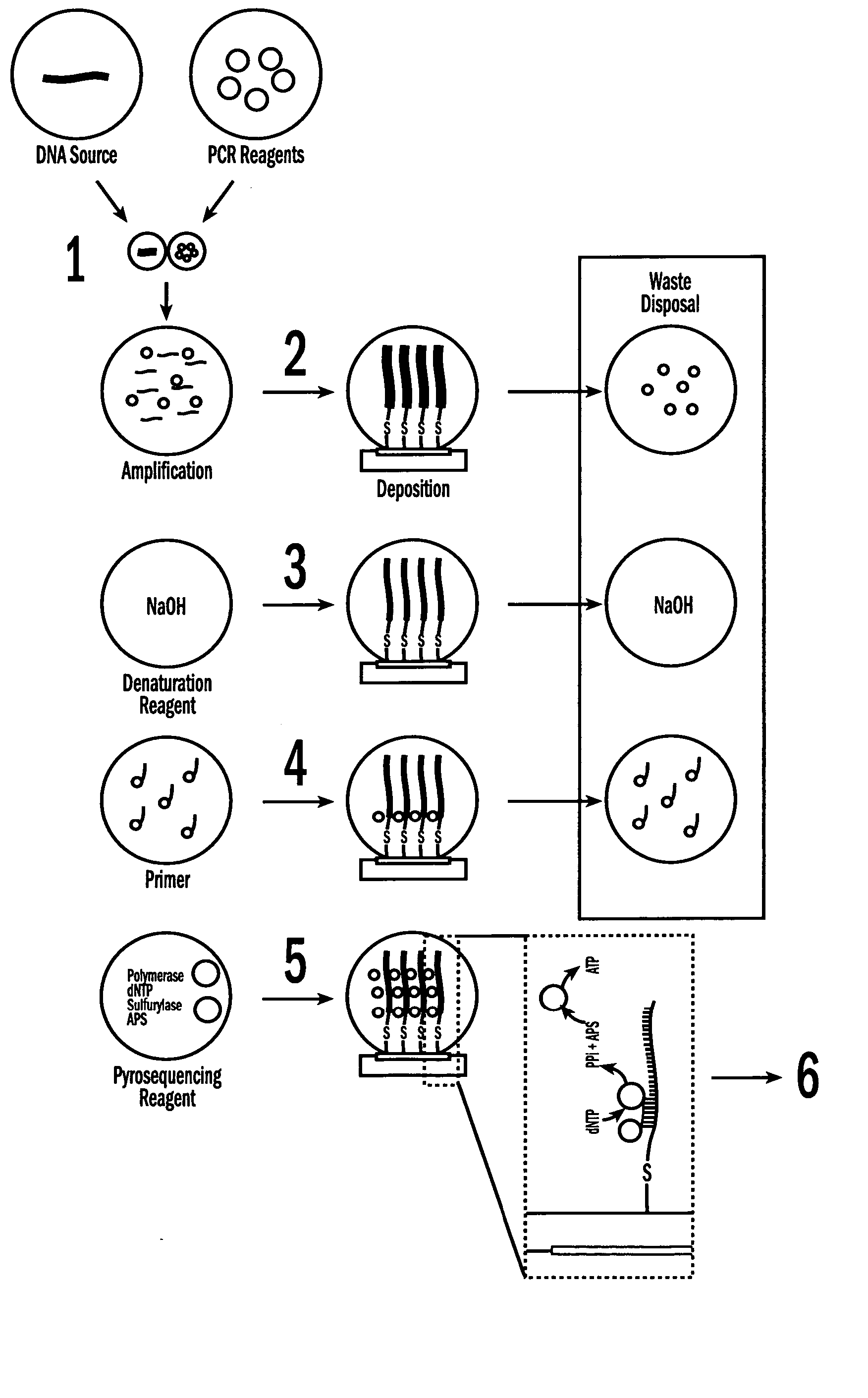
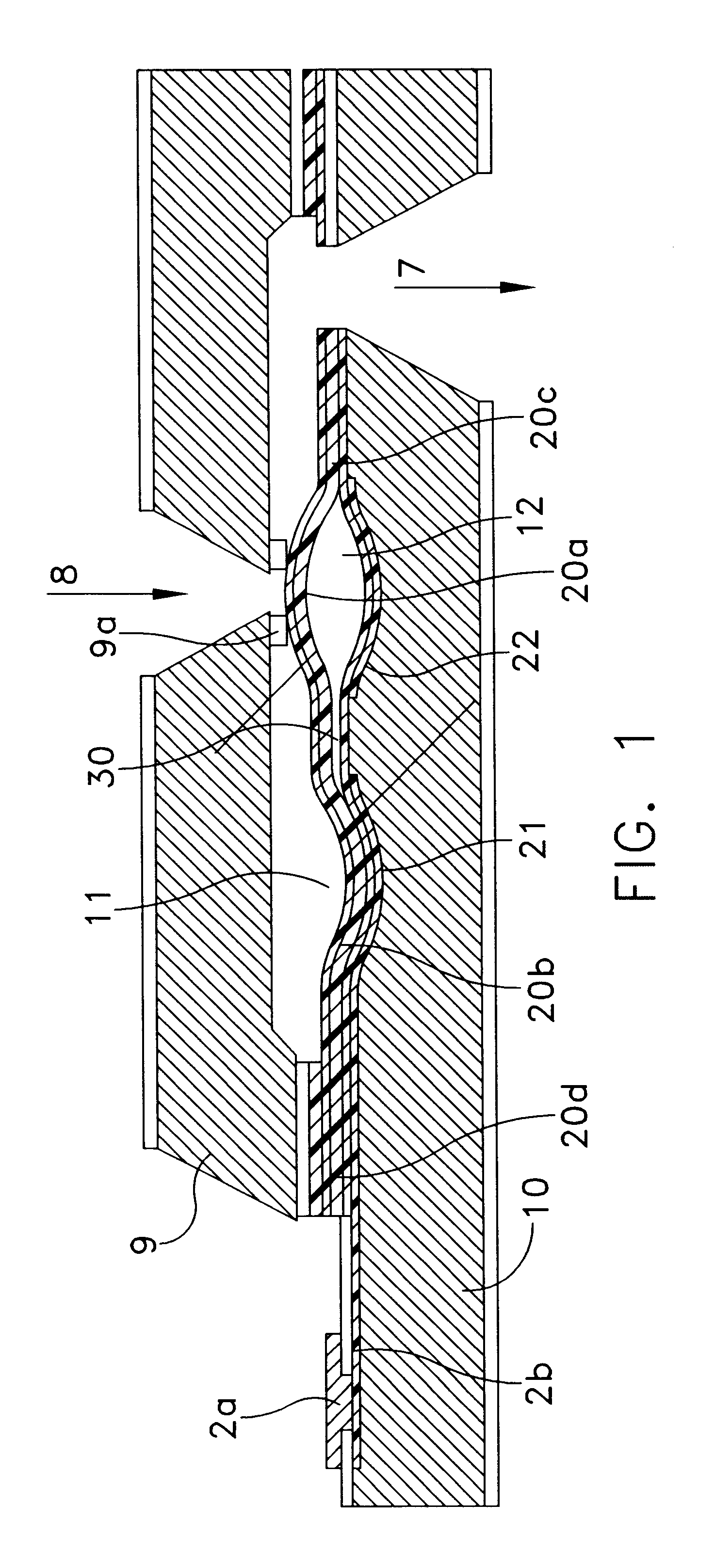
A biochip and apparatus is disclosed for performing biological assays in a self-contained microfluidic platform. The disposable biochip for multi-step reactions comprises a body structure with a plurality of reagent cavities and reaction wells connected via microfluidic channels; the reagent cavities with reagent sealing means for storing a plurality of reagents; the reagent sealing means being breakable and allowing a sequence of reagents to be released into microfluidic channel and reaction well; and the reaction well allowing multi-step reactions to occur. The apparatus may further comprise a microactuator, a heating and cooling element, a detector, a moving stage, a magnetic field generator, and a processor operable to perform all necessary functions, such as reagent delivery, magnetic purification, mixing and incubation, heating and cooling, and optical detection on a microfluidic biochip.
Owner:HO WINSTON Z
Droplet-based nucleic acid amplification device, system, and method
InactiveUS20080038810A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentTemperature controlBiology
The present invention relates to a droplet-based nucleic acid amplification device, system, and method. According to one embodiment, a droplet microactuator is provided and includes: (a) a substrate comprising electrodes for conducting droplet operations; and (b) one or more temperature control means arranged in proximity with one or more of the electrodes for heating and / or cooling a region of the droplet microactuator and arranged such that a droplet can be transported on the electrodes into the region for heating.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Droplet-based surface modification and washing
ActiveUS20070243634A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyHeating or cooling apparatusTransportation and packagingSurface modificationAmount of substance
The present invention relates to droplet-based surface modification and washing. According to one embodiment, a method of providing a droplet in contact with a surface with a reduced concentration of a substance is provided, wherein the method includes: (a) providing a droplet microactuator comprising a surface in contact with a droplet comprising a starting concentration and starting quantity of the substance and having a starting volume; (b) conducting one or more droplet operations to merge a wash droplet with the droplet provided in step (a) to yield a combined droplet; and (c) conducting one or more droplet operations to divide the combined droplet to yield a set of droplets comprising: (i) a droplet in contact with the surface having a decreased concentration of the substance relative to the starting concentration; and (ii) a droplet which is separated from the surface.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Droplet-based affinity assays
InactiveUS20070275415A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyHeating or cooling apparatusTransportation and packagingBiologyMicroactuator
The present invention relates to droplet-based affinity assays. According to one embodiment, a method of detecting a target analyte in a sample is provided, wherein the method includes: (a) executing droplet operations to combine affinity-based assay reagents on a droplet microactuator with a sample potentially comprising the target analyte to generate a signal indicative of the presence, absence and / or quantity of analyte; and (b) detecting the signal, wherein the signal corresponds to the presence, absence and / or quantity of the analyte in the sample.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Droplet-based surface modification and washing
