Solid-state imagine device, line sensor, optical sensor, and method for operating solid-state imaging device
A technology of a solid-state imaging device and a working method, which is applied to radiation control devices, image communication, television, etc., can solve the problems of inability to match two images, low sensitivity, and difficulty in high sensitivity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
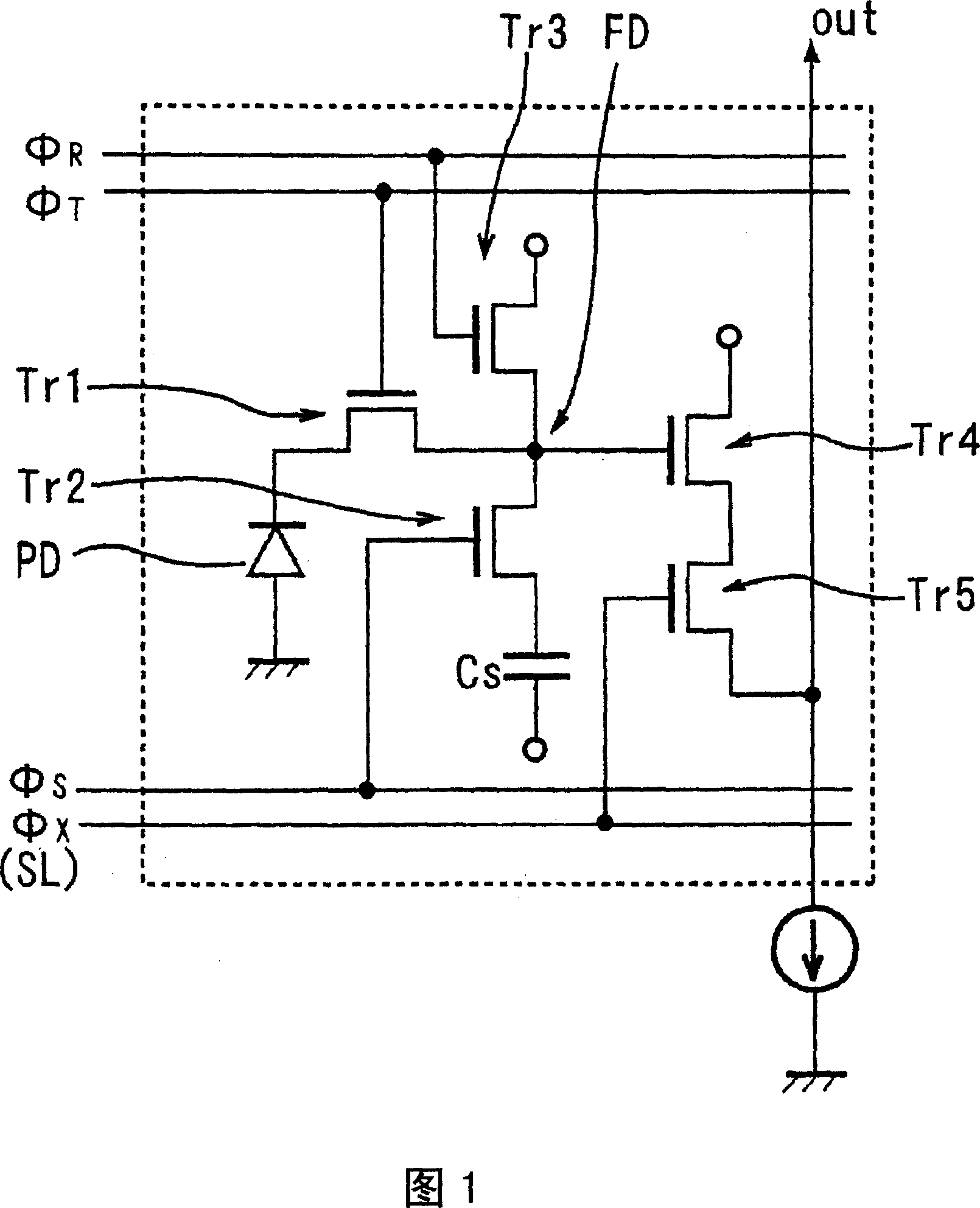
[0143] The solid-state imaging device of this embodiment is a CMOS image sensor, and FIG. 1 is an equivalent circuit diagram of one pixel.