ActiveUS7439014B2Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyHeating or cooling apparatusTransportation and packagingSurface modificationSurface modified
The present invention relates to droplet-based surface modification and washing. According to one embodiment, a method of providing a droplet in contact with a surface with a reduced concentration of a substance is provided, wherein the method includes: (a) providing a droplet microactuator comprising a surface in contact with a droplet comprising a starting concentration and starting quantity of the substance and having a starting volume; (b) conducting one or more droplet operations to merge a wash droplet with the droplet provided in step (a) to yield a combined droplet; and (c) conducting one or more droplet operations to divide the combined droplet to yield a set of droplets comprising: (i) a droplet in contact with the surface having a decreased concentration of the substance relative to the starting concentration; and (ii) a droplet which is separated from the surface.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Filler fluids for droplet operations
ActiveUS20070242105A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsFixed microstructural devicesEngineeringLiquid drop
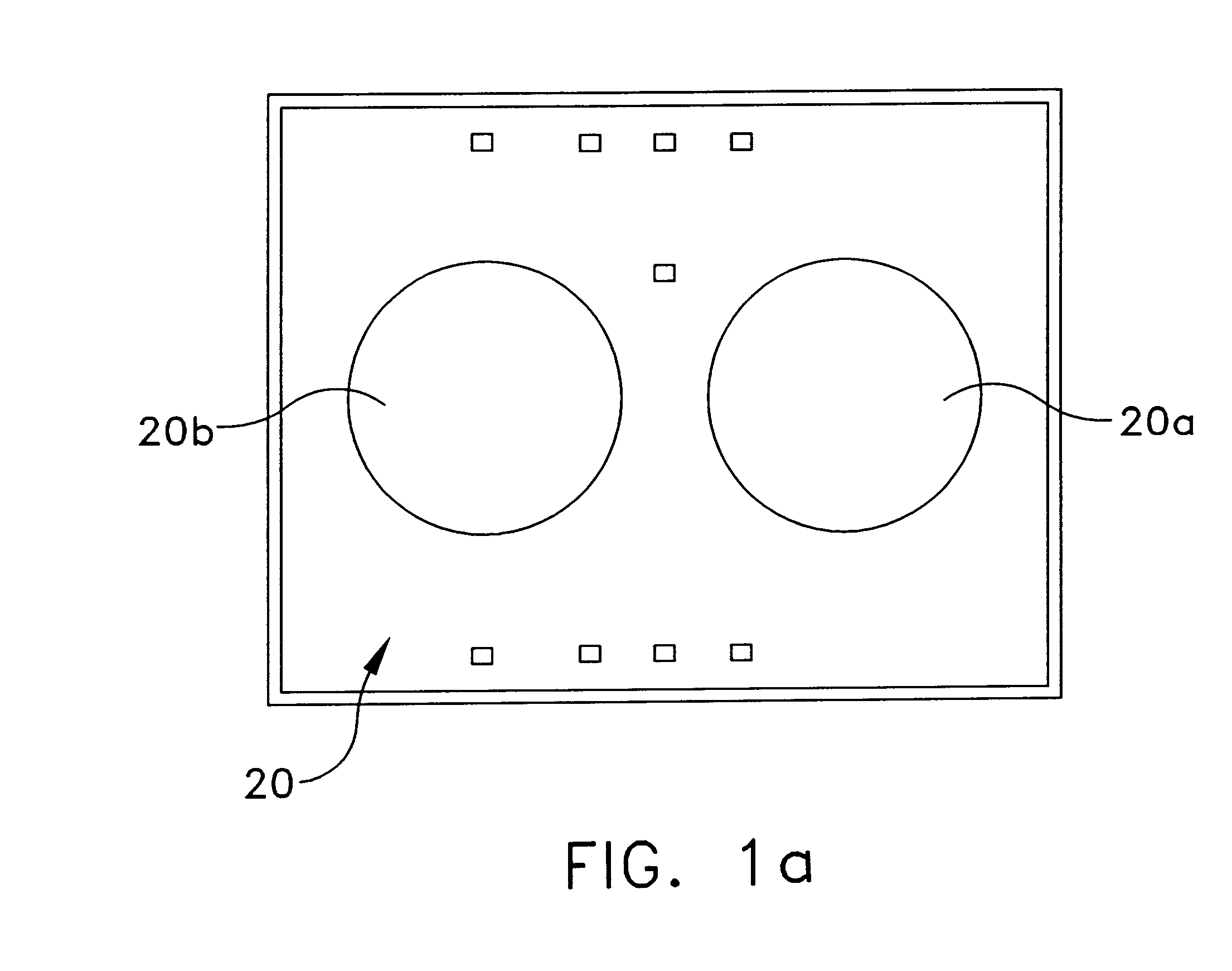
The present invention relates to filler fluids for droplet operations. According to one embodiment of this aspect, a droplet microactuator is provided and includes: (a) a first substrate comprising electrodes configured for conducting droplet operations on a surface of the substrate; (b) a second substrate spaced from the surface of the substrate by a distance sufficient to define an interior volume between the first substrate and second substrate, wherein the distance is sufficient to contain a droplet disposed in the space on the first substrate; and (c) a droplet arranged in the interior volume and arranged with respect to the electrodes in a manner which permits droplet operations to be effected on the droplet using the electrodes.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
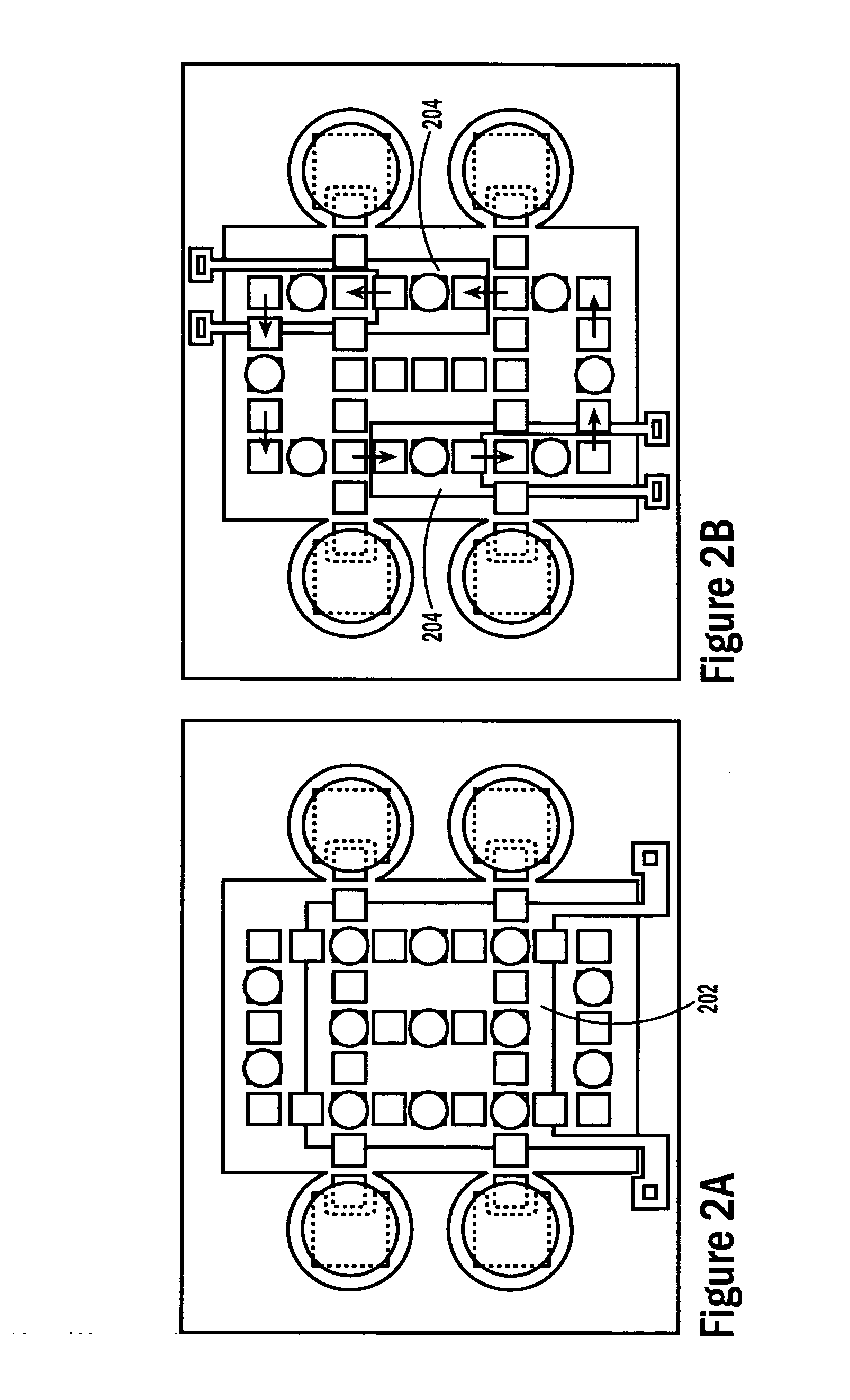
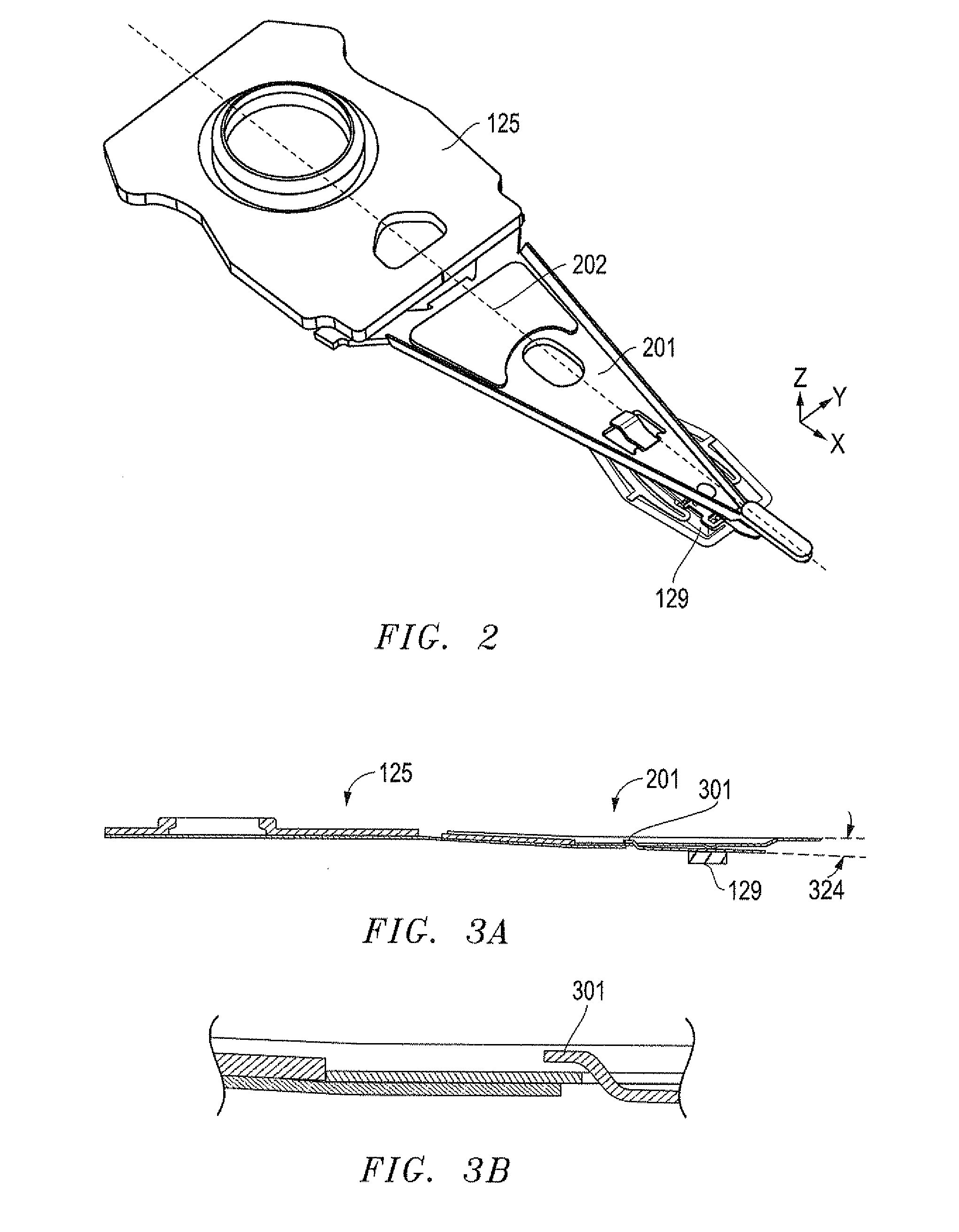
Dimple pivot post for a rotary co-located microactuator
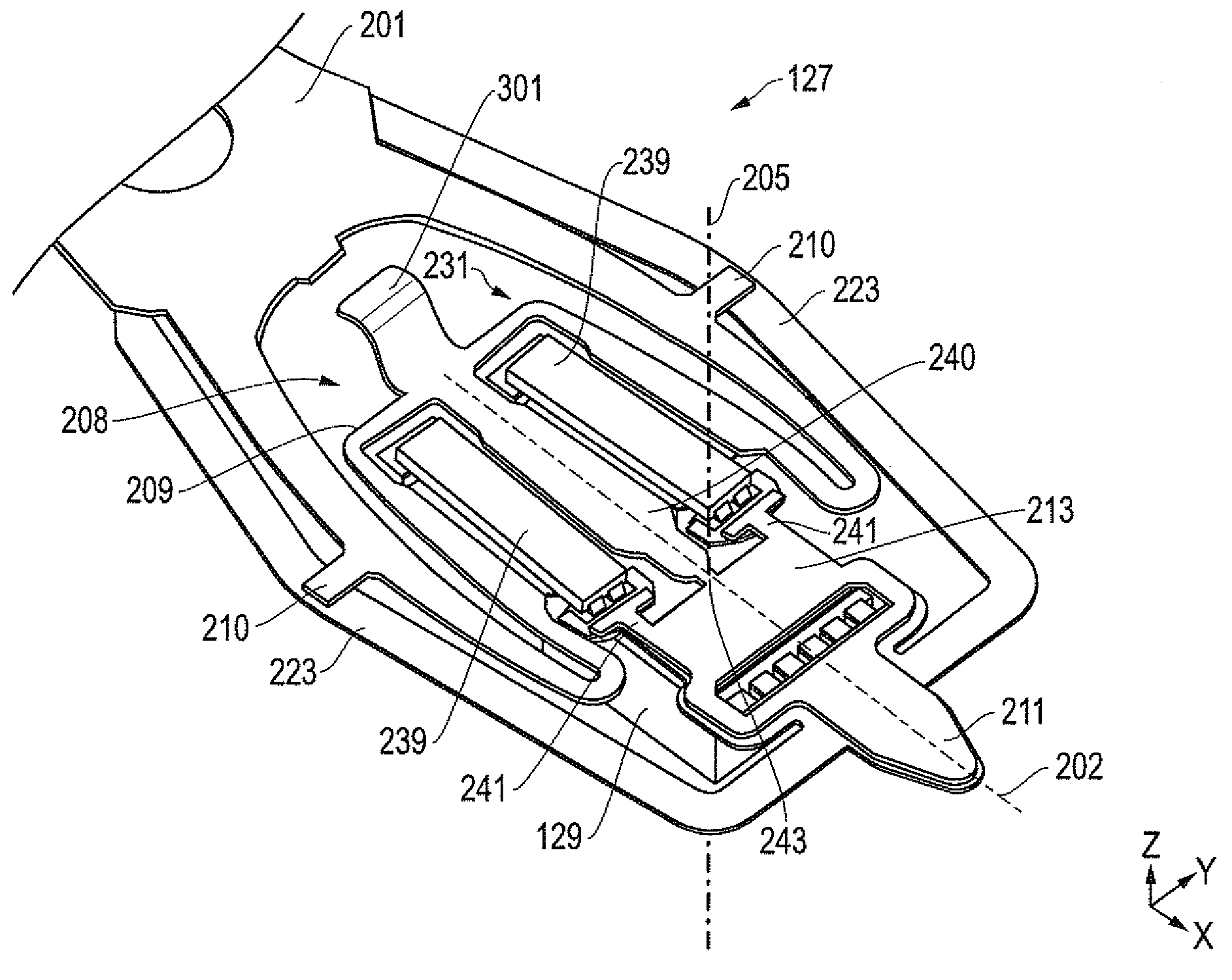
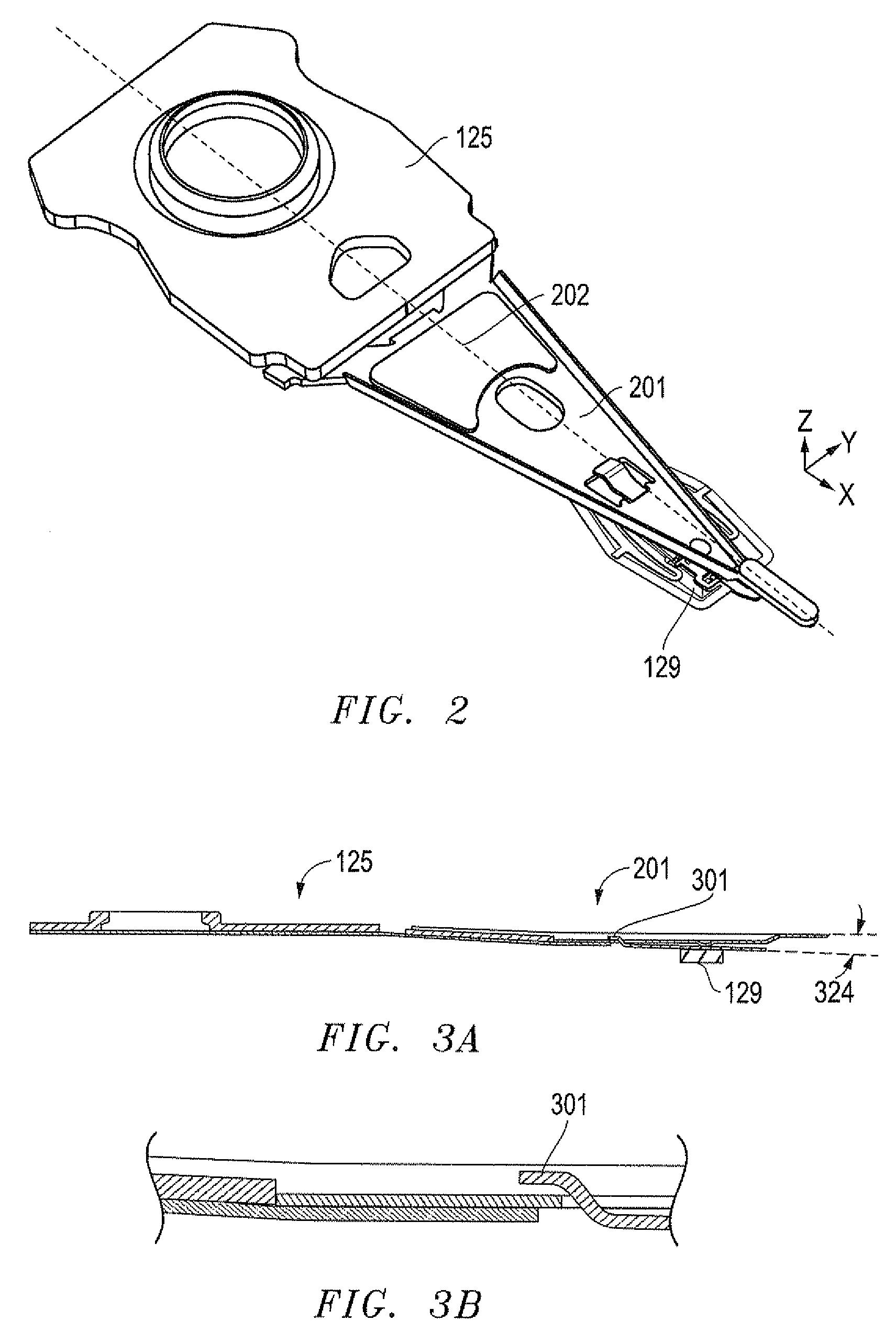
InactiveUS7057857B1Eliminate deformationImprove performanceRecord information storageMounting/attachment of transducer headAdhesiveEngineering
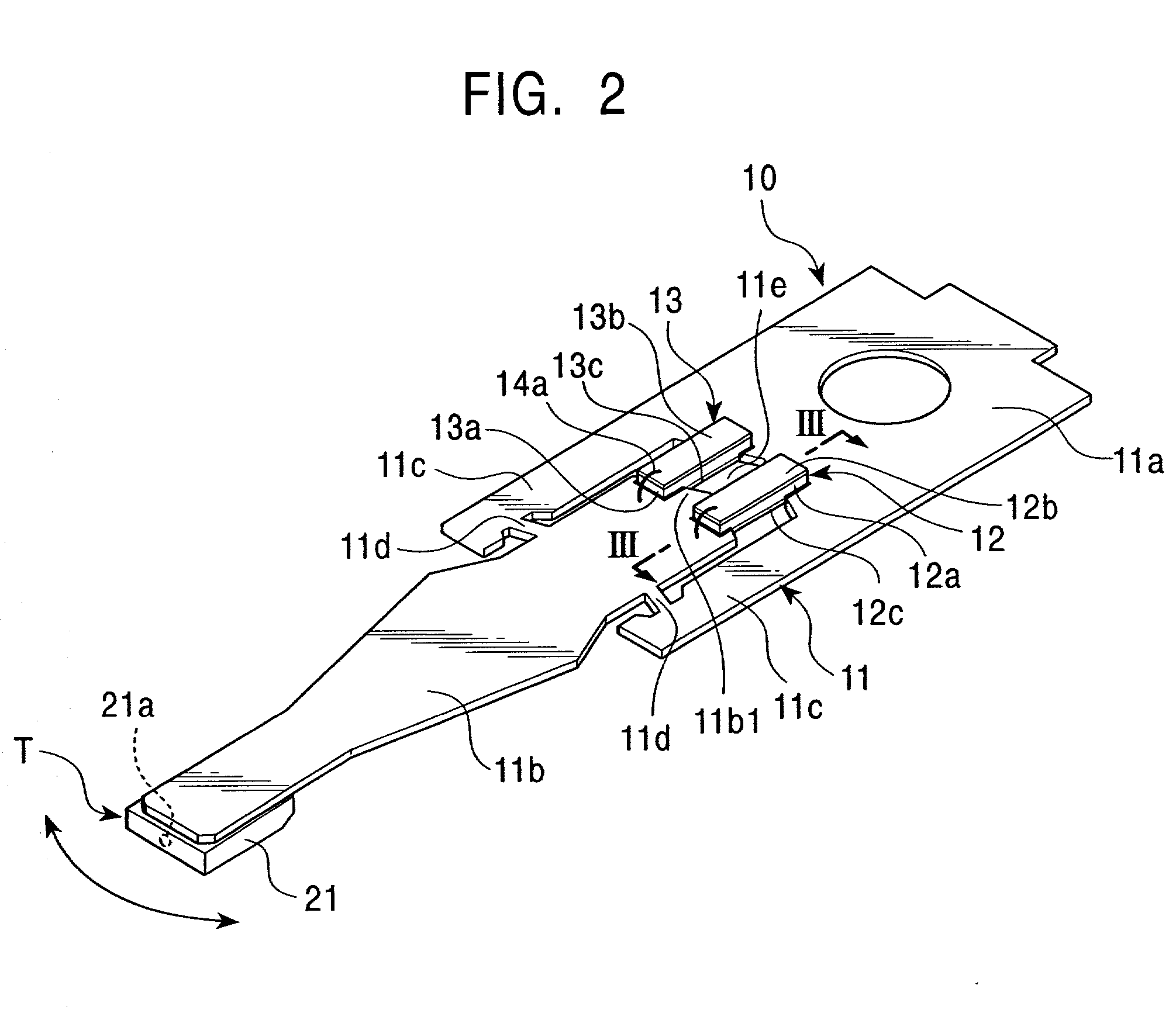
A rotary microactuator-based head-gimbal assembly design controls the unwanted deflection of a flexure in a data storage device and eliminates hinge deformation. The head-gimbal assembly maintains the co-planarity of the hinged islands in the microactuator under the applied load acting on the flexure and two associated hinged islands. The dimple post is placed at the dimple loading region of the flexure tongue and has the same height as adhesive dams on paddles secured to the hinged islands. The dimple post is formed by branching one of the existing conductive traces covered by a photoresist layer to the dimple loading region on flexure tongue. In an alternative embodiment, the dimple post is secured to the dimple loading region of the flexure tongue by means of adhesives with a variety of viscosity and elastic moduli.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
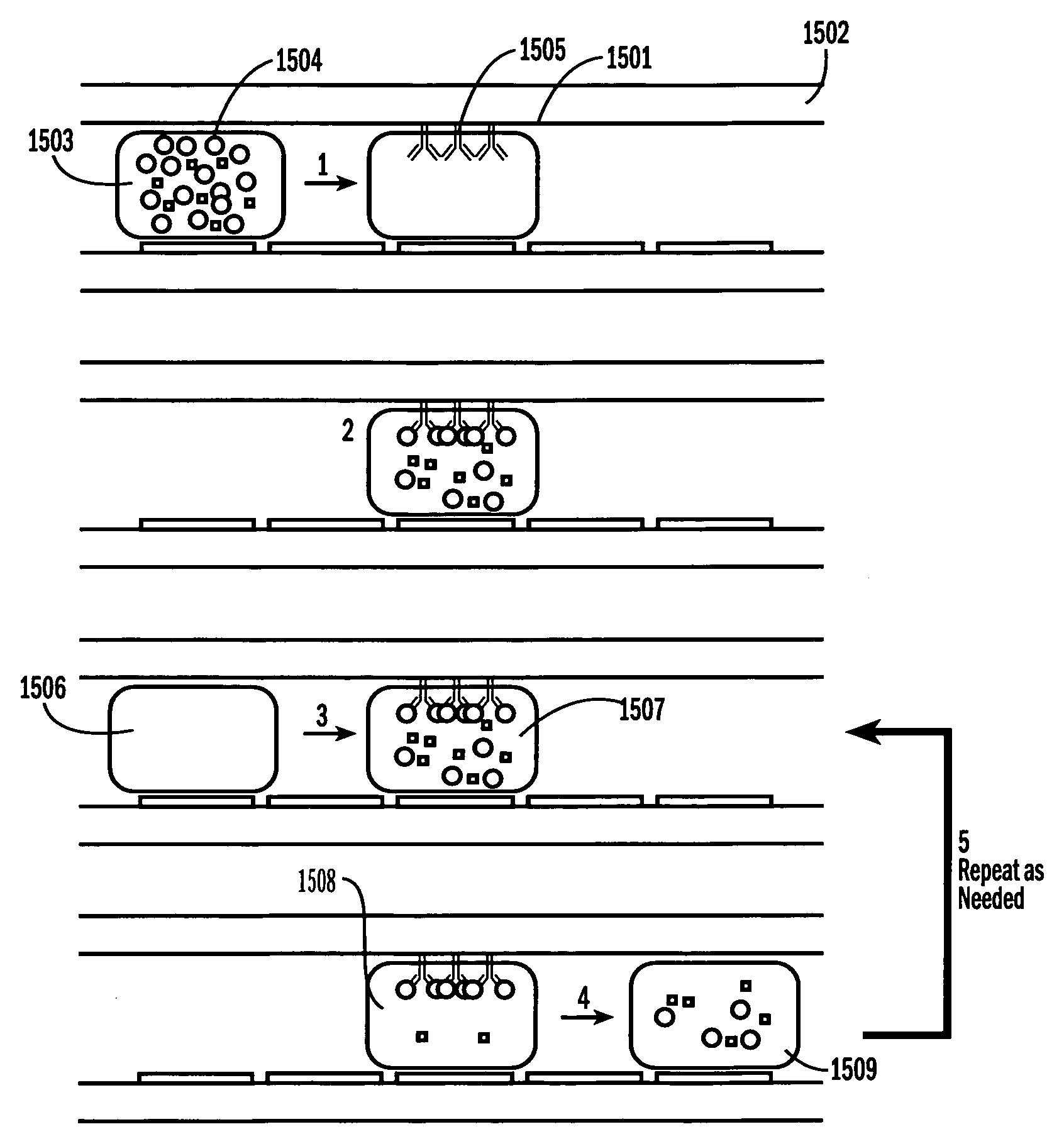
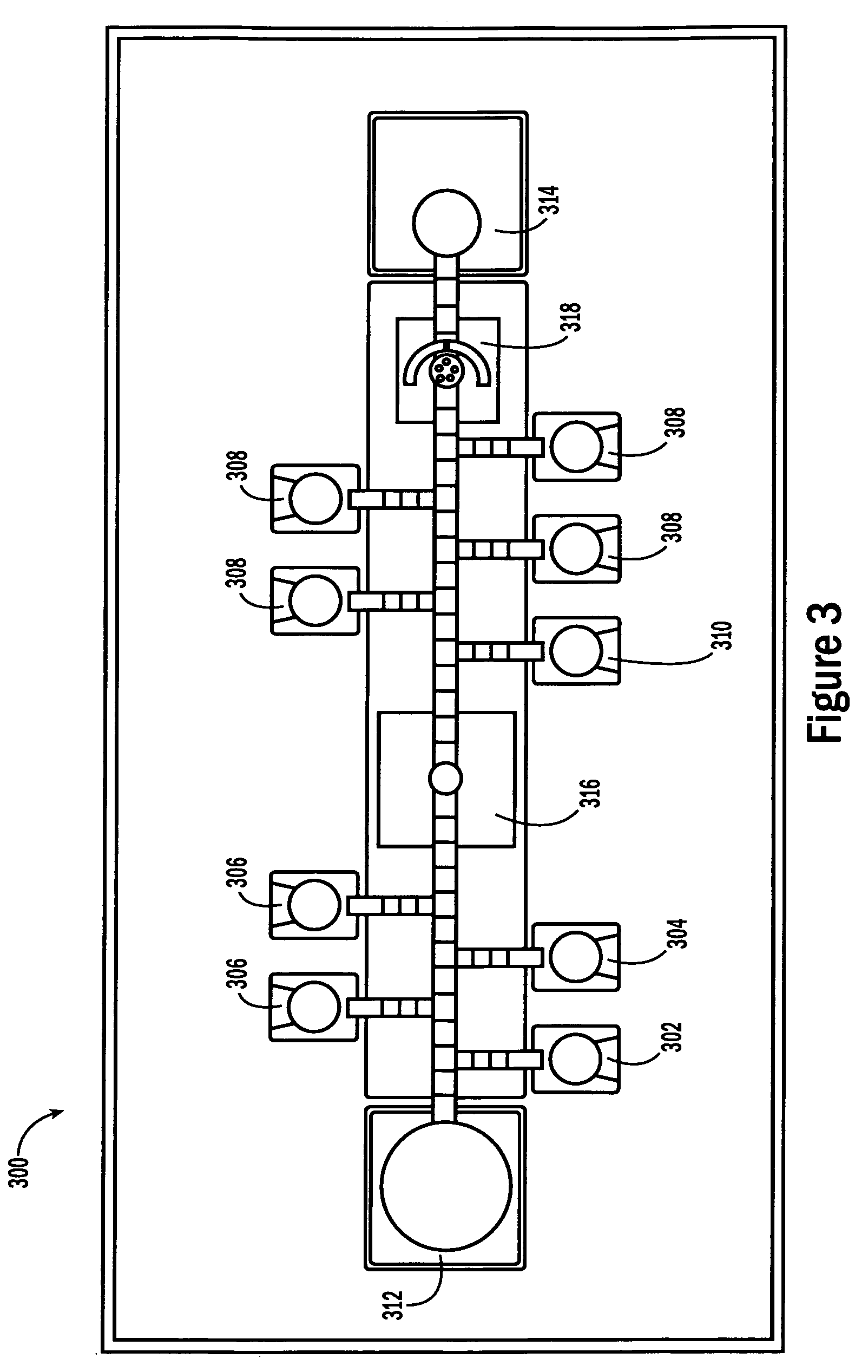
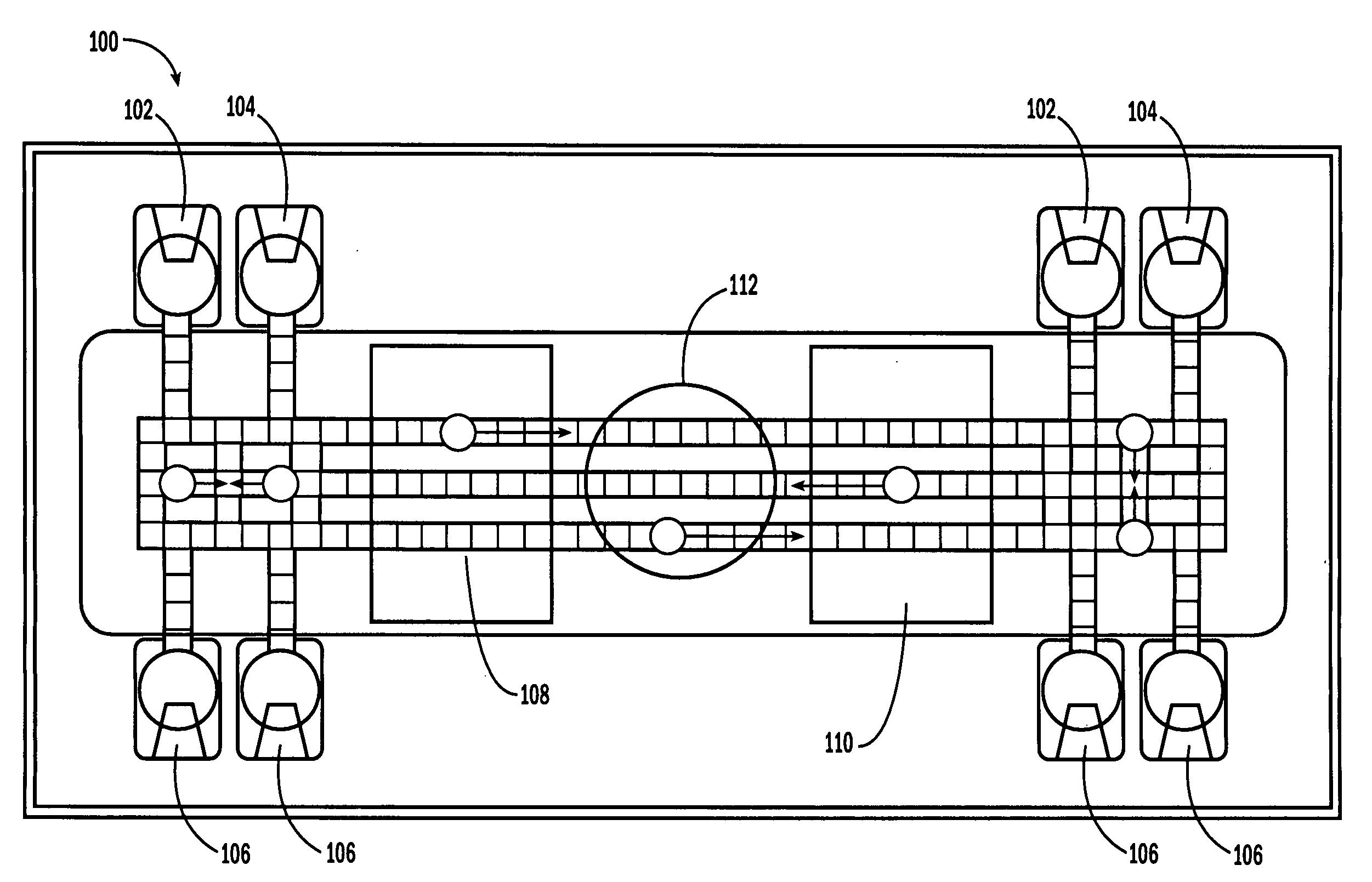
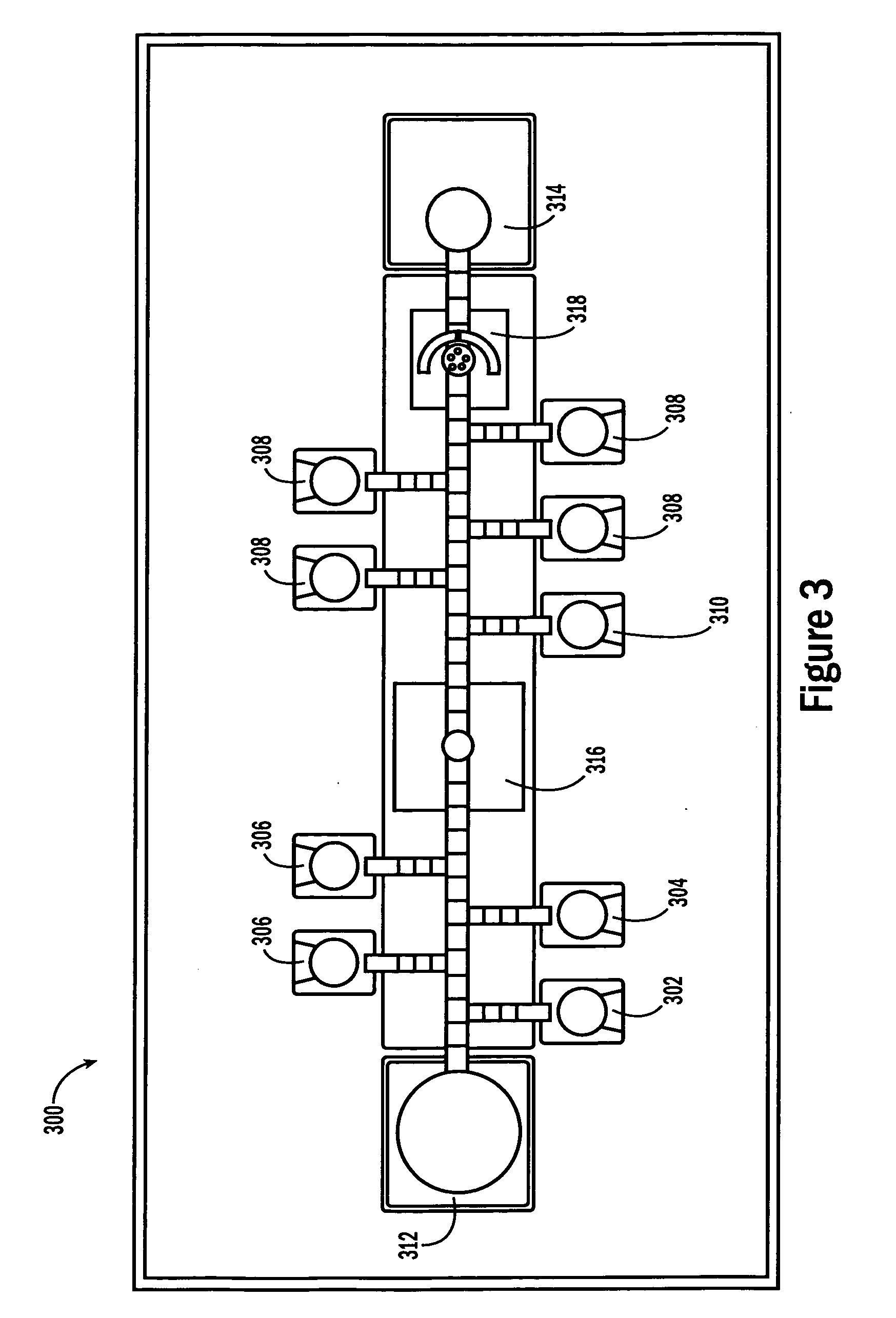
Sample Processing Droplet Actuator, System and Method
InactiveUS20080230386A1Easy to useFacilitates of propertySequential/parallel process reactionsSludge treatmentInterior spaceEngineering