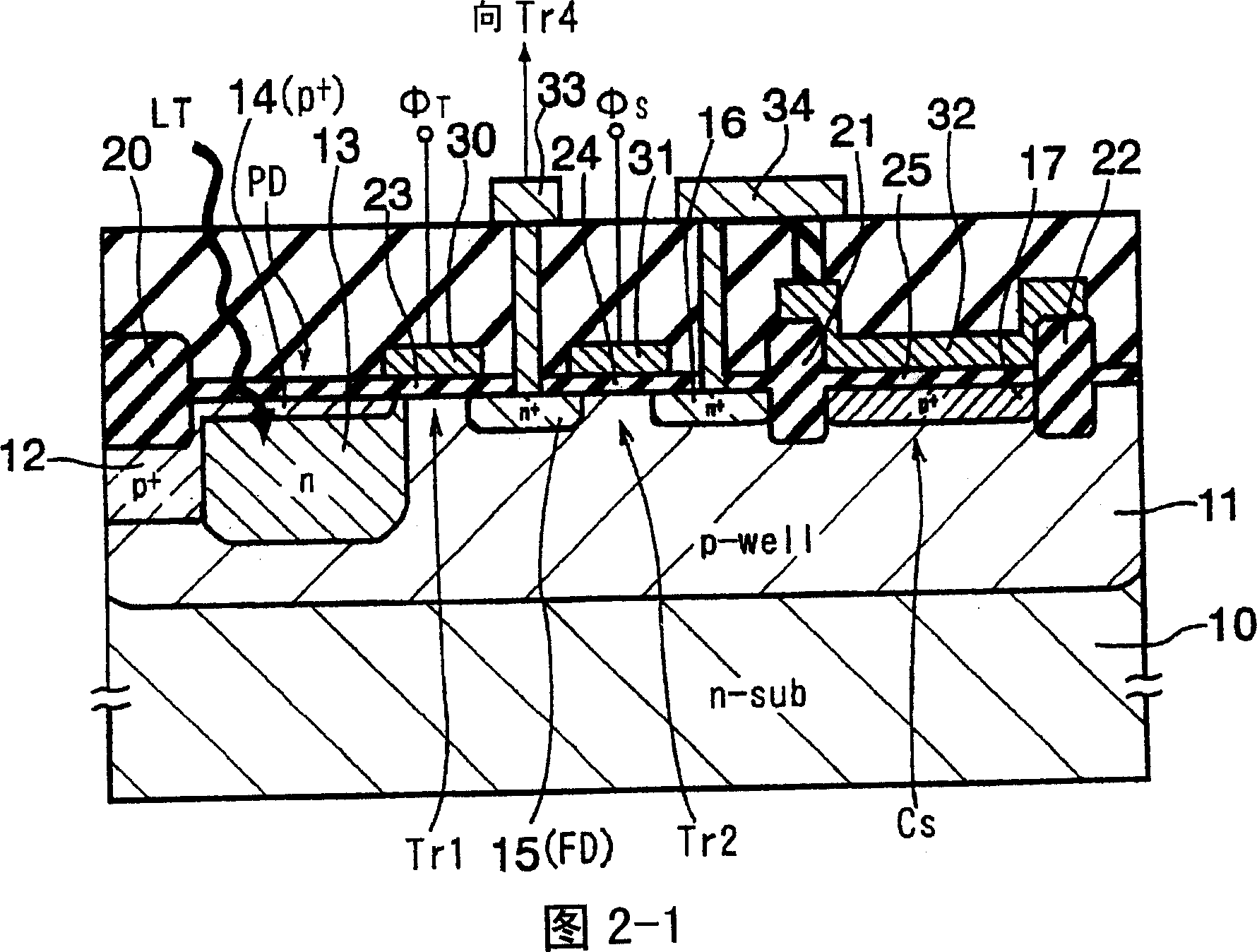
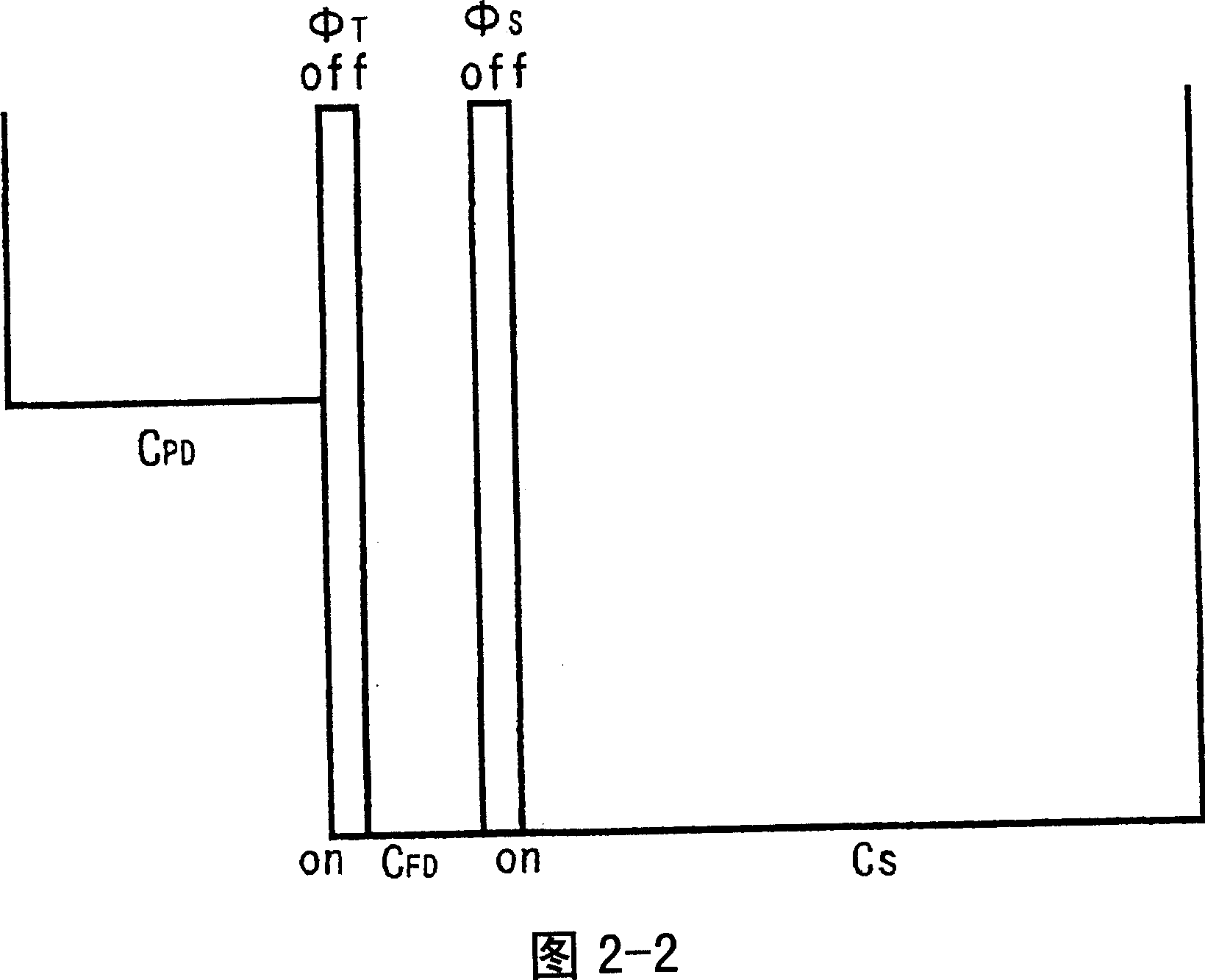
[0144] Each pixel consists of a photodiode PD that receives light and generates photocharges, a transfer transistor Tr1 that transfers photocharges from the photodiode PD, a floating region FD that transfers photocharges through the transfer transistor Tr1, and accumulates photocharges from the photodiodes during an accumulation operation. The overflow photocharge storage capacitor element C S , The floating area FD and the storage capacitor element C S The storage transistor Tr2 that is combined or divided by the potential of the floating region FD, the reset transistor Tr3 that is formed in connection with the floating region FD and used to discharge the photocharges in the floating region FD, and the amplifier that transforms the photocharges in the floating region FD into a voltage signal The transistor Tr4 and the selection transist...
Embodiment approach 2
[0219] This embodiment is a form in which the circuit configuration of the pixel of the CMOS image sensor in the first embodiment is modified.
[0220] FIG. 9-1 is an equivalent circuit diagram of one pixel of an example of the CMOS image sensor of this embodiment. It is substantially the same as the equivalent circuit diagram of FIG. 1, but the connection between the amplification transistor Tr4 and the selection transistor Tr5 is different. The selection transistor Tr5 is arranged on the upper side of the amplification transistor Tr4, and the output of the amplification transistor Tr4 is connected to the output line out. .
[0221] By connecting in this way, the gain of the amplifier of the amplifier transistor Tr4 can be increased.
[0222] 9-2 is an equivalent circuit diagram of one pixel of another example of the CMOS image sensor of this embodiment. It is substantially the same as the equivalent circuit diagram of FIG. 1, but for the five transistors including the tran...
Embodiment approach 3
[0227] The solid-state imaging device of this embodiment is a CCD image sensor.
[0228] FIG. 10-1 is an equivalent circuit diagram of one pixel of an example of the CCD image sensor of this embodiment.
[0229] φ V1 and φ V2 The first charge-coupled transfer line CCD1 and the second charge-coupled transfer line CCD2 of the 2-phase drive are arranged to extend in the vertical direction, the photodiode PD is directly connected to the first charge-coupled transfer line CCD1, and is connected to the second charge-coupled transfer line via the transfer transistor Tr1 Forwarding route to CCD2 connection.
[0230] Here, the second charge-coupled transfer line CCD2 functions as a storage capacitor element C that accumulates photocharges overflowing from the photodiode PD when the photodiode PD is saturated. S kick in.
[0231] In the CCD image sensor of the above-mentioned structure, the signal before saturation on the low-illuminance side is transferred through the first charge-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com