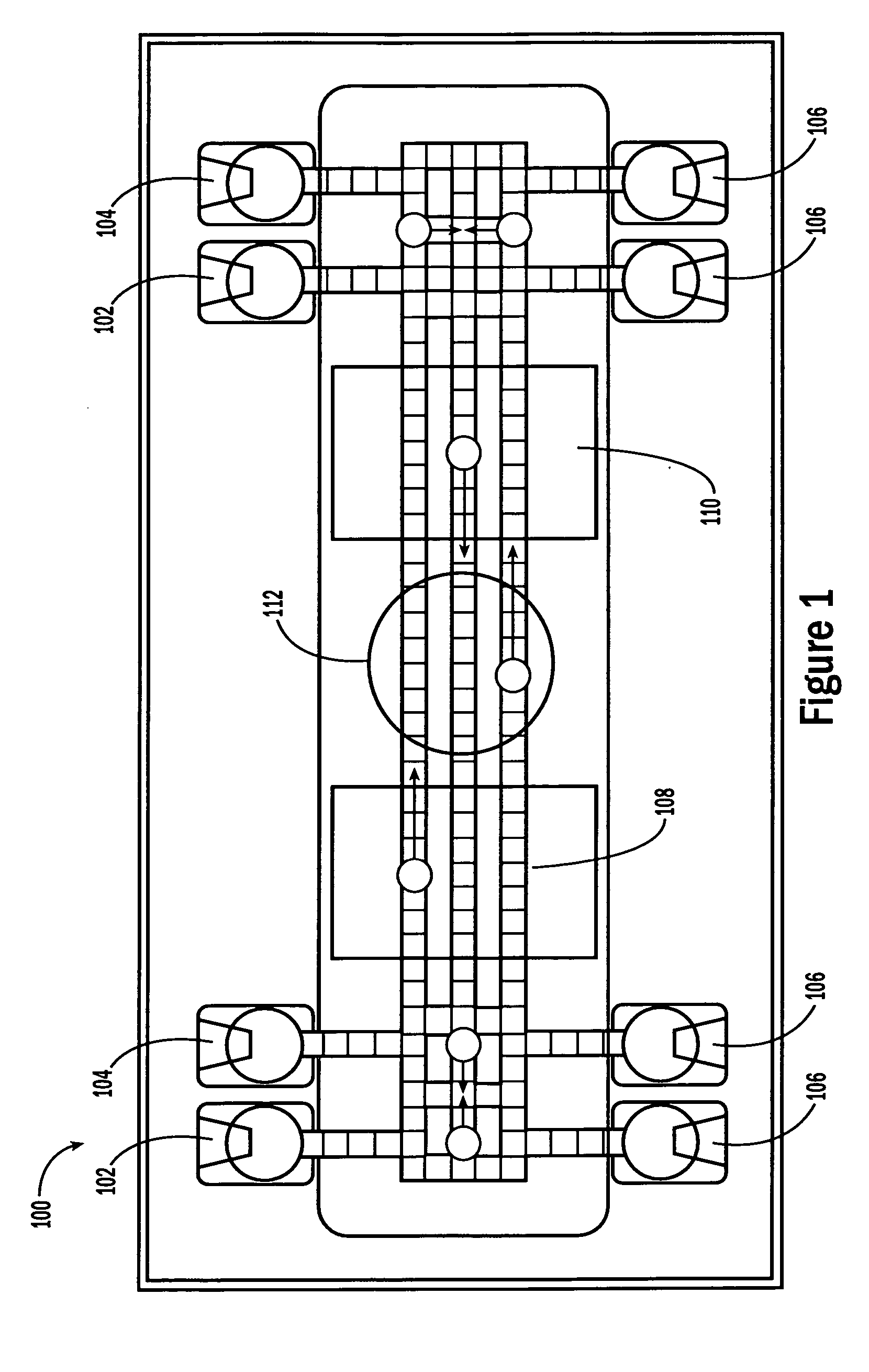
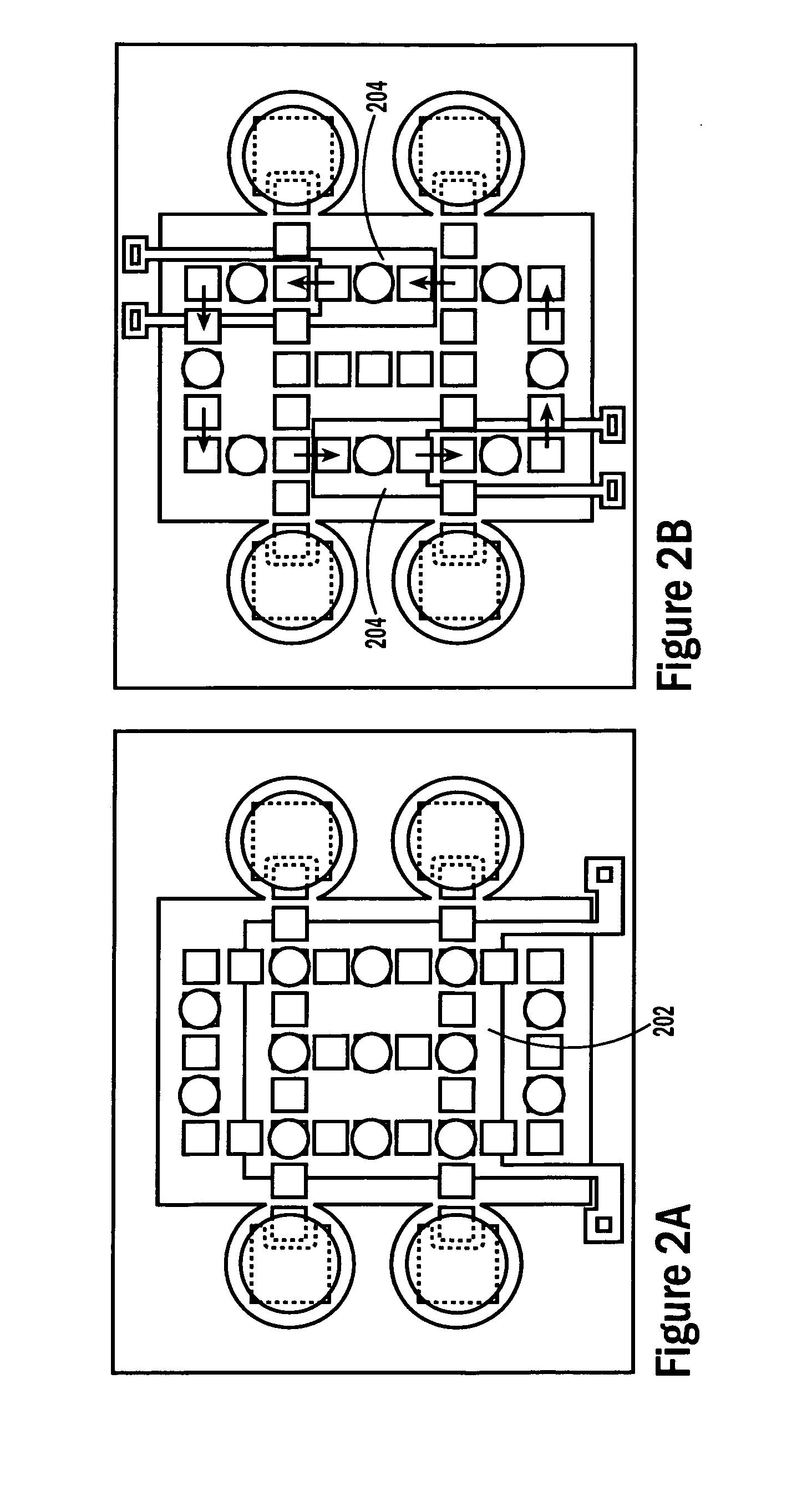
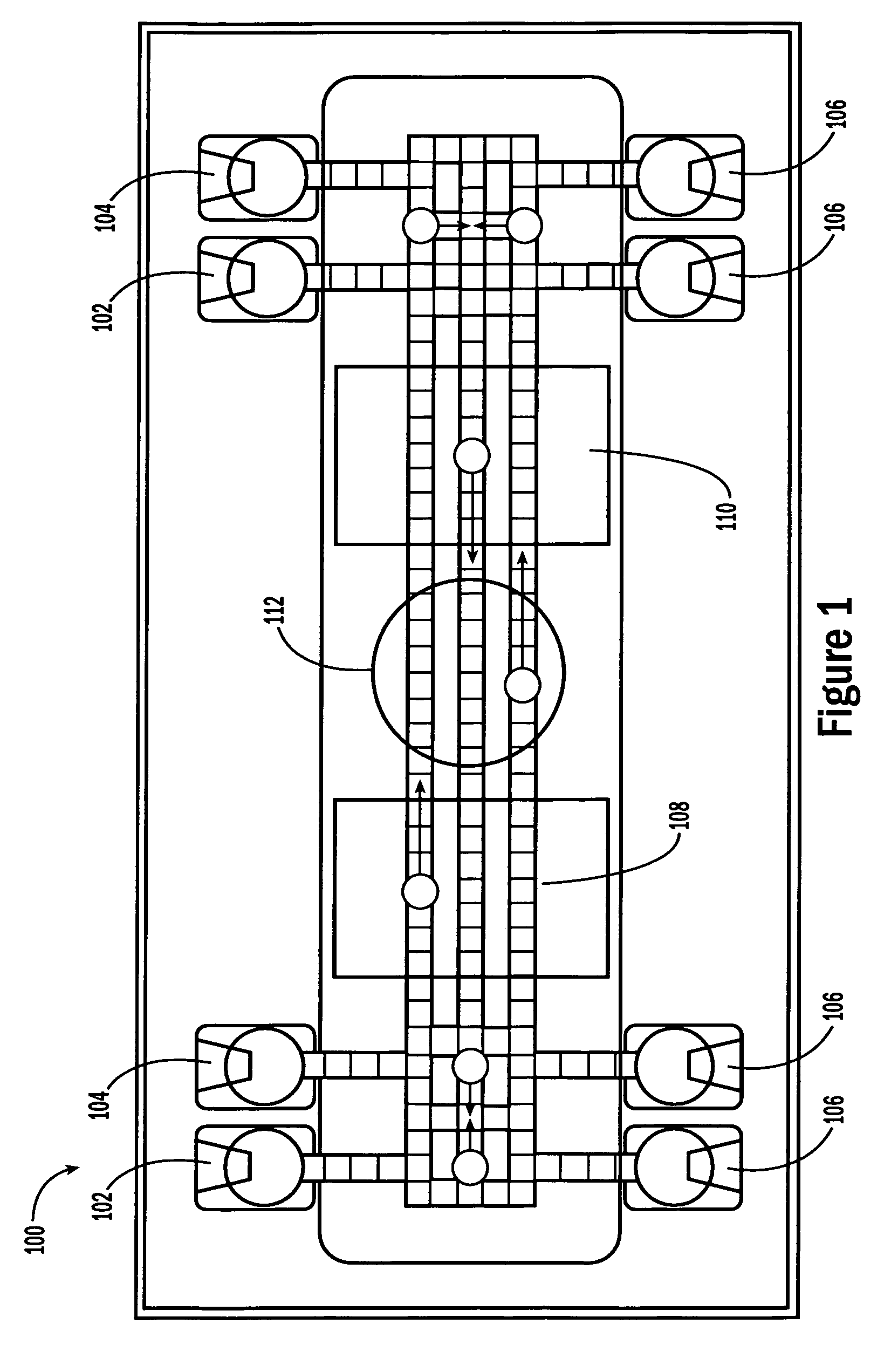
Sample processing droplet actuators, systems and methods are provided. According to one embodiment, a stamping device including a droplet microactuator is provided and includes: (a) a first plate including a path or network of control electrodes for transporting droplets on a surface thereof; (b) a second plate mounted in a substantially parallel orientation with respect to the first plate providing an interior volume between the plates, the second plate including one or more stamping ports for transporting some portion or all of a droplet from the interior volume to an exterior location; (c) a port for introducing fluid into the interior volume between the plates; and (d) a path or network of reference electrodes corresponding to the path or network of control electrodes. Associated systems and methods including the stamping device are also provided.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
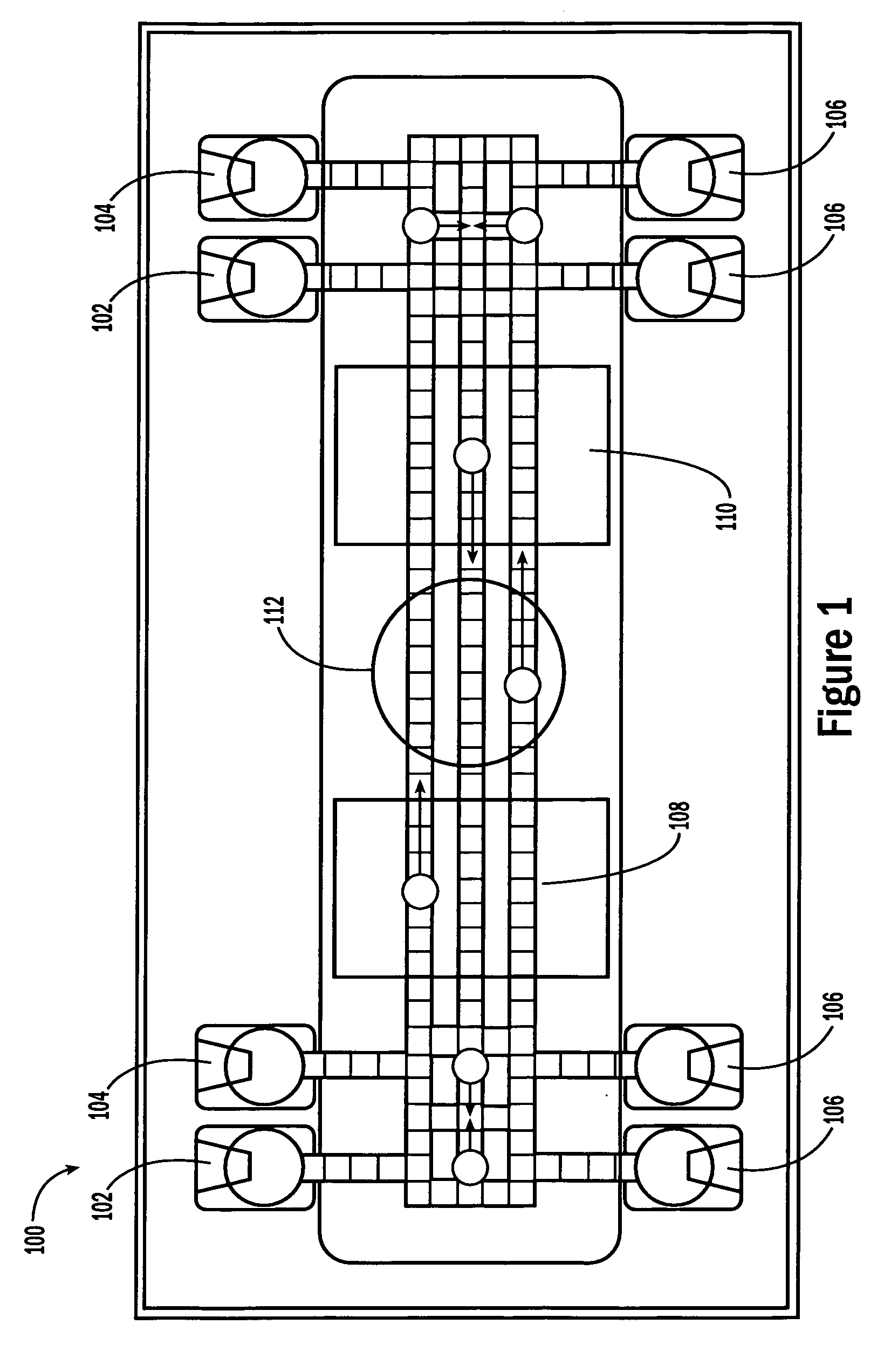
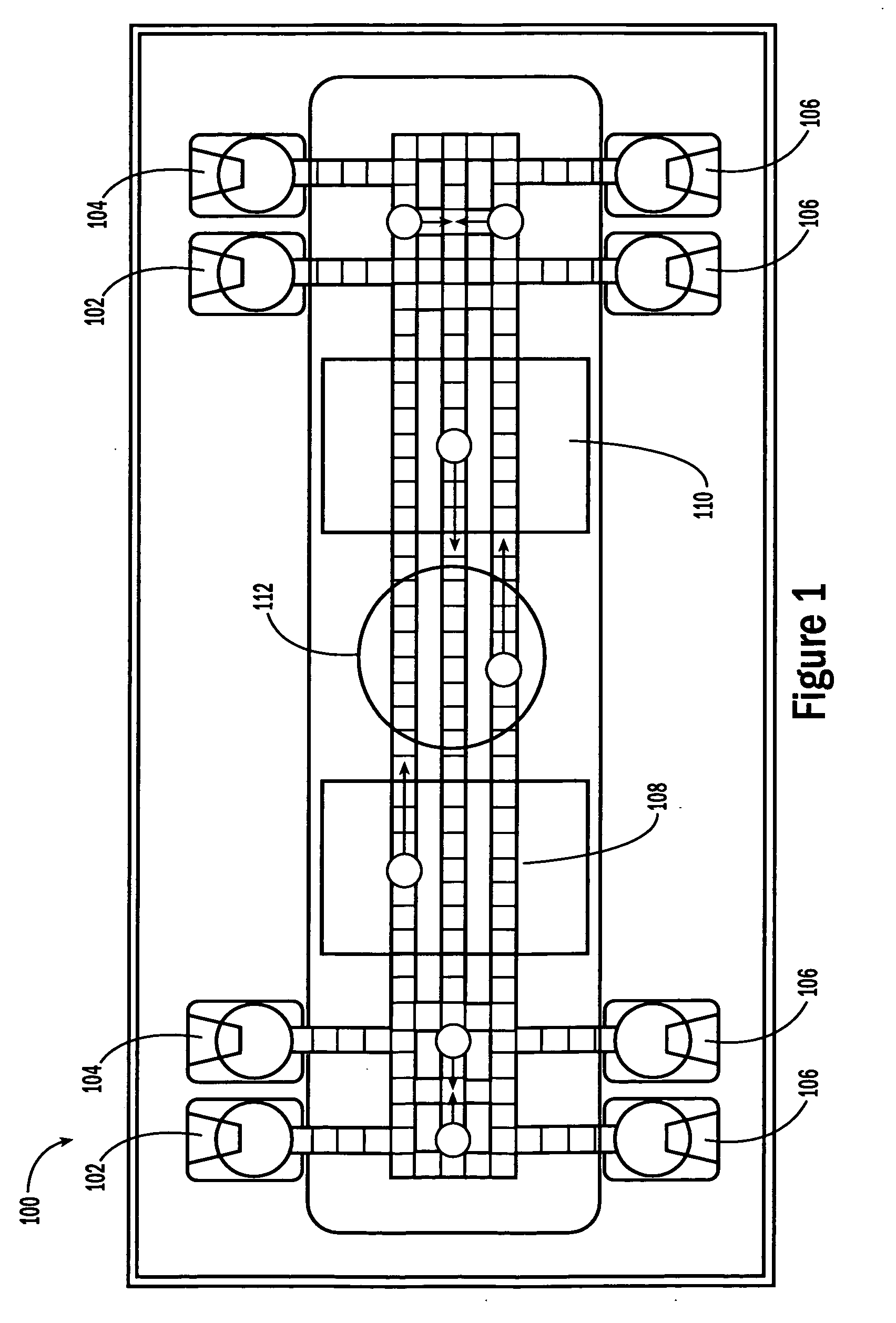
Method of using actuators for microfluidics without moving parts
InactiveUS7255780B2Maximize area overlapEffectively converting the surface into more hydrophilicSludge treatmentFlow mixersElectricityMicrofluidics
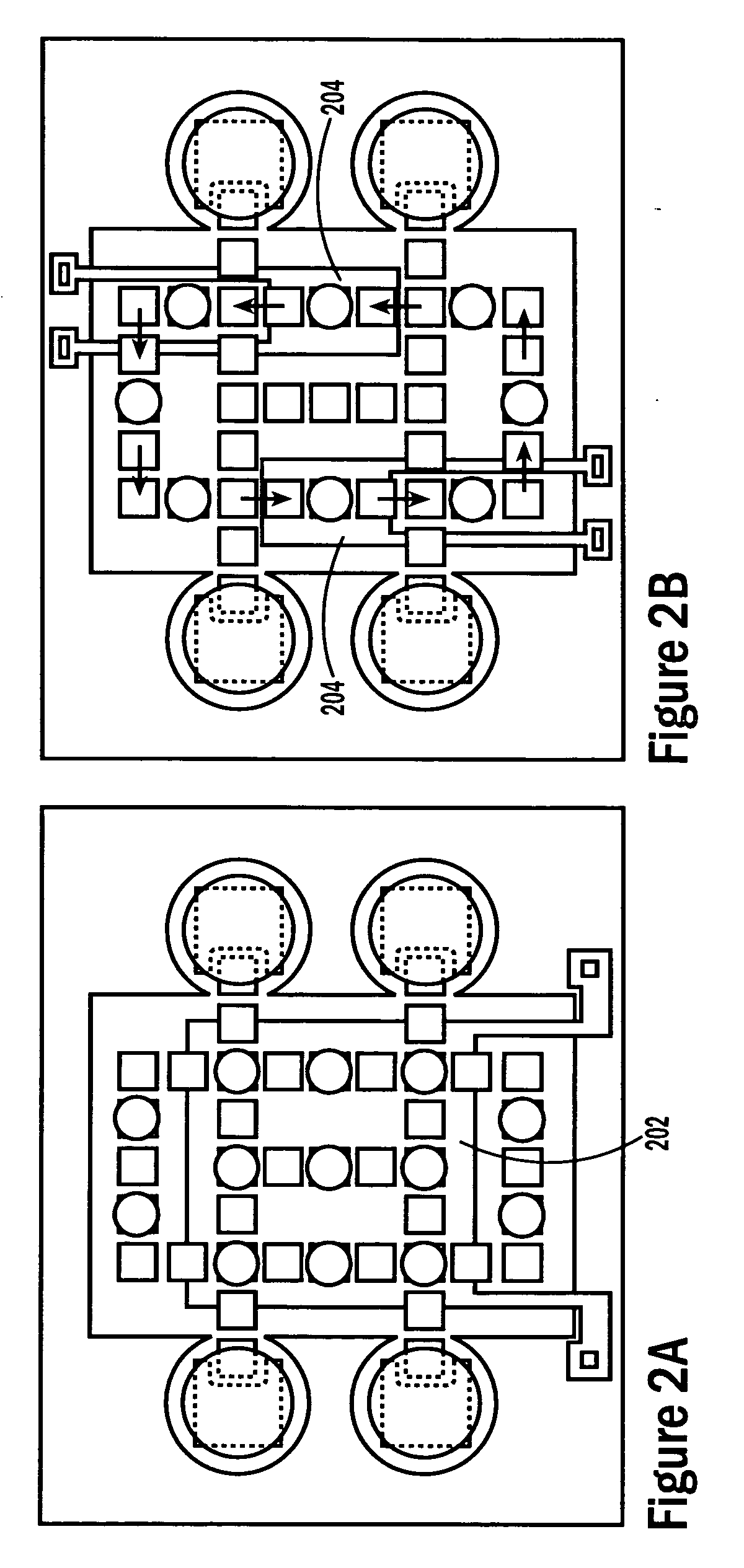
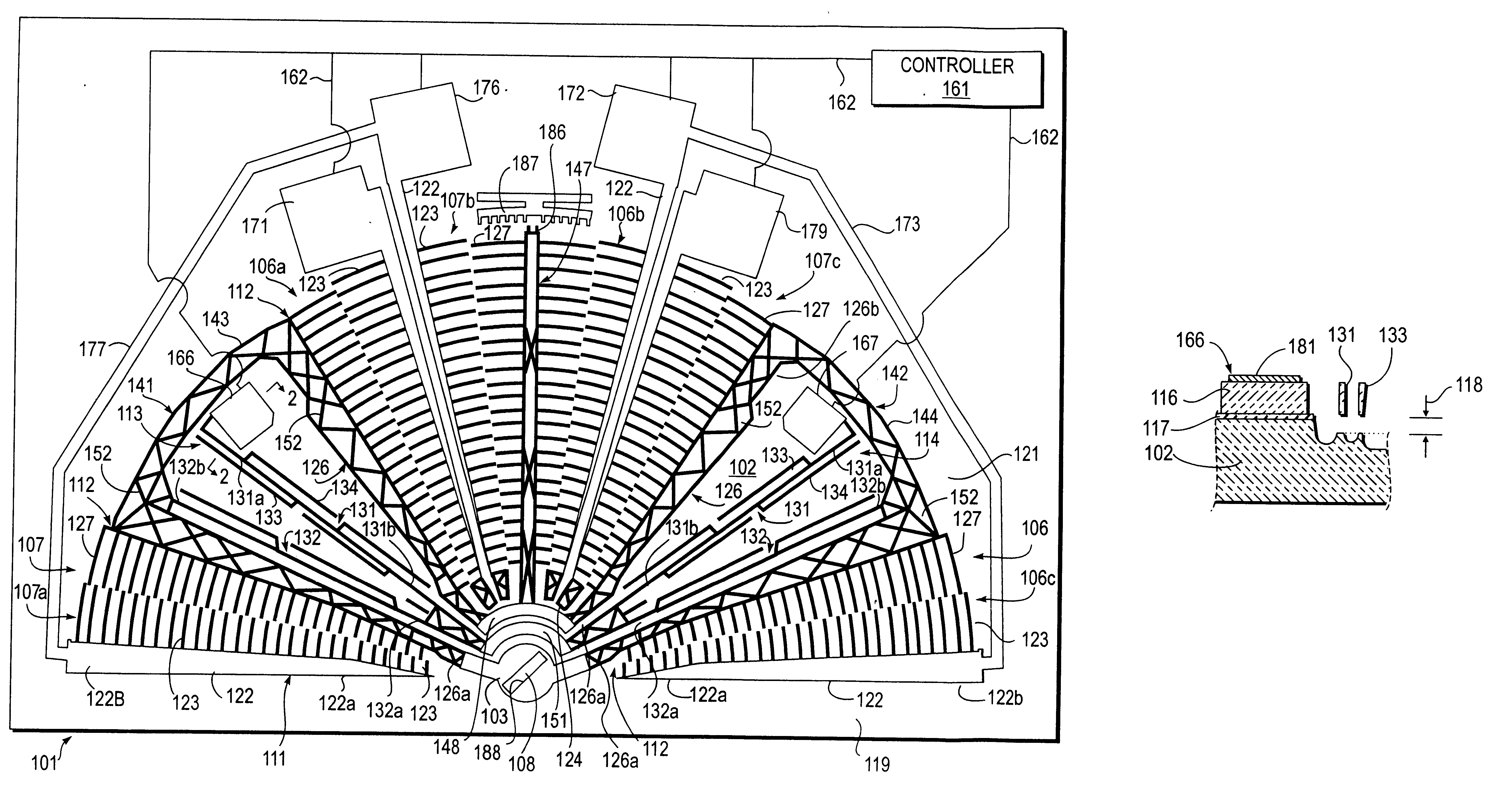
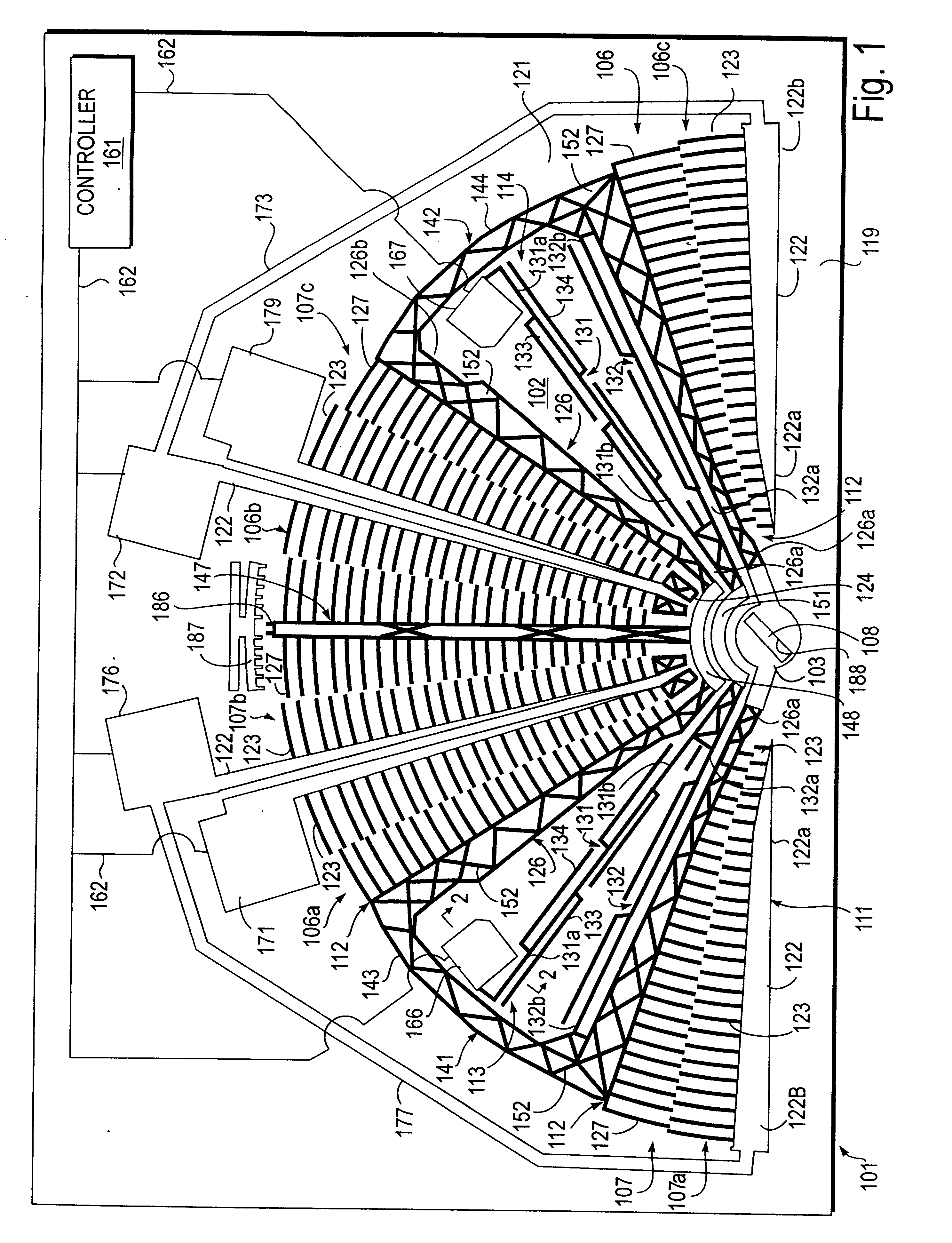
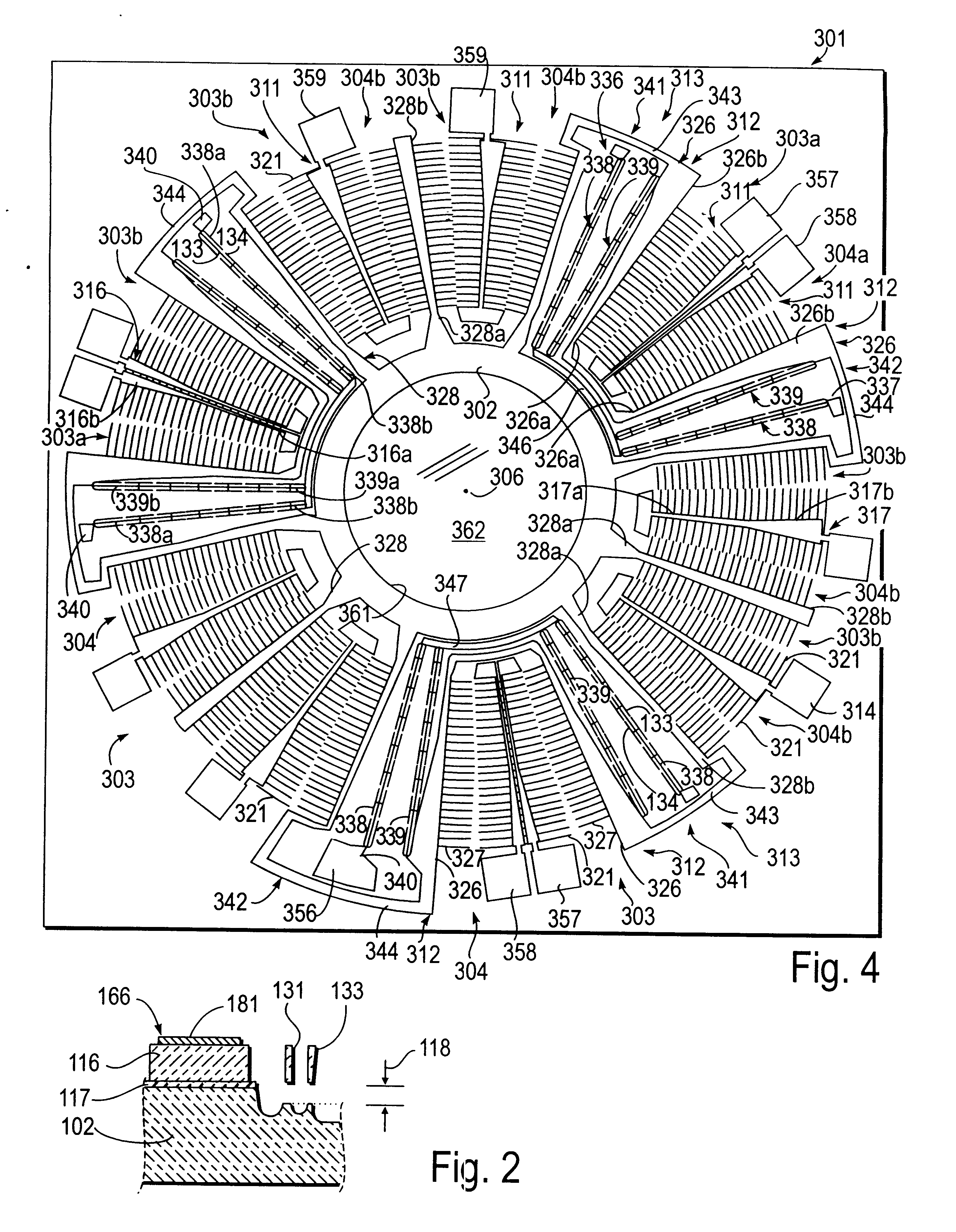
A series of microactuators for manipulating small quantities of liquids, and methods of using these for manipulating liquids, are disclosed. The microactuators are based on the phenomenon of electrowetting and contain no moving parts. The force acting on the liquid is a potential-dependent gradient of adhesion energy between the liquid and a solid insulating surface.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
Droplet-based diagnostics
InactiveUS20070242111A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentEngineeringMicroactuator
The present invention relates to droplet-based diagnostics. According to one embodiment, a droplet microactuator system is provided and includes: (a) a droplet microactuator configured to conduct droplet operations; and (b) a sensor configured in a sensing relationship with the droplet microactuator, such that the sensor is capable of sensing a signal from and / or a property of one or more droplets on the droplet microactuator.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
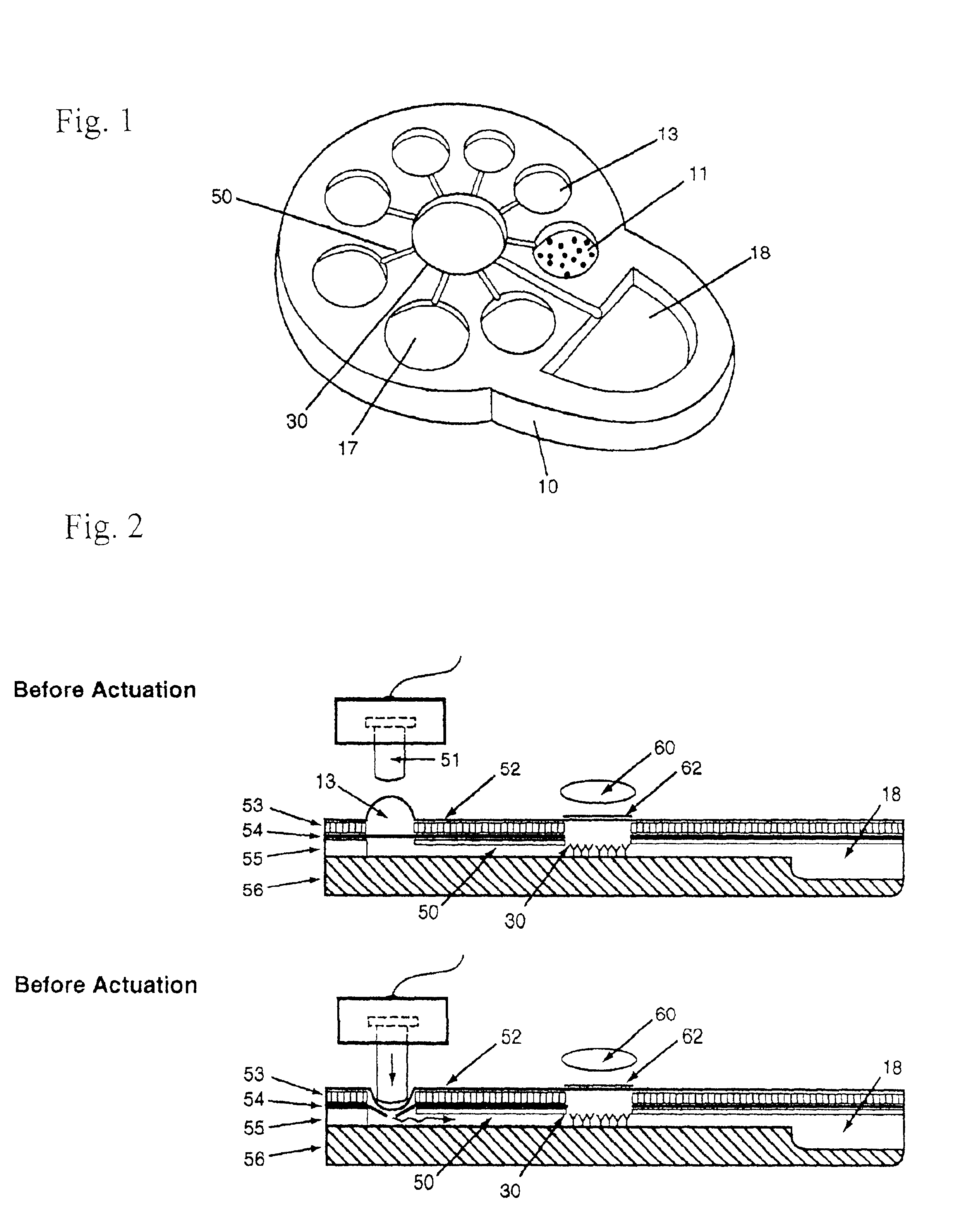
Chemiluminescence-based microfluidic biochip
InactiveUS6949377B2Accurate and reproducible resultSimple and rapid and POCT applicationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPositive pressureBiochip
The disclosure describes how to use luminescence detection mechanism, move microfluid, and control multiple-step biochemical reactions in closed confined microfluidic biochip platform. More particularly, a self-contained disposable biochip with patterned microchannels and compartments having storage means for storing a plurality of samples, reagents, and luminescent substrates. At least one external microactuator in the biochip system produces positive pressure and automates multiple-step reactions in microfluidic platforms for clinical chemistry, cell biology, immunoassay and nucleic acid analysis. The method comprises the steps of transferring sequentially at least one of samples, reagents, and then luminescent substrate from compartments through microchannels to reaction sites. The luminescent substrates react with probes to form a probe complex resulting into luminescence, which is detected by an optical detector.
Owner:HO WINSTON Z
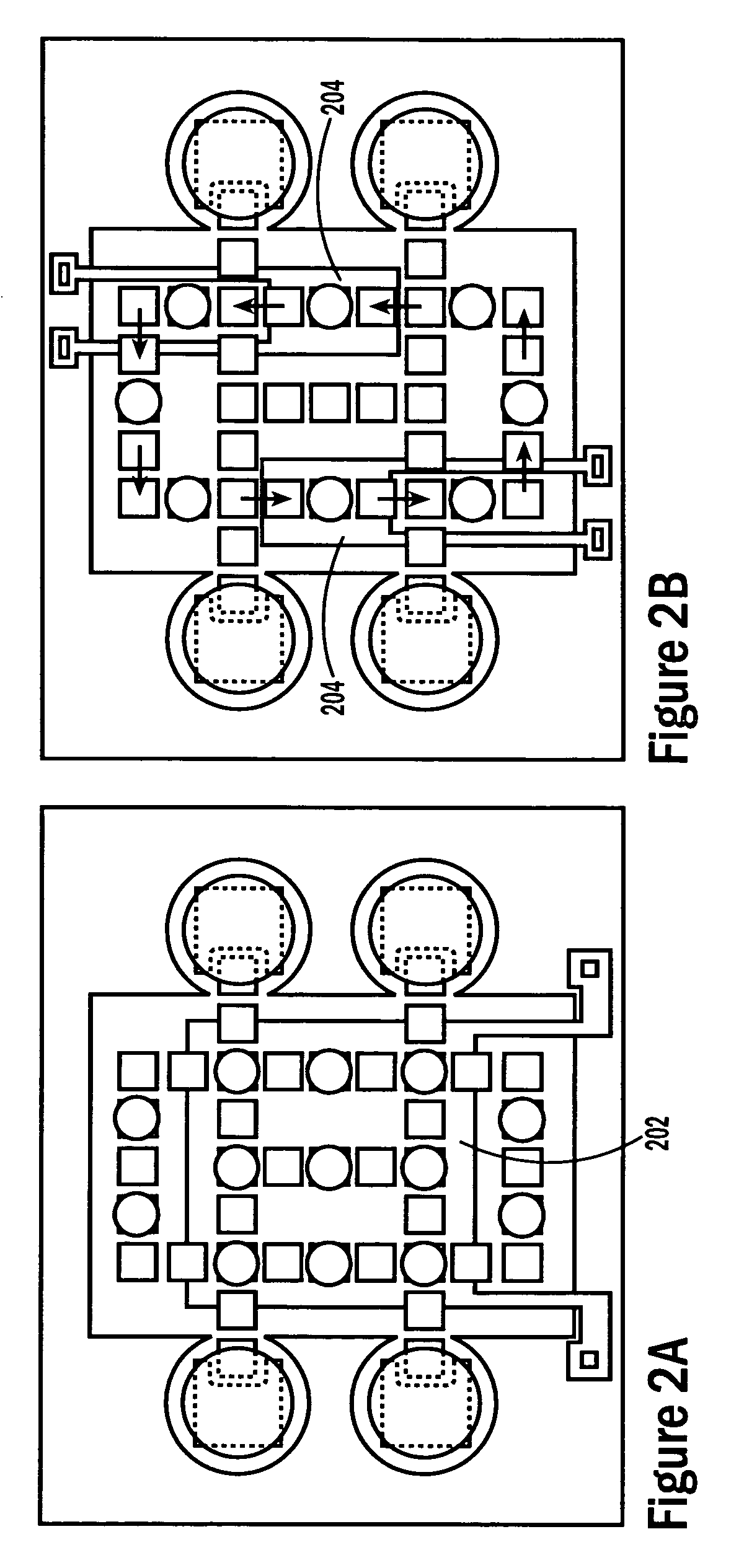
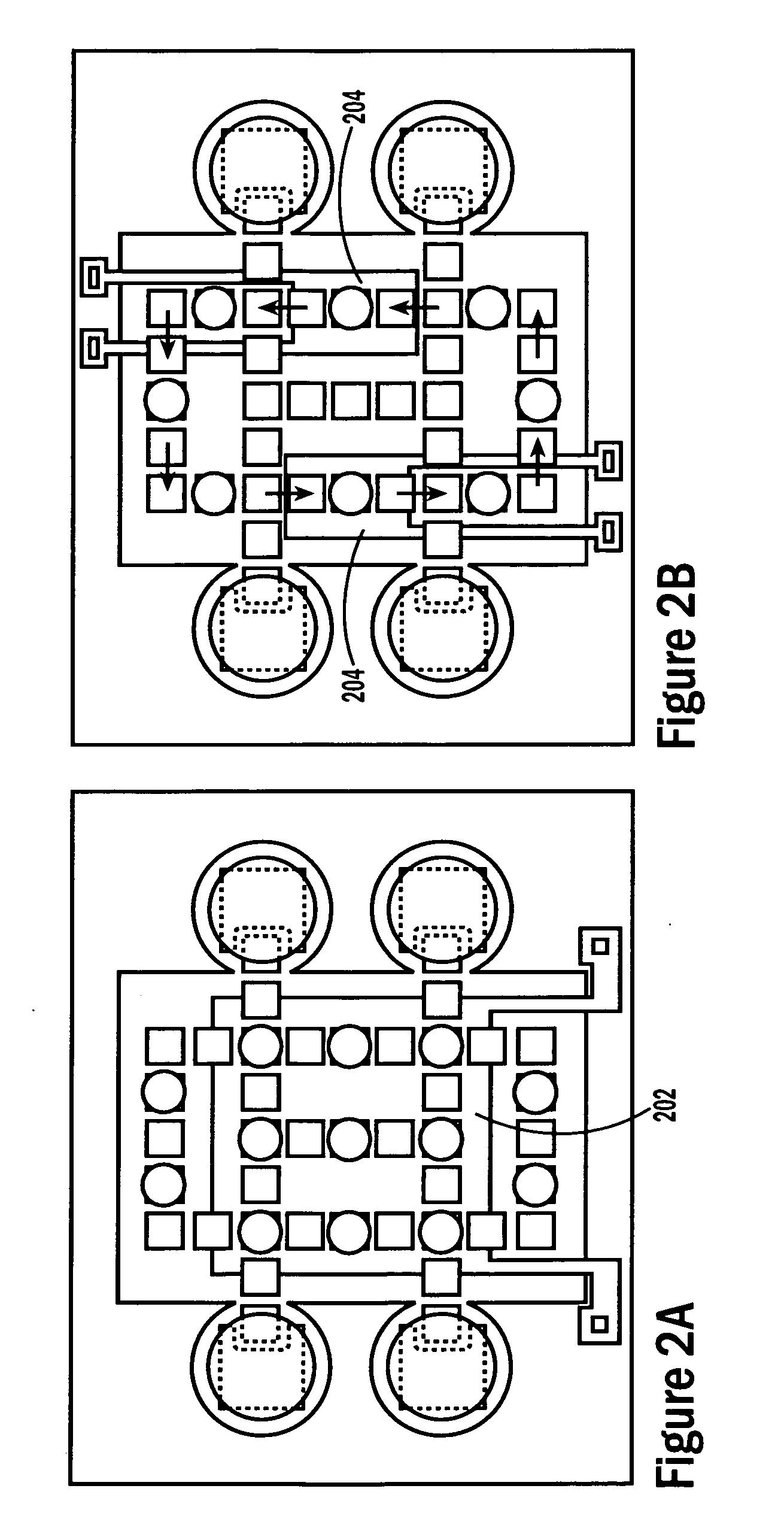
Droplet microactuator system
InactiveUS7815871B2Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentControl theoryMicroactuator
The present invention relates to a droplet microactuator system. According to one embodiment, the droplet microactuator system includes: (a) a droplet microactuator configured to conduct droplet operations; (b) a magnetic field source arranged to immobilize magnetically responsive beads in a droplet during droplet operations; (c) a sensor configured in a sensing relationship with the droplet microactuator, such that the sensor is capable of sensing a signal from and / or a property of one or more droplets on the droplet microactuator; and (d) one or more processors electronically coupled to the droplet microactuator and programmed to control electrowetting-mediated droplet operations on the droplet actuator and process electronic signals from the sensor.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
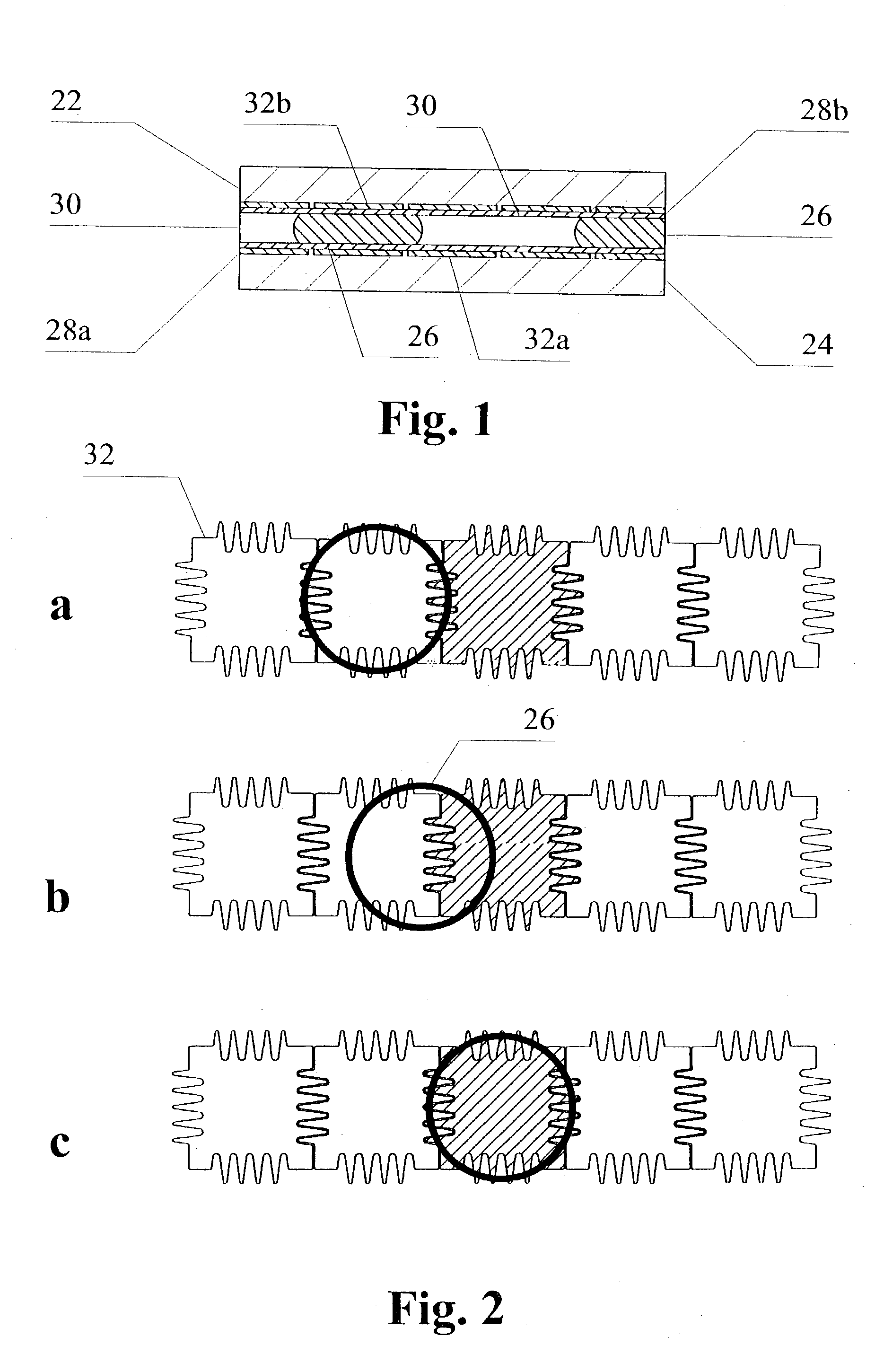
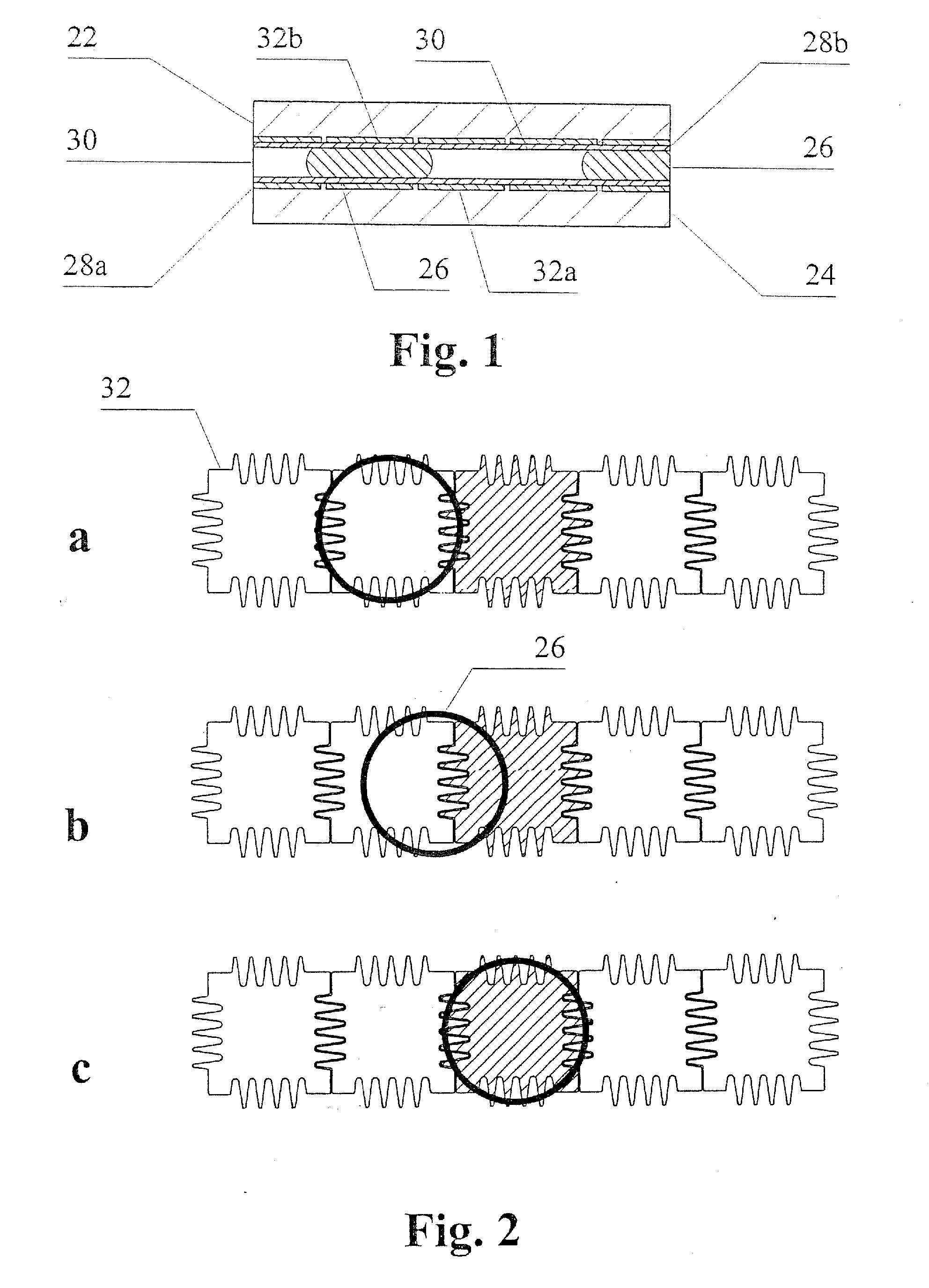
Bistable microactuator with coupled membranes
InactiveUS6168395B1Improves pneumaticImproves liquid couplingCircuit elementsDecorative surface effectsMetallic electrodeCoupling
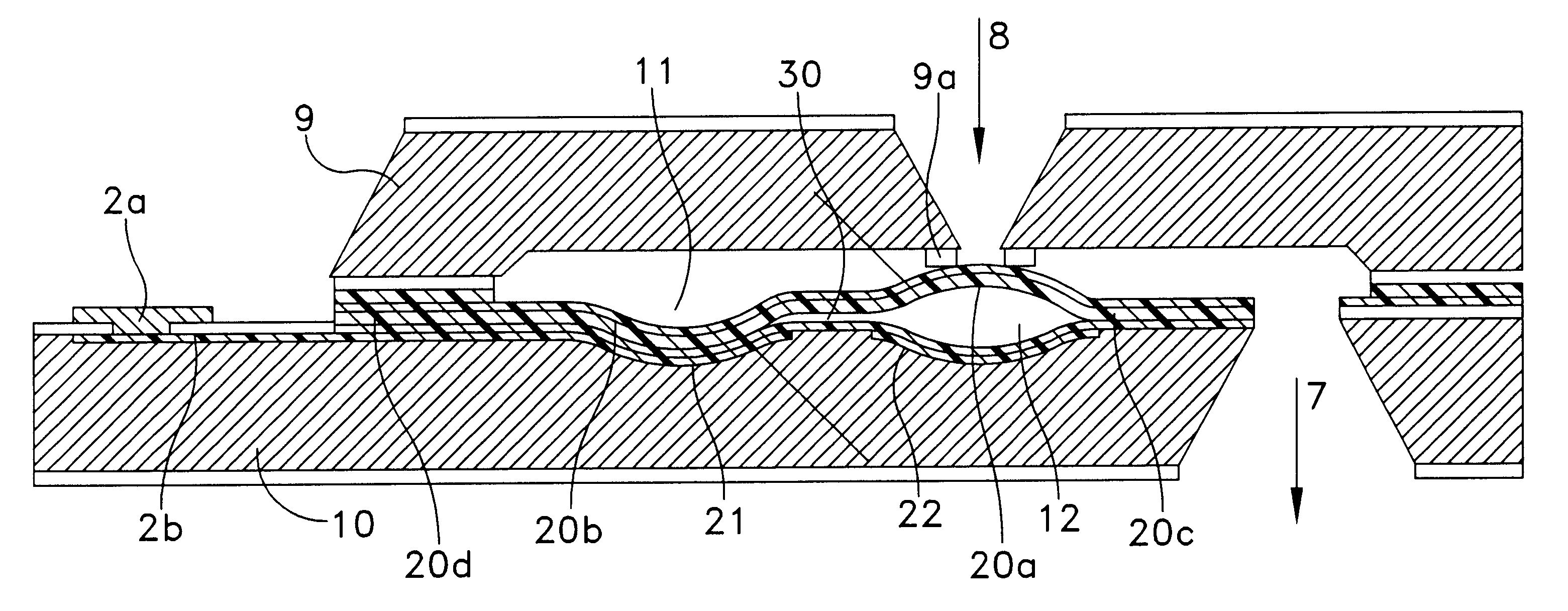
A bistable electrostatic actuator with pneumatic or liquid coupling. The actuator has enclosed metallic electrodes. It can be used for a microvalve or micropump. The actuator has buckled membrane sections in pairs and curved substrate electrodes, locally associated with said membrane sections.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Droplet-based particle sorting
InactiveUS7901947B2Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementChemical physicsParticle sorting
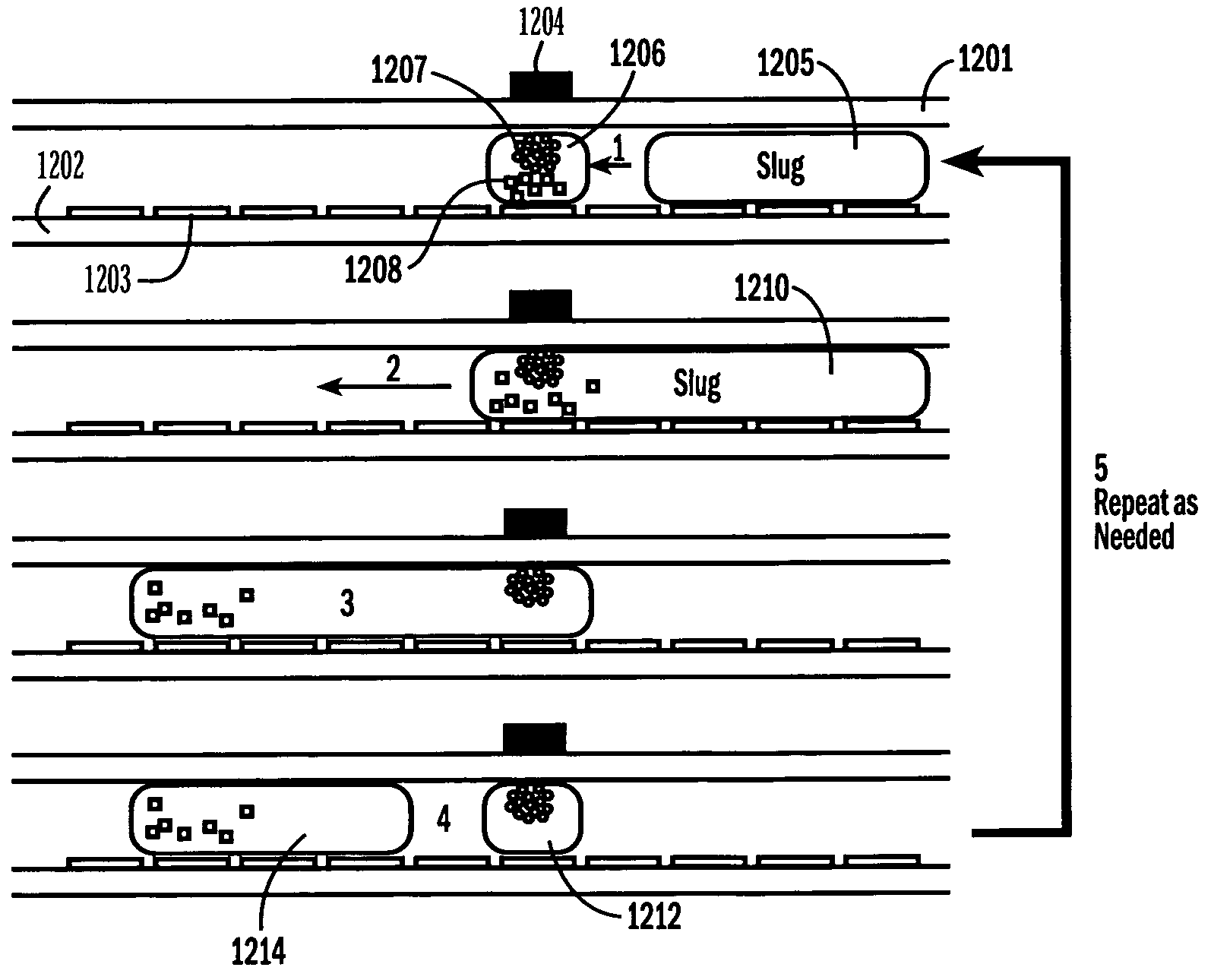
The present invention relates to droplet-based particle sorting. According to one embodiment, a droplet microactuator is provided and includes: (a) a suspension of particles; and (b) electrodes arranged for conducting droplet operations using droplets comprising particles. A method of transporting a particle is also provided, wherein the method includes providing a droplet comprising the particle and transporting the droplet on a droplet microactuator.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
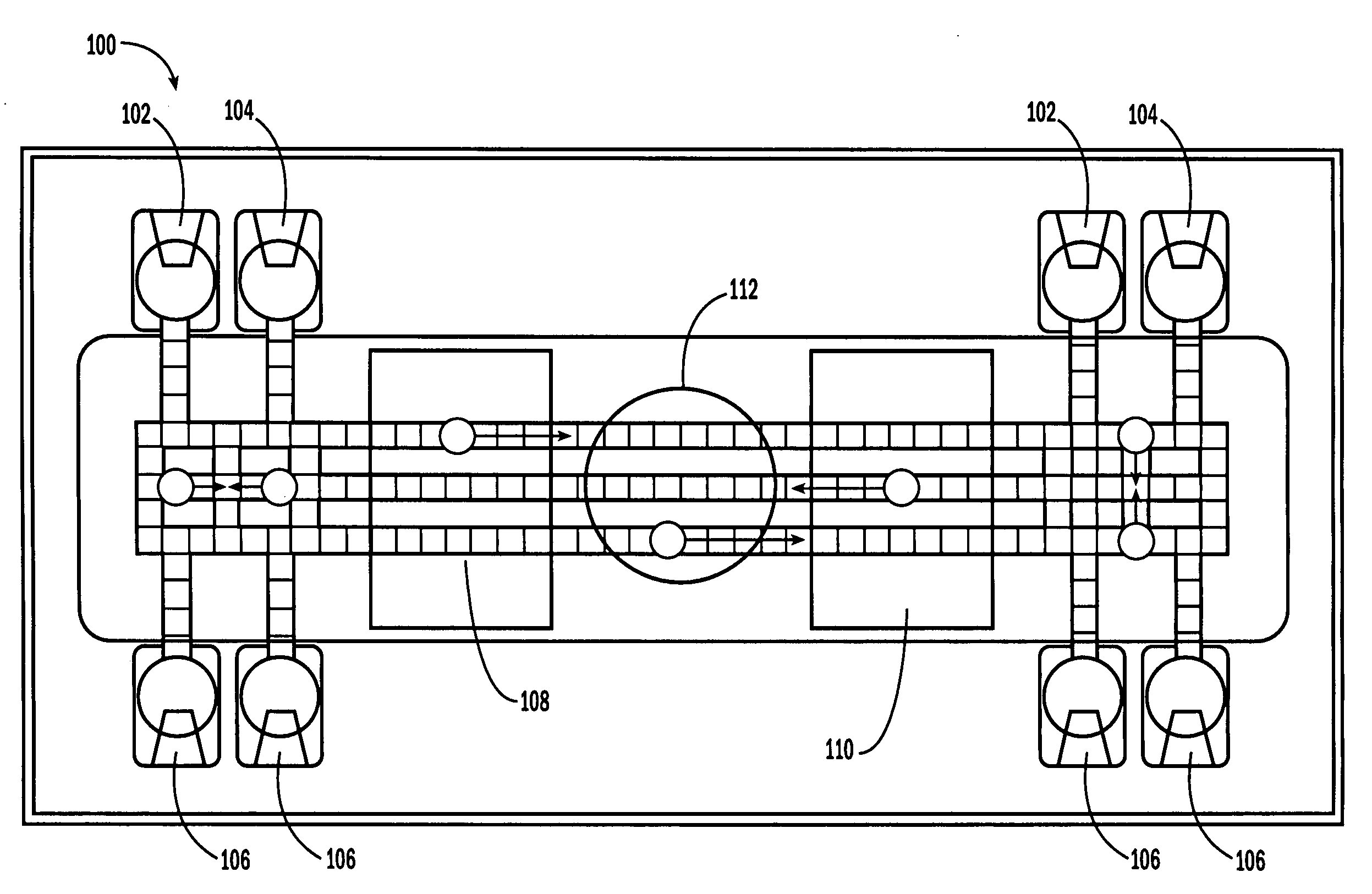
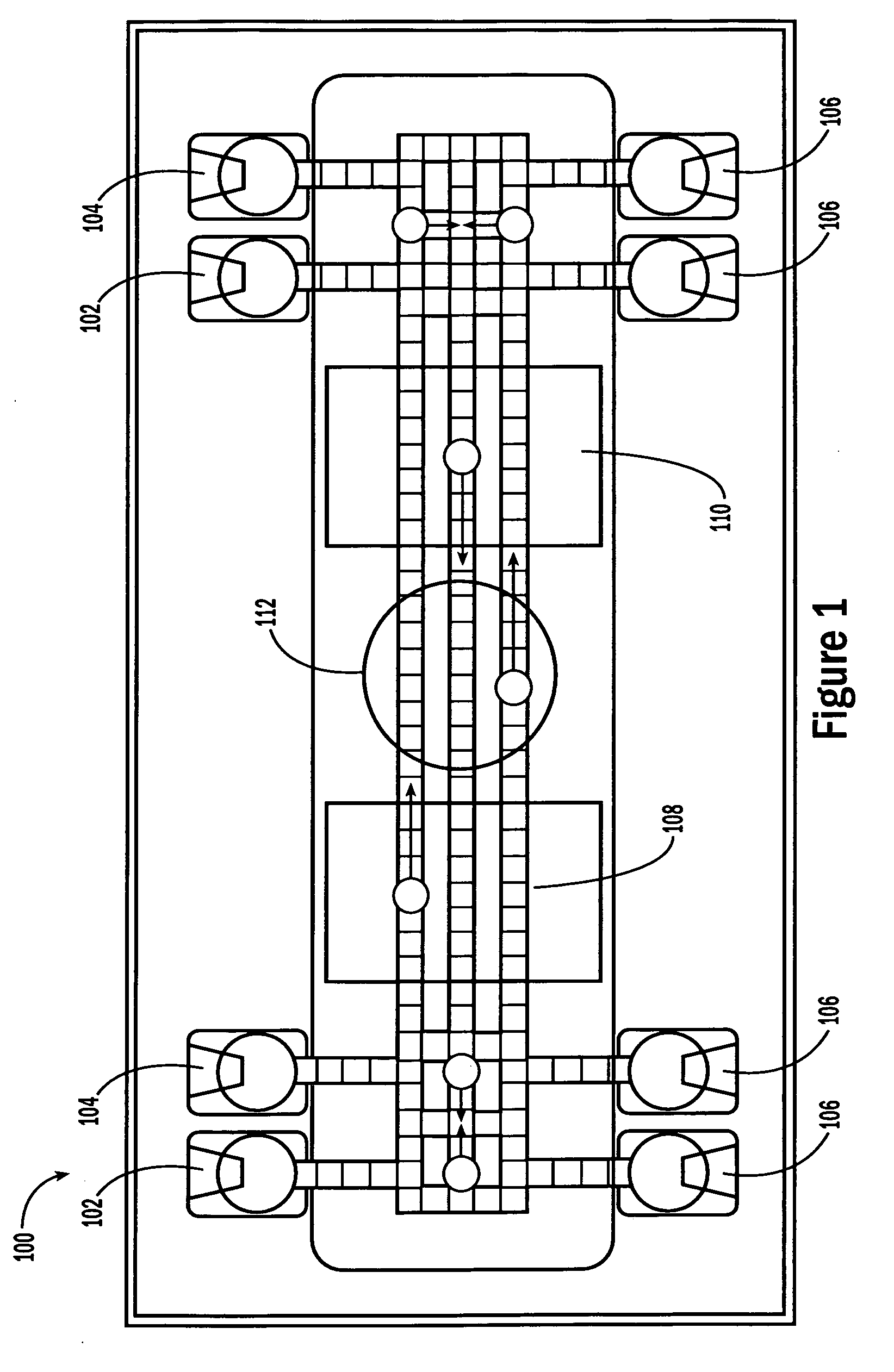
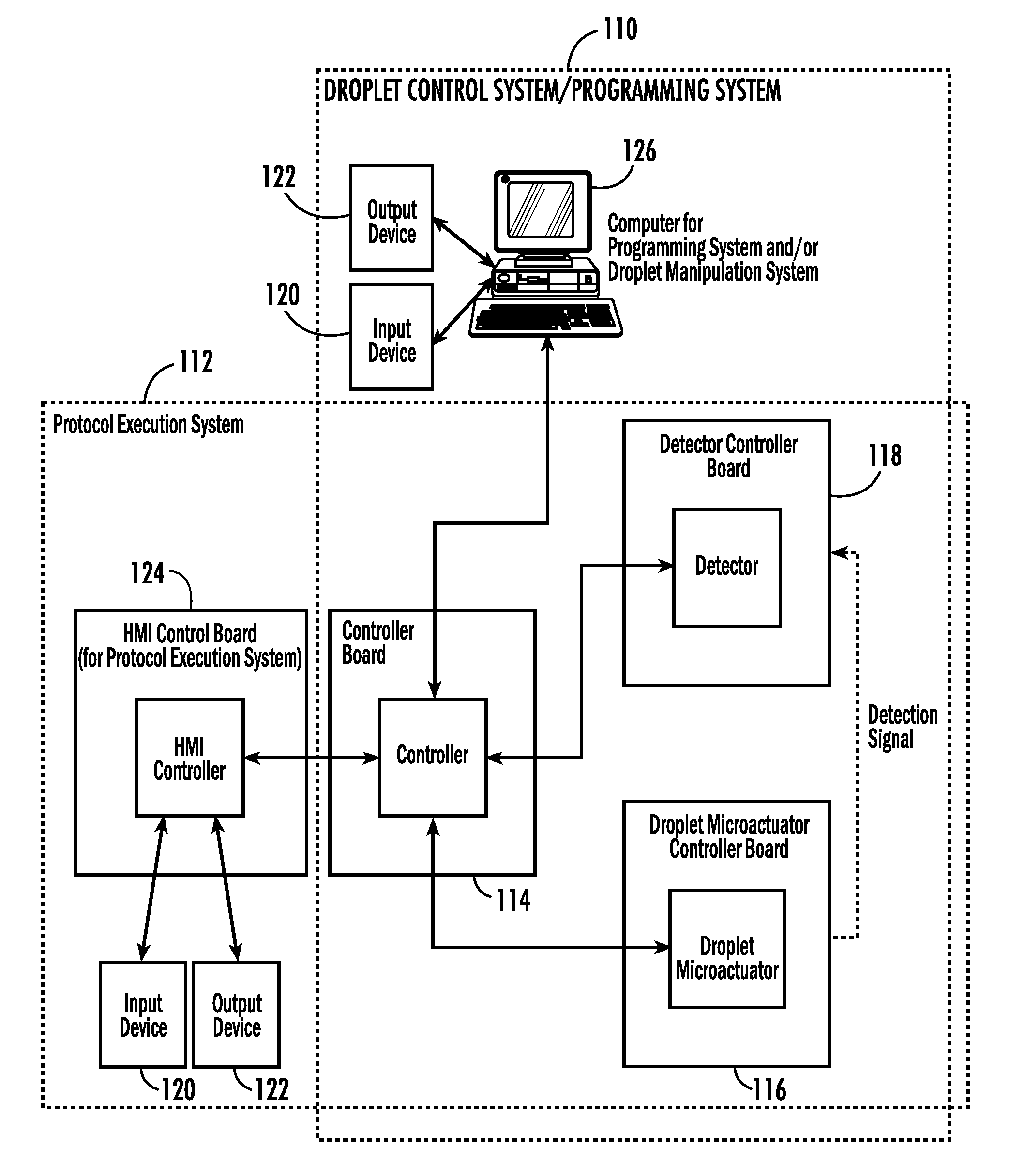
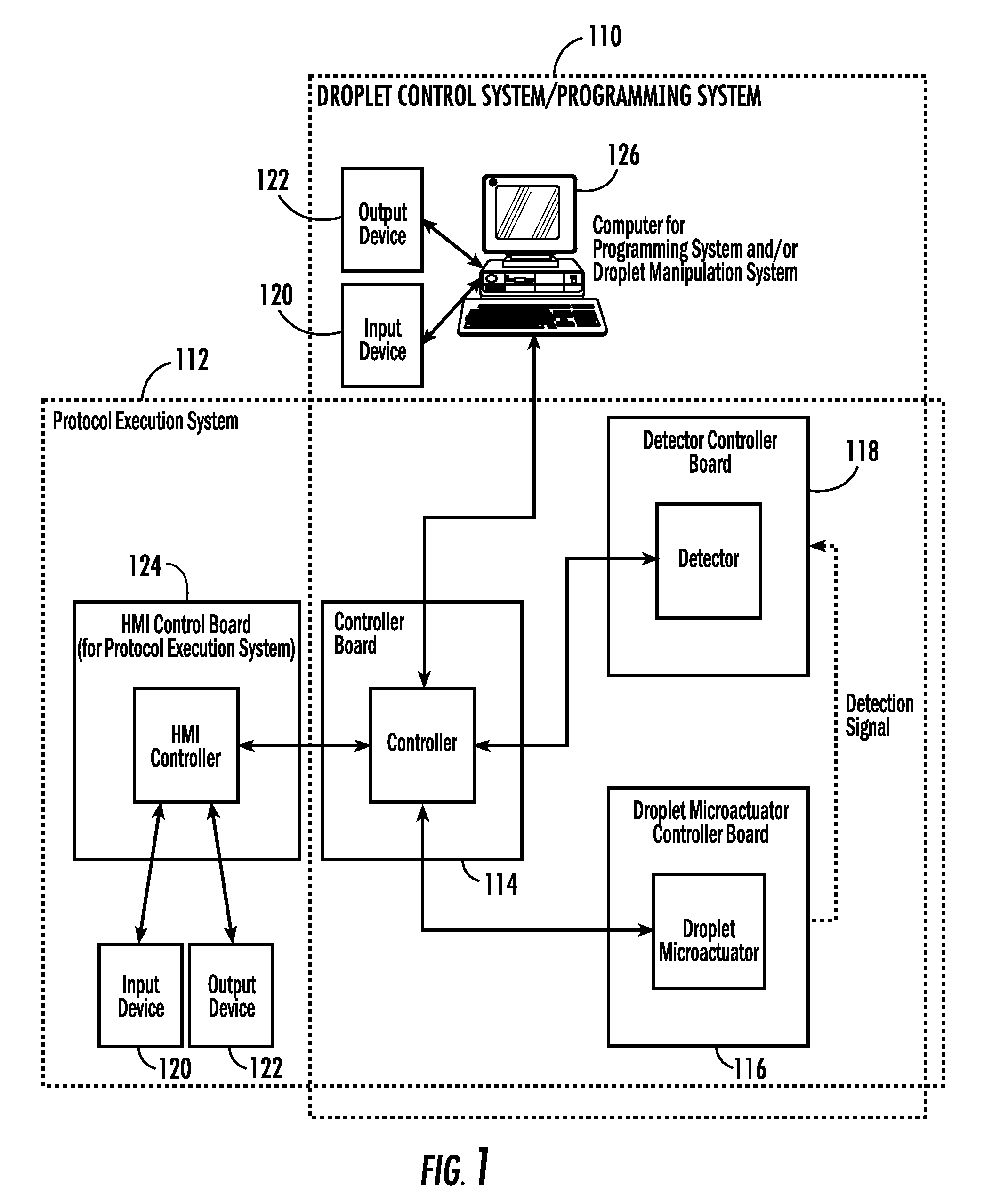
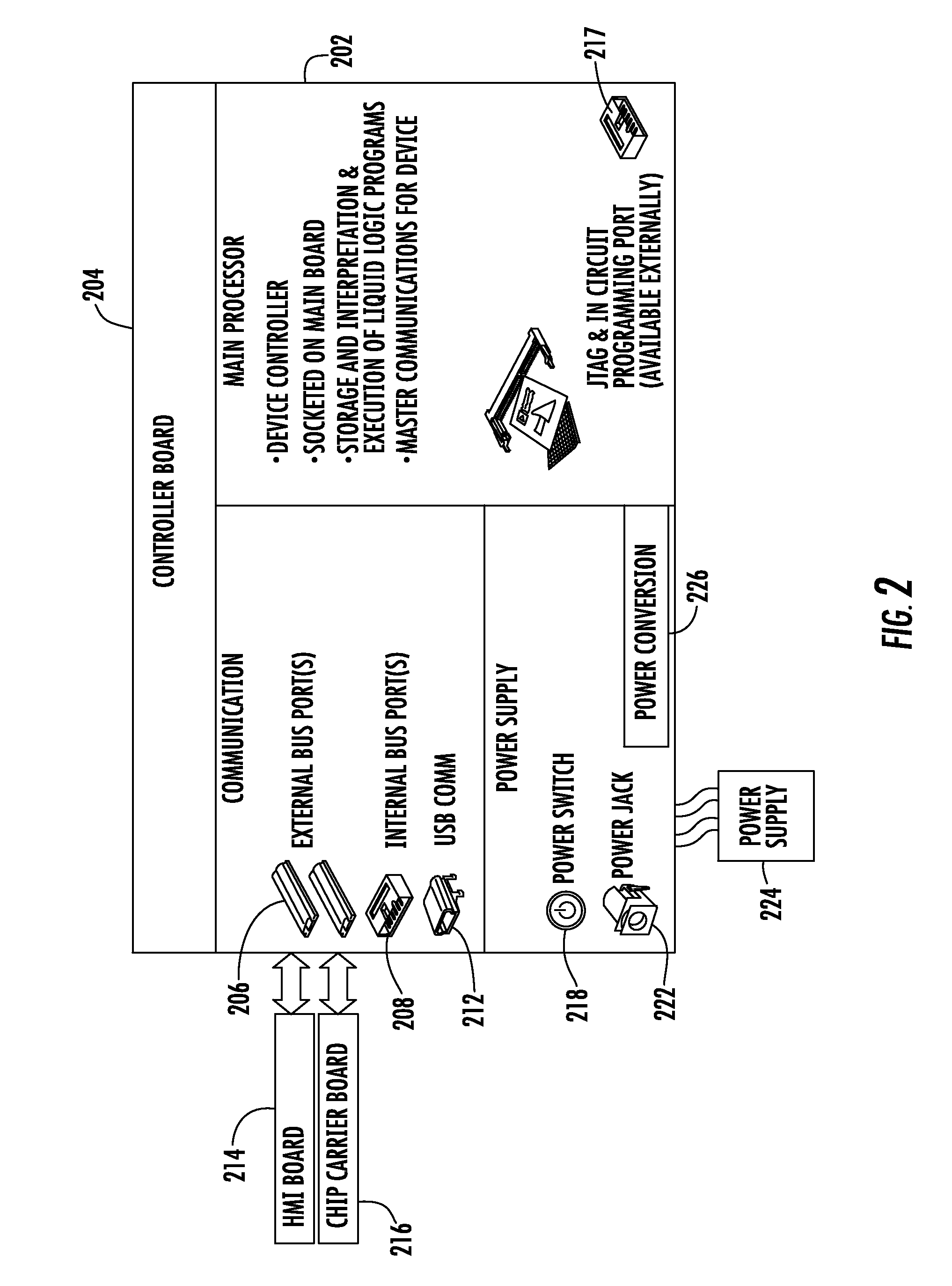
System for Controlling a Droplet Actuator
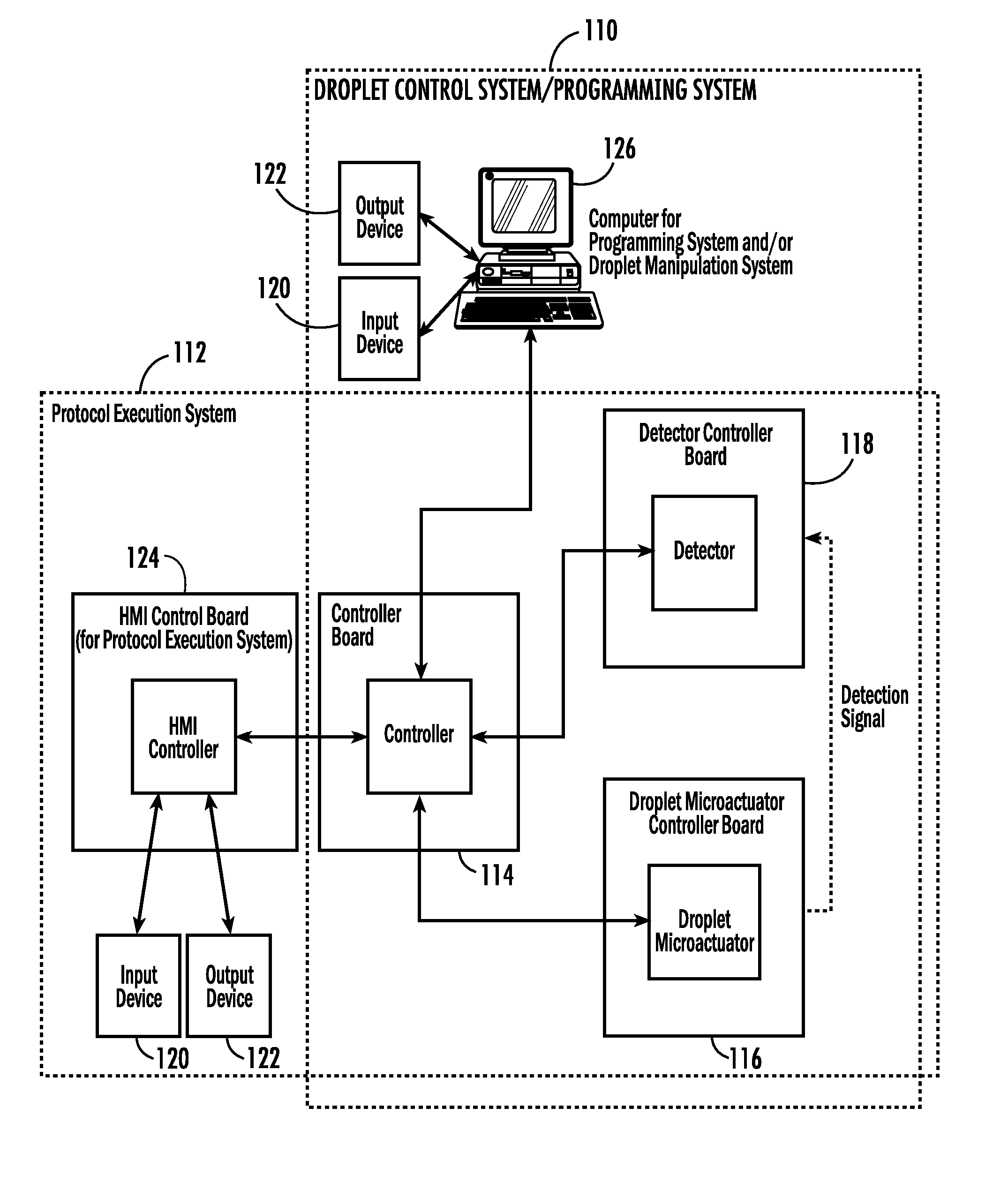
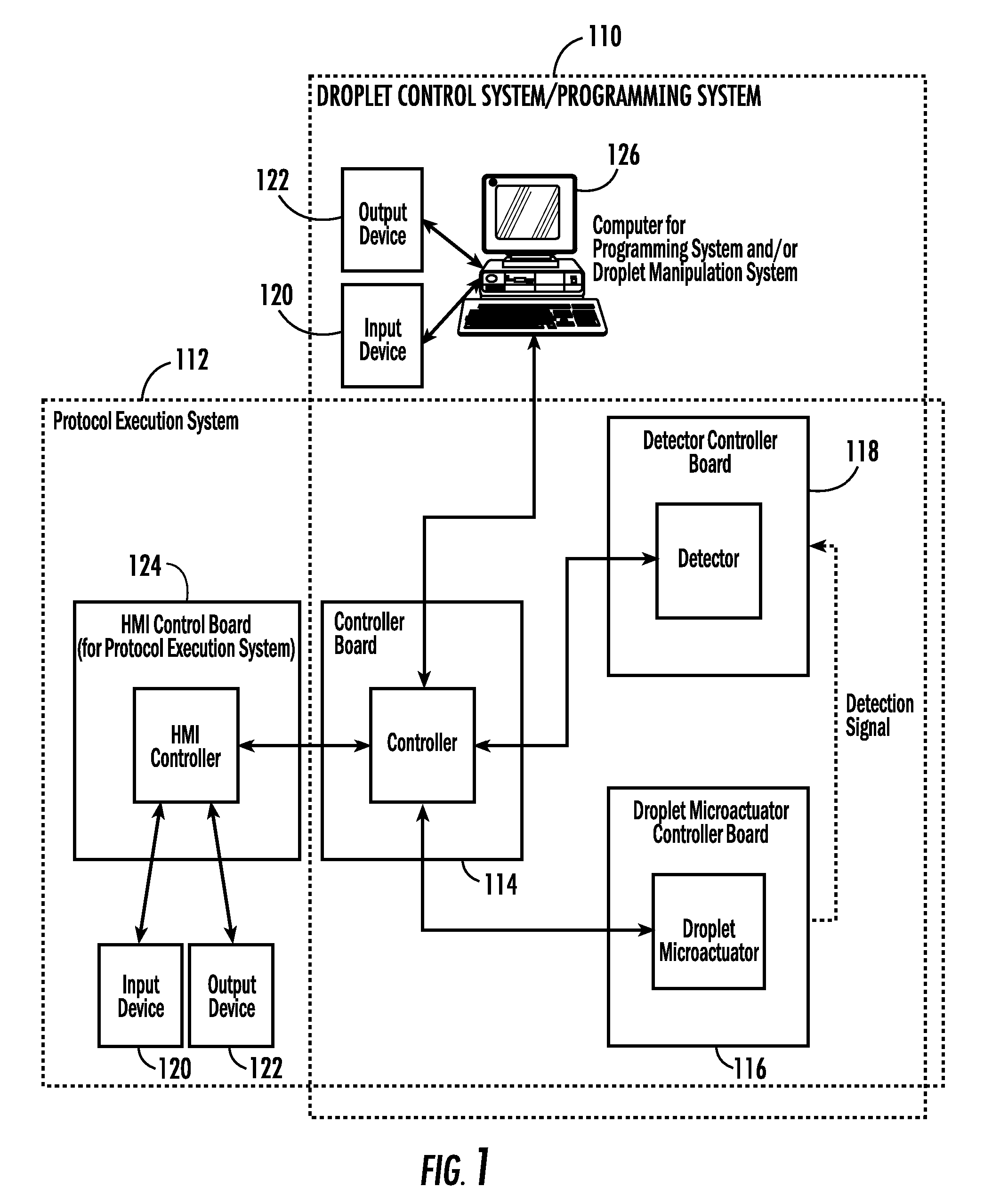
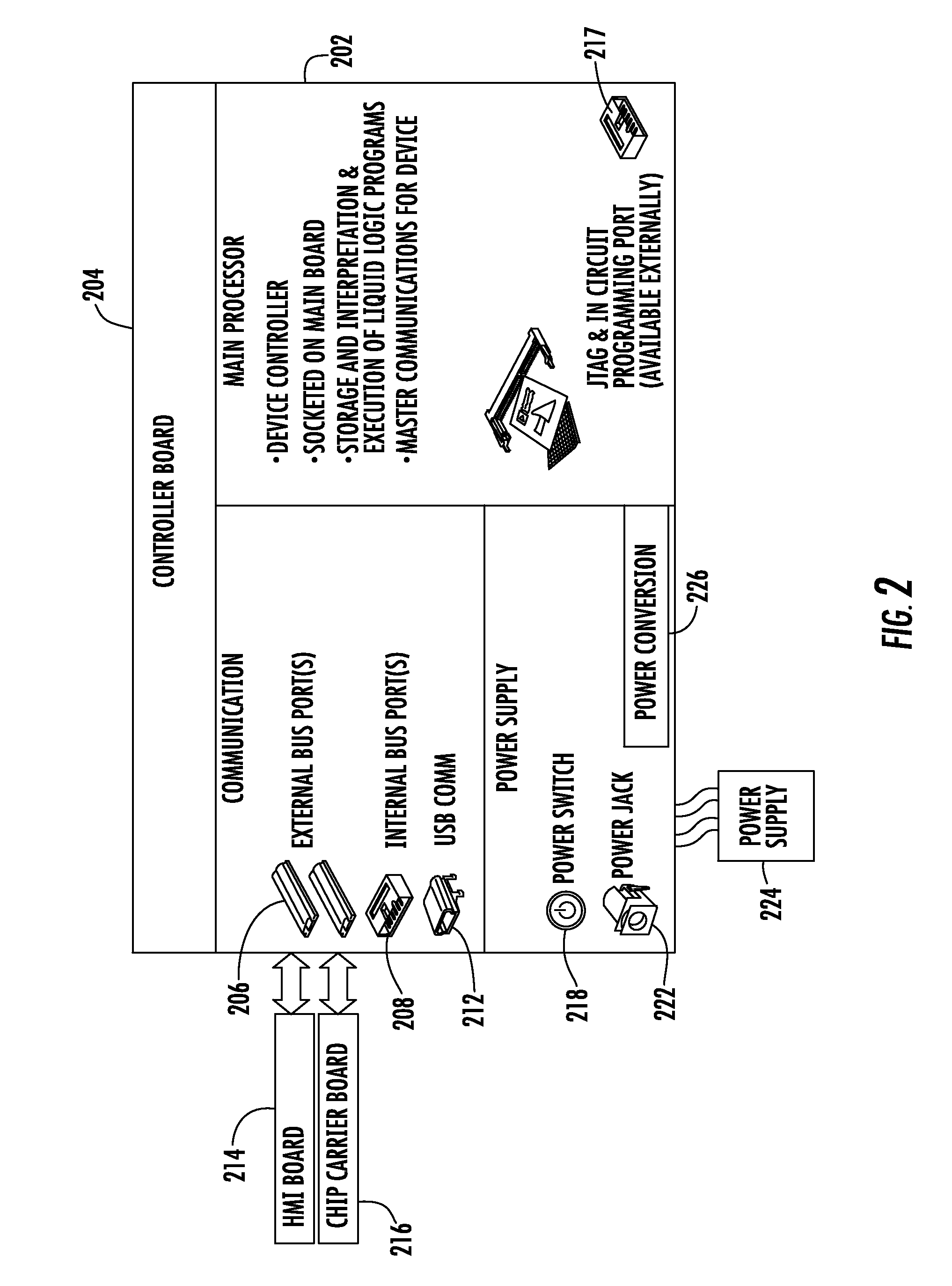
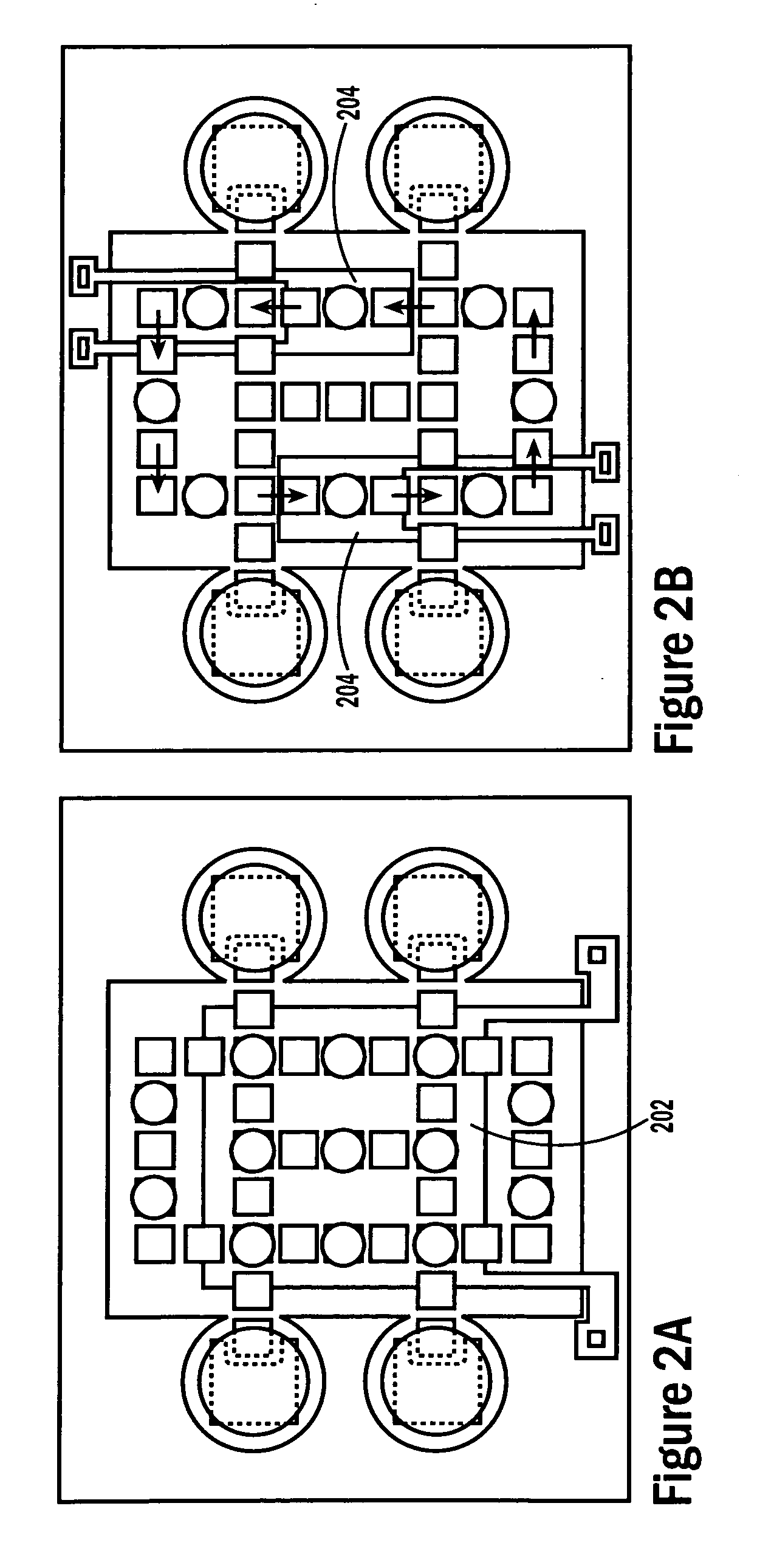
InactiveUS20080006535A1Accurate sampling volumeRestrict levelSludge treatmentLevel controlDisplay deviceEngineering
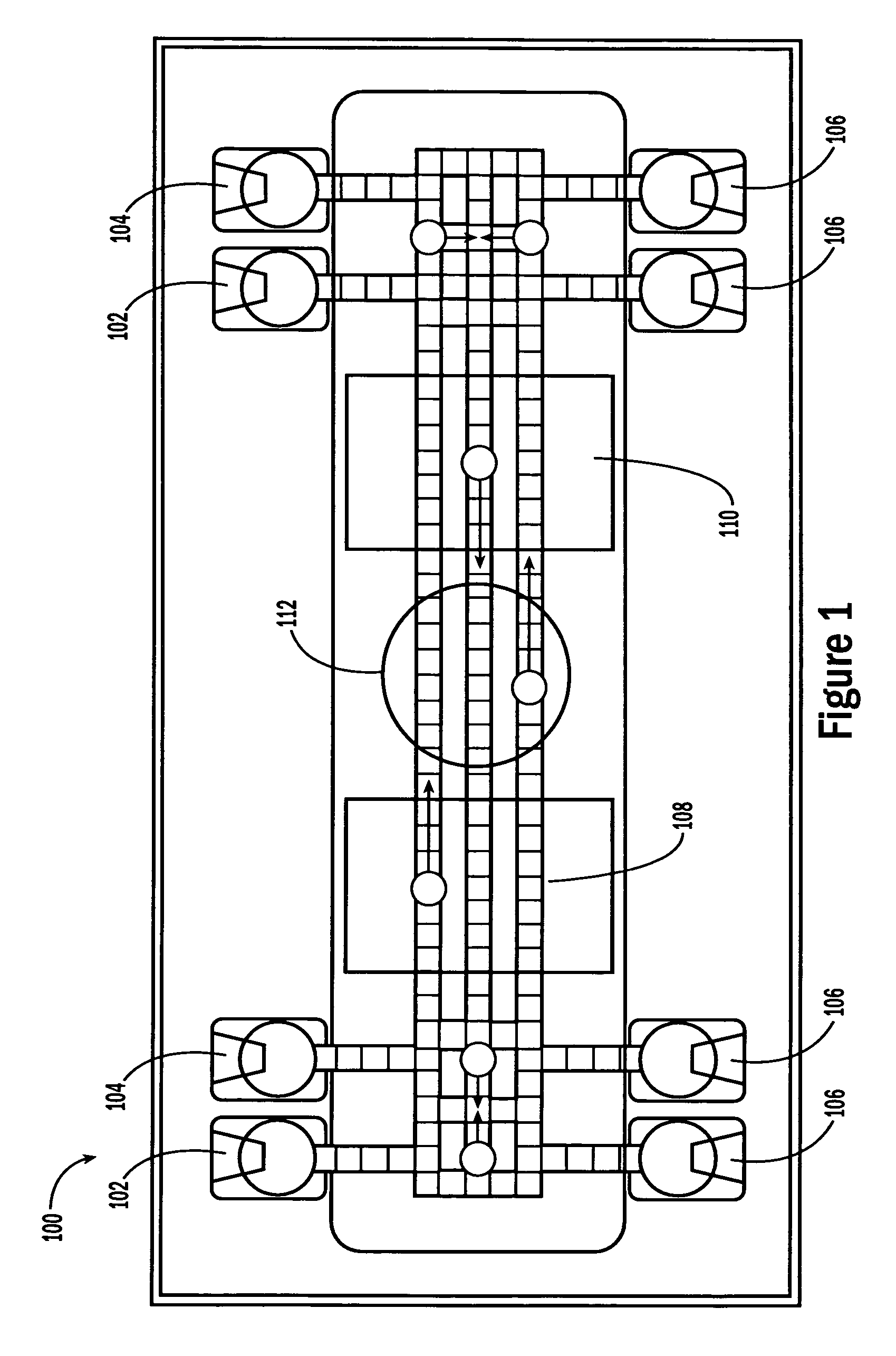
Systems for controlling a droplet microactuator are provided. According to one embodiment, a system is provided and includes a controller, a droplet microactuator electronically coupled to the controller, and a display device displaying a user interface electronically coupled to the controller, wherein the system is programmed and configured to permit a user to effect a droplet manipulation by interacting with the user interface. According to another embodiment, a system is provided and includes a processor, a display device electronically coupled to the processor, and software loaded and / or stored in a storage device electronically coupled to the controller, a memory device electronically coupled to the controller, and / or the controller and programmed to display an interactive map of a droplet microactuator. According to yet another embodiment, a system is provided and includes a controller, a droplet microactuator electronically coupled to the controller, a display device displaying a user interface electronically coupled to the controller, and software for executing a protocol loaded and / or stored in a storage device electronically coupled to the controller, a memory device electronically coupled to the controller, and / or the controller.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Systems, methods, and products for graphically illustrating and controlling a droplet actuator
Systems for controlling a droplet microactuator are provided. According to one embodiment, a system is provided and includes a controller, a droplet microactuator electronically coupled to the controller, and a display device displaying a user interface electronically coupled to the controller, wherein the system is programmed and configured to permit a user to effect a droplet manipulation by interacting with the user interface. According to another embodiment, a system is provided and includes a processor, a display device electronically coupled to the processor, and software loaded and / or stored in a storage device electronically coupled to the controller, a memory device electronically coupled to the controller, and / or the controller and programmed to display an interactive map of a droplet microactuator. According to yet another embodiment, a system is provided and includes a controller, a droplet microactuator electronically coupled to the controller, a display device displaying a user interface electronically coupled to the controller, and software for executing a protocol loaded and / or stored in a storage device electronically coupled to the controller, a memory device electronically coupled to the controller, and / or the controller.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC +1
Droplet-based nucleic acid amplification method and apparatus
ActiveUS20090291433A1Reduces and eliminates build-upImprove efficiencyHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementTemperature controlBiology
The present invention relates to a droplet-based nucleic acid amplification method and apparatus. According to one embodiment, a method of amplifying a nucleic acid in a biological sample is provided, wherein the method includes: (a) providing a system comprising a droplet microactuator electronically coupled to and controlled by a processor capable of executing instructions, the droplet microactuator comprising: (i) a sample potentially comprising a target nucleic acid; (ii) a substrate comprising electrodes for conducting droplet operations; and (iii) one or more temperature control means arranged in proximity with one or more of the electrodes for heating a region of the droplet microactuator such that a droplet can be transported into the region for heating; (b) using droplet operations to combine on the droplet microactuator one or more amplification reagent droplets and one or more sample droplets to yield an amplification-ready droplet; and (c) thermal cycling the amplification-ready droplet sufficient to result in amplification of a target nucleic acid when present in the amplification-ready droplet.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
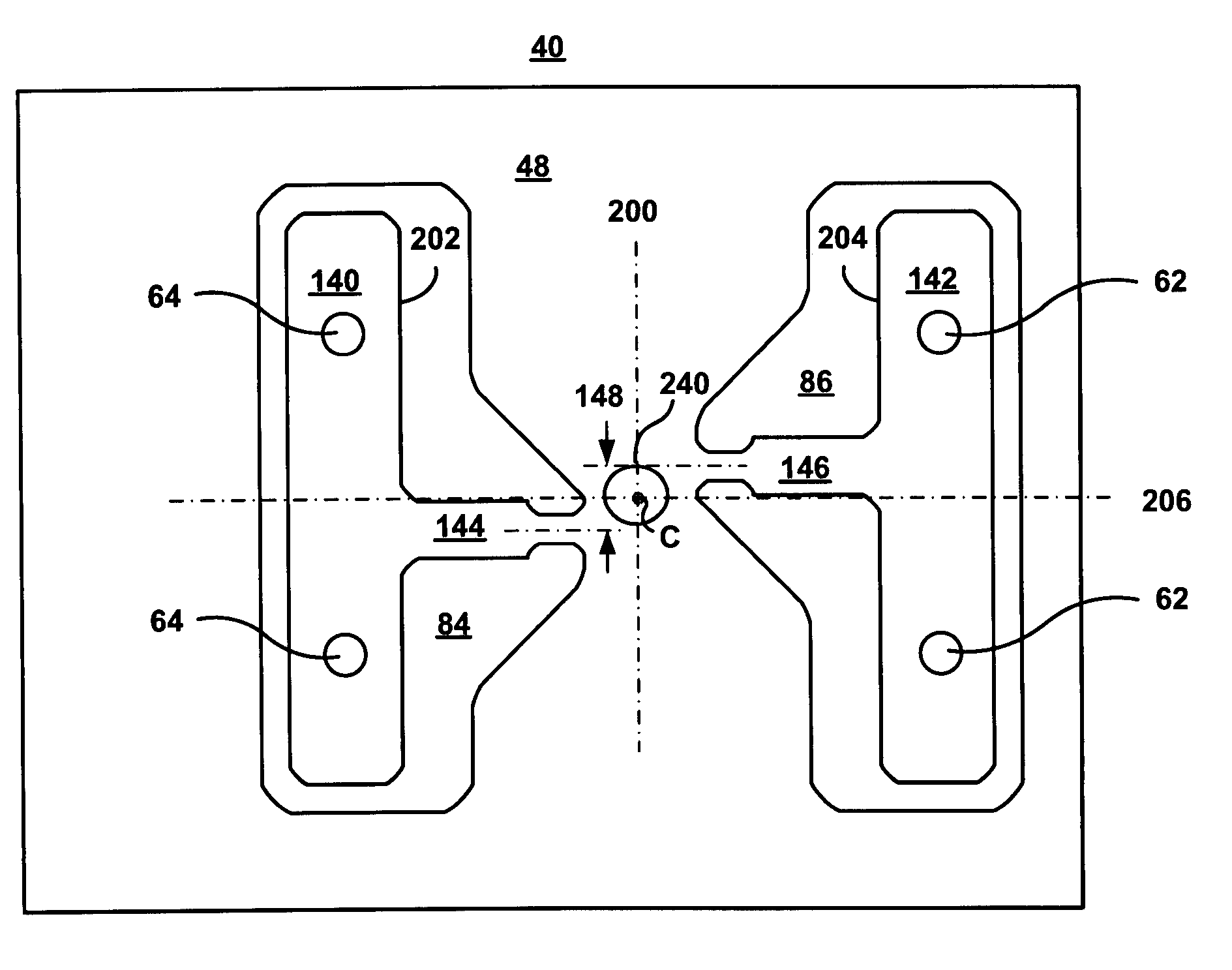
System, method and apparatus for flexure-integrated microactuator
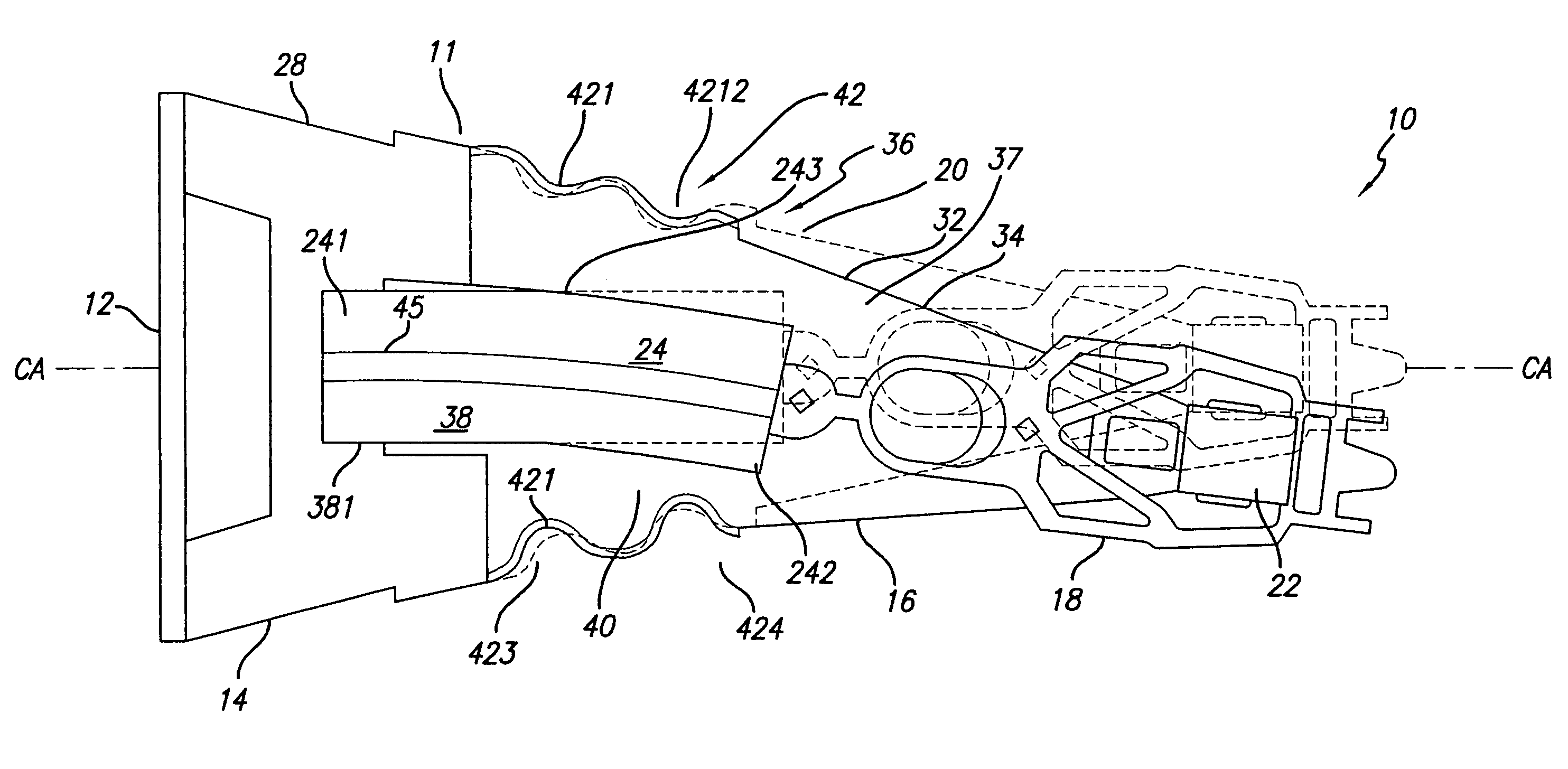
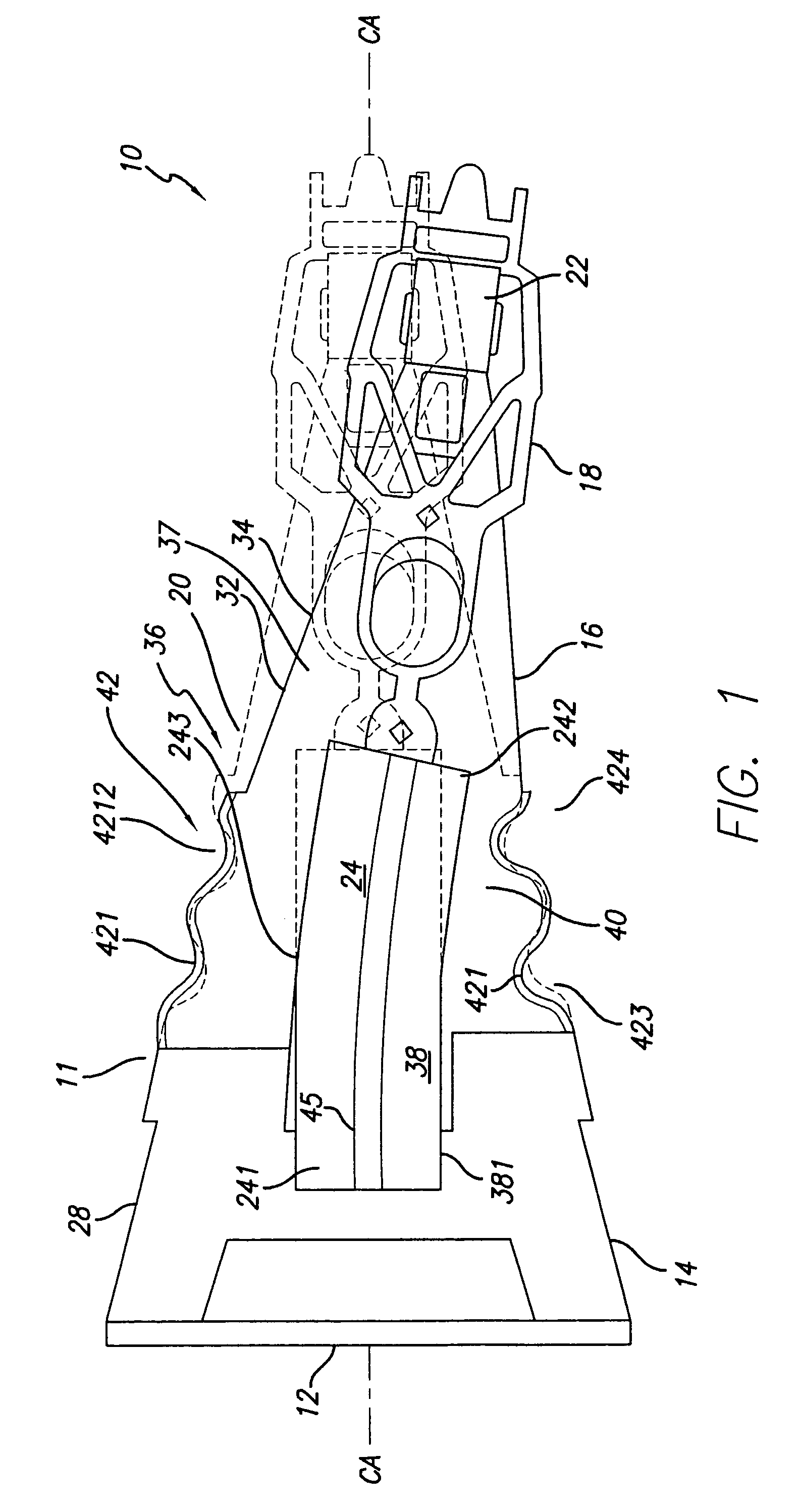
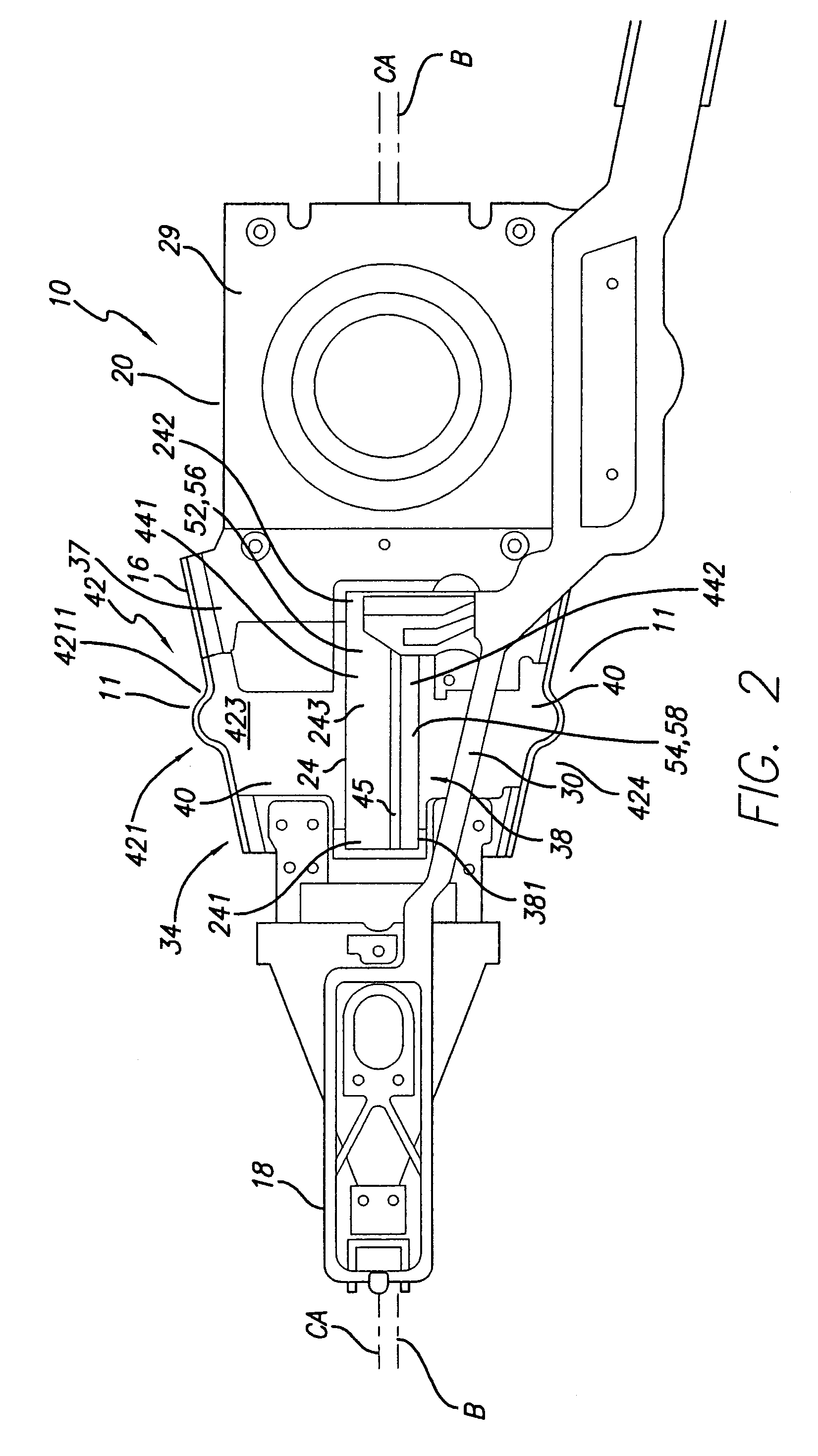
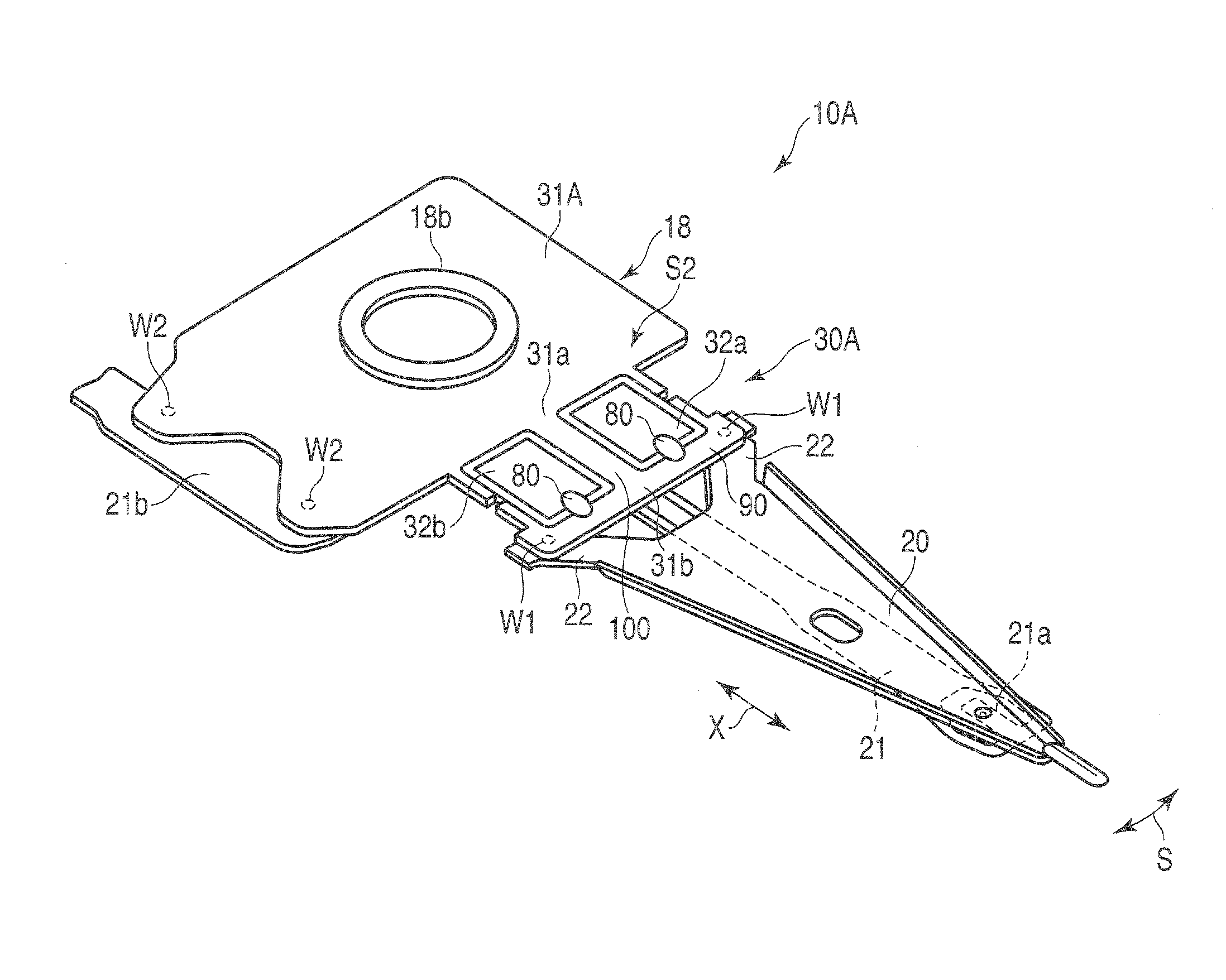
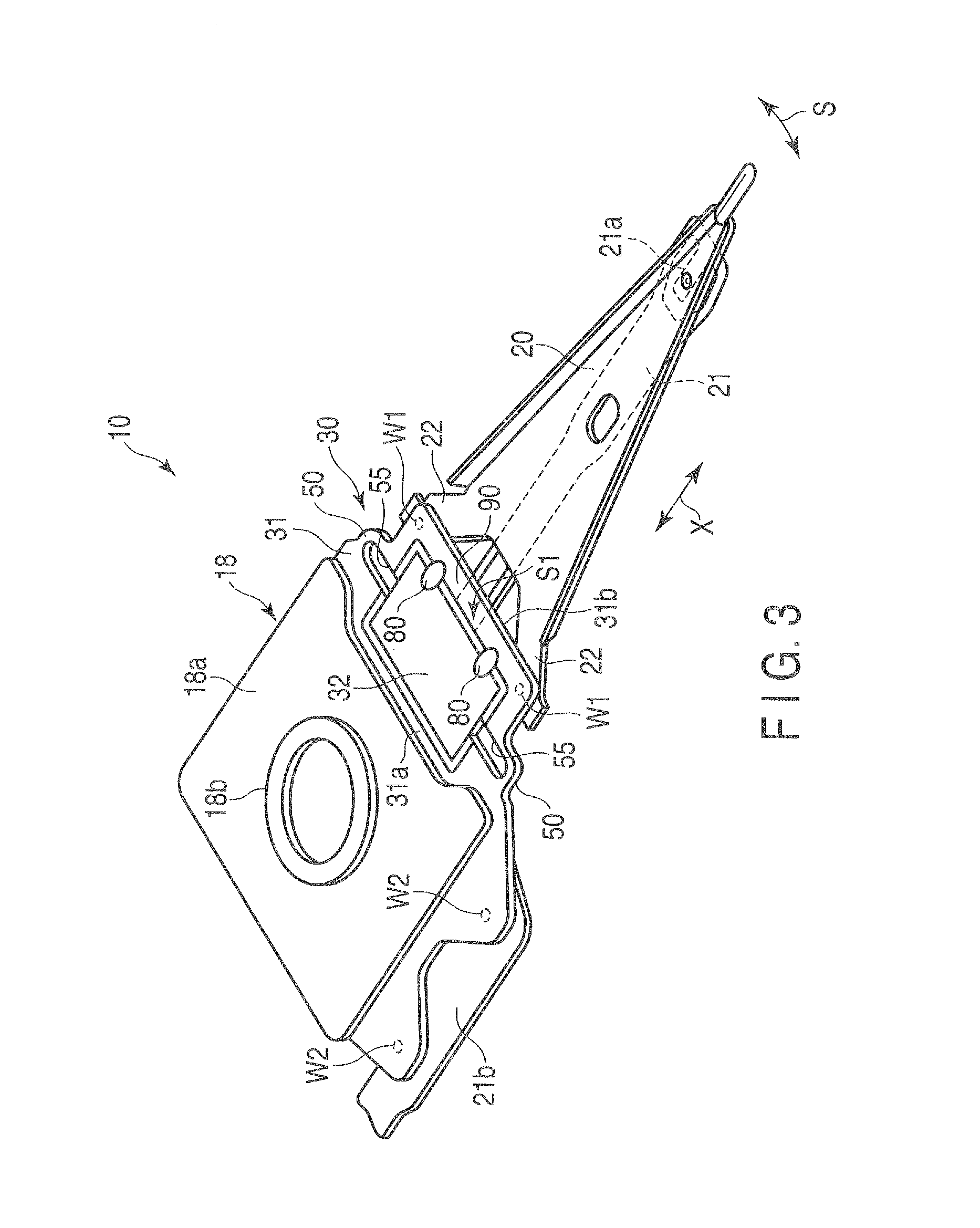
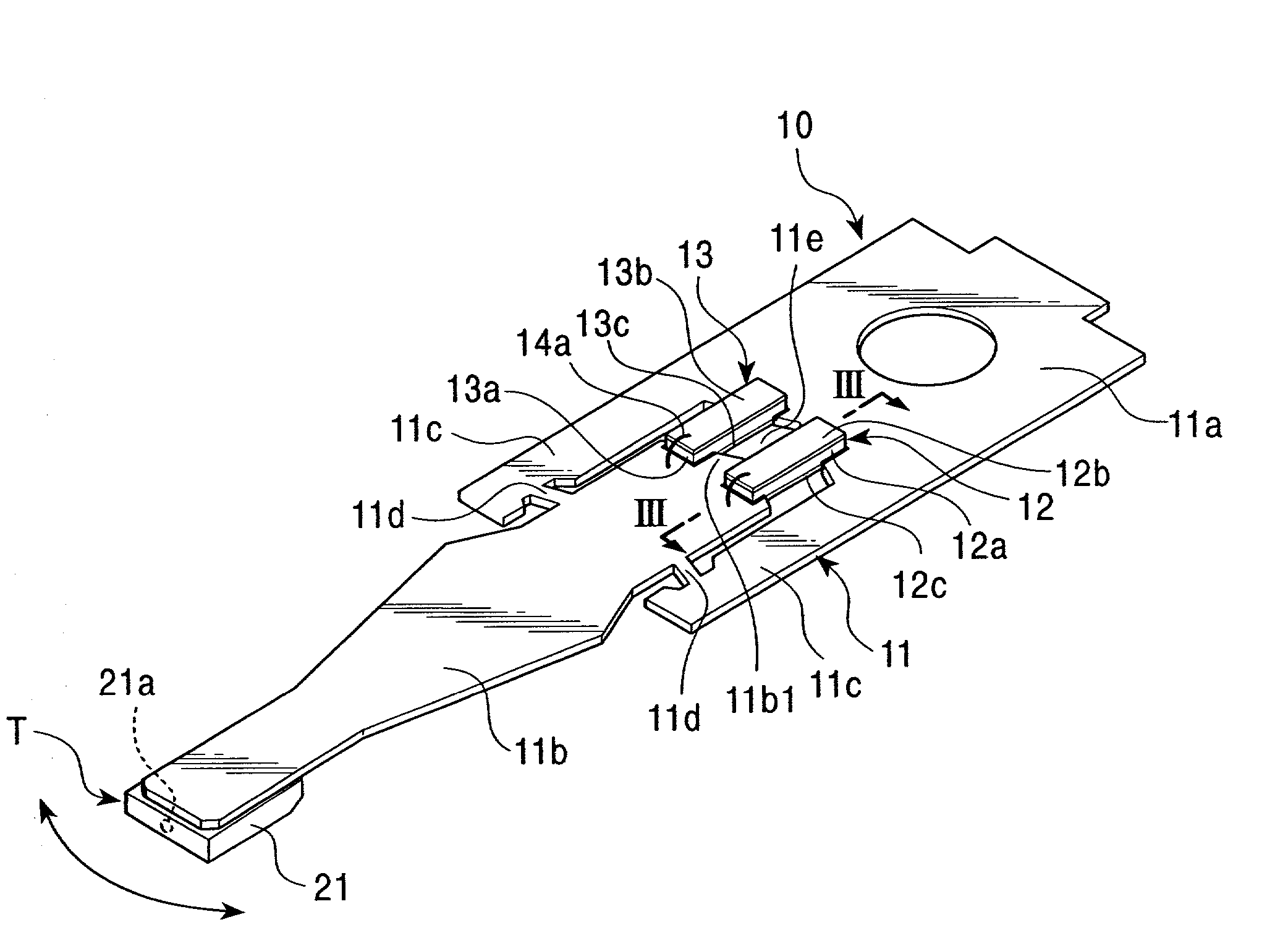
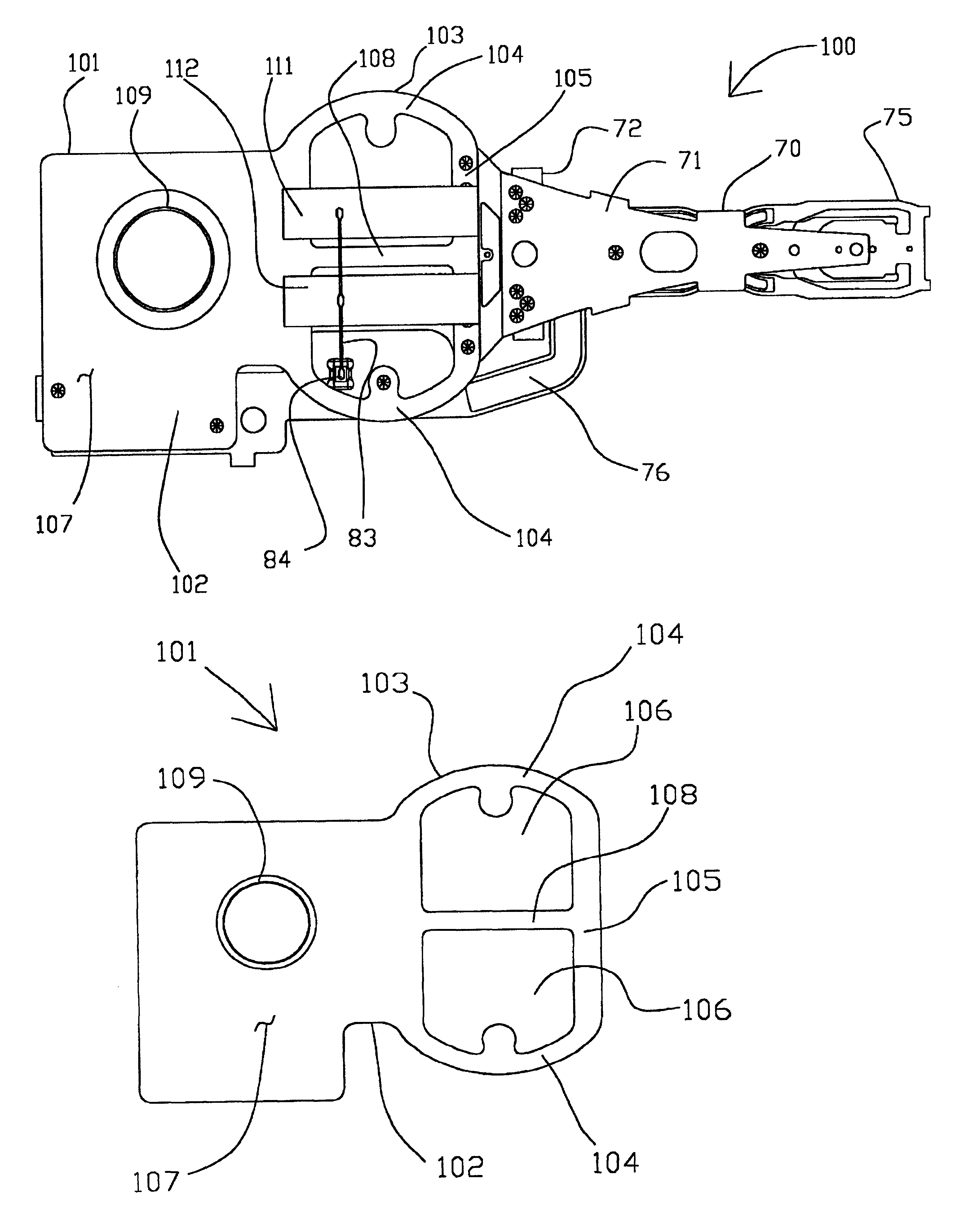
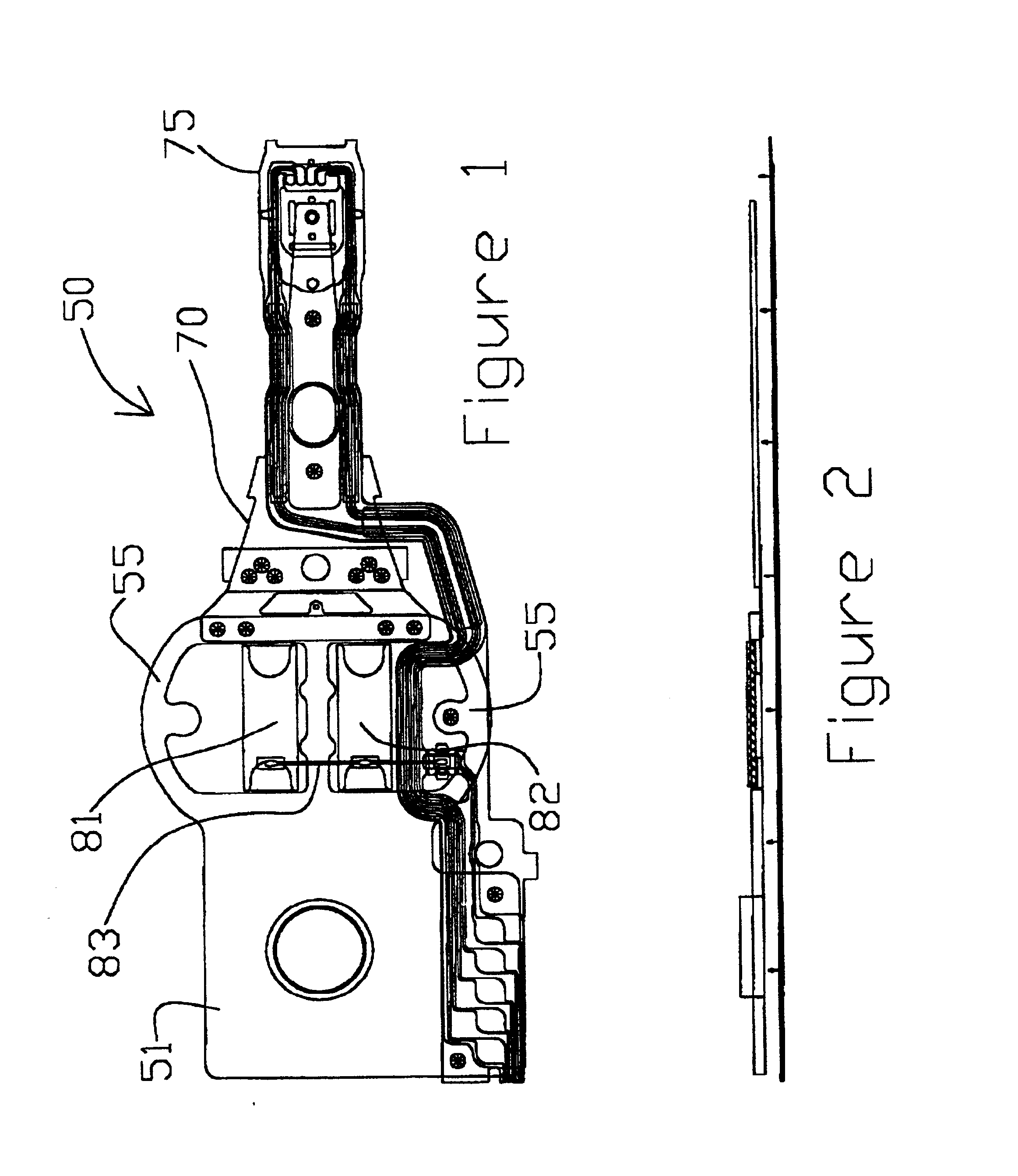
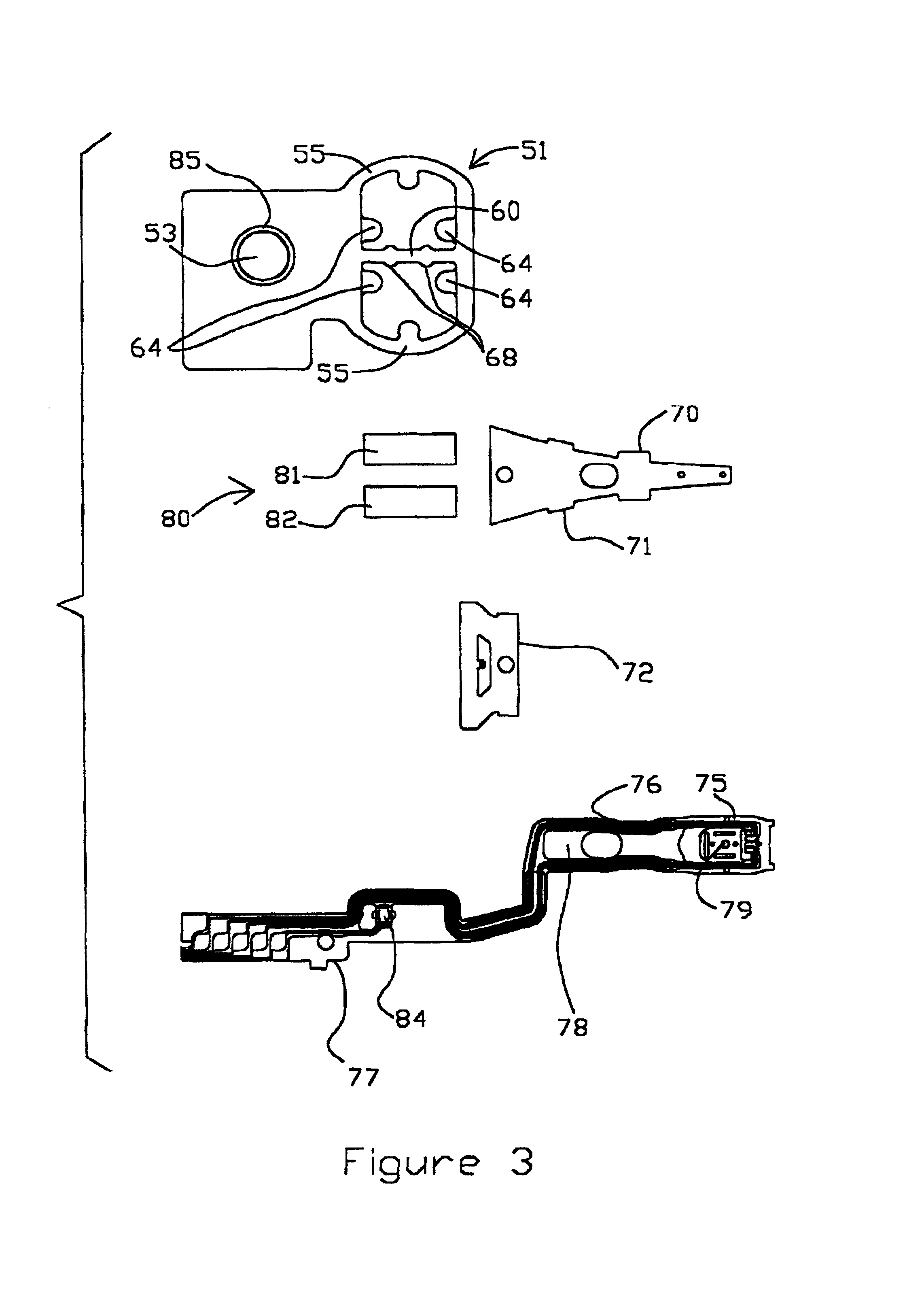
ActiveUS20090244786A1Overcome costsOvercomes manufacturabilityDriving/moving recording headsRecord information storageTrack densityHard disc drive
A piezo in-tongue microactuator includes a suspension assembly with a flexure tongue. The tongue has two slots that accept piezo actuators. The tongue also has multiple hinge flexible elements that translate the extension and / or contraction of the piezo actuators into rotary motion of the recording head. This rotary motion is then used to precisely position the recording element over the desired track on the hard disk drive and permits higher track density to be achieved.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Loading-protected bending microactuator in additive suspensions
ActiveUS7459835B1Improved disk drive suspensionLow costPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesArm with actuatorsDistal portionEngineering
A microactuated disk drive suspension for supporting a slider at a disk includes a load beam extending in a plane and having on a common axis a base section adapted for mounting to an actuator, a spring section and a beam section carrying a flexure and the slider thereon. The suspension has relatively movable proximate and distal portions on the common axis that are joined by a bending system cantilevered from the proximate portion and including a cantilevered bending motor opposed to the common axis and having a laterally bendable unsupported region. A cantilevered laterally bendable load assist structure defined by the suspension edges is provided arranged to block undue loading of the bending motor unsupported region.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
System, method and apparatus for flexure-integrated microactuator
ActiveUS8085508B2Overcome costsOvercomes manufacturabilityTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageHard disc driveTrack density
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Droplet-based affinity assay device and system
ActiveUS20090280476A1Large facilityEasy to testBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusBiologyAntibody
The present invention relates to a droplet-based affinity assay device and system. According to one embodiment, a droplet microactuator is provided and includes an antibody immobilized on a surface. According to another embodiment, a droplet microactuator is provided and includes a droplet on the droplet microactuator, the droplet comprising an antibody.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Actuators for microfluidics without moving parts
InactiveUS20070267294A1Effectively converting the surface into more hydrophilicArea maximizationSludge treatmentFlow mixersElectricityMicrofluidics
A series of microactuators for manipulating small quantities of liquids, and methods of using these for manipulating liquids, are disclosed. The microactuators are based on the phenomenon of electrowetting and contain no moving parts. The force acting on the liquid is a potential-dependent gradient of adhesion energy between the liquid and a solid insulating surface.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
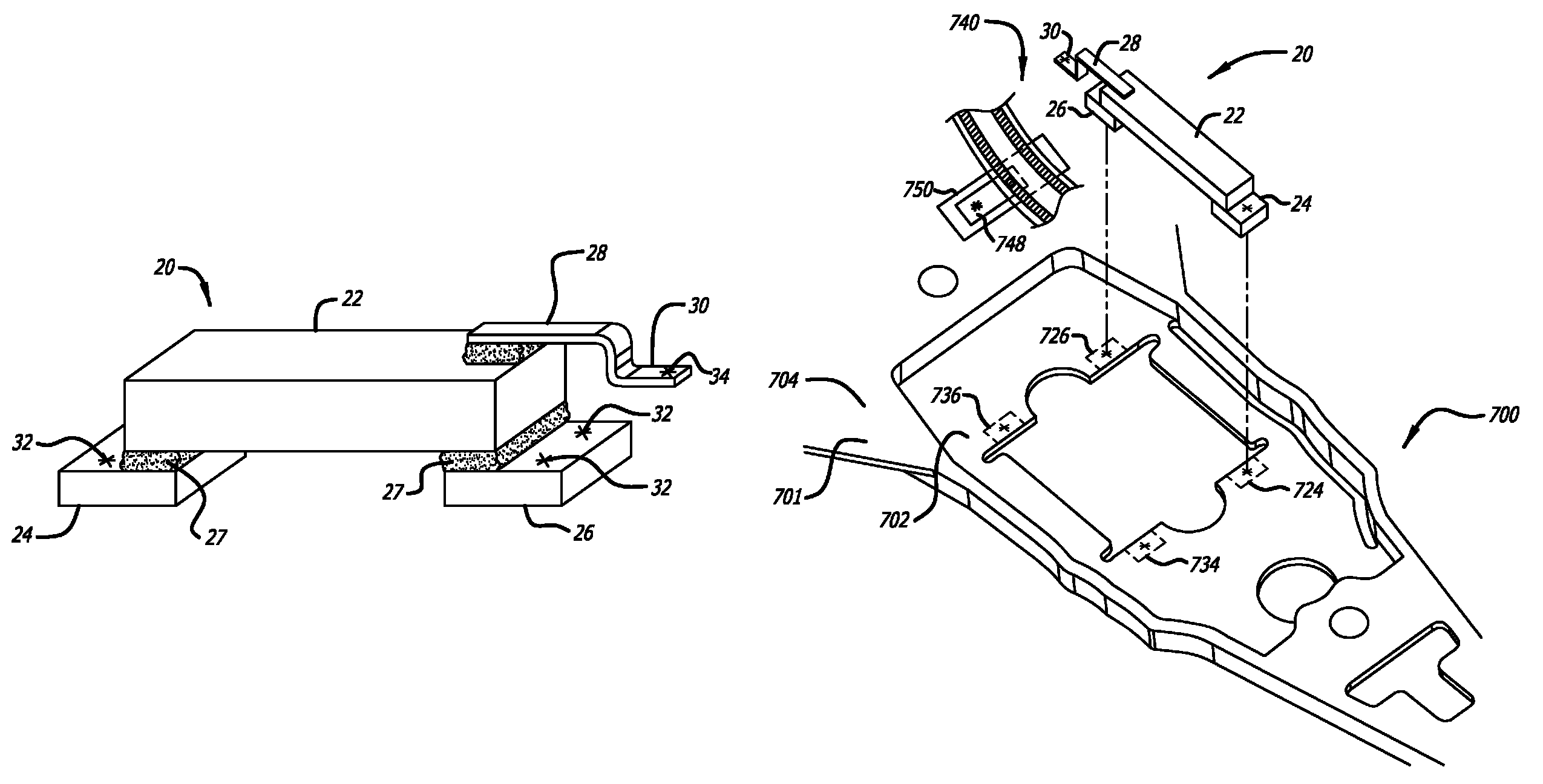
Wireless Microactuator Motor Assembly for Use in a Hard Disk Drive Suspension, and Mechanical and Electrical Connections Thereto
ActiveUS20100271735A1Sufficient resiliencyOvercome lack of conductivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyArm with actuatorsHard disc driveElectrical conductor
A microactuator assembly for a hard disk drive head suspension has an expandable base of stainless steel sheet material defining a negative lead affixed to the negative electrode on the bottom surface of a piezoelectric element, and a piece of stainless steel sheet material defining a positive lead attached to the positive electrode on the top surface of the piezoelectric element. The leads may be affixed directly to the piezoelectric element via conductive adhesive. The microactuator assembly can be assembled separately, and then laser welded into place on a suspension. A bond pad made of stainless steel sheet material extends from the flexible circuit, is electrically connected to the microactuator driving voltage conductor within the flexible circuit through a via, and is electrically isolated from the suspension substrate by an insulating film. The microactuator unit positive lead is mechanically and electrically connected to the bond pad via laser welding.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Electronic apparatus and disk drive suspension
ActiveUS20110242708A1Conductive and reliableReliable conductionArm with actuatorsRecord information storageGold particlesMicroactuator
A microactuator element as an example of an electrical component is disposed on a metallic, electrically conductive plate member. A conductive resin member is disposed on a current-carrying part of the conductive plate member and a conduction part of the microactuator element. A thin porous plating layer of thickness 100 nm or less includes a large number of gold particles is formed in a region of a surface of the conductive plate member which covers the current-carrying part. The conductive resin member is secured to the conductive plate member through the thin porous gold plating layer and electrically connected to the conductive plate member.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
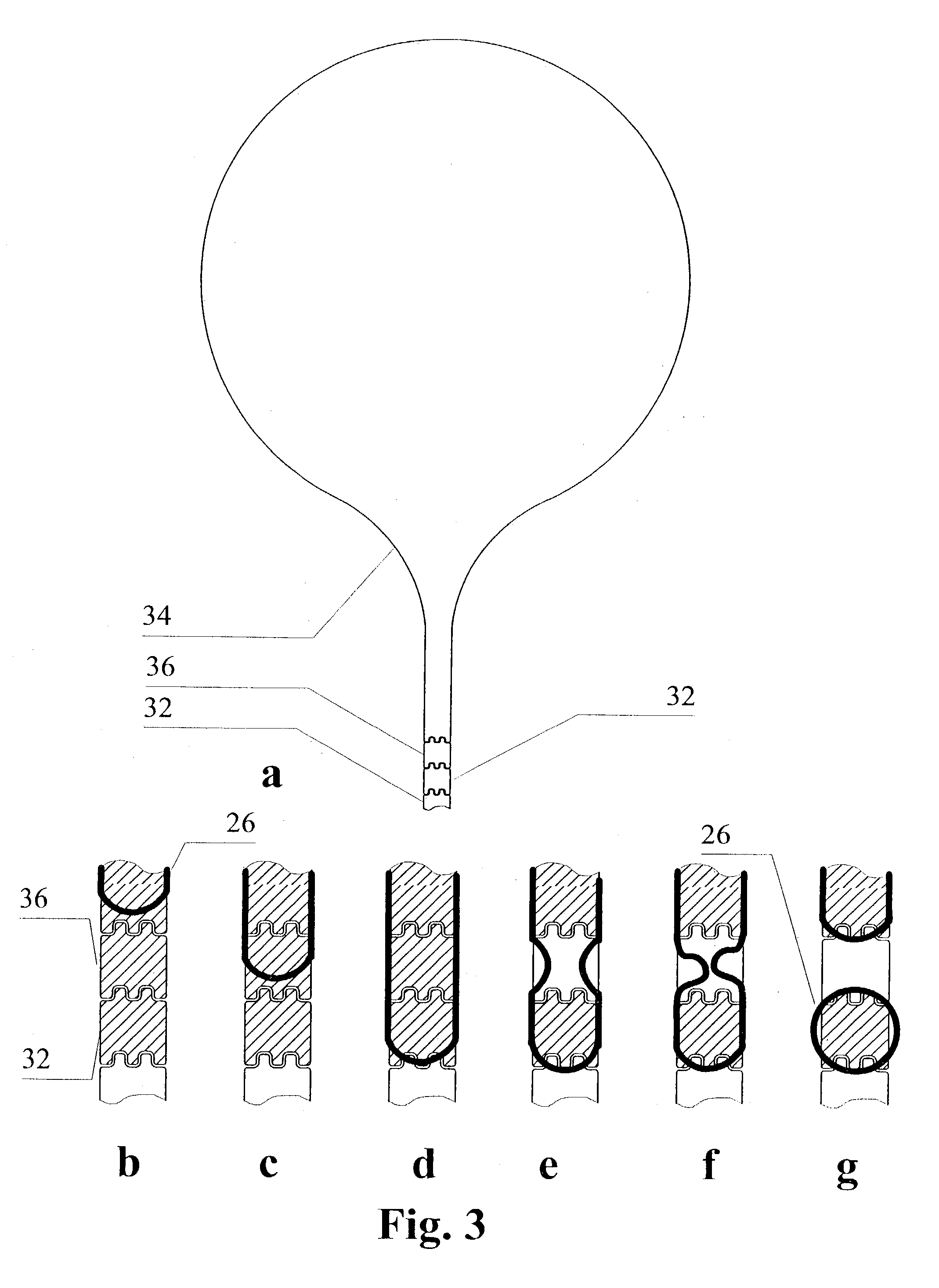
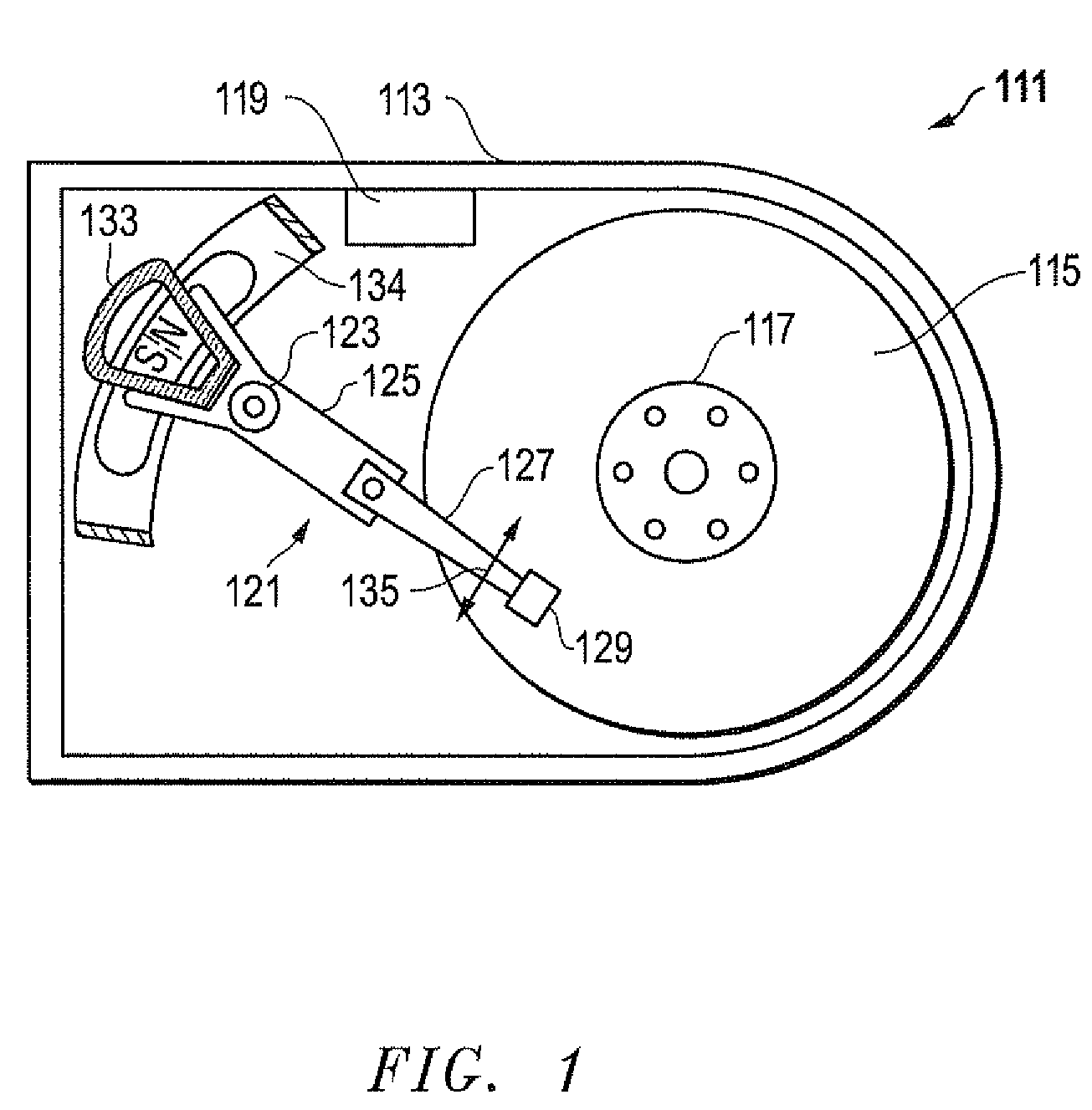
Microactuated dimple for head suspensions
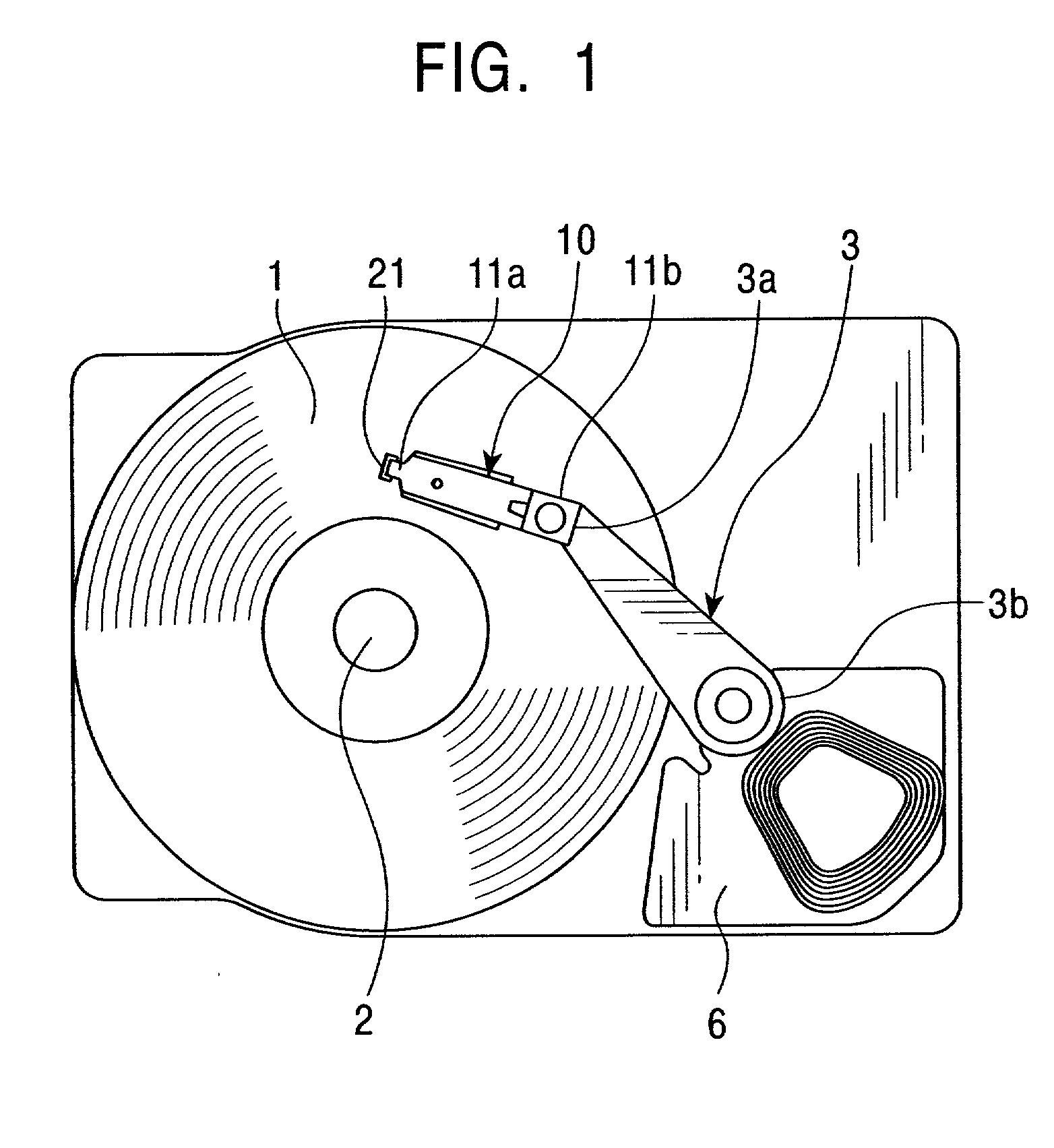
InactiveUS7256968B1Move preciselyTrack finding/aligningRecord information storageDynamic storageEngineering
A head suspension for supporting a head slider over a disk in a dynamic storage device and providing precise movement of the head slider relative to tracks on the disk. The head suspension includes a load beam, a flexure having a slider mounting region, and a dimple interface transmitting a load beam force to the slider mounting region. The head suspension further includes a microactuator mounted to the load beam. Movement of the microactuator is transmitted through the dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface so as to cause movement of the slider mounting region transverse to tracks on the disk. A method of precisely moving a head slider supported by a head suspension includes providing and driving a microactuator configured to transmit movement of the microactuator to a slider mounting region through a dimple interface by action of frictional forces at the dimple interface.
Owner:HUTCHINSON TECH
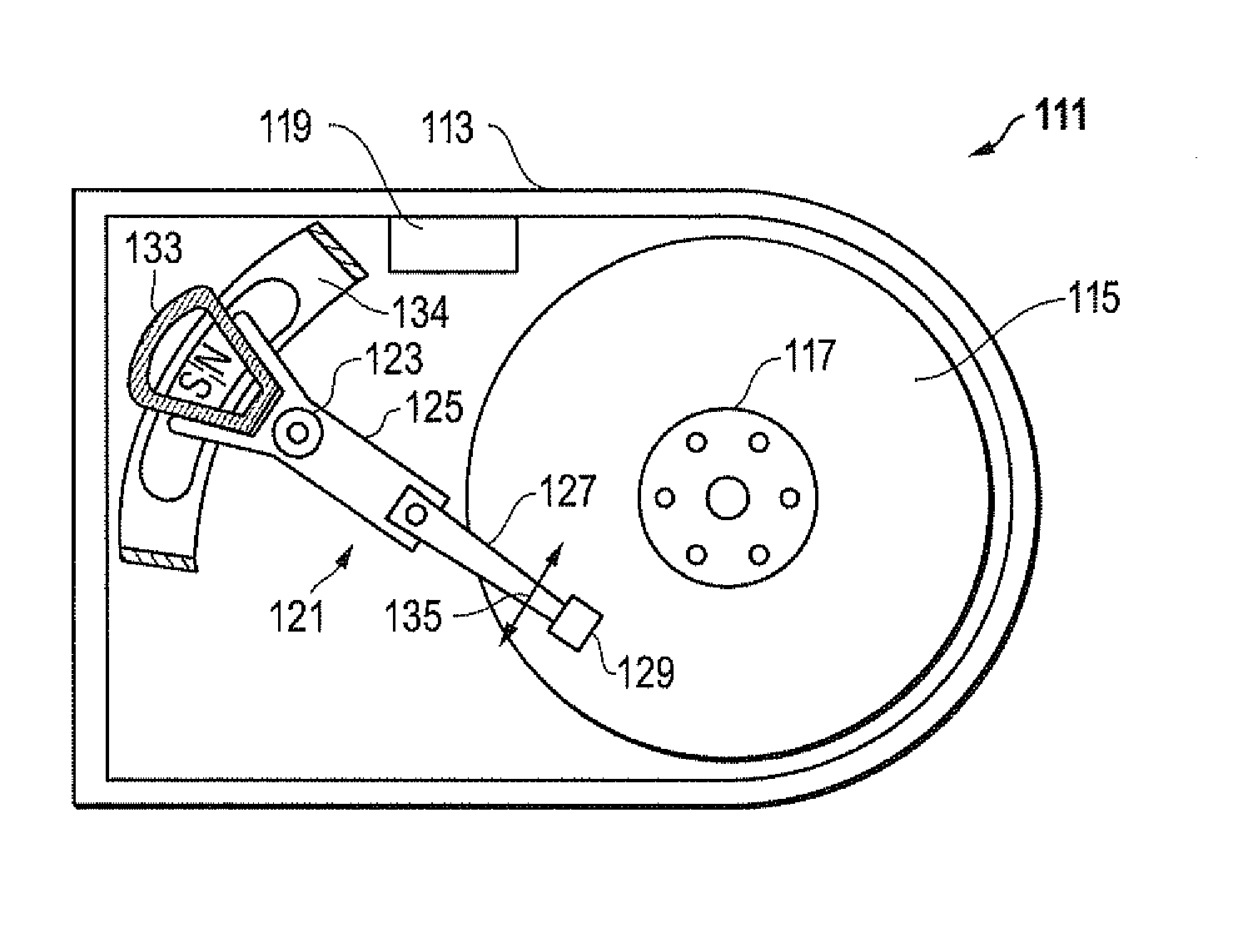
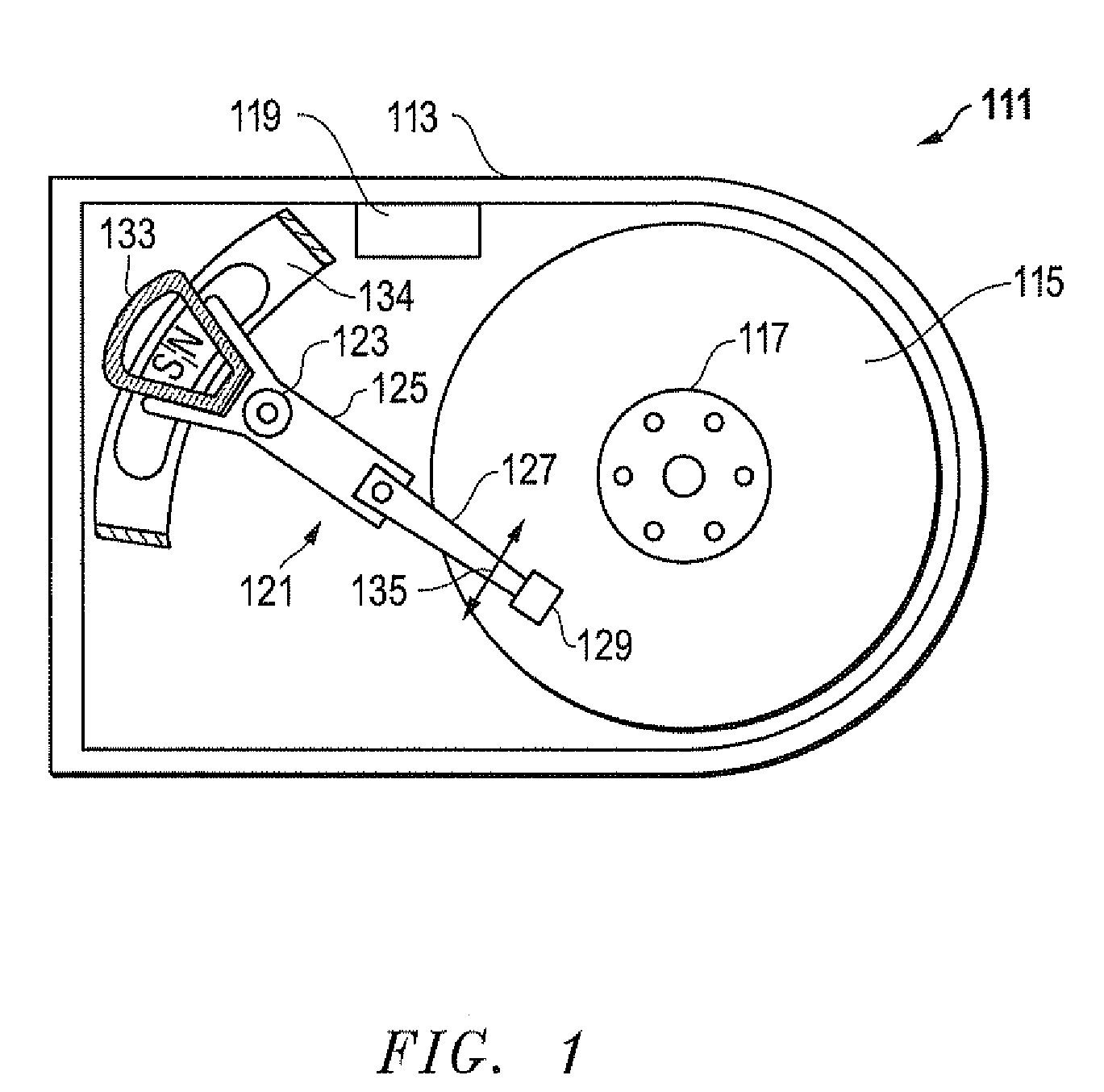
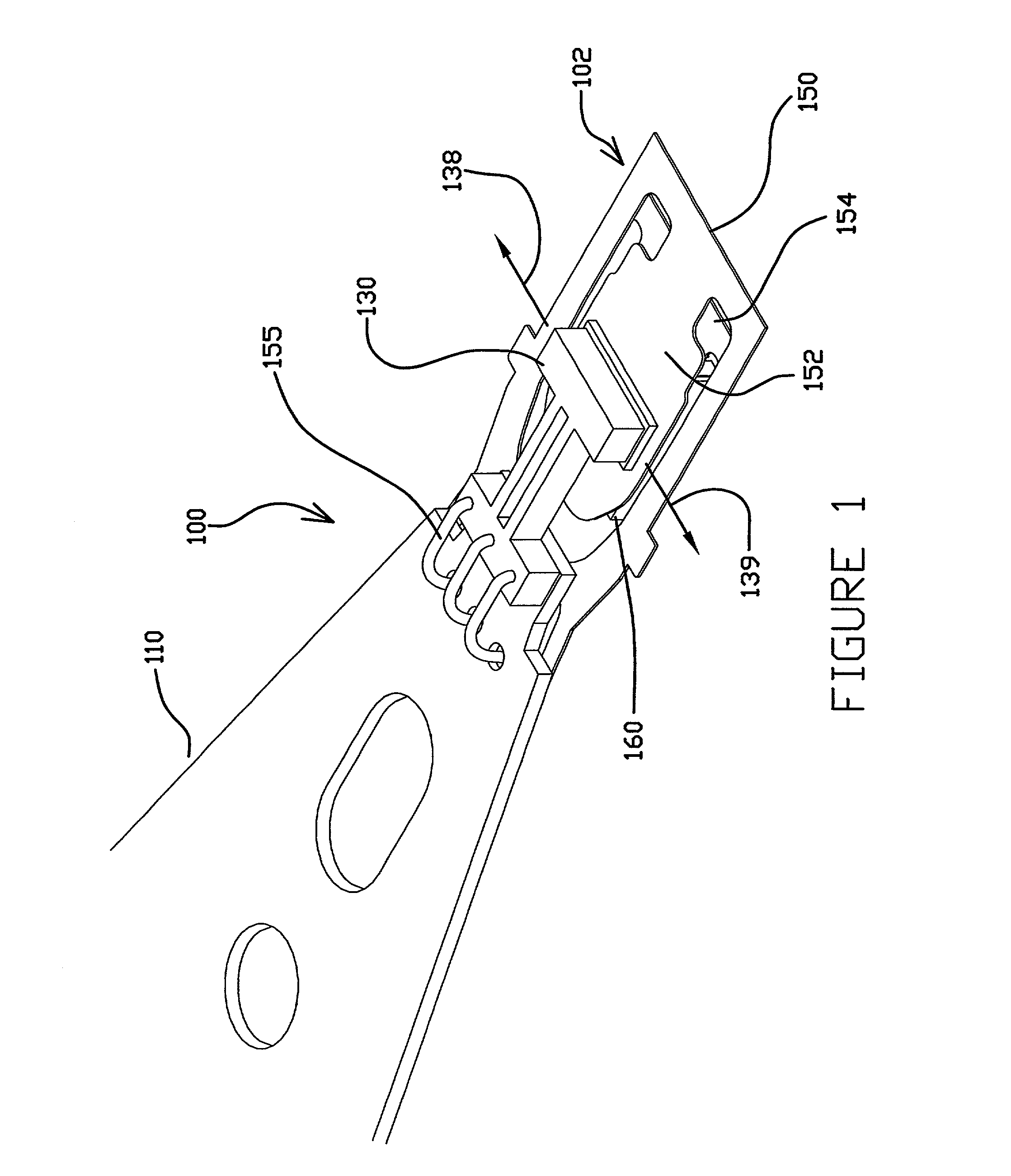
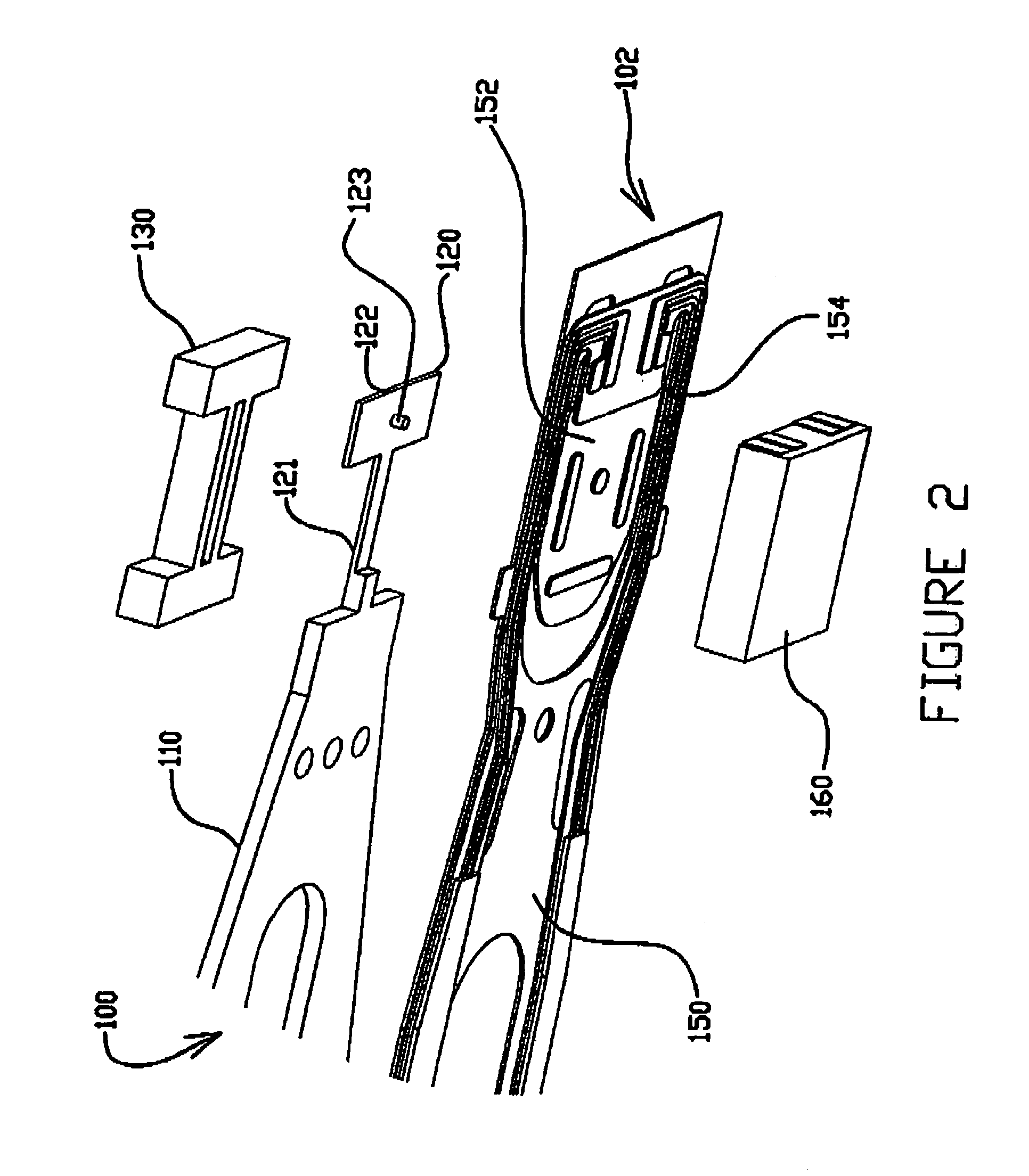
Magnetic head device having suspension with microactuator bonded thereto
The present invention provides a magnetic head device exhibiting a good bonded state of a piezoelectric element and a load beam, and excellent reliability. The magnetic head device includes a slider provided with a reproducing element for detecting a magnetic signal recorded on a recording medium, and a recording element for recording a magnetic signal on the recording medium, an elastic supporting member for supporting the slider, and piezoelectric elements mounted on the elastic supporting member, for distorting the elastic supporting member to change the position of the slider. The piezoelectric element and the elastic supporting member are bonded together with a photo-curing and thermosetting epoxy adhesive resin having a Young's modulus of 1 GPa or more at 25° C., and a glass transition temperature of 90° C. or more.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Rotary electrostatic microactuator
InactiveUS6329737B1Improved range of angular motionRecord information storageCoupling light guidesPlanar substrateComb drive
A rotary electrostatic microactuator that includes a substantially planar substrate and a rotatable member overlying the substrate for rotation about an axis of rotation extending perpendicular to the planar substrate. First and second spaced-apart springs and a plurality of comb drive assemblies are included. Each of the comb drive assemblies has a first comb drive member mounted on the substrate and a second comb drive member. Each of the first and second comb drive members are provided with arcuate comb drive fingers. Each of the first and second springs has a first end portion secured to the substrate and a second end portion secured to at least one of the second comb drive members for suspending the second comb drive members and the rotatable member over the substrate. The second comb drive members are movable in a direction of travel about the axis of rotation between a first position in which the comb drive fingers of the first and second comb drive members are not substantially fully interdigitated and a second position in which the comb drive fingers of the first and second comb drive members are substantially fully interdigitated.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Microactuated head suspension with ring springs
InactiveUS7177119B1Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksEngineeringTorsion spring
A microactuated head suspension including a mounting region for attachment of the head suspension to a source of primary actuation, a pair of generally arcuate ring springs and a connecting member. The ring springs at spaced locations extending from the mounting region with at least one aperture interposed between the pair of ring springs. Each ring spring having concave sides that are substantially free from linear sections and are oriented away from a longitudinal centerline of the head suspension. The connection member is located opposite the mounting region and is spaced from the mounting region by the at least one aperture. The connection member joins ends of the pair of ring springs. In addition, the head suspension may include at least one microactuator for secondary actuation of the head suspension. The microactuator is operationally mounted relative to the pair of ring springs.
Owner:INTRI PLEX (THAILAND) LTD
Wireless microactuator motor assembly for use in a hard disk drive suspension, and mechanical and electrical connections thereto
ActiveUS8189301B2Sufficient resiliencyOvercome lack of conductivityArm with actuatorsSolid-state devicesHard disc driveElectricity
A microactuator assembly for a hard disk drive head suspension has an expandable base of stainless steel sheet material defining a negative lead affixed to the negative electrode on the bottom surface of a piezoelectric element, and a piece of stainless steel sheet material defining a positive lead attached to the positive electrode on the top surface of the piezoelectric element. The leads may be affixed directly to the piezoelectric element via conductive adhesive. The microactuator assembly can be assembled separately, and then laser welded into place on a suspension. A bond pad made of stainless steel sheet material extends from the flexible circuit, is electrically connected to the microactuator driving voltage conductor within the flexible circuit through a via, and is electrically isolated from the suspension substrate by an insulating film. The microactuator unit positive lead is mechanically and electrically connected to the bond pad via laser welding.
Owner:MAGNECOMP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com